Patents
Literature
7802results about How to "Lower the volume" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
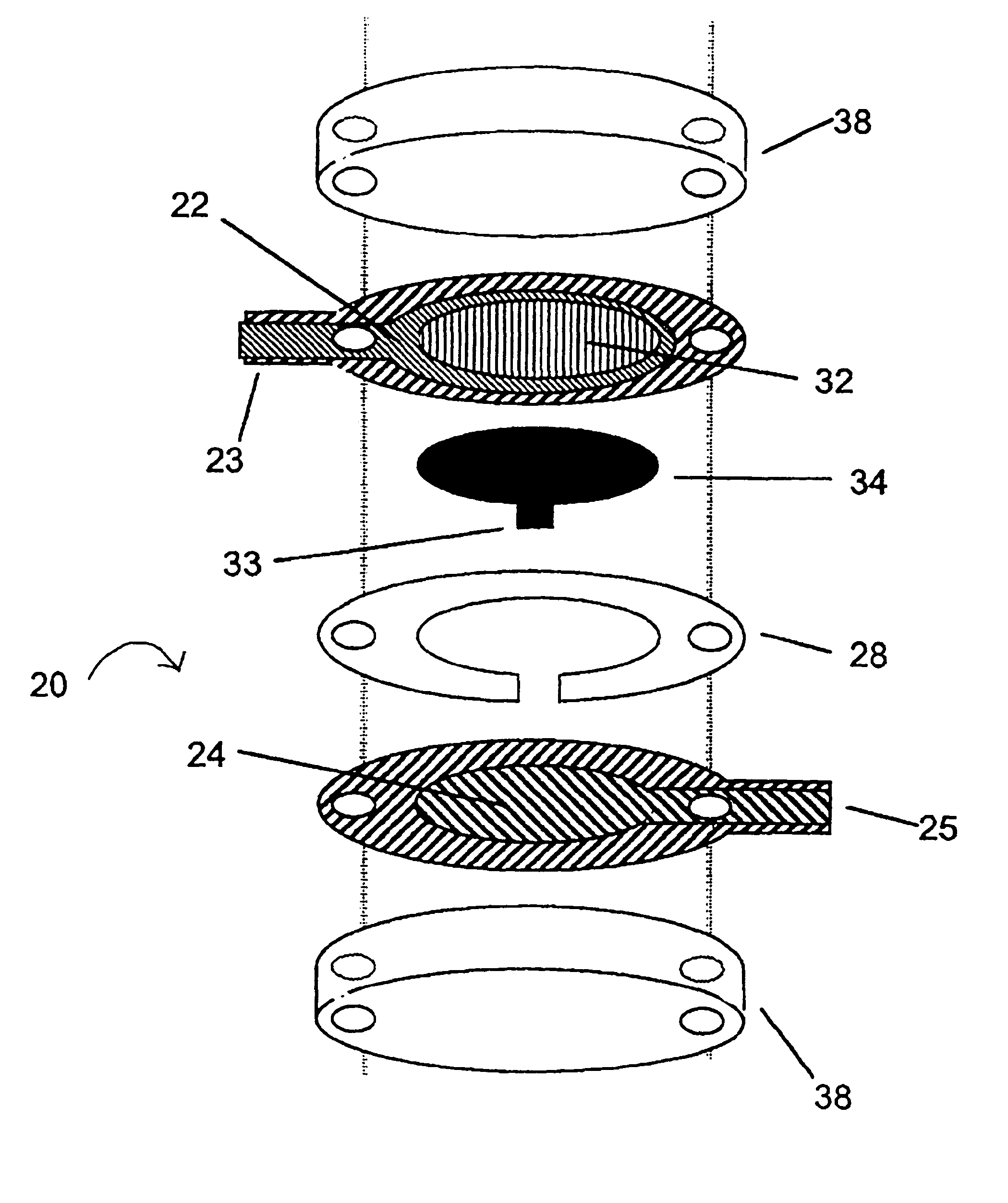
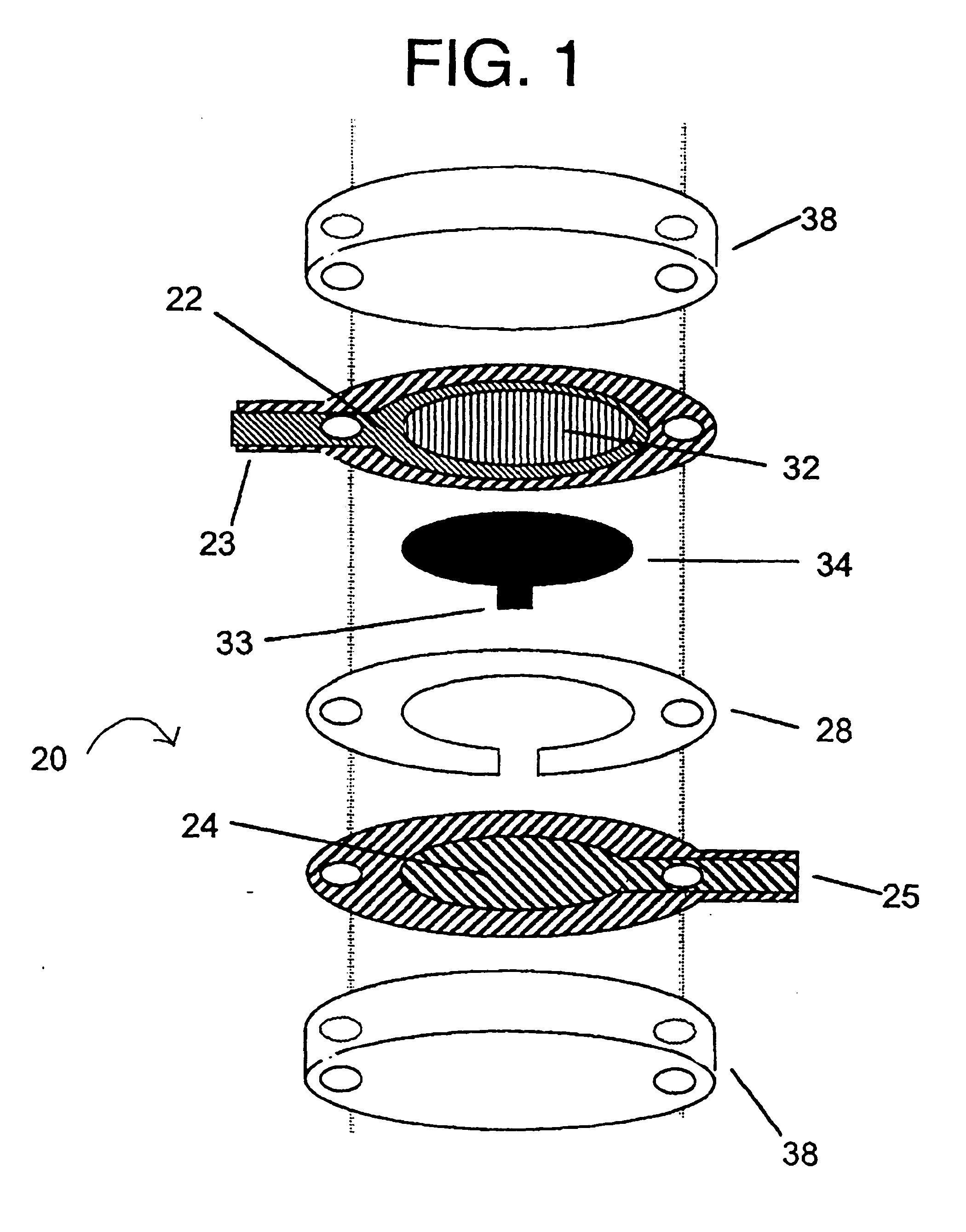
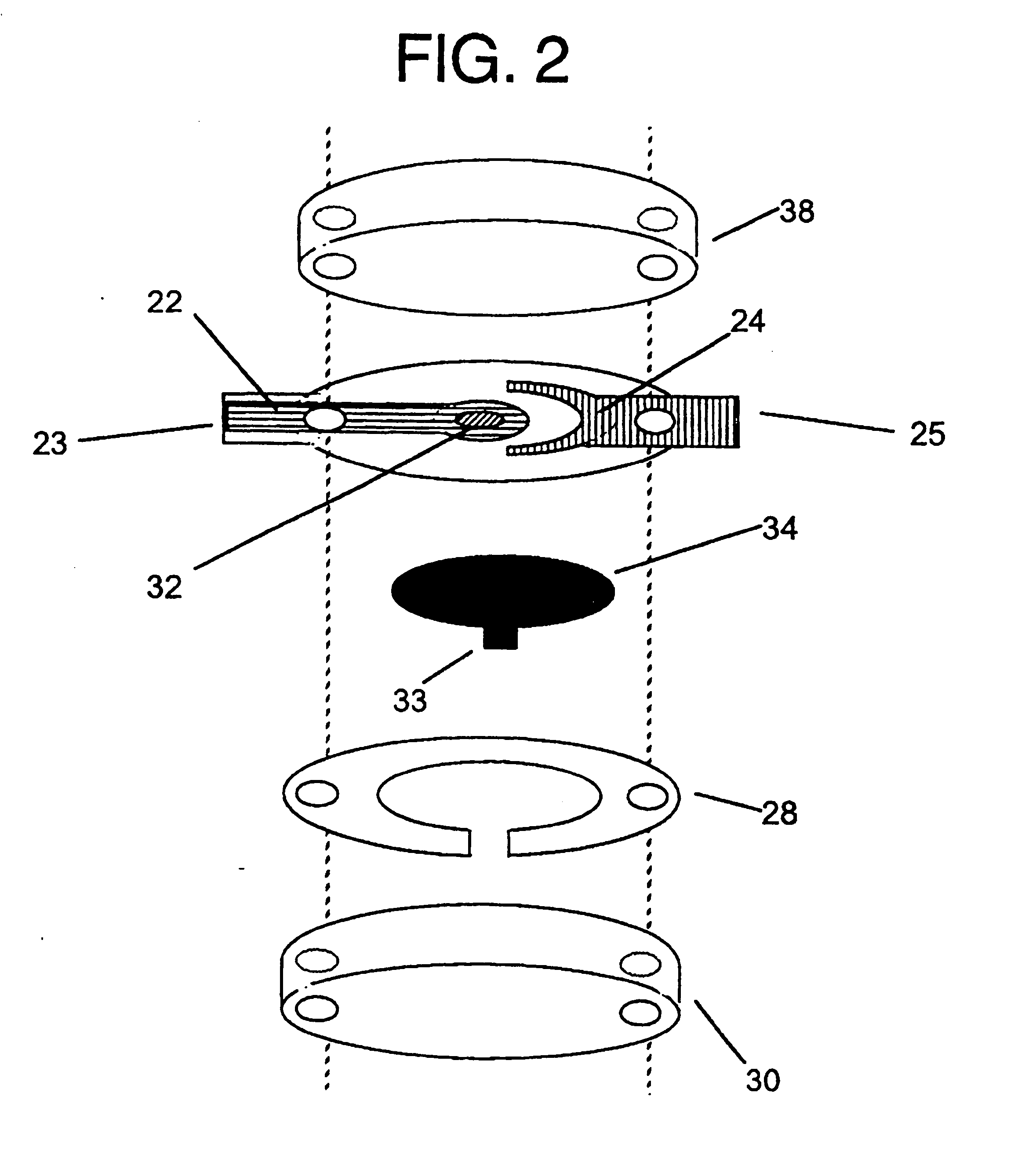
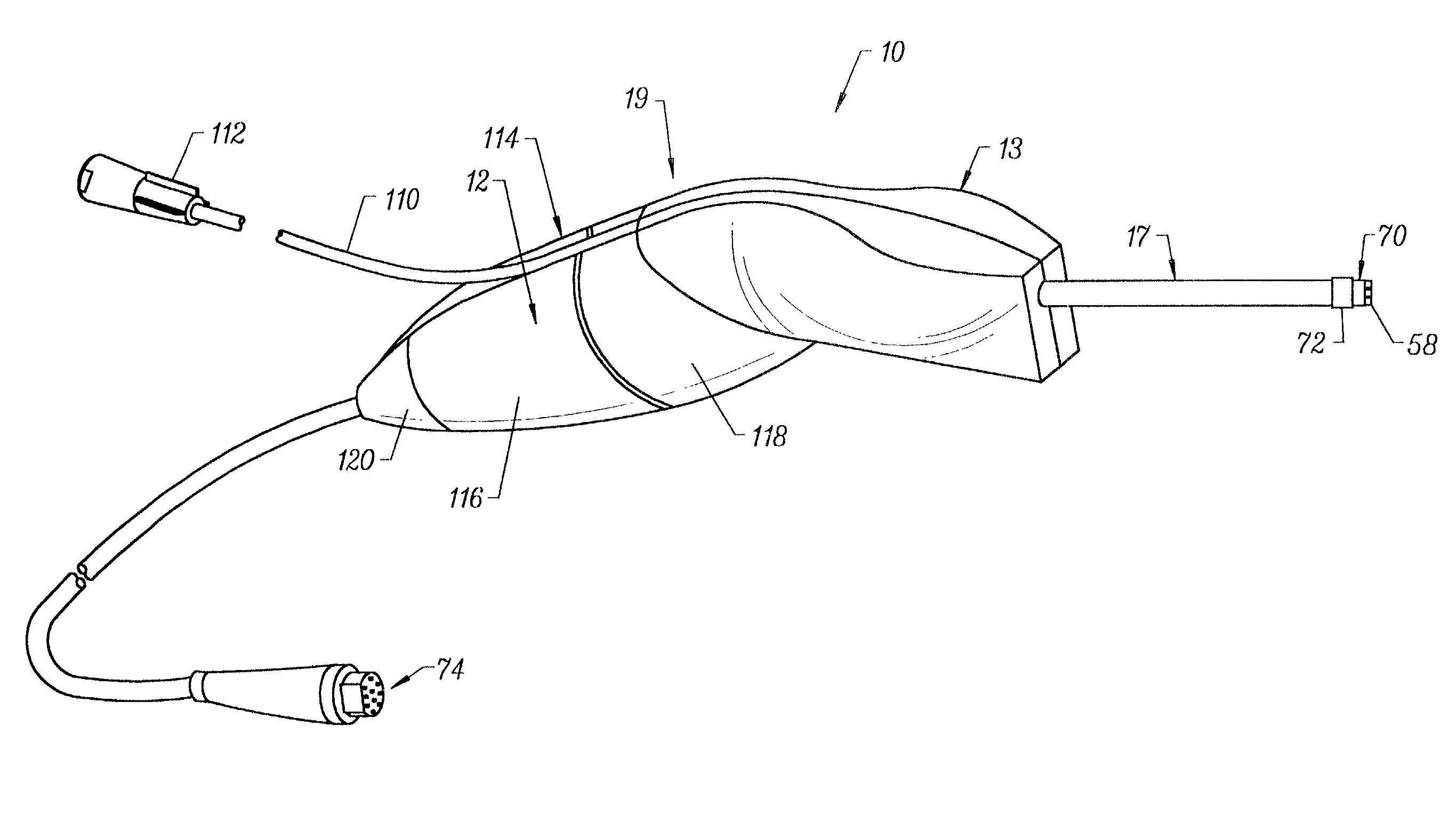
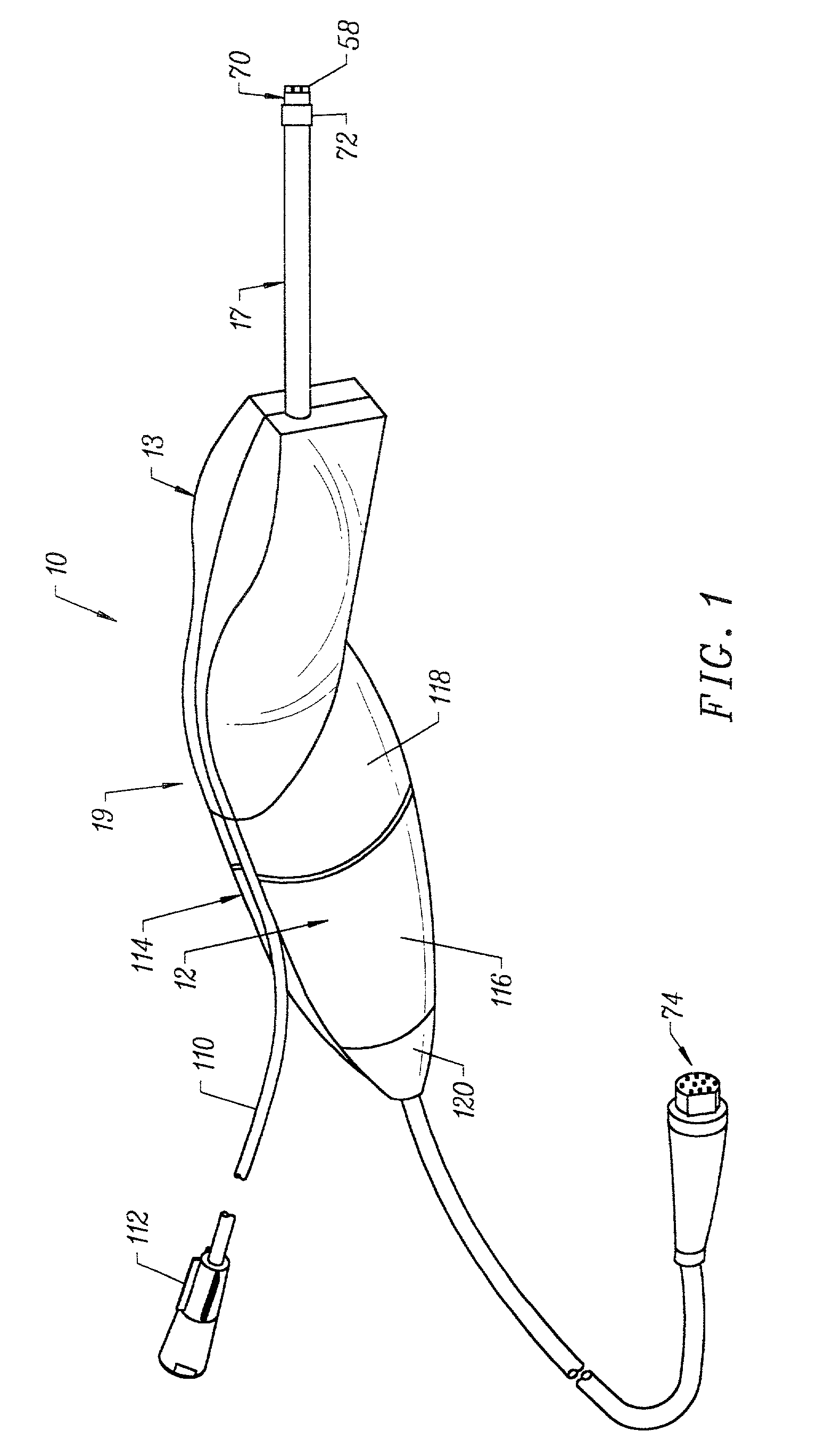
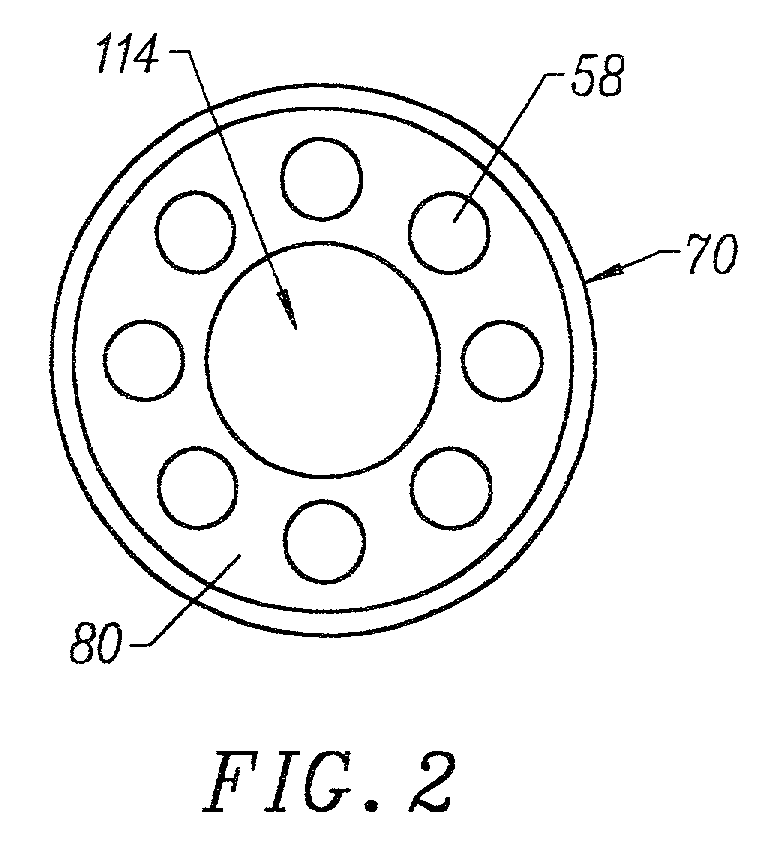
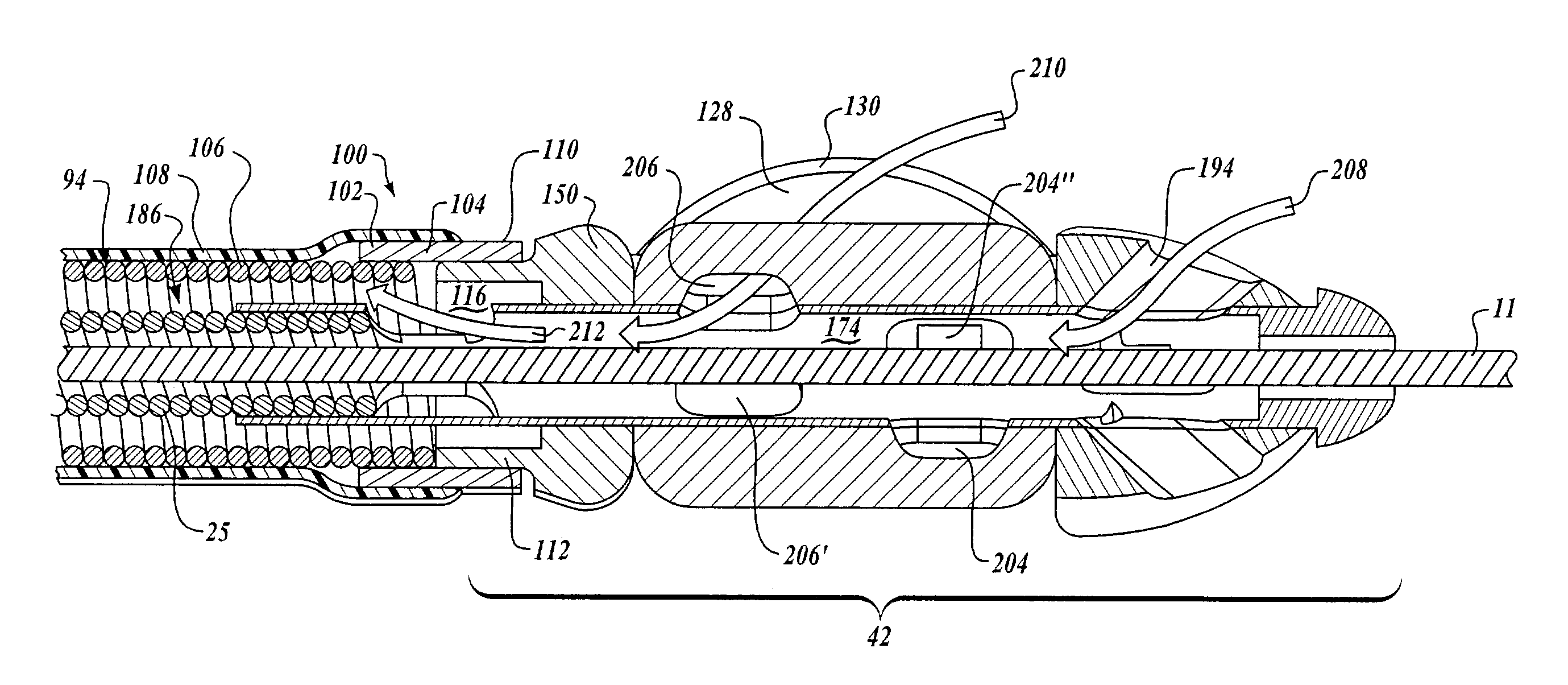
Integrated Lancing and Measurement Device
InactiveUS20080017522A1Accurate and efficient measurementLower the volumeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteMeasurement device
An integrated lancing and measurement device is provided comprising a sensor designed to determine the amount and / or concentration of analyte in a biological fluid having a volume of less than about 1 μL. A piercing member is adapted to pierce and retract from a site on the patient to cause the fluid to flow therefrom, and the sensor is positioned adjacent to the site on the patient so as to receive the fluid flowing from the site to generate an electrical signal indicative of the concentration of the analyte in the fluid. The sensor is comprised of a working electrode comprising an analyte-responsive enzyme and a redox mediator, and a counter electrode. An analyte monitor is operatively connected to the sensor and adapted to measure the signal generated by the sensor. Also provided are analyte measuring methods that optionally employ the integrated lancing and measurement device.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
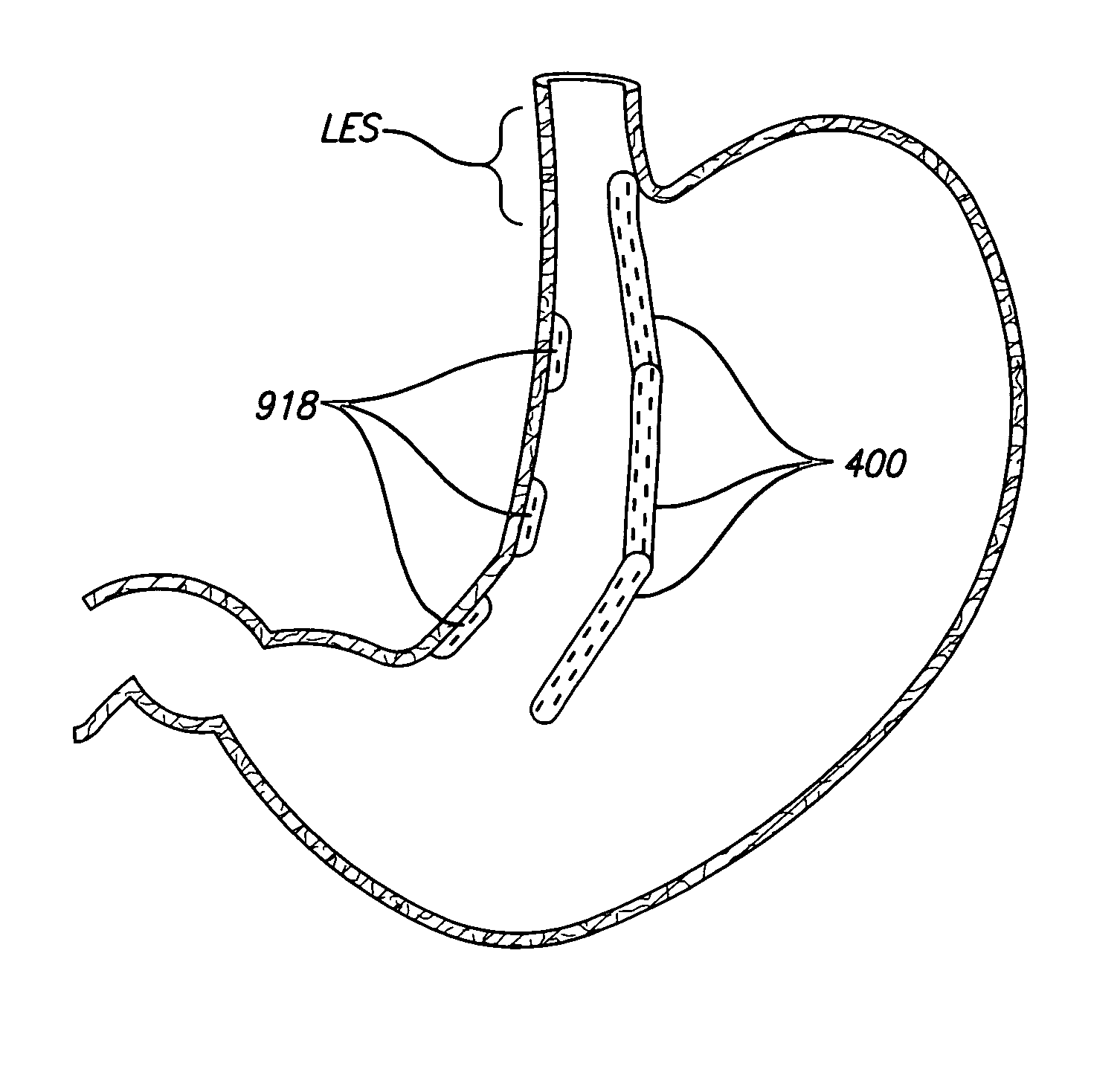
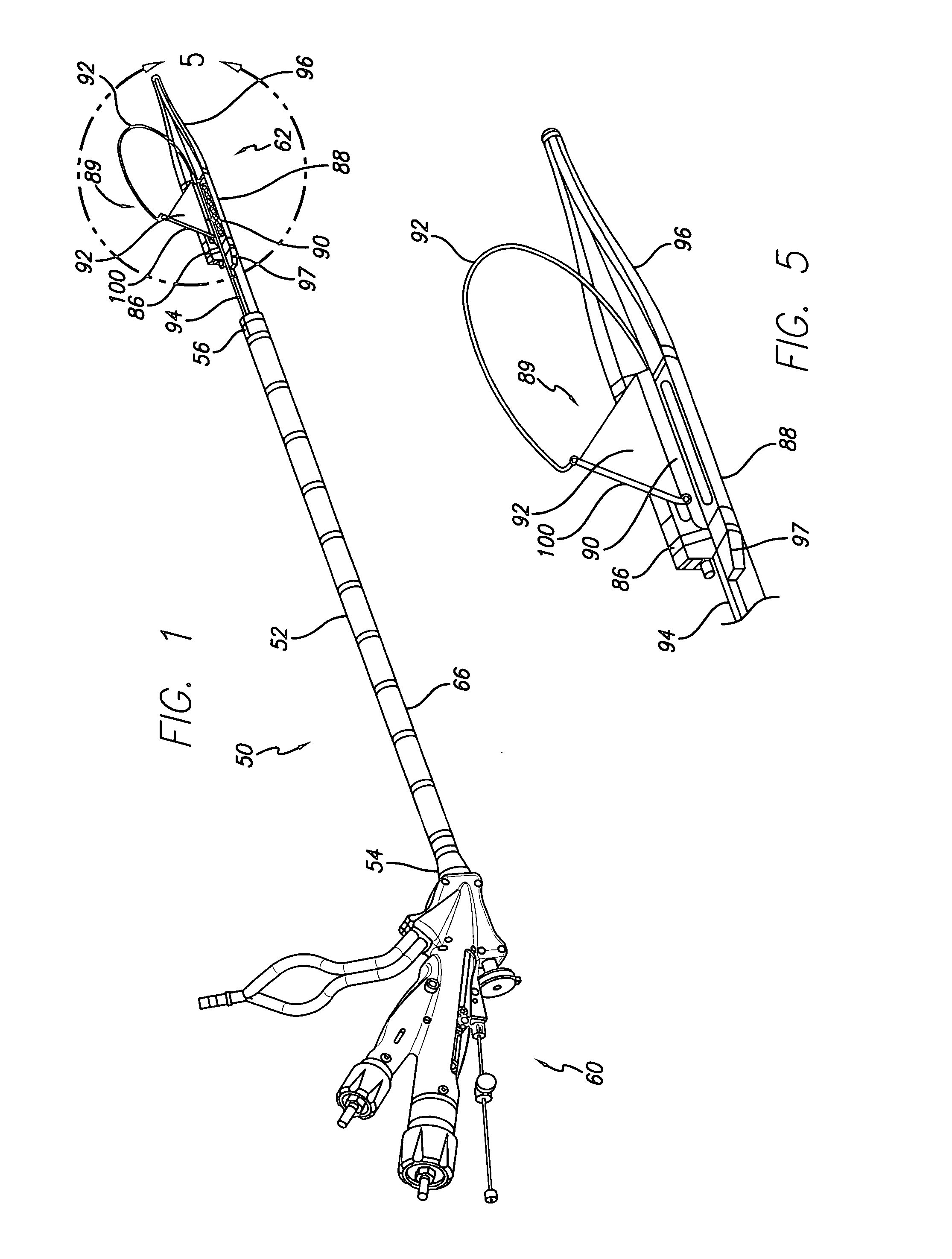
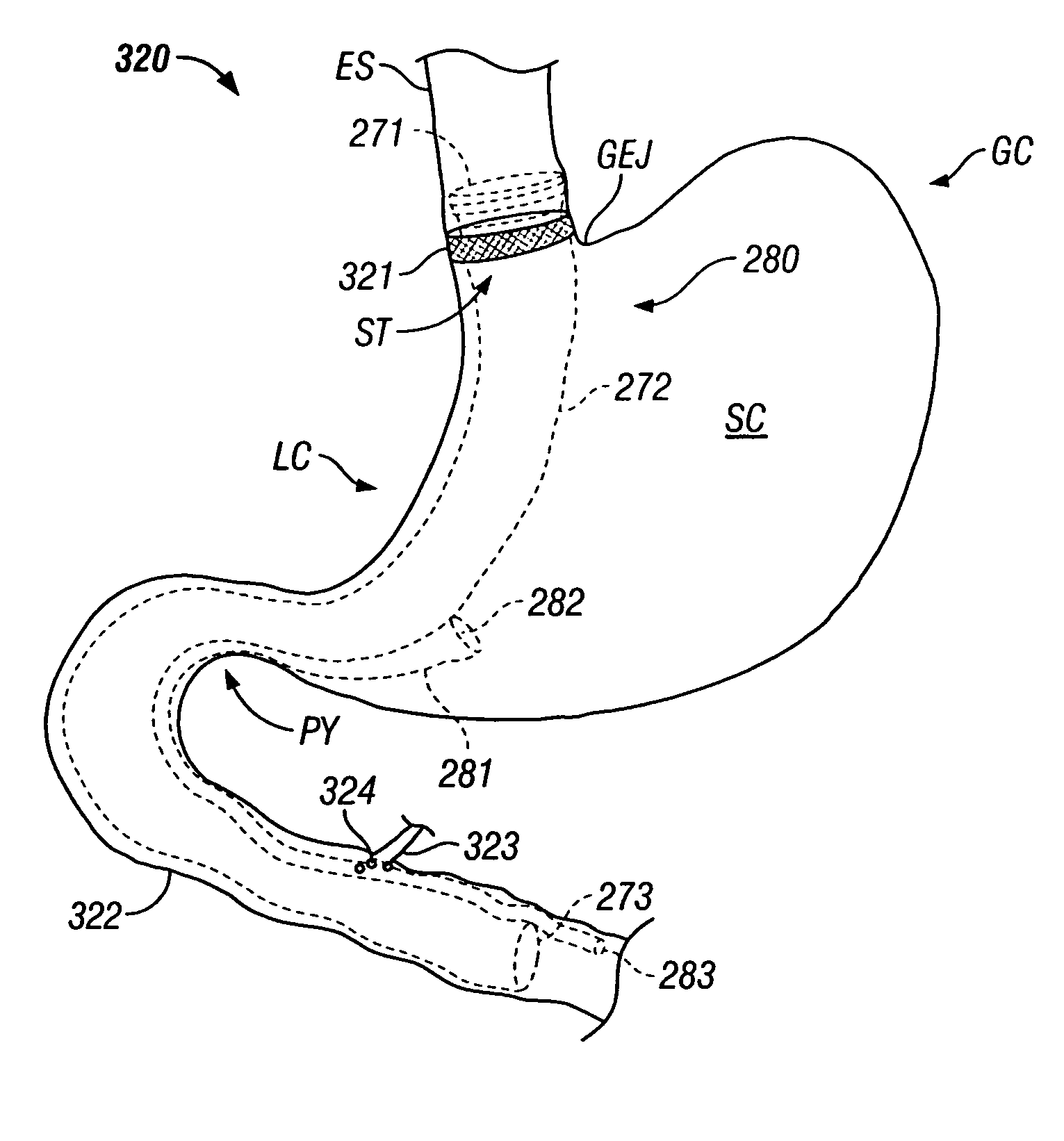
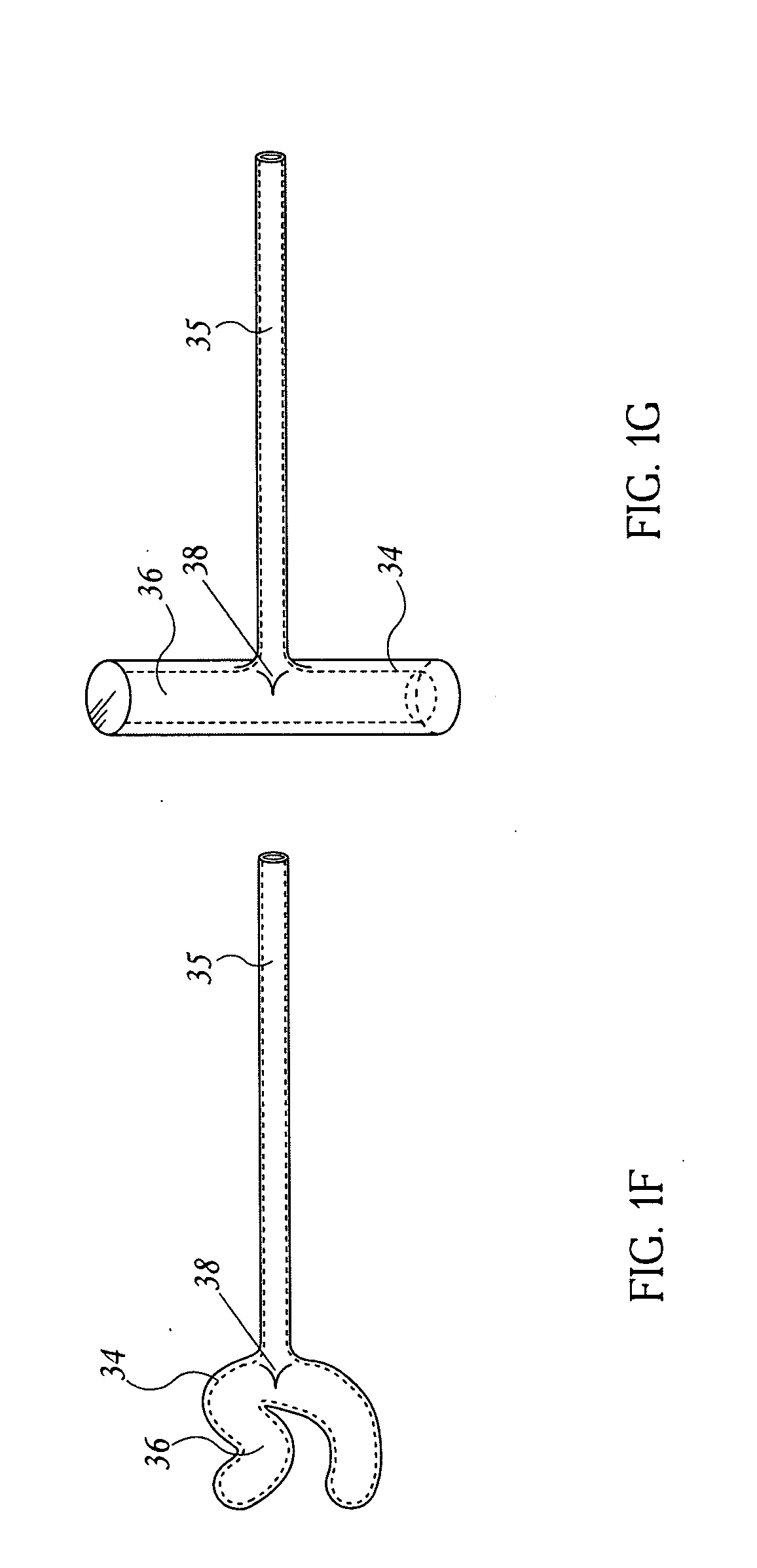
Devices and methods for placement of partitions within a hollow body organ
InactiveUS8449560B2Minimize and eliminate cross acquisitionFacilitate acquisitionSuture equipmentsStapling toolsBody organsBiomedical engineering
