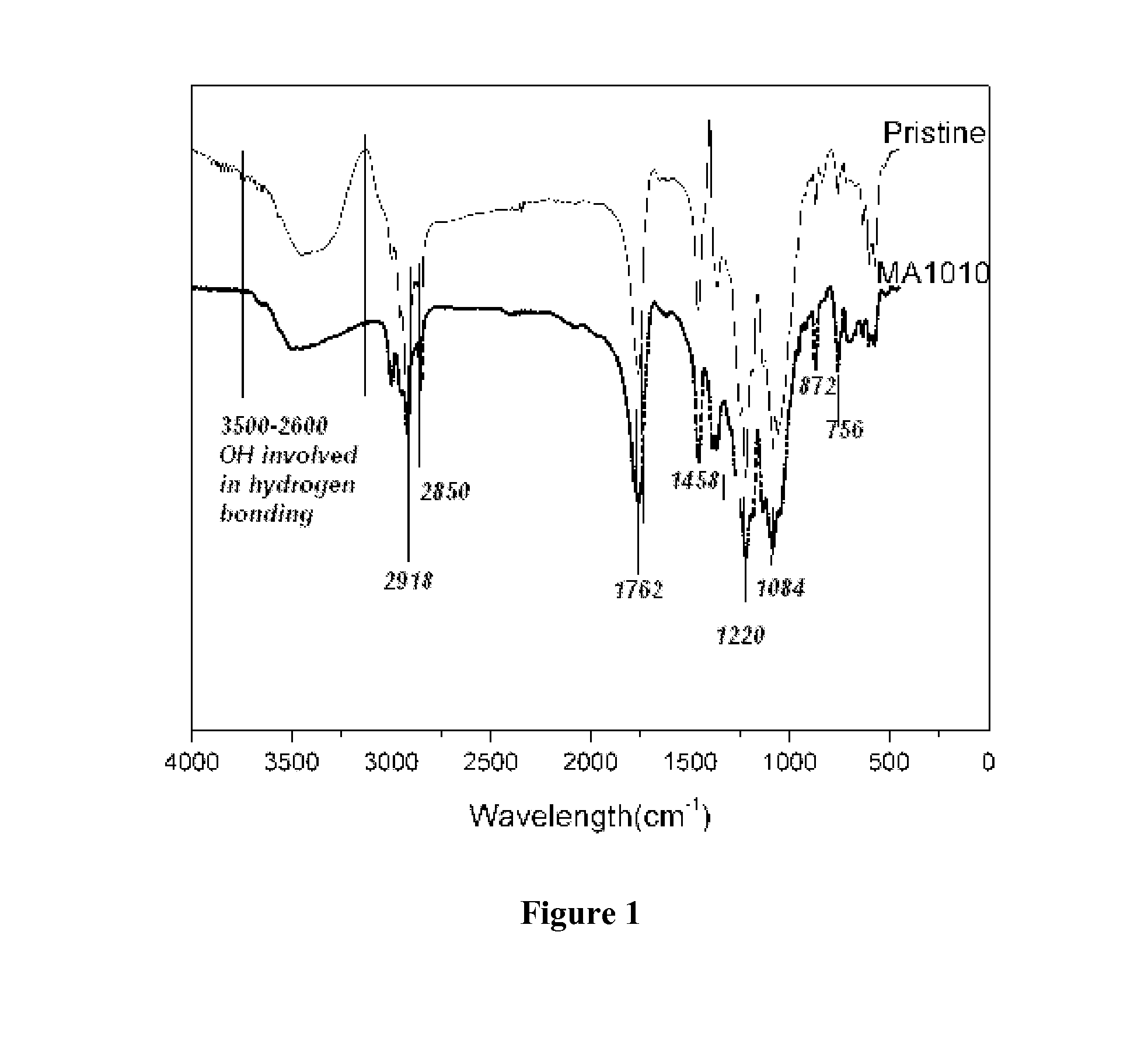
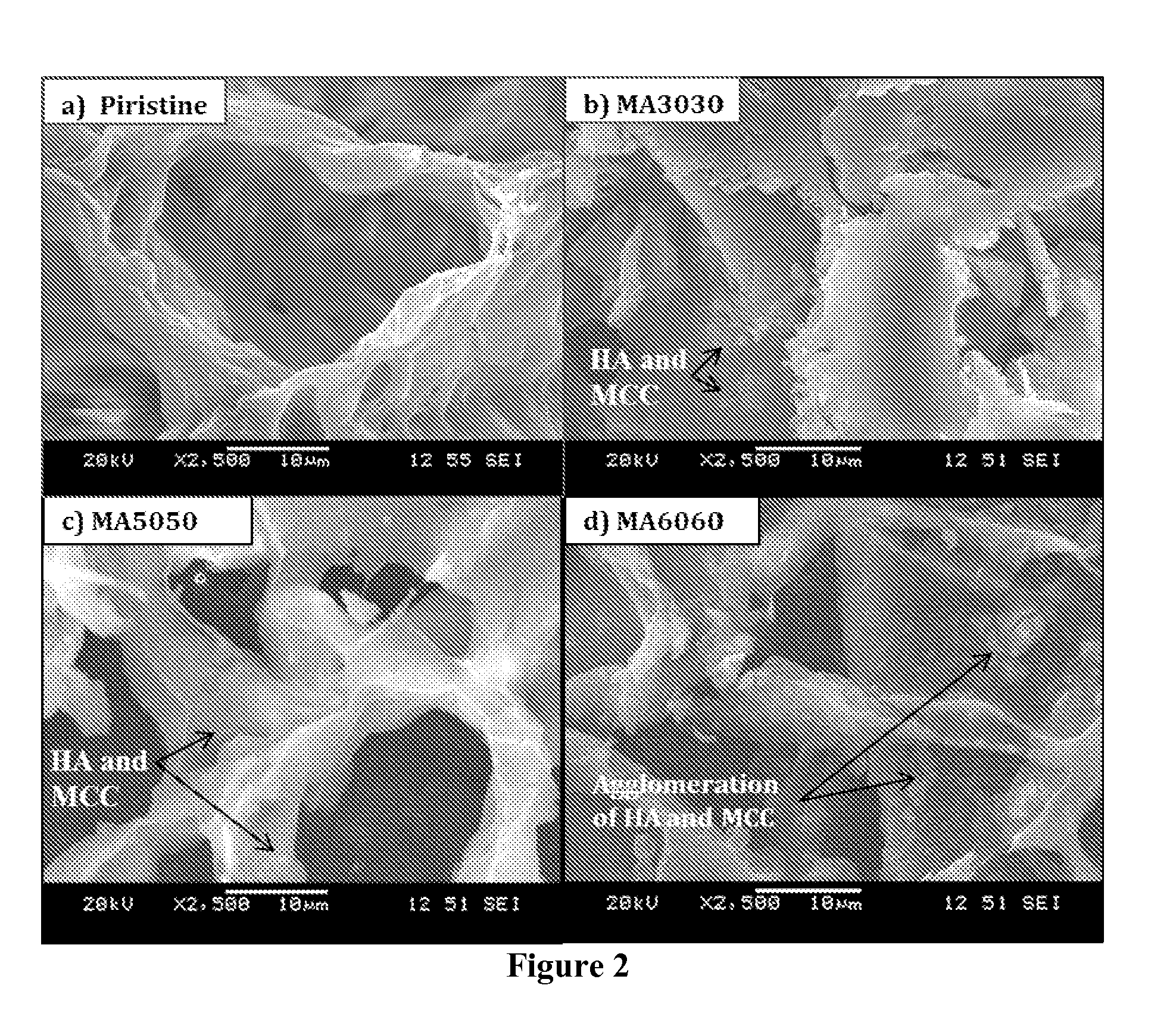
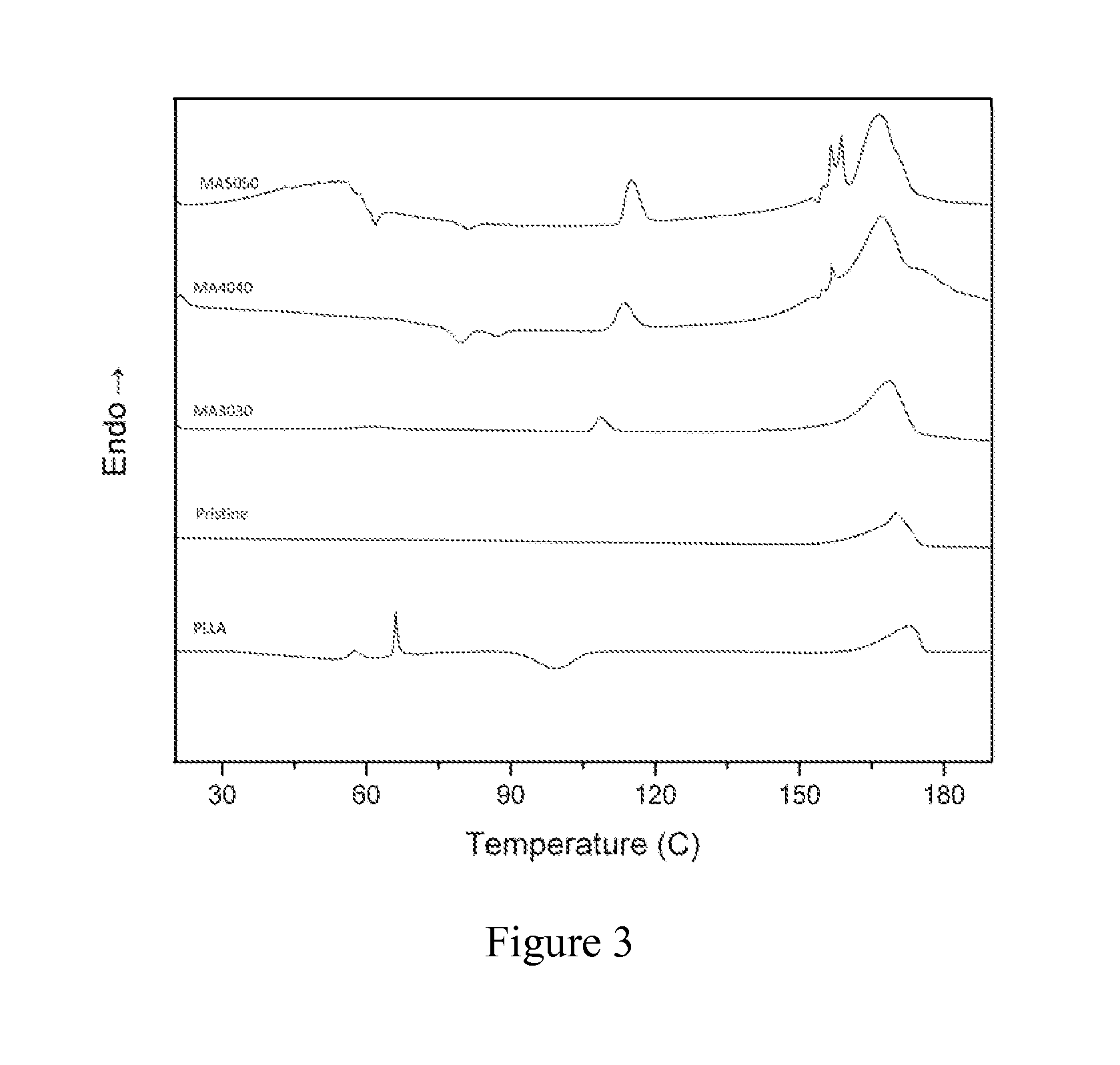
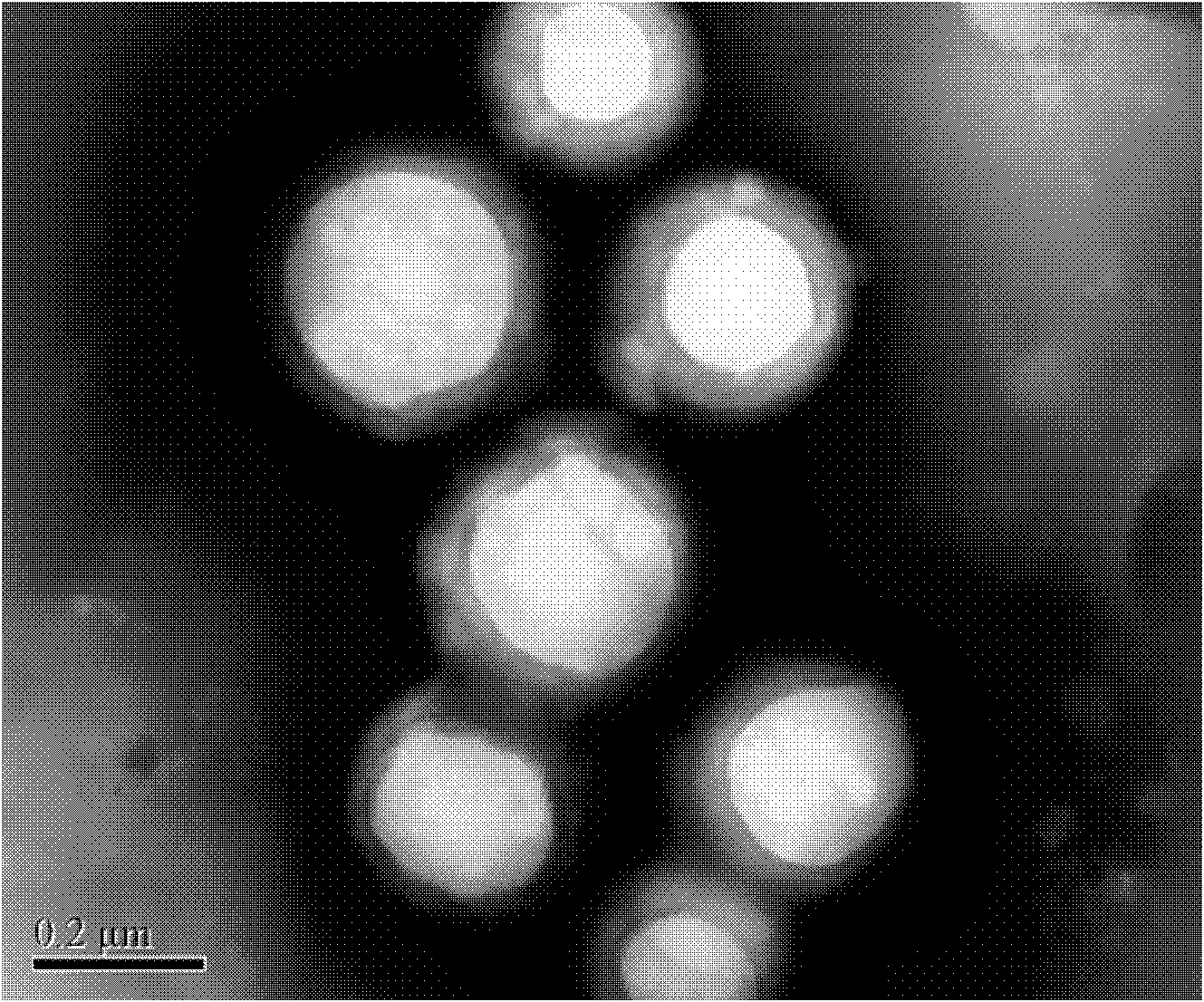Patents
Literature
171 results about "Poly-L-lactide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
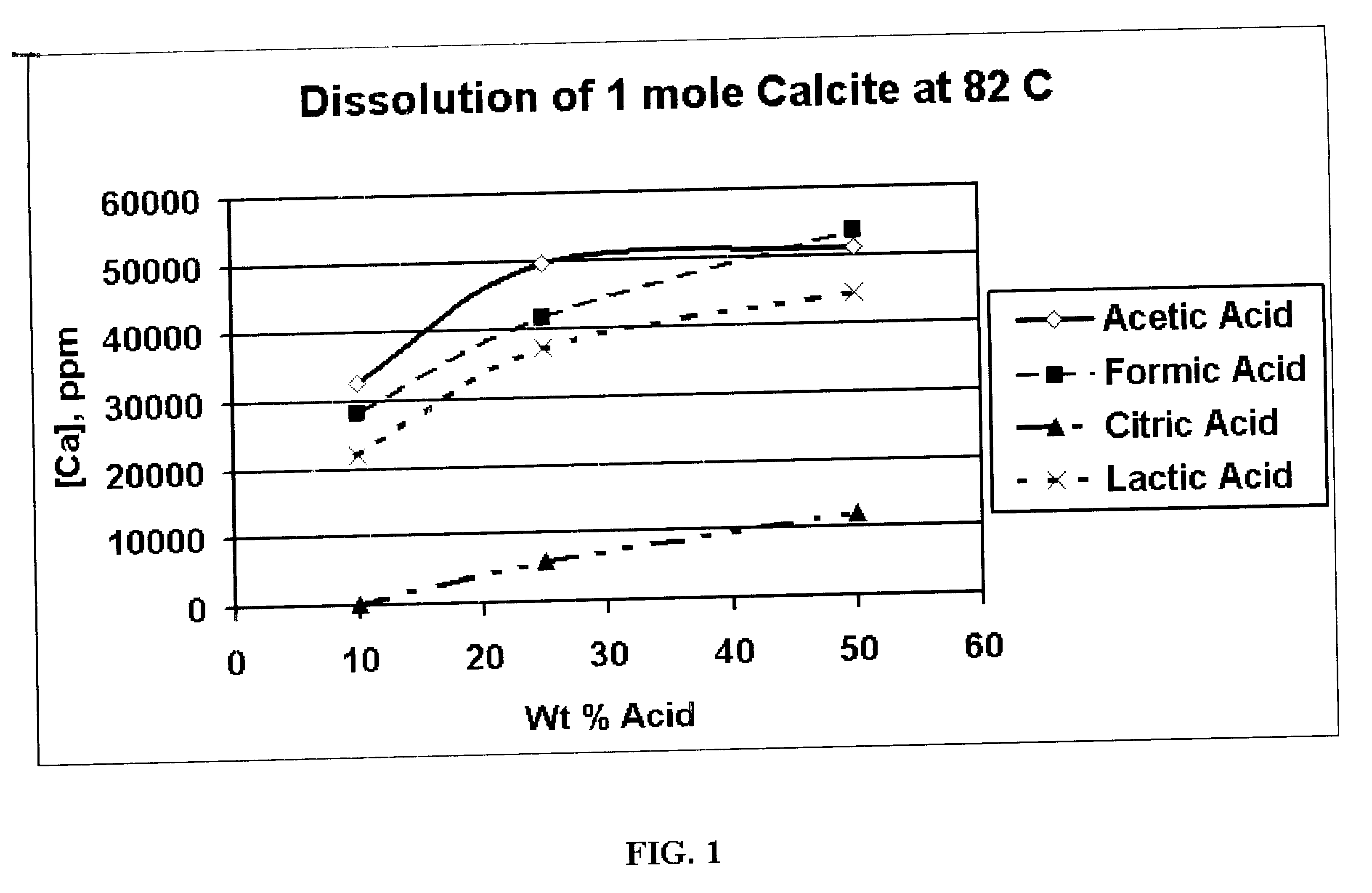
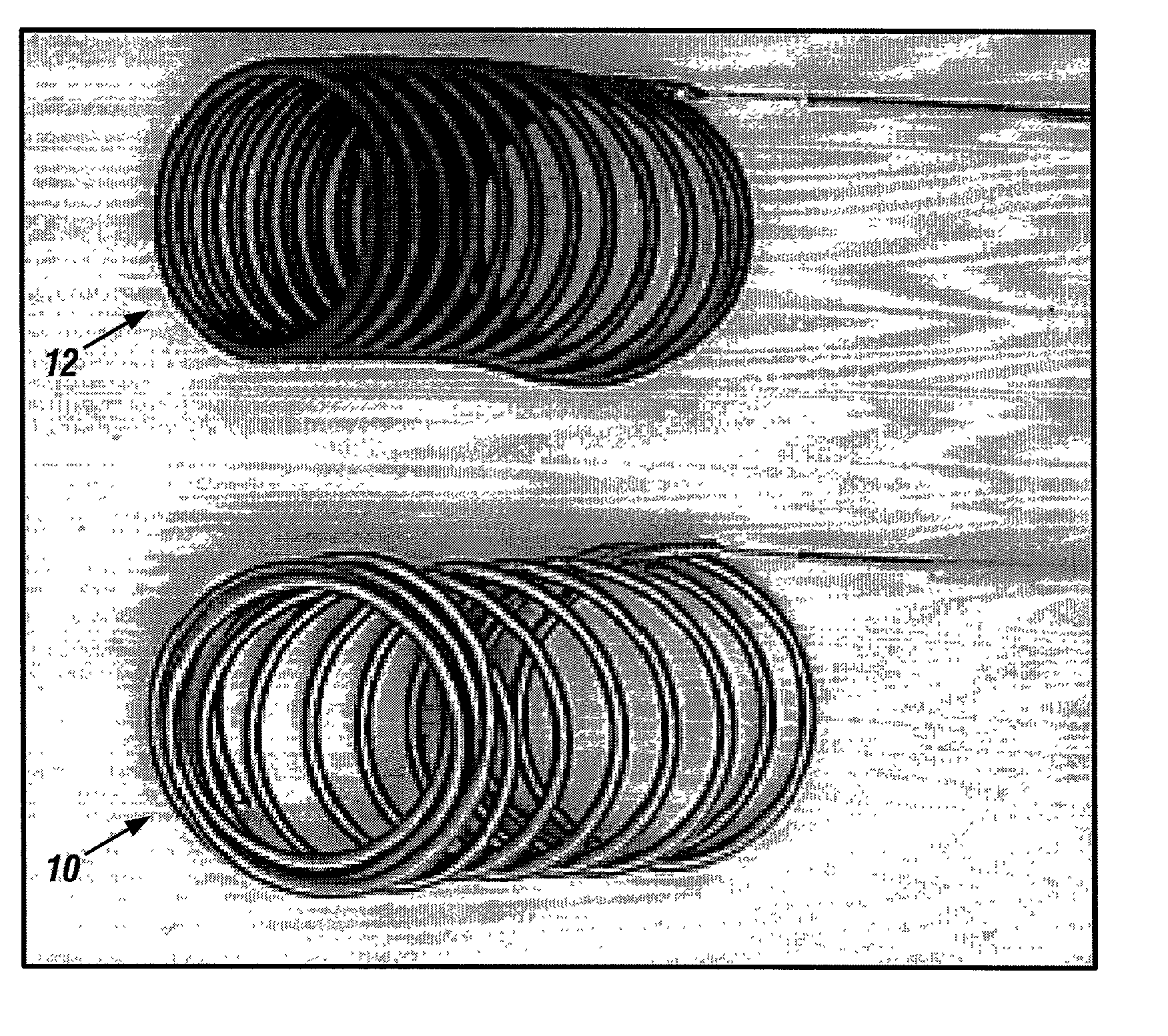
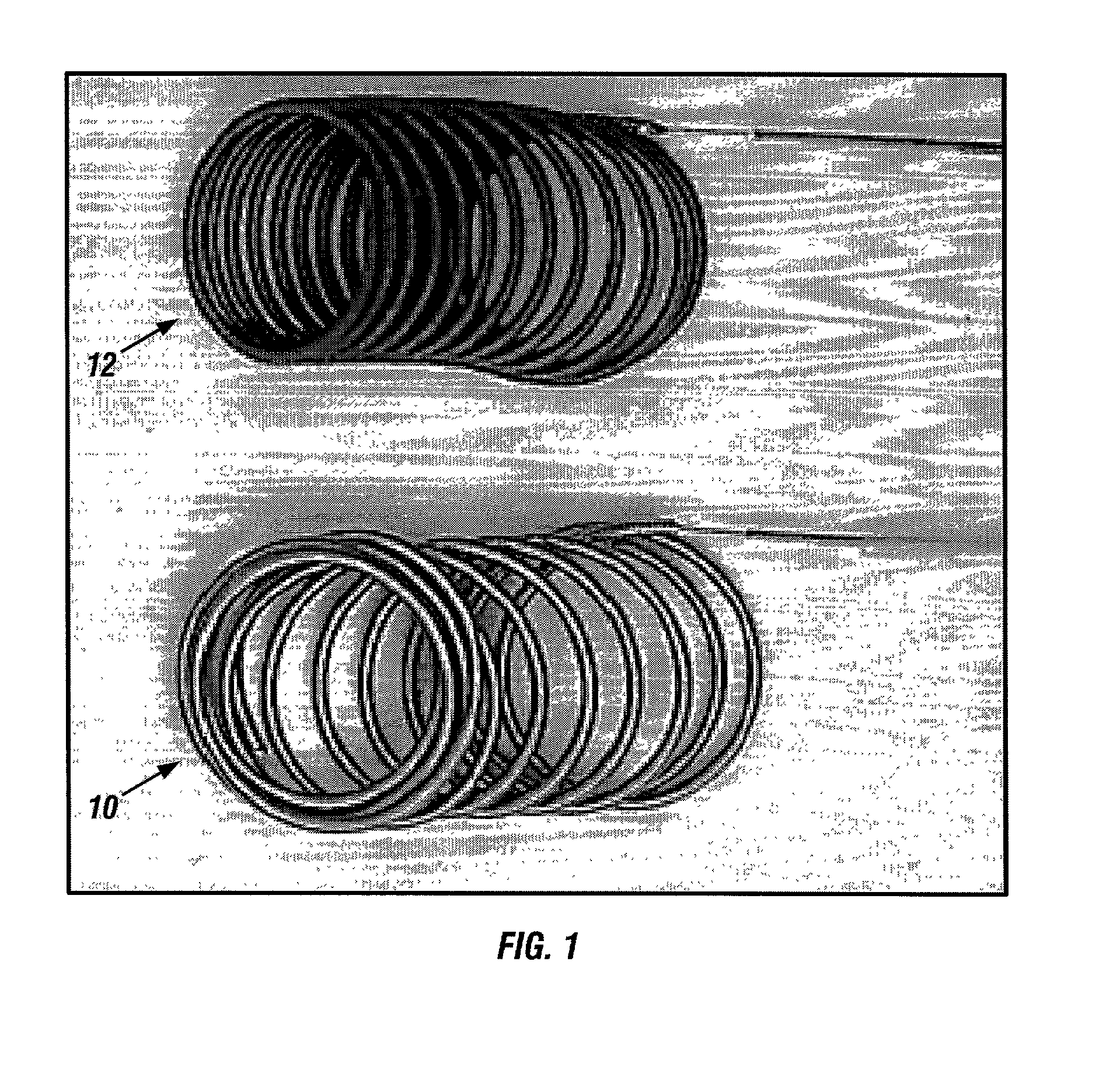
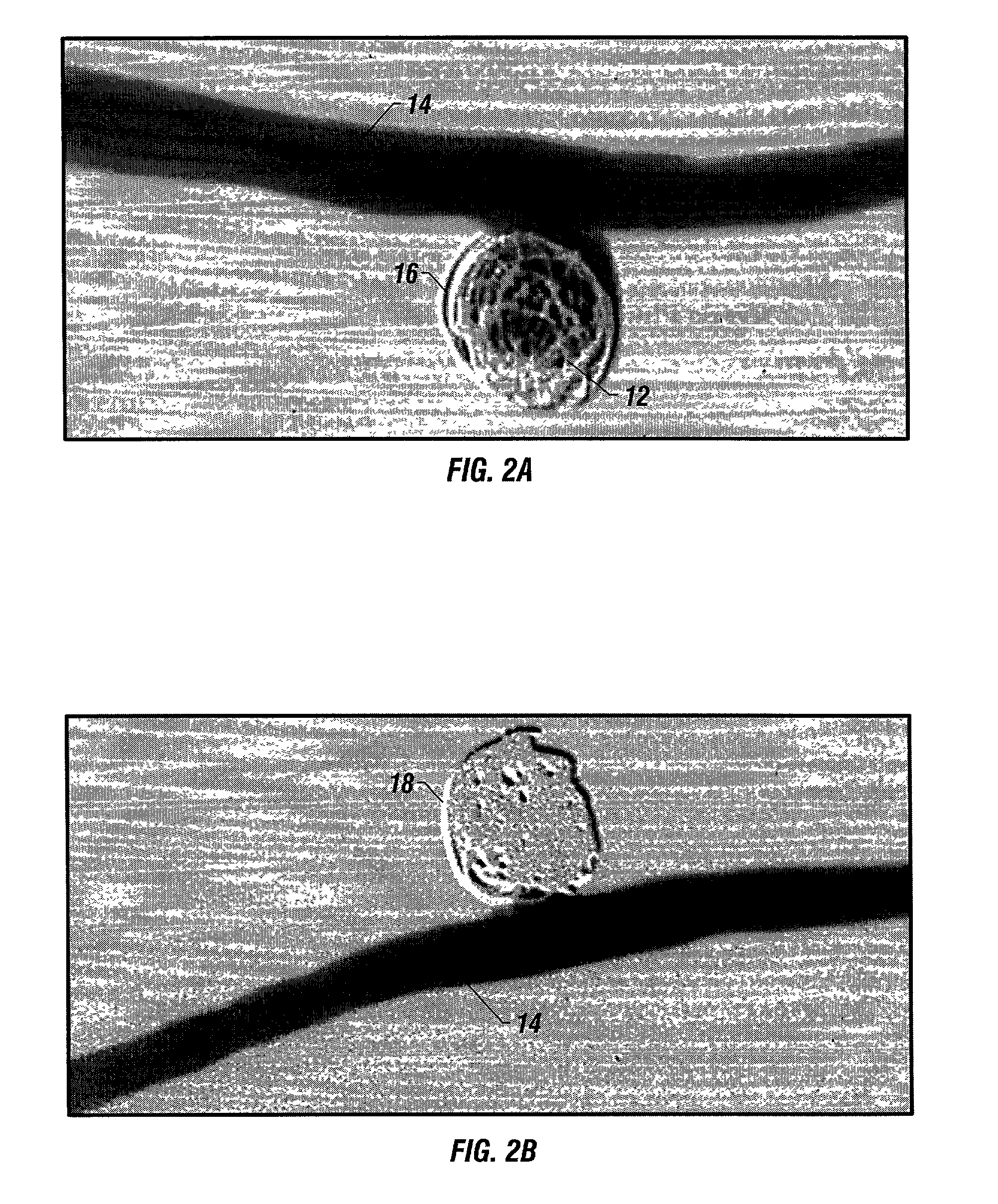
Generating Acid Downhole in Acid Fracturing
An acid fracturing method is provided in which the acid is generated in the fracture by hydrolysis of a solid acid-precursor selected from one or more than one of lactide, glycolide, polylactic acid, polyglycolic acid, a copolymer of polylactic acid and polyglycolic acid, a copolymer of glycolic acid with other hydroxy-, carboxylic acid-, or hydroxycarboxylic acid-containing moieties, and a copolymer of lactic acid with other hydroxy-, carboxylic acid or hydroxycarboxylic acid-containing moieties. The solid acid-precursor may be mixed with a solid acid-reactive material to accelerate the hydrolysis and / or coated to slow the hydrolysis. Water-soluble liquid compounds are also given that accelerate the hydrolysis. The method ensures that the acid contacts fracture faces far from the wellbore.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Bioabsorbable polymeric implants and a method of using the same to create occlusions
A new embolic agent, bioabsorbable polymeric material (BPM) is incorporated to a Guglielmi detachable coil (GDC) to improve long-term anatomic results in the endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms. The embolic agent, comprised at least in part of at least one biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer and growth factors, is carried by hybrid bioactive coils and is used to accelerate histopathologic transformation of unorganized clot into fibrous connective tissue in experimental aneurysms. An endovascular cellular manipulation and inflammatory response are elicited from implantation in a vascular compartment or any intraluminal location. Thrombogenicity of the biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer is controlled by the composition of the polymer. The coil further is comprised at least in part of a growth factor or more particularly a vascular endothelial growth factor, a basic fibroblast growth factor or other growth factors. The biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer is in the illustrated embodiment at least one polymer selected from the group consisting of polyglycolic acid, poly˜glycolic acid / poly-L-lactic acid copolymers, polycaprolactive, polyhydroxybutyrate / hydroxyvalerate copolymers, poly-L-lactide. Polydioxanone, polycarbonates, and polyanhydrides.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Biodegradable polymer coils for intraluminal implants
