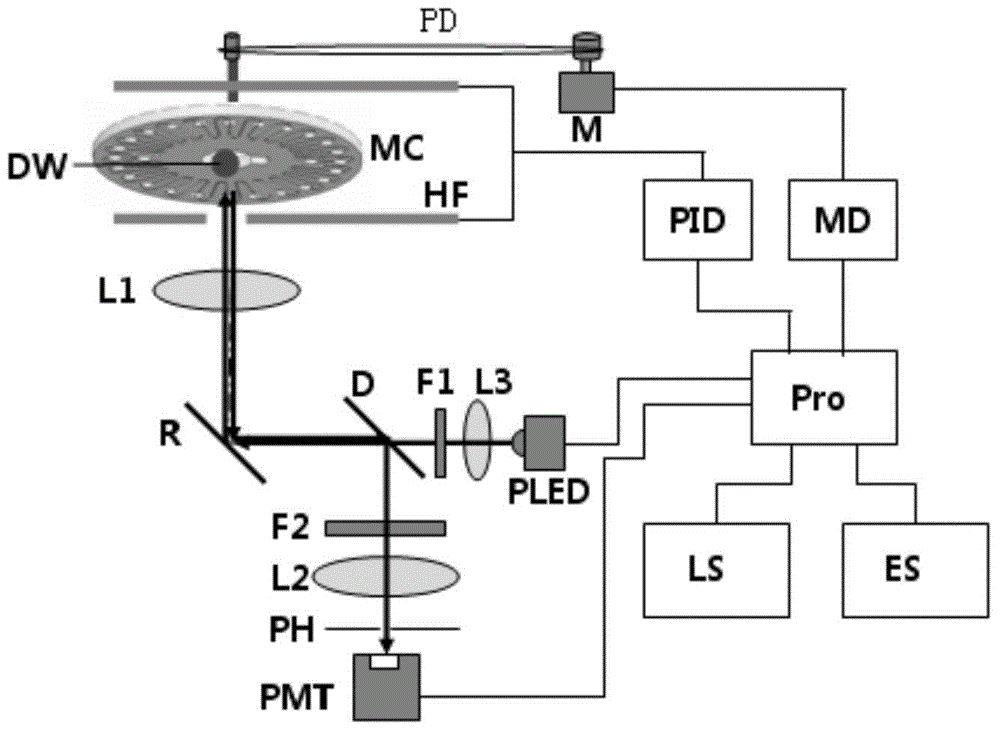
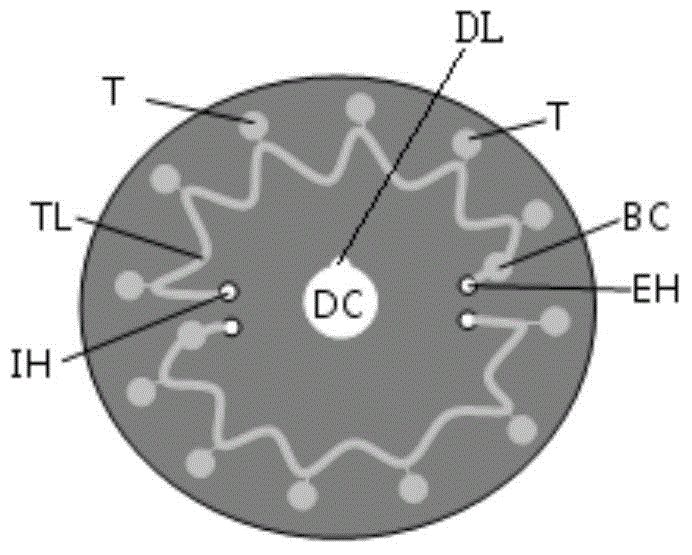
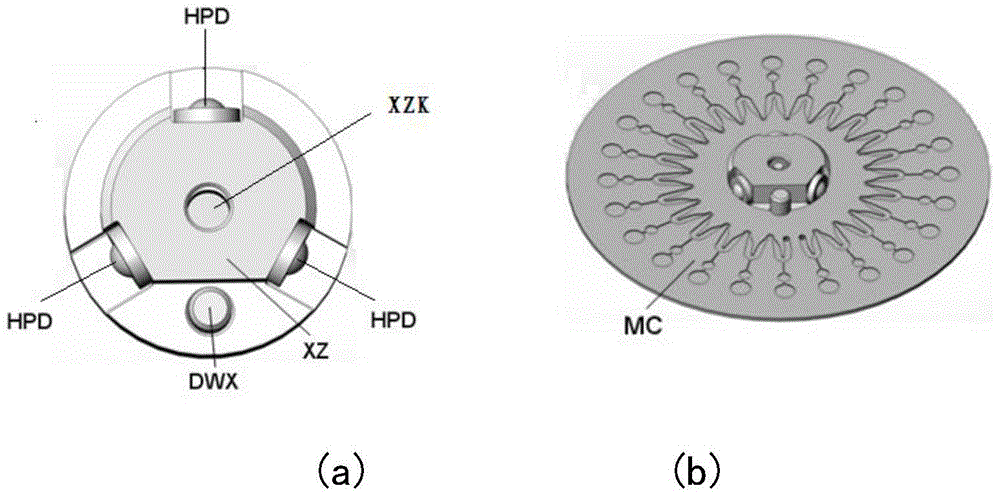
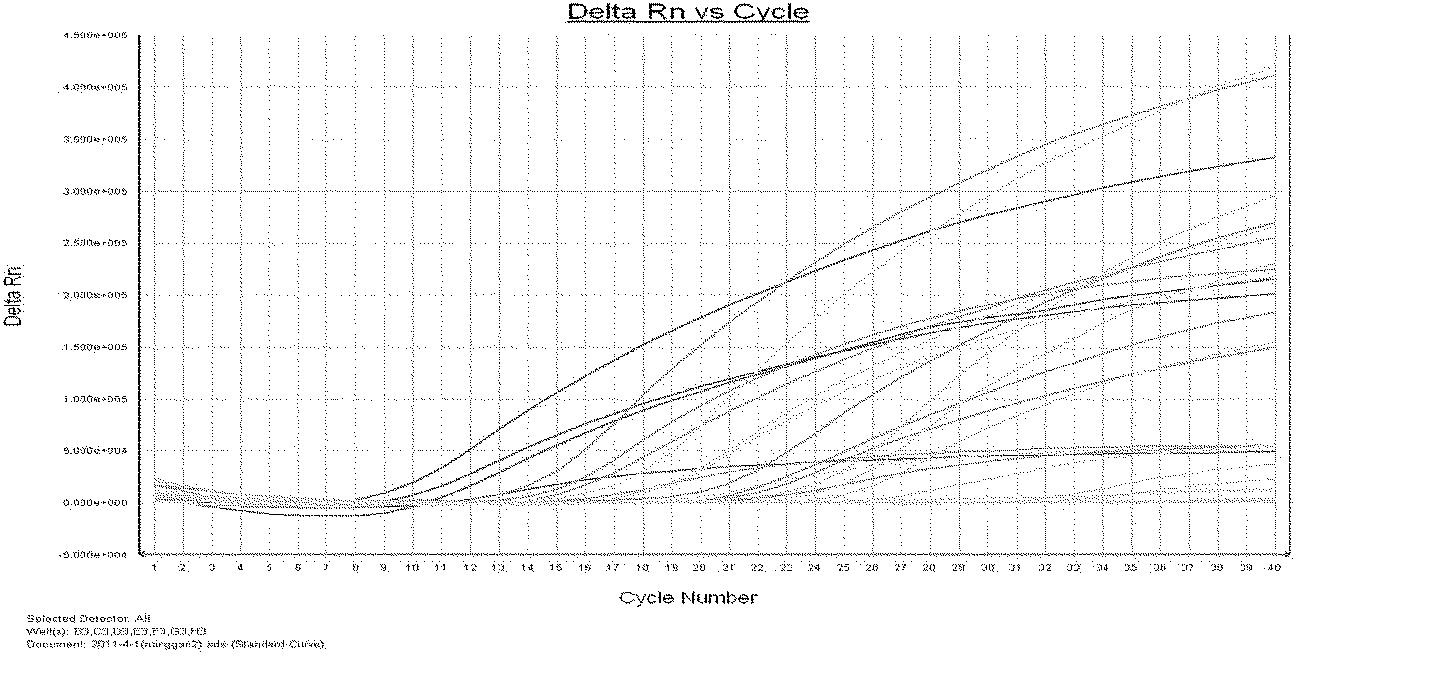
Patents
Literature
220 results about "Food poisoning" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Food borne illness resulting from consumption of contaminated or toxic food.
