Patents
Literature
424 results about "Intravascular device" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Intravascular devices are an integral component of modern-day medical practice. They are used to administer intravenous fluids, medications, blood products and parenteral nutrition.
Delivery devices
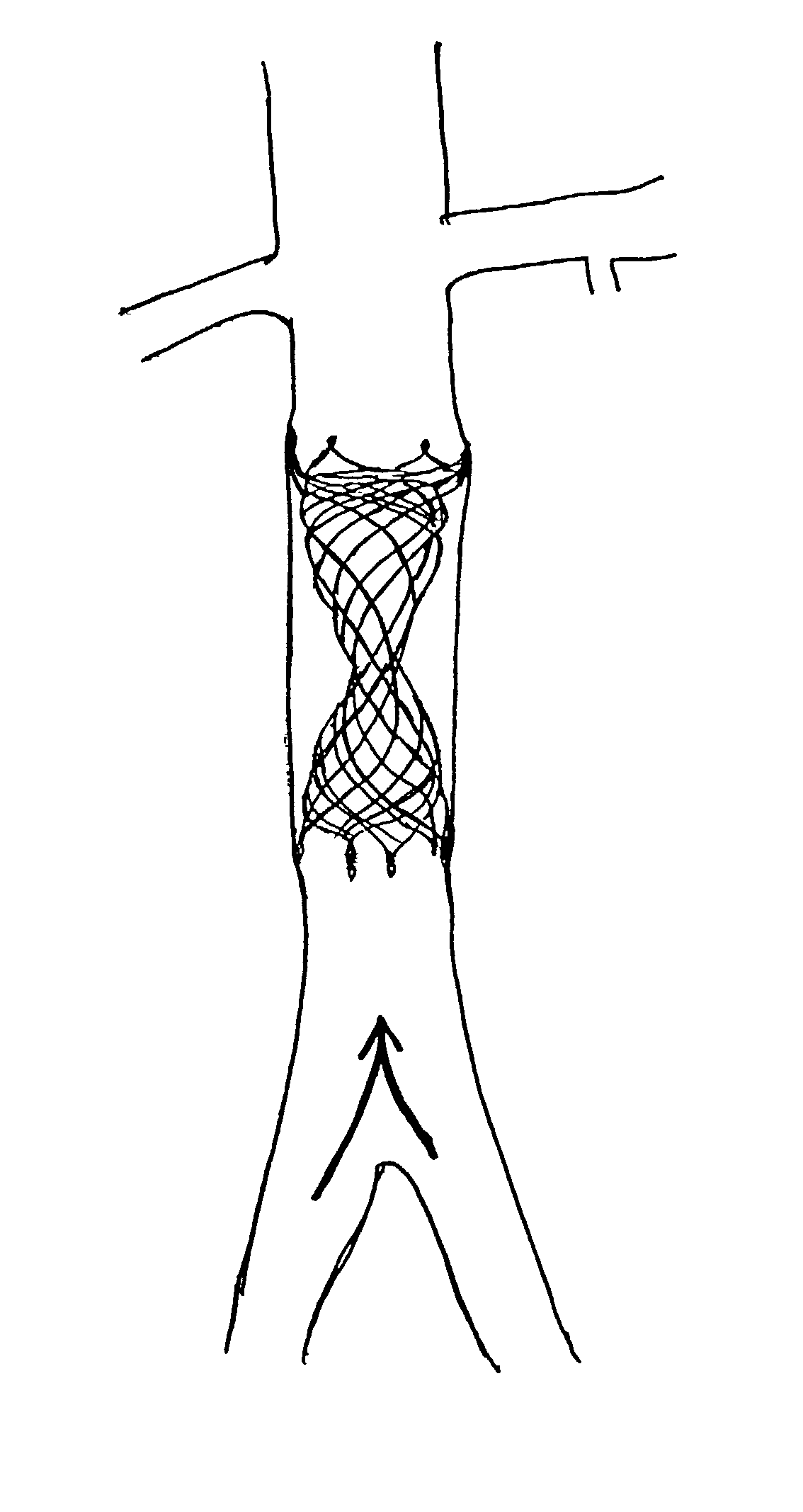
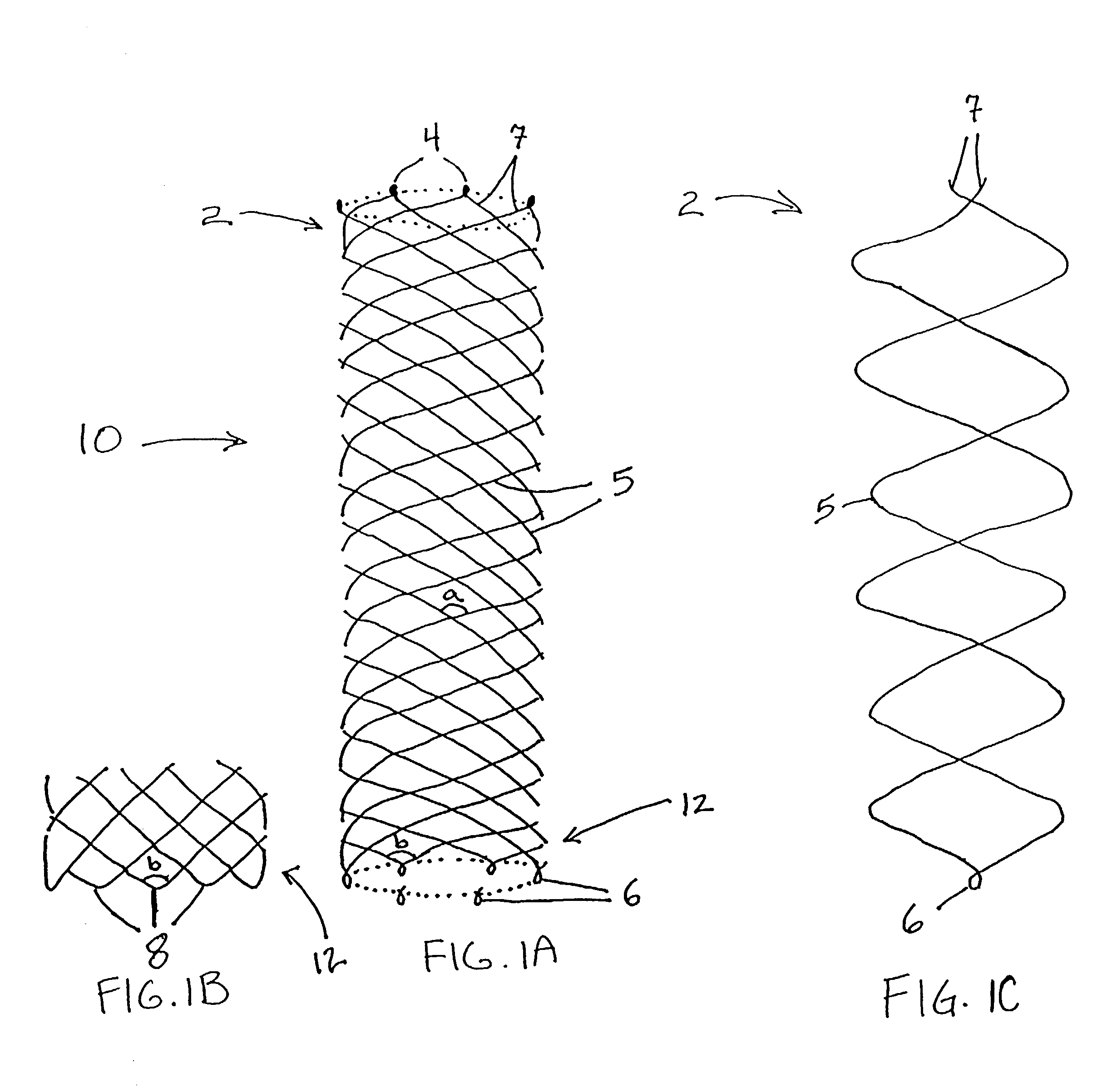
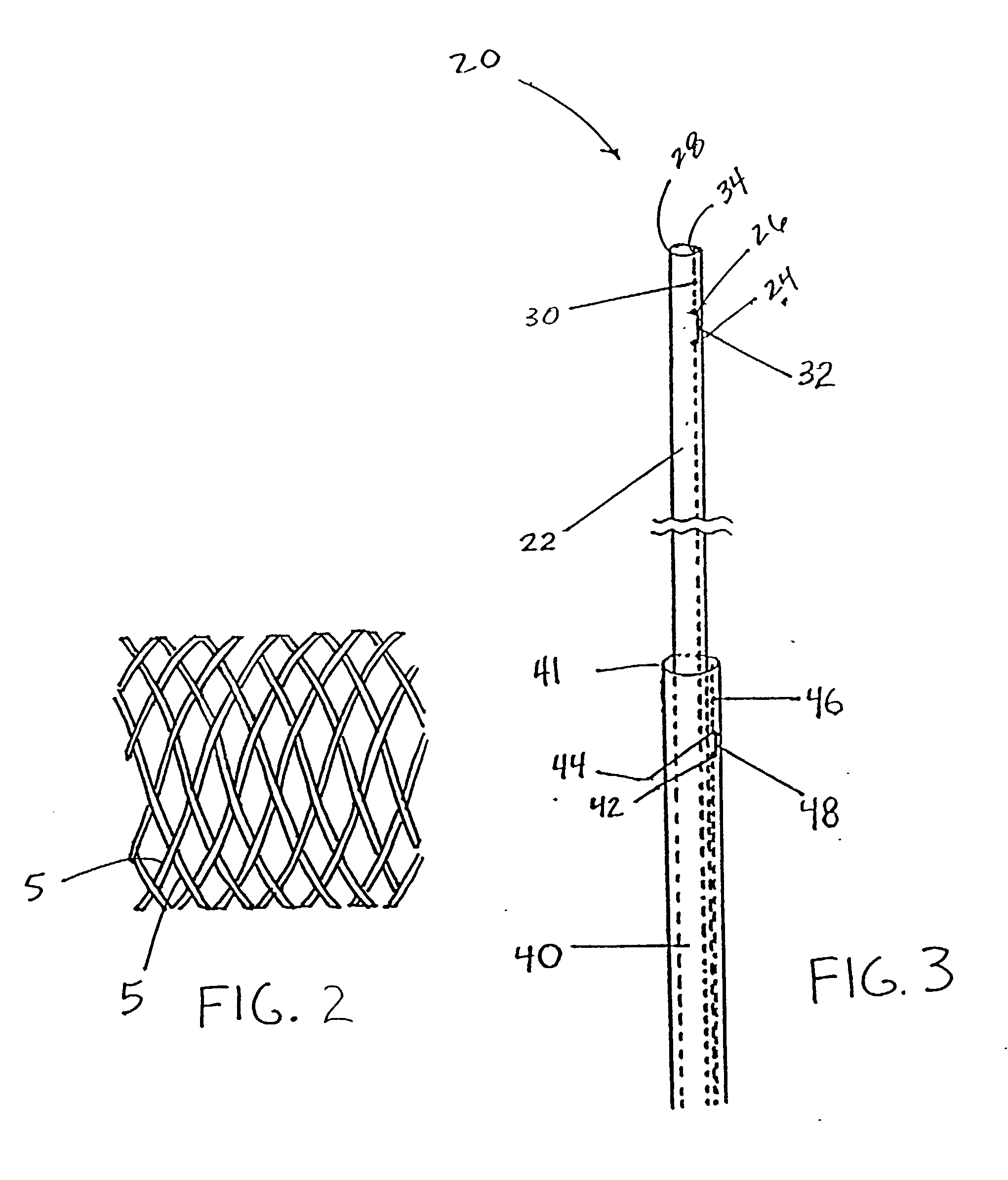
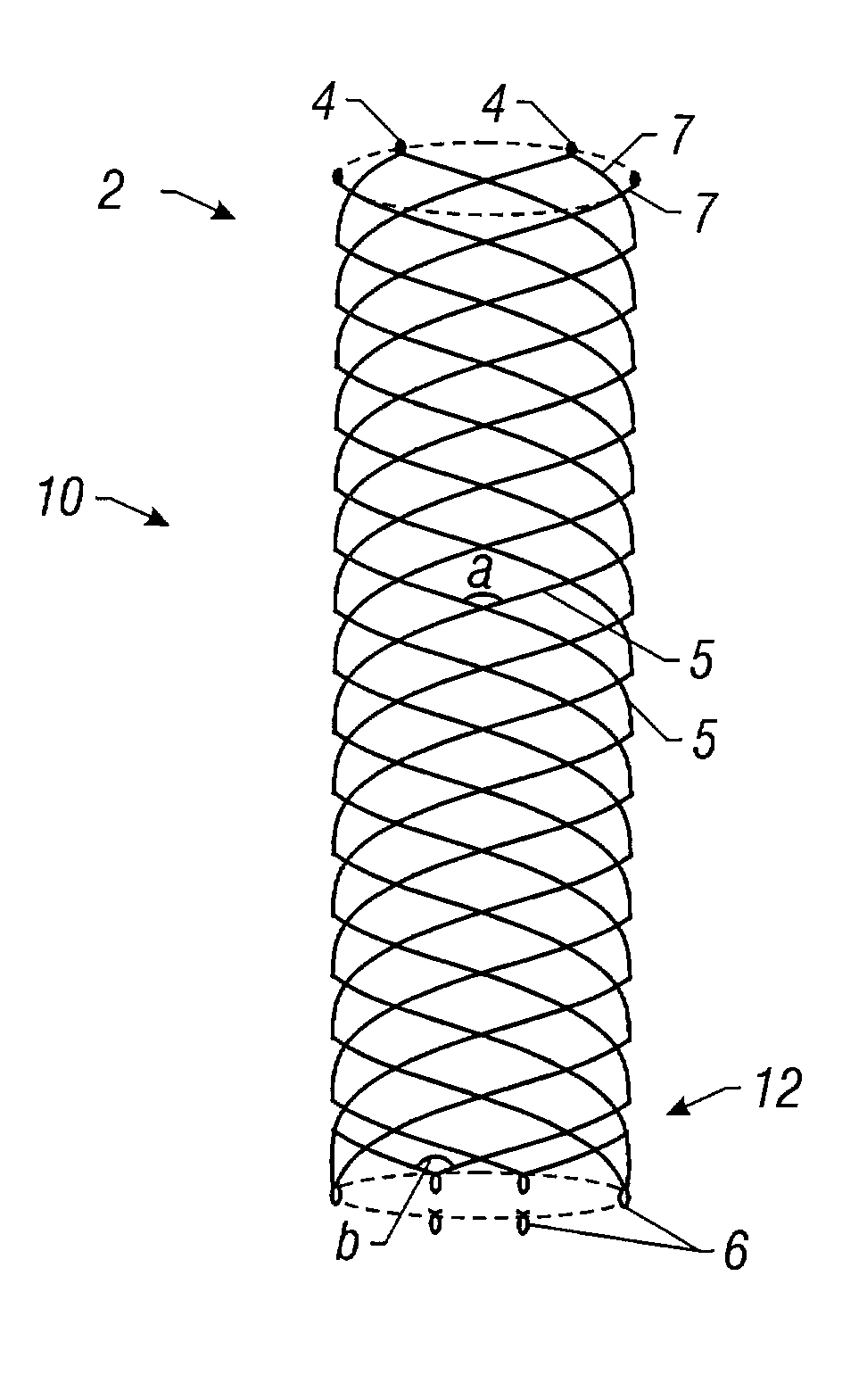
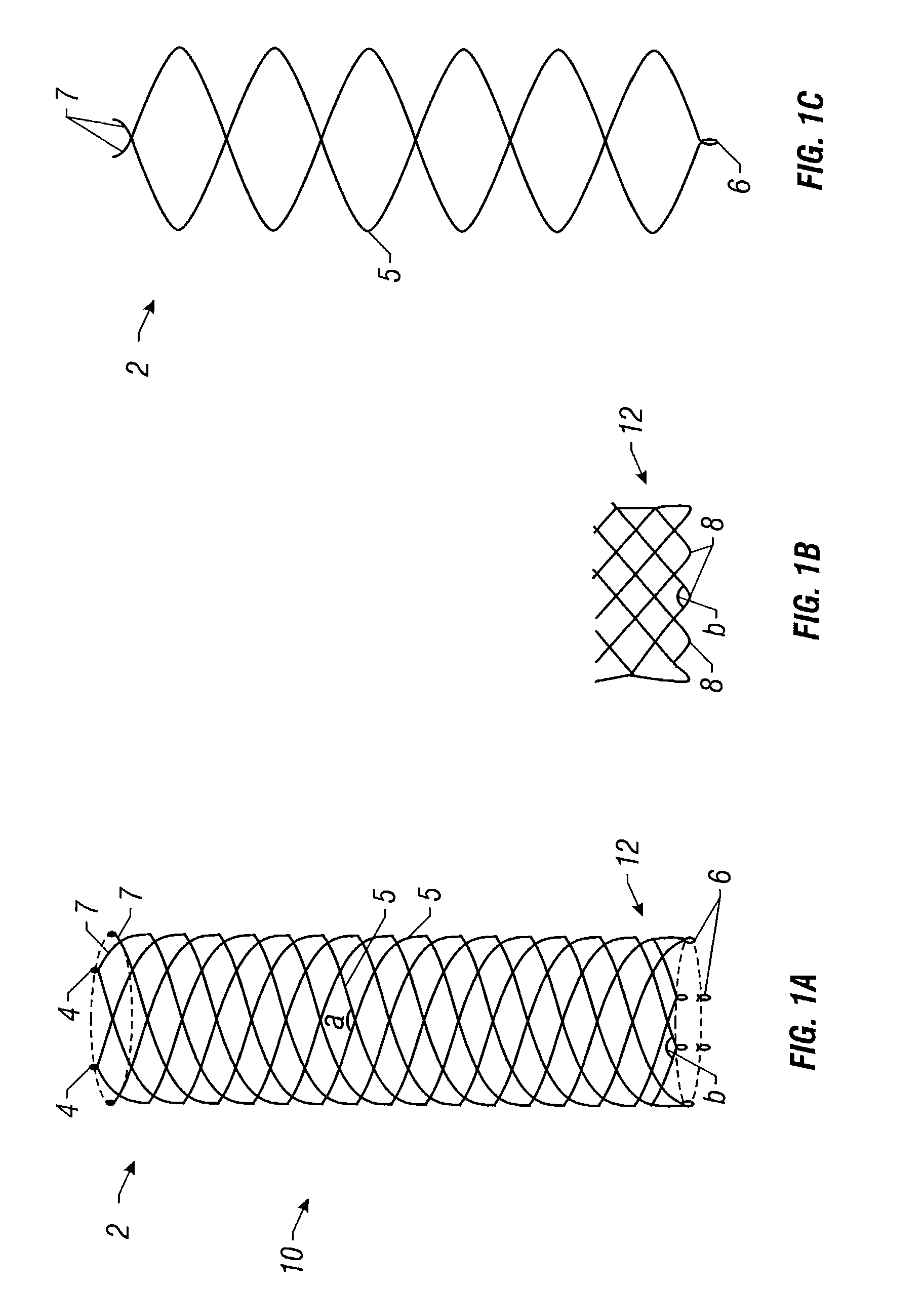
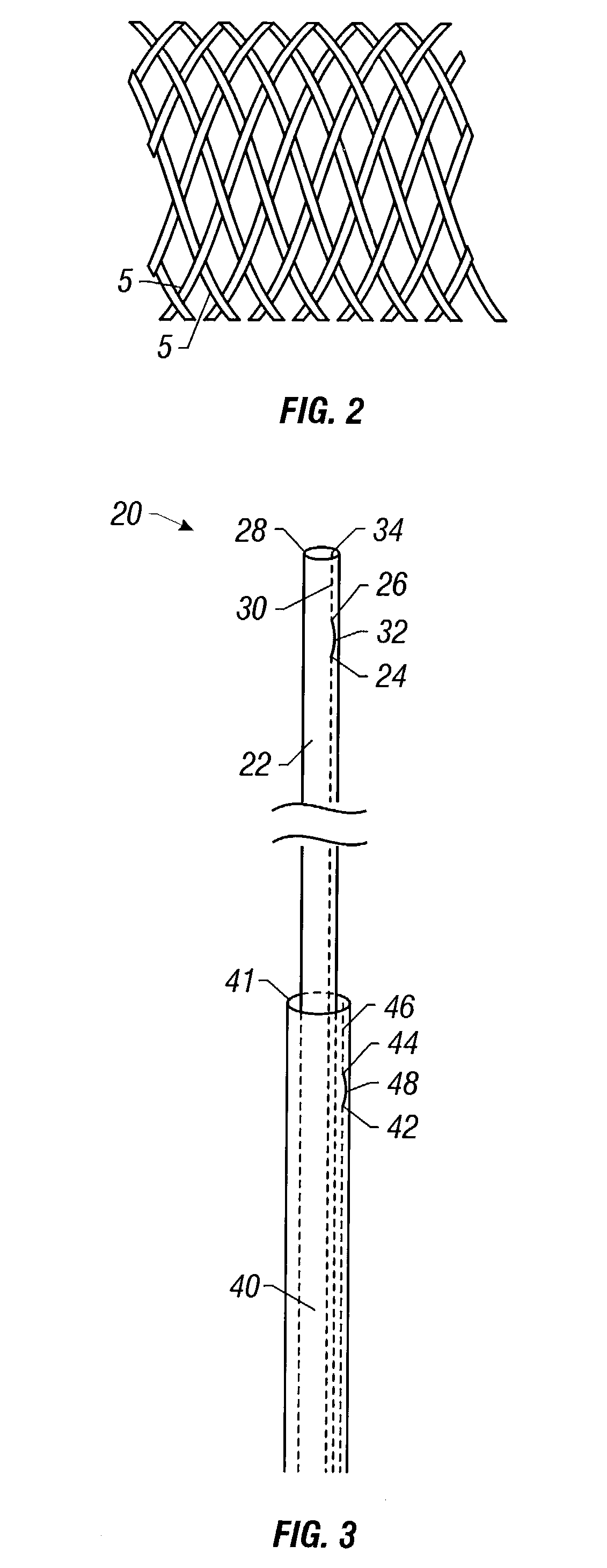
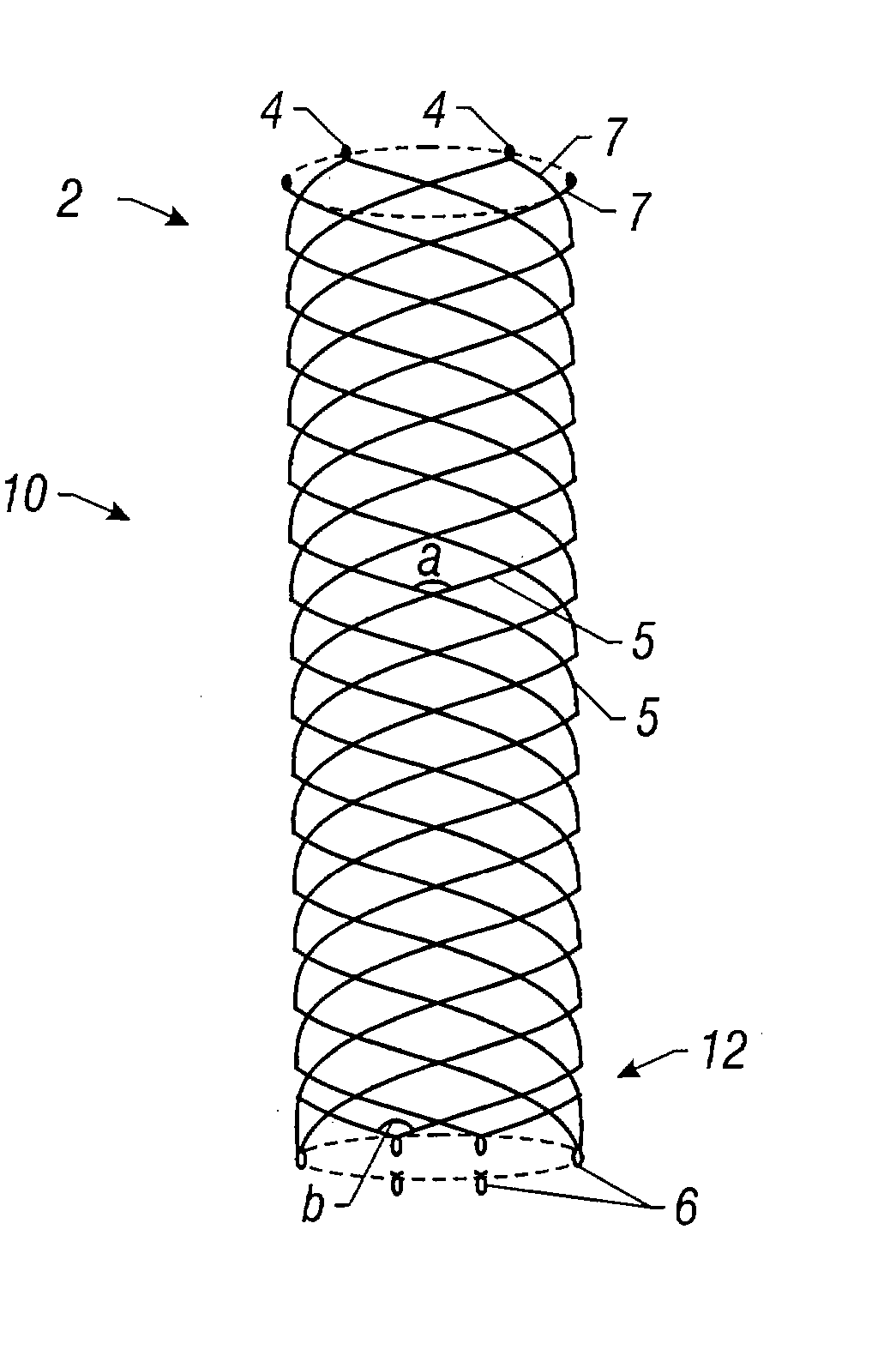
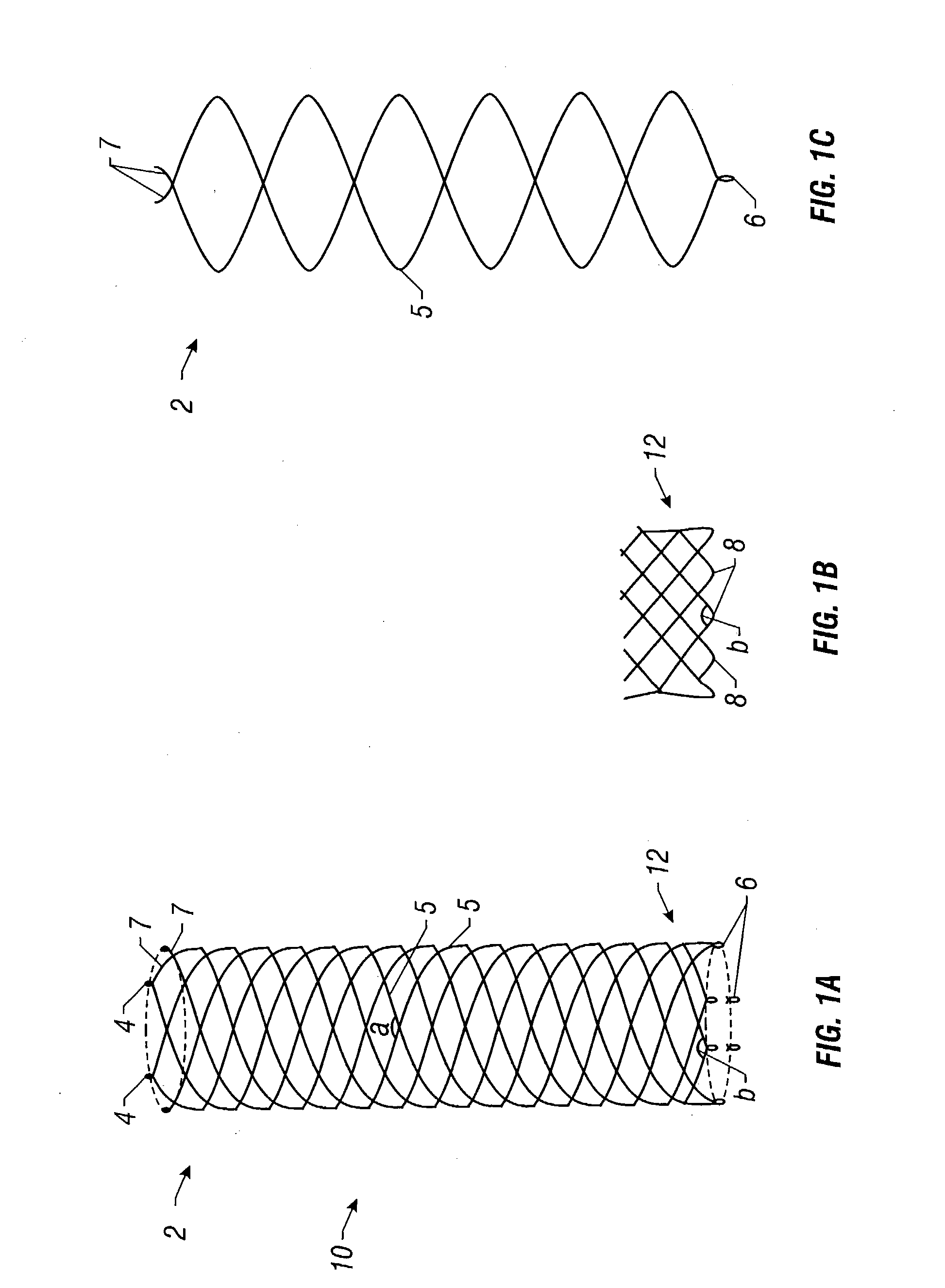
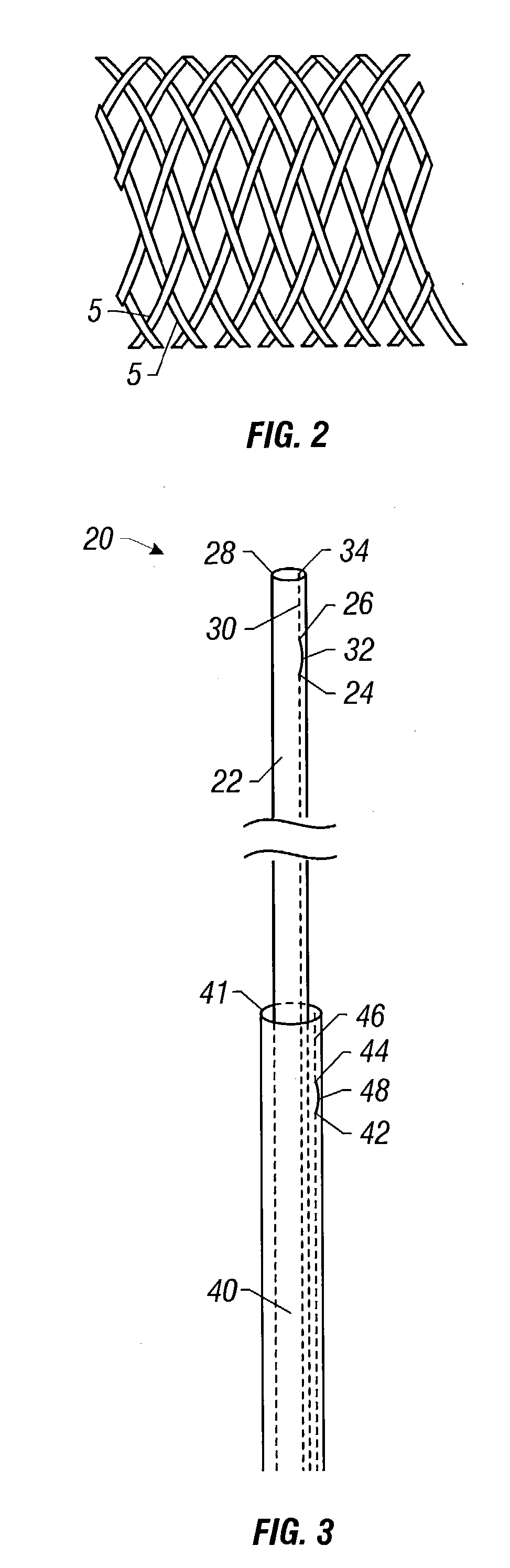
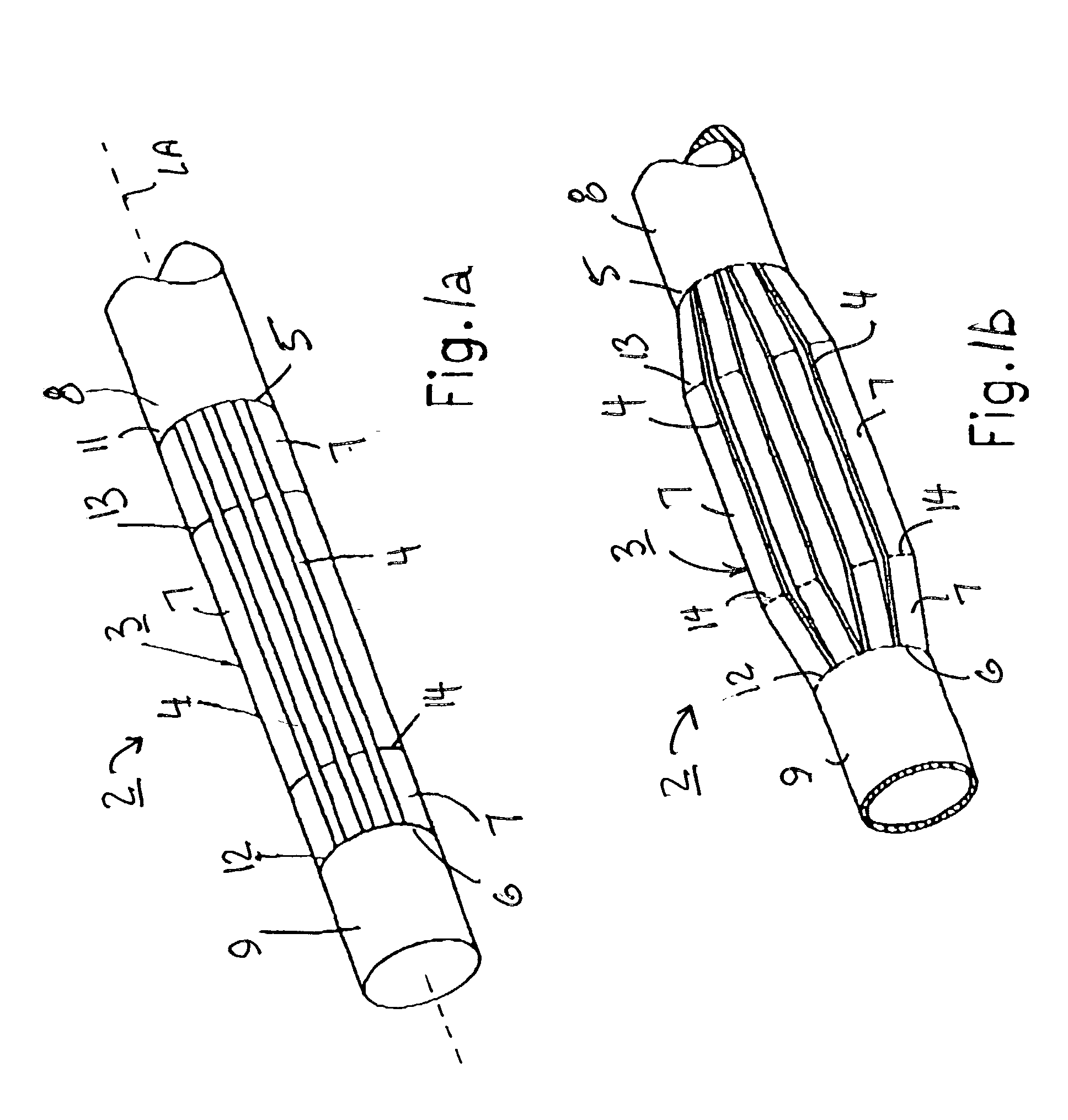
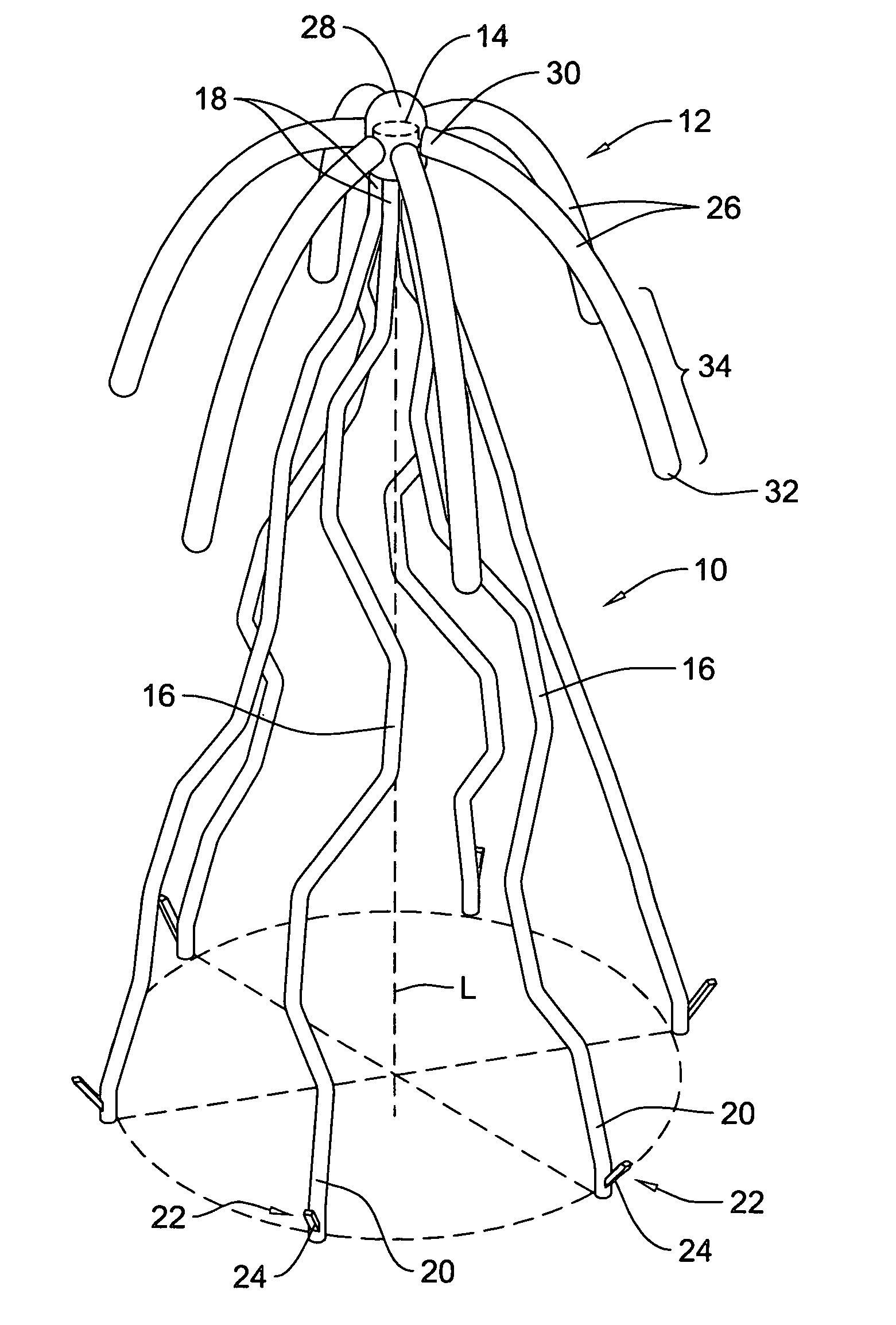
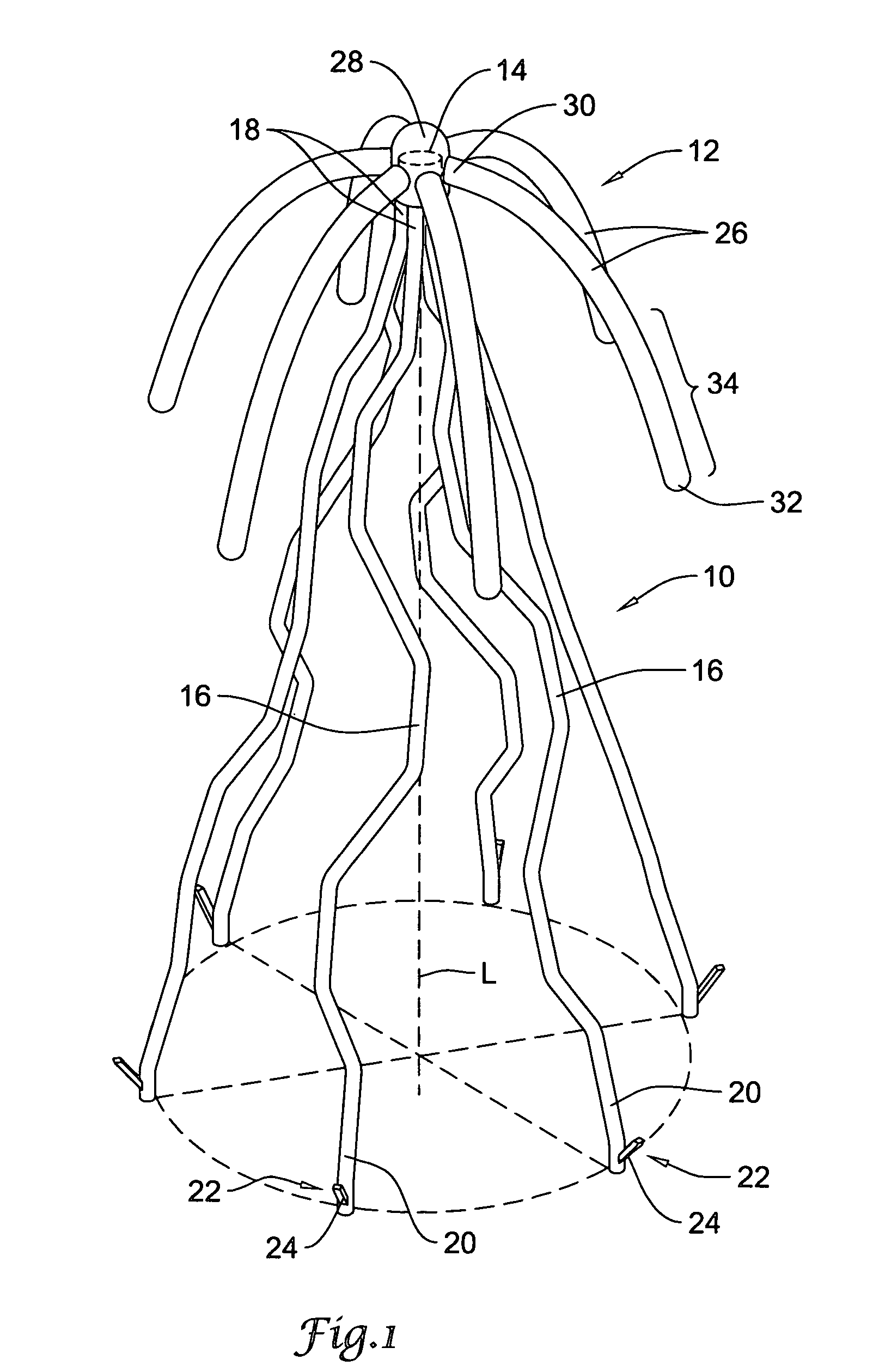
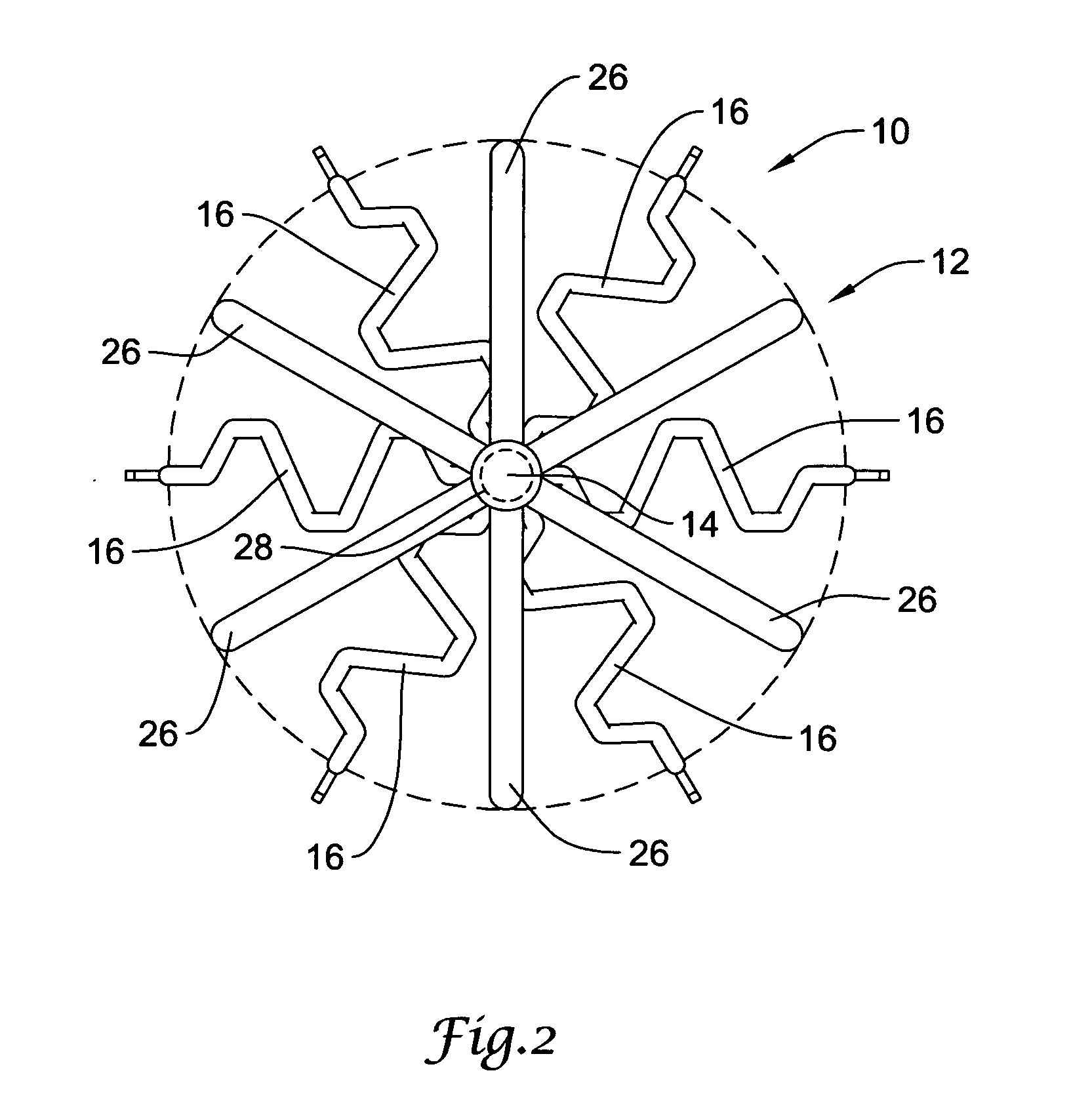
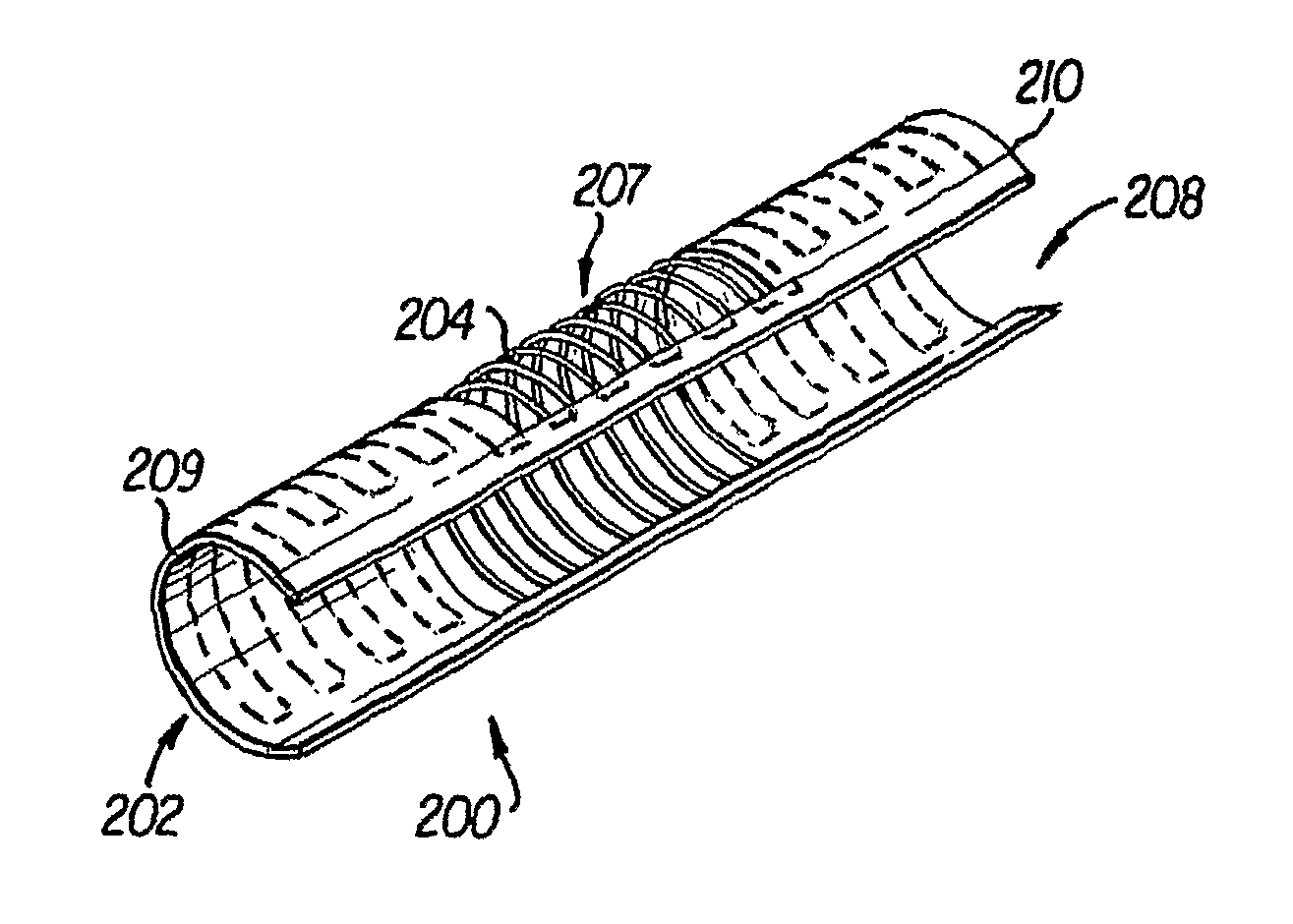
