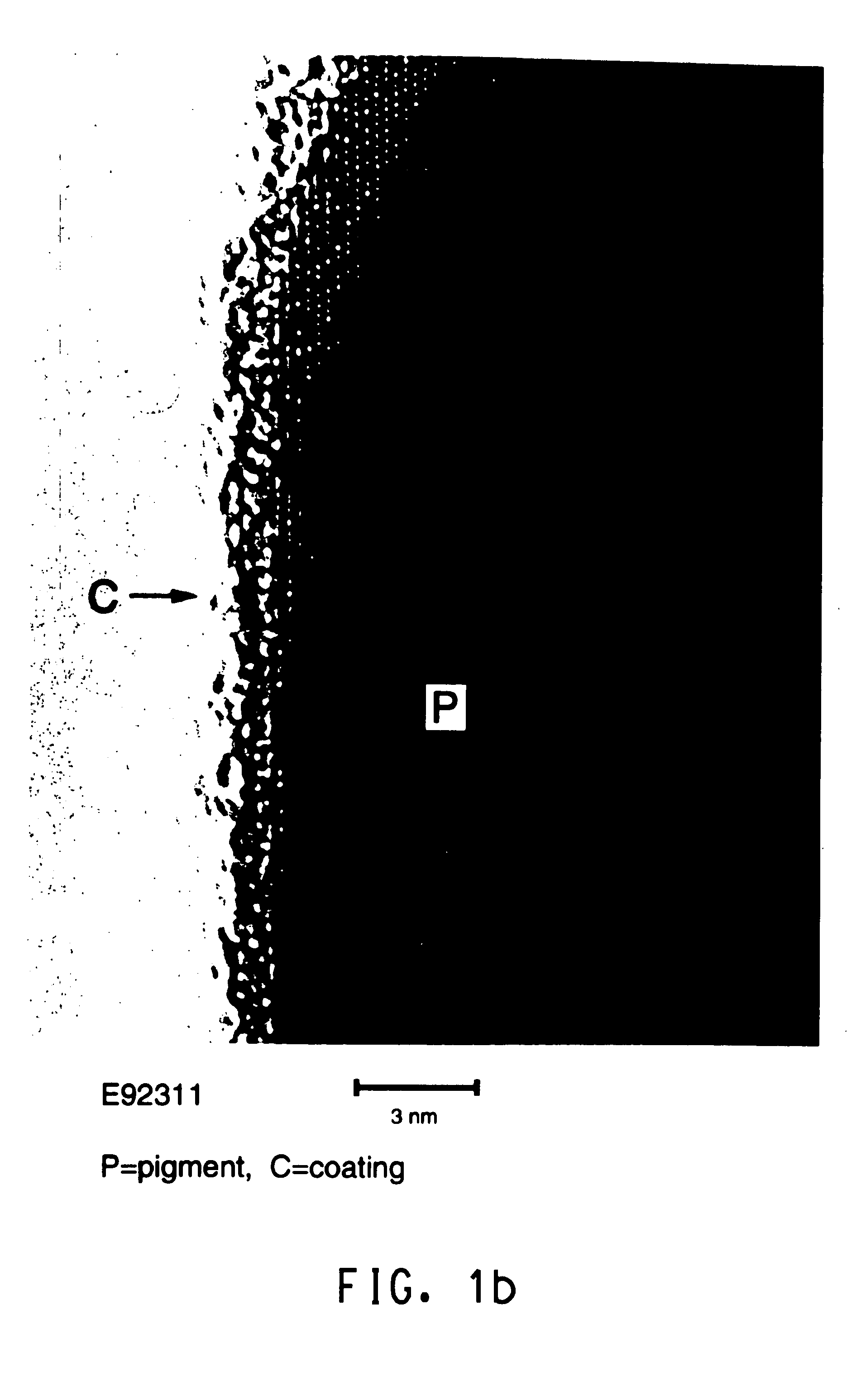
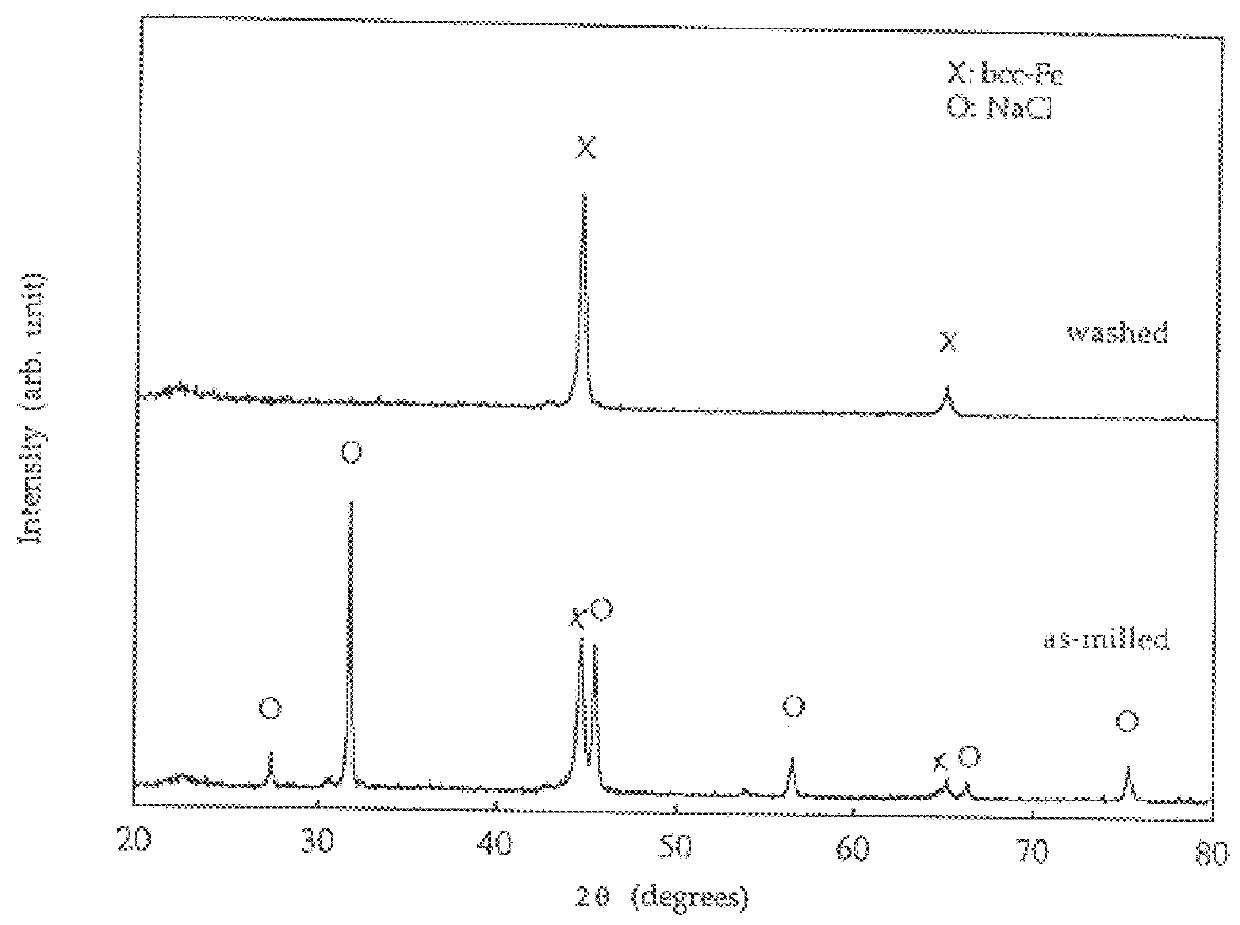
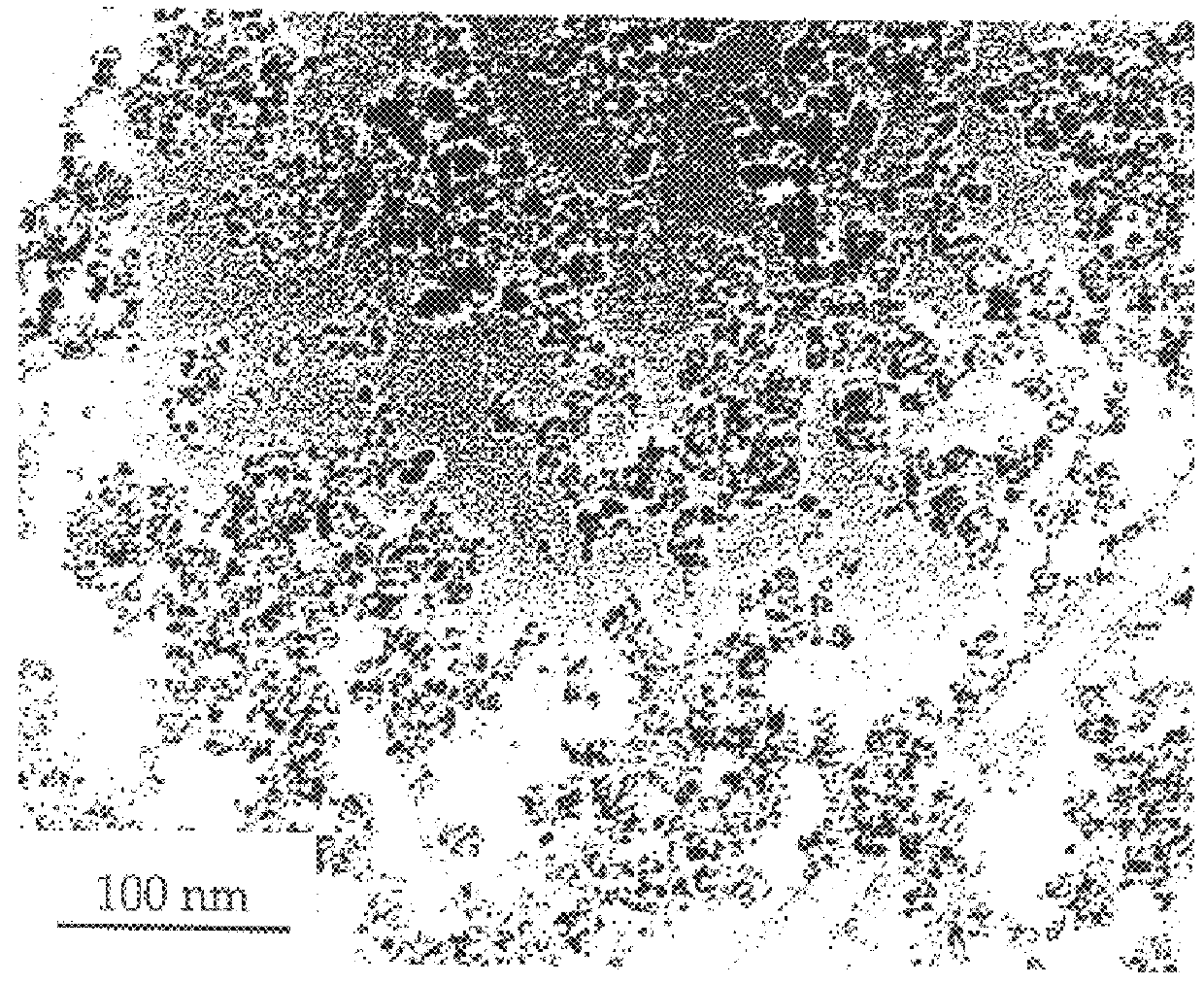
Patents
Literature
6094results about "Titanium dioxide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
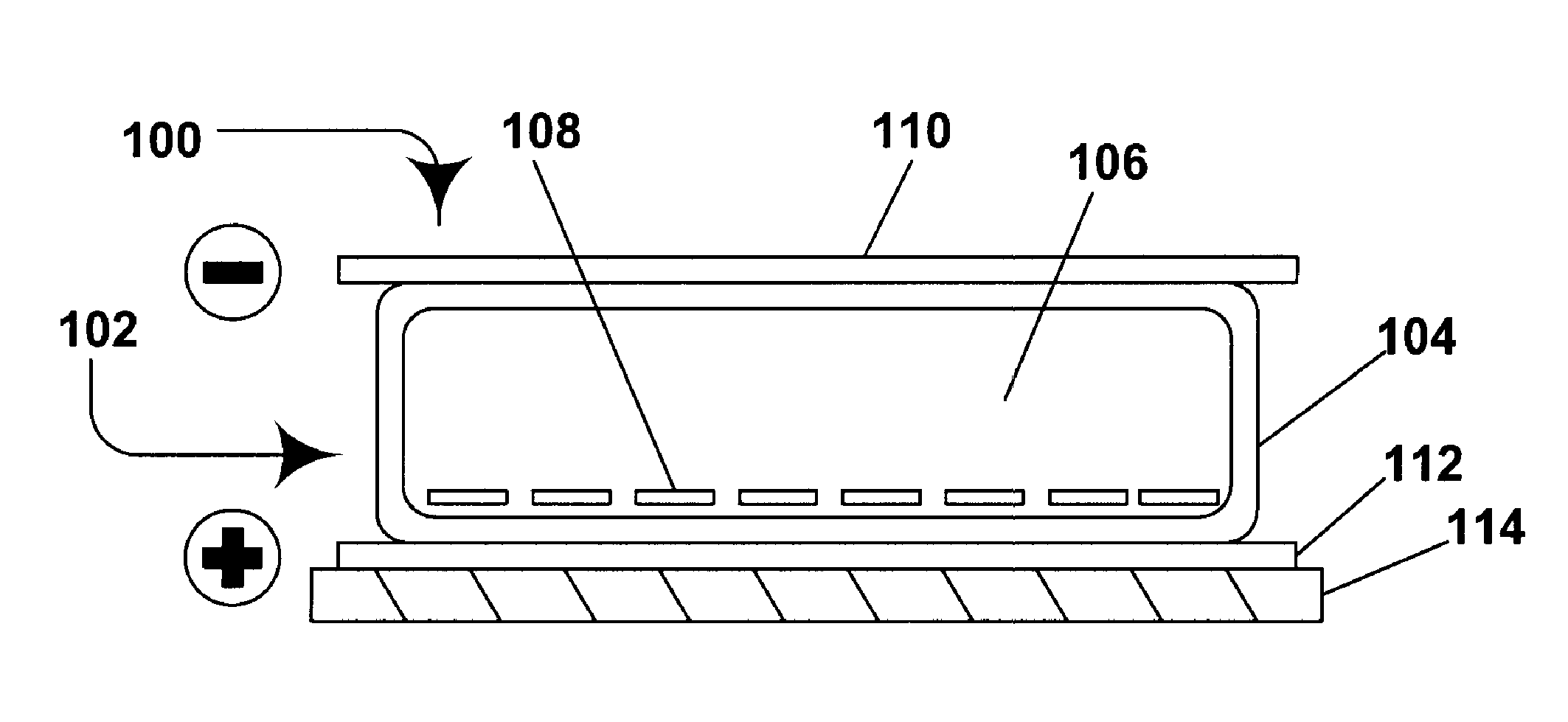
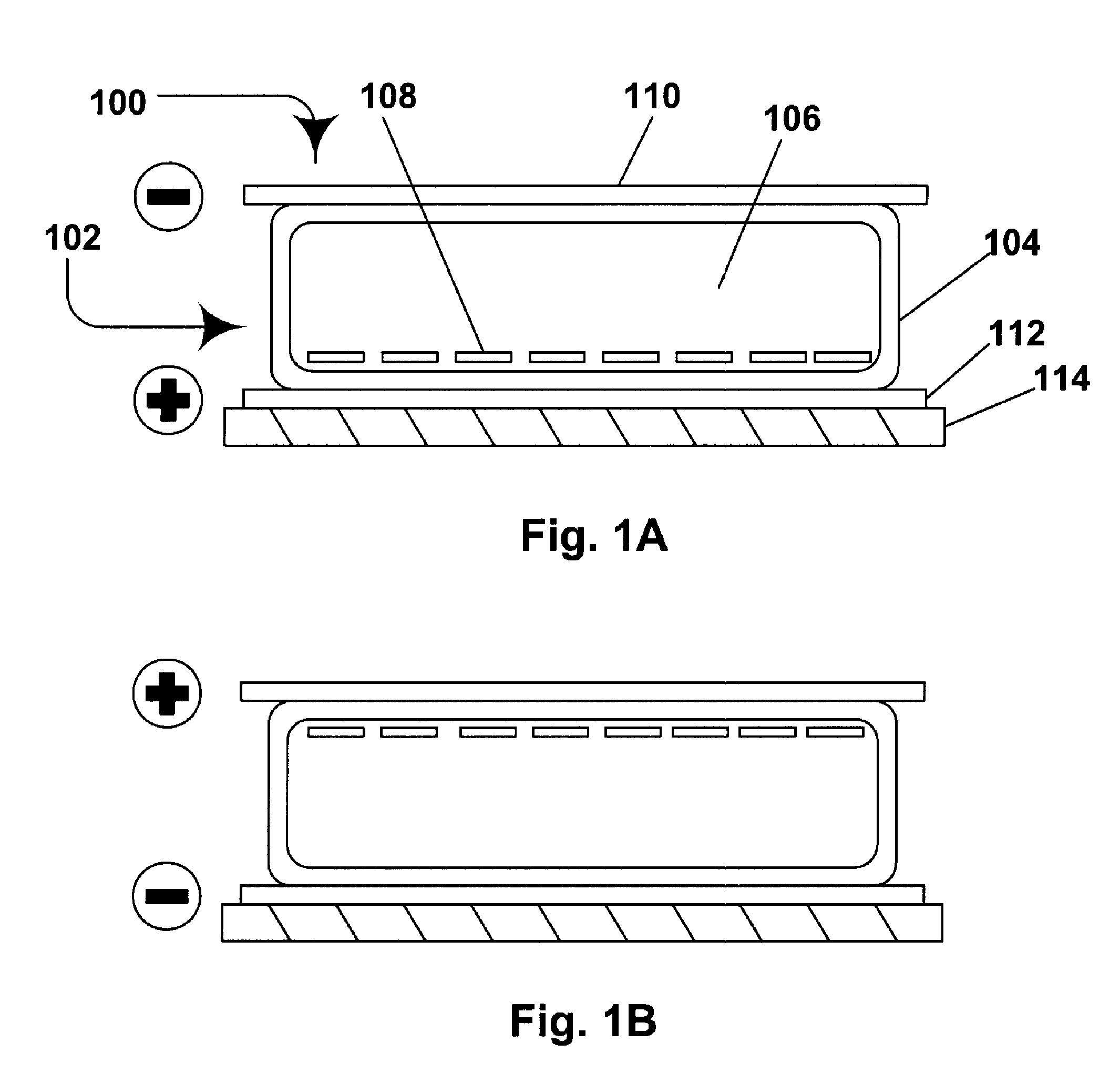
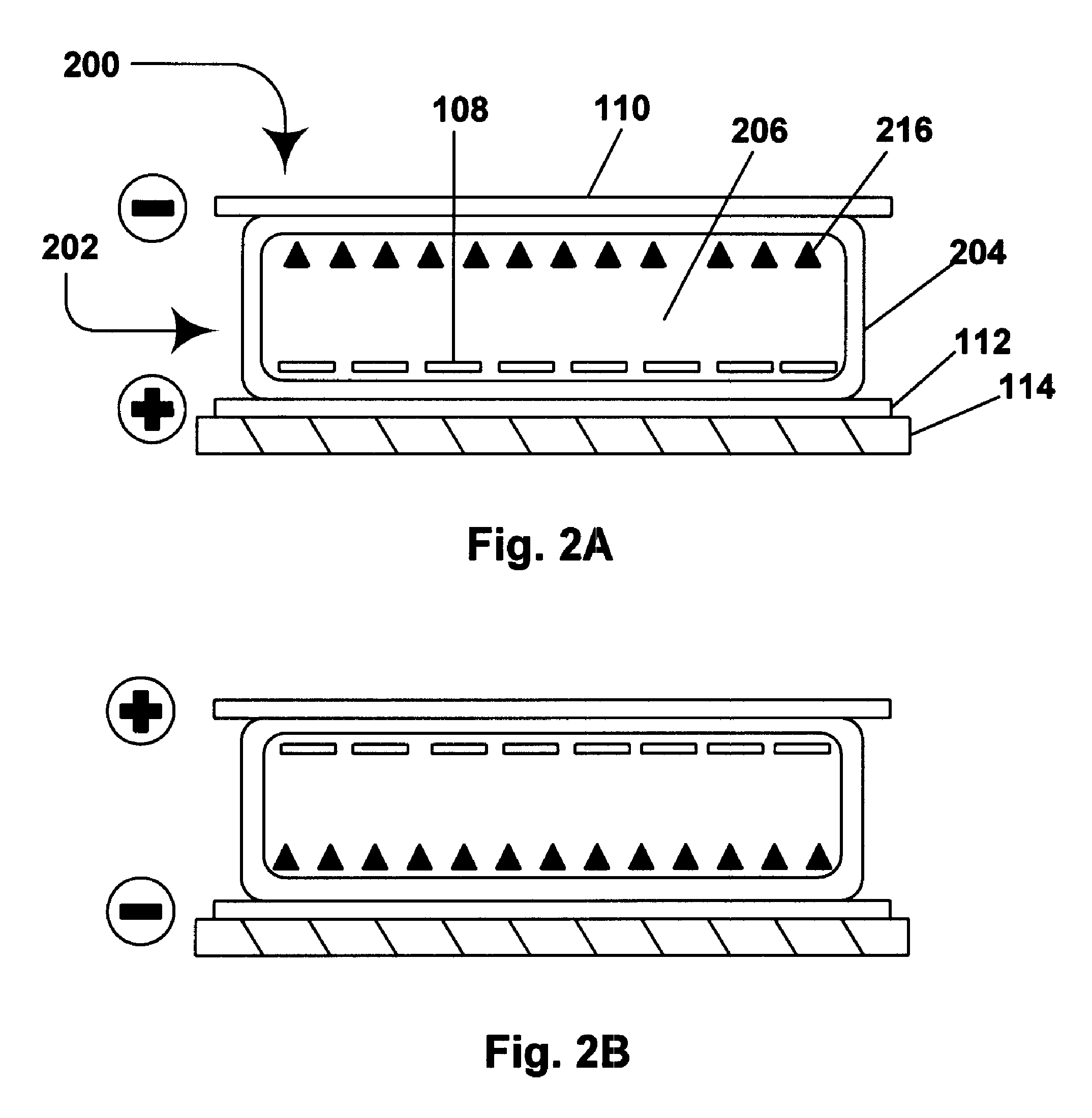
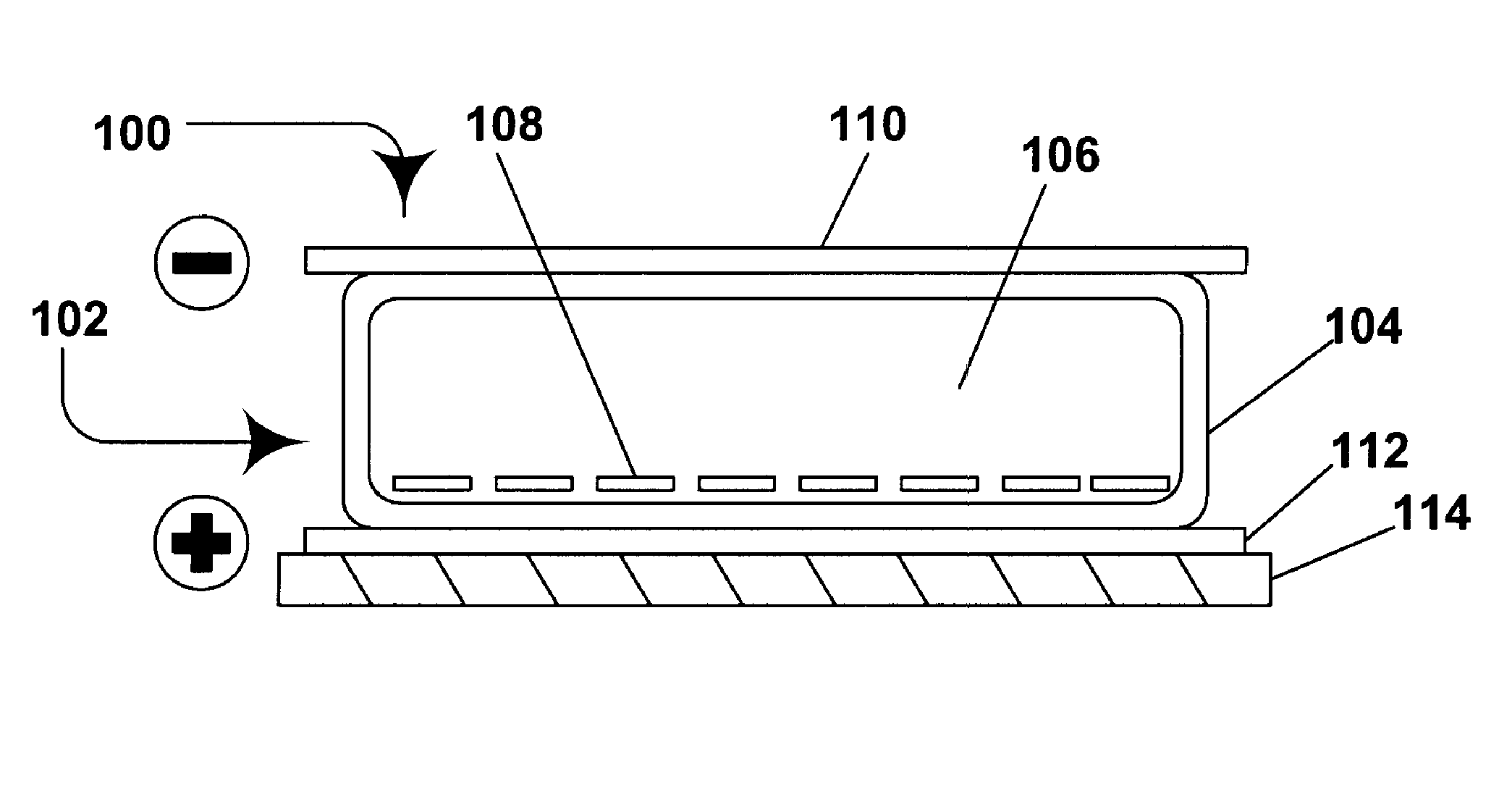
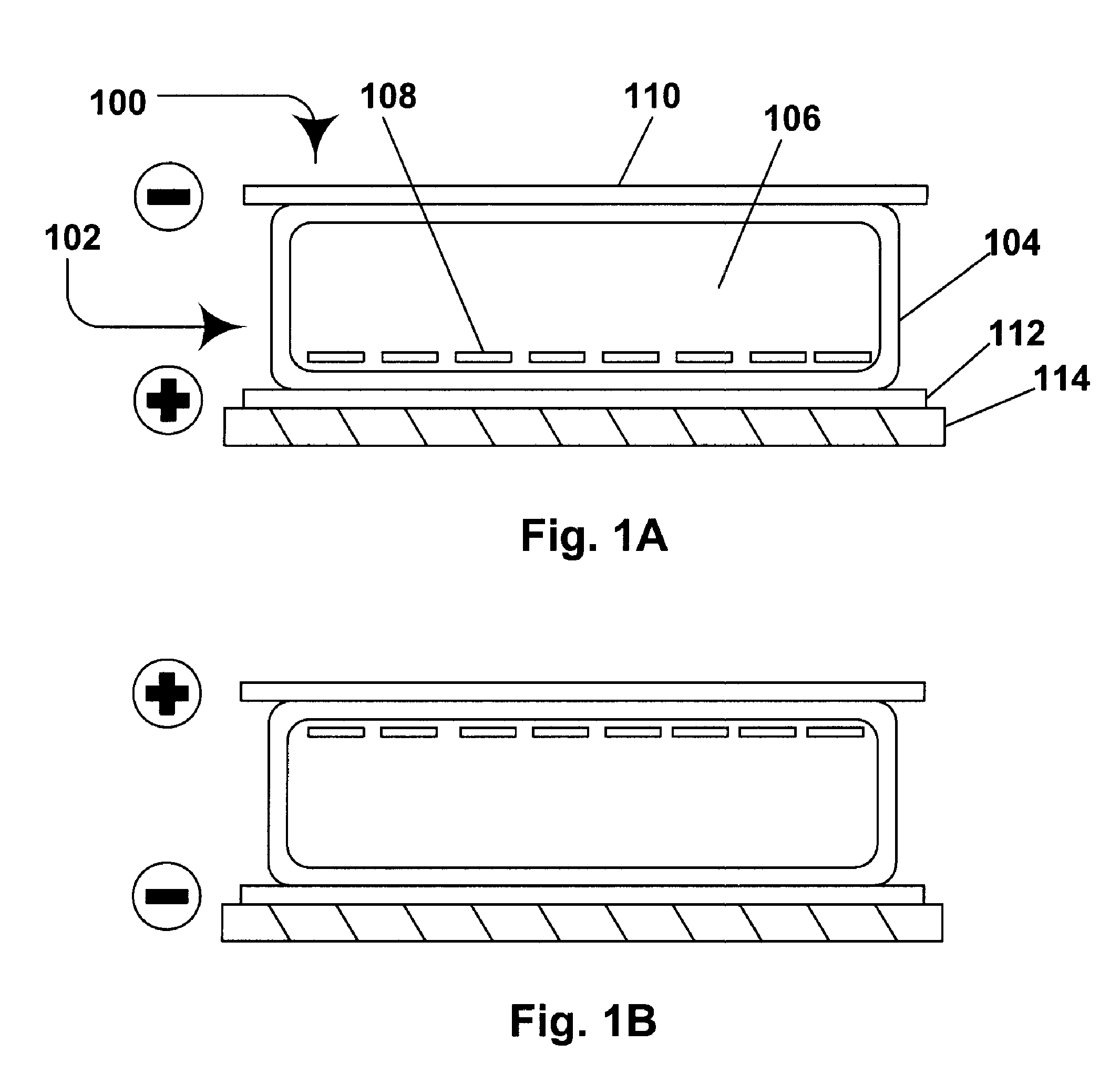
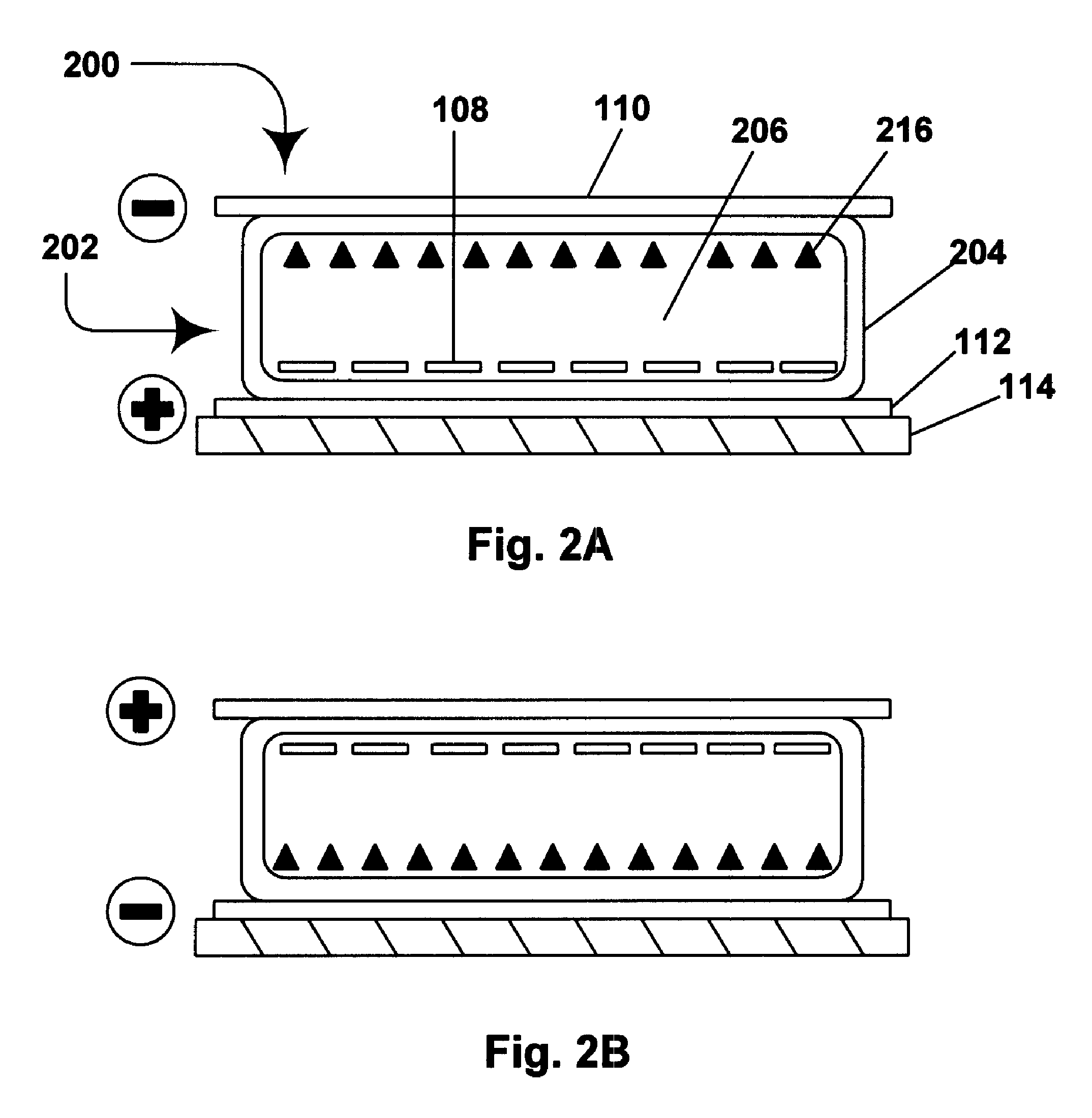
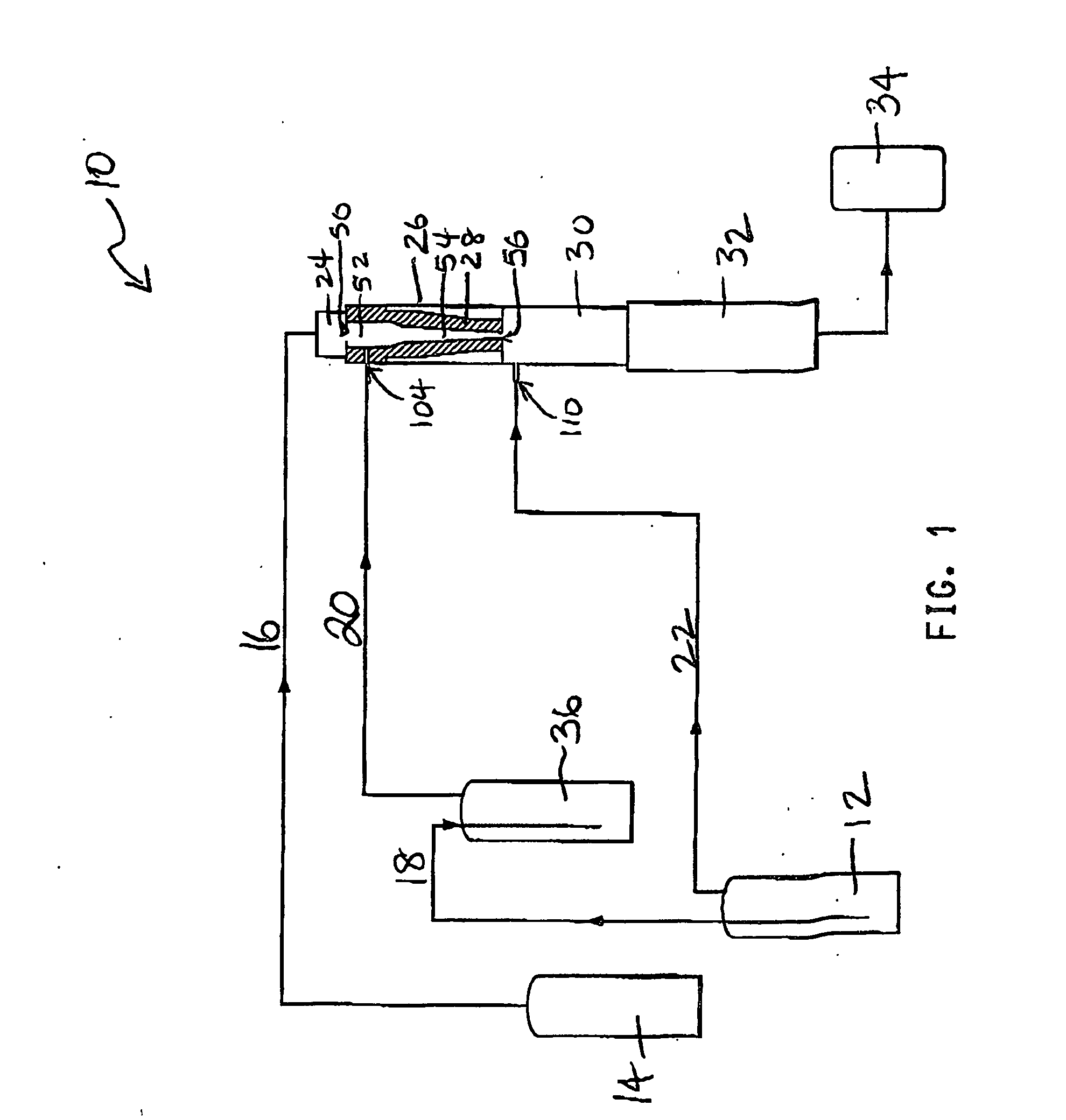
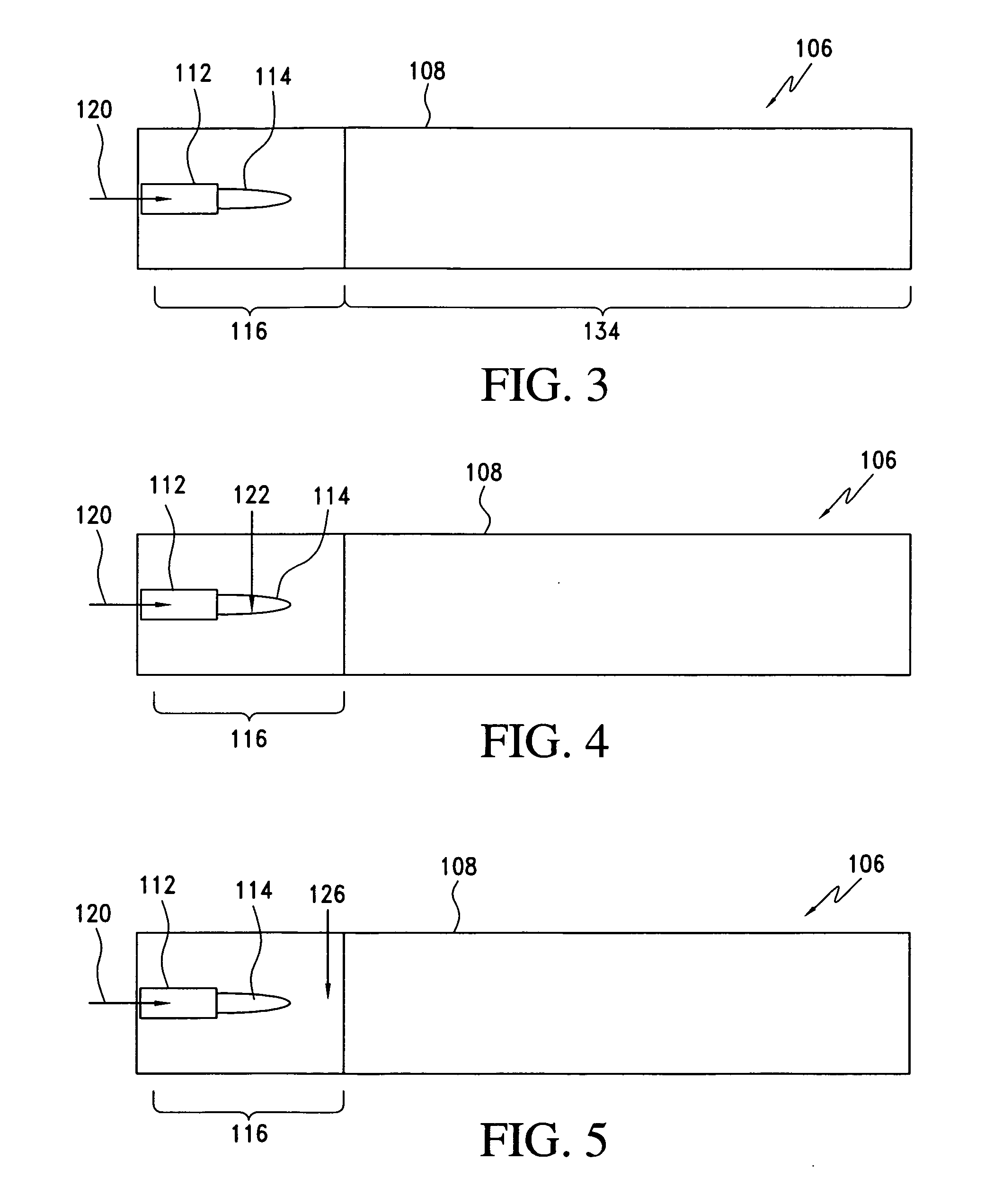
Electrophoretic media containing specularly reflective particles
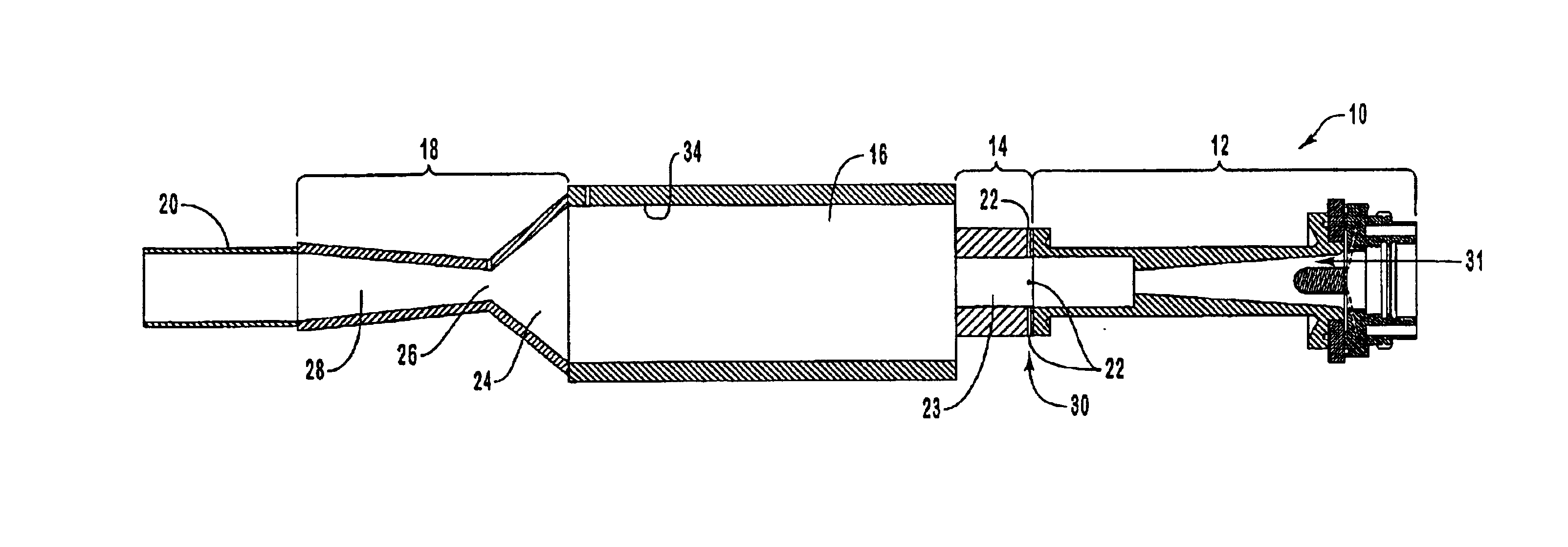
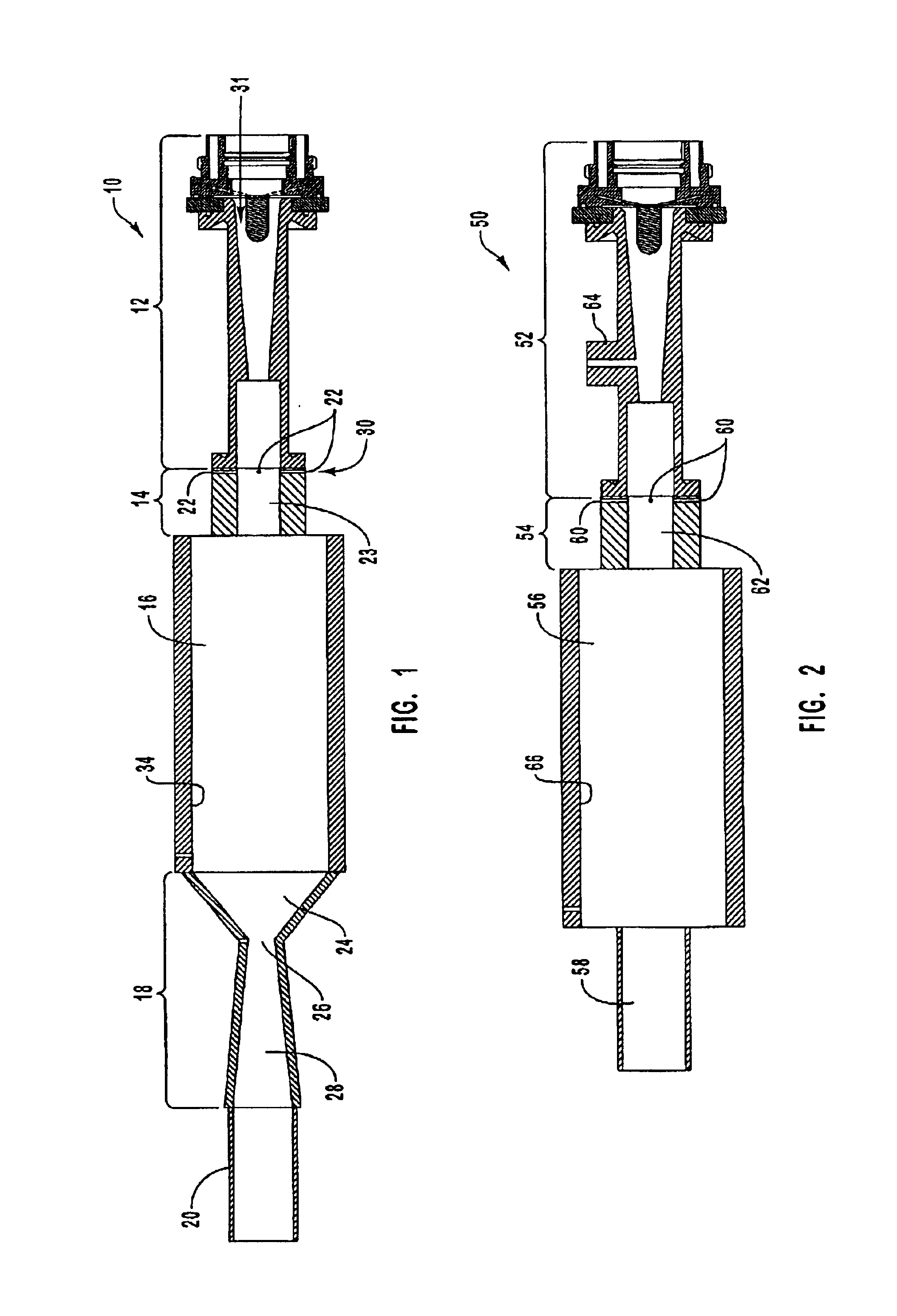
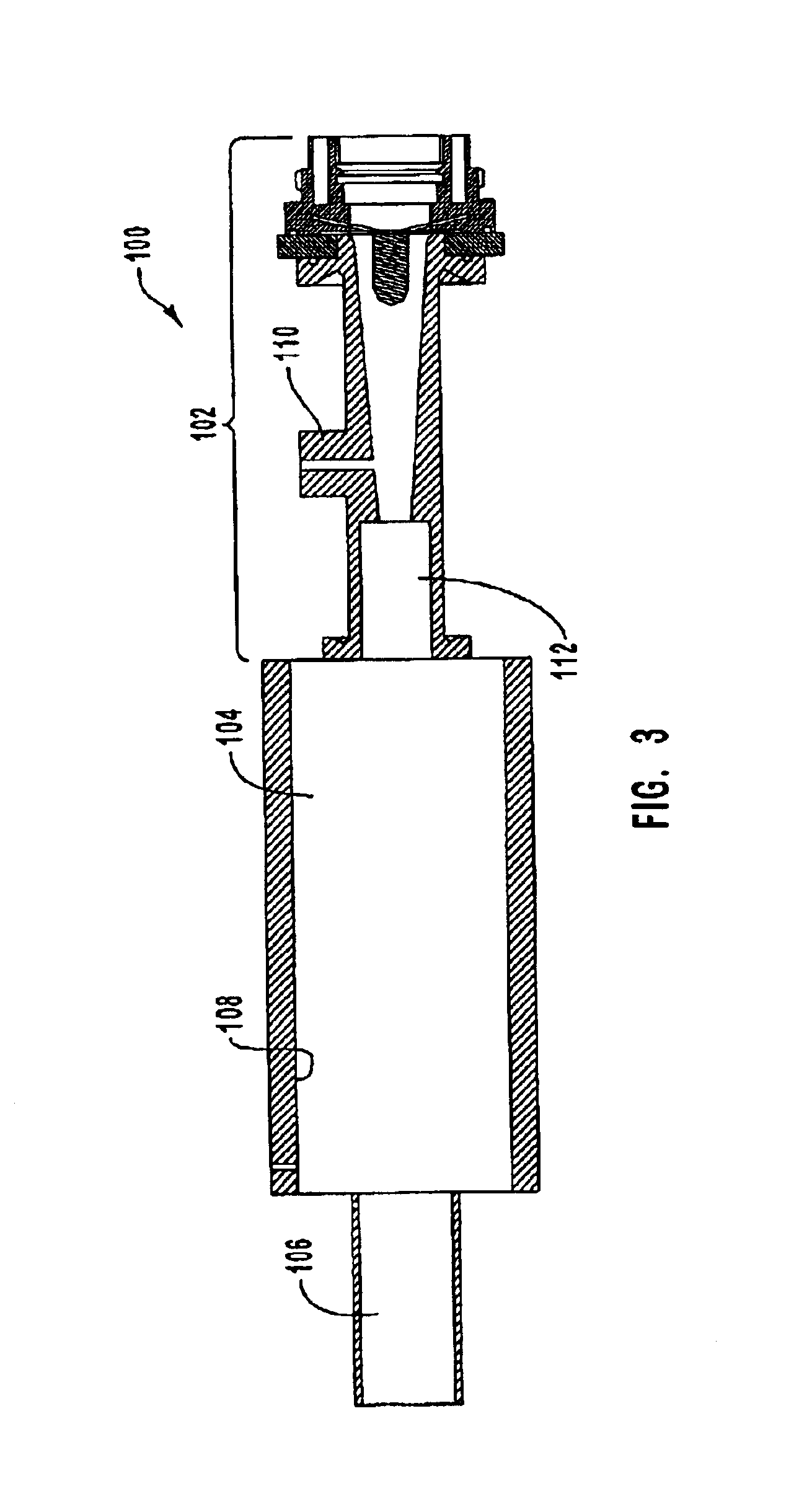
ActiveUS20040094422A1Good flexibilityImprove uniformitySludge treatmentStatic indicating devicesElectrophoresisSpecular reflection
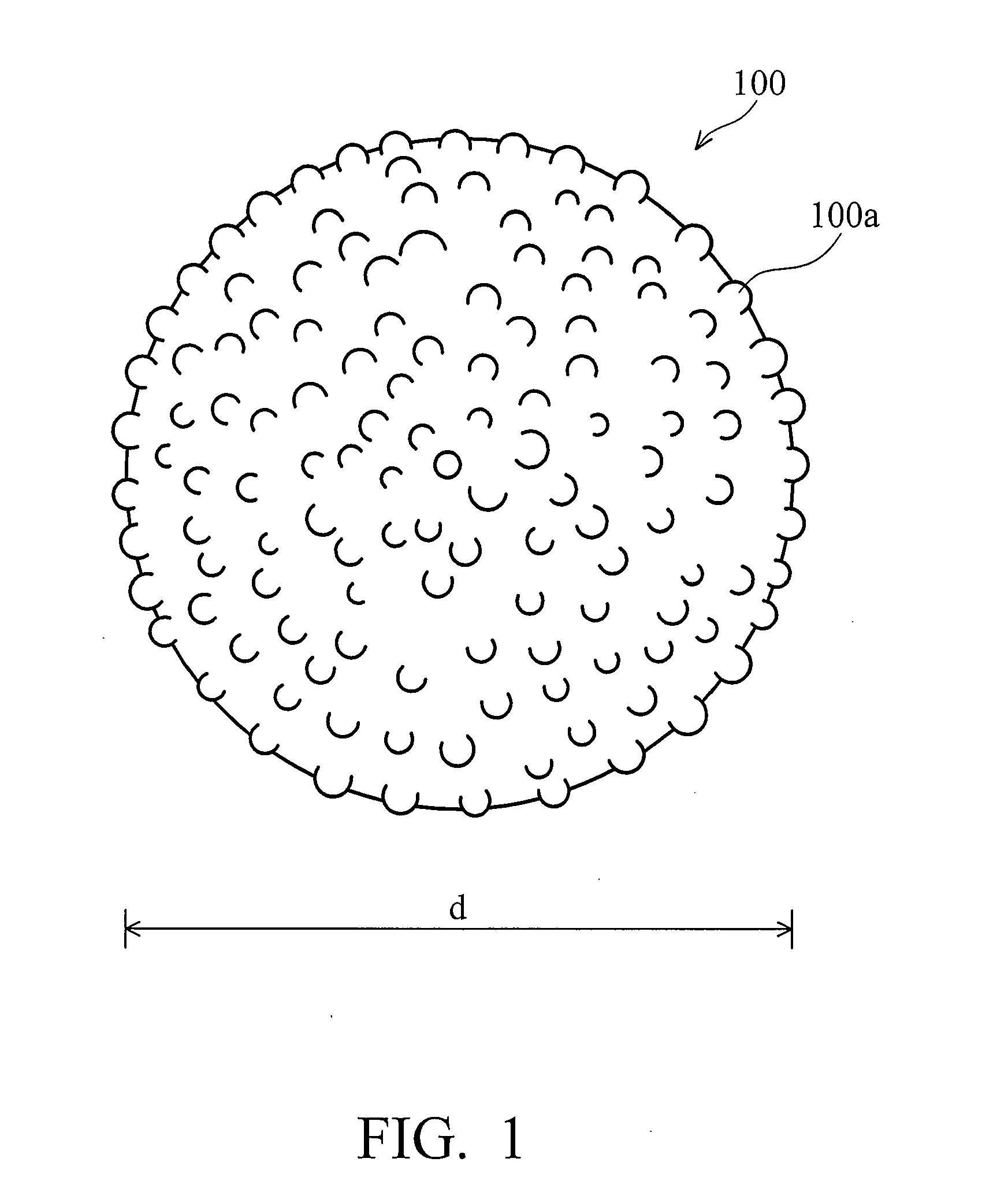
An electrophoretic medium (100) comprises at least one type of particle (108) suspended in a suspending fluid (106) and capable of moving therethrough on application of an electric field to the medium, the particles (108) including at least one electrophoretically mobile specularly reflective particle.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Electrophoretic media containing specularly reflective particles