Devices and methods for tissue acquisition and fixation, or gastroplasty, are described. Generally, the devices of the system may be advanced in a minimally invasive manner within a patient's body to create one or more plications within the hollow body organ. A tissue treatment device attached to a distal end of a flexible elongated member and has a cartridge member opposite an anvil member. The cartridge member and the anvil member are movable between a closed position and an open position, and a moveable barrier is disposed between the cartridge and anvil members to help acquire a dual fold of tissue. The tissue treatment device can be repositioned to form multiple plications within the organ.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
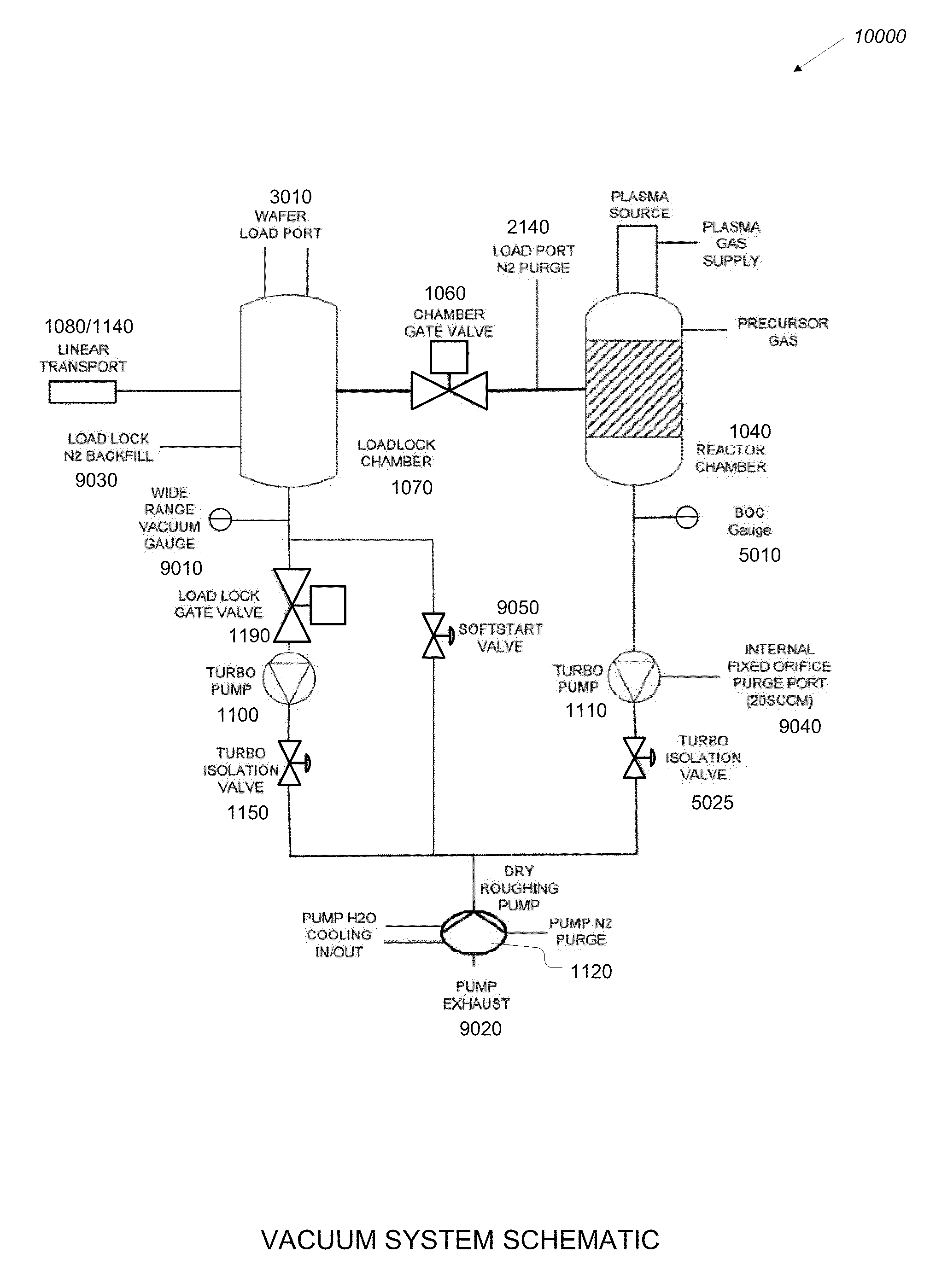
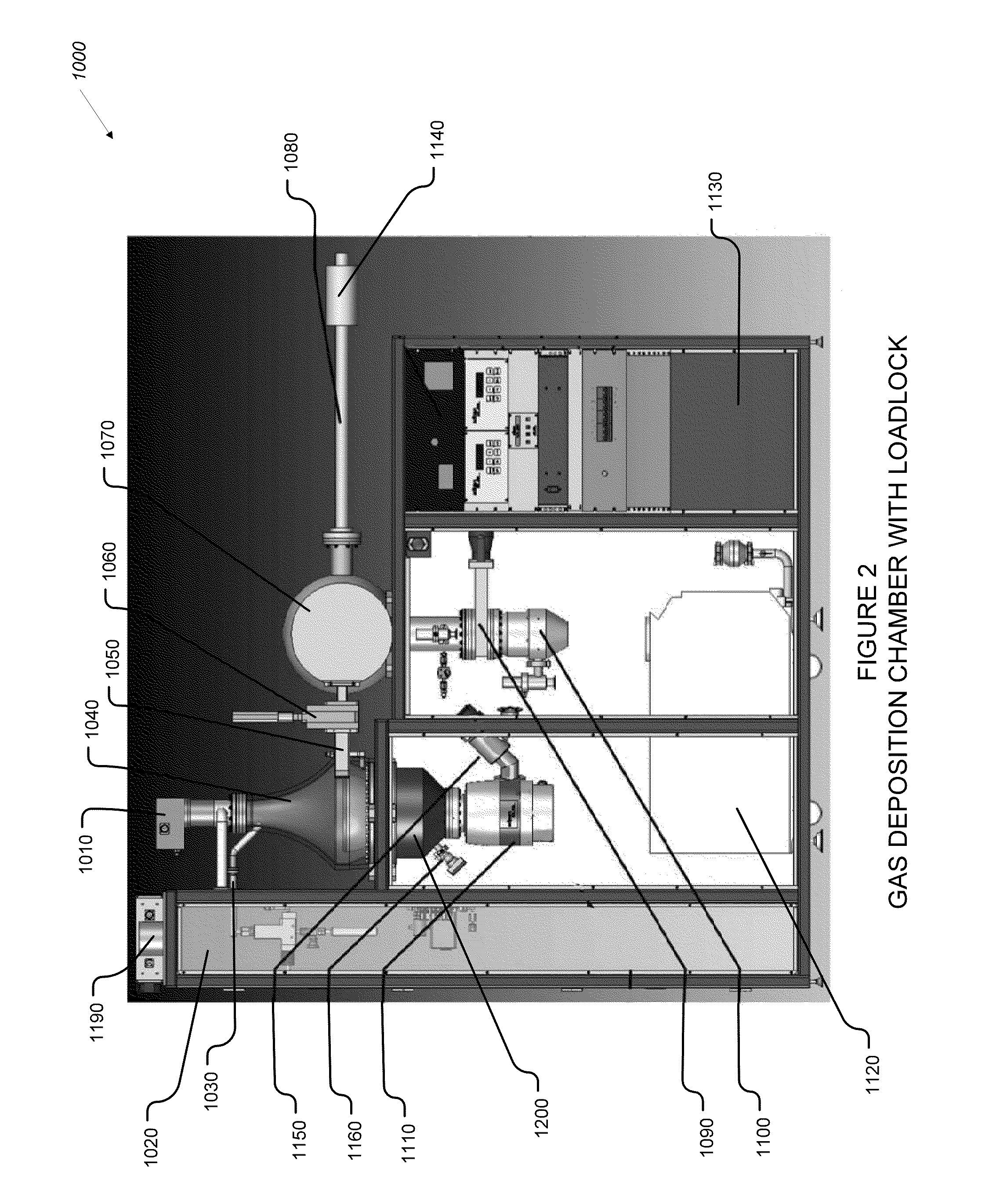
Plasma atomic layer deposition system and method
InactiveUS20100183825A1Lower the volumeShorten cycle timeChemical vapor deposition coatingPlasma techniqueEngineeringAtomic layer deposition
An improved gas deposition chamber includes a hollow gas deposition volume formed with a volume expanding top portion and a substantially constant volume cylindrical middle portion. The hollow gas deposition volume may include a volume reducing lower portion. An aerodynamically shaped substrate support chuck is disposed inside gas deposition chamber with a substrate support surface positioned in the constant volume cylindrical middle portion. The volume expanding top portion reduces gas flow velocity between gas input ports and the substrate support surface. The aerodynamic shape of the substrate support chuck reduces drag and helps to promote laminar flow over the substrate support surface. The volume reducing lower portion helps to increase gas flow velocity after the gas has past the substrate support surface. The improved gas deposition chamber is configurable to 200 mm diameter semiconductor wafers using ALD and or PALD coating cycles. An improved coating method includes expanding process gases inside the deposition chamber prior to the process gas reaching surfaces of a substrate being coated. The method further includes compressing the process gases inside the deposition chamber after the process gas has flowed past surfaces of the substrate being coated.
