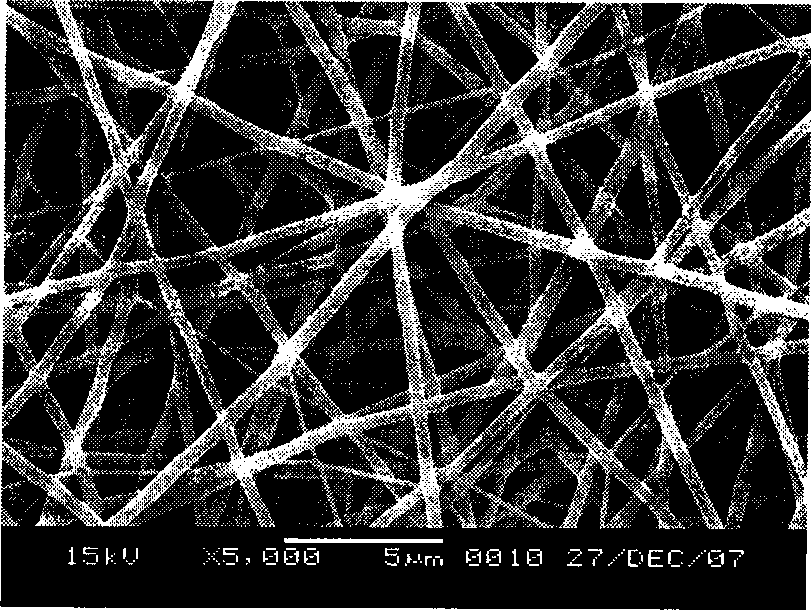
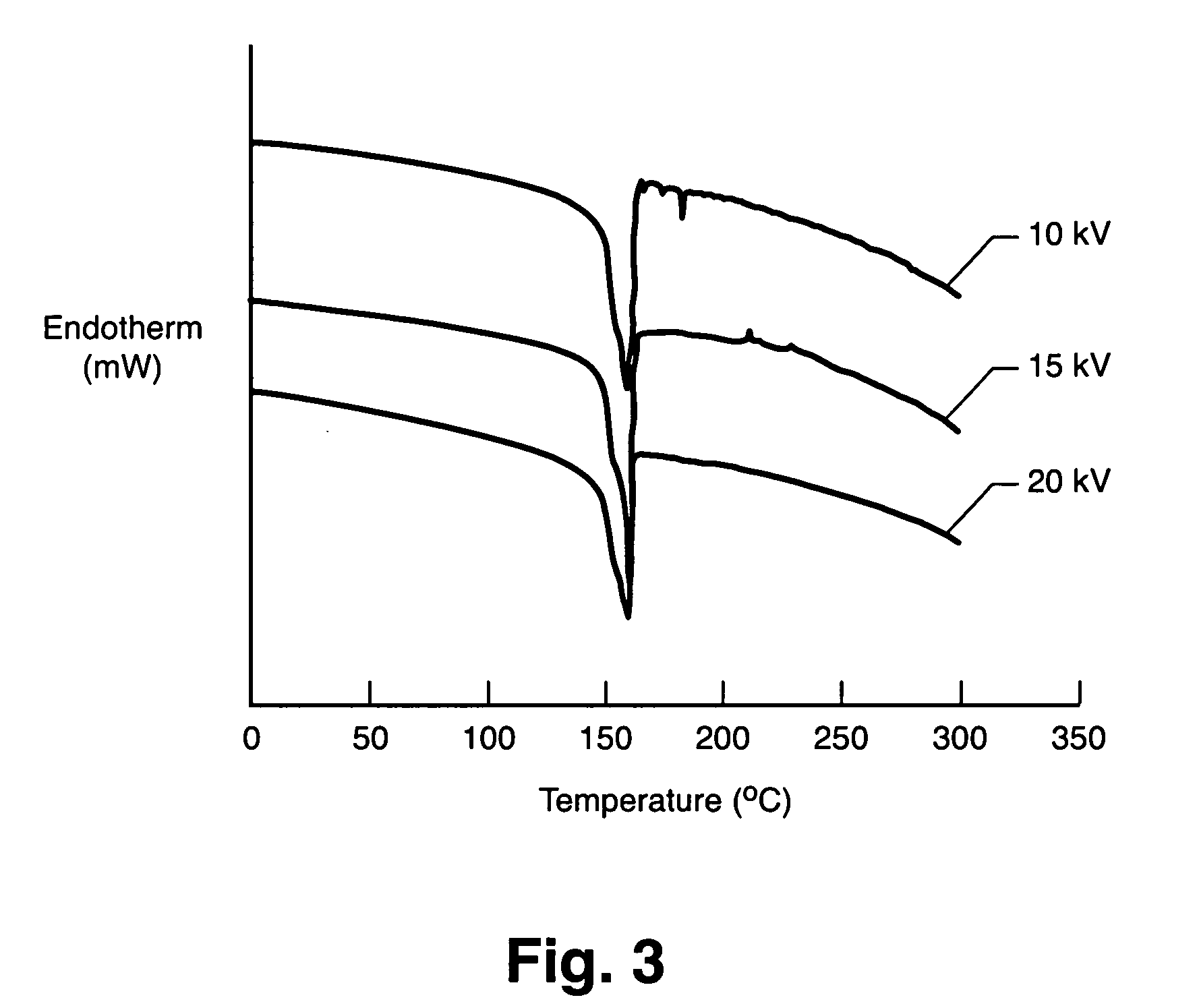
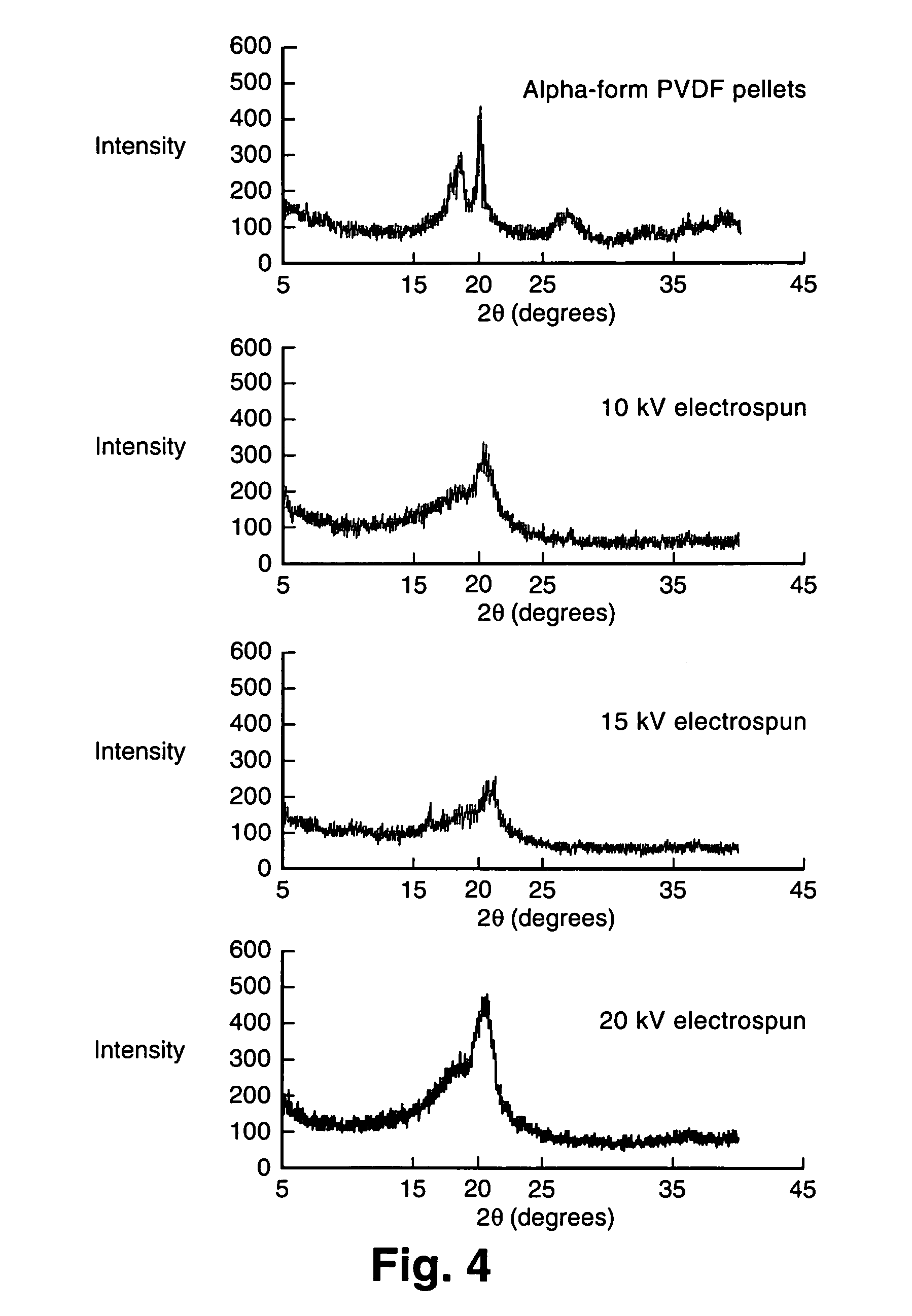
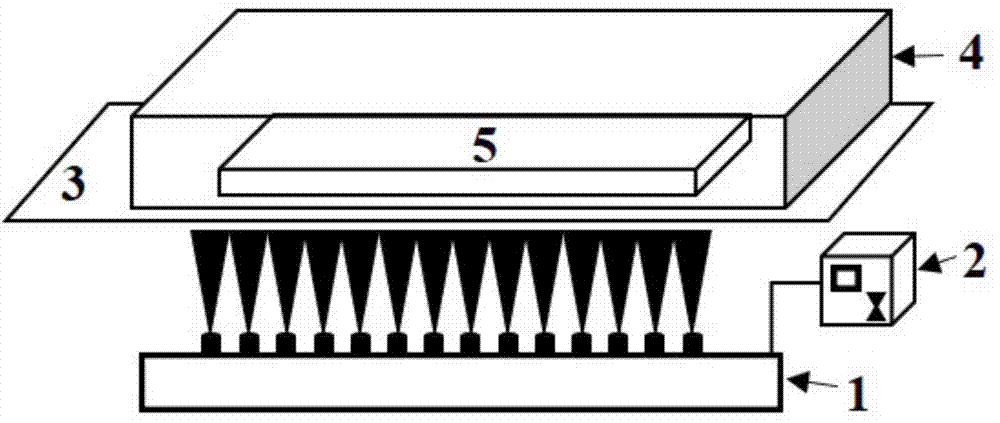
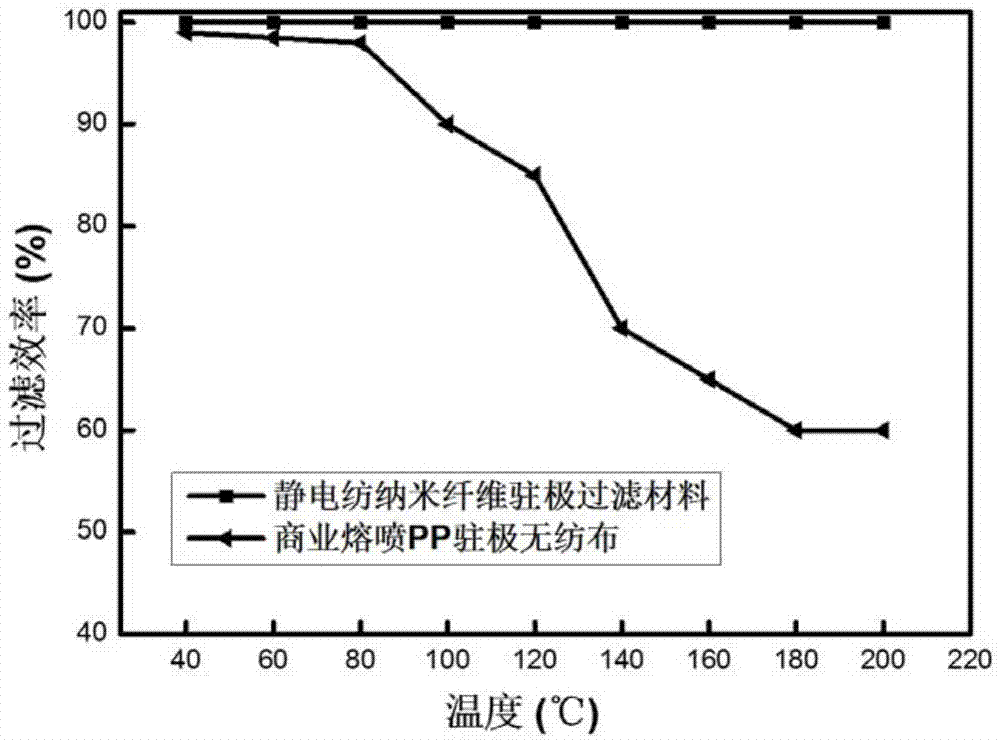
Patents
Literature
7965 results about "Electrospinning" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
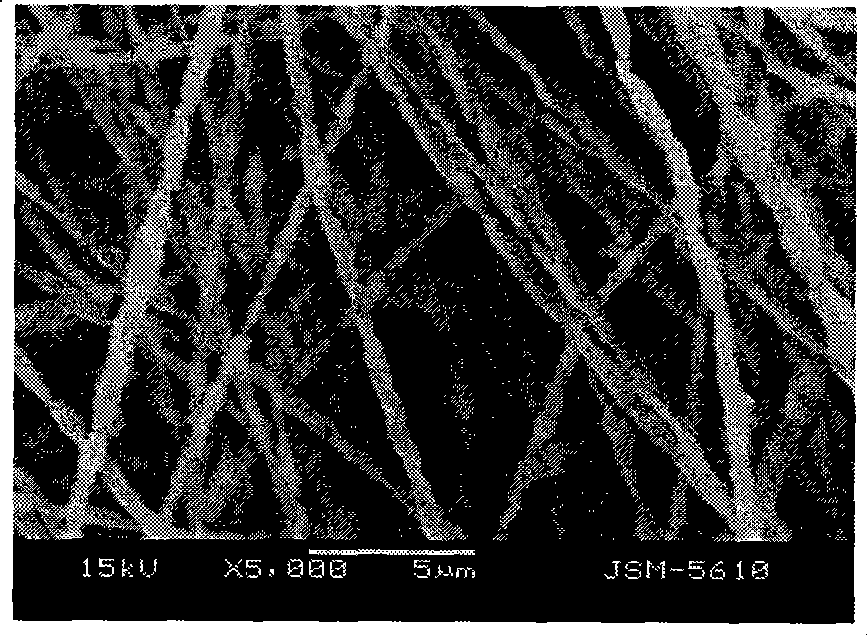
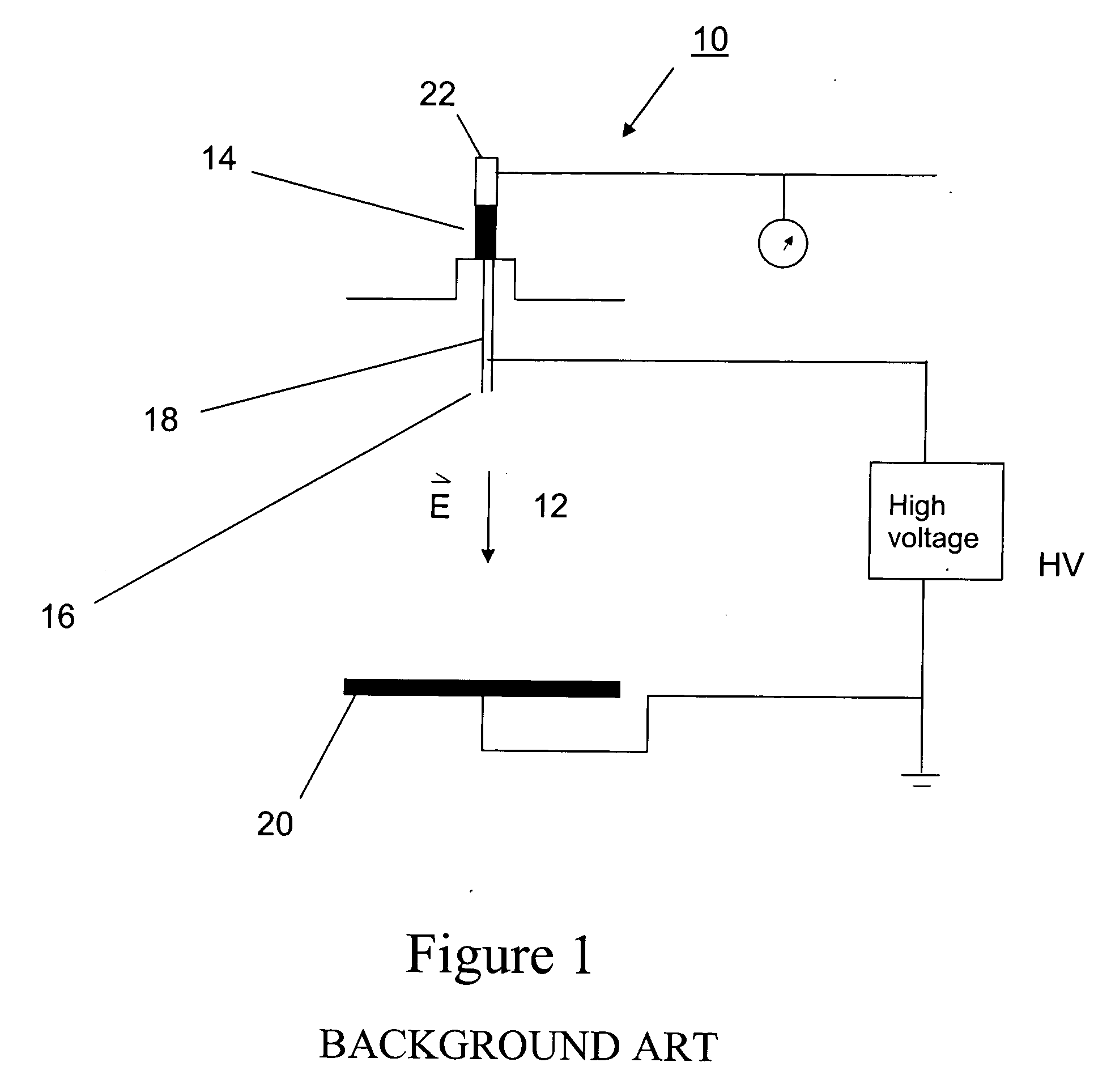
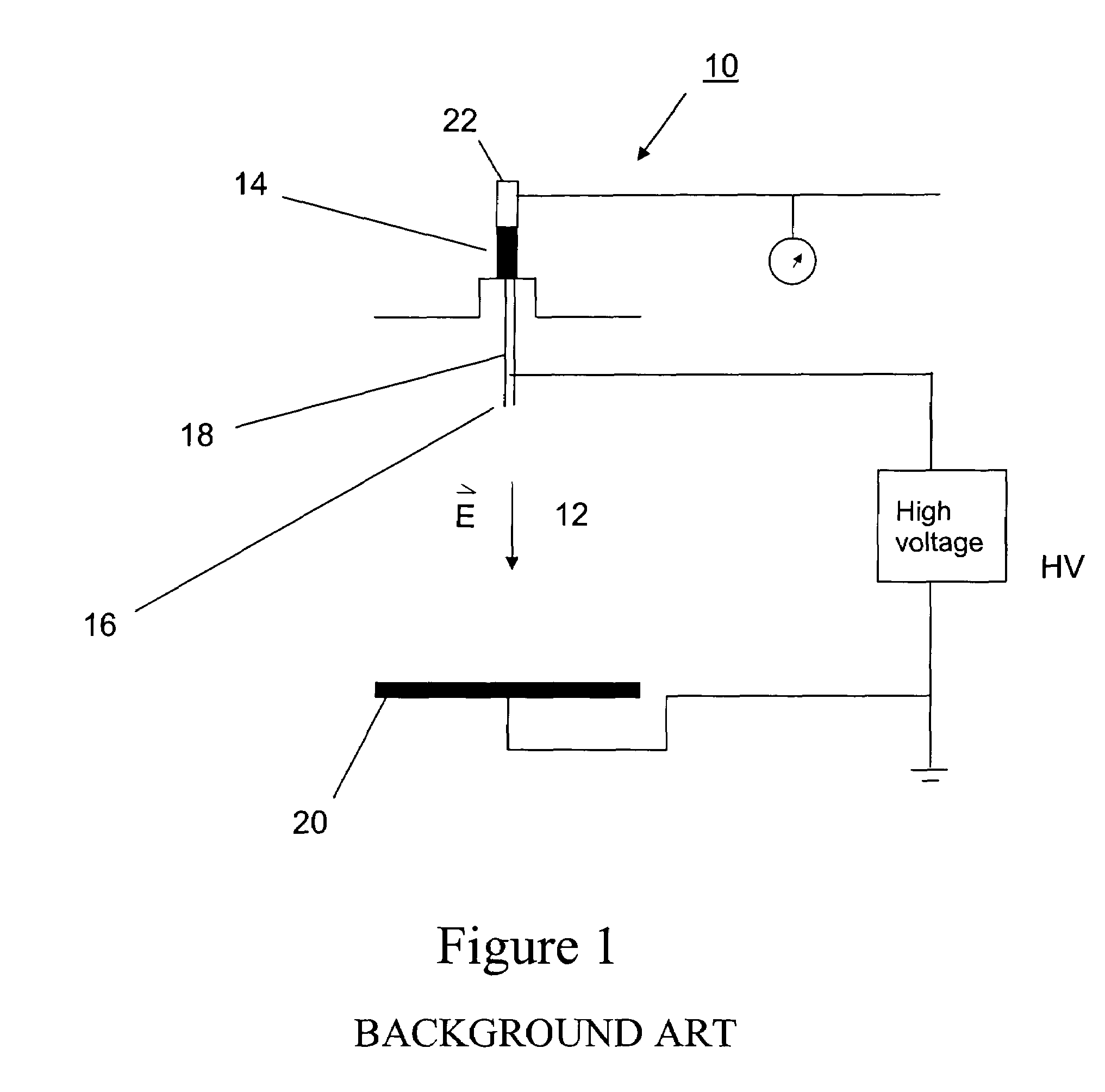
Electrospinning is a fiber production method which uses electric force to draw charged threads of polymer solutions or polymer melts up to fiber diameters in the order of some hundred nanometers. Electrospinning shares characteristics of both electrospraying and conventional solution dry spinning of fibers. The process does not require the use of coagulation chemistry or high temperatures to produce solid threads from solution. This makes the process particularly suited to the production of fibers using large and complex molecules. Electrospinning from molten precursors is also practiced; this method ensures that no solvent can be carried over into the final product.