ActiveUS7312916B2Improve reflectivityReduces backplane scatteringSludge treatmentStatic indicating devicesElectrophoresisSpecular reflection
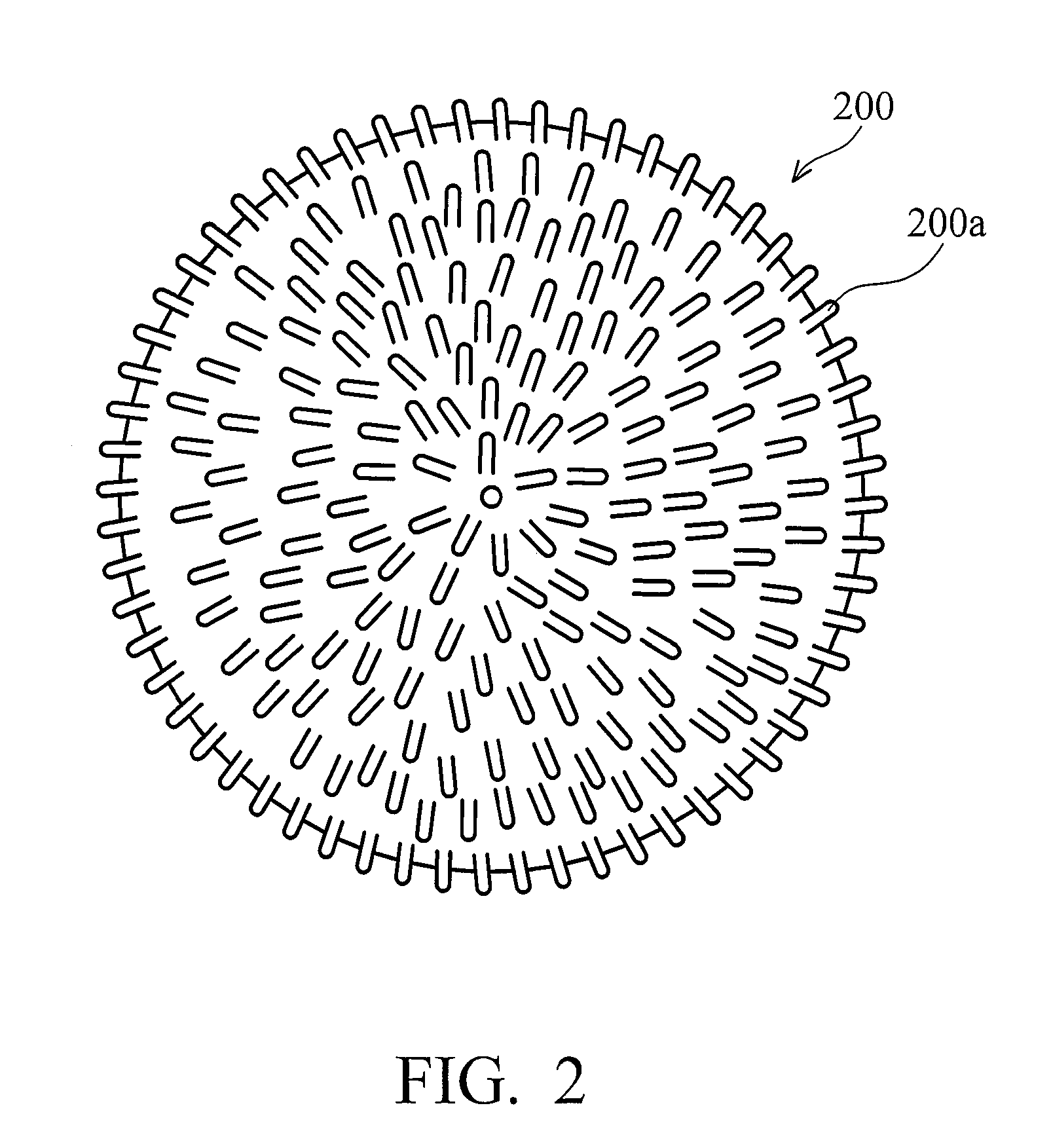
An electrophoretic medium (100) comprises at least one type of particle (108) suspended in a suspending fluid (106) and capable of moving therethrough on application of an electric field to the medium, the particles (108) including at least one electrophoretically mobile specularly reflective particle.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
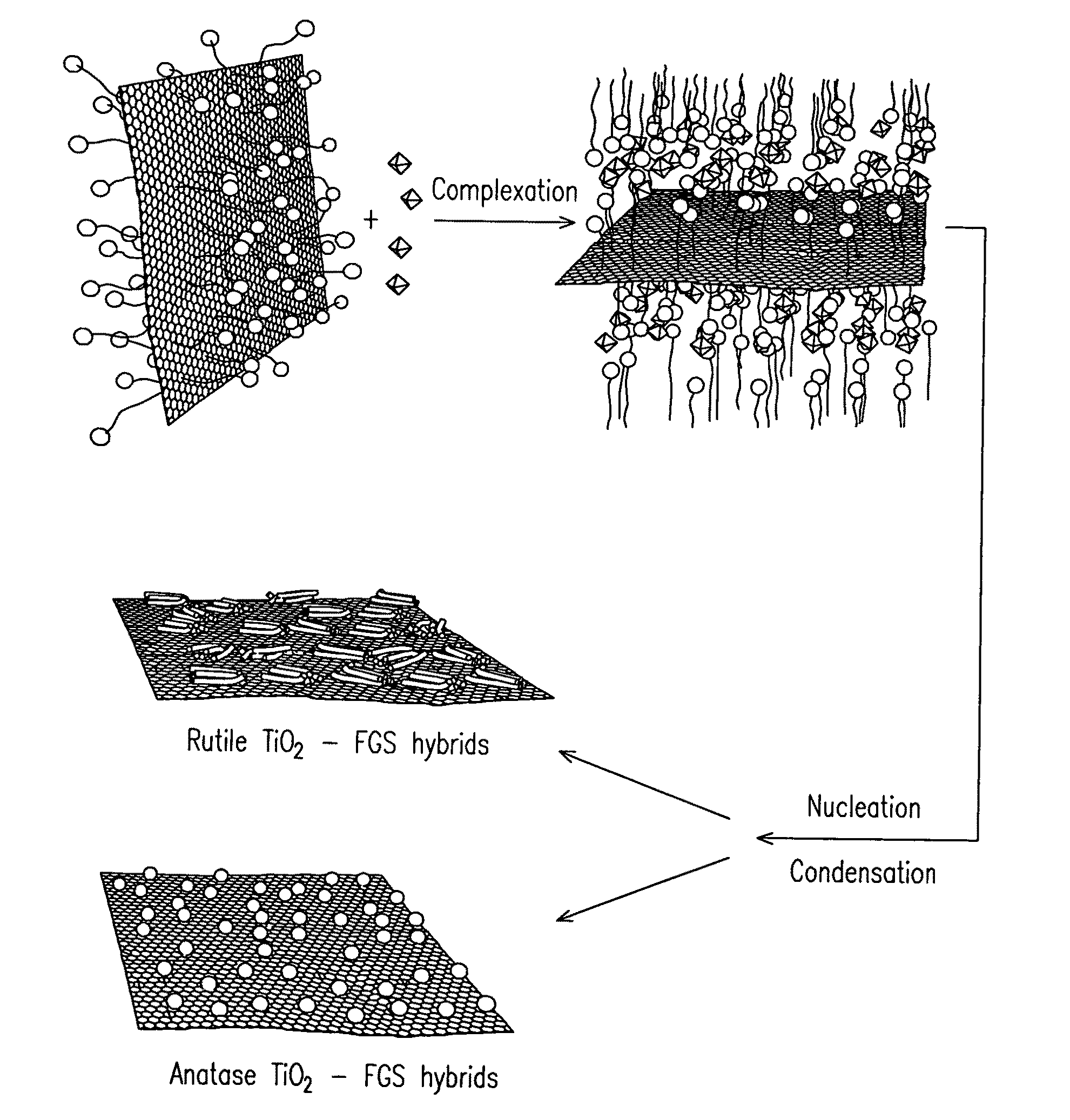
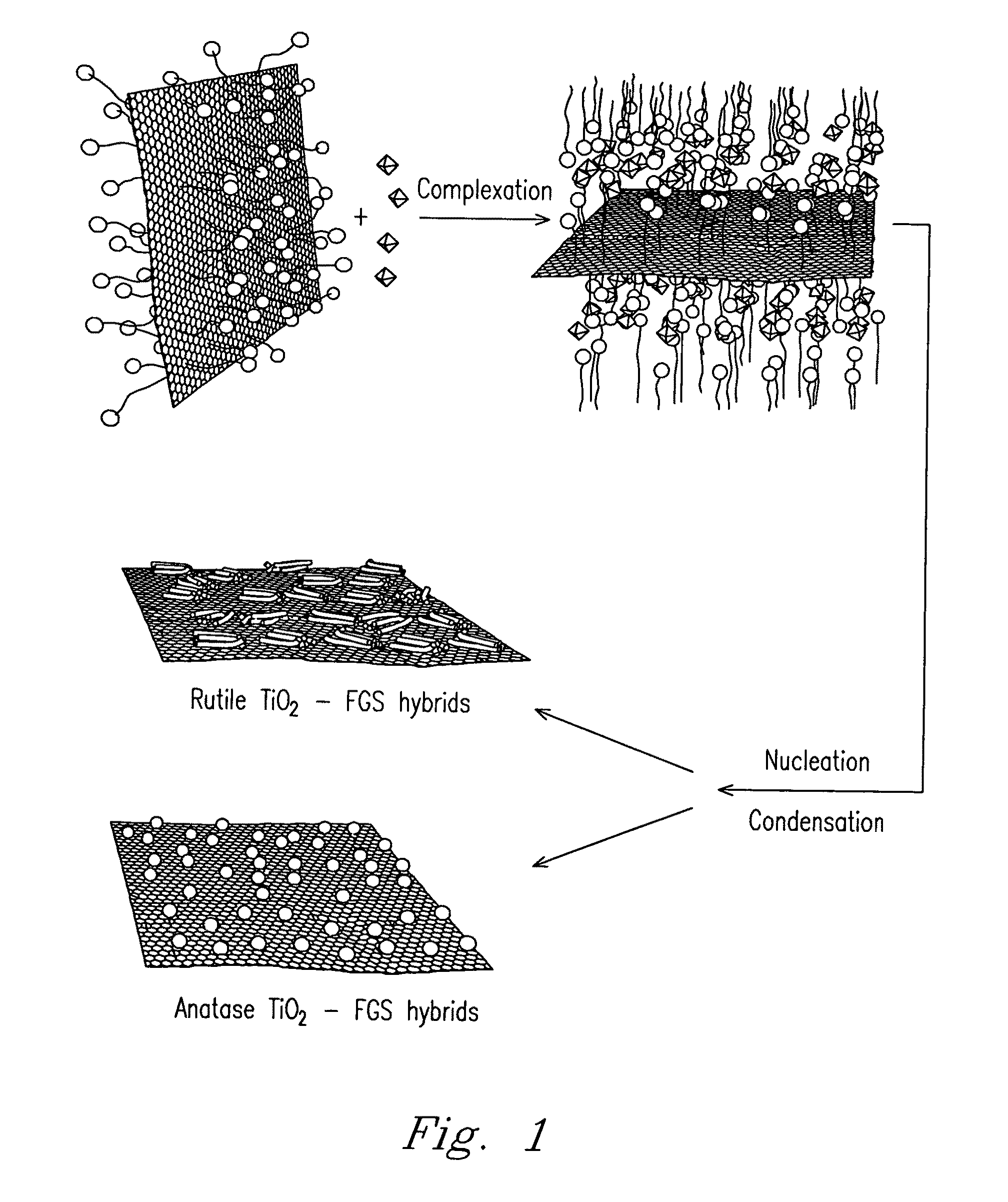
Nanocomposite of graphene and metal oxide materials
ActiveUS20100081057A1Easy to distinguishMaterial nanotechnologyRecord information storageDischarge rateCvd graphene
Nanocomposite materials comprising a metal oxide bonded to at least one graphene material. The nanocomposite materials exhibit a specific capacity of at least twice that of the metal oxide material without the graphene at a charge / discharge rate greater than about 10C.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV +1