An endovascular cellular manipulation and inflammatory response are elicited from implantation in a vascular compartment or any intraluminal location of a separable coil comprised at least in part of at least one biocompatible and absorbable polymer or protein and growth factors. Typically a catheter associated with the separable coil is used to dispose the coil into a selected body lumen. The biocompatible and absorbable polymer or protein is thrombogenic. The coil further is comprised at least in part of a growth factor or more particularly a vascular endothelial growth factor, a basic fibroblast growth factor or other growth factors. The biocompatible and absorbable polymer is in the illustrated embodiment at least one polymer selected from the group consisting of polyglycolic acid, poly~glycolic acid poly-L-lactic acid copolymers, polycaprolactive, polyhydroxybutyrate / hydroxyvalerate copolymers, poly-L-lactide. Polydioxanone, polycarbonates, and polyanhydrides. The biocompatible and absorbable protein is at least one protein selected from the group consisting of collagen, fibrinogen, fibronectin, vitronectin, laminin, and gelatin. In one embodiment the coil is composed of the biocompatible and absorbable polymer or protein with a radio-opaque material is disposed thereon. Alternatively, the coil is composed of a radio-opaque material, and the biocompatible and absorbable polymer or protein is disposed thereon. This apparatus may be positioned within intracranial aneurysms or any aneurysm in the body as well as within other body cavities.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Bioabsorbable polymeric implants and a method of using the same to create occlusions
InactiveUS20020040239A1Peptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical containersPoly-L-lactideVascular compartment
A new embolic agent, bioabsorbable polymeric material (BPM) is incorporated to a Guglielmi detachable coil (GDC) to improve long-term anatomic results in the endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms. The embolic agent, comprised at least in part of at least one biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer and growth factors, is carried by hybrid bioactive coils and is used to accelerate histopathologic transformation of unorganized clot into fibrous connective tissue in experimental aneurysms. An endovascular cellular manipulation and inflammatory response are elicited from implantation in a vascular compartment or any intraluminal location. Thrombogenicity of the biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer is controlled by the composition of the polymer. The coil further is comprised at least in part of a growth factor or more particularly a vascular endothelial growth factor, a basic fibroblast growth factor or other growth factors. The biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer is in the illustrated embodiment at least one polymer selected from the group consisting of polyglycolic acid, poly~glycolic acid / poly-L-lactic acid copolymers, polycaprolactive, polyhydroxybutyrate / hydroxyvalerate copolymers, poly-L-lactide. Polydioxanone, polycarbonates, and polyanhydrides.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
