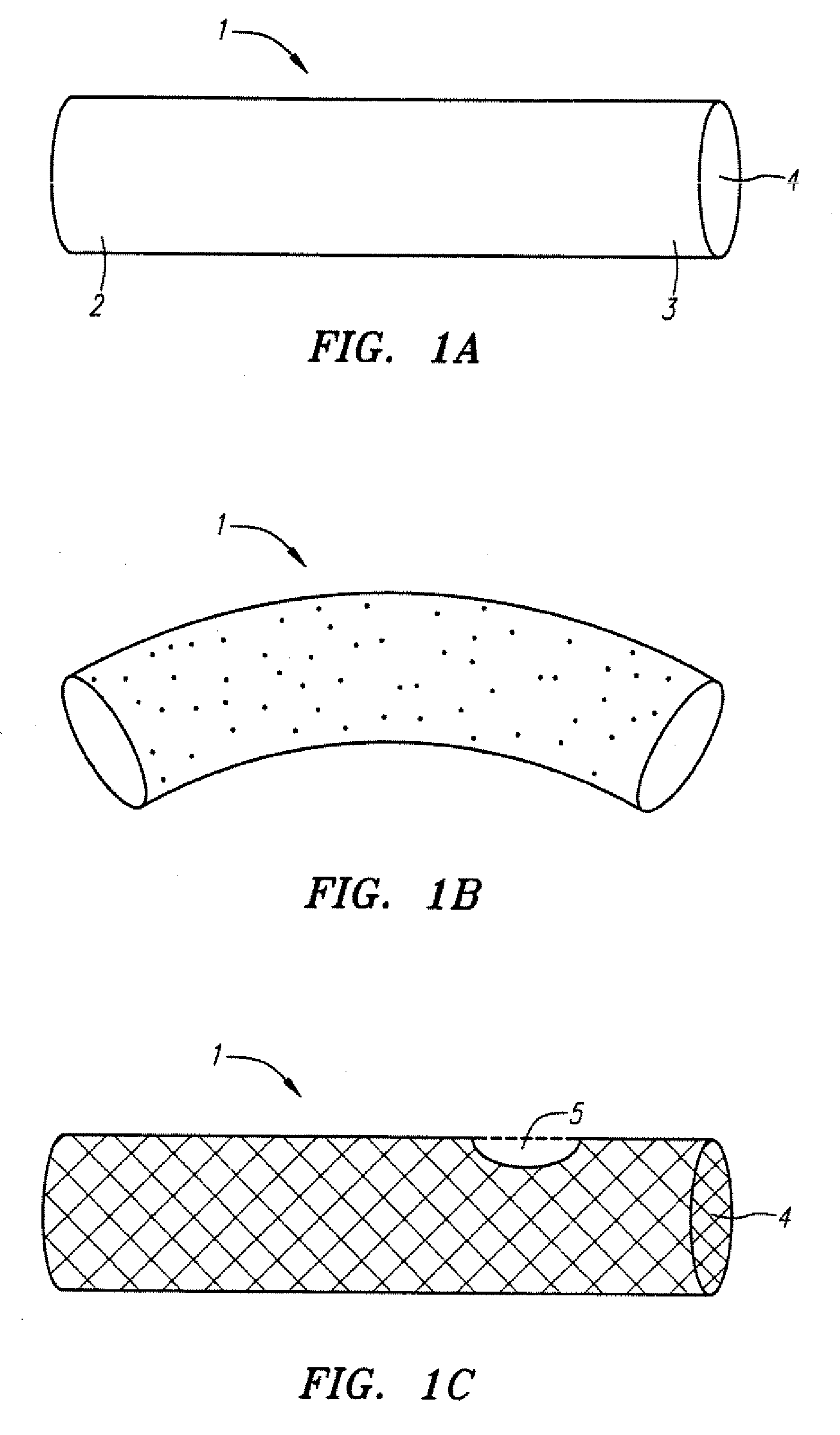
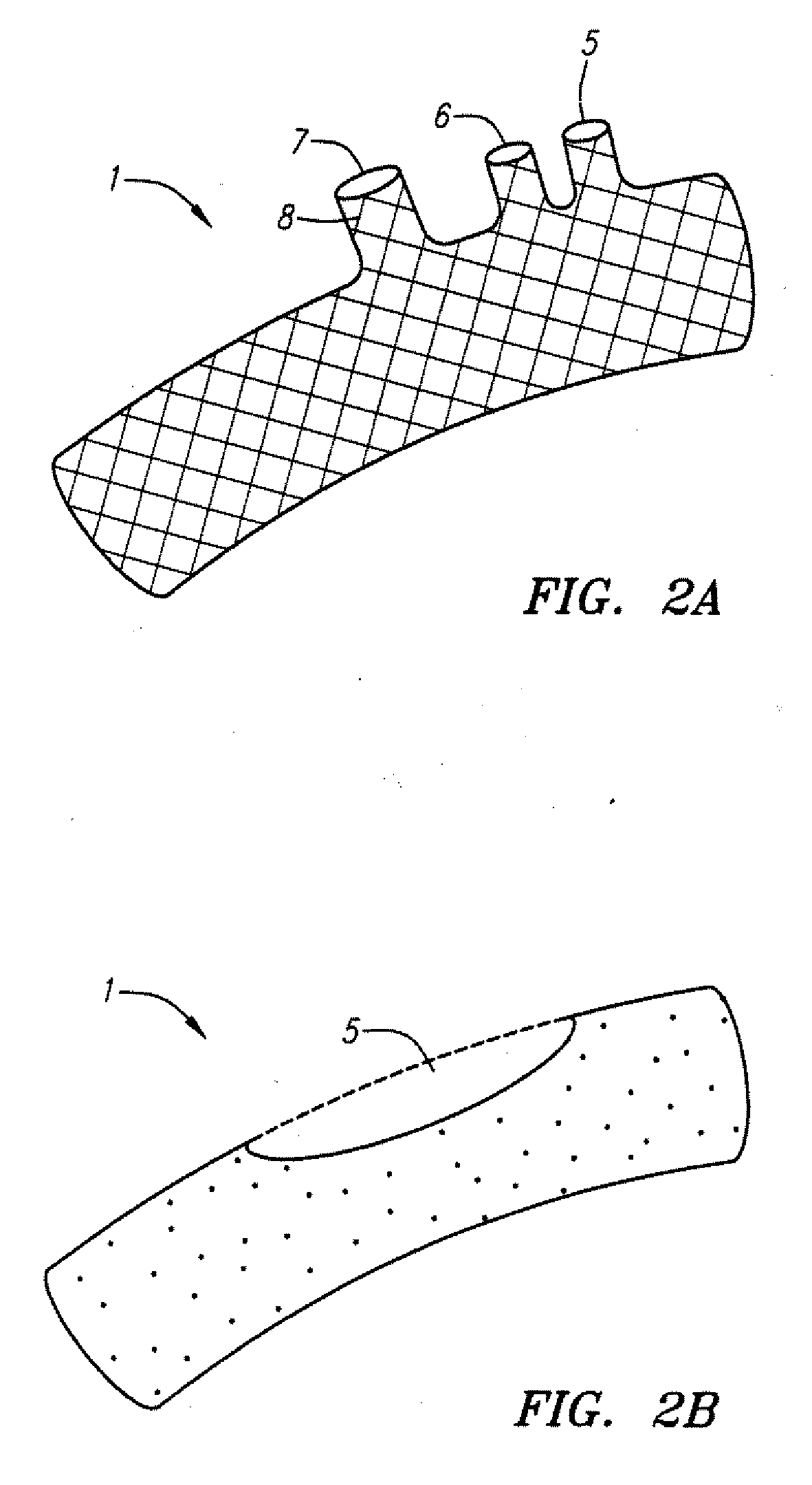
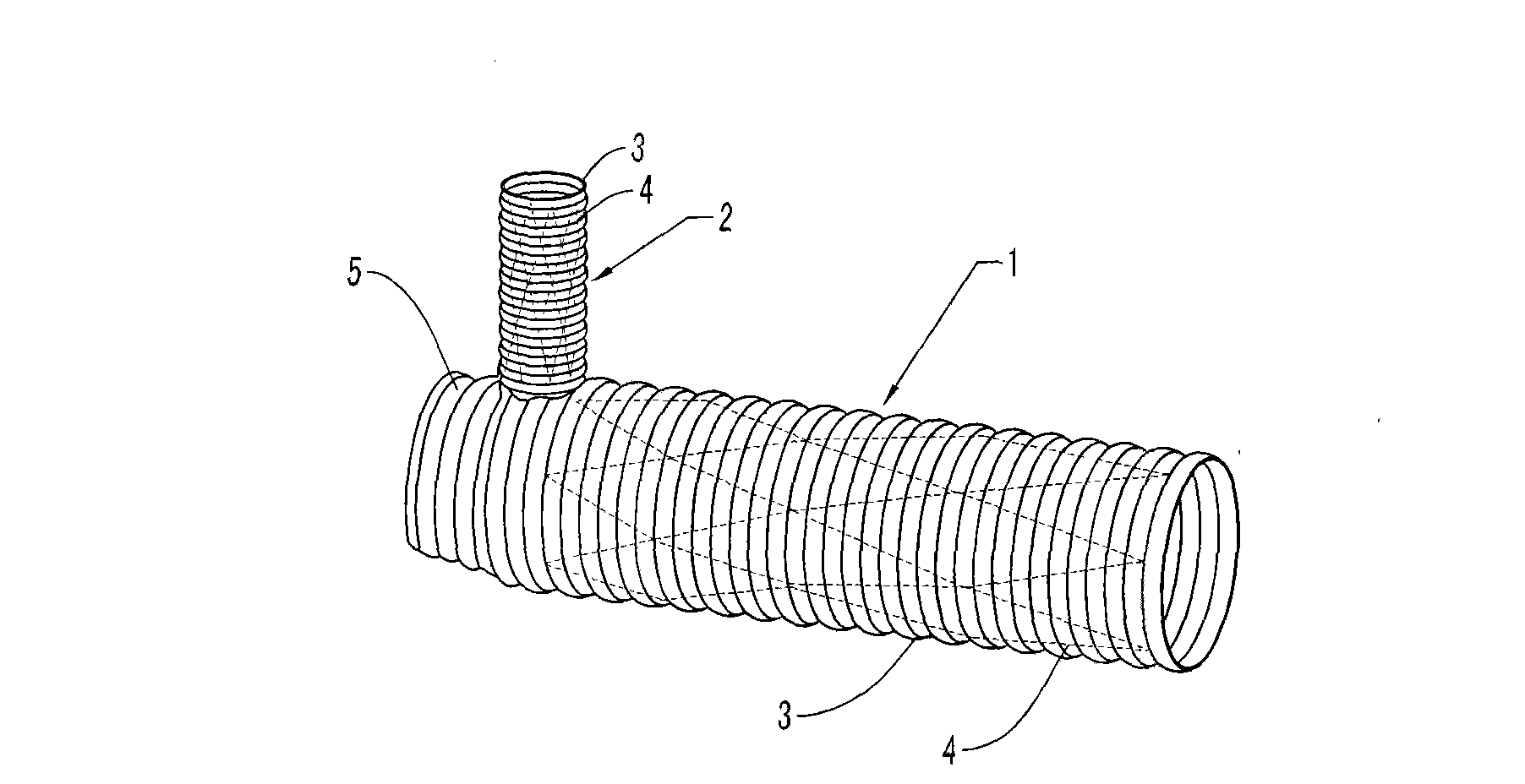
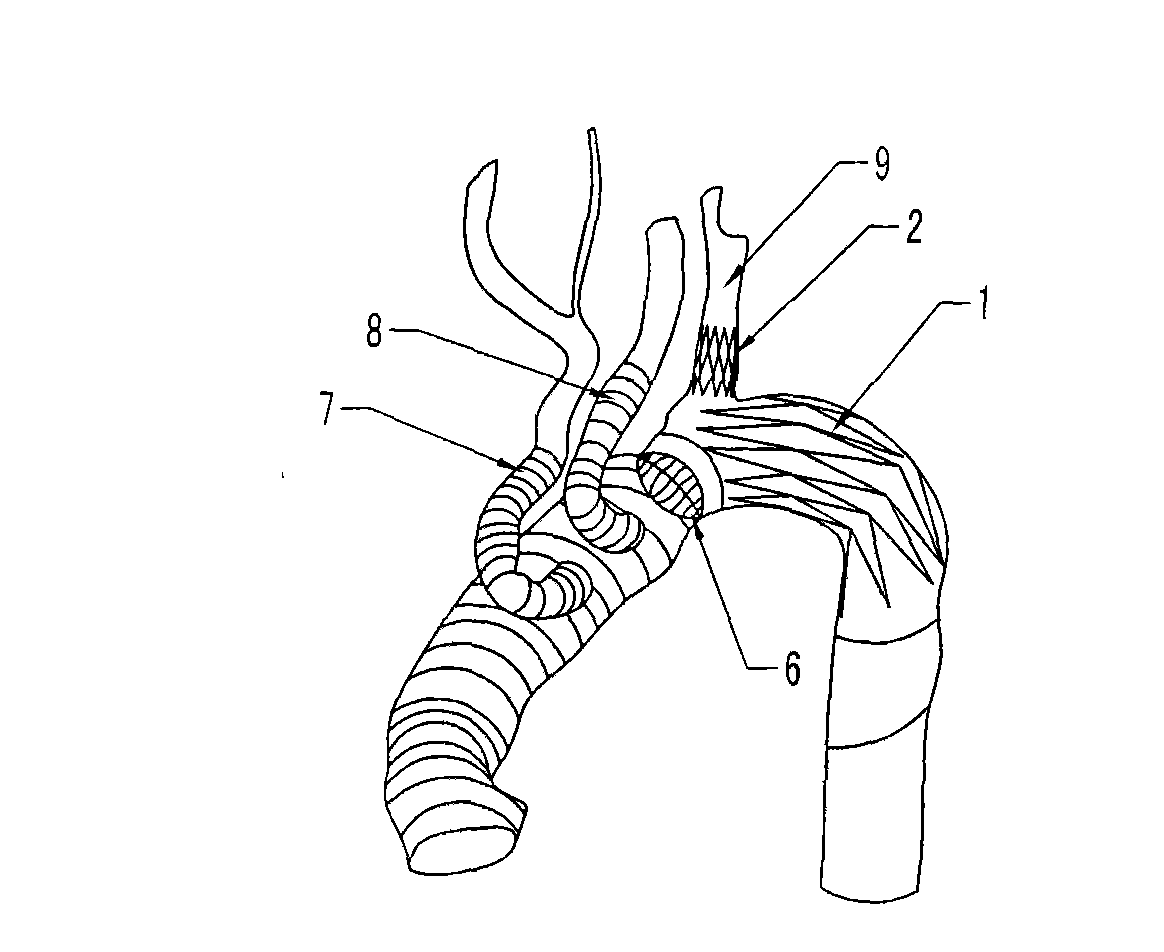
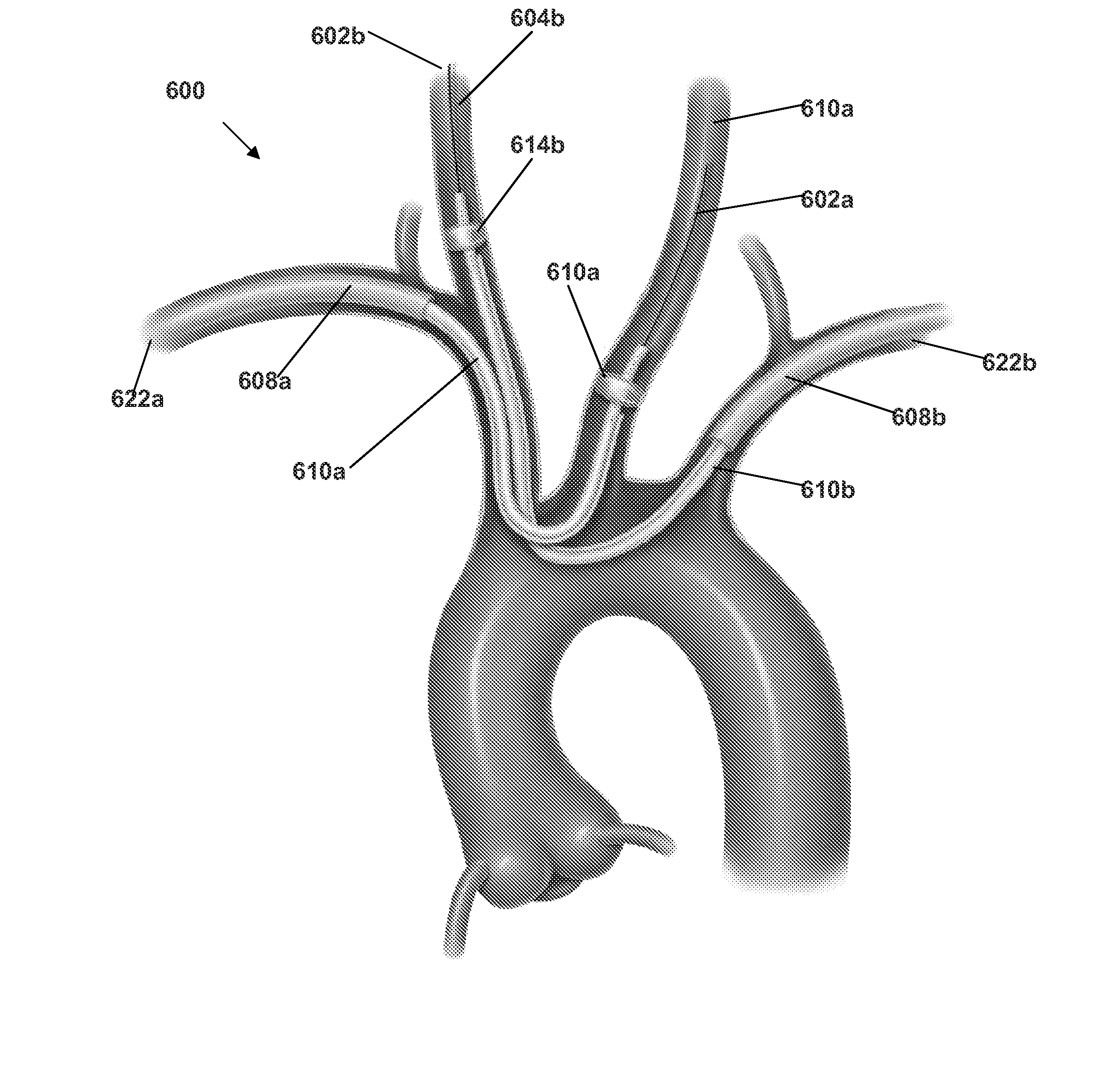
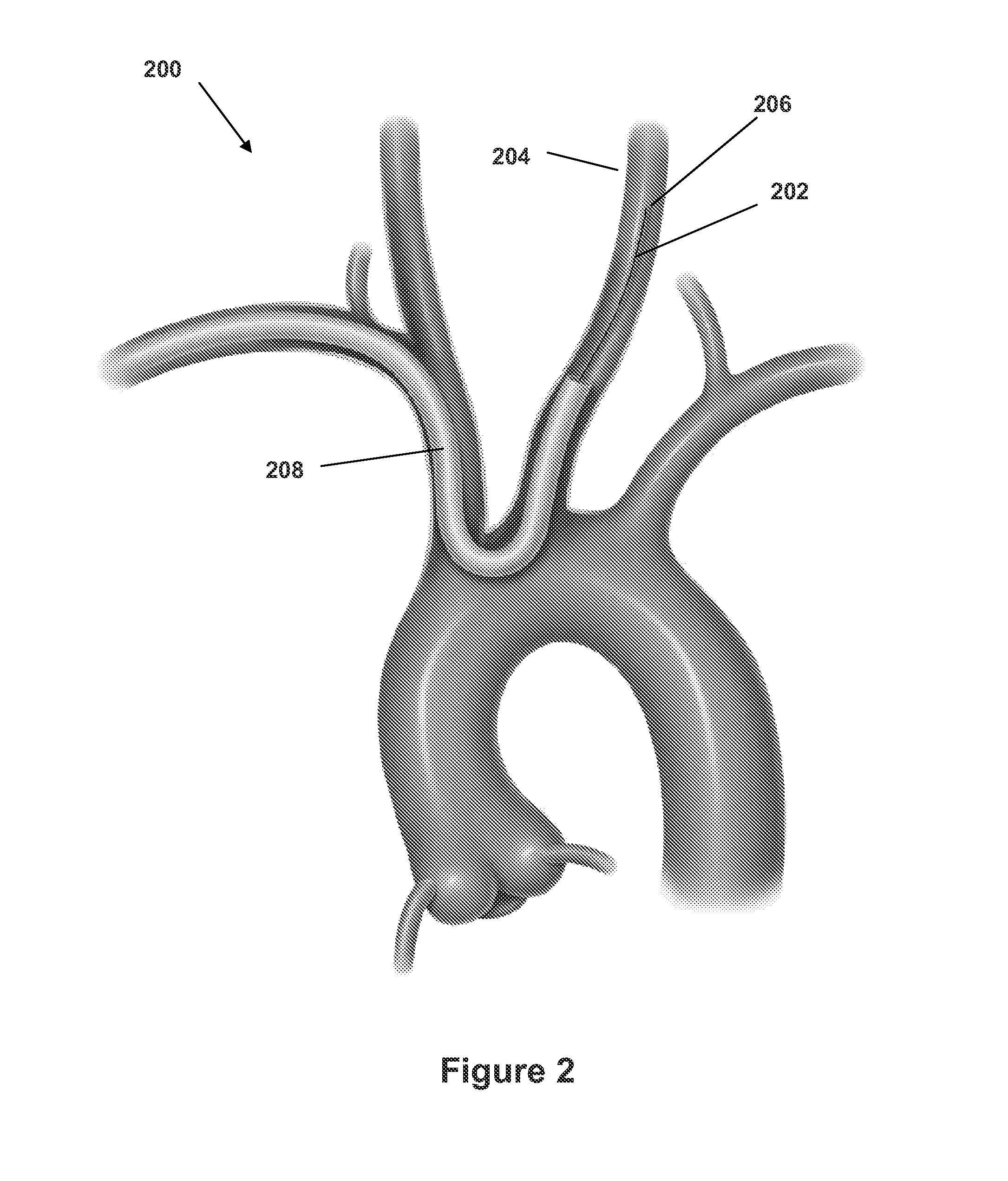
Patents
Literature
30 results about "Innominate Arteries" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
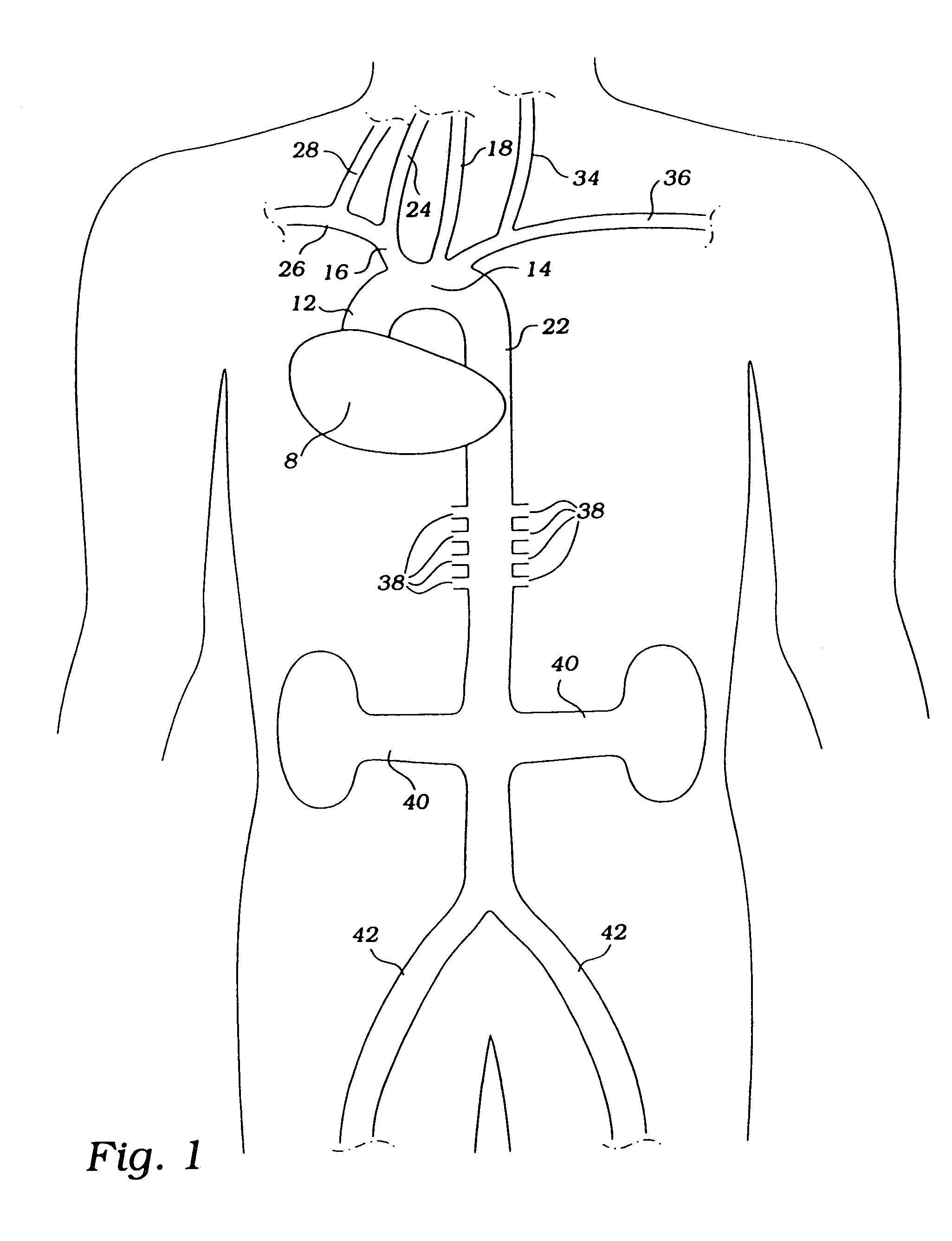
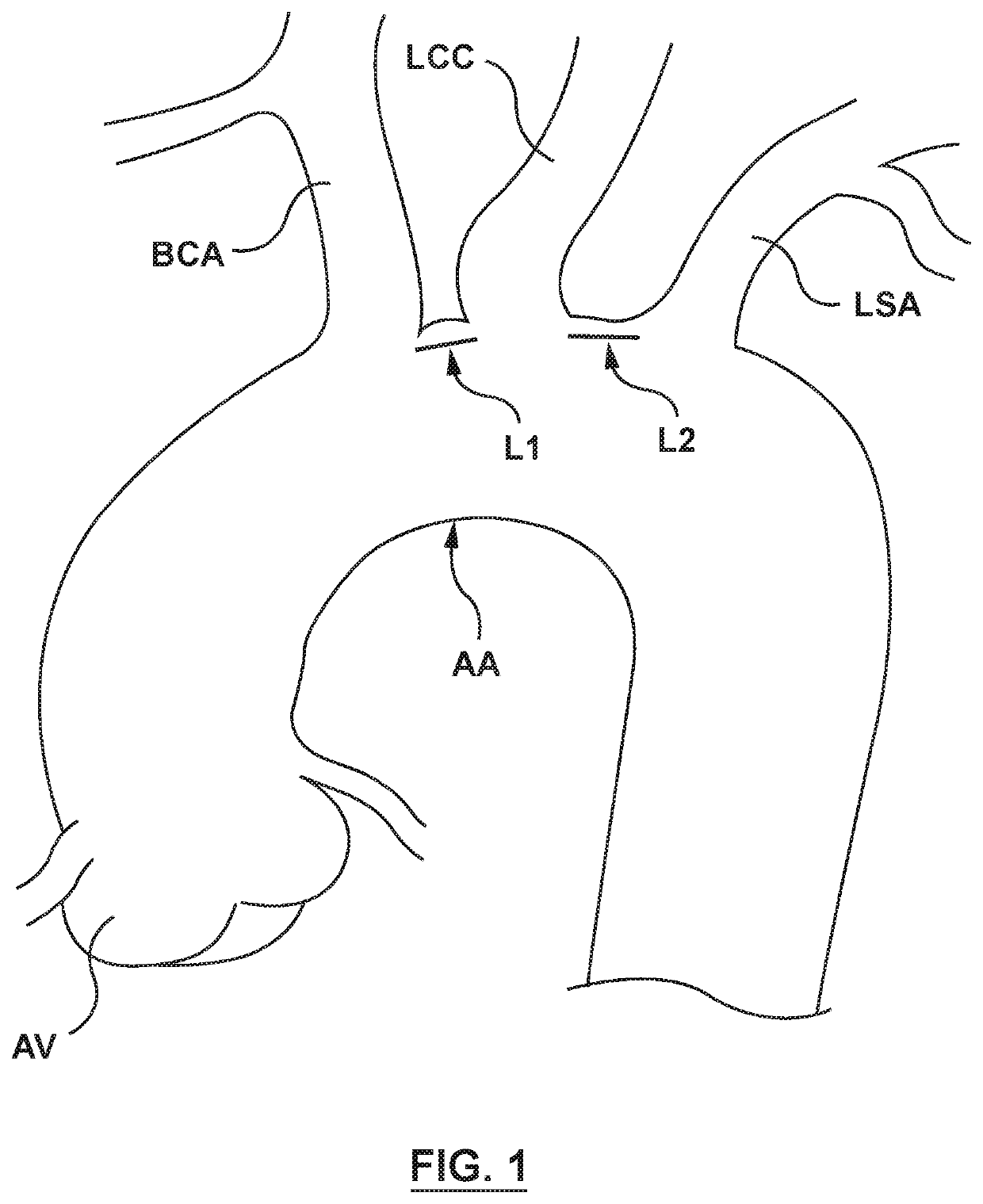
The brachiocephalic artery (or brachiocephalic trunk or innominate artery) is an artery of the mediastinum that supplies blood to the right arm and the head and neck.