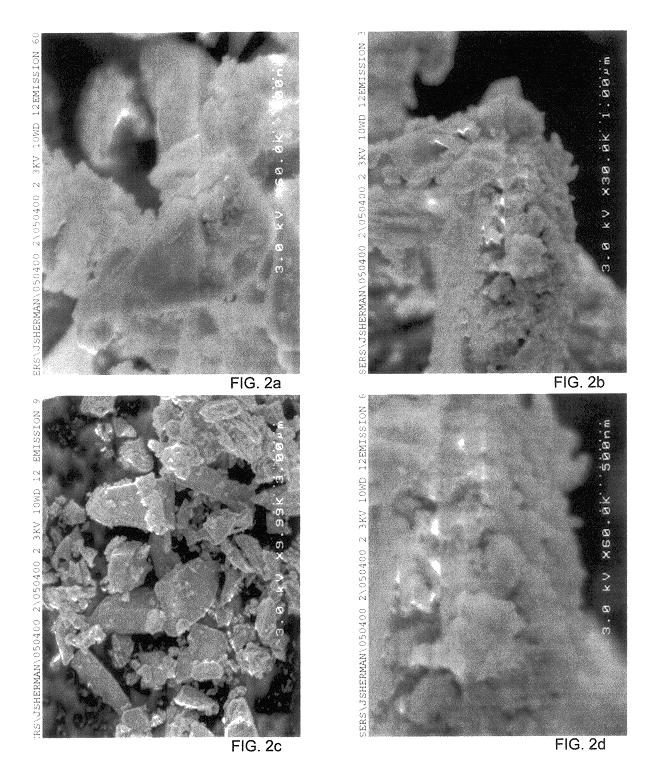
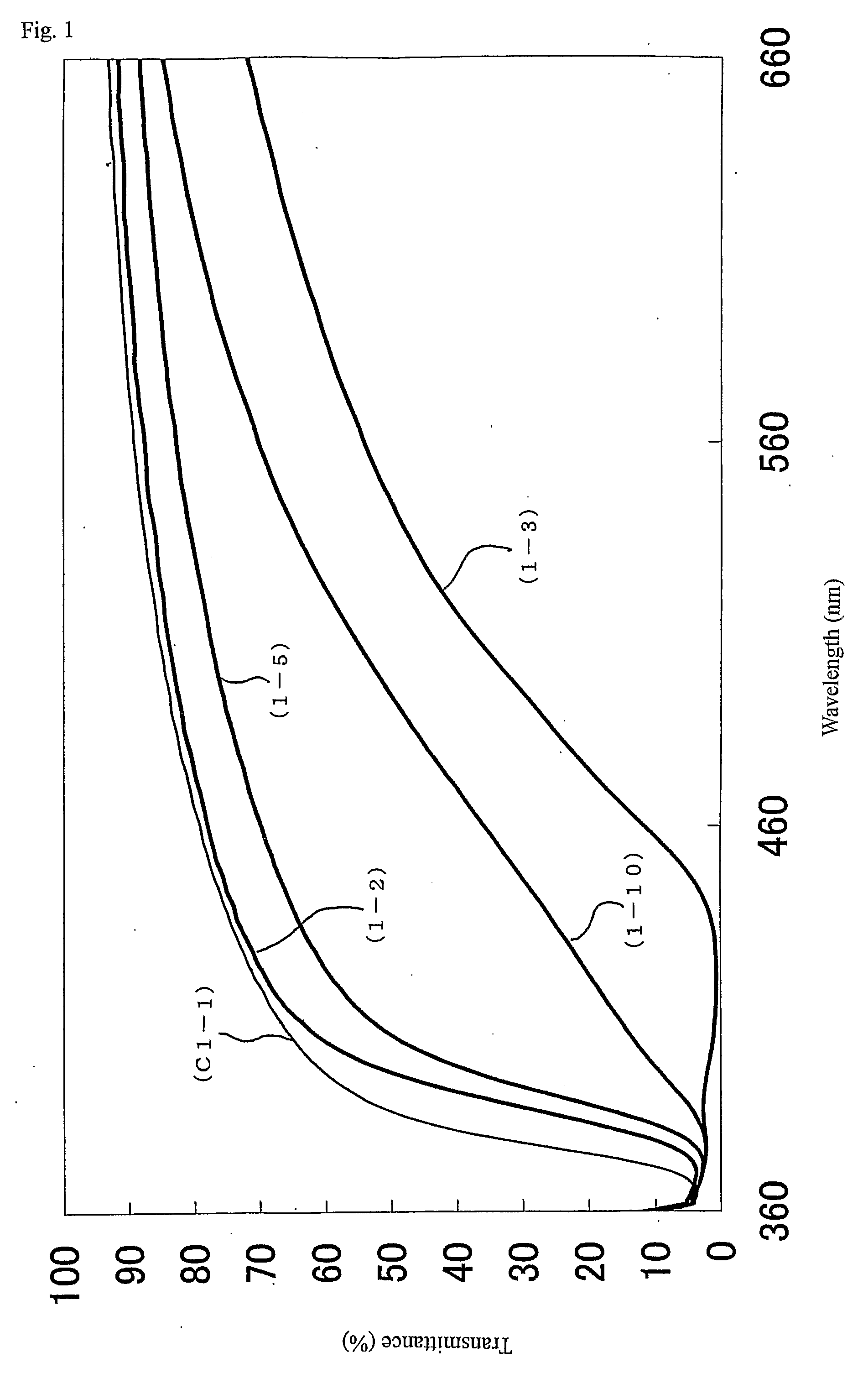
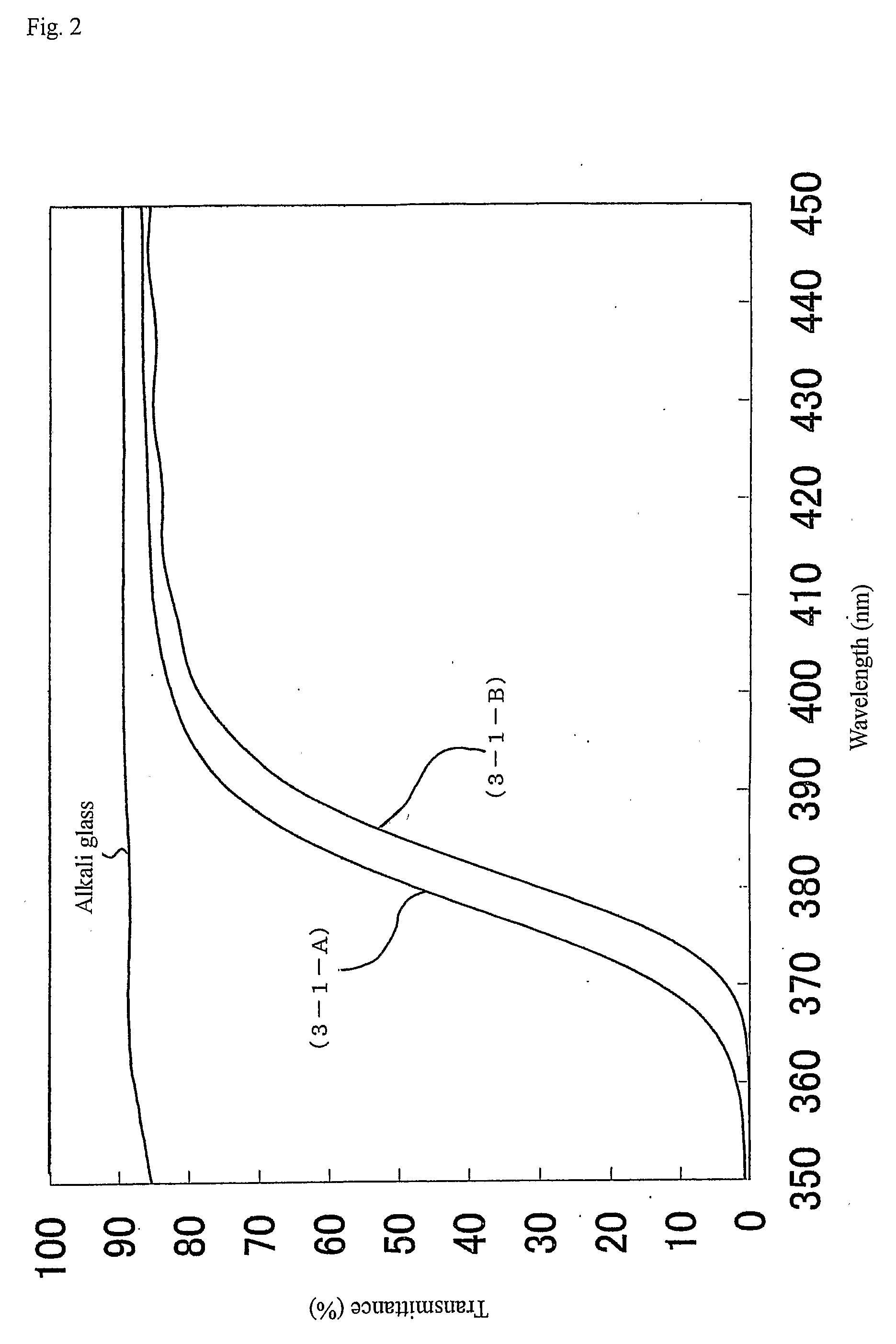
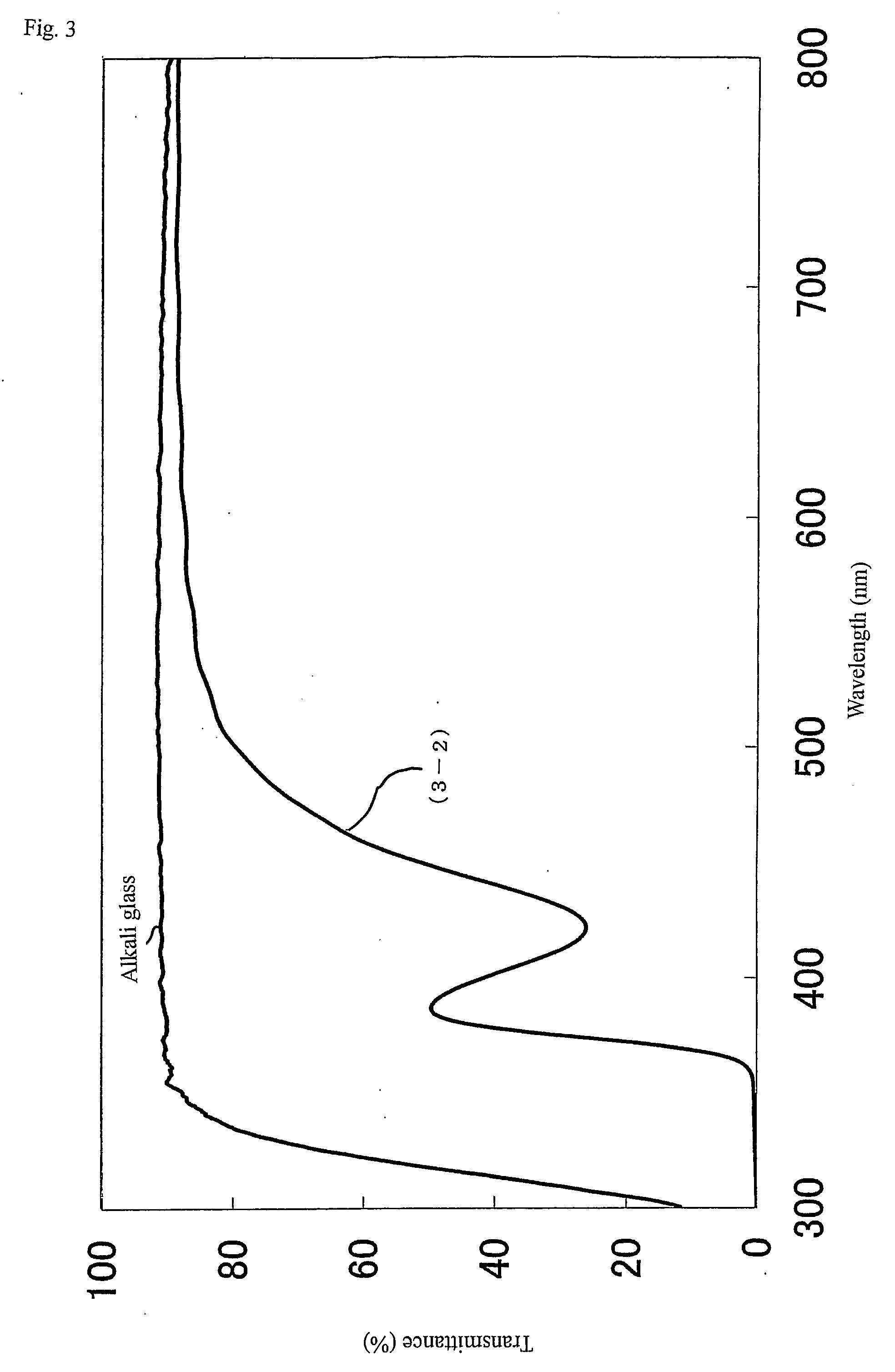
Nanoparticulate titanium dioxide coatings, and processes for the production and use thereof
Nanoparticulate titanium dioxide coating produced by educing flocculates of titanium dioxide nanoparticles from a titanyl sulfate solution and dispersing the nanoparticles in a polar sol-forming medium to make a sol suitable as a coating usable to impart photocatalytic activity, U.V. screening properties, and fire retardency to particles and to surfaces. The photocatalytic material and activity is preferably localized in dispersed concentrated nanoparticles, spots or islands both to save costs and leverage anti-microbial effects.
Owner:SHERMAN JONATHAN
Nanoparticulate titanium dioxide coatings, and processes for the production and use thereof
Nanoparticulate titanium dioxide coating produced by educing flocculates of titanium dioxide nanoparticles from a titanyl sulfate solution and dispersing the nanoparticles in a polar sol-forming medium to make a sol suitable as a coating usable to impart photocatalytic activity, U.V. screening properties, and fire retardency to particles and to surfaces. The photocatalytic material and activity is preferably localized in dispersed concentrated nanoparticles, spots or islands both to save costs and leverage anti-microbial effects.
Owner:SHERMAN JONATHAN
Process for the production of ultrafine powders of metal oxides
InactiveUS6503475B1Low costHigh yield rateAlkaline earth titanatesMaterial nanotechnologyDiluentBiological activation
A process for the production of ultrafine powders that includes subjecting a mixture of precursor metal compound and a non-reactant diluent phase to mechanical milling whereby the process of mechanical activation reduces the microstructure of the mixture to the form of nano-sized grains of the metal compound uniformly dispersed in the diluent phase. The process also includes heat treating the mixture of nano-sized grains of the metal compound uniformly dispersed in the diluent phase to convert the nano-sized grains of the metal compound into a metal oxide phase. The process further includes removing the diluent phase such that the nano-sized grains of the metal oxide phase are left behind in the form of an ultrafine powder.