Owner:ULTRATECH INT INC
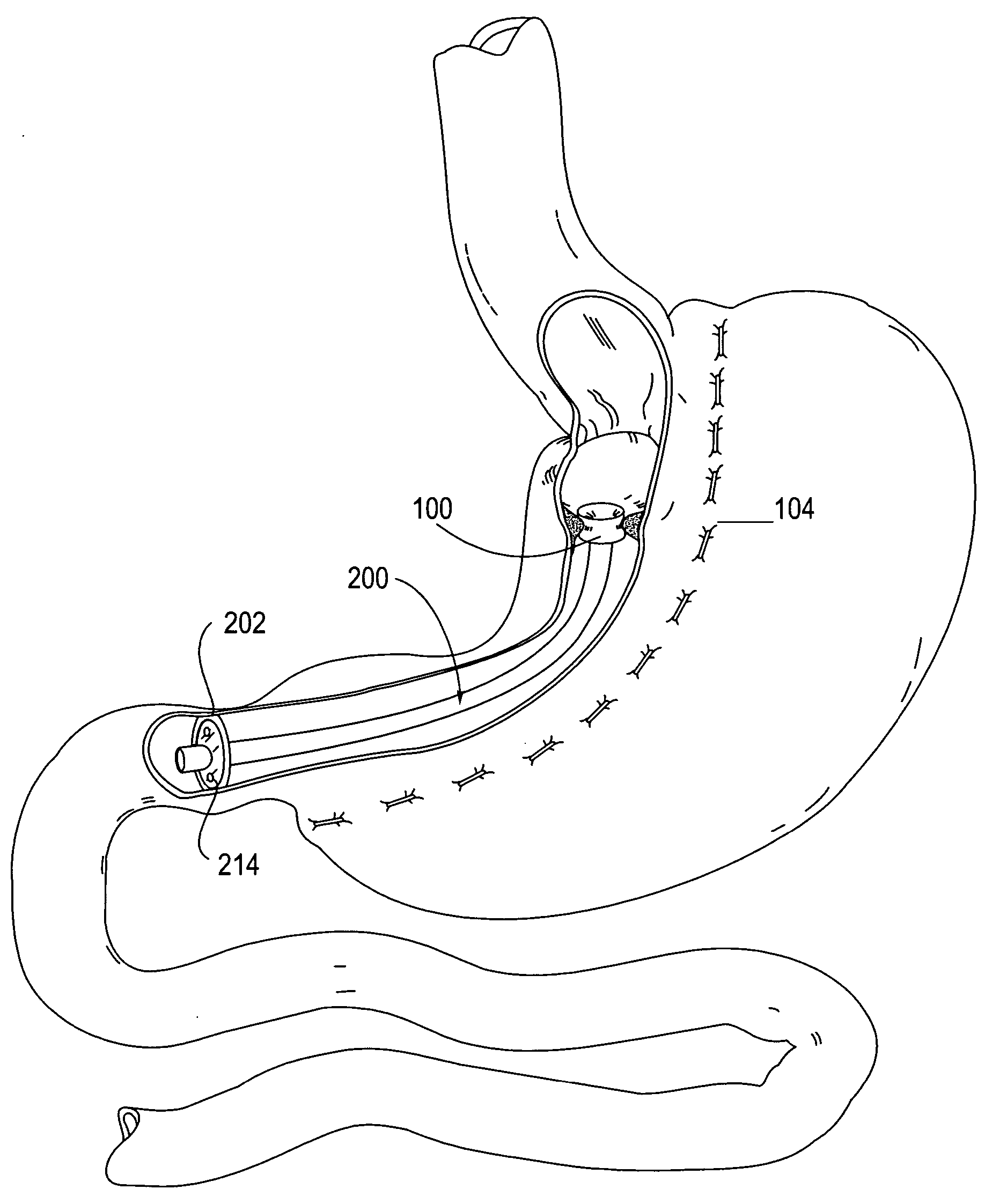
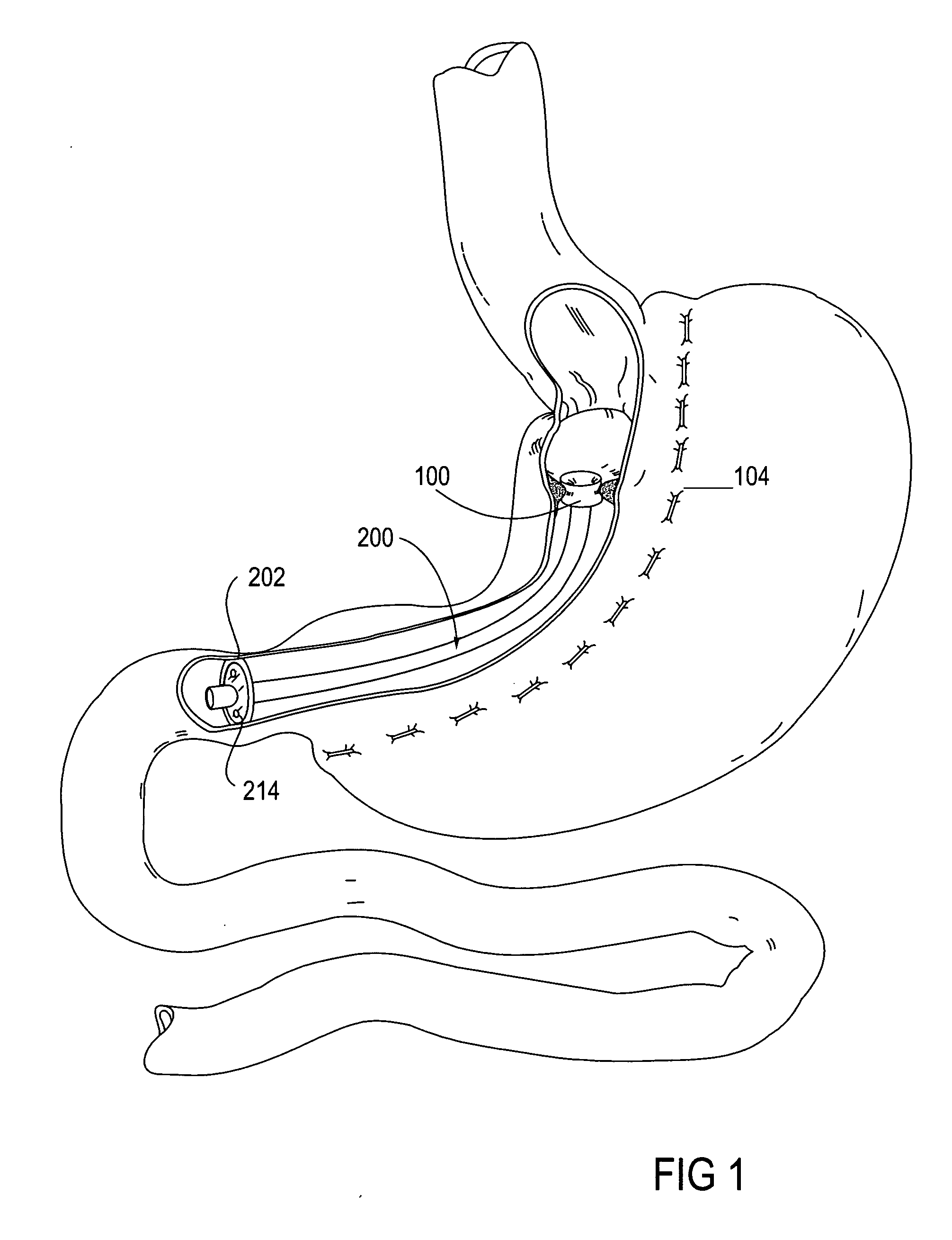
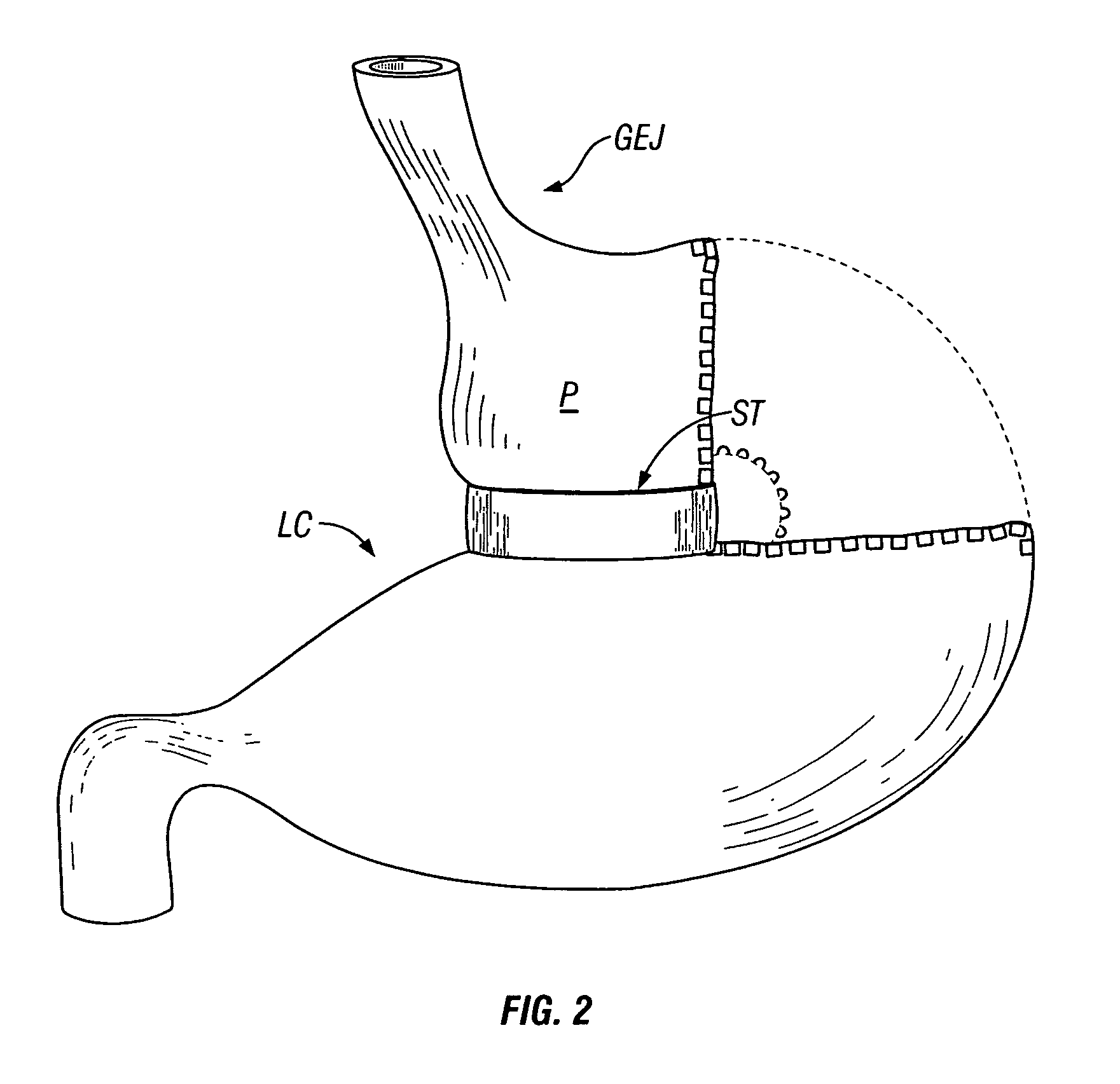
Gastrointestinal sleeve device and methods for treatment of morbid obesity
InactiveUS20050049718A1Effectively reducing stomach volumeStimulating intestinal responseMedical devicesTubular organ implantsIntestinal structureMorbid obesity
Apparatus and methods are described for treatment of morbid obesity using minimally invasive techniques. The apparatus includes a system of components that may be used separately or in combination for effectively reducing stomach volume, bypassing a portion of the stomach and / or small intestines, reducing nutrient absorption in the stomach and / or small intestines and / or depositing minimally or undigested food farther than normal into the intestines, thereby stimulating intestinal responses. The components described include a gastric sleeve device, an intestinal sleeve device, and a combined gastrointestinal sleeve device.
Owner:VALENTX
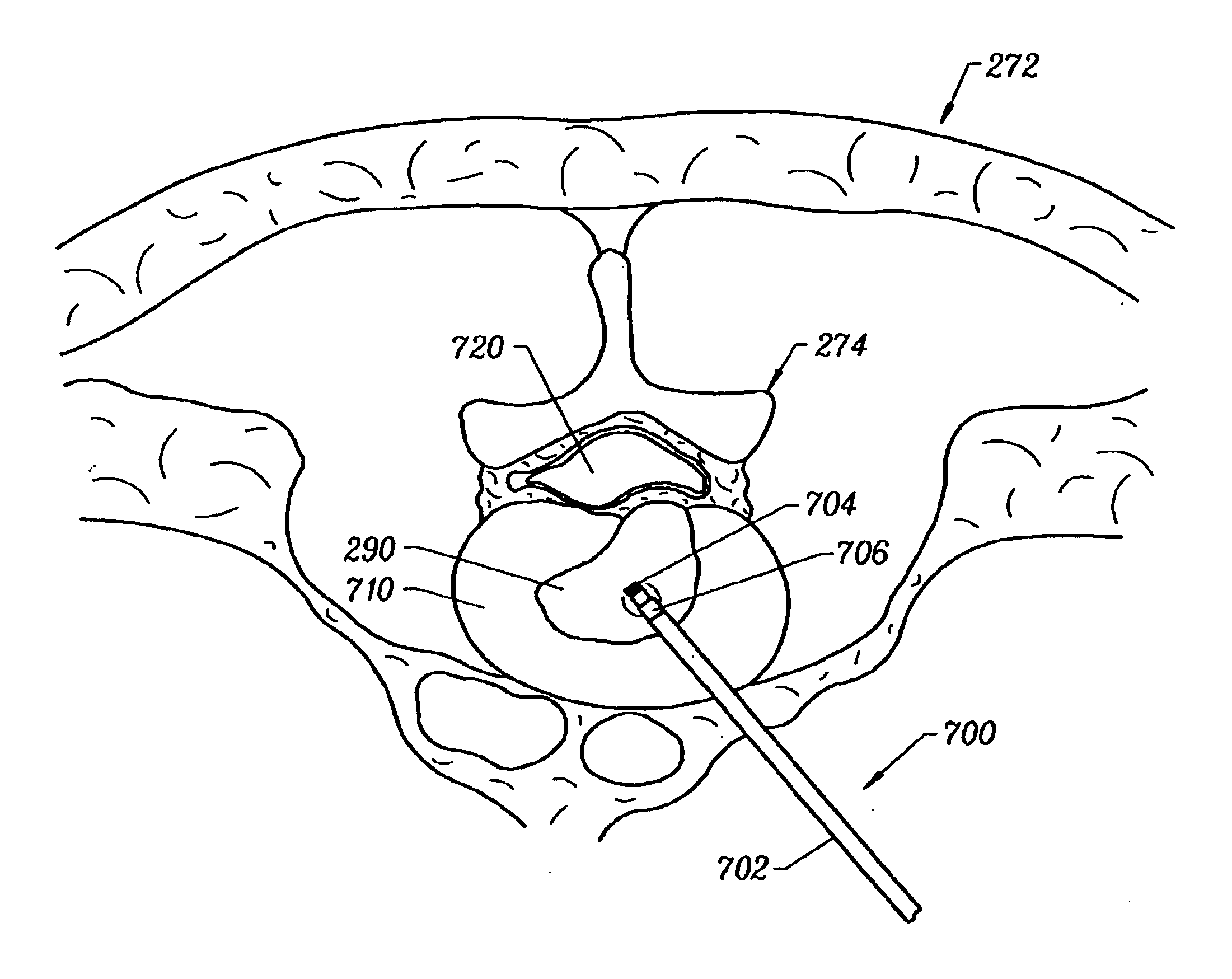
Methods for repairing damaged intervertebral discs
InactiveUS7318823B2Reduce internal pressureReduce moistureBiocideOrganic chemistryIntervertebral discActive electrode
Apparatus and methods for treating an intervertebral disc by ablation of disc tissue. A method of the invention includes positioning at least one active electrode within the intervertebral disc, and applying at least a first high frequency voltage between the active electrode(s) and one or more return electrode(s), wherein the volume of the nucleus pulposus is decreased, pressure exerted by the nucleus pulposus on the annulus fibrosus is reduced, and discogenic pain of a patient is alleviated. In other embodiments, a curved or steerable probe is guided to a specific target site within a disc to be treated, and the disc tissue at the target site is ablated by application of at least a first high frequency voltage between the active electrode(s) and one or more return electrode(s). A method of making an electrosurgical probe is also disclosed.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Porous drug matrices and methods of manufacture thereof
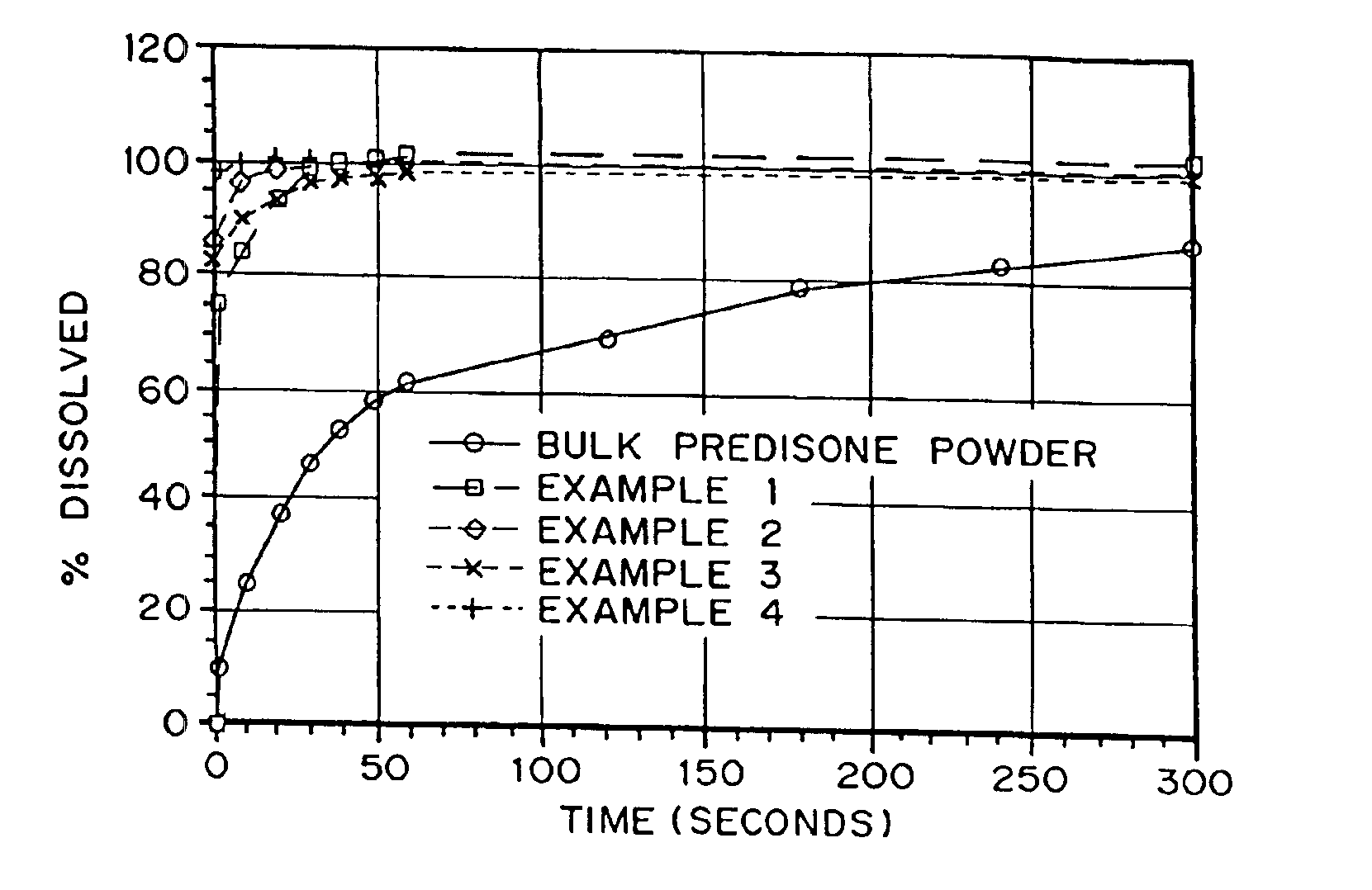
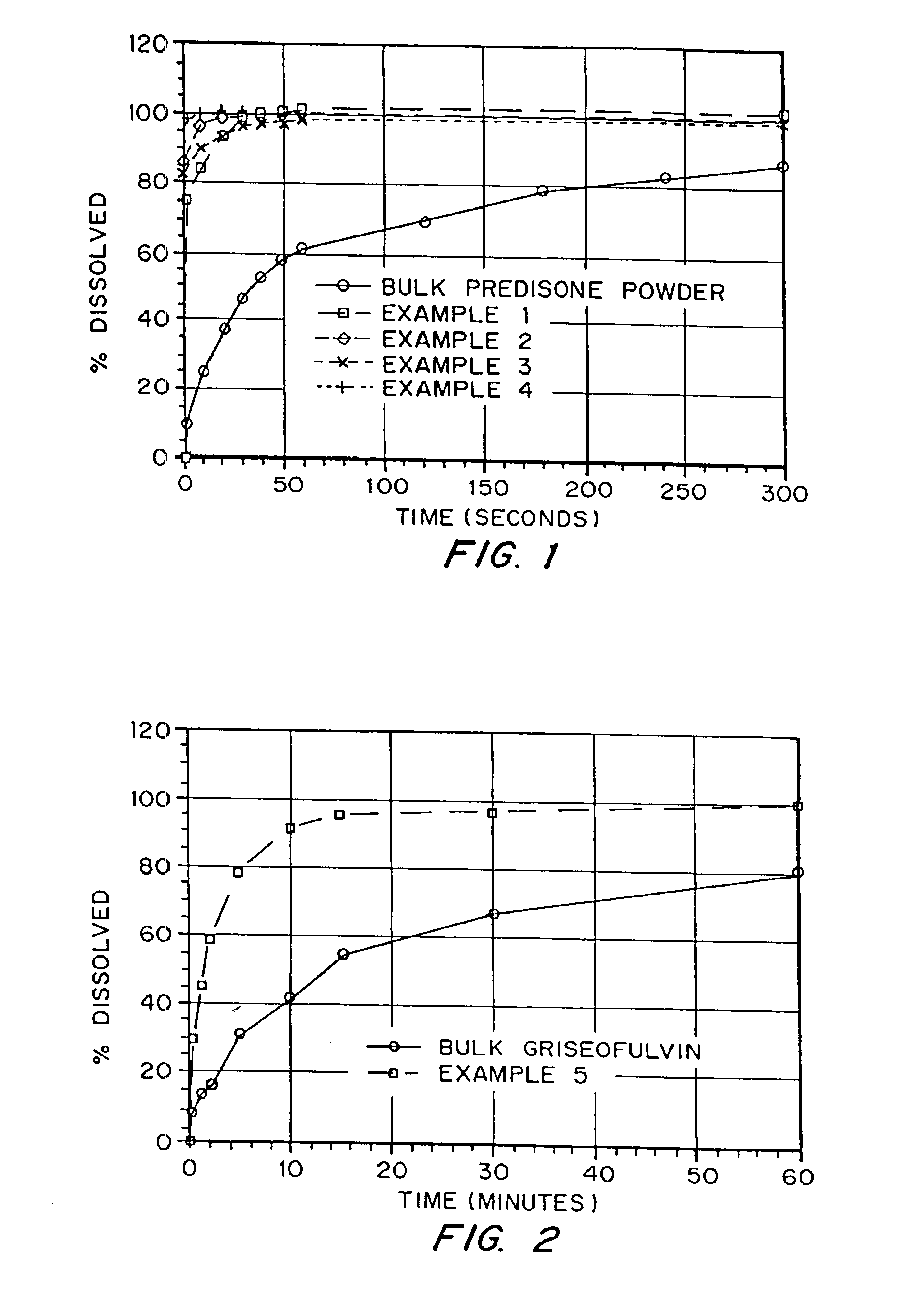
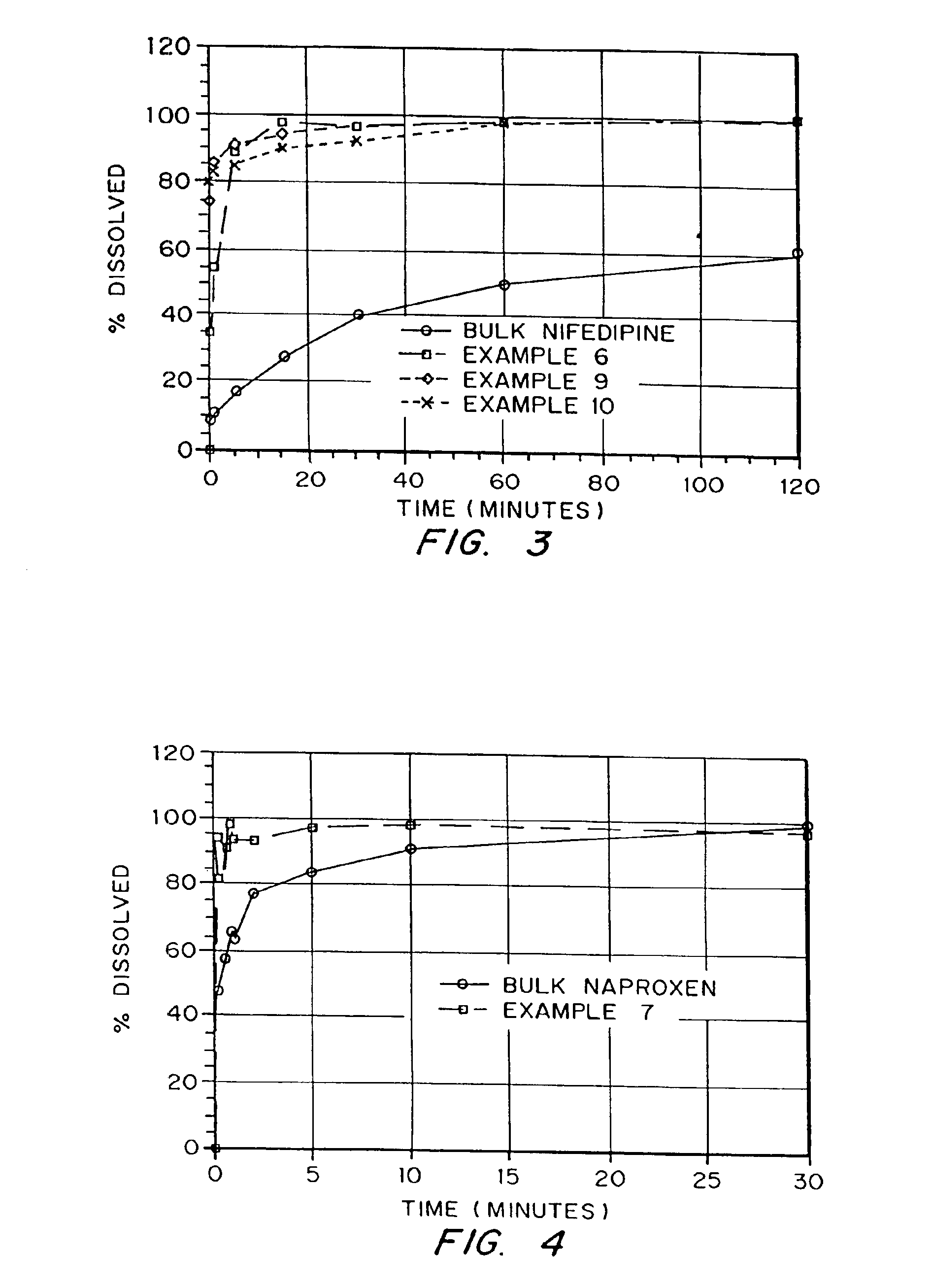
InactiveUS6932983B1Lower the volumePrevent precipitationPowder deliveryNanotechDrugs solutionWater soluble drug
