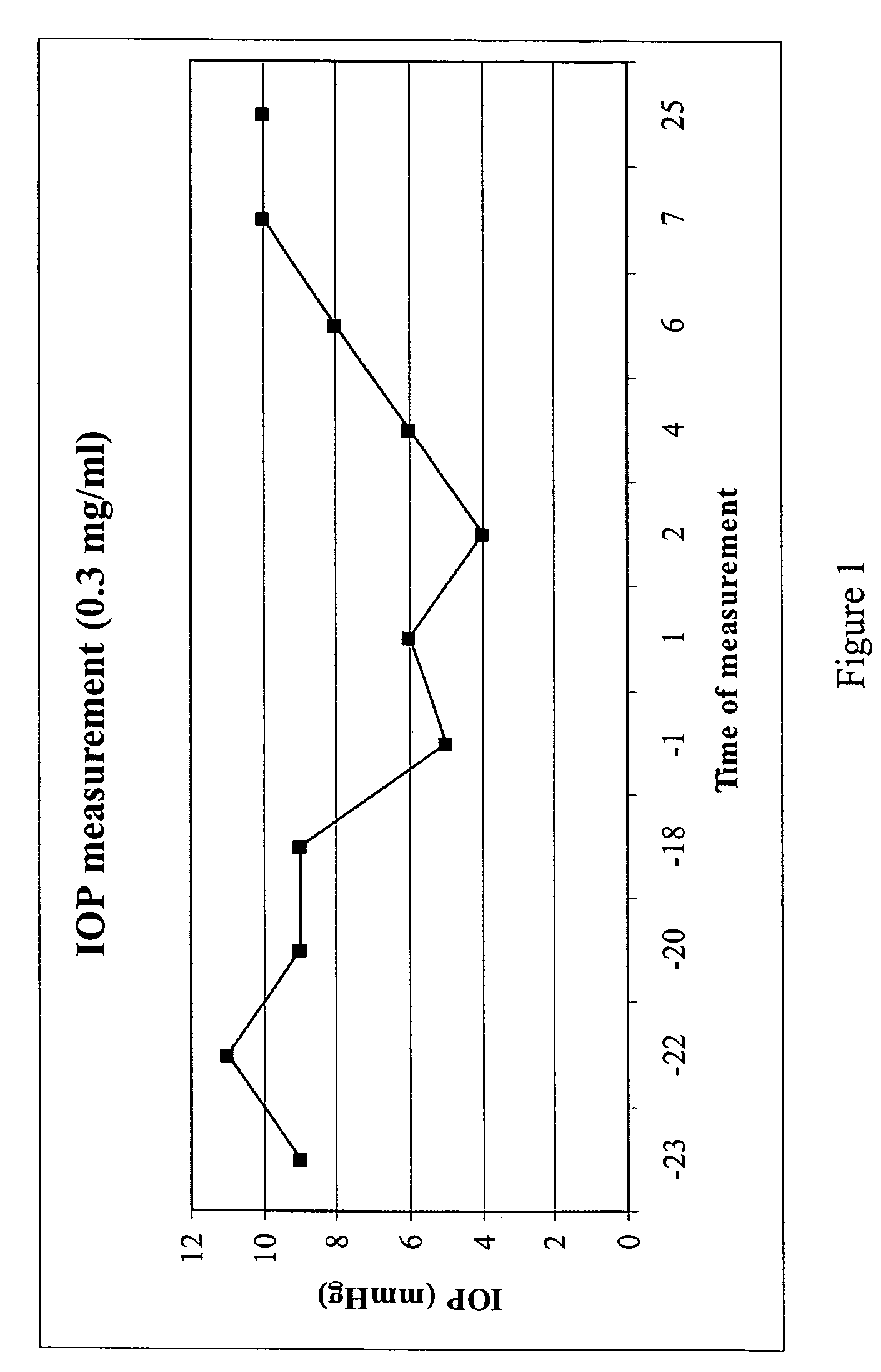
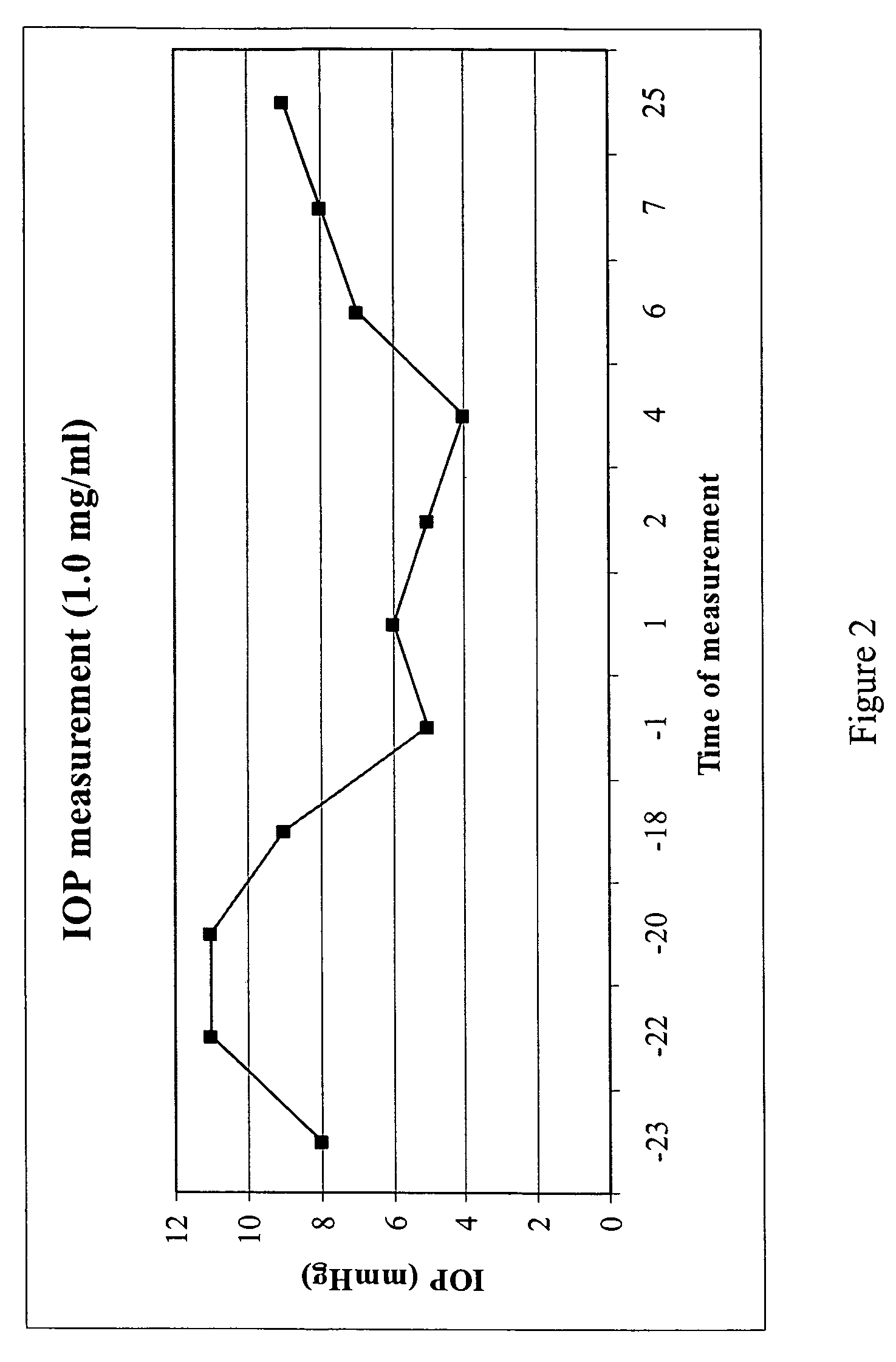
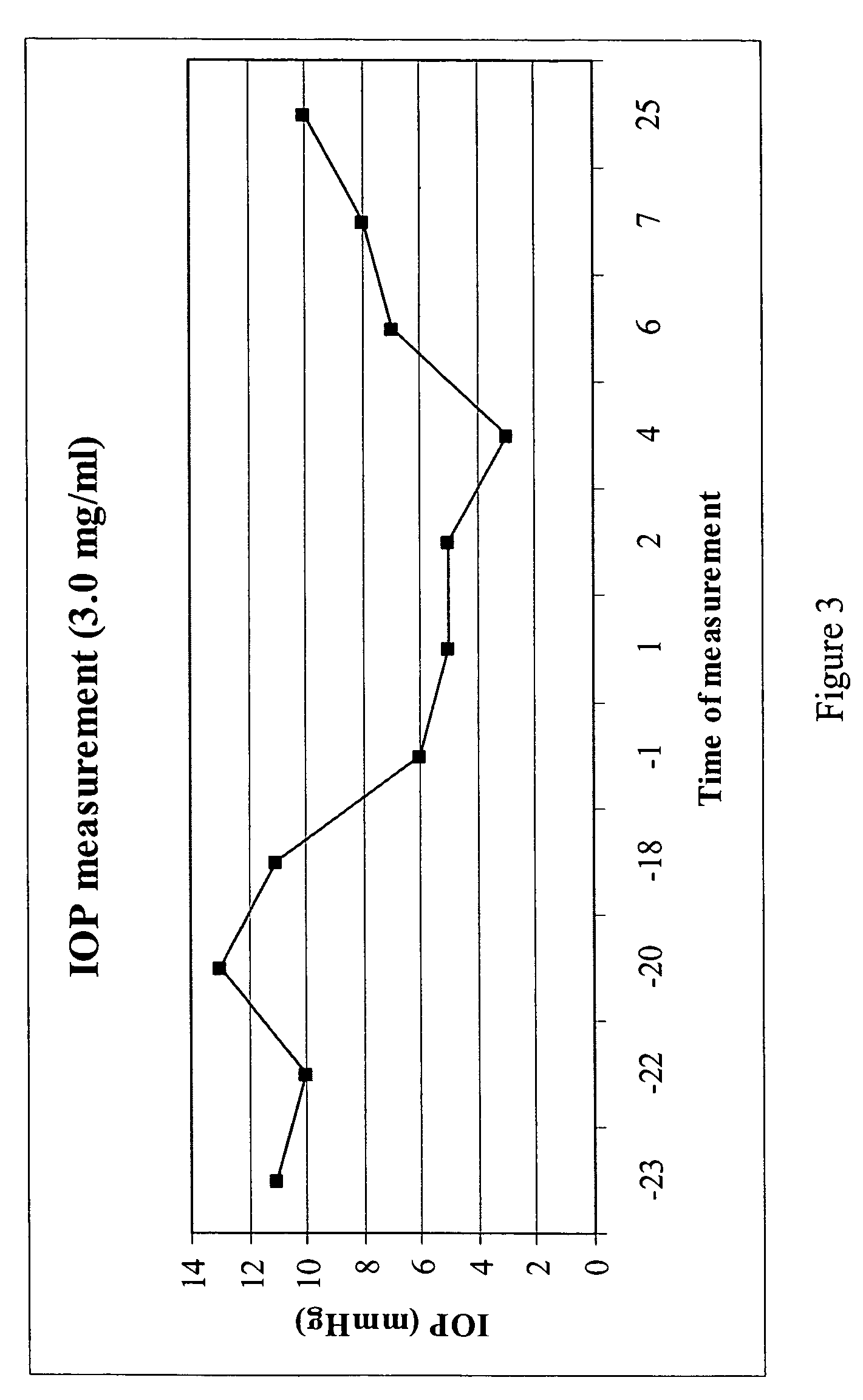
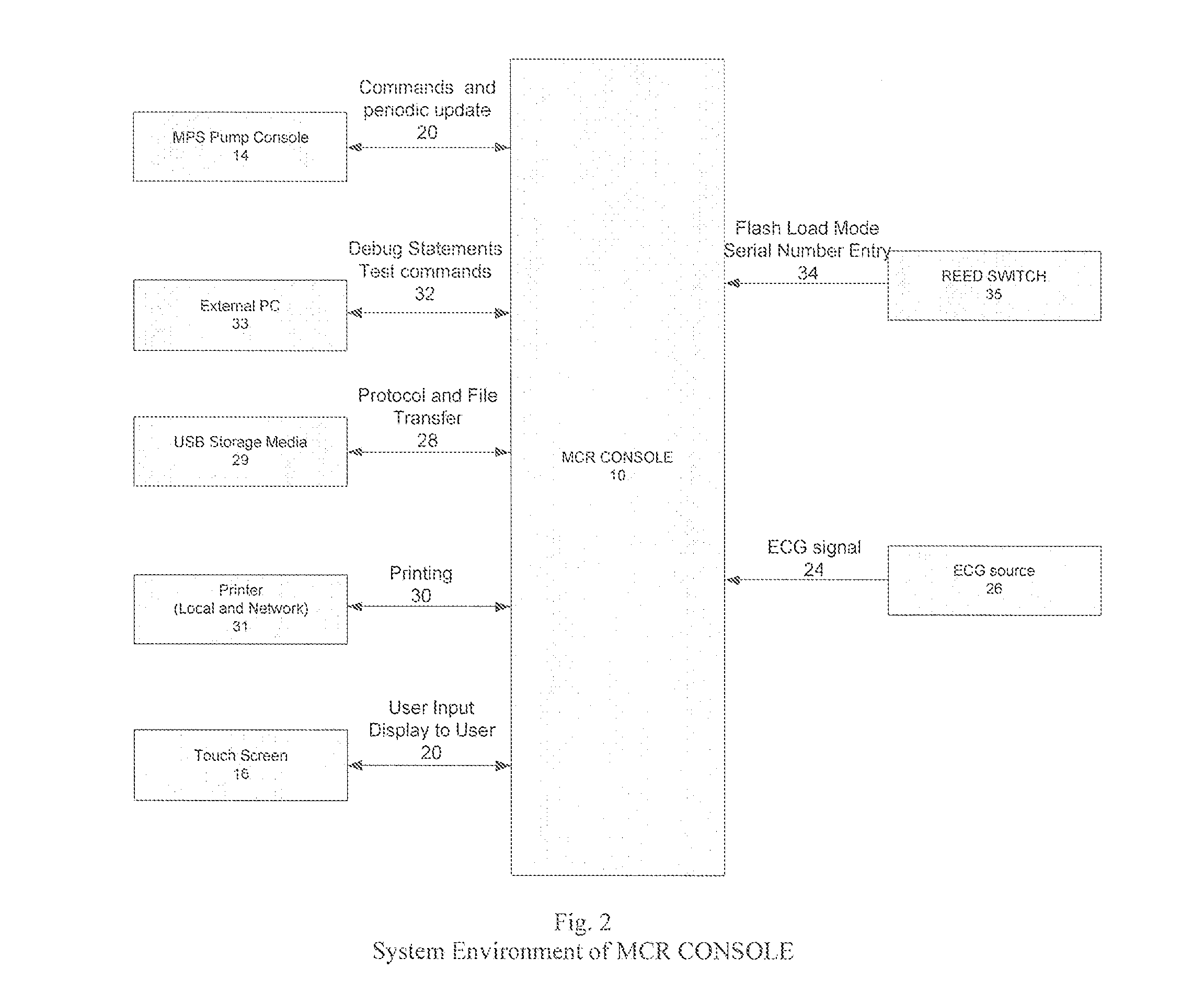Patents
Literature
51 results about "Cardioplegias" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
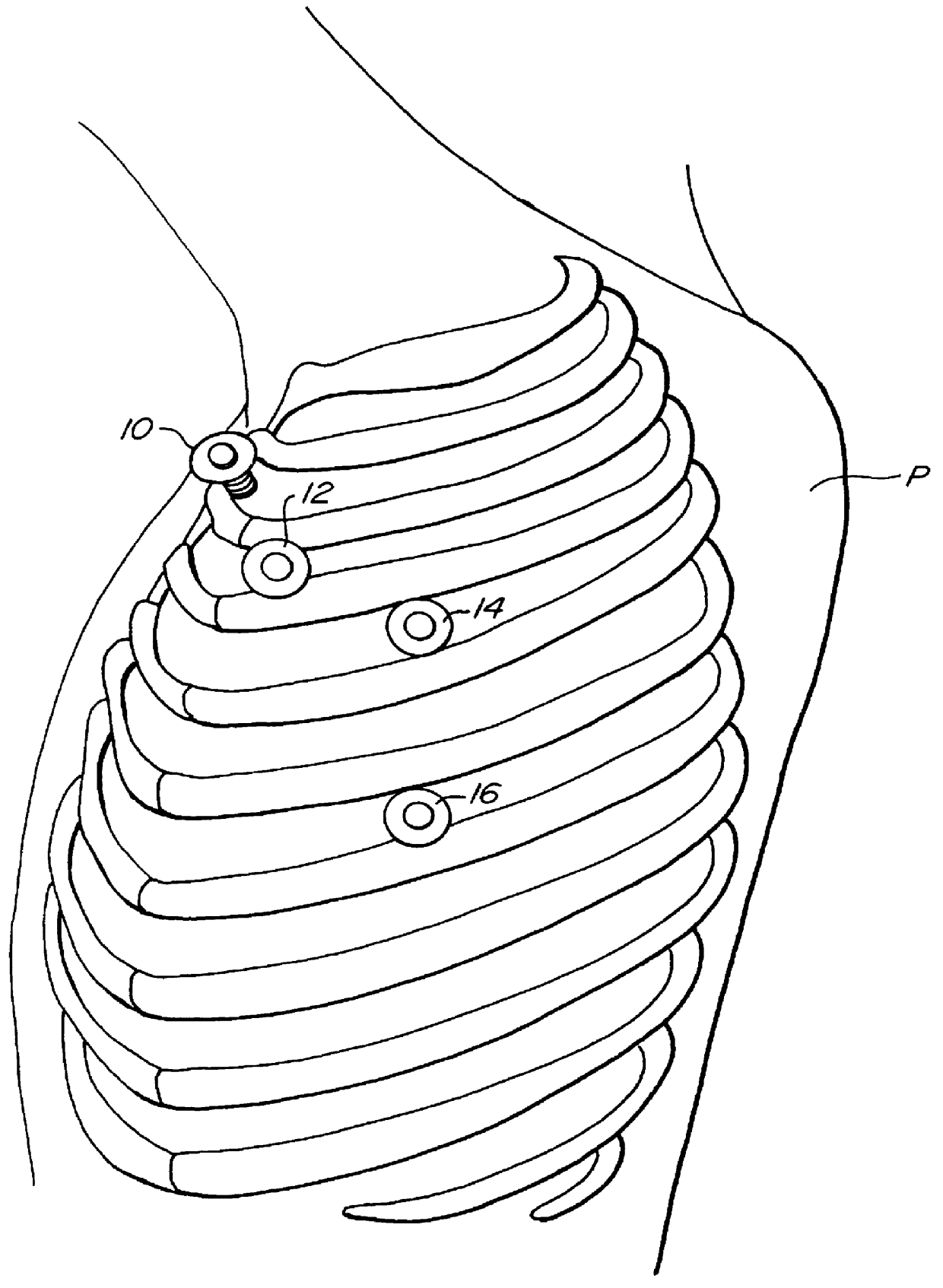
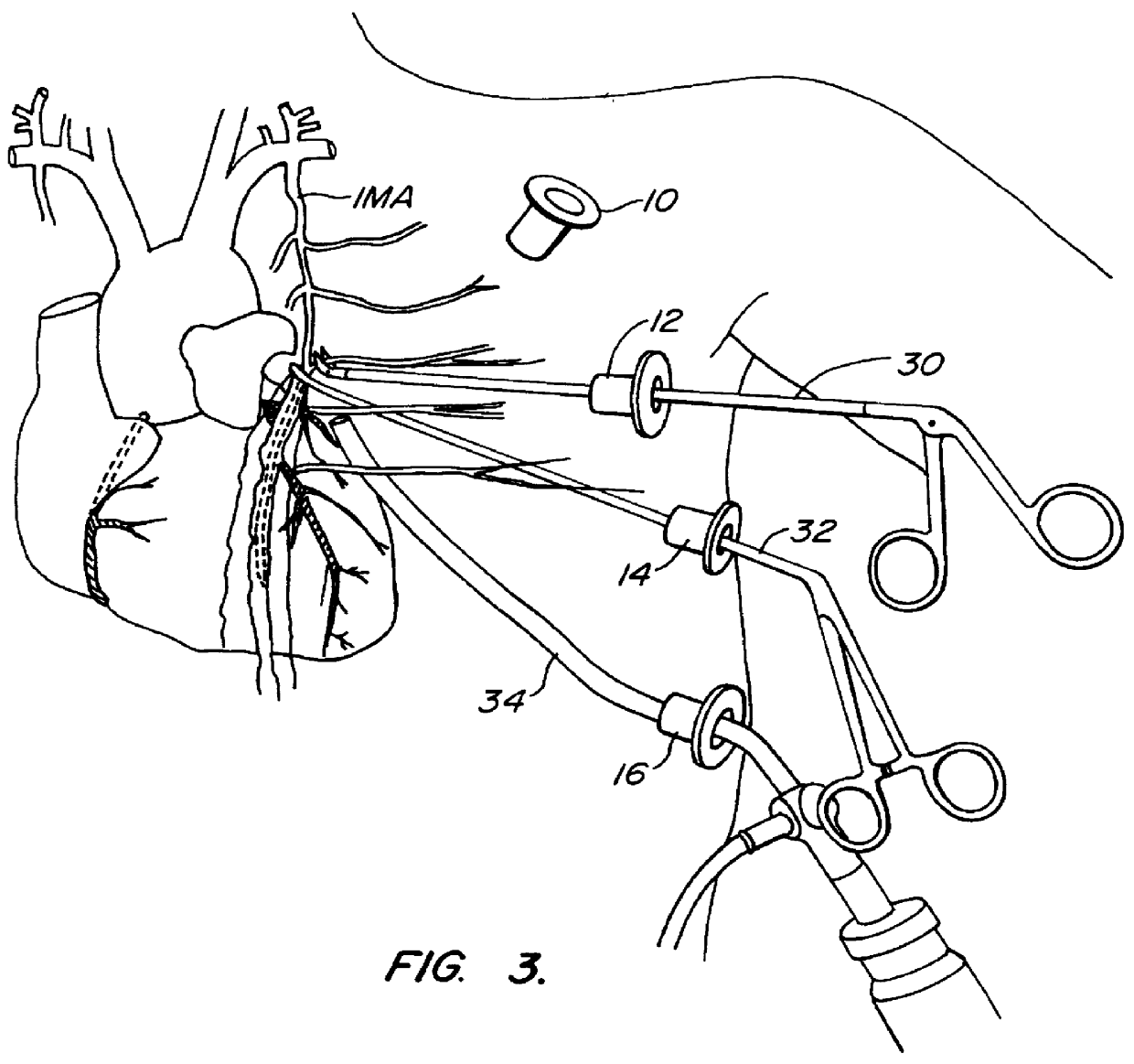
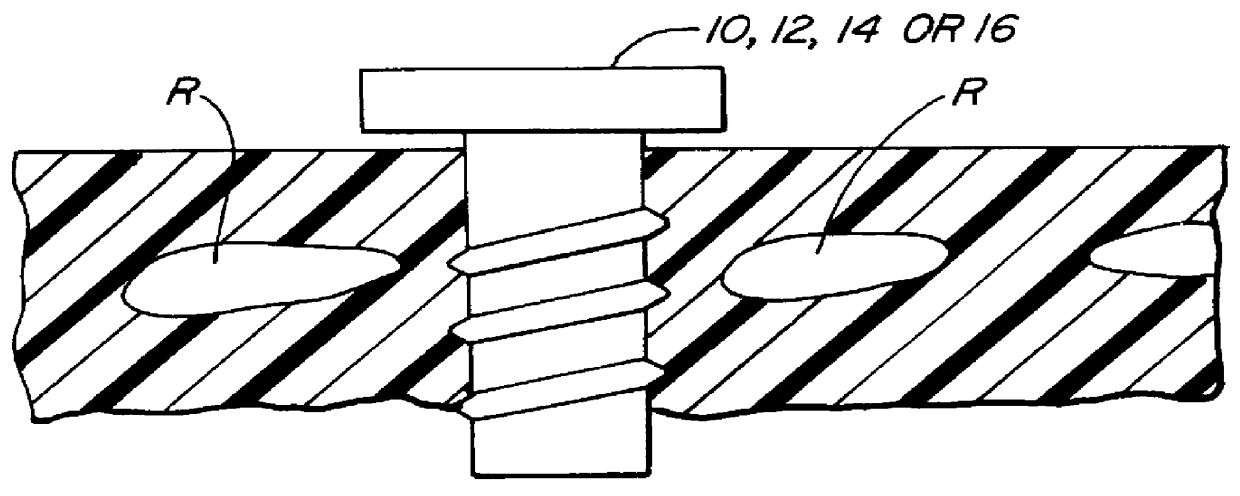
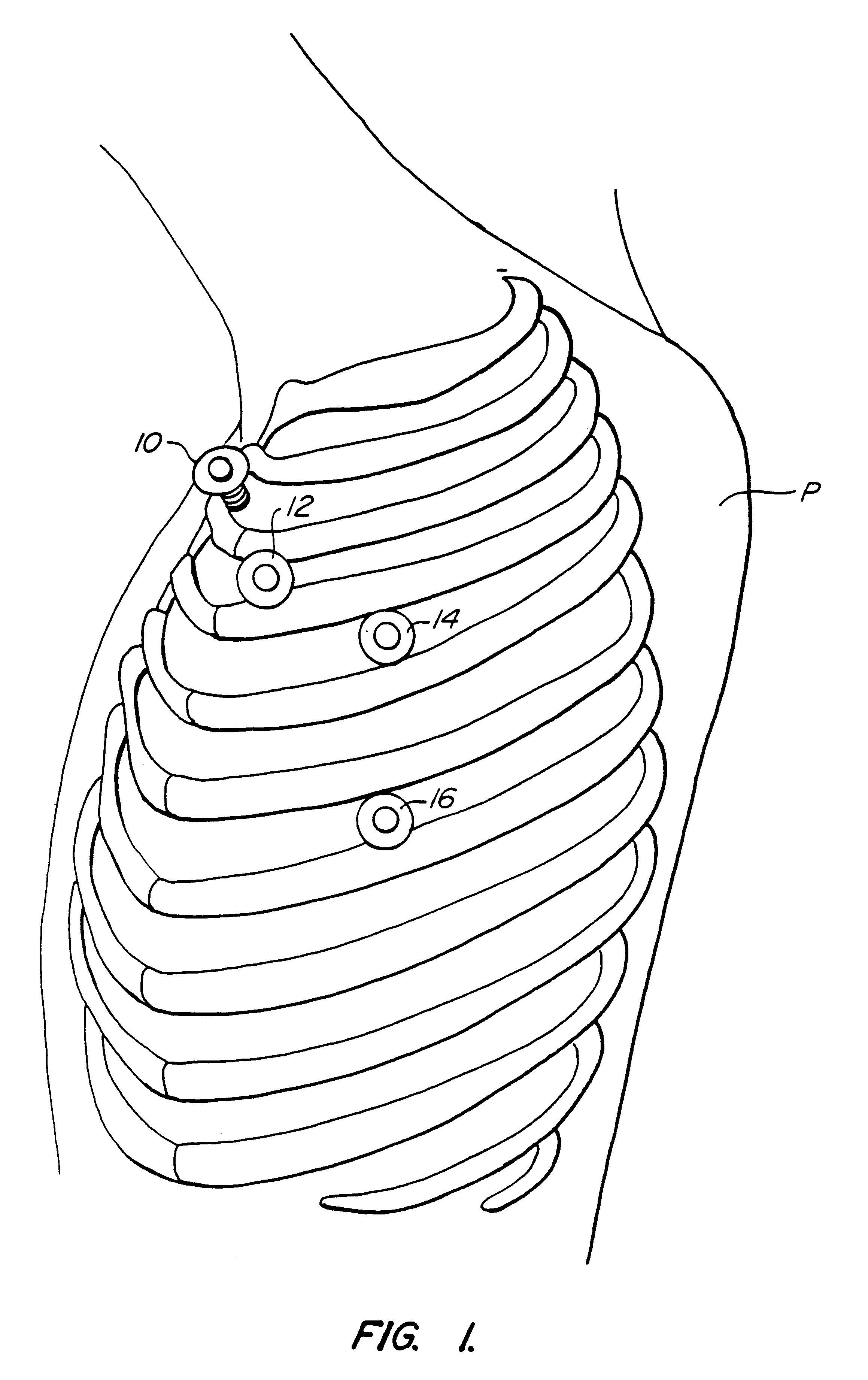
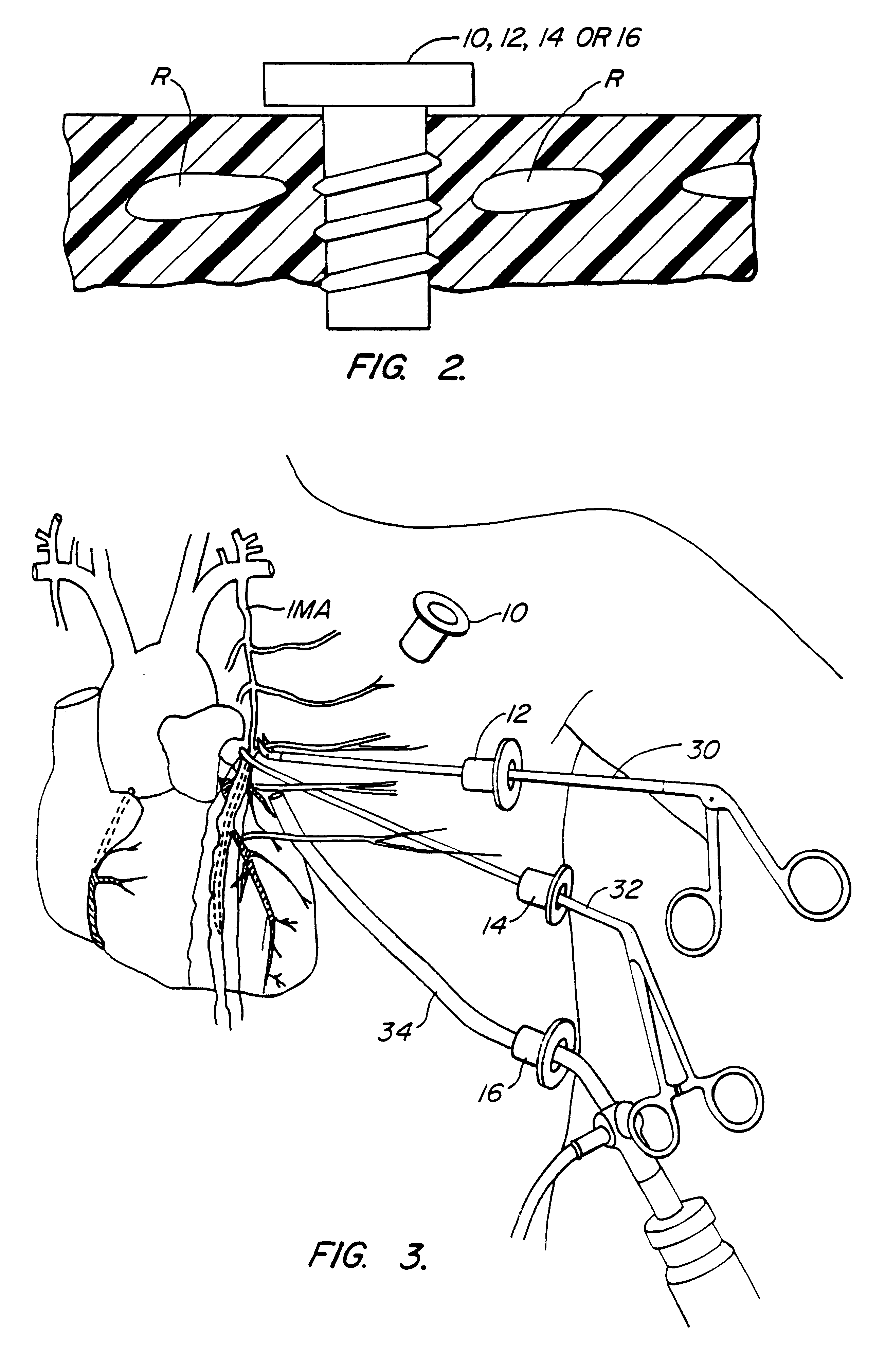
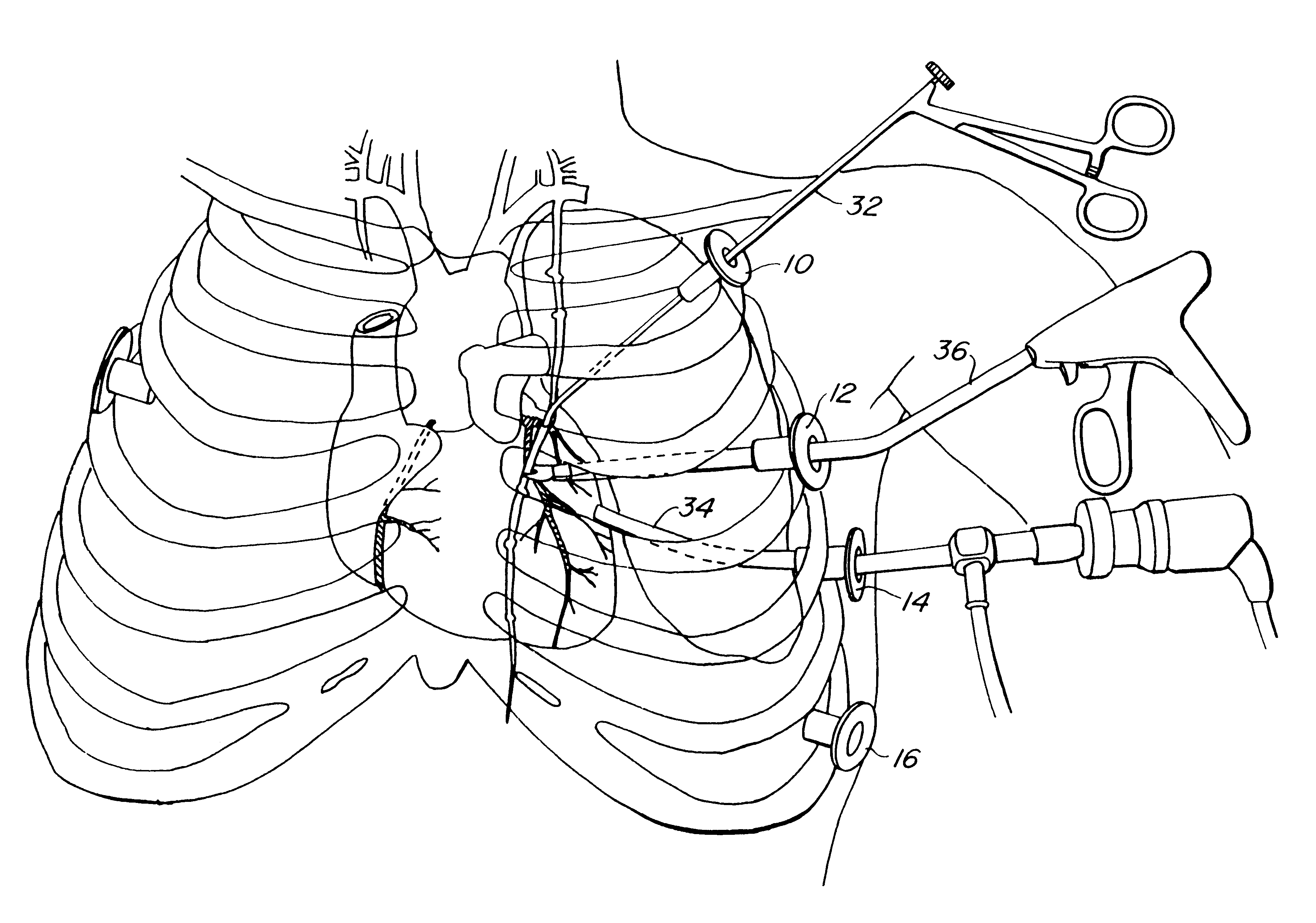
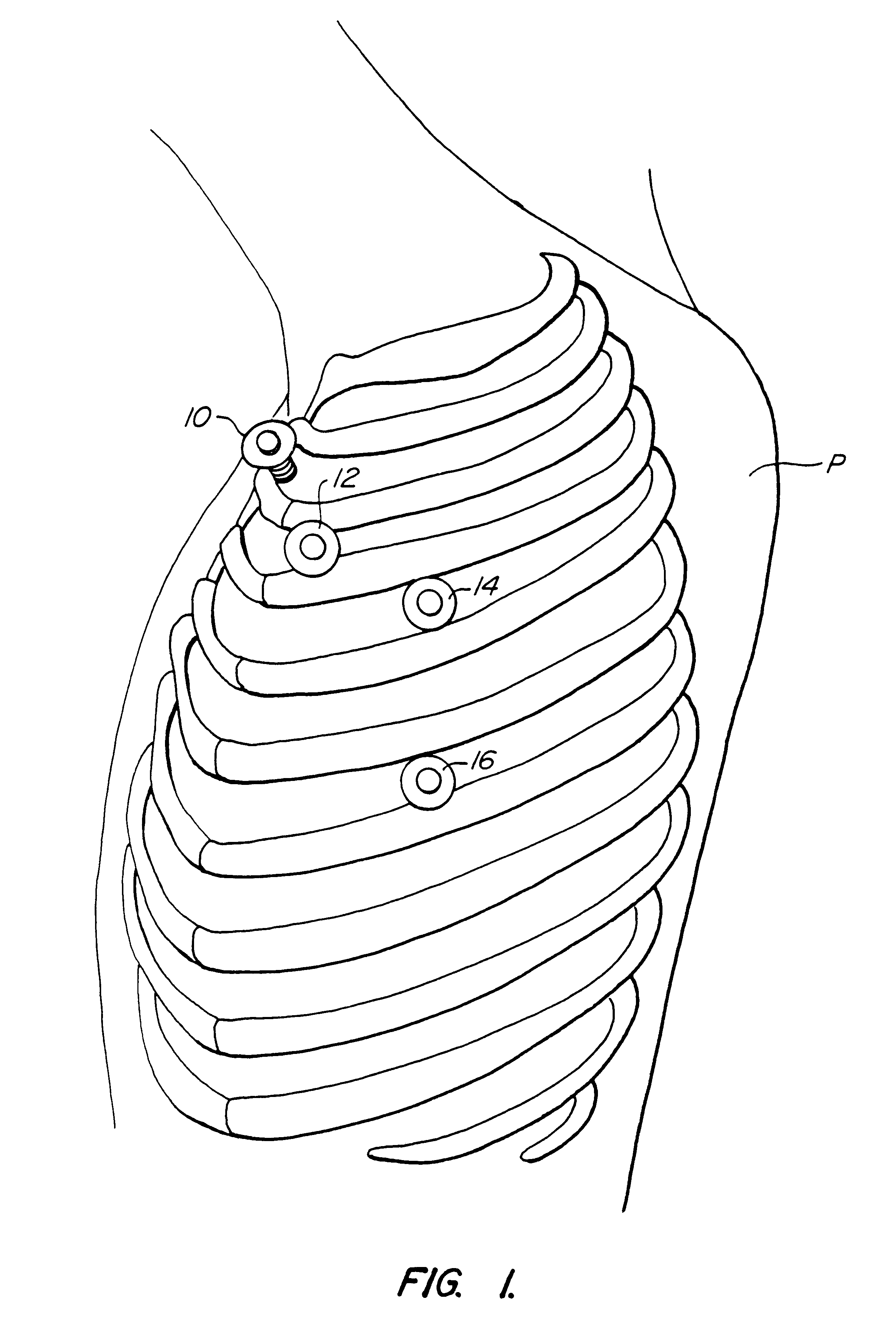
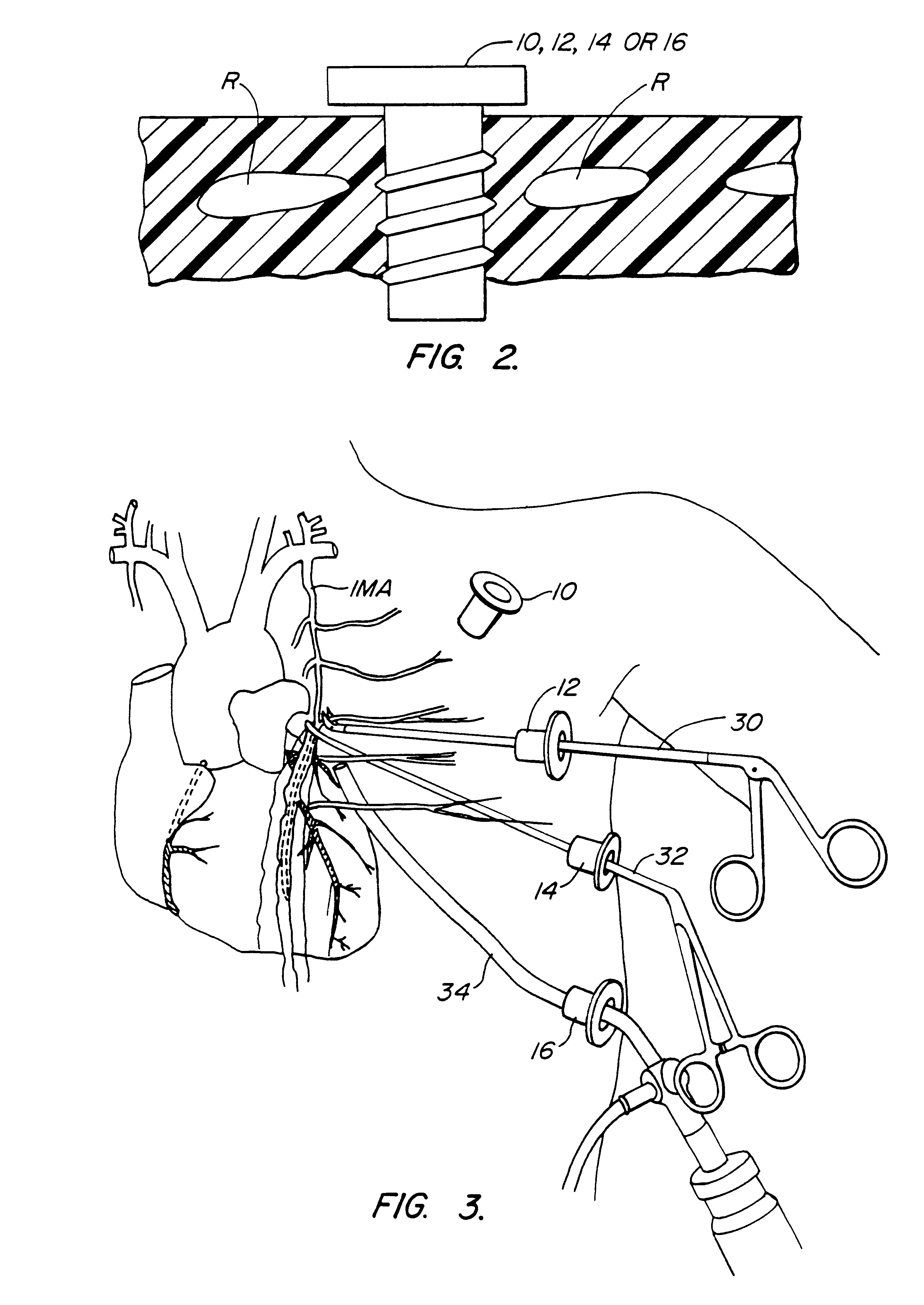
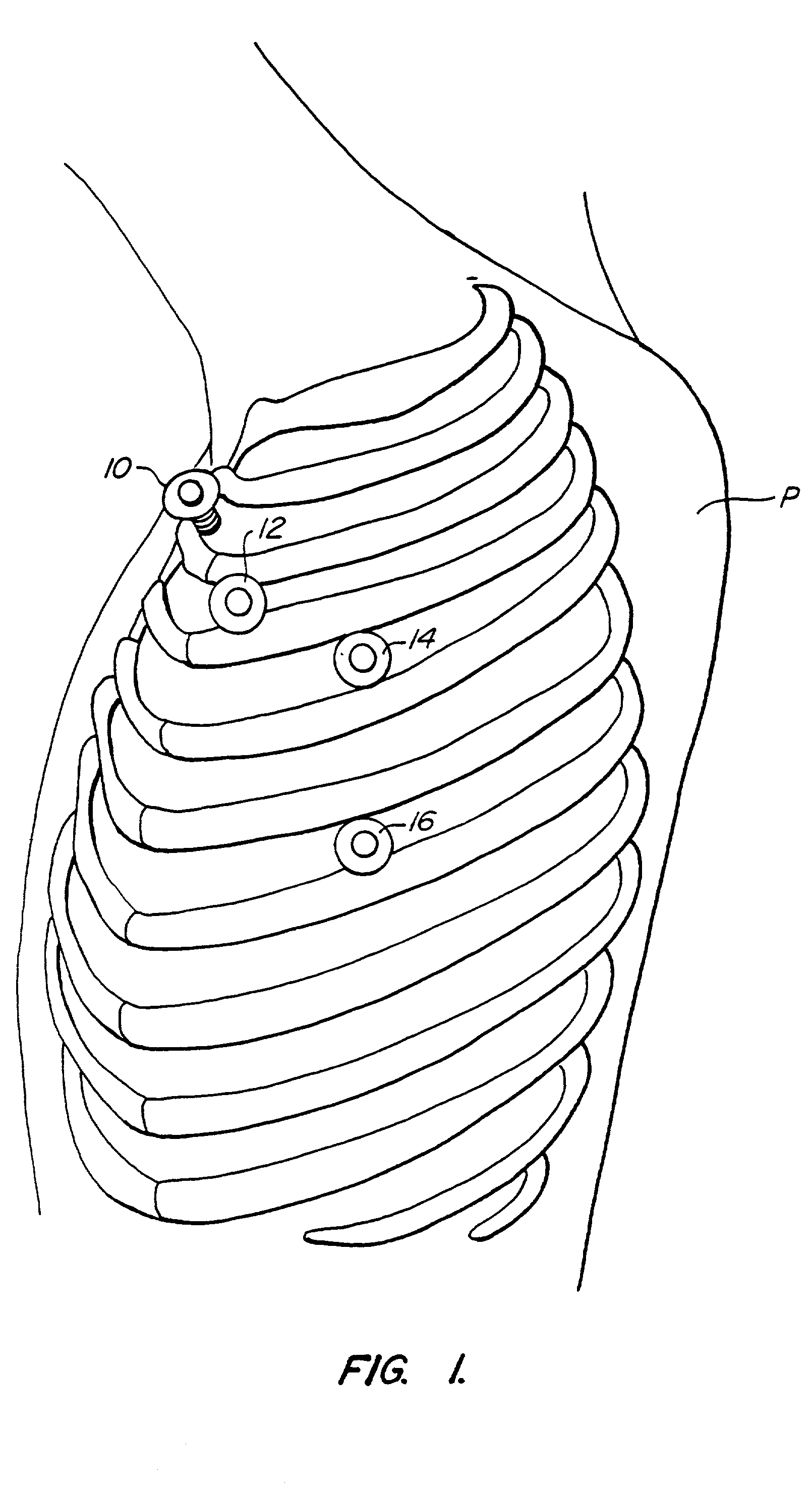
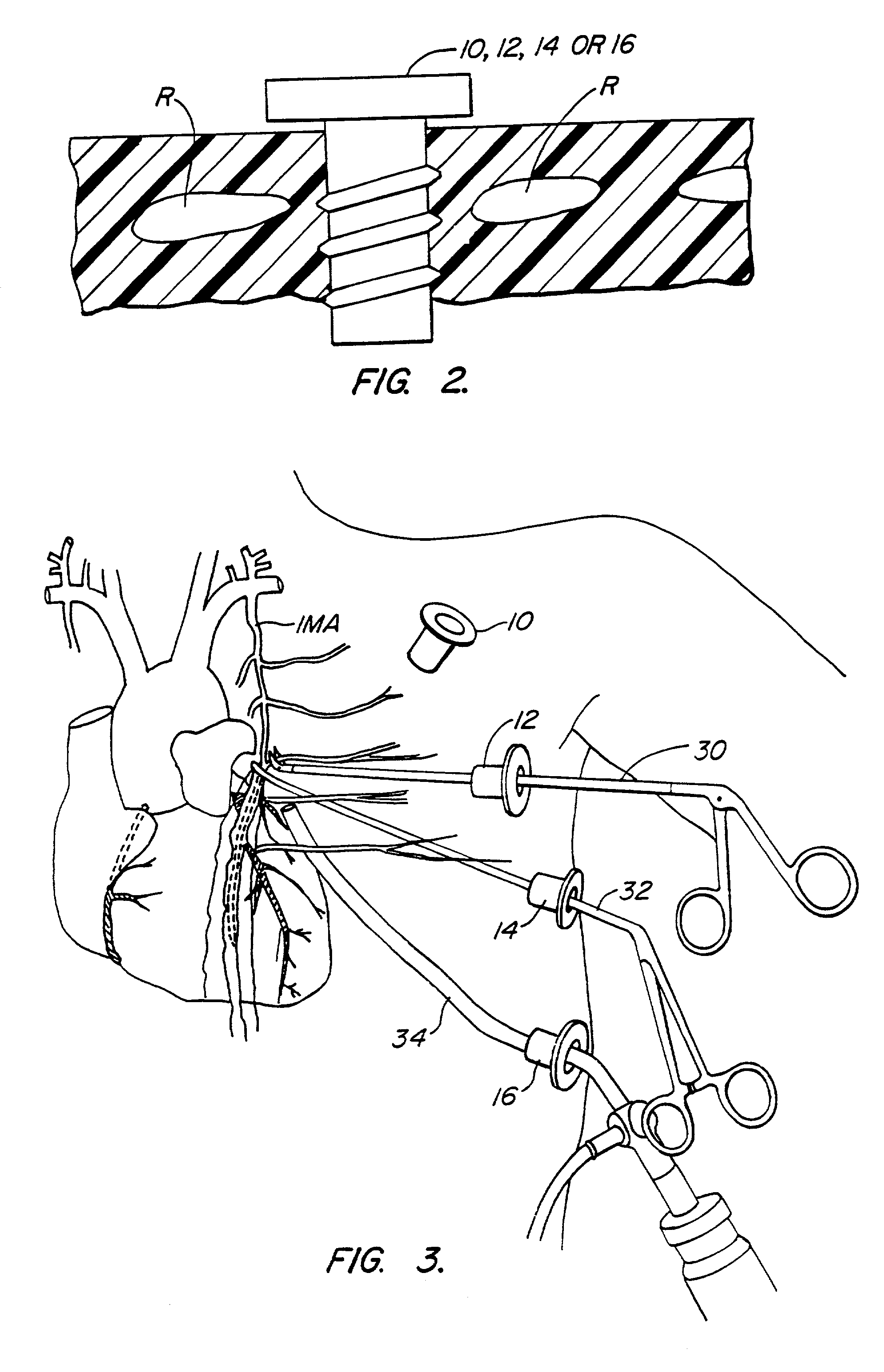
Methods and systems for performing thoracoscopic coronary bypass and other procedures
InactiveUS6027476AImprove isolationReduce complicationsSuture equipmentsCannulasThoracoscopeHeart operations
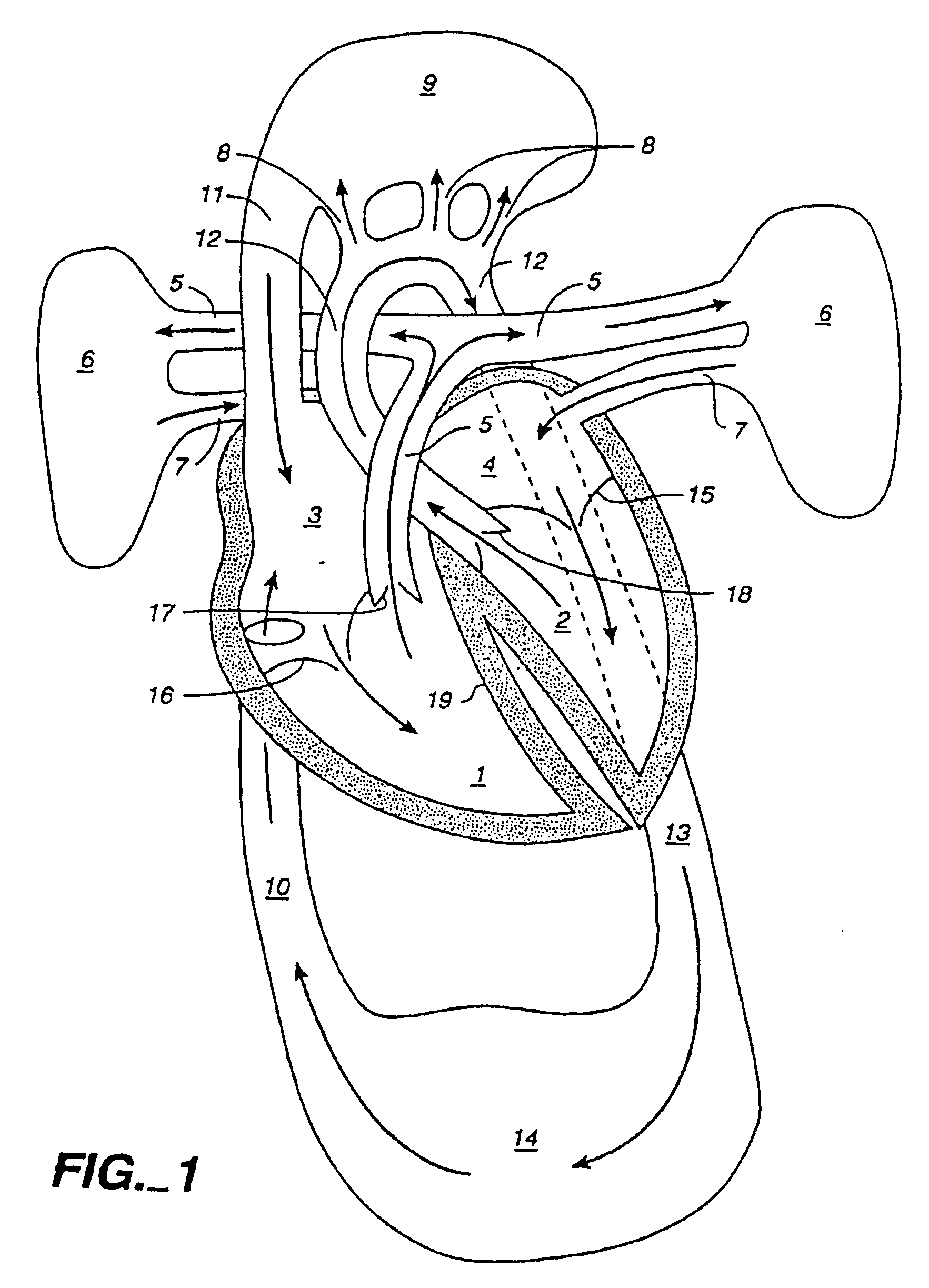
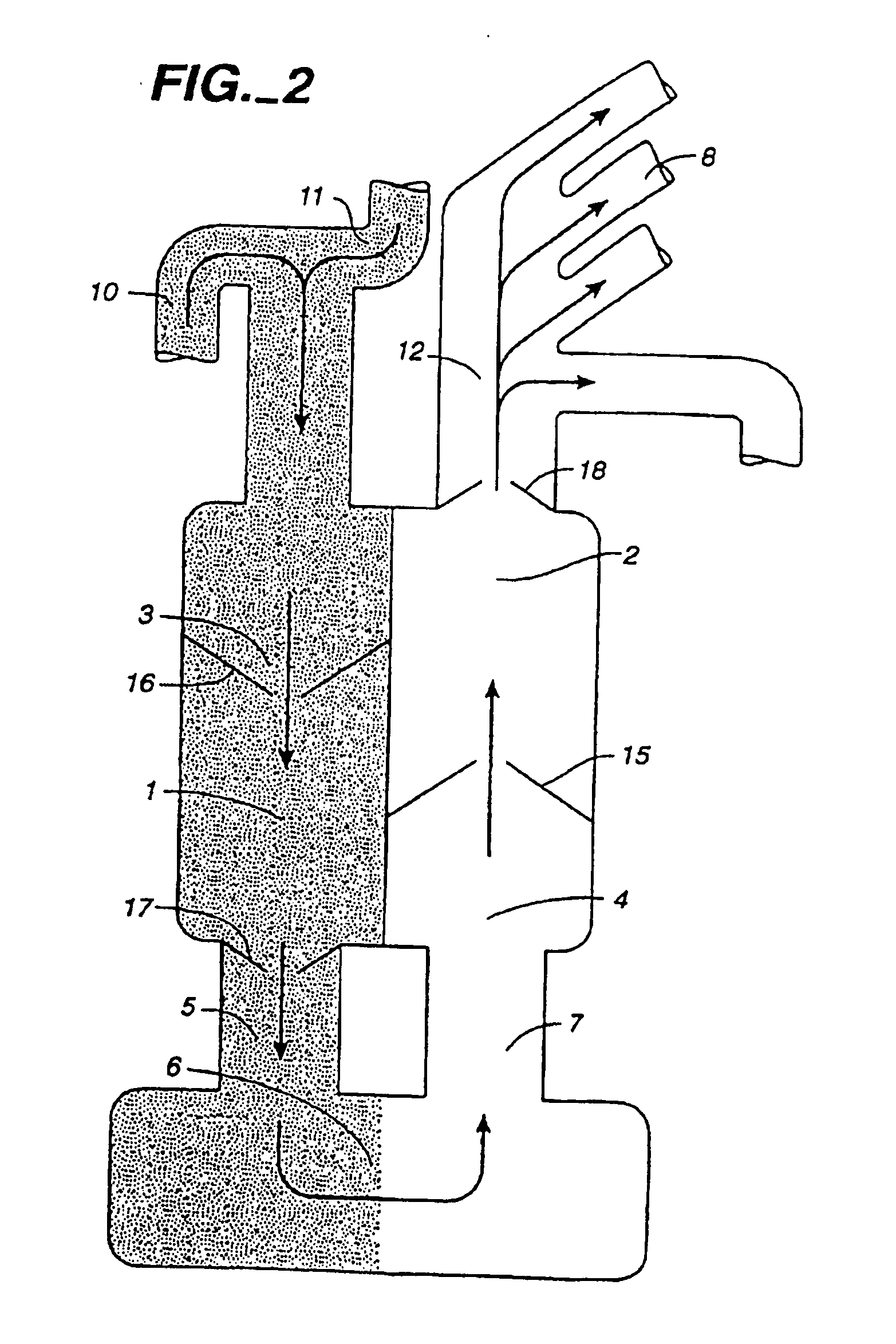
A method for closed-chest cardiac surgical intervention relies on viewing the cardiac region through a thoracoscope or other viewing scope and endovascularly partitioning the patient's arterial system at a location within the ascending aorta. The cardiopulmonary bypass and cardioplegia can be induced, and a variety of surgical procedures performed on the stopped heart using percutaneously introduced tools. The method of the present invention will be particularly suitable for forming coronary artery bypass grafts, where an arterial blood source is created using least invasive surgical techniques, and the arterial source is connected to a target location within a coronary artery while the patient is under cardiopulmonary bypass and cardioplegia.