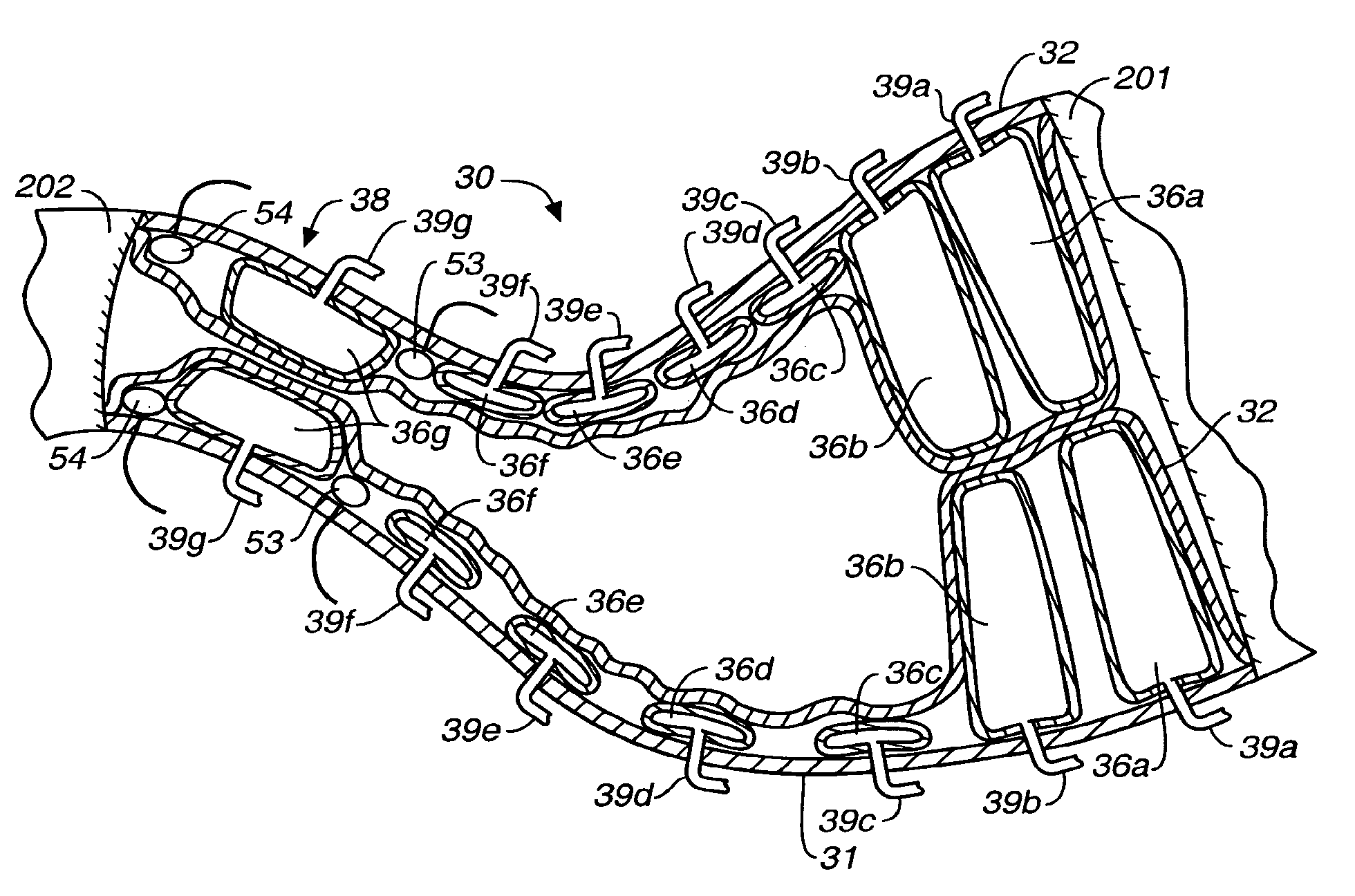
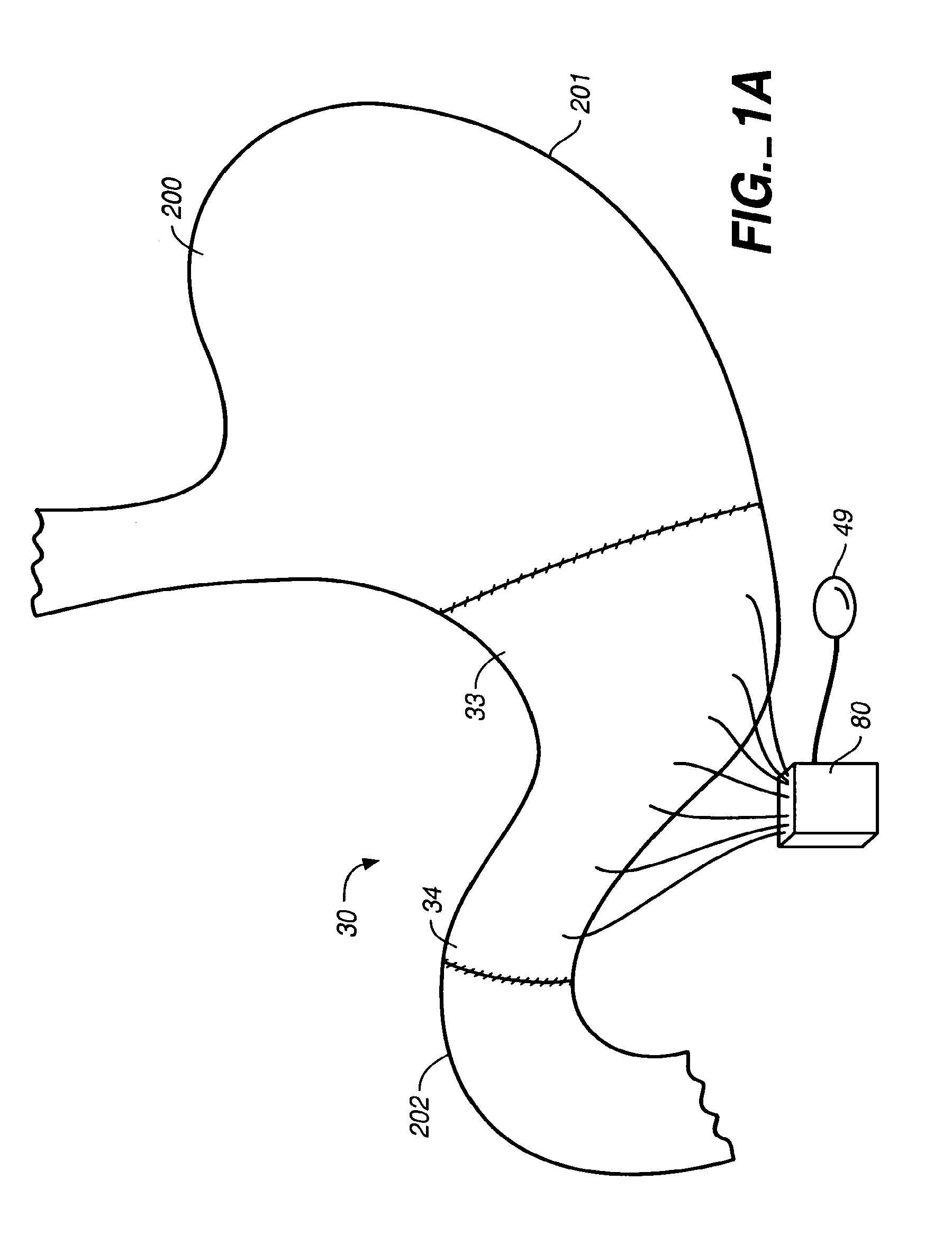
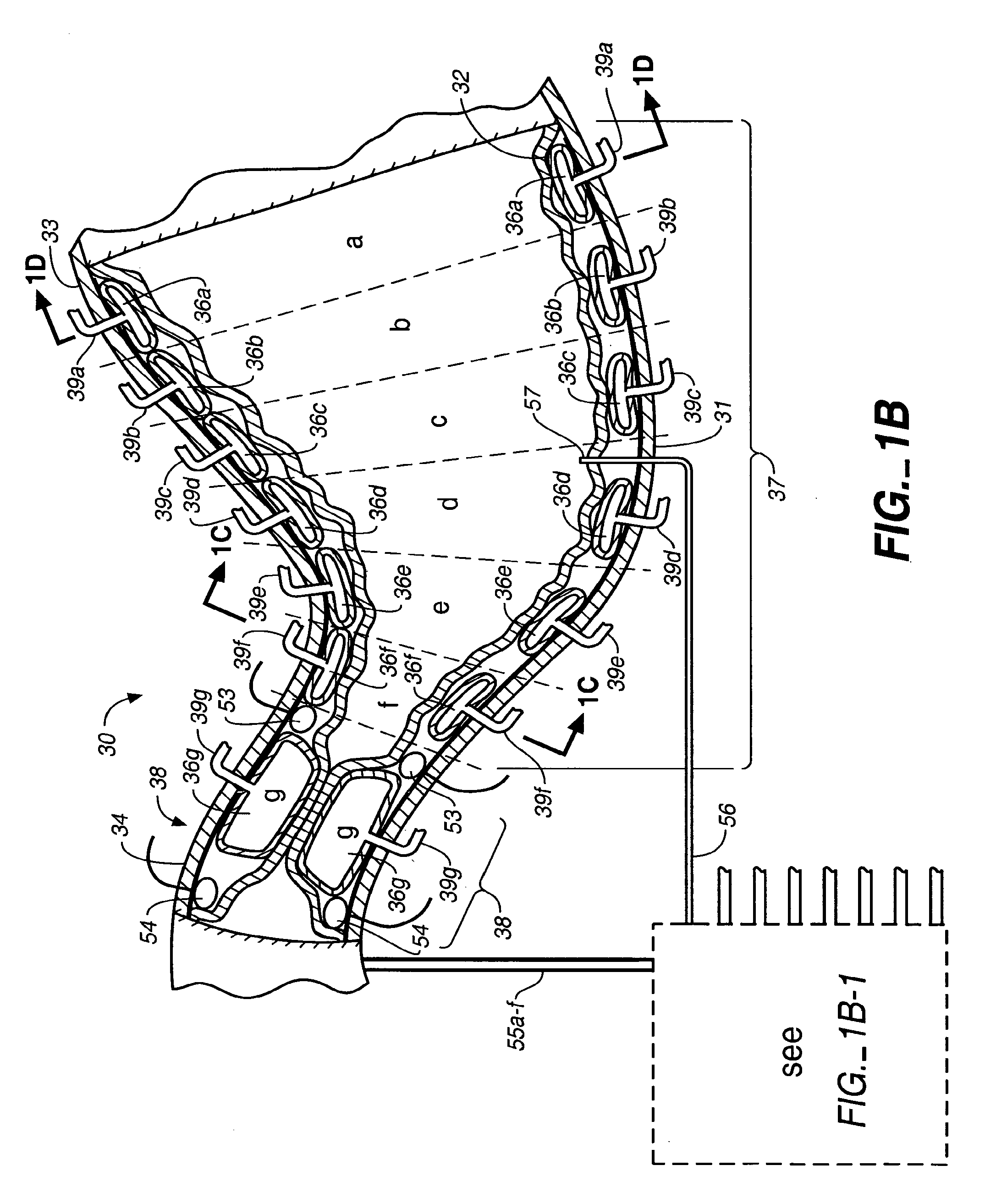
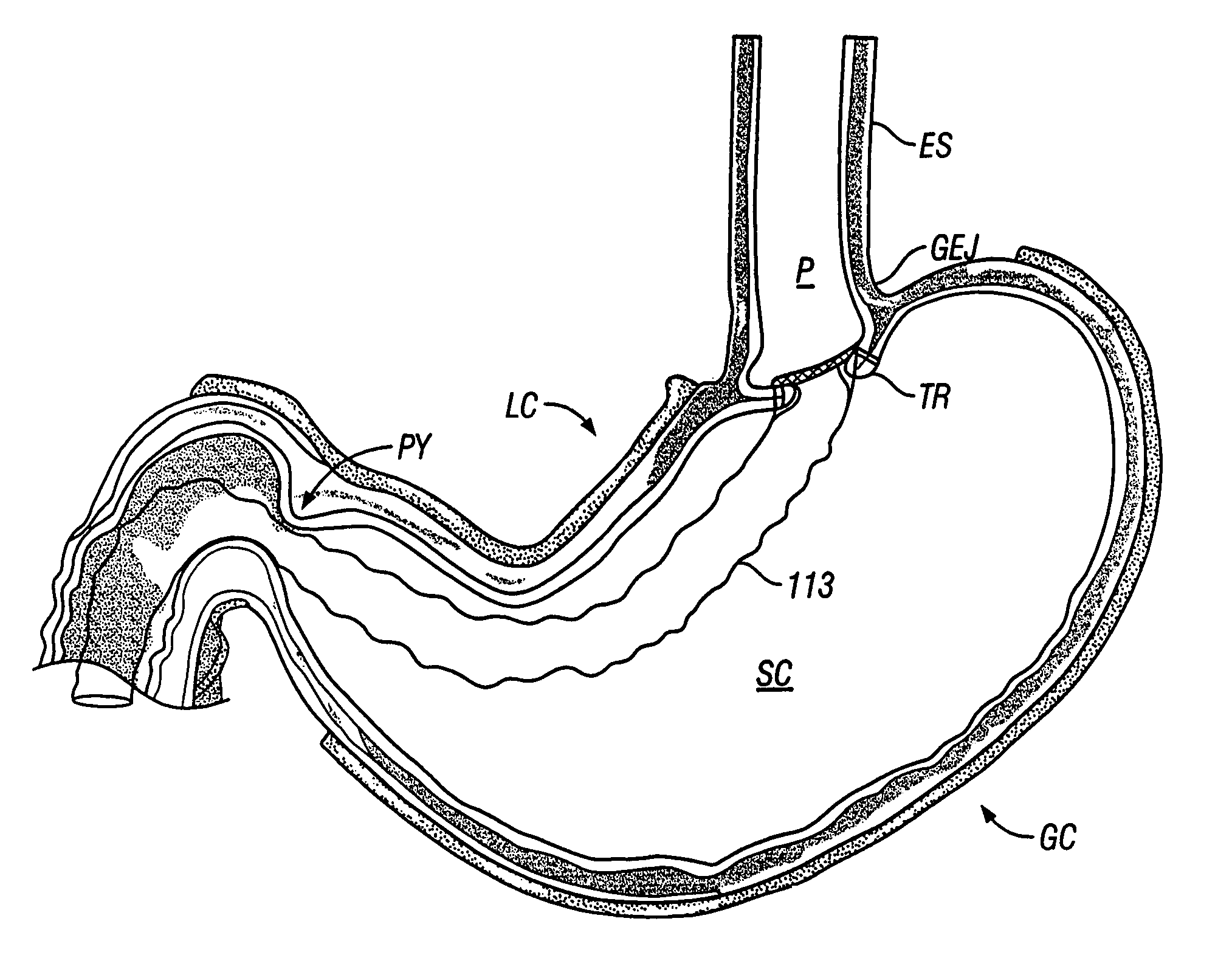
Patents
Literature
167 results about "Pylorus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
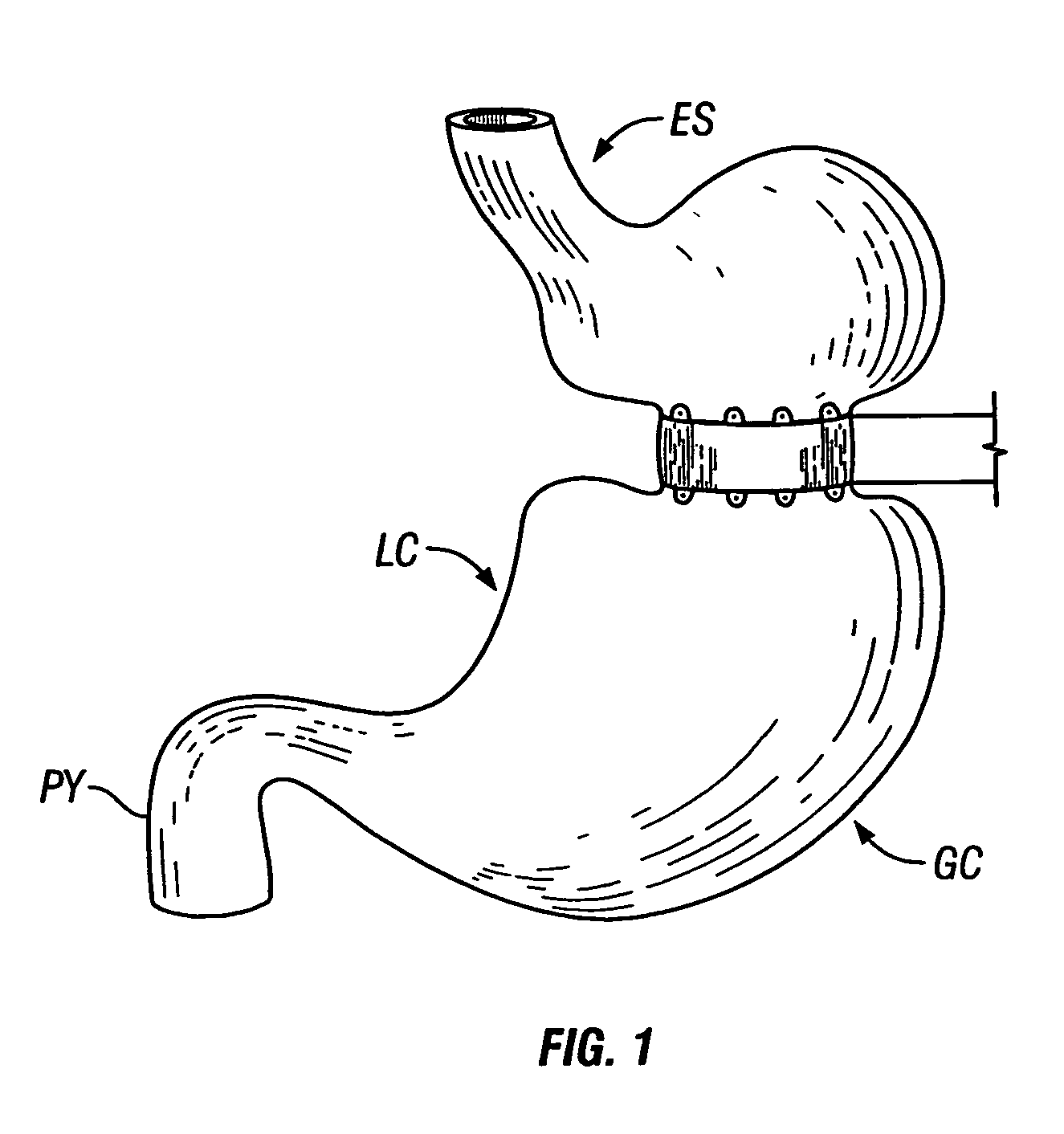
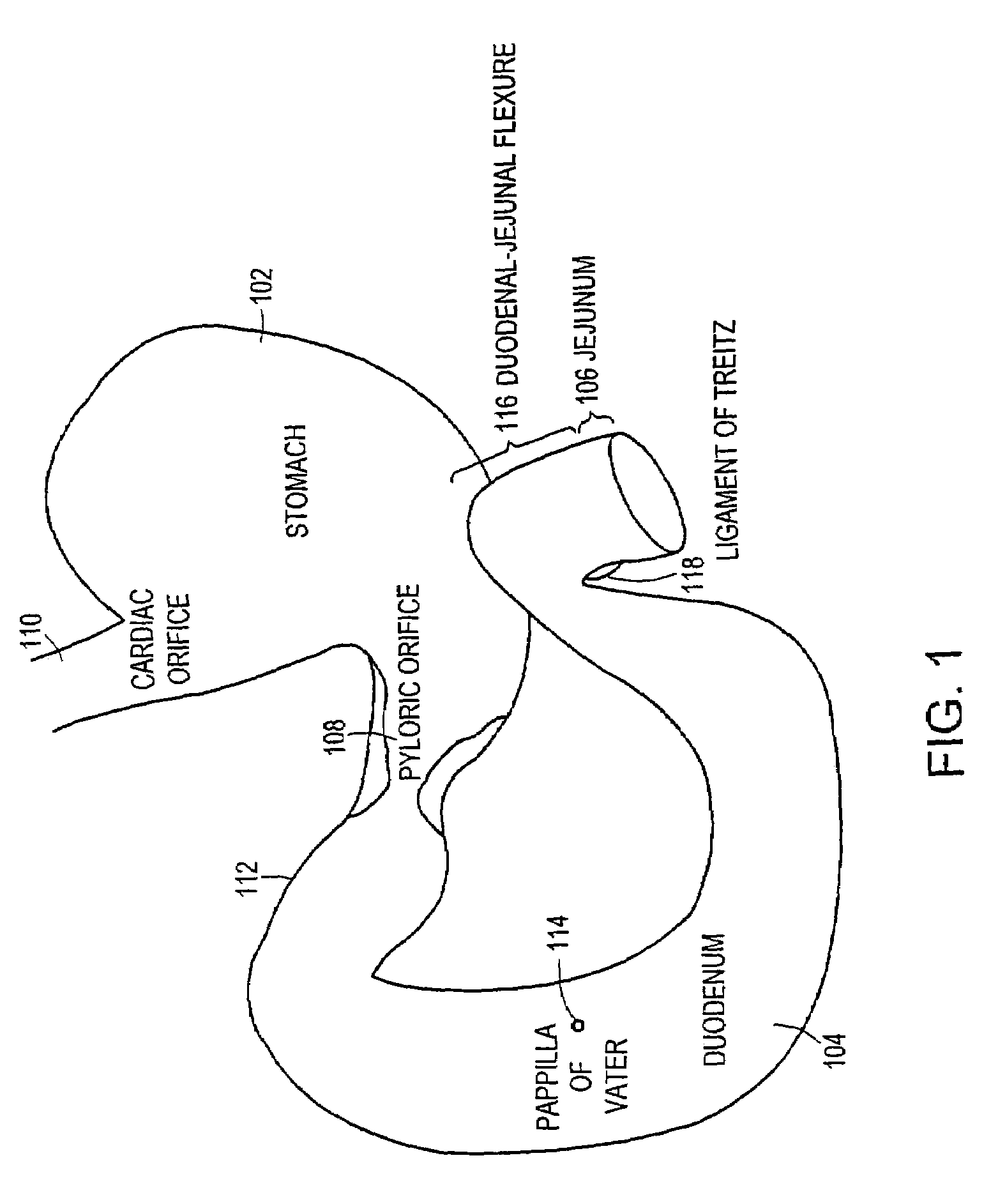
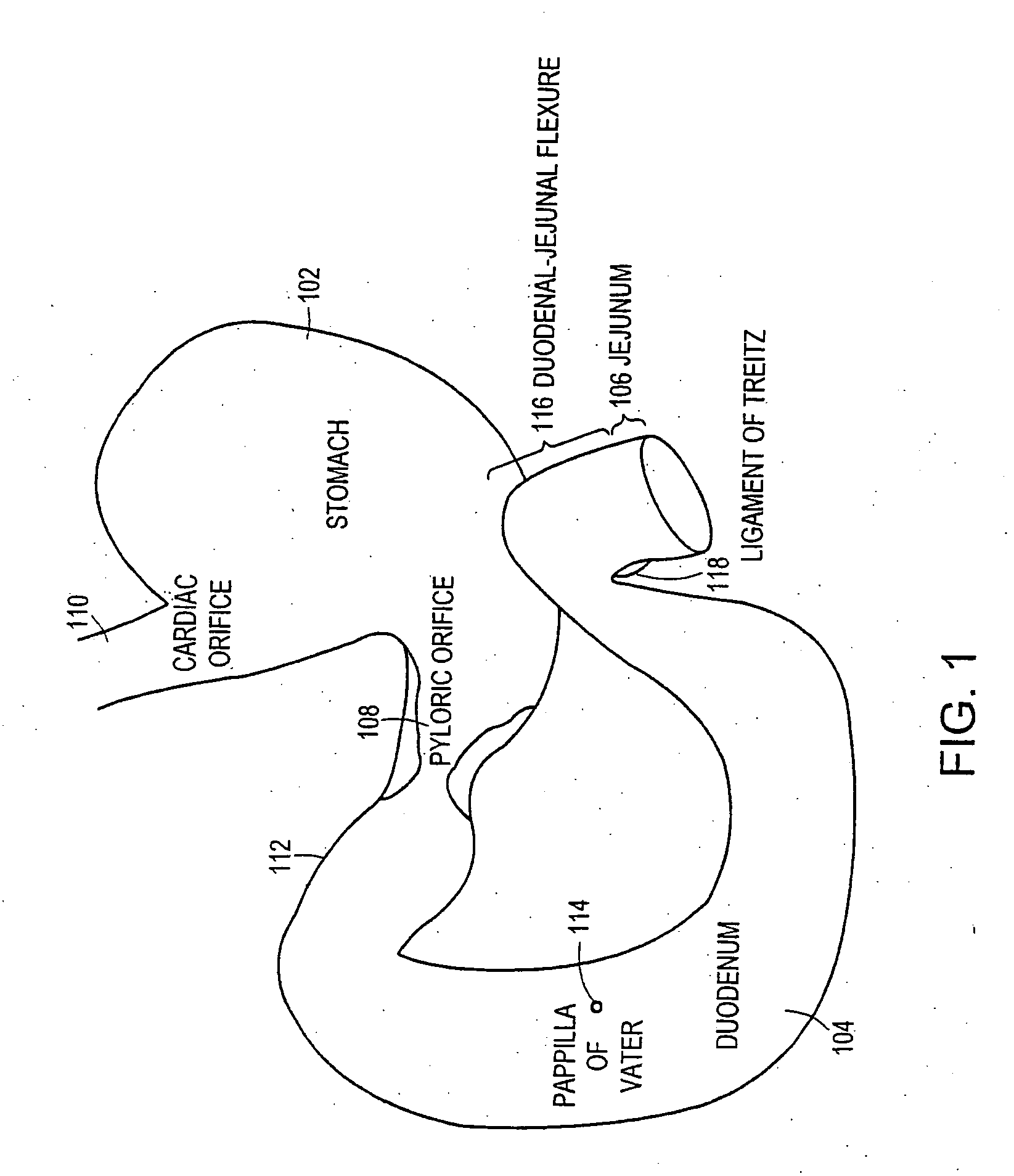
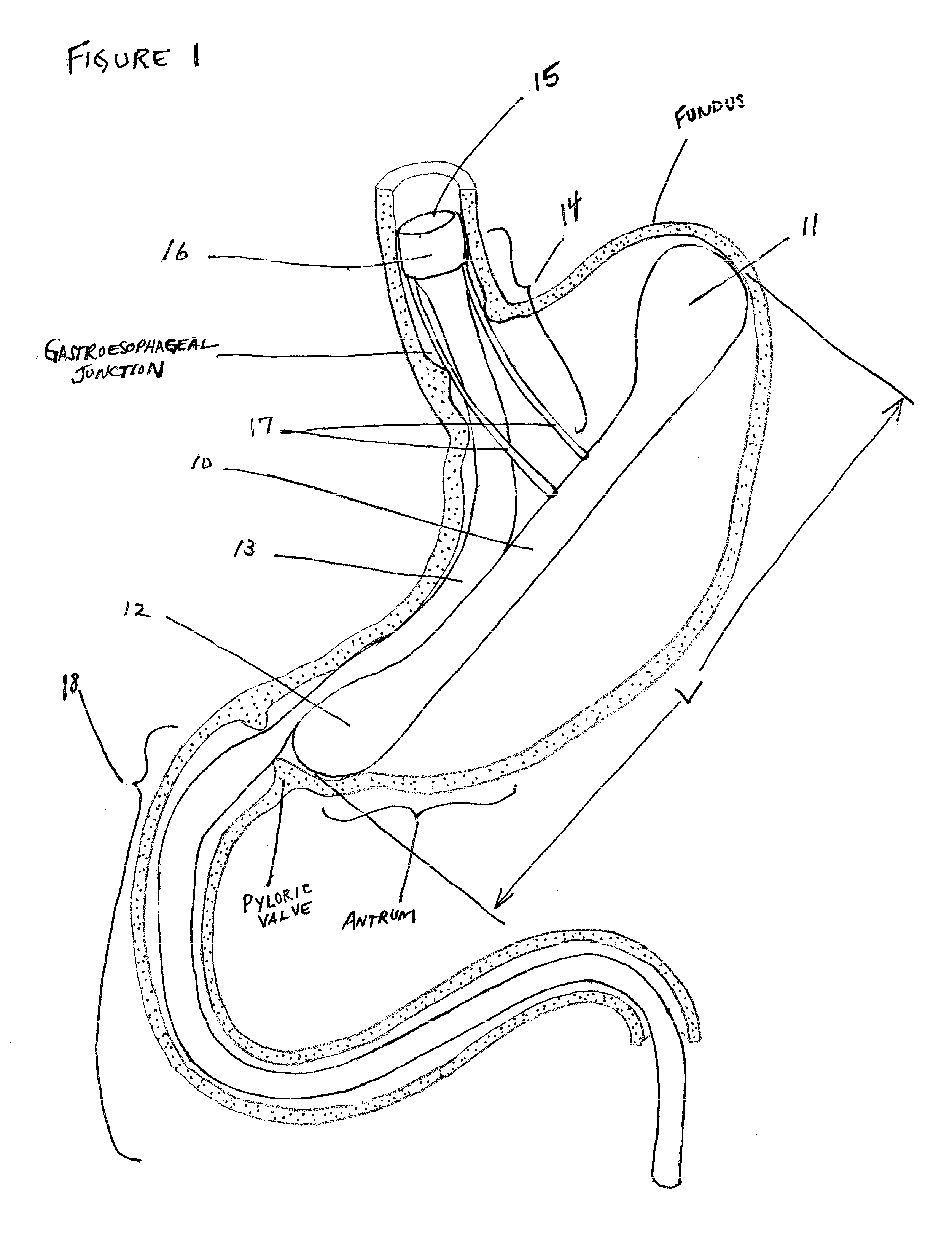
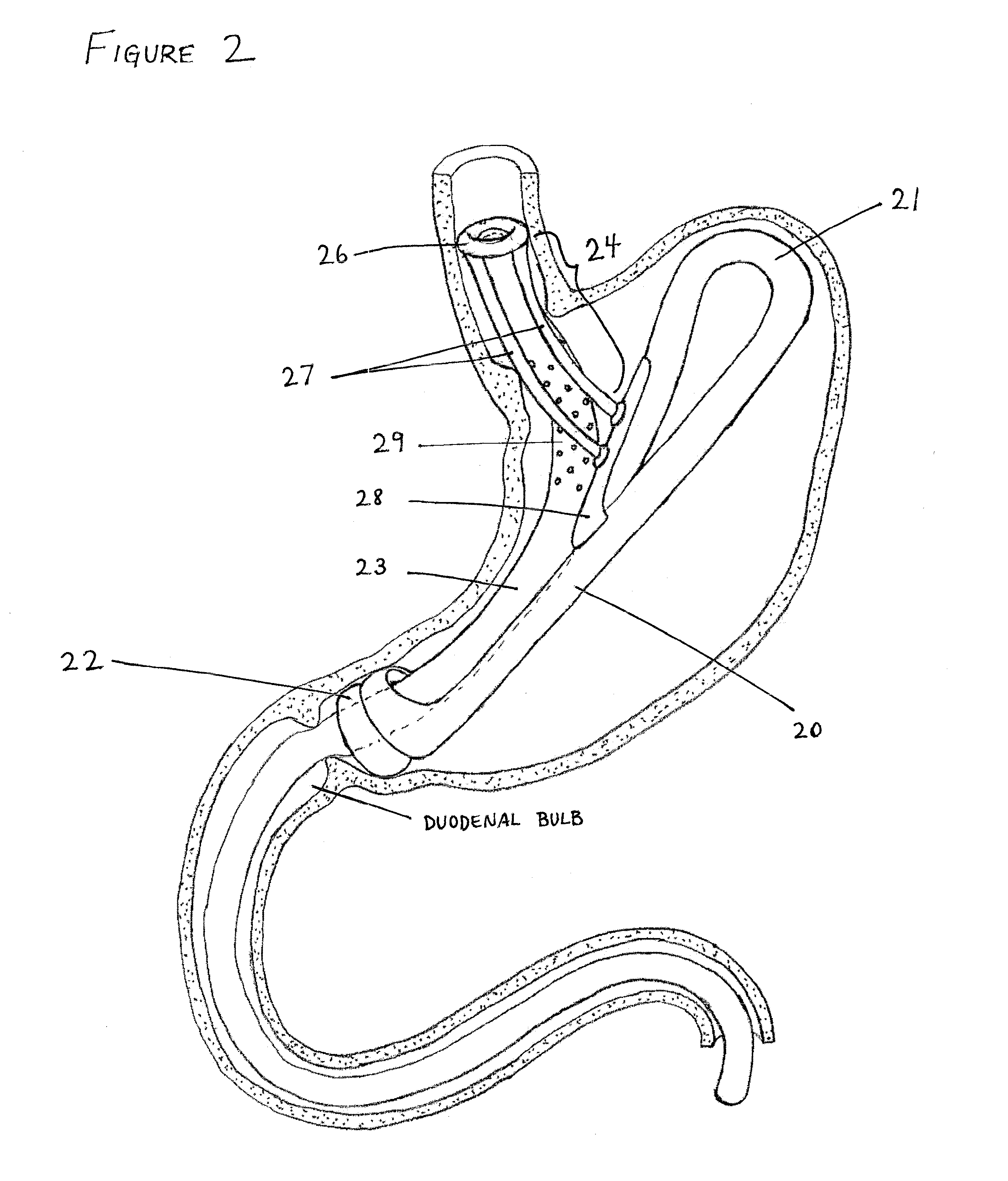
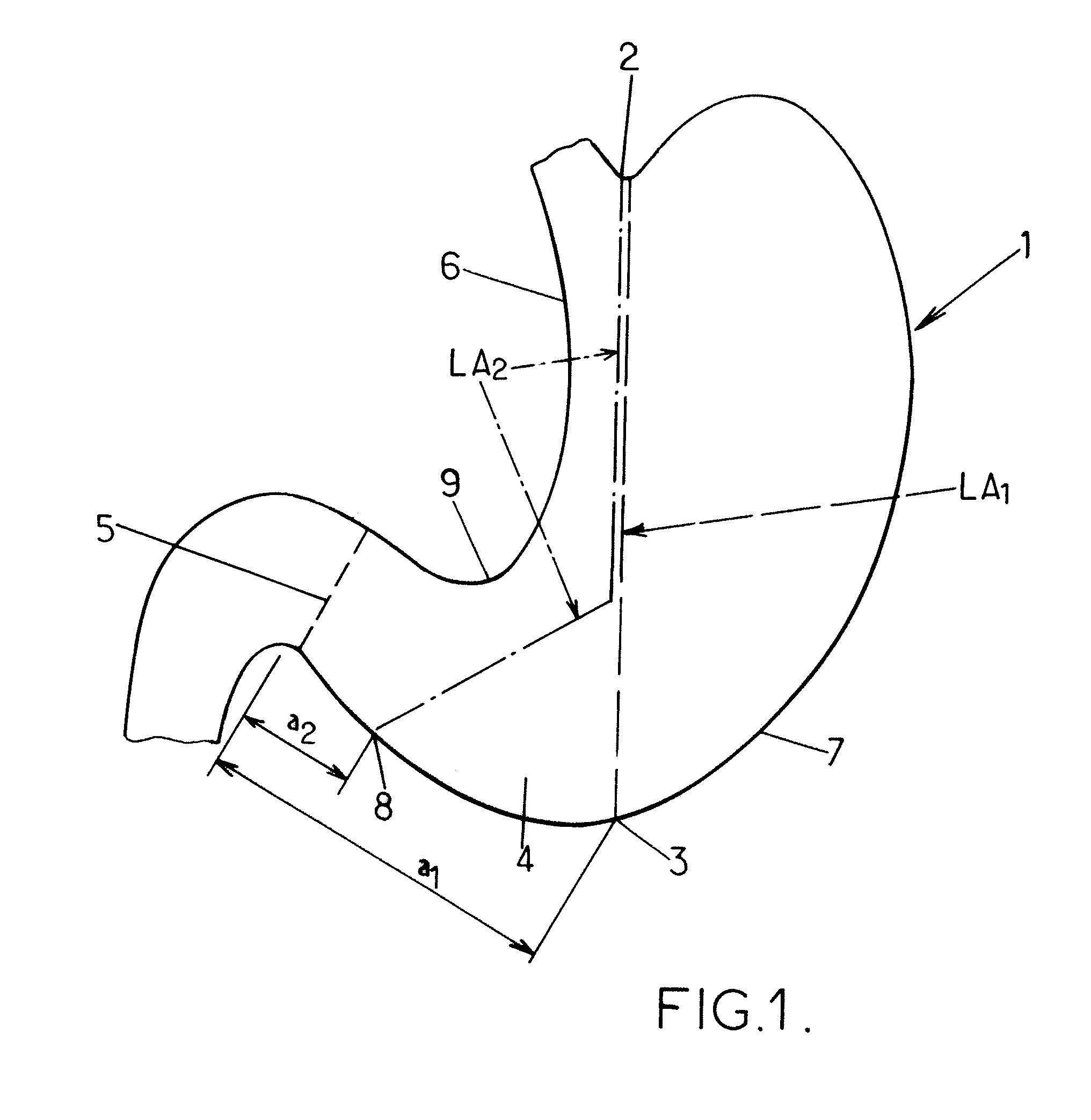
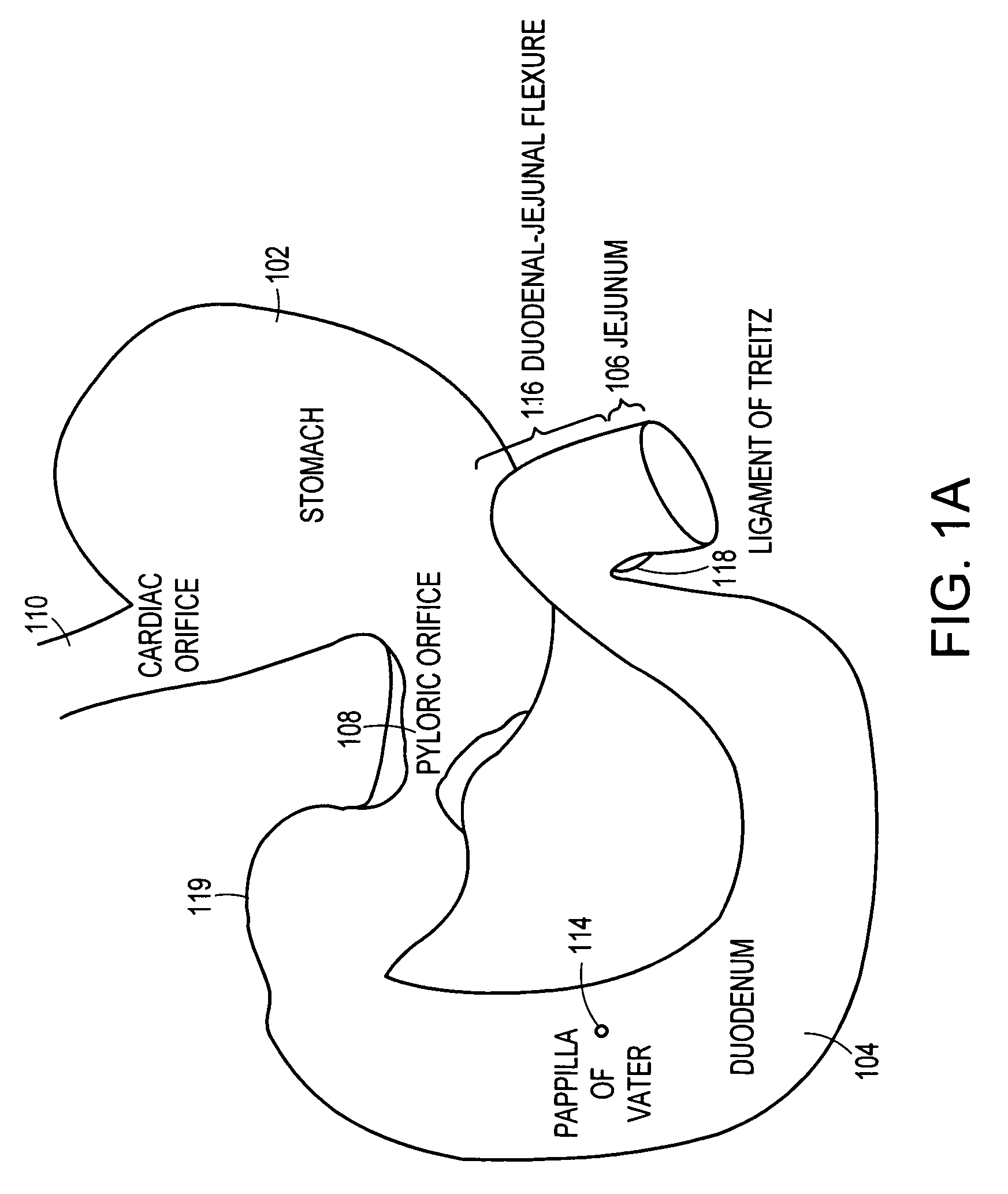
The pylorus (/paɪˈlɔːrəs/ or /pɪˈloʊrəs/), or pyloric part, connects the stomach to the duodenum. The pylorus