Drugs, especially low aqueous solubility drugs, are provided in a porous matrix form, preferably microparticles, which enhances dissolution of the drug in aqueous media. The drug matrices preferably are made using a process that includes (i) dissolving a drug, preferably a drug having low aqueous solubility, in a volatile solvent to form a drug solution, (ii) combining at least one pore forming agent with the drug solution to form an emulsion, suspension, or second solution, and (iii) removing the volatile solvent and pore forming agent from the emulsion, suspension, or second solution to yield the porous matrix of drug. The pore forming agent can be either a volatile liquid that is immiscible with the drug solvent or a volatile solid compound, preferably a volatile salt. In a preferred embodiment, spray drying is used to remove the solvents and the pore forming agent. The resulting porous matrix has a faster rate of dissolution following administration to a patient, as compared to non-porous matrix forms of the drug. In a preferred embodiment, microparticles of the porous drug matrix are reconstituted with an aqueous medium and administered parenterally, or processed using standard techniques into tablets or capsules for oral administration.
Owner:ACUSPHERE INC
Method and device for use in endoscopic organ procedures
InactiveUS7220237B2Maintain alimentary flowImprove adhesionDiagnosticsSurgical instrument detailsStomaBody organs
Methods and devices for use in tissue approximation and fixation are described herein. The present invention provides, in part, methods and devices for acquiring tissue folds in a circumferential configuration within a hollow body organ, e.g., a stomach, positioning the tissue folds for affixing within a fixation zone of the stomach, preferably to create a pouch or partition below the esophagus, and fastening the tissue folds such that a tissue ring, or stomas, forms excluding the pouch from the greater stomach cavity. The present invention further provides for a liner or bypass conduit which is affixed at a proximal end either to the tissue ring or through some other fastening mechanism. The distal end of the conduit is left either unanchored or anchored within the intestinal tract. This bypass conduit also includes a fluid bypass conduit which allows the stomach and a portion of the intestinal tract to communicate.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
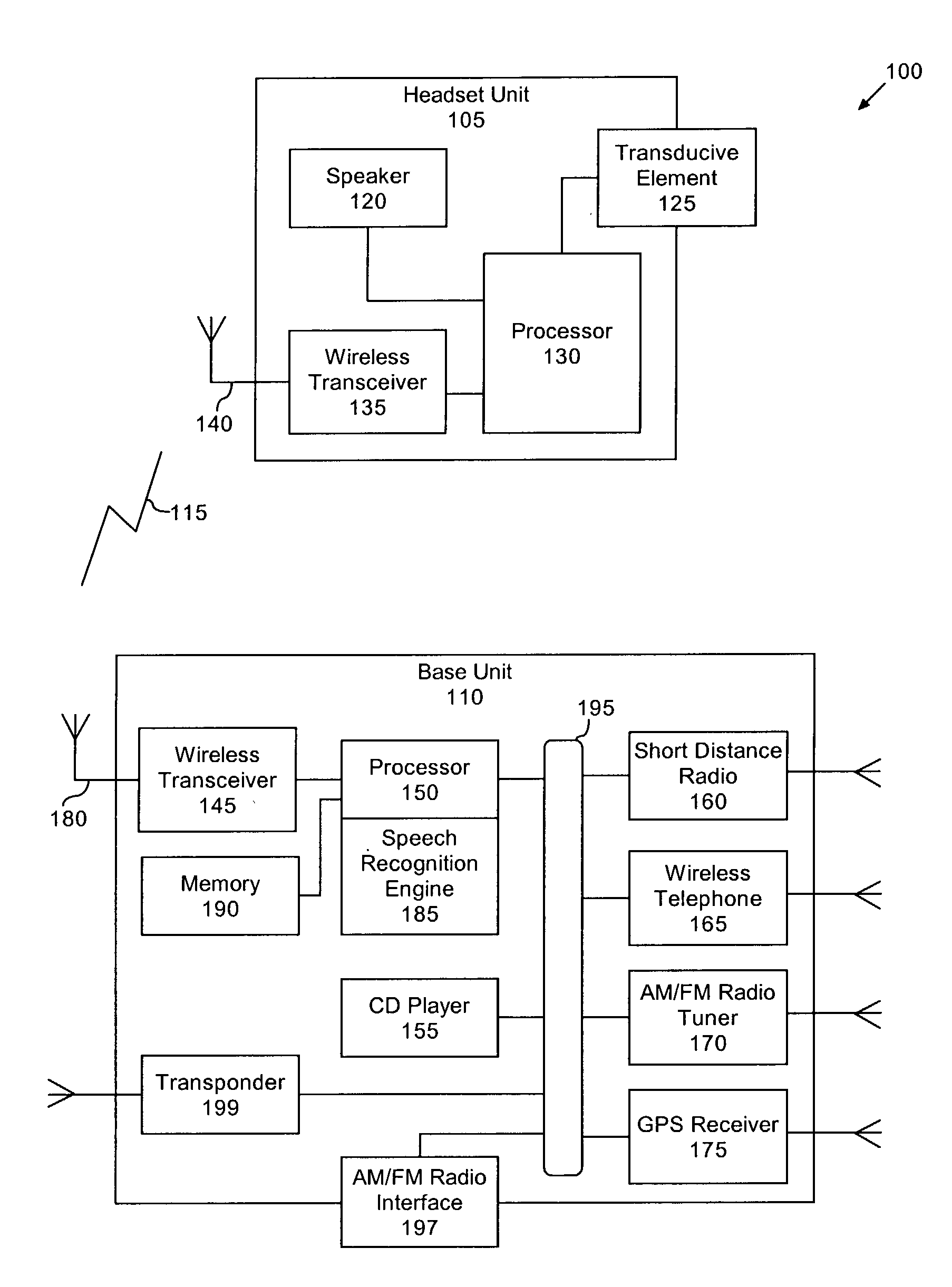
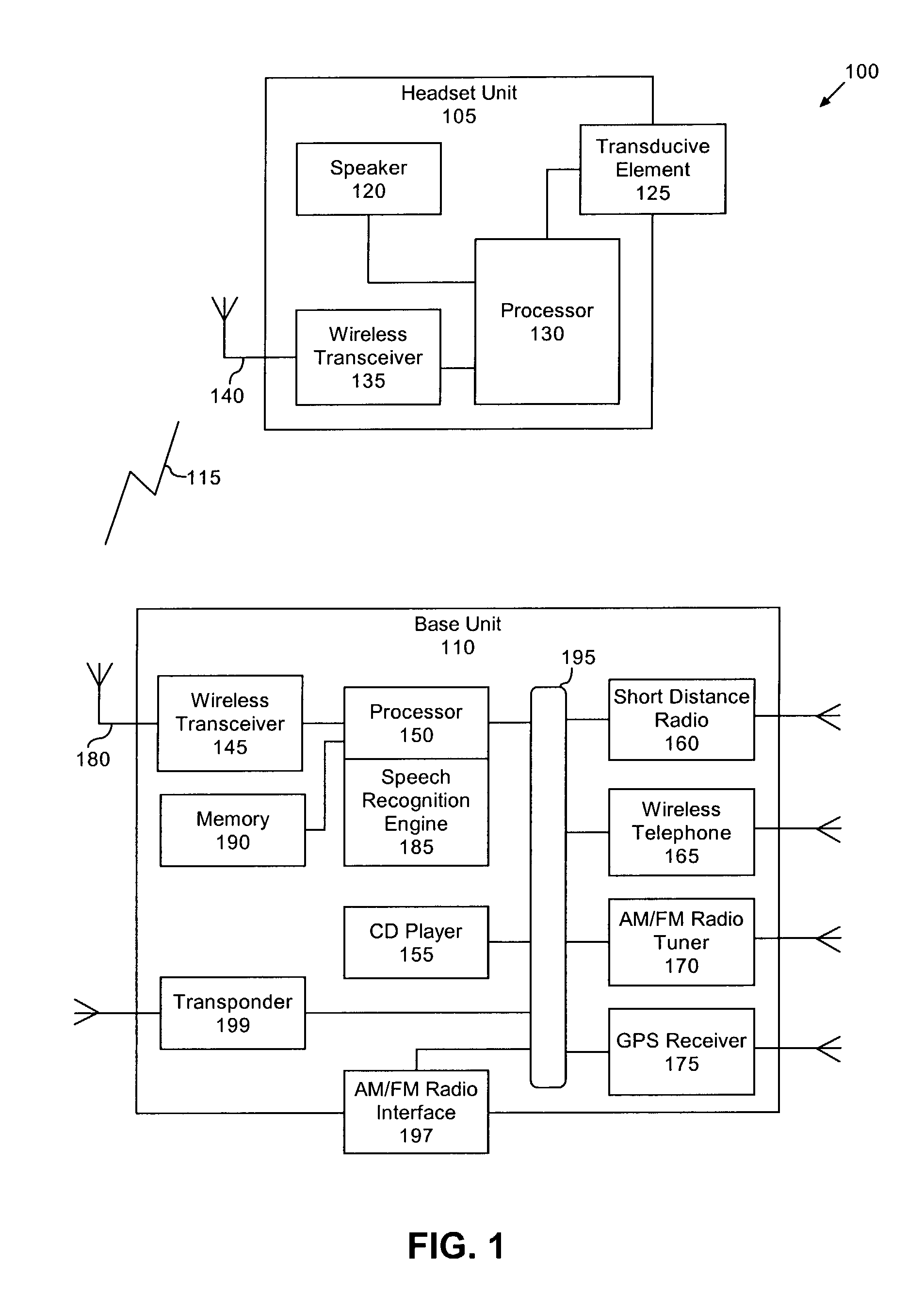
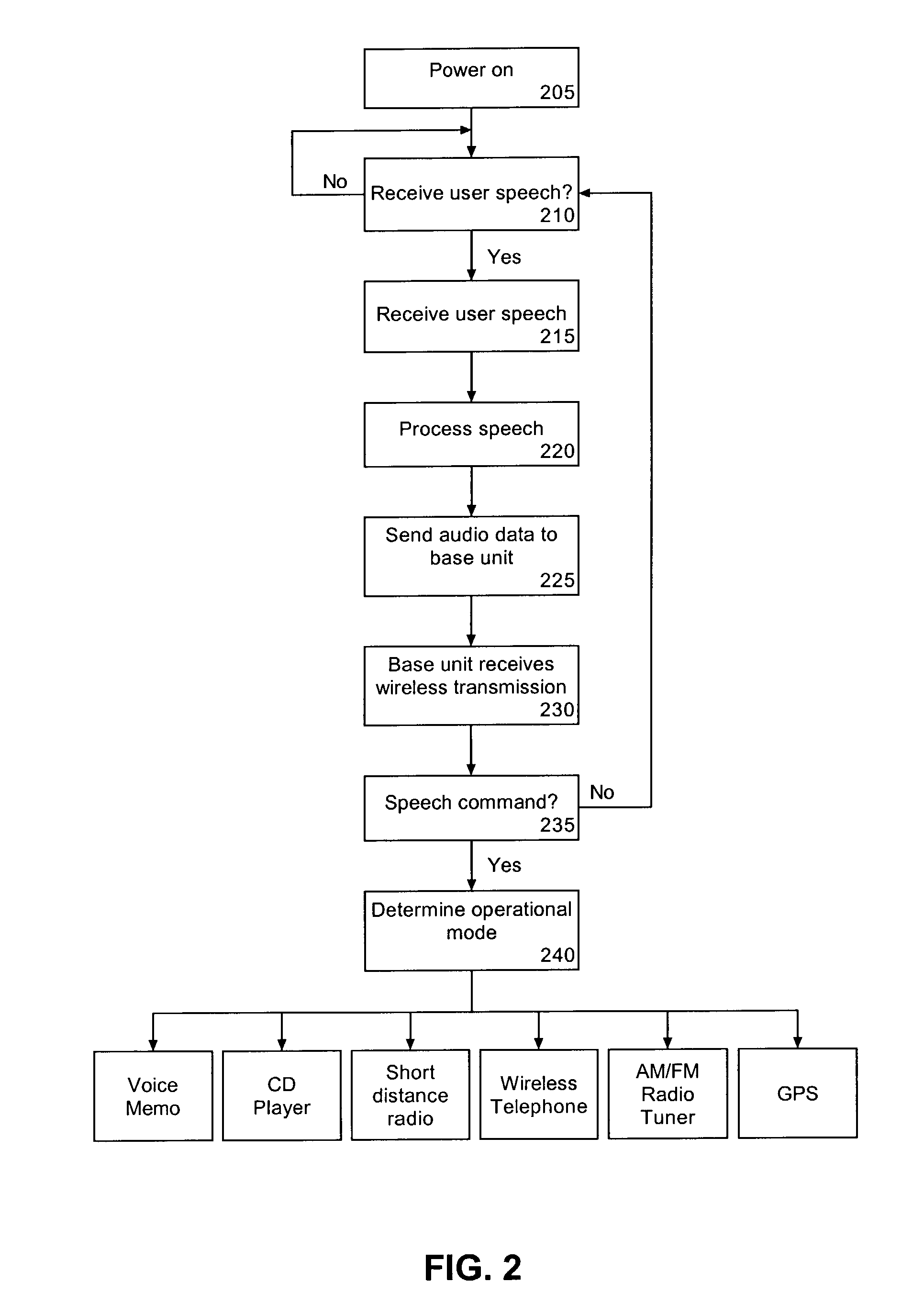
Method and System for Operating a Multi-Function Portable Electronic Device Using Voice-Activation
ActiveUS20080248797A1Lower the volumePower managementDevices with voice recognitionActivation methodComputer hardware
Methods and systems in which a portable electronic device can be voice activated are disclosed. The portable electronic device can be a multi-function electronic device. The voice activation can be robust and context sensitive. The voice activation can also be utilized without any preparatory user action with respect to the portable electronic device. The portable electronic device can also interact with a media system.