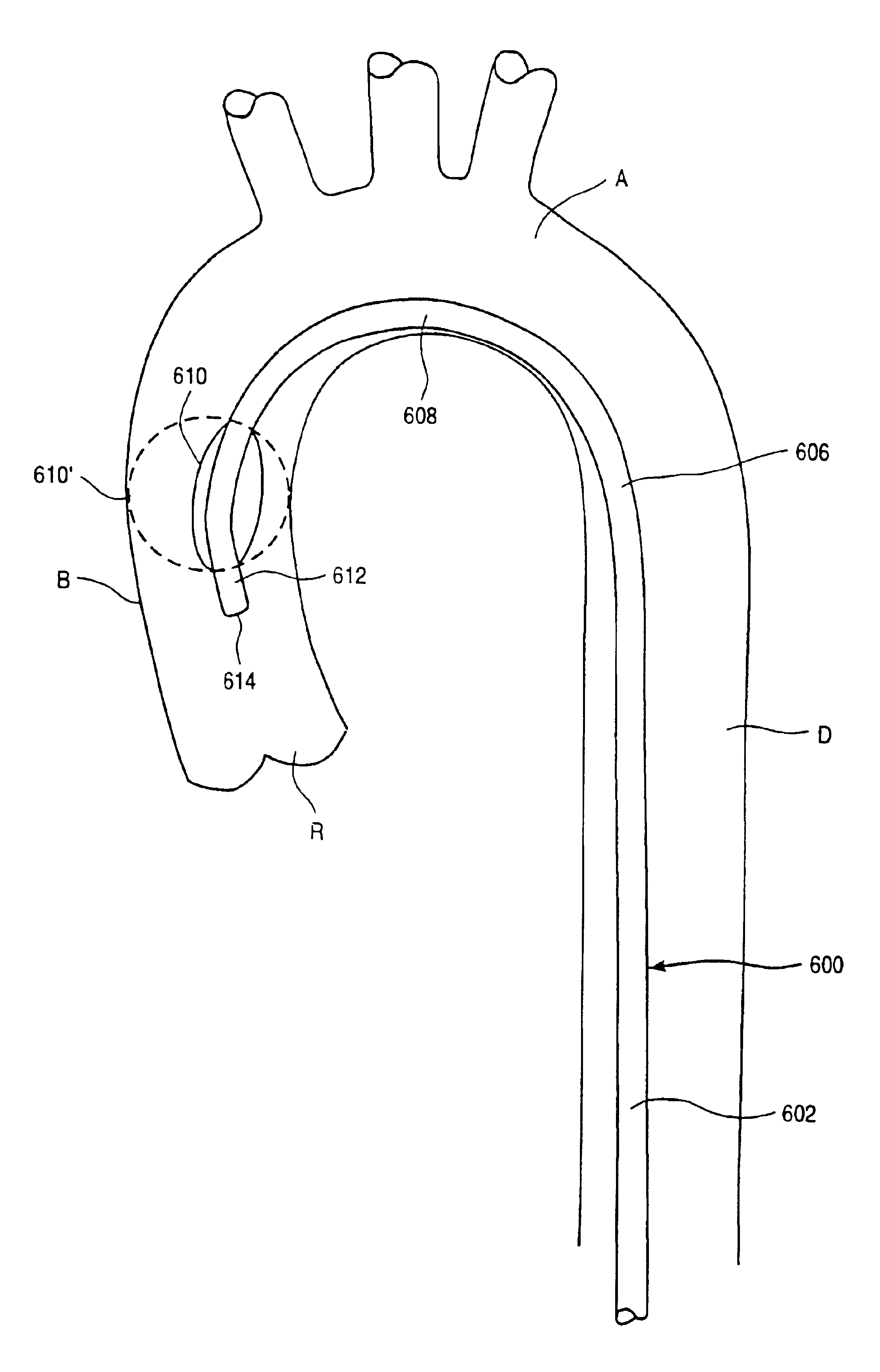
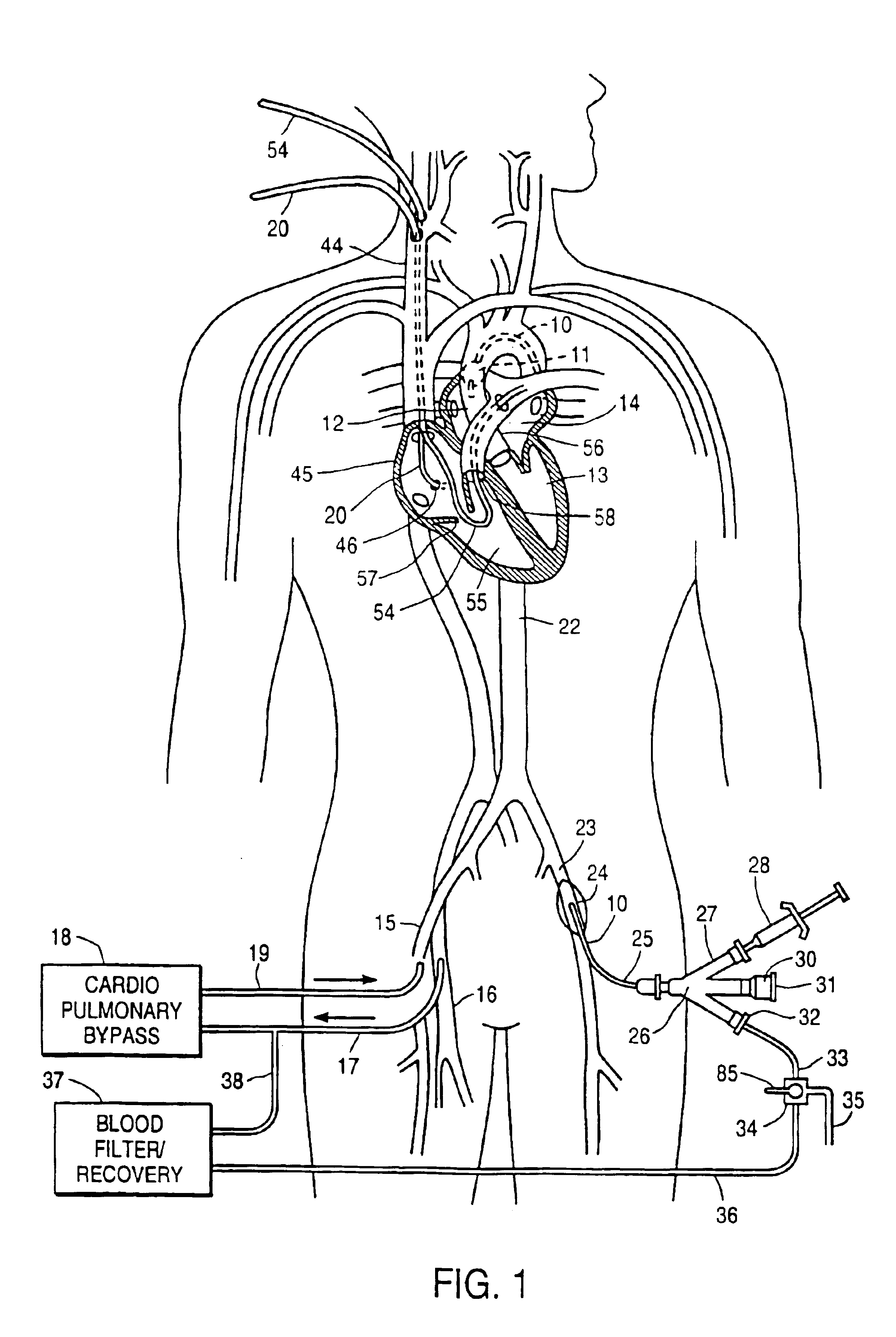
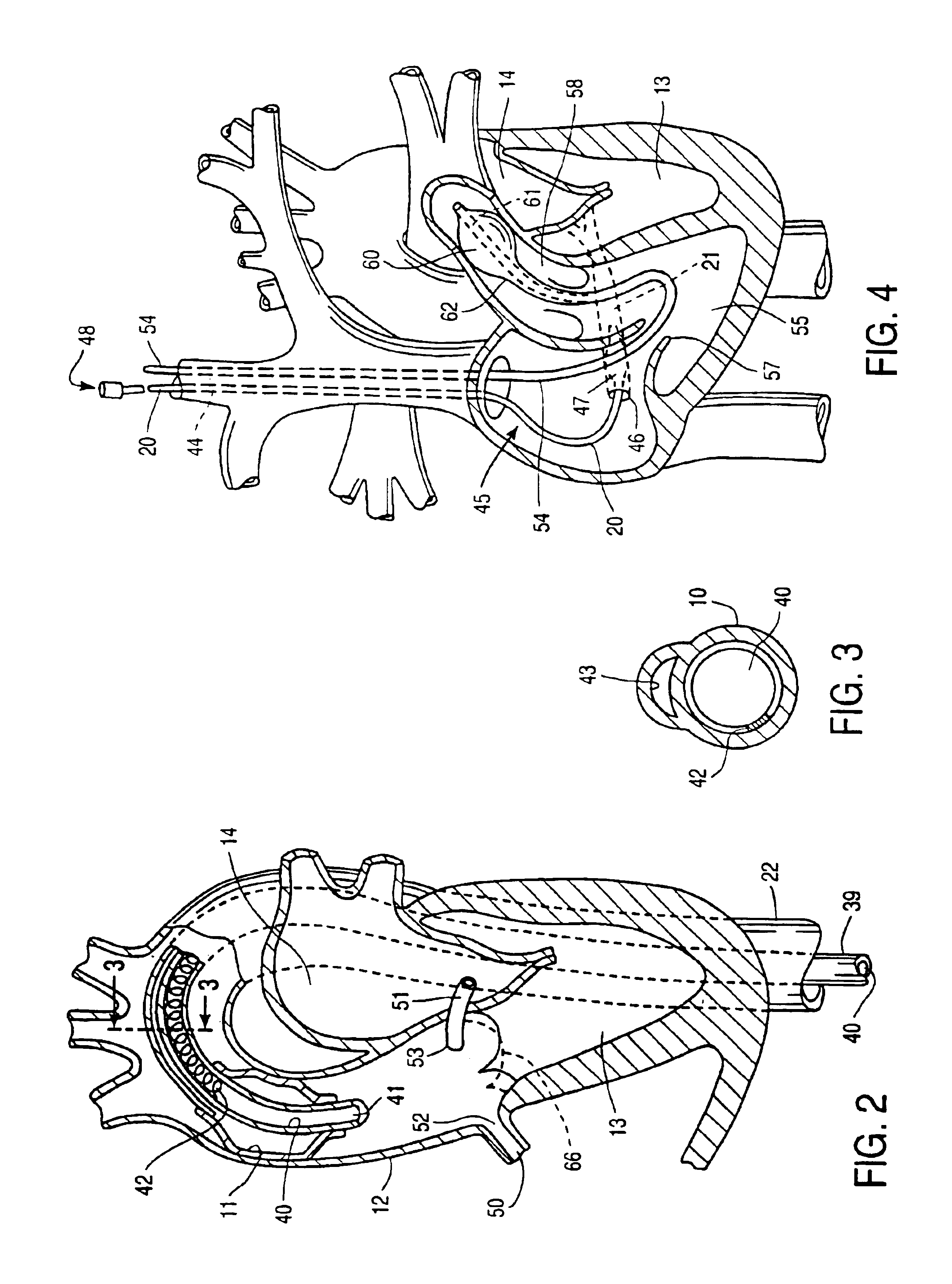
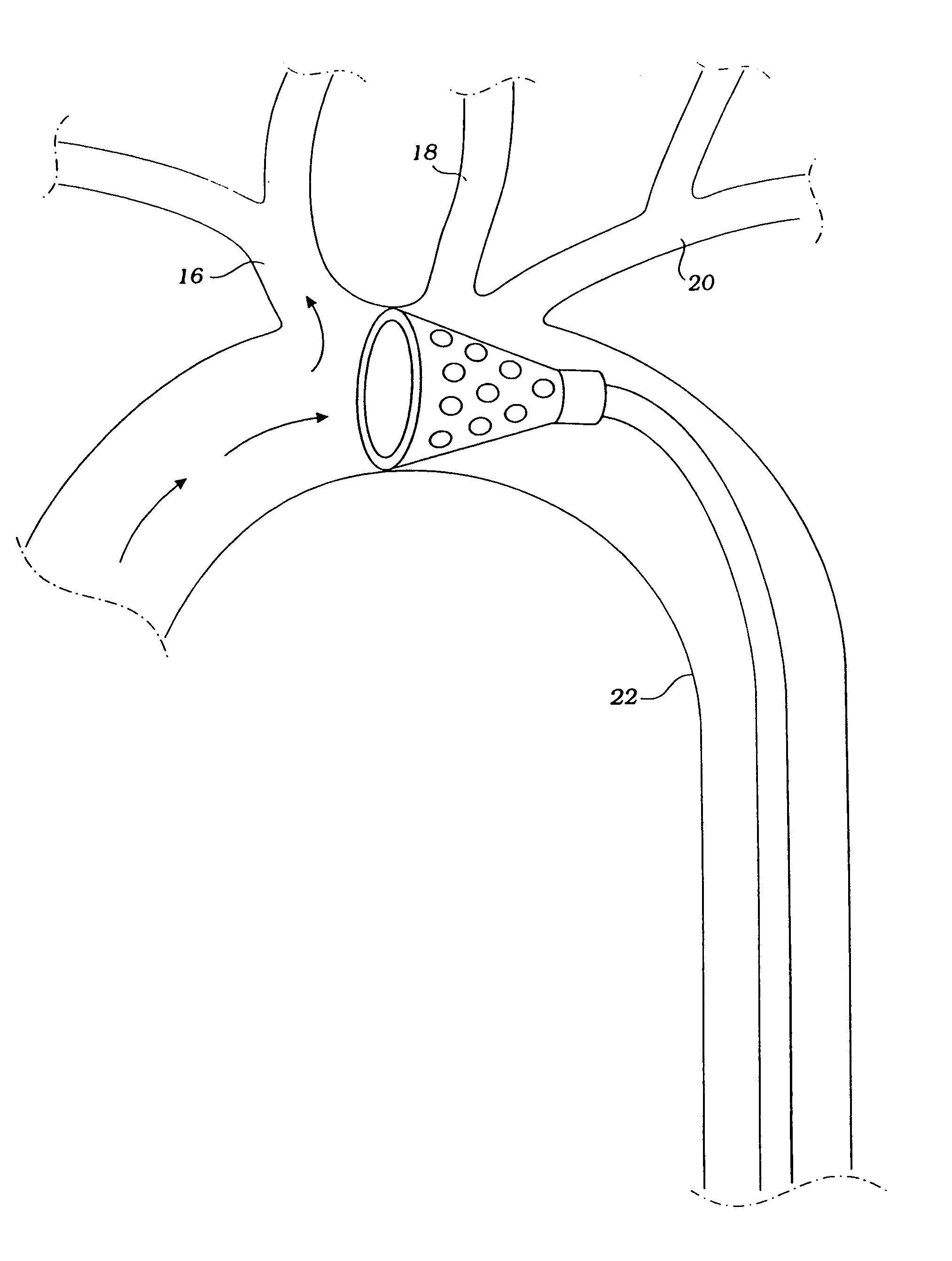
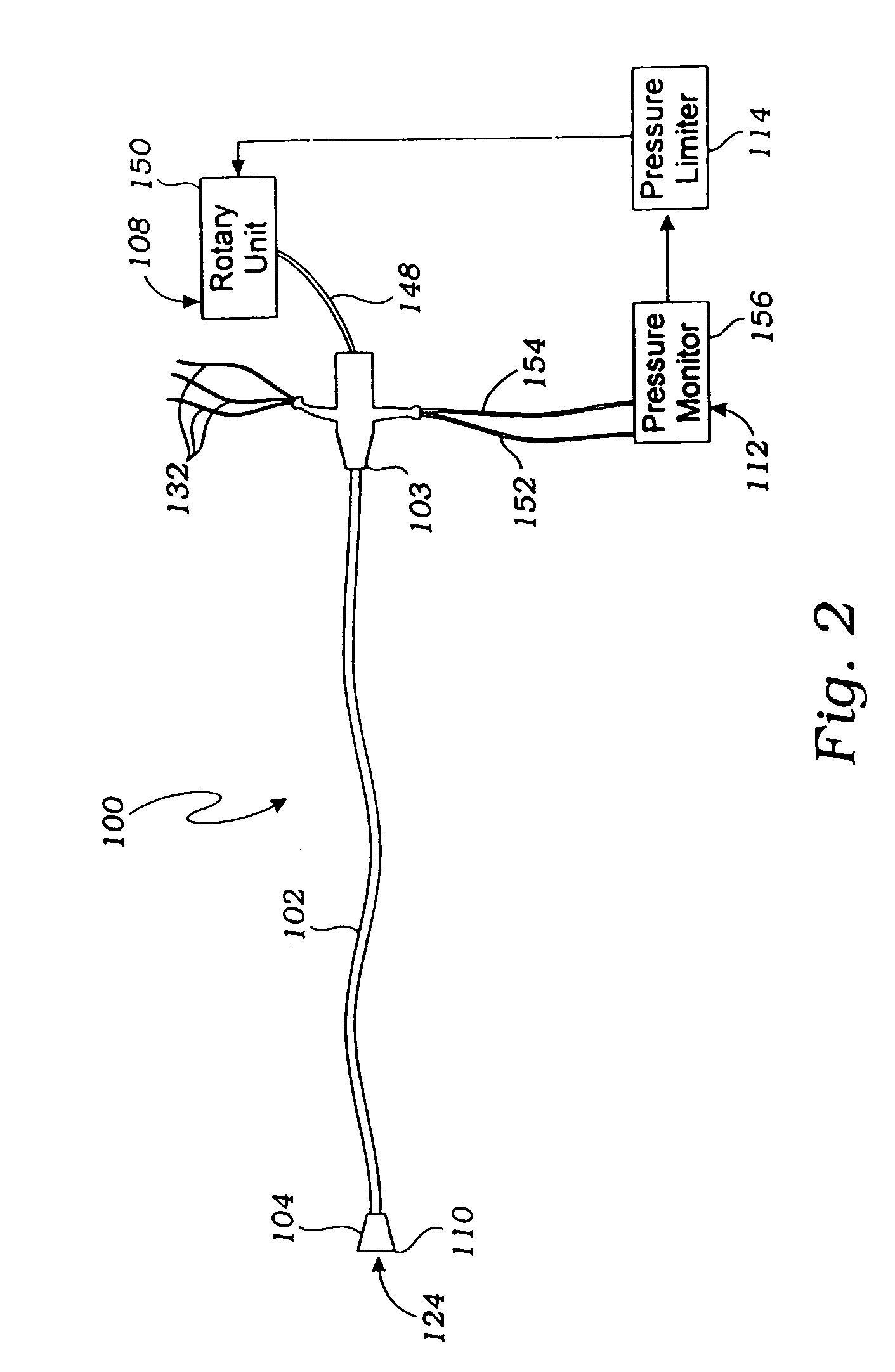
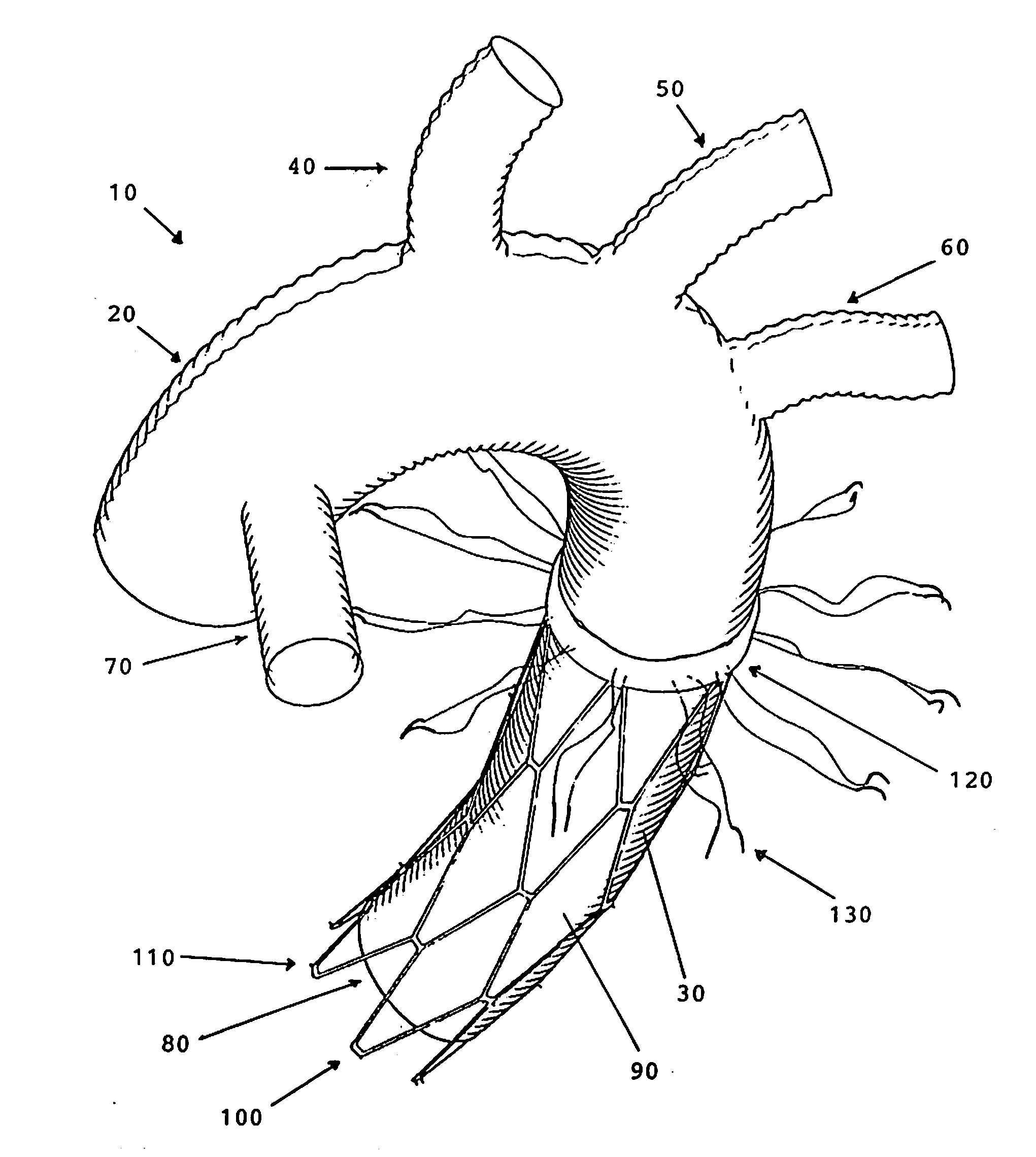
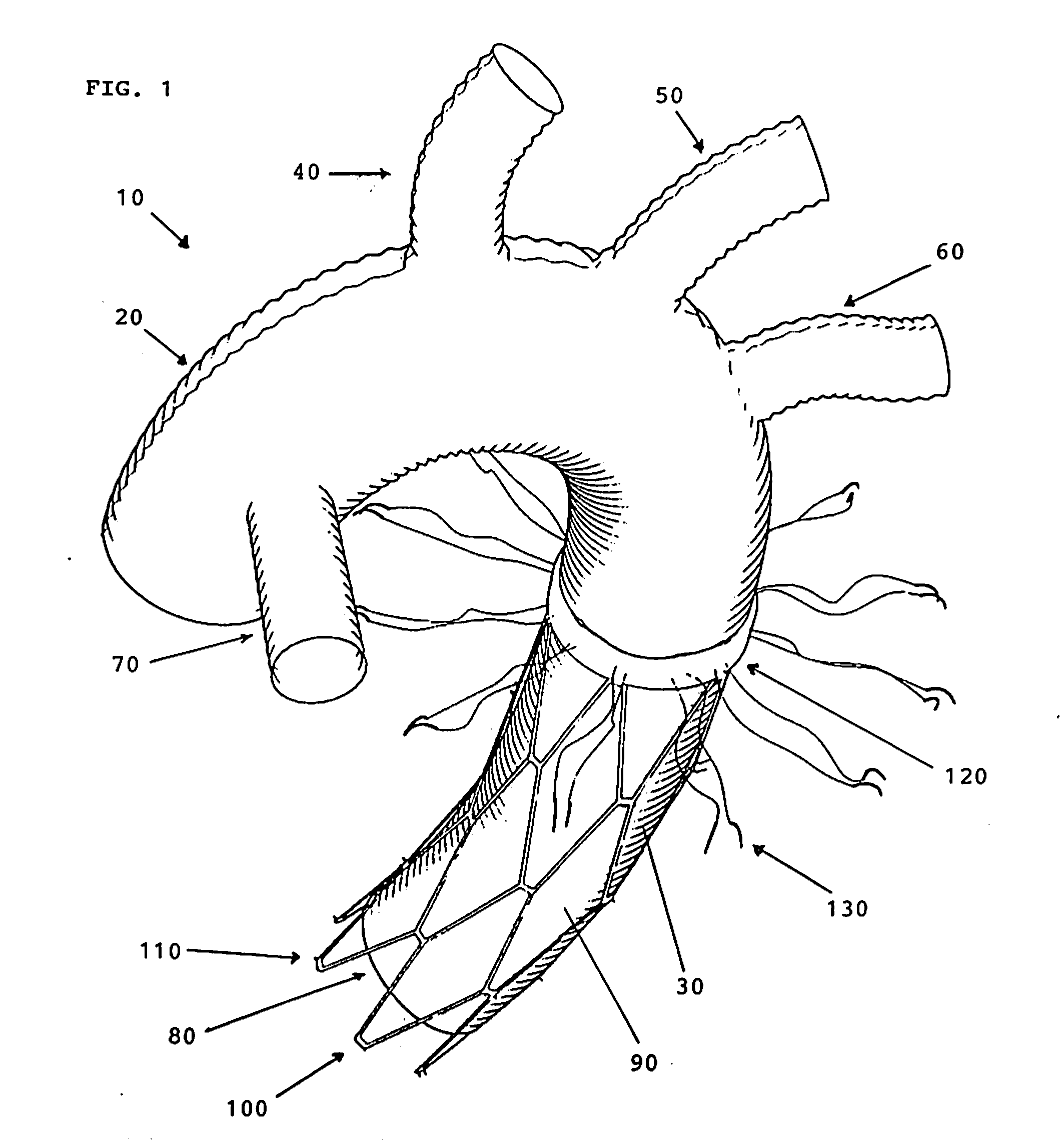
Endovascular system for arresting the heart
InactiveUS6913600B2Reduce morbidityReduce mortalitySuture equipmentsOther blood circulation devicesCardiopulmonary bypass timeSurgical department
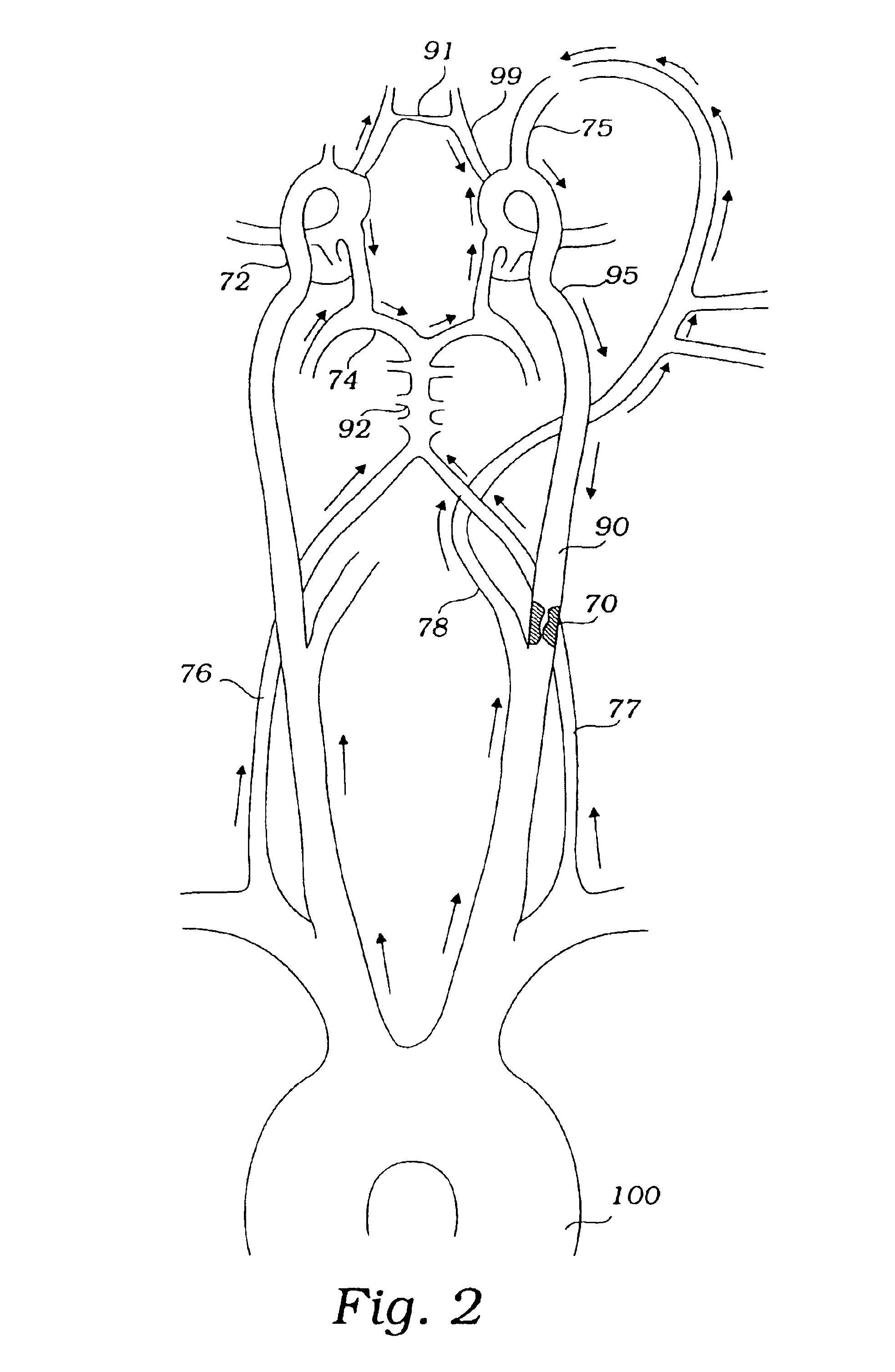
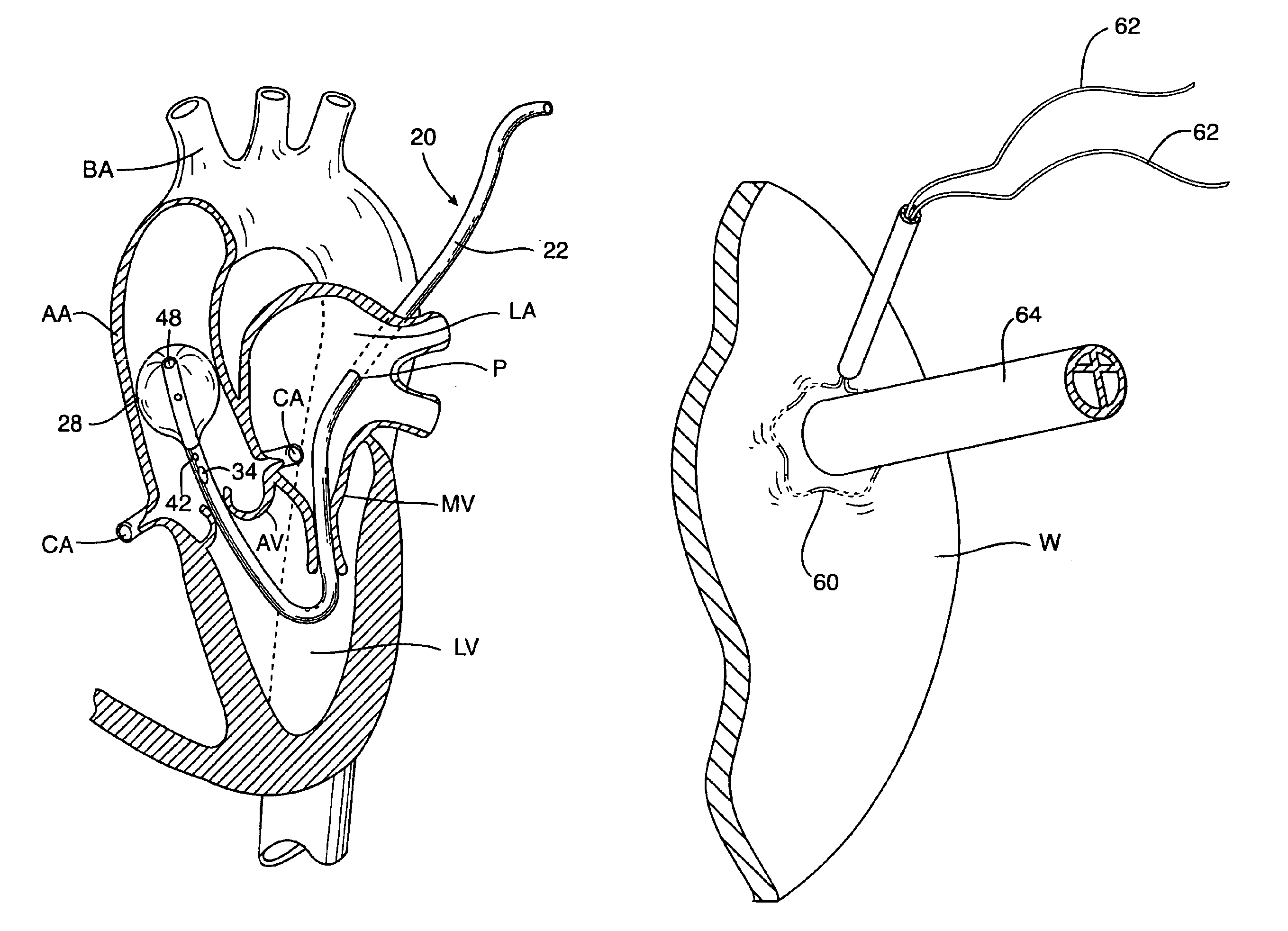
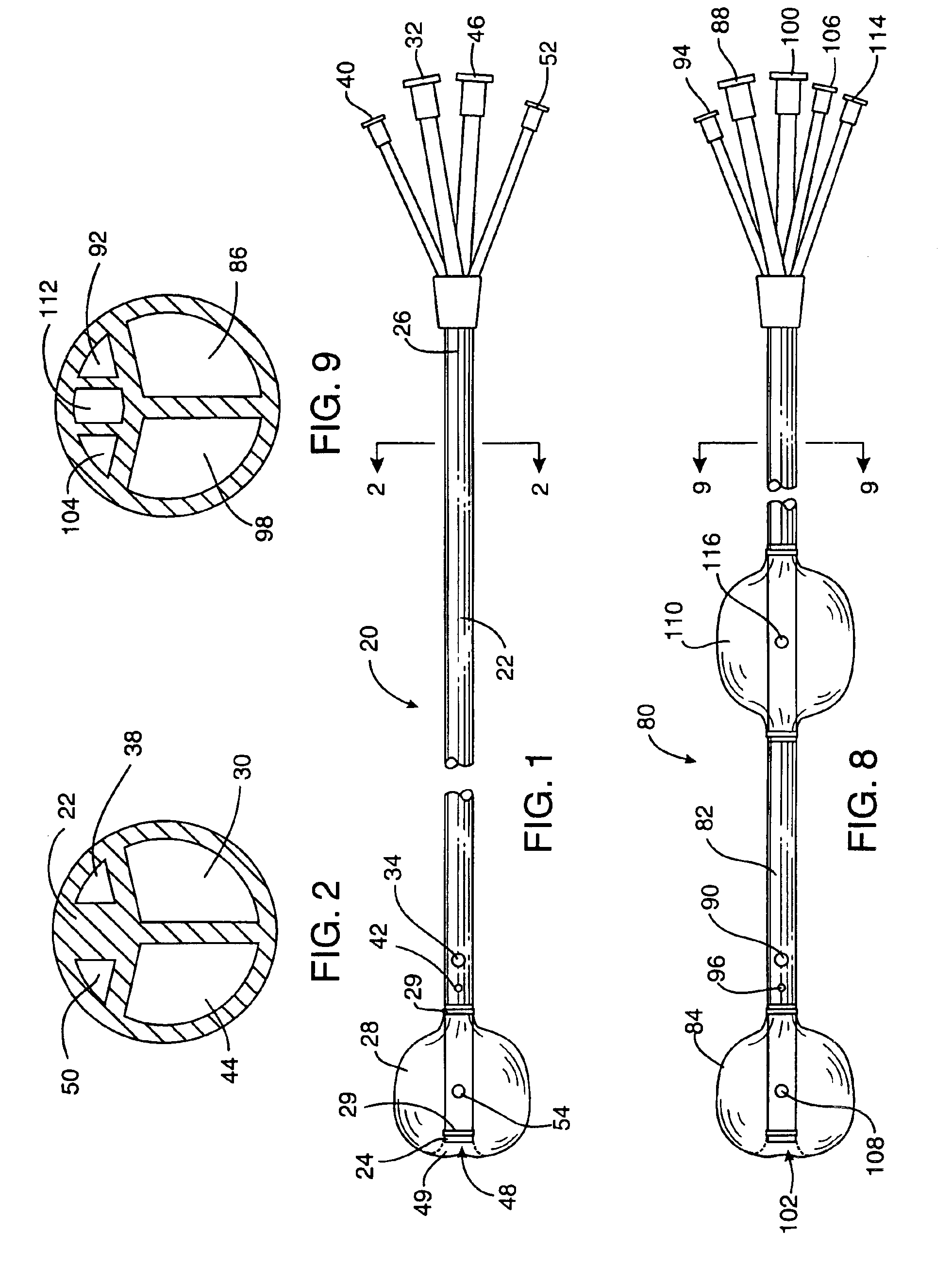
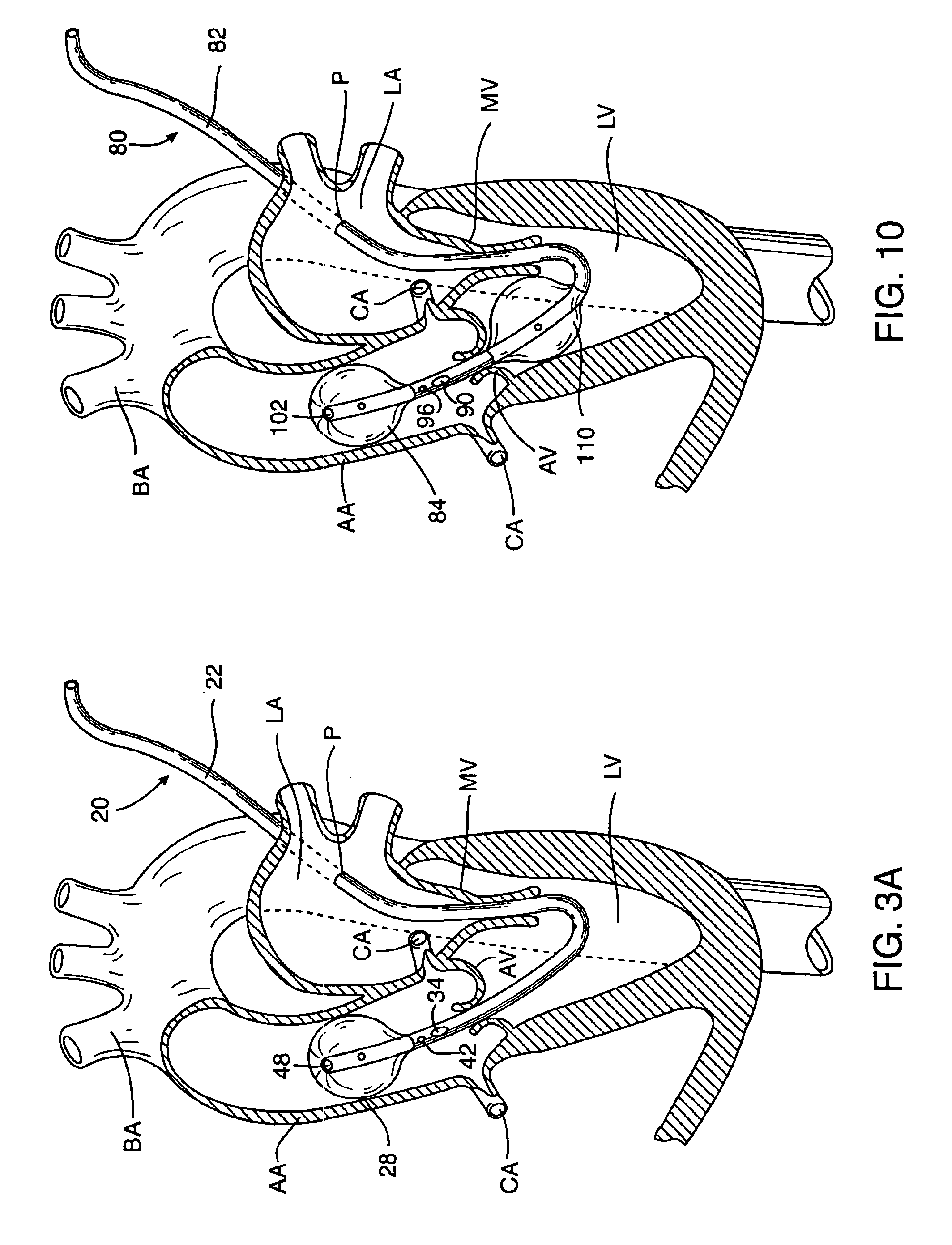
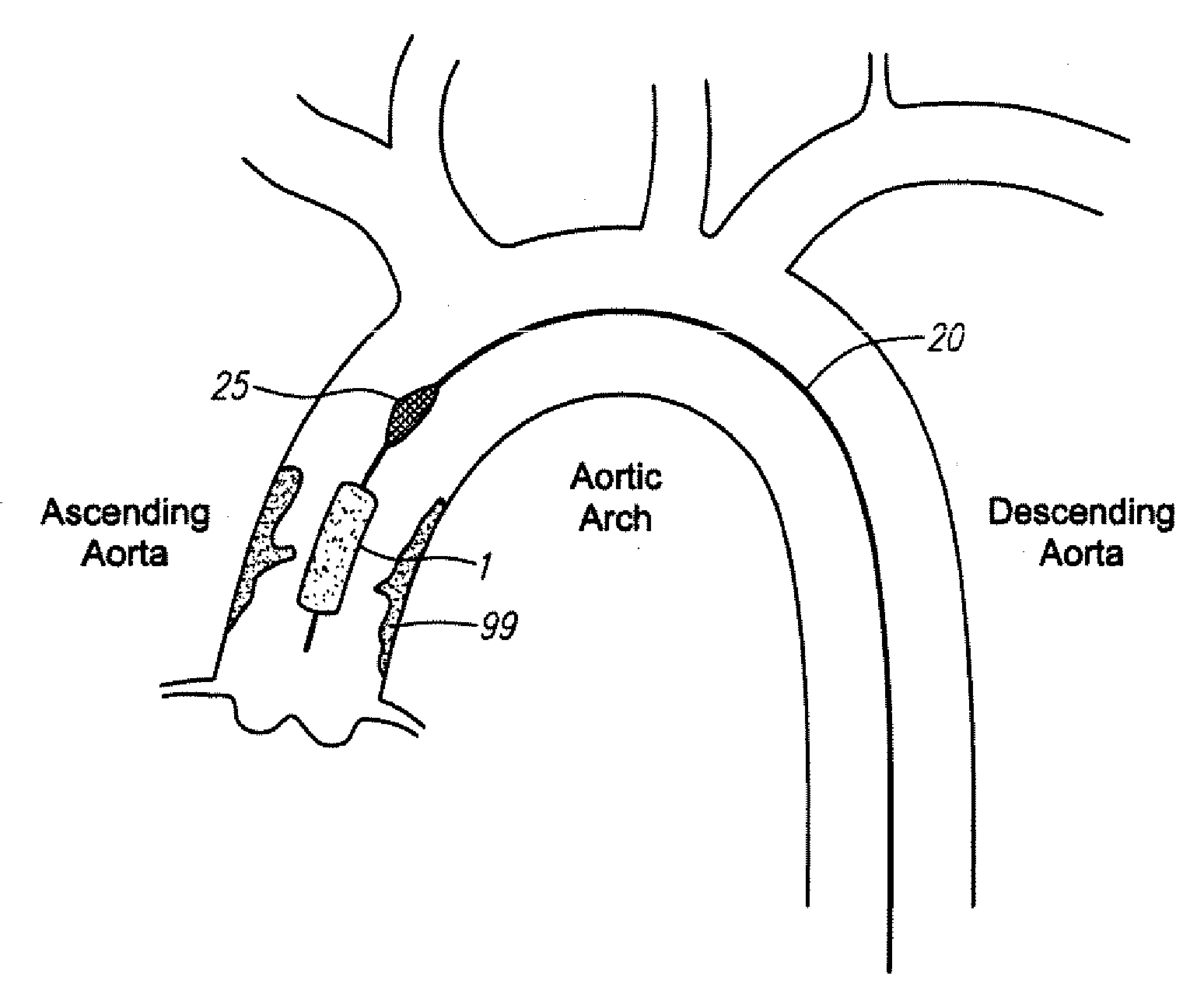
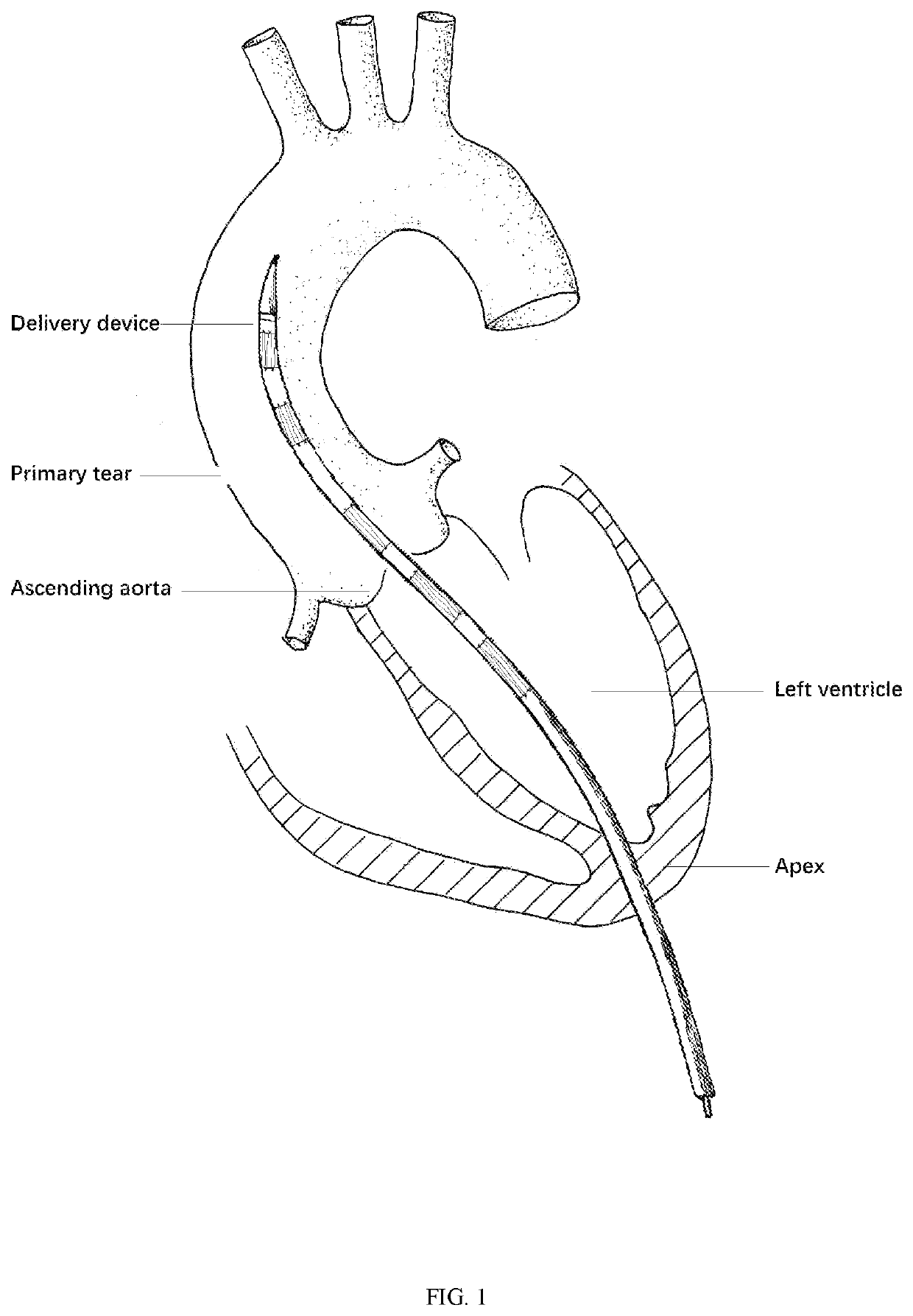
Devices and methods are provided for temporarily inducing cardioplegic arrest in the heart of a patient and for establishing cardiopulmonary bypass in order to facilitate surgical procedures on the heart and its related blood vessels. Specifically, a catheter based system is provided for isolating the heart and coronary blood vessels of a patient from the remainder of the arterial system and for infusing a cardioplegic agent into the patient's coronary arteries to induce cardioplegic arrest in the heart. The system includes an endoaortic partitioning catheter having an expandable balloon at its distal end which is expanded within the ascending aorta to occlude the aortic lumen between the coronary ostia and the brachiocephalic artery. Means for centering the catheter tip within the ascending aorta include specially curved shaft configurations, eccentric or shaped occlusion balloons and a steerable catheter tip, which may be used separately or in combination. The shaft of the catheter may have a coaxial or multilumen construction. The catheter may further include piezoelectric pressure transducers at the distal tip of the catheter and within the occlusion balloon. Means to facilitate nonfluoroscopic placement of the catheter include fiberoptic transillumination of the aorta and a secondary balloon at the distal tip of the catheter for atraumatically contacting the aortic valve. The system further includes a dual purpose arterial bypass cannula and introducer sheath for introducing the catheter into a peripheral artery of the patient.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
Cerebral perfusion augmentation
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
Methods and devices for treating aortic atheroma
InactiveUS20060161241A1Precise positioningAvoid obstructionStentsBlood vesselsLeft subclavian arteryAortic atheroma
A method for treating both sessile and mobile aortic atheroma is described. A radially expanding device, such as a stent or compliant cast, comprising a generally cylindrical member expandable between a compressed state and an enlarged state is provided. The cylindrical member has a proximal opening, a distal opening, a lumen therebetween, and at least one side opening in the wall of the generally cylindrical member. The methods comprise imaging the aorta to identify position and extent of atheroma. The stent is then advanced into the aortic arch and positioned so that the at least one side-opening is aligned with the takeoff of one or more of the right brachiocephalic artery, the left common carotid artery, or the left subclavian artery. The stent is expanded into contact with the endoluminal surface of the aorta and atheroma is trapped between the stent and the endoluminal surface of the aorta.
Owner:SAGE MEDICAL TECH
Devices and methods for preventing distal embolization using flow reversal by partial occlusion of the brachiocephalic artery
InactiveUS6837881B1Prevention of distal embolizationMinimizing blood lossStentsBalloon catheterAtherectomyPercutaneous angioplasty
The invention provides a medical device having a catheter and one or more expandable constricting / occluding members. The catheter is adapted for use with therapeutic or diagnostic devices, including an angioplasty / stent catheter and an atherectomy catheter. The constrictor / occluder is mounted at the distal end of the catheter. Manometers may be mounted distal to one or more constrictors for measuring pressure distal to the constrictor(s). Methods of using the devices for preventing distal embolization during extracranial or intracranial carotid procedures or vertebral artery procedures by reversing blood flow in an internal carotid artery, an external carotid artery, and / or a common carotid artery toward the subclavian artery are disclosed.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