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
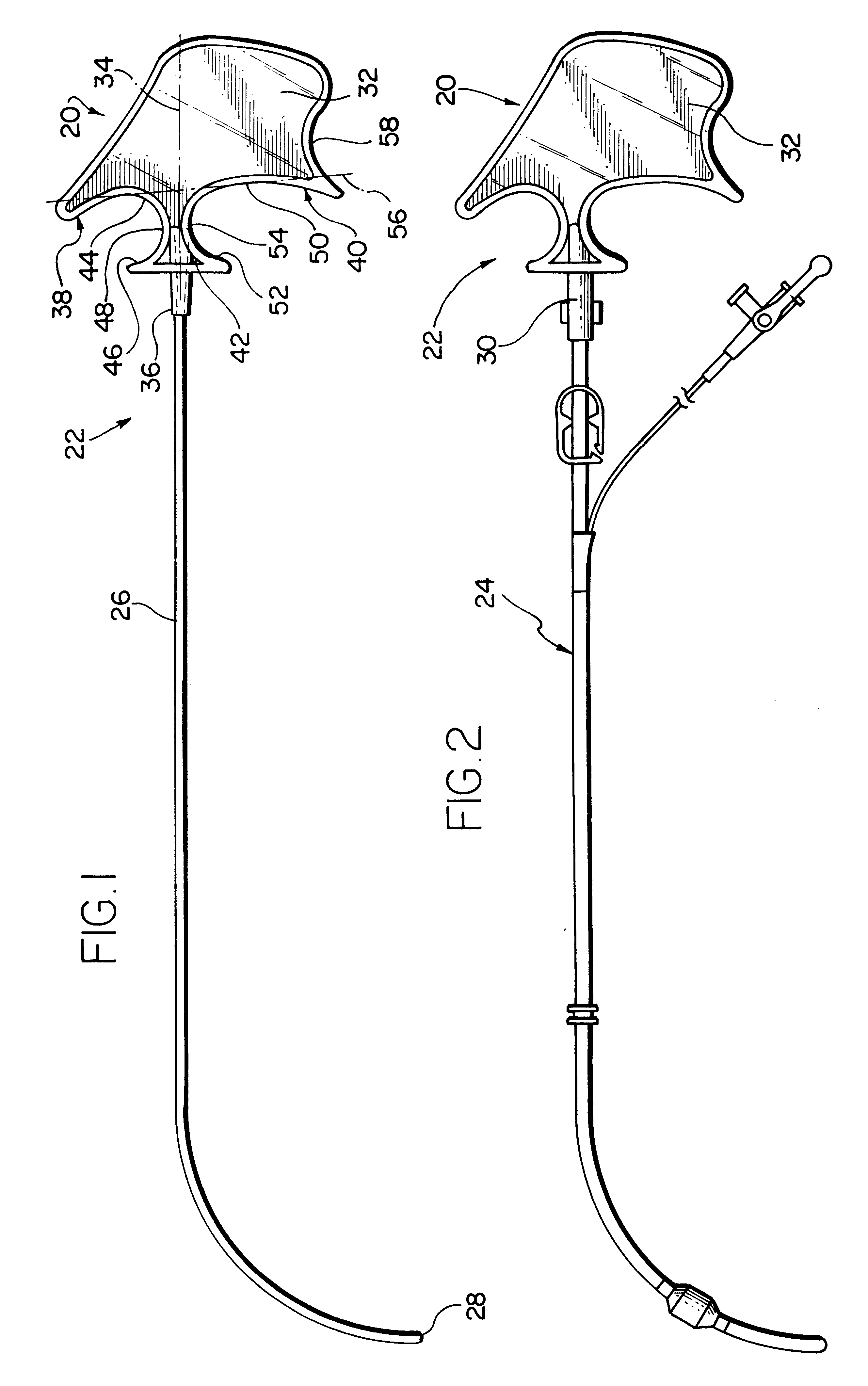
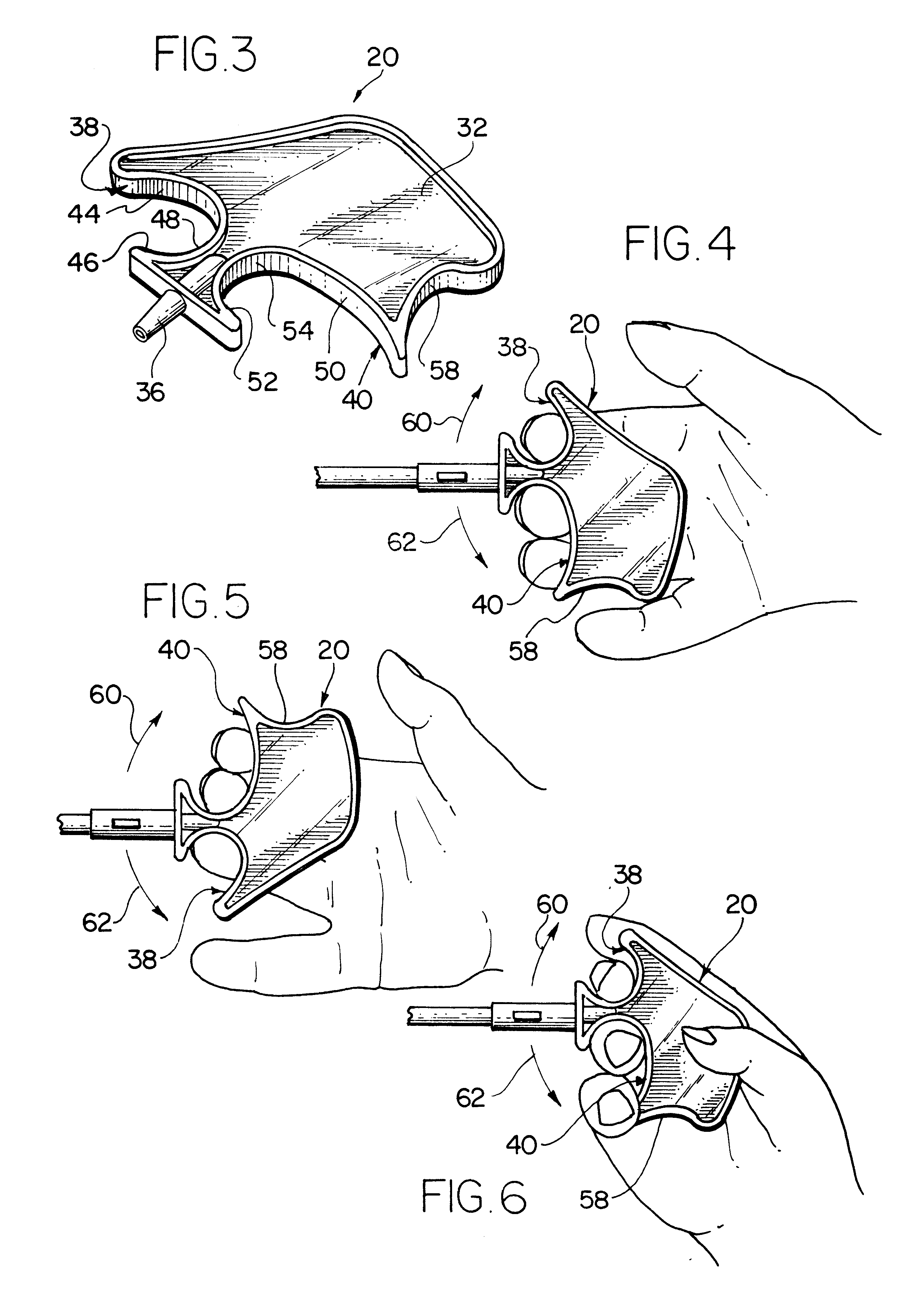
Catheter stylet handle
The present invention provides a novel ergonomic handle for a retrograde coronary sinus catheter stylet. The handle is provided at a proximal end of a thin rod. In use, the stylet is inserted into a retrograde cardioplegia catheter. The stylet handle of the present invention extends from the proximal end of the catheter. The handle includes a generally flat, substantially planar body portion having a proximal end, a distal end and an axis extending from the proximal end to the distal end. A first concave pocket is provided at the distal end of the body on one side of the axis and a second concave pocket is provided at the distal end of the body on the opposite side of the axis. Each pocket has a plurality of surfaces against which at least one of the digits of a user may be placed to manipulate the position of the stylet, and thus the catheter. The handle is manipulated in a plane defined by the body so as to manipulate the stylet and the catheter. The body also has a third concave pocket which is proximate to the second pocket. At least one of the user's digits can grip the third pocket.