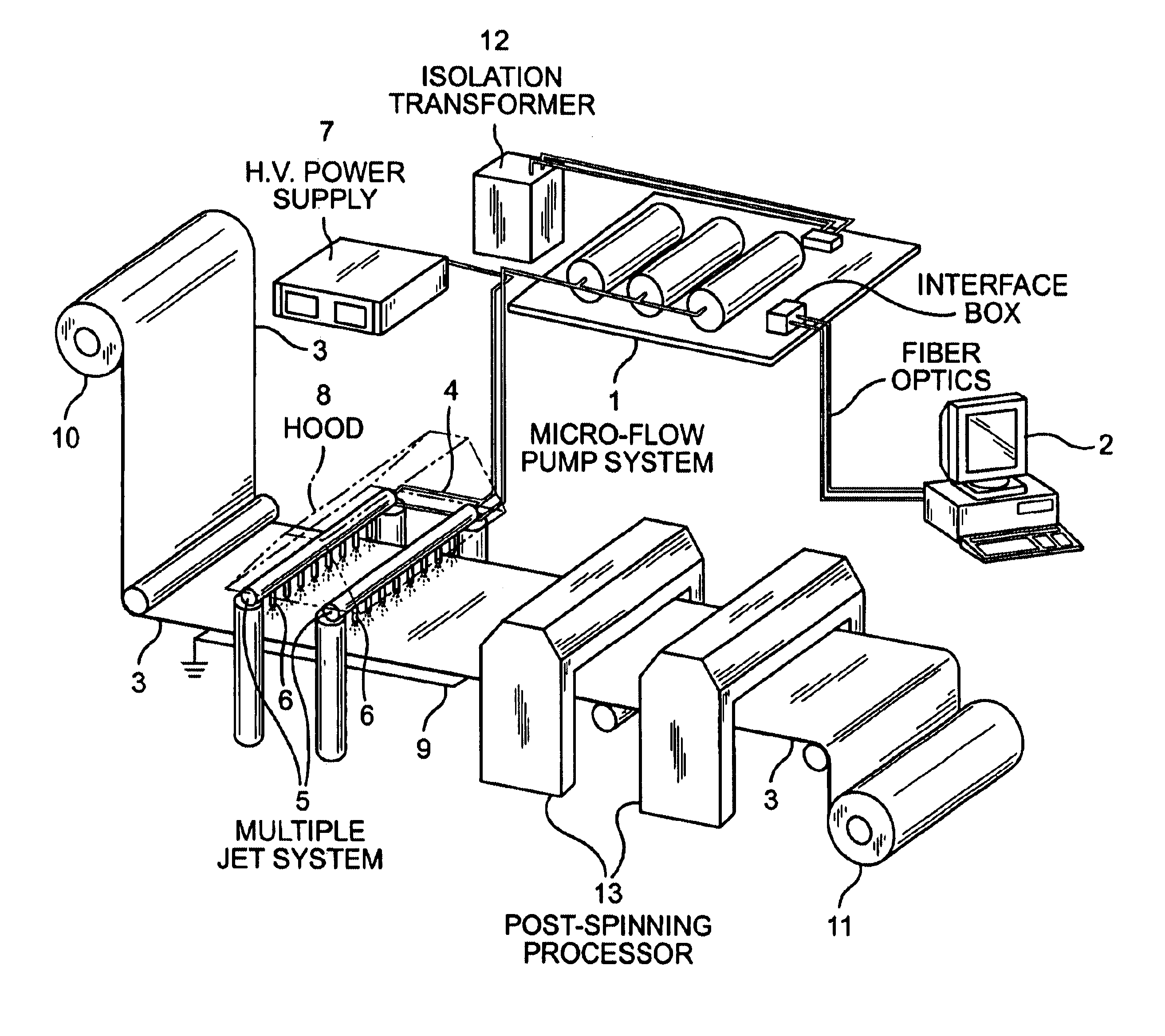
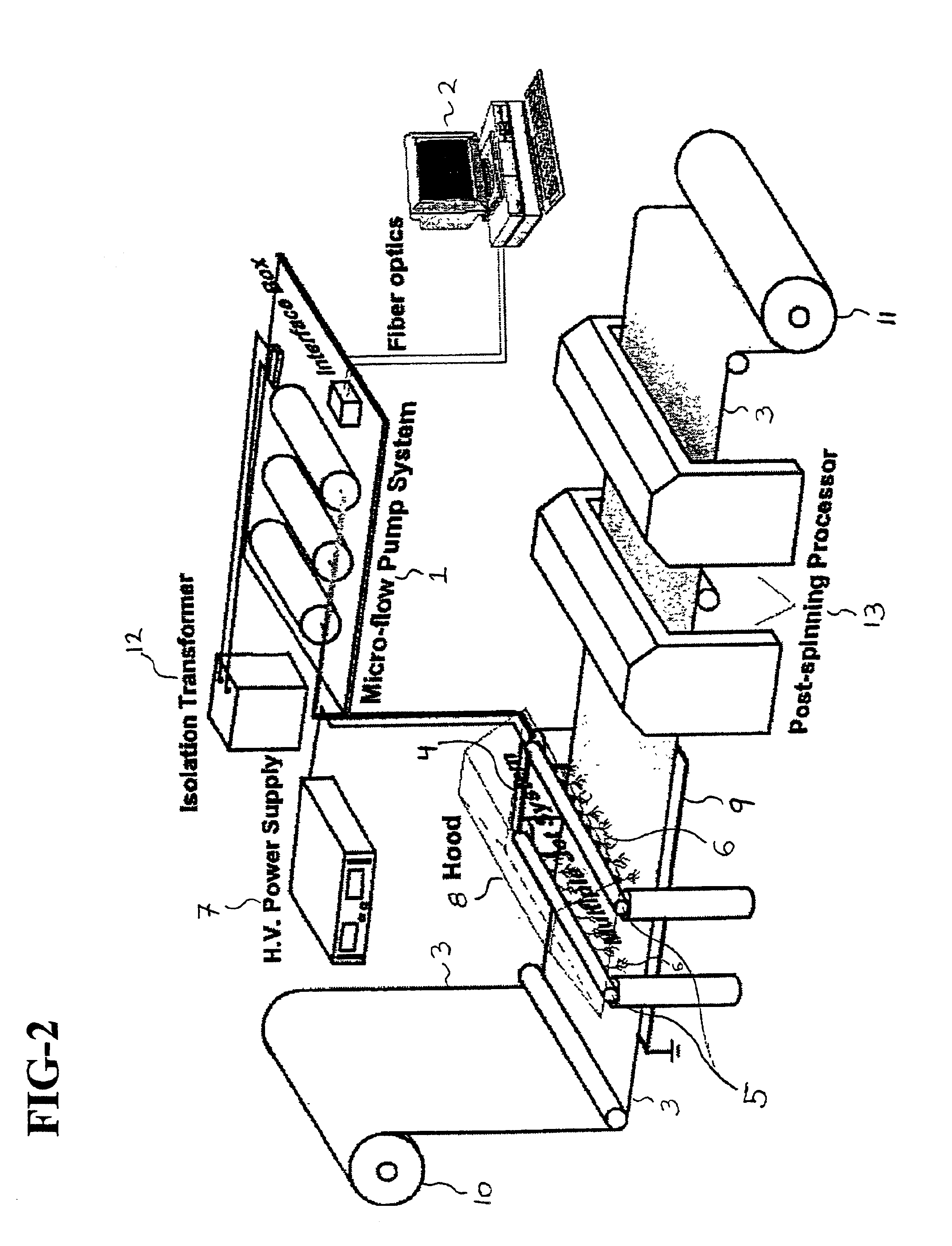
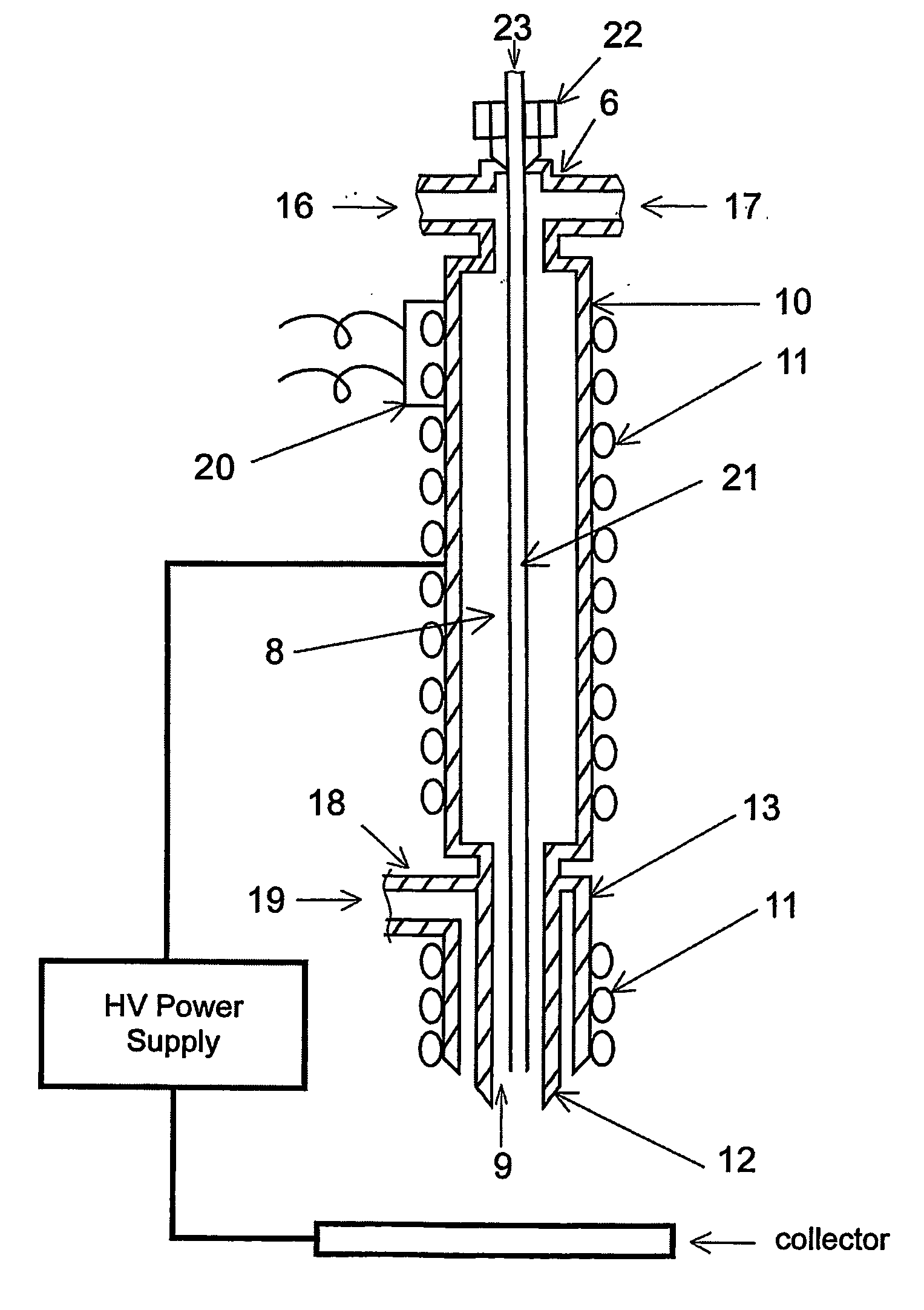
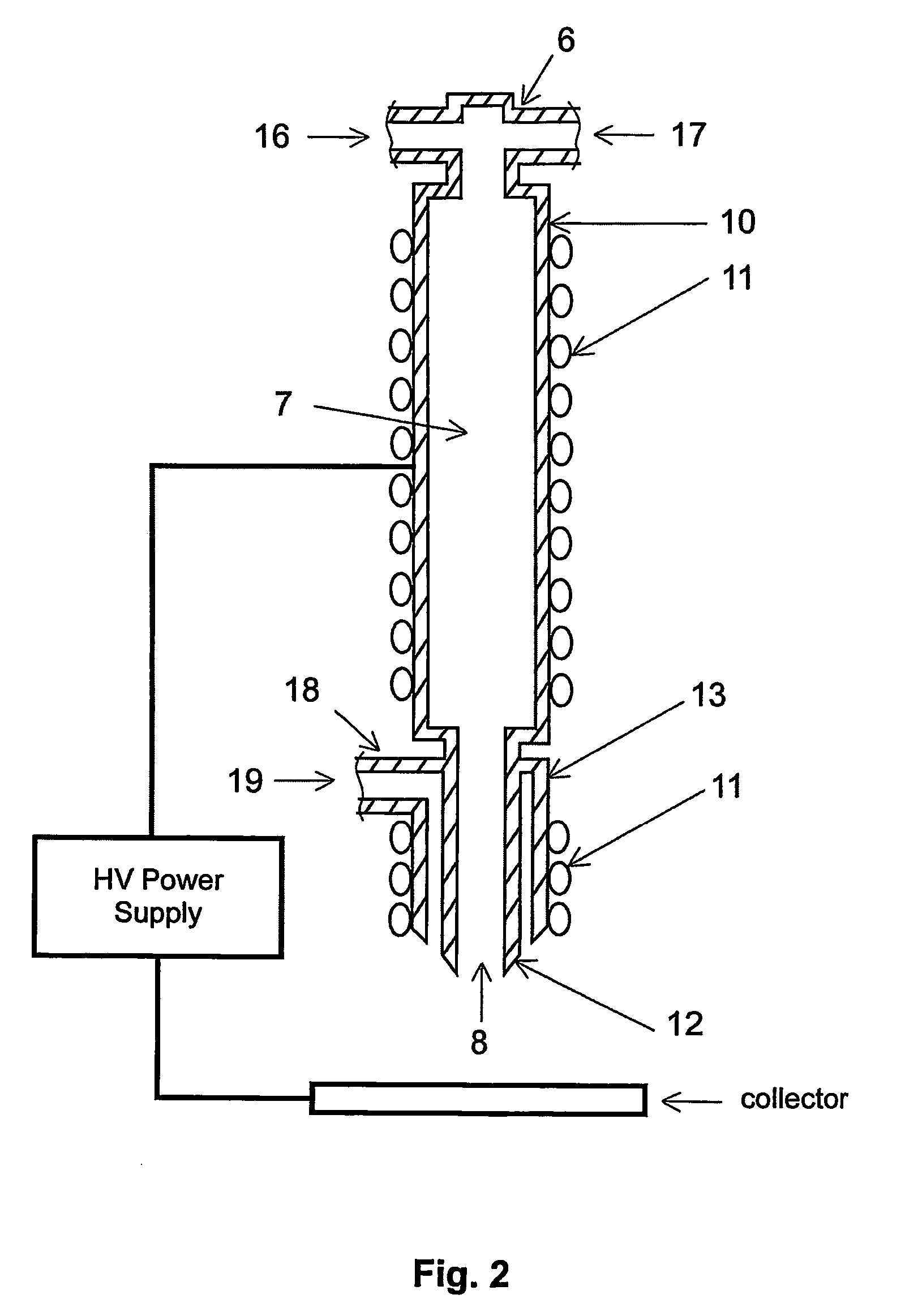
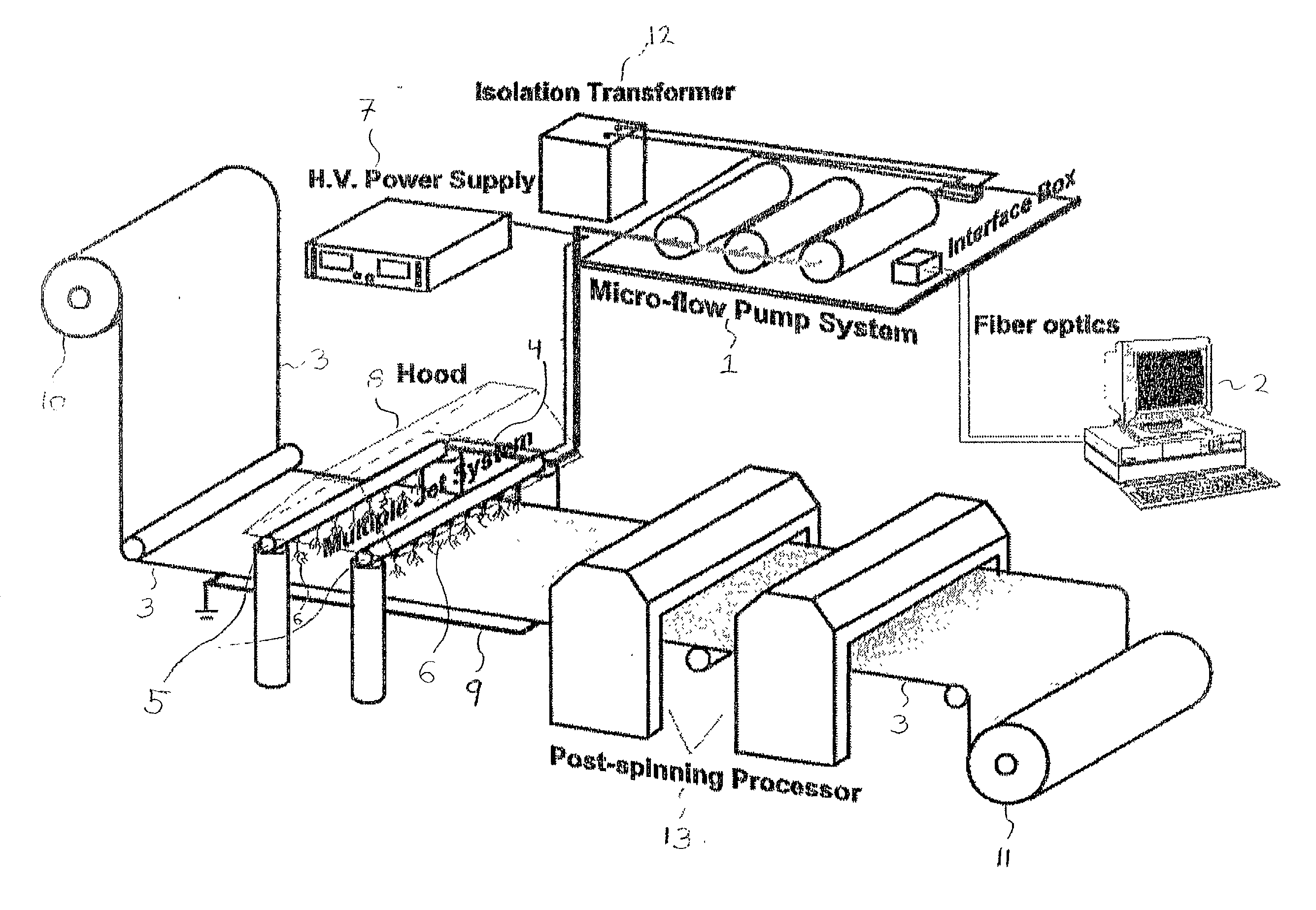
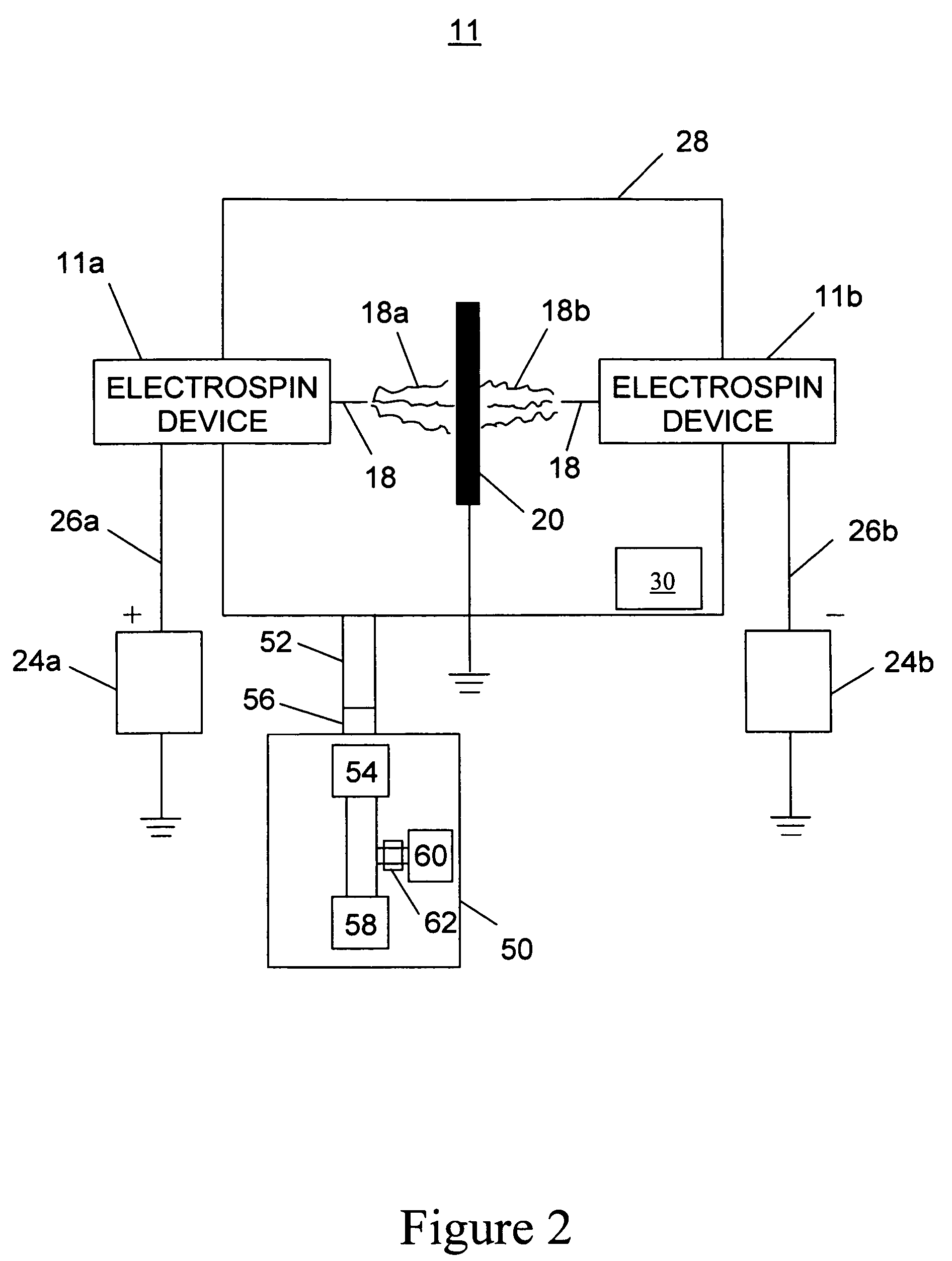
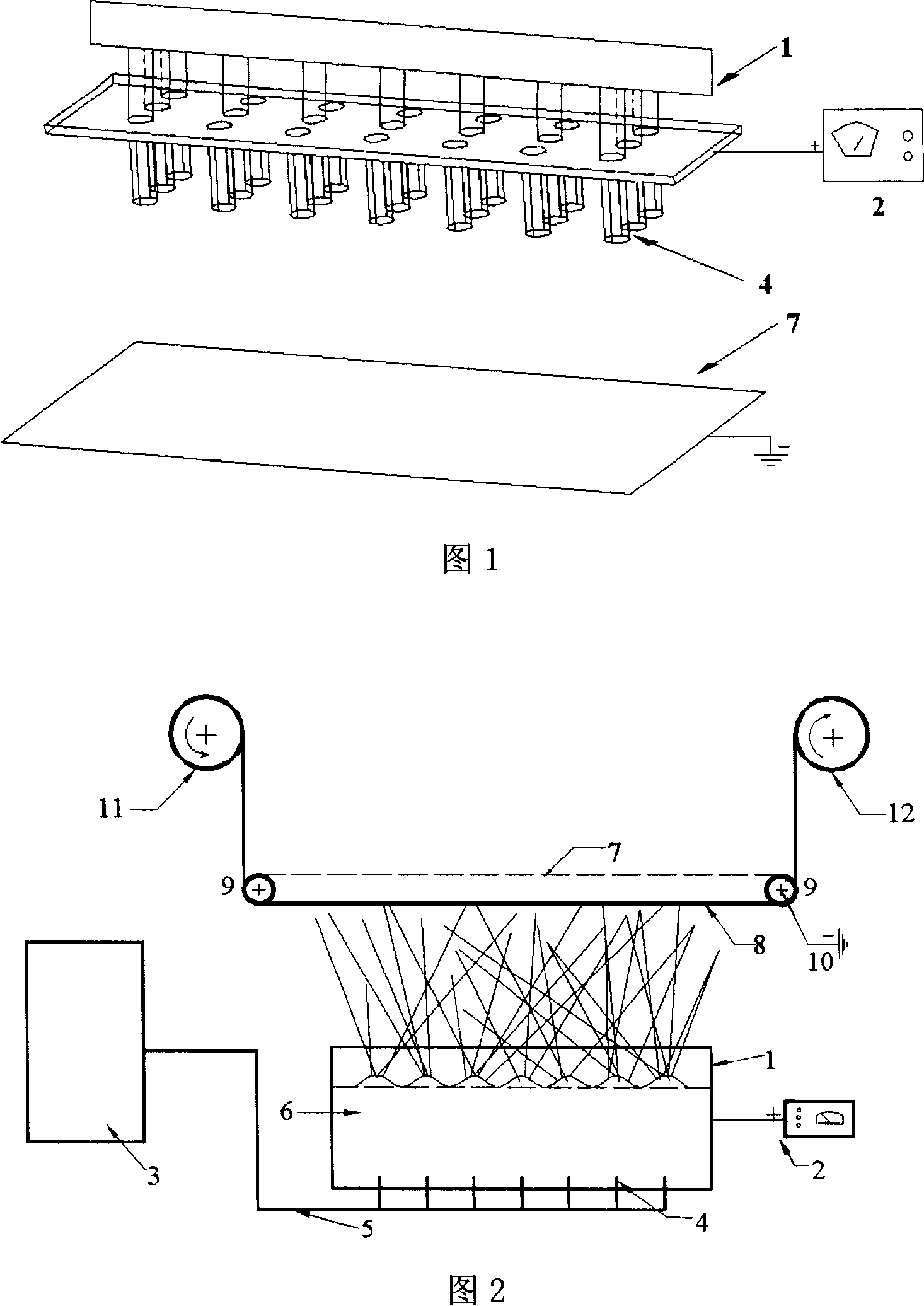
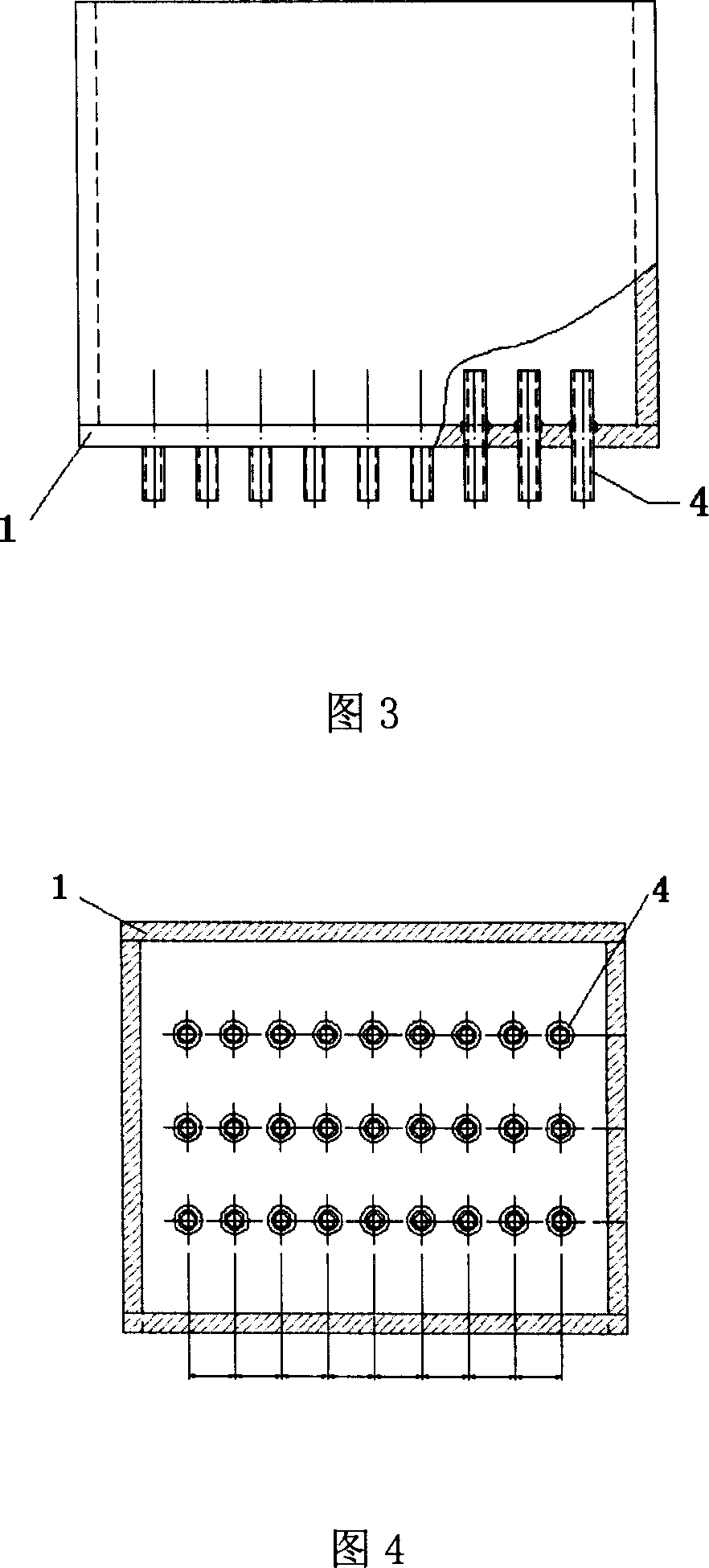
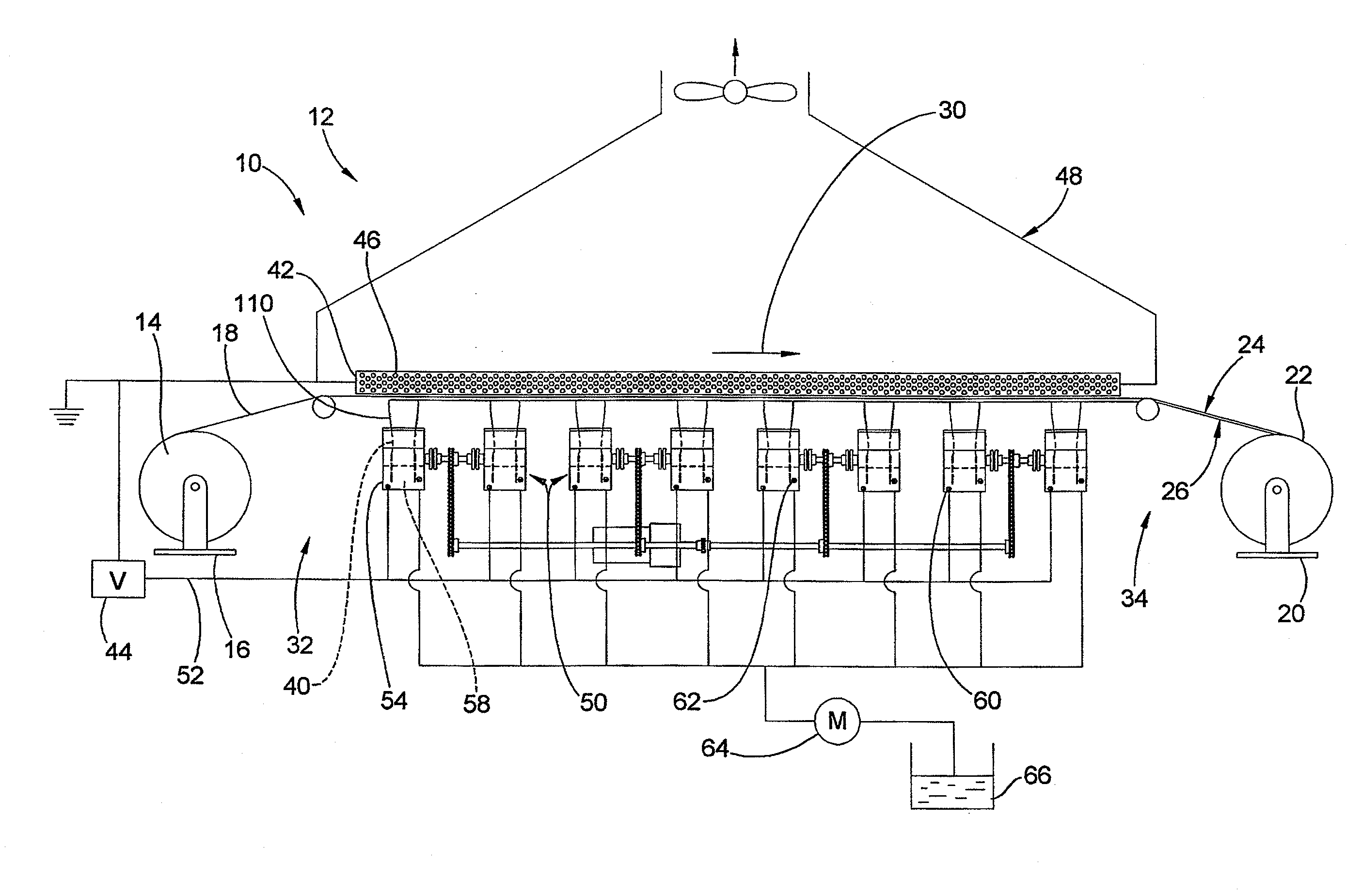
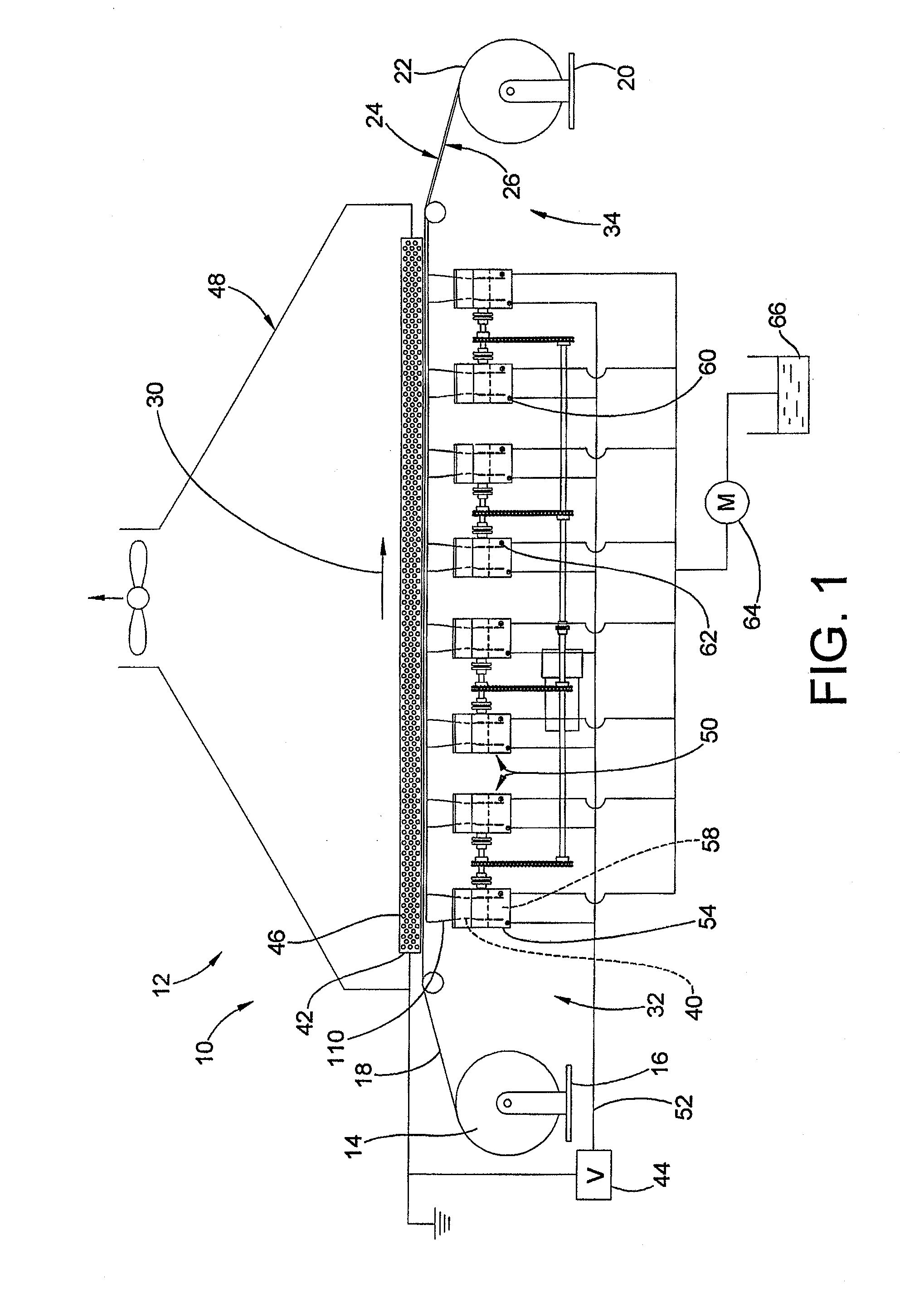
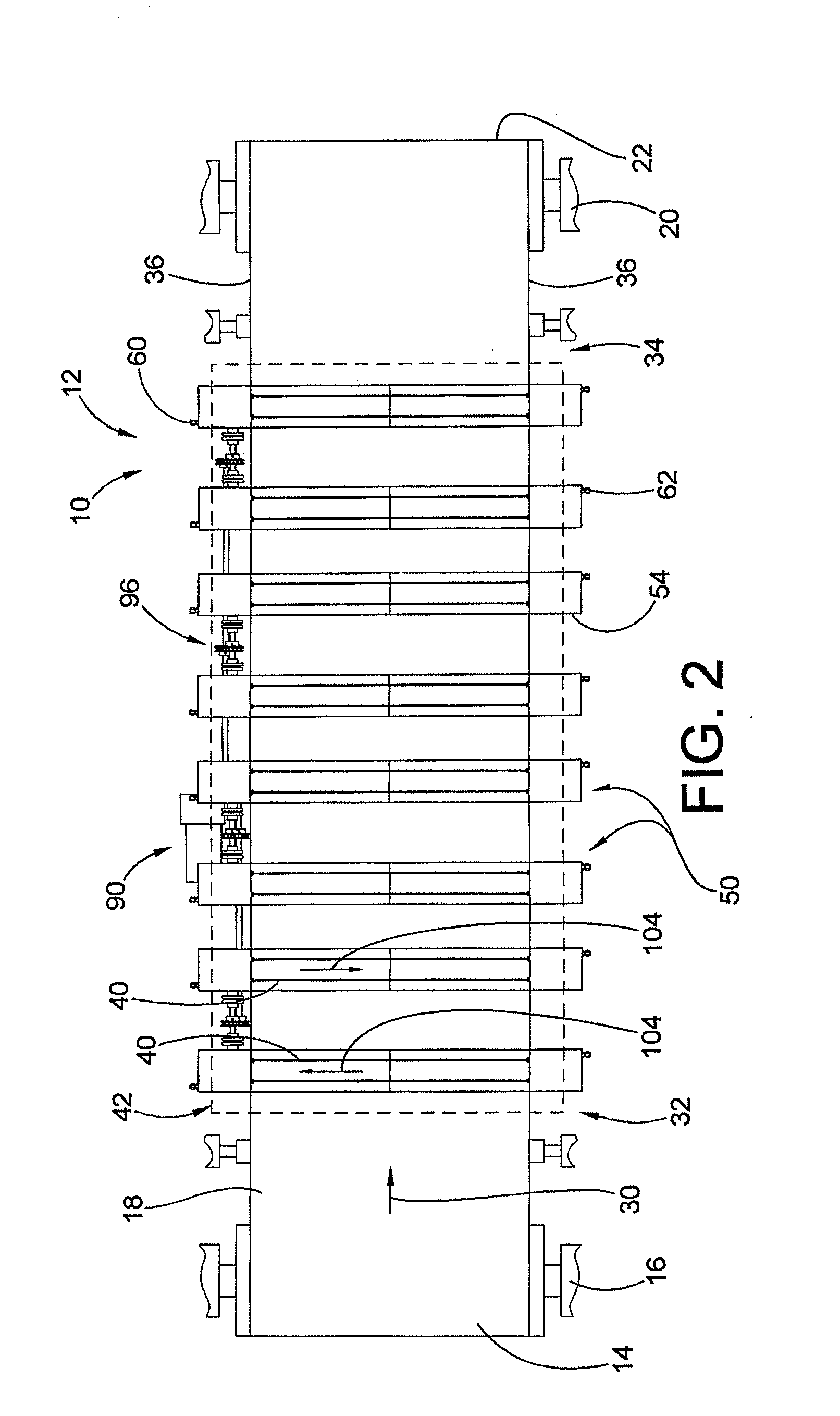
Apparatus and methods for electrospinning polymeric fibers and membranes
InactiveUS6713011B2Easy to controlLarge specific surface areaElectric discharge heatingConfectioneryFiberElectrospinning
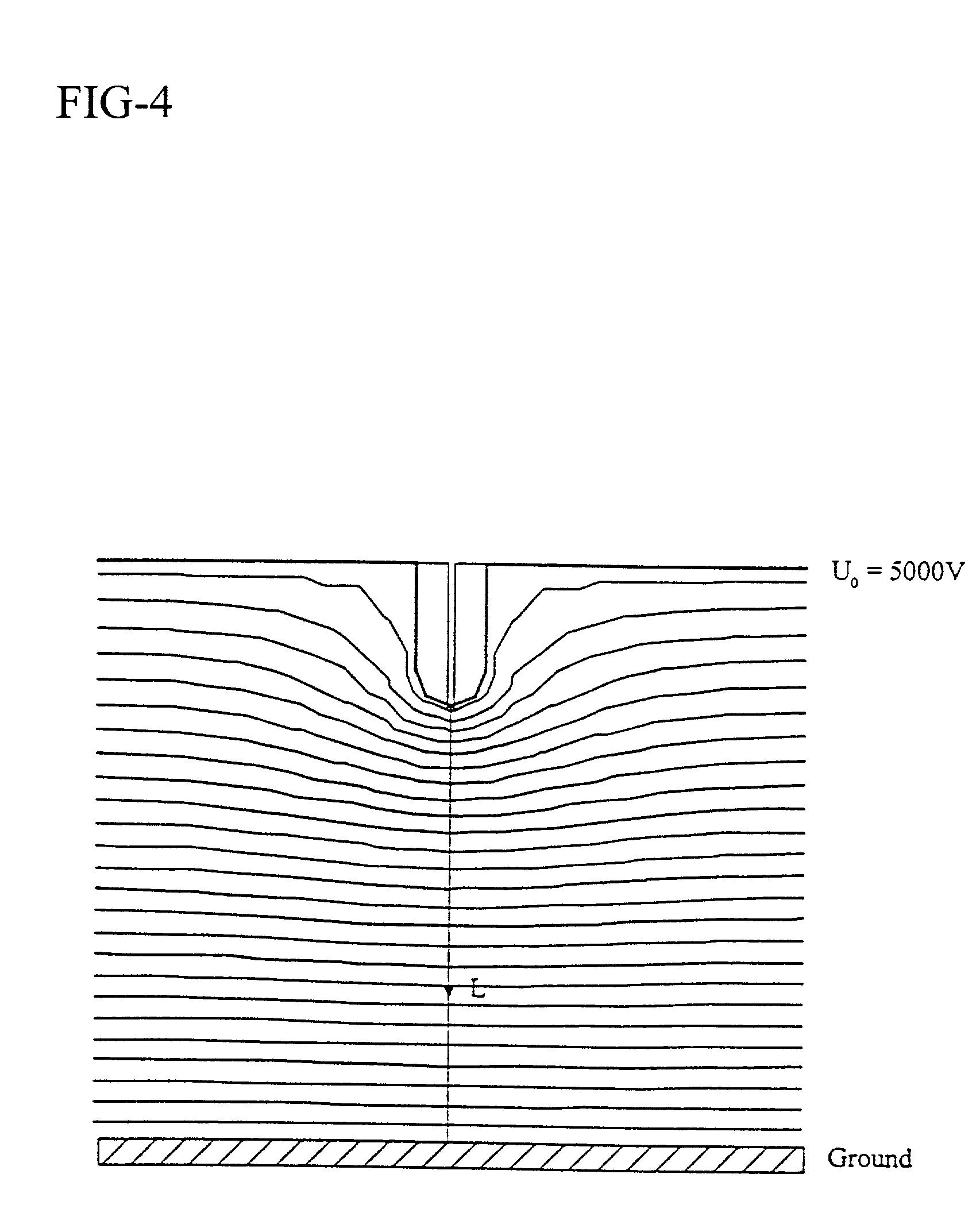
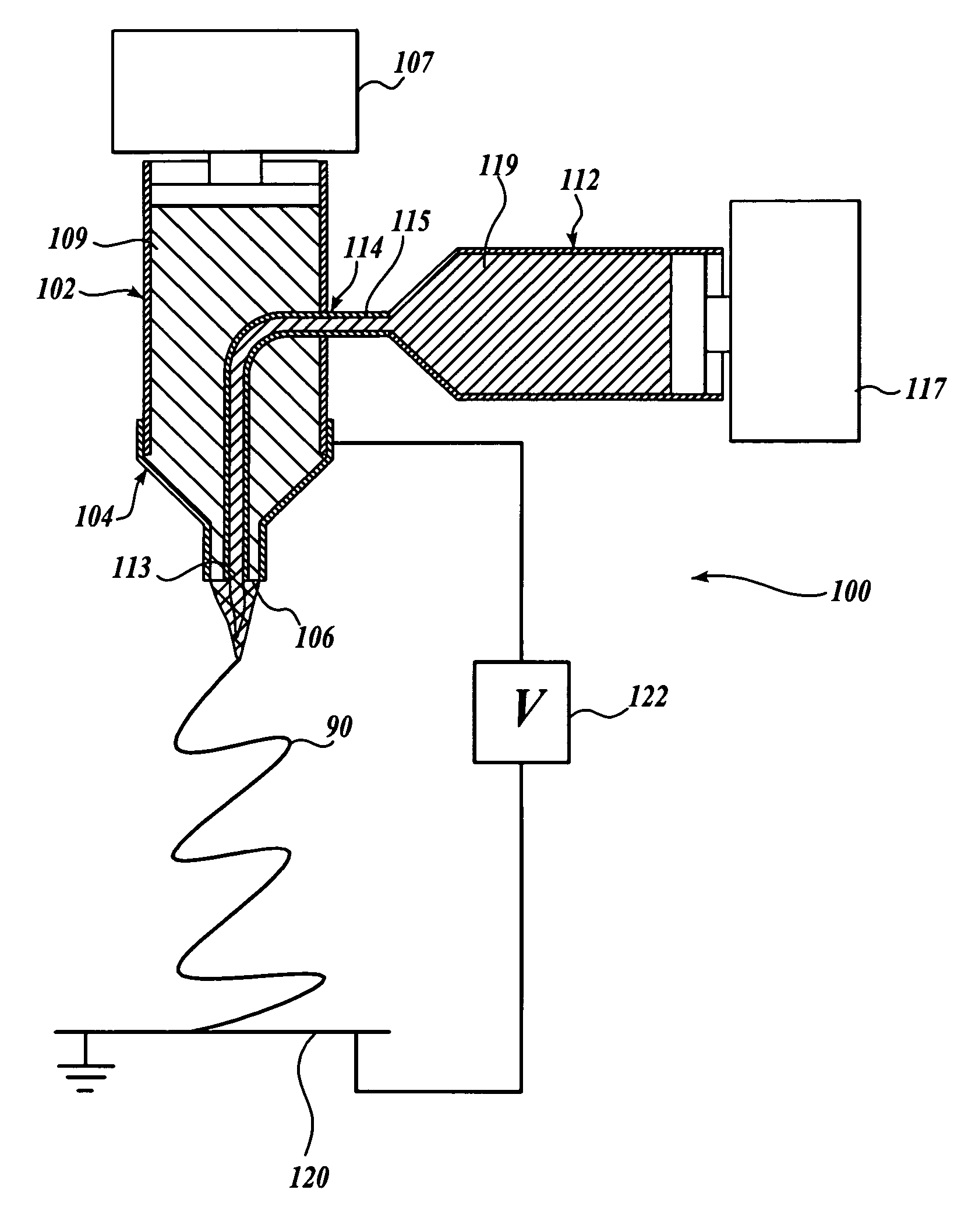
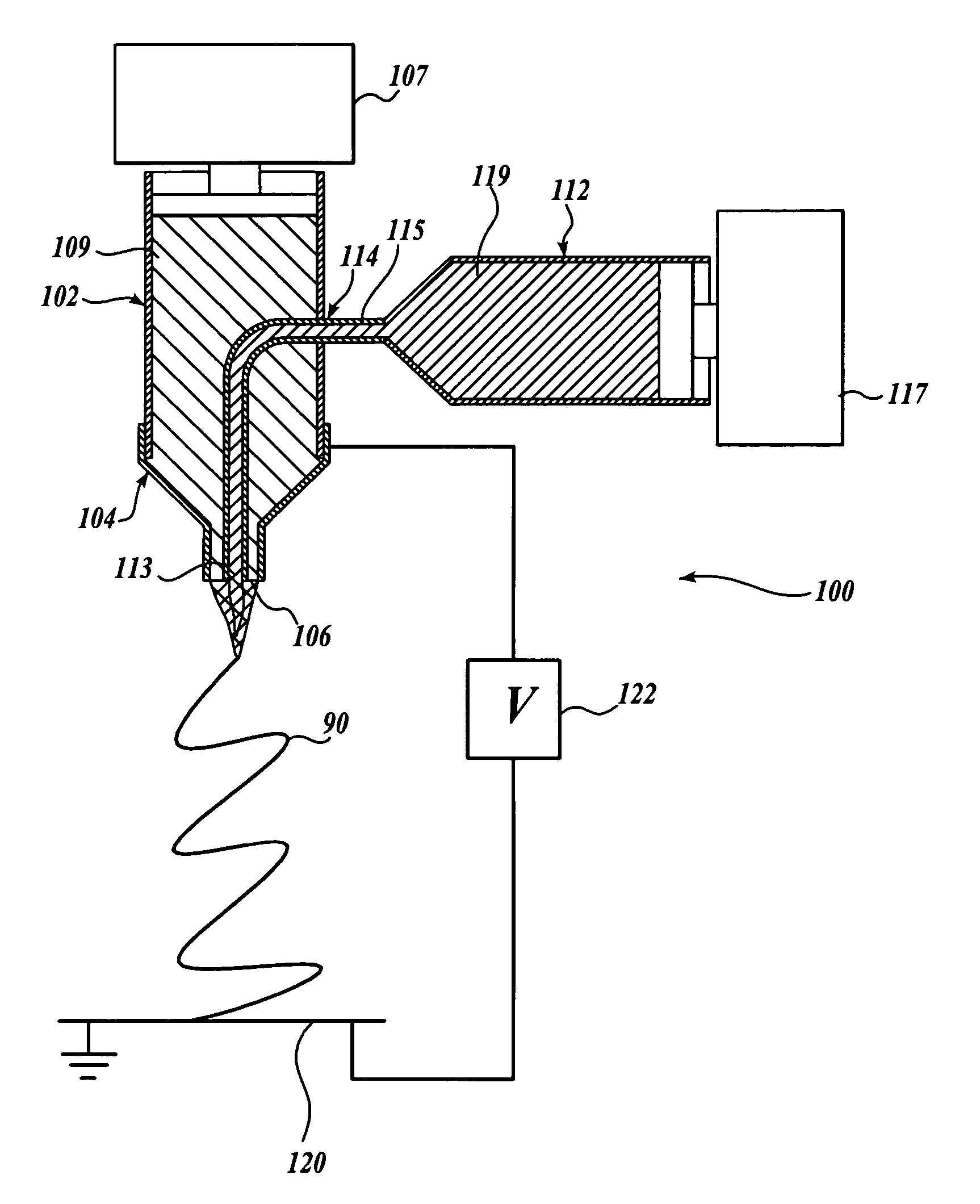
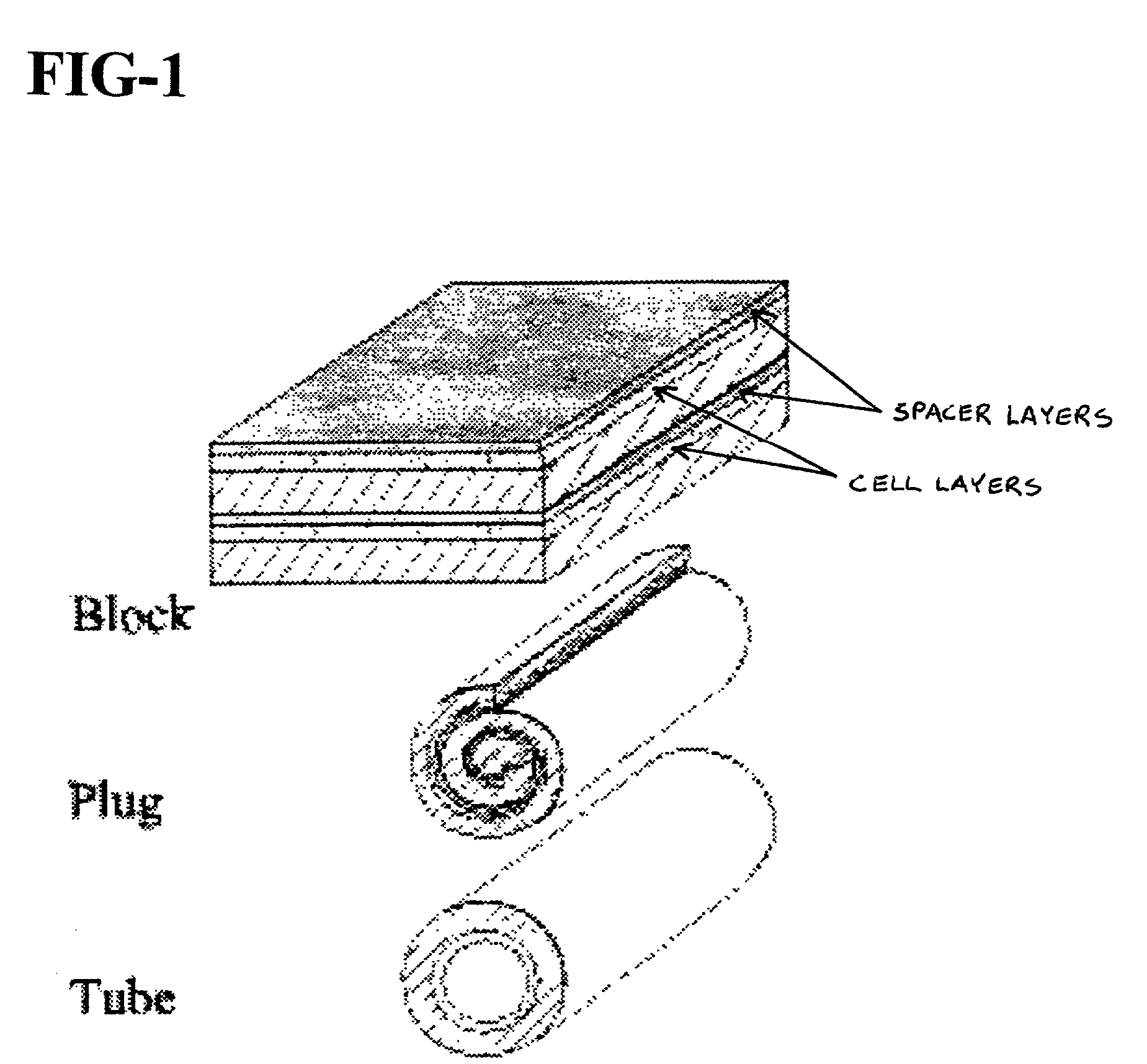
An apparatus and method for electrospinning polymer fibers and membranes. The method includes electrospinning a polymer fiber from a conducting fluid in the presence of a first electric field established between a conducting fluid introduction device and a ground source and modifying the first electric field with a second electric field to form a jet stream of the conducting fluid. The method also includes electrically controlling the flow characteristics of the jet stream, forming a plurality of electrospinning jet streams and independently controlling the flow characteristics of at least one of the jet streams. The apparatus for electrospinning includes a conducting fluid introduction device containing a plurality of electrospinning spinnerets, a ground member positioned adjacent to the spinnerets, a support member disposed between the spinnerets and the ground member and movable to receive fibers formed from the conducting fluid, and a component for controlling the flow characteristics of conducting fluid from at least one spinneret independently from another spinneret.
Owner:RES FOUND THE
Cell delivery system comprising a fibrous matrix and cells
Cell storage and delivery systems and methods for storing and delivering viable cells to a mammal are disclosed. The cell storage and delivery systems include a biodegradable and / or bioabsorbable fibrous matrix physically associated with viable cells to contain and release the cells at a controlled rate. The biodegradable and / or bioabsorbable matrix can be formed by electrospinning fibers of biodegradable and / or bioabsorbable fiberizable material. The methods include methods for storing viable cells and for delivering viable cells to a mammal using the cell storage and delivery system.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Fluoropolymer fine fiber
ActiveUS20090032475A1Advantageously employedHeat stableDispersed particle filtrationLiquid suspension thickening by filtrationPolymer scienceFiltration
