Patents
Literature
385 results about "Blood loss" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
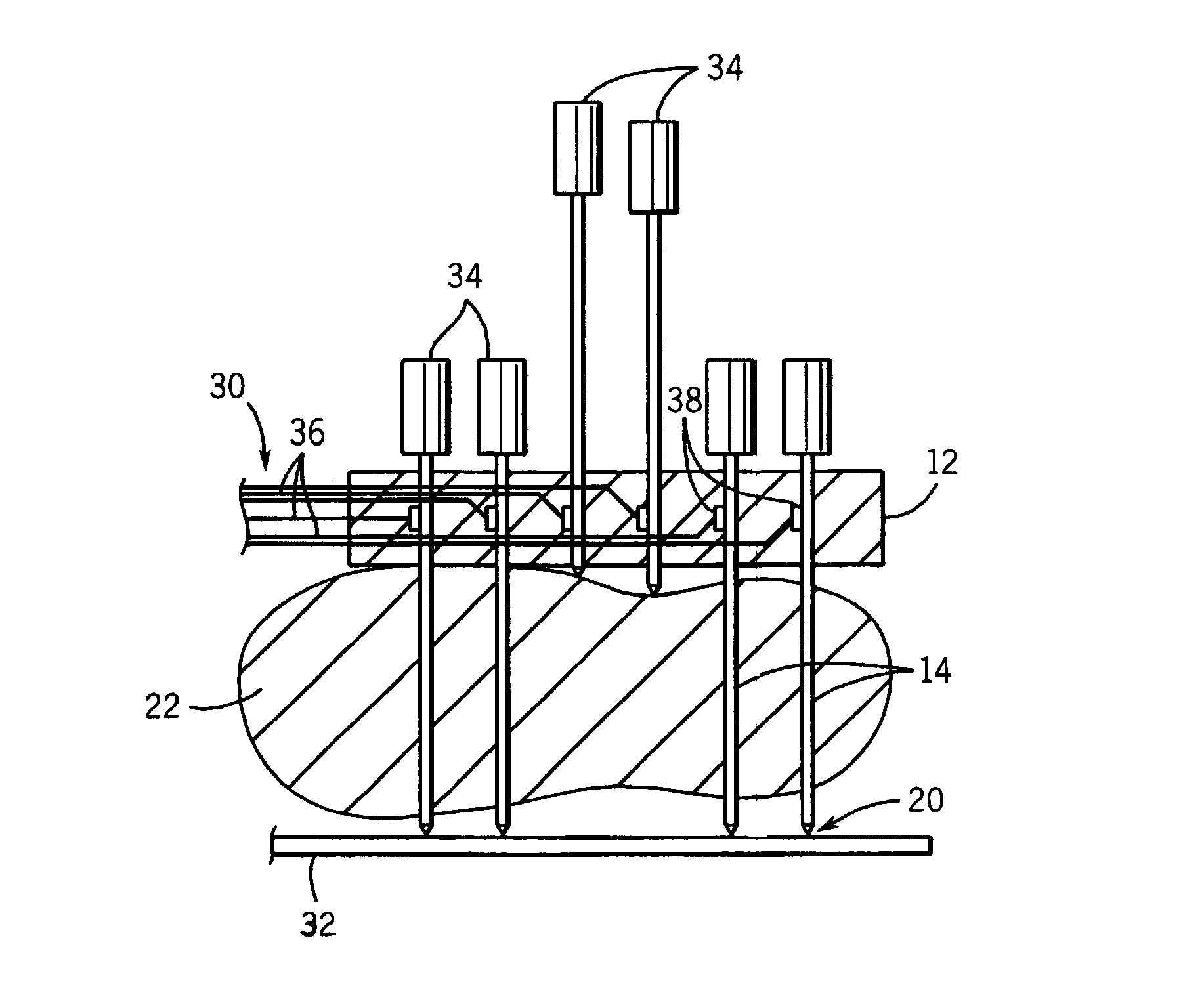
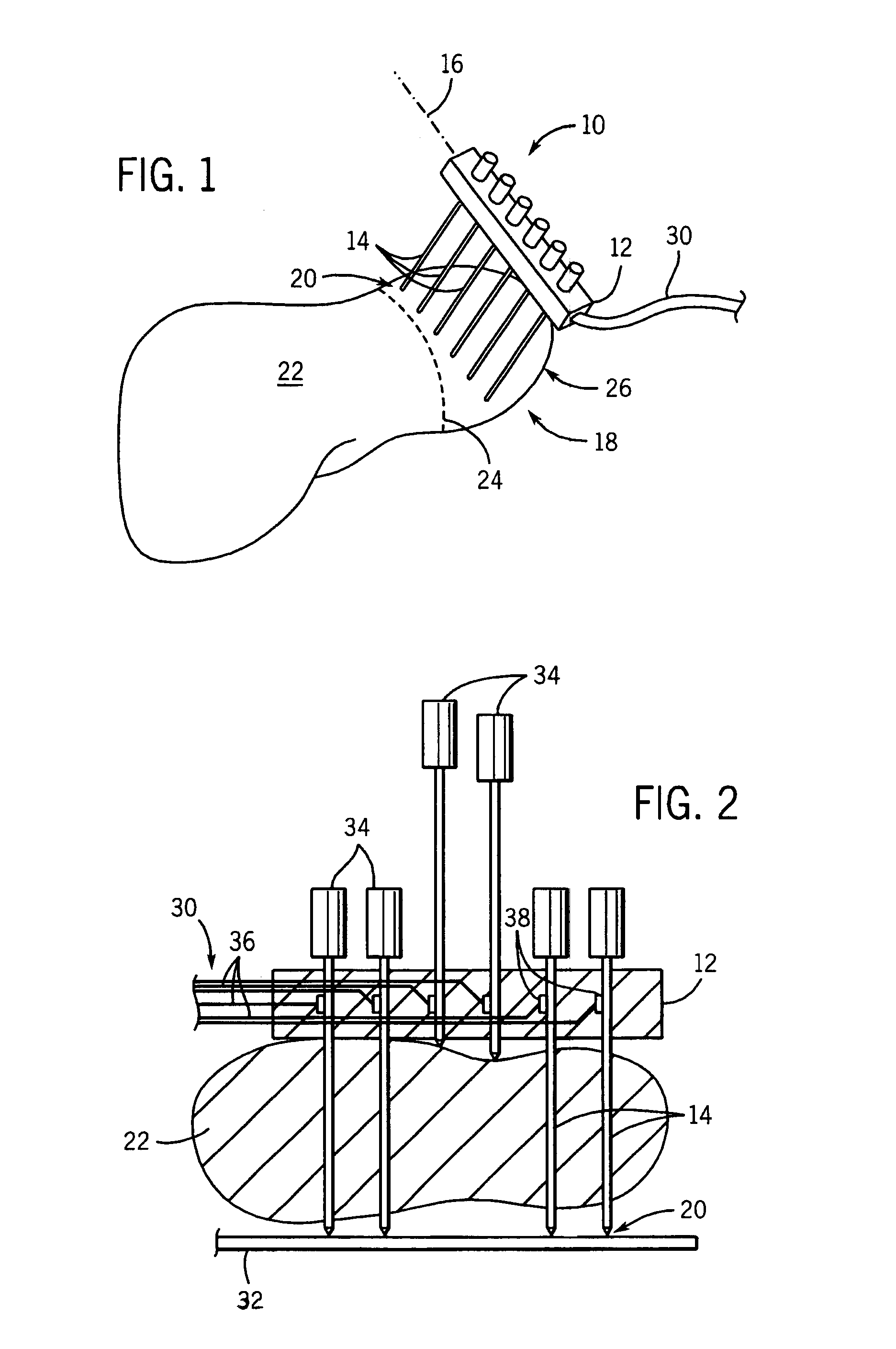
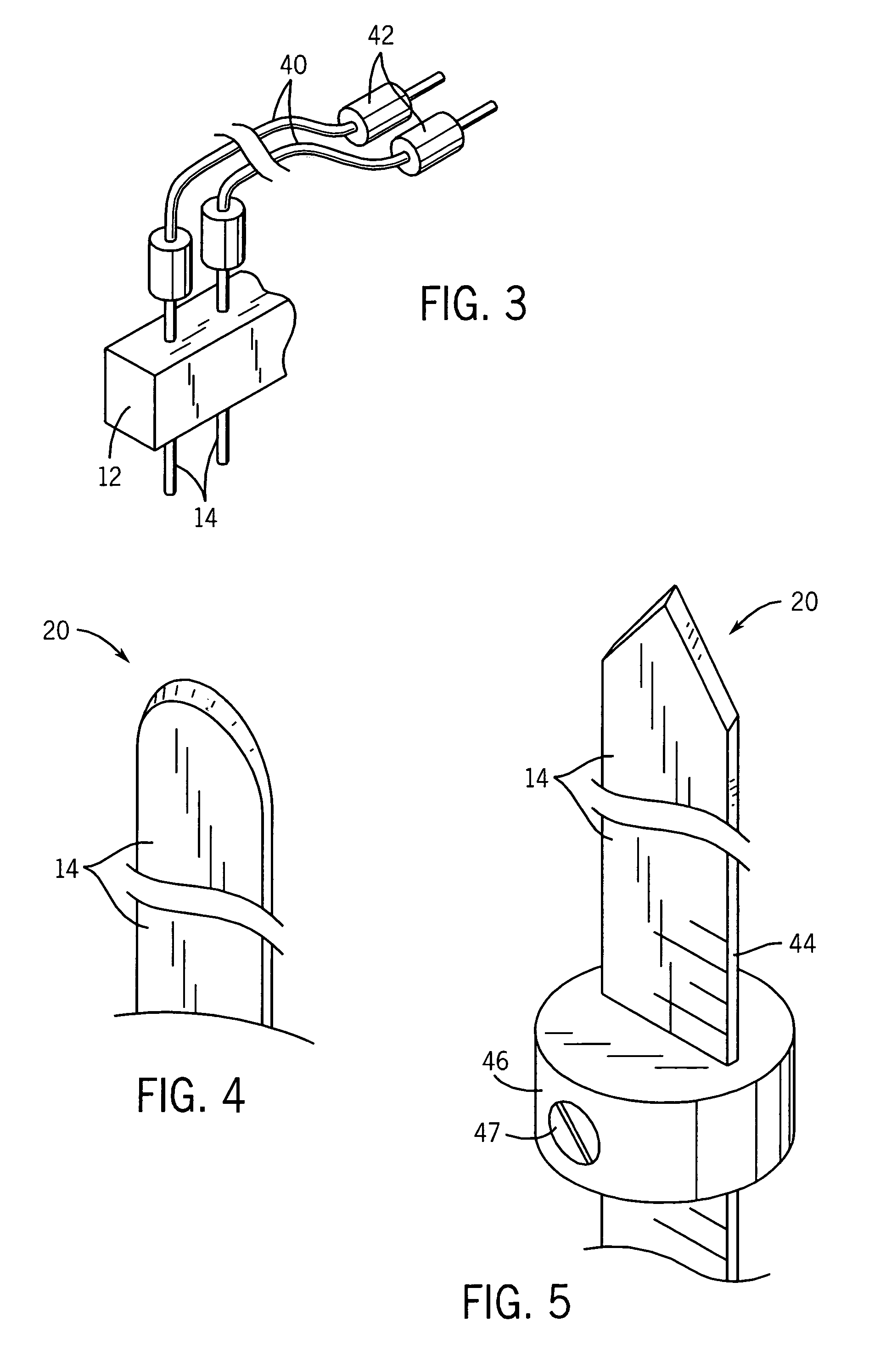
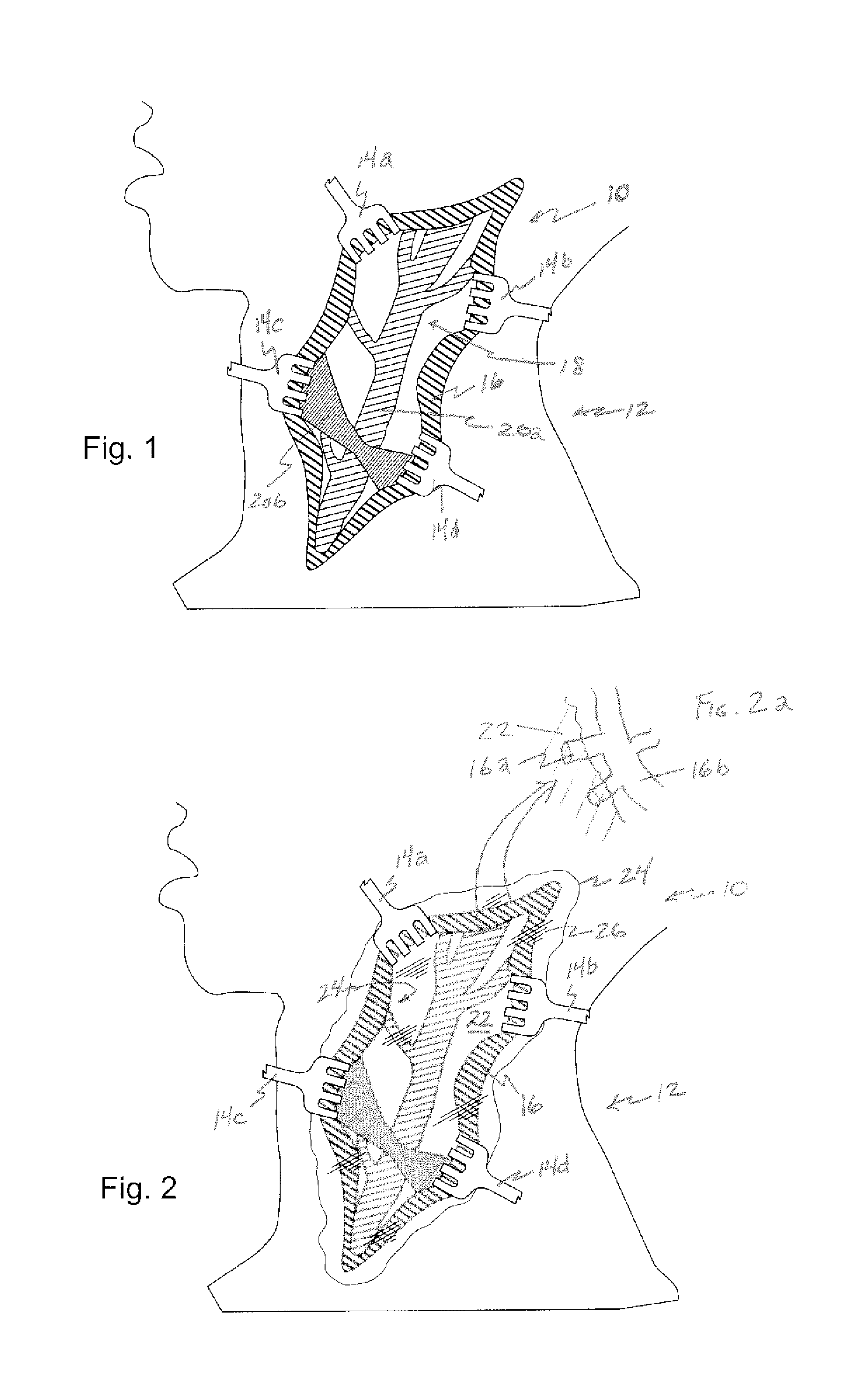
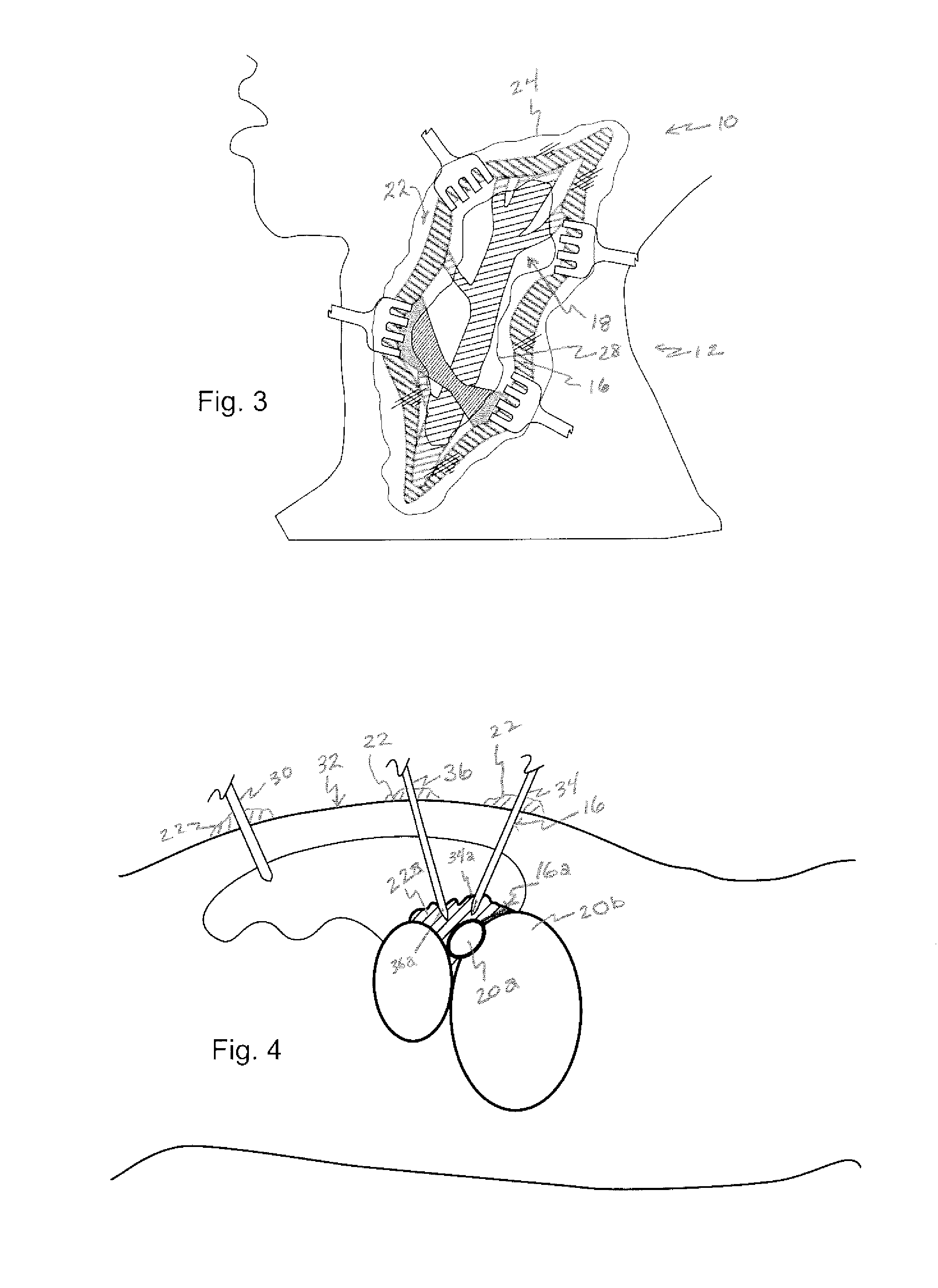
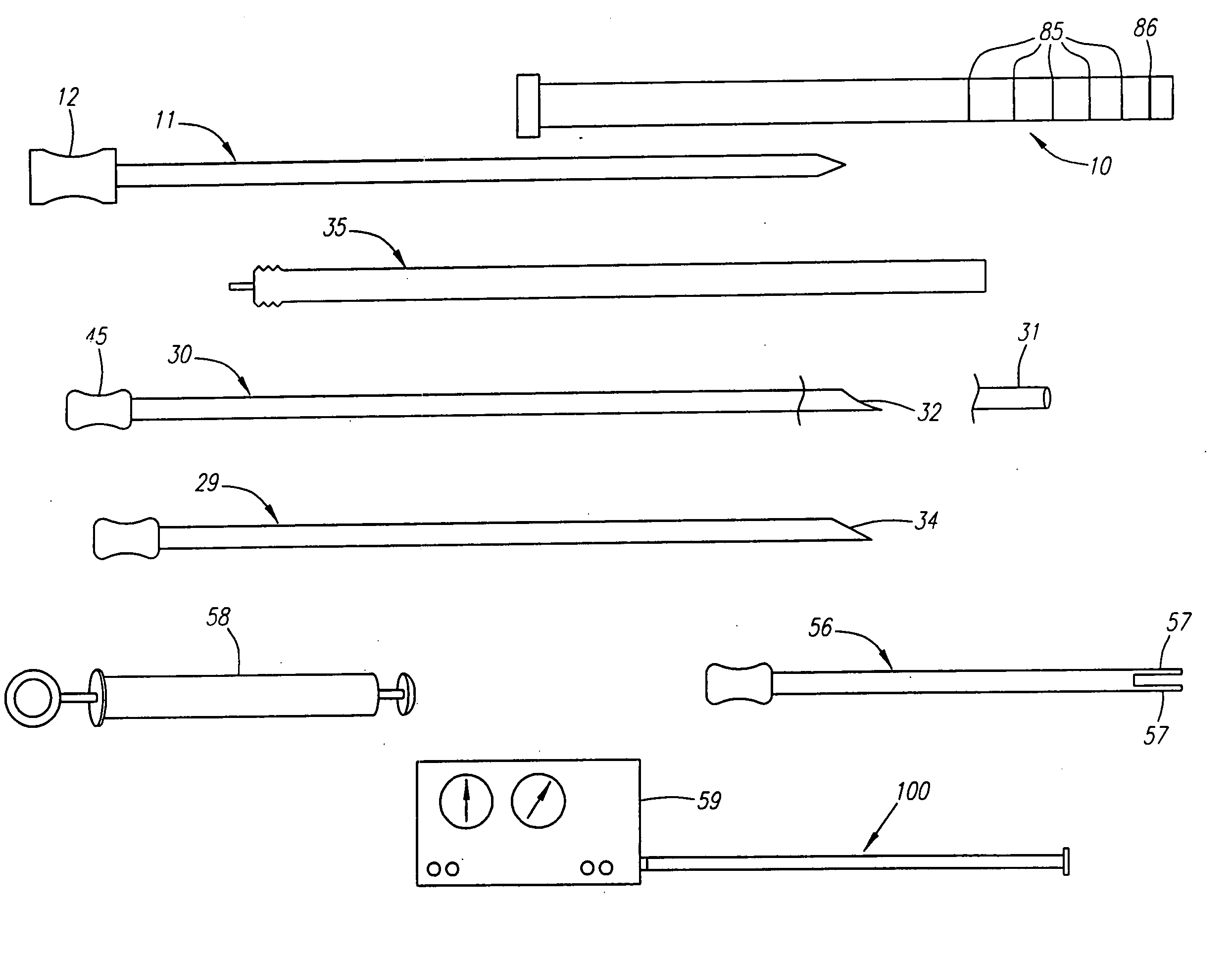
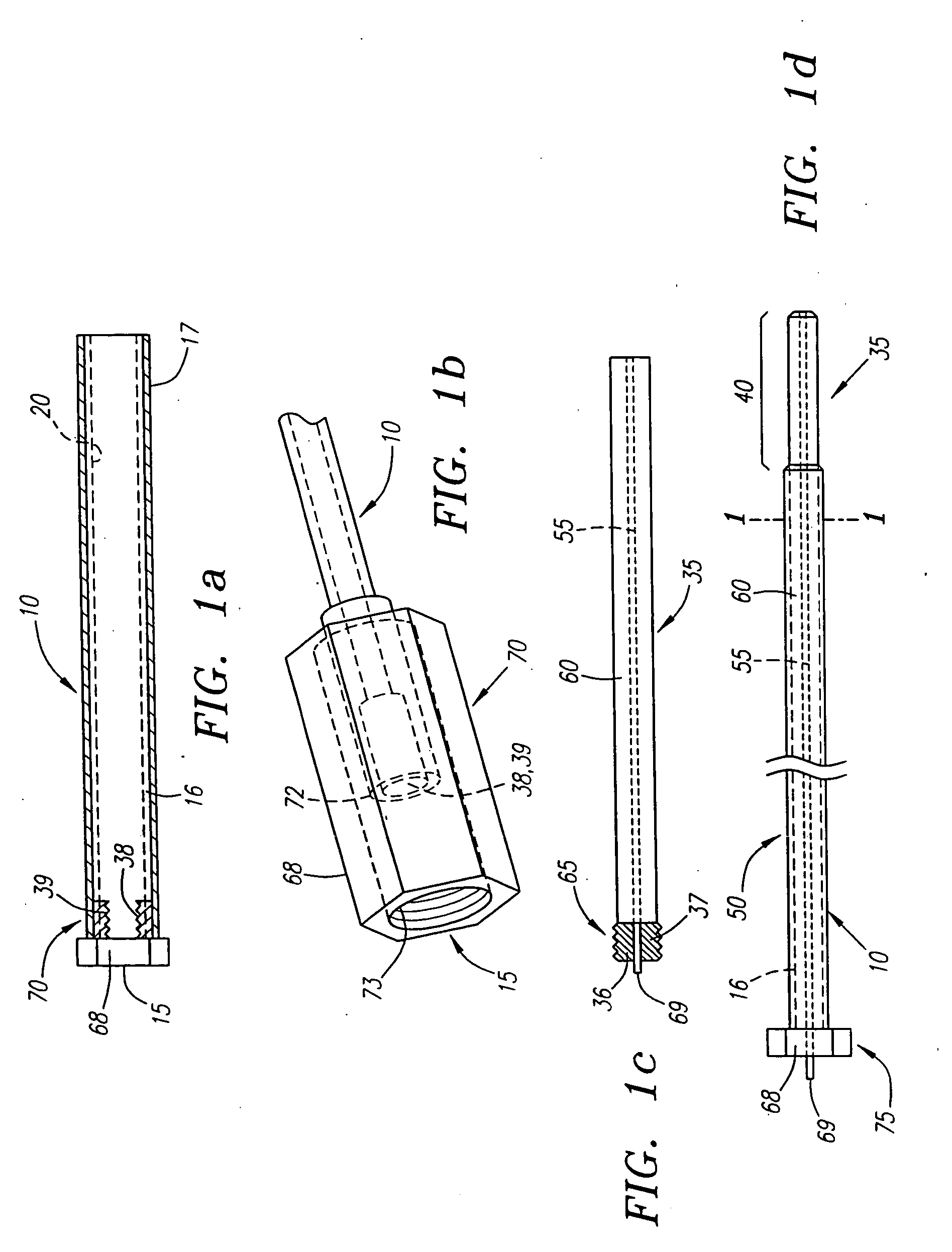
Depth and puncture control for blood vessel hemostasis system
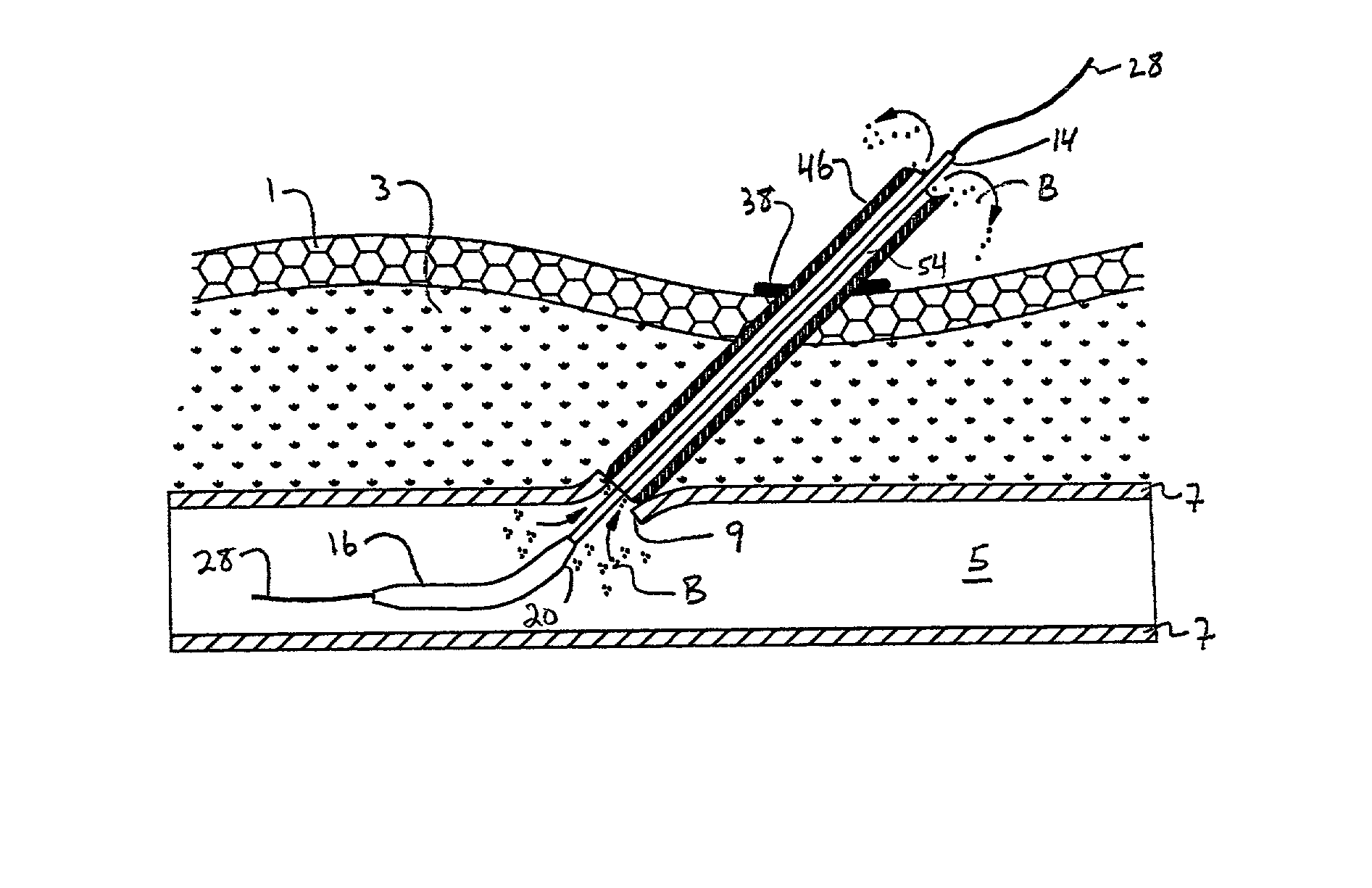
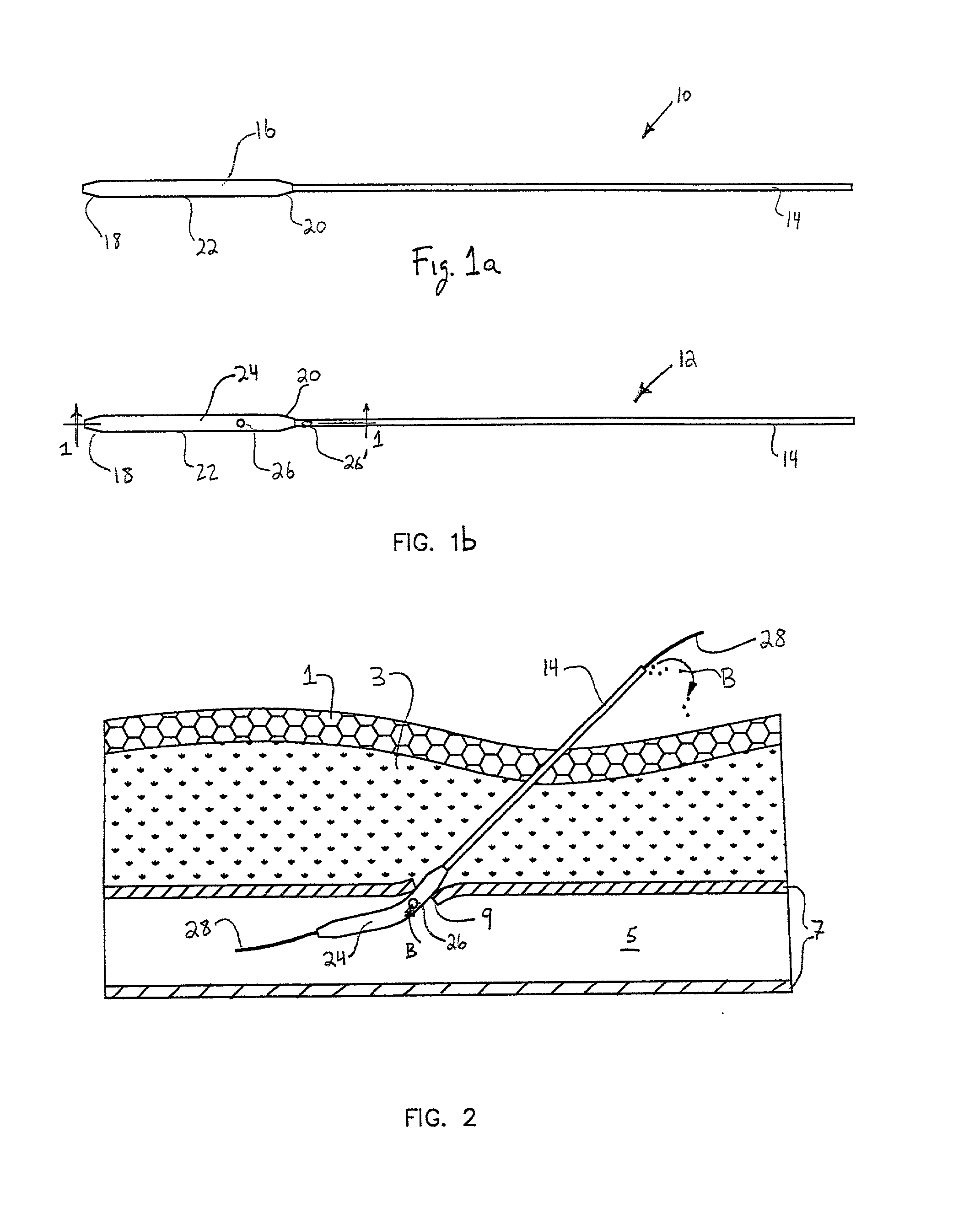
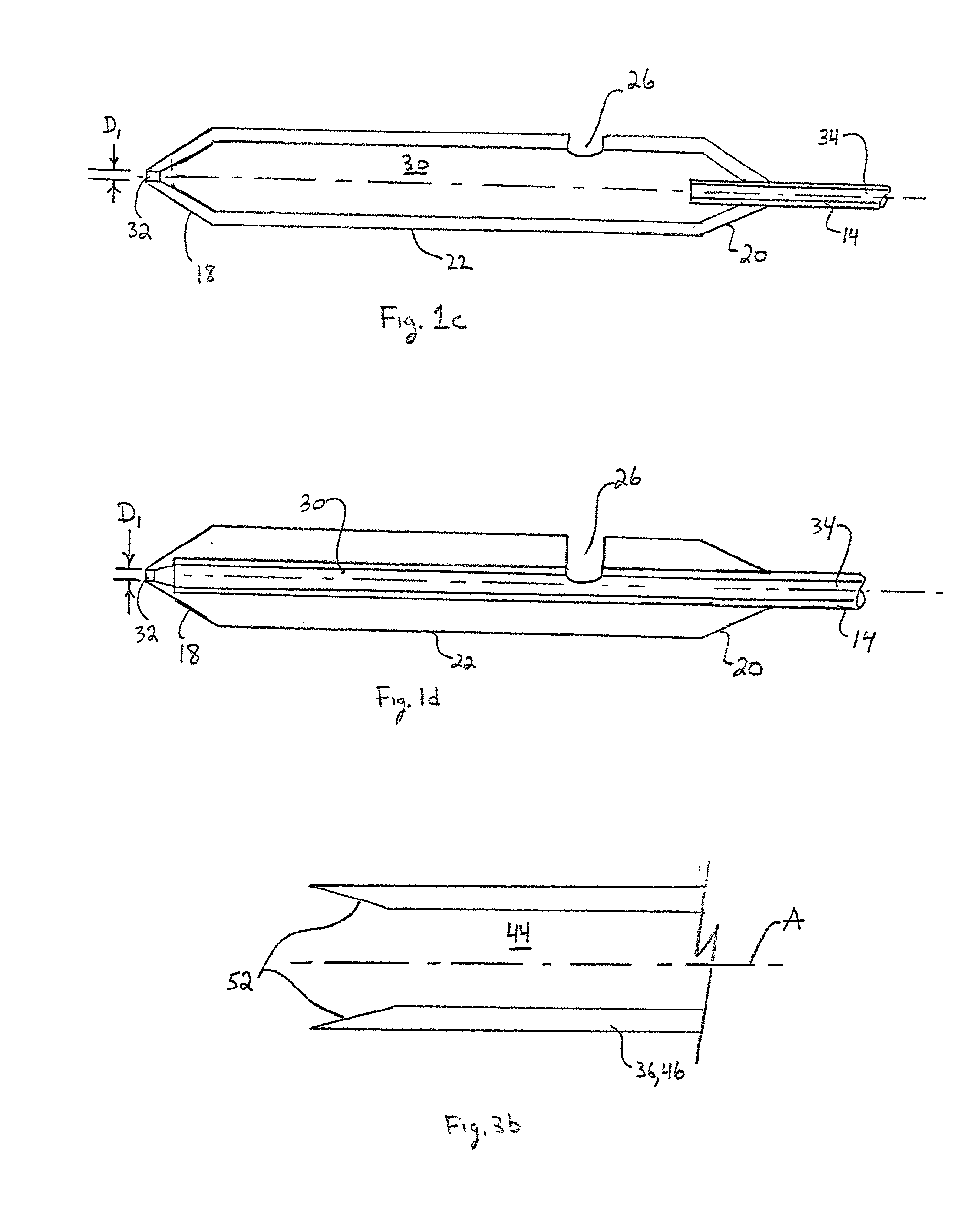
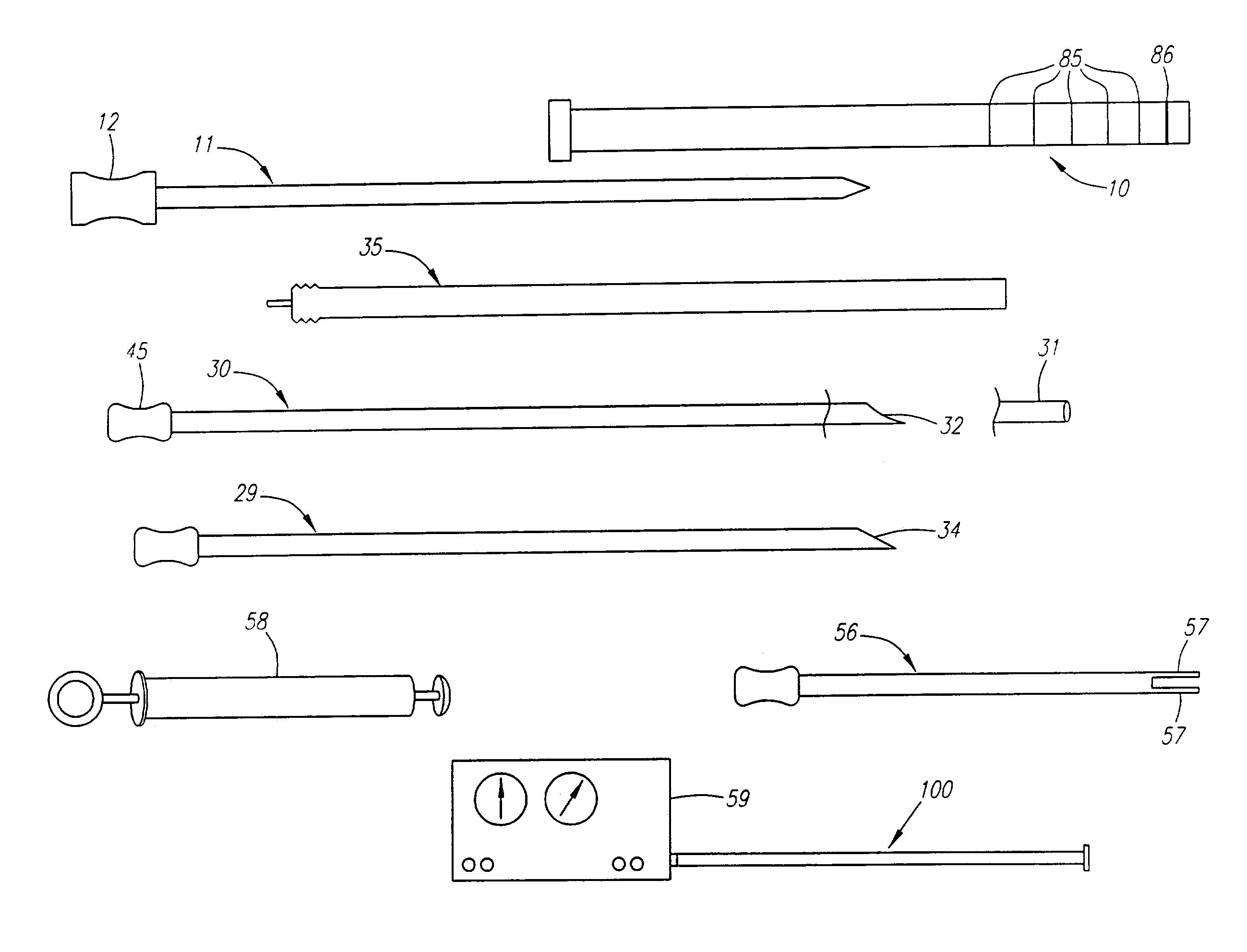
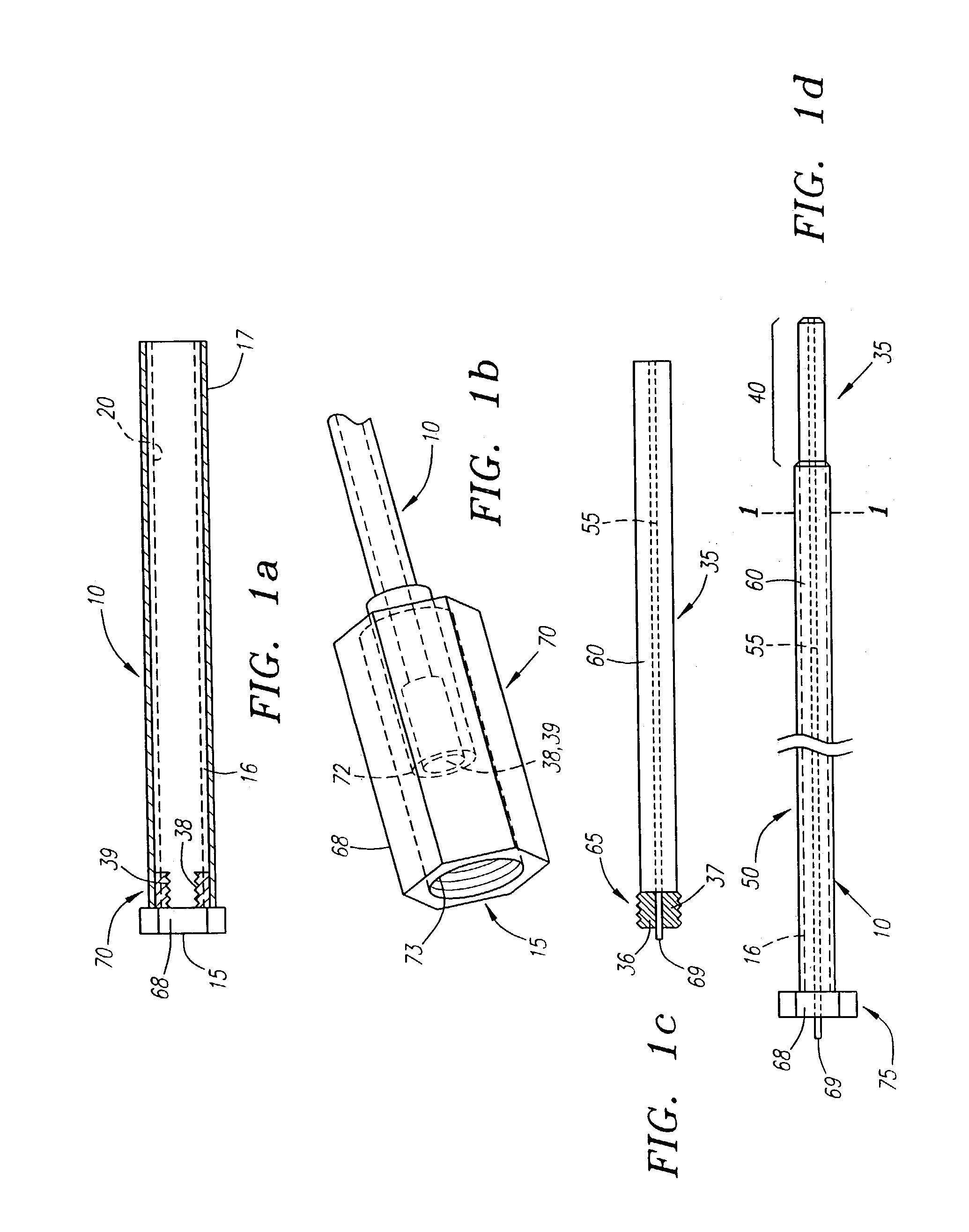
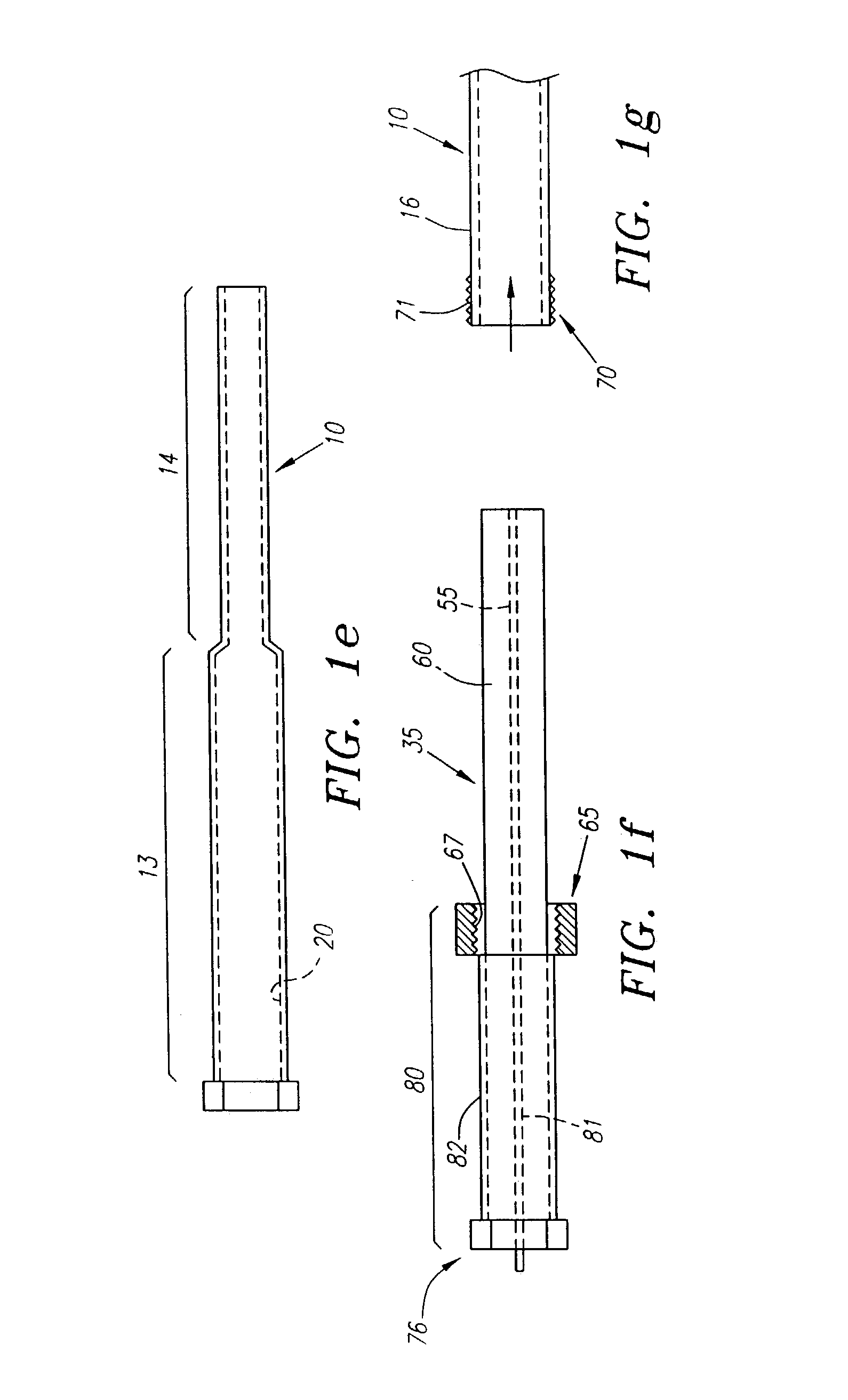
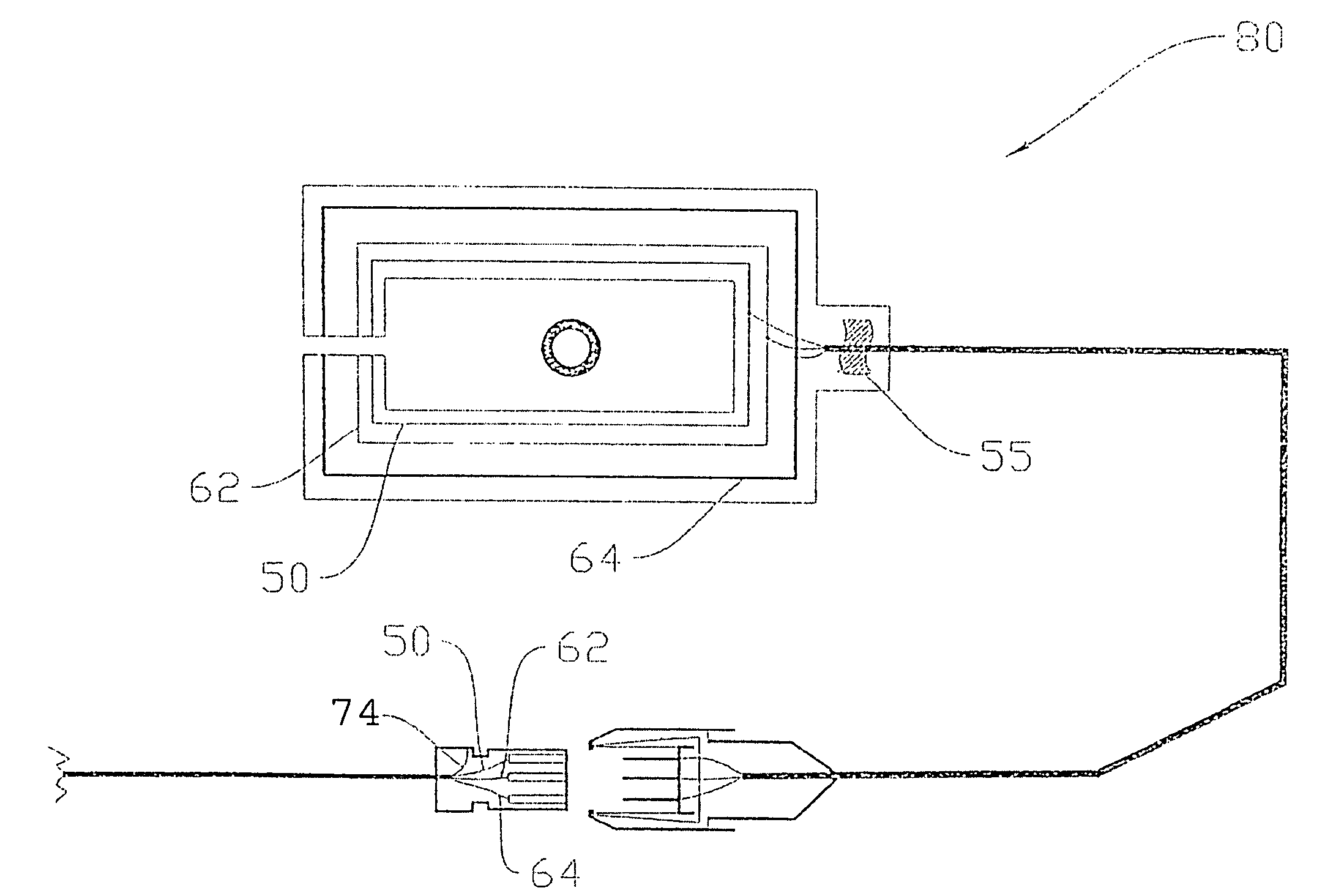
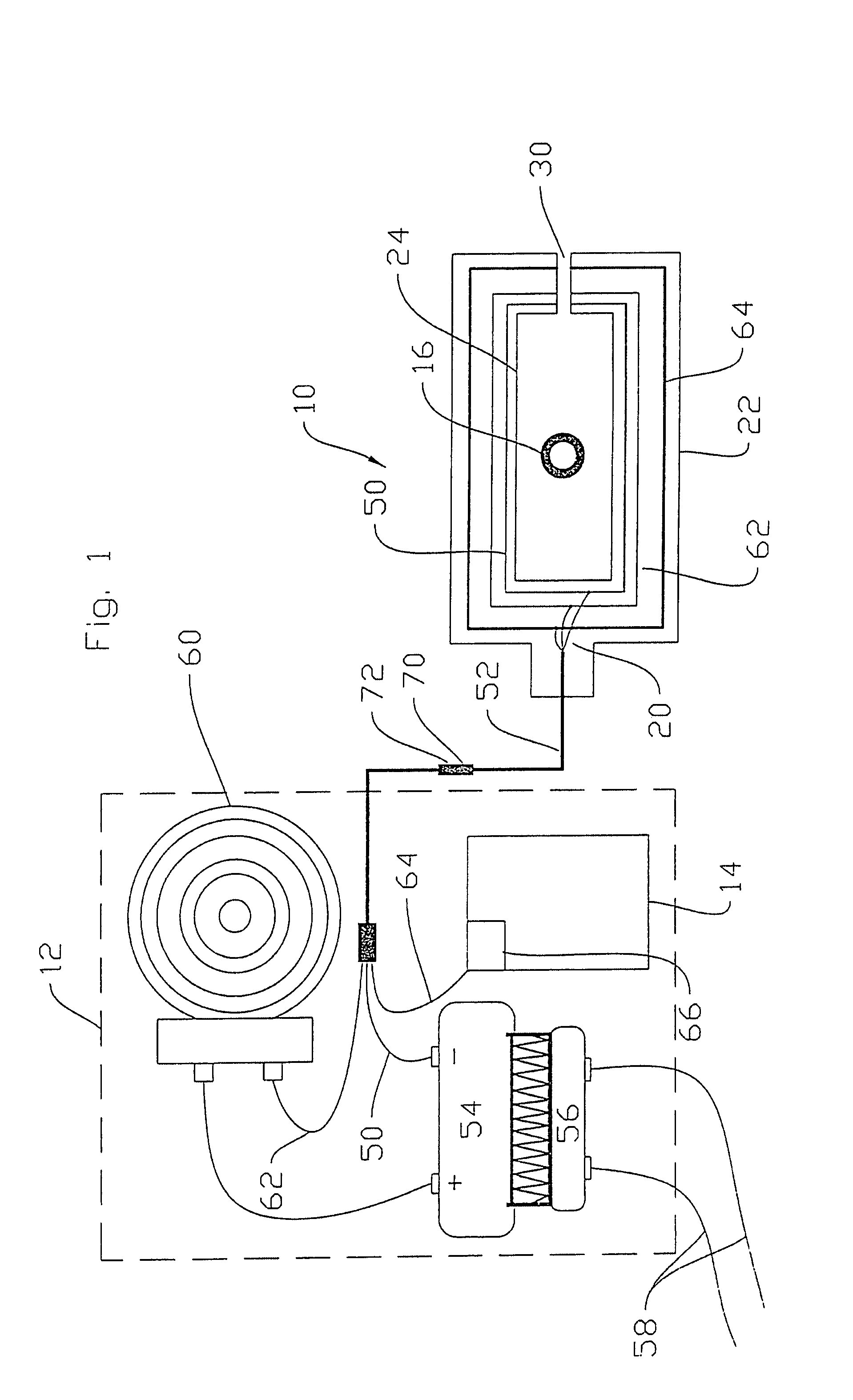
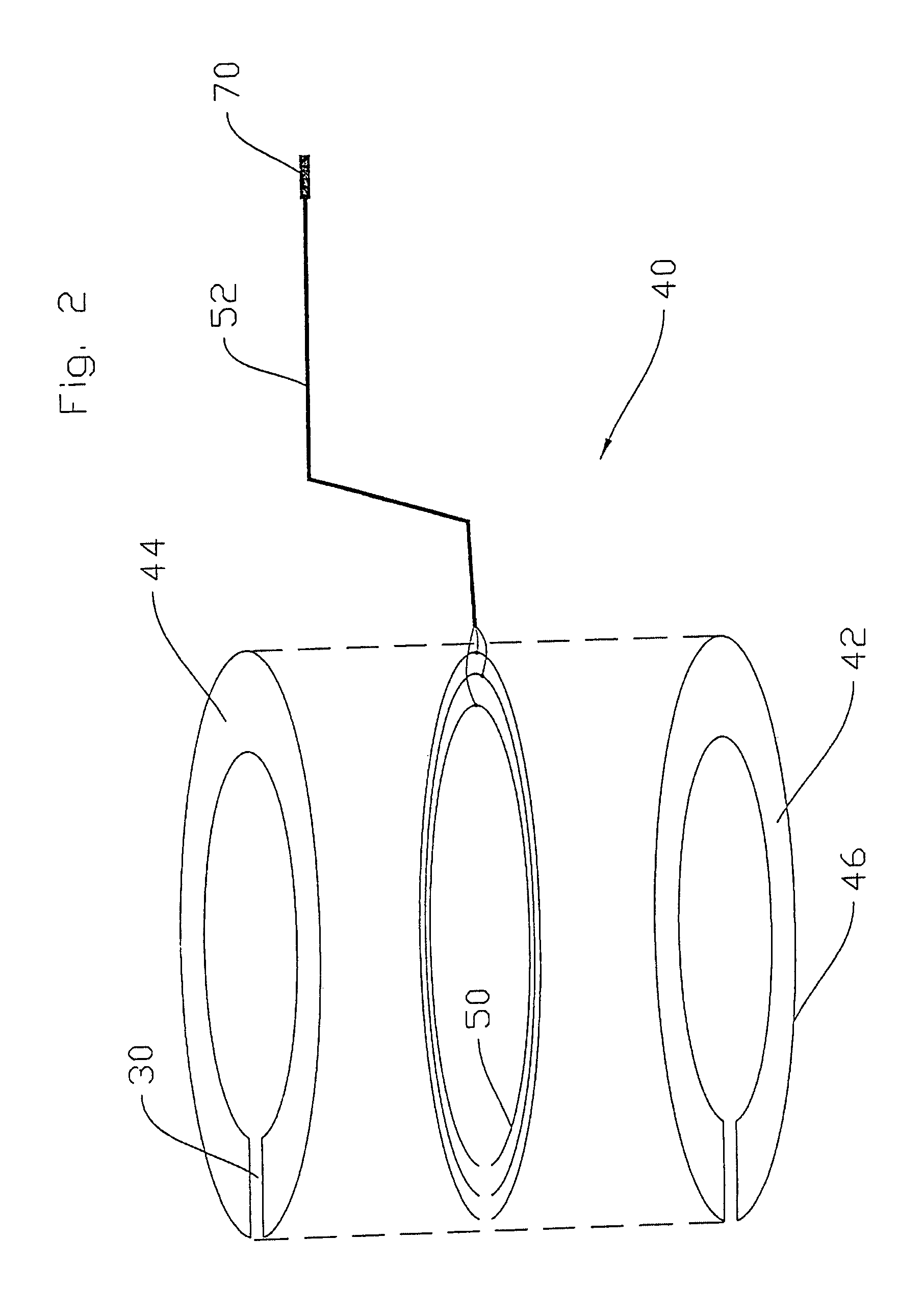
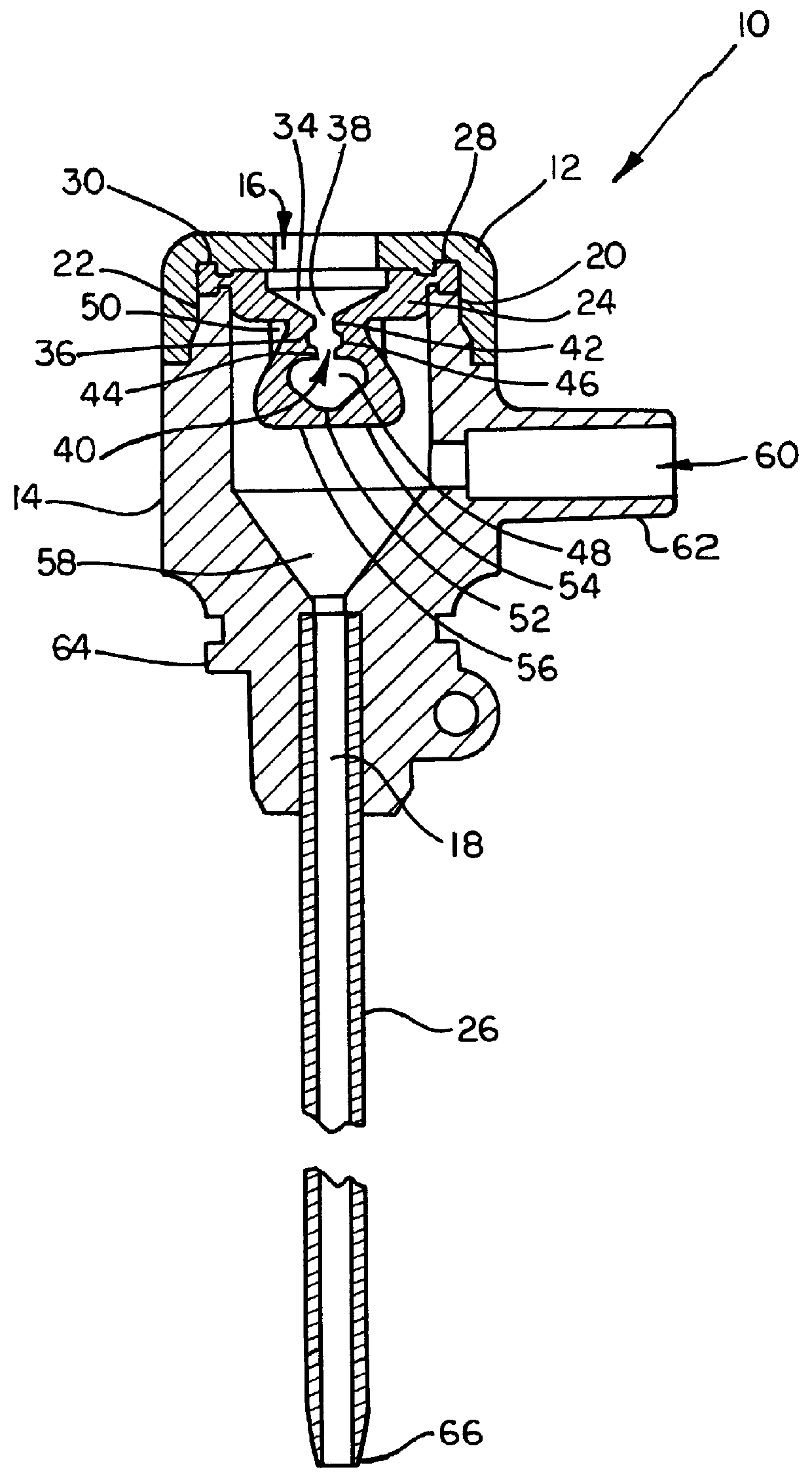
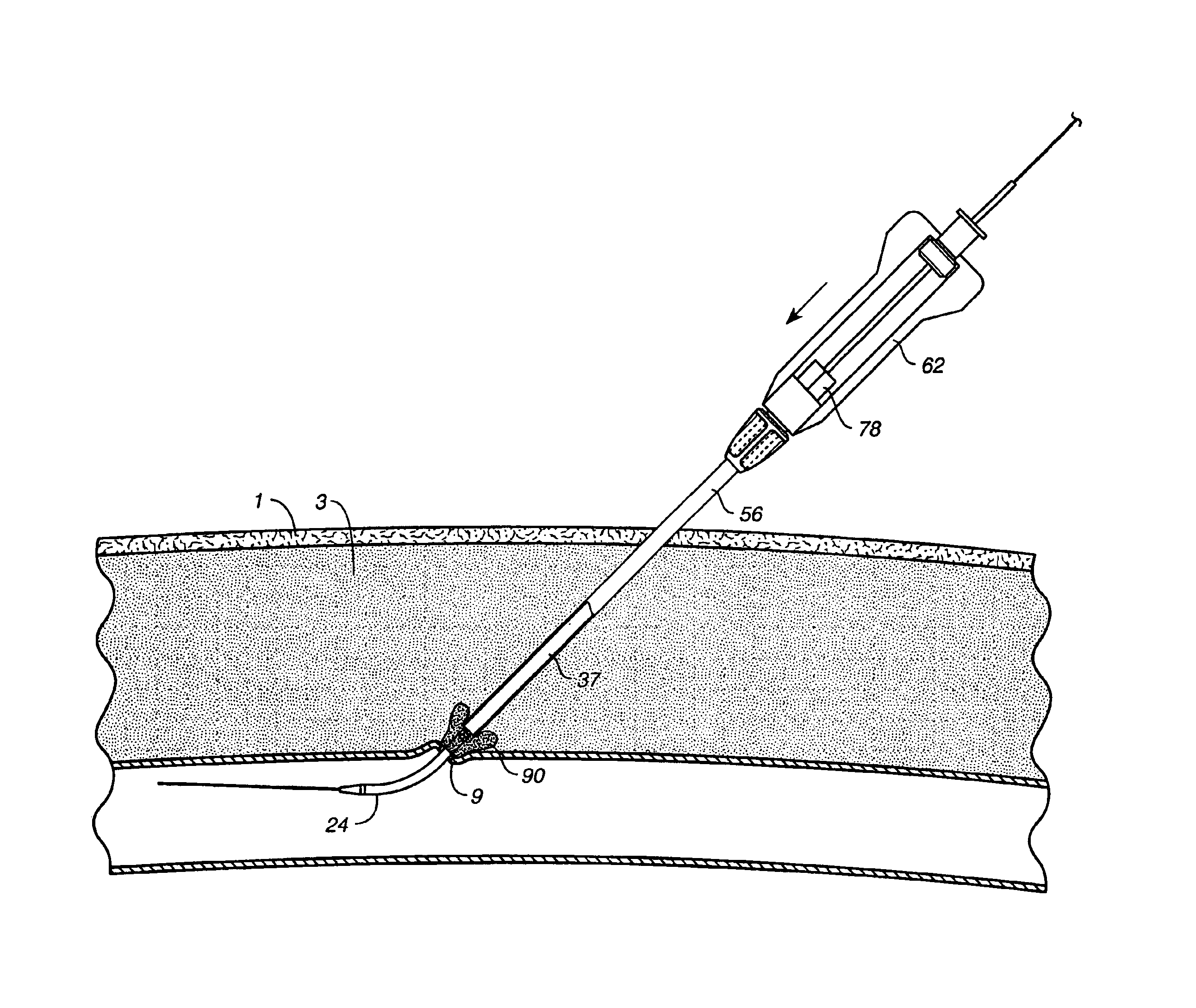
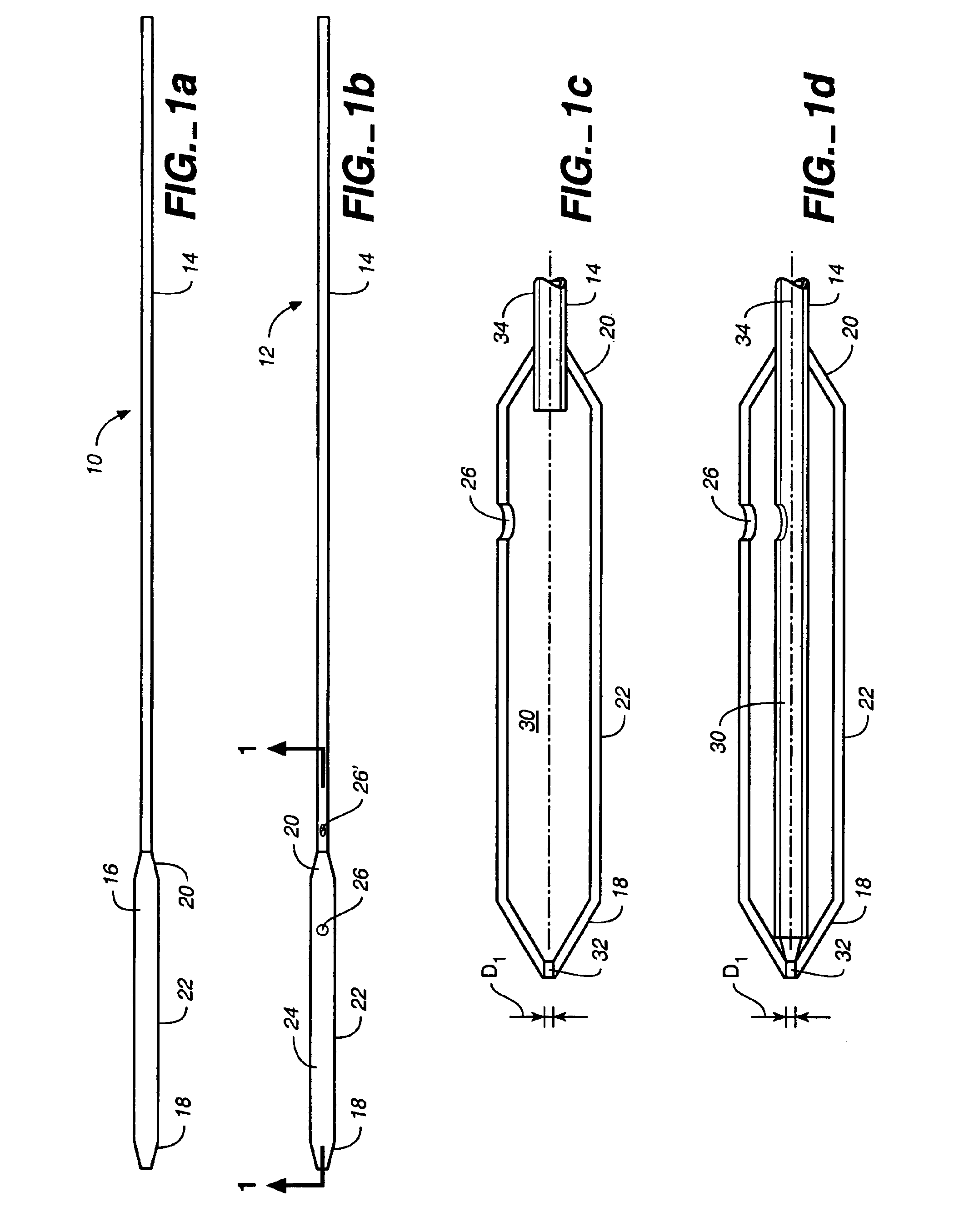
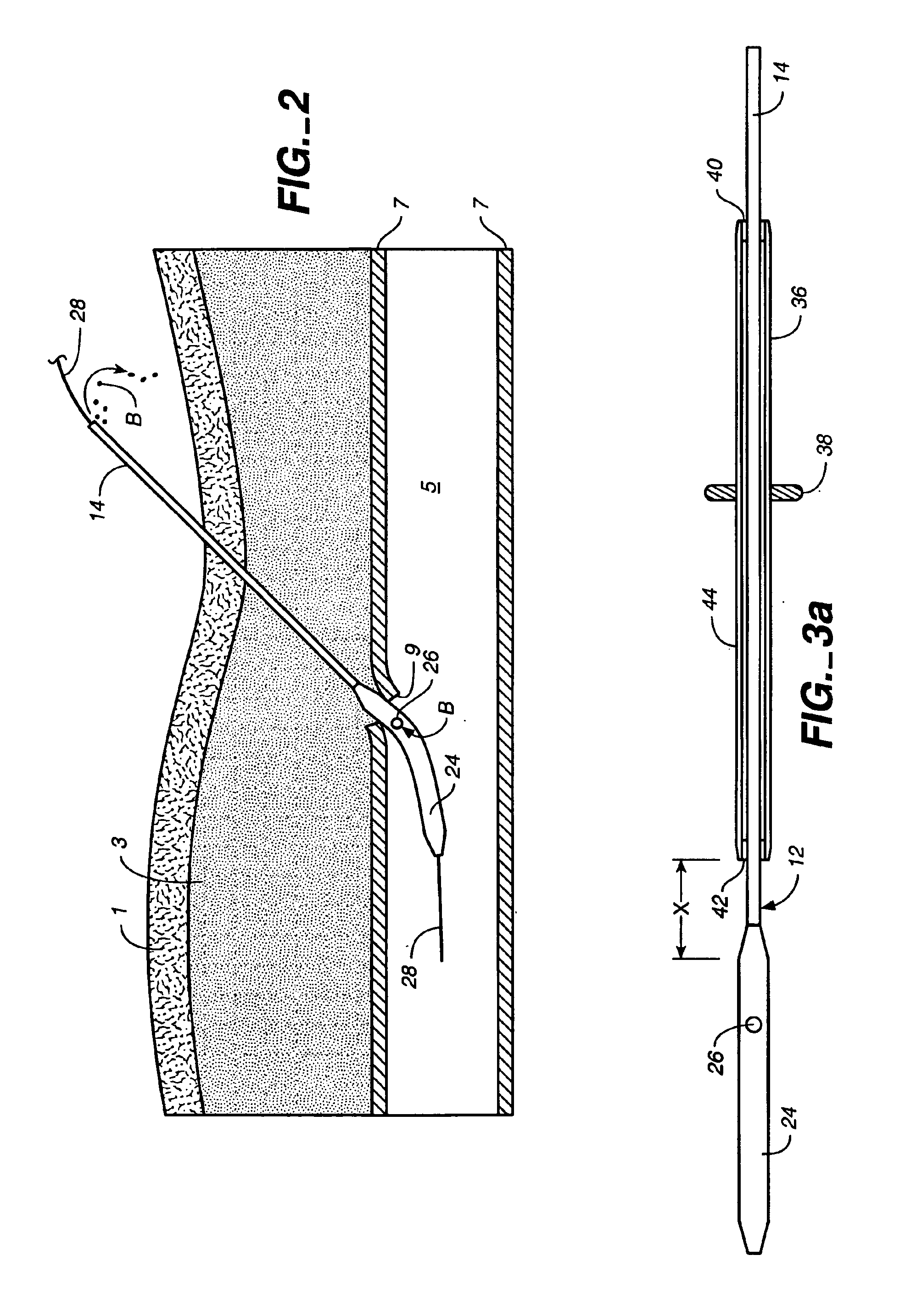
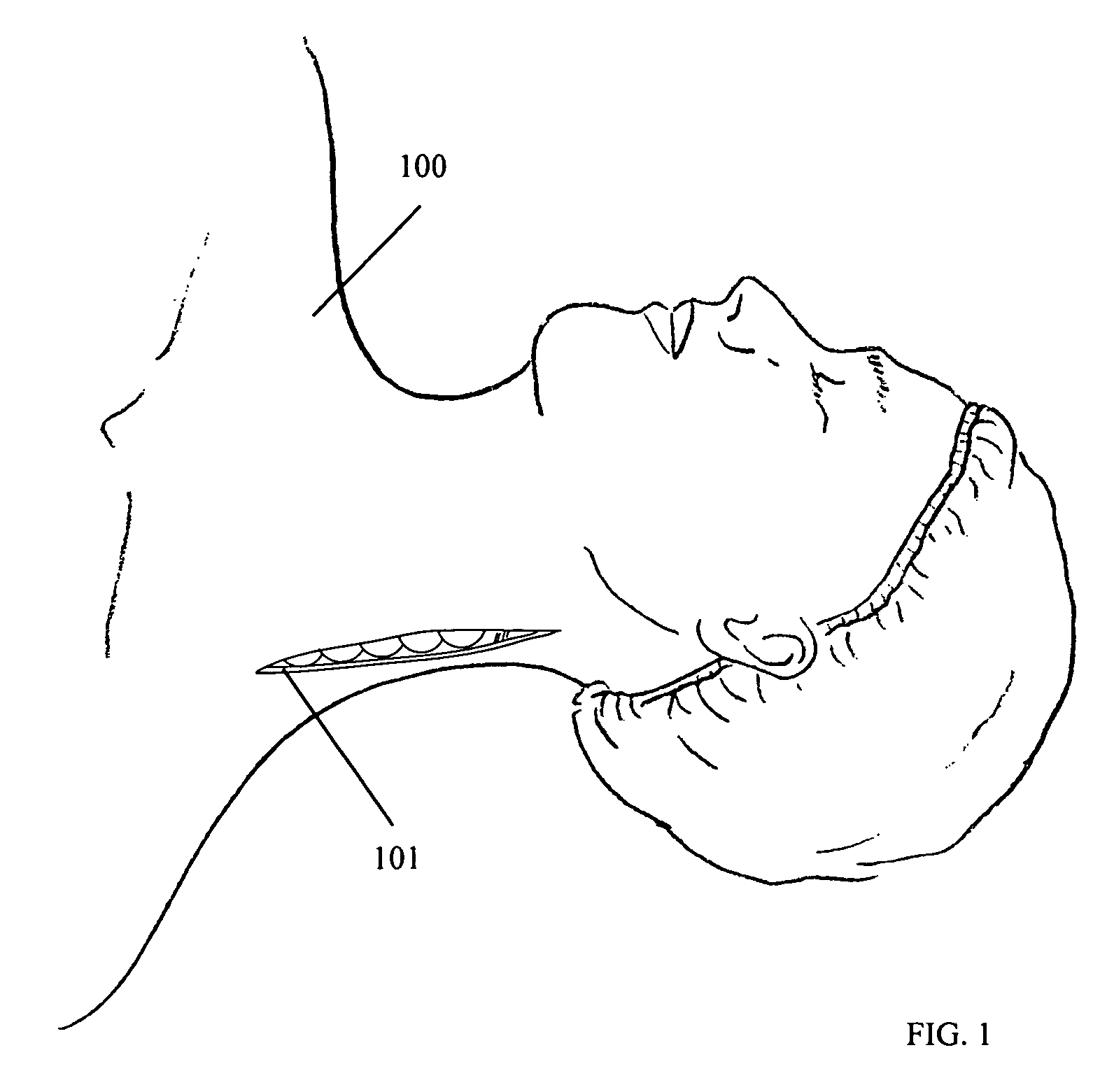
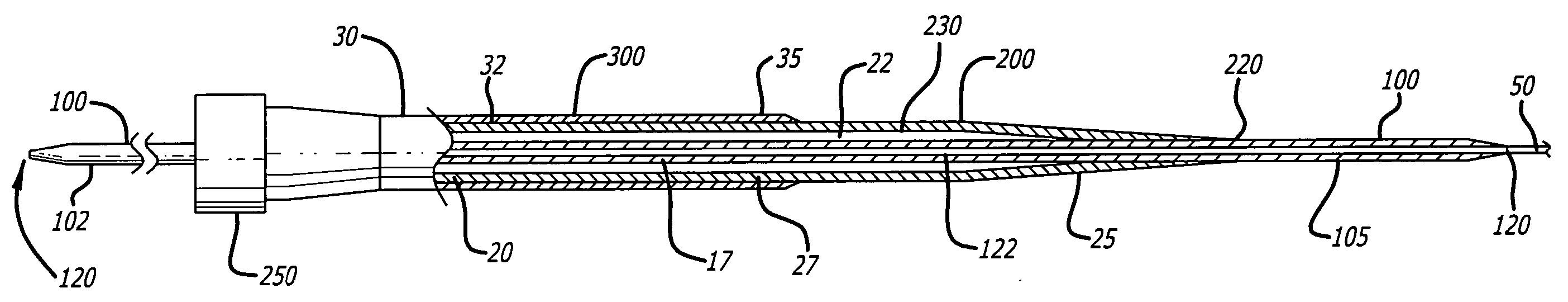
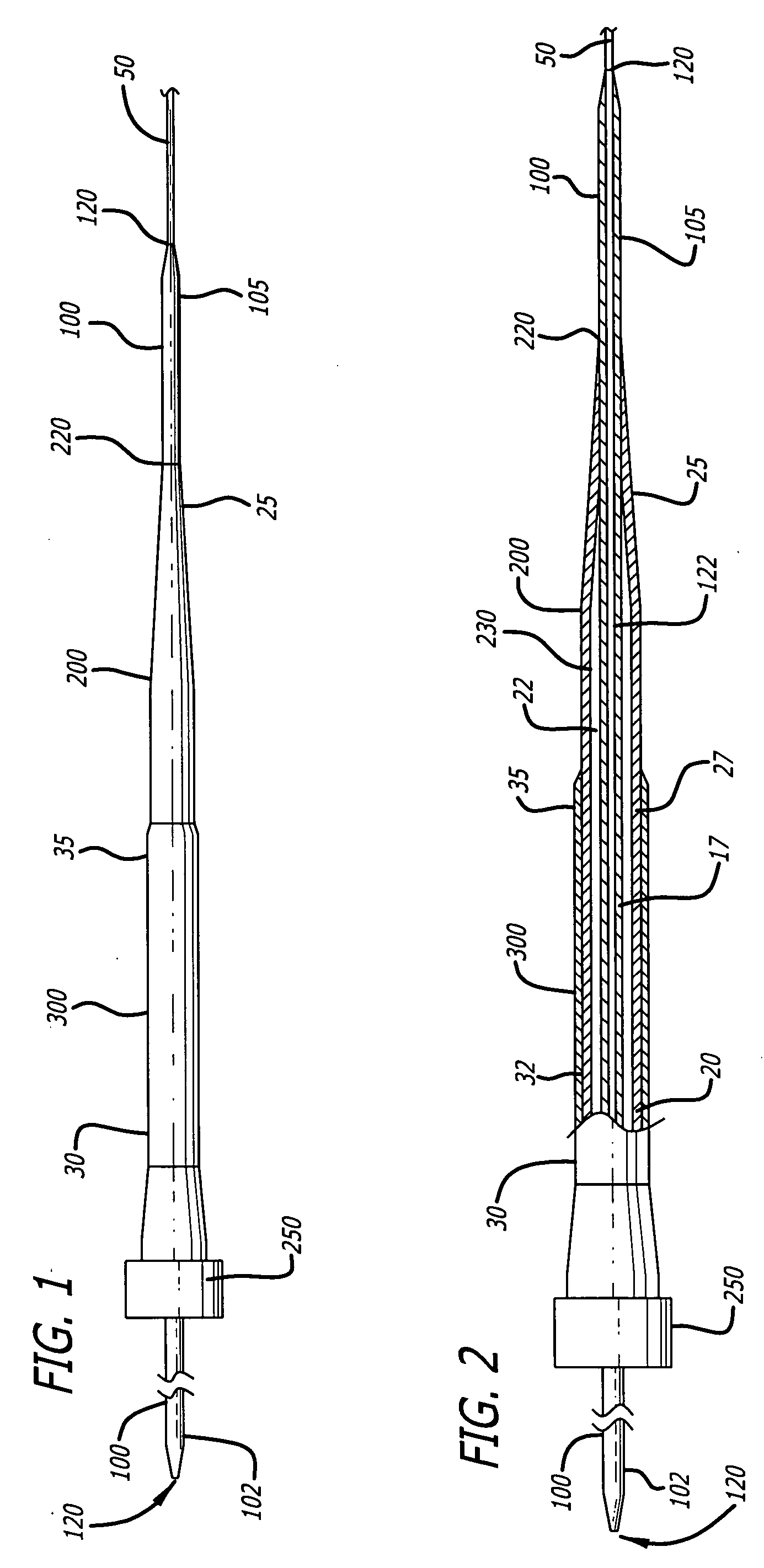
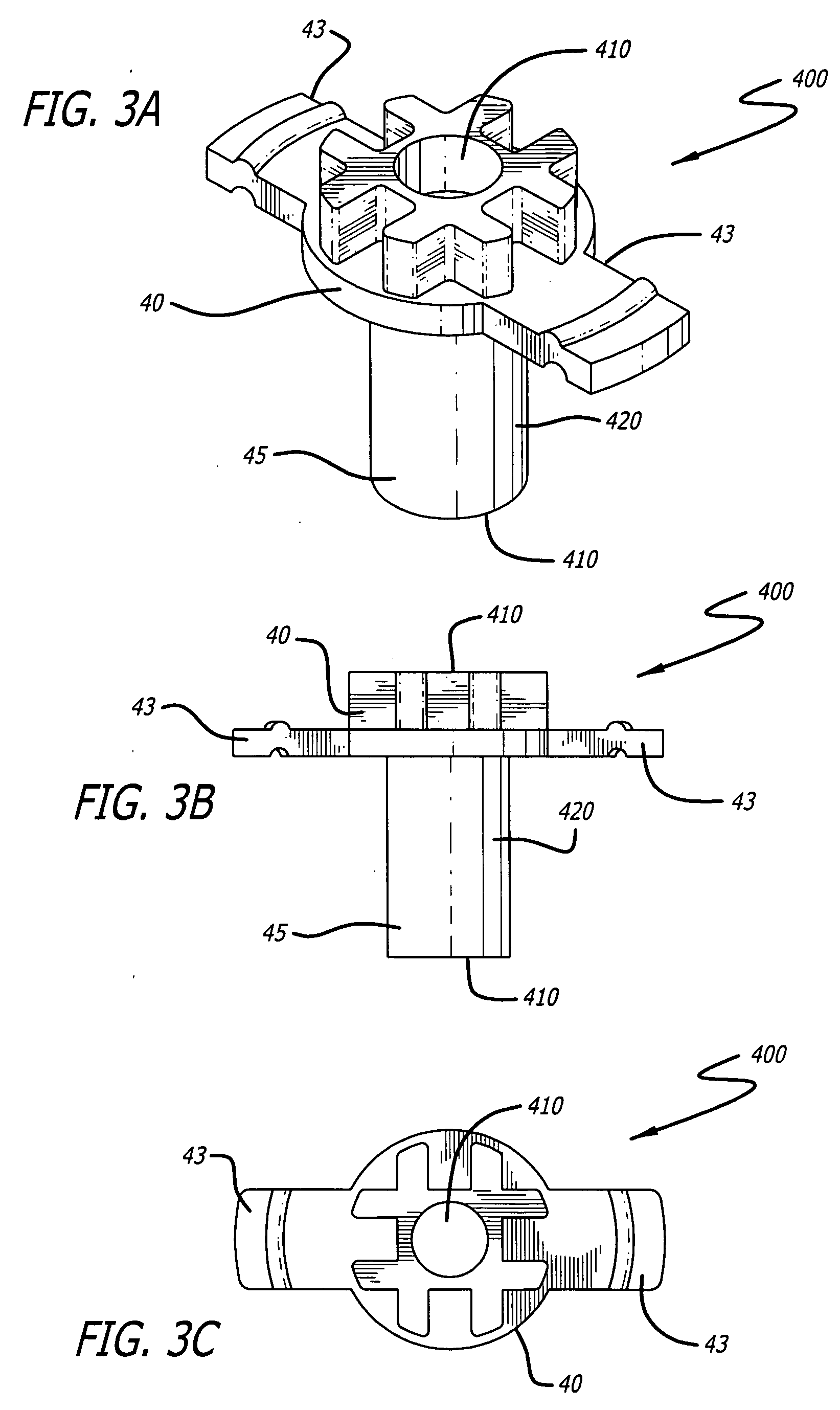
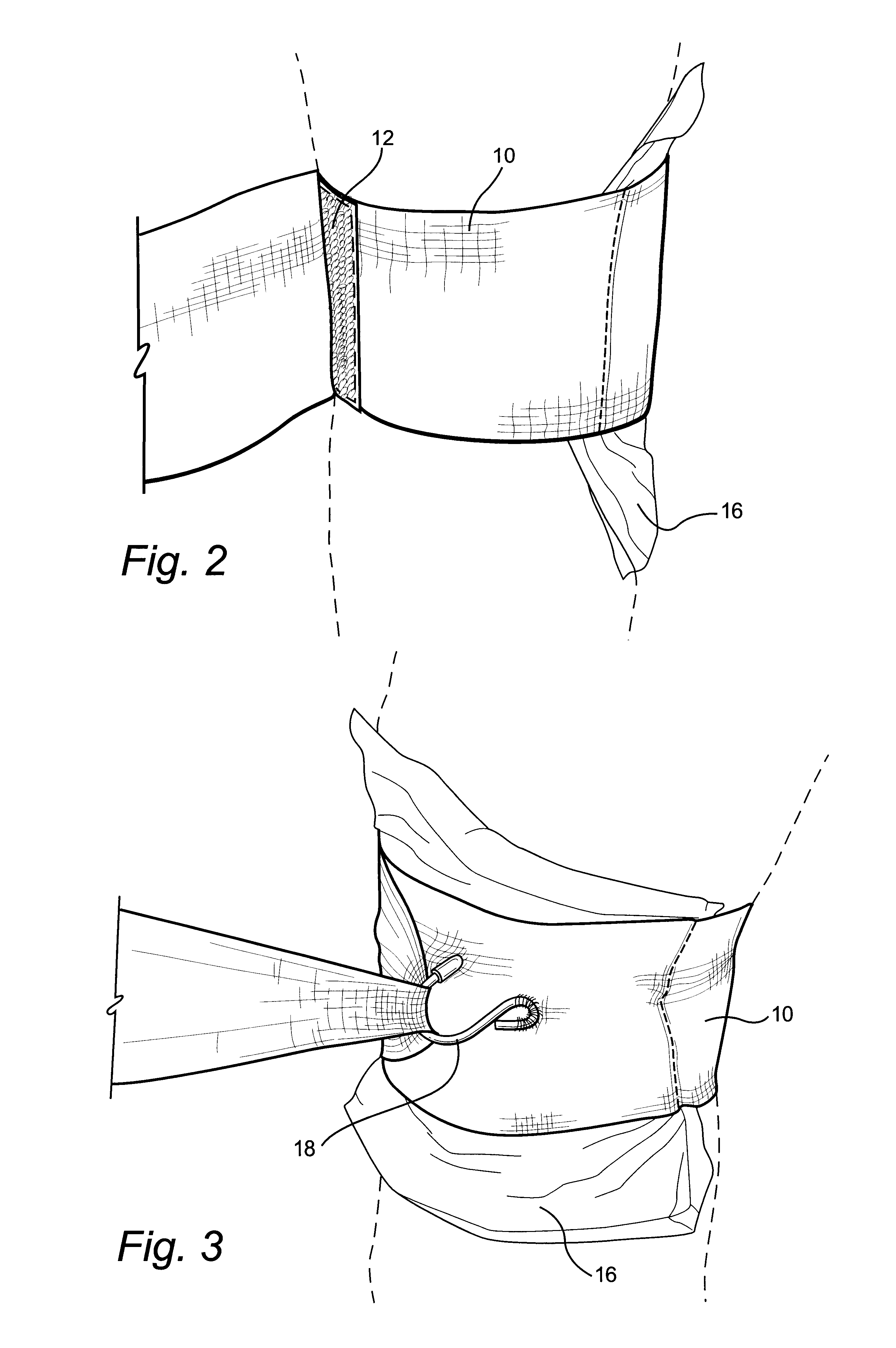
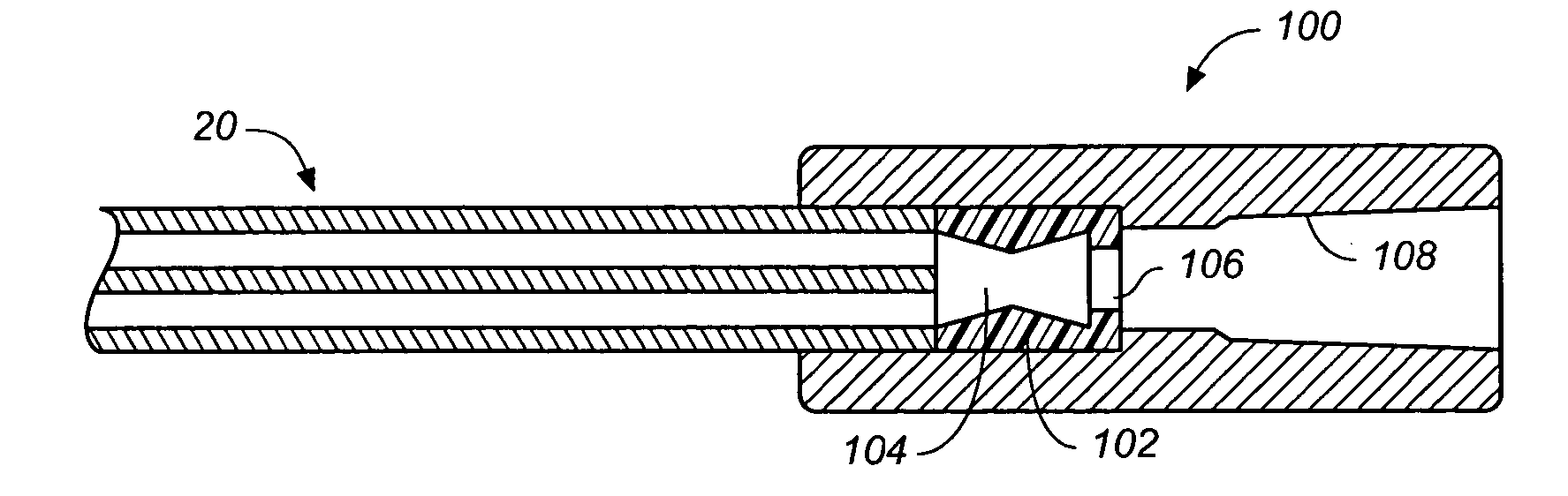
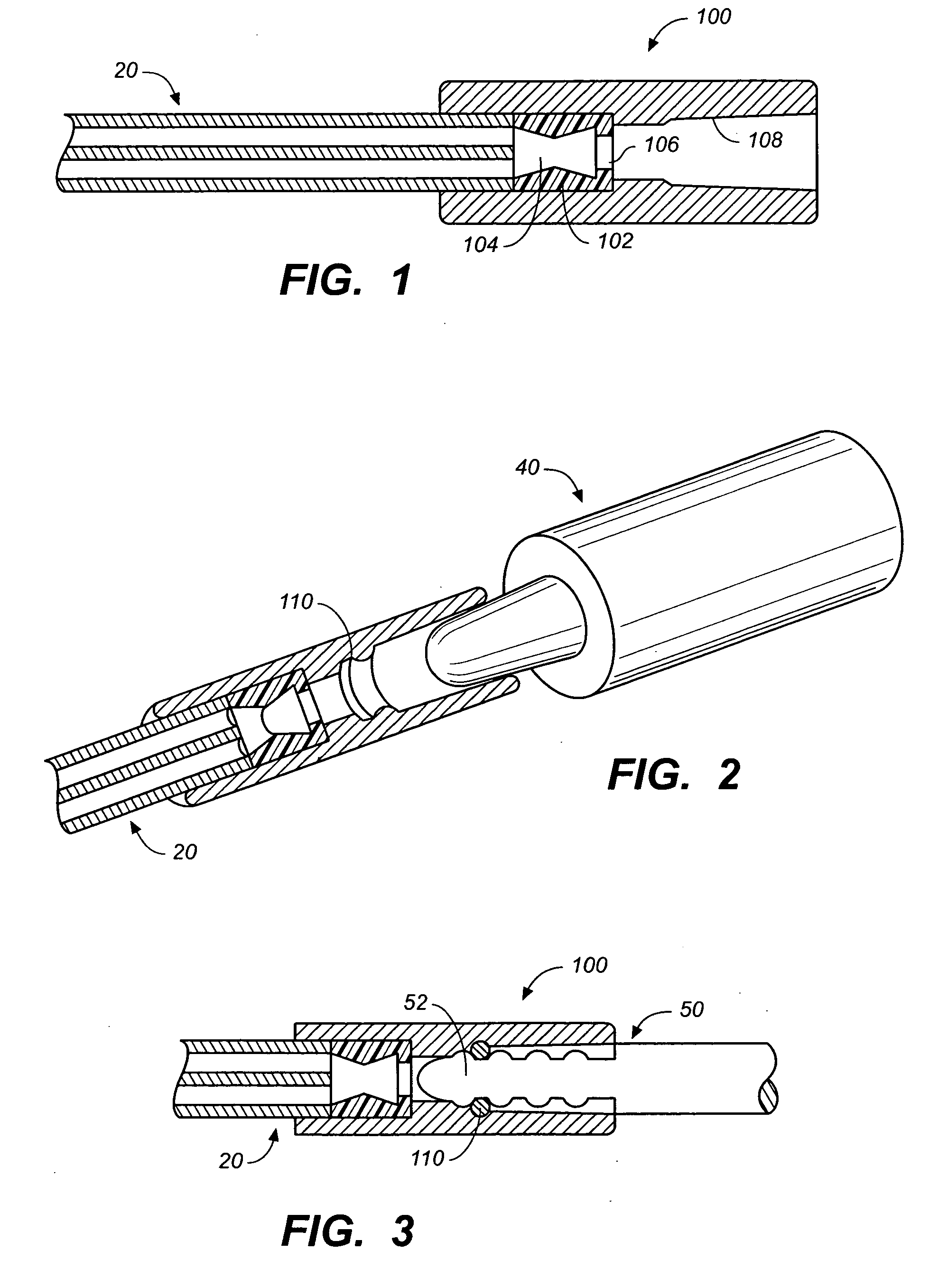
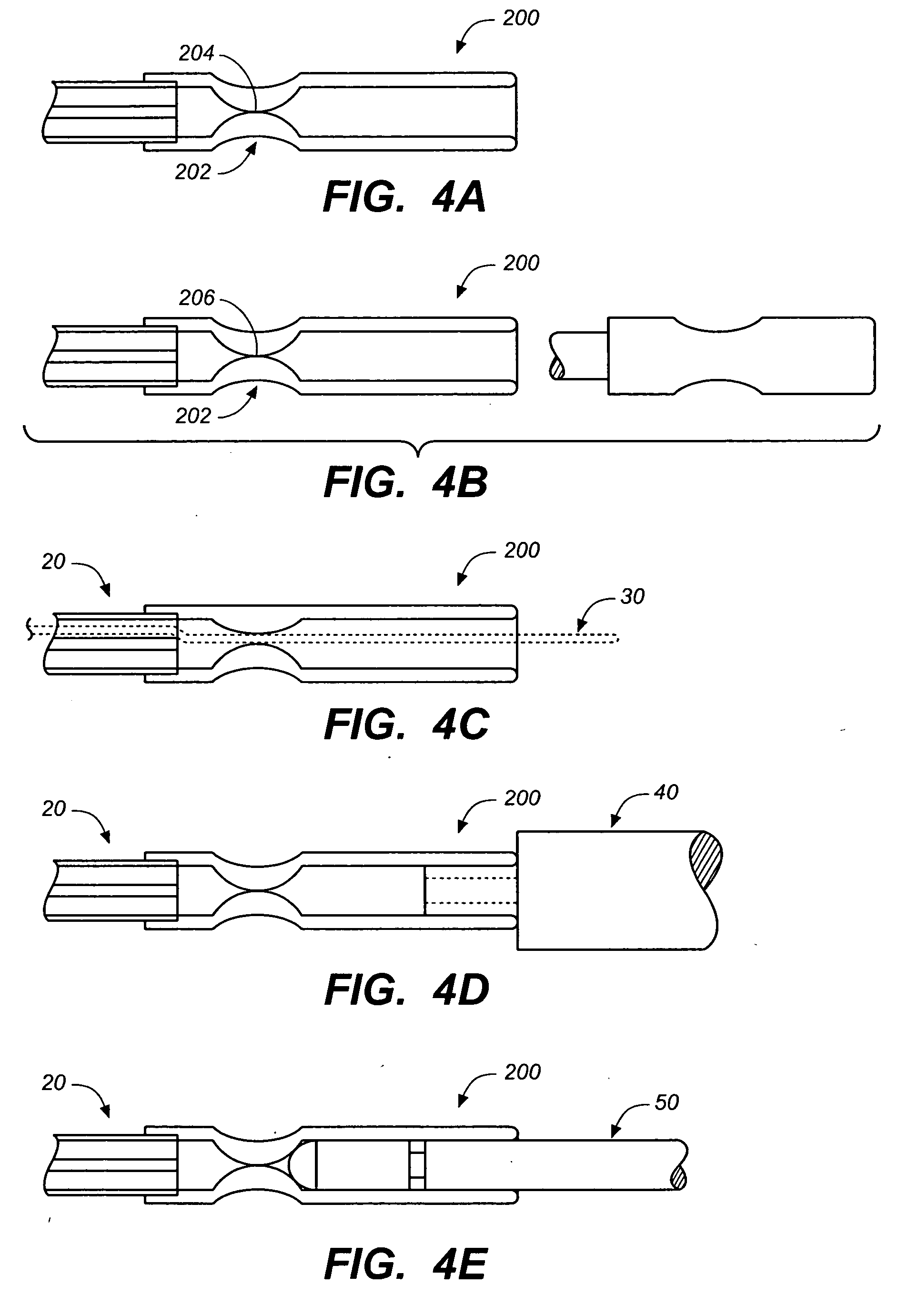
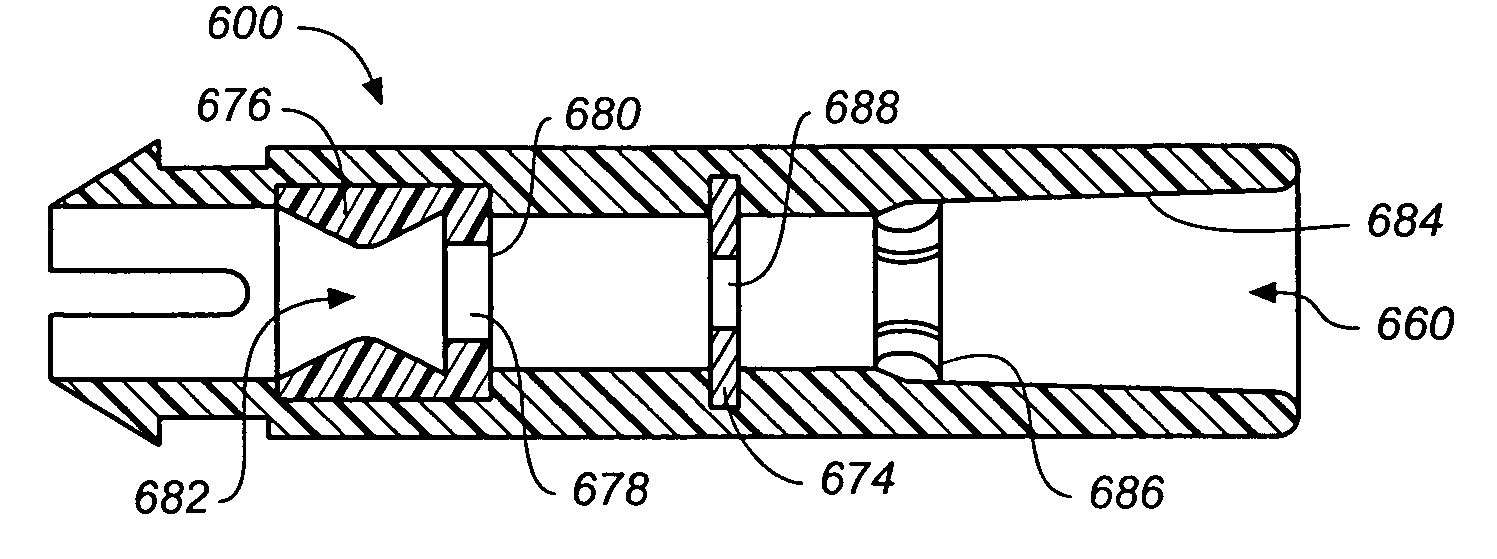
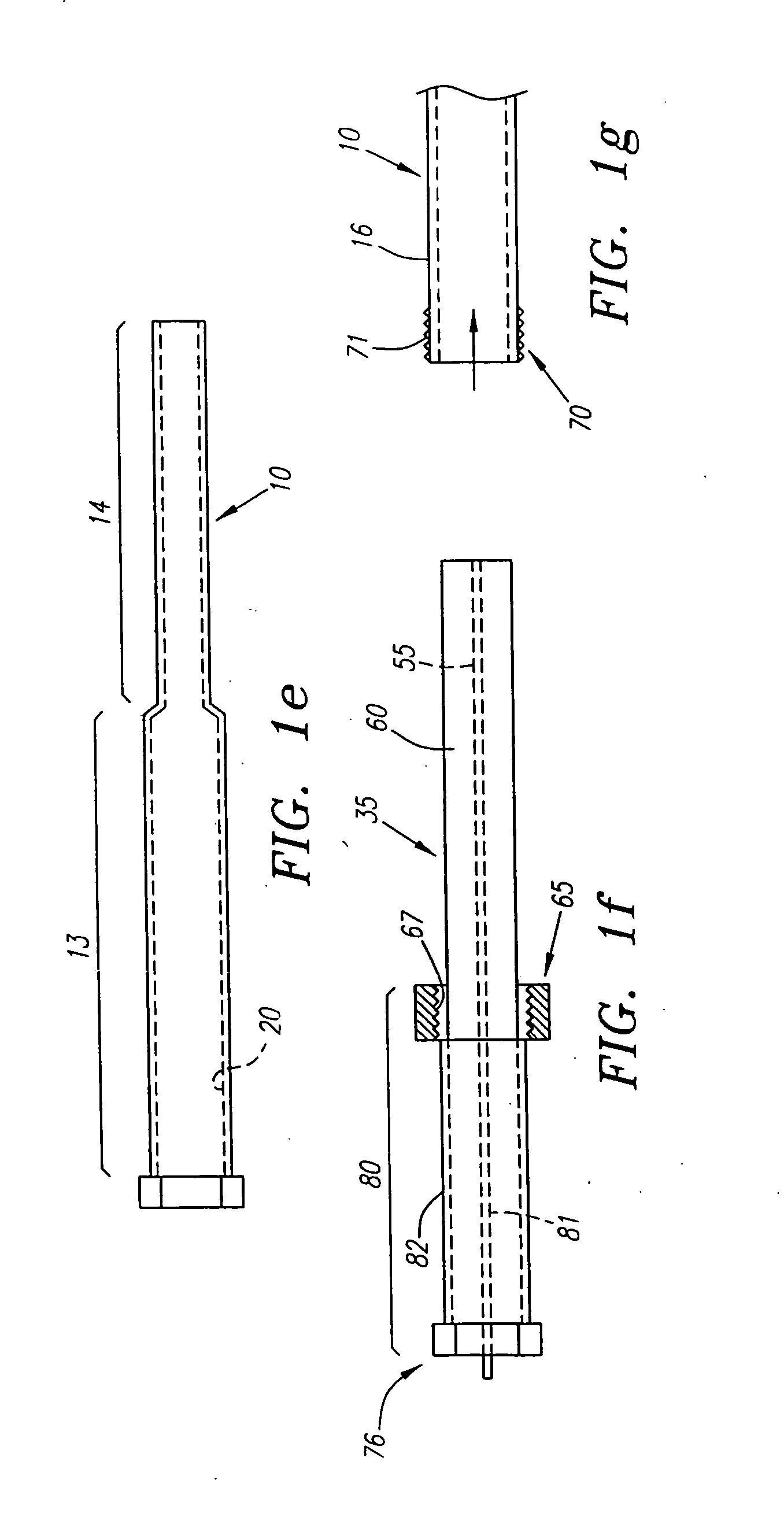
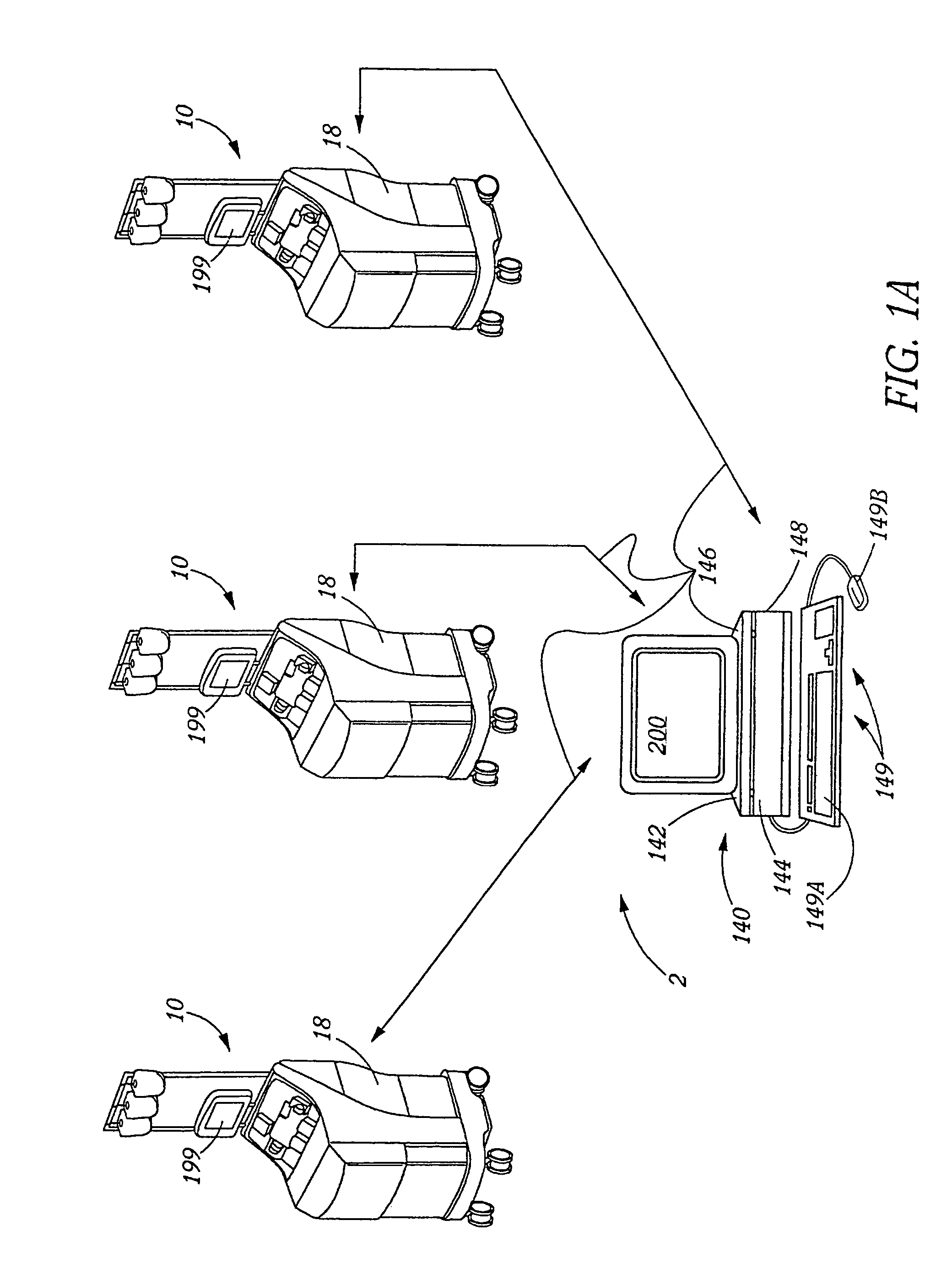
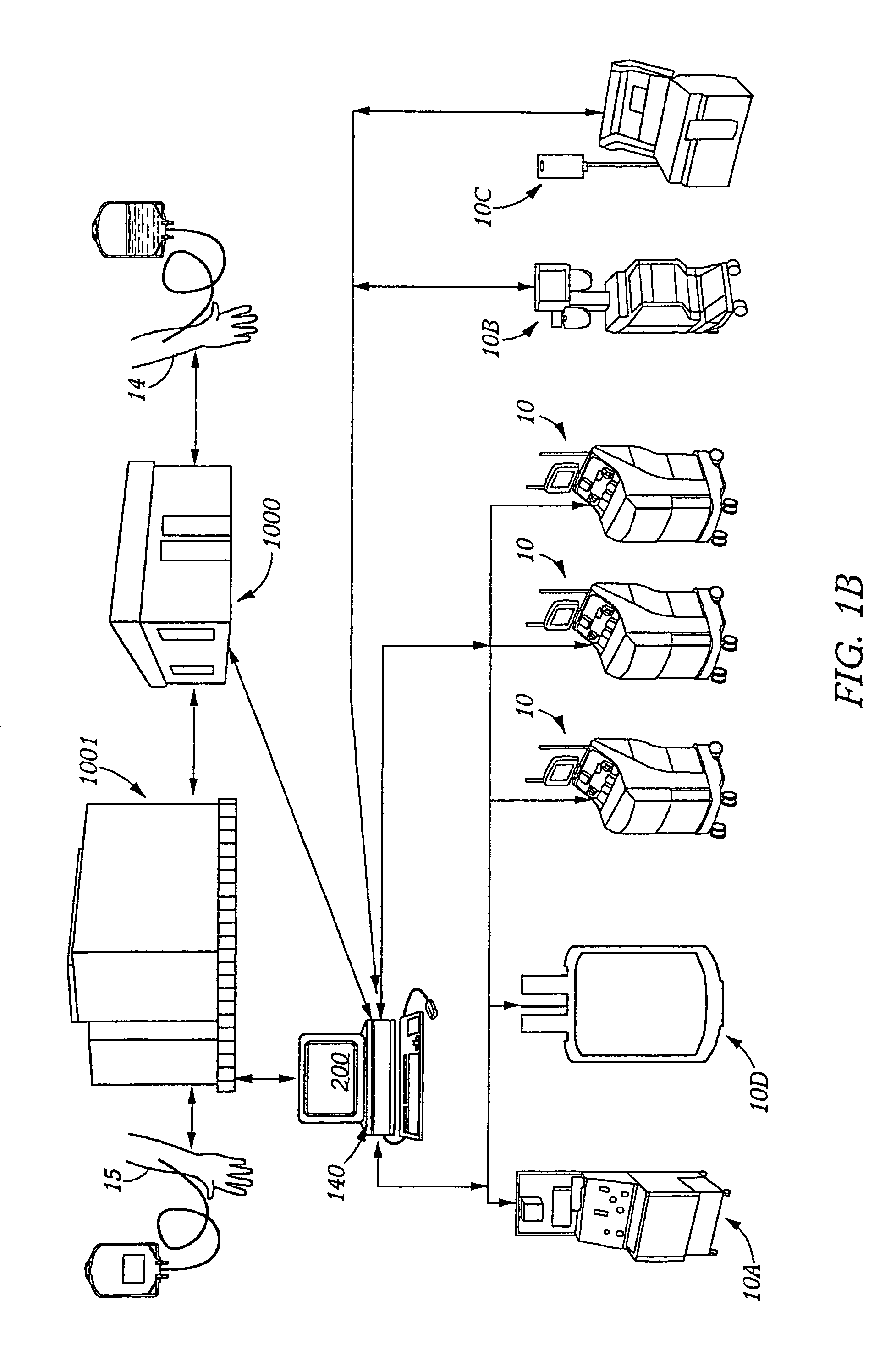
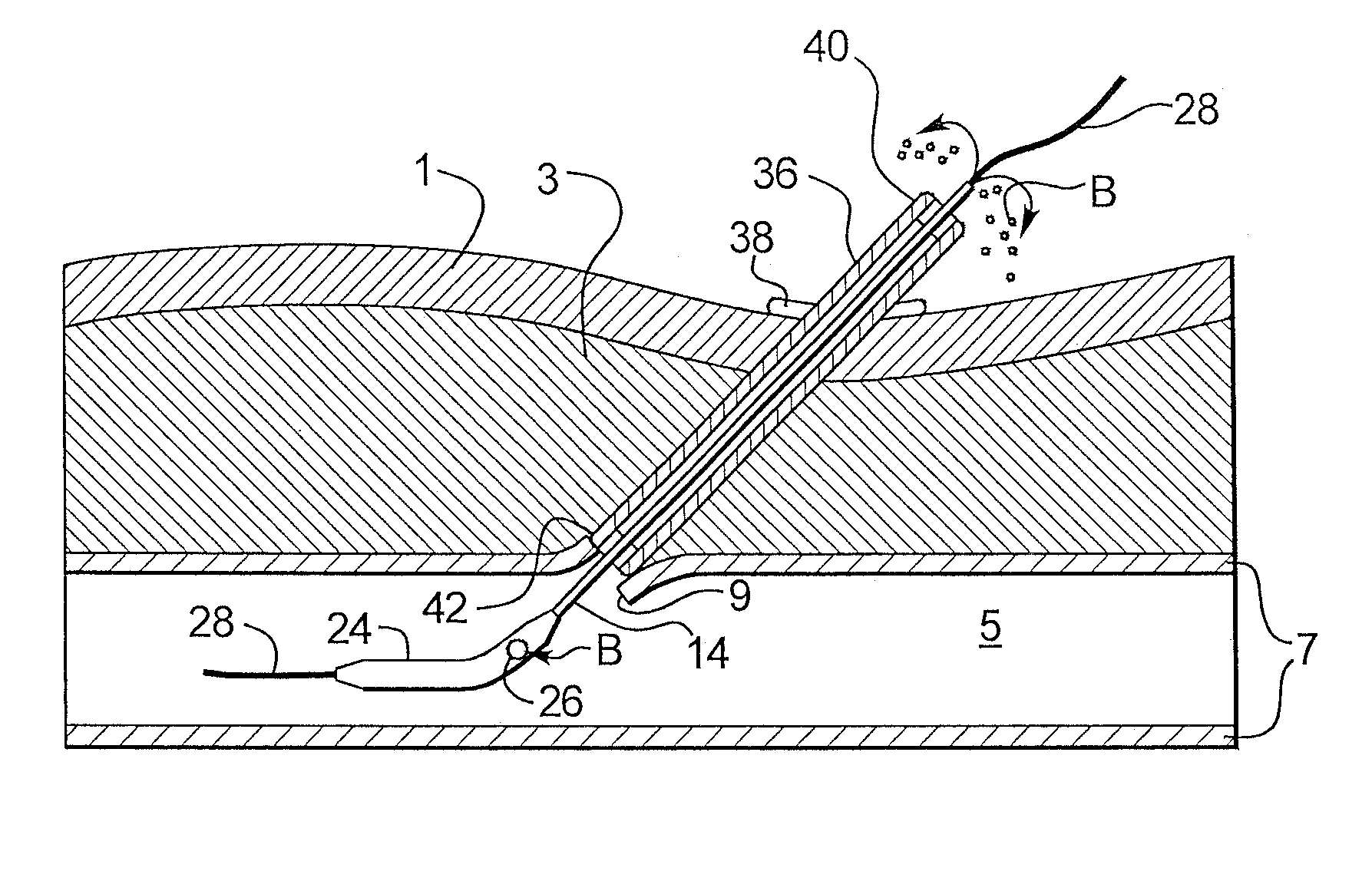
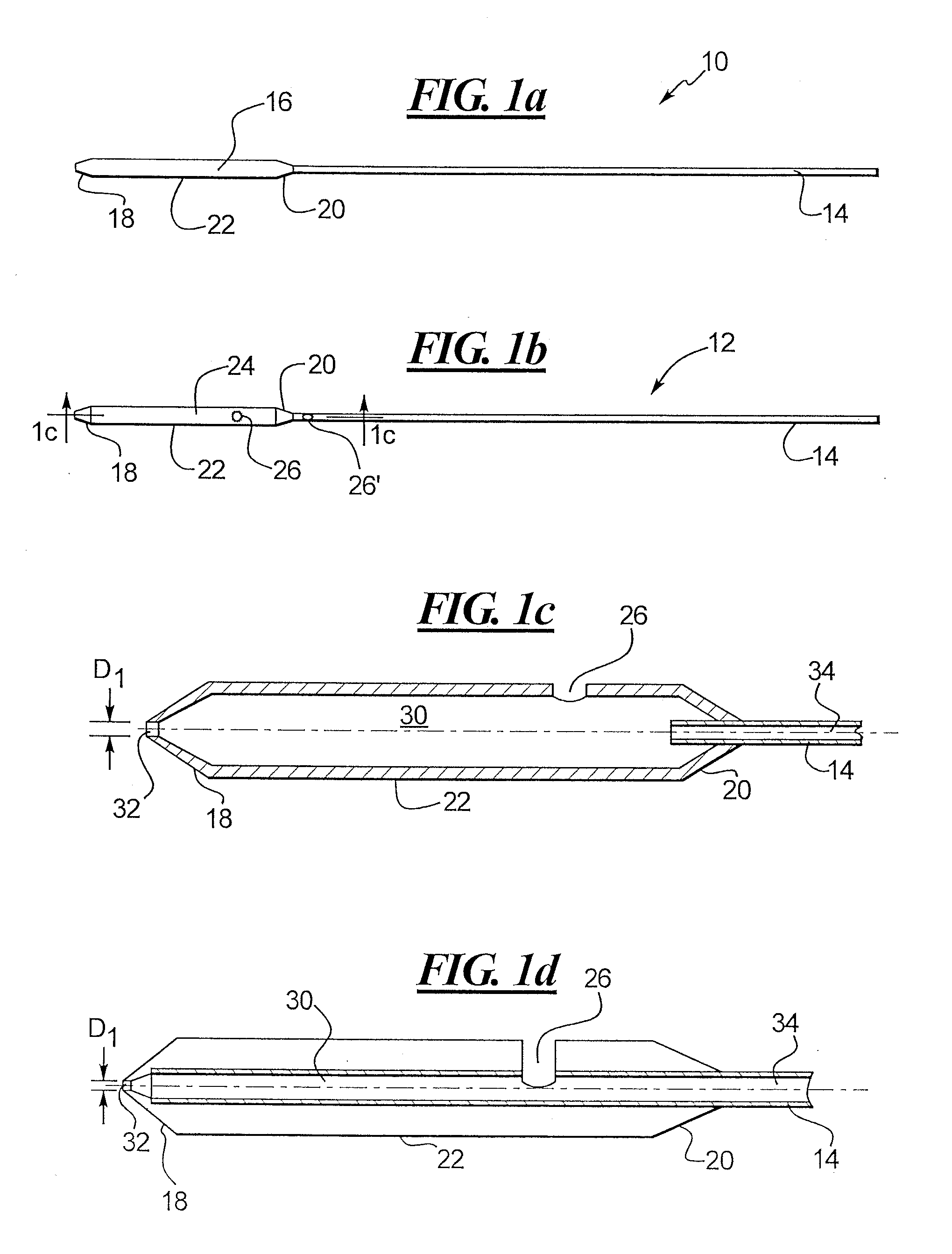
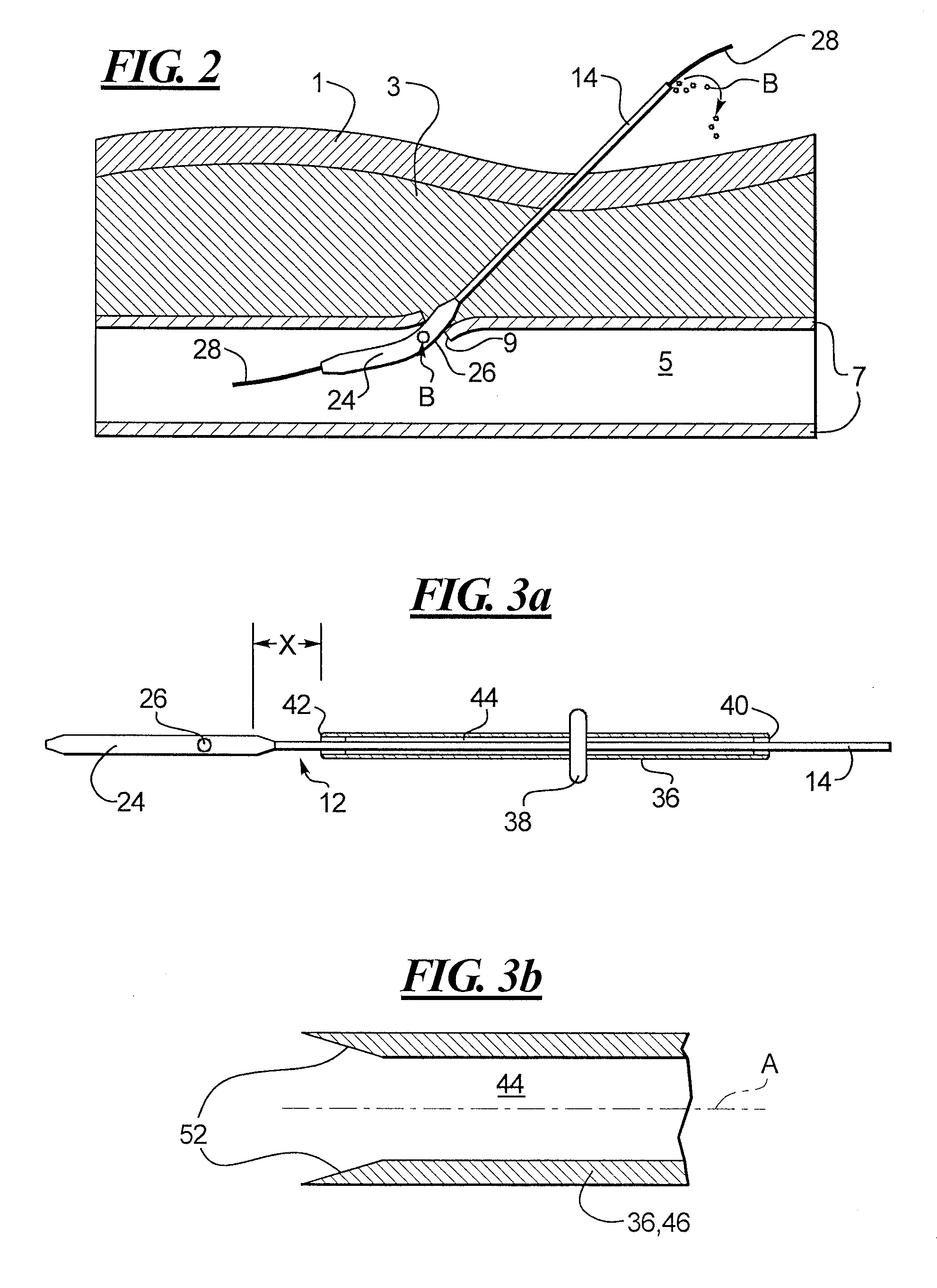
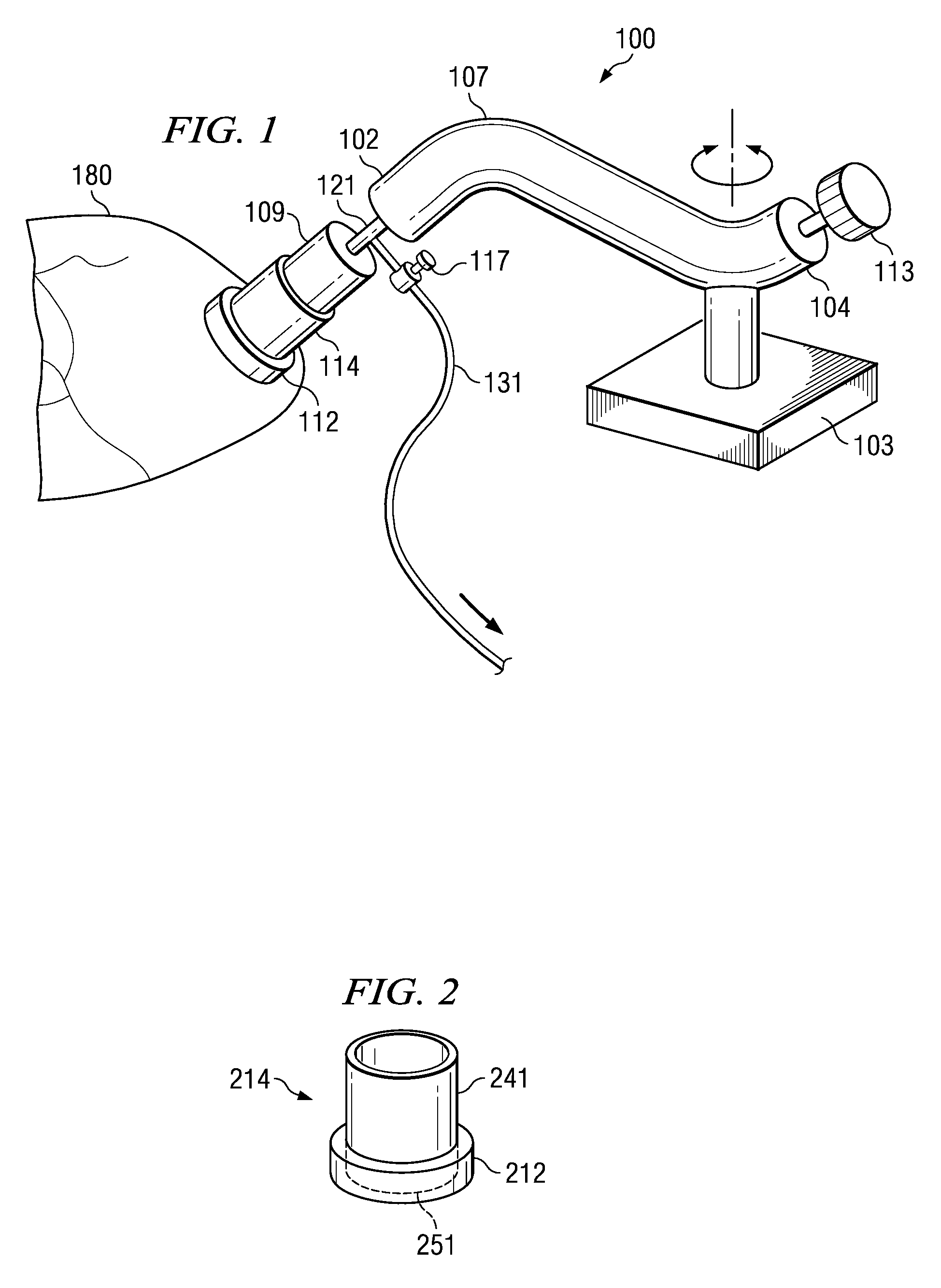
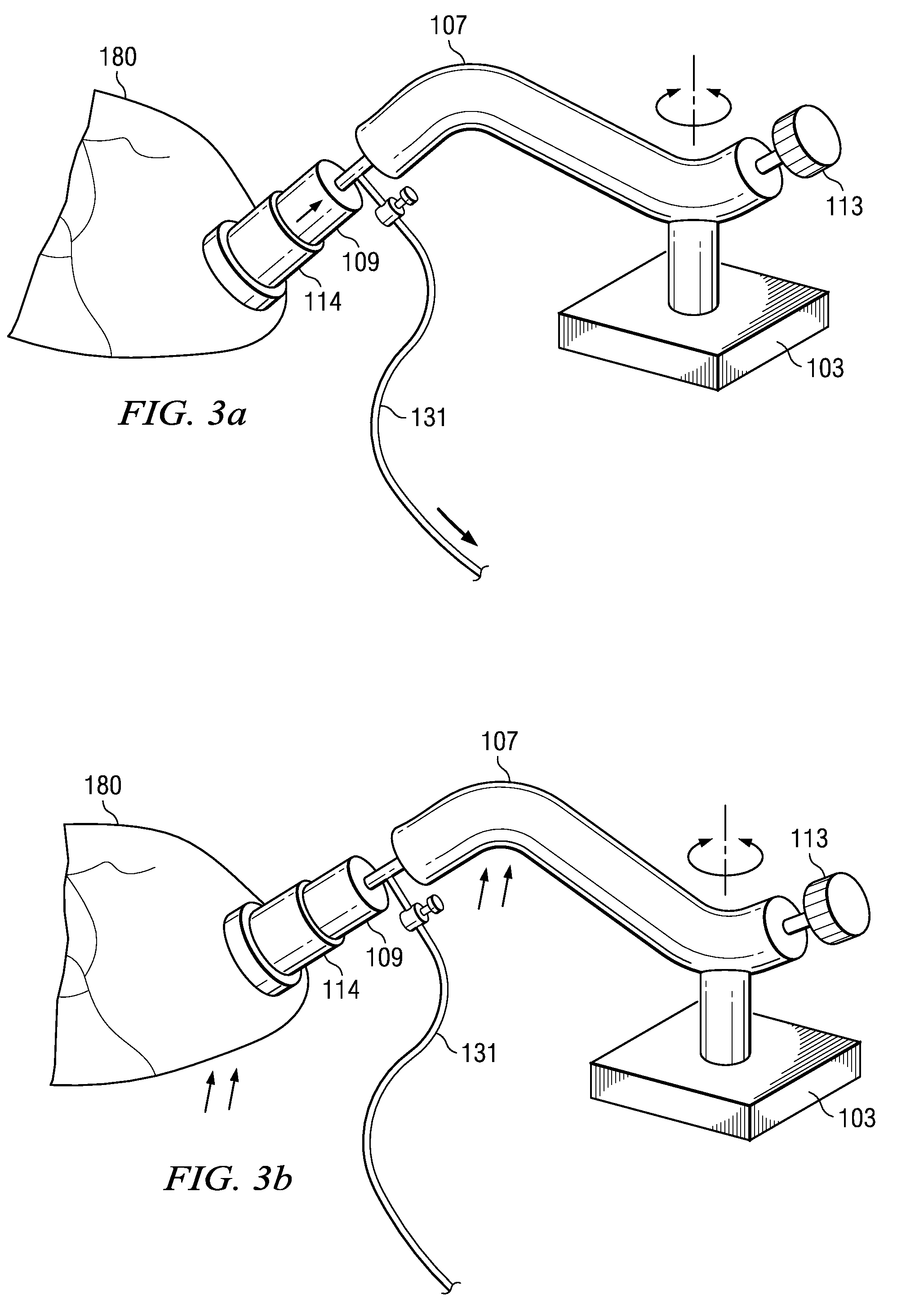
