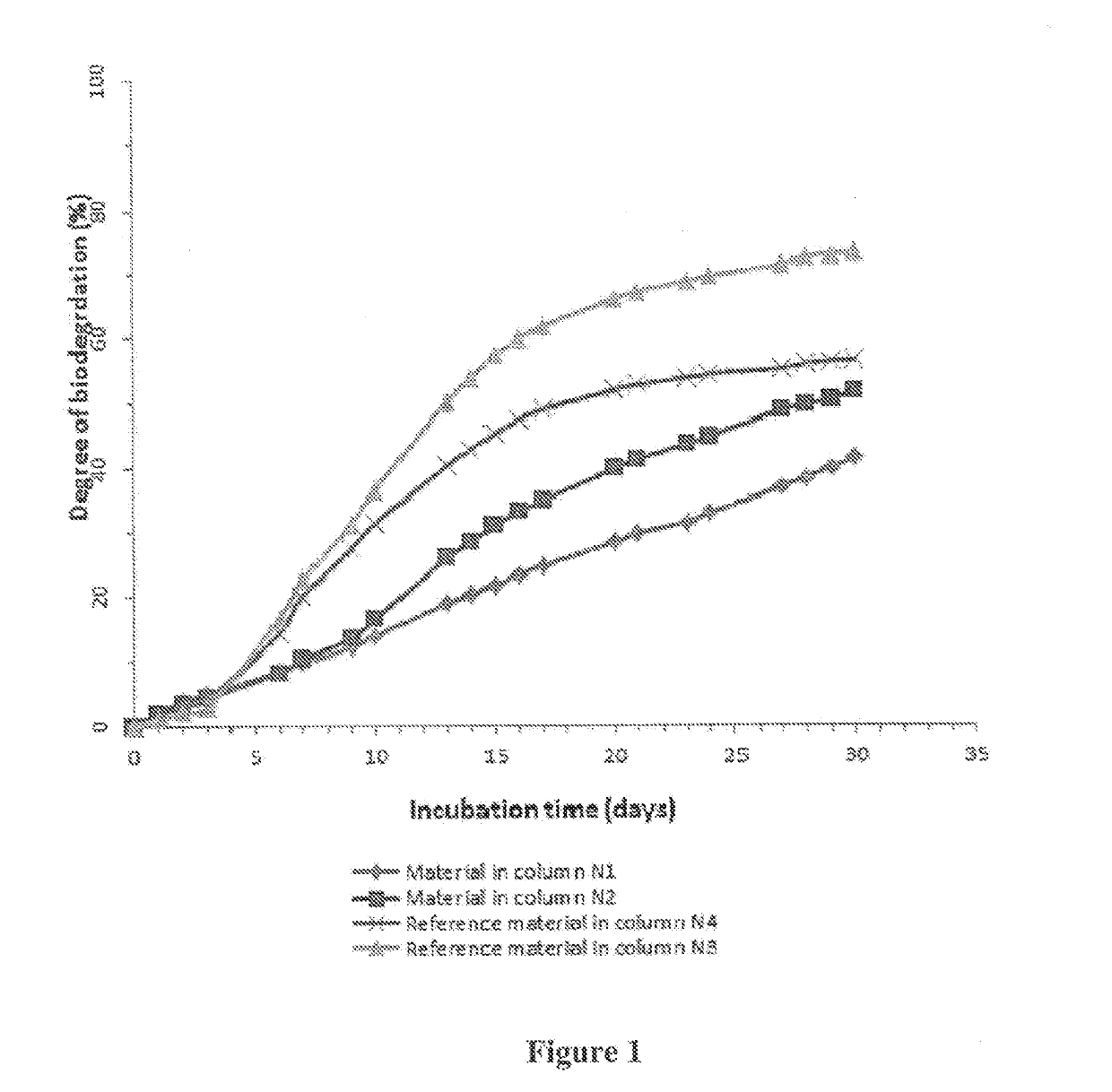
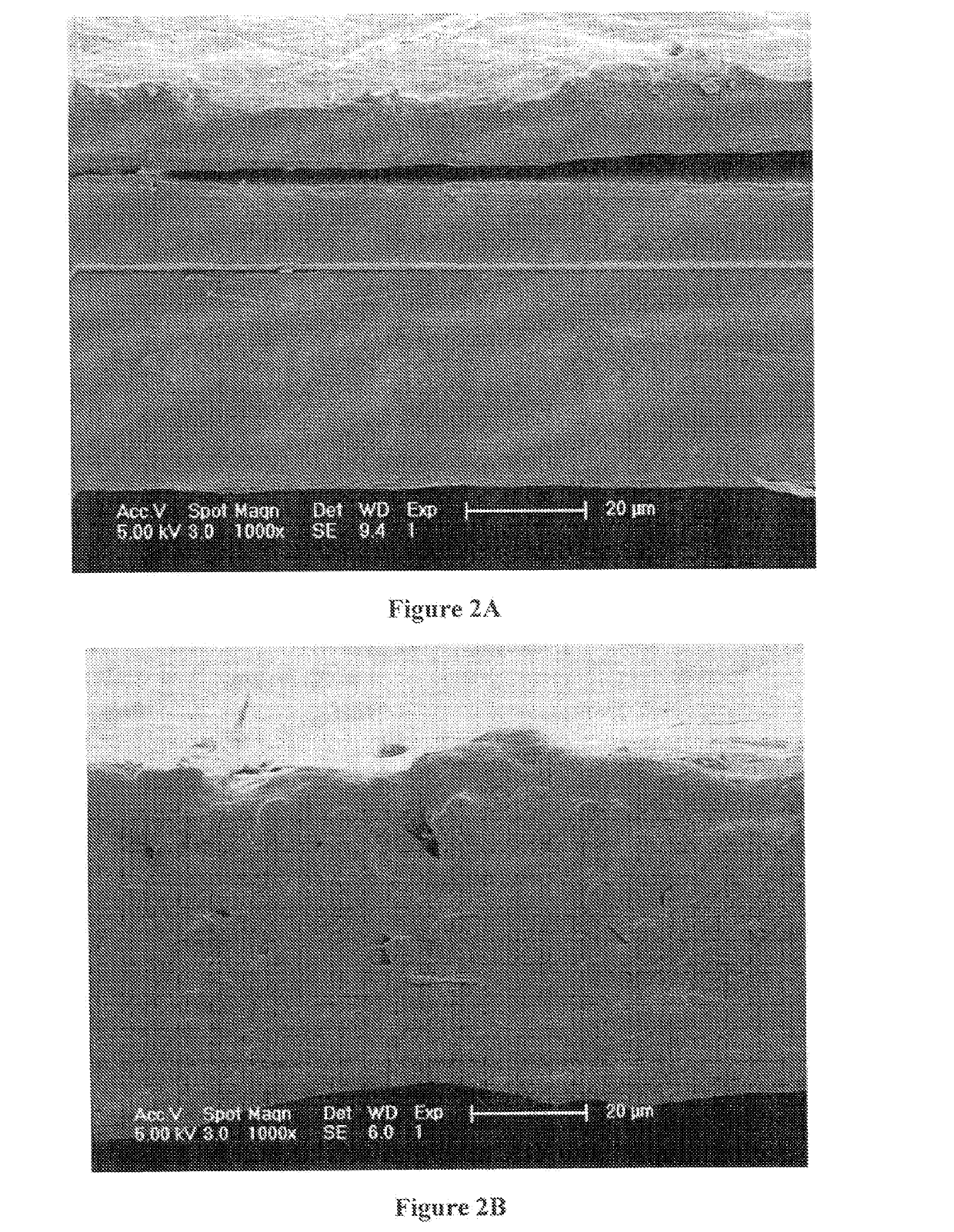
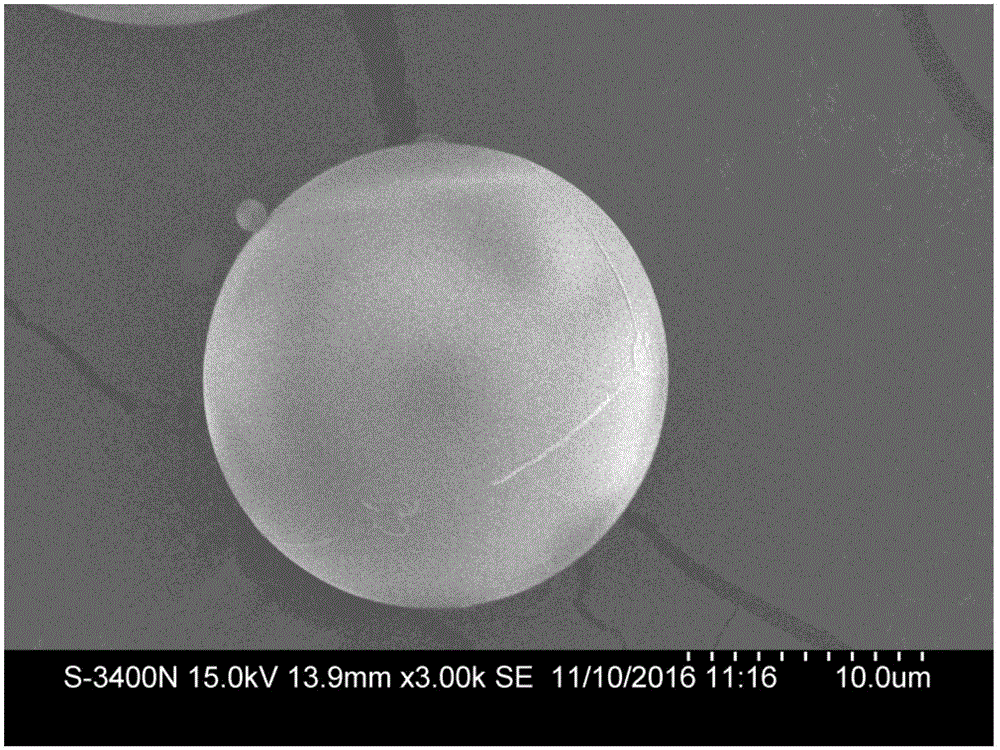
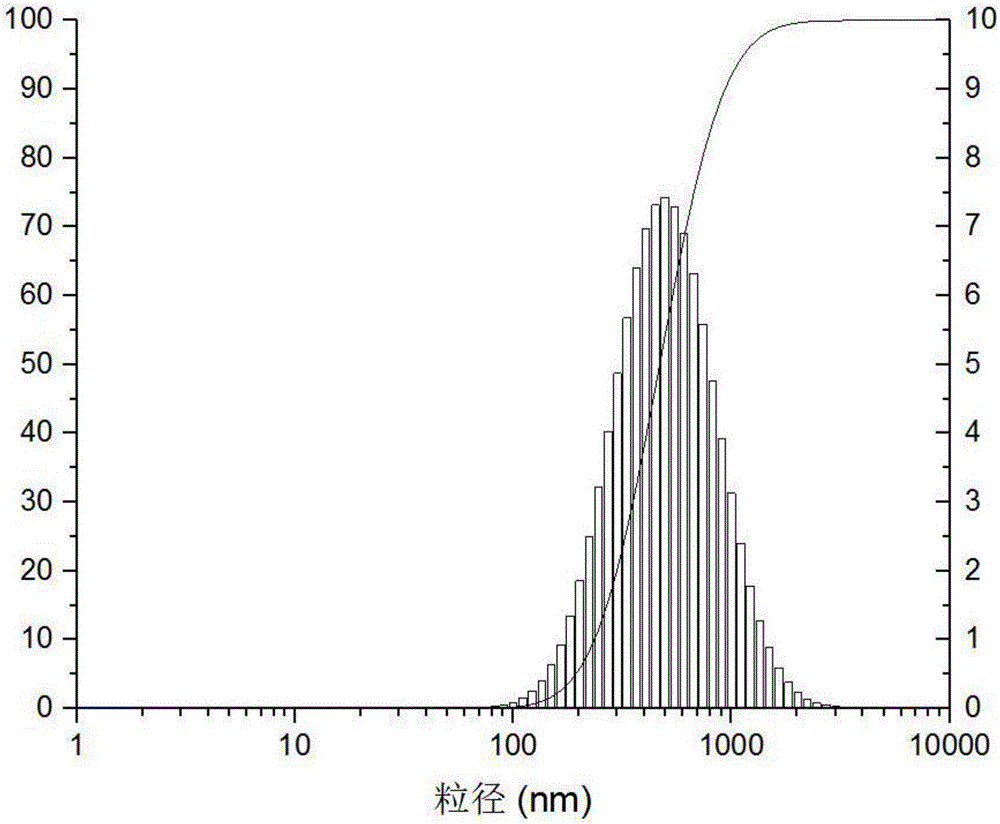
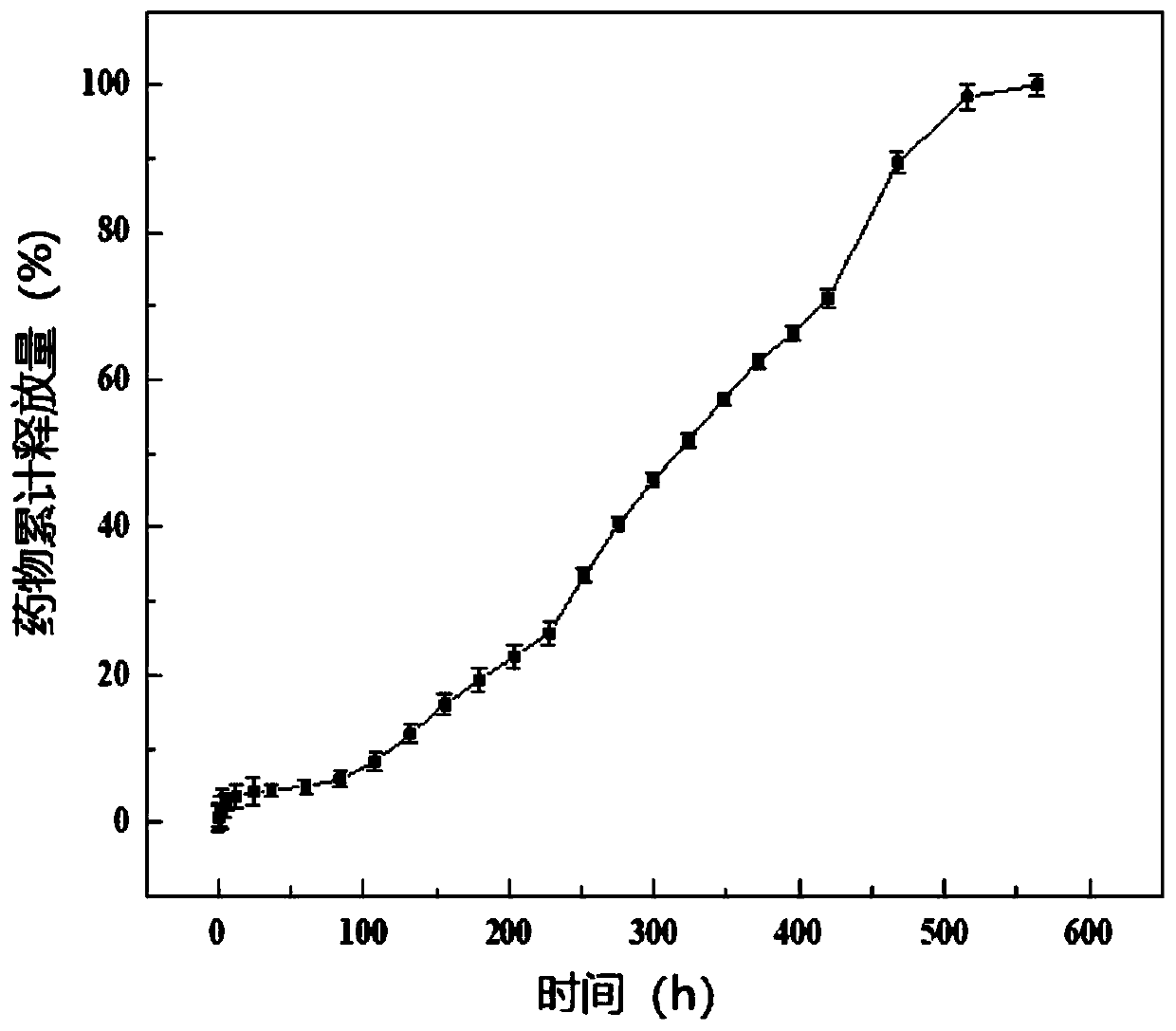
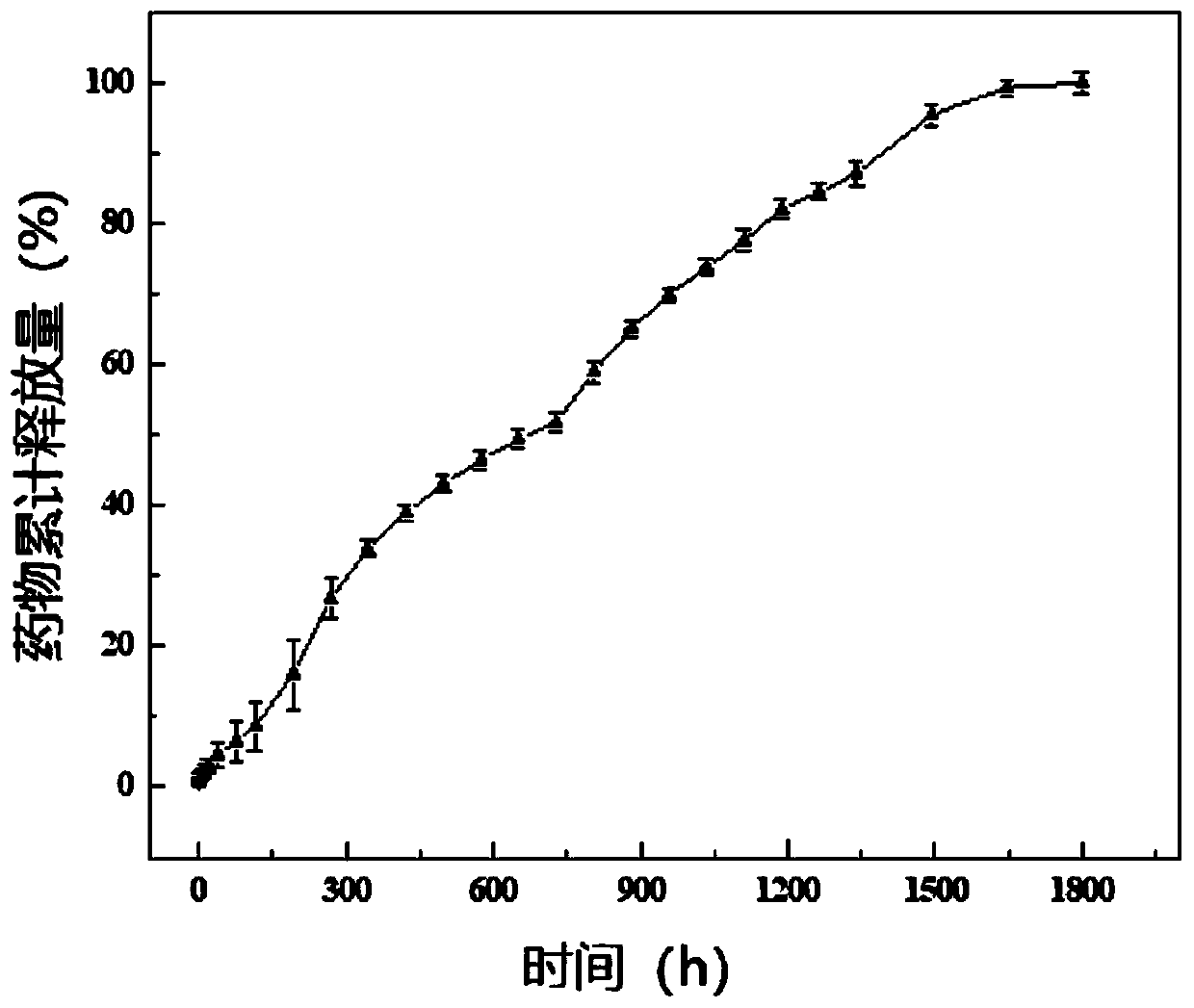
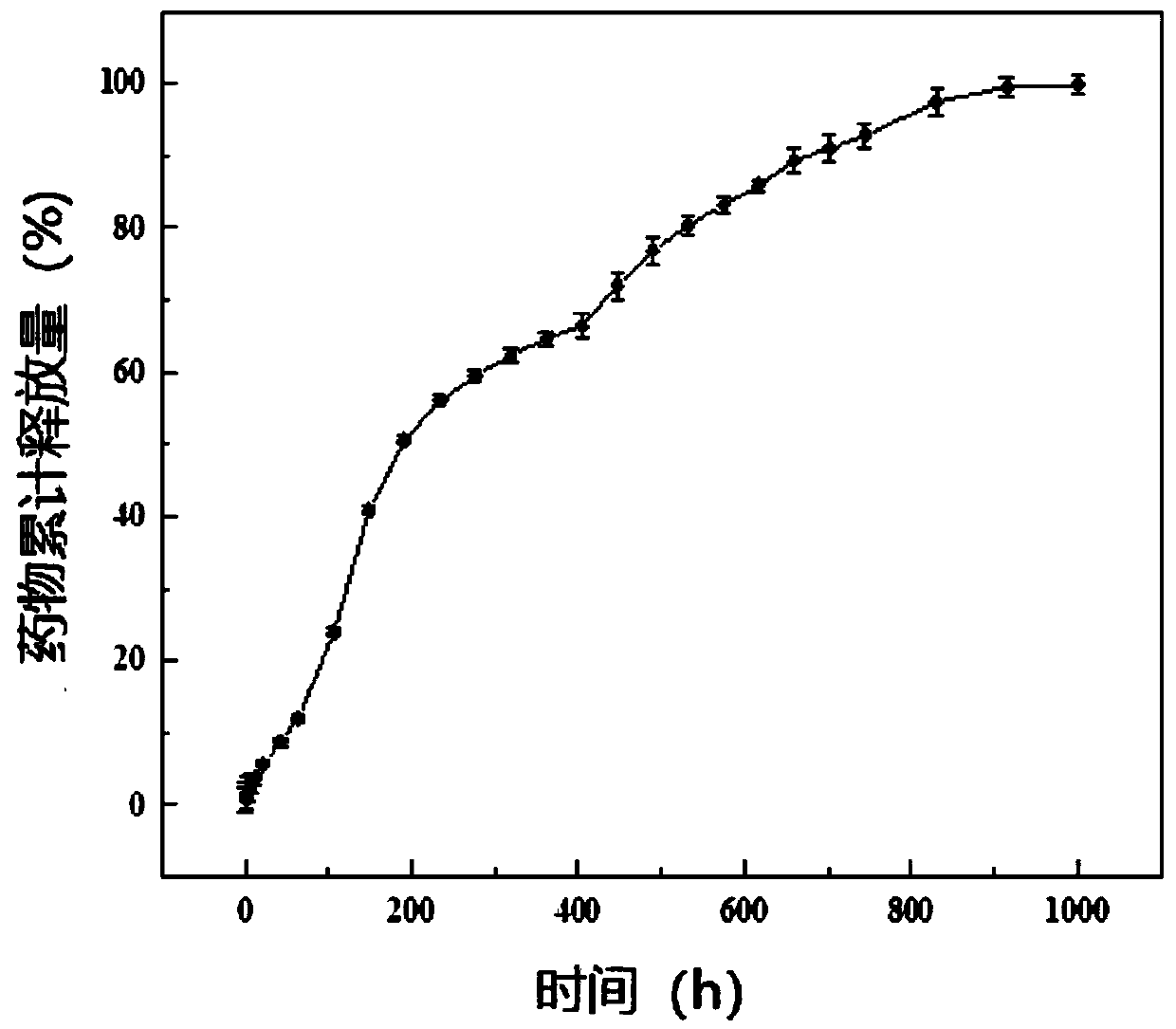
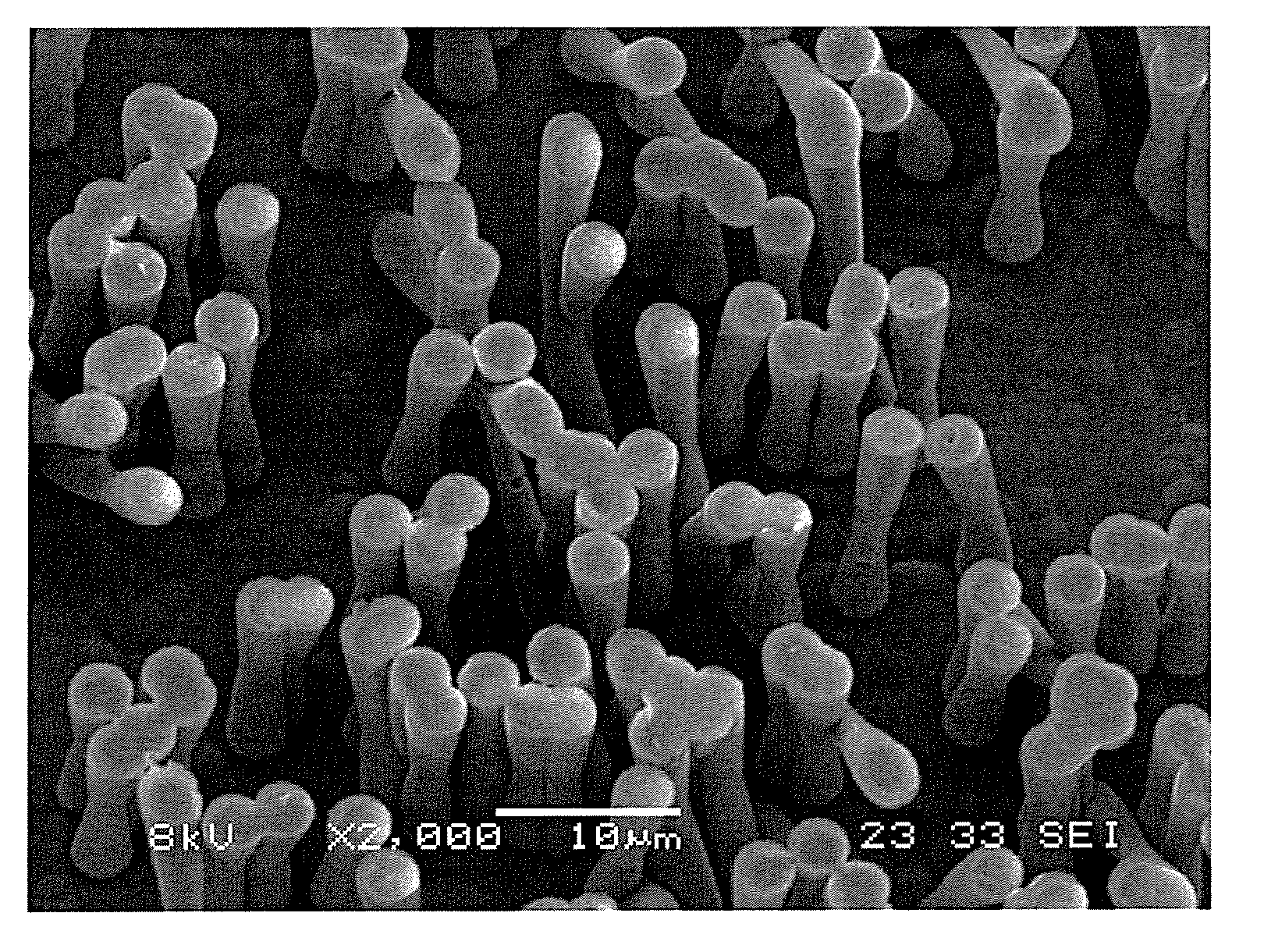Patents
Literature
85 results about "Polydioxanone" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Polydioxanone (PDO, PDS) or poly-p-dioxanone is a colorless, crystalline, biodegradable synthetic polymer.
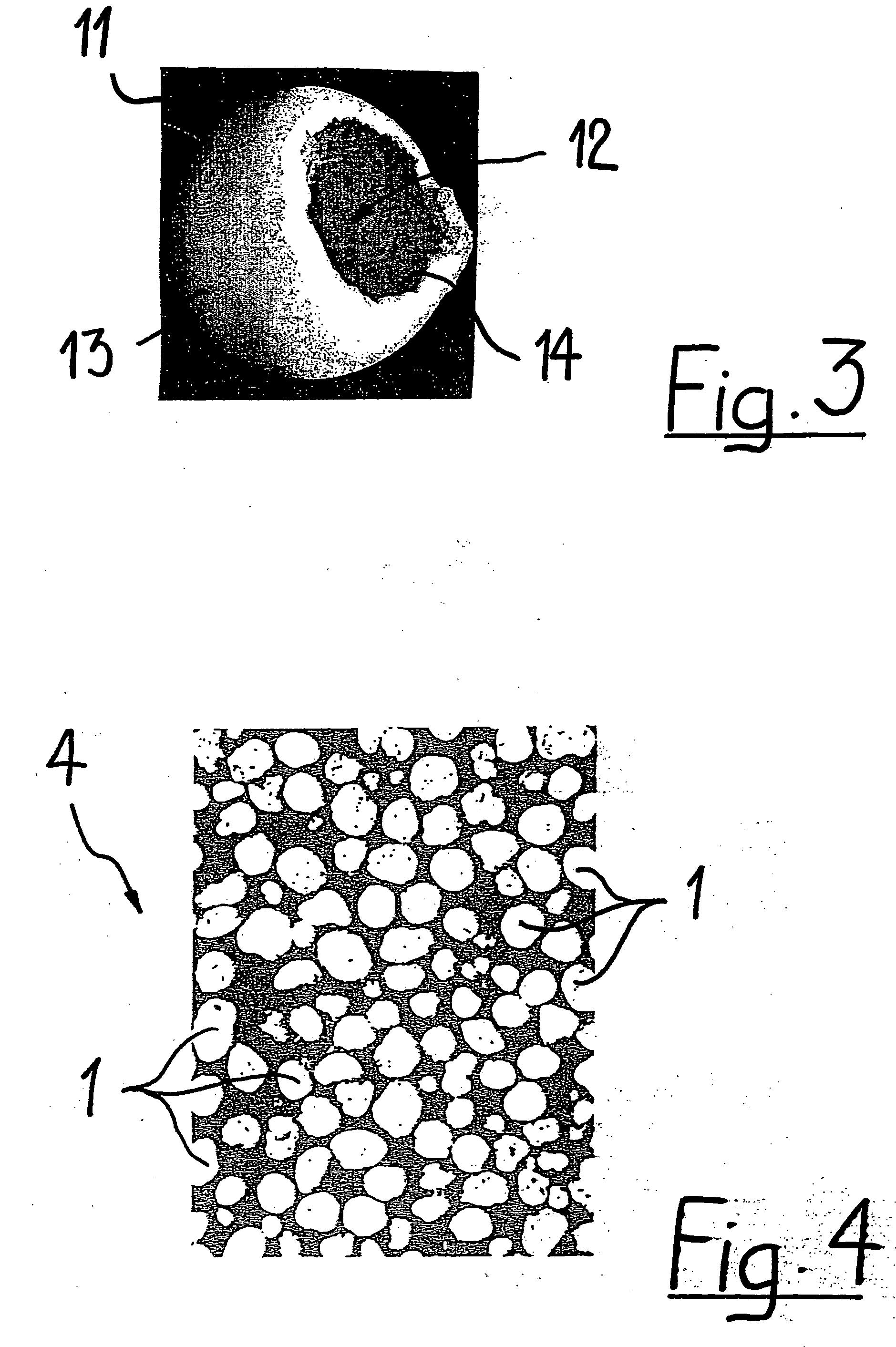
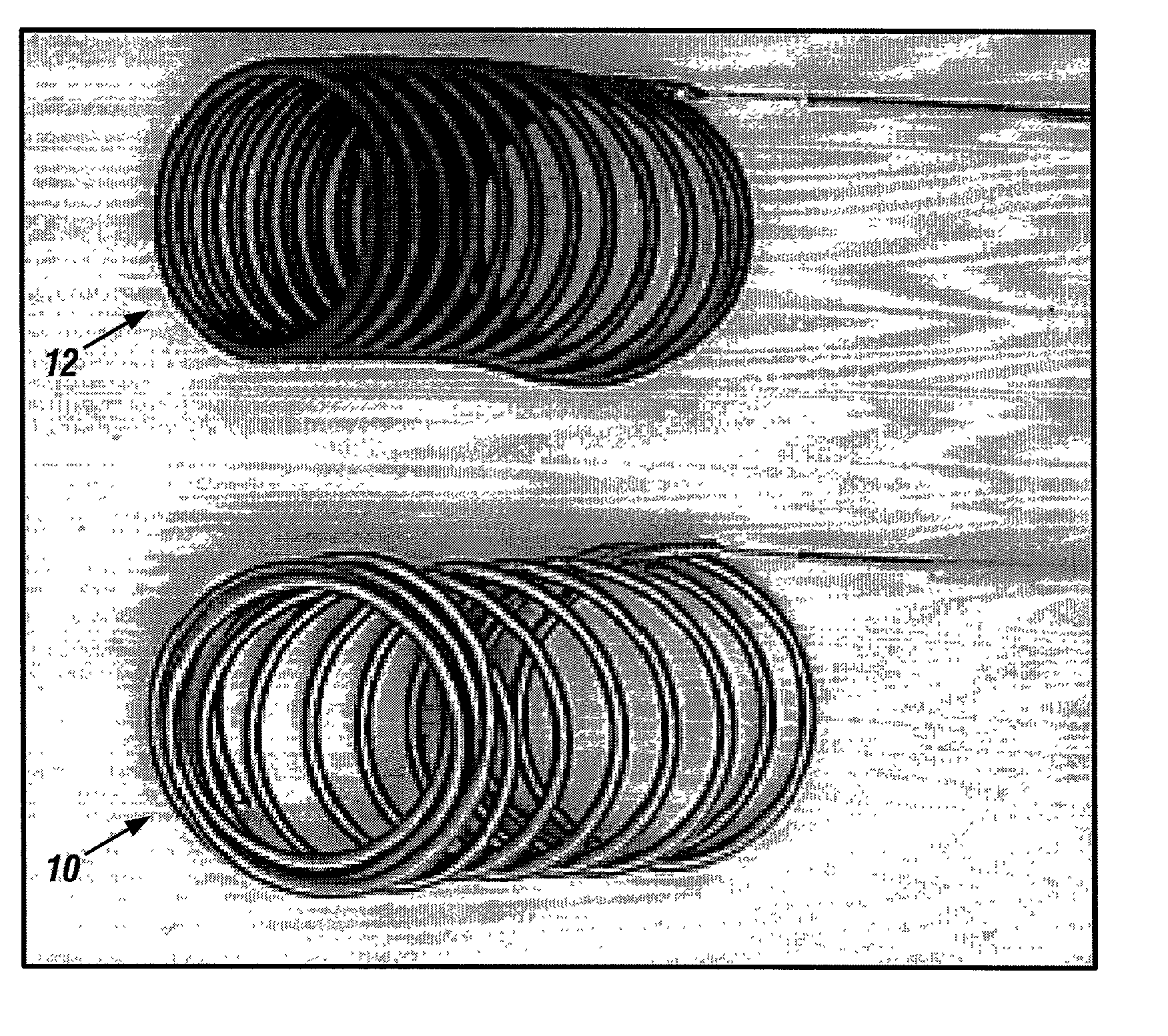
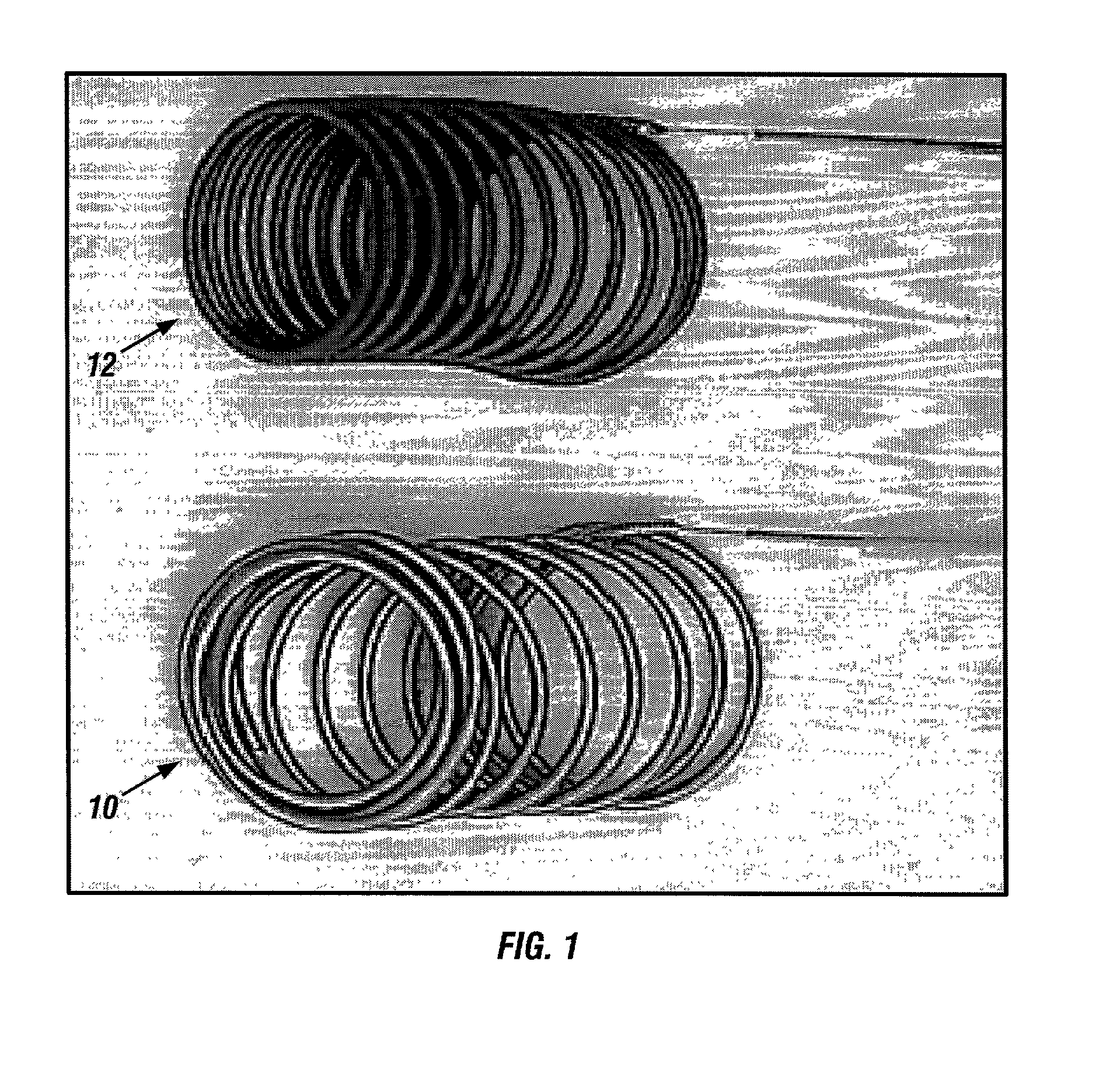
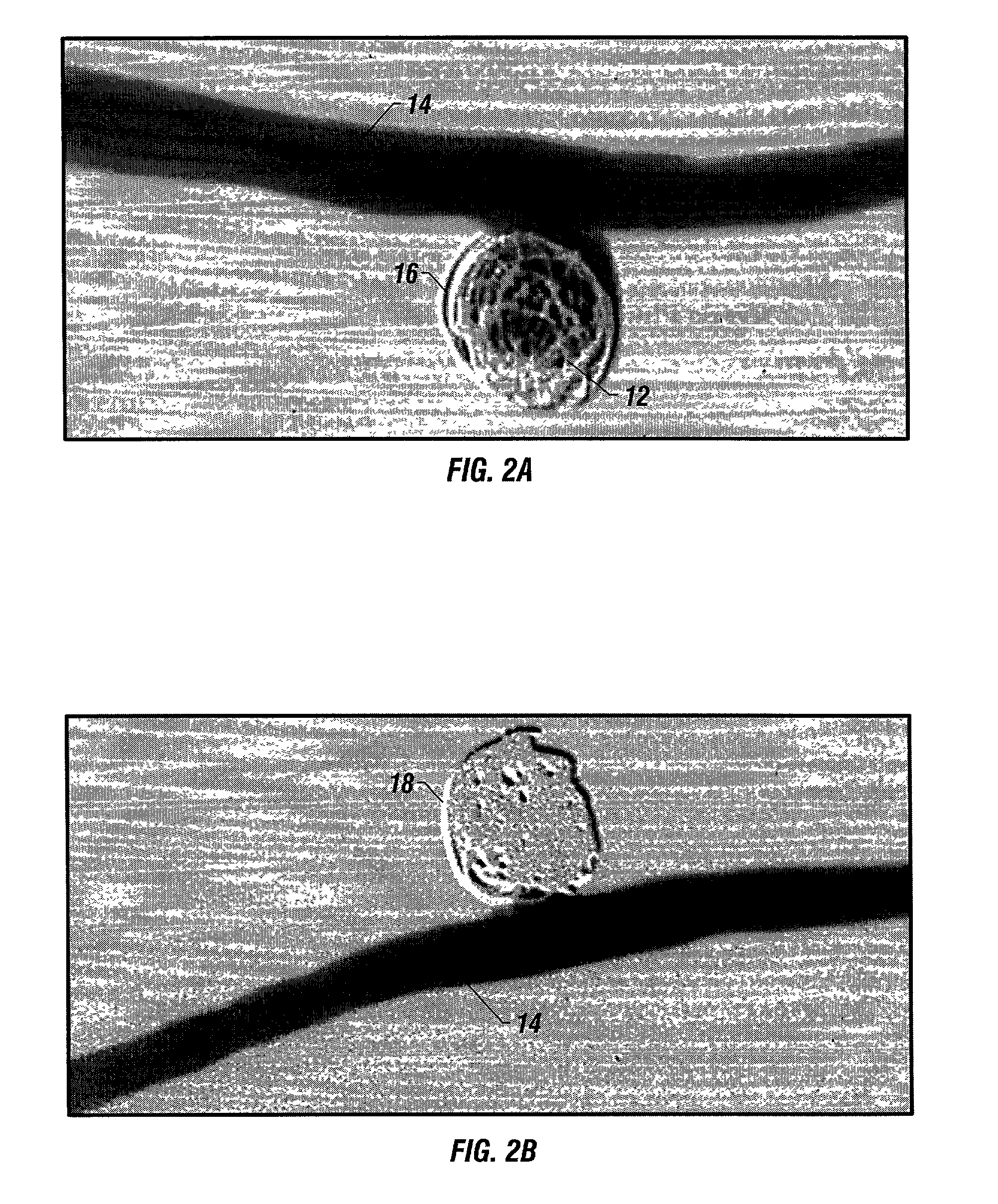
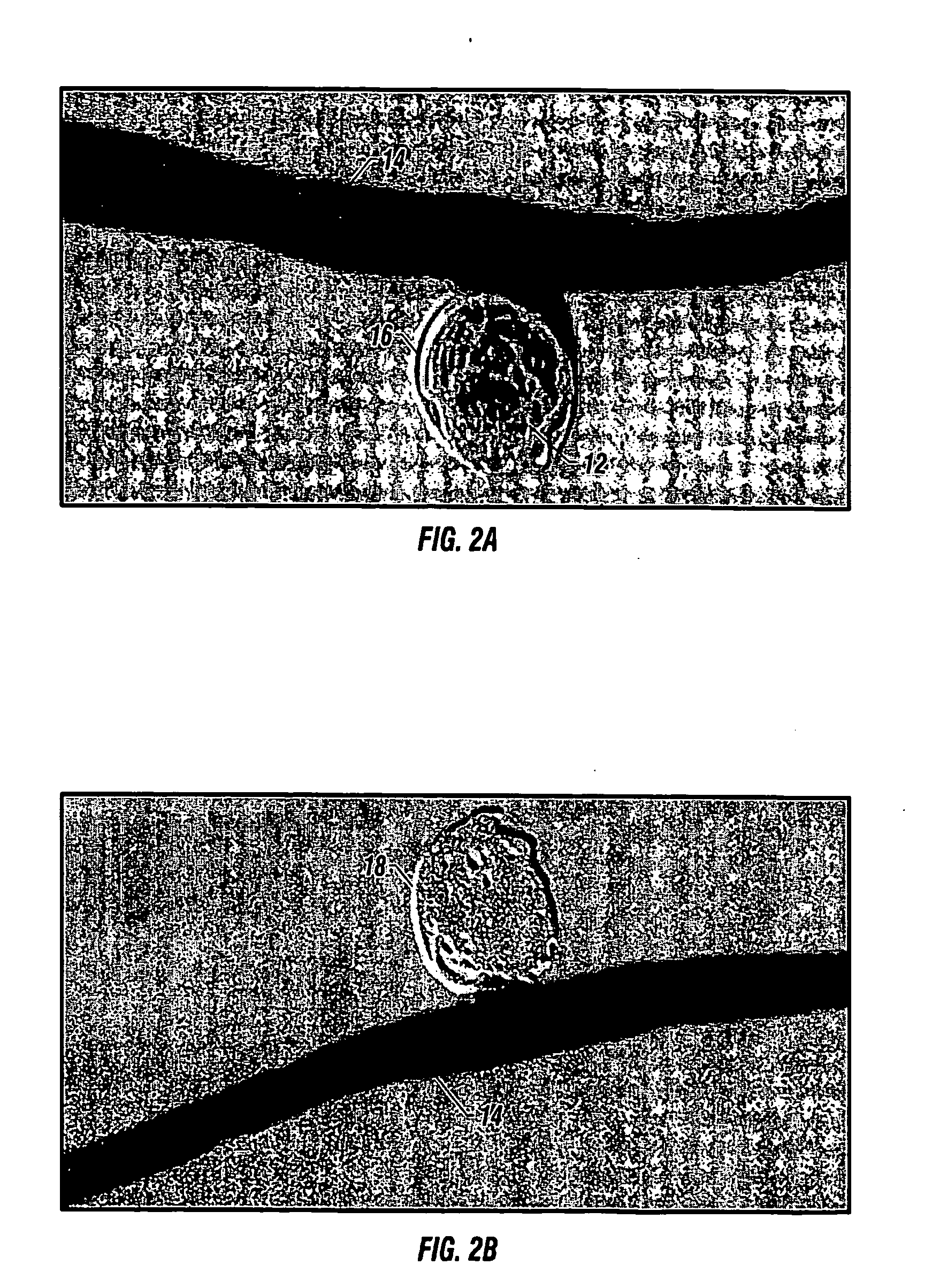
Bioabsorbable polymeric implants and a method of using the same to create occlusions
A new embolic agent, bioabsorbable polymeric material (BPM) is incorporated to a Guglielmi detachable coil (GDC) to improve long-term anatomic results in the endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms. The embolic agent, comprised at least in part of at least one biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer and growth factors, is carried by hybrid bioactive coils and is used to accelerate histopathologic transformation of unorganized clot into fibrous connective tissue in experimental aneurysms. An endovascular cellular manipulation and inflammatory response are elicited from implantation in a vascular compartment or any intraluminal location. Thrombogenicity of the biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer is controlled by the composition of the polymer. The coil further is comprised at least in part of a growth factor or more particularly a vascular endothelial growth factor, a basic fibroblast growth factor or other growth factors. The biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer