Patents
Literature
379results about How to "Decreased blood flow" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Apparatus and method for treating tumors near the surface of an organ
InactiveUS6337998B1Avoid flowPrevent heat lossElectrotherapySurgical needlesAbnormal tissue growthTherapeutic Area
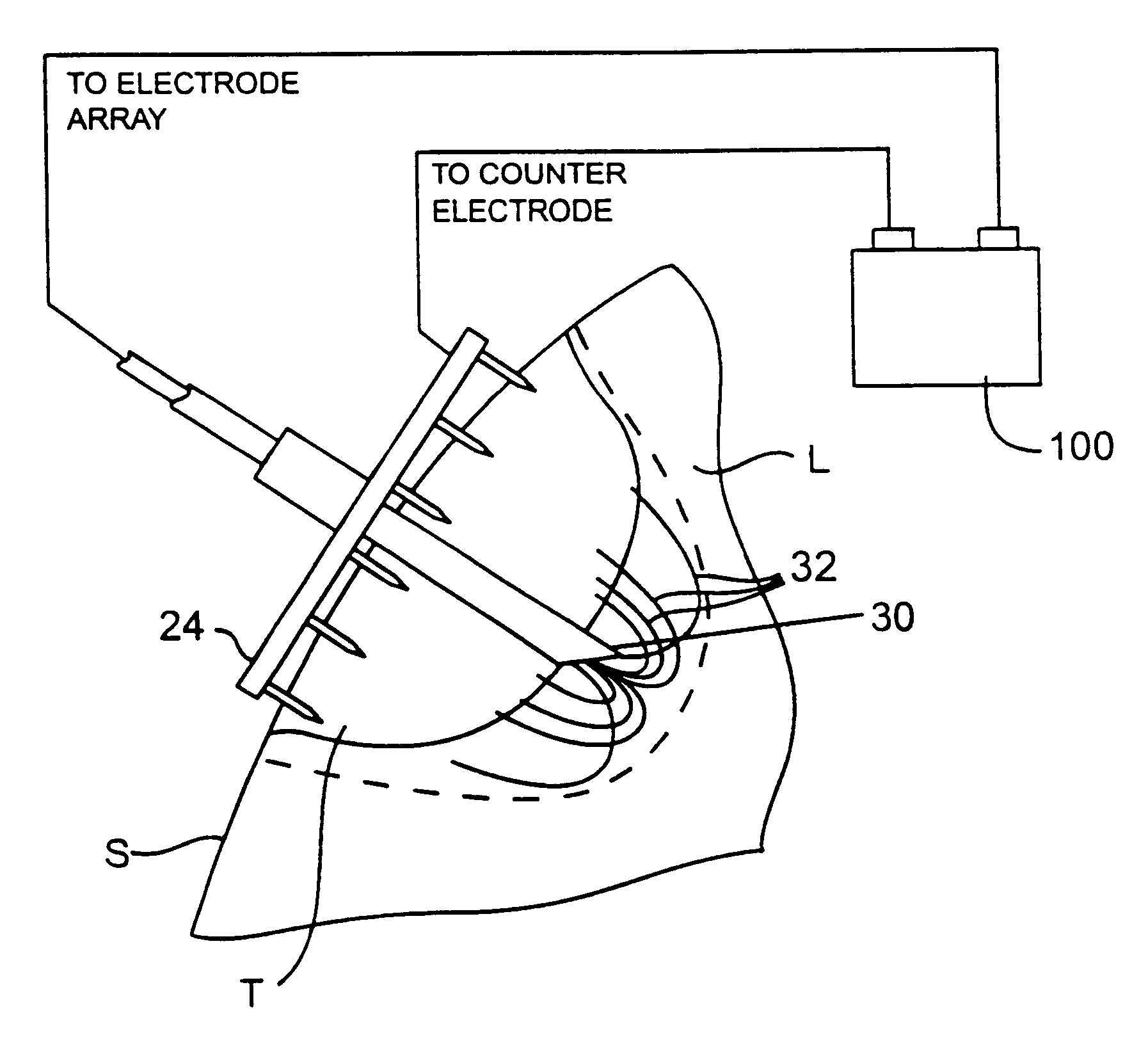
A system for treating a target region in tissue beneath a tissue surface comprises a probe for deploying an electrode array within the tissue and a surface electrode for engaging the tissue surface above the treatment site. Preferably, surface electrode includes a plurality of tissue-penetrating elements which advance into the tissue, and the surface electrode is removably attachable to the probe. The tissue may be treated in a monopolar fashion where the electrode array and surface electrode are attached to a common pole on an electrode surgical power supply and powered simultaneously or successively, or in a bipolar fashion where the electrode array and surface electrode are attached to opposite poles of the power supply. The systems are particularly useful for treating tumors and other tissue treatment regions which lie near the surface.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Intra-aortic renal drug delivery catheter
InactiveUS7329236B2Avoid and limit detrimental effectIncrease concentrationBalloon catheterMulti-lumen catheterDiagnostic agentGuide tube
A catheter for delivering a therapeutic or diagnostic agent to a branch blond vessel of a major blood vessel comprises an elongated shaft having at least one lumen in fluid communication with an agent delivery port in a distal section of the shaft, an expandable tubular member on the distal section of the shaft, and a radially expandable member on the tubular member. The tubular member is configured to extend within the blood vessel up-stream and down-stream of a branch vessel, and has an interior passageway which is radially expandable within the blood vessel to separate blood flow through the blood vessel into an outer blood flow stream exterior to the tubular member and an inner blood flow stream within the interior passageway of the tubular member.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
Medical device suitable for use in treatment of a valve
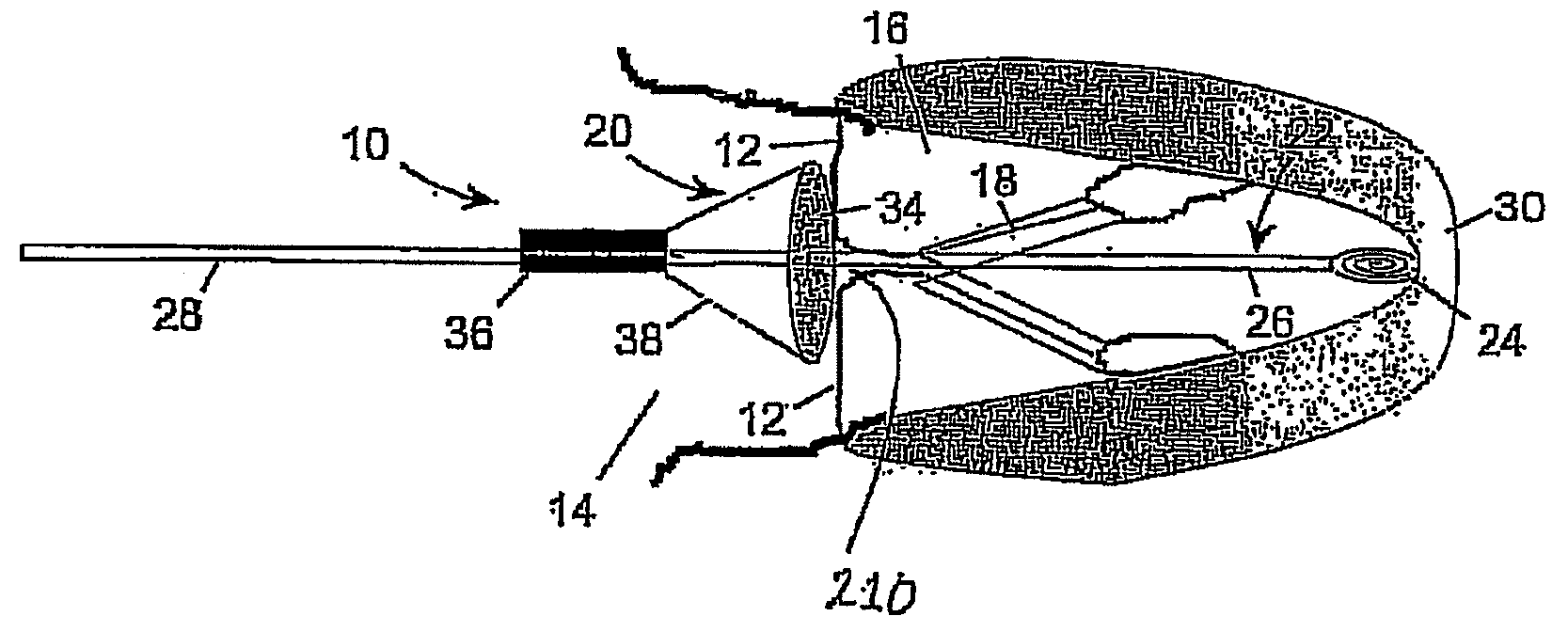
InactiveUS20060178700A1Prevent leakageProfound clinical consequencesSuture equipmentsHeart valvesSeptal wallMedical device
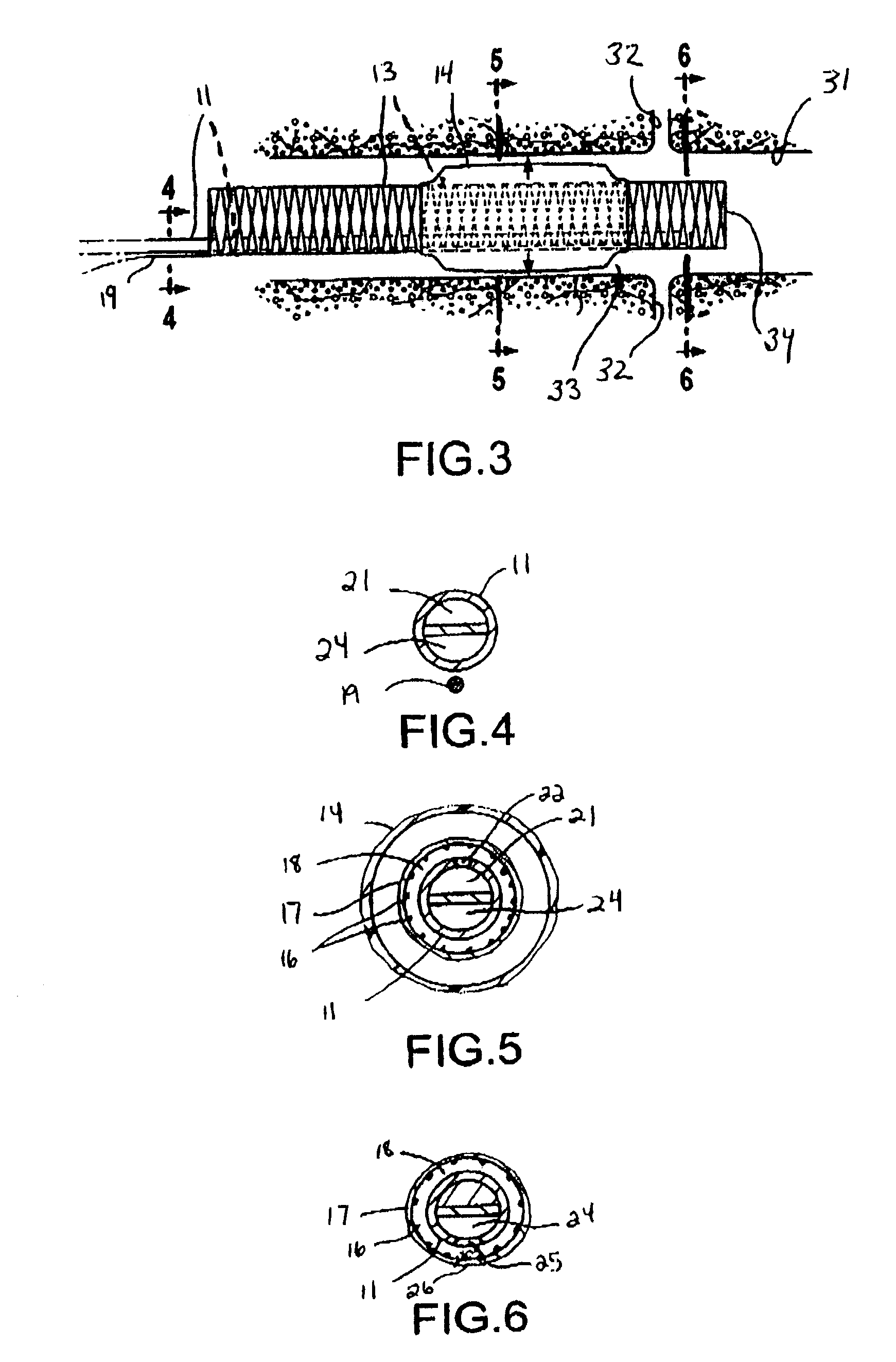
A medical device (1210) comprises a generally cylindrical treatment element (1220) for location between a pair of valve leaflets (1212) situated between an atrium (1214) and a ventricle (1216) of a heart. The treatment element (1220) supports the valve leaflets (1212) at the region of co-aptation of the valve leaflets (1212) and occludes the valve opening to resist fluid flow in the retrograde direction through the valve opening. The device (1210) comprises a support (1222) to support the treatment element (1210) at the region of co-aptation of the valve leaflets (1212). The support has an anchor (1224) and a tether (1226), the tether (1226) being provided at the end of a guide wire (1228) which is initially utilised in the percutaneous insertion of the treatment element (1220). The anchor (1224) is secured, in use, to a septal wall (1230), while the guide wire (1228) exits the atrium (1214) through a vein adjacent a rear wall (1224) thereof. The treatment element (1220) includes a remotely actuatable clamp therein, in order to allow the treatment element (1220) to be secured to the guide wire (1228) or the tether (1226).
Owner:MEDNUA
Modulation and analysis of cerebral perfusion in epilepsy and other neurological disorders
InactiveUS20060265022A1Increase perfusionReduce perfusionElectroencephalographyUltrasound therapyDiseaseNervous system
A system including an implantable neurostimulator device capable of modulating cerebral blood flow to treat epilepsy and other neurological disorders. In one embodiment, the system is capable of modulating cerebral blood flow (also referred to as cerebral perfusion) in response to measurements and other observed conditions. Perfusion may be increased or decreased by systems and methods according to the invention as clinically required.
