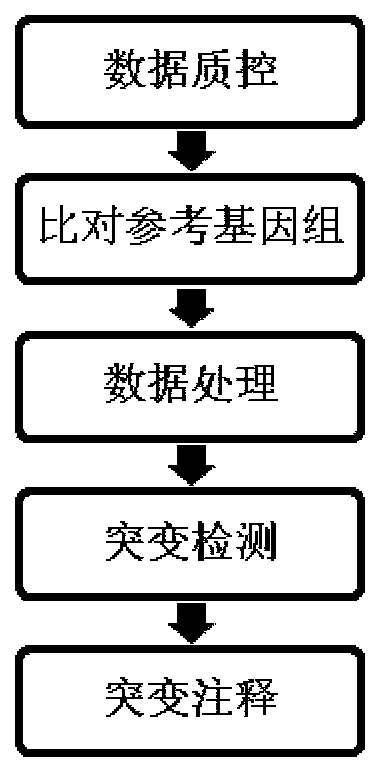
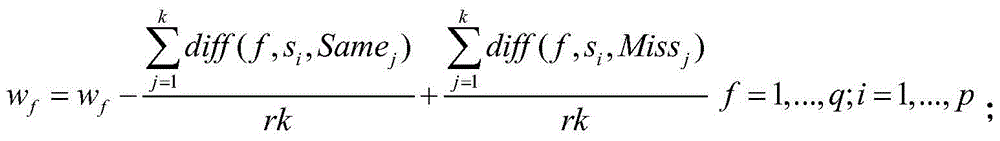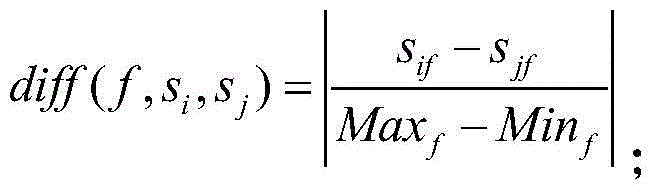Patents
Literature
65 results about "Cancer genome" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
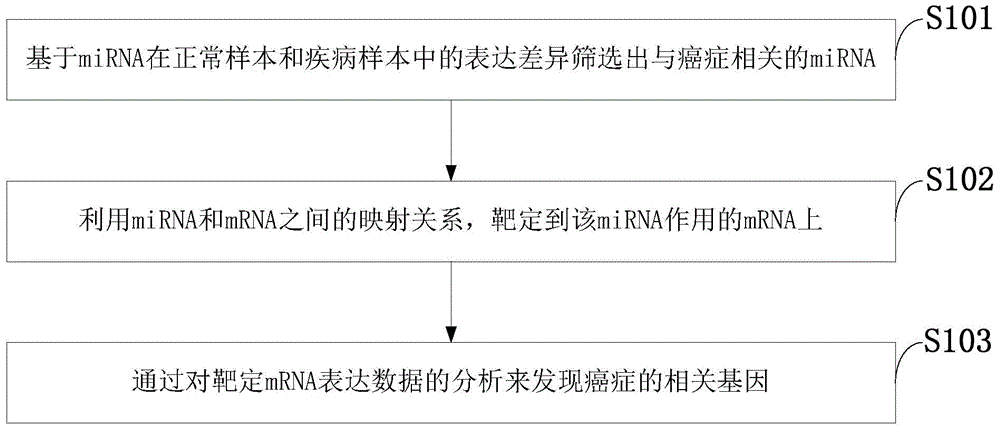
Cancer-related genes finding method by using miRNA expression data
ActiveCN105701365AReduce disease riskReduce dimensionalitySequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsStatistical analysisCancer genome
The present invention discloses a cancer-related genes finding method by using miRNA expression data, based on a pan-cancer program PanCancer under The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), and uses statistical analysis and a machine learning algorithm to carry out analysis and processing on the gene expression data, and to identify complex diseases related genes. The method comprises: sorting out sample data; carrying out statistical analysis on the miRNA expression data; sorting miRNA in order of an average change rate; selecting a target gene; extracting a corresponding disease sample and normal sample; and using a Relief algorithm to sort genes in the extracted miRNA sample. The method disclosed by the present invention can find a plurality of risk genes related to cancer and other complex diseases, and has important significance to a biological target therapy, biomedical research, pathogenesis explanation, risk prediction, and the like.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Multi-omic search engine for integrative analysis of cancer genomic and clinical data
A method is provided for utilizing multi-omic data indices for tumor profiling. The method can comprise the steps of storing a plurality of multi-omic data indices, wherein each of the plurality of multi-omic data indices comprises cancer-specific tokenized data; ingesting additional multi-omic data and any annotations associated with the additional multi-omic data, the additional multi-omic data related to one or more indices; indexing the ingested additional multi-omic data and annotations while preserving gene names, gene variant names and multi-omic mapping between different data streams for the same patient in the specific index, to produce tokenized ingested additional multi-omic data; receiving a user query; selecting one or more relevant multi-omic data indices based on the user query; ranking the selected one or more multi-omic data indices based on at least one of clinical actionability, pathogenicity, feature weight, or frequency; and returning the ranked one or more multi-omic data indices to the user.
Owner:HUMAN LONGEVITY
Target region enrichment sequencing method for 165 genes
The invention provides a target region enrichment sequencing method for 165 genes. According to the method, 165 group-entering genes are screened according to the cancer genome and medicine data of TCGA, NCCN, FDA and the like. The 165 genes comprise detection genes recommended by NCCN, target genes corresponding to target medicines and important clinical medicines approved by FDA, genes influencing the medication effect of the target medicines, and genes influencing the chemical drug sensibility and toxic and side effects. According to the method, the exon regions of the 165 genes are enriched at once through the probe capturing technology, the multi-gene and multi-target parallel depth high-throughput sequencing is realized, the various variation types (such as point mutation, deletion, insertion, fusion and copy number amplification) of the genes can be simultaneously detected, and the detection depth and accuracy are superior to those of the prior art.
Owner:刘鹏飞
Non-invasive blood based monitoring of genomic alterations in cancer
ActiveUS20160138112A1Diagnostic and prognostic utilityAccurate measurementBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementControl subjectsHousekeeping gene
The invention provides methods to monitor cell free nucleic acids. The method comprises obtaining a plasma sample from a subject known to have a cancer characterized by a pair of mutually exclusive mutations specific to the cancer; isolating cell free nucleic acids from the plasma sample obtained from the subject; measuring the amount a housekeeping gene and / or total DNA in the cell free nucleic acids isolated from the plasma sample to confirm that the amount of housekeeping gene and / or total DNA in the sample is within a selected range; measuring the amount of a first of the pair of mutually exclusive mutations specific to the cancer in the cell free nucleic acids isolated from the plasma sample; and indicating in a report that the subject has the first mutation when (a) the amount of the housekeeping gene and / or total DNA in the cell free nucleic acids isolated from the plasma sample is within the selected range and (b) the amount of the first mutation is increased as compared to a control amount, wherein the control amount is determined by measuring the apparent amount of the first mutation in control cell free nucleic acids isolated from plasma samples obtained from control subjects known to have the second of the pair of mutually exclusive mutations specific to the cancer using measuring conditions substantially the same as those used to measure the amount of the first mutation in the cell free nucleic acids isolated from the plasma sample from the subject.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
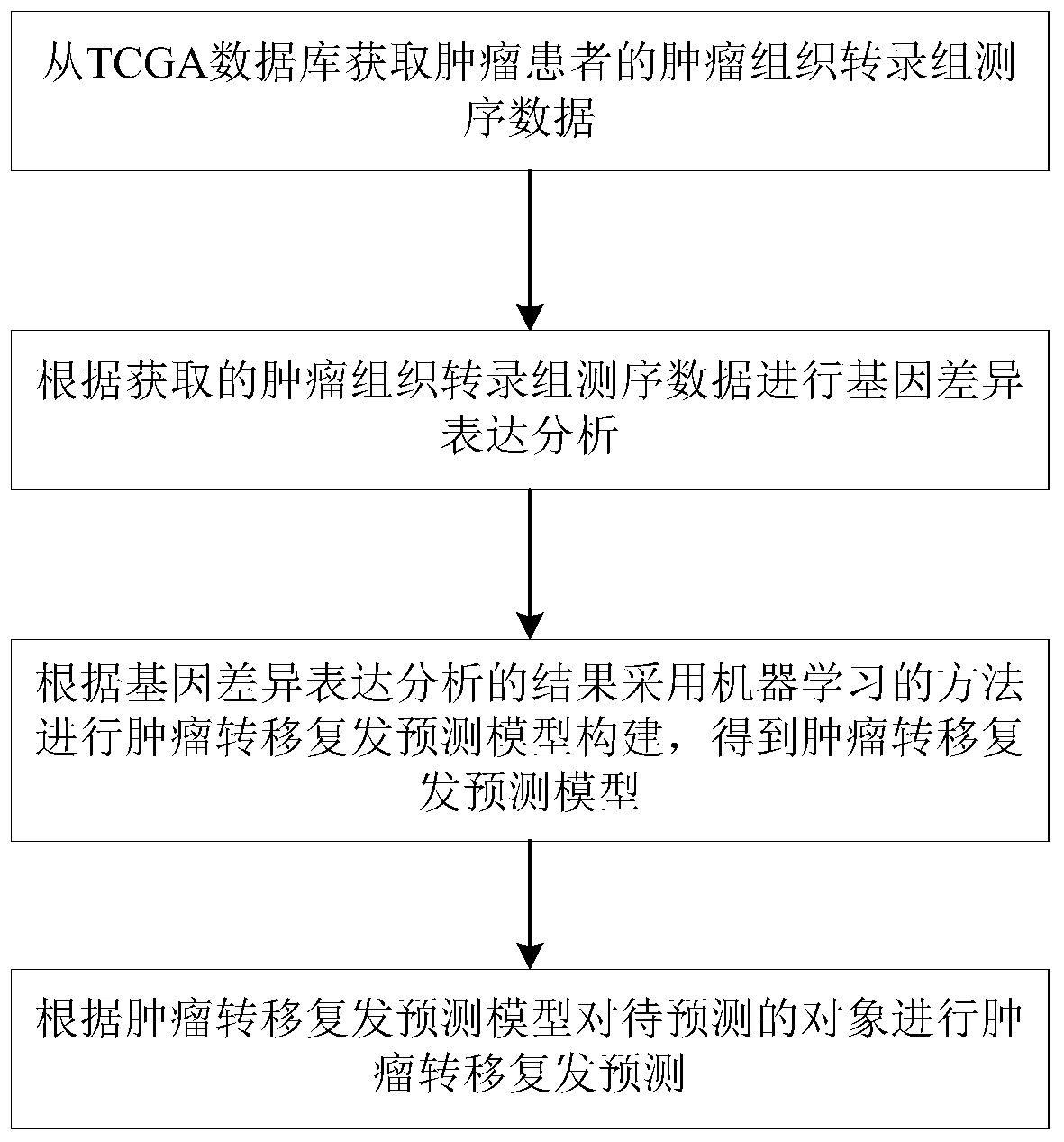
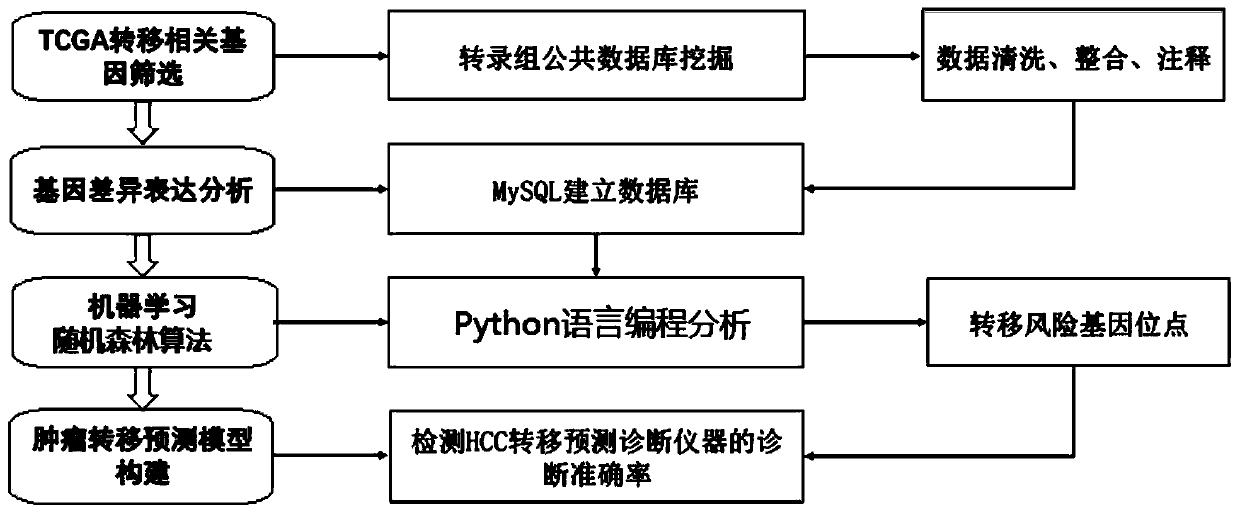
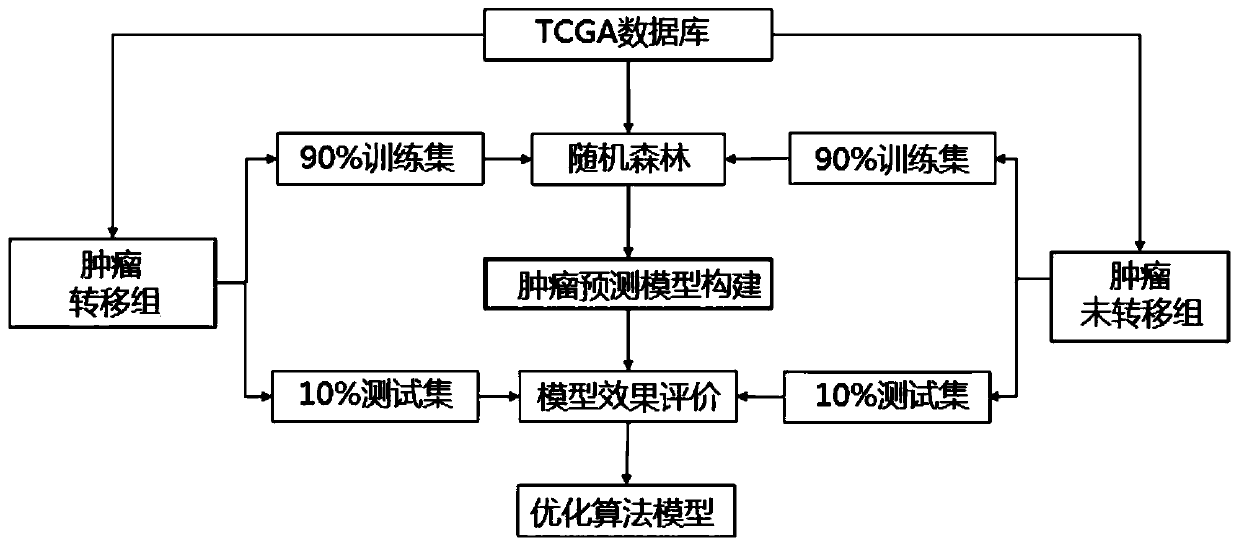
Tumor metastasis and recurrence prediction method and system based on TCGA database
ActiveCN109801680ARealize fully automated managementHealth-index calculationBiostatisticsCancer genomeRecurrence prediction
The invention discloses a tumor metastasis and recurrence prediction method and system based on a TCGA (The Cancer Genome Atlas) database. The tumor metastasis and recurrence prediction method includes the steps: obtaining transcriptome sequencing data of tumor tissues of tumor patients from the TCGA database; performing gene differential expression analysis according to the acquired transcriptomesequencing data of tumor tissues; performing construction of a tumor metastasis and recurrence prediction model by using a machine learning method according to results of gene differential expressionanalysis to obtain a tumor metastasis and recurrence model; and performing tumor metastasis and recurrence prediction on an object to be predicted according to the tumor metastasis and recurrence prediction model. The tumor metastasis and recurrence prediction method based on a TCGA database utilizes the machine learning method and the TCGA database to realize the fully automated management of the tumor metastasis and recurrence prediction, can directly provide a clear diagnosis and prognosis reference and guidance for tumor patients, and is more timely, accurate and efficient. The tumor metastasis and recurrence prediction method based on a TCGA database can be widely applied to the field of medical computer applications.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF CHINESE MEDICINE
Breast cancer occurrence related characteristic gene screening method
InactiveCN107729718AAvoid missingImprove accuracyBiostatisticsCharacter and pattern recognitionGenomicsCancer genome
The invention discloses a breast cancer occurrence related characteristic gene screening method. With breast cancer data in a TCGA database being a study object, a multi-characteristic gene screeningmethod is adopted, and a real characteristic gene is screened from the aspects of correlation, specificity, biological functions and the like. Based on cancer genomic data, through the characteristicgene extracting method, the gene related to early cancer occurrence is extracted, a classification model is built, and therefore early breast cancer automatic diagnosis is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Cancer genome and non-specific gene tag-based large-scale drug relocation method
The invention relates to a cancer genome and non-specific gene tag-based large-scale drug relocation method, and discloses a method for expression profile core labels of single human coding gene mutations without organization resource backgrounds through integrating and analyzing large-scale transcriptome data in different cancer types for the first time. On the basis of core labels, the inventionprovides a drug relocation method which aims at the in-vivo environment, is not based on model animals or cells and is capable of comprehensively covering more than 8000 human genome potential targetgenes for the first time, and designs a quantitative index for measuring interaction specificity between drugs and target genes for the first time, so that a drug relocation analysis method for comprehensively analyzing human drug target genes in a large scale is realized and a new way is provided or drug target point design and human disease treatment.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Flow correction method for second-generation cancer genome high-throughput sequencing data
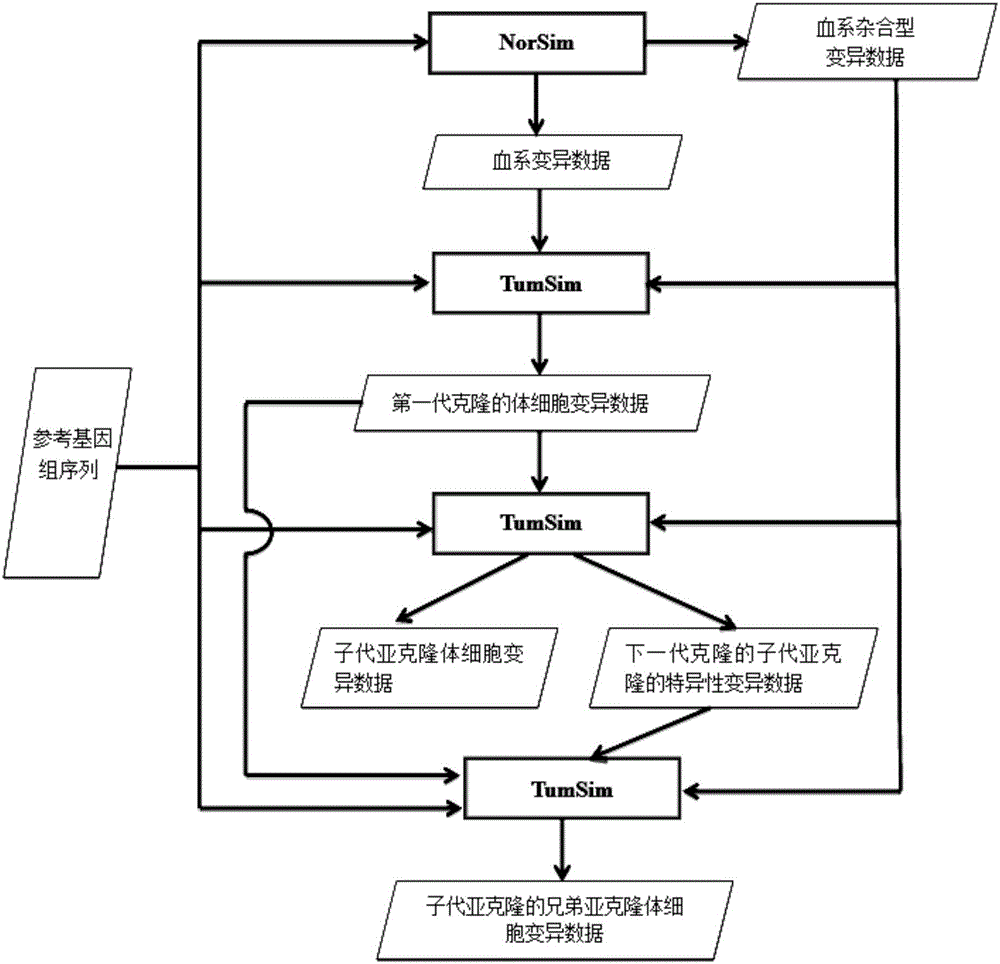
ActiveCN106778072AHigh precisionSave storage spaceHybridisationSpecial data processing applicationsCancer genomeSubcloning
The invention discloses a flow correction method for second-generation cancer genome high-throughput sequencing data; in the method, a series of 32-bit unsigned numbers are used as identification quantities to record corresponding bloodline variation or somatic cell variation data respectively to generate read data embodying purity and different subcloning ratios, somatic cell variation correction data for offspring subcloning and its brother subcloning are acquired according to variation relationship between farther-son subcloning inheritance and brother subcloning mutual exclusion, and the data are used to correct a processing flow of second-generation cancer genome high-throughput sequencing data.