Owner:QUEST MEDICAL
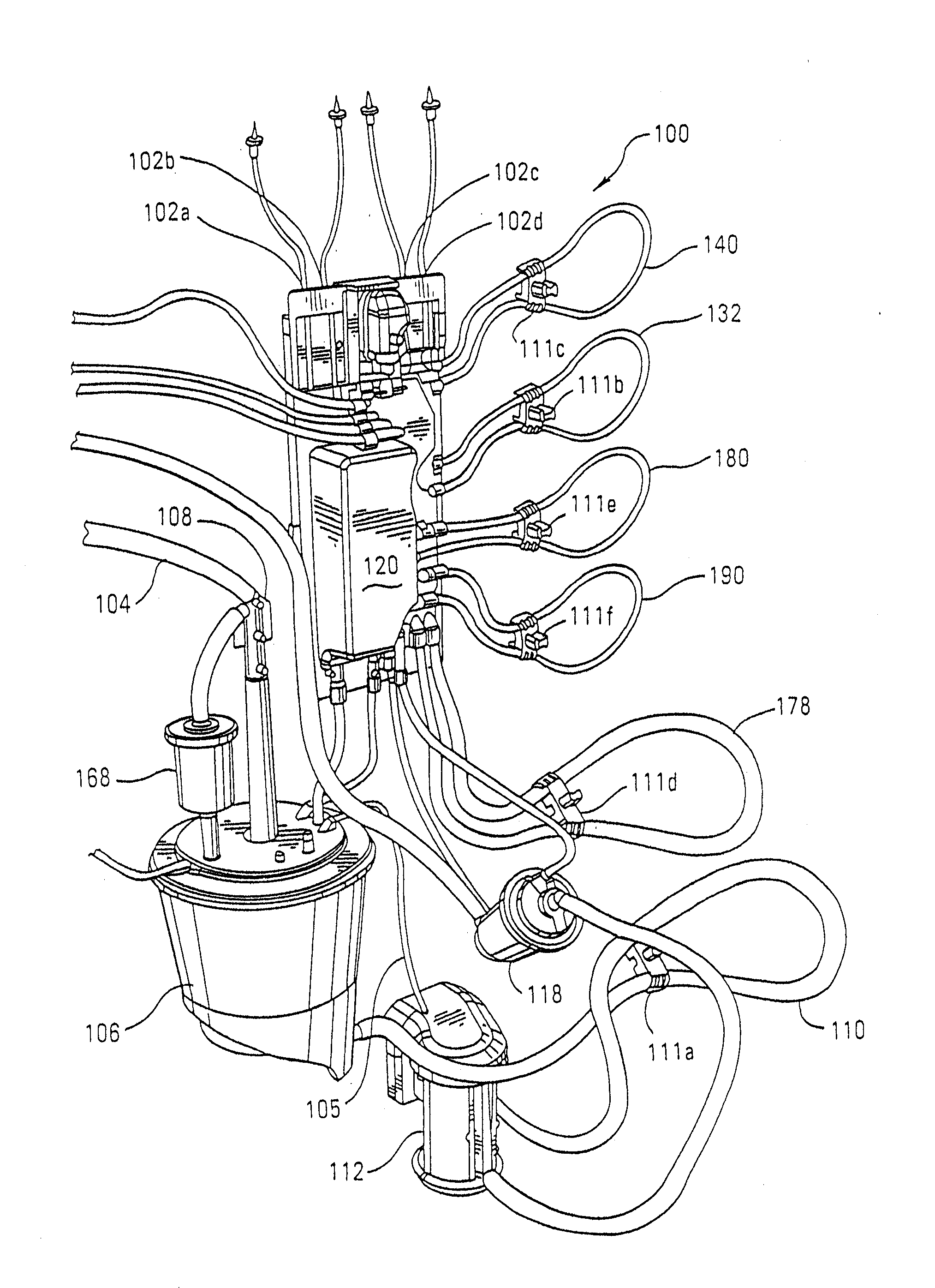
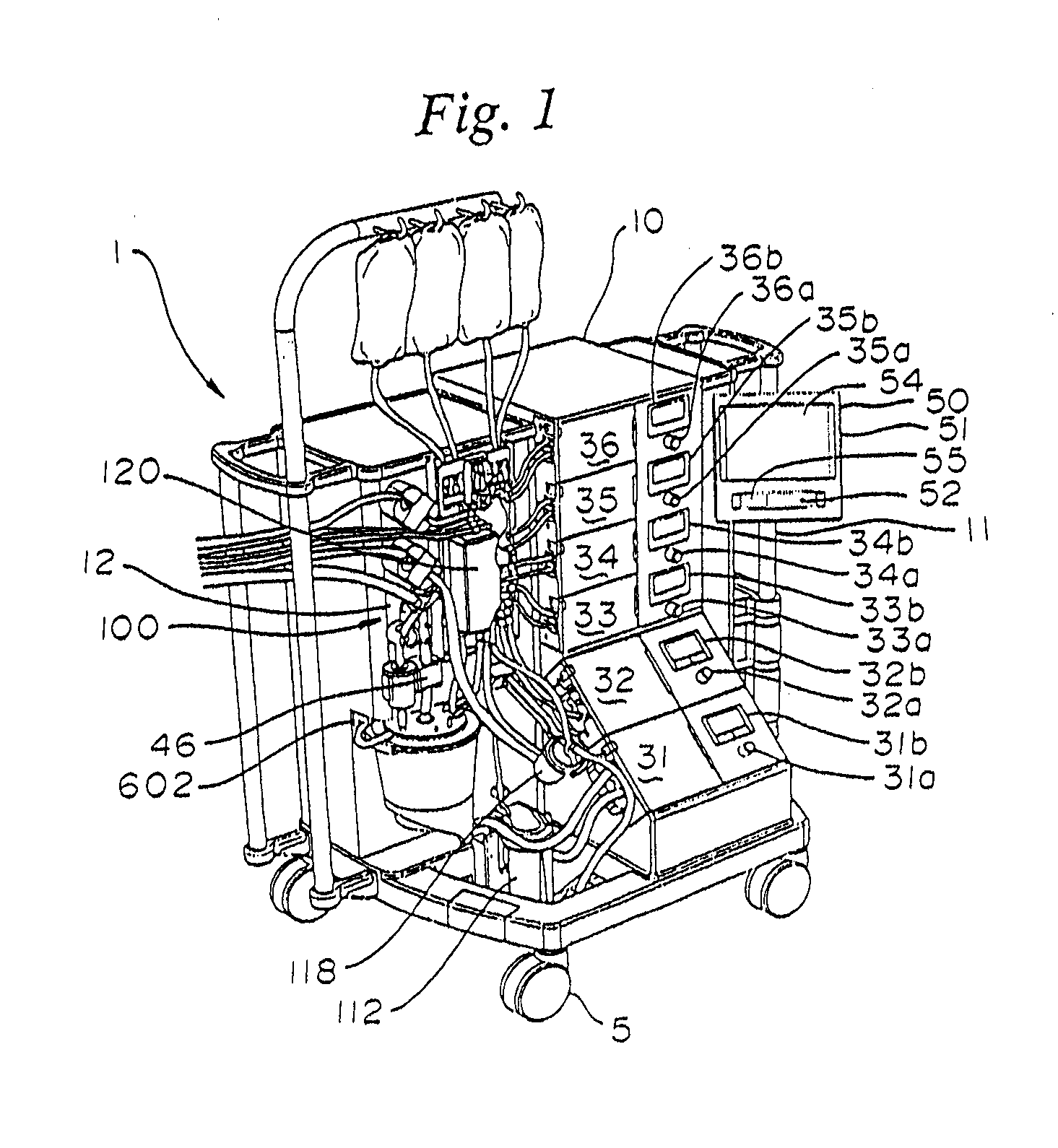
Disposable cartridge for a blood perfusion system
InactiveUS20080027368A1Simplified interconnection/disconnectionSimple setupDialysis systemsMedical devicesCardioplegiasEngineering
A disposable cartridge for use in extracorporeal blood perfusions systems that have a control unit for controlling the flow of fluids. The cartridge has a housing defining a plurality of internal passageways that connect to a cardiopulmonary circuit, a cardioplegia circuit and a suction circuit. The cartridge may be fitted with one or more of a bubble trap, a filter, and a valve.
Owner:SORIN GRP USA INC
Blood perfusion system
ActiveUS20060167400A1Simplified interconnection/disconnectionSimple setupOther blood circulation devicesMedical devicesVenous bloodDisplay device
An extracorporeal blood perfusion system includes a disposable assembly and a control unit having a control interface region. The interface region includes pump assemblies for selective pumping of venous blood, arterial blood, cardioplegia solution, suctioned blood and blood removed from the left ventricle. Valve assemblies control the flow of fluids through the assembly and to / from the patient and sensors monitor various fluid parameters including temperature and pressure within the various fluid circuits. The user interface is a functional screen interface for effecting the operation of the control unit and valve assemblies. The screen interface may be a touch screen having objects that corresponds to the component interface region. The display may be selectively controlled to provide graphic depictions of disposable assembly components with corresponding narrative instructions.
Owner:SORIN GRP USA INC
Antegrade cardioplegia catheter and method
InactiveUS6932792B1Facilitate occlusionOvercome disadvantagesStentsBalloon catheterCardioplegiasAscending aorta
A cardioplegia catheter is configured to extend into the ascending aorta with a proximal portion of the shaft extending into a left chamber of the heart through a aortic valve and out of the heart through a penetration in a wall thereof. The cardioplegia catheter has an occlusion member configured to occlude the ascending aorta between the brachiocephalic artery and the coronary ostia. An arterial return cannula delivers oxygenated blood to the arterial system downstream of the occlusion member, while cardioplegic fluid is delivered through a lumen in the cardioplegia catheter upstream of the occlusion member to induce cardioplegic arrest.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
Method and systems for performing thoracoscopic cardiac bypass and other procedures
InactiveUS6311693B1Promote healingEqual efficacySuture equipmentsCannulasHeart operationsThoracoscopes
A method for closed-chest cardiac surgical intervention relies on viewing the cardiac region through a thoracoscope or other viewing scope and endovascularly partitioning the patient's arterial system at a location within the ascending aorta. The cardiopulmonary bypass and cardioplegia can be induced, and a variety of surgical procedures performed on the stopped heart using percutaneously introduced tools. The method of the present invention will be particularly suitable for forming coronary artery bypass grafts, where an arterial blood source is created using least invasive surgical techniques, and the arterial source is connected to a target location within a coronary artery while the patient is under cardiopulmonary bypass and cardioplegia.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
Methods and systems for performing thoracoscopic coronary bypass and other procedures
InactiveUS6325067B1Reduce complicationsAllows can be cooledSuture equipmentsCannulasHeart operationsThoracoscopes
A method for closed-chest cardiac surgical intervention relies on viewing the cardiac region through a thoracoscope or other viewing scope and endovascularly partitioning the patient's arterial system at a location within the ascending aorta. The cardiopulmonary bypass and cardioplegia can be induced, and a variety of surgical procedures performed on the stopped heart using percutaneously introduced tools. The method of the present invention will be particularly suitable for forming coronary artery bypass grafts, where an arterial blood source is created using least invasive surgical techniques, and the arterial source is connected to a target location within a coronary artery while the patient is under cardiopulmonary bypass and cardioplegia
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
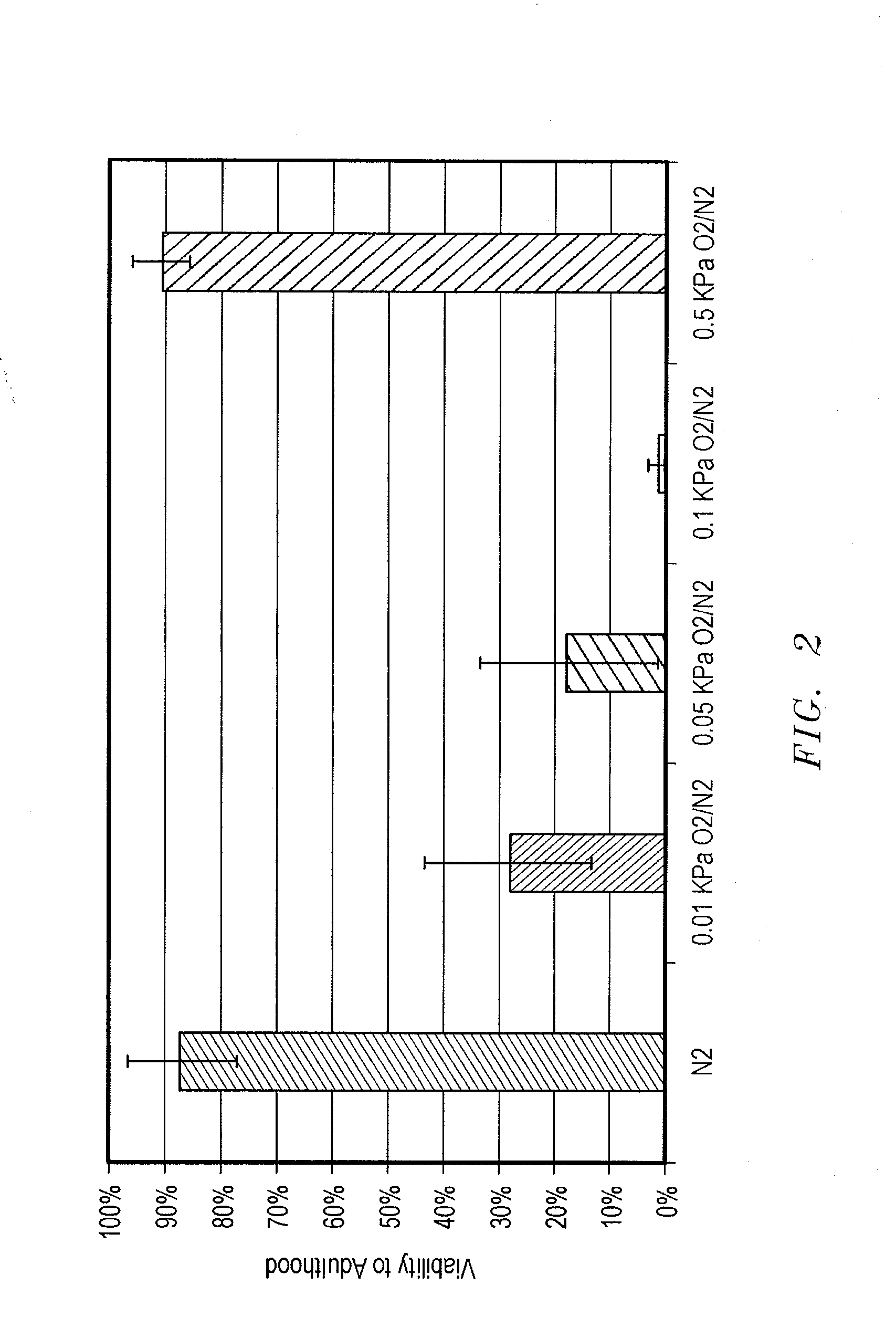
Methods, compositions and devices for inducing stasis in cells, tissues, organs, and organisms
InactiveUS20050136125A1Effective in inducing stasisReduces and eliminates amount of oxygenBiocideIn-vivo radioactive preparationsInducer CellsIn vivo
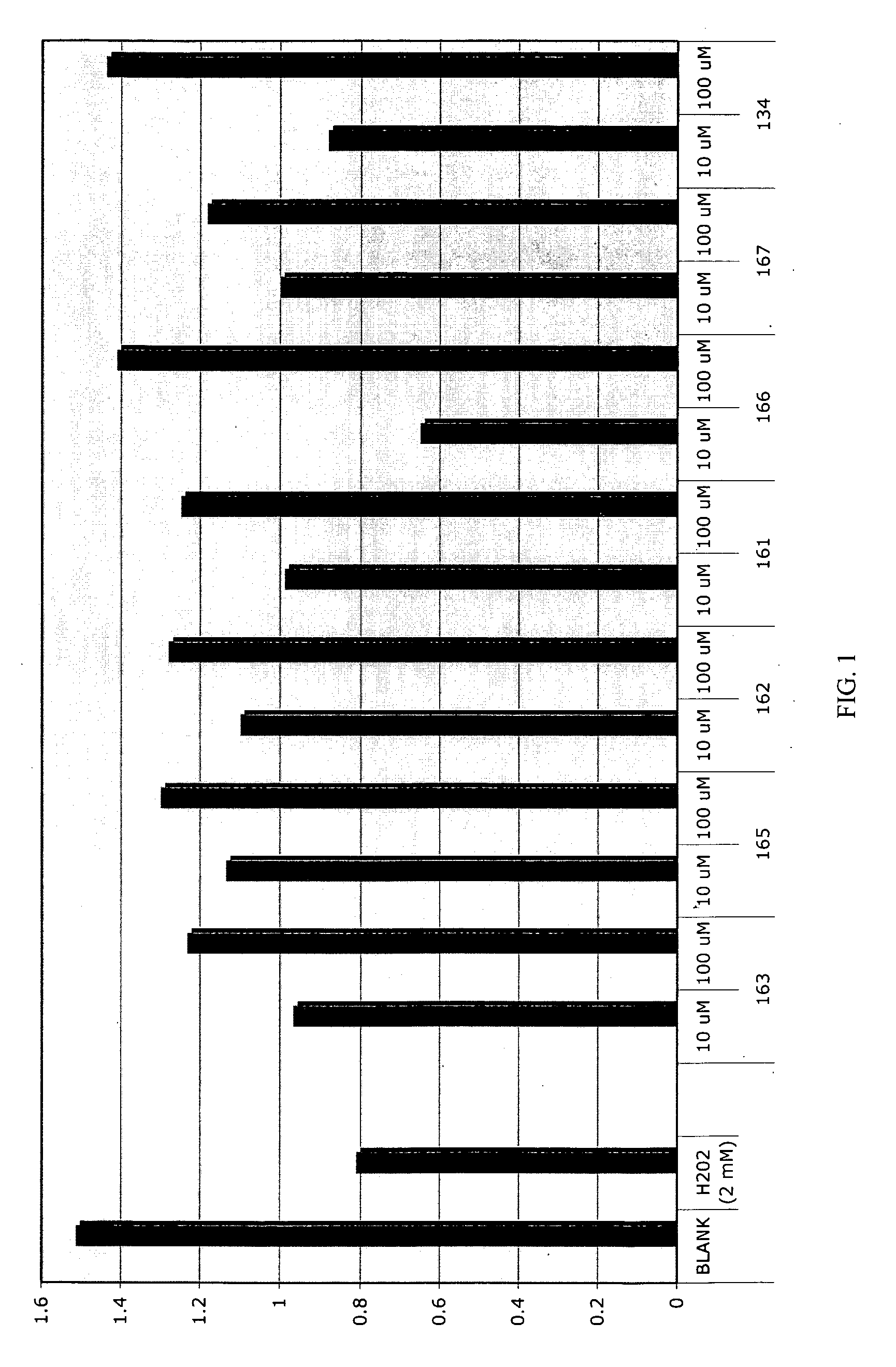
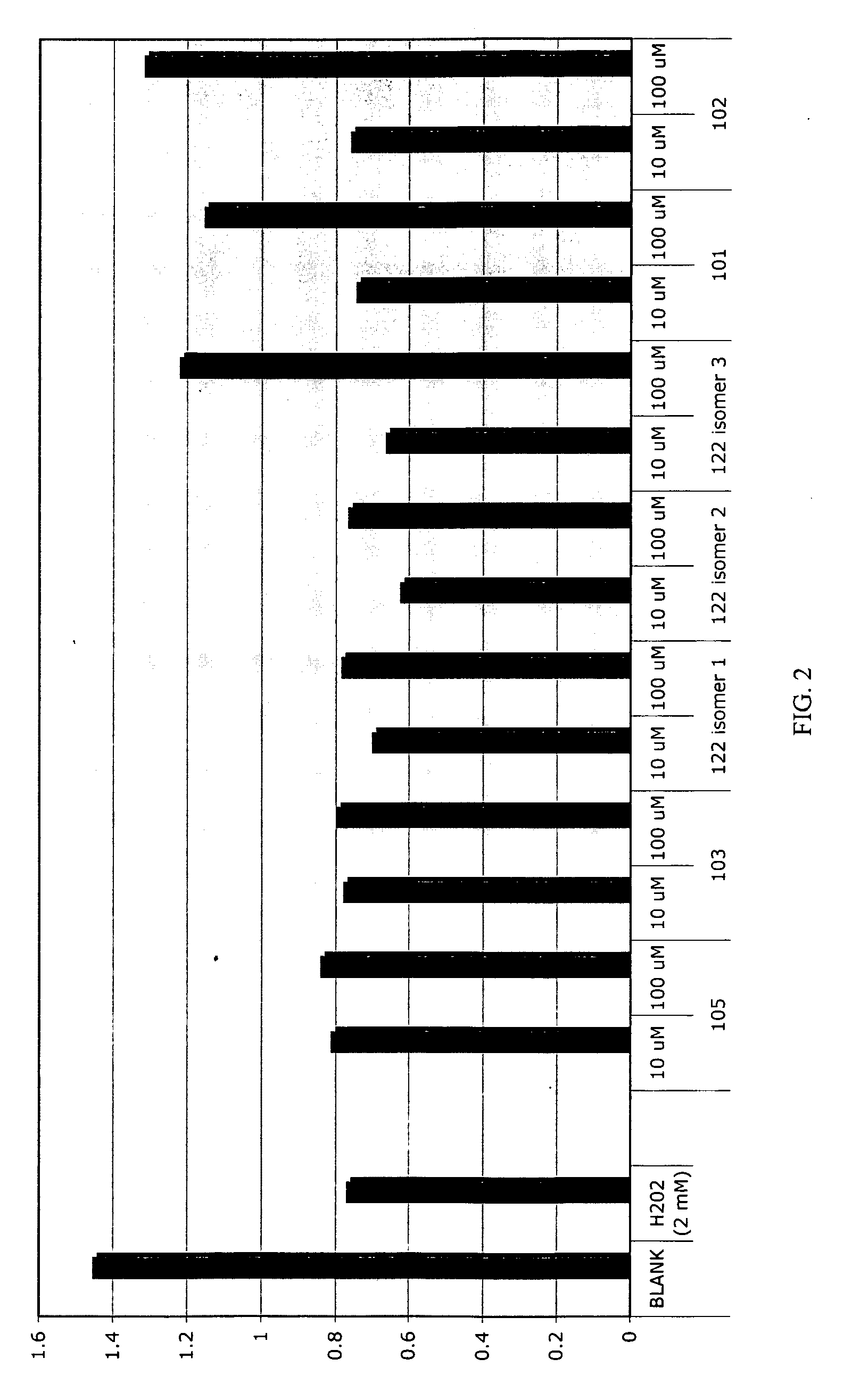
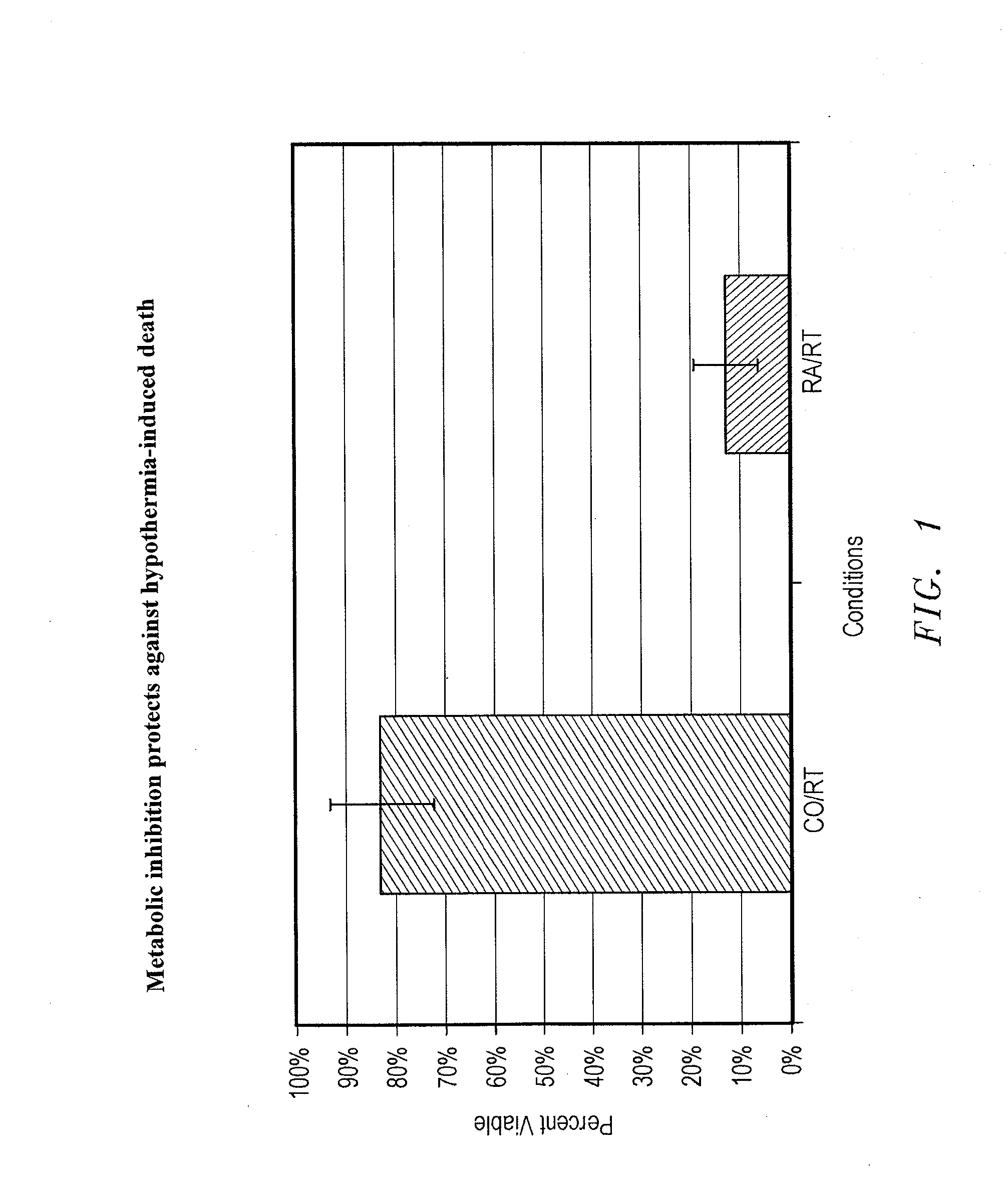
The present invention concerns the use of oxygen antagonists for inducing stasis in cells, tissues, and / or organs in vivo or in an organism overall. It includes methods and apparatuses for achieving stasis in any of these biological materials, so as to preserve and / or protect them. In specific embodiments, therapeutic methods and apparatuses for organ transplantation, hyperthermia, wound healing, hemorrhagic shock, cardioplegia for bypass surgery, neurodegeneration, hypothermia, and cancer is provided.