Antegrade cardioplegia catheter and method
InactiveUS6932792B1Facilitate occlusionOvercome disadvantagesStentsBalloon catheterCardioplegiasAscending aorta
A cardioplegia catheter is configured to extend into the ascending aorta with a proximal portion of the shaft extending into a left chamber of the heart through a aortic valve and out of the heart through a penetration in a wall thereof. The cardioplegia catheter has an occlusion member configured to occlude the ascending aorta between the brachiocephalic artery and the coronary ostia. An arterial return cannula delivers oxygenated blood to the arterial system downstream of the occlusion member, while cardioplegic fluid is delivered through a lumen in the cardioplegia catheter upstream of the occlusion member to induce cardioplegic arrest.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
Methods and devices for treatging aortic atheroma
InactiveUS20080004687A1Avoid obstructionPrecise positioningStentsBlood vesselsLeft subclavian arteryAortic atheroma
A method for treating both sessile and mobile aortic atheroma is described. A radially expanding device, such as a stent or compliant cast, comprising a generally cylindrical member expandable between a compressed state and an enlarged state is provided. The cylindrical member has a proximal opening, a distal opening, a lumen therebetween, and at least one side opening in the wall of the generally cylindrical member. The methods comprise imaging the aorta to identify position and extent of atheroma. The stent is then advanced into the aortic arch and positioned so that the at least one side-opening is aligned with the takeoff of one or more of the right brachiocephalic artery, the left common carotid artery, or the left subclavian artery. The stent is expanded into contact with the endoluminal surface of the aorta and atheroma is trapped between the stent and the endoluminal surface of the aorta.
Owner:SAGE MEDICAL TECH
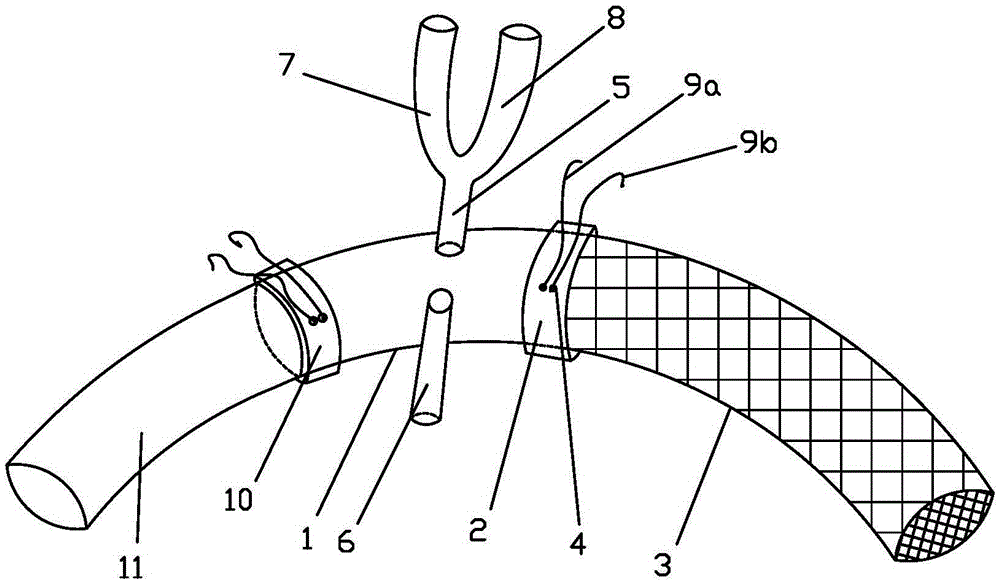
Branch artificial blood vessel bracket applied in surgery
The invention relates to a branch artificial blood vessel bracket applied in surgery, which is provided with a terylene fabric blood vessel and a large bracket lined with a harder memory alloy wire; an artificial blood vessel of 1cm long without alloy wires is arranged at the near end and taken as a sewing ring; the branch artificial blood vessel bracket is characterized in that the near end of the large bracket is sewed by a small bracket; and the small bracket consists of the terylene fabric blood vessel and the lined soft memory alloy wire. The branch artificial blood vessel bracket creatively adds a branch bracket used for supporting the true lumen of left subclavian artery so as to keep smooth and complete left subclavian artery and the distal end of thoracic descending aorta, overcome the defects of the current surgery and avoid the coincidence of the left subclavian artery; and the distal end coincident hole is arranged between the innominate artery and the left common carotid artery, thus solving the most difficult point of the technique.
Owner:陈良万 +2
Embolism protection device
Disclosed herein are systems and methods for protecting a subject from embolisms during TAVI and other percutaneous valve procedures. Some embodiments include two flexible catheters designed to pass over a guidewire into two separate arteries, such as carotid or innominate arteries, each flexible catheter including a vessel blocking mechanism and a bypass feature that prevents ischemia while the vessel blocking mechanism is in use. Other embodiments include a single, bifurcated flexible catheter having two arms, each of which is configured to protect a different artery. In some embodiments, each arm includes a vessel blocking mechanism and a bypass feature that prevents ischemia while the vessel blocking mechanism is in use. In some embodiments, the systems also may include one or more concentric guidewires.
