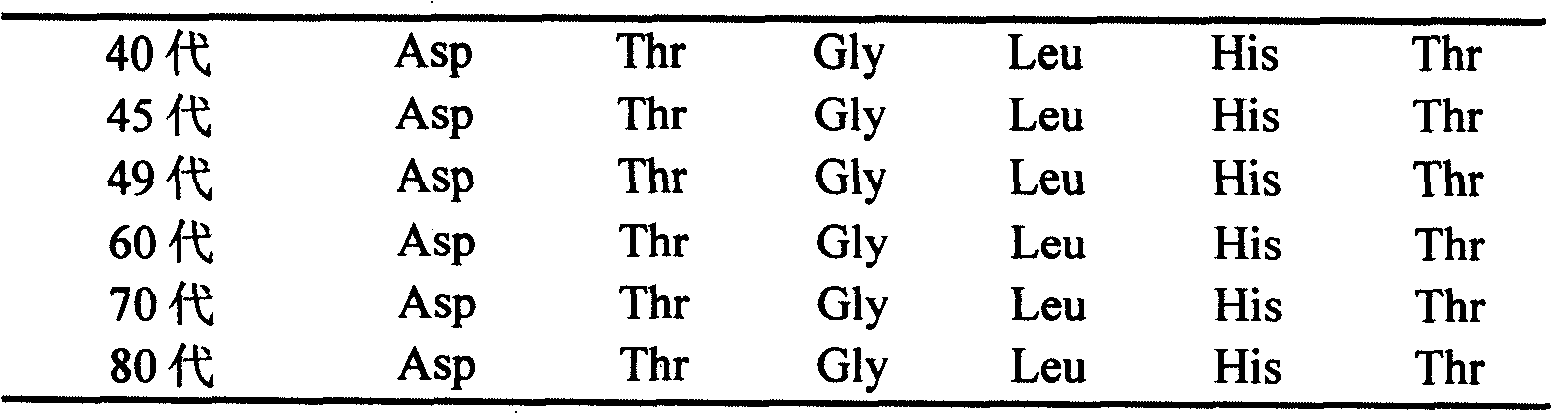Patents
Literature
2503 results about "Pathogenicity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Pathogenicity is the potential capacity of certain species of microbes or viruses to cause a disease. Pathogenicity is characterized by complex pathogenic properties which evolve during their struggle for existence. Pathogens are characterized by specific actions. Each species is able to give rise to different infectious processes. It is often used interchangeably with the term "virulence", although virulence is used more specifically to describe the relative degree of damage done by a pathogen, or the degree of pathogenicity caused by an organism. A pathogen is described partly through its virulence by its ability to produce toxins, enter tissue, colonize, hijack nutrients, and its ability to immunosuppress the host.
Probiotic recolonisation therapy
The present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions suitable for the treatment of chronic diseases associated with the presence of abnormal or an abnormal distribution of microflora in the gastrointestinal tract of a mammalian host, which compositions comprise viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic Clostridia. The compositions further comprise one or more additional viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic microorganisms selected from the group consisting of Bacteroides, Eubacteria, Fusobacteria, Propionibacteria, Lactobacilli, anaerobic cocci, Ruminococcus, E.Coli, Gemmiger, Desullomonas, Peptostreptococcus, and fungi. The present invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions suitable for the treatment of the same chronic diseases comprising viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic Escherichia coli, at least one strain of viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathoenic Bacteroides and at least one strain of viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic microorganism.
Owner:FINCH THERAPEUTICS HLDG LLC
Probiotic recolonisation therapy