is in the illustrated embodiment at least one polymer selected from the group consisting of polyglycolic acid, poly˜glycolic acid / poly-L-lactic acid copolymers, polycaprolactive, polyhydroxybutyrate / hydroxyvalerate copolymers, poly-L-lactide. Polydioxanone, polycarbonates, and polyanhydrides.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Biodegradable polymer coils for intraluminal implants
An endovascular cellular manipulation and inflammatory response are elicited from implantation in a vascular compartment or any intraluminal location of a separable coil comprised at least in part of at least one biocompatible and absorbable polymer or protein and growth factors. Typically a catheter associated with the separable coil is used to dispose the coil into a selected body lumen. The biocompatible and absorbable polymer or protein is thrombogenic. The coil further is comprised at least in part of a growth factor or more particularly a vascular endothelial growth factor, a basic fibroblast growth factor or other growth factors. The biocompatible and absorbable polymer is in the illustrated embodiment at least one polymer selected from the group consisting of polyglycolic acid, poly~glycolic acid poly-L-lactic acid copolymers, polycaprolactive, polyhydroxybutyrate / hydroxyvalerate copolymers, poly-L-lactide. Polydioxanone, polycarbonates, and polyanhydrides. The biocompatible and absorbable protein is at least one protein selected from the group consisting of collagen, fibrinogen, fibronectin, vitronectin, laminin, and gelatin. In one embodiment the coil is composed of the biocompatible and absorbable polymer or protein with a radio-opaque material is disposed thereon. Alternatively, the coil is composed of a radio-opaque material, and the biocompatible and absorbable polymer or protein is disposed thereon. This apparatus may be positioned within intracranial aneurysms or any aneurysm in the body as well as within other body cavities.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