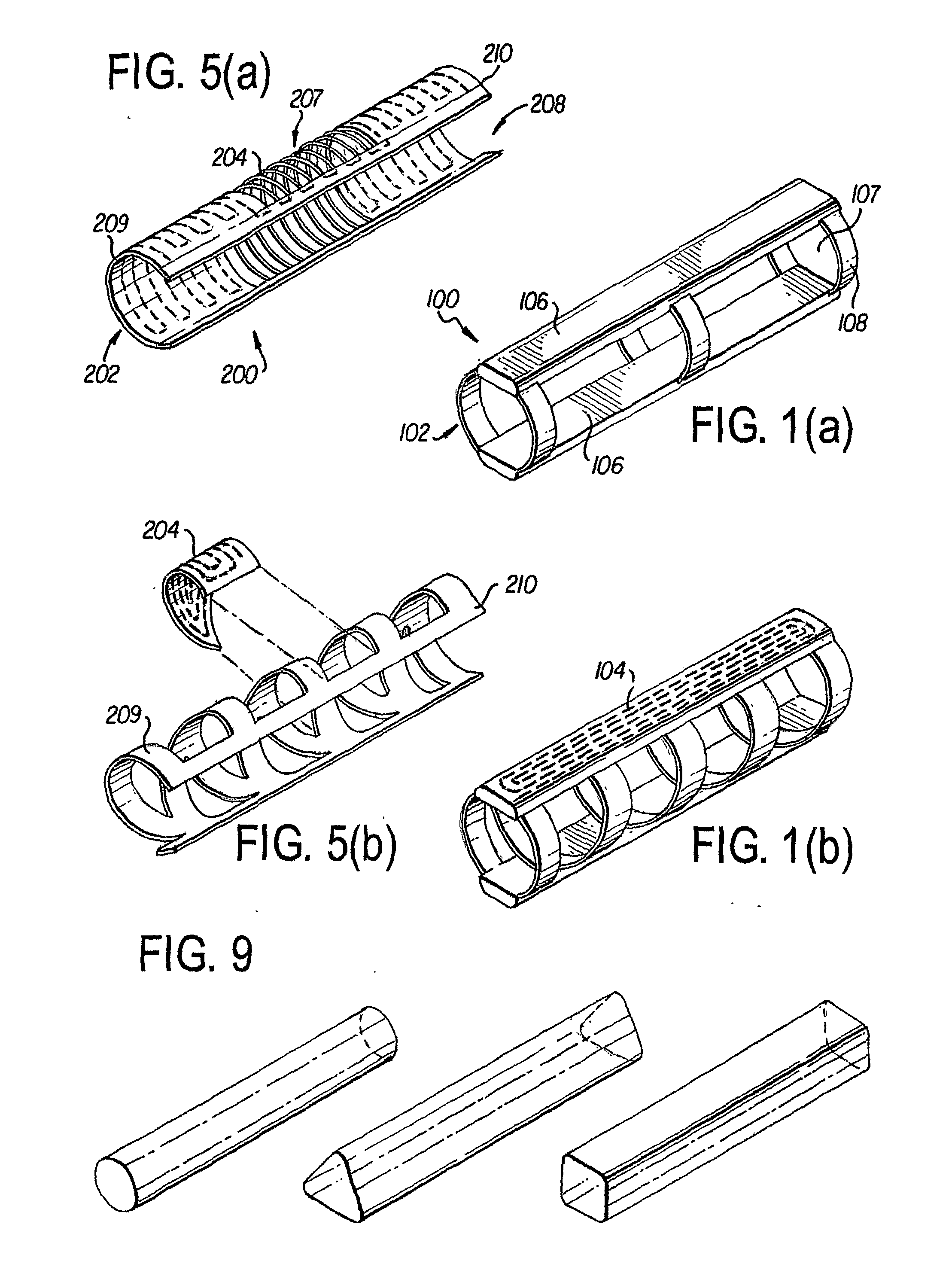
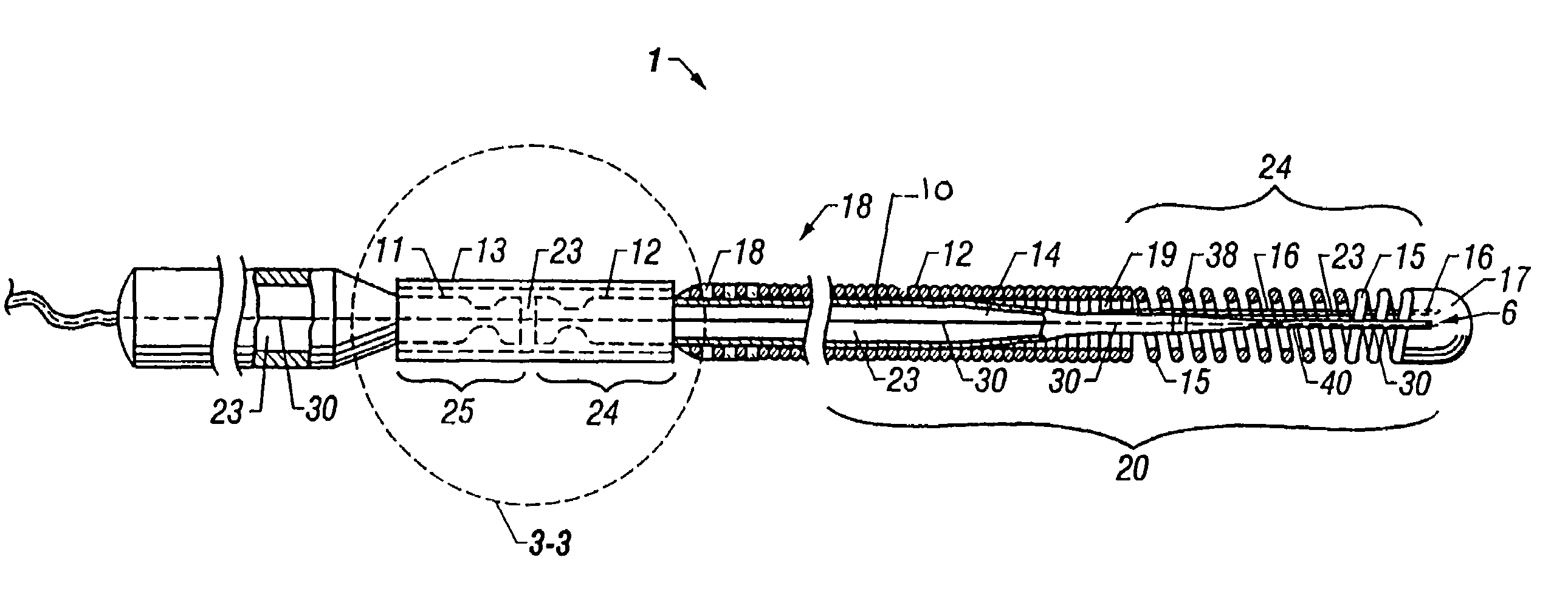
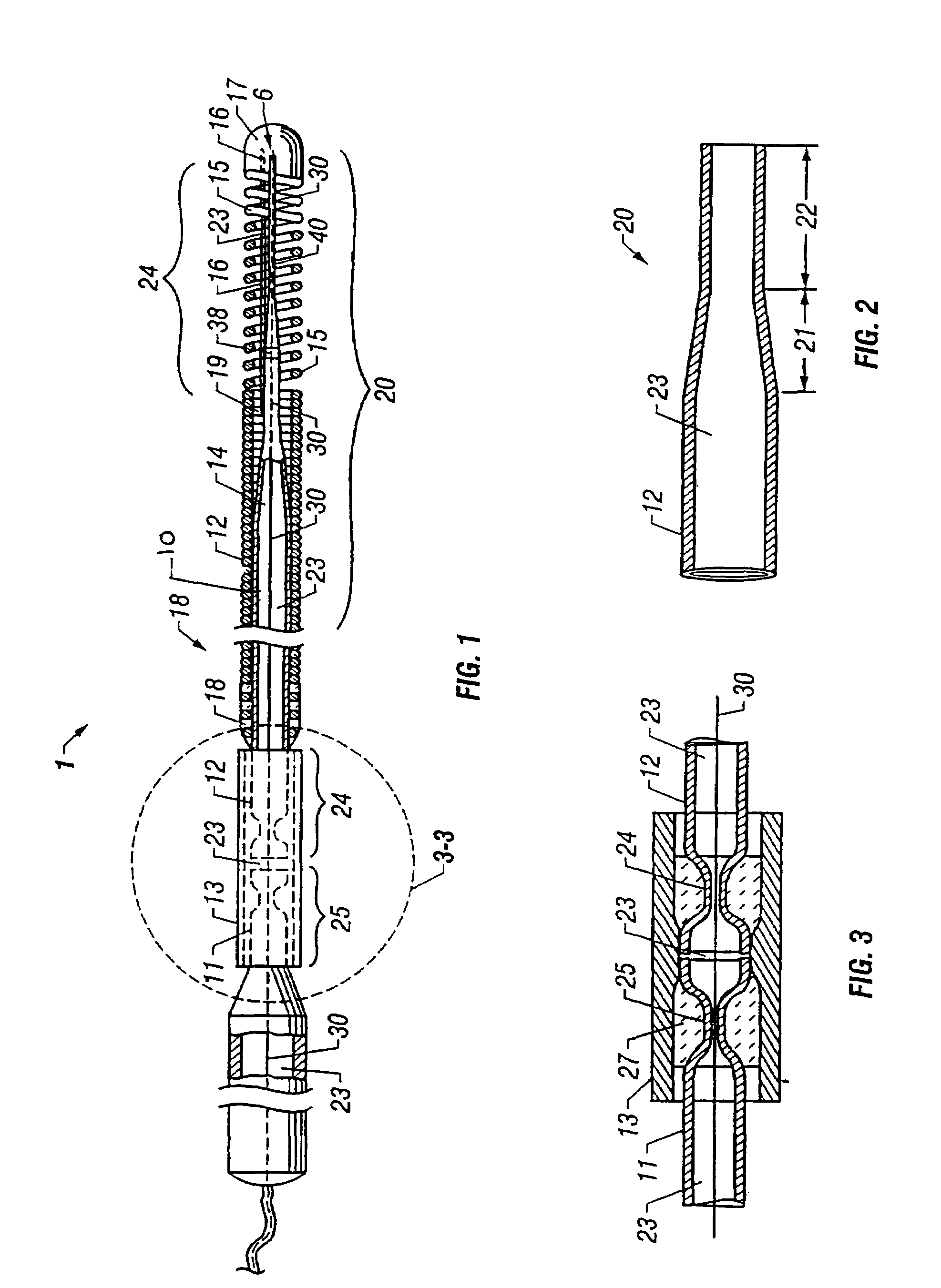
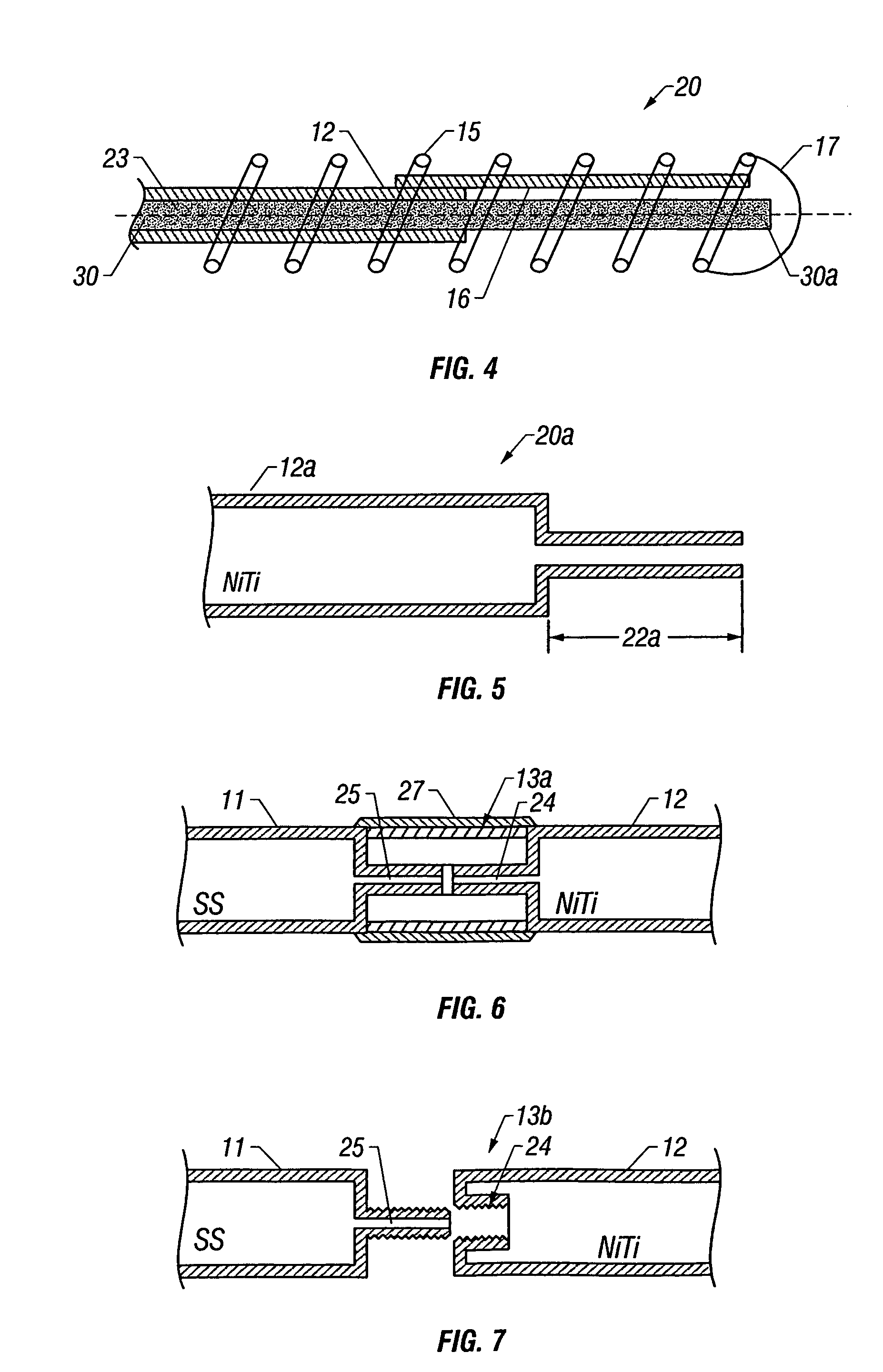
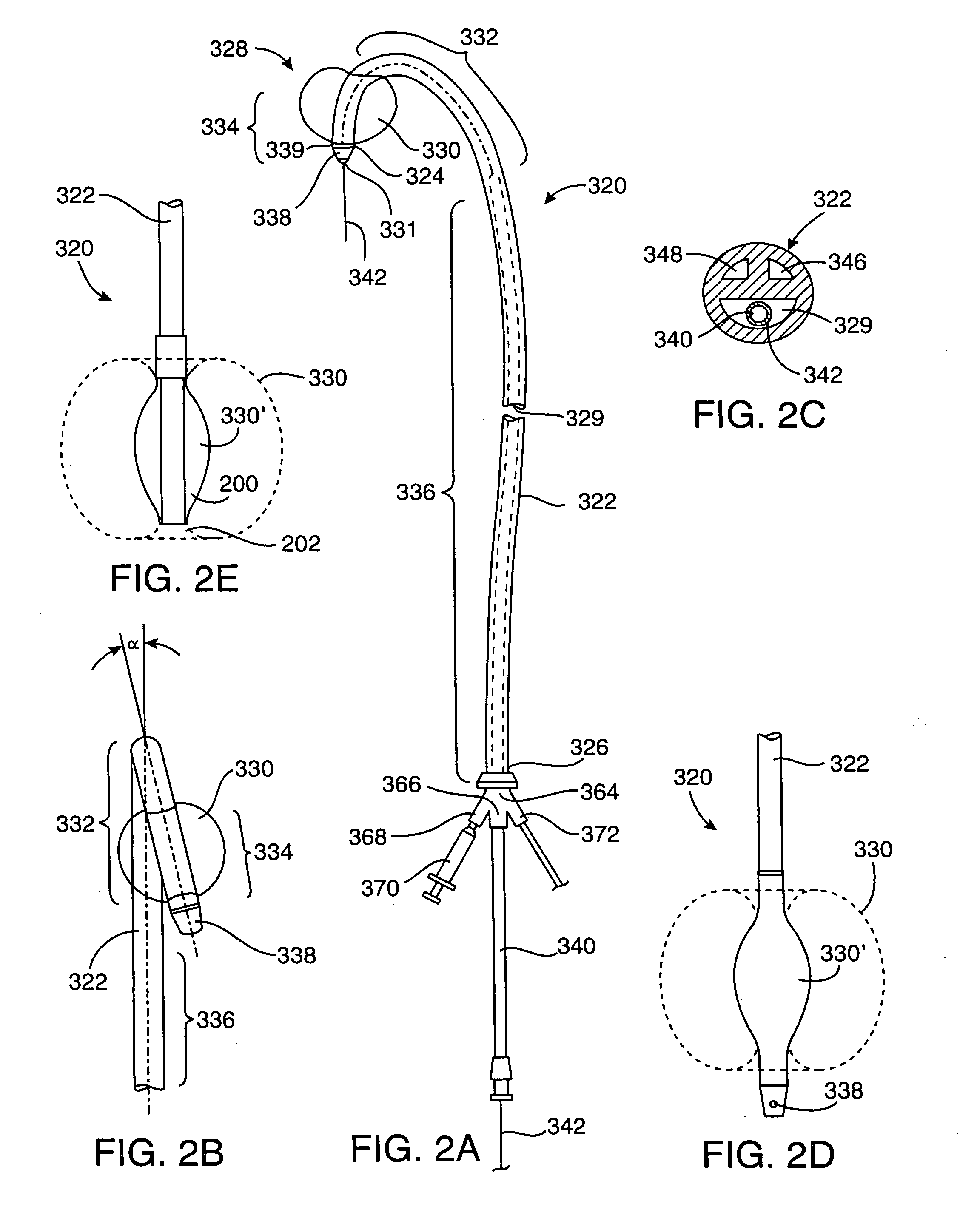
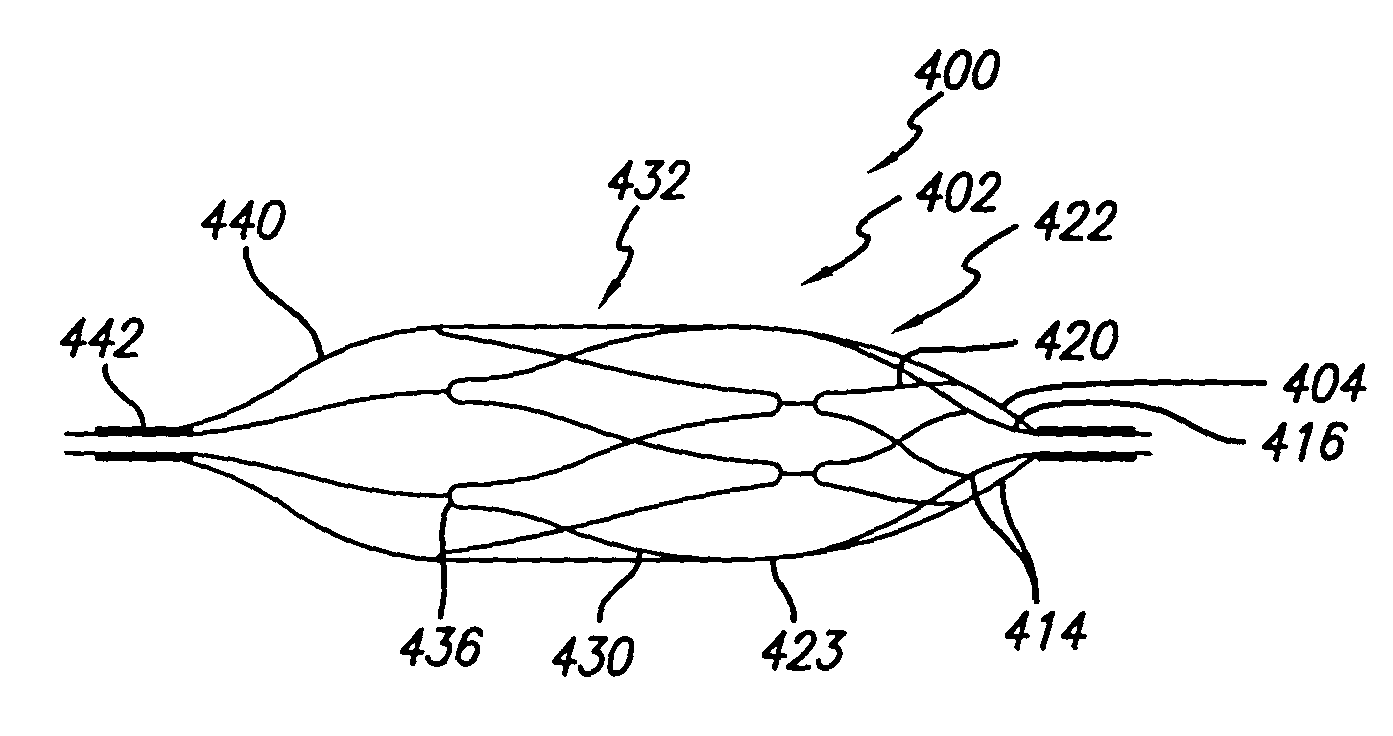
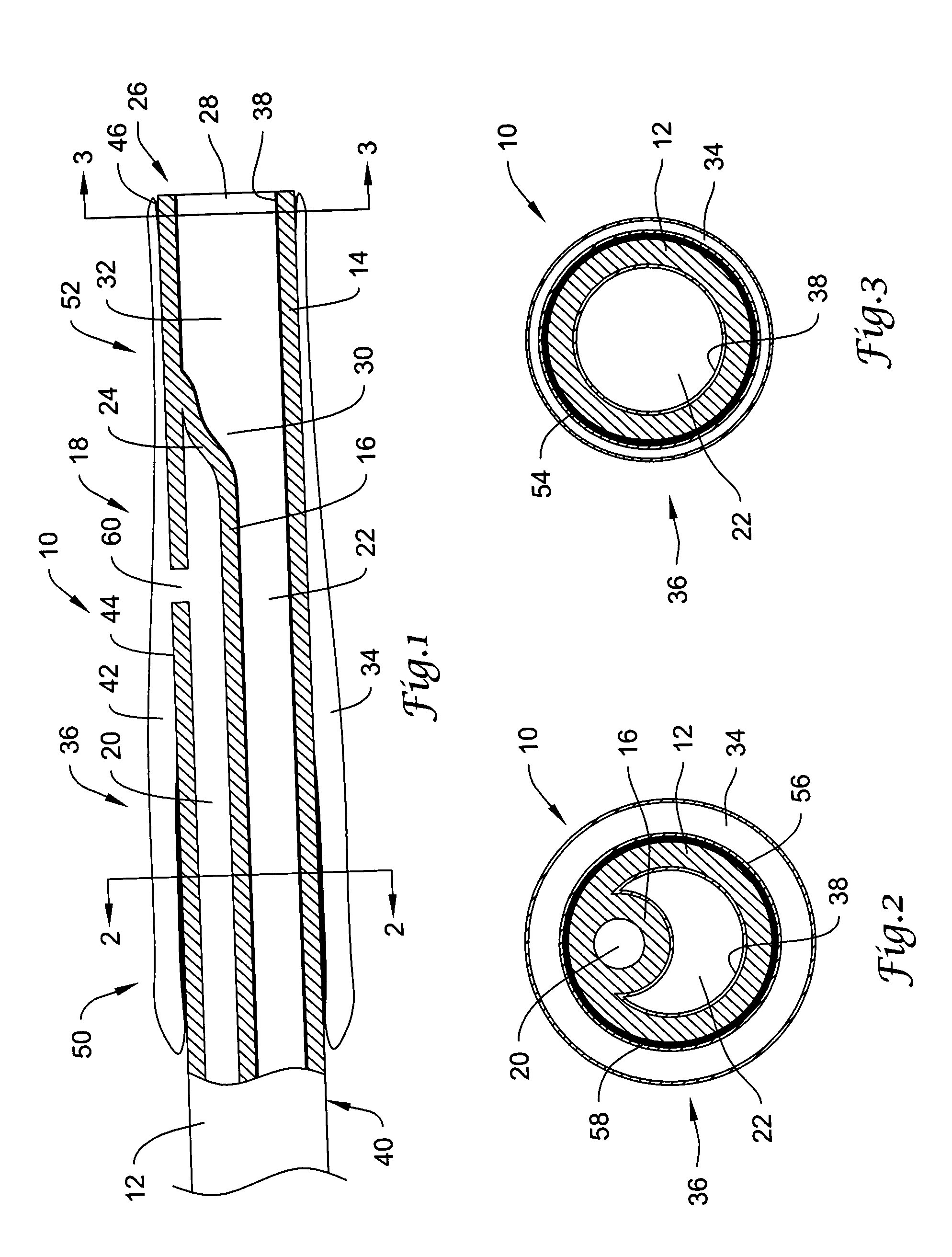
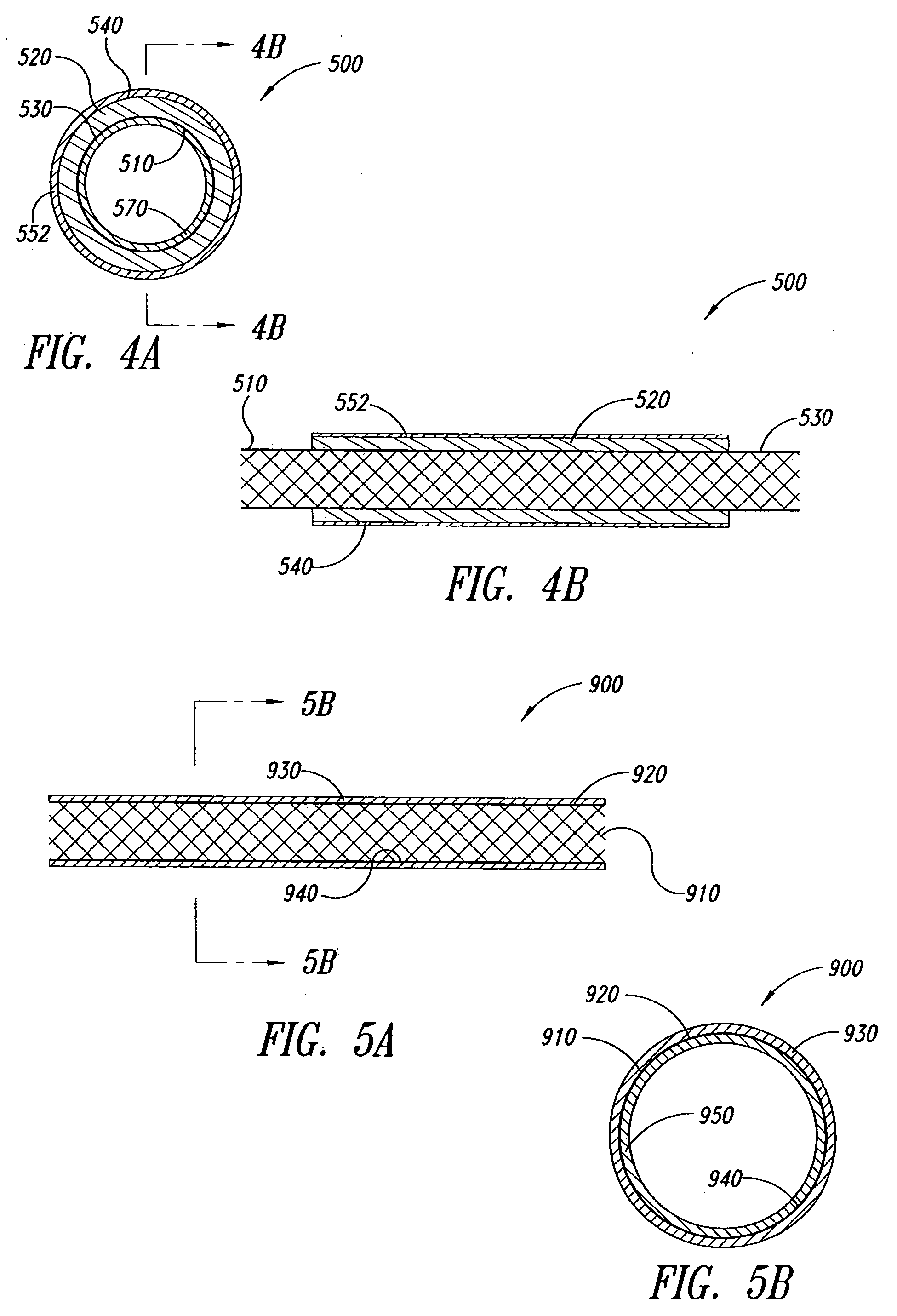
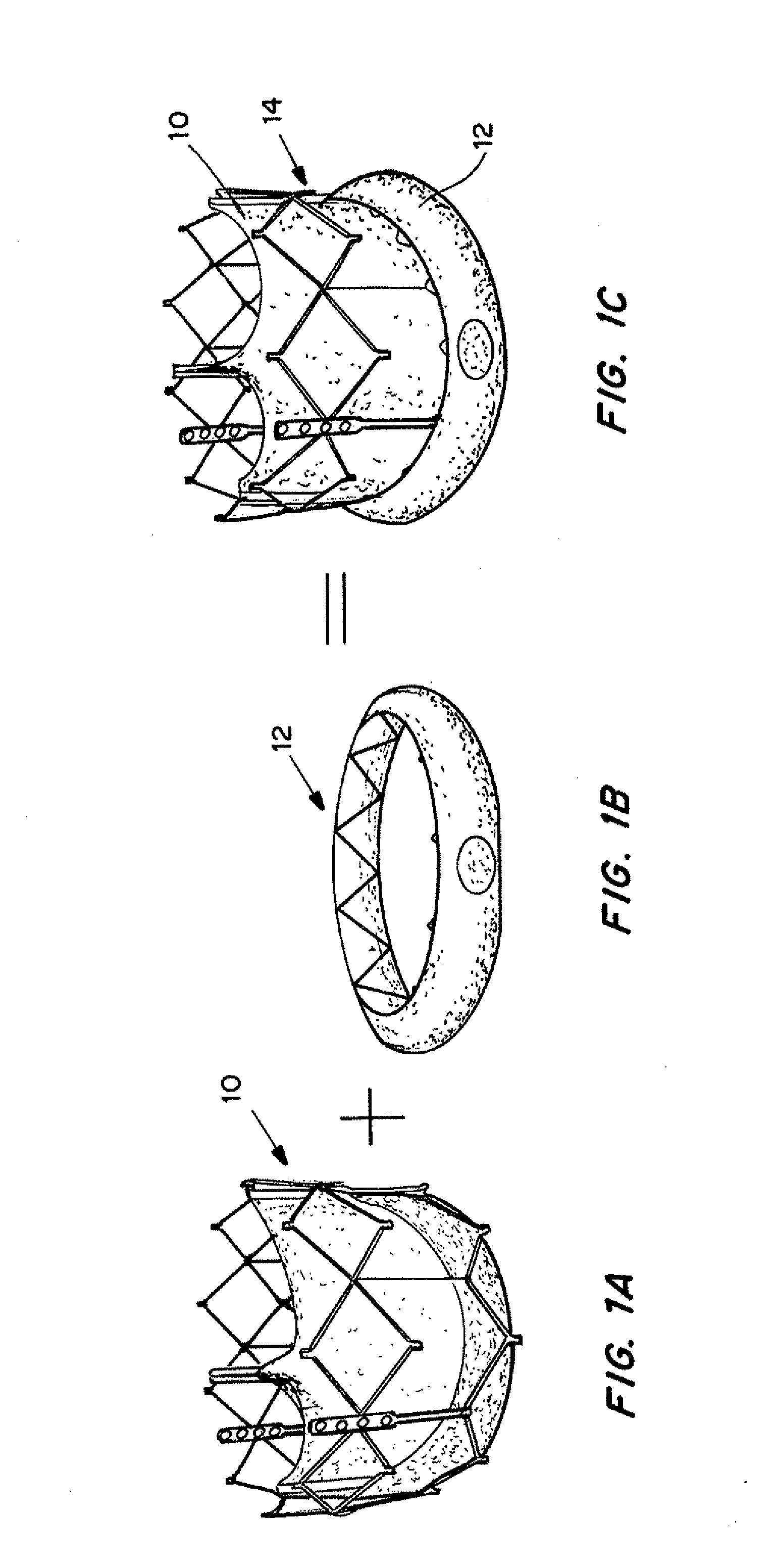
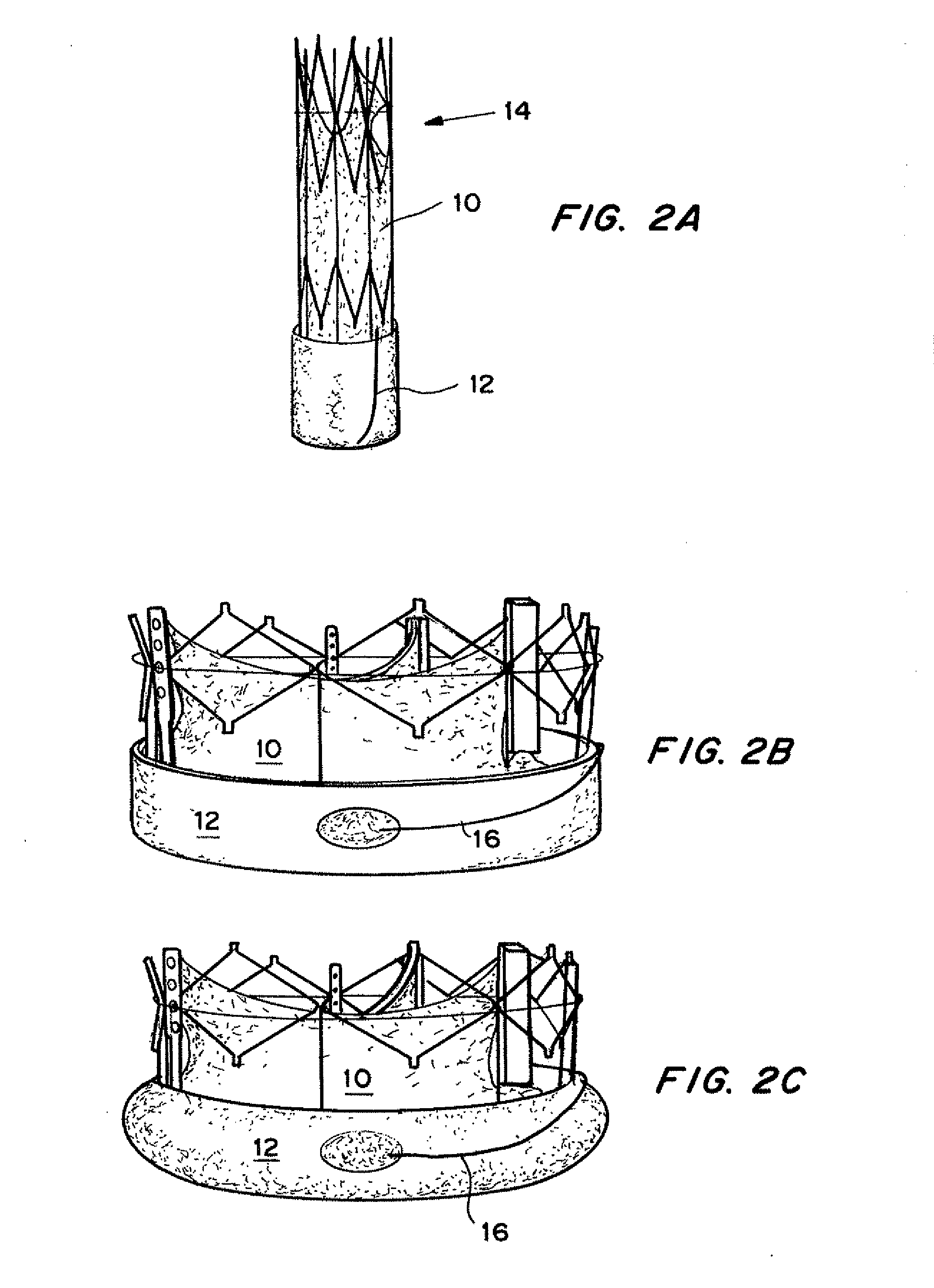
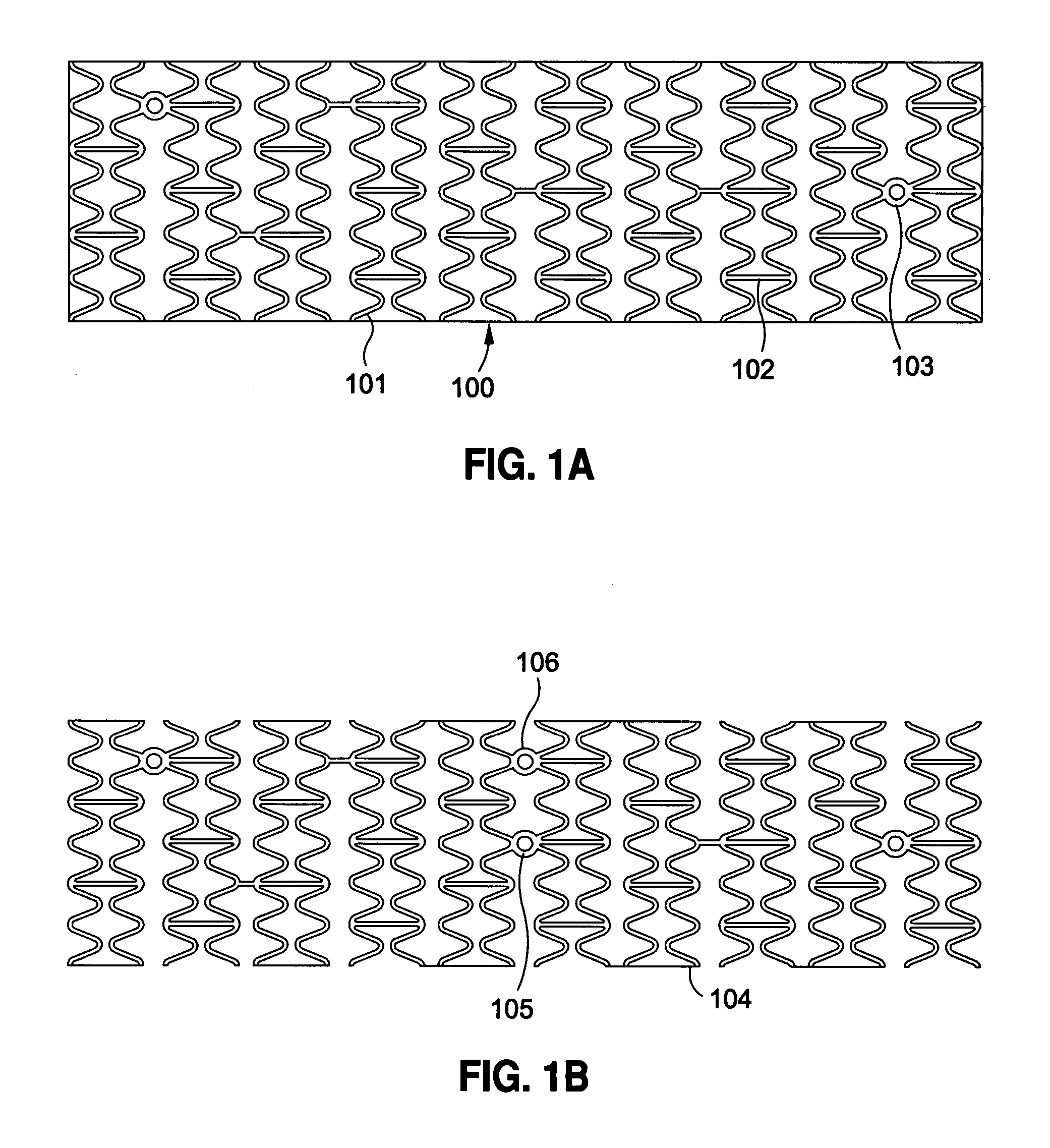
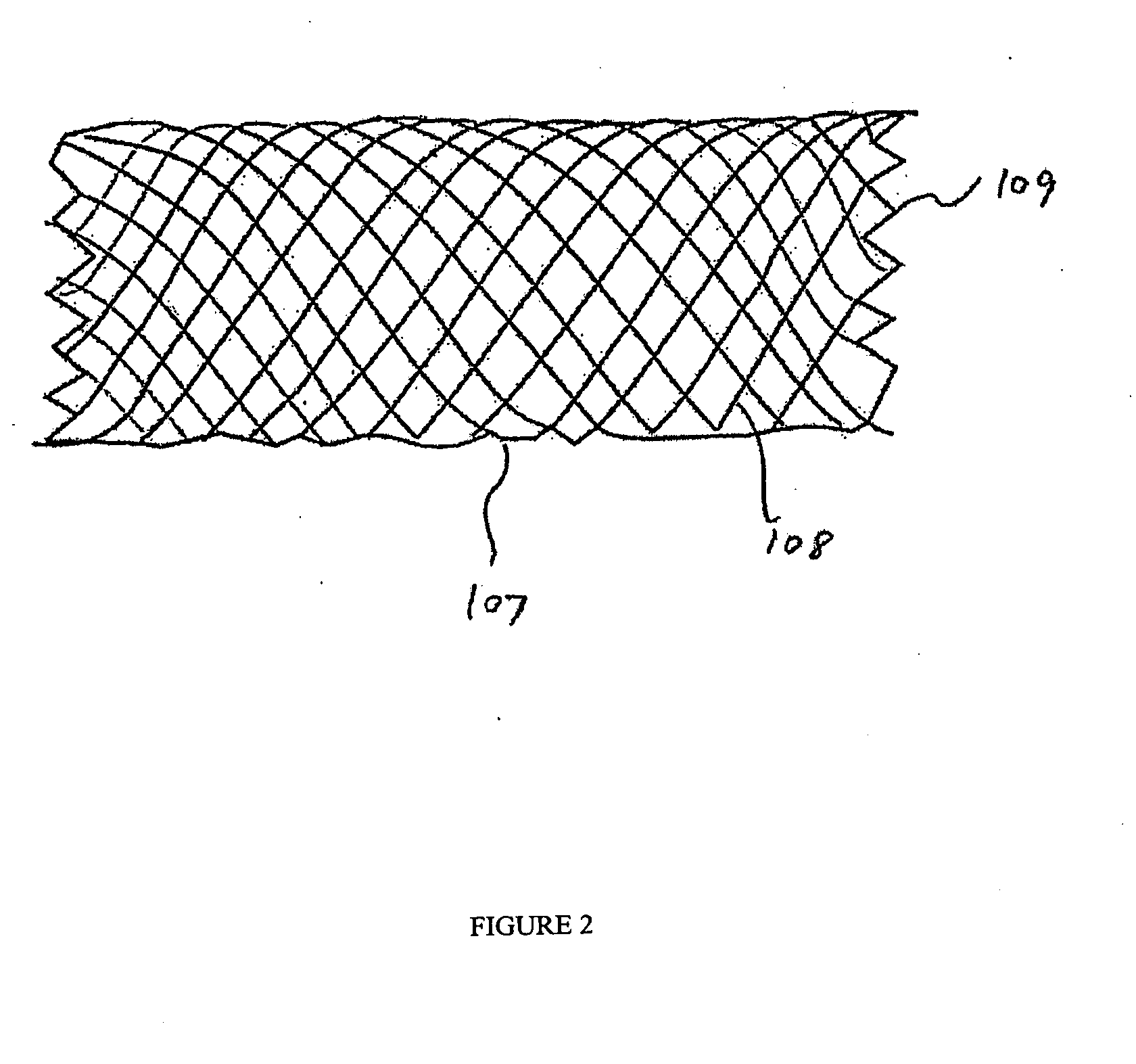
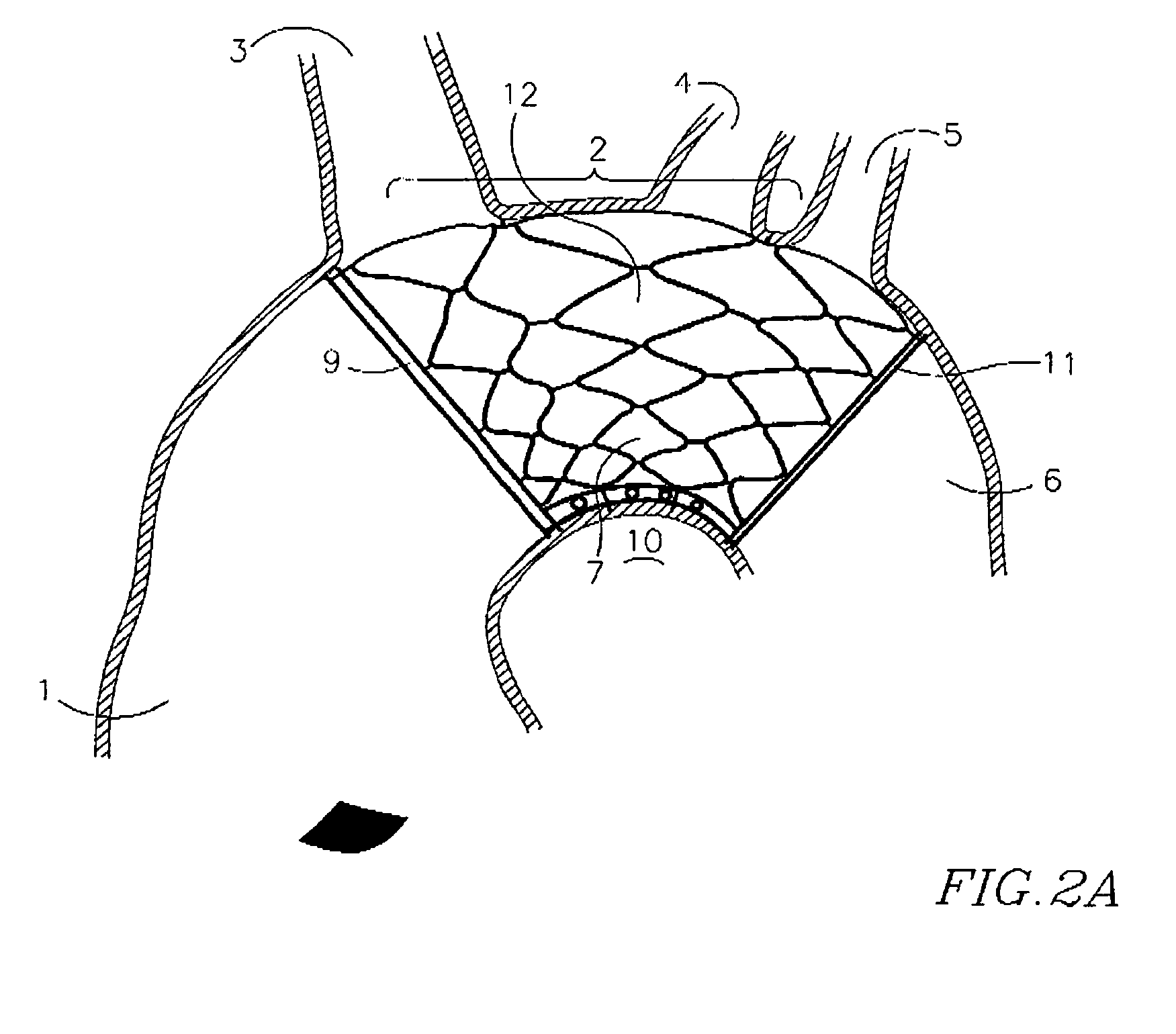
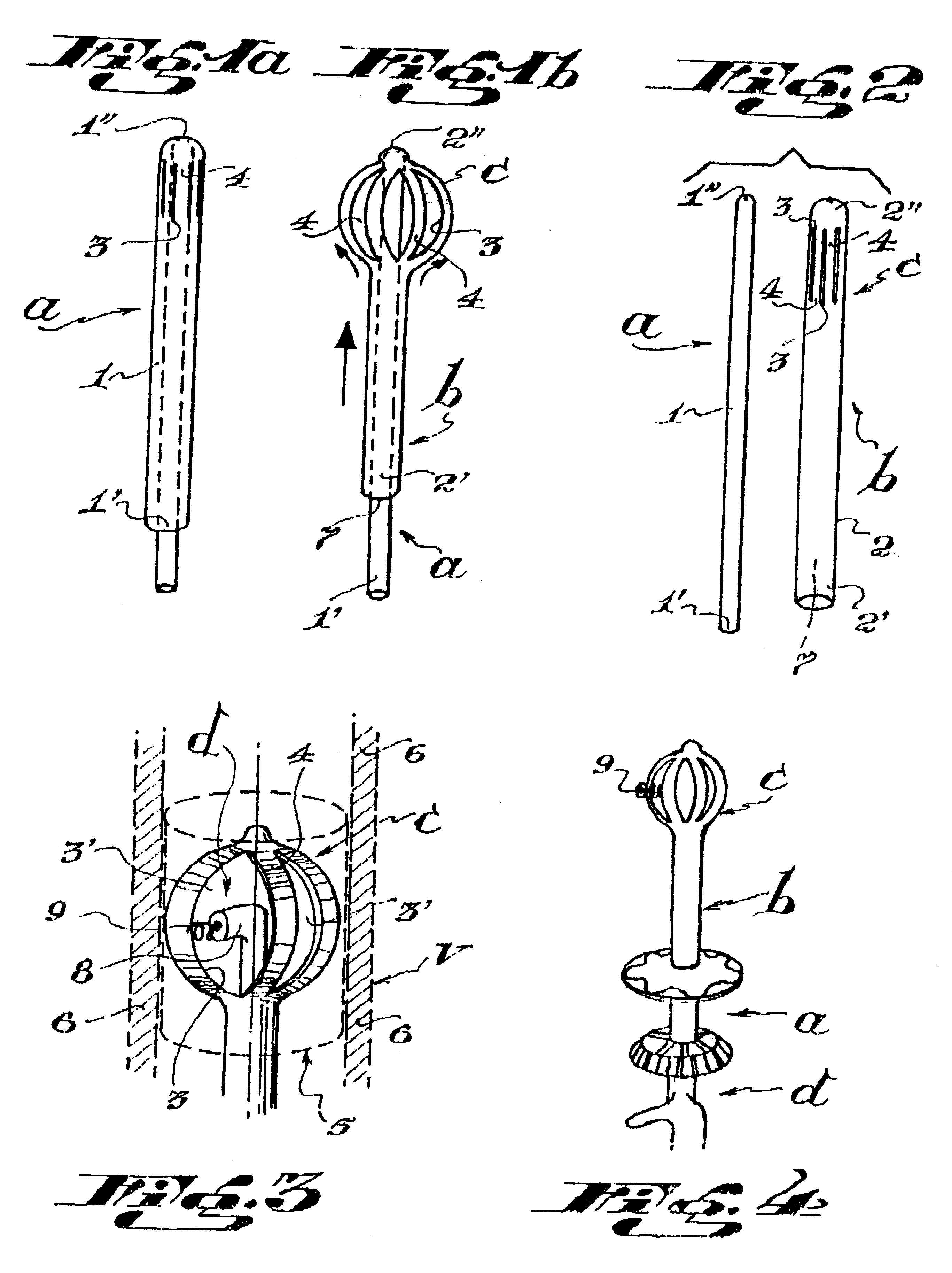
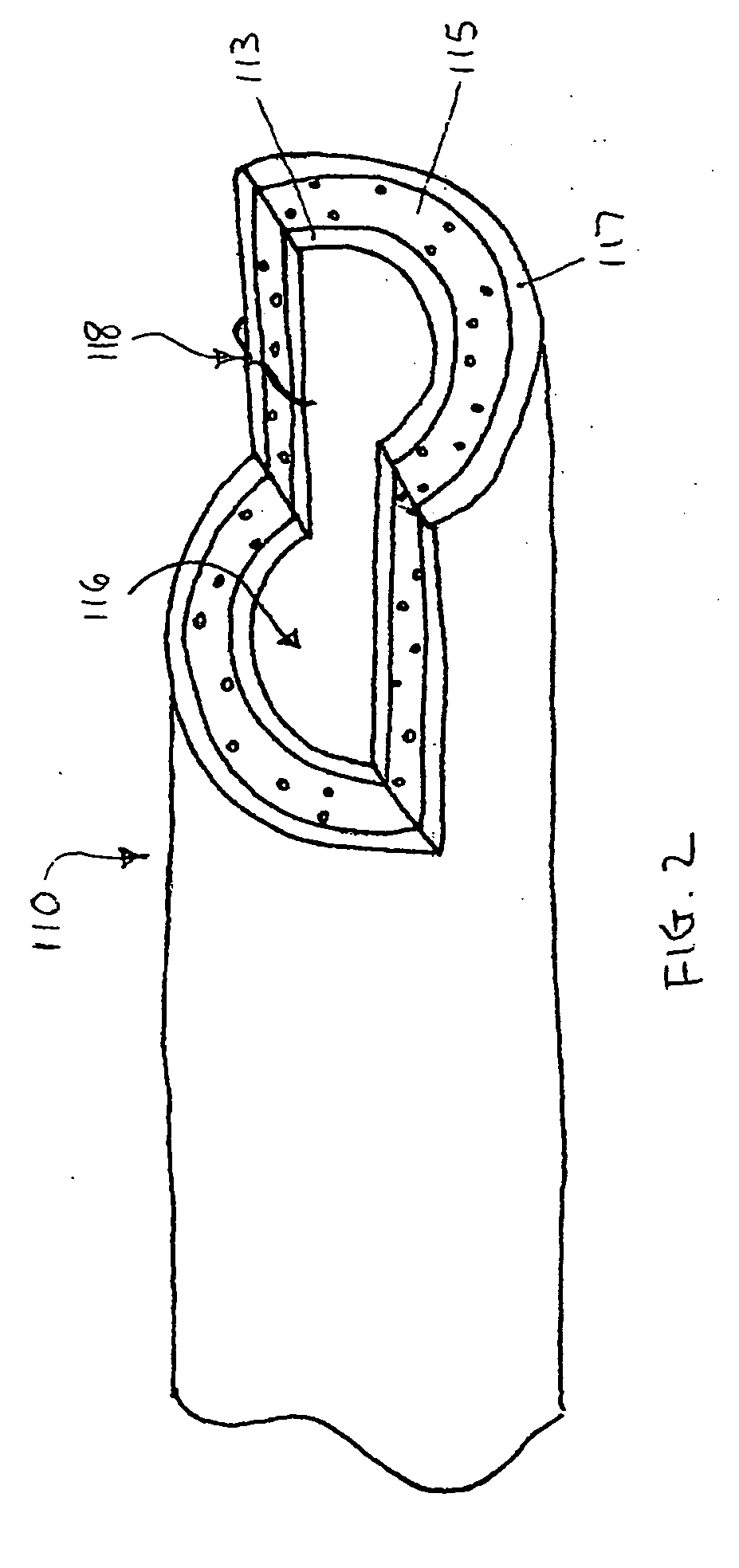
Self-expandable, woven intravascular devices for use as stents (both straight and tapered), filters (both temporary and permanent) and occluders for insertion and implantation into a variety of anatomical structures. The devices may be formed from shape memory metals such as nitinol. The devices may also be formed from biodegradable materials. Delivery systems for the devices include two hollow tubes that operate coaxially. A device is secured to the tubes prior to the implantation and delivery of the device by securing one end of the device to the outside of the inner tube and by securing the other end of the device to the outside of the outer tube. The stents may be partially or completely covered by graft materials, but may also be bare. The devices may be formed from a single wire. The devices may be formed by either hand or machine weaving. The devices may be created by bending shape memory wires around tabs projecting from a template, and weaving the ends of the wires to create the body of the device such that the wires cross each other to form a plurality of angles, at least one of the angles being obtuse. The value of the obtuse angle may be increased by axially compressing the body.