Owner:北京吉因加医学检验实验室有限公司
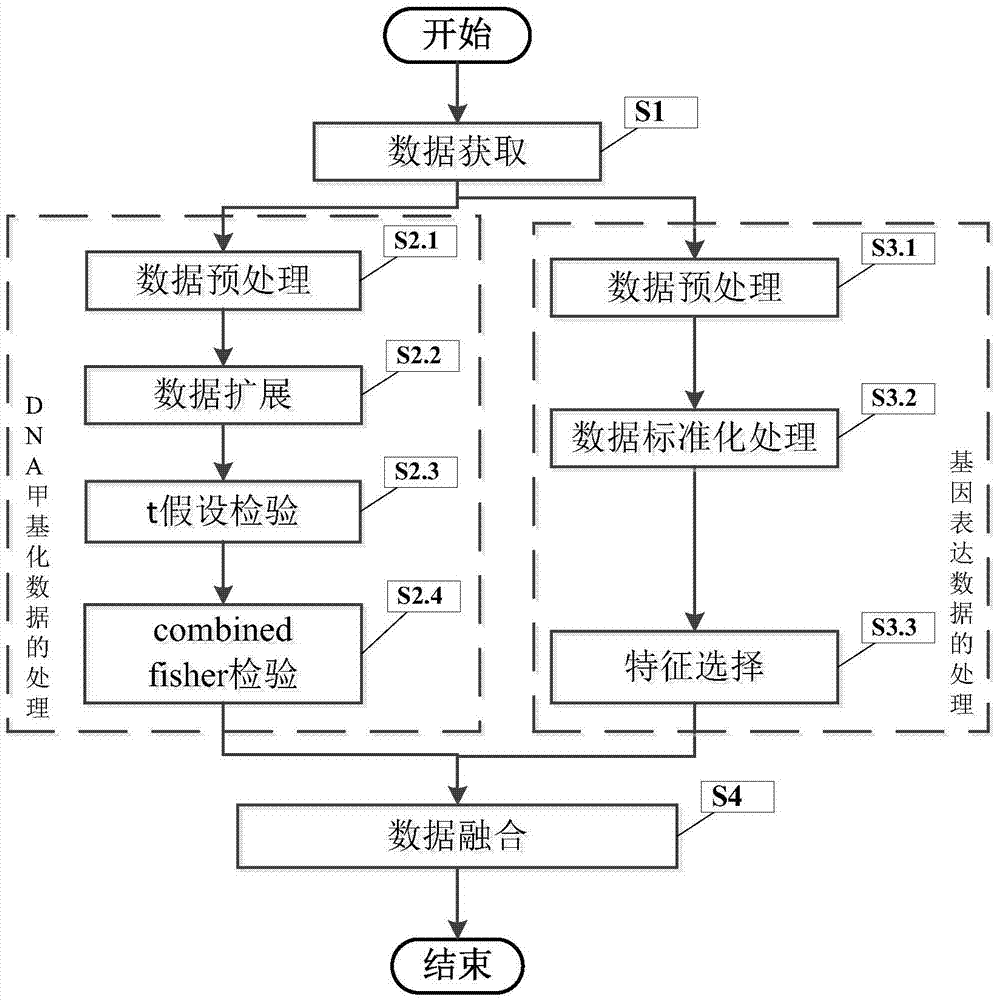
Fusion method for gene expression and methylation data
The invention discloses a fusion method for gene expression and methylation data. The fusion method includes the steps of firstly obtaining the gene expression data of a certain cancer and the DNA methylation data measured by a 450K chip from a database of cancer genome maps, then respectively performing pretreatment on the gene expression data and the DNA methylation data to obtain their respective differential gene, then cross-matching the two differential genes to obtain overlapping genes, and finally analyzing the pathways of the overlapping genes by a David online tool, and finding out cancer- and immune-related pathways in the significantly enriched pathways for the expansion of the DNA methylation data to obtain a greater number of genome-wide CpG sites.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Gene detection kit for prognosis risk evaluation of patients with liver cancer and application
ActiveCN108611419ALow degree of biased amplificationLittle mutual interferenceMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGene modelMathematical model
The invention relates to a gene detection kit for liver cancer grouping and prognosis risk evaluation and a mathematical model, and application thereof in liver cancer grouping and prognosis risk evaluation. The gene detection kit is characterized in that a liver cancer grouping and liver cancer prognosis risk evaluation model is built based on a second generation sequence detection technology anda TCGA (The Cancer Genome Atlas) database, and the result shows that liver cancer has two obviously-different prognosis subgroups, and a genetic group for prognosis risk evaluation of the liver cancer. According to the gene detection kit, a 6 gene model composed of CA9, CXCL5, G6PD, MMP12, MYBL2 and SLC1A5 is found, and the prognosis index is defined as PI=exp(p') / exp(1+p'), wherein p'=zCA9*1.64+zCXCL5*1.22+zMMP12*1.52+1.93*zMYBL12+0.76*zSLC1A5+2.43*zG6PD-3.86. The model is capable of recognizing and determining different liver cancer prognosis subgroups and reflecting the prognosis risk ofpatients with liver cancer.
Owner:MENGCHAO HEPATOBILIARY HOSPITAL OF FUJIAN MEDICAL UNIV
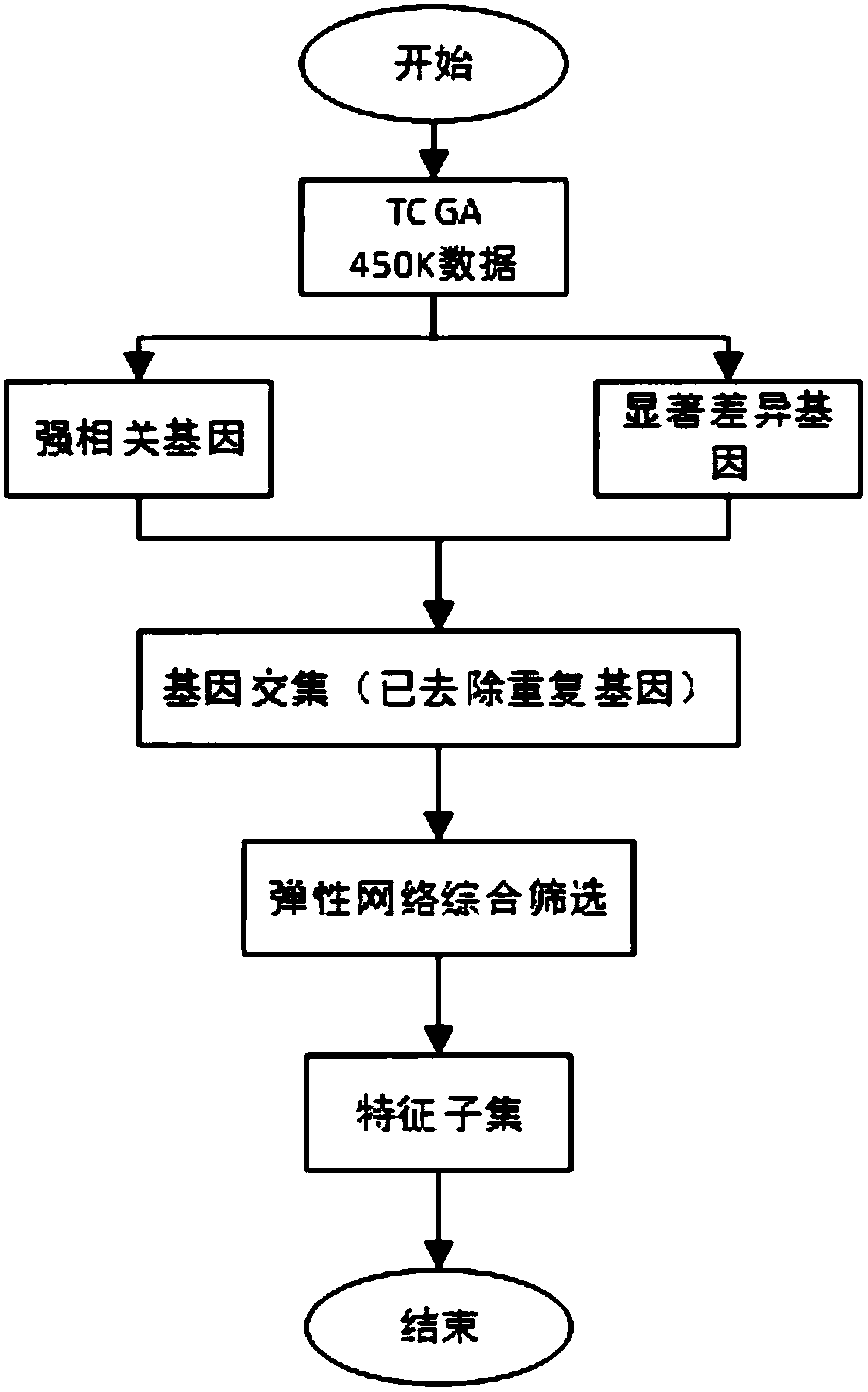
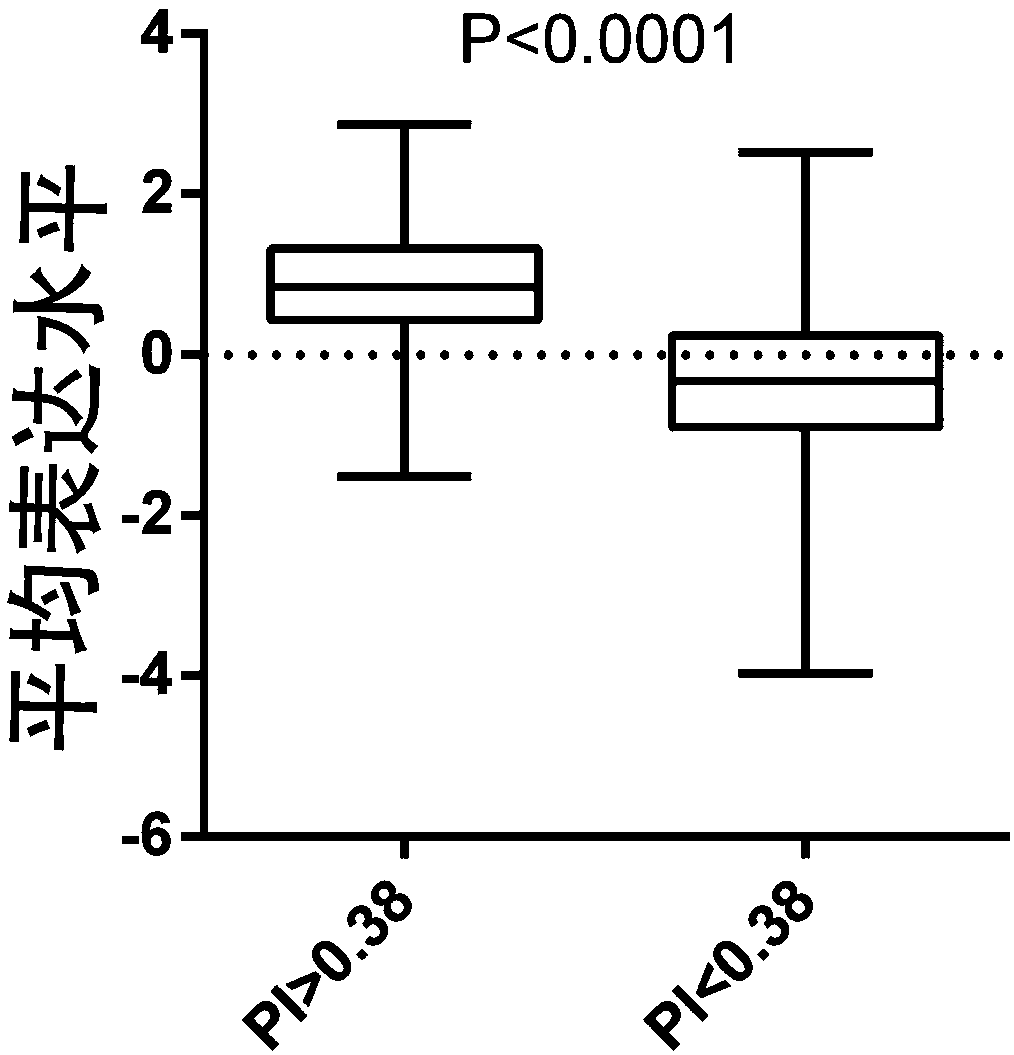
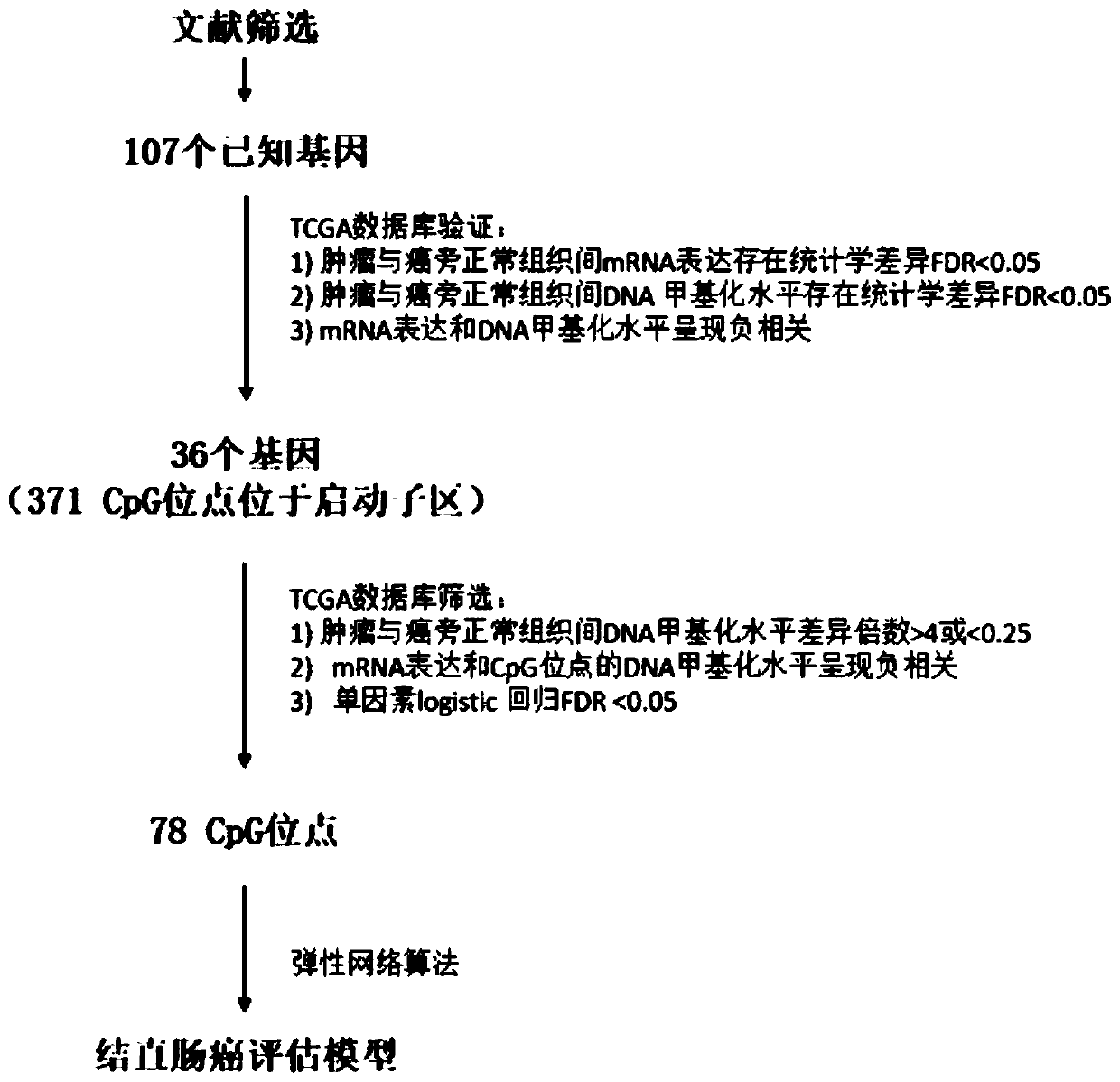
Colorectal cancer judgment model for distinguishing cancer tissue of colorectal cancer from paracancerous normal tissue and establishing method of colorectal cancer judgment model
The invention discloses a colorectal cancer judgment model for distinguishing cancer tissue of colorectal cancer from paracancerous normal tissue and an establishing method of the colorectal cancer judgment model. The method includes: selecting 107 genes related to colorectal cancer with methylation differences in the promoter region of the genes; verifying the expression of the 107 genes and the level of methylation in the promoter region by the aid of patients with both methylation and gene expression data in a TCGA (the cancer genome