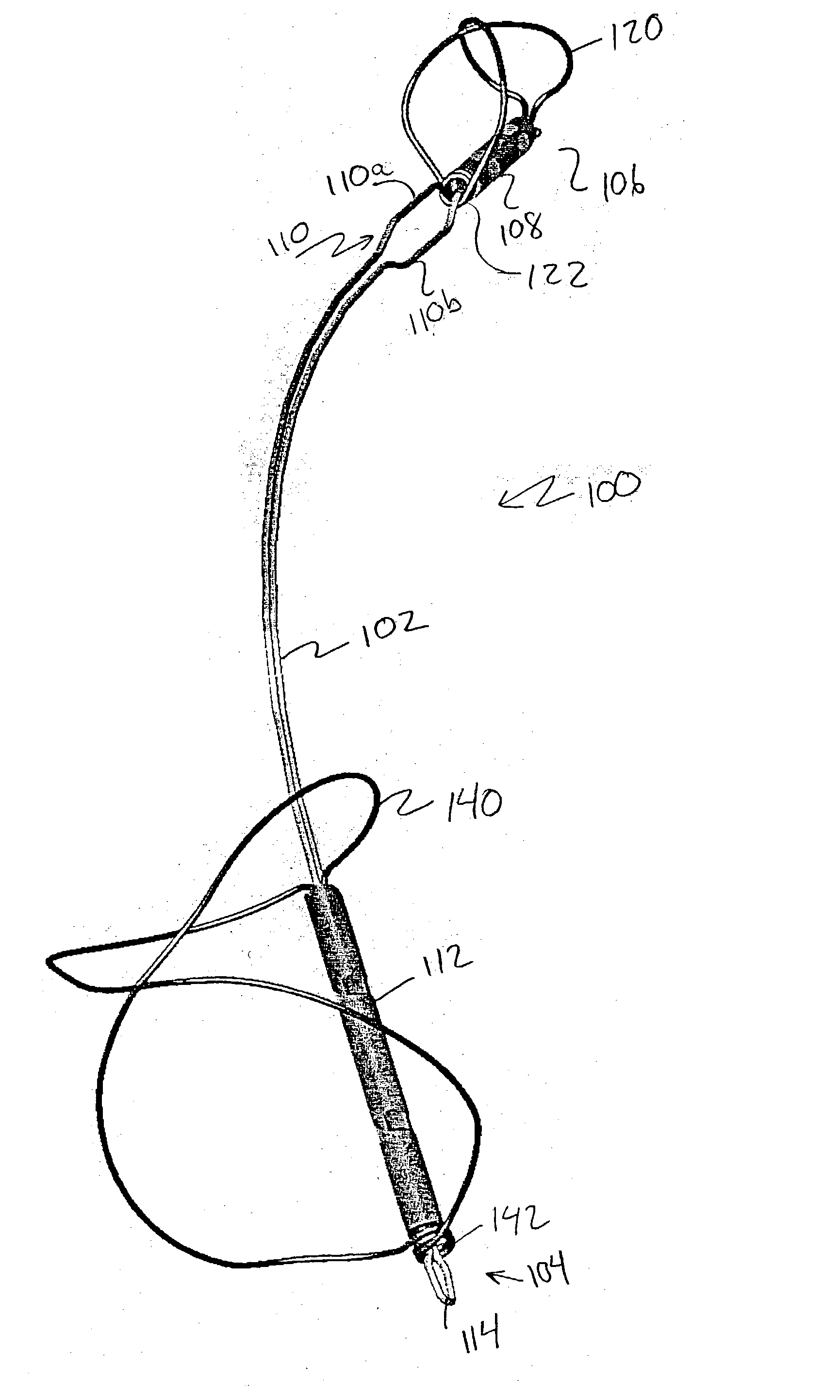
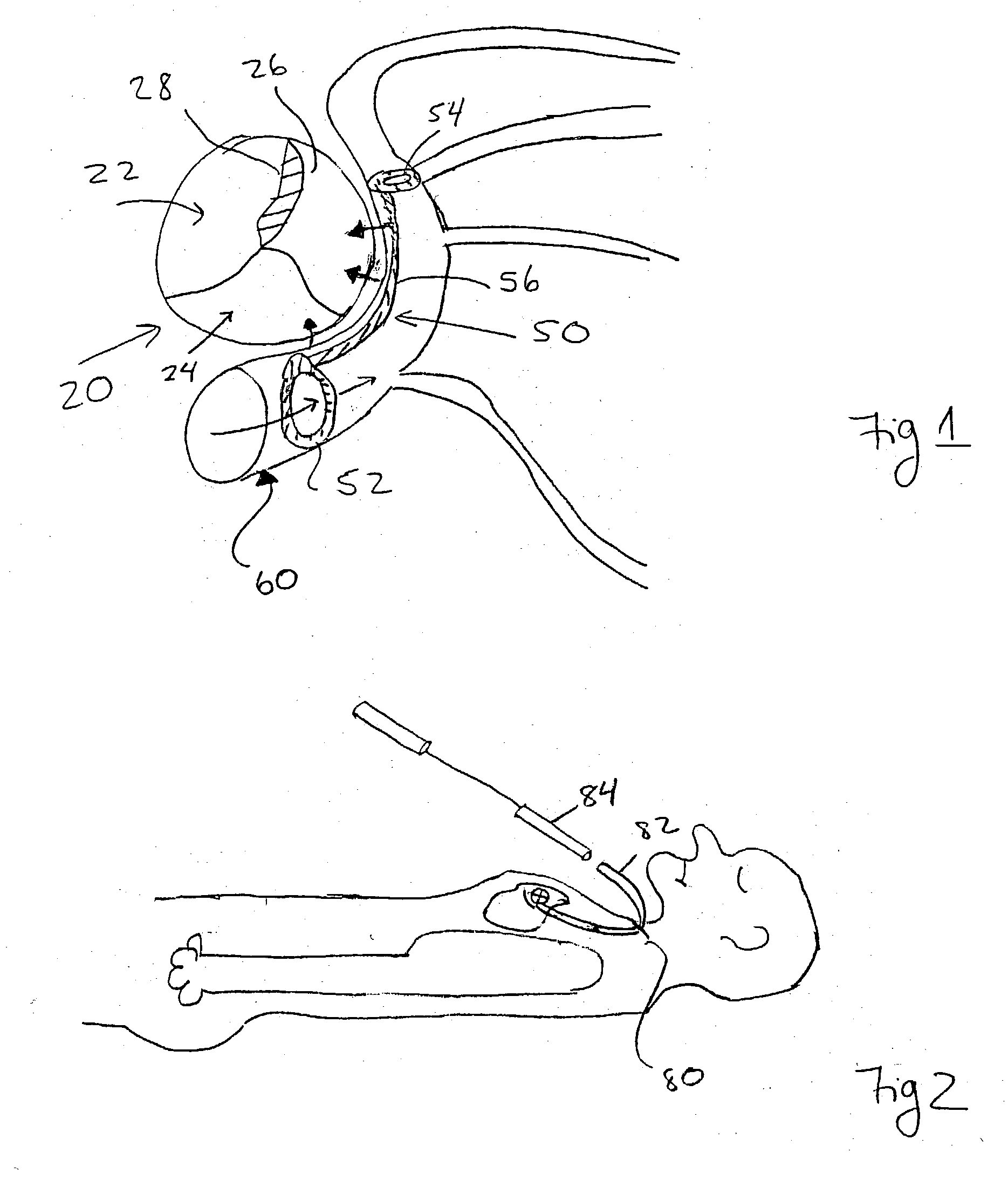
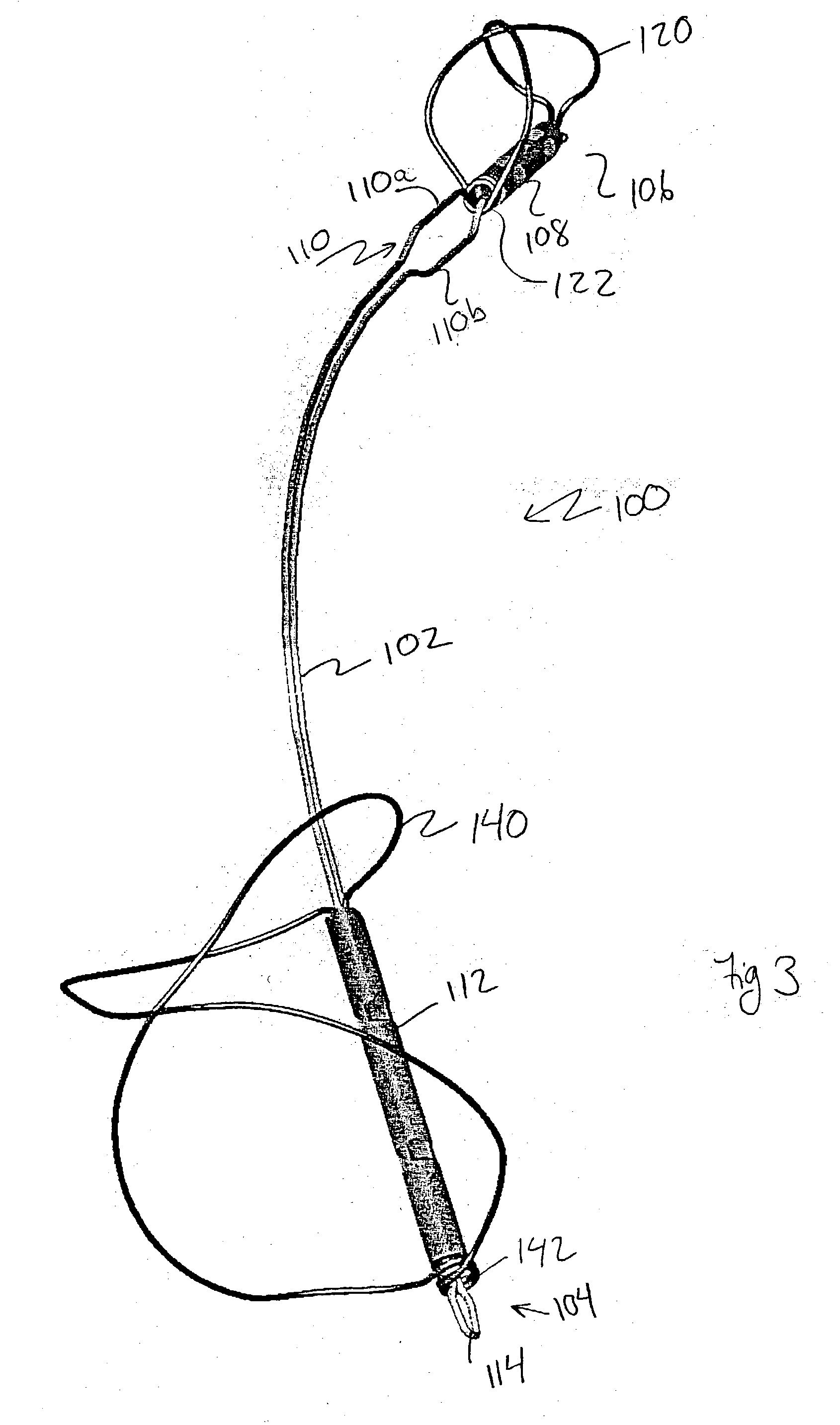
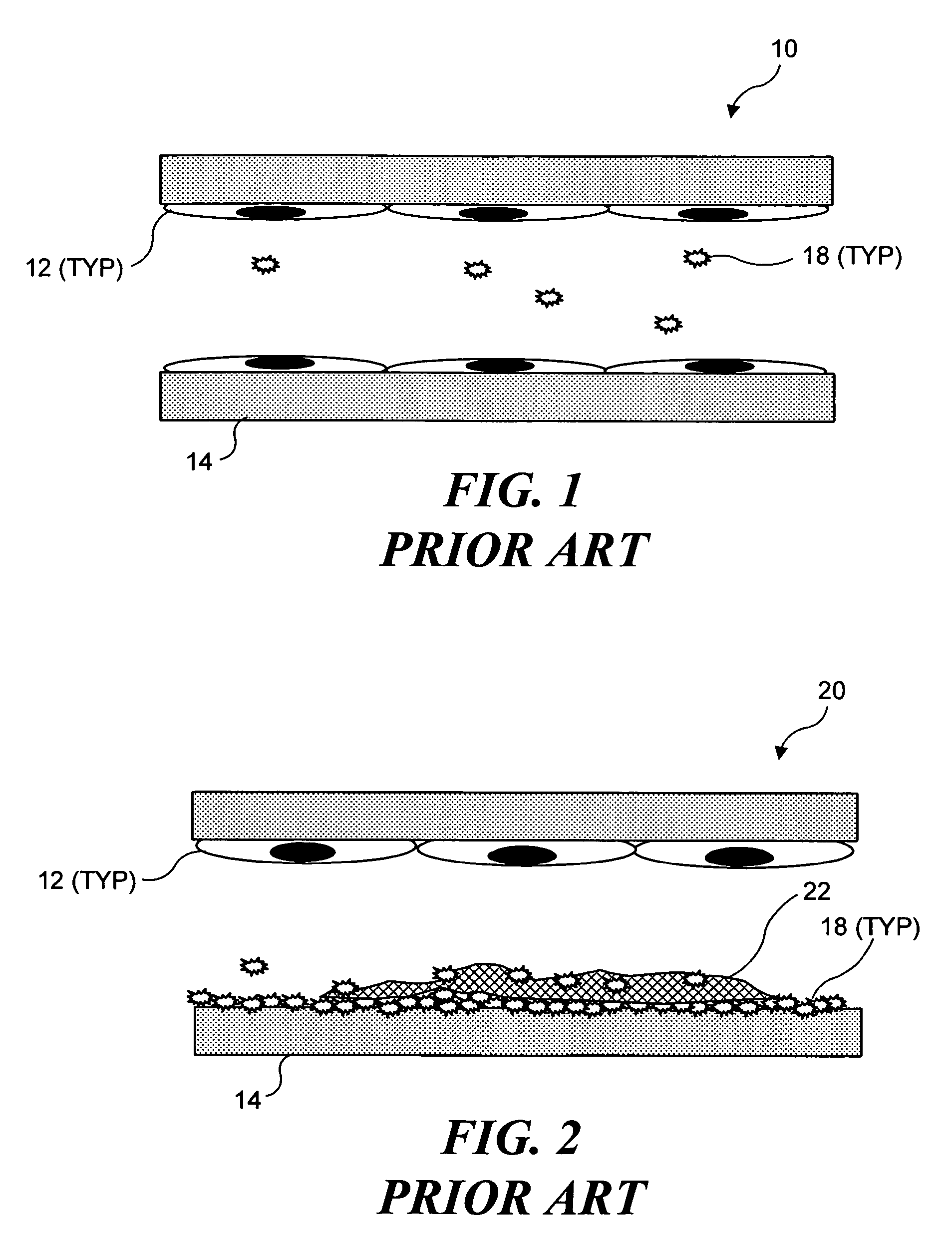
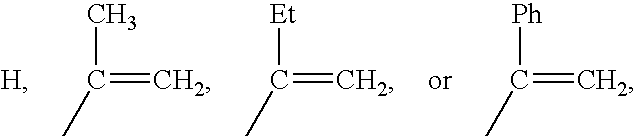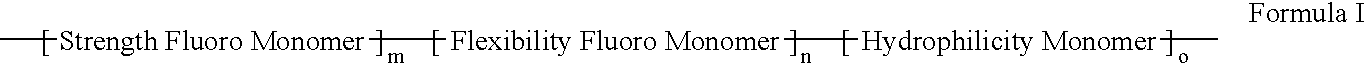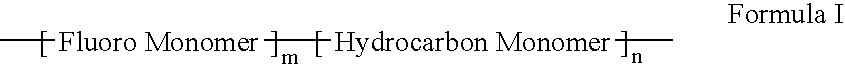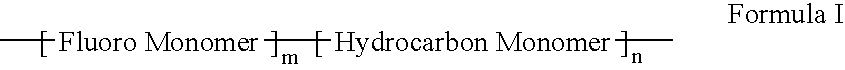Patents
Literature
2196 results about "Thrombosis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
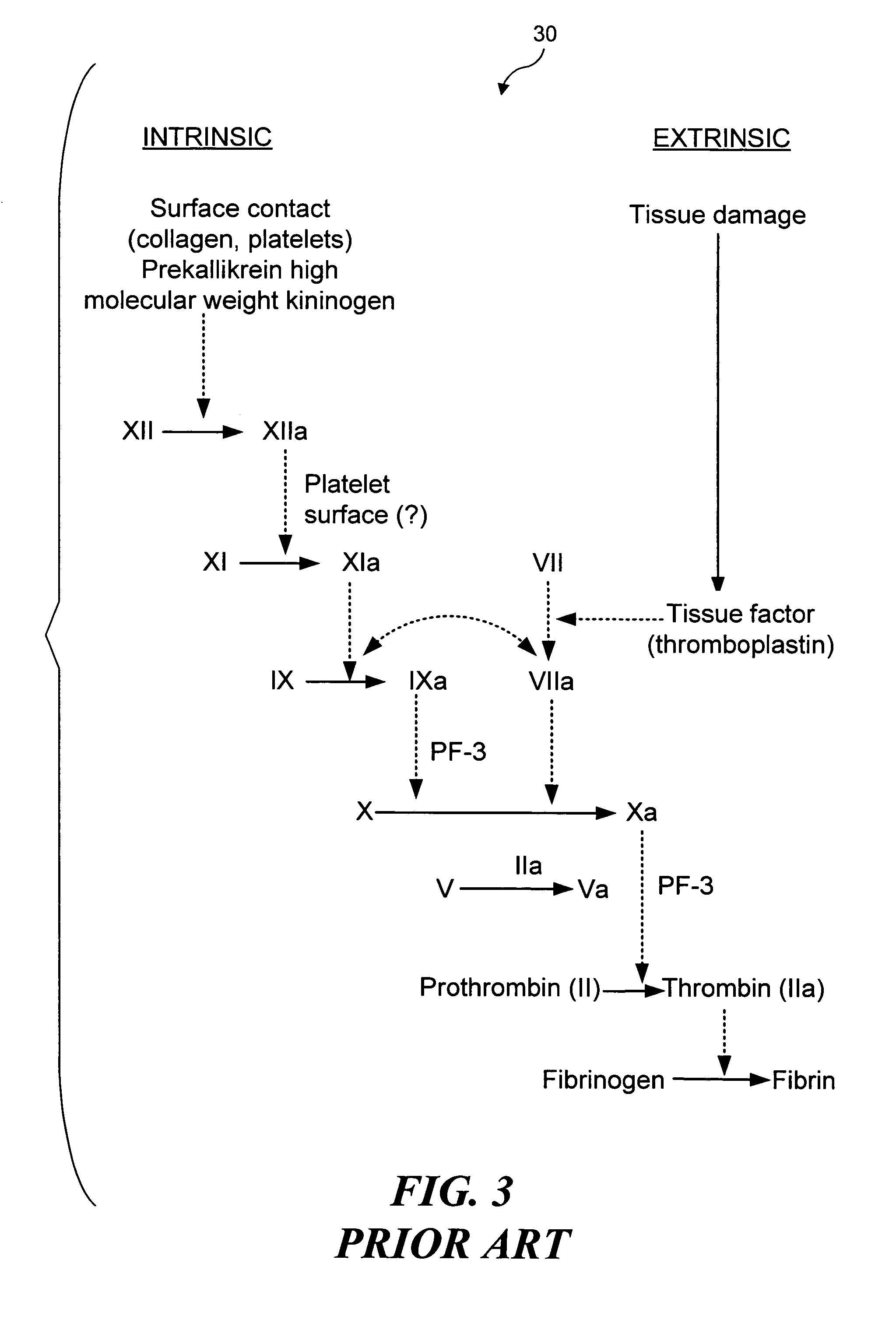
Thrombosis (from Ancient Greek θρόμβωσις thrómbōsis "clotting”) is the formation of a blood clot inside a blood vessel, obstructing the flow of blood through the circulatory system. When a blood vessel (a vein or an artery) is injured, the body uses platelets (thrombocytes) and fibrin to form a blood clot to prevent blood loss. Even when a blood vessel is not injured, blood clots may form in the body under certain conditions. A clot, or a piece of the clot, that breaks free and begins to travel around the body is known as an embolus.