Owner:NEUROPACE
Method and device for performing cooling or cryo-therapies, for, e.g., angioplasty with reduced restenosis or pulmonary vein cell necrosis to inhibit atrial fibrillation employing tissue protection
InactiveUS7001378B2Minimize and inhibit bio-chemical eventRobust designCatheterSurgical instruments for heatingPercent Diameter StenosisPercutaneous angioplasty
An enhanced method and device are provided to treat atrial fibrillation or inhibit or reduce restenosis following angioplasty or stent placement. A balloon-tipped catheter is disposed in the area treated or opened through balloon angioplasty immediately following angioplasty. The balloon, which can have a dual balloon structure, may be delivered through a guiding catheter and over a guidewire already in place. A fluid such as a perfluorocarbon flows into the balloon to freeze the tissue adjacent the balloon, this cooling being associated with reduction of restenosis. A similar catheter may be used to reduce atrial fibrillation by inserting and inflating the balloon such that an exterior surface of the balloon contacts at least a partial circumference of the portion of the pulmonary vein adjacent the left atrium. In another embodiment, blood perfusion is performed simultaneously. In another embodiment, tissue contacted by the cryoablation catheter, undesired to be ablated, is protected against damage by a separate heating step.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
Exclusion Device and System For Delivery
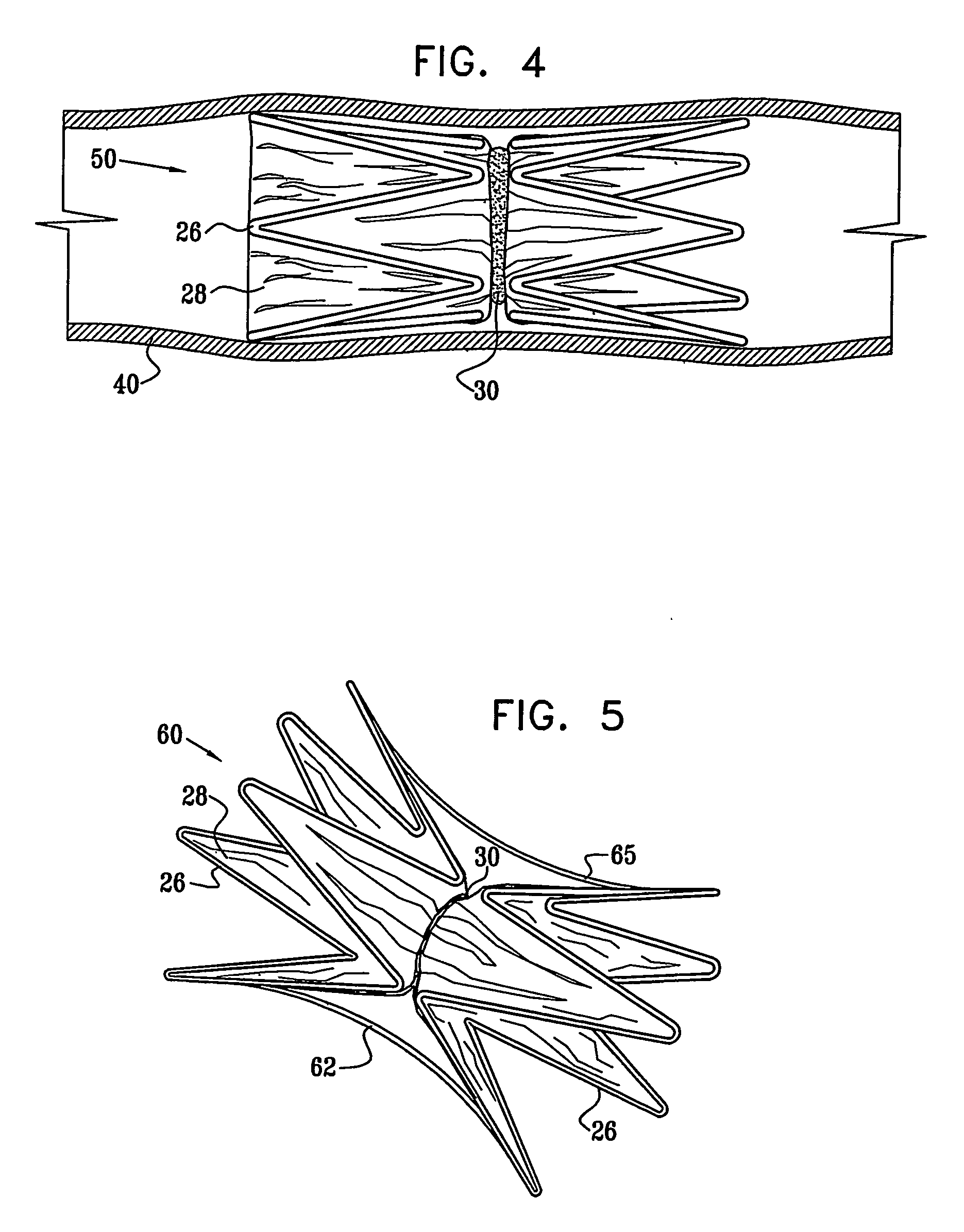
InactiveUS20070288083A1Reduce flowReduce blood flowPretreated surfacesOcculdersAnterior Cerebral Artery AneurysmNeck of pancreas
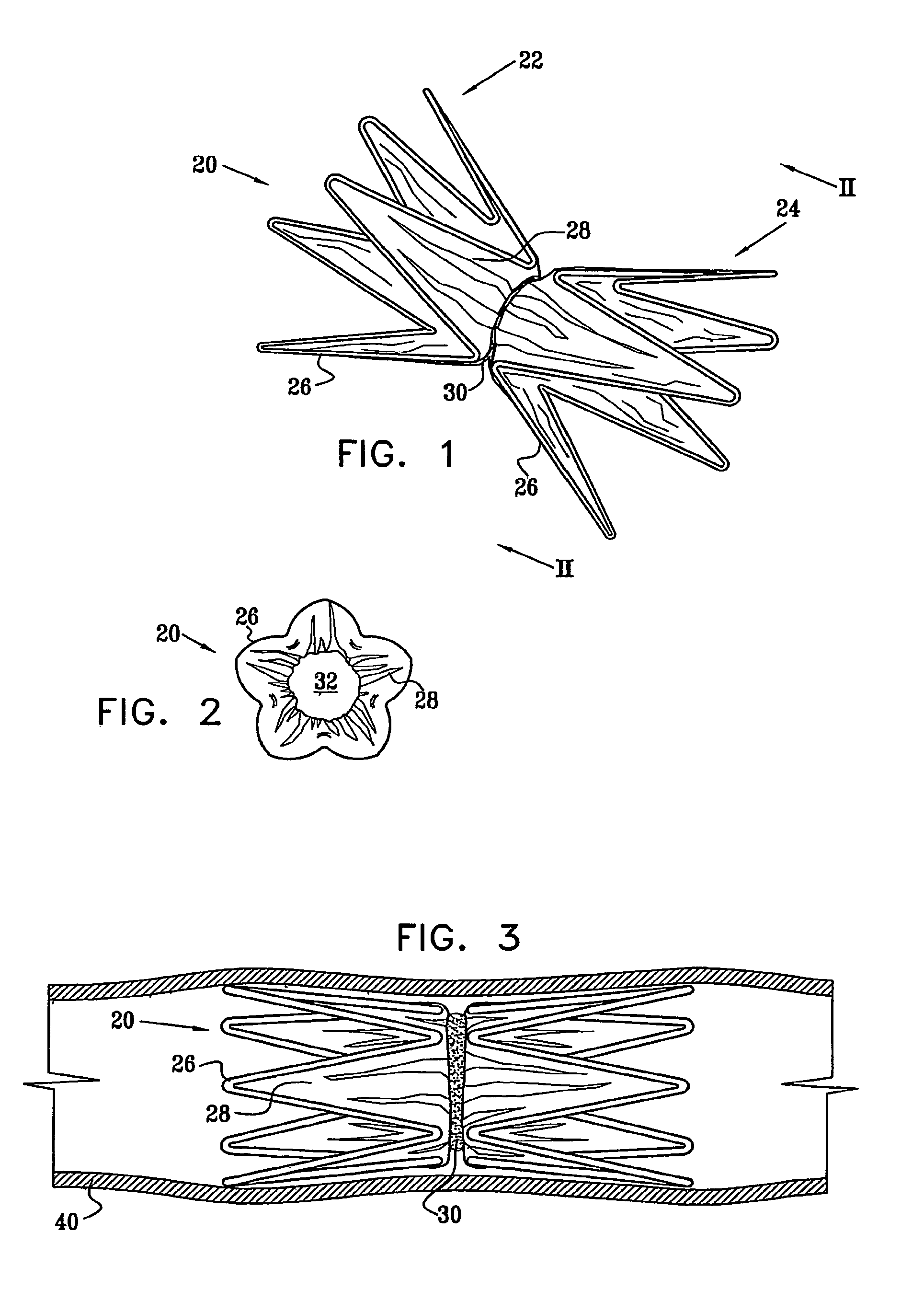
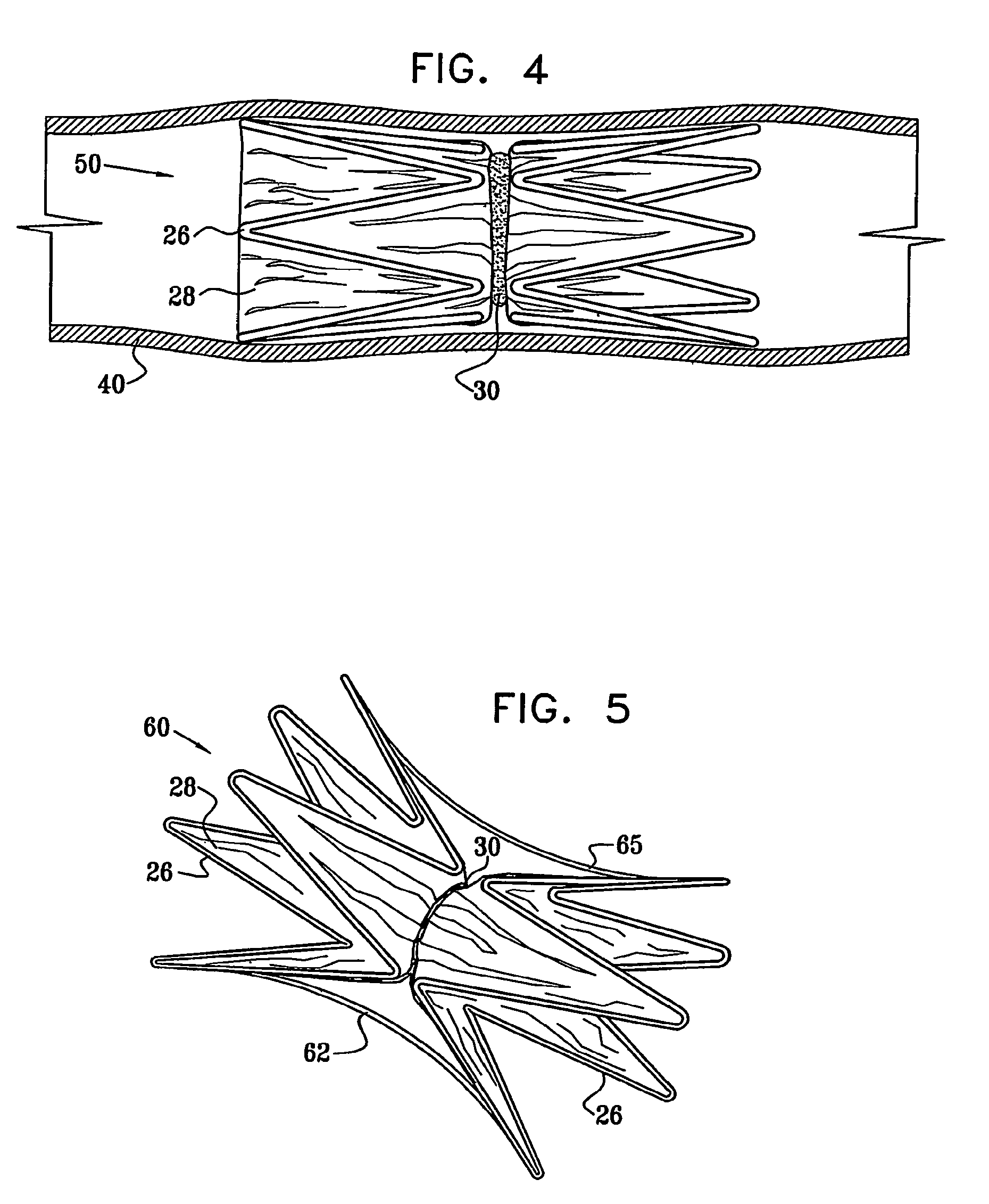
A medical flow restrictor that may be used to exclude a saccular aneurysm from the circulatory system. The device, a thin walled, foil-like shell, is compacted for delivery. The invention includes the device, electroforming fabrication methods, delivery assemblies, and methods of placing, and using, the device. A device with an aneurysm lobe and an artery lobe self-aligns its waist at the neck of an aneurysm as the device shell is pressure expanded. Negative pressure is used to collapse both the aneurysm lobe and the artery lobe, captivating the neck of the aneurysm and securing the device. The device works for aneurysms at bifurcations and aneurysms near side-branch arteries. The device, unlike endovascular coiling, excludes the weak neck of the aneurysm from circulation, while leaving the aneurysm relatively empty. Unlike stent-based exclusion, the device does not block perforator arteries. This exclusion device can also limit flow through body lumens or orifices.
Owner:ELECTROFORMED STENTS
Cerebral perfusion augmentation
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
Method and device for performing cooling- or cryo-therapies for, e.g., angioplasty with reduced restenosis or pulmonary vein cell necrosis to inhibit atrial fibrillation employing tissue protection
InactiveUS6905494B2Minimize and inhibit biochemical eventRobust designCatheterSurgical instruments for heatingPercent Diameter StenosisPercutaneous angioplasty
An enhanced method and device are provided to treat atrial fibrillation or inhibit or reduce restenosis following angioplasty or stent placement. A balloon-tipped catheter is disposed in the area treated or opened through balloon angioplasty immediately following angioplasty. The balloon, which can have a dual balloon structure, may be delivered through a guiding catheter and over a guidewire already in place. A fluid such as a perfluorocarbon flows into the balloon to freeze the tissue adjacent the balloon, this cooling being associated with reduction of restenosis. A similar catheter may be used to reduce atrial fibrillation by inserting and inflating the balloon such that an exterior surface of the balloon contacts at least a partial circumference of the portion of the pulmonary vein adjacent the left atrium. In another embodiment, blood perfusion is performed simultaneously. In another embodiment, tissue contacted by the cryoablation catheter, undesired to be ablated, is protected against damage by a separate heating step.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
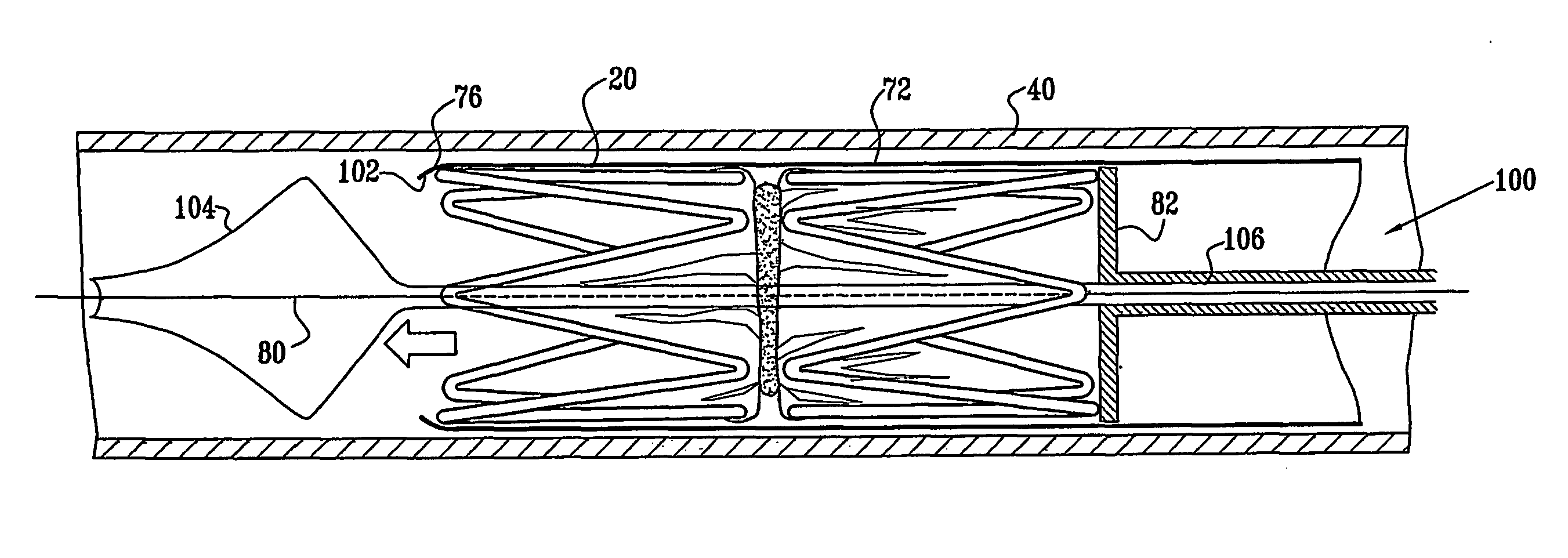
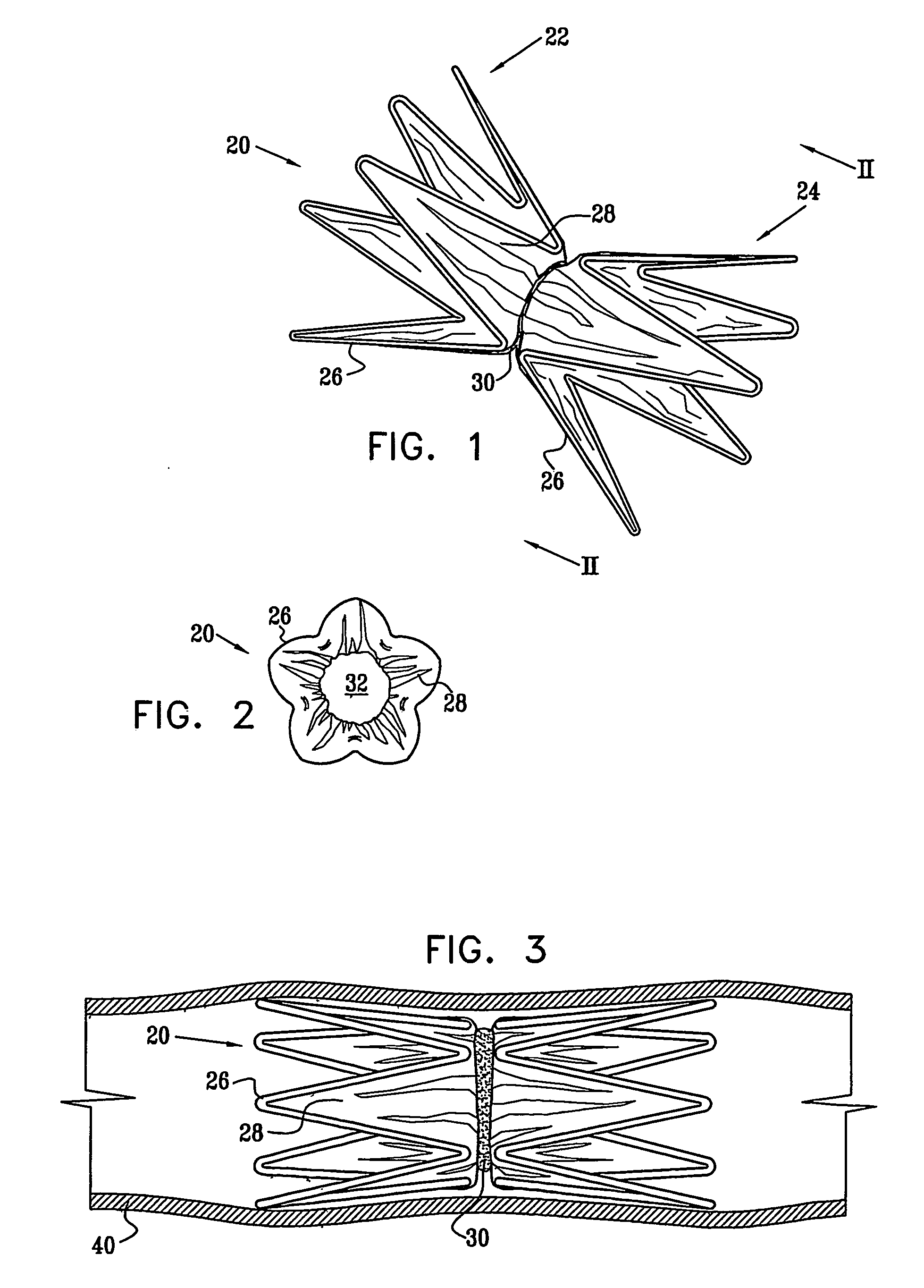
Implantable intraluminal device and method of using same in treating aneurysms
An intraluminal device implantable in a blood vessel having an aneurysm therein in the vicinity of a perforating vessel and / or of a bifurcation leading to a branch vessel. The intraluminal device includes a mesh-like tube of bio-compatible material having an expanded condition in which the tube diameter is slightly larger than the diameter of the blood vessel in which it is to be implanted, and the tube length is sufficient to straddle the aneurysm and to be anchored to the blood vessel on the opposite sides of the aneurysm. The mesh-like tube also has a contracted condition wherein it is sufficiently flexible so as to be easily manipulatable through the blood vessel to straddle the aneurysm. In its expanded condition, the mesh-like tube has a porosity index of 55%-80% such as to reduce the flow of blood through its wall to the aneurysm sufficiently to decrease the possibility of rupture of the aneurysm but not to unduly reduce the blood flow to a perforating or branch vessel to the degree likely to cause significant damage to tissues supplied with blood by such perforating or branch vessel.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