The present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions suitable for the treatment of chronic diseases associated with the presence of abnormal or an abnormal distribution of microflora in the gastrointestinal tract of a mammalian host, which compositions comprise viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic Clostridia. The compositions further comprise one or more additional viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic microorganisms selected from the group consisting of Bacteroides, Eubacteria, Fusobacteria, Propionibacteria, Lactobacilli, anaerobic cocci, Ruminococcus, E.Coli, Gemmiger, Desullomonas, Peptostreptococcus, and fungi. The present invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions suitable for the treatment of the same chronic diseases comprising viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic Escherichia coli, at least one strain of viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathoenic Bacteroides and at least one strain of viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic microorganism.
Owner:FINCH THERAPEUTICS HLDG LLC
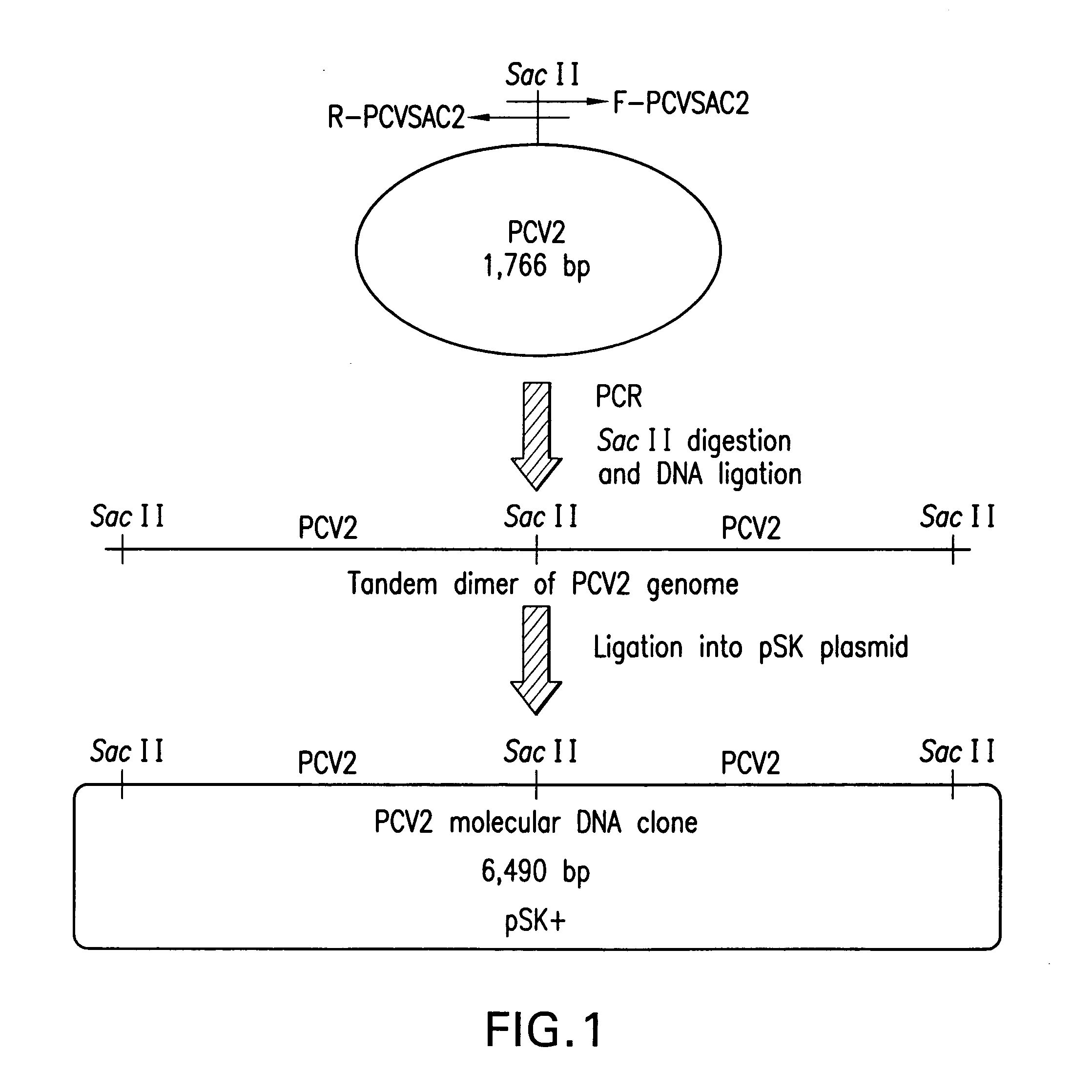
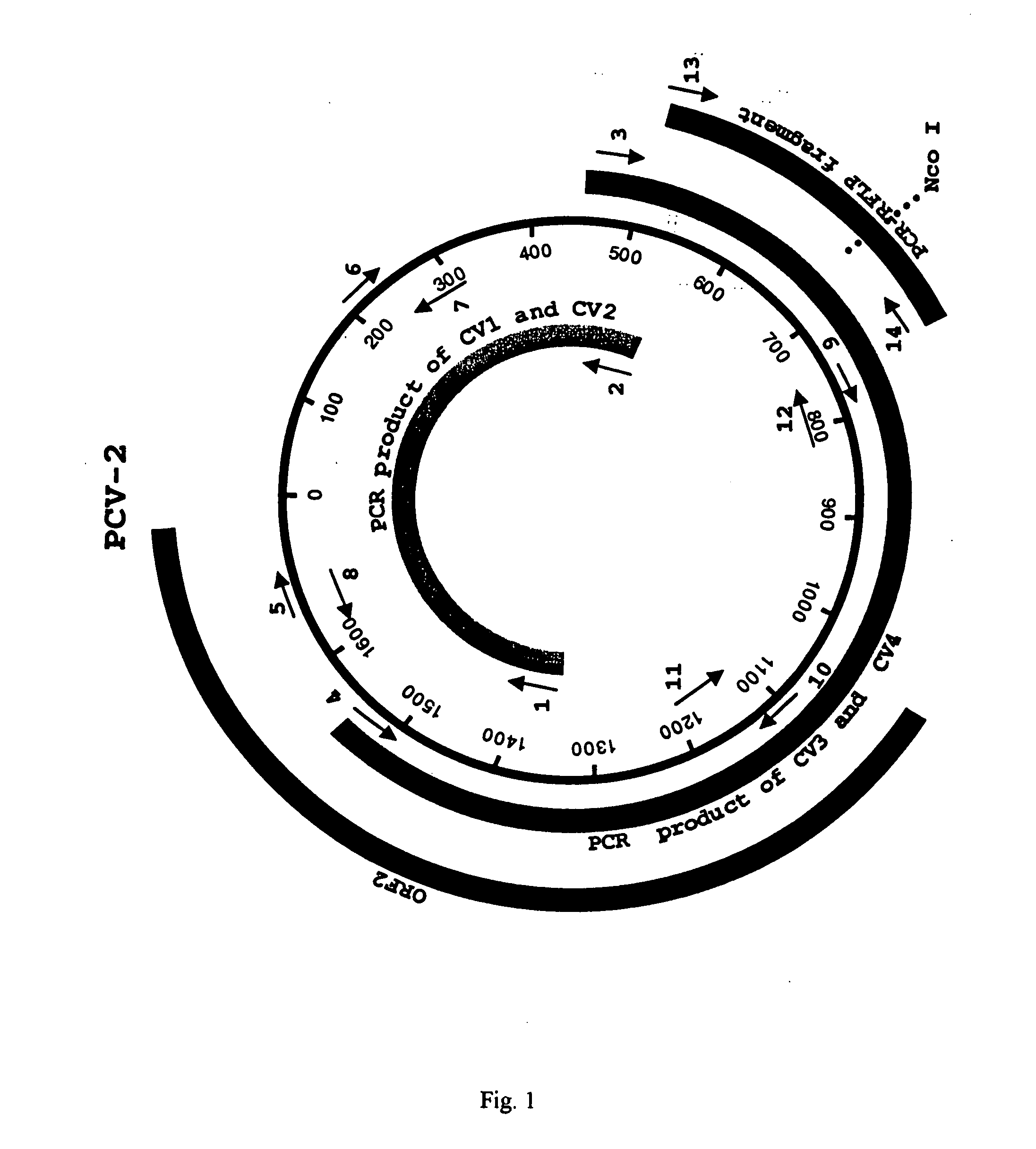
Chimeric infectious DNA clones, chimeric porcine circoviruses and uses thereof
InactiveUS7279166B2Facilitate cell culture growthEnsure vaccine safetyFungiBacteriaSpecific immunityADAMTS Proteins
The present invention relates to infectious DNA clones, infectious chimeric DNA clones of porcine circovirus (PCV), vaccines and means of protecting pigs against viral infection or postweaning multisystemic wasting syndrome (PMWS) caused by PCV2. The new chimeric infectious DNA clone and its derived, avirulent chimeric virus are constructed from the nonpathogenic PCV1 in which the immunogenic ORF gene of the pathogenic PCV2 replaces a gene of the nonpathogenic PCV1, preferably in the same position. The chimeric virus advantageously retains the nonpathogenic phenotype of PCV1 but elicits specific immune responses against the pathogenic PCV2. The invention further embraces the immunogenic polypeptide expression products. In addition, the invention encompasses two mutations in the PCV2 immunogenic capsid gene and protein, and the introduction of the ORF2 mutations in the chimeric clones.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND +1
Anti-FcRn antibodies for treatment of auto/allo immune conditions
