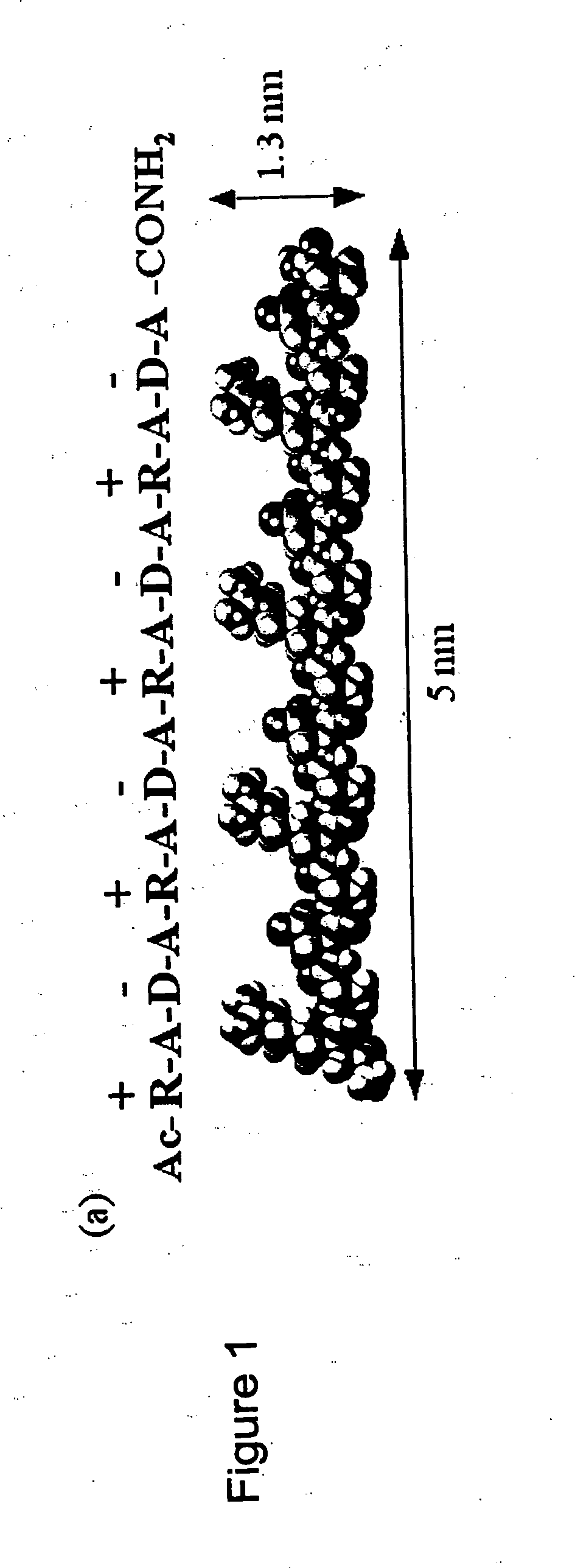
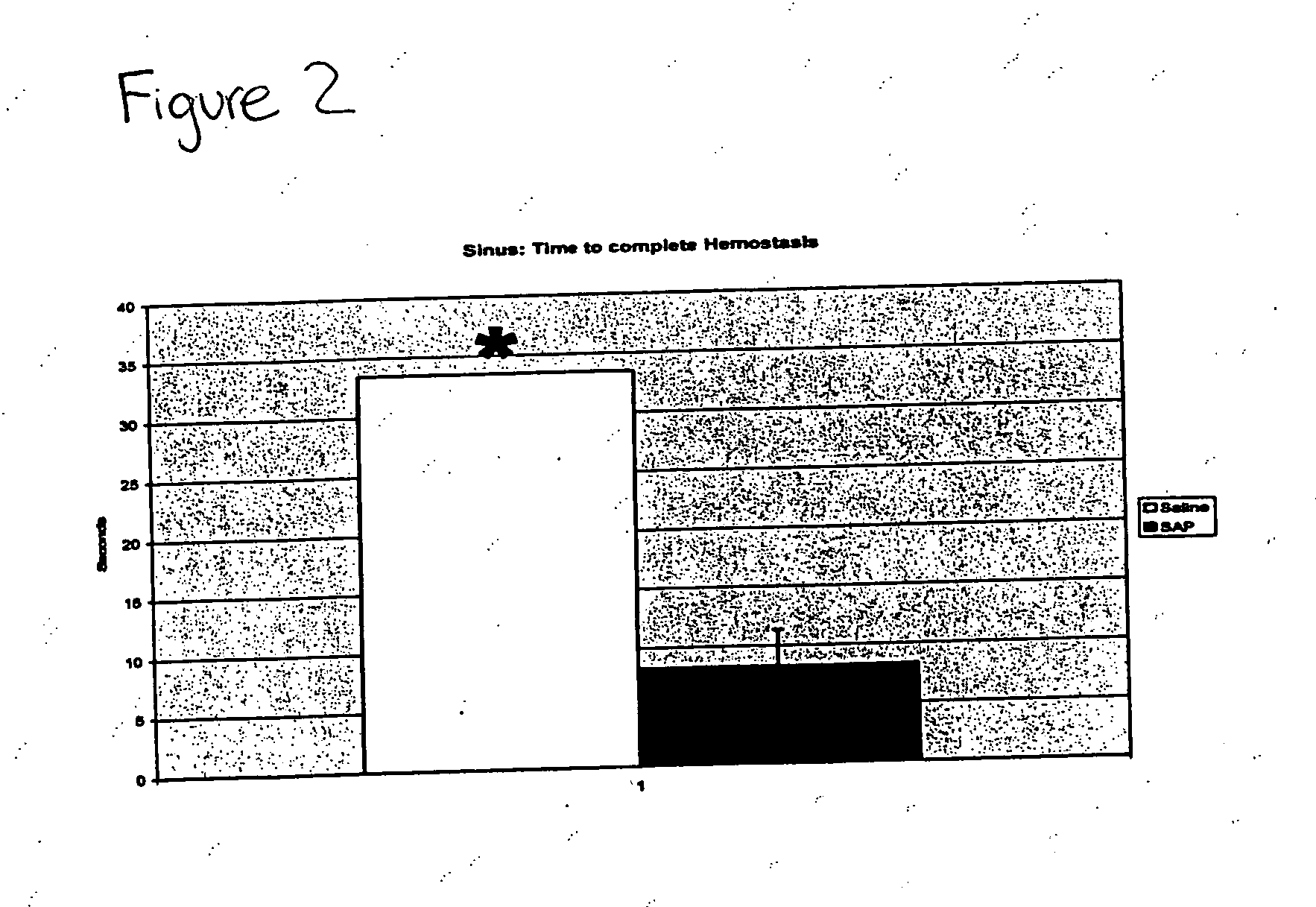
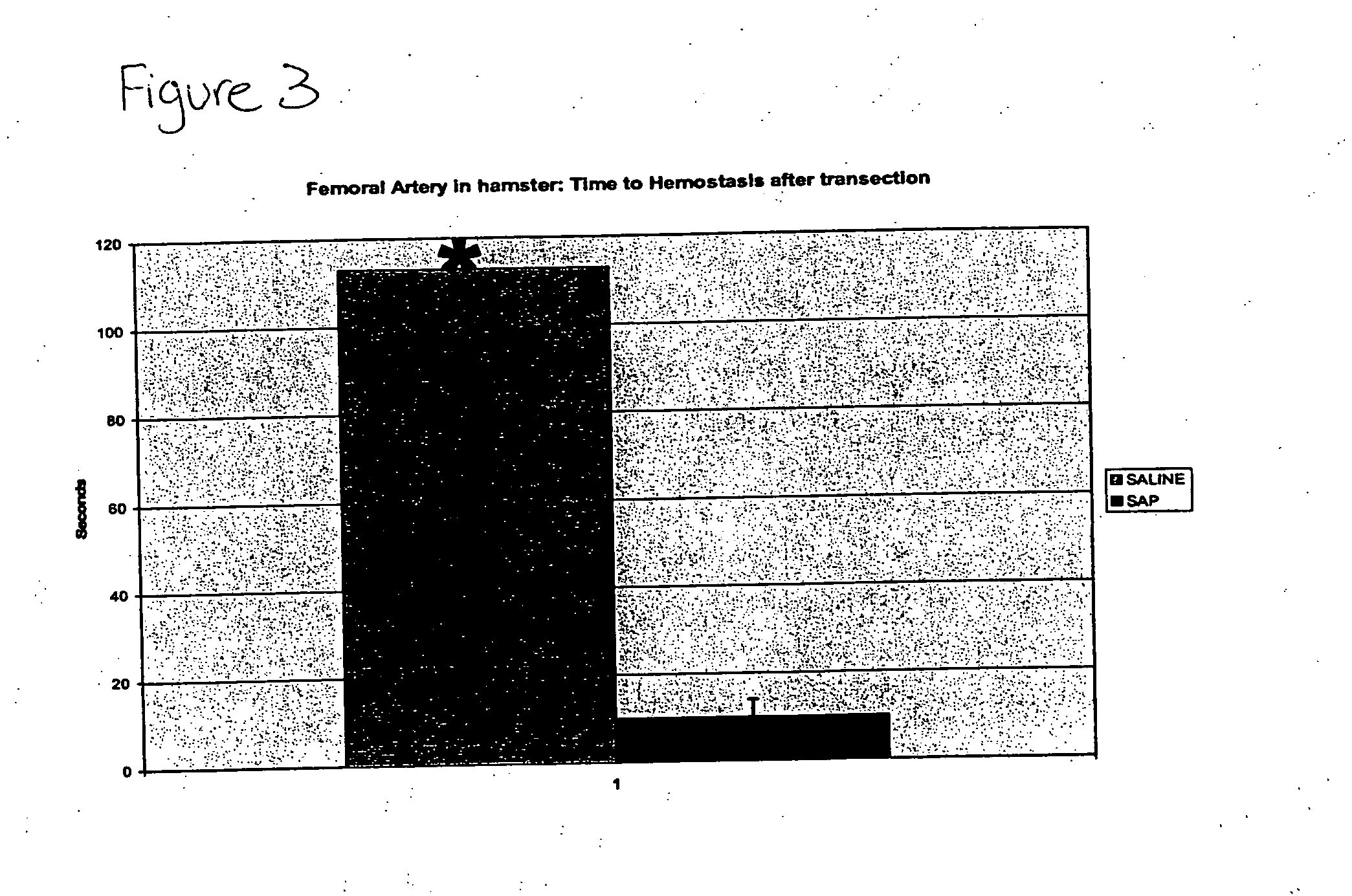
Patents
Literature
841results about How to "Good hemostasis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
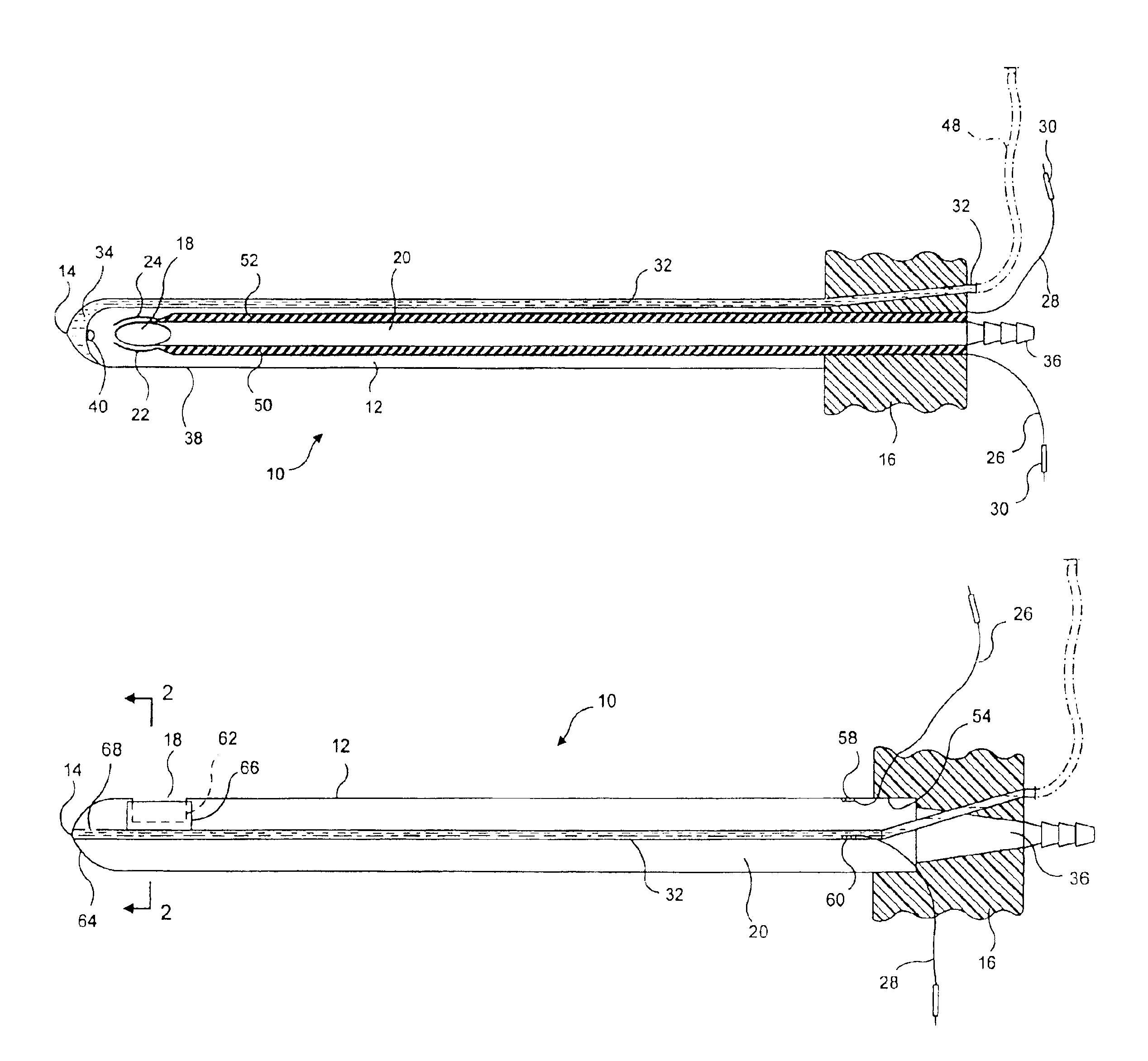
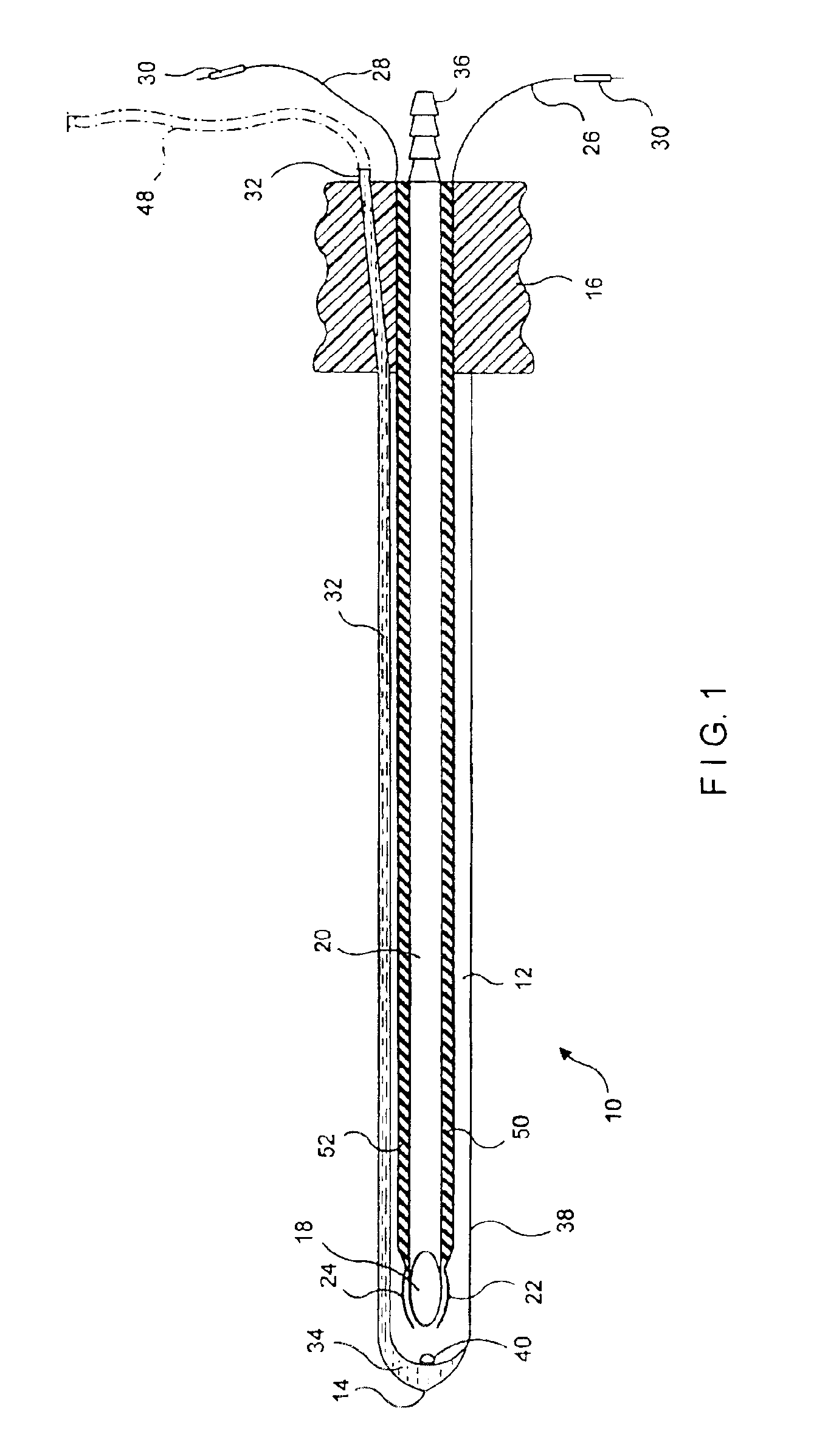
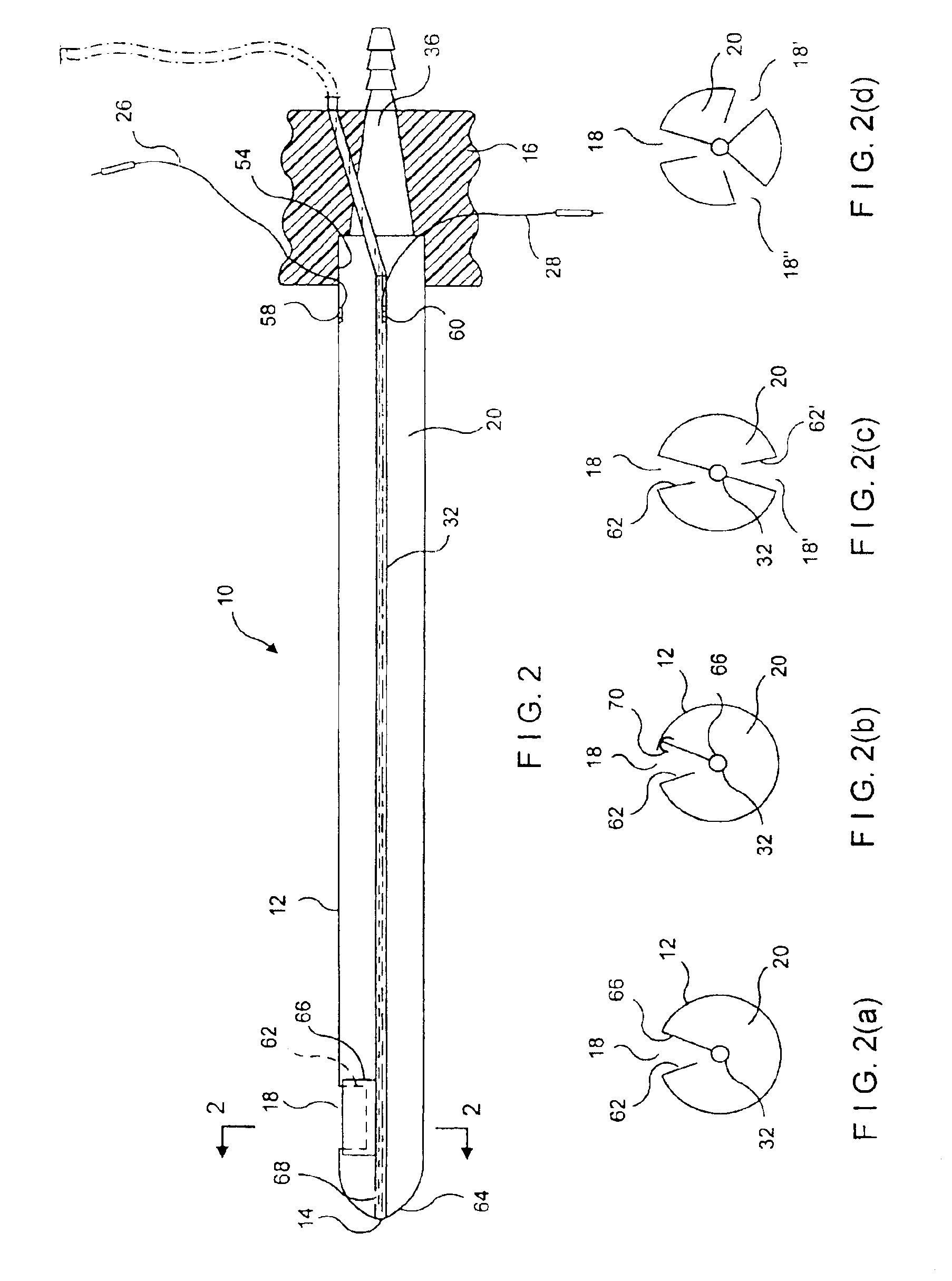
Coagulating electrosurgical instrument with tissue dam
InactiveUS20050004569A1Reduce heat damageGood hemostasisSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical forcepsBipolar electrosurgeryBiomedical engineering
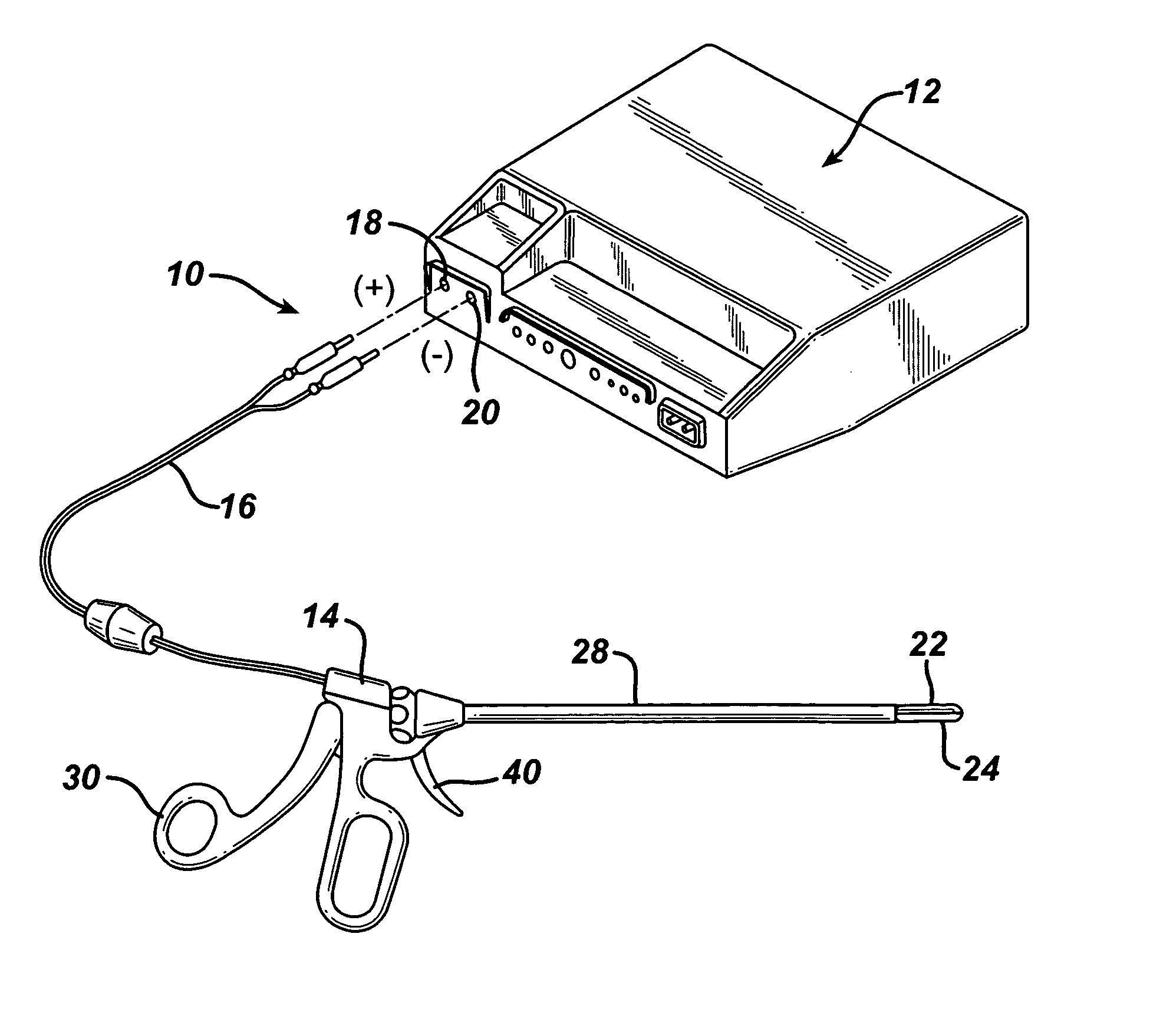
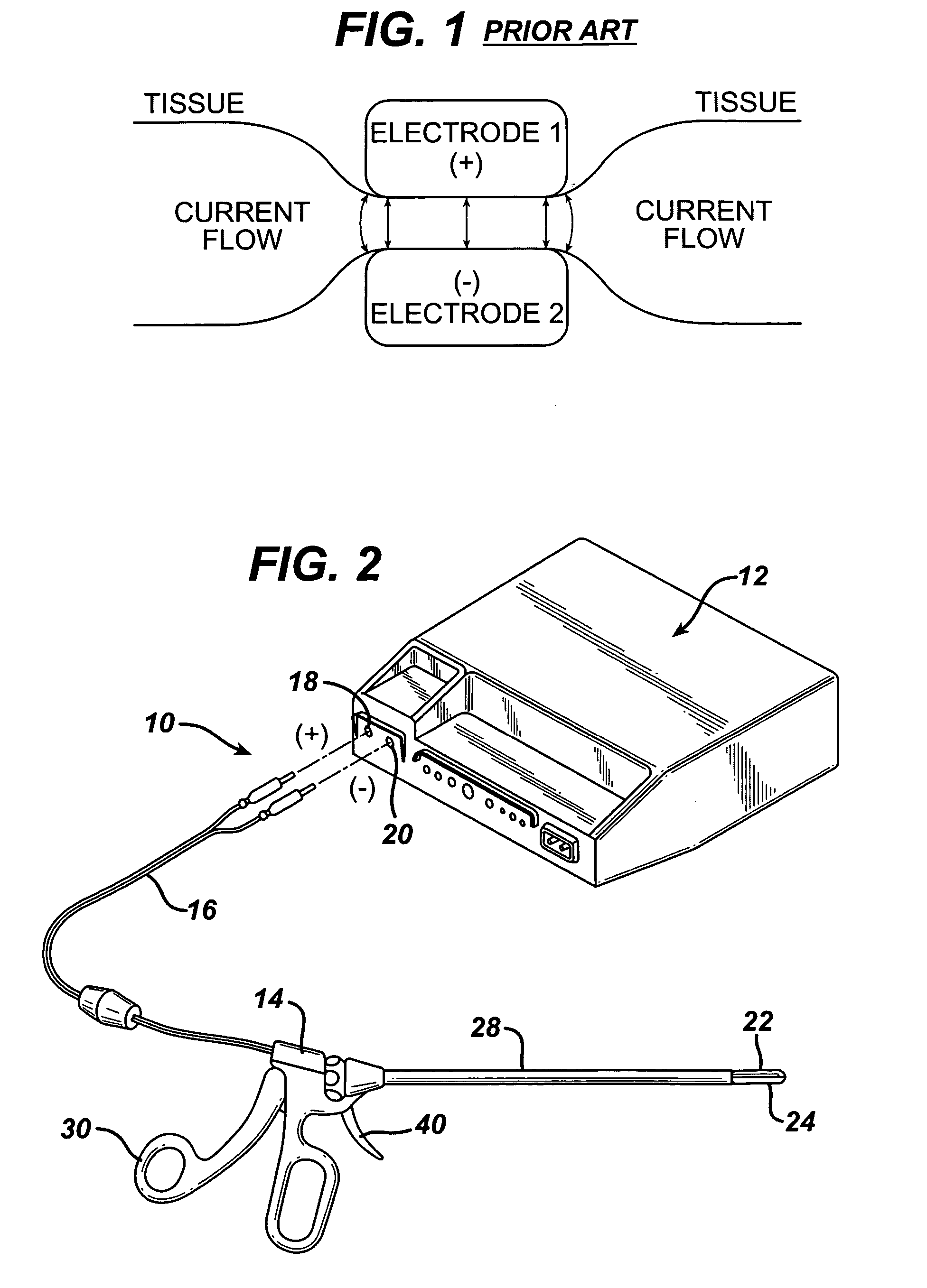
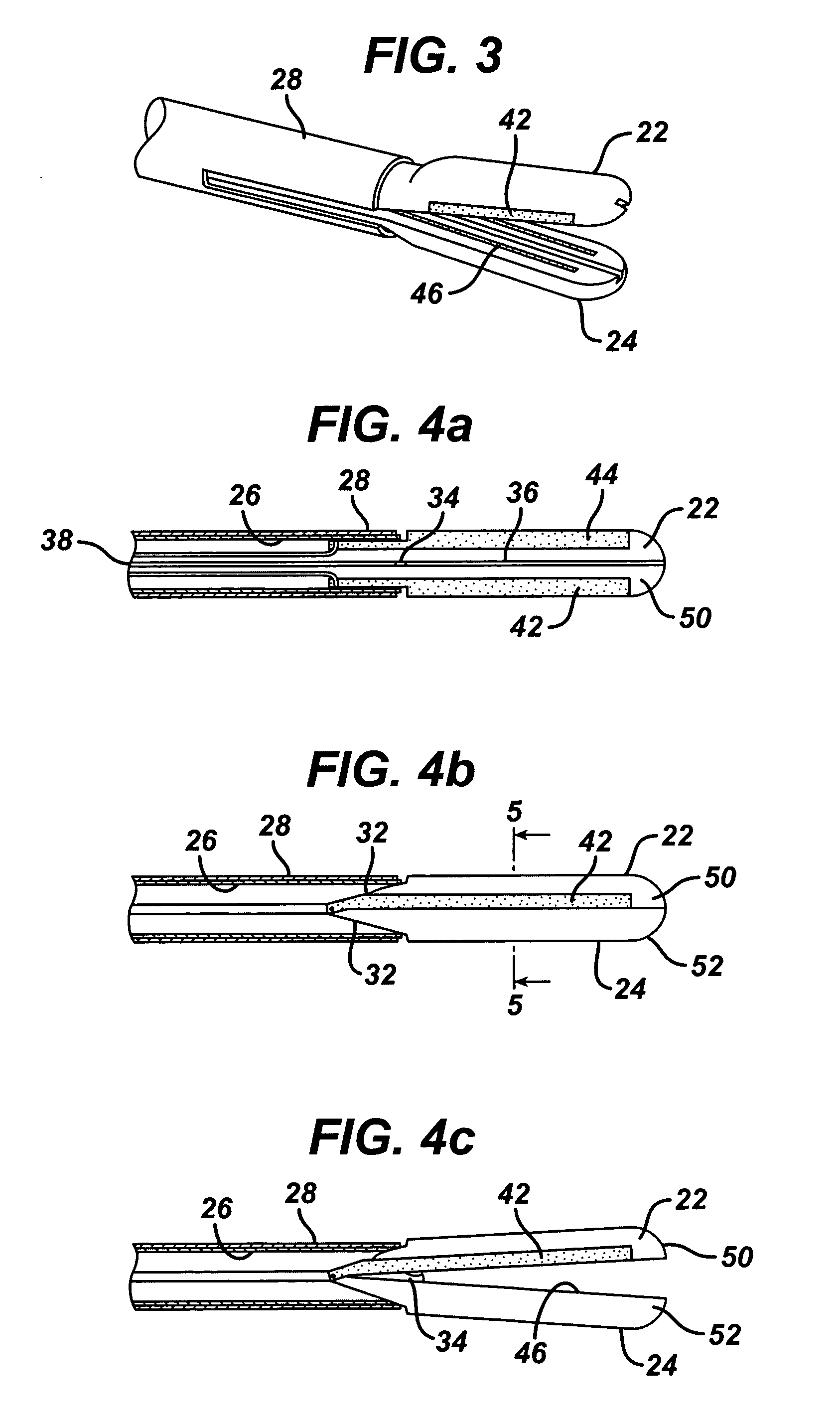
A bipolar electrosurgical instrument having a pair of relatively moveable jaws, each of which includes a tissue contacting surface. The tissue contacting surfaces of the jaws are in face-to-face relation with one another, and adjacent each of the tissue contacting surfaces are first and second spaced-apart electrodes that are adapted for connection to the opposite terminals of a bipolar RF generator so as to generator a current flow between the electrodes. The first and second electrodes of one jaw are in offset opposed relation, respectively, with the first and second electrodes of the other jaw. A cutting portion is provided between the jaws. The cutting portion is moveable to provide the instrument with a scissors-like capability or a grasper-like capability, depending on the position of the cutting portion. A tissue dam is included on at least one jaw to help contain tissue within the desired coagulation area, and thereby help contain current density between the electrodes, thereby decreasing lateral tissue thermal damage and increasing hemostasis.
Owner:WITT DAVID A +3
Apparatus and method for temporary hemostasis
ActiveUS20080009794A1Good hemostasisPrevent over-pressurizationBalloon catheterSurgeryVALVE PORTPlunger