Owner:FRED HUTCHINSON CANCER RES CENT
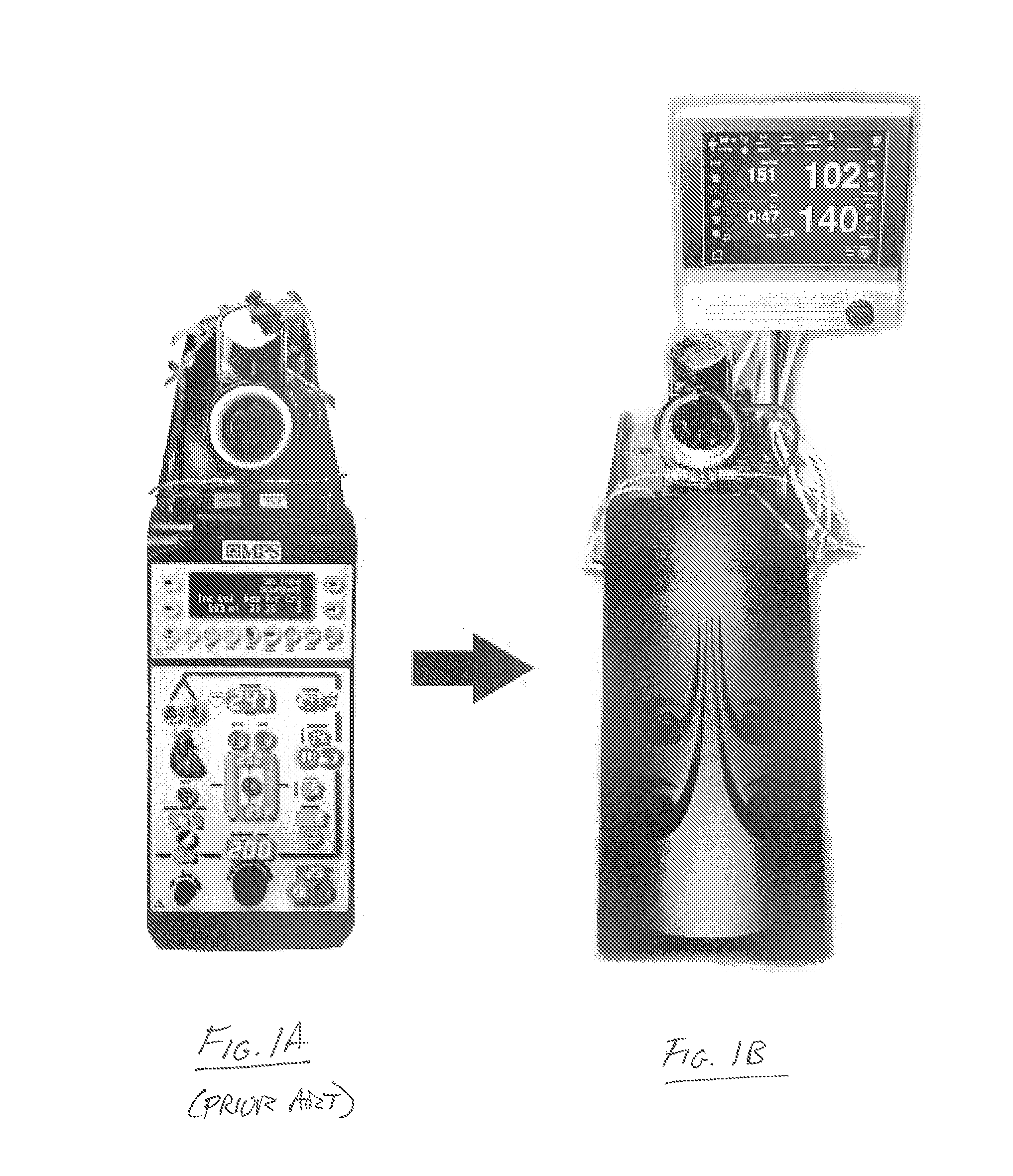
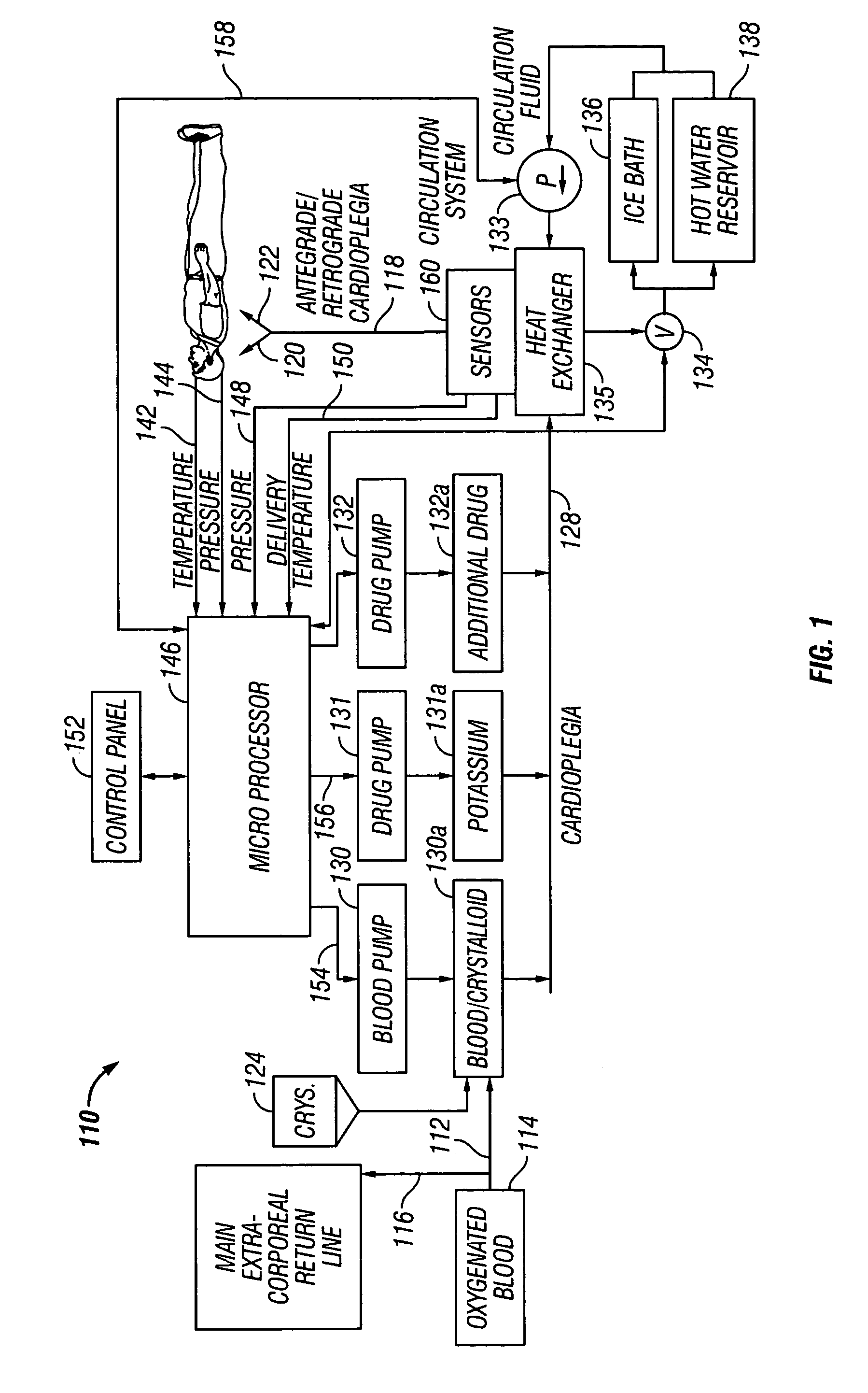
Cardioplegia Apparatus and Method
A microplegia console for controlling the delivery of cardioplegia to a patient, comprising an integrated display / touch screen for displaying cardioplegia information and patient information and allowing inputting of parameters via the display / touch screen into the console for computer-controlled perfusion of cardioplegia into the patient. The invention further comprises a method for delivery of cardioplegia to a patient, including defining and selecting a protocol from a displayed list and sequencing a series of the protocols. The invention also comprises a method for cardioplegia delivery to achieve aortic valve closure. Additionally, the invention comprises a method for activating an icon whereby, upon a first selection of the icon, displaying an indicia indicating that the icon has been first selected; and upon a second selection of the icon, activating the icon.
Owner:QUEST MEDICAL
Methods, Compositions and Articles of Manufacture for Enhancing Survivability of Cells, Tissues, Organs, and Organisms
InactiveUS20080171726A1Improve survivabilityPrevent and reduce damageBiocideSulfur/selenium/tellurium active ingredientsSurvivabilityIn vivo
The present invention concerns the use of oxygen antagonists and other active compounds for inducing stasis or pre-stasis in cells, tissues, and / or organs in vivo or in an organism overall, in addition to enhancing their survivability. It includes compositions, methods, articles of manufacture and apparatuses for enhancing survivability and for achieving stasis or pre-stasis in any of these biological materials, so as to preserve and / or protect them. In specific embodiments, there are also therapeutic methods and apparatuses for organ transplantation, hyperthermia, wound healing, hemorrhagic shock, cardioplegia for bypass surgery, neurodegeneration, hypothermia, and cancer using the active compounds described.
Owner:ROTH MARK B +3
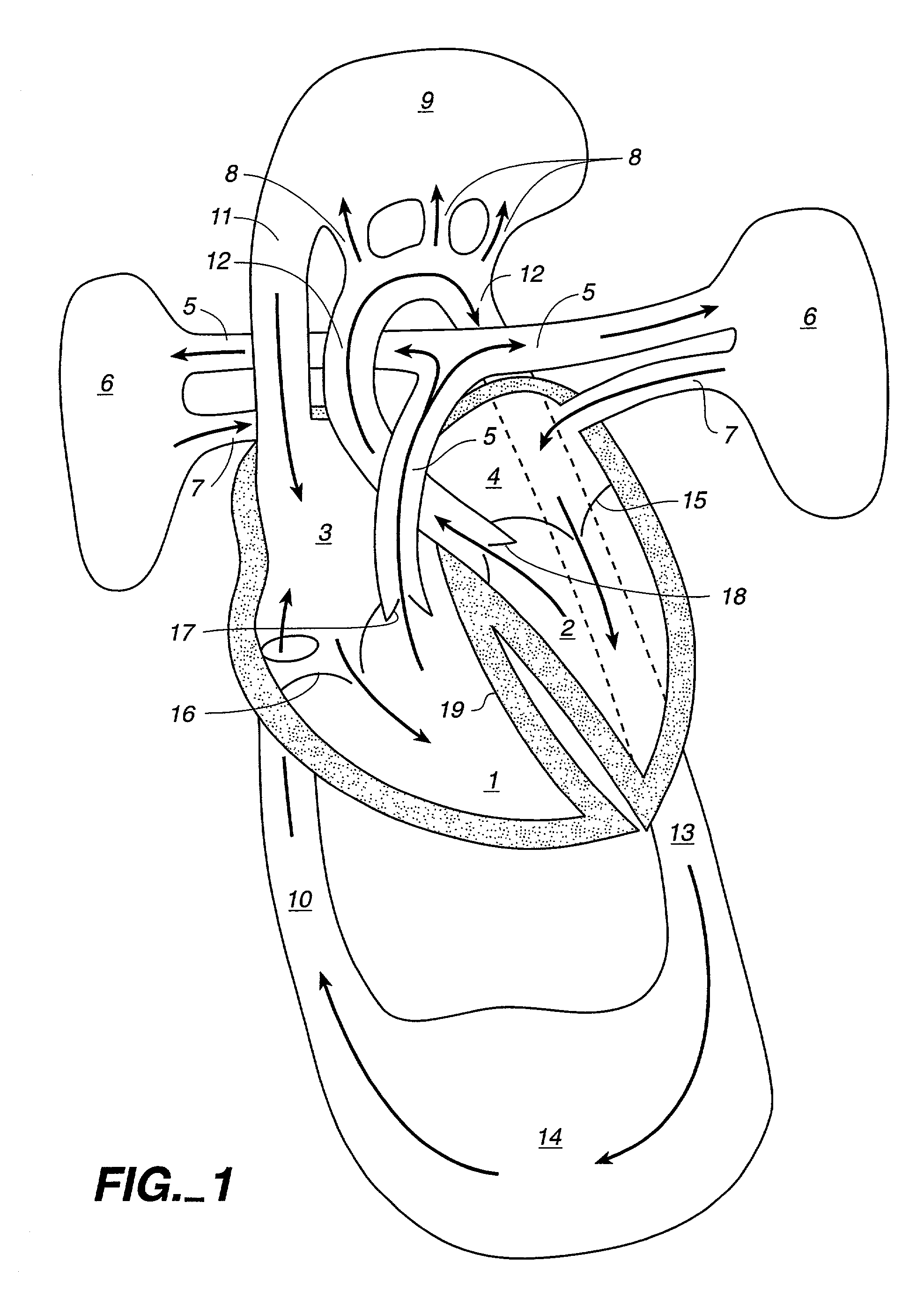
Method and apparatus for venous drainage and retrograde coronary perfusion
InactiveUS20050113799A1Improve protectionFacilitate surgeryBalloon catheterOther blood circulation devicesIschemic heartExtracorporeal circulation
A system is disclosed for cannulating the vena cava of a patient during cardiopulmonary bypass procedures. Such cannulation is necessary for drainage of venous blood from the patient so that it may be oxygenated and pumped back to the patient to perfuse tissues during cardiac surgery and, more specifically, during periods of ischemic cardiac arrest or dysfunction. The device of the present invention not only provides venous drainage for cardiopulmonary bypass, but also performs the function of routing cardioplegic solution through the heart in the retrograde direction. Such cardioplegia provides protection to the heart during periods of ischemic cardiac arrest. This invention replaces a plurality of cannulae currently used for open-heart surgery, thus simplifying the surgical field and improving visibility of the heart. The device allows for the delivery of retrograde cardioplegia to the coronary circulation of both the right and the left side of the heart. The device further includes protection mechanisms to prevent overinflation or excessive pressurization of the right atrium during retrograde delivery of cardioplegia solution.
Owner:INDIAN WELLS MEDICAL
Balloon occlusion device and methods of use
A cardioplegia occluder and methods of using the device during cardiac surgery are disclosed. The system typically includes a substantially rigid cannula with an occluder mounted on the distal region of the cannula that expands upon activation to occlude the aorta downstream of an infusion port which delivers cardioplegia solution to arrest the heart. Systems including cutting blades, blade guards, flanges, radiopaque markers and occluder aligners are also disclosed. In use, the distal end of the cannula is inserted through an incision into the aorta, the occluder is expanded and cardioplegia solution is infused upstream of the aorta to arrest the heart. The infusion port can alternately be used to aspirate cardioplegia or embolic debris or other unwanted material from the aorta.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Retrograde cannula having automatically inflatable balloon
InactiveUS20050085792A1Prevent drainageHalting the flow of cardioplegiaStentsBalloon catheterCardioplegiasCoronary sinus
Cardioplegia is delivered to a heart vessel by conducting the cardioplegia through an infusion lumen of a cannula. The cardioplegia communicates with a balloon disposed on a distal end of the cannula to cause the cardioplegia to inflate the balloon into sealing contact with a wall of the coronary sinus. The flow of cardioplegia is halted while preventing drainage of cardioplegia from the balloon, to maintain the balloon in its inflated state until such time as the flow of cardioplegia is resumed. Drainage of cardioplegia from the balloon is prevented by causing a valve to be shifted to a closed position blocking communication between the infusion lumen and the balloon. The valve can be shifted manually, or automatically in response to the halting of the delivery of cardioplegia.
Owner:MICHIGAN CRITICAL CARE CONSULTANTS
Disposable cartridge for a blood perfusion system
InactiveUS7278981B2Simplified interconnection/disconnectionSimple setupOther blood circulation devicesFlexible member pumpsCardioplegiasEngineering
A disposable cartridge for use in extracorporeal blood perfusions systems that have a control unit for controlling the flow of fluids. The cartridge has a housing defining a plurality of internal passageways that connect to a cardiopulmonary circuit, a cardioplegia circuit and a suction circuit. The cartridge may be fitted with one or more of a bubble trap, a filter, and a valve.
Owner:SORIN GRP USA INC
Pyridyl-substituted porphyrin compounds and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20060003982A1Extended half-lifeAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsSexual impotenceReperfusion injury
The present invention relates to Pyridyl-Substituted Porphyrin Compounds, compositions comprising an effective amount of a Pyridyl-Substituted Porphyrin Compound and methods for treating or preventing injury due to exposure to a reactive species, erectile dysfunction due to surgery, lung disease, hyperoxia, neurodegenerative disease, liver disease, myocardial damage during cardioplegia, an inflammatory condition, a reperfusion injury, an ischemic condition, a cardiovascular disease, diabetes, a diabetic complication, cancer, a side effect of cancer chemotherapy, or a radiation-induced injury, or to prolong the half-life of an oxidation-prone compound, comprising administering to a subject in need thereof an effective amount of a Pyridyl-Substituted Porphyrin Compound.
Owner:INOTECK PHARMA CORP
N-benzyl substituted pyridyl porphyrin compounds and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20070072825A1Extended half-lifeAvoid adjustmentAntibacterial agentsBiocideSide effectReperfusion injury
The present invention relates to N-Benzyl-Substituted Pyridyl Porphyrin Compounds, compositions comprising an effective amount of an N-Benzyl-Substituted Pyridyl Porphyrin Compound and methods for treating or preventing injury due to exposure to a reactive species, erectile dysfunction, urinary incontinence, lung disease, hyperoxia, neurodegenerative disease, liver disease, myocardial damage during cardioplegia, an inflammatory condition, a reperfusion injury, an ischemic condition, a cardiovascular disease, diabetes, a diabetic complication, cancer, a side effect of cancer chemotherapy, or a radiation-induced injury, and methods for prolonging the half-life of an oxidation-prone compound, comprising administering to a subject in need thereof an effective amount of an N-Benzyl-Substituted Pyridyl Porphyrin Compound.
Owner:INOTECK PHARMA CORP
Methods, Compositions and Devices for Inducing Stasis in Cells, Tissues, Organs, and Organisms
InactiveUS20080085329A1Effective in inducing stasisReduces and eliminates amount of oxygenBiocideSulfur/selenium/tellurium active ingredientsIn vivoBiological materials
The present invention concerns the use of oxygen antagonists for inducing stasis in cells, tissues, and / or organs in vivo or in an organism overall. It includes methods and apparatuses for achieving stasis in any of these biological materials, so as to preserve and / or protect them. In specific embodiments, therapeutic methods and apparatuses for organ transplantation, hyperthermia, wound healing, hemorrhagic shock, cardioplegia for bypass surgery, neurodegeneration, hypothermia, and cancer is provided.
Owner:FRED HUTCHINSON CANCER RES CENT
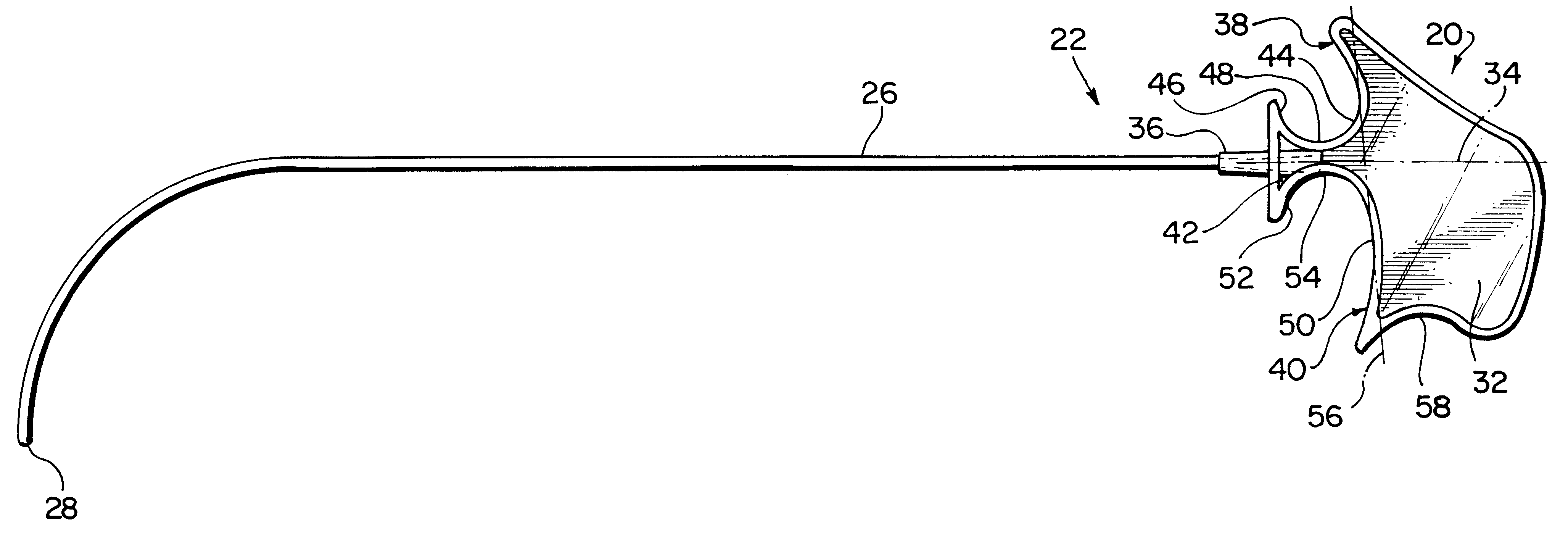
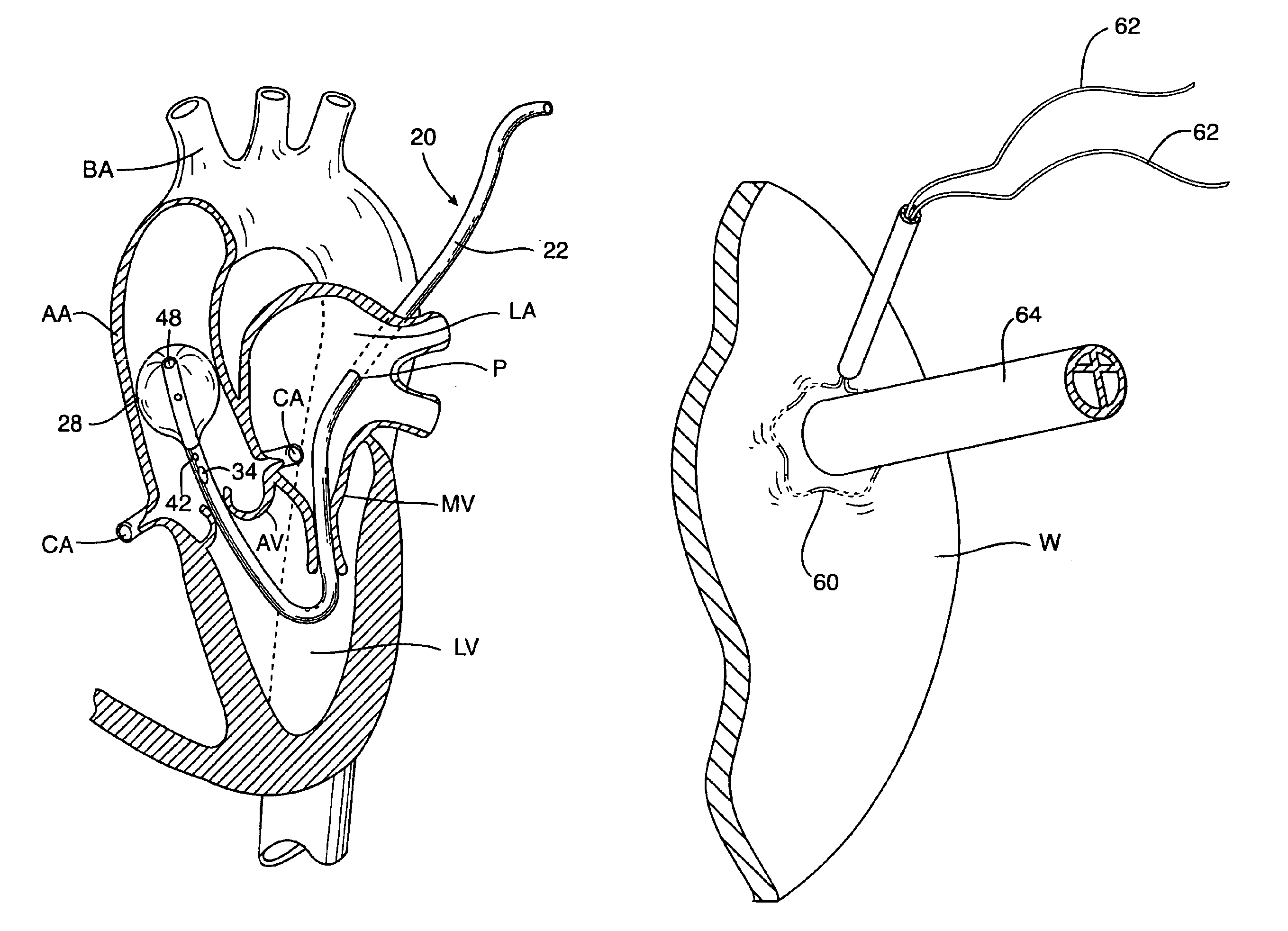
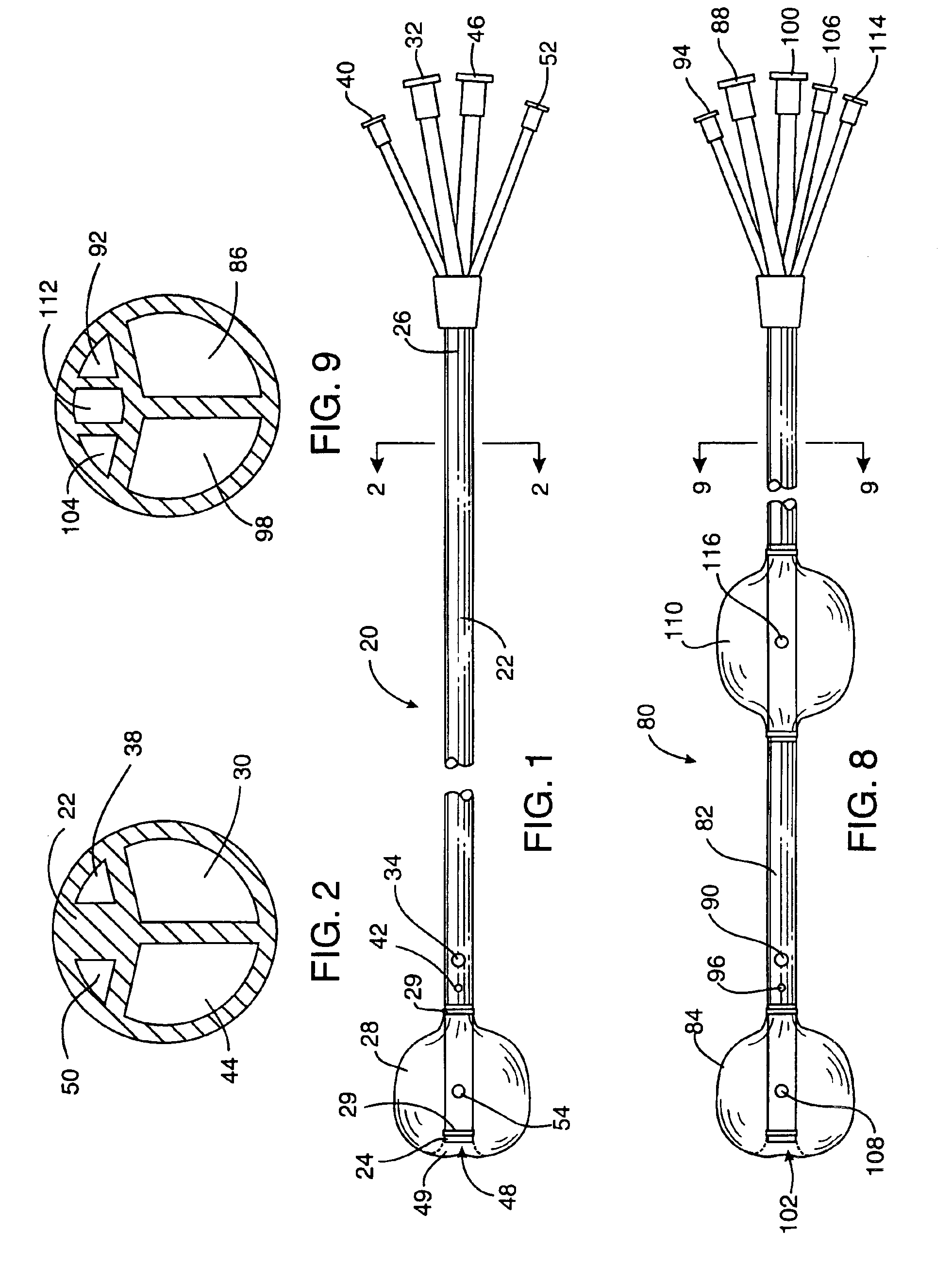
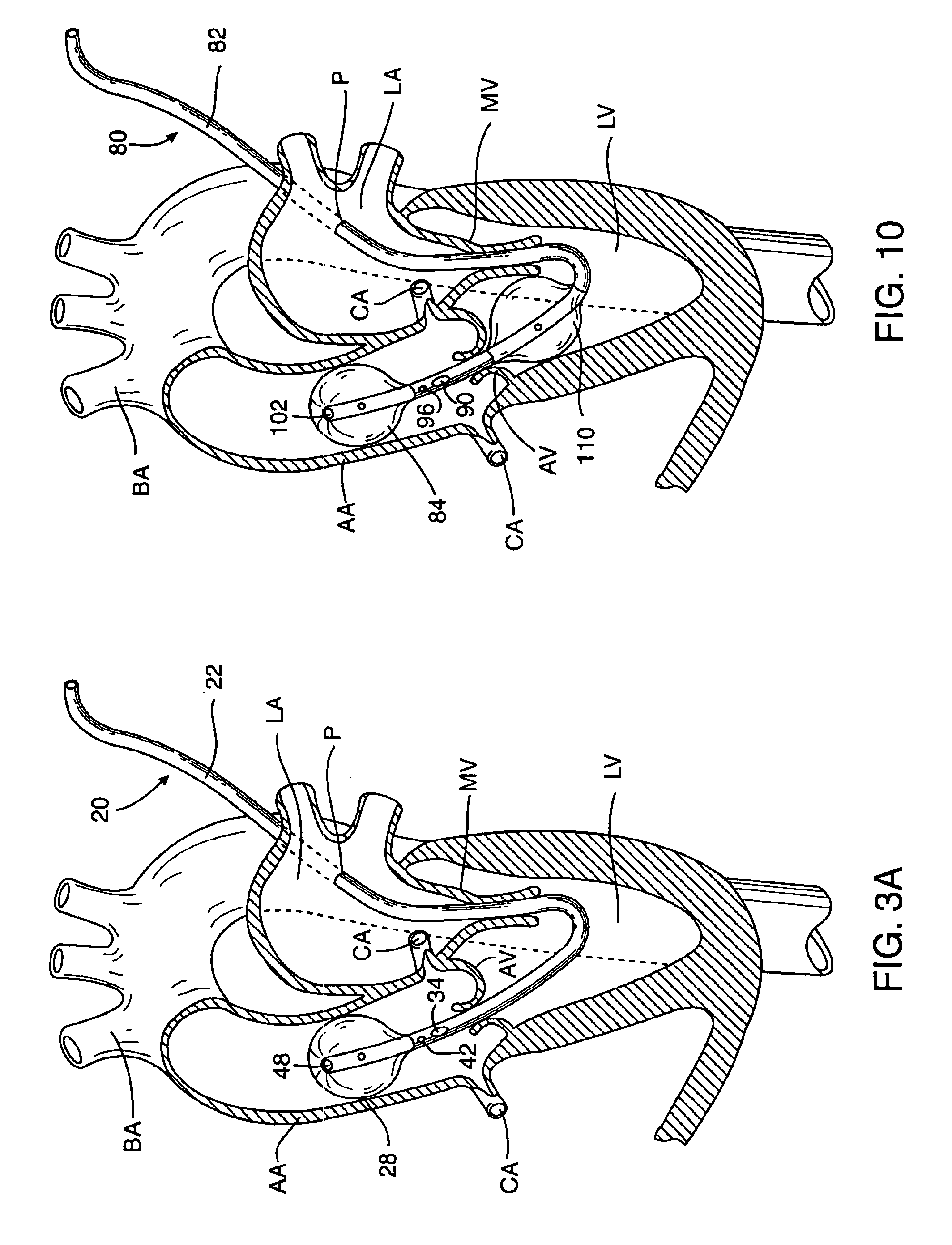
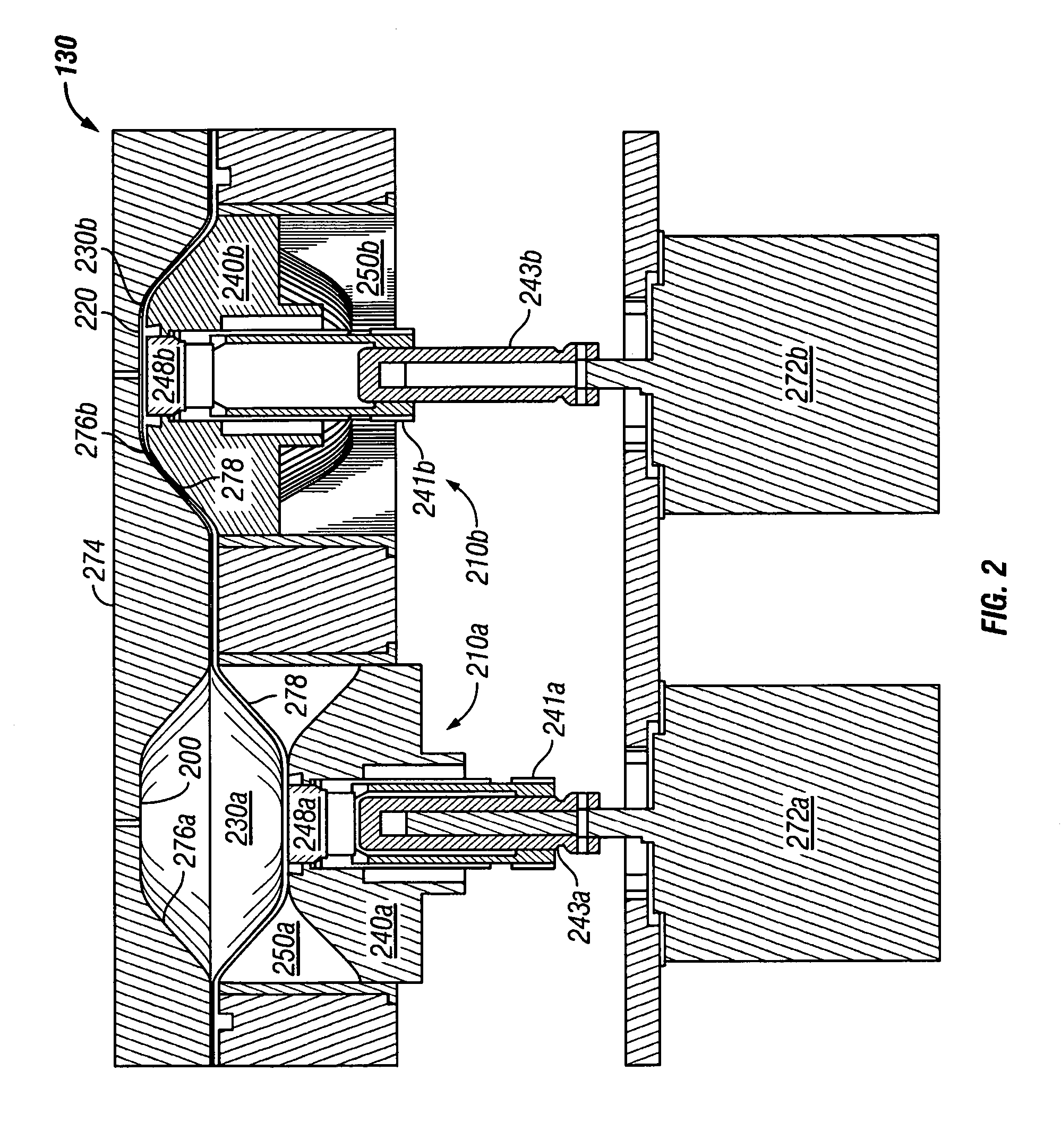
Cardioplegia Catheter System
A cardioplegia catheter system for delivery of a cardioplegia solution, comprising a cardioplegia catheter comprising an elongate tubular catheter body that defines a continuous central lumen and a flange that is connected to and extends therefrom an exterior surface of the catheter body, the flange defining a plurality of suture openings that extend therethrough the flange from a top surface to a bottom surface thereof. The cardioplegia system further comprising at least one stay suture and at least one suture capture stylet having a distal portion that is adapted to extend through one suture opening of the plurality of suture openings in the flange of the catheter body, wherein the distal portion of the rod has a shape that is adapted for slideably grasping a portion of the at least one stay suture.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
Syringeability cardiac muscle tissue engineering products based on thermo-sensitive chitosan hydrogel
InactiveCN101288779APromote regenerationImprove retentionProsthesisExtracorporeal circulationLiquid temperature
The invention discloses an injective myocardial tissue engineering product basing on temperature responsive chitosan hydrogel and more particularly relates to liquid temperature responsive chitosan hydrogel which is used as stent material that is combined with seed cells from different sources, such as embryonic stem cells, mesenchymal stem cells, human fetal cadiacmyocytes, etc., and is injected and transplanted into the specific region of an animal myocardial infarction model for observing the condition of repairing the myocardial infarction region. Constructed by the stent material, the injective myocardial tissue engineering product can improve the retention rate and the survival rate of the seed cells, can promote the regeneration of myocardial tissues, can increase the wall thickness of the infarction region and can remold the shape of an original ventricular and improve the heart function. The product is provided with the injective character and is convenient for the treatment operation, thereby avoiding risks brought by the operations of cardioplegia arrest, extracorporeal circulation, etc. The injective myocardial tissue engineering product basing on the temperature responsive chitosan hydrogel has the advantages of simple operation process and mild implementation condition, provides a new product for the myocardial tissue engineering and has great significance for the clinical development of the tissue engineering myocardial treatment on heart diseases.