A depth and puncture control system for a blood vessel hemostasis system includes a blood vessel puncture control tip which, when positioned in the lumen of a blood vessel, can inhibit the flow of blood out of the puncture site. When used together with a pledget delivery cannula and a pledget pusher, the control tip and the delivery catheter can both inhibit blood loss out the puncture site and inhibit the introduction of pledget material and tissue fragments into the blood vessel. The system also includes a handle which releasably connects together the control tip, pusher, and delivery cannula to permit limited longitudinal motion between the control tip and the delivery cannula, and between the pusher and the delivery cannula.
Owner:BOSTON SCI CORP +11
Needle kit and method for microwave ablation, track coagulation, and biopsy
InactiveUS7160292B2Minimize damageMinimize bleedingSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsFungating tumourMicrowave ablation
A modular biopsy, ablation and track coagulation needle apparatus is disclosed that allows the biopsy needle to be inserted into the delivery needle and removed when not needed, and that allows an inner ablation needle to be introduced and coaxially engaged with the delivery needle to more effectively biopsy a tumor, ablate it and coagulate the track through ablation while reducing blood loss and track seeding. The ablation needle and biopsy needle are adapted to in situ assembly with the delivery needle. In a preferred embodiment, the ablation needle, when engaged with the delivery needle forms a coaxial connector adapted to electrically couple to an ablating source. Methods for biopsying and ablating tumors using the device and coagulating the track upon device removal are also provided.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Surgical system and procedure for treatment of medically refractory atrial fibrillation
InactiveUS7387126B2Reduce complicationsShorten the timeSuture equipmentsCannulasMedicineBiomedical engineering
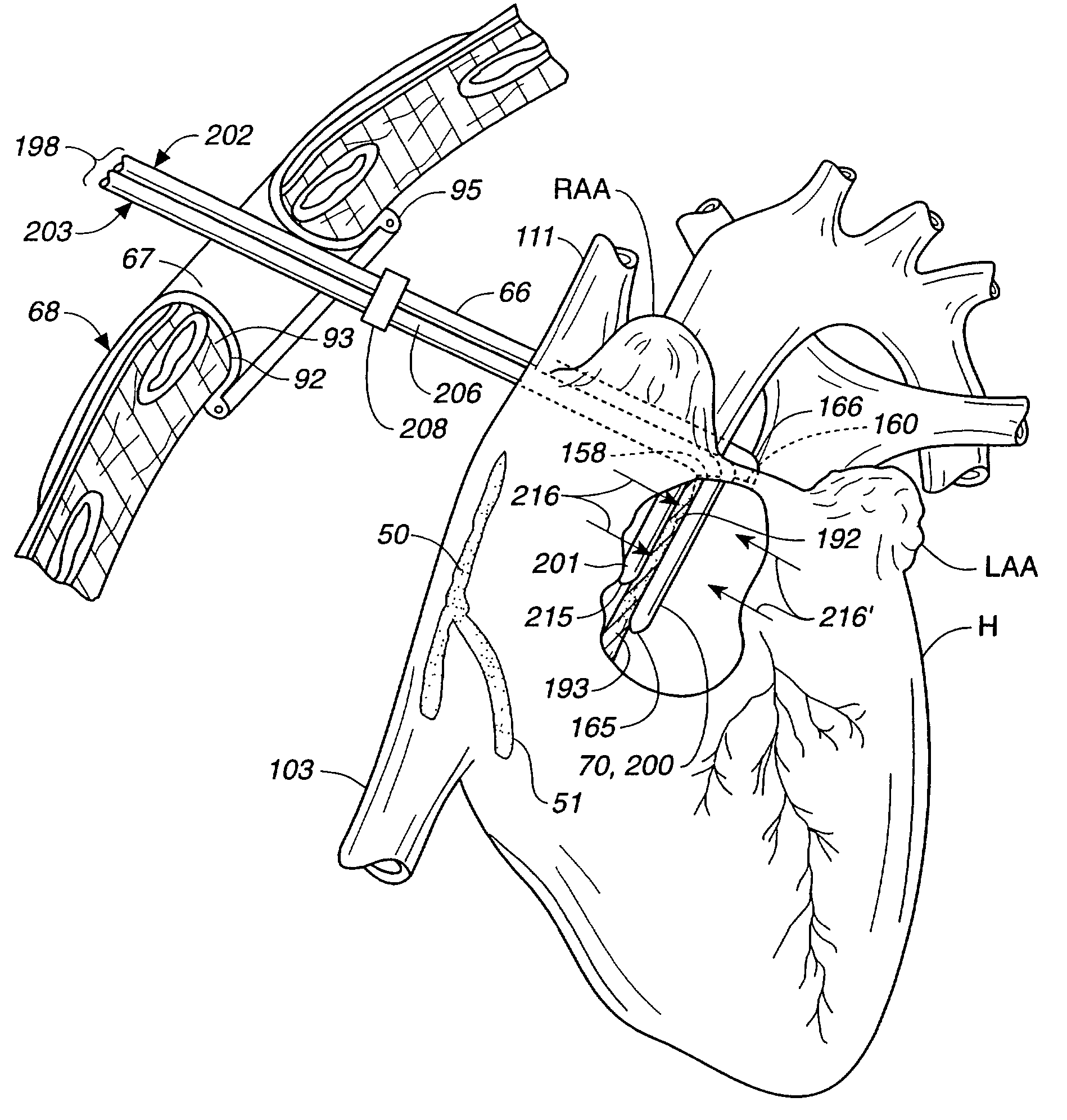
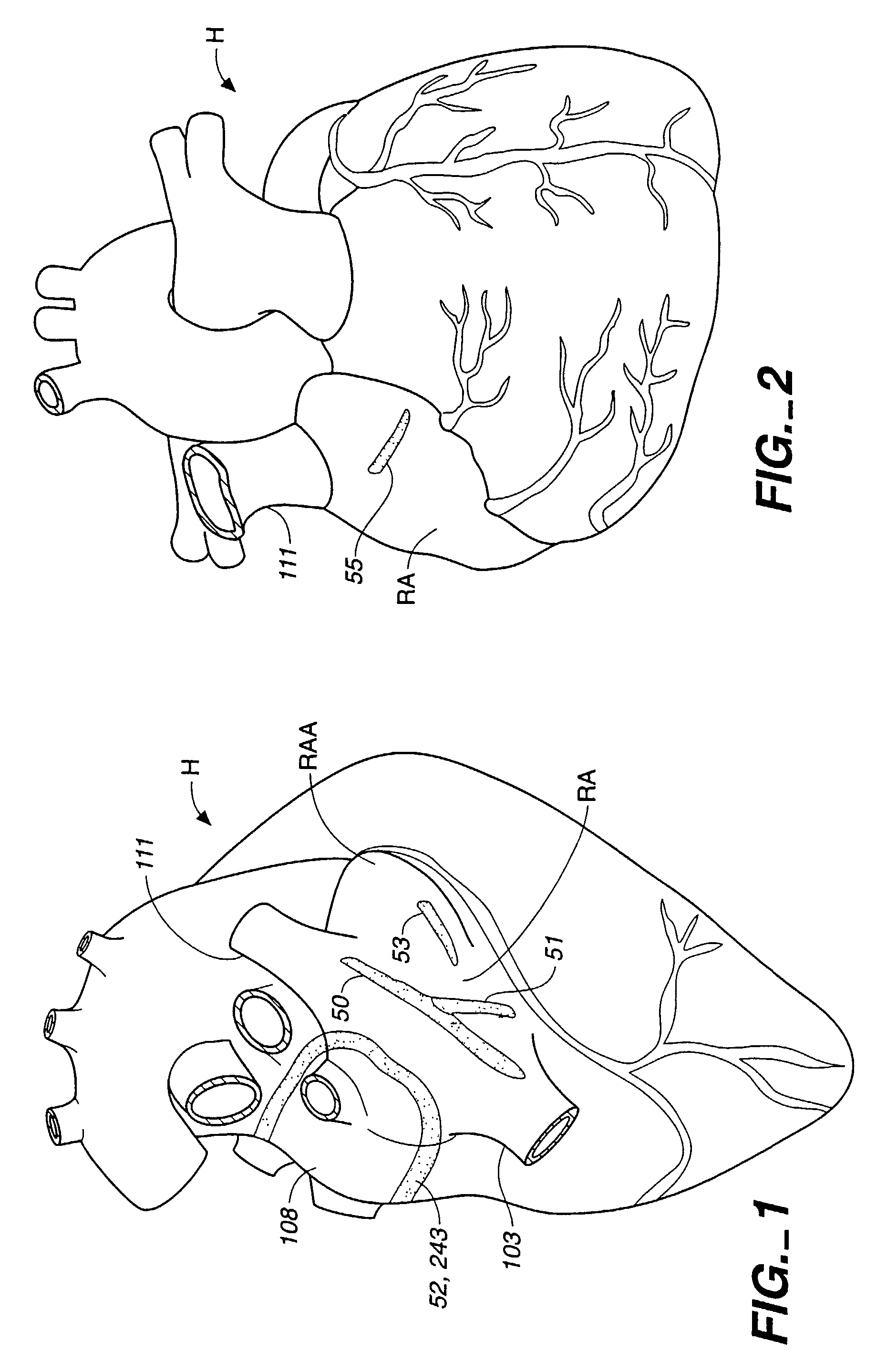
