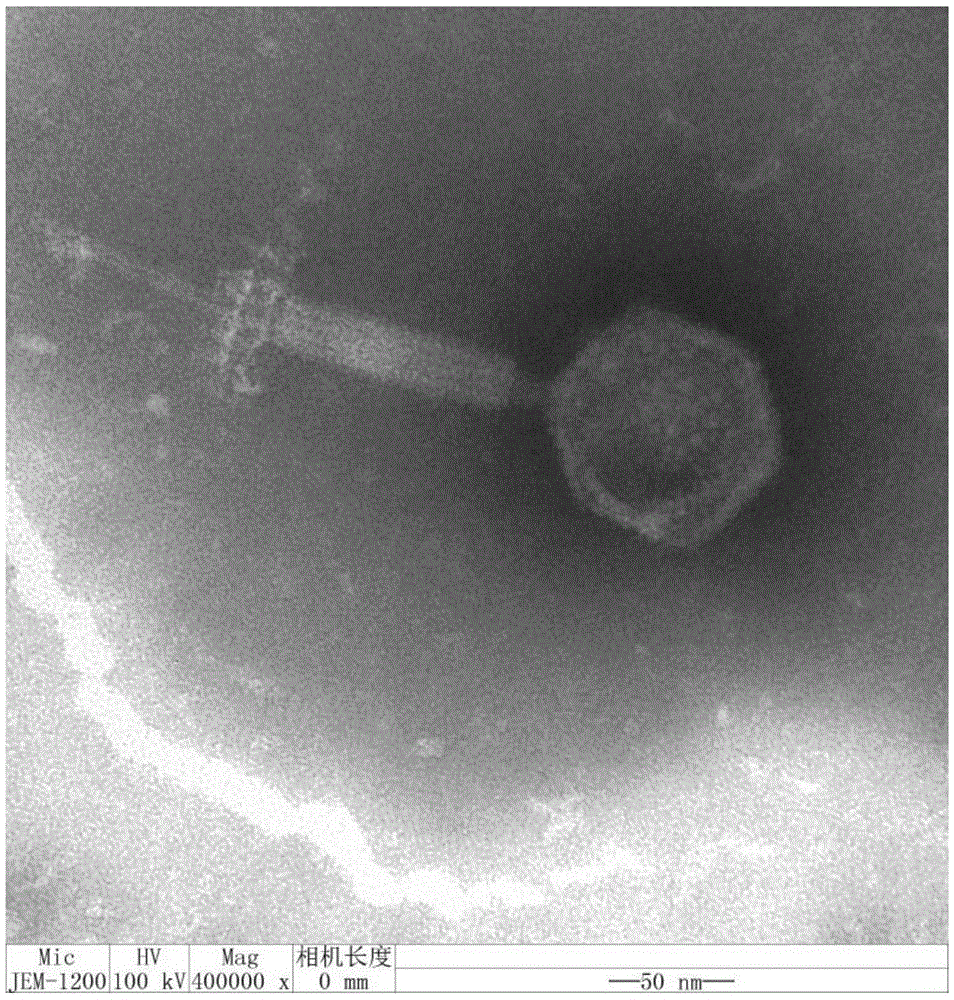
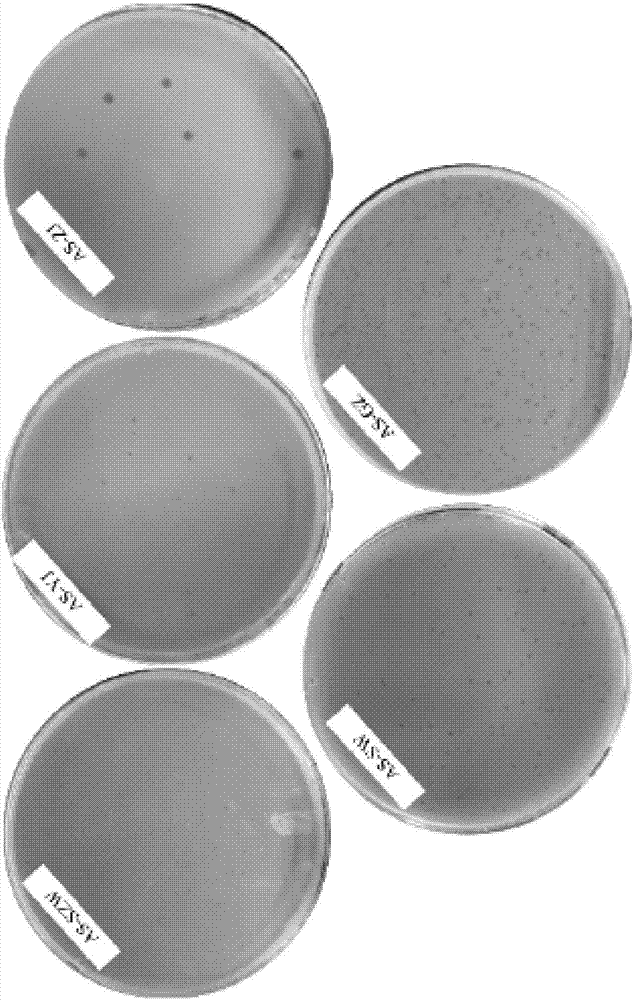
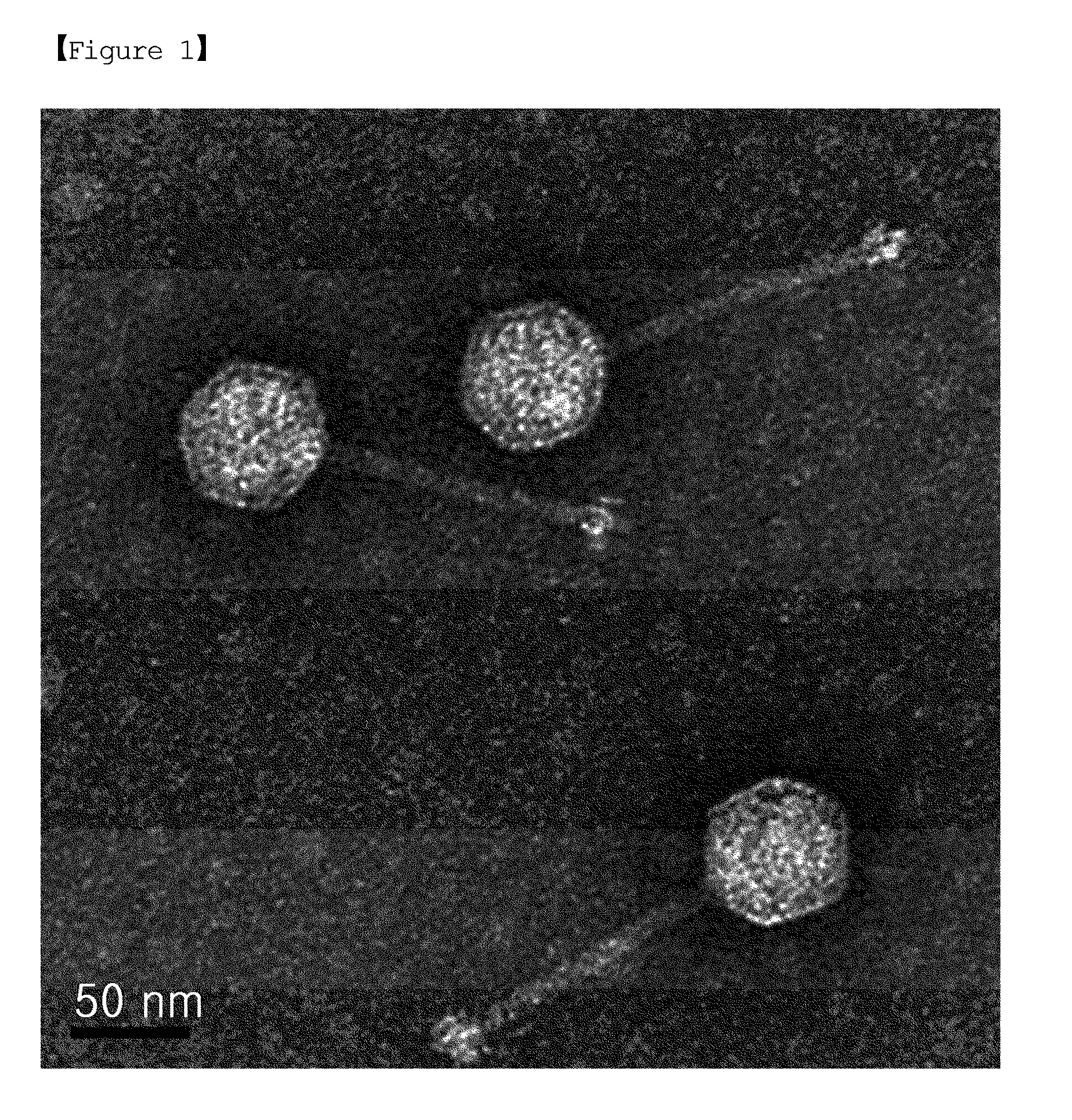
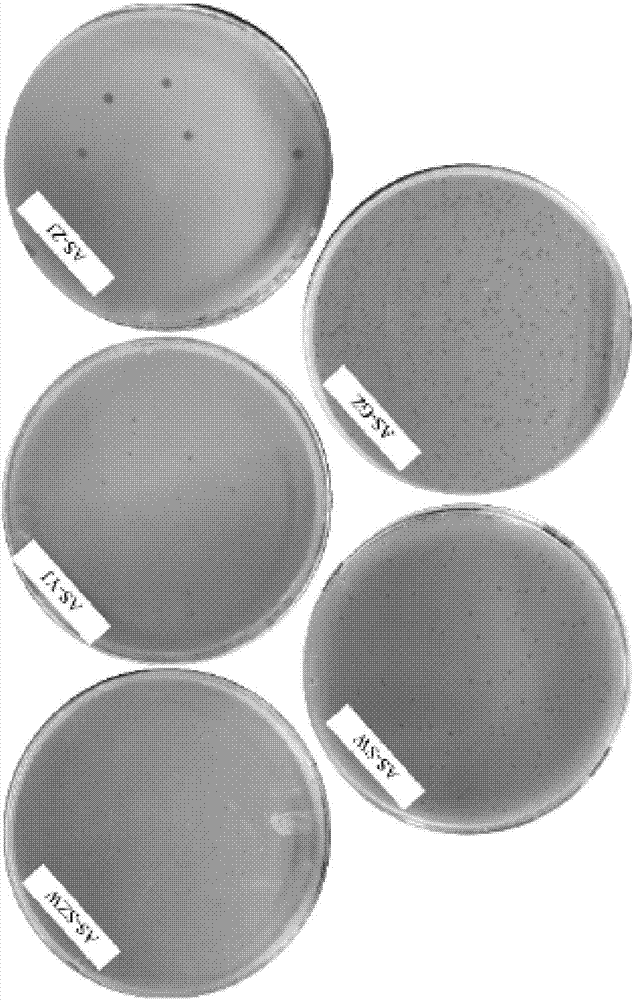
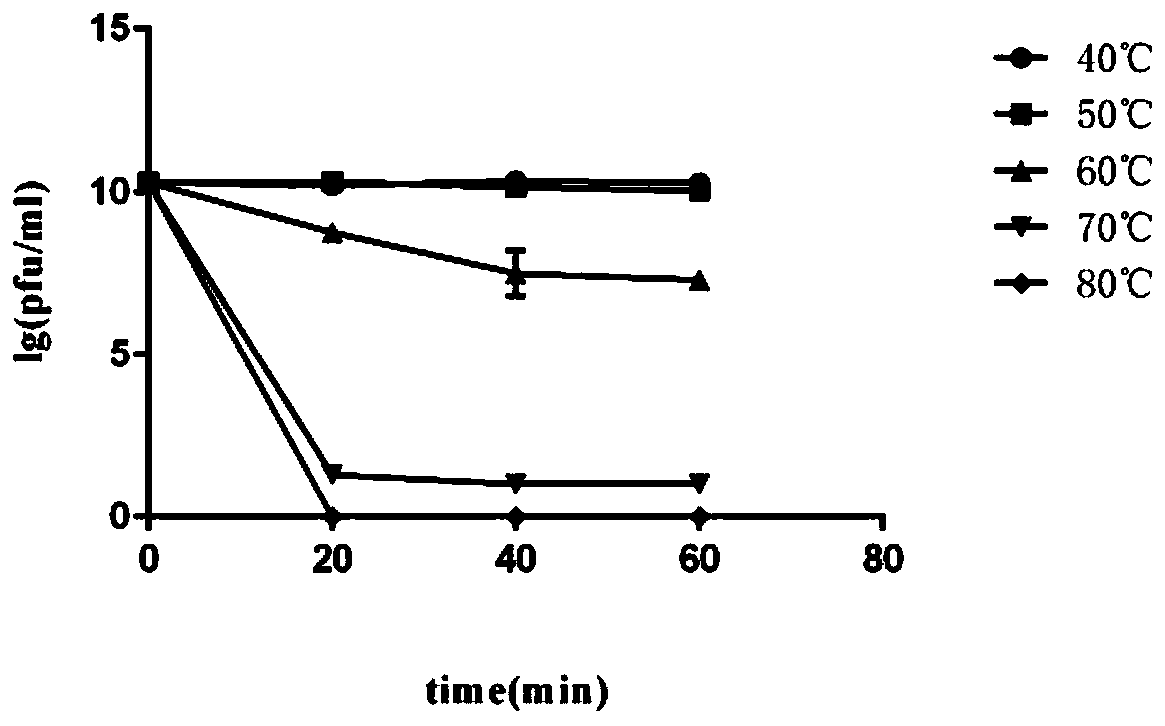
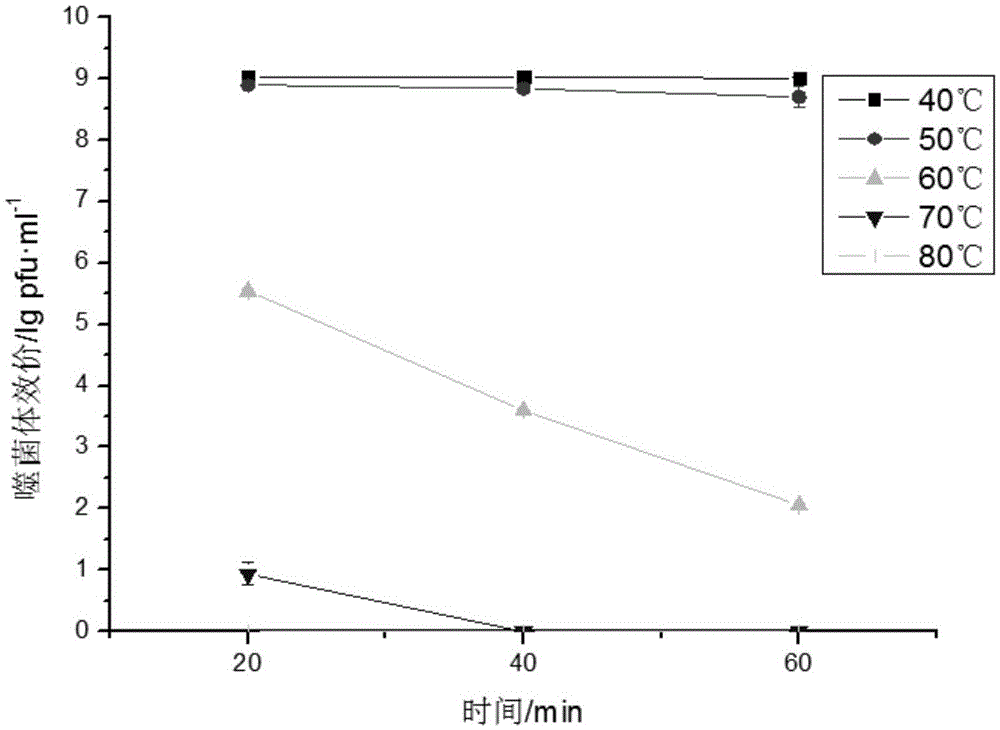
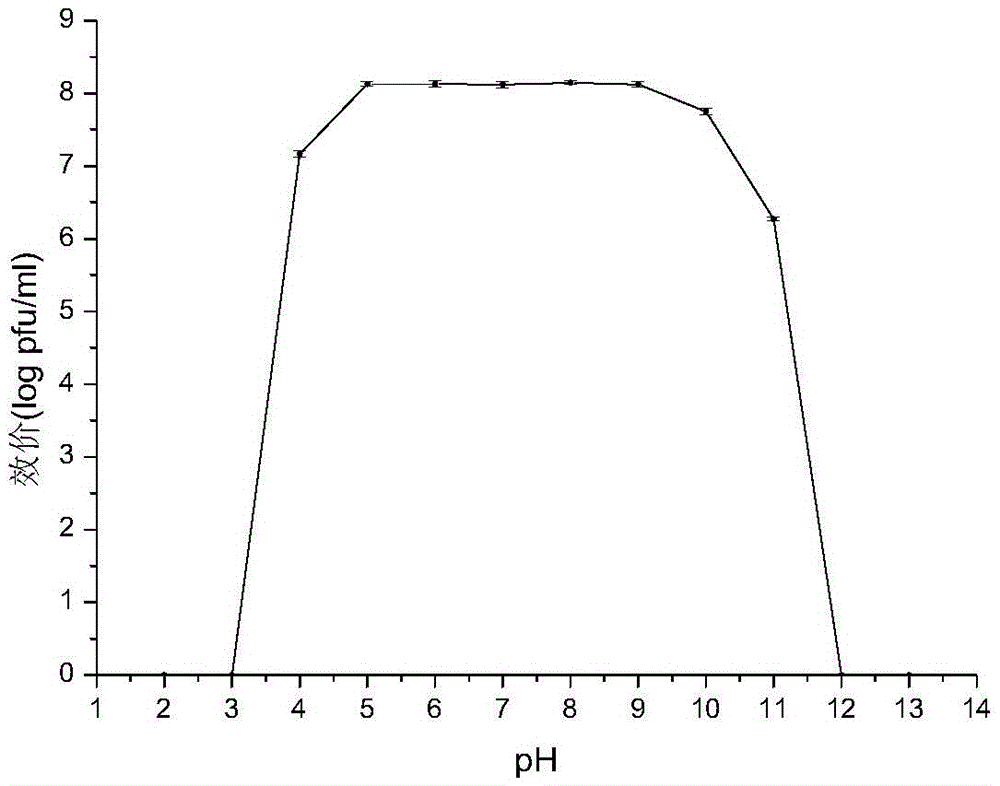
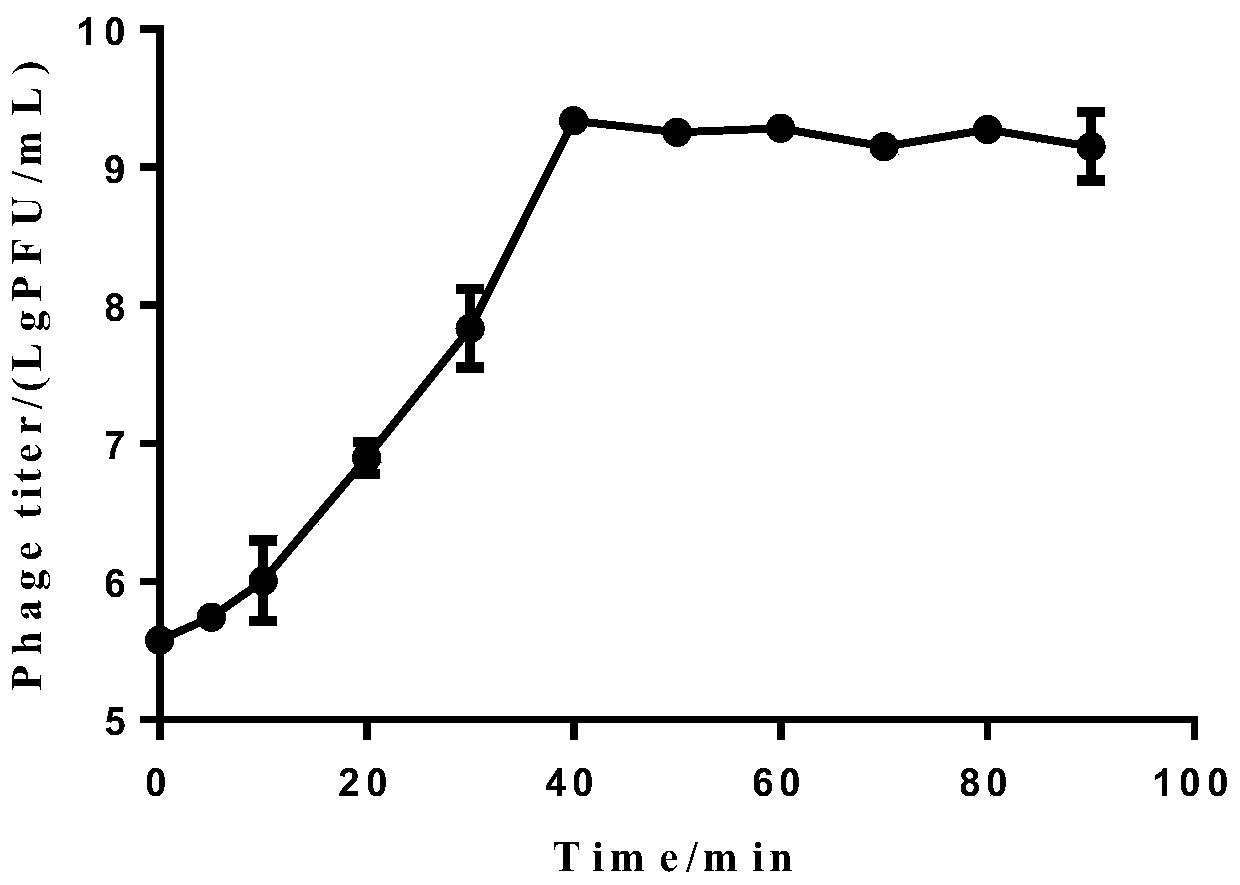
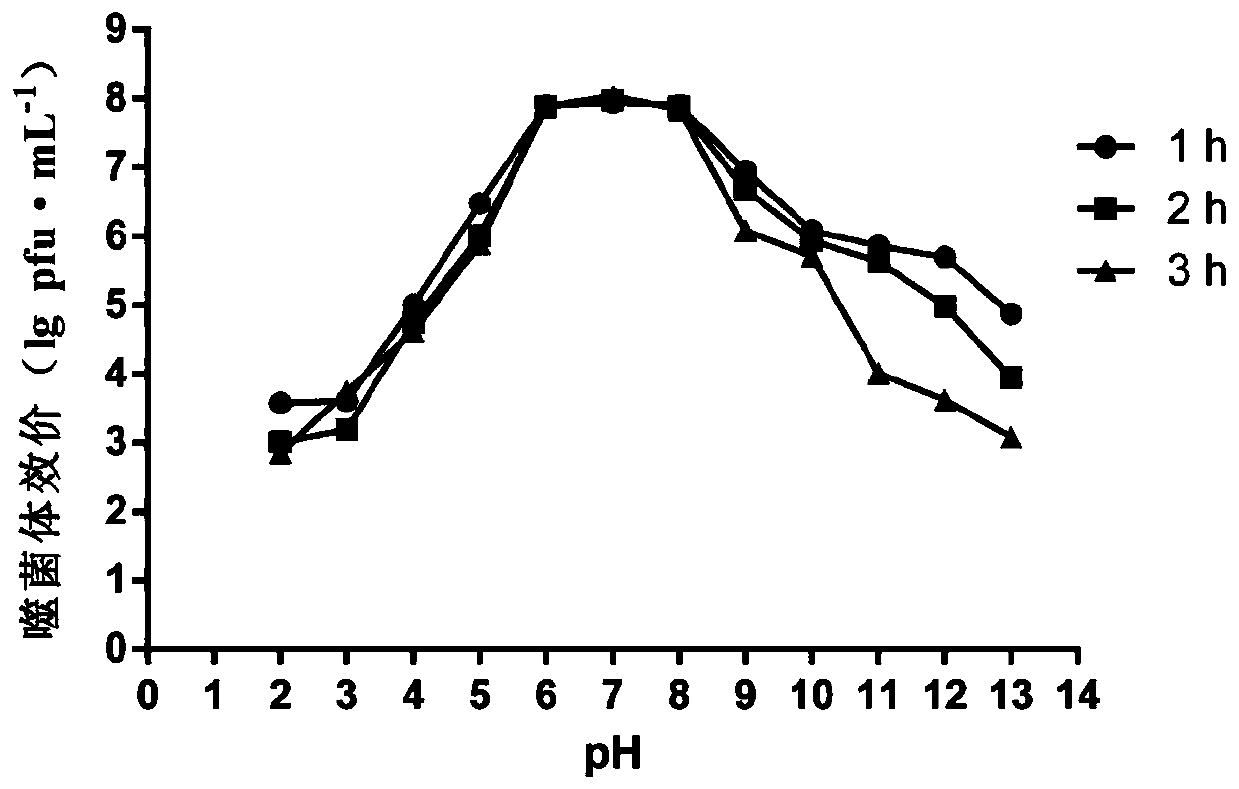
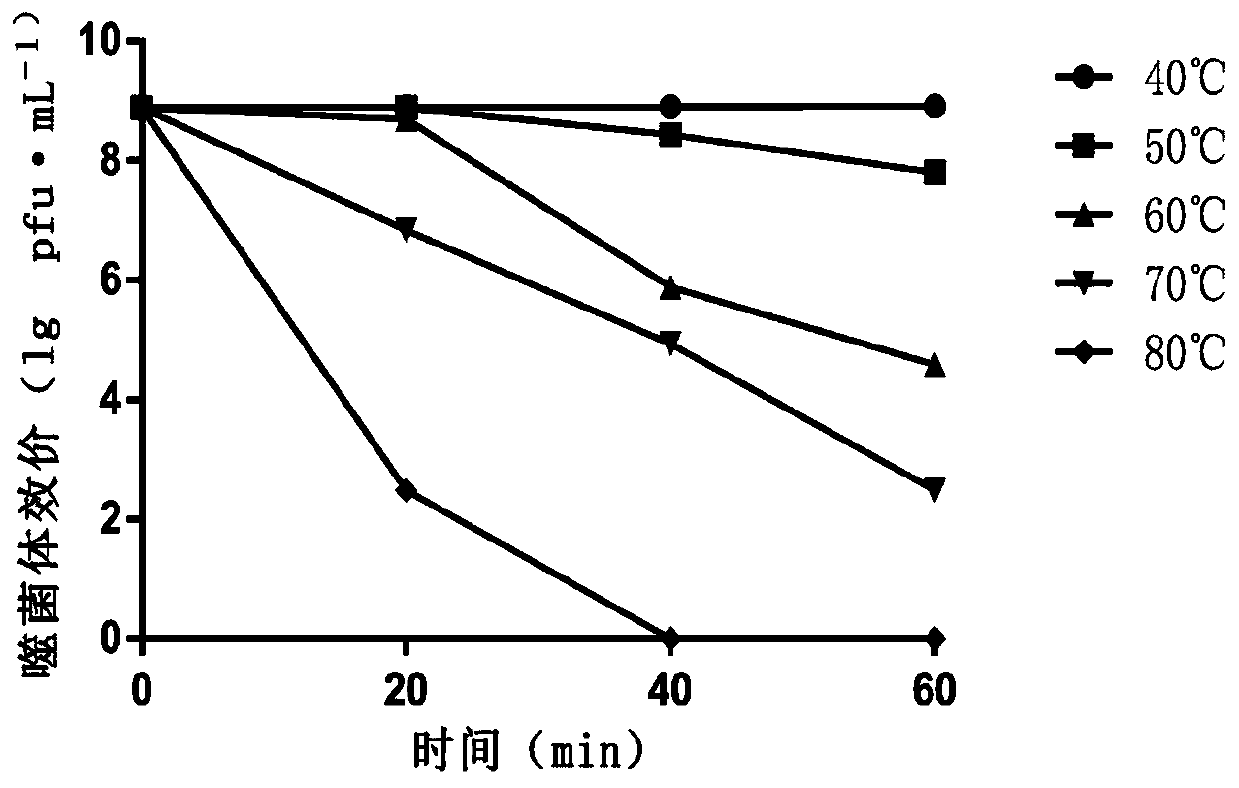
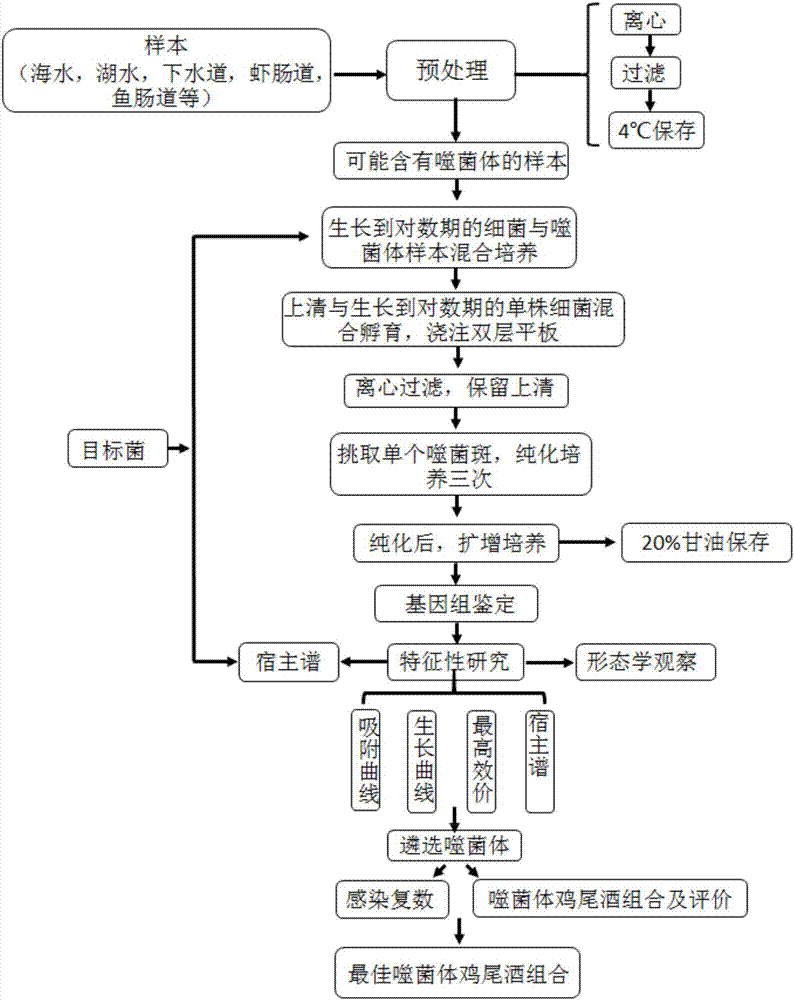
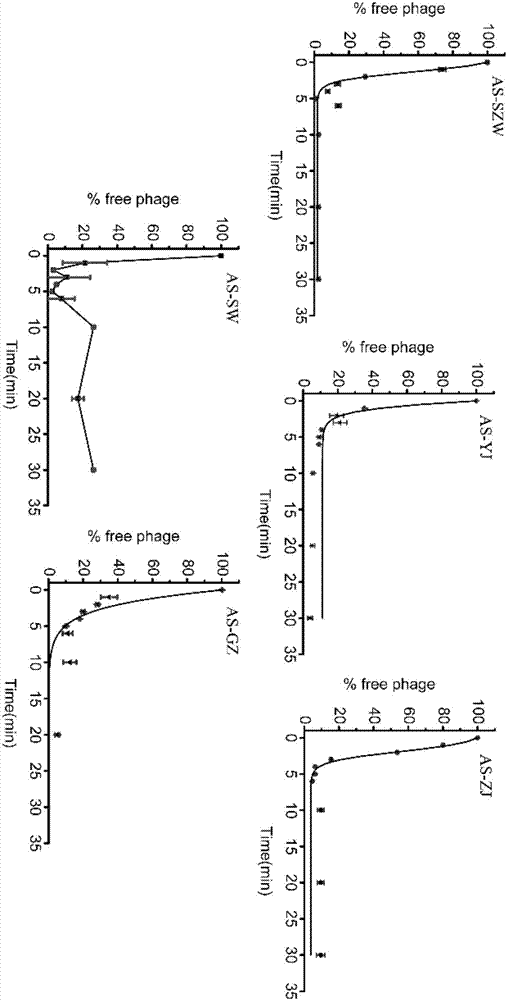
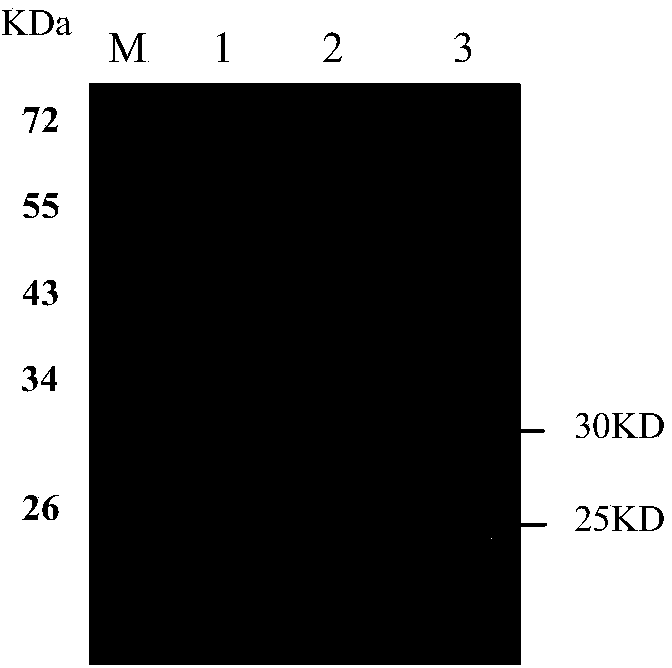
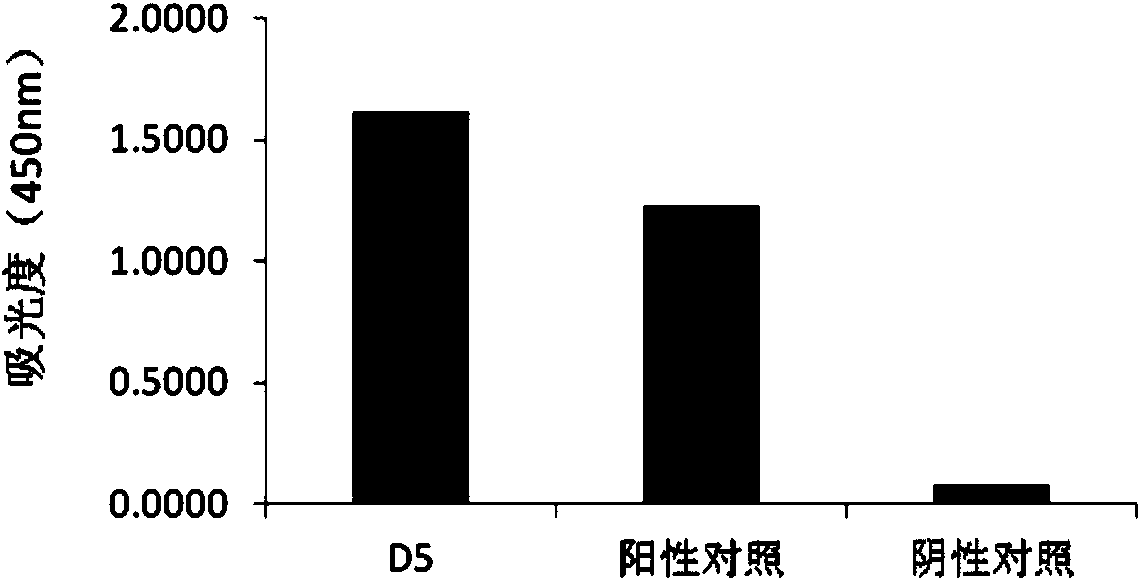
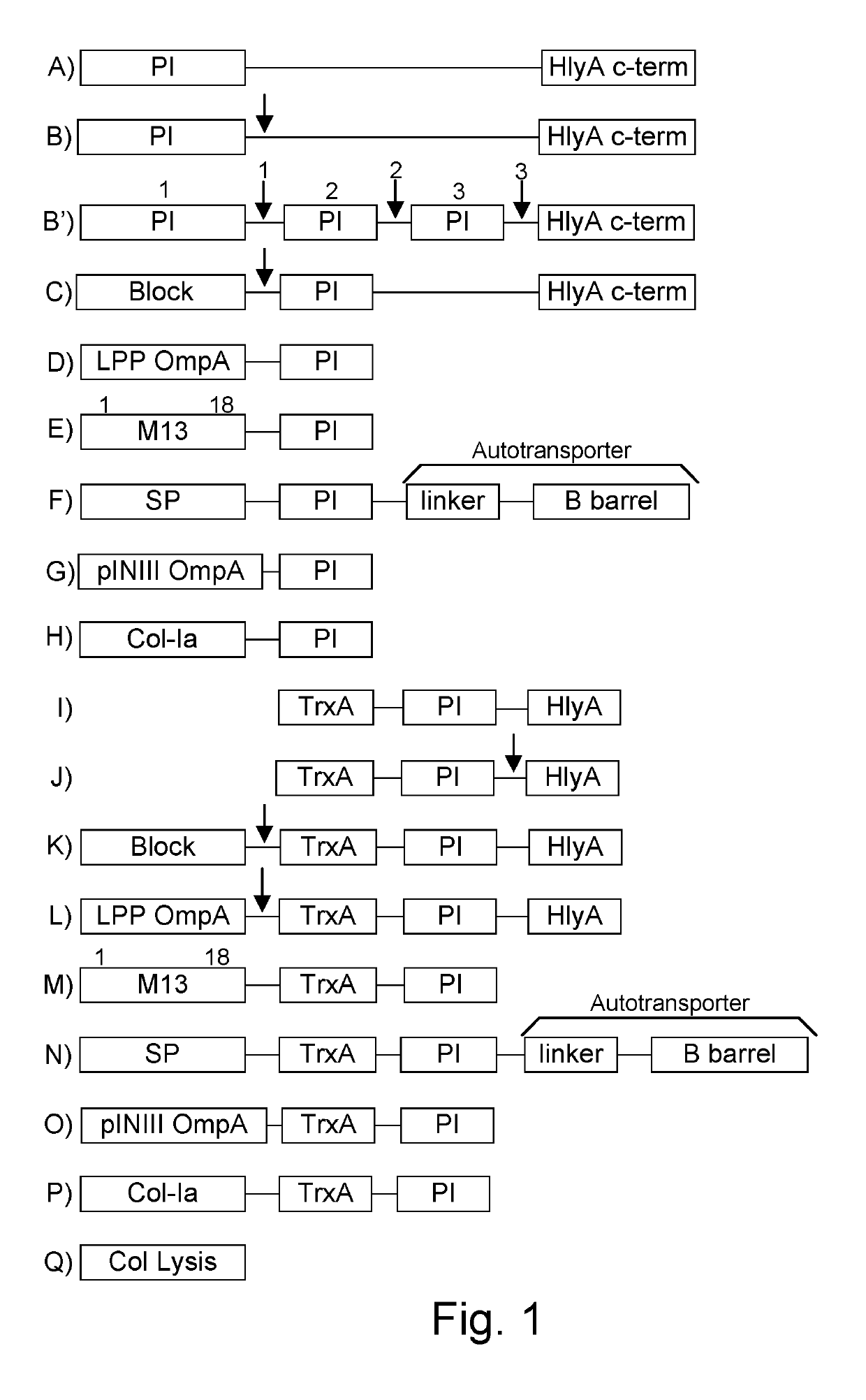
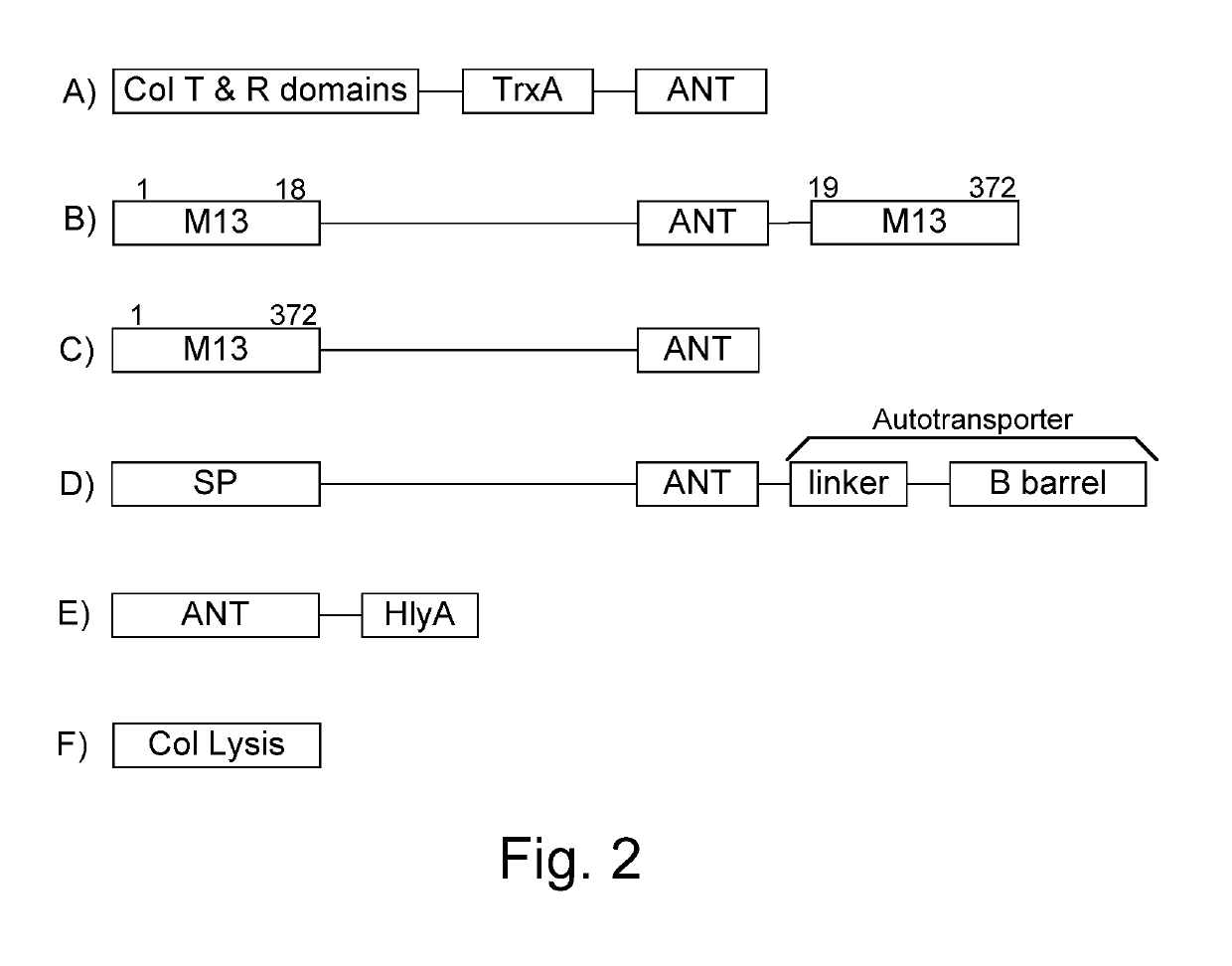
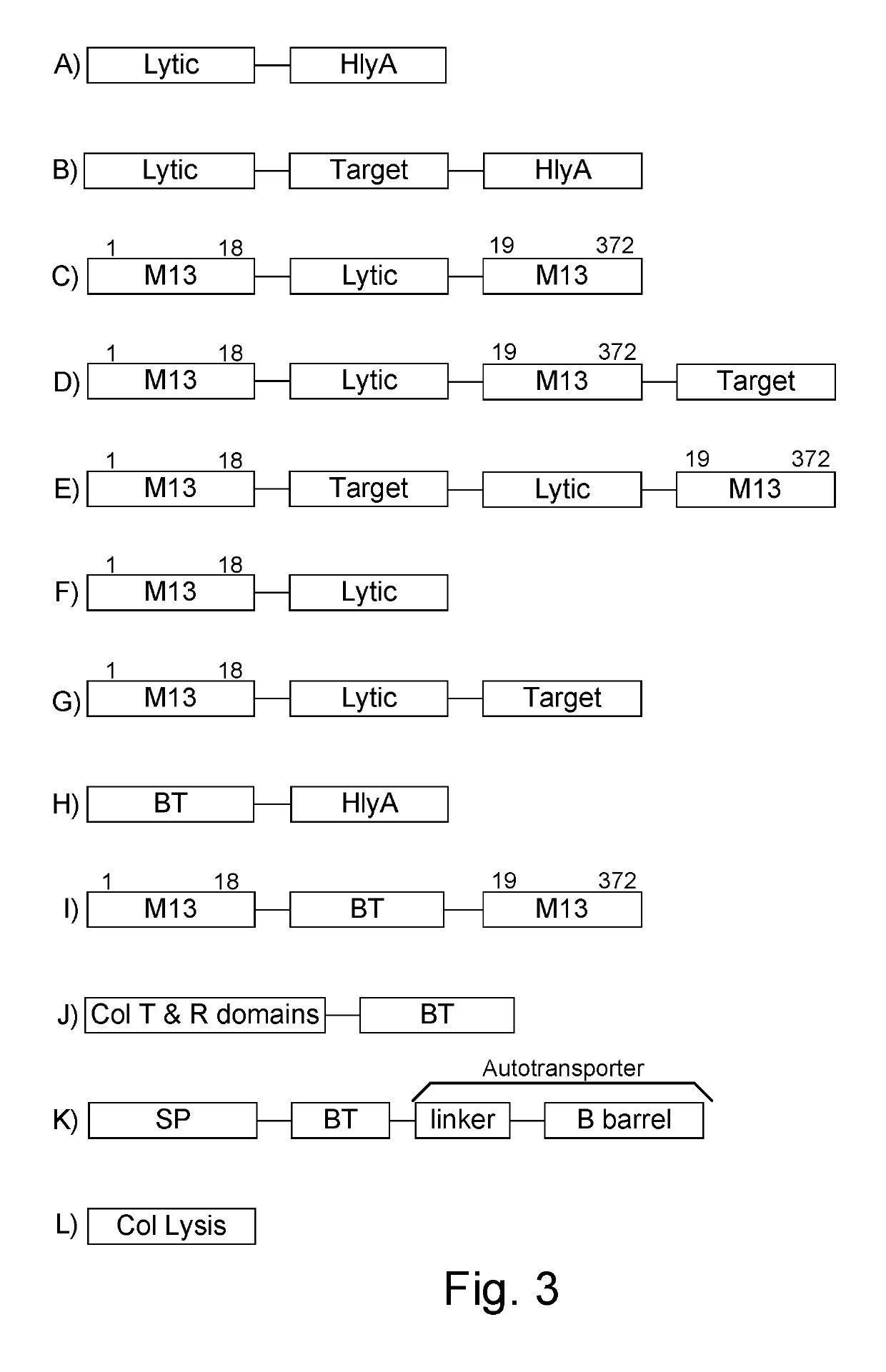
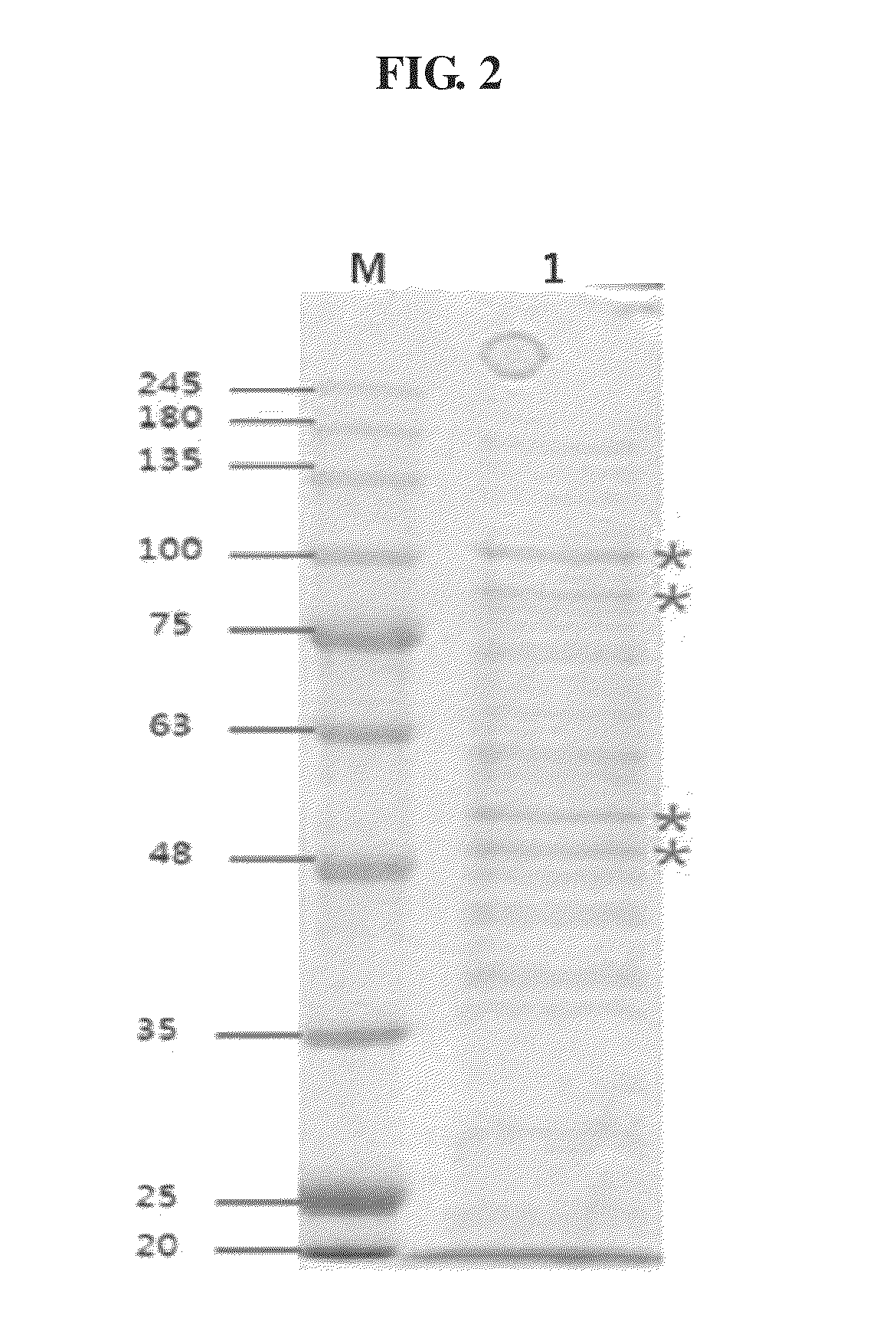
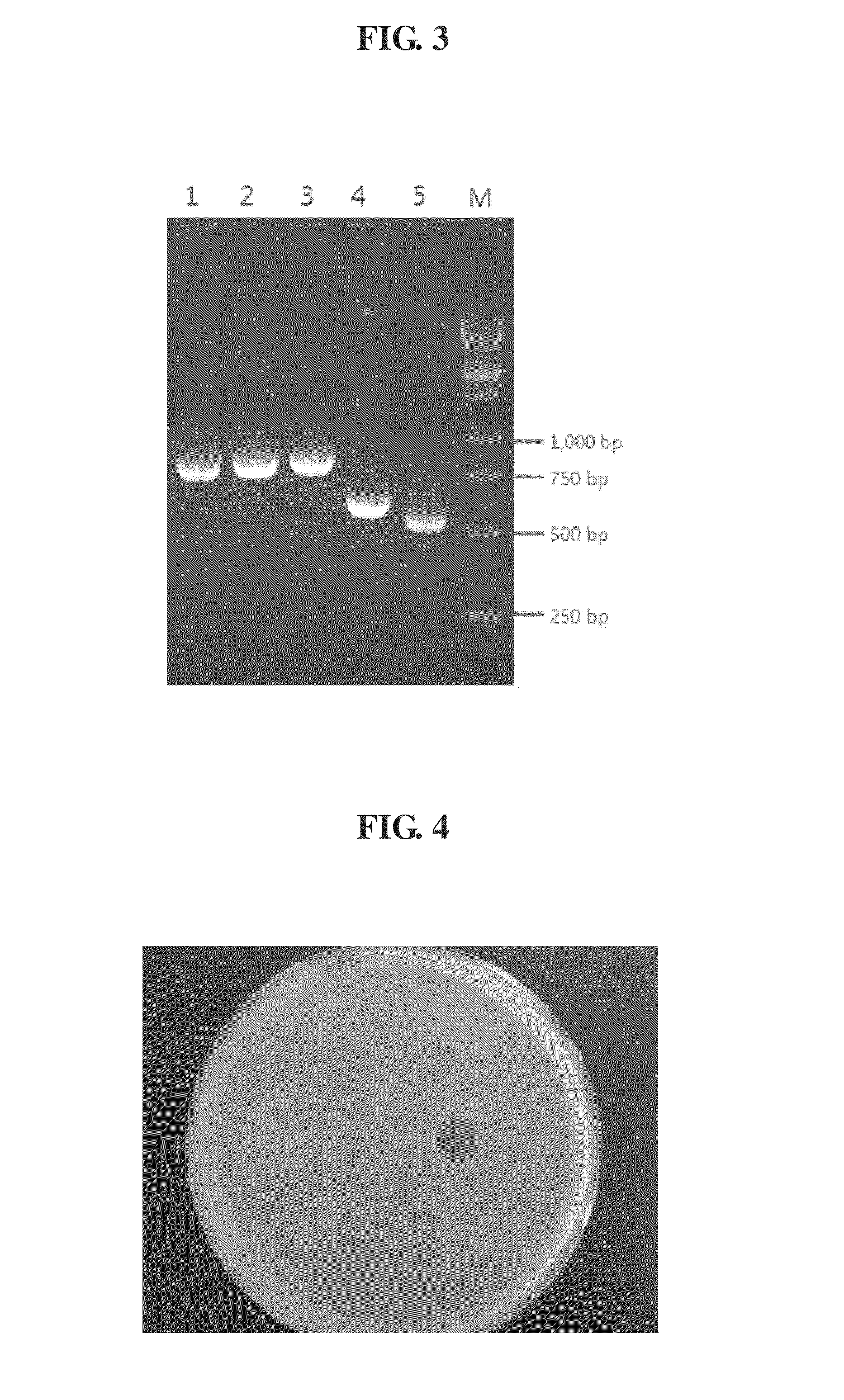
Patents
Literature
114 results about "Anaplasma phagocytophilum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Anaplasma phagocytophilum (formerly Ehrlichia phagocytophilum) is