A layer of fluoropolymer fine fiber can be made. The fine fiber can be made by electrospinning from a solvent or a solvent blend. The layers of the invention are useful in general filtration of fluid streams including gaseous and liquid streams. The fine fiber layers are also useful as hydrophobic filtration layers that can be used to separate water from a hydrocarbon stream.
Owner:DONALDSON CO INC
Nanofibers, and apparatus and methods for fabricating nanofibers by reactive electrospinning
ActiveUS20070018361A1Broaden applicationEasy to controlElectric discharge heatingInorganic material artificial filamentsFiberElectrospinning
Apparatus and methods for fabricating nanofibers by reactive electrospinning are described. An electrospinning process is coupled with an in-line reactor where chemical or photochemical reactions take place. This invention expands the application of the electrospinning and allows the production of nanofibers of crosslinked polymers and other new materials, such as gel nanofibers of ceramic precursors.
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE
Silk biomaterials and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS7674882B2Avoid problemsReduce usagePeptide/protein ingredientsFilament/thread formingFiberIn vivo
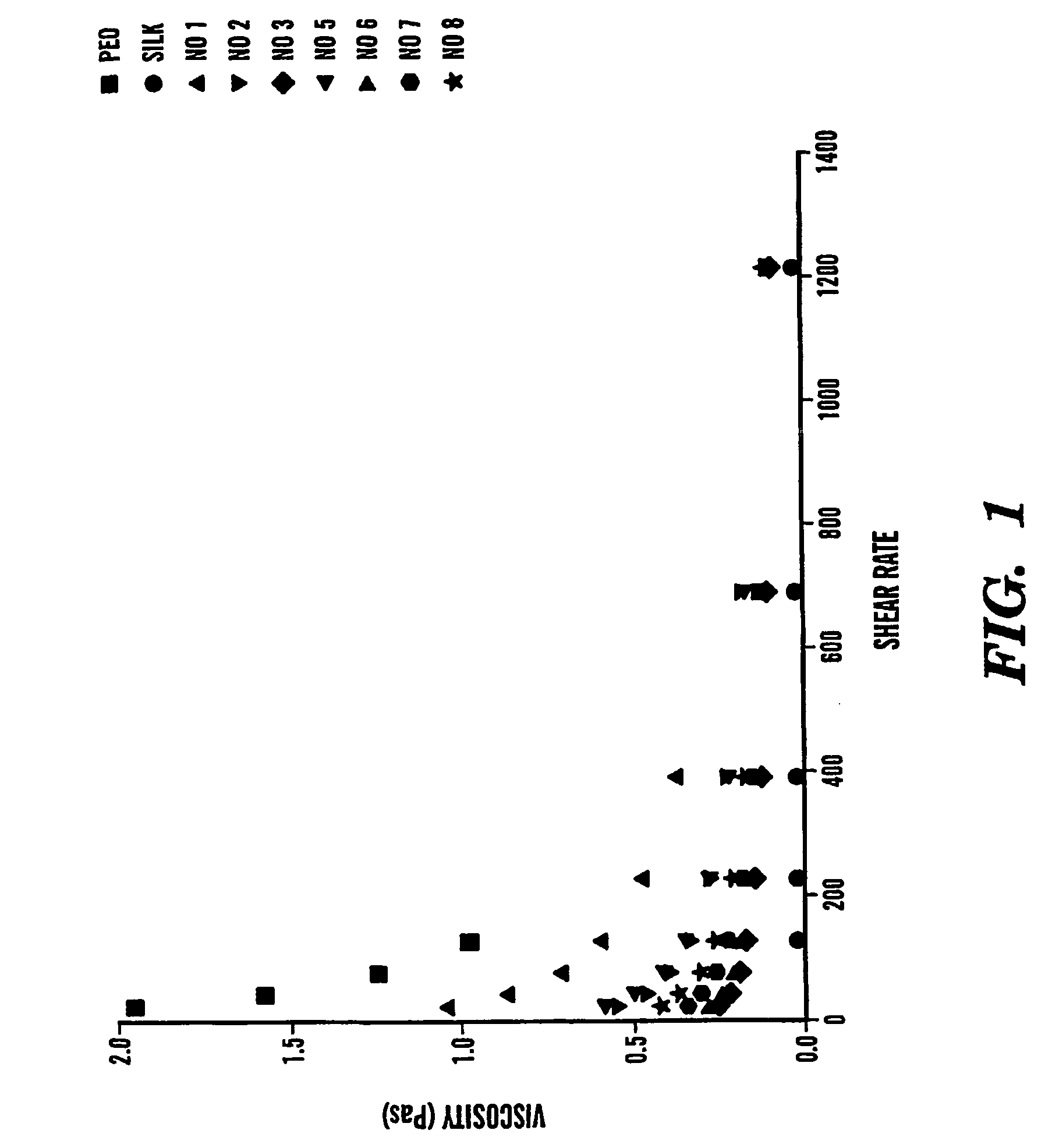
The present invention provides an all-aqueous process and composition for production of silk biomaterials, e.g., fibers, films, foams and mats. In the process, at least one biocompatible polymer, such as poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO) (a well-documented biocompatible material), was blended with the silk protein prior to processing e.g., electrospinning. We discovered that this step avoids problems associated with conformational transitions of fibroin during solubilization and reprocessing from aqueous solution which lead to embrittled materials. Moreover, the process avoids the use of organic solvents that can pose problems when the processed biomaterials are exposed to cells in vitro or in vivo.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
Apparatus and methods for electrospinning polymeric fibers and membranes
An apparatus and methods for electrospinning polymer fibers and membranes are described. The methods include in one aspect electrospinning a polymer fiber from a conducting fluid containing the polymer in the presence of a first electric field established between a conducting fluid introduction device and a ground source and modifying the first electric field with a second electric field to form a jet stream of the conducting fluid. In another aspect the methods include forming an electrospinning jet stream of the conducting fluid and electrically controlling the flow characteristics of the jet stream. In yet another aspect the methods include forming