Vital sign monitor for measuring blood pressure using optical, electrical and pressure waveforms
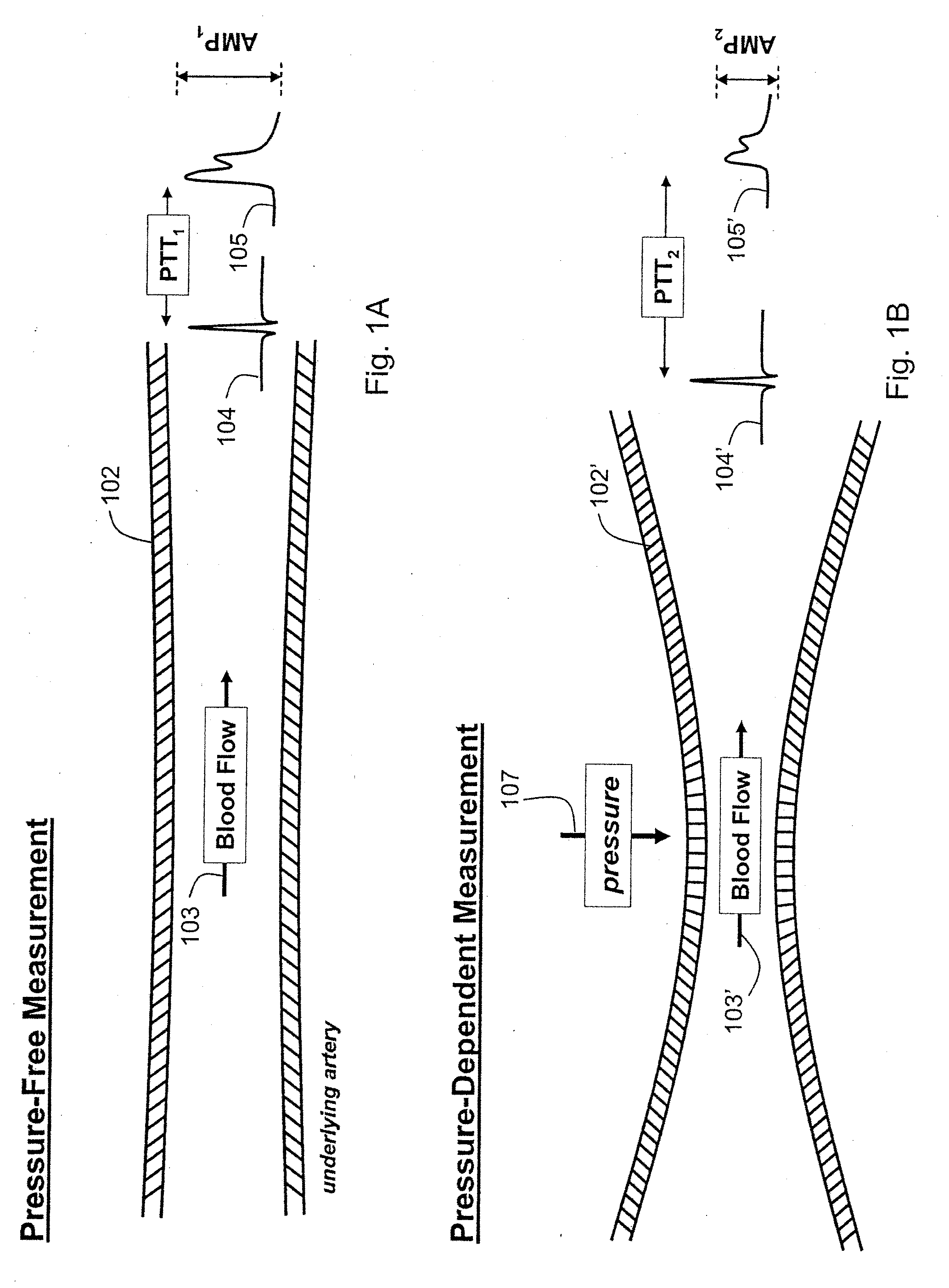
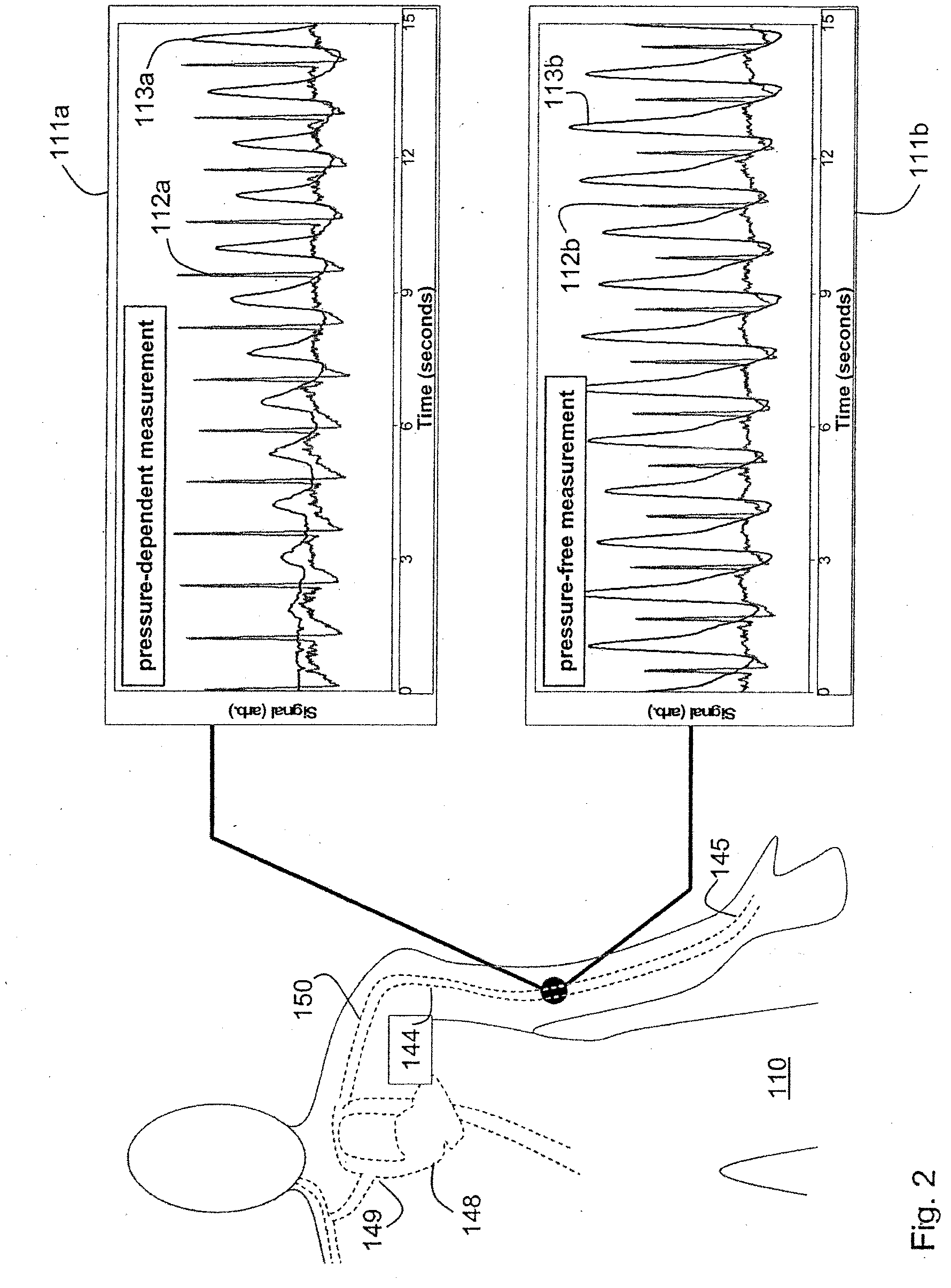
ActiveUS20090018453A1Decreased blood flowEliminate amplitudeElectrocardiographyEvaluation of blood vesselsContinuous measurementPhotodiode
A method and apparatus for continuous measurement of blood pressure, based on pulse transit time, which does not require any external calibration. This technique, referred to herein as the ‘composite technique’, is carried out with a body-won sensor that measures blood pressure and other vital signs, and wirelessly transmits them to a remote monitor. A network of disposable sensors, typically placed on the patient's right arm and chest, connect to the body sensor and measure a time-dependent electrical waveform, optical waveform, and pressure waveform. The disposable sensors typically include an armband that features an inflatable bladder coupled to a pressure sensor, at least 3 electrical sensors (e.g. electrodes), and an optical sensor (e.g., a light source and photodiode) attached to a wrist-worn band.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
Intra-aortic renal drug delivery catheter
InactiveUS7481803B2Reduce the amount requiredDecreased blood flowStentsBalloon catheterDiagnostic agentBlood vessel
A catheter for delivering a therapeutic or diagnostic agent to a branch blood vessel of a major blood vessel, generally comprising an elongated shaft having at least one lumen in fluid communication with an agent delivery port in a distal section of the shaft, an expandable tubular member on the distal section of the shaft, and a radially expandable member on the tubular member. The tubular member is configured to extend within the blood vessel up-stream and down-stream of a branch vessel, and has an interior passageway which is radially expandable within the blood vessel to separate blood flow through the blood vessel into an outer blood flow stream exterior to the tubular member and an inner blood flow stream within the interior passageway of the tubular member.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
Medical device suitable for use in treatment of a valve
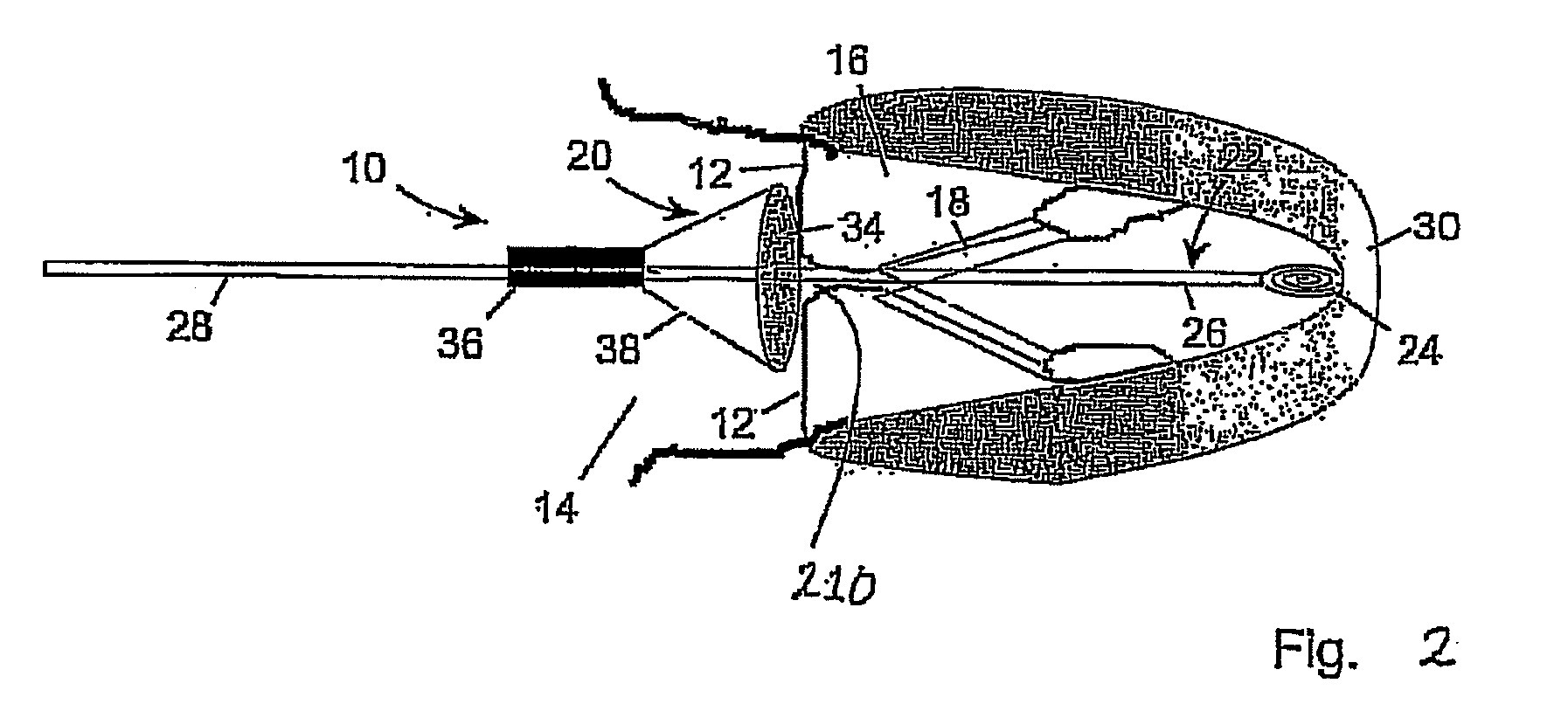
InactiveUS20070293943A1Secure supportProfound clinical consequencesHeart valvesMitral valve leafletMedical device
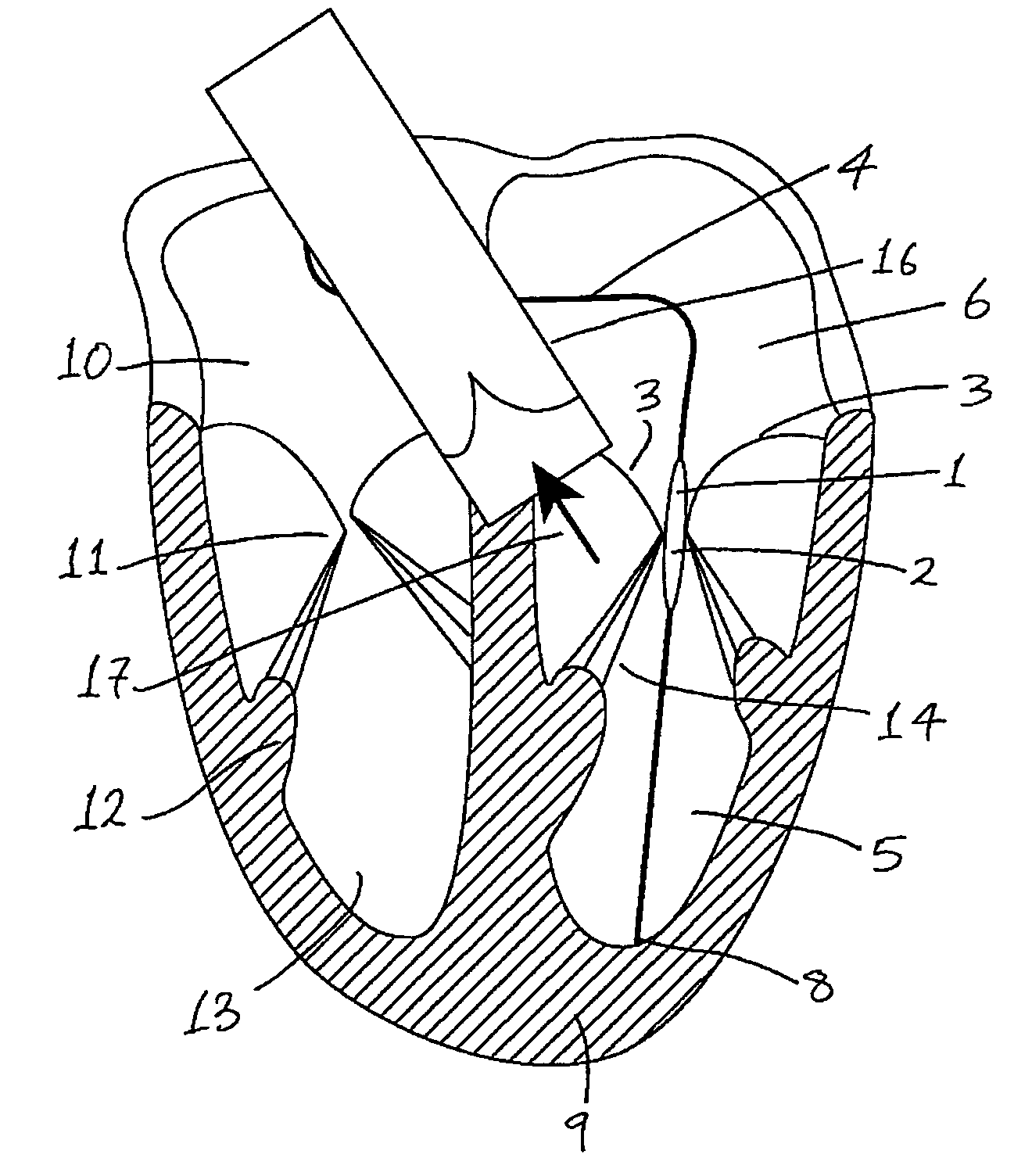
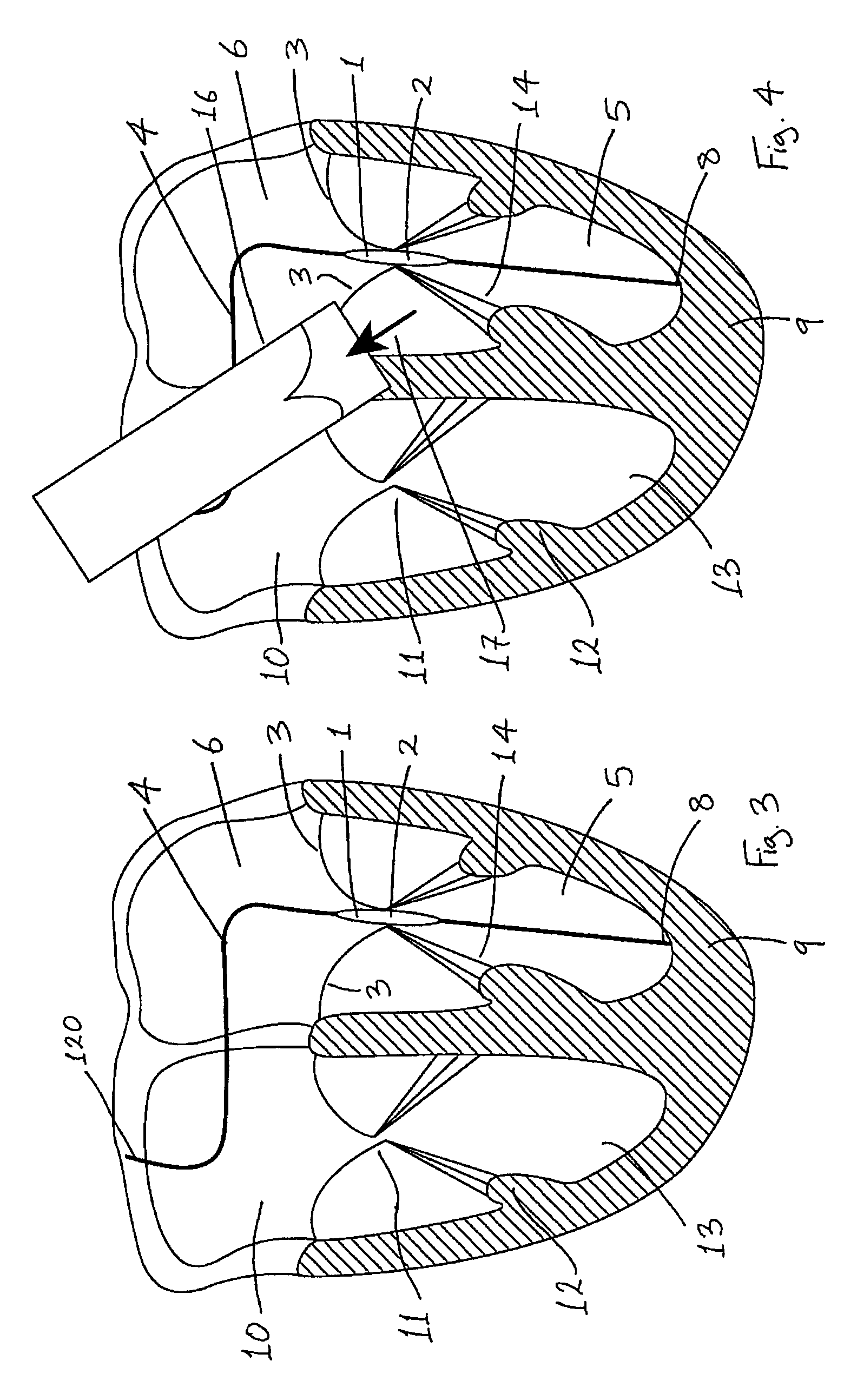
A medical device (1) suitable for use in treatment of a mitral valve comprises a treatment element (2) located at the region of co-aptation of the leaflets (3) of the mitral valve, a support element (4) which supports the treatment element (2) at the region of co-aptation of the valve leaflets (3), and an anchor element (8) to anchor the support element (4) to the ventricle wall at the apex (9) of the ventricle (5). The anchor element (8) is located at the distal end of the support element (4), and the proximal end (120) of the support element (4) is unconstrained relative to the wall of the ventricle (5) and the wall of the atrium (6). The treatment element (2) acts to resist blood flow in the retrograde direction through the valve opening.
Owner:MEDNUA
Medical device suitable for use in treatment of a valve
InactiveUS20090076600A1Profound clinical consequencesIncrease pressureSuture equipmentsHeart valvesSeptal wallSurgery
A medical device (1210) comprises a generally cylindrical treatment element (1220) for location between a pair of valve leaflets (1212) situated between an atrium (1214) and a ventricle (1216) of a heart. The treatment element (1220) supports the valve leaflets (1212) at the region of co-aptation of the valve leaflets (1212) and occludes the valve opening to resist fluid flow in the retrograde direction through the valve opening. The device (1210) comprises a support (1222) to support the treatment element (1210) at the region of co-aptation of the valve leaflets (1212). The support has an anchor (1224) and a tether (1226), the tether (1226) being provided at the end of a guide wire (1228) which is initially utilised in the percutaneous insertion of the treatment element (1220). The anchor (1224) is secured, in use, to a septal wall (1230), while the guide wire (1228) exits the atrium (1214) through a vein adjacent a rear wall (1224) thereof. The treatment element (1220) includes a remotely actuatable clamp therein, in order to allow the treatment element (1220) to be secured to the guide wire (1228) or the tether (1226).