Method for treatment of disorders of the gastrointestinal system
There are provided novel synthetic stool preparations comprising bacteria isolated from a fecal sample from a healthy donor. The synthetic stool preparations are used for treating disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, including dysbiosis, Clostridium difficile infection and recurrent Clostridium difficile infection, prevention of recurrence of Clostridium difficile infection, treatment of Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, irritable bowel syndrome, inflammatory bowel disease, and diverticular disease, and treatment of food poisoning such as salmonella. Methods of preparation and methods of use of the synthetic stool preparations are also provided.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GUELPH +2
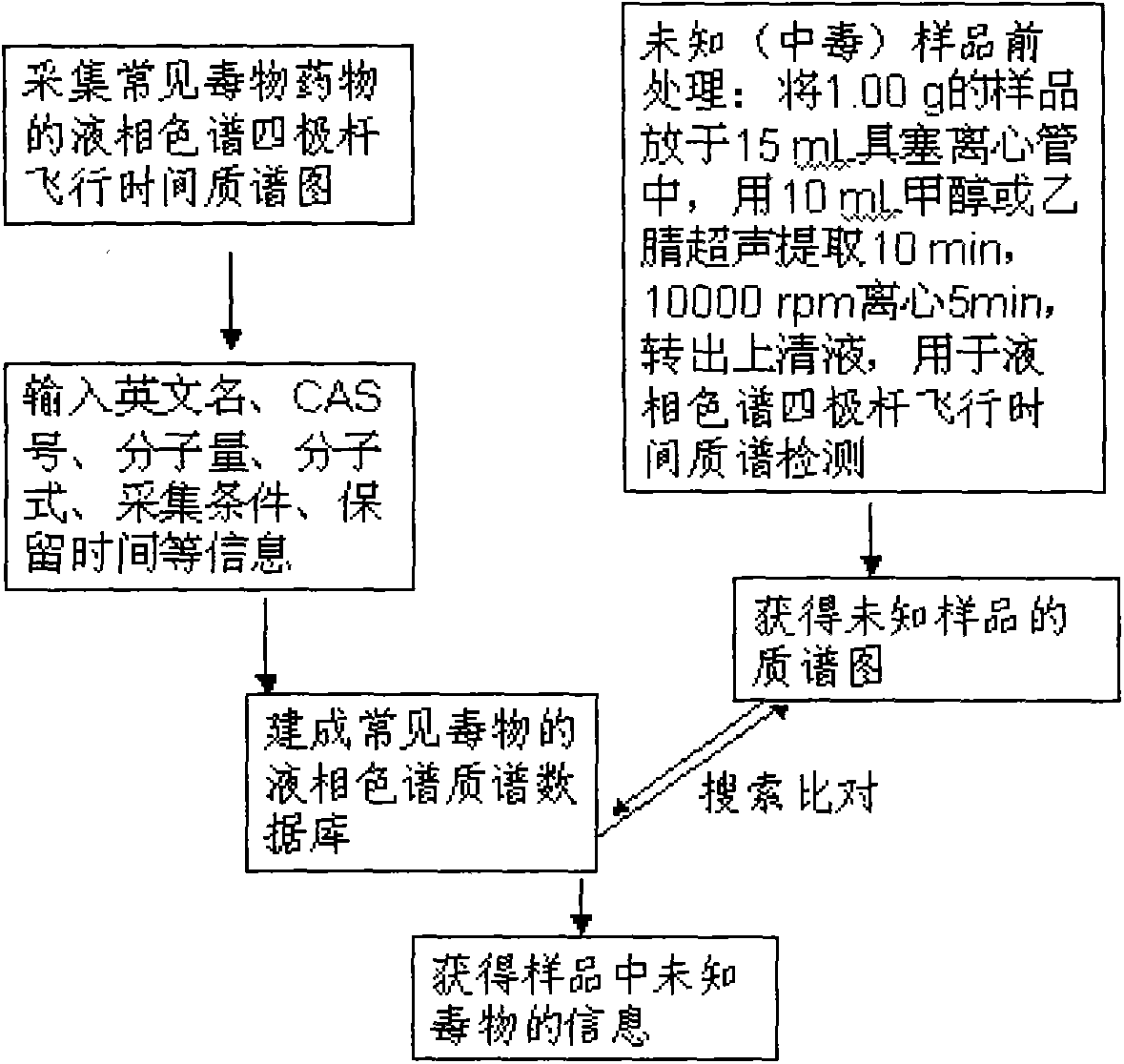
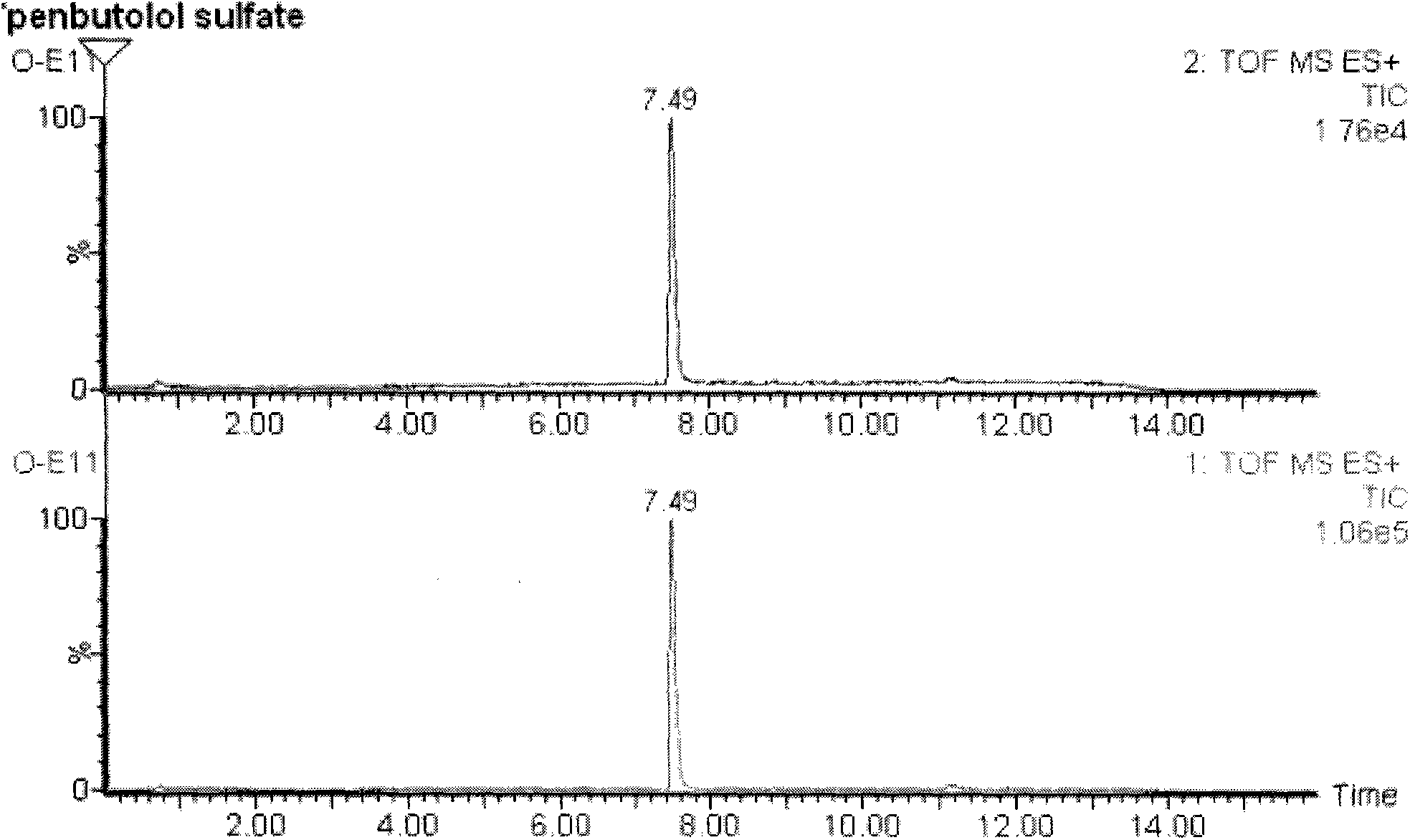
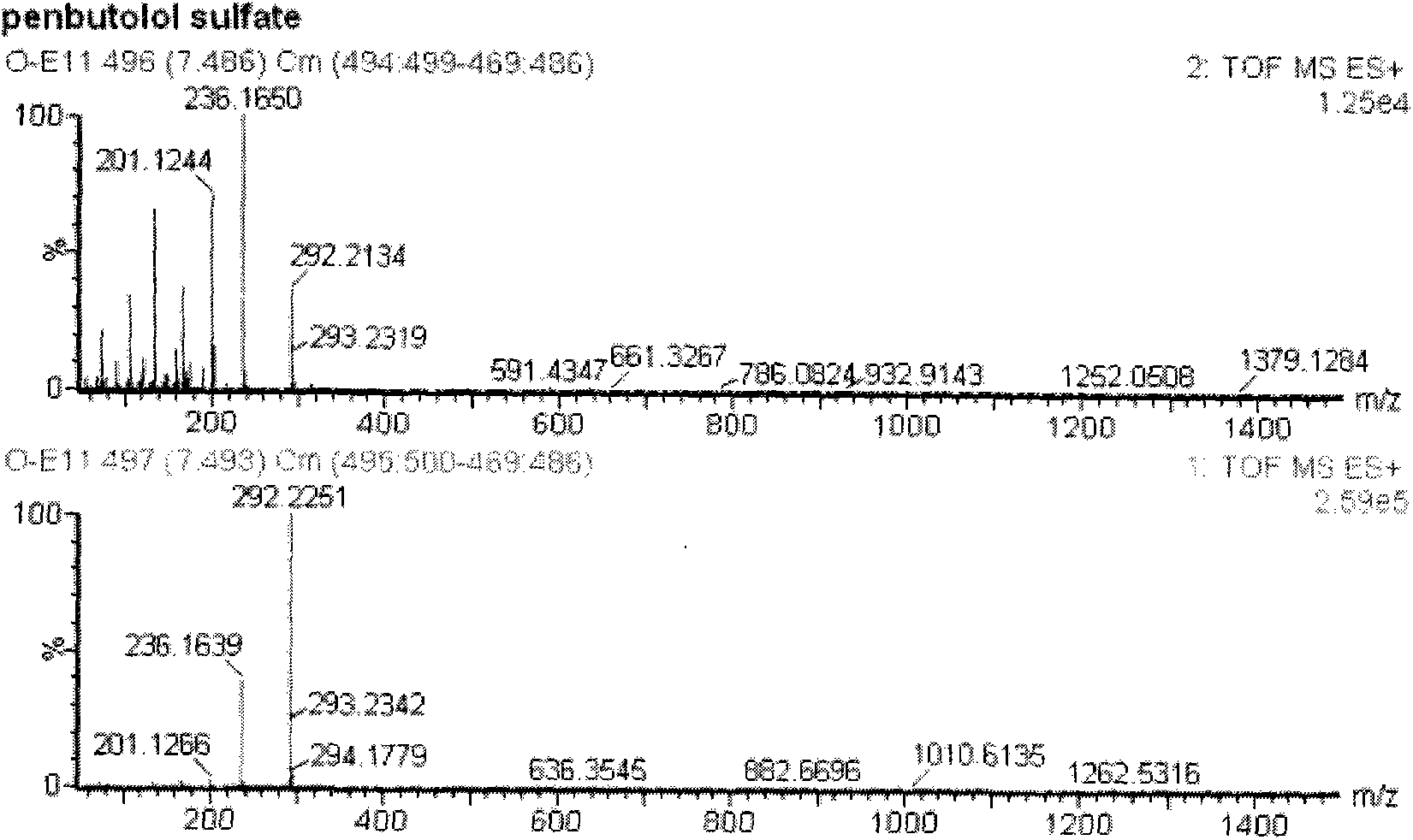
Method for detecting unknown poison by establishing liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry database
ActiveCN103823008AShorten detection timeReduce processing timeComponent separationMass spectrometry measurementToxicant
The invention relates to a method for detecting unknown poison by establishing a liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry database, in particular to a method used for detecting unknown poison during food poisoning. According to the method, firstly, an ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry method is used for establishing a liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry database of common poison; then, a sample is subjected to supersonic extraction with methyl alcohol or acetonitrile, liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry data of an extracting solution are measured similarly and searched and compared in the liquid chromatogram-mass spectrometry database of common poison according to the retention time of the sample and mass spectrometry fragments, and the variety of the unknown poison in the sample is judged; and the unknown poisoning sample is simply extracted and directly measured and compared, and a screening result can be acquired in one hour, so that the detecting and treating time of the sample is greatly shortened, the detecting efficiency is improved, and technical support is provided for related events such as food poisoning and the like caused by unknown reasons.