Owner:CLARET MEDICAL
Embolic protection device
Embolic protection devices useful for filtering emboli during interventional cardiac, vascular, or other procedures are described. The device can include first and second expandable mesh filters having open and closed ends. The first filter is attached to a catheter at its closed end. The second filter is attached to a steerable guide wire at its closed end. The second filter includes a cinching wire circumferentially attached to the filter. The filters are deployed in separate vessels, such as the brachiocephalic artery and the left common carotid artery. A procedure is performed, and the filters trap any emboli travelling through the path of the filters. At the end of the procedure, the second filter is closed using the cinching wire, and retracted into the first filter. Both the first and second filters are collapsed into a sheath and removed from the body with along with any emboli trapped in the filters.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
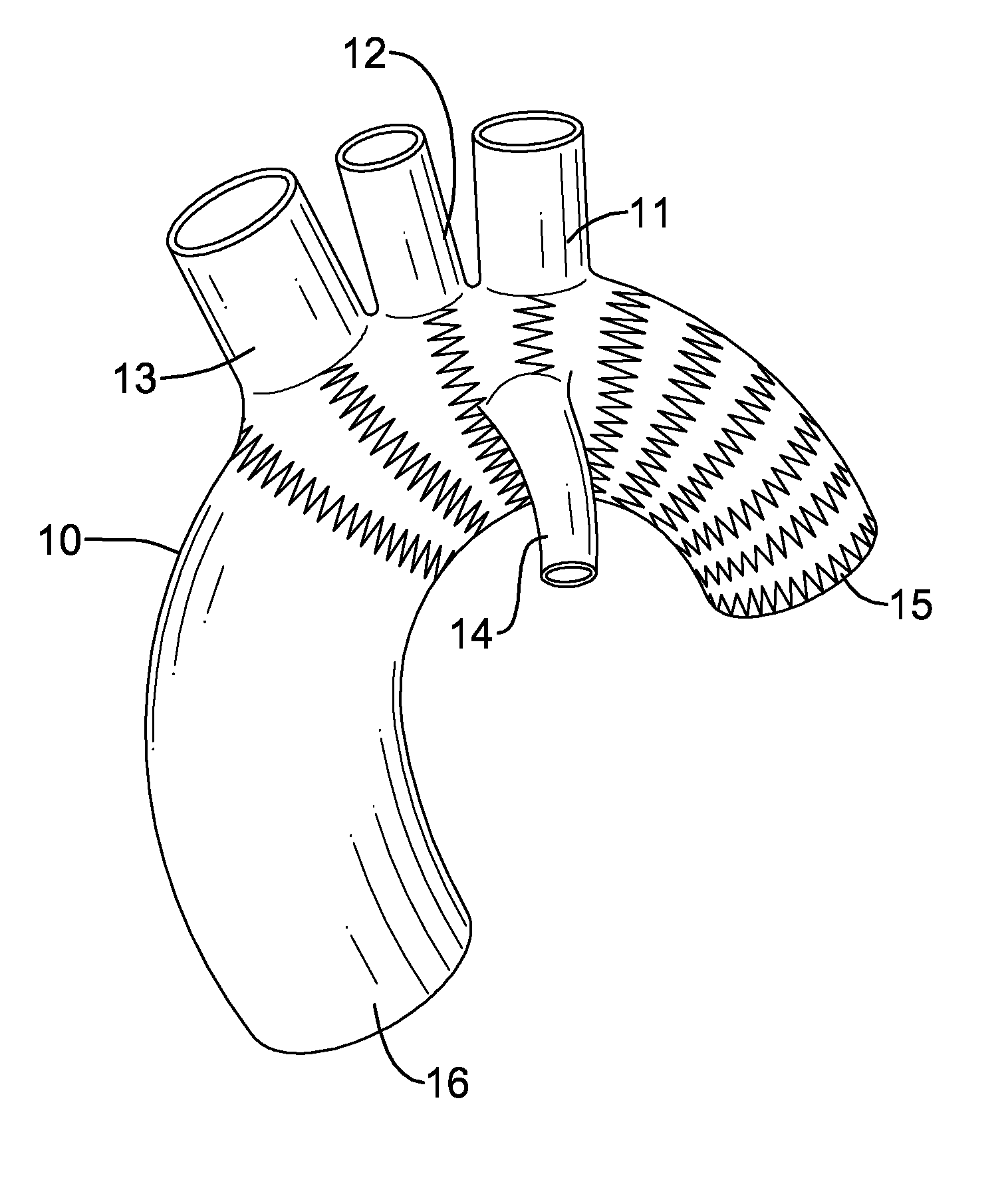
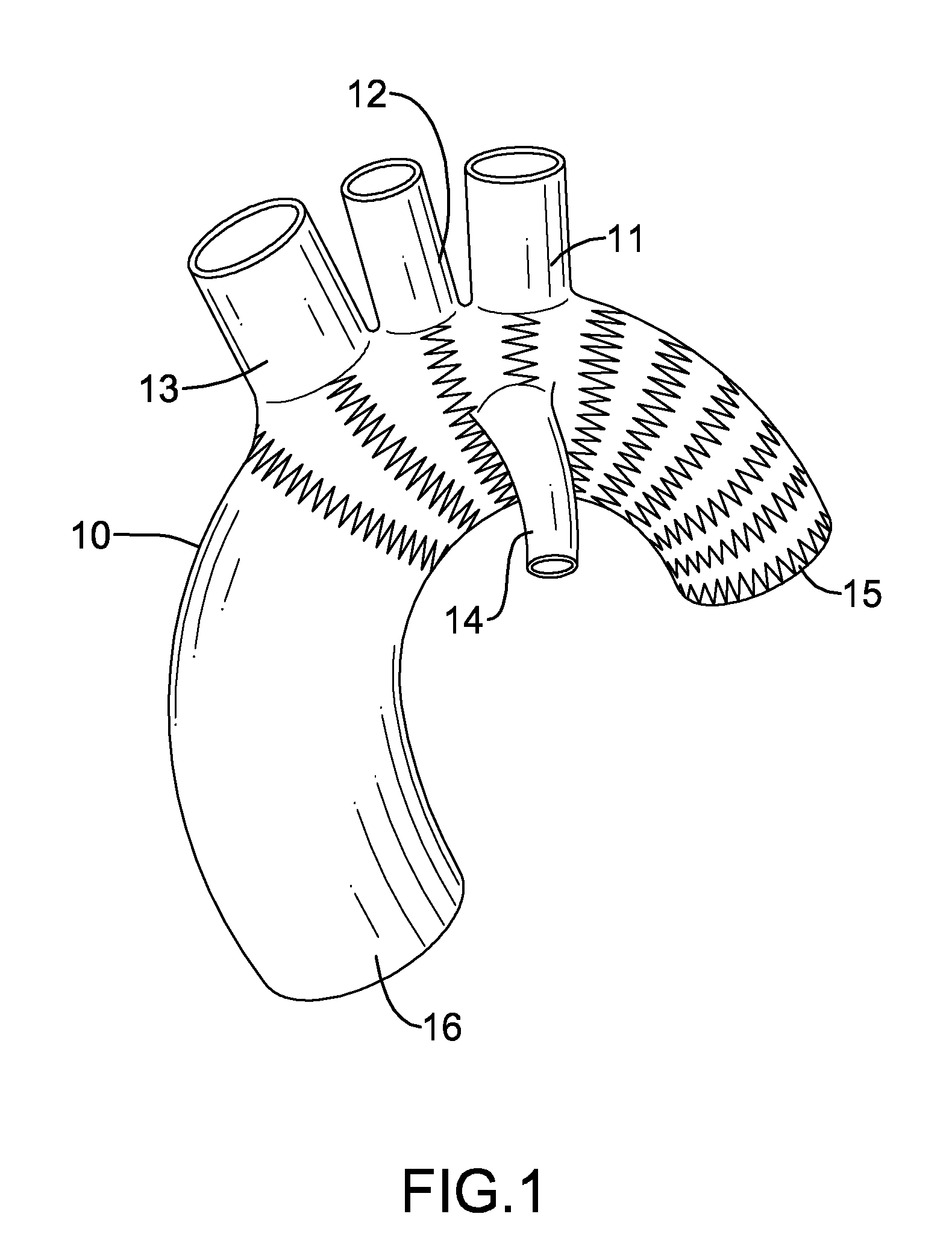
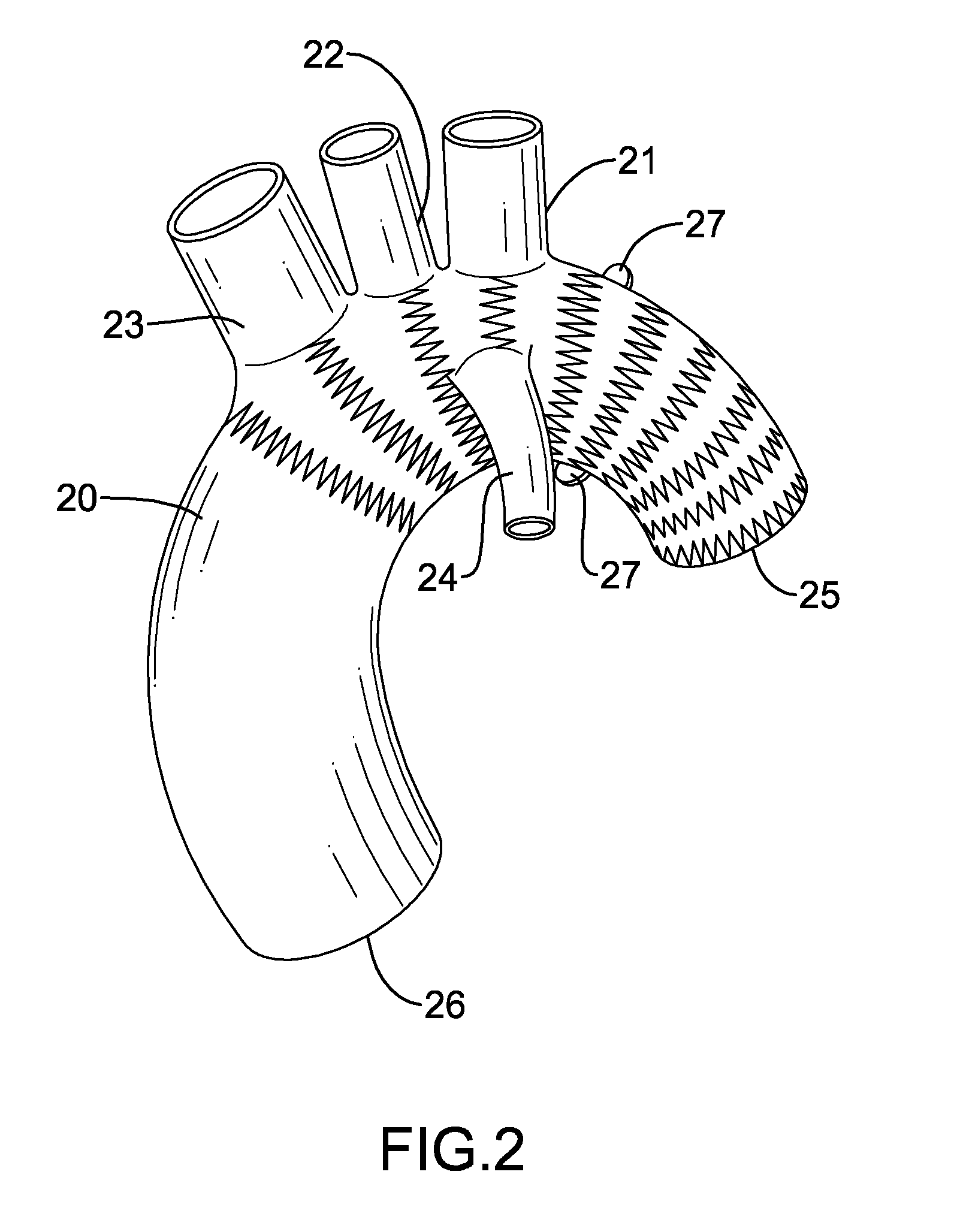
Total aortic arch reconstruction graft
A total aortic arch reconstruction graft, includinga) a first, hollow cylindrical segment in the shape of an aortic arch and adapted to be joined to a patient's ascending aorta, and including three side hollow cylindrical branches in communication therewith and adapted to be joined to a patient's left subclavian artery, left common carotid artery and innominate artery, respectively, and a fourth hollow cylindrical branch adapted to be joined to a heart-lung machine;b) a second, hollow cylindrical segment having a first end being joined to the second end of the first segment, and a second end adapted to be inserted into the descending aorta of a patient, the second segment having an expandable outer wall covered with an expandable open-mesh stent having means for attaching the second segment to an internal surface of a patient's descending aorta,c) a collar having a diameter slightly larger than the diameter of said first segment, the collar located at a juncture where the first end of the second segment is joined to the second end of the first segment, with the collar having means for attachment to the open end of a patient's descending aorta. A surgical procedure for total replacement of the aortic arch of a patient is also disclosed.
Owner:SHERIF HISHAM M F
Stent graft system
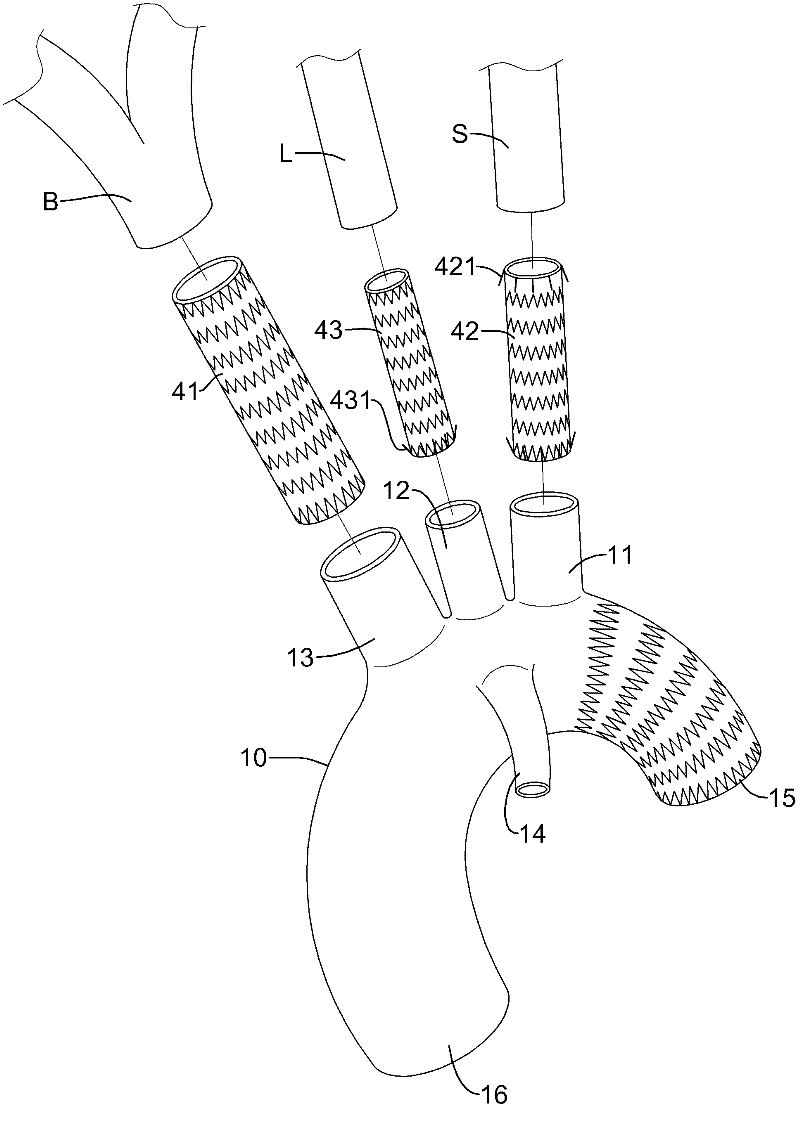
The stent graft system in accordance with the present invention has a trunk, a left subclavian tube, a left common carotid tube and a brachiocephalic tube. The trunk is tubular and expandable and has a descending end, an ascending end, a left subclavian mount, a left common carotid mount and a brachiocephalic mount, for receiving the aforementioned branch tubes that are elastic and self-expandable for respectively connecting the left subclavian artery, the left common carotid artery and the brachiocephalic artery to the trunk. With the above-described structure, the present invention allows fast determination of a suitable trunk and branch tubes for a patient and allows a medical institute to prepare compatible branch tubes and trunks for a composite stent graft system instead of numerous stent grafts of various combinations of differently sized tubular bodies and branches, wherein the former requires significantly less warehousing cost than the latter.
Owner:陈玮慧
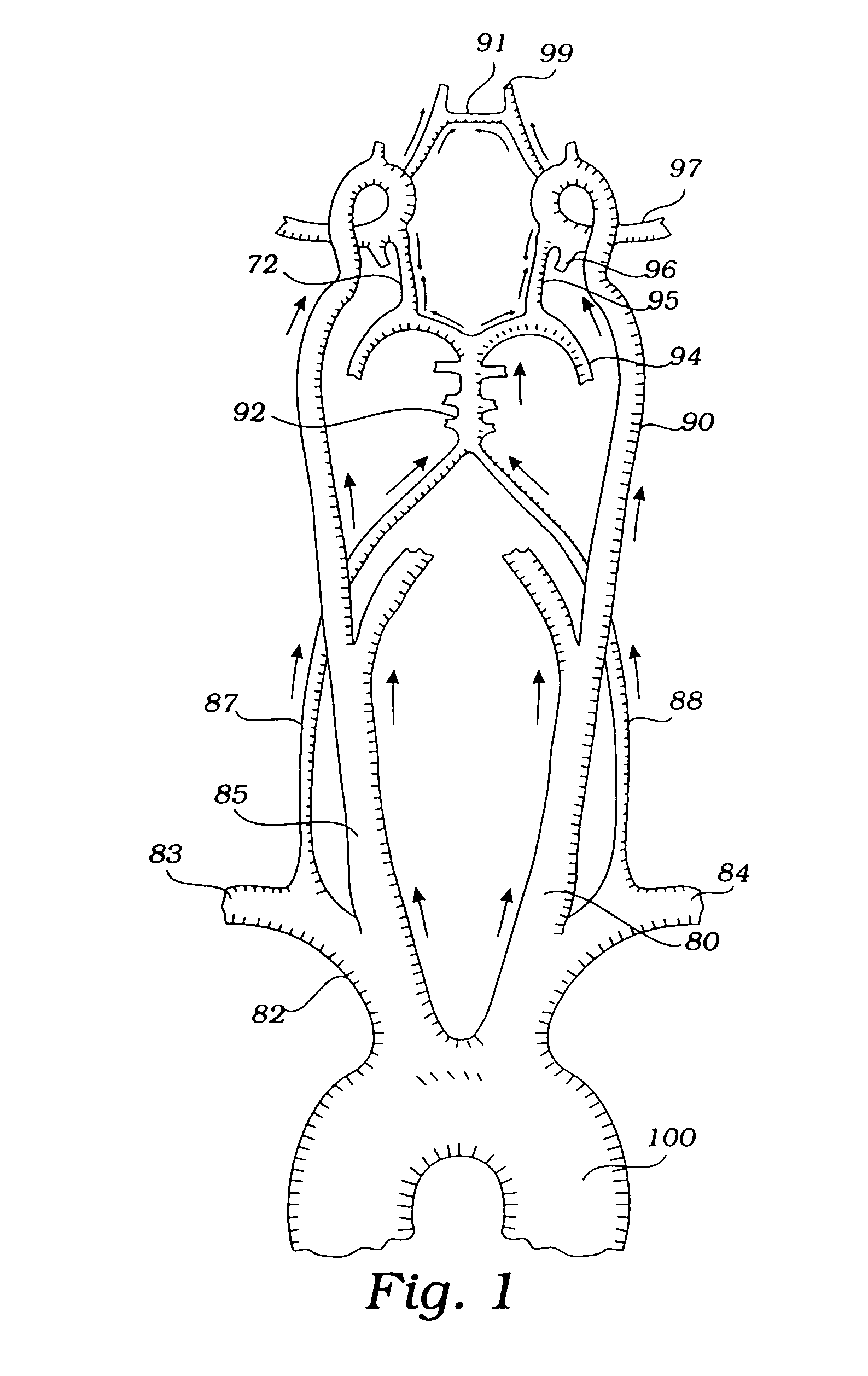
Devices and methods for preventing distal embolization using flow reversal and perfusion augmentation within the cerebral vasculature