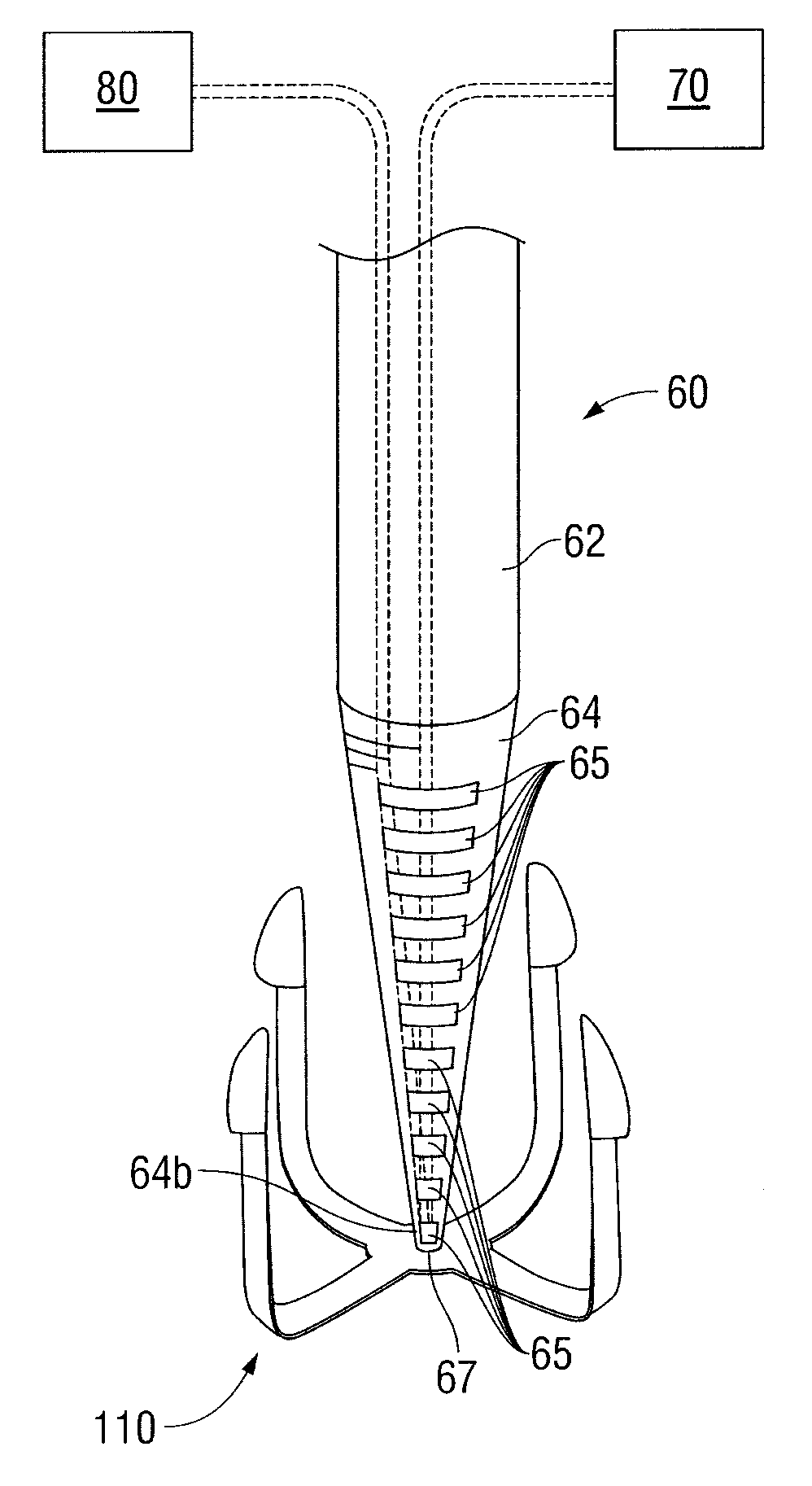
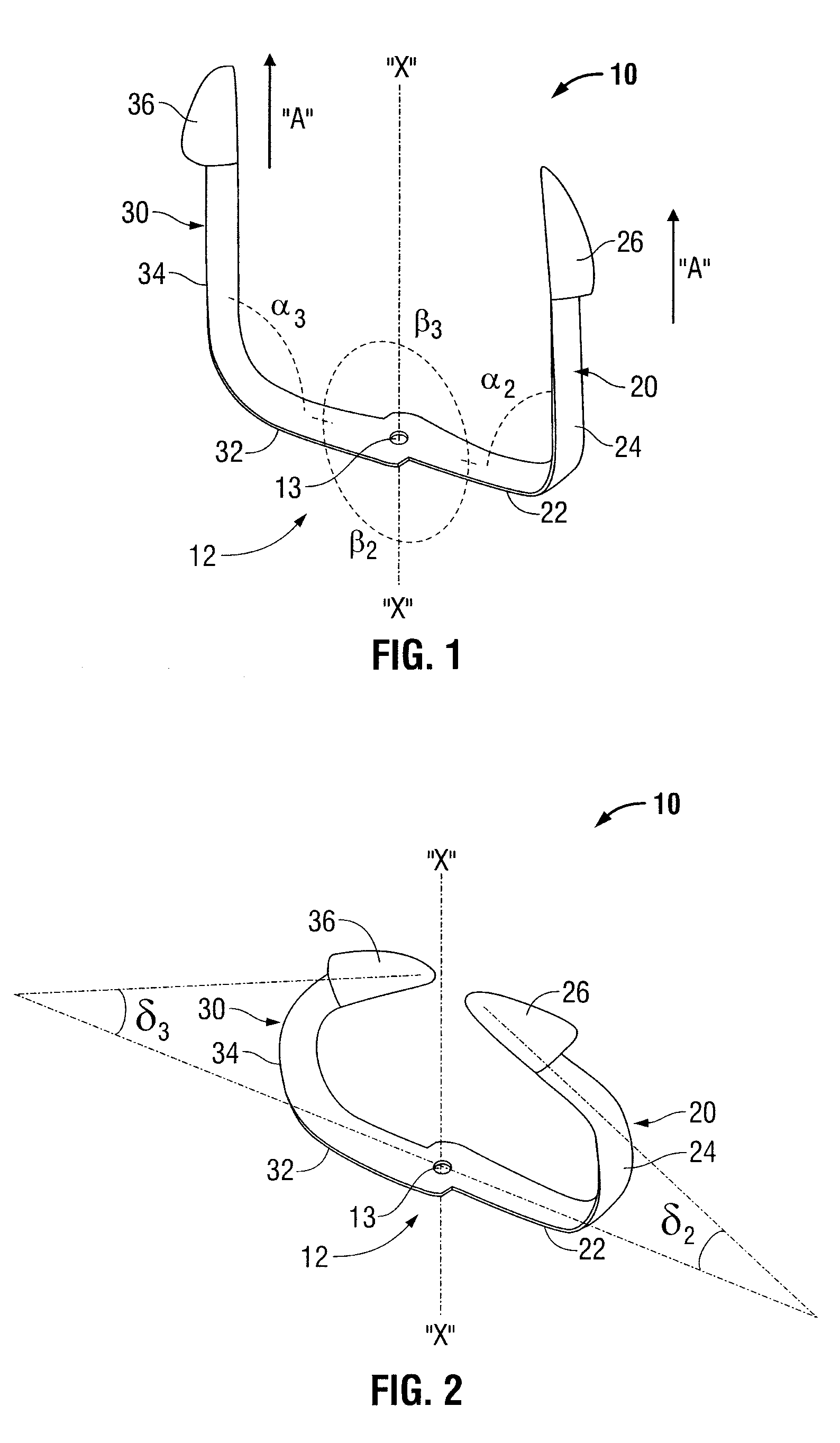
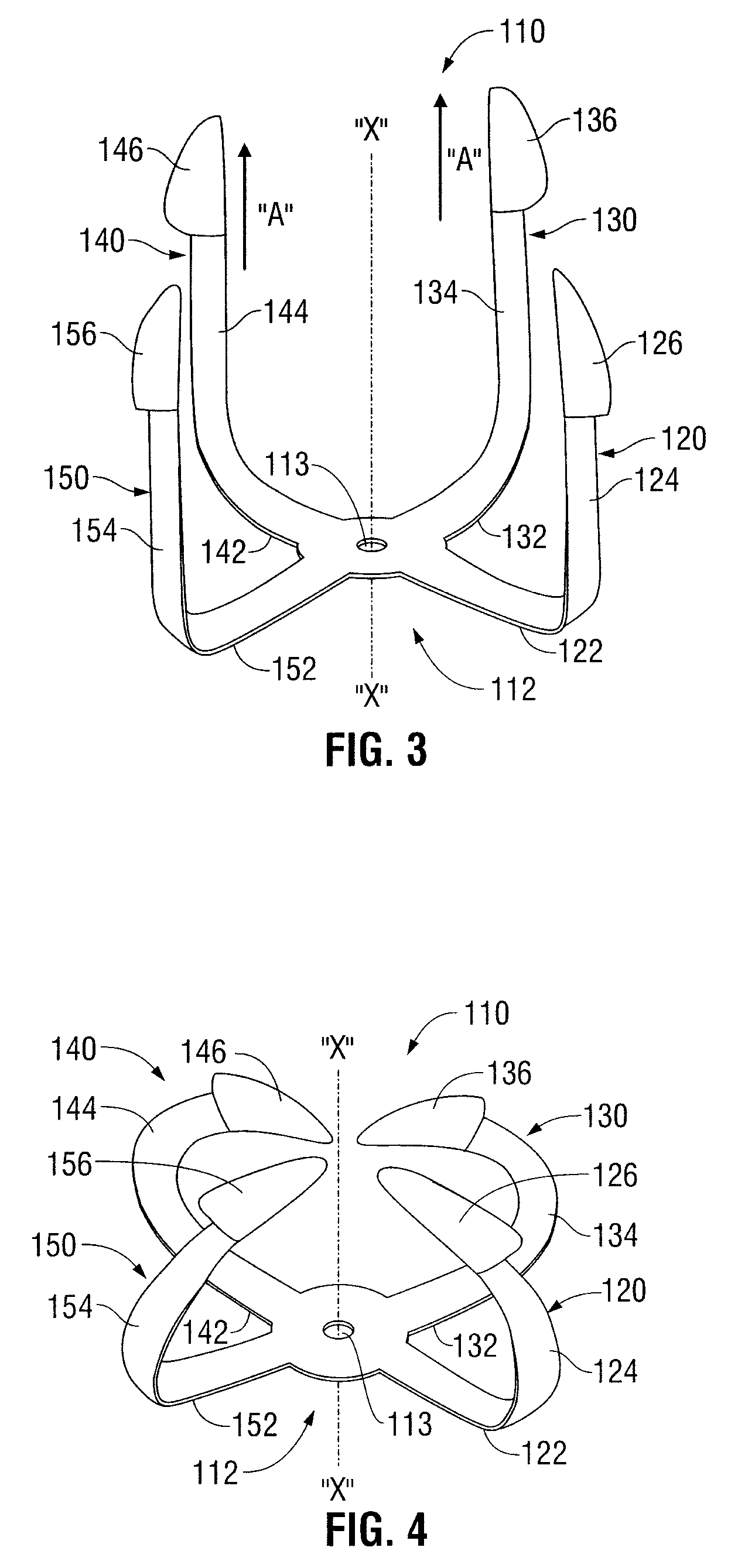
Shape memory fasteners and method of use
ActiveUS9295463B2DiagnosticsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTrimethylene carbonateBiological activation
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
Porous biocompatible implant material and method for its fabrication
a biocompatible and biodegradable implant for a cavity in a bone of a living organism is made of a biocompatible and biodegradable granules which are selected from the group including biopolymers, bioglasses, bioceramics preferably calcium sulfate, calcium phosphate such as monocalcium phosphate monohydrate, monocalcium phosphate anhydrous, dicalcium phosphate dihydrate, dicalcium phosphate anhydrous, tetracalcium phosphate, calcium orthophosphate phosphate, α-tricalcium phosphate, β-tricalcium phosphate, apatite such as hydroxyapatite, or a mixture thereof. The biocompatible and biodegradable granules are provided with a coating, which comprises at least one layer of a biocompatible and biodegradable polymer which is selected from the group including poly((α-hydroxyesters), poly(orthoesters), polyanhydrides, poly(phosphazenes), poly(propylene fumarate), poly(ester amides), poly(ethylene fumarate), polylactide, polyglycolide, polycaprolactone, poly(glycolide-co-trimethylene carbonate), polydioxanone, co-polymers thereof and blends of those polymers. The biocompatible and biodegradable implants are obtained by fusing together the polymer-coated granules through polymer-linkage of the polymer coatings of neighboring granules.