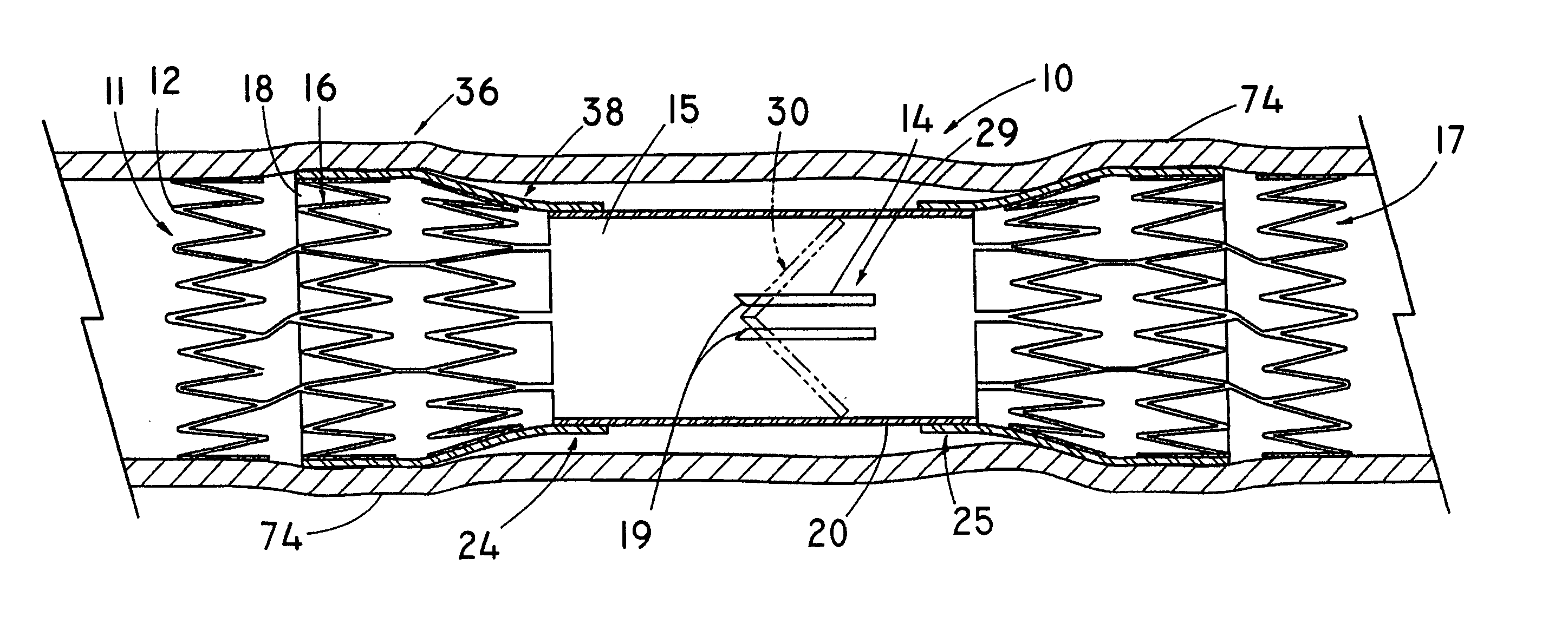
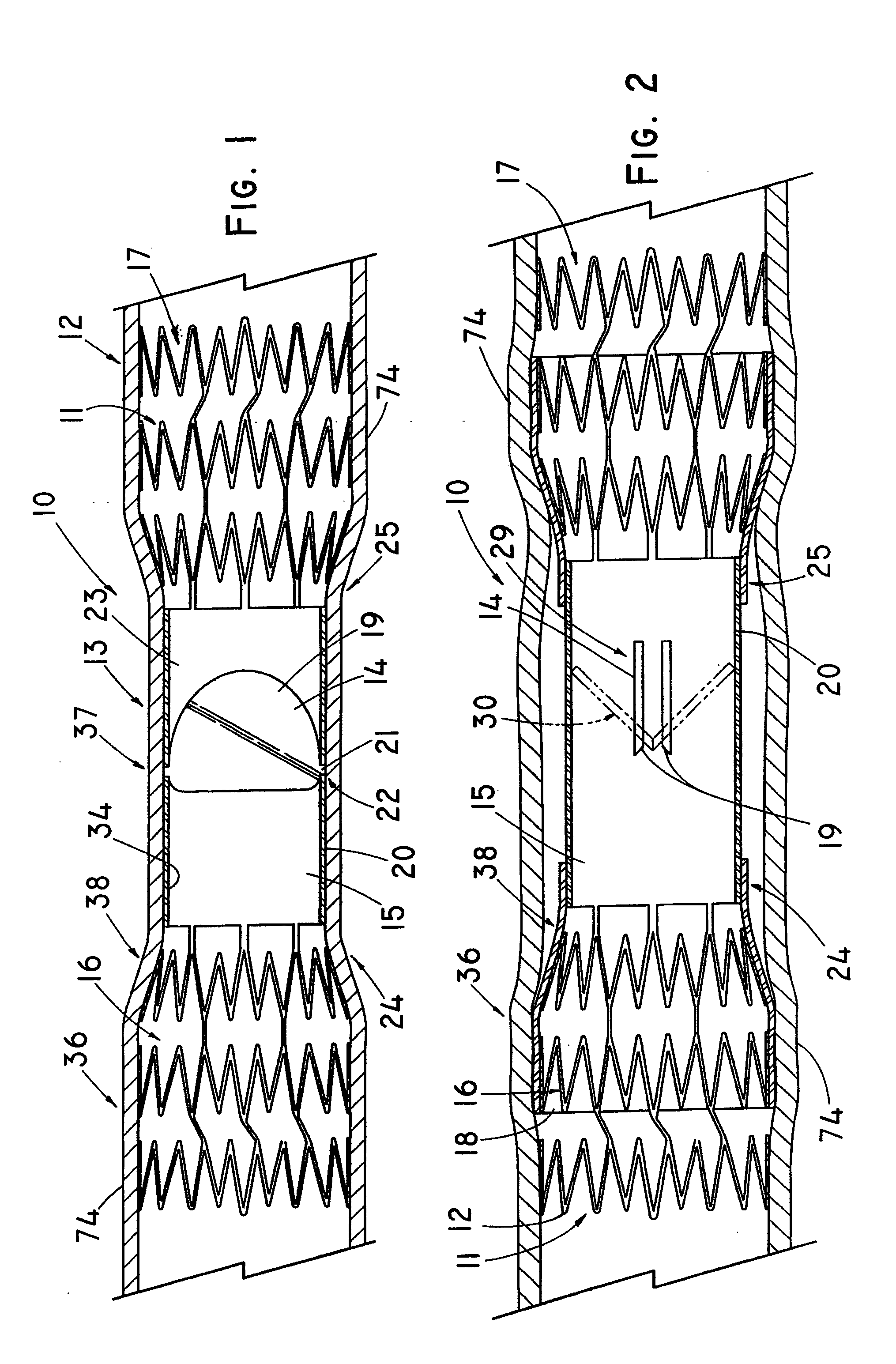
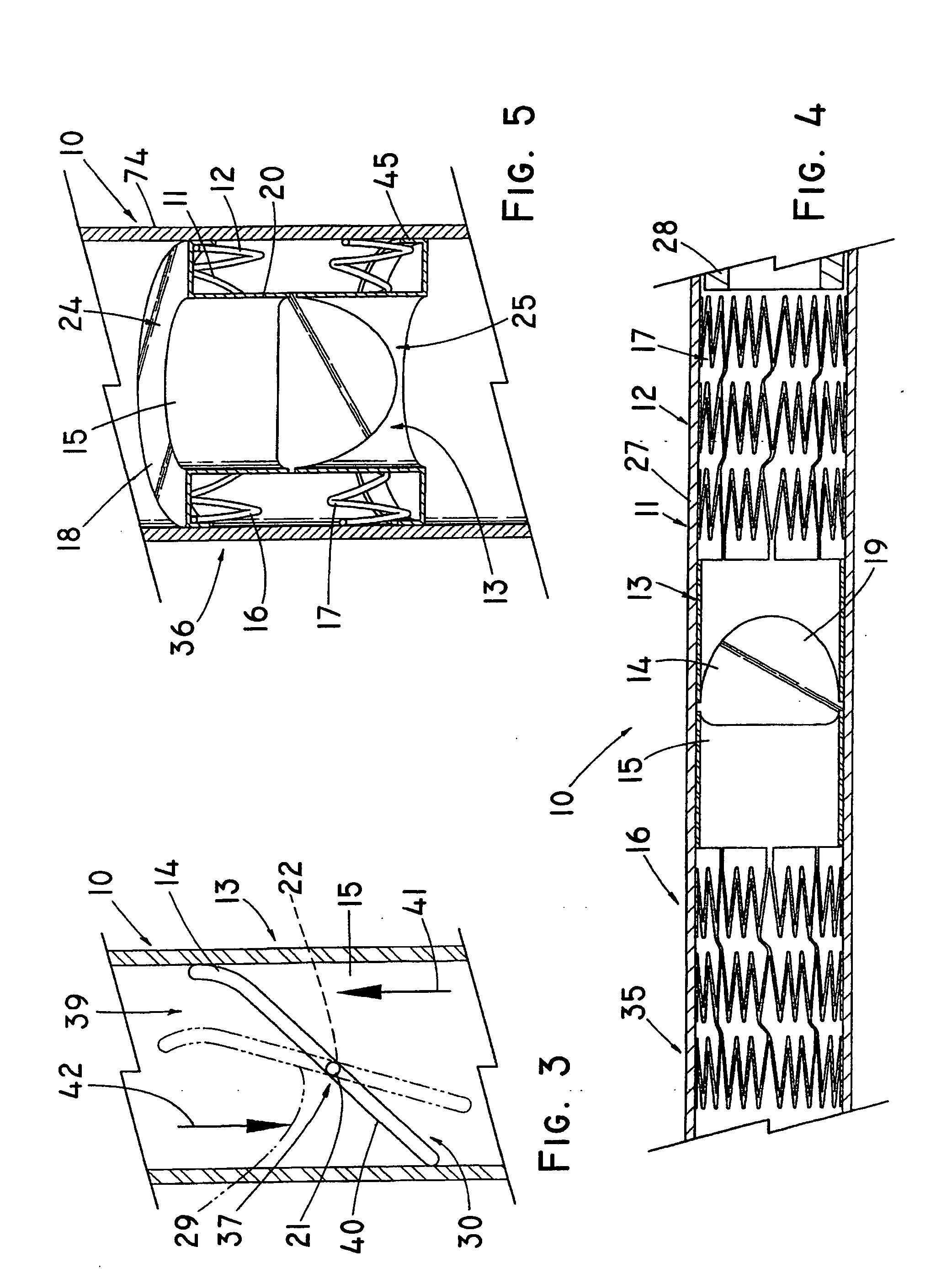
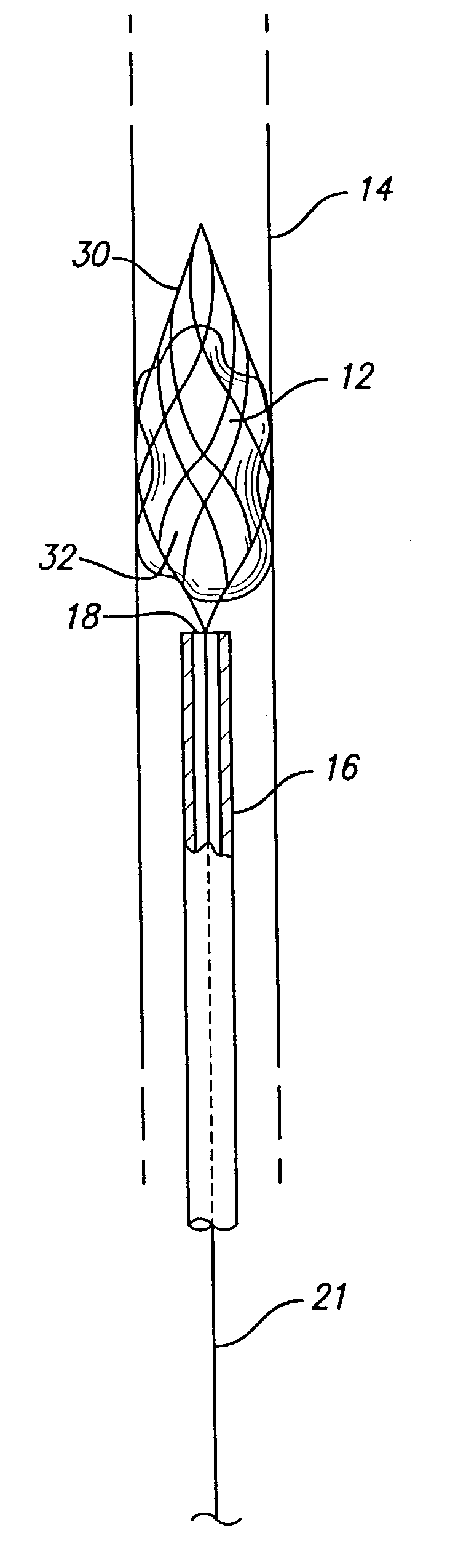
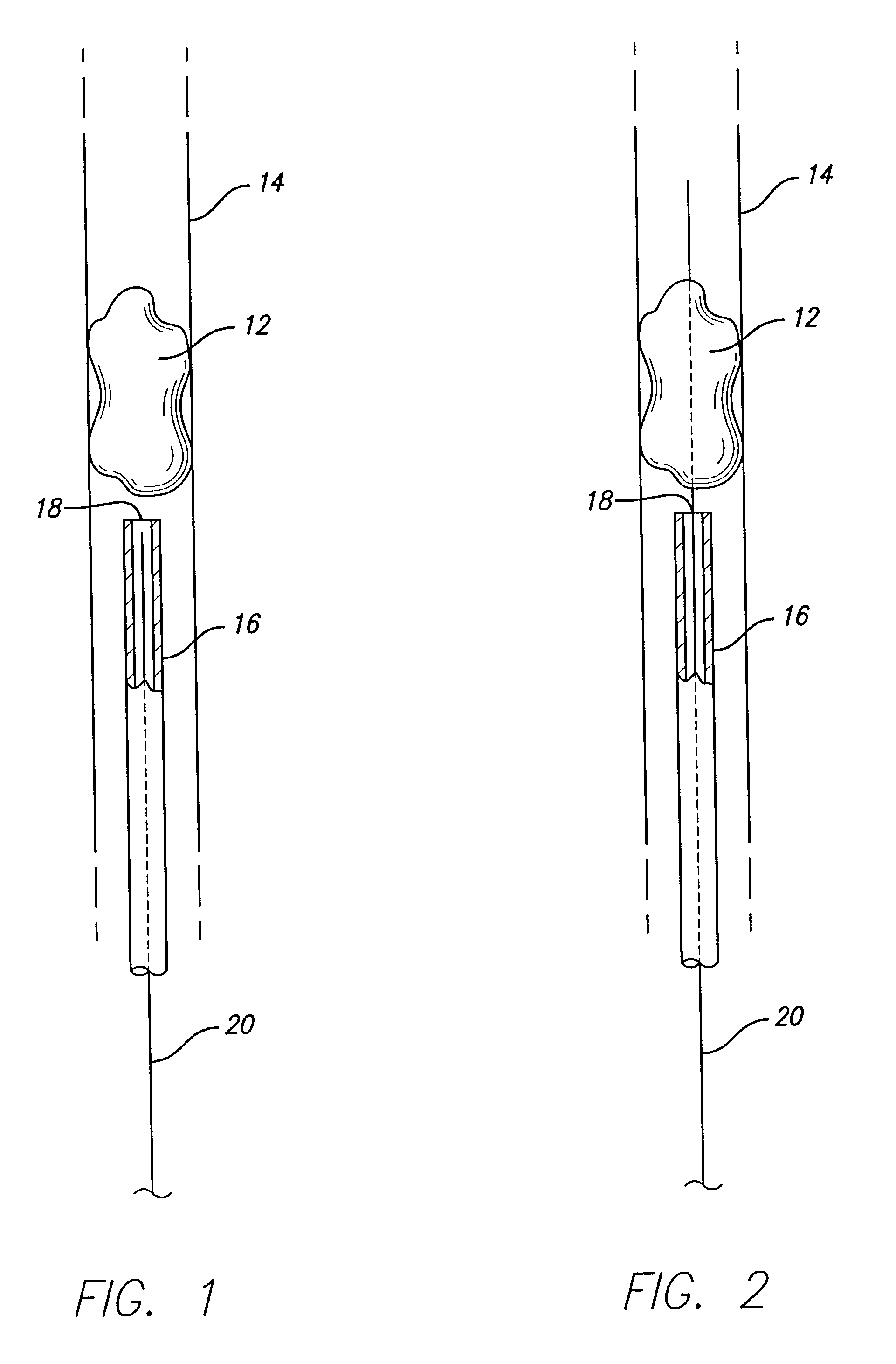
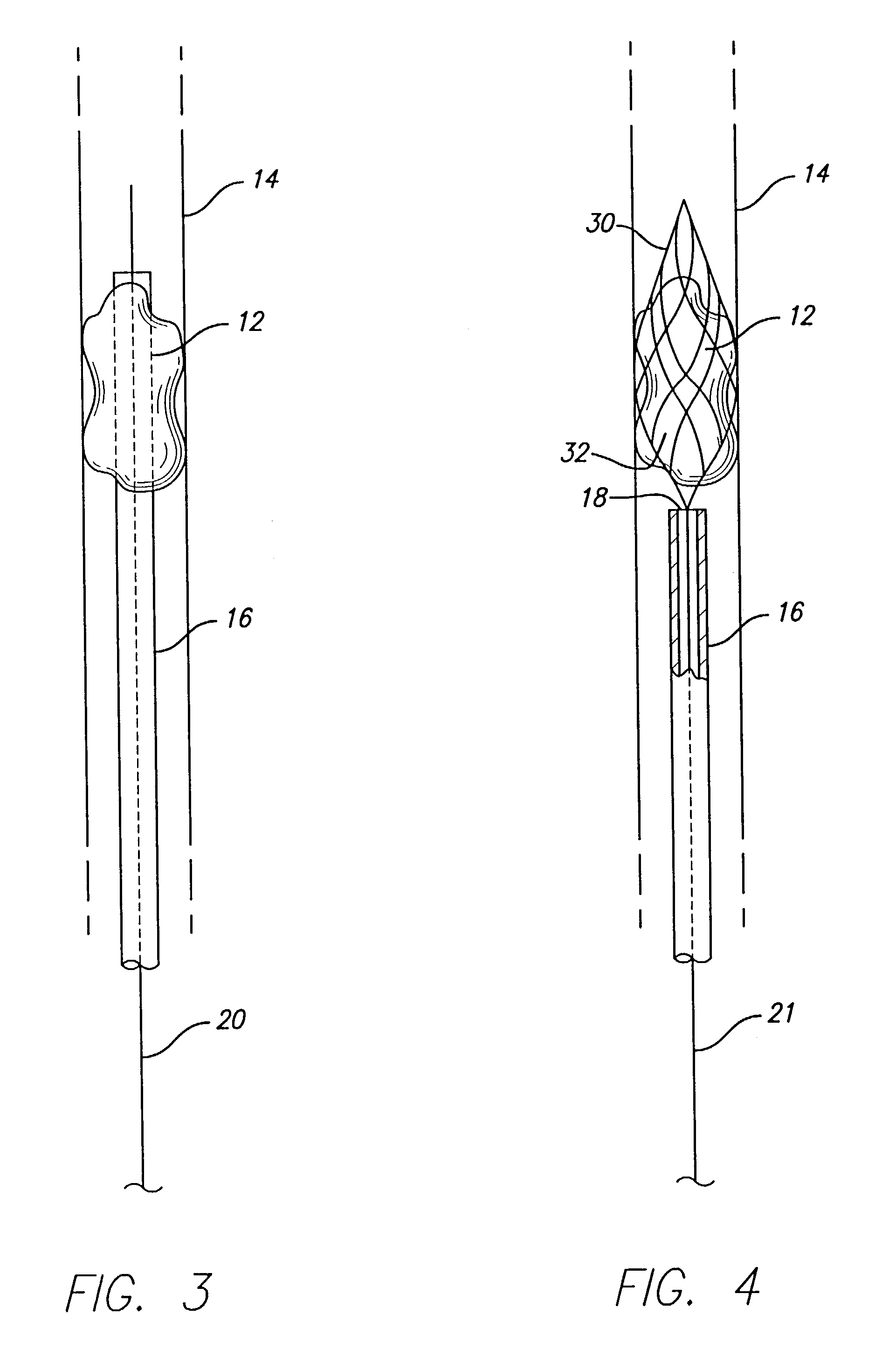
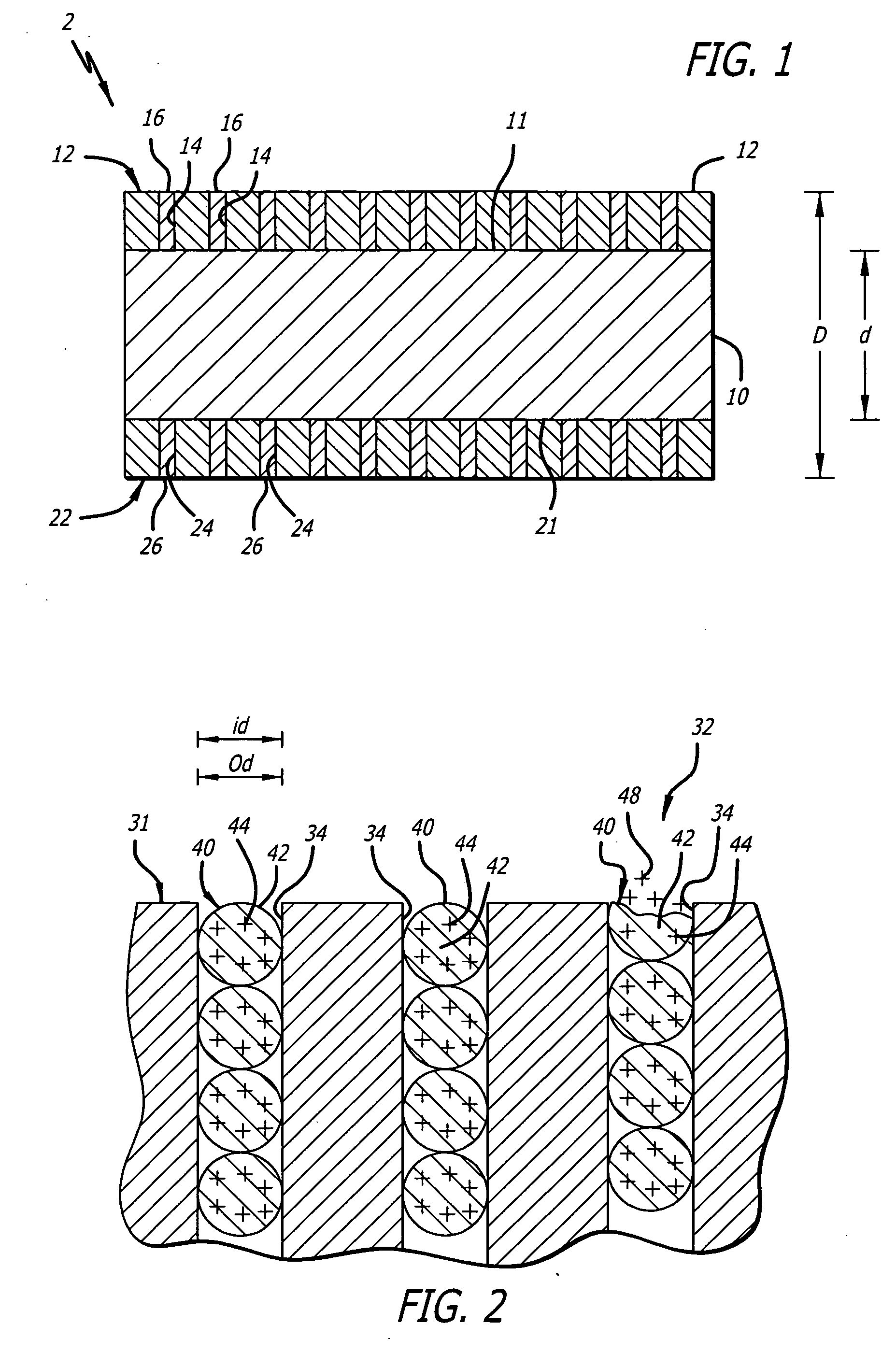
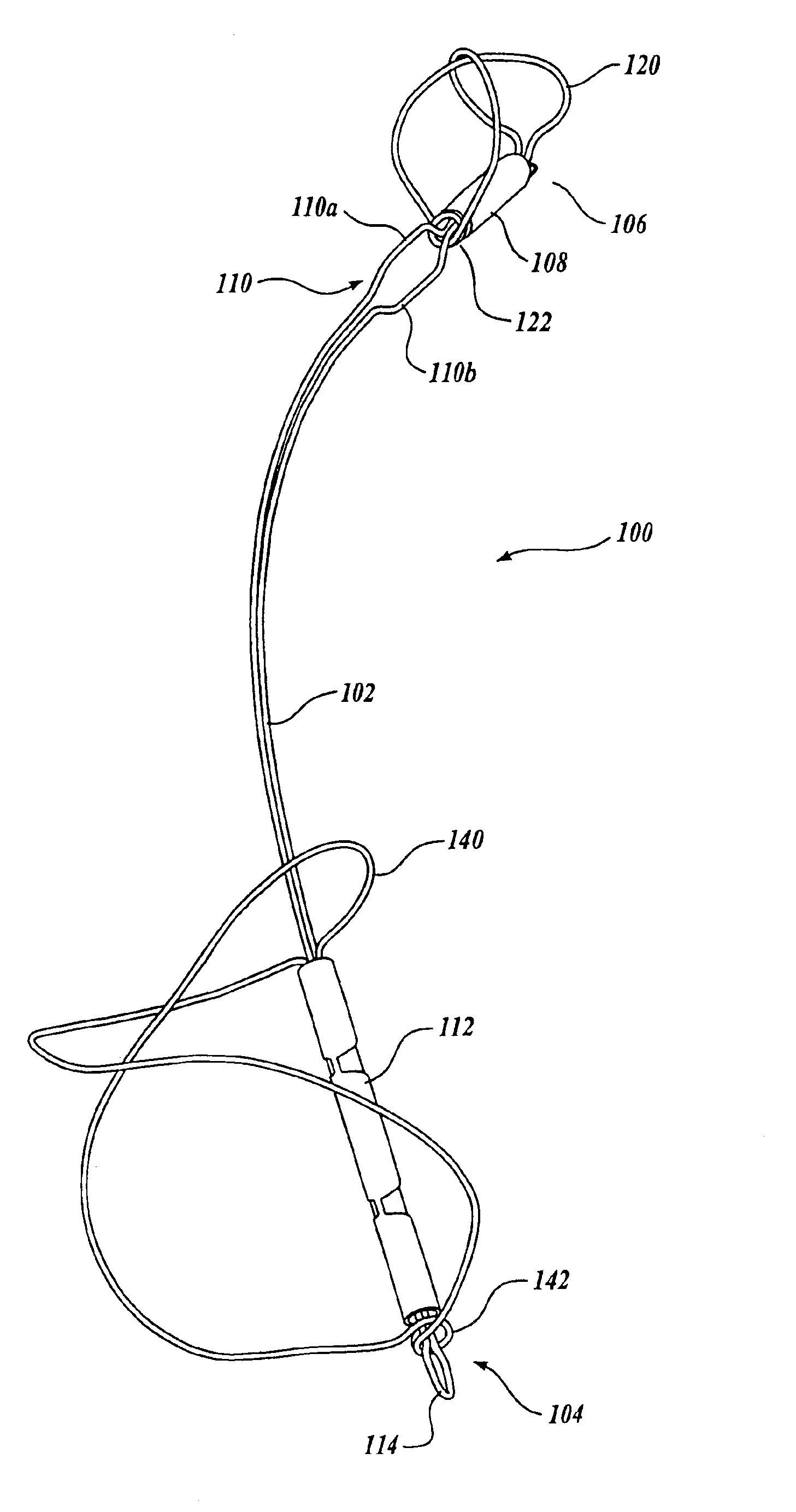
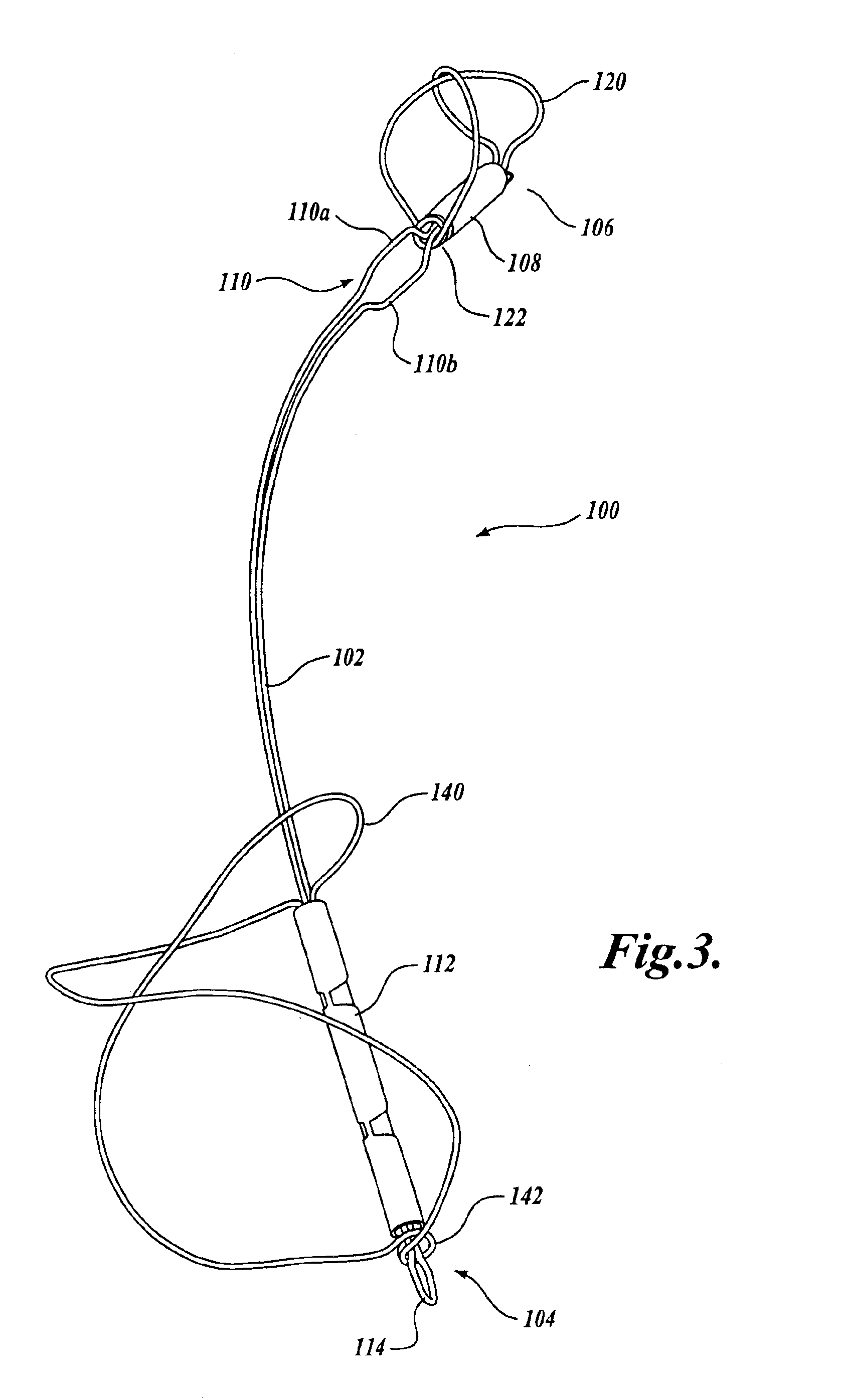
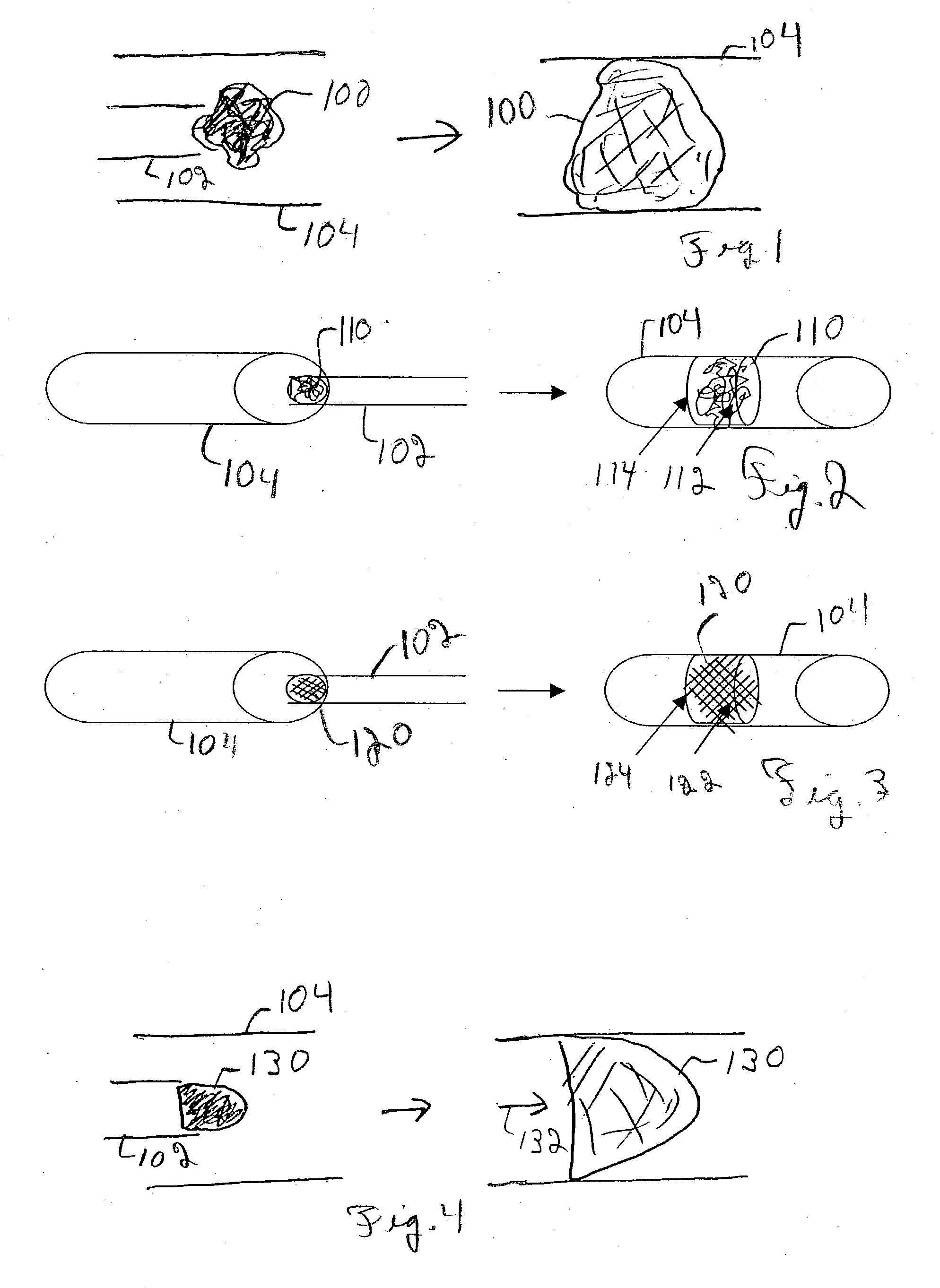
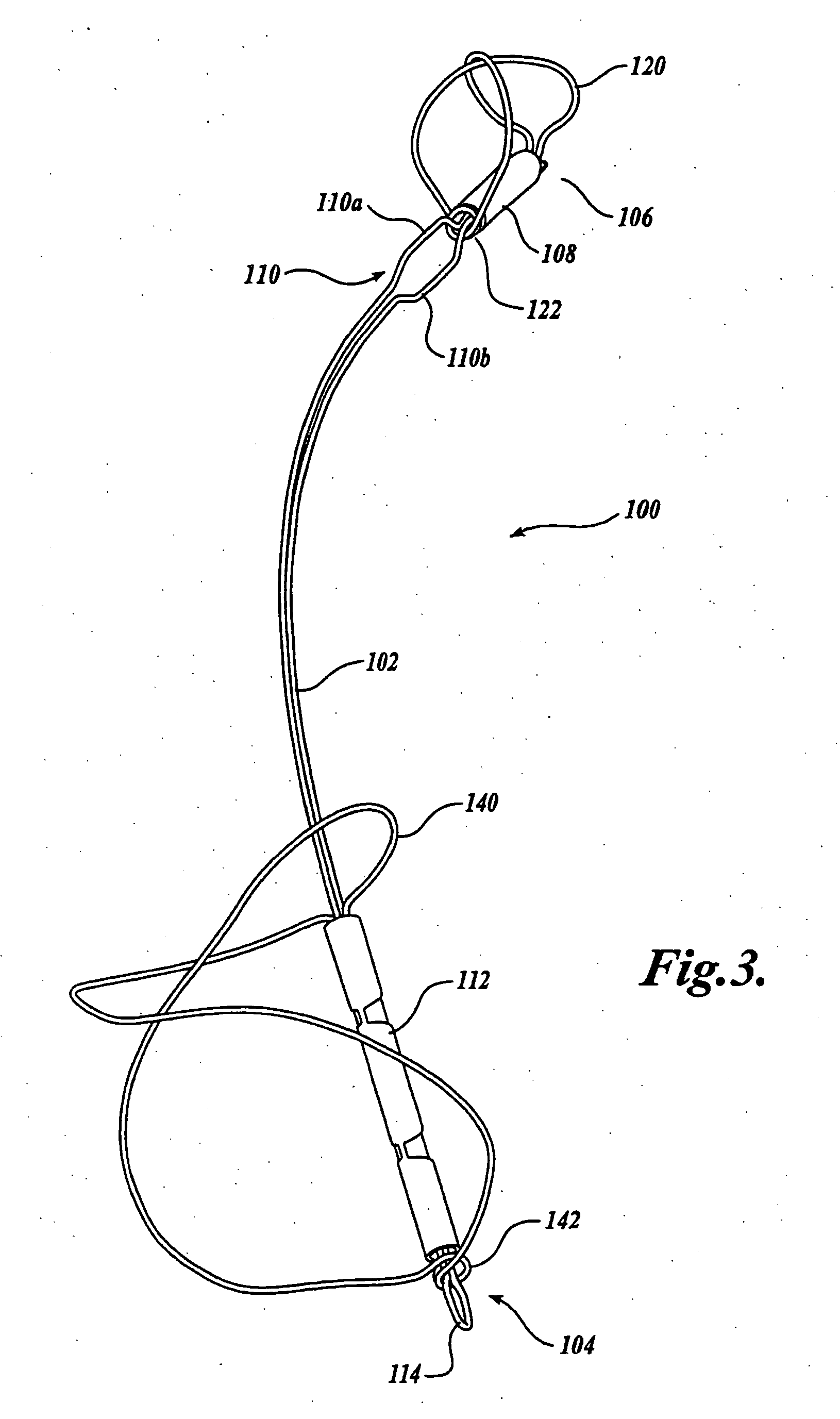
Device for occluding vascular defects
A multi-layer occluder for treating a target site within the body is provided. The occluder may include first and second layers. For example, the first layer may include braided strands of metallic material, and the second layer may include braided strands of polymeric material. At least one of the first or second layers may be configured to facilitate thrombosis.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
Percutaneously placed prosthesis with thromboresistant valve portion
InactiveUS20050182483A1Prevent and limit refluxAvoid poolingBall valvesVenous valvesVenous ValvesBlood flow
A venous valve prosthesis having a substantially non-expandable, valve portion comprising a valve-closing mechanism, such as a pair of opposing leaflets; and an anchoring portion, such as one or more self-expanding frames or stents that are expandable to anchor the prosthesis at the implantation site. In one embodiment, the rigid valve portion includes a deposition of material such as pyrolitic carbon to reduce the thrombogenecity of the blood-contacting surfaces. The anchoring portions preferably include a covering, such as a tubular construct of synthetic or collagen-derived material (such as a bioremodelable ECM material), which attaches about the support structure such that blood flow is directed through the valve mechanism as it transitions from the larger diameter anchoring portion to the intermediate, smaller-diameter portion of the prosthesis. In another embodiment, the valve support housing and valve-closing elements are delivered in a collapsed, folded, and / or dissembled state sized for delivery, then manipulated in situ to the second expanded configured following deployment.