atlas) database, wherein a total of 37 genes are successfully verified, and 371 CpG sites are located in the promoter regions thereof; screening the 371 CpG sites by the aid of the data in the TCGA database, wherein a total of 78 CpG sites is selected; for the 78 CpG sites and on the basis of the data in the TCGA database, establishing the colorectal cancer judgment model by the aid of the elastic network algorithm. With the method, a theoretical basis is provided for blood screening of colorectal cancer in the future.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
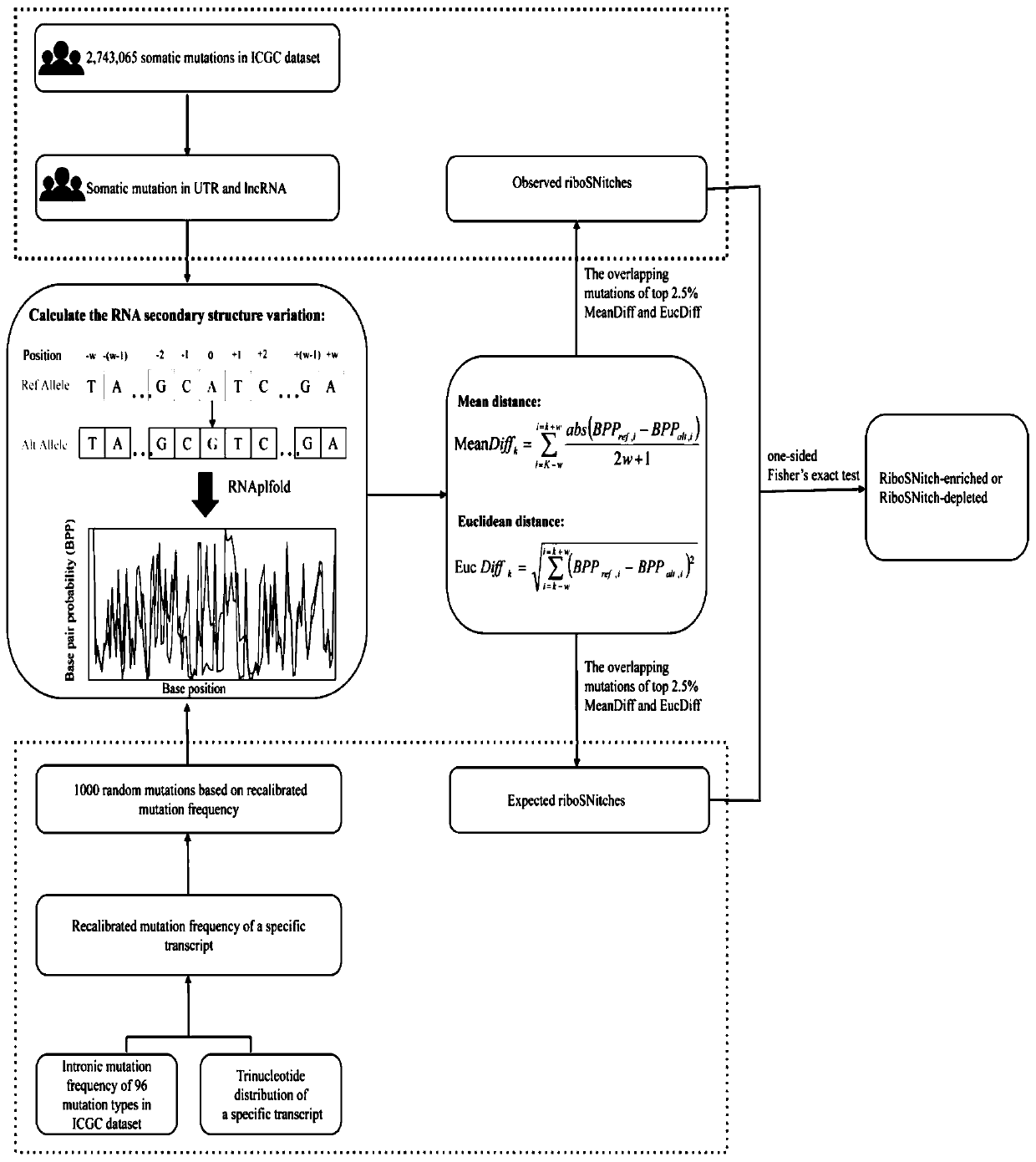
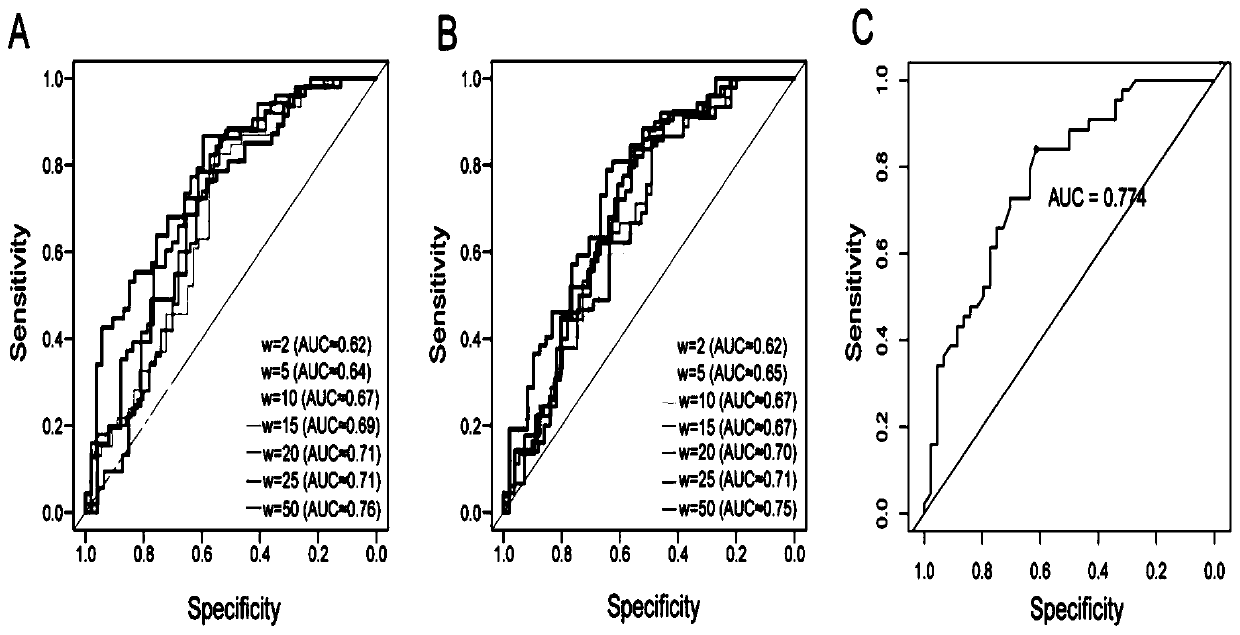
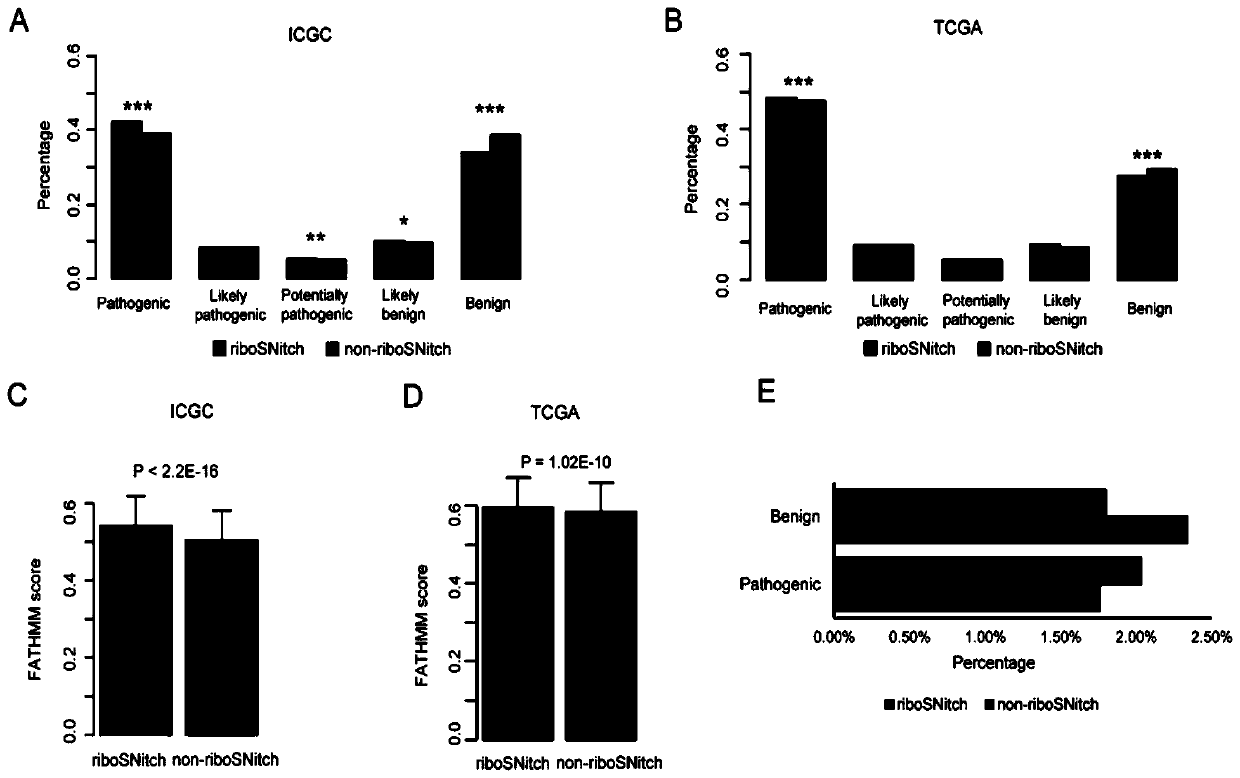
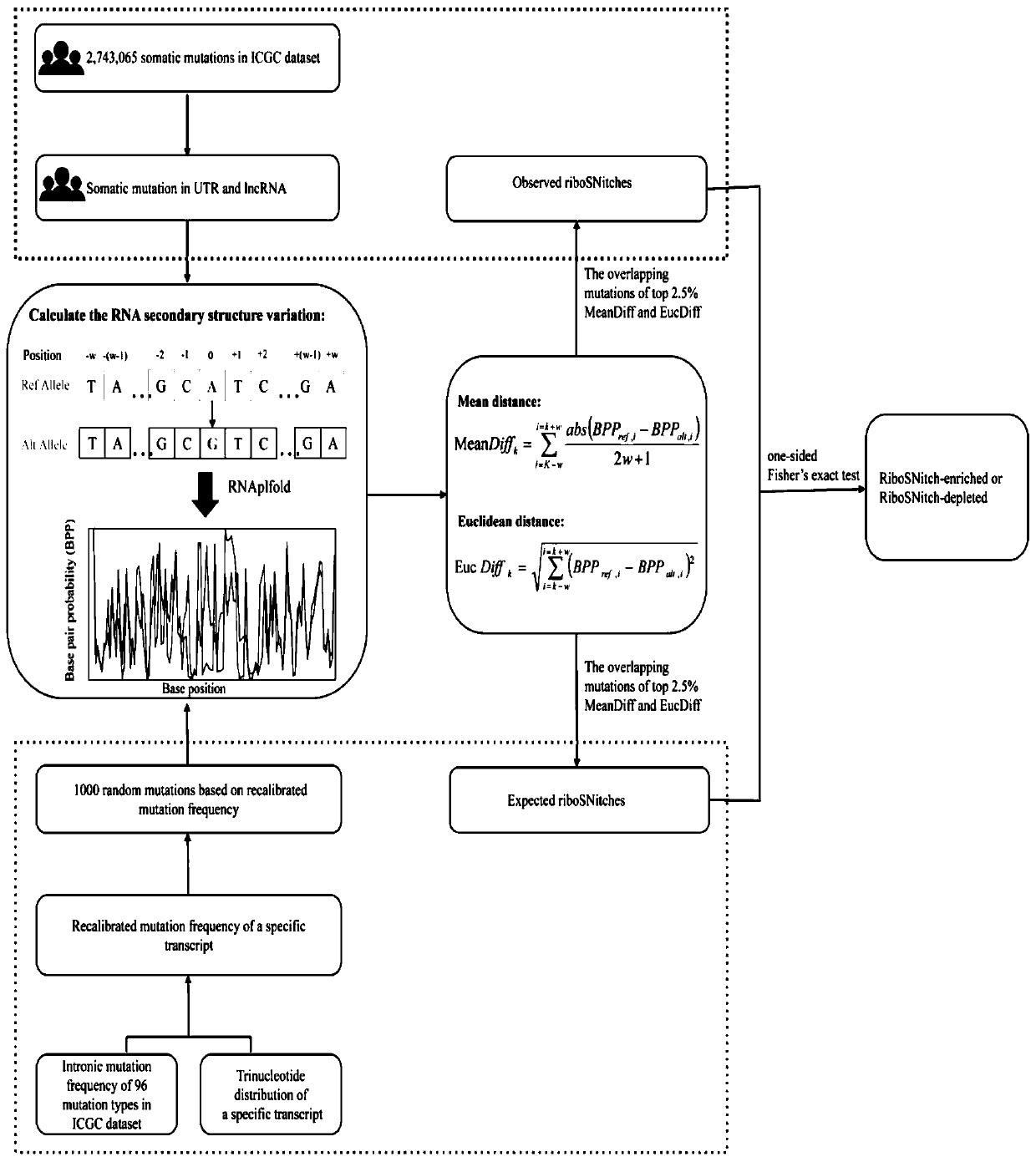
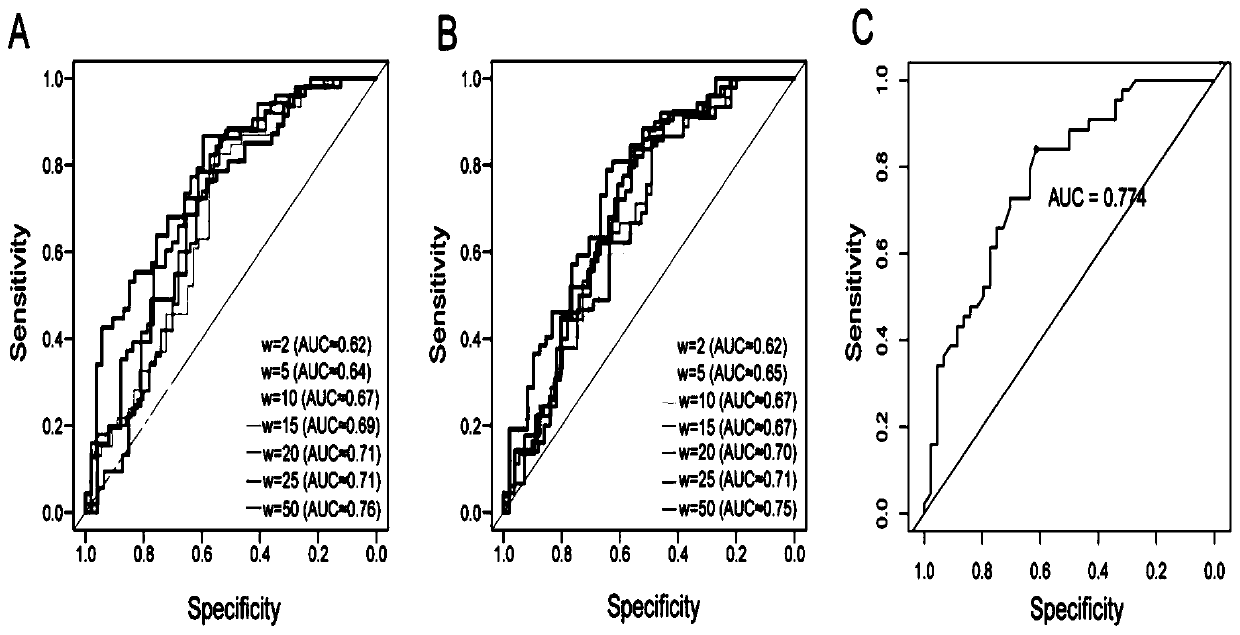
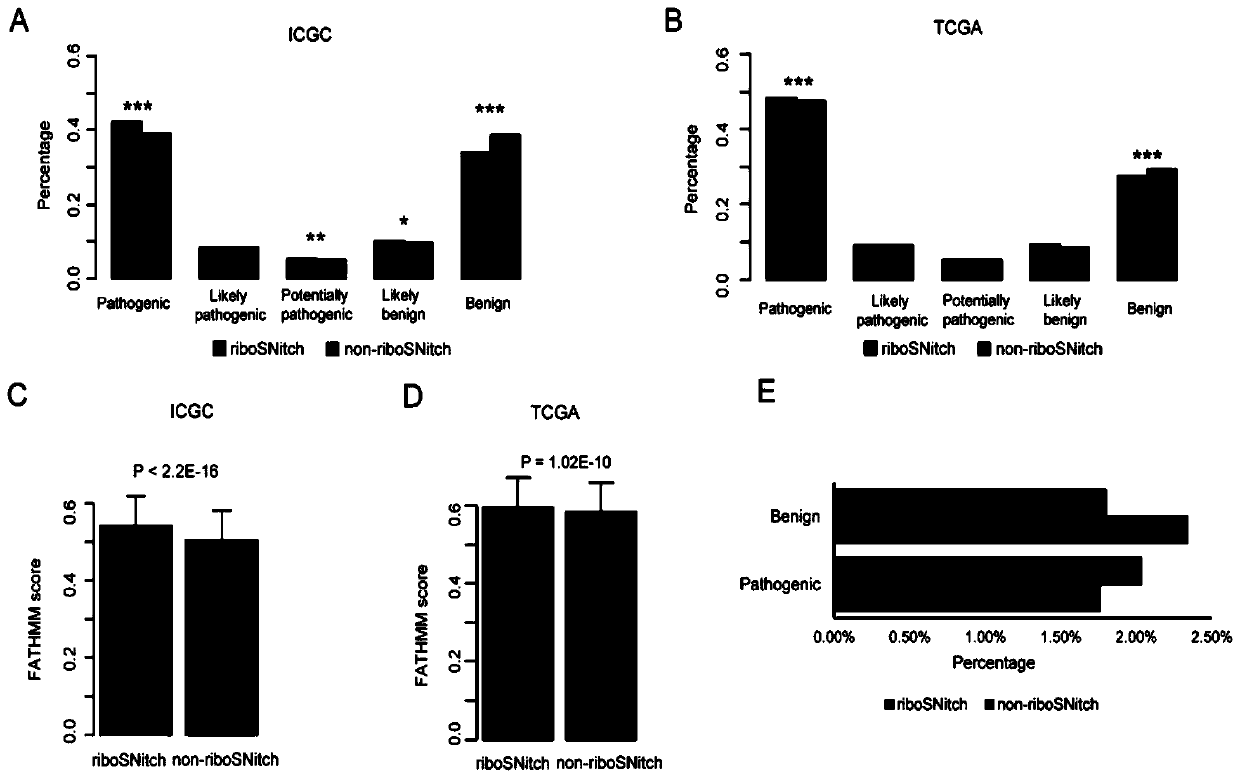
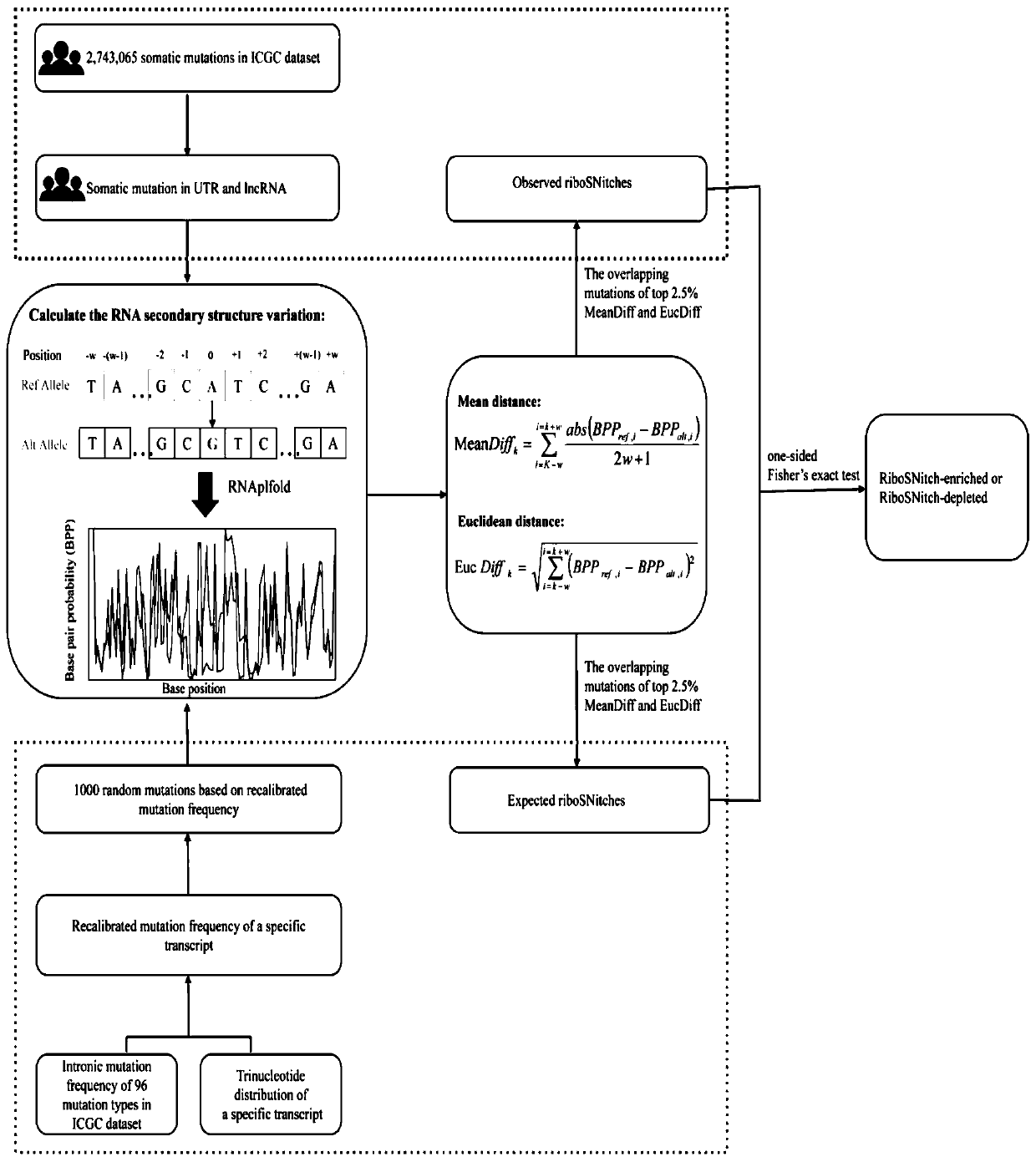
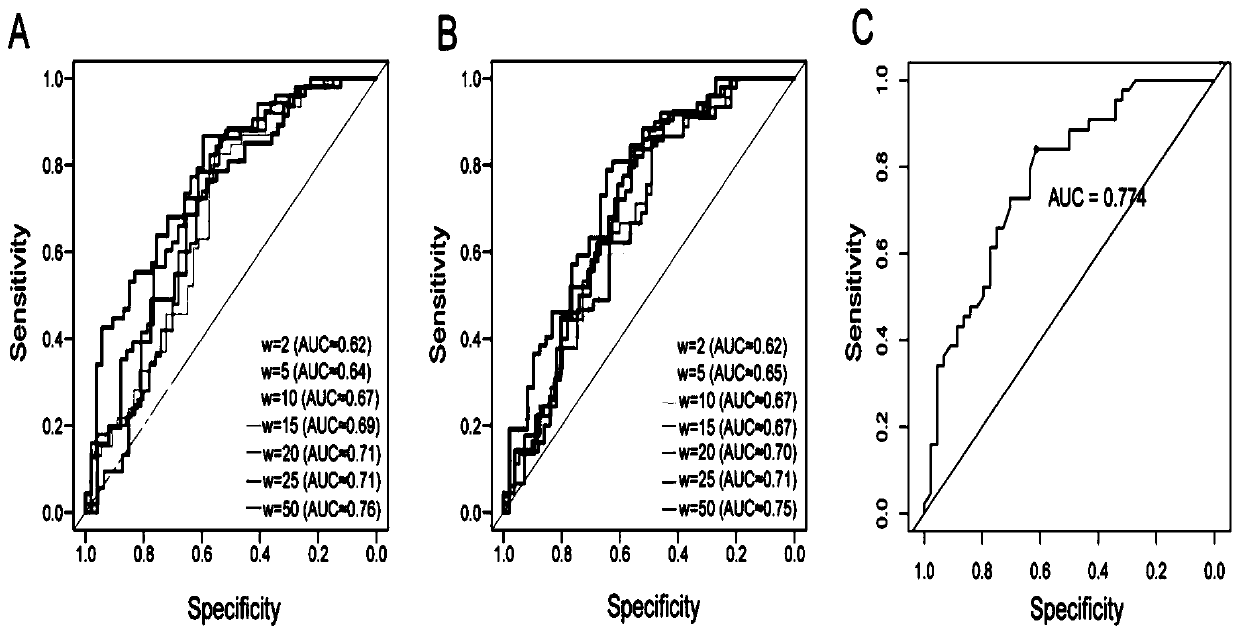
Method and device for predicting degree of influence of mutation on secondary structure of RNA based on EucDiff value
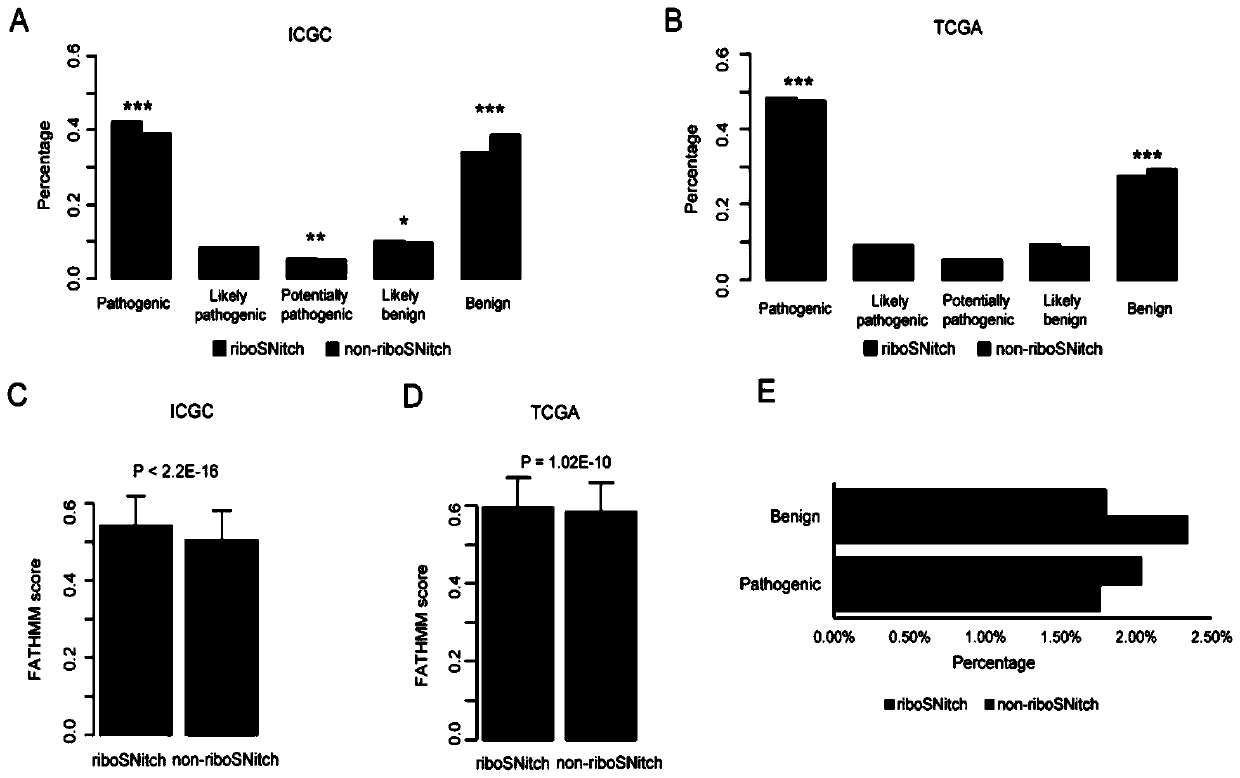
The invention relates to the technical field of detection of the influence of mutation on the secondary structure of RNA, and particularly relates to a method and a device for predicting the degree ofinfluence of mutation on the secondary structure of RNA based on a EucDiff value. The invention also provides a method for predicting a riboSNitch element rich or deleted in a cancer genome. The present invention further provides software named SNIPER, used for predicting the riboSNitch and identifying non-coding elements rich or absent in tumors.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
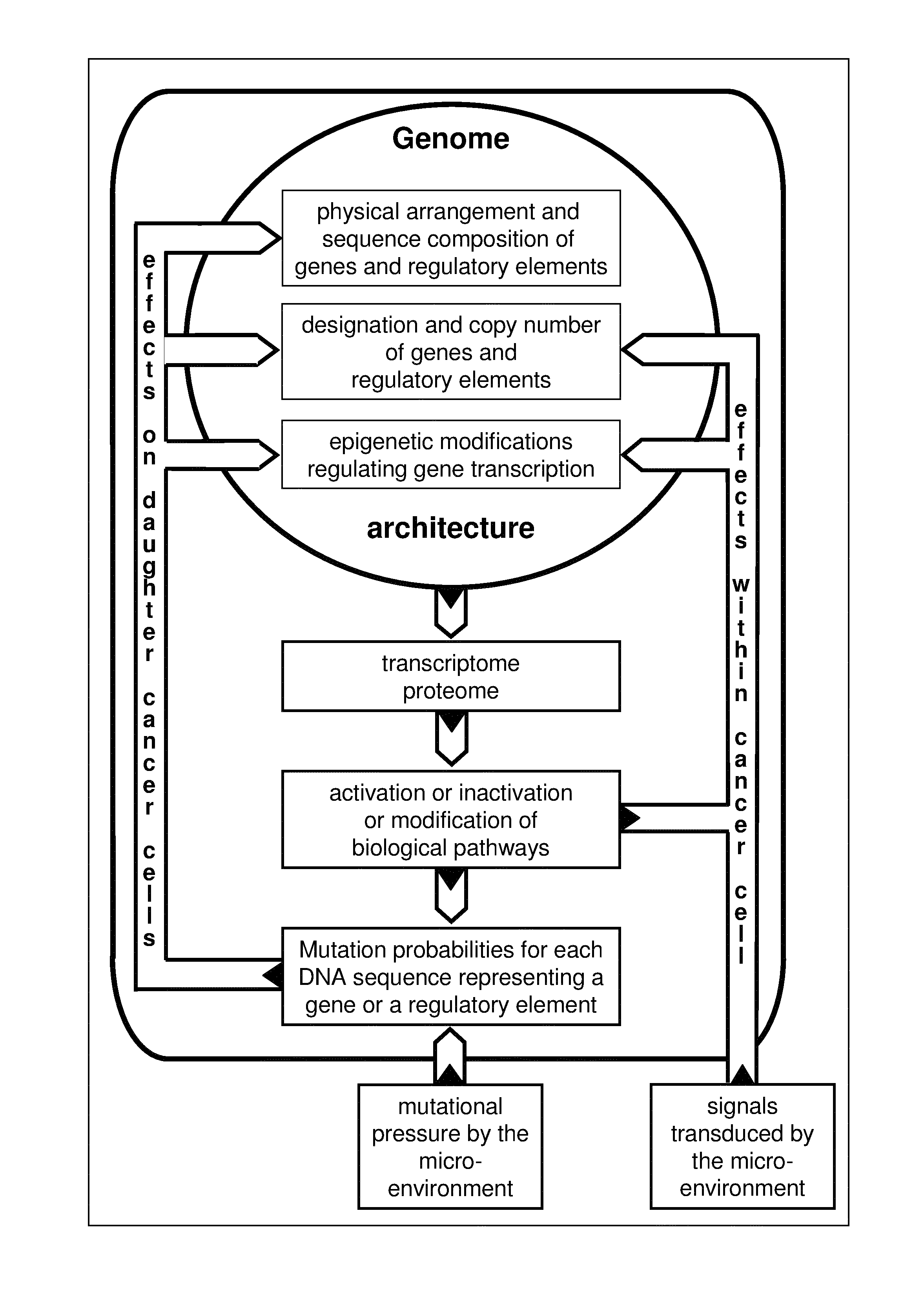
Algorithm for modification of somatic cancer evolution
Owner:RUBBEN ALBERT
Method and system for selecting customized drug using genomic nucleotide sequence variation information and survival information of cancer patient
PendingCN108475300AIncrease credibilityQuick and easy to provideProteomicsGenomicsGenomic mutationLymphatic Spread
The present invention relates to a method and system for selecting a customized drug using information of cancer genomic nucleotide sequence variations and patient survival and, more specifically, toa method and system for selecting a customized anticancer therapeutic drug using variation information of a synthetic cancer survival gene among cancer genomic nucleotide sequence variations. The method and system for customized anticancer therapy of the present invention using information of cancer genomic mutations and patient survival or the evaluation of invasive or metastatic ability of cancer cells or tissues correspond to a technique to effectively select an anticancer therapeutic drug having a good therapeutic effect and prognosis according to the individual through the variation analysis of synthetic cancer survival gene pairs, which is derived from the information of cancer genomic nucleotide sequence variations and cancer survival and metastasis, and the method and system of thepresent invention have high reliability and can provide related information promptly and simply.