Owner:HYODOH HIDEKI +2
Methods for creating woven devices
Self-expandable, woven intravascular devices for use as stents (both straight and tapered), filters (both temporary and permanent) and occluders for insertion and implantation into a variety of anatomical structures. The devices may be formed from shape memory metals such as nitinol. The devices may also be formed from biodegradable materials. Delivery systems for the devices include two hollow tubes that operate coaxially. A device is secured to the tubes prior to the implantation and delivery of the device by securing one end of the device to the outside of the inner tube and by securing the other end of the device to the outside of the outer tube. The stents may be partially or completely covered by graft materials, but may also be bare. The devices may be formed from a single wire. The devices may be formed by either hand or machine weaving. The devices may be created by bending shape memory wires around tabs projecting from a template, and weaving the ends of the wires to create the body of the device such that the wires cross each other to form a plurality of angles, at least one of the angles being obtuse. The value of the obtuse angle may be increased by axially compressing the body.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Methods for creating woven devices
Self-expandable, woven intravascular devices for use as stents (both straight and tapered), filters (both temporary and permanent) and occluders for insertion and implantation into a variety of anatomical structures. The devices may be formed from shape memory metals such as nitinol. The devices may also be formed from biodegradable materials. Delivery systems for the devices include two hollow tubes that operate coaxially. A device is secured to the tubes prior to the implantation and delivery of the device by securing one end of the device to the outside of the inner tube and by securing the other end of the device to the outside of the outer tube. The stents may be partially or completely covered by graft materials, but may also be bare. The devices may be formed from a single wire. The devices may be formed by either hand or machine weaving. The devices may be created by bending shape memory wires around tabs projecting from a template, and weaving the ends of the wires to create the body of the device such that the wires cross each other to form a plurality of angles, at least one of the angles being obtuse. The value of the obtuse angle may be increased by axially compressing the body.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
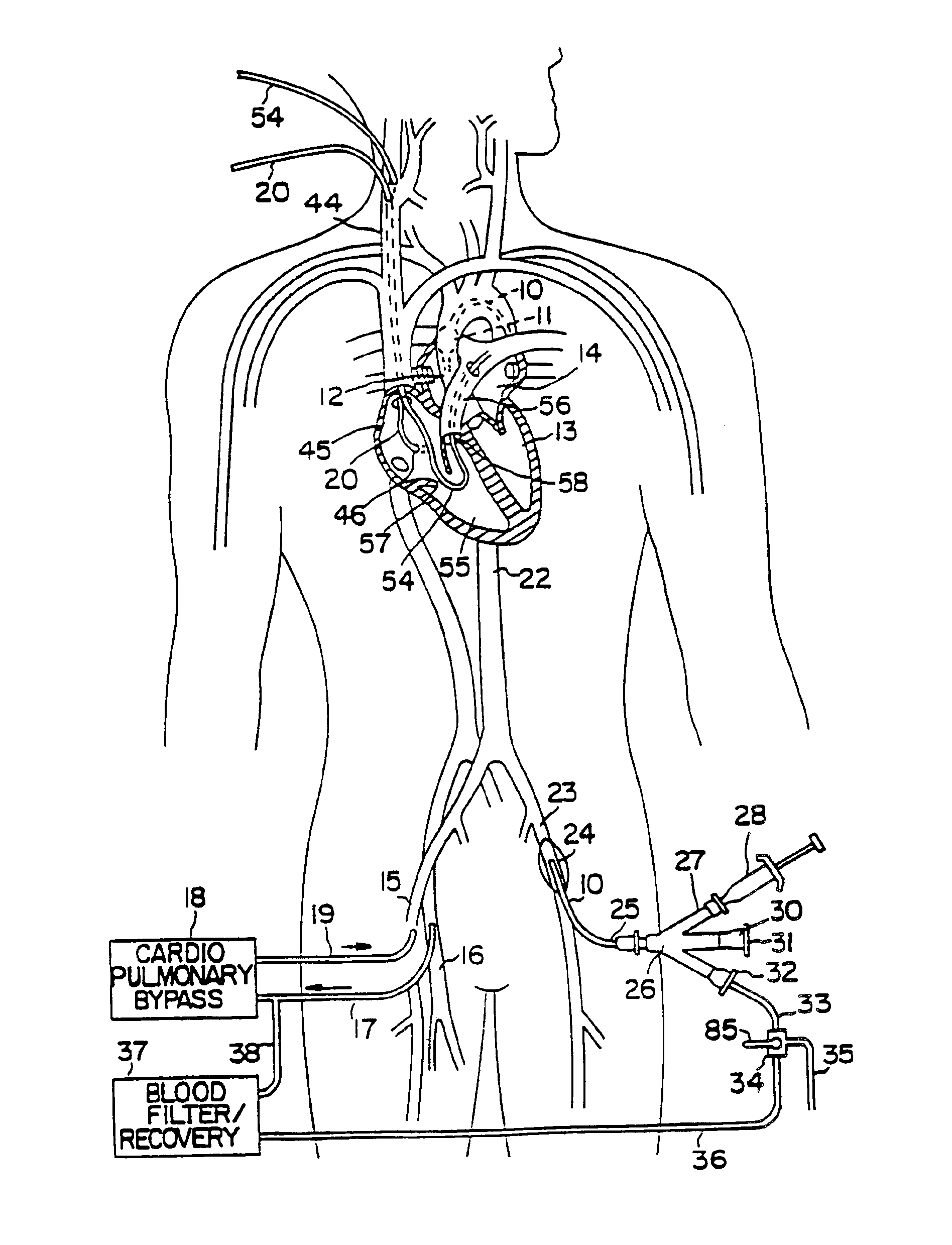
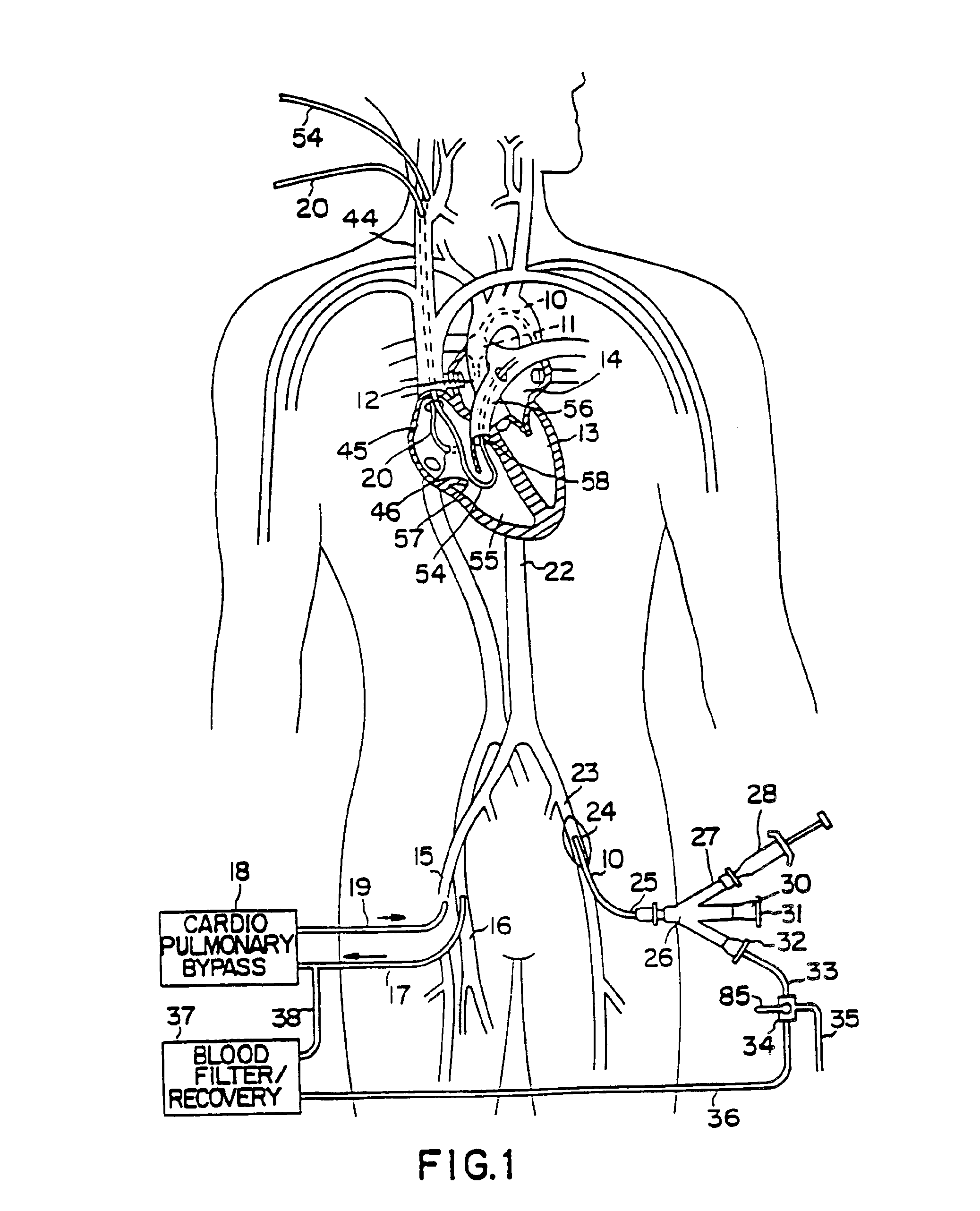
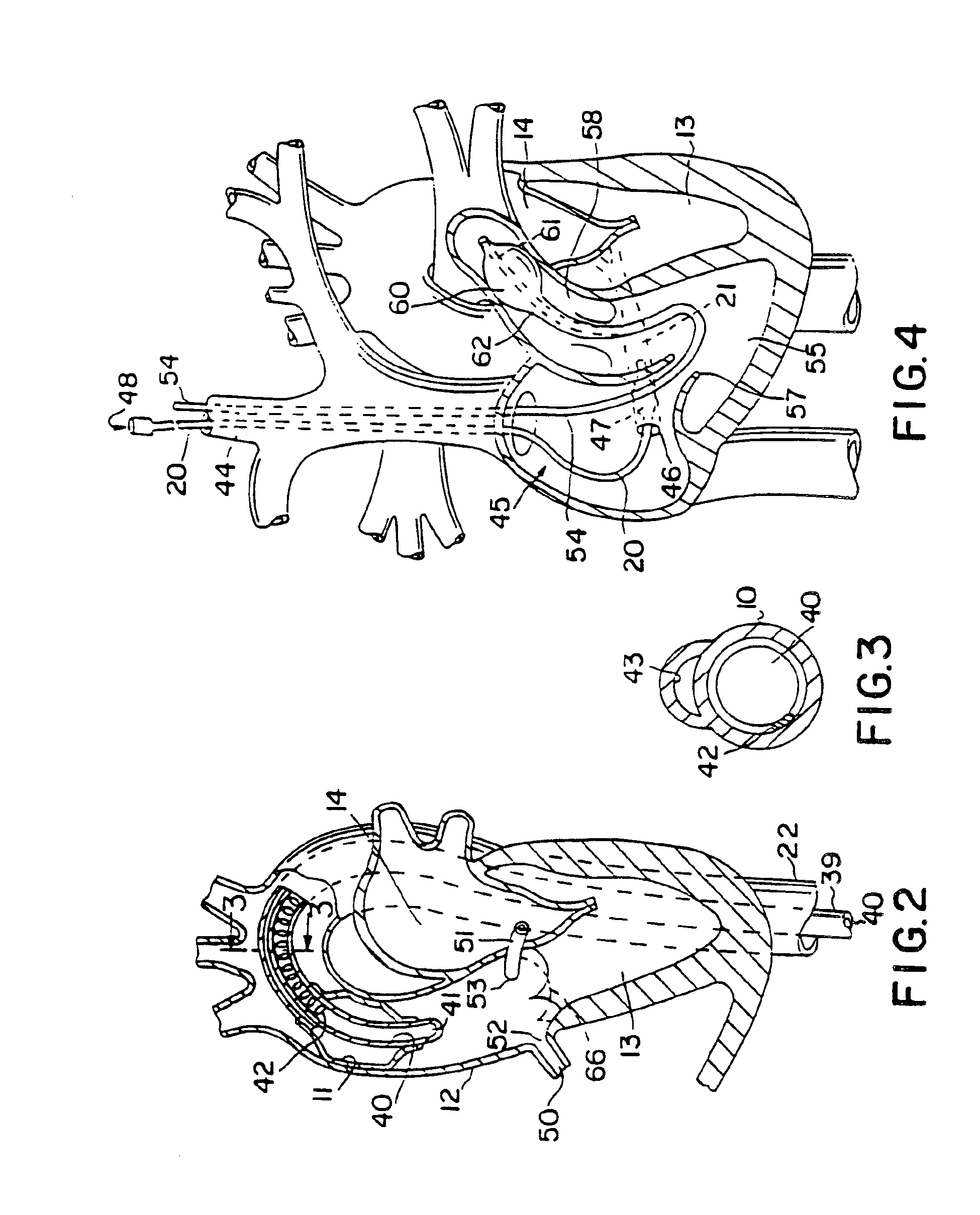
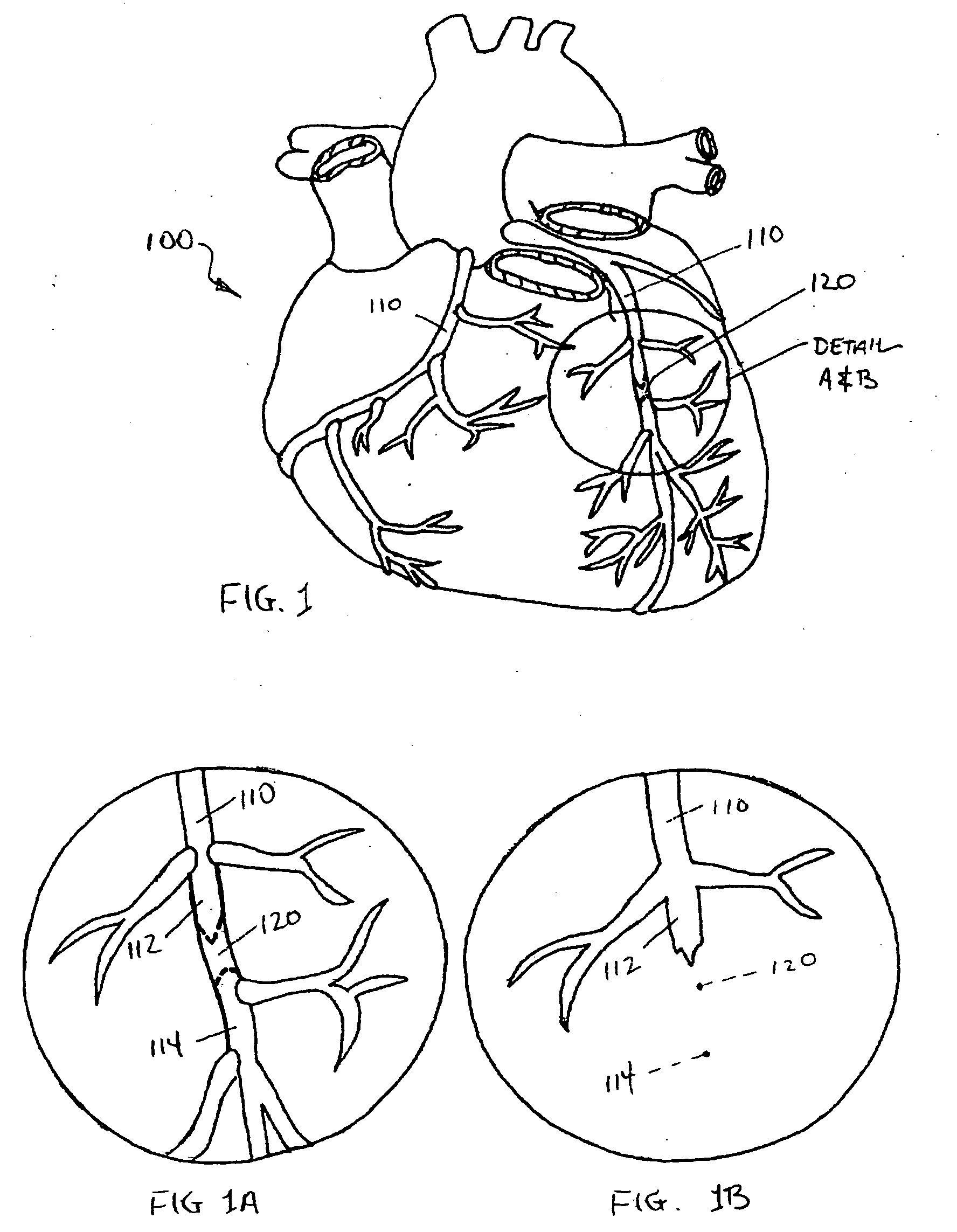
System for cardiac procedures
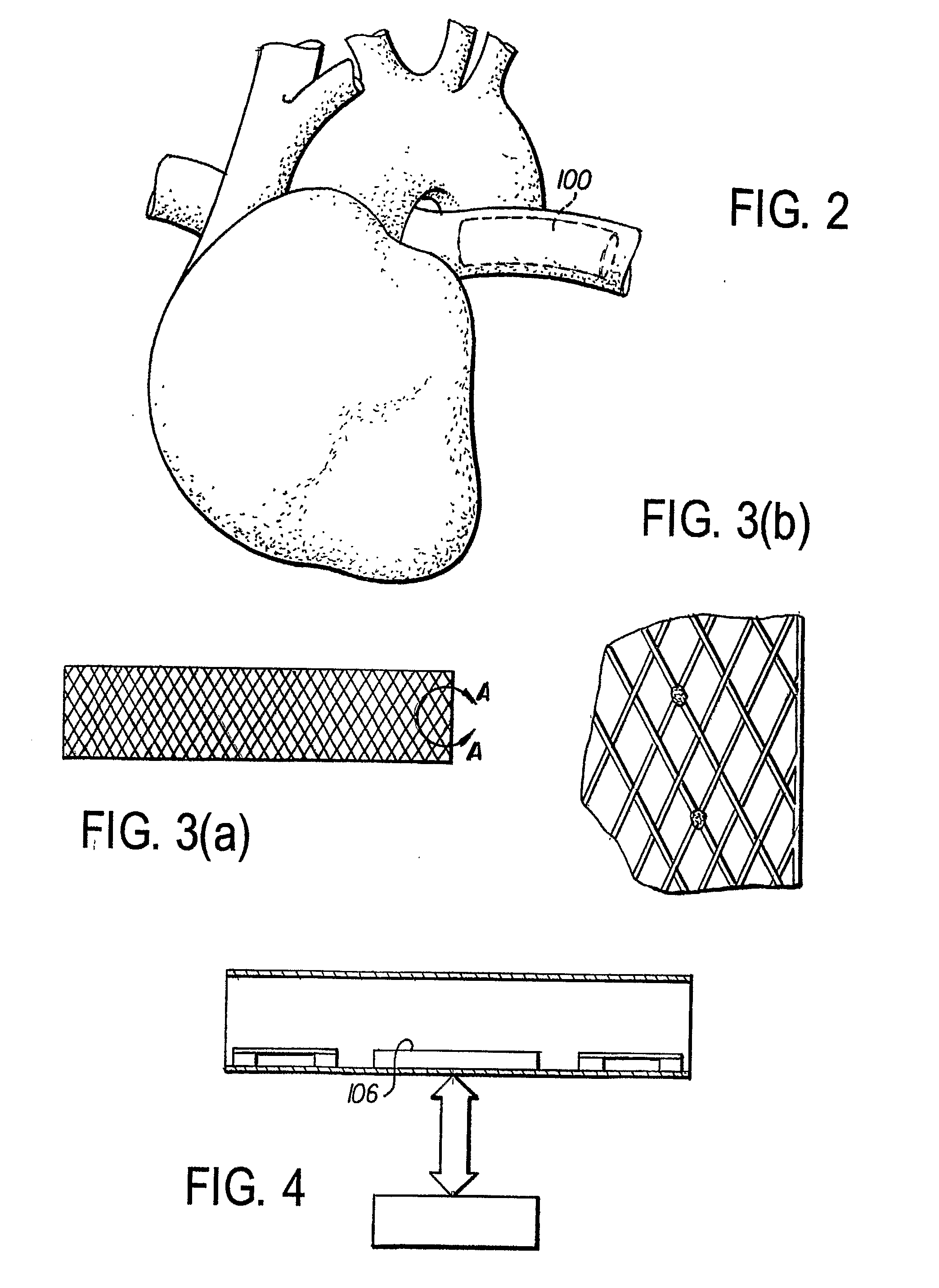
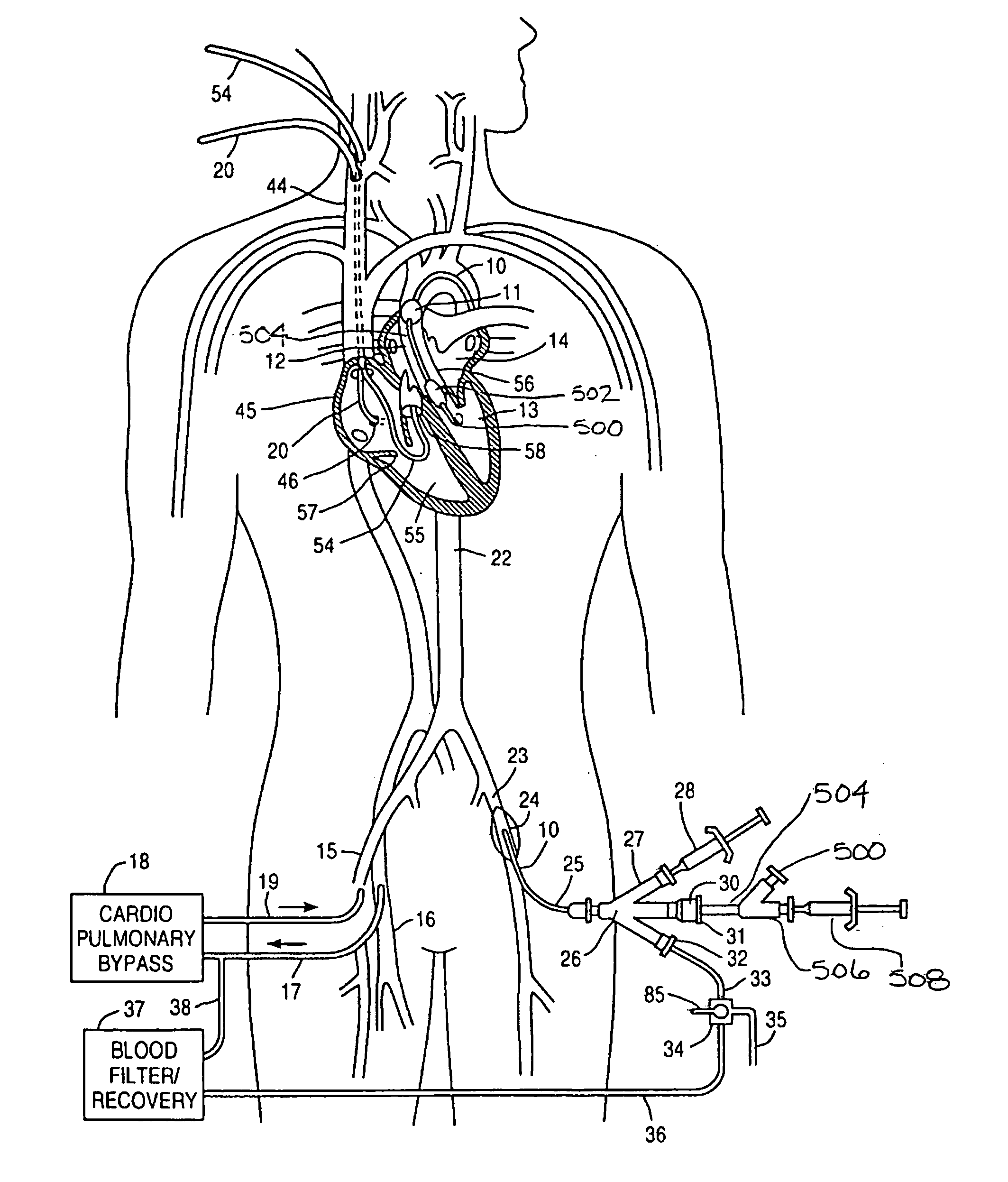
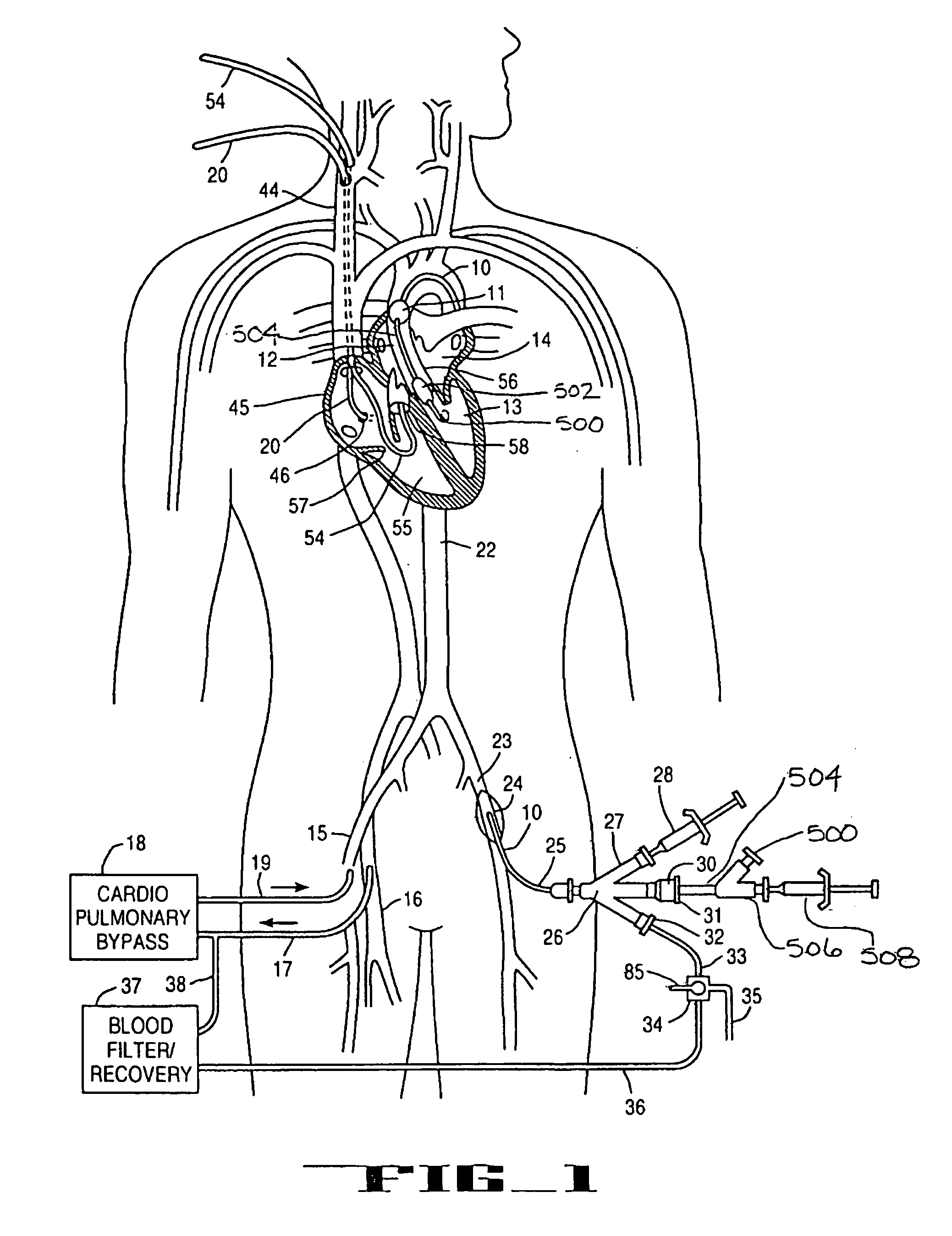
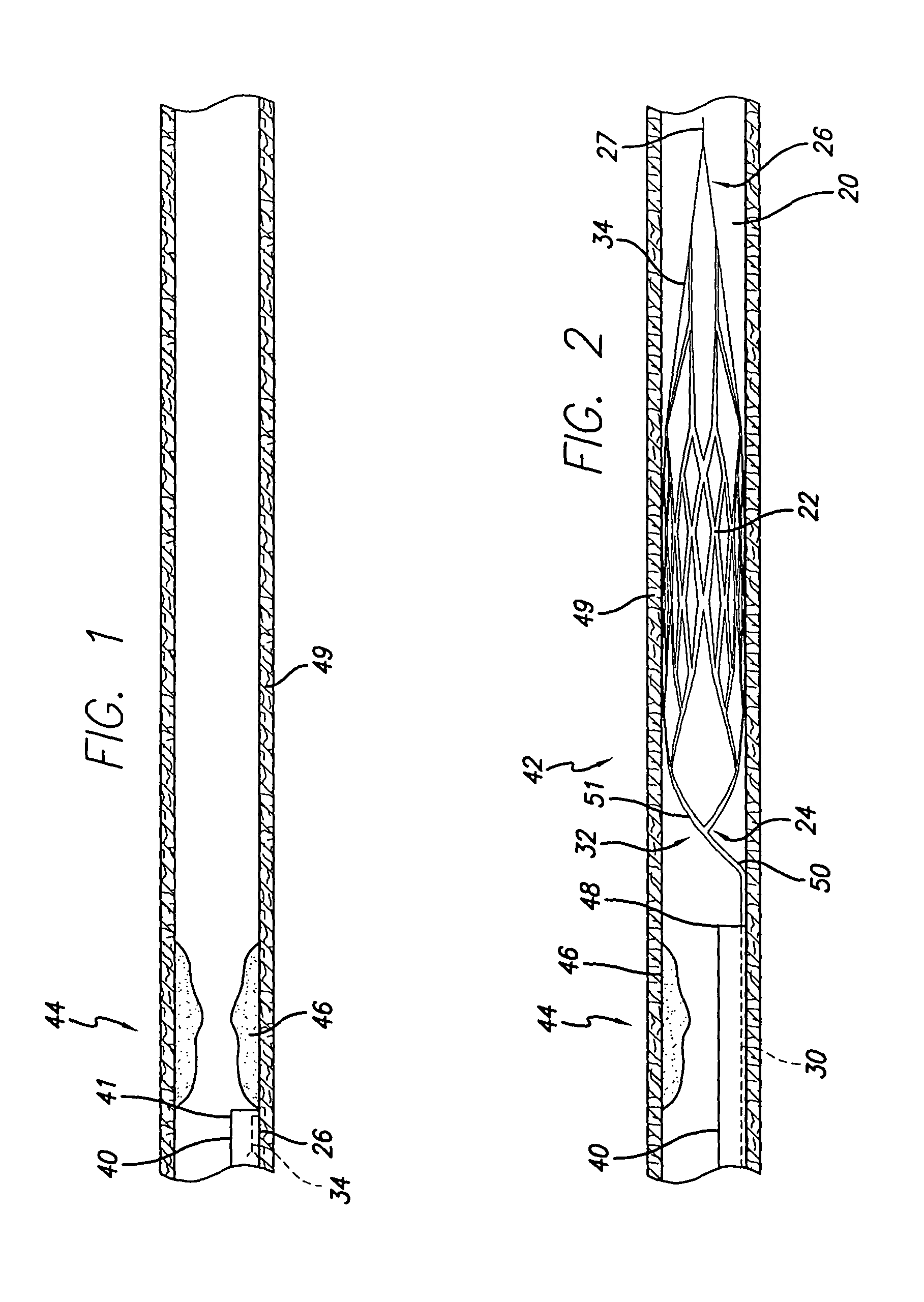
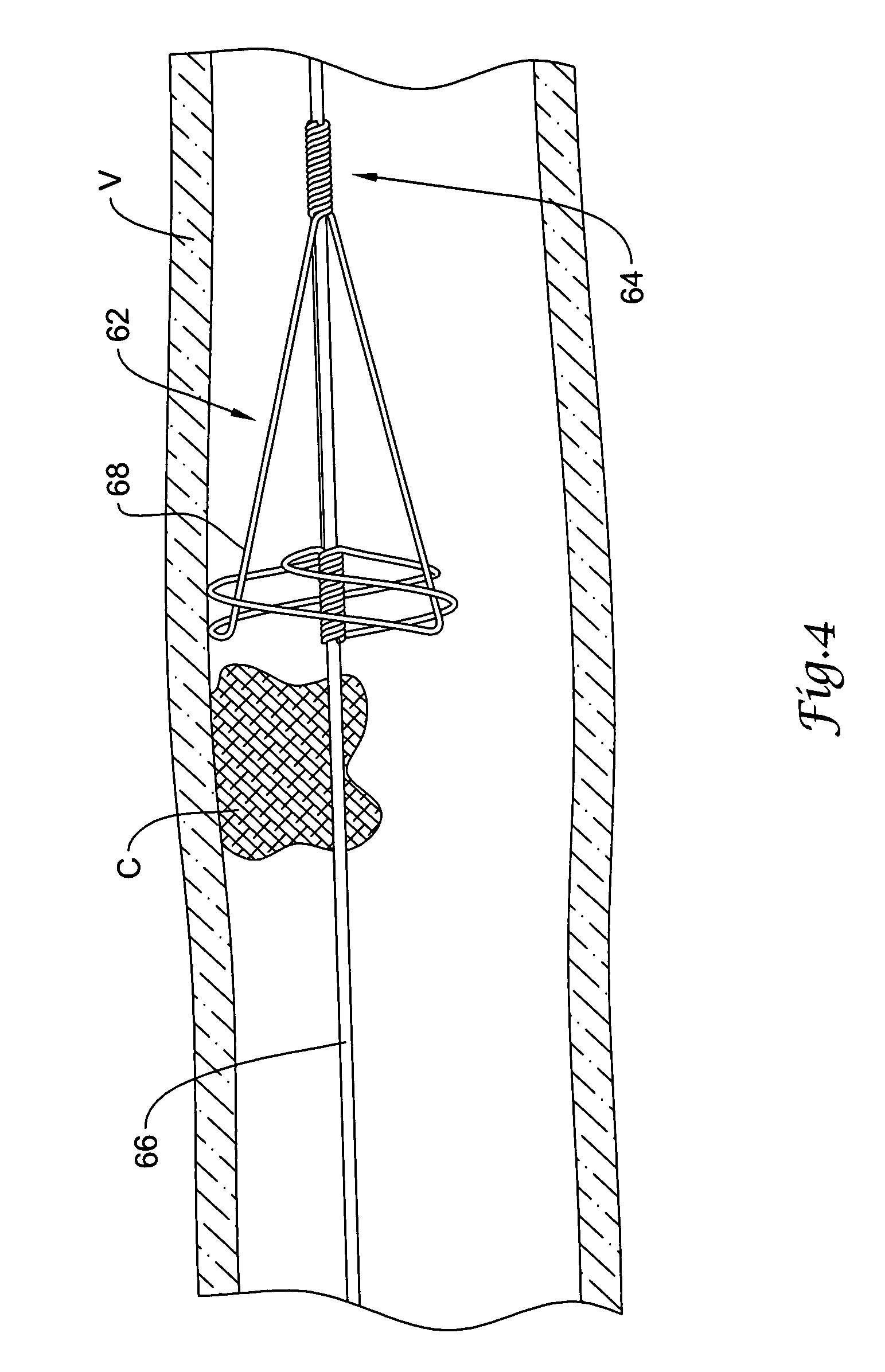
A system for accessing a patient's cardiac anatomy which includes an endovascular aortic partitioning device that separates the coronary arteries and the heart from the rest of the patient's arterial system. The endovascular device for partitioning a patient's ascending aorta comprises a flexible shaft having a distal end, a proximal end, and a first inner lumen therebetween with an opening at the distal end. The shaft may have a preshaped distal portion with a curvature generally corresponding to the curvature of the patient's aortic arch. An expandable means, e.g. a balloon, is disposed near the distal end of the shaft proximal to the opening in the first inner lumen for occluding the ascending aorta so as to block substantially all blood flow therethrough for a plurality of cardiac cycles, while the patient is supported by cardiopulmonary bypass. The endovascular aortic partitioning device may be coupled to an arterial bypass cannula for delivering oxygenated blood to the patient's arterial system. The heart muscle or myocardium is paralyzed by the retrograde delivery of a cardioplegic fluid to the myocardium through patient's coronary sinus and coronary veins, or by antegrade delivery of cardioplegic fluid through a lumen in the endovascular aortic partitioning device to infuse cardioplegic fluid into the coronary arteries. The pulmonary trunk may be vented by withdrawing liquid from the trunk through an inner lumen of an elongated catheter. The cardiac accessing system is particularly suitable for removing the aortic valve and replacing the removed valve with a prosthetic valve.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
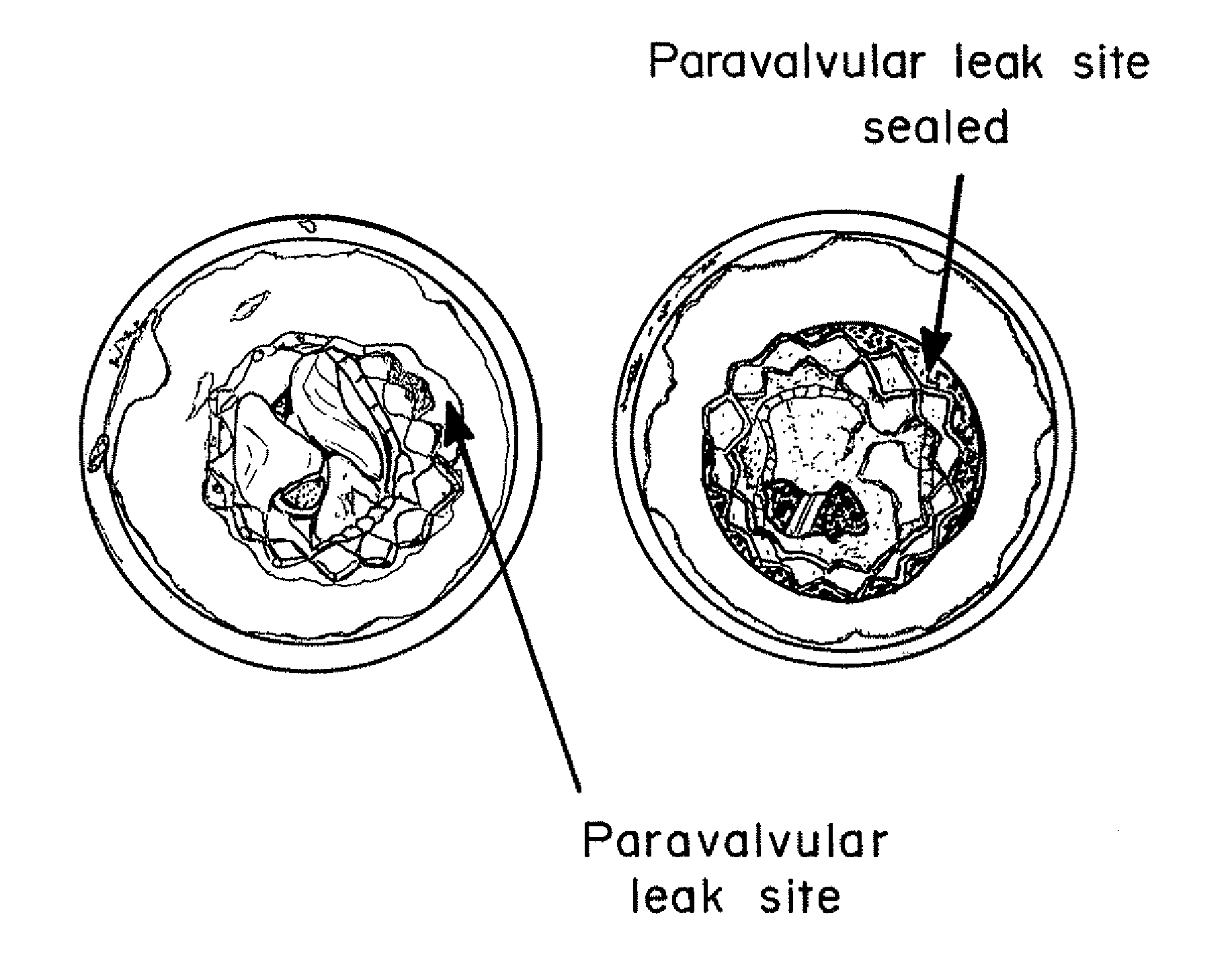
Means for Controlled Sealing of Endovascular Devices
InactiveUS20130331929A1Improve sealingEliminate prosthetic-annular incongruenceSurgical adhesivesHeart valvesProsthesisFunctional integrity
Expandable sealing means for endoluminal devices have been developed for controlled activation. The devices have the benefits of a low profile mechanism (for both self-expanding and balloon-expanding prostheses), contained, not open, release of the material, active conformation to the “leak sites” such that leakage areas are filled without disrupting the physical and functional integrity of the prosthesis, and on-demand, controlled activation, that may not be pressure activated.