Owner:COOK INC
Device for removal of thrombus through physiological adhesion
InactiveUS7004954B1Raise the level of performanceRestoring native blood flowBalloon catheterSurgeryMedicineThrombus
A device that is useful for removing obstructions from vessels. Various embodiments and methods of use are contemplated for the effective removal of obstructions. The disclosed devices utilize a thrombogenic material to promote the formation of fibrin bonds, thus enhancing adhesion. It is further contemplated that the disclosed devices may be used in all vasculature including the cerebral vasculature and the neurovasculature.
Owner:ENDOVASCULAR TECH
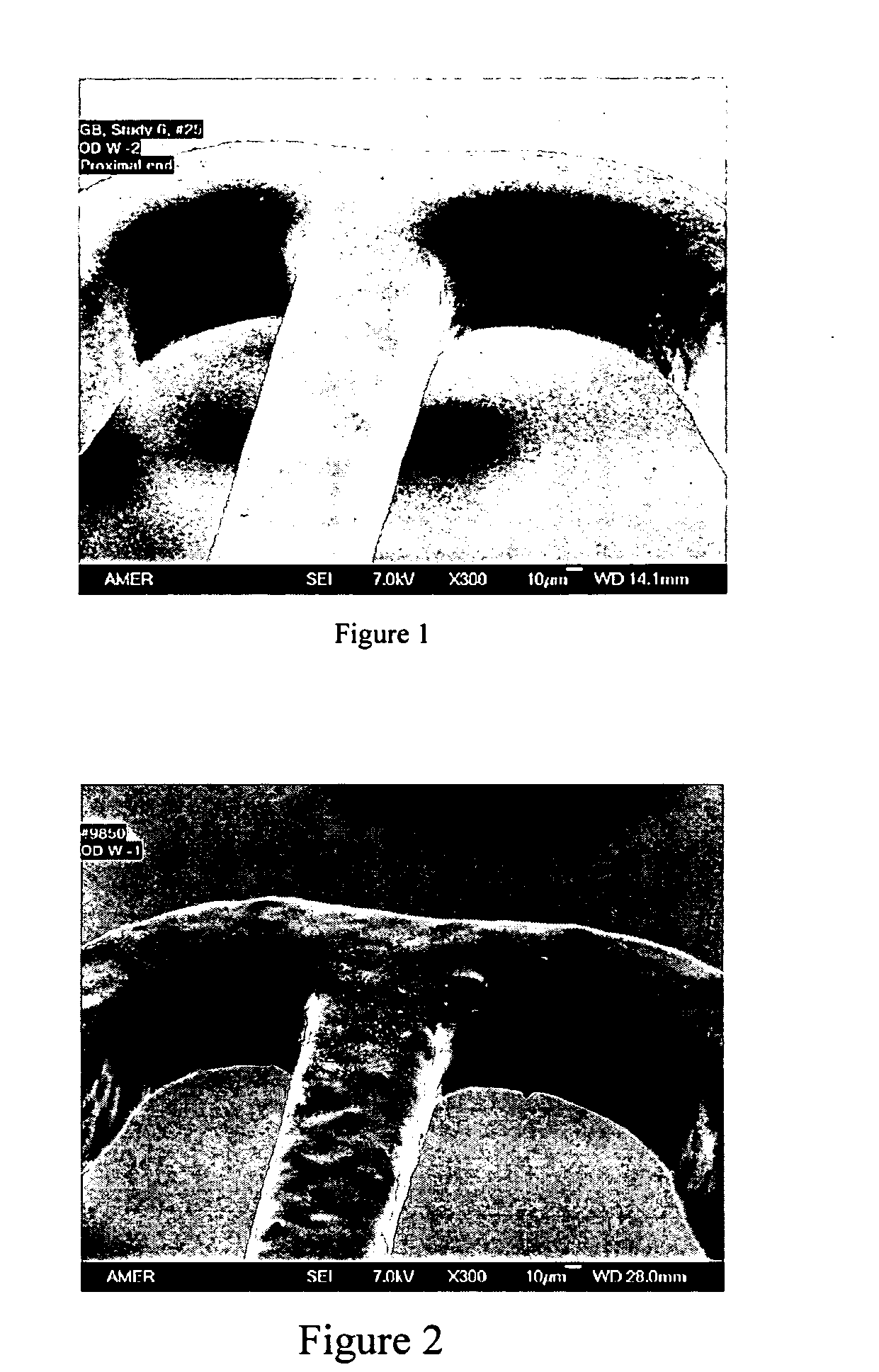
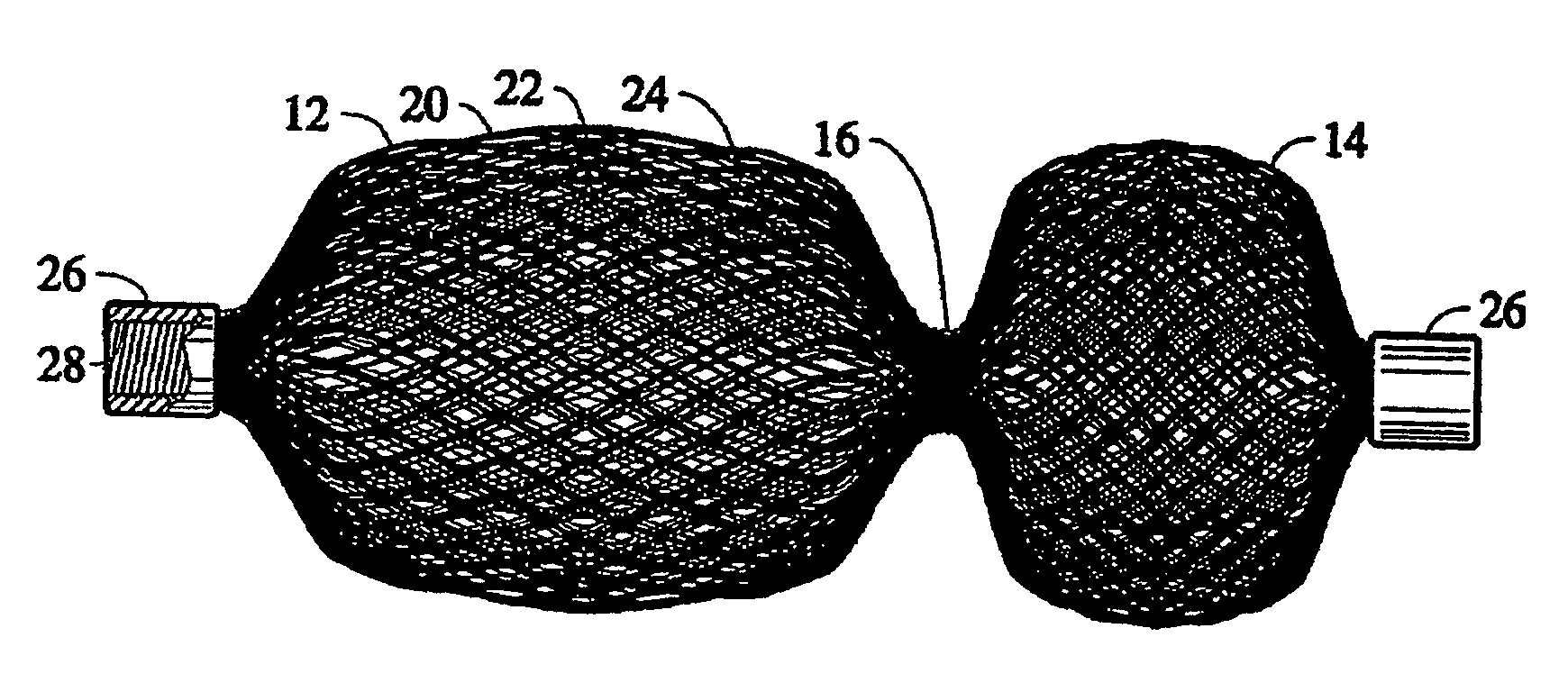
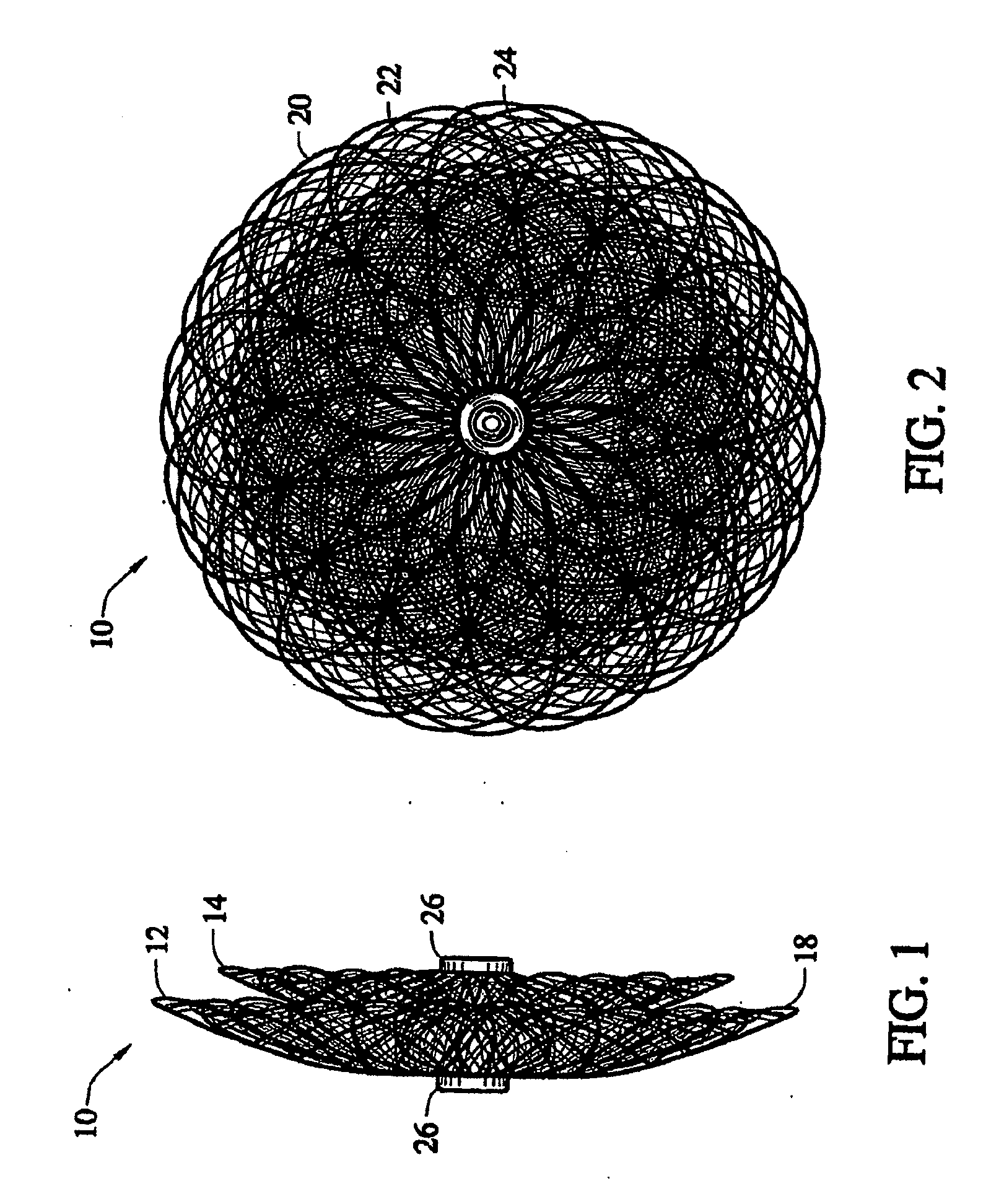
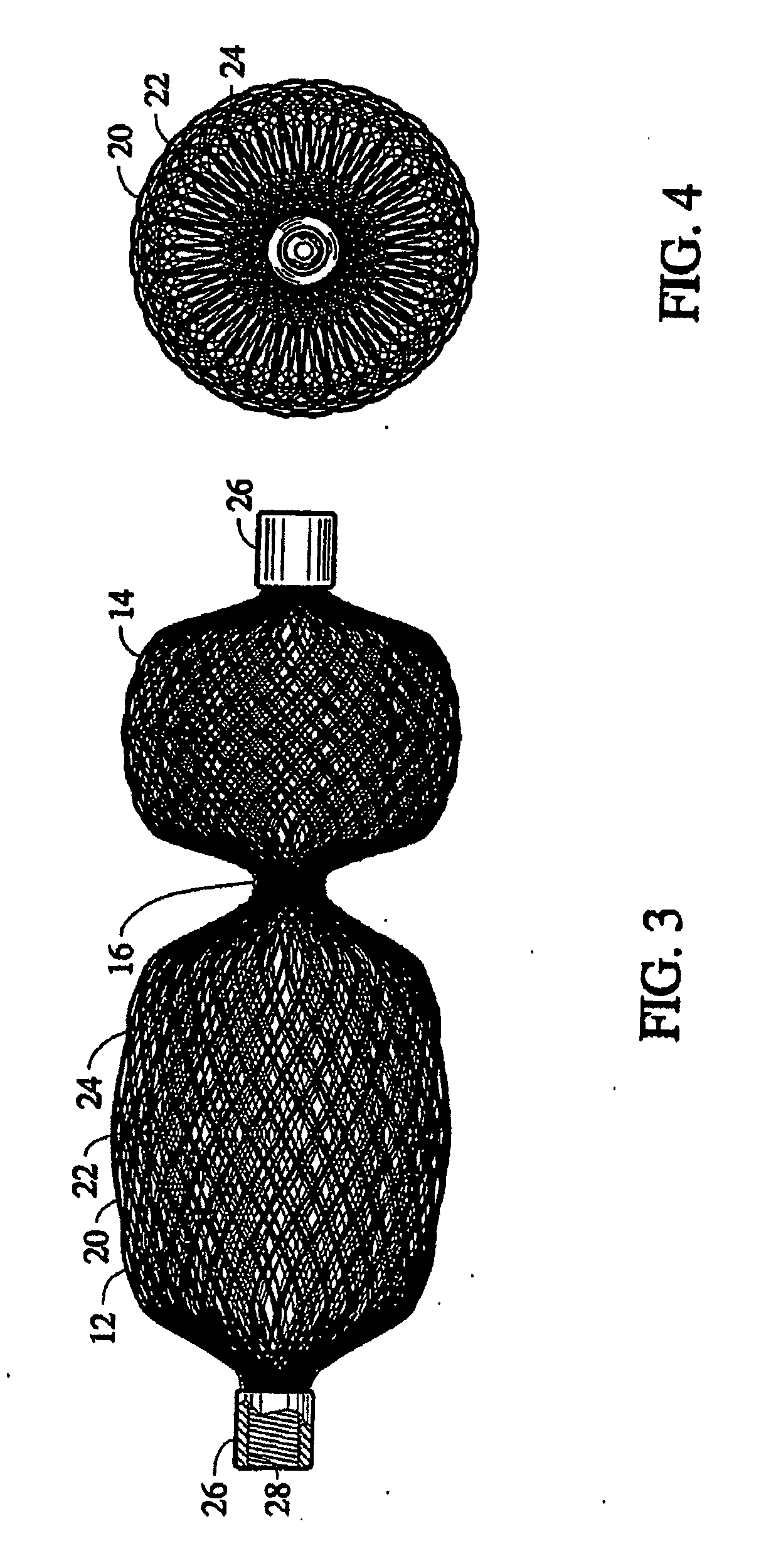
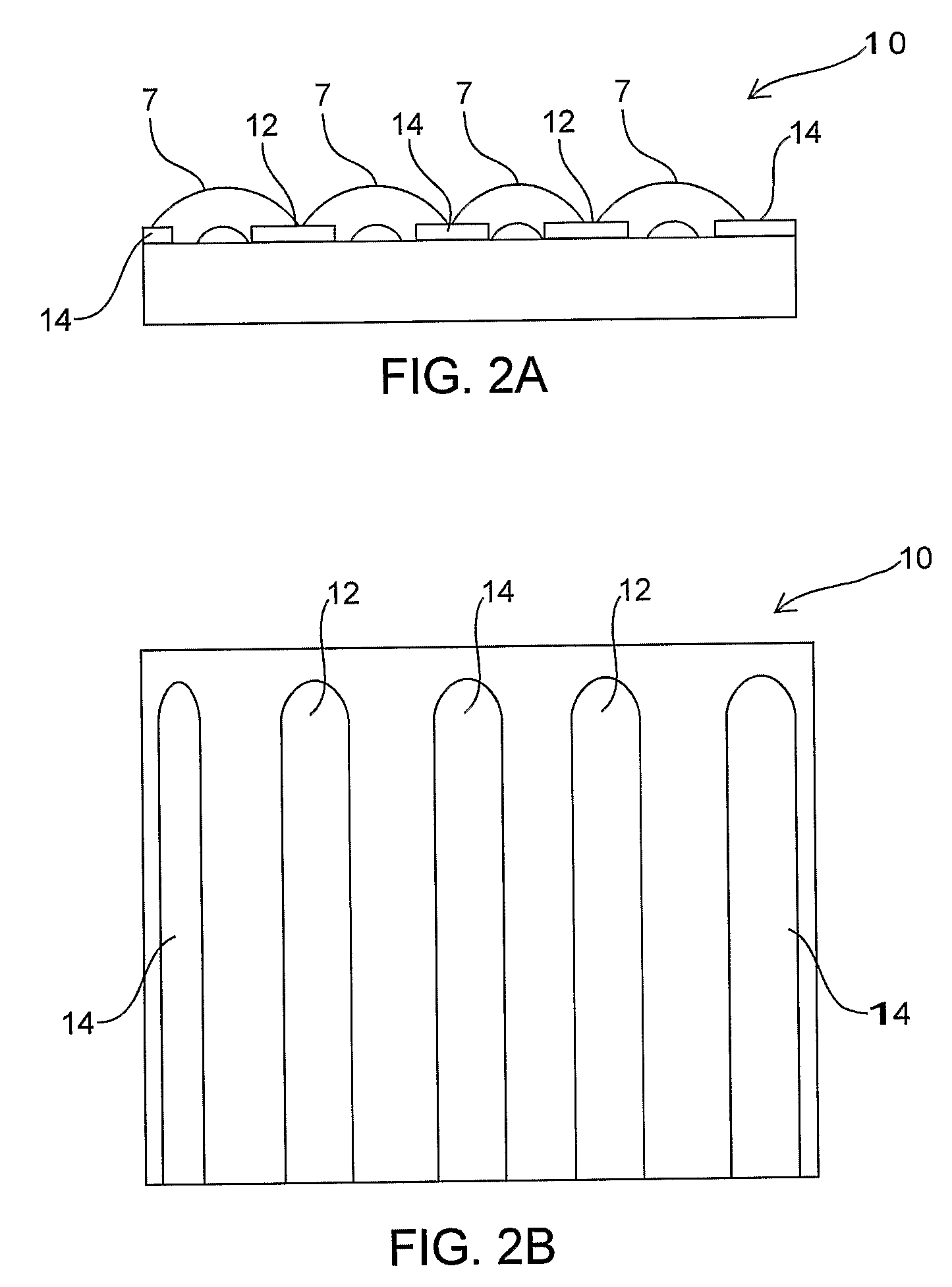
Braided vascular devices having no end clamps
InactiveUS20090082803A1Less cross-sectional dimensionOcculdersSurgical veterinaryThrombusVascular device
In some embodiments, a medical device may include one or more of the following features: (a) a metal fabric formed of braided metal strands, (b) the medical device having a collapsed configuration for delivery through a channel in a patient's body and having a generally dumbbell-shaped expanded configuration with two expanded diameter portions separated by a reduced diameter portion formed between opposed ends of the device and unsecured metal strand ends at the opposed ends, and (d) a thrombogenic agent located on the metal fabric.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
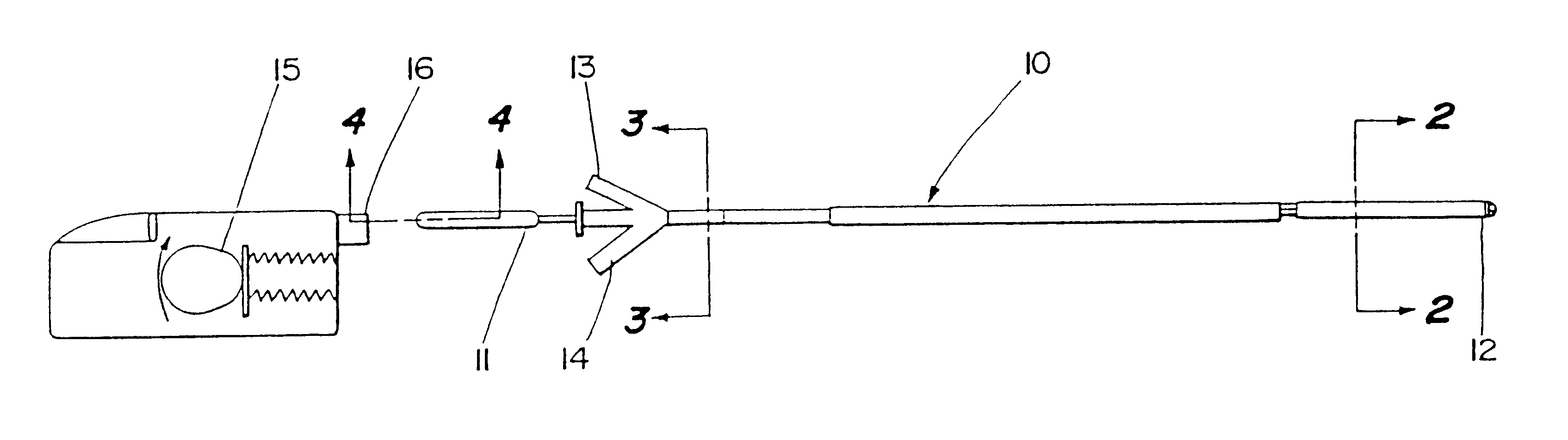
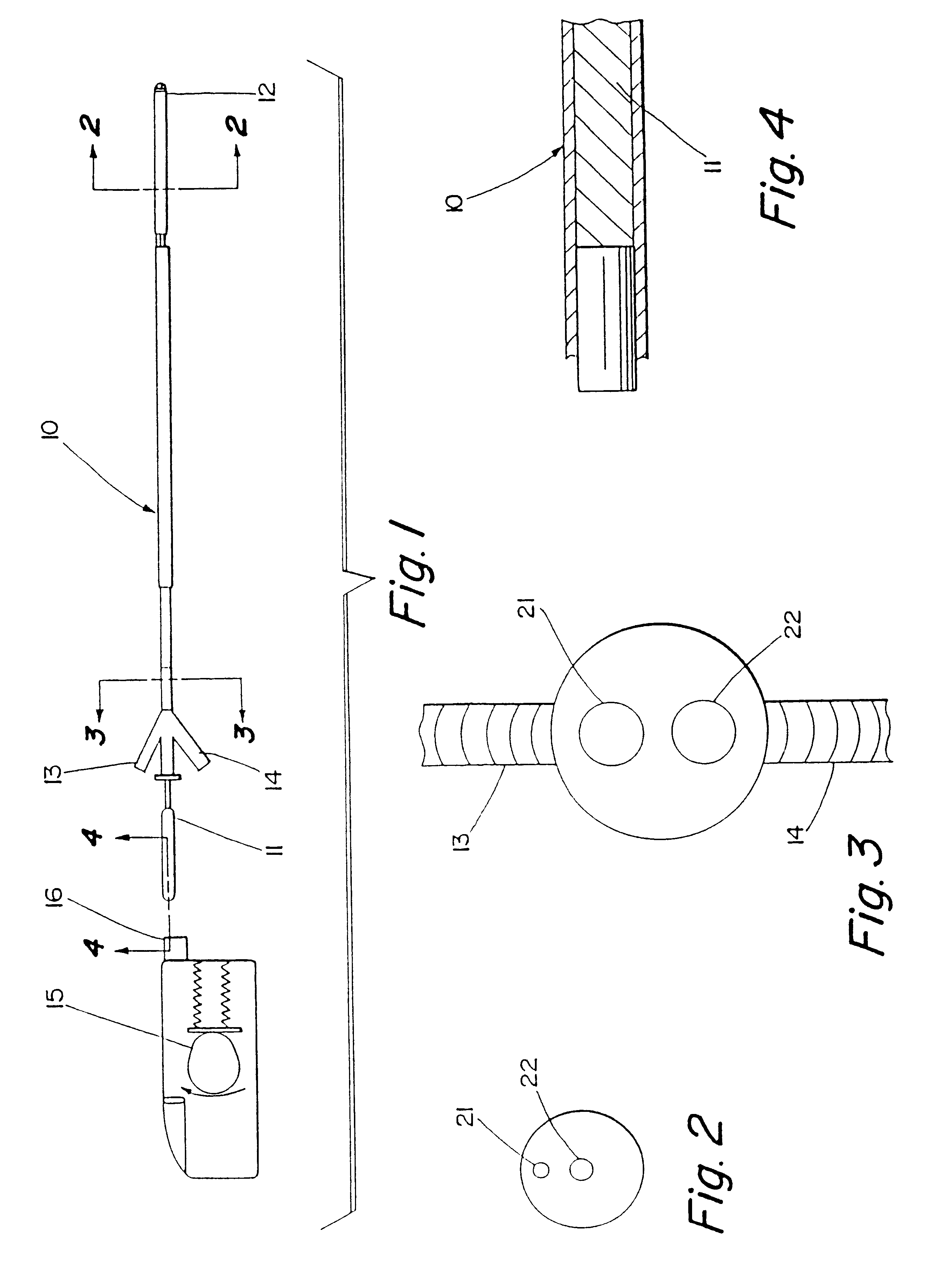
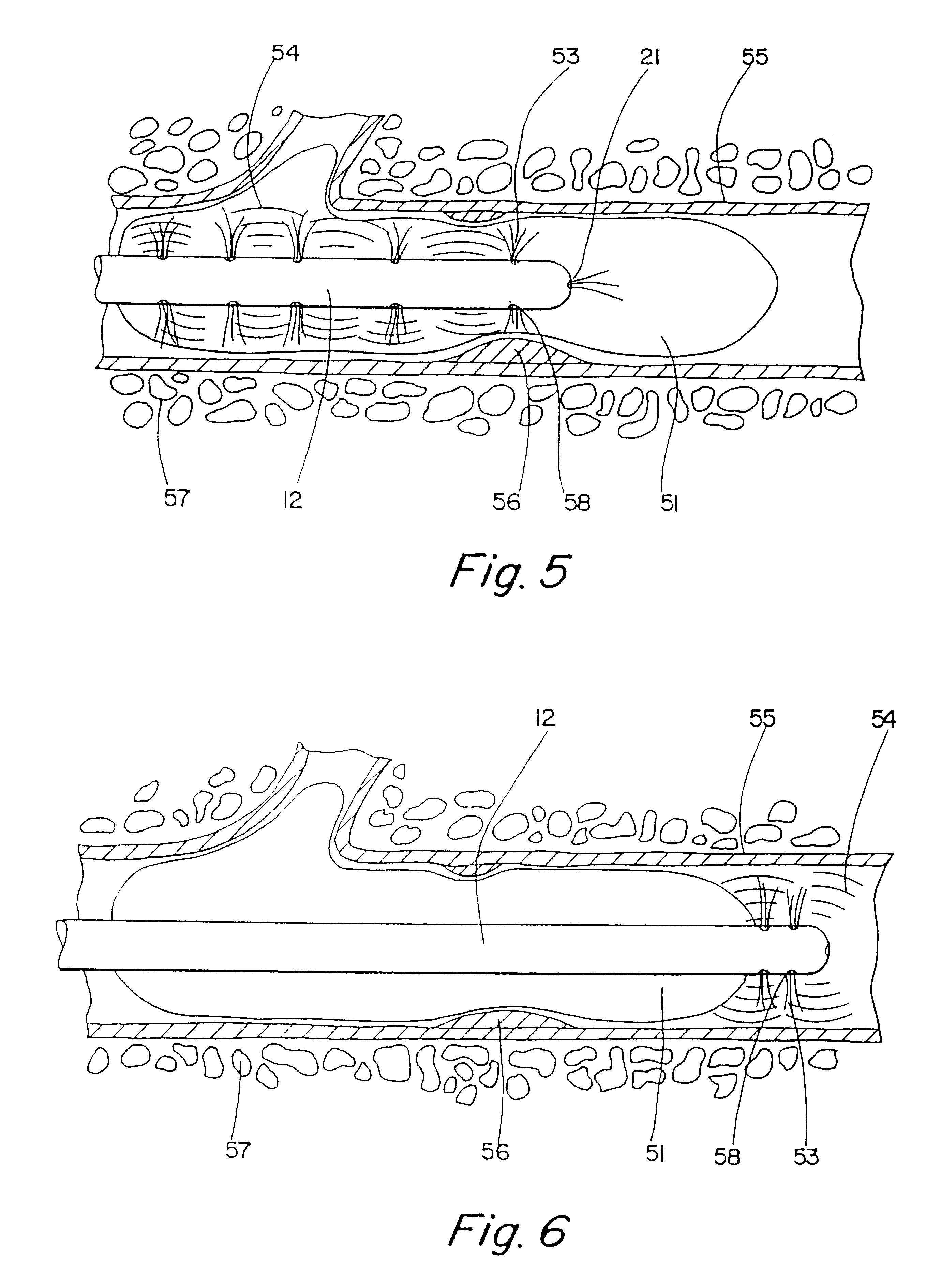
Motion catheter
The present invention describes a catheter suitable for introduction into a tubular tissue for dissolving blockages in such tissue. The catheter is particularly useful for removing thrombi within blood vessels. In accordance with the preferred embodiments, a combination of vibrating motion and injection of a lysing agent is utilized to break up blockages in vessels. The vessels may be