is considered as having two parts, the pyloric antrum (opening to the body of the stomach) and the pyloric canal (opening to the duodenum). The pyloric canal ends as the pyloric orifice, which marks the junction between the stomach and the duodenum. The orifice is surrounded by a sphincter, a band of muscle, called the pyloric sphincter. The word pylorus comes from Greek πυλωρός, via Latin. The word pylorus in Greek means "gatekeeper", related to "gate" (Greek: pyle) and is thus linguistically related to the word "pylon".
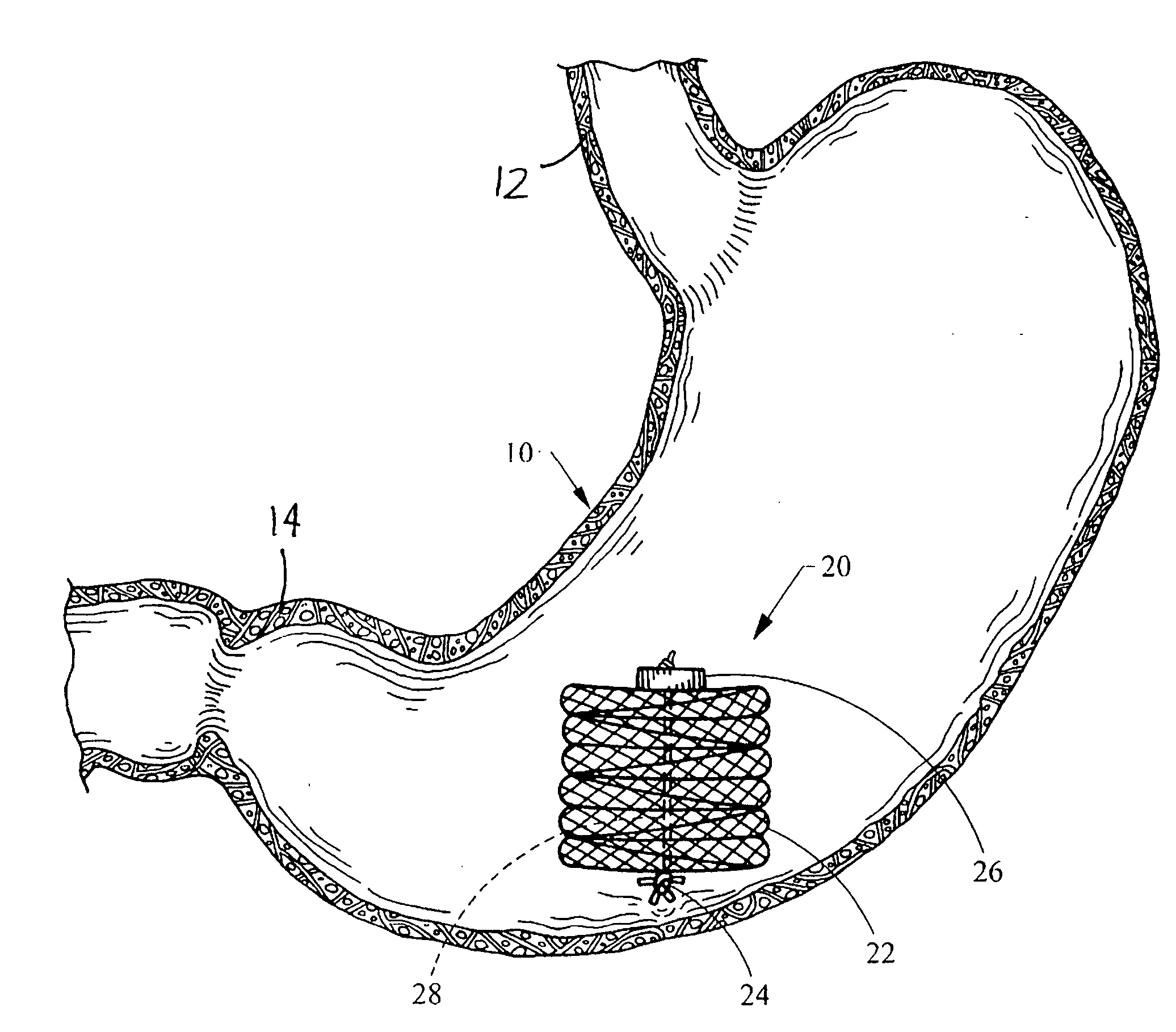
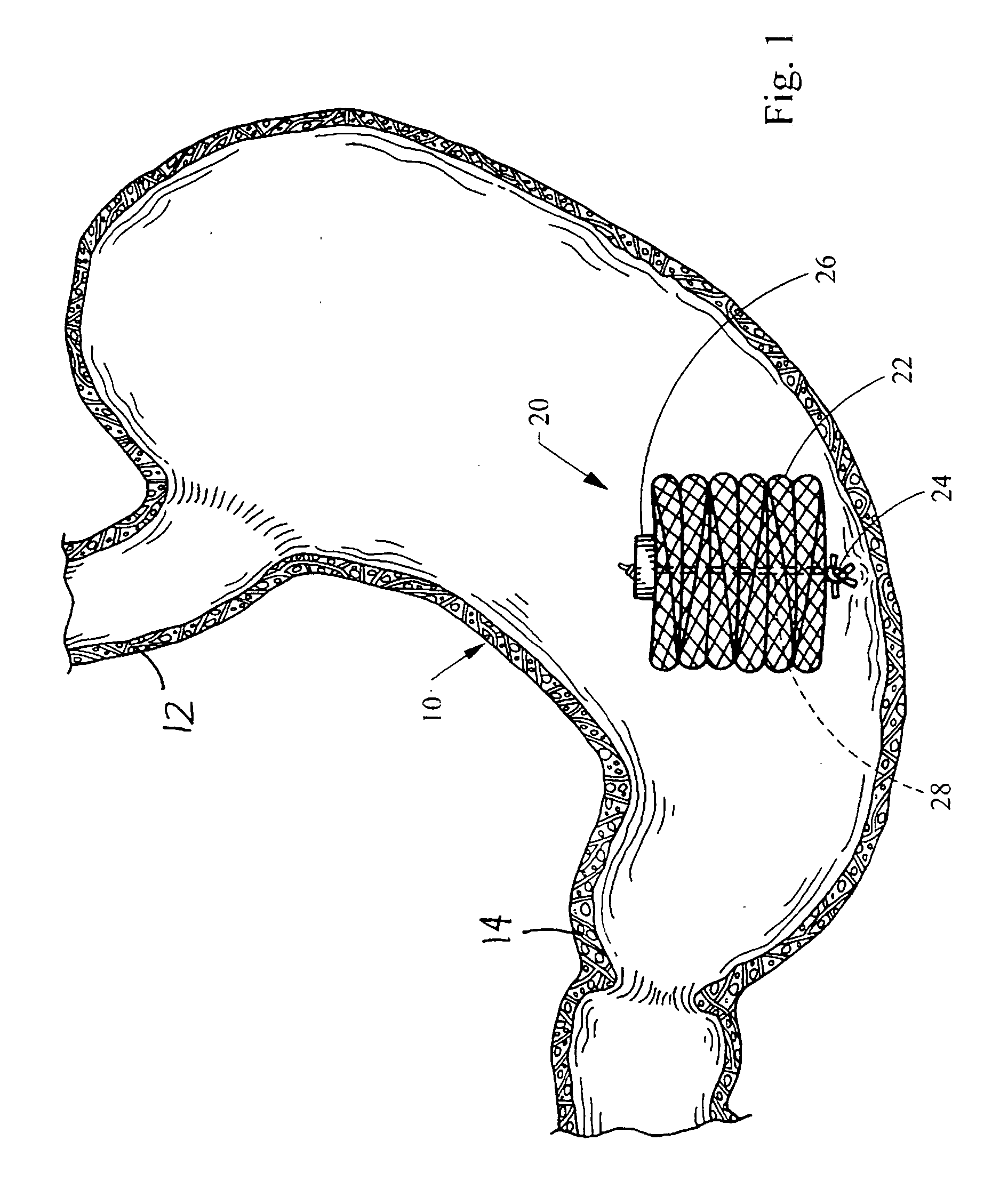
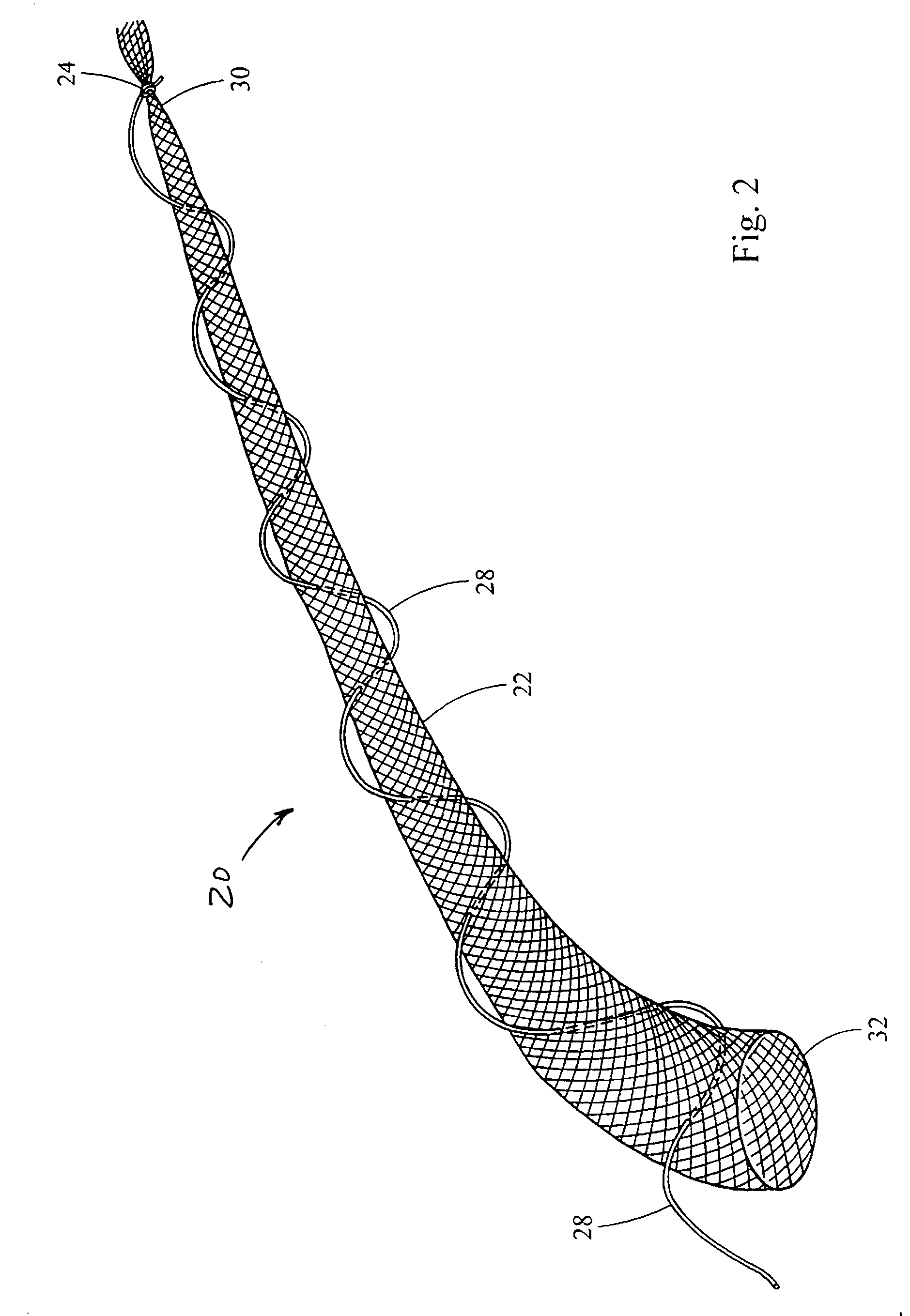