Owner:ENDOLUMINAL SCI
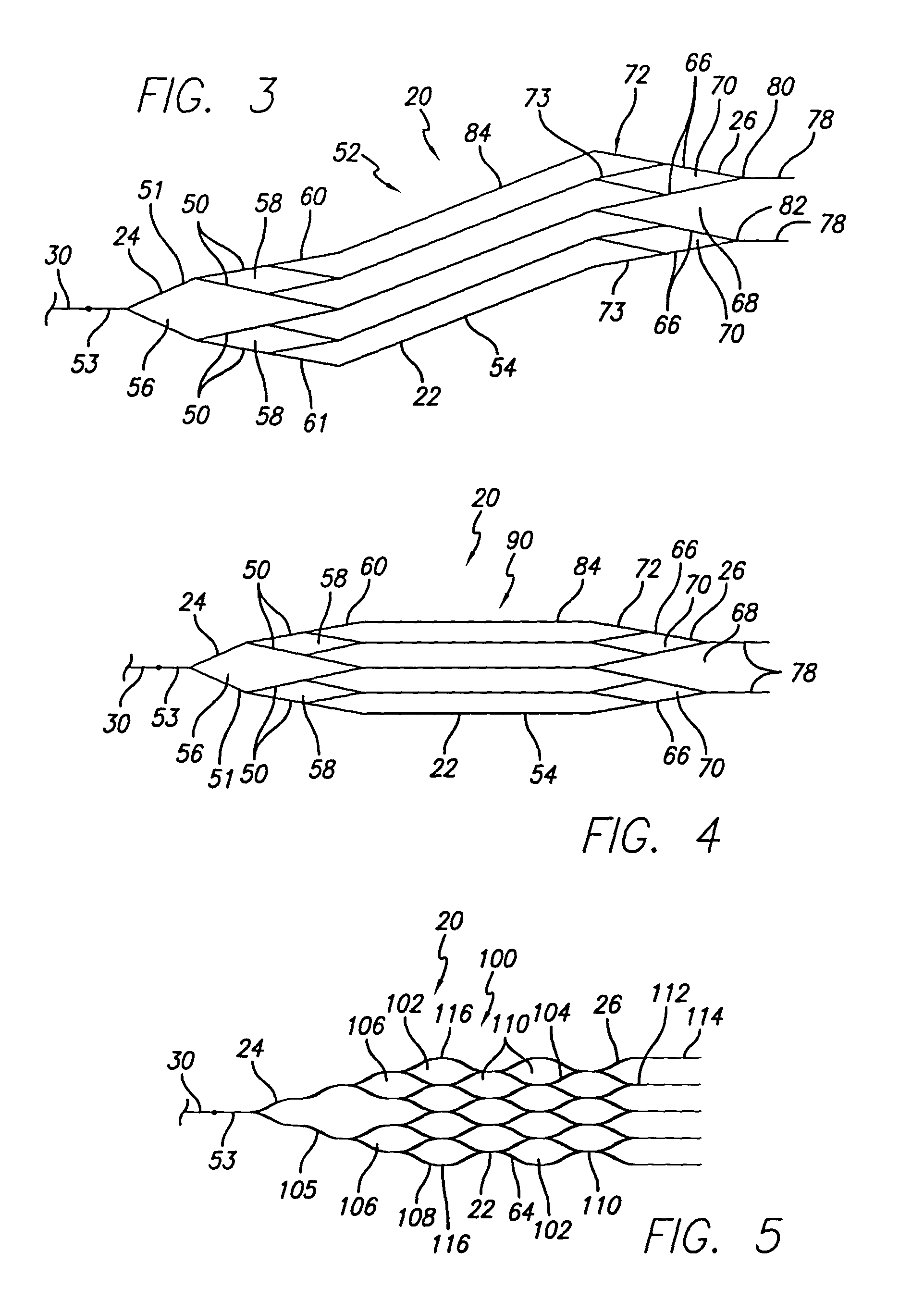
Expandable delivery appliance particularly for delivering intravascular devices
A delivery appliance for delivering an expandable annular device, particularly an expandable intravascular device, to a desired location in a lumen, includes an annular array of supporting strips extending from a proximal end of the annular array to a distal end of the annular array, to define an annular supporting surface for the expandable annular device. Each of the supporting strips is laterally deformable to radially expand or radially contract the annular array and the annular supporting surface defined thereby. A connecting stem passes through the annular array of supporting strips and has a distal end coupled to the supporting strips at the distal end of the annular array for axial movement therewith, and a proximal end passing through the proximal end of the annular array of supporting strips for axial movement with respect thereto. The proximal end of the connecting stem is axially movable in opposite directions to move the distal end of the annular array axially away from or towards, the proximal end of the annular array to radially contract or radially expand the annular supporting surface.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC +1
Endovascular devices and methods of use
ActiveUS20090177090A1StethoscopeHeart/pulse rate measurement devicesBalloon catheterIntravascular device
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
Intravascular filter with bioabsorbable centering element
Bioabsorbable centering elements for use in centering an implantable intravascular device within a body vessel are disclosed. The bioabsorbable centering element may include a number of support members configured to self-expand and engage the wall of the vessel when deployed. The support members may be formed from a biodegradable material adapted to degrade in vivo within a pre-determined period of time.
Owner:LIFESCREEN SCI
Intravascular devices and fibrosis-inducing agents
InactiveUS20050149173A1Reducing perigraft leakageFacilitate “anchoring”StentsPeptide/protein ingredientsFibrosisCoil embolization
Intravascular devices (e.g., stents, stent grafts, covered stents, aneurysm coils, embolic agents and drug delivery catheters and balloons) are used in combination with fibrosing agents in order to induce fibrosis that may otherwise not occur when the implant is placed within an animal or to promote fibrosis betweent the devices and the host tissues. Compositions and methods are described for use in the treatment of aneurysms and unstable arterial (vulnerable) plaque.
Owner:ANGIOTECH INT AG (CH)
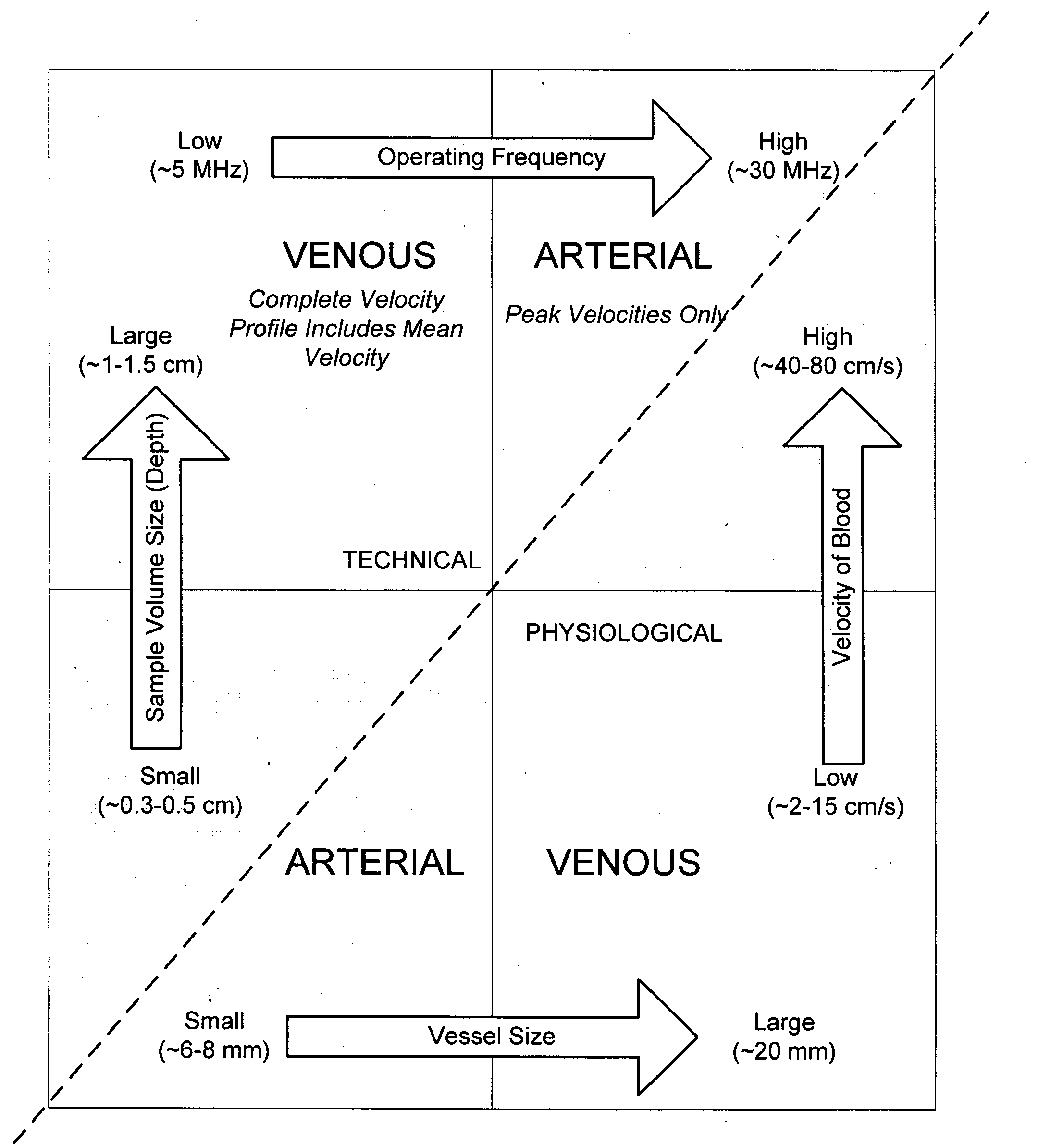
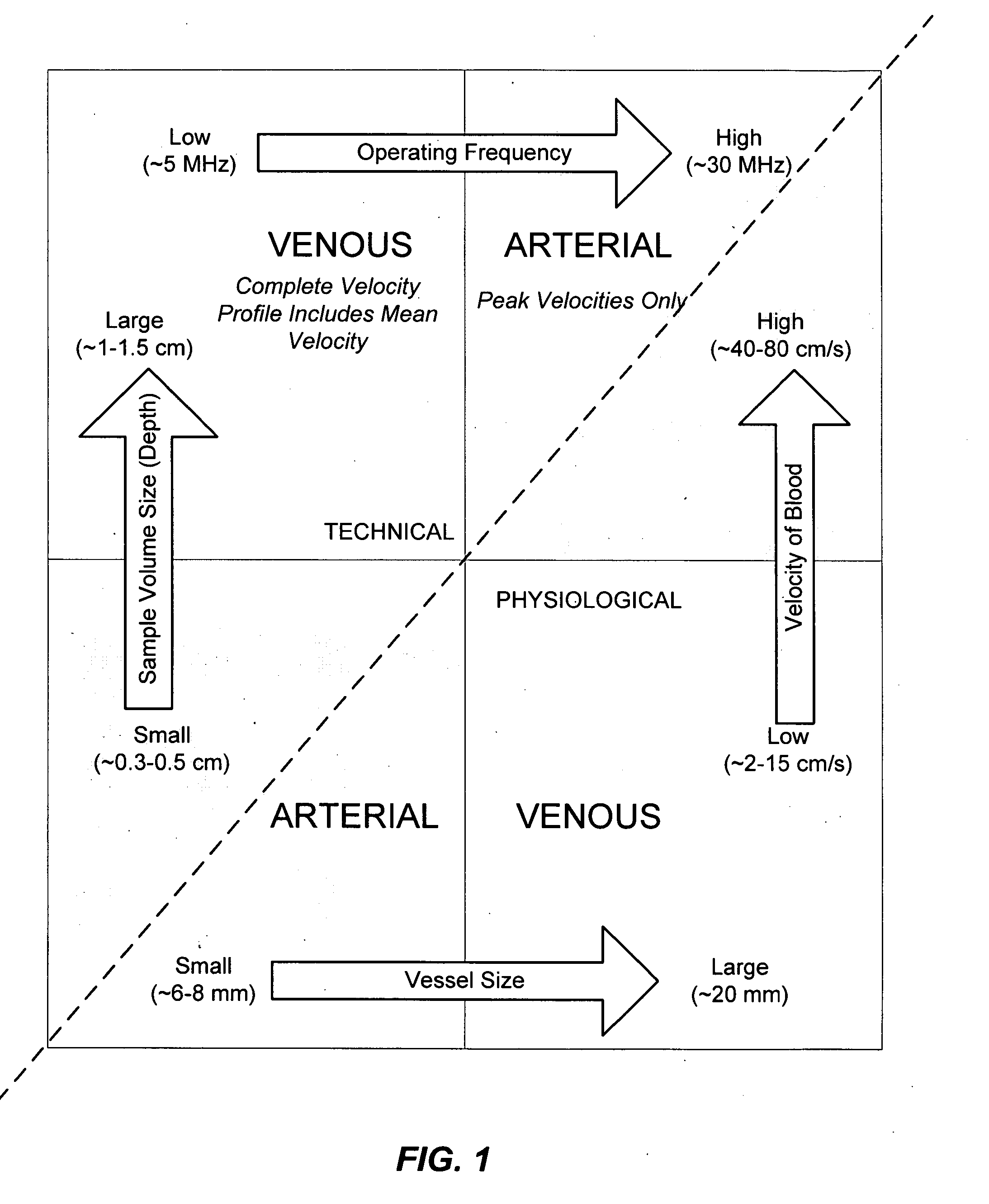
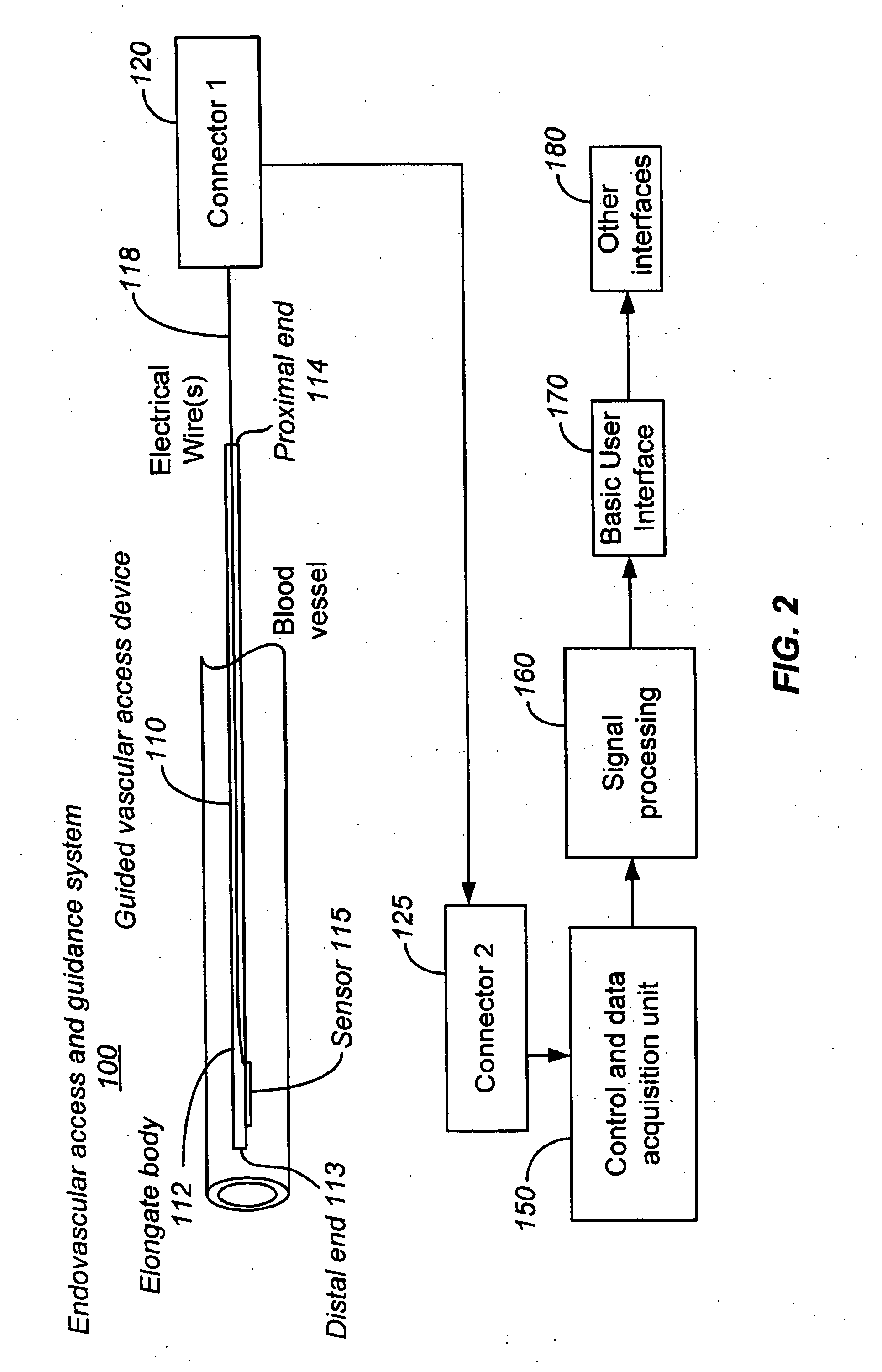
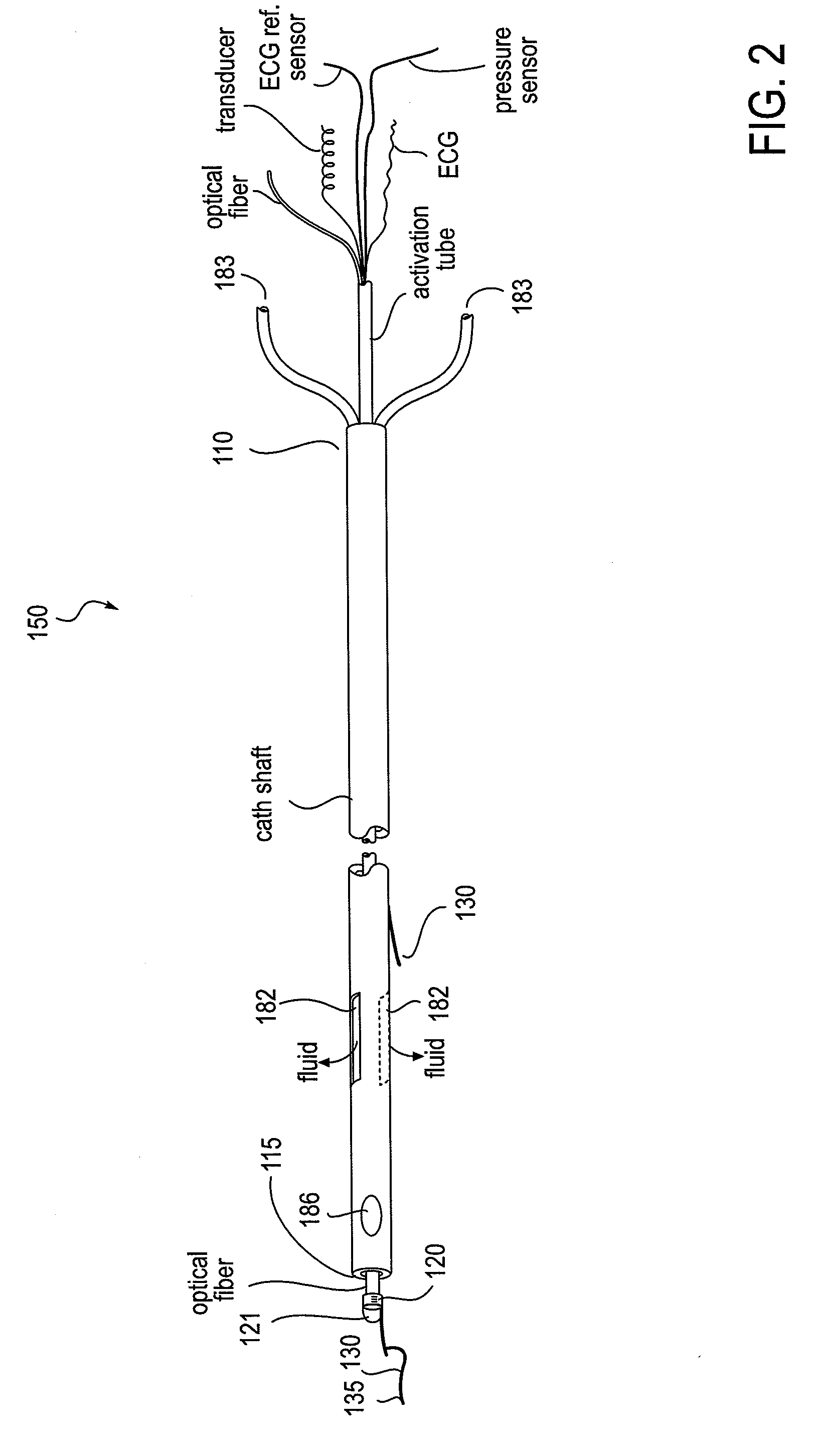
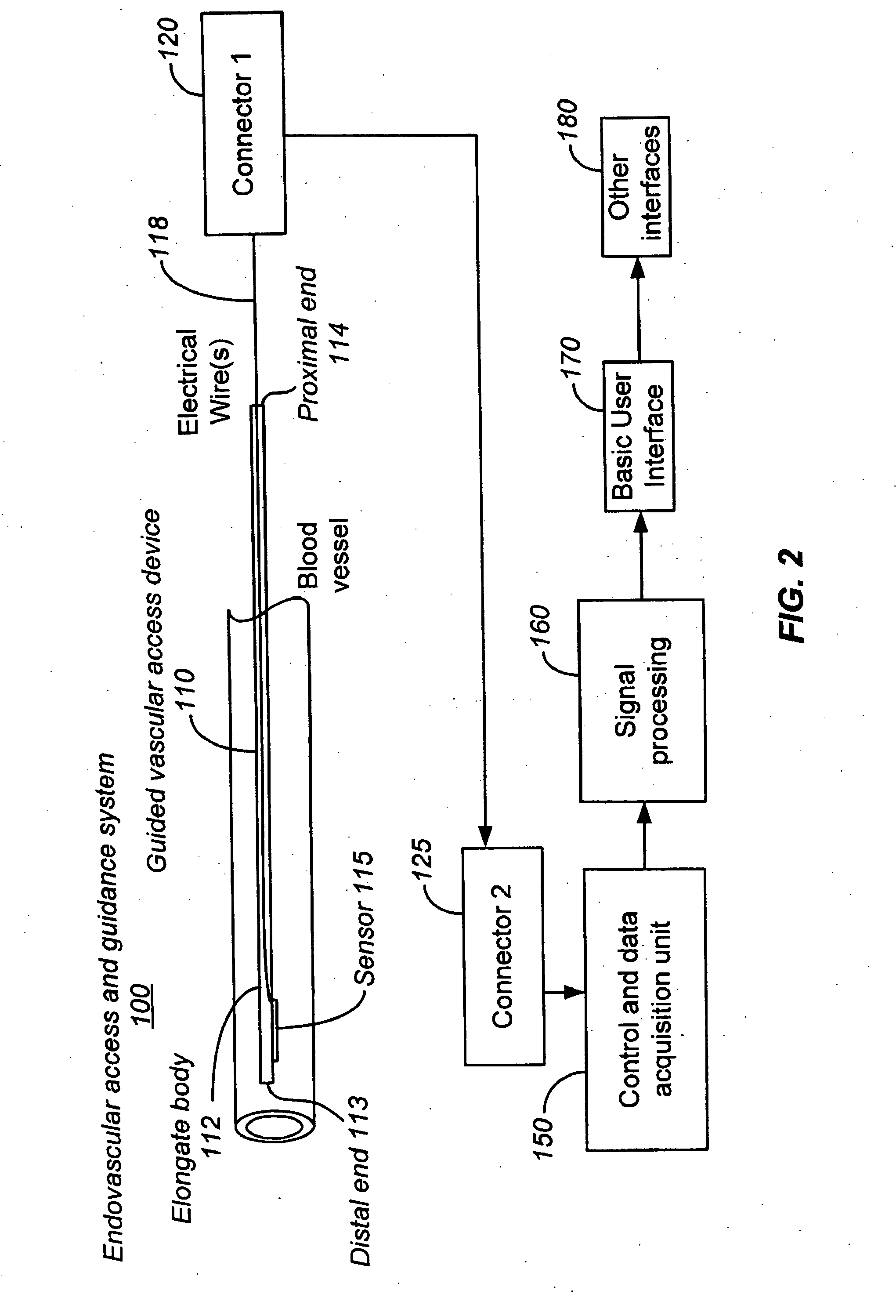
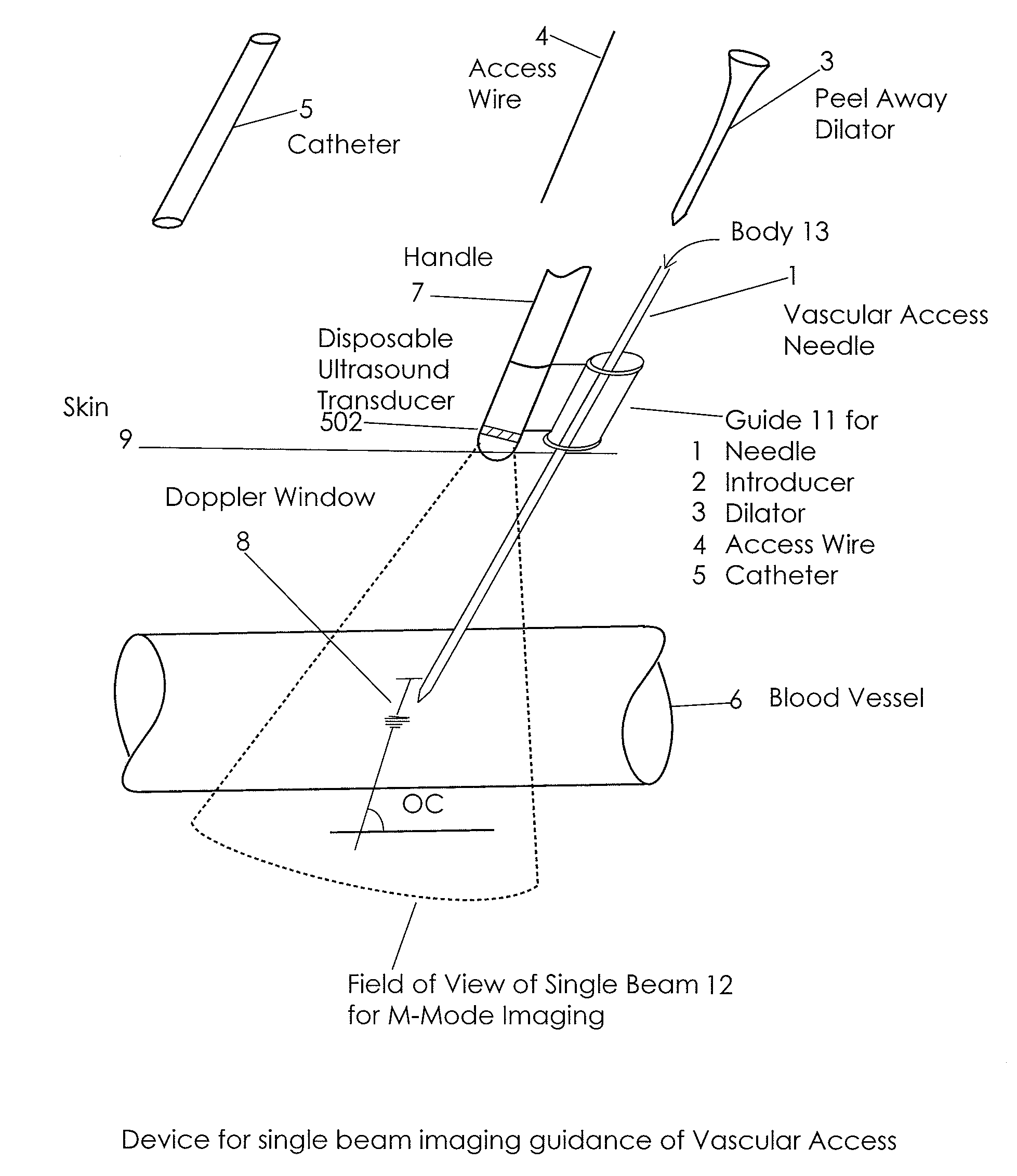
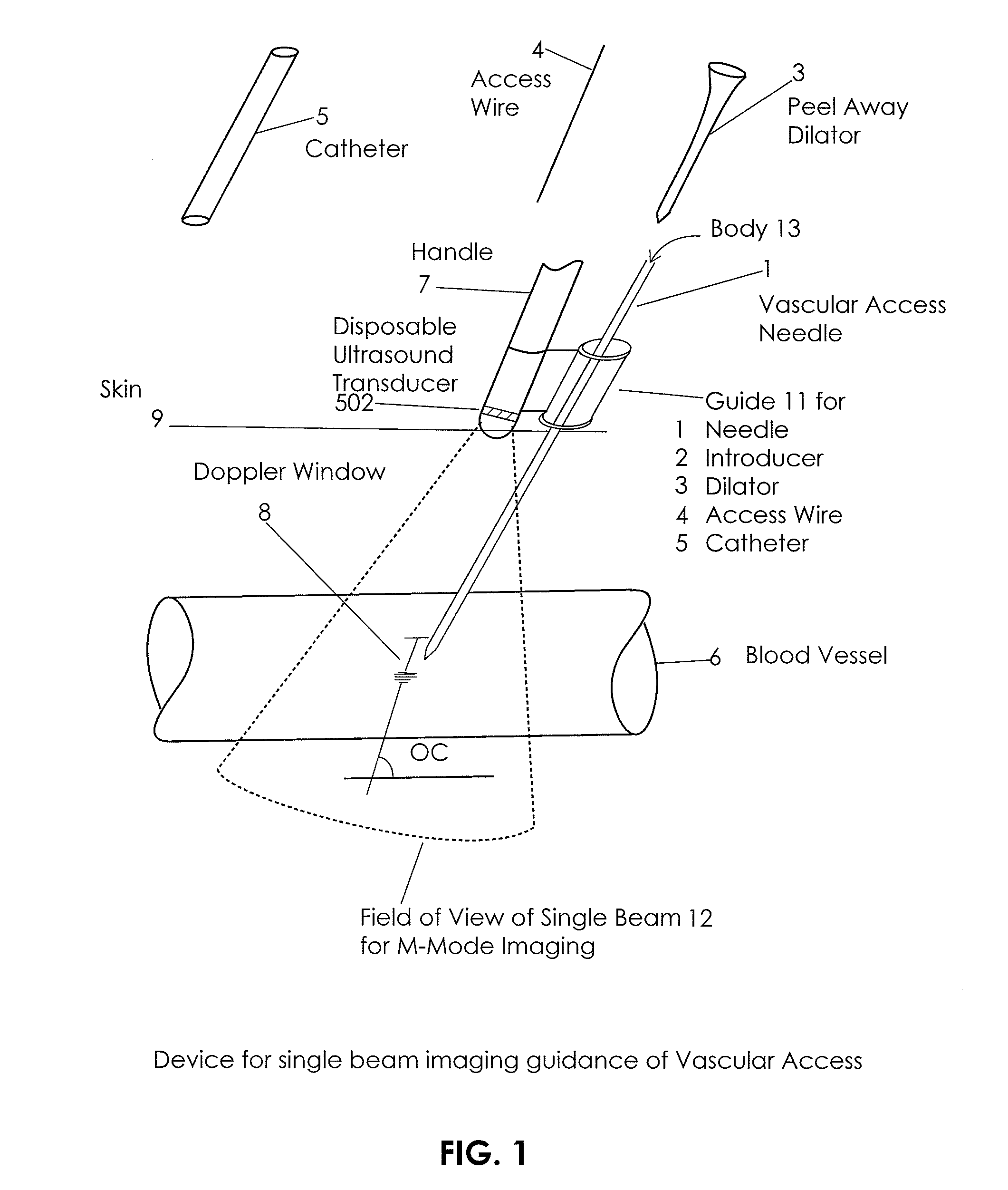