a Gram-negative bacterium that is unusual in its tropism to neutrophils. It causes anaplasmosis in sheep and cattle, also known as tick-borne fever and pasture fever, and also causes the zoonotic disease human granulocytic anaplasmosis.
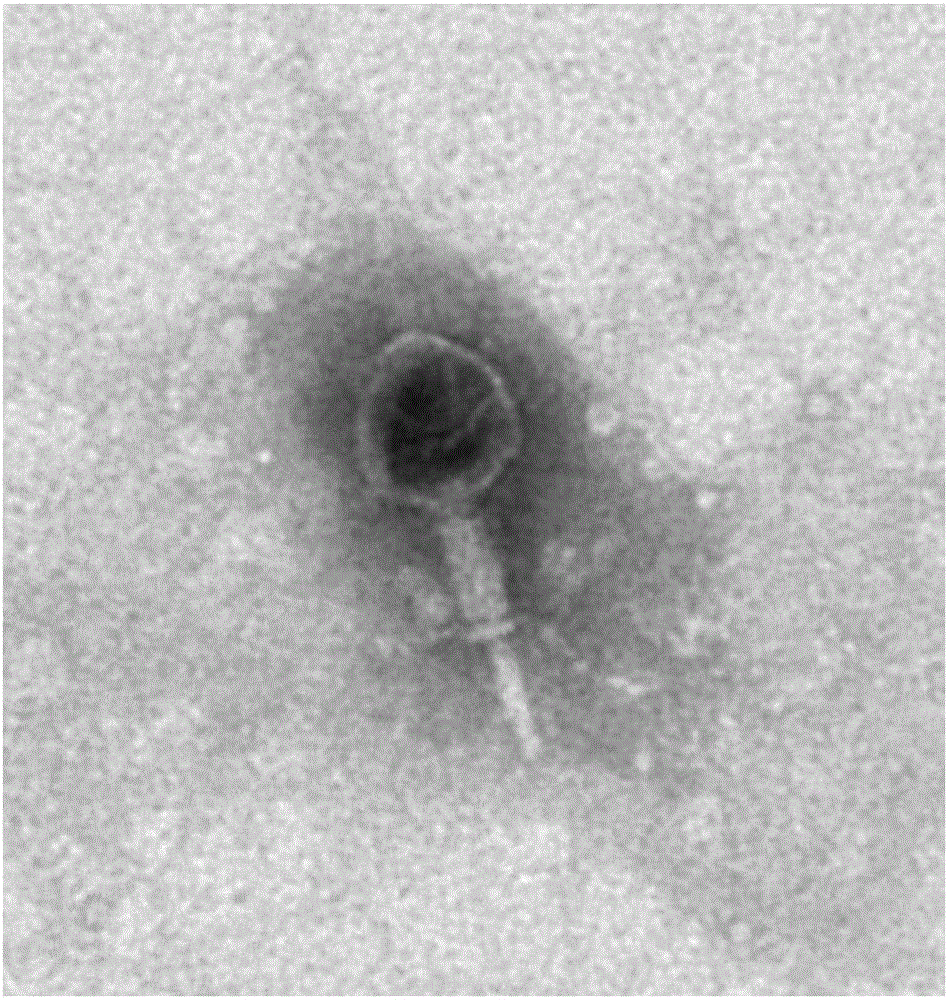
Novel bacteriophage and antibacterial composition comprising the same
Disclosed herein are is a novel bacteriophage which has specific bactericidal activity against one or more Salmonella bacteria selected from the group consisting of Salmonella Enteritidis, Salmonella Typhimurium, Salmonella Gallinarum, and Salmonella Pullorum without affecting beneficial bacteria. Disclosed are also compositions, animal feeds or drinking water, cleaners and sanitizers for preventing and treating the infectious diseases caused by Salmonella Enteritidis, Salmonella Typhimurium, Salmonella Gallinarum or Salmonella Pullorum including salmonellosis, Salmonella food poisoning, Fowl Typhoid, and Pullorum disease or for controlling the salmonella bacteria.