Owner:COLLAGEN MATRIX
Bioabsorbable polymeric implants and a method of using the same to create occlusions
InactiveUS20020040239A1Peptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical containersPoly-L-lactideVascular compartment
A new embolic agent, bioabsorbable polymeric material (BPM) is incorporated to a Guglielmi detachable coil (GDC) to improve long-term anatomic results in the endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms. The embolic agent, comprised at least in part of at least one biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer and growth factors, is carried by hybrid bioactive coils and is used to accelerate histopathologic transformation of unorganized clot into fibrous connective tissue in experimental aneurysms. An endovascular cellular manipulation and inflammatory response are elicited from implantation in a vascular compartment or any intraluminal location. Thrombogenicity of the biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer is controlled by the composition of the polymer. The coil further is comprised at least in part of a growth factor or more particularly a vascular endothelial growth factor, a basic fibroblast growth factor or other growth factors. The biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer is in the illustrated embodiment at least one polymer selected from the group consisting of polyglycolic acid, poly~glycolic acid / poly-L-lactic acid copolymers, polycaprolactive, polyhydroxybutyrate / hydroxyvalerate copolymers, poly-L-lactide. Polydioxanone, polycarbonates, and polyanhydrides.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
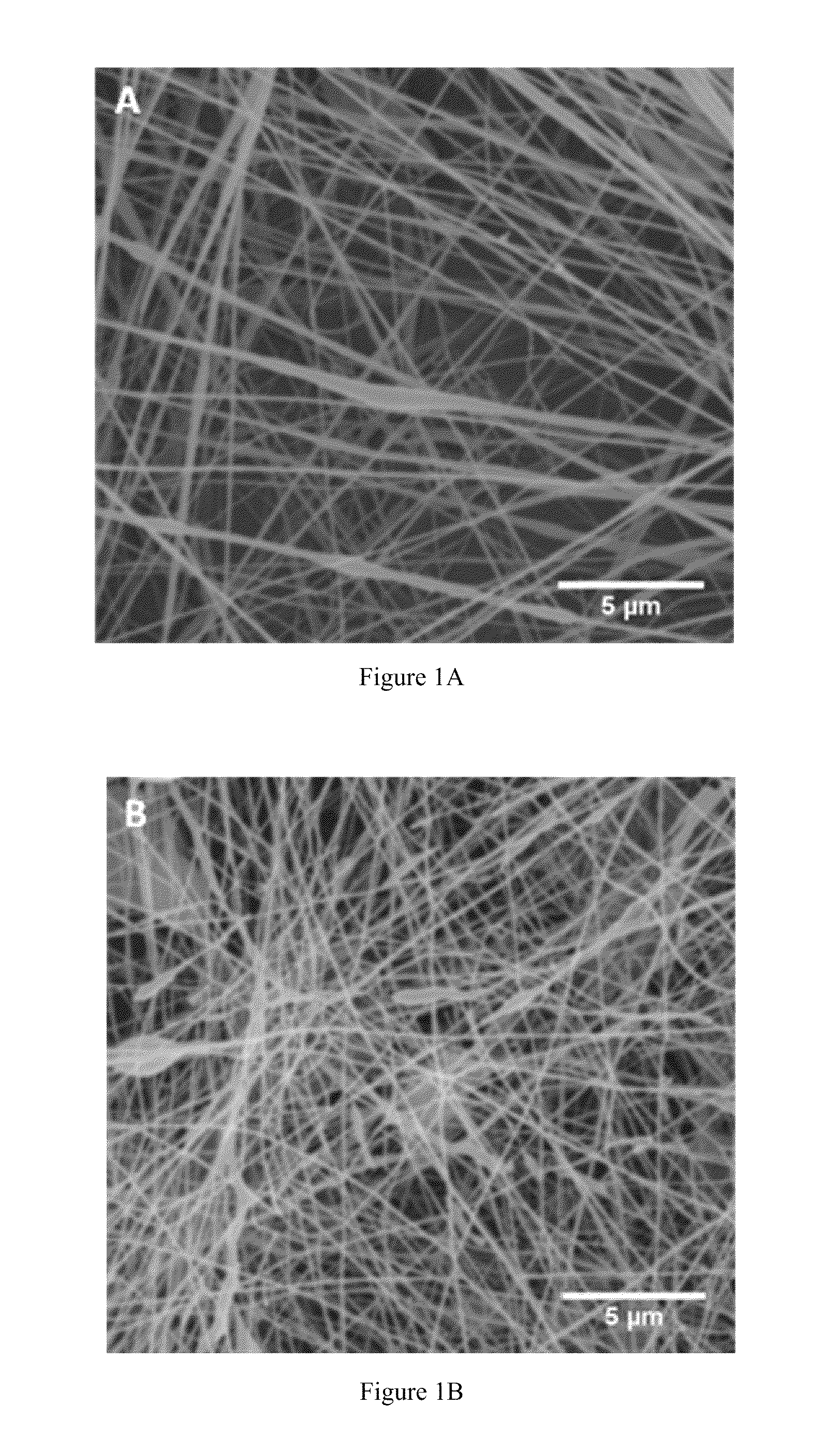
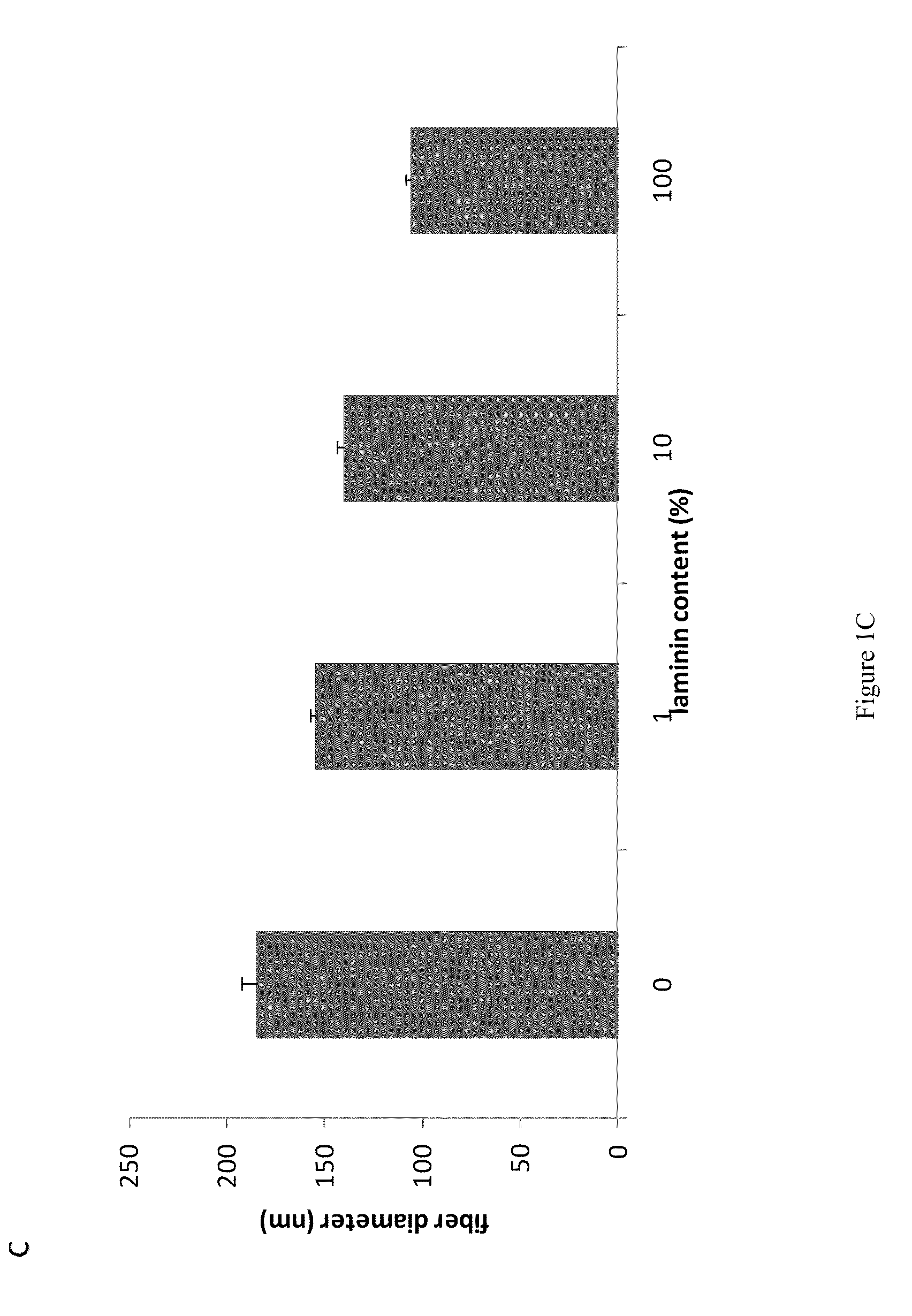
Compositions and methods for making and using laminin nanofibers
ActiveUS20110236974A1Low costHigh manufacturing requirementsElectric discharge heatingNanomedicineMicrosphereBiopolymer
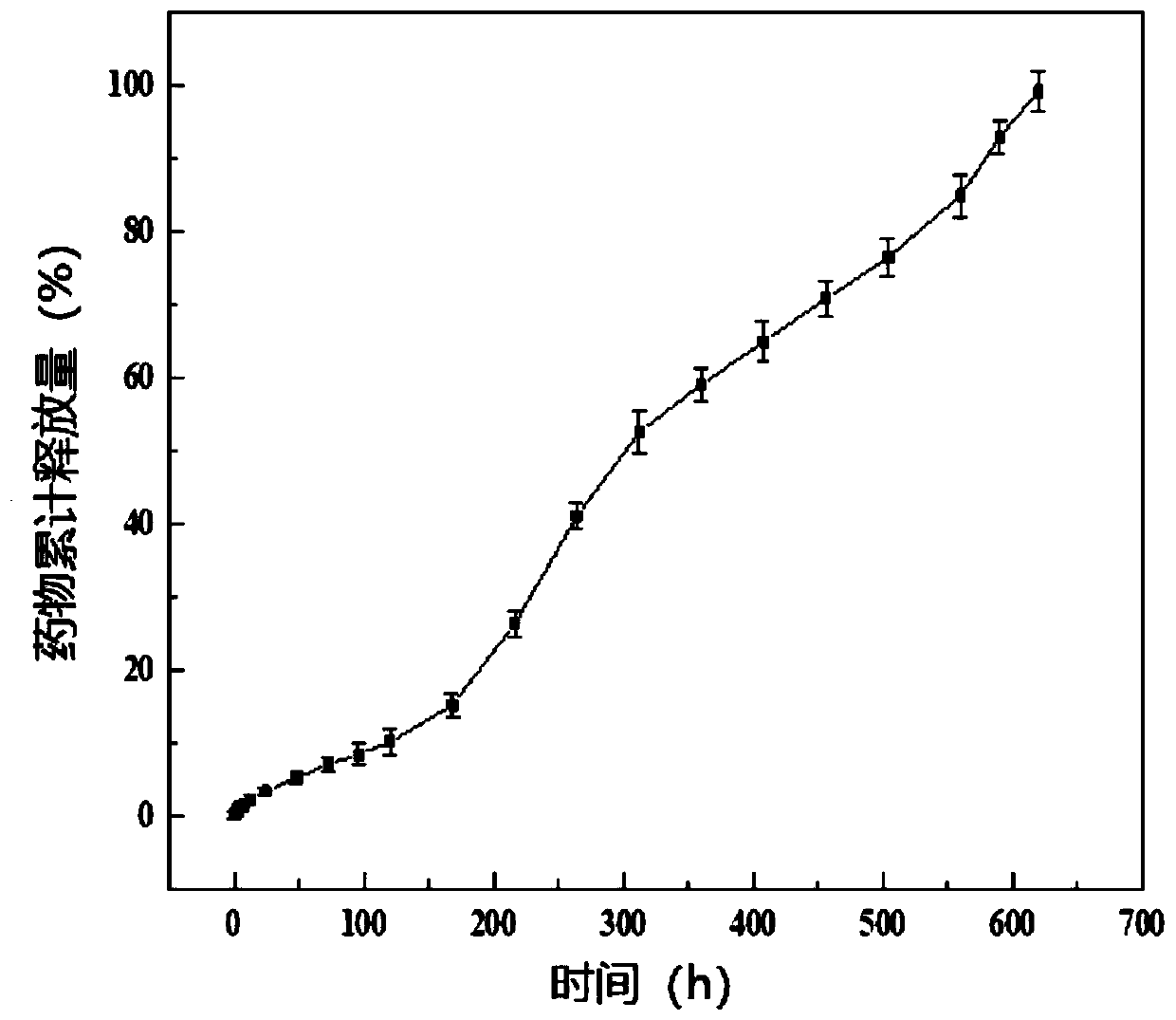
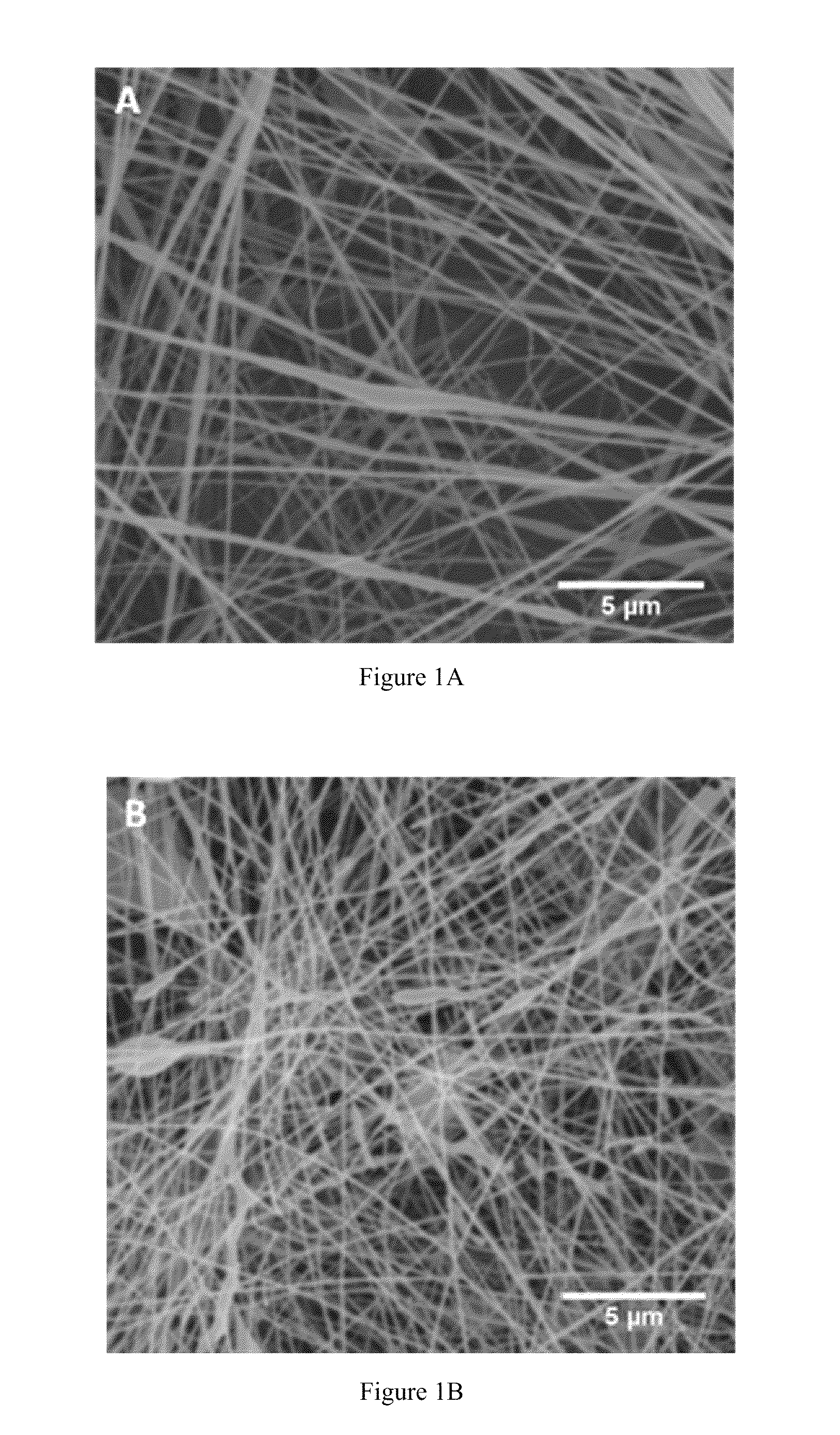
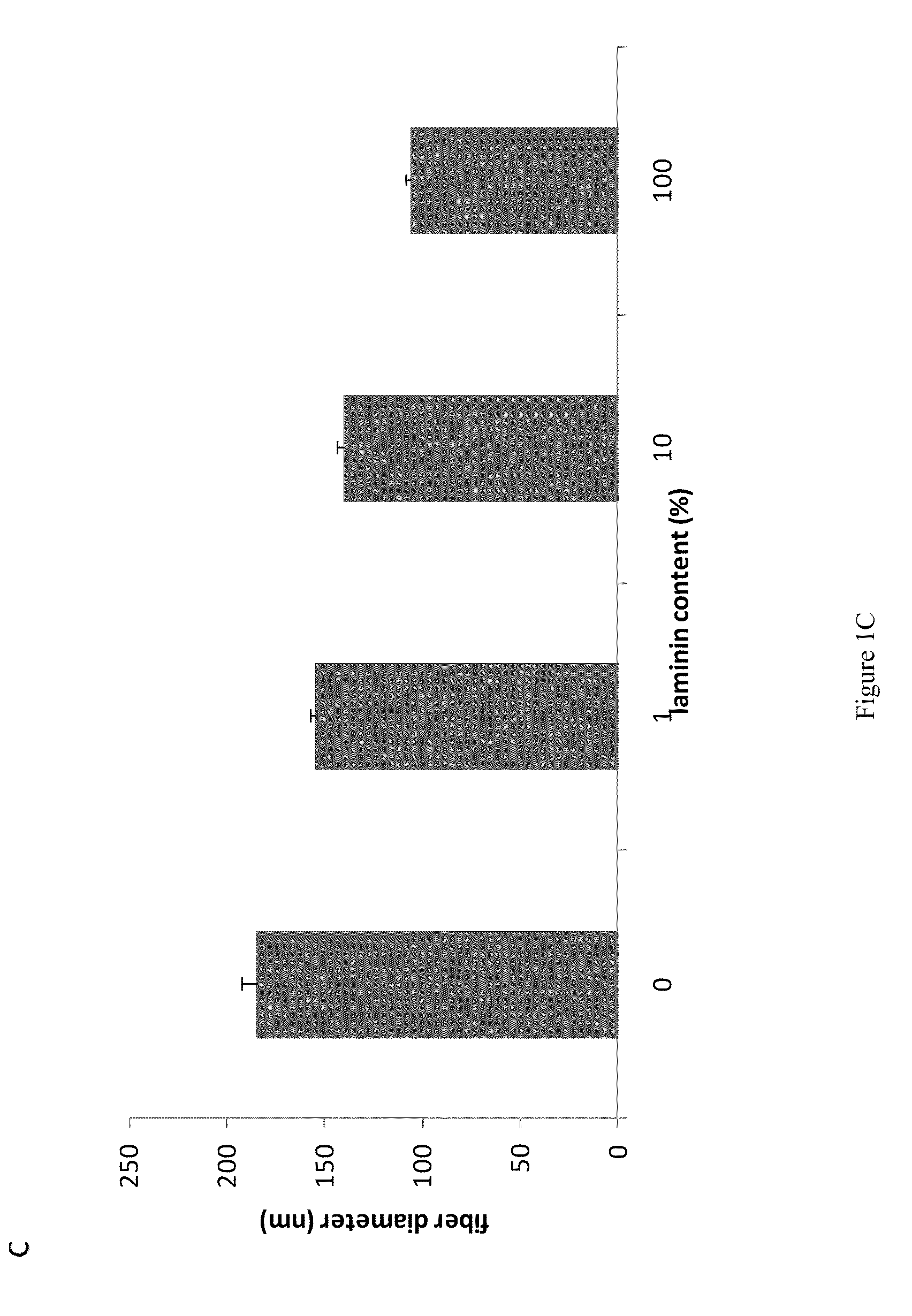
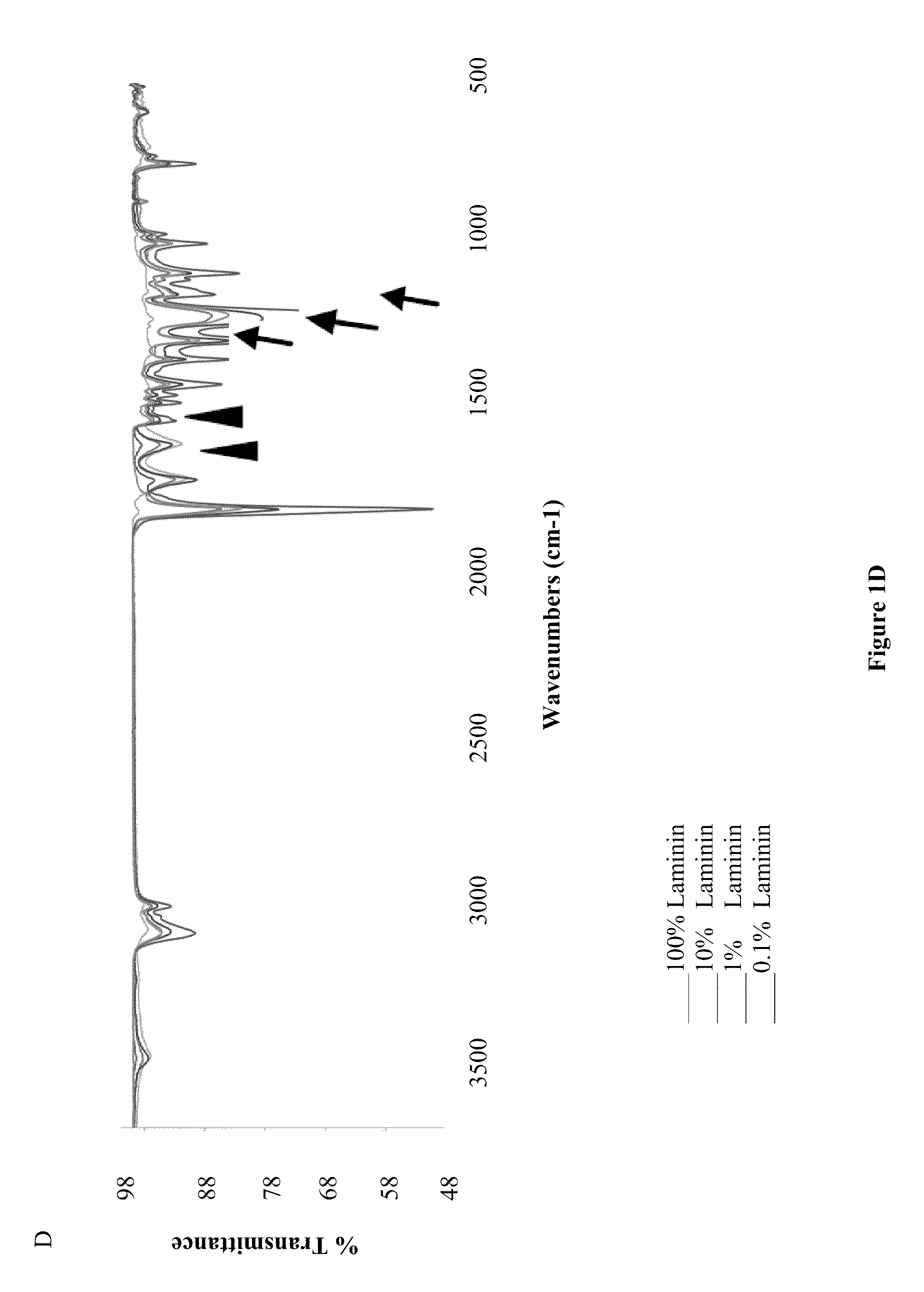
The present invention provides methodologies and parameters for fabrication of the hybrid biomaterial by blending pure laminin or complex extracts of tissues containing laminin with biopolymers such as polycaprolactone (PCL), polylactic / polyglycolic acid copolymer (PLGA) or Polydioxanone (PDO) in fluoroalcohols (HFP, TFA), fabrication of substrates and scaffolds and devices from the hybrid biomaterial in forms such as films, nanofibers by electrospinning or microspheres, and the biological or biomedical use of the material or devices derived from it.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Self-expanding biodegradable stent
The self-expanding biodegradable stent is a compressible, resilient mesh stent, which is compressed during delivery to a biological vessel or channel, and which expands to the contours of the vessel or channel upon delivery. The self-expanding biodegradable stent includes a substantially cylindrical main body portion having slightly flared, longitudinally opposed first and second open ends. The substantially cylindrical main body portion is hollow and is formed from an open mesh material, preferably formed as a unitary body from a biodegradable monofilament, such as a polydioxanone monofilament fiber. In order to reduce the possibility of trauma to the interior of the vessel, the open ends are blunted, with end points of the mesh forming a plurality of loops being about each of the first and second open ends, and opposing ends of the filament are interleaved with and bonded to a medial portion of the cylinder.
Owner:ELLA CS
Reinforced absorbable synthetic matrix for hemostatic applications
The present invention is directed to a reinforced absorbable hemostat comprising at least one hemostatic agent in a single layer of nonwoven synthetic fabric having a mixture of compressed fiber staples of a polyglycolide / polylactide copolymer and a polydioxanone.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Shape Memory Fasteners And Method Of Use
ActiveUS20110087277A1DiagnosticsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTrimethylene carbonateBiological activation
A surgical fastener configured to close an opening in tissue is provided. The surgical fastener includes a base defining a central axis at least one pair of legs extending from the base. Each of the legs includes a base portion and a tissue engaging portion. When in a first position, each of the tissue engaging portions is arranged to define an insertion direction and when in a second position, each of the tissue engaging portions extends inward towards the central axis. The surgical fastener is at least partially formed from a shape memory material including a combination of Polydioxanone and Poly(L-lactide) or a combination of Trimethylene Carbonate and Poly(L-lactide). The pair of legs are configured to move from the first position to the second position upon activation of the shape memory material.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Reinforced Absorbable Synthethic Matrix for Hemostatic Applications