Owner:INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF PLA
Purine derivatives and methods of use thereof
The present invention relates to Purine Derivatives; compositions comprising an effective amount of a Purine Derivative; and methods for reducing an animal's core body temperature, protecting an animal's heart against myocardial damage during cardioplegia; or for treating or preventing a cardiovascular disease, a neurological disorder, an ophthalmic condition, an ischemic condition, a reperfusion injury, obesity, a wasting disease, or diabetes, comprising administering an effective amount of a Purine Derivative to an animal in need thereof. The Purine Derivatives include compounds of the following formula:or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereofwhereinA is —CH2OHB and C are —OH:D isA and B are trans with respect to each other:B and C are cis with respect to each other:C and D are cis or trans with respect to each other:R1 is —H, -halo, —CN, —N(R2)2, —OR2, —SR2, —NHC(O)R2, —NHC(O)N(R2)2, —NHC(O)OR2, —C(O)OR2, —C(O)R2, —C(O)N(R2)2, —OC(O)N(R2)2, —C(halo)3, or —NO2;each R2 is independently —H, —C1-C10 alkyl, —C2-C6 alkenyl, —C2-C6 alkynyl, —(CH2)n-aryl, —(CH2)n-(3- to 7-membered monocyclic heterocycle, —(CH2)n-(8- to 12-membered bicyclic heterocycle), —(CH2)n—(C3-C8 monocyclic cycloalkyl), —(CH2)n—(C3-C8 monocyclic cycloalkenyl), —(CH2)n—(C8-C12 bicyclic cycloalkyl), or —(CH2)n—(C8-C12 bicyclic cycloalkenyl);each n is an integer ranging from 0 to 6;each p is an integer ranging from 1 to 6; andeach q is an integer ranging from 1 to 6.
Owner:INOTECK PHARMA CORP
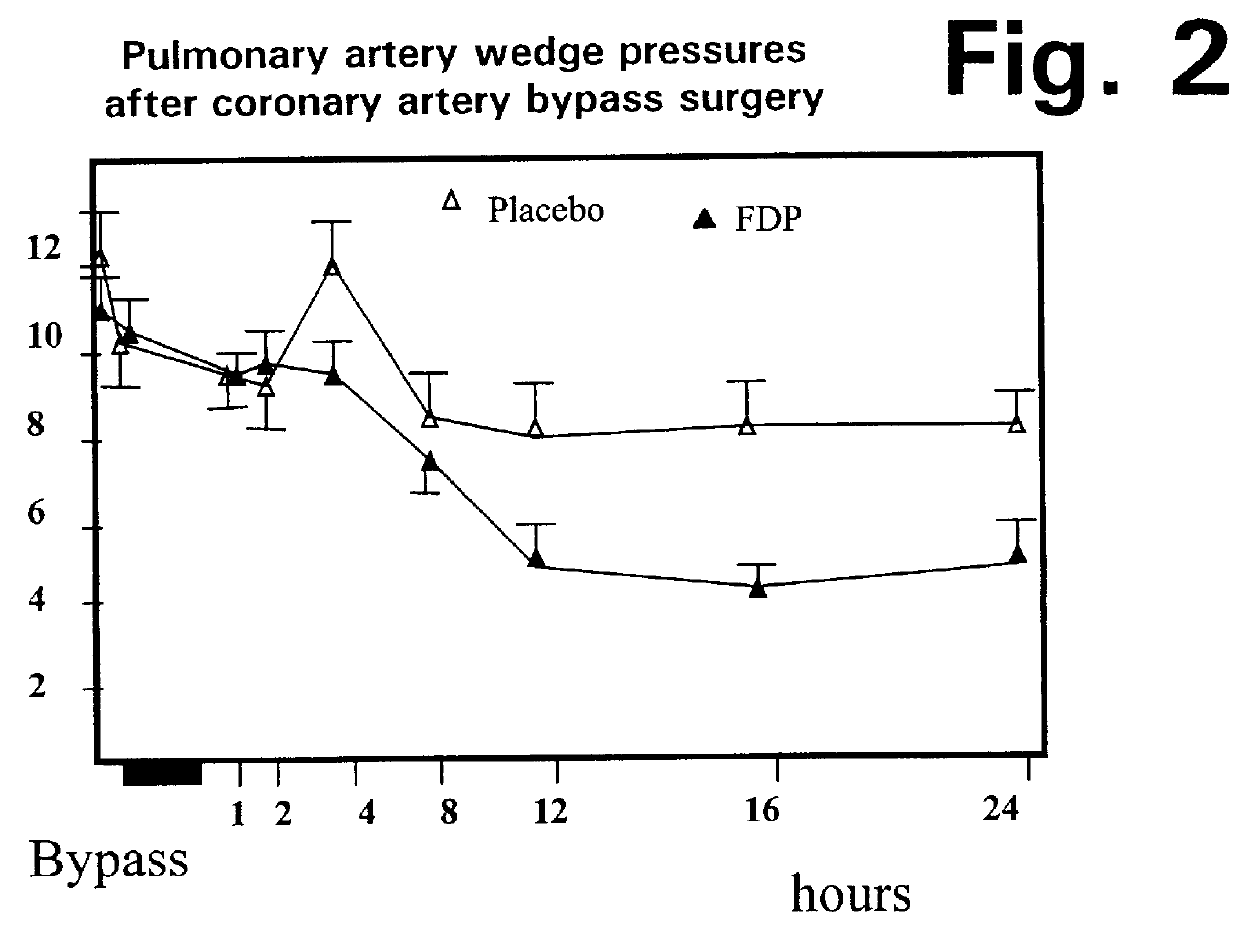
Method of reducing pulmonary hypertension and atrial fibrillation after surgery using cardiopulmonary bypass
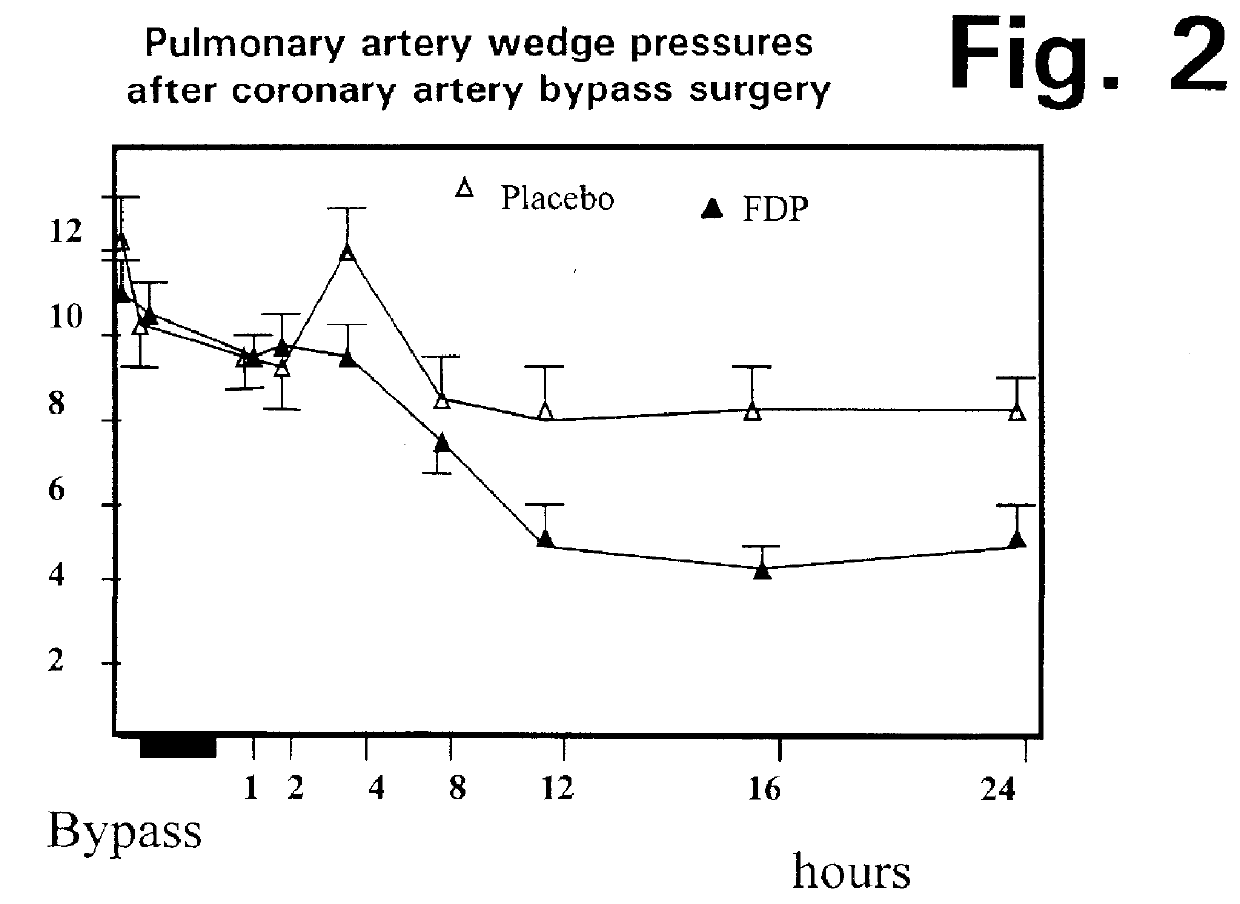
A method is disclosed for using fructose-1,6-diphosphate (FDP) to reduce and prevent two very serious problems caused by surgery that requires cardiopulmonary bypass. Before bypass begins, a liquid that contains FDP is intravenously injected into the patient, preferably over a period such as about 10 to 30 minutes, to allow the FDP to permeate in significant quantity into the heart and lungs while the heart is still beating. FDP can be added to the cardioplegia solution that is pumped through the heart to stop the heartbeat, and / or during bypass. This treatment was found to reduce two very important and serious problems that have unavoidably plagued CPB surgery in the past, which are: (1) elevated levels of pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR), which includes pulmonary hypertension; and (2) high occurrence rates for atrial fibrillation. Prior to this discovery, there has never been any satisfactory treatment which could reduce the severity and occurrence rates for these two major problems. FDP also can be co-administered in this manner, along with (1) a buffering or alkalizing agent that counteracts acidosis, such as sodium bicarbonate or THAM, and / or (2) a drug that reduces the formation of lactic acid, such as dichloroacetate.
Owner:QUESTCOR PHARMA
Injection of fructose-1,6-diphosphate (FDP) prior to coronary artery bypass grafting surgery
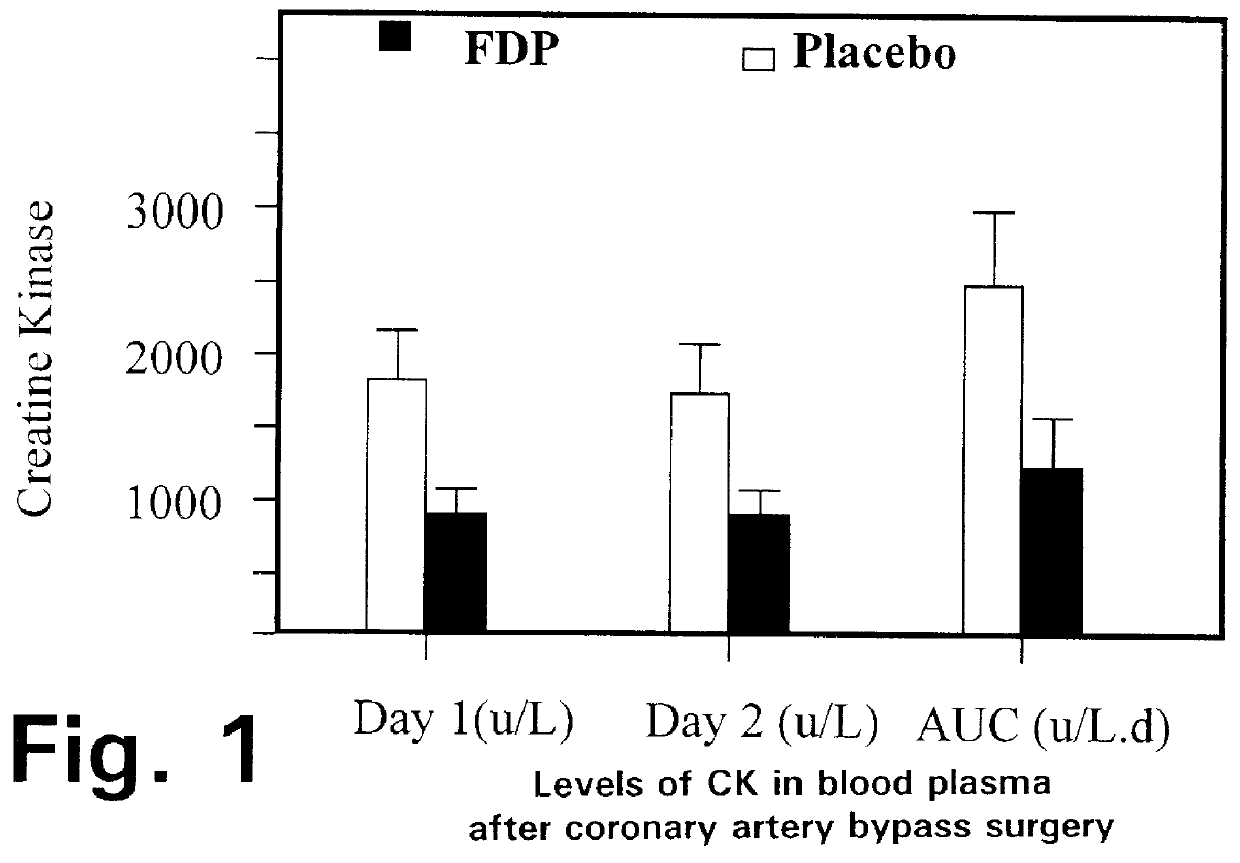
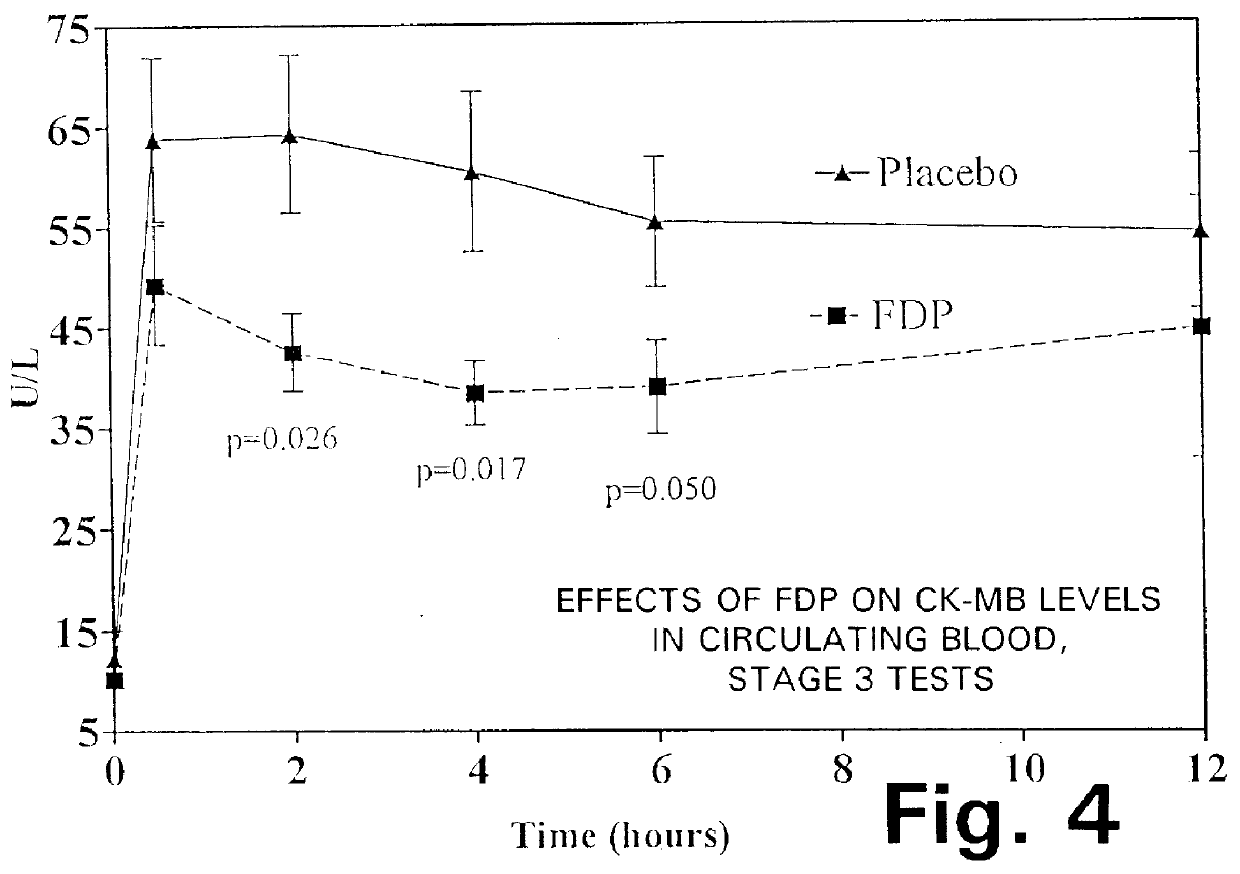
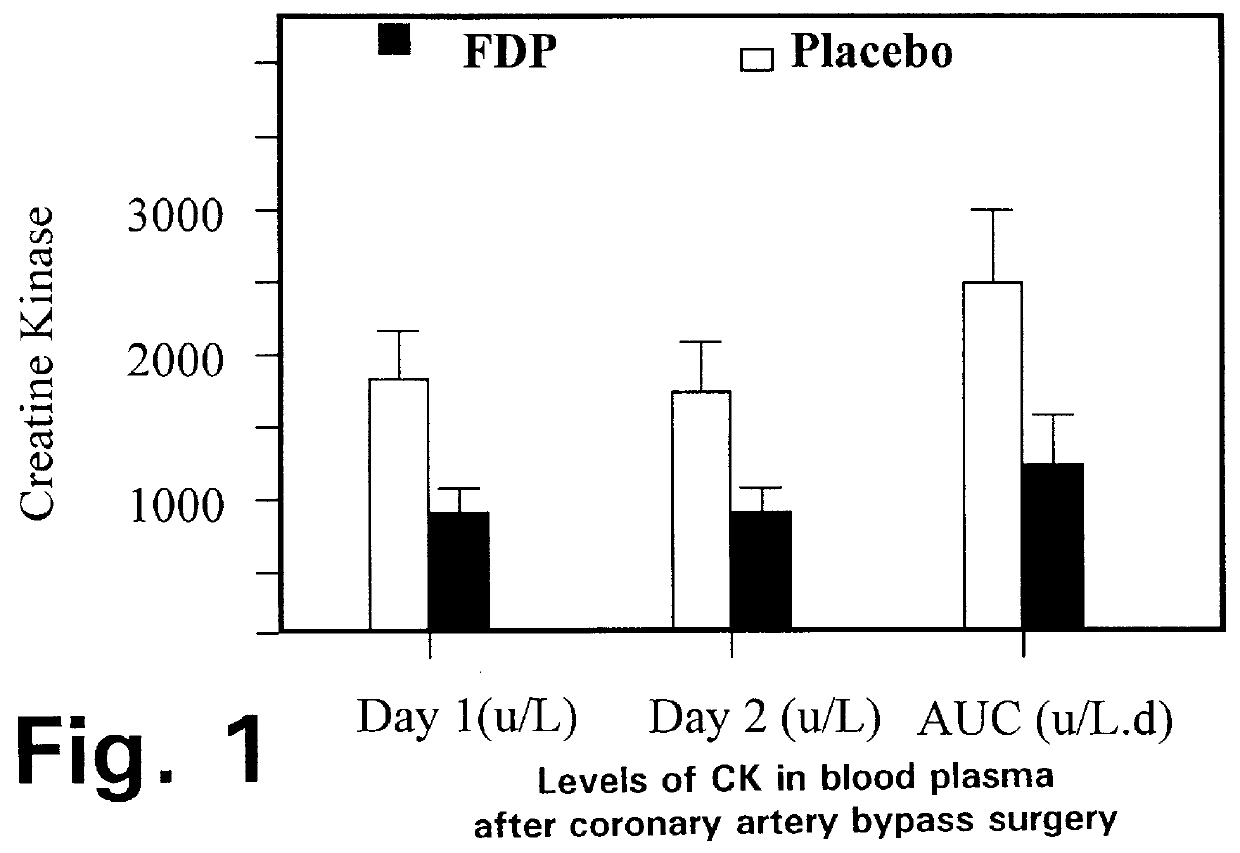
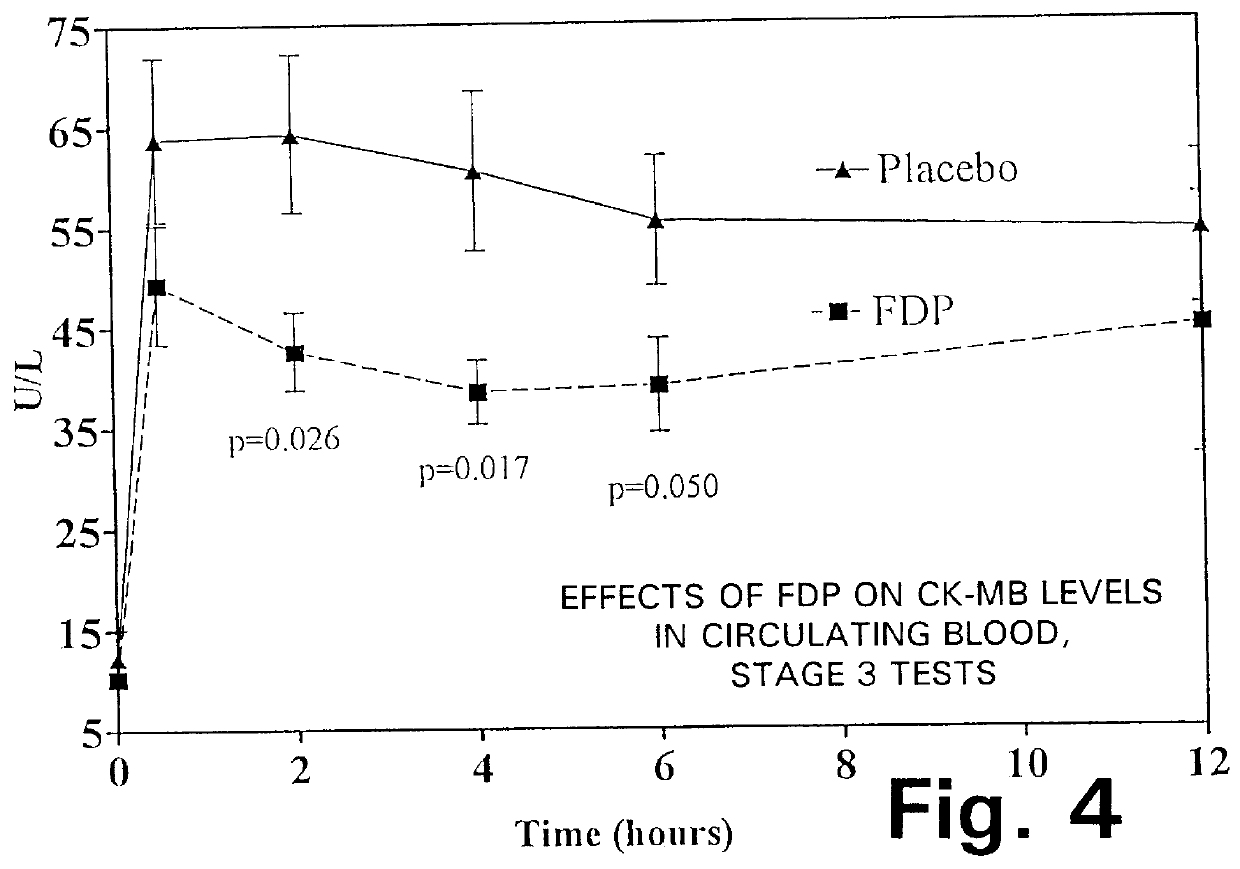
Fructose-1,6-diphosphate (FDP) is used to treat patients who are undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) surgery. Before cardiopulmonary bypass begins, a liquid that contains FDP is intravenously infused in the patient, preferably for about 10 to 30 minutes, to allow the FDP to enter the heart and lung tissue while the heart is still beating. FDP can also be added to cardioplegia solution; in addition, FDP can be injected after bypass is terminated, but if post-bypass injection is used, steps should be taken to avoid excess lactic acid accumulation, which appears to increase the risk of atrial fibrillation. To prevent or control lactic acidosis, a buffering or alkalizing agent, such as sodium bicarbonate, or an agent which reduces lactic acid formation, such as dichloroacetate, can be used. In double-blinded trials, this use of FDP substantially reduced heart damage and improved overall outcomes, as shown by lower levels of creatine kinase in blood, improvements in pumping performance, reduced requirements for vasodilator and inotropic drugs, and shorter stays in intensive care units. Certain dosages also reduced the likelihood of atrial fibrillation; however, FDP at high dosages increased the likelihood of A-fib. FDP also helped reduce pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR); this is an important finding, since pulmonary hypertension following cardiopulmonary bypass is a very difficult and often intractable problem, and is a contributing factor in nearly all deaths following CPB surgery.