Antibodies to heavy chain of human FcRn are provided which function as non-competitive inhibitors of IgG binding to FcRn. The antibodies may be polyclonal, monoclonal, chimeric or humanized, or antigen binding fragments thereof. These antibodies are useful for reducing the concentration of pathogenic IgGs in individuals and therefore used as a therapeutic tool in autoimmune and alloimmune conditions.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Probiotic lactic acid bacterium to treat bacterial infections associated with SIDS
Compositions including a non-pathogenic lactic acid-producing bacteria, such as a Bacillus species, spores or an extracellular product of B. coagulans, formulated for oral administration to the intestinal tract for inhibiting bacterial gastrointestinal infections are described. Methods and systems using the compositions for treating gastrointestinal infections, particularly sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) are also disclosed.
Owner:GANEDEN BIOTECH
Probiotic recolonisation therapy
The present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions suitable for the treatment of chronic diseases associated with the presence of abnormal or an abnormal distribution of microflora in the gastrointestinal tract of a mammalian host, which compositions comprise viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic Clostridia. The compositions further comprise one or more additional viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic microorganisms selected from the group consisting of Bacteroides, Eubacteria, Fusobacteria, Propionibacteria, Lactobacilli, anaerobic cocci, Ruminococcus, E. Coli, Gemmiger, Desulfamonas, Peptostreptococcus, and fungi. The present invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions suitable for the treatment of the same chronic diseases comprising viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic Escherichia coli, at least one strain of viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathoenic Bacteroides and at least one strain of viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic microorganism.
Owner:FINCH THERAPEUTICS HLDG LLC
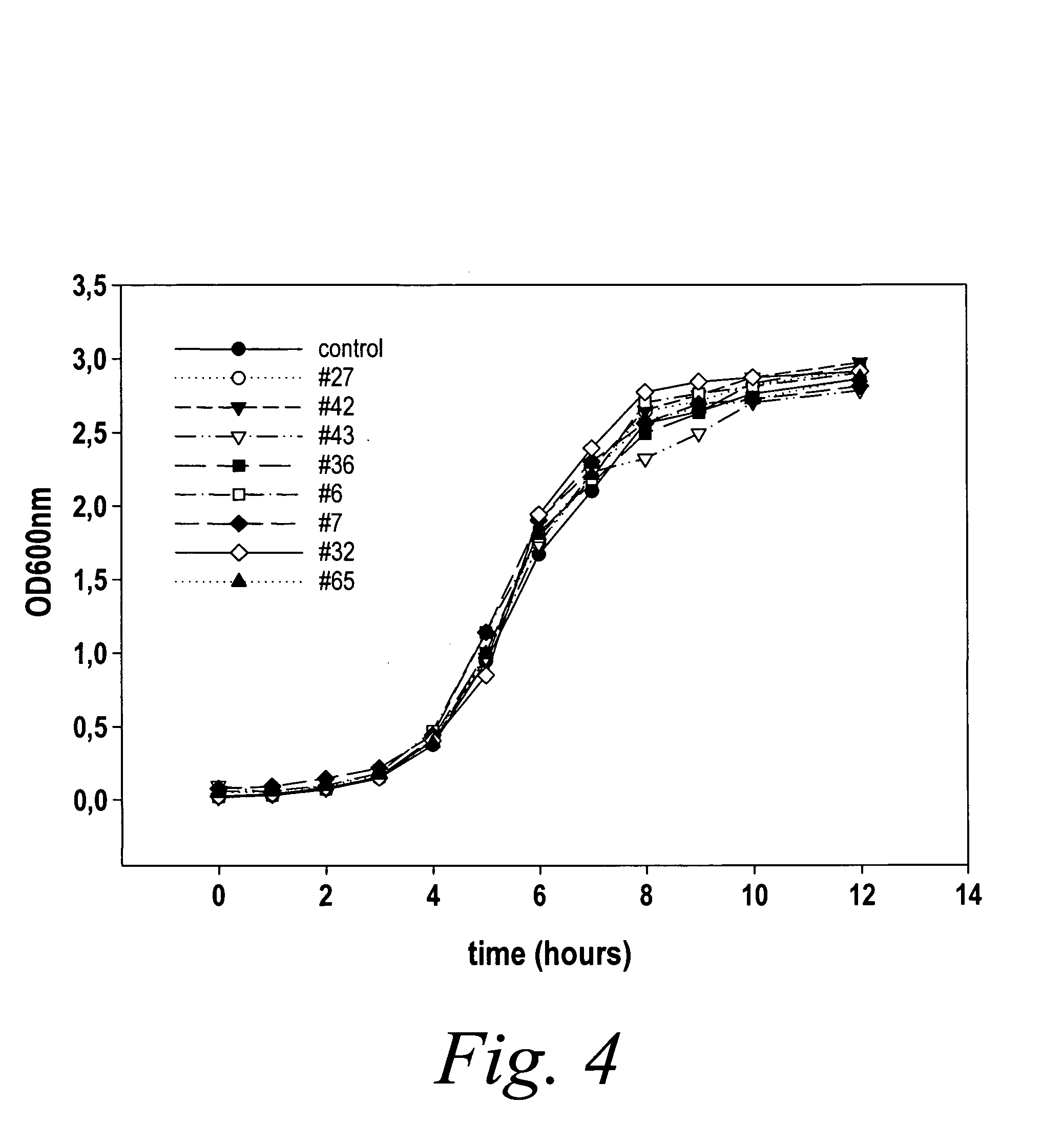
Attenuated negative strand viruses with altered interferon antagonist activity for use as vaccines and pharmaceuticals
InactiveUS6669943B1Impaired ability to antagonizeAvoiding and minimizing side effectSsRNA viruses negative-senseVirus peptidesNegative strandPharmaceutical drug
