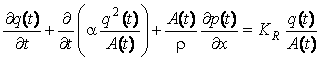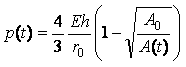Patents
Literature
240 results about "Coronary circulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
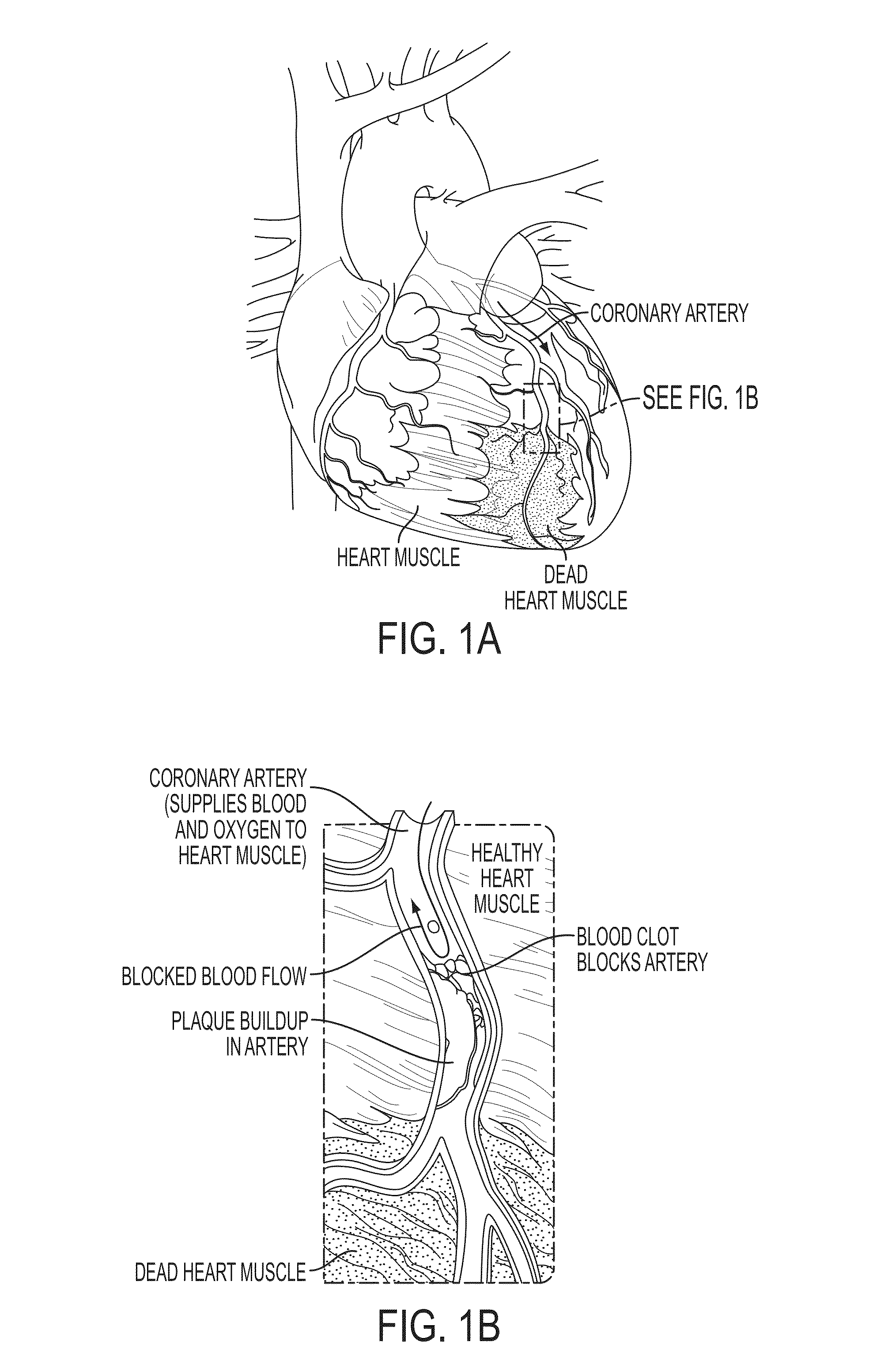
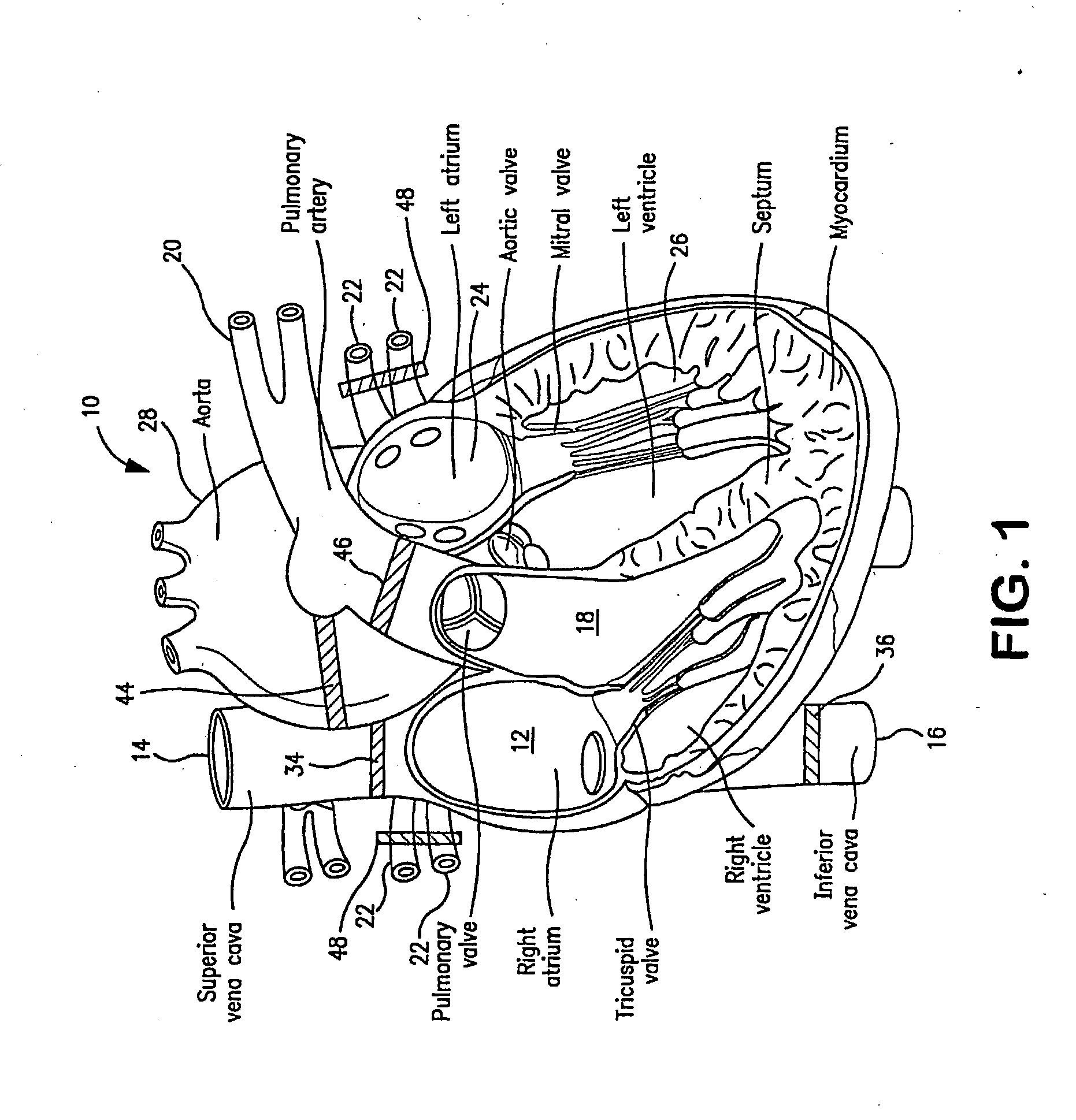
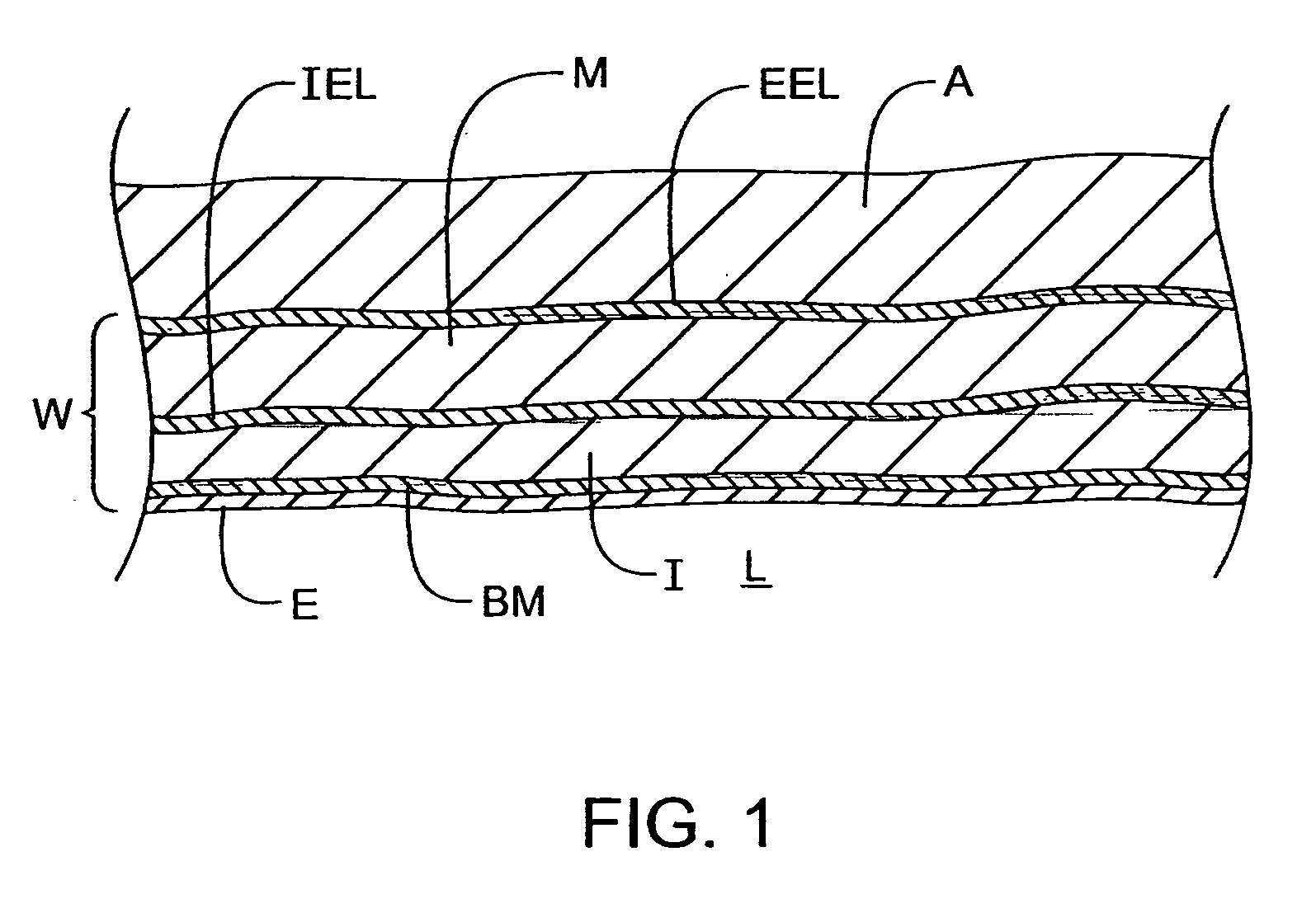
Coronary circulation is the circulation of blood in the blood vessels that supply the heart muscle (myocardium). Coronary arteries supply oxygenated blood to the heart muscle, and cardiac veins drain away the blood once it has been deoxygenated. Because the rest of the body, and most especially the brain, needs a steady supply of oxygenated blood that is free of all but the slightest interruptions, the heart is required to function continuously. Therefore its circulation is of major importance not only to its own tissues but to the entire body and even the level of consciousness of the brain from moment to moment. Interruptions of coronary circulation quickly cause heart attacks (myocardial infarctions), in which the heart muscle is damaged by oxygen starvation. Such interruptions are usually caused by ischemic heart disease (coronary artery disease) and sometimes by embolism from other causes like obstruction in blood flow through vessels.
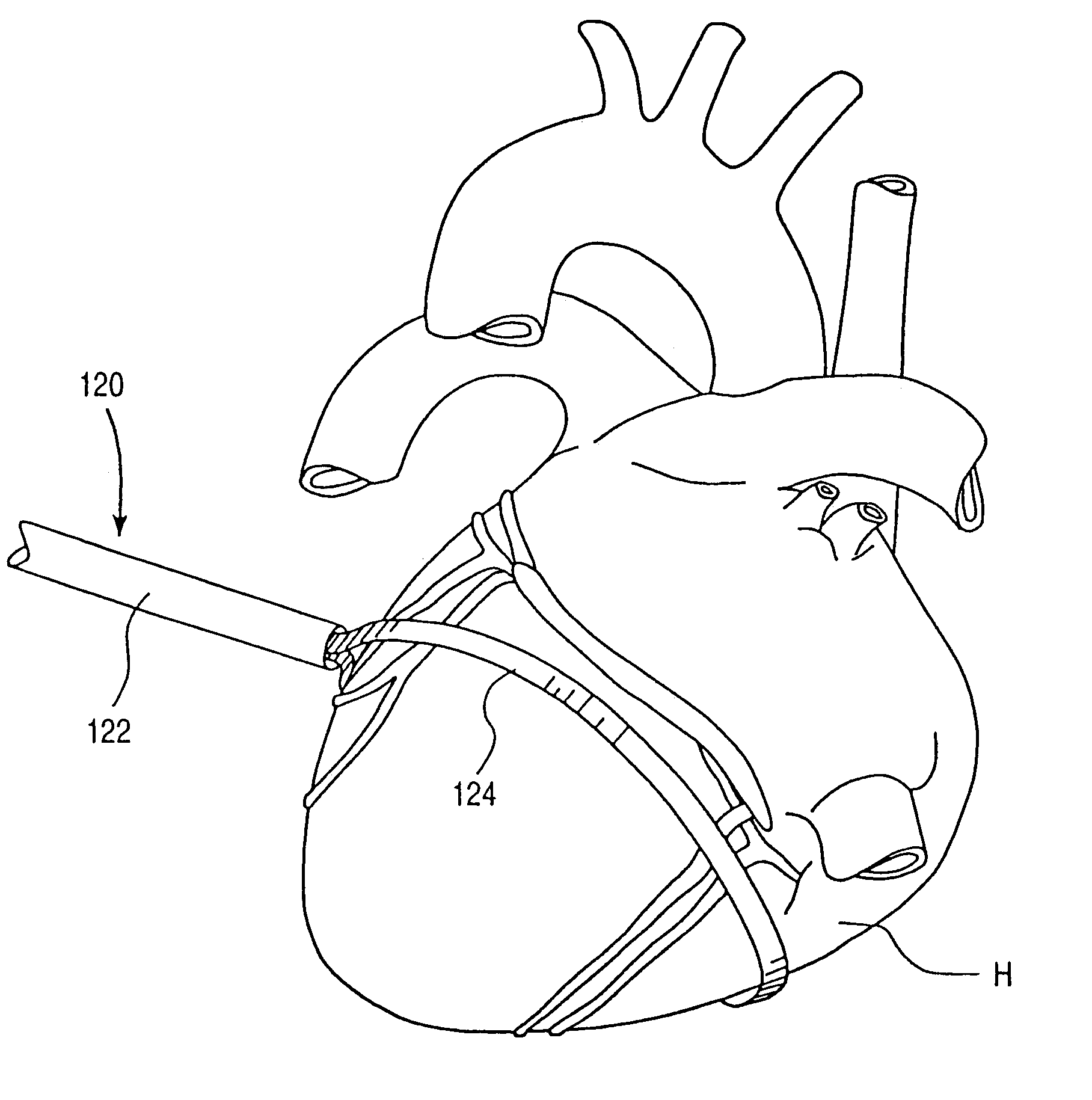
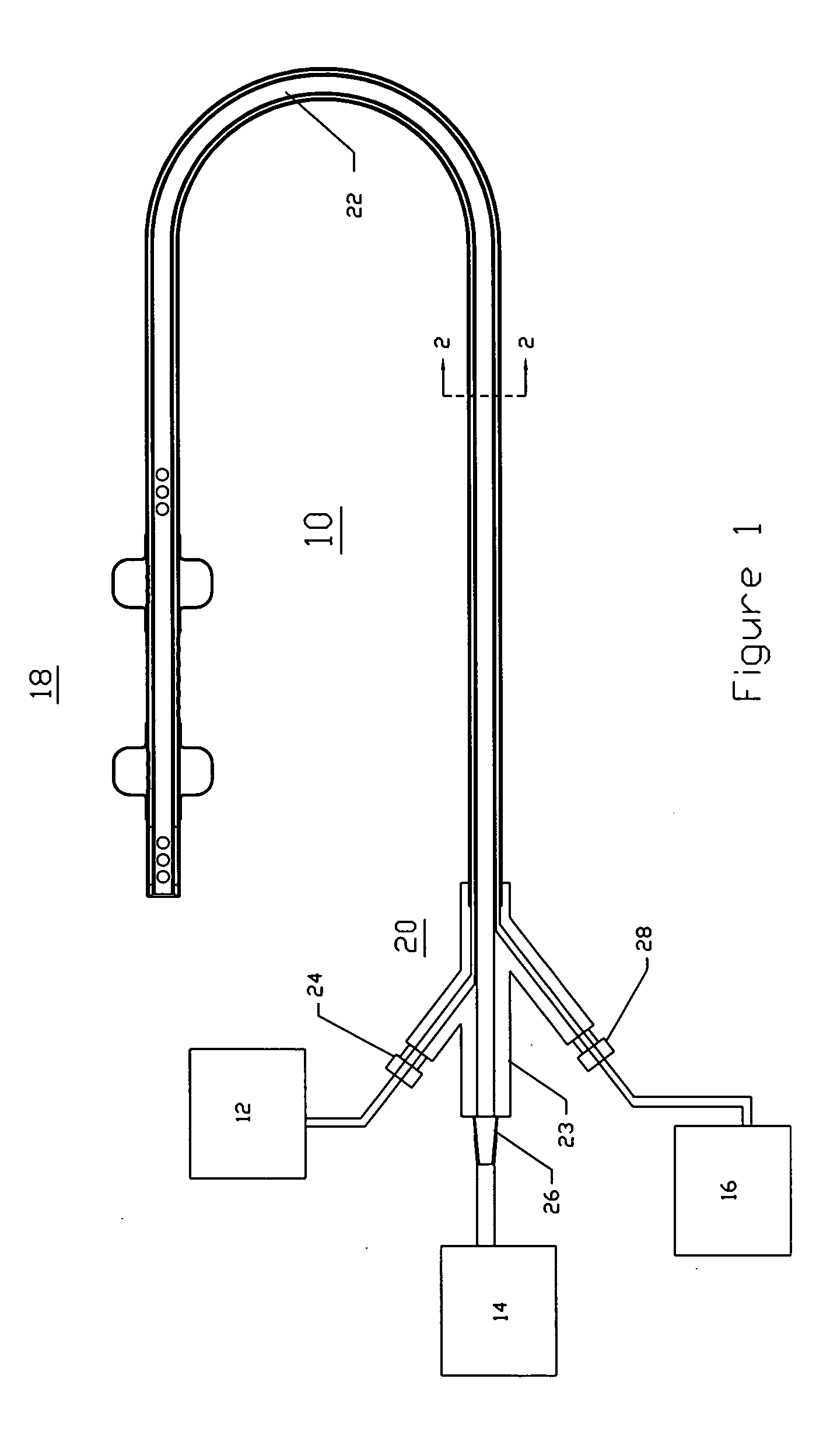
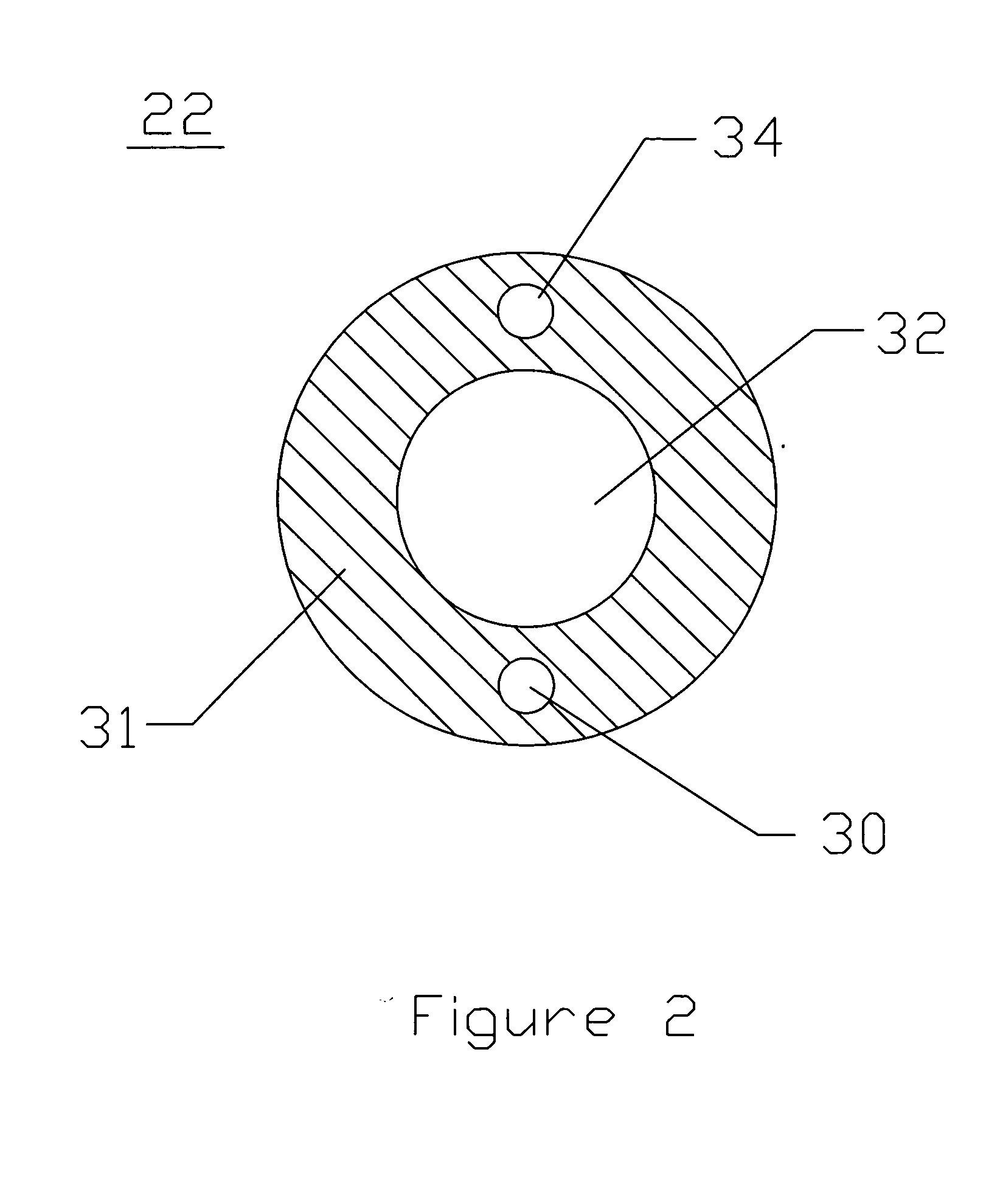
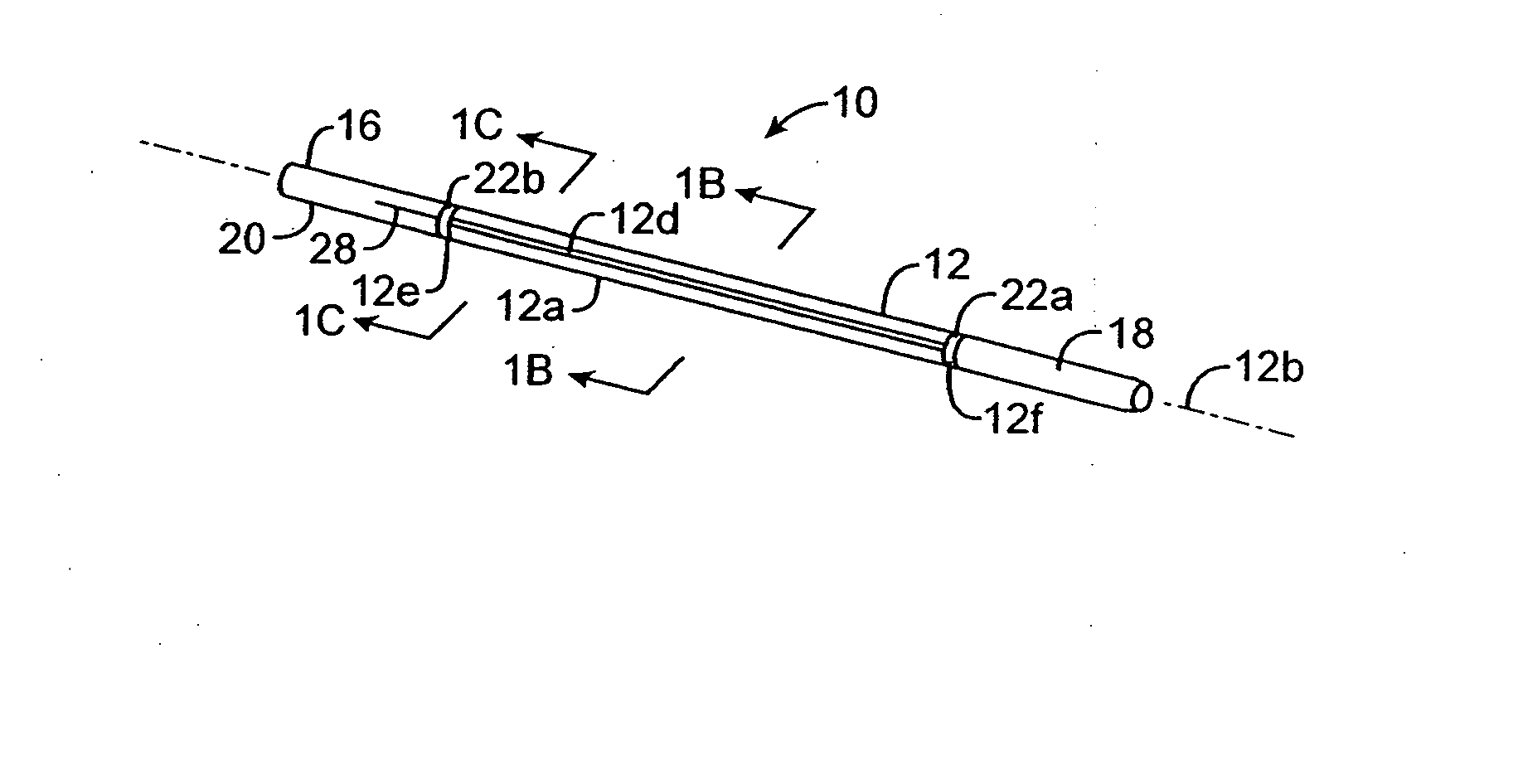
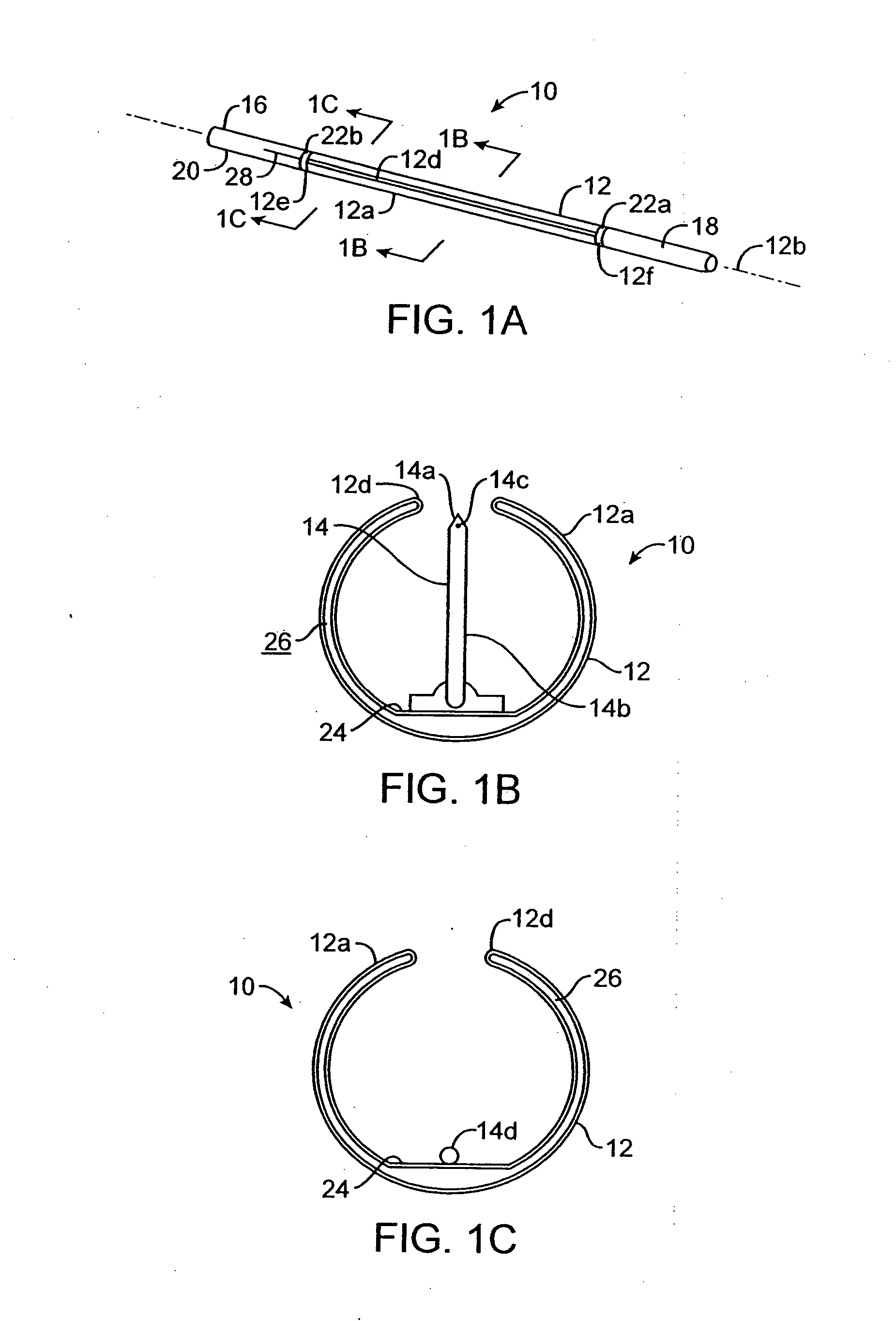
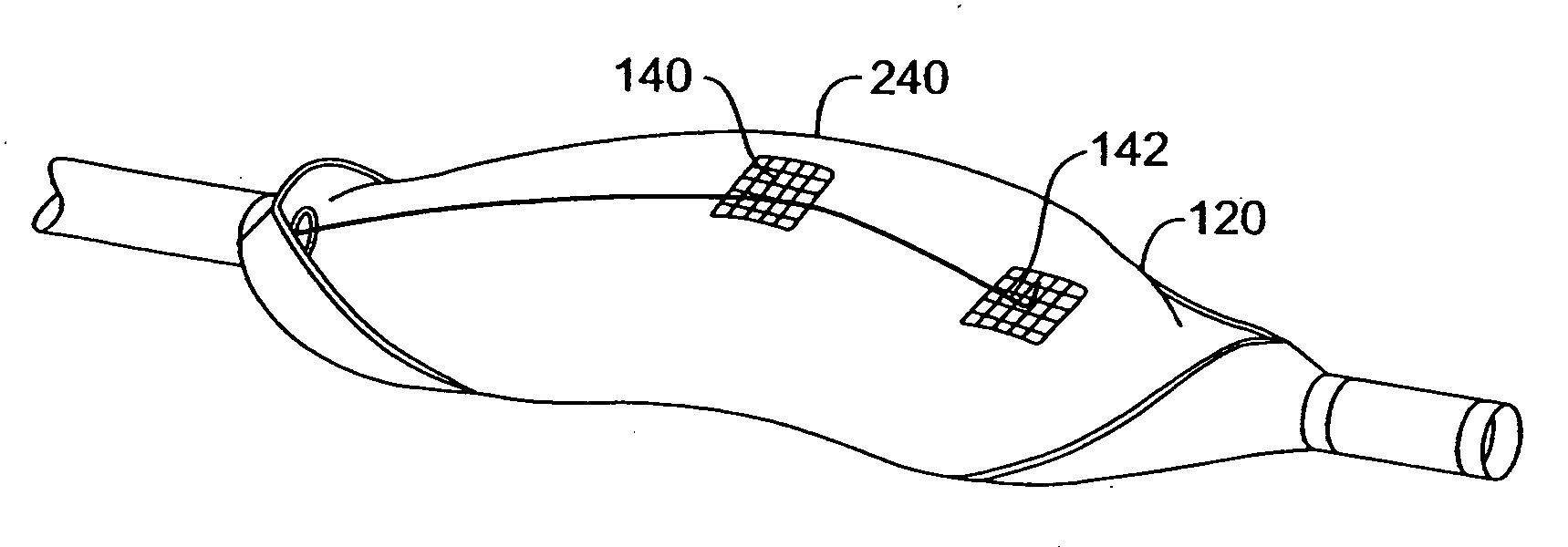
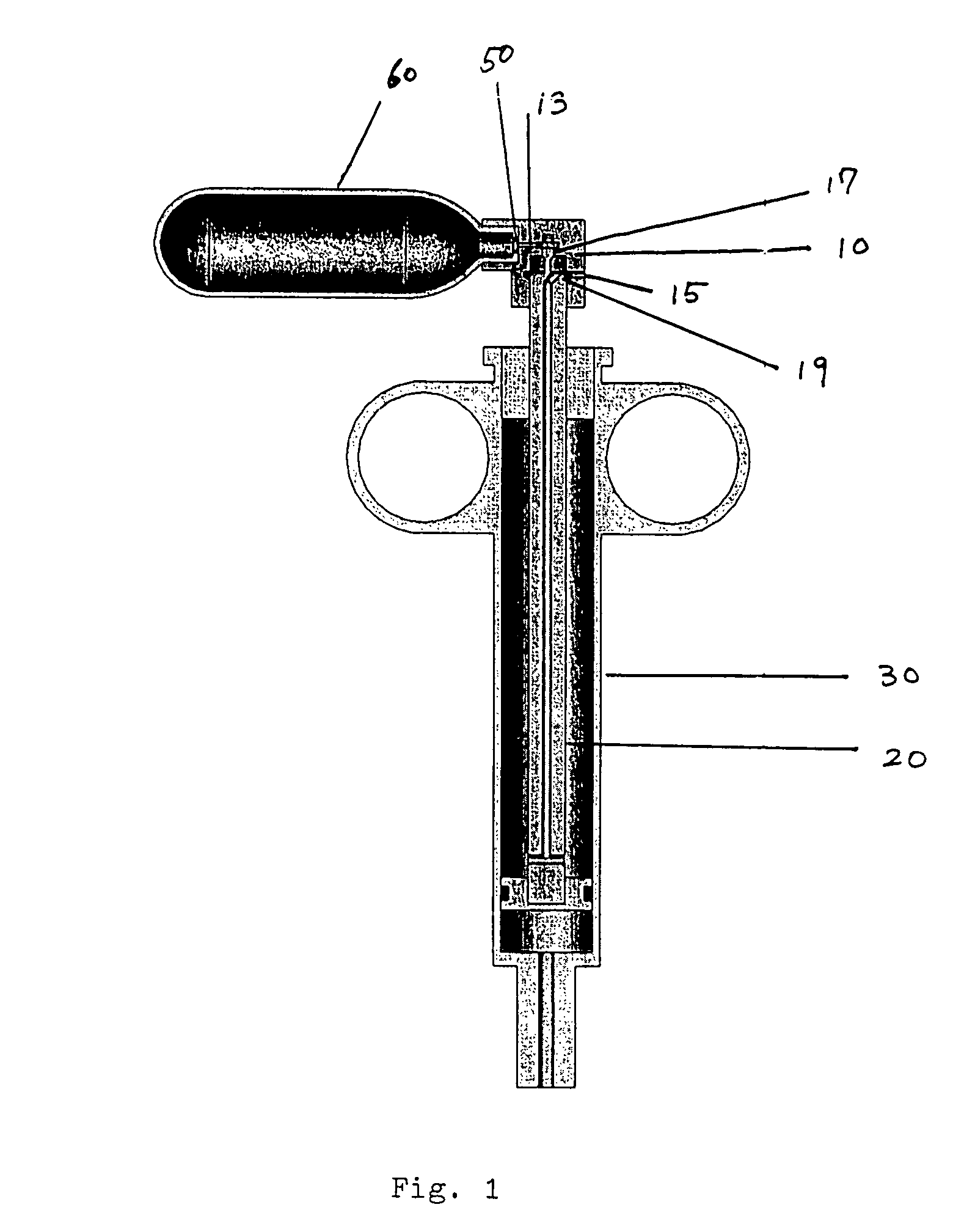
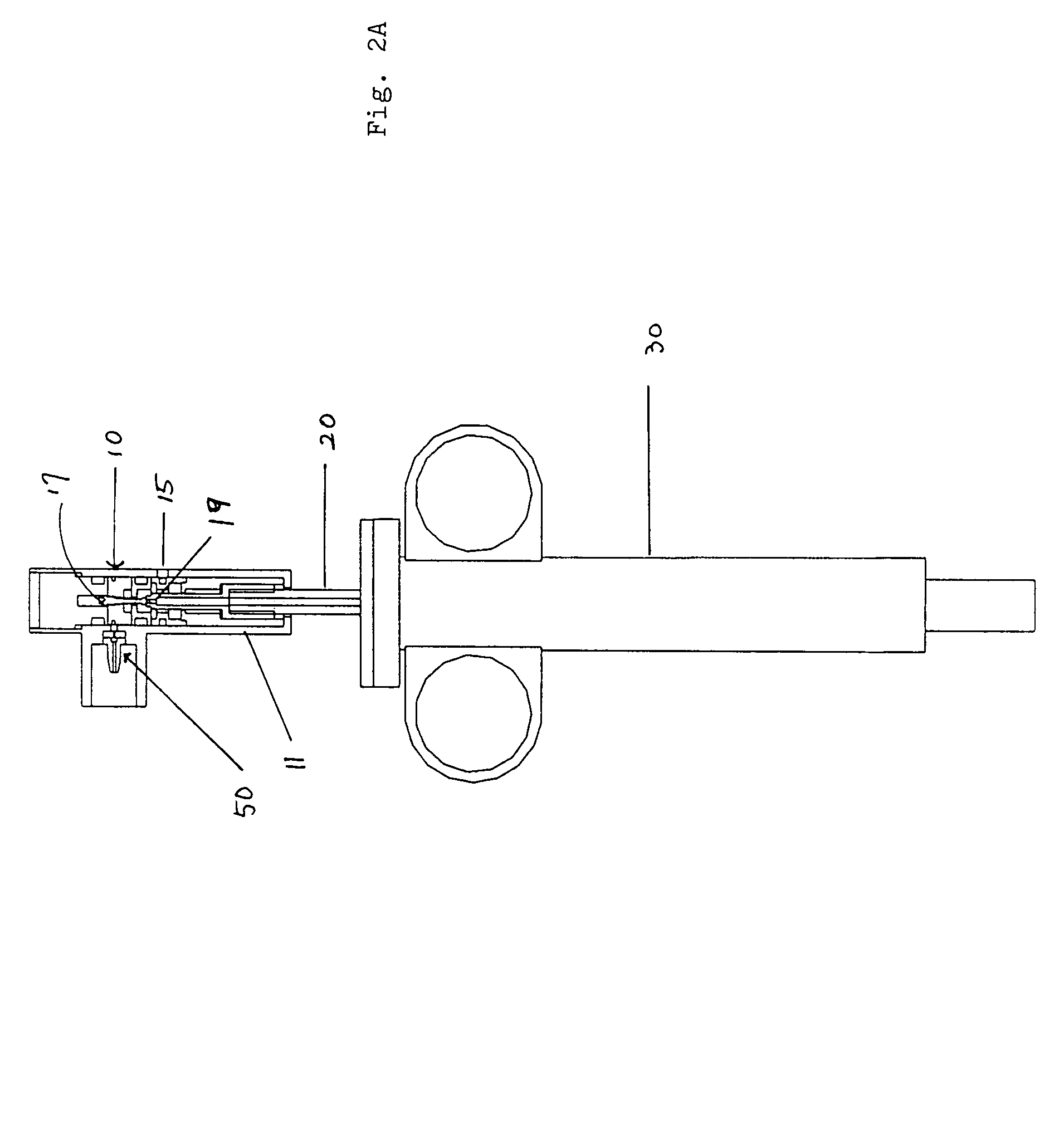
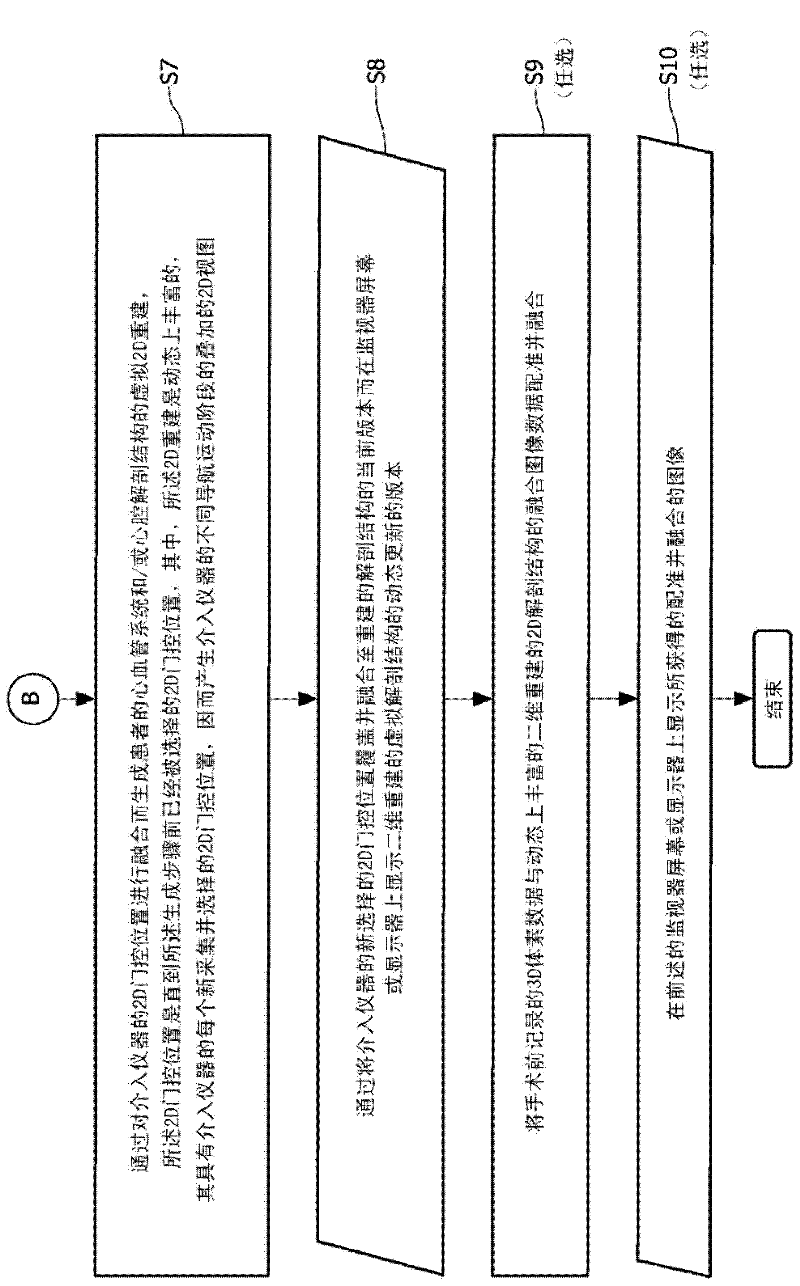
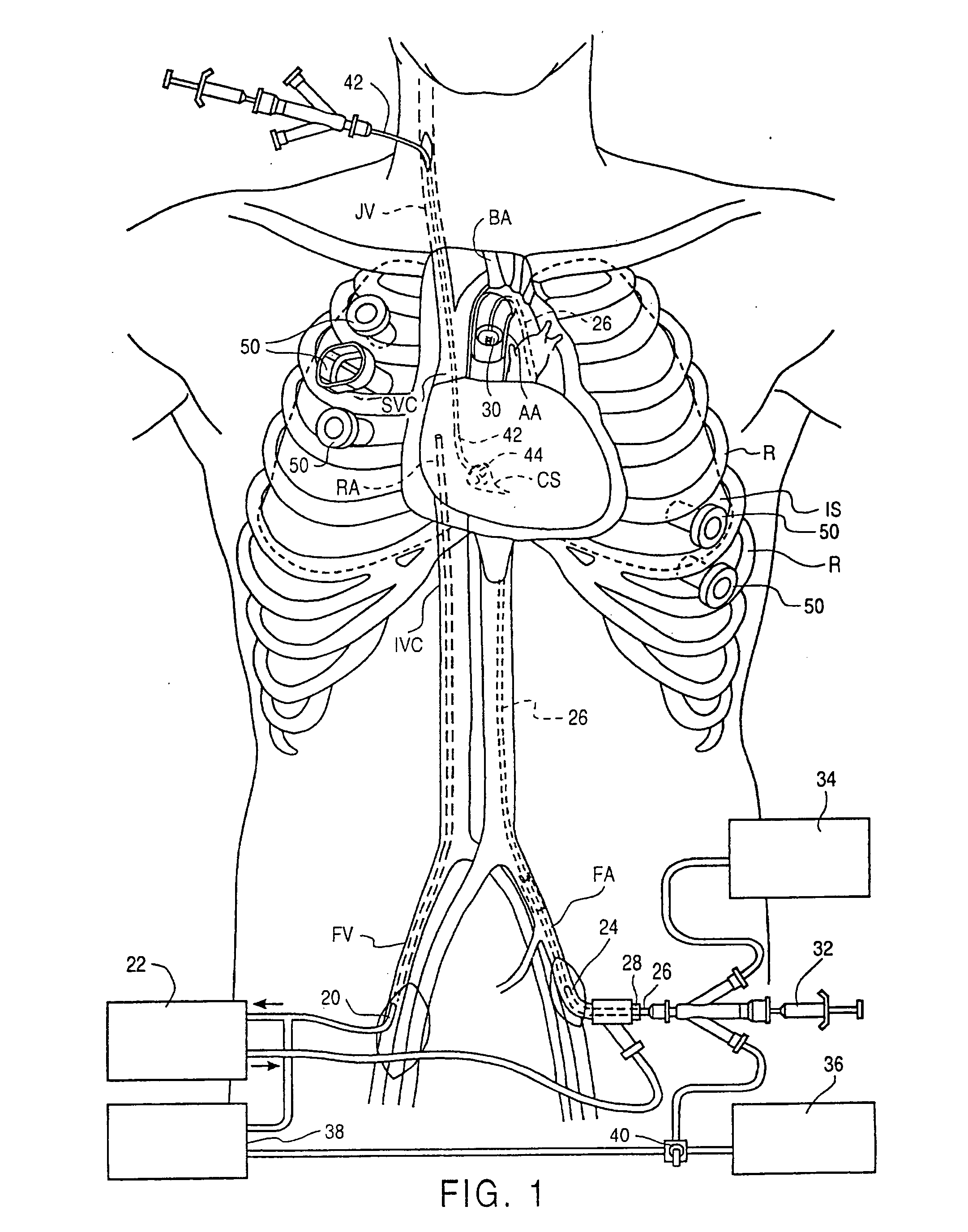
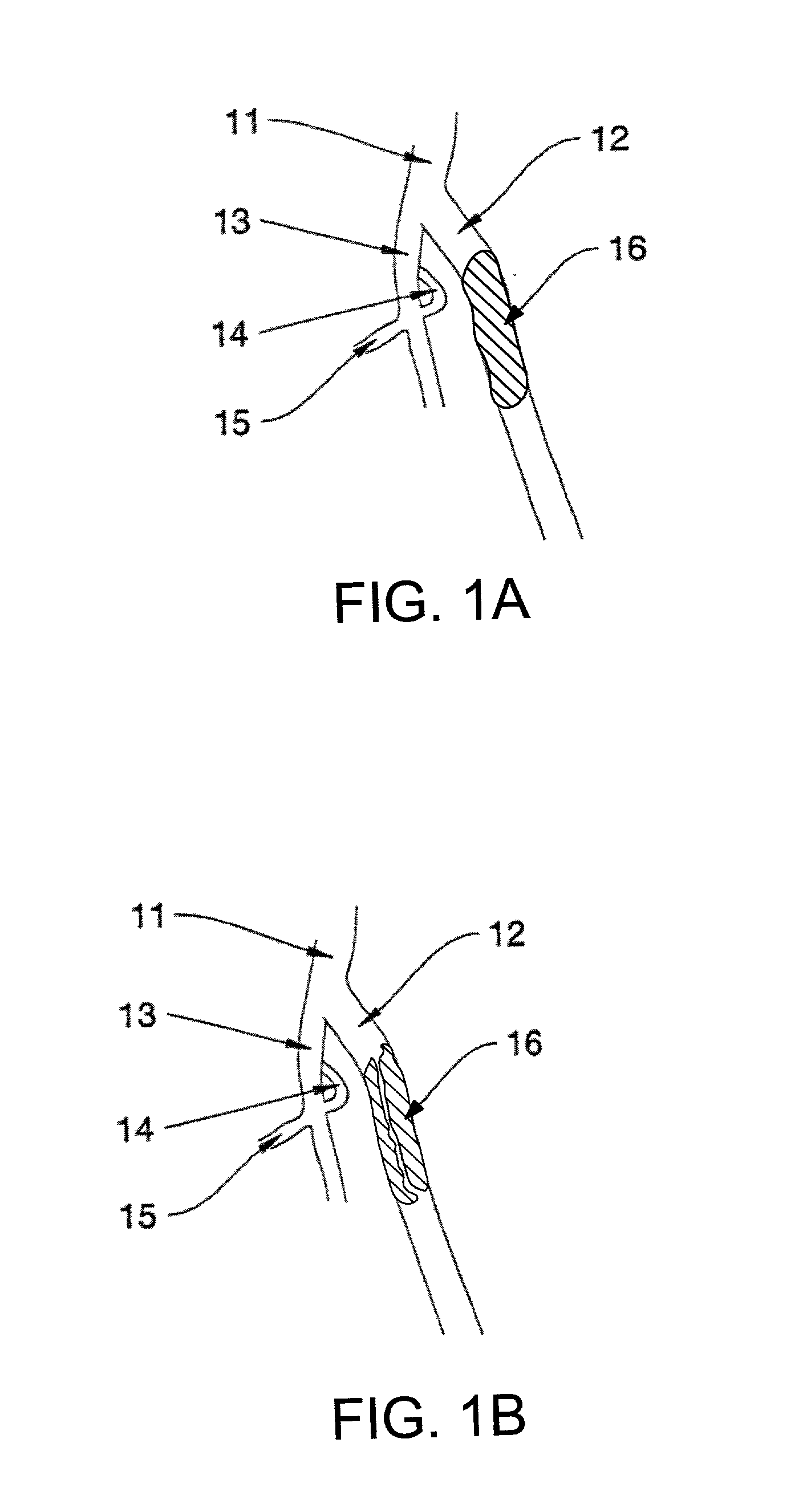
Endovascular system for arresting the heart
InactiveUS6913600B2Reduce morbidityReduce mortalitySuture equipmentsOther blood circulation devicesCardiopulmonary bypass timeSurgical department
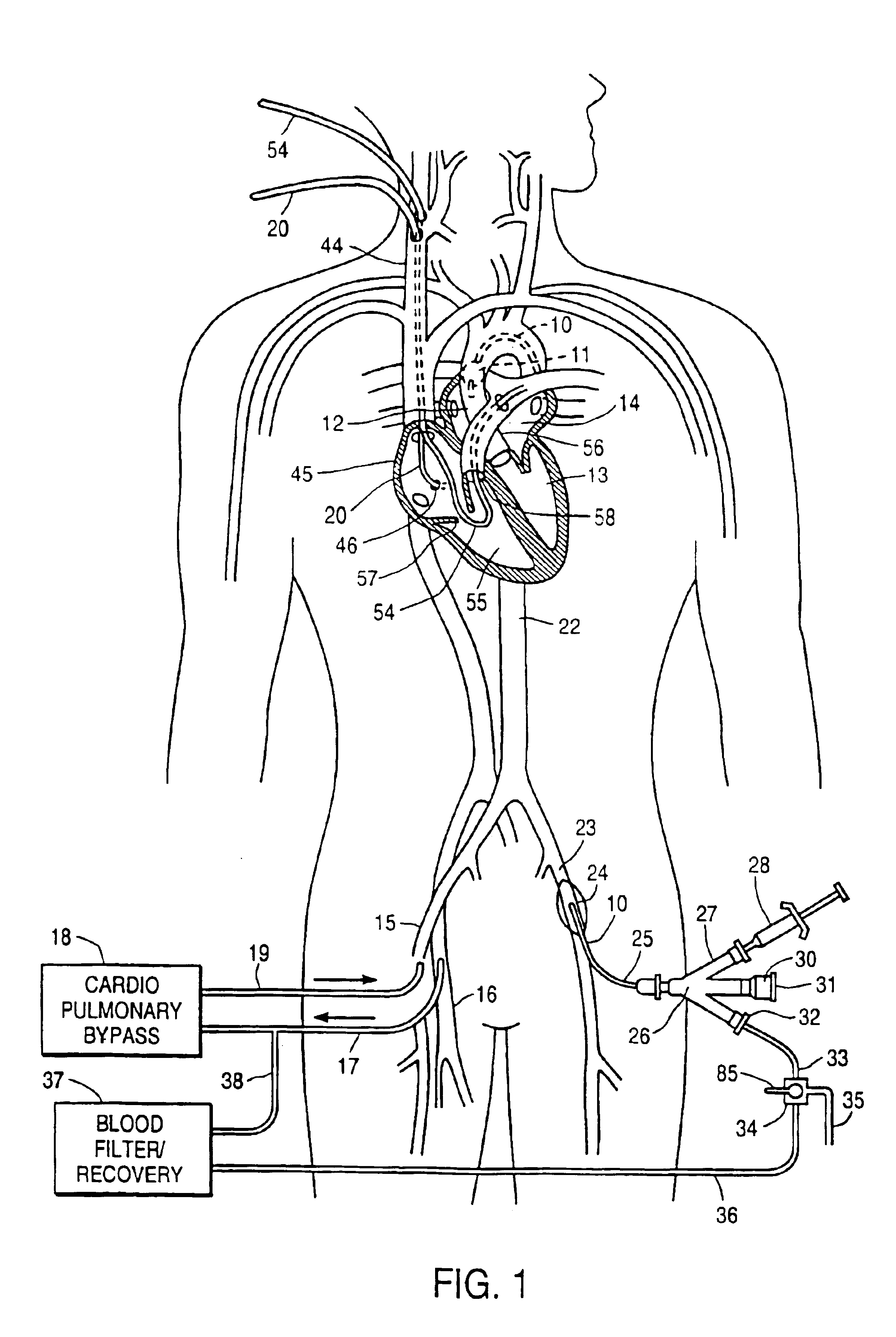
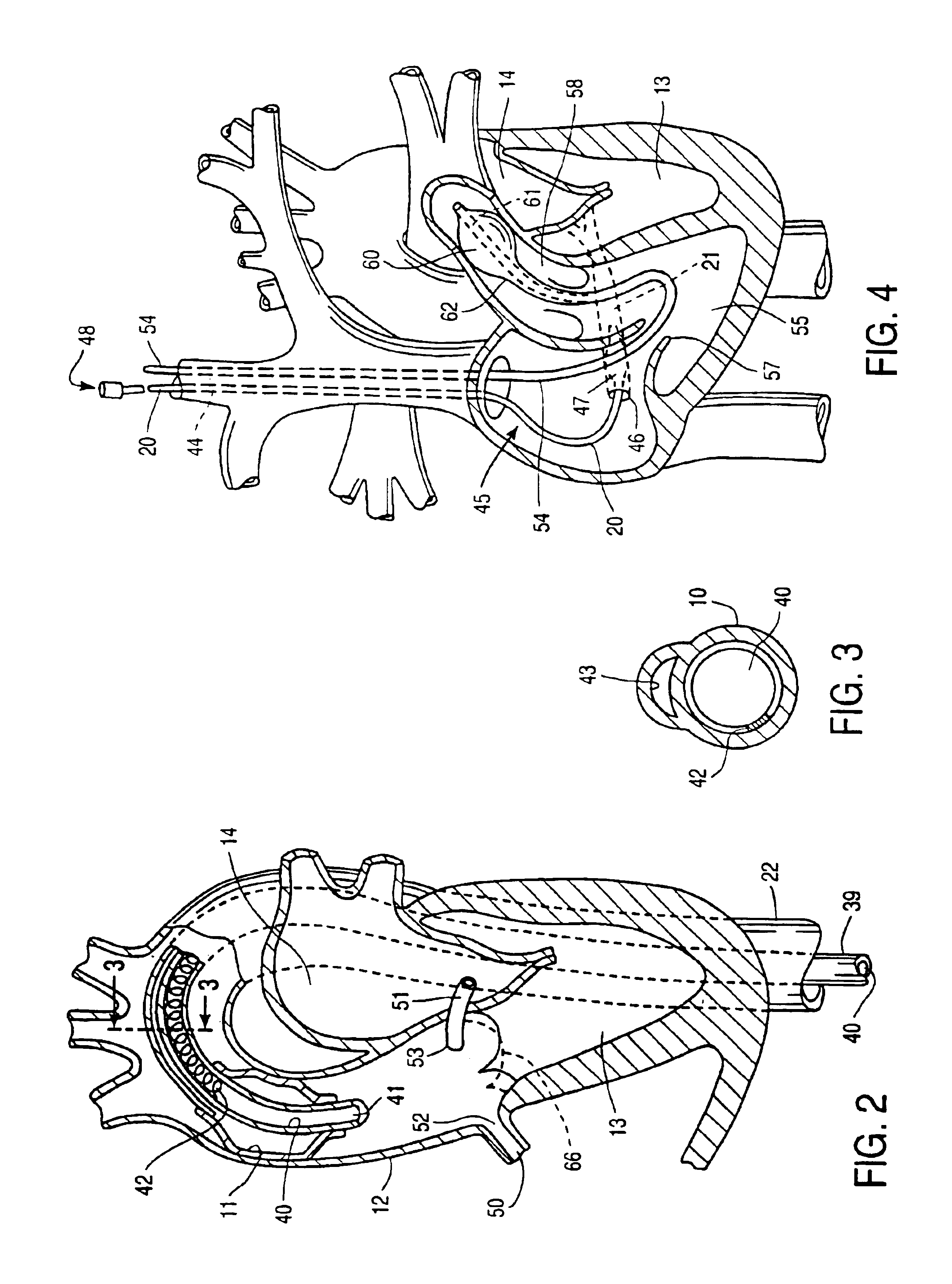
Devices and methods are provided for temporarily inducing cardioplegic arrest in the heart of a patient and for establishing cardiopulmonary bypass in order to facilitate surgical procedures on the heart and its related blood vessels. Specifically, a catheter based system is provided for isolating the heart and coronary blood vessels of a patient from the remainder of the arterial system and for