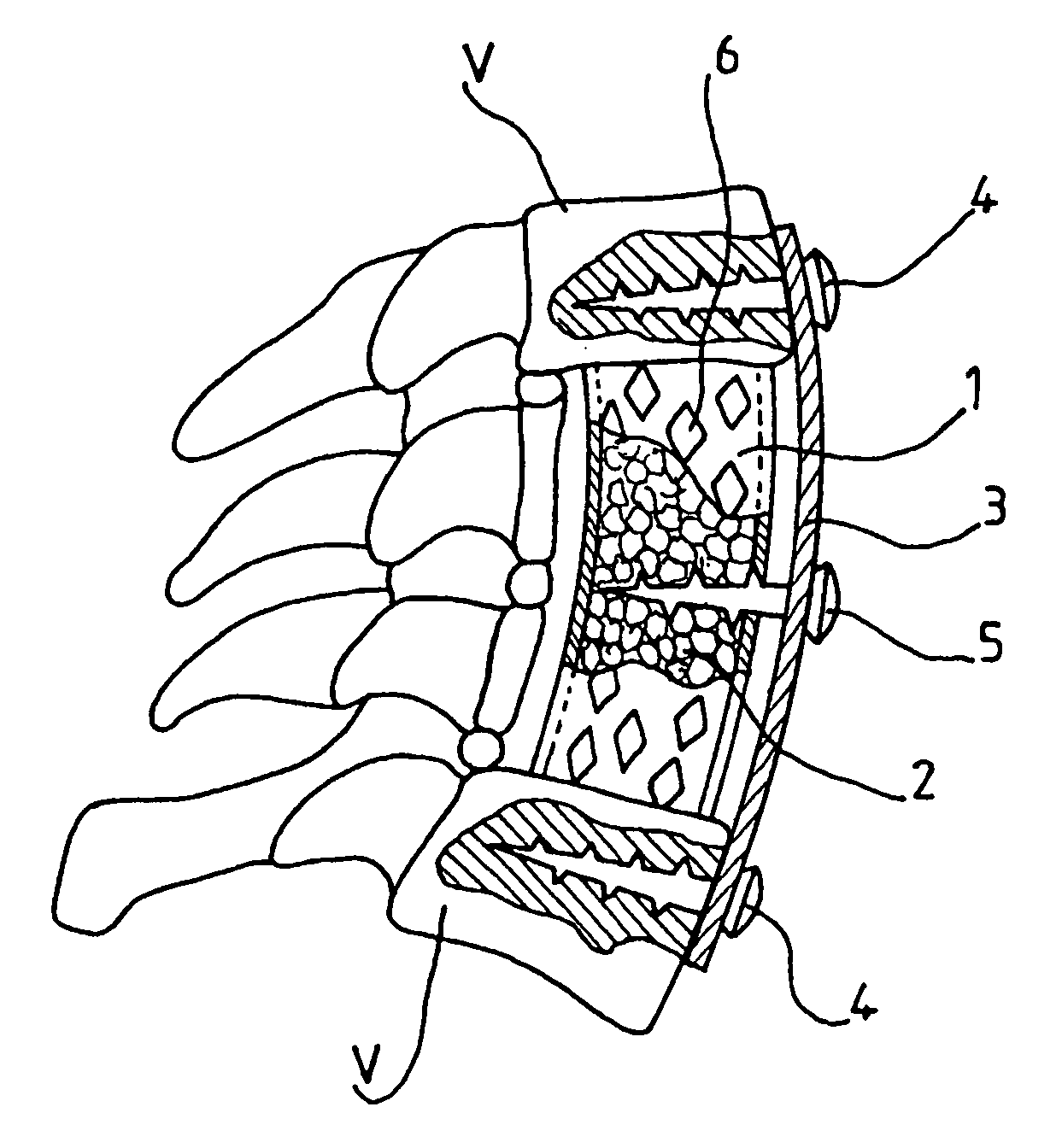
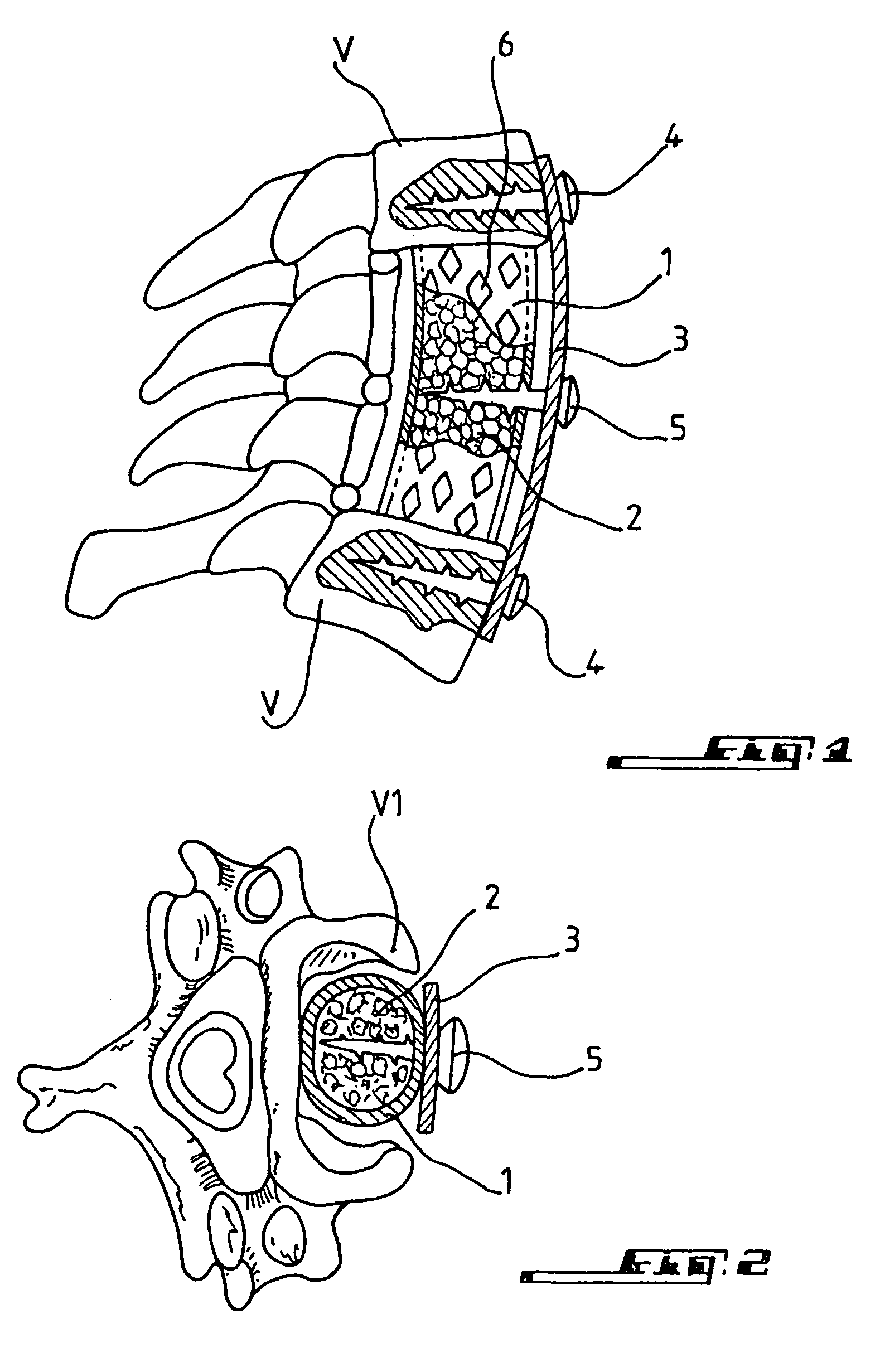
Bone repair device
A bone repair device includes a mesh tube coated with poly-L-Lactide and in which a graft is inserted. The tube is maintained in position by a plate fixed with screws to healthy bone portions. The invention is useful for filling bone cavities.
Owner:COUSIN BIOTECH R L
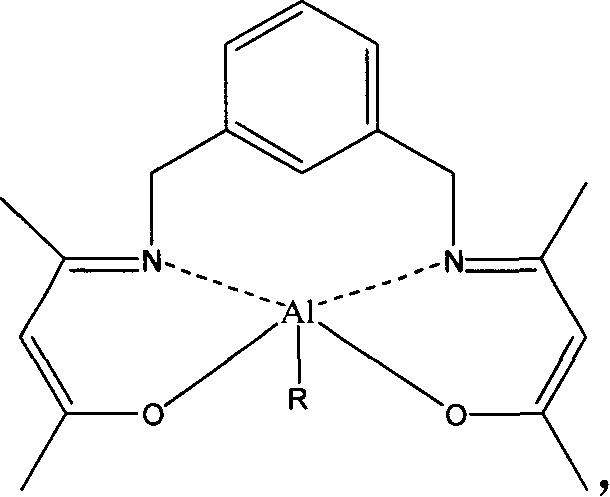
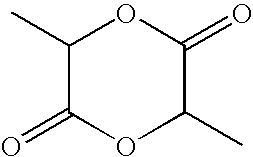
Enol form lactide open-ring polymerization catalyst and its preparing method and use
This invention relates to an enol form lactide open loop polymerized catalyst and its preparation method and also a method for polymerizing lactide by the catalyst including levo-lactied, right handed lactide, meso-lactide, dl-lactide and a mixer of any proportions between levo-lactide and right handed lactide, in which, the catalyst refers to the product reacted by an enol form Schiff base and Alethyl and their derivation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HISUN BIOMATERIALS
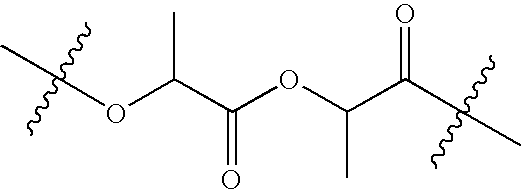
Bioabsorbable Polymeric Compositions and Medical Devices
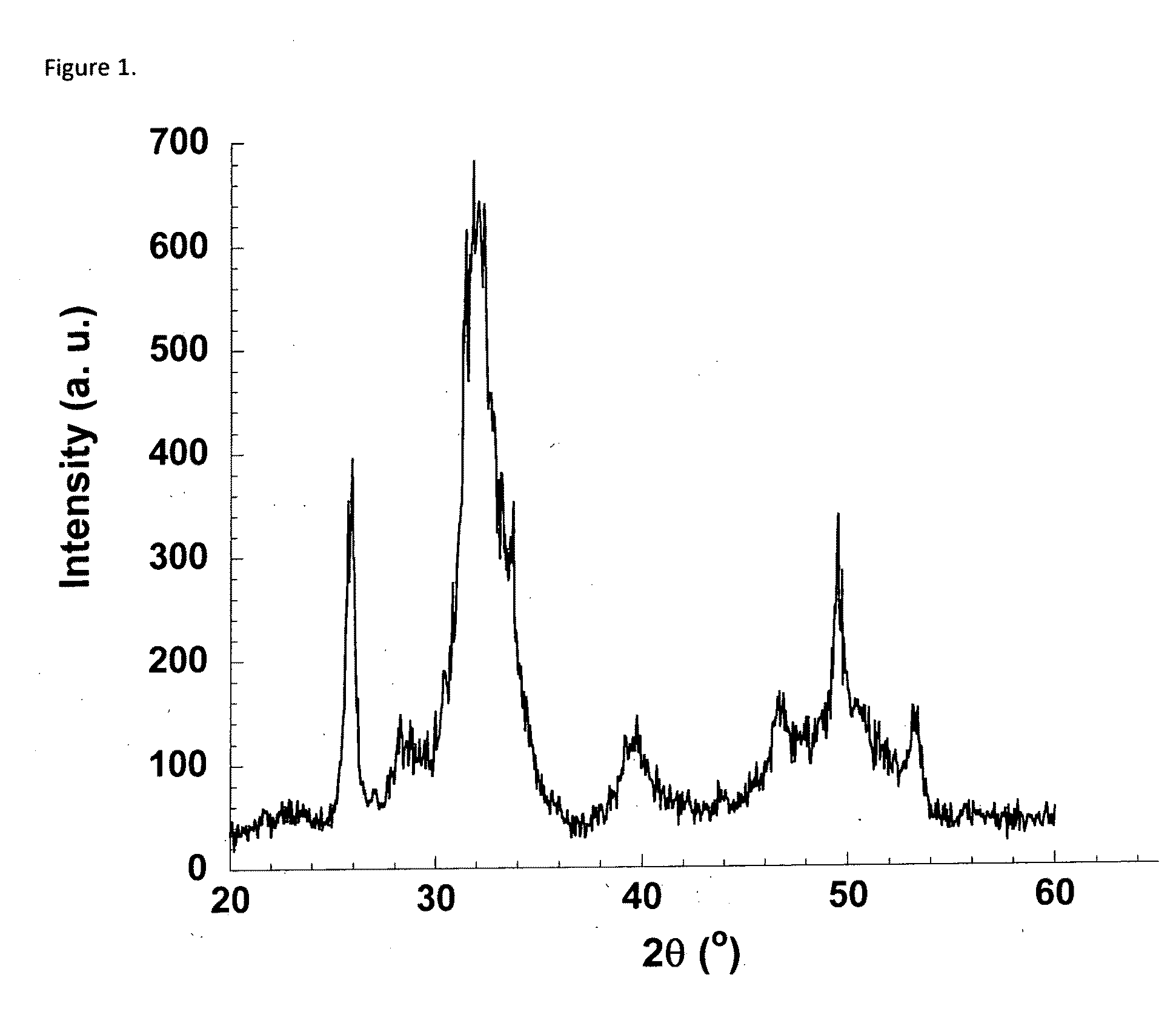
The present invention comprises a stent forming a plurality of meandering elements comprising a blend formed from a polymer. The polymer comprises poly-L-lactide, poly-D-lactide or mixtures thereof and a copolymer moiety comprising poly-L-lactide or poly-D-lactide linked with ε-caprolactone or trimethylcarbonate. The poly-L-lactide or poly-D-lactide sequence in the copolymer moiety is random with respect to the distribution of ε-caprolactone or trimethylcarbonate and the copolymer moiety molecular weight ranges from about 1.2 IV to about 4.8 IV. The meandering elements may be stretched to a modulus ranging from about 250000 PSI to about 550,000 PSI, one segment of the meandering element has a decreased cross-sectional area and may have a wide-angle X-ray scattering (WAXS) 2θ values of ranging from about 1 to about 35. In various embodiment, two, three or n segments of the meandering element have a decreased cross-sectional area and may also have a wide-angle X-ray scattering (WAXS) 2θ values of ranging from about 1 to about 35 after stretching. In another embodiment, all segments of the meandering element have a decreased cross-sectional area and may also have a wide-angle X-ray scattering (WAXS) 2θ values of ranging from about 1 to about 35 after stretching. The meandering element may comprise a helical winding, a circumferential winding or stent ringlet. The properties of the bioabsorbable polymers allow for both crimping and expansion of the stent. The crystal properties of the bioabsorbable polymers may change during crimping and / or expansion allowing for improved mechanical properties such as tensile strength and slower degradation kinetics.