InactiveUS7635376B2Preventing ischemic strokeStroke preventionBalloon catheterSurgeryAtherectomyCoarctation of the aorta
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
Stent Graft System
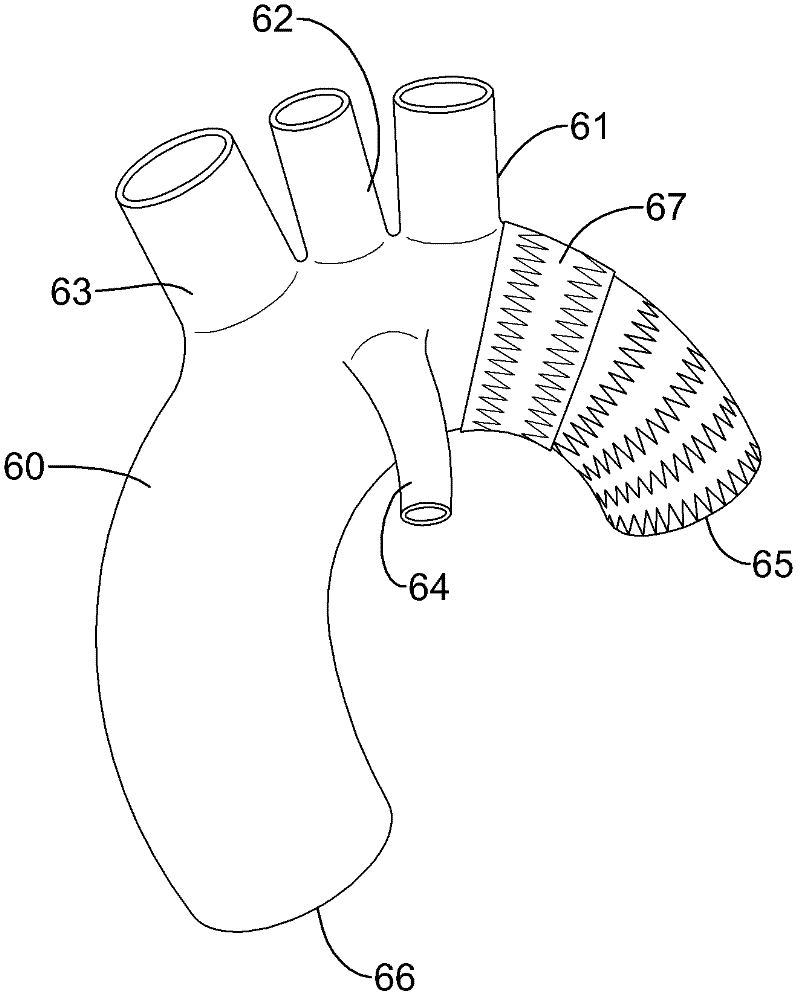
The stent graft system in accordance with the present invention has a trunk, a left subclavian tube, a left common carotid tube and a brachiocephalic tube. The trunk is tubular and expandable and has a descending end, an ascending end, a left subclavian mount, a left common carotid mount and a brachiocephalic mount, for receiving the aforementioned branch tubes that are elastic and self-expandable for respectively connecting the left subclavian artery, the left common carotid artery and the brachiocephalic artery to the trunk. With the above-described structure, the present invention allows fast determination of a suitable trunk and branch tubes for a patient and allows a medical institute to prepare compatible branch tubes and trunks for a composite stent graft system instead of numerous stent grafts of various combinations of differently sized tubular bodies and branches, wherein the former requires significantly less warehousing cost than the latter.
Owner:CHEN WEI HUI
Devices and methods for preventing distal embolization using flow reversal by partial occlusion of the brachiocephalic artery
InactiveUS8034043B1Preventing ischemic strokeStroke preventionStentsBalloon catheterAtherectomyPercutaneous angioplasty
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
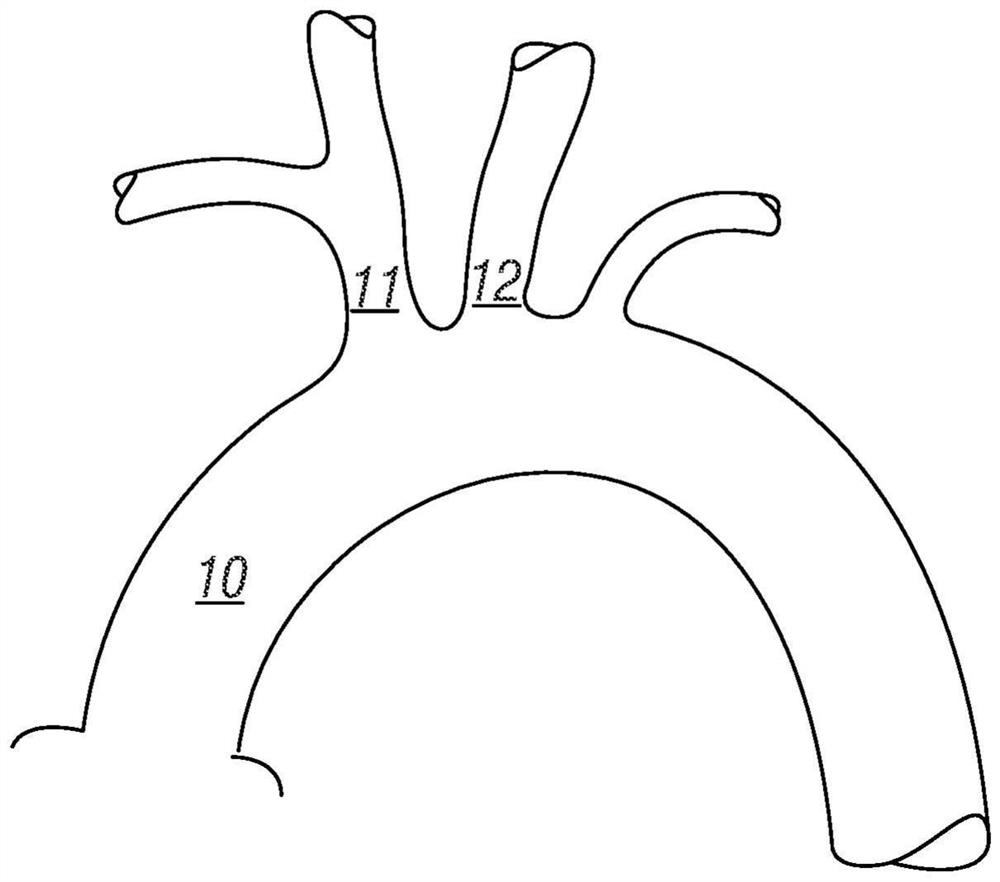
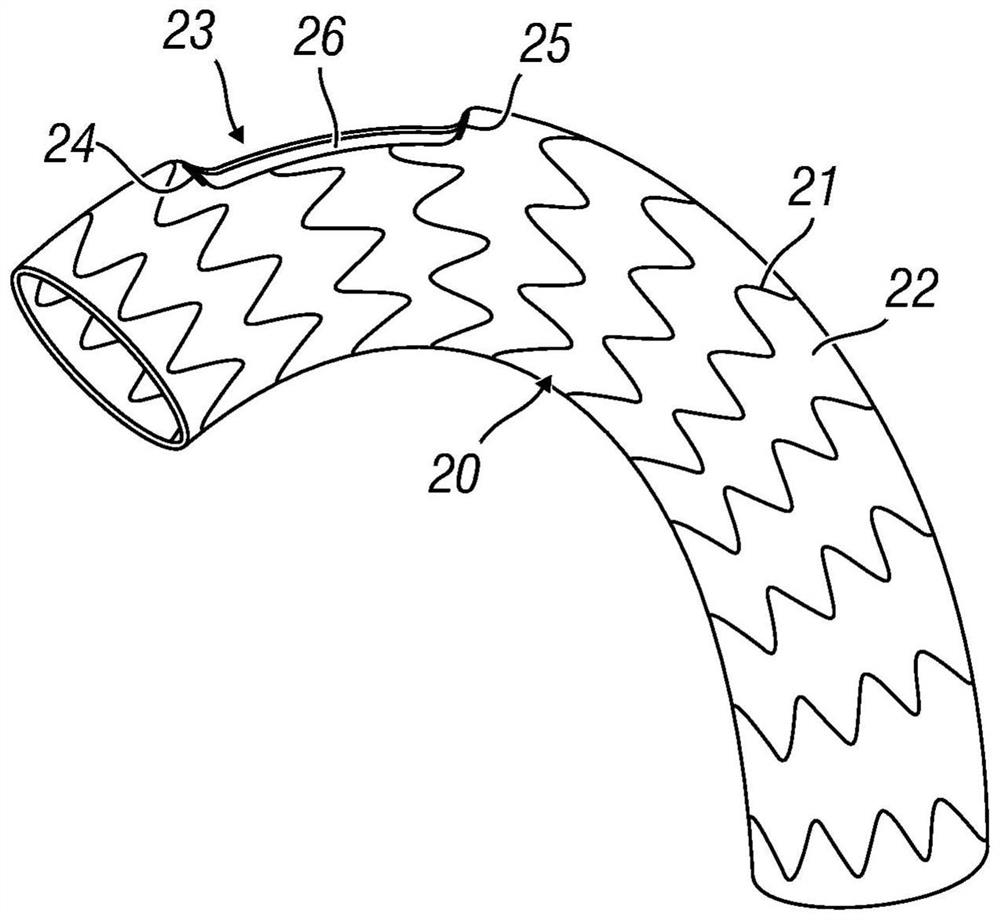
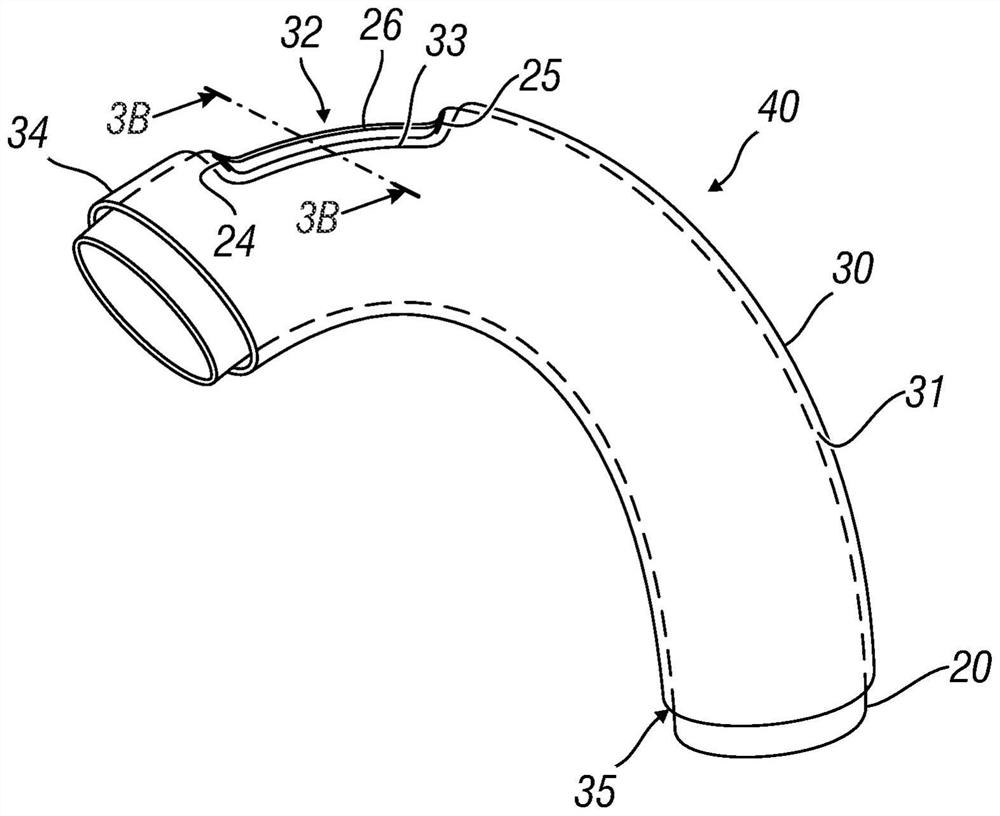
Ascending aorta stent anchored by innominate artery for dissection, and delivery system
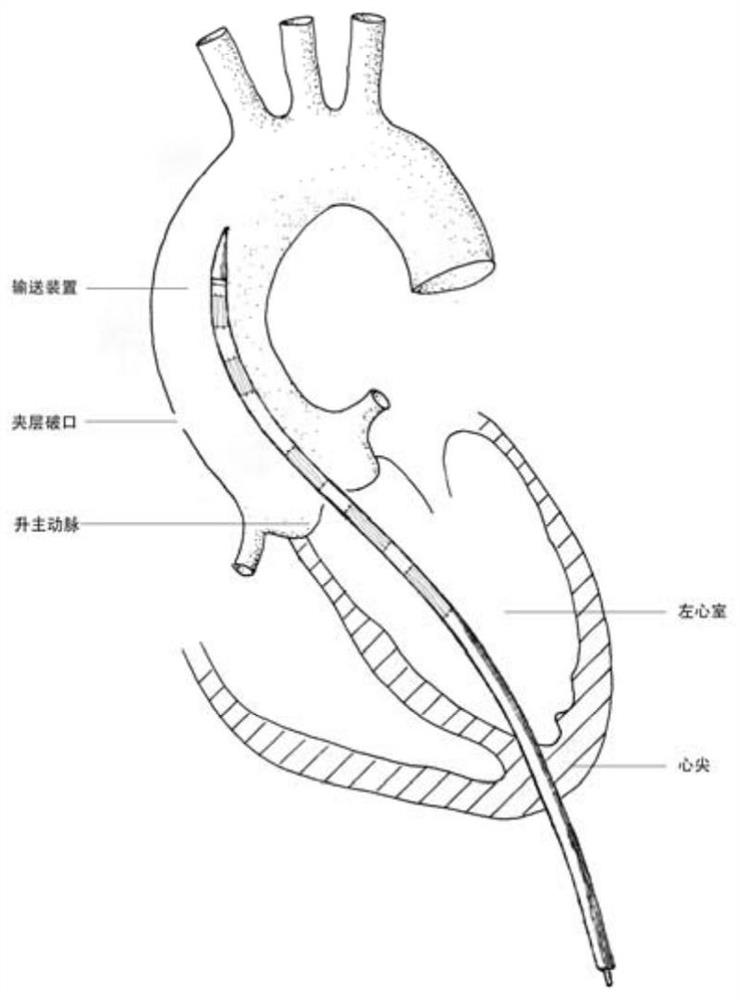
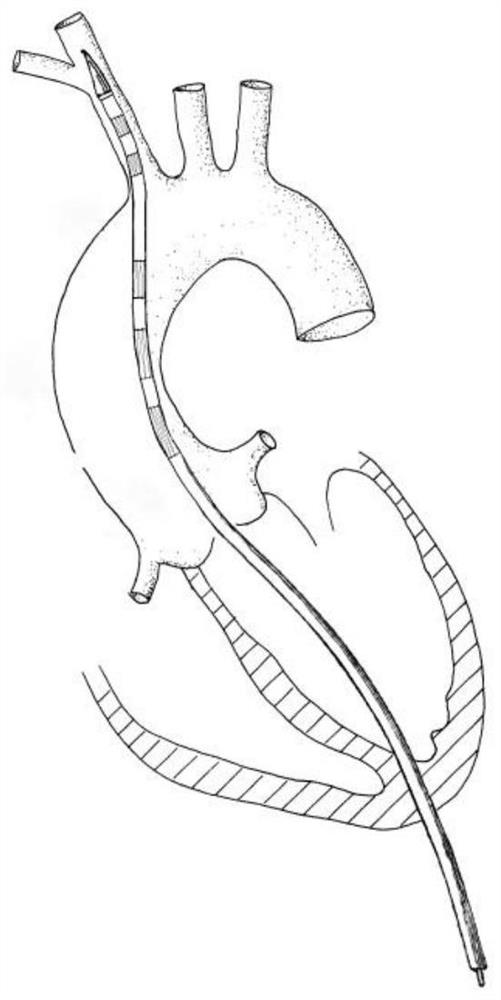
ActiveCN109172043ASecurity anchoring methodNo entry into the false cavityStentsBlood vesselsAortic dissectionThird aortic arch
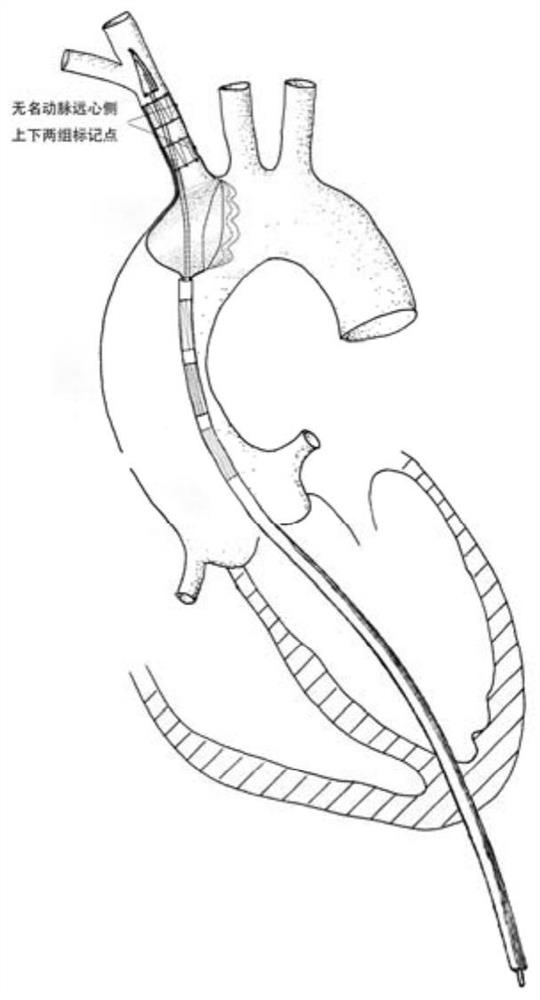
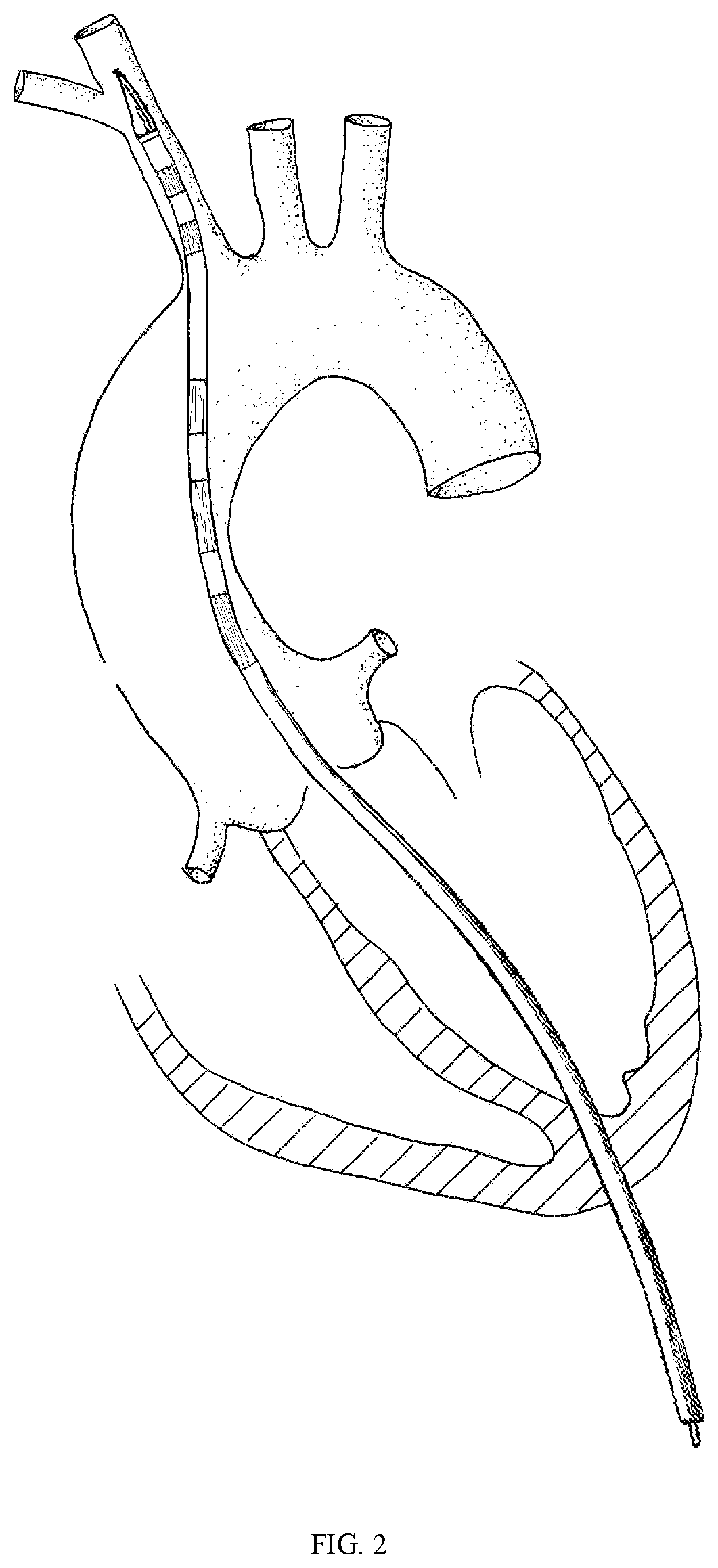
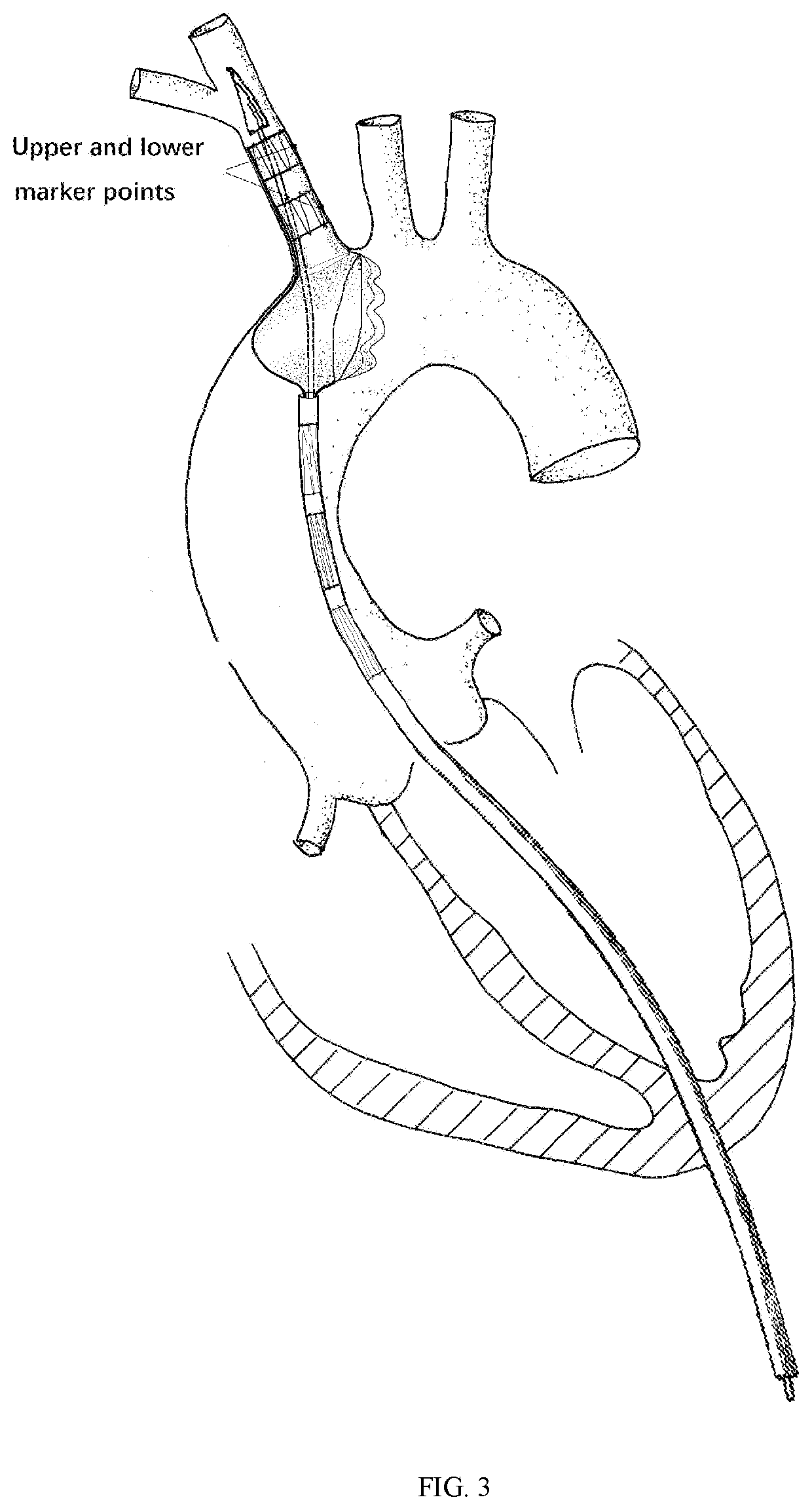
The invention provides an ascending aorta repair stent anchored by innominate artery, comprising an ascending aorta stent segment and an innominate artery stent segment, wherein an innominate artery portion of the stent is first released and a body portion is then released; the distal end opening of the body portion facing the distal end of the aortic arch lumen, and the body portion of the stentcovers the dissection at the primary rupture of the ascending aorta. When the release is completed, the main body terminates above the junction of the sinus canal. The longitudinal beam structure is made of a temperature-dependent shape memory metal material extending to the great curvature side of the aortic arch of the innominate artery and to the minor curvature side of the aortic arch, and isreleased so as to satisfy the individualized ascending aortic anatomical arc of different patients to abut against the aortic wall. The stent is anchored only according to the special anatomical shapeof the ascending aorta and the innominate artery and the memory metal longitudinal beam structure. Used in patients with type A aortic dissection in the acute phase of surgical contraindication whenwaiting for the transitional phase of surgery for patients with high surgical risk of acute type A aortic dissection to provide follow-up surgical treatment opportunities.
Owner:FUWAI HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI & PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE
Arcus aortae stent graft vascular structure for department of surgery and application