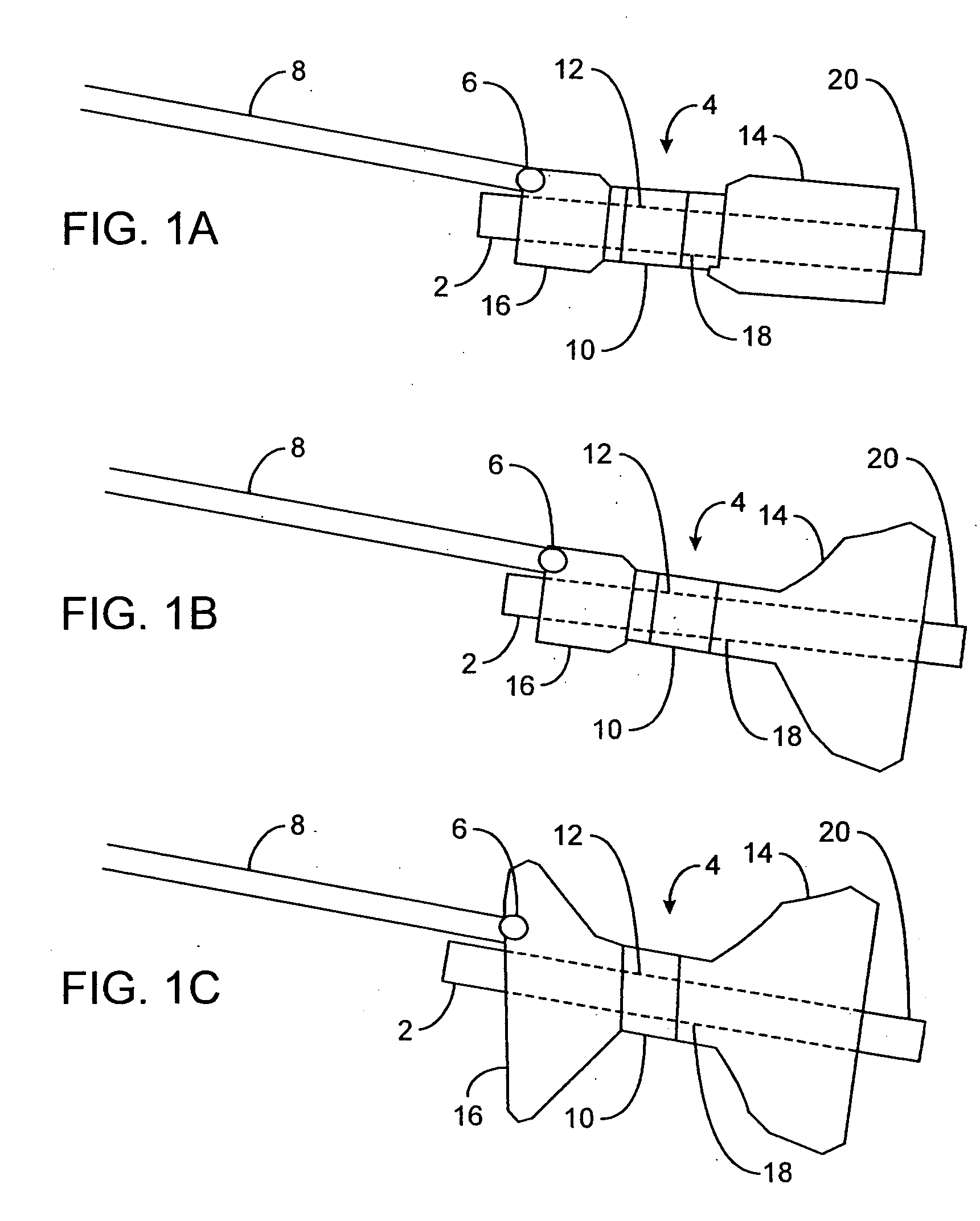
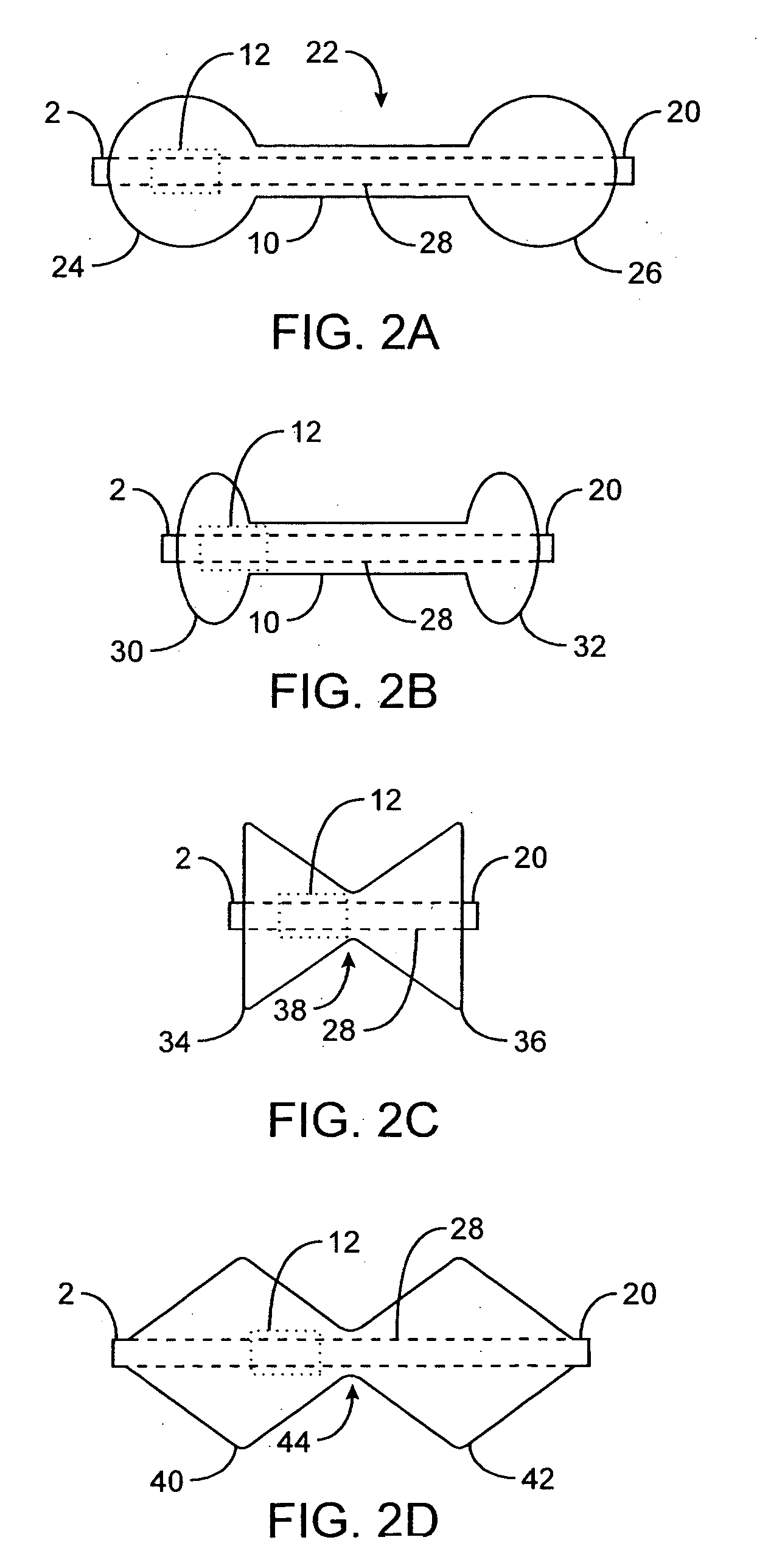
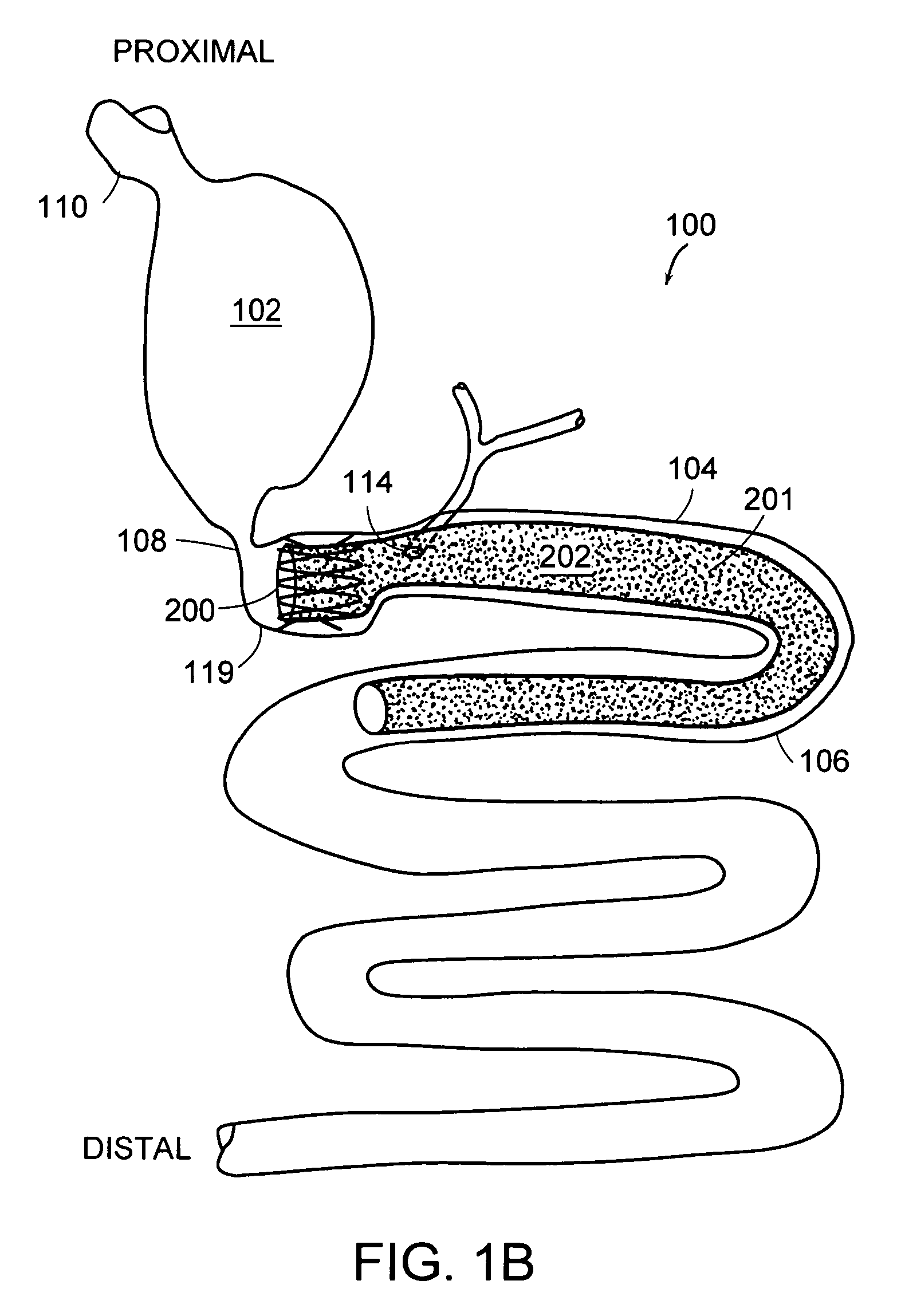
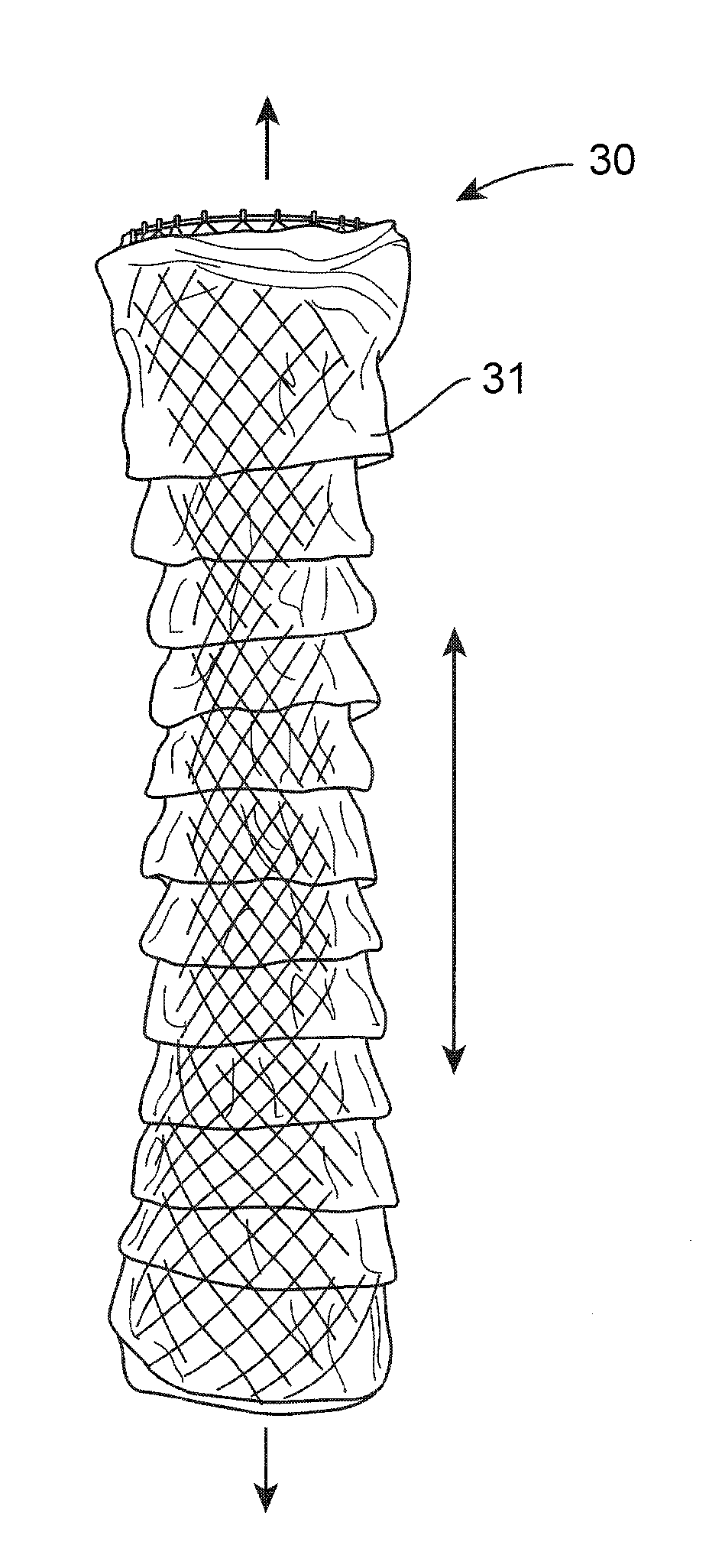
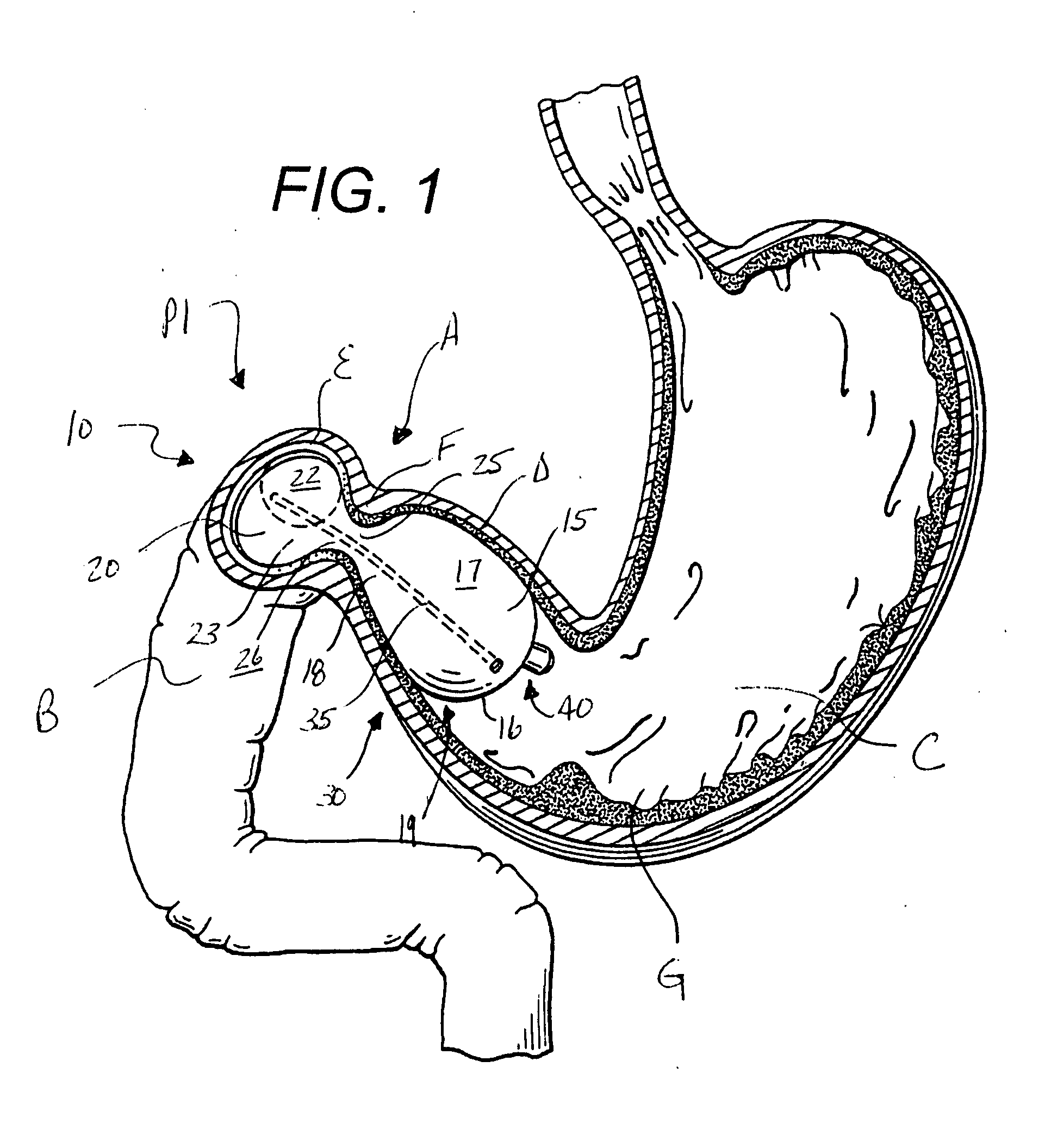
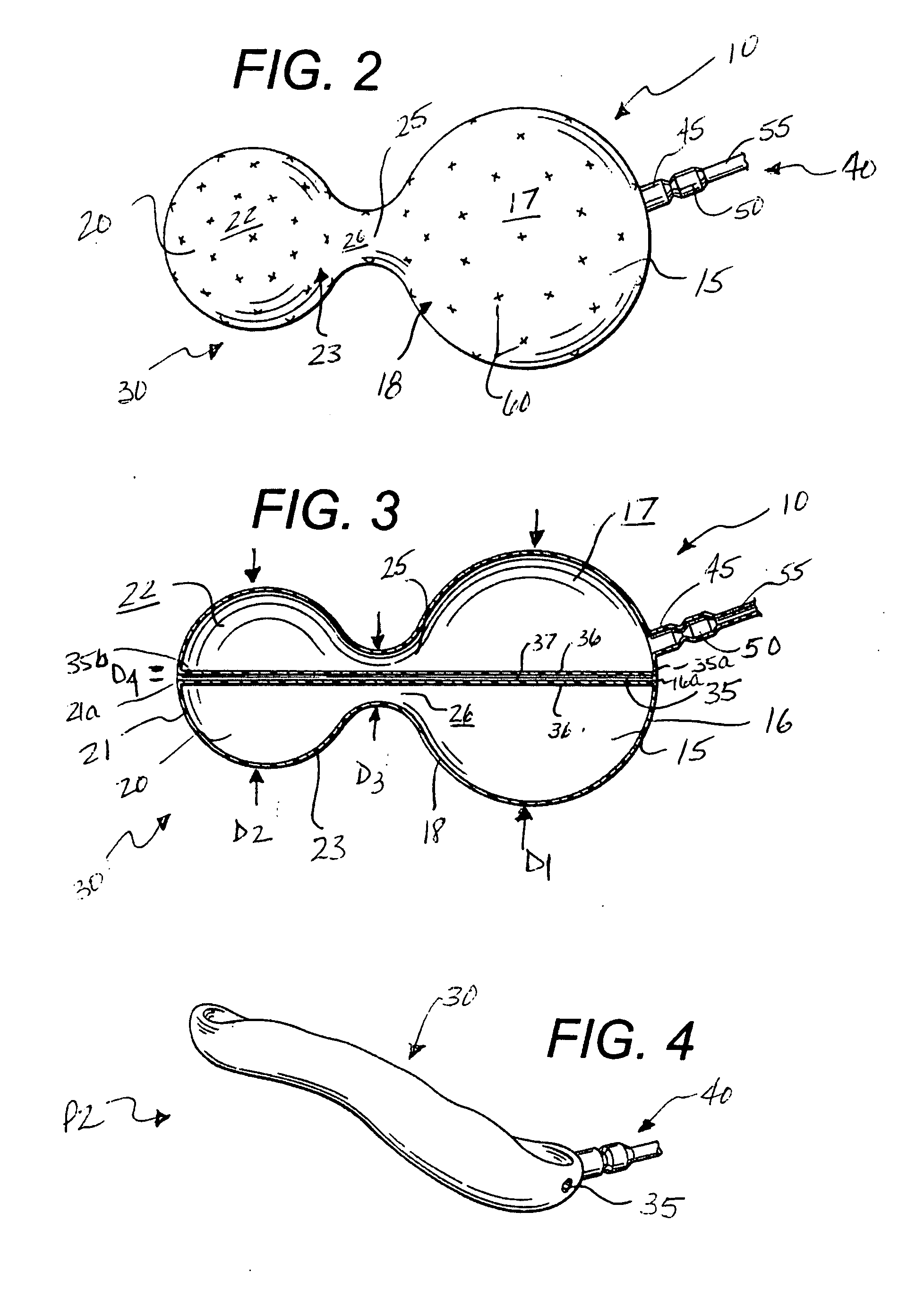
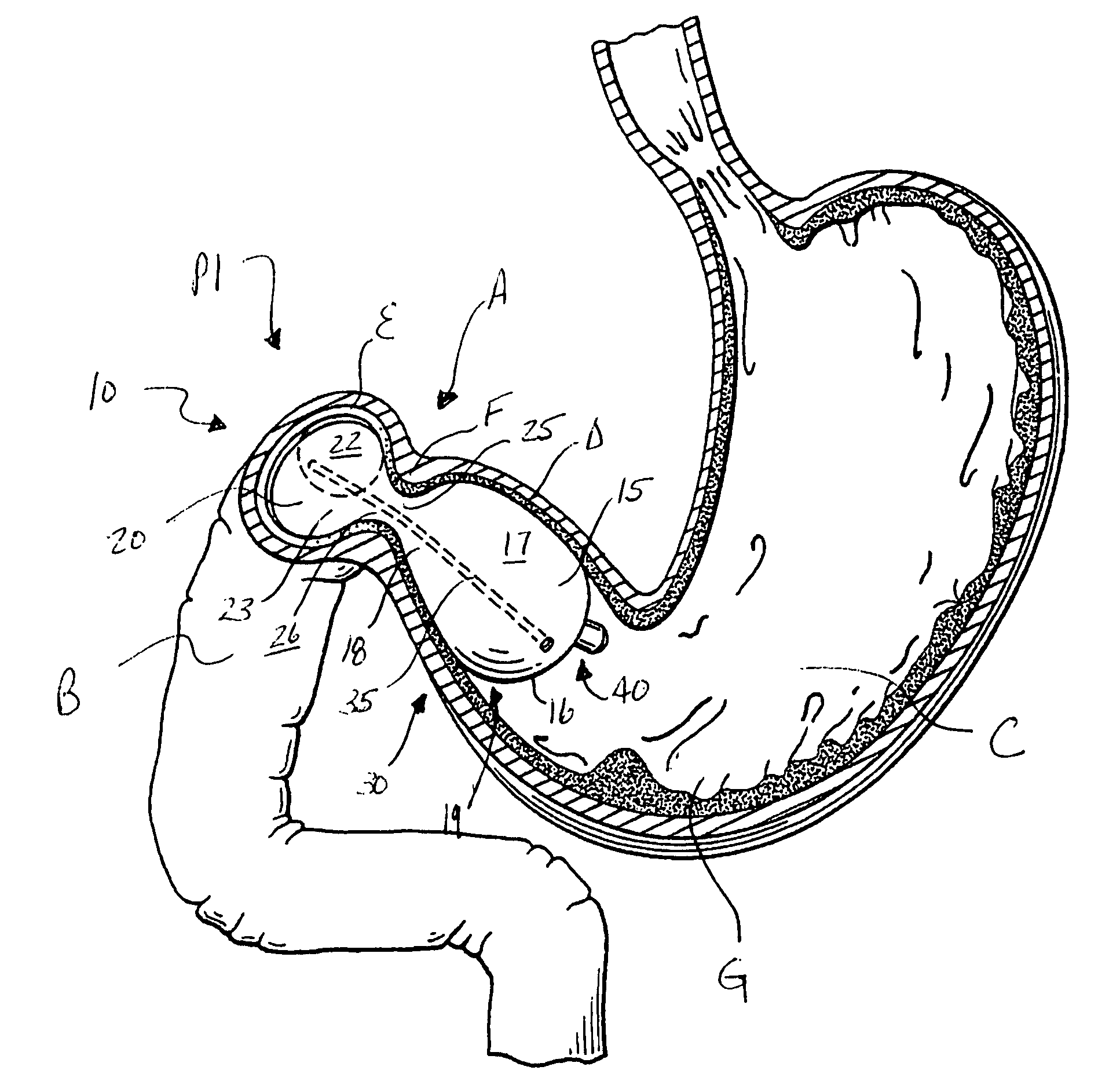
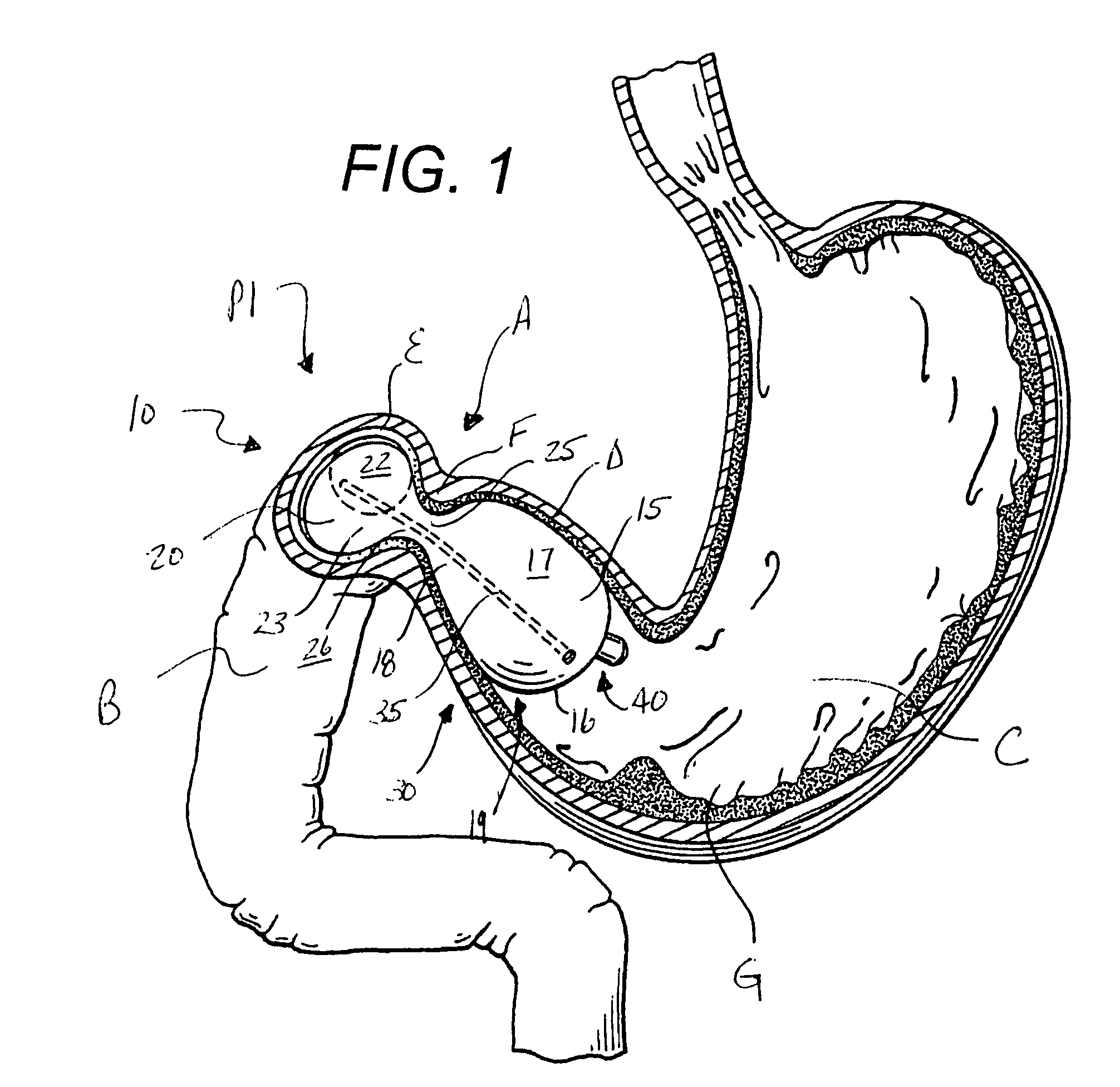
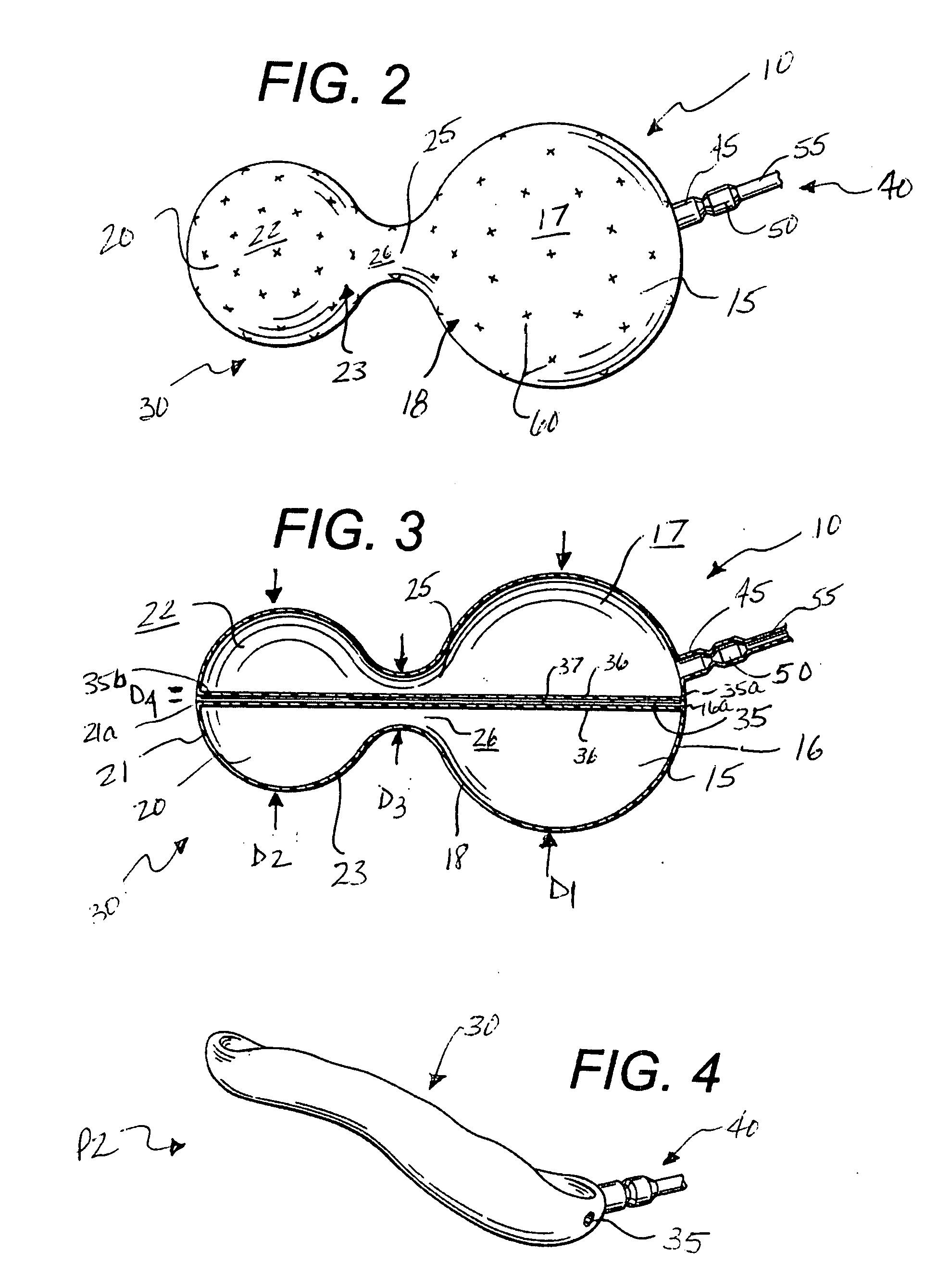
Intragastric device for treating obesity
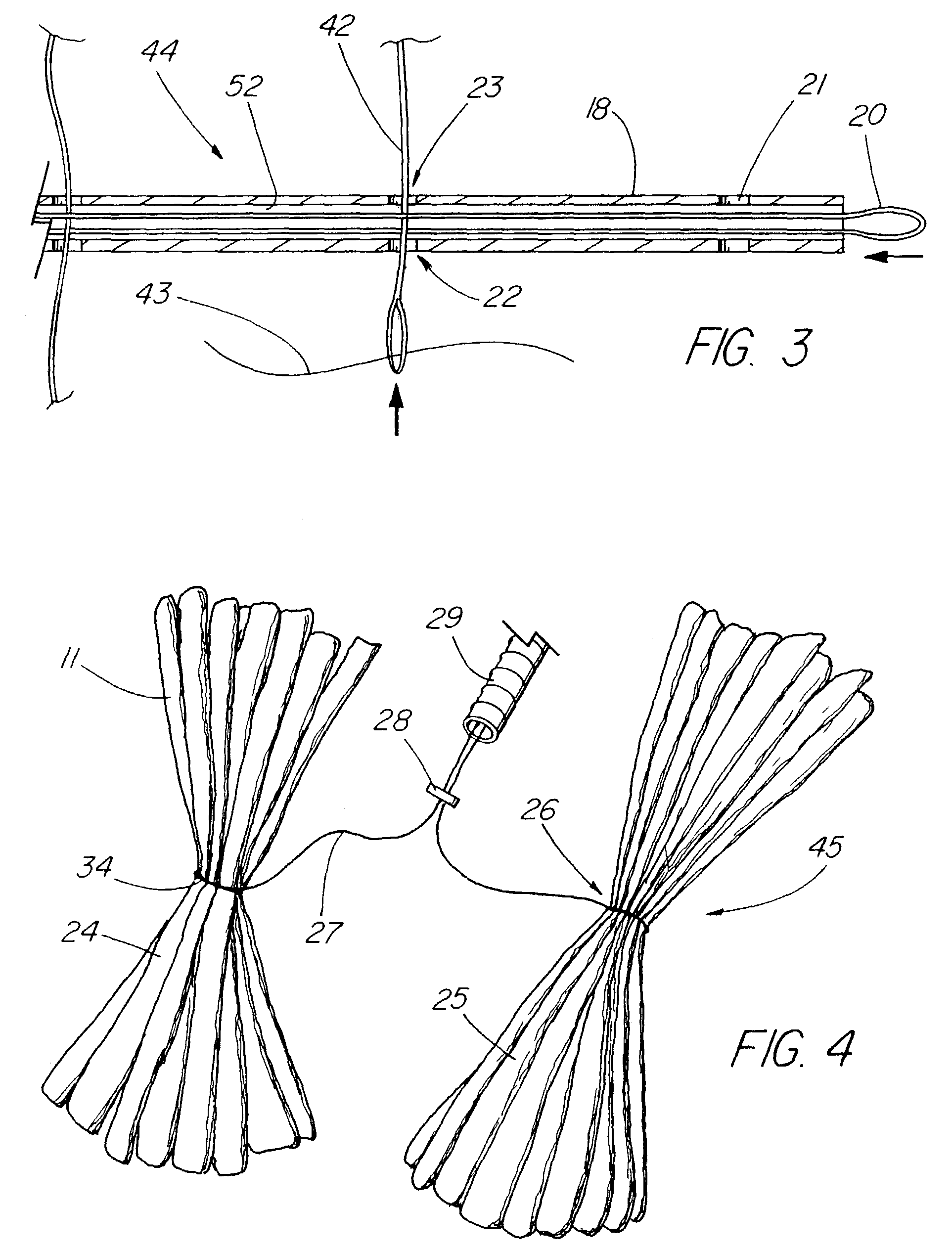
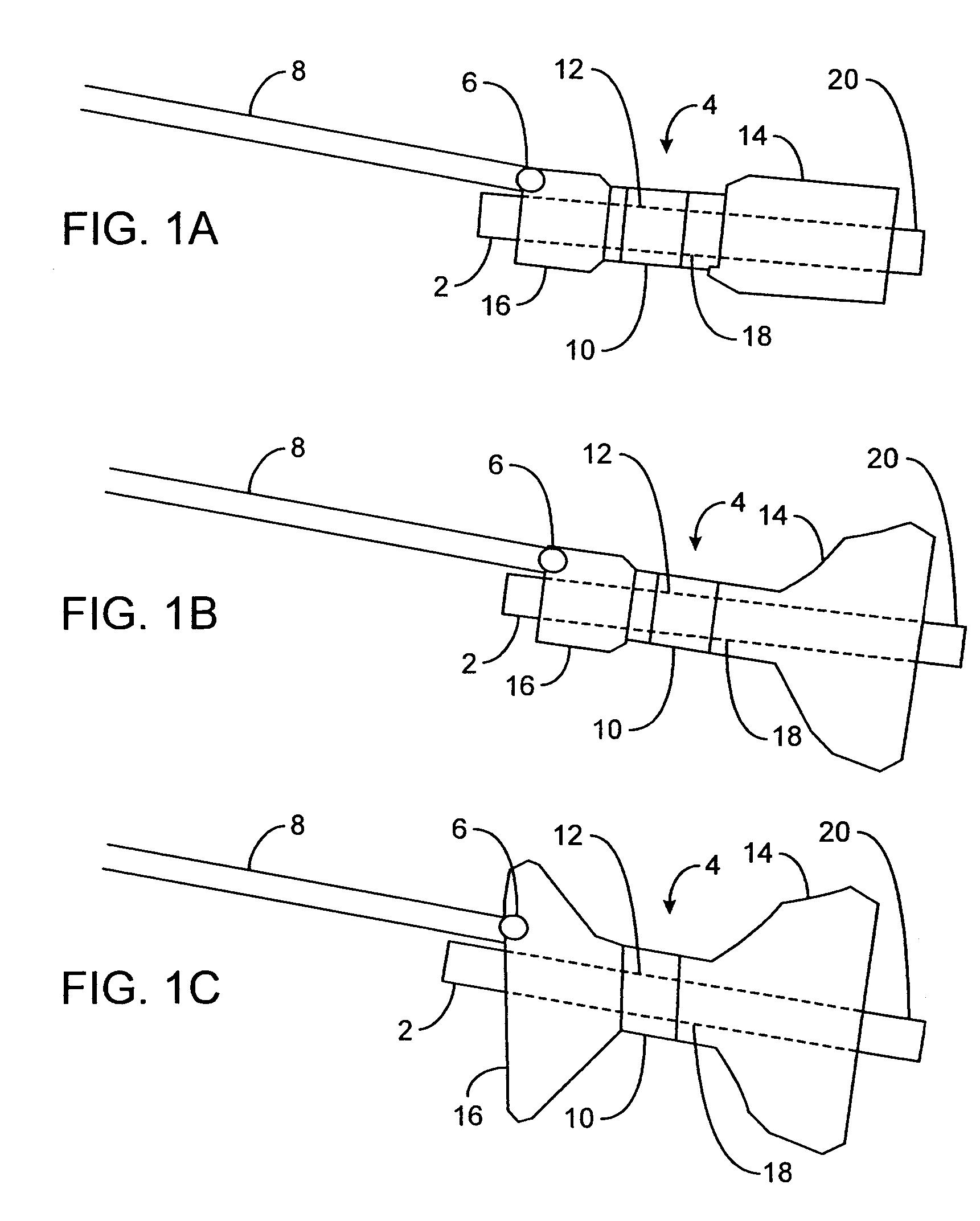
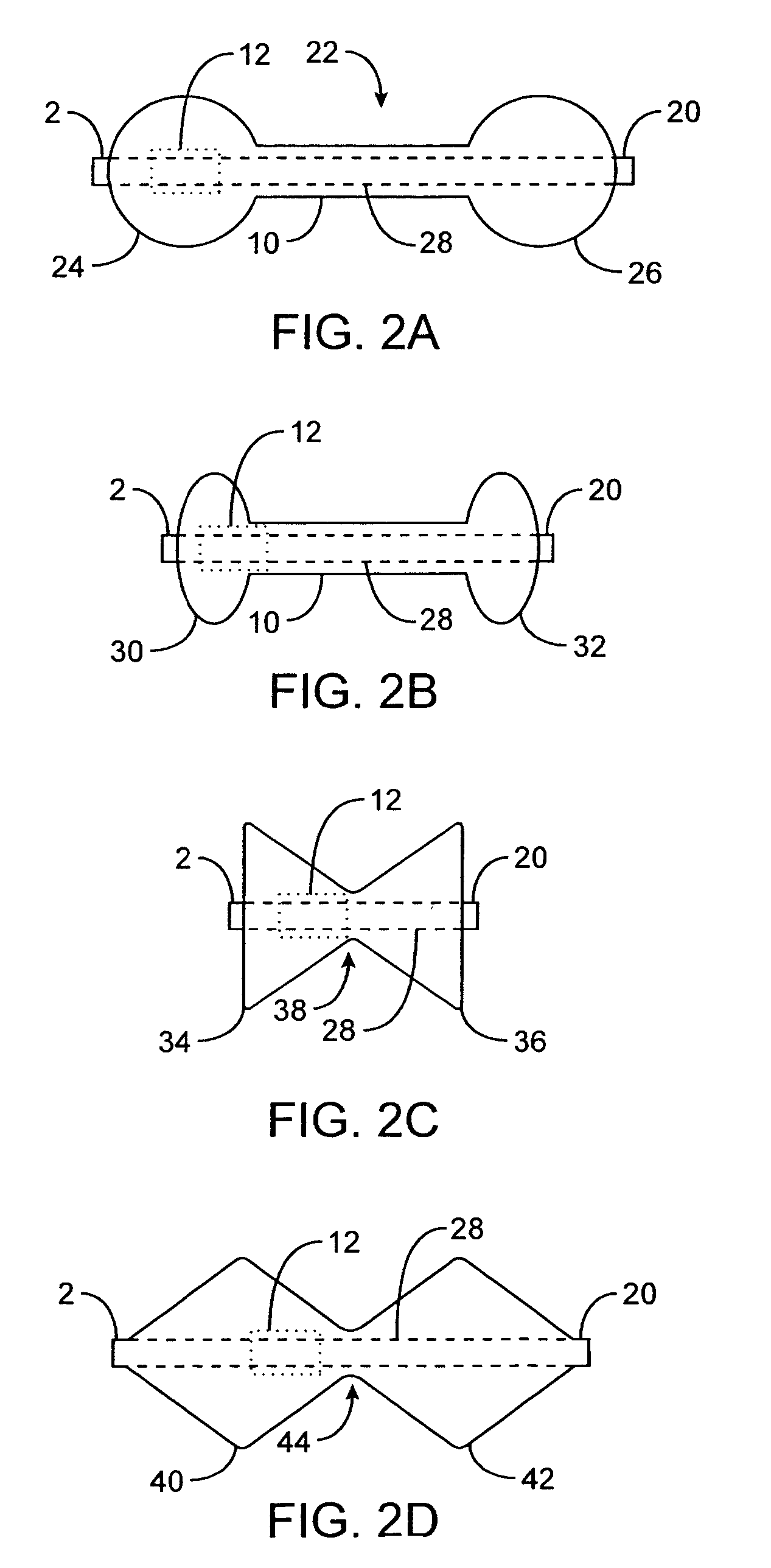
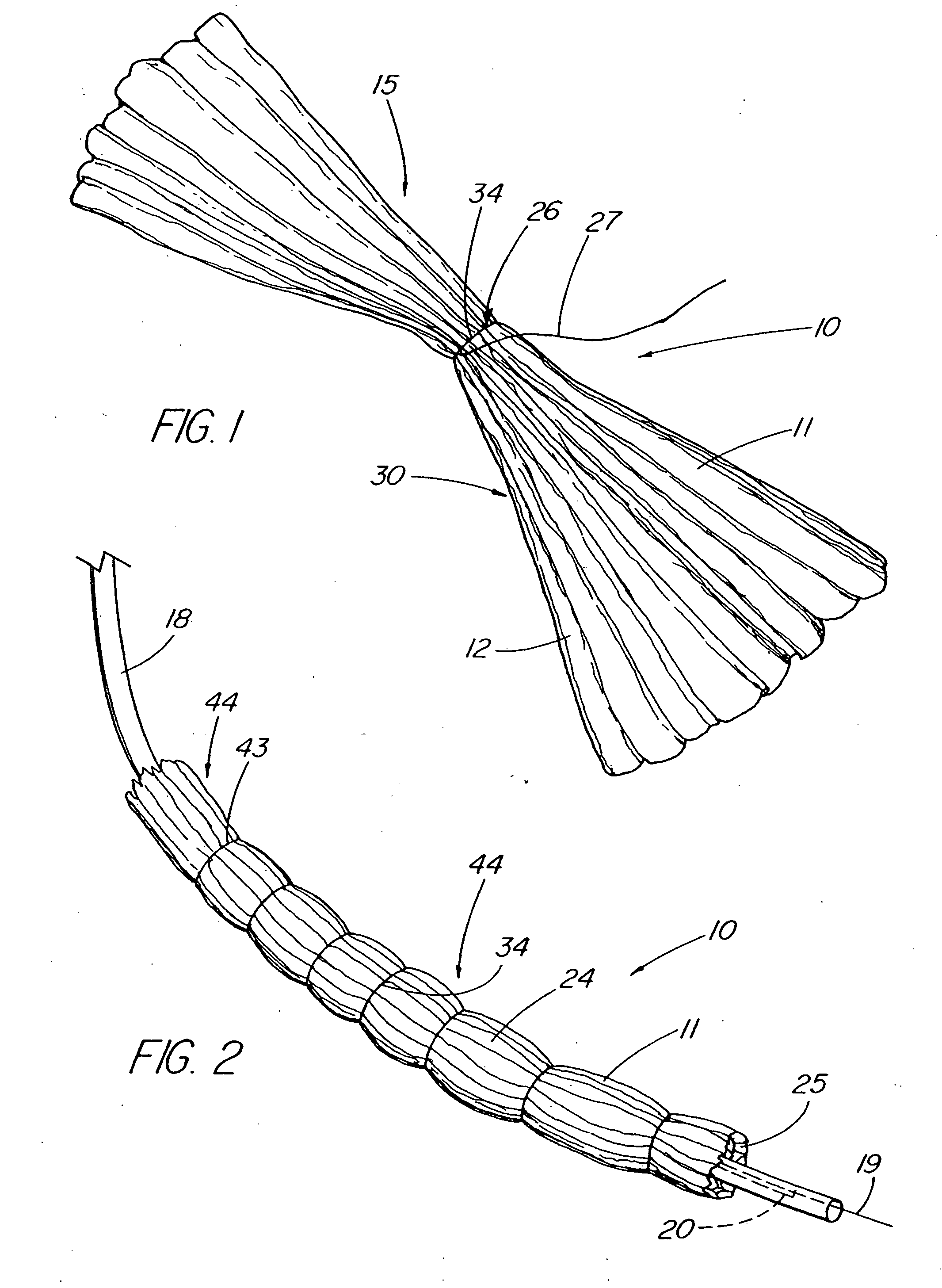
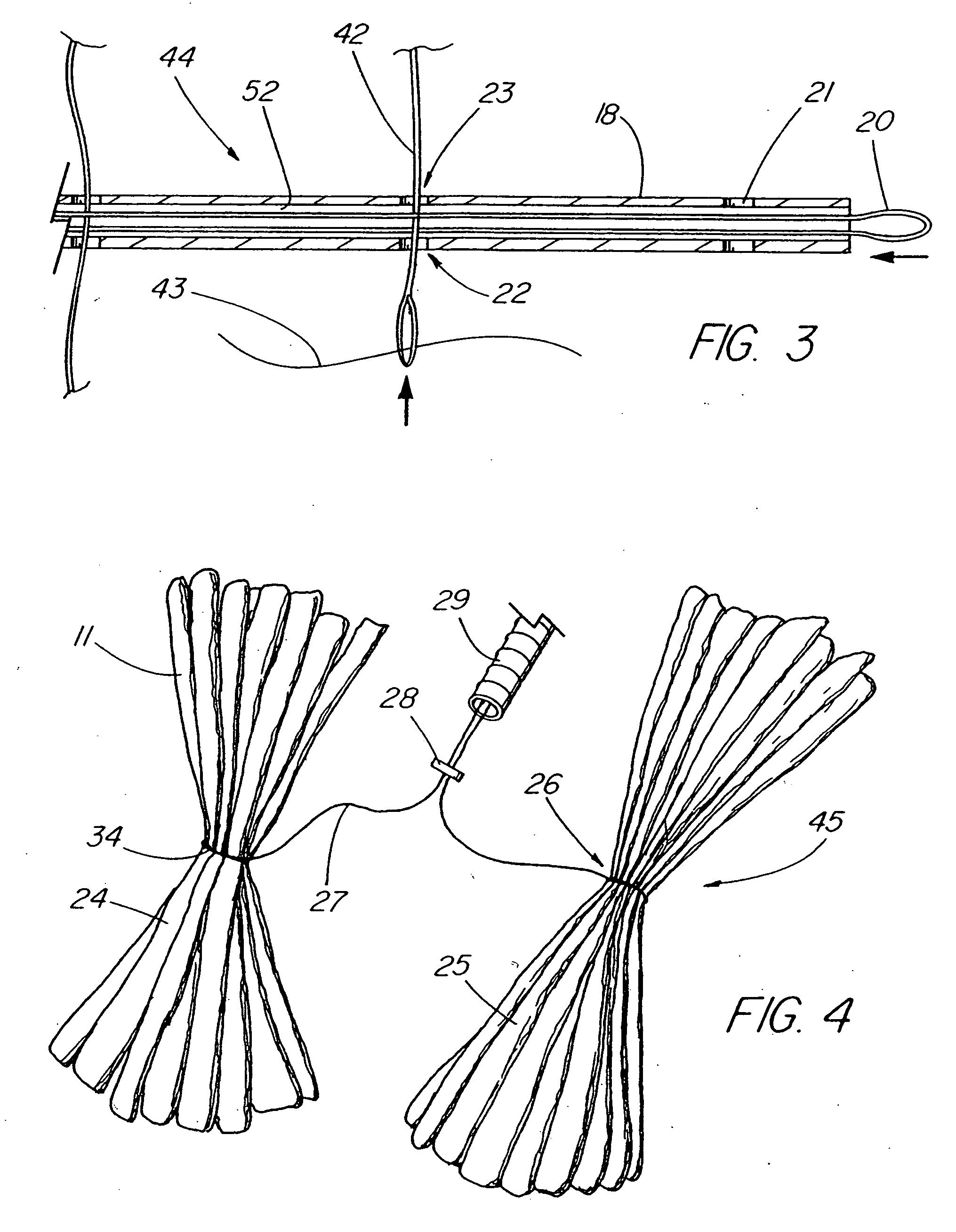
An intragastric device generally comprises a strip digestive-resistant mesh material that is operable between a first configuration and a second configuration. The first configuration is sufficiently small to permit introduction of the digestive-resistant mesh material into a gastric lumen of the mammal. The second configuration is sufficiently large to prevent the digestive-resistant mesh material from passing through the mammals pylorus, thereby permitting the mesh member to act as an artificial bezoar. Methods and devices for delivering the mesh member are also provided, including a pusher that is operable to engage and disengage the mesh member for delivery through the gastric lumen via a delivery sheath.