Owner:MEDNUA
Intra-aortic renal drug delivery catheter
InactiveUS20060189960A1Reduce the amount requiredDecreased blood flowBalloon catheterMulti-lumen catheterDiagnostic agentBlood vessel
A catheter for delivering a therapeutic or diagnostic agent to a branch blond vessel of a major blood vessel comprises an elongated shaft having at least one lumen in fluid communication with an agent delivery port in a distal section of the shaft, an expandable tubular member on the distal section of the shaft, and a radially expandable member on the tubular member. The tubular member is configured to extend within the blood vessel up-stream and down-stream of a branch vessel, and has an interior passageway which is radially expandable within the blood vessel to separate blood flow through the blood vessel into an outer blood flow stream exterior to the tubular member and an inner blood flow stream within the interior passageway of the tubular member.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
Ablation in the Gastrointestinal Tract to Achieve Hemostasis and Eradicate Lesions With a Propensity for Bleeding
ActiveUS20090012513A1High failure rateReduced blood flowDilatorsSurgical instruments for heatingArteriovenous malformationGastric antral vascular ectasia
Devices and methods are provided for the ablation of regions of the digestive tract to achieve hemostasis and to eradicate chronically bleeding lesions as occur with gastric antral vascular ectasia (GAVE), portal hypertensive gastropathy (PHG), radiation proctopathy and colopathy, arteriovenous malformations, and angiodysplasia. Ablation is typically provided in a wide-field manner, and in conjunction with sufficient pressure to achieve coaptive coagulation. Ablation, as provided the invention, starts at the mucosa and penetrates deeper into the gastrointestinal wall in a controlled manner. Ablation control may be exerted by way of electrode design and size, energy density, power density, number of applications, pattern of applications, and pressure. Control may also be provided by a fractional ablation that ablates some tissue within a target region and leaves a portion substantially unaffected. Embodiments of the device include an ablational electrode array that spans 360 degrees and an array that spans an arc of less than 360 degrees.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Device for treatment of tissue adjacent a bodily conduit by thermocompression
InactiveUS7811313B2Guaranteed functionAvoid heatCatheterMicrowave therapyInsertion stentCatheter device
A method and apparatus of treating tissue adjacent to a bodily conduit using thermotherapy, while preventing obstructions of the bodily conduit due to edema employs the circulation of warmed fluid to maintain the temperature of the bodily conduit walls and compresses the tissue to be treated to increase the effectiveness of the irradiated heat. An energy-emitting source containing catheter is inserted in a bodily conduit and is positioned in a region of the tissue to be treated so that the energy-emitting source radiates energy to the tissue to be treated. Fluid warmed to over 30° C. is circulated into and through the catheter to warm walls of the bodily conduit adjacent the catheter. The circulated fluid inflates a balloon to a pressure to compress the tissue to be treated. The combination of warmed fluid over 30° C. being circulated adjacent the bodily conduit to maintain the warmth in its walls and the compression of the tissue to be treated enables a natural stent to be formed that remains after the catheter and compression balloon is removed.
Owner:MEDIFOCUS
Method and apparatus treating tissue adjacent a bodily conduit with thermocompression and drugs
InactiveUS7833220B2Guaranteed functionAvoid heatElectrotherapyDrug compositionsSufficient timeHeat sensitive
Owner:MEDIFOCUS
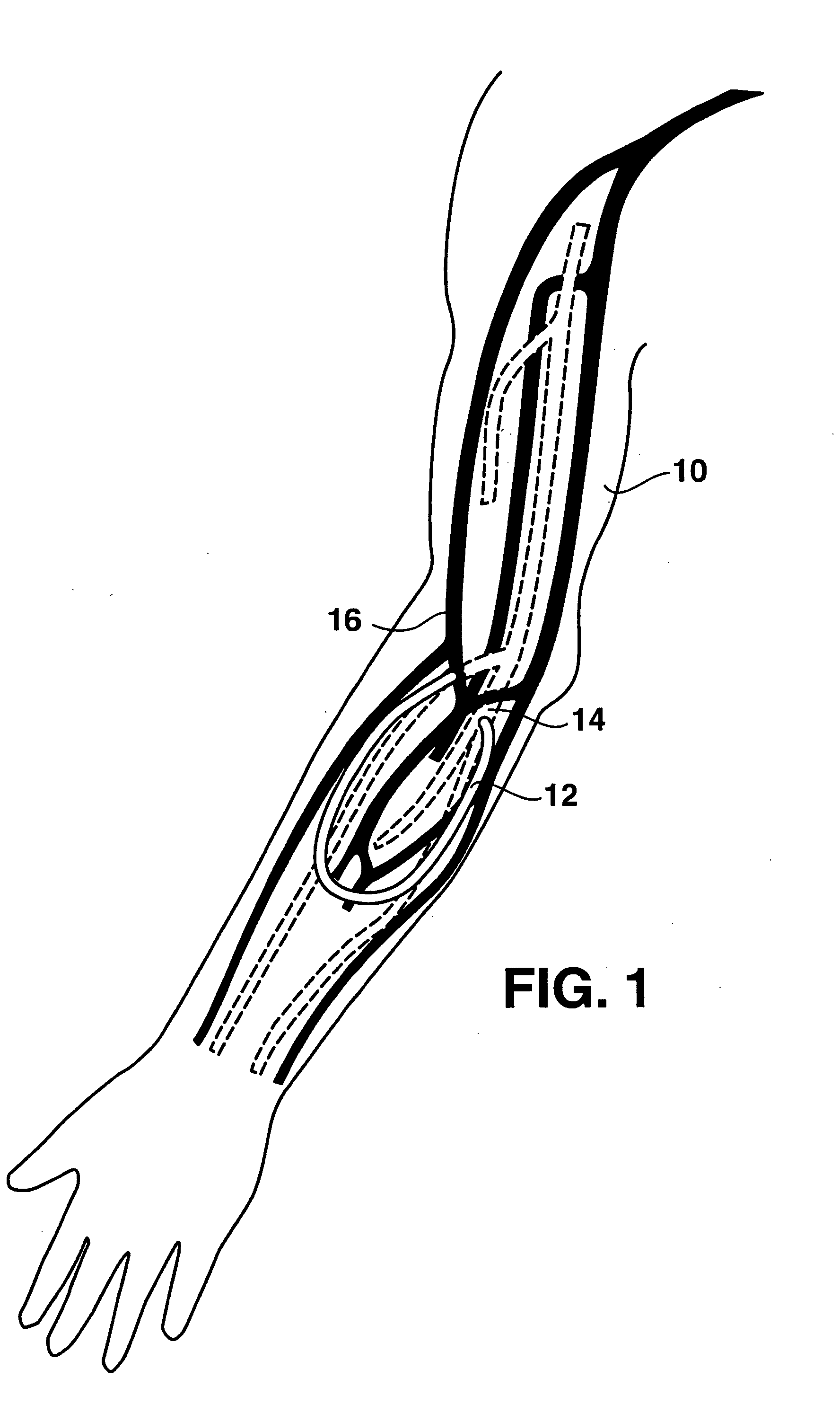
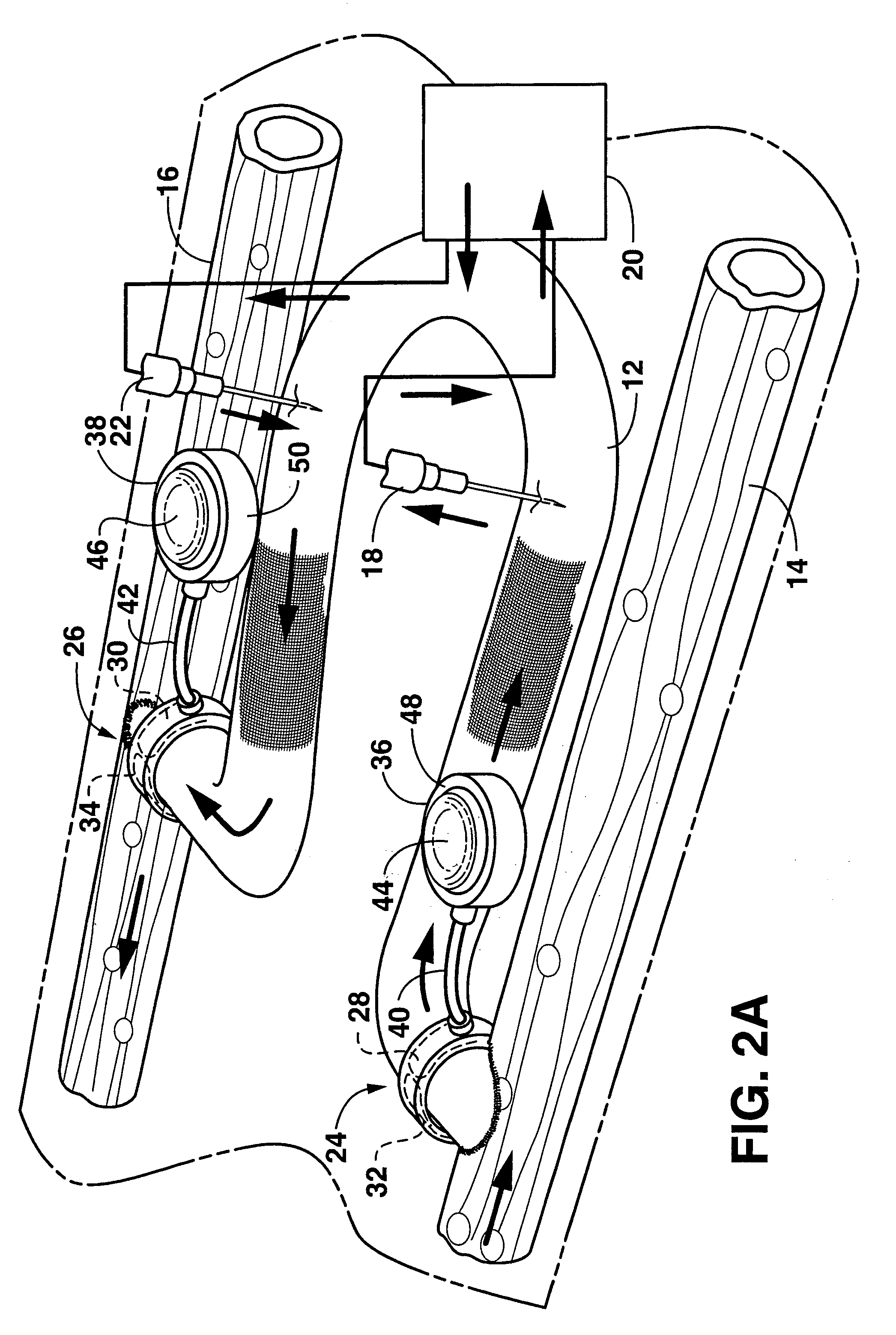
Arteriovenous access valve system and process
InactiveUS7025741B2Eliminates orReduces arterial steal and graft thrombosisOther blood circulation devicesDilatorsHaemodialysis machineVein graft
An arteriovenous graft system is described. The arteriovenous graft system includes an arteriovenous graft that is well suited for use during hemodialysis. In order to minimize or prevent arterial steal, at least one valve device is positioned at the arterial end of the arteriovenous graft. In one embodiment, for instance, the arteriovenous graft system includes a first valve device positioned at the arterial end and a second valve device positioned at the venous end. In one embodiment, the valve devices may include an inflatable balloon that, when inflated, constricts and closes off the arteriovenous graft. By minimizing or preventing arterial steal, other complications associated with arteriovenous grafts are also avoided. For instance, the present invention is also well suited to preventing arteriovenous graft thrombosis, eliminating dialysis needle hole bleeding, and eliminating or minimizing arteriovenous graft pseudoaneurism formation.