Owner:爱富体人
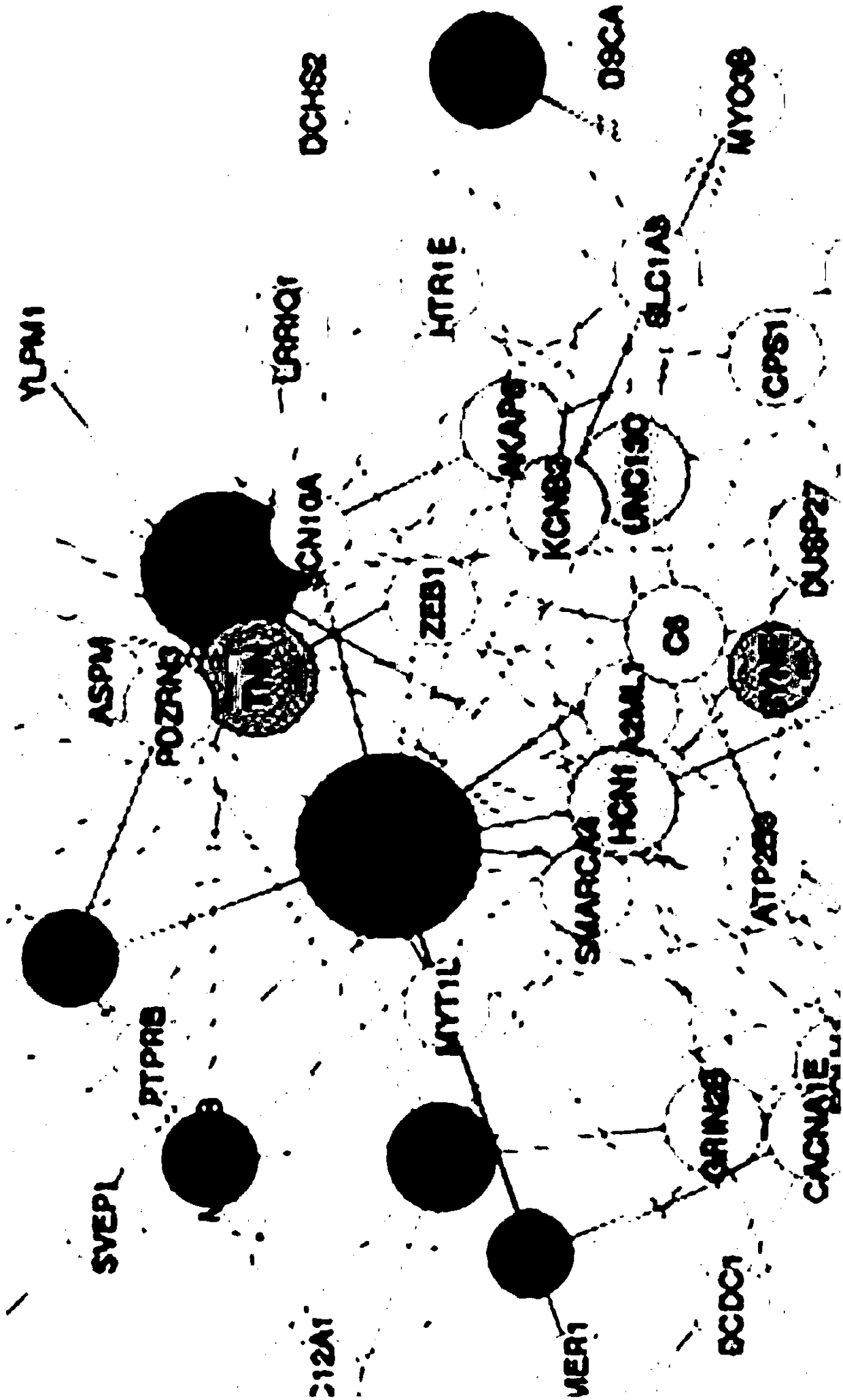
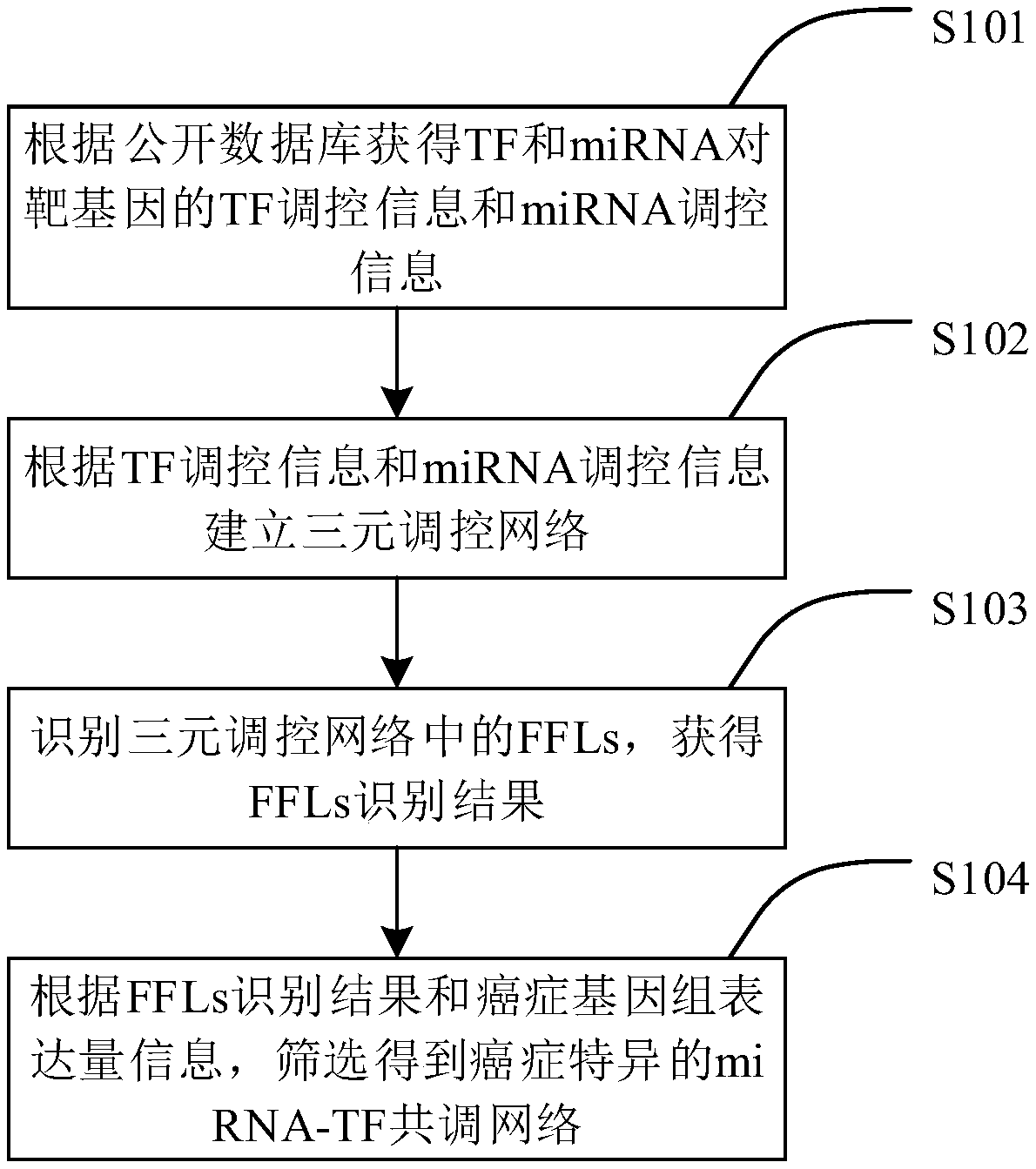
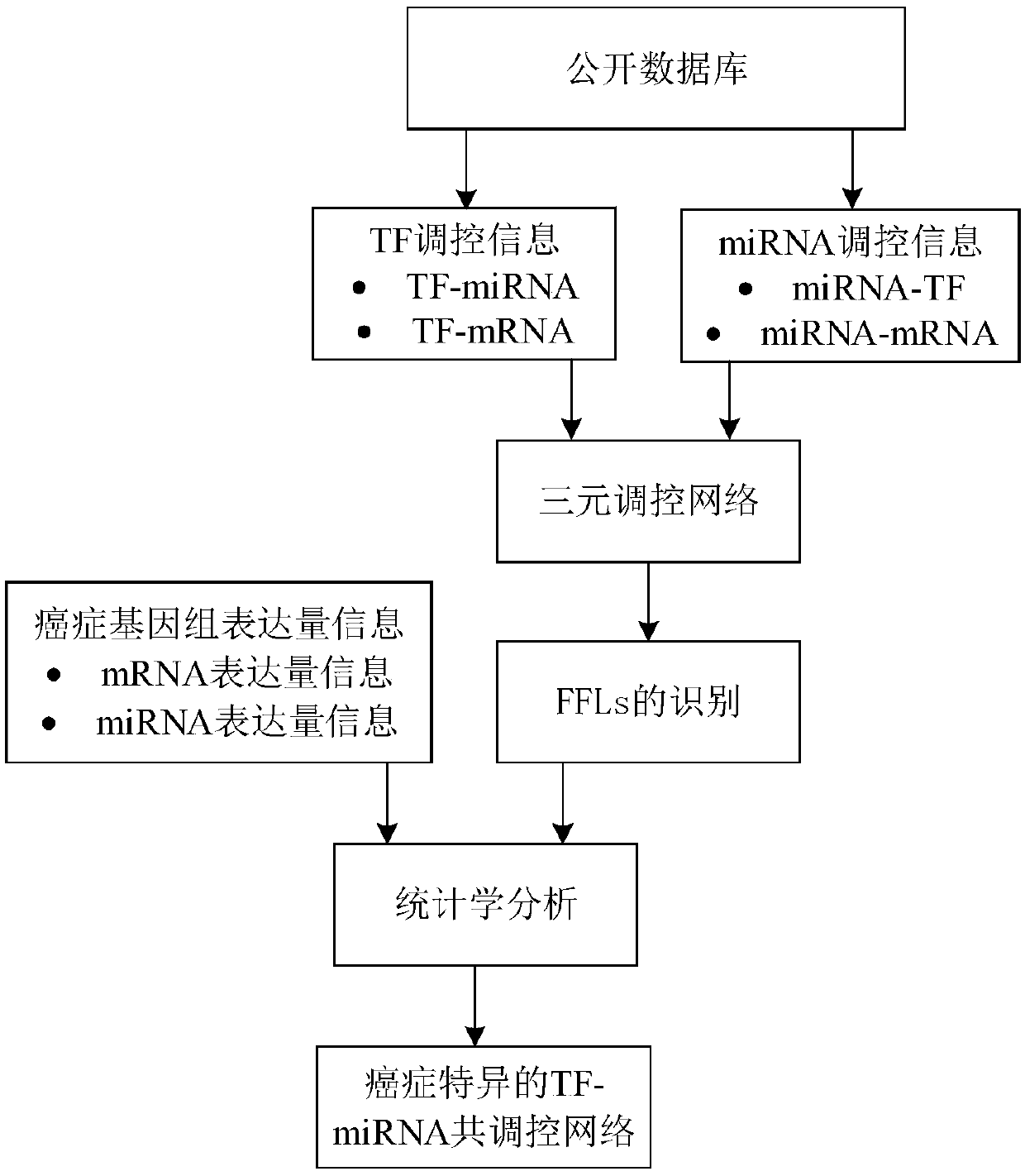
Specific cancer coregulatory network establishment method and device
The invention provides a specific cancer coregulatory network establishment method and device and belongs to the technical field of regulatory network establishment. The method comprises the followingsteps: according to a public databank, acquiring TF regulatory information and miRNA regulatory information of TF and miRNA upon target genets; according to the TF regulatory information and the miRNA regulatory information, establishing a ternary regulatory network; recognizing FFLs in the ternary regulatory network, and acquiring FFLs recognition results; according to the FFLs recognition results and cancer genome expression information, screening, thereby obtaining a specific cancer miRNA-TF coregulatory network. According to the method, the ternary regulatory network of TF, miRNA and target genes is established, together with gene expression information, the miRNA-TF coregulatory network is obtained, and the accuracy of miRNA-TF coregulatory relationships is improved.
Owner:ACADEMY OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI
Standard substance for extensive oncogene detection and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111334505AFit closelyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationInsertion deletionCancer genome
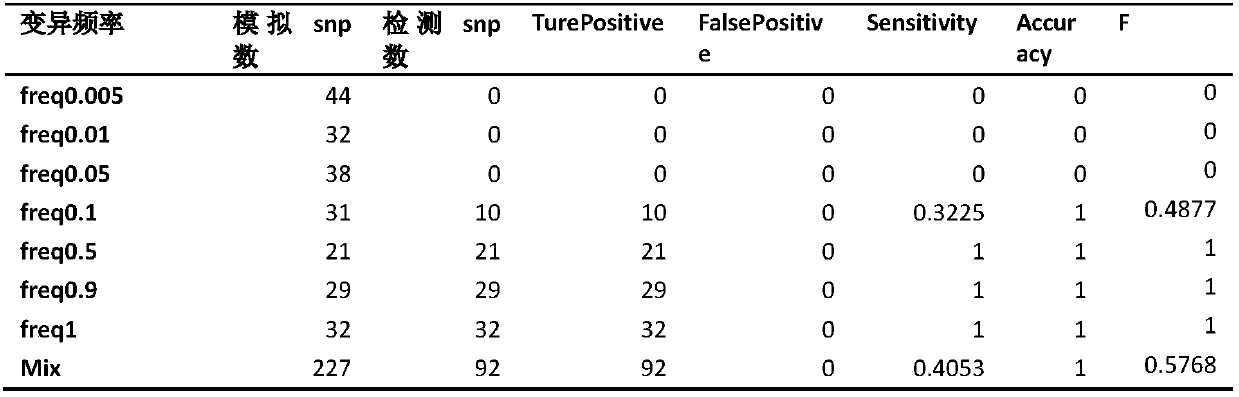
The invention provides a standard substance for extensive oncogene detection. The standard substance includes 13 mutation sites verified by Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR) and 500X high-throughput whole exome sequencing verified site information, has more than 700 variation sites of over 330 genes, also includes common structural variations of cancer genomes, such as common gene SNV, base insertion deletion and the like, has corresponding mutation site frequencies within a range of 1% to 100%, and is wide in application scene and platform. The standard substance can be used for evaluating stability, specificity and sensitivity of the working flow from sample extraction to biological information analysis, evaluating each sample treatment method and detecting performance differences among platforms. The standard substance belongs to a major innovation in the industry, and has wide application prospect and great industrial application value.