The present invention is directed to a reinforced absorbable hemostat comprising at least one hemostatic agent in a single layer of nonwoven synthetic fabric having a mixture of compressed fiber staples of a polyglycolide / polylactide copolymer and a polydioxanone.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Methods of making composite prosthetic devices having improved bond strength
ActiveUS8206632B2High strengthMinimize the possibilityAdhesive processes with surface pretreatmentLaminationPolypropylene meshUltimate tensile strength
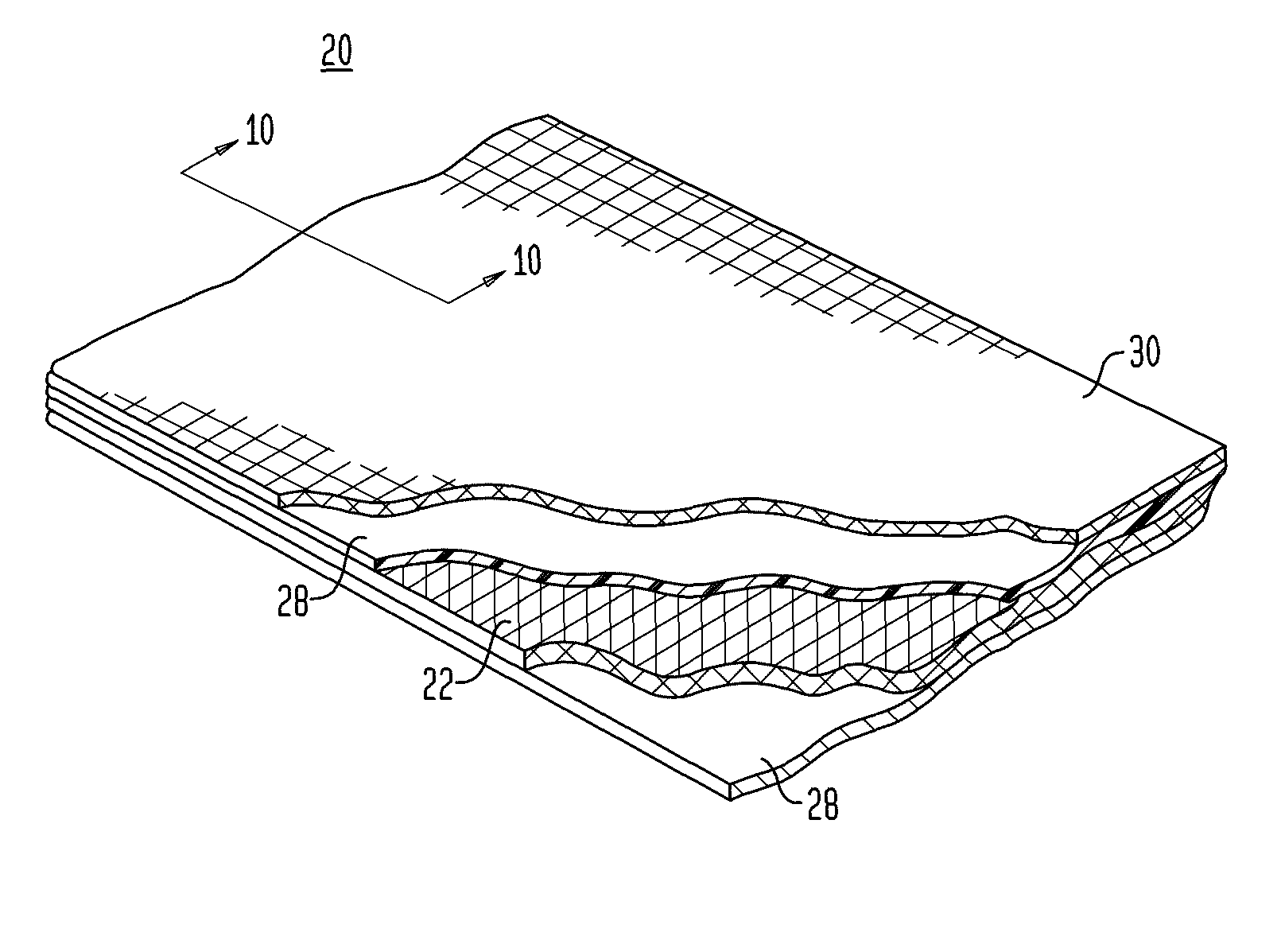
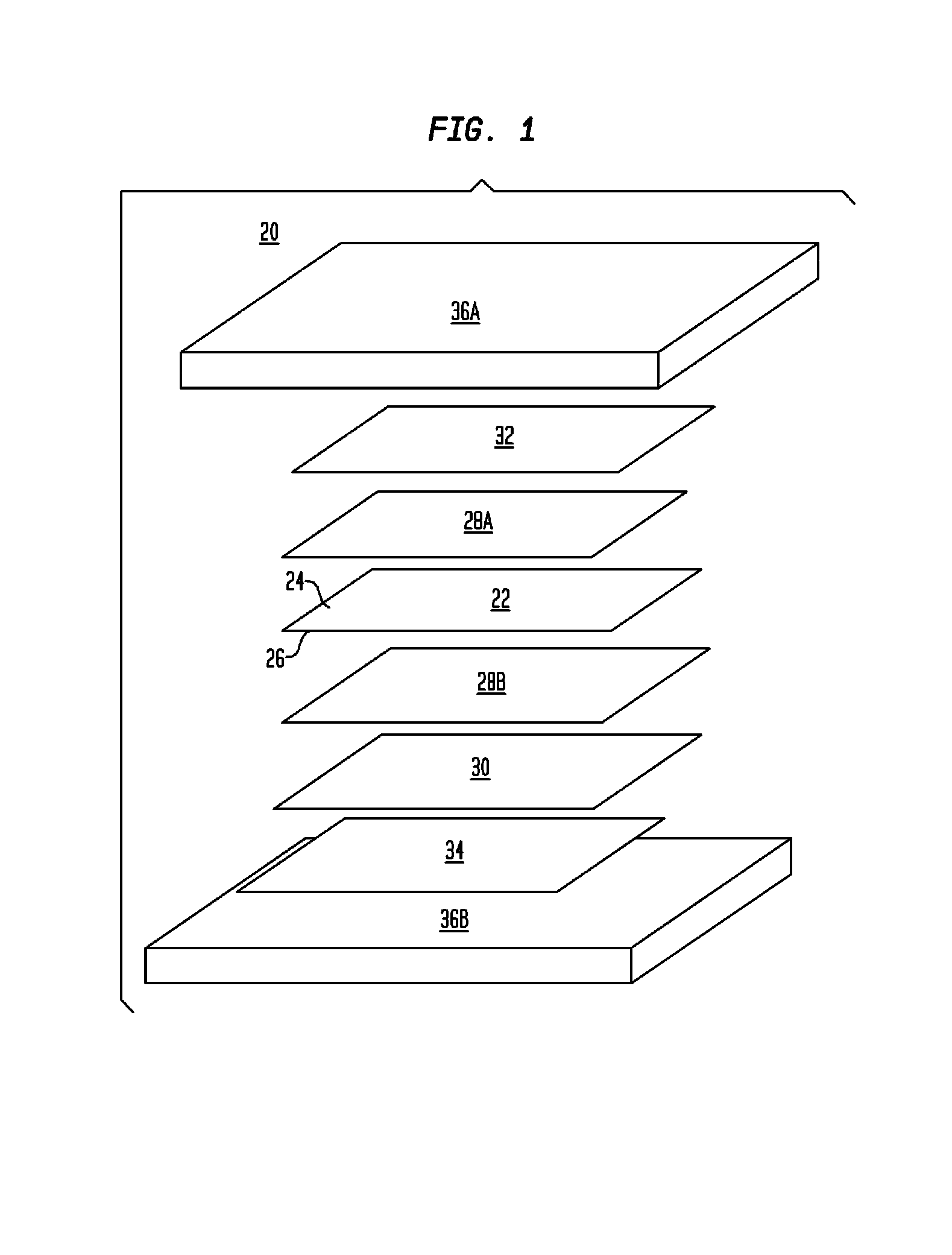
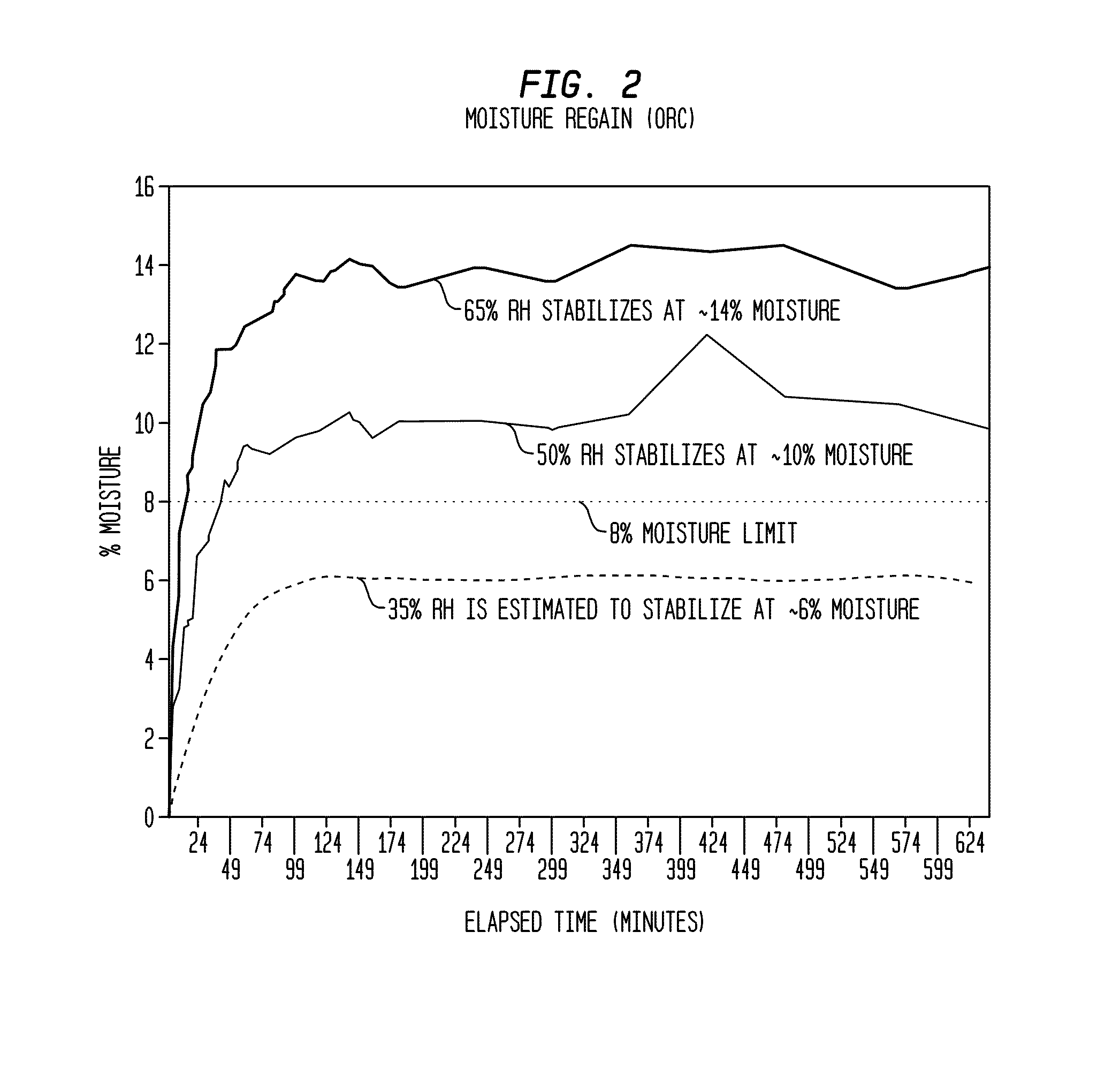
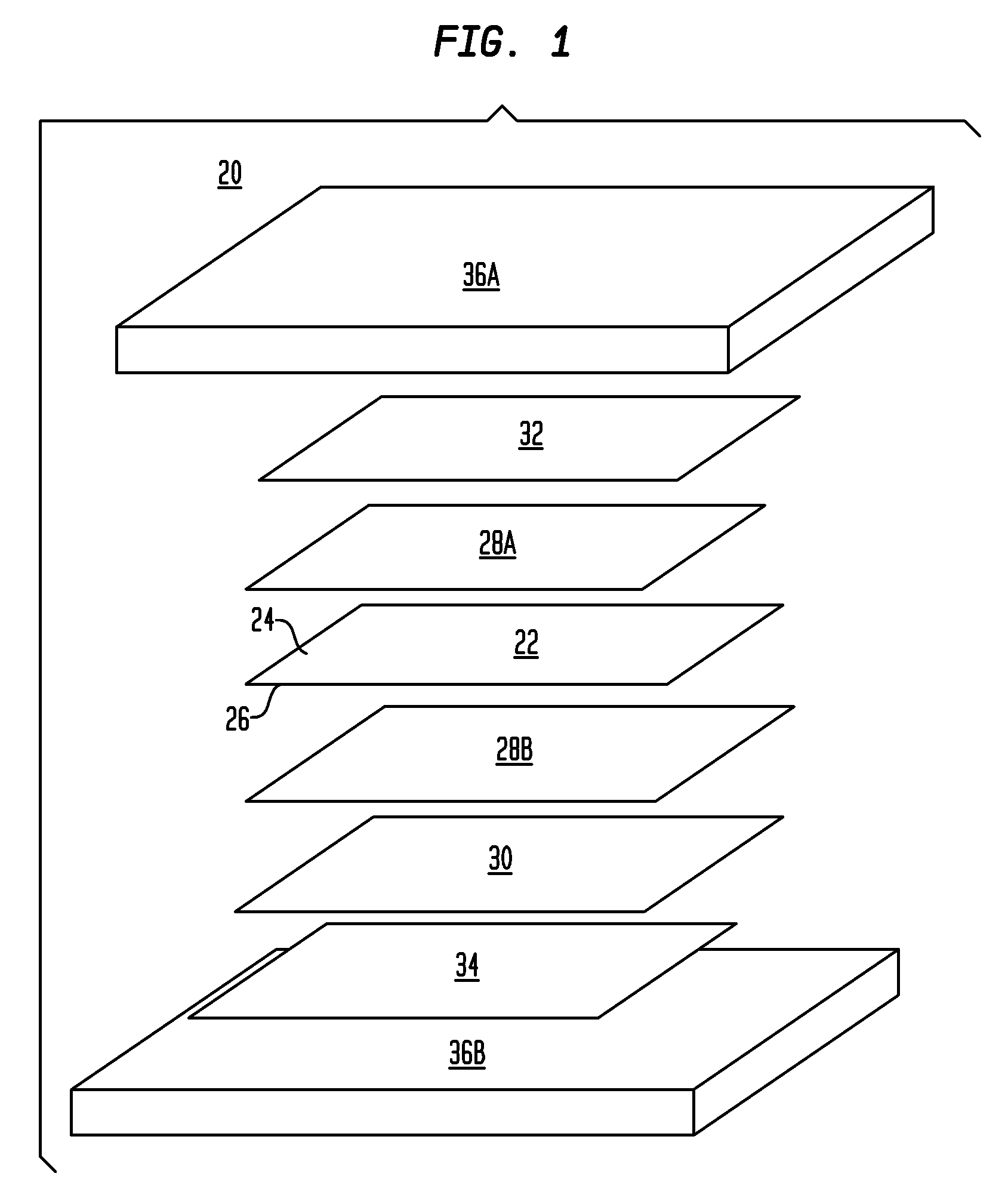
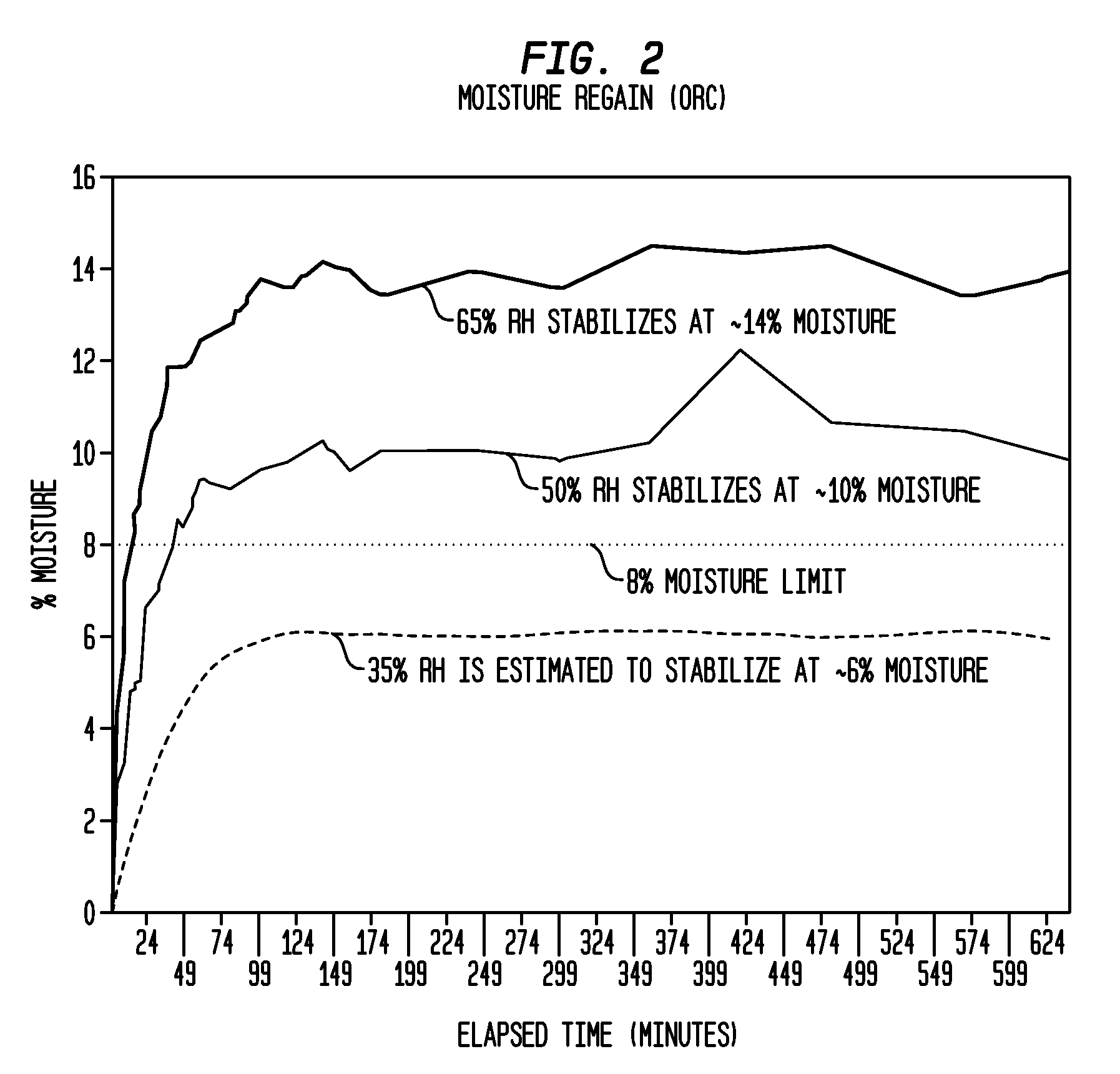
A method of making a composite prosthetic device, such as a hernia repair device, includes providing a support layer, juxtaposing a layer of an absorbable material with the support layer, and disposing an absorbable adhesive between the support layer and the layer of an absorbable material. The method includes heating the layers for melting the absorbable adhesive so as to bond the support layer with the layer of the absorbable material. Before the heating step, the moisture content of at least one of the layers is increased for improving thermal conductivity between the layers so as to enhance the strength of the bonds formed between the layers. The moisture content may be increased by exposing at least one of the layers to an environment having elevated relative humidity. In one embodiment, the support layer is polypropylene mesh, the layer of the absorbable material is oxidized regenerated cellulose, and the absorbable adhesive is polydioxanone.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Bioabsorbable polymeric implants and a method of using the same to create occlusions
A new embolic agent, bioabsorbable polymeric material (BPM) is incorporated to a Guglielmi detachable coil (GDC) to improve long-term anatomic results in the endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms. The embolic agent, comprised at least in part of at least one biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer and growth factors, is carried by hybrid bioactive coils and is used to accelerate histopathologic transformation of unorganized clot into fibrous connective tissue in experimental aneurysms. An endovascular cellular manipulation and inflammatory response are elicited from implantation in a vascular compartment or any intraluminal location. Thrombogenicity of the biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer is controlled by the composition of the polymer. The coil further is comprised at least in part of a growth factor or more particularly a vascular endothelial growth factor, a basic fibroblast growth factor or other growth factors. The biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer is in the illustrated embodiment at least one polymer selected from the group consisting of polyglycolic acid, poly˜glycolic acid / poly-L-lactic acid copolymers, polycaprolactive, polyhydroxybutyrate / hydroxyvalerate copolymers, poly-L-lactide. Polydioxanone, polycarbonates, and polyanhydrides.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods and Compositions for Tissue Augmentation
InactiveUS20080075749A1Avoid intakeInhibit migrationCosmetic preparationsPowder deliveryParticulatesPolyolefin
Methods and compositions for use in tissue volume replacement are provided. The present invention comprises compositions comprising a combination of materials, comprising preferably a solid polymer particle phase and a gel phase, and also comprises single phase compositions. More particularly, preferred embodiments comprise a solid polymer particle phase made of materials comprising Gore-Tex (micronized e-PTFE), PDS II (polydioxanone, a monofilament), NUROLON (a long chain aliphatic polymer Nylon 6 or Nylon 6,6) ETHILON (a long chain aliphatic polymer Nylon 6 and Nylon 6,6), PROLENE (Polypropylene, isotactic crystalline stereoisomer of polypropylene, a synthetic linear polyolefin.), VICRYL (copolymer made from 90% glycolide and 10% L-lactide), silk, MONACRYL (poly ε-caprolactone.), polylactide, polyglycolide, poly lactide-co-glycolide, and BIOPOL (polyhydroxyvalerate), MEDPOR (biocompatible (micronized) polyethylene), BIOGLASS (bioactive glass particulate), NOVABONE and NOVABONE-CM, and the gel phase comprises polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP). Preferred single phase compositions comprise PVP. Methods of the present invention comprising injection of such compositions for tissue augmentation.