Owner:DIAXAMED LLC
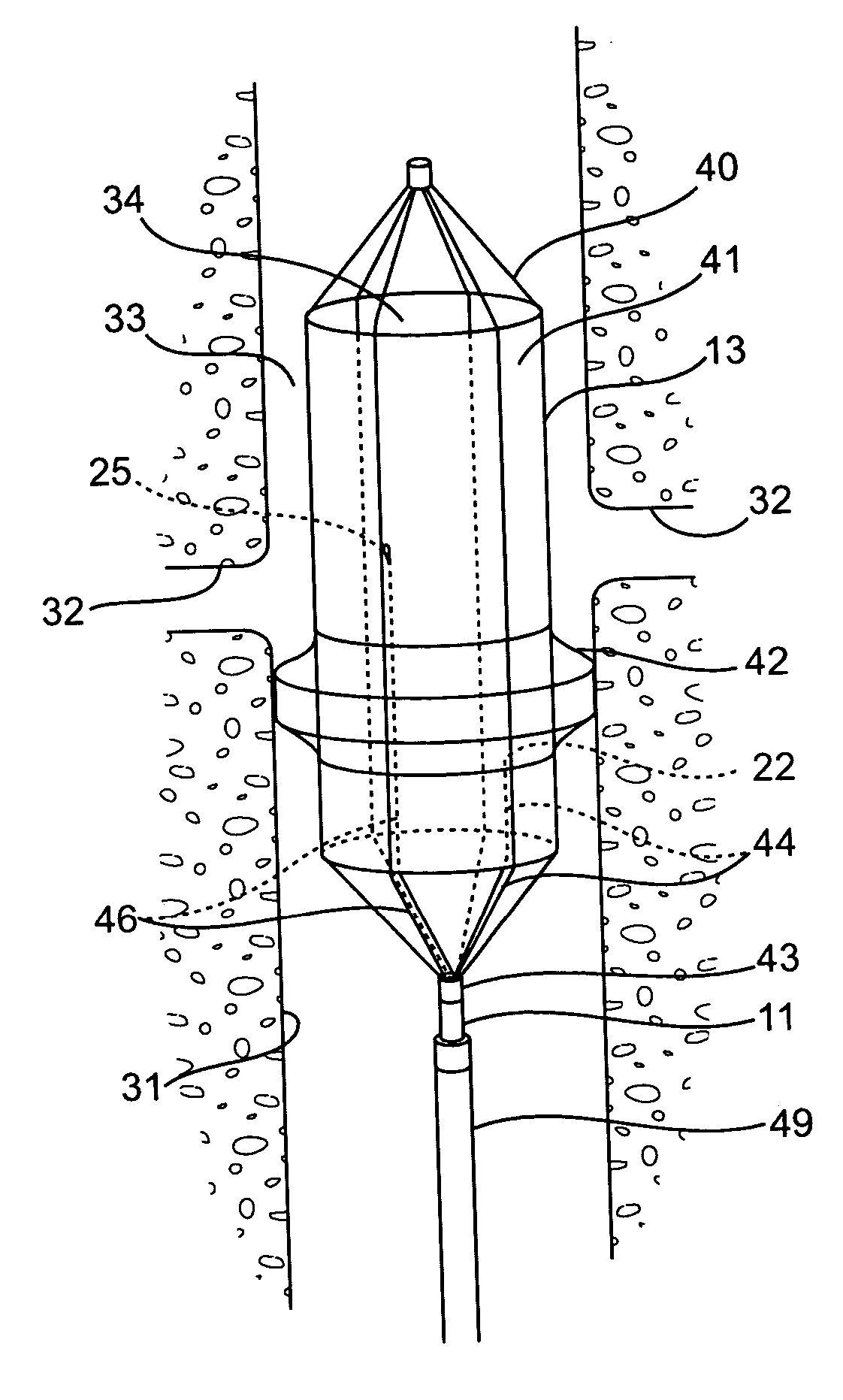
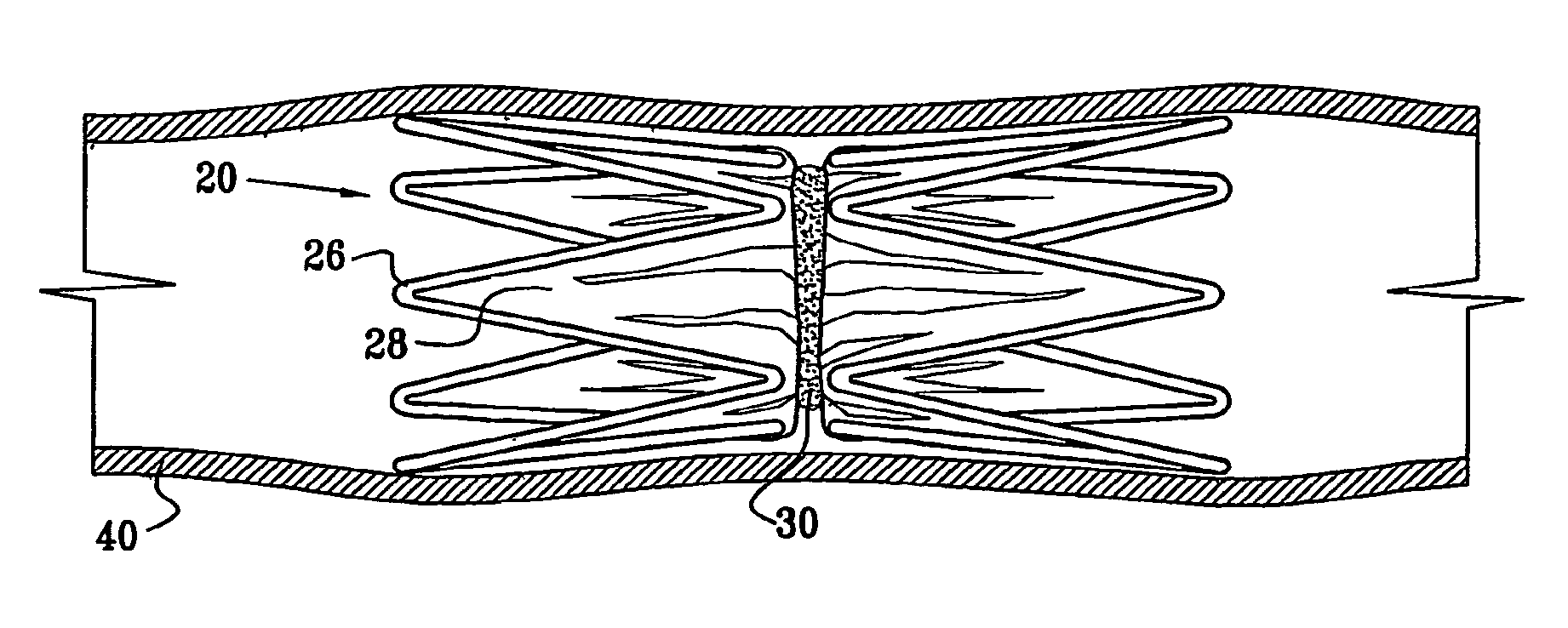
Vascular implant
InactiveUS20070027525A1Simple and inexpensive to manufactureReduce the overall diameterStentsBlood vesselsVascular implantEngineering
A medical implant (20) includes first and second ring members (22,24), each including a resilient framework (26) having a generally cylindrical form. A tubular sleeve (28) is fixed to the first and second ring members so as to hold the ring members in mutual longitudinal alignment, thereby defining a lumen (32) passing through the ring members. A constricting element (30) is fit around the sleeve at a location intermediate the first and second ring members so as to reduce a diameter of the lumen at the location.
Owner:NEOVASC MEDICAL LTD
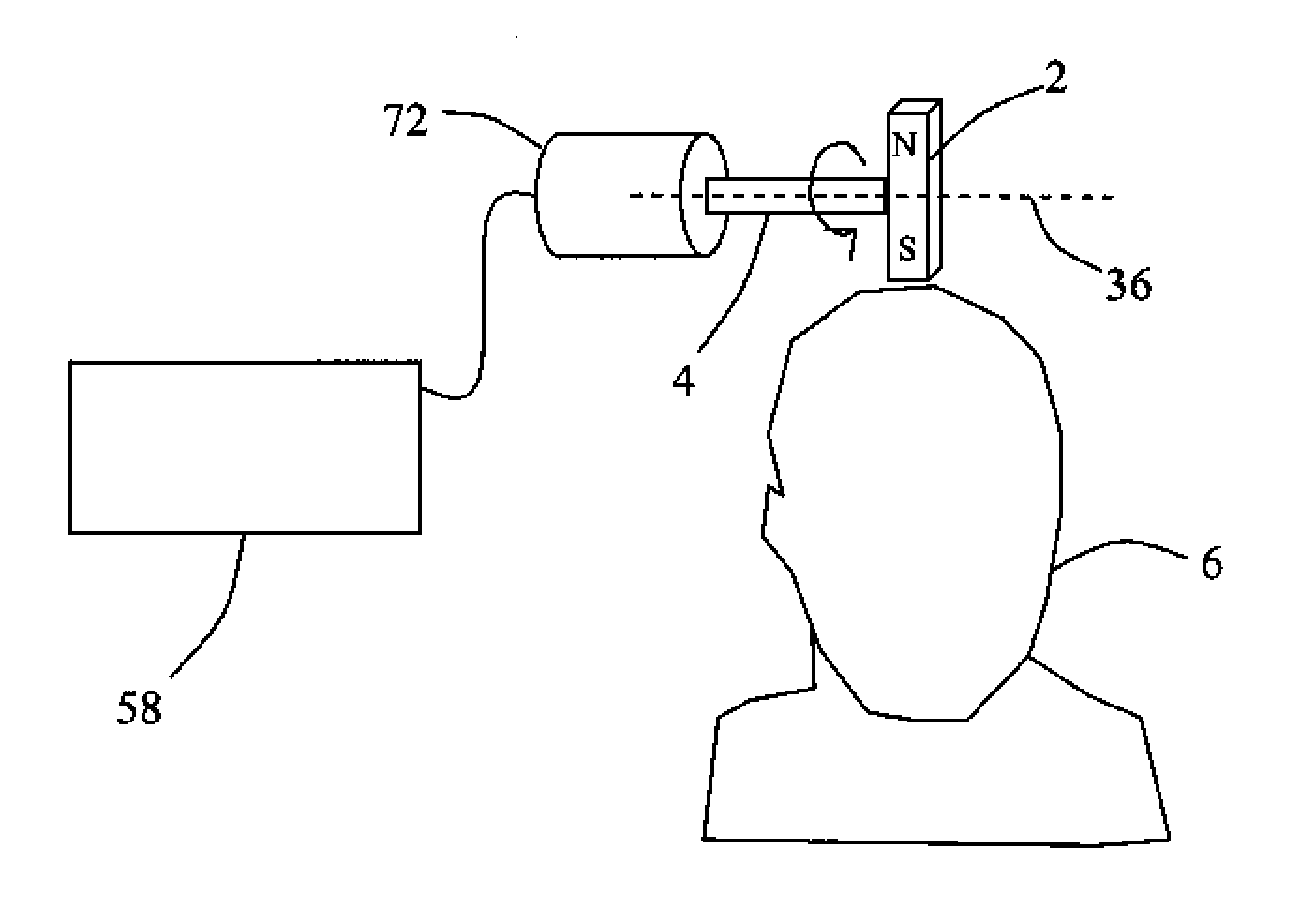
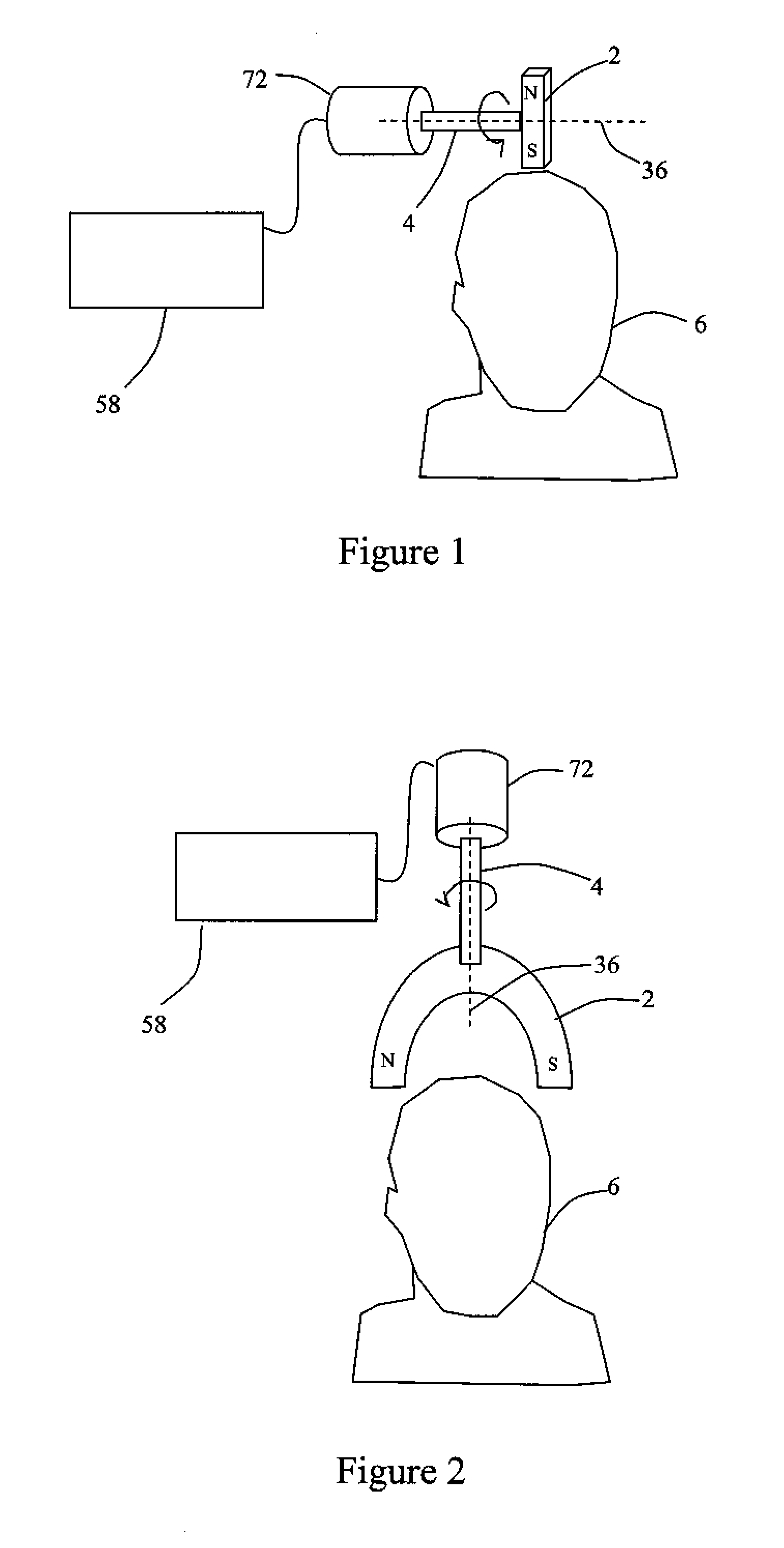
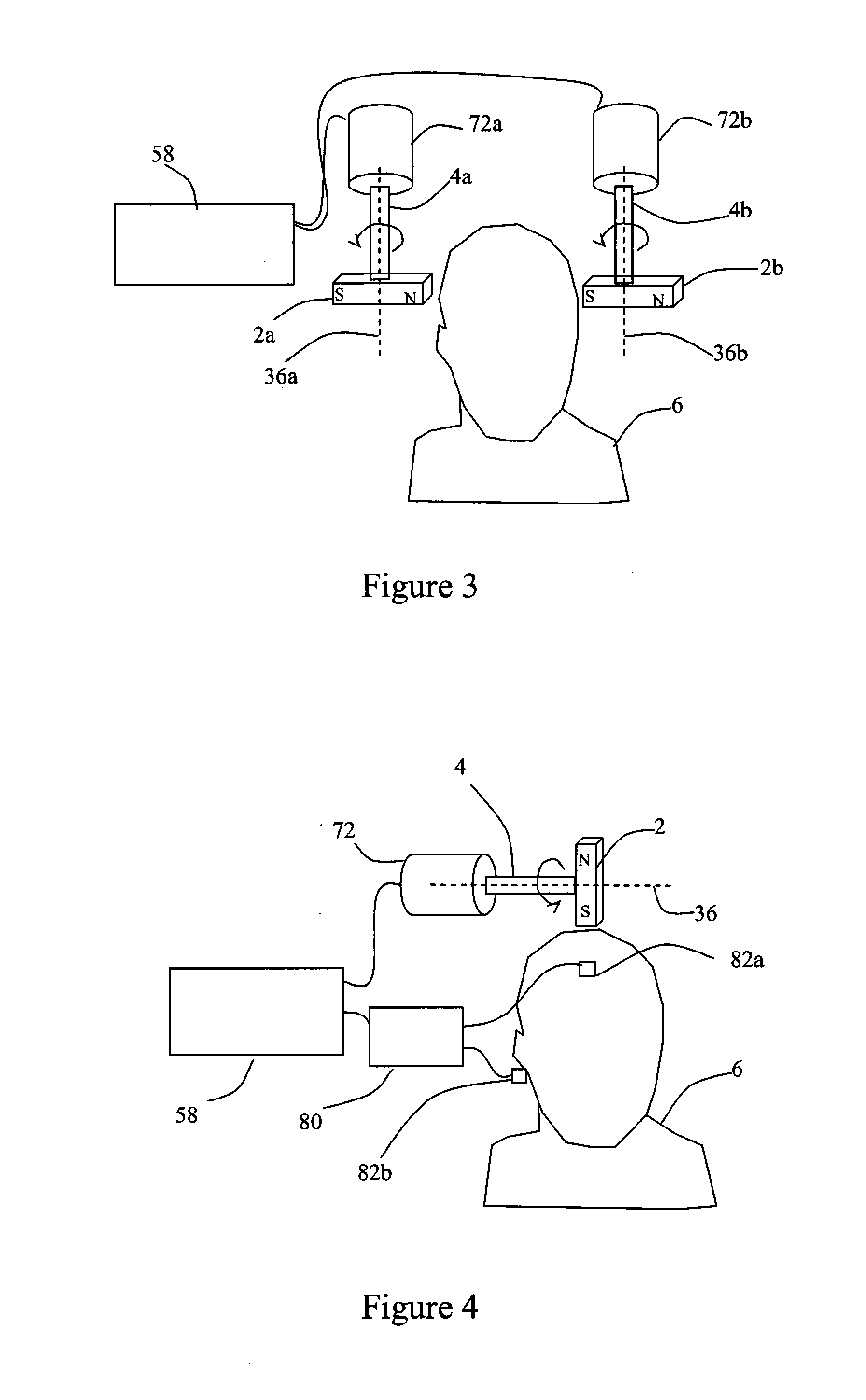
Systems and methods for neuro-eeg synchronization therapy
ActiveUS20110112427A1Lower blood pressureIncrease libidoElectroencephalographyElectrotherapyDrugDisease
Described are methods, devices, and systems for a novel, inexpensive, easy to use therapy for a number of disorders. Described are methods and devices to treat disorders that involves no medication. Methods and devices described herein use alternating magnetic fields to gently “tune” the brain and affect mood, focus, and cognition of subjects.