Owner:WILSONCOOK MEDICAL
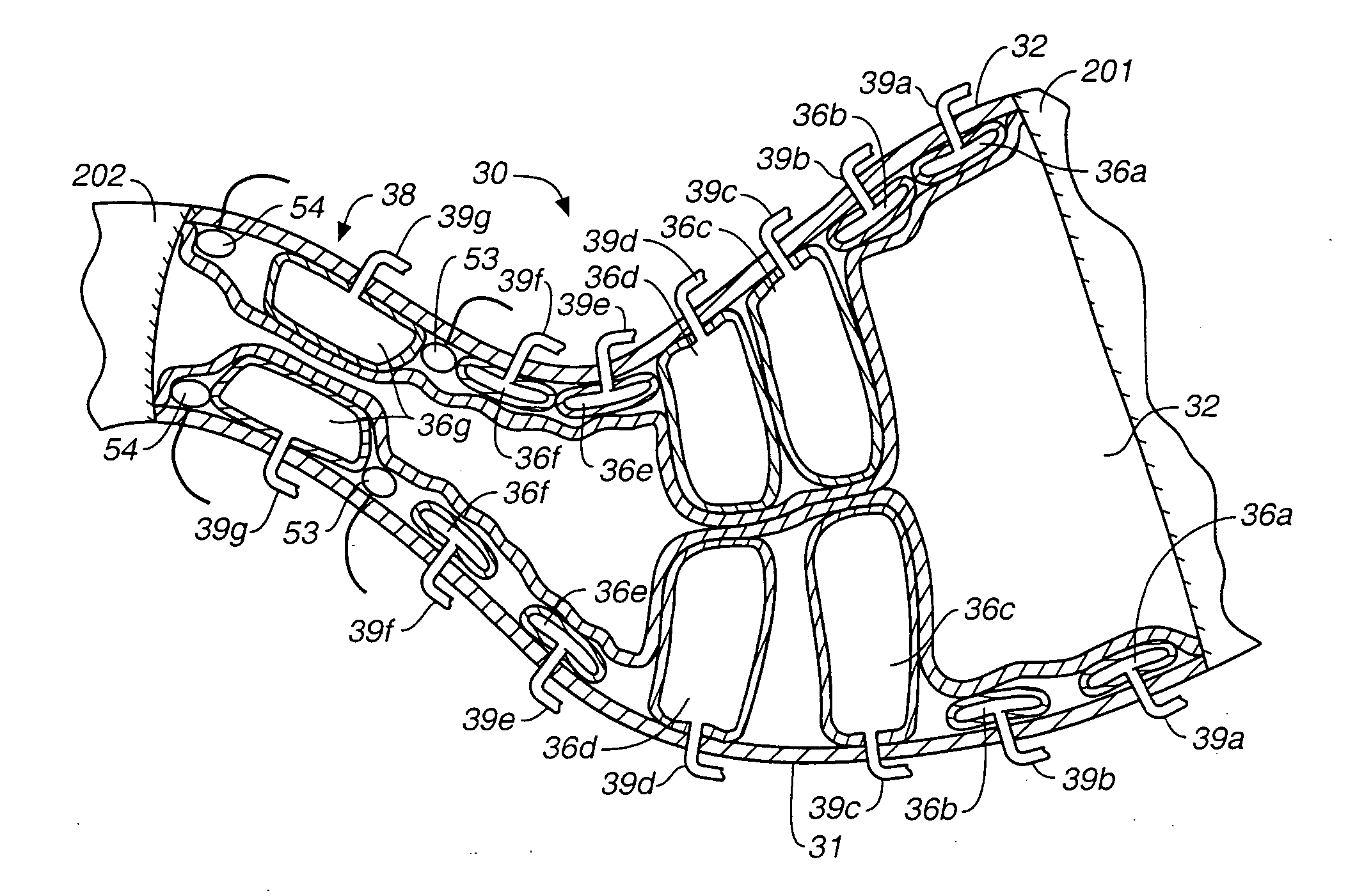
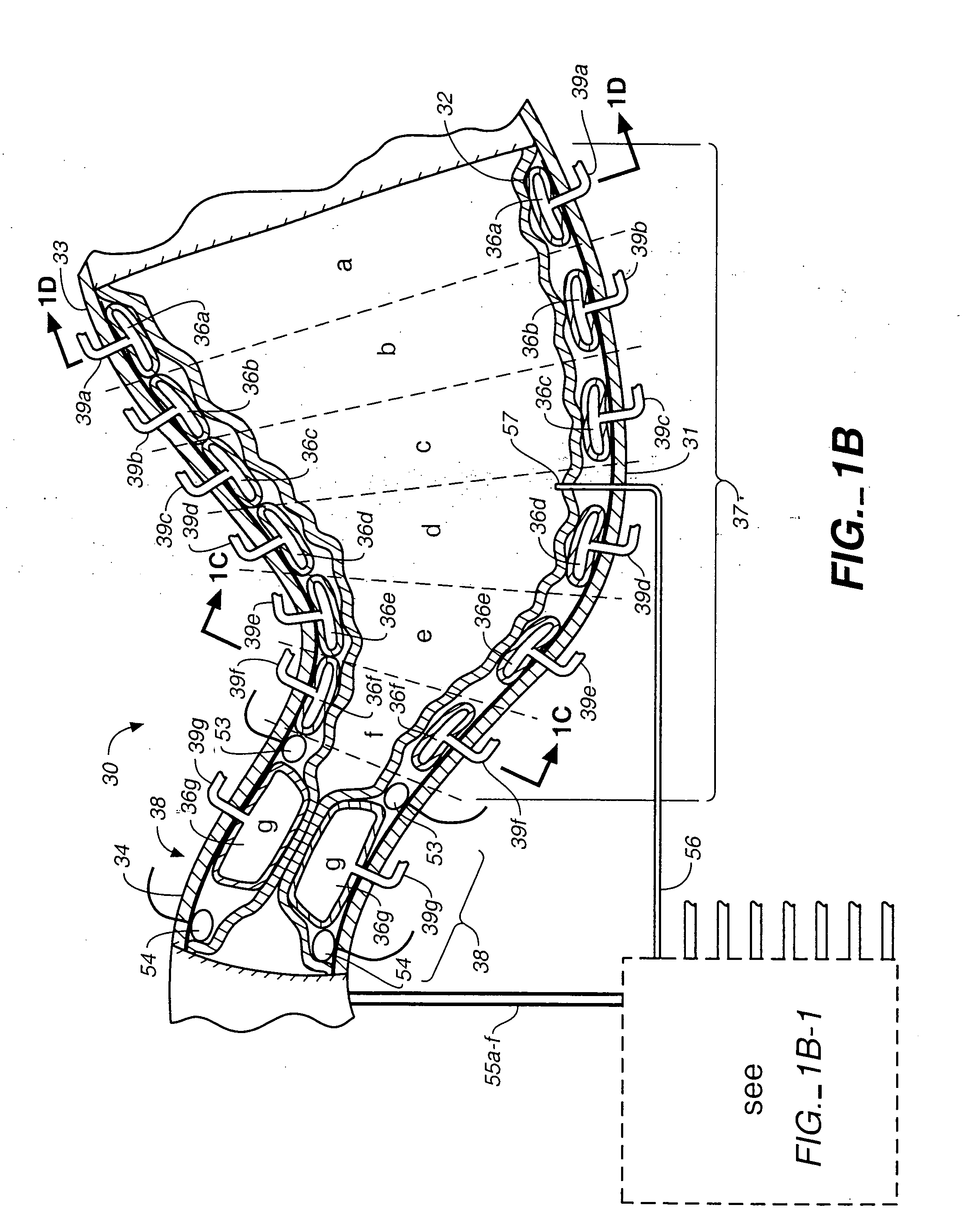
Devices and methods for pyloric anchoring
ActiveUS20050055039A1Avoiding erosion and ulcerationSuture equipmentsElectrotherapyPylorusPatient characteristics
A device for performing one or more functions in a gastrointestinal tract of a patient includes an anchoring member and at least one actuator, sensor, or combination of both coupled with the anchoring device. The anchoring device is adapted to maintain at least part of the device within a pyloric portion of the patient's stomach and to intermittently engage, without directly attaching to, stomach tissue. Actuators perform any suitable function, such as transmitting energy to tissue, acting as a sleeve to reduce nutrient absorption, occupying space in the stomach, eluting a drug and / or the like. Sensors may be adapted to sense any suitable patient characteristic within the patient's gastrointestinal tract, such as pH, temperature, bile content, nutrient content, fats, sugars, alcohol, opiates, drugs, analytes, electrolytes and / or hemoglobin.
Owner:BARONOVA
Methods of forming a laparoscopic greater curvature plication using a surgical stapler
A method of plicating a stomach by accessing the exterior of a stomach of a patient and grasping tissue on a first and second location on a first side of the greater curvature of the stomach. Also forming a plication therebetween with a first staple. The method involves grasping tissue on a third and fourth location on a second side of the greater curvature of the stomach and forming a plication with a second staple. The first and second plications are near a location selected from the group consisting of a gastroesophageal junction, a pylorus, and an incisura angularis. The method further includes grasping tissue on a first and second side of a greater curvature of the stomach and forming a fold along a length of the greater curvature by attaching the first and second sides together along a first attachment line with a first plurality of staples.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
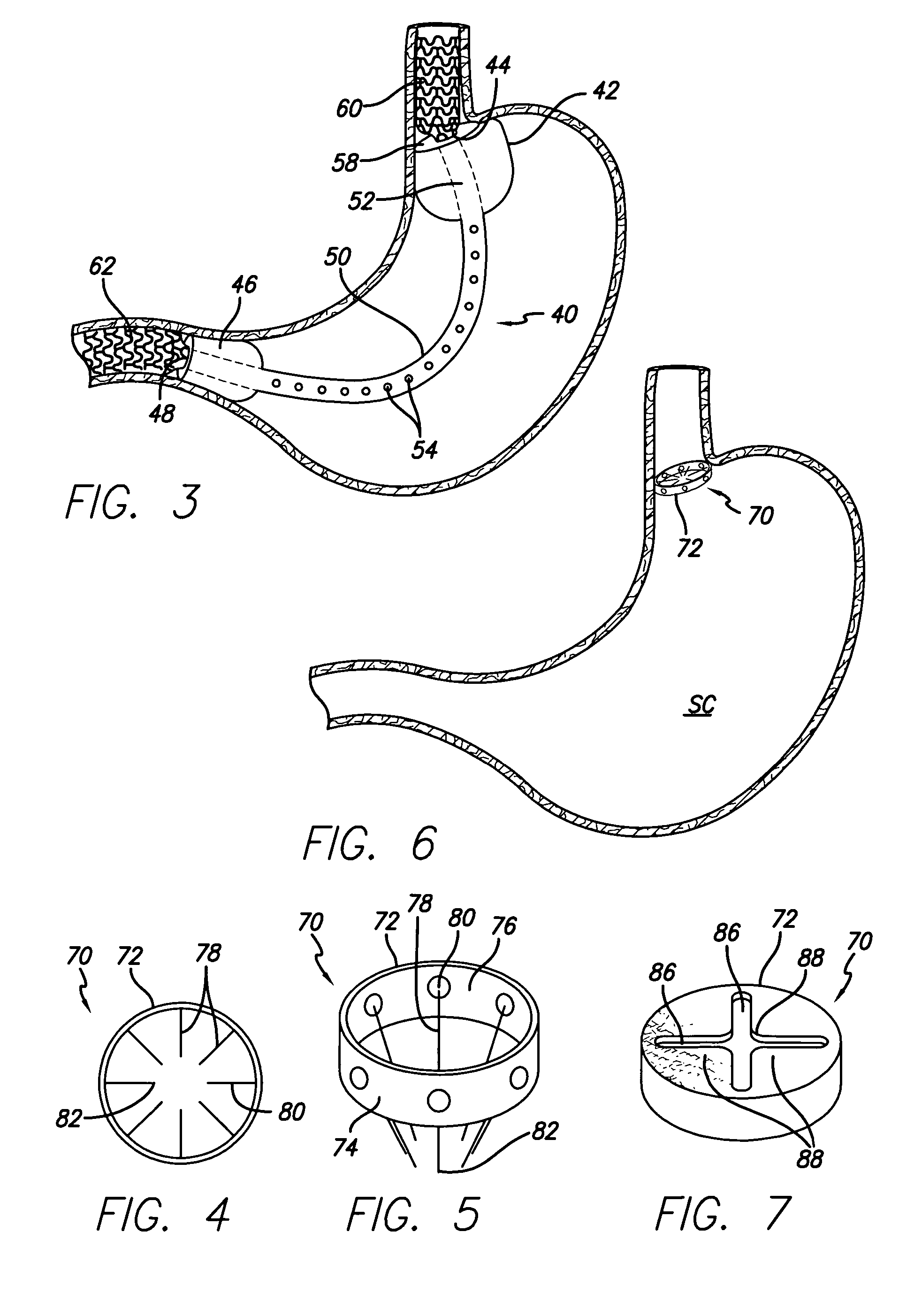
Systems and methods for treating obesity