veins, arteries, ducts, intestines, or any lumen within the body that may become blocked from the material that flows through it. As a particular example, dissolution of vascular thrombi is facilitated by advancing a catheter through the occluded vessel, the catheter causing a vibrating, stirring action in and around the thrombus usually in combination with the dispensing of a thrombolytic agent such as urokinase into the thrombus. The catheter has an inflatable or expandable member near the distal tip which, when inflated or expanded, prevents the passage of dislodged thrombus around the catheter. The dislodged portions of thrombus are directed through a perfusion channel in the catheter, where they are removed by filtration means housed within the perfusion channel before the blood exits the tip of the catheter. Catheters that allow both frequency (1-1000 Hz) vibratory motion and delivery of such agents to a blockage and a method for using such catheters are disclosed.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Medical device with porous surface containing bioerodable bioactive composites and related methods
InactiveUS20050119723A1Reduced responseImproving device-tissue interfaceStentsLiquid surface applicatorsActive agentNanoparticle
An implantable medical device includes a porous surface with a composite material located within the pores that includes a bioerodable material in combination with a bioactive agent. The composite material is adapted to erode upon exposure to the body of a patient, thus releasing the bioactive agent into the patient, whereas the porous surface remains on the device. In one embodiment, the composite material includes micro- or nano-particles that are deposited within the pores. In a further embodiment, the porous surface is an electrolessly electrochemically deposited material. Certain tie layer and other surface modification aspects are described to enhance various aspects of the bioactive composite surface. The bioactive composite surface is of particular benefit when provided on an endolumenal stent assembly in a manner adapted to elute anti-restenosis or anti-thrombosis agents or combinations thereof.