Owner:SAMSUNG CORNING PRECISION MATERIALS CO LTD +1
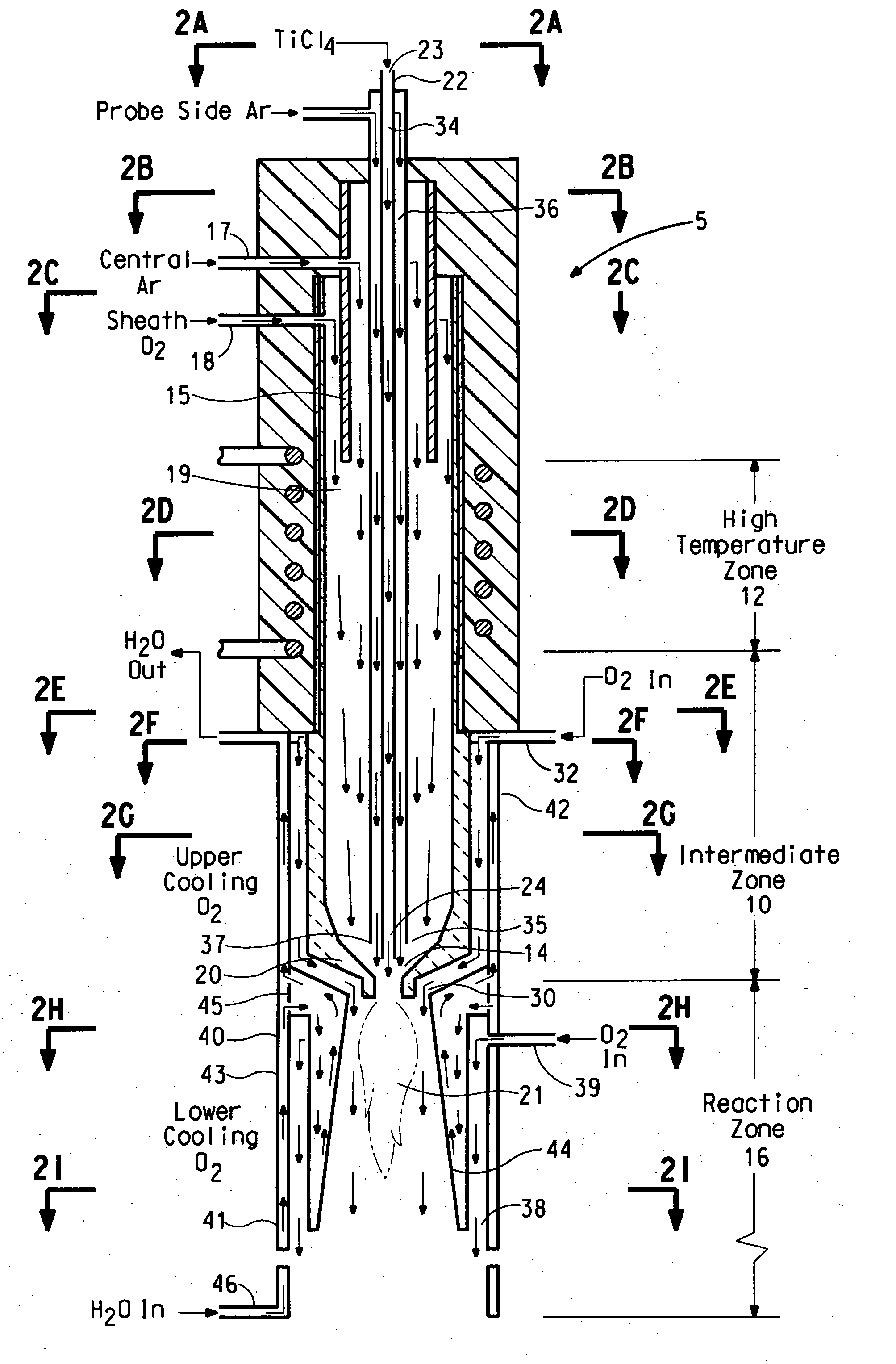
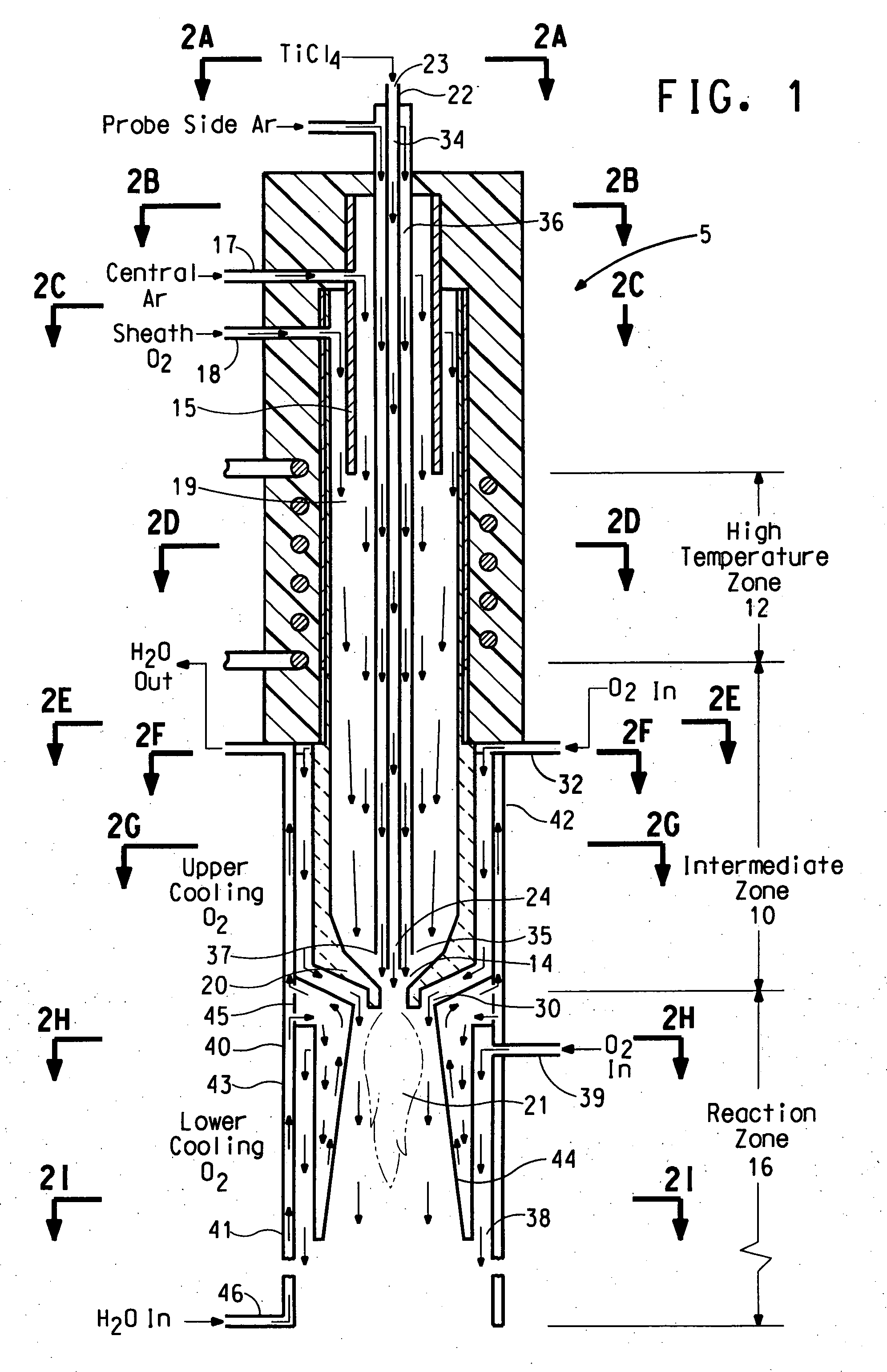
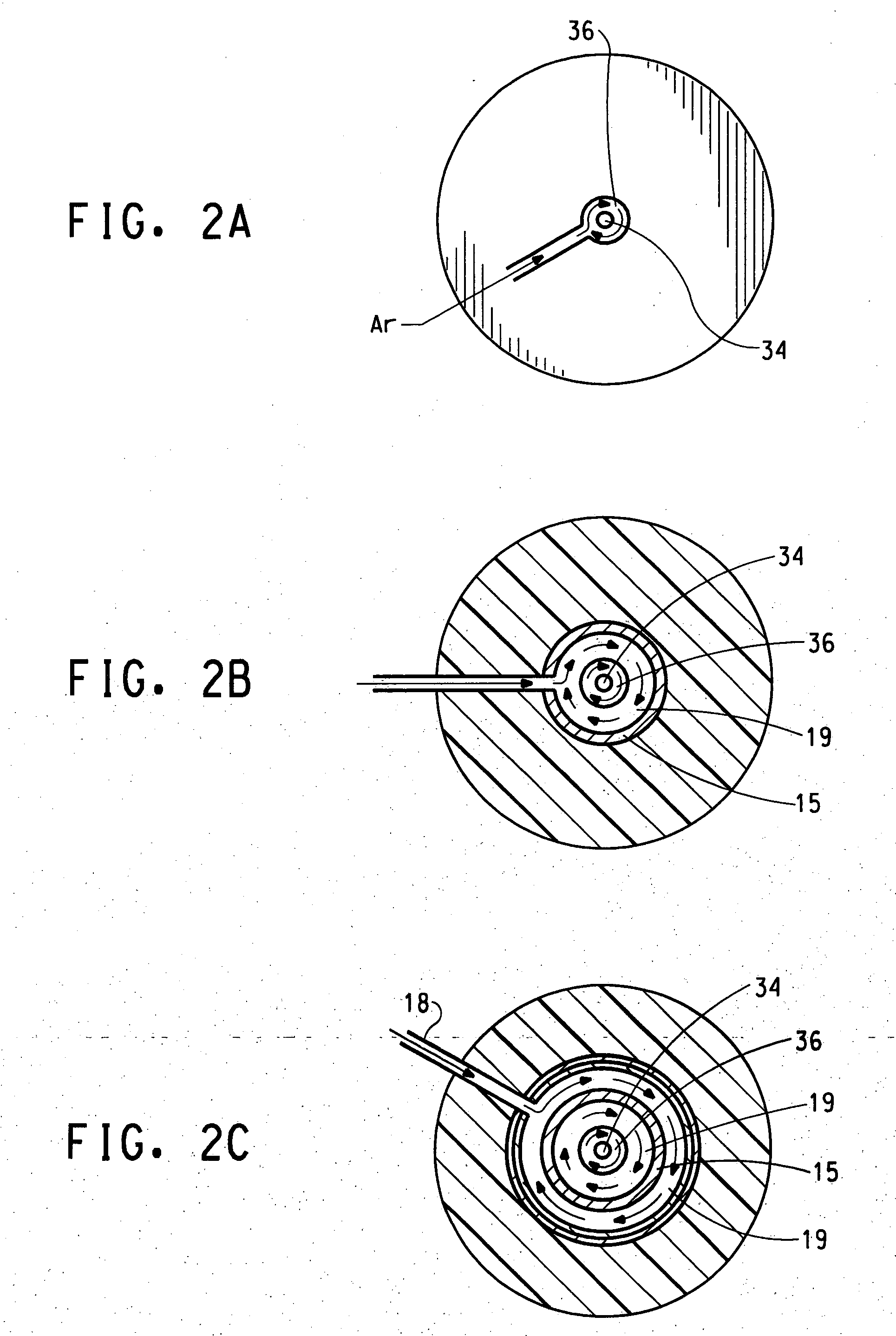
Thermal synthesis apparatus and process
InactiveUS6821500B2Improve efficiencyHigh yieldCarbon monoxideIndirect heat exchangersNuclear engineeringReaction zone
An apparatus for thermal conversion of one or more reactants to desired end products includes an insulated reactor chamber having a high temperature heater such as a plasma torch at its inlet end and, optionally, a restrictive convergent-divergent nozzle at its outlet end. In a thermal conversion method, reactants are injected upstream from the reactor chamber and thoroughly mixed with the plasma stream before entering the reactor chamber. The reactor chamber has a reaction zone that is maintained at a substantially uniform temperature. The resulting heated gaseous stream is then rapidly cooled by passage through the nozzle, which "freezes" the desired end product(s) in the heated equilibrium reaction stage, or is discharged through an outlet pipe without the convergent-divergent nozzle. The desired end products are then separated from the gaseous stream.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
Mixed-metal oxide particles by liquid feed flame spray pyrolysis of oxide precursors in oxygenated solvents
Liquid feed flame spray pyrolysis of solutions of a metal oxide precursor which is an alkoxide or C1-6 carboxylate and at least one second metal oxide precursor and / or second metal compound dissolved in oxygenated solvent by combustion with oxygen lead to the formation of sub-micron mixed-metal oxide powders not accessible by other processes or by the pyrolysis of metal chlorides or nitrates. The powders have numerous uses in advanced materials applications including particulate solid state lasers, advanced ceramic materials, and as catalysts in organic synthesis and automobile exhaust systems.
Owner:TAL MATERIALS +1
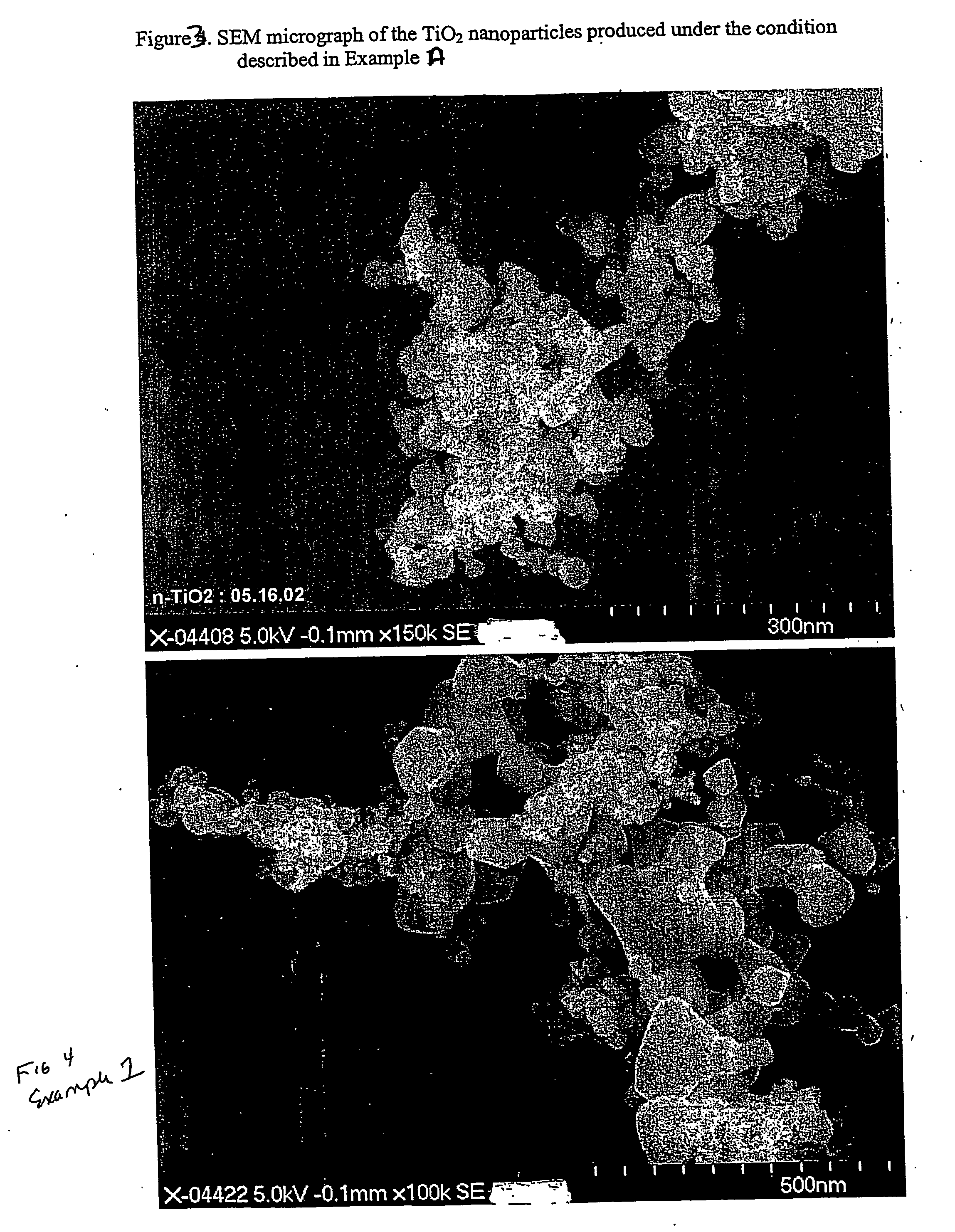
Plasma synthesis of metal oxide nanopowder and apparatus therefor
InactiveUS6994837B2Large dischargeKeep for a long timePigmenting treatmentMaterial nanotechnologyDopantPhysical chemistry
A process and apparatus for the synthesis of metal oxide nanopowder from a metal compound vapour is presented. In particular a process and apparatus for the synthesis of TiO2 nanopowder from TiCl4 is disclosed. The metal compound vapour is reacted with an oxidizing gas in electrically induced RF frequency plasma thus forming a metal oxide vapour. The metal oxide vapour is rapidly cooled using a highly turbulent gas quench zone which quickly halts the particle growth process, yielding a substantial reduction in the size of metal oxide particles formed compared with known processes. The metal compound vapour can also react with a doping agent to create a doped metal oxide nanopowder. Additionally, a process and apparatus for the inline synthesis of a coated metal oxide is disclosed wherein the metal oxide particles are coated with a surface agent after being cooled in a highly turbulent gas quench zone.
Owner:TEKNA PLASMA SYST INC
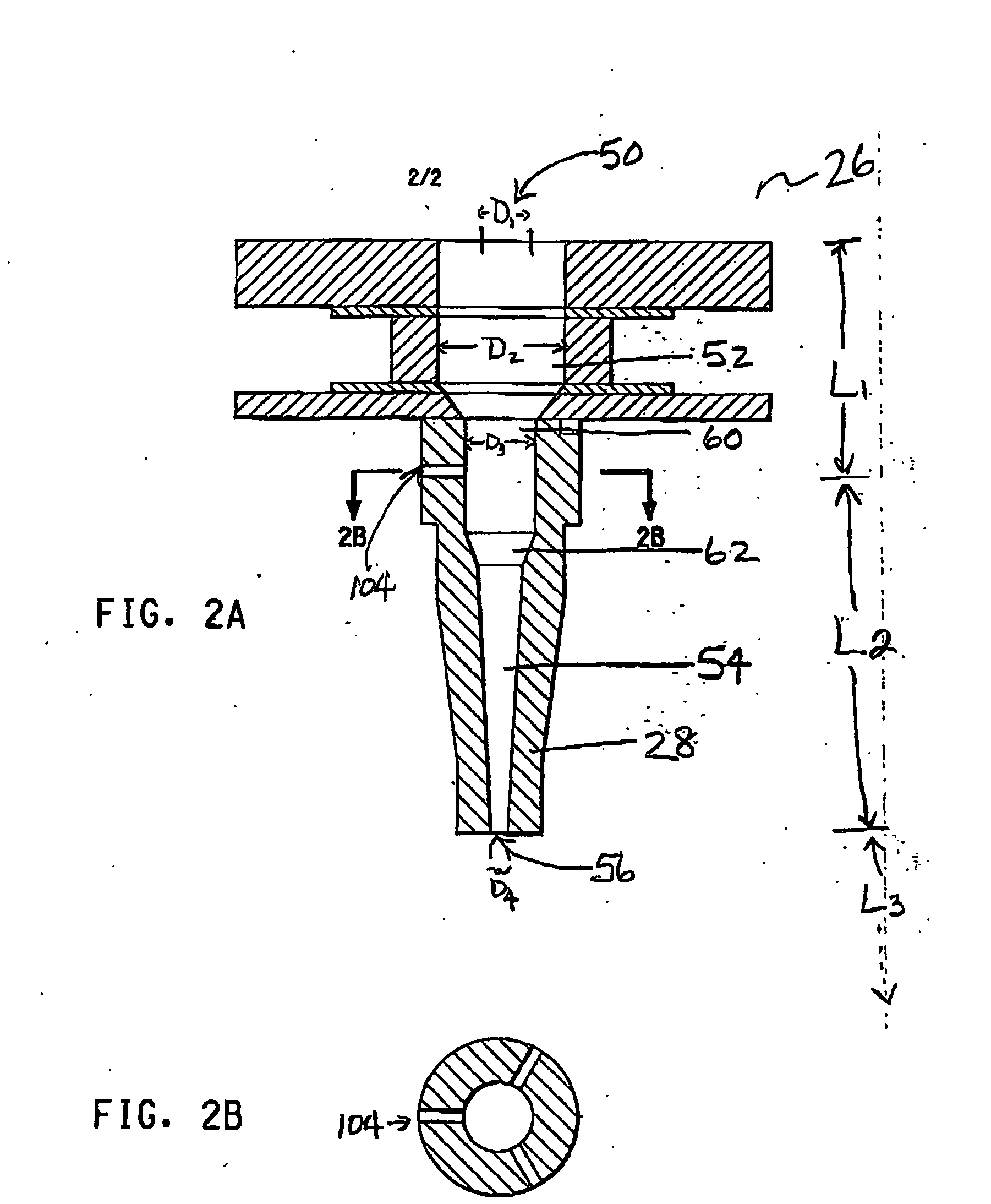
Tubular titanium oxide particles, method for preparing the same, and use of the same
InactiveUS20040265587A1Large specific surface areaImprove detection accuracyMaterial nanotechnologyLight-sensitive devicesReduction treatmentSorbent
The process for preparing tubular titanium oxide particles comprises subjecting a water dispersion sol, which is obtained by dispersing (i) titanium oxide particles and / or (ii) titanium oxide type composite oxide particles comprising titanium oxide and an oxide other than titanium oxide in water, said particles having an average particle diameter of 2 to 100 nm, to hydrothermal treatment in the presence of an alkali metal hydroxide. After the hydrothermal treatment, reduction treatment (including nitriding treatment) may be carried out. The tubular titanium oxide particles obtained in this process are useful as catalysts, catalyst carriers, adsorbents, photocatalysts, decorative materials, optical materials and photoelectric conversion materials. Especially when the particles are used for semiconductor films for photovoltaic cells or photocatalysts, prominently excellent effects are exhibited.
Owner:JGC CATALYSTS & CHEM LTD
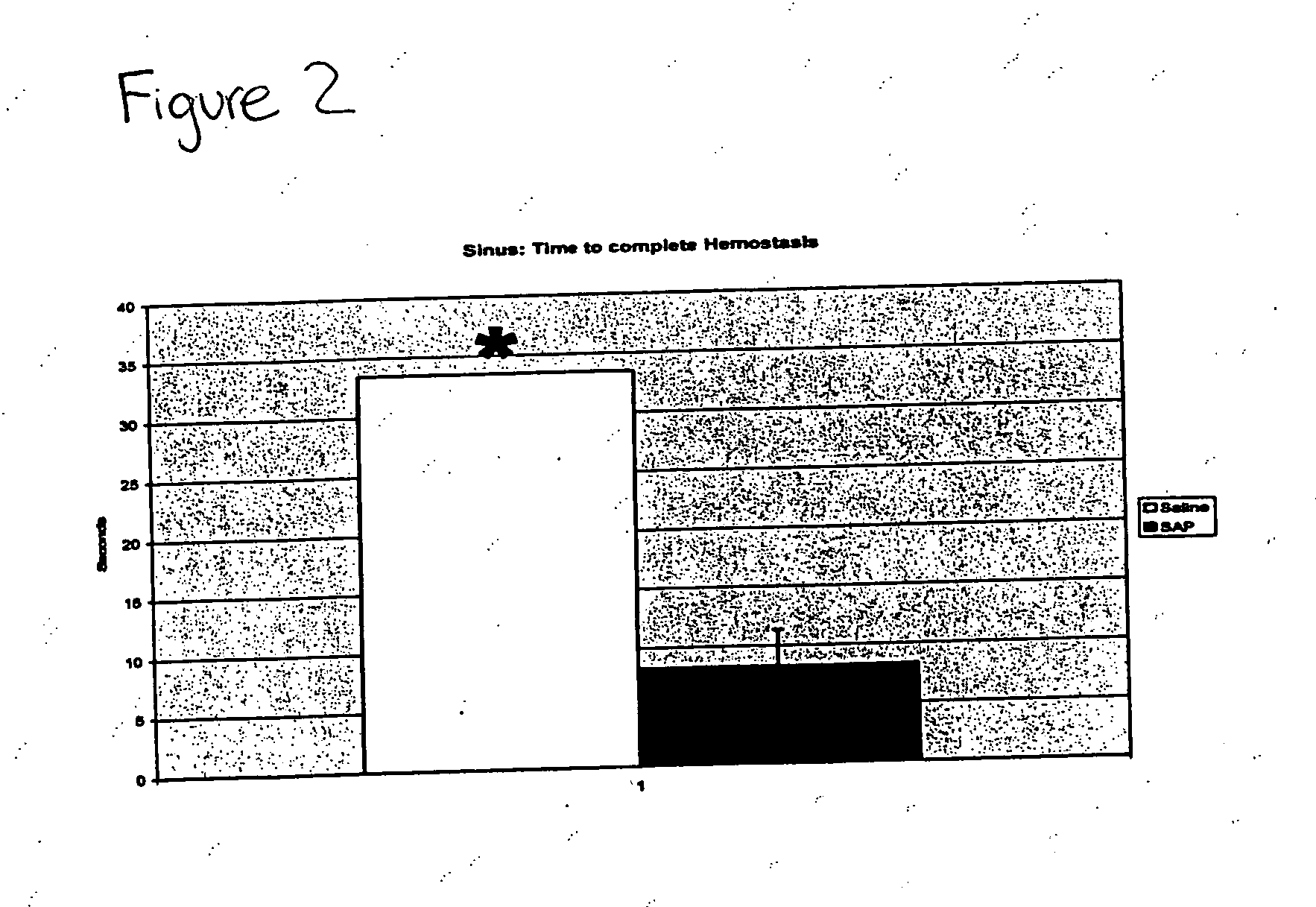
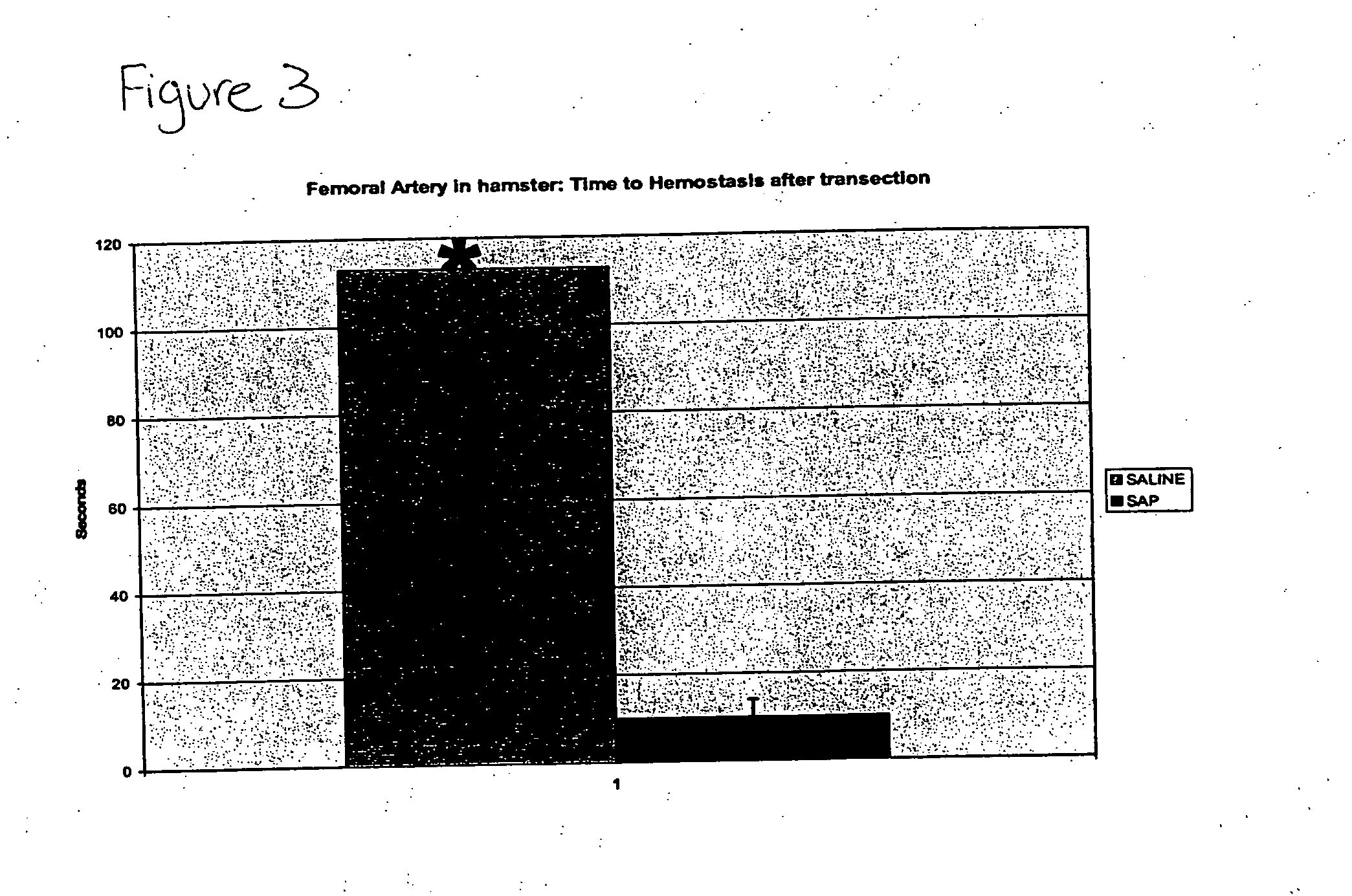
Compositions and methods for promoting hemostasis and other physiological activities
ActiveUS20070203062A1Good hemostasisControl bleedingBiocideTripeptide ingredientsWound dressingVasoconstrictor Agents
Compositions that include nanoscale structured materials or precursors thereof (e.g., self-assembling peptides) are described. The compositions can include other substances (e.g., a vasoconstrictor). Also described are methods for using the compositions to promote hemostasis, to protect the skin or wounds from contamination, to decontaminate a site upon removal of previously applied compositions that provided a protective coating, and to inhibit the movement of bodily substances other than blood. The compositions are also useful in isolating tissue, removing tissue, preserving tissue (for, e.g., subsequent transplantation or reattachment), and as bulking, stabilizing or hydrating agents. Medical devices that include the compositions (e.g., a stent or catheter), bandages or other wound dressings, sutures, and kits that include the compositions are also described.