The invention provides surgical systems and methods for ablating heart tissue within the interior and / or exterior of the heart. A plurality of probes is provided with each probe configured for introduction into the chest for engaging the heart. Each probe includes an elongated shaft having an elongated ablating surface of a predetermined shape. The elongated shaft and the elongated ablating surface of each probe are configured to ablate a portion of the heart. A sealing device affixed to the heart tissue forms a hemostatic seal between the probe and the penetration in the heart to inhibit blood loss therethrough.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
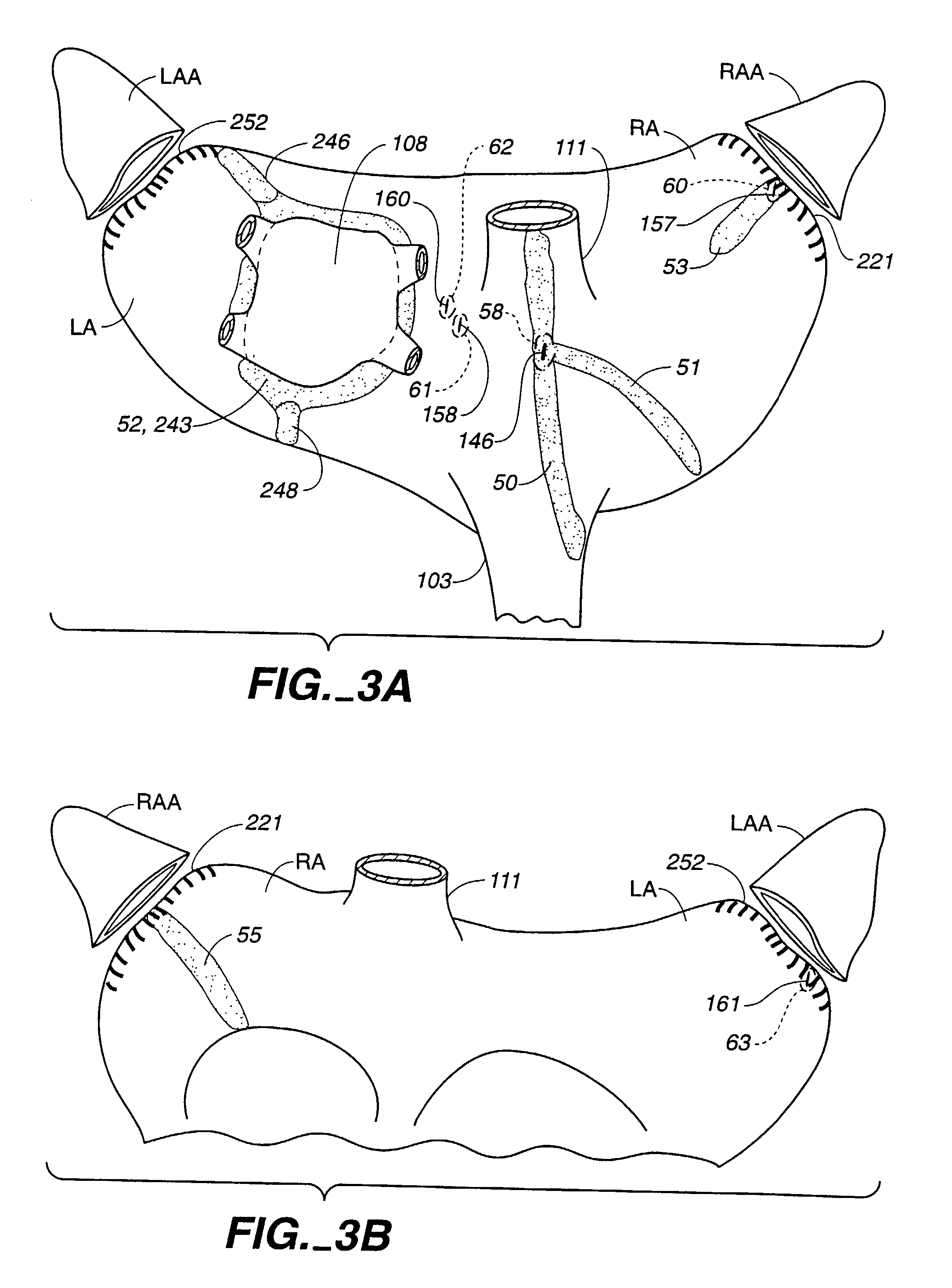
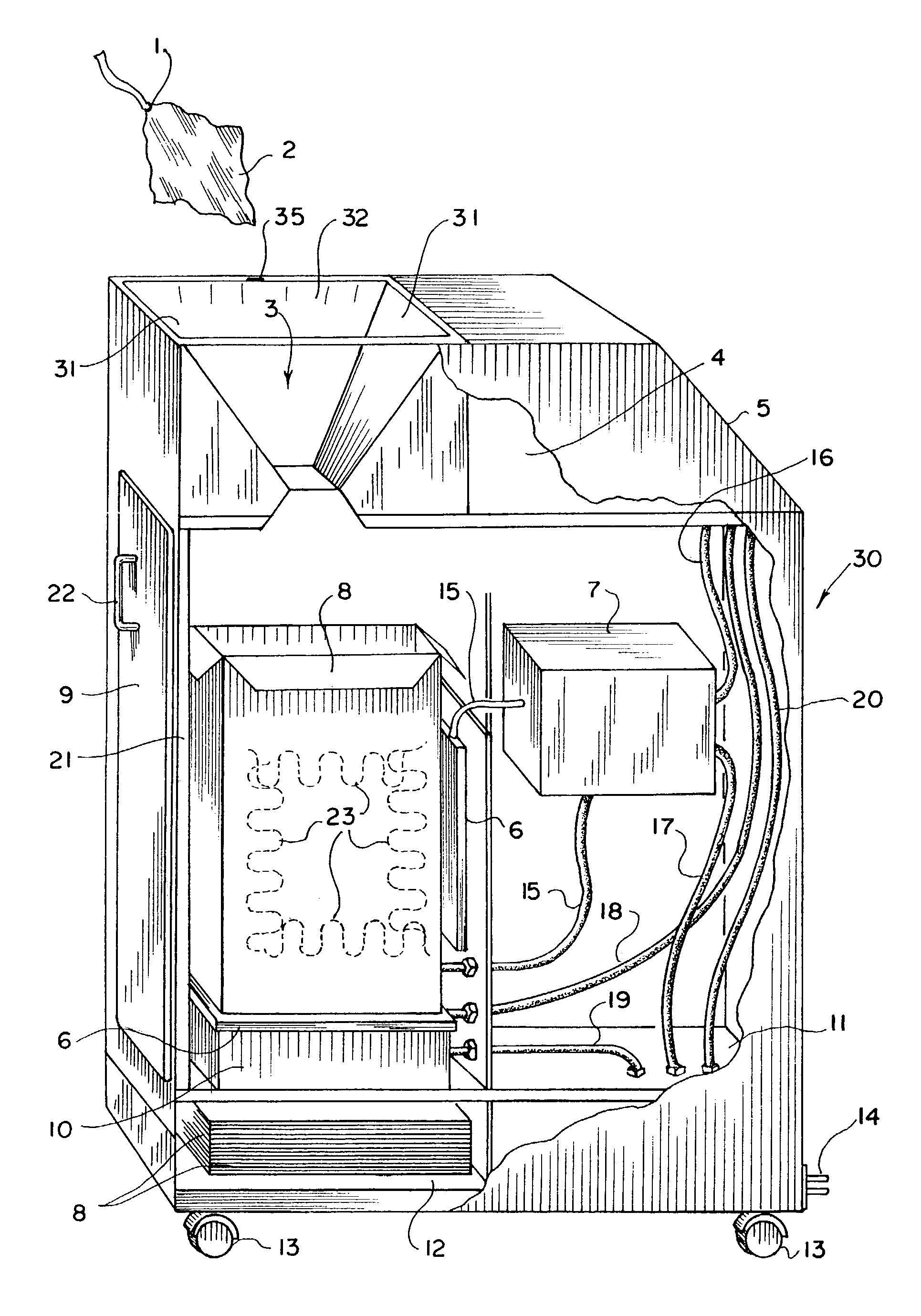
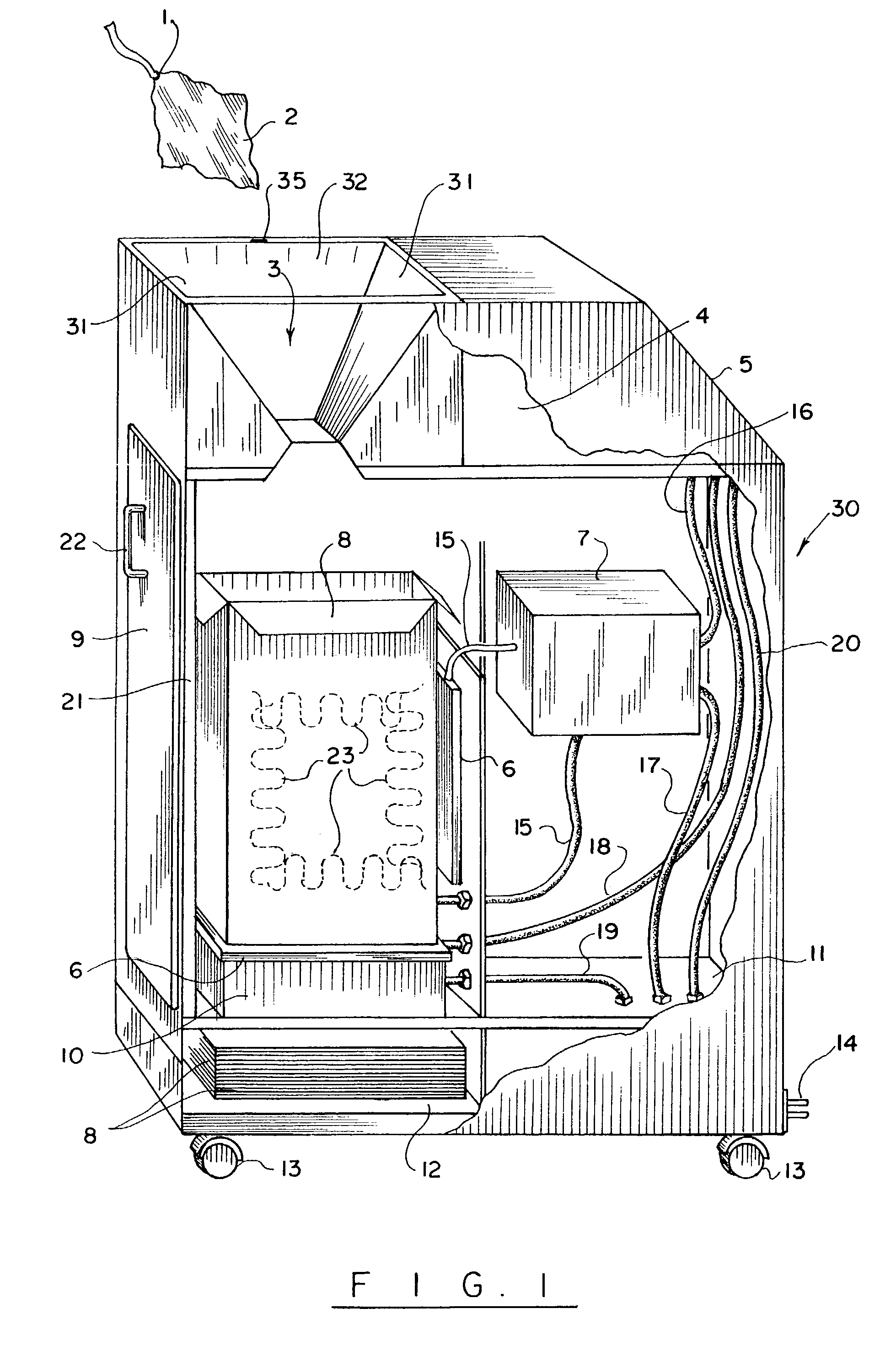
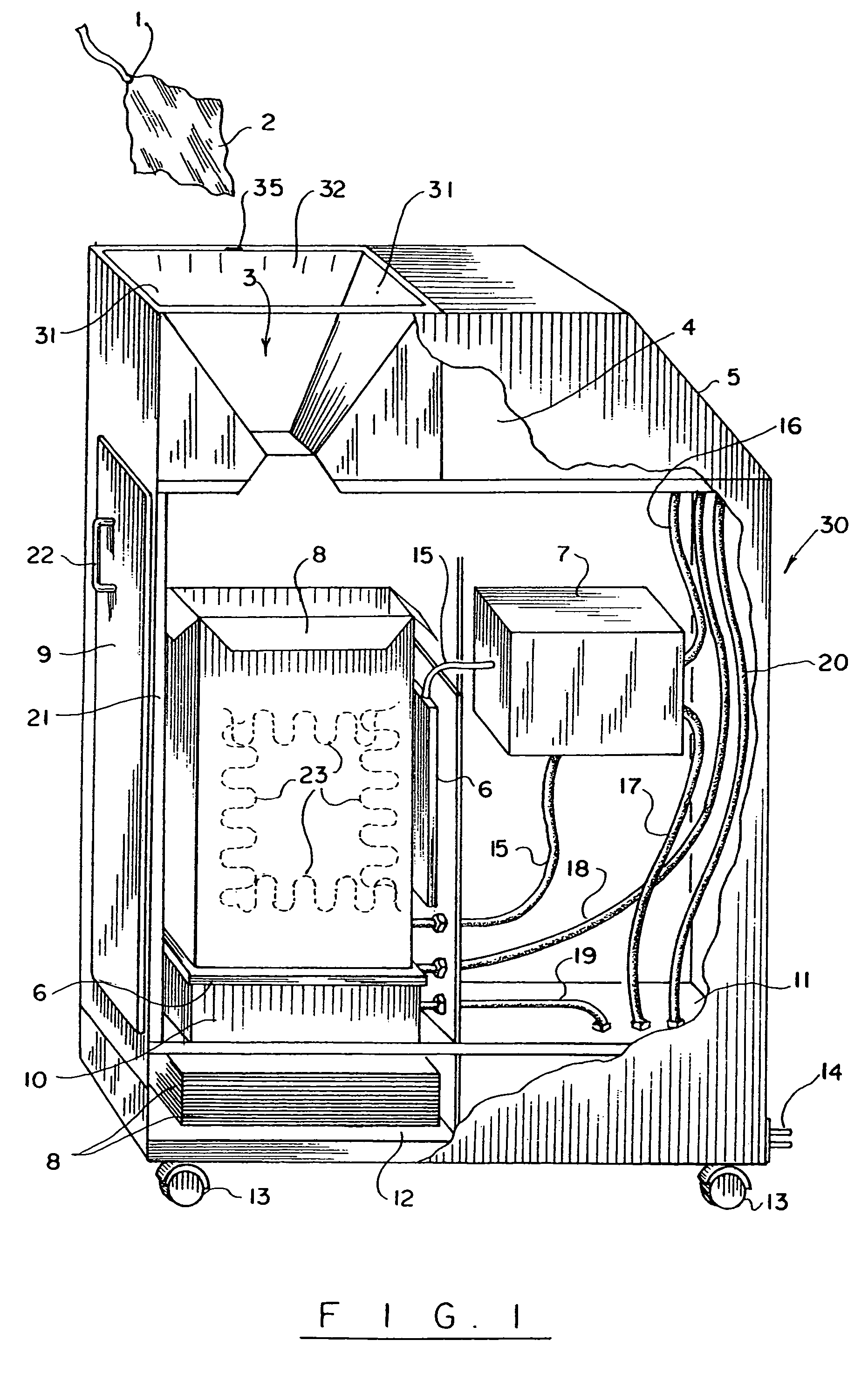
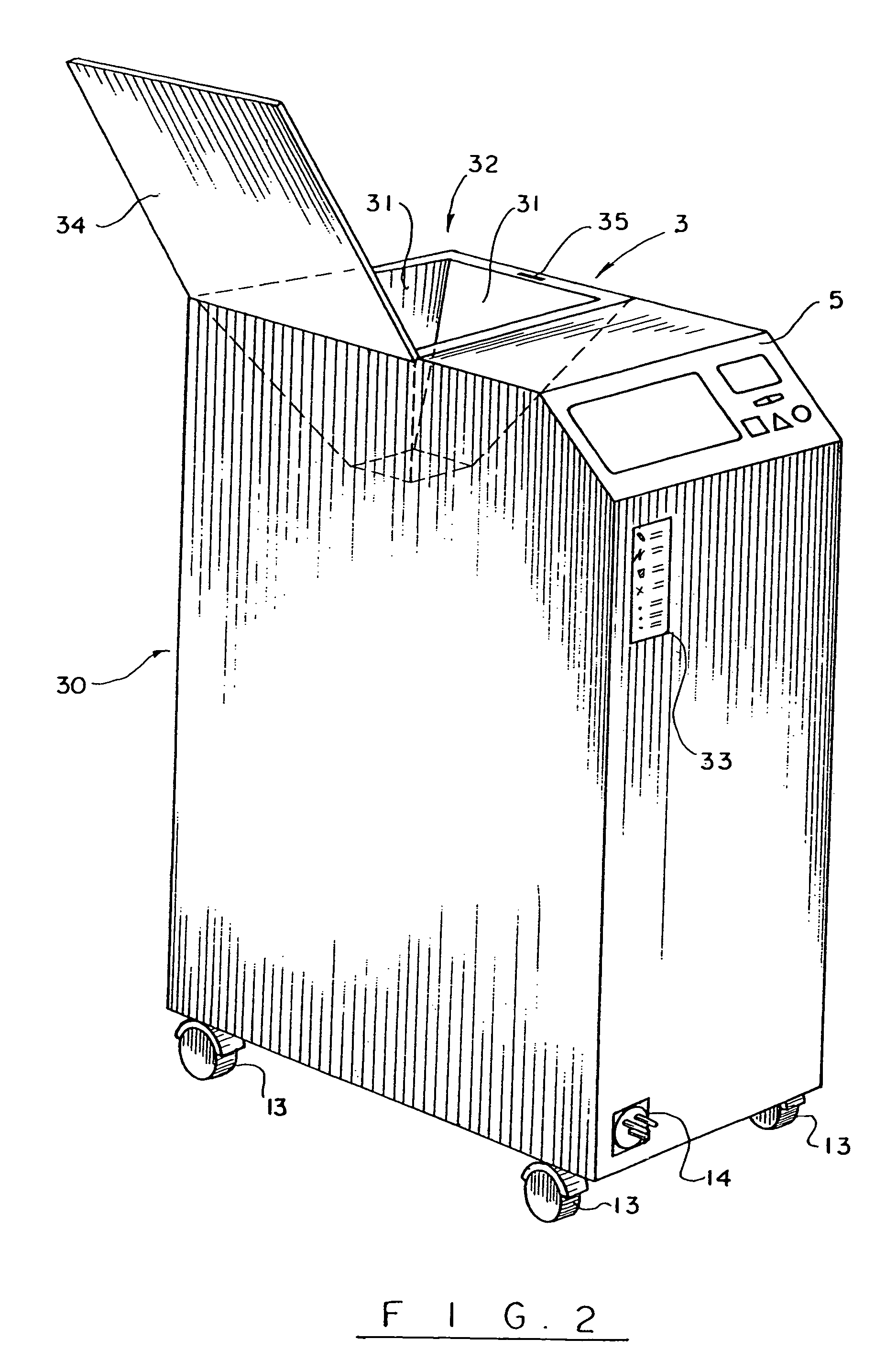
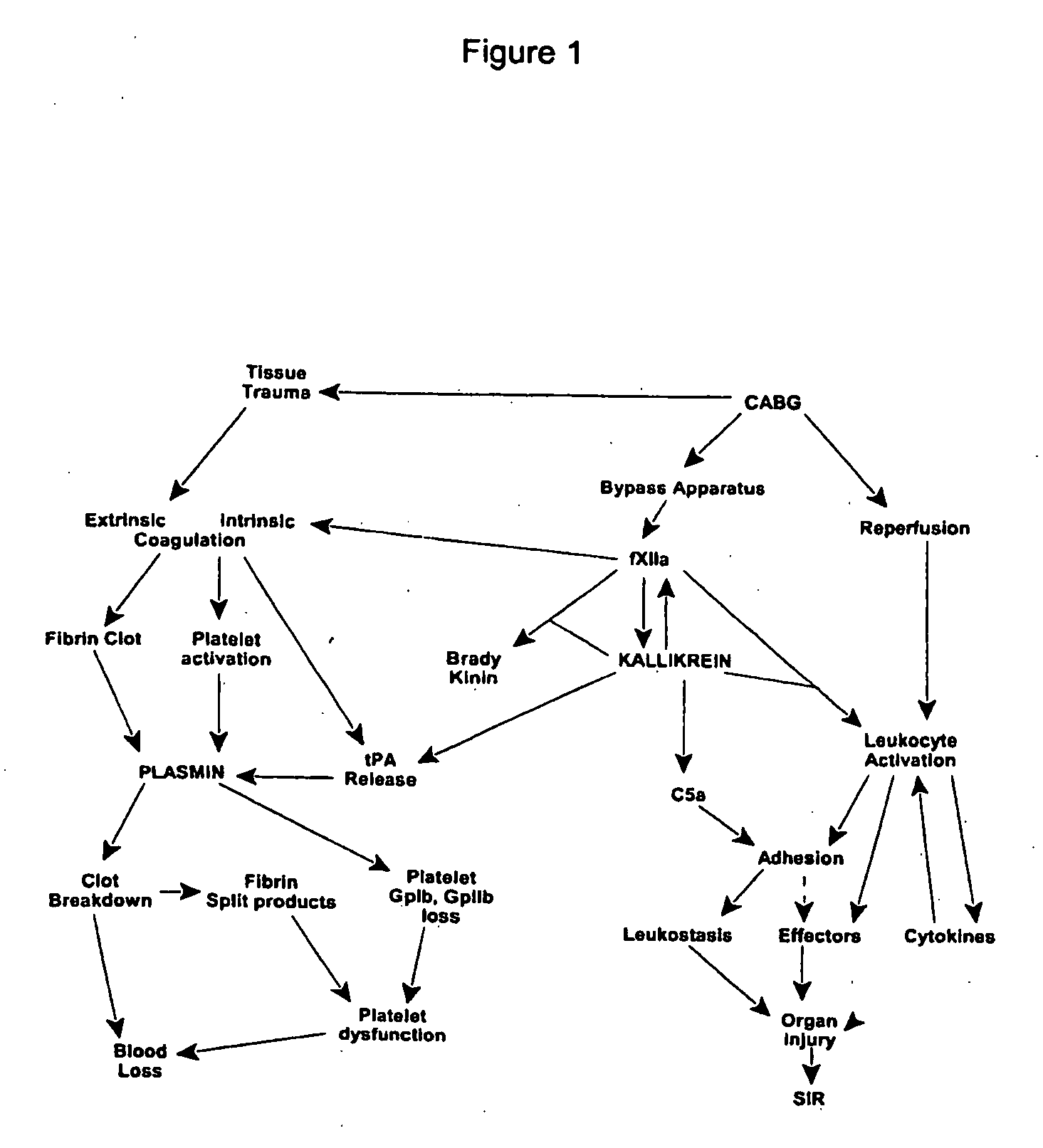
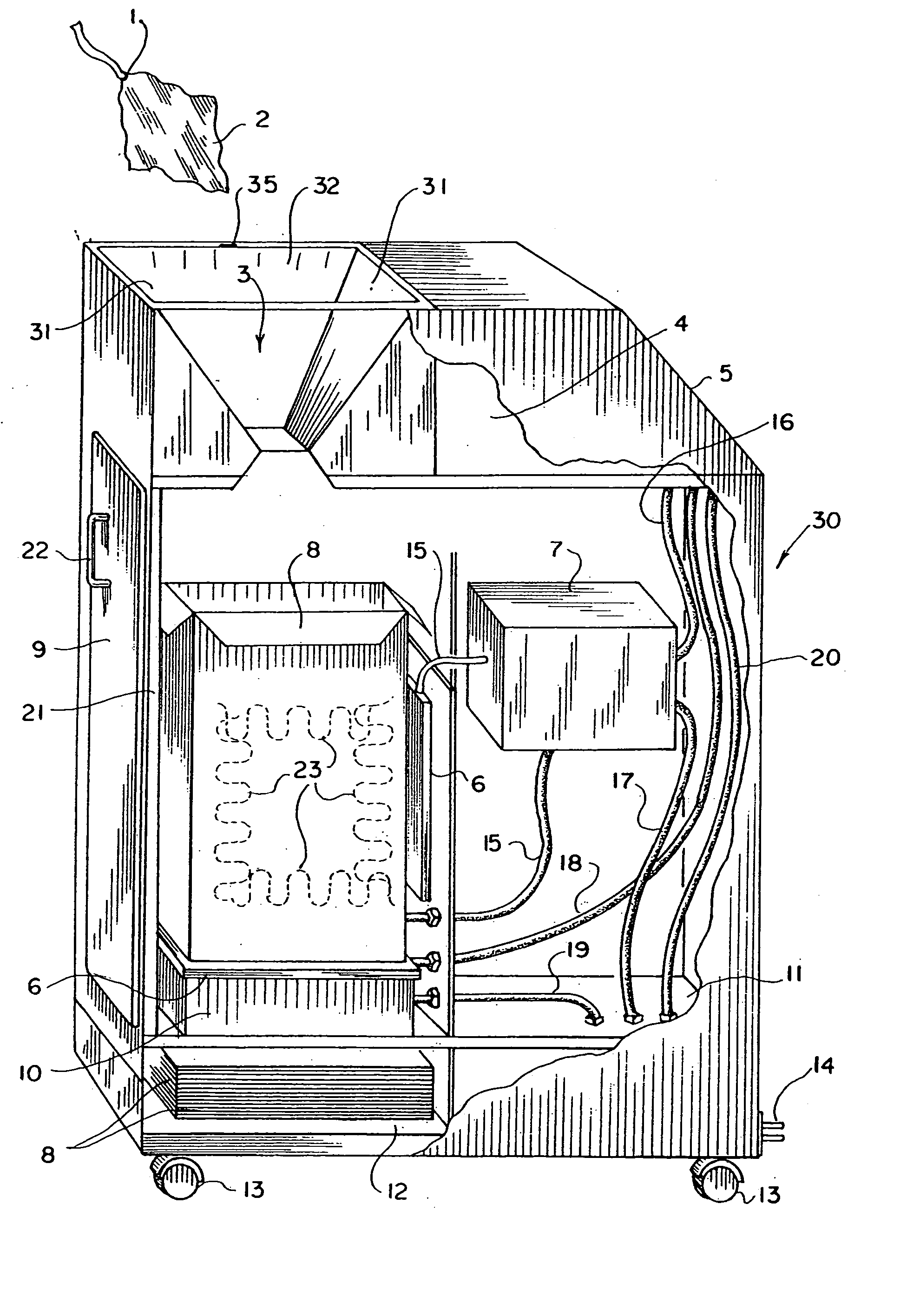
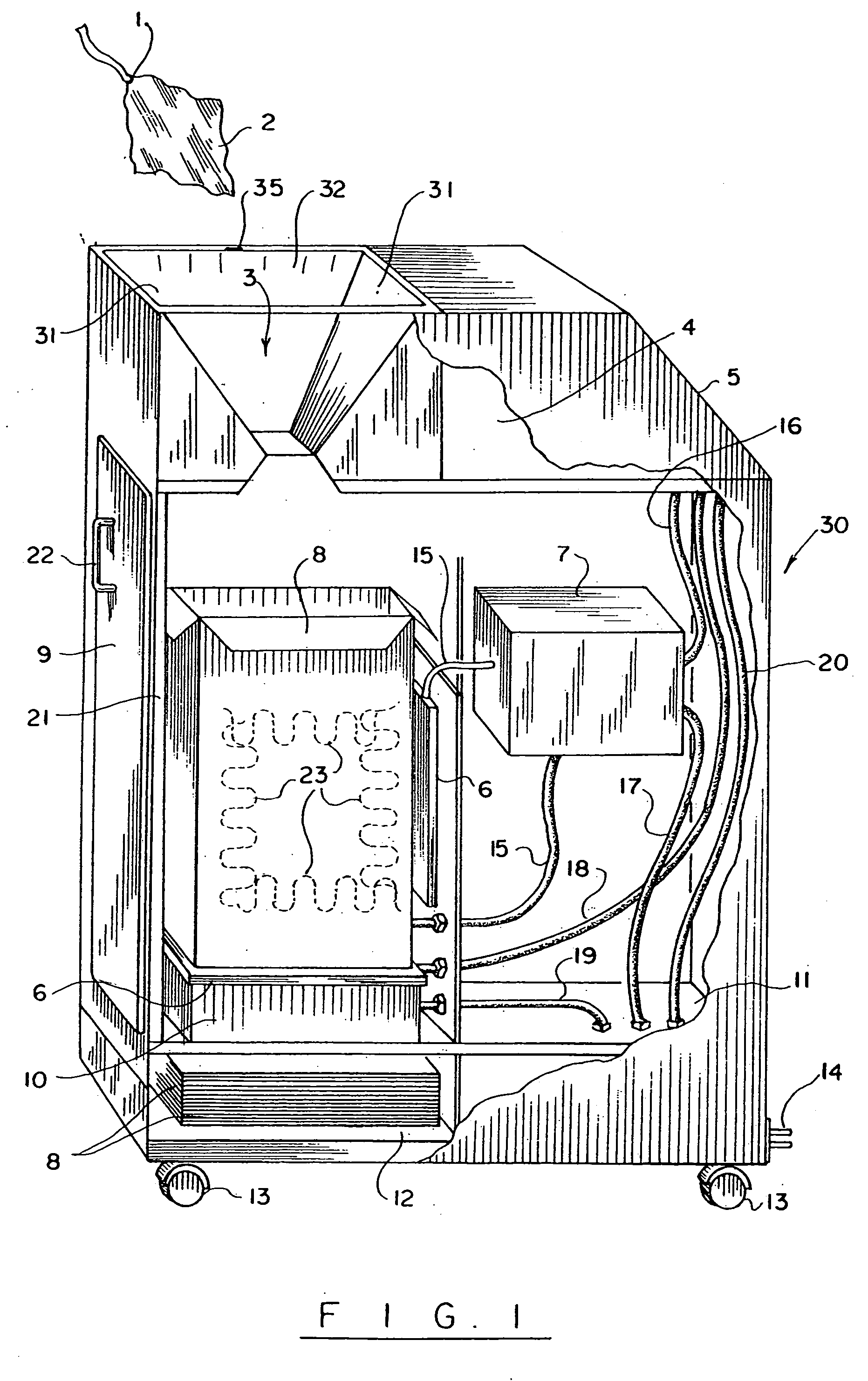
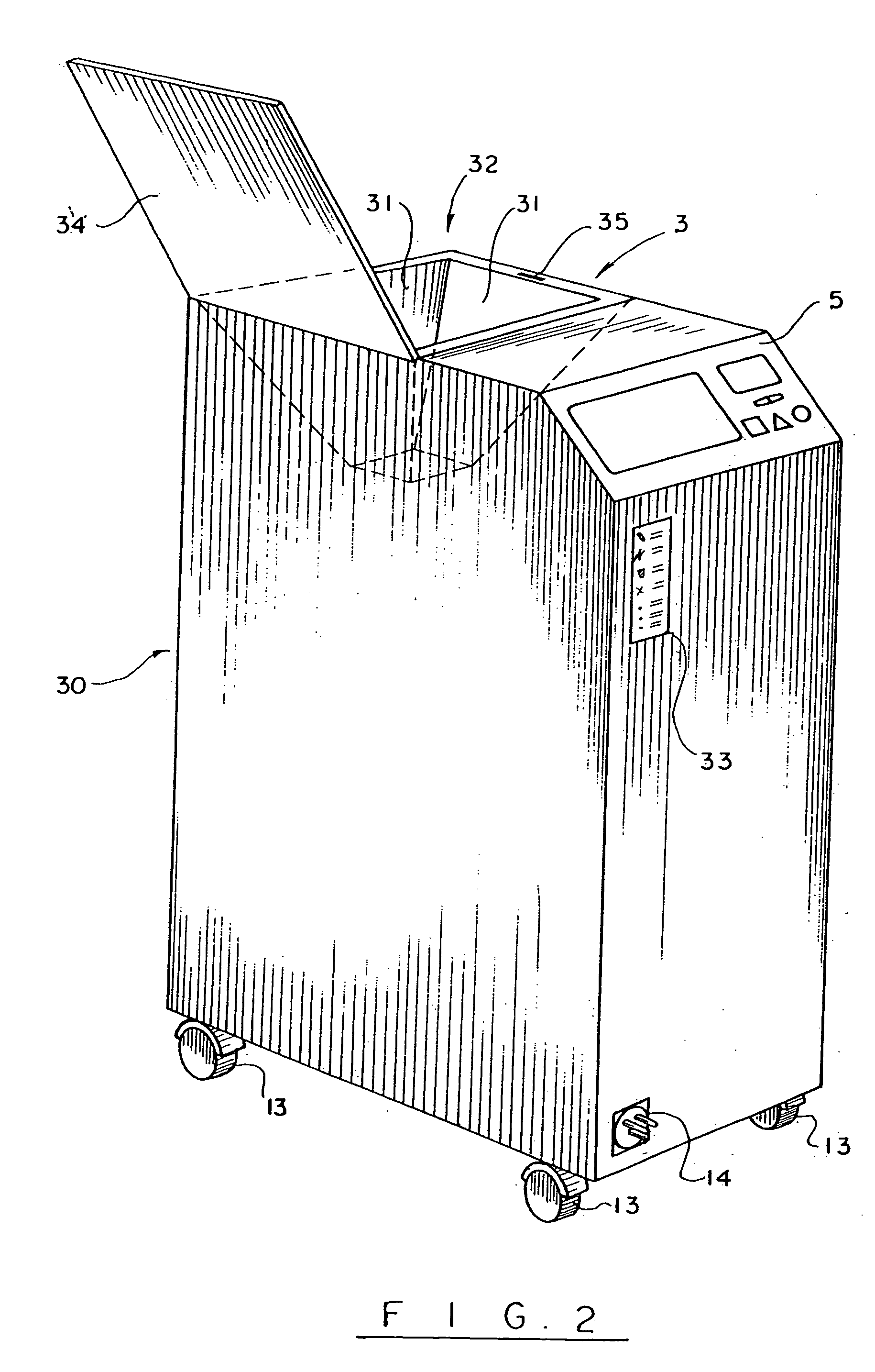
Automatic surgical sponge counter and blood loss determination system
InactiveUS6998541B2Inhibition retentionEliminate dangerSurgical furnitureDiagnosticsOptical scannersRechargeable cell
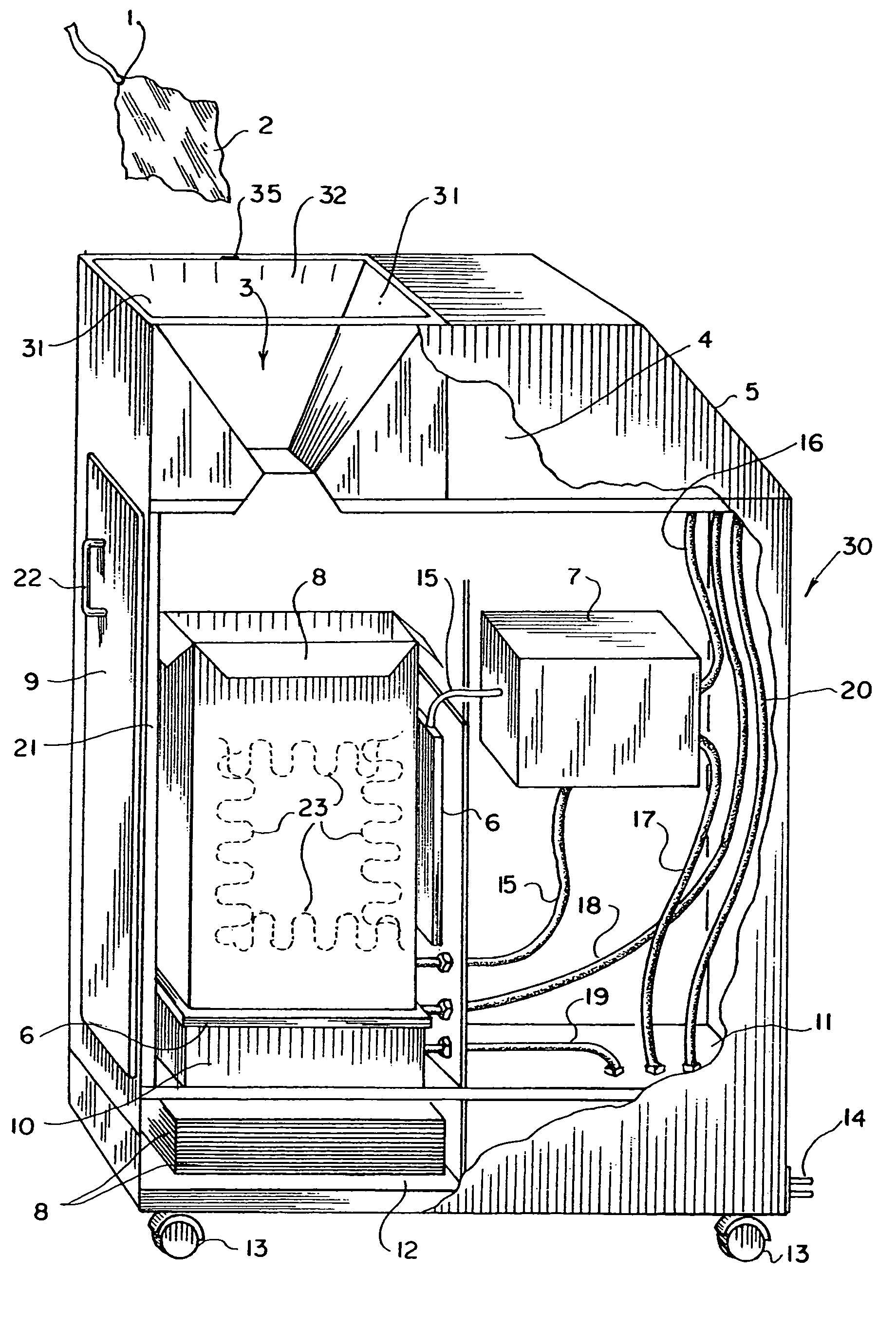
A surgical sponge detection system includes a plurality of surgical sponges (2) having radio frequency identification tags (1) securely attached thereto and a non-optical hand-held reader (40) for detecting the sponges by detecting the tags (1). Also disclosed is a device (30) for automatically counting, weighing, and calculating blood loss contained within, soiled surgical sponges (2) which includes a cabinet with an opening (3) at the top through which sponges (2) are deposited, a reader (6) which scans each sponge (2) entered and determines sponge type from a tag (1) affixed to each sponge (2), and a disposable bag (8) into which the sponges (2) are deposited. The disposable bag (8) is removably mounted to a weighing scale (10); there is also a rear door (9) from which the disposable bag (8) can be easily removed, a rechargeable battery (11), a