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Novel bacteriophage and antibacterial composition comprising the same
ActiveUS20110052542A1Effective preventionEffective treatmentAntibacterial agentsBiocideBacteroidesFood poisoning
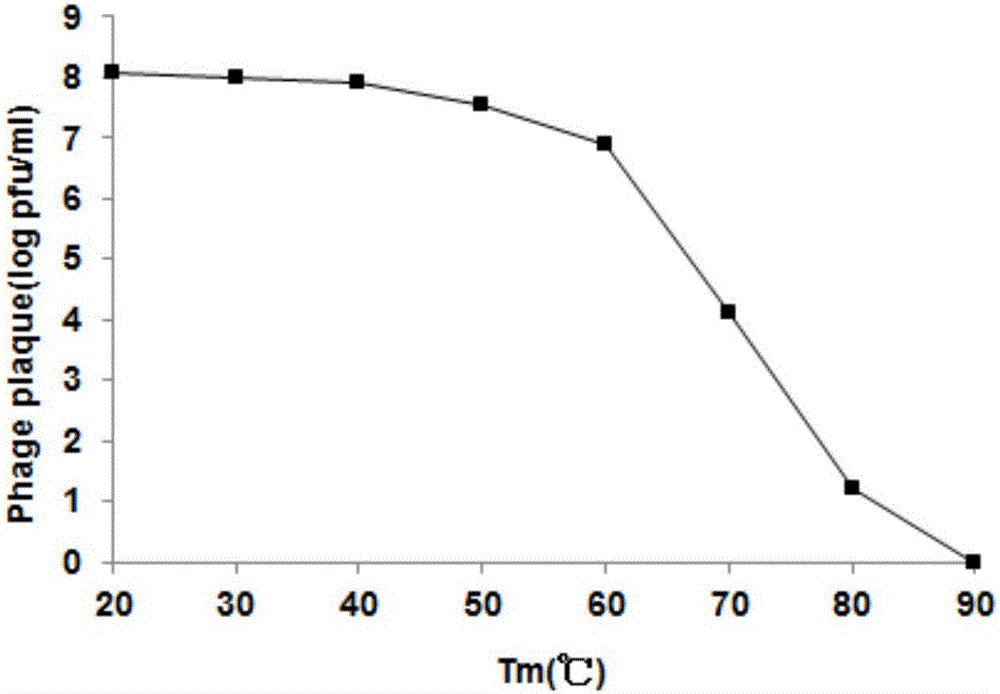
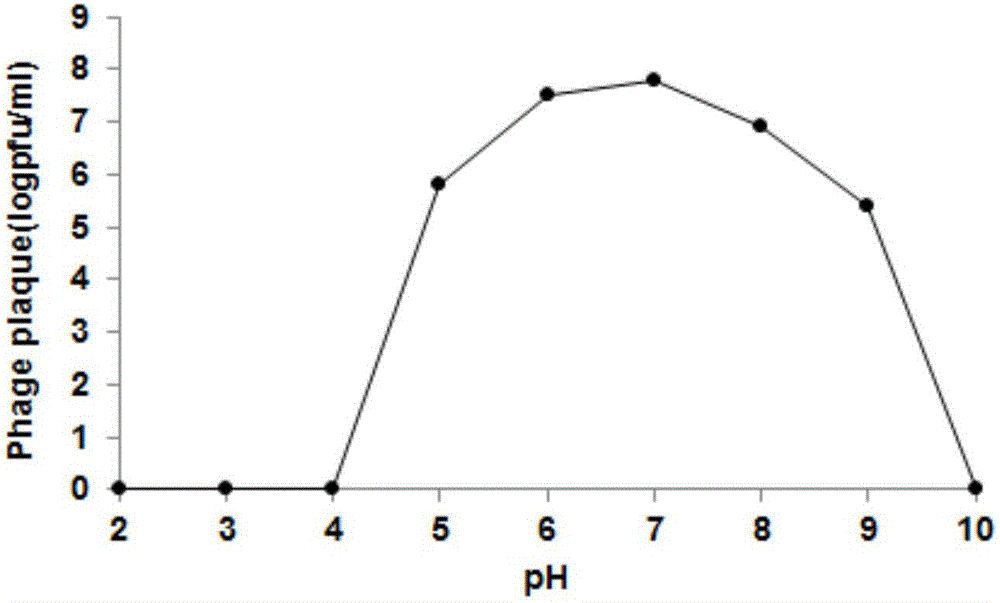
Disclosed herein is a novel bacteriophage which has specific bactericidal activity against one or more Salmonella bacteria selected from the group consisting of Salmonella Enteritidis, Salmonella Typhimurium, Salmonella Gallinarum, and Salmonella Pullorum without affecting beneficial bacteria, in addition to showing excellent tolerance to acid, heat and desiccation. The novel bacteriophage can be widely used as an active ingredient for therapeutic agents, animal feeds or drinking water, cleaners and sanitizers for preventing and treating the infectious diseases caused by Salmonella Enteritidis, Salmonella Typhimurium, Salmonella Gallinarum or Salmonella Pullorum including salmonellosis, Salmonella food poisoning, Fowl Typhoid, and Pullorum disease or for controlling the salmonella bacteria.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Short-tailed coliphage and application thereof
ActiveCN110129283AIncrease lytic activityNo side effectsAntibacterial agentsBiocideEscherichia coliMicroorganism
The invention relates to a coliphage and application thereof, in particular to a short-tailed highly-lytic coliphage. The coliphage named PD38 is collected in the China General Microbiological CultureCollection Center on September 26, 2018, wherein the collection number is CGMCC No. 16391. The coliphage has a good lytic effect on escherichia coli, has a good killing effect on the escherichia coliin food and culture environment, and can prevent and treat diseases caused by the escherichia coli of chicken.