Owner:APPLE INC
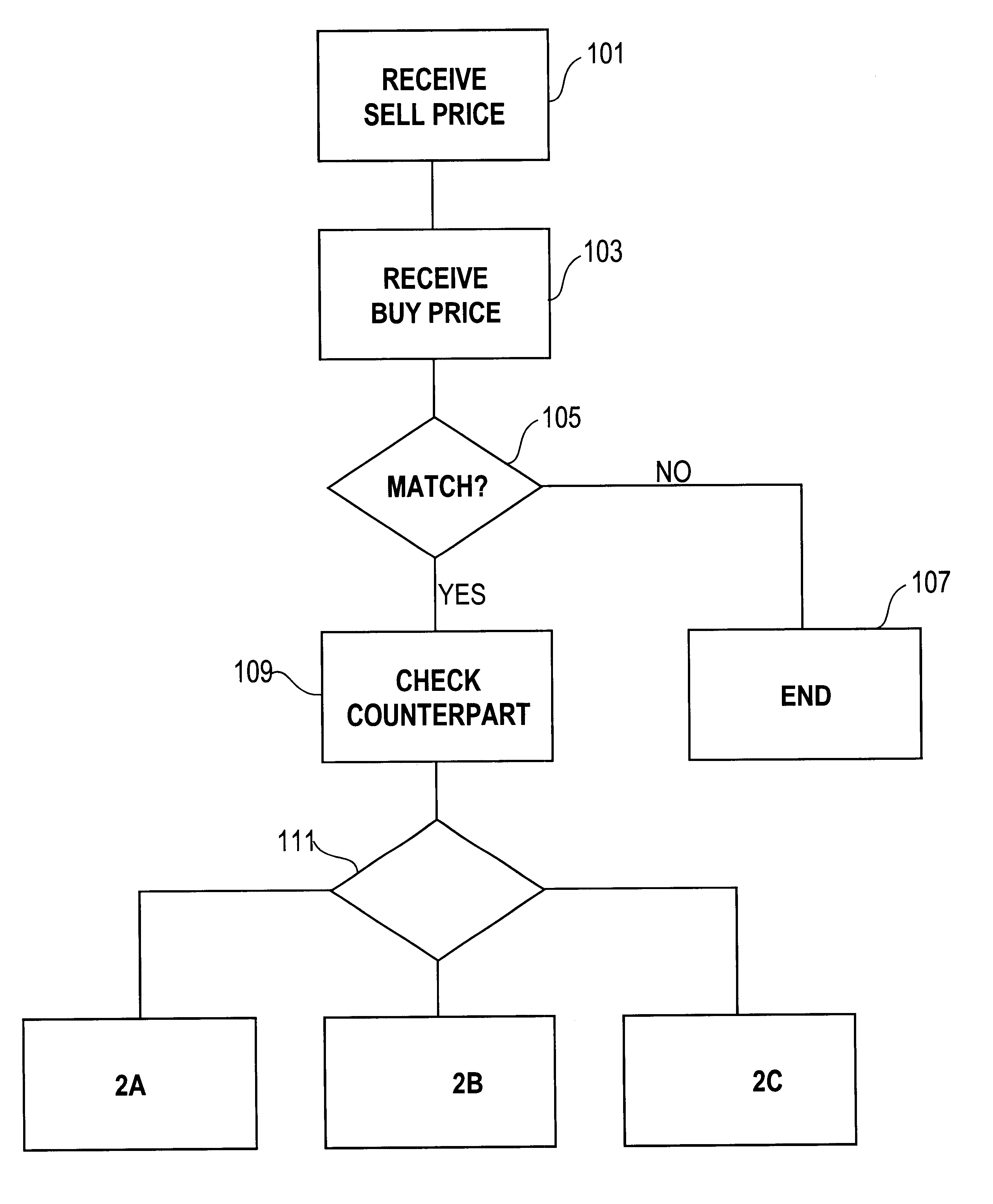
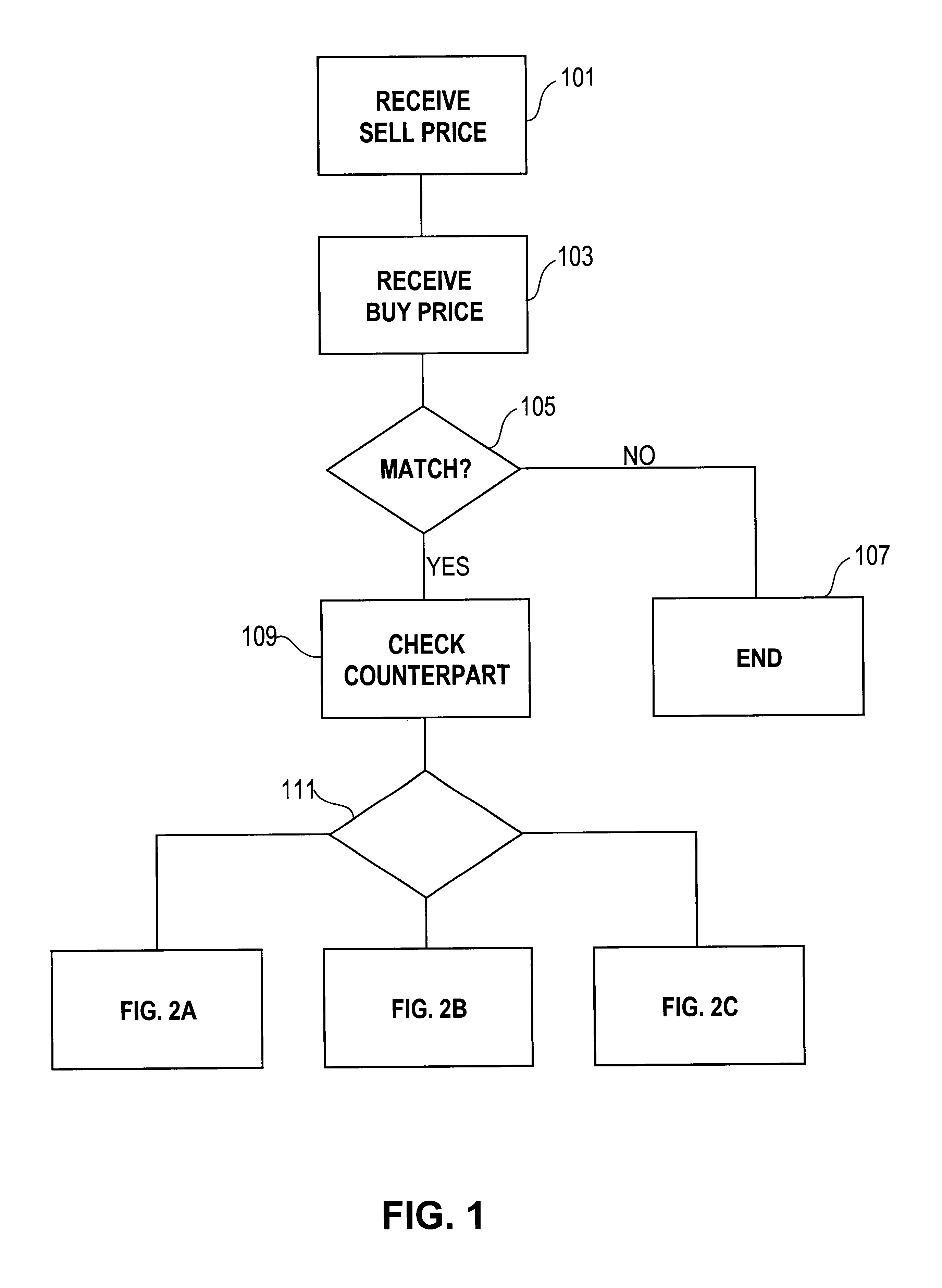
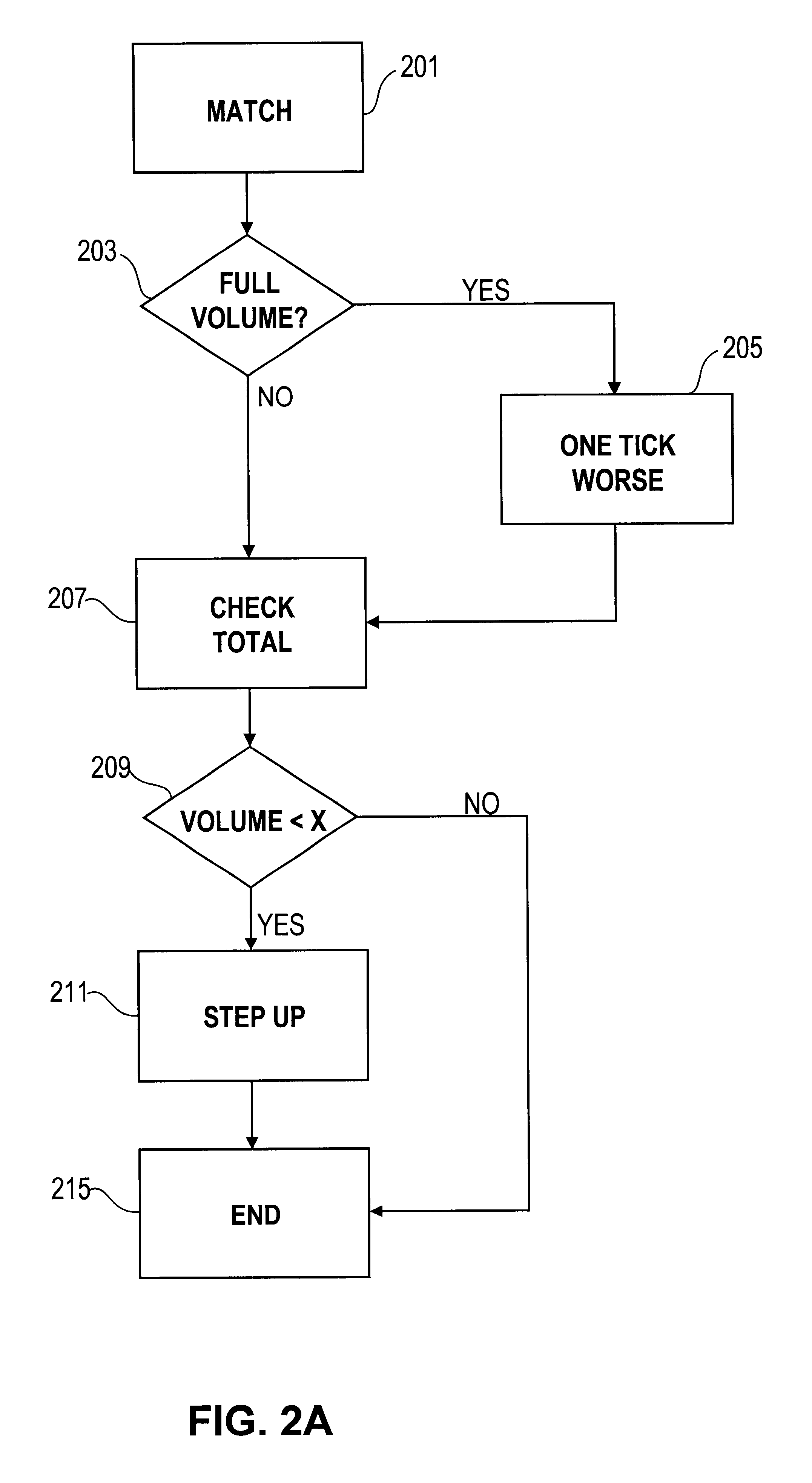
Automated exchange for matching bids between a party and a counterparty based on a relationship between the counterparty and the exchange
InactiveUS6405180B2Tight spreadReduced volume (risk)Special service provision for substationFinanceOrder formCourse of action
In an automated exchange system means are provided by means of which a market maker can enter a course of action in advance, so that the volume in the orderbook is continuously updated, and where the updating is performed differently with respect to different counter parts. Also, quotes that may result in a trade between Market Makers are hidden for some time before being matched, thus giving the Market Makers a chance to back off. The system employs a function that supports that Market Makers through pre-defined parameters will have new orders generated by the system and that a market maker can act differently with respect to different counterparts. The parameters specify if a Market Maker should add extra volume on an existing price or generate a new order at a worse price. In order to make it possible for market makers to have a very tight spread without forcing them to take larger risks, additional logic is used when matching orders. The algorithm used for this purpose protects the market makers in certain situations and gives market makers the possibility to have a tight spread without taking a large risk. The algorithm also supports that the market makers can take the risk to quote large volumes.
Owner:ISE LLC
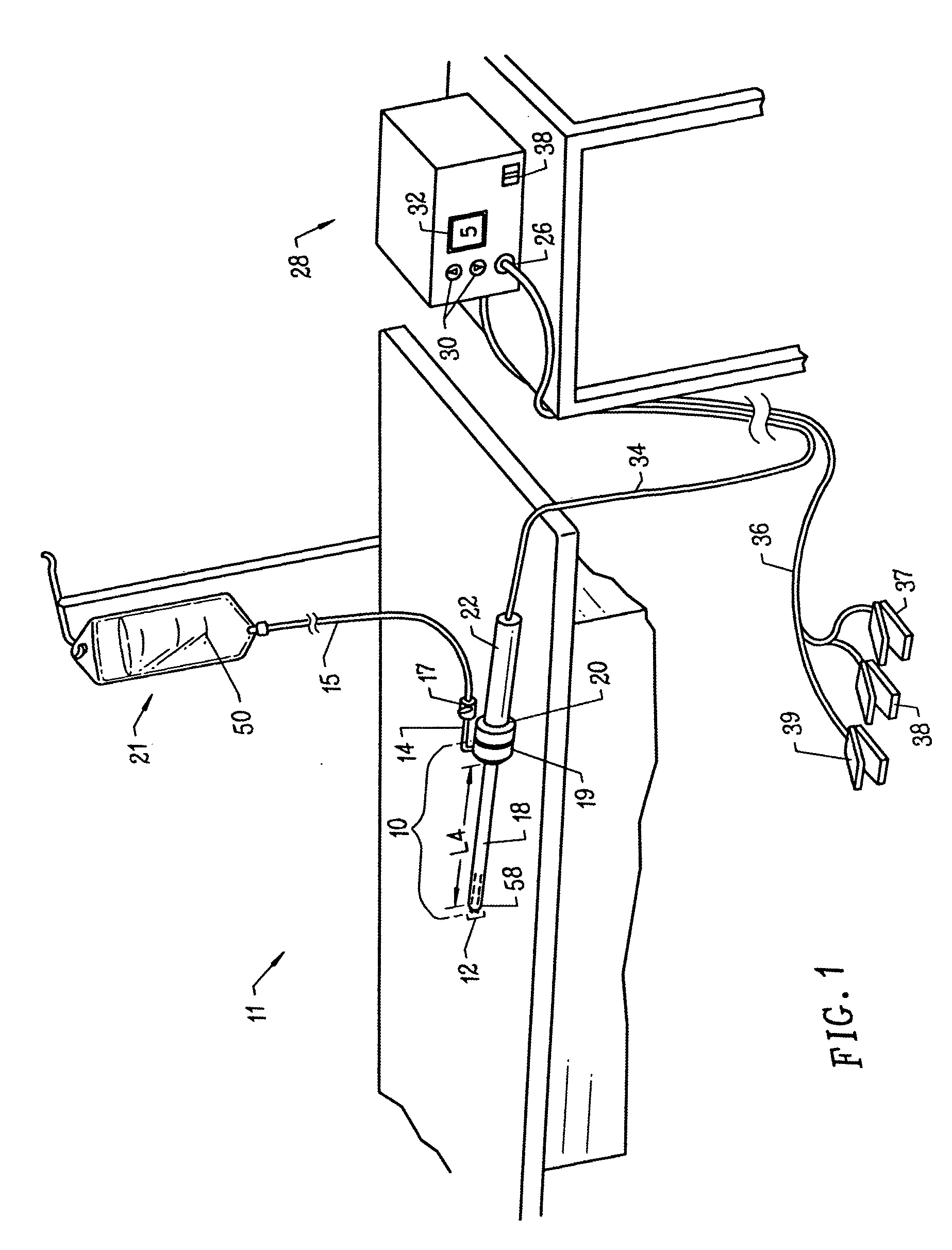
Methods of determining concentration of glucose
InactiveUS7058437B2Lower the volumePrecise processMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAnalyteMedicine
A region of skin, other than the fingertips, is stimulated. After stimulation, an opening is created in the skin (e.g., by lancing the skin) to cause a flow of body fluid from the region. At least a portion of this body fluid is transported to a testing device where the concentration of analyte (e.g., glucose) in the body fluid is then determined. It is found that the stimulation of the skin provides results that are generally closer to the results of measurements from the fingertips, the traditional site for obtaining body fluid for analyte testing.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Systems and methods for modifying broadcast programming
InactiveUS6931451B1Lower the volumeFacilitate selection and playback and archiving and erasureElectrophonic musical instrumentsMultiple digital computer combinationsClient-sideRadio program
A system for selecting, erasing or reproducing program recordings using marking and descriptive data which is transmitted to a client location from a remote processing location. A database of identification signals specifying the characteristics of a known programming is maintained at a remote processing location. In a first embodiment, selected identification signals are downloaded from the database to the client location and are used by a processor at the client location to identify desired programming within a locally stored collection of previously received broadcast programming signals. In a second arrangement, locally stored programming signals are processed to extract identification data which is uploaded from the client location to the remote processing location for comparison to the database, and information describing the content of the matching programs is returned to the client location for use as a program guide, facilitating the selection, permanent storage, or playback of desired program records and / or the erasure of undesired programming. To conserve local storage space, identified program records may be uploaded and stored at the remote processing location, or shared program records in a central library may be made available for remote playback after an the identity of equivalent locally stored programming is confirmed.
Owner:TIVO SOLUTIONS INC
Semiconductor processing apparatus comprising chamber partitioned into reaction and transfer sections
InactiveUS6899507B2Reduce adhesionImprove efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCharge manipulationEngineeringSemiconductor
Semiconductor processing equipment that has increased efficiency, throughput, and stability, as well as reduced operating cost, footprint, and faceprint is provided. Other than during deposition, the atmosphere of both the reaction chamber and the transfer chamber are evacuated using the transfer chamber exhaust port, which is located below the surface of the semiconductor wafer. This configuration prevents particles generated during wafer transfer or during deposition from adhering to the surface of the semiconductor wafer. Additionally, by introducing a purge gas into the transfer chamber during deposition, and by using an insulation separating plate 34, the atmospheres of the transfer and reaction chambers can be effectively isolated from each other, thereby preventing deposition on the walls and components of the transfer chamber. Finally, the configuration described herein permits a wafer buffer mechanism to be used with the semiconductor processing equipment, thereby further increasing throughput and efficiency.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Remote computer virus scanning
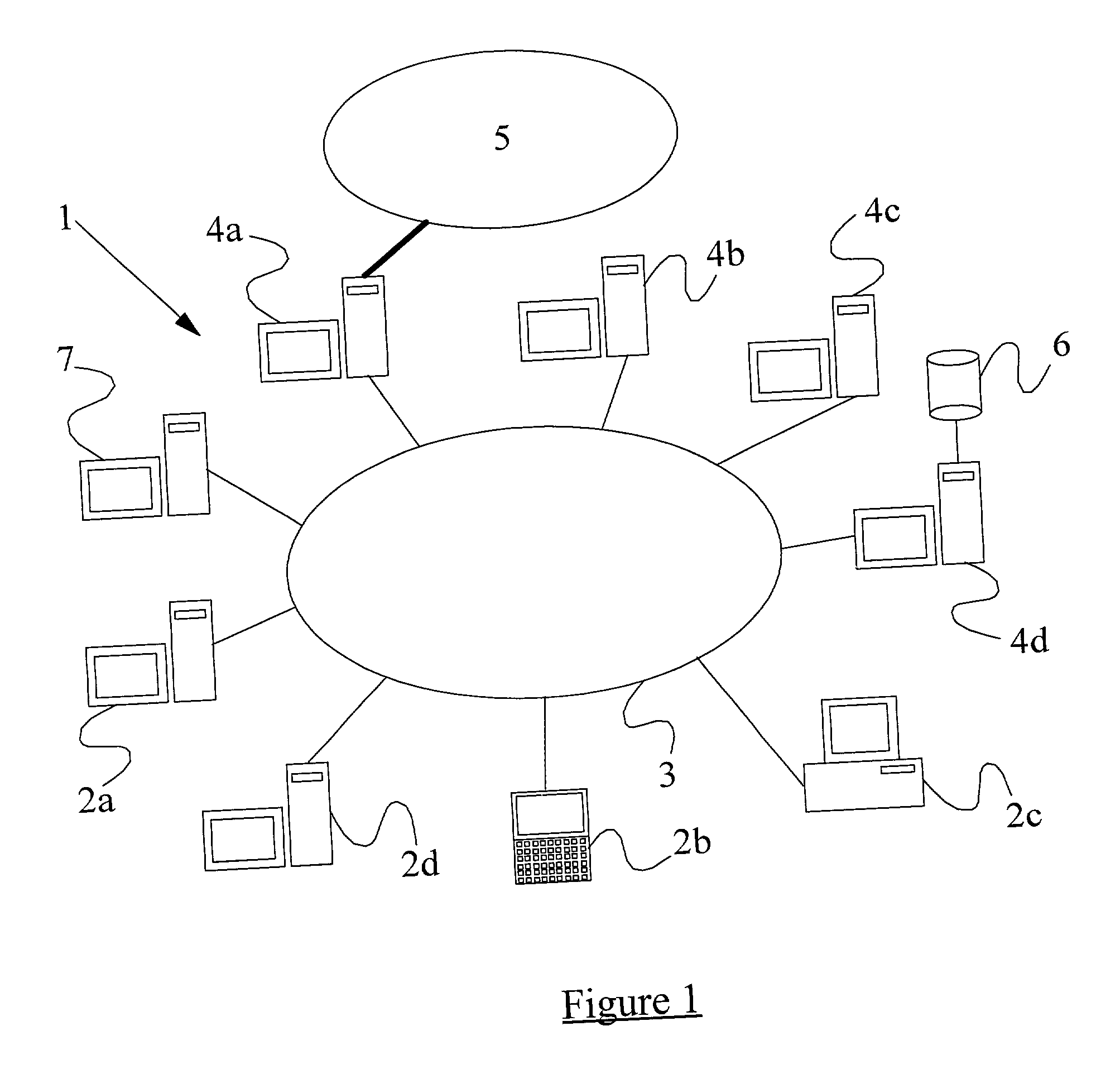
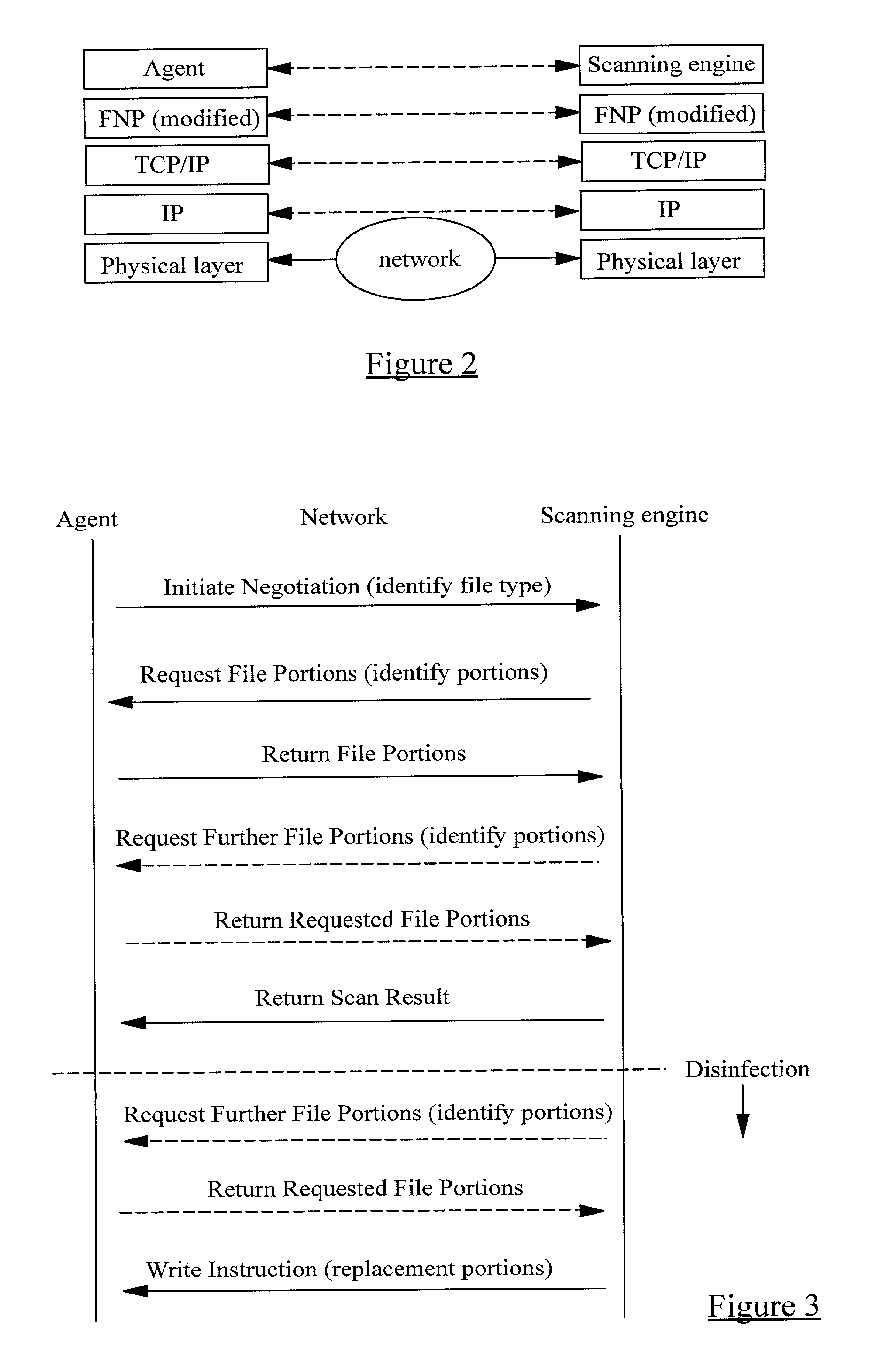
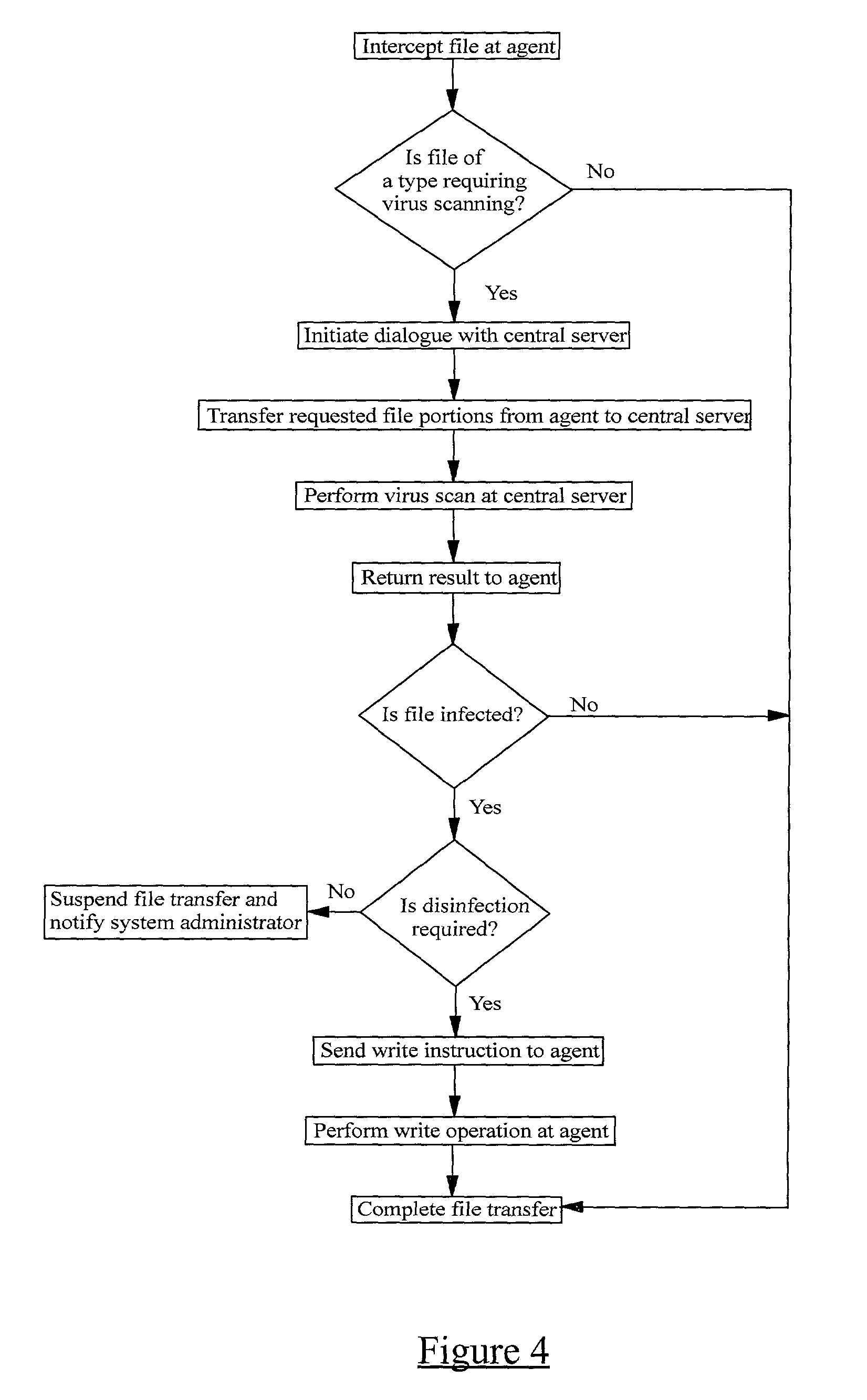
InactiveUS20010005889A1Improve network securityLower the volumeMemory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsRemote computerVirus
A method of scanning electronic files for computer viruses comprises identifying at a first node 4 of a computer network 1, electronic files which require to be scanned for computer viruses. The first node 4 initiates a dialogue with a second node 7 of the network 1, the second node comprising a virus scanning application. During the dialogue, the second node 7 identifies to the first node 4 one or more portions of the electronic file required by the virus scanning application. The first node 4 transfers the identified portions to the second node 7 which then carries out a virus scanning operation. The result of this operation is then returned to the first node 4.