An apparatus for providing hemostasis within a puncture through tissue includes an elongate member having a lumen extending between proximal and distal ends thereof, an expandable member carried on the distal end and a housing on the proximal end, the housing including an interior communicating with the lumen, and further including a valve assembly with a one-way valve allowing access into the housing interior upon application of a pressure differential across the valve, and a movable plunger for overriding and opening the valve.
Owner:ACCESSCLOSURE
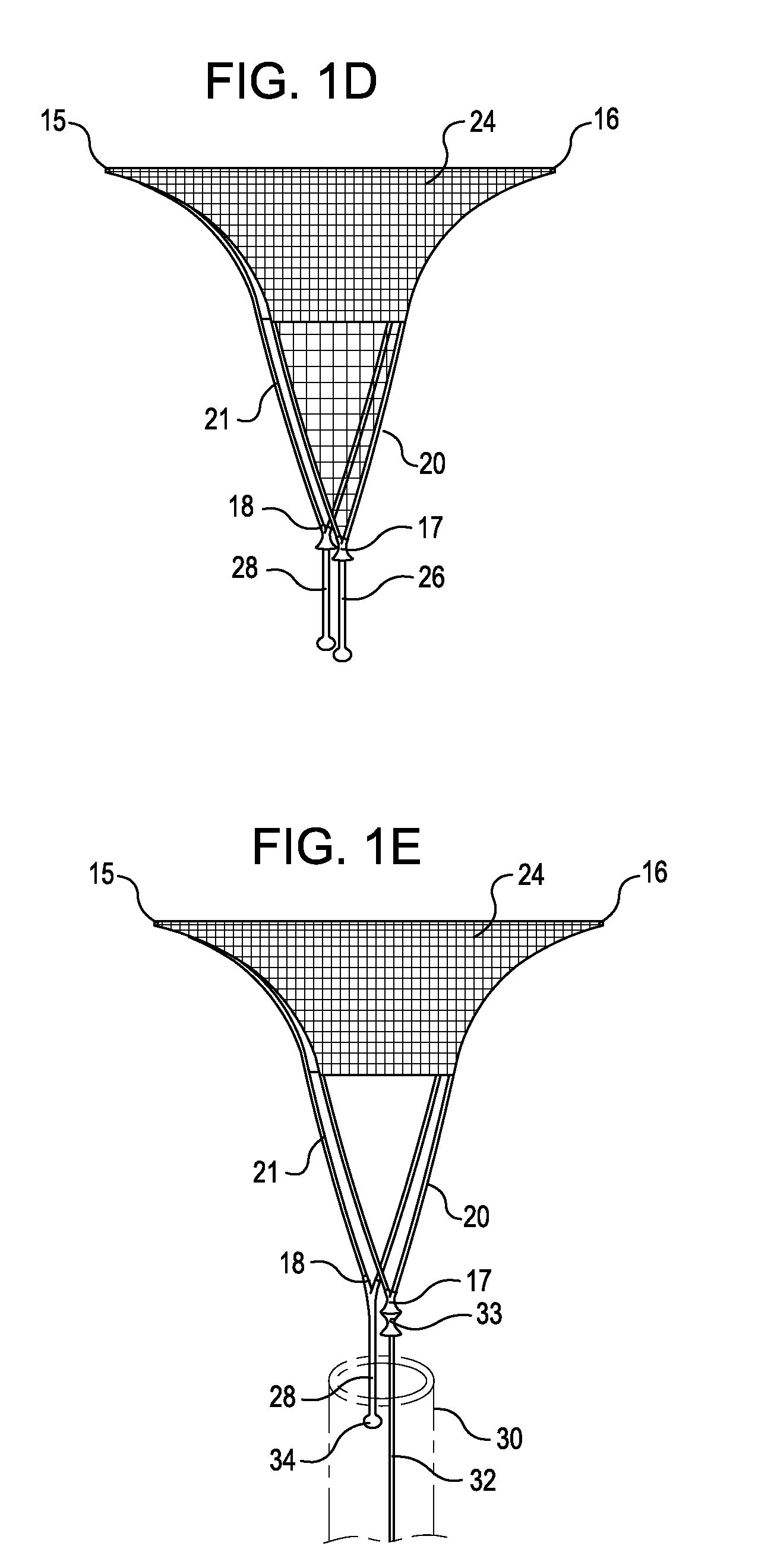
Compression anastomosis ring assembly and applicator for use therewith
InactiveUS7527185B2Reduced dimensionIncrease rangeSuture equipmentsStapling toolsOrgan wallShape-memory alloy
A compression anastomosis ring (CAR) assembly for use in joining severed organ wall portions of a hollow organ. The assembly comprises a first portion which includes an anvil assembly and a second portion which comprises a bottom ring, at least one ring element, and at least one spring element formed of a shape-memory alloy. The at least one spring element provides a restorative force and is in compressive force contact with the bottom ring and the tissue to be joined is positioned between the anvil ring and the bottom ring. A plurality of needles on one of the ring elements is operative, upon application of a closure force, to pierce the tissue and the anvil ring, holding the anvil ring to the second portion of the CAR assembly. An applicator for applying the CAR assembly and a method for using the assembly and applicator are taught.
Owner:NITI SURGICAL SOLUTIONS
Apparatus and methods for delivering sealing materials during a percutaneous procedure to facilitate hemostasis
InactiveUS20050149117A1Good hemostasisImprove sealingInfusion syringesSurgical veterinaryIntroducer sheathPrecursor polymer