Owner:AVIR GREEN HILLS BIOTECH RES DEVMENT TRADE +1
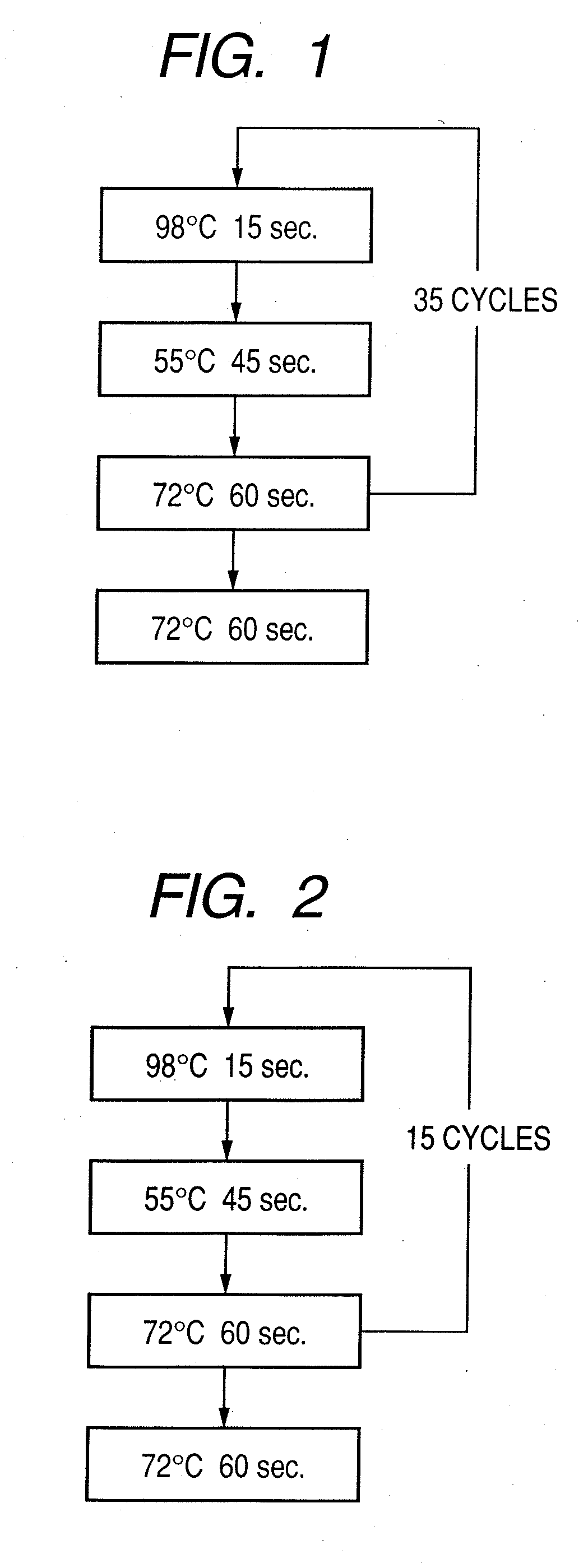
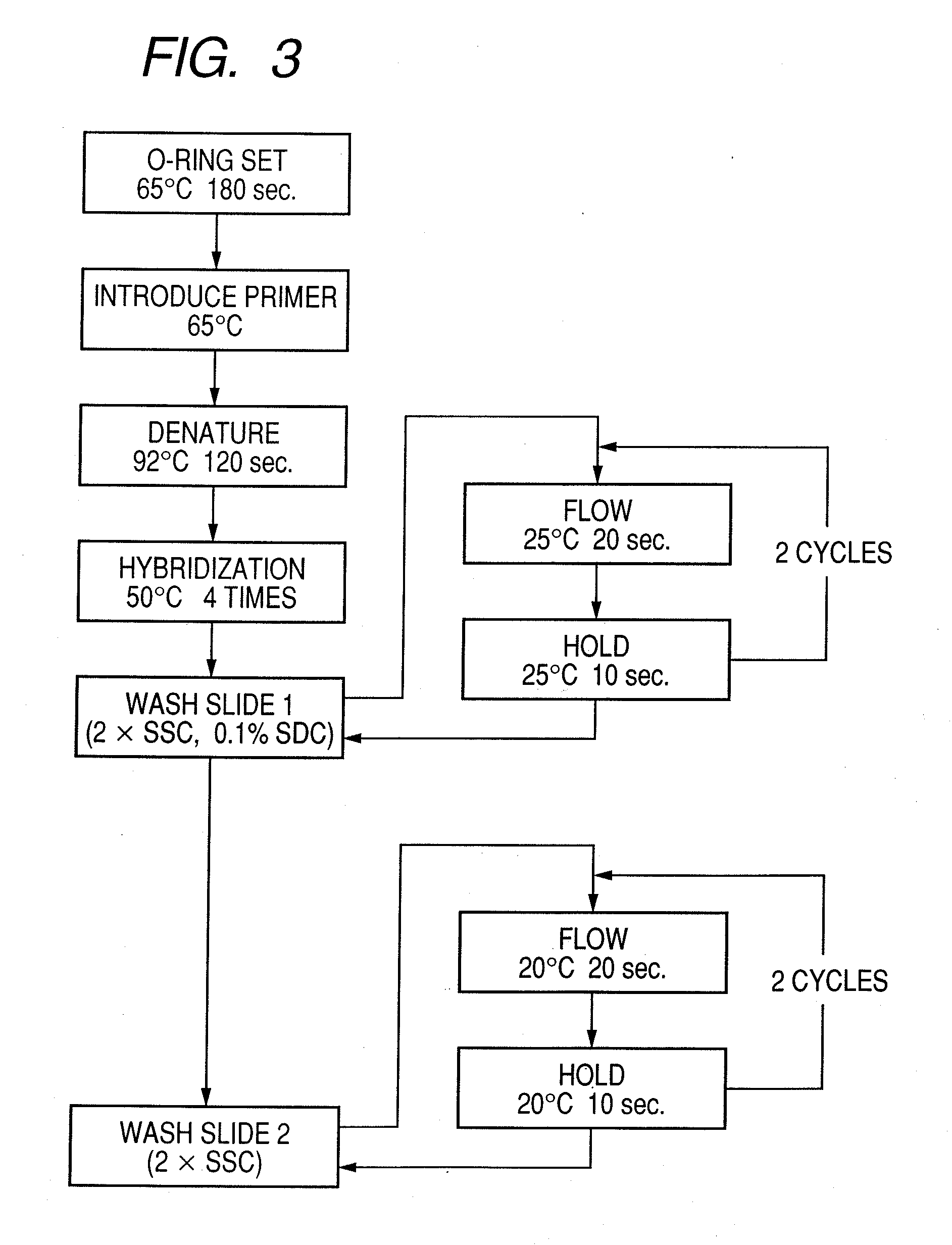
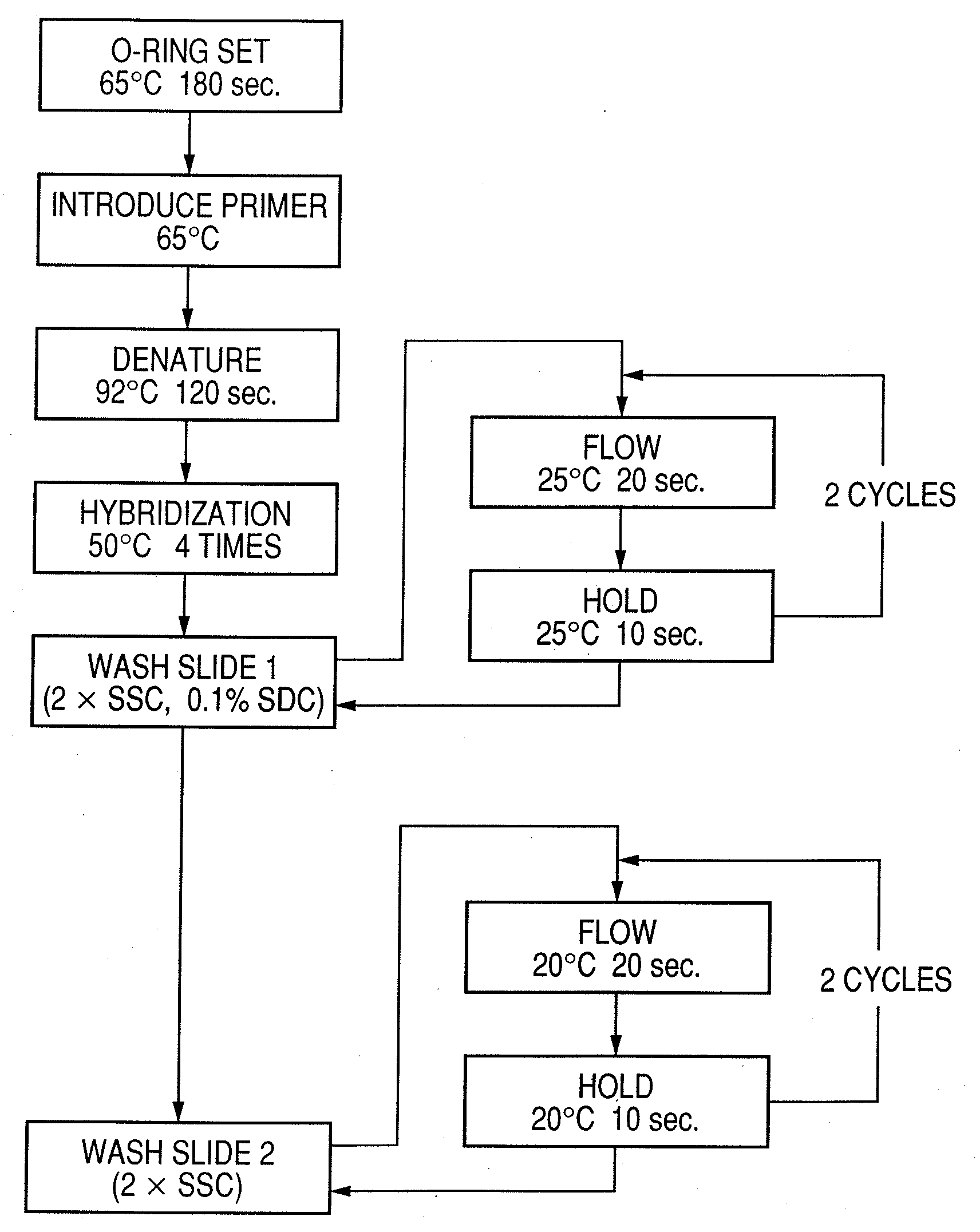
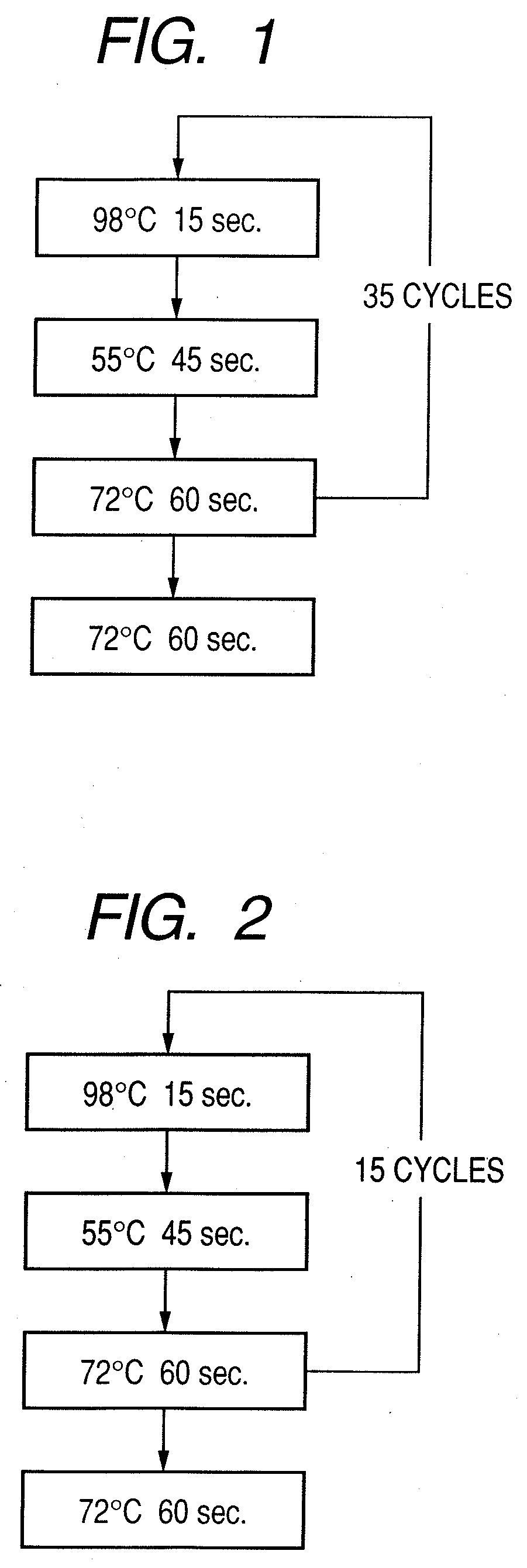
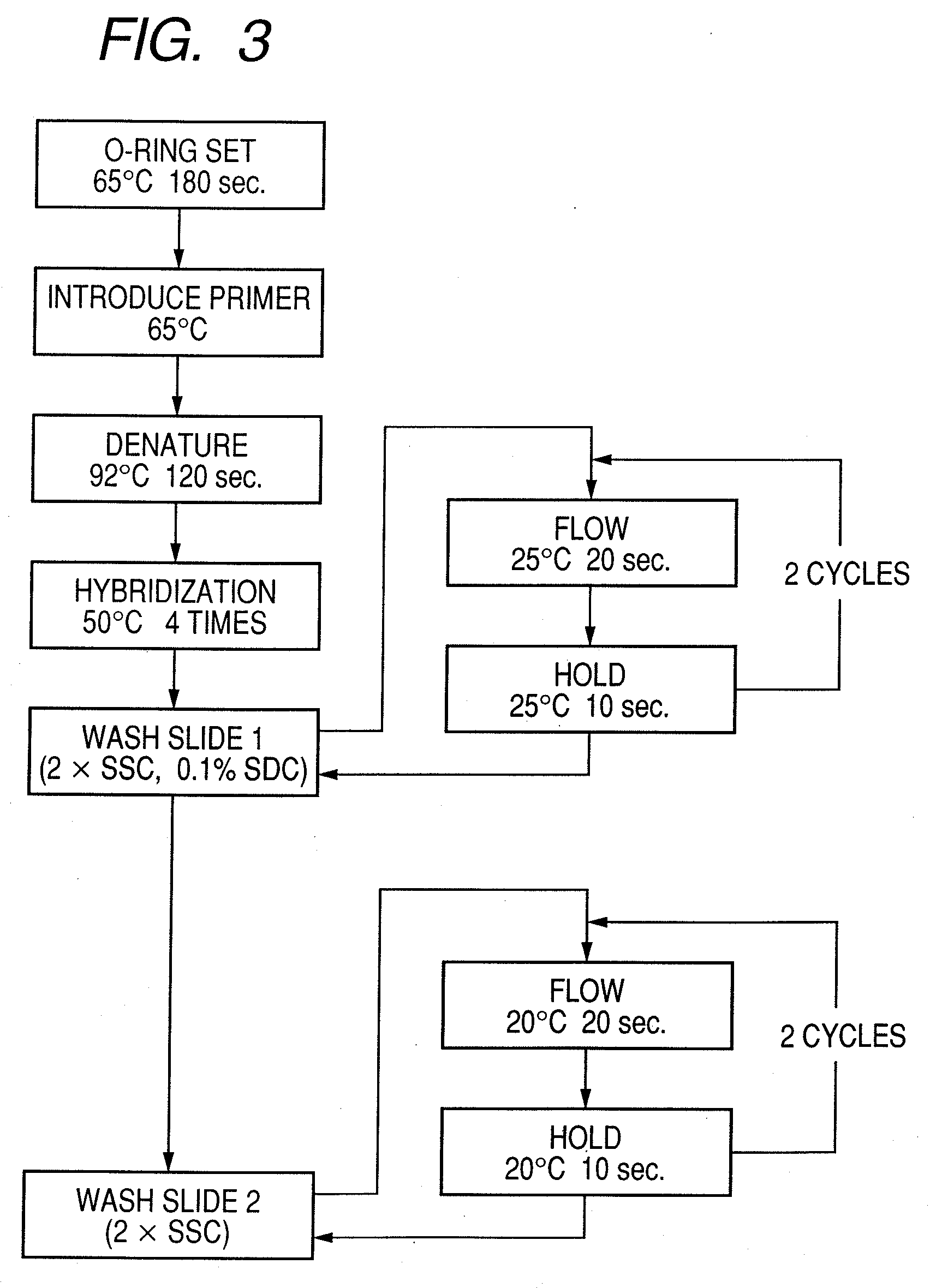
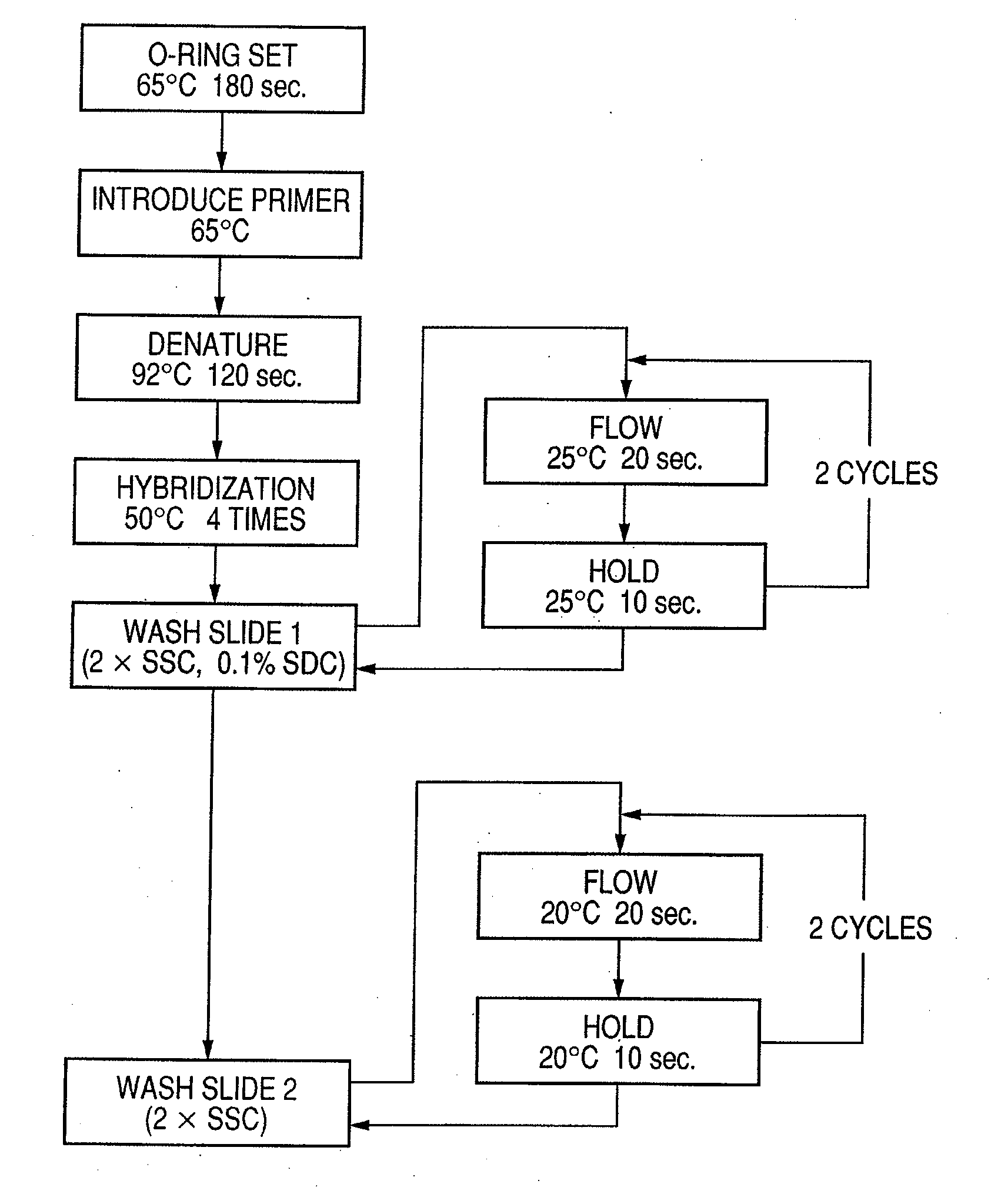
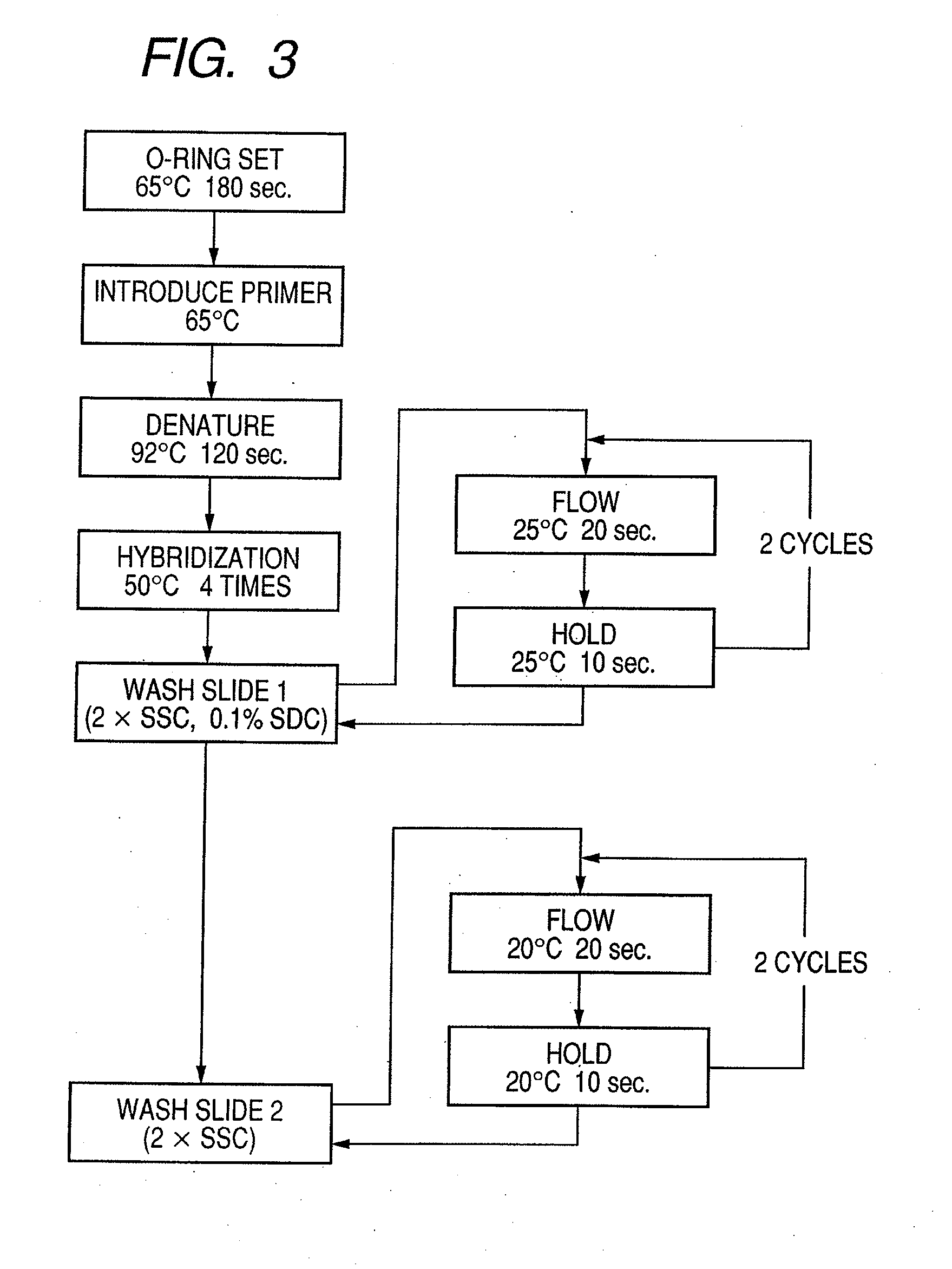
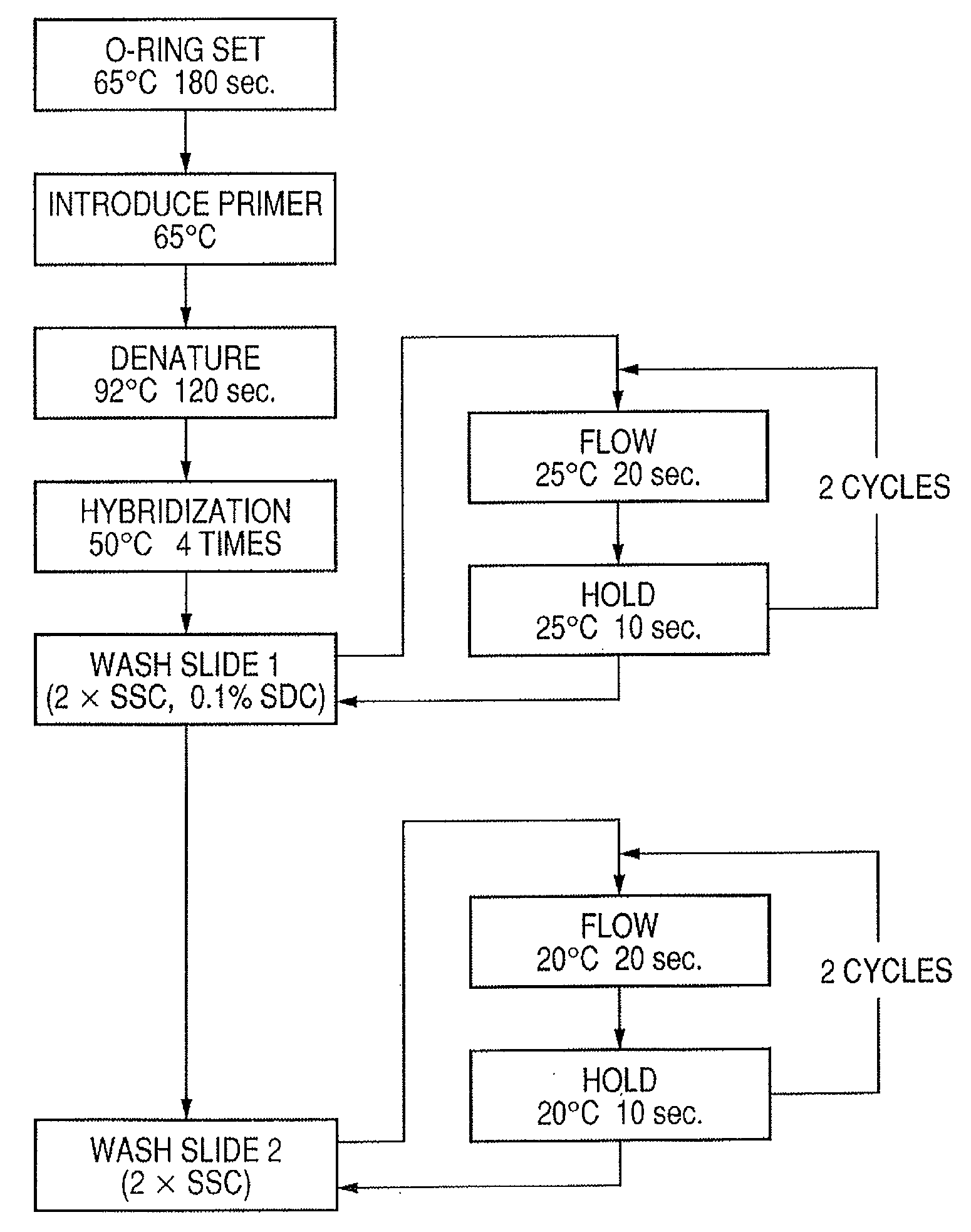
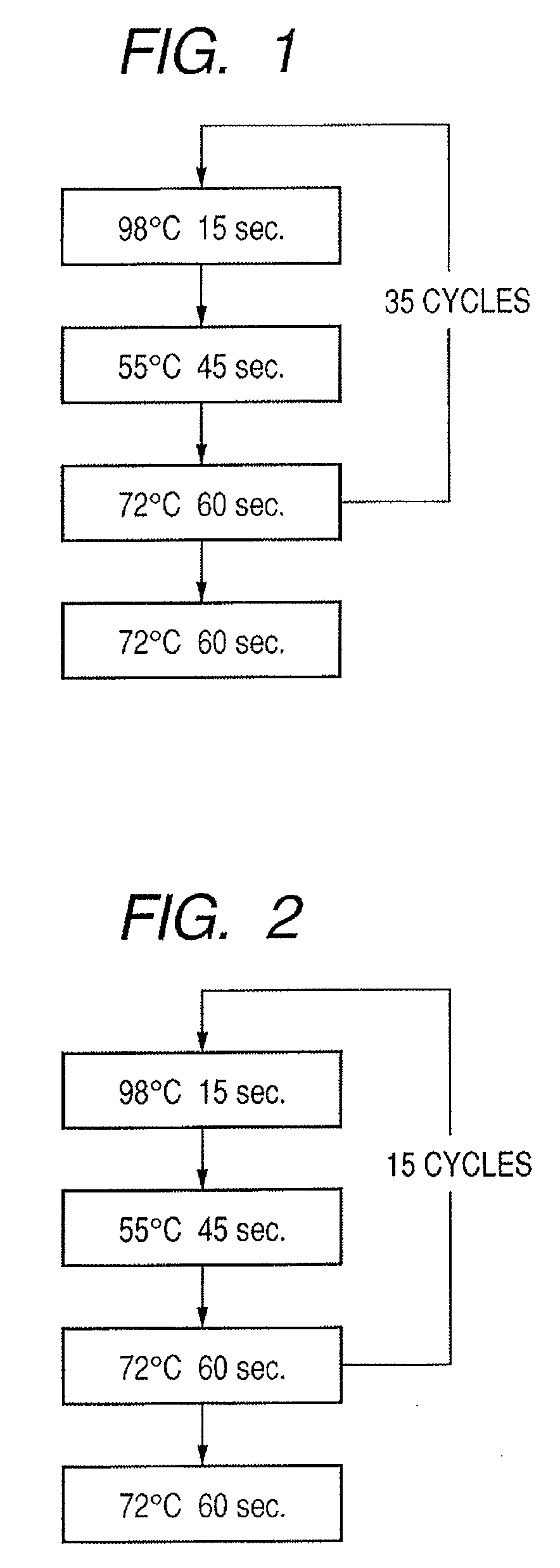
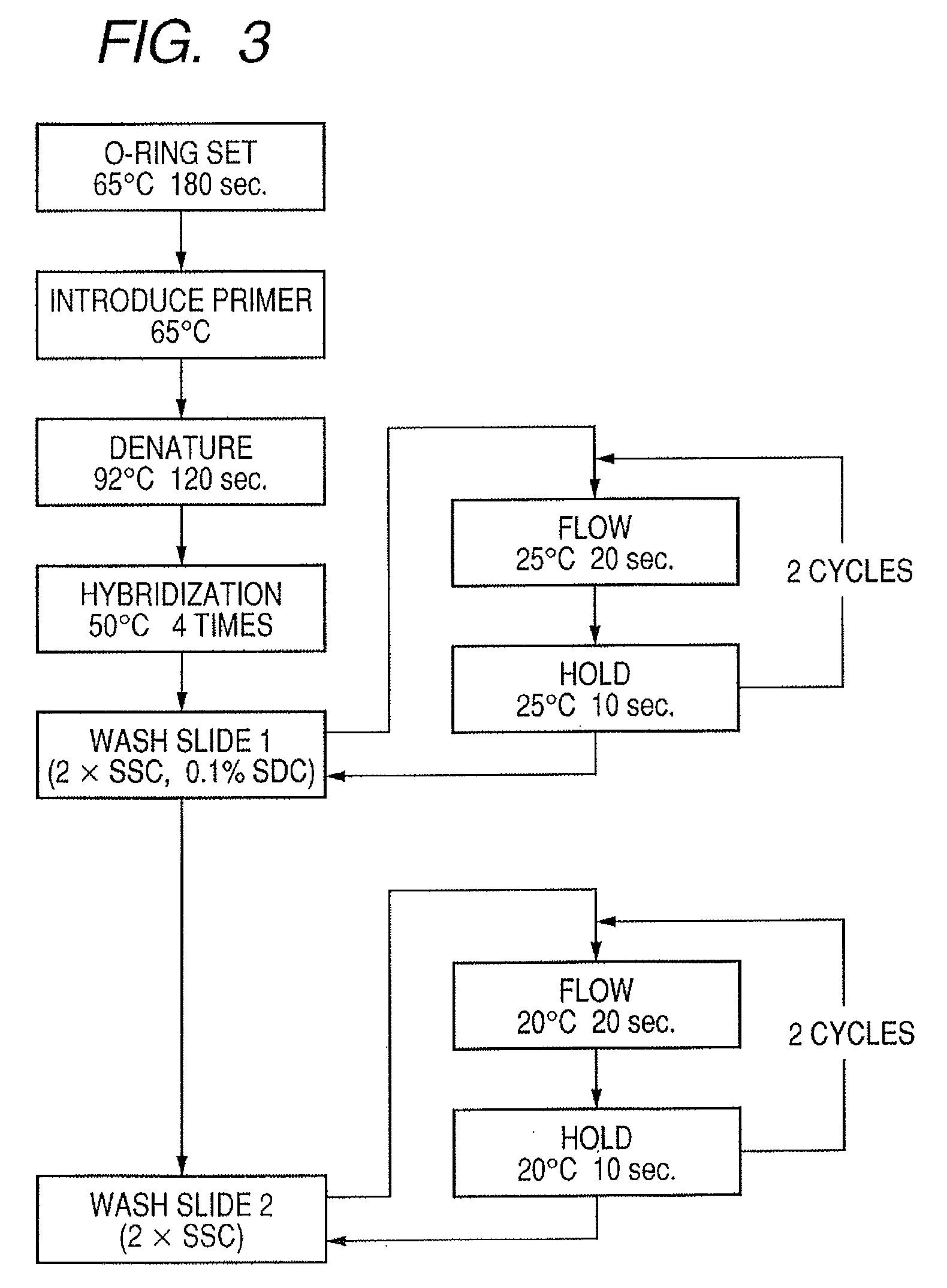
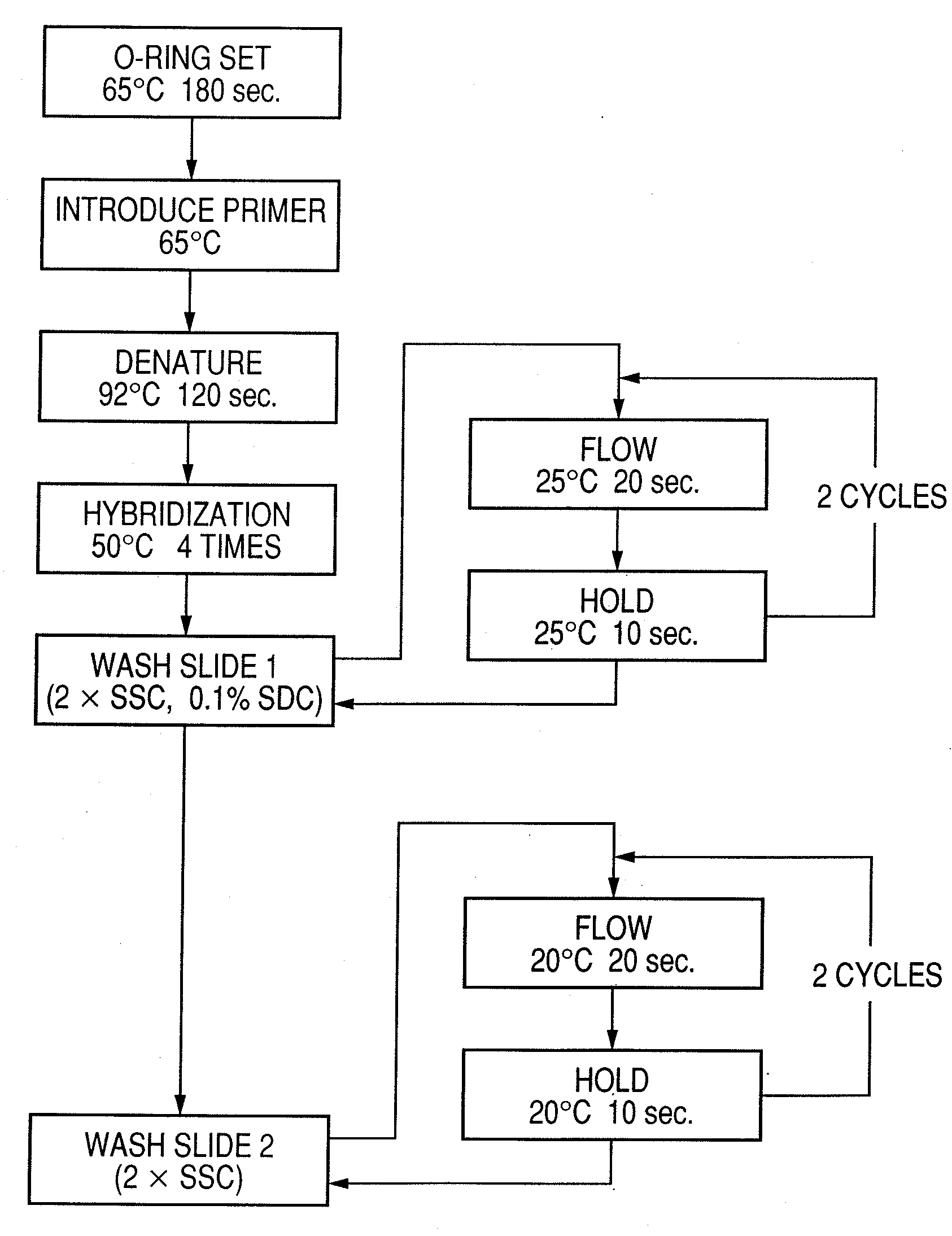
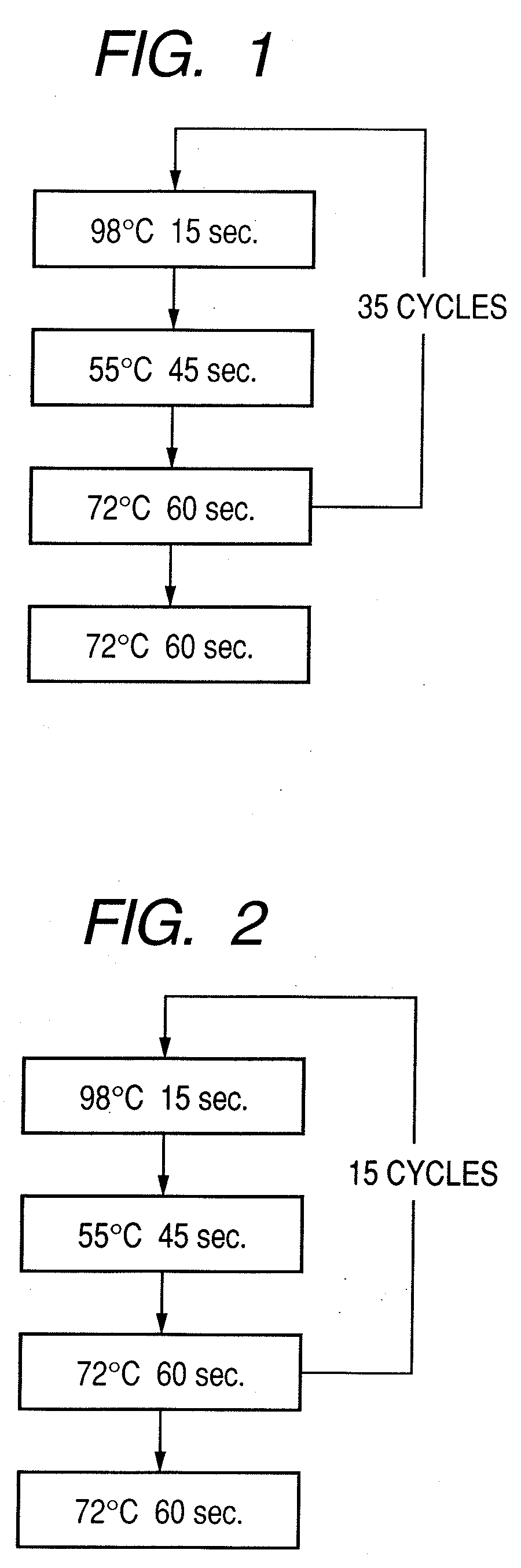
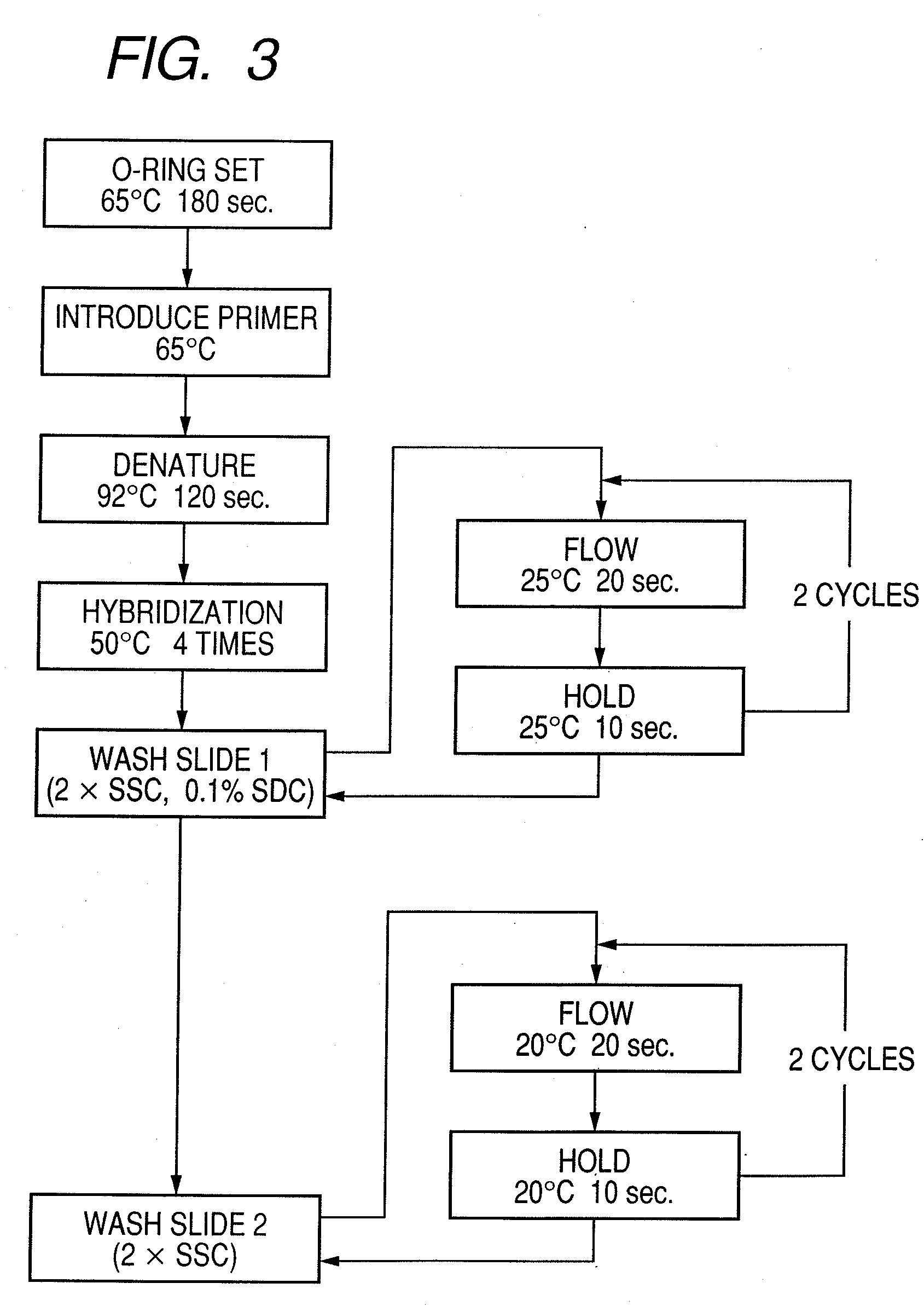
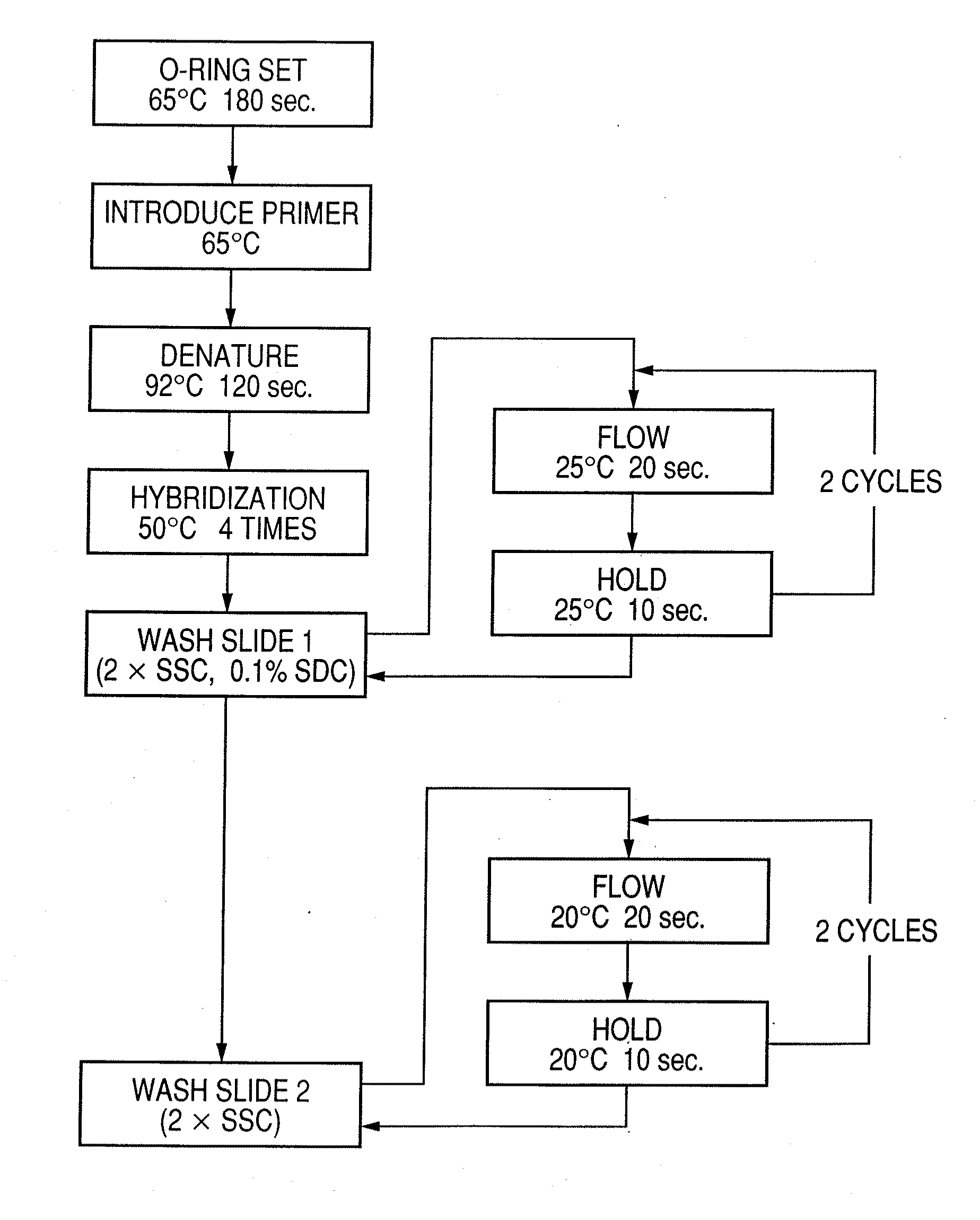
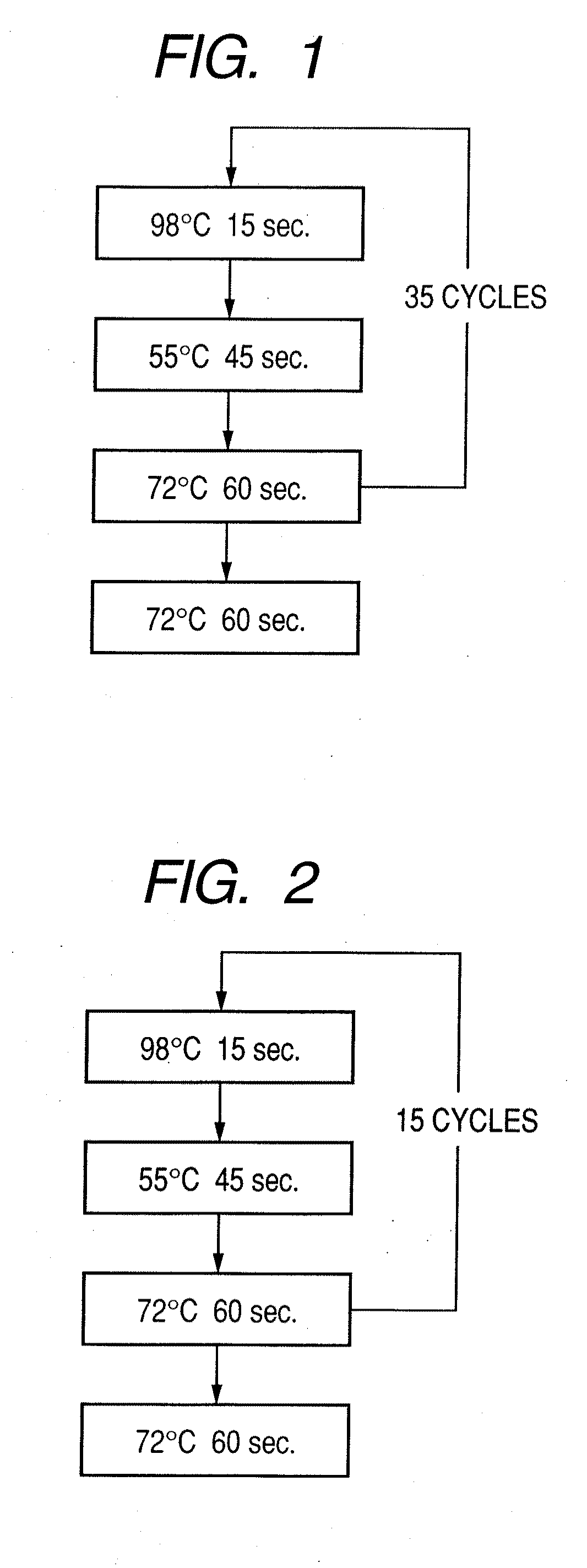
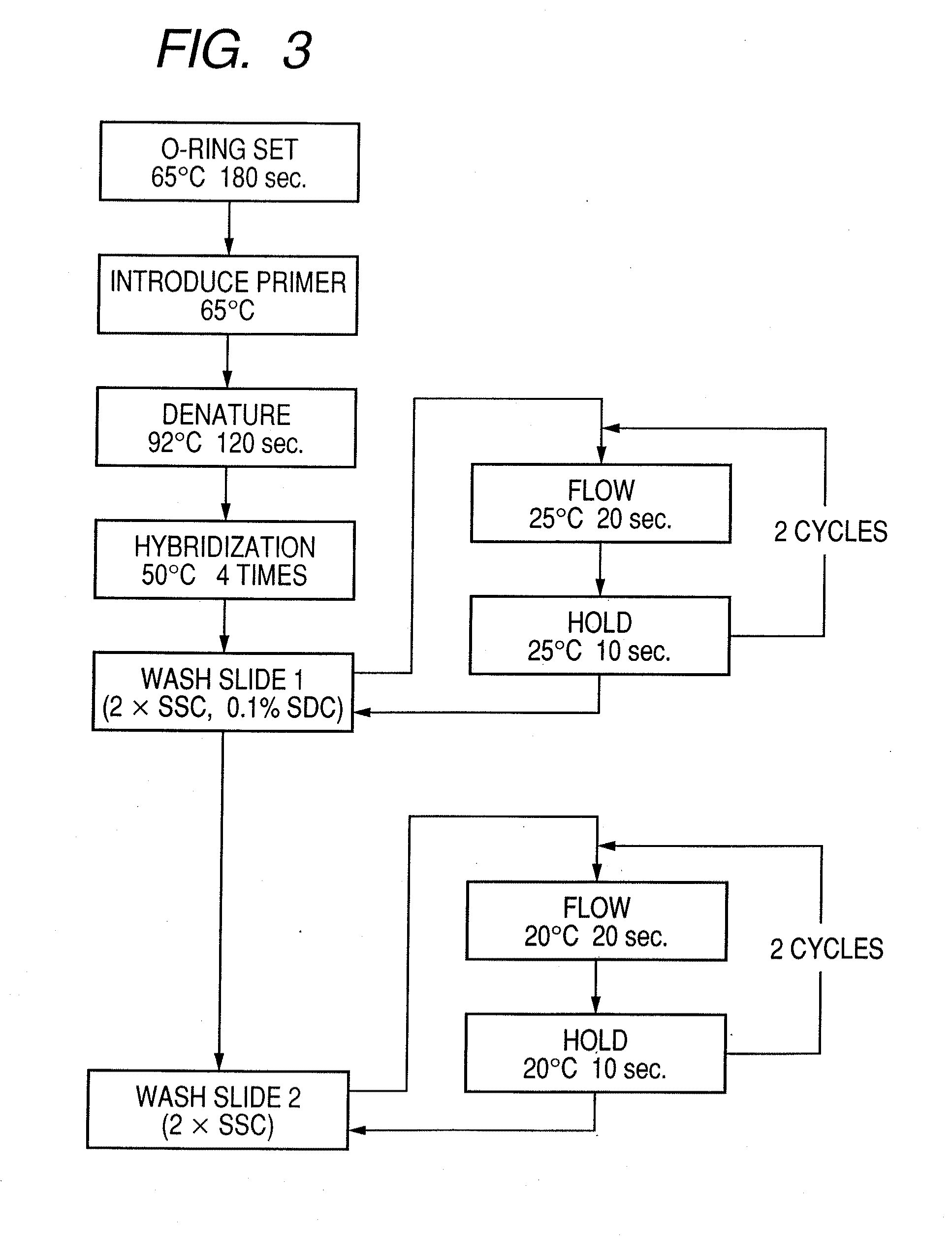
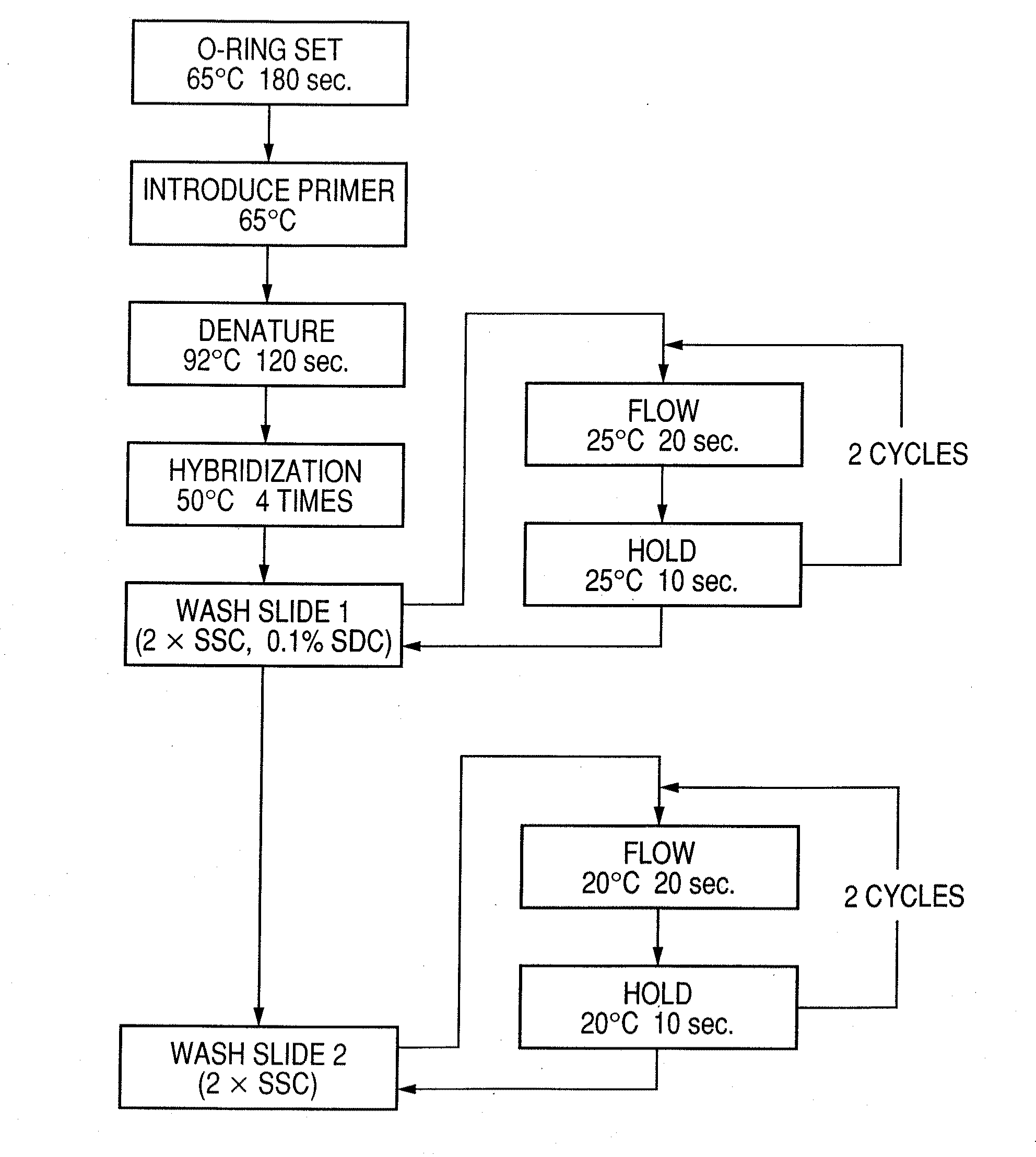
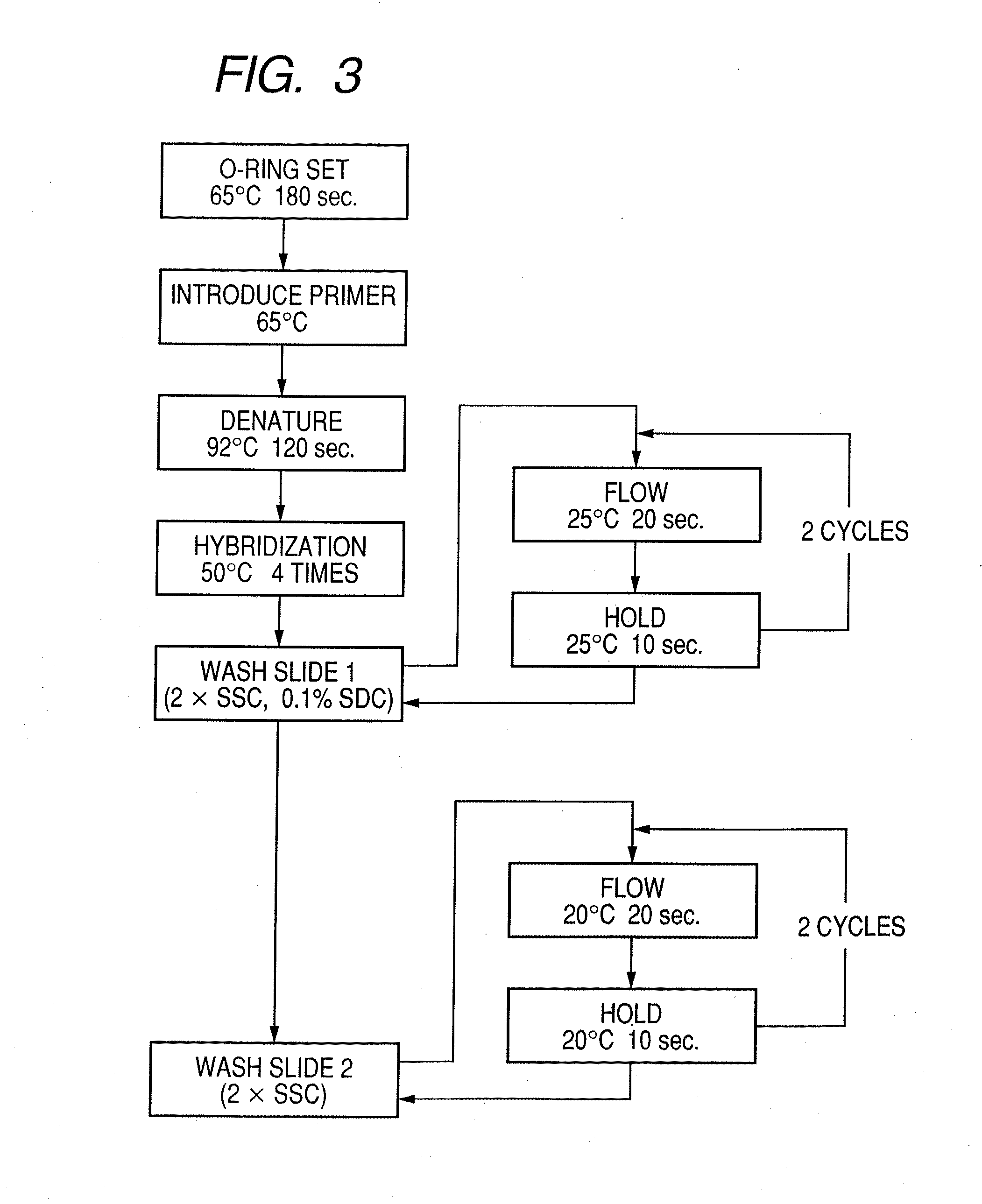
Probe, probe set, probe carrier, and testing method
InactiveUS20080286792A1Accurate identificationQuickly and more detectSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPathogenicityOligonucleotide
A probe, a set of probes, and a probe carrier on which the probe or the set of probes is immobilized, are provided for classification of fungus species. The probe or the set of probes is capable of collectively detecting fungus of the same species and distinguishingly detecting those fungus from fungus of other species. The probe is an oligonucleotide probe for detecting a pathogenic fungus DNA and includes at least one of base sequences of SEQ ID NOS. 1 to 3 and mutated sequences thereof.
Owner:CANON KK
Probe, probe set, probe carrier, and testing method
InactiveUS20090004659A1Accurate identificationQuickly and more accurately detect a target fungusSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPathogenicityOligonucleotide
A probe, a set of probes, and a probe carrier on which the probe or the set of probes is immobilized, are provided for classification of fungus species. The probe or the set of probes is capable of collectively detecting fungus of the same species and distinguishingly detecting those fungus from fungus of other species. The probe is an oligonucleotide probe for detecting a pathogenic fungus DNA and includes at least one of base sequences of SEQ ID NOS. 1 to 4 and mutated sequences thereof.