Owner:F SECURE CORP
System for tissue cavity closure
InactiveUS20060004388A1Lower the volumeLess invasive treatmentSuture equipmentsSurgical staplesSurgical operationAnatomical structures
Surgical systems for less invasive access to and isolation of an atrial appendage are provided. A suturing grasper compresses soft tissue structures and deploys one or more sutures through complimentary pledget(s) carried by the grasper. The pledgets are reinforced, containing support members that define the profile of the stitch and distribute stresses applied by the stitch, once tightened, over a length of tissue. This hardware may be applicable to other surgical and catheter based applications as well including: compressing soft tissue structures lung resections and volume reductions; gastric procedures associated with reduction in volume, aneurysm repair, vessel ligation, or other procedure involving isolation of, resection of, and reduction of anatomic structures.
Owner:ATRICURE
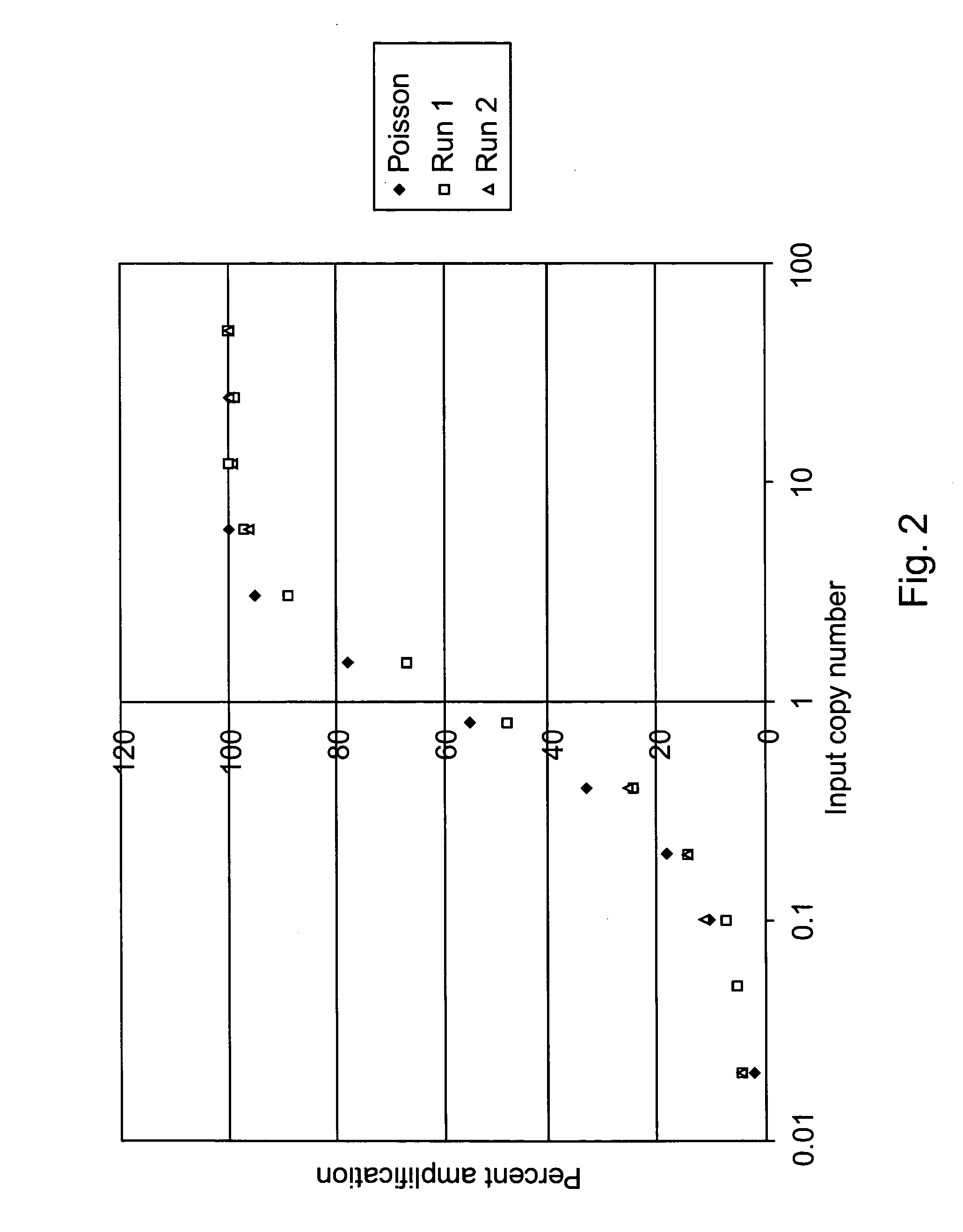
Single molecule amplification and detection of DNA length
InactiveUS20050042639A1Reliable resultsImprove reliabilityHeating or cooling apparatusMicrobiological testing/measurementStatistical analysisDNA
Methods and systems for performing single molecule amplification for detection, quantification and statistical analysis of nucleic acids are provided. Methods and systems are provided for determining and quantifying lengths of nucleic acids of interest.
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
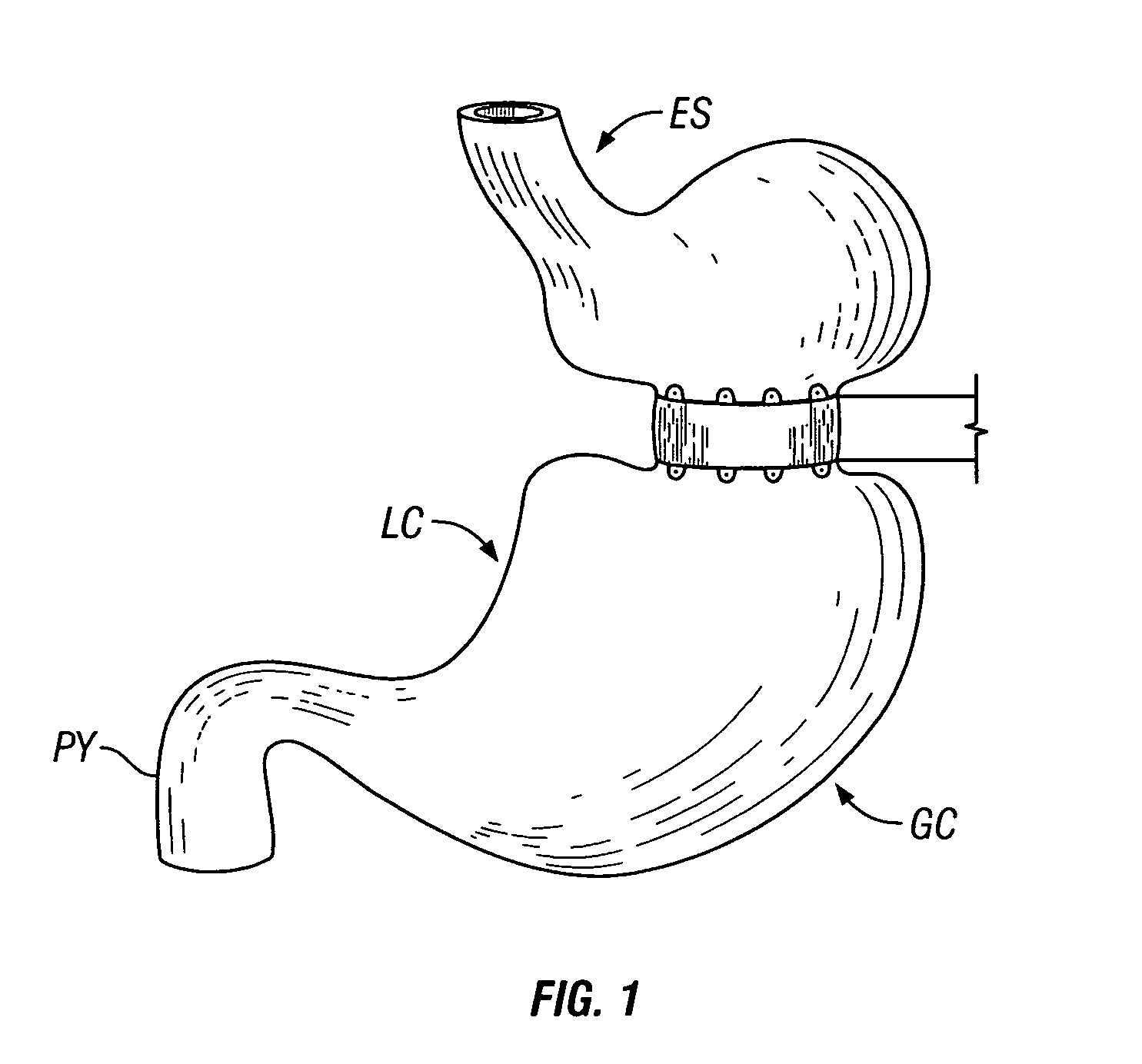
Systems and methods for treating obesity
ActiveUS20050228504A1Good for weight lossStimulatesIntravenous devicesTubular organ implantsPylorusGastric emptying
Methods and devices for simulating a gastric bypass and reducing the volume of the stomach involve placing a tubular liner along the lesser curve of the stomach cavity. Also, methods and devices for slowing gastric emptying involve placing valves within the stomach cavity near the gastrointestinal junction and / or the pylorus. These methods and devices may prevent a patient from drinking and eating large volumes at one time and from eating slowly all day.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Systems and methods for electrosurgical treatment of turbinates
InactiveUS7442191B2Minimize thermal damageLower the volumeCannulasEnemata/irrigatorsVoltageCartilage
The present invention provides systems and methods for selectively applying electrical energy to a target location within the head and neck of a patient's body, particularly including tissue in the ear, nose and throat. In one aspect, a method is provided for reducing the volume of enlarge swollen tissue in the patient's nose, such as swollen nasal tissue, mucus membranes, turbinates, polyps, neoplasms, cartilage (e.g., the nasal septum) or the like. In particular, the turbinates are treated by positioning one or more electrode terminal(s) adjacent to the turbinates, and delivering electrically conductive fluid, such as isotonic saline, to the nasal cavity to substantially surround the electrode terminal(s) with the fluid. High frequency voltage is applied between the electrode terminal(s) and one or more return electrode(s) to remove a small tissue segment, channel or hole from the region near or in the turbinates to shrink the turbinates and prevent swelling, due to the formation of scar tissue as the wound heals. The high frequency voltage may be selected to effect a small amount of thermal damage to the walls of the channel or hole to facilitate the formation of scar tissue without extending this thermal damage beyond the immediate region of the target site.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Intralumenal material removal using a cutting device for differential cutting
InactiveUS7344546B2Minimal damageFacilitates translation and navigationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCannulasDrive shaftMaterial removal
Intralumenal material removal systems are provided using an advanceable and rotatable cutter assembly designed for differential cutting. The intralumenal material removal system includes a cutter assembly positionable in the body cavity of a mammalian subject. One embodiment of the cutter assembly includes a cutter with blades that are designed and arranged to form an acute blade angle of attack with the matter-to-be-removed. The cutter assembly is axially advanceable by translating the drive shaft and rotatable by rotating the drive shaft. The occlusive material is scraped by the cutter assembly and may be aspirated to remove the material from the body cavity. The cutter assembly may provide aspiration ports positioned between facing surfaces of the blades.
Owner:BOSTON SCI LTD
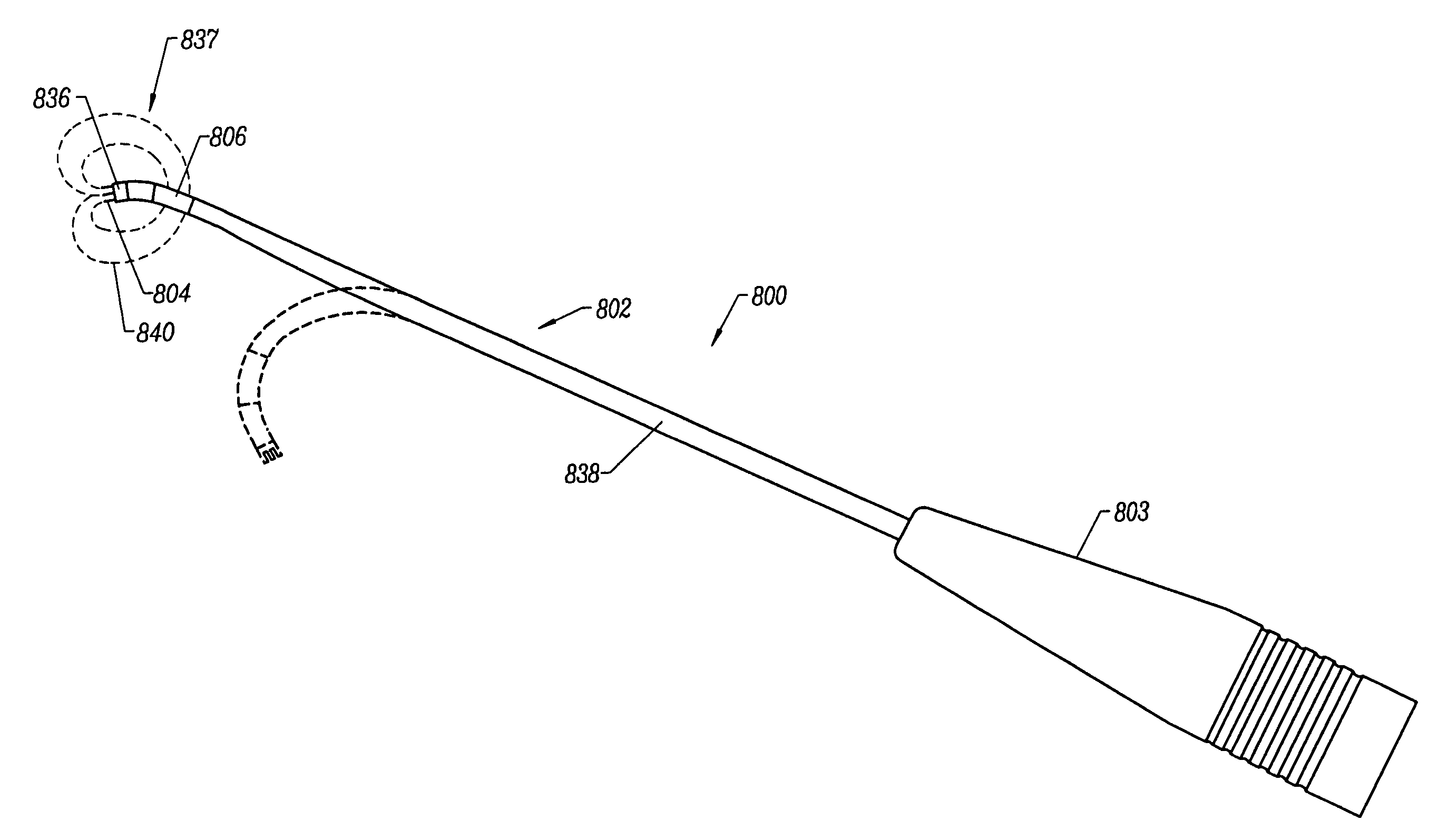
Systems and methods for electrosurgery
InactiveUS7270658B2Use performanceAvoid cloggingSurgical needlesEndoscopesIntervertebral discSpinal cord
Methods and apparatus for selectively applying electrical energy to a target location within a patient's body, particularly including tissue in the spine. In a method of the invention high frequency (RF) electrical energy is applied to one or more active electrodes on an electrosurgical probe in the presence of an electrically conductive fluid to remove, contract or otherwise modify the structure of tissue targeted for treatment. In one aspect, a dura mater and spinal cord are insulated from the electrical energy by an insulator positioned on a non-active side of the probe. In another aspect, a plasma is aggressively formed in the electrically conductive fluid by delivering a conductive fluid to a distal end portion of the probe and aspirating the fluid from a location proximal of the return electrode. In another aspect, a distal end of an electrosurgical probe having at least one electrode on a biased, curved, bent, or steerable shaft is guided or steered to a target site within an intervertebral disc having a disc defect for treatment of tissue to be treated at the target site by the selective application of electrical energy thereto.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Impulse chamber for jet delivery device
InactiveUS20070049873A1Lower the volumeSimple and cost-efficient to manufactureAmpoule syringesJet injection syringesCost effectivenessEngineering
The invention relates to an impulse chamber which can be used for expelling an amount of a fluid compound at a high pressure. The impulse chamber comprises a variable-volume impulse chamber adapted for containing a volume of a flowable drug, an outlet nozzle in fluid communication with the impulse chamber and being adapted to be arranged against the skin of a subject, and a fluid inlet in fluid communication with the impulse chamber. The impulse chamber is defined substantially by a deformable chamber portion, such that deformation thereof reduces the volume of the cavity. In an exemplary embodiment the compressible chamber portion is in the form of an elastomeric tube, this providing a simple, yet reliable and cost-effective impulse chamber unit.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Gas flow rate verification unit
ActiveUS7716993B2Increase flow rateUniform pressureMultiple way valvesPipeline systemsEngineeringGas supply
A gas flow rate verification unit capable of enhancing reliability of gas flow rate verification. The gas flow rate verification unit has a first cutoff valve that is connected to a flow rate control device and to which gas is inputted, a second cutoff valve for discharging the gas, a communication member for allowing the first cutoff valve and the second cutoff valve to communicate with each other, a pressure sensor for detecting the pressure of the gas supplied between the first cutoff valve and the second cutoff valve, a temperature detector for detecting the temperature of the gas supplied between the first cutoff valve and the second cutoff valve, and a control means for verifying the flow of the gas flowing in the flow control device, the verification being performed by using both the result of the pressure detected by the pressure sensor and the result of the temperatures detected by the temperature detector. The volume (Vk) between the valve seat of the first cutoff valve and the valve seat of the second cutoff valve is equal to or less than the volume (Ve) between the outlet of the flow control device and the valve seat of the first cutoff valve.