Owner:菁良科技(深圳)有限公司
Method for predicting element being rich in riboSnitch or with lost riboSnitch in cancer genome and related equipment
The invention relates to the technical field for detecting influence of mutation to an RNA secondary structure, and particularly to a method for predicting an element being rich in riboSnitch or with lost riboSnitch in a cancer genome and related equipment. The invention provides software which is named as SNIPER. The software can be used for predicting the riboSNitch and identifying a non-coded element which is rich in riboSNitch or has lost riboSnitch in a tumor. The content of the invention includes introduction to the software SNIPER and firstly analyzes the riboSnitch in somatic cell mutation in a cancer.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method for predicting influence degree of mutation on RNA secondary structure based on MeanDiff value and related equipment
The invention provides a method for predicting the influence degree of mutation on an RNA secondary structure based on a Mean Diff value and related equipment. The present invention also provides methods of predicting the enrichment or deletion of riboSNitch elements in a cancer genome. The invention also provides software named as SNIPER, and the software can be used for predicting riboSNitch andidentifying a non-coding element which is rich in riboSNitch or lacks riboSNitch in a tumor.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
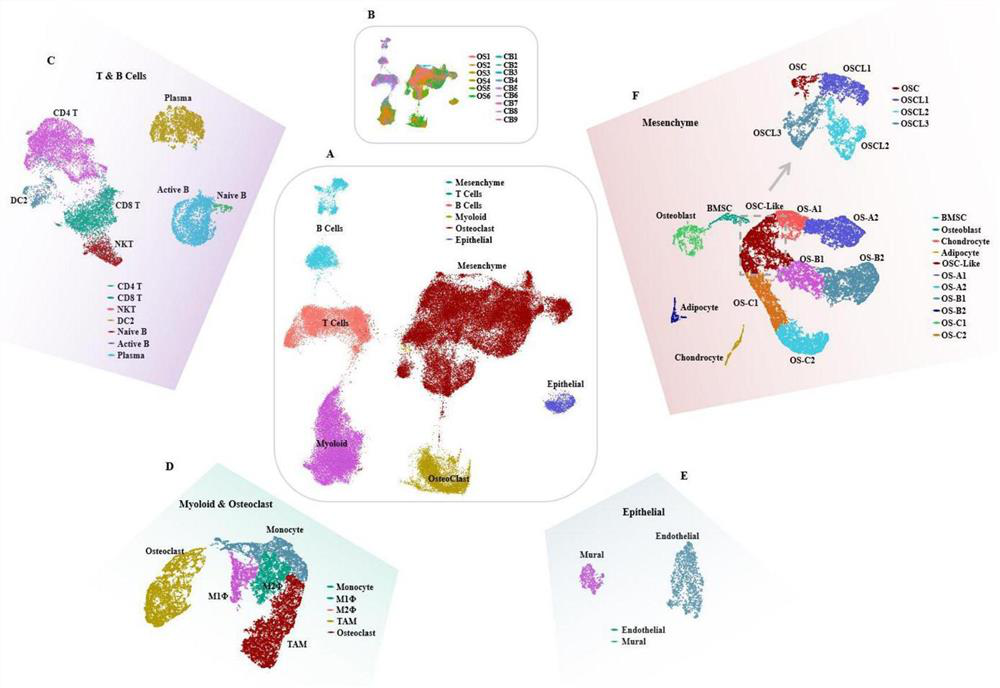
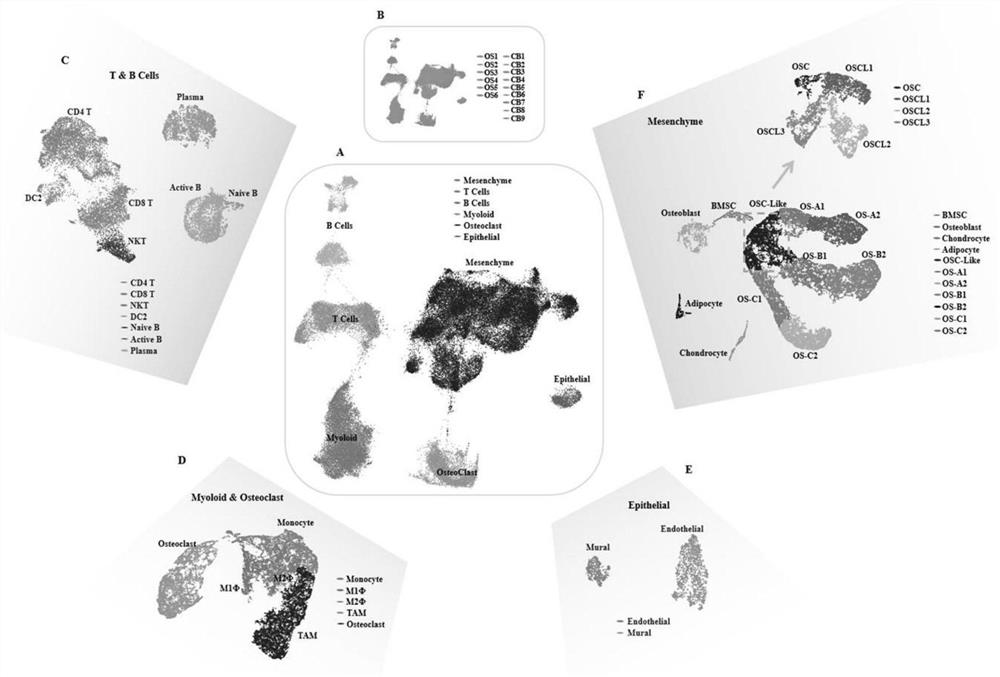
Gene for osteosarcoma typing and osteosarcoma prognosis evaluation and application thereof
ActiveCN113355418AMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisConventional OsteosarcomaCancer genome
The invention provides a gene for osteosarcoma typing and osteosarcoma prognosis evaluation and application thereof. Aiming at tumor heterogeneity, the difference of cytodynamics and molecular characteristics between conventional osteosarcoma and normal cancellous bone is compared, the obvious differentiation direction of osteosarcoma cells is detected based on a single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) technology, or a gene detection kit, a gene detection chip technology or an immunohistochemical method, and the possible interaction between each cell type in the tumor microenvironment is researched. According to the differentiation direction of osteosarcoma cells, conventional osteosarcoma can be divided into three types, microenvironment characteristics of each type are described, and prognosis of type-B genotyping is verified according to cancer genome atlas (TCGA) data.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHANGZHENG HOSPITAL +1
Kit for detecting gene mutation related to anti-oxidative stress pathway of lung adenocarcinoma
ActiveCN113444793AEffectively guide individualized treatmentAvoid wastingMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsAntioxidative stressCancer genome
The invention relates to a kit for detecting gene mutation related to an anti-oxidative stress pathway of lung adenocarcinoma. The kit contains detection reagents for detecting the expression quantity of the following genes: RP11-539L10.2, AKR1C2, RP11-572H4.1, TRIM16L, RARA, SESN2, RP5-827L5.2, CTD-2139B15.5, Metazoa_SRP, snoU13, RP11-545H22.1, KRT8P30, TALDO1, TRAPPC13P1, GS1-388B5.2, RP11-267L5.1, TRAV11, RP11-699A7.1 and AL132671.1. Compared with the prior art, the kit has the advantages that the genes related to the anti-oxidative stress pathway are screened through RNA sequencing, LASSO and binary classification Logistic regression, the score Score is constructed, the cut-off value of the corresponding score in the lung adenocarcinoma is obtained through ROC curve analysis, and the kit can be used for predicting mutation of the genes (KEAP1, NFE2L2 and CUL3) related to the anti-oxidative stress pathway in the lung adenocarcinoma. The specific gene mutation of the lung adenocarcinoma is predicted by utilizing the expression quantity of the gene composition, the prediction method has the advantages of high accuracy and good specificity through verification of a TCGA (The Cancer Genome Atlas) database, an experiment and a multi-omics database, and the kit has a very good application prospect.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
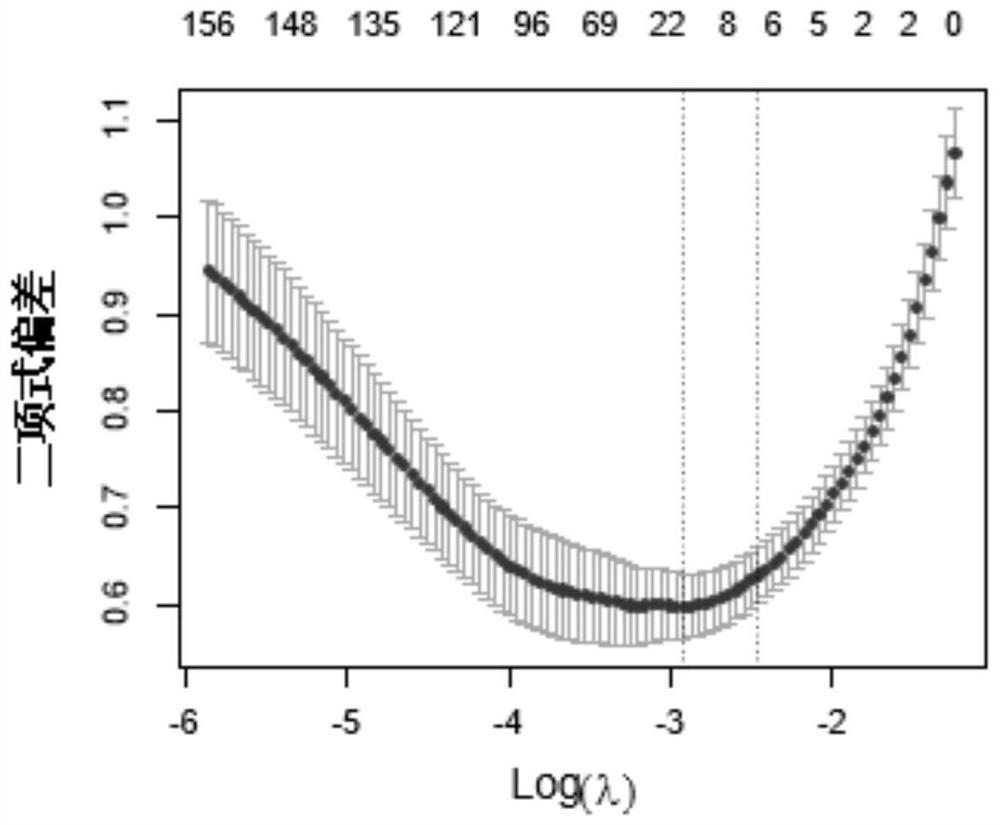
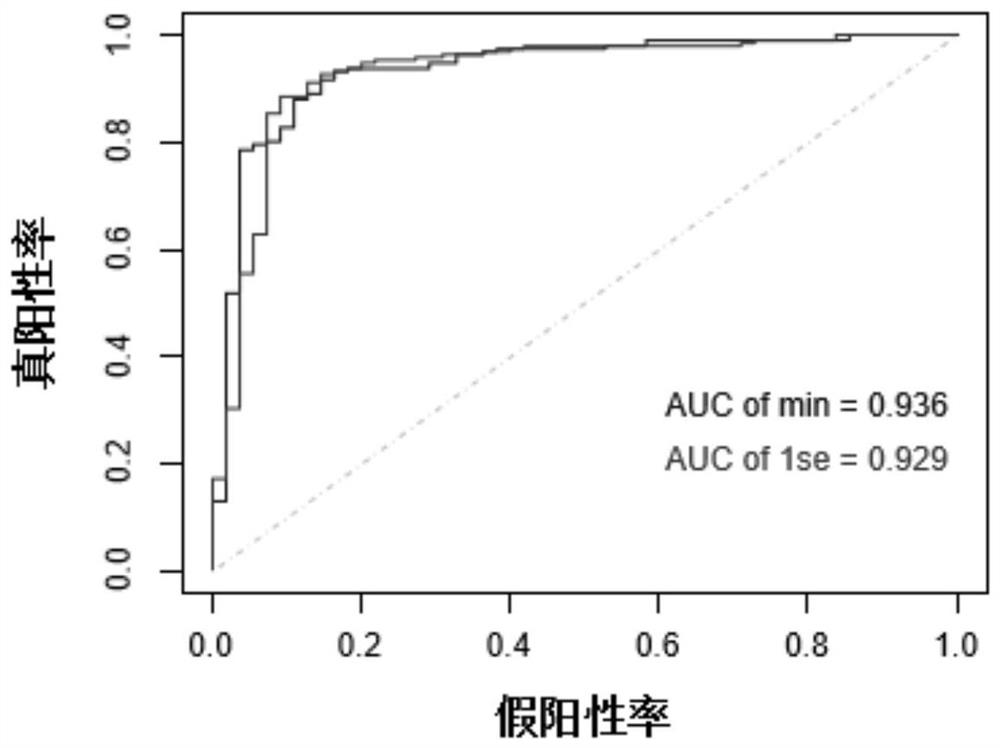
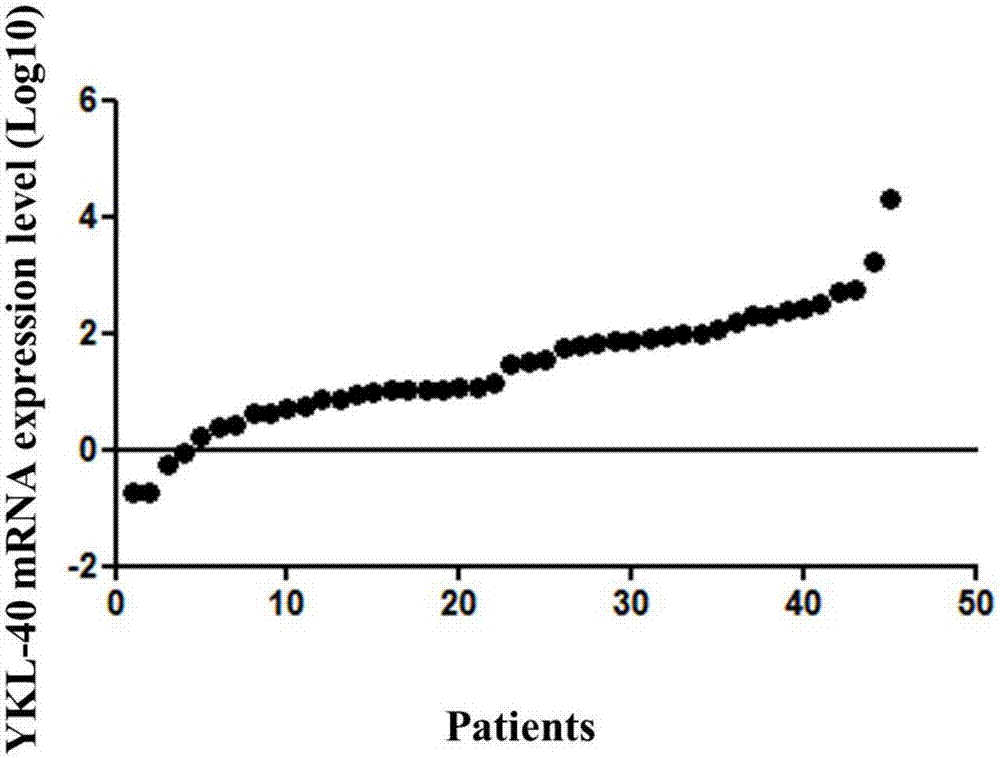
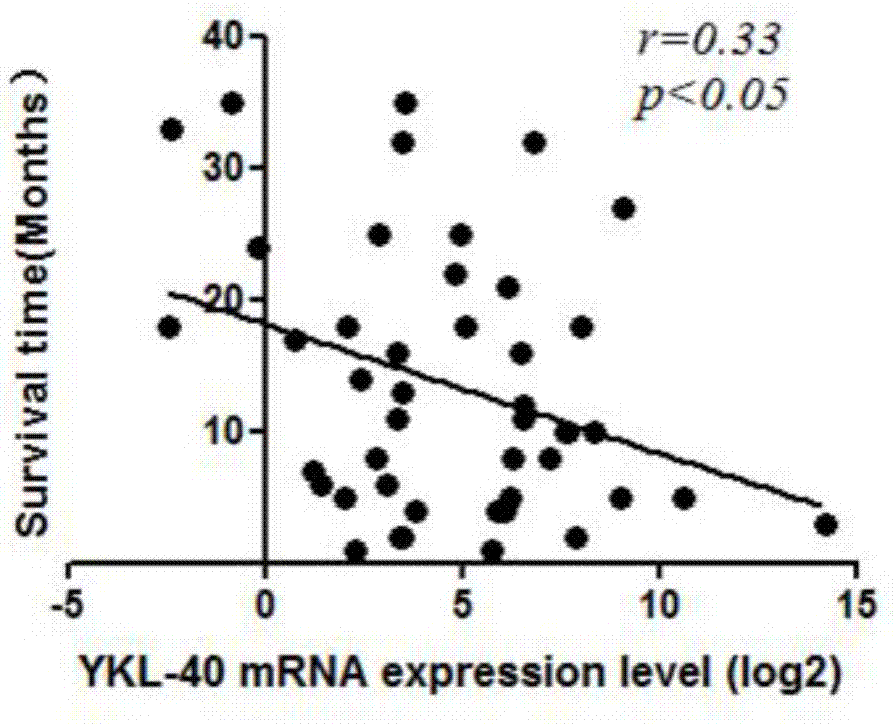
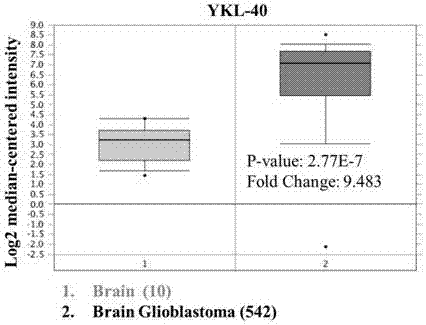
Application of YKL-40 as glioblastoma biomarker
The invention relates to application of human cartilage glycoprotein (YKL-40) as a glioblastoma biomarker. The glioblastoma (Glioblastoma, GBM) patient is low in survival rate and poor in prognosis. Effective biomarker and monitoring method are absent at present. The invention finds that the overall YKL-40 meso-position expression is obviously increased (Fold change=9.483, P<0.0001) by analyzing the YKL-40 mRNA gene expression data of the glioblastoma patient in a TCGA (The Cancer Genome Atlas) database. 45 IV-stage Chinese people glycoprotein clinic samples are further collected, and after qPCR process is adopted for quantitatively analyzing the YKL-40 expression and the prognosis correlation analysis is performed, the YKL-40 mRNA transcriptional level of 41 patients is obviously increased and the patients are short in lifetime and poor in prognosis. The invention analyzes and verifies that the YKL-40 is closely related to the lifetime and poor prognosis, the YKL-40 can be used as a potential glioblastoma biomarker, and a qPCR or protein quantitative monitoring method can be utilized to indicate the lifetime and prognosis of the glioblastoma patient.