shelf (12) for unused disposable bag storage, a control unit (4) which processes data received from reader (6) and scale (10) and instantaneously calculates total weight of liquid contained within sponges entered, a display panel (5) continuously displays the number and type of sponges entered during a given procedure as well as the total weight of liquids retained in those sponges. There is a means for automatically determining the weight of the sponges when dry which includes a non-optical scanner means (6) which can read an indicating means (1) on the sponges (2) even when the indicating means (1) is covered with blood or other body fluids.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
Dressing and integrated system for detection of fluid loss
InactiveUS7670289B1Quick installationEasy to removeSemi-permeable membranesSolvent extractionHemodialysisHaemodialysis machine
Owner:MCCALL KENNETH SHAWN
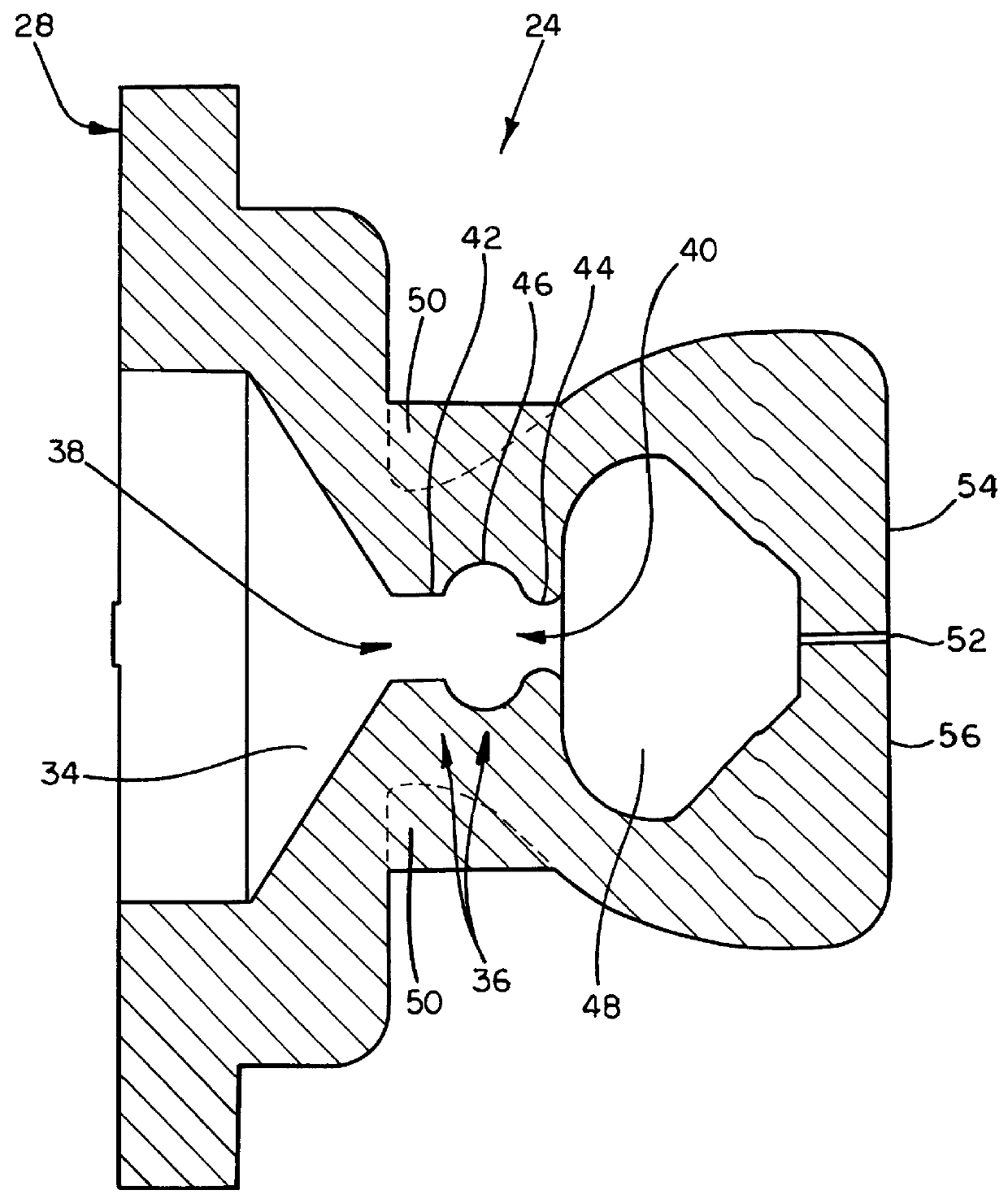
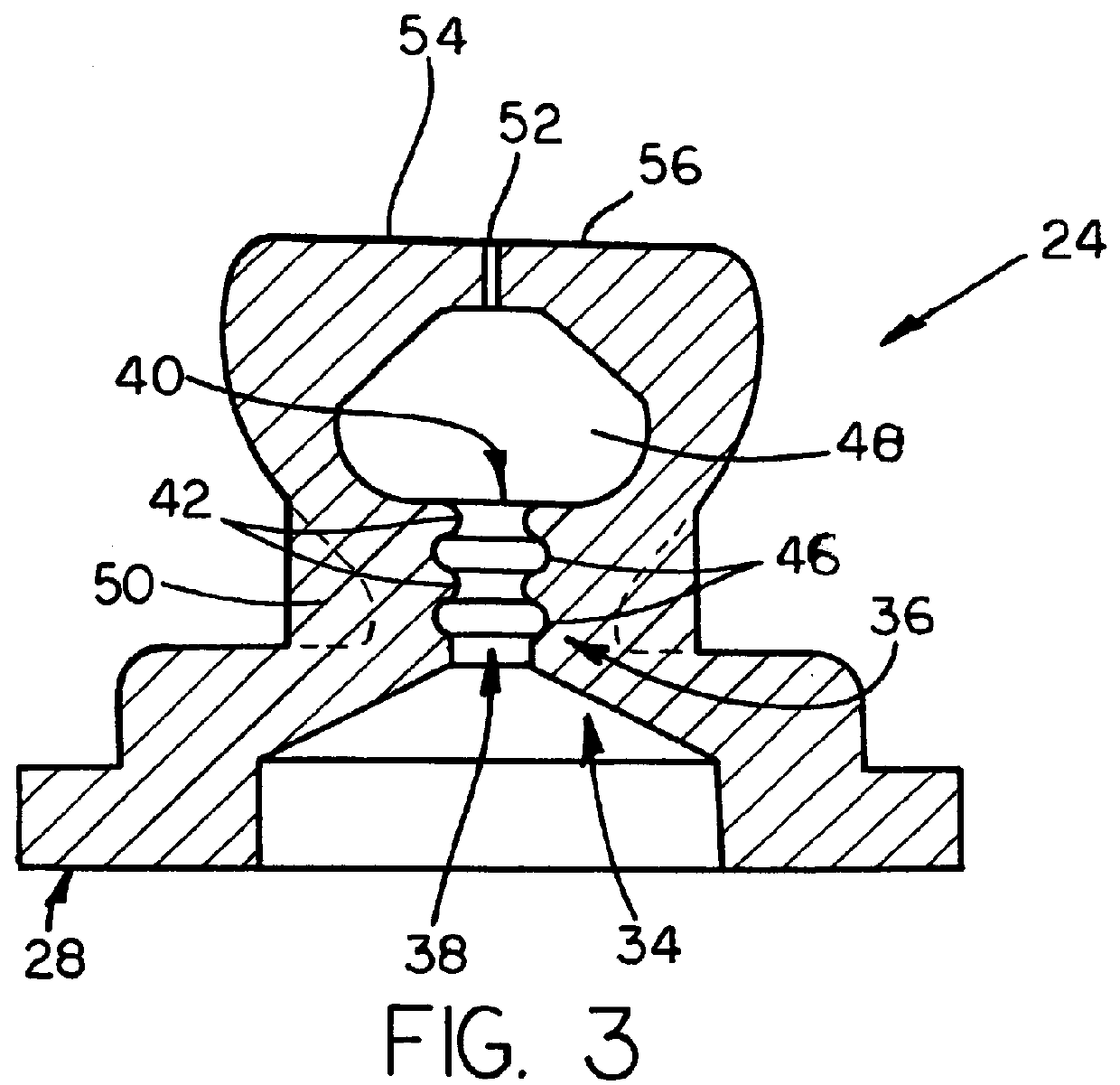
Hemostasis valve
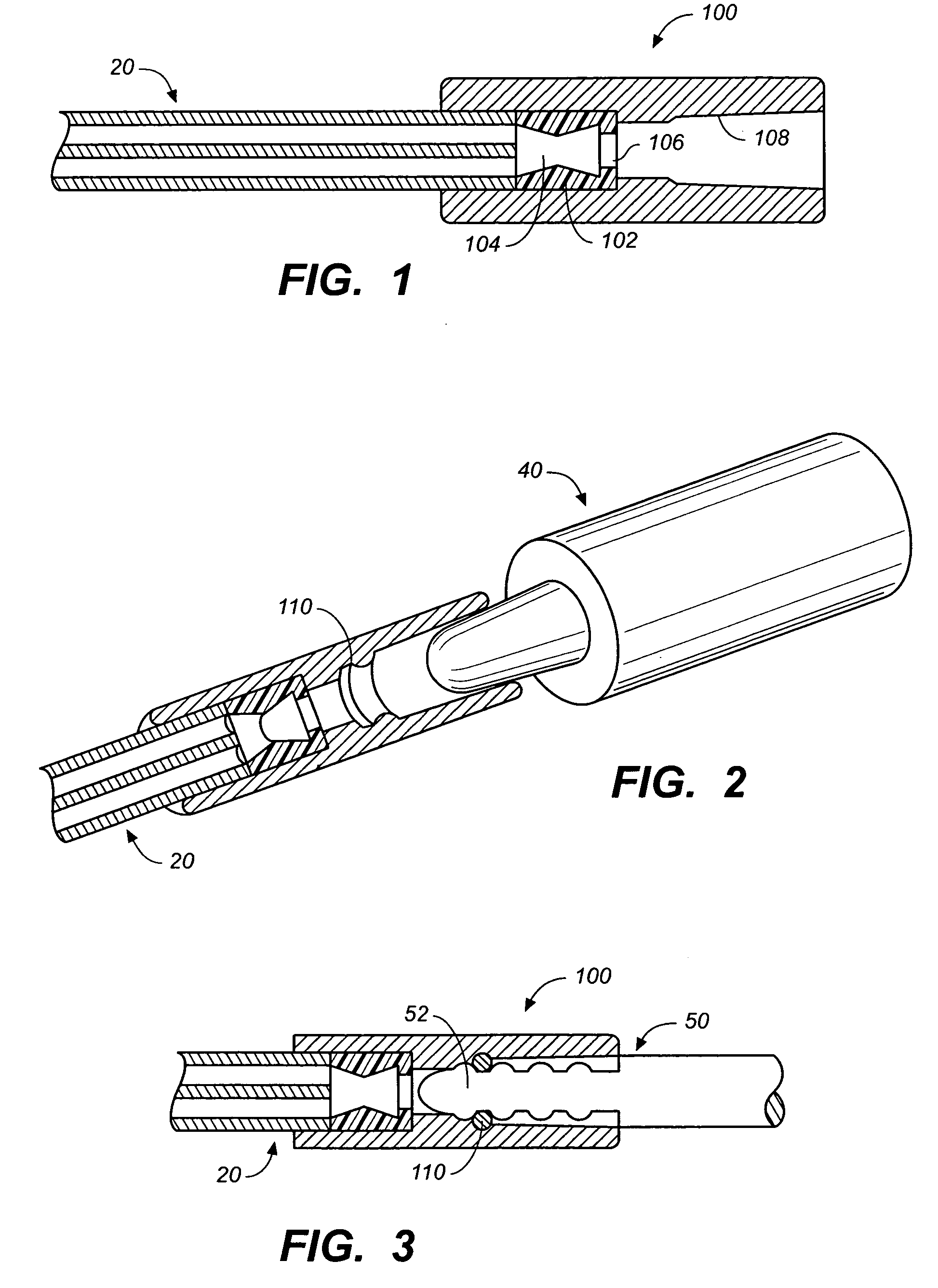
A one-piece hemostasis valve located within a longitudinally extended housing, with the valve comprising an extended sealing neck having a passageway therethrough, communicating with a sealing chamber having opposing sealing exit lips and preferably support shoulders on the outside of the valve adjacent to the sealing neck to provide support for the valve. The passageway of the extended sealing neck contains narrowed and broadened portions to prevent blood loss when receiving a guidewire and catheter inserted through the passageway of the sealing neck.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
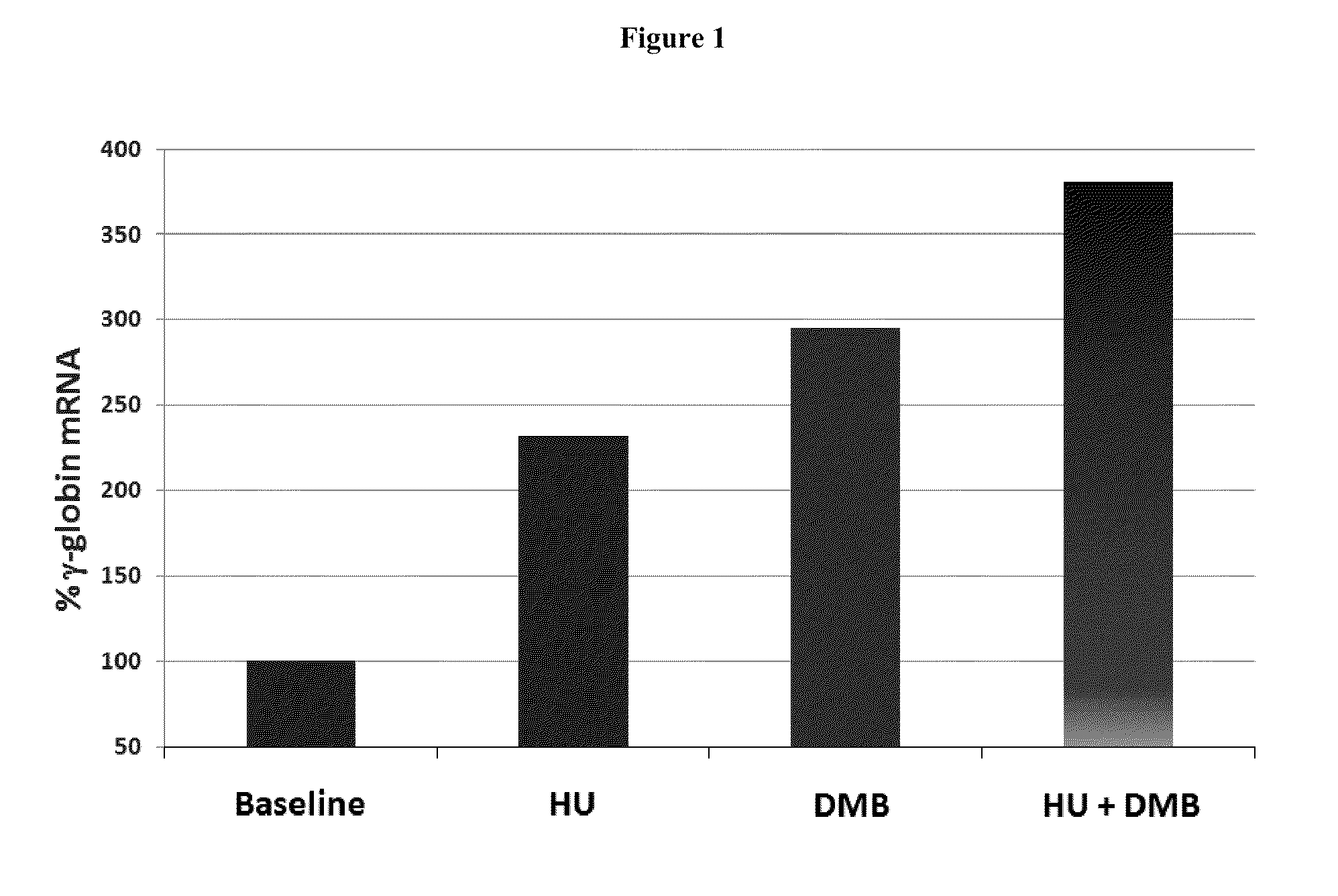
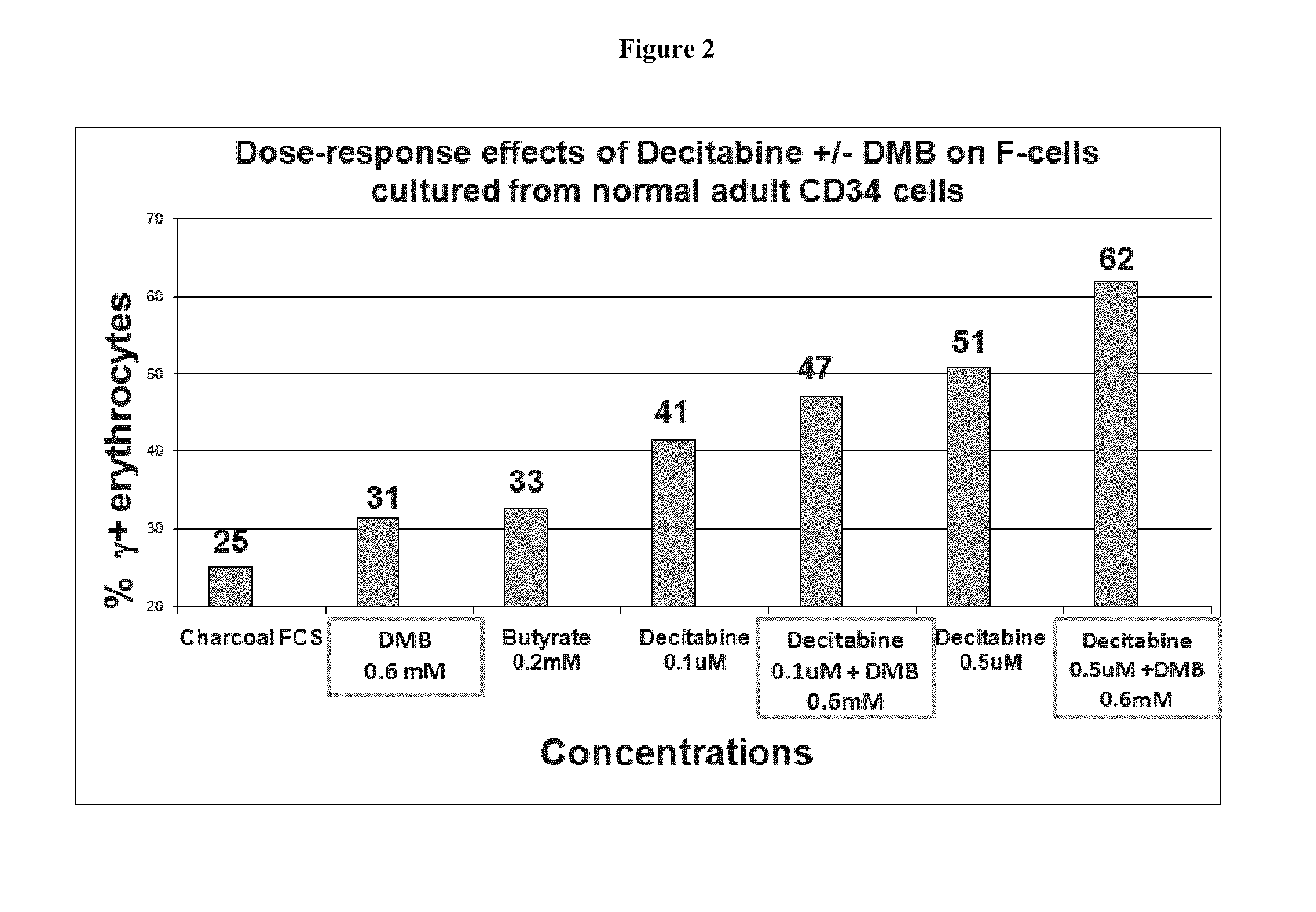
Methods and low dose regimens for treating red blood cell disorders
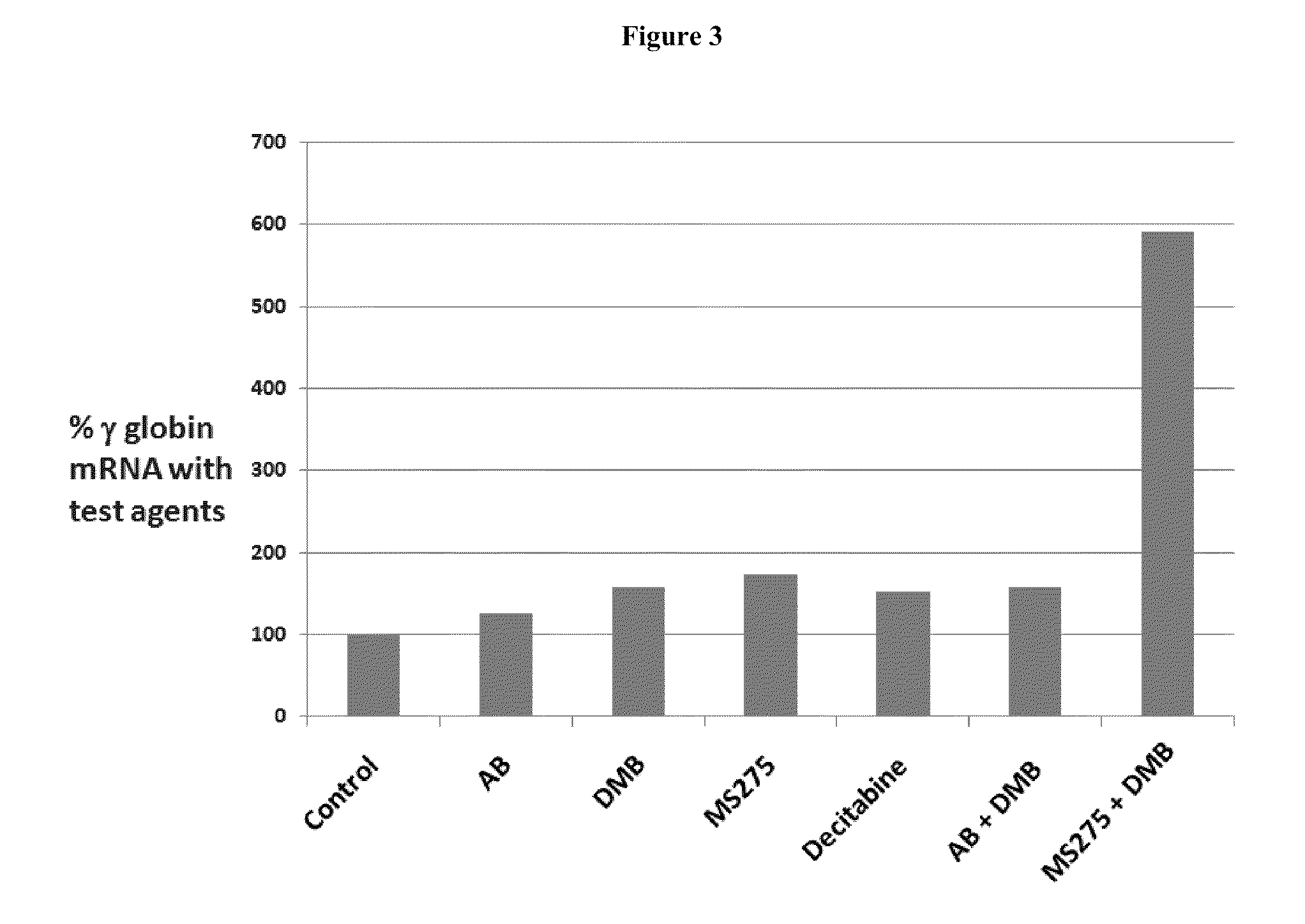
ActiveUS20110251149A1Increase volumeIncrease the number ofBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsBeta thalassemiaRegimen