infusing a cardioplegic agent into the patient's coronary arteries to induce cardioplegic arrest in the heart. The system includes an endoaortic partitioning catheter having an expandable balloon at its distal end which is expanded within the ascending aorta to occlude the aortic lumen between the coronary ostia and the brachiocephalic artery. Means for centering the catheter tip within the ascending aorta include specially curved shaft configurations, eccentric or shaped occlusion balloons and a steerable catheter tip, which may be used separately or in combination. The shaft of the catheter may have a coaxial or multilumen construction. The catheter may further include piezoelectric pressure transducers at the distal tip of the catheter and within the occlusion balloon. Means to facilitate nonfluoroscopic placement of the catheter include fiberoptic transillumination of the aorta and a secondary balloon at the distal tip of the catheter for atraumatically contacting the aortic valve. The system further includes a dual purpose arterial bypass cannula and introducer sheath for introducing the catheter into a peripheral artery of the patient.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
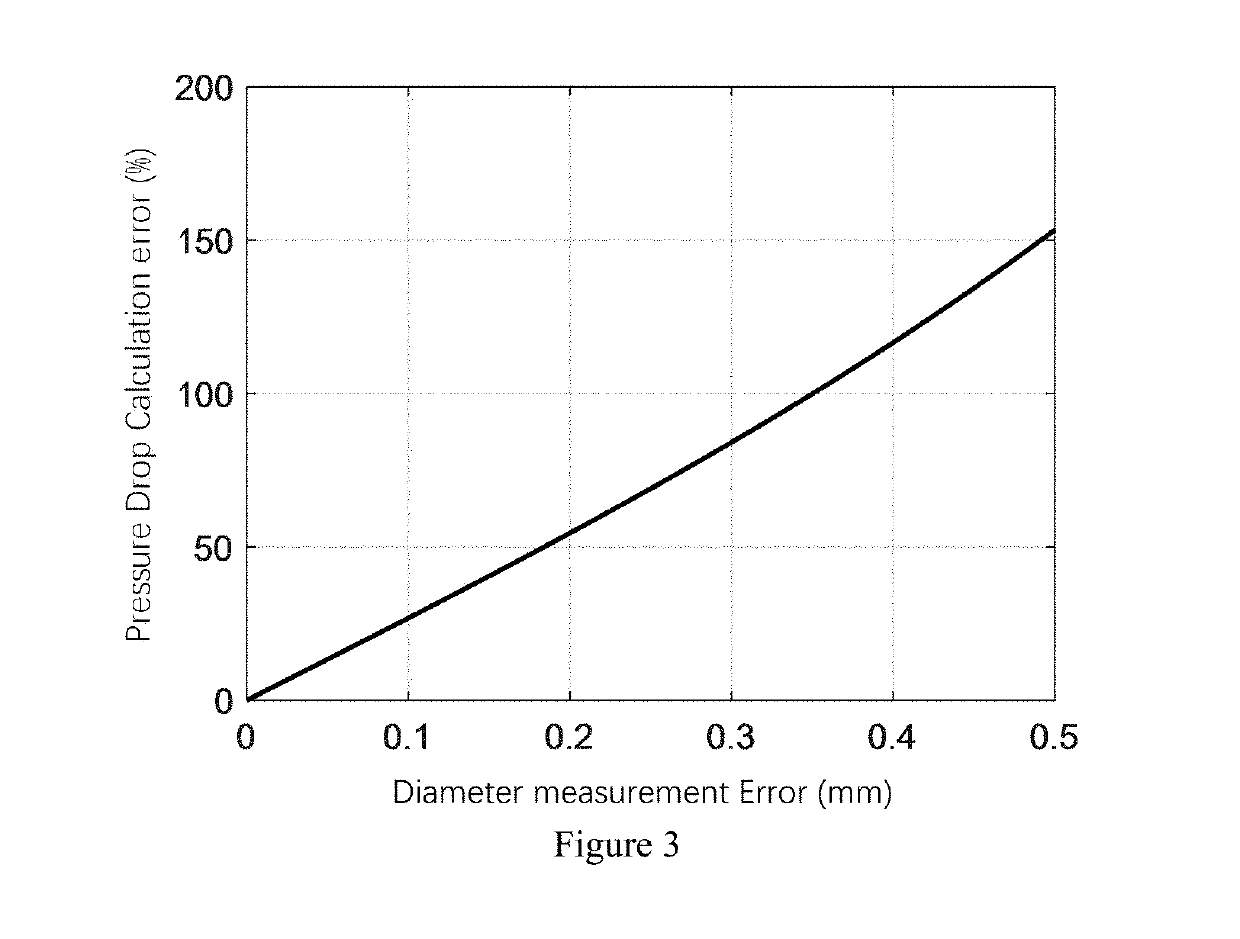
Method and System for Non-Invasive Functional Assessment of Coronary Artery Stenosis
InactiveUS20130246034A1Non-invasive functional assessmentMedical simulationMedical imagingCoronary arteriesAnatomical measurement
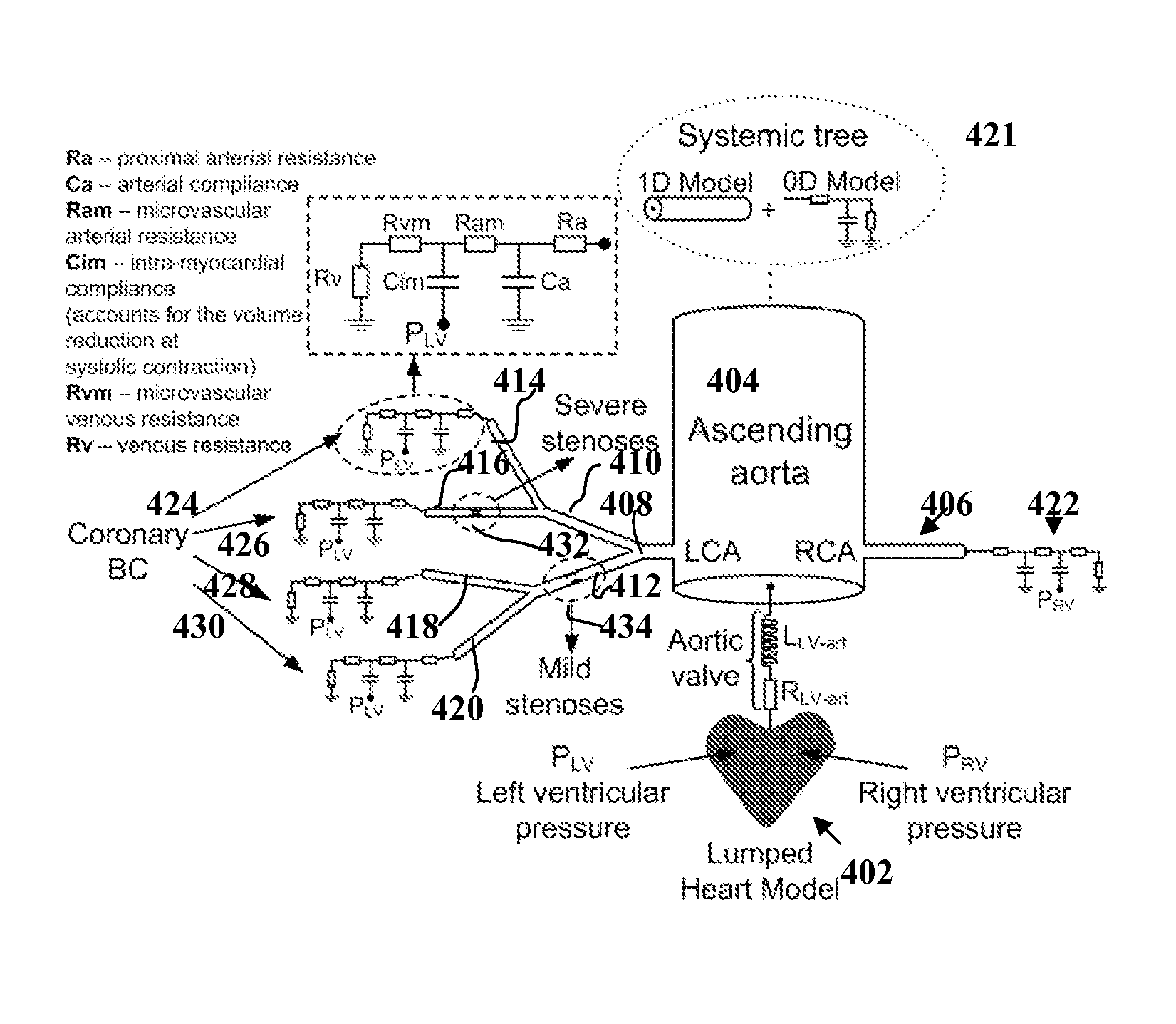
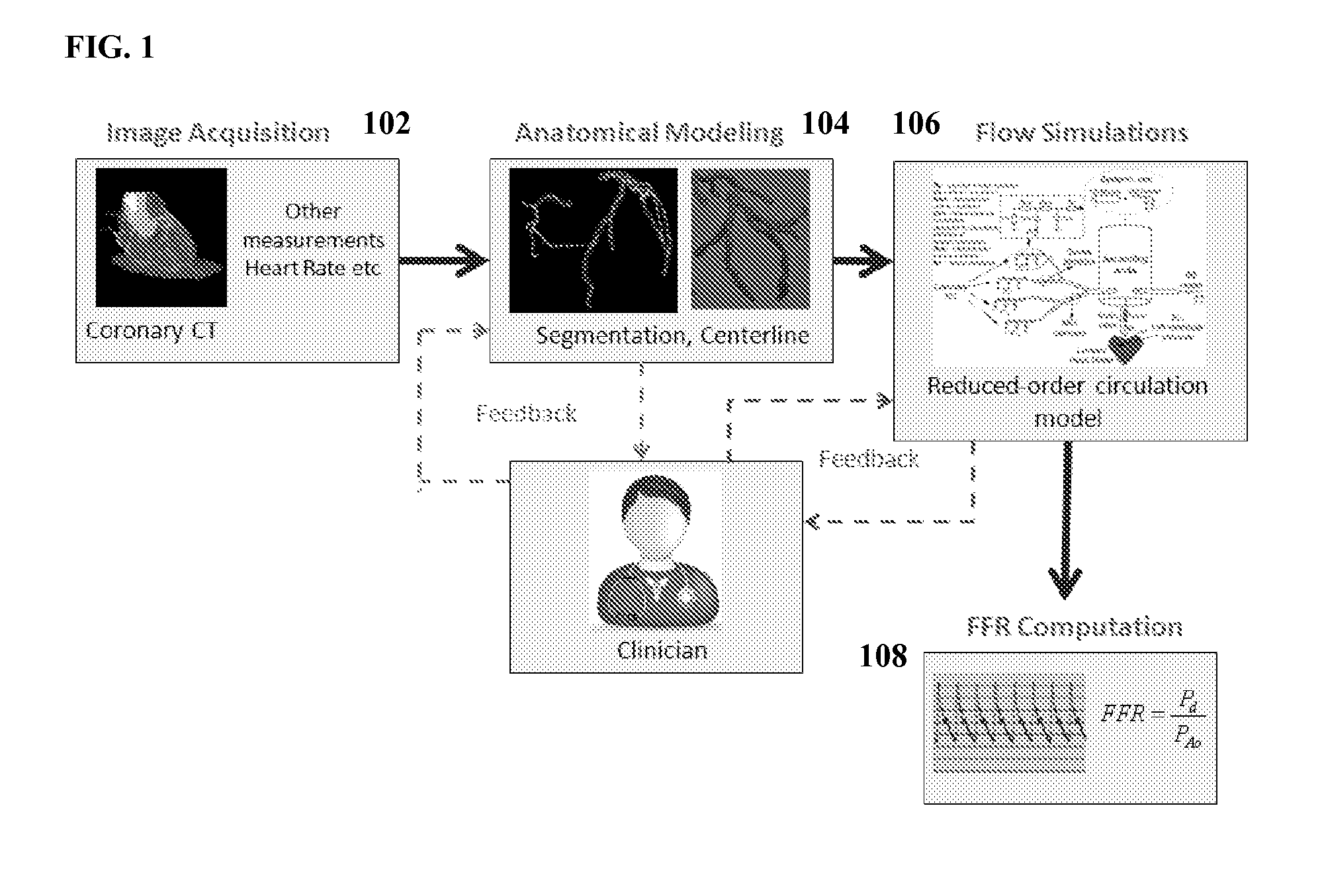
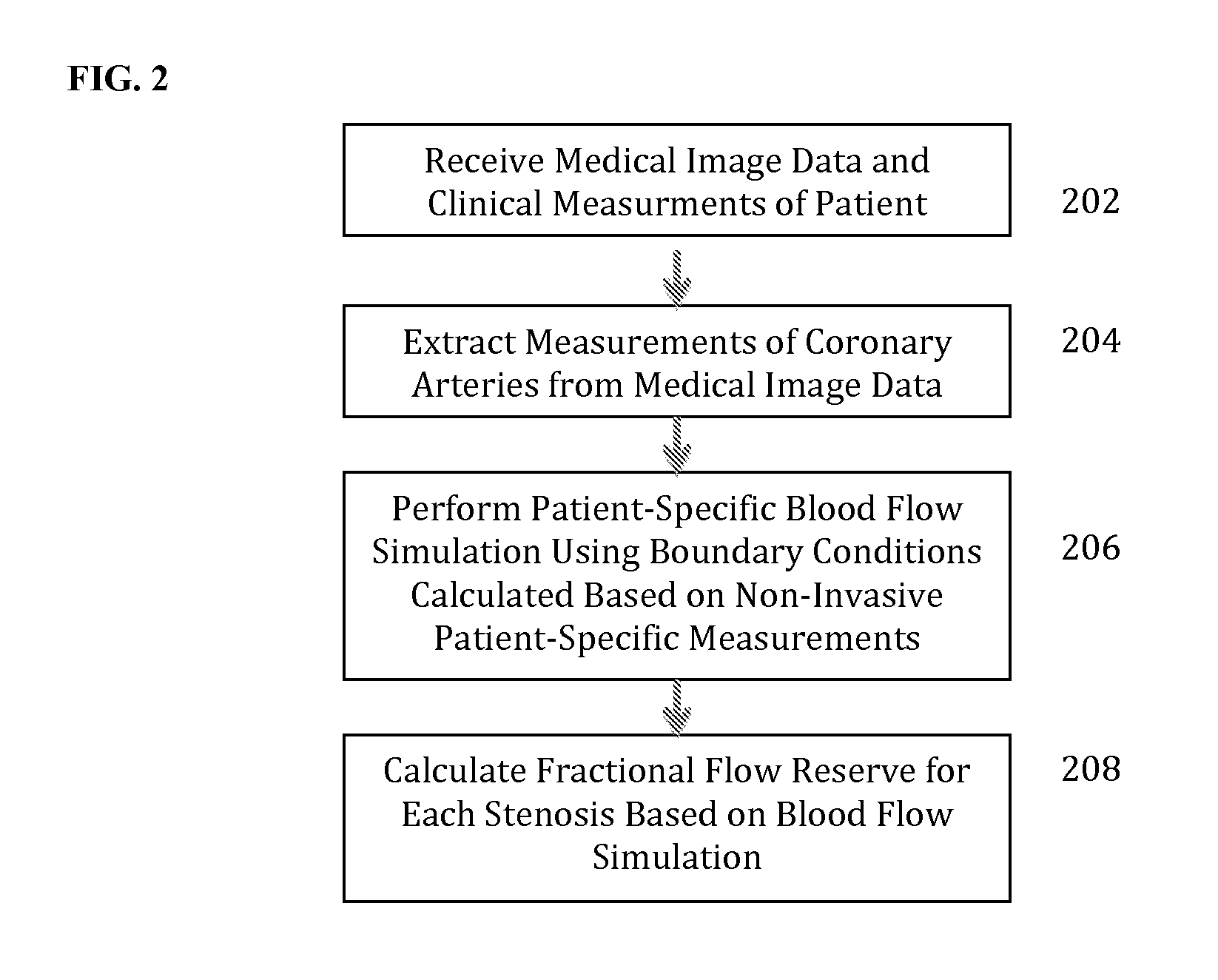
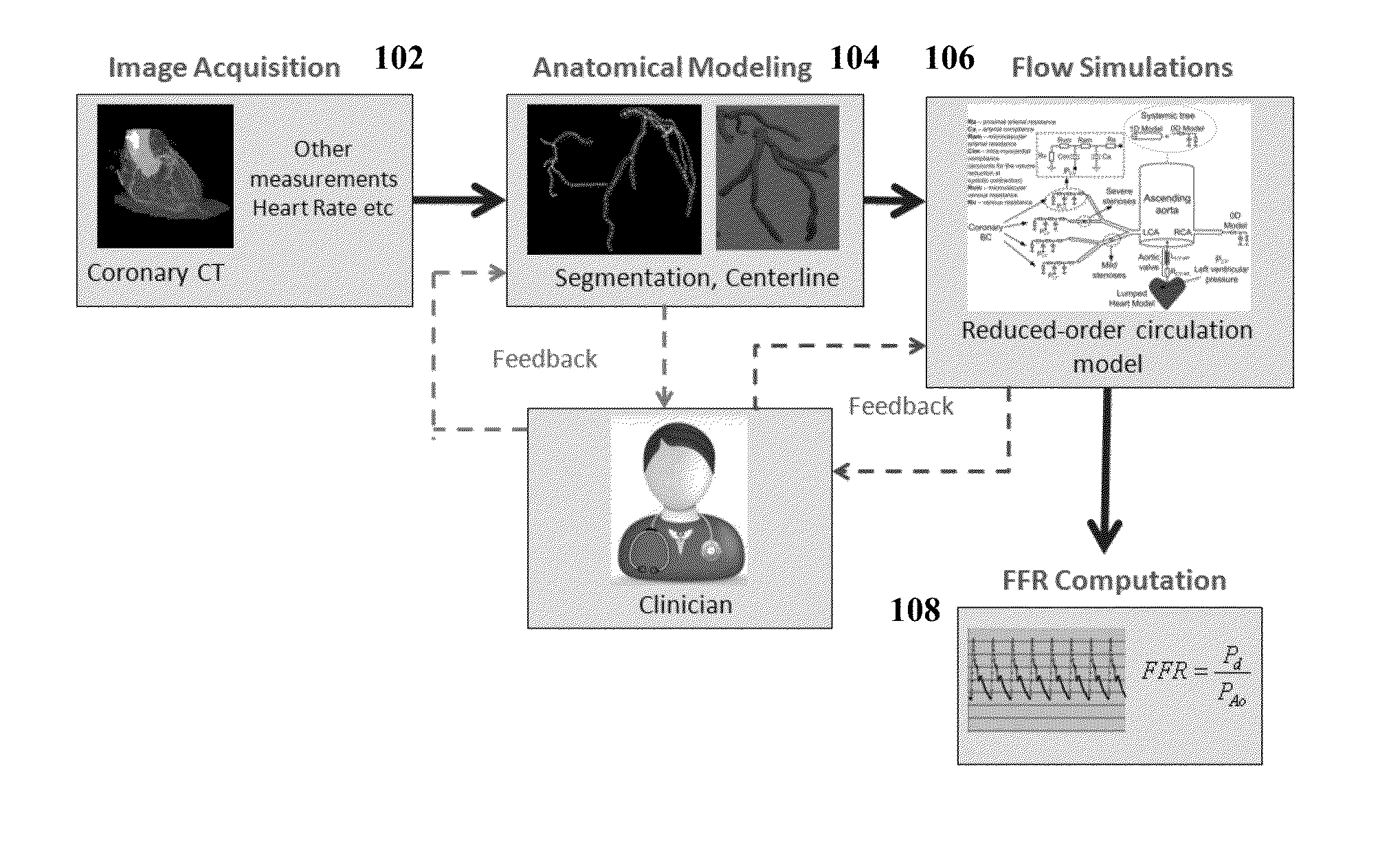
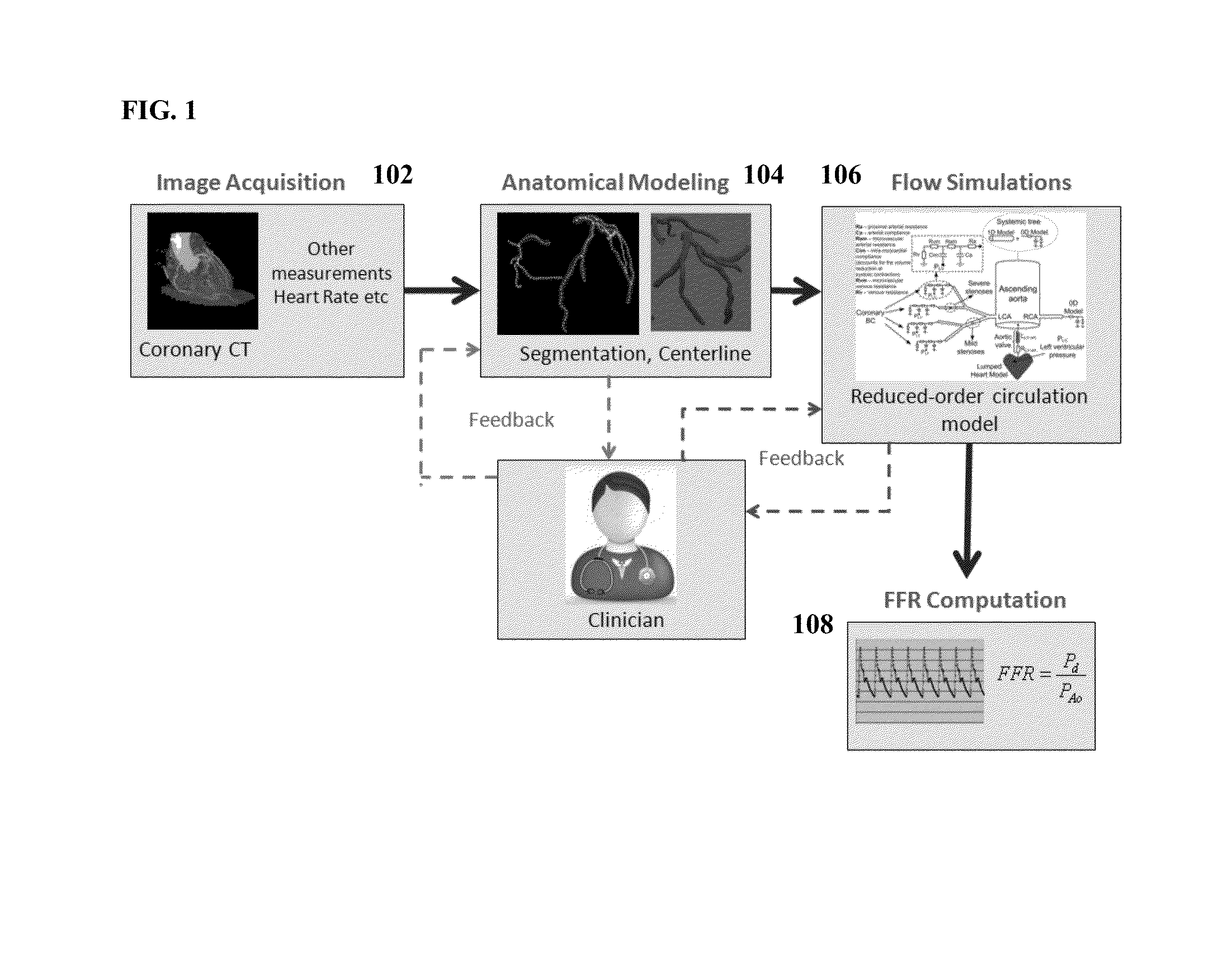
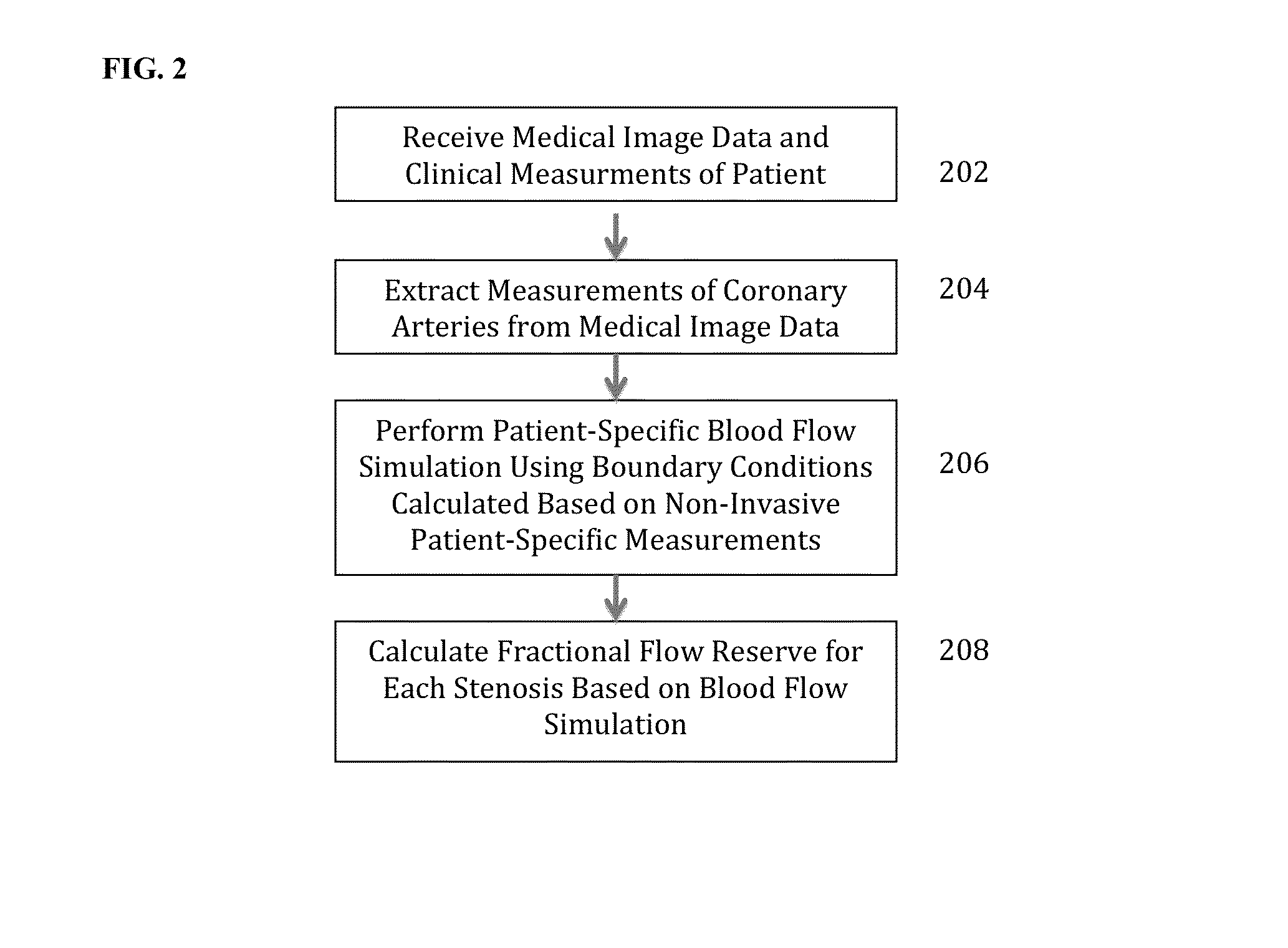
A method and system for non-invasive assessment of coronary artery stenosis is disclosed. Patient-specific anatomical measurements of the coronary arteries are extracted from medical image data of a patient acquired during rest state. Patient-specific rest state boundary conditions of a model of coronary circulation representing the coronary arteries are calculated based on the patient-specific anatomical measurements and non-invasive clinical measurements of the patient at rest. Patient-specific rest state boundary conditions of the model of coronary circulation representing the coronary arteries are calculated based on the patient-specific anatomical measurements and