Owner:BEIJING TRICISIONBIO THERAPEUTICS INC
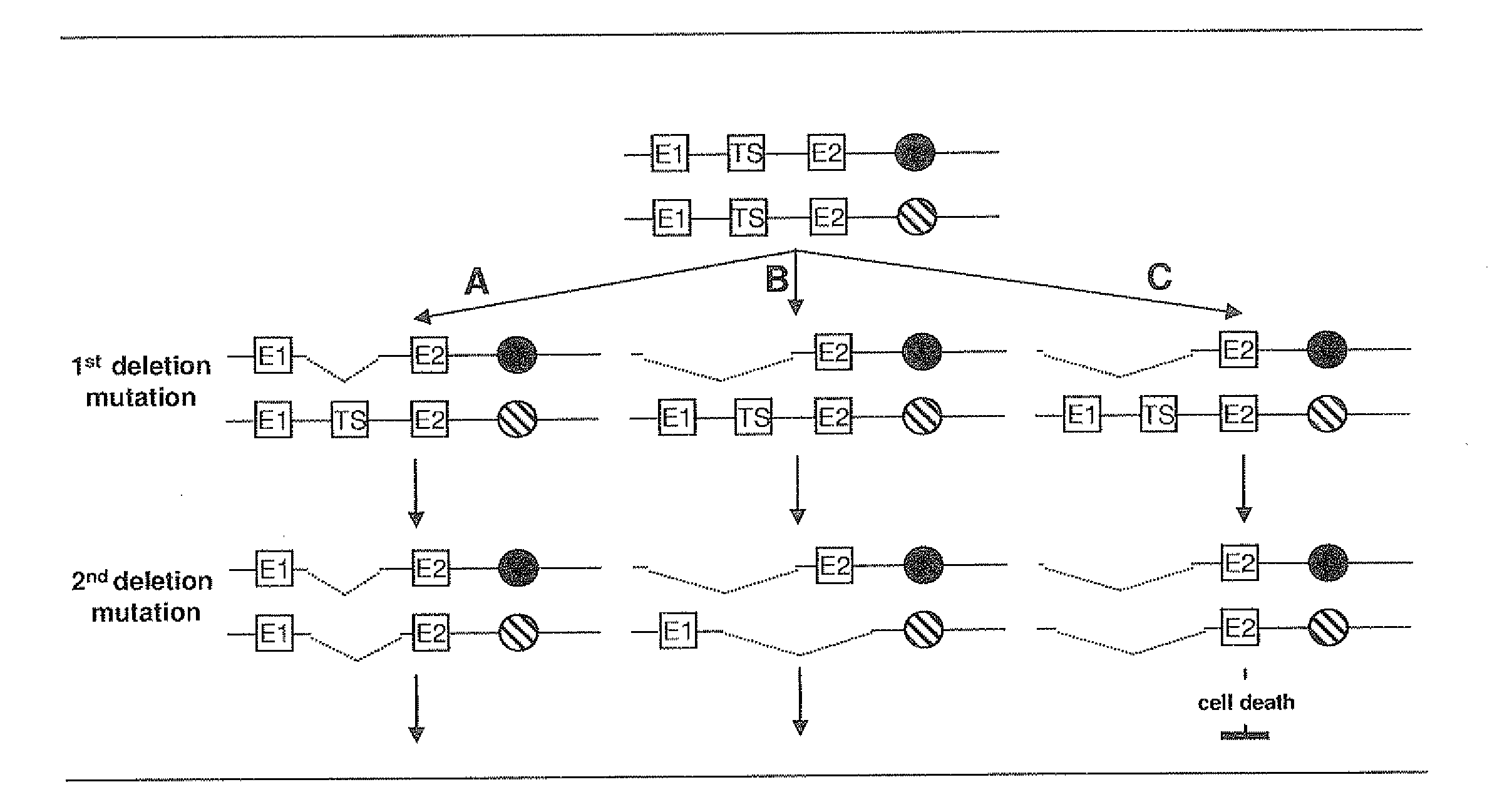
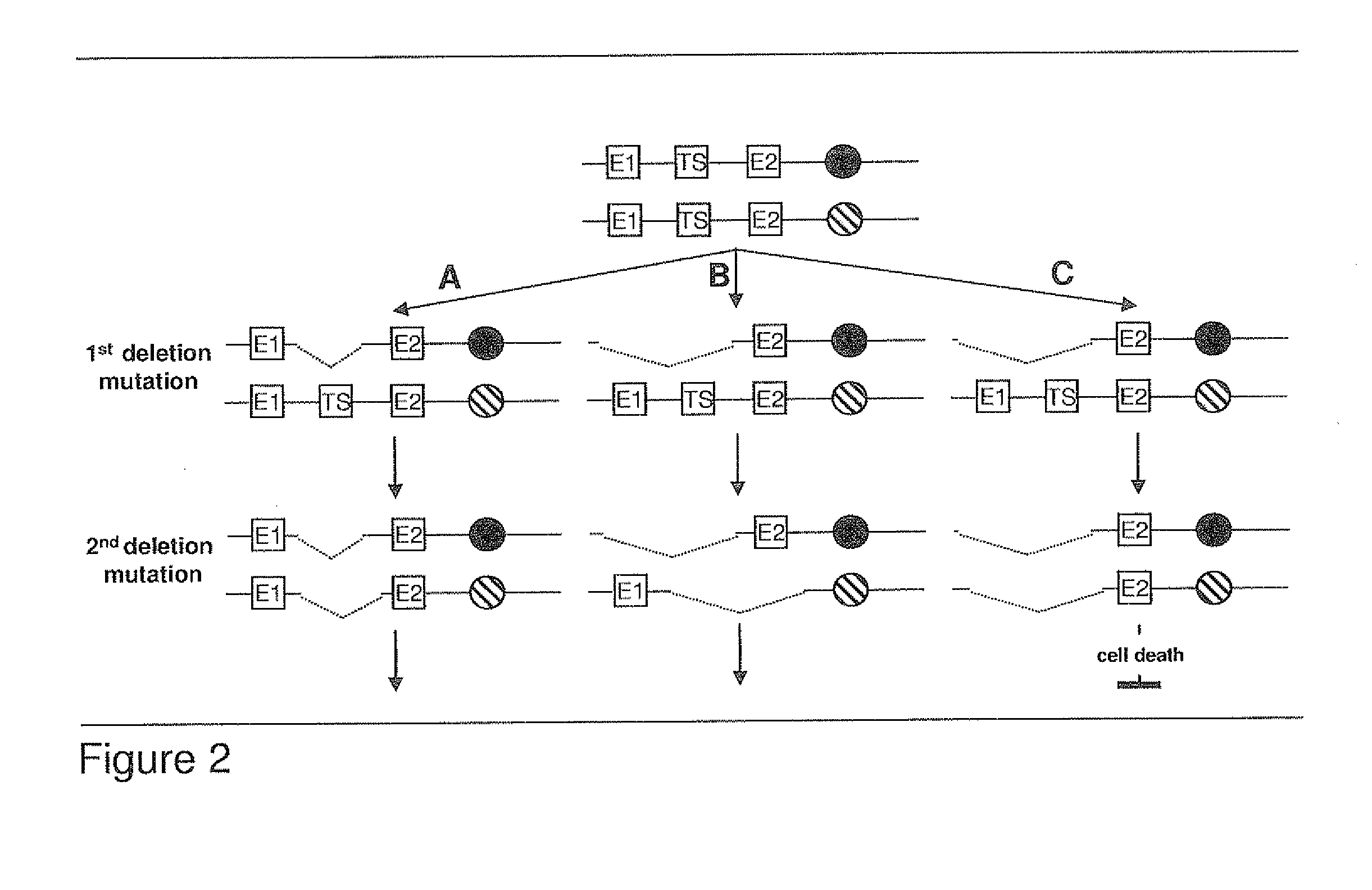
Algorithm for Modification of Somatic Cancer Evolution
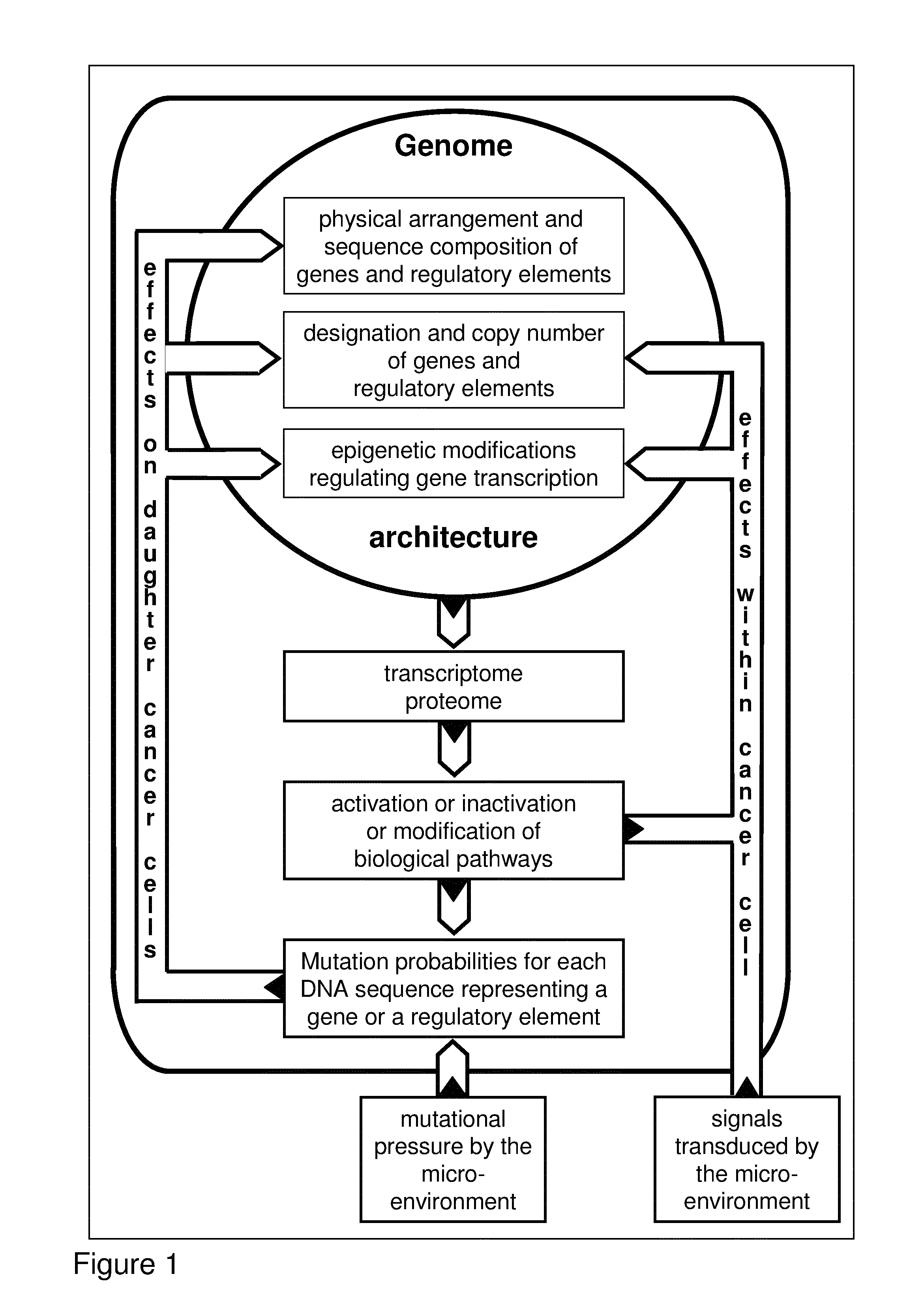
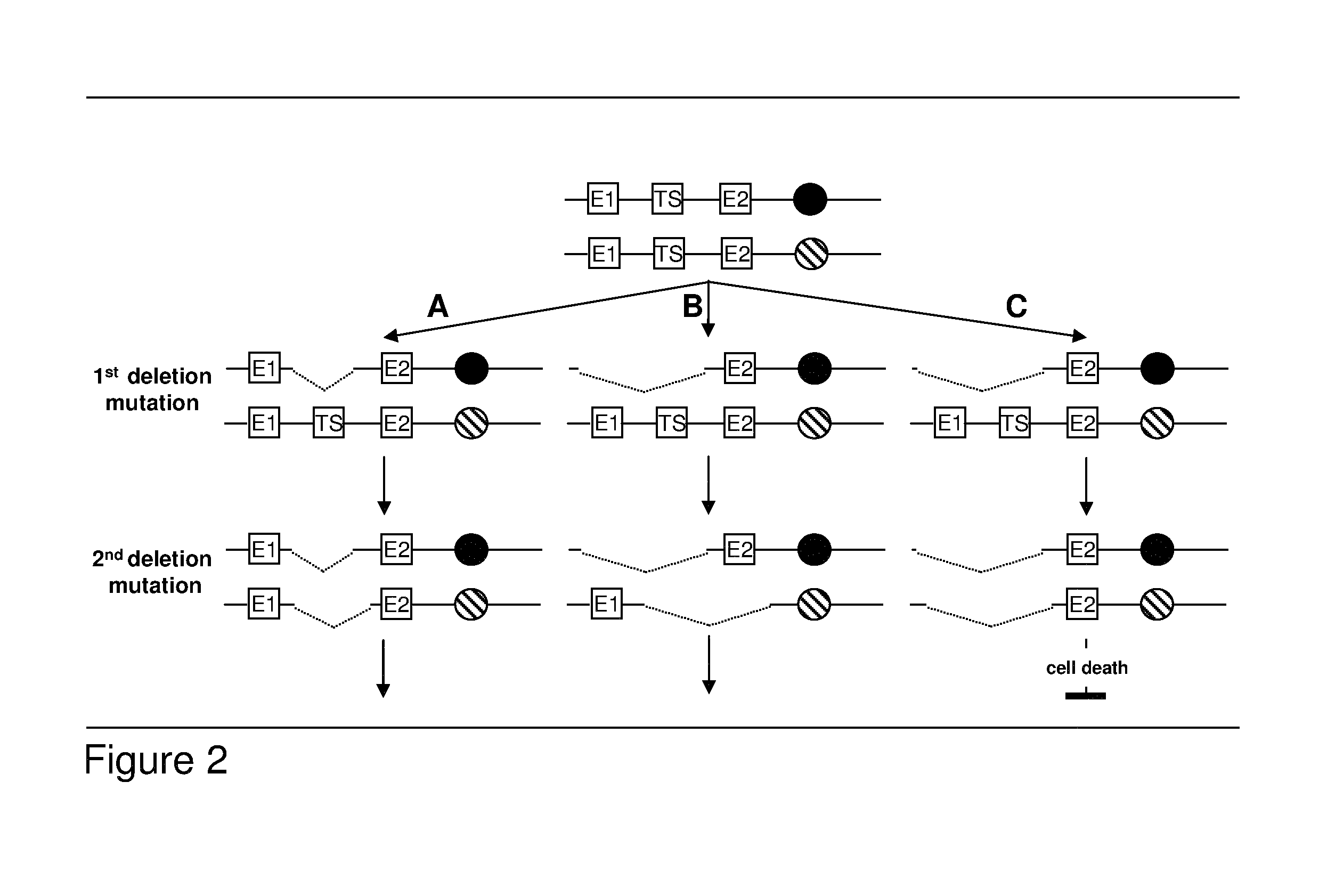
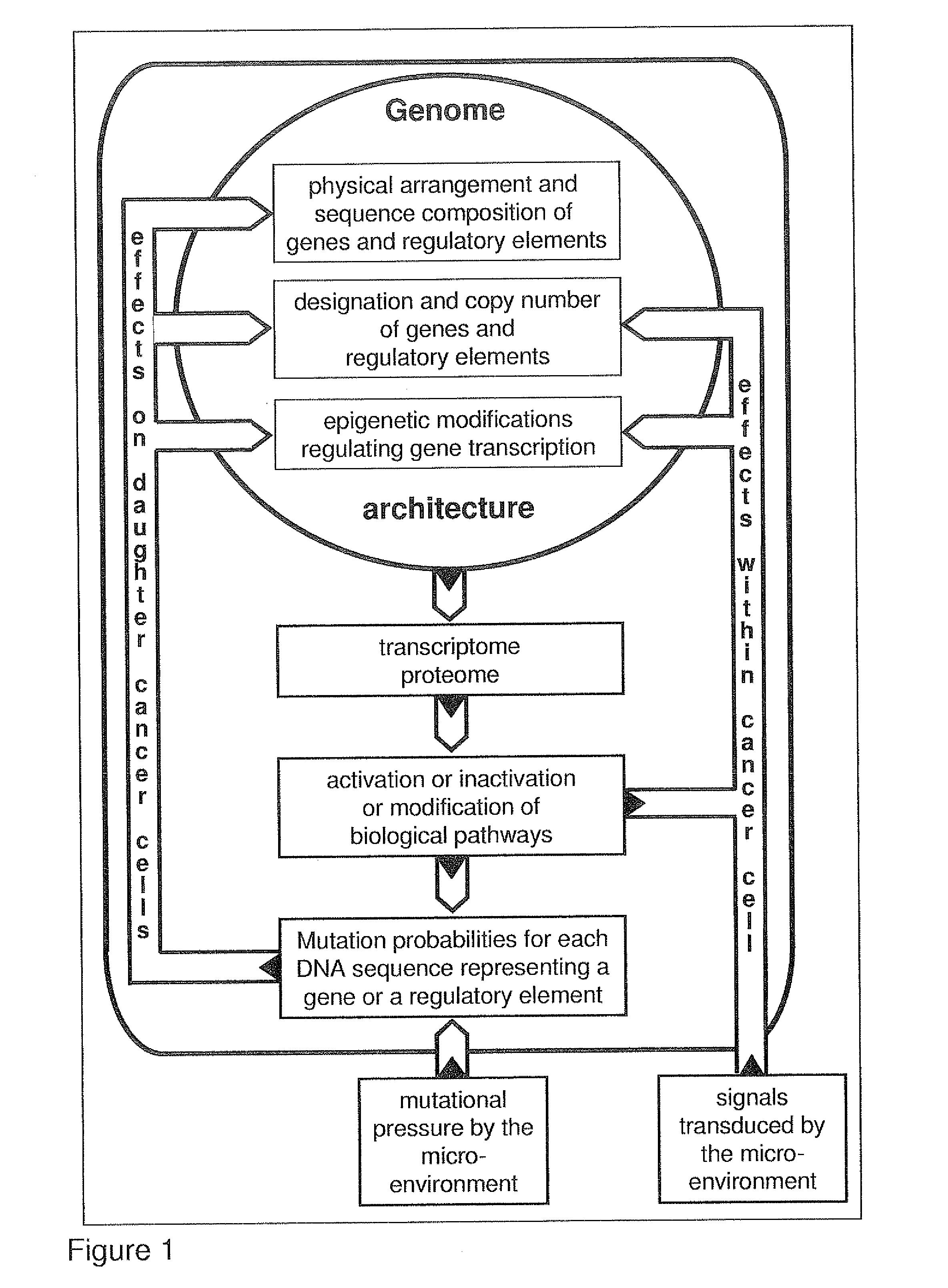
Most clinically distinguishable malignant tumors are characterized by specific mutations, specific patterns of chromosomal rearrangements and a predominant mechanism of genetic instability. It has been suggested that the internal dynamics of genomic modifications as opposed to the external evolutionary forces have a significant and complex impact on Darwinian species evolution. A similar situation can be expected for somatic cancer evolution as the key mechanisms encountered in species evolution such as duplications, rearrangements or deletions of genes also constitute prevalent mutation mechanisms in cancers with chromosomal instability. The invention is an algorithm which is based on a systems concept describing the putative constraints of the cancer genome architecture on somatic cancer evolution. The algorithm allows the identification of therapeutic target genes in individual cancer patients which do not represent oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes but have become putative therapeutic targets due to constraints of the cancer genome architecture on individual somatic cancer evolution. Target genes or regulatory elements may be identified by their designation as essential genes or regulatory elements in cancer cells of the patient but not in normal tissue cells or they may be identified by their impact on the process of somatic cancer evolution in individual patients based on phylogenetic trees of somatic cancer evolution and on the constructed multilayered cancer genome maps. The algorithm can be used for delivering personalized cancer therapy as well as for the industrial identification of novel anti-cancer drugs. The algorithm is essential for designing software programs which allow the prediction of the natural history of cancer disease in individual patients.
Owner:RUBBEN ALBERT
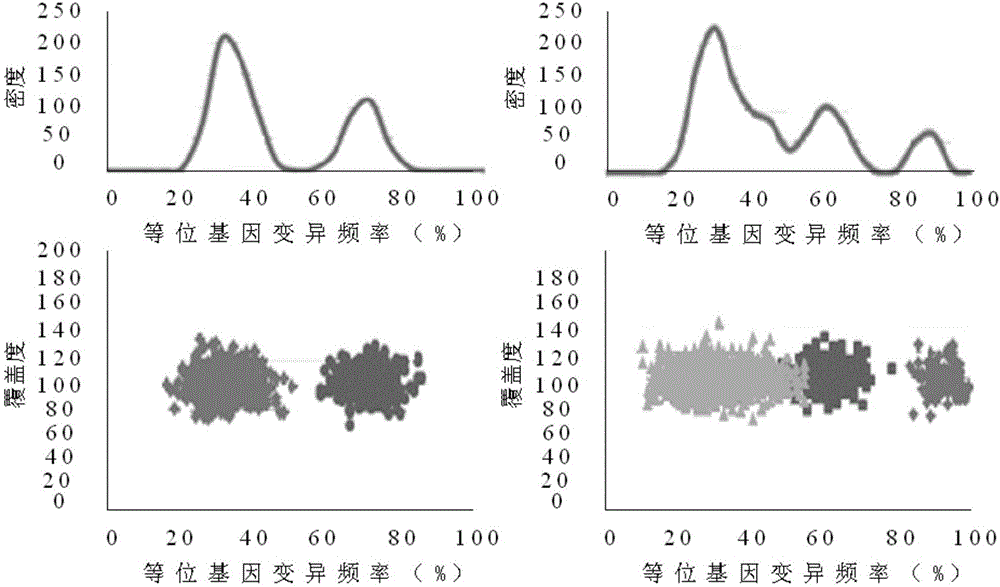
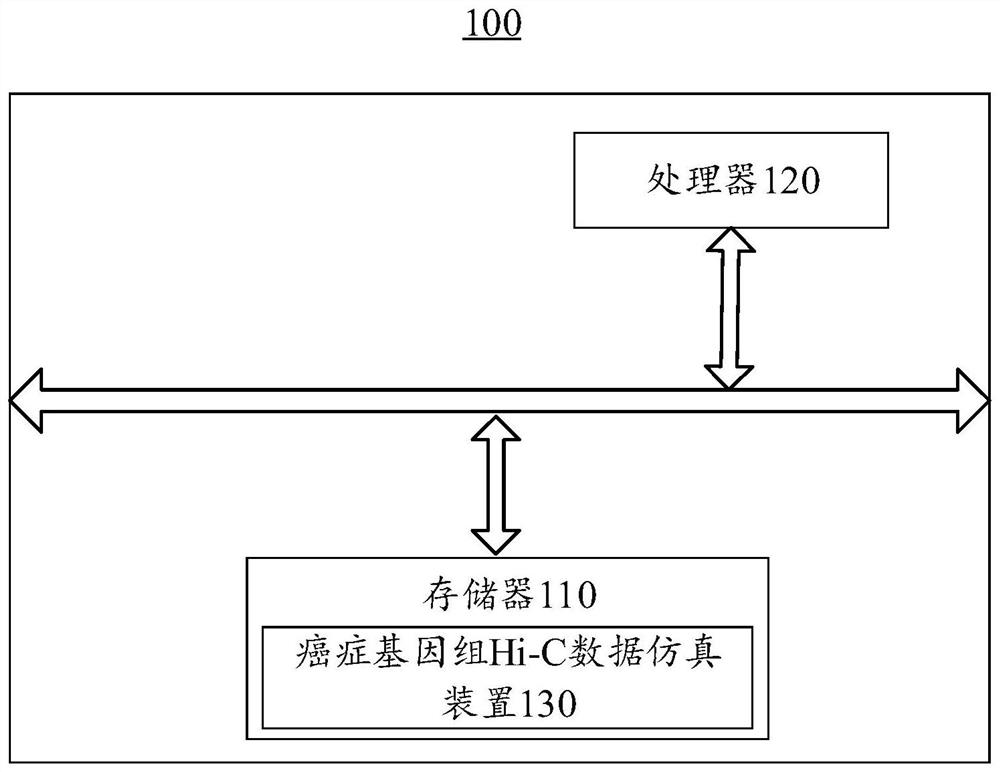
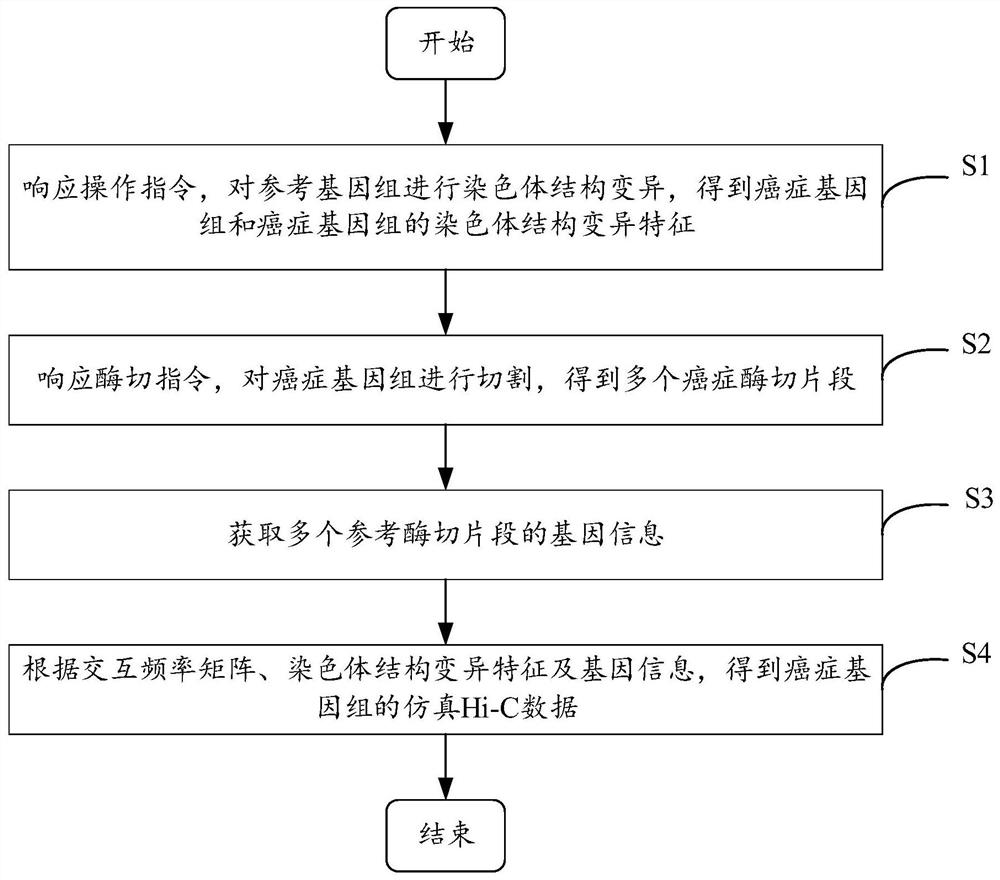
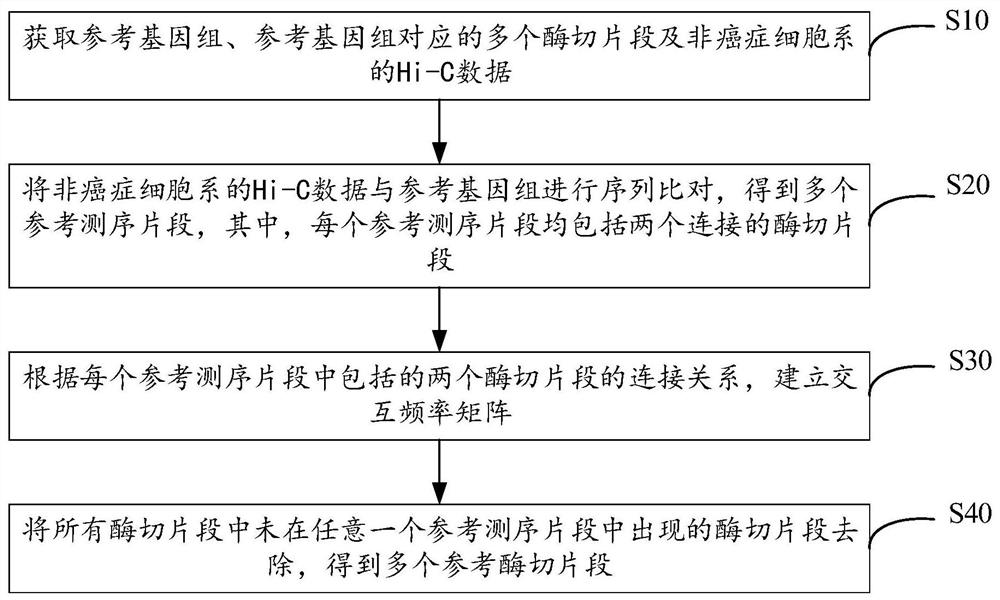
Cancer genome Hi-C data simulation method and device and electronic equipment
The embodiment of the invention provides a cancer genome Hi-C data simulation method and device and electronic equipment, and relates to the technical field of genomics. According to the method, a specified variation mode can be adopted to simulate chromosome structure variation of a cancer genome and the interaction frequency matrix and the gene information of the reference enzyme digestion fragment are taken as templates; the simulated Hi-C data of the cancer genome is obtained in combination with the chromosome structure variation characteristics, various variation conditions of the chromosome are simulated, and the interaction characteristics of different positions of the cancer genome can be reflected, so that the accuracy of simulating the Hi-C data of the cancer genome is improved.