Owner:QUESTCOR PHARMA
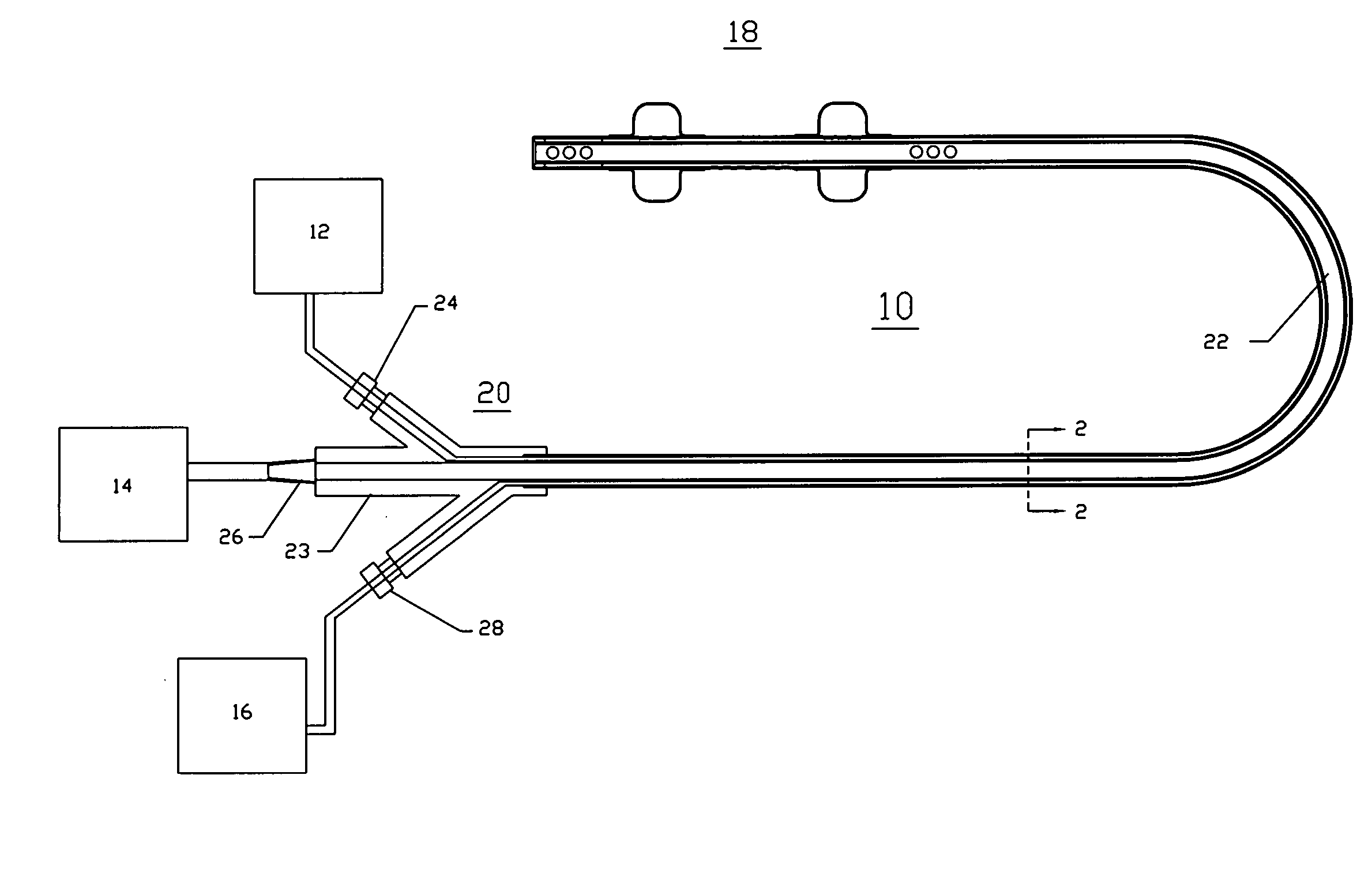
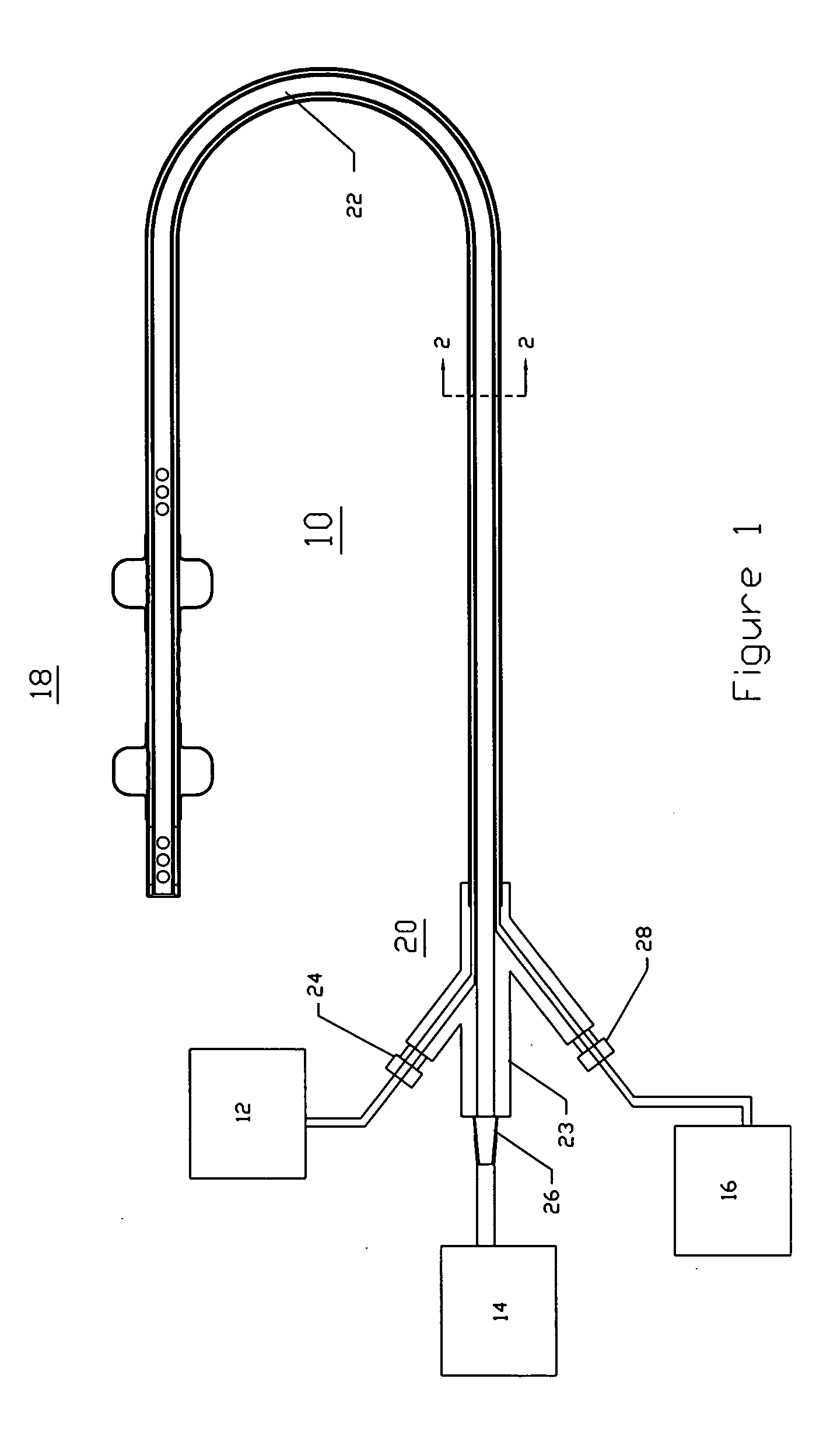
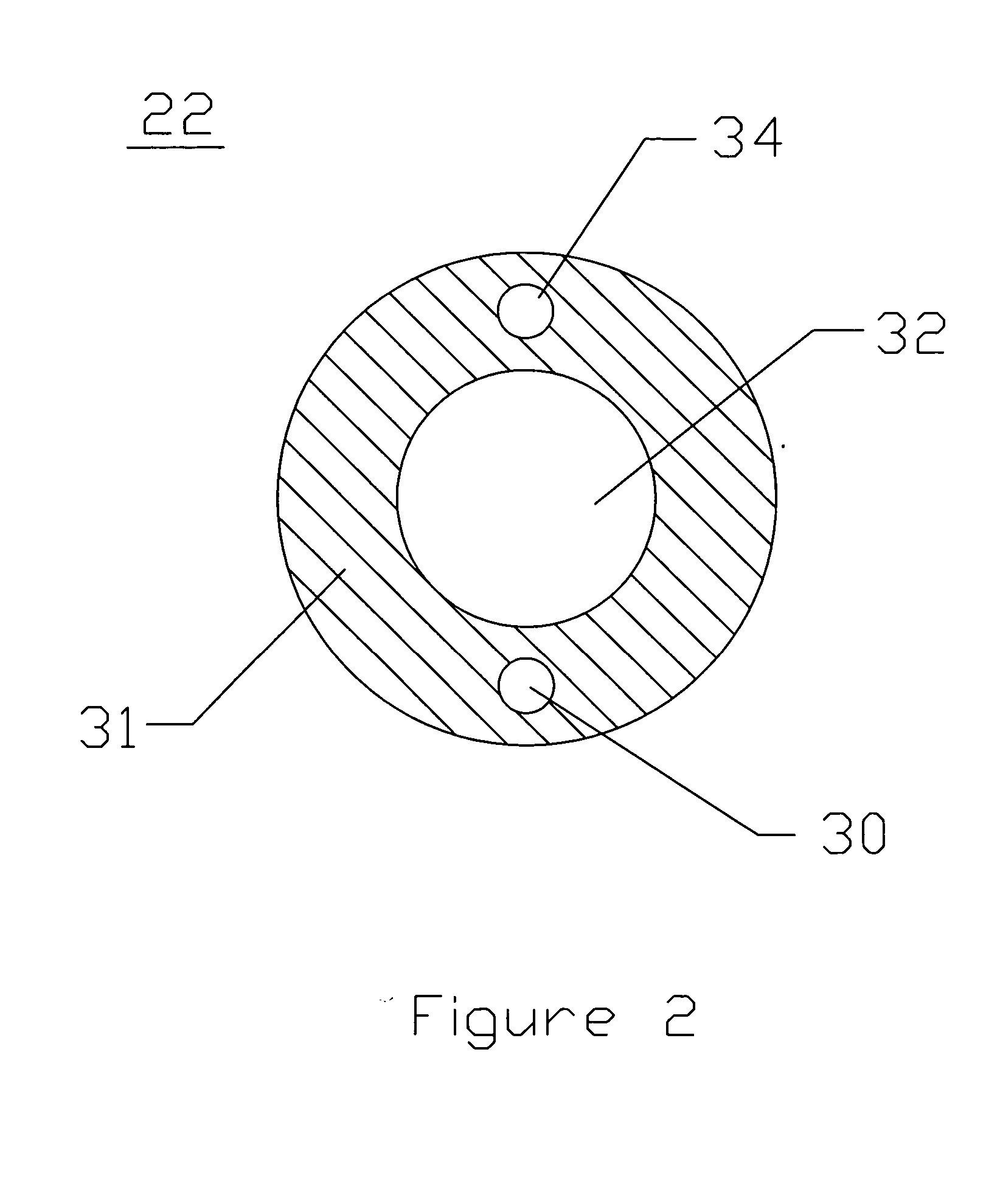
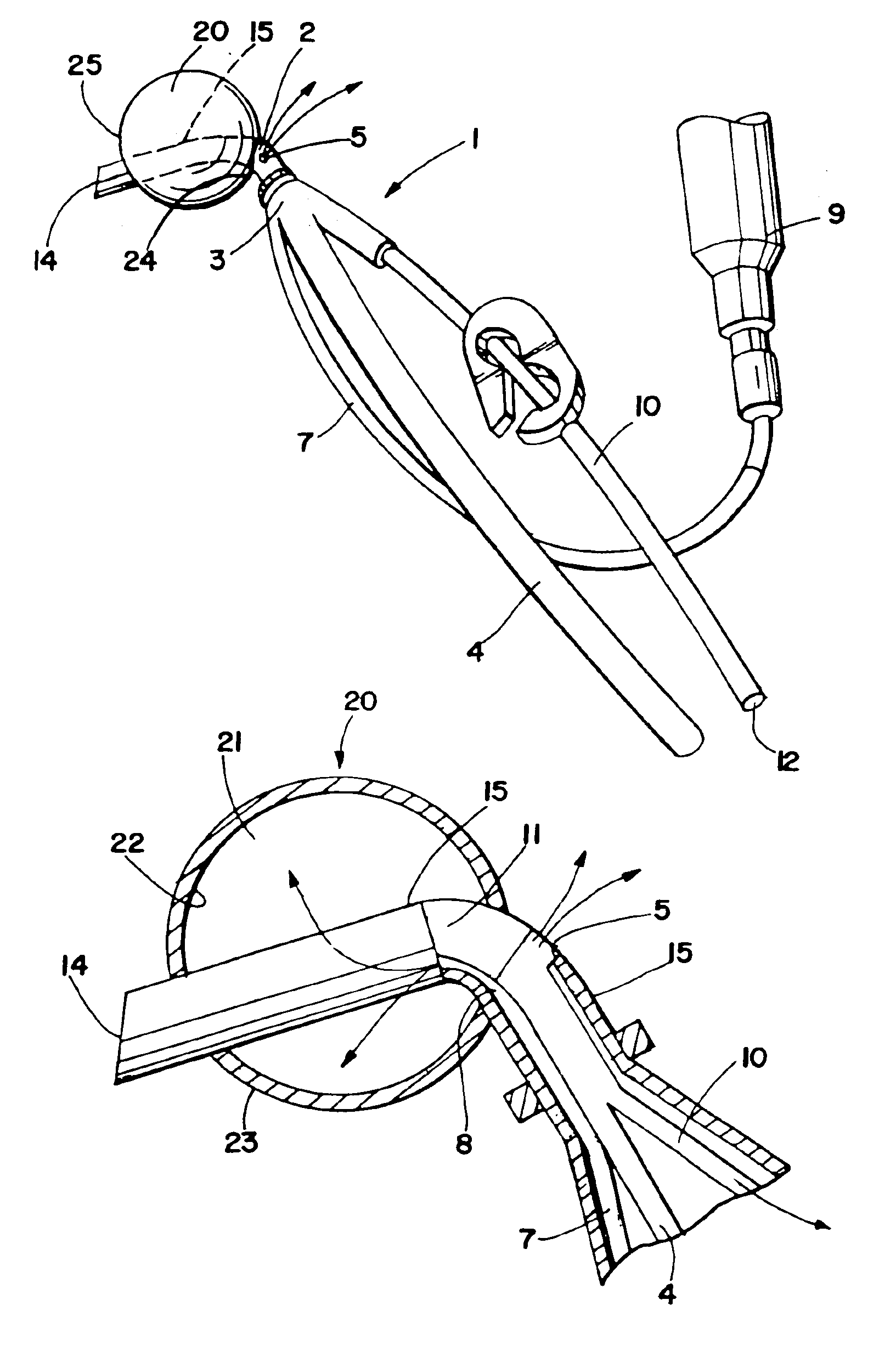
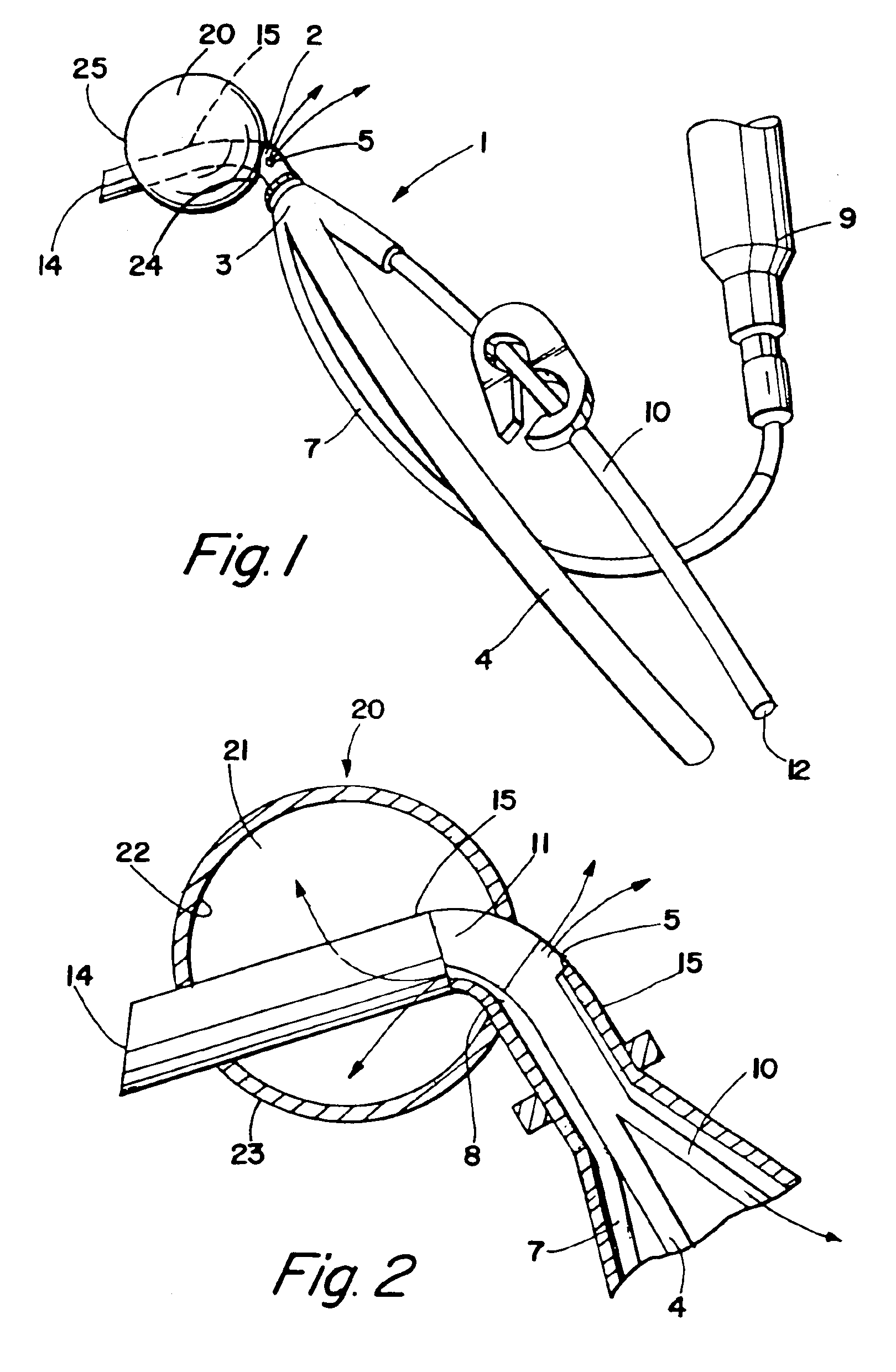
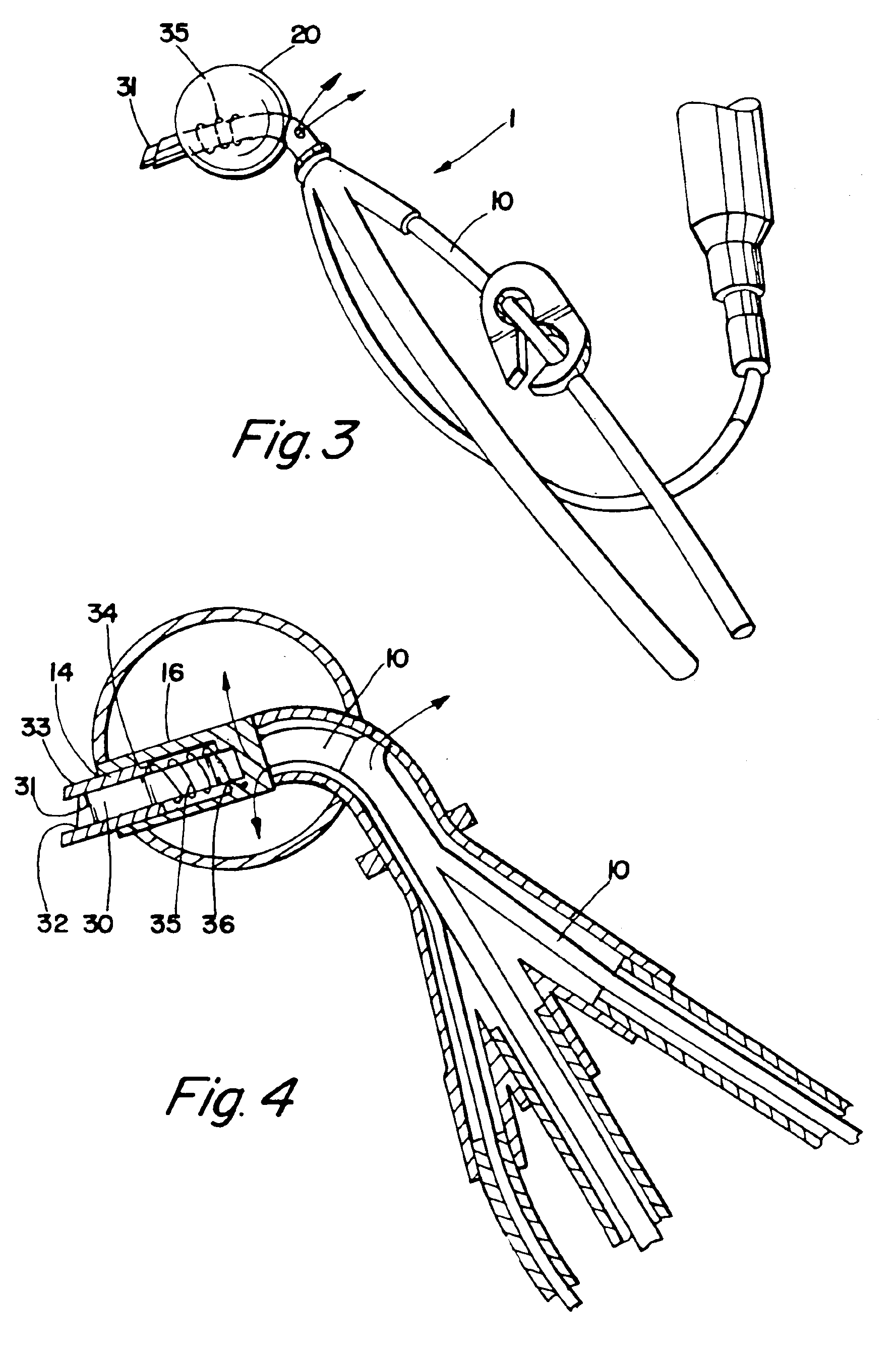
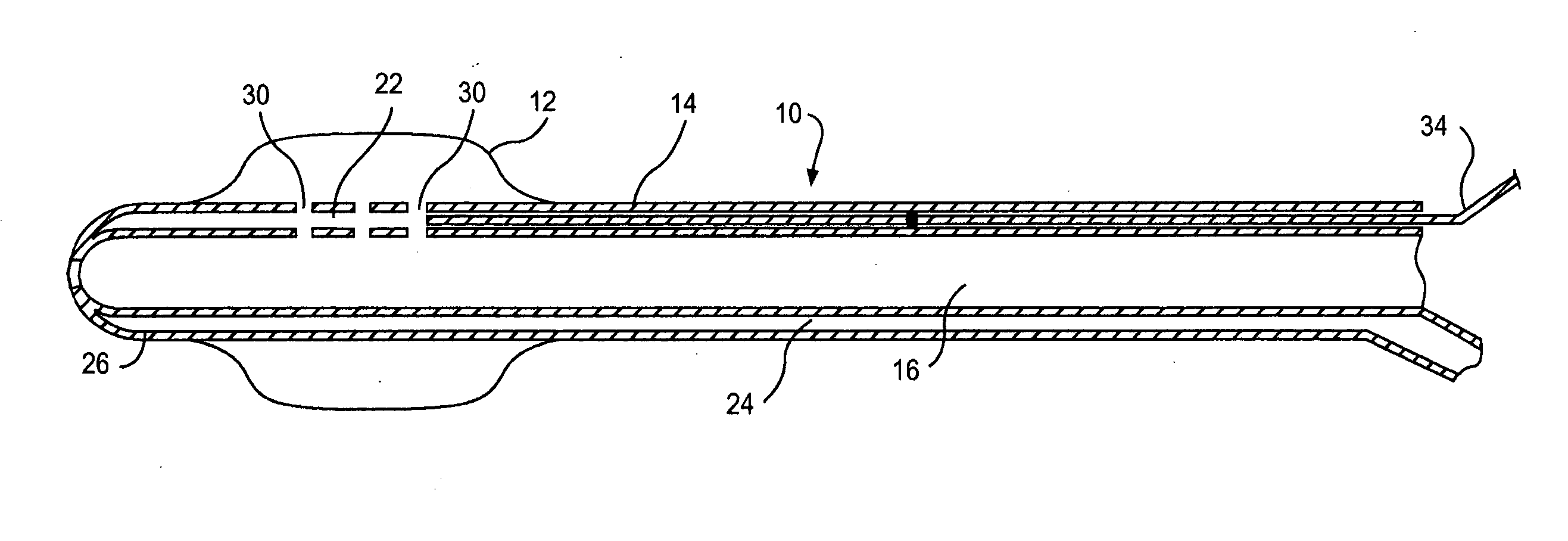
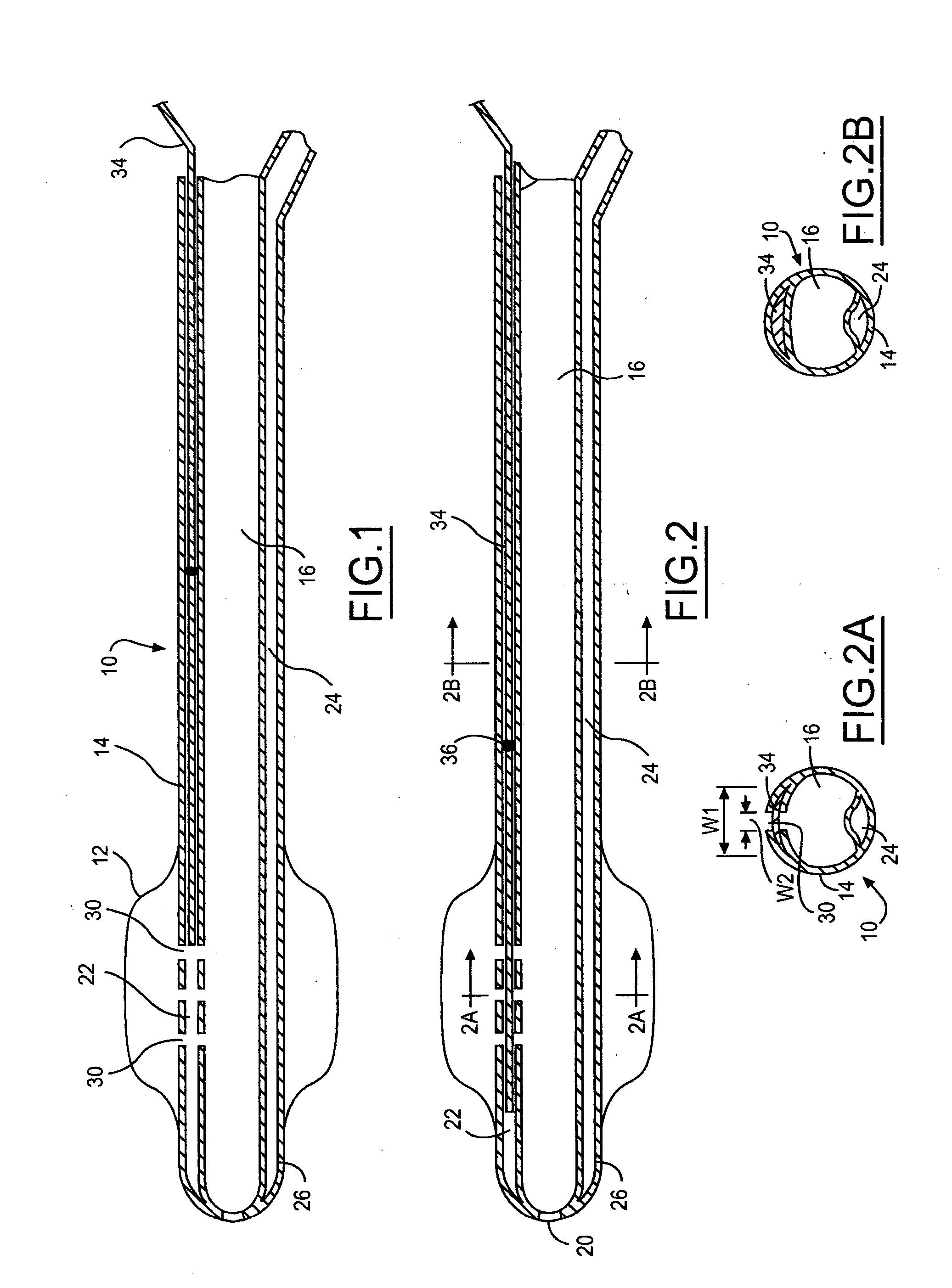
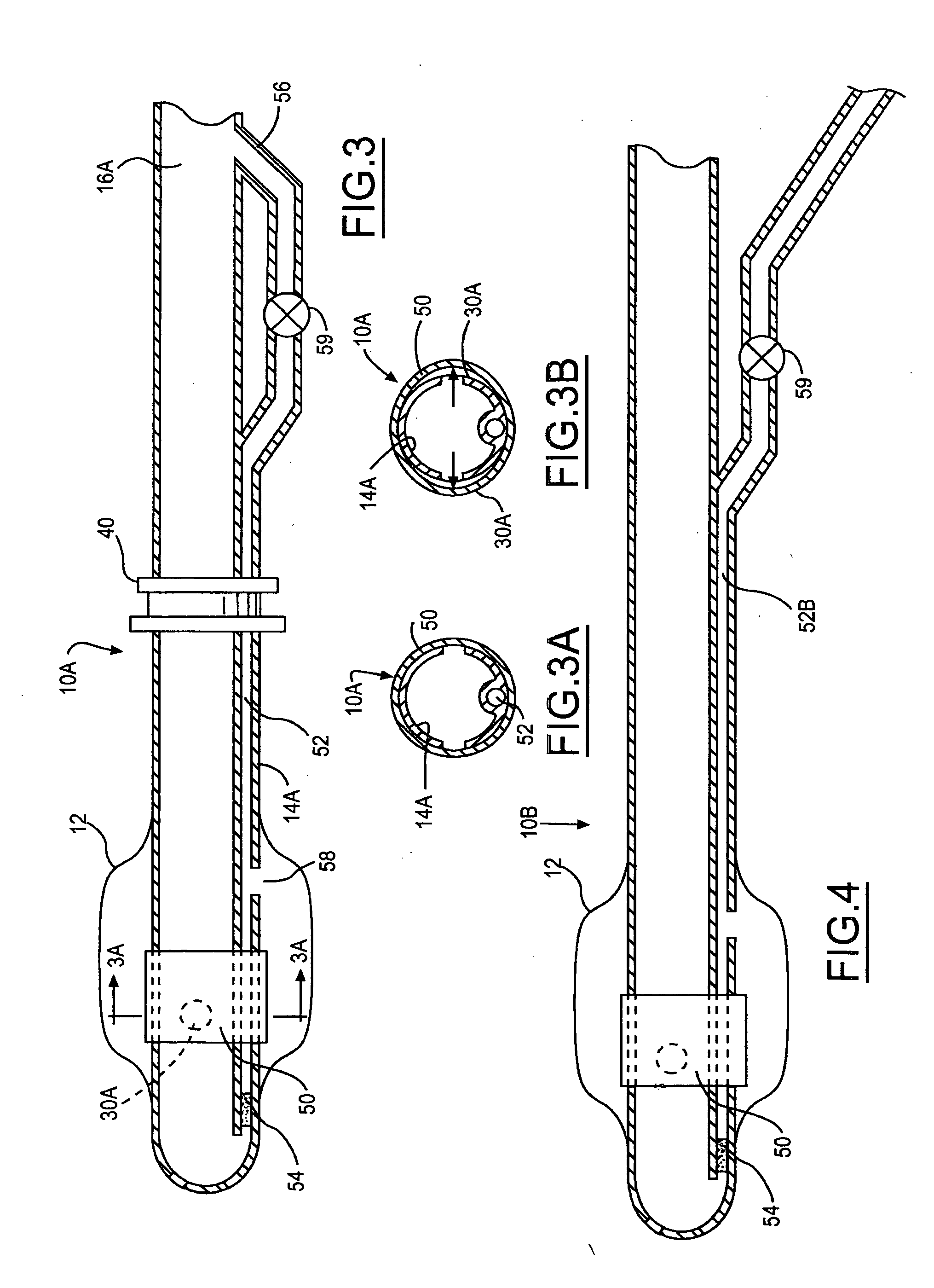
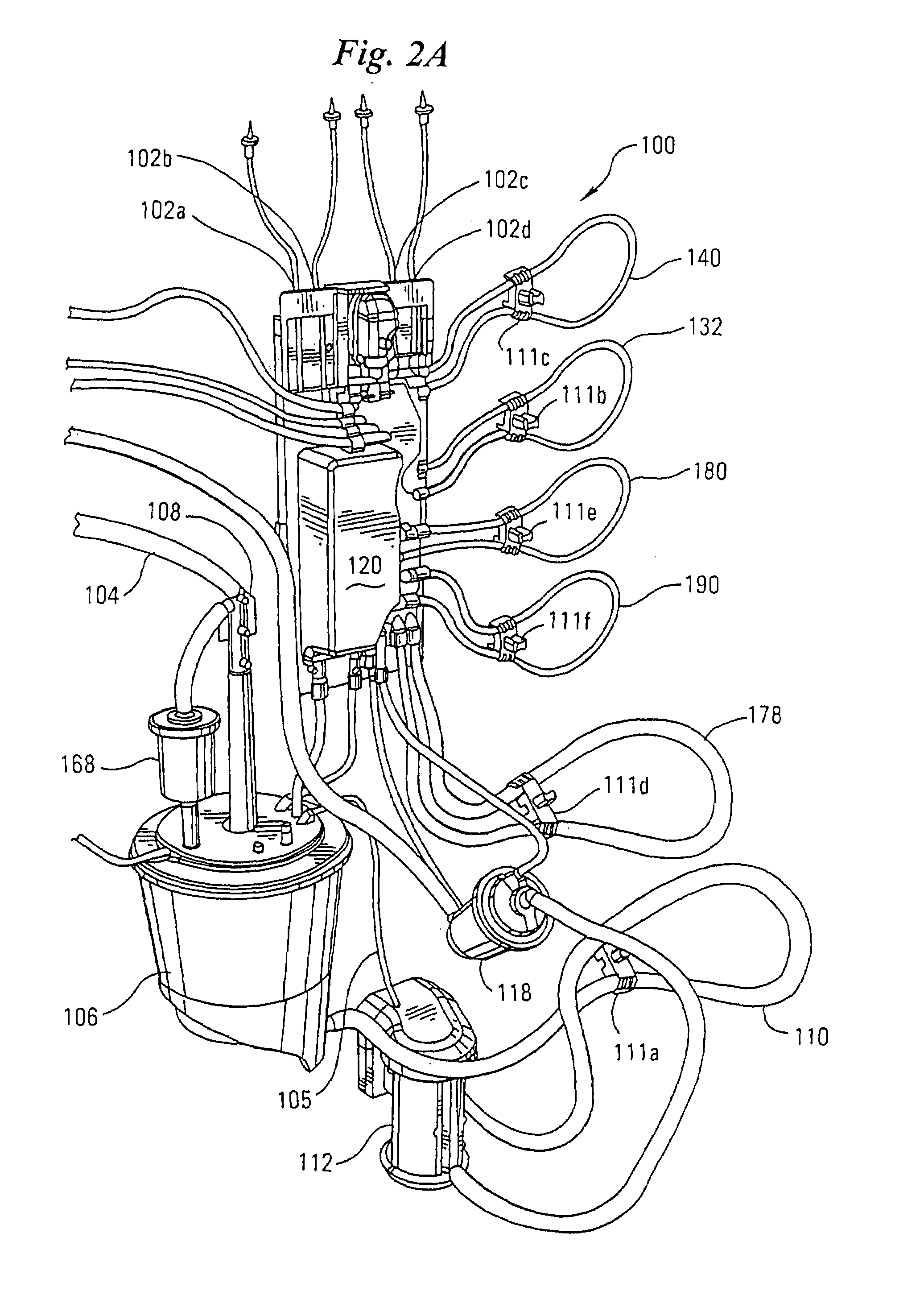
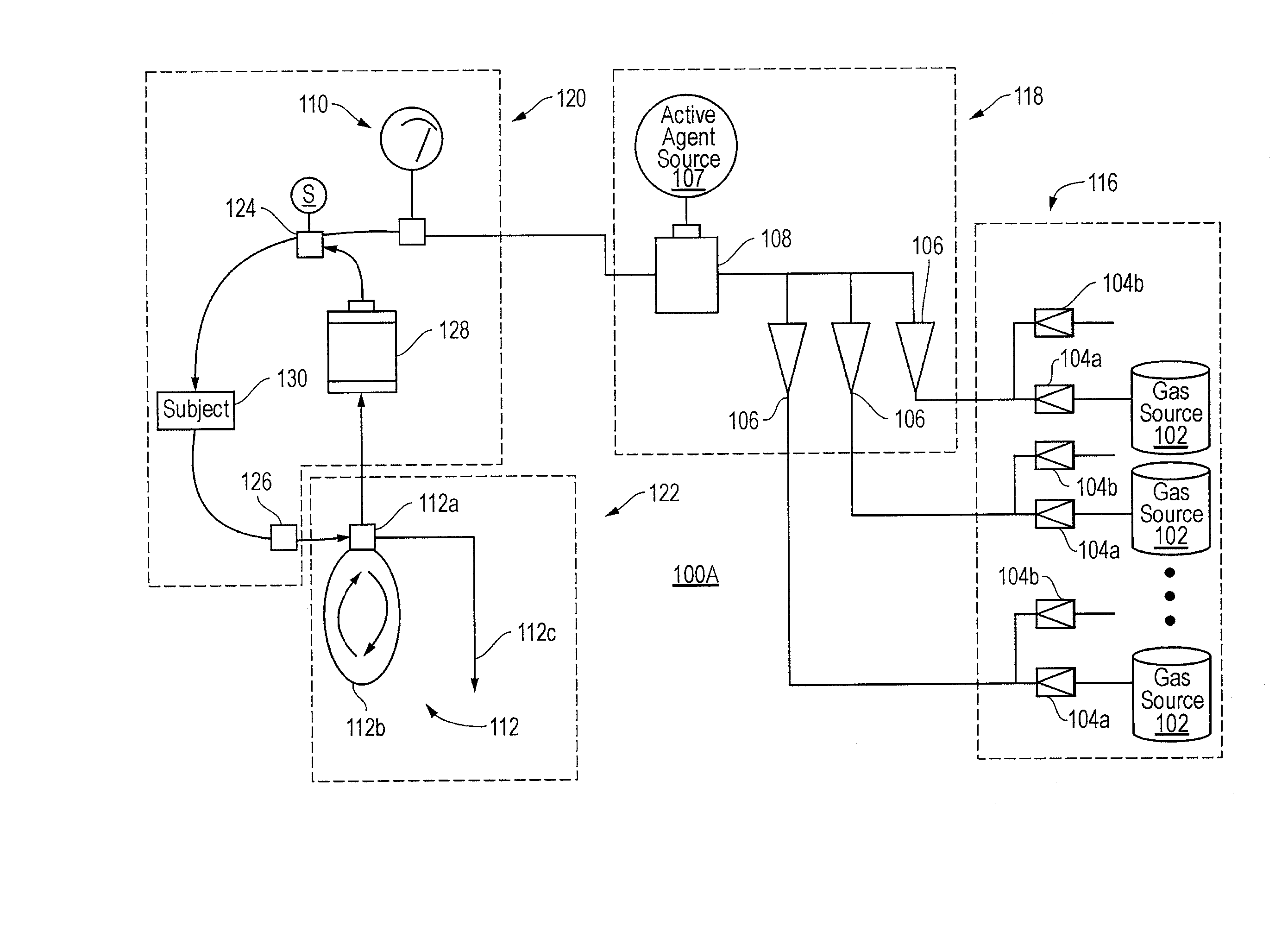
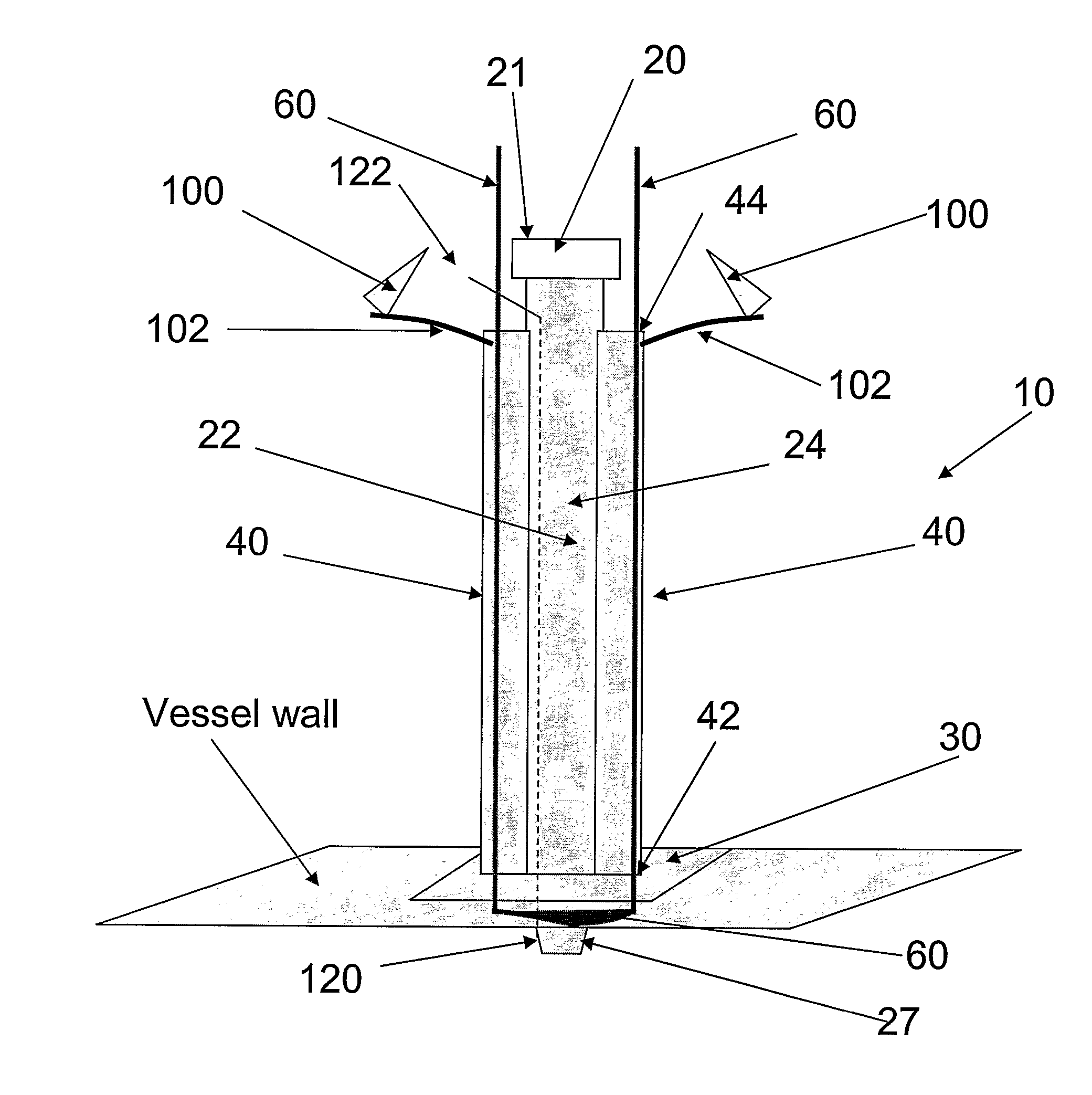
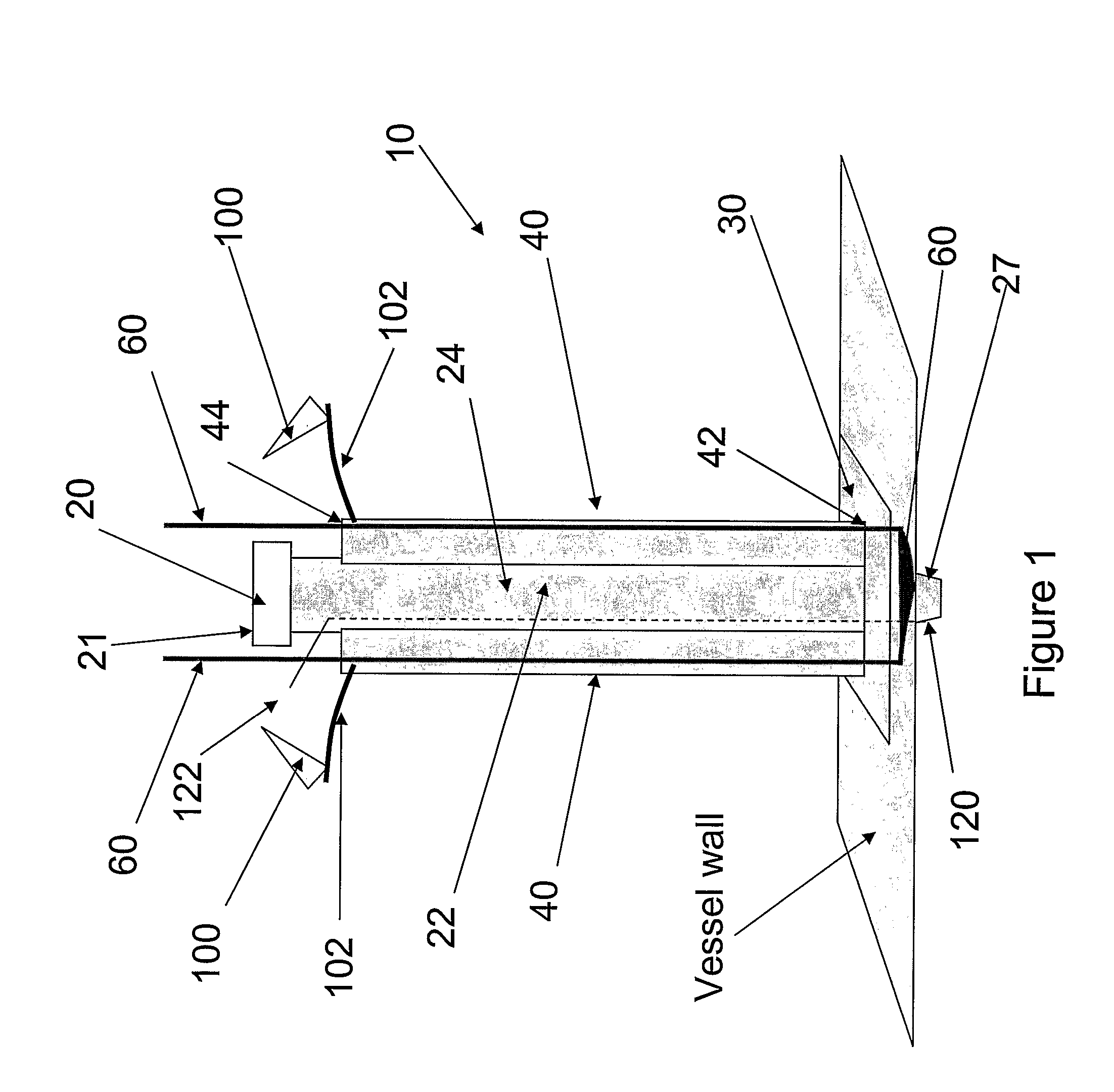
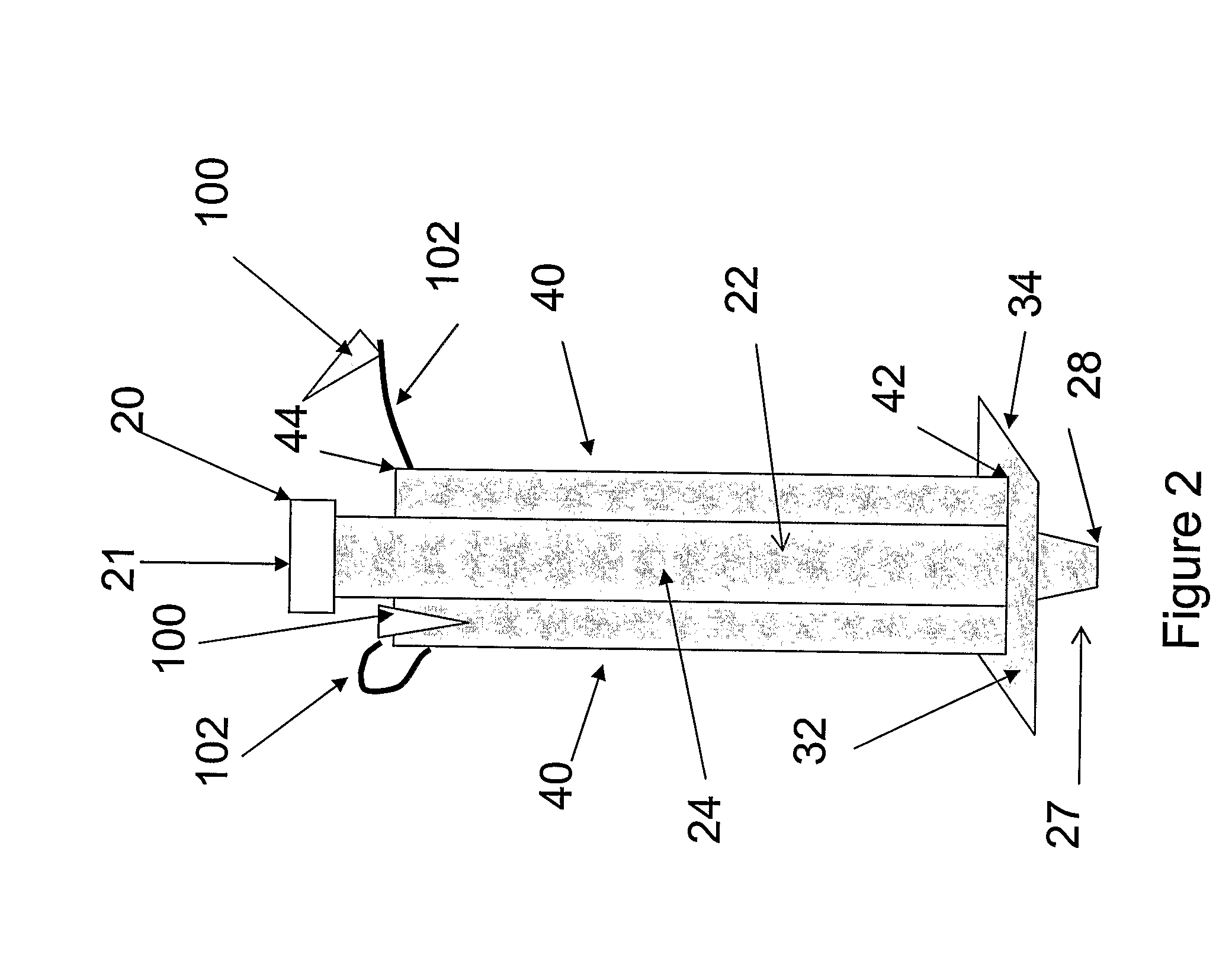
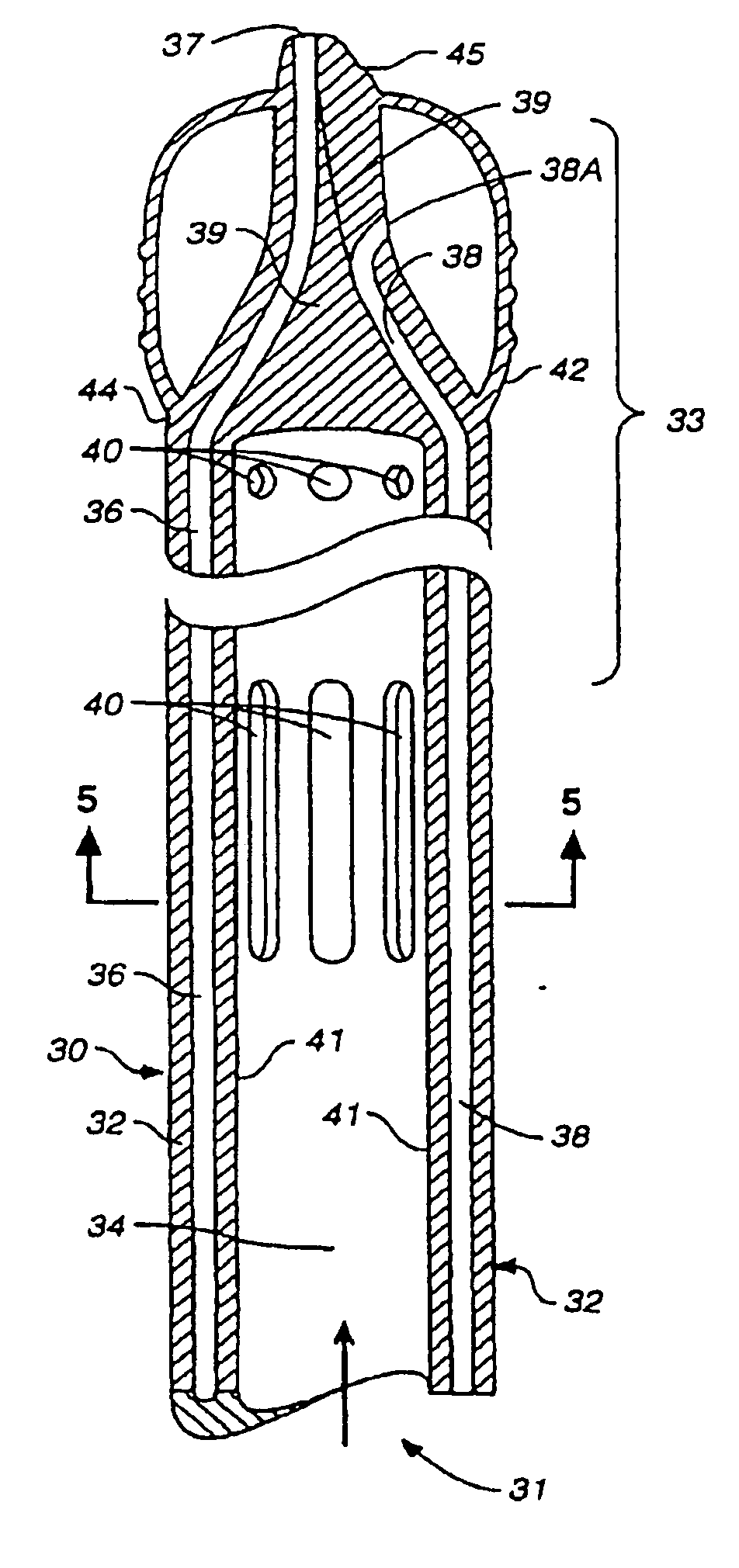
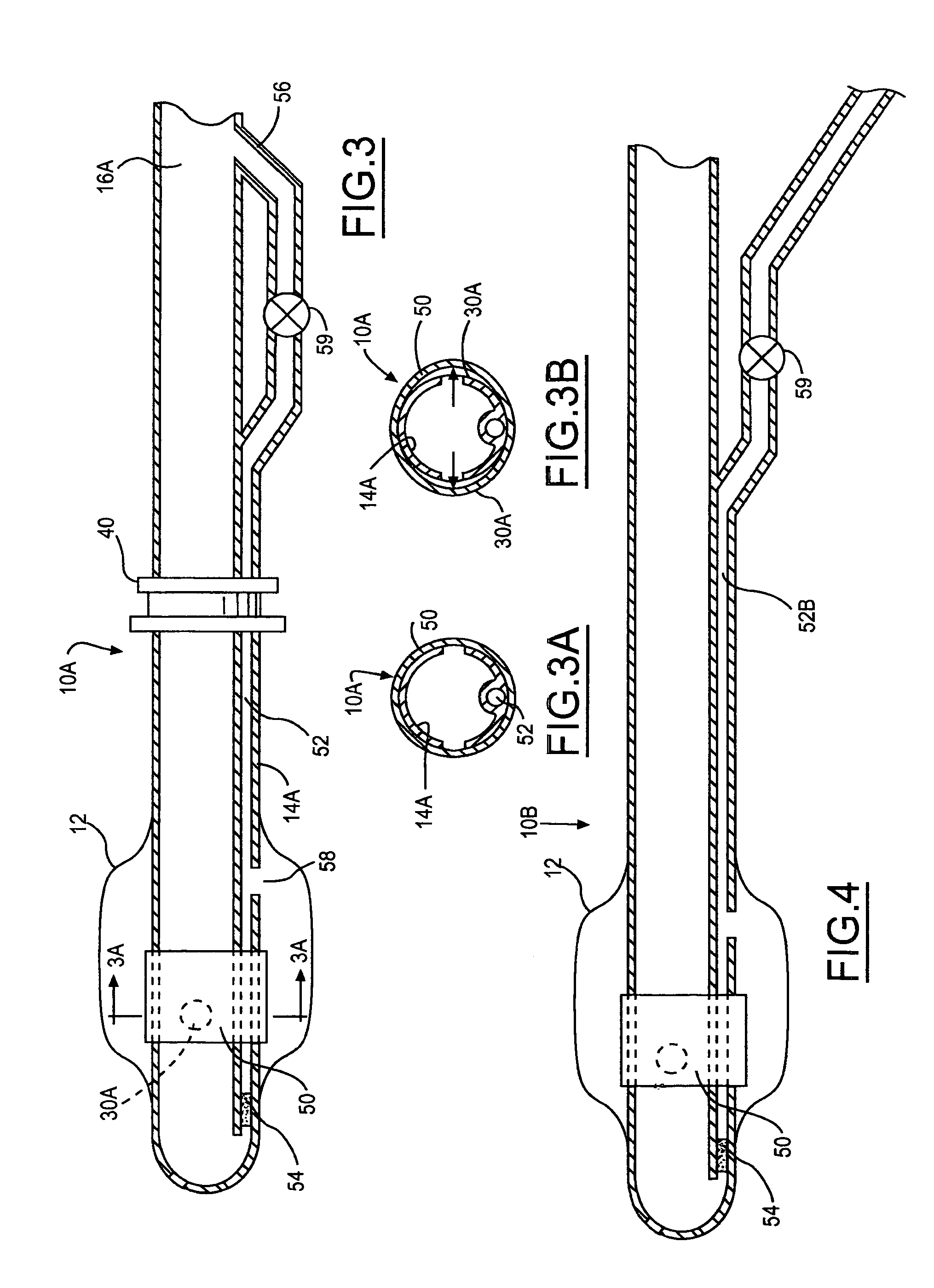
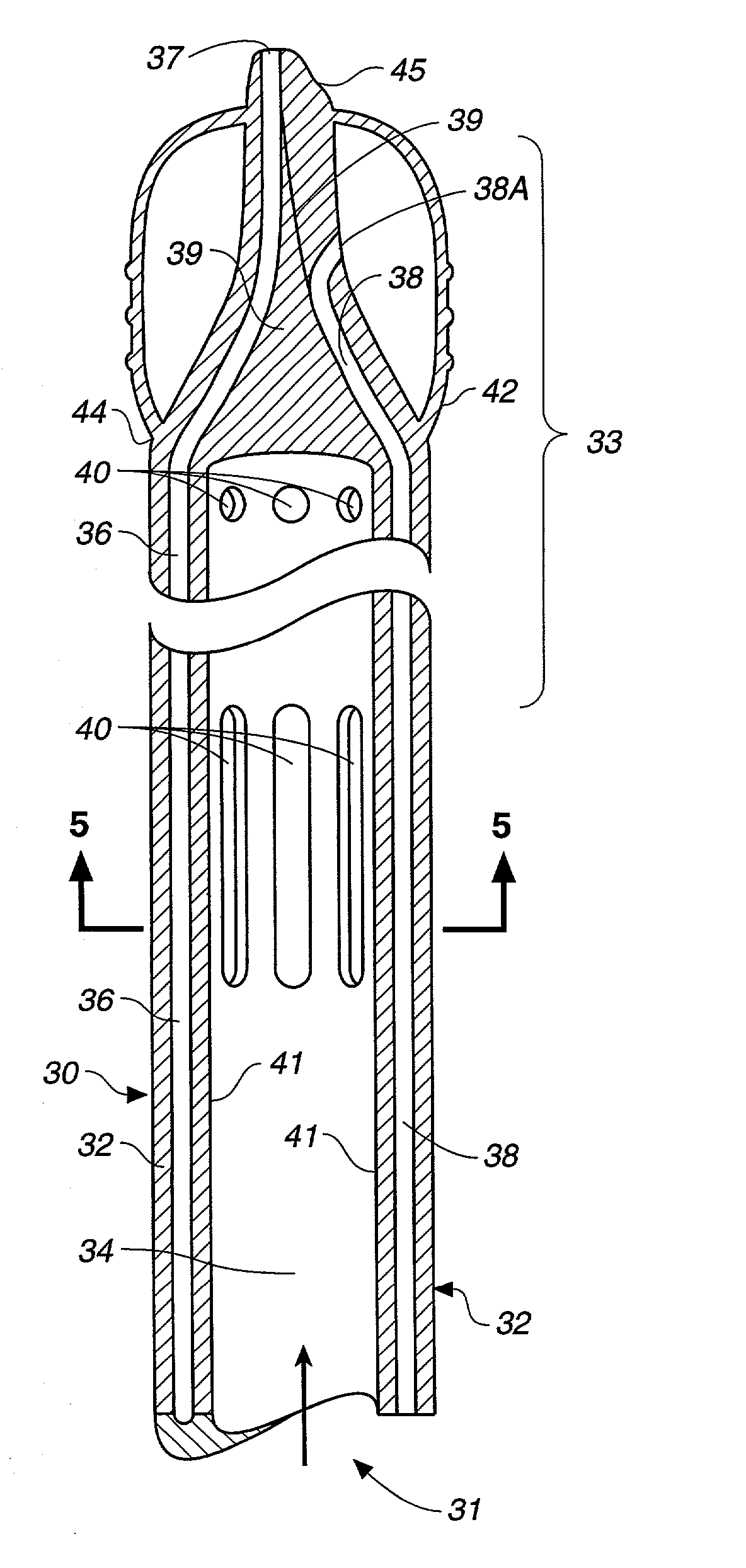
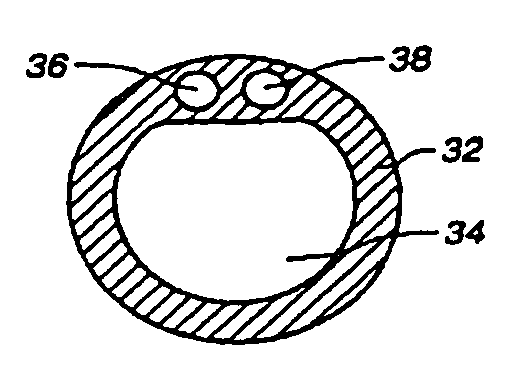
Multichannel catheter
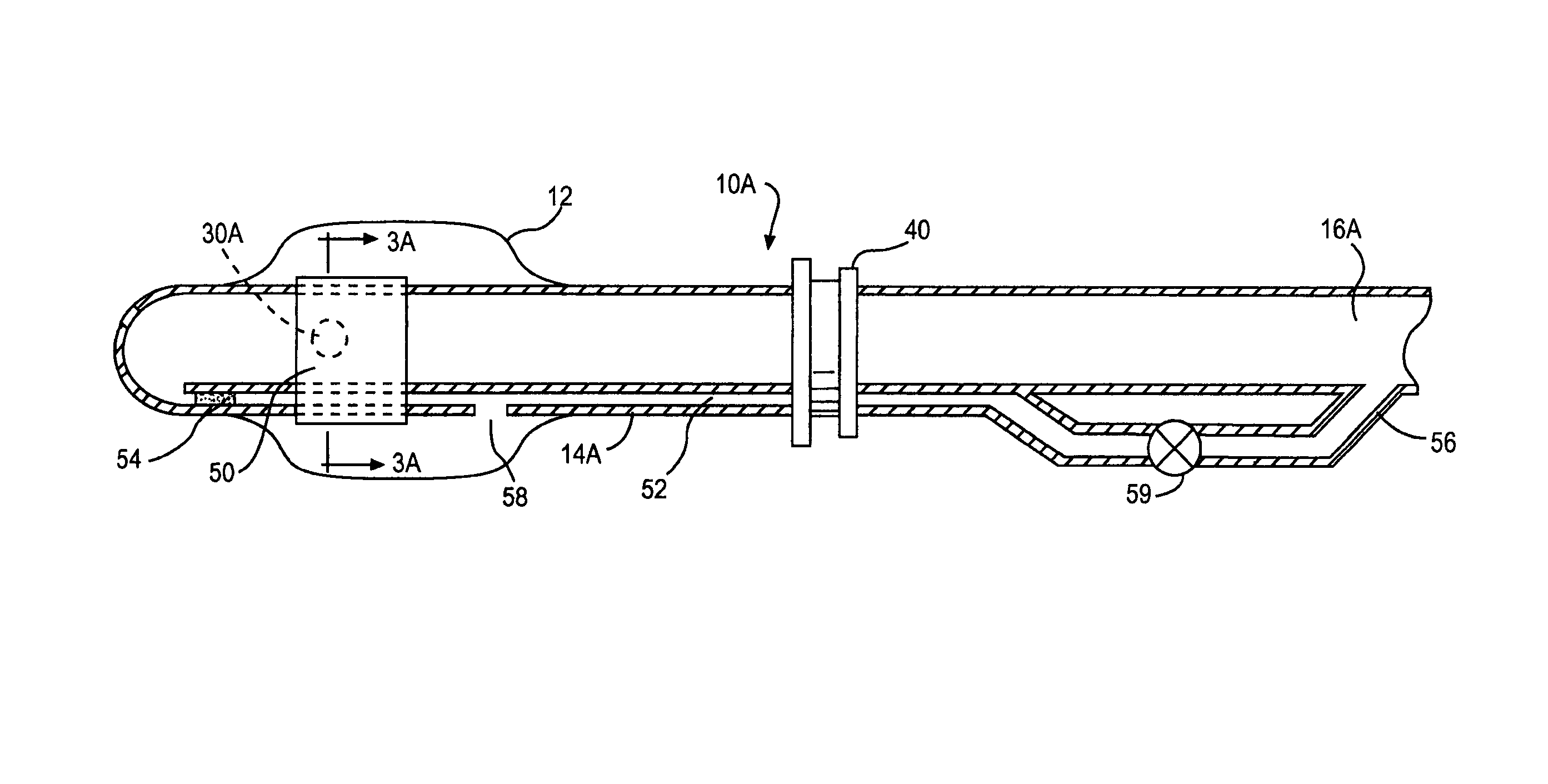
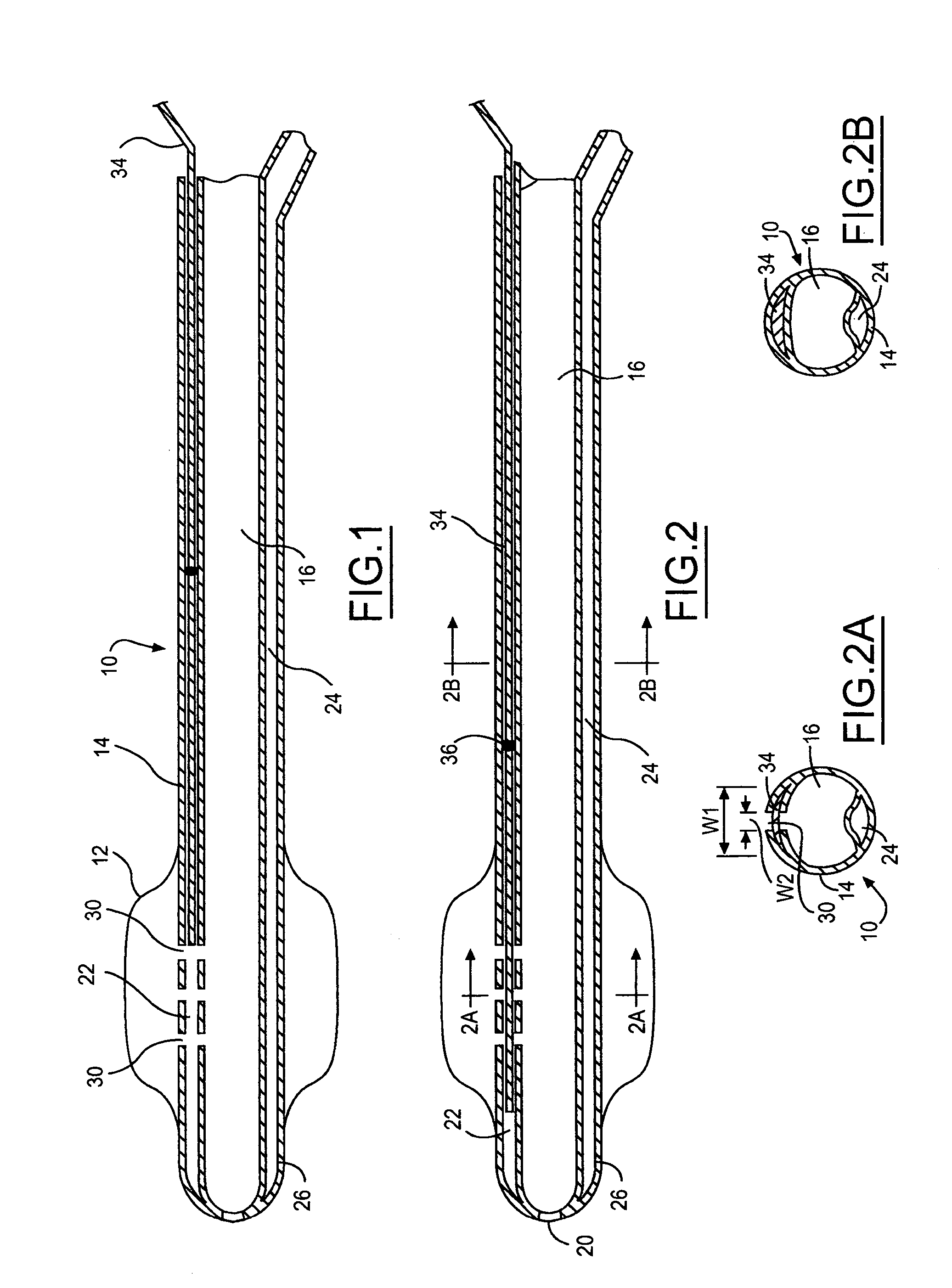
InactiveUS20050171505A1Efficient deliveryMaximizes rate of blood flowSuture equipmentsOther blood circulation devicesExtracorporeal circulationHeart operations
This invention is a single, multichannel catheter useful for extracorporeal circulation of blood to a patient undergoing cardiovascular treatments or surgery. The catheter has three independent channels and an expandable balloon at one end of the catheter. The first channel (34) is the largest and is of a size that allows for delivery of blood to a patient in an amount sufficient to maintain the patient's metabolism and perfusion throughout the treatment or surgery. A second channel (36), smaller than the first, is integrated into the wall of the first channel, and is suitable for delivering a biologically active fluid (e.g., for cardioplegia) to the heart and / or venting the left heart. A third channel (38), also smaller than the first, is integrated into the wall of the first channel, and suitable for delivering a fluid to the balloon for its expansion when positioned in the ascending aorta to occlude the flow of blood to the heart. It is important that the first channel accounts for at least about 70% of the total channel volume. The catheter provides an improved means of performing cardiovascular surgery on a patient using a cardiopulmonary machine for extracorporeal circulation of blood. The catheter is particularly useful for cardiac surgery. The multichannel catheter is best prepared using an extrusion molding technique.
Owner:SORIN GRP USA INC
Retrograde cannula having automatically inflatable balloon
Cardioplegia is delivered to a heart vessel by conducting the cardioplegia through an infusion lumen of a cannula. The cardioplegia communicates with a balloon disposed on a distal end of the cannula to cause the cardioplegia to inflate the balloon into sealing contact with a wall of the coronary sinus. The flow of cardioplegia is halted while preventing drainage of cardioplegia from the balloon, to maintain the balloon in its inflated state until such time as the flow of cardioplegia is resumed. Drainage of cardioplegia from the balloon is prevented by causing a valve to be shifted to a closed position blocking communication between the infusion lumen and the balloon. The valve can be shifted manually, or automatically in response to the halting of the delivery of cardioplegia.
Owner:MICHIGAN CRITICAL CARE CONSULTANTS
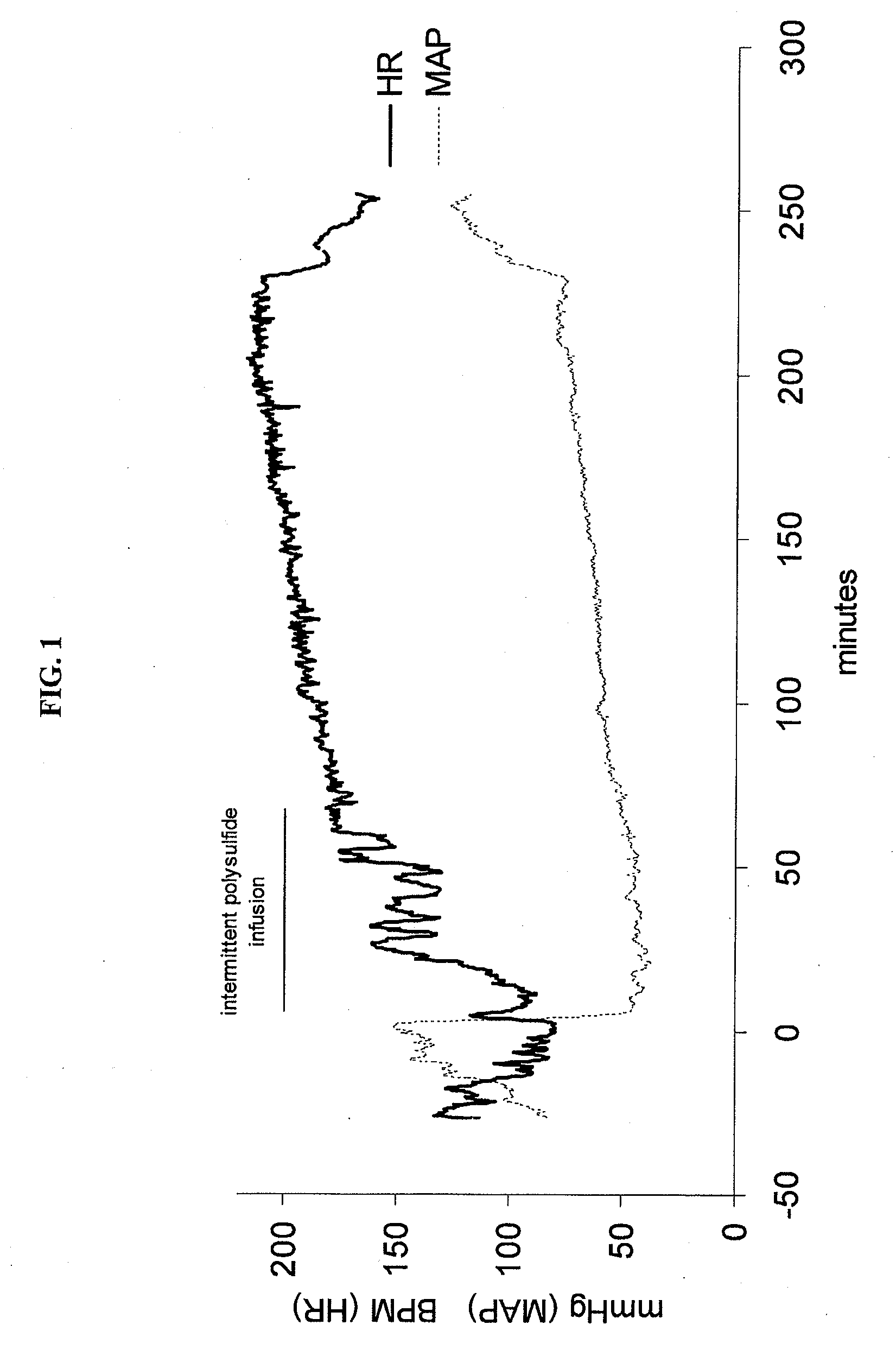