Owner:ORBUSNEICH MEDICAL PTE LTD
Super-tough high heat-resistant polylactic acid / elastomer blended material or article and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104910598AEffective control of decentralizationEffective control of dispersed phase morphologyElastomerPolymer science
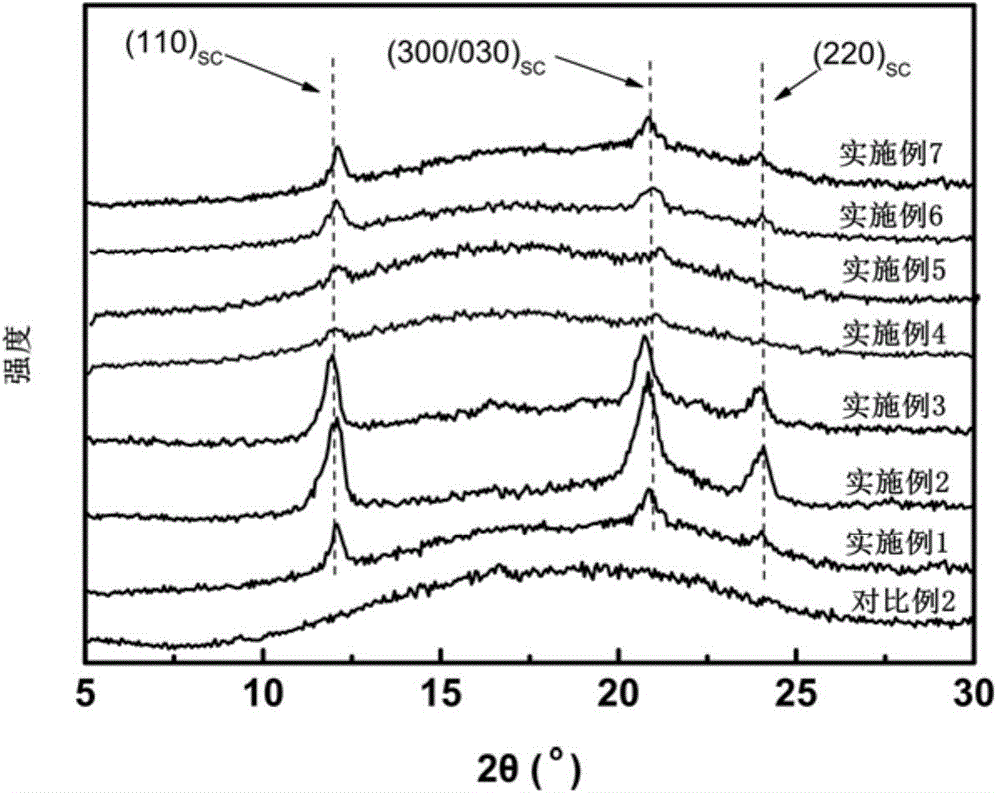
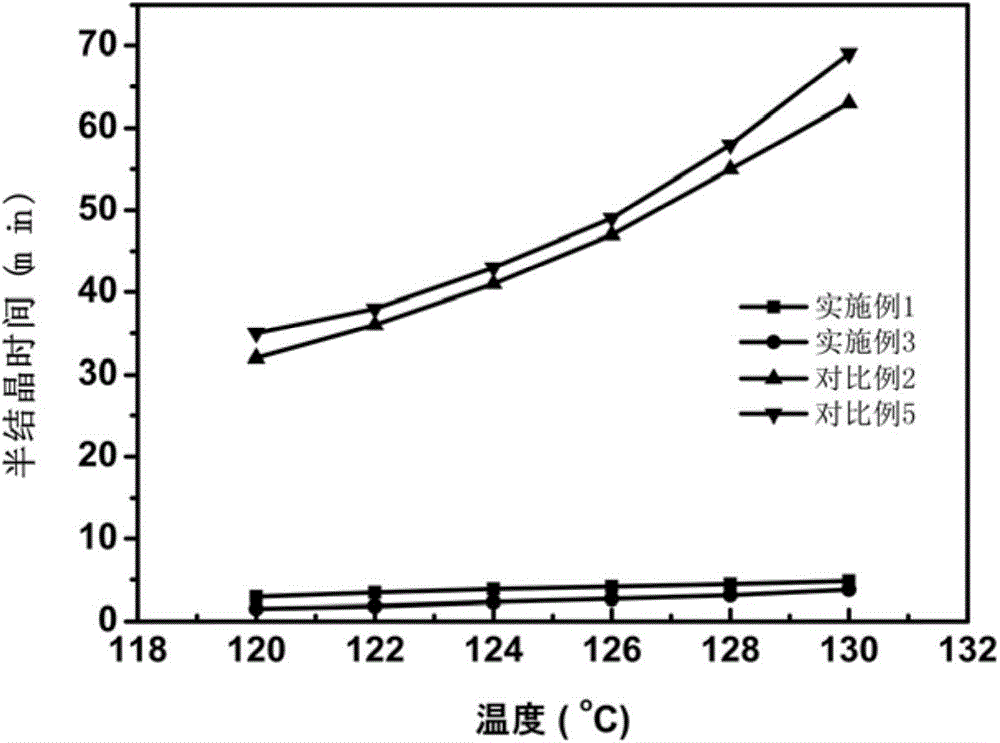
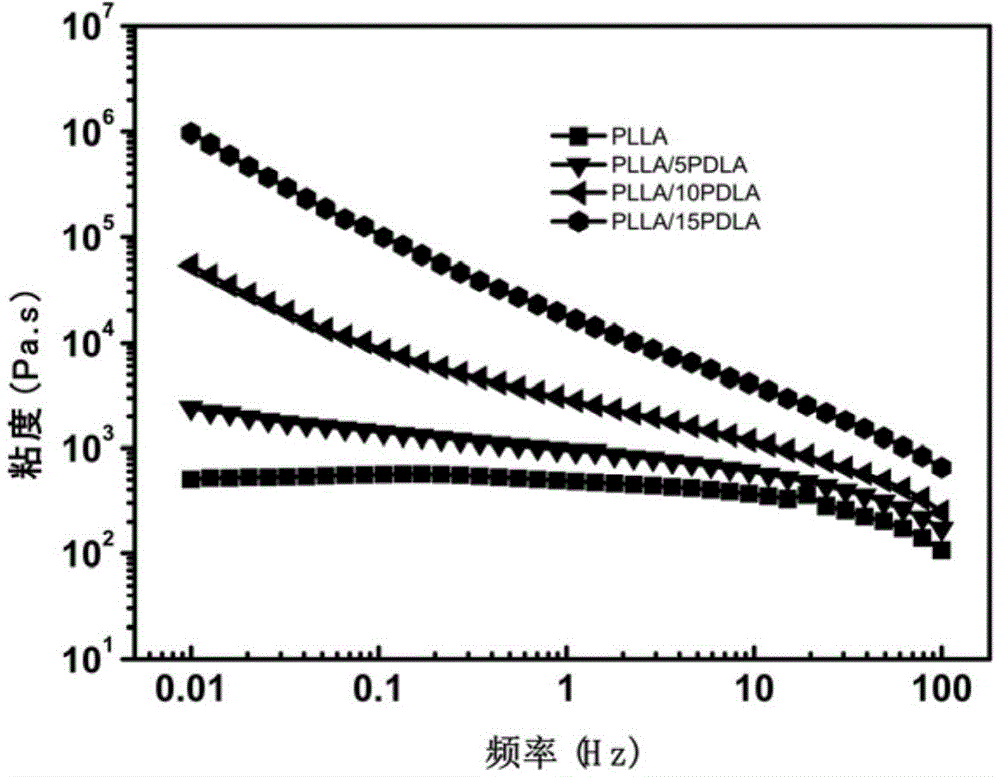
The present invention discloses a super-tough high heat resistant polylactic acid / elastomer blended material or an article, which is prepared by melting and blending or further processing and molding the following components: 75 to 99 parts of poly-L-lactic acid or poly-D-lactic acid, 1 to 25 parts of third component poly-D-lactic acid or poly-L-lactic acid, and elastomer accounting to 5-30wt% of the total amount of the polylactic acid, the crystallinity of the obtained blended material or article is 43-53%, the heat resistant temperature is 113.5-140.5 DEG C, and notch impact strength is 20.5-93.3kJ / m<2>. By use of the characteristic of easy stereocomplexing of chiral polylactic acid molecules, stereocomplex crystals are formed in suit in a melt from small amount of third component molecular chains and matrix molecular chains, on the one hand the stereocomplex crystals can be used as a rheology modifier to change the dispersion state of the elastomer in a matrix to improve the toughening efficiency of the elastomer on the matrix, and on the other hand the stereocomplex crystals can be used as a nucleating agent to greatly accelerate matrix crystallization. The method is not only ingenious in design, but also provides an effective and simple way for the development of super-tough high heat-resistant polylactic acid blended materials or articles.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Bioabsorbable Polymeric Compositions and Medical Devices
The bioabsorbable polymers and compositions of the present invention may be formed into medical devices such as stents that can be crimped onto a catheter system for delivery into a blood vessel. The properties of the bioabsorbable polymers allow for both crimping and expansion of the stent. The crystal properties of the bioabsorbable polymers may change during crimping and / or expansion allowing for improved mechanical properties such as tensile strength and slower degradation kinetics. Typically, bioabsorbable polymers comprise aliphatic polyesters based on lactide backbone such as poly L-lactide, poly D-lactide, poly D,L-lactide, mesolactide, glycolides, lactones, as homopolymers or copolymers, as well as formed in copolymer moieties with co-monomers such as, trimethylene carbonate (TMC) or ε-caprolactone (ECL).
Owner:ORBUSNEICH MEDICAL PTE LTD
Bioabsorbable polymeric implants and a method of using the same to create occlusions
A new embolic agent, bioabsorbable polymeric material (BPM) is incorporated to a Guglielmi detachable coil (GDC) to improve long-term anatomic results in the endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms. The embolic agent, comprised at least in part of at least one biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer and growth factors, is carried by hybrid bioactive coils and is used to accelerate histopathologic transformation of unorganized clot into fibrous connective tissue in experimental aneurysms. An endovascular cellular manipulation and inflammatory response are elicited from implantation in a vascular compartment or any intraluminal location. Thrombogenicity of the biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer is controlled by the composition of the polymer. The coil further is comprised at least in part of a growth factor or more particularly a vascular endothelial growth factor, a basic fibroblast growth factor or other growth factors. The biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer is in the illustrated embodiment at least one polymer selected from the group consisting of polyglycolic acid, poly˜glycolic acid / poly-L-lactic acid copolymers, polycaprolactive, polyhydroxybutyrate / hydroxyvalerate copolymers, poly-L-lactide. Polydioxanone, polycarbonates, and polyanhydrides.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
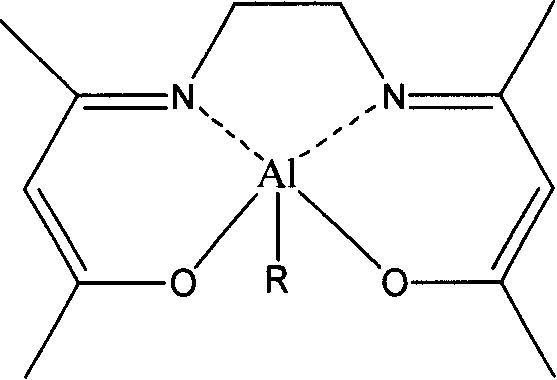
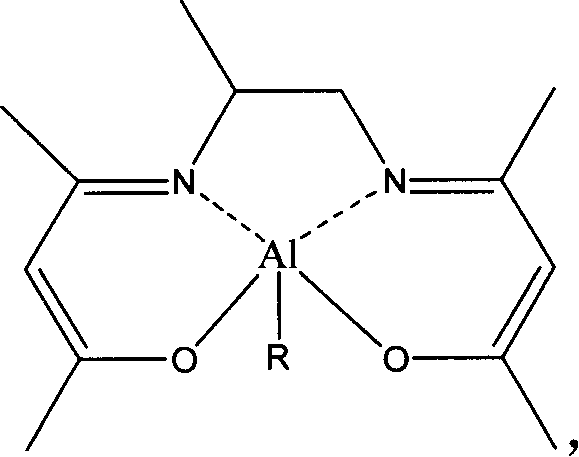
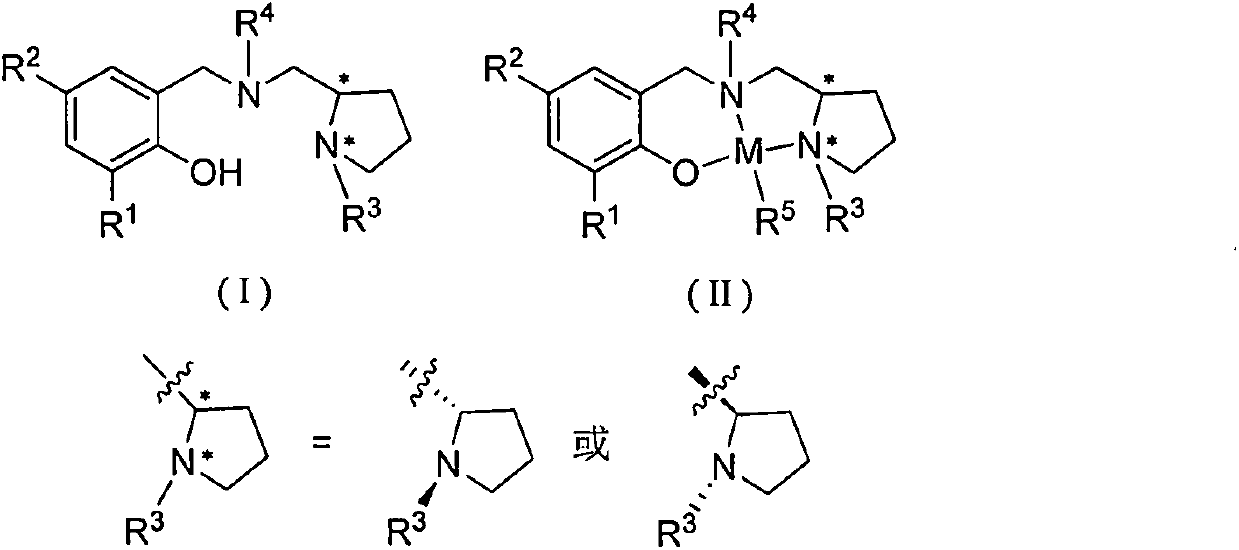
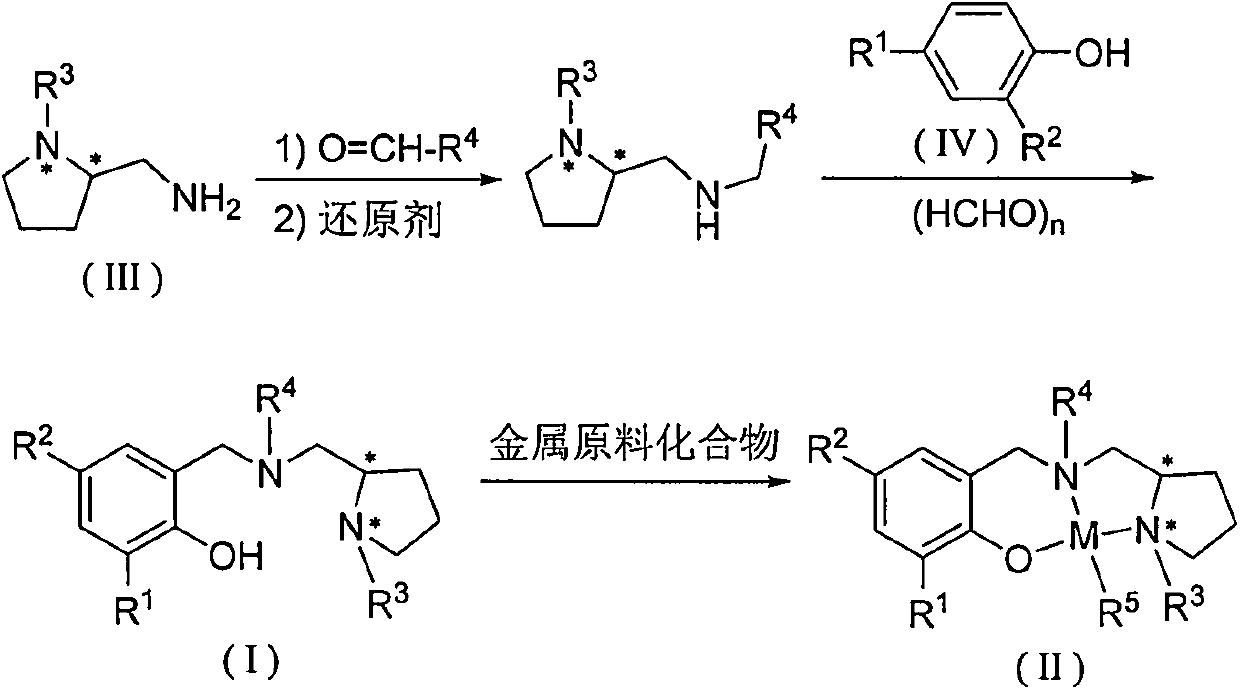
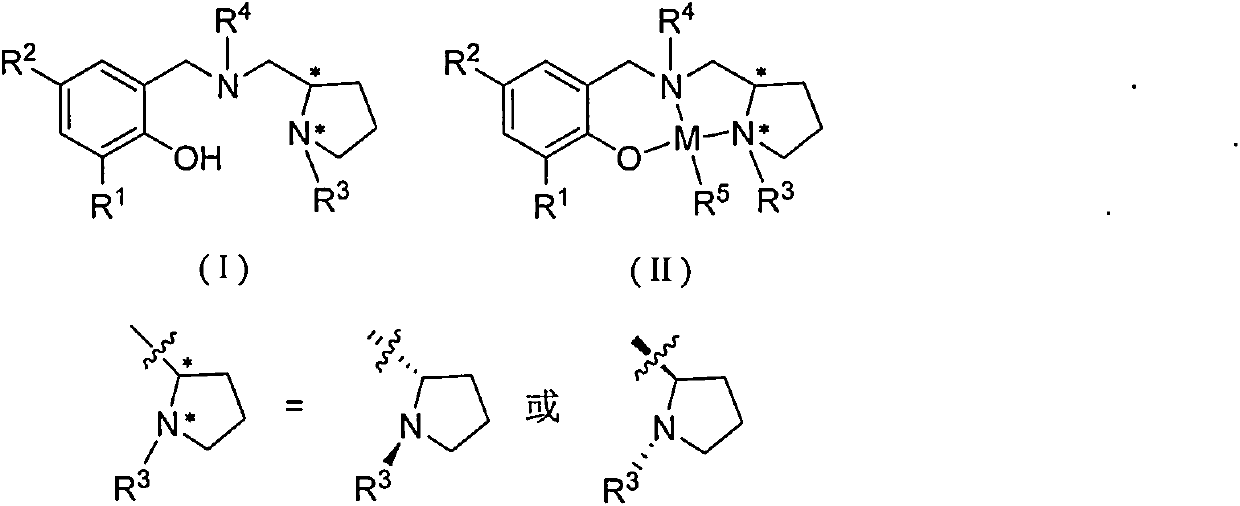
Chiral amino phenoxyl zinc and magnesium compound, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103787943ALigand raw materials are readily availableLigand raw materials are convenientGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsGroup 2/12 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesPolyesterLactide
The invention discloses a chiral amino phenoxyl zinc and magnesium compound, a preparation method of the chiral amino phenoxyl zinc and magnesium compound, and application of the chiral amino phenoxyl zinc and magnesium compound in ring opening polymerization of catalytic lactone with high activity and high selectivity. The preparation method comprises the following steps: directly reacting a neutral ligand with a metal raw material compound in an organic medium; performing filtration, concentration and re-crystallization to obtain a target compound. The chiral amino phenoxyl zinc and magnesium compound is an efficient lactone ring opening polymerization and can be applied to polymerization reaction of catalytic lactide and the like; particularly, high-isotacticity or high-heterotacticity polylactic acid can be obtained for racemization lactide. The chiral amino phenoxyl zinc and magnesium compound has the obvious advantages that raw materials are easily obtained; a synthetic route is simple; high product yield, high catalytic activity and high stereo selectivity are realized; a high-regularity and high-molecular-weight polymer material can be obtained; requirements of industrial departments can be met. A structural formula is shown as (img file='DSA00000897420700011.TIF' wi='860'he='608' / ).
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for continuously refining L-lactide from crude L-lactide
The invention discloses a method for continuously refining L-lactide from crude L-lactide, which comprises the following steps of: firstly, performing at least once lightness removal to the crude L-lactide by using a lightness-removing column, sending melted crude L-lactide into the middle of the lightness-removing column, refluxing and separating as well as distilling the crude L-lactide in the lightness-removing column, condensing vapor distillate at the upper end of the lightness-removing column for removing water, L-lactate and meso-lactide; secondly, enabling column bottom liquid to enter a reboiler for vaporization and then enter into the column, performing at least once rectification to the left column bottom liquid through a treating column after cooling, wherein the lower end of the lightness-removing column mainly has high-boiling point distillate liquid comprising the L-lactide and lactate oligomer; and when in rectification, refluxing and separating the column bottom liquid of the lightness-removing column to obtain a refined L-lactide; refining column bottom flow to obtain concentrated lactate oligomer. The L-lactide purified by the method can be directly used in the polymerization of poly L-lactate, thereby lowering the purifying cost of the L-lactide, increasing the yield, and being environmental friendly without organic solvents.