Apparatus and methods are provided for sealing a puncture extending through tissue to a blood vessel. A delivery sheath is introduced-into the puncture, and a sealing compound, e.g., precursor polymers that mix to create a hydrogel, is introduced through the delivery sheath into the puncture. The delivery sheath is then removed, an introducer sheath is advanced through the puncture into the vessel, and instruments are introduced through the introducer sheath into the vessel to perform a medical procedure. After completing the procedure, the introducer sheath is withdrawn. The sealing compound may expand into the puncture and / or tissue recoil of the surrounding tissue may cause the sealing compound to at least partially occlude the puncture to facilitate sealing and / or hemostasis.
Owner:ACCESSCLOSURE
Device for suction-assisted lipectomy and method of using same
InactiveUS6918903B2Shorten recovery timeSmall sizeMedical devicesIntravenous devicesSuction assisted lipectomyAdipectomy
A device is described which allows simultaneous application of suction or vacuum for evacuation of fat with application of energy to the fat inside an opening in a cannula. A pair of electrodes is situated within the cavity of the cannula just under the surface of cannula tip opening(s) or as part of the walls of such openings. The electrodes are spaced to allow coagulation of fat entering the cannula. Irrigation may be applied in a continuous or discontinuous or intermittent stream within the cannula to cool the tip and facilitate removal of suctioned tissue and prevent buildup of debris on electrodes. A method for using the cannula to remove adipose tissue or fat destroyed by the energy application through the use of suction with mechanical motion of the cannula, with energy application and optionally with the use of irrigation is also disclosed.