Disclosed herein are methods and low dose regimens for increasing fetal hemoglobin levels in patients with red blood cell disorders, such as beta thalassemia, sickle cell disease, other anemias, or blood loss. Fetal and total hemoglobin levels and red blood cell counts are increased by administering 2,2-dimethylbutyrate (DMB) alone or in combination with hydroxyurea, decitabine or an HDAC inhibitor. Treatment can be continued for at least two weeks.
Owner:HEMAQUEST PHARMA INC +1
Electrode array for tissue ablation
ActiveUS7367974B2Fast ablationFlow of bloodDiagnosticsSurgical needlesElectrode arrayTissue ablation
An electrode array allows for rapid ablation of a strip of tissue in an organ providing a barrier to blood loss during resection operations.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Depth and puncture control for blood vessel hemostasis system
A depth and puncture control system for a blood vessel hemostasis system includes a blood vessel puncture control tip which, when positioned in the lumen of a blood vessel, can inhibit the flow of blood out of the puncture site. When used together with a pledget delivery cannula and a pledget pusher, the control tip and the delivery catheter can both inhibit blood loss out the puncture site and inhibit the introduction of pledget material and tissue fragments into the blood vessel. The system also includes a handle which releasably connects together the control tip, pusher, and delivery cannula to permit limited longitudinal motion between the control tip and the delivery cannula, and between the pusher and the delivery cannula.
Owner:BOSTON SCI CORP +11
Agents for controlling biological fluids and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20070059350A1Good hemostasisHigh viscosityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideMedicineIncision Site