a plurality of electrospinning jet streams of the conducting fluid and independently controlling the flow characteristics of at least one of the jet streams. The apparatus for electrospinning includes a conducting fluid introduction device containing a plurality of electrospinning spinnerets for delivering the conducting fluid, a ground member positioned adjacent to the spinnerets, a support member disposed between the spinnerets and the ground member and movable to receive fibers formed from the conducting fluid, and a means for controlling the flow characteristics of conducting fluid from at least one spinneret independently from the flow characteristics of conducting fluid from another spinneret. An improved conducting fluid introduction device which includes a plurality of spinnerets, each for independently delivering a controlled quantity of conducting fluid at a controlled pressure or flow rate, the spinnerets being charged at an electric potential and being disposed relative to each other to normally interfere with the electric field produced by adjacent spinnerets, each of the spinnerets having a tip at which conducting fluid exits configured to have an electrostatic field strength at each tip stronger than the liquid surface tension at each of the tips is also described.
Owner:RES FOUND THE
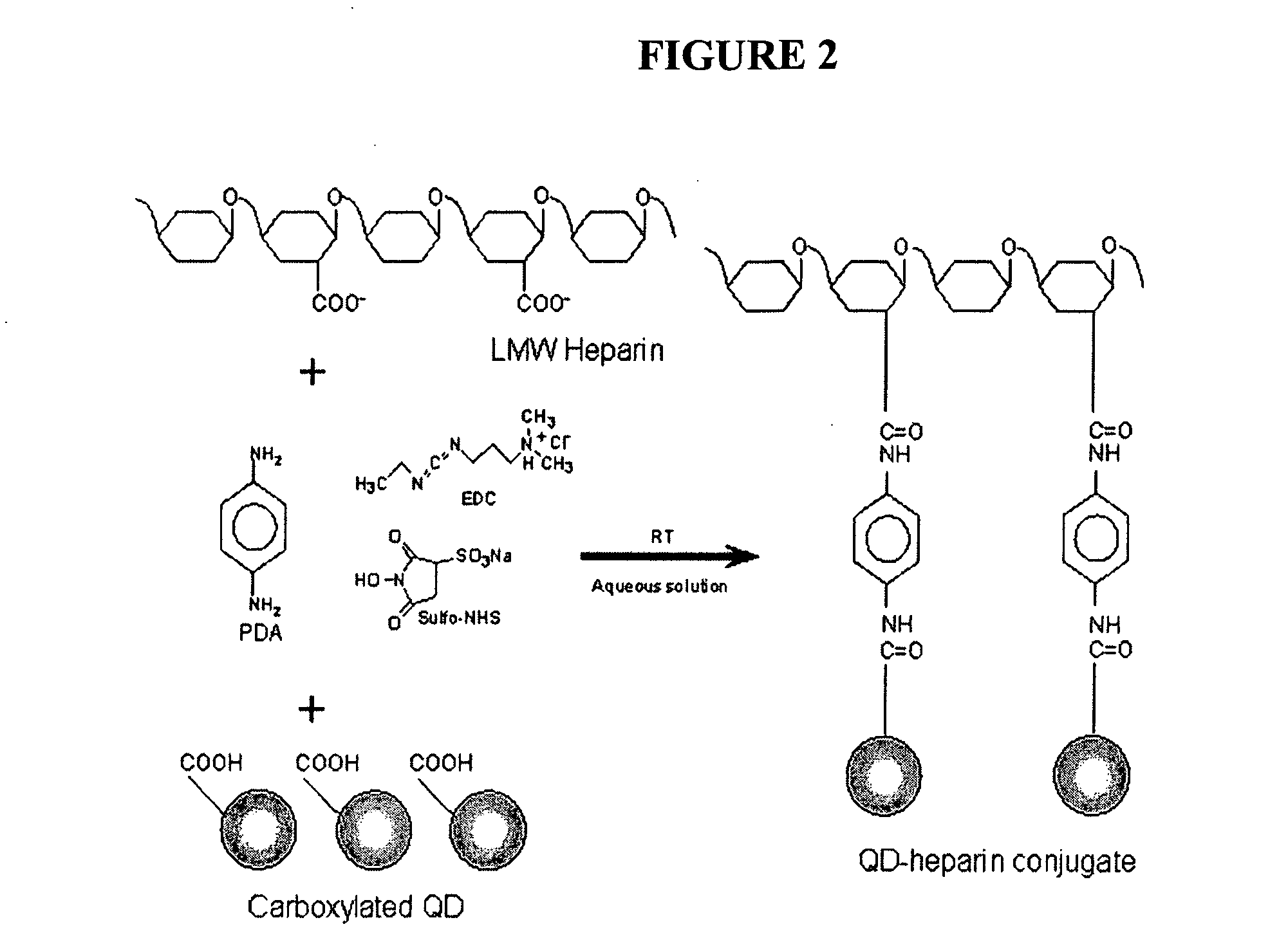
Multifunctional and biologically active matrices from multicomponent polymeric solutions
The present invention relates to a biologically active functionalized electrospun matrix to permit immobilization and long-term delivery of biologically active agents. In particular the invention relates to a functionalized polymer matrix comprising a matrix polymer, a compatibilizing polymer and a biomolecule or other small functioning molecule. In certain aspects the electrospun polymer fibers comprise at least one biologically active molecule functionalized with low molecular weight heparin. Examples of active molecules that may be used with the multicomponent polymer of the invention include, for example, a drug, a biopolymer, for example a growth factor, a protein, a peptide, a nucleotide, a polysaccharide, a biological macromolecule or the like. The invention is further directed to the formation of functionalized crosslinked matrices, such as hydrogels, that include at least one functionalized compatibilizing polymer capable of assembly.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DELAWARE
Electrospun blends of natural and synthetic polymer fibers as tissue engineering scaffolds
InactiveUS20060263417A1Facilitate cell penetrationFacilitate proliferationBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsFiberPolymer science
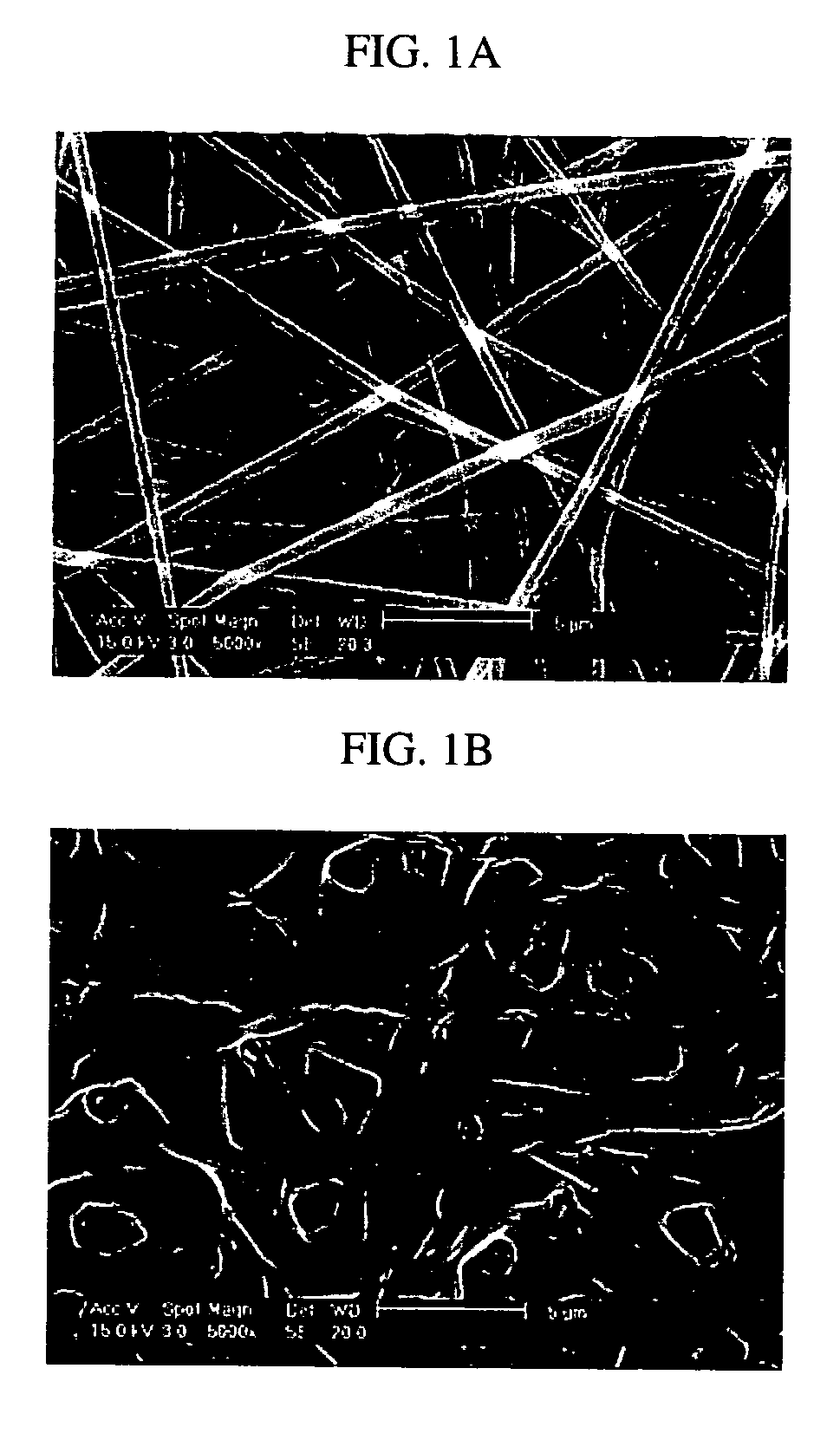
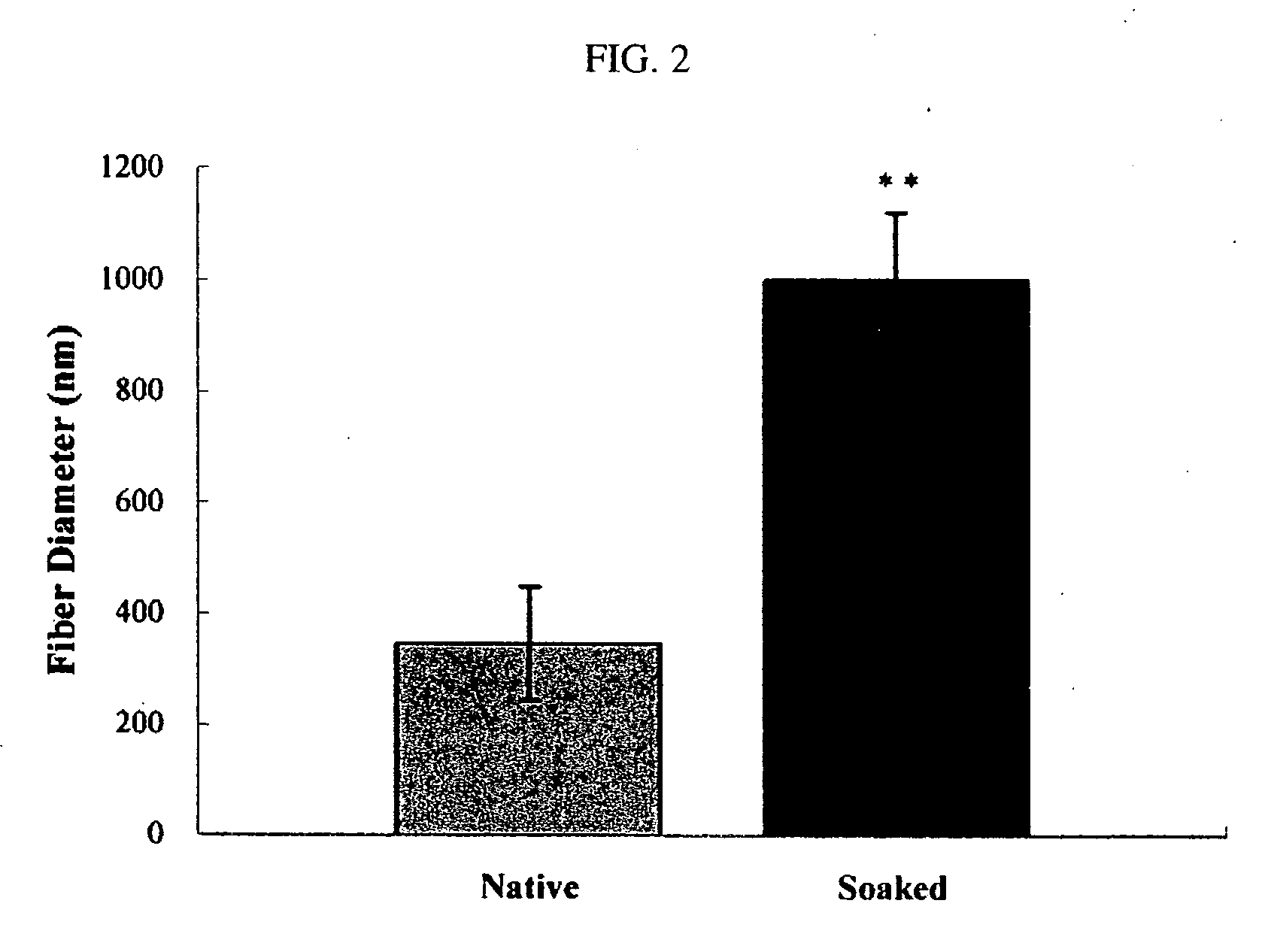
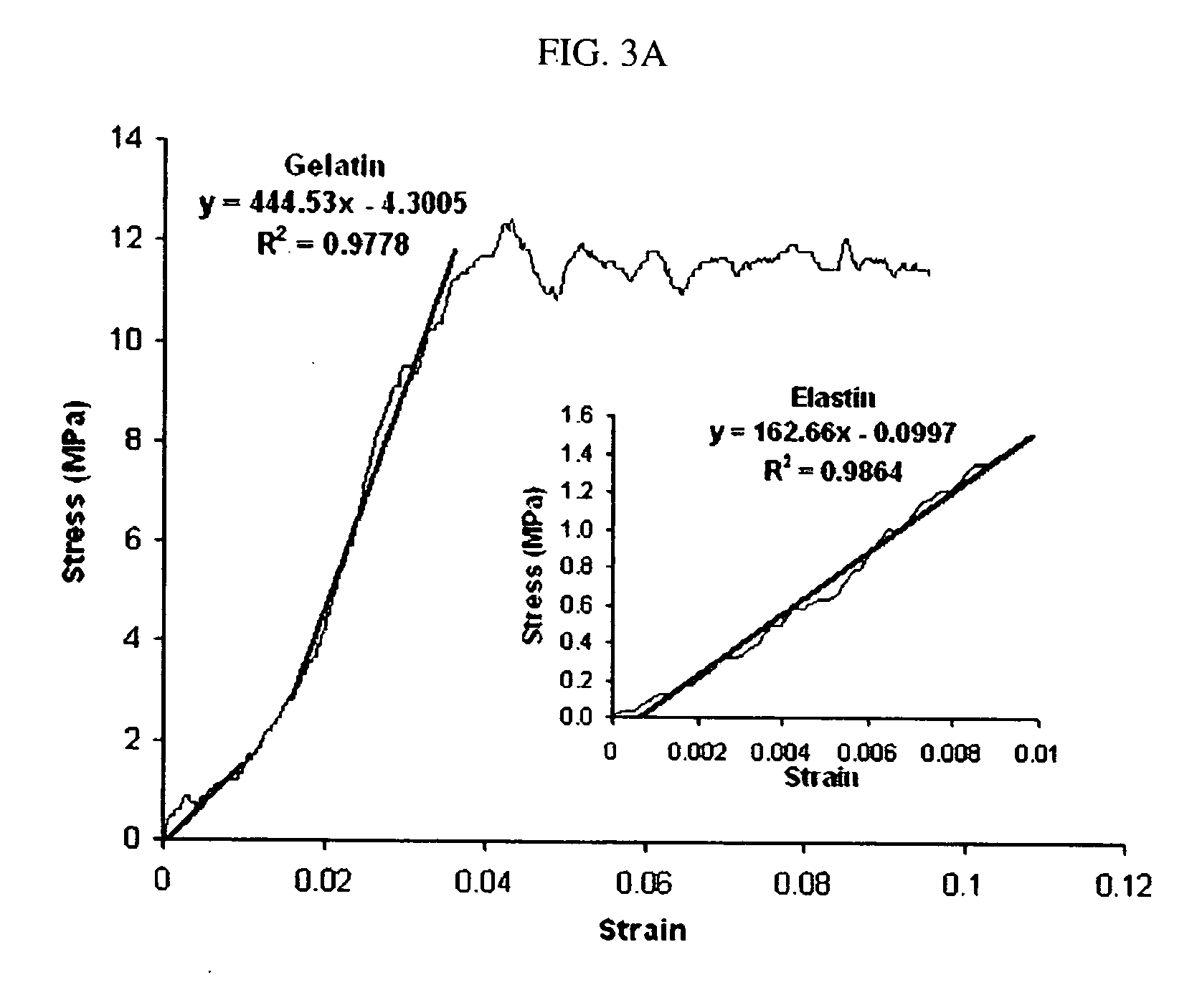