Owner:VERSITECH LTD +1
Mixed-metal oxide particles by liquid feed flame spray pyrolysis of oxide precursors in oxygenated solvents
Liquid feed flame spray pyrolysis of solutions of a metal oxide precursor which is an alkoxide or C1-6 carboxylate and at least one second metal oxide precursor and / or second metal compound dissolved in oxygenated solvent by combustion with oxygen lead to the formation of sub-micron mixed-metal oxide powders not accessible by other processes or by the pyrolysis of metal chlorides or nitrates. The powders have numerous uses in advanced materials applications including particulate solid state lasers, advanced ceramic materials, and as catalysts in organic synthesis and automobile exhaust systems.
Owner:TAL MATERIALS +1
Process for making durable rutile titanium dioxide pigment by vapor phase deposition of surface treatment
The present invention relates to a process for making durable titanium dioxide pigment by vapor phase deposition of surface treatments on the titanium dioxide particle surface by reacting titanium tetrachloride vapor, an oxygen containing gas and aluminum chloride in a plug flow reactor to form a product stream containing titanium dioxide particles; and introducing silicon tetrachloride into the reactor at a point down stream of the point where the titanium tetrachloride and oxygen were contacted and where at least 97% of the titanium tetrachloride has been converted to titanium dioxide or where the reaction temperature is no greater than about 1200° C., and preferably not more than about 1100° C.
Owner:THE CHEMOURS CO FC LLC
Process for the production of ultrafine particles
A new, cost effective process for the production of ultrafine particles which is based on mechanically activated chemical reaction of a metal compound with a suitable reagent. The process involves subjecting a mixture of a metal compound and a suitable reagent to mechanical activation to increase the chemical reactivity of the reactants and / or reaction kinetics such that a chemical reaction can occur which produces a solid nano-phase substance. Concomitantly, a by-product phase is also formed. This by-product phase is removed so that the solid nano-phase substance is left behind in the form of ultrafine particles. During mechanical activation a composite structure is formed which consists of an intimate mixture of nano-sized grains of the nano-phase substance and the reaction by-product phase. The step of removing the by-product phase, following mechanical activation, may involve subjecting the composite structure to a suitable solvent which dissolves the by-product phase, while not reacting with the solid nano-phase substance. The process according to the invention may be used to form ultrafine metal powders as well as ultrafine ceramic powders. Advantages of the process include a significant degree of control over the size and size distribution of the ultrafine particles, and over the nature of interfaces created between the solid nano-phase substance and the reaction by-product phase.
Owner:WESTERN AUSTRALIA UNIV OF THE
Titanium-containing materials
The invention relates to a method of preparing a solution containing colloidal particles which contain crystalline titanium dioxide wherein one or more hydrolysable titanium-containing compound(s) is stabilised by oxalic acid in a reaction medium. The reaction further relates to the preparation of titania materials (including particulate materials, coating solutions and films) which comprise or include anatase phase titania, and so are suitable in photocatalytic applications. The invention also deals with a method of preparing B-phase titania.
Owner:IND RES LTD
Method of producing nanoparticles using a evaporation-condensation process with a reaction chamber plasma reactor system
InactiveUS20060159596A1Reduce the temperatureMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureNanoparticleReaction zone
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for the controlled synthesis of nanoparticles using a high temperature process. The reactor chamber includes a high temperature gas heated by means such as a plasma torch, and a reaction chamber. The homogenizer includes a region between the reactant inlets and the plasma (the spacer zone) to ensure that feeds from the reactant inlets are downstream of the recirculation zone induced by the high temperature gas. It also includes a region downstream of the reactant inlets that provides a nearly I dimensional (varying only in the axial direction) flow and concentration profile in the reaction zone to produce nanoparticles with narrow size distribution.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
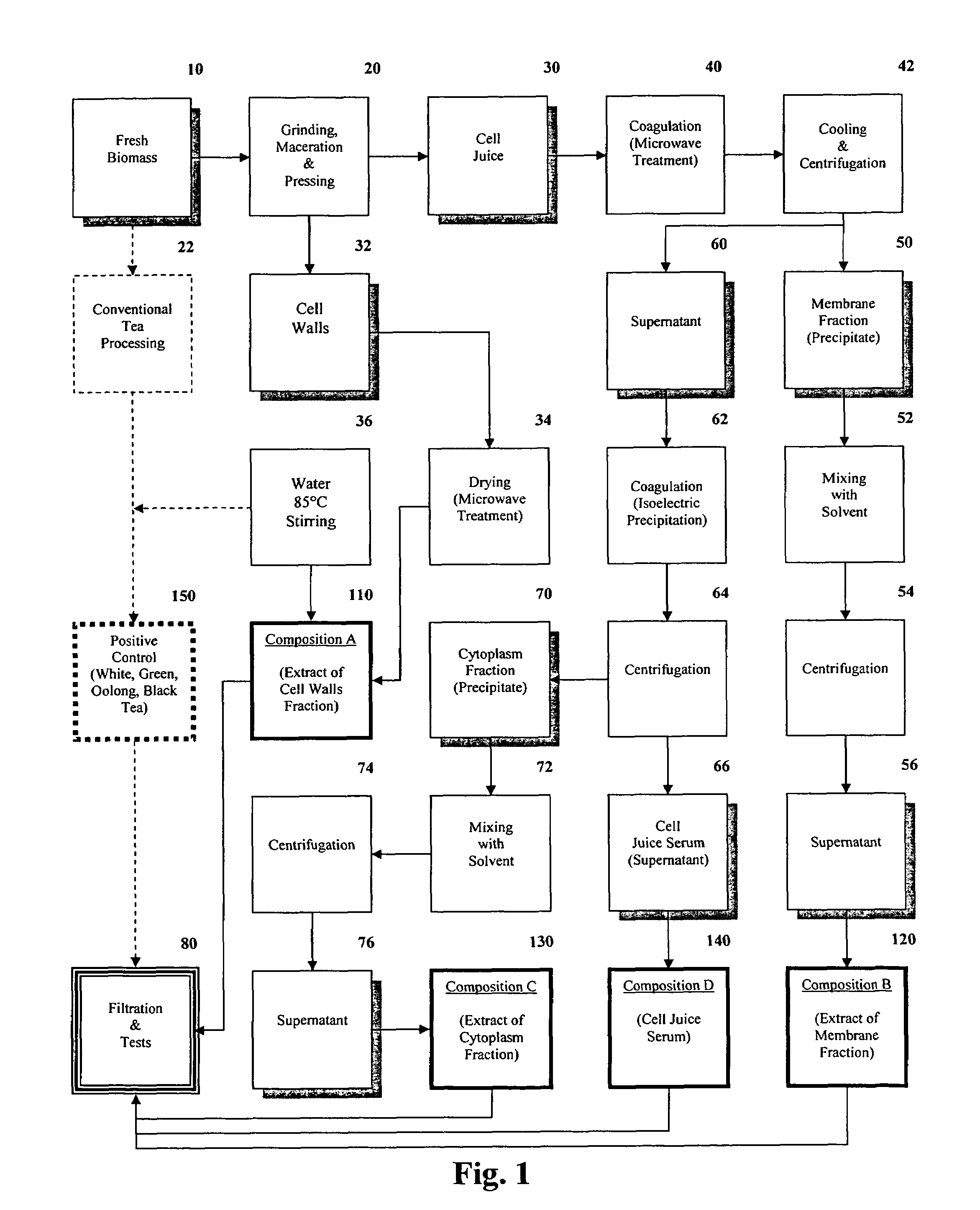
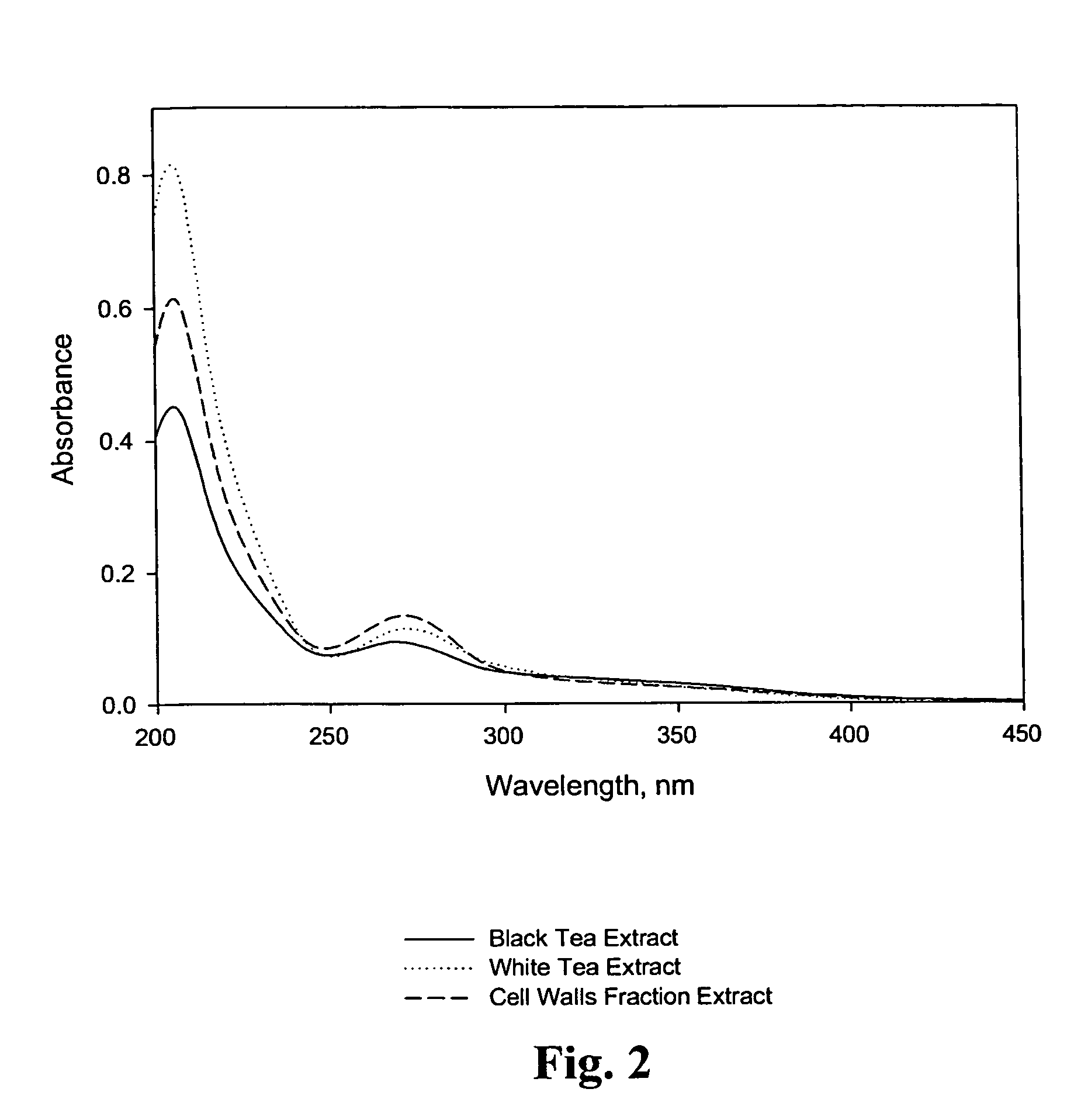
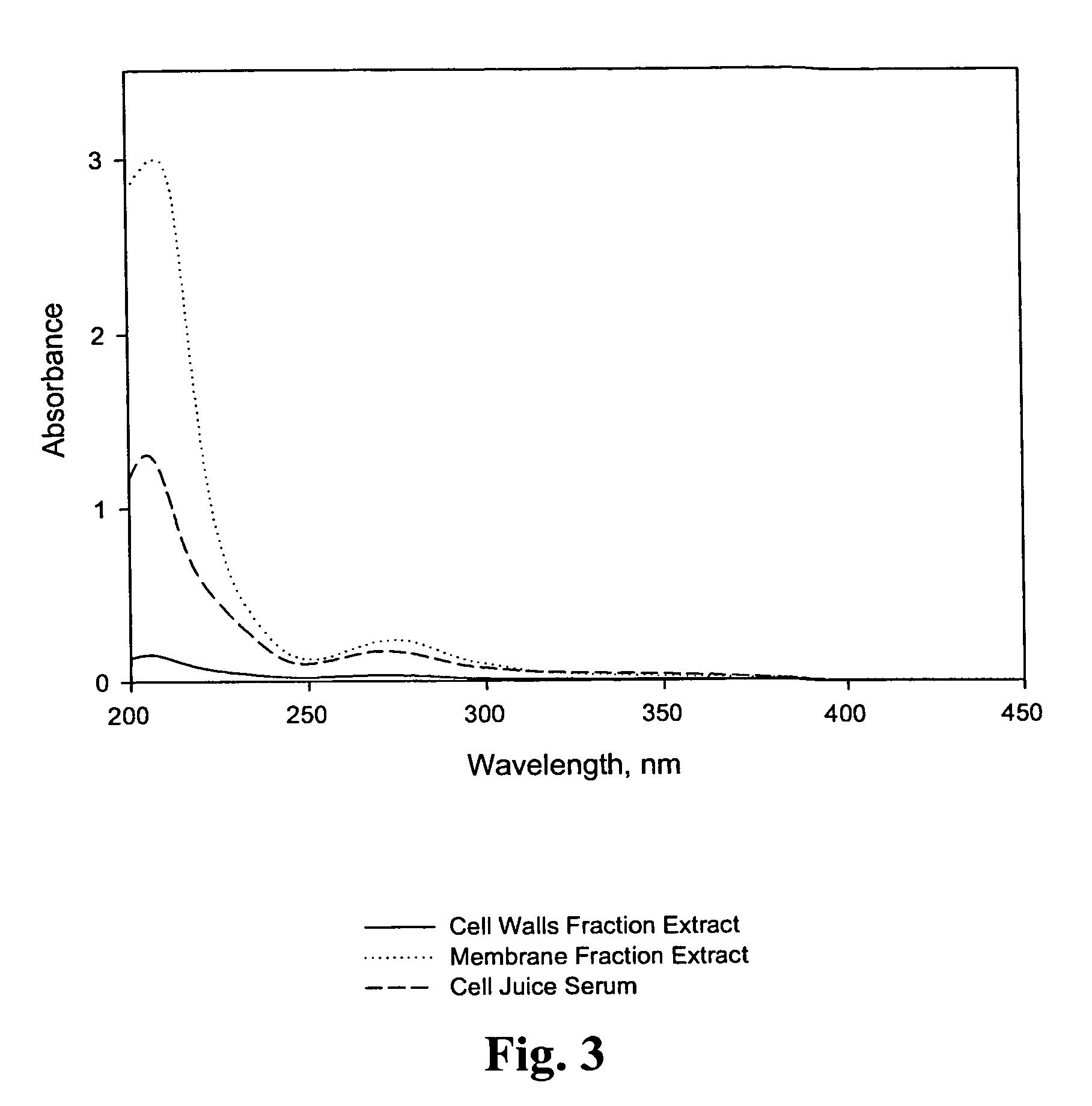
Bioactive compositions from Theacea plants and processes for their production and use
ActiveUS7473435B2Reduce ultraviolet light-induced damageProtects against oxidative damagePigmenting treatmentOrganic active ingredientsUltraviolet lightsCell wall
The present invention relates to isolated bioactive compositions containing bioactive fractions derived from Theacea plants. The present invention also relates to bioactive topical formulations containing the bioactive compositions. The present invention further relates to methods of using the bioactive compositions of the present invention, including, for example, methods for inhibiting inflammatory activity in skin tissue of a mammal, for protecting skin tissue of a mammal from ultraviolet light-induced damage, and for normalizing skin disorders in skin tissue of a mammal. The present invention also relates to methods for isolating bioactive fractions derived from cell juice or a cell walls component a Theacea plant.