Owner:CANON KK
Probe, probe set, probe carrier, and testing method
ActiveUS20080299574A1Accurate identificationQuickly and more detectAnimal cellsSugar derivativesPathogenicityOligonucleotide
A probe, a set of probes, and a probe carrier on which the probe or the set of probes is immobilized, are provided for classification of fungus species. The probe or the set of probes is capable of collectively detecting fungus of the same species and distinguishingly detecting those fungus from fungus of other species. The probe is an oligonucleotide probe for detecting a pathogenic fungus DNA and includes at least one of base sequences of SEQ ID NOS. 1 to 4 and mutated sequences thereof.
Owner:CANON KK
Probe, probe set, probe carrier, and testing method
InactiveUS20080293065A1Accurate identificationQuickly and more detectSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPathogenicityOligonucleotide
A probe, a set of probes, and a probe carrier on which the probe or the set of probes is immobilized, are provided for classification of fungus species. The probe or the set of probes is capable of collectively detecting fungus of the same species and distinguishingly detecting those fungus from fungus of other species. The probe is an oligonucleotide probe for detecting a pathogenic fungus DNA and includes at least one of base sequences of SEQ ID NOS. 1 to 2 and mutated sequences thereof.
Owner:CANON KK
Probe, probe set, probe carrier, and testing method
InactiveUS20080299578A1Accurate identificationQuickly and more accurately detect a target fungusSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPathogenicityOligonucleotide
A probe, a set of probes, and a probe carrier on which the probe or the set of probes is immobilized, are provided for classification of fungus species. The probe or the set of probes is capable of collectively detecting fungus of the same species and distinguishingly detecting those fungus from fungus of other species. The probe is an oligonucleotide probe for detecting a pathogenic fungus DNA and includes at least one of base sequences of SEQ ID NOS. 1 to 3 and mutated sequences thereof.
Owner:CANON KK
Probe, probe set, probe carrier, and testing method
InactiveUS20080305487A1Accurate identificationQuickly and more detectSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPathogenicityOligonucleotide
A probe, a set of probes, and a probe carrier on which the probe or the set of probes is immobilized, are provided for classification of fungus species. The probe or the set of probes is capable of collectively detecting fungus of the same species and distinguishingly detecting those fungus from fungus of other species. The probe is an oligonucleotide probe for detecting a pathogenic fungus DNA and includes at least one of base sequences of SEQ ID NOS. 1 to 3 and mutated sequences thereof.
Owner:CANON KK
Probe, probe set, probe carrier, and testing method
InactiveUS20080293064A1Accurate identificationQuickly and more detectSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPathogenicityOligonucleotide
A probe, a set of probes, and a probe carrier on which the probe or the set of probes is immobilized, are provided for classification of fungus species. The probe or the set of probes is capable of collectively detecting fungus of the same species and distinguishingly detecting those fungus from fungus of other species. The probe is an oligonucleotide probe for detecting a pathogenic fungus DNA and includes at least one of base sequences of SEQ ID NOS. 1 to 2 and mutated sequences thereof.
Owner:CANON KK
Probe, probe set, probe carrier, and testing method
InactiveUS20090068661A1Accurate identificationQuickly and more detectSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPathogenicityOligonucleotide
A probe, a set of probes, and a probe carrier on which the probe or the set of probes is immobilized, are provided for classification of fungus species. The probe or the set of probes is capable of collectively detecting fungus of the same species and distinguishingly detecting those fungus from fungus of other species. The probe is an oligonucleotide probe for detecting a pathogenic fungus DNA and includes at least one of base sequences of SEQ ID NOS. 1 to 4 and mutated sequences thereof.
Owner:CANON KK
Method for diagnosis and monitoring of pathogenic infection by analysis of pathogenic transrenal nucleic acids in urine
The present invention relates to a method for diagnosing and / or monitoring a bacterial or parasitic infection by detection and quantification of the transrenal nucleic acids, derived from bacterial pathogenic agents or from parasites, in urine. The detection method optionally includes the isolation and the purification of the nucleic acids from urine by methods known in the art including pairing with molecular probes that are specific for the pathogenic agents, PCR hybridization, PCR, nested PCR, SSCP, LCR, and SDA. Diagnostic kits based on these detection methods are also claimed.
Owner:INST NAT PER LE MALATTIE INFETTIVE LAZZARO SPALLANZANI IRCCS
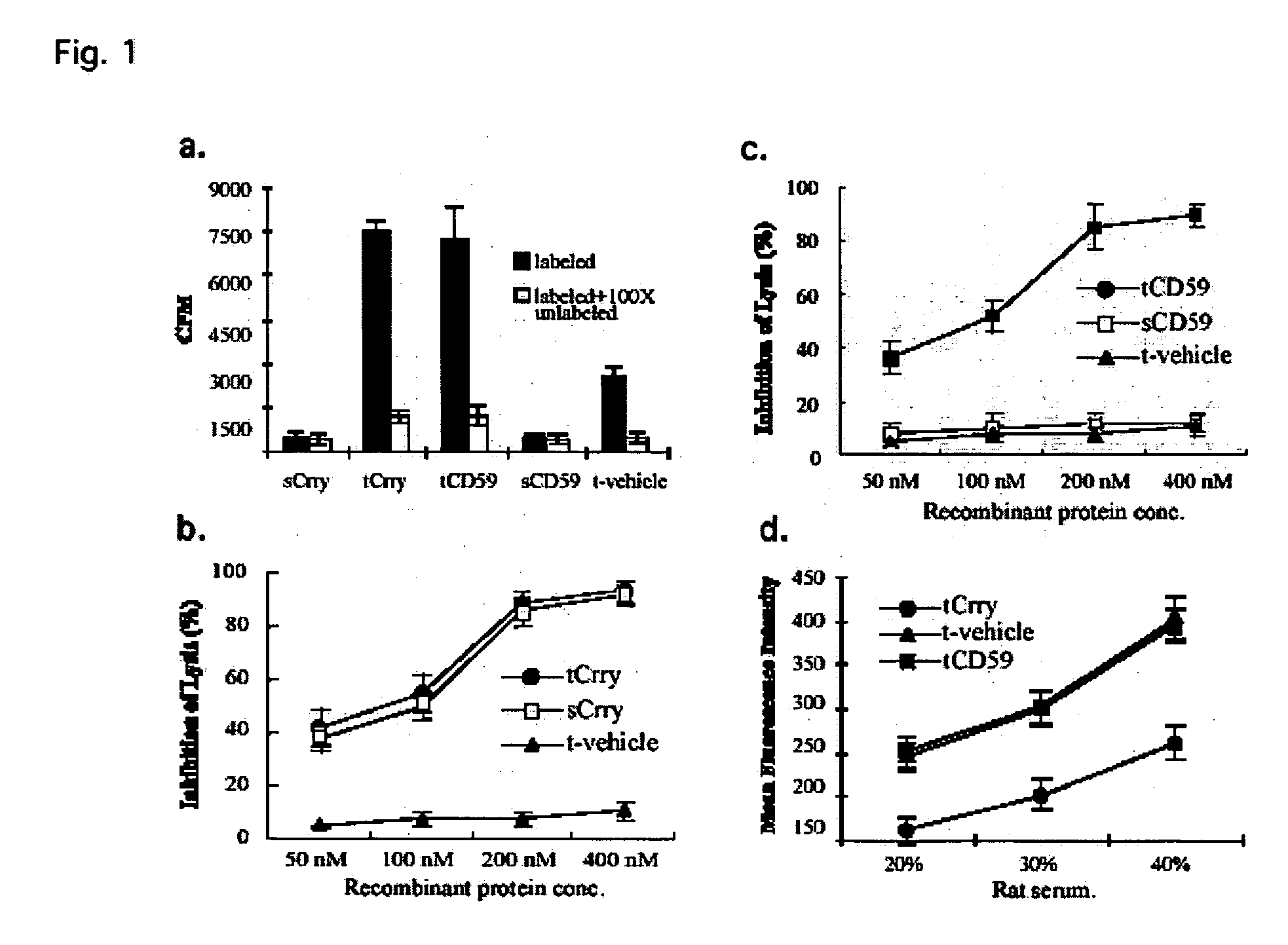
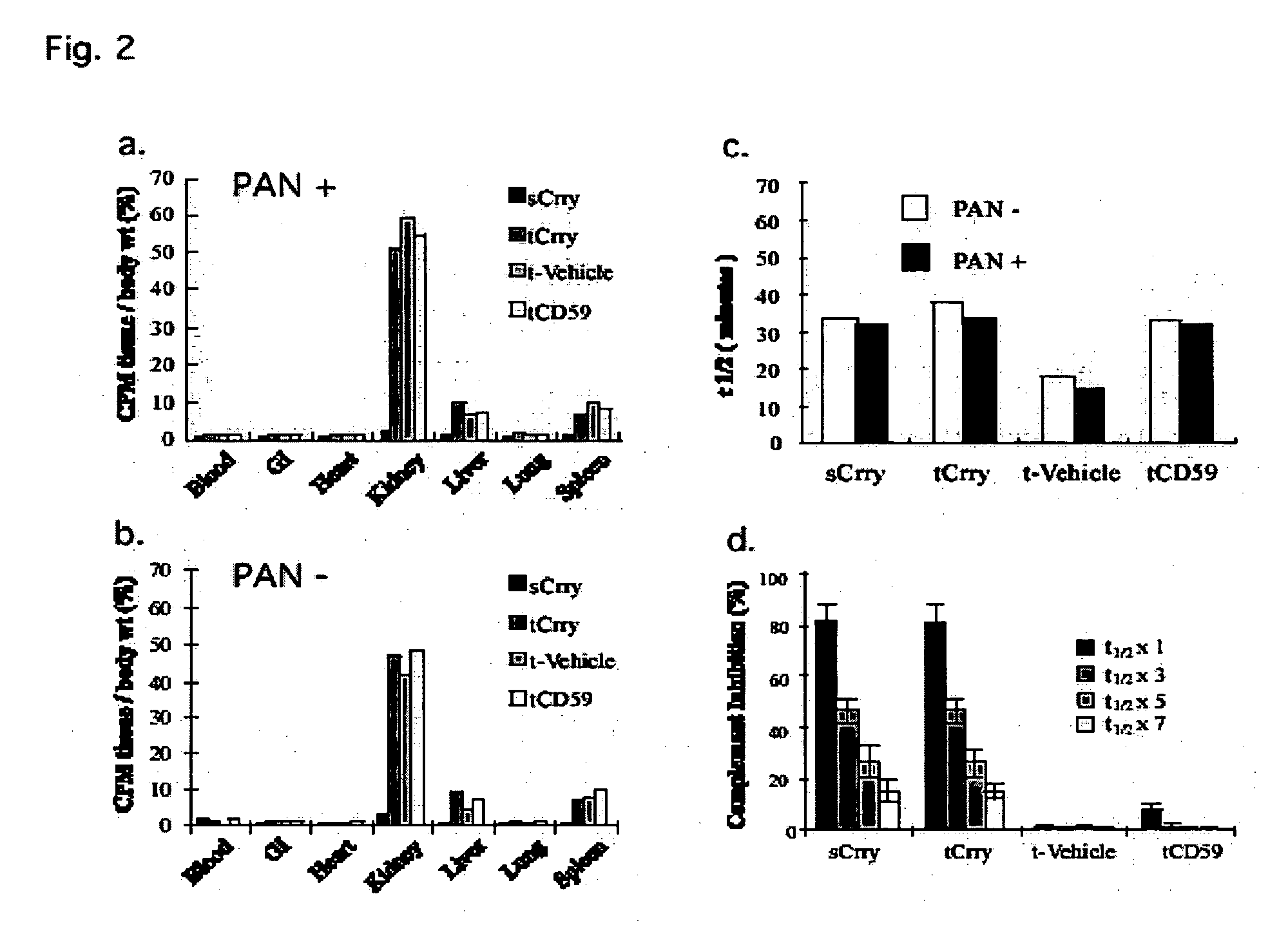
Tissue targeted complement modulators
InactiveUS20050265995A1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsEpitheliumWhole body
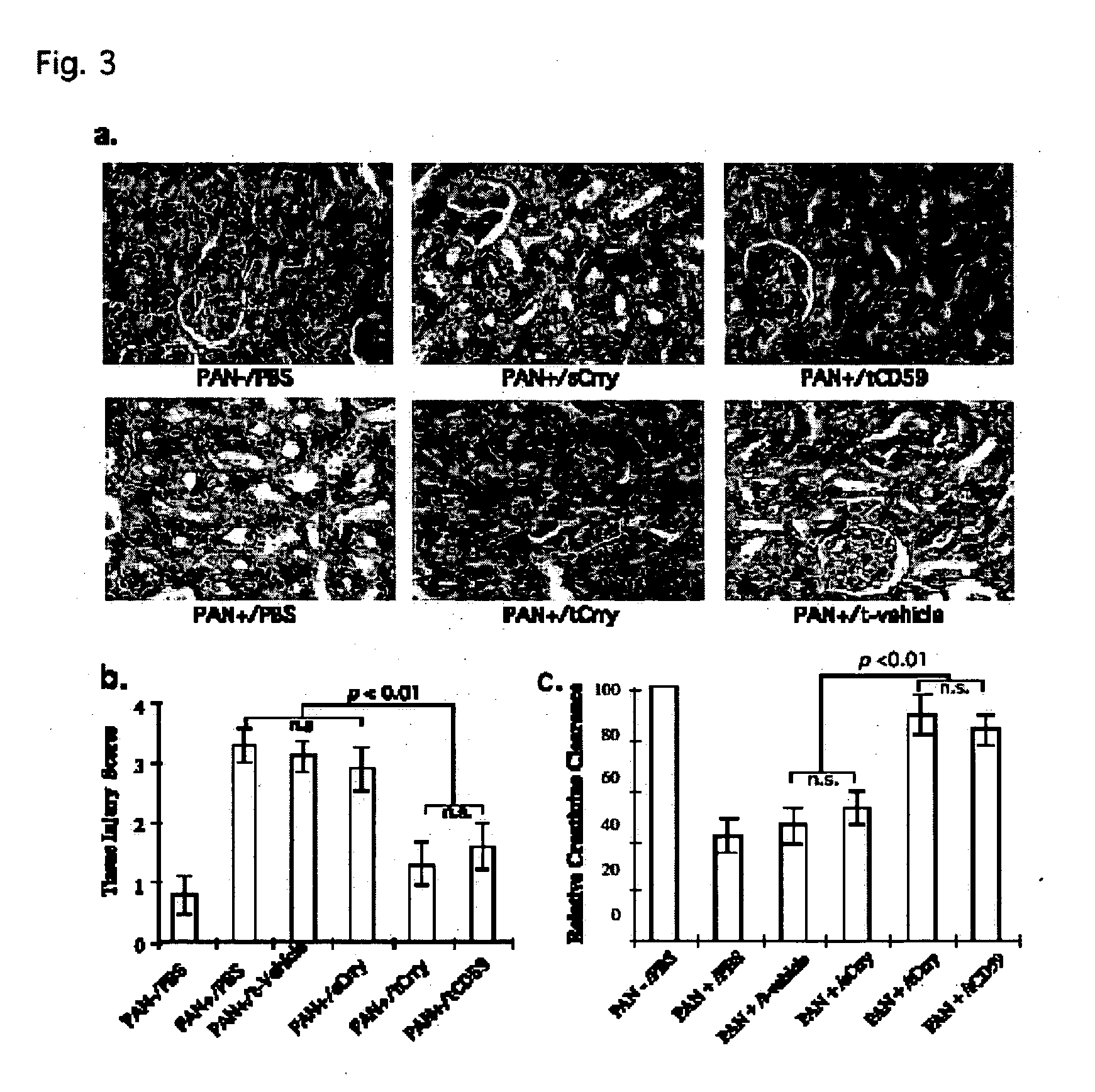
Systemic suppression of the complement system has been shown to be effective to treat inflammatory disease, yet at the potential cost of compromising host defense and immune homeostasis. Herein disclosed are methods for antigen-specific targeting of complement inhibitors that show that complement inhibitors targeted to the proximal tubular epithelium protect against tubulointerstitial injury and renal dysfunction in a rat model of nephrosis. It is shown that appropriate targeting of a systemically administered complement inhibitor to a site of disease markedy enhances efficacy and obviates the need to systemically inhibit complement. Additionally, it is shown by specifically inhibiting the terminal pathway of complement, that the membrane attack complex (MAC) plays a key role in proteinuria-induced tubulointerstitial injury, thus establishing the MAC as a valid target for pharmacological intervention in proteinuric disorders. The disclosed are compositions can be used in methods of treating pathogenic diseases and inflammatory conditions by modulating the complement system.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO +1
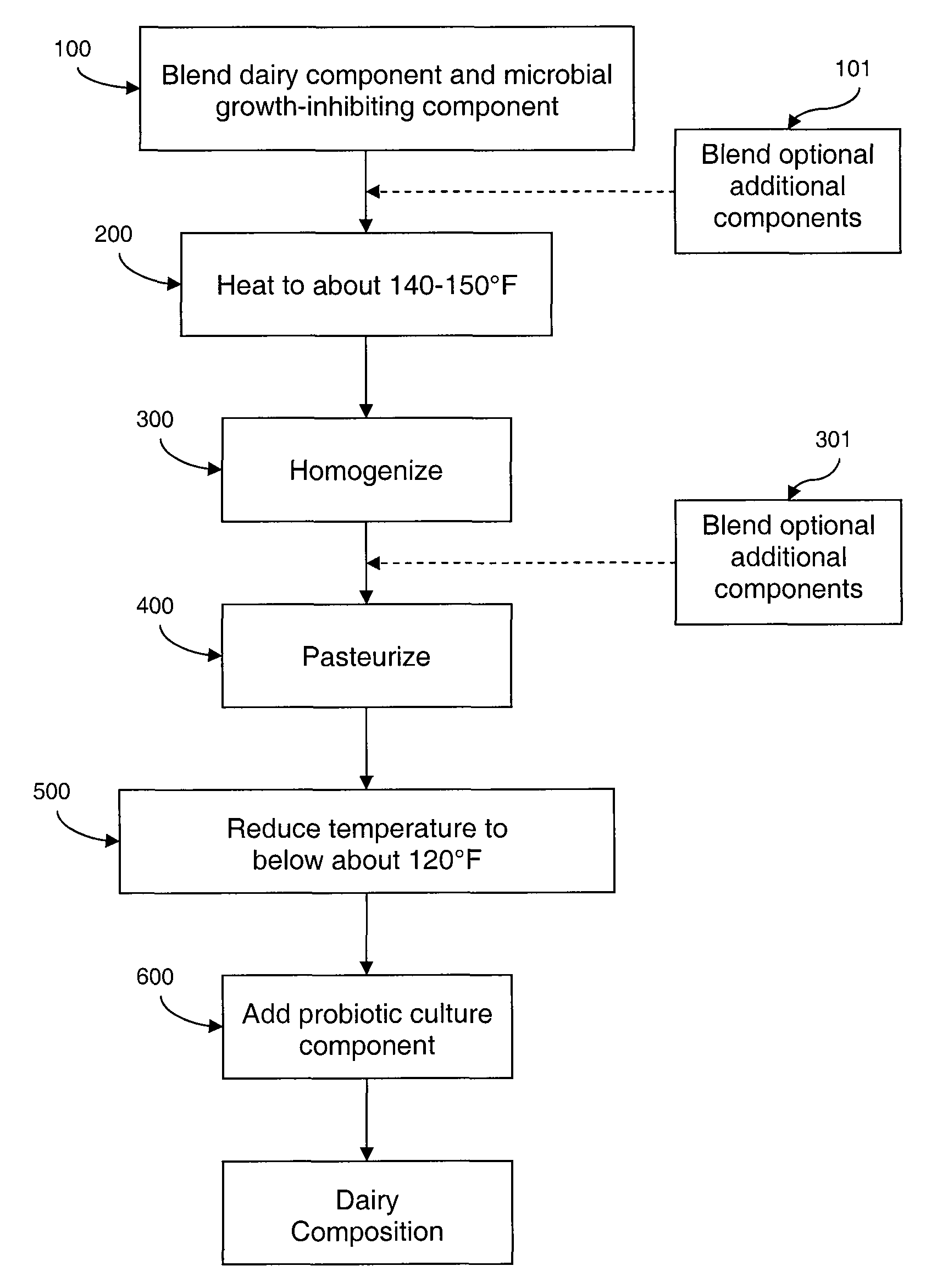
Dairy composition with probiotics and anti-microbial system
Dairy compositions are provided having a high pH, of about 4.8 to about 6.2, comprising desirable probiotic cultures as well as an anti-microbial system for inhibiting undesirable pathogenic and / or spoilage microbial growth without significantly reducing the beneficial effect of the probiotic cultures.