Owner:QINGDAO PHAGEPHARM BIO TECH CO LTD
Method for separating and screening phage for degrading Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm
InactiveCN102199576AOvercoming drug resistanceOvercoming therapeuticViruses/bacteriophagesBiofilmMicroorganism
The invention relates to a phage for degrading a Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm. The phage is characterized in that: the phage is named C12, the collection number is CGMCC No. 4249, the collection unit is China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center located at No. 3, No. 1 Yard, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing City, and the collection date is October 26, 2010. The invention provides a method for amplifying, separating and preserving the phage for degrading Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The capacity of degrading the Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm by the phage is also determined, finally the pure phage C12 with high titer and high biofilm degradation capacity is obtained, and the degradation amount of the pure phage C12 reaches 85.3 percent; the phage can degrade biofilms and crack viable bacteria in the biofilms; the clinical application of the phage can be realized; treatment problems of medicine resistance and biofilms of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa are solved; and the method is a feasible biological method.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Methicillin-resistant staphylococcus epidermidis staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage and antimicrobial application thereof
The invention relates to a bacteriophage and antimicrobial application thereof, in particular to a methicillin-resistant staphylococcus epidermidis staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage and antimicrobial application thereof, and belongs to the field of bioengineering. The methicillin-resistant staphylococcus epidermidis staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC), located in Wuhan University of Wuhan of China, on September 17, 2015. The collection number is staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage qdsa002 of CCTCC M2015554. The Latin scientific name is staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage qdsa002. The bacteriophage has high splitting effect on staphylococcus aureus, especially methicillin-resistant staphylococcus epidermidis staphylococcus aureus. The preparation can be used individually or compounded with other drugs, and a safe bacteriophage product source free of toxic and side effects is provided for control of methicillin-resistant staphylococcus epidermidis staphylococcus aureus contamination.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Bacteriophages useful for the prophylaxis and therapy of vibrio anguillarum
InactiveUS20140105866A1Infection controlEasy to applyBiocideMicroorganismsBacteroidesVibrio anguillarum
An isolated strain of bacteriophage, specific against bacteria belonging to the Vibrio genre, particularly the anguillarum species, deposited on 3 Oct. 2012 at the Polish Collection of Microorganisms (PCM) of the Ludwik Hirszfeld Institute of Immunology and Experimental Therapy of the Polish Academy of Sciences, with access number F / 00072, characterized in that said strain is efficient in the prophylaxis, control and / or treatment of the infection caused by Vibrio anguillarum in all types of species of fish, mollusks and crustaceans that are important for aquaculture susceptible to this bacteria, genome size 48.6 Kb, it is not sensitive to chloroform and its storage temperature is −80° C.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHILE
New klebsiella pneumoniae phage and application thereof
ActiveCN110438091AImprove disinfection effectBroad spectrum antibacterialAntibacterial agentsBiocideK pneumoniaeMultidrug resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae
The invention discloses new klebsiella pneumoniae phage vB_KpnM_Bp5. The klebsiella pneumoniae phage (klebsiella pneumoniae phage) phage ) vB_KpnM_Bp5 is preserved in the China Center for Type CultureCollection (CCTCC) on June 13, 2019, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO:M 2019452. The phage has better disinfecting and sterilizing effects on host multidrug resistant klebsiella pneumoniae separated from piggery sewage, also has good disinfecting and sterilizing effects on other two multidrug resistant klebsiella pneumoniae separated from hospitals, is wide in antimicrobial spectrum, and can be applied to preparation of medicines for preventing and treating multidrug resistant klebsiella pneumoniae.
Owner:南宁鑫创生物科技有限公司
Escherichia coli bacteriophage vB_EcoM_swi3 and application thereof
InactiveCN110607284AImprove securityPhysical and chemical factors are well toleratedAntibacterial agentsViral/bacteriophage medical ingredientsESCHERICHIA COLI ANTIGENAnaplasma phagocytophilum
The invention discloses escherichia coli bacteriophage vB_EcoM_swi3 of which the preservation number is CCTCC M 2019467. The bacteriophage belongs to myoviridae, and is provided with a polyhedral headand a telescopic tail structure, wherein the diameter of the head is about 80nm, and the length of the tail is about 120nm. Bright plaque can be formed on a solid culture medium, an aureole does notexist on the periphery of the plaque, the edge is clear and regular, and the diameter is about 1-1.5mm. The bacteriophage has favorable splitting effects on pig-derived escherichia coli and chicken-derived escherichia coli, especially pig-derived pathogenic escherichia coli and chicken-derived pathogenic escherichia coli, and has quite great application prospects in a plurality of respects of medicinal preparations for preventing and treating pig-derived colibacillosis and chicken-derived colibacillosis, feed additives and the like.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Staphylococcus aureus phage strain and application thereof
ActiveCN109251898ABroad cracking spectrumAntibacterial agentsViral/bacteriophage medical ingredientsFecesStaphylococcus cohnii
The invention provides a staphylococcus aureus phage strain VB_SavM_JYL01. The staphylococcus aureus phage stain VB_SavM_JYL01 has been preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection on 25th March, 2018, the preservation name is Staphylococcus aureus phage VB_SavM_JYL01, and the preservation number is CCTCC M 2018154. The staphylococcus aureus phage strain has a wide lysis spectrum, thus staphylococcus aureus can be lysed, certain staphylococcus epidermidis can also be lysed, host bacteria 206 can be lysed, and staphylococcus clinical strains separated from the environment or fecesof diseased animals can also be lysed; the staphylococcus aureus phage can be used independently or in combination with other substances, and a safe and nontoxic phage disinfecting and killing productis provided for disinfecting and purifying the environment.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
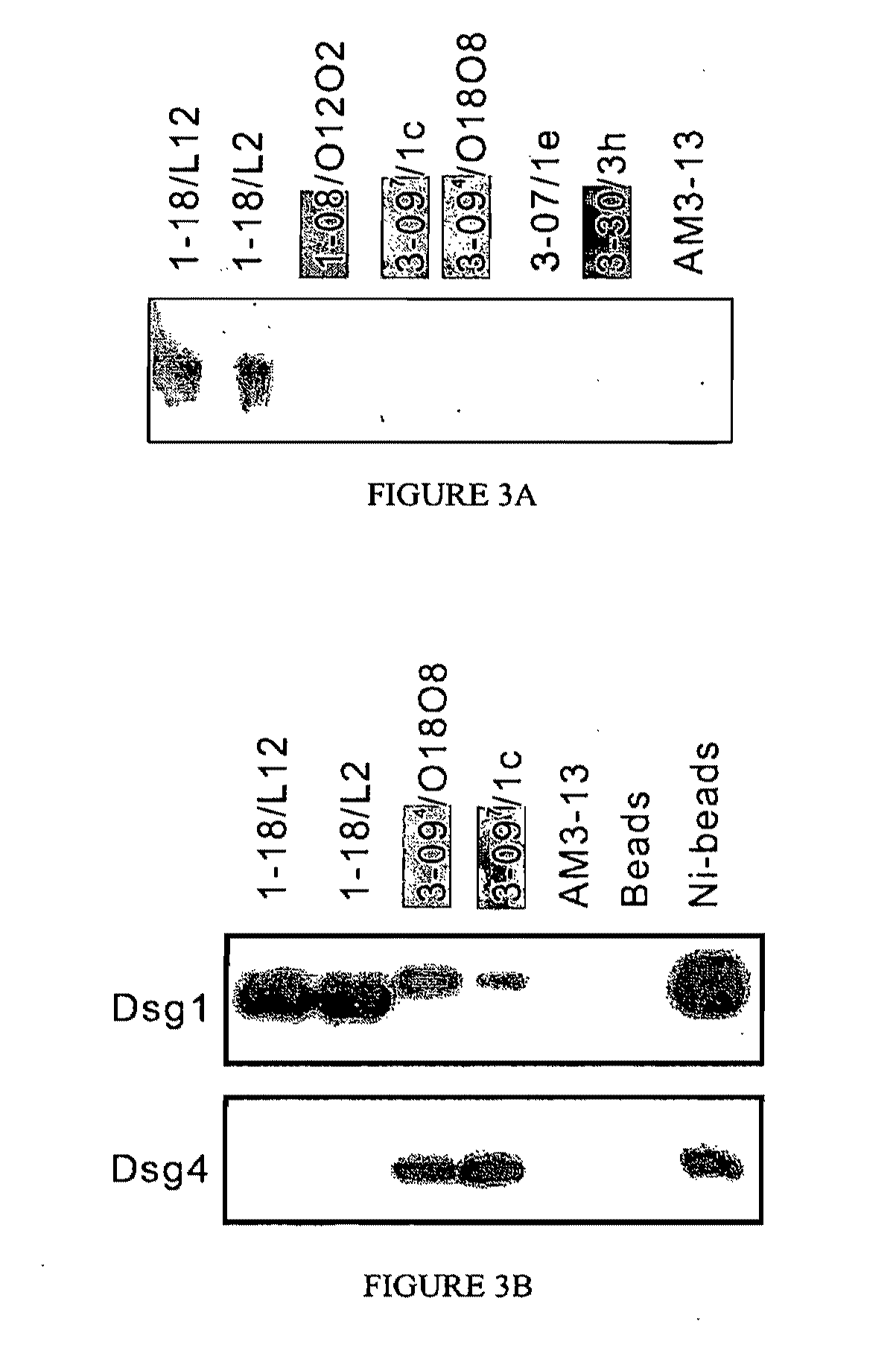
Isolation of Anti-Desmoglein 1 Antibodies by Phage Display of Pemphigus Foliaceus Autoantibodies
ActiveUS20110091449A1Inhibit expressionInhibit bindingOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsGlycophorinAnaplasma phagocytophilum
This invention relates to compositions and methods for the use of anti-autoimmune reagents that specifically bind to anti-desmoglein antibodies, which are responsible for pemphigus foliaceus. In addition, the invention relates to methods and compositions for inhibiting the expression or function of a variable region of an anti-desmoglein (anti-Dsg) pathogenic autoantibody.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Enterohaemorrhagic escherichia coli phage and application thereof
ActiveCN106754751AWide host rangeAvoid survivalAntibacterial agentsDigestive systemAnaplasma phagocytophilumMolecular biology
The invention relates to enterohaemorrhagic escherichia coli phage and an application thereof. The enterohaemorrhagic escherichia coli phage is characterized in that the preservation number of a phage strain is CCTCC NO:M 2016539, and the phage strain is preserved at the China Center for Type Culture Collection at Wuhan university in China on September 29, 2016, and is classified and named asenterohaemorrhagic coliphage vB-ECM-MIE, entero-haemorrhagic-Escherichia-coli-O157:H7 phage vB-ECM-MIE. The enterohaemorrhagic escherichia coli phage has efficient sterilization capacity on EHEC.
Owner:韩鸣
Aeromonas salmonicida phage, bactericidal composition comprising same and application of bactericidal composition
ActiveCN107099509AAntibacterial agentsMicroorganism based processesAnaplasma phagocytophilumMicrobiology
The invention relates to an aeromonas salmonicida phage, a bactericidal composition comprising the same and an application of the bactericidal composition. The phage is capable of quickly inhibiting growth of Atlantic aeromonas salmonicida within a short period of time and inhibiting generation of resistance of the pathogenic bacterium phage. In addition, the bactericidal composition comprising the phage is safe and effective, and is high in specificity and low in production cost, and the disadvantages of single phagotherapy are compensated in the control process of pathogenic bacterium.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
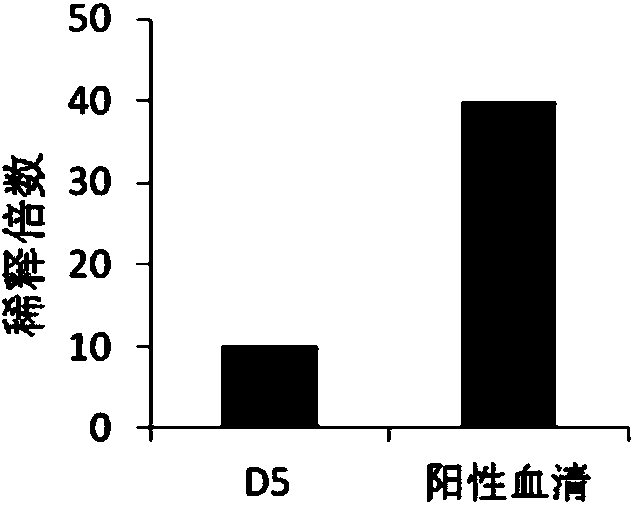
Humanized neutralizing antibody D5 against avian influenza virus (AIV) H7N9 as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention provides a humanized neutralizing antibody D5 against the avian influenza virus (AIV) H7N9. The neutralizing antibody D5 is screened by utilizing the phage surface display technique. The amino acid sequences of light and heavy chain variable regions of the neutralizing antibody D5 are respectively shown in SEQ ID No.1 and SEQ ID No.2. The antibody can specifically recognize the antigens of H7N9 virions, can carry out obvious enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with the virus H7N9, and has a neutralizing activity function of resisting infection with the virus H7N9. Besides, the antibody can be used for preparing specific antibody drugs for preventing and treating the AIV H7N9, and then the drugs are clinically used for preventing and treating acute respiratory infectious diseases caused by the virus H7N9.