Owner:ISP INVESTMENTS LLC
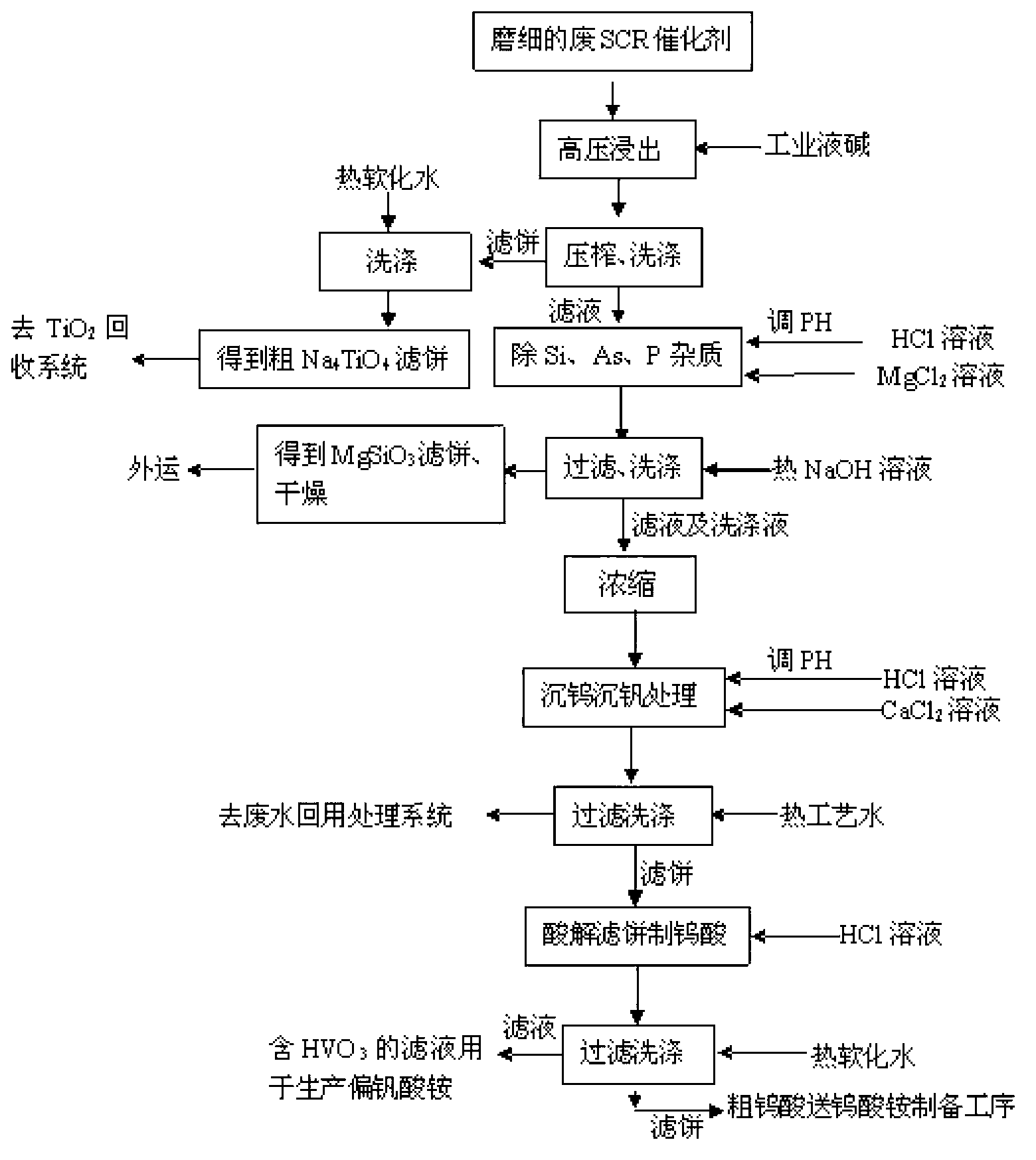
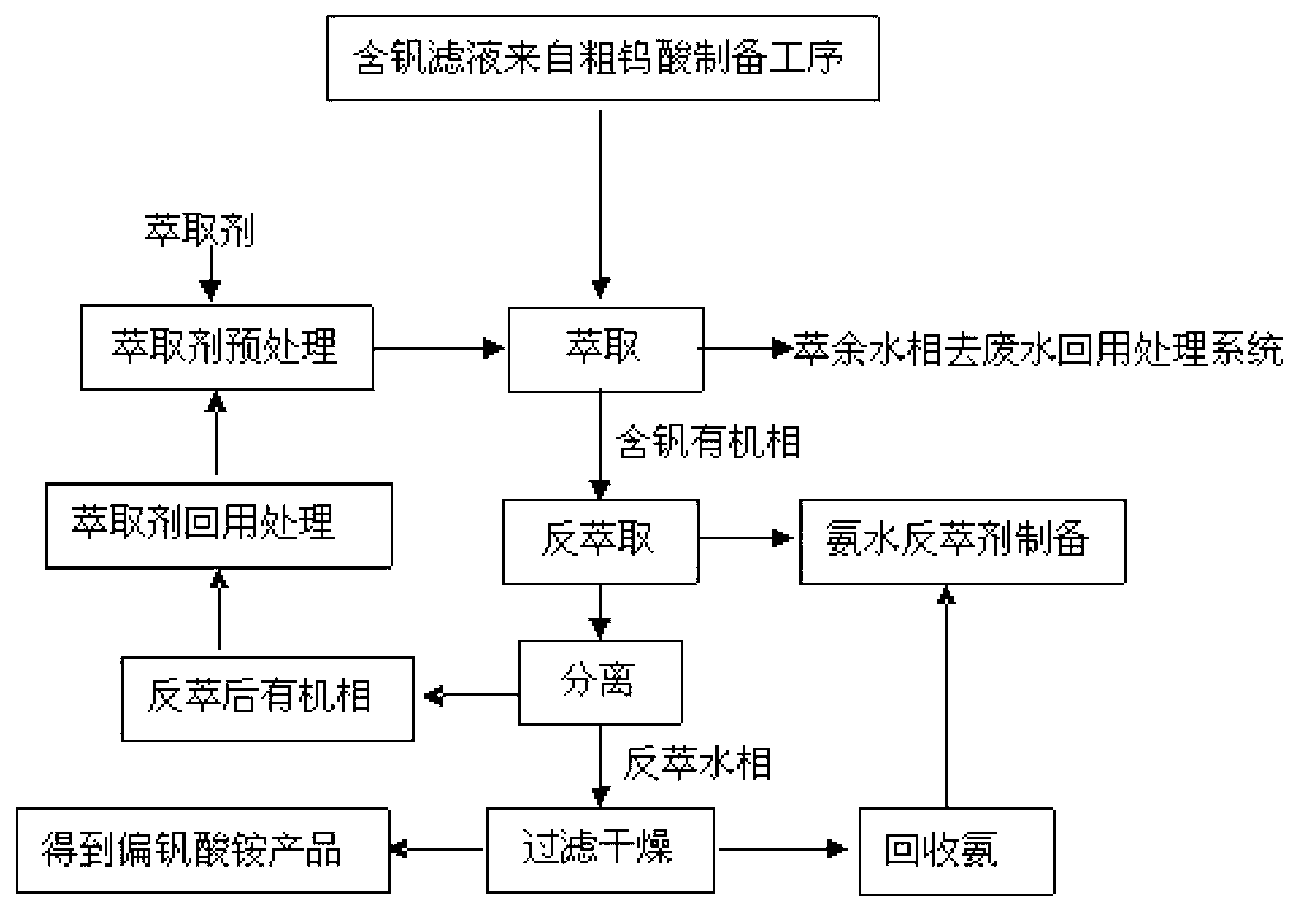
Recovery process of honeycomb type selective catalytic reduction (SCR) waste catalyst containing tungsten, vanadium and titanium
InactiveCN102936039AHigh purityHigh recovery rateTitanium dioxideVanadium compoundsHigh concentrationAmmonium paratungstate
The invention discloses recovery process of honeycomb type selective catalytic reduction (SCR) waste catalyst. The process includes the following steps: a, preprocessing the SCR waste catalyst and leaching at the high temperature and under high pressure; b, adding hydrochloric acid into leaching liquid, adjusting pH, and removing impurities; c, adding hydrochloric acid into the leaching liquid, reacting, calcining and preparing rutile titanium dioxide; d, preparing ammonium paratungstate; e, preparing ammonium metavanadate; and f, recycling and treating waste water. Main products of ammonium paratungstate, ammonium metavanadate and rutile titanium dioxide obtained in the process are high in purity and recovery rate. By-products of silicon magnesium slags, salty mud, high-concentration sodium chloride liquid and barium sulfate dregs are high-purity harmless useful goods. The process is free of harmful secondary pollutant emission, environment-friendly and capable of circulating, has high economical and social benefit and is practicable.
Owner:曾瑞
Titanium dioxide nanopowder manufacturing process
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Process for preparing titanium dioxide nano-belts
The invention provides a method for preparing a titanium dioxide nano belt, belonging to the nano material technical field. The prior methods for preparing the titanium dioxide nano belt comprise the hydro-thermal method and the combination method of the sol-gel method and the hydro-thermal method. The prior electrostatic spinning method is applied to the preparation of nano fibers. The invention comprises three steps that: 1. a spinning solution is prepared; the mixture of polymethylmethacrylate and vinylpyrrolidone is used as a macromolecule template, and the mixture of chloroform and N,N-dimethylformamide is used as a solvent; 2. a titanium alkoxide / macromolecule template compound nano belt is prepared; the electrostatic spinning method is used, and the technical parameters are as follows: the voltage is between 15 and 25kV and the curing distance is between 15 and 30cm; 3. a TiO2 nano belt is prepared; the heat treatment method is used, and the technical parameters are as follows: the rate of temperature rise is between 0.5 and 2 DEG C / min and the heat preservation time at the temperature of between 500 and 900 DEG C is between 10 and 15h; for the TiO2 nano belt prepared, the width is between 5 and 15mu m, the thickness is between 30 and 60nm and the length is more than 200mu m; the TiO2 nano belt comprises a pure phase anatase type TiO2 nano belt and a pure phase rutile type TiO2 nano belt.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for extracting tungsten, titanium and vanadium from waste SCR (selective catalytic reduction) catalyst
InactiveCN102936049ASolve the pollution of the environmentLow equipment requirementsTungsten oxides/hydroxidesTitanium dioxideSlagStrong acids
The invention discloses a method for extracting tungsten, titanium and vanadium from a waste SCR (selective catalytic reduction) catalyst, which comprises the following steps: crushing the waste SCR catalyst, adding a strongly alkaline solution, and reacting; filtering, separating, then adding strong acid into the sodium tungstate and sodium vanadate mixed solution, and reacting to obtain tungstic acid and a sodium salt and vanadic acid mixed solution; regulating the pH value of the sodium salt and vanadic acid mixed solution until precipitate is separated out, thus obtaining ammonium vanadate; then adding sulfuric acid into the tungsten-and-vanadium-removed SCR catalyst, and reacting to obtain a titanyl sulfate solution and solids such as aluminum slag and the like; then adding water into the titanyl sulfate solution, and hydrolyzing to obtain titanic acid and a waste acid solution; and finally, respectively calcining the obtained ammonium vanadate, tungstic acid and titanic acid to obtain vanadium pentoxide, tungsten trioxide and titanium dioxide. According to the invention, tungsten, titanium and vanadium can be extracted from the SCR catalyst through the reaction with strong alkali and strong acid at a low temperature, the equipment requirement is low, the energy consumption is low, some products having added values can be coproduced, and no secondary pollution is generated, thereby facilitating popularization and application.
Owner:成都新智金森环保科技有限公司
Methods for producing pattern-forming body
InactiveUS7252923B2Improve accuracyEffect can be problematicMaterial nanotechnologyPhotosensitive materialsEngineeringPost exposure
A method of producing a pattern-forming body with high accuracy with no need for a post-exposure treatment and without allowing any photocatalyst to remain in the resultant pattern-forming body and whereby any problematic effect of the photocatalyst in the pattern-forming body is eliminated. The method includes providing a photocatalyst-containing layer-sided substrate and a pattern-forming body substrate having a characteristic-changeable layer, which is changed by the effect of the photocatalyst in the photocatalyst-containing layer, and a light-shading part formed as a pattern in such a manner that the photocatalyst-containing layer and the characteristic-changeable layer are brought into contact with each other, followed by exposure on the side of the pattern-forming body substrate to change the characteristics of the characteristic-changeable layer of the exposed part, followed by removing the photocatalyst-containing layer-sided substrate.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
Apparatus for making metal oxide nanopowder
InactiveUS20070292321A1Reduce decreaseEliminate coarse tailMaterial nanotechnologyOxygen/ozone/oxide/hydroxideReaction zoneCooling fluid
There is described an apparatus for making metal oxide particles which are substantially free of coarse tail from an oxidizing agent and a metal reactant in a flow reactor. The apparatus can be a concentric tubular flow reactor comprising a substantially funnel-shaped reactant contacting region located adjacent to a reaction zone which is able to direct a flow of a hot oxidizing agent towards a flow of the metal reactant to form a reaction stream which flows downstream into a reaction zone, whereby the hot oxidizing agent of the reaction stream is able to surround the flow of metal reactant sufficient to prevent the metal reactant from contacting the wall of the reactant contacting region and forming scale on the wall. A cooling fluid conduit being able to direct a flow of a cooling fluid into the reaction zone to flow coaxially with the reaction stream and to form a fluid curtain between the reaction stream and a baffle, which defines at least a portion of the reaction zone, while the metal reactant and hot oxidizing agent within the reaction stream react to form the metal oxide nanopowder prevents scale from forming on the baffle.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Porous material having hierarchical porous structure and preparation method thereof
Disclosed are porous ceramic balls with a hierarchical porous structure ranging in size from nanometers to micrometers, and preparation methods thereof. Self-assembly polymers and sol-gel reactions are used to prepare porous ceramic balls in which pores ranging in size from ones of nanometers to tens of micrometers are hierarchically interconnected to one another. This hierarchical porous structure ensures high specific surface areas and porosities for the porous ceramic balls. Further, the size and distribution of the pores can be simply controlled with hydrophobic solvent and reaction time. The pore formation through polymer self-assembly and sol-gel reactions can be applied to ceramic and transition metals. Porous structures based on bioceramic materials, such as bioactive glass, allow the formation of apatite therein and thus can be used as biomaterials of bioengineering, including bone fillers, bone reconstruction materials, bone scaffolds, etc.
Owner:KOREA INST OF MATERIALS SCI
Methods of preparing a surface-activated titanium oxide product and of using same in water treatment processes
InactiveUS6919029B2Inhibit dissolution and migrationMaterial nanotechnologyOther chemical processesHigh rateTitanium
A method for producing a surface-activated crystalline titanium oxide product having a high adsorptive capacity and a high rate of adsorption with respect to dissolved contaminants includes the steps of preparing a titanium oxide precipitate from a mixture comprising a hydrolysable titanium compound and heating the precipitate at a temperature of less than 300° C., without calcining the precipitate. Preferably, the titanium oxide product includes crystalline anatase having primary crystallite diameters in the range of 1-30 nm. The surface-activated crystalline titanium oxide product is used in methods to remove dissolved inorganic contaminants from dilute aqueous streams by suspending the product in an aqueous stream or by filtering an aqueous stream through a bed of the product. In another method, a hydrolysable titanium compound is added to an aqueous stream so that titanium oxides form as a co-precipitate with dissolved contaminants within a bed of particulate material.
Owner:STEVENS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Metal oxide particle and its uses
InactiveUS20070154561A1High transparencyPromote absorptionMaterial nanotechnologyBiocideAcyl groupUltraviolet absorption
An object of the present invention is to provide a metal oxide particle which exercises more excellent ultraviolet absorbency as a matter of course and combines therewith merits of, for example, either being shifted in ultraviolet absorption edge toward the longer wavelength side and being excellent also in the absorption efficiency of a long-wavelength range of ultraviolet rays, or having good transparency and, for example, even in cases where added into or coated onto substrates, not damaging the transparency or hue of the substrates. As a means of achieving this object, a metal oxide particle according to the present invention is a metal oxide particle such that a hetero-element is contained in a particle comprising an oxide of a specific metal element (M), wherein the metal oxide particle is: 1) a metal oxide particle in the form of a fine particle wherein the hetero-element is at least one specific metal element (M′); 2) a metal oxide particle wherein the hetero-element includes at least two specific metal elements (M′); 3) a metal oxide particle wherein: the hetero-element is a more specified metal element (M′) and at least a part thereof is 2 in valence; or the metal element (M) is a more specified metal element and the metal oxide particle is in a specific range in crystal grain diameter in the vertical direction to each of the (002) plane and the (100) plane; or 4) a metal oxide particle wherein: the hetero-element is at least one specific nonmetal element and an acyl group is contained in the particle; or the hetero-element includes at least two specific nonmetal elements; or the hetero-element is at least one specific nonmetal element and a component derived from a metal element (M′) other than the metal element (M) is contained in the particle.
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
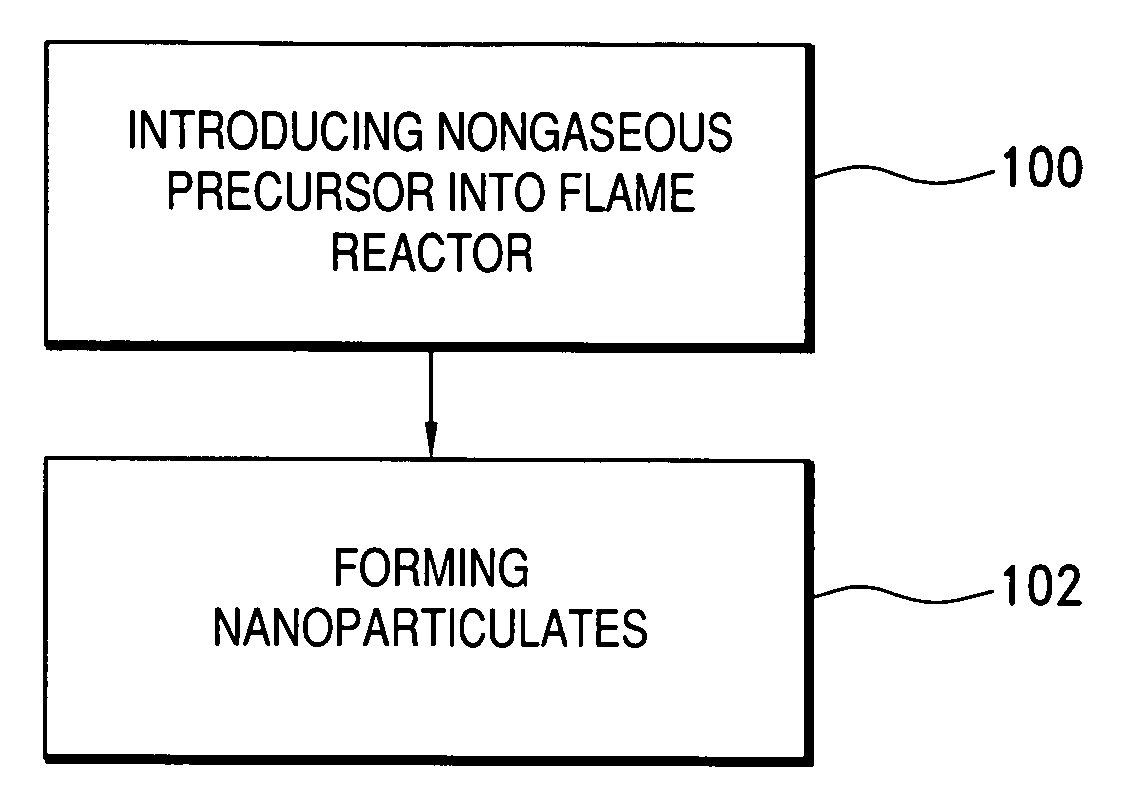
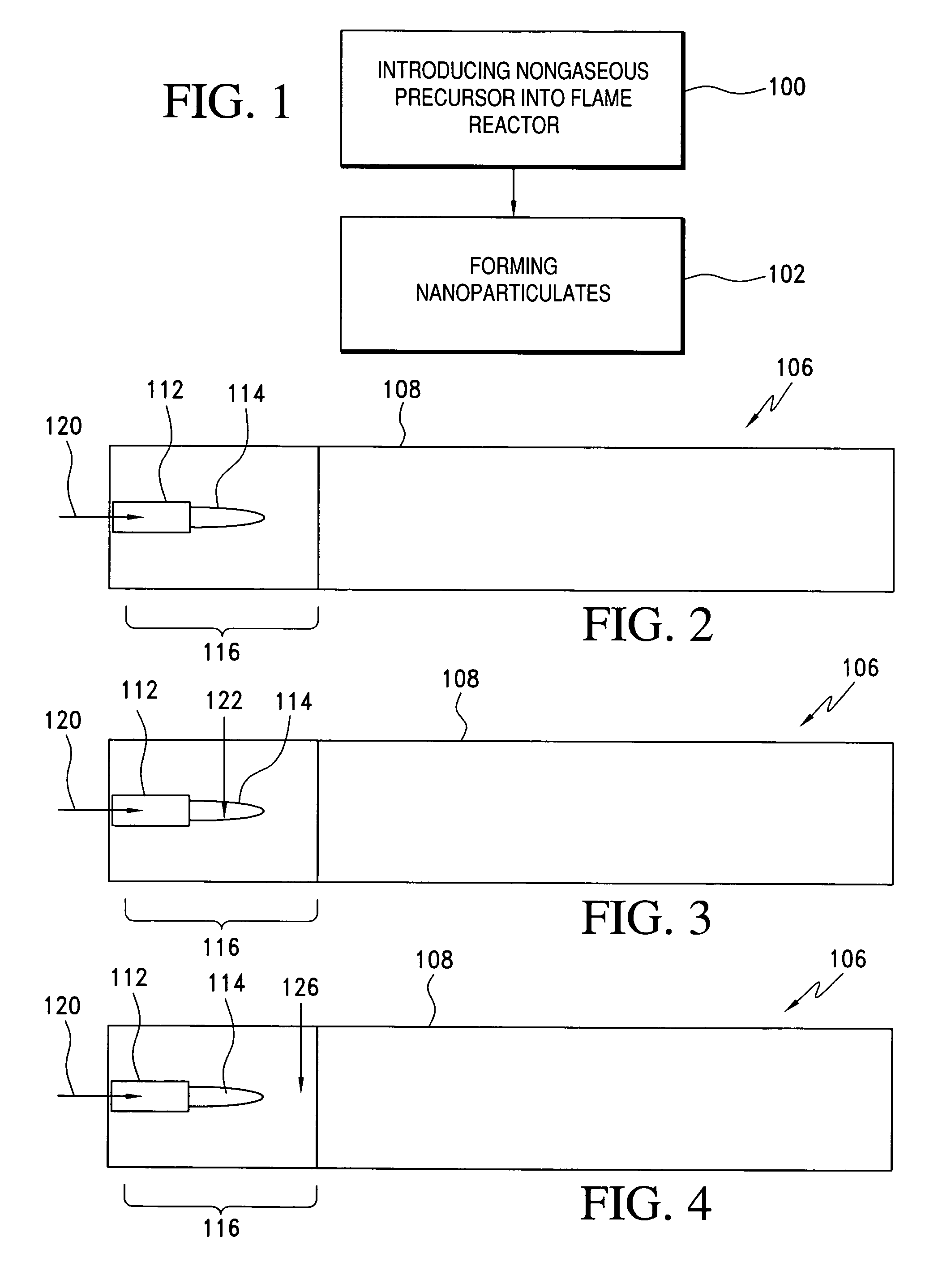
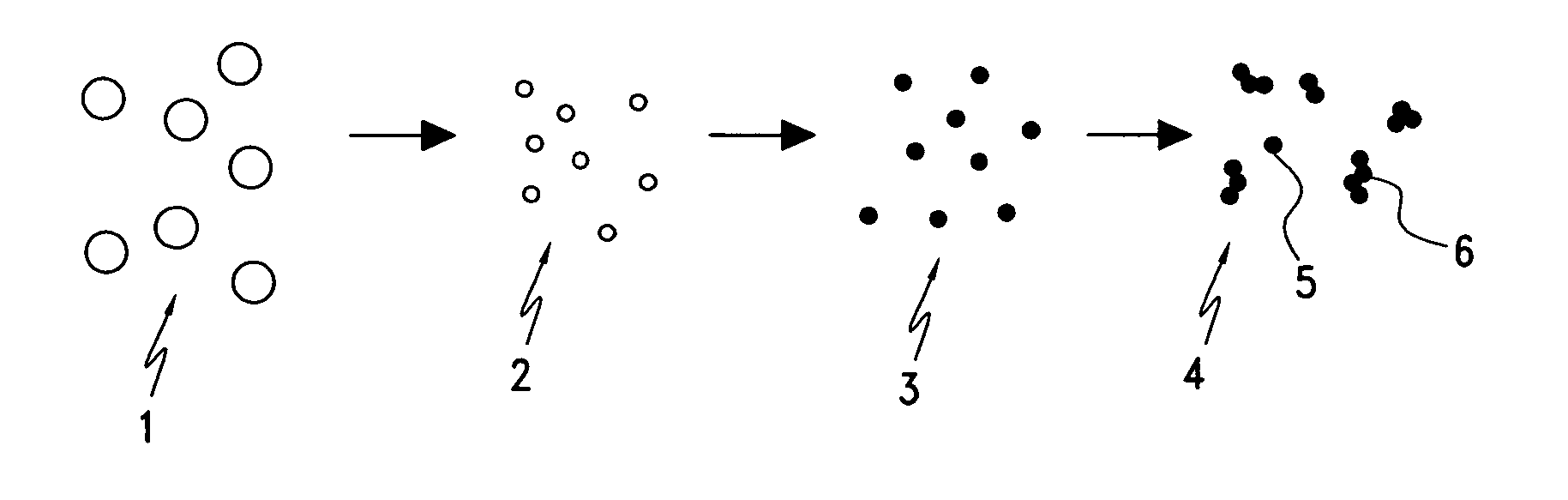
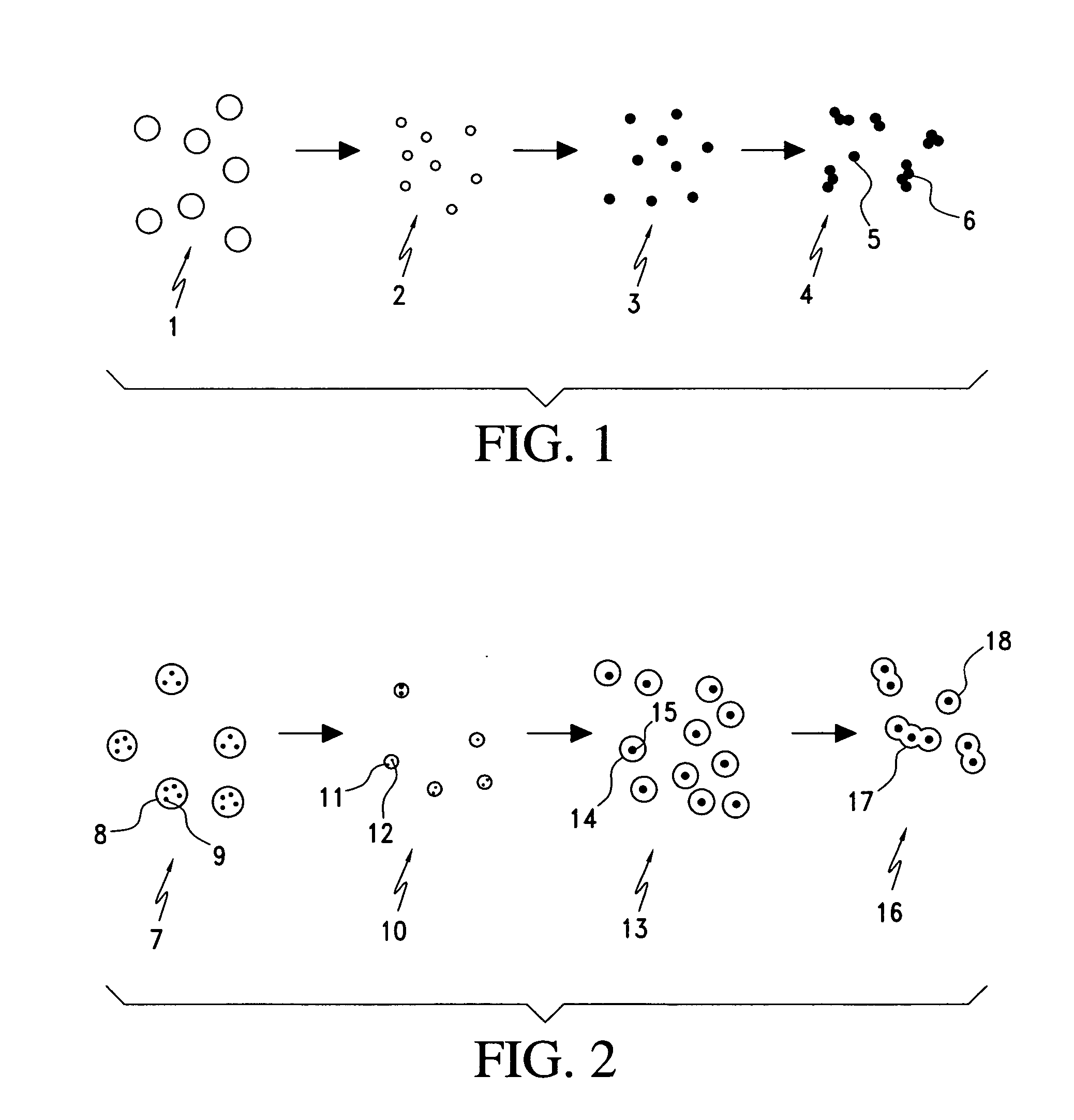
Method of making nanoparticulates and use of the nanoparticulates to make products using a flame reactor
InactiveUS20060166057A1Easy to joinLower melting temperatureMaterial nanotechnologyBurnersMulti materialNanoparticle
The present invention relates to a method of making nanoparticulates in a flame reactor, the nanoparticulates having controlled properties such as weight average particle size, composition and morphology. The nanoparticulates made with the method of present invention may be tailored to a specific weight average particle size range, such as from about 1 nm to about 500 nm. In addition to weight average particle size, the nanoparticulates made with the method of the present invention may include a variety of materials including metals, ceramics, organic materials, and combinations thereof. Moreover, the method of the present invention allows control over the morphology of the nanoparticulates, which allows the production of nanoparticulates with any desired morphology including spheroidal and unagglomerated; and agglomerated (aggregated) into larger units of hard aggregates.