Owner:BEIJING CENT FOR DISEASE PREVENTION & CONTROL
Rescue agents for treating botulinum toxin intoxications
ActiveUS20050106182A1Facilitates the nicking of the single chain toxinNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsMedicineFood poisoning
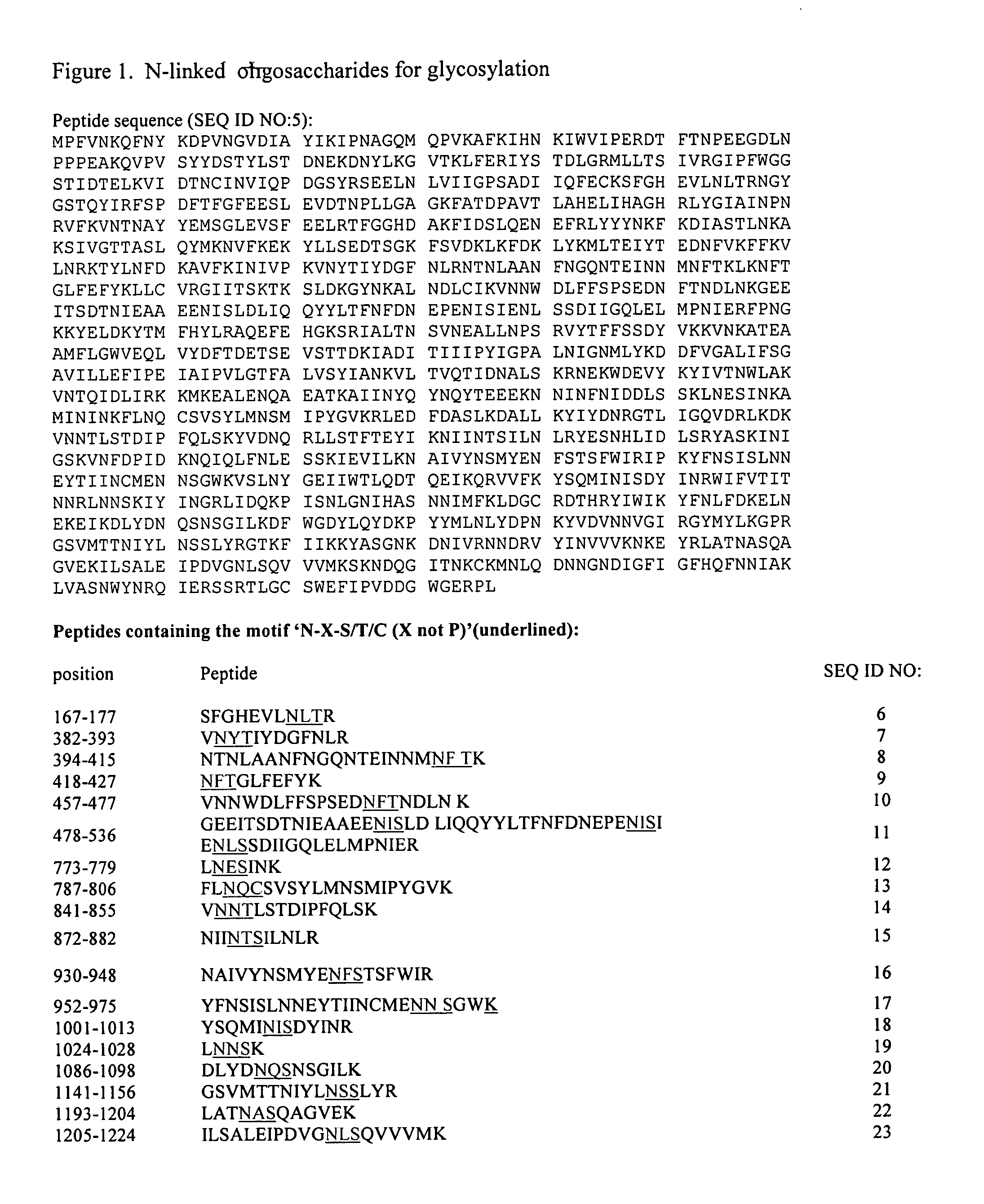
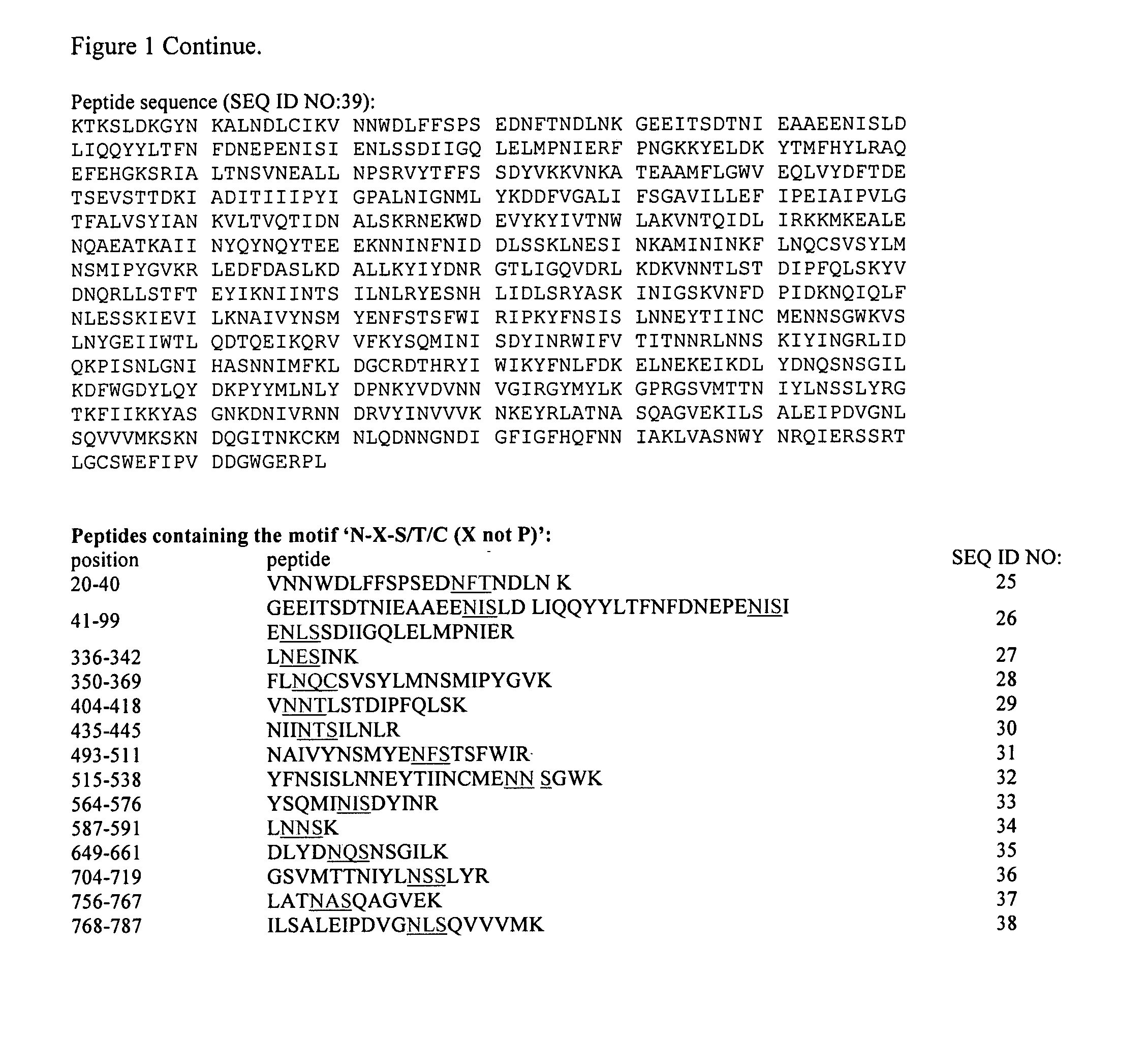
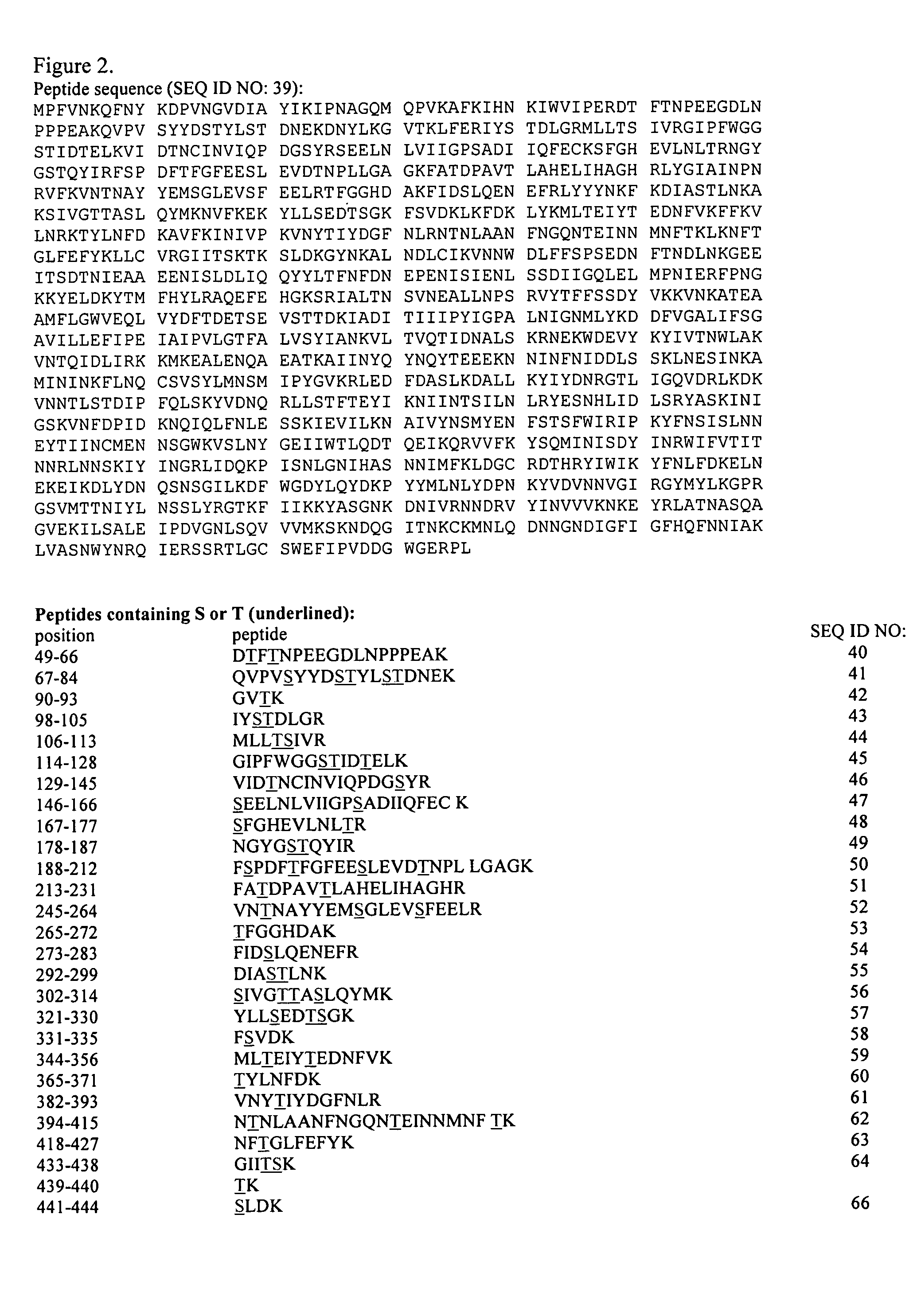
The present invention relates to rescue agents for use in the treatments of toxin intoxication—for example botulinum intoxication, which can result from food poisoning, an act of bioterrorism, or from accidental overdose in the course of treatment. In some embodiments, the rescue agents comprise at least one of an inactive botulinum toxin and a modified nontoxic nonhemagglutinin. The present invention also provides for glycosylated active and inactive toxins and methods of using same.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Use of Bdellovibrio in eliminating pathogenicity vibrio in marine products and breeding water body thereof
InactiveCN101356927AImprove applicabilityImprove elimination rateBiocideBacteriaFood poisoningAntibiotic Y
The invention discloses an application of bdellovibrios in removing pathogenic vibrio in marine food products and the culture water. The bdellovibrio concentrated solution is added into the marine food products and / or the culture water so as to lead the concentration of the bdellovibrio to reach at least 10<2>pfu / ml. When the invention is applied before eating the marine food products, in the transportation process and in the culture water, the concentration range of bdellovibrio is respectively 10<4>-10<12> pfu / ml, 10<3>-10<11> pfu / ml, and 10<2>-10<6 > pfu / ml. More than 90% pathogenic vibrio carried by marine food products before eating and / or in the transportation process is cleared by adopting a biological method, and the pathogenic vibrio in the culture water can also be controlled within10cfu / ml. The invention is suitable for the pretreatment process before being eaten or processed, the transportation process and the culture process of marine food products, especially facilitating the reduction or elimination of chemical medicine residues such as antibiotics, thus fundamentally avoiding the occurrence of food poisoning of the marine food products.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Rescue agents for treating botulinum toxin intoxications
InactiveUS7172764B2Facilitates the nicking of the single chain toxinNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsMedicineFood poisoning
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Rapid parallel nucleic acid detection method and system based on micro-fluidic chip
ActiveCN104630373AMeet automatic sampling requirementsUniform heating temperature fieldBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSequential/parallel process reactionsFluorescenceDisplay device
The invention relates to a rapid parallel nucleic acid detection method and system based on a micro-fluidic chip. The nucleic acid detection system comprises a micro-fluidic chip, a motor, exciting light, a double-focal-plane imaging lens set, a detector, a signal acquisition processor and a display; the micro-fluidic chip comprises at least one reaction channel; a heating film is arranged at the periphery of the micro-fluidic chip; a submillimeter air layer is maintained between the micro-fluidic chip and the heating film; and the micro-fluidic chip is irradiated by adopting the exciting light, so that a nucleic acid sample generates fluorescence under excitation of the exciting light, the fluorescence is gathered on the detector by virtue of the double-focal-plane imaging lens set so as to generate an analog signal, the detector transmits the generated analog signal to the signal acquisition processor so as to generate a real-time fluorescence detection signal, and the real-time fluorescence detection signal is displayed by the display. The method and the system disclosed by the invention can be applied to the fields of clinical pathogenic bacterium molecular diagnosis, food inspection and quarantine, food poisoning pathogenic bacterium detection, bacteriology classification and epidemiological investigation and have huge economical and social benefits.