Owner:CURVE MEDICAL LLC
Methods and systems for endovascularly clipping and repairing lumen and tissue defects
ActiveUS20070191884A1Reliable attachmentPromote shrinking and reabsorptionSuture equipmentsDilatorsAneurysmTissue defect
An implantable closure structure is delivered using minimally invasive techniques, and inhibits the migration of liquid and particulate matter from inside a physiological cavity or opening, such as an aneurysm or a septal defect, as well as inhibiting the flow of liquid and particulate matter, such as from an associated blood vessel or chamber, into the physiological cavity or opening. The device has a closure structure that covers the neck or opening of a cavity and has one or more anchoring structures for supporting and retaining the closure structure in place across the cavity or opening.
Owner:PULSAR VASCULAR
Apparatus and methods for delivering sealing materials during a percutaneous procedure to facilitate hemostasis
InactiveUS20070060950A1Good hemostasisImprove sealingDiagnosticsSurgical veterinaryVessel sealingBlood vessel
An apparatus for sealing a puncture extending through tissue to a blood vessel includes a guidewire including an expandable tamp, a retaining sheath for covering the tamp, and a delivery sheath including a primary lumen for receiving the guidewire therethrough and a secondary lumen for delivering sealing compound into the puncture. The guidewire is advanced into the puncture with the tamp in a contracted condition, the tamp is expanded within the vessel after retracting the retaining sheath, and the guidewire is retracted to seal the puncture from the vessel. The delivery sheath is advanced over the guidewire, and sealing compound is introduced into the puncture through the delivery sheath. After introducing the sealing compound, the delivery sheath is removed, and an introducer sheath is advanced over the guidewire to provide access to perform a medical procedure via the vessel after removing the guidewire.
Owner:ACCESSCLOSURE
Systems and methods for supporting or occluding a physiological opening or cavity
ActiveUS20100094335A1Promote re-endothelializationPromote tissue growthStentsDilatorsImplanted deviceEngineering
Implantable devices for placement at a cavity or opening such as an aneurysm are disclosed. The implantable devices, in a deployed condition, have a generally inverted U-shaped profile with a curved or angled framework support structure sized and configured for placement in proximity to tissue surrounding the opening and anchoring legs extending proximally from the framework structure sized and configured to contact the wall of a neighboring lumen at opposed locations. Occlusive and semi-occlusive membranes may be associated with the framework support structure and deployed over the opening to provide exclusion of the opening and flow diversion. Proximal anchoring segments providing additional lumen wall surface area contact for the implantable device following deployment may be incorporated.
Owner:PULSAR VASCULAR
Vascular closure device
InactiveUS20070083232A1's efficiencyEasy to useOcculdersSurgical veterinaryVascular closure deviceVascular device
The present invention provides a device for closing an opening to a body cavity and methods of closing an opening to a body cavity. The device and methods can be used to easily and effectively close a vascular puncture site resulting from a surgical procedure, an atrial or ventricular septal defect, a malfunctioning heart valve, or the left atrium appendage.
Owner:INNOVASIVE
Hemostatic device
ActiveUS7498477B2Excellent hemostatic effectGood hemostasisDiagnosticsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesHemostaticsWrap around
A hemostatic device includes a flexible band adapted to be wrapped around a patient's limb at a site on the limb where bleeding is to be stopped, a portion for securing the band in a wrapped state to the limb, a curved plate which is made of a material more rigid than the band and at least a portion of which is curved toward the inner peripheral side thereof, a main balloon which is provided on the inner peripheral side of the curved plate and which inflates when a fluid is introduced therein, and a pressing member which is provided between the curved plate and the main balloon so that at least a portion thereof overlaps with the balloon and which is adapted for pressing against the balloon. The device provides an excellent hemostatic effect and prevents numbness and poor circulation in areas peripheral to the site of attachment.
Owner:TERUMO KK
Vascular closure
InactiveUS20070083231A1's efficiencyEasy to useSurgical veterinarySurgical staplesBlood vesselSurgical procedures
The present invention provides a device for closing an opening to a body cavity and methods of closing an opening to a body cavity. The device and methods can be used to easily and effectively close a vascular puncture site resulting from a surgical procedure.
Owner:LEE BENJAMIN
Compositions and methods for promoting hemostasis and other physiological activities
ActiveUS20070203062A1Good hemostasisControl bleedingBiocideTripeptide ingredientsWound dressingVasoconstrictor Agents
Compositions that include nanoscale structured materials or precursors thereof (e.g., self-assembling peptides) are described. The compositions can include other substances (e.g., a vasoconstrictor). Also described are methods for using the compositions to promote hemostasis, to protect the skin or wounds from contamination, to decontaminate a site upon removal of previously applied compositions that provided a protective coating, and to inhibit the movement of bodily substances other than blood. The compositions are also useful in isolating tissue, removing tissue, preserving tissue (for, e.g., subsequent transplantation or reattachment), and as bulking, stabilizing or hydrating agents. Medical devices that include the compositions (e.g., a stent or catheter), bandages or other wound dressings, sutures, and kits that include the compositions are also described.
Owner:VERSITECH LTD +1
Methods and systems for endovascularly clipping and repairing lumen and tissue defects
ActiveUS8551132B2Promote shrinking and reabsorptionGood hemostasisSuture equipmentsDilatorsParticulatesTissue defect
Owner:PULSAR VASCULAR
Agents for controlling biological fluids and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20070059350A1Good hemostasisHigh viscosityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideMedicineIncision Site
Therapeutic formulations adapted for positive-pressure application for controlling biological fluid at a desired site in a subject, absorbent articles comprising therapeutic formulations, and anti-infective devices coated with therapeutic formulations, said formulations comprising about 25% to about 99% by weight liquid-crystal forming compound and 0% to about 75% by weight solvent. In addition, methods of using said formulations including methods for controlling biological fluid at a desired site in a subject, methods for controlling blood loss, and methods for facilitating effective closure of a vascular wound or incision site at a desired site in a subject are disclosed, the methods comprising administering particular formulations comprising liquid-crystal forming compounds and solvents that are described herein.
Owner:SOUTHEASTERN MEDICAL TECH
Method and apparatus for improved hemostasis and damage control operations
InactiveUS6998510B2Improved hemostatic packing in trauma careGood hemostasisPlastersBaby linensTamponadePERITONEOSCOPE
Devices and methods are disclosed for achieving hemostasis in traumatized patients. The devices utilize fluid impermeable outer surfaces and distributed pressure to achieve tamponade and hemostasis, primarily by exertion of pressure. The devices are capable of serving as carriers for throabogenic or antipathogenic agents. Peripheral haemostatic packing devices include optional adhesive hemostatic barriers to cover the entire wound area over the hemostatic pack. The hemostatic packing devices may be placed and removed by open surgery or laparoscopic access without generating excessive re-bleeding, and may further comprise antimicrobial or thrombogenic regions.
Owner:DAMAGE CONTROL SURGICAL TECH
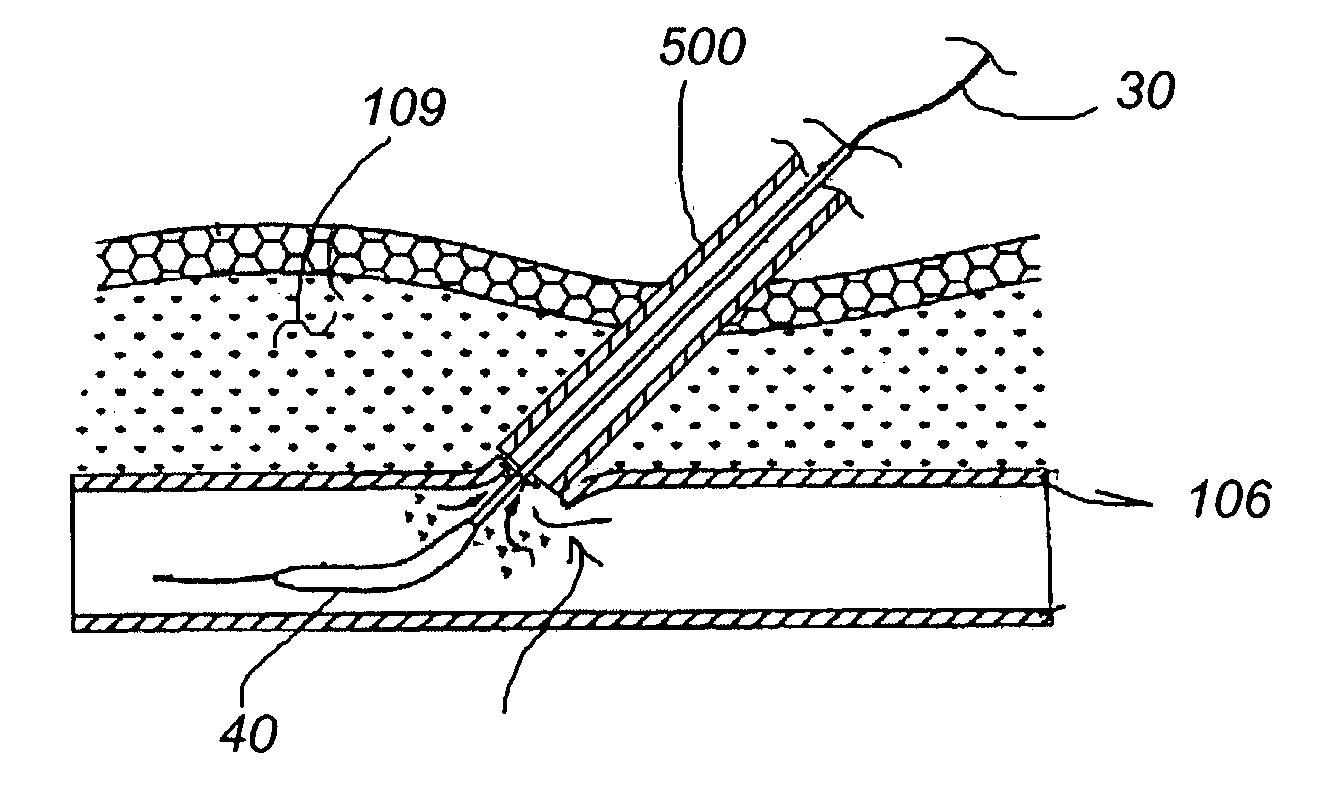