Owner:MEDLOGICS DEVICE CORP
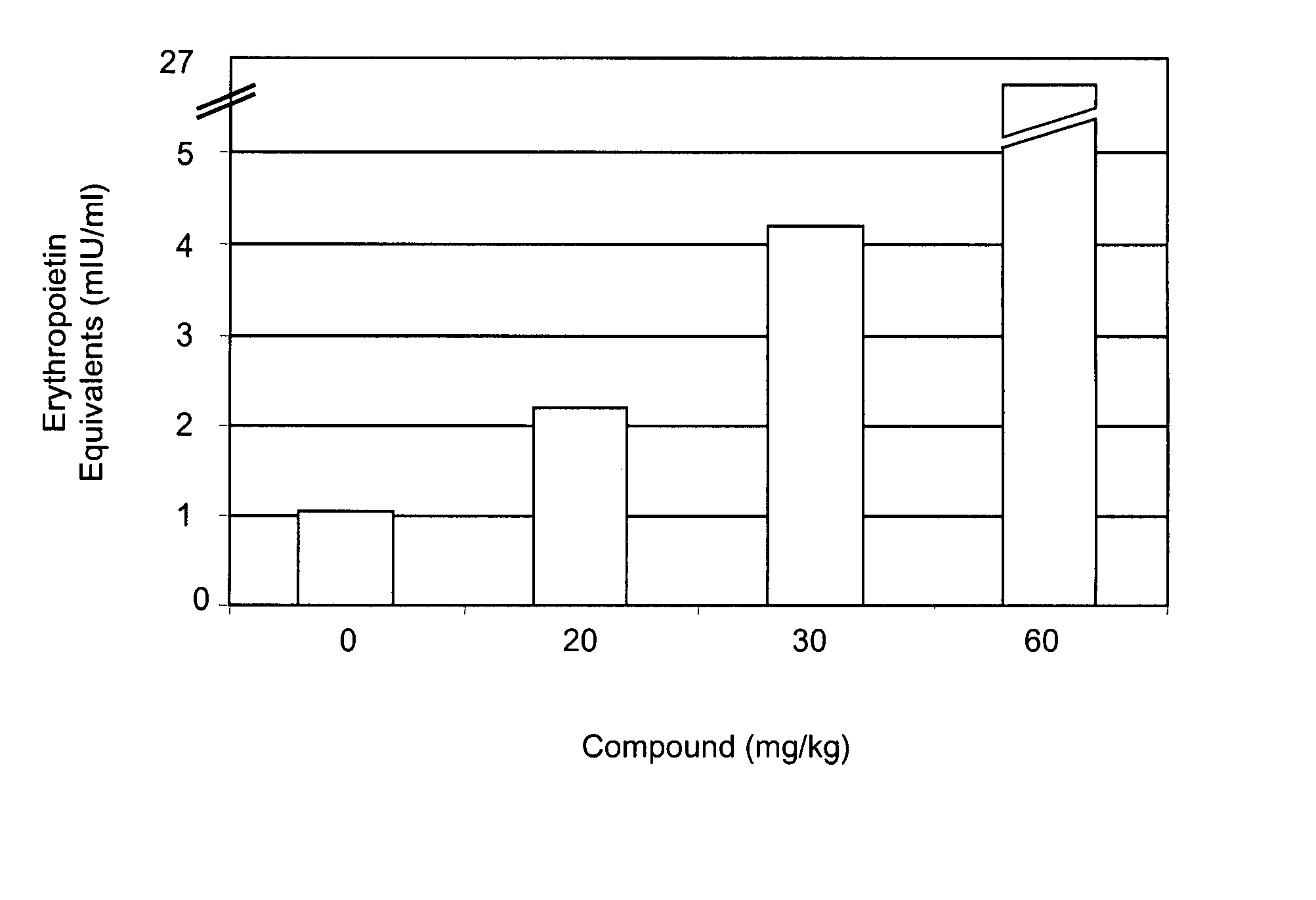
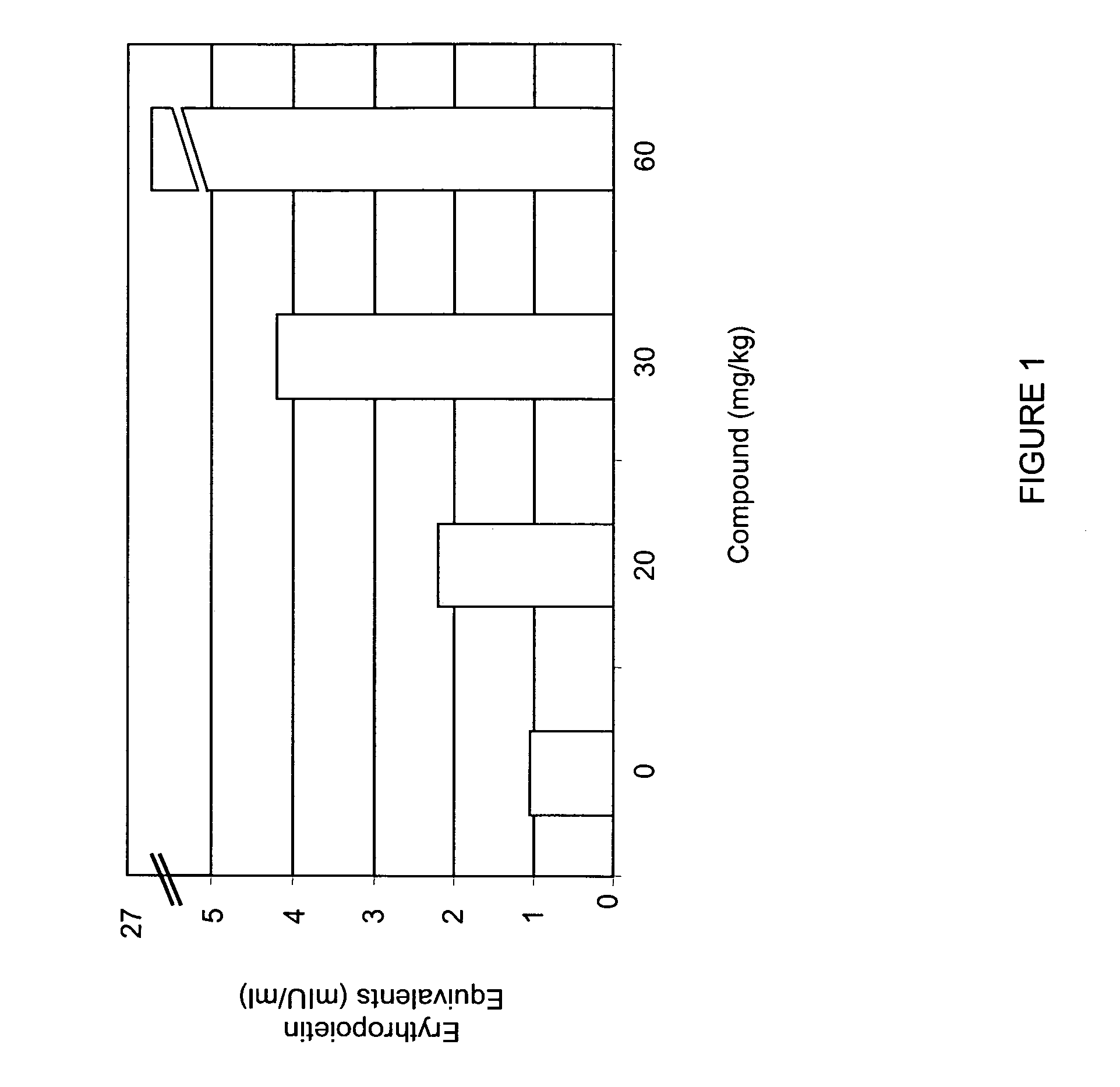
Treatment method for anemia
InactiveUS20060276477A1Promote circulationRaise hemoglobin levelsHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideLower riskMedicine
The present invention relates to improved methods for treating anemia. Methods and compounds useful for treating anemia, wherein the anemia treatment is associated with a lower risk of thrombosis or hypertension compared to that observed with rhEPO therapy, are provided.
Owner:FIBROGEN INC
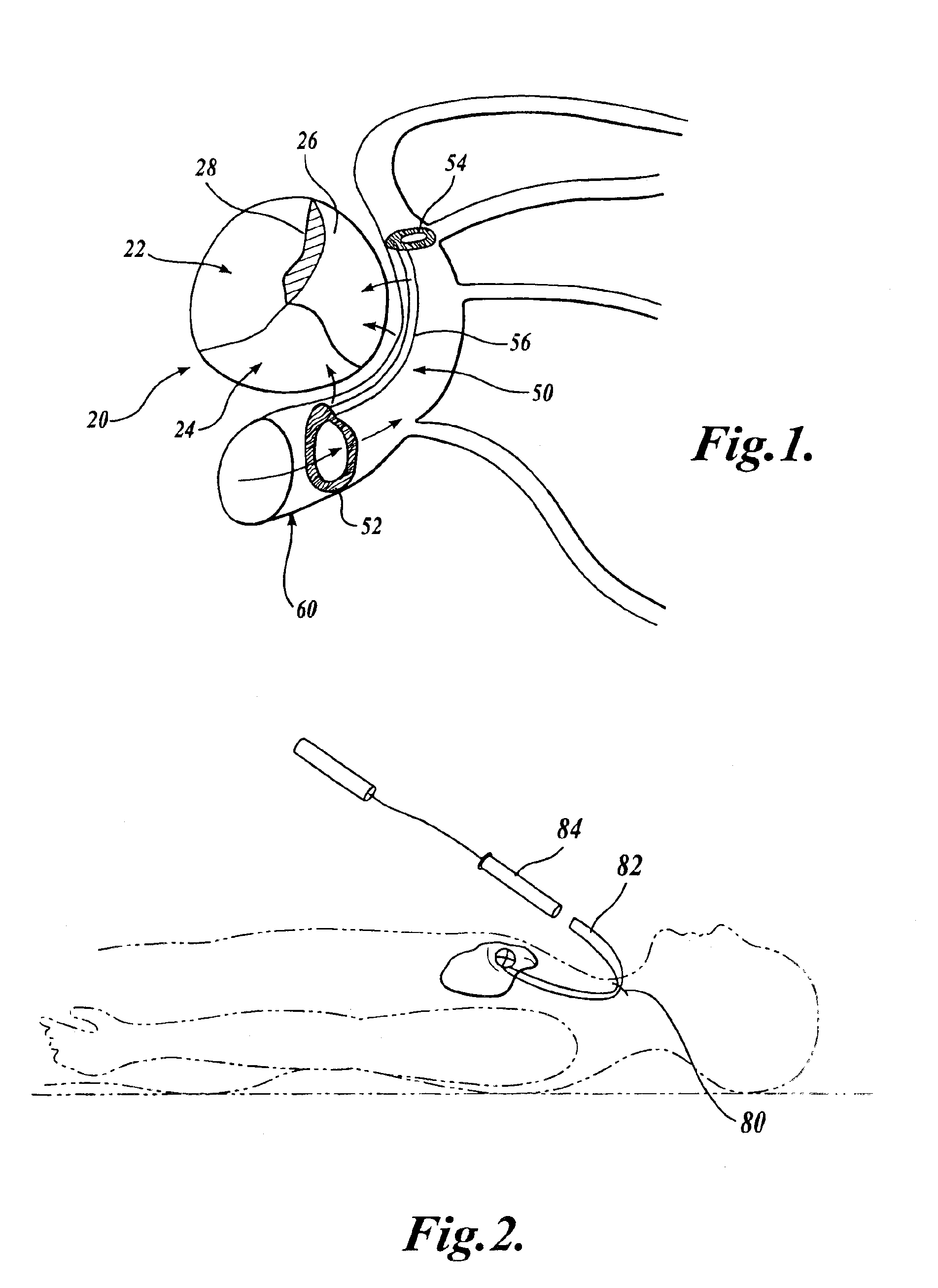
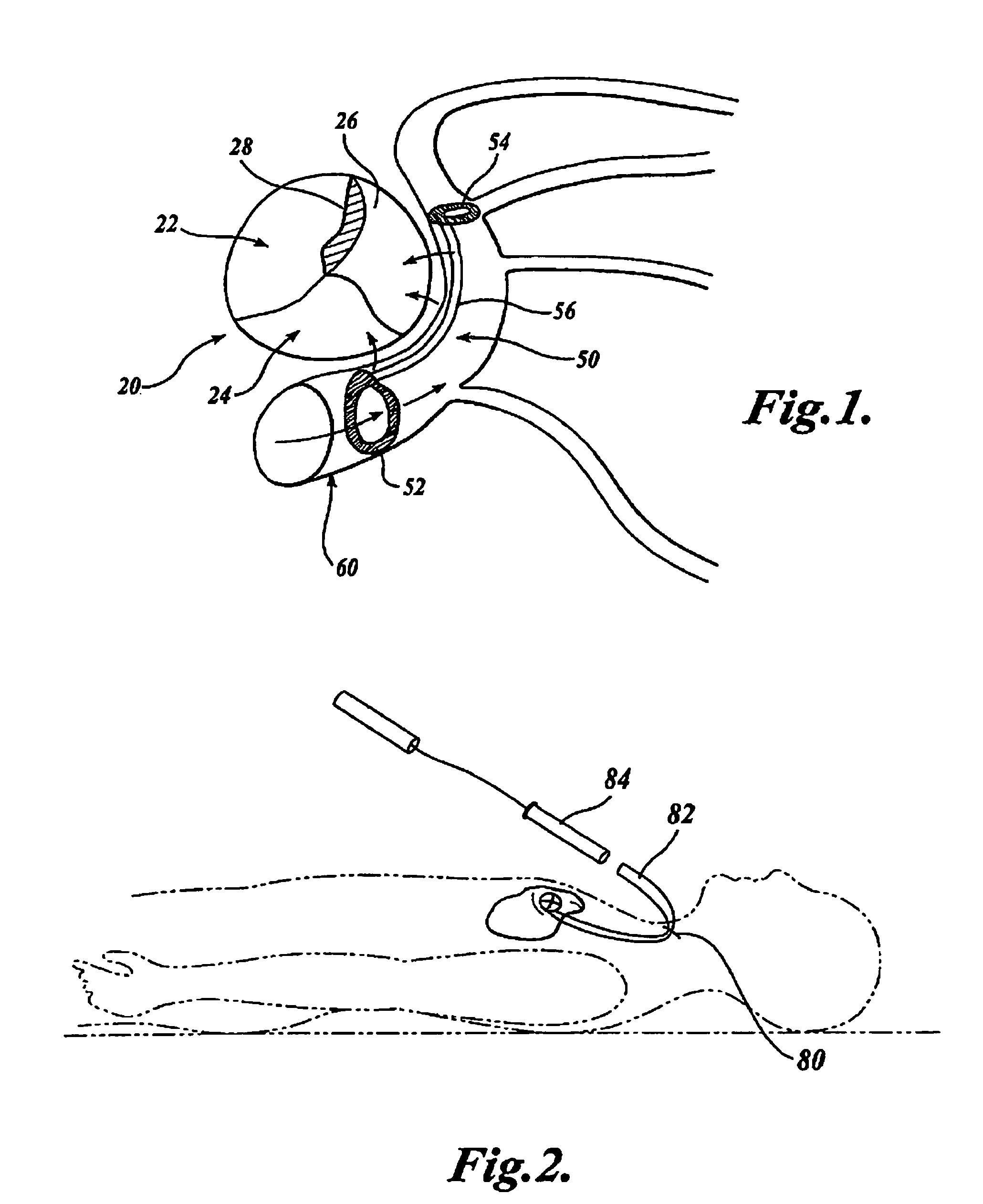
Barrier device for ostium of left atrial appendage
InactiveUS6949113B2Effective isolationPrevent escapeElectrocardiographyDilatorsBlood vessel occlusionThrombus
A membrane applied to the ostium of an atrial appendage for blocking blood from entering the atrial appendage which can form blood clots therein is disclosed. The membrane also prevents blood clots in the atrial appendage from escaping therefrom and entering the blood stream which can result in a blocked blood vessel, leading to strokes and heart attacks. The membranes are percutaneously installed in patients experiencing atrial fibrillations and other heart conditions where thrombosis may form in the atrial appendages. A variety of means for securing the membranes in place are disclosed. The membranes may be held in place over the ostium of the atrial appendage or fill the inside of the atrial appendage. The means for holding the membranes in place over the ostium of the atrial appendages include prongs, stents, anchors with tethers or springs, disks with tethers or springs, umbrellas, spiral springs filling the atrial appendages, and adhesives. After the membrane is in place a filler substance may be added inside the atrial appendage to reduce the volume, help seal the membrane against the ostium or clot the blood in the atrial appendage. The membranes may have anticoagulants to help prevent thrombosis. The membranes be porous such that endothelial cells cover the membrane presenting a living membrane wall to prevent thrombosis. The membranes may have means to center the membranes over the ostium. Sensors may be attached to the membrane to provide information about the patient.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Device and method for modifying the shape of a body organ
An intravascular support device includes a support or reshaper wire, a proximal anchor and a distal anchor. The support wire engages a vessel wall to change the shape of tissue adjacent the vessel in which the intravascular support is placed. The anchors and support wire are designed such that the vessel in which the support is placed remains open and can be accessed by other devices if necessary. The device provides a minimal metal surface area to blood flowing within the vessel to limit the creation of thrombosis. The anchors can be locked in place to secure the support within the vessel.
