Methicillin-resistant staphylococcus epidermidis staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage and antimicrobial application thereof
A methicillin-resistant staphylococcus technology, applied in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus phage and its antibacterial application, phage and its antibacterial application field, can solve human health threats, non-specific inflammatory response and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
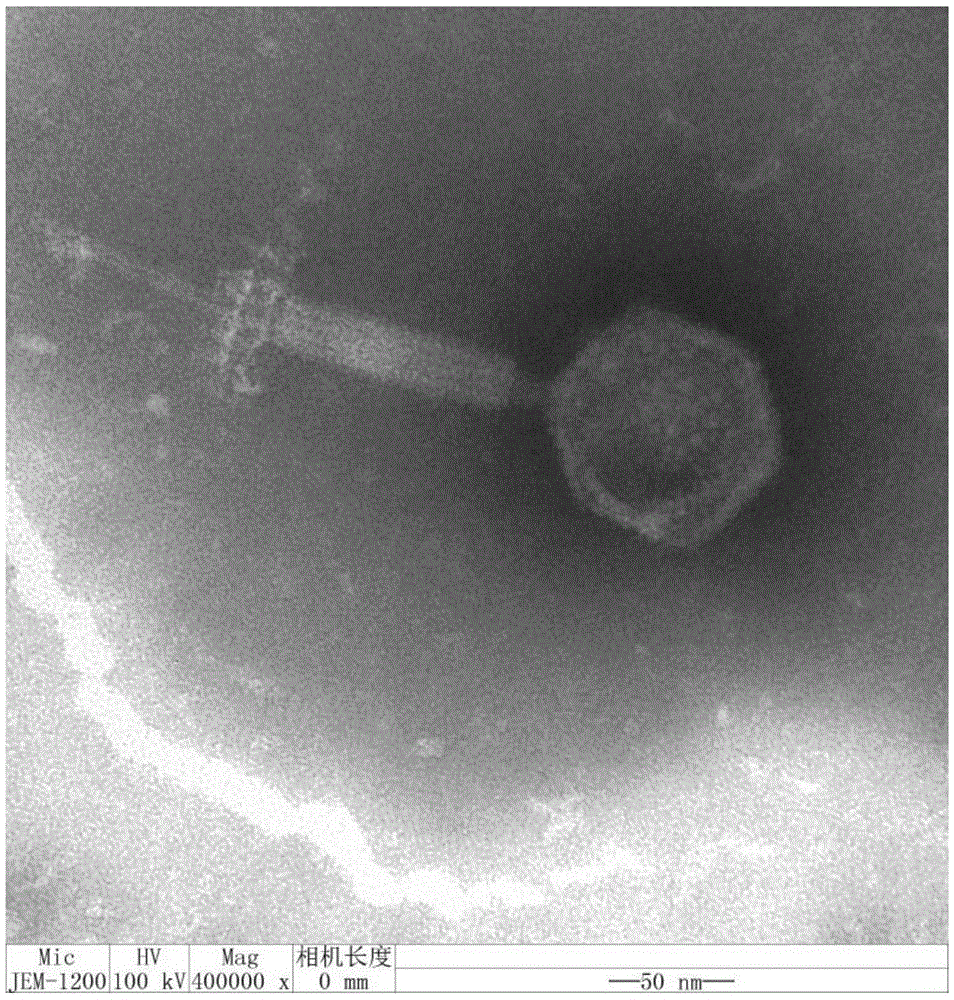
[0023] Embodiment 1: Isolation and purification of phage
[0024] Take 100 μL of ATCC43300 in the logarithmic phase and add it to 5 ml of double-concentrated nutrient broth liquid medium, then add 5 ml of centrifuged sewage to the above culture medium, and culture at 37°C for 12 hours with shaking at 120 r / min, then take The above culture solution was centrifuged at 6000r / min for 10min, and the precipitate was discarded. The supernatant was passed through a 0.22 μm sterile microporous filter membrane to obtain a phage stock solution, which was stored at 4°C.
[0025] Properly dilute the phage stock solution with SM buffer, take 100 μL logarithmic phase ATCC43300 and 100 μL phage dilution solution, add 5 ml nutrient agar and nutrient broth (1:1 volume ratio) to the semi-solid medium, mix well and pour Put it on a solid agar plate to make a double-layer plate. After the plate condenses, immediately invert it and incubate it at a constant temperature of 37°C.
[0026] On the abo...