non-invasive clinical measurements of the patient at rest. Hyperemic blood flow and pressure across at least one stenosis region of the coronary arteries are simulated using the model of coronary circulation and the patient-specific hyperemic boundary conditions. Fractional flow reserve (FFR) is calculated for the at least one stenosis region based on the simulated hyperemic blood flow and pressure.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
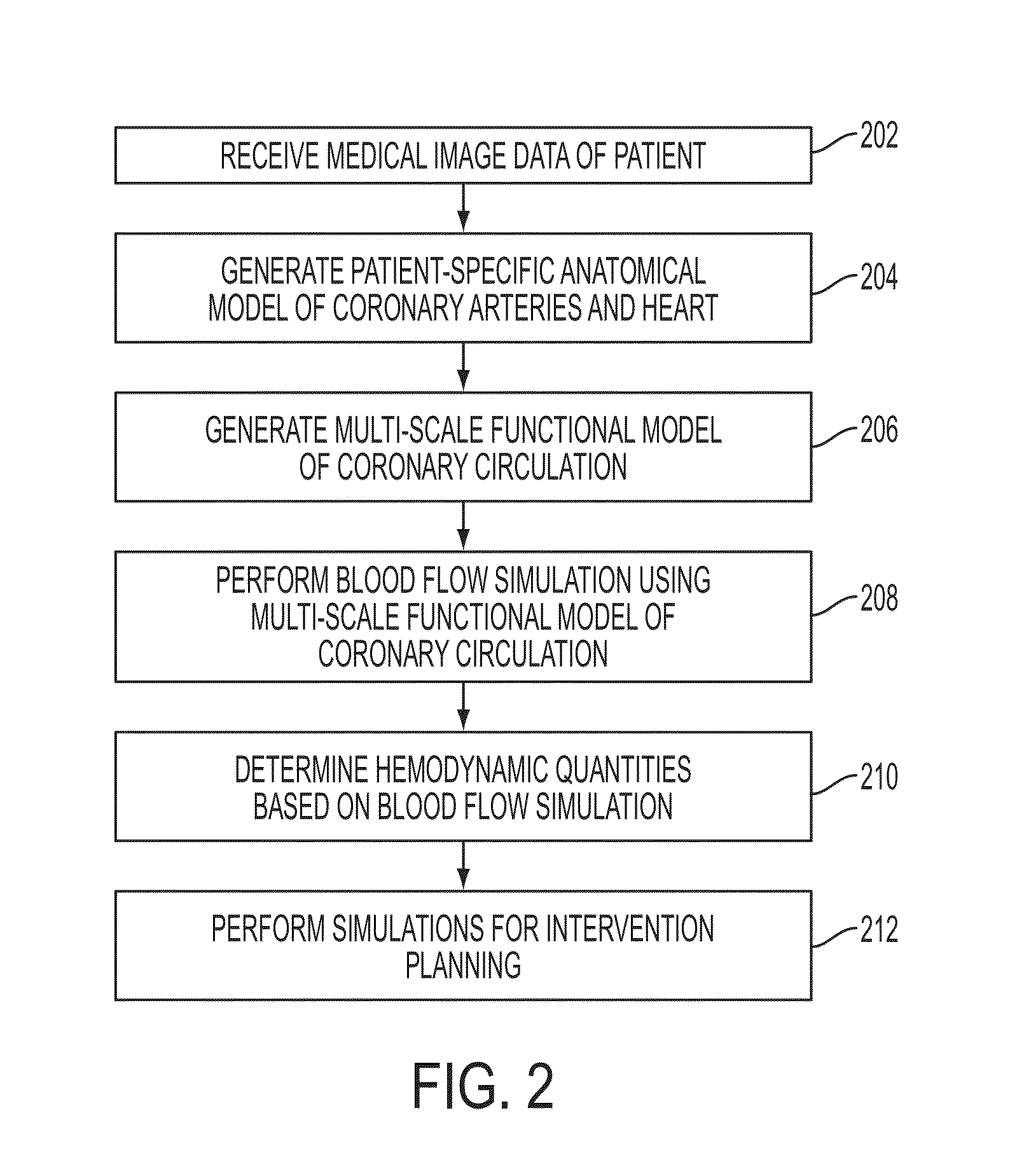
Method and System for Multi-Scale Anatomical and Functional Modeling of Coronary Circulation
ActiveUS20130132054A1Improve predictive performanceImprove clinical managementChemical property predictionChemical structure searchCoronary arteriesIntervention planning
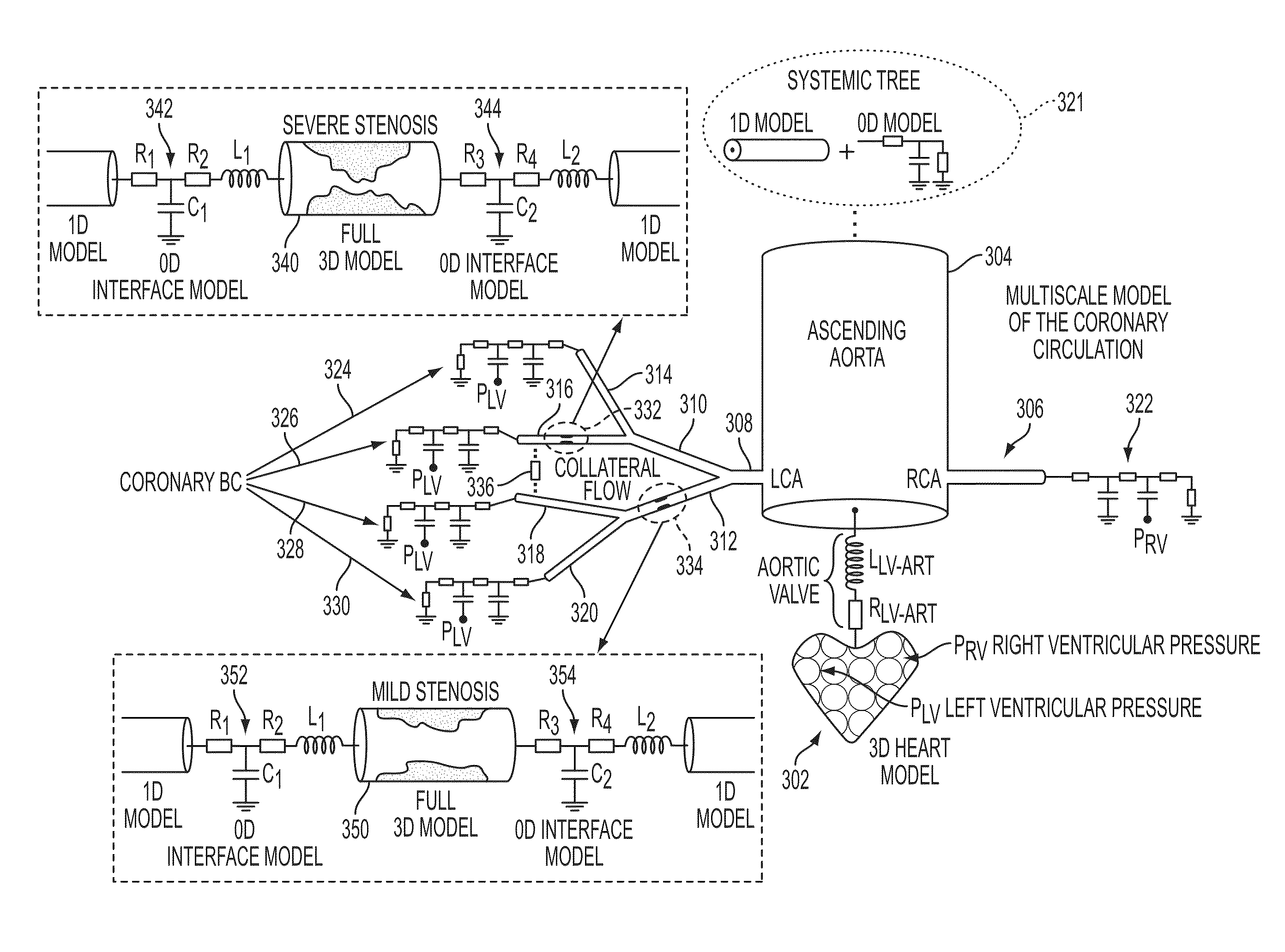
A method and system for multi-scale anatomical and functional modeling of coronary circulation is disclosed. A patient-specific anatomical model of coronary arteries and the heart is generated from medical image data of a patient. A multi-scale functional model of coronary circulation is generated based on the patient-specific anatomical model. Blood flow is simulated in at least one stenosis region of at least one coronary artery using the multi-scale function model of coronary circulation. Hemodynamic quantities, such as fractional flow reserve (FFR), are computed to determine a functional assessment of the stenosis, and virtual intervention simulations are performed using the multi-scale function model of coronary circulation for decision support and intervention planning.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH +1
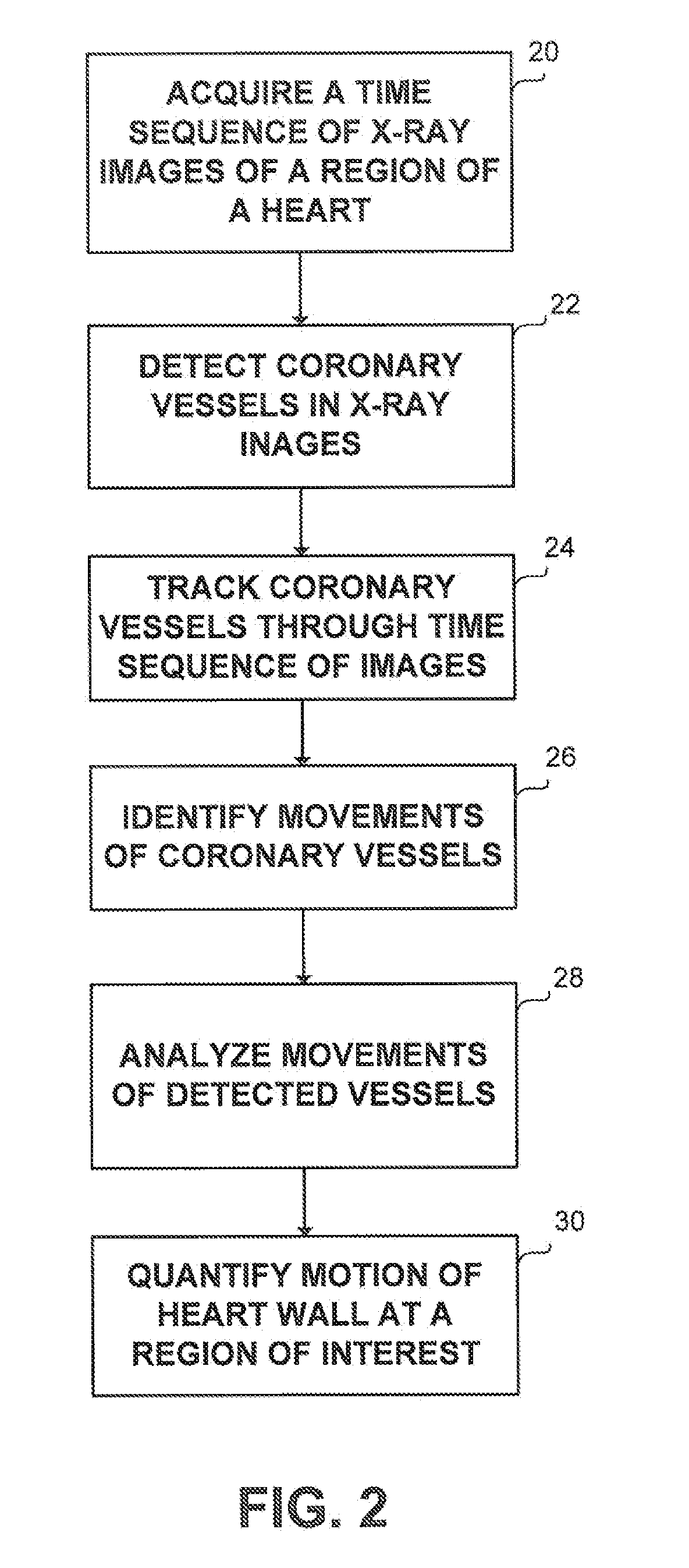
Method and system for detecting and analyzing heart mecahnics
Method and apparatus for detecting and analyzing heart mechanical activity at a region of interest of a patient's heart are provided. The method comprises acquiring a time sequence of 2-dimensional X-ray images of a region of interest over at least part of a cardiac cycle; detecting coronary vessels in the X-ray images; tracking the coronary vessels through the sequence of images to identify movements of the coronary vessels; and analyzing the movements of the coronary vessels to quantify at least one parameter characterizing heart wall motion in the region of interest.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