ActiveUS20050228504A1Good for weight lossStimulatesIntravenous devicesTubular organ implantsPylorusGastric emptying
Methods and devices for simulating a gastric bypass and reducing the volume of the stomach involve placing a tubular liner along the lesser curve of the stomach cavity. Also, methods and devices for slowing gastric emptying involve placing valves within the stomach cavity near the gastrointestinal junction and / or the pylorus. These methods and devices may prevent a patient from drinking and eating large volumes at one time and from eating slowly all day.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
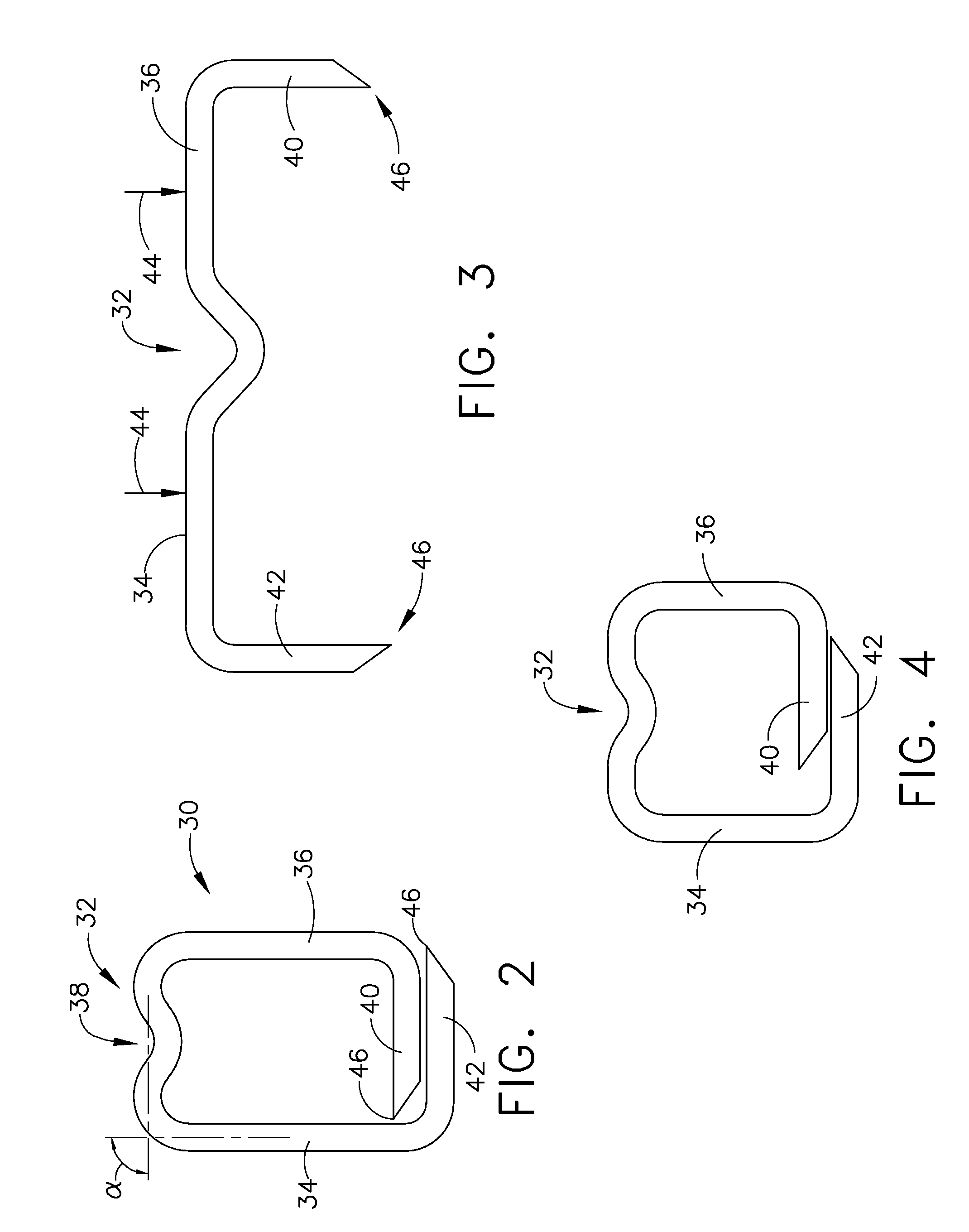
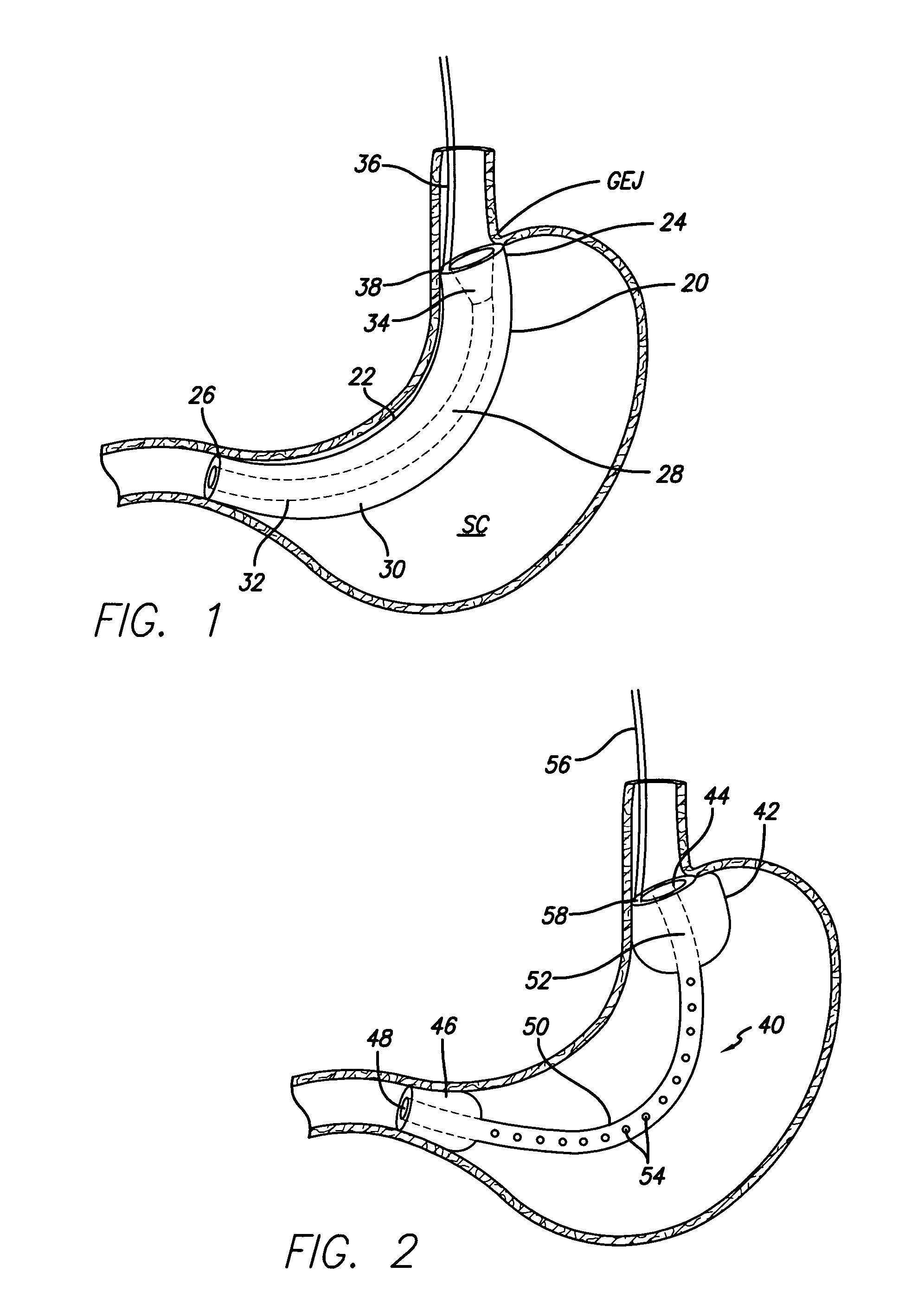
Gastric bypass prosthesis
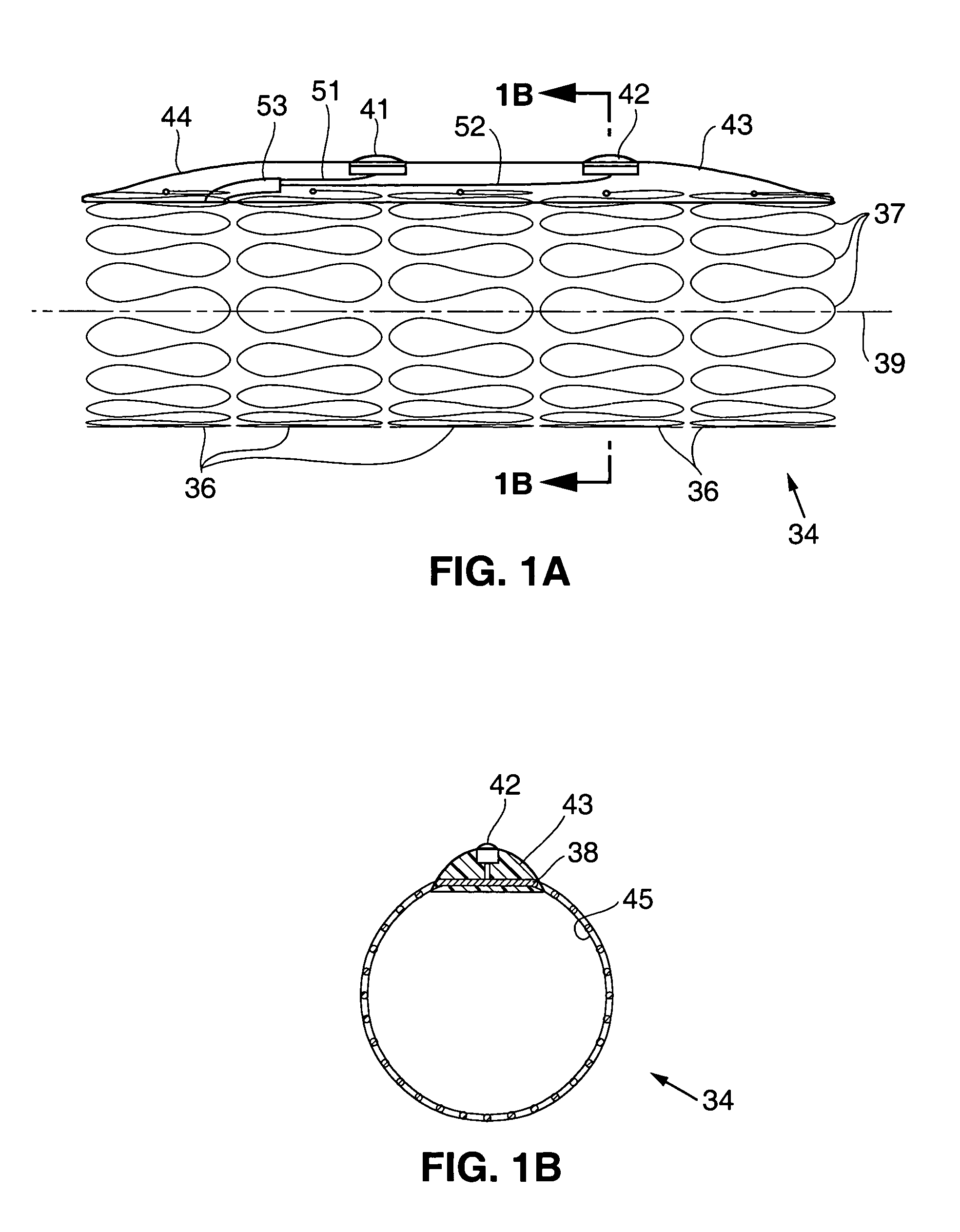
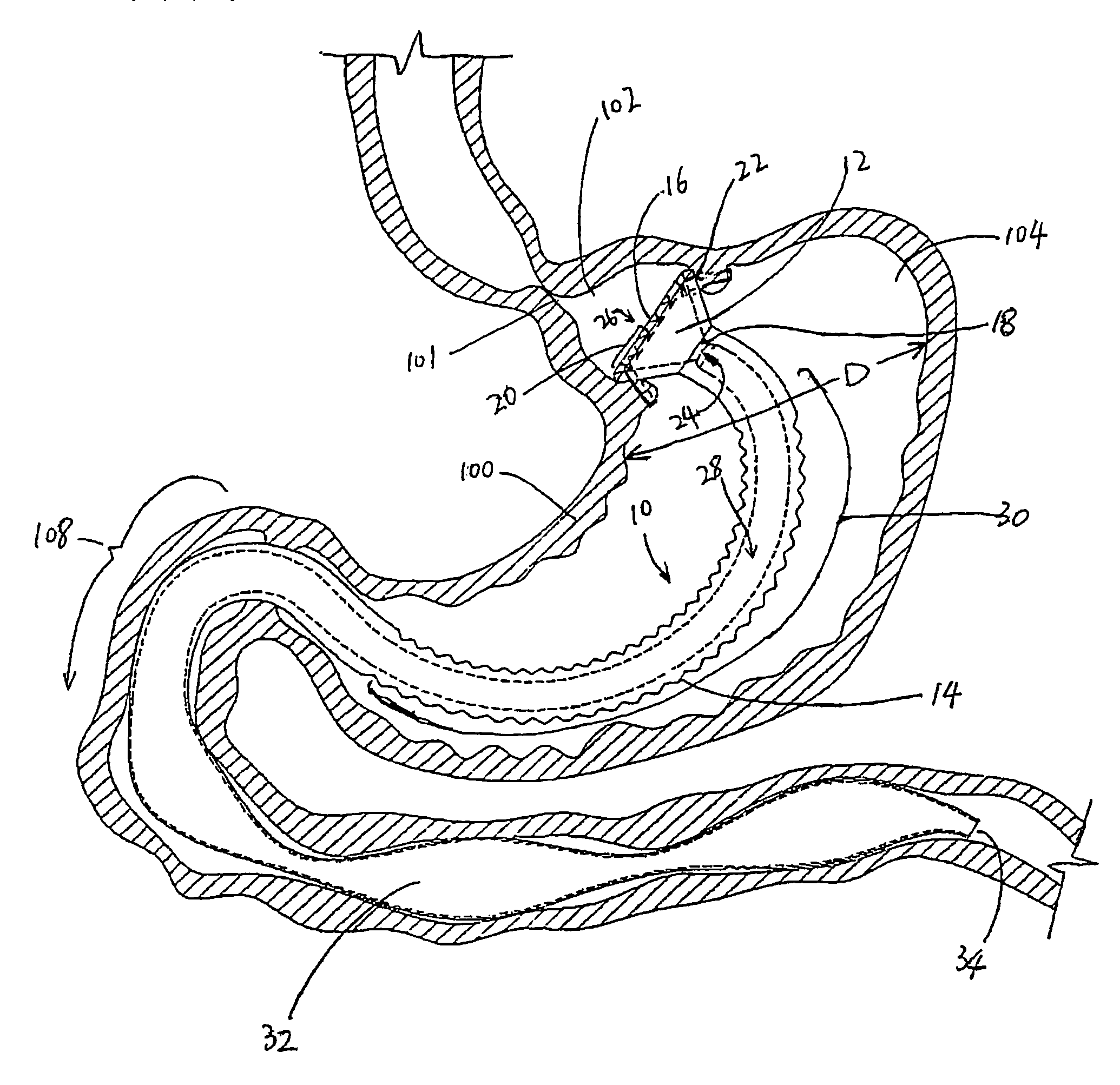
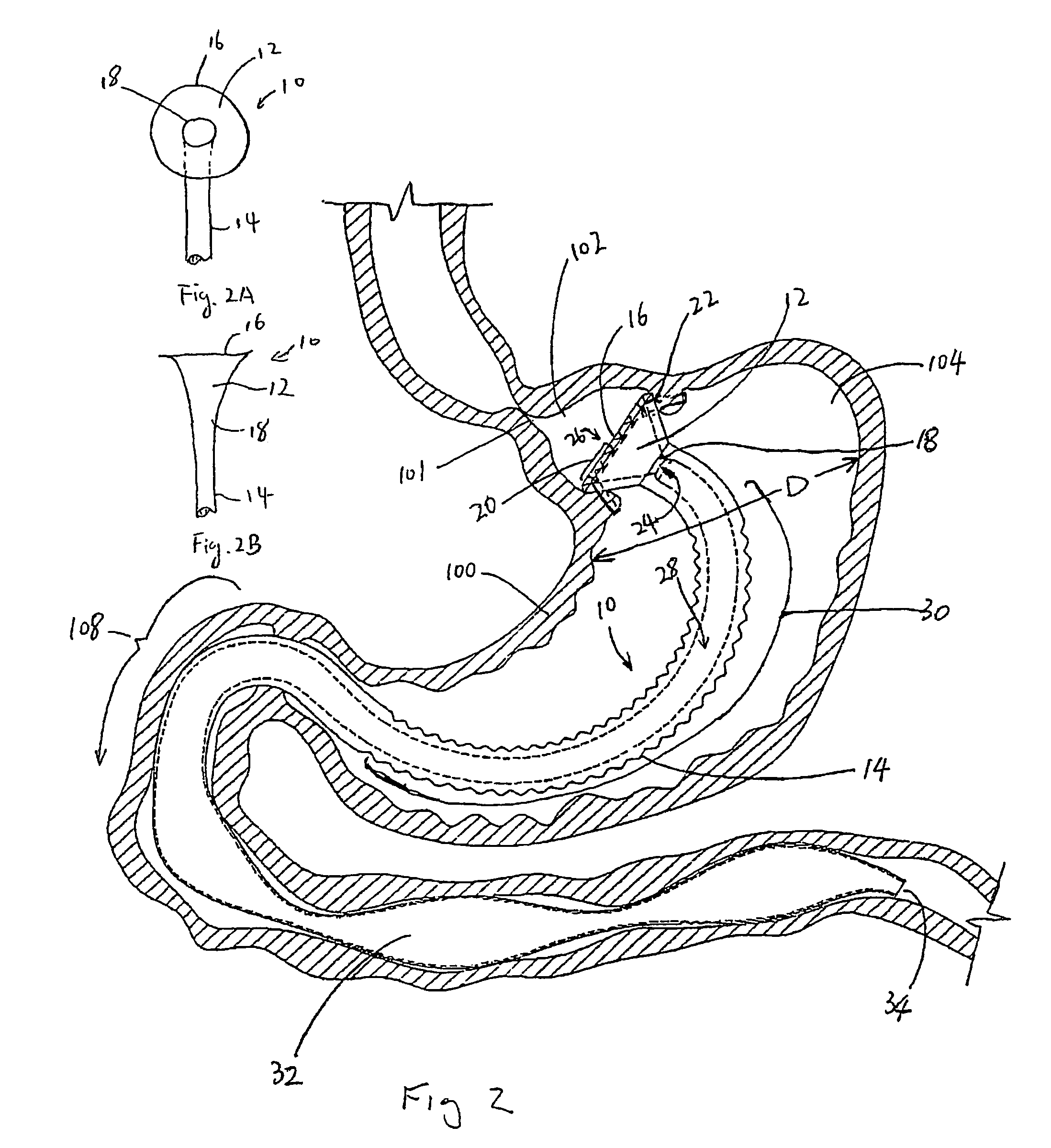
InactiveUS20050256587A1Sufficient diametric rigidityIsolated contactSuture equipmentsIntravenous devicesPylorusProsthesis
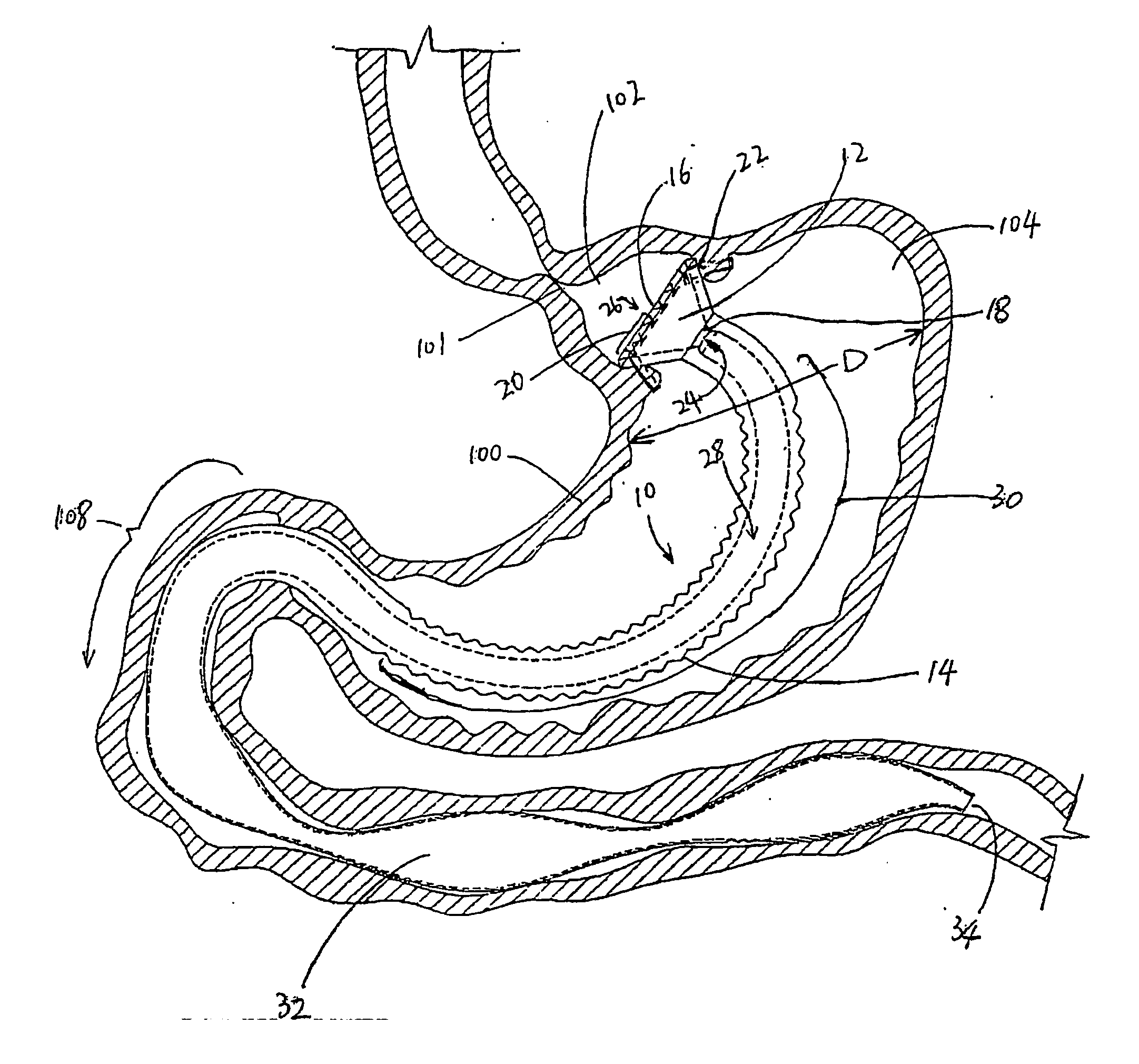
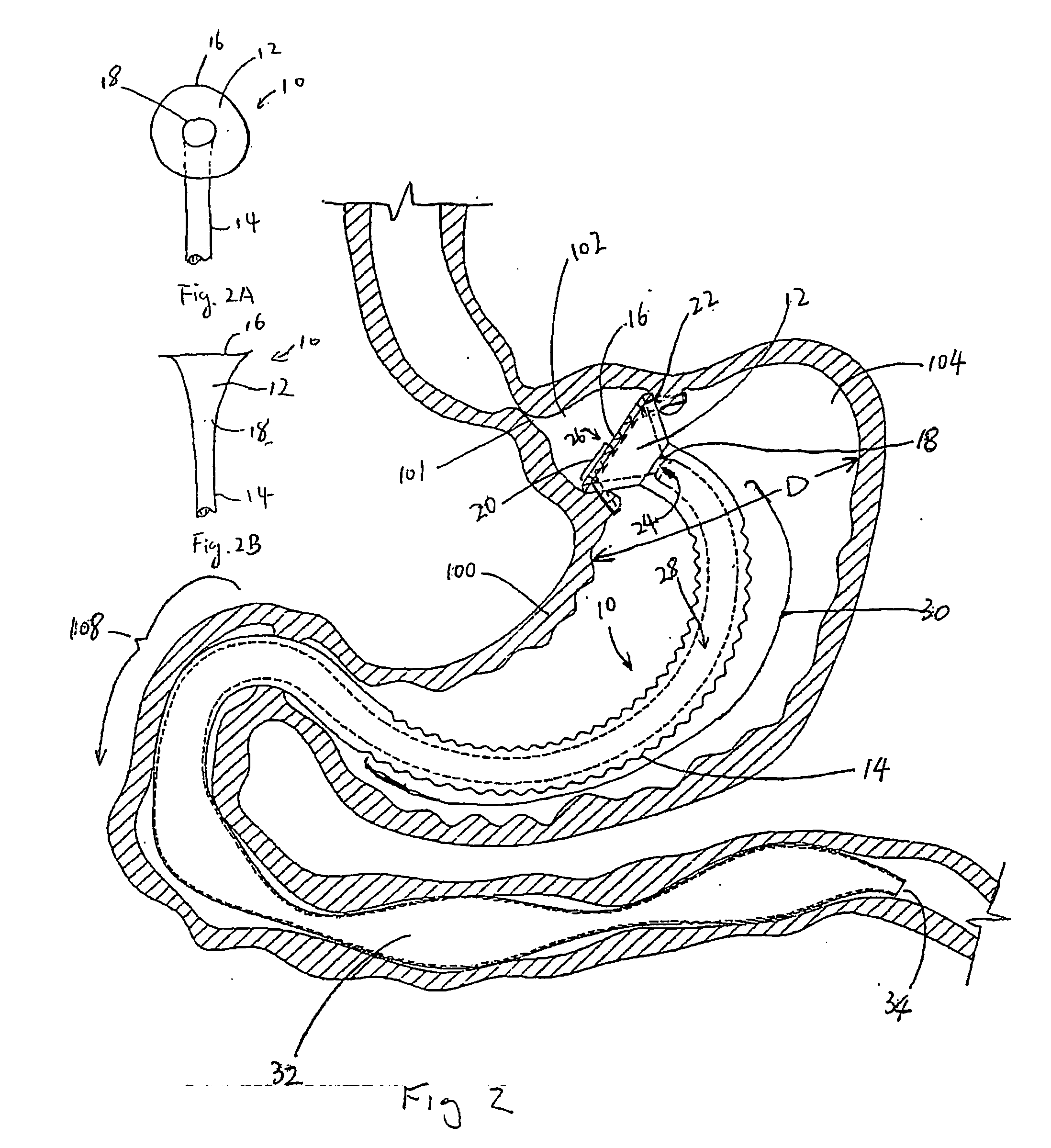
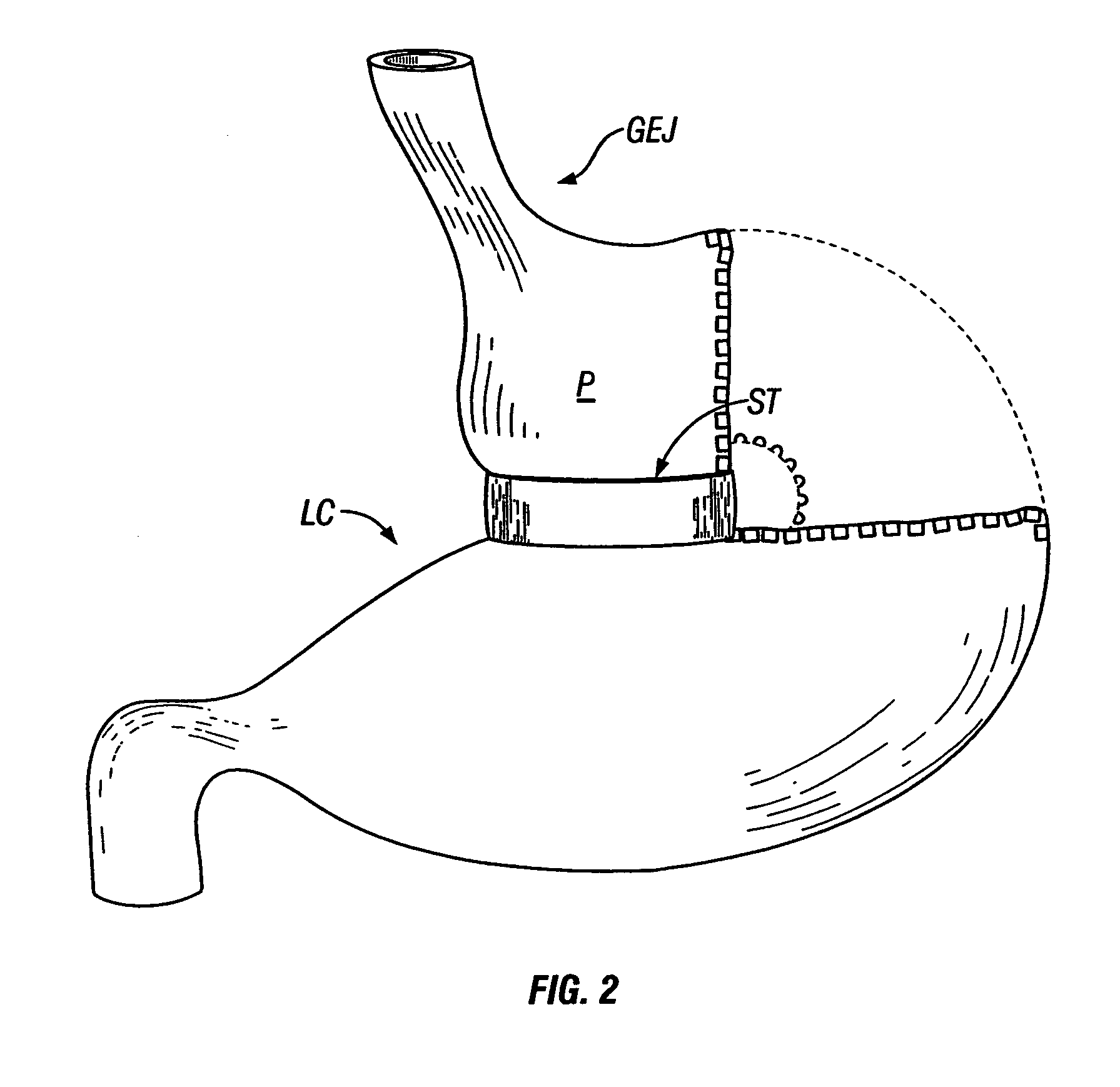
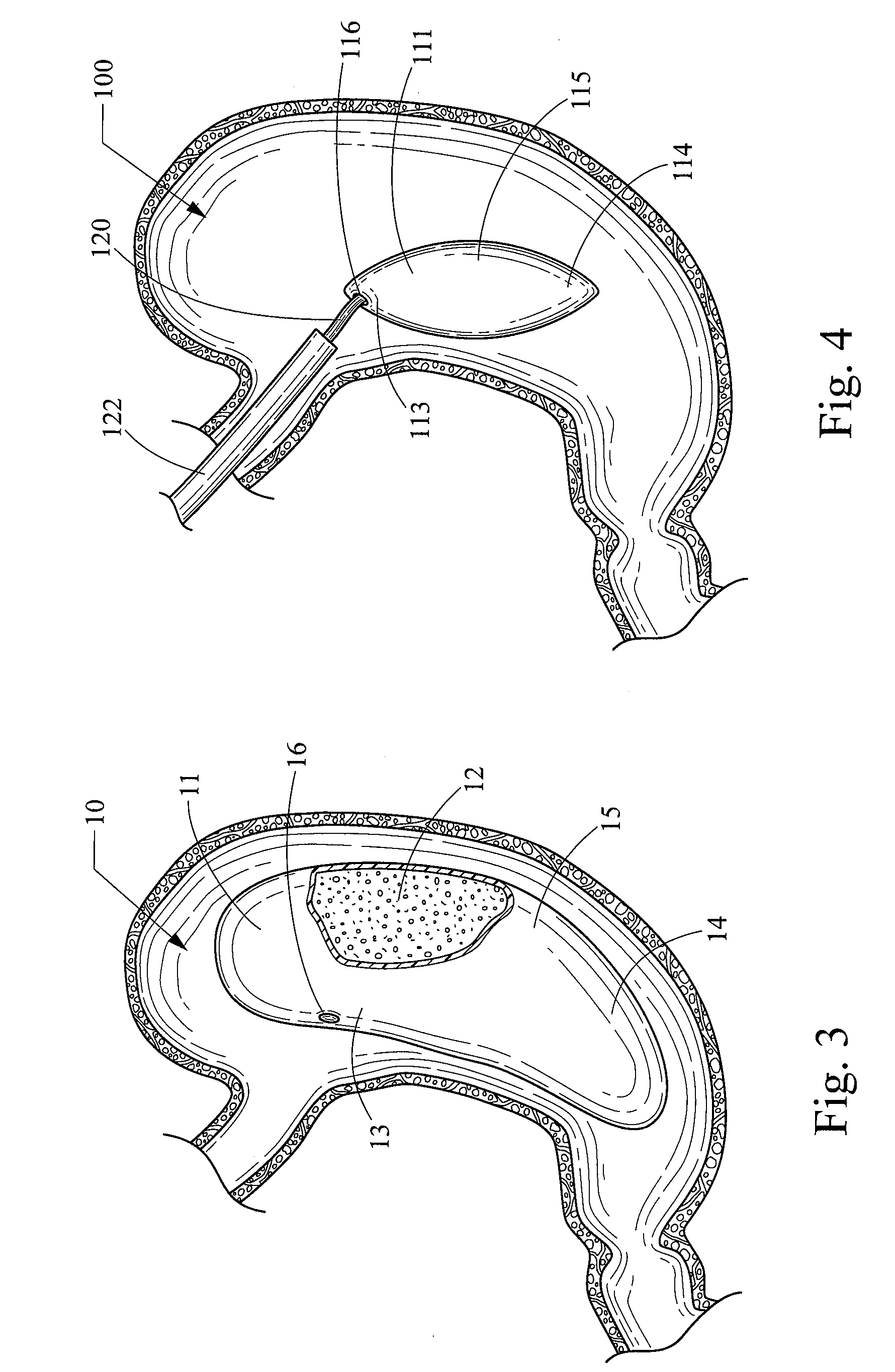
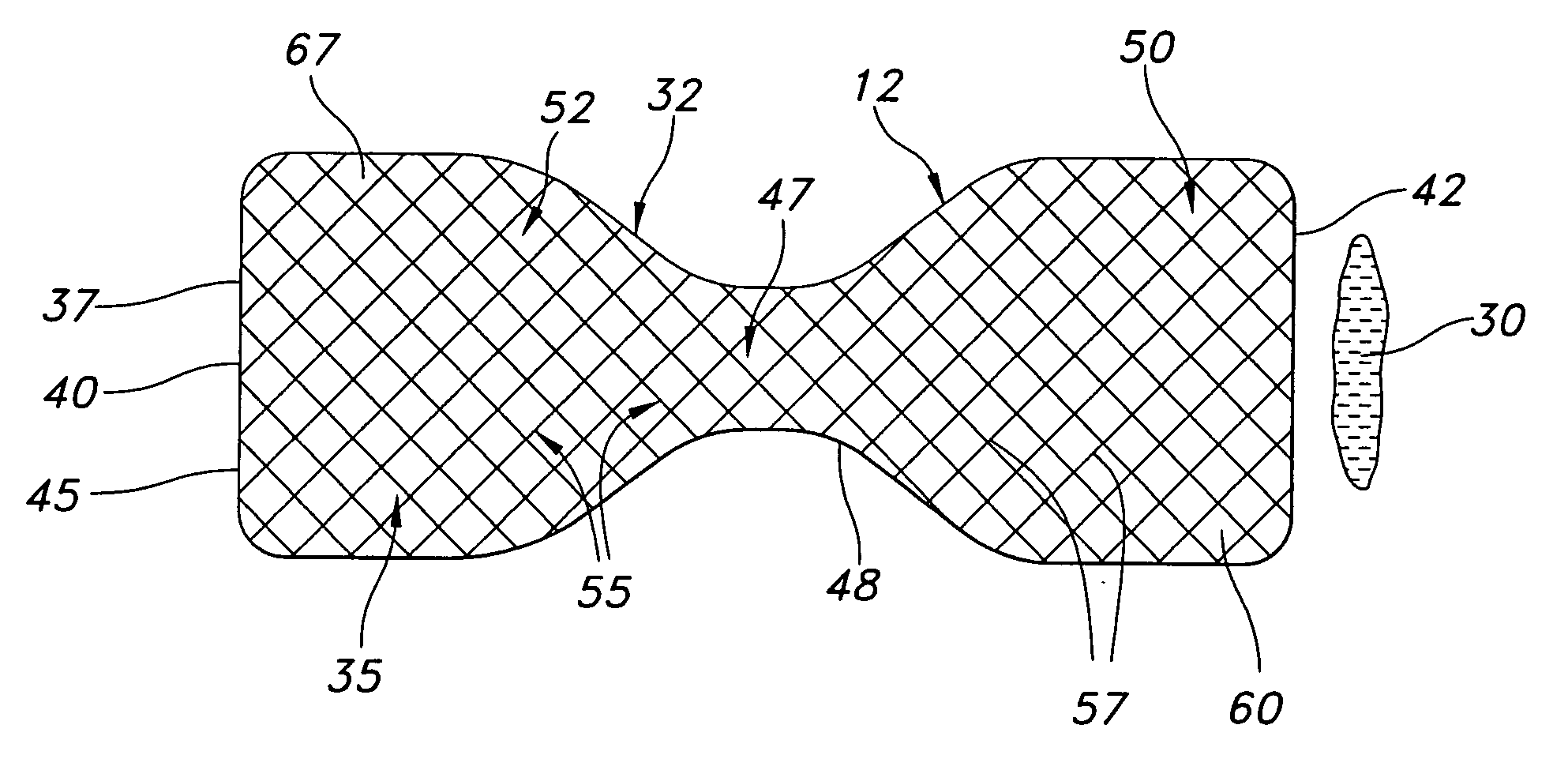
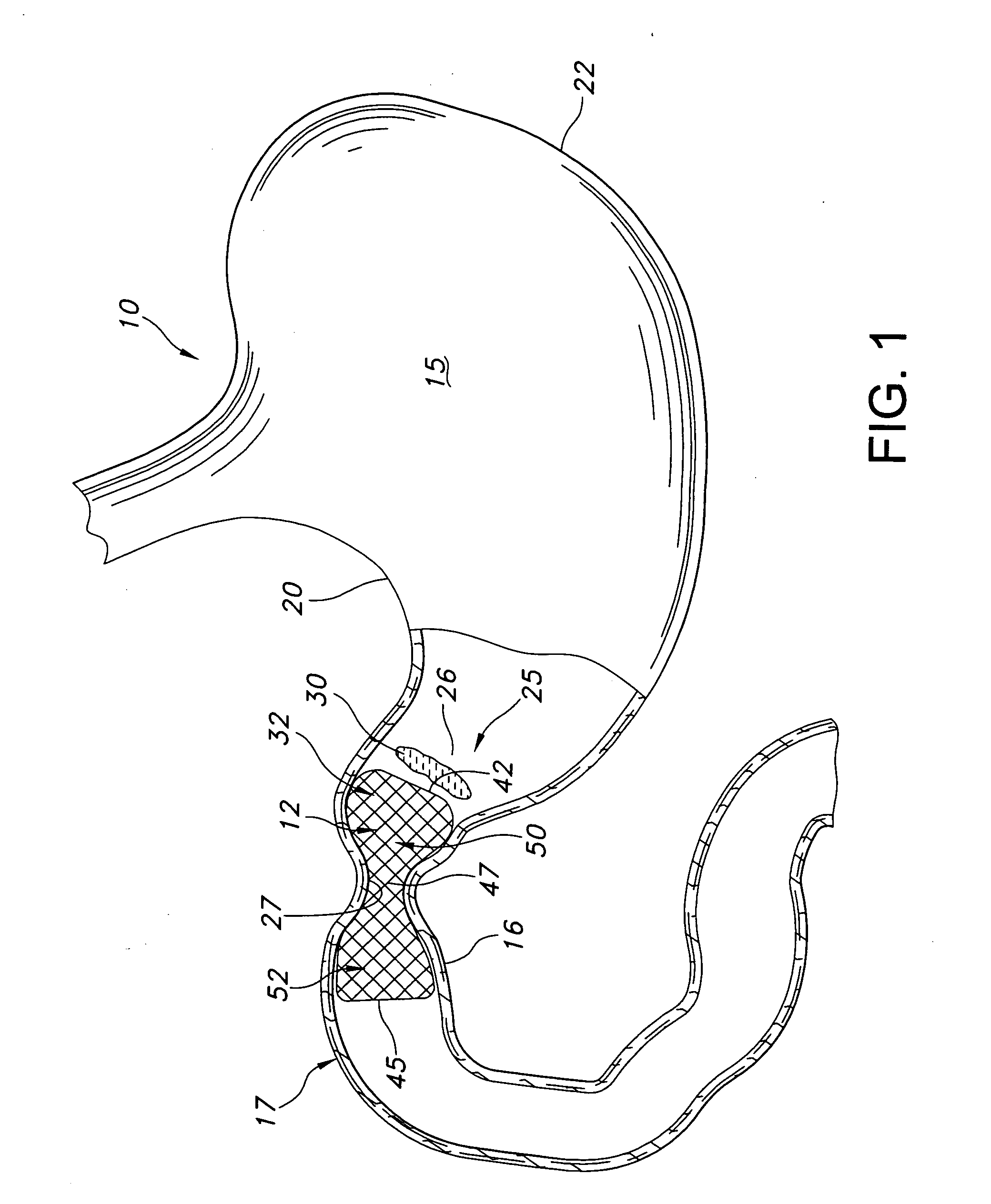
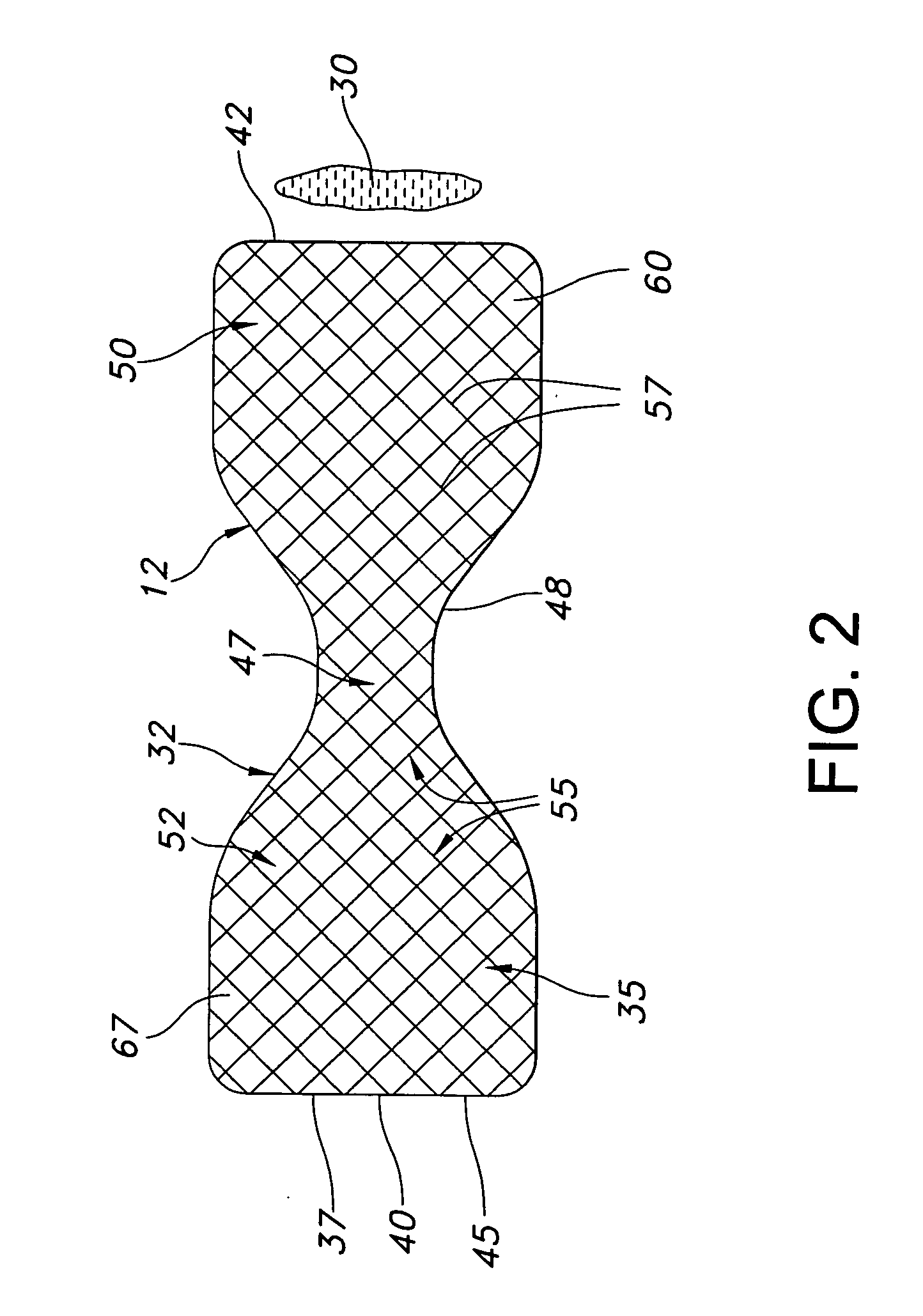
A device (10) for treatment of obesity of a patient comprises an annular element (12) having a relatively large outer boundary and a relatively small inner boundary, and an elongated flexible tube (14) extending from the relatively small inner boundary of the annular element to a distal end. The relatively large outer boundary is adapted to be attached to an inner wall of a stomach (100) of a patient, such that the annular element divides the stomach (100) into two chambers, an esophagus-end chamber close to an esophagus of the patient, and a pylorus-end chamber close to a pylorus of the patient. The invention also provides a method for treatment of obesity of a patient which includes inserting an annular element having a relatively large outer boundary and a relatively small inner boundary into a stomach of the patient, and attaching the relatively large outer boundary of the annular element to an inner circumference of the stomach of the patient.