Owner:DYER WALLACE K
Biodegradable sheet
Disclosed is a biodegradable sheet comprising at least one layer which is a direct contact layer, intended to successfully contact materials, such as liquids, while maintaining the mechanical properties of the sheet and to extend the biodegradable sheet shelf life. The direct contact layer may comprise a hydrophobic polymer selected from poly(epsilon-caprolactone) (PCL) polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB), Polydioxanone (PDO) polyglycolic acid (PGA), polybutylene succinate (PBS), polybutylene succinate adipate (PBS A), poly lactic acid (PL A), polybutylene adipate terphtalate (PBAT), polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA), such as polyhydroxybutyrates (PHB), polyhydroxyvalerates (PHV), and polyhydroxybutyrate-hydroxyvalerate copolymers (PHBV) or any mixture thereof. The biodegradable sheet may further comprise surface treated nanoclay particles, PVOH grafted with a crosslinker and PBS or PBS A The biodegradable sheet may further include at least one metalized, biodegradable, laminate layer.
Owner:TIPA CORP
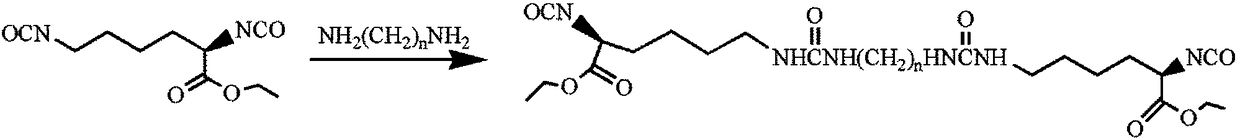
Method for improving flexibility of polypeptide membrane by polylactic acid and polydioxanone
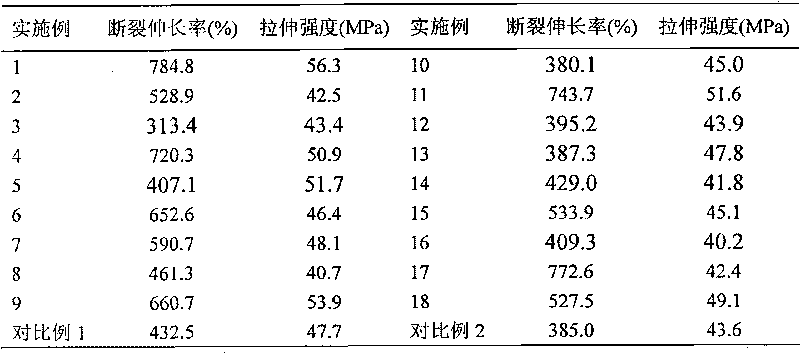
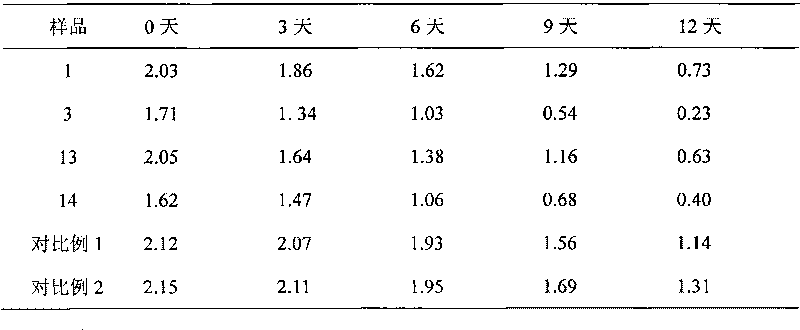
The invention discloses a method for improving the flexibility of a polypeptide membrane by polylactic acid and polydioxanone. The method comprises the following steps: (1) adding polypeptide homopolymer, diisocyanate, a catalyst and a solvent into a drying reactor, stirring to react for 40-60 minutes at 50-55 DEG C, and removing excessive diisocyanate by a dialysis method to obtain polypeptide homopolymer containing -NCO-terminated group; (2) adding the polypeptide homopolymer containing -NCO-terminated group, a catalyst and a solvent into the drying reactor, adding polylactic acid monododecyl ether, and stirring to react for 50-70 minutes at 40-50 DEG C to obtain polypeptide-poly-polylactic acid diblock copolymer; (3) adding the polypeptide-poly-polylactic acid diblock copolymer, polydioxanone and a solvent into the drying reactor, stirring and mixing for 60-70 minutes at 40-50 DEG C, forming a membrane by using a tape casting method, and drying to obtain a target product. The preparation process is simple, and the flexibility of the modified membrane is greatly improved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
Method for improving hydrophilia and flexibility of polypeptide membrane through polydioxanone and polyethylene glycol
The invention discloses a method for improving the hydrophilia and flexibility of a polypeptide membrane through polydioxanone and polyethylene glycol. The method includes the following steps that firstly, carboxyl-terminated polydioxanone monododecyl ether, a solution, a condensing agent and a polypeptide homopolymer are added in a drying reactor for reaction for 3-4 days, and a polypeptide-polydioxanone segmented copolymer is obtained; secondly, carboxyl-terminated polydioxanone monododecyl ether carboxyl, a solution, a condensing agent and amidogen-terminated ethylene glycol monomethyl ether are added in the drying reactor for reaction for 2-3 days, and a polyethylene glycol-polydioxanone segmented copolymer is obtained; thirdly, the polypeptide-polydioxanone segmented copolymer, the polyethylene glycol-polydioxanone segmented copolymer and a solvent are added in the drying reactor to be mixed for 40-50 minutes, then tape casting is used for forming the membrane, drying is conducted, and the target object of the method is obtained. The method is simple in preparation technology, and the hydrophilia and flexibility of the obtained modified membrane are greatly improved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
Biodegradable sheet
Disclosed is a biodegradable sheet comprising at least one layer which is a direct contact layer, intended to successfully contact materials, such as liquids, while maintaining the mechanical properties of the sheet and to extend the biodegradable sheet shelf life. The direct contact layer may comprise a hydrophobic polymer selected from poly(epsilon-caprolactone) (PCL) polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB), Polydioxanone (PDO) polyglycolic acid (PGA), polybutylene succinate (PBS), polybutylene succinate adipate (PBSA), poly lactic acid (PLA), polybutylene adipate terphtalate (PBAT), polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA), such as polyhydroxybutyrates (PHB), polyhydroxyvalerates (PHV), and polyhydroxybutyrate-hydroxyvalerate copolymers (PHBV) or any mixture thereof. The biodegradable sheet may further comprise surface treated nanoclay particles, PVOH grafted with a crosslinker and PBS or PBSA The biodegradable sheet may further include at least one metalized, biodegradable, laminate layer.