Owner:WAVE NEUROSCI INC
Implantable intraluminal device and method of using same in treating aneurysms
InactiveUS20050010281A1Sufficiently flexibleSufficiently pliableStentsBlood vesselsPorosityProximate
Owner:STRYKER CORP +1
Implantable system for monitoring the condition of the heart
ActiveUS20050113705A1Restore blood flowDecreased blood flowElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyCoronary circulationPeripheral
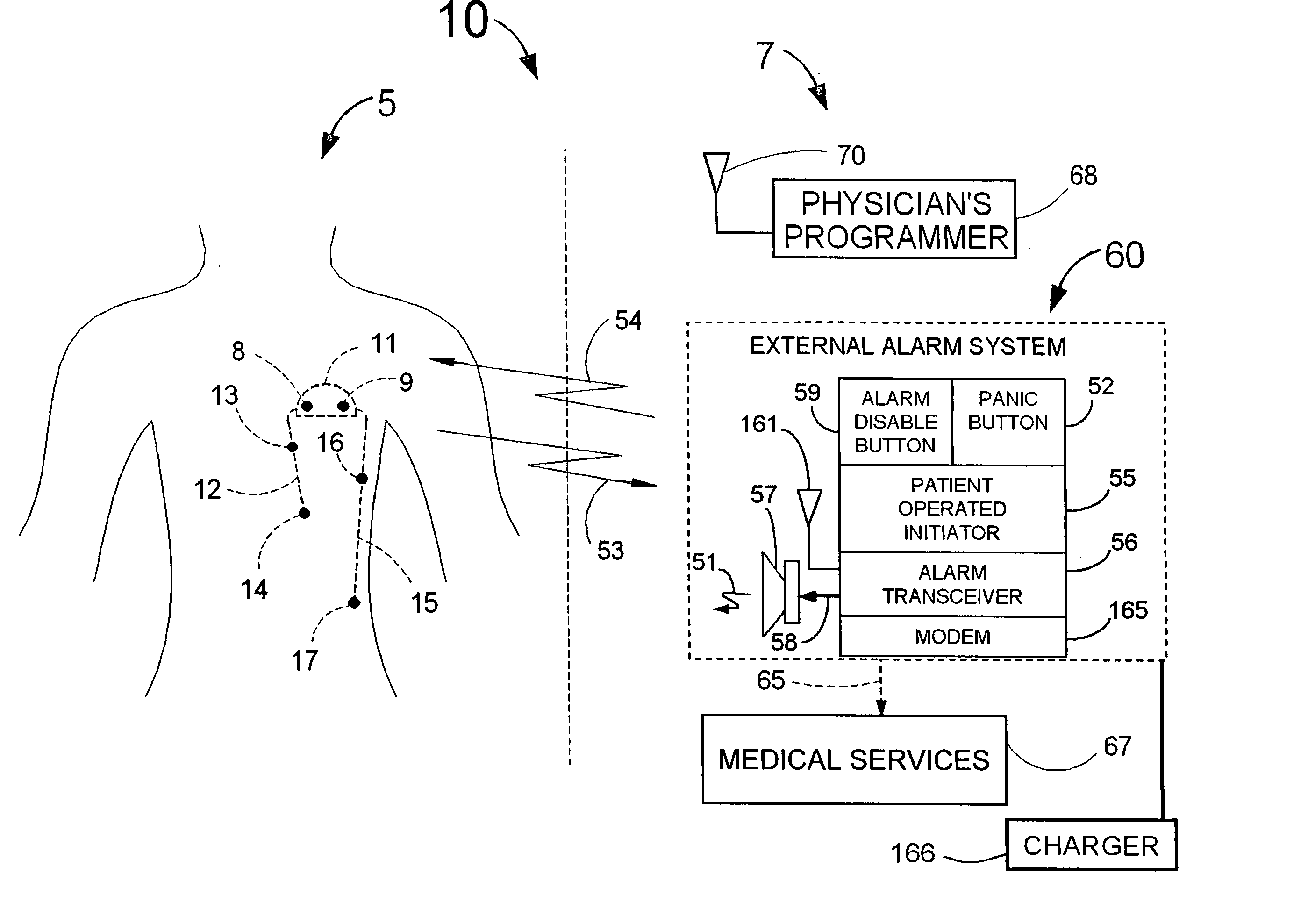
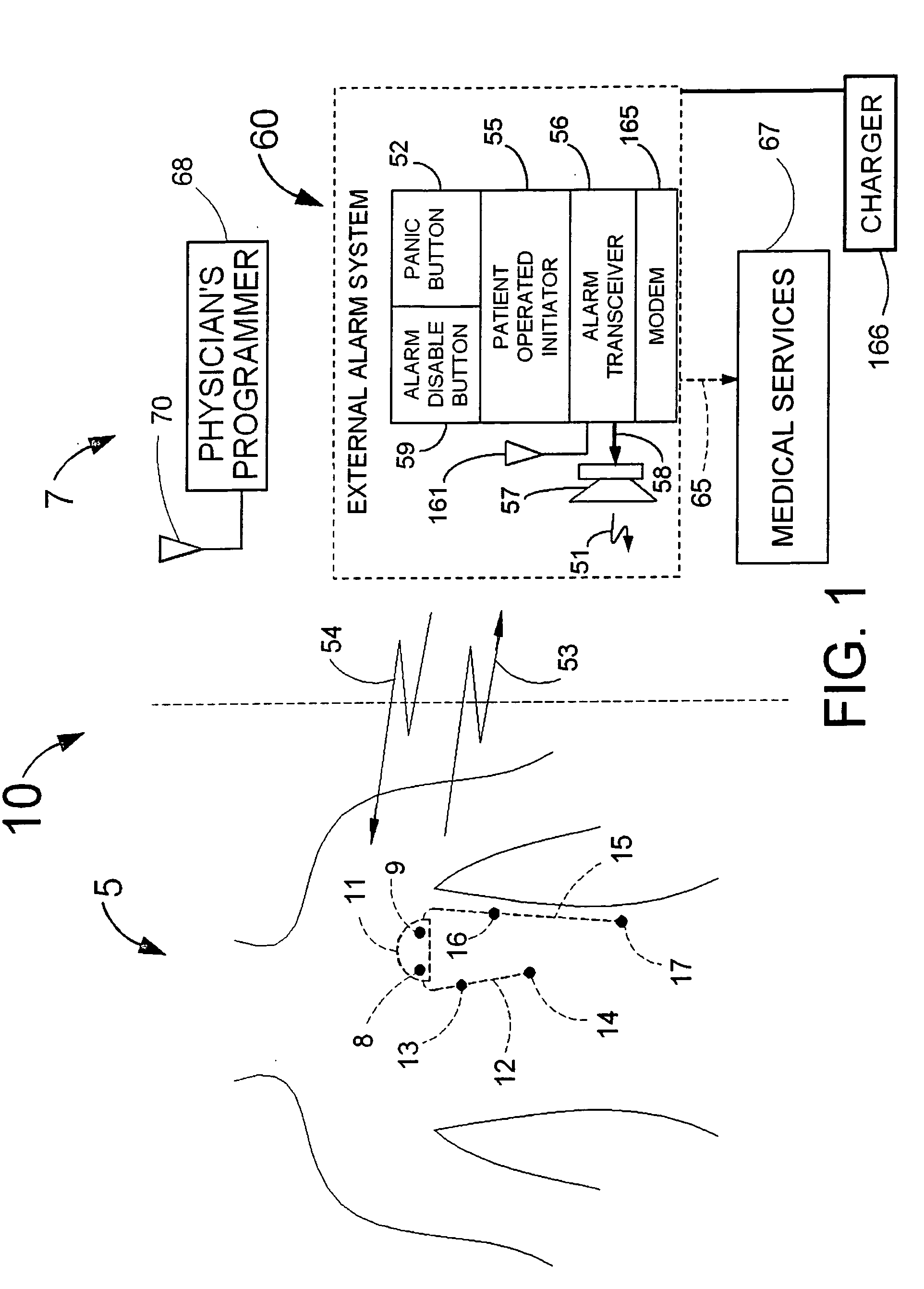
Disclosed is a “tracker system” that includes implanted electrical leads which are part of an implanted cardiotracker plus external equipment that includes external alarm means and a physician's programmer. The tracker system is designed to monitor the degradation of a patient's cardiovascular condition from one or more causes. These causes include the rejection of a transplanted heart and / or the progression of a stenosis in a coronary artery. As one or more stenoses in a coronary artery become progressively more narrow thereby causing reduced blood flow to the heart muscle coronary circulation, the tracker system can alert the patient by either or both internal and / or external alarm means to take the appropriate medical action. The physician's programmer can be used to display histograms of key heart signal parameters that are indicative of the patient's cardiovascular condition.