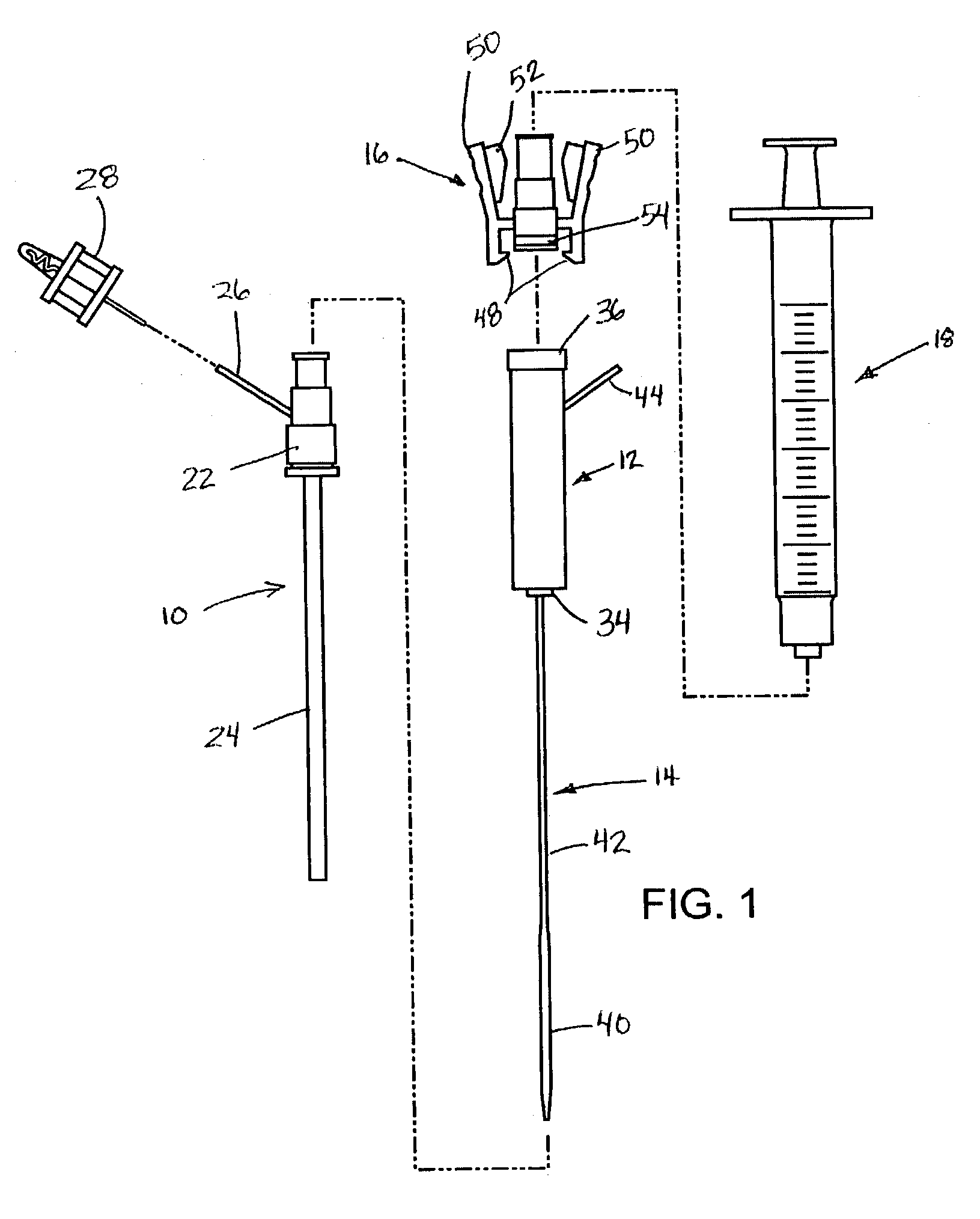
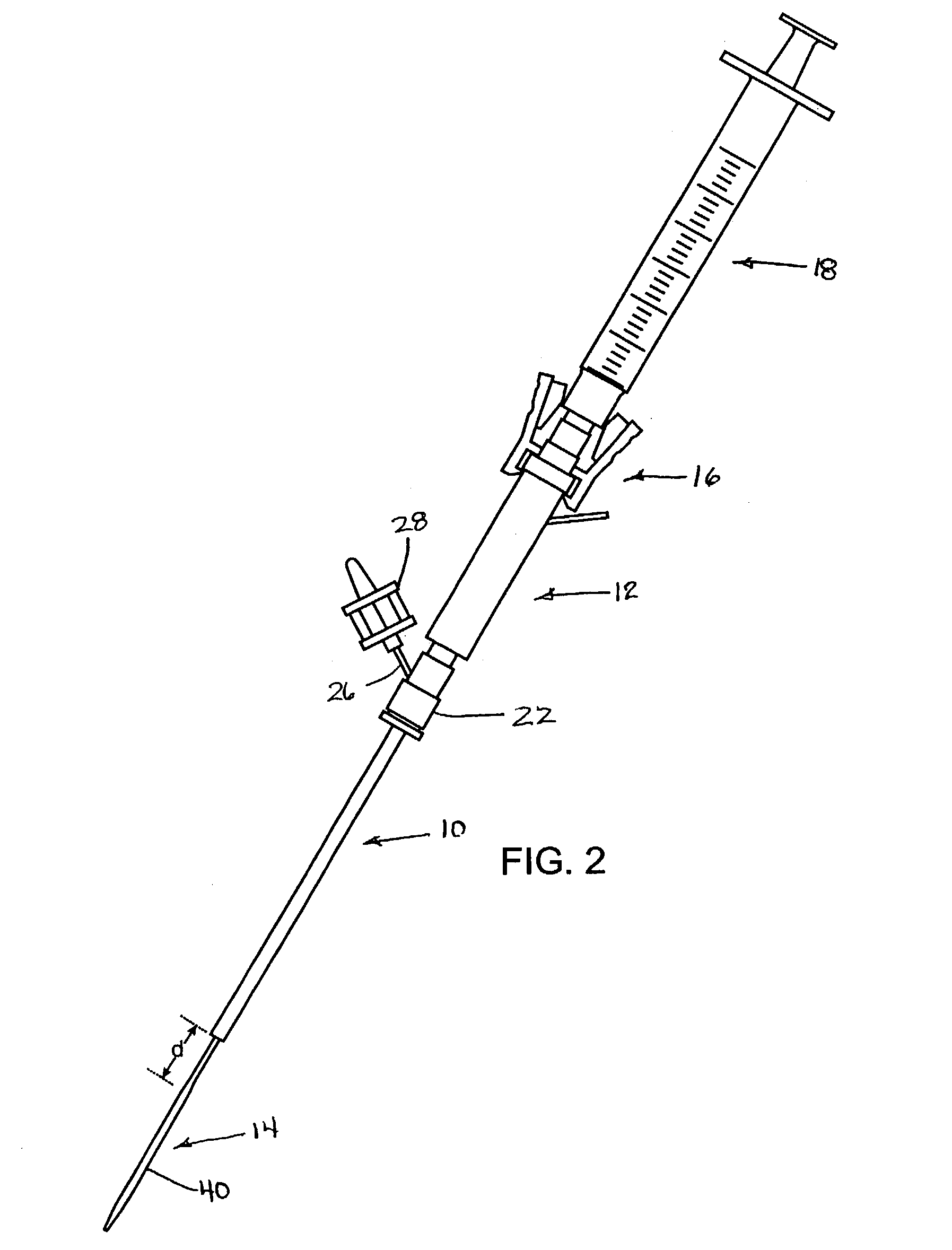
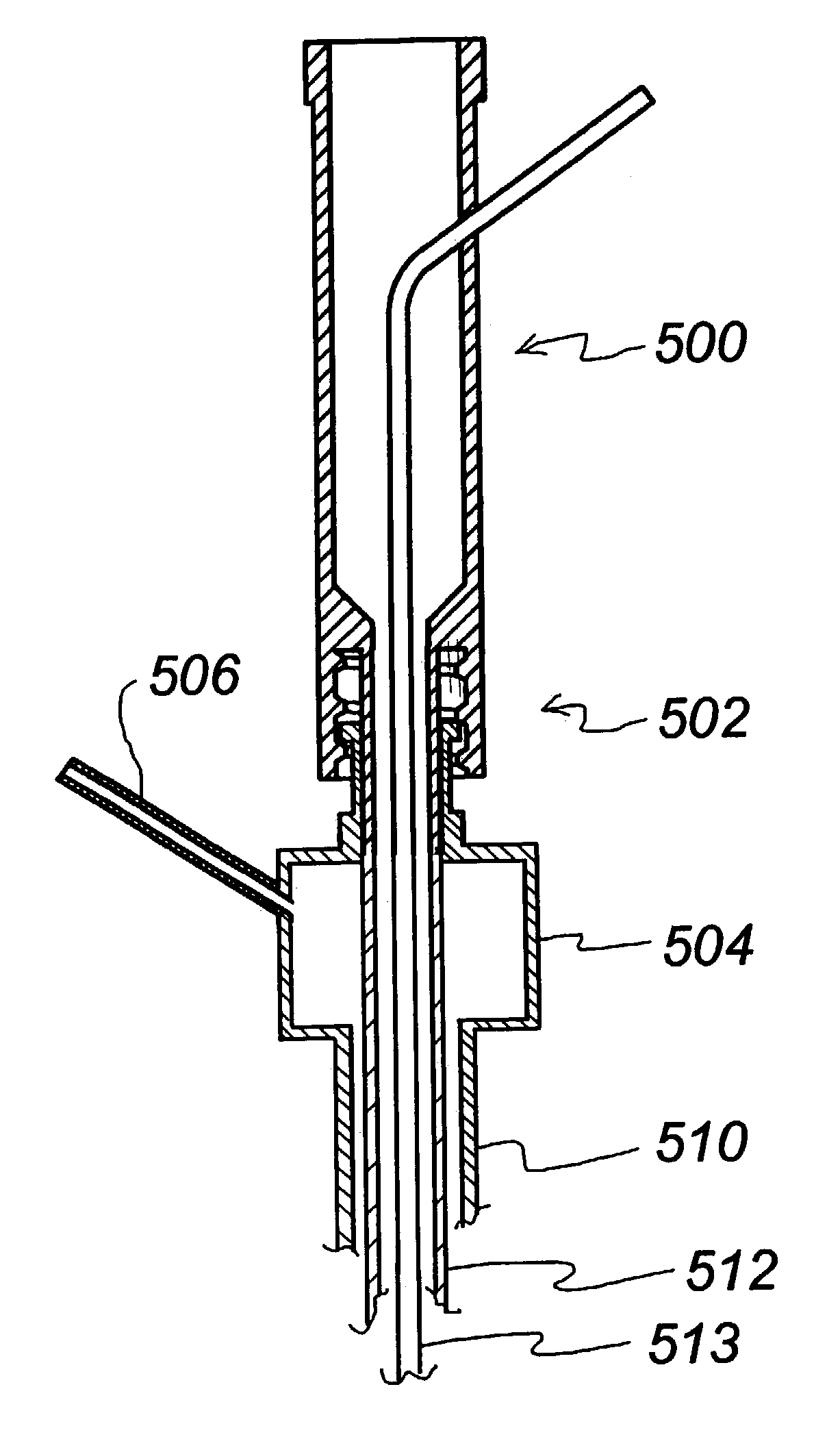
System and method for delivering hemostasis promoting material to a blood vessel puncture site by fluid pressure
InactiveUS7008440B2Good hemostasisFacilitates consistent hydrationDiagnosticsSurgical needlesIntroducer sheathBlood vessel
A system for delivering hemostasis promoting material of the present invention allows the hemostasis promoting material to be delivered to a blood vessel puncture site by fluid pressure. The system allows the hemostasis promoting material to be delivered through an producer sheath which is already in place within a tissue tract. The system includes a controlled tip which is insertable through the introducer sheath to locate and occlude the blood vessel puncture site and a hydration chamber for receiving and delivering the hemostasis promoting material to the blood vessel puncture site. The system accurately locates the blood vessel wall at a puncture site and for properly placing a hemostasis plug over the puncture site.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC +11
Hemostatic sponge
ActiveUS20100318048A1Good hemostasisImprove abilitiesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismBaby linensWound healingMaterials science
The present invention provides a hemostatic porous sponge comprising a matrix of a fibrous biomaterial and particles of a fluid absorbing, particulate material adhered to said matrix material, a method of producing these sponges and their use for wound healing.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
Hemostatic system for body cavities
InactiveUS20060271094A1Facilitates late removalFacilitate and enhance blood clot formationBalloon catheterDiagnosticsSurgeryBody cavity
Bleeding is controlled on an inner surface of a body cavity by inserting into the cavity an expandable balloon which is covered by a hemostatic shroud, expanding the balloon, and compressing the shroud against the site of bleeding. The balloon may be disposed around a central tube to supply inflation medium. The tip of the device is soft to aid with insertion. The invention includes the corresponding devices and systems for such control of bleeding within a body cavity or passageway, as well as a method of making the devices.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Sheath-mounted arterial plug delivery device
A method of facilitating hemostasis of a blood vessel puncture. The method includes the steps of inserting a tubular device into a puncture in a blood vessel to establish access to the blood vessel, providing a vessel closure system around the tubular device, introducing a hemostatic material into a space between the tubular device and vessel closure system, and delivering the hemostatic material adjacent to the puncture to facilitate hemostasis of the puncture.
Owner:BOSTON SCI CORP +11
Biocompatibility modified starch sponges
ActiveCN101455857AFlexibleActive bleeding is easily controlledAbsorbent padsBandagesFreeze-dryingBiocompatibility Testing
The invention relates to biocompatible modified starch sponge and use of the biocompatible modified starch sponge as a hemostatic material, an anti-adhesion material, a material for promoting tissue healing, a surgical sealant or a wound tissue adhesive. Modified starch is one or a combination of more than one among pre-gelatinized starch, acid modified starch, dextrin, oxidized starch, esterified starch, etherified starch, crosslinked starch, grafted starch and composite modified starch. The sponge is prepared by vacuum freeze drying of the modified starch and other biocompatible hemostatic material, coagulant, plasticizer and so on. The biocompatible modified starch sponge has the advantages that the biocompatible modified starch sponge has flexible form and good biocompatibility, can be directly acted on bloody wound surfaces, avoids the conditions of hypersusceptibility, infection and difficult healing of wounds caused by adoption of hemostatic materials such as animal source / human source collagens, obviously improves the water absorption speed, has larger viscosity, forms a zymoplastic mixture which has good adhesion, calks broken tissues and blood vessels, and is used for hemostasis of active hemorrhage.
Owner:BEIJING UNIVERSAL LIKANG TECH CO LTD
Degradable compound biomaterial membrane for medical purpose
InactiveCN1994476AHigh porosityLarge specific surface areaAbsorbent padsBandagesFiberElectrospinning
The invention relates to a method for preparing composite biological medical material used to avoid adhering organisms, wherein said film is formed by two layers; the layer used as base material is formed by degradable composite macromolecule polylactic acid, glycolic acid, or their copolymer, treated by static spin technique, to make film fiber into nanometer level; then coats one layer of degradable natural macromolecule chitose or relative derivant on the base film, to be treated to obtain the degradable composite biological medical film; and the invention can add different amounts of medical elasticizer between two layers to adjust the degrade speed. The invention can improve immunity with haemostasis function, etc.
Owner:BEIJING HUASHI BENQUAN TECH
System and method for delivering hemostasis promoting material to a blood vessel puncture site
InactiveUS7029489B1Facilitates consistent hydrationEffective stagingSurgical veterinaryWound clampsBlood vessel wallsIntroducer sheath
A system for delivering hemostasis promoting material of the present invention allows the hemostasis promoting material to be delivered to a blood vessel puncture site by fluid pressure. The system allows the hemostasis promoting material to be delivered through an introducer sheath which is already in place within a tissue tract. This system includes a controlled tip which is insertable through the introducer sheath to locate and occlude the blood vessel puncture site and a hydration chamber for receiving and delivering the hemostasis promoting material to the blood vessel puncture site. The system accurately locates the blood vessel wall at a puncture site and for properly placing a hemostasis plug over the puncture site.
Owner:BOSTON SCI CORP +11
System and method for delivering hemostasis promoting material to a blood vessel puncture with a staging tube
InactiveUS7037322B1Facilitates consistent hydrationEffective stagingDiagnosticsSurgical veterinaryIntroducer sheathBiomedical engineering
A system for delivering hemostasis promoting material of the present invention allows the hemostasis promoting material to be delivered to a blood vessel puncture site by fluid pressure. The system allows the hemostasis promoting material to be delivered through an introducer sheath which is already in place within a tissue tract. This system includes a controlled tip which is insertable through the introducer sheath to locate and occlude the blood vessel puncture site and a hydration chamber for receiving and delivering the hemostasis promoting material to the blood vessel puncture site. The system accurately locates the blood vessel wall at a puncture site and for properly placing a hemostasis plug over the puncture site.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC +11
Systems and methods for supporting or occluding a physiological opening or cavity
ActiveUS8388650B2Facilitates placement and expansionSmall diameterStentsDilatorsImplanted deviceEngineering
Implantable devices for placement at a cavity or opening such as an aneurysm are disclosed. The implantable devices, in a deployed condition, have a generally inverted U-shaped profile with a curved or angled framework support structure sized and configured for placement in proximity to tissue surrounding the opening and anchoring legs extending proximally from the framework structure sized and configured to contact the wall of a neighboring lumen at opposed locations. Occlusive and semi-occlusive membranes may be associated with the framework support structure and deployed over the opening to provide exclusion of the opening and flow diversion. Proximal anchoring segments providing additional lumen wall surface area contact for the implantable device following deployment may be incorporated.