Owner:南京冠创生物科技有限公司
Anti-cancer sustained-released injection containing epothilone derivate
InactiveCN101396342AEasy to operateGood repeatabilityOrganic active ingredientsSolution deliveryPoly dl lactidePolyethylene glycol
The invention relates to an anti-cancer sustained release injection containing epothilone derivative, consisting of sustained microspheres and menstruum. The sustained microspheres comprise anti-cancer drugs selected from taxane, alkylating agent and / or plant alkaloid and the like, the epothilone derivative and sustained release auxiliary material. The menstruum is a special menstruum containing suspending agent. The epothilone derivative is selected from epothilone B, epothilone D, iso-epothilone D, BMS-247550, azaepothilone B, furan epothilone D or BMS-310705. The sustained release auxiliary material is selected from poly-dl-lactide, the glycolic acid copolymer of the poly-dl-lactide, polyethyleneglycol, the polylactide copolymer of the polyethyleneglycol, carboxyl terminated polylactide copolymer, fatty acid and decanedioic acid copolymer, etc. The suspending agent is selected from carboxymethyl cellulose and the like with the viscosity of 100cp to 3000cp (under the temperature of 25 DEG C to 30 DEG C). The sustained release microsphere can also be made into a sustained release implant. The sustained release injection is injected or arranged in or around the tumour and can release drug at partial position for 40 days approximately, therefore, the sustained release injection improves the local drug concentration selectively and enhances the treatment effect of non-operative treatments, such as radiotherapy, chemotherapy and the like at the same time.
Owner:JINAN SHUAIHUA PHARMA TECH
Anti-cancer sustained-released injection containing epothilone derivate
InactiveCN101396340AEasy to operateGood repeatabilityOrganic active ingredientsSolution deliveryPoly dl lactidePolyethylene glycol
The invention relates to an anti-cancer sustained release injection containing epothilone derivative, consisting of sustained microspheres and menstruum. The sustained microspheres comprise anti-cancer drugs selected from taxane, alkylating agent and / or plant alkaloid and the like, the epothilone derivative and sustained release auxiliary material. The menstruum is a special menstruum containing suspending agent. The epothilone derivative is selected from epothilone B, epothilone D, iso-epothilone D, BMS-247550, azaepothilone B, furan epothilone D or BMS-310705. The sustained release auxiliary material is selected from poly-dl-lactide, the glycolic acid copolymer of the poly-dl-lactide, polyethyleneglycol, the polylactide copolymer of the polyethyleneglycol, carboxyl terminated polylactide copolymer, fatty acid and decanedioic acid copolymer, etc. The suspending agent is selected from carboxymethyl cellulose and the like with the viscosity of 100cp to 3000cp (under the temperature of 25 DEG C to 30 DEG C). The sustained release microsphere can also be made into a sustained release implant. The sustained release injection is injected or arranged in or around the tumour and can release drug at partial position for 40 days approximately, therefore, the sustained release injection improves the local drug concentration selectively and enhances the treatment effect of non-operative treatments, such as radiotherapy, chemotherapy and the like at the same time.
Owner:JINAN SHUAIHUA PHARMA TECH
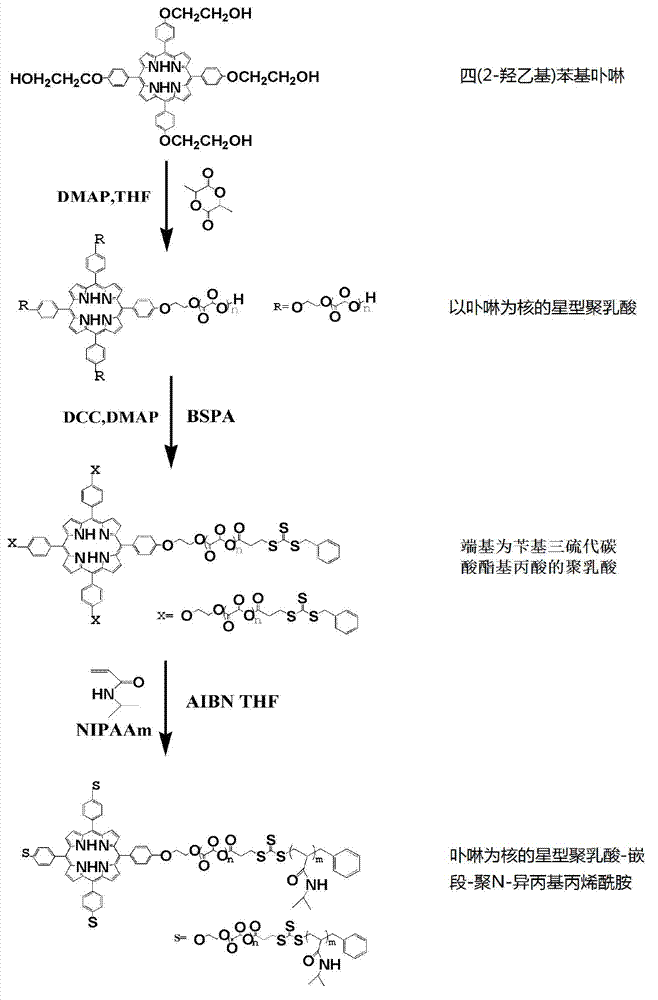
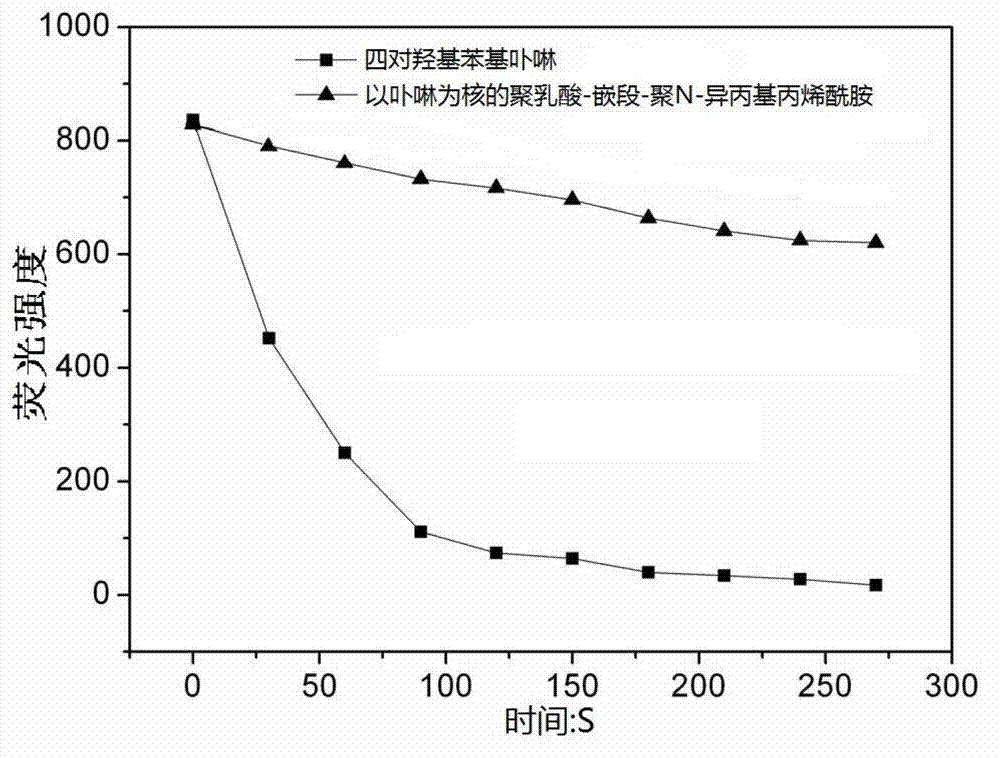
Method for synthesizing polylactic acid-block-polyN-isopropyl acrylamide temperature-sensitive material
InactiveCN103204981APrecise control over aggregate lengthConveniently preparedEnergy modified materialsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsPoly-L-lactidePolymer science
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing a polylactic acid-block-polyN-isopropyl acrylamide temperature-sensitive material, and belongs to the technical field of amphipathy block copolymers. The method comprises the following steps of: initiating ring-opening polymerization of L-lactide by using tetra(2-hydroxyethyl) phenyl porphyrin to prepare hydroxylated star-shaped polylactic acid taking porphyrin as a core terminal; carrying out esterification reaction on the hydroxylated star-shaped polylactic acid taking porphyrin as the core terminal to obtain a macromolecular chain transfer agent; and preparing a novel star-shaped polylactic acid-block-polyN-isopropyl acrylamide temperature-sensitive material from the macromolecular chain transfer agent and a temperature-sensitive N-isopropyl acrylamide monomer by using a reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer polymerization method. According to the method, a mild polymerization condition is adopted to facilitate the preparation of the star-shaped polylactic acid-block-polyN-isopropyl acrylamide temperature-sensitive biological material with polyN-isopropyl acrylamide adjustable in length and porphyrin as a core.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
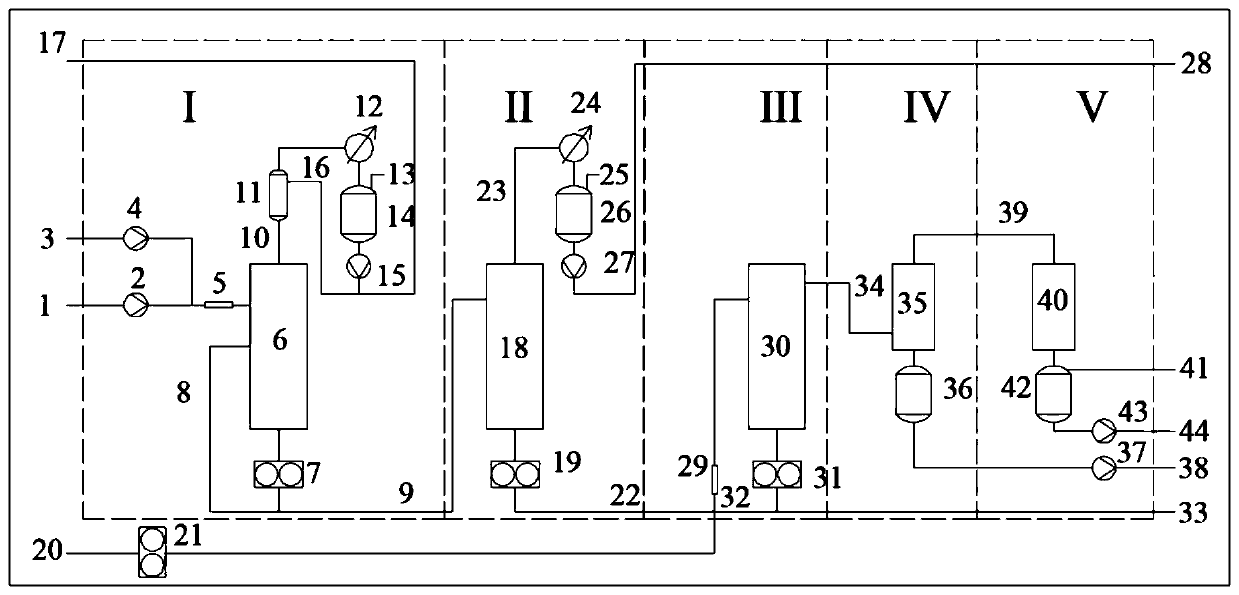
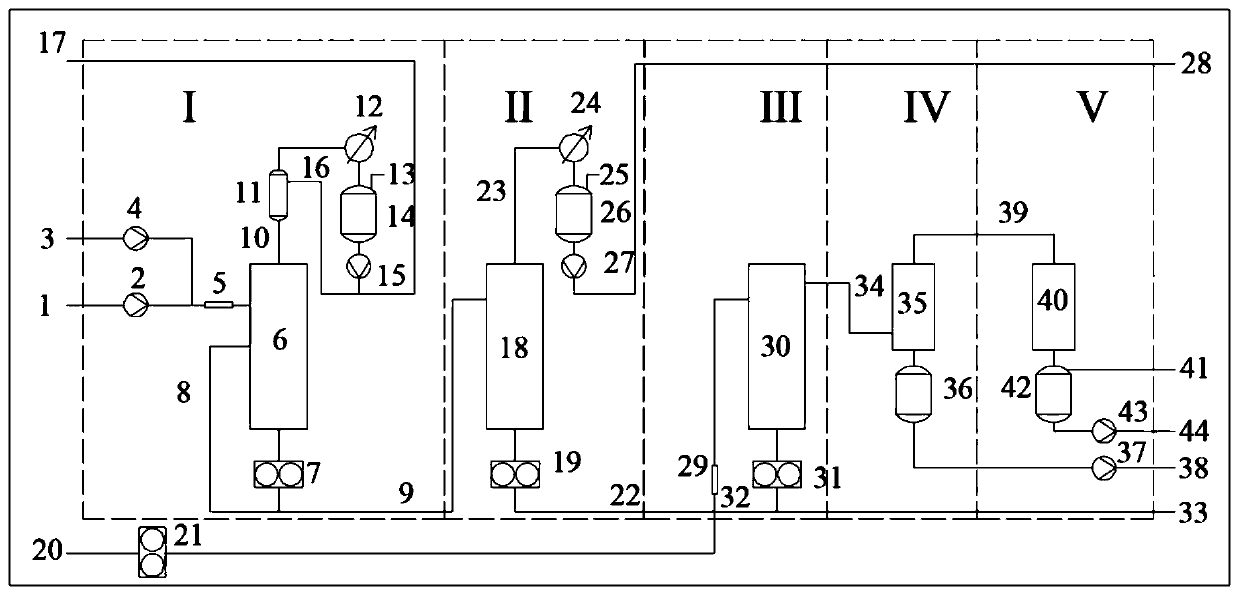
Synthesis method and device for rapidly producing lactide at high yield
ActiveCN111153886AShort manufacturing timeHigh yieldProcess control/regulationOrganic chemistryPoly-L-lactideOligomer
The invention discloses a synthesis method and device for rapidly producing lactide at high yield. The method comprises the steps: adding a lactic acid single component or lactic acid into a catalystdouble component, enabling the mixture to enter an oligomer preparation system through a mixer, increasing the residence time through bottom circulation, synthesizing oligomeric lactic acid, and enabling a gas-phase component to pass through a rectification system, so as to improve the yield of oligomeric lactic acid; removing unreacted lactic acid and water from the oligomeric lactic acid througha purification device; and adding a catalyst into the light-component-removed oligomeric lactic acid, allowing the mixture to pass through a mixer, allowing the mixture to enter a depolymerization reactor, depolymerizing so as to obtain lactide, allowing heavy components to enter the depolymerization reactor again through reflux, and allowing light components to pass through a purification and recovery system so as to obtain the lactide product. With the adoption of the device, lactide can be efficiently synthesized, crude lactide with the yield of 94-98% can be obtained within short residence time of 0.5-5 minutes, the molecular weight of the heavy-component polylactic acid is slowly increased, and the heavy-component polylactic acid can be returned for depolymerization; after the lightcomponents pass through a simple purification system, the content of L-lactide, D-lactide or DL-lactide in the lactide product is 94%-98%, and the content of meso-lactide is 0.5%-5.5%.