Non-woven fibrous scaffolds made by electrospinning from the synthetic biodegradable polymer such as, for example, poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) and natural proteins, such as, for example, gelatin (denatured collagen) and elastin and a method of making thereof.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
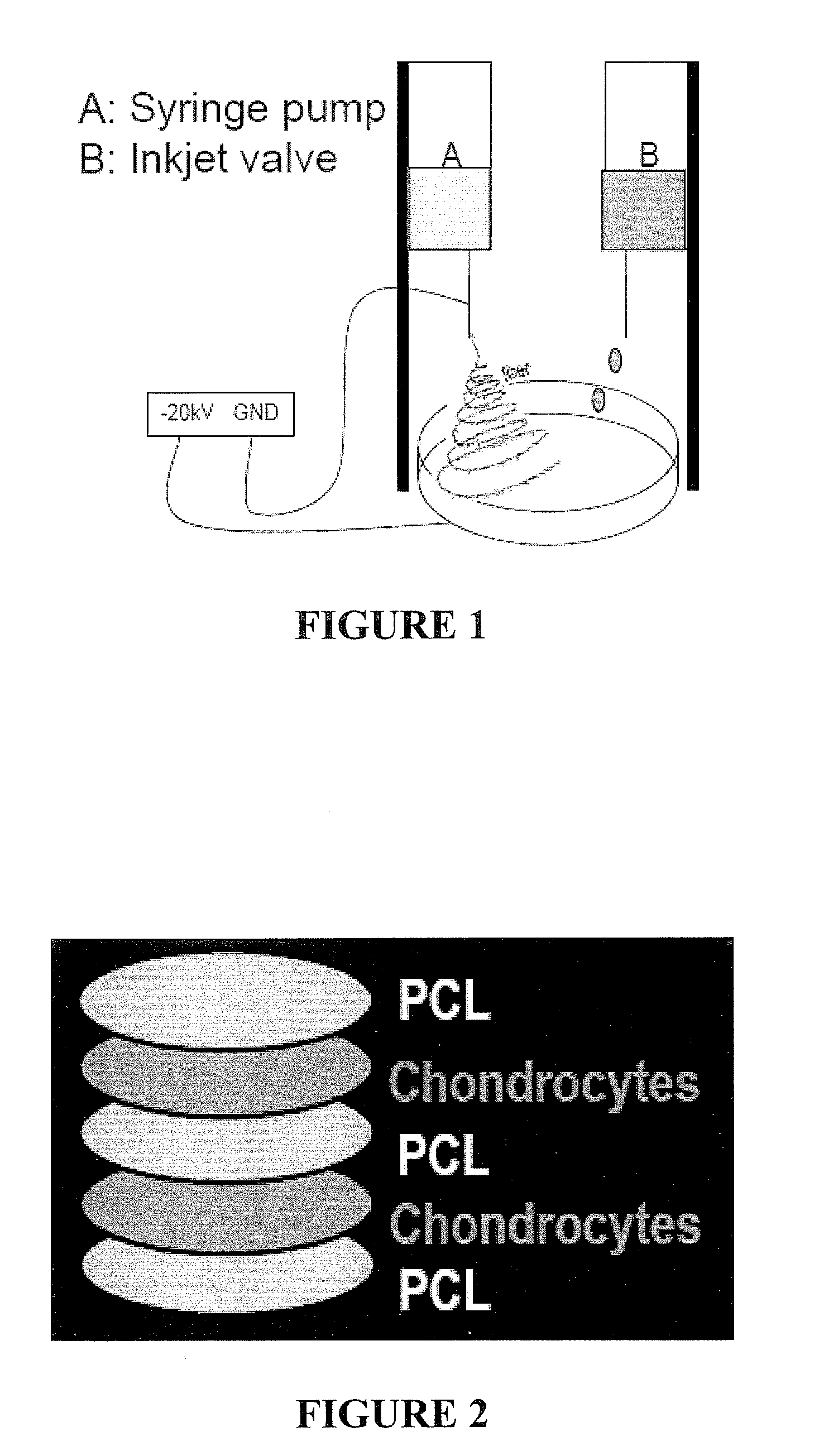
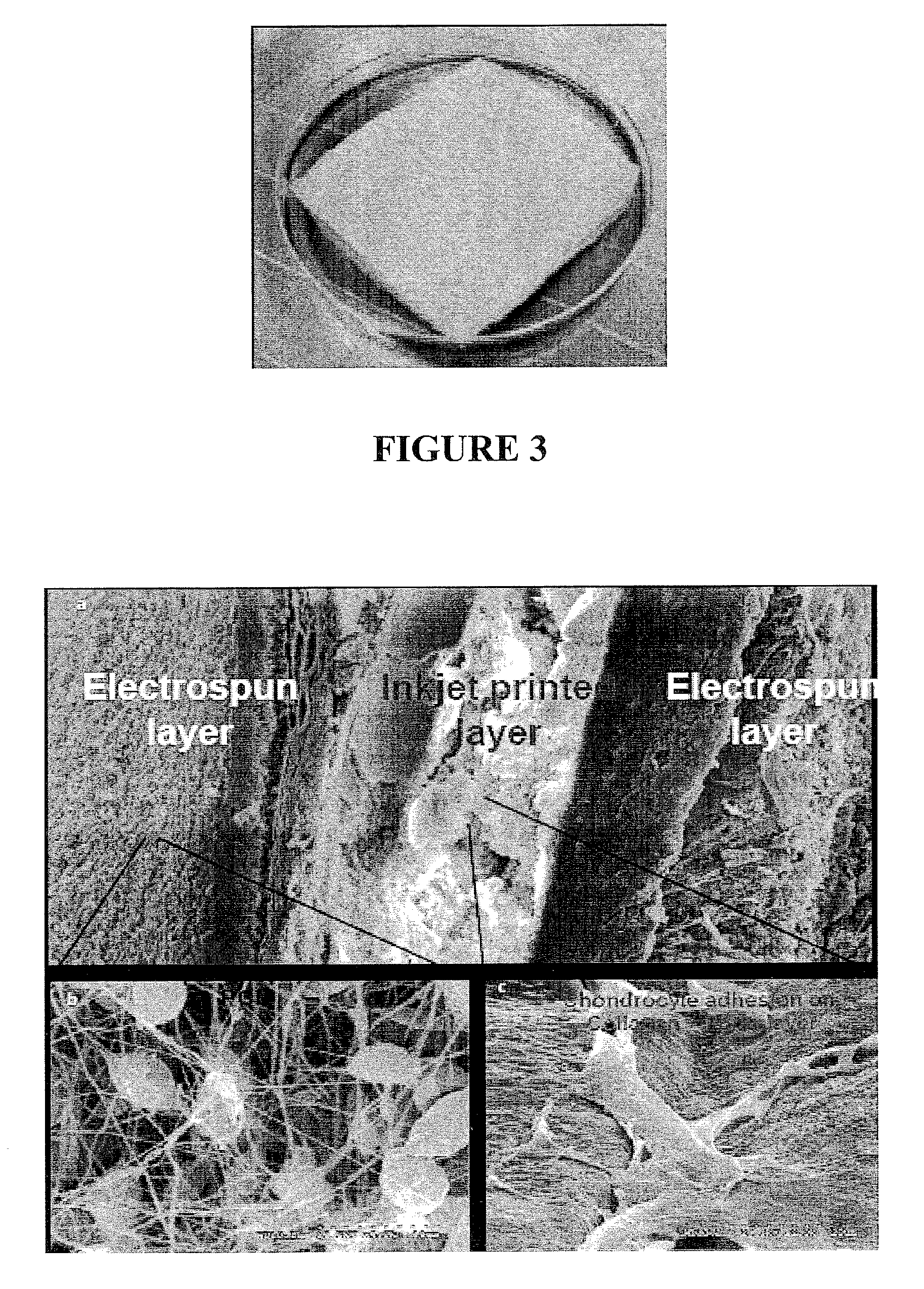
Inkjet Printing of Tissues and Cells
Provided herein is an apparatus for printing cells which includes an electrospinning device and an inkjet printing device operatively associated therewith. Methods of making a biodegradable scaffold having cells seeded therein are also provided. Methods of forming microparticles containing one or more cells encapsulated by a substrate are also provided, as are methods of forming an array of said microparticles.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
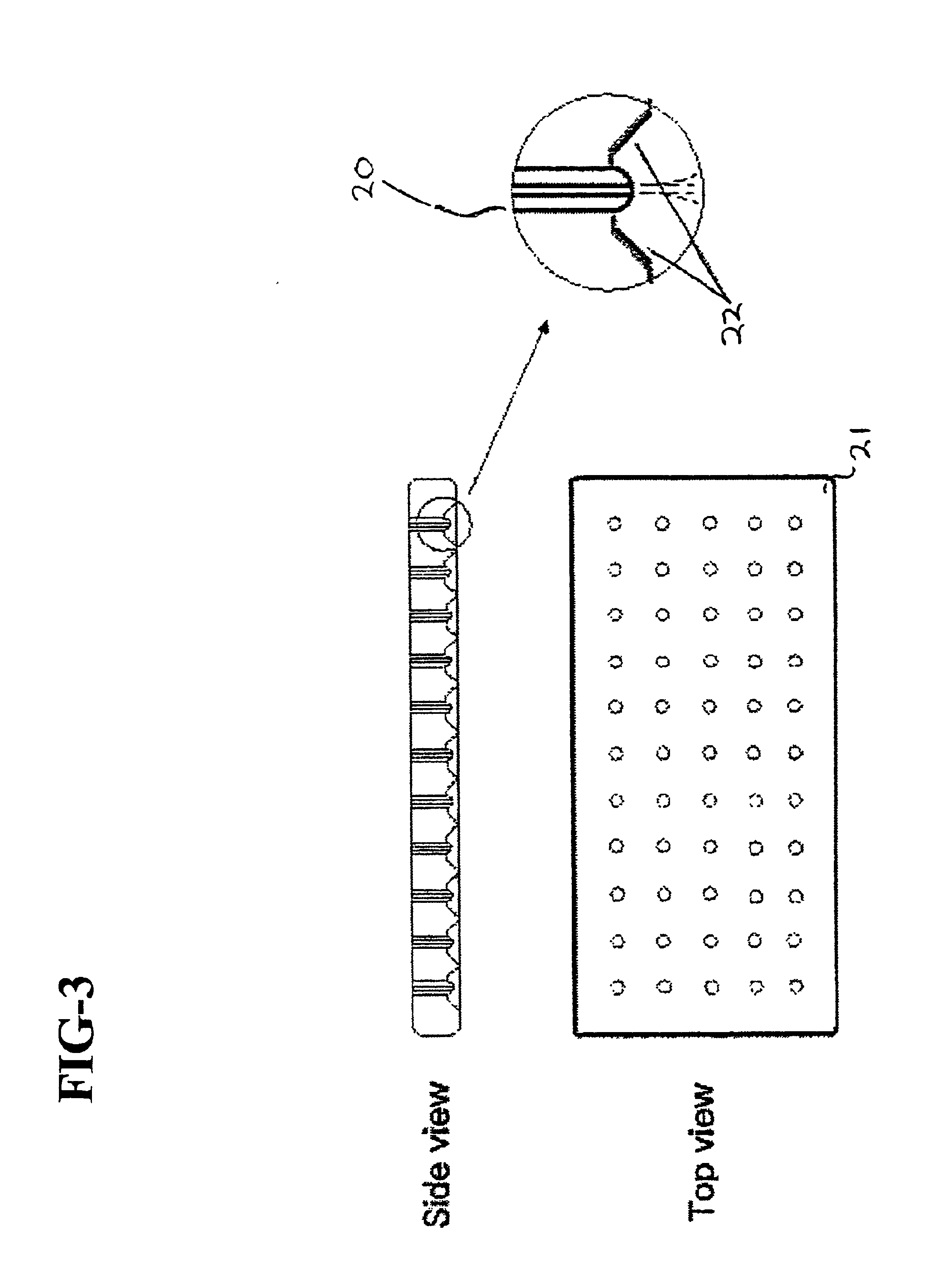
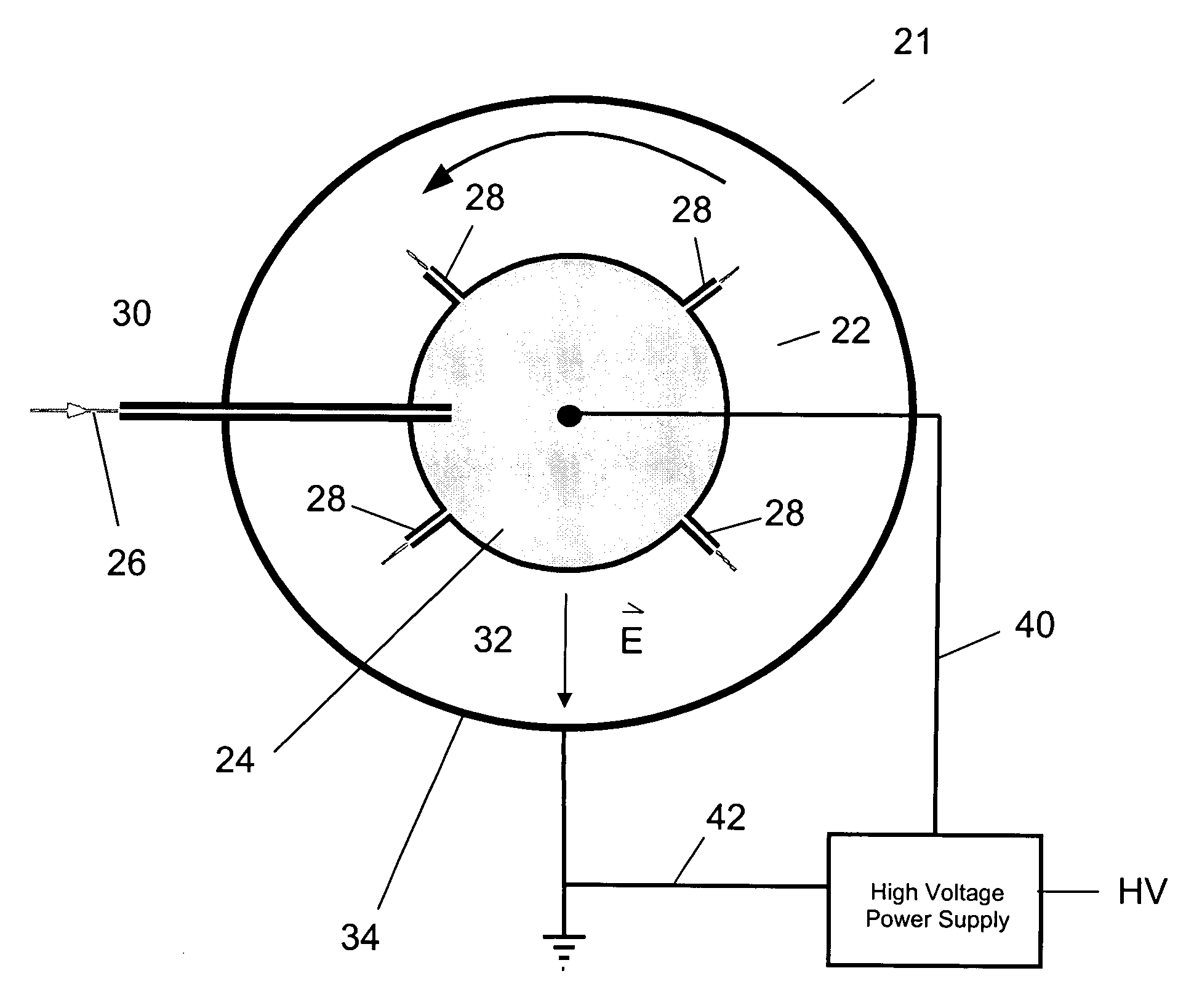
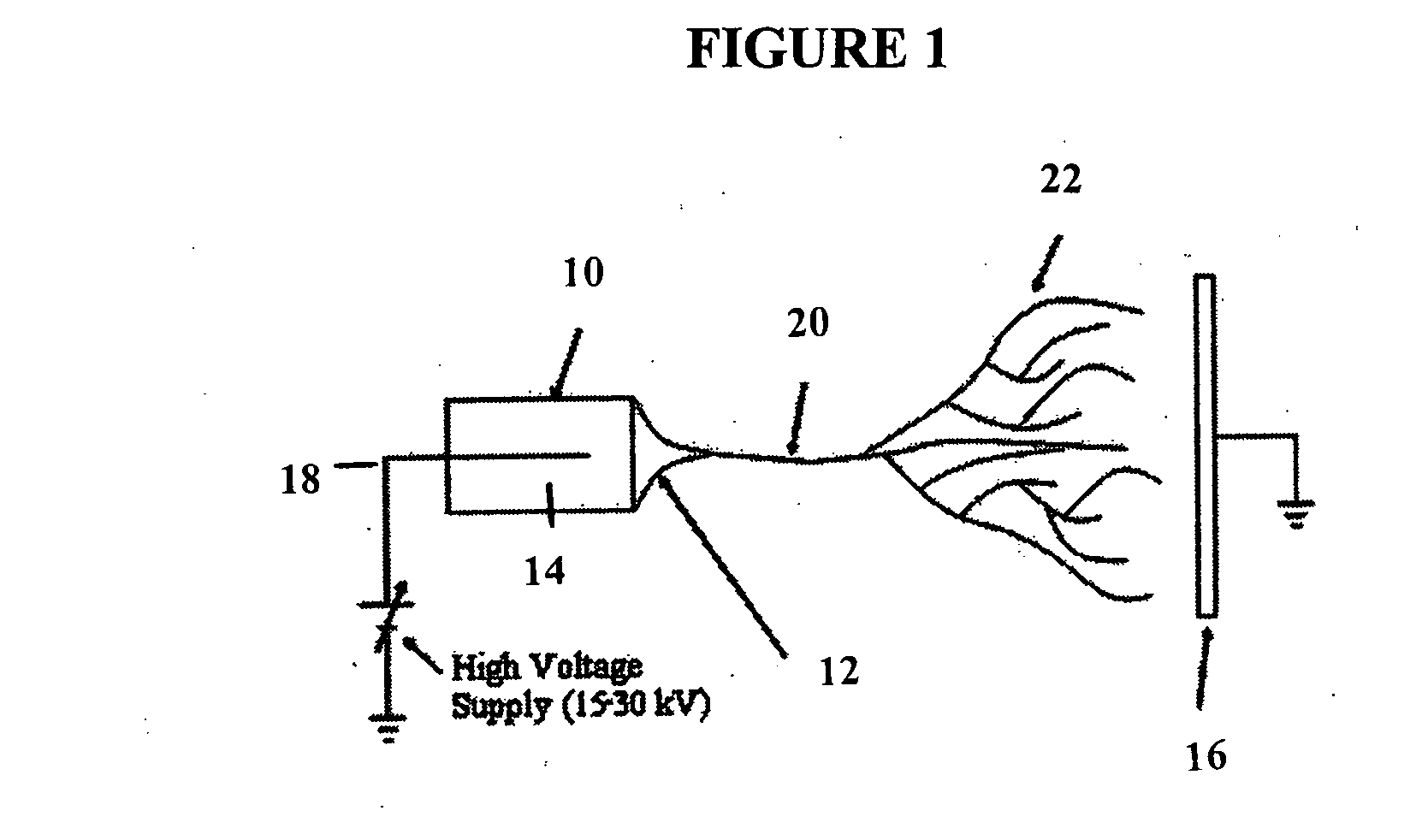
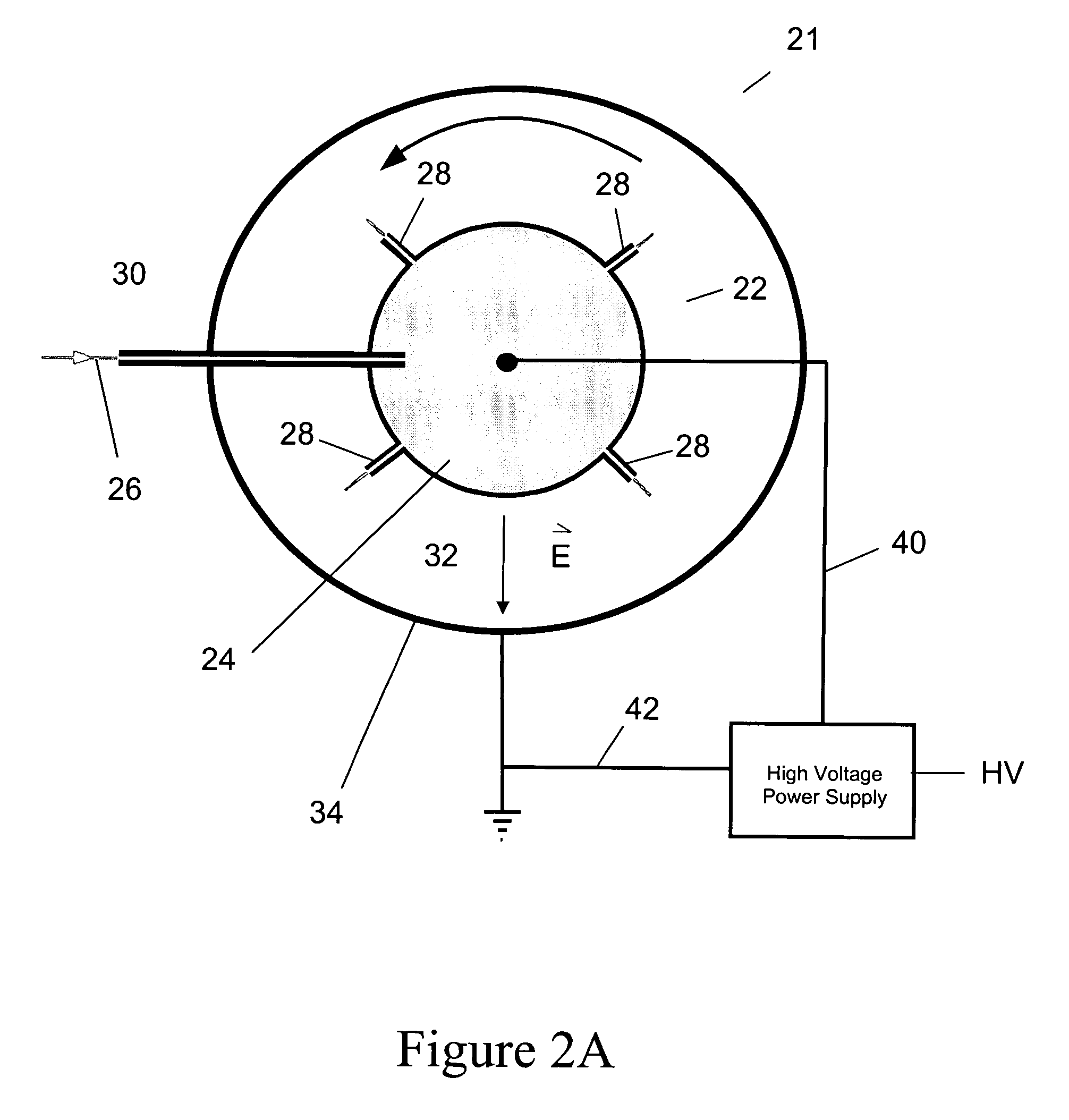
Electrospinning of fibers using a rotatable spray head
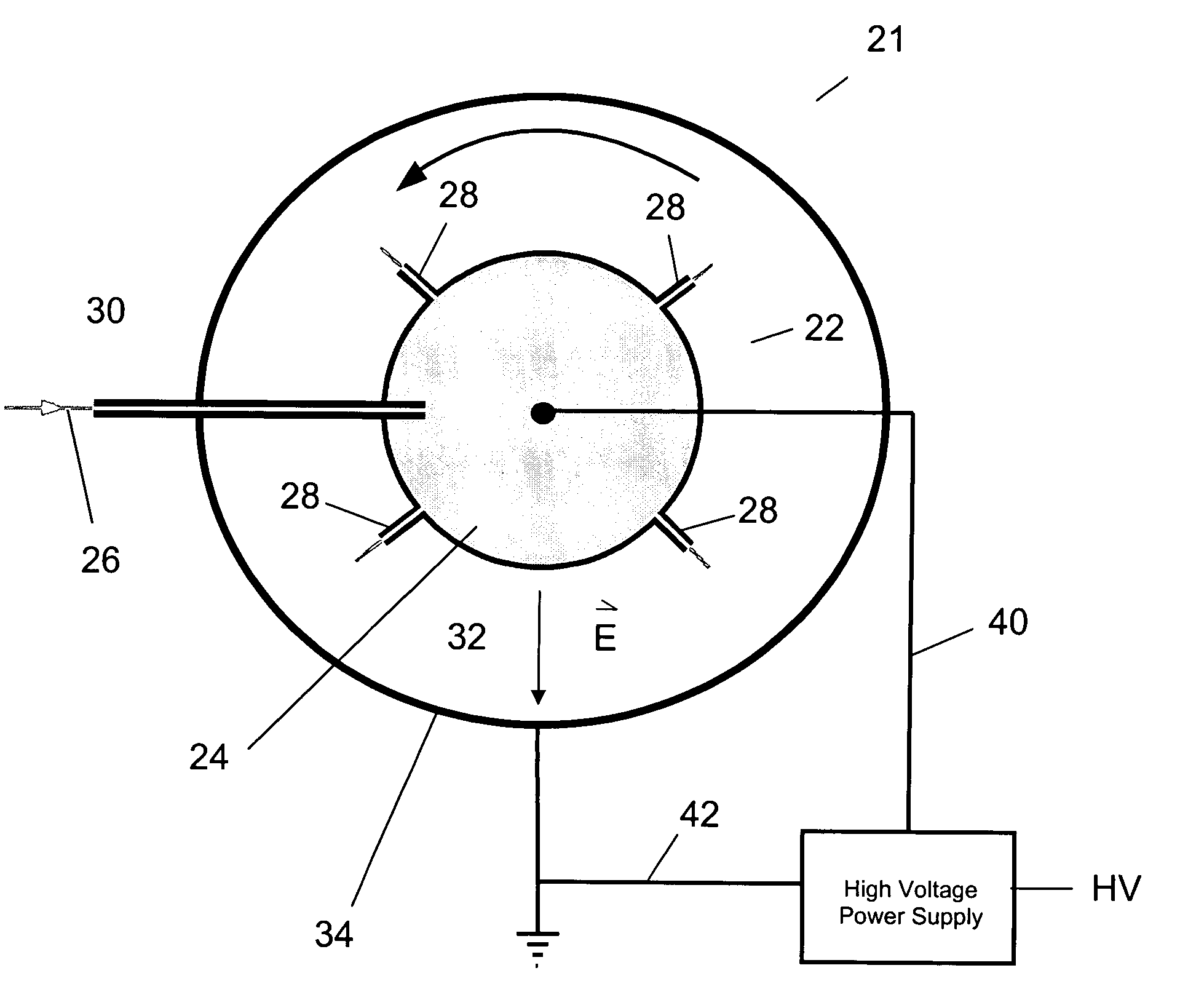
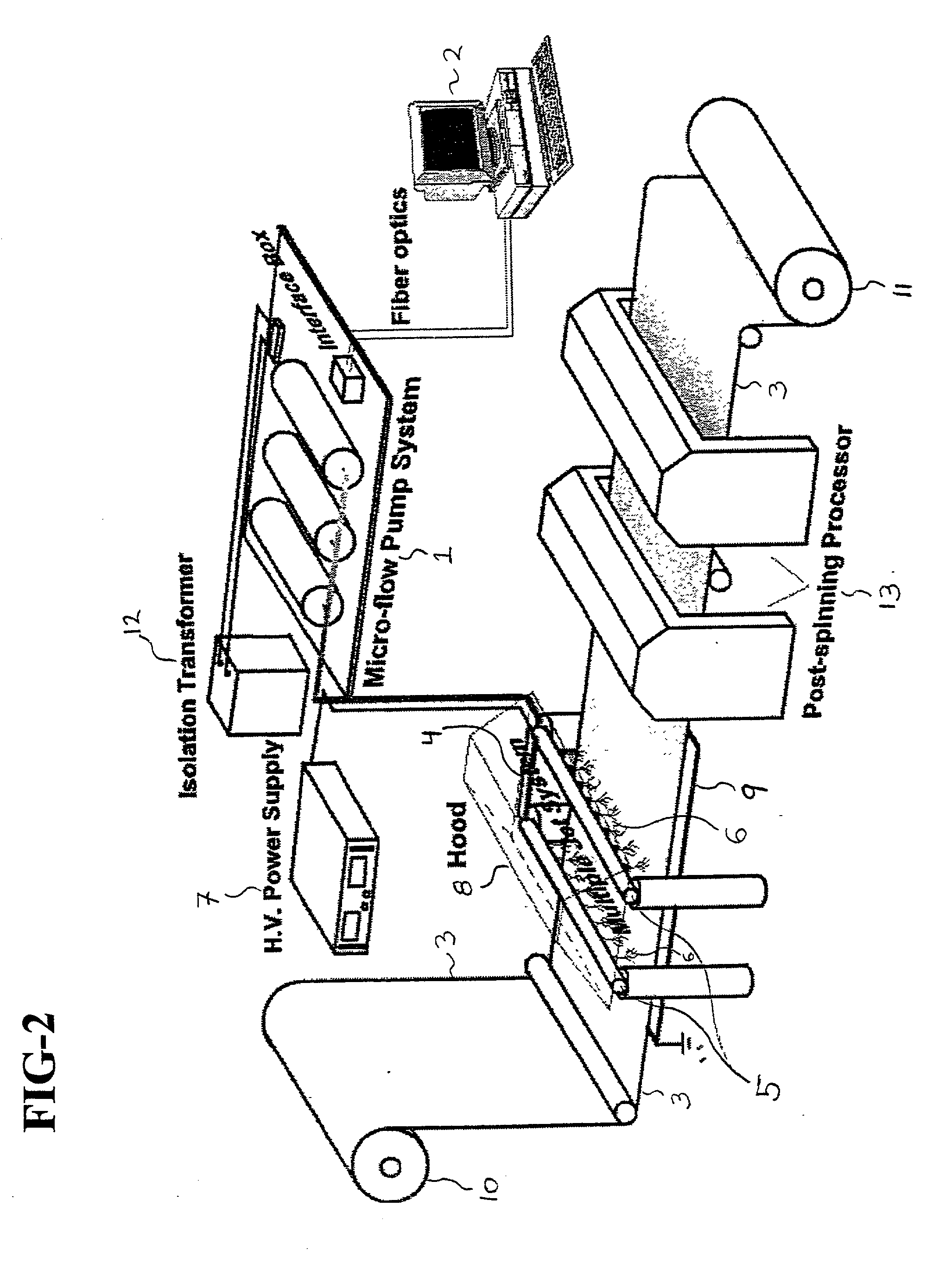
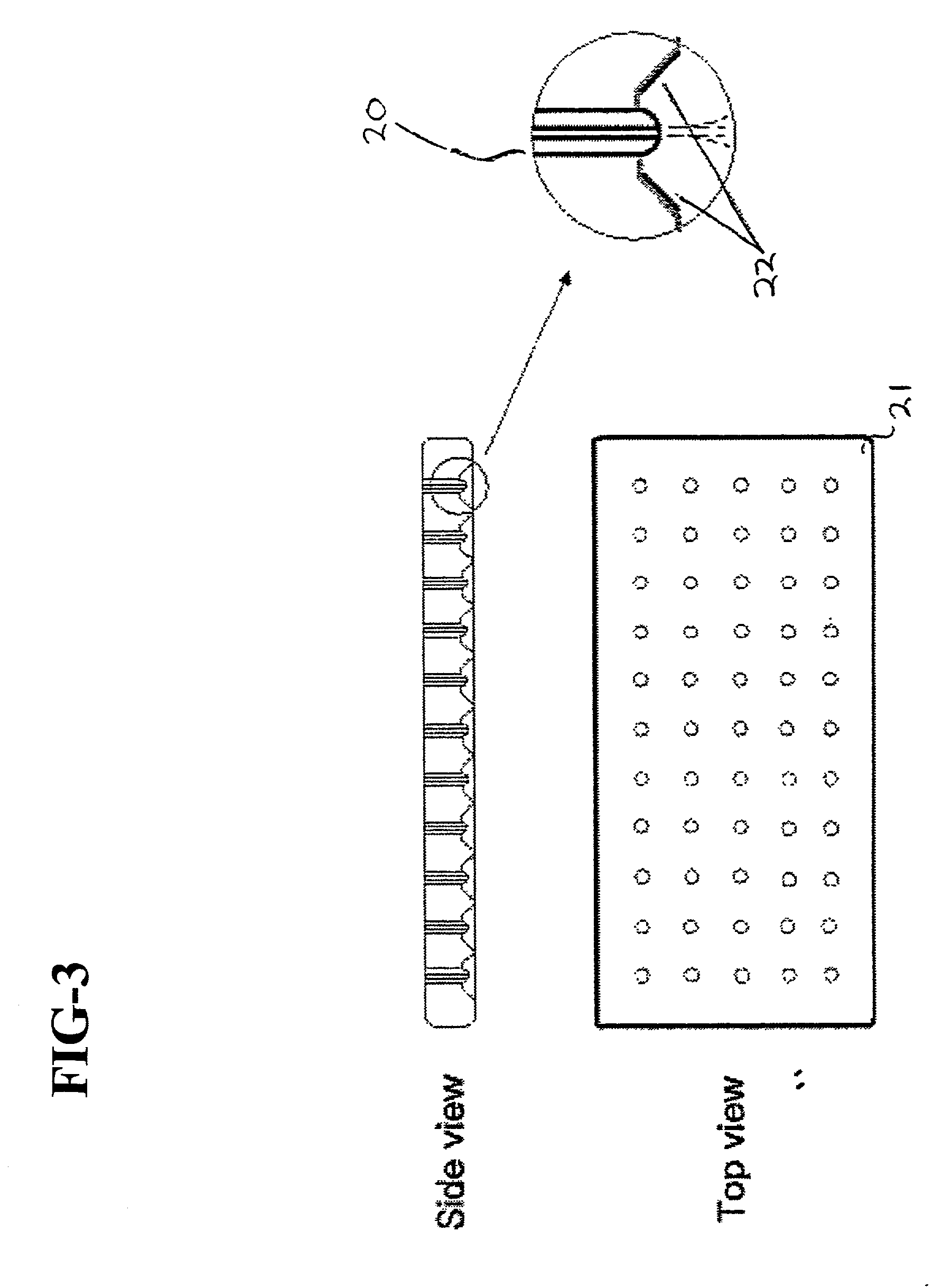
Apparatus and method for electrospinning fibers in which the apparatus includes a spray head having a longitudinal axis and including at least one electrospinning element disposed in a peripheral wall of the spray head surrounding the longitudinal axis. The electrospinning element includes a passage by which a substance from which the fibers are to be electrospun is provided to a tip of the electrospinning element. The electrospinning element extends from the peripheral wall in a direction from the longitudinal axis and is configured to electrospin the fibers by electric field extraction of the substance from the tip of the electrospinning element. Accordingly, the method includes providing a substance from which the fibers are to be composed to a tip of an electrospinning element in a peripheral wall of a spray head having a longitudinal axis, rotating the spray head or a collector configured to receive the fibers around the longitudinal axis, applying in a direction from the longitudinal axis of the spray head an electric field to the tip of the electrospinning element to electrospin by electric field extraction the substance from the tip of the electrospinning element to form the fibers, and collecting the fibers on the collector.
Owner:RES TRIANGLE INST
Antibacterial nano fiber material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101358382ANo side effects on the human bodyContinuous and stable releaseFilament/thread formingMacromolecular non-active ingredientsFiberSide effect