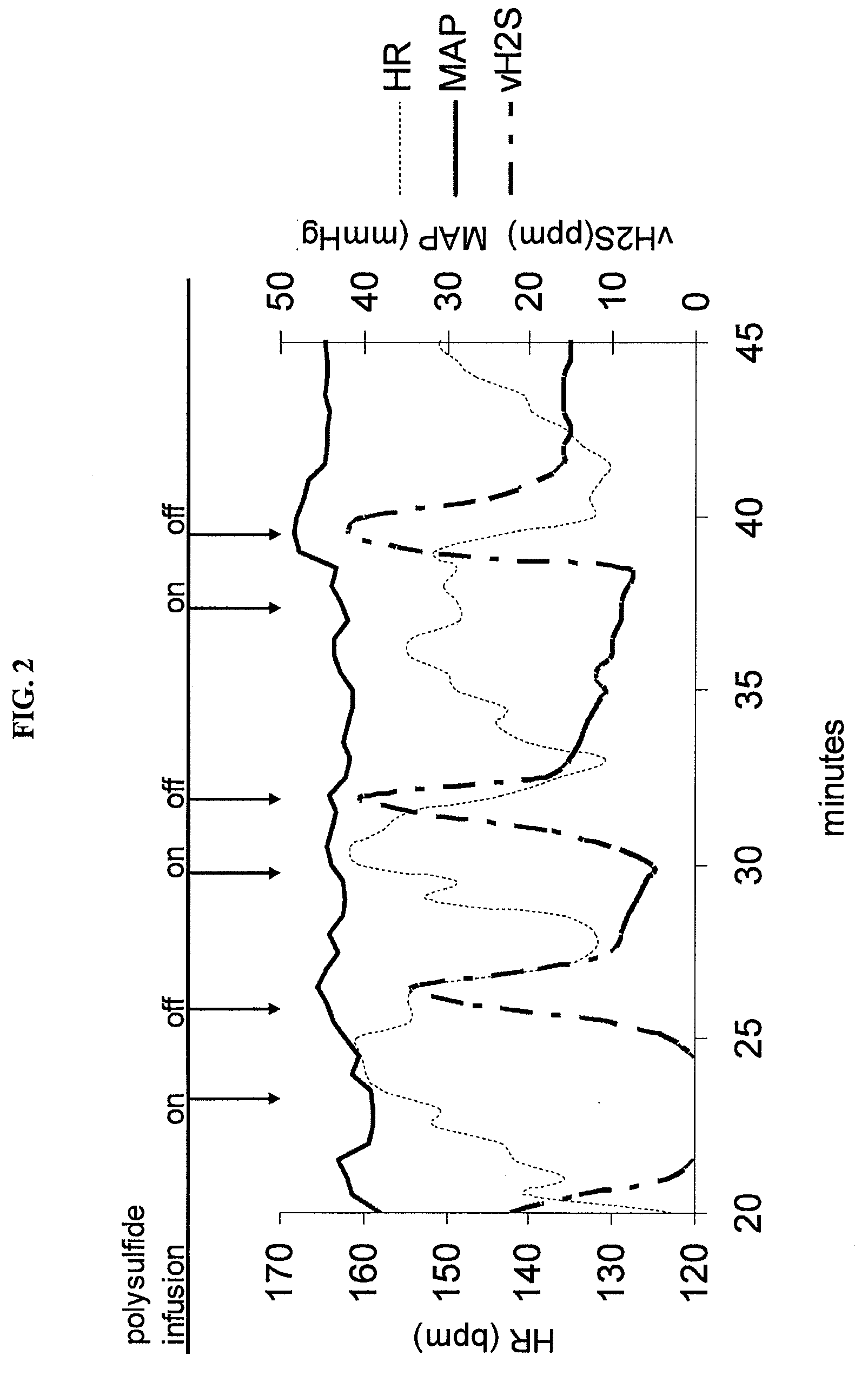
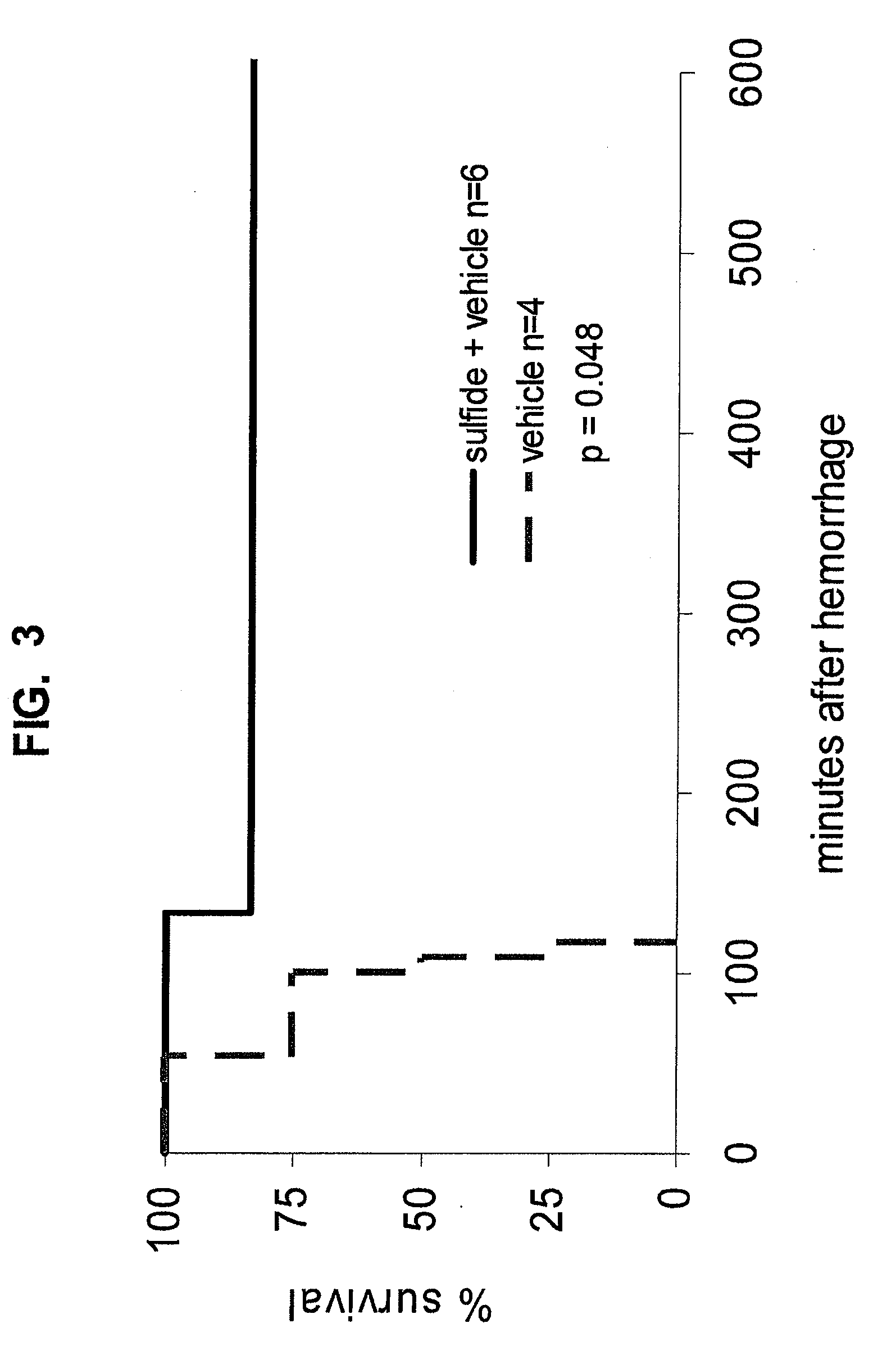
Methods and compositions regarding polychalcogenide compositions
InactiveUS20080318864A1Improve survivabilityAvoid YieldNervous disorderTripeptide ingredientsSurvivabilityNeurodegeneration
The present invention concerns the use of polychalcogenide compositions on cells, tissue, organs, and organisms to enhance their survivability. It includes compositions, compounds, methods, articles of manufacture and apparatuses for enhancing survivability and for protecting them from or treating them for injury or damage. In specific embodiments, there are also therapeutic methods and apparatuses for hypoxic / ischemic injury, organ transplantation, hyperthermia, wound healing, hemorrhagic shock, cardioplegia for bypass surgery, neurodegeneration, hypothermia, and cancer using the polychalcogenide compositions described.
Owner:FRED HUTCHINSON CANCER RES CENT
Multichannel catheter
InactiveUS20020016566A1Easy to manageImprove treatmentSuture equipmentsOther blood circulation devicesExtracorporeal circulationCardioplegias
A single, multichannel catheter useful for extracorporeal circulation of blood to a patient undergoing cardiovascular treatments or surgery. The catheter has three independent channels and an expandable balloon at one end of the catheter. The first channel is the largest and is of a size that allows for delivery of blood to a patient in an amount sufficient to maintain the patient's metabolism and perfusion throughout the treatment or surgery. A second channel, smaller than the first, is integrated into the wall of the first channel and is suitable for delivering a biologically active fluid (e.g., for cardioplegia) to the heart and / or venting the left heart. A third channel, also smaller than the first, is integrated into the wall of the first channel and suitable for delivering a fluid to the balloon for its expansion when positioned in the ascending aorta to occlude the flow of blood to the heart. It is important that the first channel accounts for at least about 70% of the total channel volume. The catheter provides an improved means of performing cardiovascular surgery on a patient using a cardiopulmonary machine for extracorporeal circulation of blood. The catheter is particularly useful for cardiac surgery. The multichannel catheter is best prepared using an extrusion molding technique.
Owner:BERTOLERO ARTHUR A +2
Methods and systems for performing thoracoscopic cardiac bypass and other procedures
InactiveUS20020023653A1Promote healingEqual efficacySuture equipmentsCannulasHeart operationsThoracoscopes
A method for closed-chest cardiac surgical intervention relies on viewing the cardiac region through a thoracoscope or other viewing scope and endovascularly partitioning the patient's arterial system at a location within the ascending aorta. The cardiopulmonary bypass and cardioplegia can be induced, and a variety of surgical procedures performed on the stopped heart using percutaneously introduced tools. The method of the present invention will be particularly suitable for forming coronary artery bypass grafts, where an arterial blood source is created using least invasive surgical techniques, and the arterial source is connected to a target location within a coronary artery while the patient is under cardiopulmonary bypass and cardioplegia.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