Owner:NANJING UNIV +1
Novel sustained release polymer
A polymer and a method for its preparation are provided. The polymer comprises poly(lactide), poly(lactide / glycolide) or poly(lactic acid / glycolic acid) segments bonded by ester linkages to both ends of an alkanediol core unit. The polymer is for use in a controlled release formulation for a medicament, preferably leuprolide acetate. The controlled release formulation is administered to a patient as a subcutaneous depot of a flowable composition comprising the polymer, a biocompatible solvent, and the medicament. Controlled release formulations comprising the polymer release leuprolide for treatment of prostate cancer patients over periods of 3-6 months.
Owner:TOLMAR INC
Synthesis of molecular weight controllable polylactic acid without metal residual
The invention provides a method for synthesizing a polylactic acid which has no metallic residue and has controllable molecular weight. The method is as follows: a reaction solvent is added into lactide to prepare a lactide solution the mol concentration of which is between 0.5 and 1.5 M under the protection of inert gas, and an initiator and catalyst are added into the lactide solution in turn, and subjected to polymerization for 0.25 to 2 hours, wherein the mol ratio of the lactide to the initiator to the catalyst is 6-350 to 1 to 0.06-0.35; a terminator is added into the lactide solution, and subjected to termination reaction for 10 to 20 minutes, wherein the mol ratio of the initiator to the terminator is 1 to 1-5; and methanol is prepared, wherein the volume ratio of the reaction solution to the methanol is 1 to 10-20, the reaction solution is dripped into the methanol to form polylactic acid deposit, and the polylactic acid deposit is separated out, filtered, subjected to methanol washing for 2 to 3 times, and subjected to vacuum drying for 24 to 48 hours at a temperature of between 20 and 40 DEG C to obtain the product. The synthesis method can be performed under the condition of room temperature and normal pressure, has high product yield and simple technique, does not require the conditions of heating and decompression, is easy to operate, and can effectively control the molecular weight of the polylactic acid product; and the product has no metallic residue and can be used as a medical material.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Biological degradable shape memory polymer and its preparation process
A biodegradable shape memory polymer is prepared through synthesizing poly-L-lactide oligomer, synthesizing poly(glycolide / caprolactone) cooligomer and using diisocyanate-type coupling agent to couple them together to obtain polyblock copolymer. Its advantage is high effect to hold the thermal deformation and thermally restoring the original shape.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Artificial bone nanocomposite and method of manufacture
A composition suitable for bone replacement is provided. The composition is a nanocomposite matrix, resembling both the structure and the properties of natural bone, including morphology, composition and mechanical characteristics. The nanocomposite is preferably porous and comprises: (1) micro or nano scale cellulose crystals or fibres; (2) hydroxyapatite nanoparticles; (3) Poly L-Lactide Acid or poly glycolic acid; and (4) a coupling agent, for example a surfactant, preferably an anionic surfactant such as sodium dodecyl sulfate. The composition is useful as an artificial bone replacement or bone graft, is preferably biomimetic, and can be suitable for use, for example, in trabecular bone substitution and osteoanagenesis applications. A method of fabrication of the nanocomposite is also provided.
Owner:EFTEKHARI SAMIN
Folate-polyethylene glycol-polylactic acid segmented copolymer micelle encapsulated with hydrophobic anticancer drug and preparation method of segmented copolymer micelle
InactiveCN103520731AImprove stabilityAct as a slow releaseOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsPoly-L-lactidePolymer science
The invention discloses a folate-polyethylene glycol-polylactic acid segmented copolymer micelle encapsulated with a hydrophobic anticancer drug and a preparation method of the segmented copolymer micelle. The preparation method comprises the steps as follows: bis-amino polyethylene glycol polymer is prepared firstly; mono amino polyethylene glycol tert-butyl ester polymer is prepared by the bis-amino polyethylene glycol polymer; the mono amino polyethylene glycol tert-butyl ester polymer is cross-linked with lactide to obtain tert-butoxy acylamino polyethylene glycol-polylactic acid polymer, and the tert-butoxy acylamino polyethylene glycol-polylactic acid polymer reacts with trifluoroacetic acid to obtain amino-terminated polyethylene glycol-polylactic acid polymer; and the amino-terminated polyethylene glycol-polylactic acid polymer and activated folate react away from light to obtain the folate-polyethylene glycol-polylactic acid polymer. The compound has hydrophilia , biocompatibility and water solubility of the hydrophobic segment, material absorption and cell adhesion of protein can be reduced, the circulation time of the drug in blood is prolonged, and the formed copolymer has modificability; a tumor target compound with low molecular weight and hydrophilic polyethylene glycol-4000 segmer are bonded to form a hydrophilic segment; and the hydrophobic segment is polylactic acid, and the hydrophobic anticancer drug is embedded into the hydrophobic segment, so that the toxic and side effects are reduced.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Poly-L-lactide-caprolactone copolymer (PLCL) three-dimensional porous scaffold, PLCL and collagen (PLCL-COL) composite scaffold and preparation methods of scaffolds
InactiveCN105343936ASimple structureHigh porositySurgeryTissue regenerationLow temperature depositionPoly-L-lactide
The invention is applicable to the field of biomedicine, and provides a poly-L-lactide-caprolactone copolymer (PLCL) three-dimensional porous scaffold, a PLCL and collagen (PLCL-COL) composite scaffold and preparation methods of the scaffolds. The preparation method of the PLCL three-dimensional porous scaffold, on the basis of a low-temperature deposition manufacturing technology, specifically comprises the following steps: implementing modeling pretreatment by virtue of CAD software, conducting hierarchical slicing by virtue of Aurora software, and implementing design of printing parameters of the PLCL three-dimensional porous scaffold by virtue of Cark software; dissolving the PLCL in an organic solvent, so that a PLCL homogenous liquid is prepared; smearing the organic solvent on a forming platform when forming room temperature drops to minus 25-35 DEG C, and printing and shaping after setting the shaping parameters by virtue of the Cark software, so that a PLCL three-dimensional porous scaffold prefabricated part is obtained; and taking out and freeze-drying the PLCL three-dimensional porous scaffold prefabricated part, so that the PLCL three-dimensional porous scaffold is obtained.