Owner:CAPITALBIO CORP +2
Multiplex quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection kit for vibrio parahaemolyticus and detection method
InactiveCN102605055AMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFood poisoningSaxitoxin
The invention provides a multiplex quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction detection kit for vibrio parahaemolyticus toxin gene and a detection method. The kit mainly comprises specific primers, probes and PCR reaction reagent, wherein the specific primers and the probes consist of specific primers and probes of vibrio parahaemolyticus thermostable direct hemolysin gene (tdh), thermolabile hemomysin gene (tlh), toxin expression regulating protein gene (toxR) and thermostable related hemolysin gene (trh). The invention provides the quick, sensitive and specific multiplex fluorescent quantitative PCR detection kit and the detection method aiming at the vibrio parahaemolyticus toxin gene, and provides basis for controlling food poisoning caused by the vibrio parahaemolyticus in time and early diagnosis of the food poisoning caused by the vibrio parahaemolyticus.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CENT FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION
Novel bacteriophage and antibacterial composition comprising the same
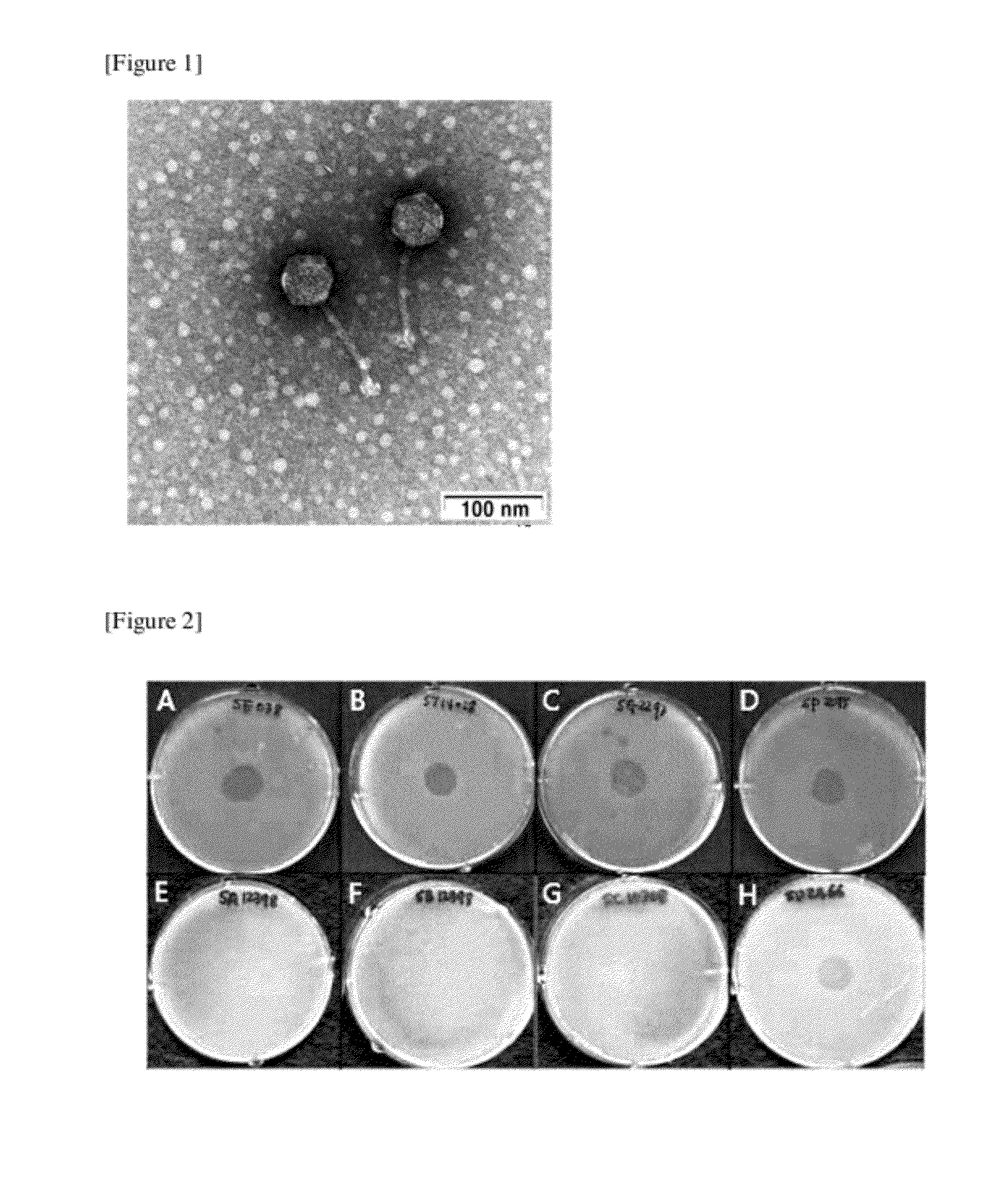
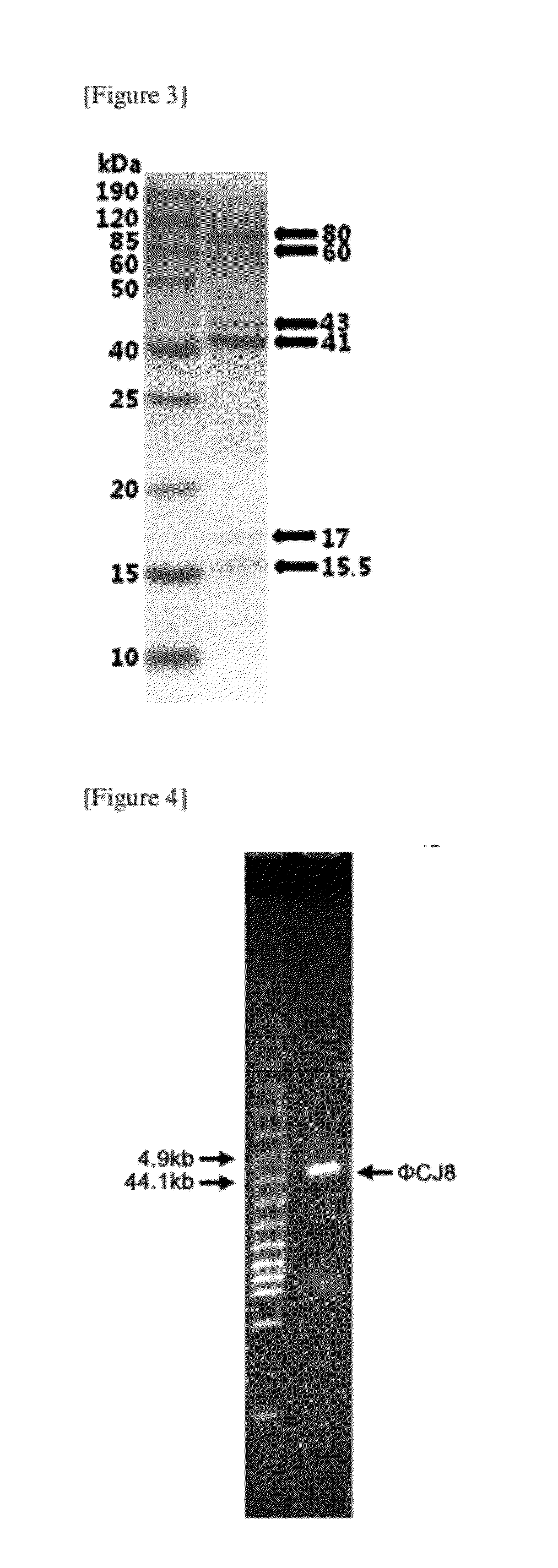
ActiveUS20110052542A1Effective preventionEffective treatmentAntibacterial agentsBiocideBacteroidesFood poisoning
Disclosed herein is a novel bacteriophage which has specific bactericidal activity against one or more Salmonella bacteria selected from the group consisting of Salmonella Enteritidis, Salmonella Typhimurium, Salmonella Gallinarum, and Salmonella Pullorum without affecting beneficial bacteria, in addition to showing excellent tolerance to acid, heat and desiccation. The novel bacteriophage can be widely used as an active ingredient for therapeutic agents, animal feeds or drinking water, cleaners and sanitizers for preventing and treating the infectious diseases caused by Salmonella Enteritidis, Salmonella Typhimurium, Salmonella Gallinarum or Salmonella Pullorum including salmonellosis, Salmonella food poisoning, Fowl Typhoid, and Pullorum disease or for controlling the salmonella bacteria.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Immune chromatographic paper strip and method for quick detecting pathogen and toxin in food
The present invention discloses a kind of immunogical chromatographic paper strip for sensitive, specific and fast detection of common pathogen and toxin in food and the detection method. The present invention is the new technology for detecting pathogen and toxin in food and its application. Now, there are great amount of reports on applying colloidal gold immunogical chromatographic test paper in detecting soluble antigen and bacteria as granular antigen are detected after being treated via extraction or other processes. The present invention features that special chromatographic film and optimized conditions are adopted so that the immunogical chromatographic paper strip may be used directly in detecting bacteria. The present invention may be used in the fast detection of common pathogen in food and the fast diagnosis of toxin in food.
Owner:INST OF HYGIENE & ENVIRONMENTAL MEDICINE PLA ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL
Novel Bacteriophage and Antibacterial Composition Comprising the Same
InactiveUS20100166709A1Good acidImprove the heating effectAntibacterial agentsBiocideFood poisoningBacteriophage
The present invention relates to a novel bacteriophage, more particularly, a bacteriophage that has a specific bactericidal activity against one or more Salmonella bacteria selected from the group consisting of Salmonella Enteritidis, Salmonella Typhimurium, Salmonella Gallinarum, and Salmonella Pullorum. Further, the present invention relates to a composition for the prevention or treatment of infectious diseases including salmonellosis and Salmonella food poisoning caused by Salmonella Enteritidis or Salmonella Typhimurium, Fowl Typhoid caused by Salmonella Gallinarum, and Pullorum disease caused by Salmonella Pullorum, comprising the bacteriophage as an active ingredient. Furthermore, the present invention relates to a feed additive, drinking water, a cleaner and a sanitizer, comprising the bacteriophage as an active ingredient.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Oligonucleotide probe kit for detecting common intestine trac kpathogenic bacteria and its use
InactiveCN1683565AQuick checkAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesAntigenBio engineering
The present invention belongs to the field of microbe detecting technology. The oligonucleotide probe for detecting common intestinal tract pathogenic bacteria is designed on 16S rRNA and 23S rRNA of bacteria, ipaH of dysentery bacillus giant plasmid, VipR of Salmonella typhi and other gene sequence, has length of 25-50 bp, and relatively high sensitivity and specificity. The oligonucleotide probe is suitable for detection based on nucleic acid hybridization principle, especially detection based on gene chip principle. Under certain use condition, it can detect Listeria, parahemolutic vibrio, Campylobacter, etc. It may be used in many aspects, such as disease diagnosis, environment detection, food poisoning detection, etc.
Owner:RADIOLOGY INST ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICINE SCI PLA
Oligonucleotide primer for detecting common pathogenic bacteria by adopting fluorescent quantitation PCR (Rich Client Platform) technology, method thereof for detecting common pathogenic bacteria and application thereof
InactiveCN101928773AEfficient and wideWide range of applicationsMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesBiotechnologyFood poisoning
The invention discloses an oligonucleotide primer for detecting common pathogenic bacteria by adopting a fluorescent quantitation PCR (Rich Client Platform) technology, a method thereof for detecting common pathogenic bacteria and the application thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: providing 10 pairs of specific oligonucleotide primer sequences at annealing temperature of 50-60 DEG C without differing 5 DEG C; and simultaneously, quickly, accurately and effectively identifying and quantificationally detecting various pathogenic bacteria at the same time. A detection range comprises bacillus cereus, enterobacter sakazakii, vibrio parahaemolyticus, enterohemorrhagic escherichia coli O157, salmonella, Listeria monocytogenes, Shigella, campylobacter jejuni, pseudomonas aeruginosa, klebsiella pneumoniae, and the like. The invention also can be used for the fields of disease diagnosis, environmental monitoring, water-quality and food supervision and detection, food poisoning pathogenicbacteria detection, bacteriological classification, epidemiological investigation, biological agent detection, and the like, is convenient, quick, accurate and effective and has wide application range.