Owner:KRAFT FOODS GRP BRANDS LLC
Annotation method and annotation system of whole-genome variant data
InactiveCN106156538AAccurate NotesSolve the screening puzzleProteomicsGenomicsReference genesAllele frequency
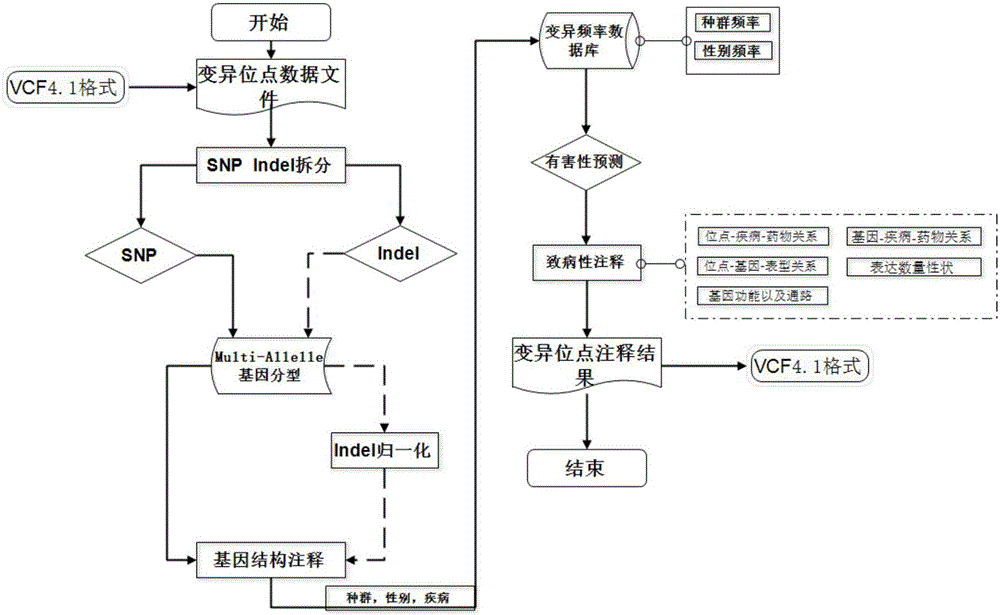
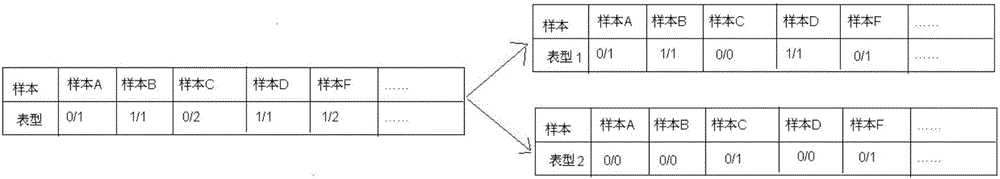
The invention discloses an annotation method and an annotation system of whole-genome variant data. The method comprises the following steps of S1, creating a variant data file, wherein the variant data are stored according to a national standard VCF format as an input file; S2, performing multi-allele genotyping, firstly performing genotype judgment, representing a basic group which is consistent with a reference genome by zero, and representing the basic groups which are inconsistent with the reference gene group by 1, 2, 3,..., then performing SNP and InDel multi-allele type resolution so that the allele type is represented by zero and one; S3, causing InDel generation position normalization, namely performing InDel generation position normalization according to a left justification and simplification normalization method; and S4, performing annotation, namely performing gene structure annotation, allele frequency annotation, variable site harm prediction and pathogenicity annotation. The annotation method and the annotation system improve integrity and accuracy of annotation information.
Owner:天津诺禾医学检验所有限公司
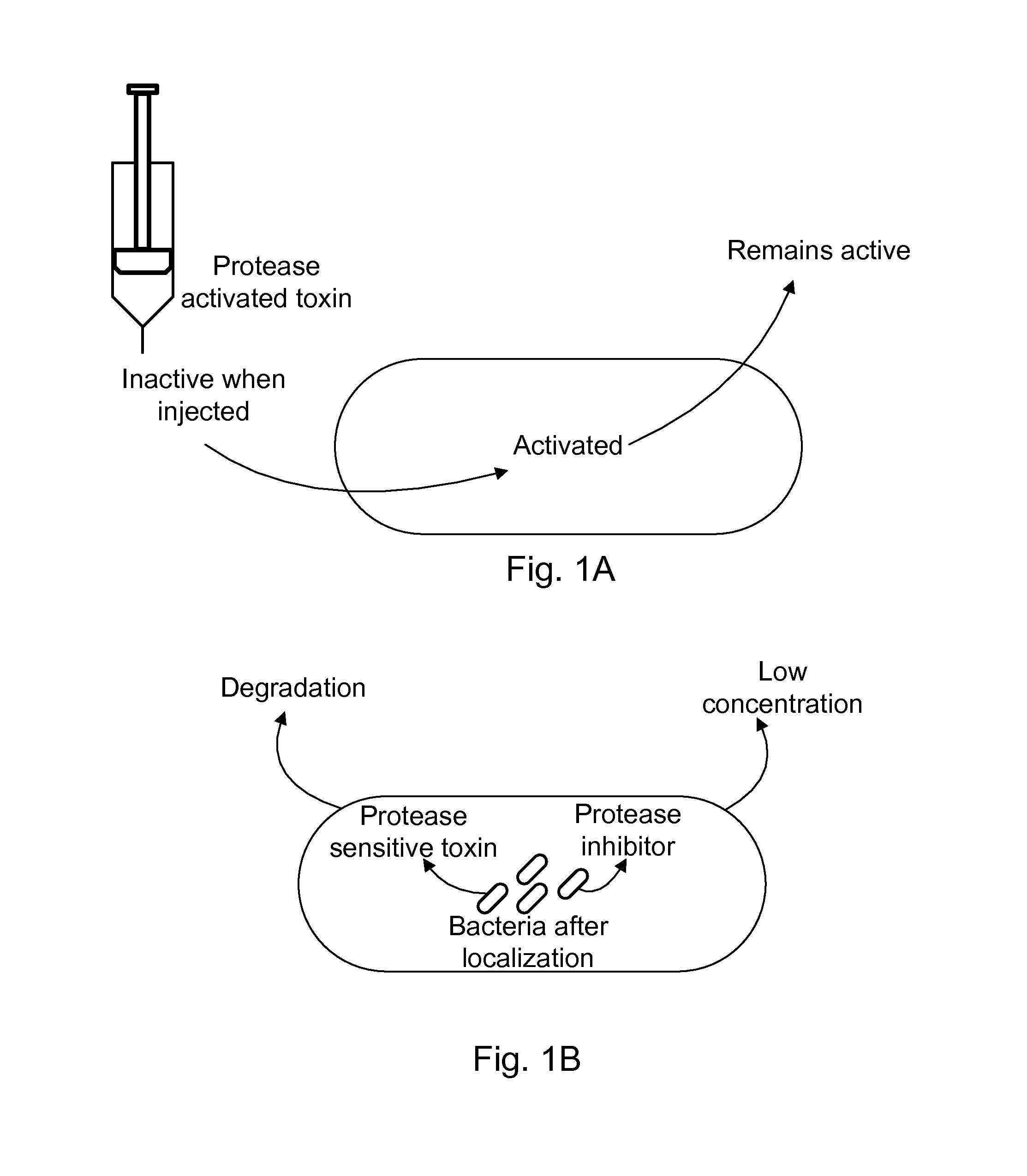
Protease inhibitor: protease sensitivity expression system composition and methods improving the therapeutic activity and specificity of proteins delivered by bacteria
Bacteria which co-express protease inhibitors and protease sensitive therapeutic agents, which are surface displayed, secreted and / or released and result in their localized production and maintenance within a target tissue and inactivation outside of the target tissue, thereby increasing therapeutic activity and reducing the systemic toxicity. The bacteria may be attenuated, non-pathogenic, low pathogenic or a probiotic. Protease sensitivity may be further accomplished by engineering protease degradation sites within the therapeutic agents, further enhancing the inactivation outside of the target tissue while retaining activity within the target tissue through co-expression of a protease inhibitor. Novel chimeric proteins secreted by bacteria, including chimeric toxins targeted to neoplastic cells, tumor matrix cells and cells of the immune system, and combination therapies of these protease inhibitor:chimeric toxin-expressing bacteria together with small-molecule and biologic agents are also described. Non-conjugative bacteria limiting exchange of genetic material, and antibody resistant bacteria are also provided.
Owner:BERMUDES DAVID GORDON
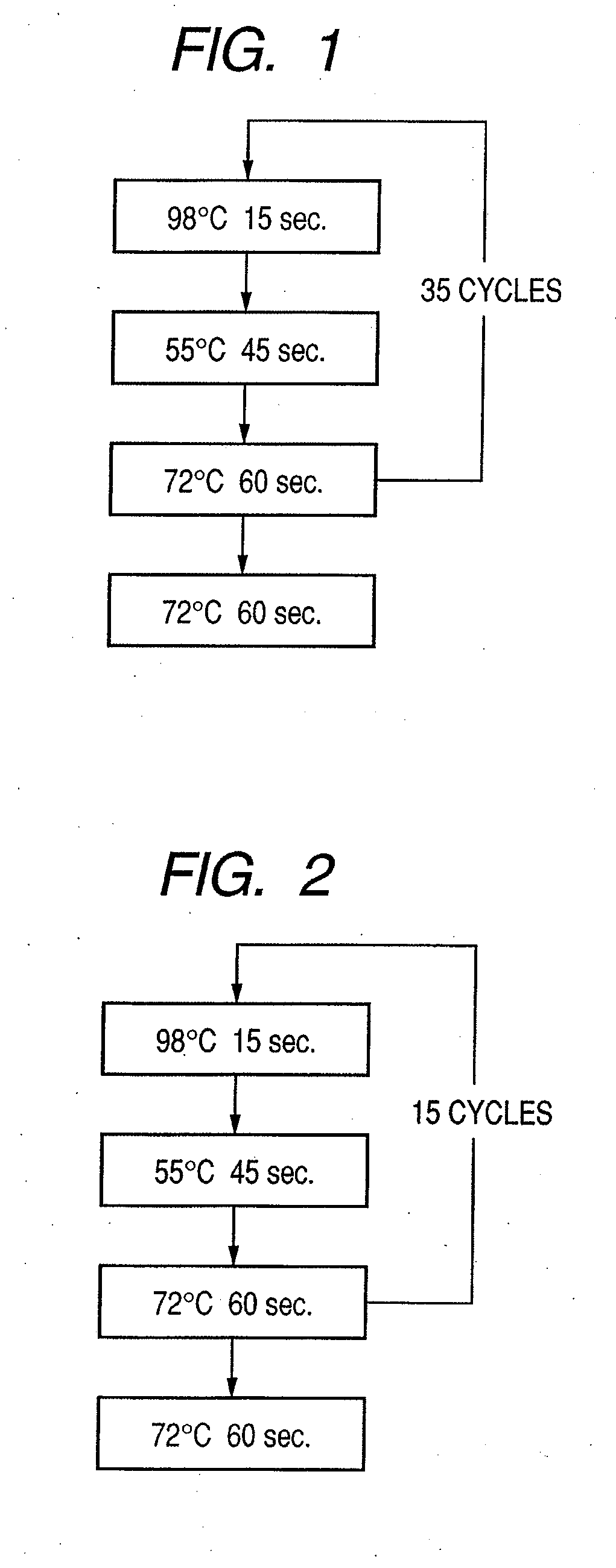
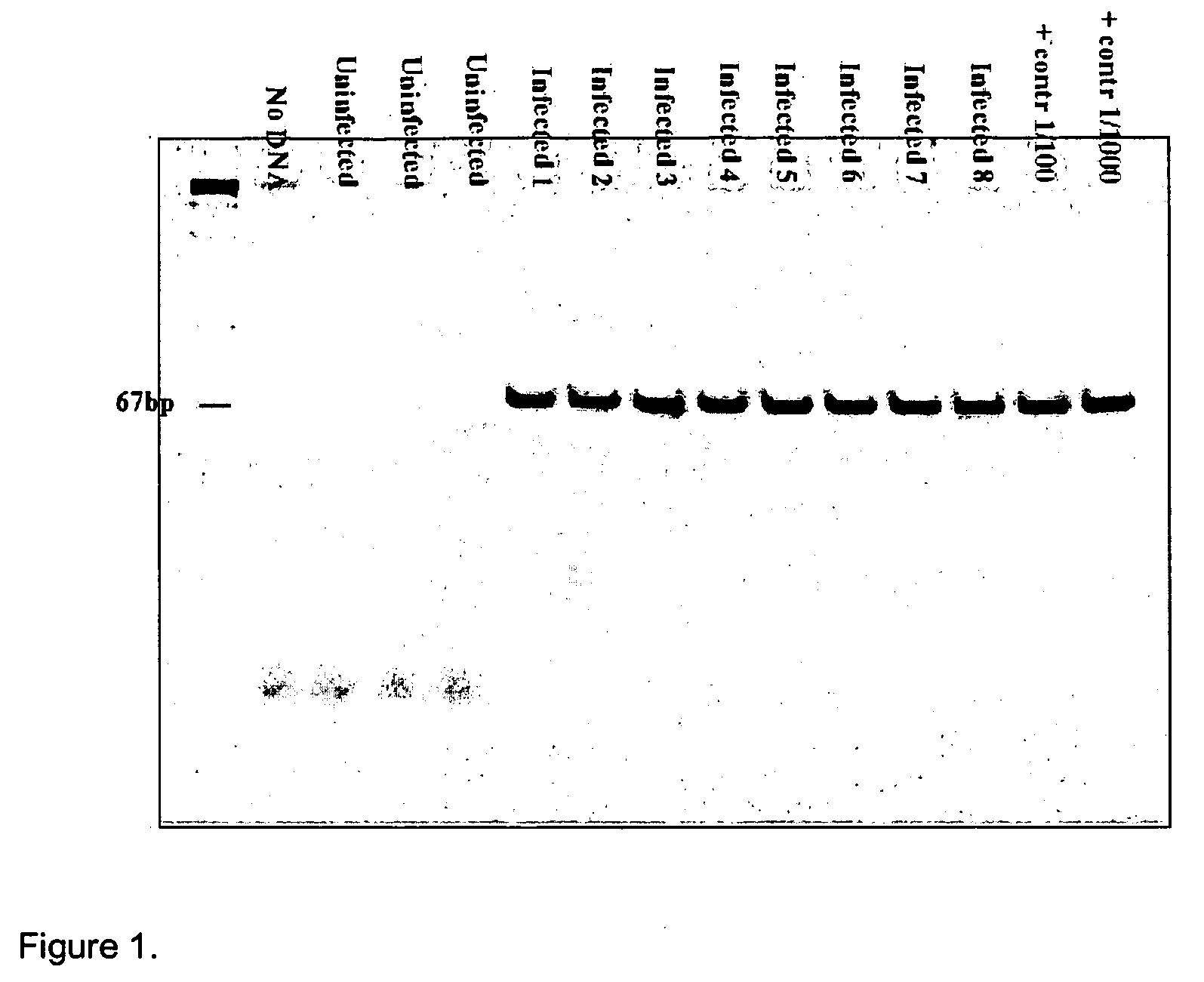
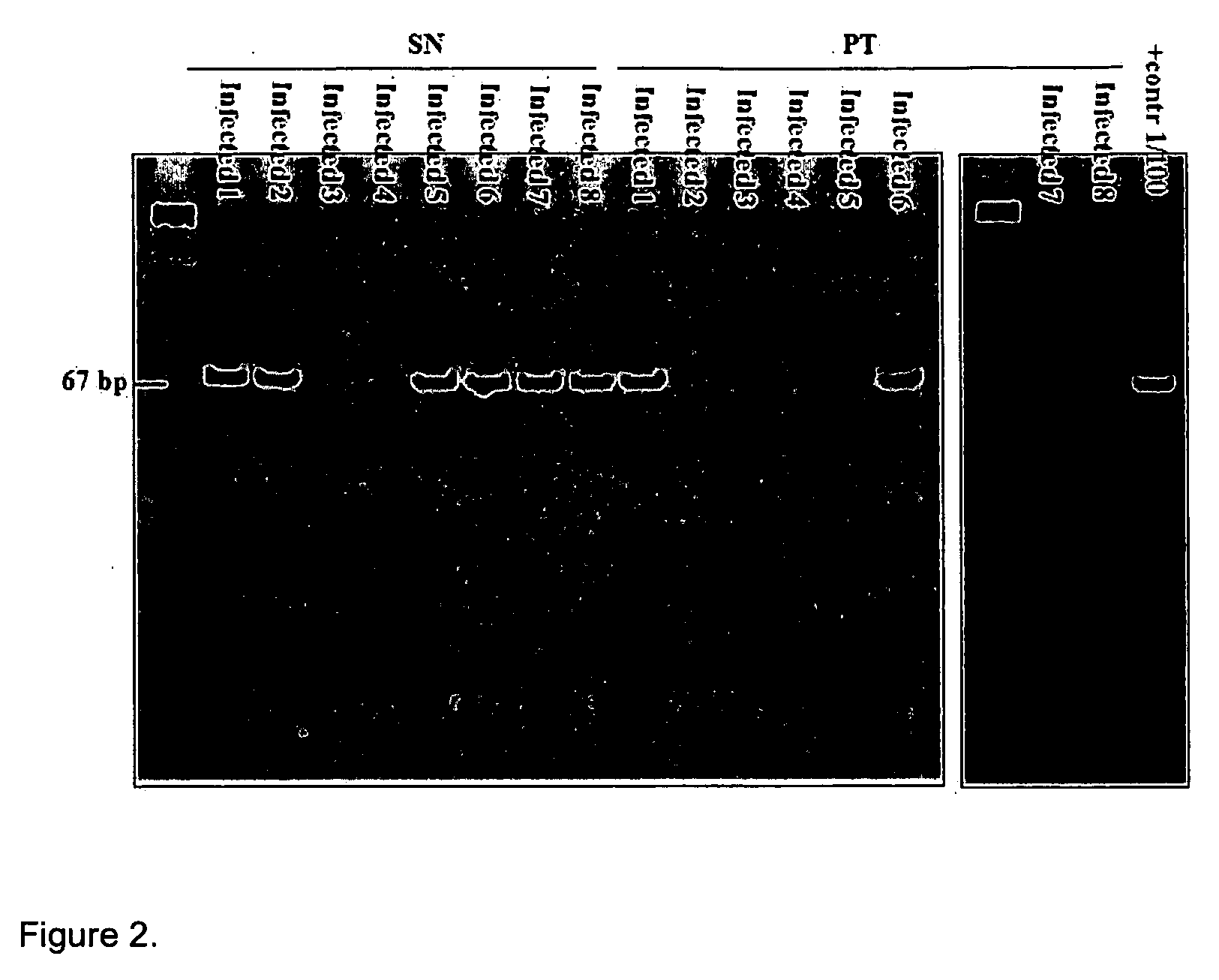
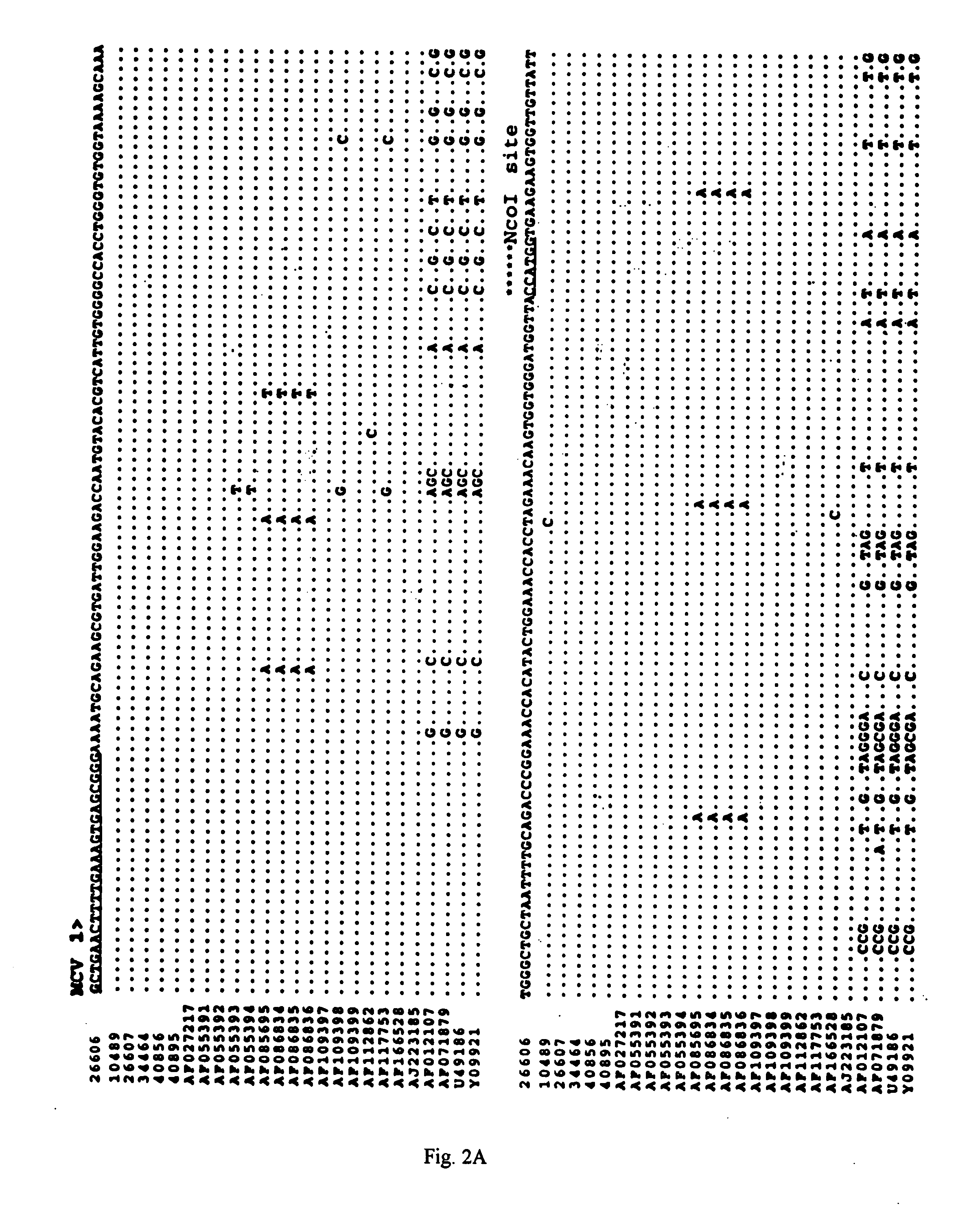
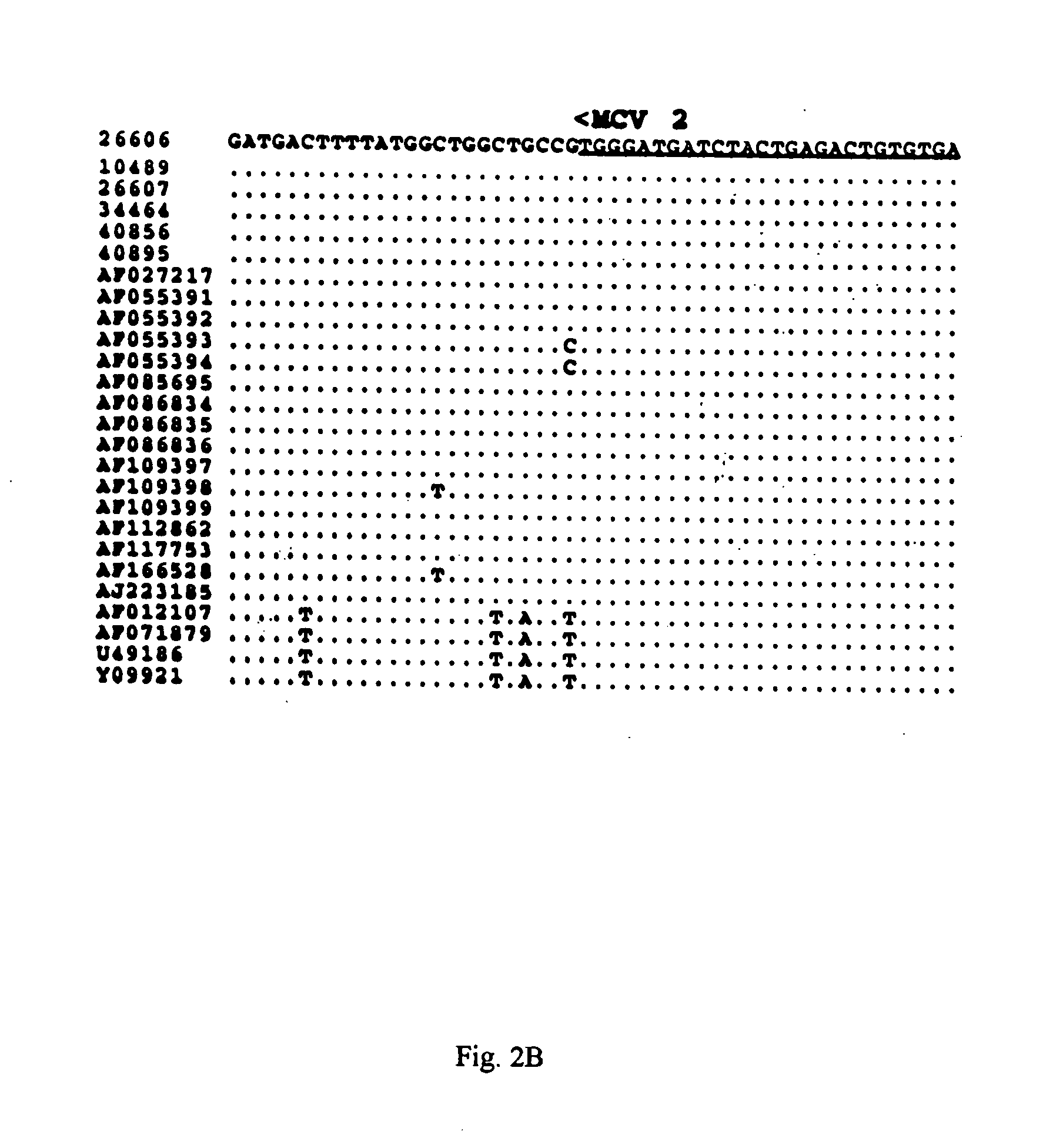
Differential PCR-RFLP assay for detecting and distinguishing between nonpathogenic PCV-1 and pathogenic PCV-2
InactiveUS20050147966A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementRestriction enzyme digestionNucleotide
The present invention relates to a method for detecting and differentiating PCV infections in a biological sample taken from a pig which involves amplifying a fragment from an extracted nucleic acid; digesting the fragment with a suitable restriction enzyme such as the unique NcoI restriction enzyme; forming a restriction fragment length polymorphism pattern; and then detecting the presence or absence of a PCV isolate. The invention further concerns the new oligonucleotide primers for differentiating PCV infections comprising a nucleotide sequence selected from the group consisting of MCV1 having a nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:1 and MCV2 having a nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:2. Moreover, this invention provides a novel kit for detecting and distinguishing PCV infections that includes the new oligonucleotide primers and the suitable restriction enzyme.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain and application thereof