Owner:CARDIAC DIMENSIONS
Embolism protection devices
InactiveUS20040093015A1Reduce adverse effectsDilatorsTissue regenerationEmbolic Protection DevicesActive agent
Embolism protection devices can be formed with a biocompatible expandable polymer that can expand upon release within a patient's vessel. Upon release, the structure can be configured to filter flow through the vessel. The material of the embolism protection devices can release one or more biologically active agents, such as a thrombolitic agent, including, for example, tPA. Alternatively or additionally, the embolism protection device can be connected to a tether that elutes one or more biologically active agents.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Methacrylate copolymers for medical devices
A polymer of hydrophobic monomers and hydrophilic monomers is provided. It is also provided a polymer blend that contains the polymer and another biocompatible polymer. The polymer or polymer blend and optionally a biobeneficial material and / or a bioactive agent can form a coating on an implantable device such as a drug delivery stent. The implantable device can be used for treating or preventing a disorder such as atherosclerosis, thrombosis, restenosis, hemorrhage, vascular dissection or perforation, vascular aneurysm, vulnerable plaque, chronic total occlusion, patent foramen ovale, claudication, anastomotic proliferation for vein and artificial grafts, bile duct obstruction, ureter obstruction, tumor obstruction, or combinations thereof.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
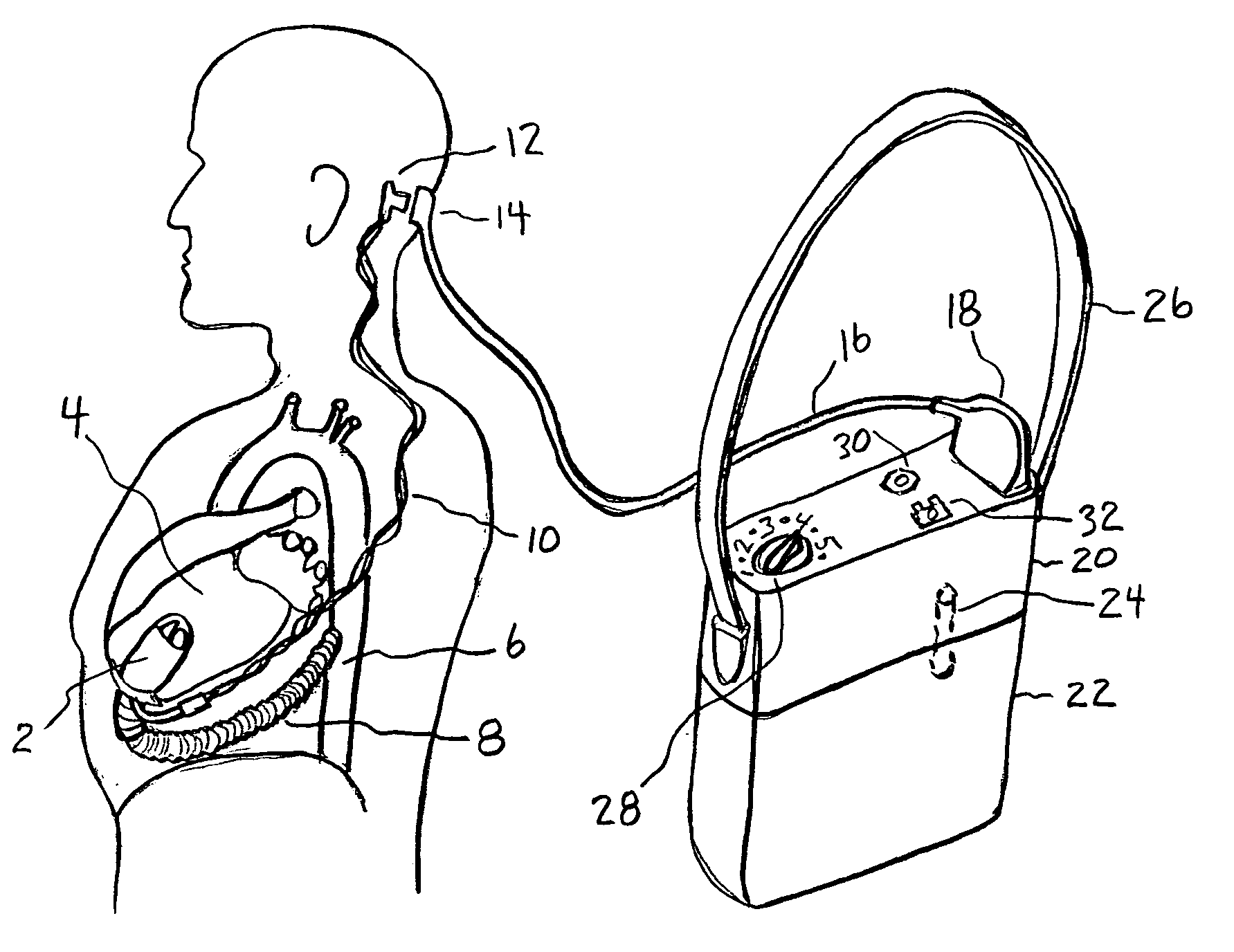
Artificial heart power and control system
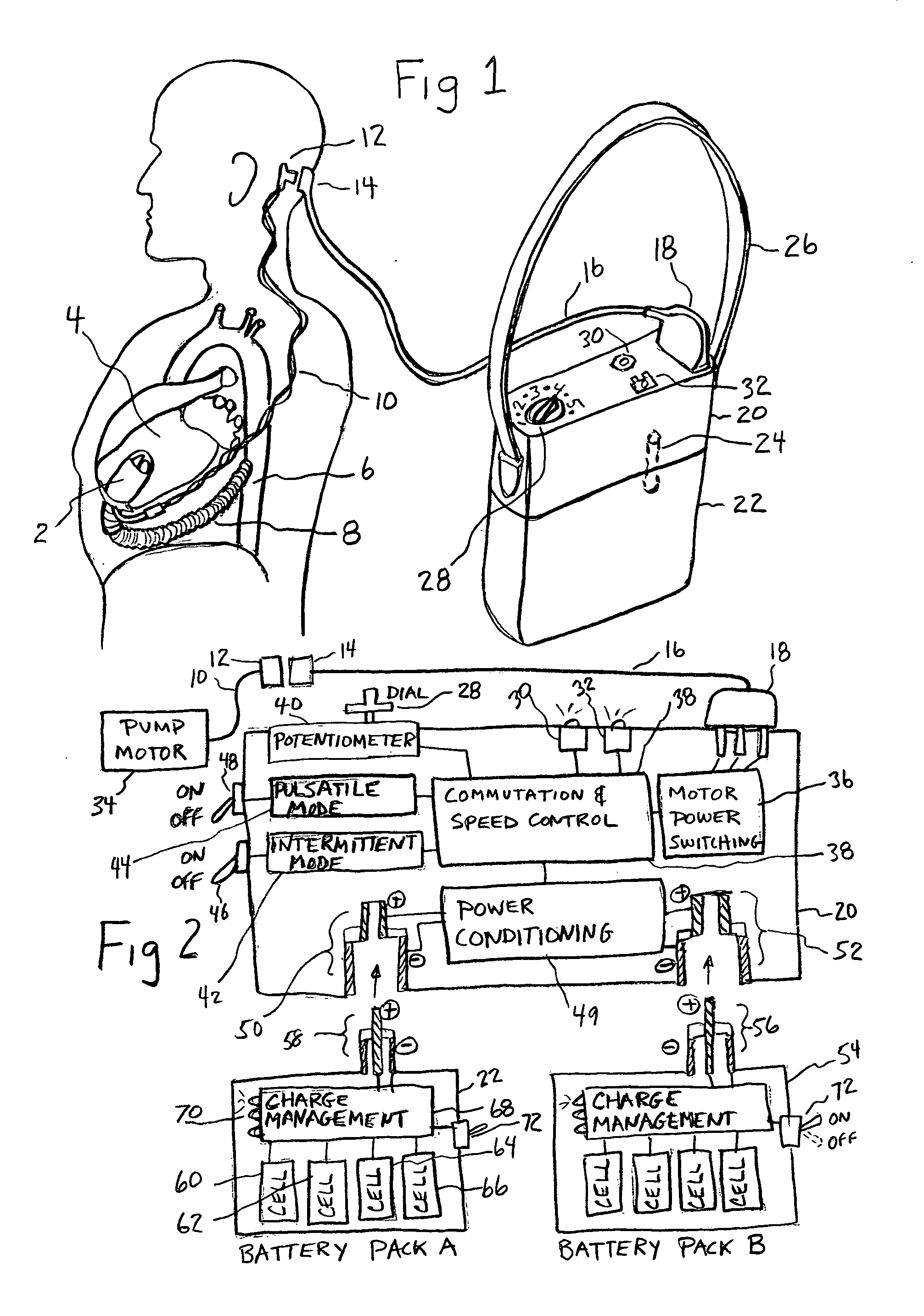
InactiveUS20050071001A1Secure attachmentReduce trafficPrimary cell maintainance/servicingControl devicesControl theoryElectric cables
The present invention provides a human engineered power and control system for artificial hearts or assist devices configured for ease of use, ruggedness, and high reliability. Battery powered systems of the prior art have required multiple cables and connectors that are subject to failure due to damage or wear. In the present invention, direct connection of the batteries to the control system eliminates multiple cables and connectors used with previous designs. A novel method of connecting batteries to the control system and exchanging batteries without interruption of power is provided in a compact user friendly configuration. The control system may provide periodic reductions in assist device flow to permit the natural ventricle to eject blood through the natural outflow valve, open the valve leaflets to prevent them from adhering together, and achieve sufficient washout to prevent thrombosis. Using either software based control or software independent electronic circuitry, the flow pumped by the artificial heart is reduced for a long enough period of time to permit at least a few beats of the natural heart to generate sufficient pressure to open the outflow valve. In a control system embodiment in which the patient manually adjusts the pump speed to incremental settings for rest and exercise conditions, a pulsatile flow mode is disclosed which provides approximately the same flow at a given incremental setting as the pump produces when running in a constant speed mode at the same setting. As the patient learns which speed setting is best for daily activities, the patient may use the same setting with either a pulsatile or constant pump speed mode.
Owner:EDER JEFFREY
Cross stream thrombectomy catheter with flexible and expandable cage
A cross stream thrombectomy catheter with a flexible and expandable cage preferably formed of nitinol for removal of hardened and aged thrombotic material stubbornly attached to the interior of a blood vessel. The cage, which can be mesh or of straight or spiral filament design, is located close to inflow and outflow orifices at the distal portion of a catheter tube and is deployed and extended at a thrombus site for intimate contact therewith and for action of a positionable assembly and subsequent rotation and lineal actuation to abrade, grate, scrape, or otherwise loosen and dislodge difficult to remove thrombus which can interact with cross stream flows to exhaust free and loosened thrombotic particulate through the catheter tube. An alternative embodiment discloses a mechanism involving a threaded tube in rotatable engagement with an internally threaded sleeve to incrementally control the deployment and expansion of the flexible and expandable cages.
Owner:BOSTON SCI LTD
Radioactive intraluminal endovascular prosthesis and method for the treatment of aneurysms
A method for increasing the rate of thrombus formation and / or proliferative cell growth of a selected region (21) of cellular tissue (22) including the step of endovascularly irradiating the selected region (21) with radiation, having a dose range of endovascular radiation of about 1 Gy to about 600 Gy at a low dose rate of about 1 cGy / hr to about 320 cGy / hr, to increase thrombus formation and / or cell proliferation of the affected selected region (21). Preferably, the delivery means includes a deformable endovascular prosthesis (25) adapted for secured positioning adjacent to the selected region (21) of cellular tissue (22), and a radioactive source. This source cooperates with the deformable endovascular device (25) in a manner endovascularly irradiating the selected region with radiation, having the above-indicated dose range and low dose rate of endovascular radiation to increase thrombus formation and / or cell proliferation of the affected selected region (21).
Owner:ISOSTENT
Compounds and methods for delivery of prostacyclin analogs
Owner:UNITED THERAPEUTICS CORP
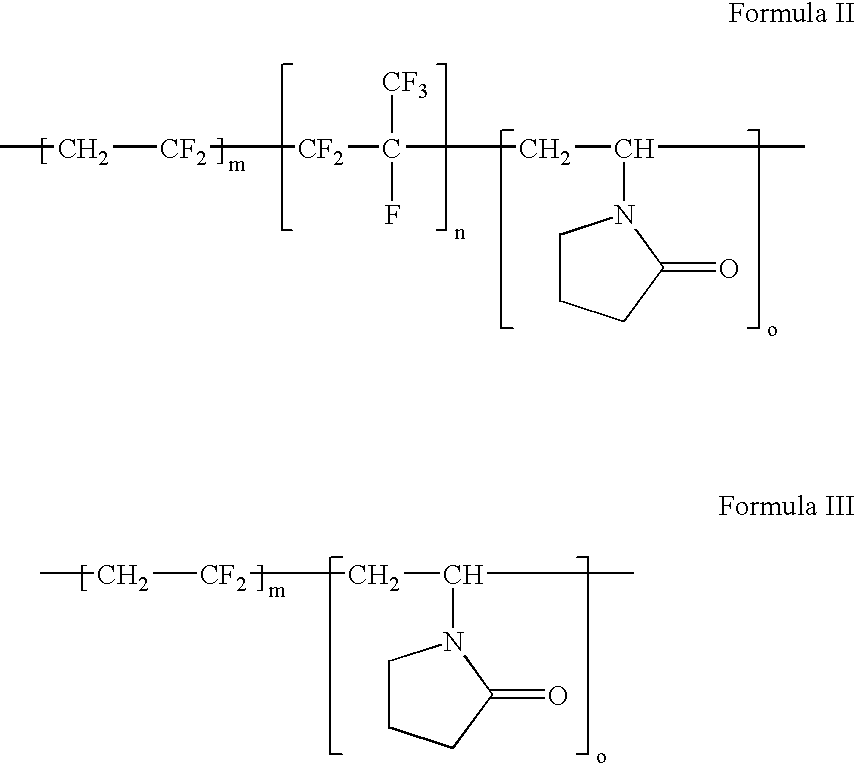
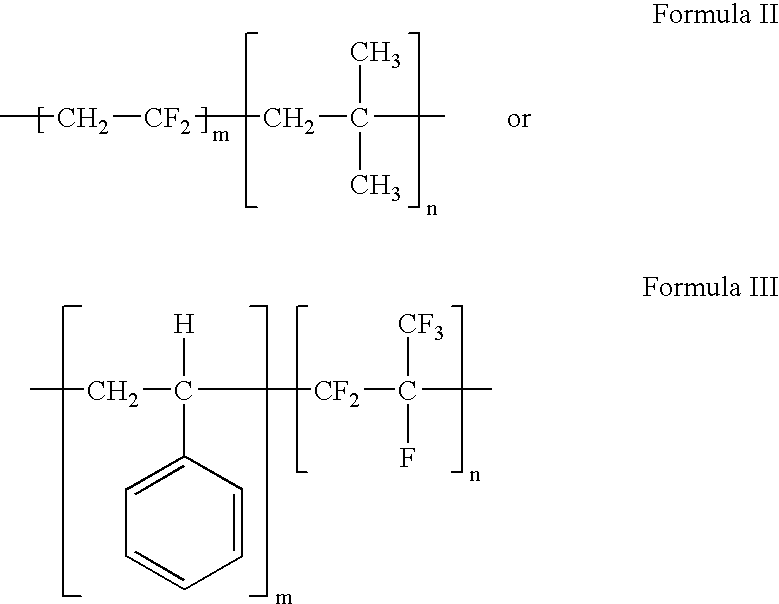
Polymers of fluorinated monomers and hydrophilic monomers
ActiveUS20060047095A1Improve propertiesProvide flexibilityFibre treatmentSurgeryDiseasePolymer science
A polymer of fluorinated monomers and hydrophilic monomers is provided. It is also provided a polymer blend that contains a polymer of fluorinated monomers and another biocompatible polymer. The polymer of fluorinated monomers or polymer blend described herein and optionally a bioactive agent can form a coating on an implantable device such as a drug-delivery stent. The implantable device can be used for treating or preventing a disorder such as atherosclerosis, thrombosis, restenosis, hemorrhage, vascular dissection or perforation, vascular aneurysm, vulnerable plaque, chronic total occlusion, patent foramen ovale, claudication, anastomotic proliferation for vein and artificial grafts, bile duct obstruction, ureter obstruction, tumor obstruction, or combinations thereof.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
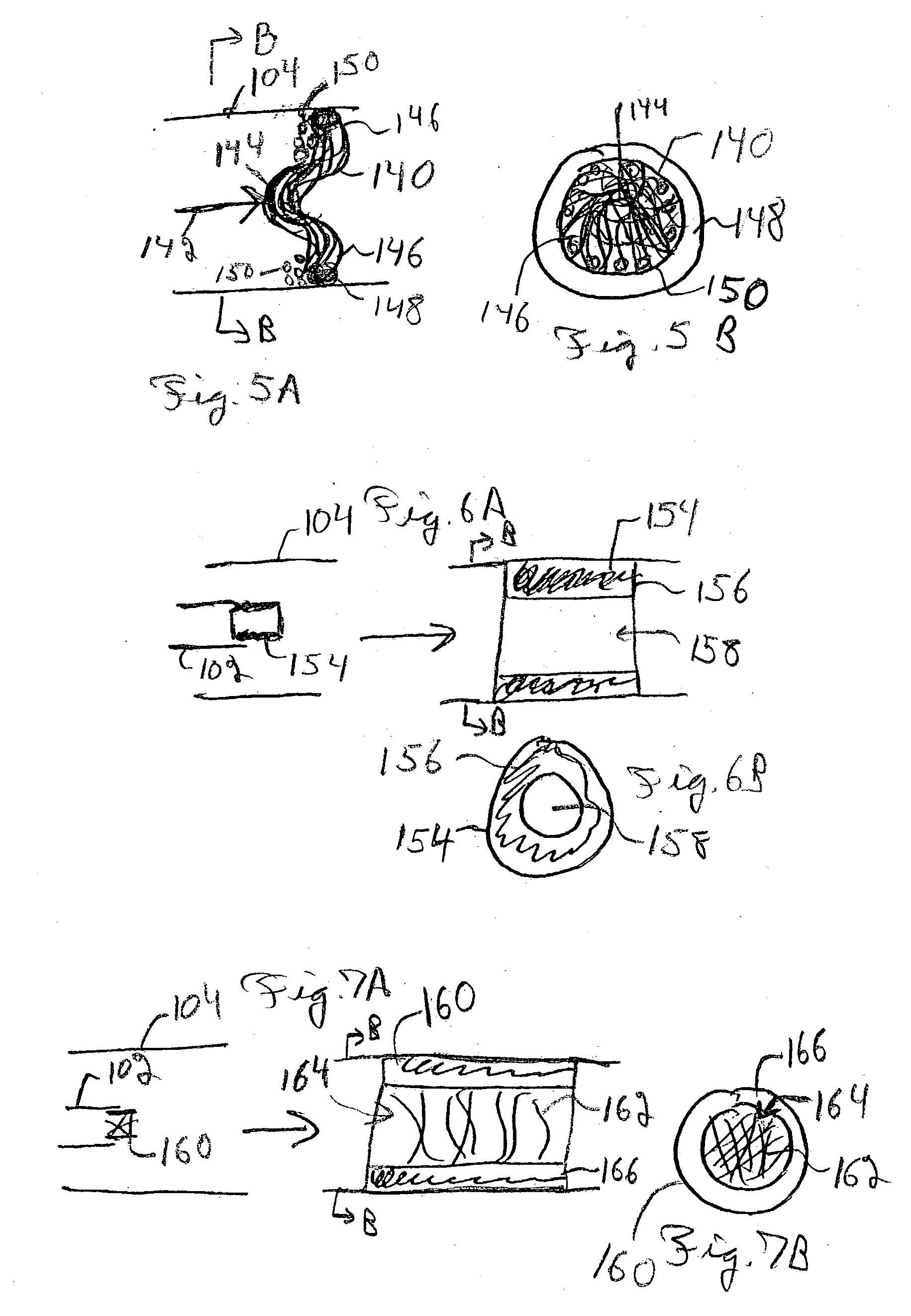
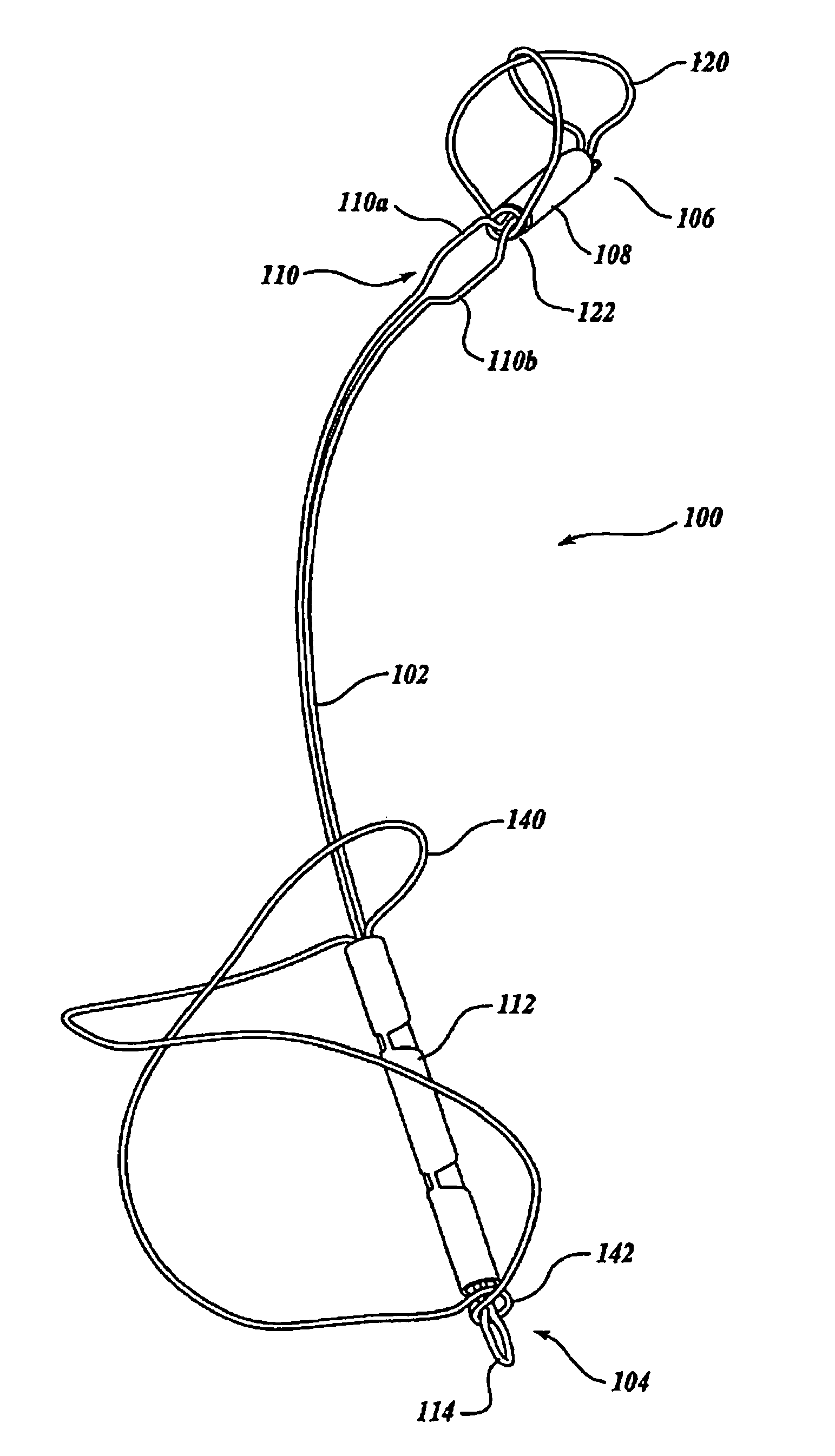
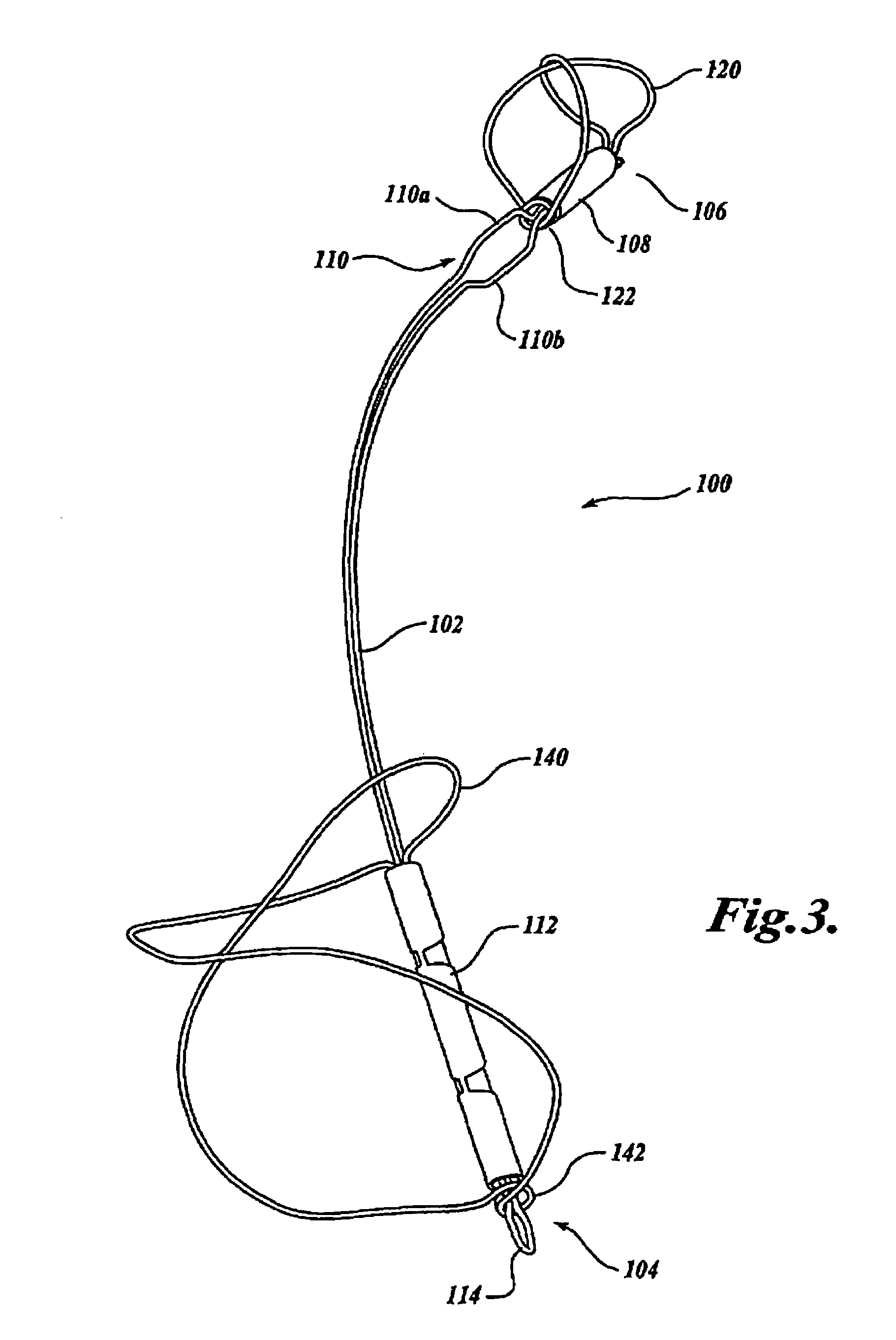
Biodegradable polymer coils for intraluminal implants
An endovascular cellular manipulation and inflammatory response are elicited from implantation in a vascular compartment or any intraluminal location of a separable coil comprised at least in part of at least one biocompatible and absorbable polymer or protein and growth factors. Typically a catheter associated with the separable coil is used to dispose the coil into a selected body lumen. The biocompatible and absorbable polymer or protein is thrombogenic. The coil further is comprised at least in part of a growth factor or more particularly a vascular endothelial growth factor, a basic fibroblast growth factor or other growth factors. The biocompatible and absorbable polymer is in the illustrated embodiment at least one polymer selected from the group consisting of polyglycolic acid, poly~glycolic acid poly-L-lactic acid copolymers, polycaprolactive, polyhydroxybutyrate / hydroxyvalerate copolymers, poly-L-lactide. Polydioxanone, polycarbonates, and polyanhydrides. The biocompatible and absorbable protein is at least one protein selected from the group consisting of collagen, fibrinogen, fibronectin, vitronectin, laminin, and gelatin. In one embodiment the coil is composed of the biocompatible and absorbable polymer or protein with a radio-opaque material is disposed thereon. Alternatively, the coil is composed of a radio-opaque material, and the biocompatible and absorbable polymer or protein is disposed thereon. This apparatus may be positioned within intracranial aneurysms or any aneurysm in the body as well as within other body cavities.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods and devices for the non-thermal, electrically-induced closure of blood vessels
ActiveUS8105324B2Less discomfortSelectively induce hemostasis within blood vesselsElectrotherapySurgical instruments for heatingElectricityArteriolar Vasoconstriction
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Device and method for modifying the shape of a body organ
An intravascular support device includes a support or reshaper wire, a proximal anchor and a distal anchor. The support wire engages a vessel wall to change the shape of tissue adjacent the vessel in which the intravascular support is placed. The anchors and support wire are designed such that the vessel in which the support is placed remains open and can be accessed by other devices if necessary. The device provides a minimal metal surface area to blood flowing within the vessel to limit the creation of thrombosis. The anchors can be locked in place to secure the support within the vessel.