Owner:TIPA CORP
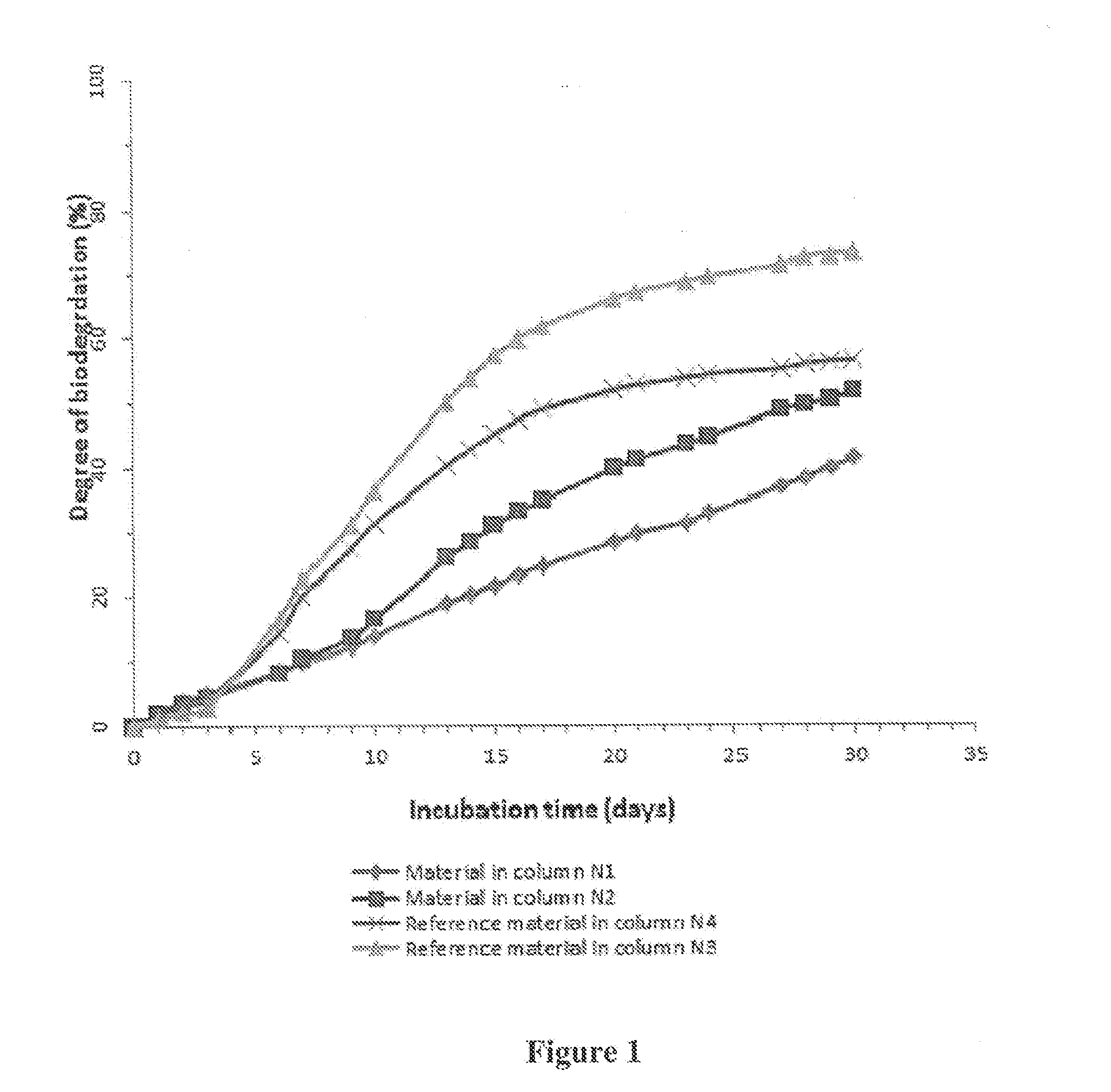
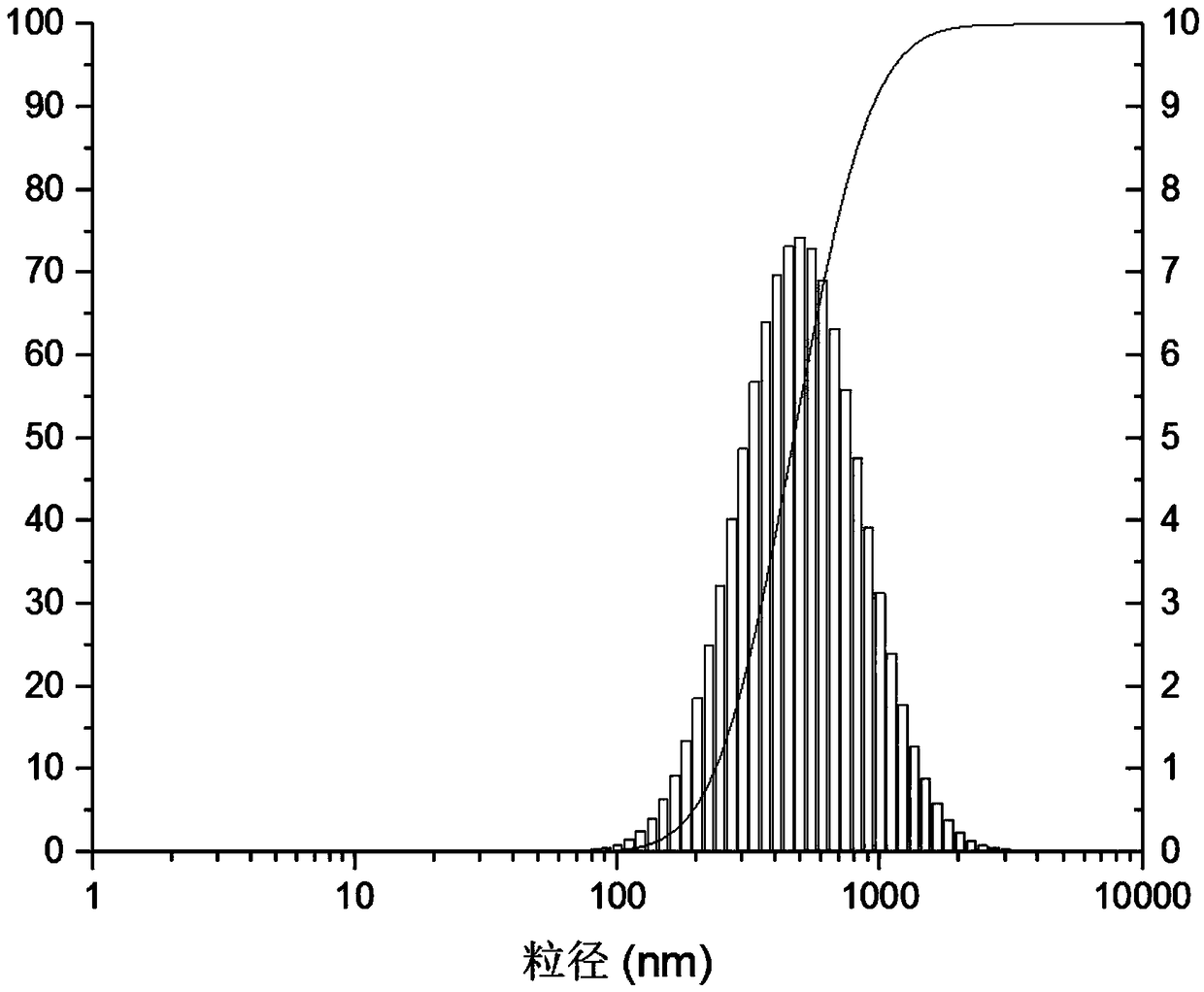
Method for preparing biodegradable filling materials, product prepared by aid of method and application of product
ActiveCN106492284AEasy to fillEasy to operatePowder deliveryAerosol deliveryGel preparationMass ratio
The invention relates to a method for preparing biodegradable filling materials, a product prepared by the aid of the method and application of the product. The method mainly includes steps of (1), mixing matrix materials and dispersion-phase materials according to a mass ratio of 10:0-6:4 with one another and dissolving the matrix materials and the dispersion-phase materials in organic solvents to obtain high-polymer organic solvents; (2), treating the high-polymer organic solvents by the aid of a mechanical process or an emulsification process to obtain a micro-sphere. The matrix materials comprise polydioxanone; the dispersion-phase materials comprise a type of or a plurality of types of poly-L-lactic acid, polycaprolactone, polylactic acid and polyglycolic acid. The method, the product and the application have the advantages that the method is easy to implement, low in cost and good in repeatability, the product comprises tiny and stable particles, and the micro-sphere prepared by the aid of the method has similar and controllable particle sizes, is good in filling performance and tissue compatibility and is safe and degradable; the product can be degraded slowly, the degradation time can be regulated and controlled according to selection of the types and the adding proportions of the dispersion-phase materials; the micro-sphere can be used for preparing freeze-dried powder preparations and gel preparations, and the product is convenient to transport, store and clinically use.
Owner:重庆瑞凡德生物科技有限公司
Drug-carrying nanocomposite fiber membrane system and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109908108AStable in natureHigh porosityOrganic active ingredientsInorganic active ingredientsElectrospinningPolyethylene glycol
The invention relates to a drug-carrying nanocomposite fiber membrane system and a preparation method and application thereof. The drug-carrying nanocomposite fiber membrane system comprises a first nanofiber layer, a second nanofiber layer and a third nanofiber layer; the first nanofiber layer includes a polylactic acid-hydroxyacetic acid copolymer, polydioxanone and drugs; the second nanofiber layer includes a polylactic acid-hydroxyacetic acid copolymer, polyglycolic acid and drugs; the third nanofiber layer includes polylactic acid-hydroxyacetic acid copolymer, polyethylene glycol and drugs. The preparation method includes: respectively dissolving and mixing polymer materials and drugs contained in the nanofiber layers to obtain three kinds of mixed solutions; subjecting the mixed solutions to electrostatic spinning in sequence to obtain the drug-carrying nanocoposite fiber membrane system. The drug-carrying nanocomposite fiber membrane system is a complete 0-day to 2.5-month drugsustained release system, achieving multi-gradient, multi-stage and long-term drug release.
Owner:SHENZHEN GUANGYUAN BIOMATERIAL CO LTD
Bone screw
ActiveCN104887305AReduce intensityIncreased micromotionPharmaceutical delivery mechanismFastenersMetallic materialsScrew cap
The invention relates to a bone screw. The bone screw comprises a screw pole and a screw cap, the screw pole comprises a polish rod section and a screw rod section, a degradable material layer is compounded on the peripheral circumferential surface of the polish rod section, and the outer diameter of the degradable material layer is less than or equal to the large diameter of the screw rod section. The screw pole and screw cap are made of metal material; the degradable material layer is prepared from one or the polymer of polylactic acid, polyglycolic acid, poly trimethylene carbonate, polydioxanone and poly epsilon-caprolactone. Through operation, the bone screw is stable in fixing effect and avoided from sliding after the fracture part of a patient is fixed and before the degradable material layer is degraded; in the later degradation process of the degradable material layer and after the complete degradation of the degradable material layer, the bone moves slightly to stimulate the full healing of the bone, the achievement ratio of operation is improved, and the healing effect of the fracture part is better.
Owner:HEBEI RUINUO MEDICAL INSTR CO LTD
Methods of making composite prosthetic devices having improved bond strength
ActiveUS20090152766A1High strengthMinimize the possibilityAdhesive processes with surface pretreatmentLaminationPolypropylene meshUltimate tensile strength
A method of making a composite prosthetic device, such as a hernia repair device, includes providing a support layer, juxtaposing a layer of an absorbable material with the support layer, and disposing an absorbable adhesive between the support layer and the layer of an absorbable material. The method includes heating the layers for melting the absorbable adhesive so as to bond the support layer with the layer of the absorbable material. Before the heating step, the moisture content of at least one of the layers is increased for improving thermal conductivity between the layers so as to enhance the strength of the bonds formed between the layers. The moisture content may be increased by exposing at least one of the layers to an environment having elevated relative humidity. In one embodiment, the support layer is polypropylene mesh, the layer of the absorbable material is oxidized regenerated cellulose, and the absorbable adhesive is polydioxanone.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Medicine carrying nanofiber membrane and preparation and application methods thereof
ActiveCN109898236AAchieving Linear Control ReleasePromote swellingOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismFiberPorosity
The invention relates to a medicine carrying nanofiber membrane and preparation and application methods thereof. The medicine carrying nanofiber membrane is composed of polylactic acid-hydroxyacetic acid copolymer fiber, polydioxanone fiber and medicines, wherein the medicines are dispersed inside the polylactic acid-hydroxyacetic acid copolymer fiber. The preparation method of the medicine carrying nanofiber membrane comprises (1) mixing the medicines and polylactic acid-hydroxyacetic acid copolymer with solvent and then mixing polydioxanone with solvent to obtain two mixed solutions; (2) independently loading the two mixed solutions and performing electrostatic spinning with multi-spinneret electrostatic spinning equipment to obtain the medicine carrying nanofiber membrane. The obtainedmedicine carrying nanofiber membrane is prepared through electrostatic spinning and is stable in property, high in porosity and similar to extracellular matrices, and when applied to postoperative stumps, can be extracted without secondary surgery, be degradable in vivo and achieve linear release of the medicines.