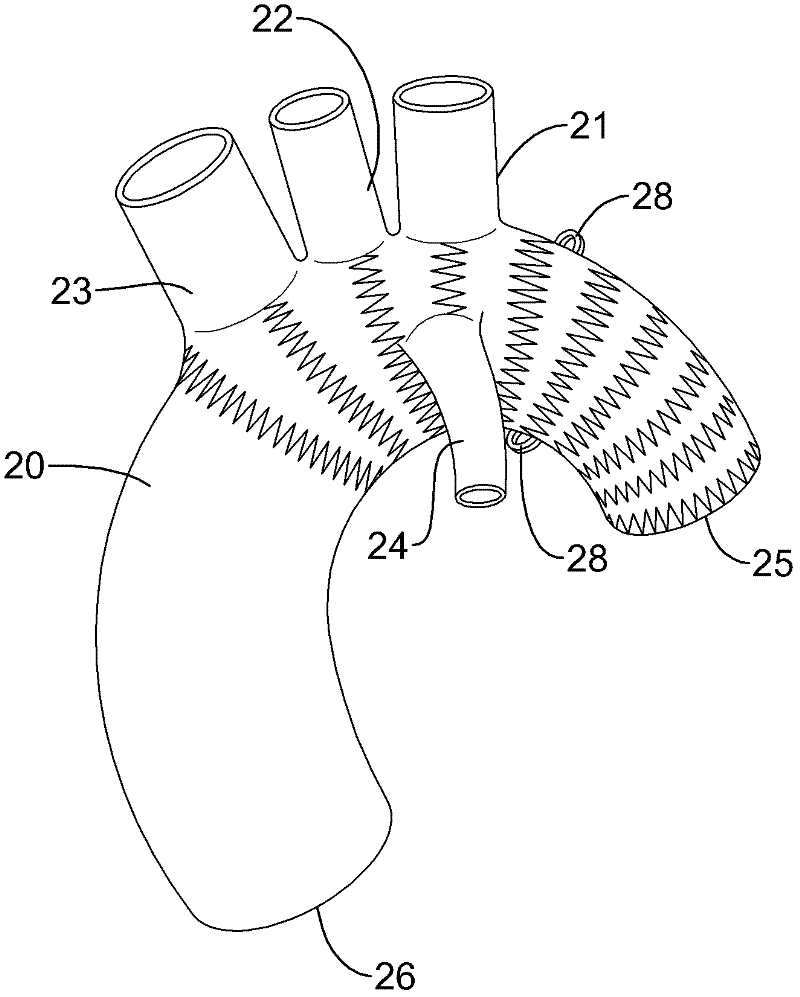
The invention discloses an arcus aortae stent graft vascular structure for the department of surgery. The structure comprises a first artificial blood vessel, a connecting ring and a second artificial blood vessel. The connecting ring is embedded into the exterior of one side of the first artificial blood vessel. A reflection portion is reserved at the connecting ring and the end of the first artificial blood vessel. The reflection portion is turned outwards to wrap the connecting ring to form the compound end. One end of the second artificial blood vessel is embedded at the compound end to form a connecting portion. A threading hole is formed in the peripheral side wall of the connecting ring. A first branch and a second branch are arranged on the periphery of the first artificial blood vessel. The first branch comprises a first forked portion for being connected with an innominate artery and a second forked portion for being connected with the left common carotid artery. The second branch is connected with a pump blood vessel and then disconnected with the left subclavian artery. The second artificial blood vessel is the stent graft artificial blood vessel, and the far end of the second artificial blood vessel is used for being connected with the thoracic descending aorta.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE HOSPITAL
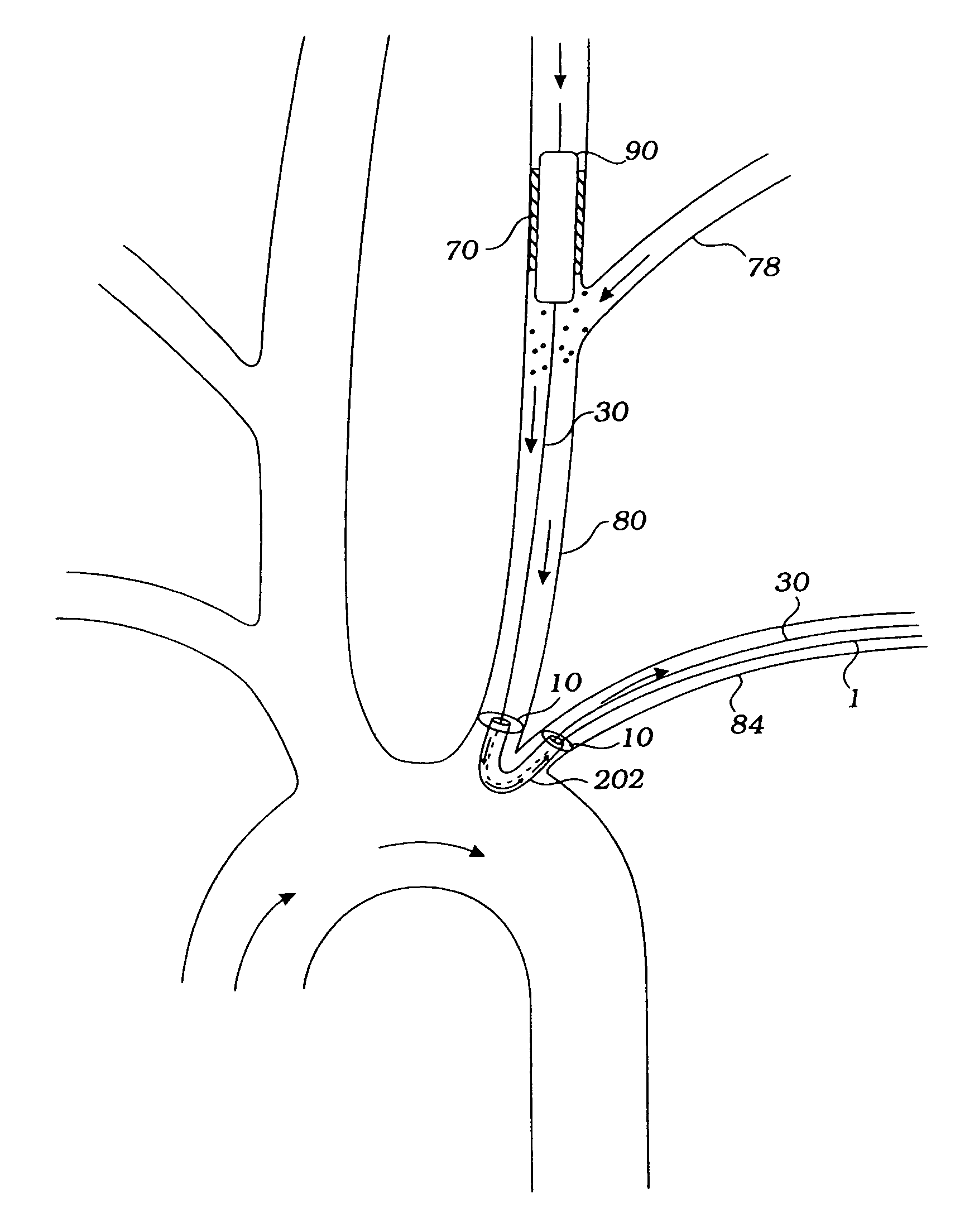
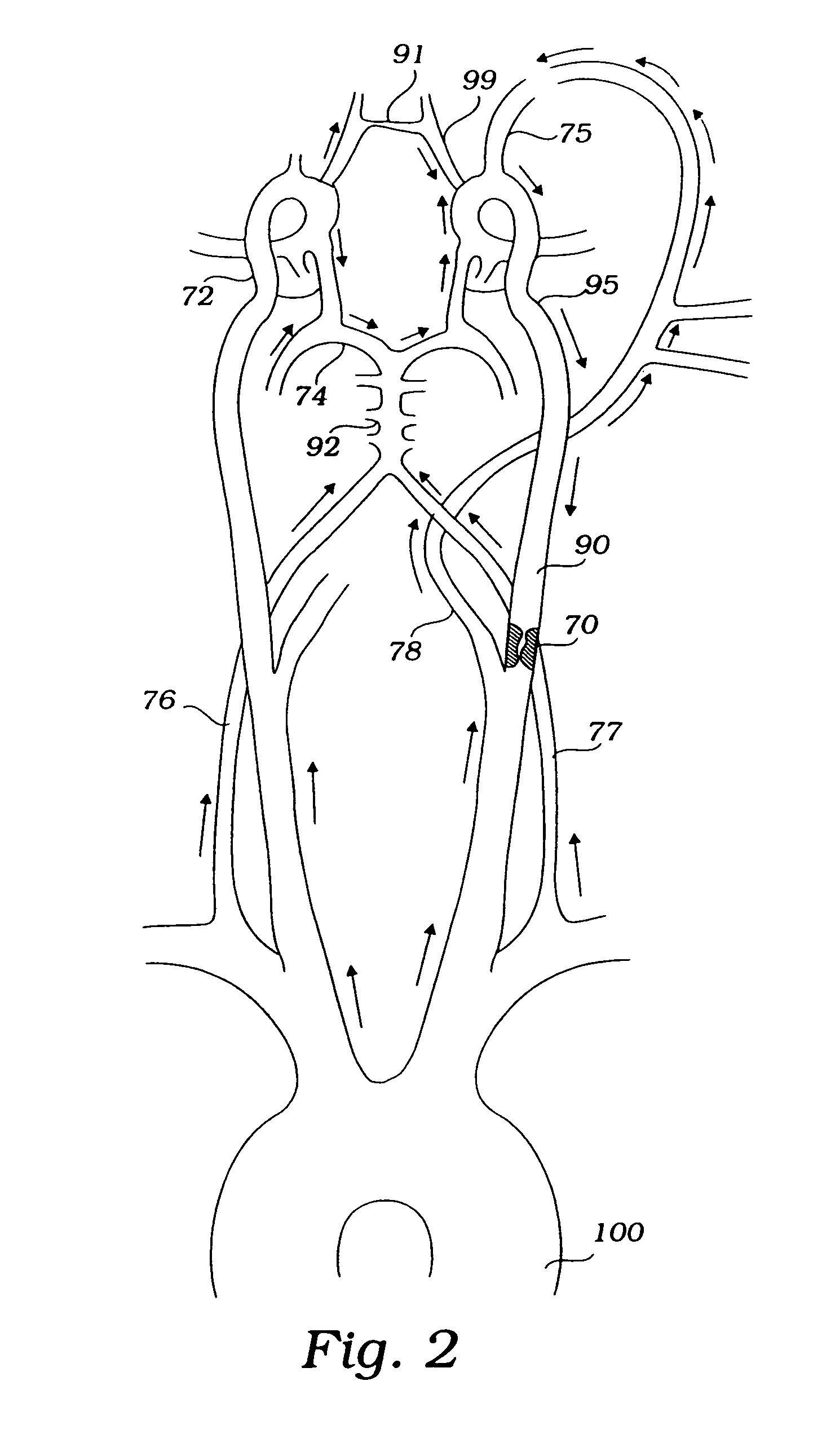
Systems for protecting the cerebral vasculature
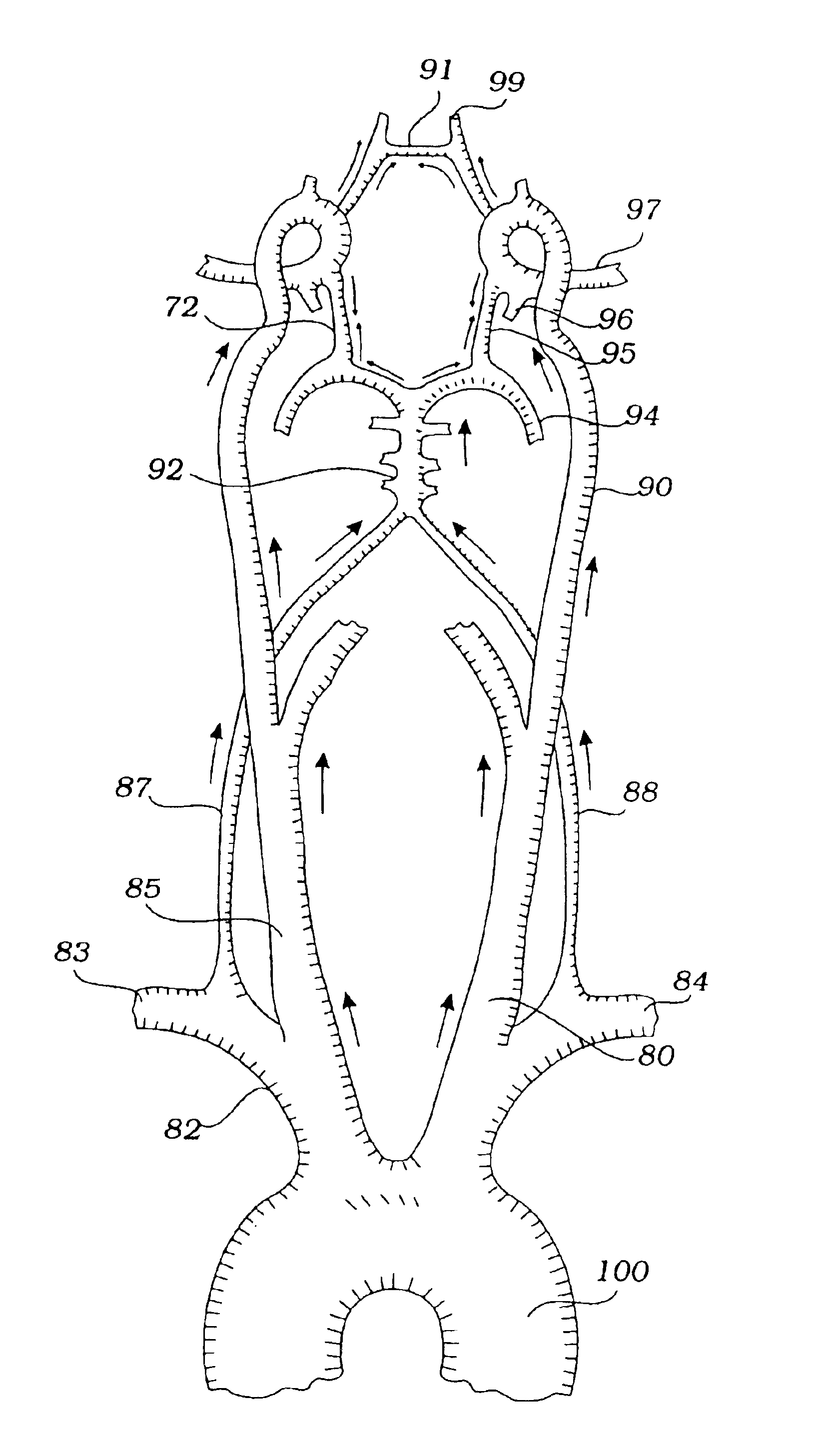
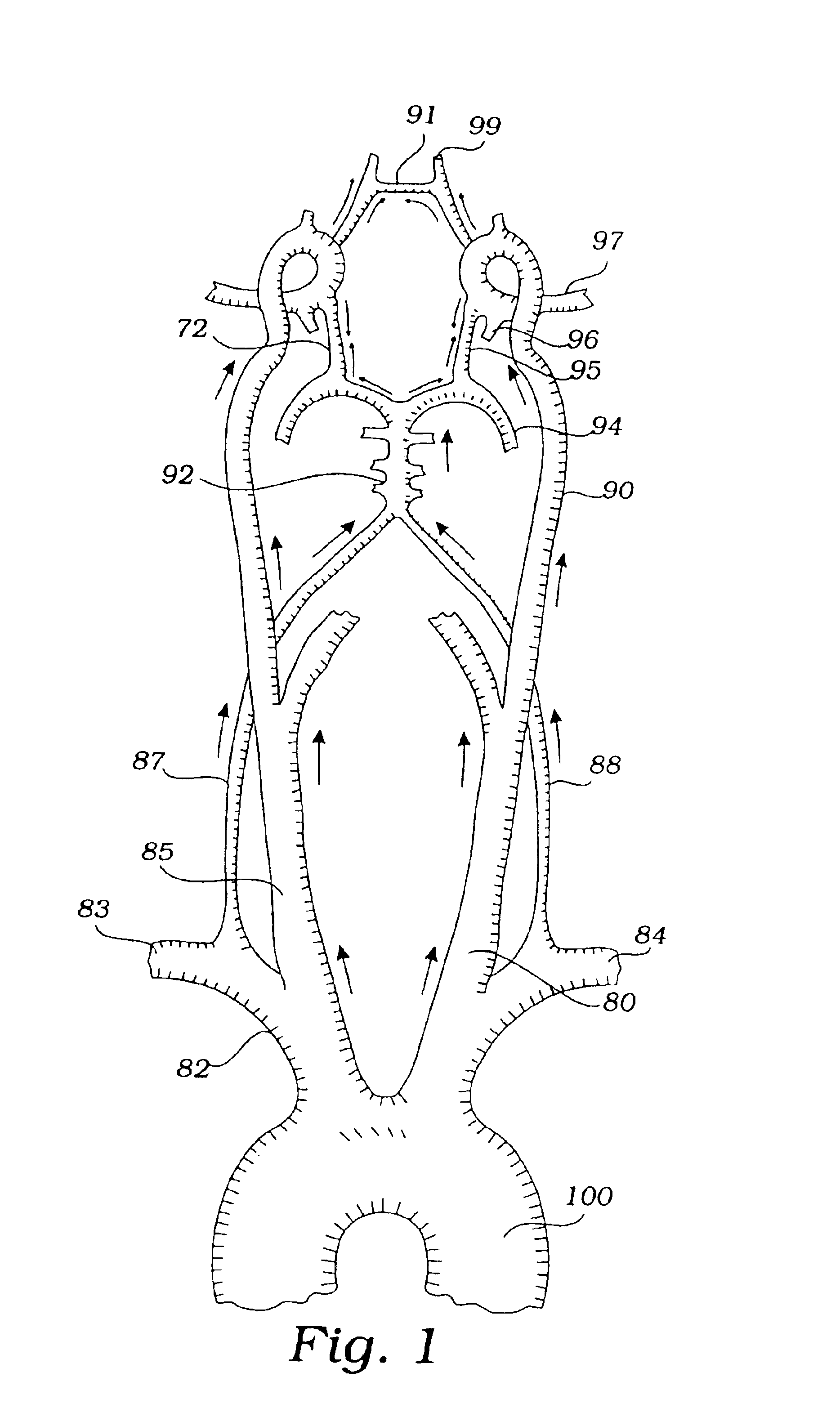
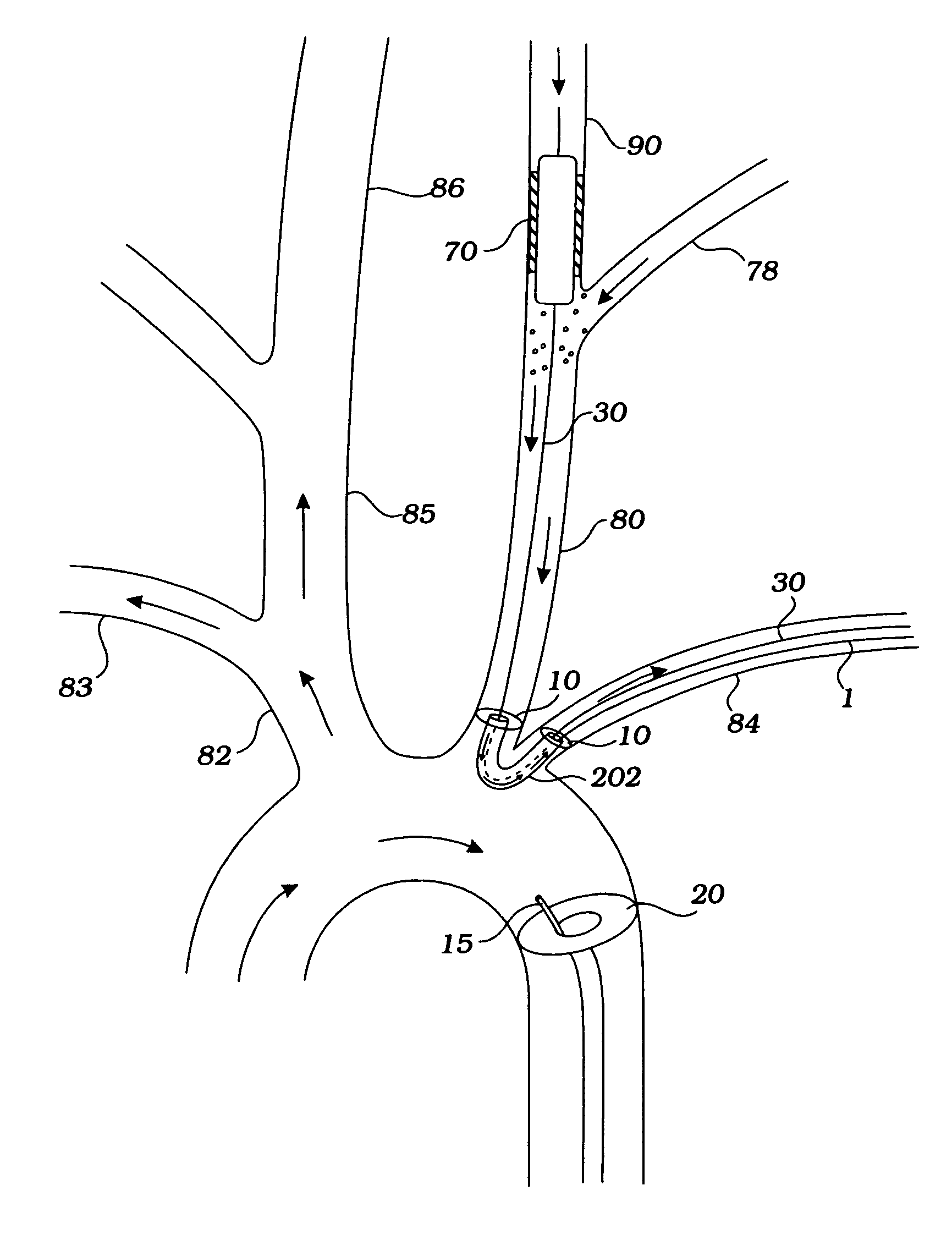
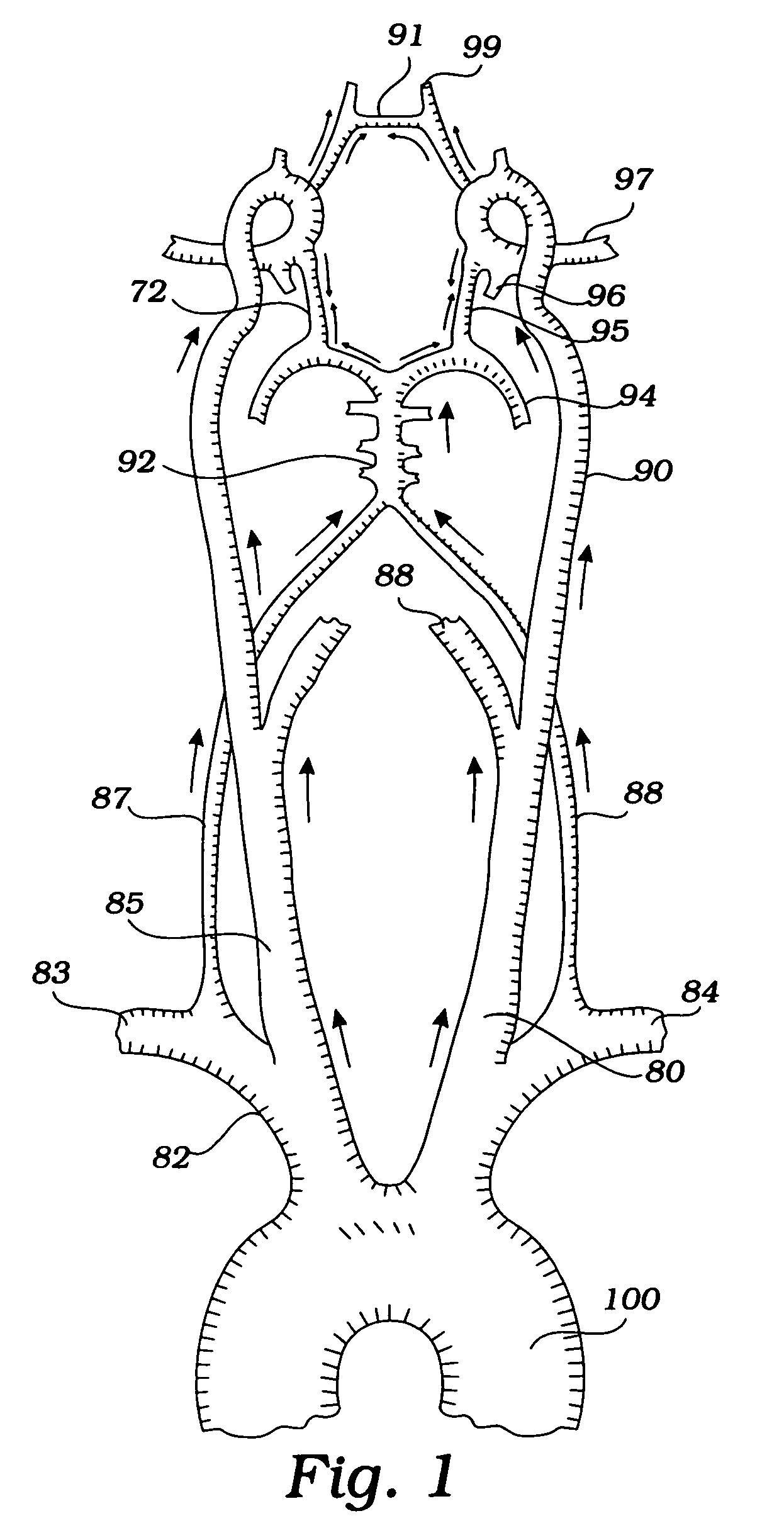
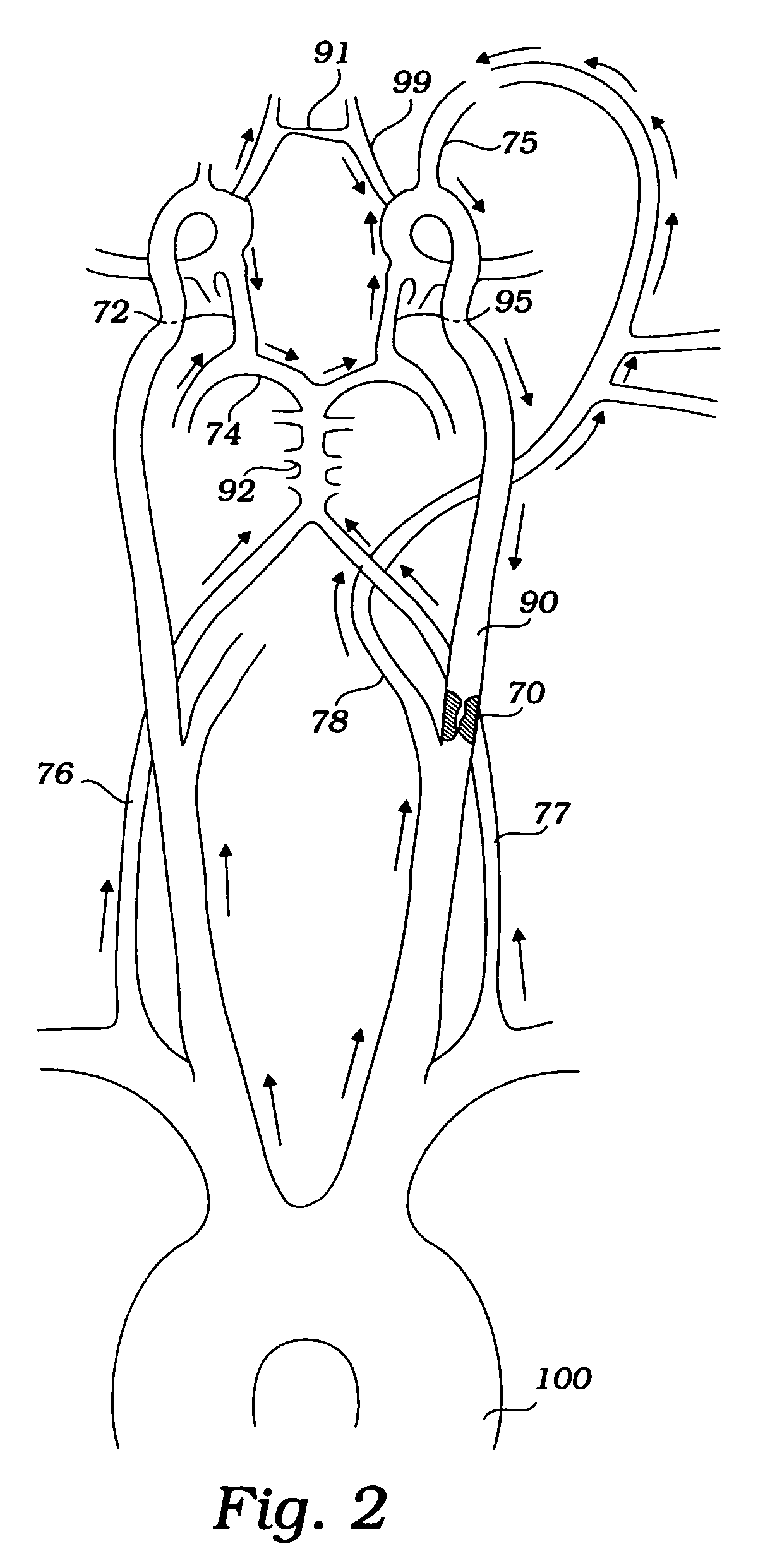
Disclosed are methods and devices for isolating all three of the left subclavian, left common carotid and brachiocephalic arteries from embolic debris that might flow through the aortic arch, via a single access point. A system may include an elongate flexible tubular sheath, having a proximal end and a distal end, and an inner member extending through the sheath and moveable relative to the sheath. A left subclavian element may be supported by the inner member. A filter membrane may be configured to isolate the aorta from the brachiocephalic, left common carotid and left subclavian arteries when the left subclavian element is expanded within the left subclavian artery and the sheath is retracted to expose the membrane. The left subclavian element may include a self expandable frame, whichmay carry a left subclavian filter.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Method for delivery of an embolic protection unit
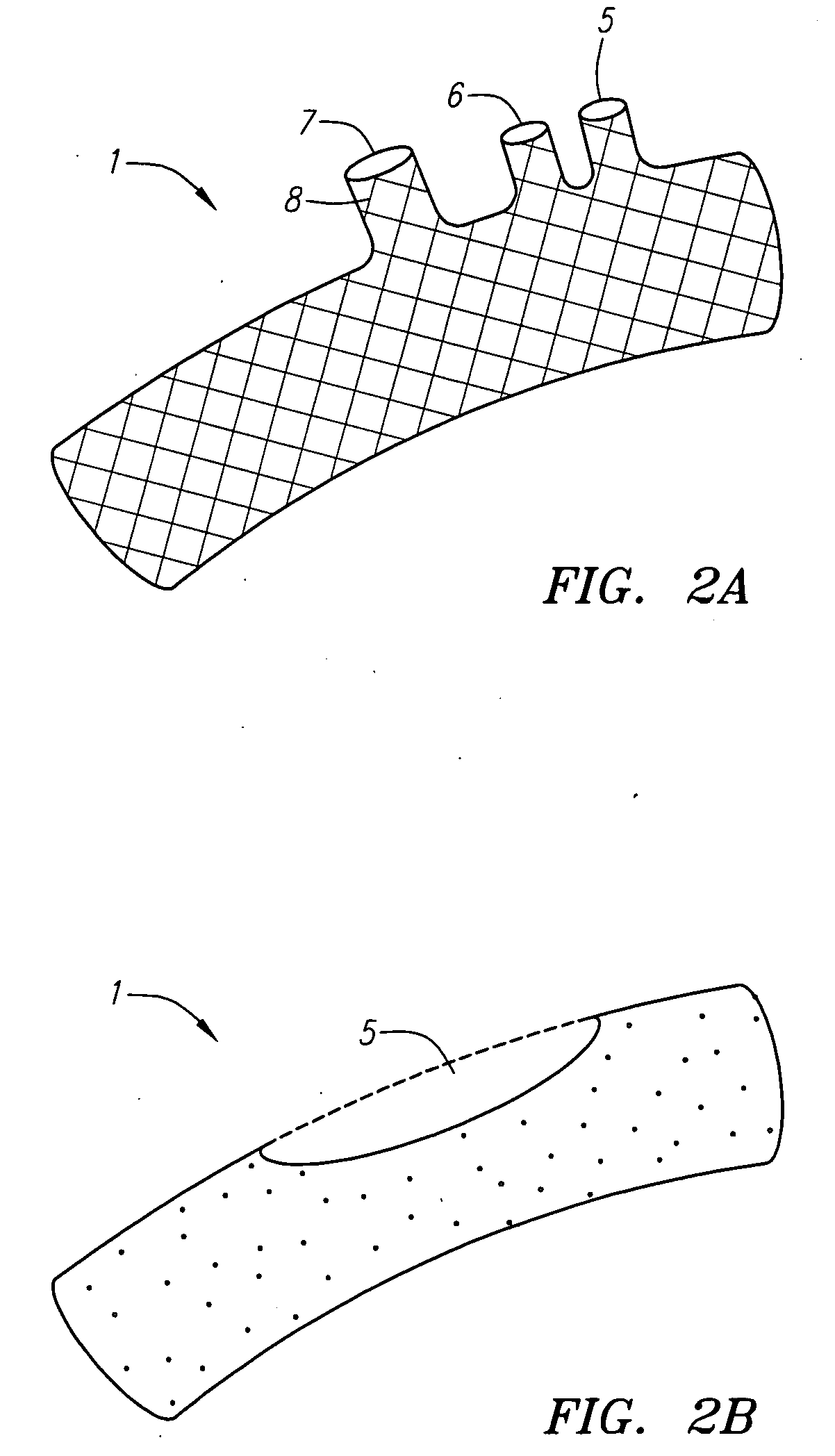
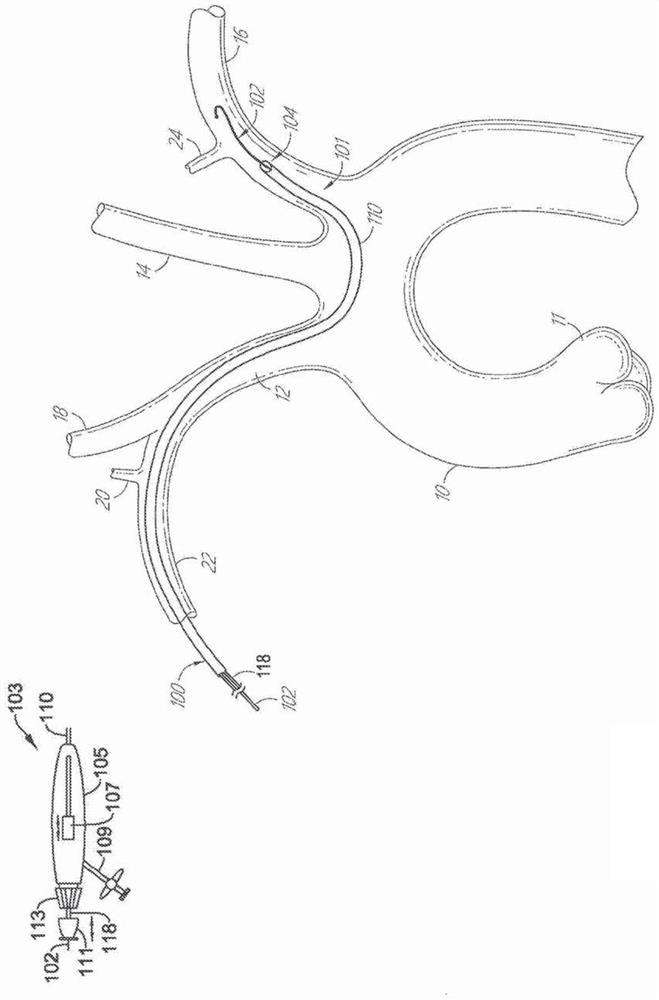
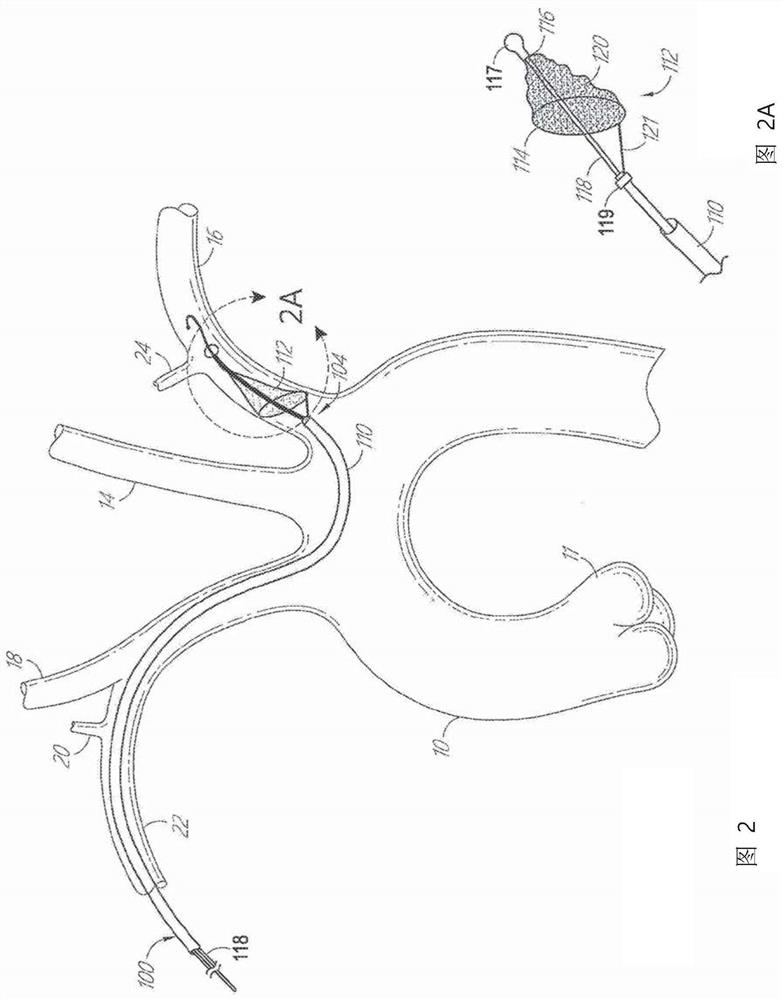
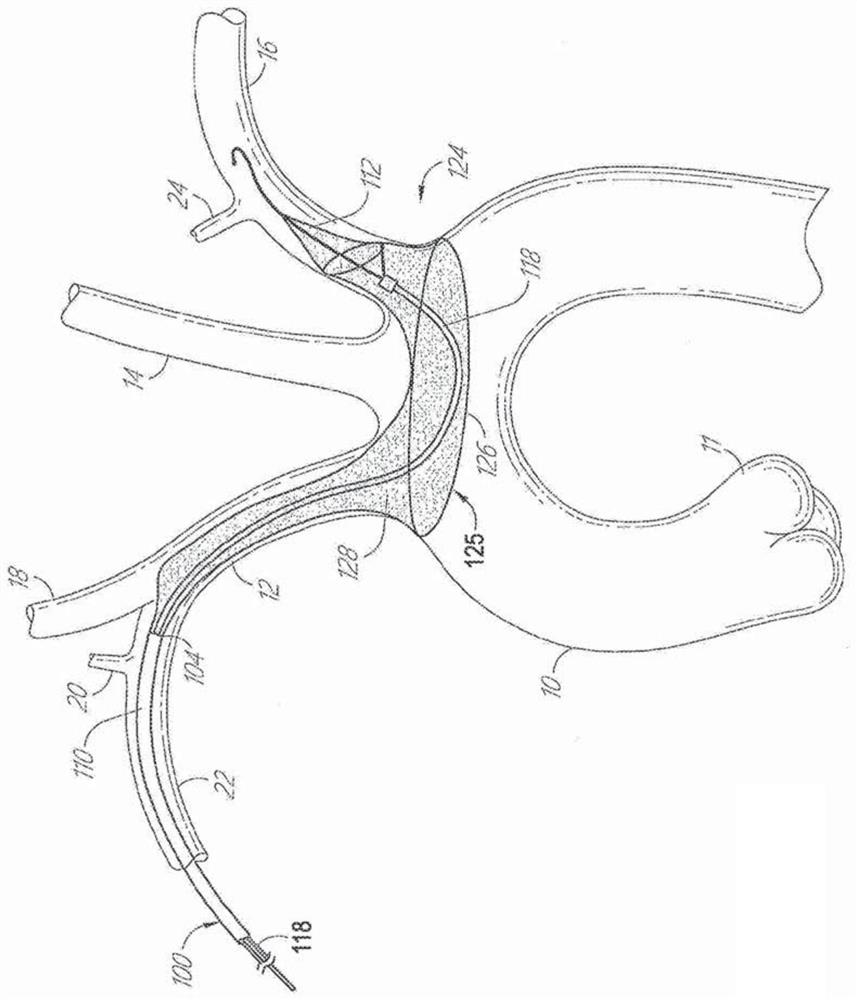
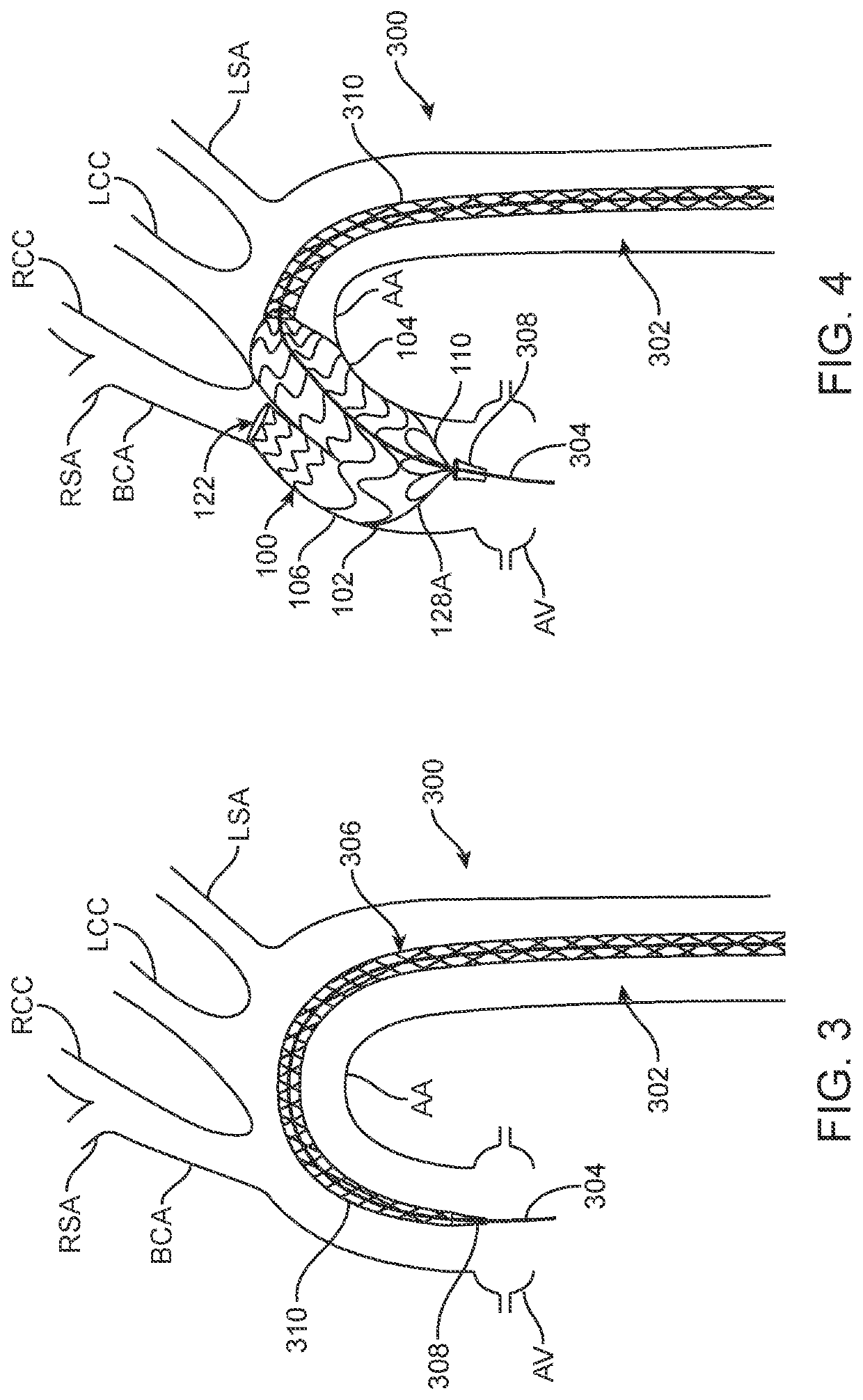
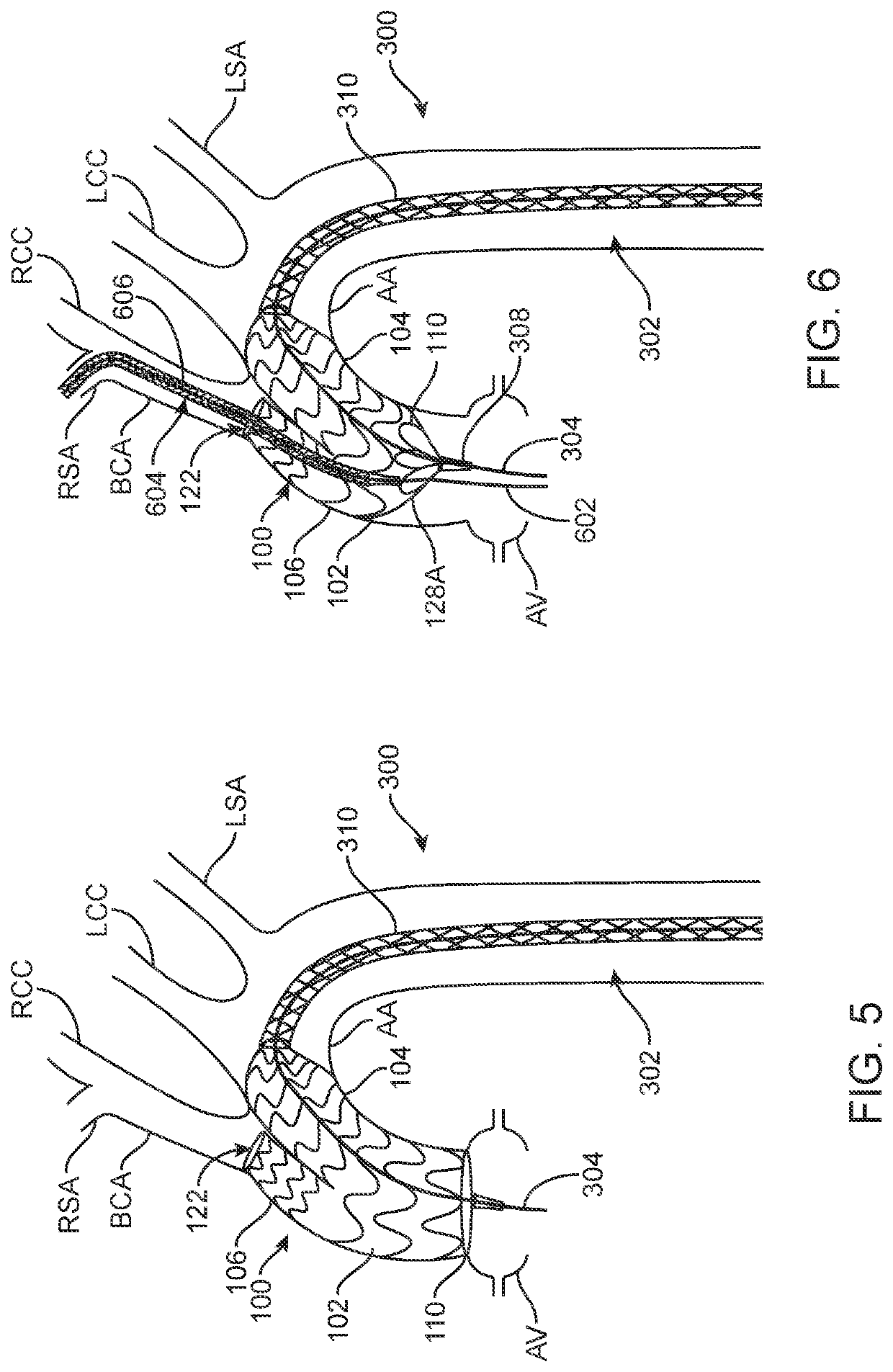
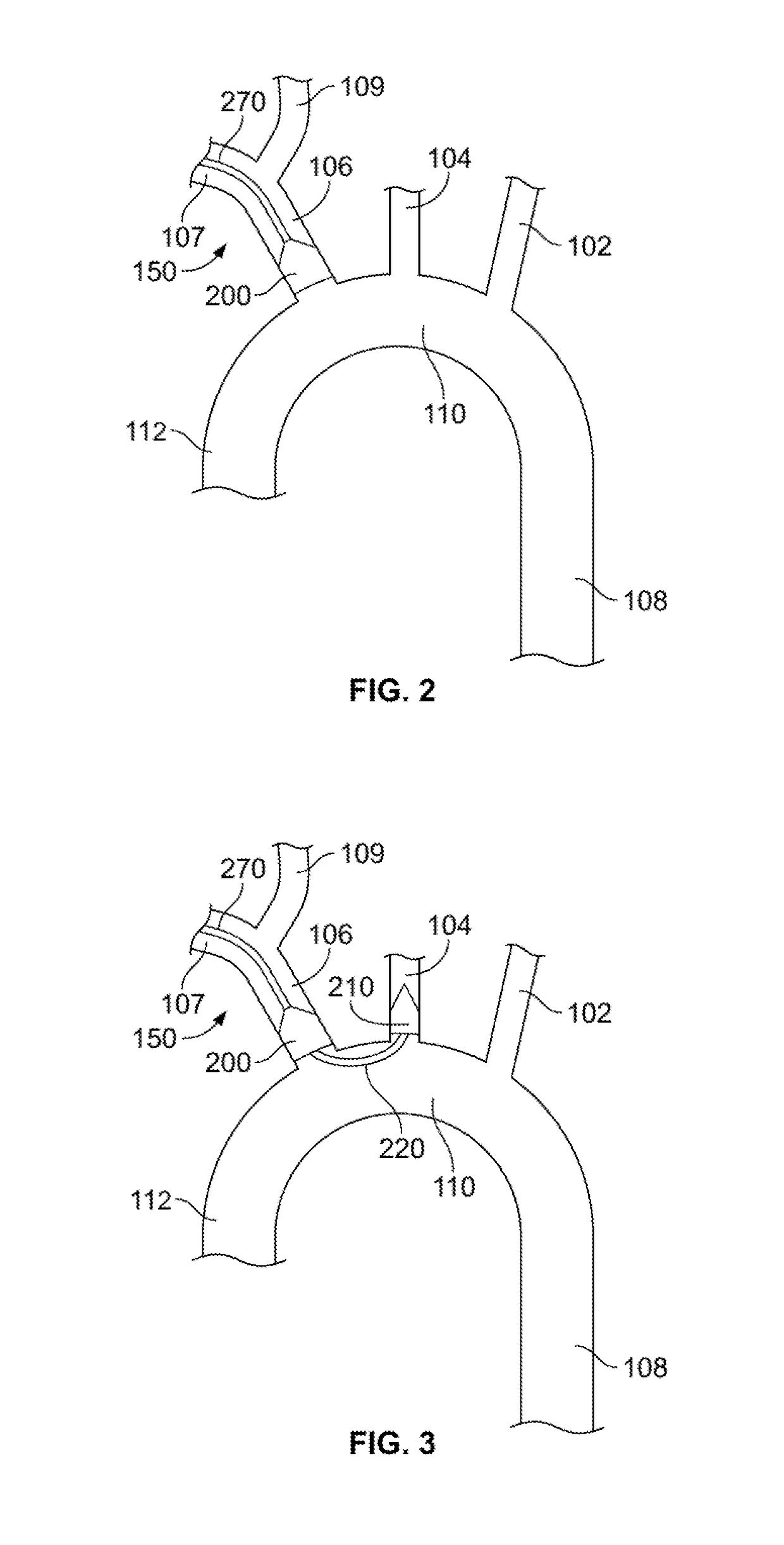
ActiveUS9579182B2Facilitate introducing and directingImprove sealingHeart valvesSurgeryAscending aortaInnominate Arteries
A method of delivering a embolic protection unit to the aorta arch of a patient. The method comprising, introducing a catheter from brachiocephalic artery or through an incision in a wall of the ascending aorta, the catheter comprising an embolic protection unit having an off-center connection point. Advancing the embolic protection unit in a downstream direction from the catheter. Expanding the embolic protection unit in the aorta arch to cover said ostia. Delivering a medical device into the ascending aorta while the embolic protection unit is hold by the catheter covering the ostia.