Owner:CARDIAC DIMENSIONS
Device and method for modifying the shape of a body organ
InactiveUS20060142854A1Low metal coverage areaReduce chanceHeart valvesBlood vesselsBody organsBlood flow
An intravascular support device includes a support or reshaper wire, a proximal anchor and a distal anchor. The support wire engages a vessel wall to change the shape of tissue adjacent the vessel in which the intravascular support is placed. The anchors and support wire are designed such that the vessel in which the support is placed remains open and can be accessed by other devices if necessary. The device provides a minimal metal surface area to blood flowing within the vessel to limit the creation of thrombosis. The anchors can be locked in place to secure the support within the vessel.
Owner:CARDIAC DIMENSIONS
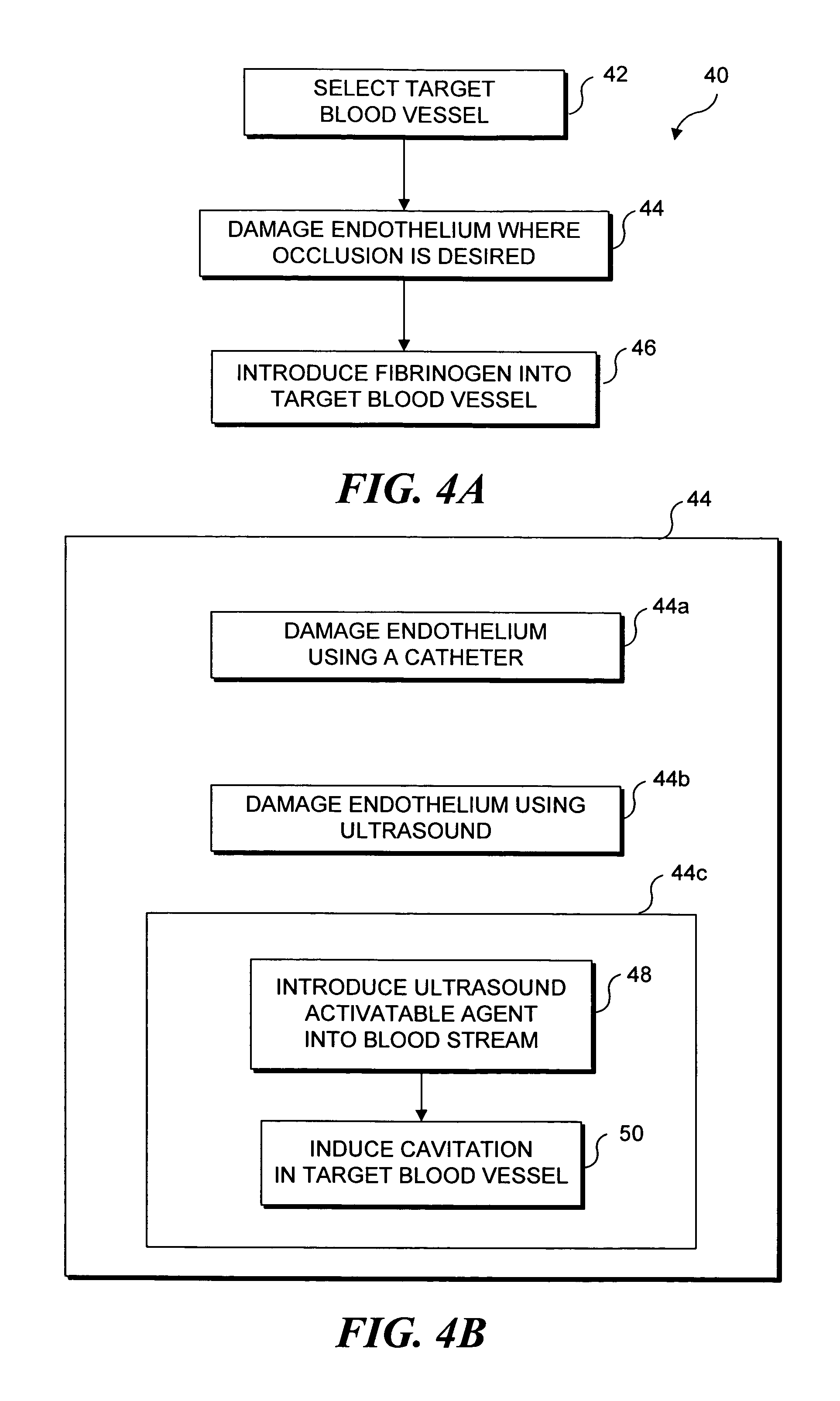
Ultrasound target vessel occlusion using microbubbles
InactiveUS7591996B2Eliminate heat damageFew techniqueUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyCavitationThrombus
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Device and method for modifying the shape of a body organ
InactiveUS20050272969A1Low metal coverage areaReduce chanceHeart valvesBlood vesselsBody organsBlood flow
An intravascular support device includes a support or reshaper wire, a proximal anchor and a distal anchor. The support wire engages a vessel wall to change the shape of tissue adjacent the vessel in which the intravascular support is placed. The anchors and support wire are designed such that the vessel in which the support is placed remains open and can be accessed by other devices if necessary. The device provides a minimal metal surface area to blood flowing within the vessel to limit the creation of thrombosis. The anchors can be locked in place to secure the support within the vessel.
Owner:CARDIAC DIMENSIONS
Method and apparatus for stenting comprising enhanced embolic protection coupled with improved protections against restenosis and thrombus formation
Apparatus and methods for stenting are provided comprising a stent attached to a porous biocompatible material that is permeable to endothelial cell ingrowth, but impermeable to release of emboli of predetermined size. Preferred stent designs are provided, as well as preferred manufacturing techniques. Apparatus and methods are also provided for use at a vessel branching. Moreover, embodiments of the present invention may comprise a coating configured for localized delivery of therapeutic agents. Embodiments of the present invention are expected to provide enhanced embolic protection, improved force distribution, and improved recrossability, while reducing a risk of restenosis and thrombus formation.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB VASCULAR ENTERPRISE
Methods and devices for plasmon enhanced medical and cosmetic procedures
InactiveUS20050203495A1Enhanced and very confined body surgeryBetter-controlled surgery and treatment conditionsCosmetic preparationsHair removalHair removalMedical treatment
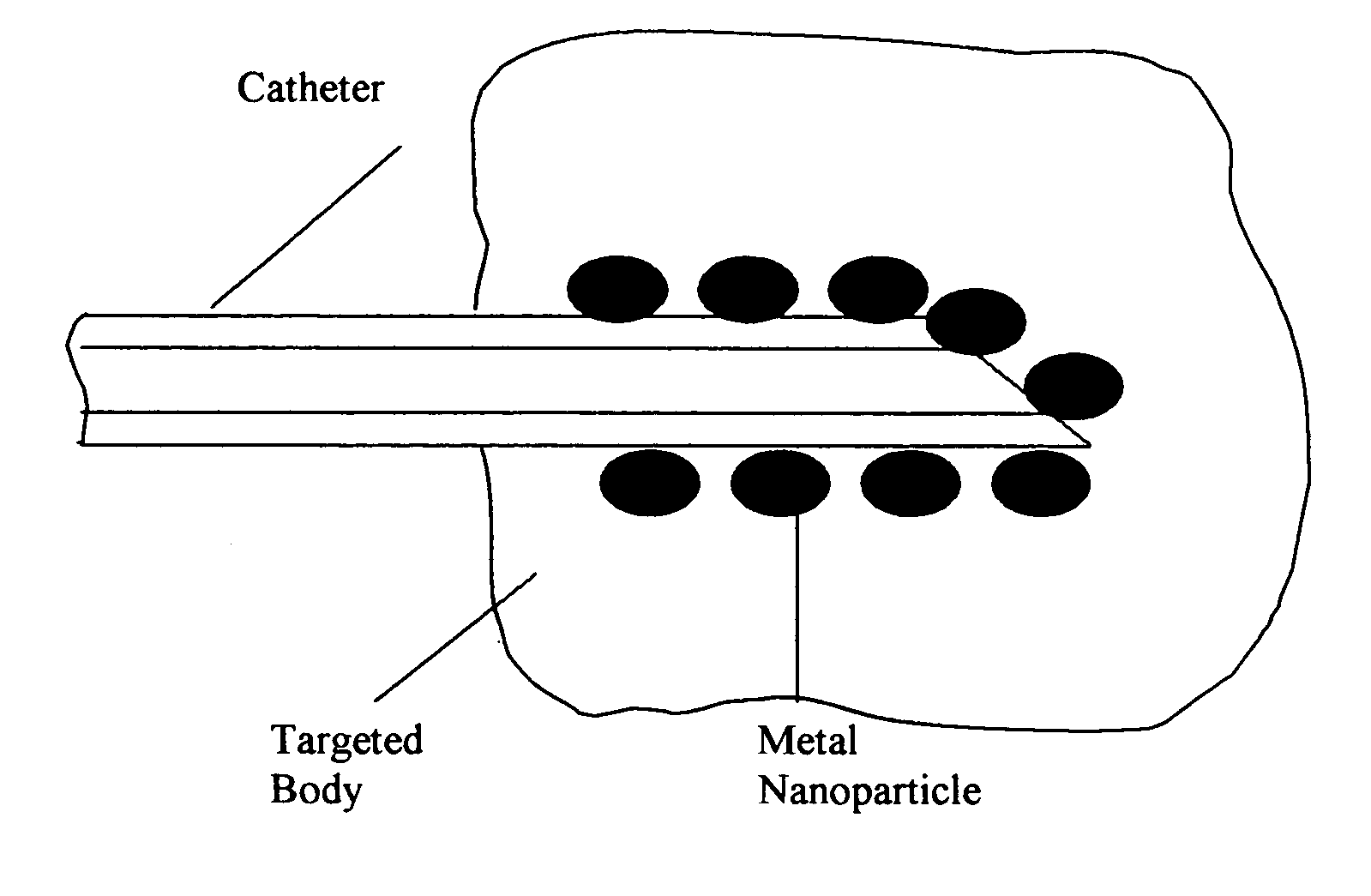
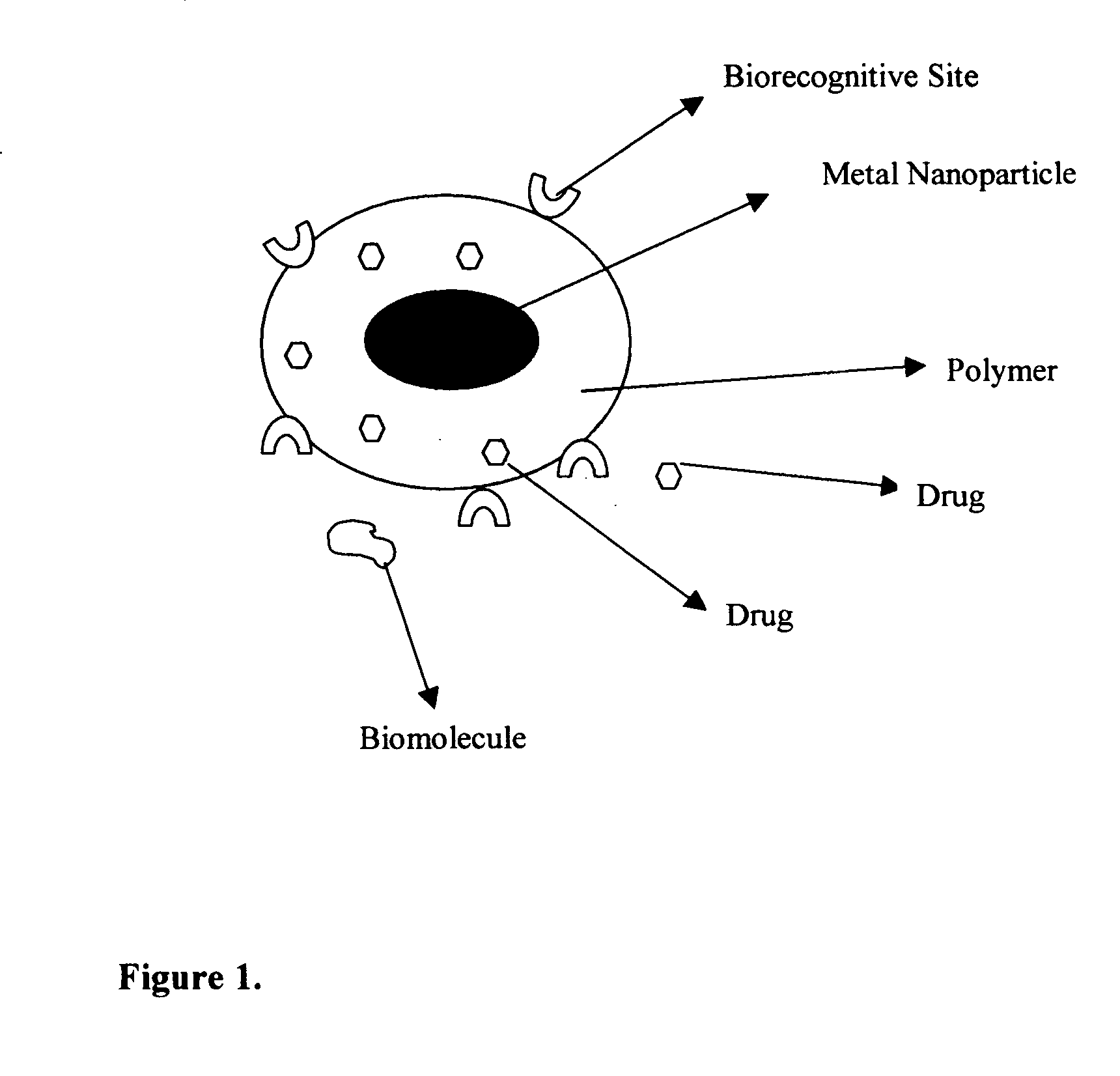
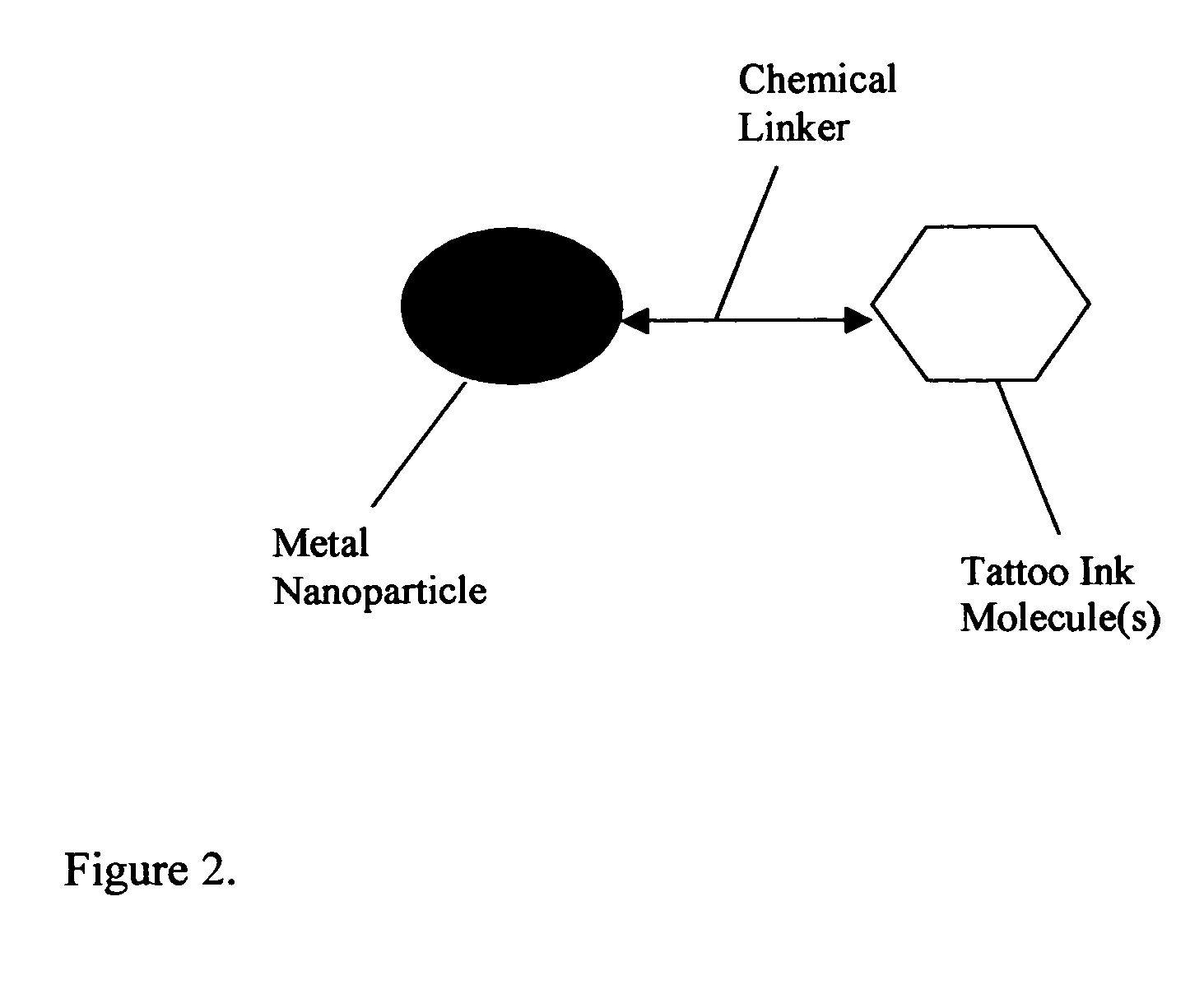
Composition of methods and devices for surface plasmon resonance-enhanced medical and cosmetic procedures are disclosed. The invention relates to the use of a nonlinear surface plasmon resonance generation source and metal nanoparticles embedded to a body to enhance medical and cosmetic procedures in the body. The methods and devices in this invention can be applied for very effective three-dimensionally localized body surgery, tattoo removal, skin pigmentation removal, hair removal, drug delivery, photodynamic therapy, thrombosis, lithotripsy and cosmetic body treatment. The present invention relates also to a method of making temporary, semi-permanent and permanent tattoos with surface plasmon resonance technique.
Owner:US PATENT & TRADEMARK OFFICE
Benzimidazole derivatives and their use as KDR kinase protein inhibitors
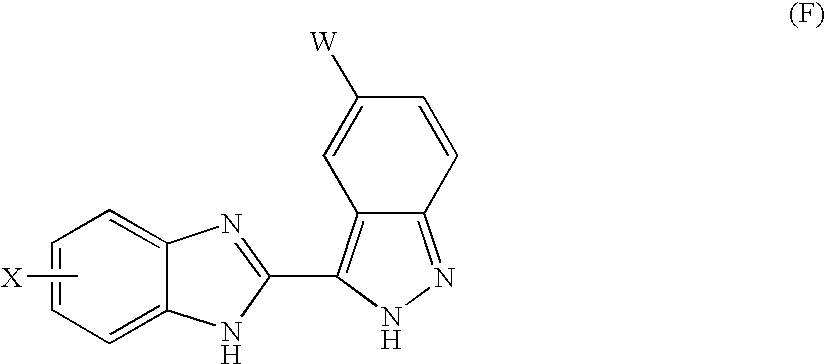
The invention discloses and claims benzimidazole compounds of formula (I): wherein X is C—R2; Y is C—R2 or C—R3; W and Z are each C—R3; R1 is an optionally substituted aryl, heteroaryl or a saturated 5- or 6-membered monocyclic heterocyclic radical or a bicyclic heterocyclic radical; and A5 is H or alkyl; or a stereoisomer, a racemate, an enantiomer or a diastereoisomer of said compound of formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof; the use of compounds of formula (I) for the treatment of a disorder of proliferation of blood vessels, uncontrolled angiogenesis, a fibrotic disorder, a disorder of proliferation of mesangial cells, a metabolic disorder, allergy, asthma, thrombosis, a disease of the nervous system, retinopathy, psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes, muscle degeneration, solid tumors and cancers, pharmaceutical compositions comprising a compound of formula (I) and one or more pharmaceutically acceptable adjuvants or diluents and pharmaceutical compositions comprising a compound of formula (I) and one or more. antimitiotic agents.