The invention relates to an antibacterium nano fiber material and a preparation method thereof; the material comprises polymer superfine fiber and antibacterial agent, and the weight ratio is 60 to 98: 2 to 40; the preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) the antibacterial agent is dissolved in distilled water to prepare solution; the polymer superfine fiber is dissolved in methylene dichloride or chloroform organic solvent, emulsifier is added to be mixed evenly, to obtain solution which is dispersed evenly; (2) the two types of solution are mixed to obtain even water-in-oil W / O latex, and then electrostatic spinning is conducted to the latex, to obtain the antibacterium nano fiber material. The nano fiber material has good ventilation property and filterability, still has bacteriostasis and sterilization functions for a long time after stably releasing the antibacterial agent, has simple preparation method, adopts the biodegradable and bioabsorbable polymer as carrier materials, can be absorbed by the human body after fully releasing, is not left, does not need secondary operation and has no side effect.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Nanofiber Mats and production methods thereof
An apparatus and method in which the apparatus includes a first electrospinning device configured to electrospin first fibers of a first substance, a second electrospinning device configured to electrospin second fibers of a second substance such that first and second fibers combine in a mat formation region, and a biasing device configured to bias the first electrospinning device with a first electric polarity and to bias the second electrospinning device with a second electric polarity of opposite polarity to the first electric polarity to promote attraction and coalescence between the first and second fibers. The method electrospins under the first electric polarity first fibers from the first substance, electrospins under the second electric polarity fibers from the second substance, and coalesces the first and second fibers to form the fiber mat.
Owner:RES TRIANGLE INST
Vascular graft having a chemicaly bonded electrospun fibrous layer and method for making same
InactiveUS20030100944A1Improve surface morphologyGood tissue responseNon-woven fabricsCoatingsChemical LinkageElectrospinning
A vascular graft comprising a traditional graft material and an electrospun fibrous layer. The solvent used to reduce the material for the electrospun layer is also capable of reducing the graft material to a liquid solution. The electrospun layer is chemically bonded to the graft material, without adhesives, by either spraying the graft with the solvent prior to electrospinning or by assuring that a sufficient amount of residual solvent reaches the graft while electrospinning.