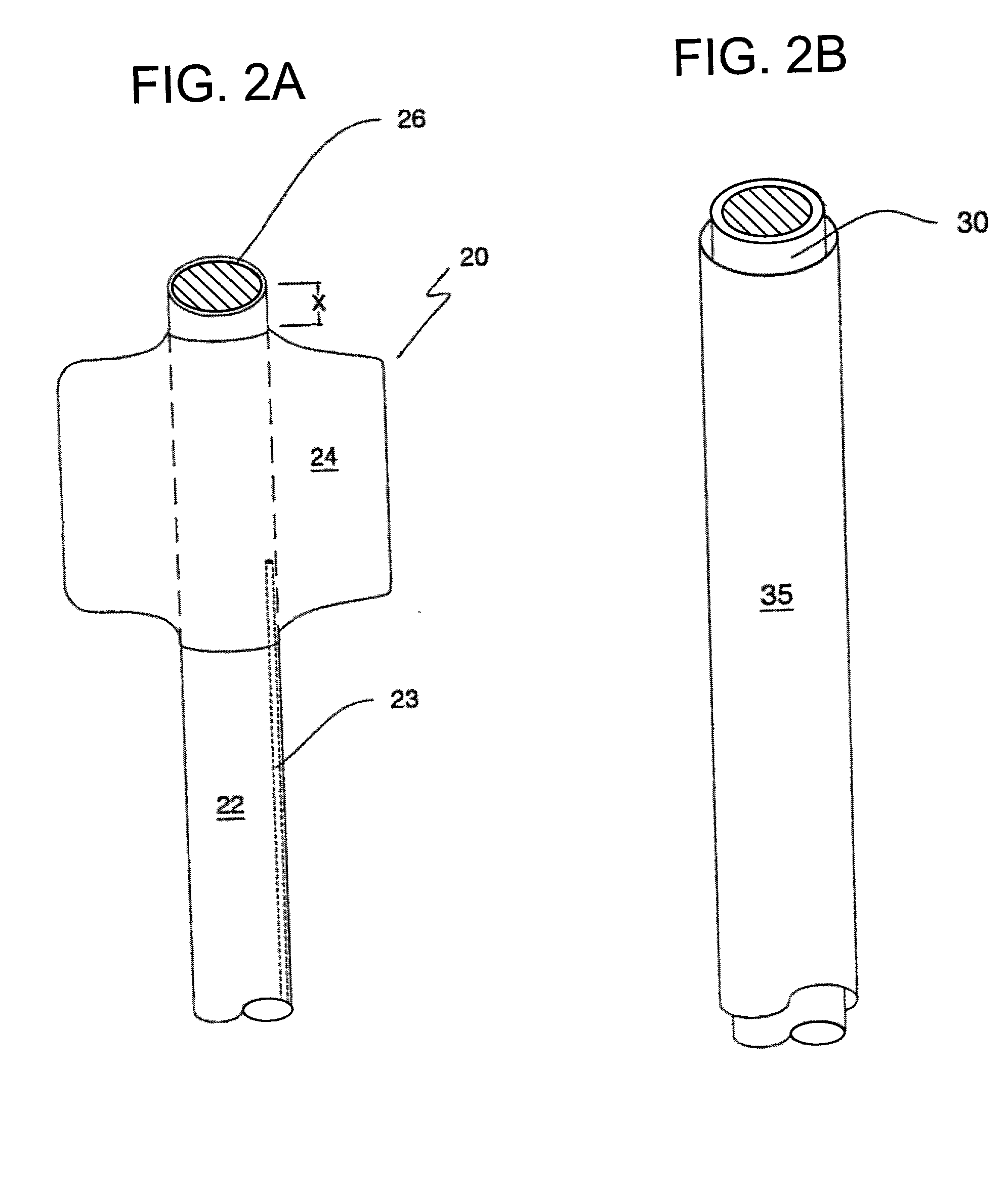
Guide catheter having selected flexural modulus segments
InactiveUS6858024B1Prevent guide catheter back-outIncreasing back-out resistanceGuide needlesFlexible pipesFlexural modulusAortic arch
A guiding catheter for use in coronary angioplasty and other cardiovascular interventions which incorporates a plurality of segment of selected flexural modulus in the shaft of the device. The segments which have a different flexibility than the sections immediately proximal and distal to them, creating zones in the catheter shaft which are either more or less flexible than other zones of the shaft. The flexibility and length of the shaft in a given zone is then matched to its clinical function and role. A mid-shaft zone is significantly softer than a proximal shaft or distal secondary curve to better traverse the aortic arch shape without storing too much energy. A secondary zone section is designed to have maximum stiffness to provide optimum backup support and stability.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
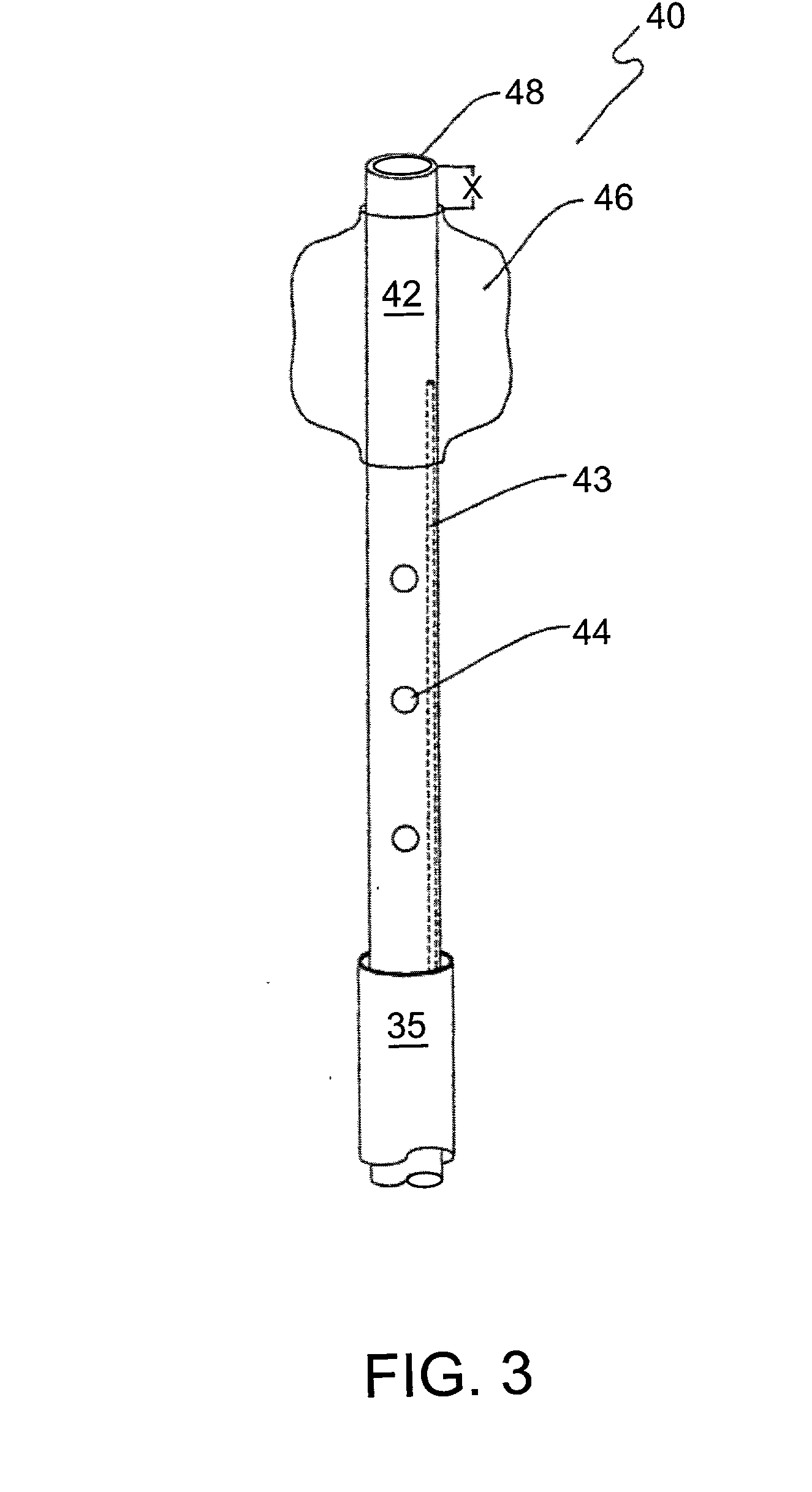
Catheter devices and methods for their use in the treatment of calcified vascular occlusions
Owner:CARDINAL HEALTH SWITZERLAND 515 GMBH
Method and System for Non-Invasive Functional Assessment of Coronary Artery Stenosis
ActiveUS20140058715A1Non-invasive functional assessmentMedical simulationMedical imagingCoronary arteriesAnatomical measurement
A method and system for non-invasive assessment of coronary artery stenosis is disclosed. Patient-specific anatomical measurements of the coronary arteries are extracted from medical image data of a patient acquired during rest state. Patient-specific rest state boundary conditions of a model of coronary circulation representing the coronary arteries are calculated based on the patient-specific anatomical measurements and non-invasive clinical measurements of the patient at rest. Patient-specific rest state boundary conditions of the model of coronary circulation representing the coronary arteries are calculated based on the patient-specific anatomical measurements and non-invasive clinical measurements of the patient at rest. Hyperemic blood flow and pressure across at least one stenosis region of the coronary arteries are simulated using the model of coronary circulation and the patient-specific hyperemic boundary conditions. Fractional flow reserve (FFR) is calculated for the at least one stenosis region based on the simulated hyperemic blood flow and pressure.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