Owner:ANGEL MEDICAL SYST
Permanent thrombus filtering stent
InactiveUS20070093744A1Stroke preventionGood blood pressureStentsSurgeryInsertion stentStent implantation
A permanent thrombus and plaque filtering stent blocks and / or filters potential emboli in patients undergoing intravascular treatment and / or stent implantation. The stent has a plurality of movable magnetic or ultrasonic agitating elements attached thereto, which when remotely activated move, vibrate or rotate to break up the thrombus, plaque or tissue debris.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
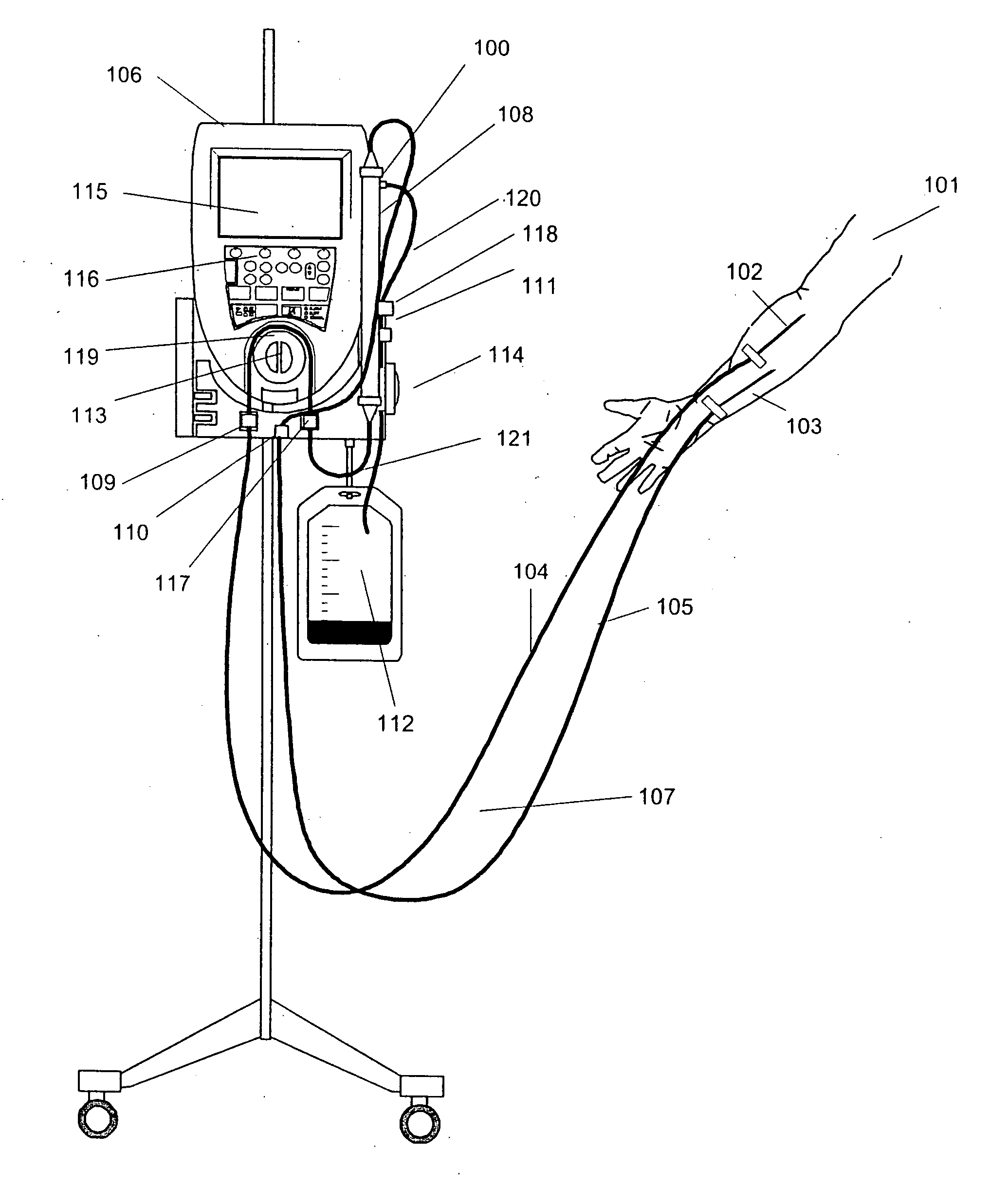
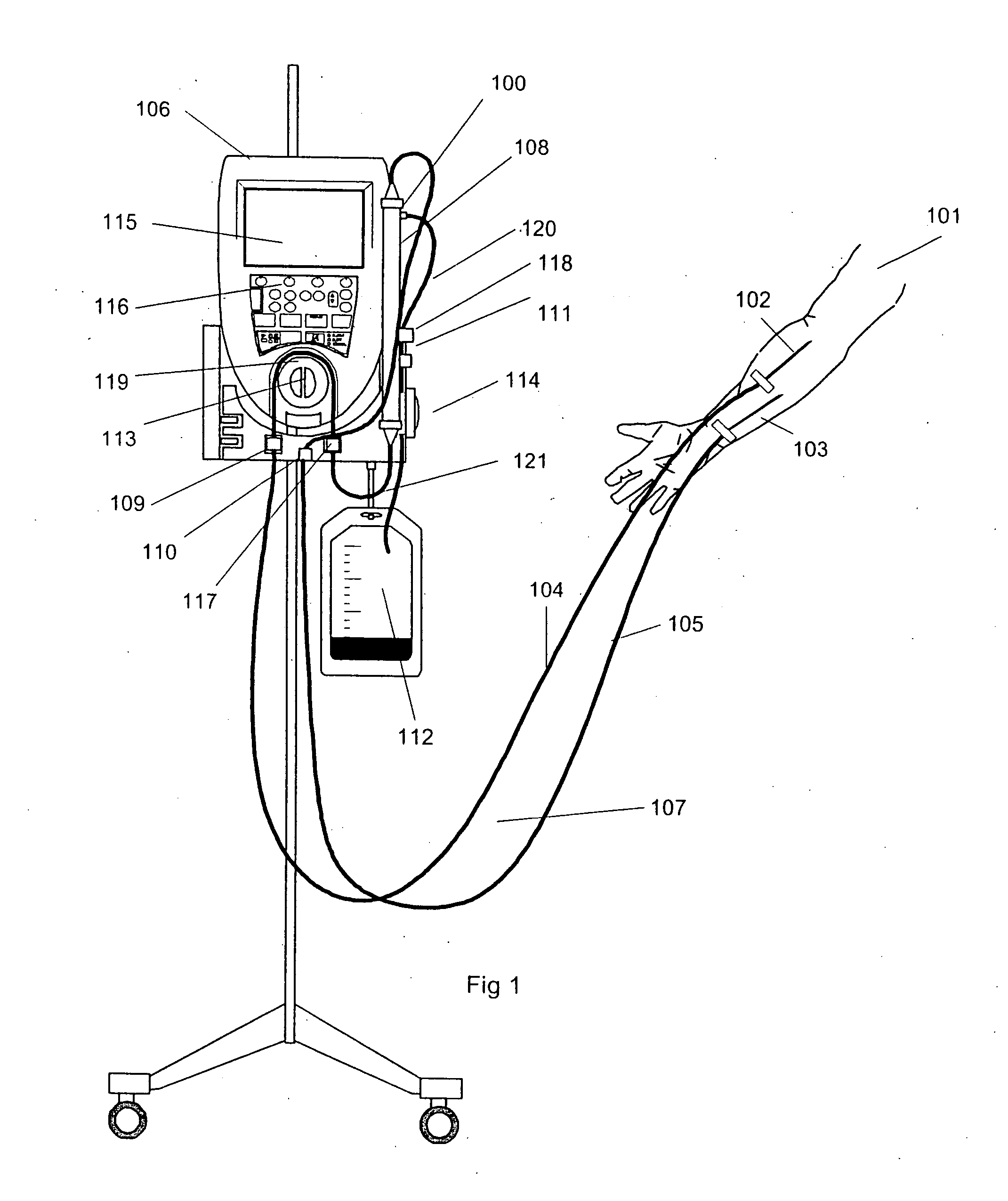
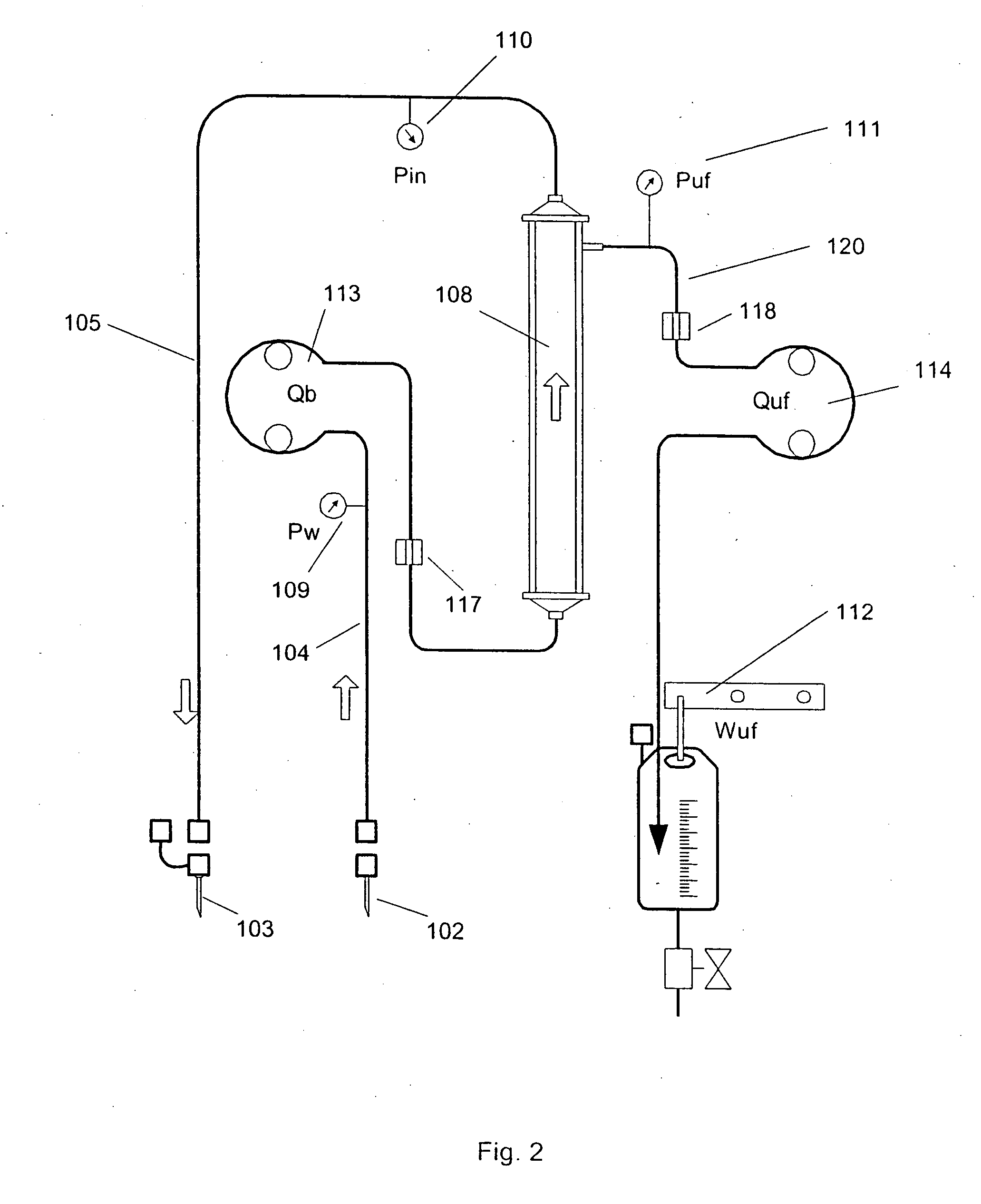
Method to control blood and filtrate flowing through an extracorporeal device
InactiveUS20050004502A1Alleviate occlusionReduce partSemi-permeable membranesSolvent extractionBiomedical engineeringBlood velocity
A method and apparatus are disclosed for controlling blood flow through an extracorporeal blood circuit having a controller comprising the steps of: withdrawing the blood from a withdrawl blood vessel in a patient into the extracorporeal circuit, treating the blood in the circuit and infusing the treated blood into the patient; detecting an occlusion which at least partially blocks the withdrawl or infusion of the blood; reducing the blood flow rate and the rate of filtration in response to the occlusion, and further prompting the patient to move his arm in an effort to alleviate the occlusion.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
Vascular implant
ActiveUS8911489B2Simple and inexpensive to manufactureReduce the overall diameterStentsEar treatmentVascular implantEngineering
A medical implant (20) includes first and second ring members (22, 24), each including a resilient framework (26) having a generally cylindrical form. A tubular sleeve (28) is fixed to the first and second ring members so as to hold the ring members in mutual longitudinal alignment, thereby defining a lumen (32) passing through the ring members. A constricting element (30) is fit around the sleeve at a location intermediate the first and second ring members so as to reduce a diameter of the lumen at the location.
Owner:SHOCKWAVE MEDICAL
Injection site for male luer or other tubular connector
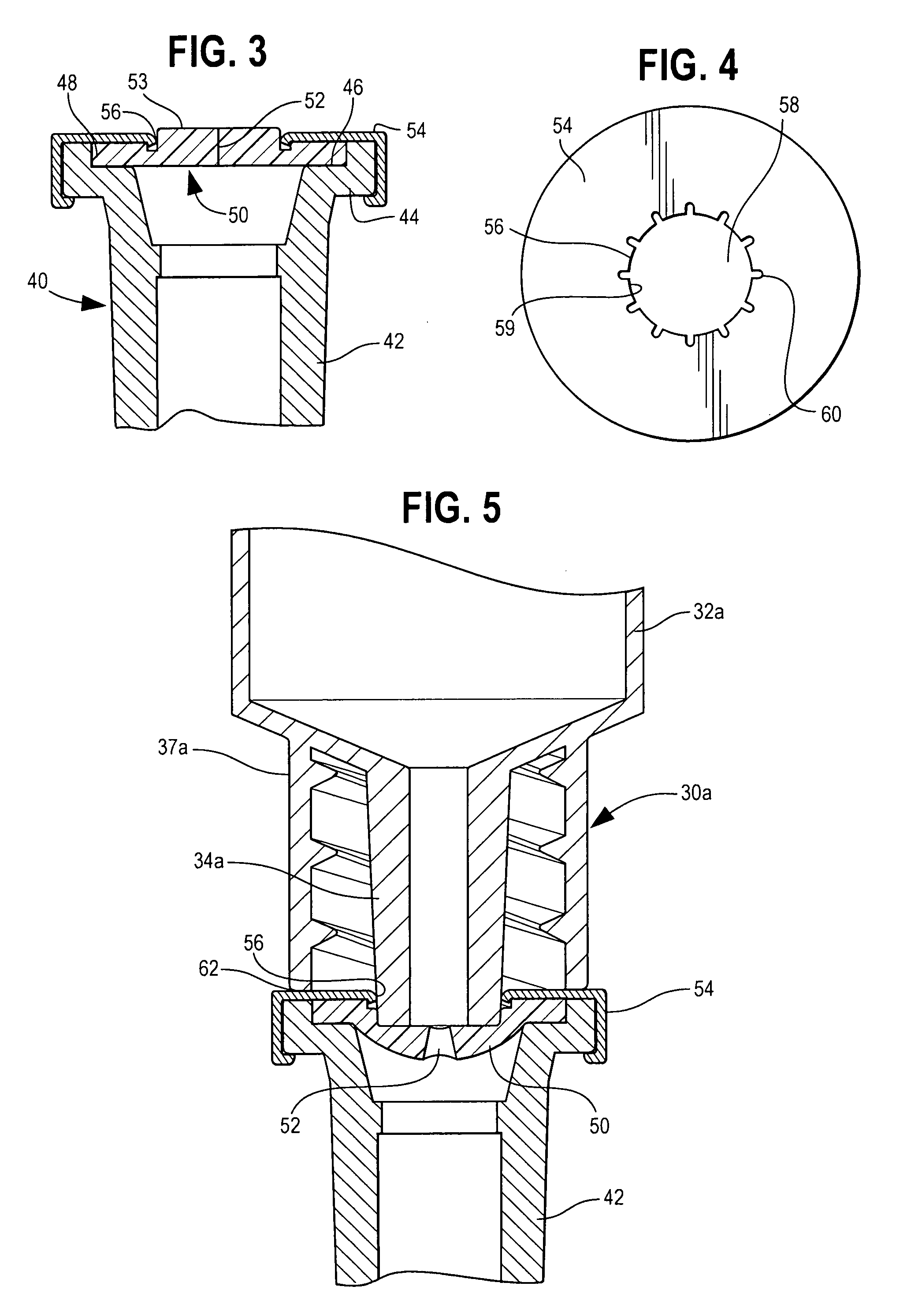
ActiveUS7025744B2Decreased blood flowReduce turbulenceInfusion devicesMedical devicesInjection siteEngineering
A medical device has an interior for containment of fluids; an opening into the interior, an elastomeric wall comprising a fixedly placed, flexible barrier across the opening; and a retention wall positioned adjacent to a peripheral portion of the elastomeric wall. The retention wall defines a central opening and has a generally rigid retention zone surrounding the central opening, to engage and retain a connector tube which is advanced into the central opening to displace the elastomeric wall and to open a flow aperture through the elastomeric wall, for flow through the wall and connector tube. One of the retention zone and connector tube are made of a material of sufficient hardness that material of the other engaging member is deformed by engagement therewith, which increases the strength of retention between the retention wall and the connector tube.