Owner:DATASCOPE INVESTMENT
Jet type electrostatic spinning equipment capable of producing Nano fiber in bulk
InactiveCN101003916AThe need for large-scale productionNo frequent replacementSpinnerette packsFilament/thread formingFiberHigh volume manufacturing
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Electrospun cell matrices
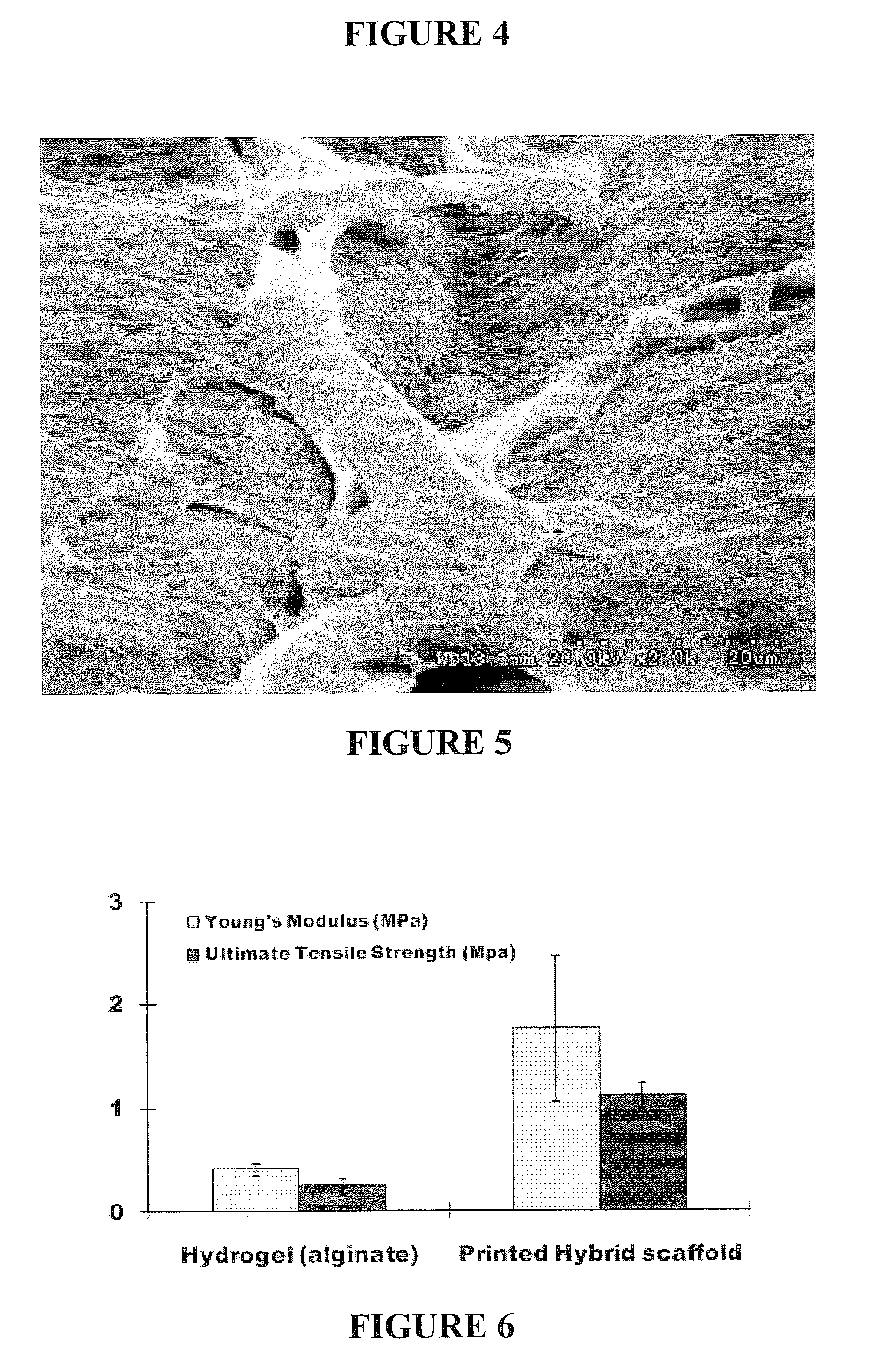
InactiveUS20060204539A1Function increaseFiber sizeMonocomponent protein artificial filamentElectro-spinningElectrospinningUltimate tensile strength
The invention is directed to compositions and methods for preparing electrospun matrices comprising at least one natural biological material component and at least one synthetic polymer material. The natural component makes the matrices highly biocompatible while the molecular weight polymer component can impart additional strength mechanical strength to the scaffold and / or improve ease of manufacture by increasing viscosity and spinning characteristics of the solution during electrospining.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV
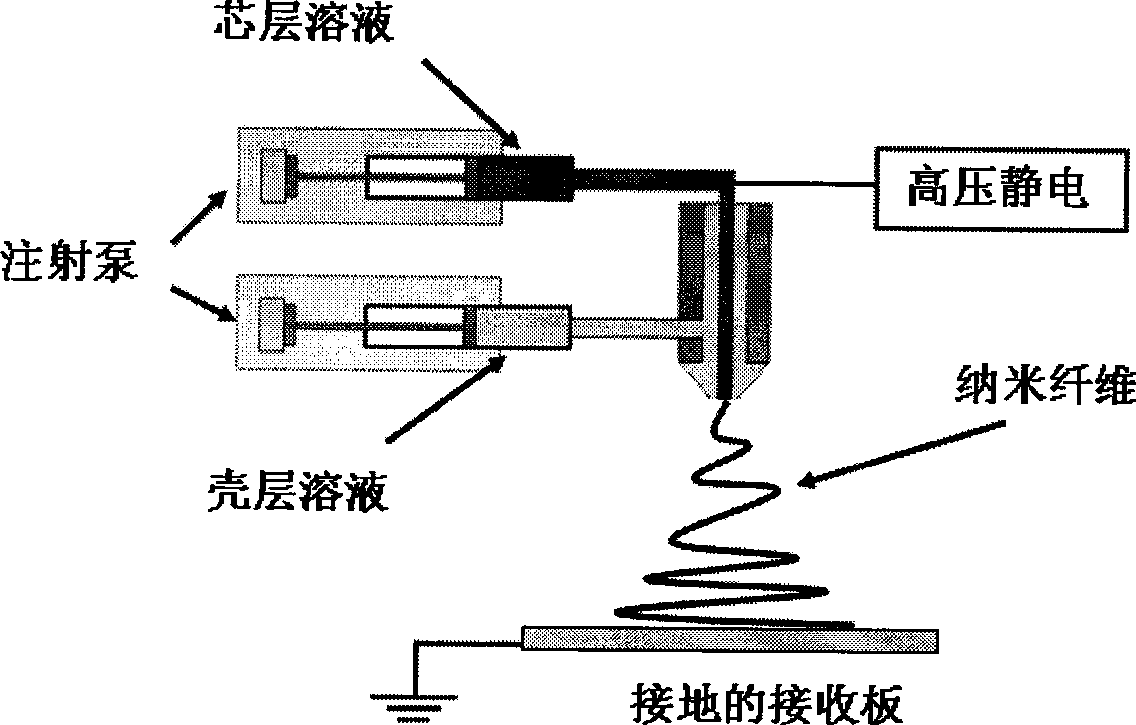
Electrospinning of fine hollow fibers
A method for electrospinning nanofibers having a core-sheath, tubular, or composite structure is disclosed. The process uses a spinneret having first and second capillaries that channel first and second fluids in the spinneret, the second capillary surrounding the first. A high voltage is applied between the spinneret and a spaced conductive collector. In one embodiment, the first fluid is a mineral oil and the second fluid is a polymeric solution that may include a polymer, a catalyst, a solvent, and a sol-gel precursor. The as-spun nanofiber includes an oil core and a composite sheath. The oil may be removed to produce a composite tubular fiber or the polymer and oil may be removed by calcination to produce a ceramic tubular fiber. In other embodiments, miscible fluids are used to produce porous nanofibers, selected additives functionalize the surfaces of the nanofibers and / or conjugated polymers are used.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Method of nanofibres production from a polymer solution using electrostatic spinning and a device for carrying out the method
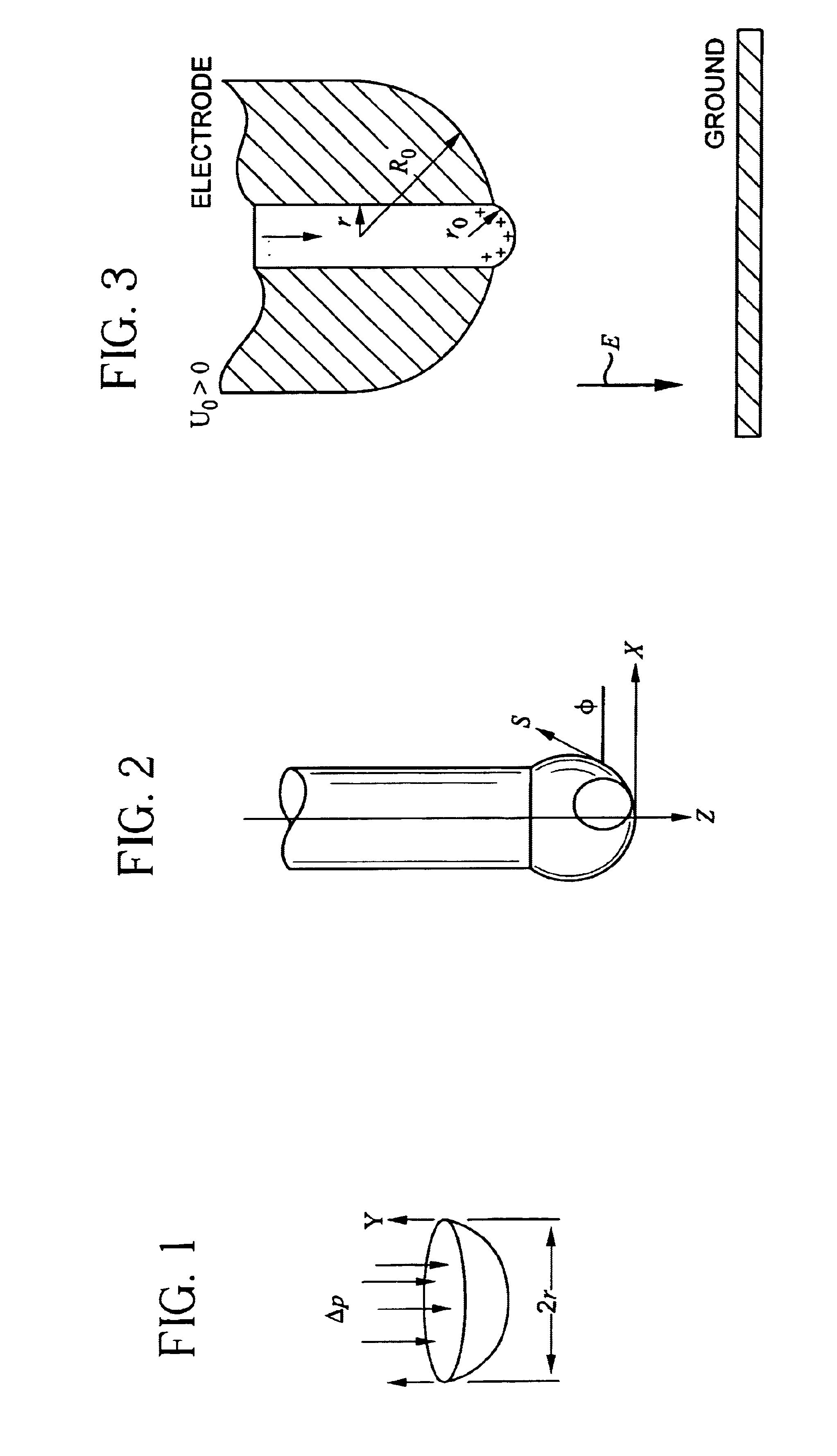
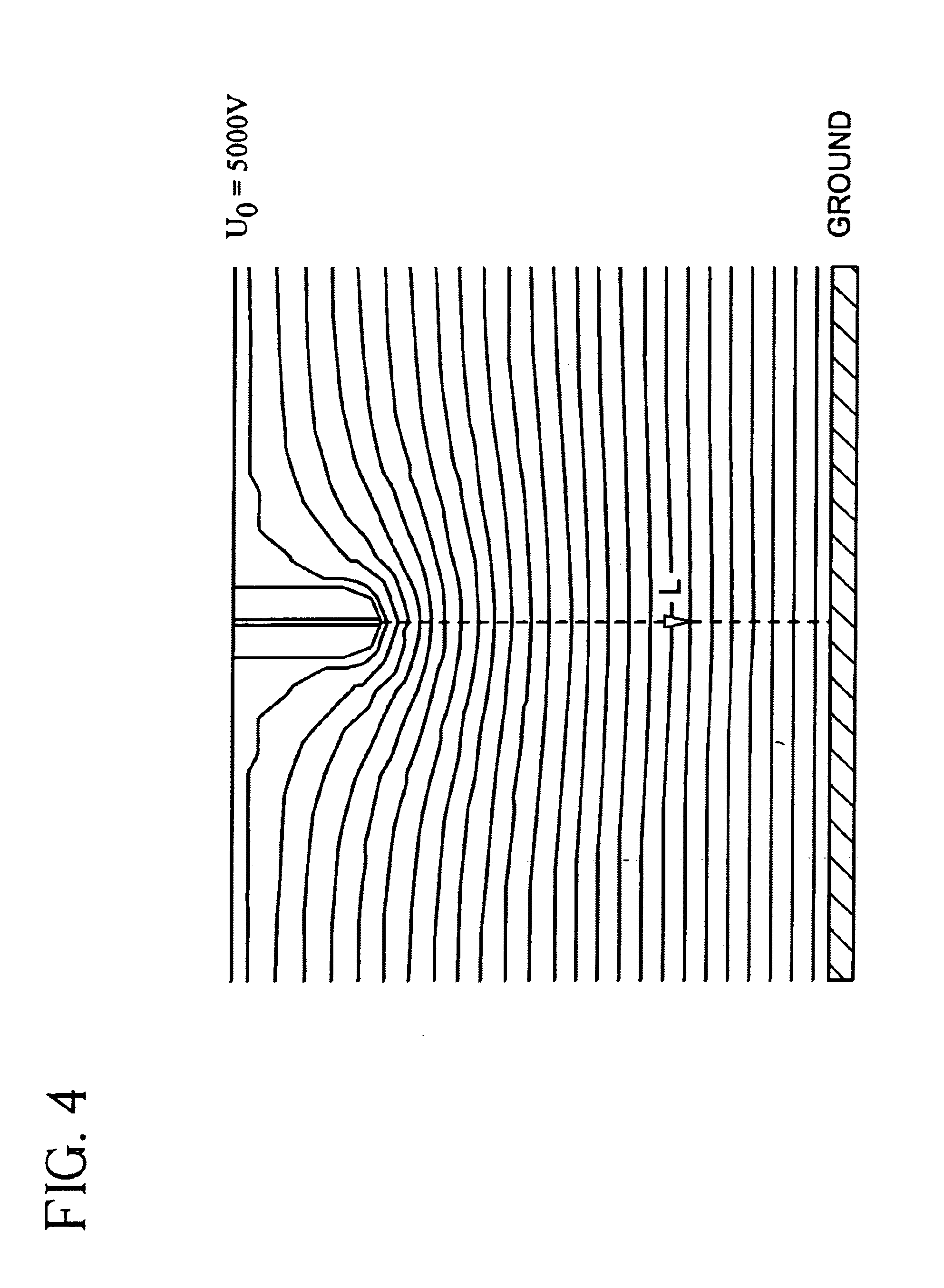
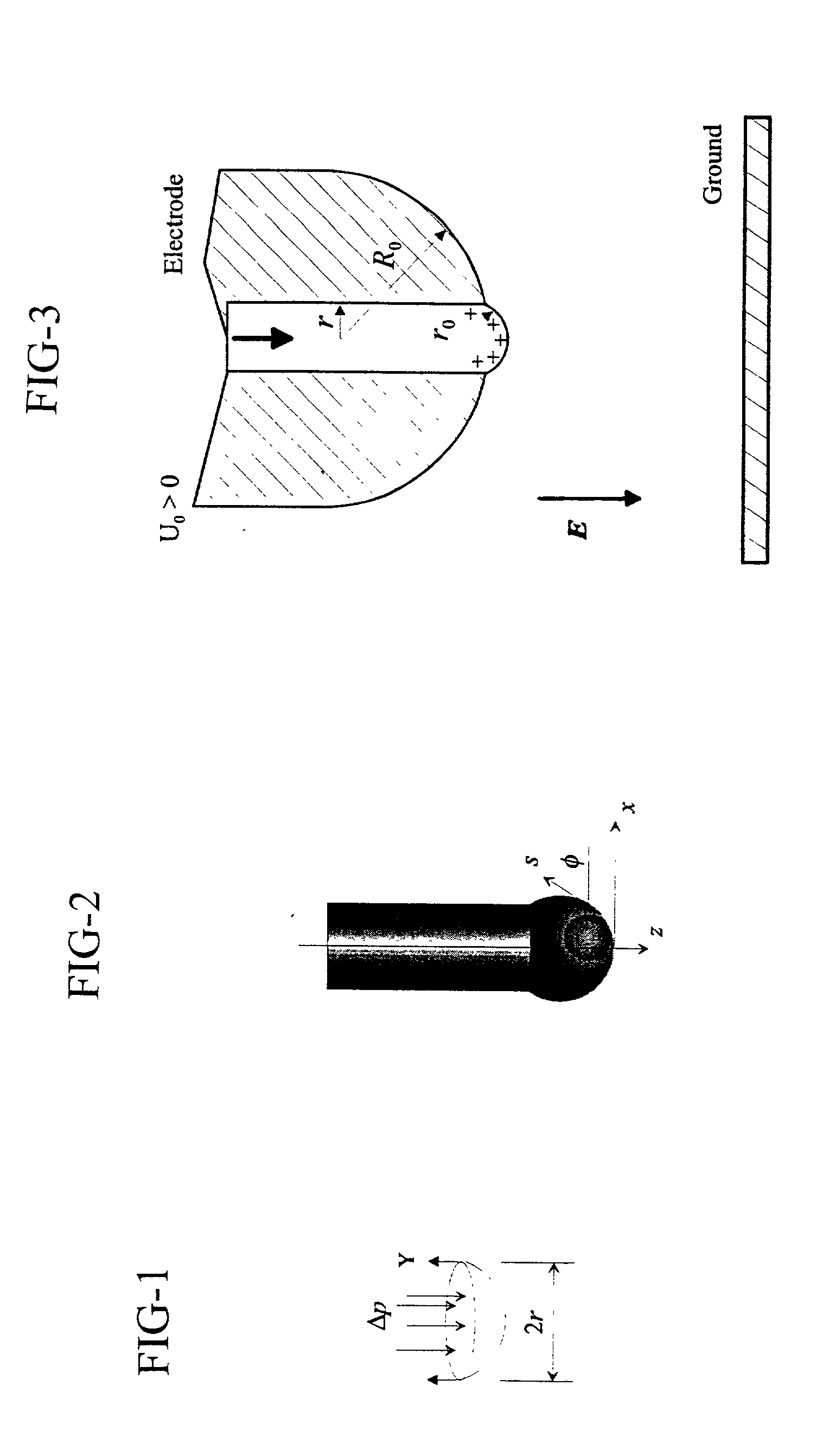
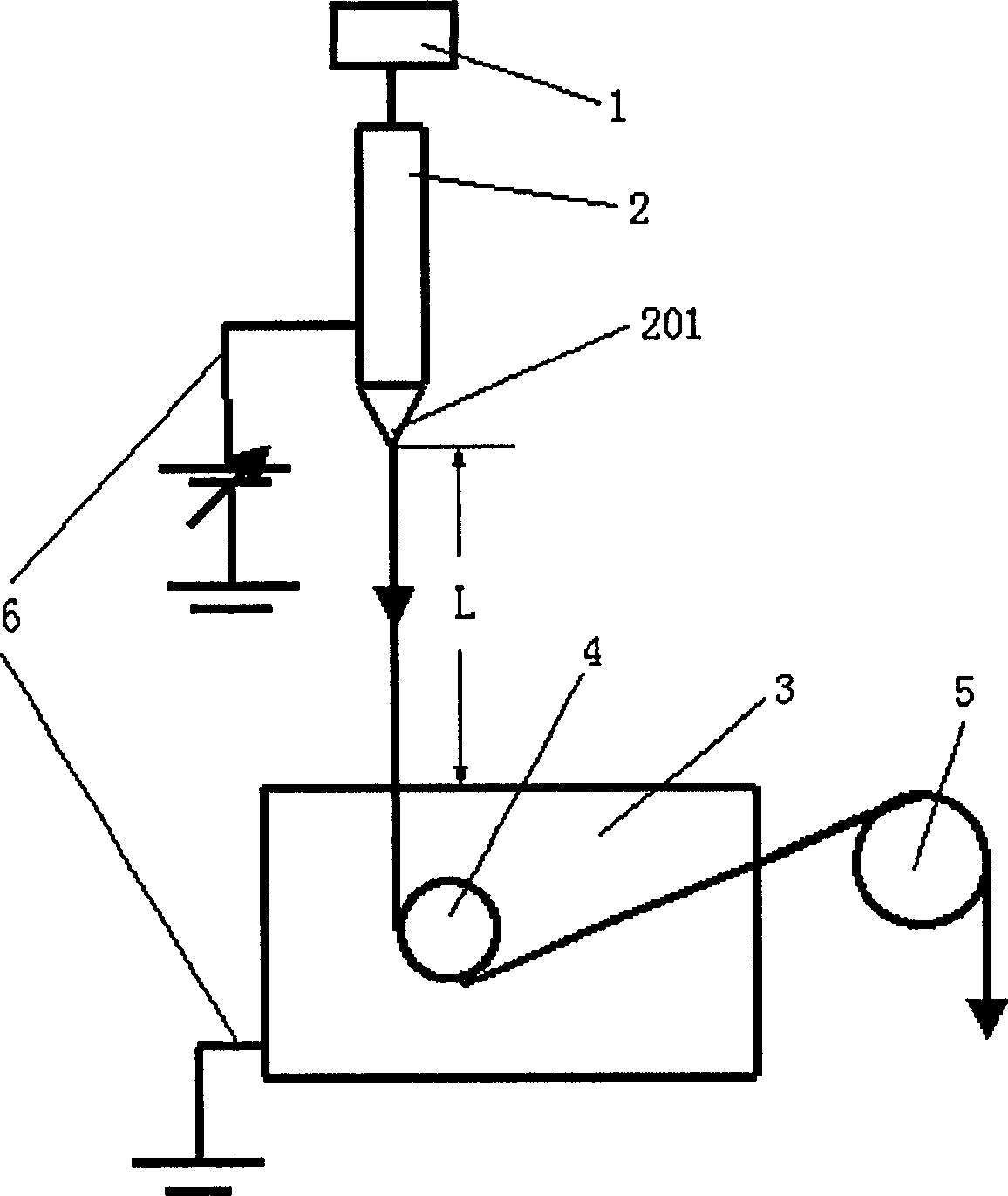
ActiveUS7585437B2High quality and uniformity of layerSpinnerette packsNanotechnologyPotential differenceElectrospinning
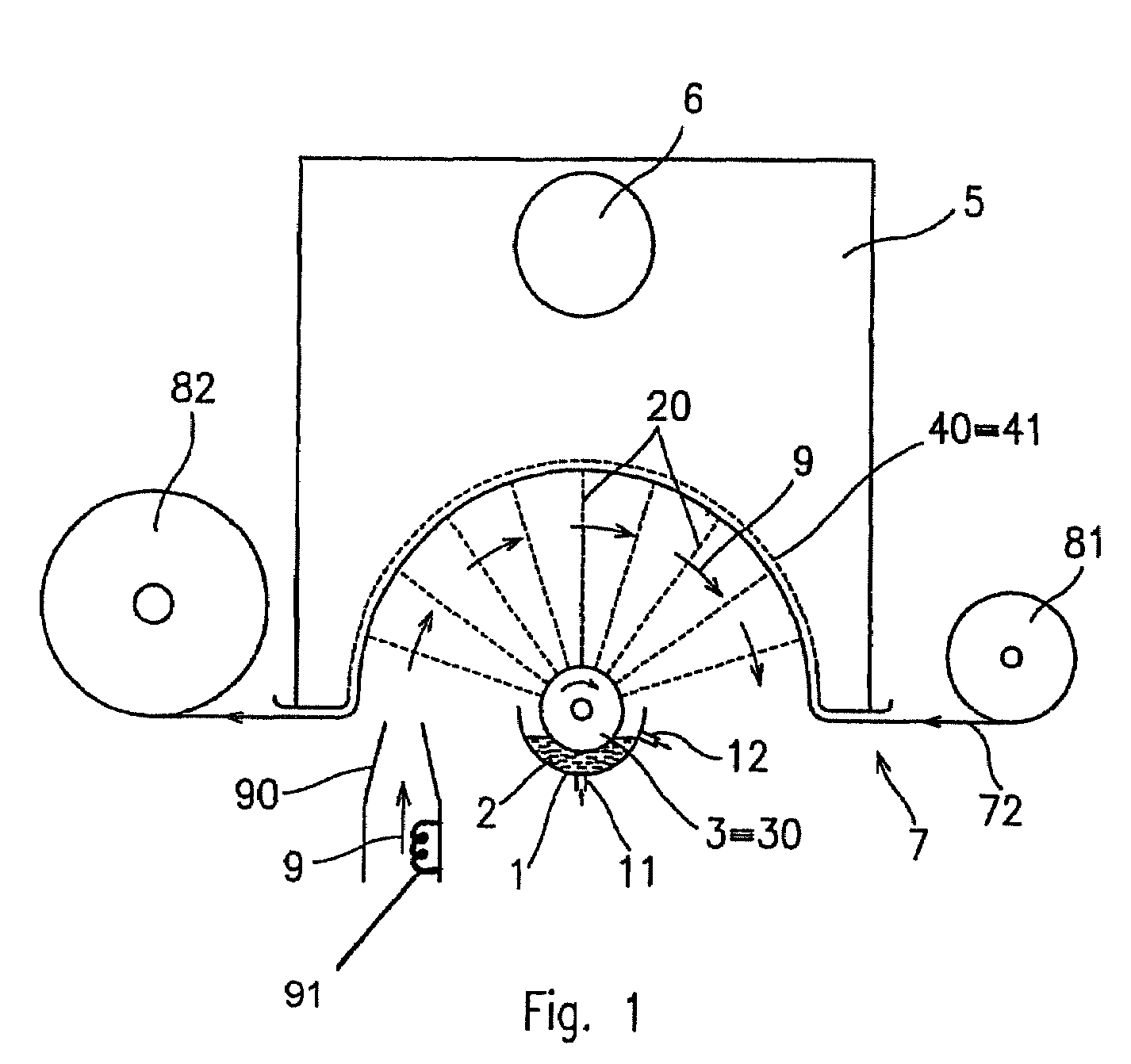
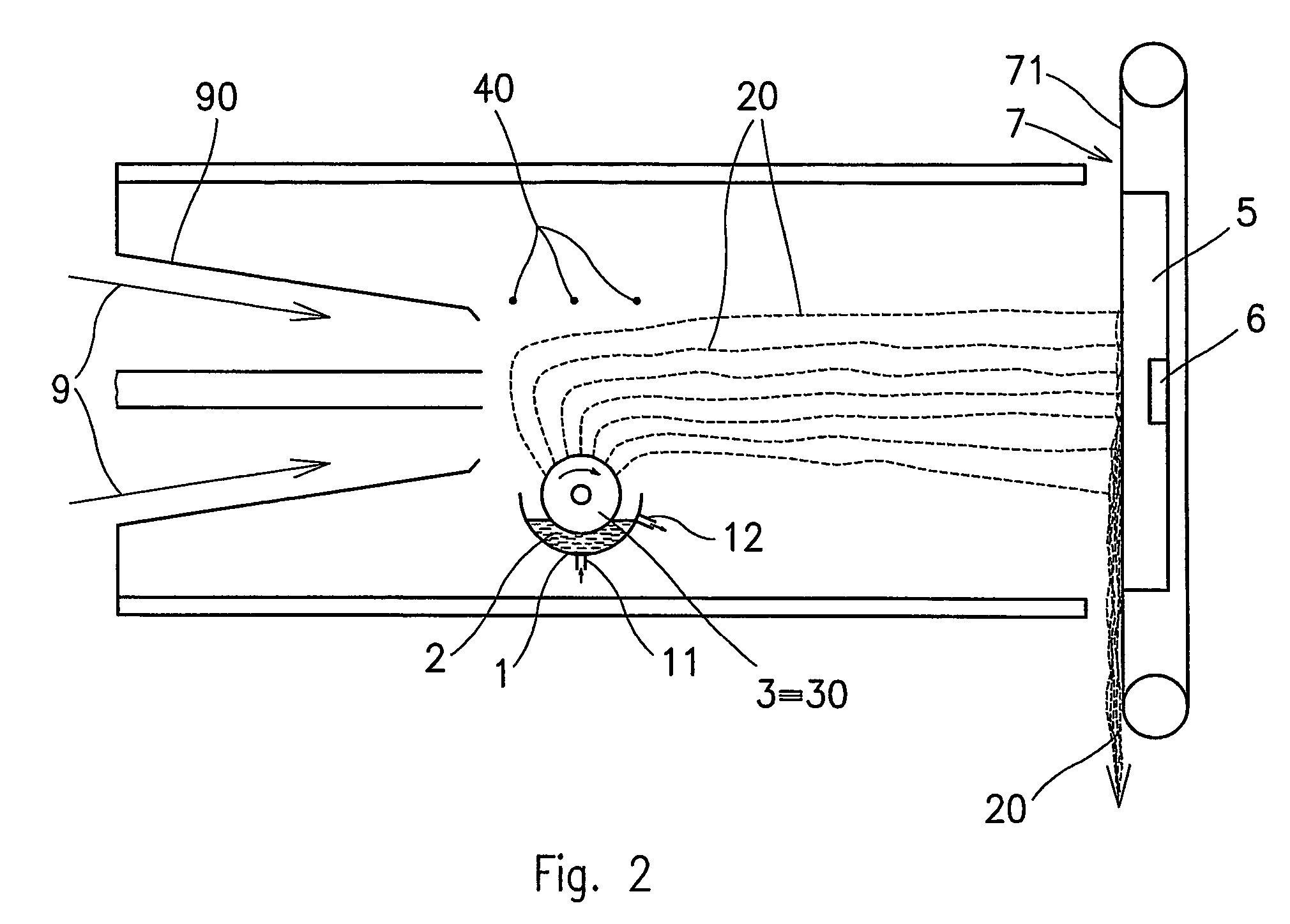
A method of nanofibers production from a polymer solution uses electrostatic spinning in an electric field created by a potential difference between a charged electrode and a counter electrode. The polymer solution for spinning is supplied into the electric field using the surface of a rotating charged electrode. On a part of the circumference of the charged electrode near to the counter electrode, a spinning surface is created for attaining a high spinning capacity. In a device for carrying out the method, the charged electrode is pivoted and part of its circumference is immersed in the polymer solution. The free part of the circumference of the charged electrode is positioned opposite the counter electrode.