Owner:PULSAR VASCULAR
Compression anastomosis ring assembly and applicator for use therewith
InactiveUS20080015617A1Reduced dimensionIncrease the scope of applicationSuture equipmentsStapling toolsOrgan wallShape-memory alloy
A compression anastomosis ring (CAR) assembly for use in joining severed organ wall portions of a hollow organ. The assembly comprises a first portion which includes an anvil ring and a second portion which comprises a bottom ring, at least one ring element, and at least one spring element formed of a shape-memory alloy. The at least one spring element provides a restorative force and is in compressive force contact with the bottom ring and the tissue to be joined is positioned between the anvil ring and the bottom ring. A plurality of needles on one of the ring elements is operative, upon application of a closure force, to pierce the tissue and the anvil ring, holding the disk to the second portion of the CAR assembly. An applicator for applying the CAR assembly and a method for using the assembly and applicator are taught.
Owner:NITI SURGICAL SOLUTIONS
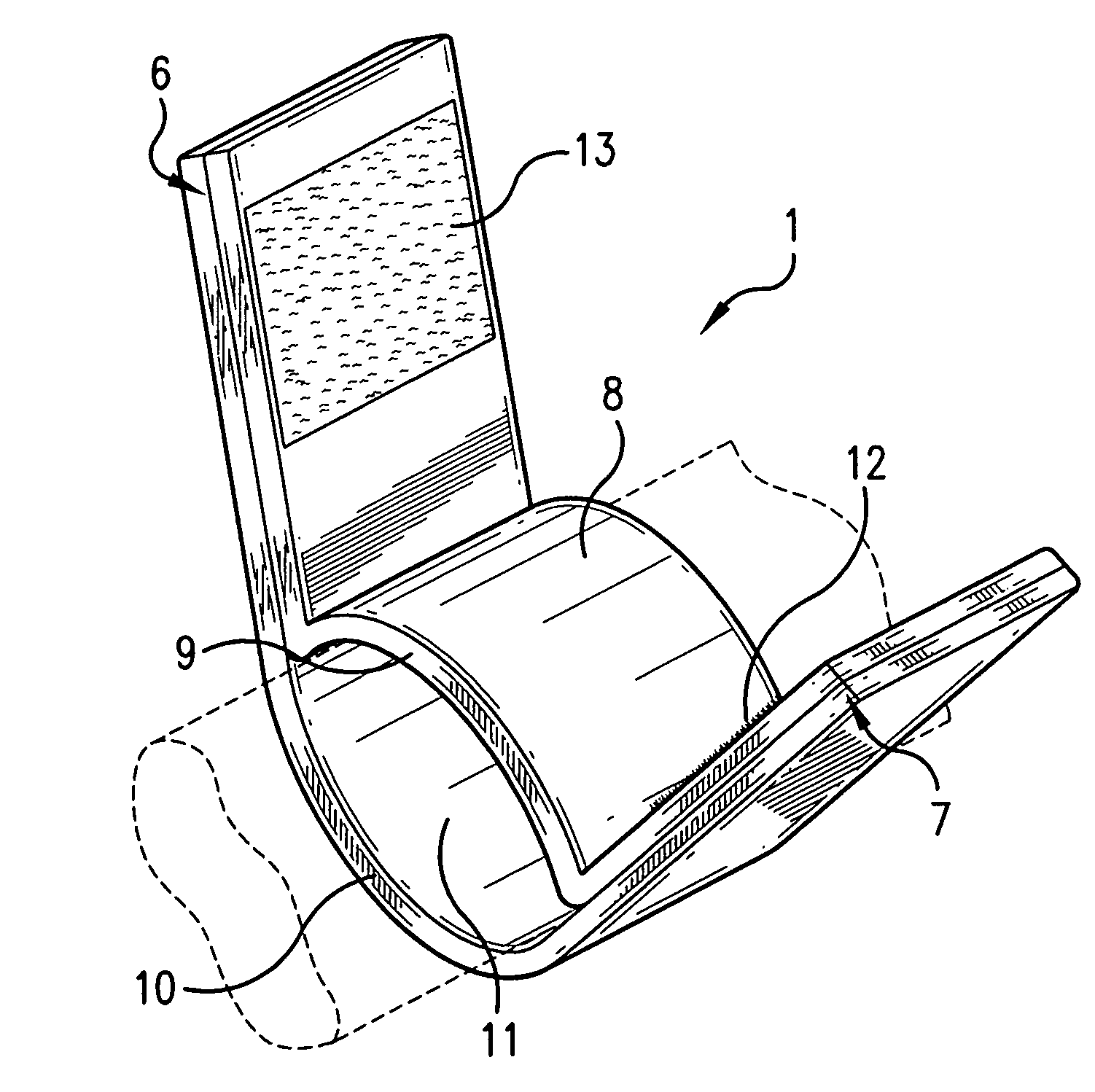
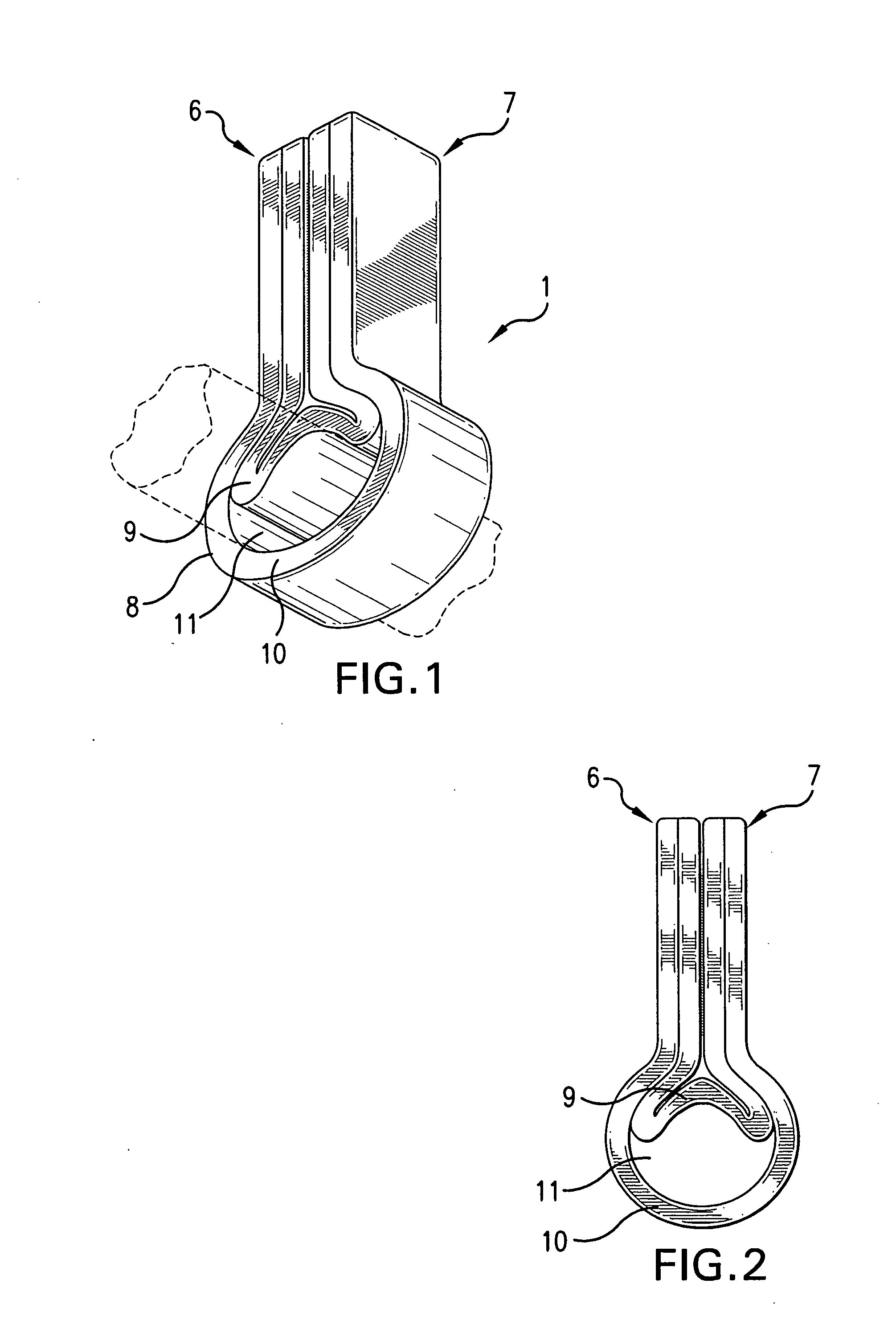
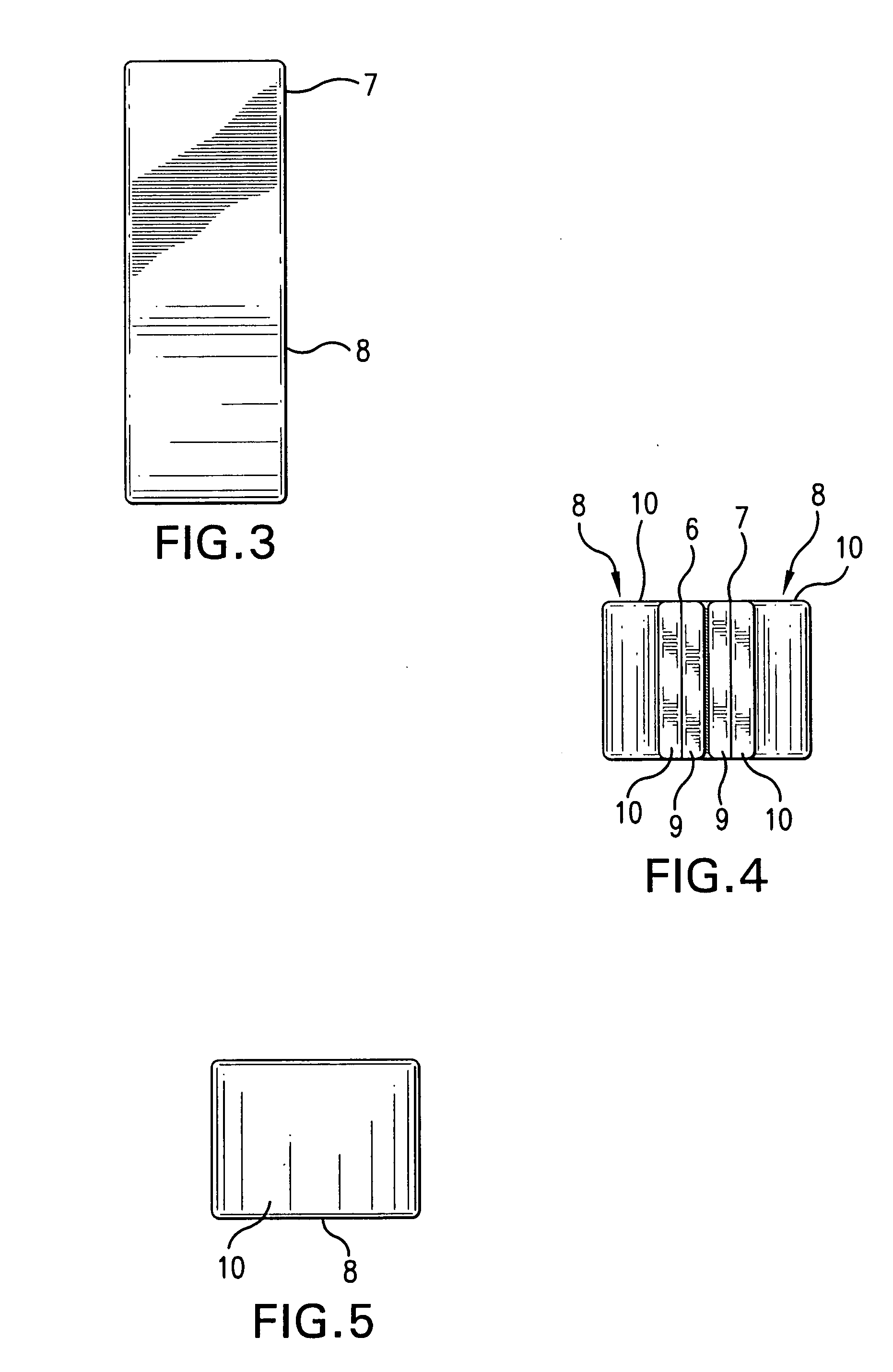
Skin-contacting-adhesive free dressing
A dressing having a flexible sleeve shaped to accommodate a substantially cylindrical body portion, the sleeve having a lining which is substantially non-adherent to the body part being bandaged and having a peripheral securement means which attaches two peripheral portions to each other without those portions being circumferentially adhered to the sleeve portion.