InactiveCN101985608AGood control effectControl epidemicBiocideBacteriaEcological environmentOrganism
The invention relates to a bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain, which is characterized in that the collection No. of the strain is CGMCC No.3789; and the 16S rRNA of the strain accesses to GenBank, with accession No. of HQ179100. The strain is used for controlling rice bacterial leaf streak. The strain has the following advantages: the strain has good control effect on the rice bacterial leaf streak, is free of toxin and pathogenicity, is harmless to people and livestock and is environment-friendly; the prepared biocontrol bacteria or the compound biocontrol bacteria formed by compounding the prepared biocontrol bacteria and bismerthiazol are sprayed after being diluted, so that reasonable distribution of the microfloras in the ecological environment around the root leaves of the rice can be controlled and managed and the living environment of the pathogenic bacteria is worsened to form a rice ecosystem with biodiversity, thus effectively and enduringly controlling prevalence of the rice bacterial leaf streak.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Immunization and/or treatment of parasites and infectious agents by live bacteria
ActiveUS8771669B1Reducing eliminatingReducing or eliminating the targeted parasite, infectious diseaseVirusesBacteriaLytic peptideHuntingtons chorea
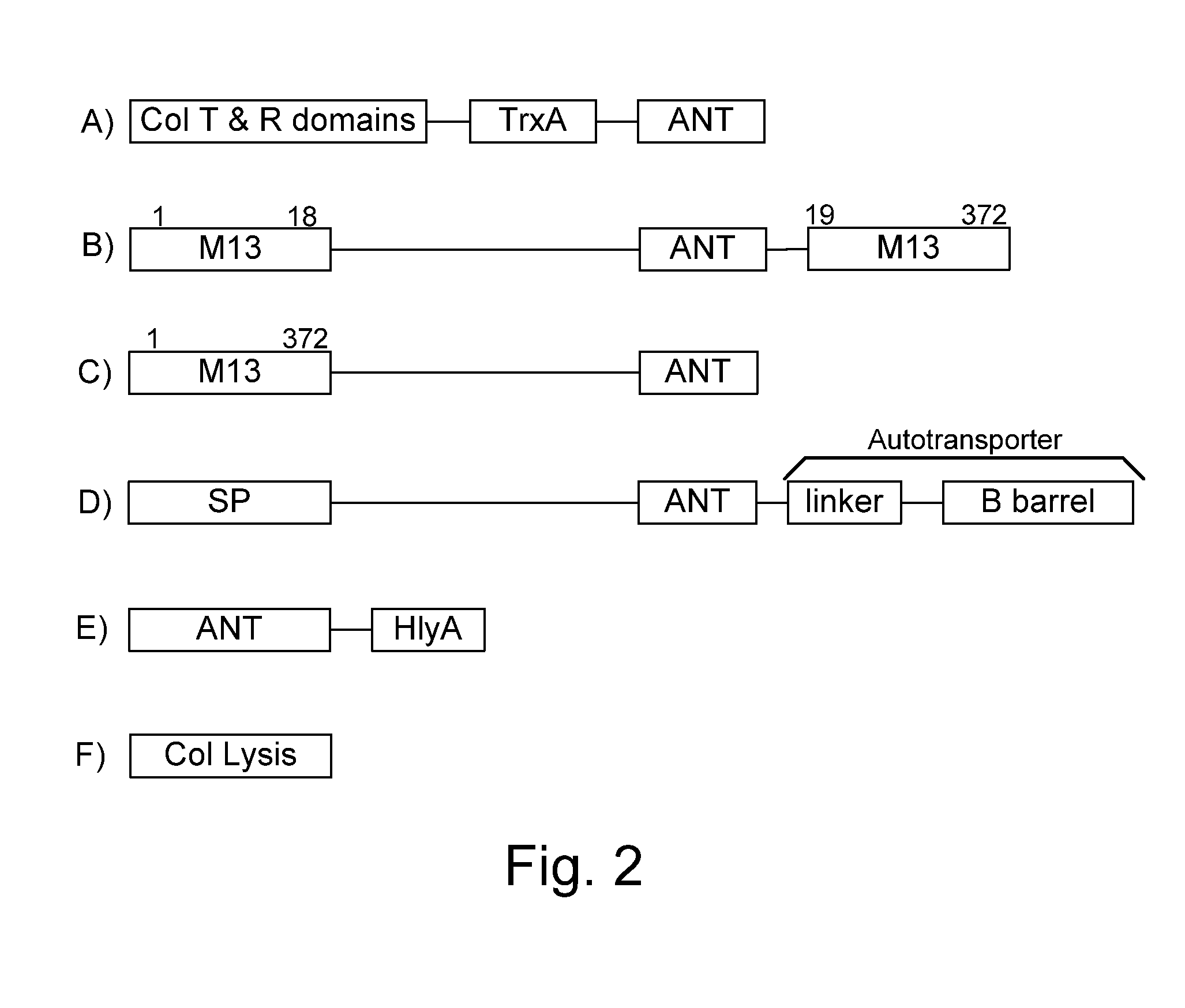
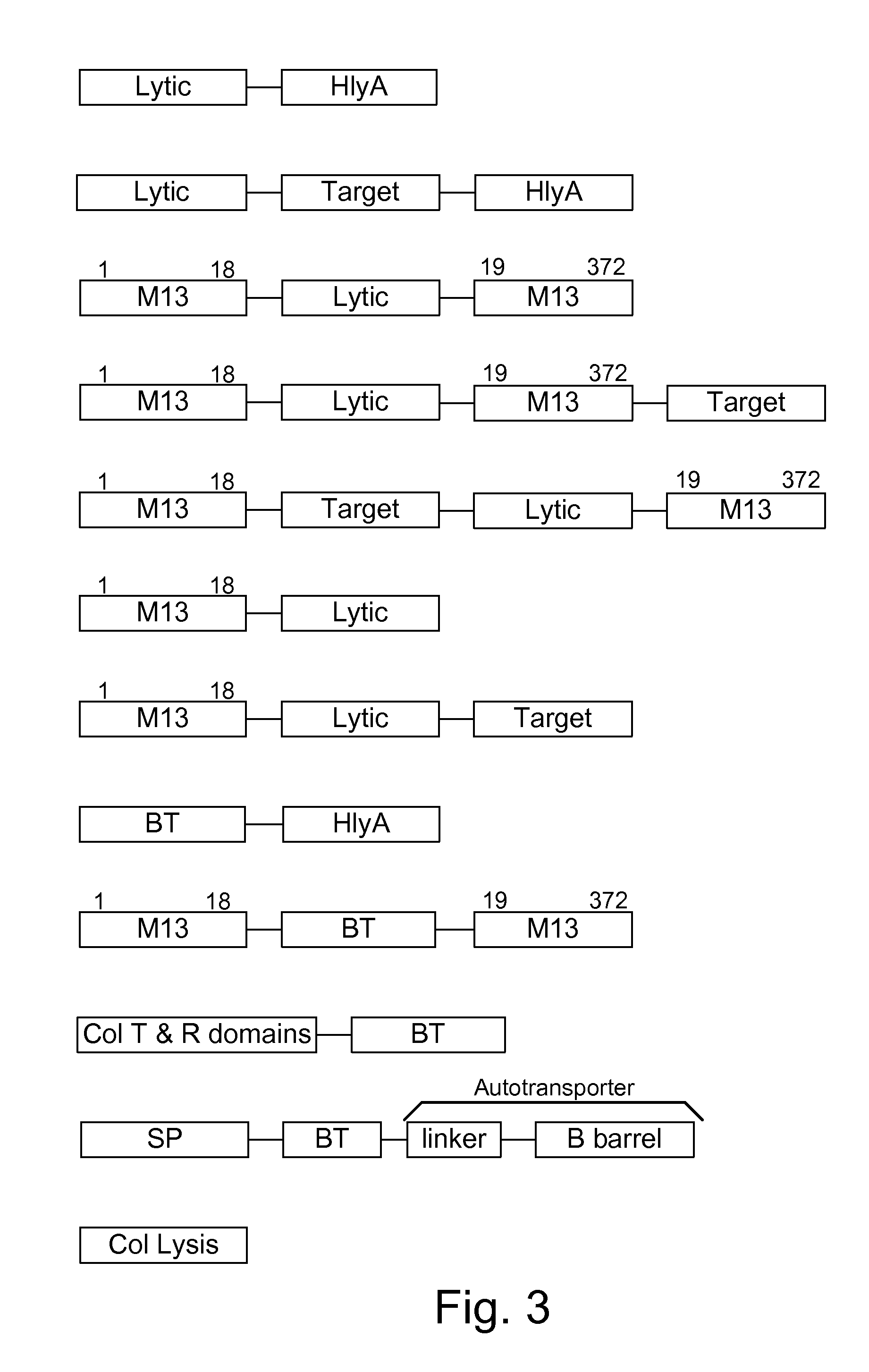
Chimeric proteins are expressed, secreted or released by a bacterium to immunize against or treat a parasite, infectious disease or malignancy. The delivery vector may also be attenuated, non-pathogenic, low pathogenic, or a probiotic bacterium. The chimeric proteins include chimeras of, e.g., phage coat and / or colicin proteins, bacterial toxins and / or enzymes, autotransporter peptides, lytic peptides, multimerization domains, and / or membrane transducing (ferry) peptides. The active portion of the immunogenic chimeric proteins can include antigens against a wide range of parasites and infectious agents, cancers, Alzheimer's and Huntington's diseases, and have enhanced activity when secreted or released by the bacteria, and / or have direct anti-parasite or infectious agent activity. The activity of the secreted proteins is further increased by co-expression of a protease inhibitor that prevents degradation of the effector peptides. Addition of an antibody binding or antibody-degrading protein further prevents the premature elimination of the vector and enhances the immune response.
Owner:BERMUDES DAVID G DR
Modulation of pathogenicity
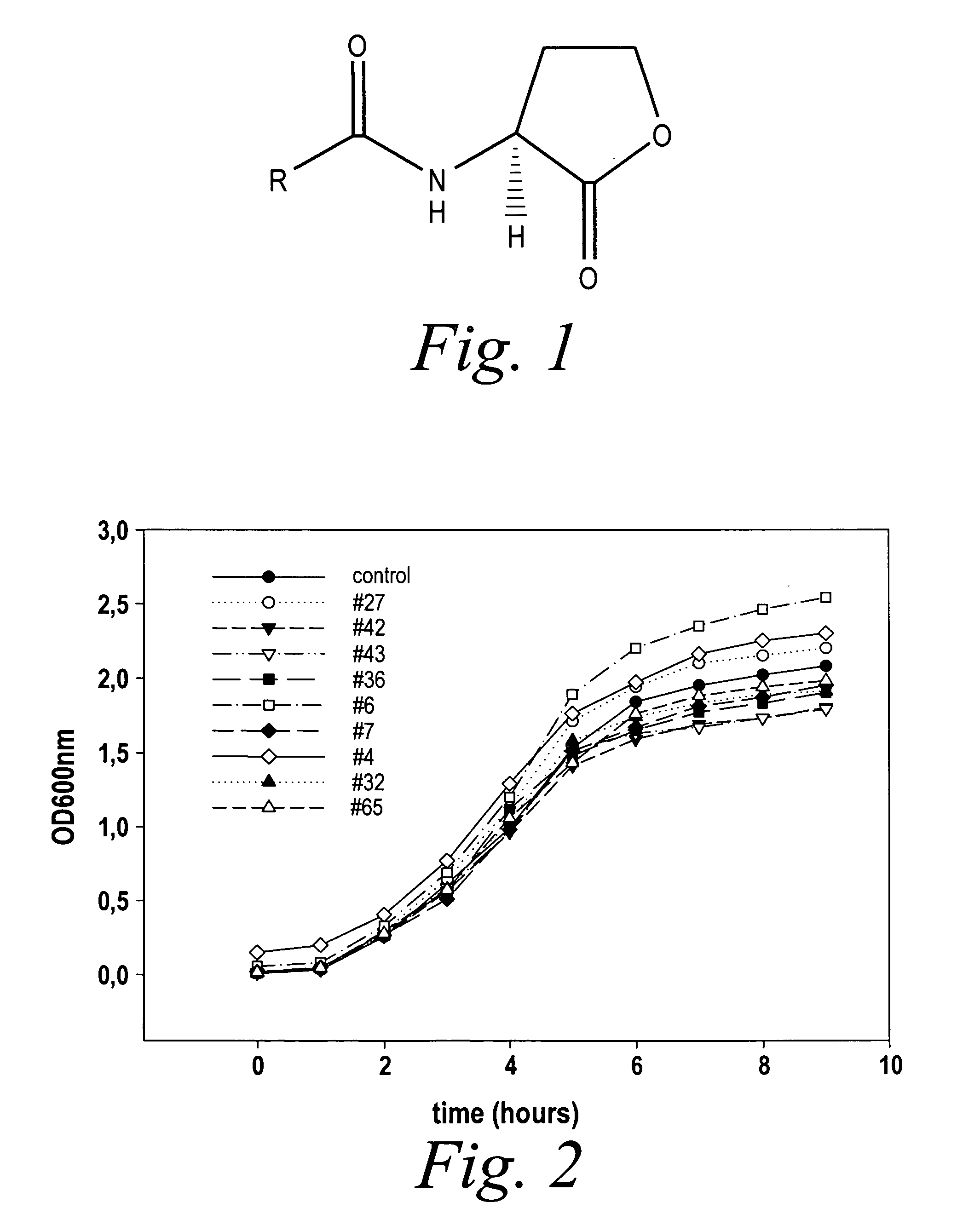
InactiveUS7335779B2Modulating bacterial cell-cell communicationReduce formationAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsArylPathogenicity
The present invention relates to the use of compounds of the general Formula (I):wherein in Formula (I),R is H, alkyl, cycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl;R1 is H, alkyl, cycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl;R2 is H, alkyl, cycloalkyl, aryl or heteroaryl;A1 and A2 each independently represent an optionally substituted C1-C20-alkyl group which may contain one or more group(s) Z, or a monocyclic or polycyclic optionally substituted aromatic or non-aromatic ring system which may contain one or more group(s) X, and in case of a polycyclic ring system, said system contains at least one aromatic ring;Z is selected from the group consisting of S, O, N, NR4, CO, CO2, CS, SO or SO2 X is selected from the group consisting of S, O, N, NR4, SO or SO2.