Owner:ACADEMY OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI
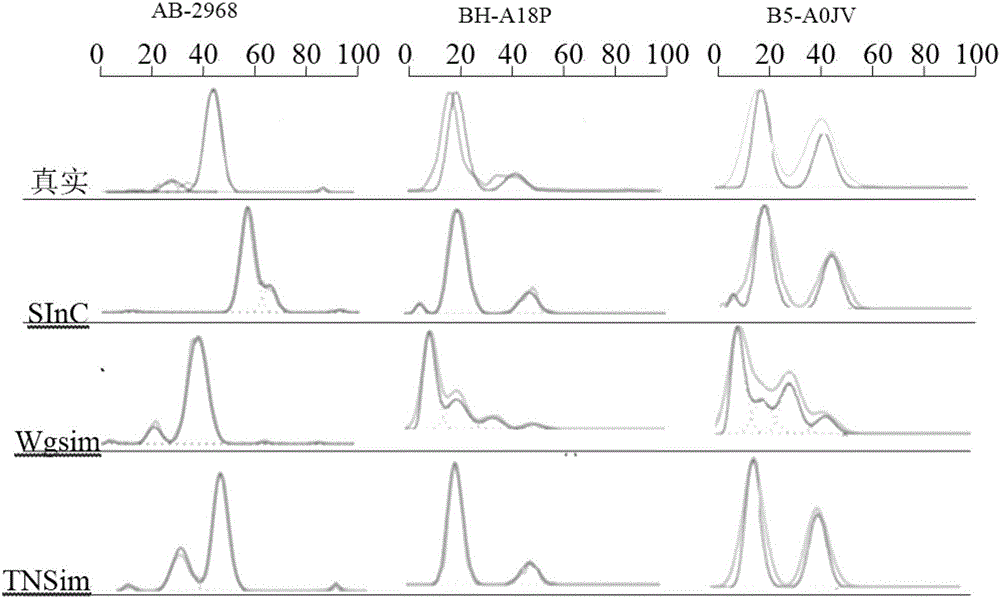
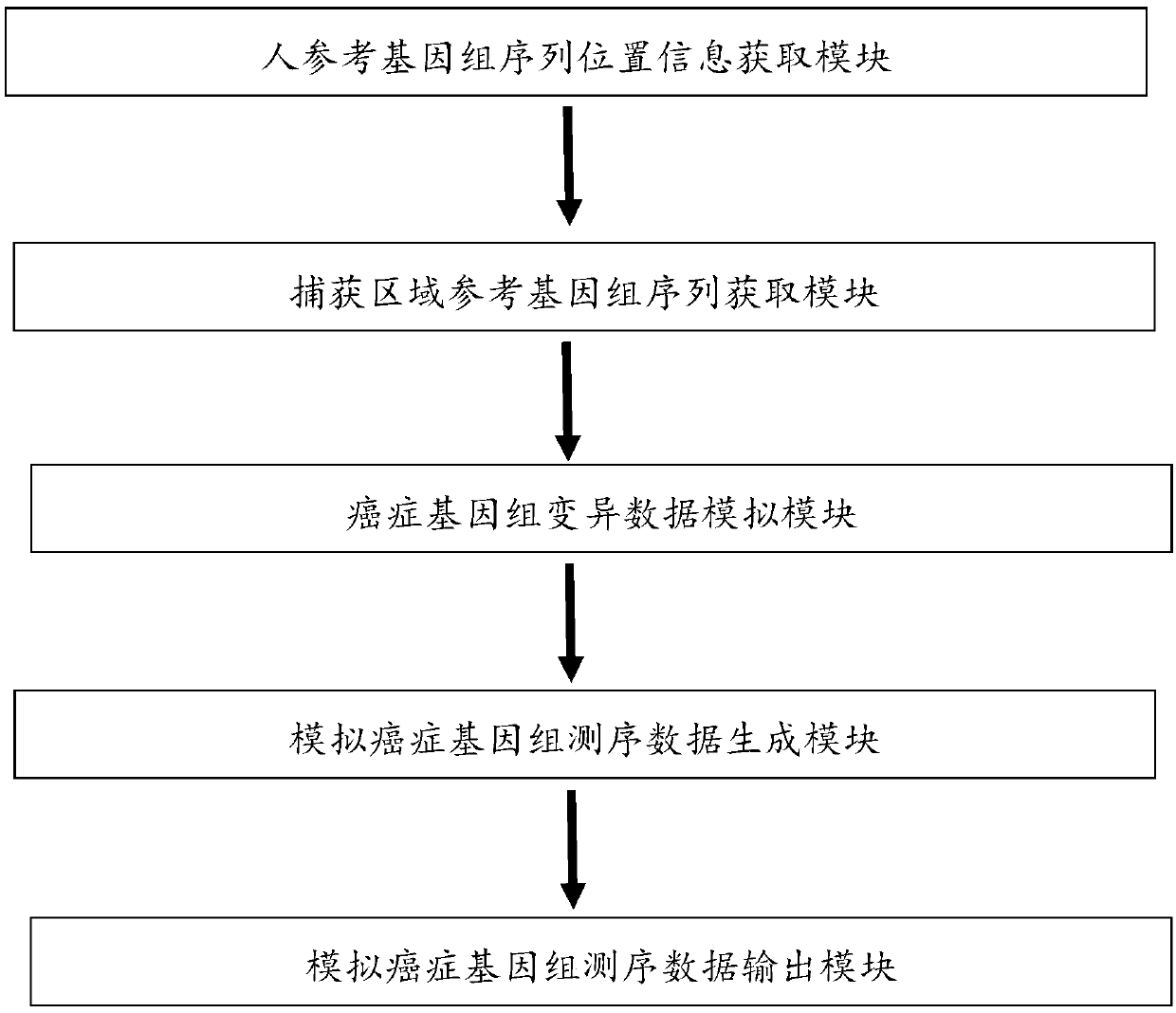
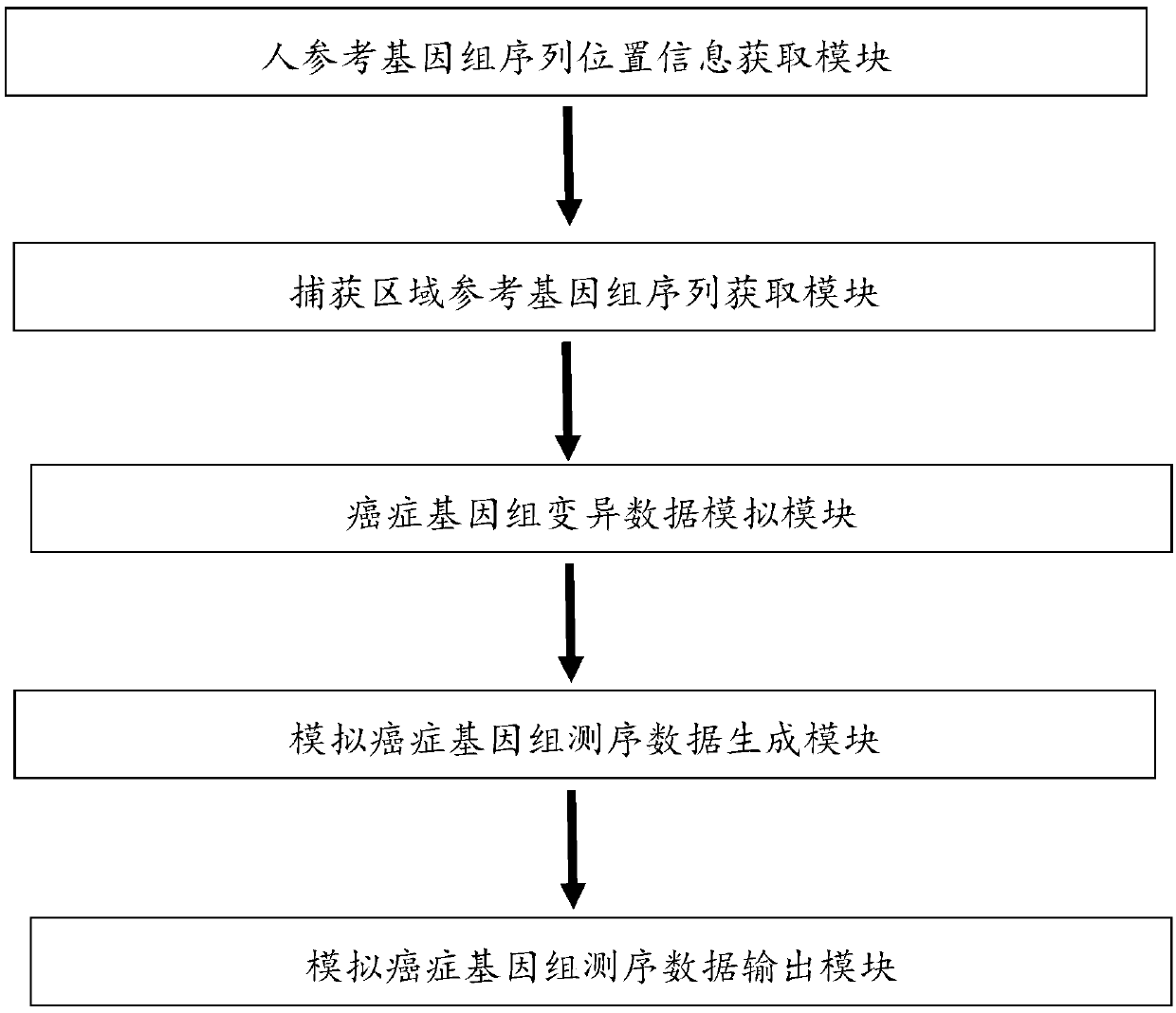
Analog cancer genome sequencing data generating device
The invention relates to an analog cancer genome sequencing data generating device. The device comprises a human reference genome sequence position information acquiring module, a capturing area reference genome sequence acquiring module, a cancer genome variation data analog module, an analog cancer genome sequencing data generating module and an analog cancer genome sequencing data output module. The invention provides an algorithm and a device which can simulate various kinds of variations so that the generated analog sequencing data is suitable for evaluation of properties of various kindsof detection software.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ANNOROAD BIO TECH CO LTD +1
Gene for osteosarcoma typing and osteosarcoma prognosis evaluation, and application thereof
ActiveCN113512588AMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisConventional OsteosarcomaCancer genome
According to a gene for osteosarcoma typing and osteosarcoma prognosis evaluation, and application thereof, aiming at tumor heterogeneity, the difference of cytodynamics and molecular characteristics between conventional osteosarcoma and normal cancellous bone is compared, and based on a single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) technology or a gene detection kit, a gene detection chip technology or an immunohistochemical method, the obvious differentiation direction of osteosarcoma cells is detected, and possible interaction among all cell types in a tumor microenvironment is researched. According to the differentiation direction of osteosarcoma cells, conventional osteosarcoma can be divided into three types, the tumor microenvironment characteristics of each type are described, and prognosis of each type is verified according to cancer genome map (TCGA) data.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHANGZHENG HOSPITAL +1
Multi-resolution modeling of discrete stochastic processes for computationally-efficient information search and retrieval
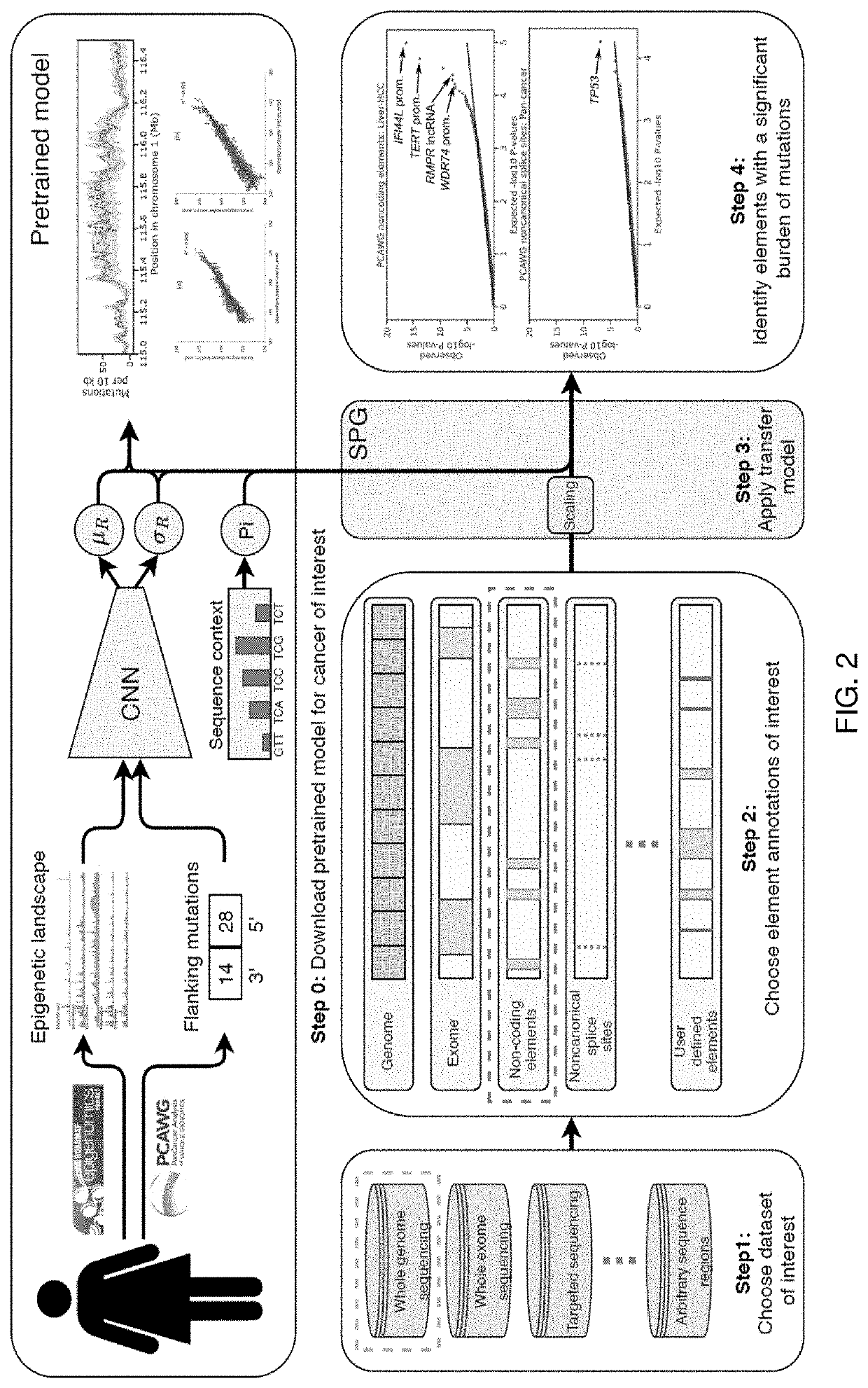
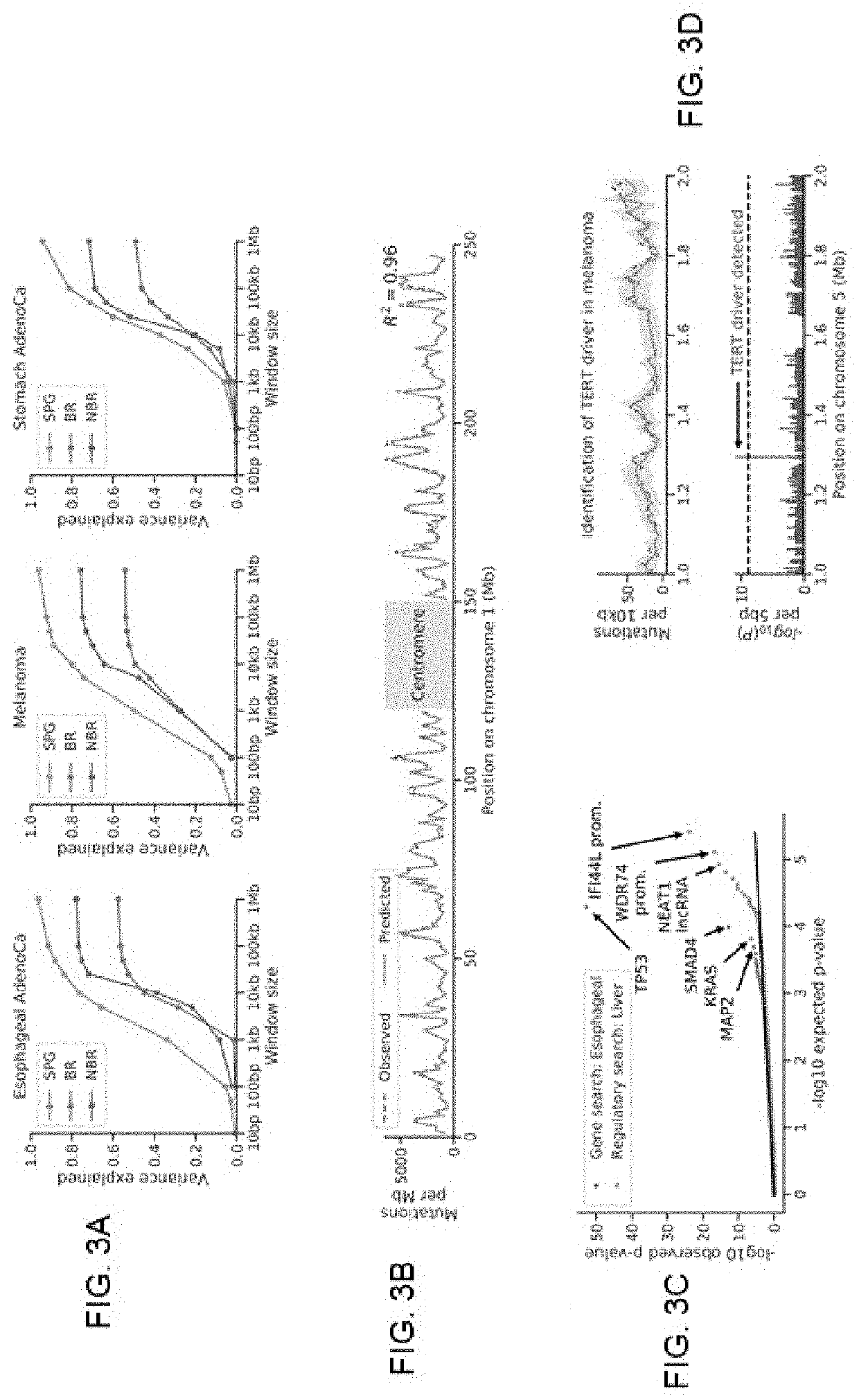
An activity of interest is modeled by a non-stationary discrete stochastic process, such as a pattern of mutations across a cancer genome. Initially, input genomic data is used to train a model to predict rate parameters and their associated uncertainty estimation for each of a set of process regions. For any arbitrary set of indexed positions of the stochastic process that are identified in an information query, the rate parameters and their associated estimation uncertainties are scaled using the model to obtain a distribution of the events of interest and their associated estimation uncertainties for the set of indexed positions. In one practical application, and in response to a search query associated with one or more base-pairs, a result is then returned. The result, which represents deviations between the estimated and observed mutation rates, is used to identify genomic elements that have more mutations than expected and therefore constitute previously unknown driver mutations.