Owner:INST OF HYGIENE & ENVIRONMENTAL MEDICINE PLA ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL
Food-originated pathogenic bactenium quick detection gene chip and its application
InactiveCN1536090AMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesFood poisoningBeta-hemolytic streptococcus
The present invention provides a gene chip for quickly detecting pathogens from food source, discloses the preparation method of said gene chip and provides 26 oligonucleotide probe sequences for detection. Said gene chip can quickly, accurately and high-effectively detect and identify the class of the pathogens in food, and its detection range includes staphylococcus aureus, Shiga's bacillus, salmonella, colibacillus 0157, bacillus proteus, mononuclear hyperplastic listerella, enterocolitis yersinia, aeruginous pseudomonads, vibrio parahaemolyticus, vibrio cholerae, bacillus cereus, beta hemolytic streptococcus, coconut fermentation pseudomonads, boticin, vibrio jejuni and bacillus perfringens, etc.
Owner:INST OF HYGIENE & ENVIRONMENTAL MEDICINE PLA ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL
Culture medium capable of simultaneously enriching five kinds of food-borne pathogenic bacteria and preparation method for culture medium
ActiveCN102660474AImprove detection efficiencyLow costBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementEscherichia coliFood borne
The invention relates to a culture medium for simultaneous composite enrichment of five kinds of food-borne pathogenic bacteria, namely Salmonella, Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Listeria monocytogenes and Shigella, and a preparation method for the culture medium. Food-borne pathogenic bacteria are a significant reason to cause food positioning, so the rapid and accurate detection of the food-borne pathogenic bacteria has an important practical significance for preventing and controlling food safety incidents. The culture medium is characterized by comprising the following components: 10.0 g of peptone, 10.0 g of sodium chloride, 9.0 g of disodium hydrogen phosphate, 1.5 g of monopotassium phosphate, 0.1 g of cholate, 0.1 mg of potassium tellurite, 1.0 g of lithium chloride, 3.0 g of glucose, 2.0 g of mannitol, 2.5 g of sodium pyruvate, 1.0 g of aesculin and 1,000 mL of distilled water, wherein the pH value is 7.1 to 7.5. The culture medium can simultaneously enrich five kinds of target pathogenic bacteria, can be used for separation and identification of target bacteria, can also be used for the molecular detection of multiple pathogenic bacteria on the same detection platform, provides technical support for a method for rapidly detecting five kinds of pathogenic bacteria in food, and meets the requirement of simultaneous detection of five kinds of food-borne pathogenic bacteria.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES +1
Novel adsorbent
InactiveUS20050101482A1Efficient removalIncrease surface areaOther chemical processesFood preparationMetaboliteHazardous substance
An adsorbent is disclosed which is formed either by coating an adsorption mass such as active carbon with a gel-like substance such as the dibasic metallic salt of a macromolecular polycarboxylic acid, soybean curd, jelly, konjak, agar, perilla, gelidium jelly, or chitosanoxalic acid salt gel and subsequently subjecting the coated basis to a freezing treatment or by effecting the coating with the gel-like substance already made to contain a frost damage preventing substance such as glycerin and subsequently depriving the coated basis of the frost damage preventing substance. This adsorbent, on being brought into direct contact with foodstuffs or ingested directly into the digestive system, effects highly efficient removal by adsorption of such food additive, feed additive, agricultural pesticide, food poisoning substance, allergen, heavy metal or highly poisonous organic compound as are suffered to adhere to or exist in the foodstuffs, such surplus nutrients as persist in the digestive system, such oligomers and additives as are contained in liquors, such metabolites of alcohol as are formed in the digestive system after assimilation of alcohol, such harmful substances as hydroperoxides of unsaturated fatty acids as are suffered to exist in oils and fats, and such components of offensive odor as emanate from fish.
Owner:AOYAGI JUURO +1
Method for quickly screening and confirming common pesticides and rodenticides in poisoning samples of complex matrixes
InactiveCN108333286AShorten detection timeReduce processing timeComponent separationRetention timeGas phase
The invention discloses a method for quickly screening and confirming common pesticides and rodenticides in poisoning samples of complex matrixes. The method comprises the steps as follows: 1) a second-level mass spectrum database, including Chinese names, English names, CAS numbers, molecular weights, molecular formulas, retention time, quantitative ion pairs, qualitative ion pairs and collisionvoltage, of common pesticides is constructed by use of gas chromatography triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry and ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography triple quadrupole tandem linear iontrap mass spectrometry; a second-level mass spectrum database of common rodenticides is constructed by use of ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography triple quadrupole tandem linear ion trap massspectrometry; 2) samples causing food poisoning are extracted and purified, detection is performed through gas chromatography triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry and ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography triple quadrupole tandem linear ion trap mass spectrometry respectively, and detection conditions are identical with those of a method adopted during construction of the second-levelmass spectrum database.