Owner:THE SECOND PEOPLES HOSPITAL OF SHENZHEN
Composite drug carried microsphere, minocycline hydrochloride nano controlled-release composite drug carried microsphere system and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101836961ALow toxicityGood slow releaseAntibacterial agentsTetracycline active ingredientsMicrosphereCholesterol
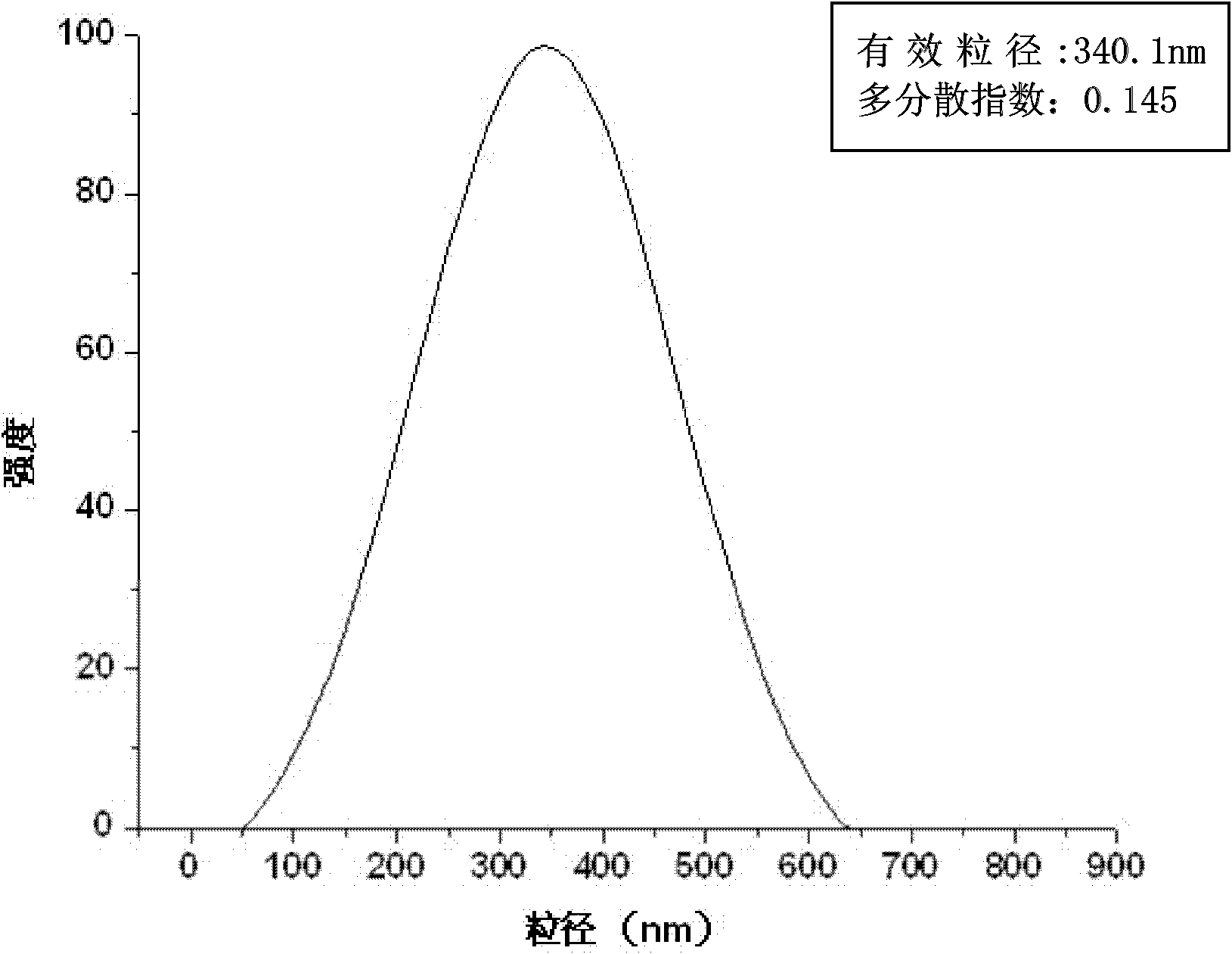
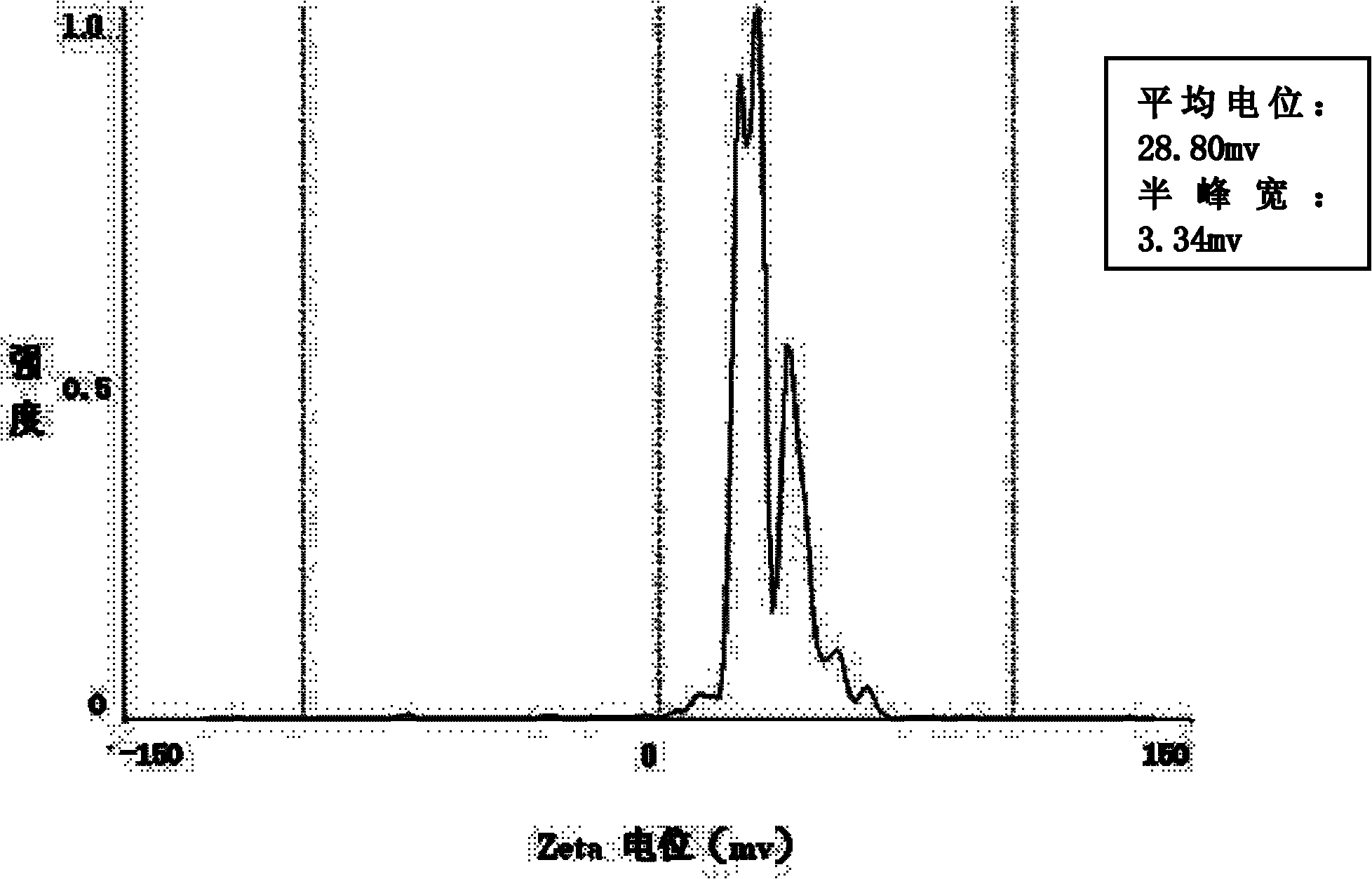
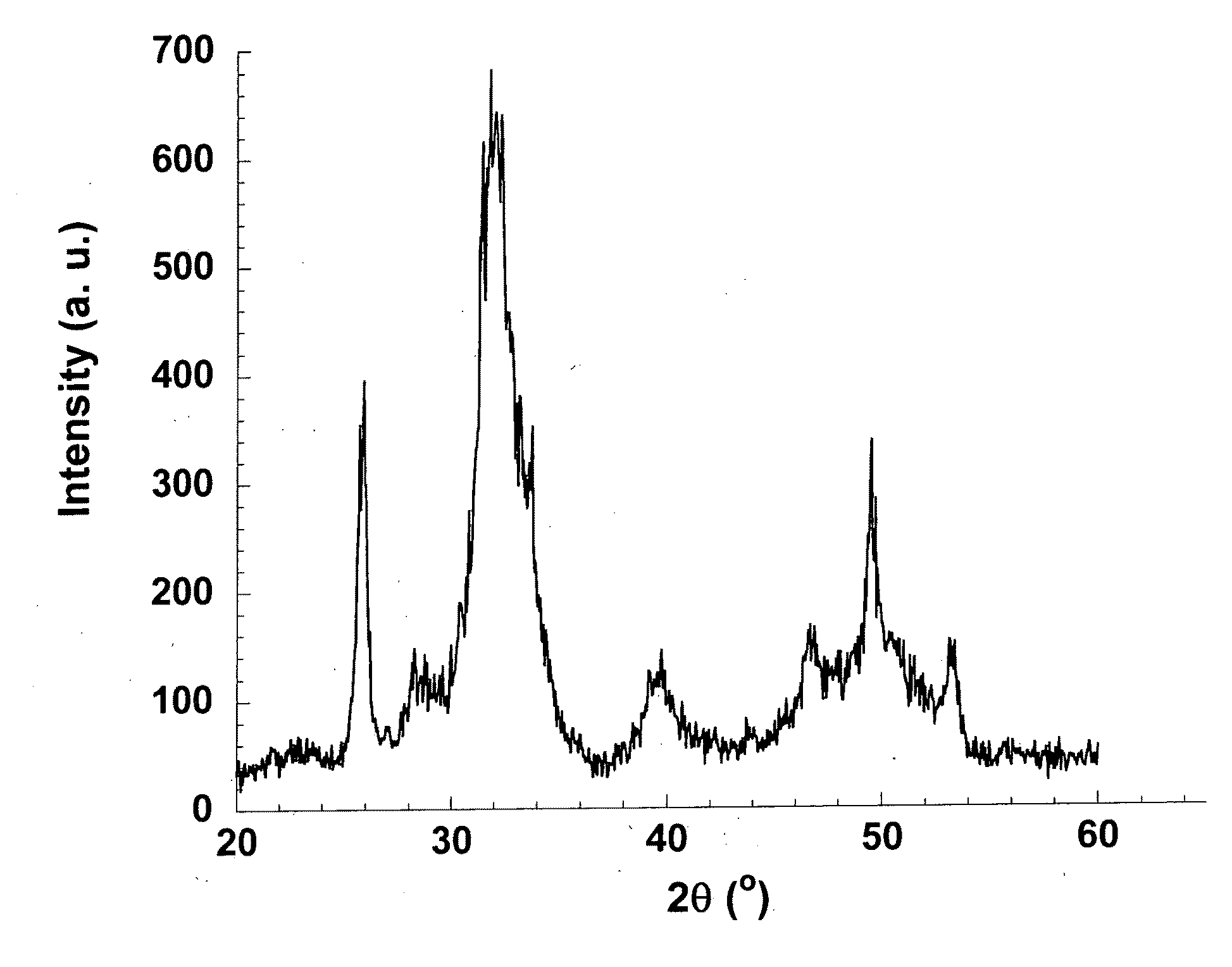
The invention relates to a composite drug carried microsphere, a minocycline hydrochloride nano controlled-release composite drug carried microsphere system and a preparation method thereof. A drug carried system with a nuclear shell structure is formed by embedding minocycline hydrochloride inside a poly D,L-lactide-co-glycolic acid polymer microsphere and covering a cationic polymeric liposome prepared from O-QACMC modified by polyethylene glycol, O-QACMC and cholesterol outside the poly D, L-lactide-co-glycolic acid polymer microsphere; and the composite drug carried microsphere system covered and carried with the minocycline hydrochloride has the grain diameter ranging from 340 nm to 400 nm and positive surface Zeta electric potential. The composite drug carried microsphere system can be remained in a water solution for at least 2 months, has high entrapment rate reaching larger than 90 percent on drugs and strong drug carrying capacity reaching 9 percent. The minocycline hydrochloride nano controlled-release composite drug carried microsphere system has the characteristics of uniform and controllable grain diameter, good preparation stability, simple preparation process, high drug carrying rate, favorable controlled release function, and the like, and is suitable for batch production.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Production of moldable bone substitute
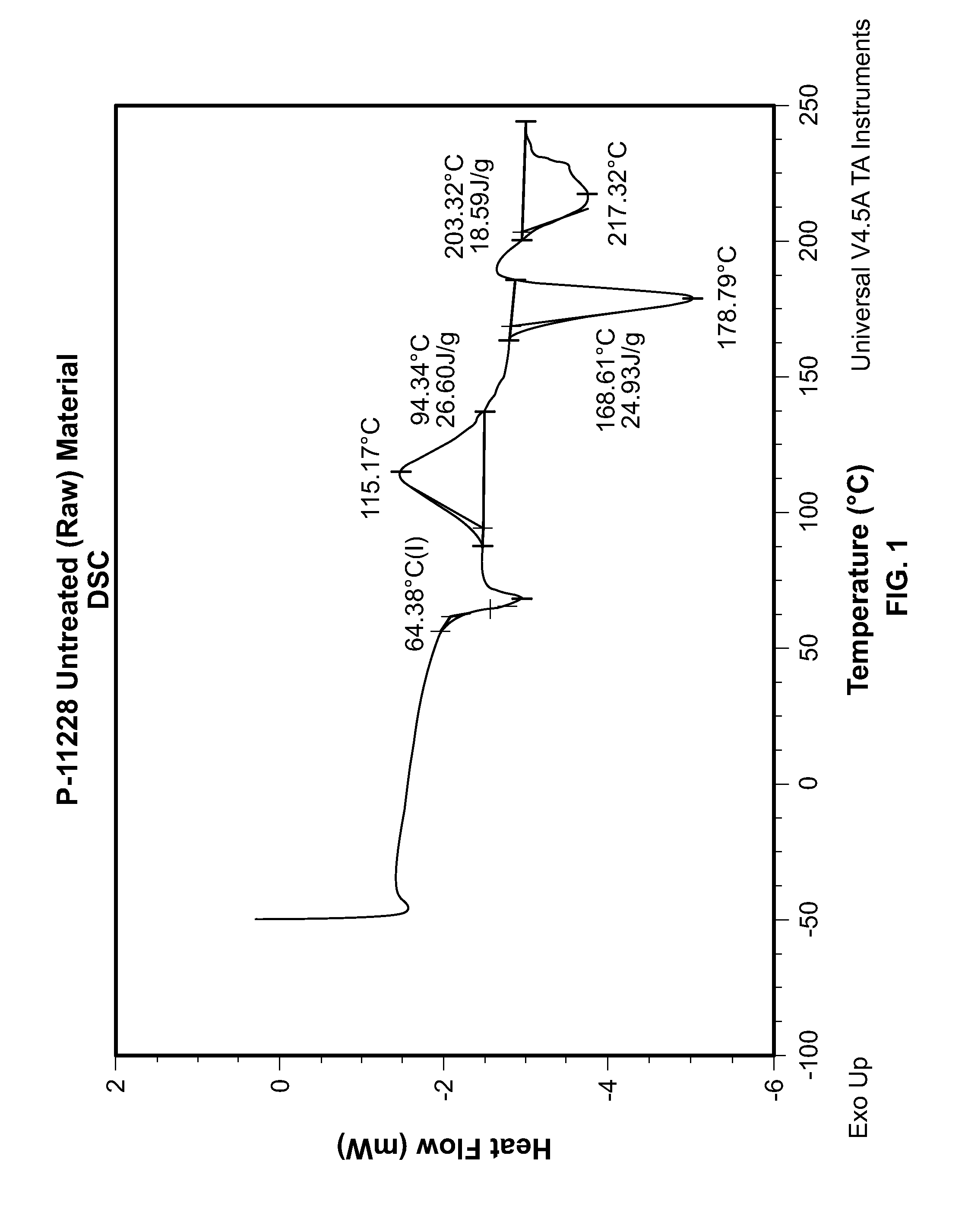
InactiveUS20100226956A1Long shapeability timeHigh final strengthInorganic phosphorous active ingredientsSkeletal disorderPorosityLactide
Composites and methods of producing a mouldable bone substitute are described. A scaffold for bone growth comprises nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite (HA), a bioresorbable plasticizer, and a biodegradable polymer. Plasticizers of the invention include oleic acid, tocopherol, eugenol, 1,2,3-triacetoxypropane, monoolein, and octyl-beta-D-glucopyranoside. Polymers of the invention include poly(caprolactone), poly(D,L-Lactic acid), and poly(glycolide-co lactide). Methods of regulating porosity, hardening speed, and shapeability are also described. Composites and methods are described using nanocrystalline HA produced with and without amino acids. The scaffold for bone growth described herein displays increased strength and shapeability.