Owner:TECHNICKA UNIVEZITA V LIBERCI
Static spinning device and its industrial use
InactiveCN1715463AHigh speedImprove mechanical propertiesFilament/thread formingElectrospinningMagnification
The present invention provides electrostatic spinning apparatus and its industrial application. The apparatus includes polymer solution conveying machine, spinning nozzle device connected to the outlet of the polymer solution conveying machine, spinning bath below the spinning nozzle device, fiber turning guide roller set inside the spinning bath and electrodes set on the spinning nozzle device and the spinning bath. The apparatus of the present invention is used in spinning polymer, and has greatly raised wet spinning speed, great fiber drafting magnification, well oriented fiber molecule chain, compact fiber structure, greatly raised mechanical performance of fiber, wide solvent selecting range, simplified electrostatic spinning equipment, raised solvent recovering rate and less environmental pollution caused by the solvent.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Nano-bionic material for tissue repair and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101829361AImprove regenerative abilityTo achieve the effect of graft repairProsthesisNano-scaffoldTissue repair
The invention provides a nano-bionic material for tissue repair and a preparation method thereof. The nano-bionic material comprises a nano-bionic bracket and hydrosol attached to the nano-bionic bracket, wherein one or more cell factors and / or cells are coated in the hydrosol. The preparation method of the nano-bionic material comprises the following steps of: preparing an electrospinning solution and a hydrosol solution containing the cell factors and / or the cells; preparing the nano-bionic bracket by using the electrospinning; printing the hydrosol solution containing the cell factors and / or the cells on the nano-bionic bracket by using a ink-jet printer; and the like, and repeating the electrospinning and the ink jet to obtain the nano-bionic material with different thicknesses. By combining with an electrospinning technology and a biological printing technology, the invention combines specific medicines and / or the cell factors and / or the cells in the nano-bracket and / or the surface of the nano-bracket, thereby greatly enhancing the effects of the nano-bionic material on tissue repair and tissue regeneration; in addition, the invention has broad application prospect.
Owner:MEDPRIN REGENERATIVE MEDICAL TECH
Electrospinning of fibers using a rotatable spray head
Apparatus and method for electrospinning fibers in which the apparatus includes a spray head having a longitudinal axis and including at least one electrospinning element disposed in a peripheral wall of the spray head surrounding the longitudinal axis. The electrospinning element includes a passage by which a substance from which the fibers are to be electrospun is provided to a tip of the extrusion electrospinning element. The electrospinning element extends from the peripheral wall in a direction from the longitudinal axis and is configured to electrospin the fibers by electric field extraction of the substance from the tip of the extrusion electrospinning element. Accordingly, the method includes providing a substance from which the fibers are to be composed to a tip of an electrospinning element in a peripheral wall of a spray head having a longitudinal axis, rotating the spray head or a collector configured to receive the fibers around the longitudinal axis, applying in a direction from the longitudinal axis of the spray head an electric field to the tip of the electrospinning element to electrospin by electric field extraction the substance from the tip of the electrospinning element to form the fibers, and collecting the fibers on the collector.
Owner:RES TRIANGLE INST
Method for producing shell-core structure medicament nano-fibre with coaxial electrostatic spinning technology
InactiveCN101509153AFix monotonic release behaviorMeet needsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismFilament/thread formingFiberDissolution
The invention relates to a method for preparing shell-core structured medicament nano fiber by coaxial electrostatic spinning technology, comprising: (1) dissolving high molecular polymer and medicament in mass proportion of 60-99.9:0.1-40 in organic solvent with high volatility, and stirring until complete dissolution to obtain shell solution; (2) dissolving one or more than one of natural polymer, medicament, and bioactive factor in the solvent, or dissolving the same in super pure water under aseptic condition to obtain core solution; and (3) carrying out coaxial electrostatic spinning, setting the spinning voltage at 15-25kv, the reception distance at 8-20cm, the spinning pushing speed at 0.1-1.5mL / h, and the spinning nozzle as 0.9mm, to obtain the shell-core structured medicament nano fiber. The preparation method is simple in operation, mild in reaction condition, low in cost and favorable for economic benefit; in preparing the shell-core structured medicament nano fiber, two or more than two medicaments can be simultaneously loaded and released, thus meeting requirements of tissue regeneration or patients.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
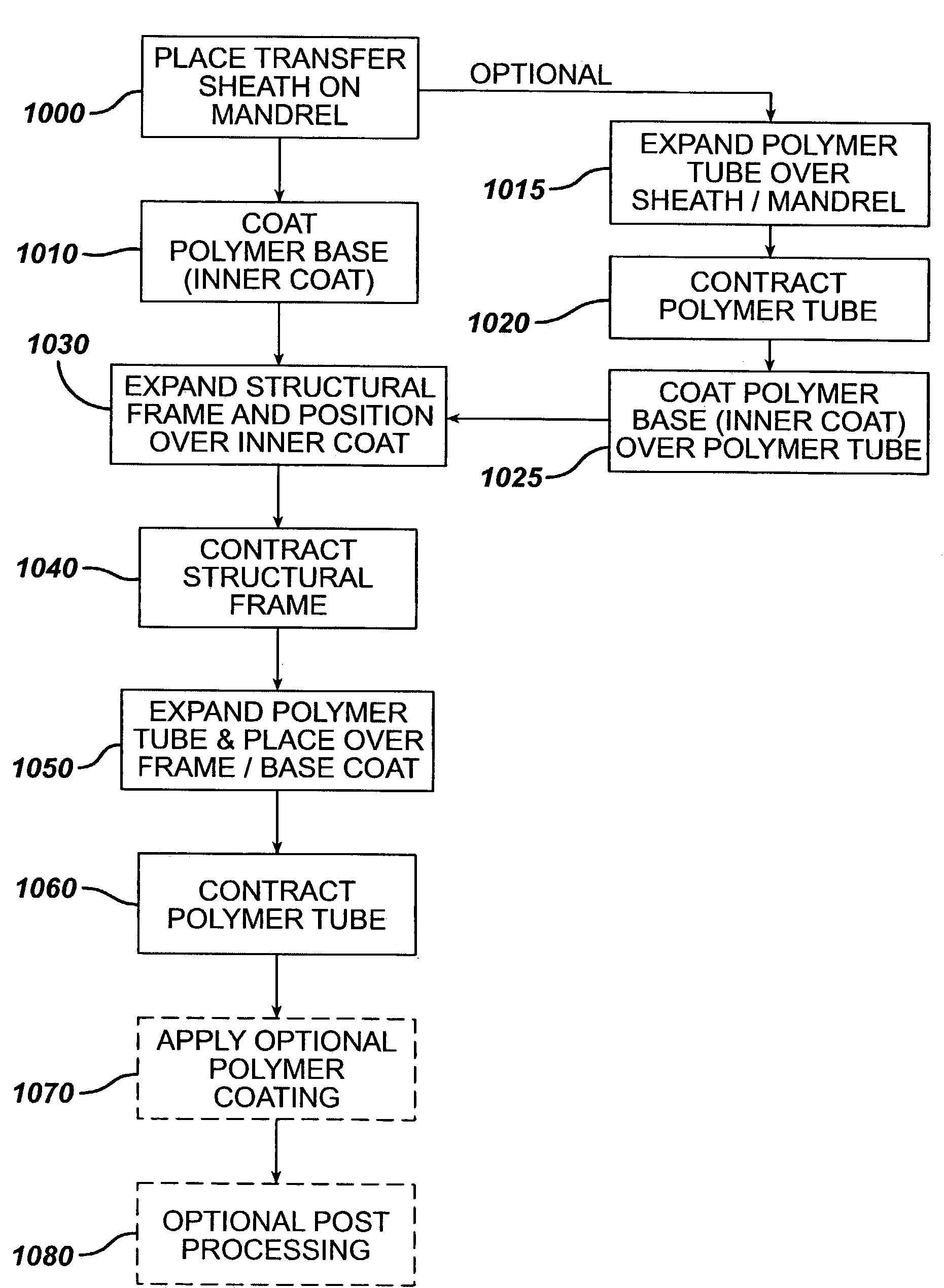
Method of placing a tubular membrane on a structural frame
The present invention relates to a medical device, and more particularly to a method of forming a tubular membrane on a radially expandable structural frame. In one aspect, a structural frame is placed over a spinning mandrel and a fiber is electro-statically spun over at least a portion of the structural frame forming a membrane. A transfer sheath may be used between the mandrel and structural frame to prevent the electrostatically spun fiber from adhering to the mandrel. In another aspect, a first membrane is spun over the mandrel before the structural frame is placed over the mandrel. In this aspect, at least a portion of the structural frame is sandwiched between the membranes. The membrane or membranes and structural frame form a fiber spun frame assembly. The fiber spun frame assembly may be coated with an elastic polymer. In addition, the membrane or membranes may go through some post processing to achieve desired characteristics or configurations.
Owner:CARDINAL HEALTH SWITZERLAND 515 GMBH
Methods of Applying Skin Wellness Agents to a Nonwoven Web Through Electrospinning Nanofibers
Generally, the present invention is directed to, in one embodiment, a method for forming a composite nonwoven web configured to deliver skin wellness agents to the skin of a user. According to the method, an aqueous system of a hydrophilic polymer and a skin wellness agent is formed. The aqueous system is then electrospun onto a surface of a nonwoven web containing synthetic fibers. The resulting nanofibers have an average diameter of from about 50 nanometers to about 5000 nanometers, such as from about 200 nanometers to about 700 nanometers.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Nanofibrous materials as drug, protein, or genetic release vehicles
InactiveUS20060200232A1Electric discharge heatingSynthetic resin layered productsElectrospinningActive agent
The present invention is a bioactive, nanofibrous material construct which is manufactured using an unique electrospinning perfusion methodology. One preferred embodiment provides a nanofibrous biocomposite material formed as a discrete textile fabric from a prepared liquid admixture of (i) a biodurable synthetic polymer; (ii) a biologically active agent; and (iii) a liquid organic carrier. The prepared liquid admixture and fluid blending of diverse matter is employed in a novel electrospinning perfusion process to form an agent-releasing nanofibrous fabric, which in turn, can serve as the antecedent precursor and tangible workpiece for subsequently making the desired medical article or device suitable for use in-vivo. As the fabric is generated as a discrete article in either tubular or flat sheet form, one or more of the pre-chosen biologically-active agents will have become non-permanently immobilized and releaseably attached to the nanofibrous material of the fabric. These non-permanently immobilized biologically-active agents are chemical compounds which retain their recognized biological activity both before and after becoming non-permanently bound to the formed textile material; and will become subsequently released in-situ as discrete freely mobile agents from the fabric upon uptake of water from the ambient environment. Accordingly, the agent-releasing nanofibrous fabric is very suitable for inclusion and use in-vivo as a clinical / therapeutic medical article or device.
Owner:PHANEUF MATTHEW D +2
Filtration Medias, Fine Fibers Under 100 Nanometers, and Methods
InactiveUS20090199717A1Avoid layeringMaterial nanotechnologyIsotope separationAcetic acidElectrospinning
An electrospinning fine fiber production methodology for generating a significant amount of fibers with diameters of less than 100 nanometers is provided. Also, a filter media composite comprising a substrate layer and an electrospun fine fiber layer having a increased efficiency relative to pressure drop and / or a controlled pore size distribution is provided. According to some embodiments nylon is electrospun from a solvent combination of formic and acetic acids.
Owner:ELMARCO SRO
Electrospun electroactive polymers
InactiveUS20060057377A1Easy to set upFast and easy to runMaterial nanotechnologyPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPolyesterFiber
Electroactive polymers are produced via electrospinning. The induction of electroactivity via electrospinning can be utilized with one or more soluble polymers with polarizable moieties. Suitable polymer classes include but are not limited to polyimides, polyamides, vinyl polymers, polyurethanes, polyureas, polythioureas, polyacrylates, polyesters, and biopolymers. Any one or more solvents sufficient to dissolve the one or more polymers of interest and make a spinnable solution can be utilized. The polymer can be electrospun into fiber and fibrous nonwoven mat. The electroactive polymer can be doped with inclusions, such as nanotubes, nanofibers, and piezoceramic powders for dielectric enhancement The availability of electroactive polymer fibers and fibrous nonwoven mat will enable many new applications for electroactive polymers.
Owner:NASA +2
Electrospinning nano-fiber electret filtering material and its preparation method
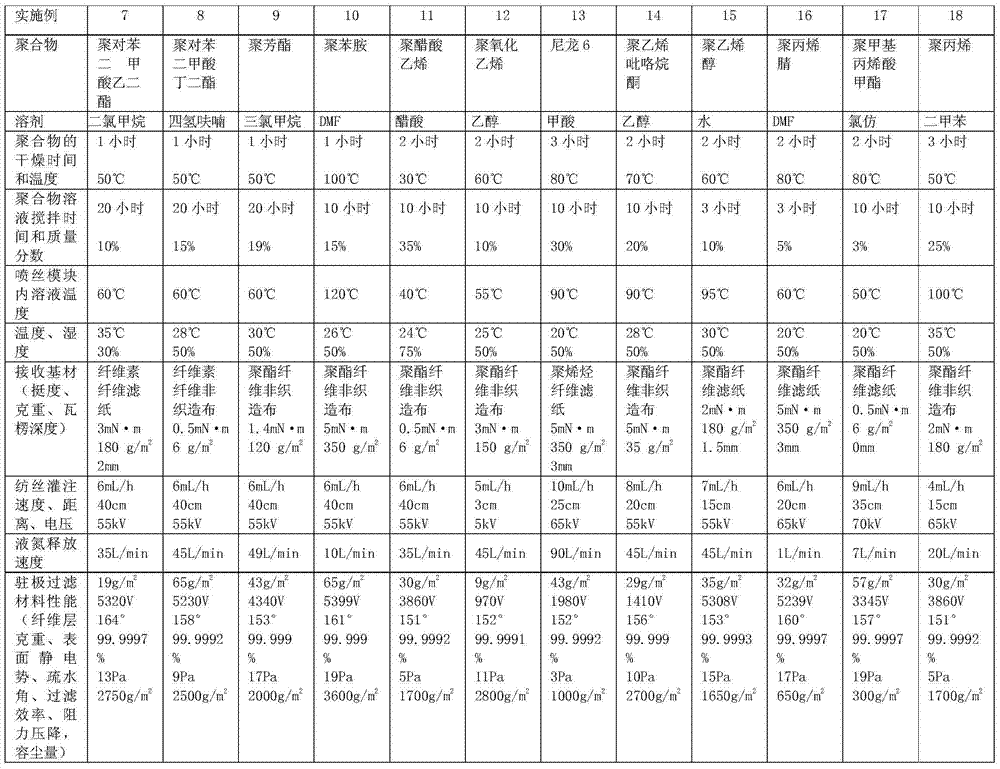
ActiveCN104289042AHigh surface electrostatic potentialHigh super strong electrostatic adsorption performanceSynthetic resin layered productsFiltration separationPorosityFiber
The invention relates to an electrospinning nano-fiber electret filtering material and its preparation method. The high-efficiency and low-resistsance nano-fiber electret filtering material having no interfibrous adhesion and having a fluffy three-dimensional netted intercommunication structure is prepared through controlling the component and the temperatures of a polymer solution in an electrospinning process and carrying out one-step forming in the nano-fiber forming rapid cooling process, wherein the gram weight of the above nanofiber layer is 0.01-70g / m<2>, and the porosity is not less than 80%. The surface electrostatic potential of the nano-fiber electret filtering material is 800-6000V, and the surface charges have lasting storage stability, the hydrophobic angle is greater than 150DEG, the filtering efficiency of the material to particles of 0.006-1[mu]m can reach above 99.999%, the piezoresistance is less than 20Pa, and the dust containing capacity is 300-3600g / m<2>. The preparation method is simple, and the filtering material has wide application prospects in the fields of individual protection mouth mask filtration, indoor air purification and filtration, and high efficiency / ultrahigh efficiency air filtration.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Cell storage and delivery system
Cell storage and delivery systems and methods for storing and delivering viable cells to a mammal are disclosed. The cell storage and delivery systems include a biodegradable and / or bioabsorbable fibrous matrix physically associated with viable cells to contain and release the cells at a controlled rate. The biodegradable and / or bioabsorbable matrix can be formed by electrospinning fibers of biodegradable and / or bioabsorbable fiberizable material. The methods include methods for storing viable cells and for delivering viable cells to a mammal using the cell storage and delivery system.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Process for preparing titanium dioxide nano-belts
The invention provides a method for preparing a titanium dioxide nano belt, belonging to the nano material technical field. The prior methods for preparing the titanium dioxide nano belt comprise the hydro-thermal method and the combination method of the sol-gel method and the hydro-thermal method. The prior electrostatic spinning method is applied to the preparation of nano fibers. The invention comprises three steps that: 1. a spinning solution is prepared; the mixture of polymethylmethacrylate and vinylpyrrolidone is used as a macromolecule template, and the mixture of chloroform and N,N-dimethylformamide is used as a solvent; 2. a titanium alkoxide / macromolecule template compound nano belt is prepared; the electrostatic spinning method is used, and the technical parameters are as follows: the voltage is between 15 and 25kV and the curing distance is between 15 and 30cm; 3. a TiO2 nano belt is prepared; the heat treatment method is used, and the technical parameters are as follows: the rate of temperature rise is between 0.5 and 2 DEG C / min and the heat preservation time at the temperature of between 500 and 900 DEG C is between 10 and 15h; for the TiO2 nano belt prepared, the width is between 5 and 15mu m, the thickness is between 30 and 60nm and the length is more than 200mu m; the TiO2 nano belt comprises a pure phase anatase type TiO2 nano belt and a pure phase rutile type TiO2 nano belt.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation method of polytetrafluoroethylene superfine fiber porous membrane
InactiveCN101530750AUniform pore sizeHigh porositySemi-permeable membranesHigh concentrationVoid ratio
The invention discloses a preparation method of polytetrafluoroethylene superfine fiber porous membrane. In the method, high concentration polytetrafluoroethylene aqueous emulsion is mixed with matrix polymer uniformly to prepare spinning solution. With the effect of high voltage electric field, polytetrafluoroethylene / matrix polymer composite superfine fiber porous membrane with the diameter of 100 nm to 2 [mu]m is obtained by electrostatic spinning, and then polytetrafluoroethylene superfine fiber porous membrane is formed at the conditions of sintering temperature being 330 to 500 DEG C and the sintering time lasting 30s to 5min so that the aperture diameter is 100 nm to 10 [mu]m and the porosity is 50% to 80%. The polytetrafluoroethylene superfine fiber porous membrane prepared by using the method has uniform aperture diameter and high porosity, and can be widely applied to filter material. Compared with the existing technology, the preparation method has the characteristics of simple processing technology, short process and low cost.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com