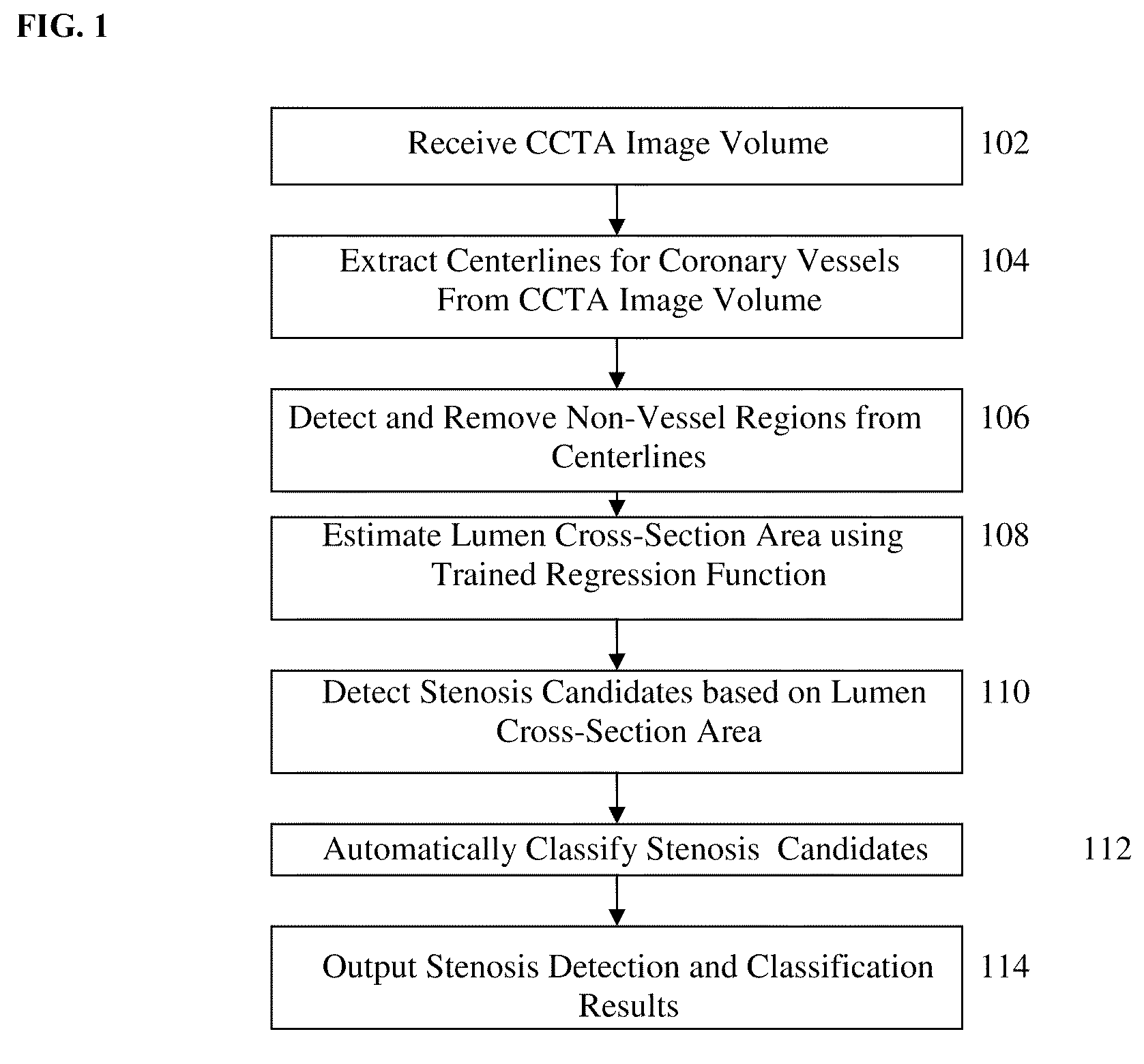
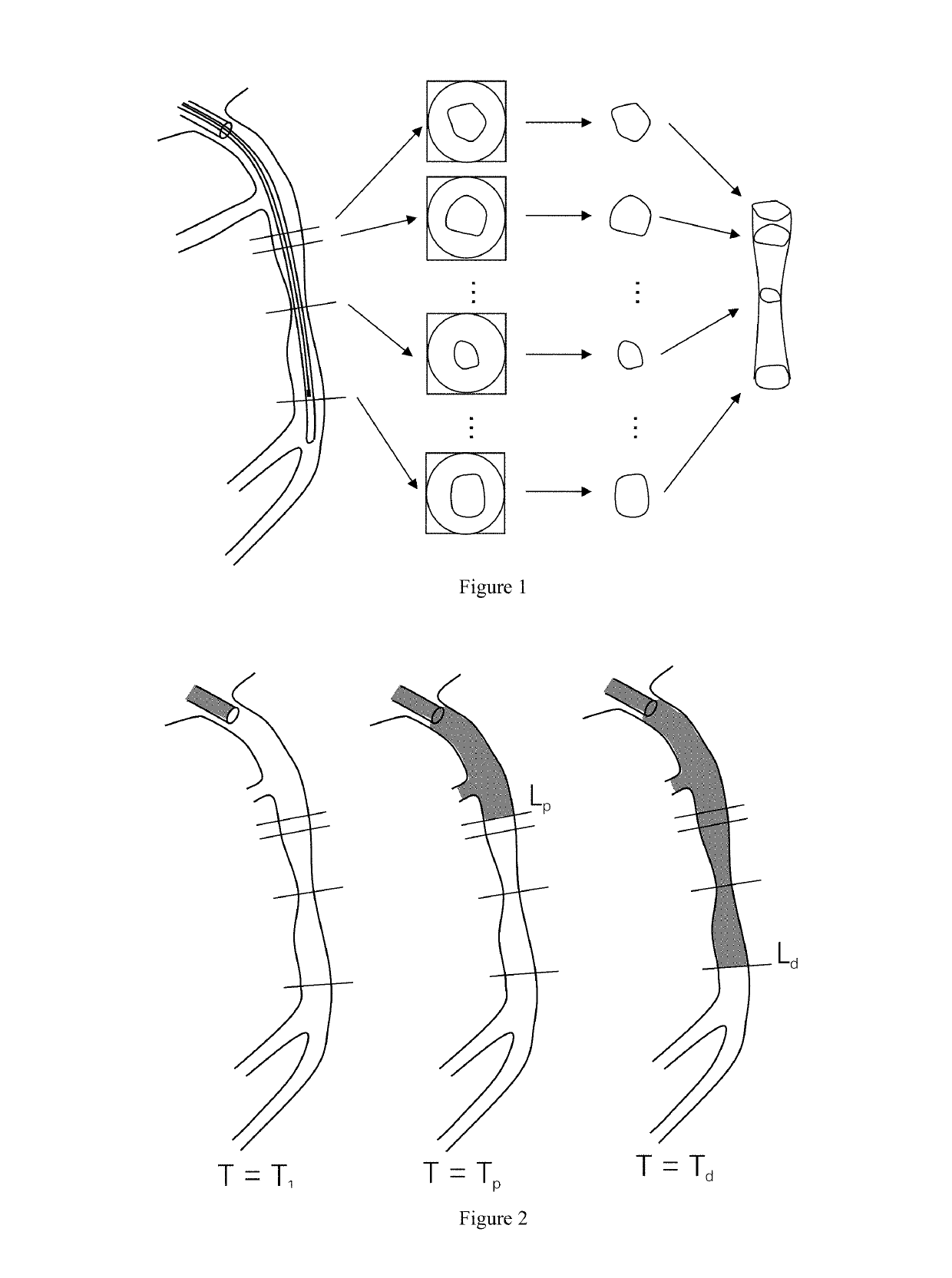
Method and System for Automatic Detection and Classification of Coronary Stenoses in Cardiac CT Volumes
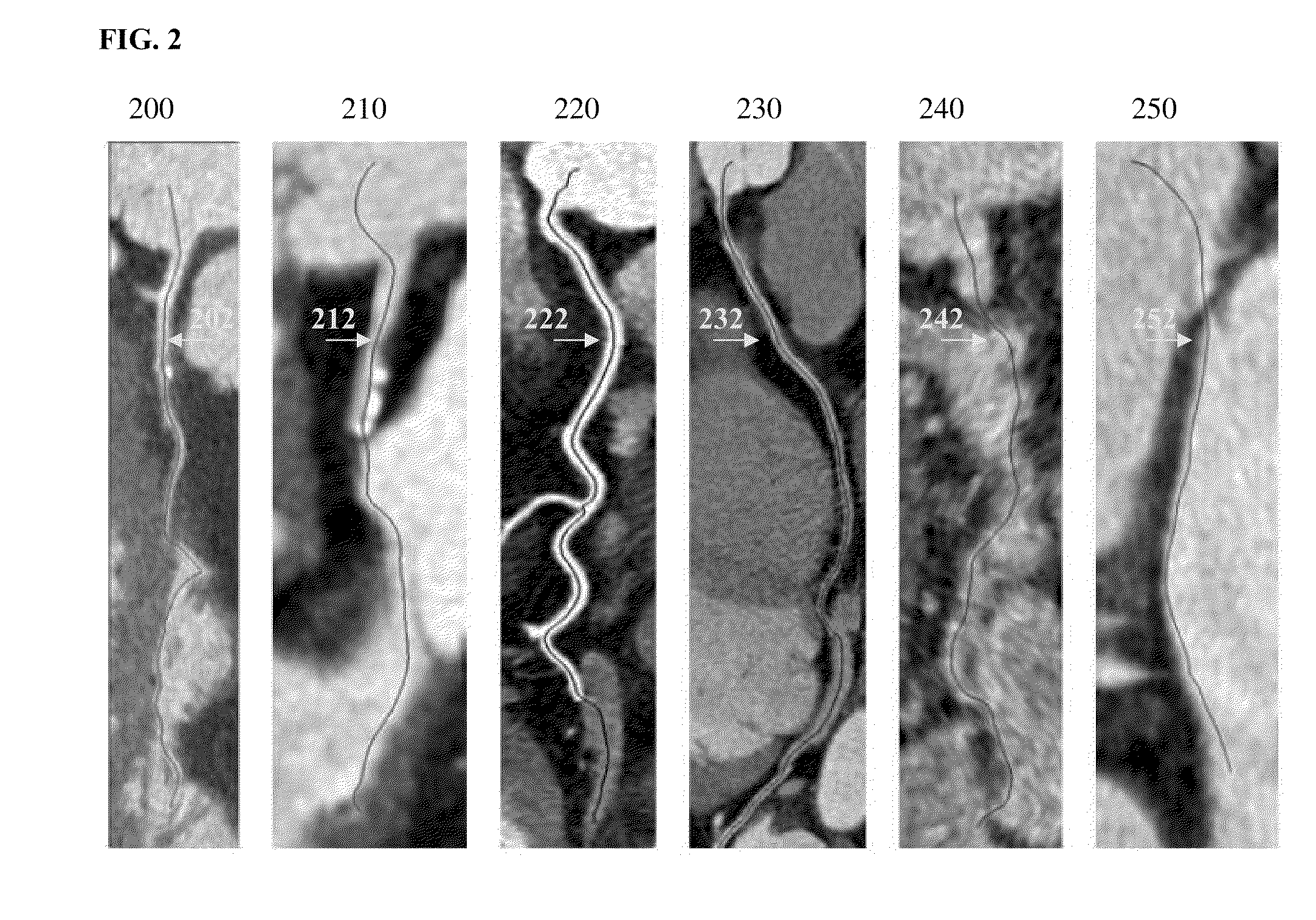
A method and system for providing detecting and classifying coronary stenoses in 3D CT image data is disclosed. Centerlines of coronary vessels are extracted from the CT image data. Non-vessel regions are detected and removed from the coronary vessel centerlines. The cross-section area of the lumen is estimated based on the coronary vessel centerlines using a trained regression function. Stenosis candidates are detected in the coronary vessels based on the estimated lumen cross-section area, and the significant stenosis candidates are automatically classified as calcified, non-calcified, or mixed.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
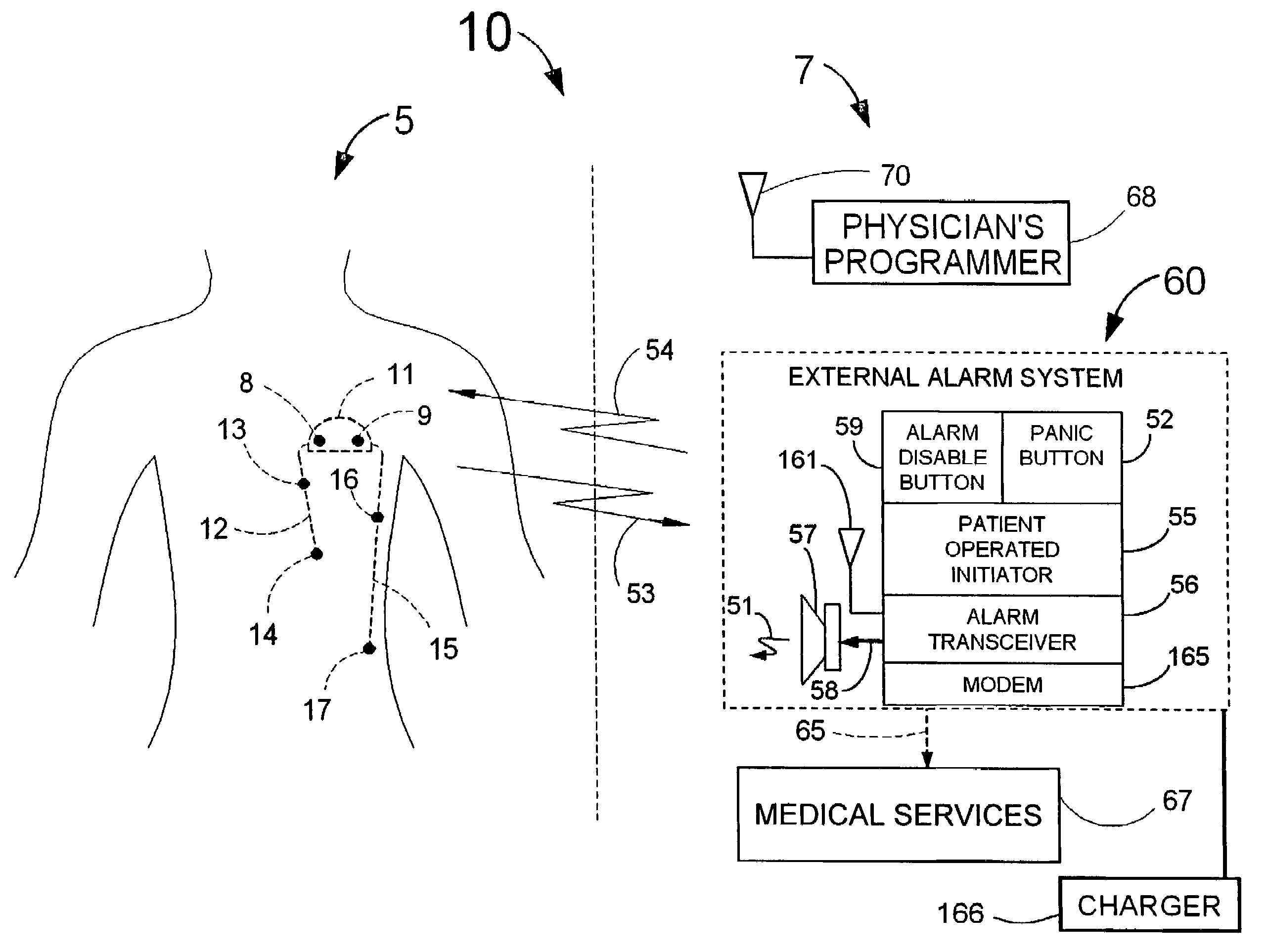
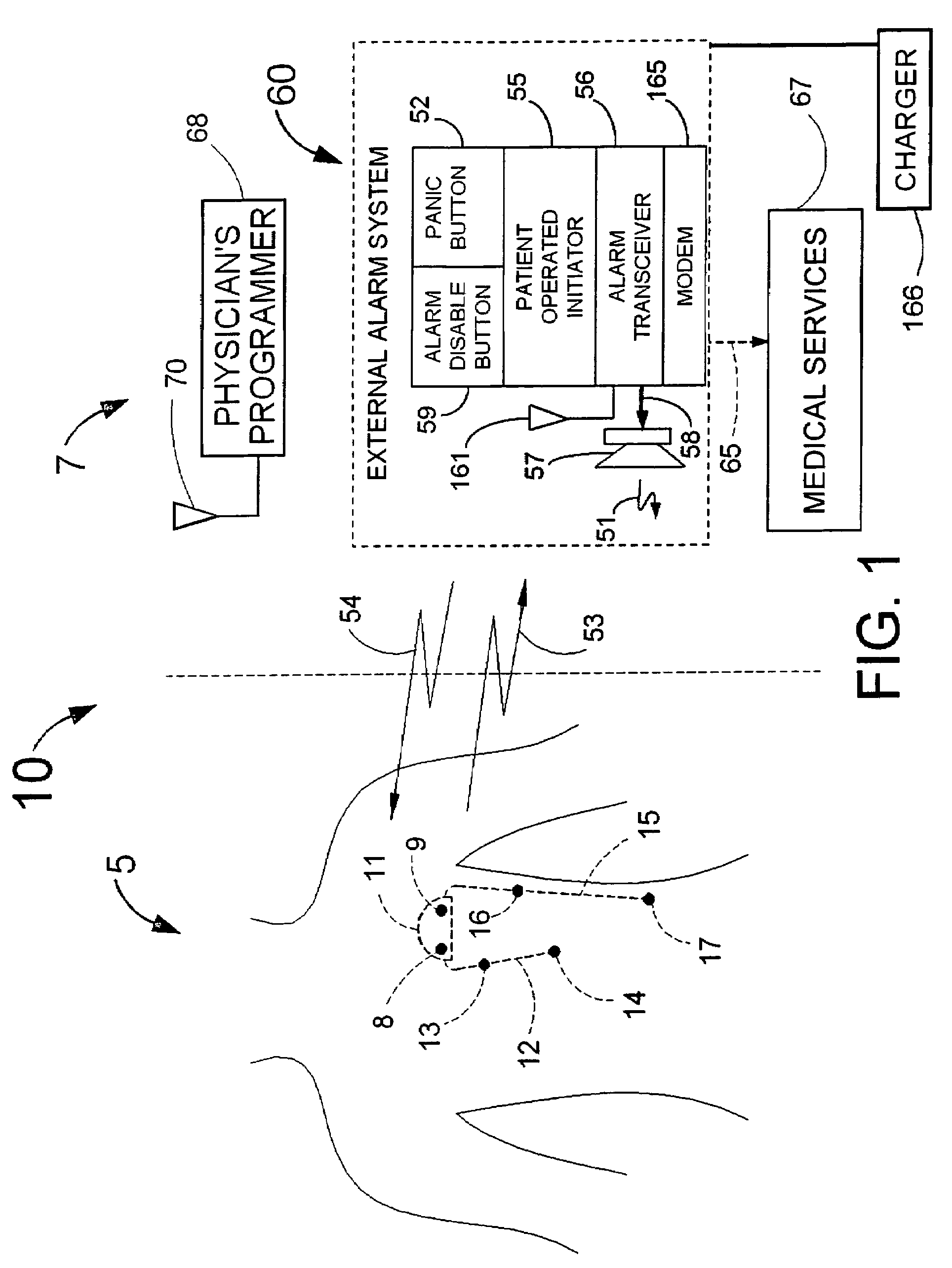
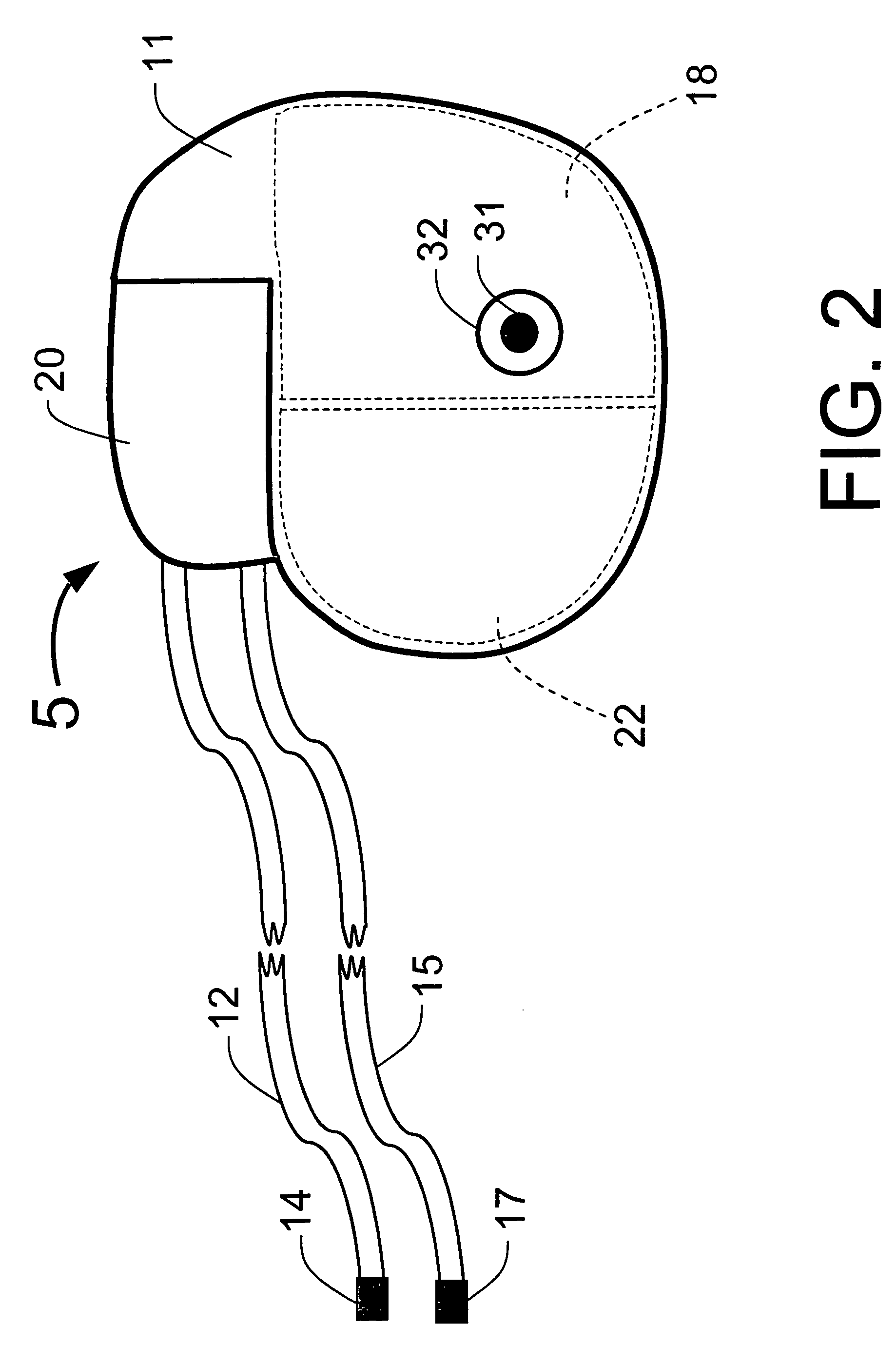
Implantable system for monitoring the condition of the heart
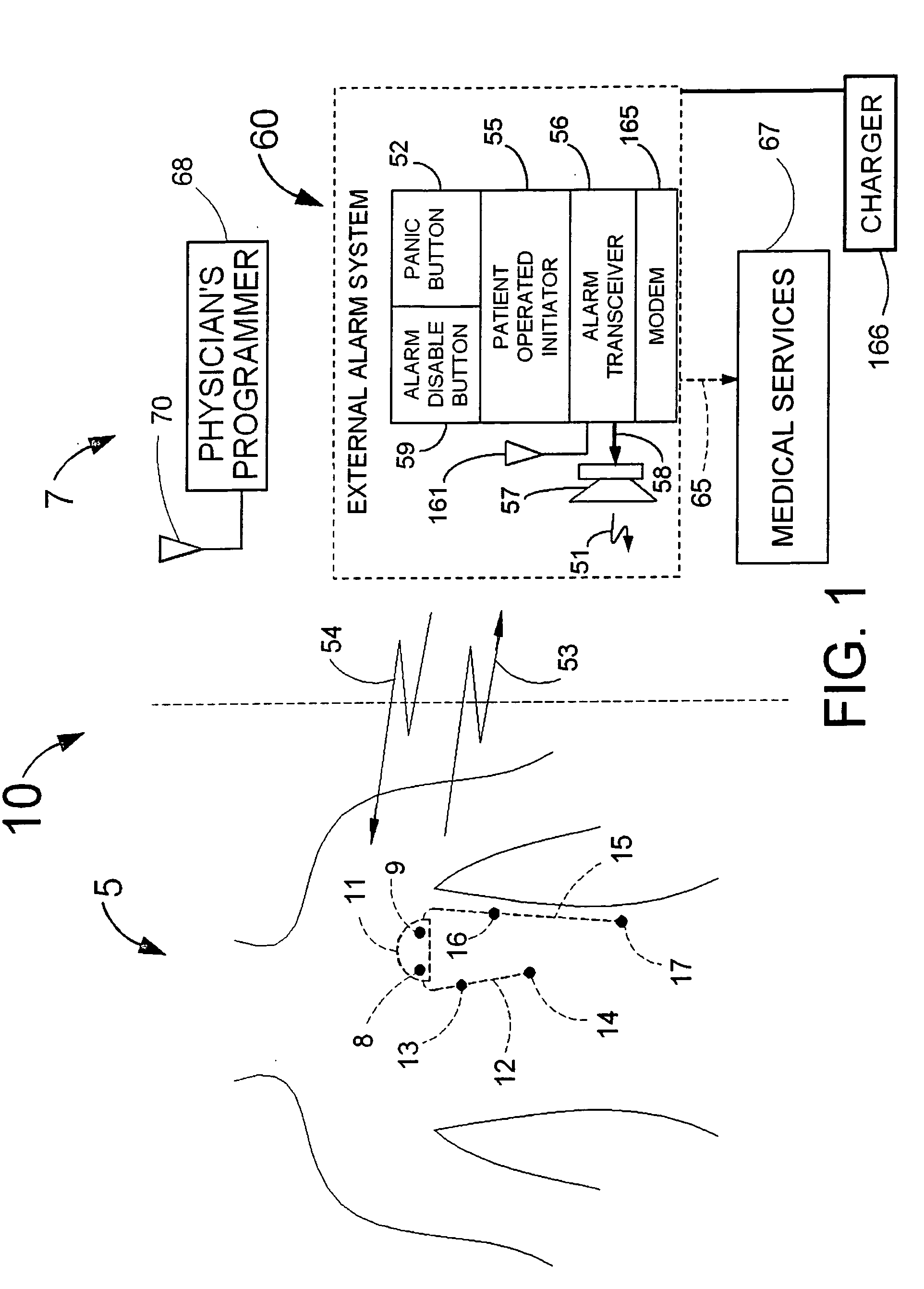
ActiveUS20050113705A1Restore blood flowDecreased blood flowElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyCoronary circulationPeripheral
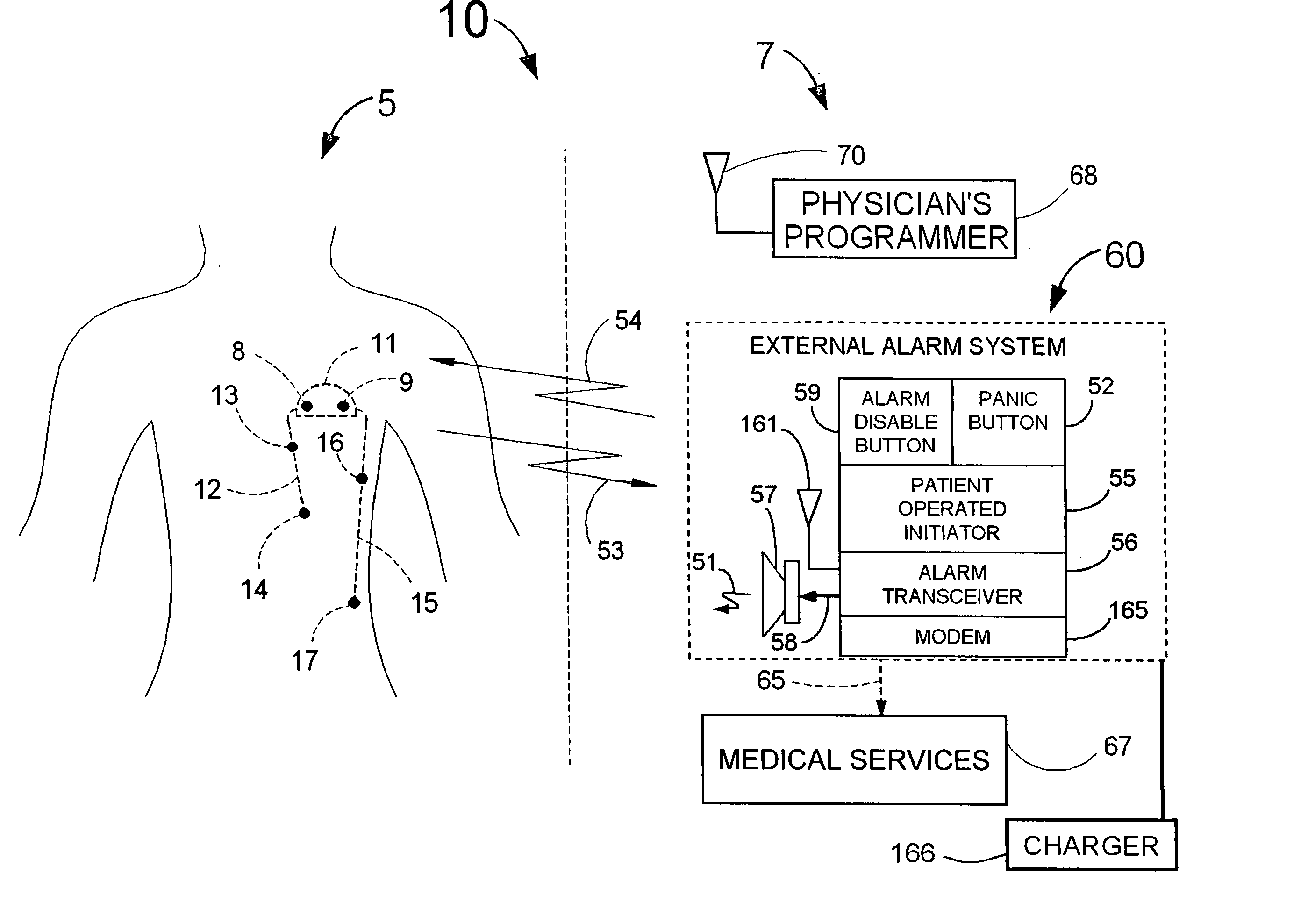
Disclosed is a “tracker system” that includes implanted electrical leads which are part of an implanted cardiotracker plus external equipment that includes external alarm means and a physician's programmer. The tracker system is designed to monitor the degradation of a patient's cardiovascular condition from one or more causes. These causes include the rejection of a transplanted heart and / or the progression of a stenosis in a coronary artery. As one or more stenoses in a coronary artery become progressively more narrow thereby causing reduced blood flow to the heart muscle coronary circulation, the tracker system can alert the patient by either or both internal and / or external alarm means to take the appropriate medical action. The physician's programmer can be used to display histograms of key heart signal parameters that are indicative of the patient's cardiovascular condition.