Owner:济南市疾病预防控制中心
Method for detecting Vibrio parahaemolyticus
InactiveCN106191298AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesForward primerFood poisoning
The invention provides a method for detecting Vibrio parahaemolyticus. The sequence of the forward primer is SEQ ID NO:1, the sequence of the reverse primer is SEQ ID NO:2, and the sequence of the probe is SEQ ID NO:3. A real-time RPA (recombinase polymerase amplification) process is utilized to detect the food-borne pathogen Vibrio parahaemolyticus, thereby implementing safe, specific, quick, sensitive and simple field quick detection on the Vibrio parahaemolyticus, and further overcoming the defects in the existing traditional detection technique. The method is suitable for field detection, can effectively inhibit the epidemic situation caused by Vibrio parahaemolyticus food poisoning in time, and perfects the food safety control system.
Owner:宁波海洋研究院 +1
Method for the production of the egg containing anti-pathogenic bacteria specific antbodies(igy) and the yogurt and ice cream containing the igy
InactiveUS20030185856A1Sterilization can be minimizedAvoid infectionMilk preparationBacterial antigen ingredientsEscherichia coliYolk
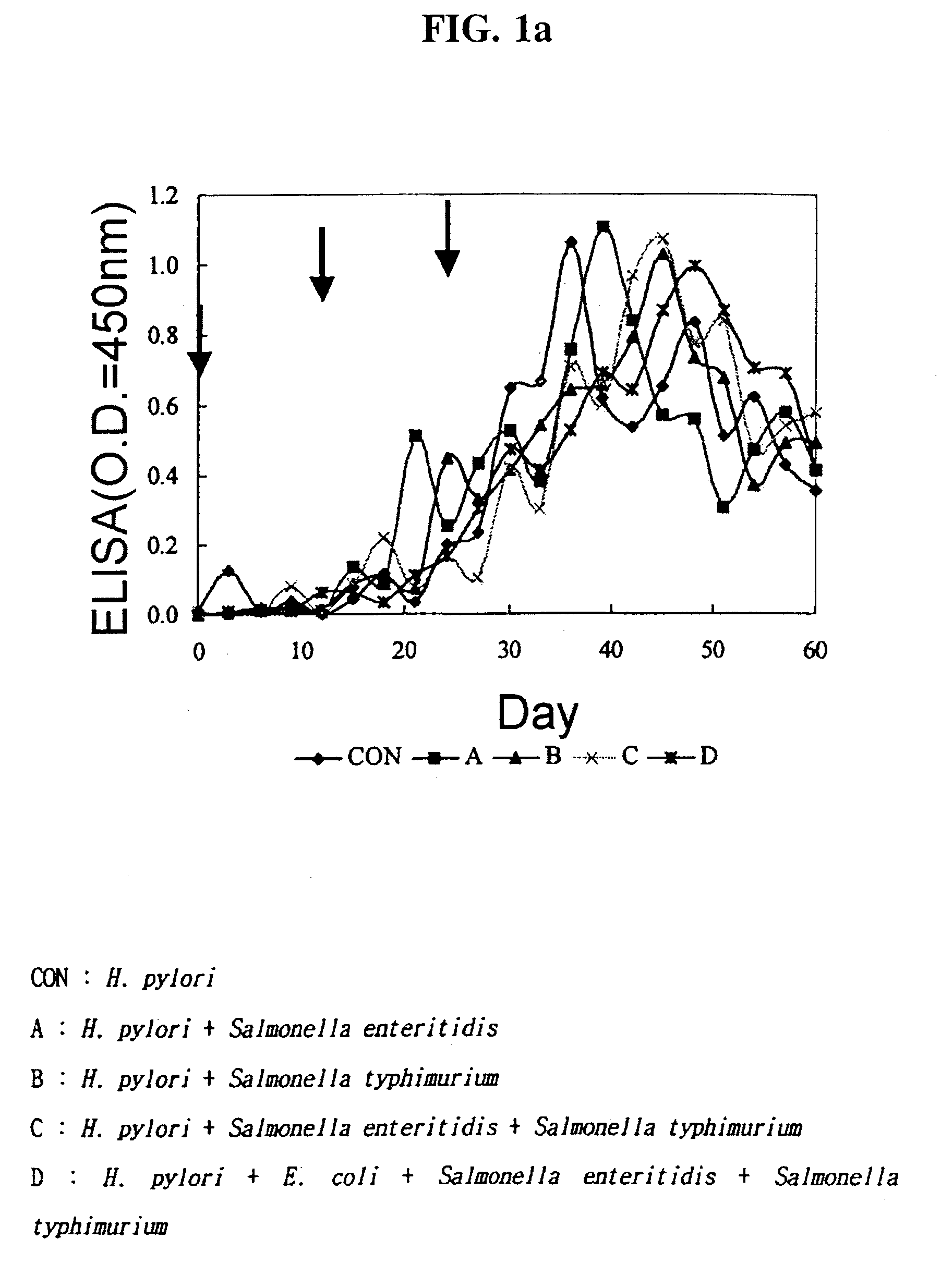
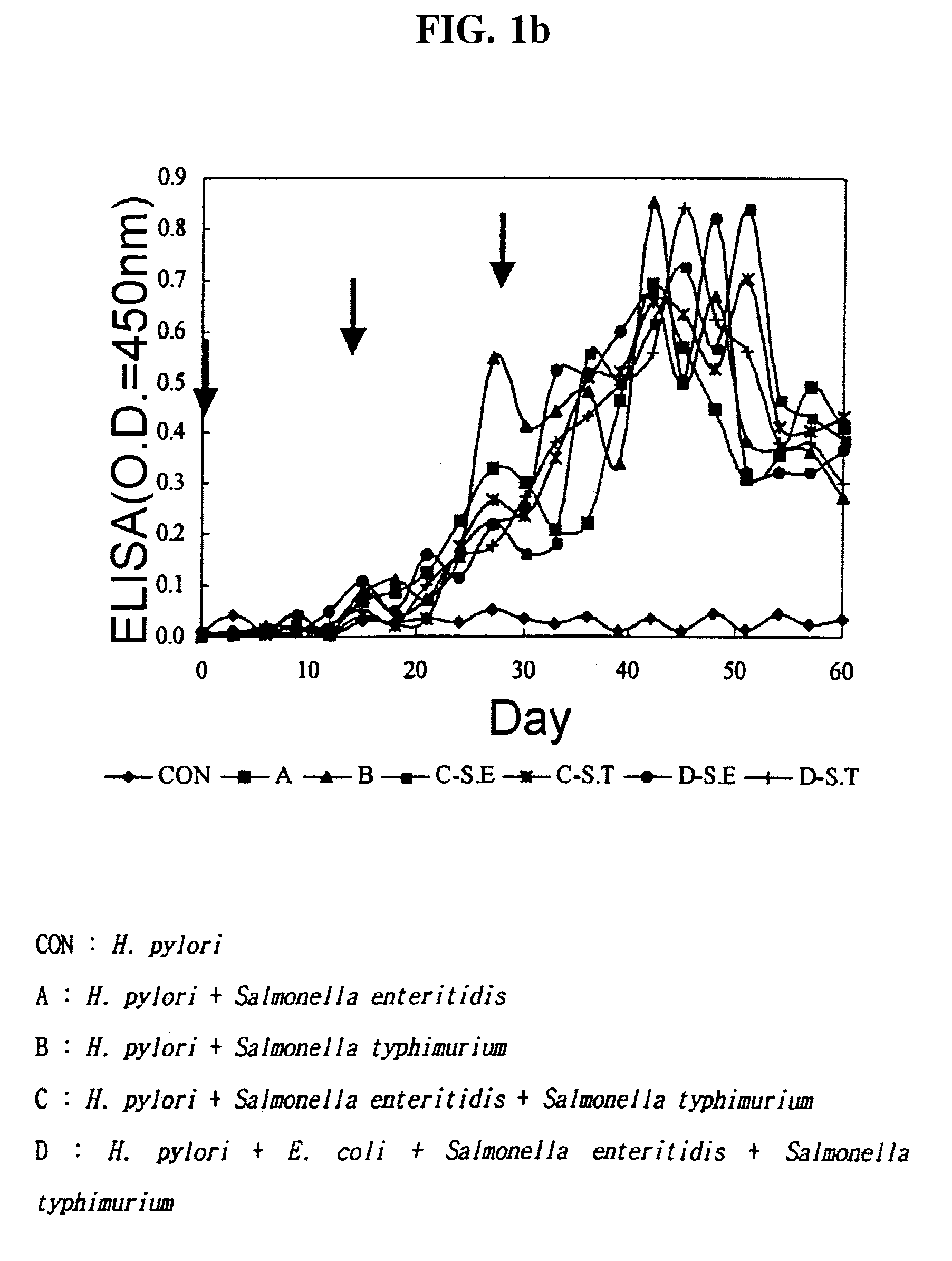
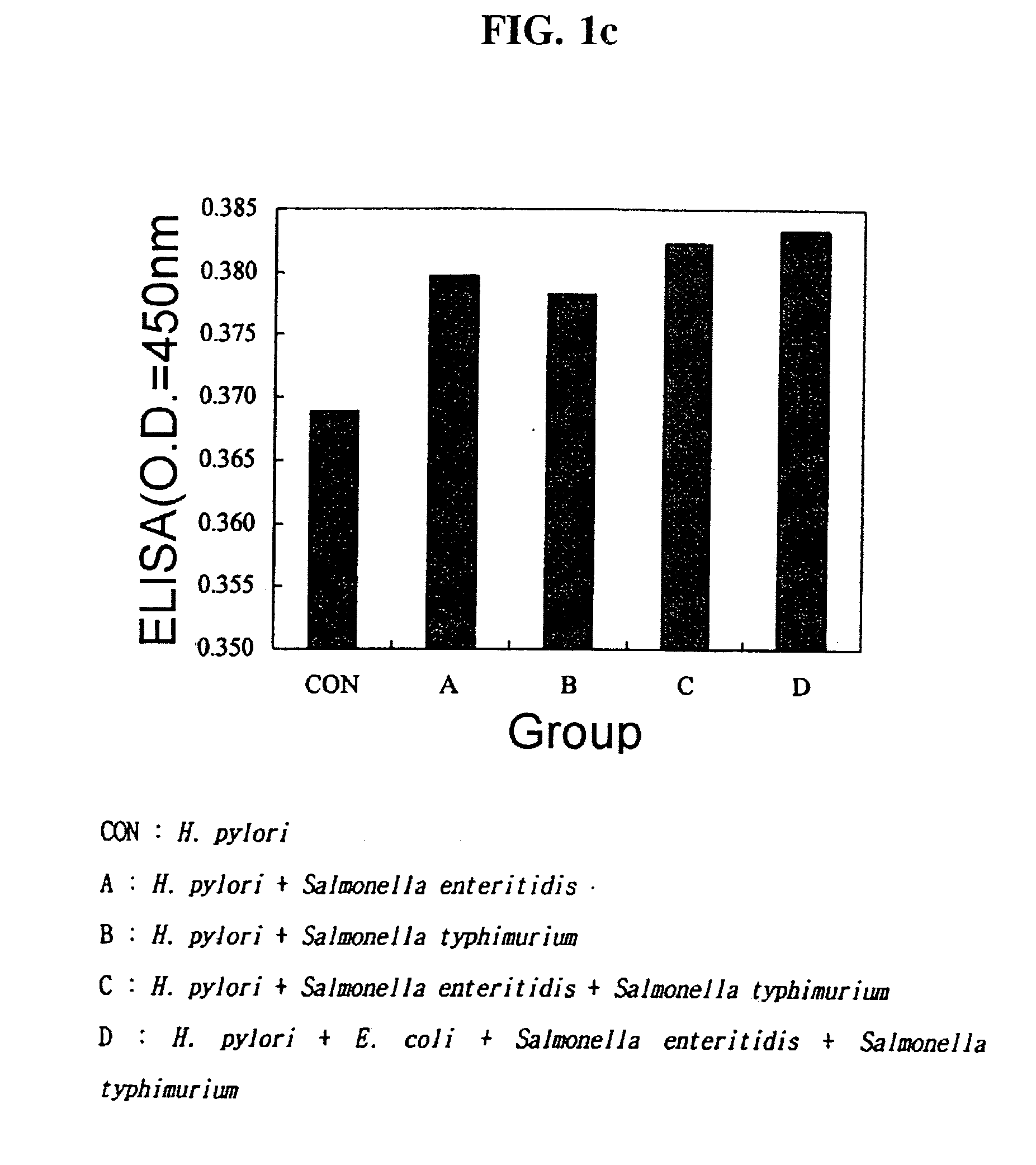
The present invention provides the method for the production of the egg containing anti-pathogenic bacteria specific antibodies (IgY) preventing gastritis, diarrhea, and food poisoning by immunizing young hens with antigen proteins of E. coli causing enteritis, Helicobacter pylori causing gastritis, and Salmonella enteritidis and Salmonella typhimurium, causing food poisoning, simultaneously. This invention also relates to composition containing the specific IgY antibodies described above and the foodstuff such as the yogurt and ice cream containing the anti-pathogenic IgY. Additionally, the present invention provides the separation method of the IgY containing protein powders from egg yolk. particularly, this separation method involves diluting egg yolk with water at 1:1 ratio and adding the appropriate amount of ammonium sulfate which enables water-soluble protein and phospholipid to separate.
Owner:LEE NAM HYUNG +4
A kind of Lactobacillus pentosus, the fermentation product of the Lactobacillus and the application of the fermentation product
InactiveCN102286392AExtended shelf lifeLower pHBacteriaFood preservationMetaboliteStaphylococcus aureus
The invention relates to a lactobacillus pentosus strain and a fermentation product of the same. The preservation number of the lactobacillus pentosus LPEM818 in the invention is CGMCC No. 4583 in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center. The fermentation product of the lactobacillus pentosus in the invention can inhibit common pathogenic escherichia coli, pseudomonas aeruginosa and staphylococcus aureus in food, and particularly has a strong inhibiting effect on listeria monocytogenes which can cause serious food poisoning. In addition, the metabolite of the strain also can inhibit the growth of aspergillus flavus and cotton and tomato blight pathogens. Consequently, the lactobacillus pentosus strain and the fermentation product thereof play an active role in the fields of food preservation and plant protection.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
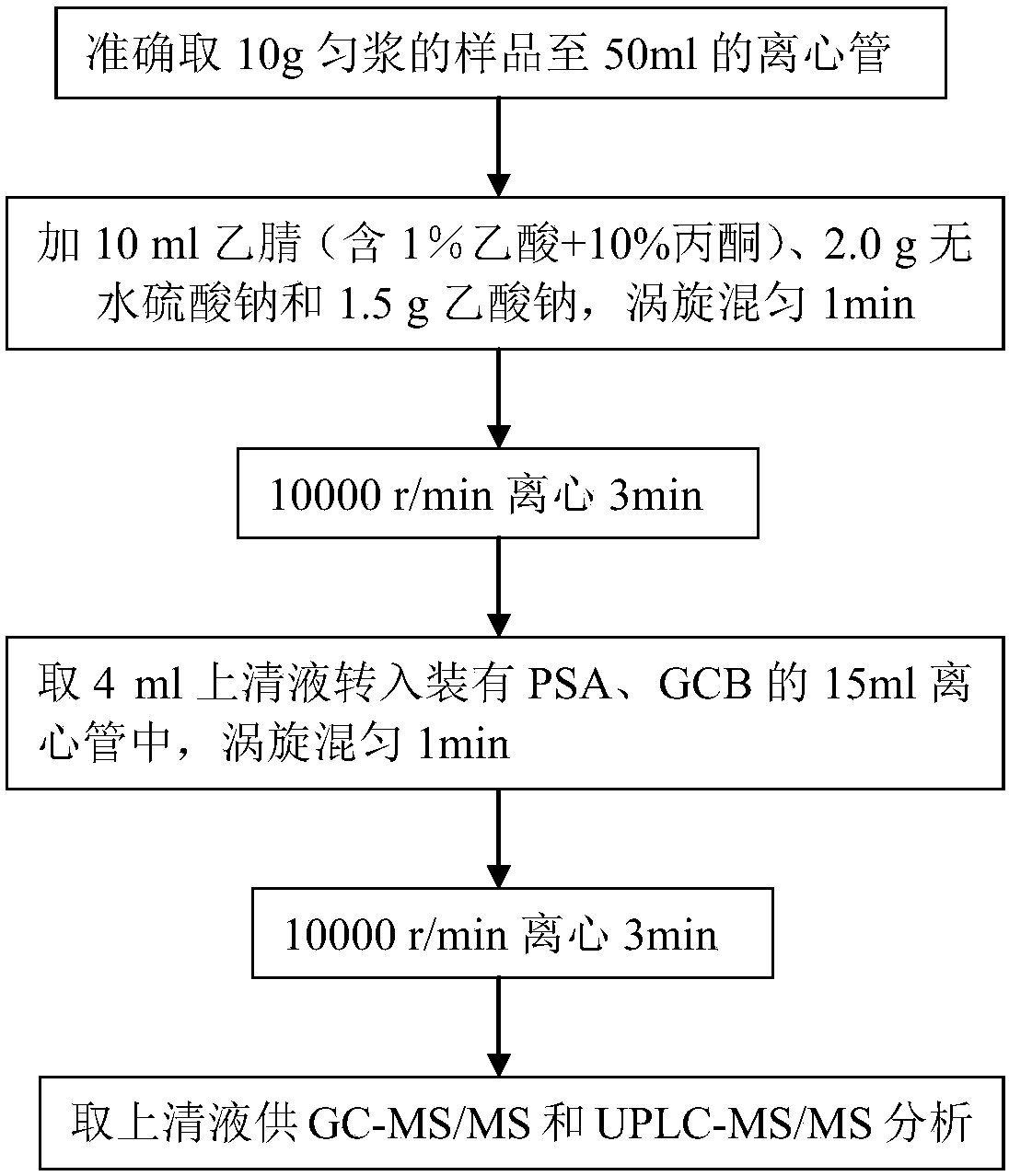
QuEChERS extraction method for poisonous substance extraction and application of QuEChERS extraction method
InactiveCN103822814AGood treatment effectConvenience to workPreparing sample for investigationPork LiverFood poisoning
The invention relates to a QuEChERS extraction method for poisonous substance extraction, which is especially suitable for extracting unknown poisonous substances in food poisoning samples. The scheme is that the extraction method comprises the following steps: at first, extracting homogenized or mixed samples with acidiferous acetonitrile or Na2 EDTA to obtain extract liquor; adding NaC1 and Na2SO4 in the extract liquor, and mixing to obtain mixed liquor; carrying out supersonic centrifuge on the mixed liquor to obtain supernate, enabling the supernate to be subjected to C18 and anhydrous sodium sulfate purification to obtain an extracting solution, and then detecting and analyzing the extracting solution. The extraction method and application are suitable for various different matrixes: pork, pork liver, milk, eggs, fruits, vegetables, gastric juice, blood and urine, are high in recovery rate and quick and reliable to test, are used for quickly screening the actual poisoning samples, and facilitate the timely treatment and criminal investigation on poisoned personnel.