Owner:EGAN THOMAS +1
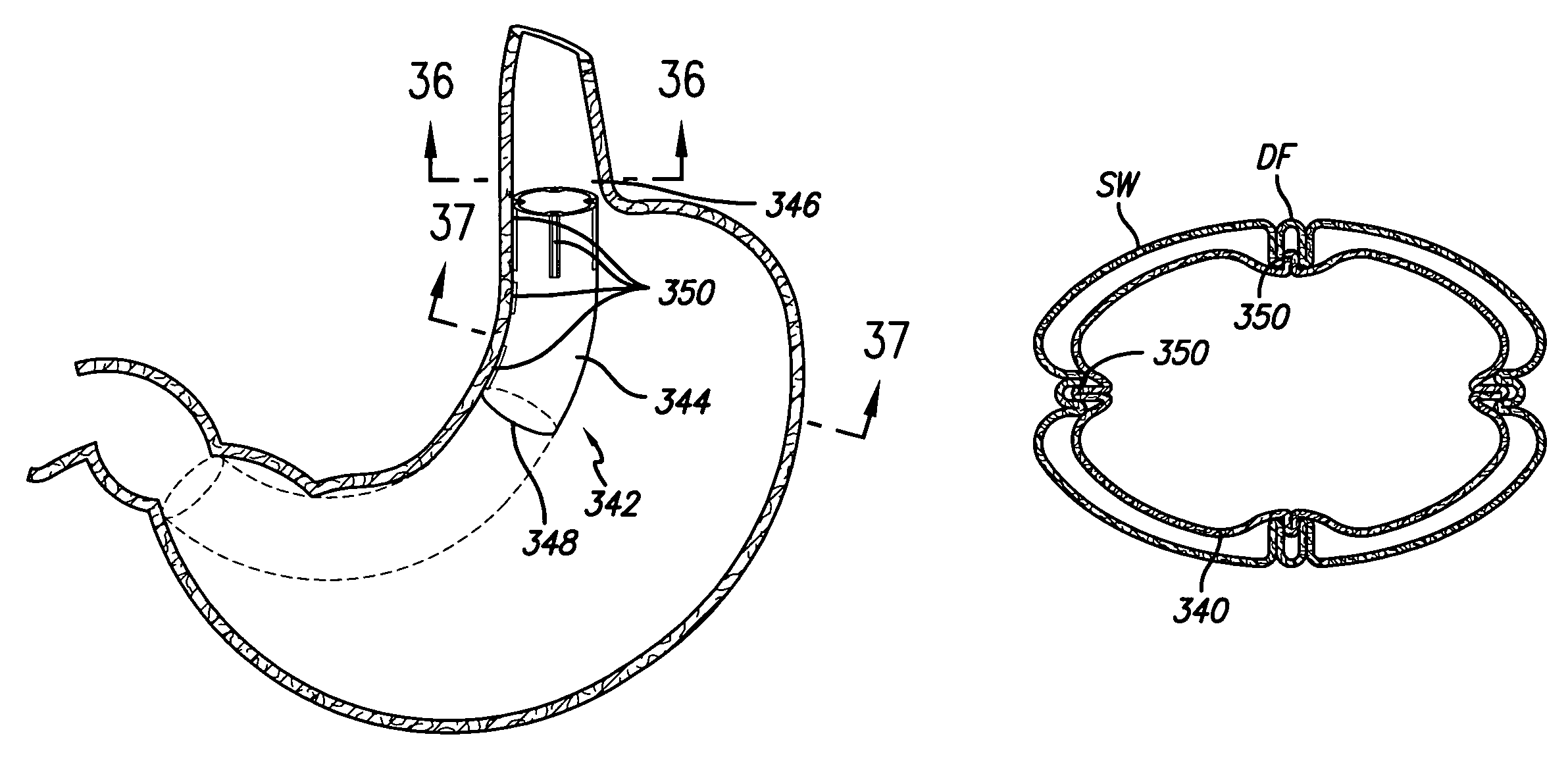
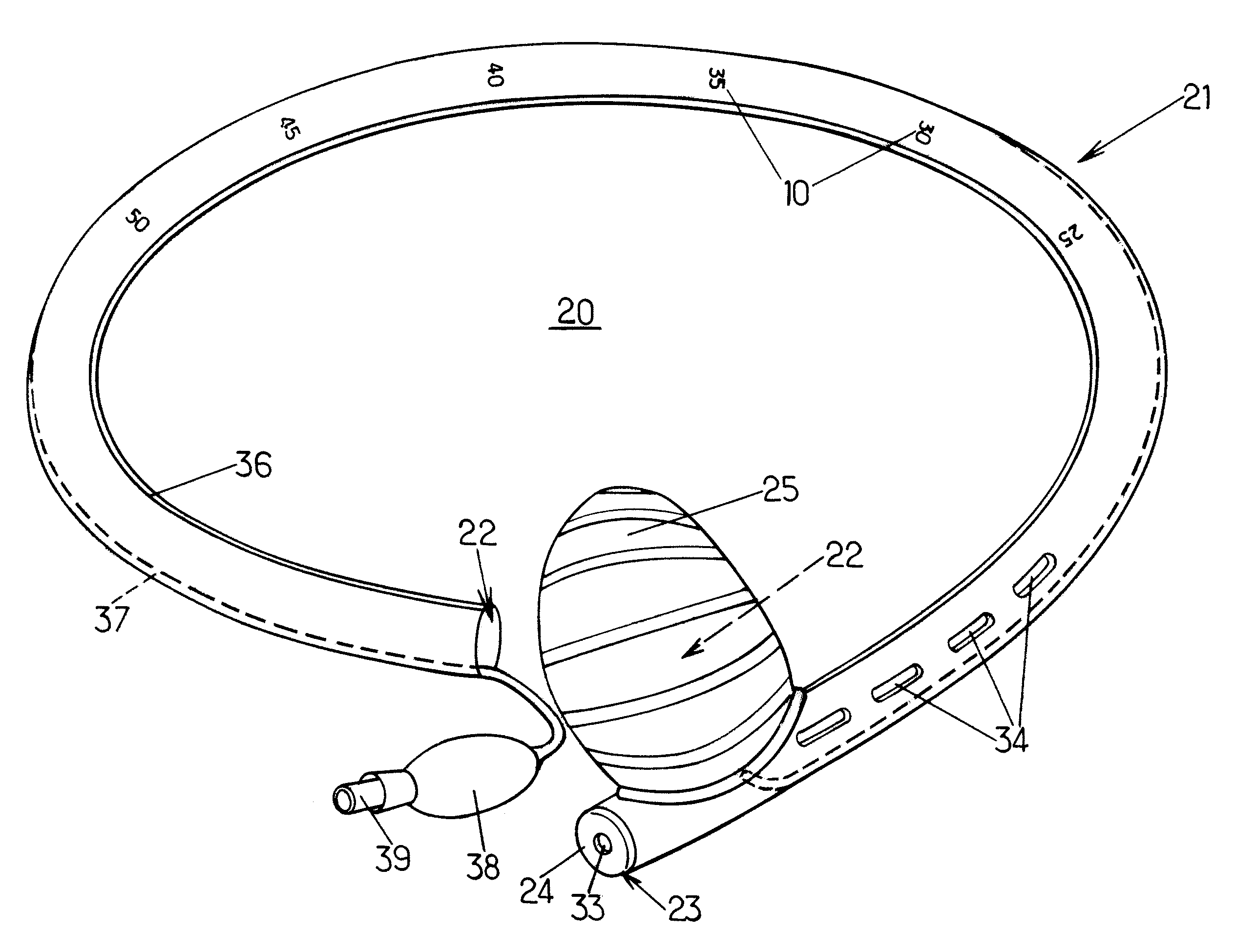
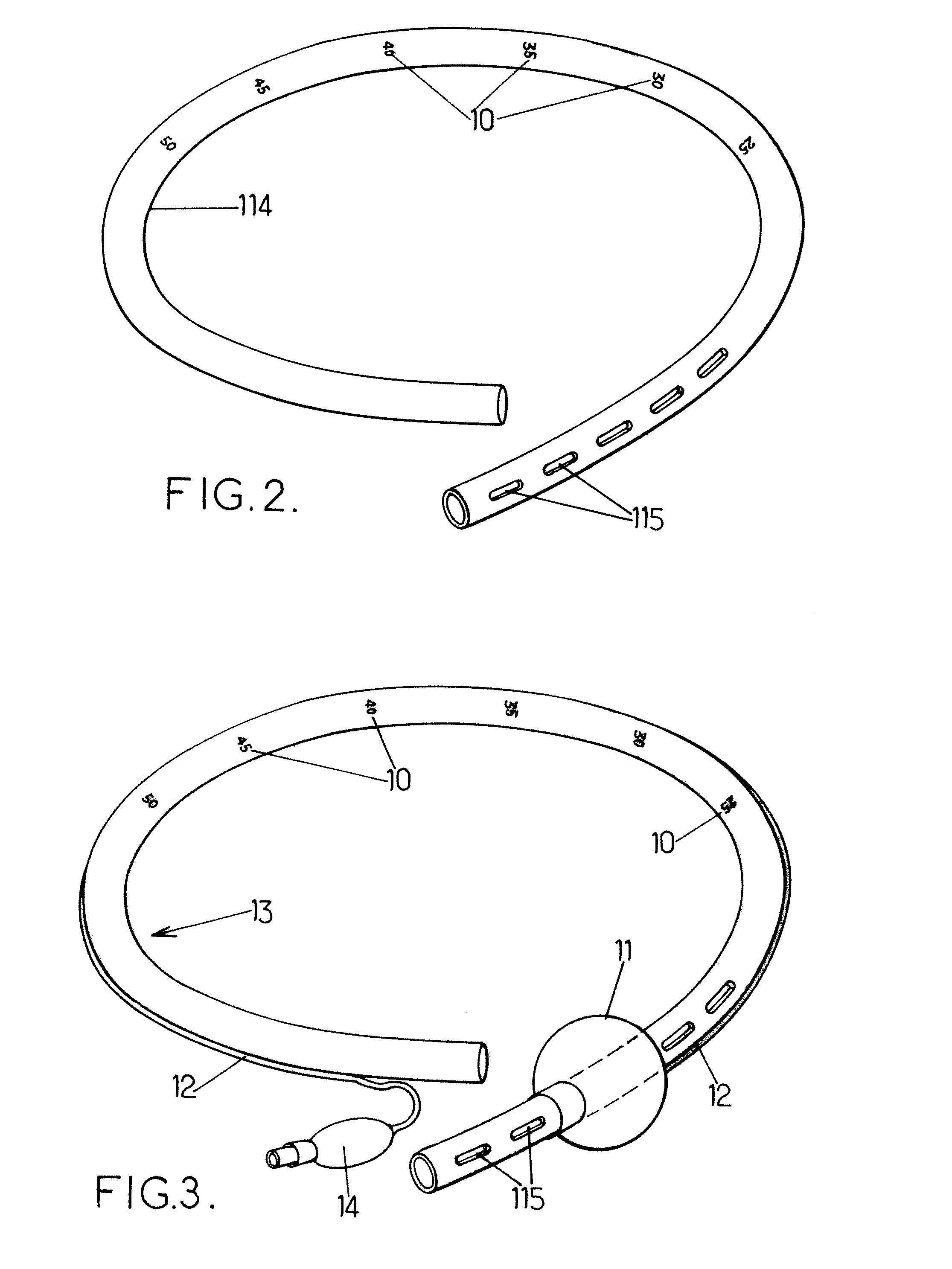
Pyloric valve obstructing devices and methods
ActiveUS20050033331A1Treat and ameliorate obesityReduced food intakeSuture equipmentsEndoradiosondesPylorusPartial obstruction
Methods, devices and systems facilitate intermittent and / or partial obstruction of a pyloric valve. Devices generally include a support portion for preventing the device from passing through the pyloric valve and a tissue engagement portion for contacting tissue adjacent the pyloric valve to obstruct the valve. Some embodiments also include a positioning member extending from the tissue engagement portion for helping position the device for obstructing the valve. A retaining member may optionally be included on the distal end of the positioning member for further maintaining a position of the device in the stomach. Some embodiments are deliverable into the stomach through the esophagus, either by swallowing or through a delivery tube or catheter. Some embodiments are fully reversible. Some embodiments self-expand within the stomach, while others are inflated or otherwise expanded.
Owner:BARONOVA
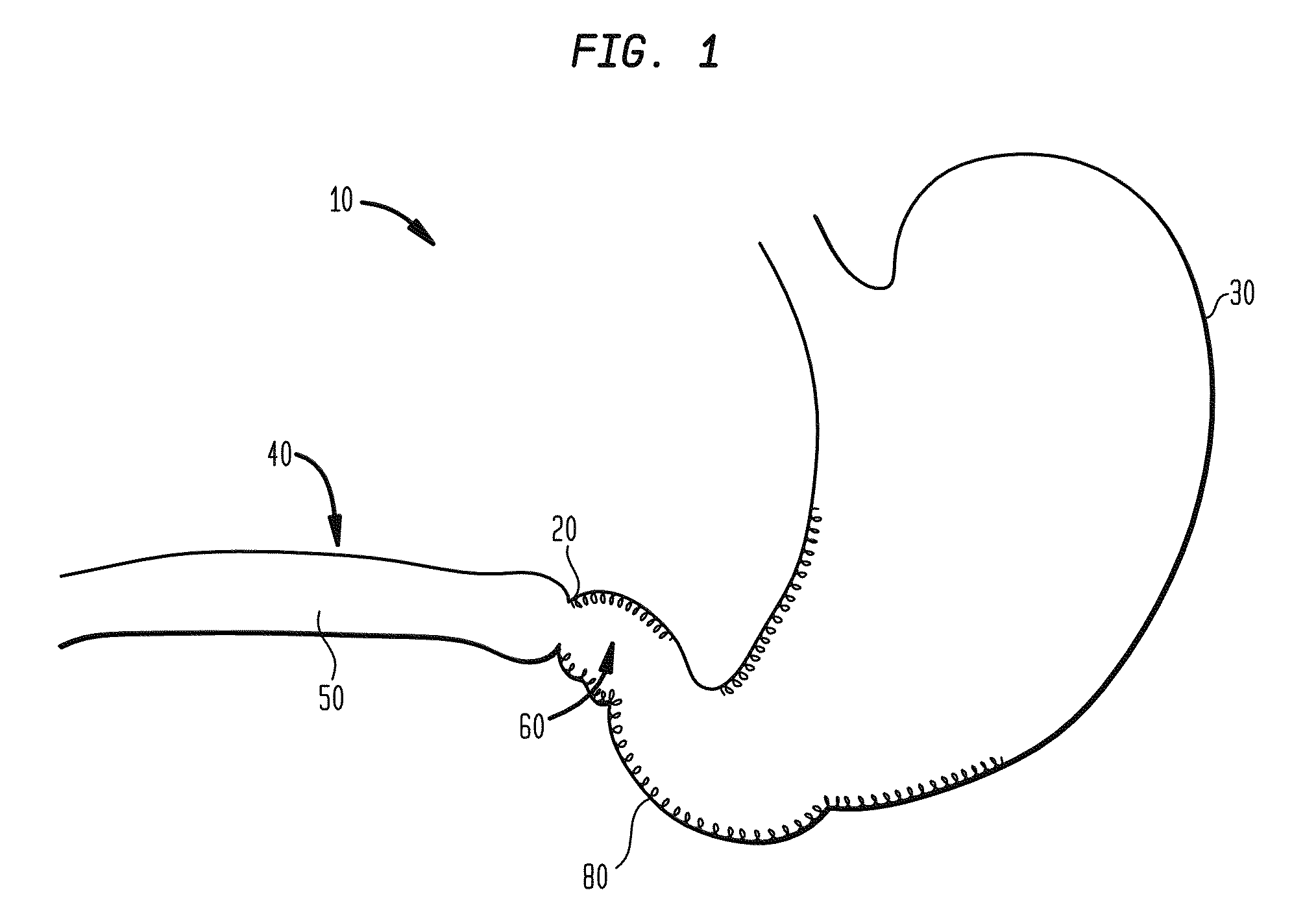
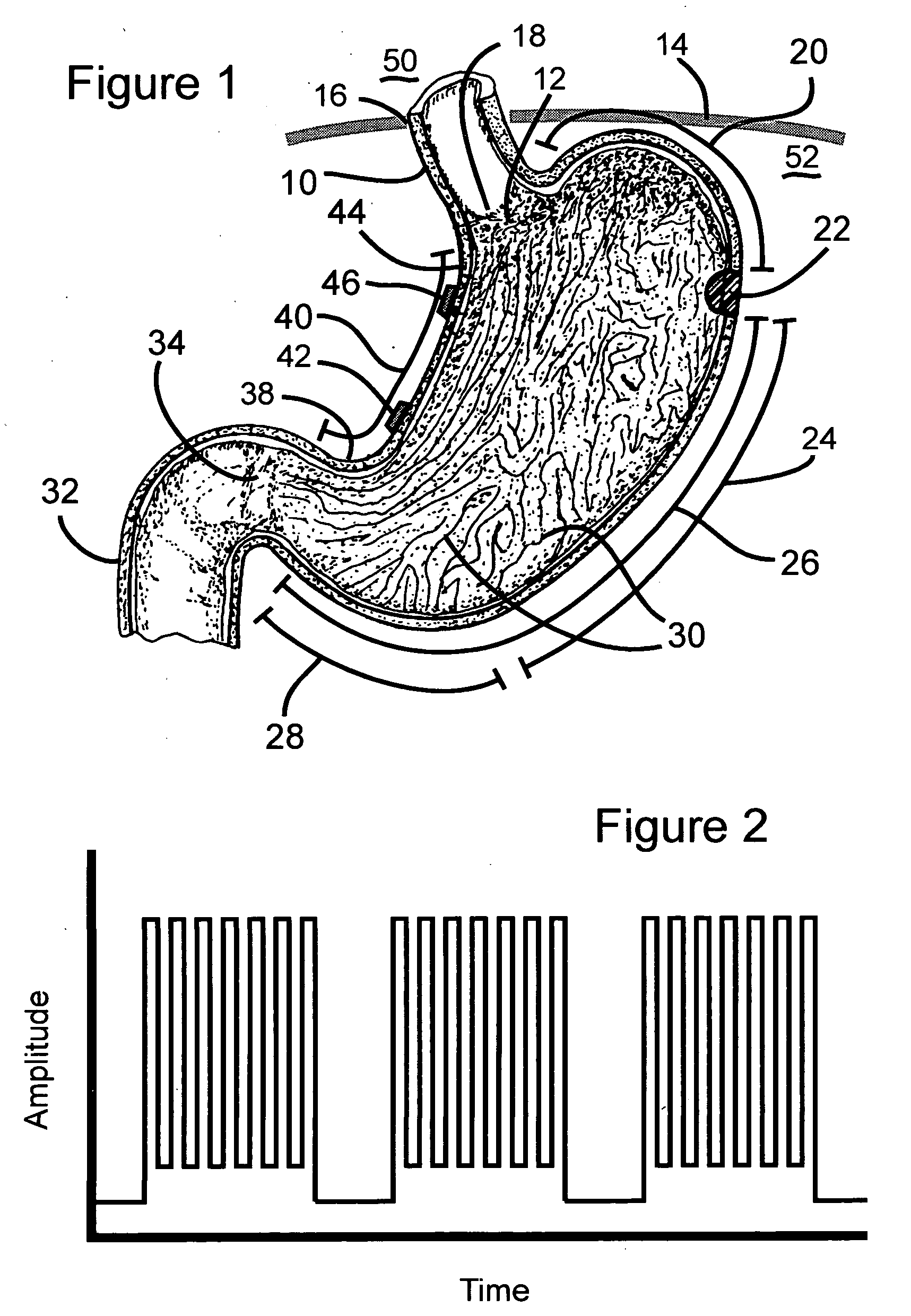
Gastrointestinal stimulation device
A fixation device for holding stimulating electrodes in electrical contact with the wall of a portion of the gastrointestinal tract is provided. In one embodiment, the fixation device includes an expandable member that fixes the electrodes in electrical contact with the gastrointestinal tract wall. Also provided is an implantable device and method for controlling the opening and / or closing of the pylorus. In particular a device and method is provided for stimulating the duodenum to control the closing / and or opening of the pylorus. Finally, a method is provided for treating obesity by controlling the pylorus to retain food in the stomach for a desired period of time, among other things to provide a feeling of satiety and / or to reduce hunger. One aspect includes controlling the pylorus's contraction by electrical stimulation of the duodenum.