Owner:ANGEL MEDICAL SYST
System and method for coronary segmentation and visualization
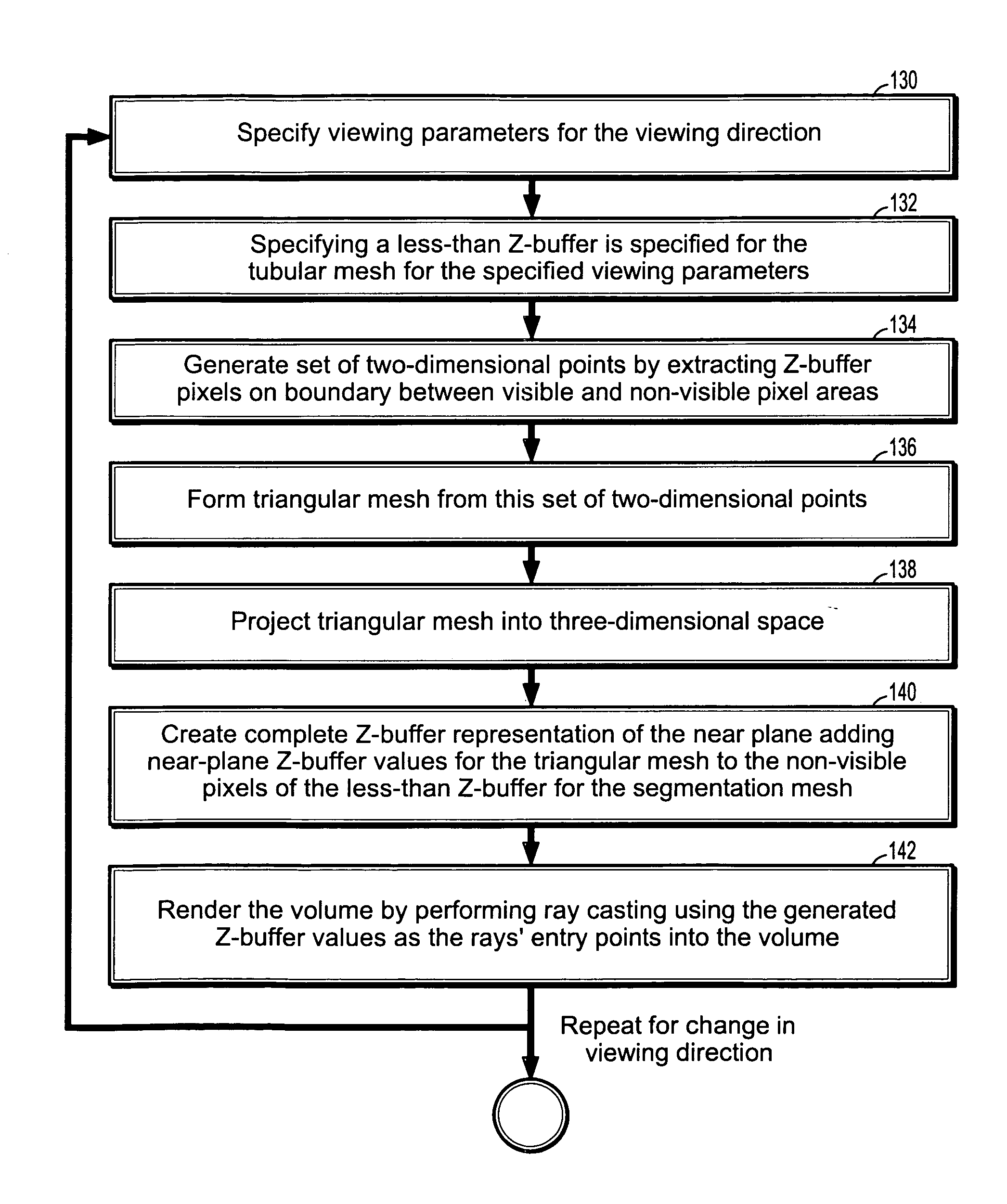
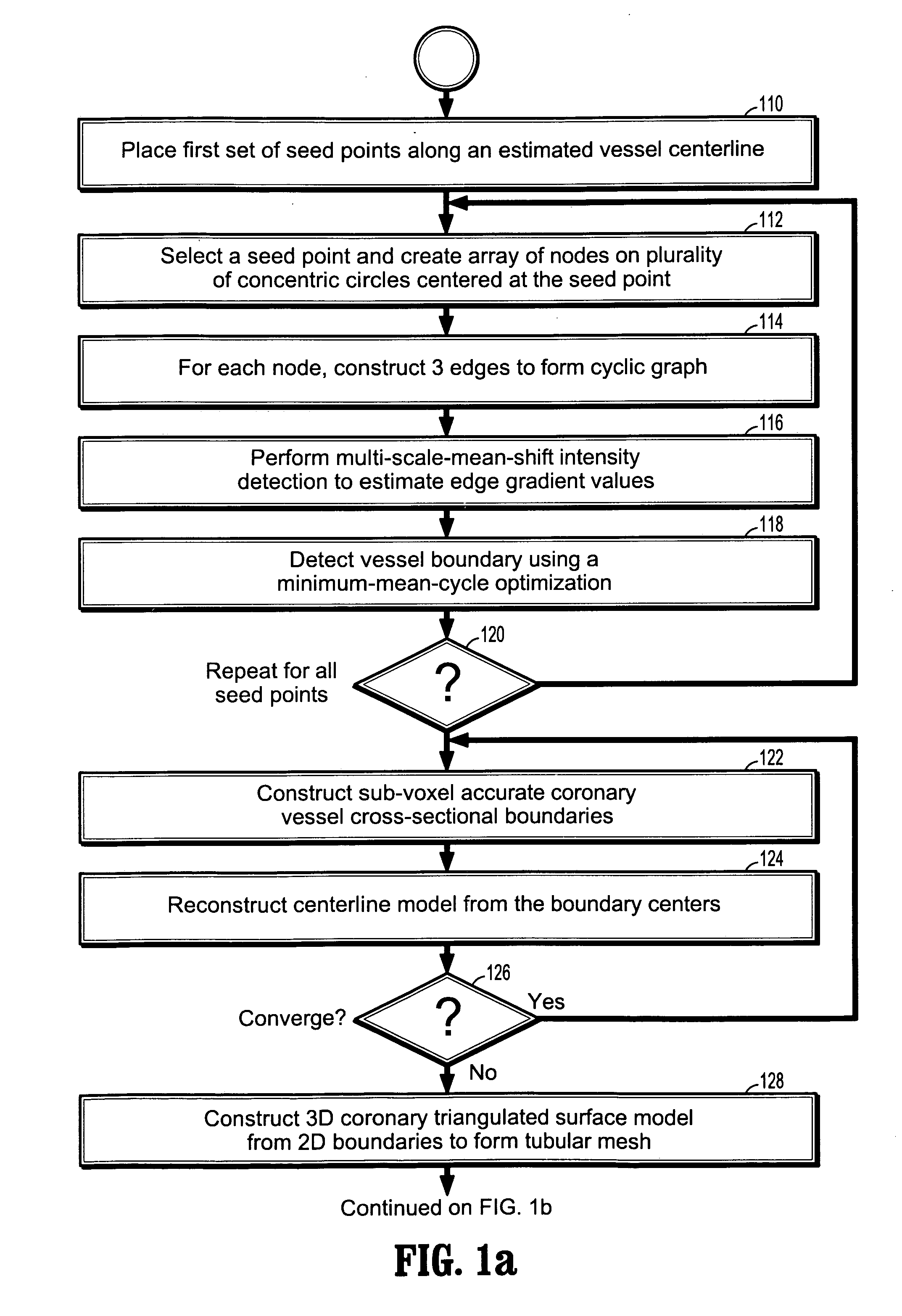
InactiveUS20080100621A1Eliminating incorrect edgeEliminating incorrect edgesImage enhancementImage analysisVoxelVertical plane
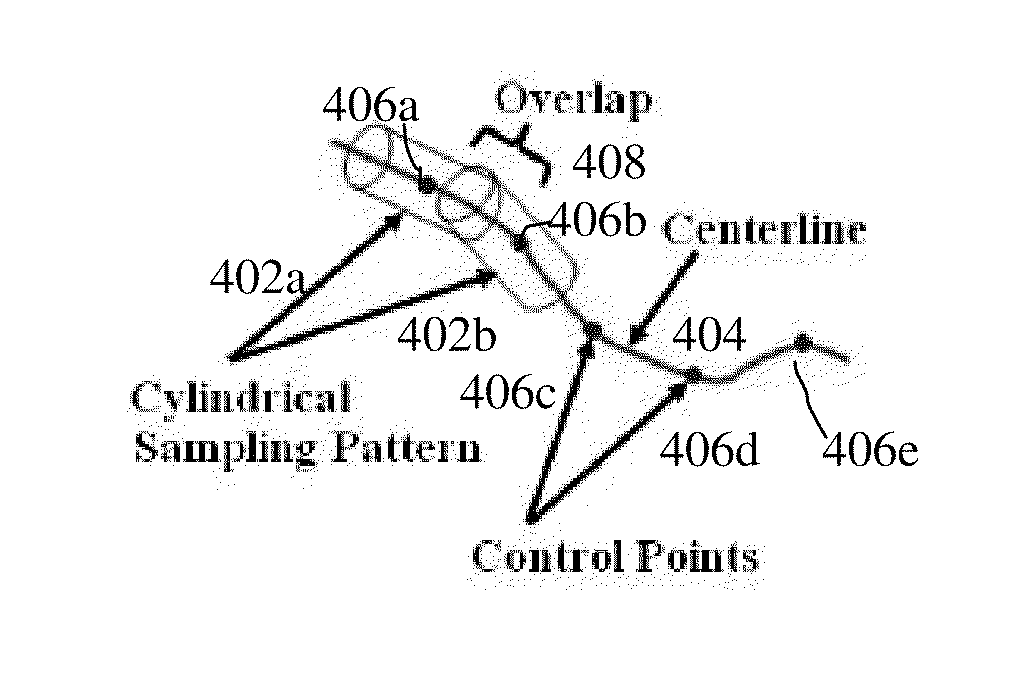
A method of coronary vessel segmentation and visualization includes providing a digitized coronary image, placing a plurality of seed points along an estimated centerline of a coronary vessel, selecting a seed point and constructing a cyclic graph around the seed point in a plane perpendicular to the centerline at the seed point, performing a multi-scale-mean shift filtering in the perpendicular plane to estimate image gradient values, detecting a vessel boundary using a minimum-mean-cycle optimization that minimizes a ratio of a cost of a cycle to a length of a cycle, constructing a sub-voxel accurate vessel boundary about a point on the centerline, and refining the location of the centerline point from the sub-voxel accurate boundary, where the steps of constructing a sub-voxel accurate vessel boundary and refining the centerline point location are repeated until convergence.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Methods and kits for delivering pharmaceutical agents into the coronary vascular adventitia
Methods and kits for delivering pharmaceutical agents to the adventitia surrounding a blood vessel utilize a catheter having a microneedle. The microneedle is positioned in the perivascular space and delivers an amount of pharmaceutical agent sufficient to circumferentially permeate around the blood vessel and, in many cases, extend longitudinally along the blood vessel and in some cases to the adventitia surrounding other blood vessels.
Owner:MERCATOR MEDSYST
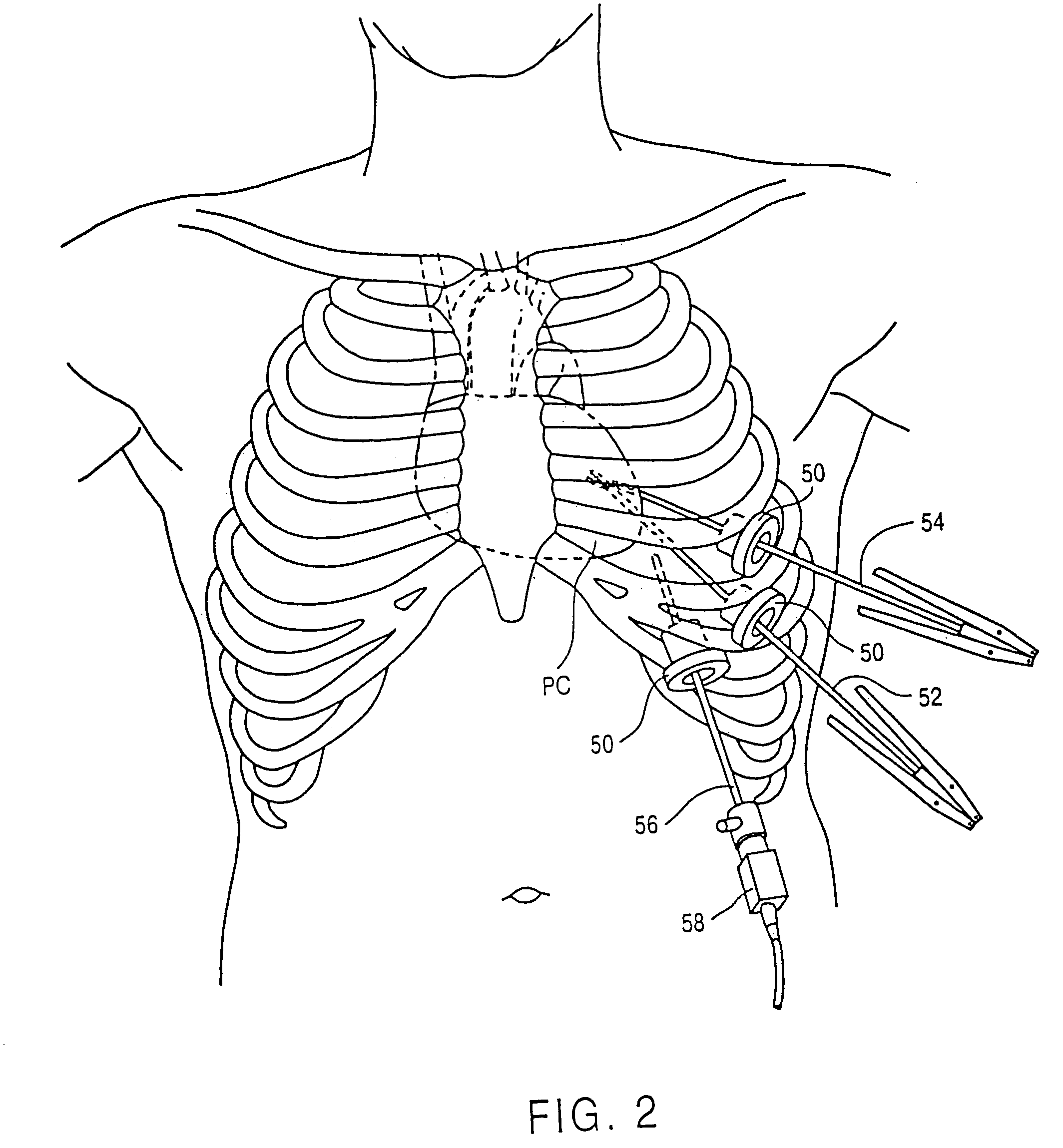
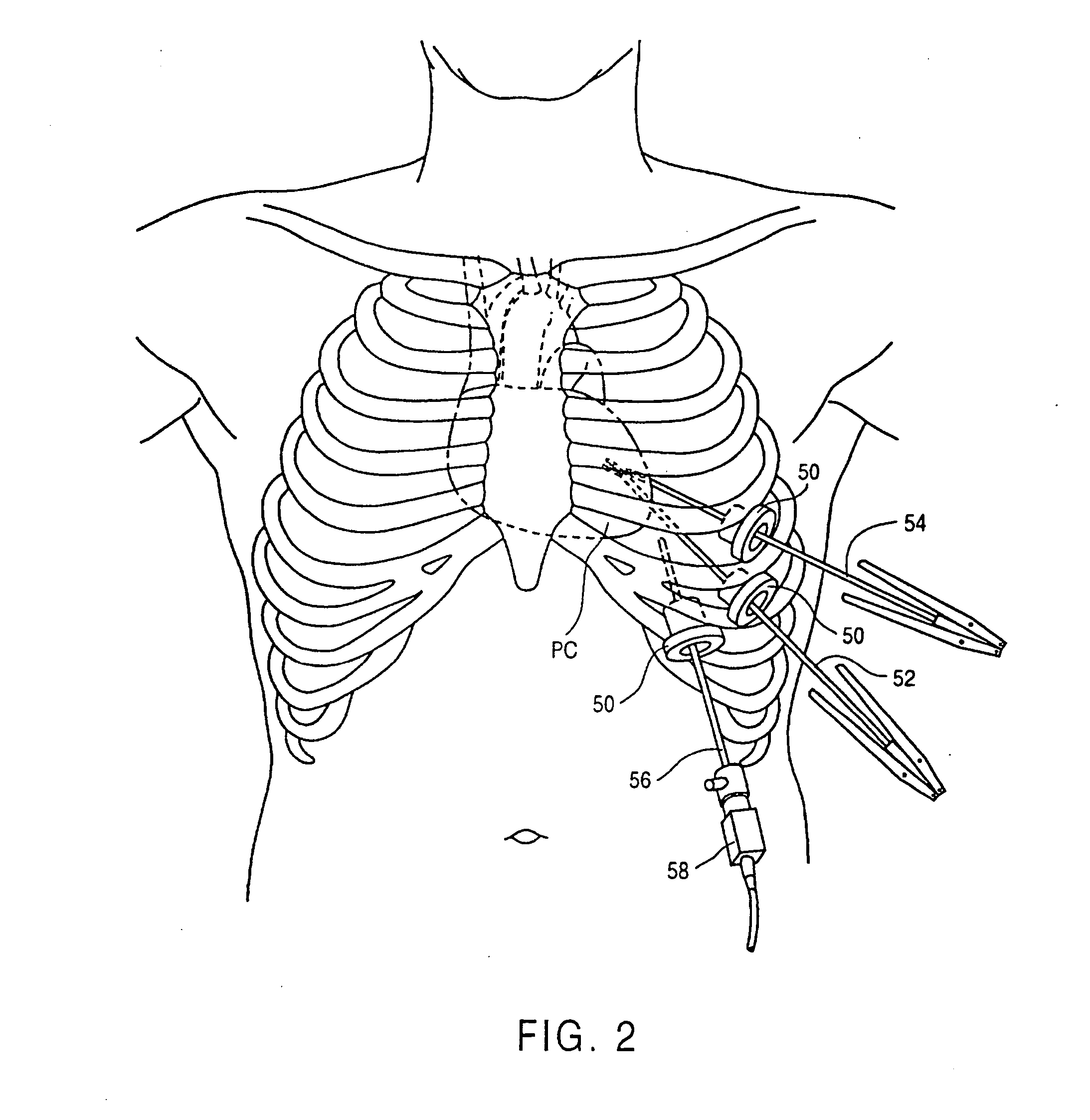
Minimally-invasive devices and methods for treatment of congestive heart failure
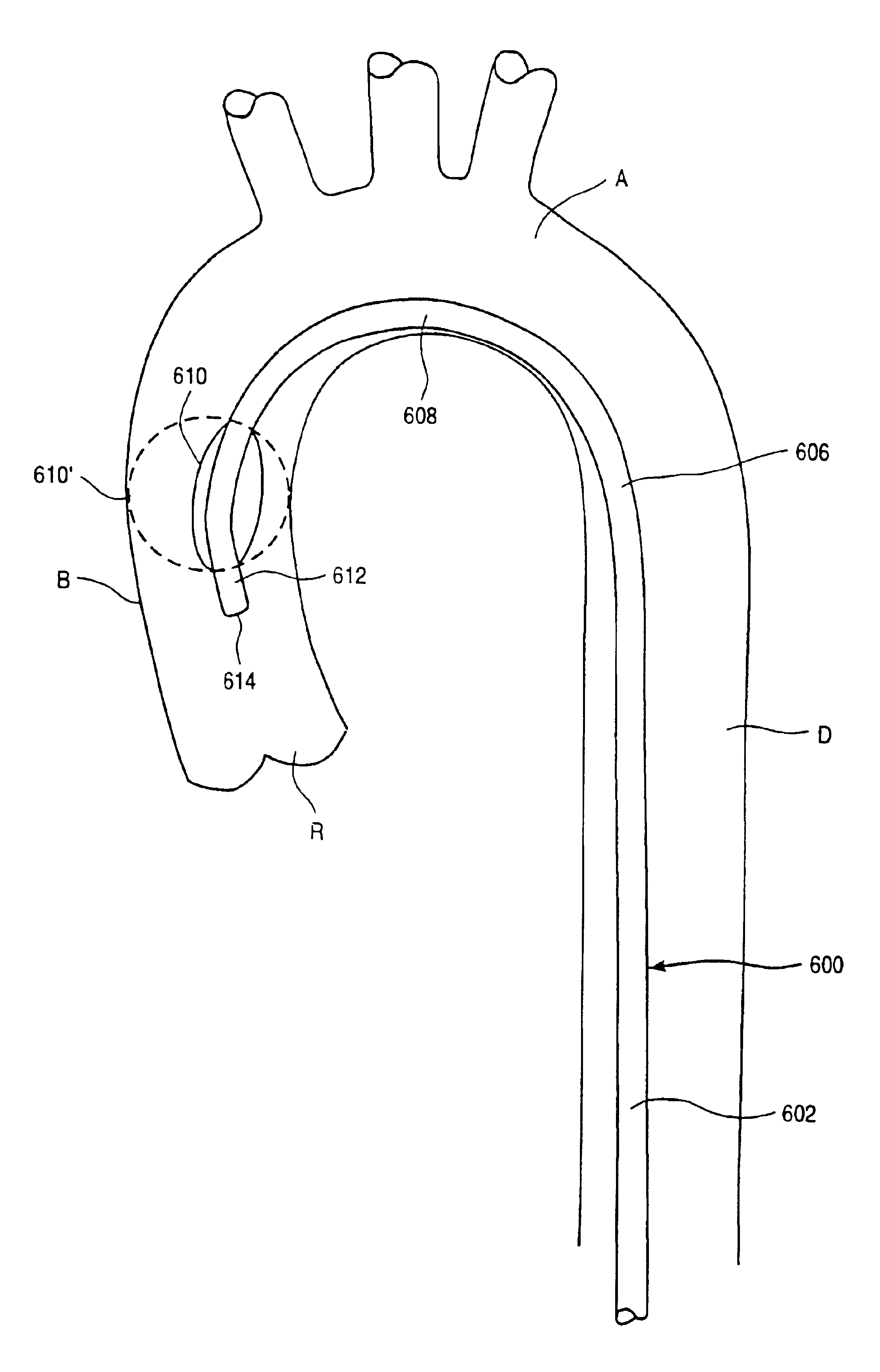
InactiveUS7213601B2Relieve painLower the volumeSuture equipmentsOther blood circulation devicesAscending aortaClavicle
A method of treatment of congestive heart failure comprises the steps of introducing an aortic occlusion catheter through a patient's peripheral artery, the aortic occlusion catheter having an occluding member movable from a collapsed position to an expanded position; positioning the occluding member in the patient's ascending aorta; moving the occluding member from the collapsed shape to the expanded shape after the positioning step; introducing cardioplegic fluid into the patient's coronary blood vessels to arrest the patient's heart; maintaining circulation of oxygenated blood through the patient's arterial system; and reshaping an outer wall of the patient's heart while the heart is arrested so as to reduce the transverse dimension of the left ventricle. The ascending aorta may be occluded and cardioplegic fluid delivered by means of an occlusion balloon attached to the distal end of an elongated catheter positioned transluminally in the aorta from a femoral, subclavian, or other appropriate peripheral artery.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Method and system for automatic detection and classification of coronary stenoses in cardiac CT volumes
A method and system for providing detecting and classifying coronary stenoses in 3D CT image data is disclosed. Centerlines of coronary vessels are extracted from the CT image data. Non-vessel regions are detected and removed from the coronary vessel centerlines. The cross-section area of the lumen is estimated based on the coronary vessel centerlines using a trained regression function. Stenosis candidates are detected in the coronary vessels based on the estimated lumen cross-section area, and the significant stenosis candidates are automatically classified as calcified, non-calcified, or mixed.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Guide catheter having selected flexural modulus segments
InactiveUS7674411B2Increase flexibilityPrevent guide catheter back-outGuide needlesLamination ancillary operationsFlexural modulusPliability
A guiding catheter for use in coronary angioplasty and other cardiovascular interventions which incorporates a plurality of segment of selected flexural modulus in the shaft of the device. The segments which have a different flexibility than the sections immediately proximal and distal to them, creating zones in the catheter shaft which are either more or less flexible than other zones of the shaft. The flexibility and length of the shaft in a given zone is then matched to its clinical function and role. A mid-shaft zone is significantly softer than a proximal shaft or distal secondary curve to better traverse the aortic arch shape without storing too much energy. A secondary zone section is designed to have maximum stiffness to provide optimum backup support and stability.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Methods and kits for delivering pharmaceutical agents into the coronary vascular adventitia
Methods and kits for delivering pharmaceutical agents to the adventitia surrounding a blood vessel utilize a catheter having a microneedle. The microneedle is positioned in the perivascular space and delivers an amount of pharmaceutical agent sufficient to circumferentially permeate around the blood vessel and, in many cases, extend longitudinally along the blood vessel and in some cases to the adventitia surrounding other blood vessels.
Owner:MERCATOR MEDSYST INC
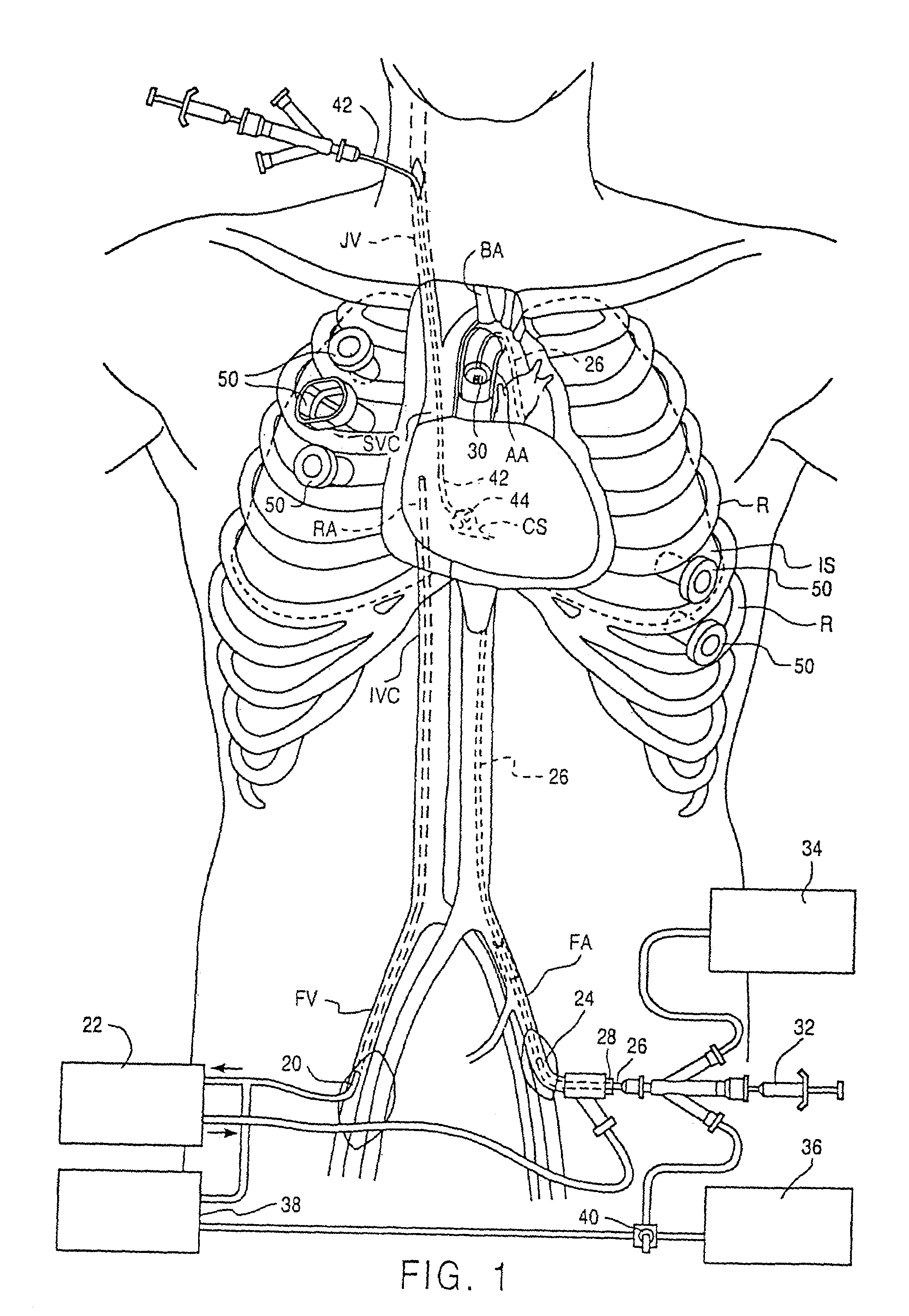
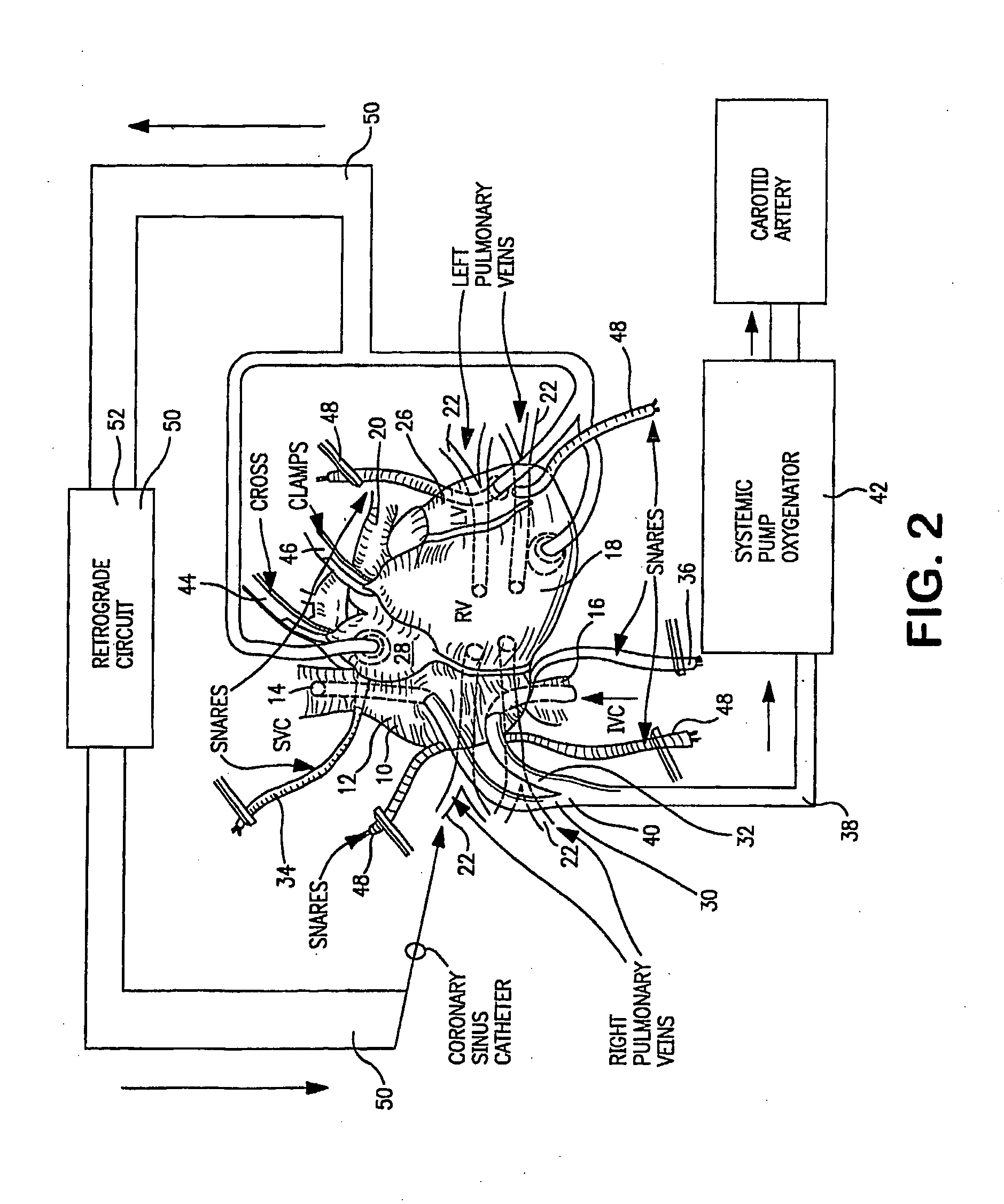
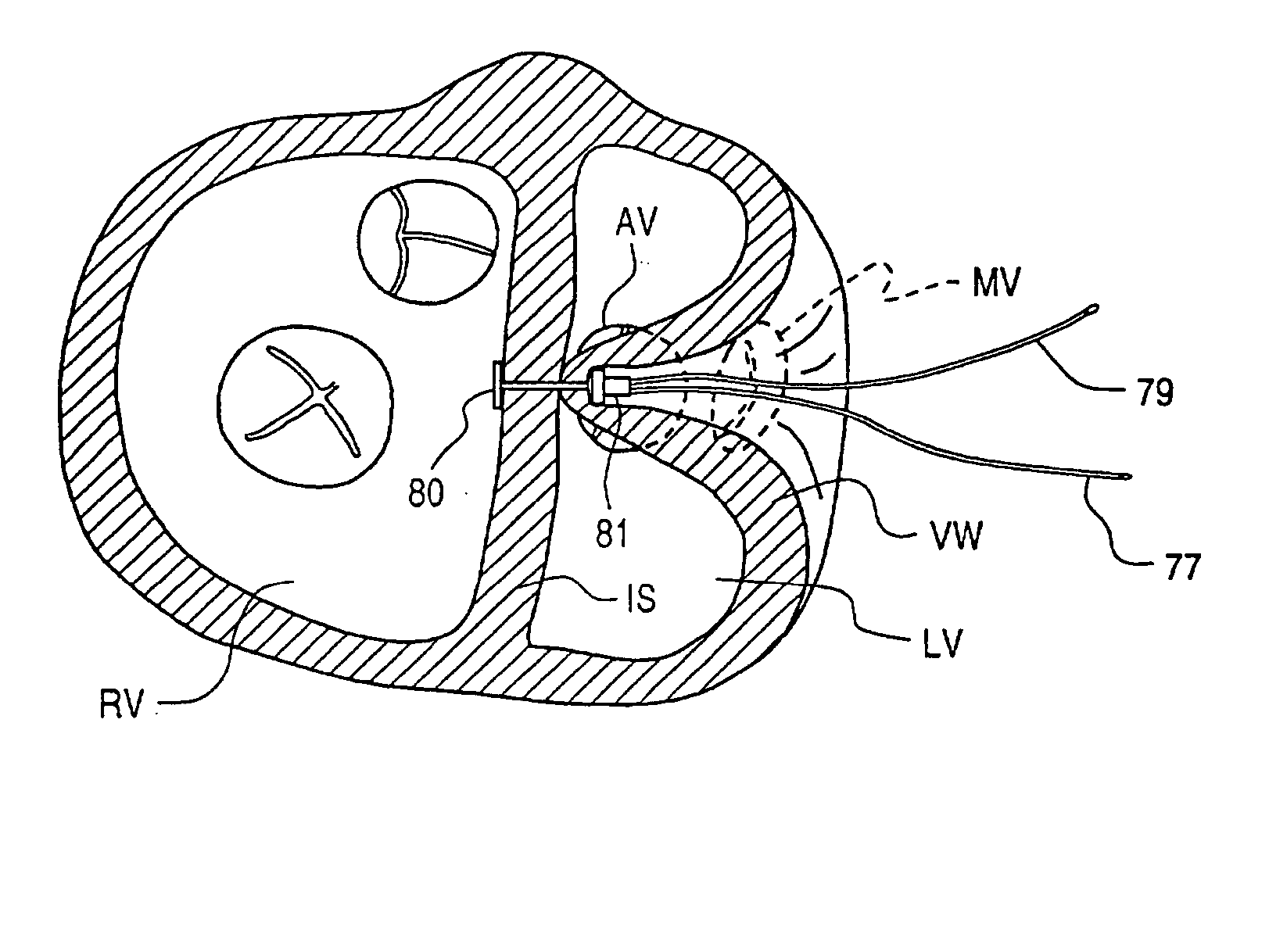
Method and apparatus for venous drainage and retrograde coronary perfusion
InactiveUS20050113799A1Improve protectionFacilitate surgeryBalloon catheterOther blood circulation devicesIschemic heartExtracorporeal circulation
A system is disclosed for cannulating the vena cava of a patient during cardiopulmonary bypass procedures. Such cannulation is necessary for drainage of venous blood from the patient so that it may be oxygenated and pumped back to the patient to perfuse tissues during cardiac surgery and, more specifically, during periods of ischemic cardiac arrest or dysfunction. The device of the present invention not only provides venous drainage for cardiopulmonary bypass, but also performs the function of routing cardioplegic solution through the heart in the retrograde direction. Such cardioplegia provides protection to the heart during periods of ischemic cardiac arrest. This invention replaces a plurality of cannulae currently used for open-heart surgery, thus simplifying the surgical field and improving visibility of the heart. The device allows for the delivery of retrograde cardioplegia to the coronary circulation of both the right and the left side of the heart. The device further includes protection mechanisms to prevent overinflation or excessive pressurization of the right atrium during retrograde delivery of cardioplegia solution.