Owner:B BRAUN MEDICAL
Methods for treating endoleaks during endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysms
InactiveUS6203779B1Decreased blood flowReducing or eliminating the possible rupture of the aneurysmCosmetic preparationsBiocideEndovascular prosthesisFluid composition
Disclosed are methods for treating endoleaks arising from endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysms. The disclosed methods involve the in situ sealing of endoleaks after placement of an endovascular prostheses in the abdominal aorta. Sealing of endoleaks is achieved by injection of either a biocompatible polymer or prepolymer fluid composition into the endoleak which composition in situ solidifies to seal the leak. Preferably, the biocompatible fluid composition comprises a contrast agent to allow the clinician to visualize the sealing process.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Compositions and methods for the treatment and prevention of cardiovascular diseases and disorders, and for identifying agents therapeutic therefor
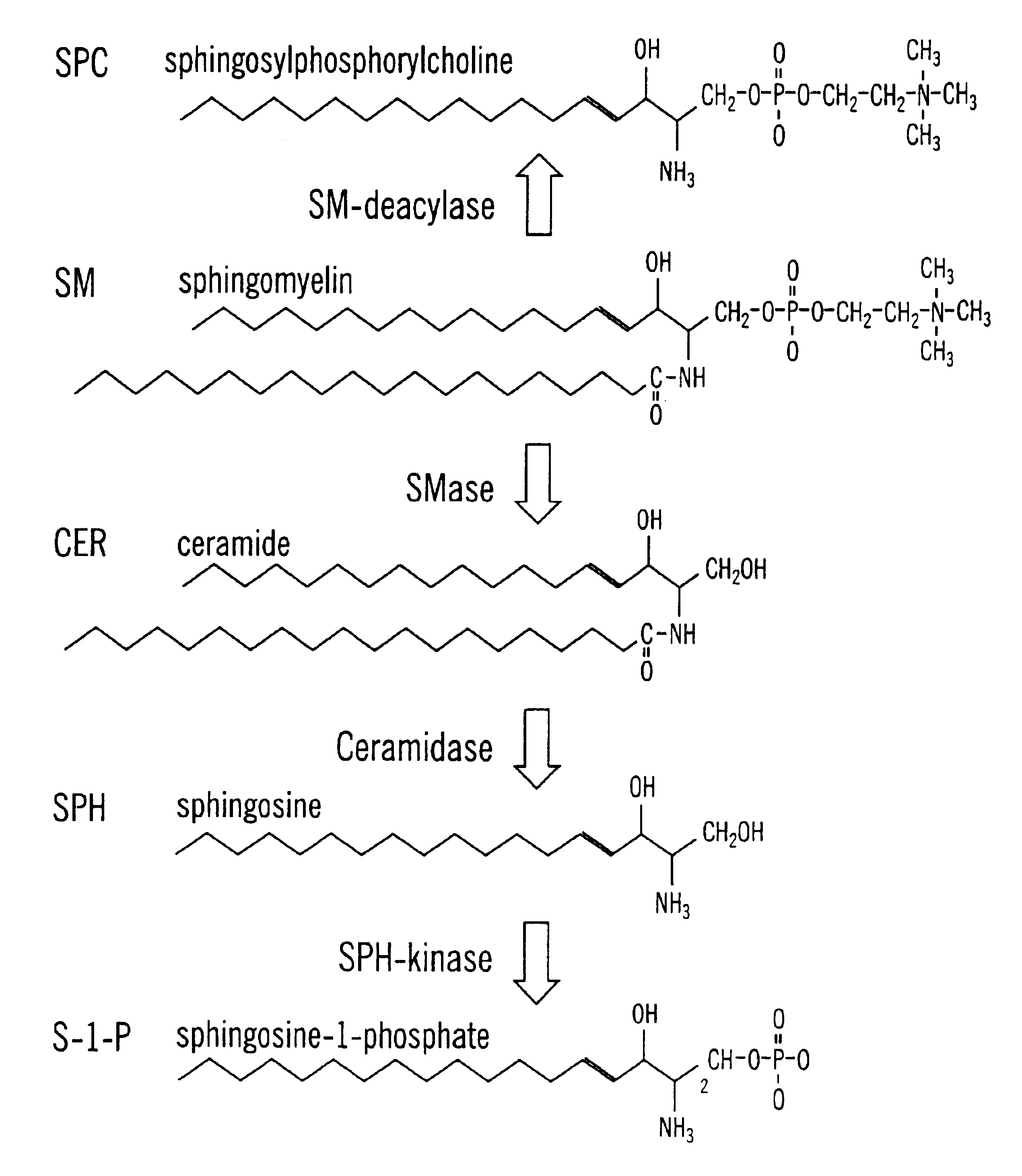
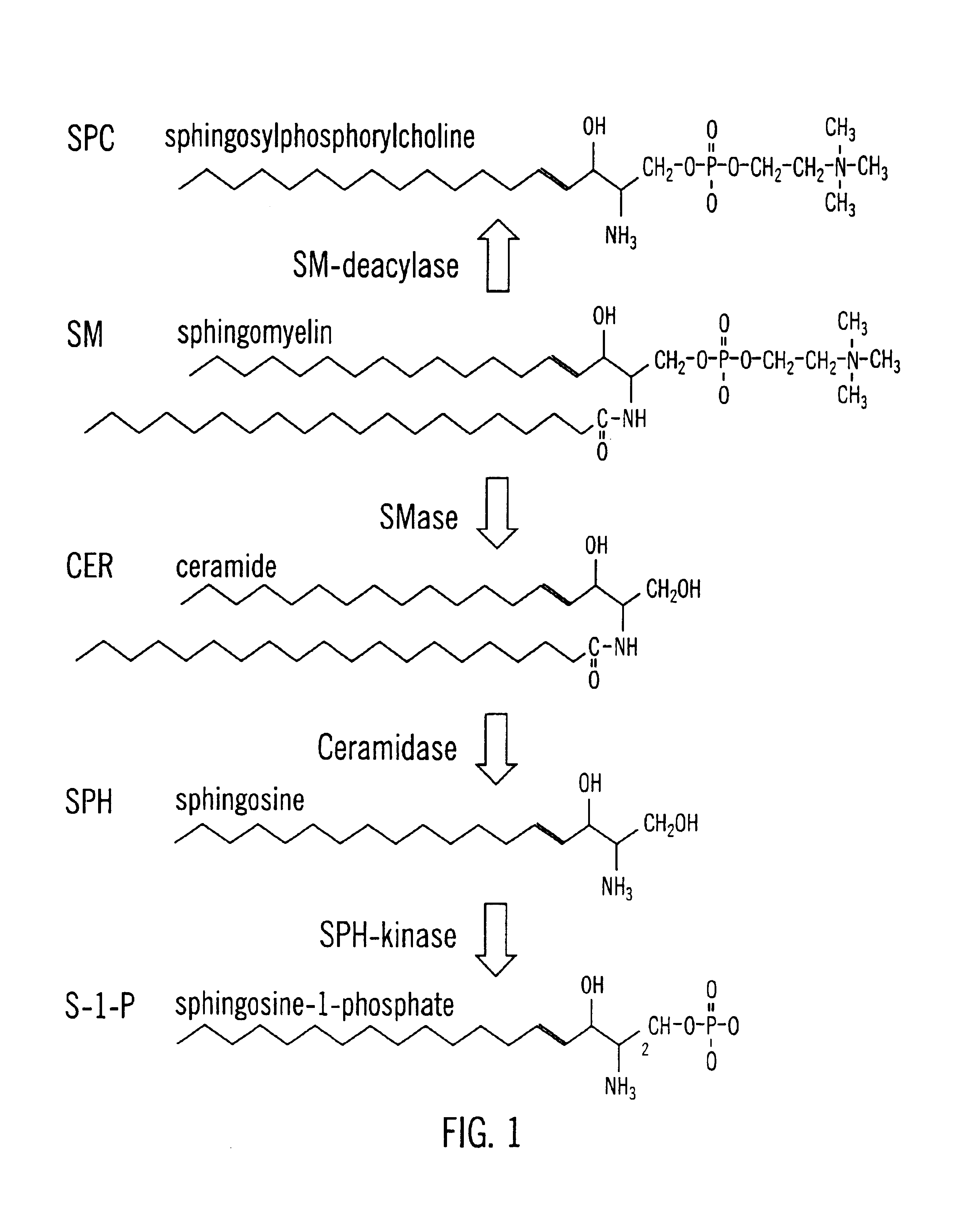
InactiveUS6858383B2High serum cholesterol levelDecreased blood flowOrganic active ingredientsHydrolasesMetaboliteSphingolipid metabolism
Methods and compositions are disclosed that are useful for the prevention and / or treatment of cardiovascular and cardiac diseases and disorders, or damage resulting from surgical or medical procedures that may cause ischemic or ischemic / reperfusion damage in humans; and cardiovascular trauma. The beneficial effects of the compositions and methods are achieved through the use of pharmaceutical compositions that include agents that interfere with the production and / or biological activities of sphingolipids and their metabolites, particularly sphingosine (SPH) and sphingosine-1-phosphate (S-1-P). Also disclosed are methods for identifying and isolating therapeutic agents.
Owner:APOLLO ENDOSURGERY INC
System for performing remote ischemic preconditioning
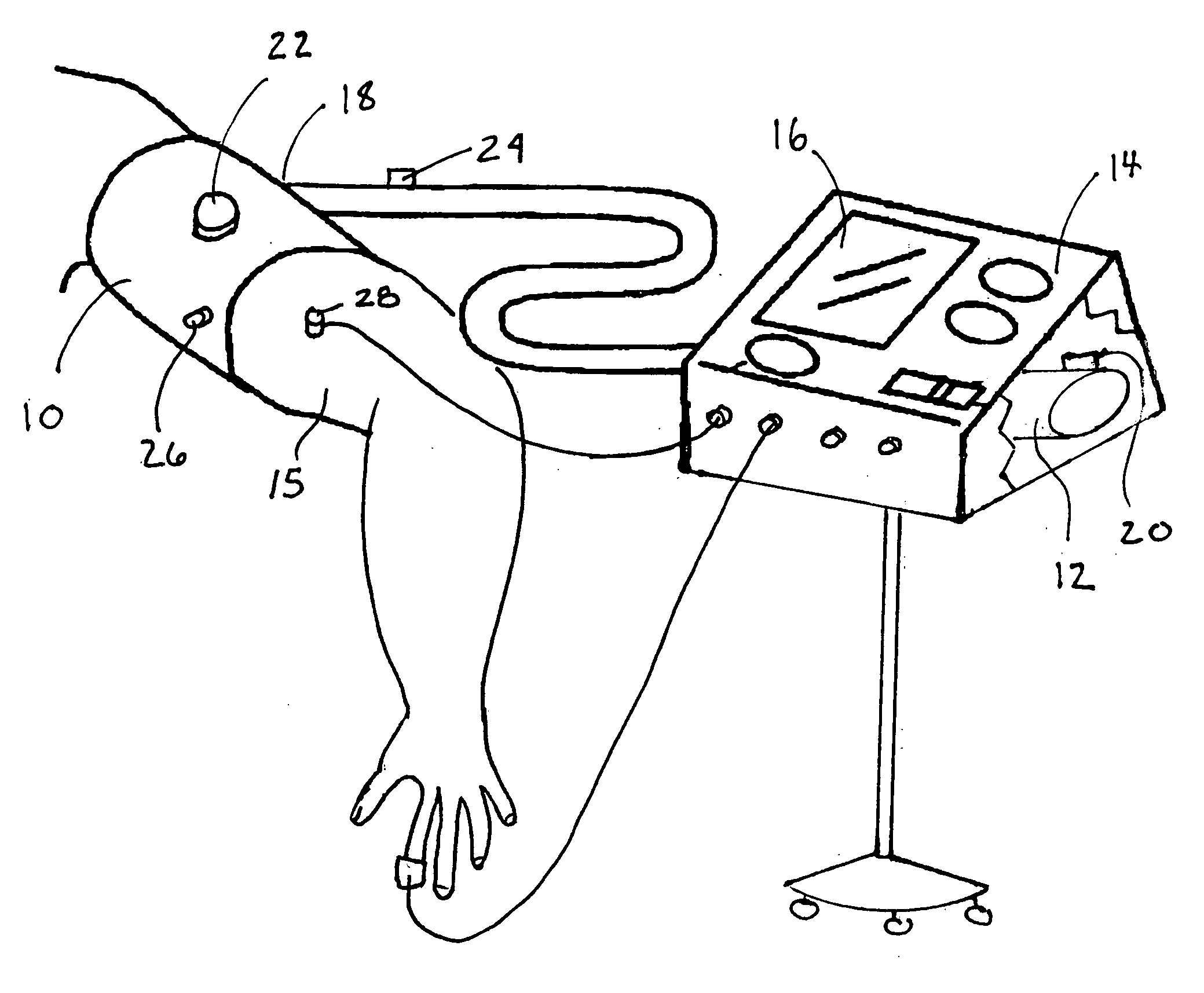
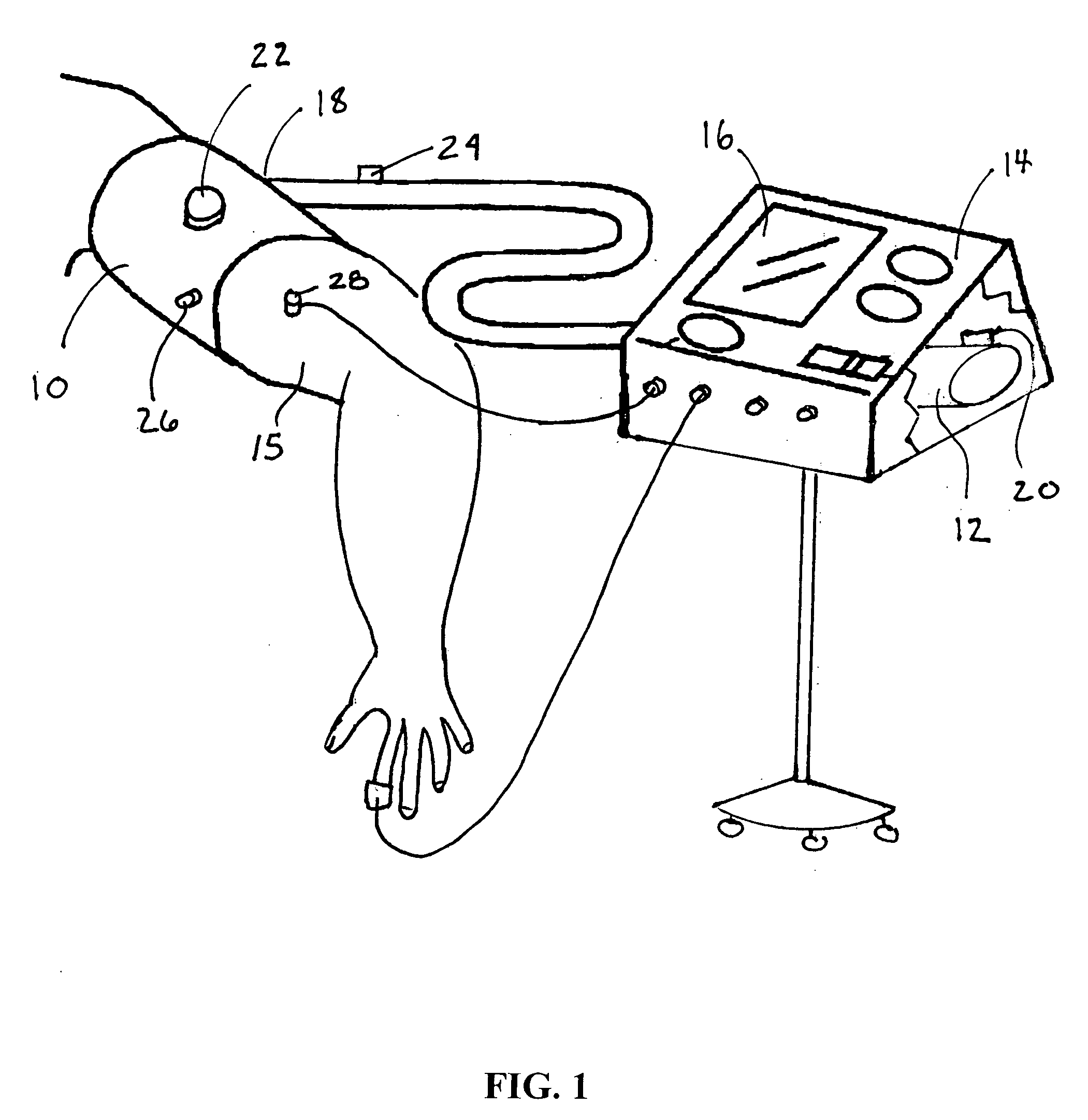
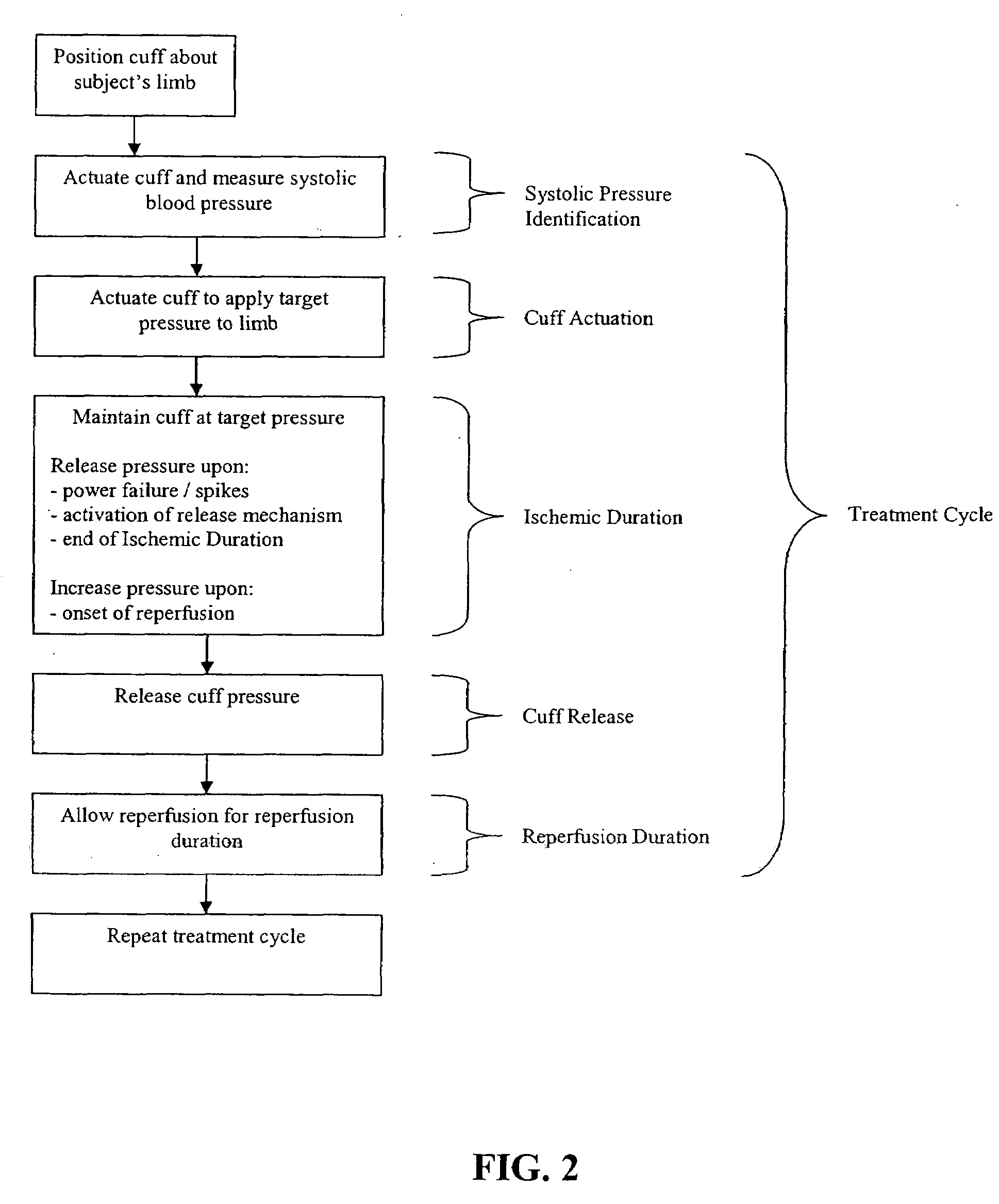
ActiveUS20080139949A1Decreased blood flowPneumatic massageEvaluation of blood vesselsMedicinePre treatment
A system for remote ischemic preconditioning that includes a cuff, and actuator, and a controller that operates the actuator according to a treatment protocol. The treatment protocol includes a plurality of treatment cycles that each comprise cuff actuation, an ischemic duration, cuff release, and a reperfusion duration.
Owner:HOSPITAL FOR SICK CHILDREN
Occlusive implant and methods for hollow anatomical structure
ActiveUS20070248640A1Promoting occlusive ingrowthInhibit migrationSuture equipmentsOcculdersFiberAnatomical structures
Apparatus and methods for treating a hollow anatomical structure comprises an implant sized for insertion into a hollow anatomical structure. The implant comprises a plurality of loose, bulked fibers. The fibers are formed from one or more bioabsorbable materials. Upon implantation, the apparatus causes a partial occlusion of the hollow anatomical structure, followed by a complete or substantially complete occlusion.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com