Owner:CABOT CORP
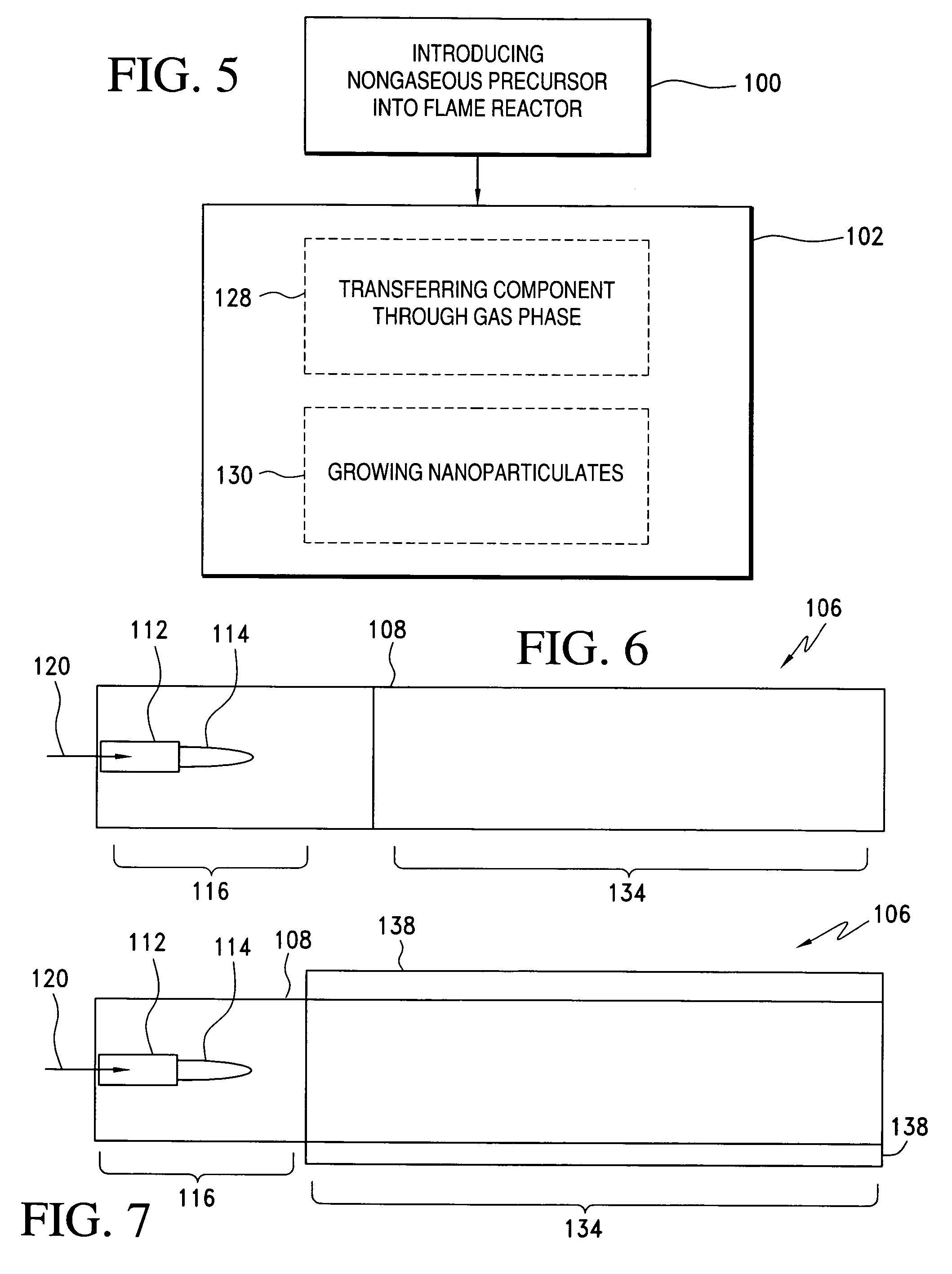
Processes for forming nanoparticles in a flame spray system
In one aspect, the process includes providing a precursor medium comprising a liquid vehicle and a precursor to a component, and flame spraying the precursor medium under conditions effective to form a population of nanoparticles, wherein the nanoparticles include the component. The population of nanoparticles, as formed, comprises less than about 5 percent by volume particles having a particle size greater than 1.0 μm. A size distribution of the population of nanoparticles may have a d50 value less than about 500 nm, and it may be unimodal. The size distribution may have a geometric standard deviation of less than about 2. The process may occur continuously for at least four hours or more. Greater than about 90 percent by weight of the precursor to the component in the precursor medium may be converted to the component in the nanoparticles. The process typically occurs in an enclosed flame spray reactor.
Owner:CABOT CORP
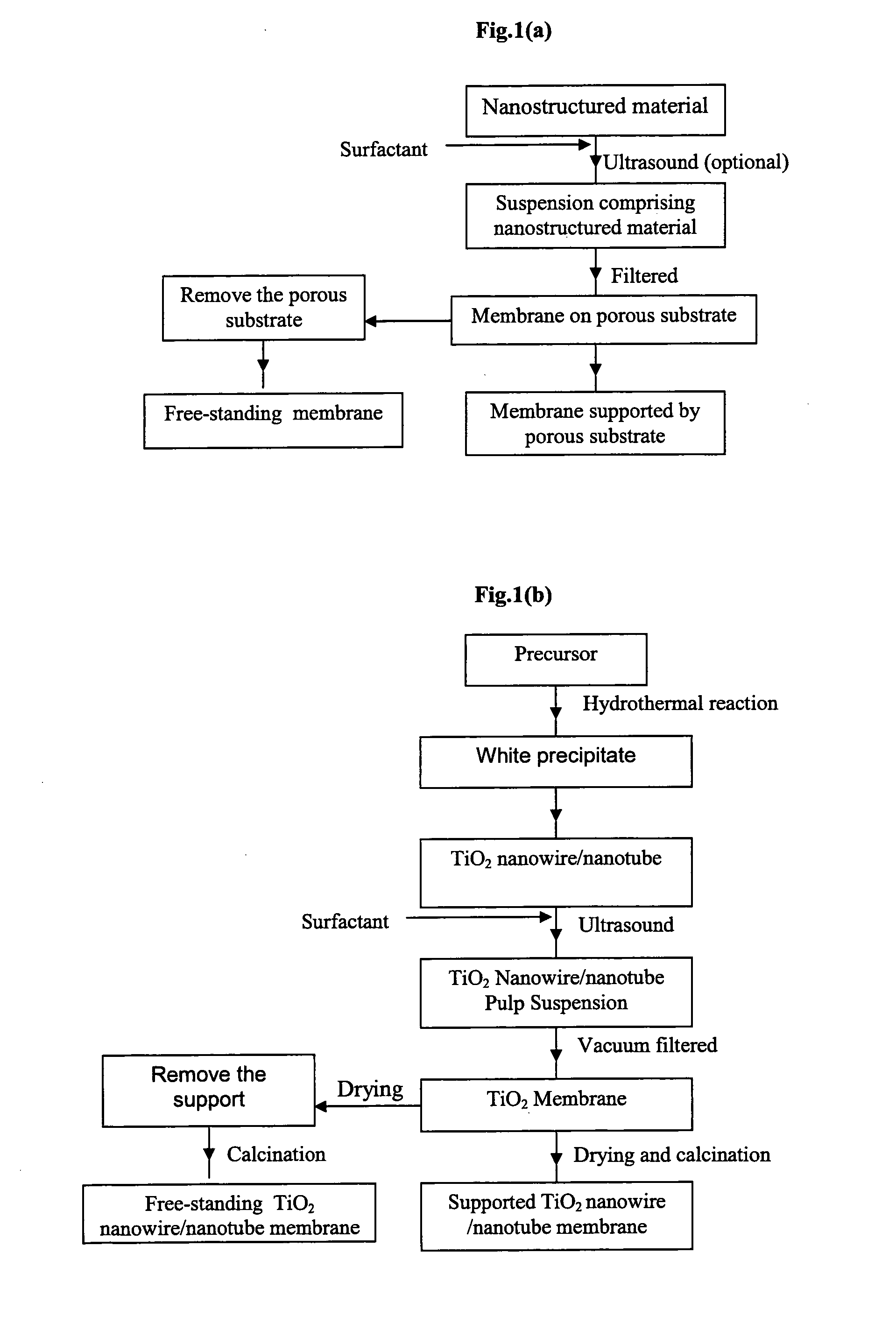
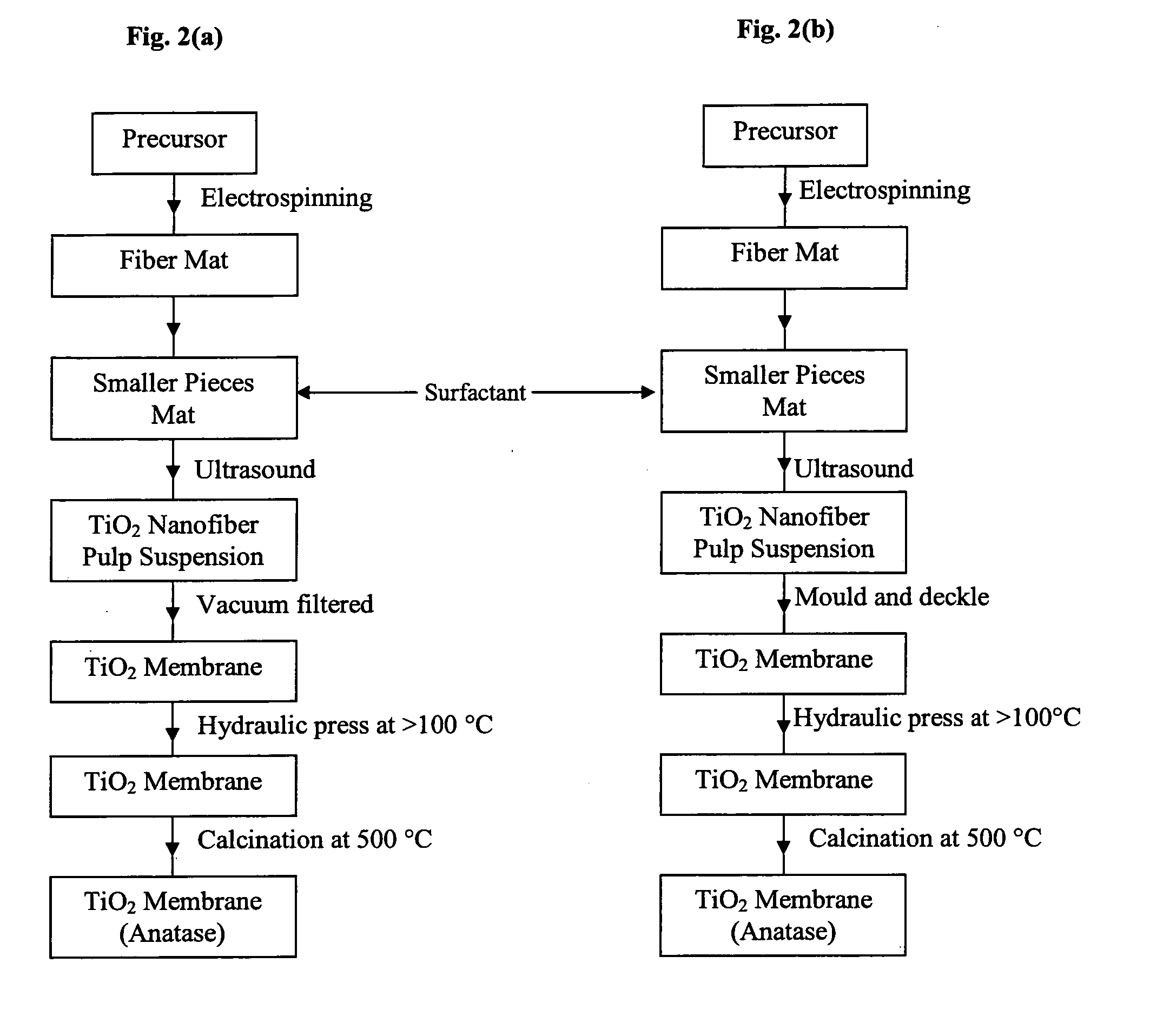
Membrane made of a nanostructured material
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV +1
Superhydrophobic and self-cleaning powders and fabrication method thereof
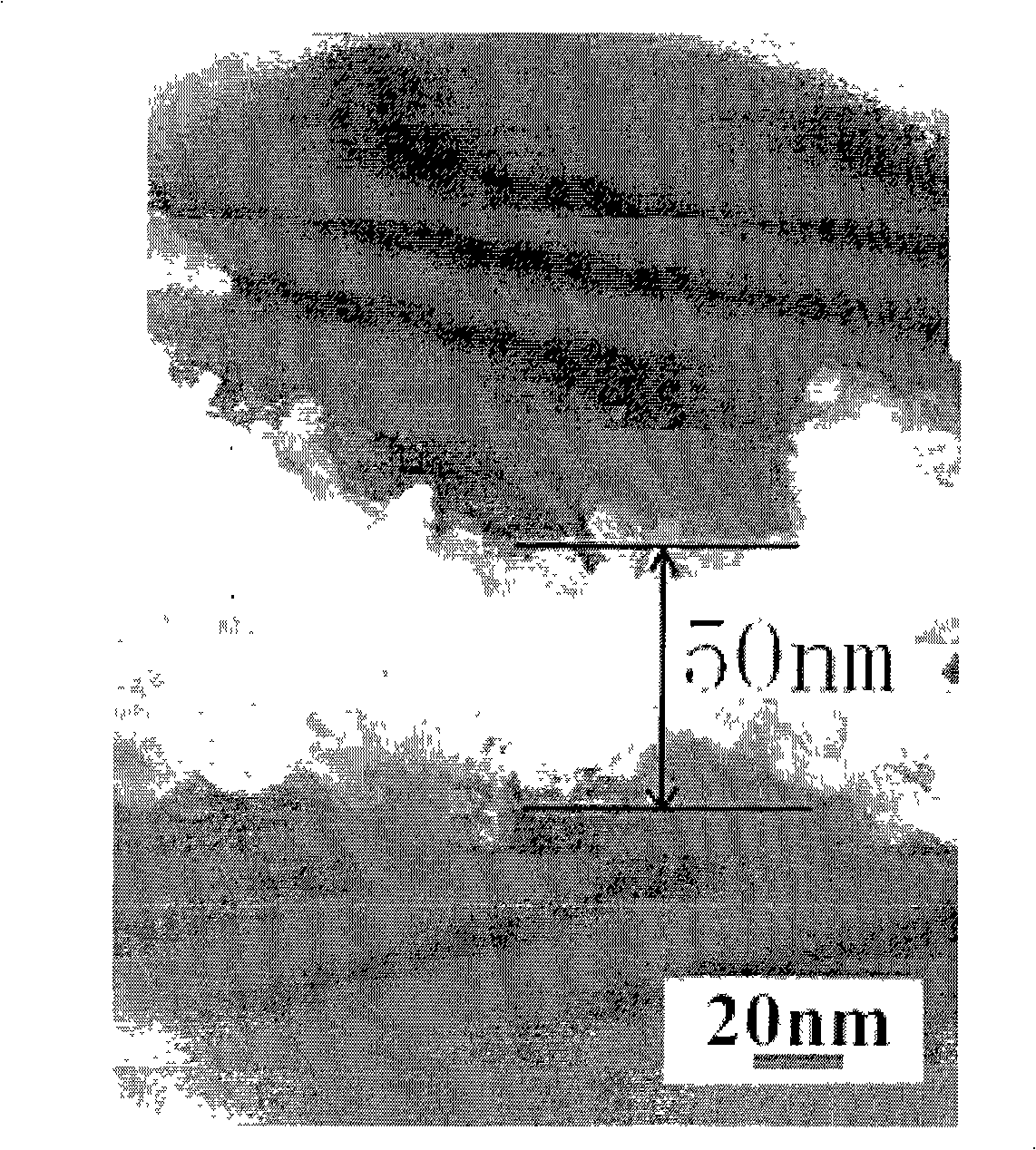
The invention discloses nano / micron binary structured powders for superhydrophobic, self-cleaning applications. The powders are featured by micron-scale diameter and nano-scale surface roughness. In one embodiment, the average diameter is about 1-25 μm, and the average roughness Ra is about 3-100 nm. The nano / micron binary structured powders may be made of silica, metal oxide, or combinations thereof.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com