Therapeutic formulations adapted for positive-pressure application for controlling biological fluid at a desired site in a subject, absorbent articles comprising therapeutic formulations, and anti-infective devices coated with therapeutic formulations, said formulations comprising about 25% to about 99% by weight liquid-crystal forming compound and 0% to about 75% by weight solvent. In addition, methods of using said formulations including methods for controlling biological fluid at a desired site in a subject, methods for controlling blood loss, and methods for facilitating effective closure of a vascular wound or incision site at a desired site in a subject are disclosed, the methods comprising administering particular formulations comprising liquid-crystal forming compounds and solvents that are described herein.
Owner:SOUTHEASTERN MEDICAL TECH
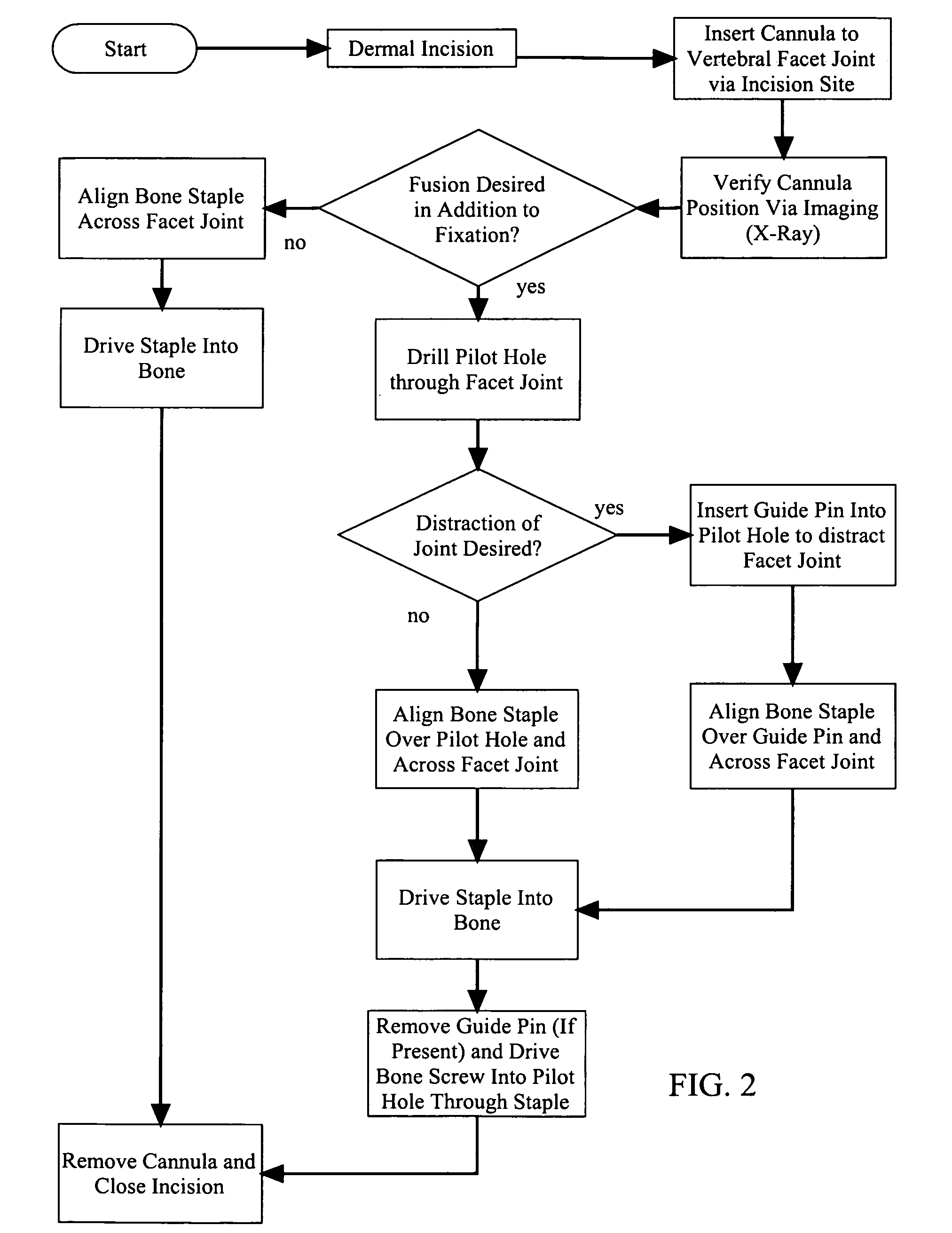
Method of lateral facet approach, decompression and fusion using screws and staples as well as arthroplasty
ActiveUS20090099602A1Improve stabilityCheap manufacturingSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisBlood lossSurgical department
A method of performing vertebral facet fusion by lateral approach and related devices. The lateral approach to facet fusion involves identifying the lateral mass and then introducing any of the fixation methods known or described herein laterally at one or more facets through the use of a hollow cannula. A surgical bone staple have a perforated bridge is used across the lateral facet joint where fixation is required. Where fusion is desired, a bone screw have lateral perforations of the shank is inserted through the bridge perforation at the joint to promote fusion. The staple and screw may be used in conjunction with one another or individually. The facet joint may be distracted prior to fixation to increase the foraminal space and decompress the neural structures to relieve pain. The method involves less surgical time, reduced blood loss and discomfort for the patient as compared to the posterior approach.