Owner:INST OF PATHOGEN BIOLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
Novel bacteriophage and antibacterial composition comprising the same
Disclosed herein are is a novel bacteriophage which has specific bactericidal activity against one or more Salmonella bacteria selected from the group consisting of Salmonella Enteritidis, Salmonella Typhimurium, Salmonella Gallinarum, and Salmonella Pullorum without affecting beneficial bacteria. Disclosed are also compositions, animal feeds or drinking water, cleaners and sanitizers for preventing and treating the infectious diseases caused by Salmonella Enteritidis, Salmonella Typhimurium, Salmonella Gallinarum or Salmonella Pullorum including salmonellosis, Salmonella food poisoning, Fowl Typhoid, and Pullorum disease or for controlling the salmonella bacteria.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Aeromonas salmonicida phage, bactericidal composition containing aeromonas salmonicida phage and application of aeromonas salmonicida phage and bactericidal composition
ActiveCN107022529AAntibacterial agentsMicroorganism based processesAnaplasma phagocytophilumPhage therapy
The invention relates to an aeromonas salmonicida phage, a bactericidal composition containing the aeromonas salmonicida phage and application of the aeromonas salmonicida phage and the bactericidal composition. The phage can rapidly inhibit the growth of Atlantic aeromonas salmonicida in a short time and inhibit the generation of resistance to the pathogenic bacterium phage. In addition, the bactericidal composition of the phage is safe and effective and is high in specificity, the production cost is low, and the defects of a single phage therapy in a pathogen control process are made up.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Vibrio alginolyticus bacteriophage and bactericidal composition containing same
InactiveCN107904213ACause some damagesGood control effectAntibacterial agentsMicroorganism based processesAnaplasma phagocytophilumMicrobiology
The invention relates to a Vibrio alginolyticus bacteriophage and a bactericidal composition containing the same. The bacteriophage can rapidly inhibit the growth of Vibrio alginolyticus in a short period of time and is long in the duration of inhibitory effect. The bactericidal composition containing the bacteriophage is safe and effective, has strong specificity and low production cost, and makes up for the deficiencies of single-bacteriophage therapy during the control of pathogenic bacteria.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Pseudomonas aeruginosa phage and application thereof
ActiveCN110144333AInhibitivePlay a killing roleAntibacterial agentsViral/bacteriophage medical ingredientsIn vitro testIn vivo
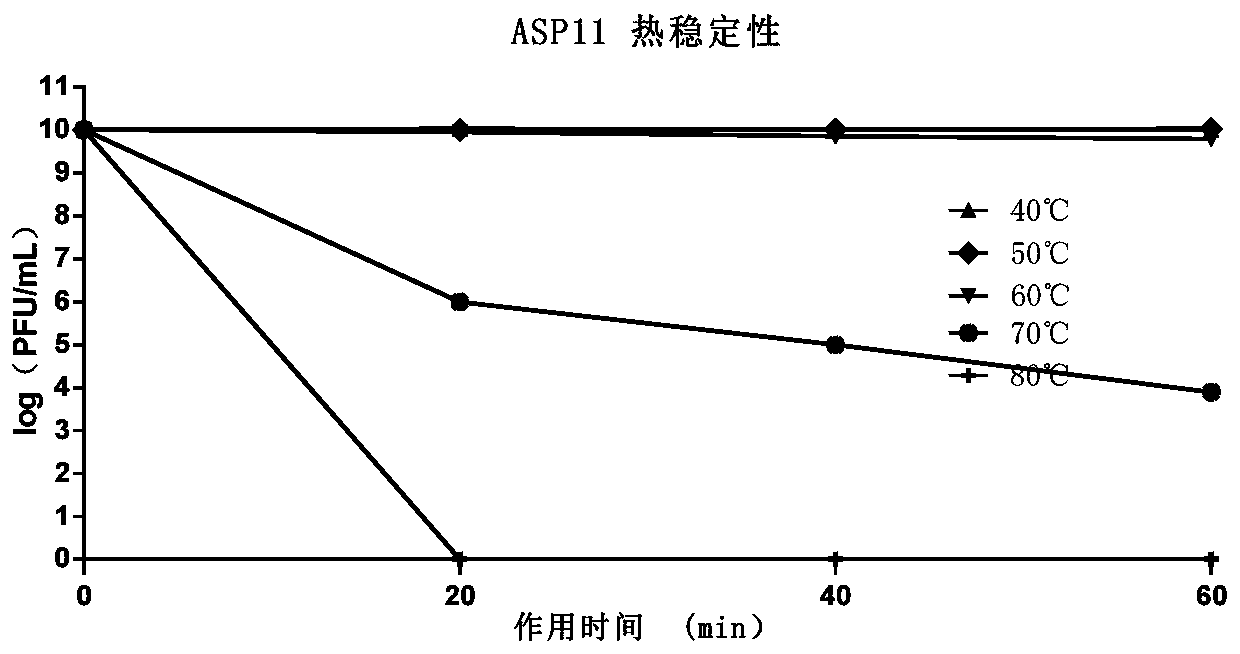
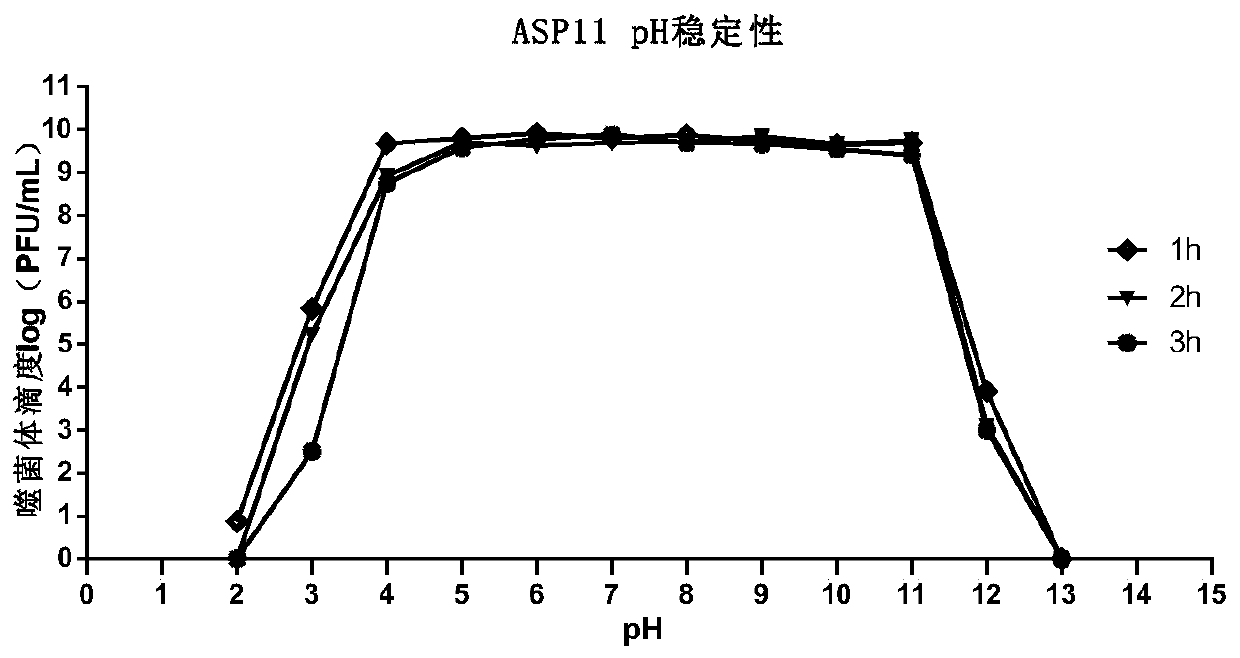
The present invention relates to a pseudomonas aeruginosa phage and an application thereof, and particularly discloses the phage capable of entering blood and the application thereof. The phage singlebody is the pseudomonas aeruginosa phage with a Latin name P. Aeruginosaphage, and named as ASP11, and has a broad-spectrum bactericidal ability against pseudomonas aeruginosa. The phage ASP11 is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, a preservation date is September 26, 2018 and a preservation number is CGMCC NO.16395. Both in vivo and in vitro tests show that thephage has a strong cleavage effect on the pseudomonas aeruginosa and provides an effective method for prevention and treatment of pseudomonas aeruginosa infected diseases.
Owner:QINGDAO PHAGEPHARM BIO TECH CO LTD
Immunization and/or treatment of parasites and infectious agents by live bacteria
ActiveUS10364435B1Reducing or eliminating the targeted parasite, infectious diseaseSsRNA viruses negative-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsBacteroidesLytic peptide
Chimeric proteins are expressed, secreted or released by a bacterium to immunize against or treat a parasite, infectious disease or malignancy. The delivery vector may also be attenuated, non-pathogenic, low pathogenic, or a probiotic bacterium. The chimeric proteins include chimeras of, e.g., phage coat and / or colicin proteins, bacterial toxins and / or enzymes, autotransporter peptides, lytic peptides, multimerization domains, and / or membrane transducing (ferry) peptides. The active portion of the immunogenic chimeric proteins can include antigens against a wide range of parasites and infectious agents, cancers, Alzheimer's and Huntington's diseases, and have enhanced activity when secreted or released by the bacteria, and / or have direct anti-parasite or infectious agent activity. The activity of the secreted proteins is further increased by co-expression of a protease inhibitor that prevents degradation of the effector peptides. Addition of an antibody binding or antibody-degrading protein further prevents the premature elimination of the vector and enhances the immune response.
Owner:BERMUDES DAVID GORDON
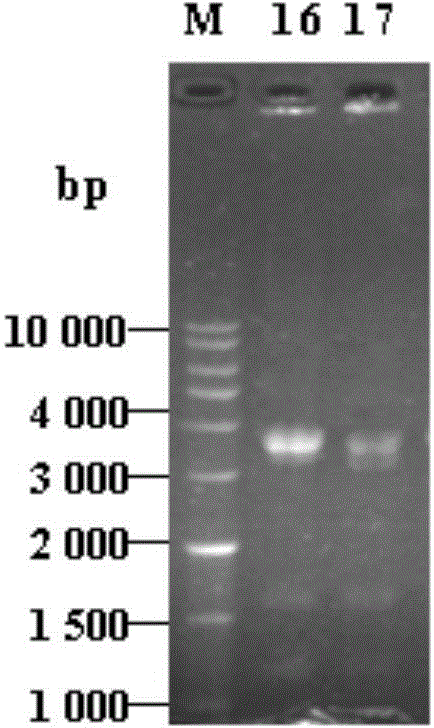
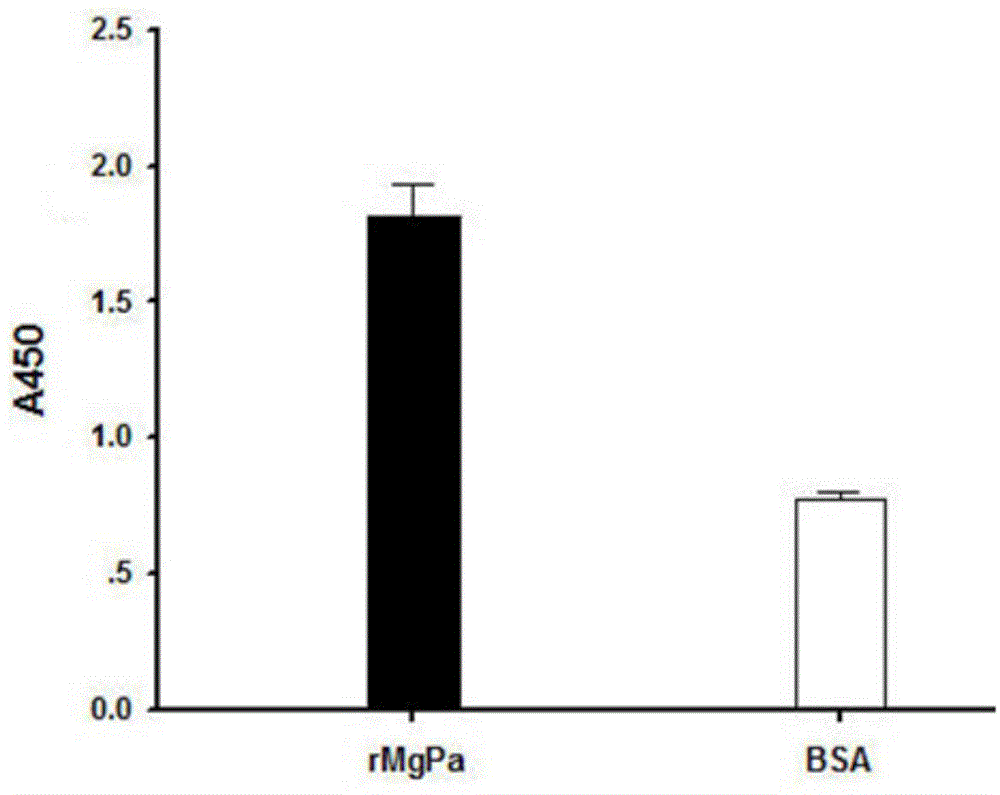
Polypeptide available for specific binding to mycoplasma genitalium adhesin protein MgPa and application thereof
InactiveCN104829693AGood effectAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsDNA IntercalationAmino acid
Owner:NANHUA UNIV
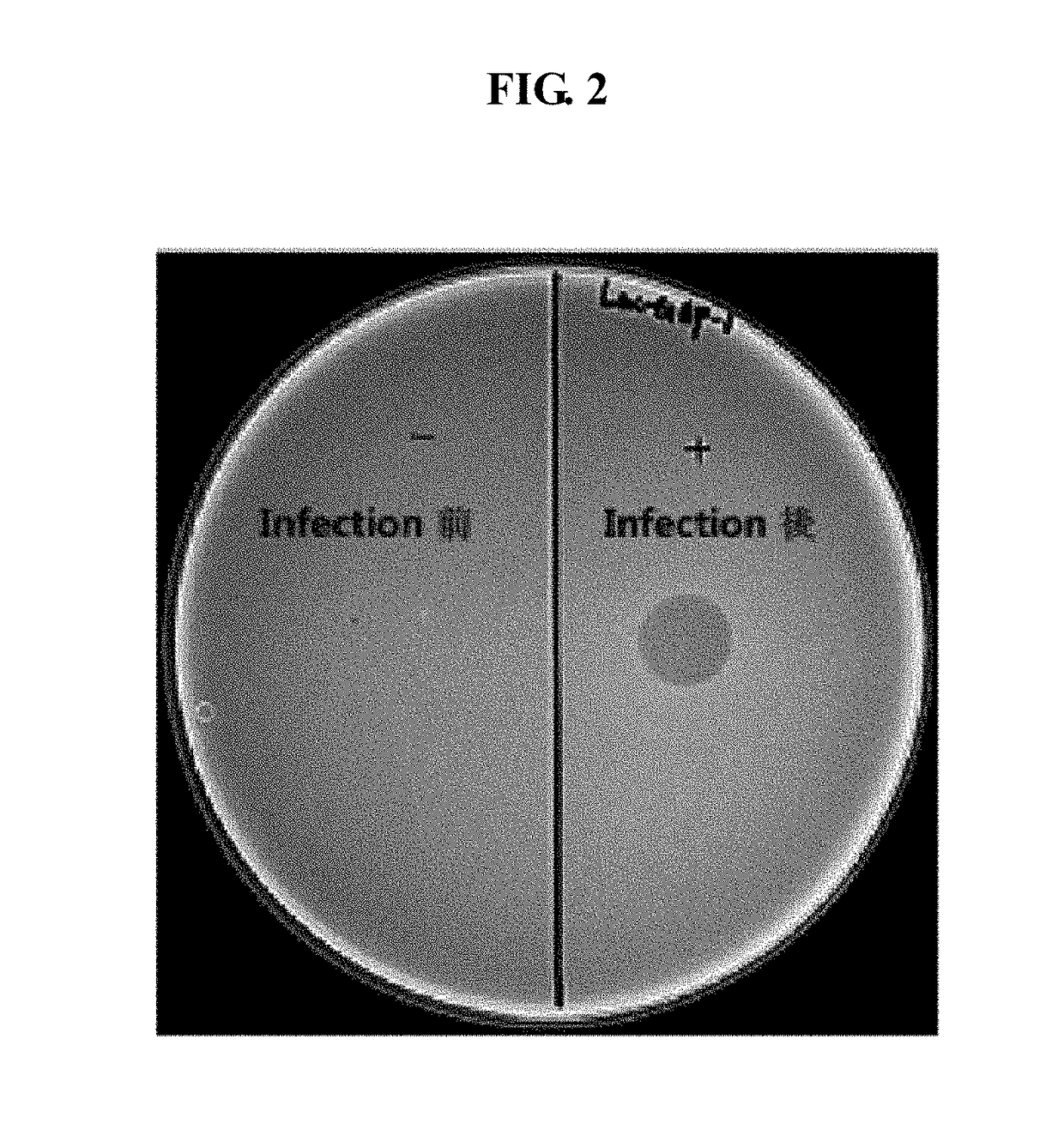
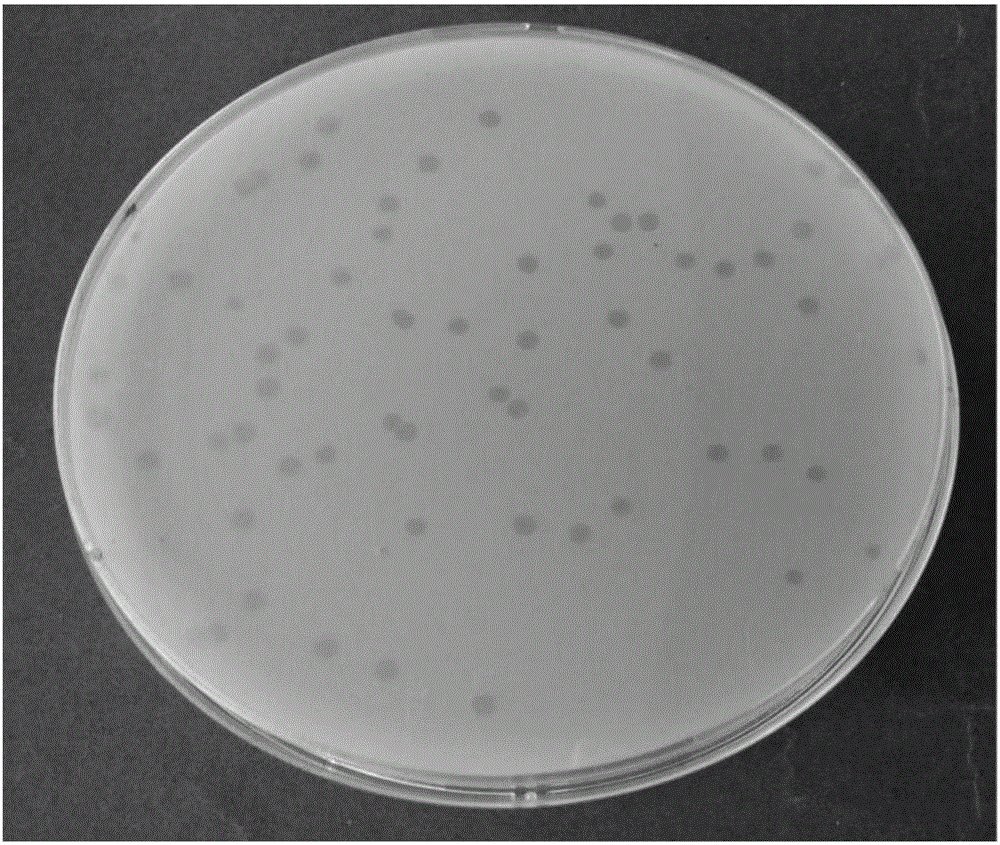
Novel lactococcus garvieae bacteriophage lac-gap-1 and use thereof in suppressing proliferation of lactococcus garvieae bacteria
ActiveUS20180000125A1Strong specificityLess side effectsAnimal feeding stuffViral/bacteriophage medical ingredientsAnaplasma phagocytophilumNucleotide
The present invention relates to a Myoviridae bacteriophage Lac-GAP-1 that is isolated from the nature and can kill specifically Lactococcus garvieae cells, which has a genome represented by the nucleotide sequence of SEQ. ID. NO: 1 (Accession NO: KCTC 12686BP), and a method for preventing and treating the infections of Lactococcus garvieae using the composition comprising said bacteriophage as an active ingredient.