Pulsatile fluid delivery system
A system for delivering blood, cardioplegia solution, and other medications or fluids in a pulsatile flow pattern to a patient during cardiopulmonary bypass is disclosed. In a preferred embodiment, a pumping apparatus having at least one chamber is utilized in which a pumping action is achieved by compressing one of the chambers with a piston mechanism, while allowing the other chamber to fill with fluid via retracting its respective piston. The instantaneous flow rate of either of the chambers is determined by the speed of the piston. In a preferred embodiment, a pulsatile flow of fluid is achieved by cyclically alternating the velocity of the piston between two different speeds. A desired average flow rate and / or delivery pressure and / or constant pulse pressure is maintained by adjusting the alternating velocities at the desired frequency and duty cycle. The calculations necessary to obtain a desired average flow rate are performed by a microprocessor, which also controls the movement of the pistons.
Owner:QUEST MEDICAL
Pyridyl-substituted porphyrin compounds and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20080009473A1Extended half-lifeAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsSexual impotenceReperfusion injury
The present invention relates to Pyridyl-Substituted Porphyrin Compounds, compositions comprising an effective amount of a Pyridyl-Substituted Porphyrin Compound and methods for treating or preventing injury due to exposure to a reactive species, erectile dysfunction due to surgery, lung disease, hyperoxia, neurodegenerative disease, liver disease, myocardial damage during cardioplegia, an inflammatory condition, a reperfusion injury, an ischemic condition, a cardiovascular disease, diabetes, a diabetic complication, cancer, a side effect of cancer chemotherapy, or a radiation-induced injury, or to prolong the half-life of an oxidation-prone compound, comprising administering to a subject in need thereof an effective amount of a Pyridyl-Substituted Porphyrin Compound.
Owner:INOTECK PHARMA CORP
Multichannel catheter
InactiveUS20050215949A1Efficient deliveryMaximizes rate of blood flowSuture equipmentsOther blood circulation devicesCardioplegiasExtracorporeal circulation
A single, multichannel catheter for extracorporeal circulation of blood to a patient undergoing cardiac treatments or surgery. The catheter has three independent channels and an expandable balloon. The first channel is the largest and delivers blood to a patient to maintain the patient's metabolism and perfusion throughout the treatment or surgery. A second, smaller channel is integrated into the wall of the first channel and delivers a biologically active fluid (e.g., for cardioplegia) to the heart and / or venting the left heart. A third, smaller channel is integrated into the wall of the first channel, and delivers an expansion fluid to the balloon to occlude the flow of blood to the heart. Preferably, the first channel accounts for at least about 70% of the total channel volume. The multichannel catheter is best prepared using an extrusion molding technique.
Owner:SORIN GRP USA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com