Owner:AVENTIS PHARMA SA (US)
Polymers of fluorinated monomers and hydrocarbon monomers
InactiveUS20060134165A1Provide mechanical strengthGive flexibilityStentsSurgeryAbnormal tissue growthPolymer science
A polymer of fluorinated monomers and hydrocarbon monomers is provided. It is also provided a polymer blend that contains a polymer formed of fluorinated monomers and hydrocarbon monomers and another biocompatible polymer. The polymer or polymer blend described herein and optionally a bioactive agent can form an implantable device such as a stent or a coating on an implantable device such as a drug-delivery stent, which can be used for treating or preventing a disorder such as atherosclerosis, thrombosis, restenosis, hemorrhage, vascular dissection or perforation, vascular aneurysm, vulnerable plaque, chronic total occlusion, claudication, anastomotic proliferation for vein and artificial grafts, bile duct obstruction, ureter obstruction, tumor obstruction, or combinations thereof.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
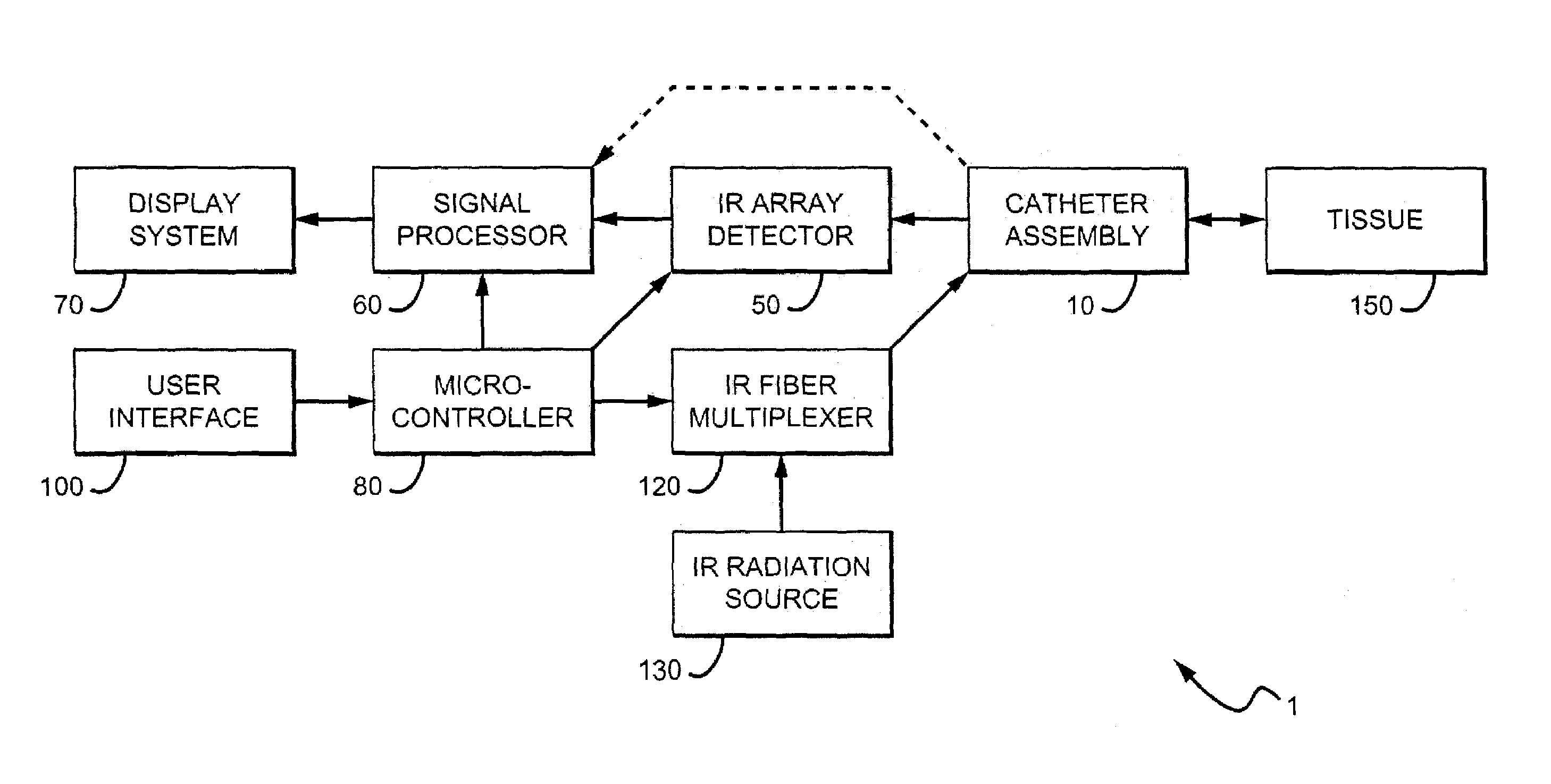
Method and apparatus for detecting vulnerable atherosclerotic plaque
Methods and devices are disclosed for detecting vulnerable atherosclerotic plaque, or plaque at risk of reducing blood flow in a vessel, by identifying a region of elevated temperature along a living vessel wall. The disclosure that human atherosclerotic plaque with measurable temperature heterogeneity has the morphological characteristics of plaque that is likely to ulcerate provides a new and sensitive technique for detecting and treating these dangerous plaques before myocardial infarction and its consequences occur. The disclosed methods are advantageous over conventional plaque detection techniques because they are capable of differentiating between those plaques that are at great risk of rupture, fissure, or ulceration, and consequent thrombosis and occlusion of the artery, and those that are not presently at risk. Infrared heat-sensing catheters useful for identifying potentially fatal arterial plaques in patients with disease of the coronary or other arteries are also described. In some embodiments a coherent infrared fiber optic bundle is employed to radially and longitudinally explore a luminal wall to identify inflamed, heat-producing, atherosclerotic plaque. Certain other methods and devices are disclosed which are particularly suited for non-invasively identifying and then monitoring the progression or amelioration of an inflamed plaque in a patient, and for monitoring for onset of inflammation in an implanted arteriovenous graft. Also disclosed are thermocouple basket catheters and thermistor basket catheters which are also capable of detecting temperature heterogeneity along a vessel wall.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
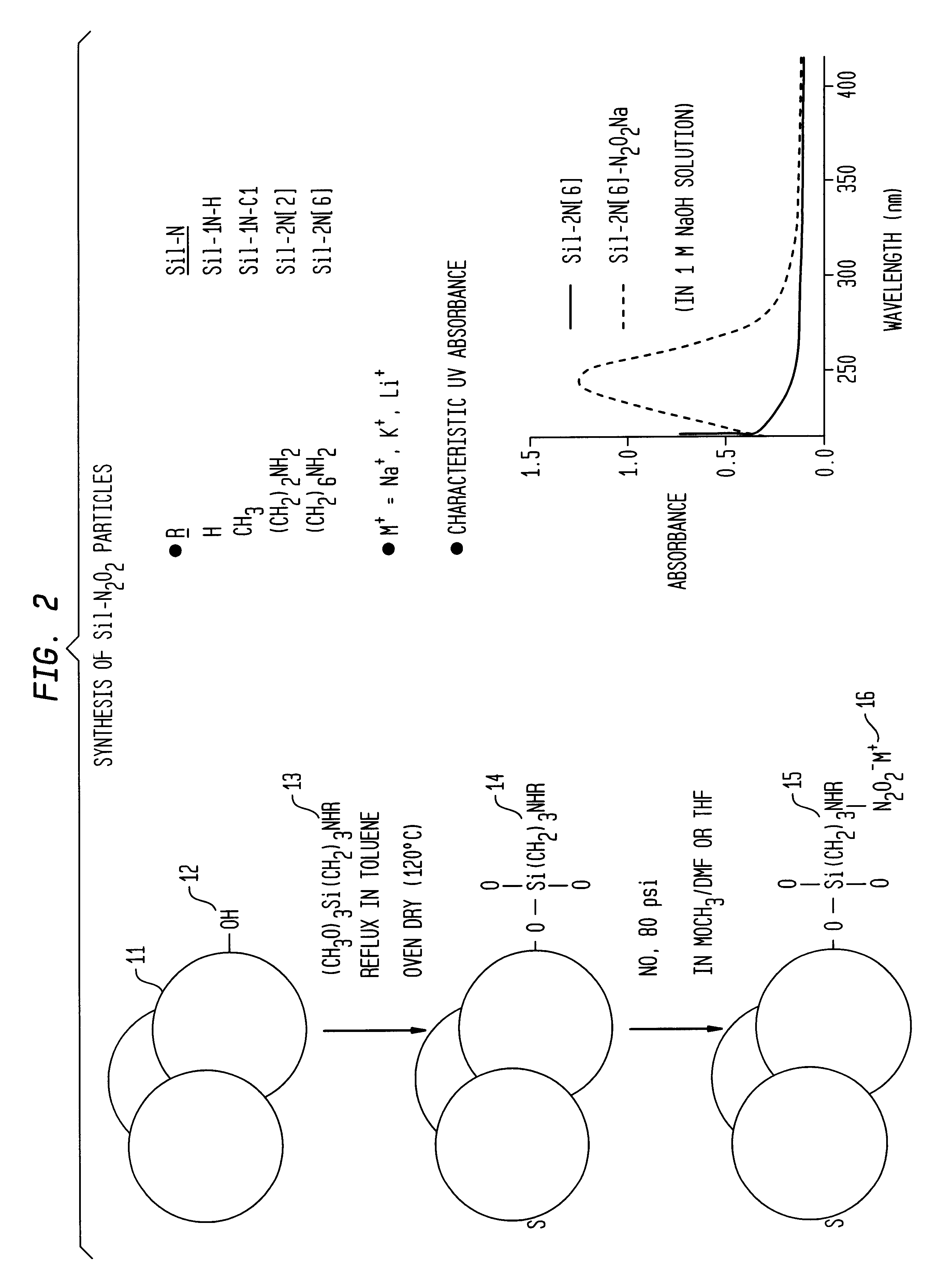
Nitric oxide-releasing polymers incorporating diazeniumdiolated silane derivatives
InactiveUS6841166B1Reduce activationReduce aggregationBiocideInorganic active ingredientsPolymeric surfaceSilanes
Biocompatible polymeric materials capable of providing in situ release of nitric oxide (NO) included diazeniumdiolated fumed silica as a filler in a multilayer polymer structure to release NO upon contact with water (blood). The blood-contacting polymer surface is preferably multi-layered so that the NO-releasing layer, containing the diazeniumdiolated fumed silica, is shielded from blood contact by one or more top (or base) coats. When in contact with blood, the NO released at the surface of the polymer prevents platelet activation and adhesion to the surface, thereby reducing platelet consumption, risk of thrombus formation and other clinical complications associated with interactions between blood and foreign materials.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
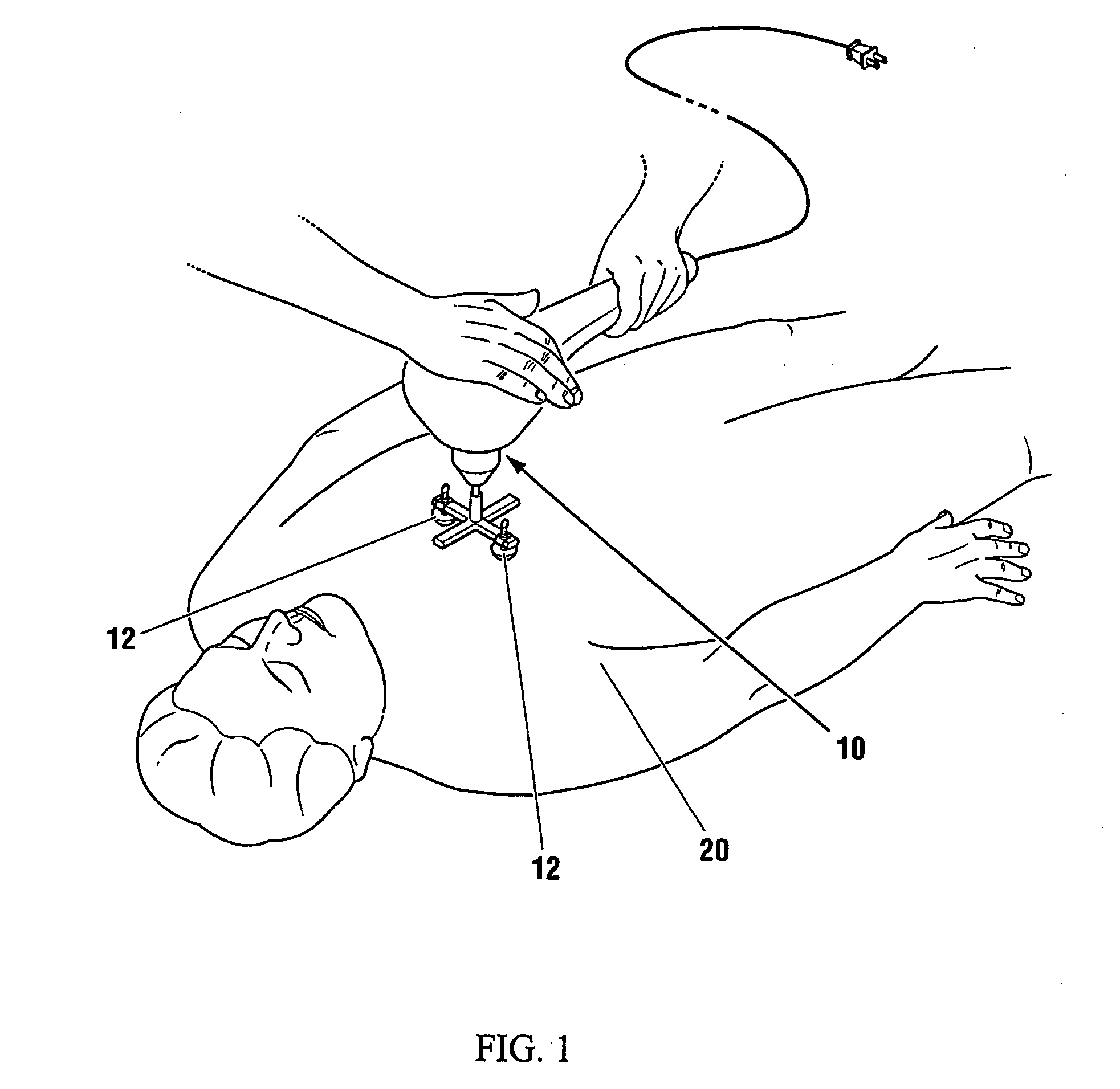
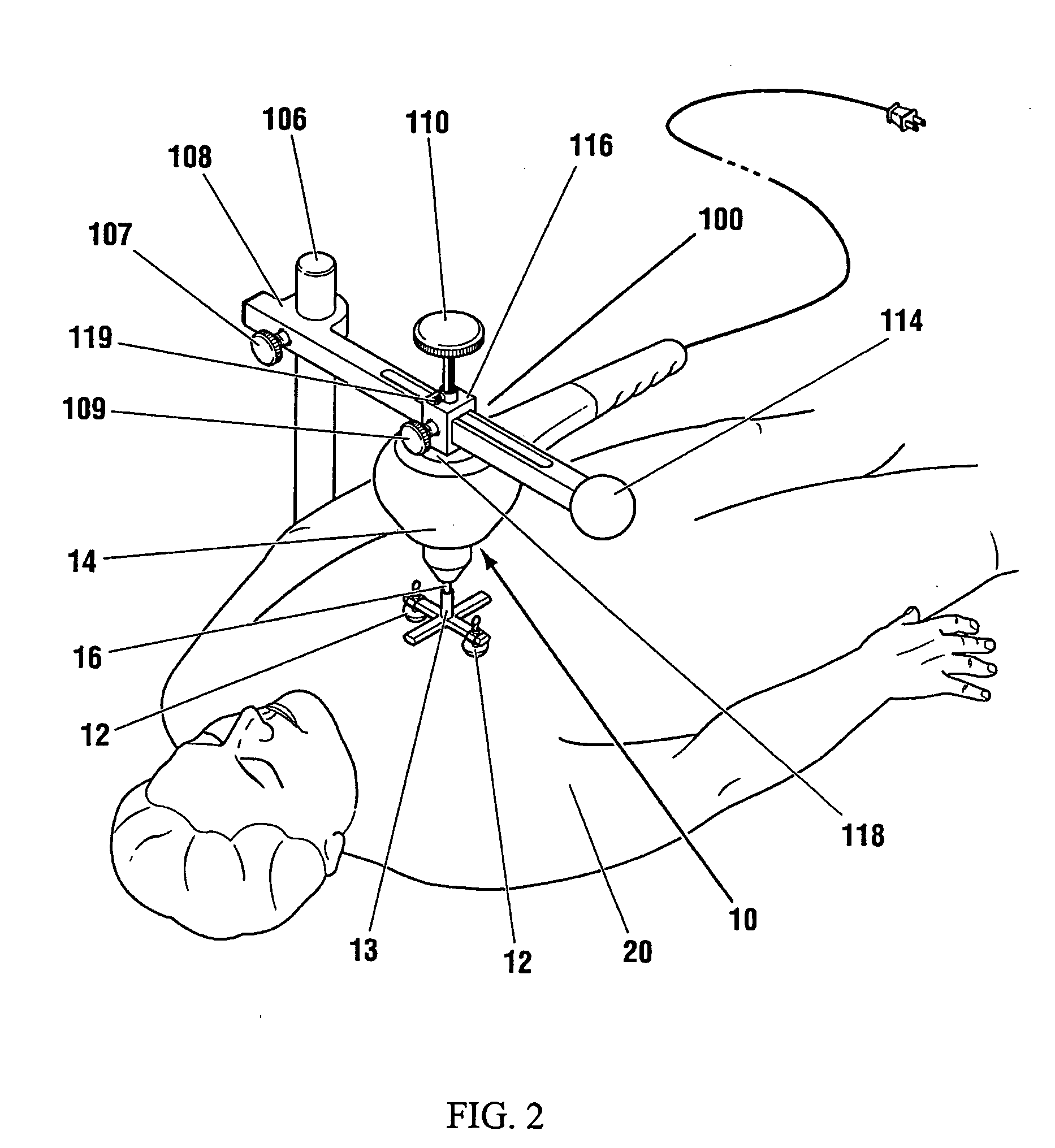
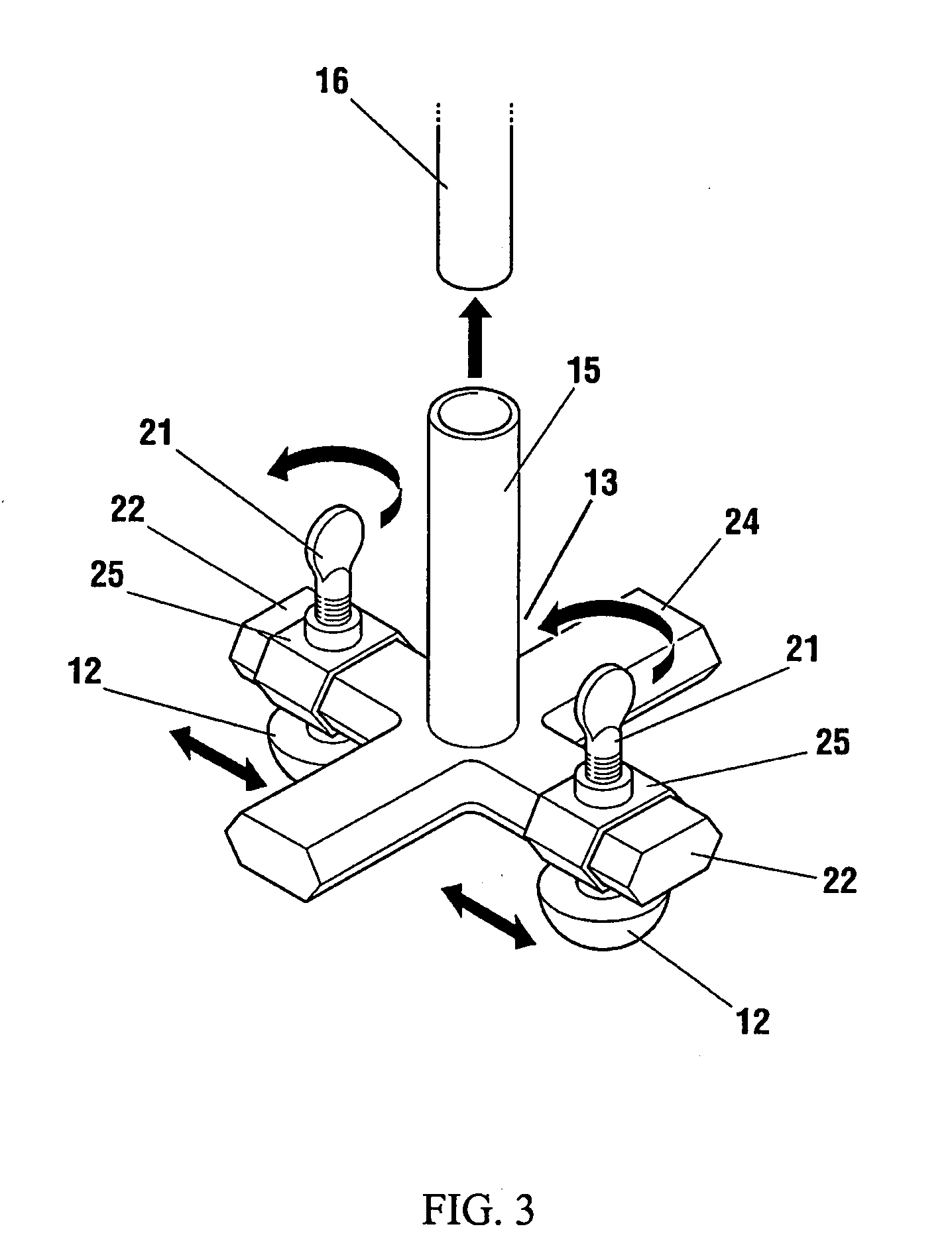
Low frequency vibration assisted blood perfusion emergency system
InactiveUS20050054958A1Improve localized drug effectivenessImprove vibrationElectrotherapySurgeryVascular obstructionFourth intercostal space
An emergency system for treatment of a patient (20) experiencing an acute vascular obstruction, employing a non-invasive vibrator (10), optimally in conjunction with drugs, for disrupting and lysing thromboses, relieving spasm (if associated), and thereby restoring blood perfusion. Vibrator (10) is operable in the sonic to infrasonic range, with a source output of up to 15 mm. For acute myocardial infarction cases, a pair of contacts (12), are advantageously placed to bridge the sternum at the fourth intercostal space. Vibration is initiated at 50 Hz (or any frequency, preferably within the 20-120 Hz range), and is ideally adjusted to a maximal amplitude (or force) deemed tolerable and safe to the patient (20), preferably with the administration of thrombolytic agents or other form of drug therapy. A synergistic effect is achieved between vibration and drugs to facilitate the disruption of thromboses, relieve spasm, and restore blood perfusion. In a variation, ultrasonic imaging may be used to direct vibration therapy.
Owner:PARALLEL BIOTECH LLP +1
Stent covered with heterologous tissue
A covered stent assembly comprising a tubular, expandable stent having a metallic framework covered with a cylinder of biocompatible, non-thrombogenic expandable material, such as heterologous tissue. In a preferred embodiment, the metallic framework is positioned coaxially within a cylinder of bovine pericardial tissue. A catheter may be used to deliver the stent assembly to a desired region in the lumen of a patient. The metallic framework is then expanded to seat the assembly within the lumen.
Owner:AMNIS THERAPEUTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com