Owner:INTRON BIOTECHNOLOGY INC
Salmonella bacteriophage and bacteriophage anti-bacterium composition and application thereof
ActiveCN106497888AStock solution titer is highHigh potencyAntibacterial agentsAnimal feeding stuffAnaplasma phagocytophilumSalmonella enteritidis
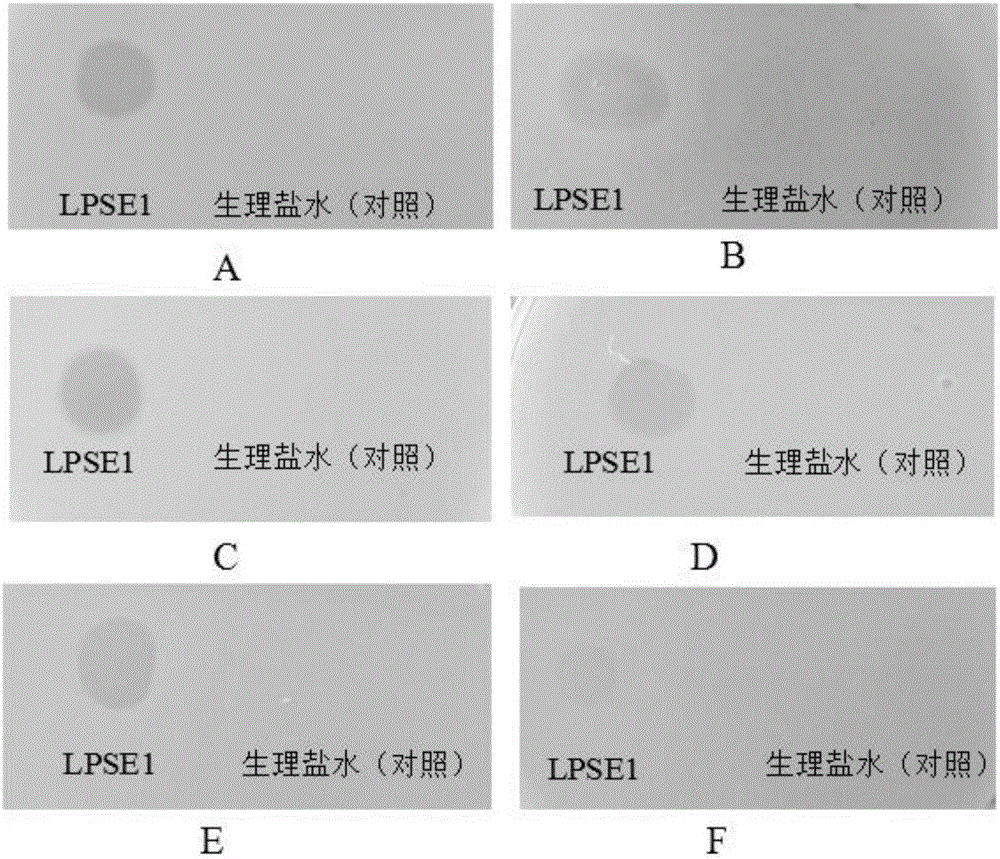
The invention discloses a salmonella bacteriophage and bacteriophage anti-bacterium composition and an application thereof. A bacteriophage is salmonella enteritidis bacteriophage LPSE1 and salmonella typhimurium bacteriophage LPST10, and both the salmonella enteritidis bacteriophage LPSE1 and the salmonella typhimurium bacteriophage LPST10 have excellent inhibiting effect on salmonellas and good tolerance for pH (potential of hydrogen) and temperature. Application examples of the salmonella bacteriophage to food systems verify that the bacteriophage has excellent effect when being used for bacteriostatic agents. The salmonella enteritidis bacteriophage LPSE1 and the salmonella typhimurium bacteriophage LPST10 have synergistic effects after being mixed and have more beneficial inhibiting effect as compared with a single bacteriophage.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
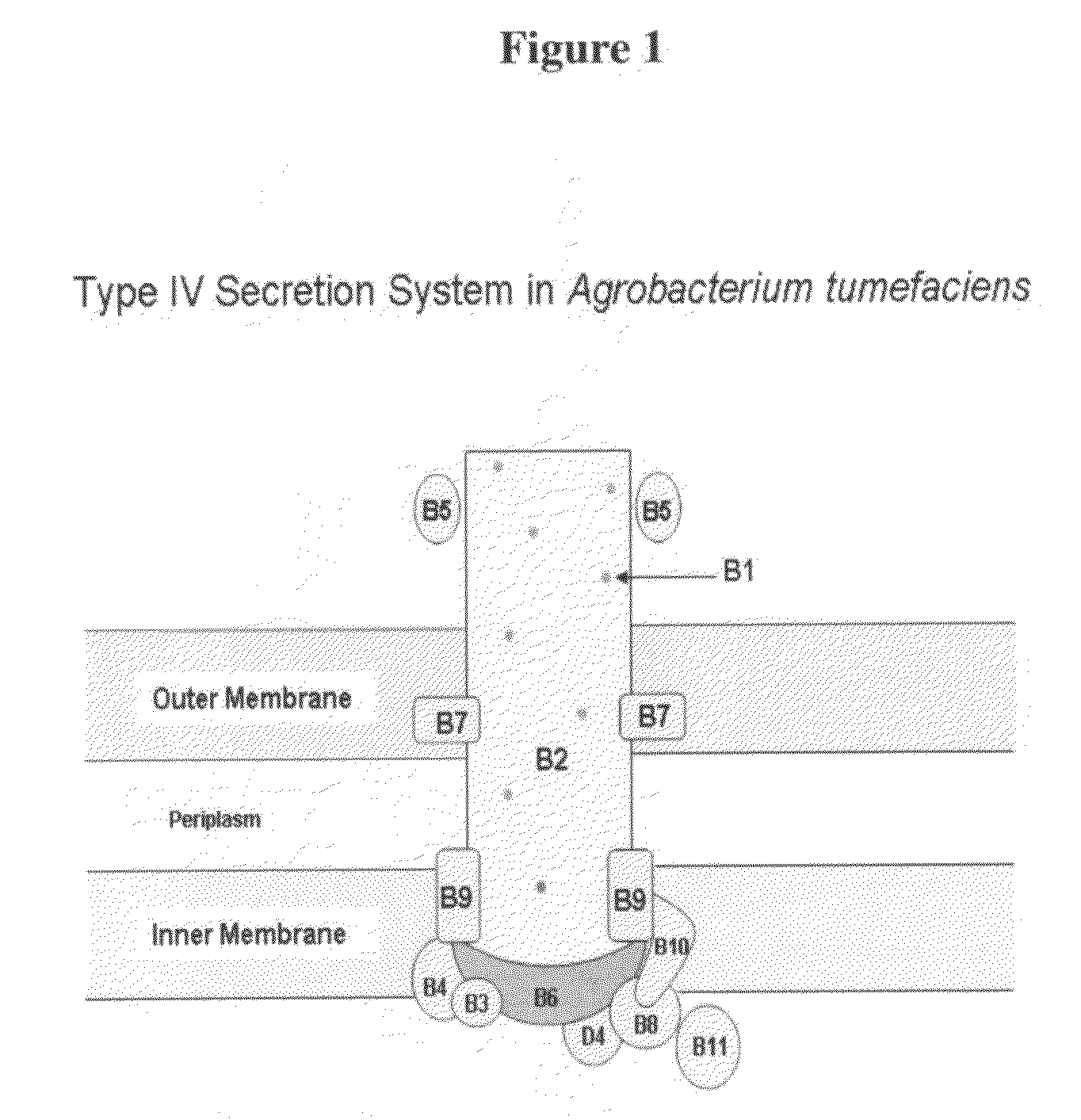
Type IV secretion system proteins in sero-detection of Anaplasma phagocytophium
Disclosed are two (2) proteins in the Type IV Secretion System (TIVSS) in Anaplasma phagocytophilum (namely, virB 10 and virB11) useful in the ELISA detection of Anaplasma pathogen. The recombinant expression of virB 10 and virB 11 and their use as kits for ELISA are also disclosed.
Owner:MEDICAL DIAGNOSTIC LAB
Vibrio alginolyticus bacteriophage and bactericidal composition containing same
InactiveCN107904212ACause some damagesGood control effectAntibacterial agentsMicroorganism based processesAnaplasma phagocytophilumMicrobiology
The invention relates to a Vibrio alginolyticus bacteriophage and a bactericidal composition containing the same. The bacteriophage can rapidly inhibit the growth of Vibrio alginolyticus in a short period of time and is long in the duration of inhibitory effect. The bactericidal composition containing the bacteriophage is safe and effective, has strong specificity and low production cost, and makes up for the deficiencies of single-bacteriophage therapy during the control of pathogenic bacteria.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Novel bacteriophage and antibacterial composition comprising the same
Disclosed herein are is a novel bacteriophage which has specific bactericidal activity against one or more Salmonella bacteria selected from the group consisting of Salmonella Enteritidis, Salmonella Typhimurium, Salmonella Gallinarum, and Salmonella Pullorum without affecting beneficial bacteria. Disclosed are also compositions, animal feeds or drinking water, cleaners and sanitizers for preventing and treating the infectious diseases caused by Salmonella Enteritidis, Salmonella Typhimurium, Salmonella Gallinarum or Salmonella Pullorum including salmonellosis, Salmonella food poisoning, Fowl Typhoid, and Pullorum disease or for controlling the salmonella bacteria.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Method for prevention and treatment of Escherichia coli infections using a bacteriophage with broad antibacterial spectrum against Escherichia coli
ActiveUS9433653B2Strong specificityLess side effectsAntibacterial agentsViral/bacteriophage medical ingredientsEscherichia coliAnaplasma phagocytophilum
Owner:INTRON BIOTECHNOLOGY INC
Technique for allowing aquatic invertebrate larvae and parents to harmlessly carry Vibrio phages
InactiveCN102550458AMeet production needsMaintain lytic activityClimate change adaptationMicroorganism based processesLysisAnaplasma phagocytophilum
The invention discloses a technique for allowing aquatic invertebrate larvae and parents to harmlessly carry Vibrio phages. The technique of the invention utilizes the feature that invertebrates do not display specific antibody response, and comprises soaking aquatic invertebrate larvae and parents with phages, collecting culture samples from the aquatic invertebrate larvae and parents, isolating phages from invertebrates, soaking again, repeating the soaking steps for a plurality of times successively, and culturing and selecting phages to obtain phages which can survive in aquatic invertebrates for a long period of time. Phages obtained by use of the technique of the invention are not virulent or harmful, can retain the lysis activity for host bacteria during a long period of time, and can meet the requirements of production of aquatic invertebrate larvae and parents. The invention provides a new technique for preventing and treating vibriosis of aquatic invertebrates.