Owner:INDIAN WELLS MEDICAL
Methods and kits for delivering pharmaceutical agents into the coronary vascular adventitia
Methods and kits for delivering pharmaceutical agents to the adventitia surrounding a blood vessel utilize a catheter having a microneedle. The microneedle is positioned in the perivascular space and delivers an amount of pharmaceutical agent sufficient to circumferentially permeate around the blood vessel and, in many cases, extend longitudinally along the blood vessel and in some cases to the adventitia surrounding other blood vessels.
Owner:MERCATOR MEDSYST INC
Methods for Computing Coronary Physiology Indexes Using a High Precision Registration Model
InactiveUS20190110776A1Improve accuracyHigh registrationImage enhancementImage analysisArterial blood flowCoronary physiology
Owner:QUANJING HENGSHENG BEIJING SCI & TECH CO LTD
Methods and kits for delivering pharmaceutical agents into the coronary vascular adventitia
InactiveUS20070078620A1Improve concentrationBalloon catheterSurgical needlesCatheterVirchow-Robin space
Owner:MERCATOR MEDSYST
Perfusion circuit and use therein in targeted delivery of macromolecules
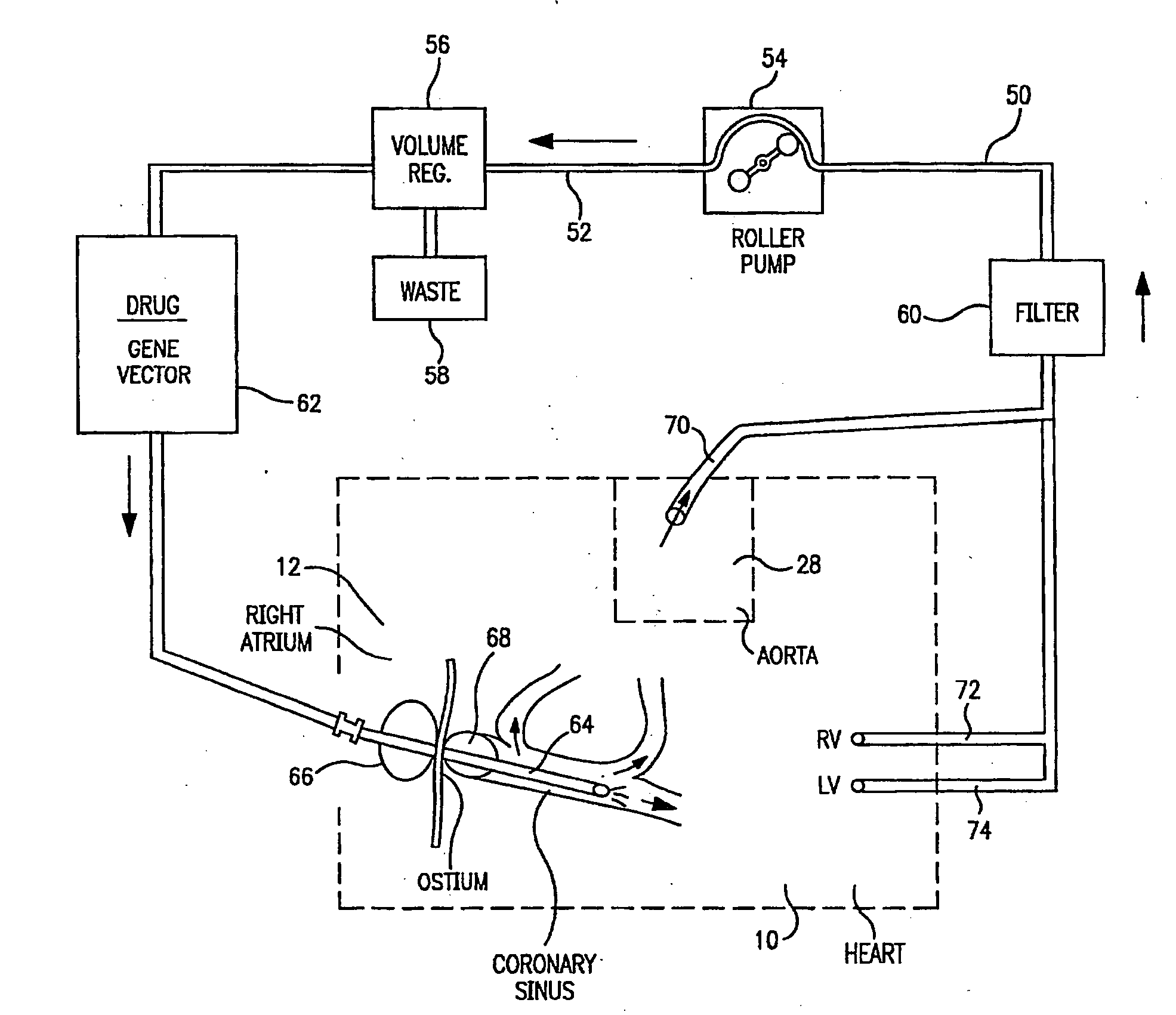
InactiveUS20090054823A1Efficient myocyte gene deliveryMaximize safetyDialysis systemsMedical devicesCardiopulmonary bypass surgeryIntensive care medicine
A perfusion circuit and a use thereof for delivering a substance to a subject's heart in situ during cardiopulmonary bypass surgery are provided. The perfusion circuit defines a path for re-circulating a solution containing a macromolecular complex through a coronary circulation circuit (50) through a subject's heart during a surgical procedure in which the substance is prevented from being delivered to the subject's other organs.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Implantable system for monitoring the condition of the heart
ActiveUS7512438B2Restore blood flowDecreased blood flowElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyHistogramMedical treatment
A “tracker system” that includes electrical leads which are part of an implanted cardiotracker plus external equipment that includes external alarm and a physician's programmer. The tracker system is designed to monitor the degradation of a patient's cardiovascular condition from one or more causes, These causes include the rejection of a transplanted heart and / or the progression of a stenosis in a coronary artery. As one or more stenoses in a coronary artery become progressively more narrow thereby causing reduced blood flow to the heart muscle coronary circulation, the tracker system can alert the patient by either or both internal and / or external alarm to take the appropriate medical action. The physician's programmer can be used to display histograms of key heart signal parameters that are indicative of the patient's cardiovascular condition.
Owner:ANGEL MEDICAL SYST
Methods and kits for delivering pharmaceutical agents into the coronary vascular adventitia
Methods and kits for delivering pharmaceutical agents to the adventitia surrounding a blood vessel utilize a catheter having a microneedle. The microneedle is positioned in the perivascular space and delivers an amount of pharmaceutical agent sufficient to circumferentially permeate around the blood vessel and, in many cases, extend longitudinally along the blood vessel and in some cases to the adventitia surrounding other blood vessels.
Owner:MERCATOR MEDSYST INC
Self-contained power-assisted syringe
A self-contained and hand-held power-assisted syringe is provided which is suitable for the controlled injection of fluid material during medical procedures such as coronary angiography procedures which utilize small-bore and small sized guide catheter systems. The present invention provides a greater degree of injection power on-demand than was previously possible in a portable and hand-held syringe; and it can deliver larger volumes of radiopaque contrast medium at greater pressures than was previously possible using a conventional manual syringe. The power assisted syringe, along with all components necessary for its effective use and operation, may be pre-packaged and steriled within a single container and then disposed of after use.
Owner:KIM DUCKSOO +2
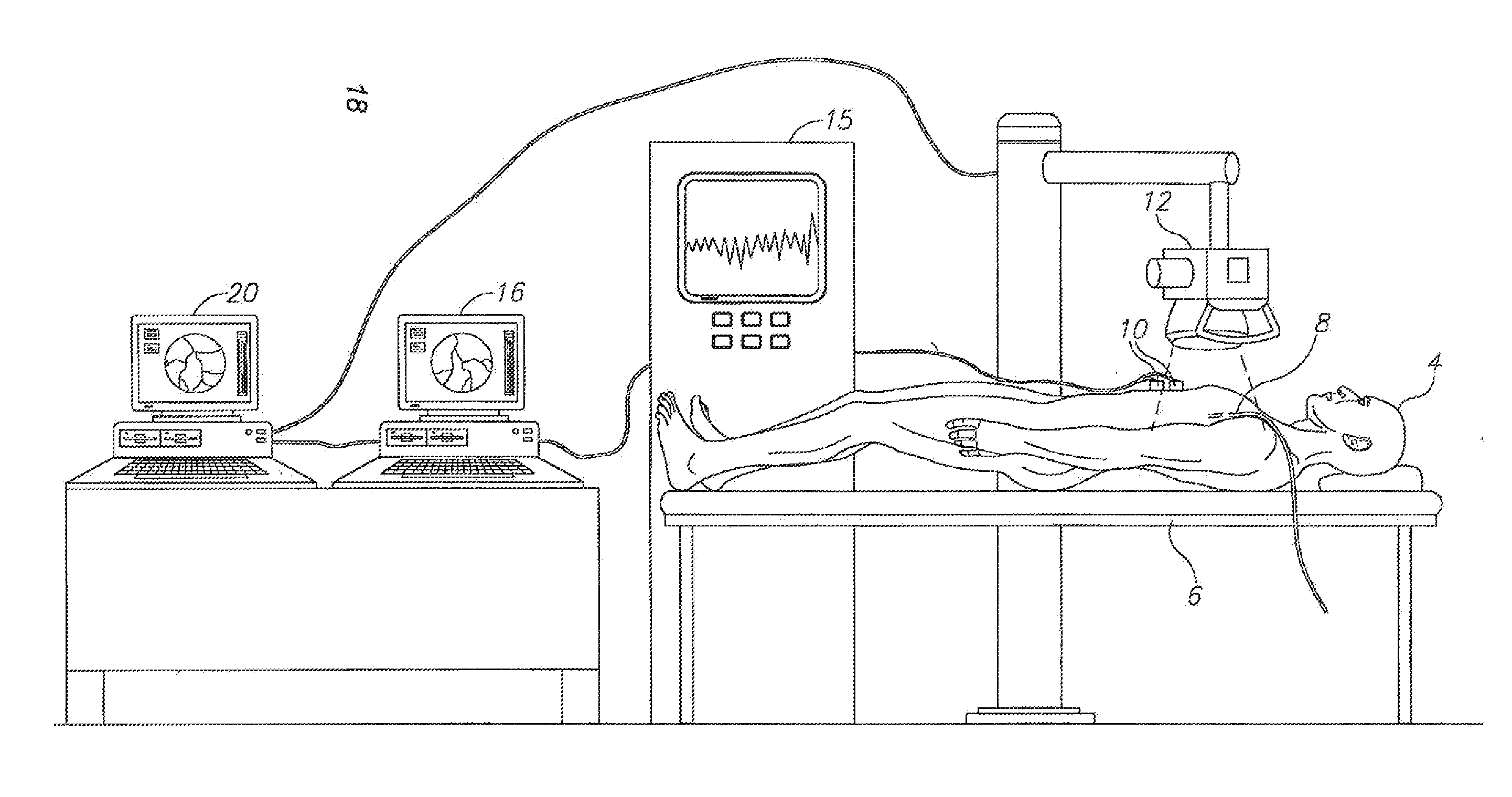
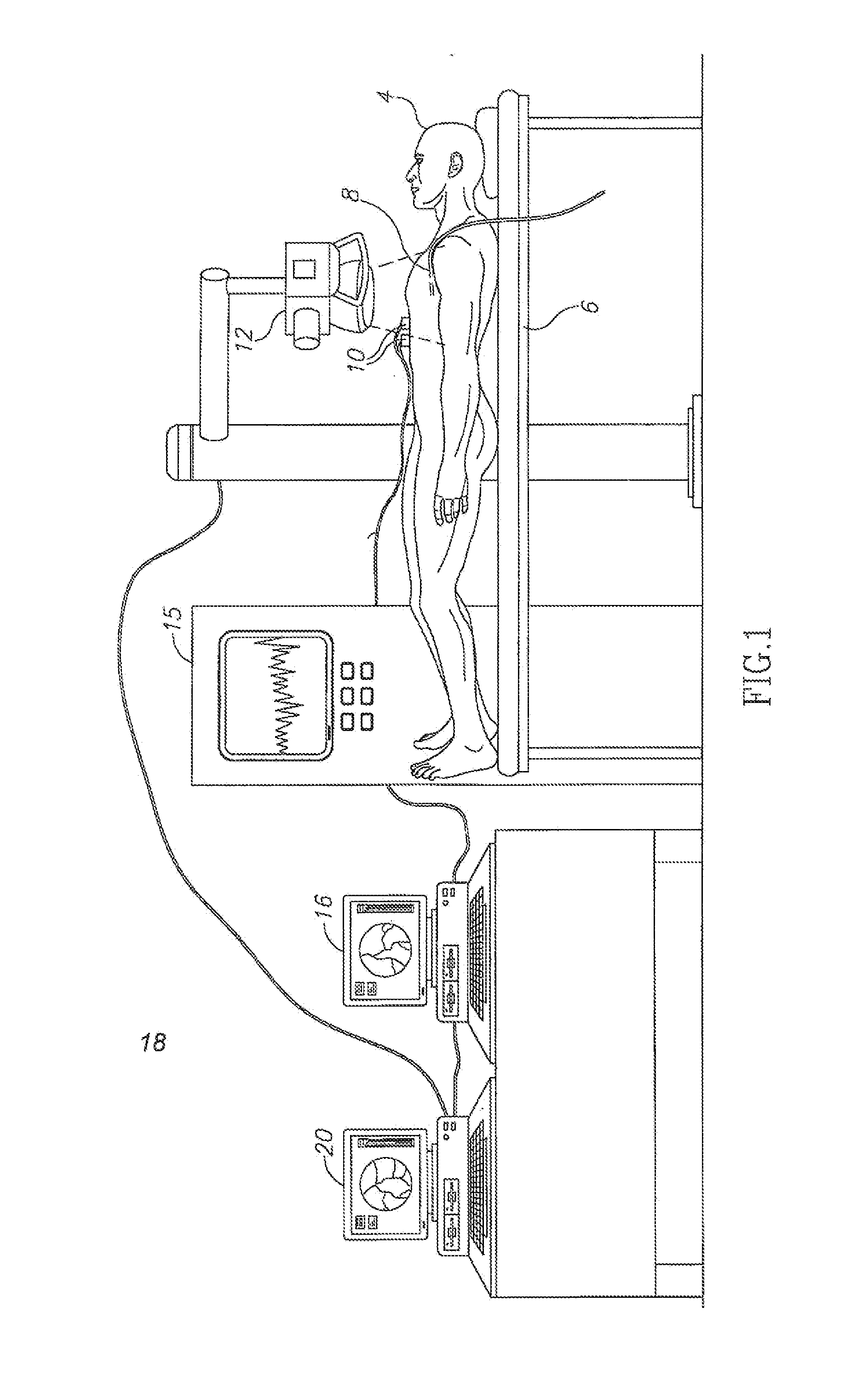
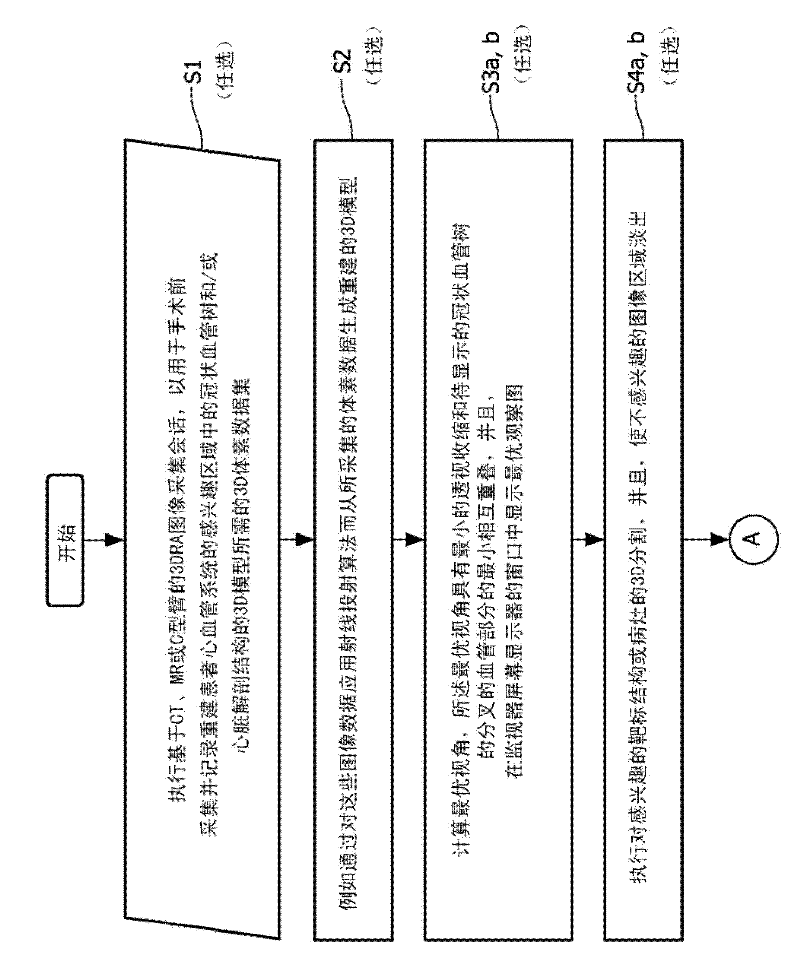
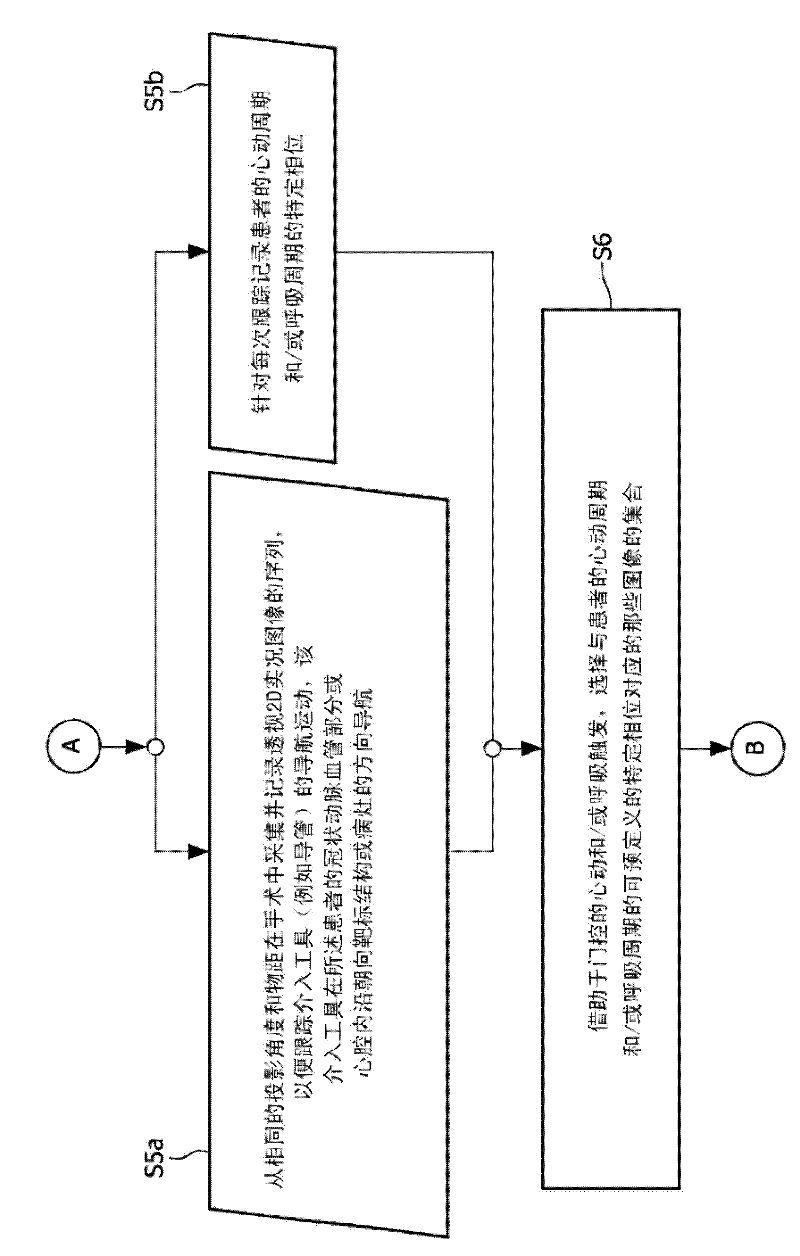
Cardiac- and/or respiratory-gated image acquisition system and method for virtual anatomy enriched real-time 2D imaging in interventional radiofrequency ablation or pacemaker placement procedures
ActiveCN102196768AUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrocardiographyCardiac cyclePacemaker Placement
The present invention refers to the field of cardiac electrophysiology (EP) and, more specifically, to image-guided radio frequency ablation and pacemaker placement procedures. For those procedures, it is proposed to display the overlaid 2D navigation motions of an interventional tool intraoperatively obtained from the same projection angle for tracking navigation motions of an interventional tool during an image-guided intervention procedure while being navigated through a patient's bifurcated coronary vessel or cardiac chambers anatomy in order to guide e.g. a cardiovascular catheter to a target structure or lesion in a cardiac vessel segment of the patient's coronary venous tree or to a region of interest within the myocard. In such a way, a dynamically enriched 2D reconstruction of the patient's anatomy is obtained while moving the interventional instrument. By applying a cardiac and / or respiratory gating technique, it can be provided that the 2D live images are acquired during the same phases of the patient's cardiac and / or respiratory cycles. Compared to prior-art solutions which are based on a registration and fusion of image data independently acquired by two distinct imaging modalities, the accuracy of the two-dimensionally reconstructed anatomy is significantly enhanced.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