Owner:PROMIMIC
Preparation method of composite small-caliber artificial blood vessel, and product thereof
InactiveCN108478863AImprove mechanical propertiesImprove antithromboticPharmaceutical containersMedical packagingPoly-L-lactideCell adhesion
The invention relates to a preparation method of a composite small-caliber artificial blood vessel, and a product thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of decellularizing a coronary artery to obtain a decellularized blood vessel; then heparinizing the decellularized blood vessel, using a mixed electrospinning solution of gelatin and poly L-lactide-caprolactone (PLCL) for spinning, and removing an organic solvent, thus obtaining the small-caliber artificial blood vessel. The prepared artificial blood vessel is a double-layer tissue engineering blood vessel, adopts decellularized porcine coronary artery as an artificial blood vessel inner layer, has good compliance and cytocompatibility, and can promote cell adhesion, proliferation and differentiation, and spreading so as to accomplish reendothelialization of the blood vessel; an outer layer is a blending layer of the PLCL and the gelatin, so that the mechanical property of the blood vessel is improved, cells of smooth muscle and the like are favorably intruded, and a middle layer of the blood vessel is formed; the inner surface of the inner layer can be modified by different drugs such as heparin, so that theantithrombus of the artificial blood vessel is improved, the blood vessel intima formation is promoted, and the blood vessel is favorably rebuilt.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
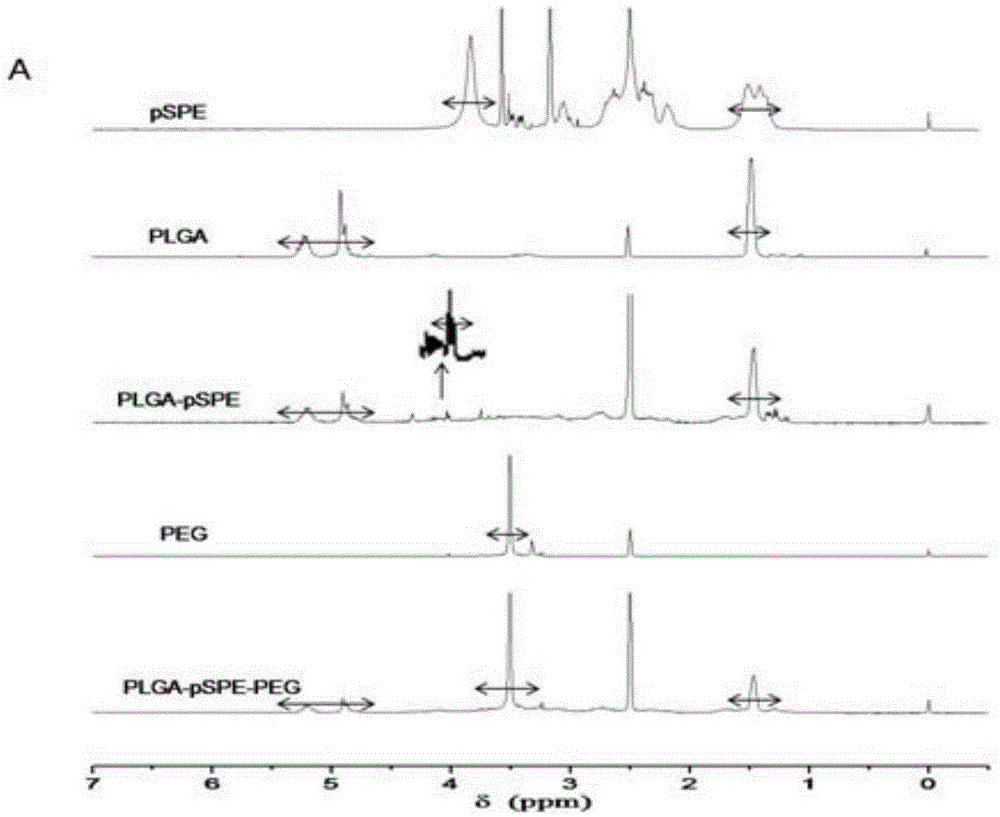
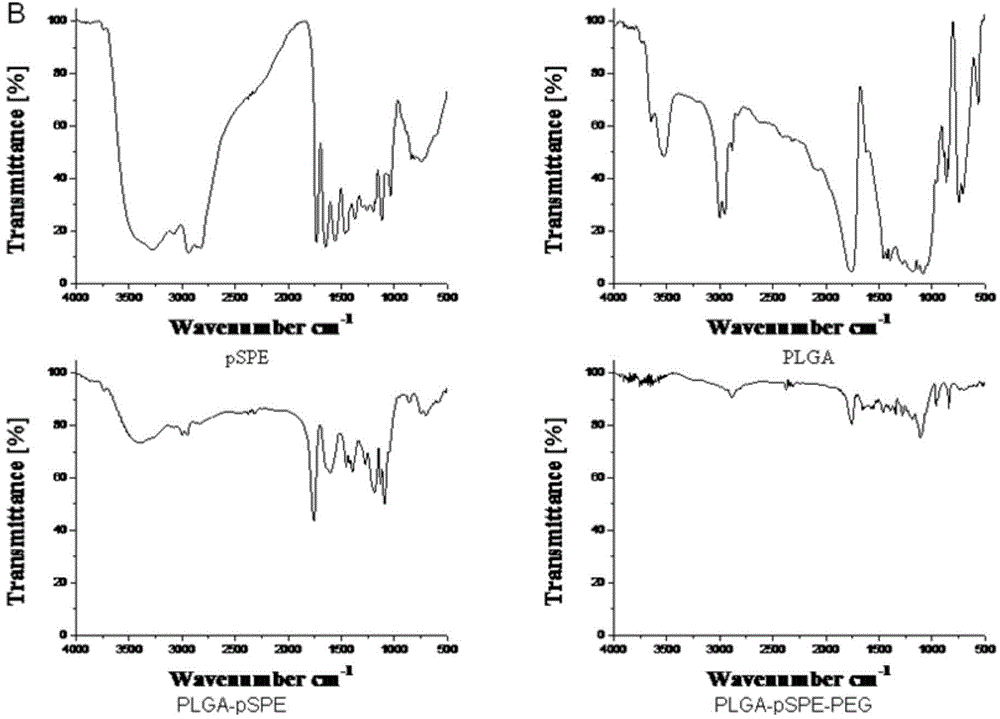
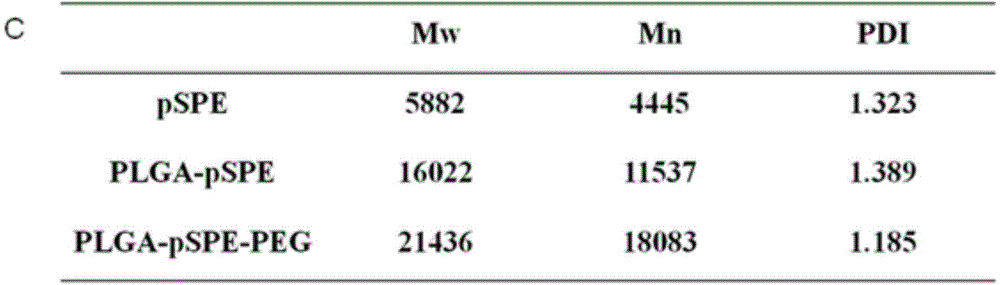
Simultaneous-delivery nanometer carrier and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104906075AGood biocompatibilityParticle size controllableGenetic material ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsLactidePolyethylene glycol
The invention discloses a nanometer carrier for simultaneous delivery of medicines and genes and a preparation method of the nanometer carrier, and particularly relates to a simultaneous-delivery nanometer carrier PLGA-pSPE (polyspermine)-PEG (polyethylene glycol)-Ligand capable of simultaneously loading medicines and genes. The medicine delivery system is realized by the following steps: synthesizing pSPE with spermine at two ends by using spermine and polyethylene glycol acrylate (PEGDA) through Michael addition reaction; generating amphipathic PLGA-pSPE from a pSPE and poly(lactide-co-glycolide) copolymer PLGA through condensation reaction of amino and carboxyl; and generating PLGA-pSPE-PEG-Ligand by using PLGA-pSPE and PEG (HOOC-PEG-Ligand) of which one end is provided with carboxyl and the other end is connected with a target head through condensation reaction of amino and carboxyl, and self-assembling to form nano particles, wherein kernel PLGA is capable of well loading insoluble medicines as a hydrophobic material; the pSPE contains a lot of secondary amino groups, is positively charged, is capable of well loading negatively charged genes and grafting an invisible material PEG with the target head; relatively good target medicine delivery can be realized under the combined action of the PEG and the target head; and the medicines and the genes are delivered to the same target cell.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Alternating magnetic field driven shape memory biological degradable polymer and preparation method thereof
The present invention is preparation process of biodegradable alternating magnetic field driven shape memory composite polymer material. The composite polymer material is mixture of copolymer of L-lactide and glycolide and / or epsilon-caprolactone and nanometer Fe3O4 particle coated with poly-L-lactide, polyglycolide or poly-epsilon-caprolactone in the weight ratio of 70-90 to 10-30. Compared with available technology, the present invention has the features of non-contact initiated shape memory function, high restoring ability and mechanical performance suitable for use in medical product, capacity of being used in developing in nuclear magnetic resonance, and targeting function for no-duct conveyance.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
In-situ fiber-forming strengthened degradable medical elastic composite material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101623516AHigh tensile strengthAppropriate compatibilityCatheterProsthesisPoly-L-lactideFiber
The invention discloses an in-situ fiber-forming strengthened degradable medical elastic composite material and a preparation method thereof. The composite material is prepared by premixing polyglycolic acid or poly-(L-lactic acid) and poly-(L-lactide-tao-caprolactone) by a weight ratio of 20:80 to 5:95 in an inert gas atmosphere; extruding the mixture in a plastic extruder with a screw rotation speed of 10-80 r / min; hauling the extruded mixture by a hauling machine at a hauling speed of 1-30 m / min; controlling a die diameter / a spline diameter to be 1-6; and quenching with water in a hauling process. The composite material can be fully biologically degraded, has obviously improved tensile strength, enables fused mass to have little abrasion on the inner wall of an equipment cavity in the processing process and can be used in medical fields, such as degradable catheters, elastic fascia, artificial skin, and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG APELOA JIAYUAN BIOMEDICAL MATERIAL +1
Process for preparing fatty polyester with variable degradative speed rate and preparation proces sof product thereof
The invention relates to a method of preparing acyclic polyesters with different degrading speeds or their products, and the characteristic: in the polymerizing course and / or in processing course of them and their products, adding in lewis acid catalyst in weight percent of 0.1-6%. The method is simple and easy to apply, the addition of the lewis acid catalyst is low and the degrading and accelerating effects of the lewis catalyst are remarkable and the lewis acid catalyst has no effect on the biocompatibility and biodegradability of the acyclic polyester, and according to practical requirements, by adding different quantities of catalyst, it can regulate and control the degrading speed of the acyclic polyester, so as to meet different use requirements, especially able to enlarging the application range of acyclic polyesters with slower degrading speeds, such as poly-epsilon-caprolactone, poly L-lactide, etc.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
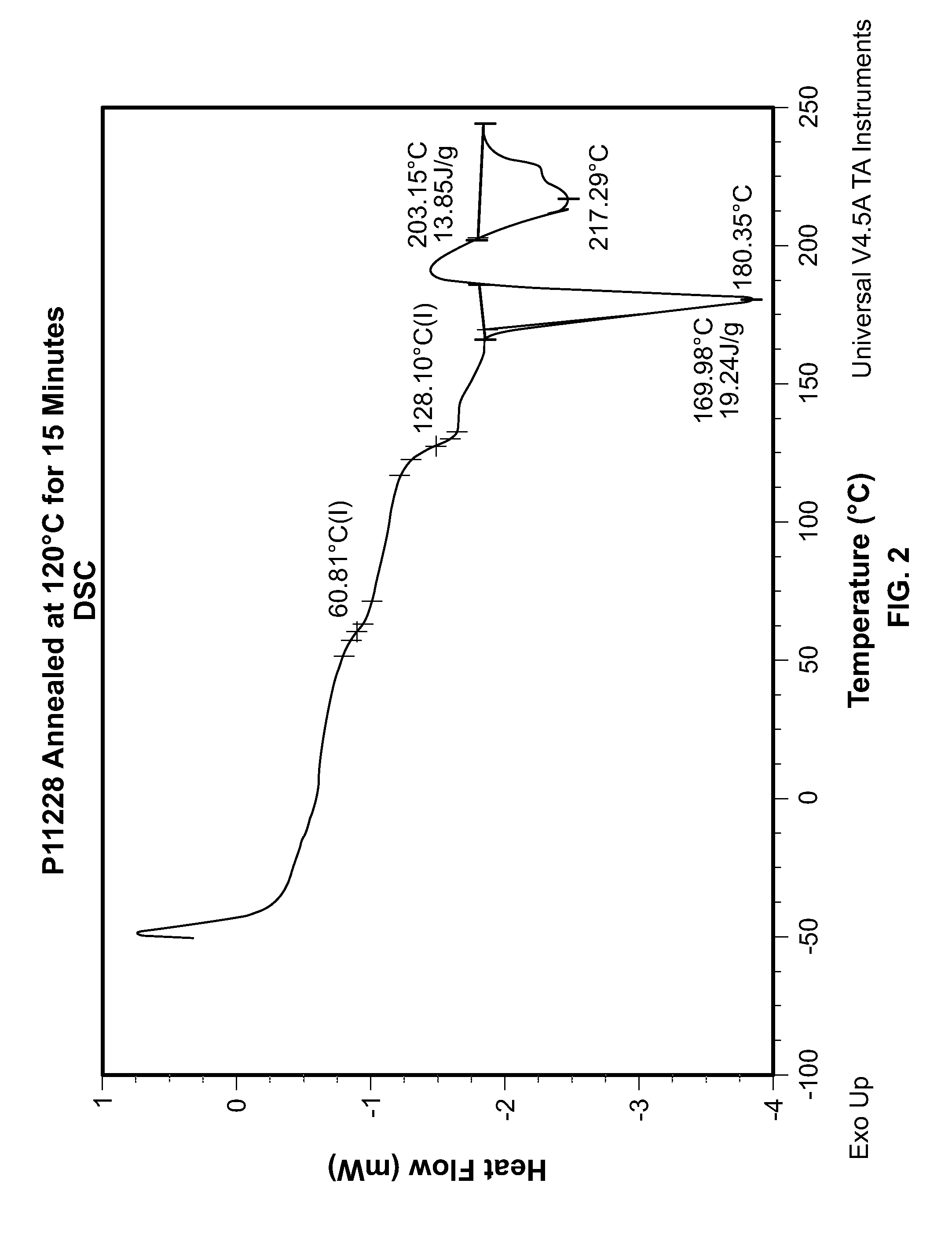
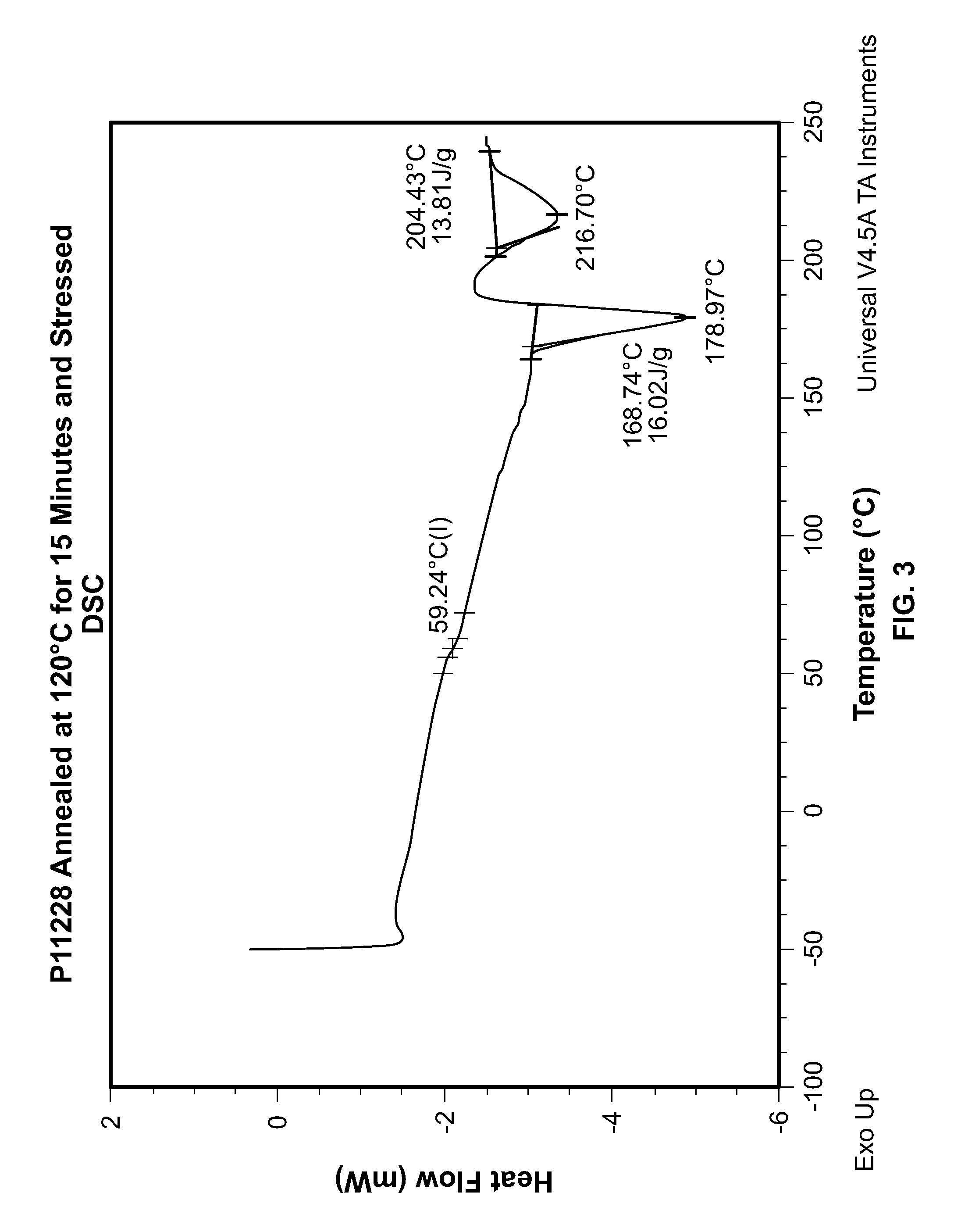
Resin composition and molded article
Provided is a resin composition that produces molded articles with excellent shock resistance and stiffness. Also provided is a resin composition with 50% or more biomass content. Also provided is a resin composition with a low coefficient of moisture absorption, excellent hydrolysis resistance and high recyclability. Also provided is a resin composition that produces molded articles with excellent heat resistance. This invention is a resin composition that comprises an aromatic polyester (component A) that has a butylene terephthalate backbone as the main structural unit, and a polylactide (component B) made from poly-L-lactide and poly-D-lactide, as well as a modifier (component C). Said resin composition (i) exhibits a crystal fusion peak in the stereocomplex phase polylactide of 190 DEG C or greater with differential scanning calorimetry, (ii) has biomass content of 50% or more, (iii) has a notched Izod impact strength of 4-15 kJ / m2 and (iv) has a bending elastic modulus of 2.5-6 GPa.
Owner:TEIJIN LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com