Owner:SHENZHEN GUANGYUAN BIOMATERIAL CO LTD
Compositions and methods for making and using laminin nanofibers
ActiveUS8728817B2Low costHigh manufacturing requirementsNervous disorderElectric discharge heatingMicrosphereBiopolymer
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
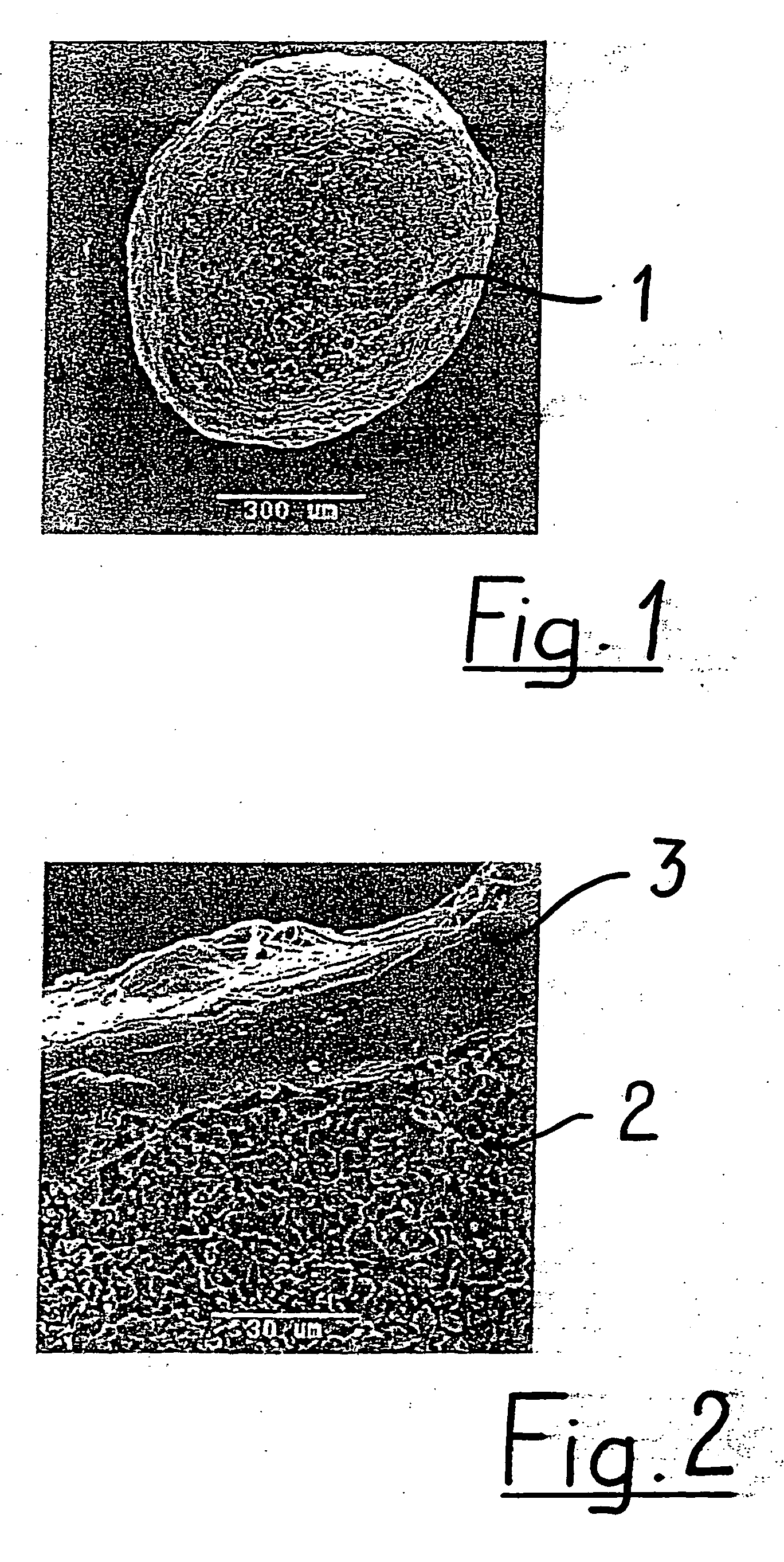
Super-hydrophilic structures
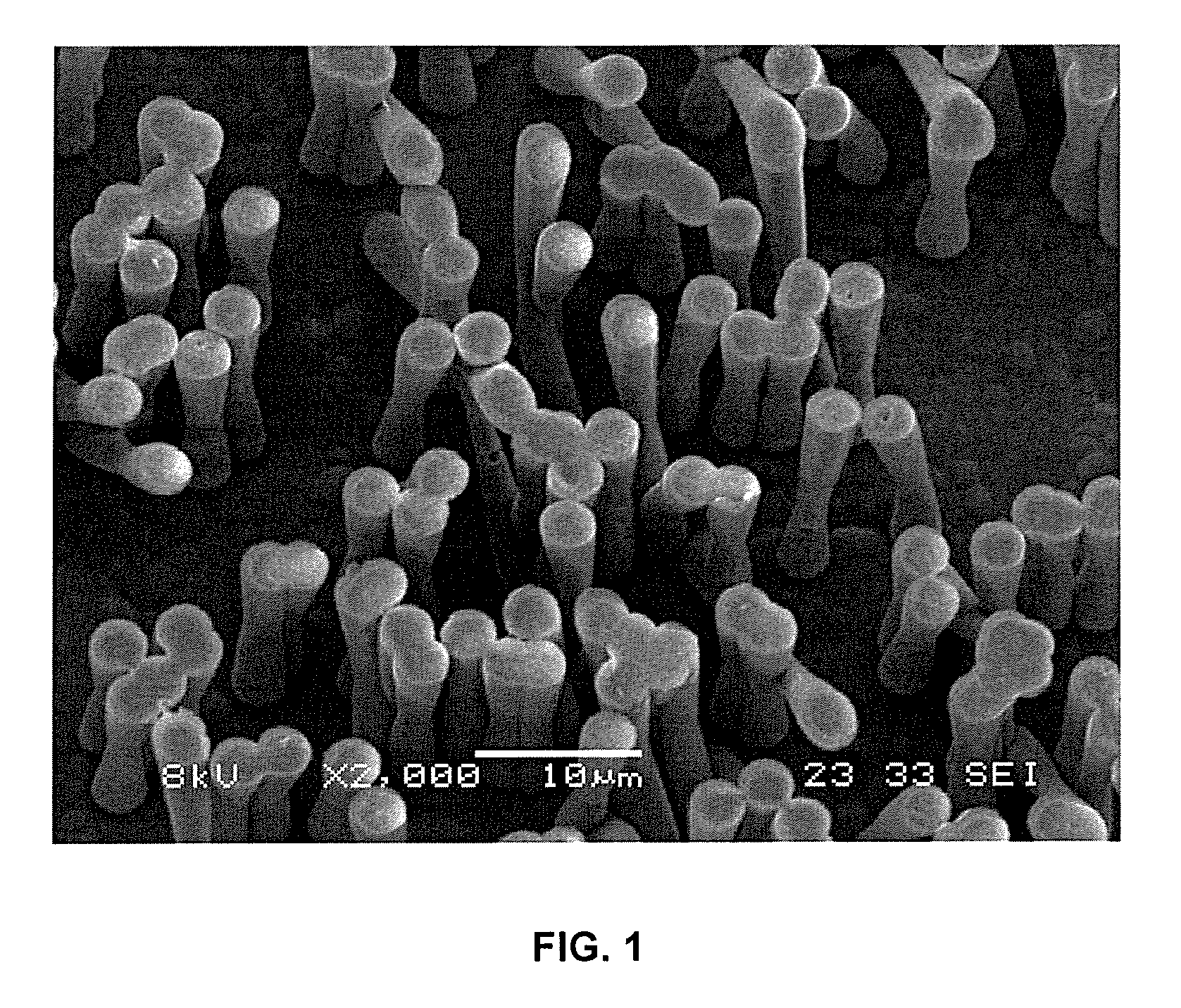
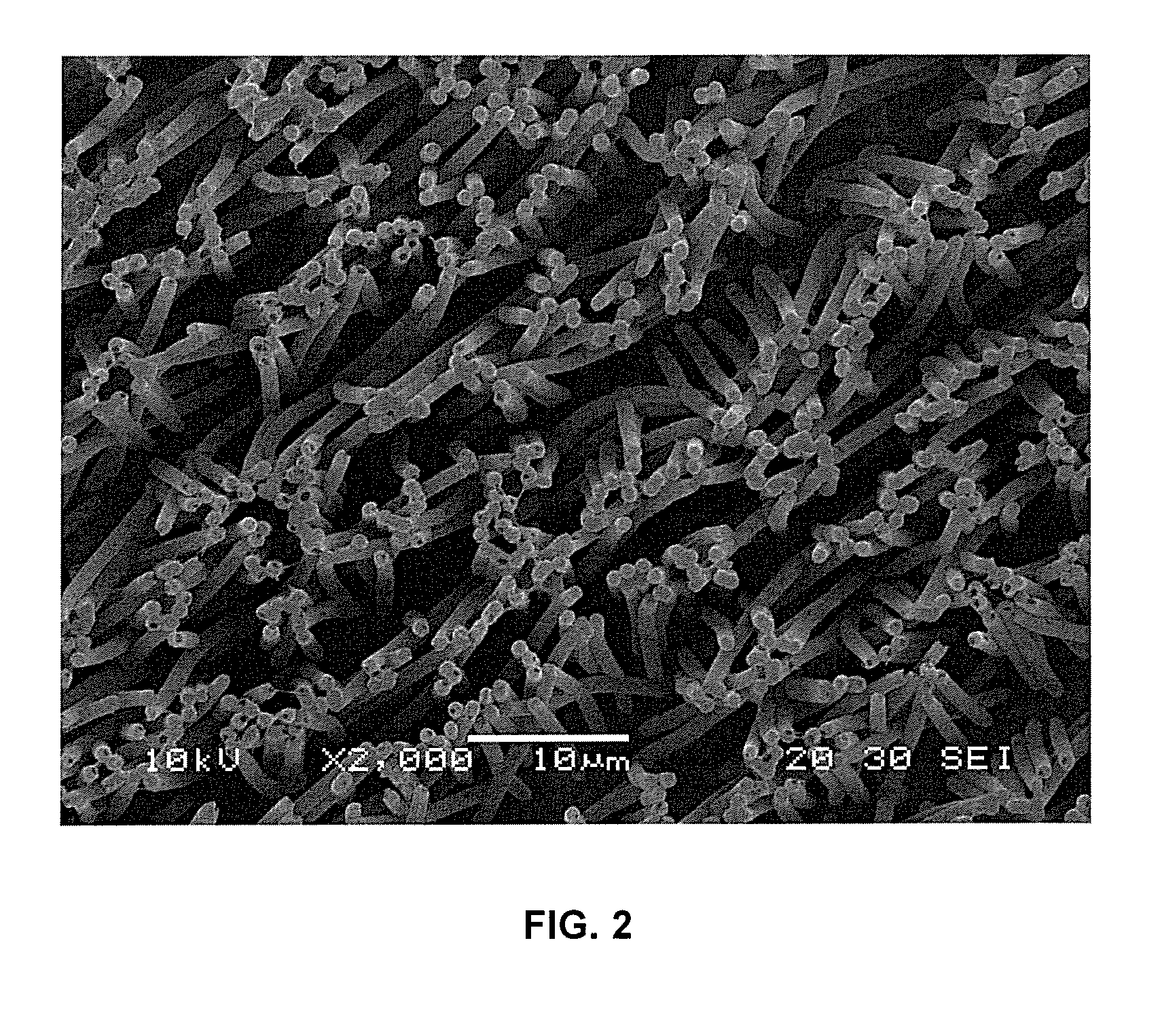
A polydioxanone film comprising substantially cylindrical polydioxanone pillars on at least one side thereof, said pillars having diameters from about 0.2 μm to about 3 μm, and heights from about 2 μm to about 20 μm from the surface of the film, a process for adsorbing proteins using the film and medical devices incorporating the film.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC +1
A kind of preparation method of biodegradable filling material and its product and application
ActiveCN106492284BEasy to fillEasy to operatePowder deliveryAerosol deliveryGel preparationPolymer science
The invention relates to a method for preparing biodegradable filling materials, a product prepared by the aid of the method and application of the product. The method mainly includes steps of (1), mixing matrix materials and dispersion-phase materials according to a mass ratio of 10:0-6:4 with one another and dissolving the matrix materials and the dispersion-phase materials in organic solvents to obtain high-polymer organic solvents; (2), treating the high-polymer organic solvents by the aid of a mechanical process or an emulsification process to obtain a micro-sphere. The matrix materials comprise polydioxanone; the dispersion-phase materials comprise a type of or a plurality of types of poly-L-lactic acid, polycaprolactone, polylactic acid and polyglycolic acid. The method, the product and the application have the advantages that the method is easy to implement, low in cost and good in repeatability, the product comprises tiny and stable particles, and the micro-sphere prepared by the aid of the method has similar and controllable particle sizes, is good in filling performance and tissue compatibility and is safe and degradable; the product can be degraded slowly, the degradation time can be regulated and controlled according to selection of the types and the adding proportions of the dispersion-phase materials; the micro-sphere can be used for preparing freeze-dried powder preparations and gel preparations, and the product is convenient to transport, store and clinically use.
Owner:重庆瑞凡德生物科技有限公司
Nano-hydroxyapatite-modified polyurethane urea bone repair material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108421086AImprove fragile featuresGood biocompatibilityPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTissue regenerationPorosityChemical reaction
The invention discloses a nano-hydroxyapatite-modified polyurethane urea bone repair material and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding nano-hydroxyapatite into a dihydroxy-terminal polydioxanone solution, uniformly dispersing and then heating; adding a diisocyanate chain extender containing a ureido structure and carrying out chain extension reaction to obtain a dual-terminal isocyanate prepolymer; carrying out self-crosslinking reaction on the dual-terminal isocyanate prepolymer and polyatomic alcohol, removing a solvent and carrying out vacuum drying at normal temperature to obtain the nano-hydroxyapatite-modified polyurethane urea bone repair material, wherein the chain extension reaction is a chemical reaction that hydroxyl reacts with isocyanato to generate a mephenesin carbamate group. According to the method, a polyurethane-urea high polymer material is integrated with nano-hydroxyapatite with high biocompatibility to obtaina framework material with high porosity and proper aperture size; and the obtained bone repair material has the advantages of controllable degradation performance, good repair effect, high mechanicalproperty, high biocompatibility, absorbable degradation product and the like.
Owner:济南羽时信息科技有限公司
Periodically degrading type tear drainage rebuilding system
InactiveCN101347365AWith bending resistanceMaintain pressure resistanceStentsEye implantsDiseaseP-dioxanone
The invention relates to a tear drainage reconstruction system that can be regularly degraded. The reconstruction system is made by adopting polydioxanone (PDO) that is a degradable polymeric biomaterial. The system comprises an upper lacrimal duct part, a lower lacrimal dust part, a main lacrimal duct, a concave dacryocyst part and a nasolacrimal duct part. The system has good flexibility, certain elasticity, extensibility, breaking strength and compression strength performance and is a lamella micro-porous tubular structure that integrates stable nasolacrimal duct supporting function, 'tears pump' function, dacryocyst drainage function, 'drug control-release' function, the function of accelerating the fade-away of chronic inflammation of a lacrimal duct and the repairing function of mucous membrane injury of the lacrimal duct together. The reconstruction system has the advantages that an implanting method is a simple and convenient, the fixation in the lacrimal duct is the stable and reliable and the iatrogenic lacrimal duct injury can not appear, the regular degradation can be realized without secondary take-out and the reconstruction system is suitable for various lacrimal duct obstruction diseases and has high curative ratio of the lacrimal duct obstruction, especially, the reconstruction system has the stable and reliable medium-to-long term effect. The tears drainage reconstruction system currently is the only perfect material for high-degree lacrimal duct reconstruction that combines the physiological drainage of the tears with the pathological mechanism of lacrimal injury repair.
Owner:吴文灿 +1
Absorbable suture anchor and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN112007216ASimple preparation processPerfect Biological FusionSuture equipmentsStaplesHydroxybutyric acidPhosphoric acid
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical equipment, and particularly relates to an absorbable suture anchor and a preparation method thereof. The suture anchor comprises an anchor bodyand a suture. The material of the anchor is formed by compounding polylactic acid and inorganic calcium phosphate, wherein the polylactic acid is L-polylactic acid (PLLA) or L-racemic polylactic acid(PLDLLA) or a combination of the L-polylactic acid (PLLA) and the L-racemic polylactic acid (PLDLLA), and the inorganic calcium phosphate is hydroxyapatite (HA) or beta-tricalcium phosphate (TCP) ora combination of the HA and the TCP. The suture is formed by weaving absorbable monofilament materials, and the absorbable monofilament materials comprise one or more of polylactic acid-glycolic acid(PLGA), polycaprolactone (PCL), polydioxanone (PPDO), polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) and polyhydroxybutyric acid (PHB). The anchor disclosed by the invention is formed by compounding the polylactic acid and the calcium phosphate, and meanwhile, the absorbable suture is adopted, so that degradation and absorption are carried out while bones and soft tissues grow together, and perfect biological fusionis achieved.
Owner:花沐医疗科技(上海)有限公司
Absorbable and knotting-free surgical suture capable of continuously resisting infection and used for thoracic surgery department
InactiveCN108853562AGood biocompatibilityHigh tensile strengthSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesFiberSide effect
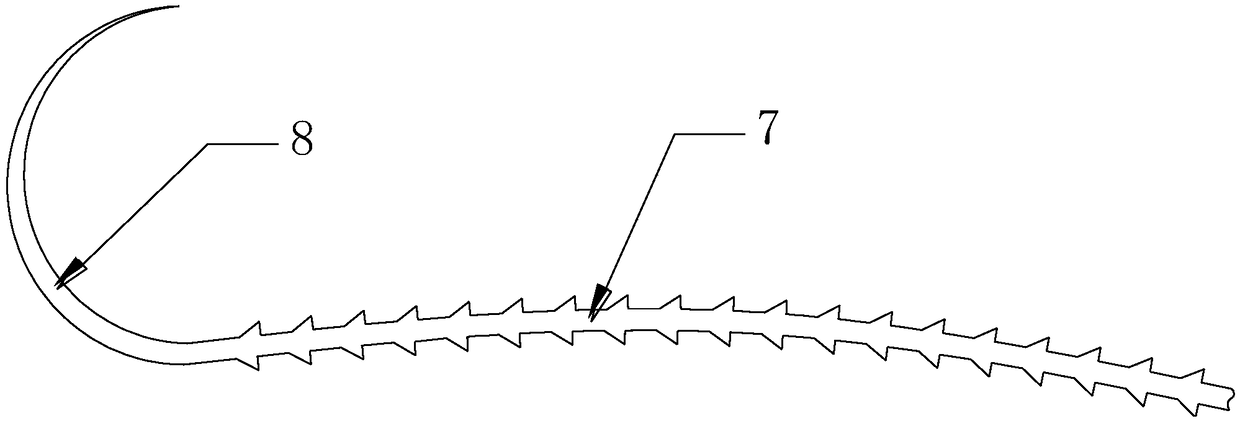
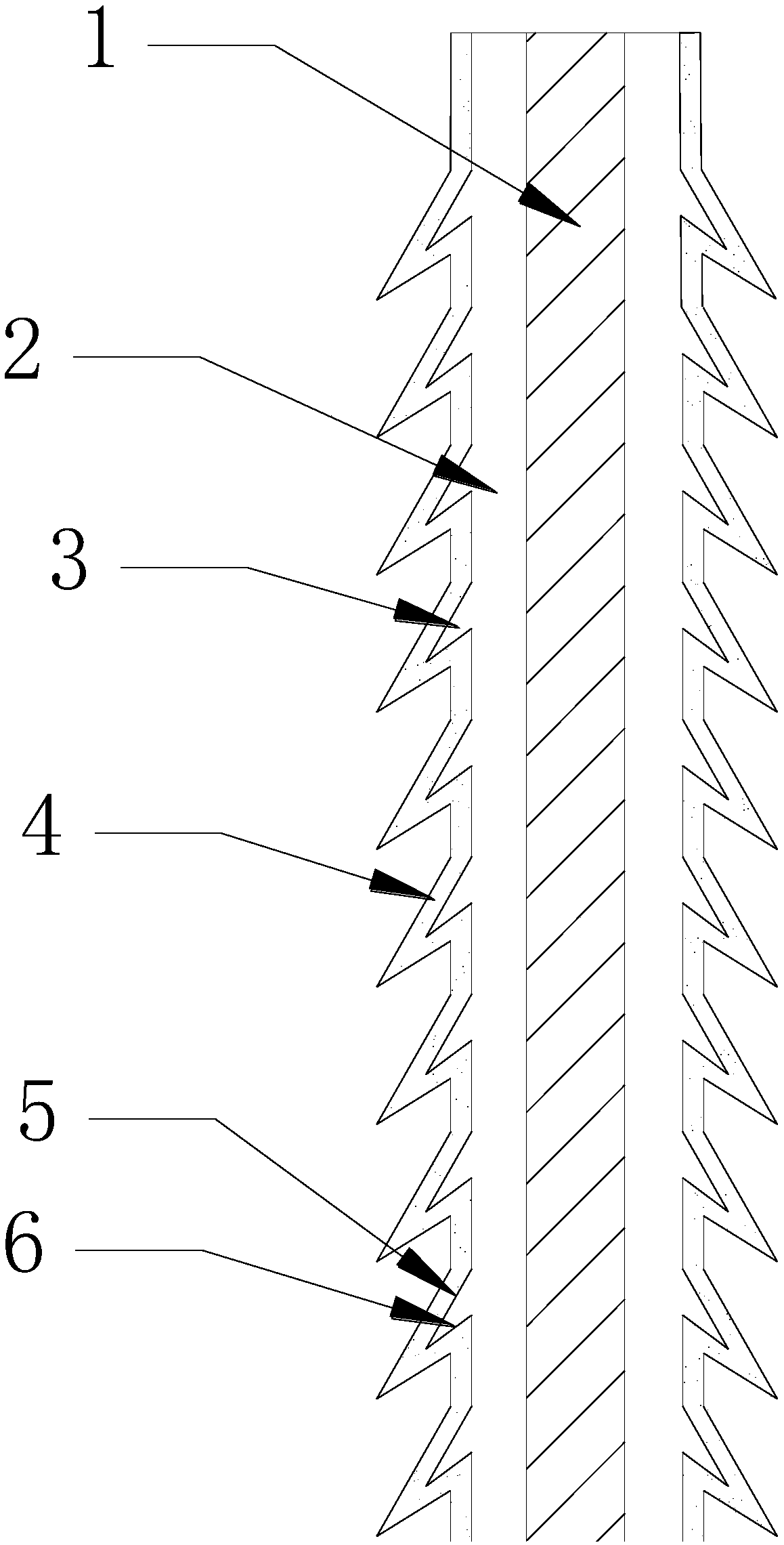
The invention provides an absorbable and knotting-free surgical suture capable of continuously resisting infection and used for thoracic surgery department. The absorbable and knotting-free surgical suture is composed of a PPDO (polydioxanone) fiber core located at the inner part, a compound drug-loading layer located in a middle layer and a collagen layer located on the outermost layer, wherein aplurality of tapered lug bosses are uniformly distributed on the compound drug-loading layer; the tapered lug bosses and the compound drug-loading layer are integrally molded; each tapered lug boss is composed of an inclined plane and a tabletop; the compound drug-loading layer is prepared from konjac glucomannan, quatemary ammonium salt chitosan, hyaluronic acid and genipin. The surgical sutureprepared by the invention does not need to be knotted in a surgery suturing process, can smoothly pass through muscle, does not easily slip off and has good biocompatibility; the absorbable and knotting-free surgical suture has a slow-release and antibacterial effect; after the absorbable and knotting-free surgical suture is degraded in a body, a product is discharged out of the body through metabolism, so that the absorbable and knotting-free surgical suture has no dangers and no toxic side effect.
Owner:王传强
Starch acetate-polydioxanone graft copolymer/inorganic particulate nano composite material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a starch acetate-polydioxanone graft copolymer / inorganic particulate nano composite material which is prepared from a starch acetate-polydioxanone graft copolymer base material and nanometer inorganic particulates, wherein the weight ratio of starch acetate to graft copolymers is 1 to 40:100, and the weight ratio of the nanometer inorganic particulates to the starch acetate-polydioxanone graft copolymers is 0.5 to 10:100. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the starch acetate-polydioxanone graft copolymer / inorganic particulate nano composite material. Because the starch acetate and the nanometer inorganic particulates are introduced into the copolymer, the production cost is reduced, the thermal property, the mechanical property and the biodegradation rate of the polydioxanone are increased, and the preparation method has lower requirements for a monomer and a reaction condition and has simple operation, high production efficiency and no environment pollution.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com