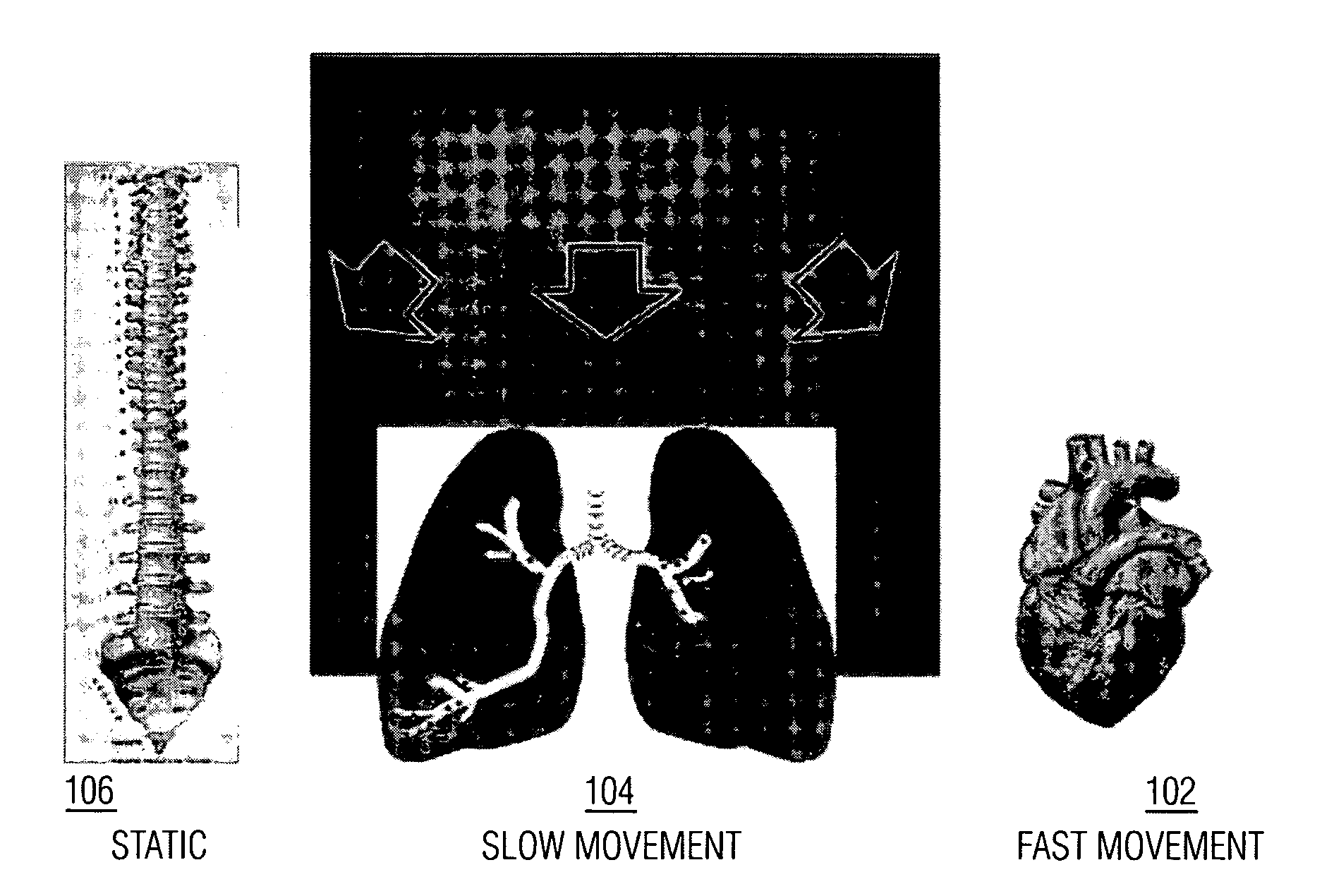
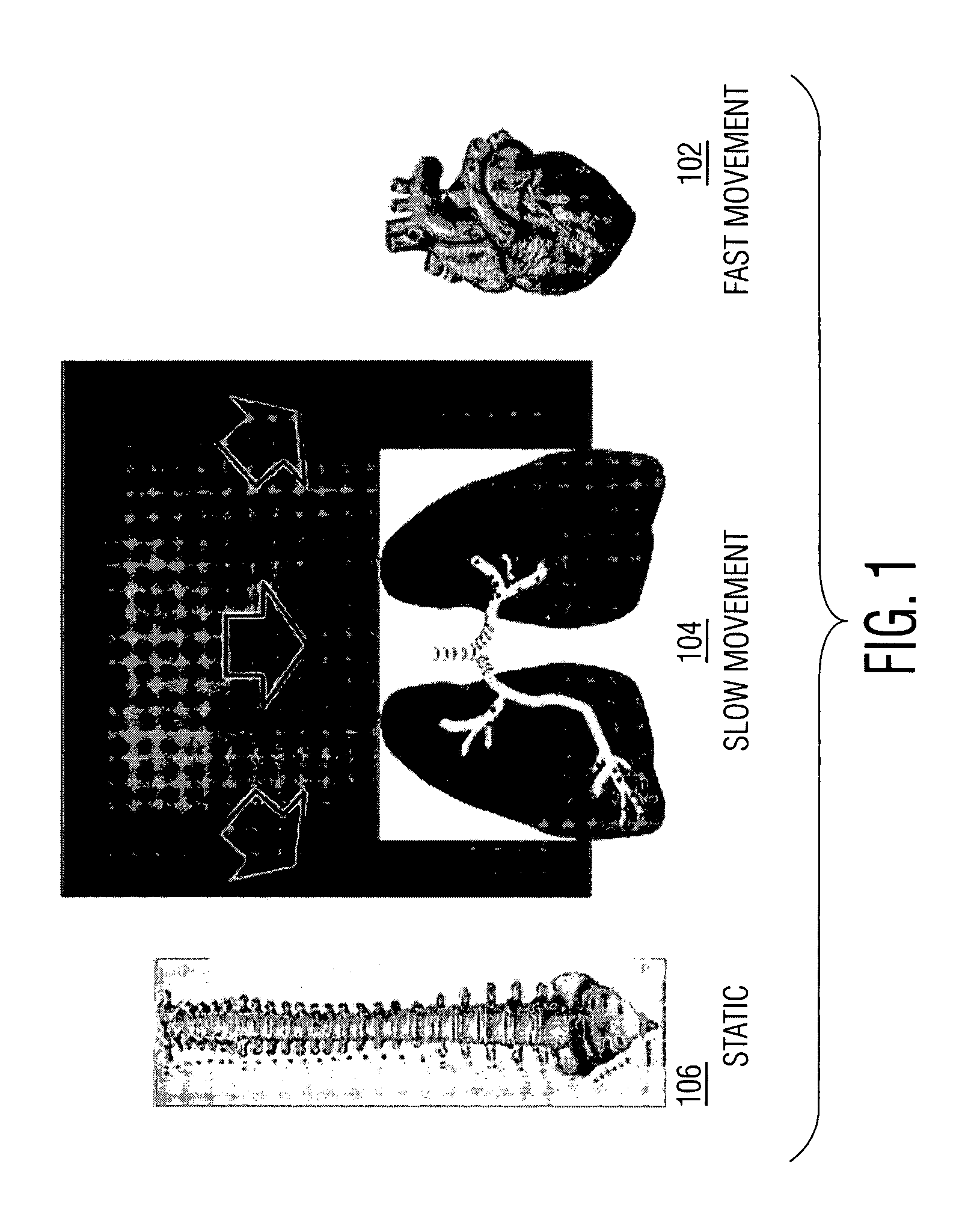
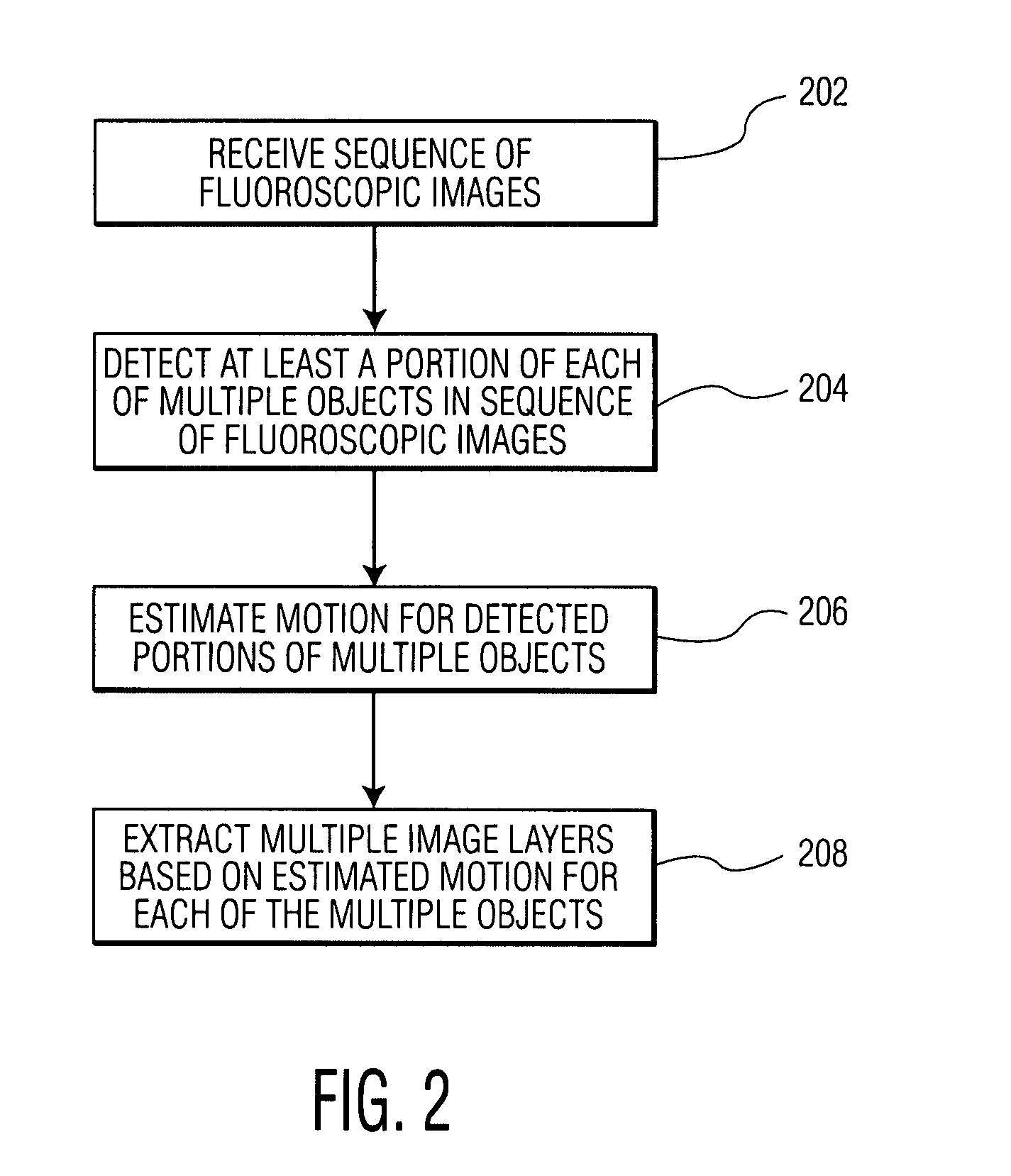
System and Method For Coronary Digital Subtraction Angiography
InactiveUS20080025588A1SurgeryRecognition of medical/anatomical patternsAnatomical structuresFluoroscopic image
A method and system for extracting motion-based layers from fluoroscopic image sequences are disclosed. Portions of multiple objects, such as anatomical structures, are detected in the fluoroscopic images. Motion of the objects is estimated between the images is the sequence of fluoroscopic images. The images in the fluoroscopic image sequence are then divided into layers based on the estimated motion. In a particular implementation, the coronary vessel tree and the diaphragm can be extracted in separate motion layers from coronary angiograph fluoroscopic image sequence.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC +1
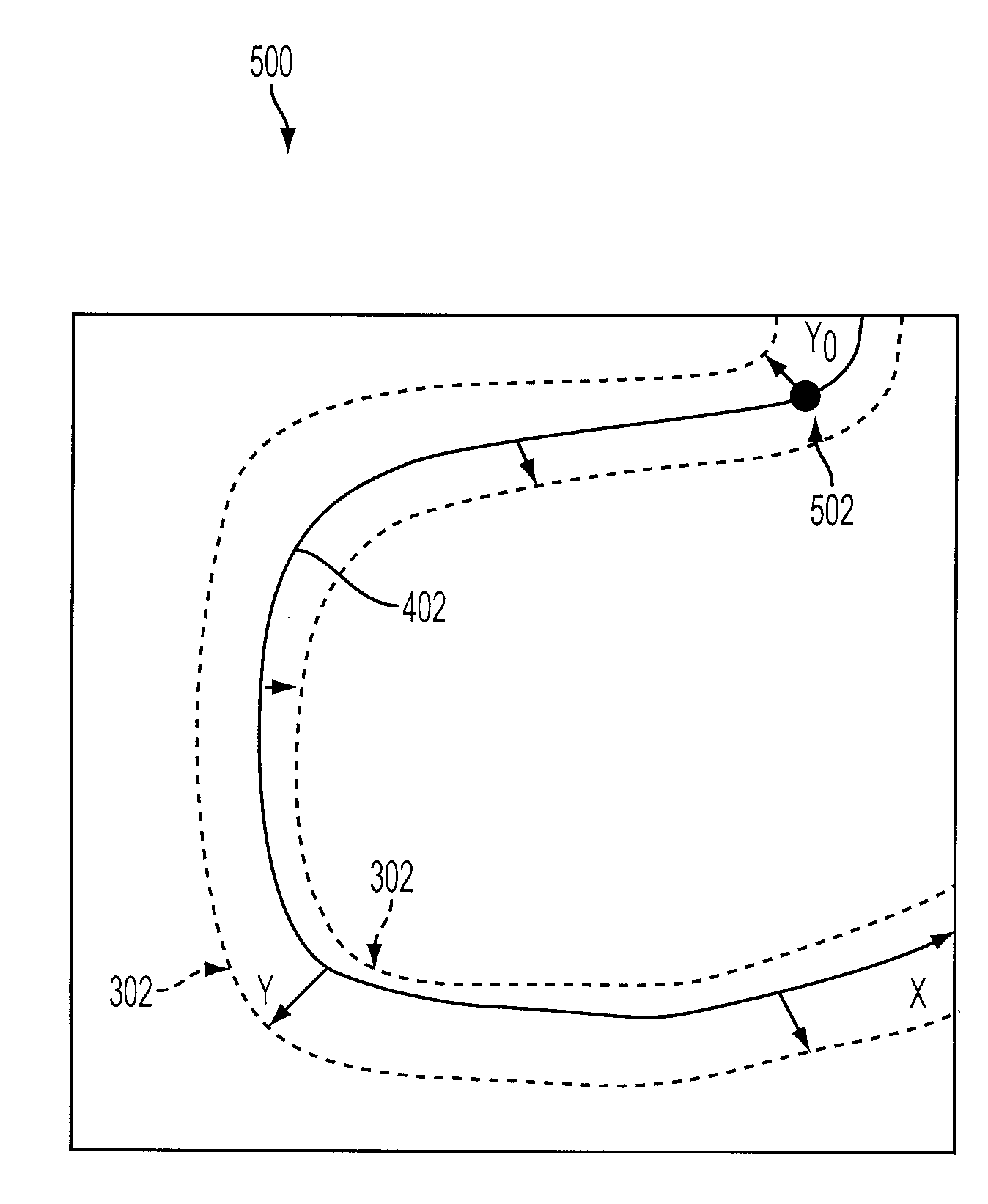
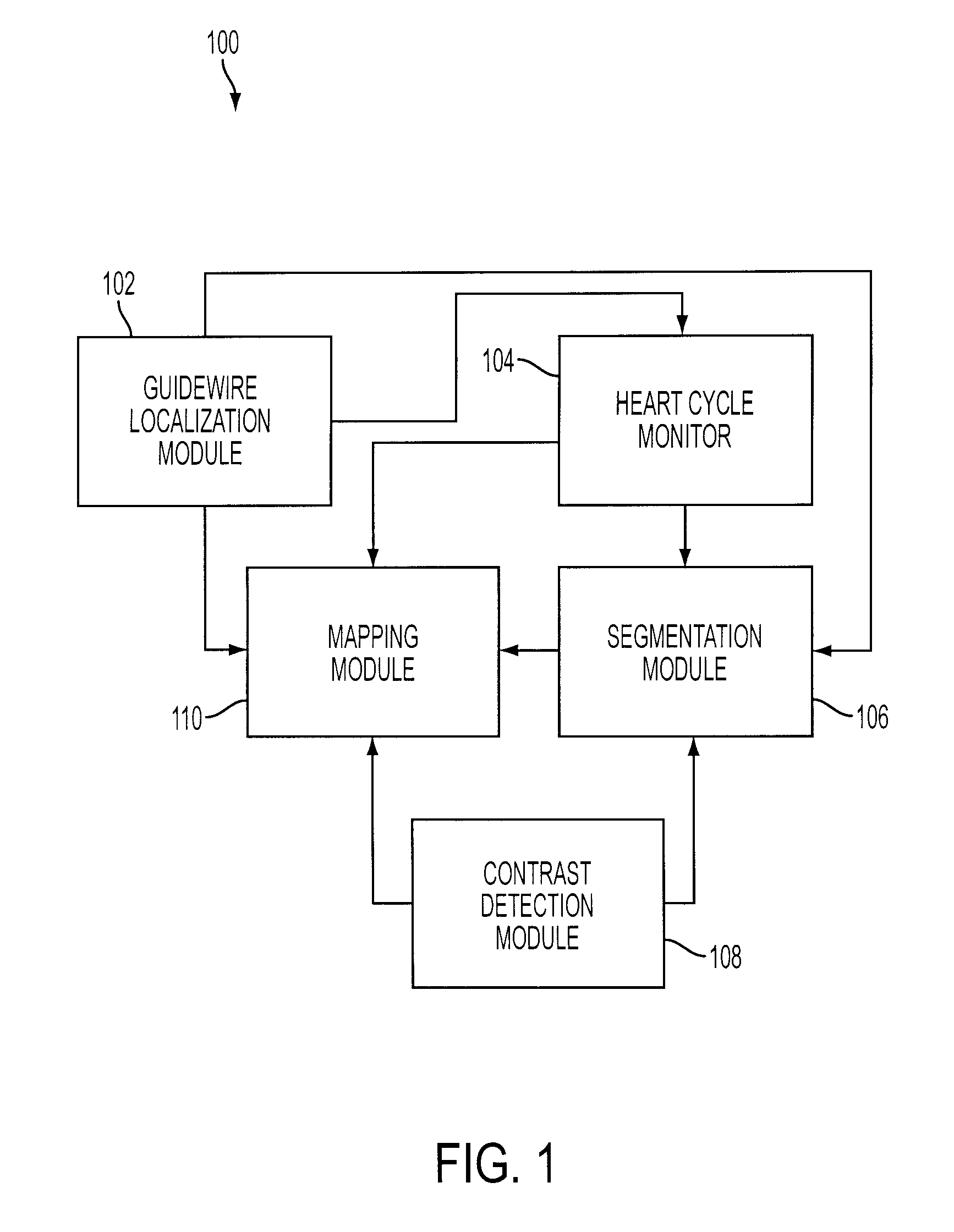
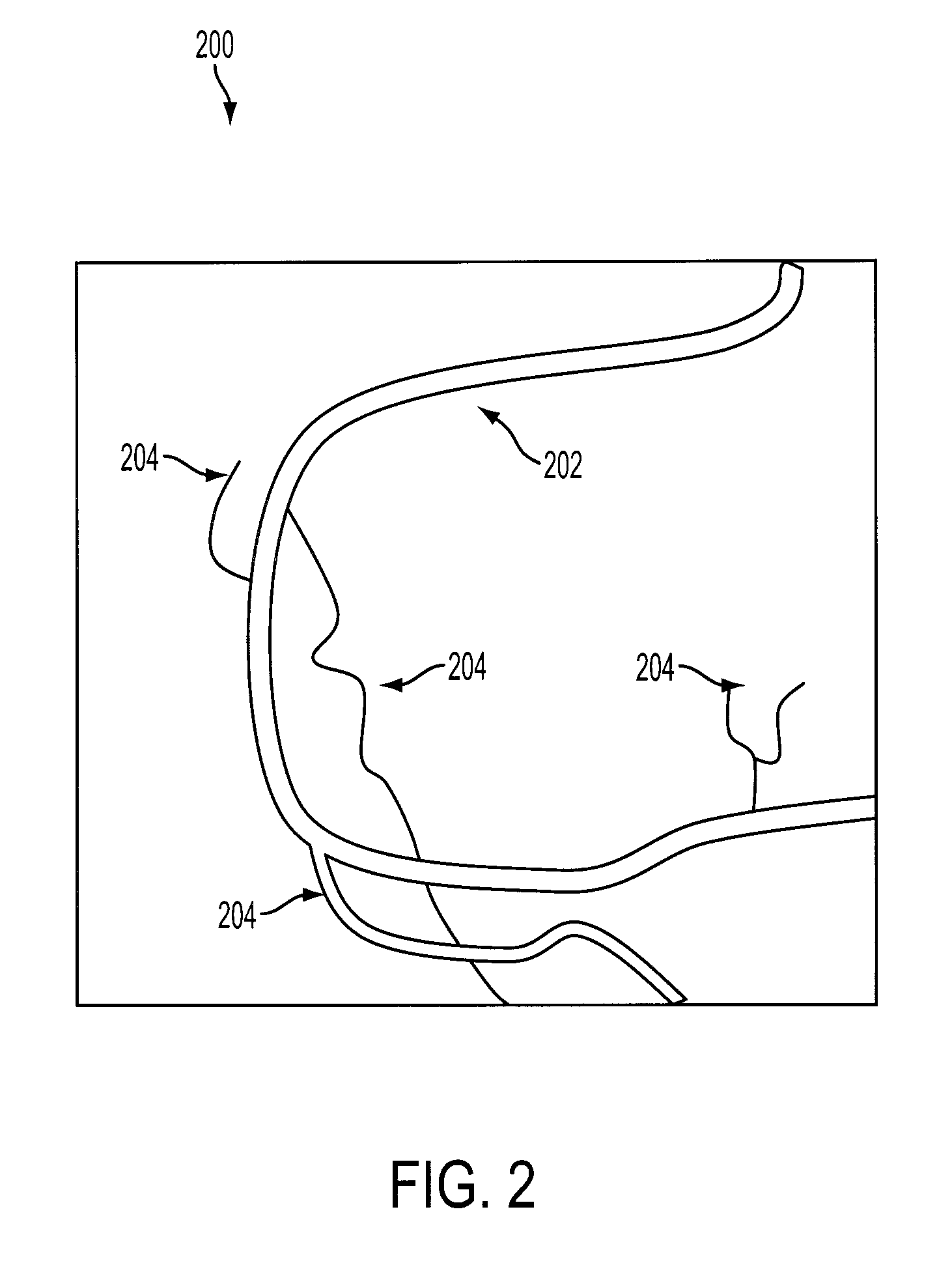
Methods and apparatus for virtual coronary mapping
A virtual map of vessels of interest in medical procedures, such as coronary angioplasty is created so that doses of contrasting agent given to a patient may be reduced. A position of a coronary guidewire is determined and locations of vessel boundaries are found. When the contrast agent has dissipated, virtual maps of the vessels are created as new images. The locations of the determined vessel boundaries are imported to a mapping system and an image obtained without using a contrast agent is modified based on the imported locations of vessel boundaries. This creates a virtual map of the vessels.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and system for non-invasive functional assessment of coronary artery stenosis
A method and system for non-invasive assessment of coronary artery stenosis is disclosed. Patient-specific anatomical measurements of the coronary arteries are extracted from medical image data of a patient acquired during rest state. Patient-specific rest state boundary conditions of a model of coronary circulation representing the coronary arteries are calculated based on the patient-specific anatomical measurements and non-invasive clinical measurements of the patient at rest. Patient-specific rest state boundary conditions of the model of coronary circulation representing the coronary arteries are calculated based on the patient-specific anatomical measurements and non-invasive clinical measurements of the patient at rest. Hyperemic blood flow and pressure across at least one stenosisregion of the coronary arteries are simulated using the model of coronary circulation and the patient-specific hyperemic boundary conditions. Fractional flow reserve (FFR) is calculated for the at least one stenosis region based on the simulated hyperemic blood flow and pressure.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
System and method for coronary digital subtraction angiography
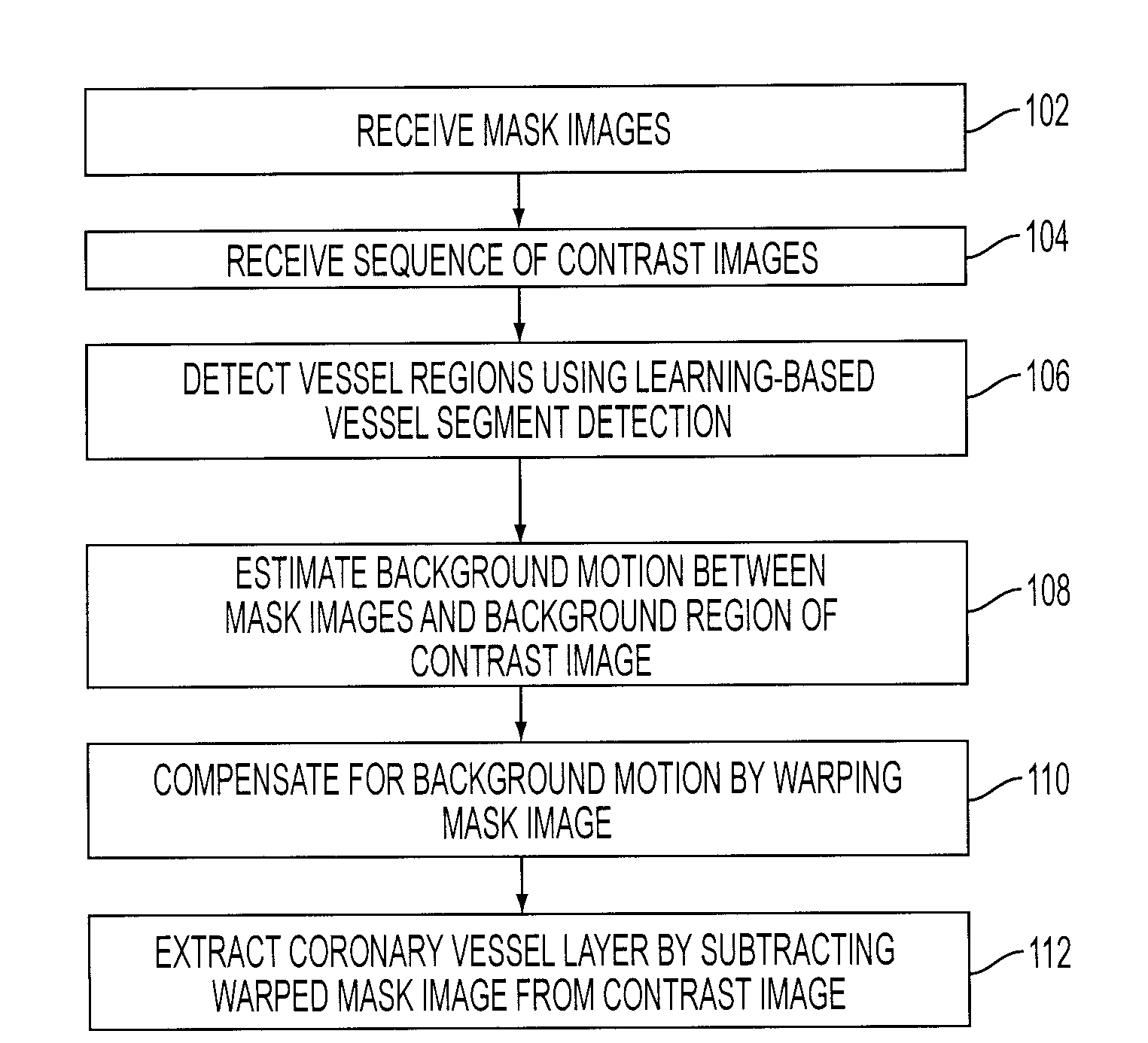
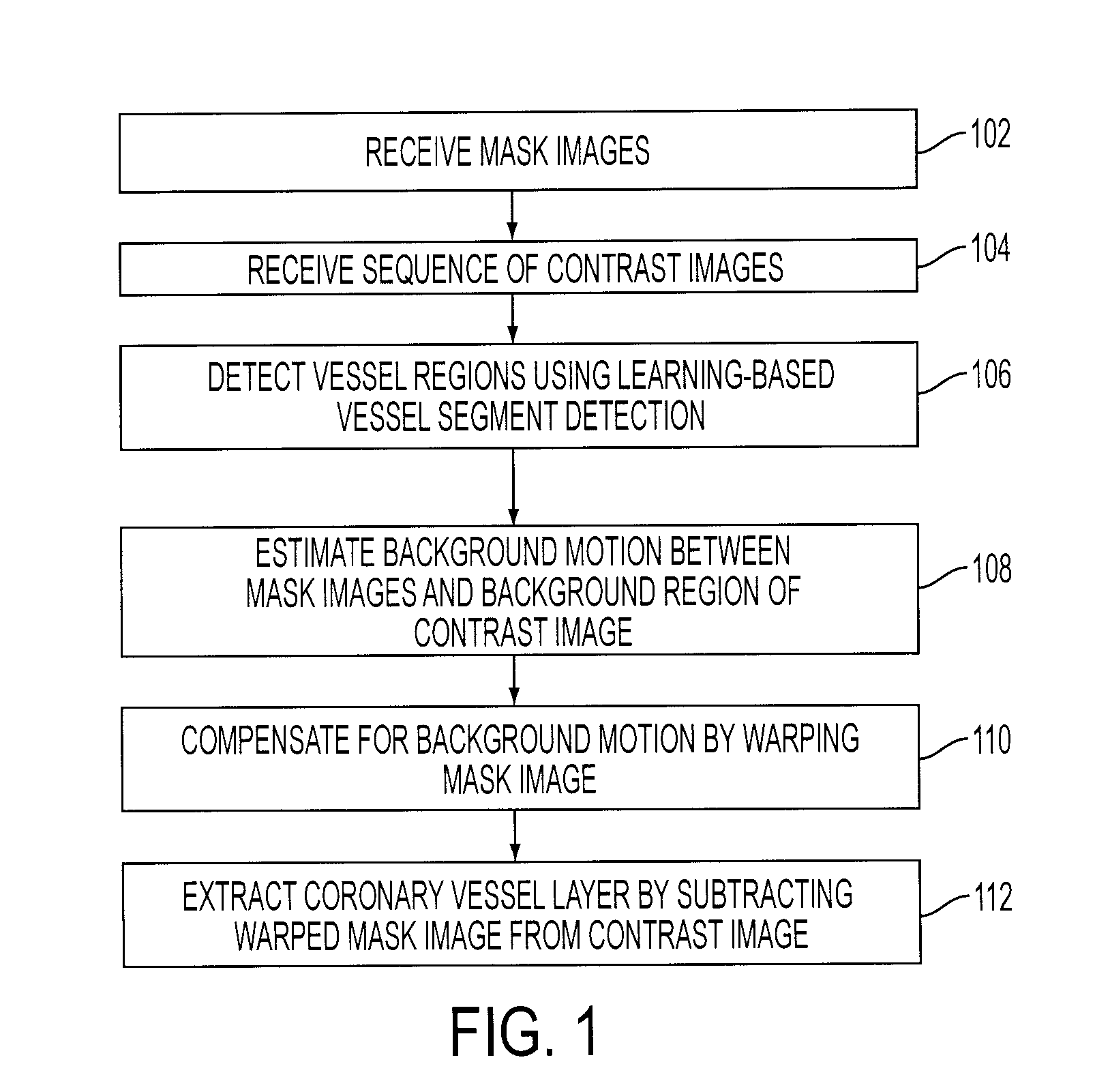
A method and system for extracting coronary vessels fluoroscopic image sequences using coronary digital subtraction angiography (DSA) are disclosed. A set of mask images of a coronary region is received, and a sequence of contrast images for the coronary region is received. For each contrast image, vessel regions are detected in the contrast image using learning-based vessel segment detection and a background region of the contrast image is determined based on the detected vessel regions. Background motion is estimated between one of the mask images and the background region of the contrast image, and the mask image is warped based on the estimated background motion to generate an estimated background layer. The estimated background layer is subtracted from the contrast image to extract a coronary vessel layer for the contrast image.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
Minimally-invasive devices and methods for treatment of congestive heart failure
InactiveUS20080029105A1Relieve painReduce riskSuture equipmentsCannulasAscending aortaCongestive heart failure chf
Owner:ETHICON INC
Catheter devices and methods for their use in the treatment of calcified vascular occlusions
Catheter devices and methods for their use in enhancing fluid flow through a vascular site occupied by a vascular occlusion are provided. The subject catheter devices include at least a first, second and third lumen, where: (a) the first lumen is used for delivery of an acidic dissolution solution to the vascular site; (b) the second lumen is used for delivery of a buffer solution to the vascular site; and (c) the third lumen is used for removal of fluid from the vascular site. In many preferred embodiments, the first, second and third lumens are coaxial. In practicing the subject methods, the vascular site is flushed simultaneously with an acidic dissolution fluid and a buffer solution, where flushing is carried out in a manner such that only a surface of the vascular occlusion is contacted with the acidic dissolution fluid and the remainder of the vascular site is not contacted with fluid having a pH that is lower than about 4. Flushing is carried out in this manner for a period of time sufficient for fluid flow through the vascular site to be enhanced, e.g. increased or established. The subject catheter devices and methods find use in the treatment of a variety of different vascular diseases characterized by the presence of calcified vascular occlusions, including peripheral and coronary vascular diseases.
Owner:CARDINAL HEALTH SWITZERLAND 515 GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com