Owner:AFLATOON KAMRAN
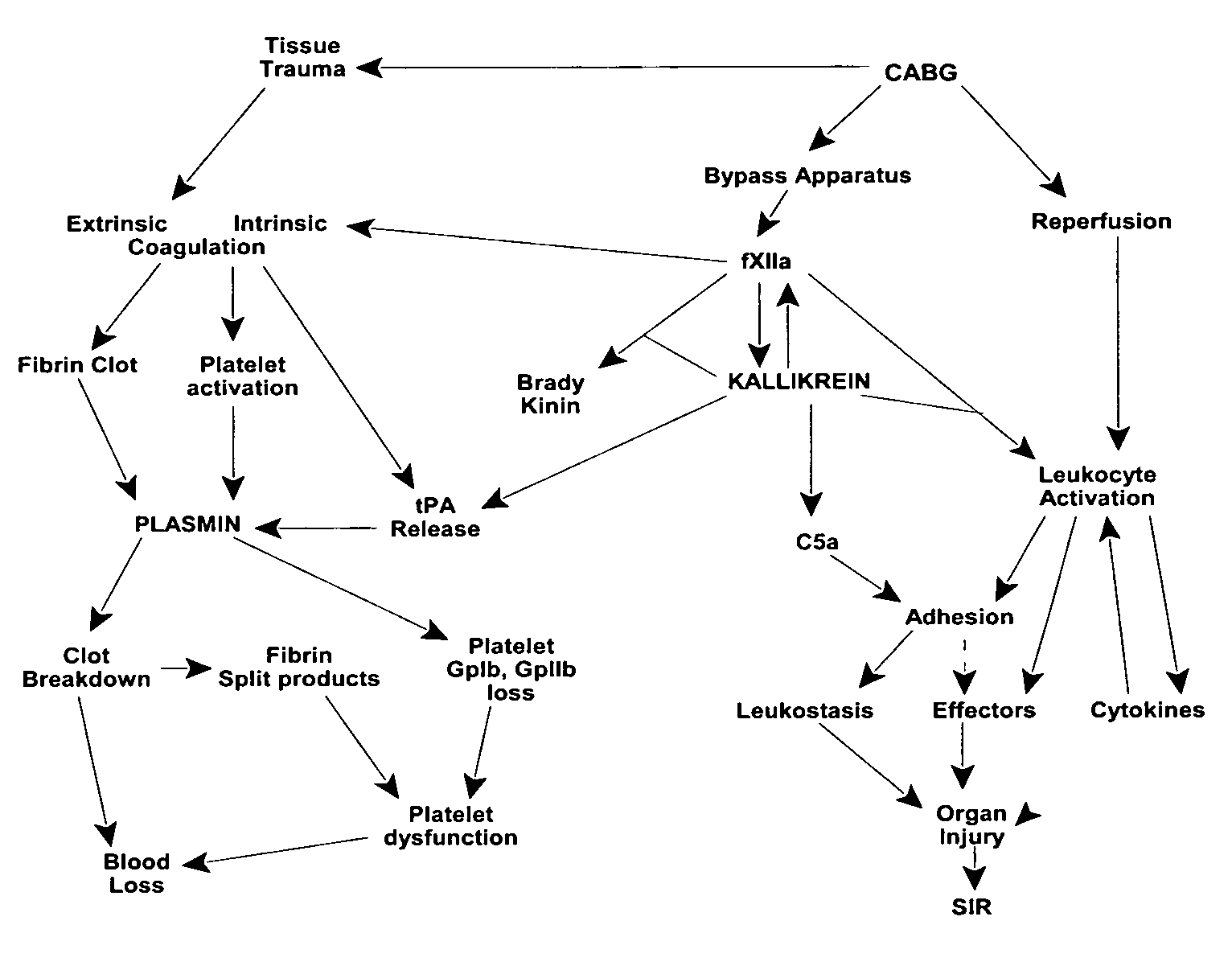
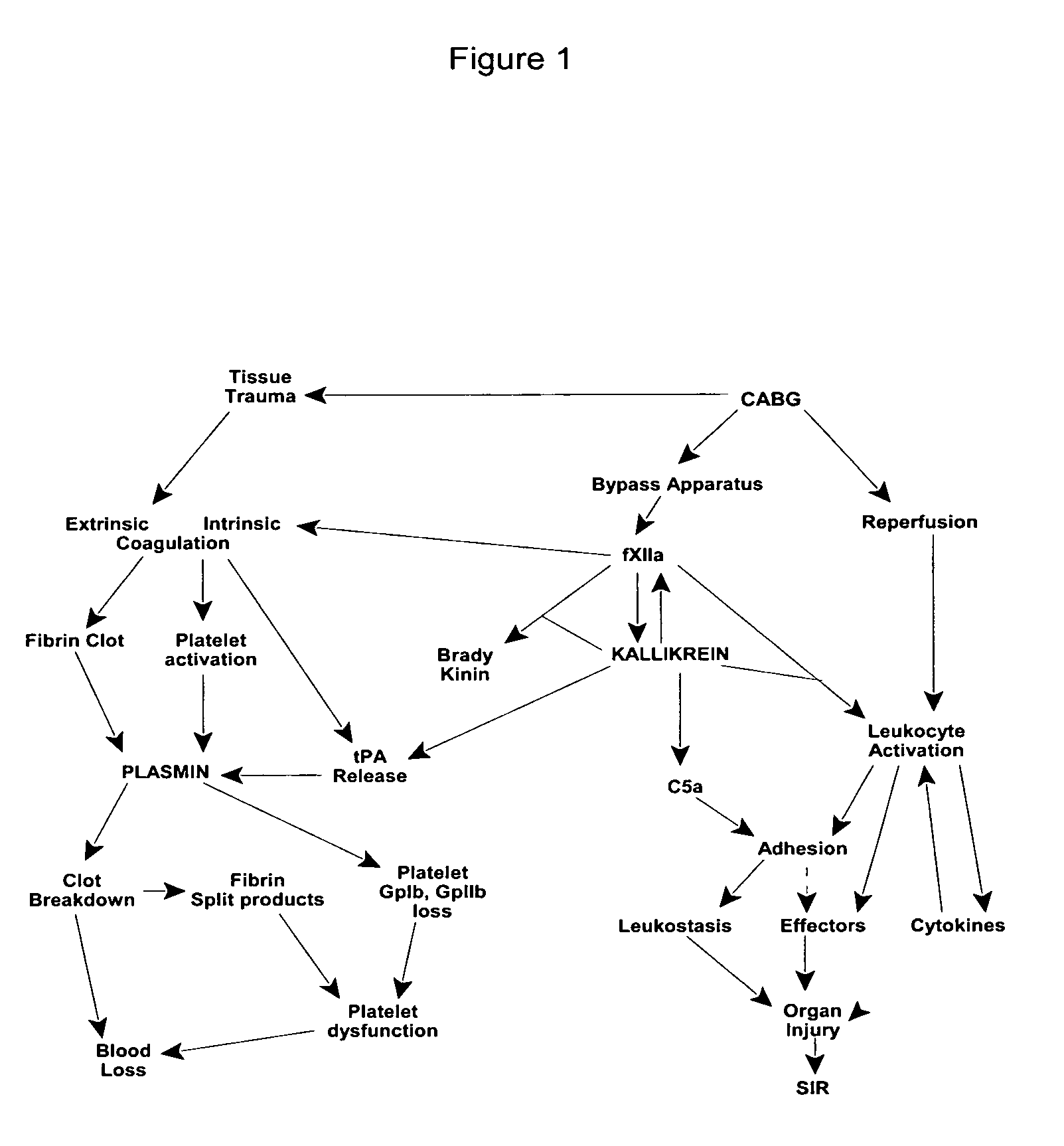
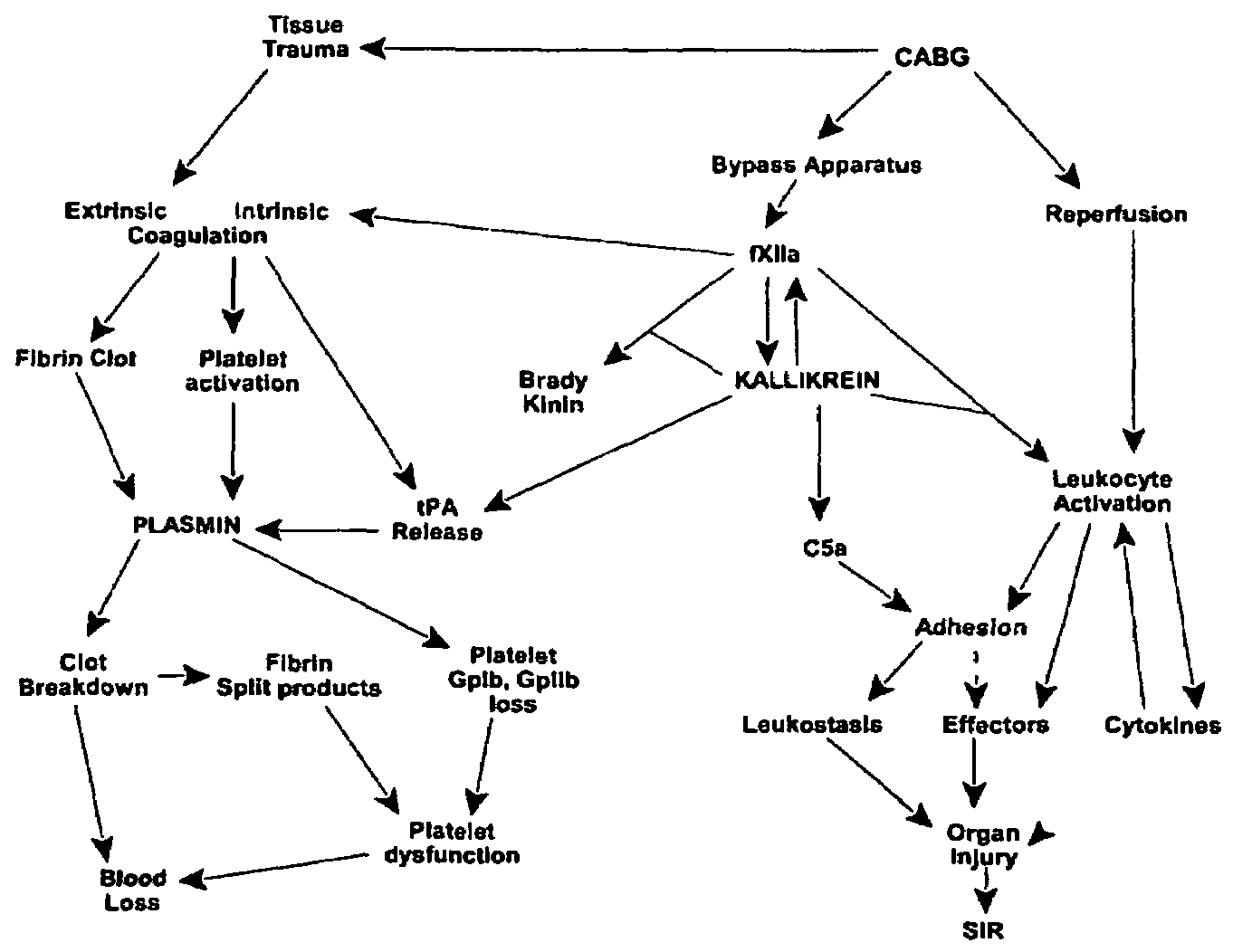
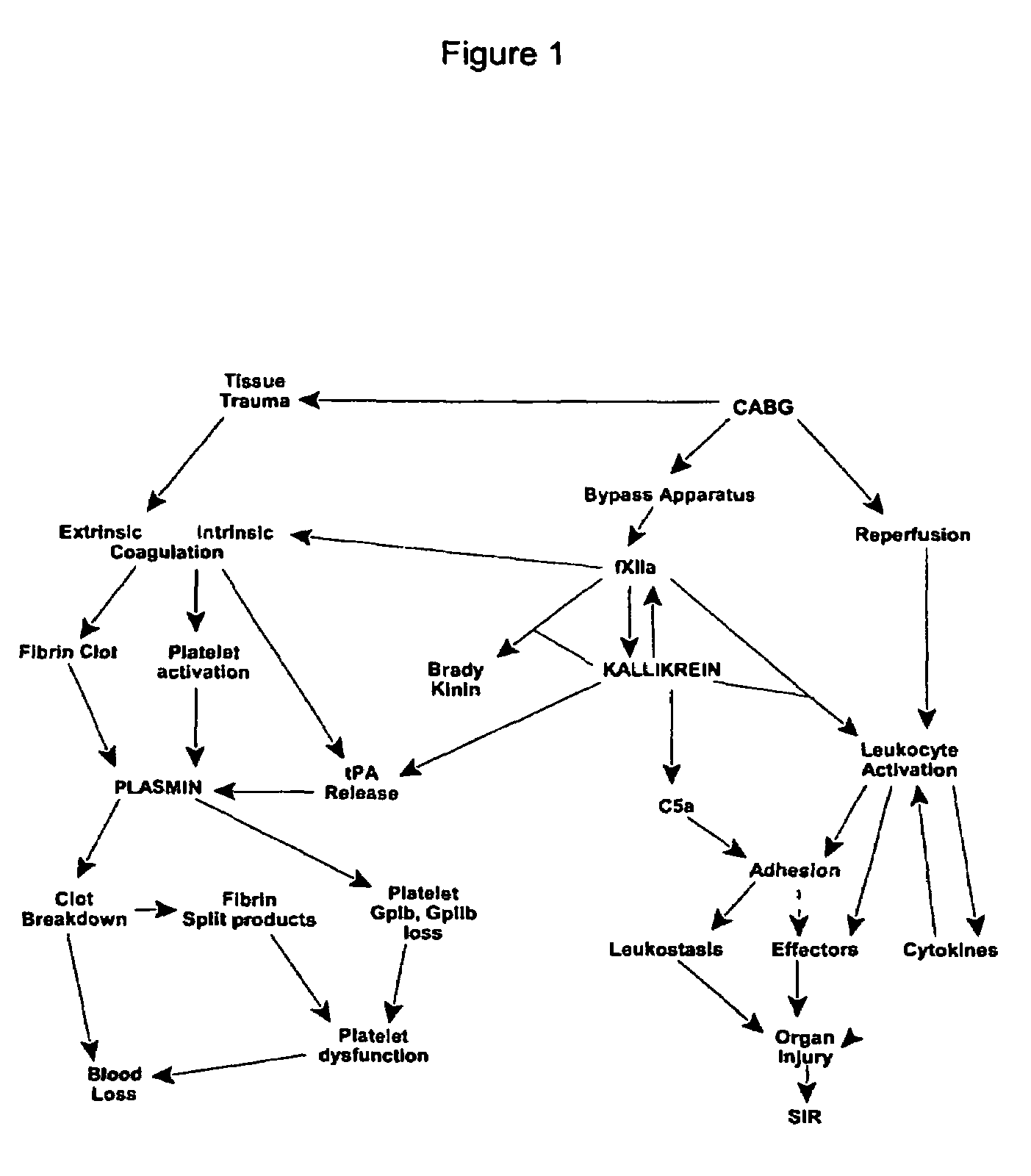
Prevention and reduction of blood loss
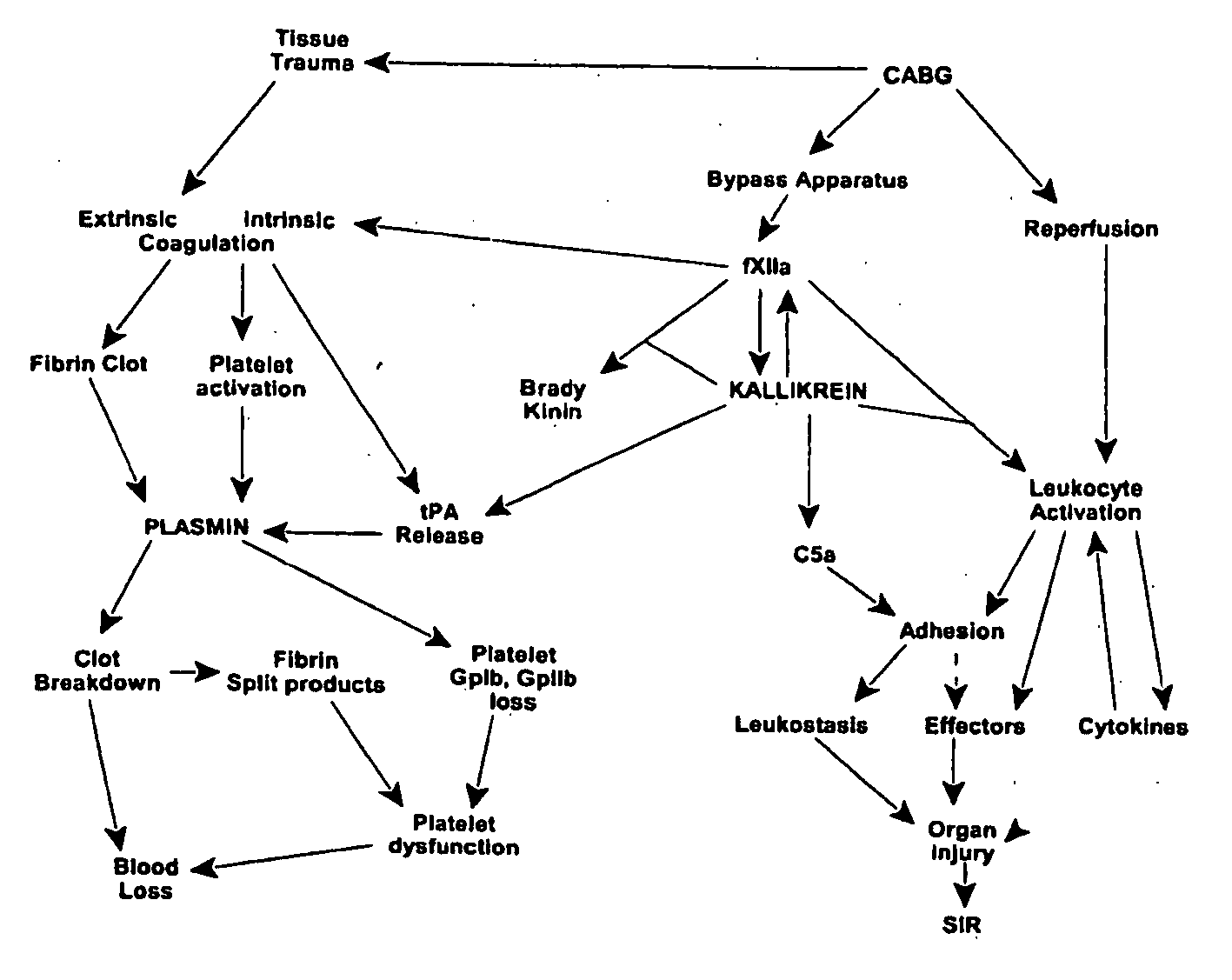
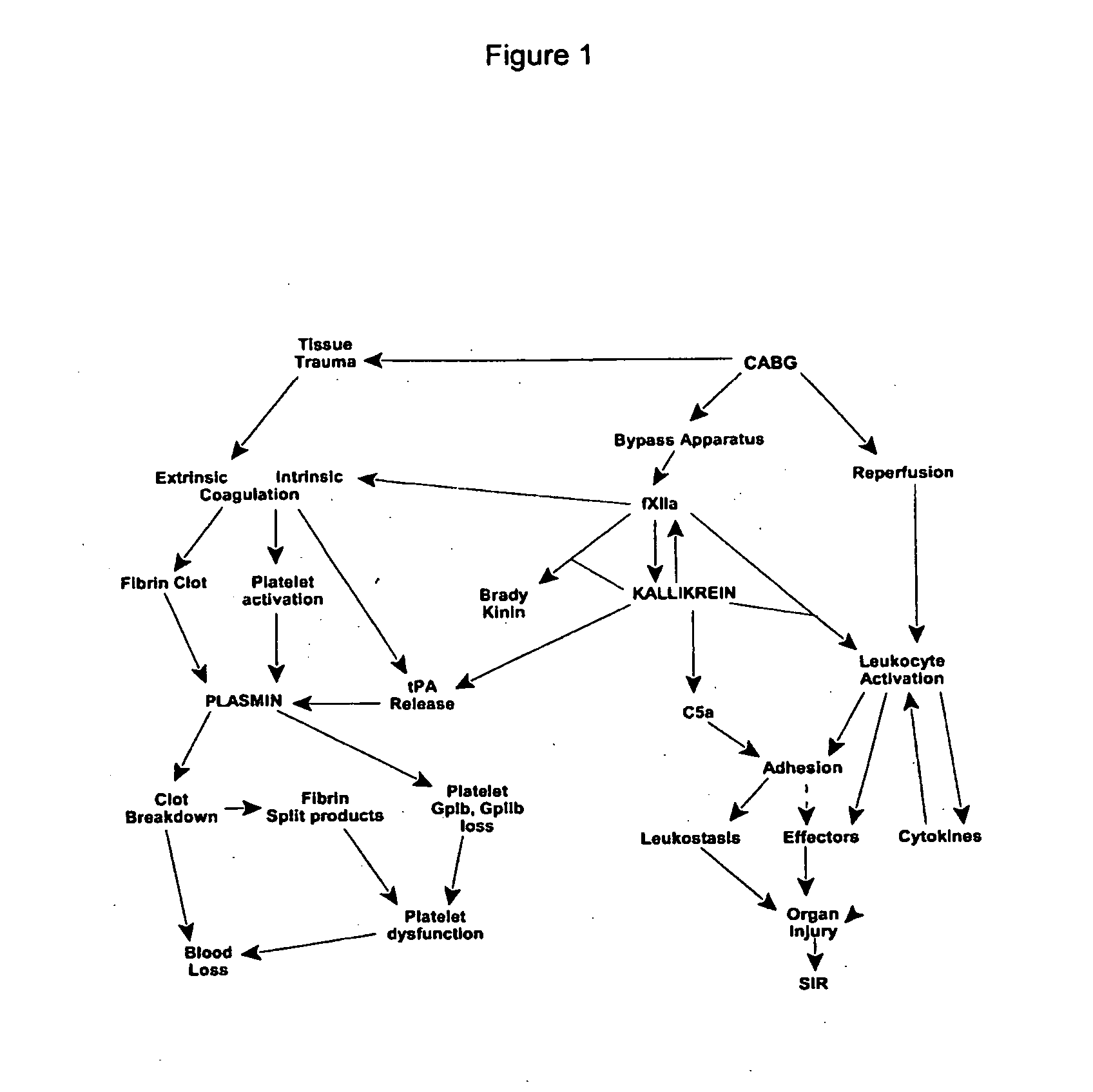
InactiveUS7064107B2Preventing and reducing onsetReduce and preventNervous disorderHydrolasesWhole bodySurgical department
Methods are described for preventing or reducing ischemia and / or systemic inflammatory response in a patient such as perioperative blood loss and / or systemic inflammatory response in a patient subjected to cardiothoracic surgery, e.g., coronary artery bypass grafting and other surgical procedures, especially when such procedures involve extra-corporeal circulation, such as cardiopulmonary bypass.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Prevention and reduction of blood loss
Methods are described for preventing or reducing ischemia and / or systemic inflammatory response in a patient such as perioperative blood loss and / or systemic inflammatory response in a patient subjected to cardiothoracic surgery, e.g. coronary artery bypass grafting and other surgical procedures, especially when such procedures involve extra-corporeal circulation, such as cardiopulmonary bypass.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
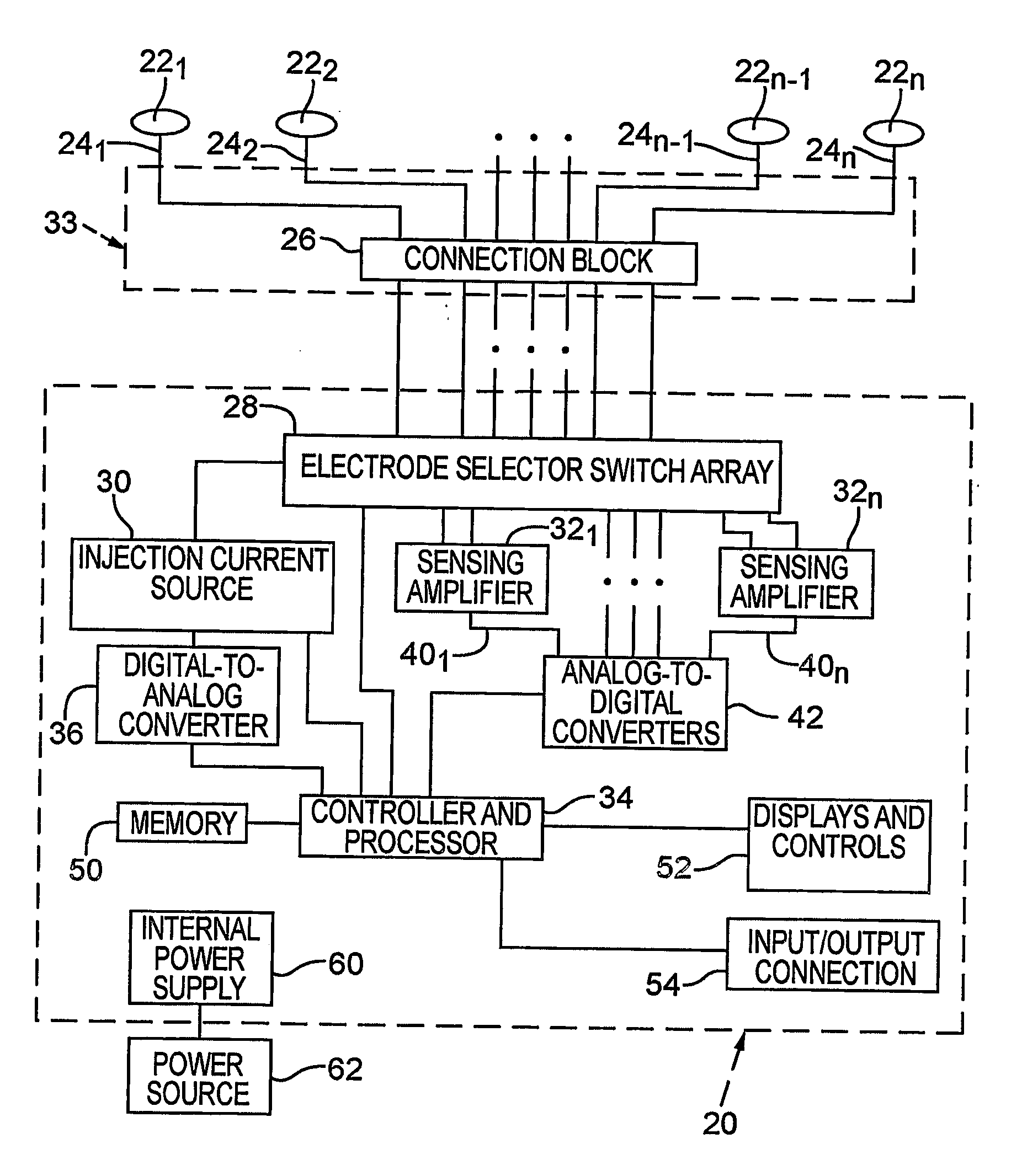
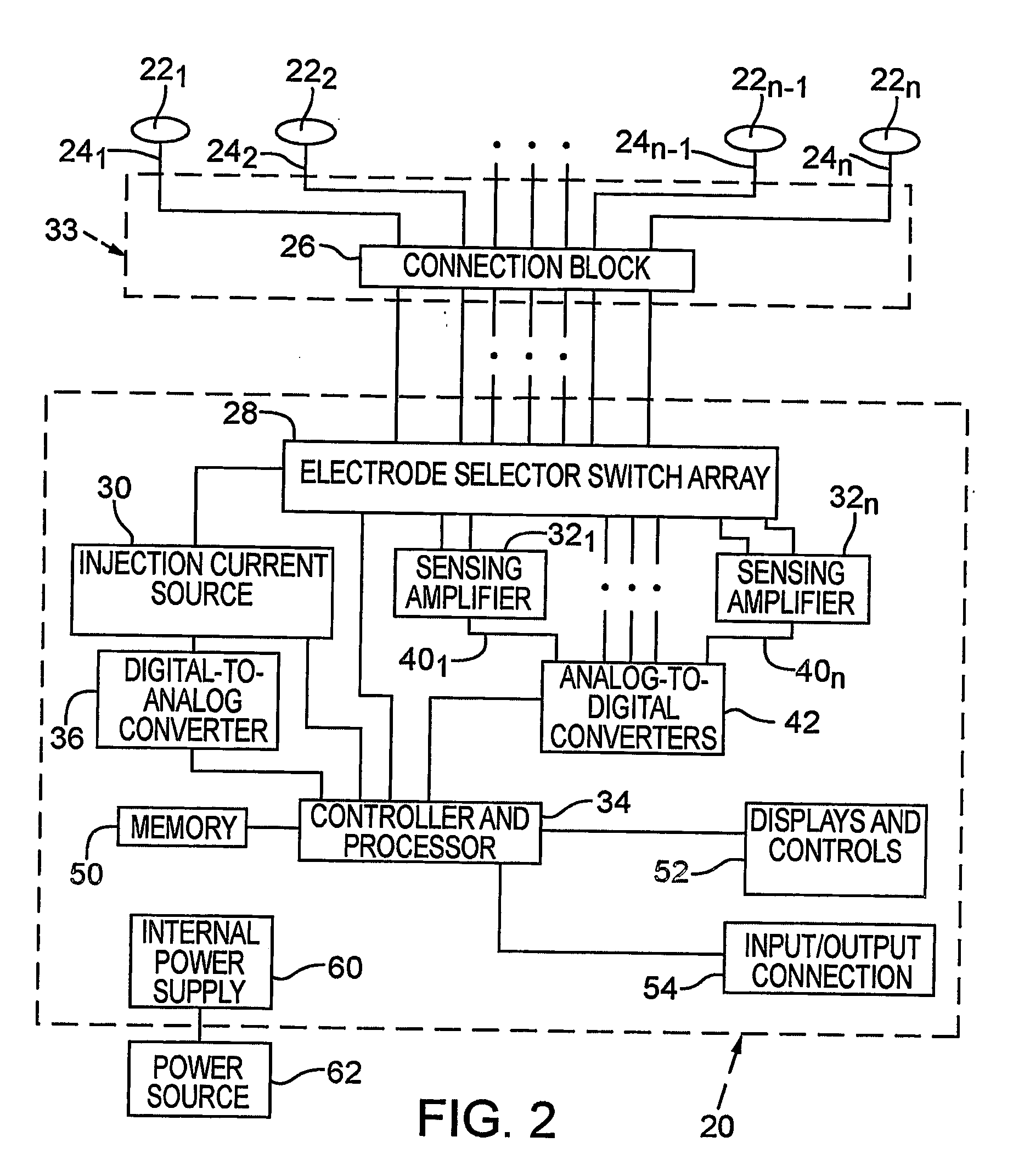
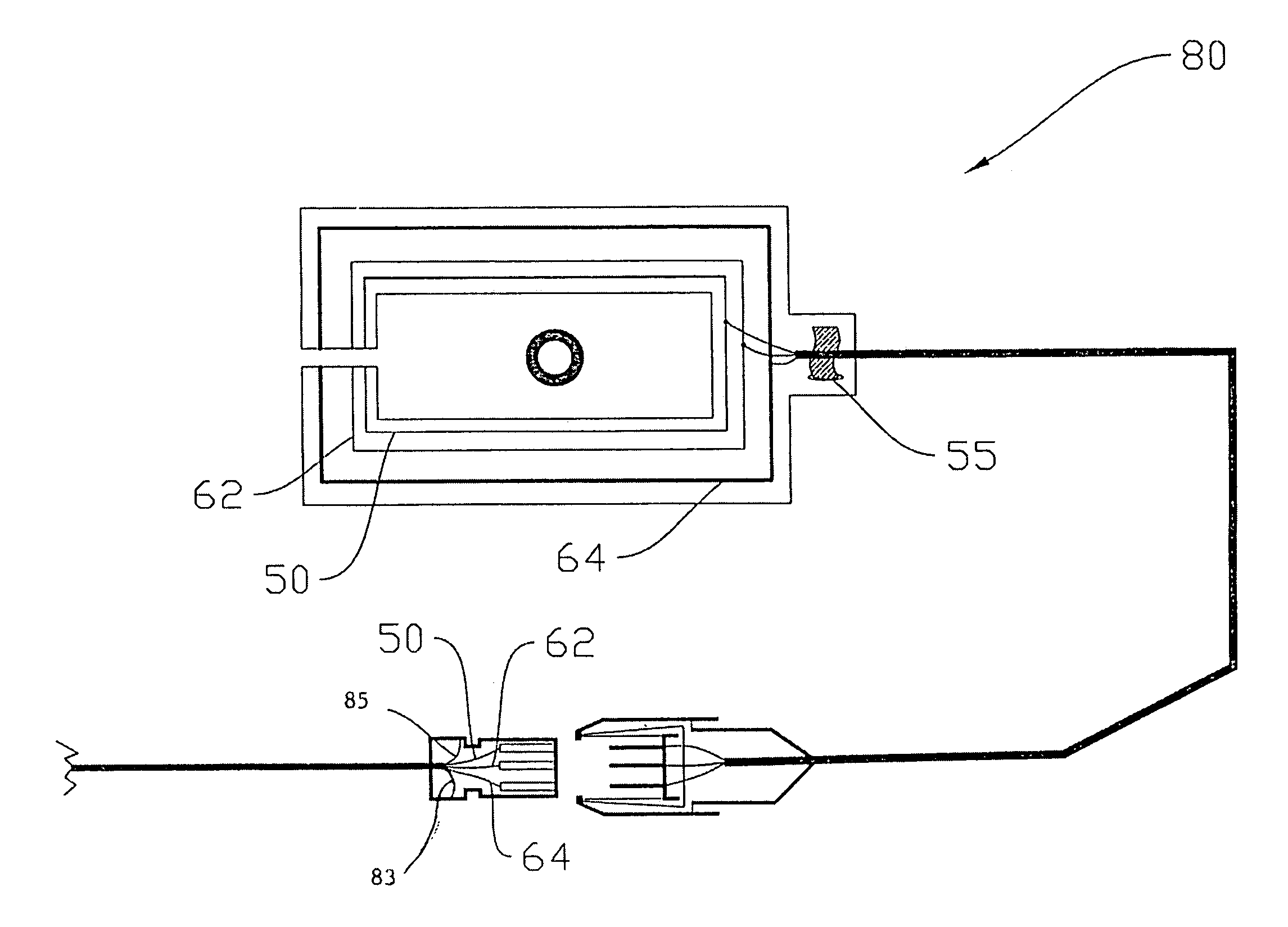
Methods of and apparatus for determining fluid volume presence in mammalian tissue
Methods and apparatus (20 ) process noninvasively measured electrical bio-impedence values and perform a technique that indicates whether there exists a change from a homeostatic fluid condition, preferably with respect to blood loss, in mammalian tissue. Analyses can be performed to determine a presence or a change in volume of fluid in an anatomical space of a mammal. A preferred implementation of such technique is embodied in an instrument that carries out a method that may predict an onset of a hemorrhagic shock condition.
Owner:SCHOCK & CO GMBH
Telescoping vascular dilator
InactiveUS20060217664A1Minimal blood lossMinimally invasiveInfusion syringesDilatorsDilatorThree vessels
A telescoping dilator assembly is configured for percutaneous insertion of large diameter intravascular devices into a blood vessel while avoiding kinking of a guidewire and minimizing blood loss. The assembly includes a first smaller diameter dilator with an inner lumen that fits snugly over a guidewire. The smaller dilator may be tapered on both ends. A second larger diameter dilator is configured to slide over the first smaller dilator. A tear away sheath is configured to slide over the dilators and into a blood vessel. A tear away sheath plug is configured to form a seal at a proximal end of the sheath. When the dilators are removed from the blood vessel, an intravascular device may be passed through the sheath into the blood vessel.
Owner:HATTLER BRACK G +1
Automatic surgical sponge counter and blood loss determination system
InactiveUS8105296B2Inhibition retentionEliminate dangerElectric signal transmission systemsSurgical furnitureOptical scannersHand held
A surgical sponge detection system includes a plurality of surgical sponges (2) having radio frequency identification tags (1) securely attached thereto and a non-optical hand-held reader (40) for detecting the sponges by detecting the tags (1). Also disclosed is a device (30) for automatically counting, weighing, and calculating blood loss contained within, soiled surgical sponges (2) which includes a cabinet with an opening (3) at the top through which sponges (2) are deposited, a reader (6) which scans each sponge (2) entered and determines sponge type from a tag (1) affixed to each sponge (2), and a disposable bag (8) into which the sponges (2) are deposited. The disposable bag (8) is removably mounted to a weighing scale (10); there is also a rear door (9) from which the disposable bag (8) can be easily removed, a rechargeable battery (11), a shelf (12) for unused disposable bag storage, a control unit (4) which processes data received from reader (6) and scale (10) and instantaneously calculates total weight of liquid contained within sponges entered, a display panel (5) continuously displays the number and type of sponges entered during a given procedure as well as the total weight of liquids retained in those sponges. There is a means for automatically determining the weight of the sponges when dry which includes a non-optical scanner means (6) which can read an indicating means (1) on the sponges (2) even when the indicating means (1) is covered with blood or other body fluids.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
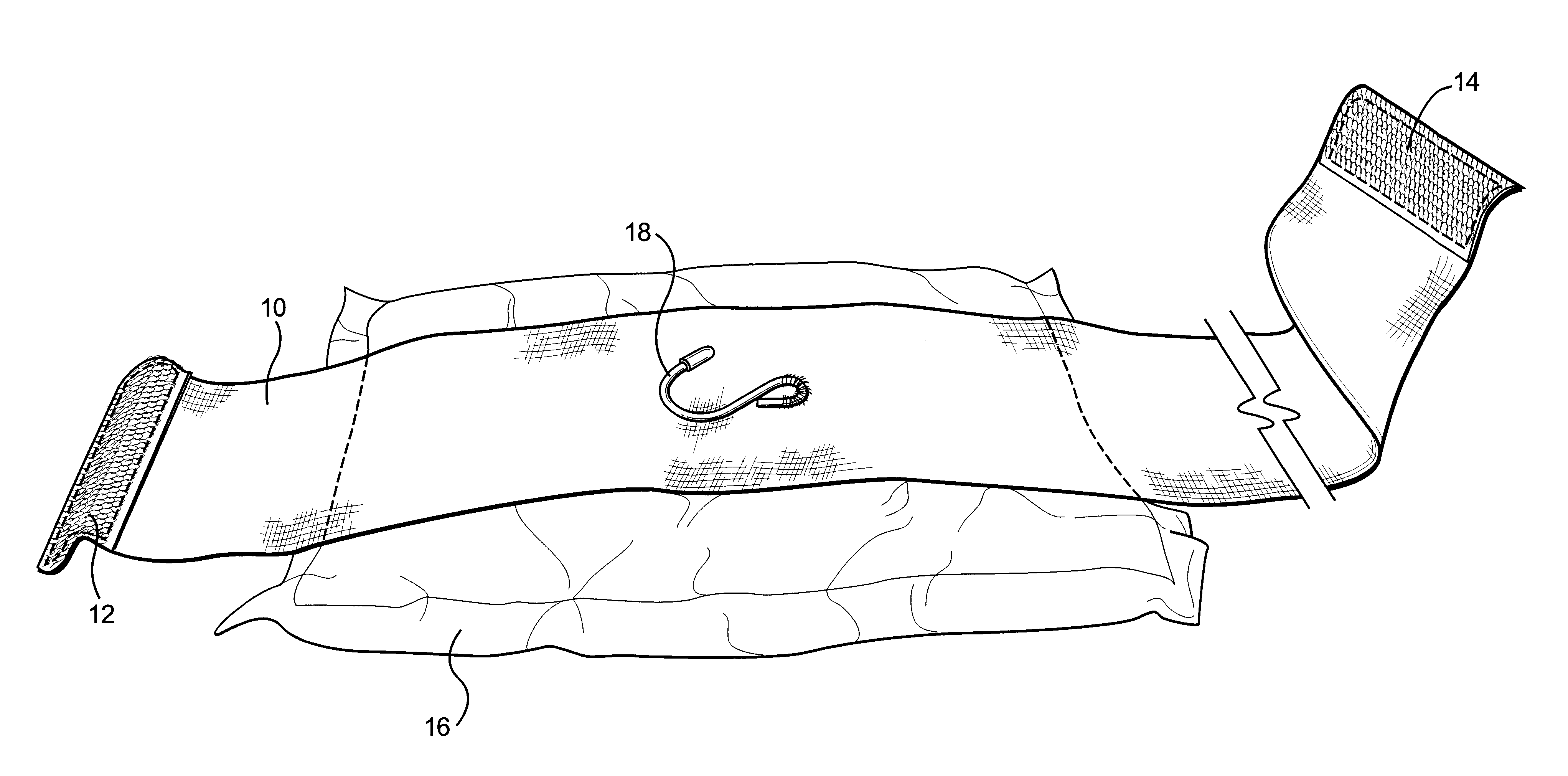
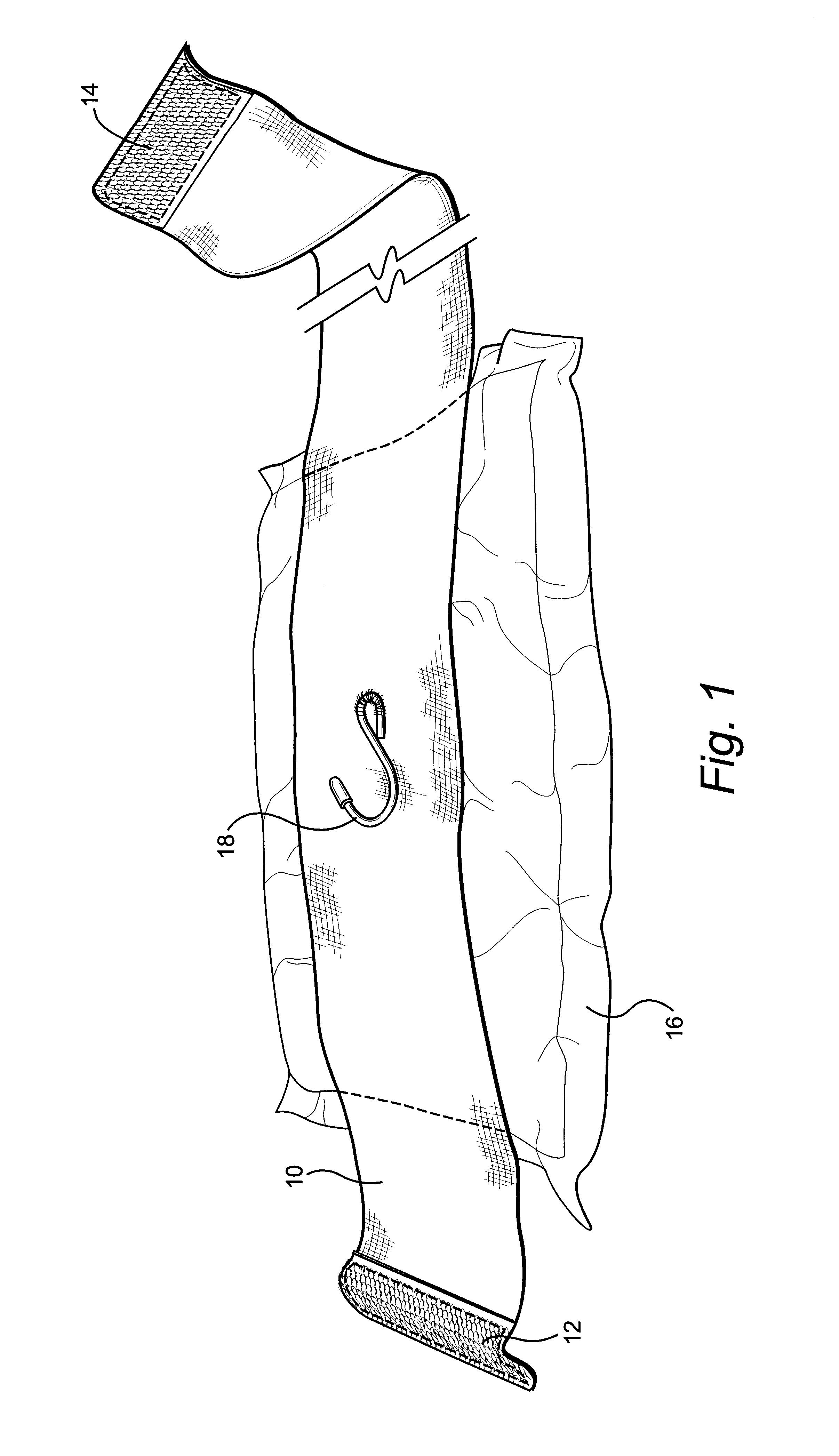
Compression bandage with tightening means
Disclosed is a strip of bandaging material having Velcro(R) strips at either end on opposite sides of the material. An absorbent pad is fixed near one end and on the side opposite the Velcro(R) strip. On the side opposite the absorbent pad, an S hook is provided with one end fastened to the material and the other end free. The absorbent pad is located over the wound and the longer end of material is wound around the extremity and fixed in place with the Velcro(R) stripe at the near end of the material. The remaining material is passed through the hook and pulled back in order to apply pressure to the wound and reduce blood loss. The remainder of the material is wrapped around the extremity and secured in place with the Velcro(R) strip on the far end.