Owner:BEIJING CENT FOR DISEASE PREVENTION & CONTROL
Method and apparatus for controlling microorganisms in food materials by vacuum and resonant ultrasonication
ActiveUS20120027898A1Effective controlEffective sterilizationDough treatmentMilk preservationBiotechnologyFood poisoning
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MIYAZAKI +1
Novel bacteriophage and antibacterial composition comprising same
InactiveCN102149816AImprove acid resistanceImprove heat resistanceAntibacterial agentsMammal material medical ingredientsDisinfectantFood poisoning
The present invention relates to a novel bacteriophage, and more specifically to a bacteriophage that can specifically destroy one or more Salmonella spp. selected from a group consisting of Salmonella enteritidis, Salmonella typhimurium, Salmonella gallinarum and Salmonella pullorum. The present invention further relates to a composition containing the bacteriophage as an active ingredient for the prevention or treatment of infectious diseases such as salmonellosis and salmonella foodborne intoxication induced by Salmonella enteritidis or Salmonella typhimurium, fowl typhoid induced by Salmonella gallinarum, pullorum induced by Salmonella pullorum, etc. Moreover, the present invention relates to animal feeds, drinking water, detergent and disinfectant containing the bacteriophage as an inactive ingredient.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Preparation method of nitrite reductase and enzyme product thereof
InactiveCN101597598AImprove stabilityImprove safety and qualityMicroorganism based processesAnimal feeding stuffFood poisoningSephadex gels
The invention discloses a preparation method of nitrite reductase, comprising the following steps: inoculating lactobacillus in a MRS culture medium to culture a first generation strain and then to culture a second generation strain; inoculating the second generation strain in a MRS fermentation culture medium to culture for 30-48h; adding sodium nitrite solution in the fermentation solution to culture for 16-32h; collecting precipitate; adding buffer solution in precipitate to fully suspend the fermentation liquor precipitate, adding lysozyme solution and treating the mixture by ultrasonication to obtain broken cell solution, collecting supernatant; filtrating the supernatant and collecting the filtrate; separating the filtrate with a sephadex chromatographic column to obtain precipitate, namely, nitrite reductase and adding 10-50% of starch in the precipitate to obtain the enzyme product. The enzyme preparation prepared by the method can be used to remove the residue of nitrite in food, feed and environment, improves the food safety and quality and prevents the poisoning, cancer and the like caused by nitrite.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
Novel bacteriophage and antibacterial composition comprising the same
The present invention relates to a novel bacteriophage, more particularly, a bacteriophage that has a specific bactericidal activity against Salmonella enteritidis, Salmonella typhimurium, Salmonella gallinarum and Salmonella pullorum, a composition for the prevention or treatment of infectious diseases including salmonellosis and Salmonella food poisoning caused by Salmonella enteritidis or Salmonella typhimurium, Fowl typhoid caused by Salmonella gallinarum, and Pullorum disease caused by Salmonella pullorum, which comprises the bacteriophage as an active ingredient, and an animal feed, drinking water, cleaner, and sanitizer which comprise the bacteriophage as an active ingredient.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
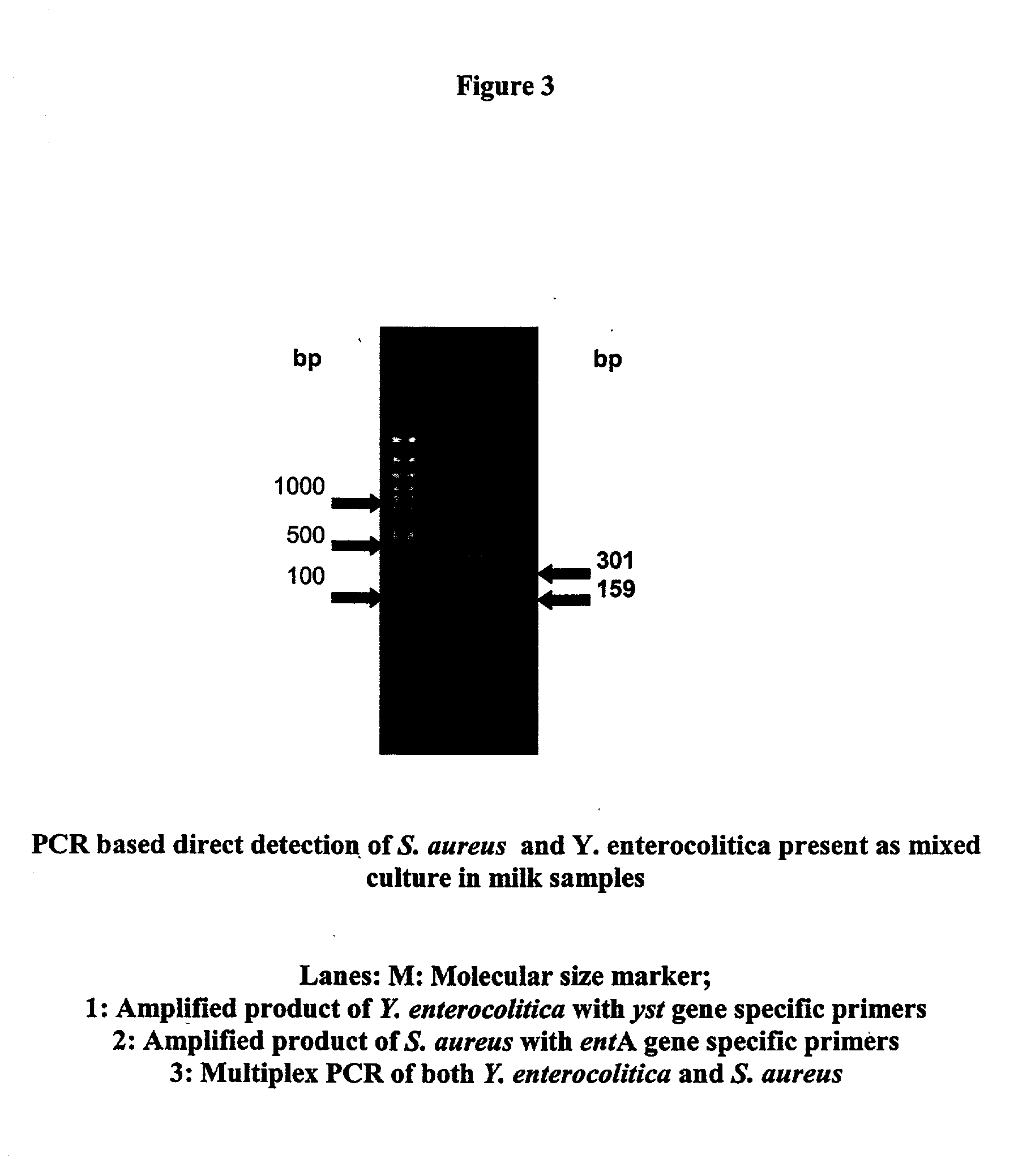
Primes for detecting food poisoning bacteria and a method thereof
InactiveUS20040248089A1Sensitive methodSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesFood poisoning
The present invention relates to novel primers of SEQ ID Nos. 1-4 useful for detecting poisoning in food articles wherein primers of SEQ ID Nos. 1 and 2 are directed against enterotoxin A gene (ent A) of bacteria Staphylococcus aureus and primers of SEQ ID Nos. 3 and 4 are directed against heat stable enterotoxin gene (yst) of bacteria yersinia enterocolitica, and a highly sensitive method of detecting said food poisoning bacterial species using said primers.
Owner:BANADA PADMANABHA PADMAPRIYA +3
Galleria mellonella derived composition for detecting peptidoglycan, a method for use thereof, and a diagnostic kit containing the same
InactiveUS20060292662A1Anthropod material medical ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementFood poisoningGalleria mellonella
The present invention relates to a composition for selectively detecting an extremely small amount of peptidoglycan in sample, a preparation method of the composition, and a detection kit for peptidoglycan. It is possible to quantify a small amount of peptidoglycan contained in human blood, tissue, body fluid, water or food, and to diagnose an infection of microorganism with peptidoglycan as a component of cell wall using the composition and the detection kit. In addition, the composition can be applied for a diagnosis reagent of detecting an infection of Gram-positive bacteria in animal or human being in advance, and thus, can be used for the prevention or treatment of food poisonings and bacterial sepsis.