Owner:CKD
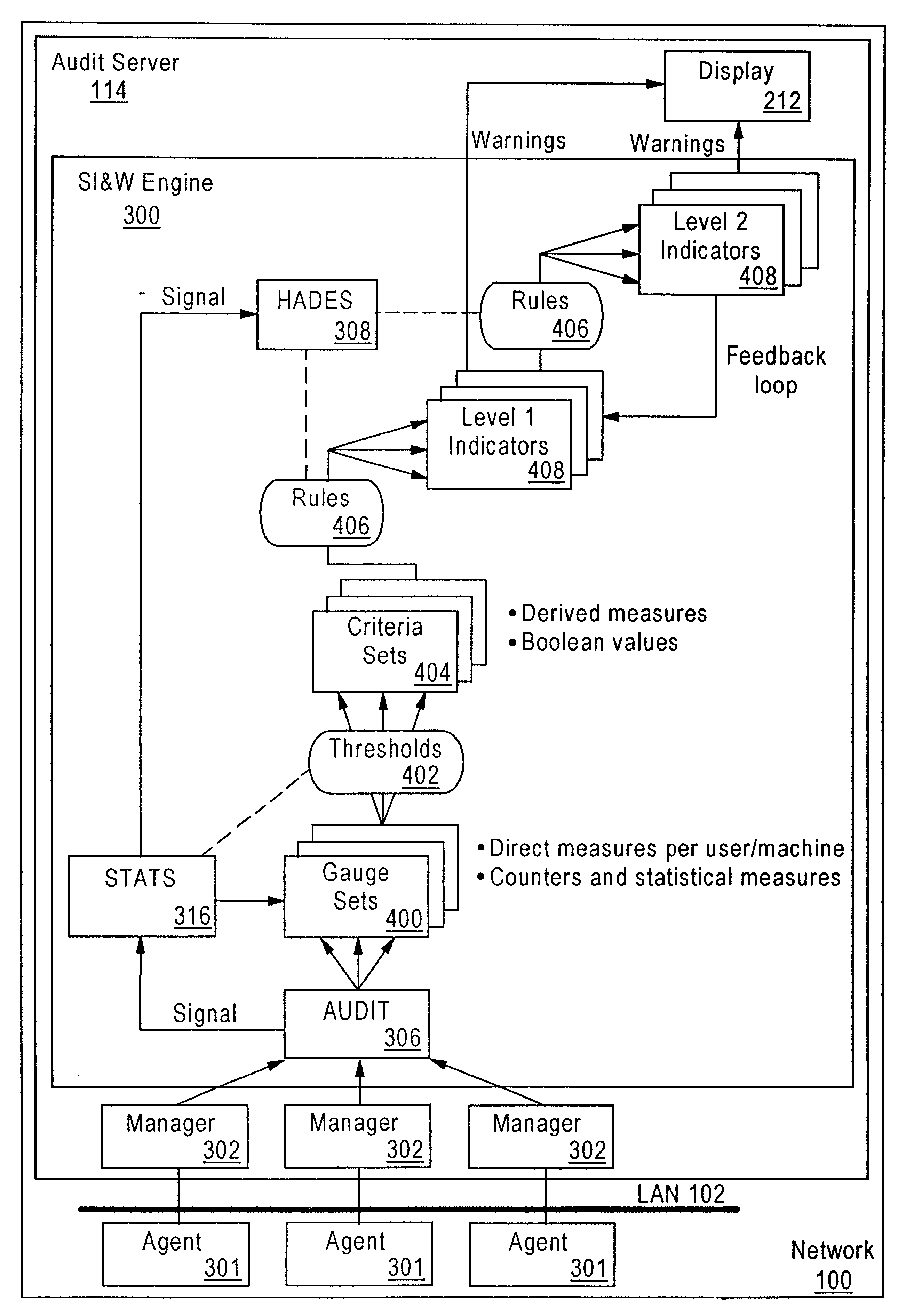
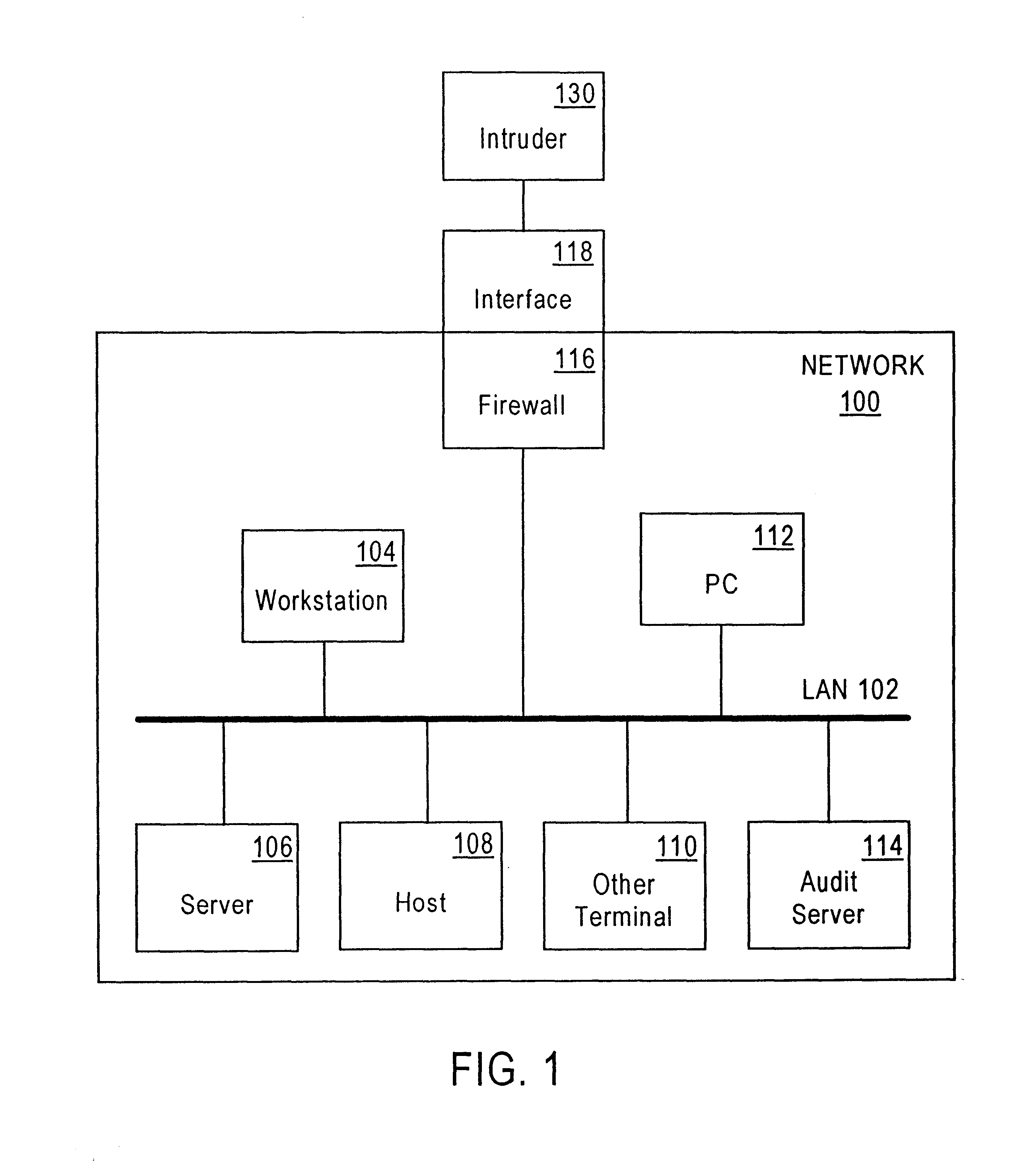
Method and system for detecting intrusion into and misuse of a data processing system
InactiveUS6839850B1Lower the volumeEasy activityMemory loss protectionUnauthorized memory use protectionData miningHandling system
Disclosed is a Security Indications and Warning (SI&W) Engine usable in conjunction with an audit agent. The audit agent forwards normalized audits to the SI&W Engine. The SI&W Engine groups the normalized audits into related groupings. Gauges are used to count the number of occurrences of audited events. A statistical engine provides statistical representations of the number of events per user, per session and per node. A predetermined number of criteria are defined a particular gauge or gauge pair. There may be many criteria for a particular network. When a predetermined number of criteria within a criteria set are triggered, an indicator is triggered. More complex indicators can use combinations of lower level indicators to provide further indications of potential security threads. Thus, a hierarchical system of gauges, criteria and indicators is used to measure boundary violations and breaches of different barriers. Advantageously, because there are no predefined scenarios or profiles that must be performed by a potential misuser or intruder, the SI&W Engine of the present invention is capable of indicating that a potential security threat exists in near-real time.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP +1
Methods for electrosurgical tissue contraction within the spine
The present invention provides systems and methods for selectively applying electrical energy to a target location within a patient's body, particularly including tissue in the spine. The present invention applies high frequency (RF) electrical energy to one or more electrode terminals in the presence of electrically conductive fluid to contract collagen fibers within the tissue structures. In one aspect of the invention, a system and method is provided for treating herniated or swollen discs within a patient's spine by applying sufficient electrical energy to the disc tissue to contract or shrink the collagen fibers within the nucleus pulposis. This causes the pulposis to shrink and withdraw from its impingement on the spinal nerve.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Method and system for remote delivery of retail banking services
A practical system and method for the remote distribution of financial services (e.g., home banking and bill-paying) involves distributing portable terminals to a user base. The terminals include a multi-line display, keys “pointing to” lines on the display, and additional keys. Contact is established between the terminals and a central computer operated by a service provider, preferably over a dial-up telephone line and a packet data network. Information exchange between the central computer and the terminal solicits information from the terminal user related to requested financial services (e.g., for billpaying, the user provides payee selection and amount and his bank account PIN number). The central computer then transmits a message over a conventional ATM network debiting the user's bank account in real time, and may pay the specified payees the specified amount electronically or in other ways as appropriate. Payments and transfers may be scheduled in advance or on a periodic basis. Because the central computer interacts with the user's bank as a standard POS or ATM network node, no significant software changes are required at the banks' computers. The terminal interface is extremely user-friendly and incorporates some features of standard ATM user interfaces so as to reduce new user anxiety.
Owner:OFFICIAL PAYMENTS
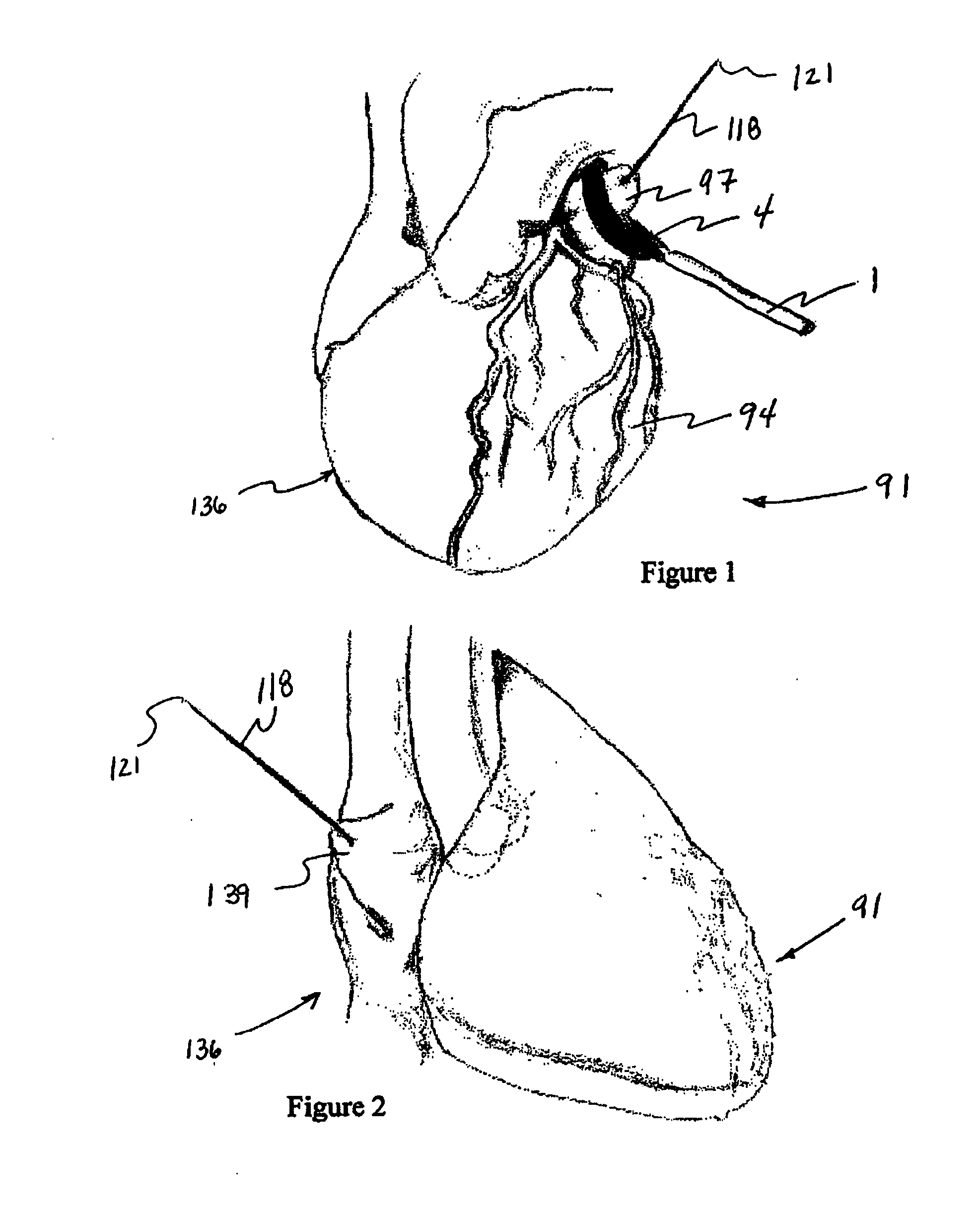
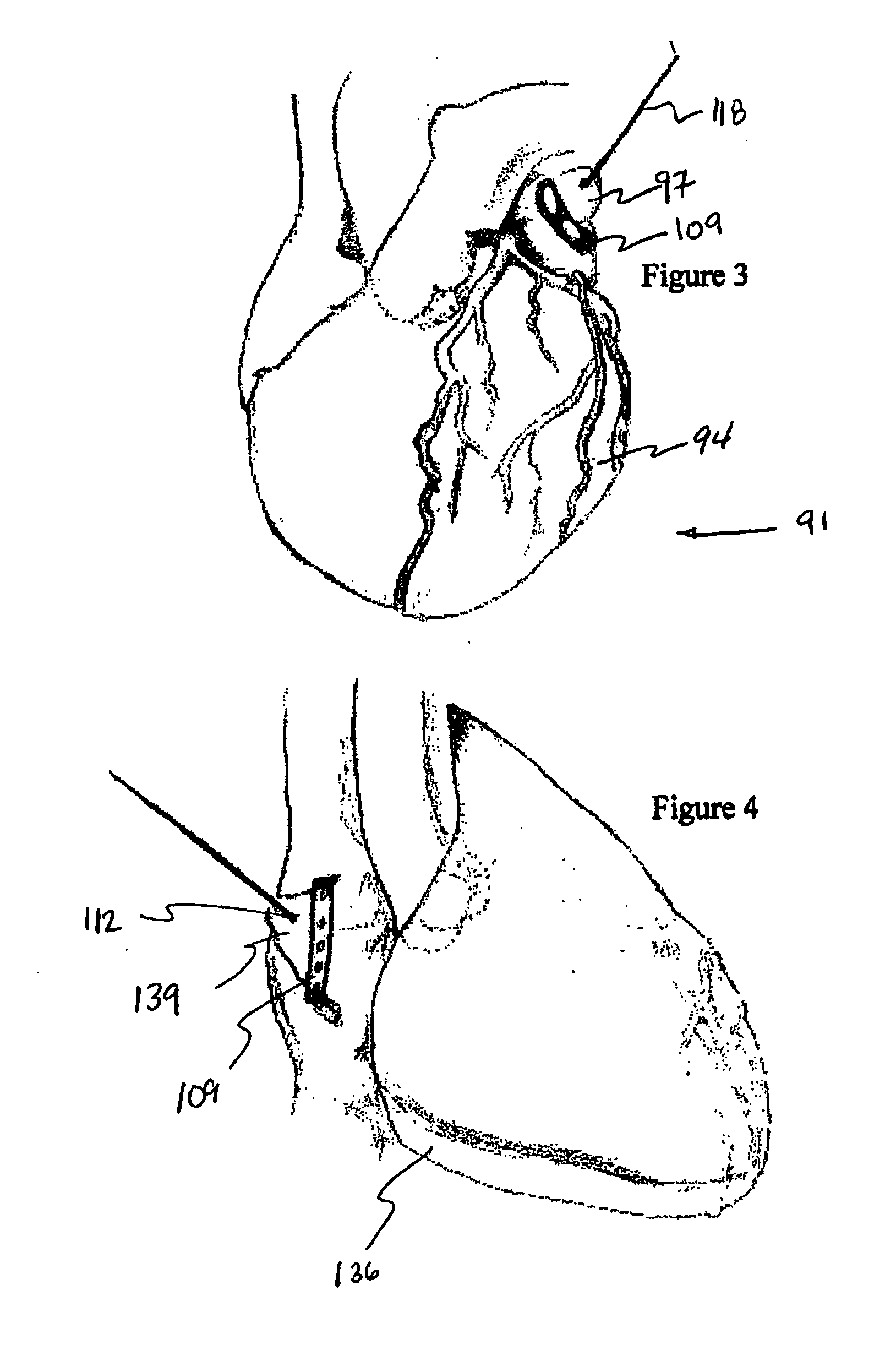
Cardiac device and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20070161846A1Reduced elastic recoilShorten speedHeart valvesInternal electrodesCardiac deviceDiastolic function
Devices and methods are described herein which are directed to the treatment of a patient's heart having, or one which is susceptible to heart failure, to improve diastolic function.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Methods for repairing damaged intervertebral discs
InactiveUSRE40156E1Reduce internal pressureReduce moistureBiocideOrganic chemistryIntervertebral discActive electrode
Apparatus and methods for treating an intervertebral disc by ablation of disc tissue. A method of the invention includes positioning at least one active electrode within the intervertebral disc, and applying at least a first high frequency voltage between the active electrode(s) and one or more return electrode(s), wherein the volume of the nucleus pulposus is decreased, pressure exerted by the nucleus pulposus on the annulus fibrosus is reduced, and discogenic pain of a patient is alleviated. In other embodiments, a curved or steerable probe is guided to a specific target site within a disc to be treated, and the disc tissue at the target site is ablated by application of at least a first high frequency voltage between the active electrode(s) and one or more return electrode(s). A method of making an electrosurgical probe is also disclosed.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Methods and devices for percutaneous, non-laparoscopic treatment of obesity
InactiveUS20050228415A1Lower the volumeEfficient use ofSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesPERITONEOSCOPEObesity
Disclosed are methods and devices to apply therapies to the walls of an organ such as the stomach. Visualization means and access means are disclosed as are devices and apparatus which can be used to perform the disclosed procedures and methods.
Owner:GERTNER MICHAEL
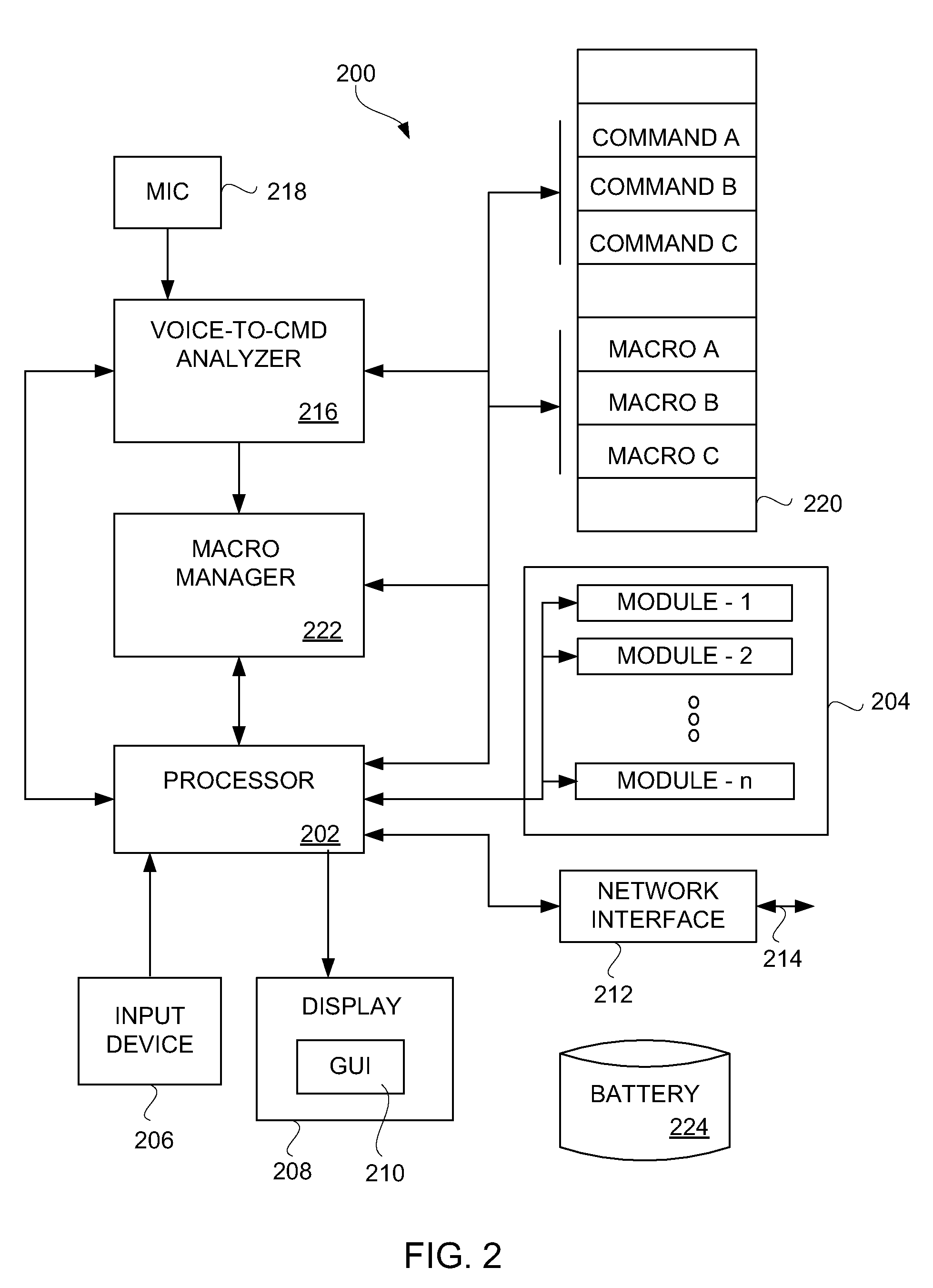
Voice controlled multimedia and communications device
ActiveUS7072686B1Lower the volumeDevices with GPS signal receiverAutomatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingSpeech controlTelecommunications link
A portable multimedia and communications device can include a transducive element for receiving sound. The device also can include a base unit having a plurality of multimedia units and a processor executing a speech recognition engine for recognizing user speech. Each of the plurality of multimedia units can be selectively enabled and operated responsive to user voice commands received via the transducive element and communicated to the base unit via a communication link.