Owner:LEIGHTON +2
Gene for osteosarcoma typing and osteosarcoma prognosis evaluation and application thereof
ActiveCN113549691AMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisConventional OsteosarcomaCancer genome
In the invention, aiming at tumor heterogeneity, the difference of cytodynamics and molecular characteristics between conventional osteosarcoma and normal cancellous bone is compared, and the obvious differentiation direction of osteosarcoma cells is detected based on a single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) technology or gene detection kit and gene detection chip technologies or an immunohistochemical method, and the possible interaction between each cell type in the tumor microenvironment is researched. According to the differentiation direction of the osteosarcoma cells, the conventional osteosarcoma can be divided into three types, microenvironment characteristics of each type are described, and prognosis of each type is verified according to The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) data.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHANGZHENG HOSPITAL +1
Reagent kit for diagnosing oral squamous cell carcinoma
ActiveCN107422123ASignificant technological progressSensitivity advantageMaterial analysisOral tissueSquamous Carcinomas
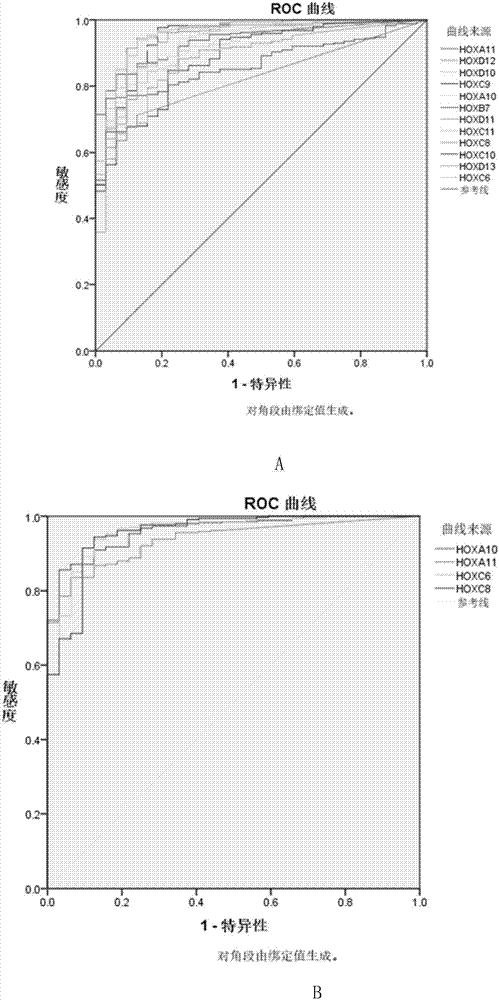
The invention provides a reagent kit for diagnosing oral squamous cell carcinoma. The reagent kit comprises specific antibodies for detecting HOXA10, specific antibodies for detecting HOXA11, specific antibodies for detecting HOXC6 or compositions with more than one or two optional specific antibodies for detecting the expression quantities of HOXC8. The reagent kit has the advantages that sequencing results for mRNA [messenger RNA (ribonucleic acid)] of the oral squamous cell carcinoma and normal oral tissues in TCGA (the cancer genome atlas) databases are statistically analyzed, data of 32 cases of normal oral tissues and 341 cases of oral squamous cell carcinoma tissues are incorporated, obvious difference of expression of partial genes in HOX families in the oral squamous cell carcinoma and the normal tissues is discovered, and accordingly the reagent kit is suitable to be applied to diagnosing the oral squamous cell carcinoma; expression of genes in the HOX families is detected in oral squamous cell carcinoma tissue pathological sections by the aid of immunohistochemical processes, and accordingly positive expression of the genes in the oral squamous cell carcinoma and application values of the genes in diagnosis can be determined.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
Genome-wide methylation analysis and use to identify genes specific to breast cancer hormone receptor status and risk of recurrance
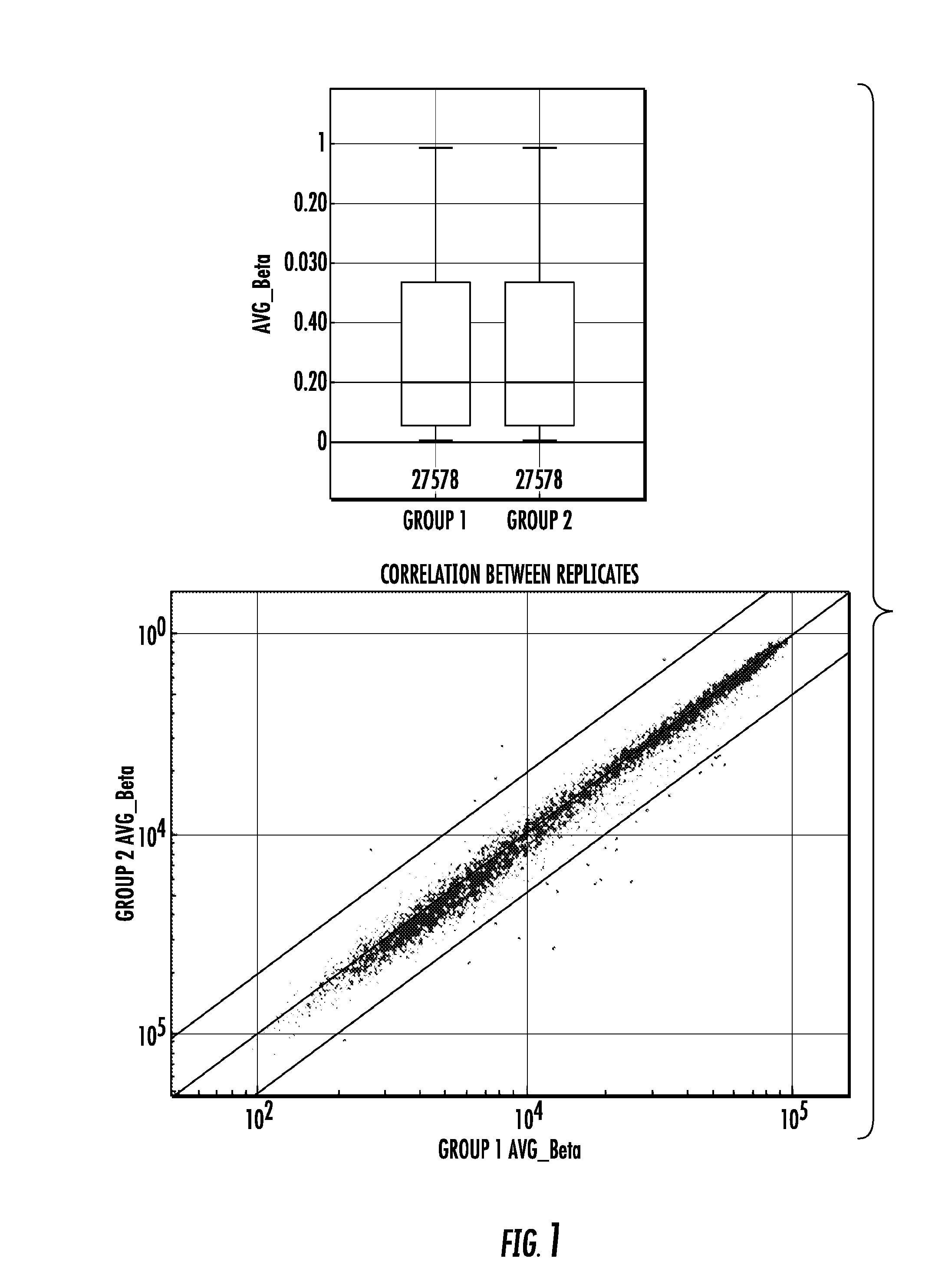
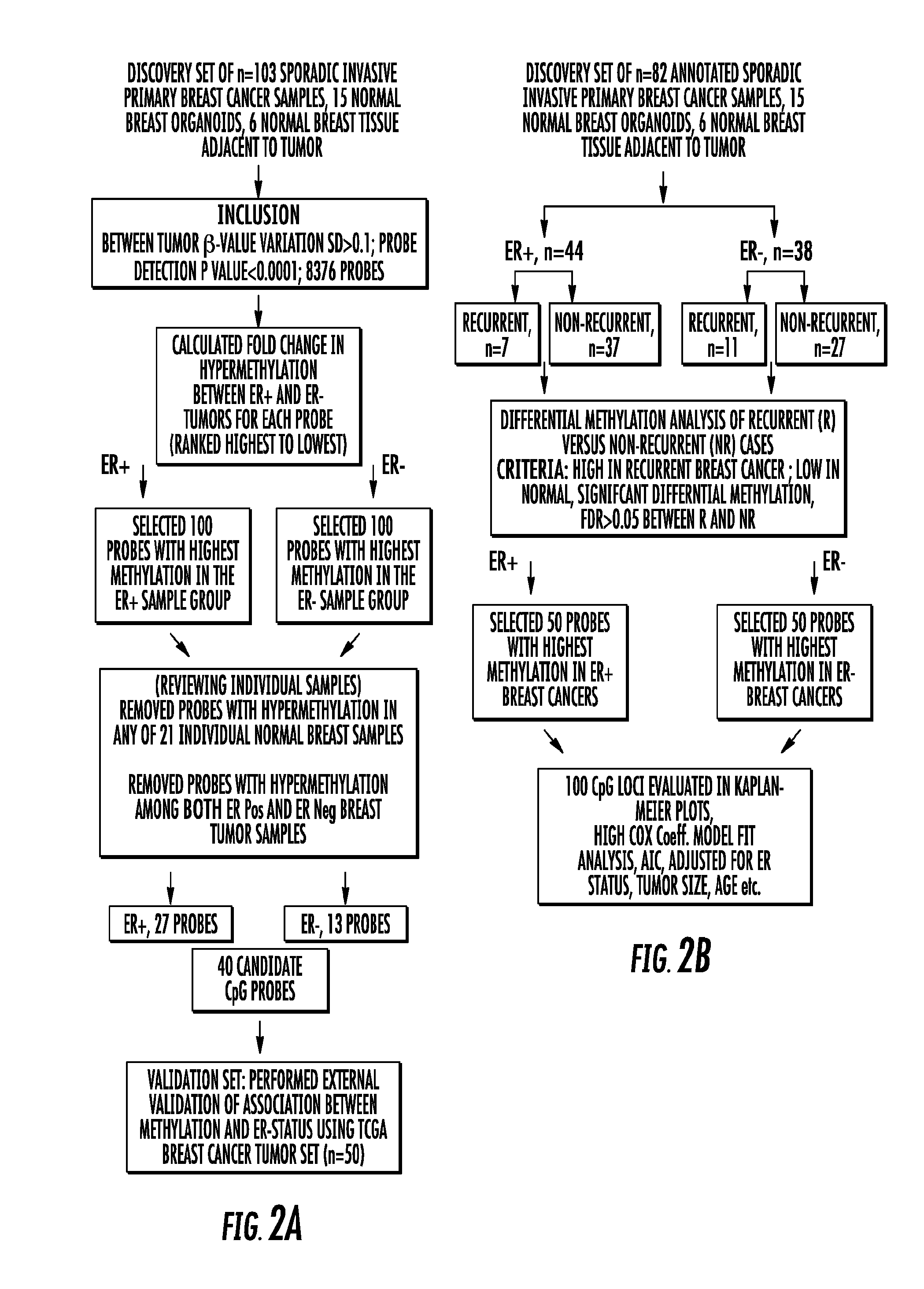
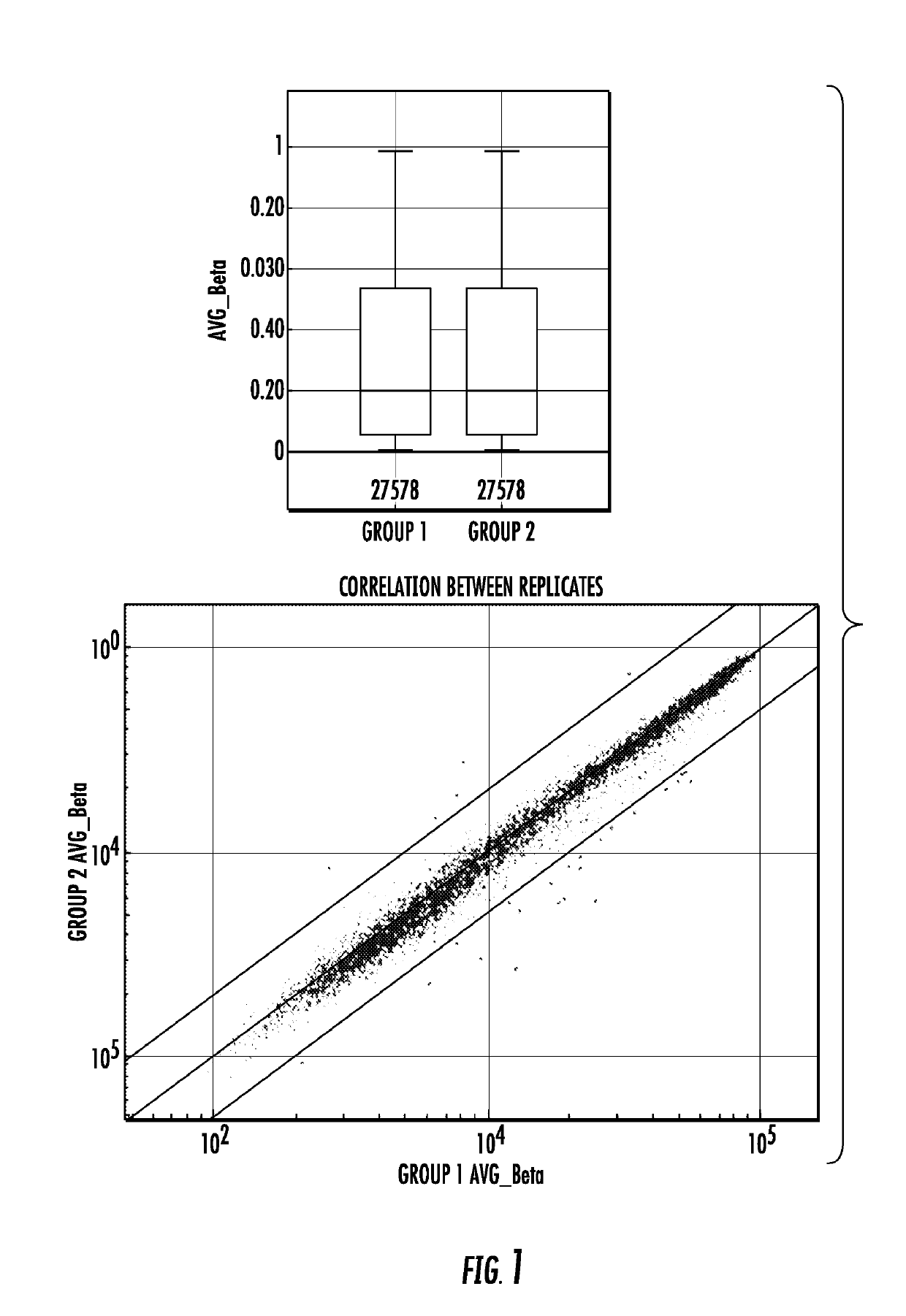
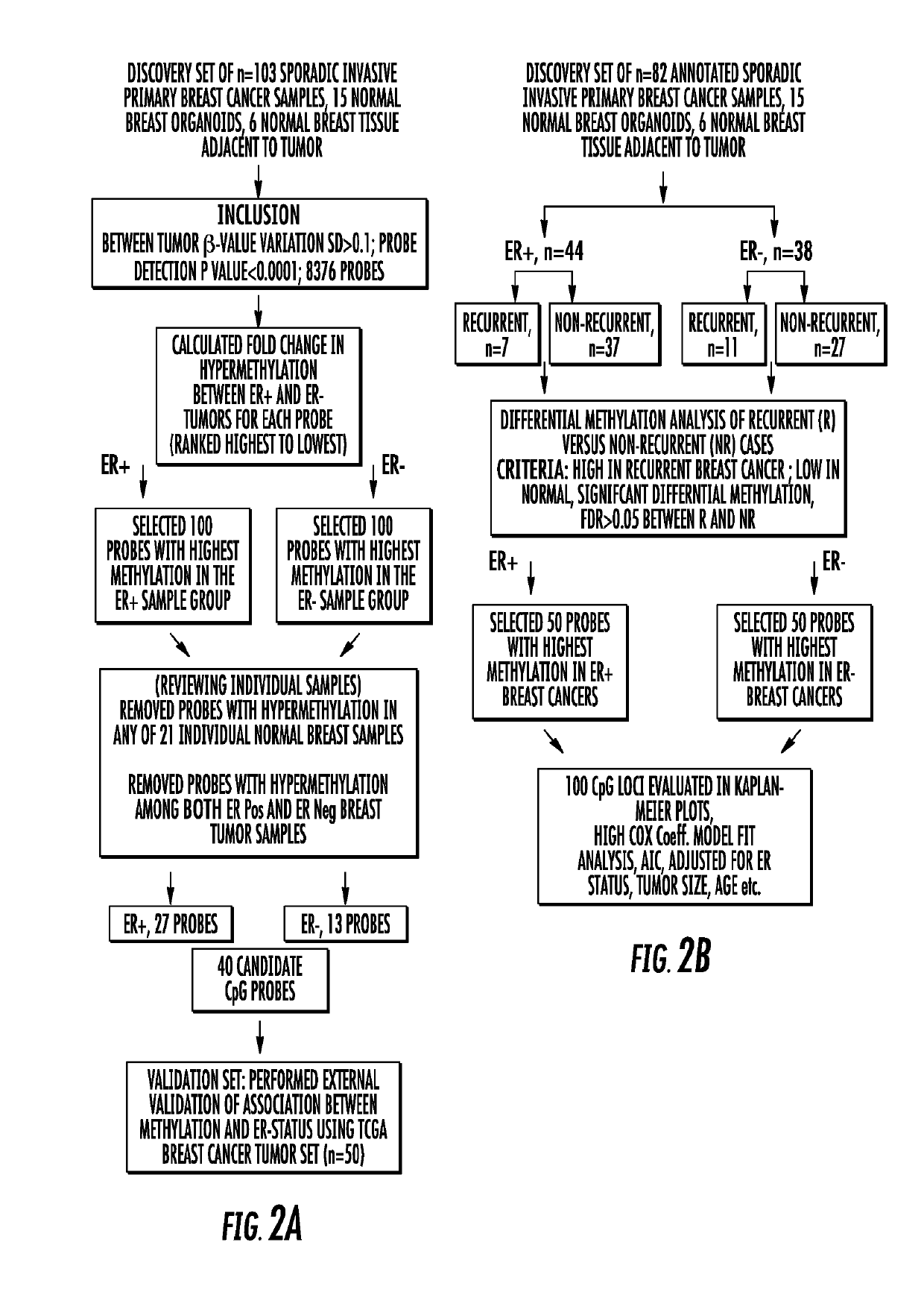
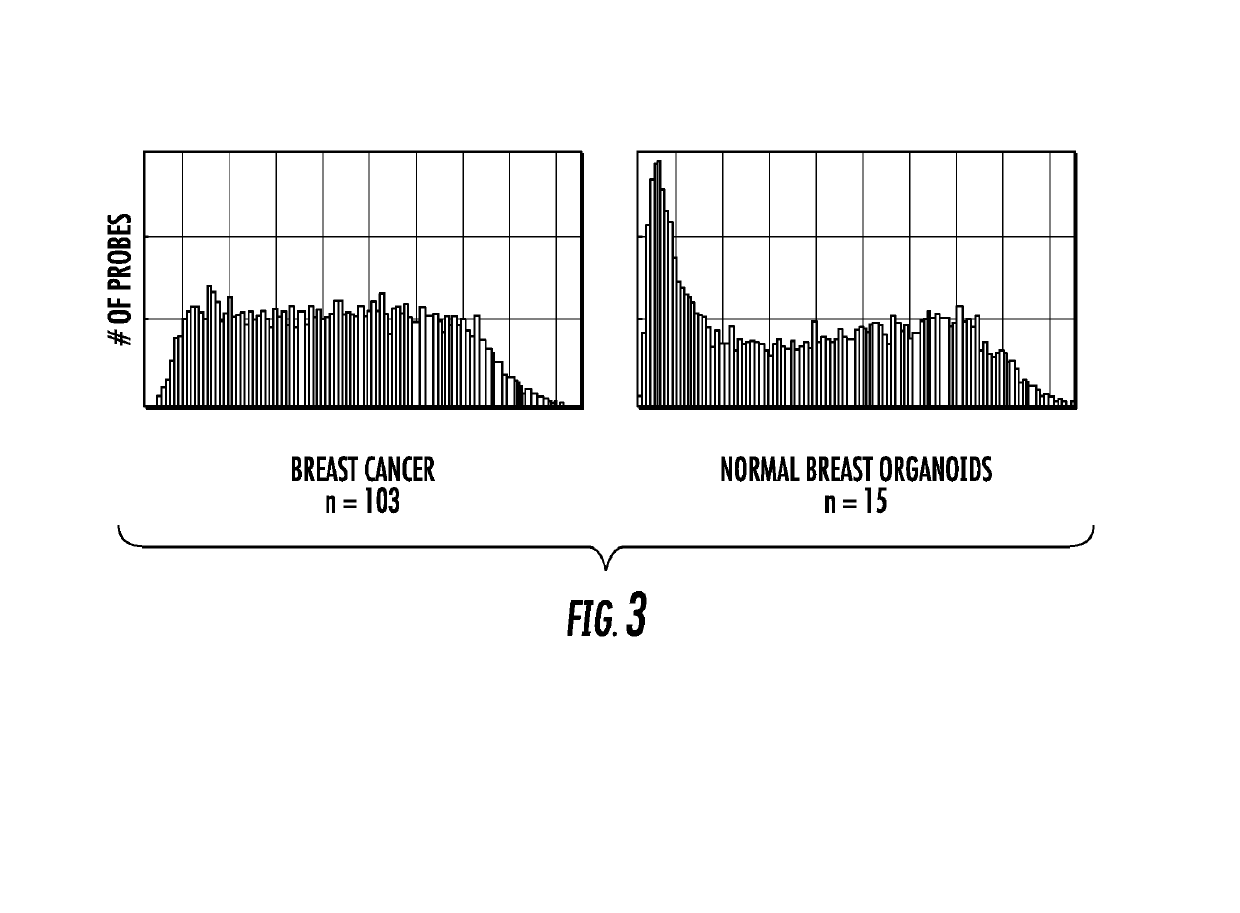
ActiveUS20140221242A1Nucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementCancer genomeMethylation analysis
To better understand the biology of hormone receptor-positive and negative breast cancer and to identify methylated gene markers of disease progression, a genome-wide methylation array analysis was performed on 103 primary invasive breast cancers and 21 normal breast samples using the Illumina Infinium HumanMethylation27 array that queried 27,578 CpG loci. Forty CpG loci showed differential methylation specific to either ER-positive or ER-negative tumors. Each of the 40 ER-subtype-specific loci was validated in silico using an independent, publicly available methylome dataset from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). In addition, 100 methylated CpG loci were identified that were significantly associated with disease progression. Arrays containing the ER-subtype-specific loci and their use in methods of diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer are provided.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Genome-wide methylation analysis and use to identify genes specific to breast cancer hormone receptor status and risk of recurrence
To better understand the biology of hormone receptor-positive and negative breast cancer and to identify methylated gene markers of disease progression, a genome-wide methylation array analysis was performed on 103 primary invasive breast cancers and 21 normal breast samples using the Illumina Infinium HumanMethylation27 array that queried 27,578 CpG loci. Forty CpG loci showed differential methylation specific to either ER-positive or ER-negative tumors. Each of the 40 ER-subtype-specific loci was validated in silico using an independent, publicly available methylome dataset from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). In addition, 100 methylated CpG loci were identified that were significantly associated with disease progression. Arrays containing the ER-subtype-specific loci and their use in methods of diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer are provided.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com