Owner:SAMYANG BIOPHARMLS CORP
Oligonucleotide for Detection of a Microorganism, Diagnostic Kits and Methods for Detection of Microorganisms Using the Oligonucleotide
InactiveUS20080261206A1Reduce diagnostic costsPrevent the abuse of antibioticsSugar derivativesNucleotide librariesBacteroidesFood poisoning
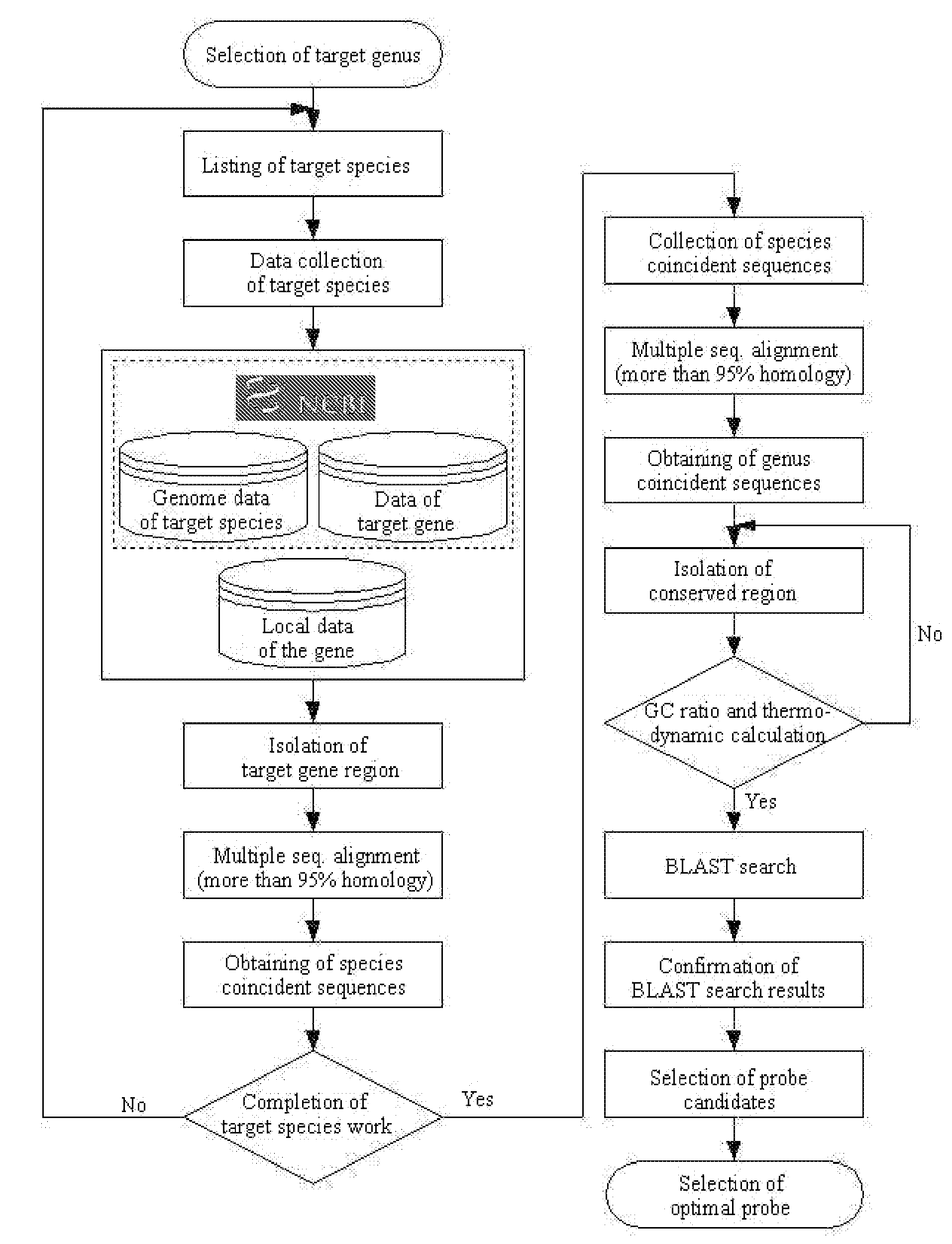
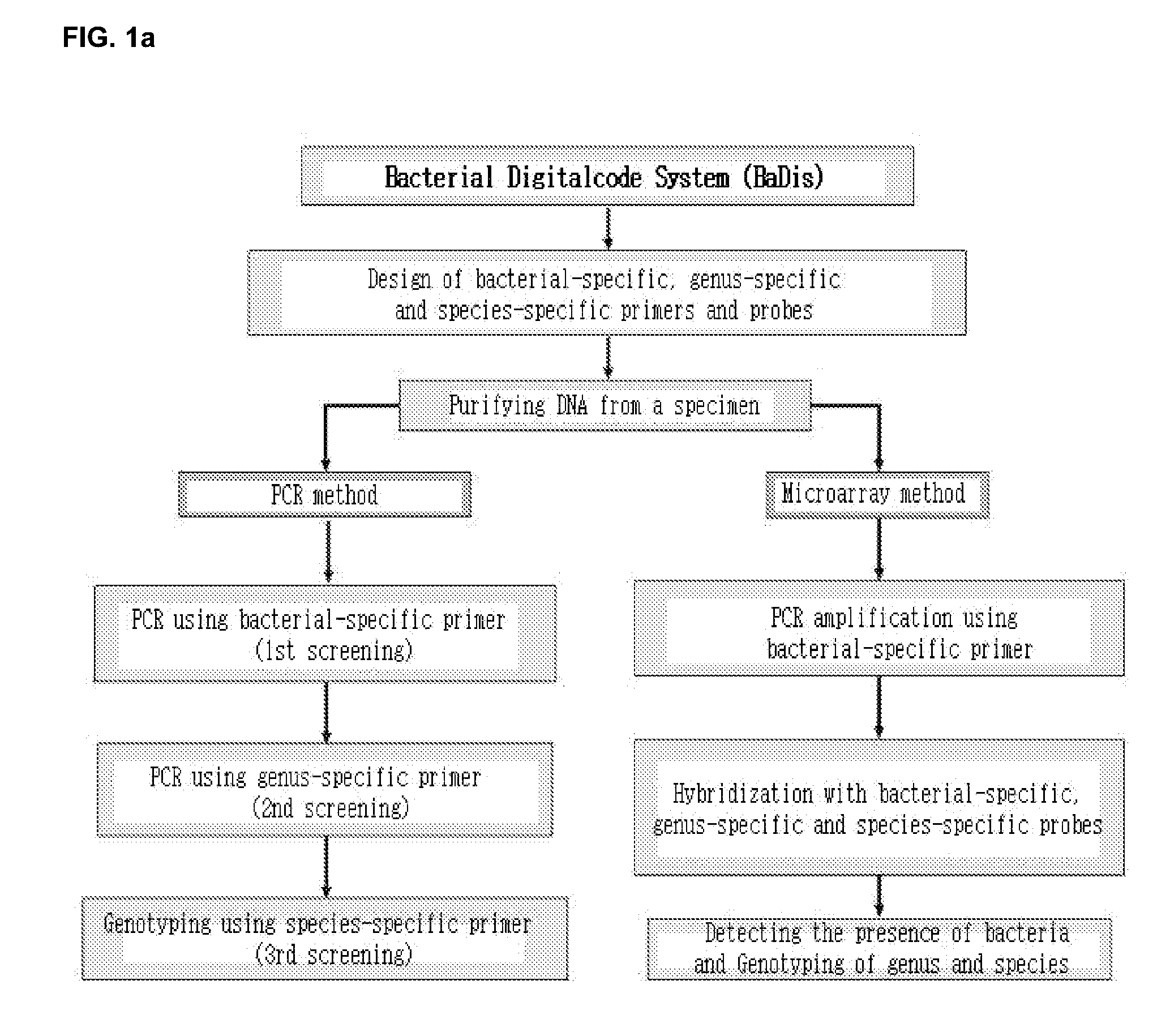
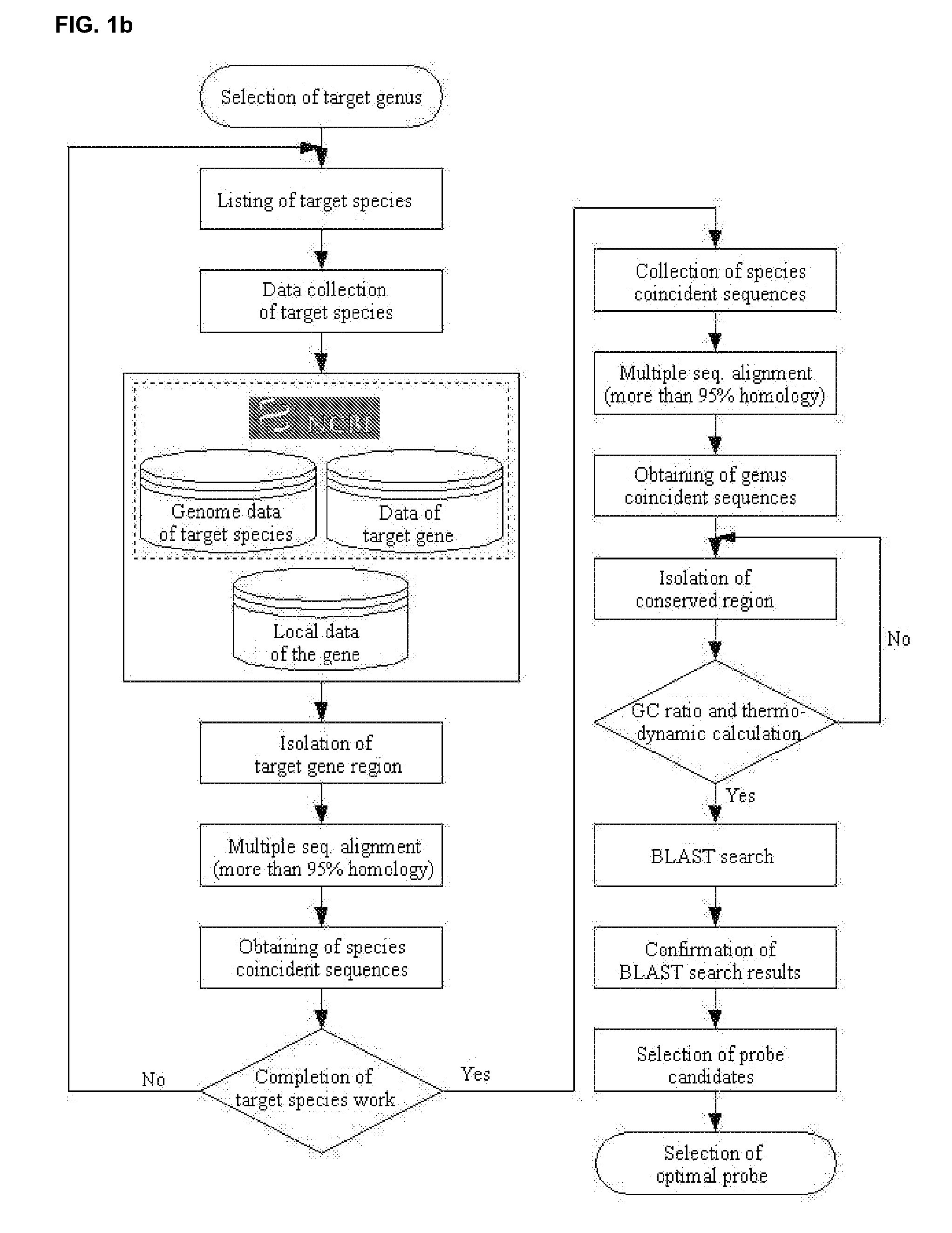
The present invention relates to a method so called Bacterial Digitalcode System (BaDis) that identifies microorganism by using bacterial-specific, genus-specific and species-specific oligonucleotides from a variety of samples or specimens for detection and differential diagnosis of microorganism. Particularly, the present invention relates to bacterial-specific, genus-specific and species-specific oligonucleotides designed by the target nucleotide sequences of 23S rDNA or ITS gene, polymerase chain reaction (hereinafter, referred to as “PCR”) kits using the oligonucleotides as a primer, the microarray containing the oligonucleotides as a probe, and methods for detecting microorganism by using the oligonucleotides. Therefore, the present invention can be applied to detect the presence of microorganism and diagnose differentially all microorganism such as pathogenic bacteria of infectious diseases, bacteria inducing food poisoning, bacteria contaminating biomedical products and environmental pollutants.
Owner:JINYIN
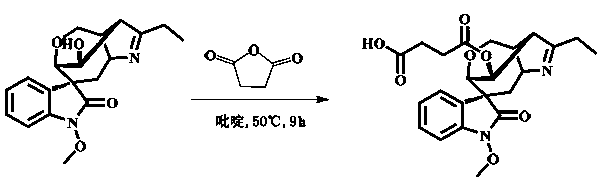
14-hydroxygelsenicine hapten and artificial antigen and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN111057064AHigh potencyHigh sensitivityOvalbuminSerum albuminGelsemium elegansFood poisoning
The invention provides a 14-hydroxygelsenicine hapten and an artificial antigen and a preparation method and application thereof. The structure of the 14-hydroxygelsenicine hapten is shown as a formula (I) as described in the specifications, the 14-hydroxygelsenicine artificial antigen shown as the formula (I) is obtained by coupling the hapten shown as the formula (I) with carrier protein. Animals are immunized by using the 14-hydroxygelsenicine artificial antigen, so that a specific antibody with high titer and high sensitivity can be obtained. The 14-hydroxygelsenicine hapten and the prepared antibody provided by the invention provide a new means for establishing a rapid, simple, cheap, sensitive and specific 14-hydroxygelsenicine detection method, and also provide a powerful means forrapid detection of gelsemium elegans toxic honey and food poisoning.
Owner:BEE RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Bacteriophage and antibacterial composition comprising the same
ActiveUS20140017205A1Good acidExcellent heat-resistanceBiocideViral/bacteriophage medical ingredientsInfectious DisorderFood poisoning
Disclosed herein is a novel bacteriophage which has specific bactericidal activity against one or more Salmonella bacteria selected from the group consisting of Salmonella enteritidis, Salmonella typhimurium, Salmonella gallinarum, and Salmonella pullorum without affecting beneficial bacteria, in addition to showing excellent tolerance to acid, heat and desiccation. The novel bacteriophage of the present invention can be widely used as an active ingredient for therapeutic agents, animal feeds or drinking water, cleaners and sanitizers for preventing and treating the infectious diseases caused by Salmonella enteritidis, Salmonella typhimurium, Salmonella gallinarum or Salmonella pullorum including salmonellosis, Salmonella food poisoning, Fowl Typhoid, and Pullorum disease or for controlling the Salmonella bacteria. The present invention also provides important insights into prevention and control strategies against Salmonella infection and suggests that the use of bacteriophage can be a novel, safe, and effectively plausible alternative to antibiotics for the prevention of Salmonella infection in poultry.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Novel bacteriophage and antibacterial composition comprising the same
Disclosed herein are is a novel bacteriophage which has specific bactericidal activity against one or more Salmonella bacteria selected from the group consisting of Salmonella Enteritidis, Salmonella Typhimurium, Salmonella Gallinarum, and Salmonella Pullorum without affecting beneficial bacteria. Disclosed are also compositions, animal feeds or drinking water, cleaners and sanitizers for preventing and treating the infectious diseases caused by Salmonella Enteritidis, Salmonella Typhimurium, Salmonella Gallinarum or Salmonella Pullorum including salmonellosis, Salmonella food poisoning, Fowl Typhoid, and Pullorum disease or for controlling the salmonella bacteria.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com