Owner:AVON ASSOCS
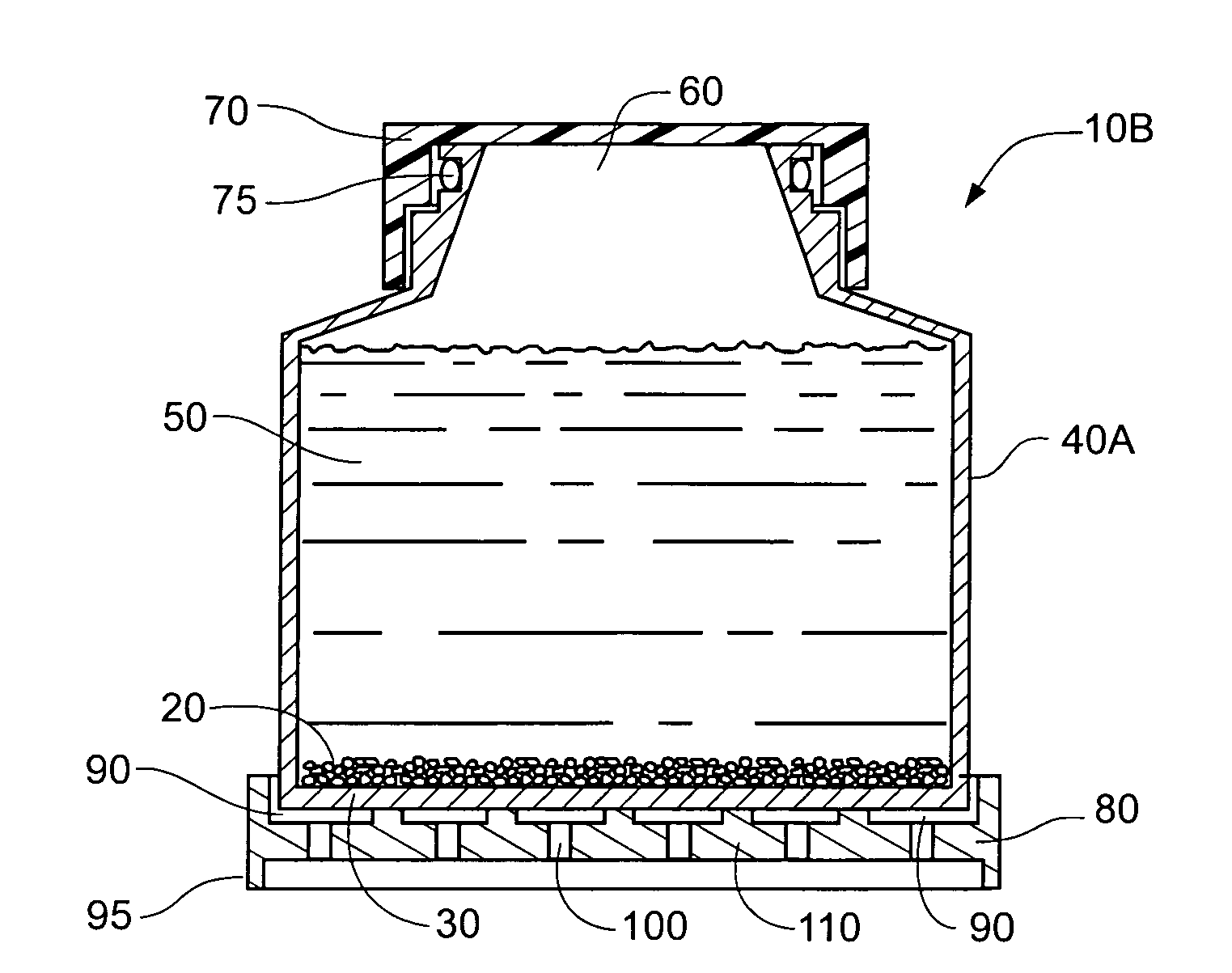
Cell culture methods and devices utilizing gas permeable materials
ActiveUS20050106717A1Increase exchange surfaceIncrease surface areaBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProduct gasBiology
Gas permeable devices and methods are disclosed for cell culture, including cell culture devices and methods that contain medium at heights, and certain gas permeable surface area to medium volume ratios. These devices and methods allow improvements in cell culture efficiency and scale up efficiency.
Owner:WILSON WOLF MFG
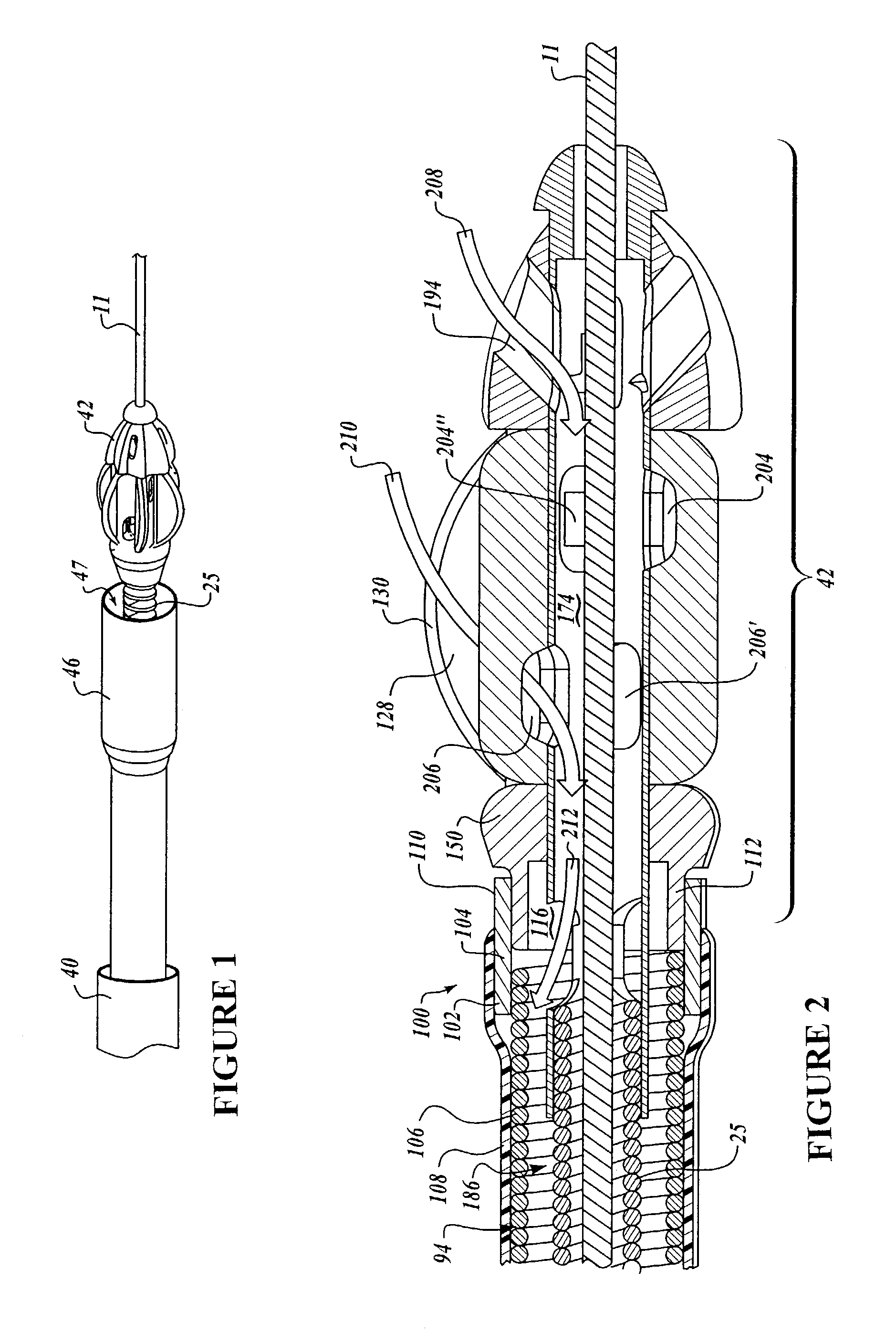
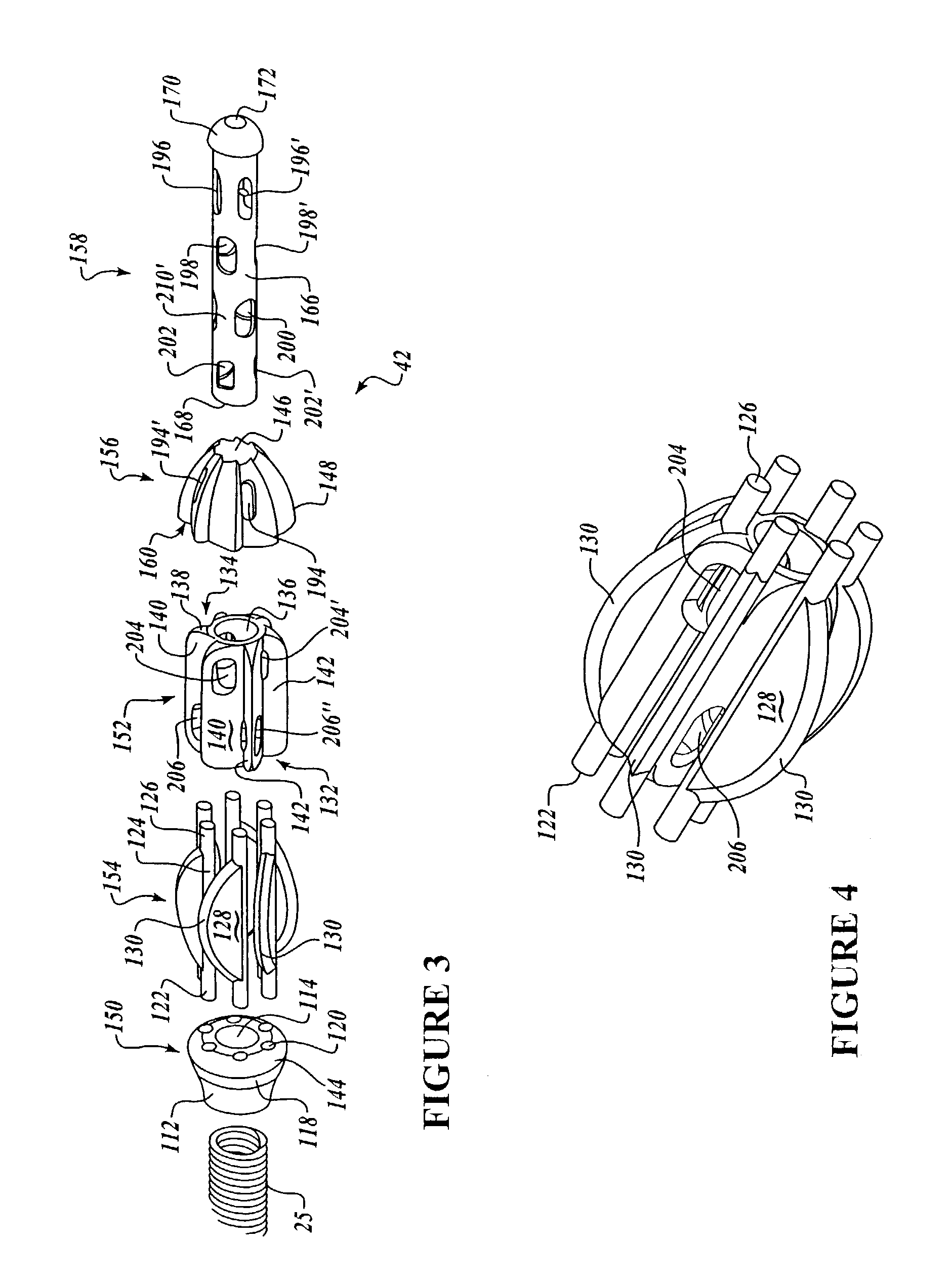
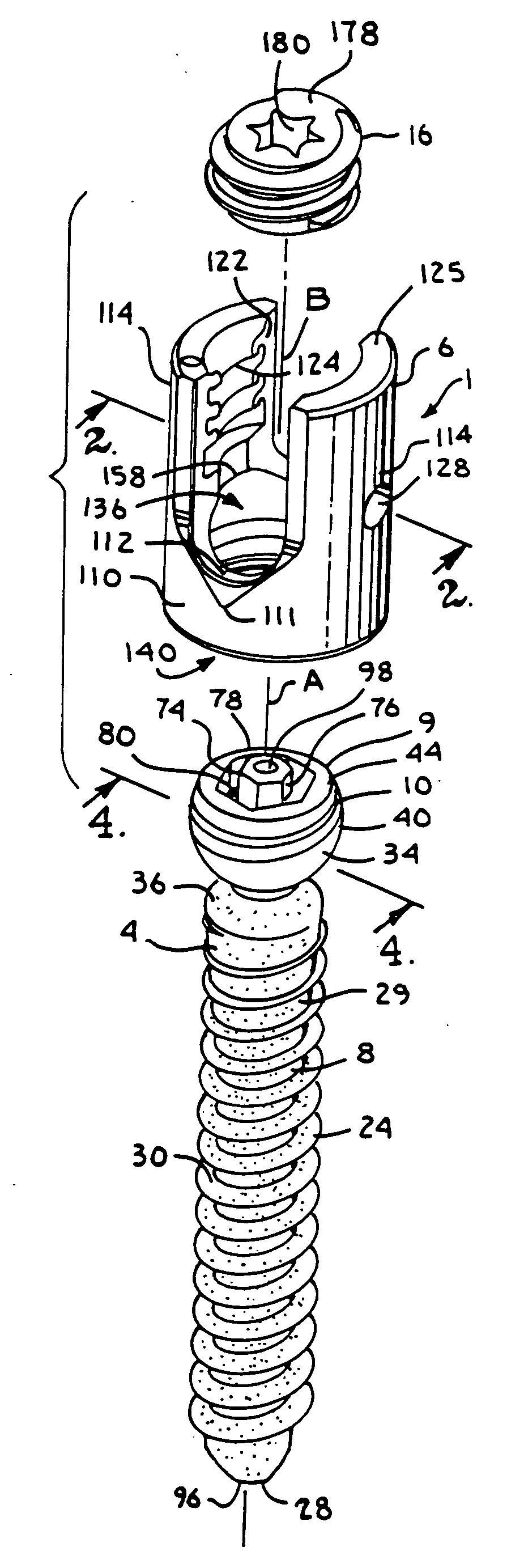
Dynamic stabilization medical implant assemblies and methods
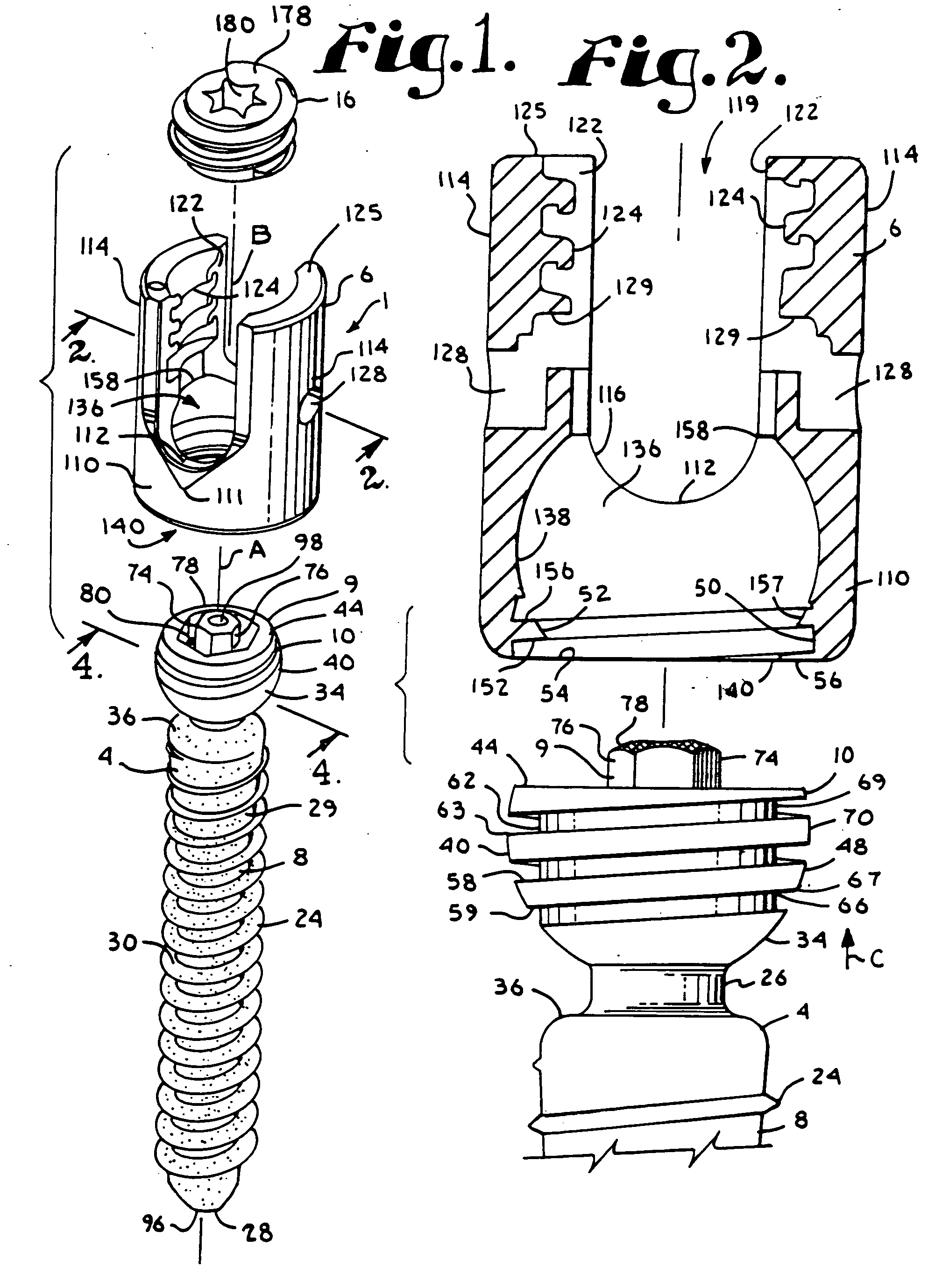
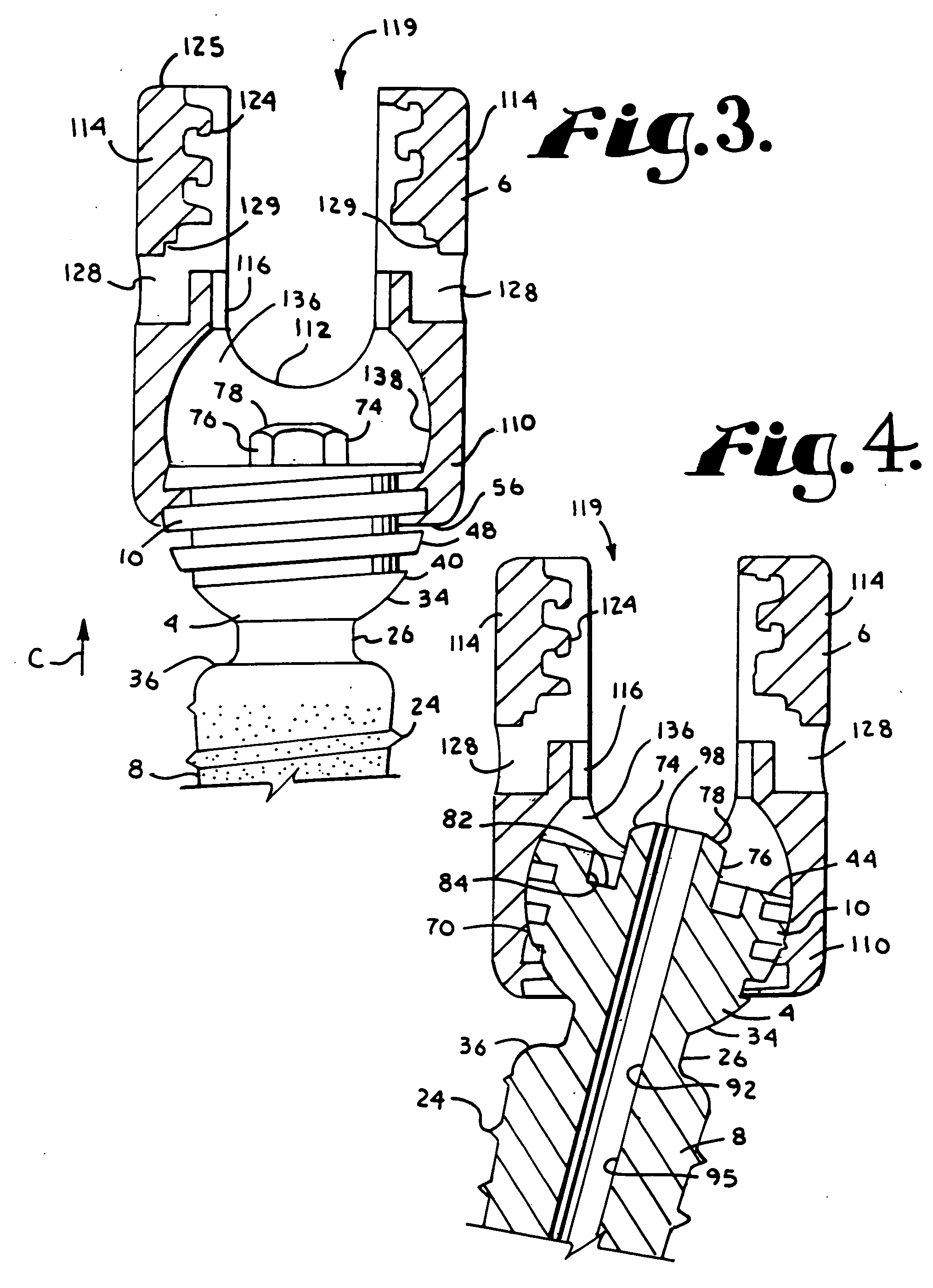
InactiveUS20070016200A1Easy to useCheap to makeInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsBiomedical engineeringBone screws
Bone screw assemblies include longitudinal connecting members that provide for dynamic stabilization, some including non-uniform portions that are configured to flex, contract or expand. Composite longitudinal connecting members include longitudinal segments made from different materials having different flexibilities. Polyaxial bone screw assemblies include change-out receivers for cooperating with replacement longitudinal connecting members having a different flexibility. Bone screw shanks for cooperating with one or more open receivers include treatment or coating to provide biologically active interface with bone.
Owner:JACKSON
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com