Owner:SWAT MEDICAL AB
Film-covered stent expander
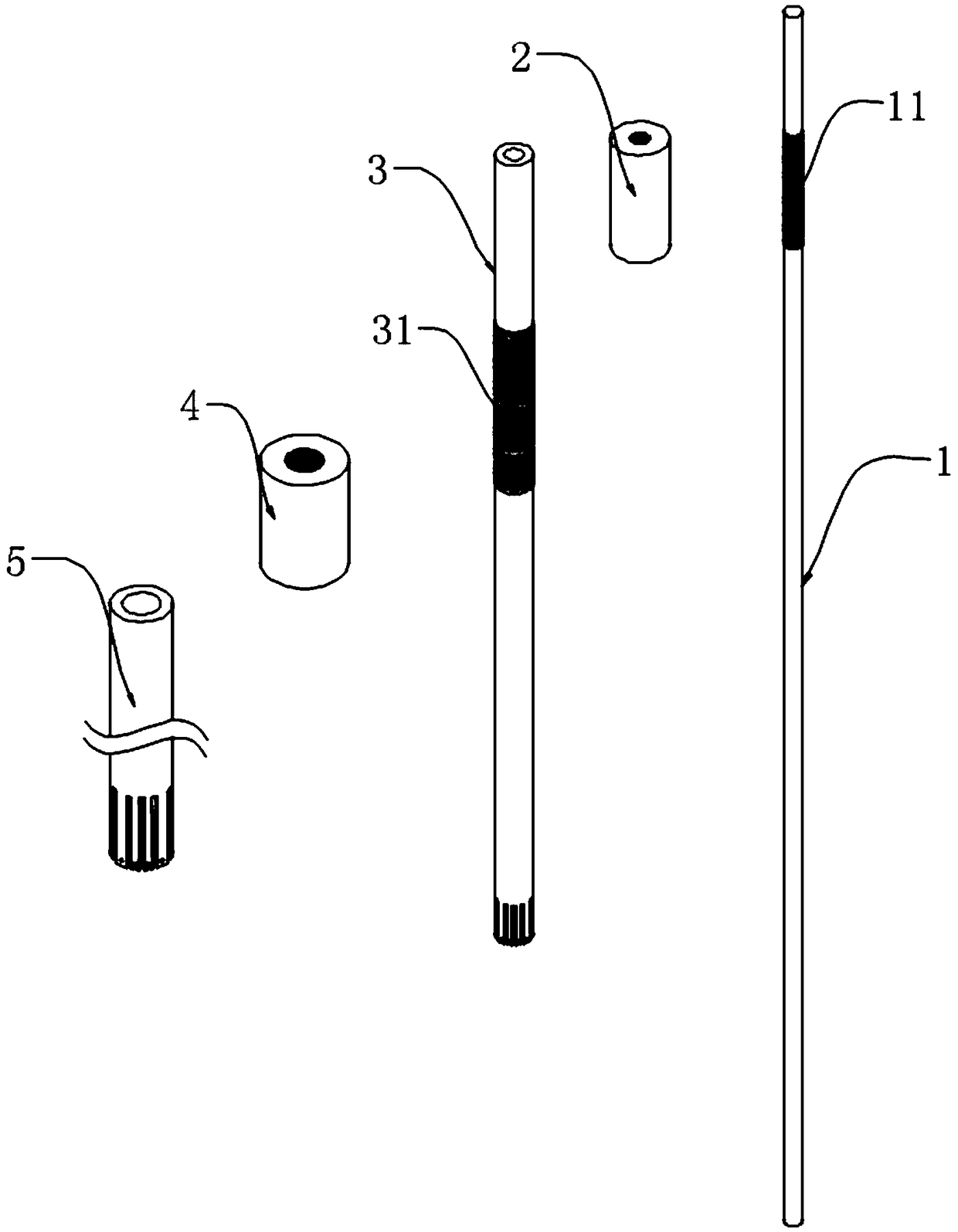
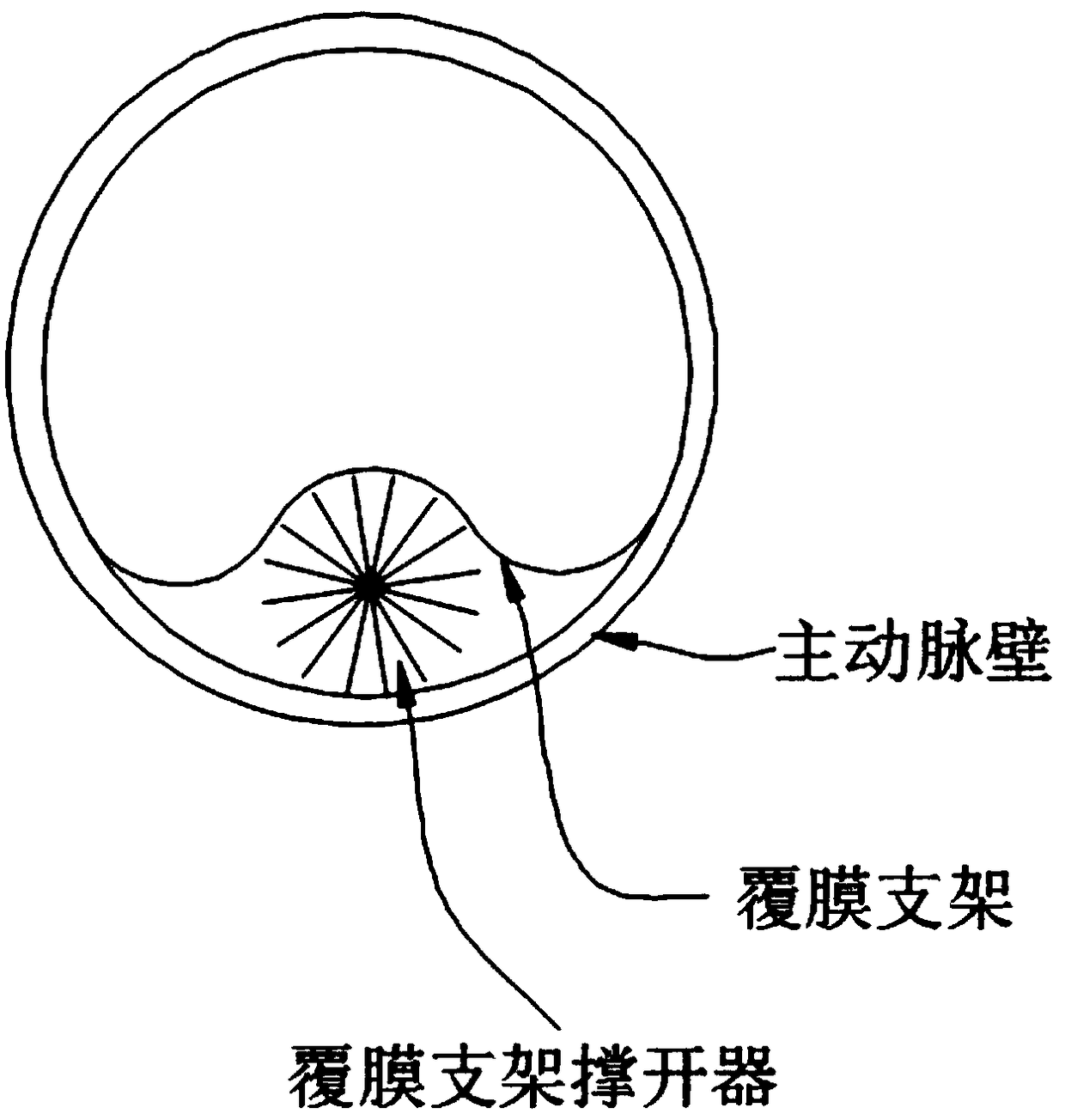
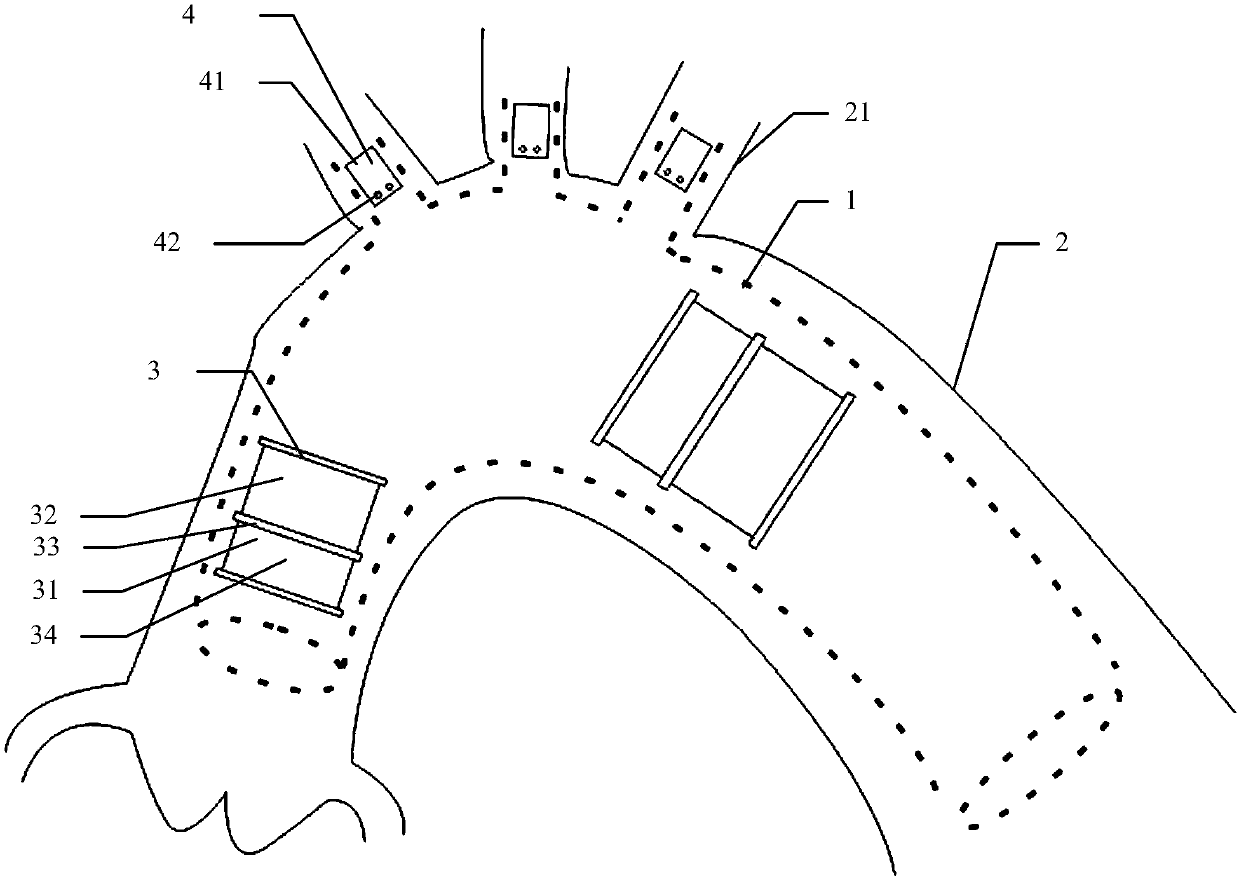
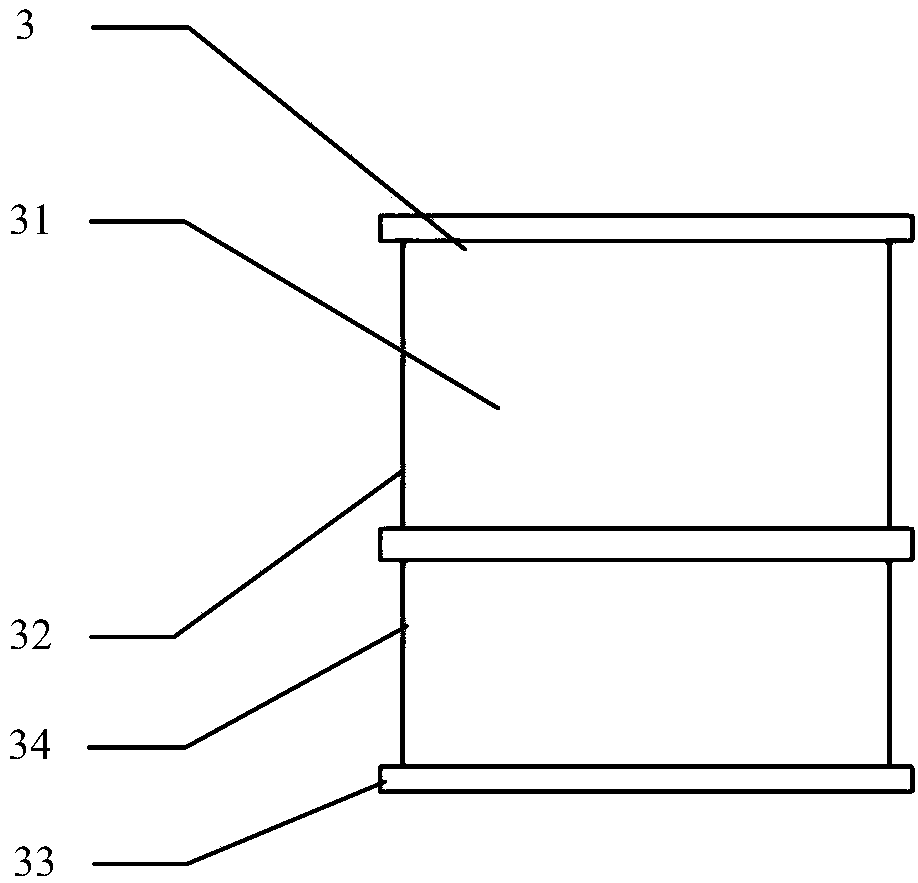
PendingCN109498212AOvercome deficienciesSimple structureStentsOther blood circulation devicesInsertion stentVascular bypass
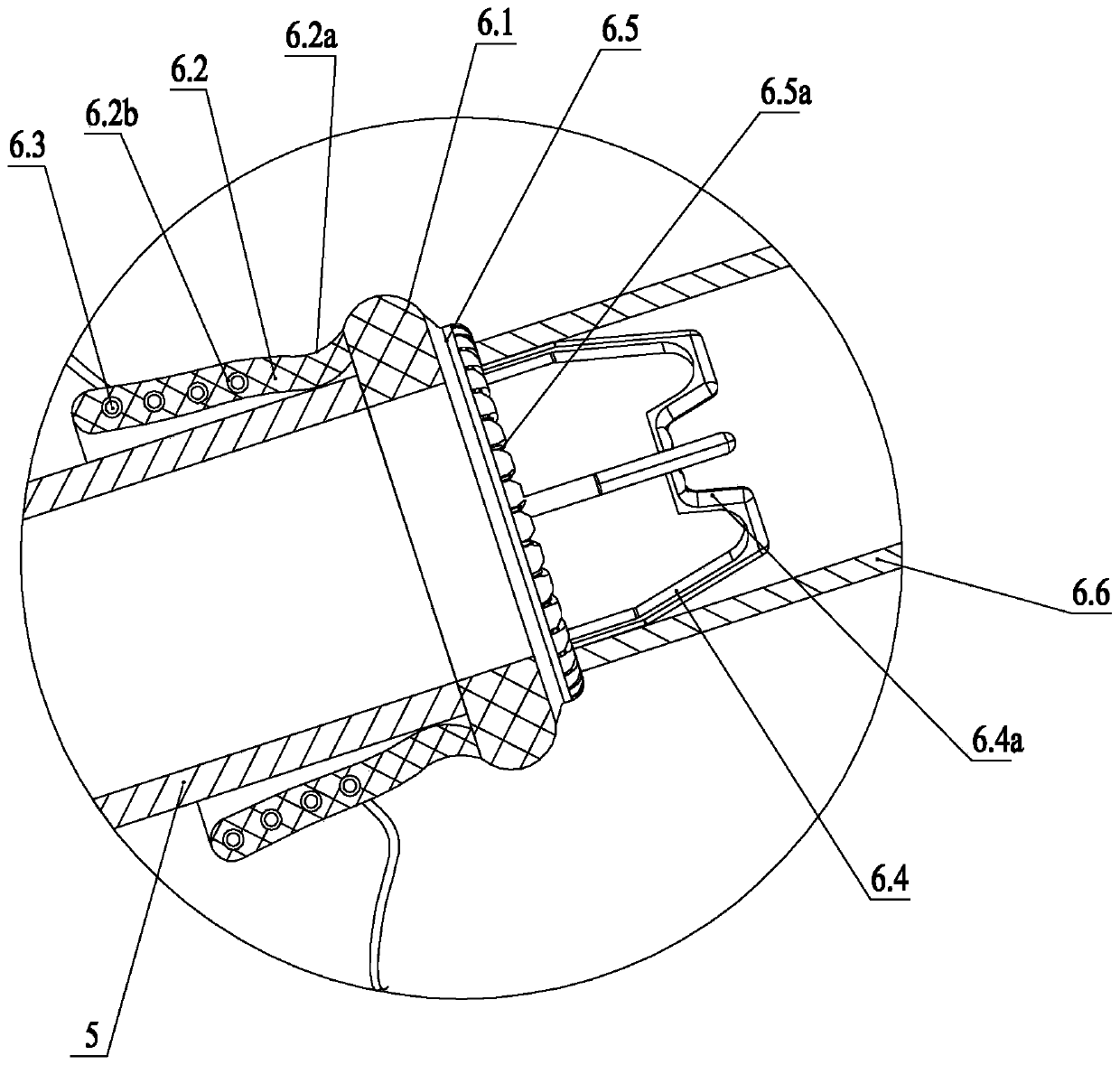
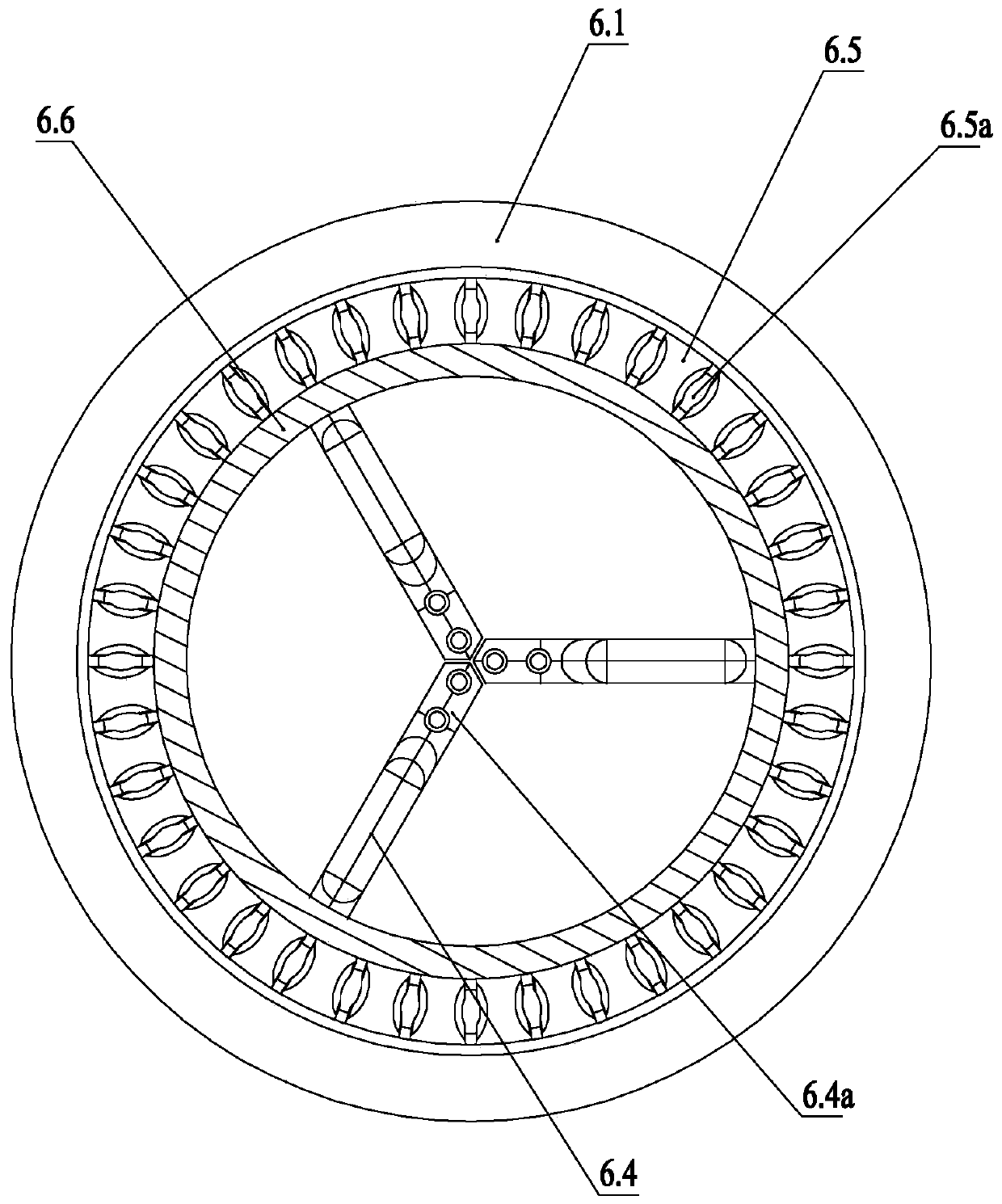
The invention relates to the technical field of covered stents, in particular to a film-covered stent expander which comprises a mandrel. The outer wall of one end of the mandrel is provided with a first external thread, a middle rod advancing and retreating adjusting nut is arranged at a position, close to the first external thread, of the mandrel, a moving middle rod sleeves the middle of the mandrel, a second external thread is arranged on the outer wall of the middle of the moving middle rod, an outer rod advancing and retreating adjusting nut is arranged at a position, close to the secondexternal thread, of the moving middle rod, a moving outer rod sleeves the middle of the moving middle rod, a plurality of first expansion frameworks are arranged on the bottom outer wall of the moving middle rod, and a plurality of second expansion frameworks are arranged on the bottom outer wall of the mandrel. The film-covered stent expander is simple in structure and convenient to use and canexpand the first expansion frameworks and the second expansion frameworks so as to expand a film-covered stent, in this way, blood can leak through from space between an aorta wall and the film-covered stent to reach innominate artery and then goes to left carotid artery from an artificial vascular bypass, and blood flow can be guided into original blood vessels, so that blood flow insufficiency is avoided.
Owner:WUXI PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Device for connecting artificial blood vessels with aortas and innominate artery blood vessels in operations
PendingCN109091187AAvoid bleedingShorten operation timeSurgeryBlood vesselsDeep hypothermic circulatory arrestCirculatory arrest time
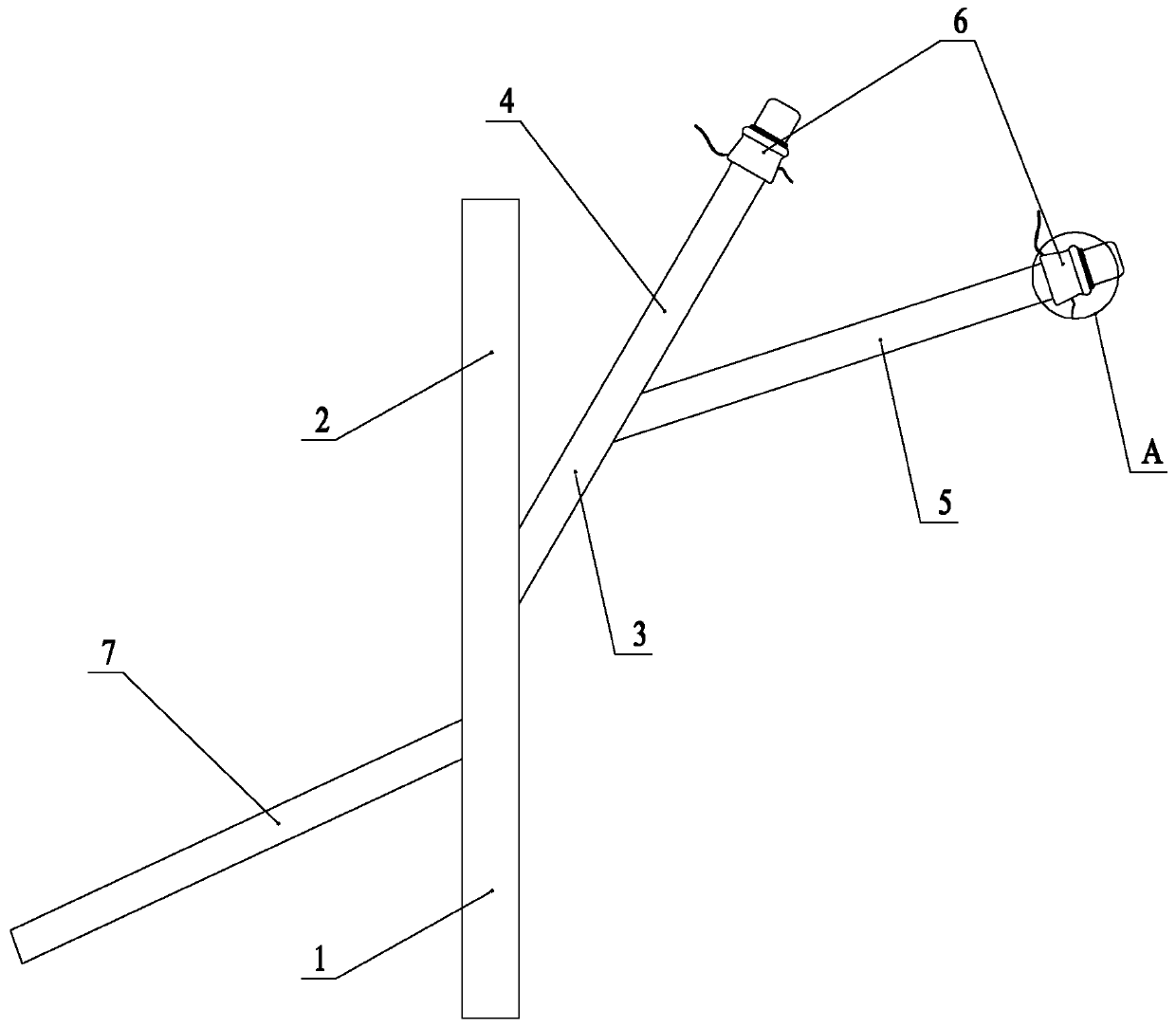
The invention provides a device for connecting artificial blood vessels with aortas and innominate artery blood vessels in operations. The device comprises a connecting device body which is of a tubular structure, the inner side wall of the connecting device body is smooth, and a groove is formed in the outer side of the tubular structure along the circumference. According to the device, a traditional suturing technology can be replaced, the operation and deep hypothermic circulatory arrest time can be effectively shortened, and complications such as anastomosis bleeding are avoided, so that the blood consumption is greatly reduced, and the operation survival rate is increased.