Embodiment 2
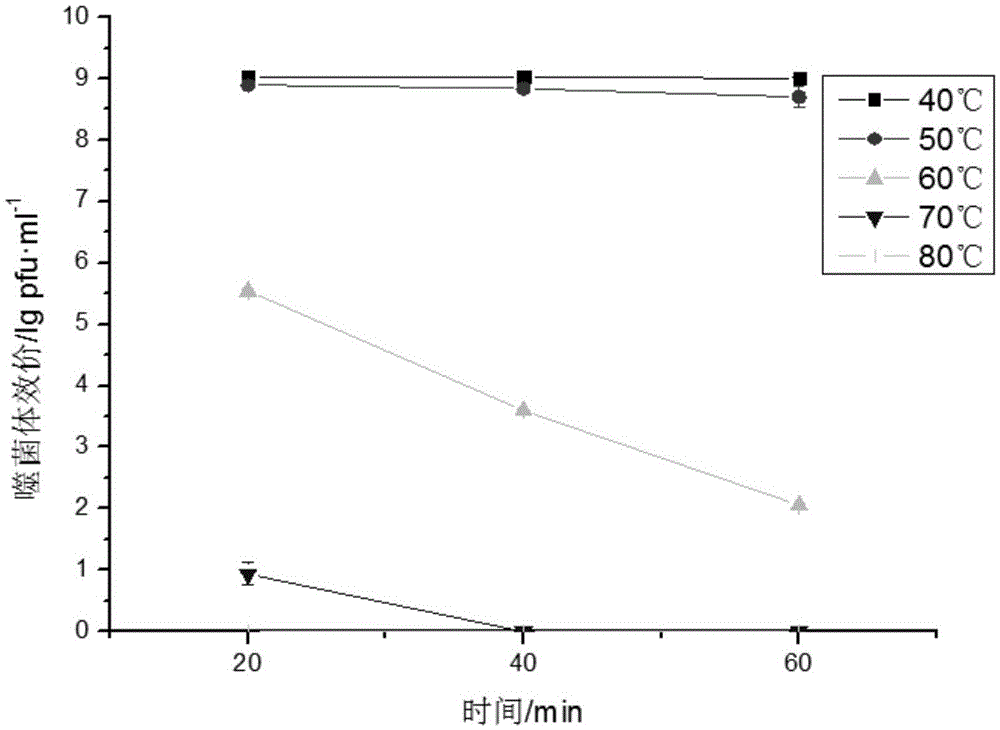
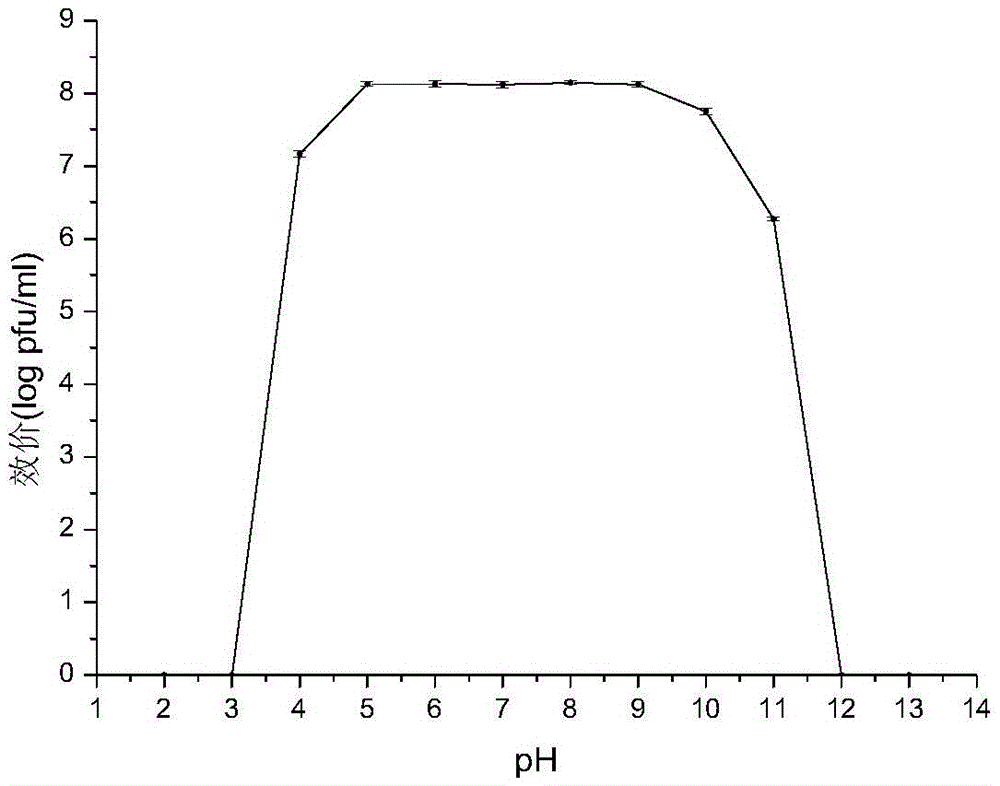
[0030] The influence of embodiment 2 temperature and pH on bacteriophage
[0031] Take 400 μL of bacteriophage qdsa002 in a sterile EP tube, and act in water baths at 40°C, 50°C, 60°C, 70°C, and 80°C for 20 minutes, 40 minutes, and 60 minutes, respectively. Immediately after the reaction, the sample was cooled at 4°C, and the titer of the phage was determined after appropriate serial dilution.
[0032] The pH gradients selected for the phage pH stability experiment were 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, and 13. Take 900 μL of sterile nutrient broth liquid medium with different pH values into sterile EP tubes, and treat them in a water bath at 37°C. After the temperature is balanced, add 100 μL of phage qdsa002, act in a water bath at 37°C for 2 hours, and use the double-layer plate method to determine the phage potency.
[0033] The thermal stability results showed that ( figure 2 ), the activity of bacteriophage qdsa001 remained basically unchanged after acting at 40°...
Embodiment 3
[0035] The mensuration of embodiment 3 phage one-step growth curves
[0036]Add the purified phage and ATCC43300 in the logarithmic phase to the nutrient broth medium at the ratio of the optimal multiplicity of infection of 0.1, incubate at 37°C for 10 minutes, centrifuge at 12000r / min for 30s, discard the supernatant, and wash with the nutrient broth liquid medium Twice to remove free phages that do not adsorb the host bacteria. Then add preheated nutrient broth liquid medium and mix well, quickly place at 37°C, shake culture at 150r / min, start timing at the same time, take samples at intervals of 10min between 0 time and 250min, and measure the titer of phage. Finally, the one-step growth curve of the phage is drawn with the action time of the phage infecting the host bacteria as the abscissa and the titer corresponding to the phage as the ordinate.
[0037] One-step growth curve of phage ( Figure 4 ) shows that within 40 minutes after the phage infects the host bacteria,...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Head diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com