Owner:QUONOVA
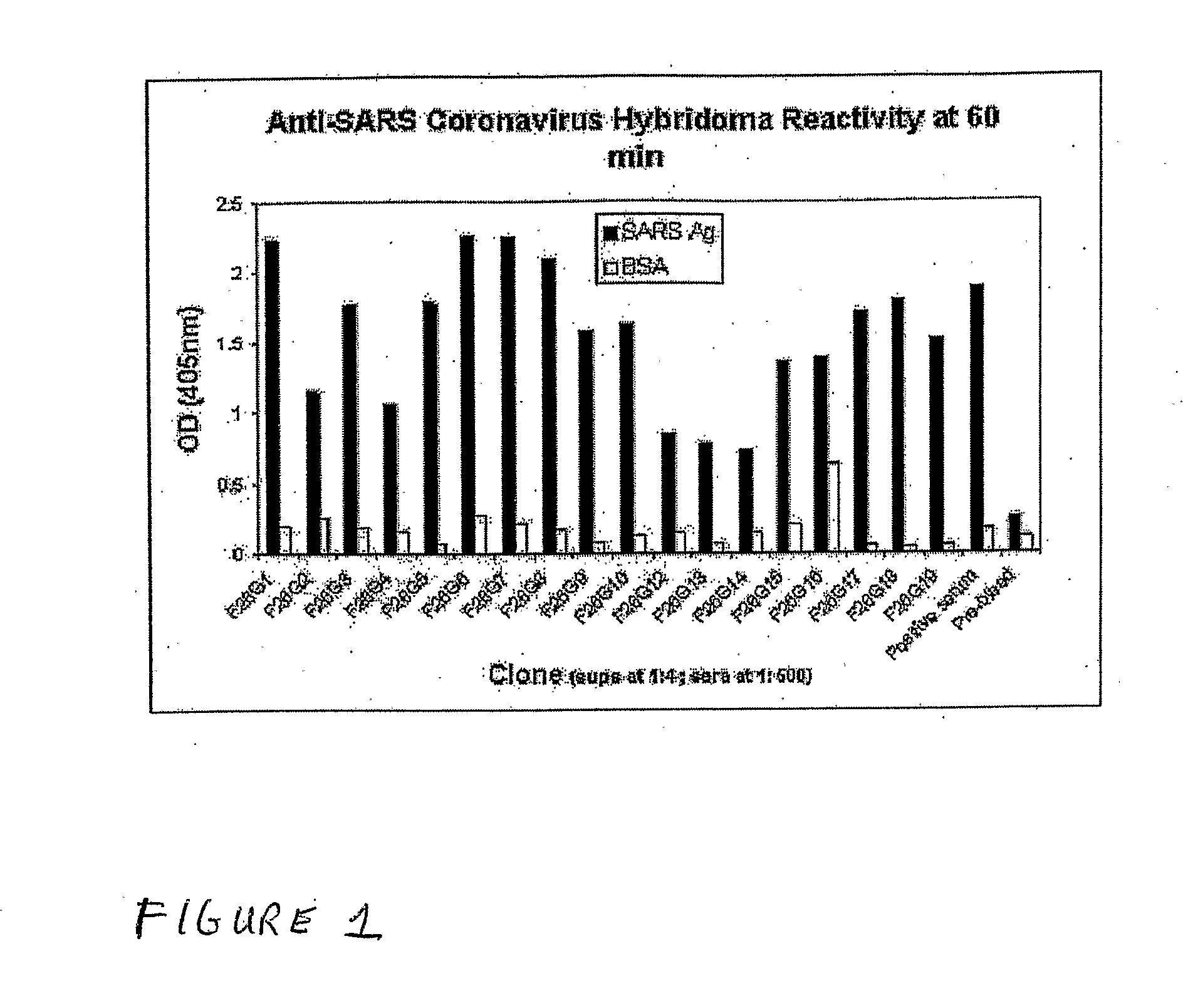
Anti-Sars Monoclonal Antibodies
ActiveUS20080081047A1Sugar derivativesViral antigen ingredientsDrug biological activityWestern immunoblot
Monoclonal antibody reagents that recognize the SARS-coronavirus (SARS-HCoV) are needed urgently. In this report we describe the development and immunochemical characterisation of mAbs against the SARS-HCoV based upon their specificity, binding requirements, and biological activity. Initial screening by ELISA, using highly purified virus as the coating antigen, resulted in the selection of seventeen mAbs. Five mAbs exhibited Western immunoblot reactivity with the denatured spike protein, of which two demonstrated the ability to neutralize SARS-HCoV in vitro. Another four Western immunoblot-negative mAbs also neutralize the virus. These antibodies will be useful for the development of diagnostic tests, pathogenicity and vaccine studies.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF HEALTH
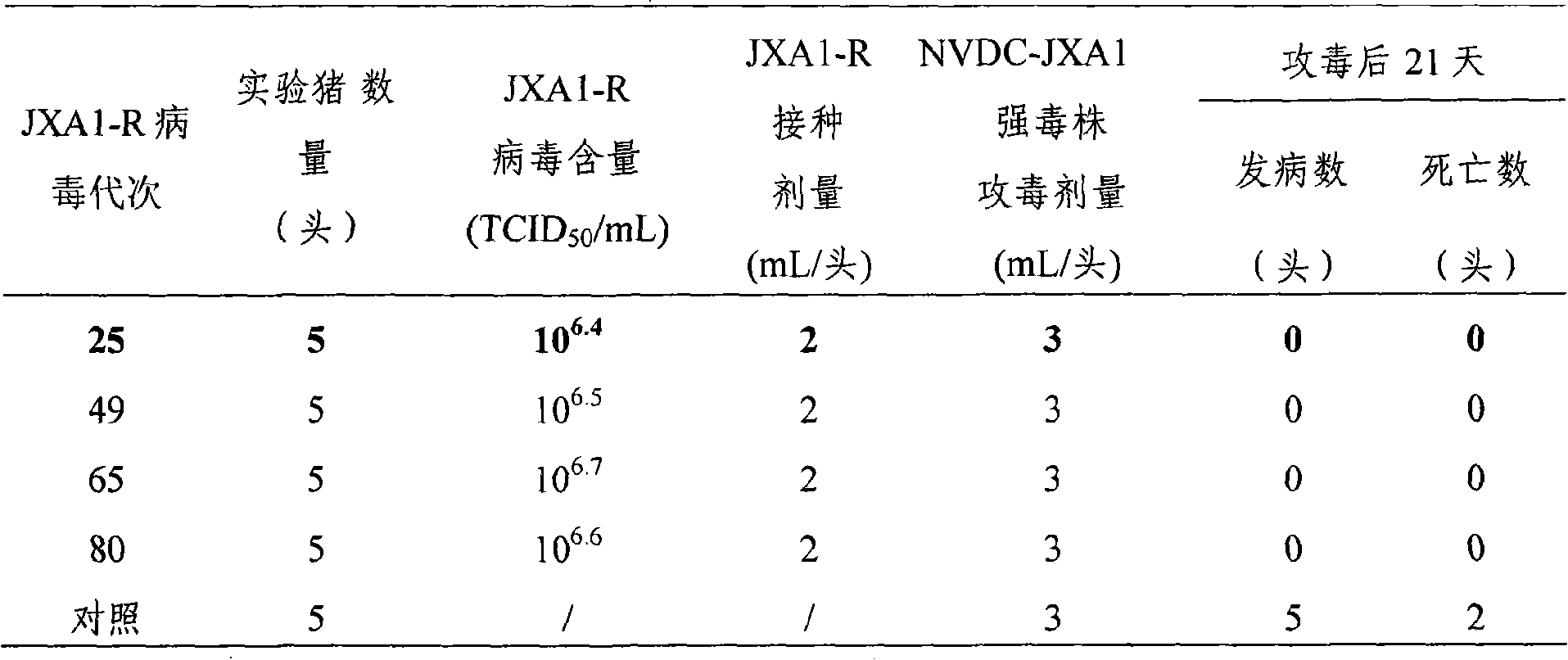
Low virulent strain of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus, immunogenicity immunogenicity material and vaccine
The application relates to a domesticated porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus low virulent strain (JXA1-R strain), immunogenicity substance containing the viral strain, and a porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus low virulent live vaccine developed through making use of the strain. The live vaccine is used to prevent the porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome, in particular the highly pathogenic blue-ear porcine disease.
Owner:CHINA ANIMAL DISEASE CONTROL CENT
Use of Bdellovibrio in eliminating pathogenicity vibrio in marine products and breeding water body thereof
InactiveCN101356927AImprove applicabilityImprove elimination rateBiocideBacteriaFood poisoningAntibiotic Y
The invention discloses an application of bdellovibrios in removing pathogenic vibrio in marine food products and the culture water. The bdellovibrio concentrated solution is added into the marine food products and / or the culture water so as to lead the concentration of the bdellovibrio to reach at least 10<2>pfu / ml. When the invention is applied before eating the marine food products, in the transportation process and in the culture water, the concentration range of bdellovibrio is respectively 10<4>-10<12> pfu / ml, 10<3>-10<11> pfu / ml, and 10<2>-10<6 > pfu / ml. More than 90% pathogenic vibrio carried by marine food products before eating and / or in the transportation process is cleared by adopting a biological method, and the pathogenic vibrio in the culture water can also be controlled within10cfu / ml. The invention is suitable for the pretreatment process before being eaten or processed, the transportation process and the culture process of marine food products, especially facilitating the reduction or elimination of chemical medicine residues such as antibiotics, thus fundamentally avoiding the occurrence of food poisoning of the marine food products.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Therapeutic agents—I
InactiveUS7449492B2Antibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsChemical fractionChemical synthesis
The present invention relates generally to chemical agents useful in the treatment and prophylaxis of infection by pathogenic or potentially pathogenic entities, or entities capable of opportunistic infection in mammals, including humans and primates, non-mammalian animals and avian species. More particularly, the present invention provides a chemical agent of the macrocyclic diterpene family obtainable from a member of the Euphorbiaceae family of plants or botanical or horticultural relatives thereof or derivatives or chemical analogues or chemically synthetic forms of the agents for use in the treatment or prophylaxis of infection by pathogenic entities in mammalian, animal and avian subjects. The present invention further contemplates a method for the prophylaxis and / or treatment in mammalian, animal or avian subjects of infection or potential infection by pathogenic entities by the topical or systemic administration of a macrocyclic diterpene obtainable from a member of the Euphorbiaceae family of plants or their botanical or horticultural derivatives or a derivative, chemical analogue or chemically synthetic form of the agent. The chemical agent of the present invention may be in the form of a purified compound, mixture of compounds, a precursor form of one or more of the compounds capable of chemical transformation into a therapeutically active agent or in the form of a chemical fraction, sub-fraction, preparation or extract of the plant.
Owner:AF 30 APRIL 2003 +1
Protease inhibitor: protease sensitivity expression system composition and methods improving the therapeutic activity and specificity of proteins delivered by bacteria
ActiveUS9068187B1Direct cytotoxicDirect inhibitoryBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsBacteroidesSurface display
Bacteria which co-express protease inhibitors and protease sensitive therapeutic agents, which are surface displayed, secreted and / or released and result in their localized production and maintenance within a target tissue and inactivation outside of the target tissue, thereby increasing therapeutic activity and reducing the systemic toxicity. The bacteria may be attenuated, non-pathogenic, low pathogenic or a probiotic. Protease sensitivity may be further accomplished by engineering protease degradation sites within the therapeutic agents, further enhancing the inactivation outside of the target tissue while retaining activity within the target tissue through co-expression of a protease inhibitor. Novel chimeric proteins secreted by bacteria, including chimeric toxins targeted to neoplastic cells, tumor matrix cells and cells of the immune system, and combination therapies of these protease inhibitor:chimeric toxin-expressing bacteria together with small-molecule and biologic agents are also described. Non-conjugative bacteria limiting exchange of genetic material, and antibody resistant bacteria are also provided.
Owner:BERMUDES DAVID GORDON
Attenuated negative strand viruses with altered interferon antagonist activity for use as vaccines and pharmaceuticals
InactiveUS20040109877A1Inhibition of replicationReduce the numberSsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsNegative strandPharmaceutical drug
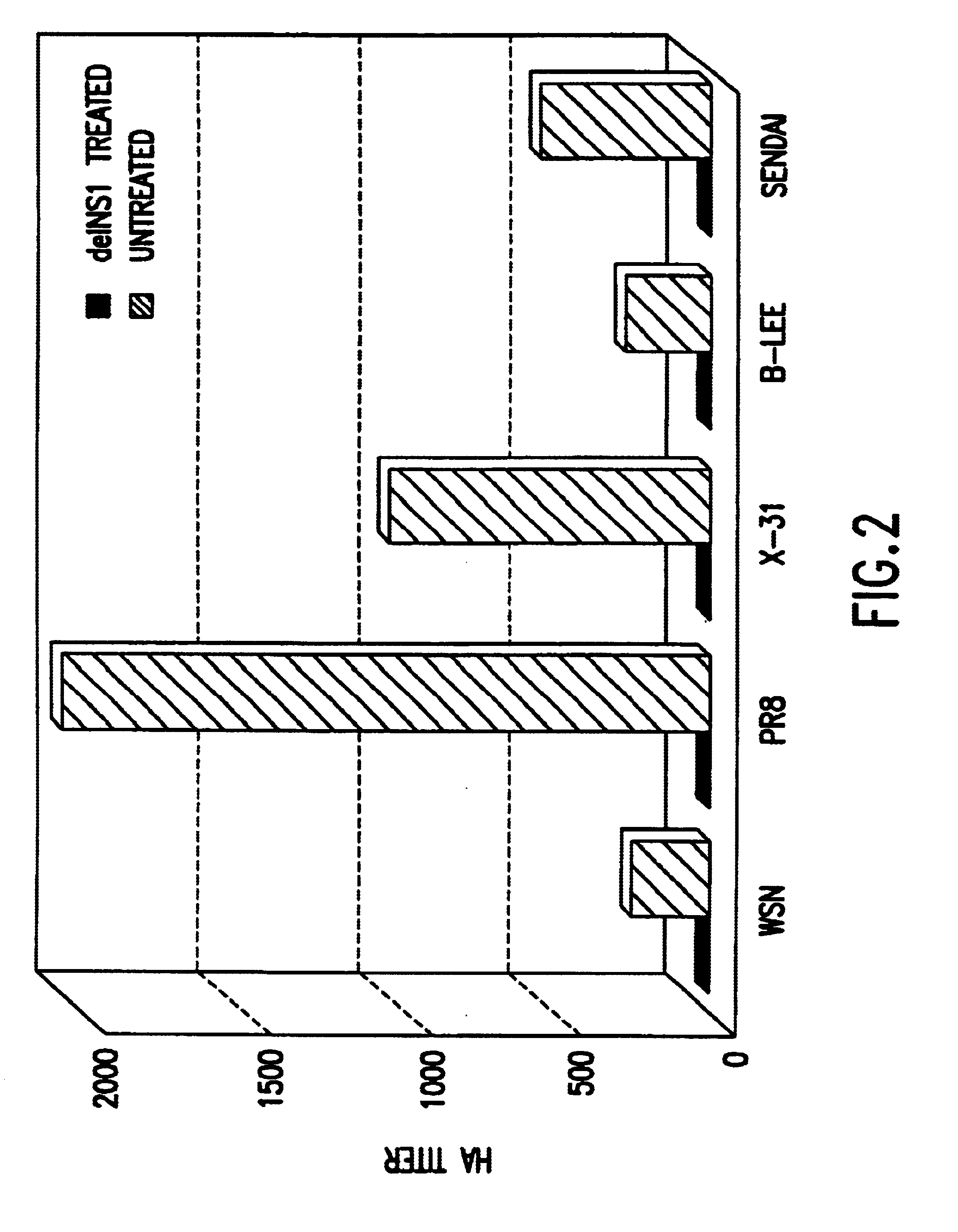
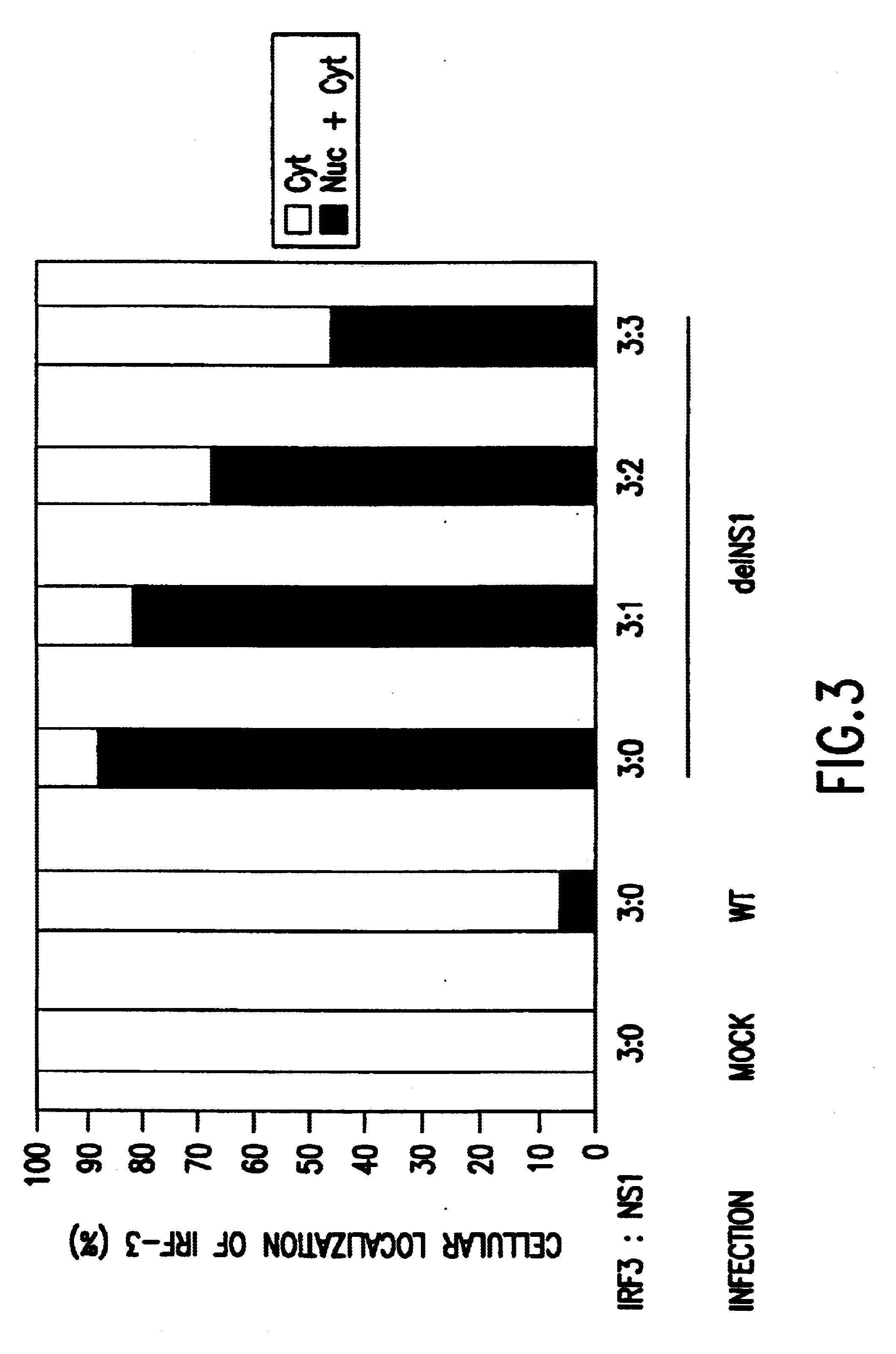
The present invention relates, in general, to attenuated negative-strand RNA viruses having an impaired ability to antagonize the cellular interferon (IFN) response, and the use of such attenuated viruses in vaccine and pharmaceutical formulations. The invention also relates to the development and use of IFN-deficient systems for selection of such attenuated viruses. In particular, the invention relates to attenuated influenza viruses having modifications to the NS1 gene that diminish or eliminate the ability of the NS1 gene product to antagonize the cellular IFN response. The mutant viruses replicate in vivo but demonstrate reduced pathogenicity, and therefore are well suited for live virus vaccines, and pharmaceutical formulations.
Owner:AVIR GREEN HILLS BIOTECH RES DEVMENT TRADE +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com