Owner:JENNINGS SPRING BARBARA
Therapeutic use of factor XI
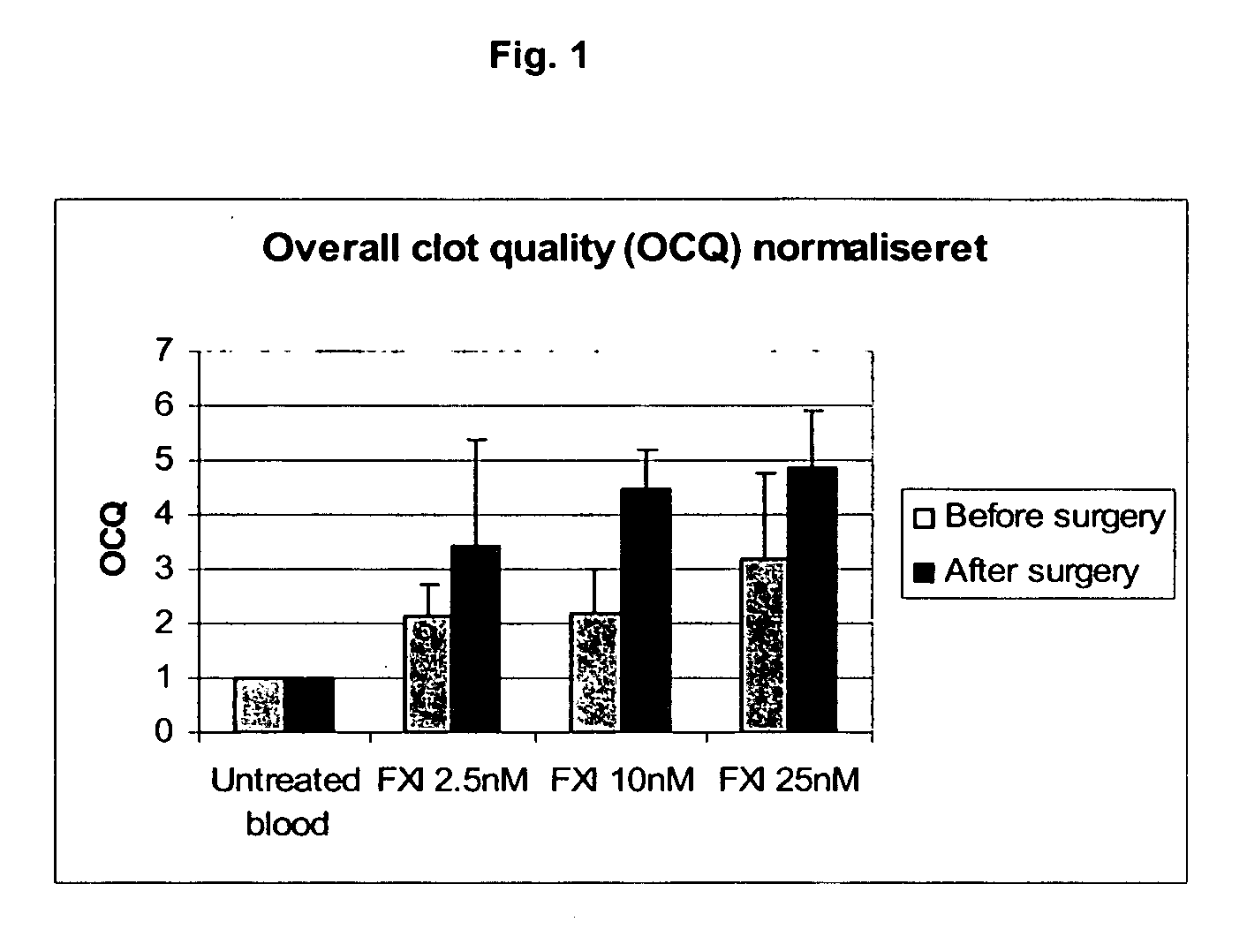
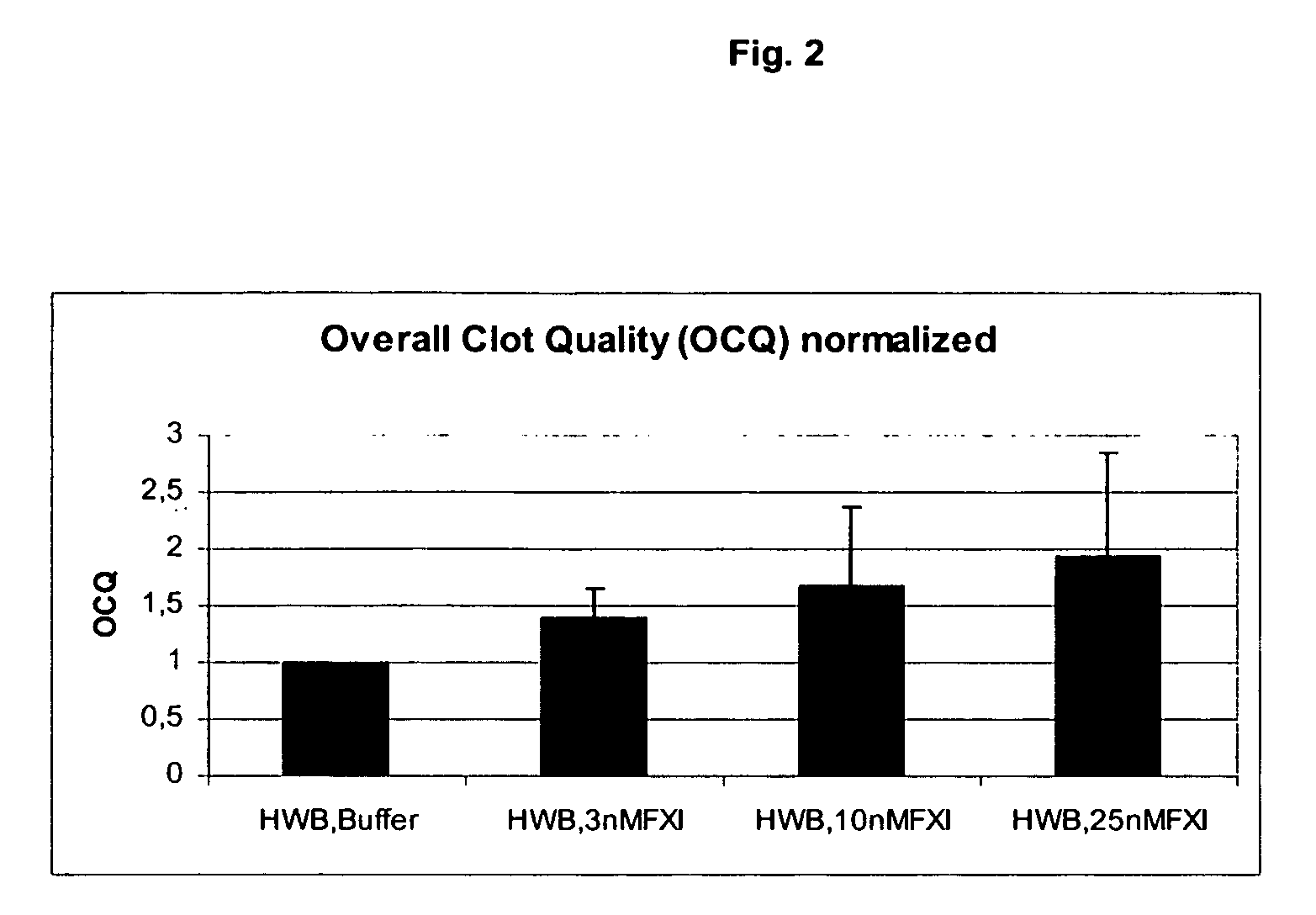
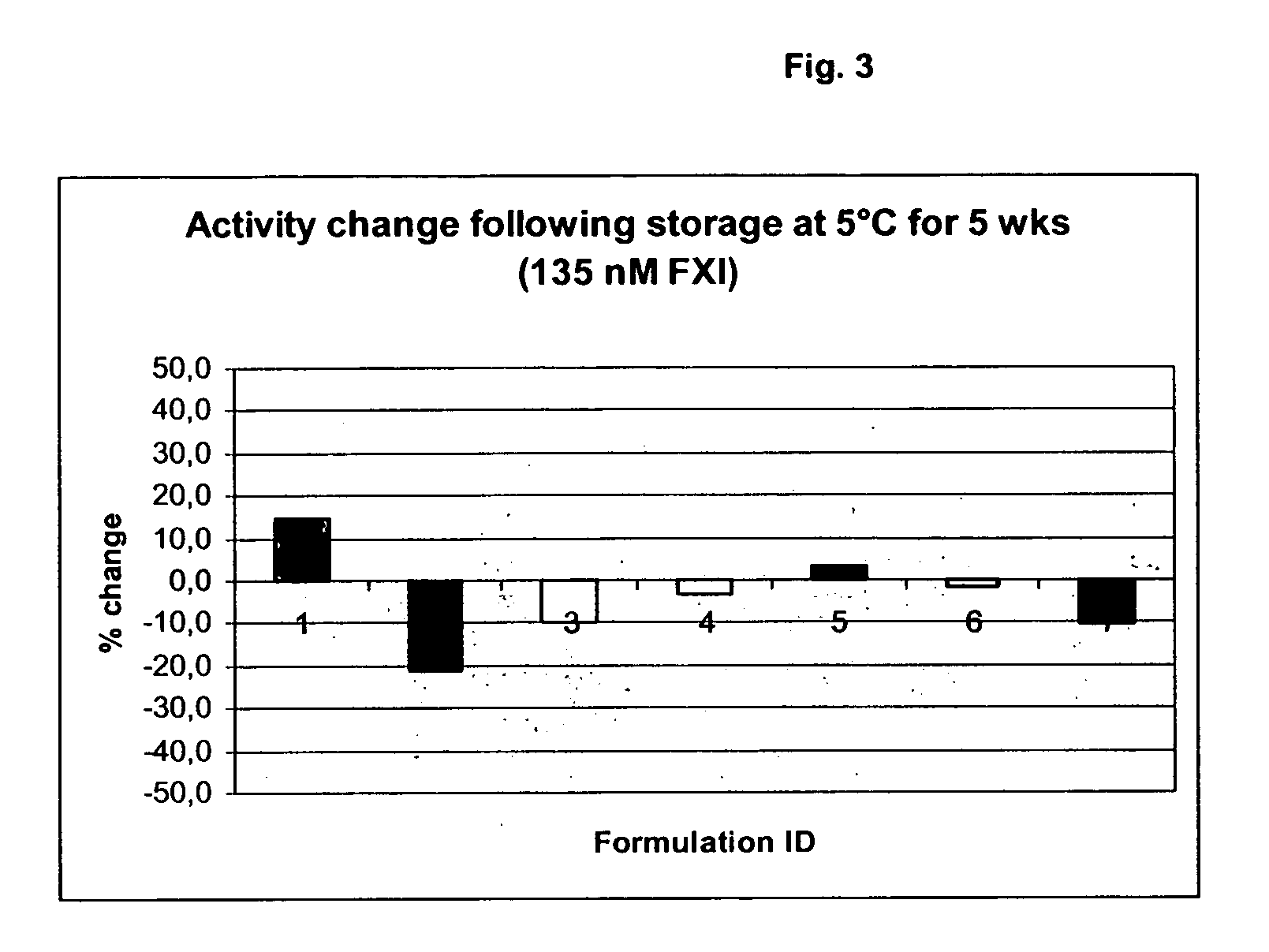
InactiveUS20050181978A1Shorten clotting timeGood hemostasisPeptide/protein ingredientsBlood disorderMedicineFactor XI
The present invention provides methods and compositions for treating bleeding episodes. The methods are carried out by administering to a patient in need thereof a preparation comprising a factor XI polypeptide, in an amount effective for such treatment. The methods of the invention result in one or more of: reduced clotting time; enhancement of hemostasis; increase in clot lysis time; increase in clot strength; and / or increase in overall clot quality (OCQ) in said patient.