Owner:张健
Four-branch artificial blood vessel for arcus aortae portion replacement perfusion
InactiveCN107468374APerfusion assuranceReduce complicationsBlood vesselsExtracorporeal circulationLeft subclavian artery
The invention provides a four-branch artificial blood vessel for arcus aortae portion replacement perfusion. The artificial blood vessel comprises a body artificial blood vessel for introducing blood for perfusion and a brachiocephalic artery branch artificial blood vessel, a left common carotid artery branch artificial blood vessel and a left subclavian artery branch artificial blood vessel which are communicated with the body artificial blood vessel. An arterial perfusion branch artificial blood vessel communicated with extracorporeal circulation is further arranged on the body artificial blood vessel. Perfusion can be performed on the bilateral whole brain and the whole body during operation, the brain perfusion during operation during profound hypothermia circulation arrest is ensured to the maximum extent, postoperative neurological complications can be reduced, the operation technique can be simplified, and the operation time is shortened, so that the purposes of improving the operation success rate and reducing related operation complications are achieved.
Owner:马路遥
Animal disease model capable of accurately positioning thoraco-abdominal aortic aneurysm
InactiveCN109620457ALarge degree of narrowingReduce manufacturing costSurgical veterinaryDiseaseCoarctation of the aorta
The invention provides an animal disease model capable of accurately positioning thoraco-abdominal aortic aneurysm. According to a method, aorta ligation is used, and the thoraco-abdominal aortic aneurysm model capable of achieving accurate positioning is built, so that the aortic constriction degree is higher on the basis of thoracic aorta constriction, and the ligation position is more flexibleand is located on the arcus aortae part or the subhepatic aorta abdominalis part between the right innominate artery and the left common carotid artery; changes of high pressure and blood flow speed at the ligation position are used for inducing aortectasis, then the aorta structure and the hemodynamics are changed, the aortic aneurysm is caused, and observation can be conveniently achieved through modern medical means such as Doppler color ultrasound and section.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SOOCHOW UNIV
Quick connecting type four-branch artificial blood vessel for irrigation
PendingCN110584830AImprove survival rateIngenious structureBlood vesselsLeft subclavian arteryNervous system
The invention relates to a quick connecting type four-branch artificial blood vessel for irrigation. The quick connecting type four-branch artificial blood vessel comprises a main body artificial blood vessel, a brachiocephalic artery branch artificial blood vessel, a left common carotid secondary branch artificial blood vessel and a left subclavian artery secondary branch artificial blood vessel,wherein the brachiocephalic artery branch artificial blood vessel, the left common carotid secondary branch artificial blood vessel and the left subclavian artery secondary branch artificial blood vessel are connected with the main body artificial blood vessel in a communicating manner. The quick connecting type four-branch artificial blood vessel is characterized in that left-hand threaded typeconnectors are respectively arranged at the far end of the left common carotid secondary branch artificial blood vessel and the far end of the left subclavian artery secondary branch artificial bloodvessel; and an intra-arterial infusion branch artificial blood vessel which communicates with the outer circulation of a connector is also arranged on the main body artificial blood vessel. The quickconnecting type four-branch artificial blood vessel disclosed by the invention is ingenious in structure and reasonable in design, so that the problem that in the prior art, in an aortic arch replacement operation, cerebral perfusion is insufficient, and nervous system complications are liable to generate can be solved; the quick connecting type four-branch artificial blood vessel can be quickly and reliably fixed, the situation that time is consumed for suturing is not needed, the operation is quick and convenient, the operation time can be greatly saved, the operation procedure difficulty isreduced, and the survival rate of a patient is increased.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE HOSPITAL THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL WITH NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Femoral aortic access modular stent assembly and method
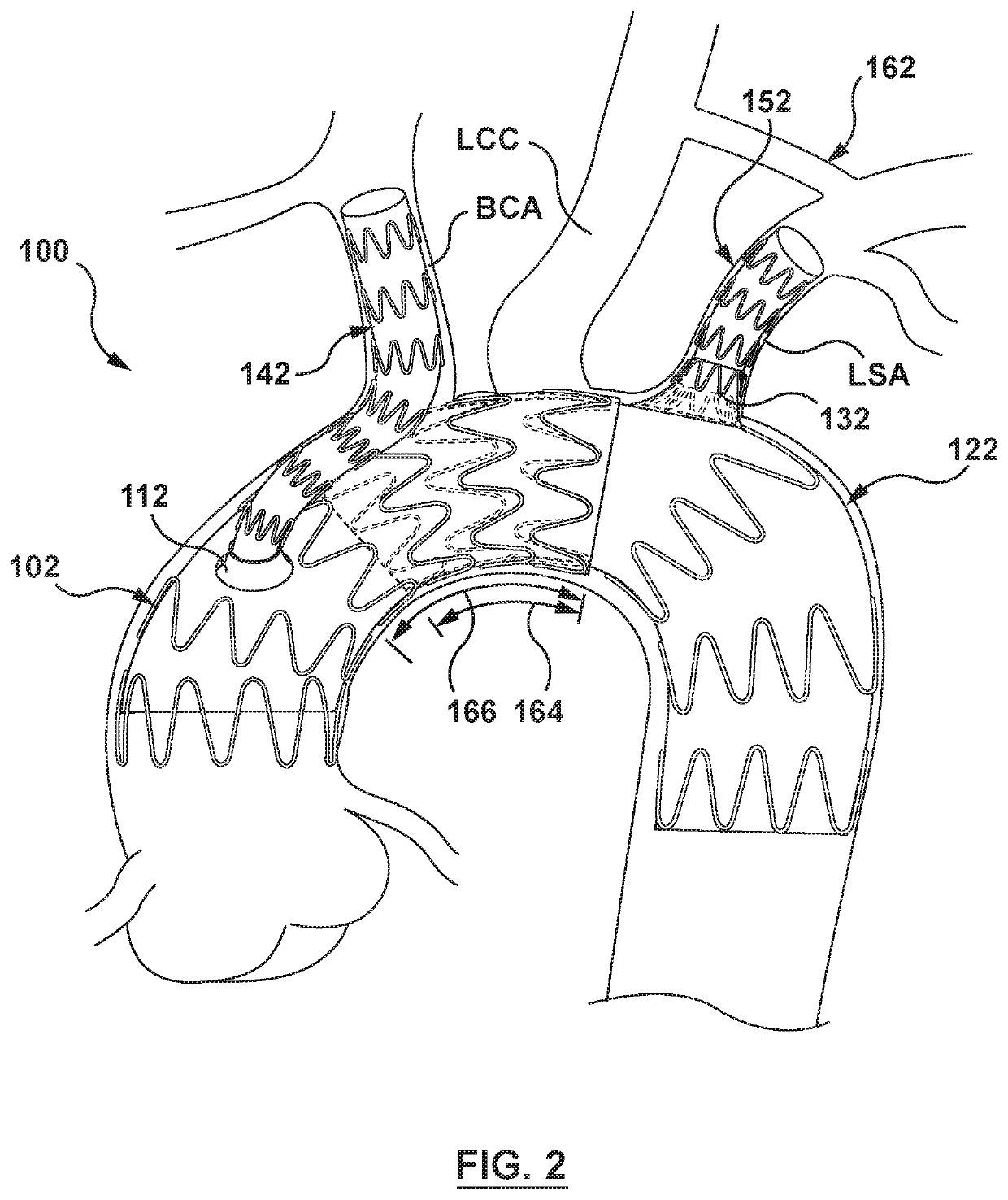
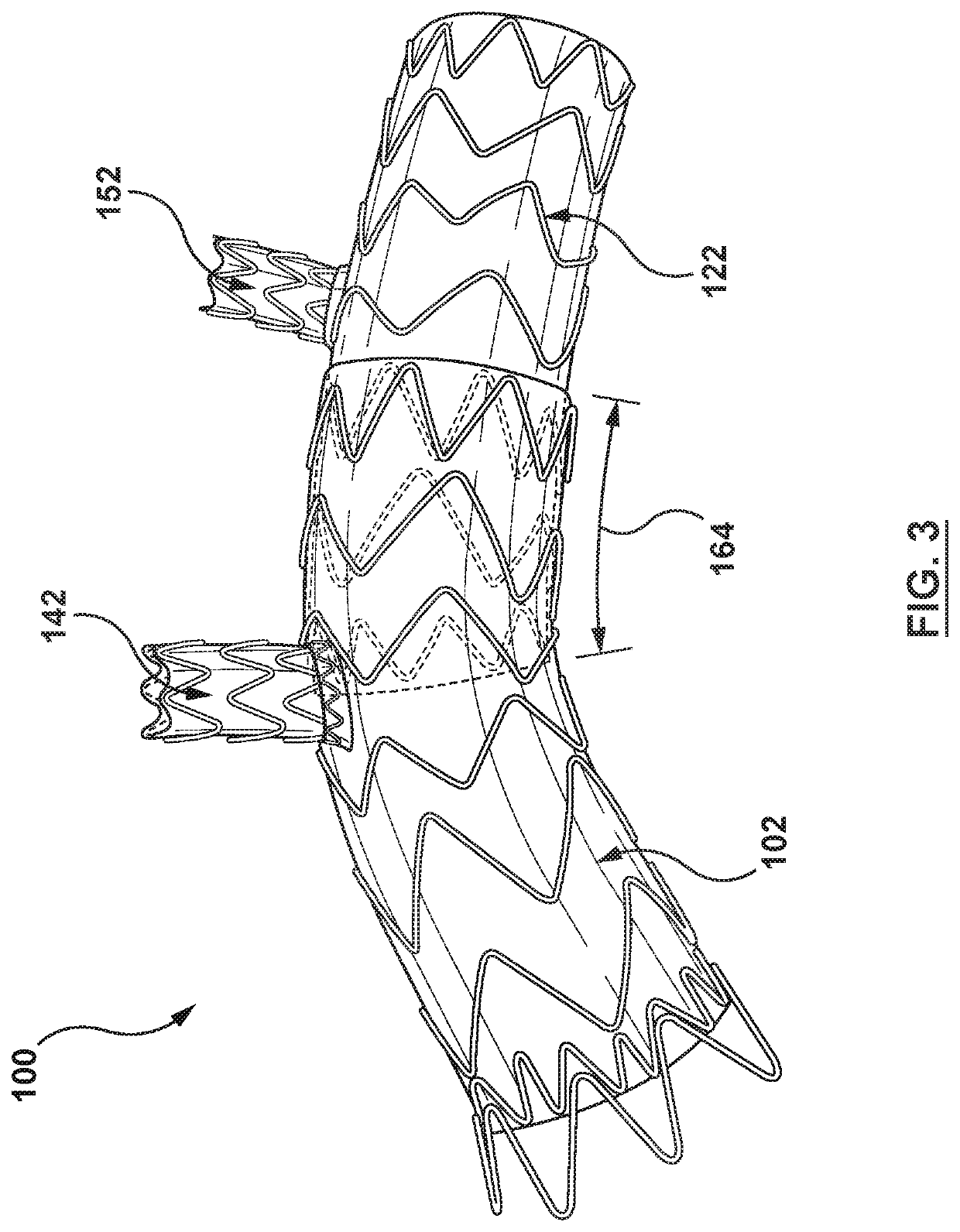
The techniques of this disclosure generally relate to a modular stent device that is deployed into the ascending aorta via femoral access. The modular stent device is a base or anchor component to which additional modular stent devices can be attached to exclude diseased areas of the aorta while at the same time allowing perfusion of the brachiocephalic artery, the left common carotid artery, and / or the left subclavian artery.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
The anchoring of an anchoring of an anatomical anchoring and the anchoring of the anchor and the conveyor system
ActiveCN109172043BSecurity anchoring methodNo entry into the false cavityStentsBlood vesselsThird aortic archDelivery system
An ascending aorta repair stent anchored by the innominate artery, including the ascending aorta stent segment and the innominate artery stent segment, the innominate artery part of the stent is first released, and then the main part is released, and the distal opening of the main part is facing the aortic arch lumen far away end, the main part of the stent covers the primary tear of the ascending aorta with dissection. After release, the body portion terminates above the sinotubular junction. The longitudinal beam structure is made of temperature-dependent shape-memory metal materials extending to the greater curvature of the aortic arch and the lesser curvature of the aortic arch that continue to the innominate artery. Stick to the aortic wall. The stent is anchored only by the special anatomical shape of the ascending aorta and the innominate artery and the memory metal stringer structure. It is used for patients with type A aortic dissection who are waiting for surgery when there are surgical contraindications in the acute stage, and provides opportunities for follow-up surgical treatment for patients with acute type A aortic dissection with high surgical risk.
Owner:FUWAI HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI & PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE
A transapical anatomical stent to repair ascending aorta and hemi arch
InactiveUS20210282916A1Safer anchoring methodSafer and convenient apical approachStentsBlood vesselsAortic dissectionSinotubular Junction
This is an ascending aorta and hemi arch repair stent graft anchored by innominate artery. The graft includes two basic parts: ascending aortic segment and innominate artery segment. The innominate artery portion of the stent graft is firstly released, then the main stent graft is continuously released. The distal end of the main stent graft is against the distal end of the aortic arch, and the main stent graft covers the primary tear location. The proximal stent graft should be positioned precisely above the sinotubular junction. The longitudinal metal beam structure with temperature-dependent shape memory alloy extending along the greater and lesser curvature of the aortic arch would fit to the aortic anatomic morphology perfectly. The graft is secured to the aorta by means of both innominate artery stent graft anchoring and temperature-dependent longitudinal metal beam. The invention is aimed at the patients with type A aorta dissection who cannot undergo the early surgery in the acute phase, providing opportunities for follow-up surgical treatment.
Owner:YU CUNTAO
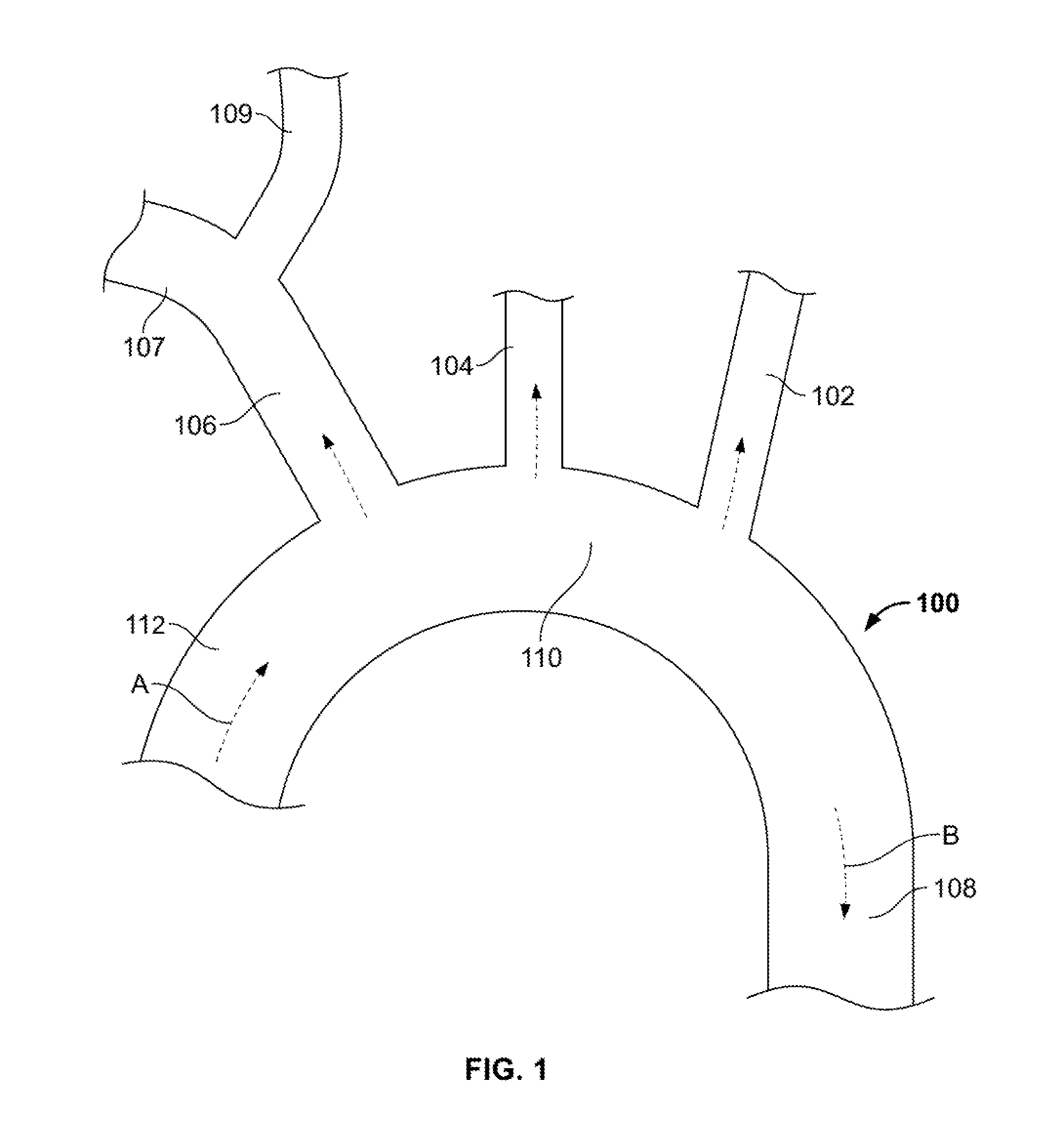
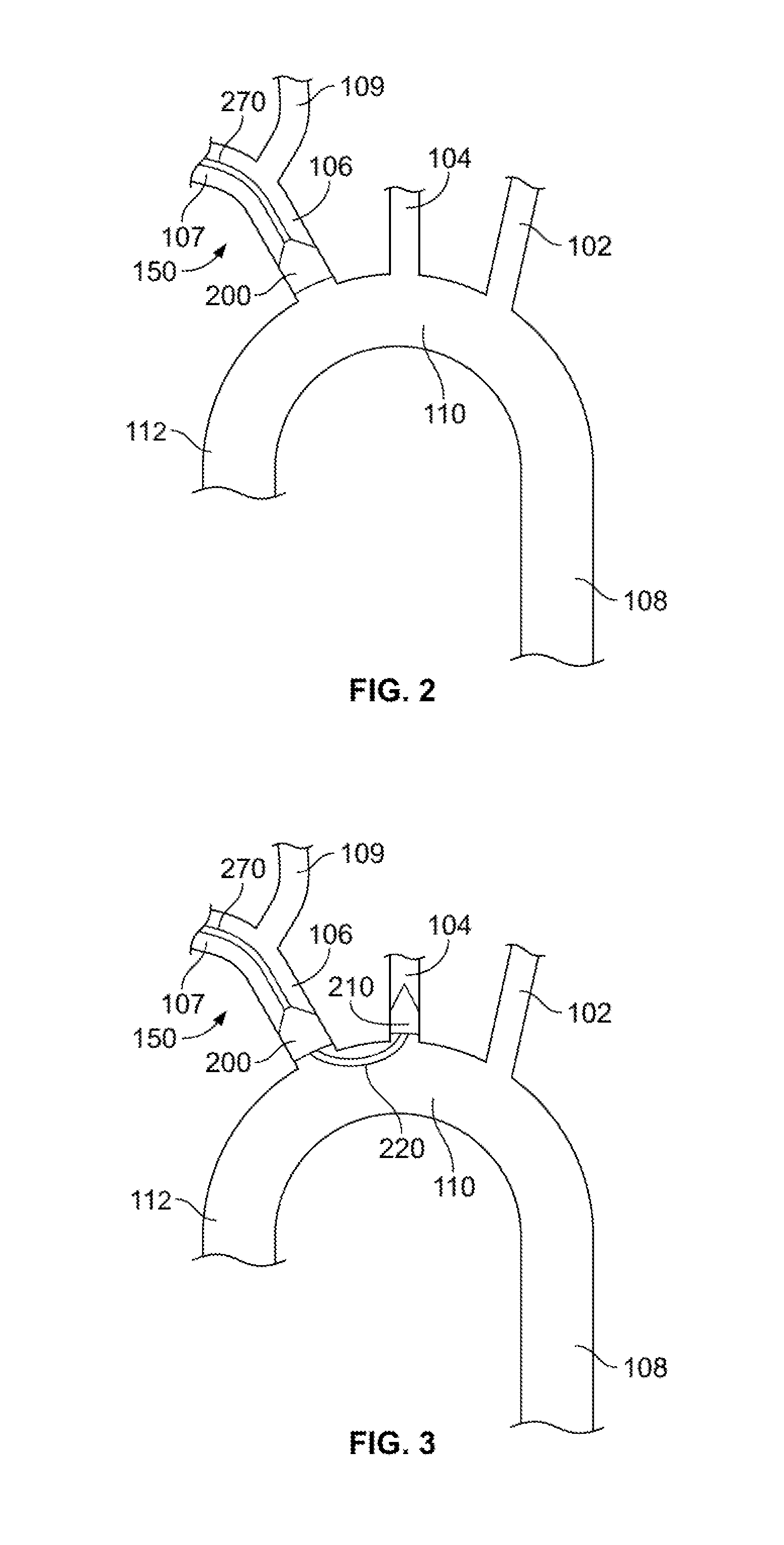
Fenestrated endoprosthesis for the correction of aortic aneurysms
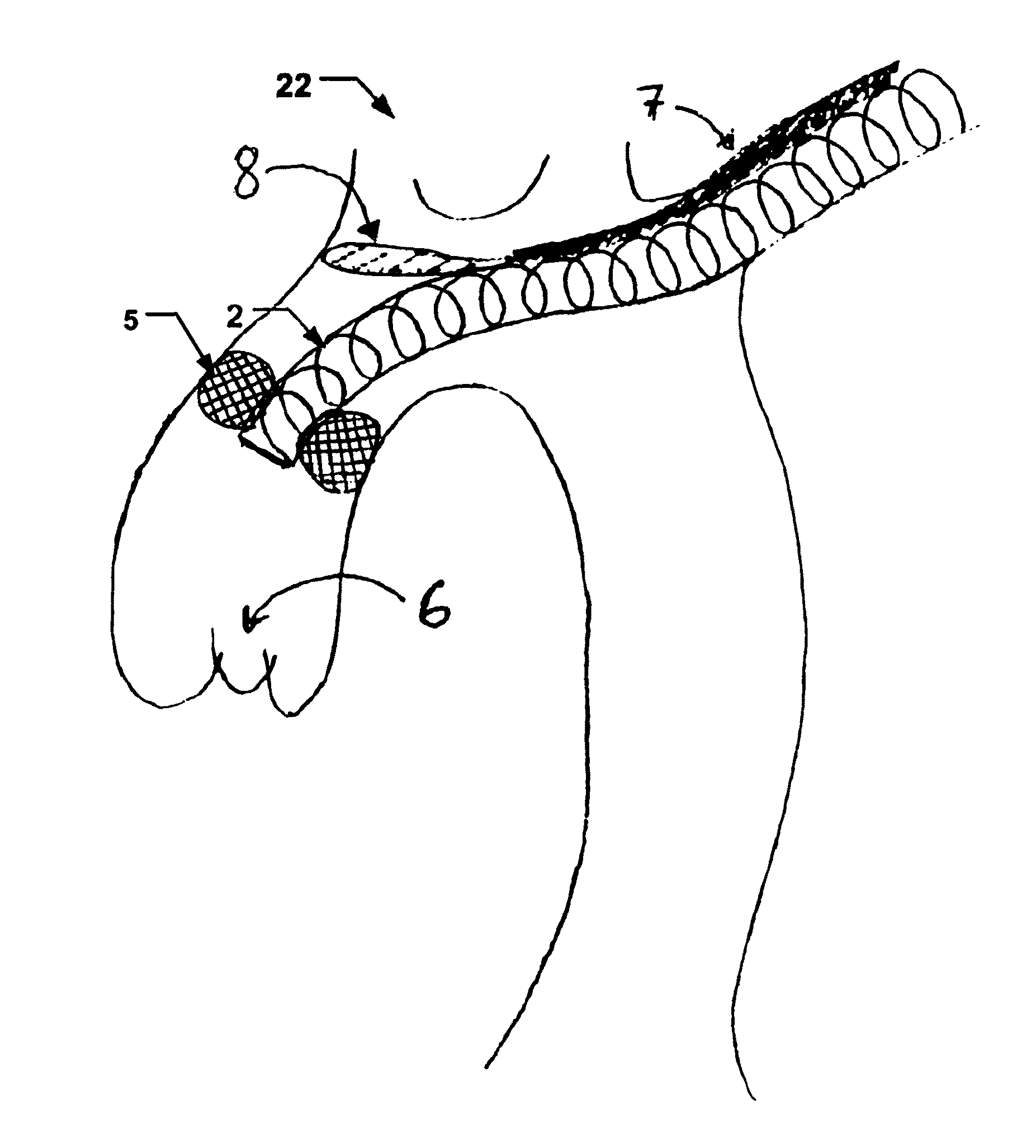
PendingCN112203614AReduce hazardsPrevent type II endoleakStentsBlood vesselsAortic arch aneurysmInnominate Arteries
A fenestrated endoprosthesis for the correction of aortic arch aneurysms comprising: a stent (20) having a first oblong lateral hole (23) having an area equal to the total area occupied by the innominate artery (11) and by the carotid artery (12); said stent (20) comprises a metal skeleton (21) covered with a fabric (22); characterized by comprising a flexible sac (30) that covers said stent (20)covered with fabric (22); said sac (30) comprises a second lateral hole (32) having an area larger than said first hole (23), so that the edges (26) of said stent (20) covered with fabric (22) that delimit said first hole (23) are visible; the edges (33) of said sac (30) that delimit the hole (32) are welded to said stent (20) covered with fabric (22); a volume (31) is created between said stent (20) covered with fabric (22) and said sac (30); said volume (31) is filled with a polymer.
Owner:UNIV DEGLI STUDI DI PADOVA
Blood flow simulation model of cerebral vessels under simulated weightlessness condition
InactiveCN110755043AReflect stress responseDiagnostics using lightSensorsSimulated weightlessnessLeft subclavian artery
The invention discloses a blood flow simulation model of cerebral vessels under the simulated weightlessness condition, and belongs to the technical field of physiologic signal simulation. The model comprises an aorta canal, an brachiocephalic artery canal, a carotid canal, a subclavian artery canal, a vertebrarterial canal, an internal carotid canal, an external carotid artery canal, a basilar artery canal, an arteria cerebri media canal, an arteria cerebri anterior canal, a posterior cerebral artery canal, an anterior communicating artery canal and a posterior communicating artery canal, wherein the aorta canal, the brachiocephalic artery canal and the subclavian artery canal form a systemic circulation arterial rete; blood flows from the systemic circulation arterial rete to the carotidcanal and the vertebrarterial canal, then flows into a cerebral circulation arterial rete formed by the internal carotid canal, the external carotid artery canal, the basilar artery canal, the arteria cerebri media canal, the arteria cerebri anterior canal, the posterior cerebral artery canal, the anterior communicating artery canal and the posterior communicating artery canal; and the tail end of the cerebral circulation arterial rete is the downstream of the arteria cerebri media canal, the downstream of the arteria cerebri anterior canal, and the downstream of the posterior cerebral arterycanal. Through the adoption of the blood flow simulation model disclosed by the invention, the analysis of the interaction of the arterial blood flow of the systemic circulation and the cerebral circulation is deeper.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Embolic protection device
Embolic protection devices useful for filtering emboli during interventional cardiac, vascular, or other procedures are described. The device can include first and second expandable mesh filters having open and closed ends. The first filter is attached to a catheter at its closed end. The second filter is attached to a steerable guide wire at its closed end. The second filter includes a cinching wire circumferentially attached to the filter. The filters are deployed in separate vessels, such as the brachiocephalic artery and the left common carotid artery. A procedure is performed, and the filters trap any emboli travelling through the path of the filters. At the end of the procedure, the second filter is closed using the cinching wire, and retracted into the first filter. Both the first and second filters are collapsed into a sheath and removed from the body with along with any emboli trapped in the filters.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
Modular aortic arch prosthetic assembly and method of use thereof
ActiveUS10702369B2Effectively proximally reroutes an ostiumStentsBlood vesselsLeft subclavian arteryInnominate Arteries
A prosthetic assembly configured for endovascular placement within an aortic arch and method of use thereof. The prosthetic assembly includes a proximal aortic stent-graft prosthesis configured to be positioned within a proximal portion of the aortic arch adjacent to the brachiocephalic artery, a distal aortic stent-graft prosthesis configured to be positioned within a distal portion of the aortic arch adjacent to the left subclavian artery, a first branch stent-graft prosthesis configured to be positioned within the brachiocephalic artery and a second branch stent-graft prosthesis configured to be positioned in one of the left common carotid and the left subclavian artery. When deployed, a proximal end of the first branch stent-graft prosthesis is disposed within a lumen of the proximal aortic stent-graft prosthesis to proximally displace the ostium of the brachiocephalic artery. When deployed, a proximal end of the distal aortic stent-graft prosthesis is disposed within the distal end of the proximal aortic stent-graft prosthesis to form an overlap between the proximal and distal aortic stent-graft prostheses. The overlap is relatively increased by the first branch stent-graft prosthesis proximally displacing the ostium of the brachiocephalic artery.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com