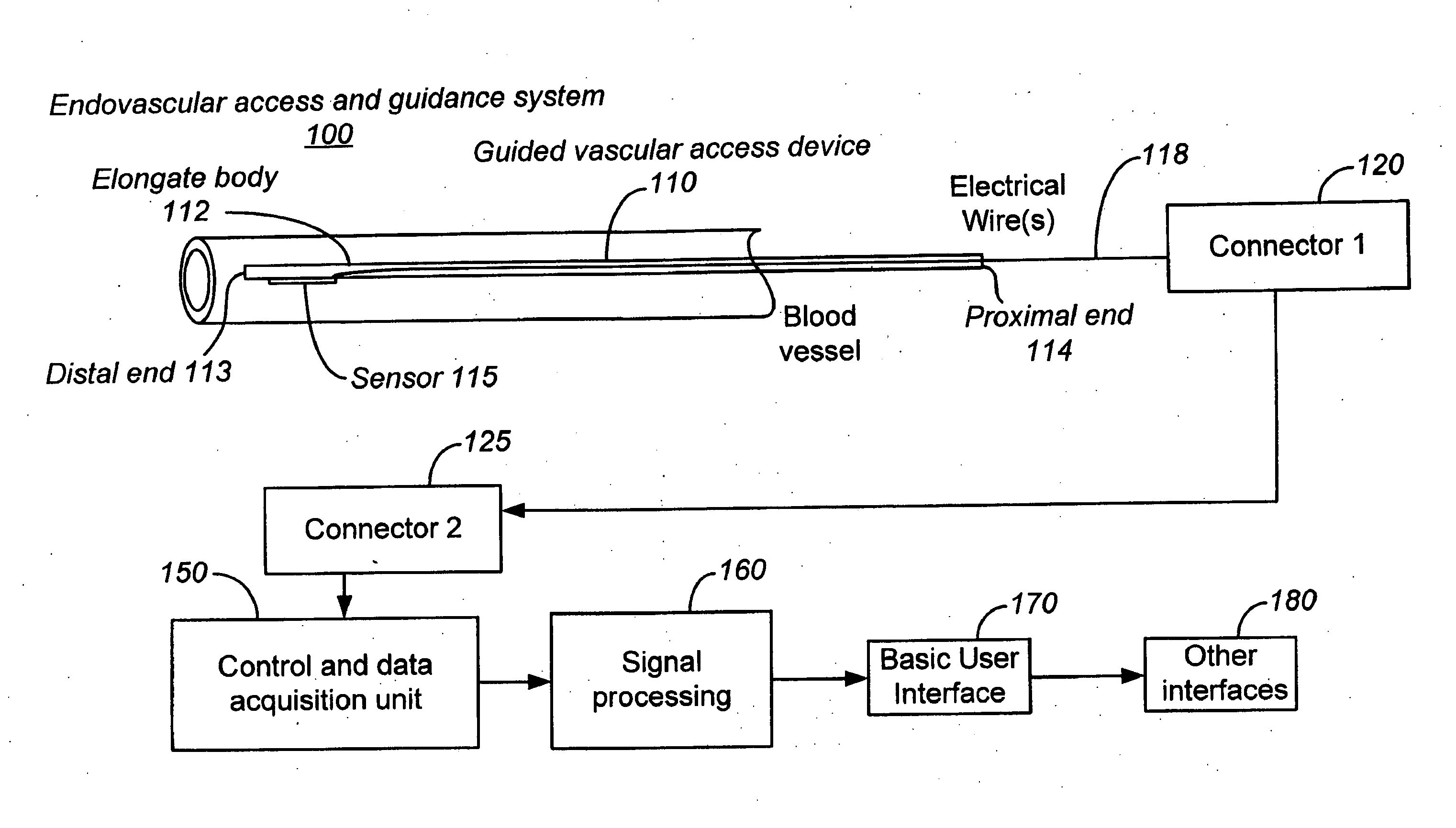
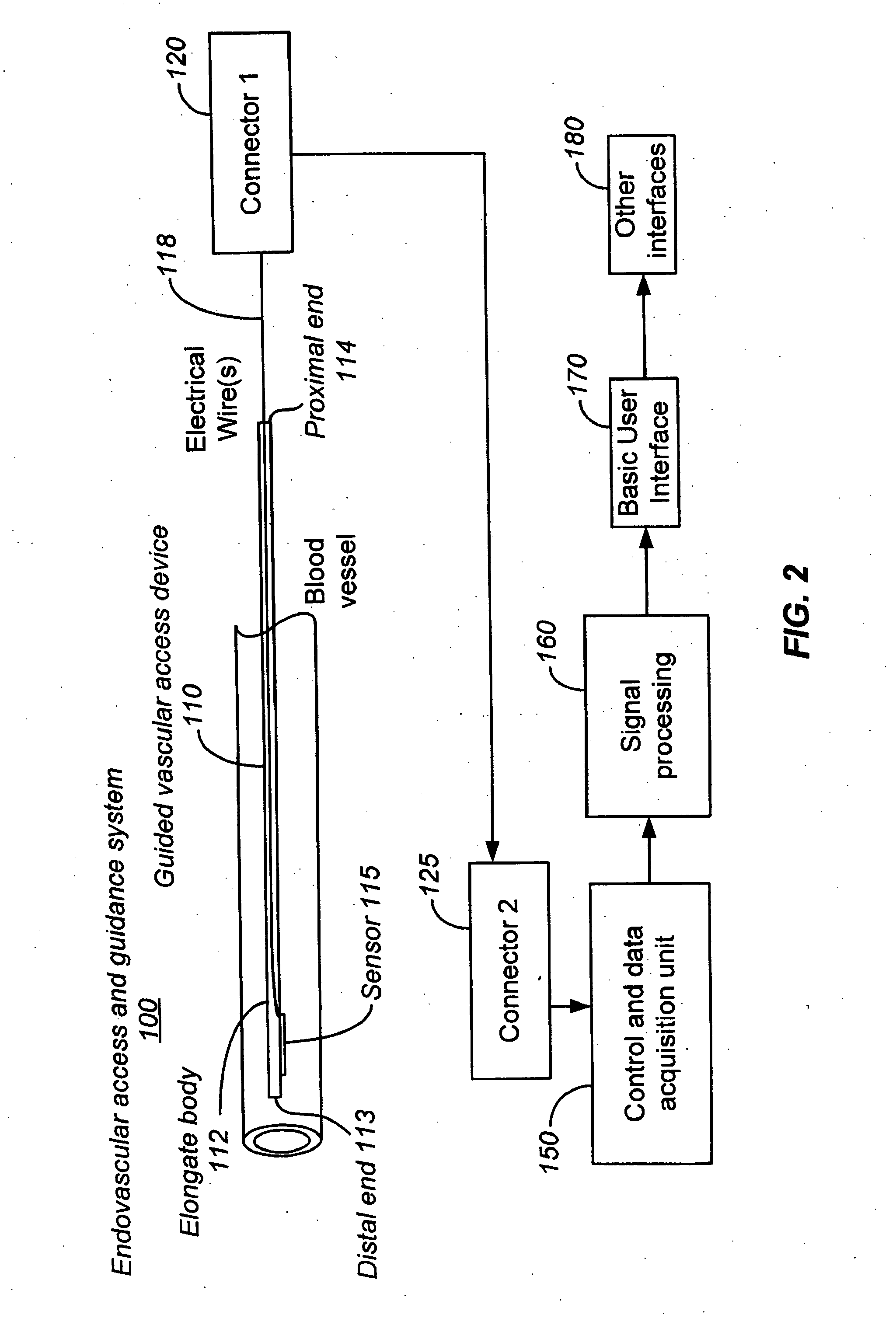
Ultrasound methods of positioning guided vascular access devices in the venous system
ActiveUS20070016068A1Diagnostic probe attachmentBlood flow measurement devicesGuidance systemVascular Access Devices
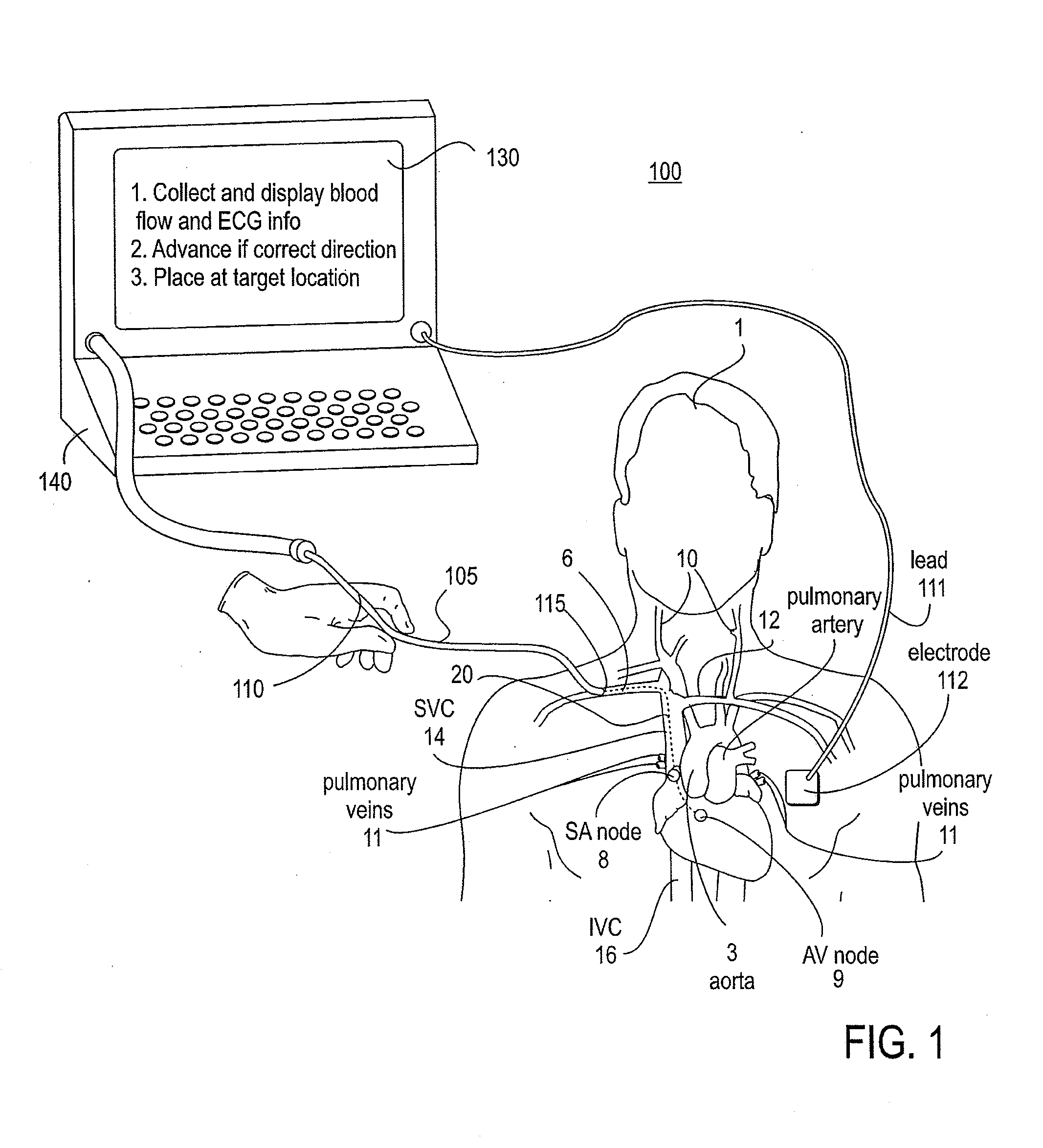
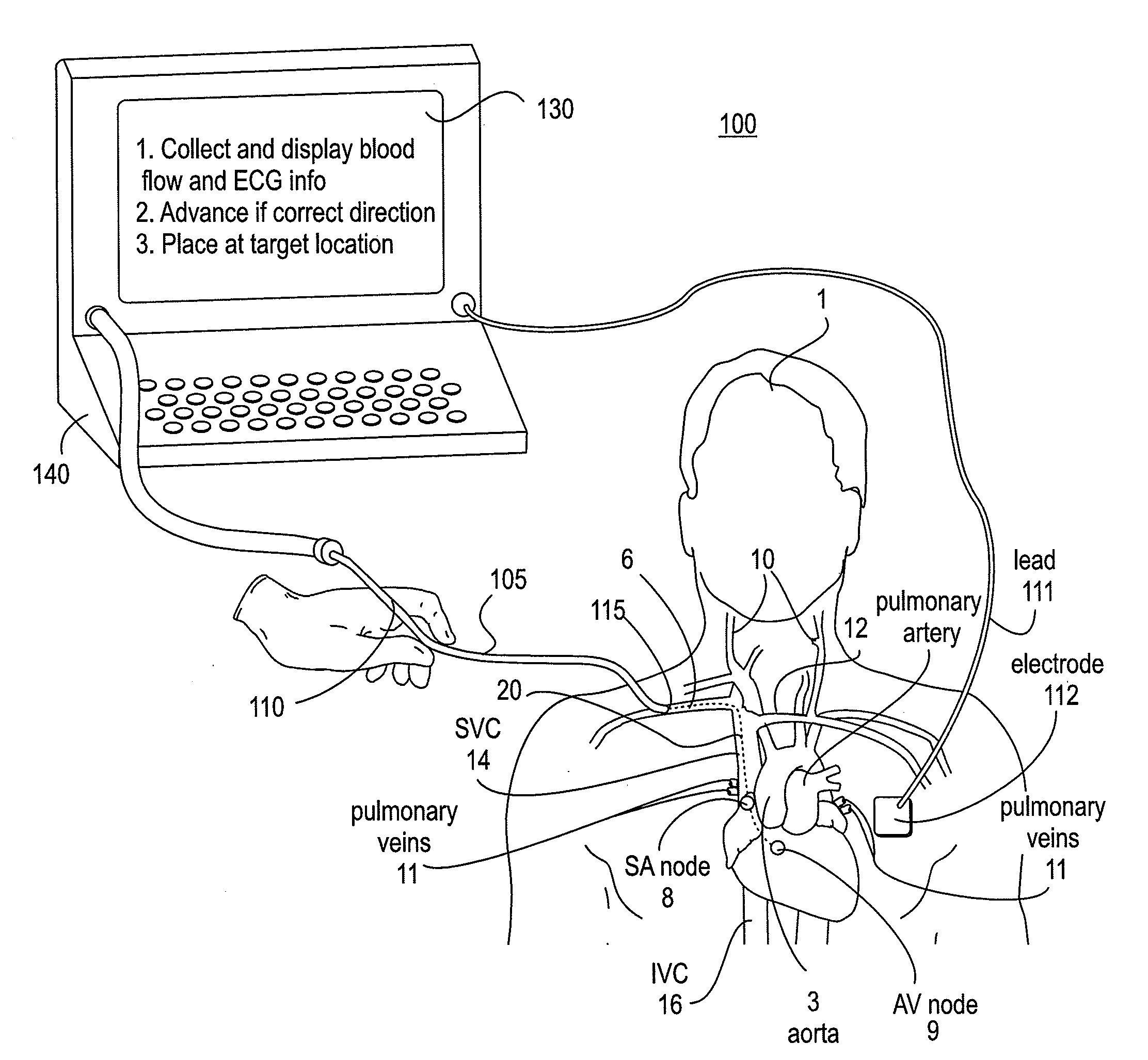
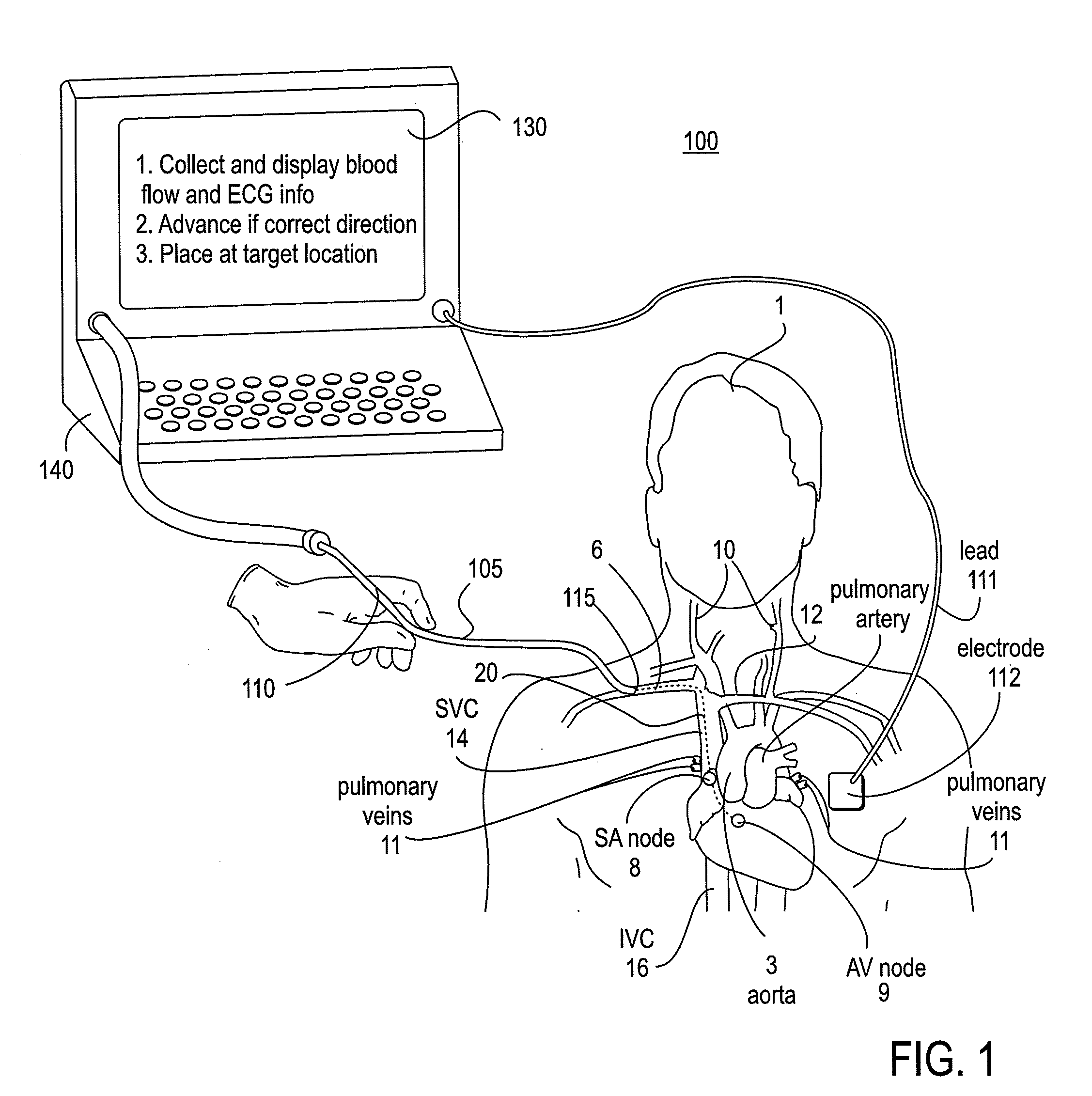
The invention relates to the guidance, positioning and placement confirmation of intravascular devices, such as catheters, stylets, guidewires and other flexible elongate bodies that are typically inserted percutaneously into the venous or arterial vasculature. Currently these goals are achieved using x-ray imaging and in some cases ultrasound imaging. This invention provides a method to substantially reduce the need for imaging related to placing an intravascular catheter or other device. Reduced imaging needs also reduce the amount of radiation that patients are subjected to, reduce the time required for the procedure, and decrease the cost of the procedure by reducing the time needed in the radiology department. An aspect of the invention includes, for example, an endovenous access and guidance system. The system comprises: an elongate flexible member adapted and configured to access the venous vasculature of a patient; a sensor disposed at a distal end of the elongate flexible member and configured to provide in vivo non-image based ultrasound information of the venous vasculature of the patient; a processor configured to receive and process in vivo non-image based ultrasound information of the venous vasculature of the patient provided by the sensor and to provide position information regarding the position of the distal end of the elongate flexible member within the venous vasculature of the patient; and an output device adapted to output the position information from the processor.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
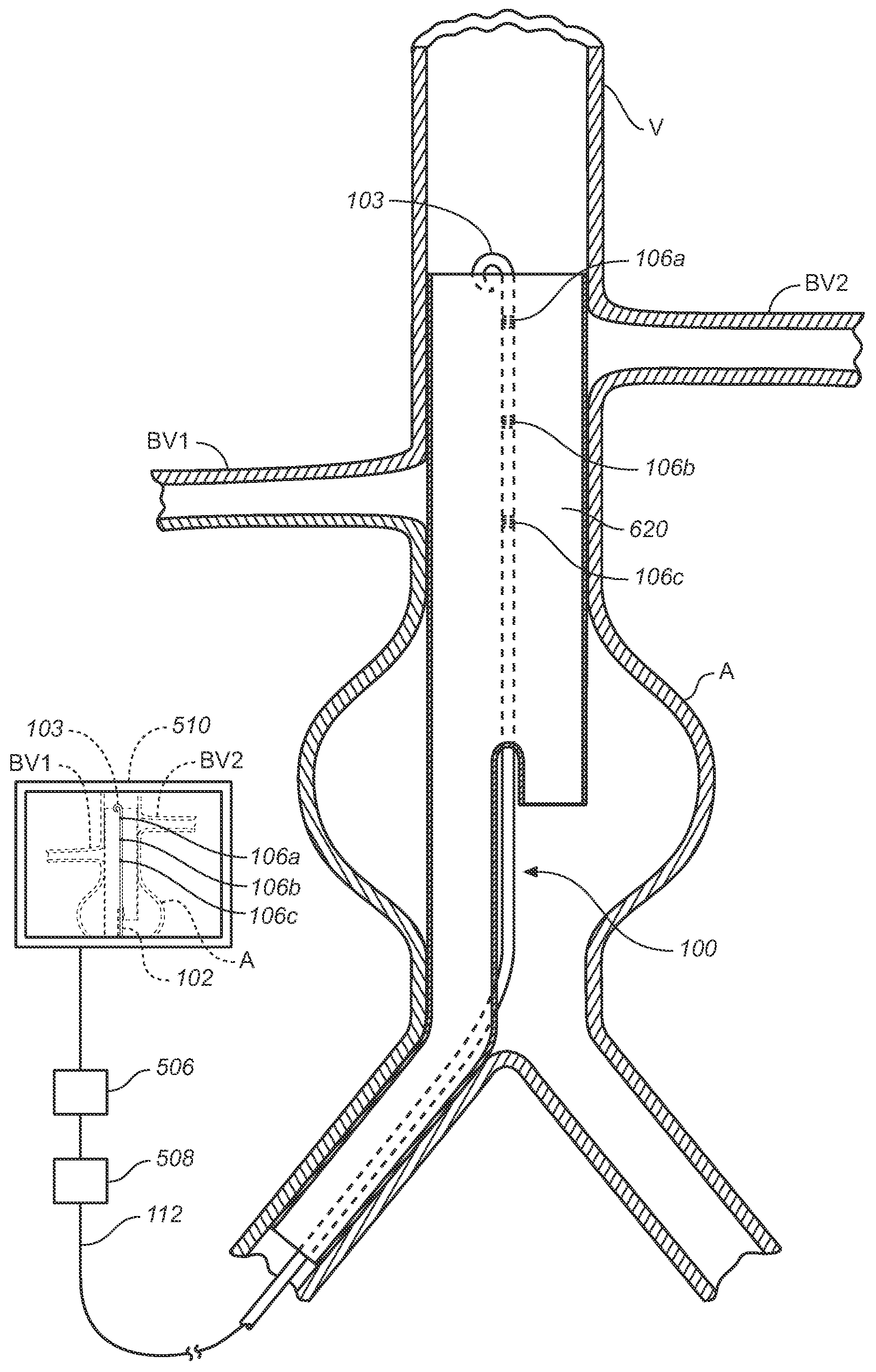
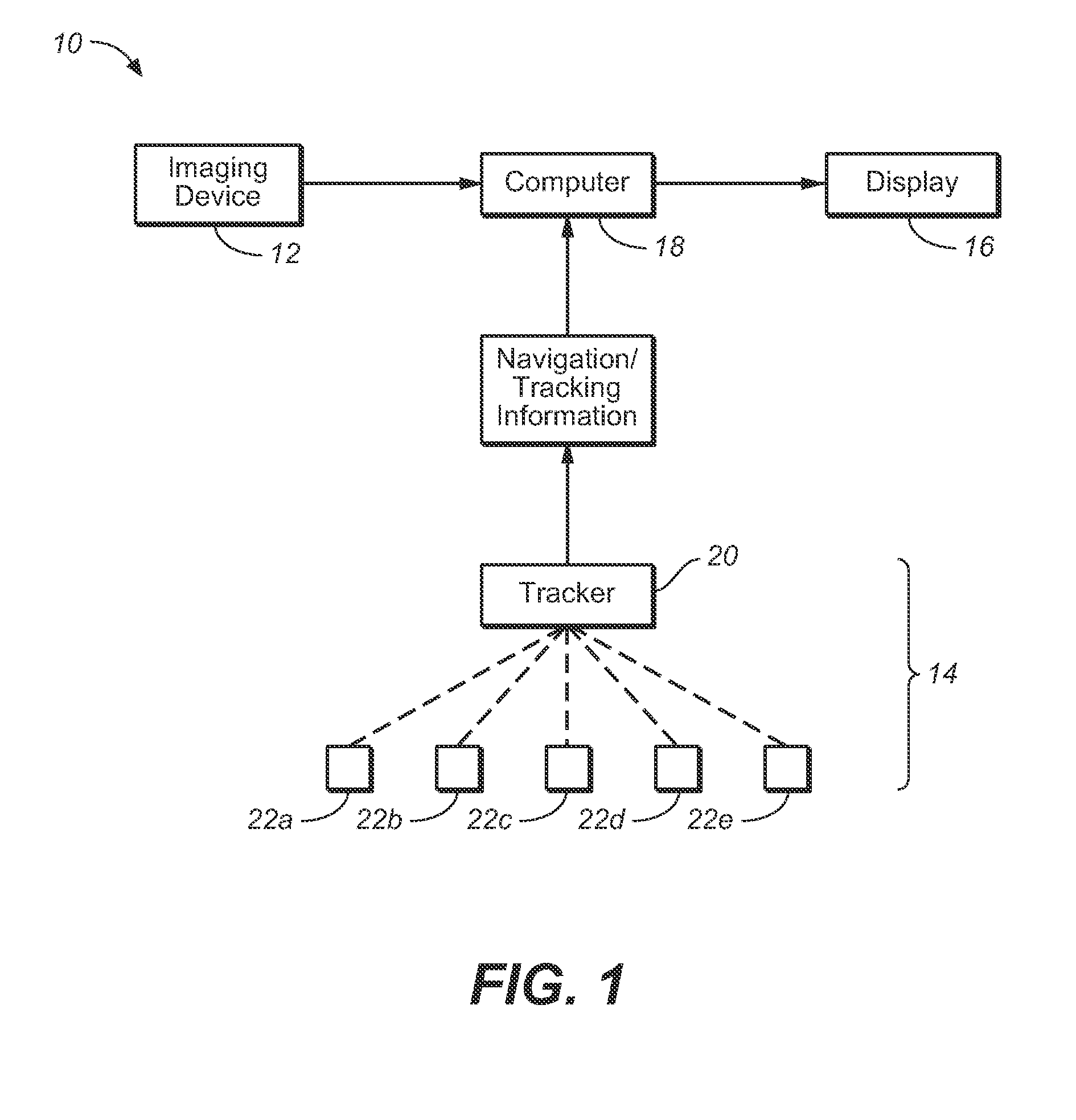
Vessel Position and Configuration Imaging Apparatus and Methods
One or more markers or sensors are positioned in the vasculature of a patient to facilitate determining the location, configuration, and / or orientation of a vessel or certain aspects thereof (e.g., a branch vessel), determining the location, configuration and / or orientation of a endovascular devices prior to and during prosthesis deployment as well as the relative position of portions of the vasculature and devices, generating an image of a virtual model of a portion of one or more vessels (e.g., branch vessels) or devices, and / or formation of one or more openings in a tubular prosthesis in situ to allow branch vessel perfusion when the prosthesis is placed over one or more branch vessels in a patient (e.g., when an aortic abdominal artery stent-graft is fixed to the aorta superior to the renal artery ostia).