Owner:ROJKJAER RASMUS +4
Oral Chinese medicine for curing osteoarthropathy
InactiveCN1400007AGood analgesic effectImprove solubilityAnthropod material medical ingredientsAntipyreticDiseaseCurative effect
Owner:郭好建
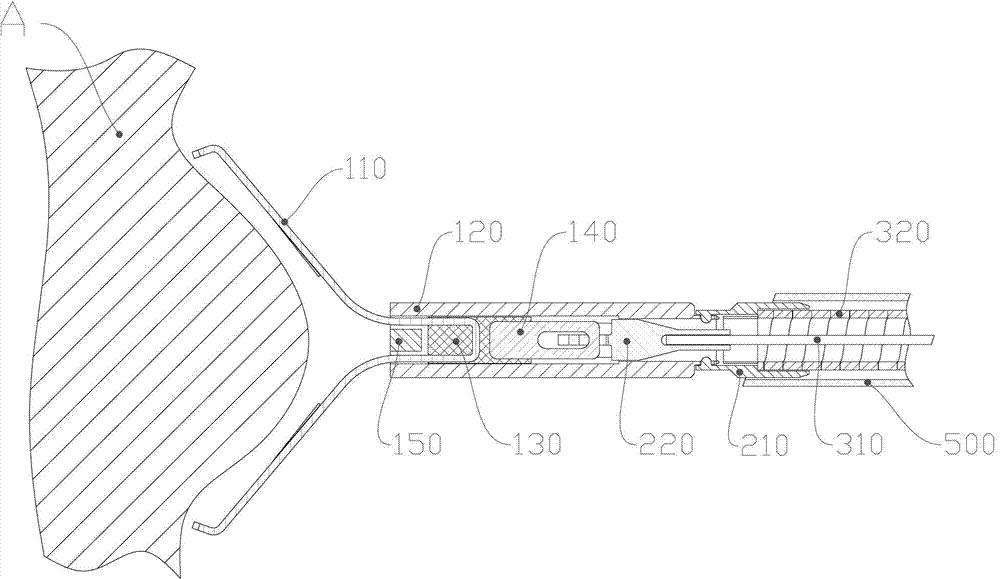
Tissue hemostasis clamping device
ActiveCN102727276AGood hemostasisAvoid scratchesSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisMechanical engineeringHemostasis
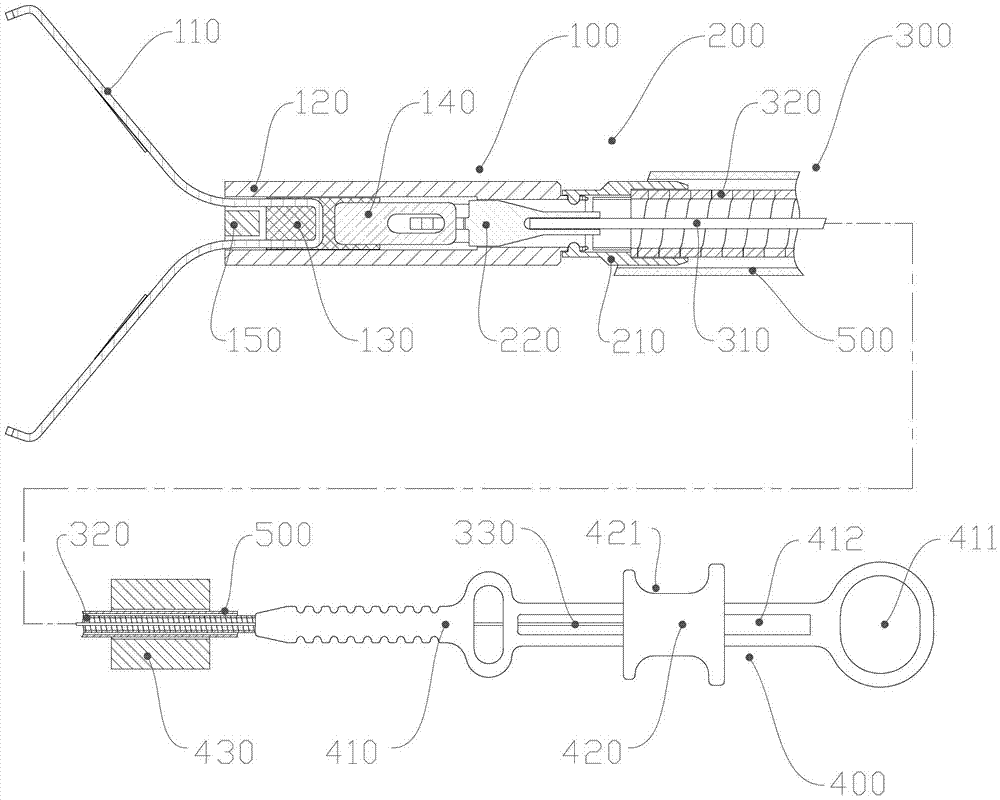
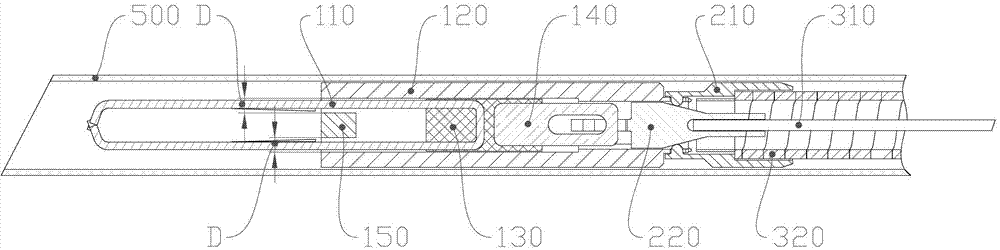
The invention discloses a tissue hemostasis clamping device, comprising a clamp, a releasing mechanism, a drawing assembly, a handle assembly and an external sheathing canal, wherein the clamp comprises a clamping plate and a connector integrally fixed with a pull-push end of the clamping plate; the pull-push end of the clamping plate and the connector can slide back and forth in a tightening pipe, the connector is buckled with the tightening pipe by a loose-preventing mechanism; the front part of the tightening pipe is provided with a stopper; a clamping arm of the clamping plate is provided with a closing stop; the releasing mechanism comprises a pull-push pipe, wherein the front part of the pull-push pipe is connected with the connector in a manner of connection failure when the front part of the pull-push pipe bears the stress exceeding a predetermined tensile force, while the rear part of the pull-push pipe is fixedly connected with a drawing steel wire; the front part of the connection pipe is connected with the rear part of the tightening pipe by a slipknot, and the rear part of the connecting pipe is fixedly connected with a sheathing tube; and the slipknot connection of the connection pipe and the tightening pipe is relieved by a pull-push pipe through the releasing mechanism. With the adoption of the technical scheme, the device has advantages of simple and reasonable structure, stable and reliable clamping, possible repeated pre-clamping, small volume of the clamp and smooth appearance.
Owner:ANREI MEDICAL HZ
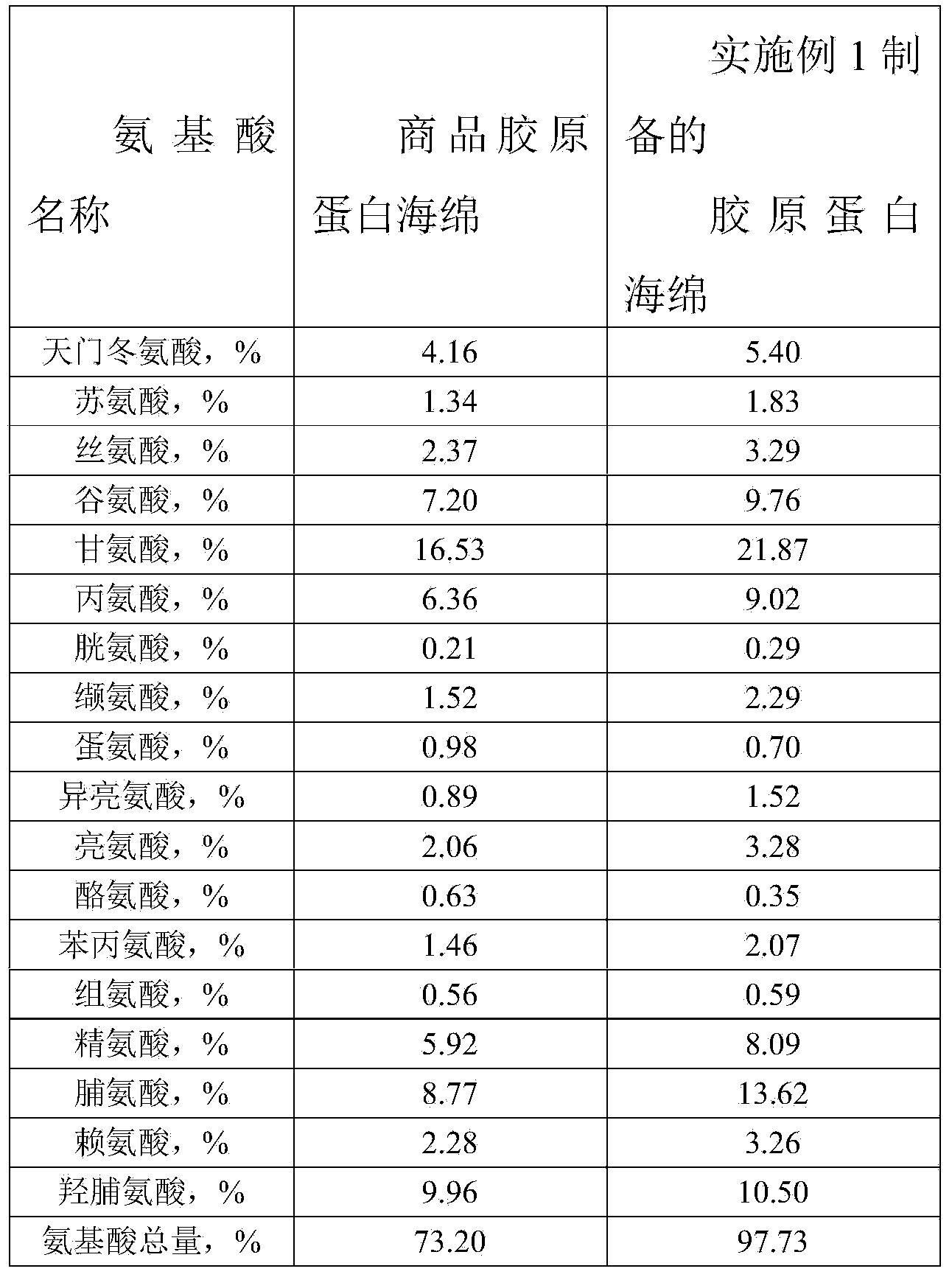
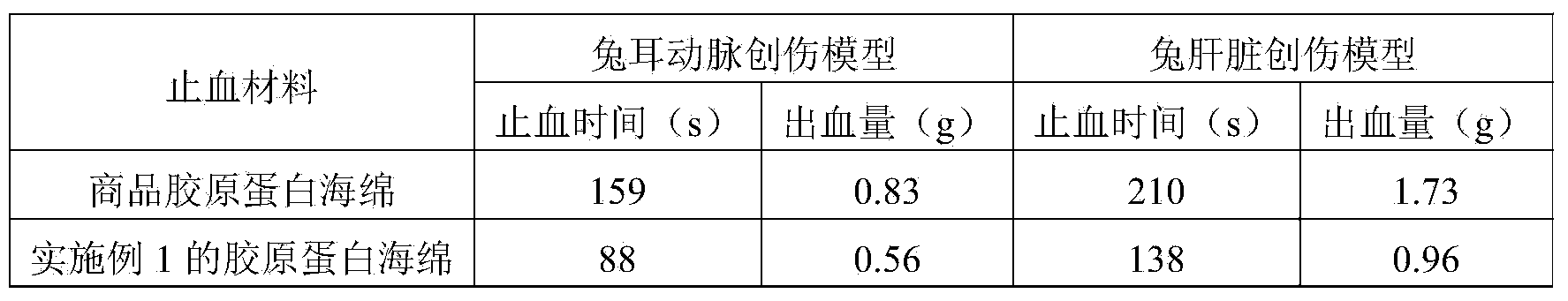
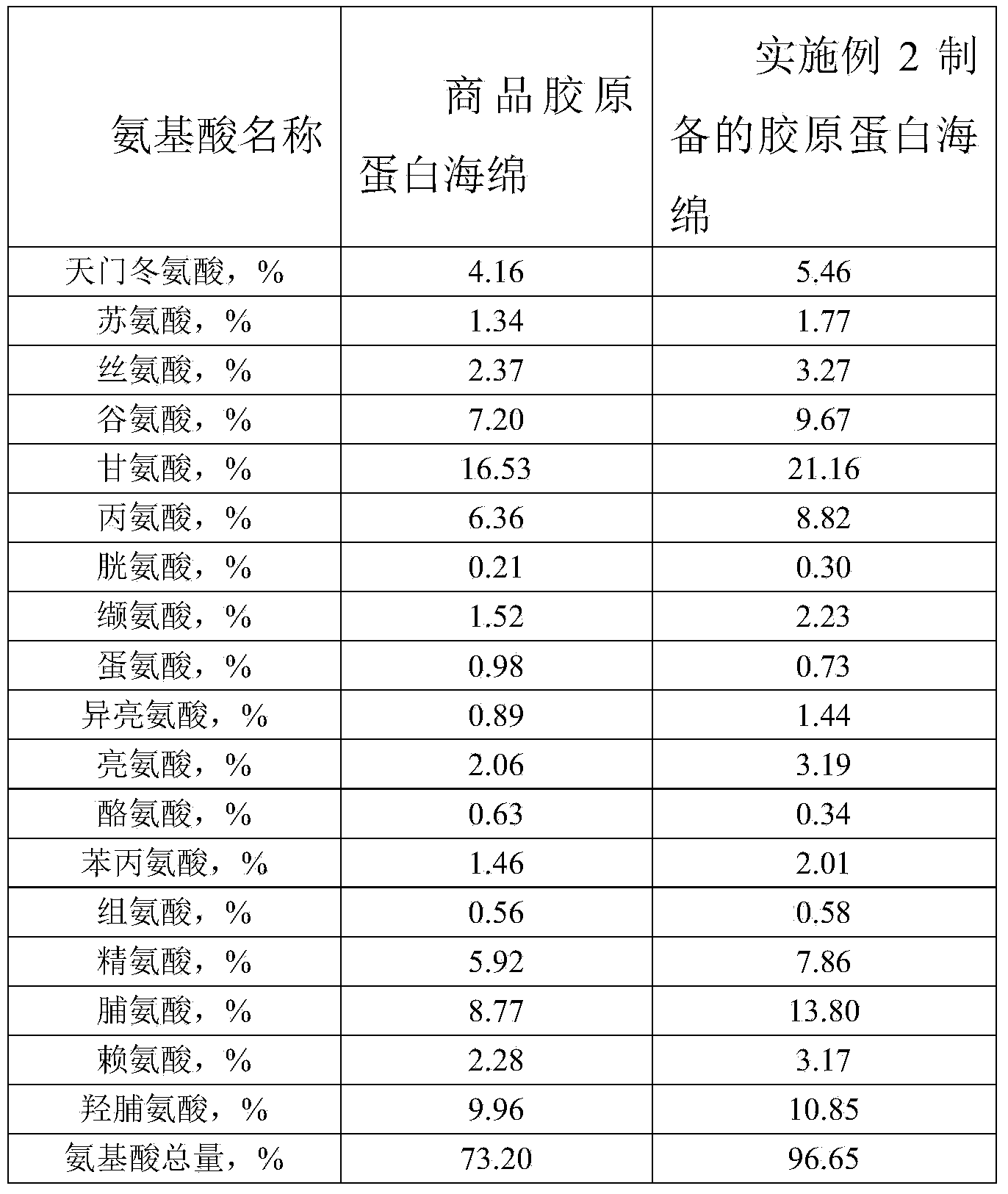
Preparation method of high-purity collagen protein sponge
InactiveCN103772734AGood removal effectHigh purityConnective tissue peptidesPeptide preparation methodsFreeze-dryingCollagen sponge
The invention provides a preparation method of high-purity collagen protein sponge, and relates to a preparation method of collagen protein sponge. The preparation method of the high-purity collagen protein sponge is used for solving the problems that the collagen protein sponge prepared by using a conventional method is long in production cycle and low in yield and purity and has poor hemostasis performance. The preparation method of the high-purity collagen protein sponge comprises the following steps: step one. pretreating fresh bovine heel tendons; step two. extracting collagen protein; step three. centrifuging; step four. salting out; step five. dissolving; step six. carrying out gradient dialysis; step seven. pre-freezing; step eight. carrying out freeze drying; and step nine. sterilizing. The final product prepared by using the method has a smooth and flat surface and relatively good hemostatic performance and is uniform in pore size distribution. The product has relatively high purity (the total amount of amino acids reaches 97.73%), an obvious hemostatic effect and no abnormal taste, is safe, non-toxic, high in yield and short in time; liquid is clear without impurities; the production cycle is shortened; the whole preparation process is carried out at a room temperature; the biological activity of the collagen protein is maintained; and the application of the high-purity collagen protein sponge in clinical is improved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com