Owner:H&H MEDICAL
Blood loss detection for hemodialysis system
InactiveUS7641612B1Quick installationEasy to removeSemi-permeable membranesSolvent extractionBlood lossLine tubing
A blood loss detection device for a hemodialysis system having a blood intake line, a dialysis machine including a pump, with the dialysis machine in communication with the blood intake line, and a blood return line in communication with the dialysis machine. The detection device includes a patch having an exterior edge and an opening through the patch forming a target for receipt of the return blood line. A slit through the patch extends between the exterior edge and the opening. A primary loop circuit terminates at two ends at the slit. An early warning alarm circuit loop terminates at two ends at the slit. An emergency shut-down circuit loop terminates at two ends at the slit. A modular connector connects the patch to an alarm activated by the early warning alarm circuit and to a switch mechanism activated by the shut-down circuit in order to shut down the dialysis machine and the pump.
Owner:MCCALL KENNETH SHAWN
Multifunction adaptor for an open-ended catheter
InactiveUS20050261664A1Prevent blood lossPrevent air embolismInfusion syringesMedical devicesCatheter deviceAir embolism
A multifunction adaptor for an open-ended catheter that allows placement of the catheter while minimizing the risk of air embolism or blood loss through the open (proximal) end of the catheter body. In one variation, the design allows passage of a standard guidewire for “over-the-guidewire” placement techniques and a connection for catheter flushing using a standard syringe. In another variation, the multifunction adaptor is configured for coupling a tunneler to the proximal end of a catheter.
Owner:CR BARD INC
Prevention and reduction of blood loss
InactiveUS20080064637A1Nervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsWhole bodyCardiopulmonary bypass time
Methods are described for preventing or reducing ischemia and / or systemic inflammatory response in a patient such as perioperative blood loss and / or systemic inflammatory response in a patient subjected to cardiothoracic surgery, e.g. coronary artery bypass grafting and other surgical procedures, especially when such procedures involve extra-corporeal circulation, such as cardiopulmonary bypass.
Owner:DYAX CORP
Automatic surgical sponge counter and blood loss determination system
InactiveUS20060044137A1Inhibition retentionEliminate dangerElectric signal transmission systemsSurgical furnitureOptical scannersHand held
A surgical sponge detection system includes a plurality of surgical sponges (2) having radio frequency identification tags (1) securely attached thereto and a non-optical hand-held reader (40) for detecting the sponges by detecting the tags (1). Also disclosed is a device (30) for automatically counting, weighing, and calculating blood loss contained within, soiled surgical sponges (2) which includes a cabinet with an opening (3) at the top through which sponges (2) are deposited, a reader (6) which scans each sponge (2) entered and determines sponge type from a tag (1) affixed to each sponge (2), and a disposable bag (8) into which the sponges (2) are deposited. The disposable bag (8) is removably mounted to a weighing scale (10); there is also a rear door (9) from which the disposable bag (8) can be easily removed, a rechargeable battery (11), a shelf (12) for unused disposable bag storage, a control unit (4) which processes data received from reader (6) and scale (10) and instantaneously calculates total weight of liquid contained within sponges entered, a display panel (5) continuously displays the number and type of sponges entered during a given procedure as well as the total weight of liquids retained in those sponges. There is a means for automatically determining the weight of the sponges when dry which includes a non-optical scanner means (6) which can read an indicating means (1) on the sponges (2) even when the indicating means (1) is covered with blood or other body fluids.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
Multifunction adaptor for an open-ended catheter
InactiveUS7578803B2Prevent blood loss or air embolismInfusion syringesMedical devicesGuide tubeCatheter device
A multifunction adaptor for an open-ended catheter that allows placement of the catheter while minimizing the risk of air embolism or blood loss through the open (proximal) end of the catheter body. In one variation, the design allows passage of a standard guidewire for “over-the-guidewire” placement techniques and a connection for catheter flushing using a standard syringe. In another variation, the multifunction adaptor is configured for coupling a tunneler to the proximal end of a catheter.
Owner:CR BARD INC
Method of inhibiting the formation of adhesions and scar tissue and reducing blood loss
InactiveUS20080069855A1Increased riskEasy to disassembleBiocideInternal osteosythesisWound siteBlood vessel
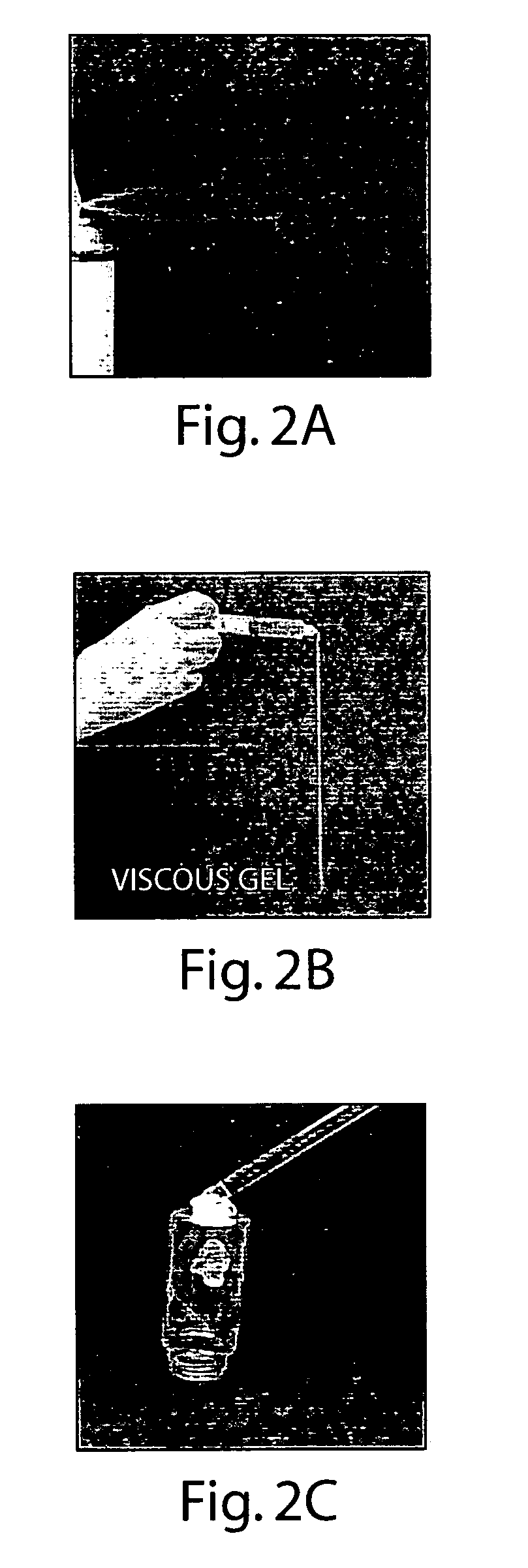
The present invention provides a method for inhibiting the formation of scar tissue and / or exogenous bone at a wound site in a body of a patient. The method includes administering an amount of a biologic agent to the wound site, wherein the biologic agent is synovial fluid or cerebrospinal fluid. A viscous substance applied to the wound site, advantageously incorporating the biologic agent, reduces the flow of blood from cut blood vessels, and contributes to a reduction in the formation of adhesions through action of the biologic agent, and through barrier properties introduced by the viscous substance.
Owner:P TECH
Needle kit and method for microwave ablation, track coagulation, and biopsy
InactiveUS20070161977A1Minimize damageMinimize bleedingSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsAbnormal tissue growthBiomedical engineering
A modular biopsy, ablation and track coagulation needle apparatus is disclosed that allows the biopsy needle to be inserted into the delivery needle and removed when not needed, and that allows an inner ablation needle to be introduced and coaxially engaged with the delivery needle to more effectively biopsy a tumor, ablate it and coagulate the track through ablation while reducing blood loss and track seeding. The ablation needle and biopsy needle are adapted to in situ assembly with the delivery needle. In a preferred embodiment, the ablation needle, when engaged with the delivery needle forms a coaxial connector adapted to electrically couple to an ablating source. Methods for biopsying and ablating tumors using the device and coagulating the track upon device removal are also provided.
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
Prevention and reduction of blood loss
InactiveUS20070249807A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticExtracorporeal circulationCardiopulmonary bypass time
Methods are described for preventing or reducing ischemia and / or systemic inflammatory response in a patient such as perioperative blood loss and / or systemic inflammatory response in a patient subjected to cardiothoracic surgery, e.g. coronary artery bypass grafting and other surgical procedures, especially when such procedures involve extra-corporeal circulation, such as cardiopulmonary bypass.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
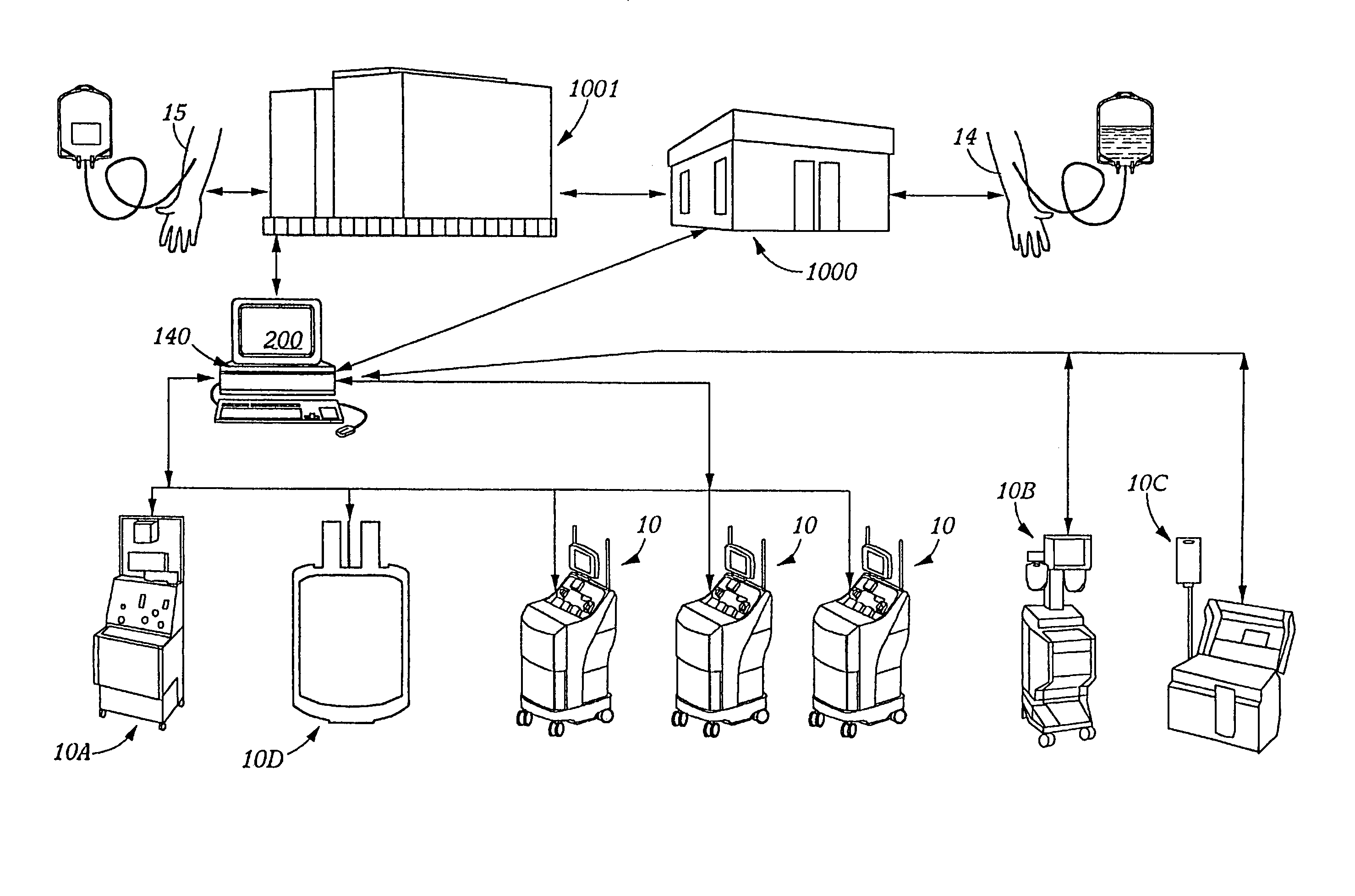
Blood processing information system with blood loss equivalency tracking
InactiveUS7430478B2Avoid wastingEasy to useOther blood circulation devicesMedical devicesBlood componentCollection system
Owner:TERUMO BCT
Depth and puncture control for system for hemostasis of blood vessel
A depth and puncture control system for a blood vessel hemostasis system includes a blood vessel puncture control tip which, when positioned in the lumen of a blood vessel, can inhibit the flow of blood out of the puncture site. When used together with a pledget delivery cannula and a pledget pusher, the control tip and the delivery catheter can both inhibit blood loss out the puncture site and inhibit the introduction of pledget material and tissue fragments into the blood vessel. The system also includes a handle which releasably connects together the control tip, pusher, and delivery cannula to permit limited longitudinal motion between the control tip and the delivery cannula, and between the pusher and the delivery cannula.
Owner:BOSTON SCI CORP +11
Electrode array for tissue ablation
ActiveUS20060064084A1Fast ablationStaunch blood flowDiagnosticsSurgical needlesElectrode arrayTissue ablation
An electrode array allows for rapid ablation of a strip of tissue in an organ providing a barrier to blood loss during resection operations.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Remote pericardial hemostasis for ventricular access and reconstruction or other organ therapies
ActiveUS20130090523A1Improve performanceFacilitate stabilizing and hemostasisSuture equipmentsHeart valvesCongestive heart failure chfPericardium
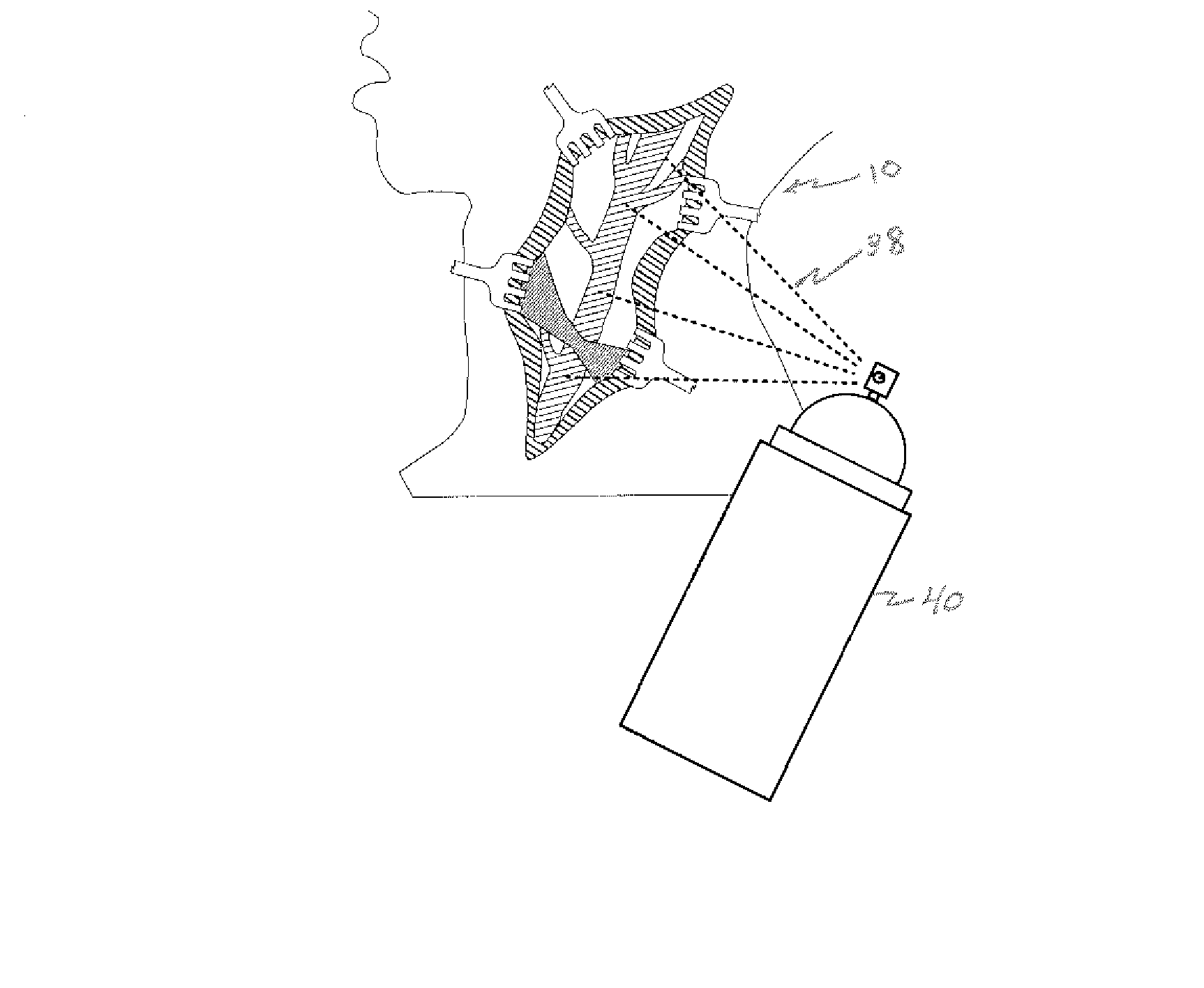
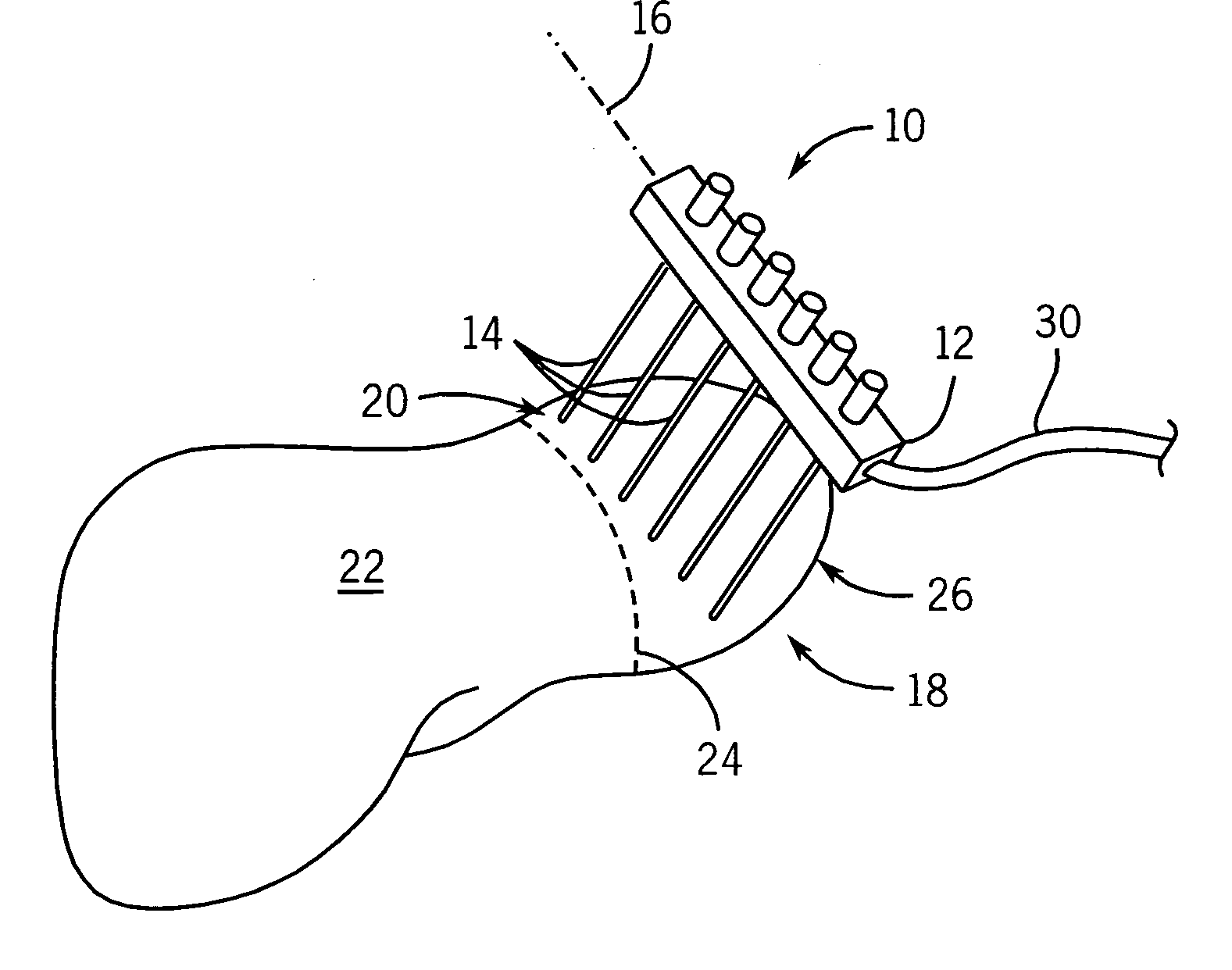
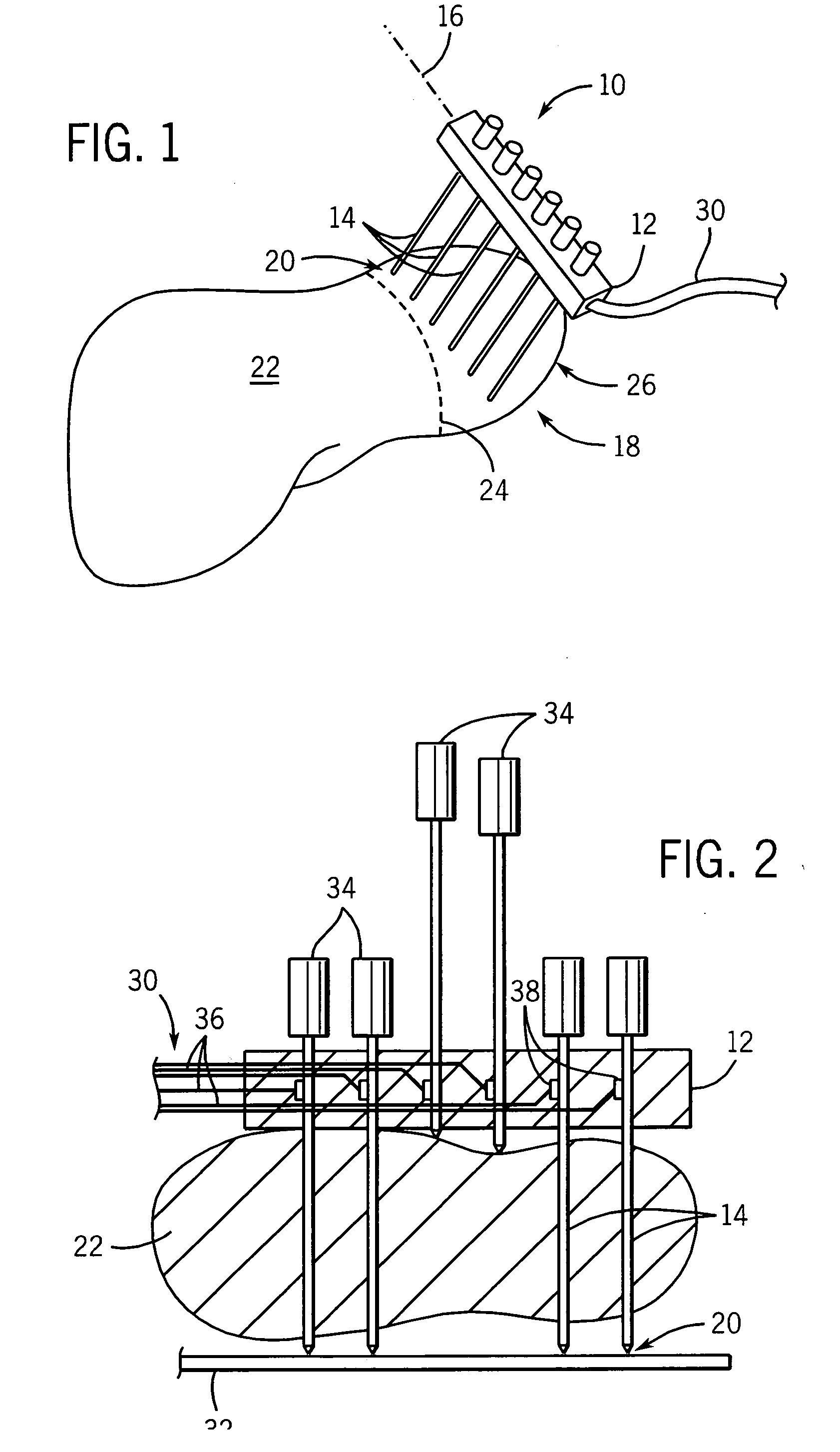
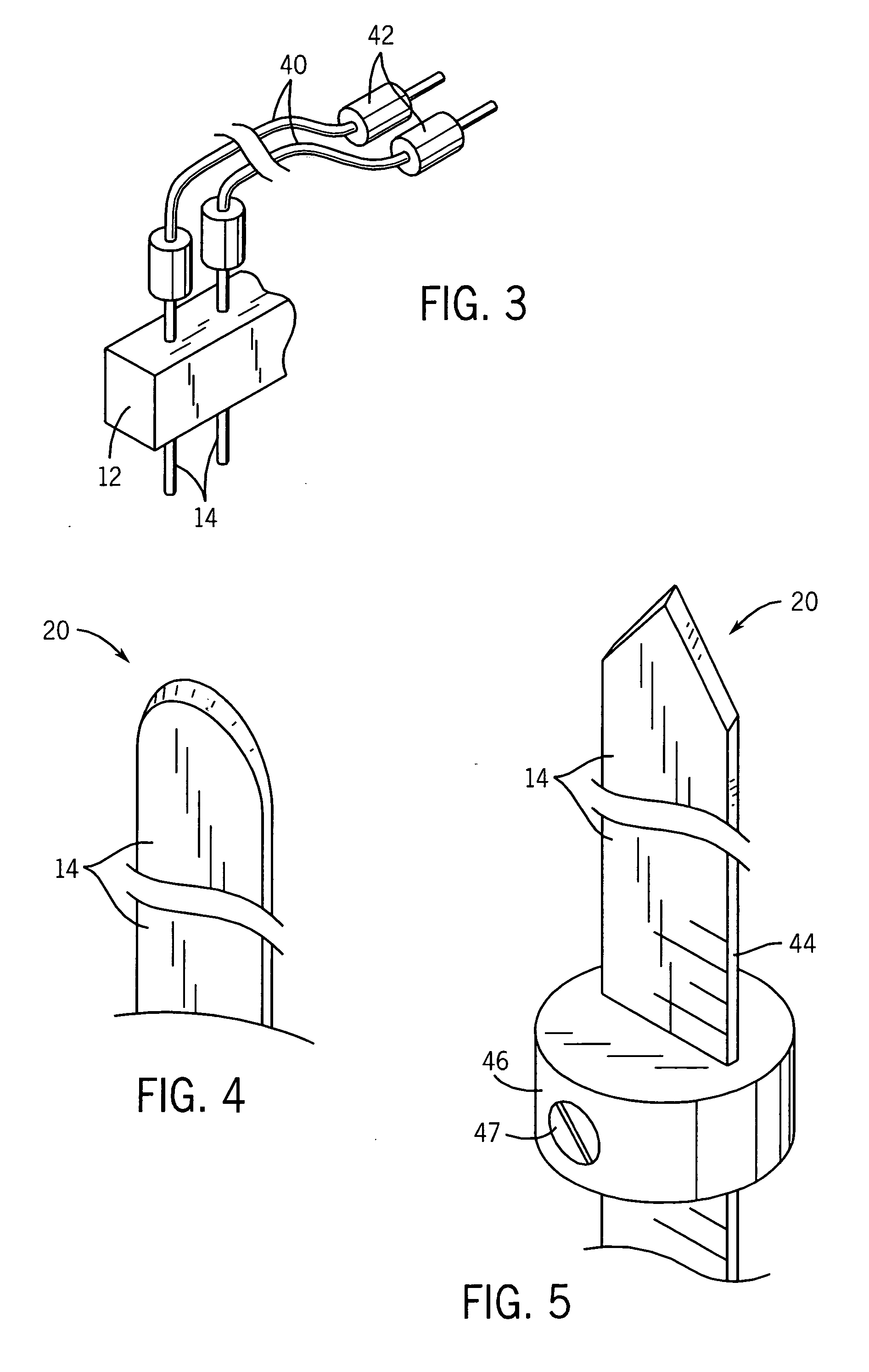
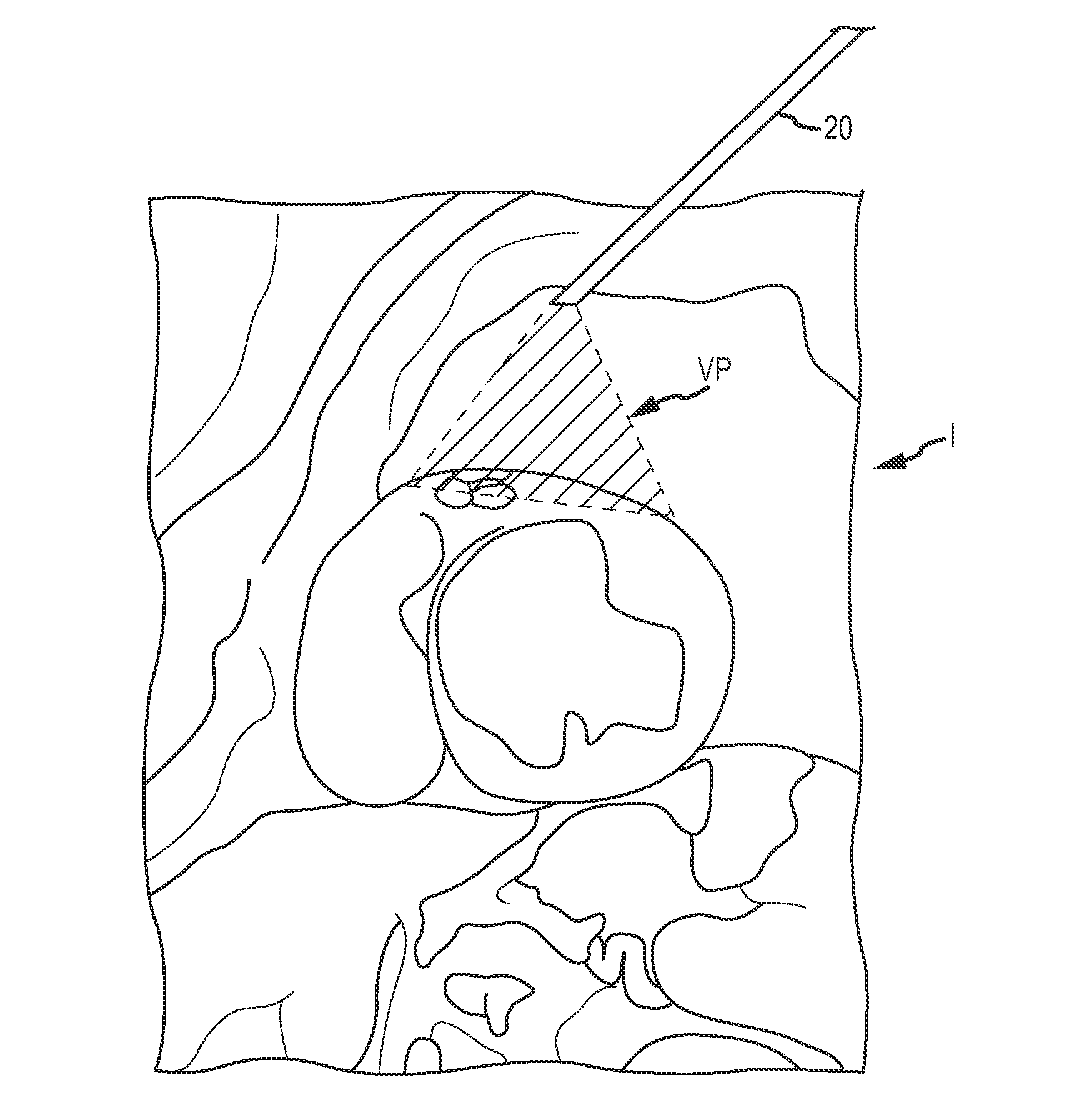
Embodiments described herein provide devices, systems, and methods that reduce the distance between two locations in tissue, often for treatment of congestive heart failure. For example, an anchor of an implant system may, when the implant system is fully deployed, reside within the right ventricle in engagement with the ventricular septum. The anchor may be deployed into the heart through a working lumen of a minimally invasive access tool. The minimally invasive access tool may have a plurality of grippers near a distal end of the working lumen. The grippers may engage epicardial tissue of the heart and may be moved radially inwardly relative so as to provide stabilization of the epicardial tissue and / or hemostasis near an access site where the anchor is inserted through the epicardium. The minimally invasive access tool may minimize blood loss from the access site and improve anchor implant processes.
Owner:BIOVENTRIX A CHF TECH
Surgical coring system
InactiveUS20080009891A1Avoid blood lossCannulasDiagnosticsExtracorporeal circulationBalloon catheter
Novel surgical tools and methods for off-pump surgery are described herein. A novel coring system is disclosed which employs a balloon catheter and a coring tool which is adapted to be threaded on to a guide wire. The guide wire serves as a track upon which the coring tool is guided. Embodiments of the coring tool ensure complete removal and excision of cored tissue. In addition, the described coring system prevents blood loss during off-pump surgery. In an embodiment, a surgical coring tool comprises a hollow body having an open distal end and a closed proximal end. The open distal end has a cutting edge. The hollow body comprises a vacuum connection to apply suction from said hollow body. The surgical coring tool also comprises a hollow elongate member disposed coaxially within said hollow body. The elongate member is adapted to be inserted on to a guide wire.
Owner:TEXAS HEART INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com