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Leadless Implantable Intravascular Electrophysiologic Device for Neurologic/Cardiovascular Sensing and Stimulation
ActiveUS20080119911A1Enhances specificity/integrityRestricted blood flowHeart defibrillatorsInternal electrodesOptical communicationRadio frequency
A leadless intravascular sensor (100, 200) uses the body tissue as a communication medium. The implantable intravascular device has a tubular stent-like structure (102) for intravascular fixation with embedded microcircuits to allow bipolar and unipolar sensing of cardiac and neurologic electrical activity, sensing of other physiologic signals, local electrical stimulation (cardiac pacing and defibrillation; neurologic stimulation and seizure therapy) as well as the ability to communicate with other implanted and non implanted devices via radio frequency and / or optical communication and / or analog signal communication using the body tissue as the conducting medium. The device can also be used in the extravascular or perivascular space. In this form, it has an open / flexible ring that can be adjusted, or self-adjusts to provide no pressure or required contact around the vessel or target region.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Guidewire with optical fiber
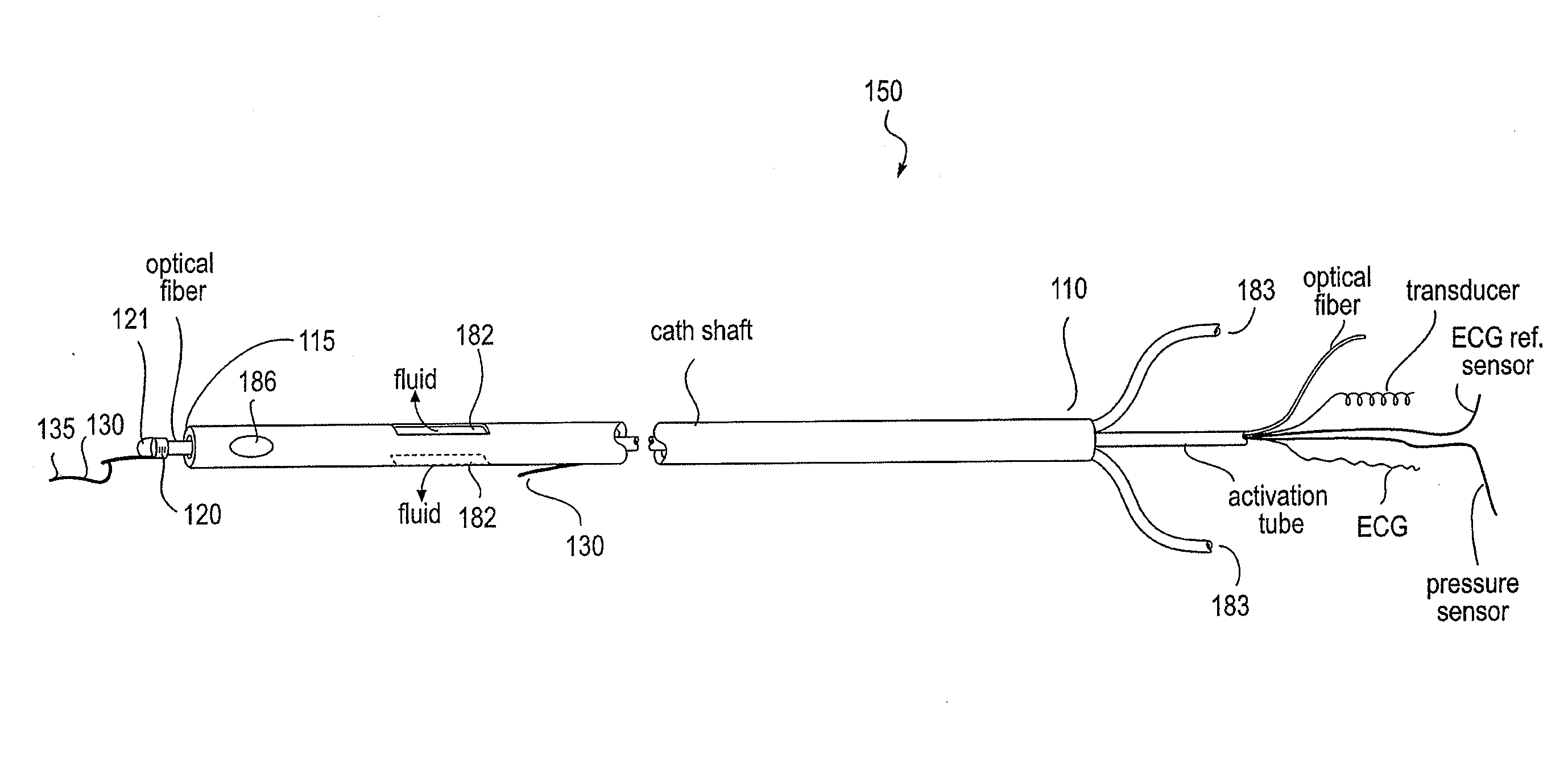
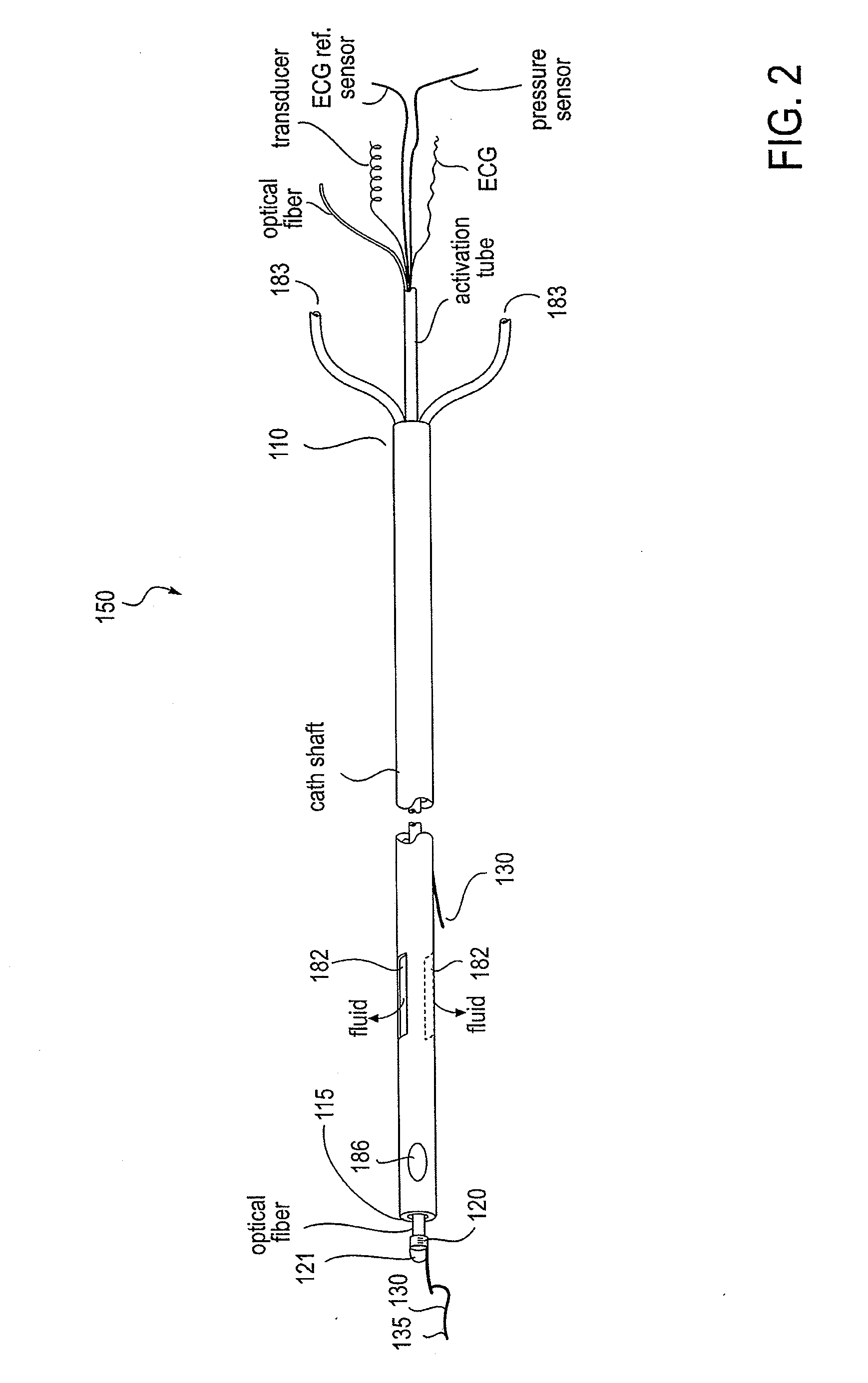
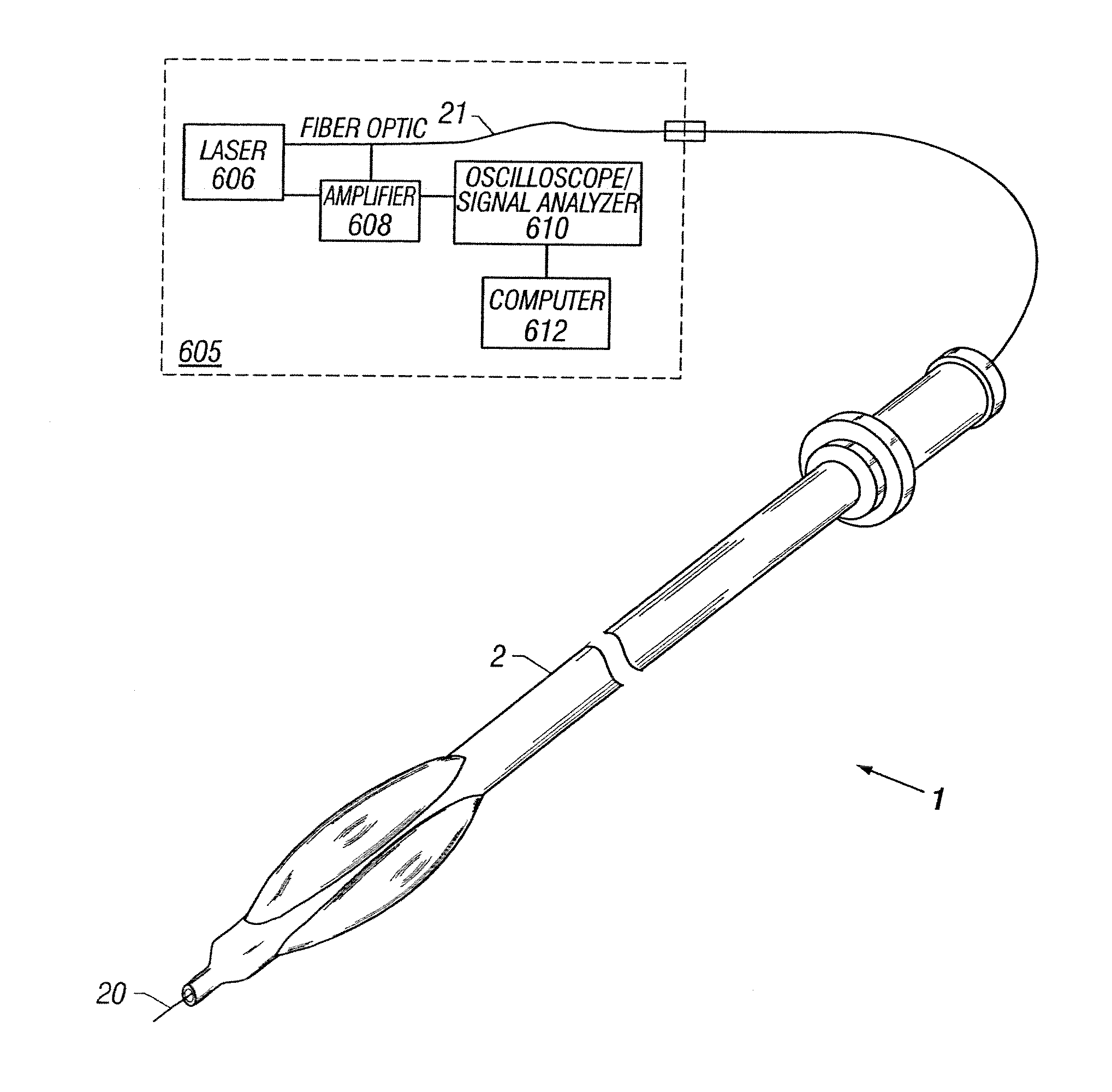
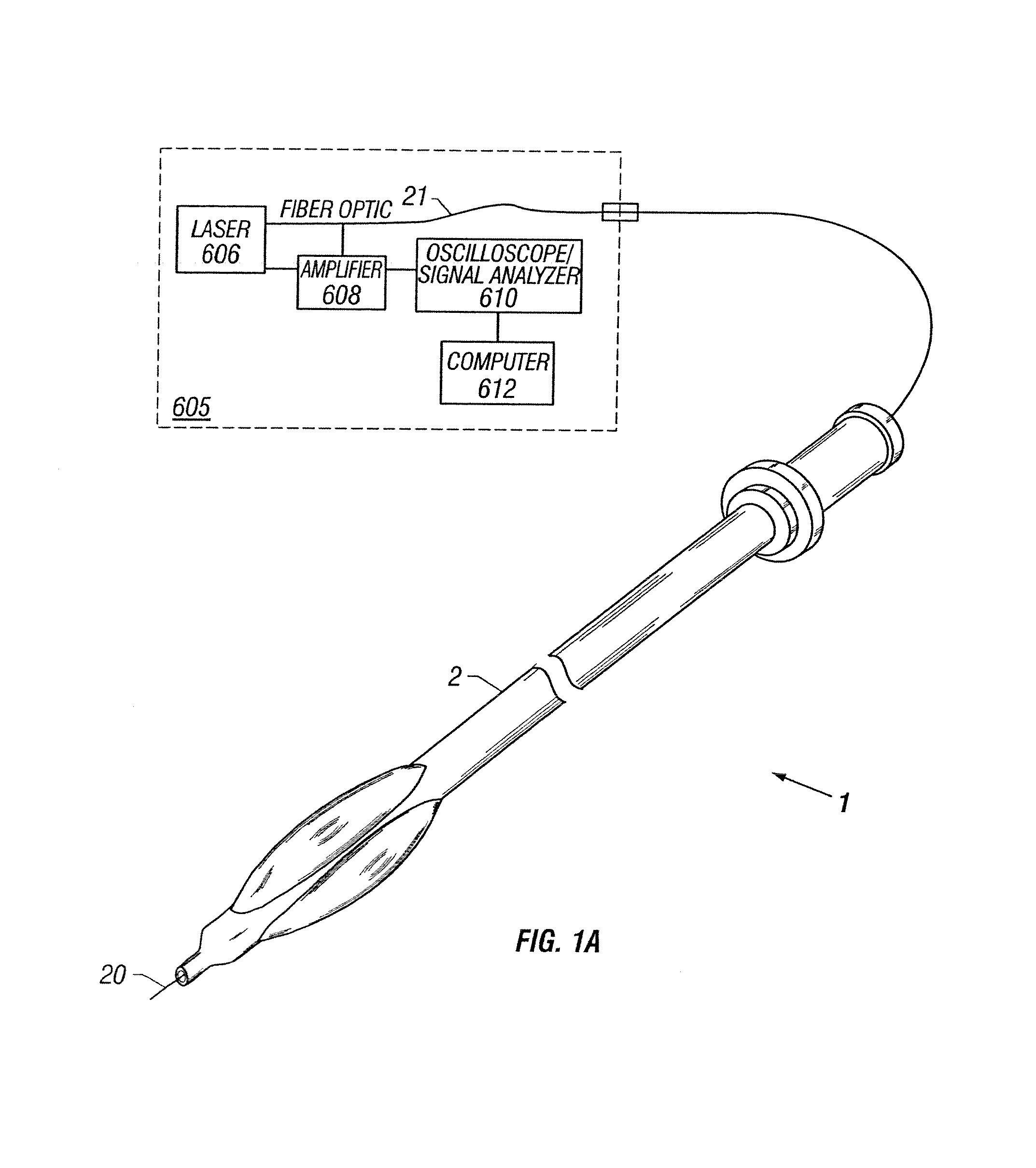
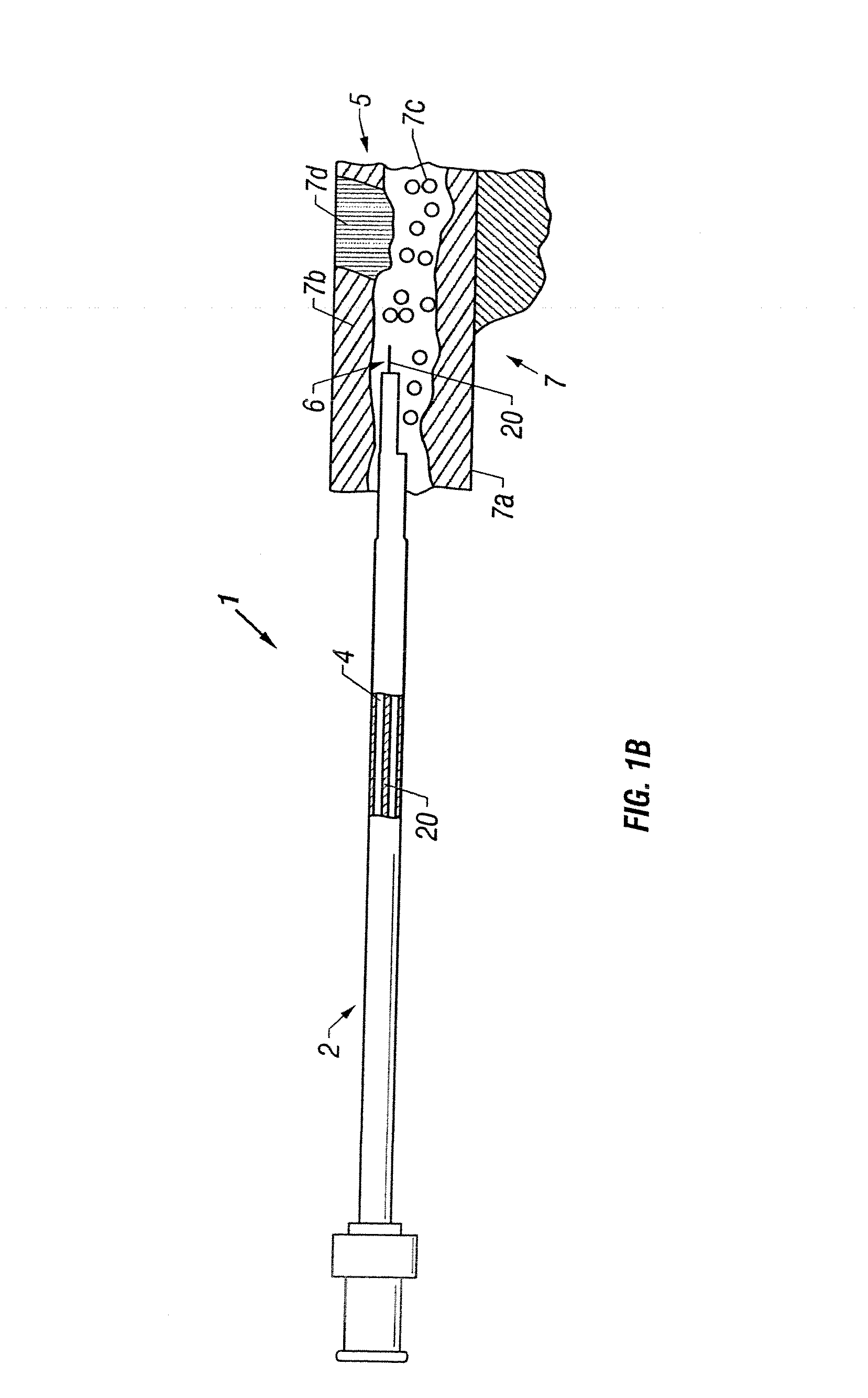
Apparatus and method to perform therapeutic treatment and diagnosis of a patient's vasculature through the use of an intravascular device having an optical fiber disposed therein. In an embodiment of this invention, the apparatus includes a therapeutic guidewire and at least one optical fiber disposed through the therapeutic guidewire, the optical fiber capable of providing diagnostic information before, during, and after the therapeutic treatment. In an embodiment, diagnostic information includes vessel and blood characteristics such as hemodynamic characteristics, hematological parameters related to blood and blood components, and thermal parameters of the vasculature.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
System and methods for performing endovascular procedures
InactiveUS20060058775A1Procedure is complicatedEasy to controlStentsGuide needlesExtracorporeal circulationAtherectomy
A system for inducing cardioplegic arrest and performing an endovascular procedure within the heart or blood vessels of a patient. An endoaortic partitioning catheter has an inflatable balloon which occludes the ascending aorta when inflated. Cardioplegic fluid may be infused through a lumen of the endoaortic partitioning catheter to stop the heart while the patient's circulatory system is supported on cardiopulmonary bypass. One or more endovascular devices are introduced through an internal lumen of the endoaortic partitioning catheter to perform a diagnostic or therapeutic endovascular procedure within the heart or blood vessels of the patient. Surgical procedures such as coronary artery bypass surgery or heart valve replacement may be performed in conjunction with the endovascular procedure while the heart is stopped. Embodiments of the system are described for performing: fiberoptic angioscopy of structures within the heart and its blood vessels, valvuloplasty for correction of valvular stenosis in the aortic or mitral valve of the heart, angioplasty for therapeutic dilatation of coronary artery stenoses, coronary stenting for dilatation and stenting of coronary artery stenoses, atherectomy or endarterectomy for removal of atheromatous material from within coronary artery stenoses, intravascular ultrasonic imaging for observation of structures and diagnosis of disease conditions within the heart and its associated blood vessels, fiberoptic laser angioplasty for removal of atheromatous material from within coronary artery stenoses, transmyocardial revascularization using a side-firing fiberoptic laser catheter from within the chambers of the heart, and electrophysiological mapping and ablation for diagnosing and treating electrophysiological conditions of the heart.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
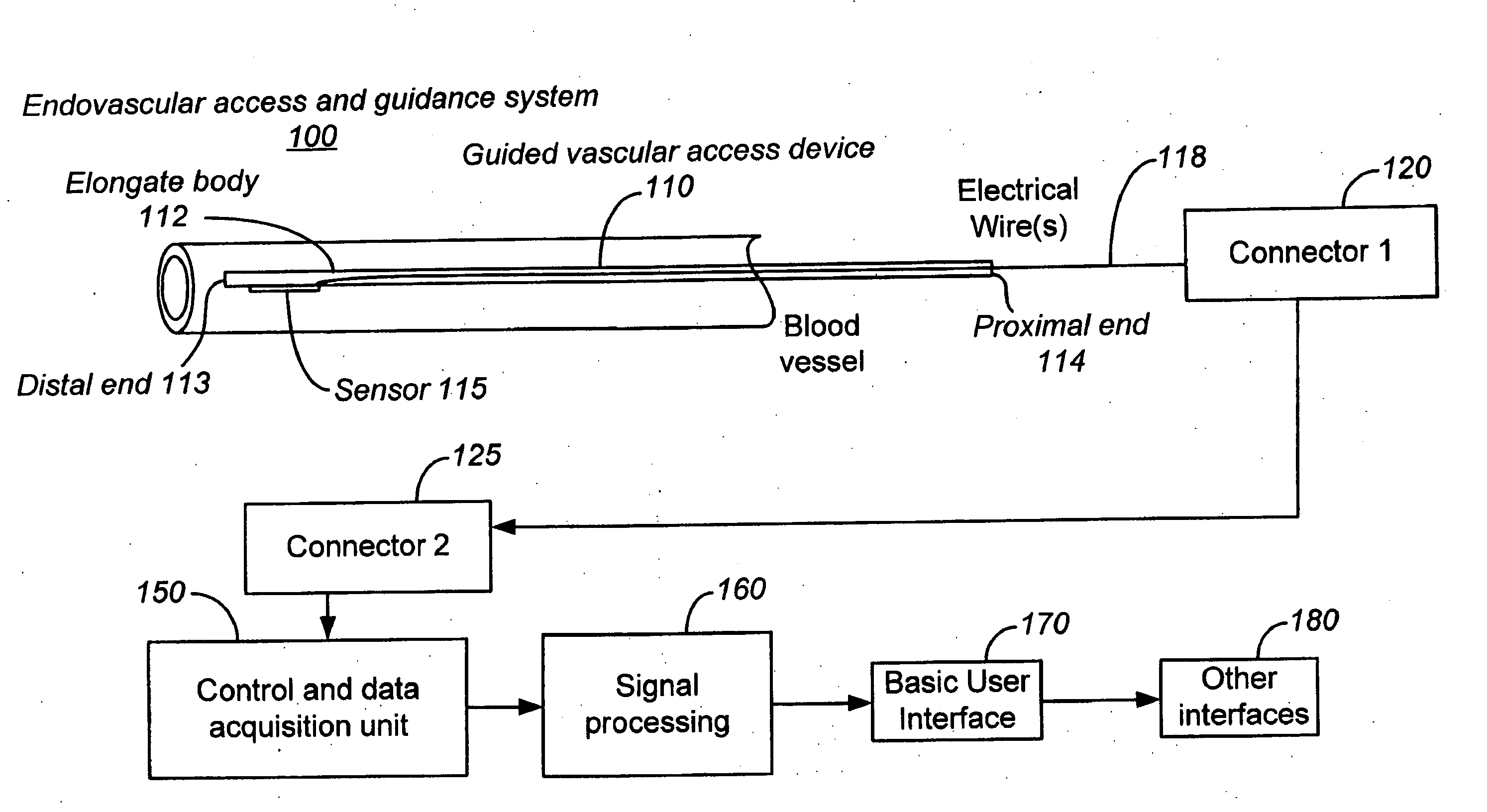
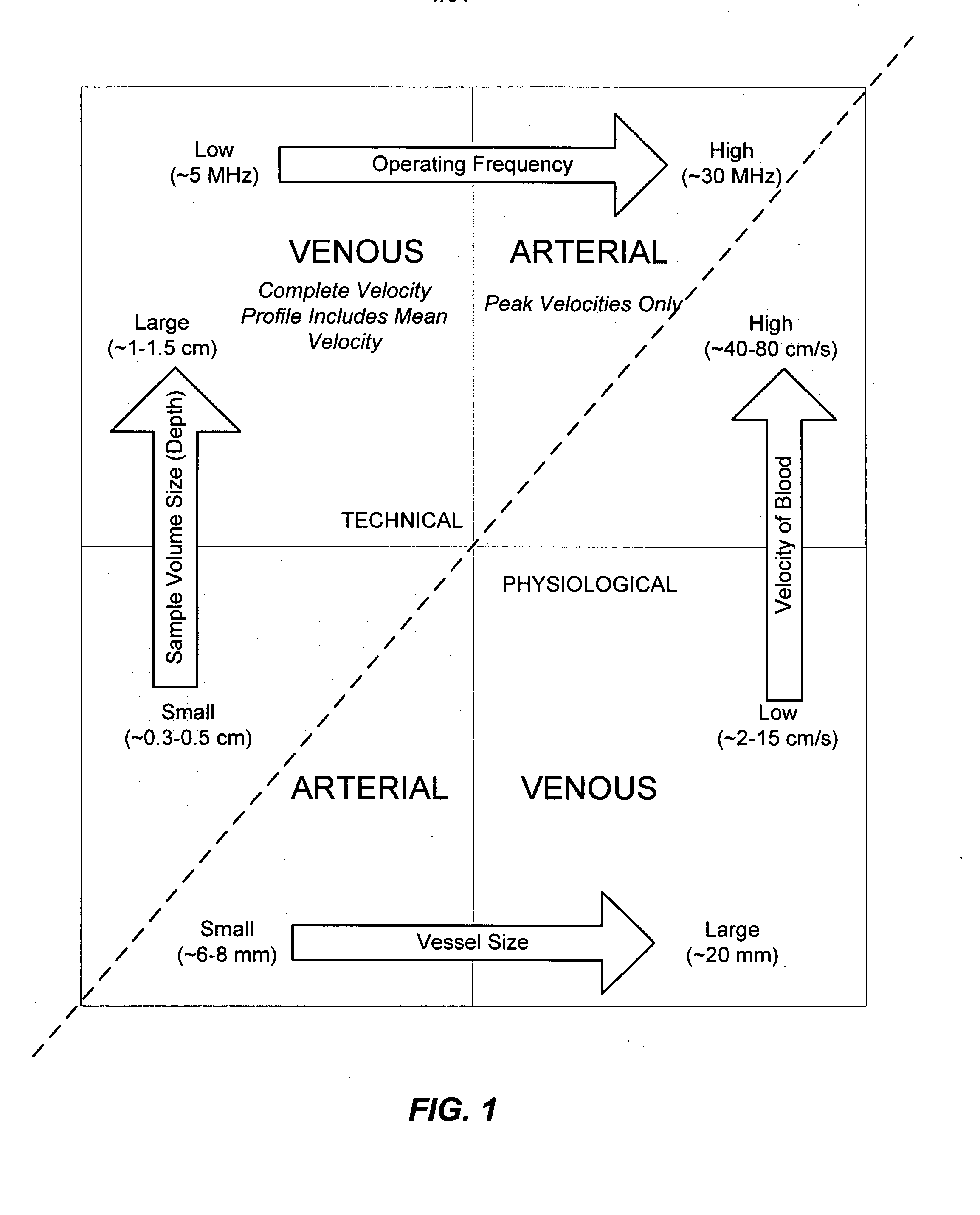
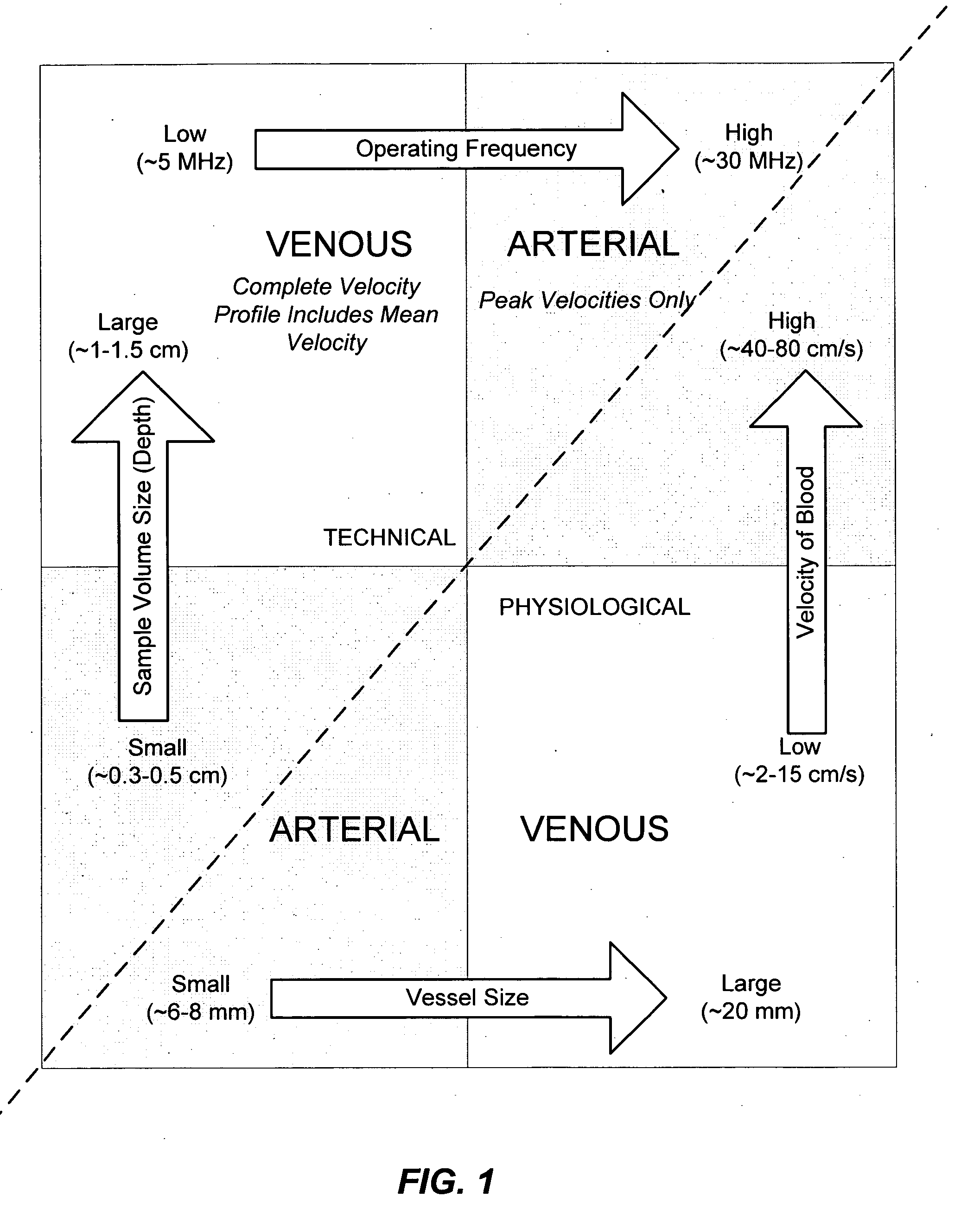
Apparatus and Method for Endovascular Device Guiding and Positioning Using Physiological Parameters
ActiveUS20090005675A1Improve accuracyImpede advancementStethoscopeHeart/pulse rate measurement devicesGuidance systemMedicine
An endovascular access and guidance system has an elongate body with a proximal end and a distal end; a non-imaging ultrasound transducer on the elongate body configured to provide in vivo non-image based ultrasound information of the vasculature of the patient; an endovascular electrogram lead on the elongate body in a position that, when the elongate body is in the vasculature, the endovascular electrogram lead electrical sensing segment provides an in vivo electrogram signal of the patient; a processor configured to receive and process a signal from the non-imaging ultrasound transducer and a signal from the endovascular electrogram lead; and an output device configured to display a result of information processed by the processor. An endovascular device has an elongate body with a proximal end and a distal end; a non-imaging ultrasound transducer on the elongate body; and an endovascular electrogram lead on the elongate body in a position that, when the endovascular device is in the vasculature, the endovascular electrogram lead is in contact with blood. The method of positioning an endovascular device in the vasculature of a body is performed by advancing the endovascular device into the vasculature; transmitting a non-imaging ultrasound signal into the vasculature using a non-imaging ultrasound transducer on the endovascular device; receiving a reflected ultrasound signal with the non-imaging ultrasound transducer; detecting an endovascular electrogram signal with a sensor on the endovascular device; processing the reflected ultrasound signal received by the non-imaging ultrasound transducer and the endovascular electrogram signal detected by the sensor; and positioning the endovascular device based on the processing step.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
Endovenous access and guidance system utilizing non-image based ultrasound
The invention relates to the guidance, positioning and placement confirmation of intravascular devices, such as catheters, stylets, guidewires and other flexible elongate bodies that are typically inserted percutaneously into the venous or arterial vasculature. Currently these goals are achieved using x-ray imaging and in some cases ultrasound imaging. This invention provides a method to substantially reduce the need for imaging related to placing an intravascular catheter or other device. Reduced imaging needs also reduce the amount of radiation that patients are subjected to, reduce the time required for the procedure, and decrease the cost of the procedure by reducing the time needed in the radiology department. An aspect of the invention includes, for example, an endovenous access and guidance system. The system comprises: an elongate flexible member adapted and configured to access the venous vasculature of a patient; a sensor disposed at a distal end of the elongate flexible member and configured to provide in vivo non-image based ultrasound information of the venous vasculature of the patient; a processor configured to receive and process in vivo non-image based ultrasound information of the venous vasculature of the patient provided by the sensor and to provide position information regarding the position of the distal end of the elongate flexible member within the venous vasculature of the patient; and an output device adapted to output the position information from the processor.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
Intravascular device and system
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
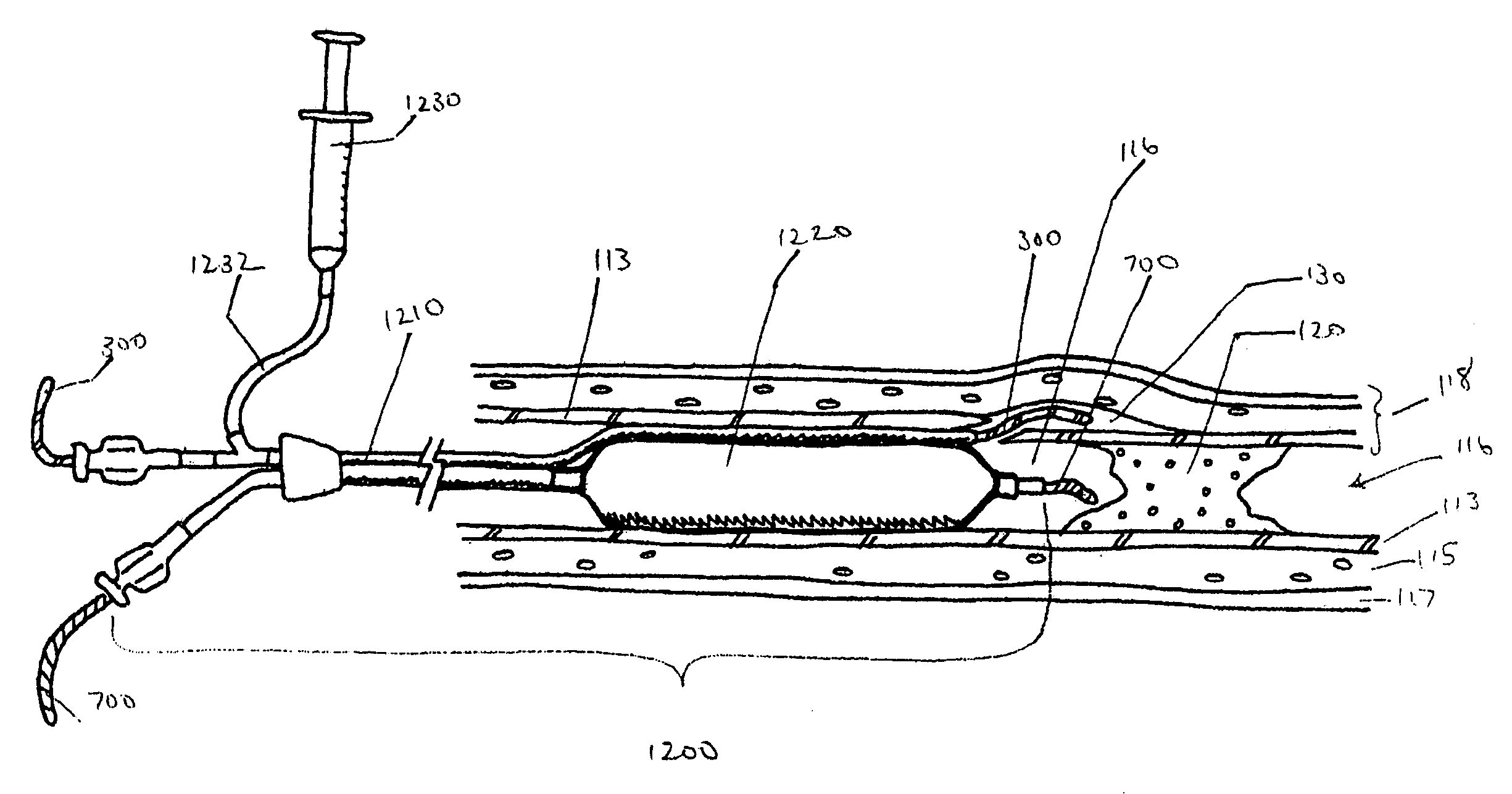
Unfolding balloon catheter for proximal embolus protection
Devices, systems and methods for removing foreign bodies within a body lumen are disclosed. An unfolding balloon catheter may include an elongated shaft having an intussuscepting balloon that can be actuated within a body lumen to capture and retrieve an intravascular device. The balloon may be configured to radially and / or axially expand when inflated, enveloping the intravascular device. In certain embodiments, the balloon may be formed by folding the ends of a distensible member inwardly, and then bonding the ends of the distensible member to the elongated shaft to form an expandable sleeve. An adhesive layer located along a portion of the elongated shaft may be used to temporarily secure the balloon to the elongated shaft.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC +1
Intravascular devices and fibrosis-inducing agents
InactiveUS20050149175A1Reducing perigraft leakageFacilitate “anchoring”StentsPeptide/protein ingredientsFibrosisCoil embolization
Intravascular devices (e.g., stents, stent grafts, covered stents, aneurysm coils, embolic agents and drug delivery catheters and balloons) are used in combination with fibrosing agents in order to induce fibrosis that may otherwise not occur when the implant is placed within an animal or to promote fibrosis betweent the devices and the host tissues. Compositions and methods are described for use in the treatment of aneurysms and unstable arterial (vulnerable) plaque.