Owner:GUANGDONG OCEAN UNIVERSITY
Use of phage AH10-Phage-QY01 in preparation of medicines for treating or preventing and controlling bacterial diseases in aquaculture
InactiveCN110093321AGood antibacterial effectReduce usageAntibacterial agentsMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesBacterial disease
The invention discloses a use of aeromonas hydrophila phage AH10-Phage-QY01 in preparation of medicines for treating or preventing and controlling bacterial diseases in aquaculture, and belongs to thetechnical field of prevention and control of bacterial diseases in aquaculture. The phage AH10-Phage-QY01 is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection and has the preservation number of CCTCC NO:M2019109. The invention also includes a use of the phage AH10-Phage-QY01 in preparation of medicines for bacterial septicemia caused by aeromonas hydrophila. The phage AH10-Phage-QY01 can be used alone or in combination with antibiotics. The universality of the phage and high specificity to host bacteria are used, the aeromonas hydrophila phage AH10-Phage-QY01 is screened for the first time from natural environment for pathogenic bacteria, and is used for inhibiting and cracking the pathogenic bacteria, treating or preventing and controlling bacterial septicemia and other bacterial fish diseases caused by the pathogenic bacteria.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Method of treating an inflammatory disease comprising administering an NR 10 antibody antagonist
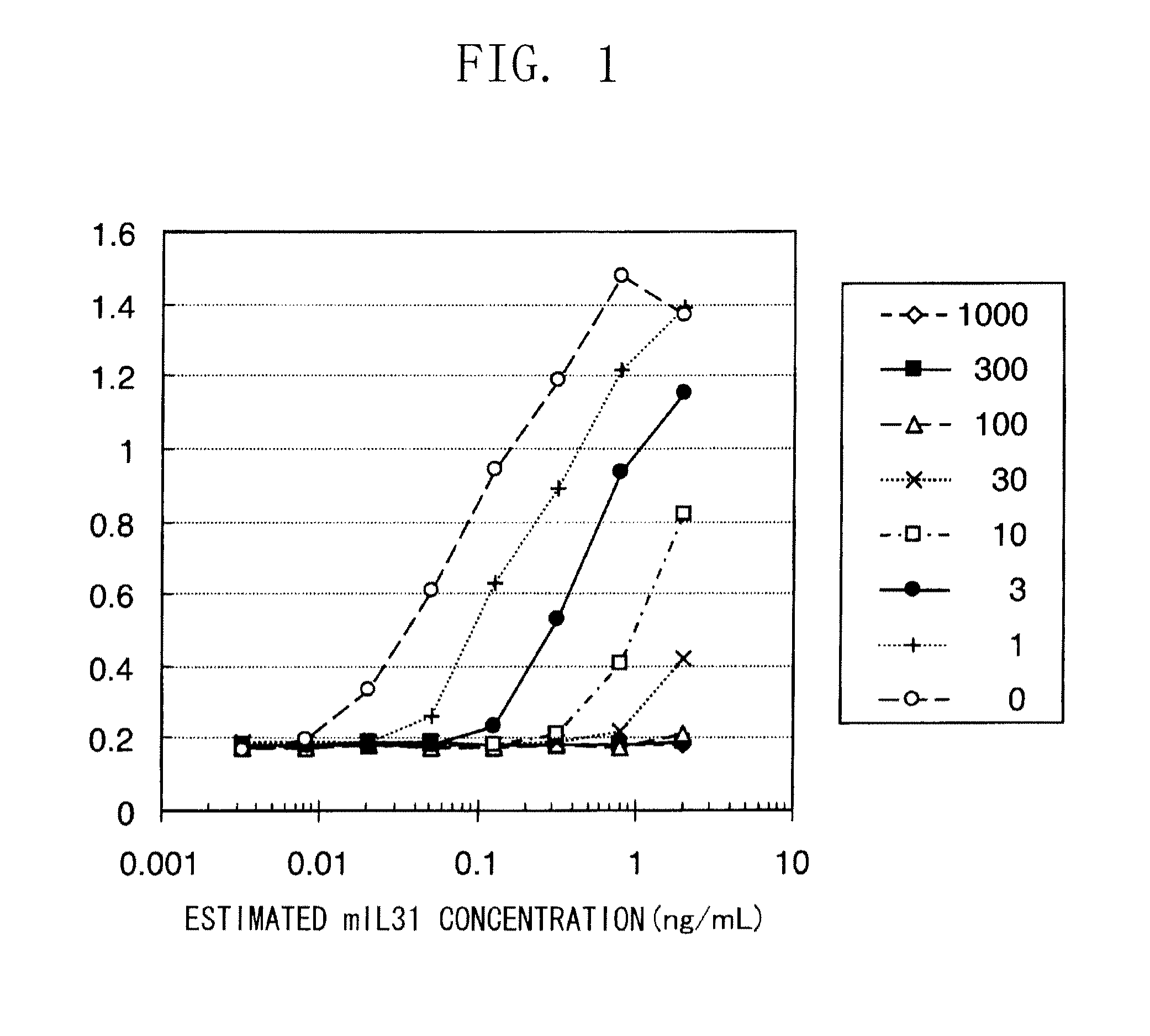
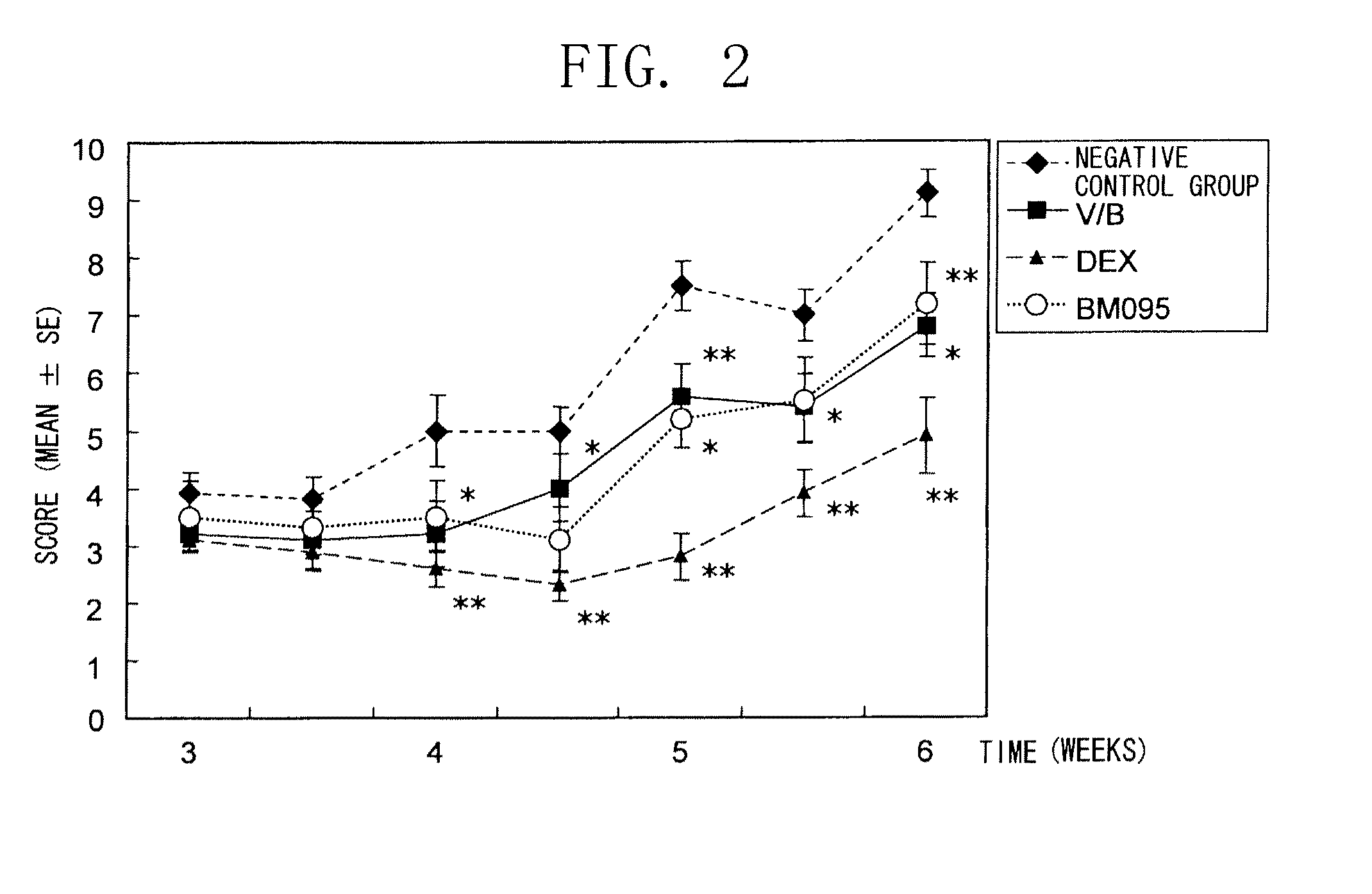
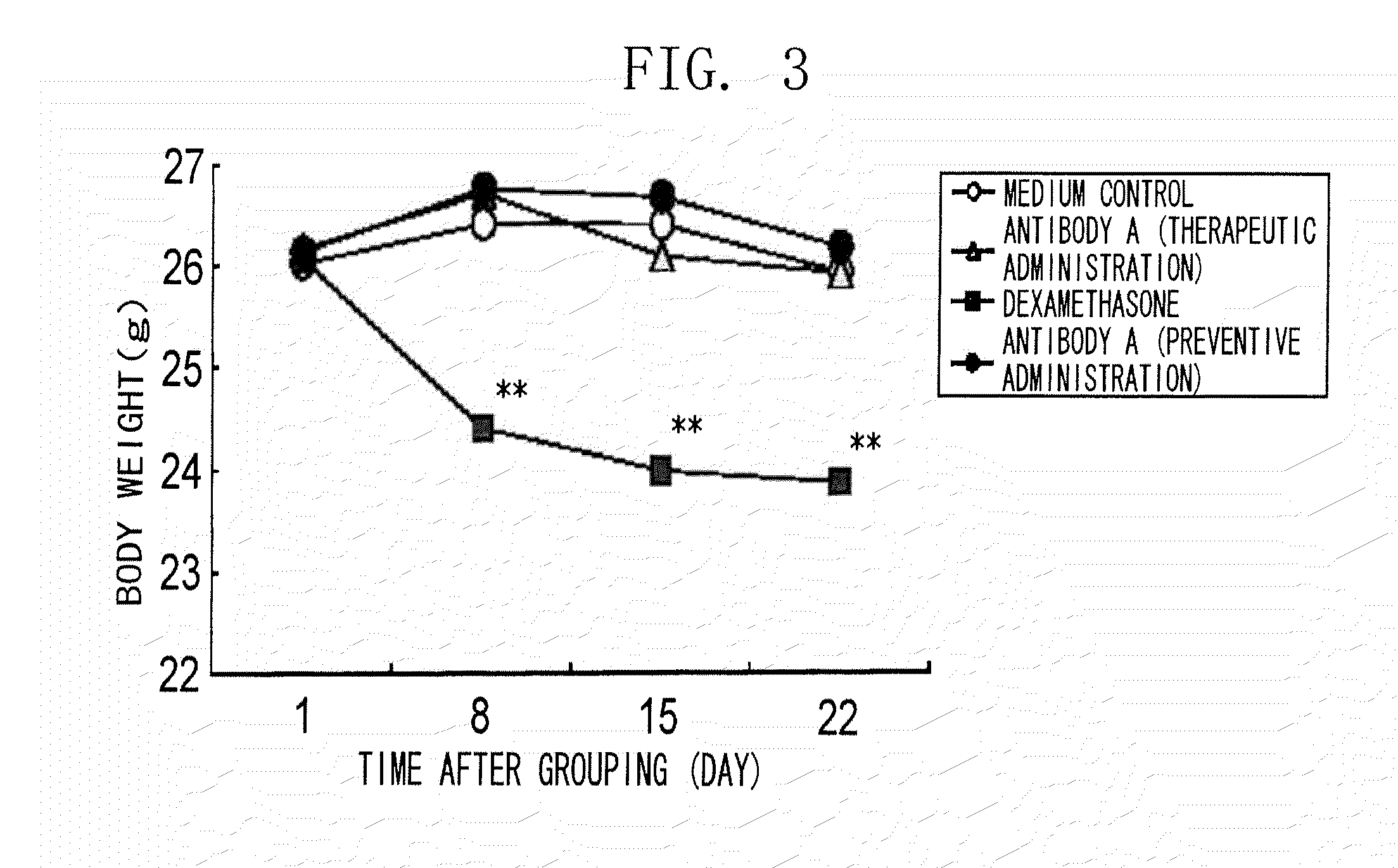
The present inventors obtained, from a phage library of human antibodies, an anti-mouse NR 10 neutralizing antibody-expressing BM095 clone that shows a strong proliferation-suppressing activity in an IL-31-dependent Ba / F3 cell proliferation assay system. When this anti-mouse NR 10 neutralizing antibody was administered to NC / Nga mice, a model of atopic dermatitis which is a mouse model of chronic dermatitis that arises as a result of repeated applications of picryl chloride, a mouse model of rheumatoid arthritis, and a mouse model of osteoarthritis, a significant effect of symptom suppression was observed. This revealed that the anti-NR 10 neutralizing antibody is indeed effective as a therapeutic agent for inflammatory diseases. In addition, the present inventors successfully obtained an anti-human NR 10 neutralizing antibody, providing extremely useful therapeutic agents with practical clinical applications.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
PCSK9 (Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin Kexin Type 9) resistant monoclonal antibody
ActiveCN107698680ABinding blockIncrease intakeMetabolism disorderMammal material medical ingredientsKexinPhage antibodies
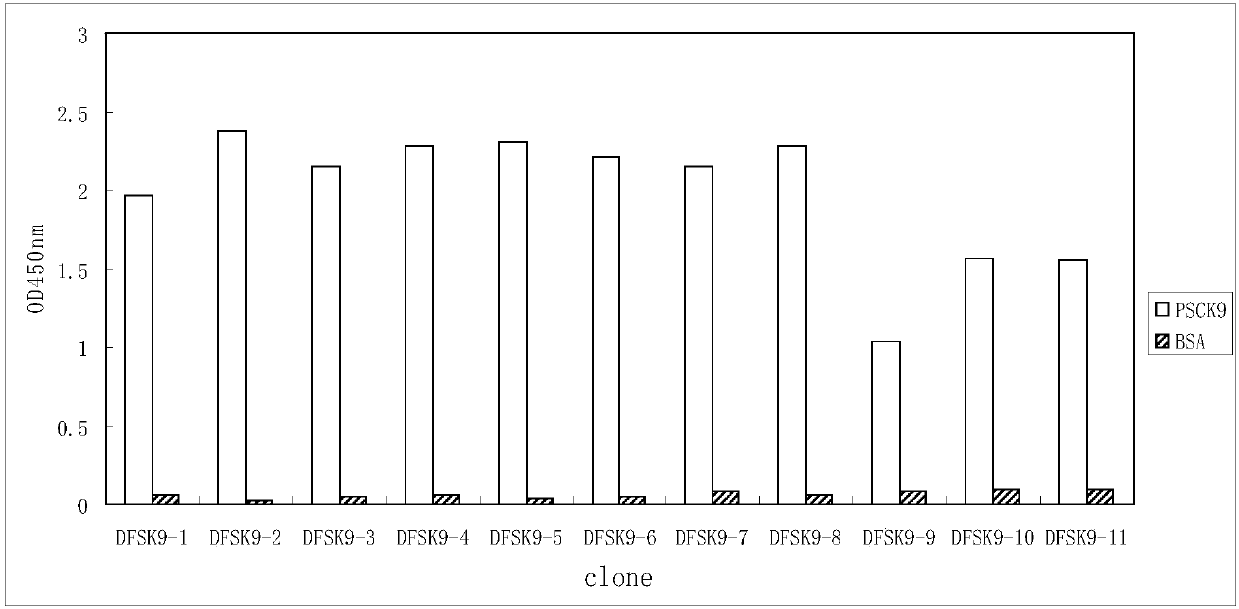
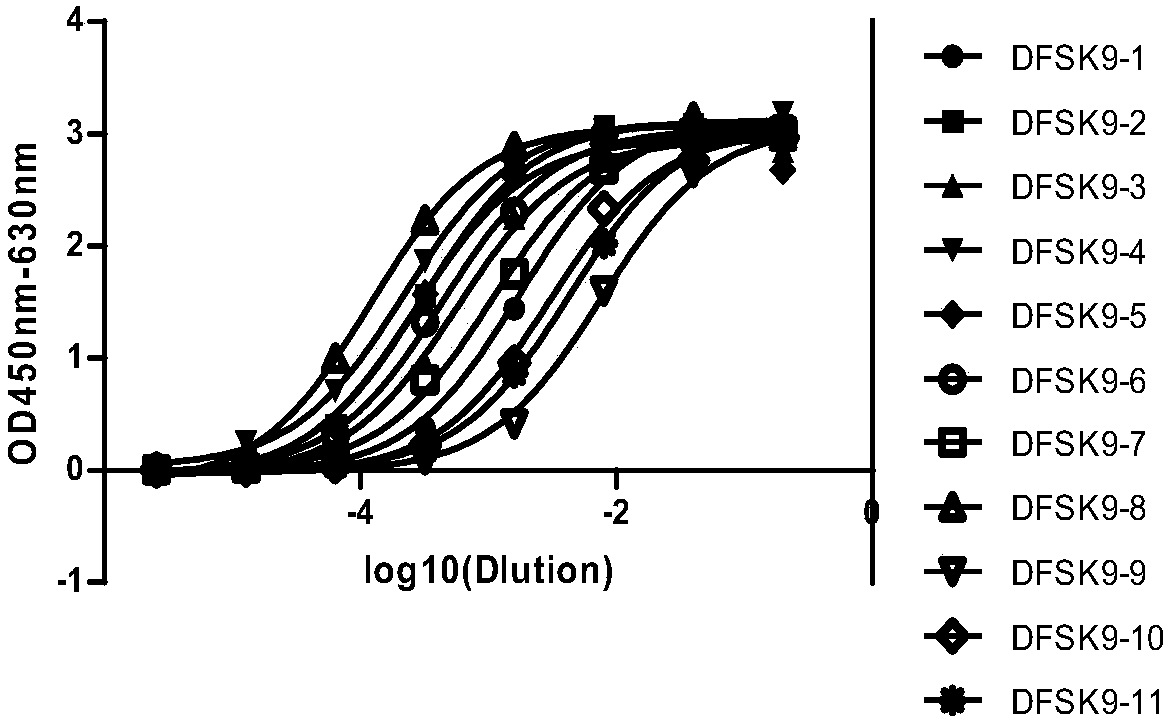
The invention relates to the technical field of antibody engineering and in particular discloses a PCSK9 (Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin Kexin Type 9) resistant monoclonal antibody. The monoclonal antibody disclosed by the invention comprises an amino acid sequence coding an antibody variable region and a CDR region. The invention further discloses an acquiring method and application of the monoclonal antibody. The method comprises the following steps: screening a PCSK9 resistant monoclonal antibody from a phage antibody library, performing affinity maturation through a method for constructing the phage antibody library by virtue of strand displacement, performing mutant library-construction screening on light-chain CDR1, 2 and 3 regions of the monoclonal antibody obtained by preliminaryscreening, selecting a monoclonal antibody with high affinity, performing mutant library-construction screening on heavy-chain CDR1, 2 and 3 regions of the monoclonal antibody, and finally screeningthe PCSK9 resistant monoclonal antibody with high affinity. The PCSK9 resistant monoclonal antibody obtained in the invention has excellent affinity to PCSK9, is capable of inhibiting binding betweenthe PCSK9 and ligands thereof, and can be used for treating dyslipidemia, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases and thrombosis-obstructive diseases.
Owner:BEIJING DONGFANG BIOTECH
Phage capable of splitting cattle streptococcus agalactiae and application thereof
ActiveCN108103029APlay a role in crackingIncrease lethalityAntibacterial agentsViral/bacteriophage medical ingredientsStreptococcus pyogenesAnaplasma phagocytophilum
The invention discloses a streptococcus phage which can split cattle streptococcus agalactiae. The applicant names the phage as vB_SagS_FSN1; the phage is preserved in China Centre for Type Culture Collection; the preservation number is CCTCC NO:M 2017670. The streptococcus phage belongs to siphoviridae, can survive stably at the temperature of 40 to 60 DEG C and the pH of 5 to 10, has high hydrophilcity, and has very strong splitting capacity to streptococcus agalactiae, particularly cattle streptococcus agalactiae epidemic strain, in vivo or in vitro, so that the feasibility of the phage inpreventing and controlling cow mastitis caused by the streptococcus agalactiae is verified, and a new way is provided for treatment of infection of the cattle streptococcus agalactiae.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com