Owner:ANGIOTECH INT AG (CH)
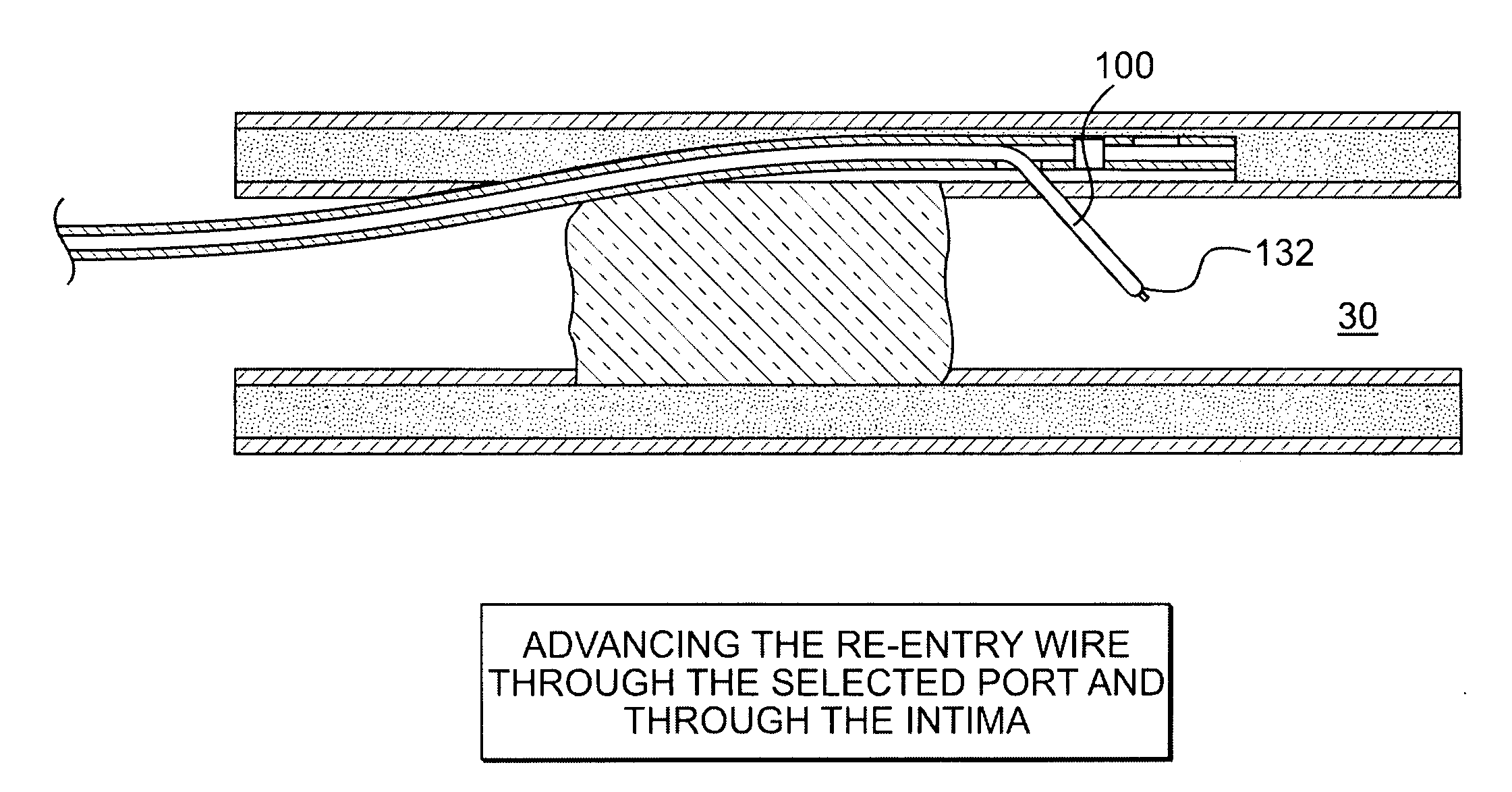
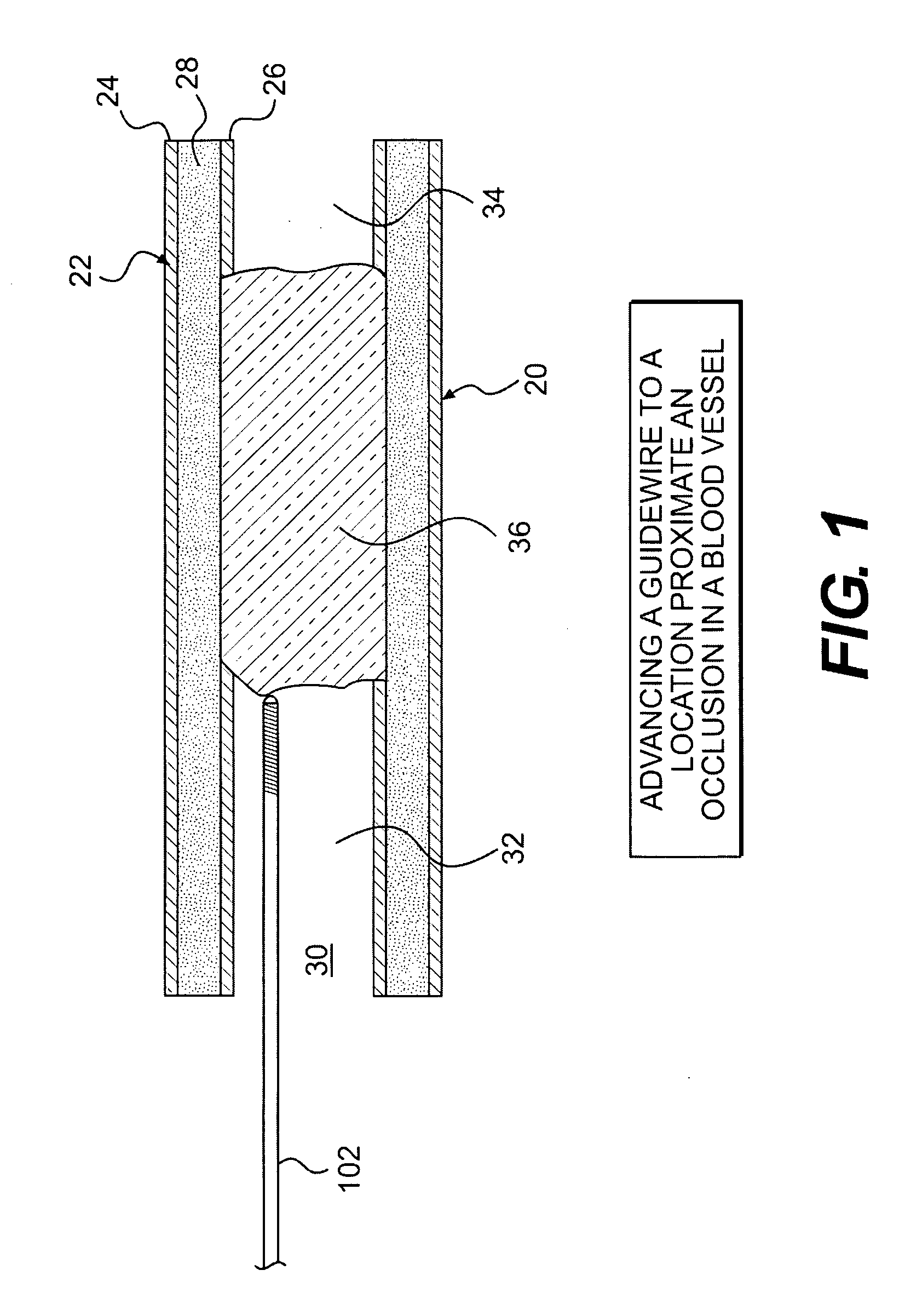
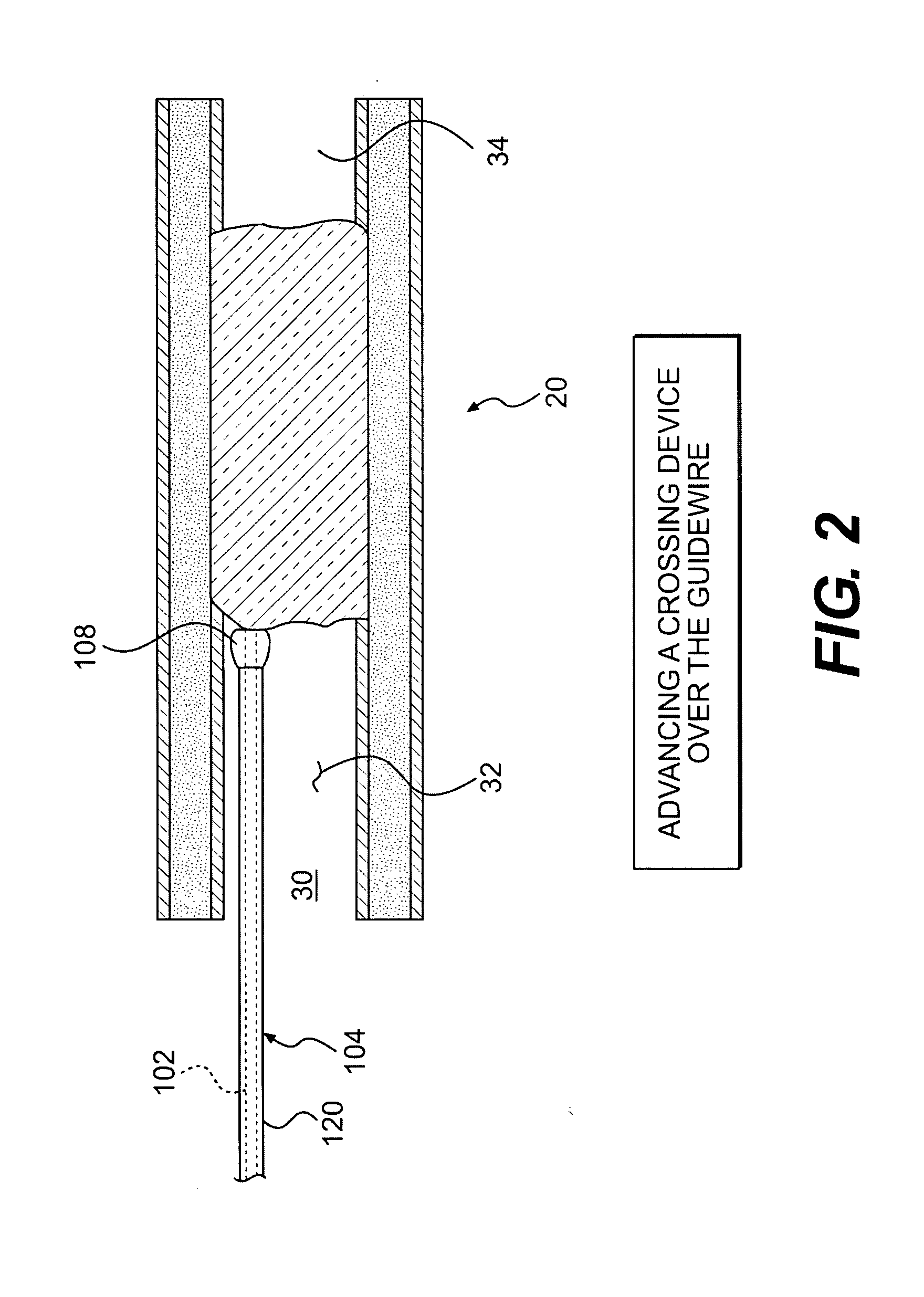
Crossing occlusions in blood vessels
The present disclosure is directed a method of facilitating treatment via a vascular wall defining a vascular lumen containing an occlusion therein. The method may include providing a first intravascular device having a distal portion and at least one aperture and positioning the distal portion of the first intravascular device in the vascular wall. The method may further include providing a reentry device having a body and a distal tip, the distal tip having a natural state and a compressed state and inserting the distal tip, in the compressed state, in the distal portion of the first intravascular device. The method may further include advancing the distal tip, in the natural state, through the at least one aperture of the first intravascular device.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Means for controlled sealing of endovascular devices
InactiveUS20130190857A1Improve sealingEliminate prosthetic-annular incongruenceStentsHeart valvesProsthesisFunctional integrity
Expandable sealing means for endoluminal devices have been developed for controlled activation. The devices have the benefits of a low profile mechanism (for both self-expanding and balloon-expanding prostheses), contained, not open, release of the material, active conformation to the “leak sites” such that leakage areas are filled without disrupting the physical and functional integrity of the prosthesis, and on-demand, controlled activation, that may not be pressure activated.
Owner:ENDOLUMINAL SCI
Endovascular device with membrane
Owner:MERLIN MD PTE
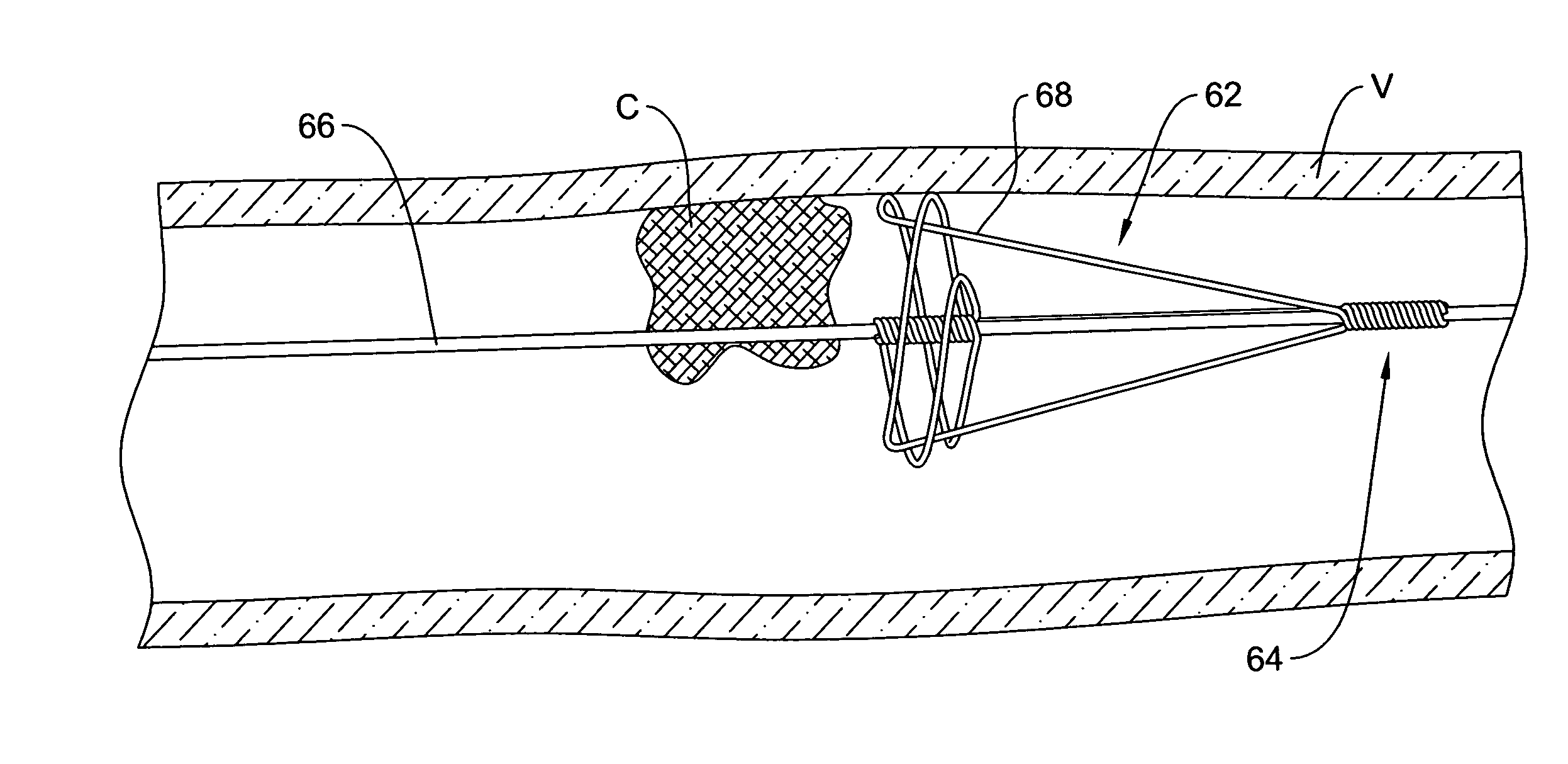
Endovascular device for entrapment of particulate matter and method for use
A device and method for protecting a blood vessel, and hence bodily tissues, against damage caused by particulate such as an embolus. The device may be a stent, for insertion in a large artery such as the ascending aorta, and may be combined with a filter. In one embodiment, the device includes an outer wire frame rather than a stent. The stent may be made of at least one layer of mesh, which is typically attached or mounted to the arterial wall. Typically only part of the stent is attached (for example at a reinforcing ring structure). Typically the size of the apertures of the mesh at the top portion of the stent is smaller than the bottom portion of the stent. The device and method are particularly useful in preventing blockages of flow to the brain, but have other uses as well. An electric charge may be placed on the device, for example, to prevent blood components from collecting.
Owner:KEYSTONE HEART
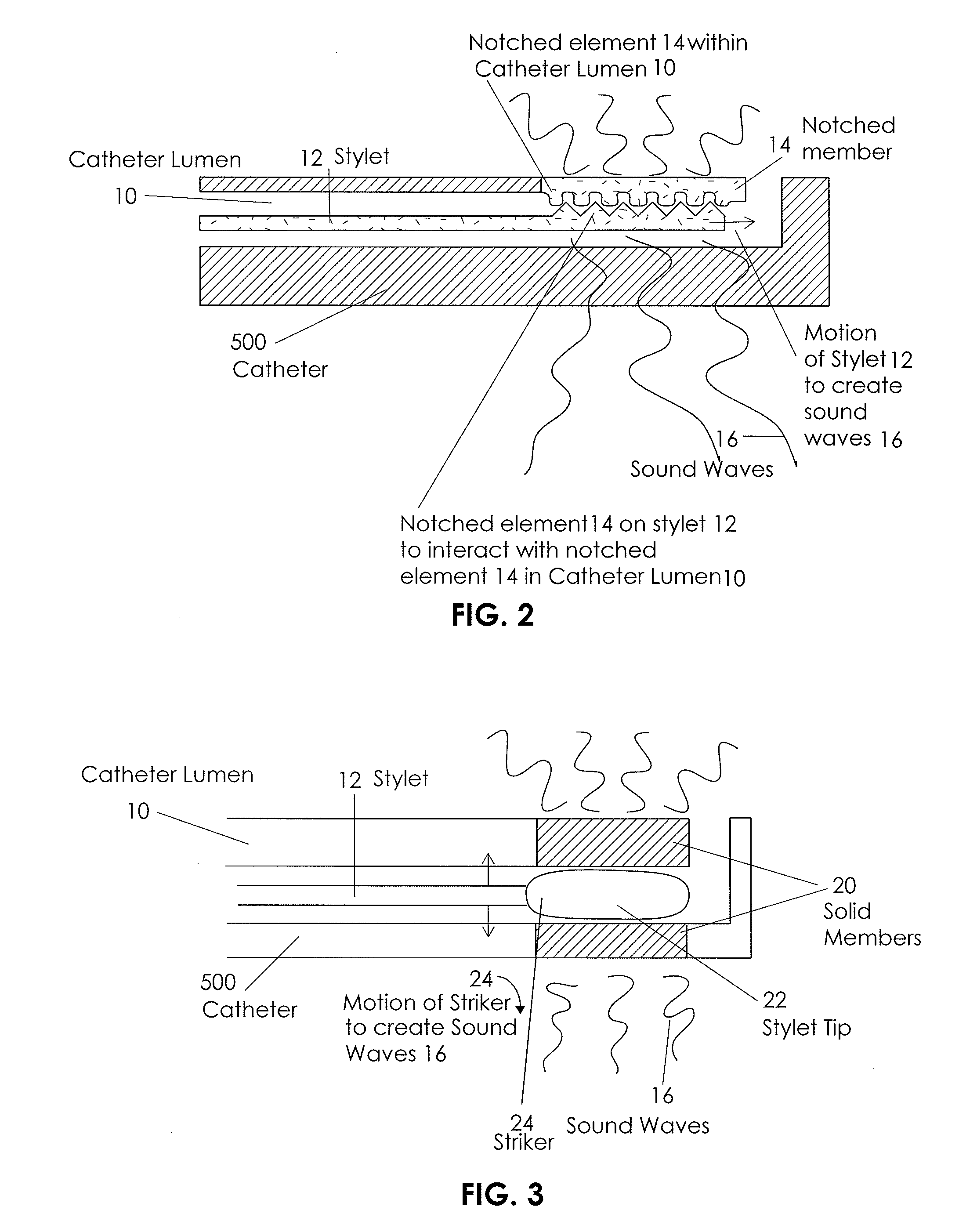
Apparatus and Method for Vascular Access
InactiveUS20090118612A1Reduce the amount requiredReduce needData processing applicationsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesVeinX-ray
In an aspect, embodiments of the invention relate to the effective and accurate placement of intravascular devices such as central venous catheters, in particular such as peripherally inserted central catheters or PICC. One aspect of the present invention relates to vascular access. It describes devices and methods for imaging guided vascular access and more effective sterile packaging and handling of such devices. A second aspect of the present invention relates to the guidance, positioning and placement confirmation of intravascular devices without the help of X-ray imaging. A third aspect of the present invention relates to devices and methods for the skin securement of intravascular devices and post-placement verification of location of such devices. A forth aspect of the present invention relates to improvement of the workflow required for the placement of intravascular devices.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
Means for Controlled Sealing of Endovascular Devices
Expandable sealing means for endoluminal devices have been developed for controlled activation. The devices have the benefits of a low profile mechanism (for both self-expanding and balloon-expanding prostheses), contained, not open, release of the material, active conformation to the “leak sites” such that leakage areas are filled without disrupting the physical and functional integrity of the prosthesis, and on-demand, controlled activation, that may not be pressure activated.
Owner:ENDOLUMINAL SCI
Endovascular device for application of prosthesis with sutures
An endovascular surgical device is disclosed for attaching an endovascular prosthesis to a vascular wall. The device includes a tubular member and an applicator device. The tubular member has longitudinal bands separated by slots that are configured to expand upon being placed in compression. The applicator device has a distal end with a rotary head for applying sutures. A portion of the suture is at least partially positioned in the rotary head. A method is described that includes positioning a prosthesis and an endovascular device within a portion of vascular wall that requires reinforcing or repairing. The tubular part is expanded, forcing the prosthesis and vascular wall to expand. The applicator device applies the suture to attach the prosthesis to the vascular wall. Additional sutures can be applied by removing the applicator device, attaching a second suture and repositioning the applicator device to attach a second suture.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Endovascular access and guidance system utilizing divergent beam ultrasound
The invention relates to the guidance, positioning and placement confirmation of intravascular devices, such as catheters, stylets, guidewires and other flexible elongate bodies that are typically inserted percutaneously into the venous or arterial vasculature. Currently these goals are achieved using x-ray imaging and in some cases ultrasound imaging. This invention provides a method to substantially reduce the need for imaging related to placing an intravascular catheter or other device. Reduced imaging needs also reduce the amount of radiation that patients are subjected to, reduce the time required for the procedure, and decrease the cost of the procedure by reducing the time needed in the radiology department. An aspect of the invention includes, for example, an endovenous access and guidance system. The system comprises: an elongate flexible member adapted and configured to access the venous vasculature of a patient; a sensor disposed at a distal end of the elongate flexible member and configured to provide in vivo non-image based ultrasound information of the venous vasculature of the patient; a processor configured to receive and process in vivo non-image based ultrasound information of the venous vasculature of the patient provided by the sensor and to provide position information regarding the position of the distal end of the elongate flexible member within the venous vasculature of the patient; and an output device adapted to output the position information from the processor.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
Catheter with optical fiber sensor
An apparatus and method to perform therapeutic treatment and diagnosis of a patient's vasculature through the use of an intravascular device having an optical fiber disposed therein. In an embodiment, the apparatus includes an intravascular device to perform a therapeutic treatment and at least one optical fiber disposed through the intravascular device. The optical fiber is configured to provide diagnostic information before, during, and after the therapeutic treatment. In an embodiment, diagnostic information includes vessel and blood characteristics such as hemodynamic characteristics, hematological parameters related to blood and blood components, and thermal parameters of the vasculature.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Endovascular devices and methods for exploiting intramural space
ActiveUS20070093780A1Convenient treatmentBypass occlusionStentsMulti-lumen catheterVascular lumenDistal portion
Devices and methods for the treatment of chronic total occlusions are provided. One disclosed embodiment comprises a method of facilitating treatment via a vascular wall defining a vascular lumen containing an occlusion therein. The method includes providing a first intravascular device having a distal portion with a concave side, inserting the first device into the vascular lumen, positioning the distal portion in the vascular wall, and orienting the concave side of the distal portion toward the vascular lumen.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
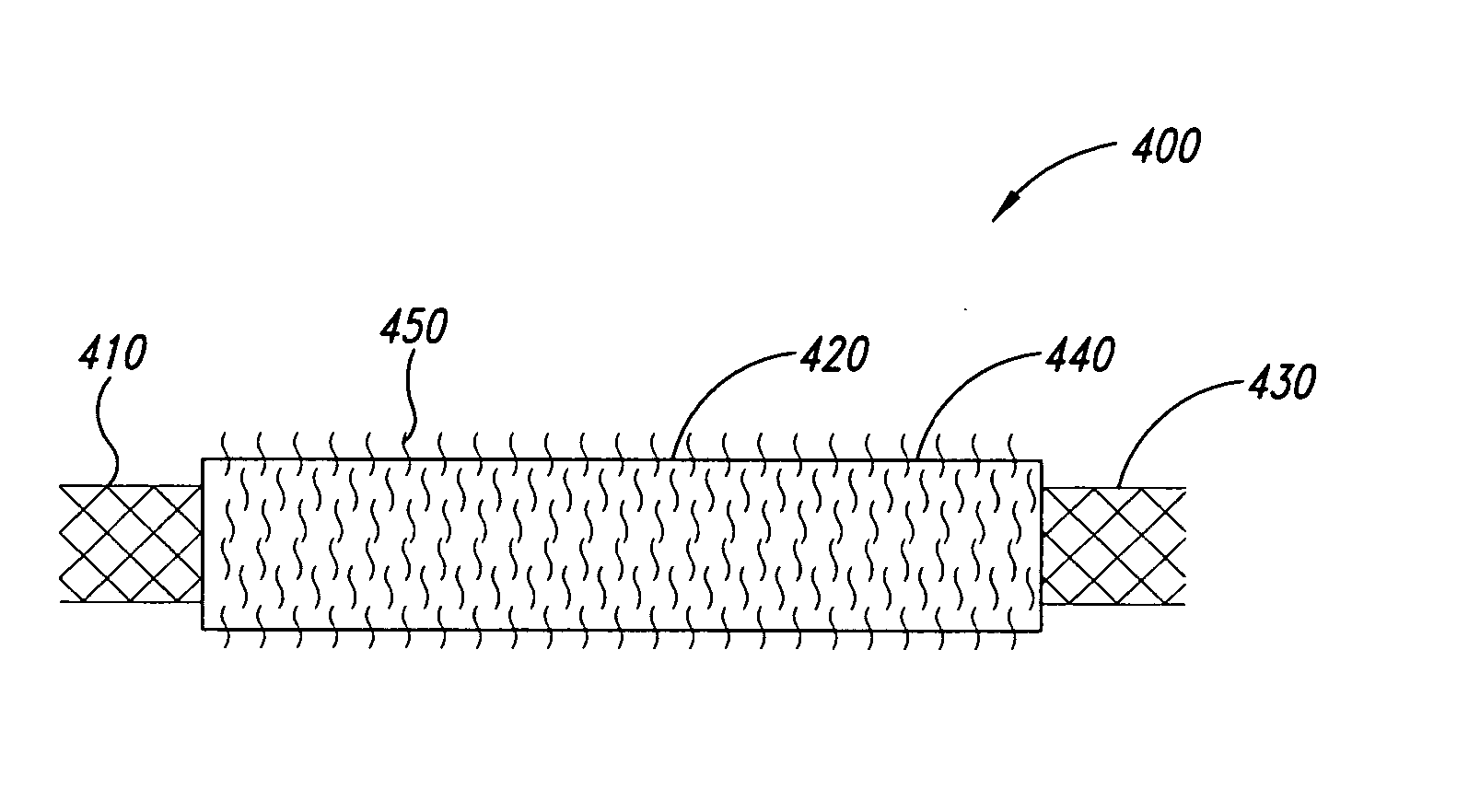
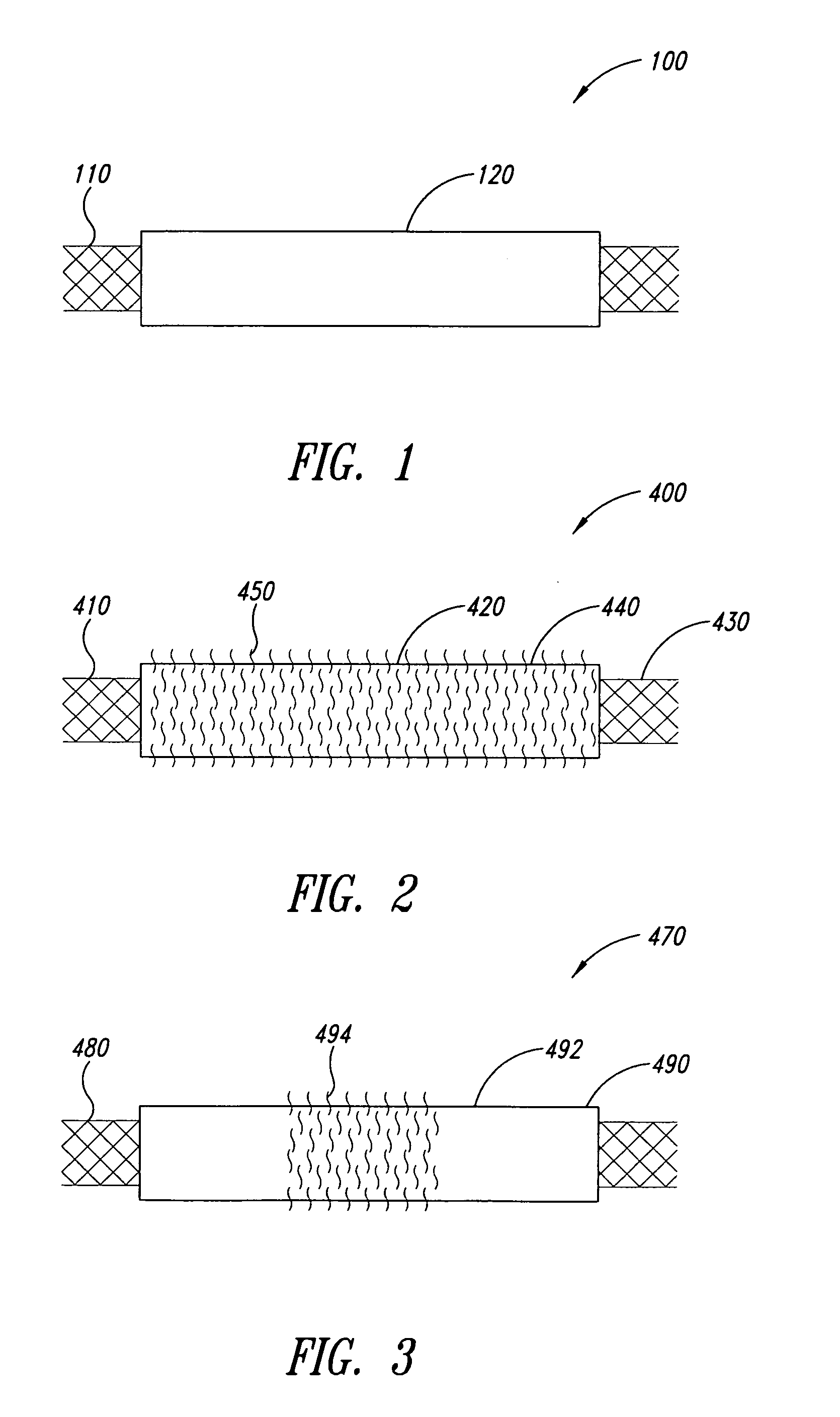
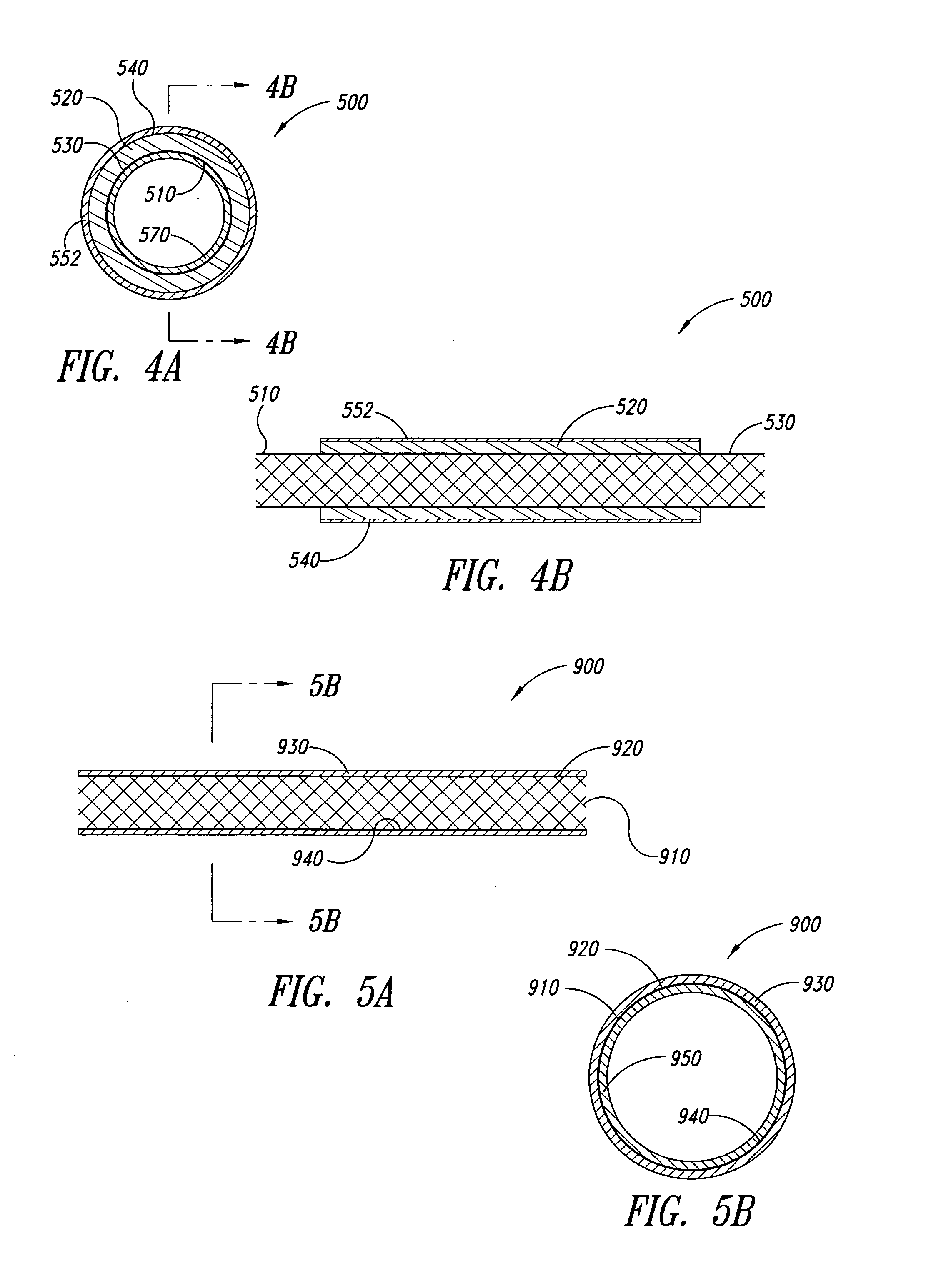
Multi-braid exterior tube
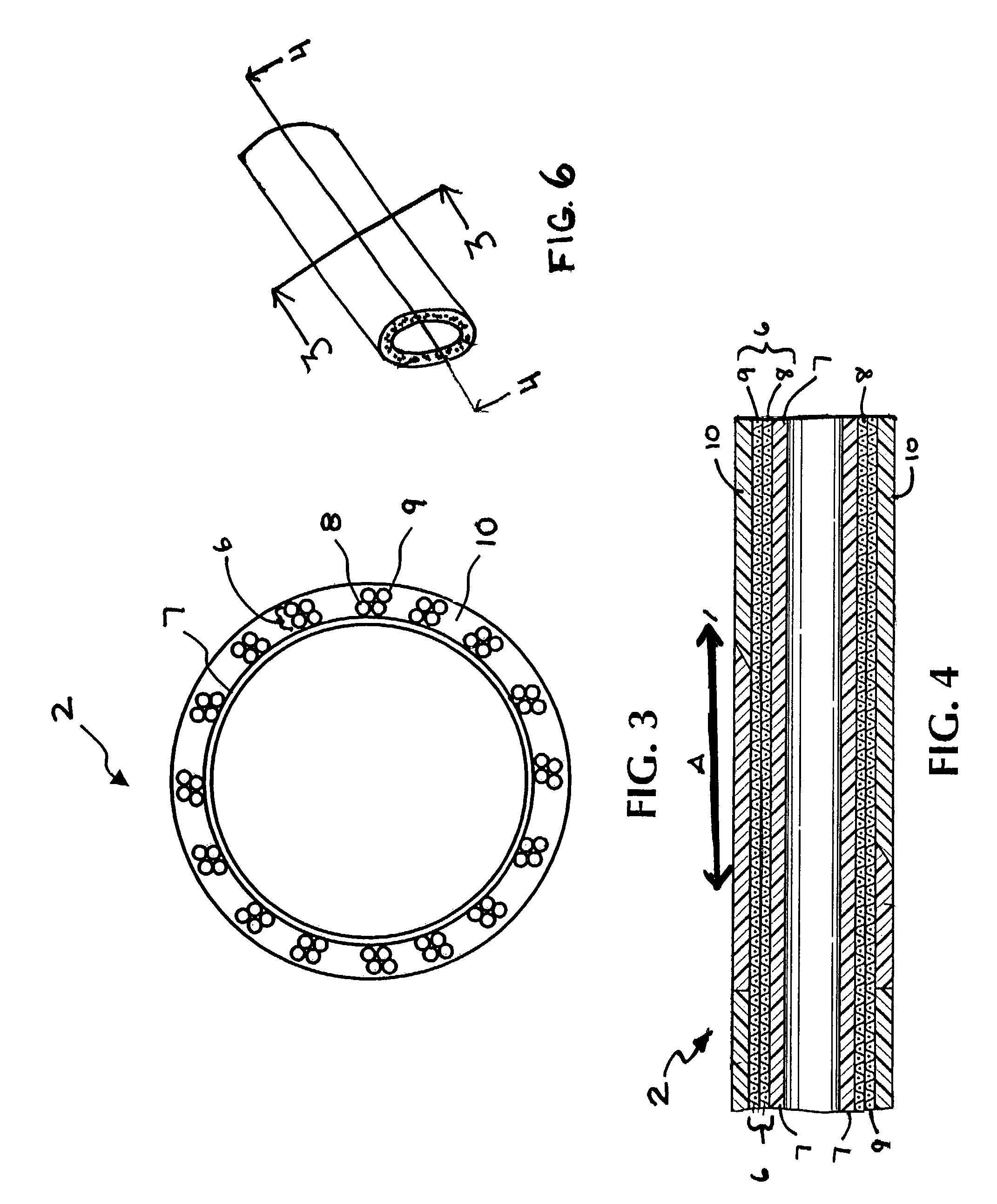
InactiveUS7438712B2Reduce frictional contactAvoid abrasionsGuide needlesStentsCompound structureUltimate tensile strength
A multiple braid exterior tube having a composite structure which includes an inner tubular layer, reinforcing layers and a polymer matrix layer. The exterior tube is formed with polymeric materials and metallic reinforcing braiding configured to provide greater tensile strength and stiffness. The exterior tube is used for a variety of medical devices such as a sheath component for intravascular devices and catheters.
Owner:LIFESHIELD SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com