Owner:INTRAPACE
Gastric bypass prosthesis
InactiveUS7316716B2Limiting the amount of food intake of a patientReduce morbiditySuture equipmentsIntravenous devicesPylorusProsthesis
A device (10) for treatment of obesity of a patient comprises an annular element (12) having a relatively large outer boundary and a relatively small inner boundary, and an elongated flexible tube (14) extending from the relatively small inner boundary of the annular element to a distal end. The relatively large outer boundary is adapted to be attached to an inner wall of a stomach (100) of a patient, such that the annular element divides the stomach (100) into two chambers, an esophagus-end chamber close to an esophagus of the patient, and a pylorus-end chamber close to a pylorus of the patient. The invention also provides a method for treatment of obesity of a patient which includes inserting an annular element having a relatively large outer boundary and a relatively small inner boundary into a stomach of the patient, and attaching the relatively large outer boundary of the annular element to an inner circumference of the stomach of the patient.
Owner:EGAN THOMAS +1
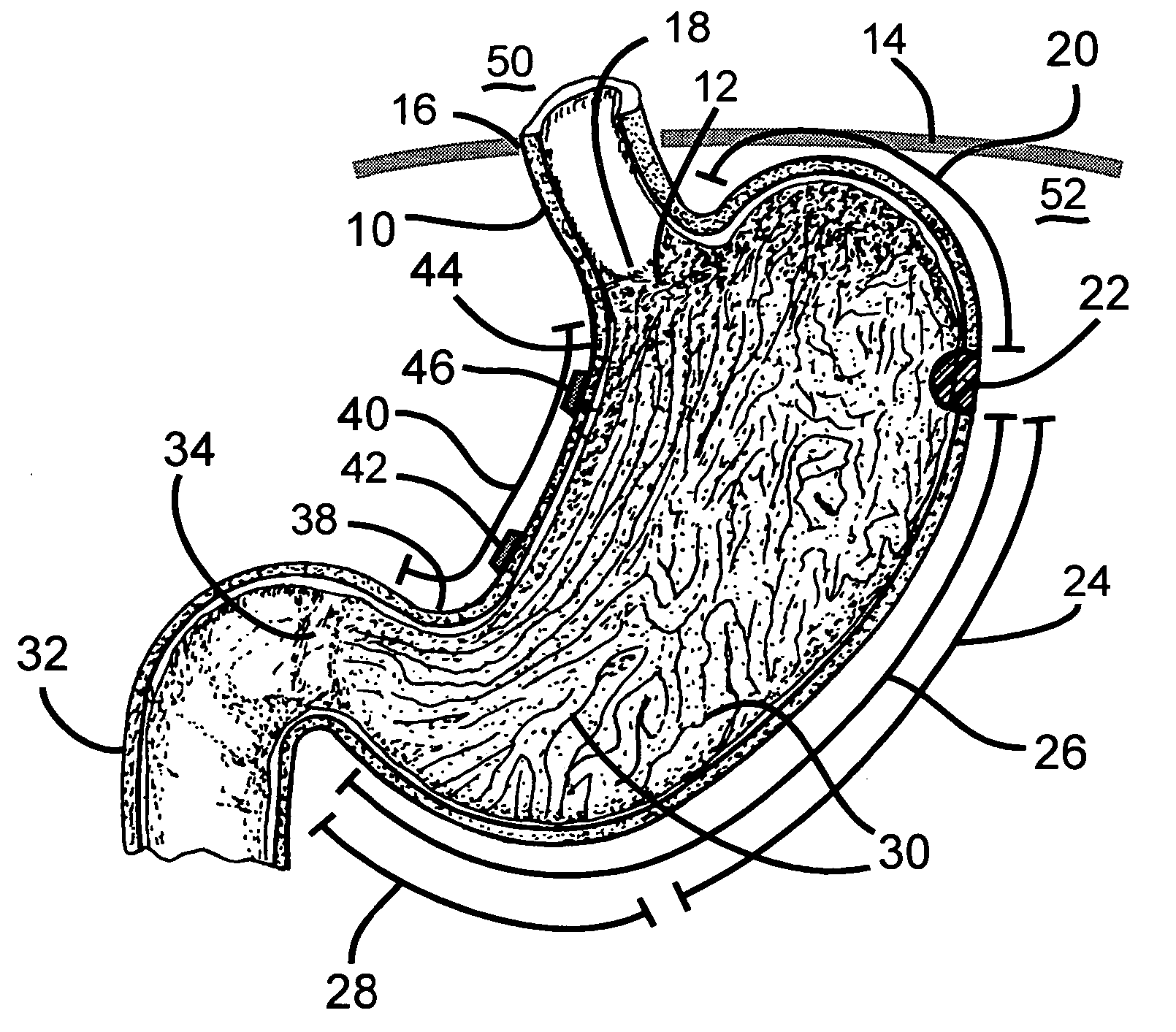
Stomach prosthesis
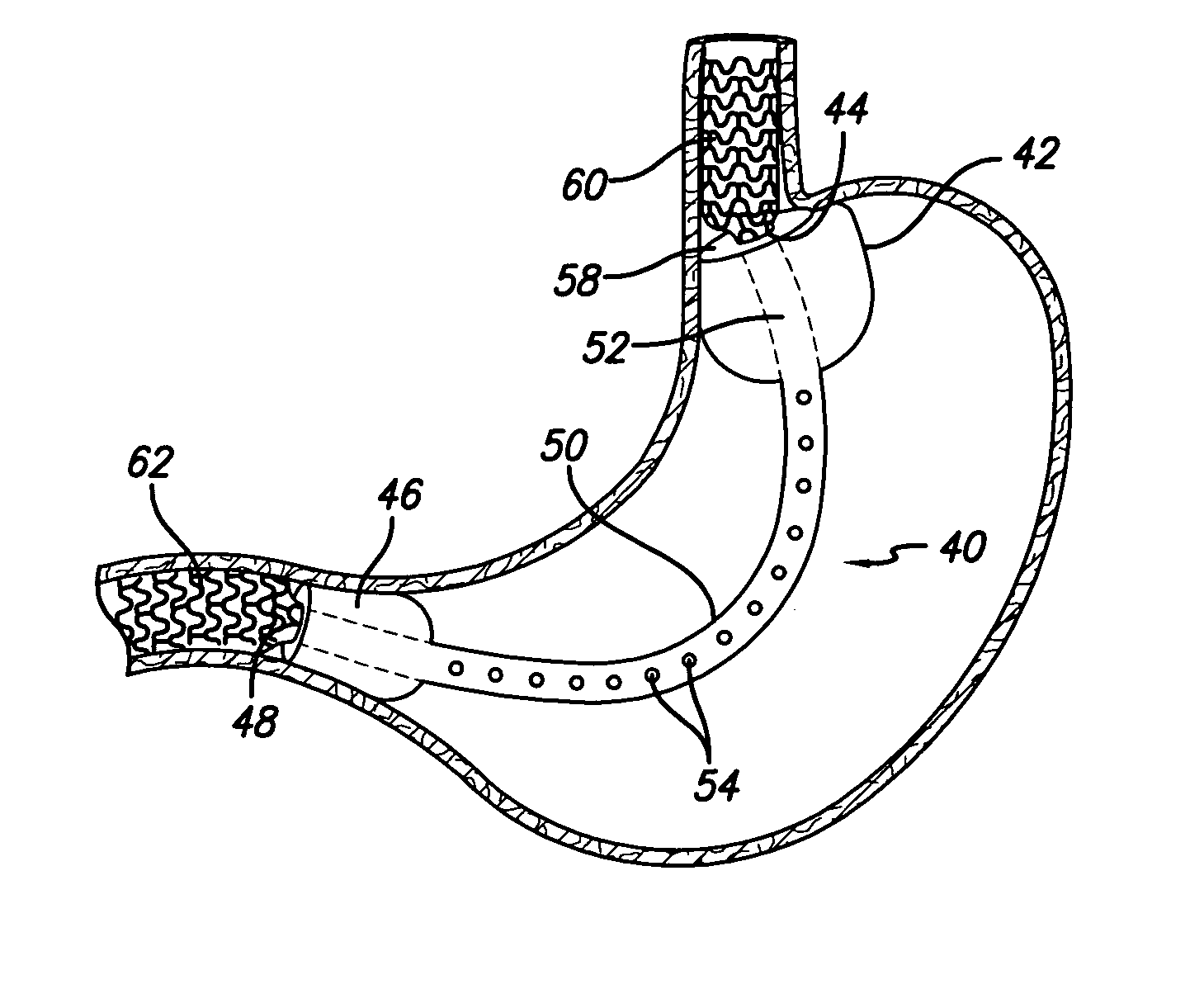
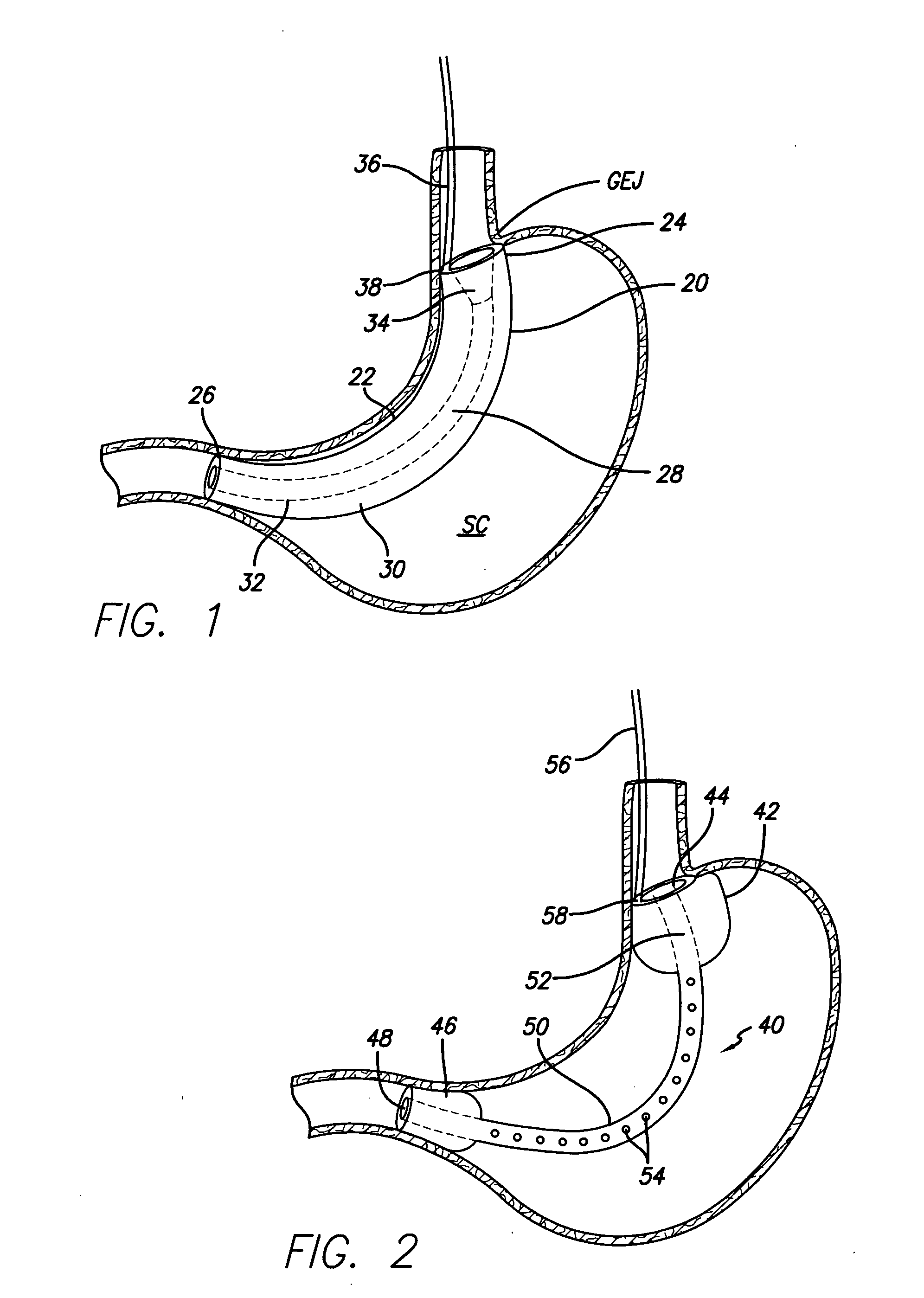
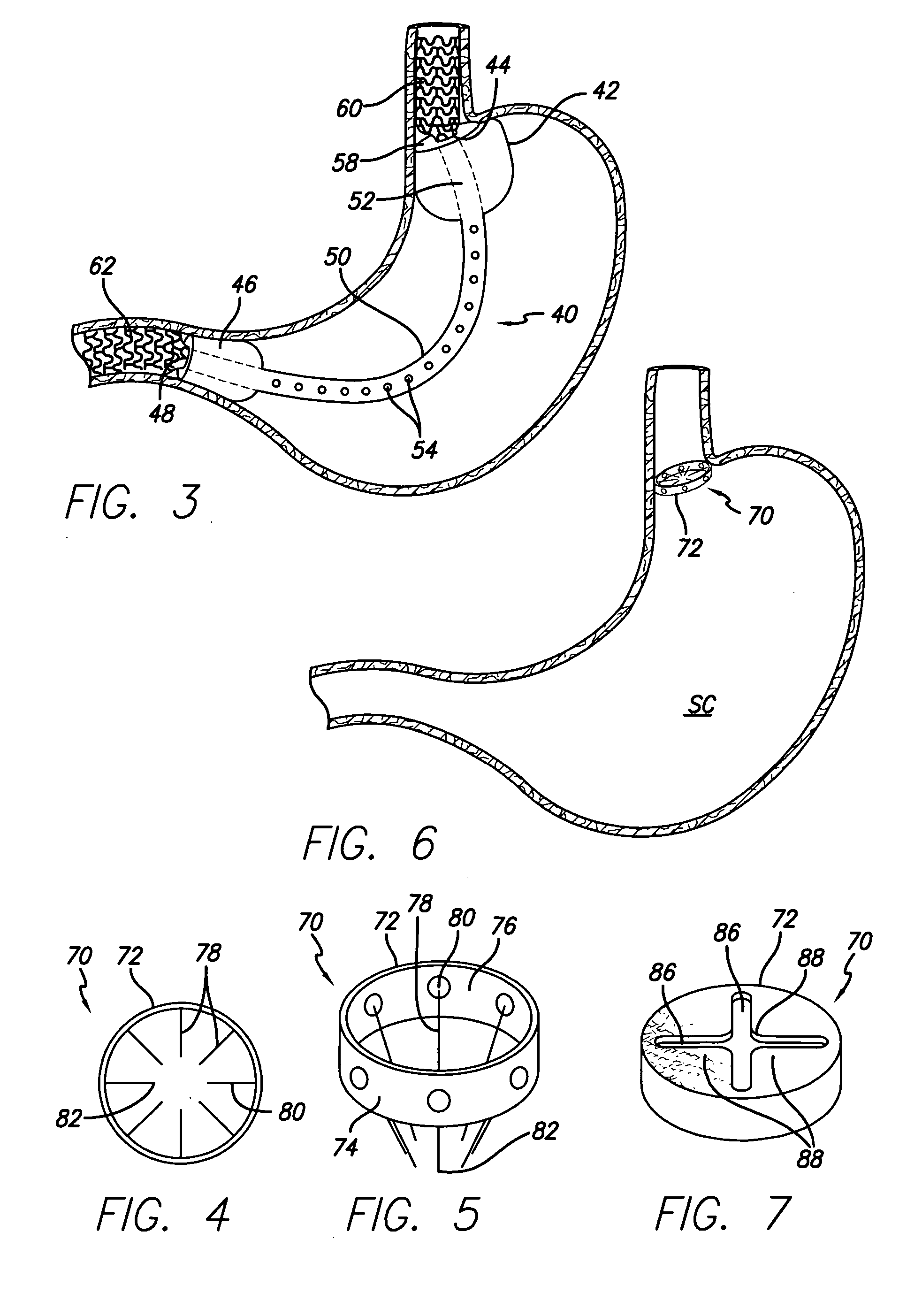
InactiveUS7037343B2Treating obesityFacilitate expedite mixing breaking downDiagnosticsSurgeryPylorusSmall intestine
An implantable stomach prosthesis is provided for surgically replacing or augmenting all or part of the antrum and / or pylorus of a stomach. The prosthesis controls the passage of food from the stomach to the small intestine. The prosthesis may be configured to churn ingested material and release it from the stomach through a prosthetic pyloric valve. At least one expandable member is arranged to be expanded to control the passage of food and / or to mimic the churning action of a patient's stomach. The prosthesis includes an outer support structure, a flexible inner member forming a conduit for the movement of material, and at least one expandable member located between the outer support structure and inner member. An implantable pump system is provided for inflating and deflating the expandable member(s).
Owner:PYTHON MEDICAL
Method and device for use in endoscopic organ procedures
InactiveUS7229428B2Minimize infection riskLower the volumeSurgical instrument detailsIntravenous devicesBody organsPylorus
A bypass conduit assembly is placed in a hollow body organ to route food and liquids past the hollow body organ. A flexible tubular member extends from a narrowed section through the hollow body organ and into either the pylorus or intestines. The tubular member is connected to tissue by fasteners such as clips, staples or stents.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Intragastric device for treating obesity
An apparatus and method comprising at least one intragastric member or artificial bezoar made of a digestive-resistant or substantially indigestible material that is introduced into a gastric lumen of a mammal for the treatment of obesity. The intragastric member or artificial bezoar is typically at inserted into the gastric lumen in a partially compacted configuration, whereby it is then manipulated into, or allowed to assume, a second expanded configuration sufficiently large to remain within the reservoir of the stomach during normal activities and not be passed through the pylorus into the intestines. In animals, the present invention has been found to be effective in achieving weight loss over a several month period, while being easy to place and retrieve.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
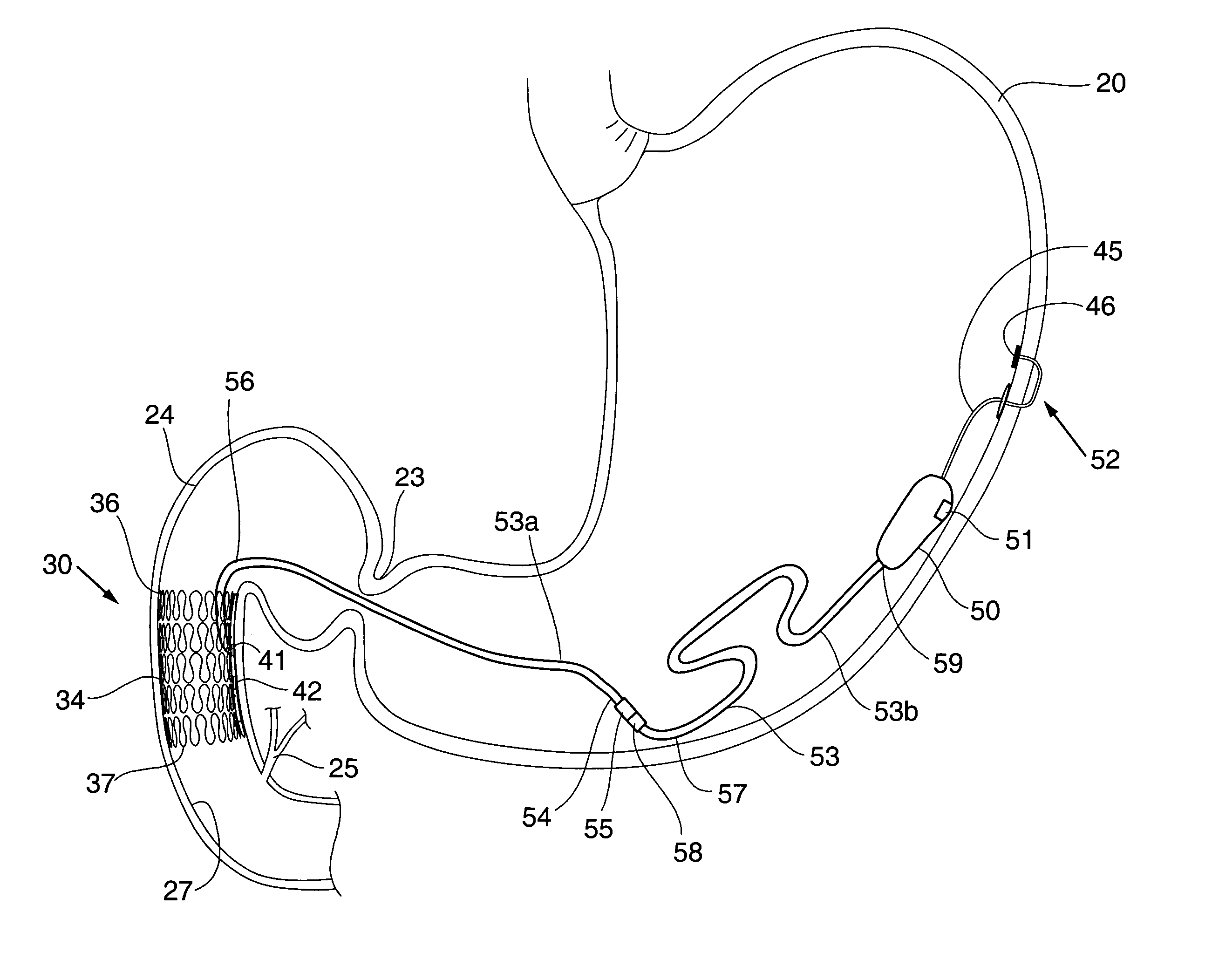
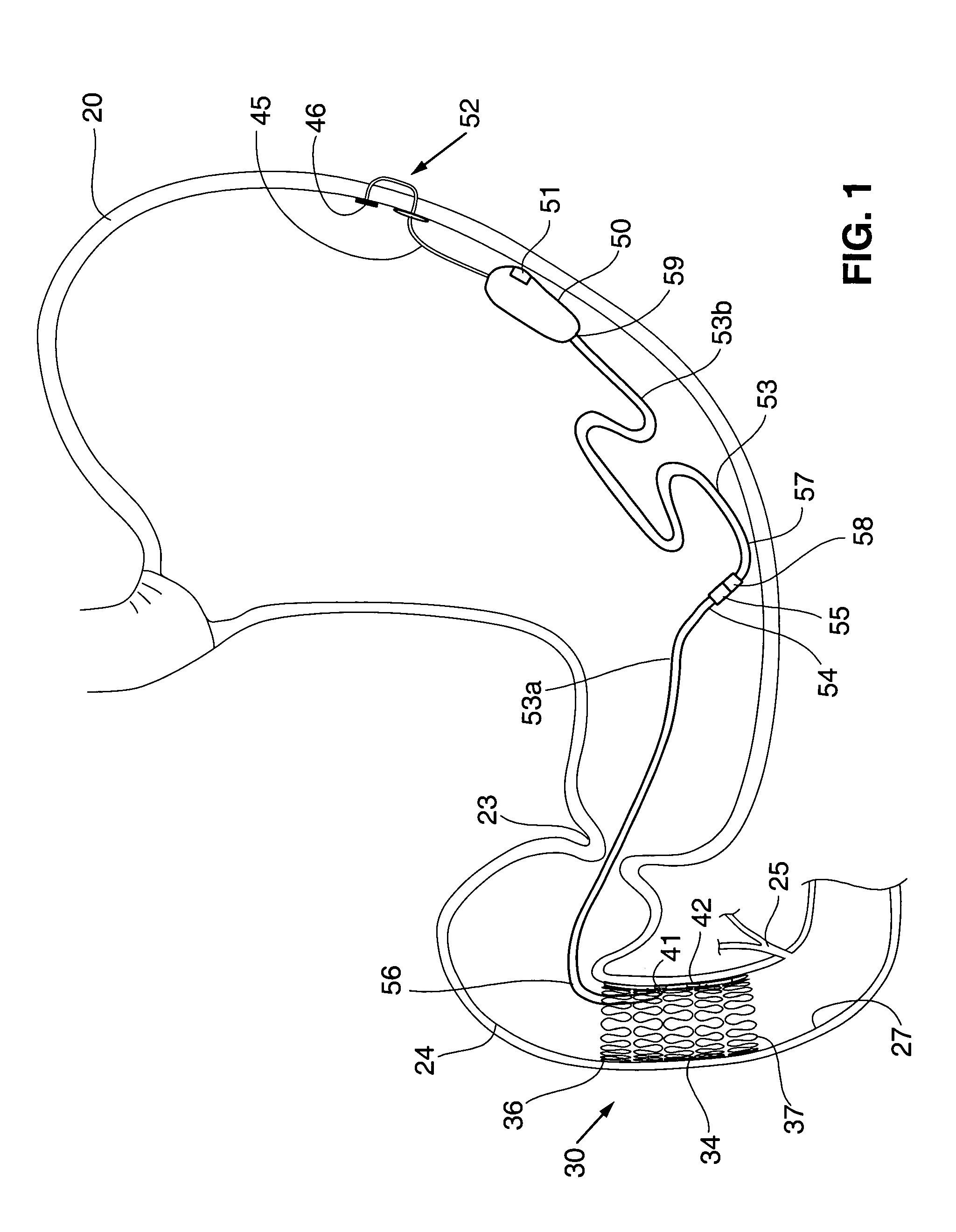
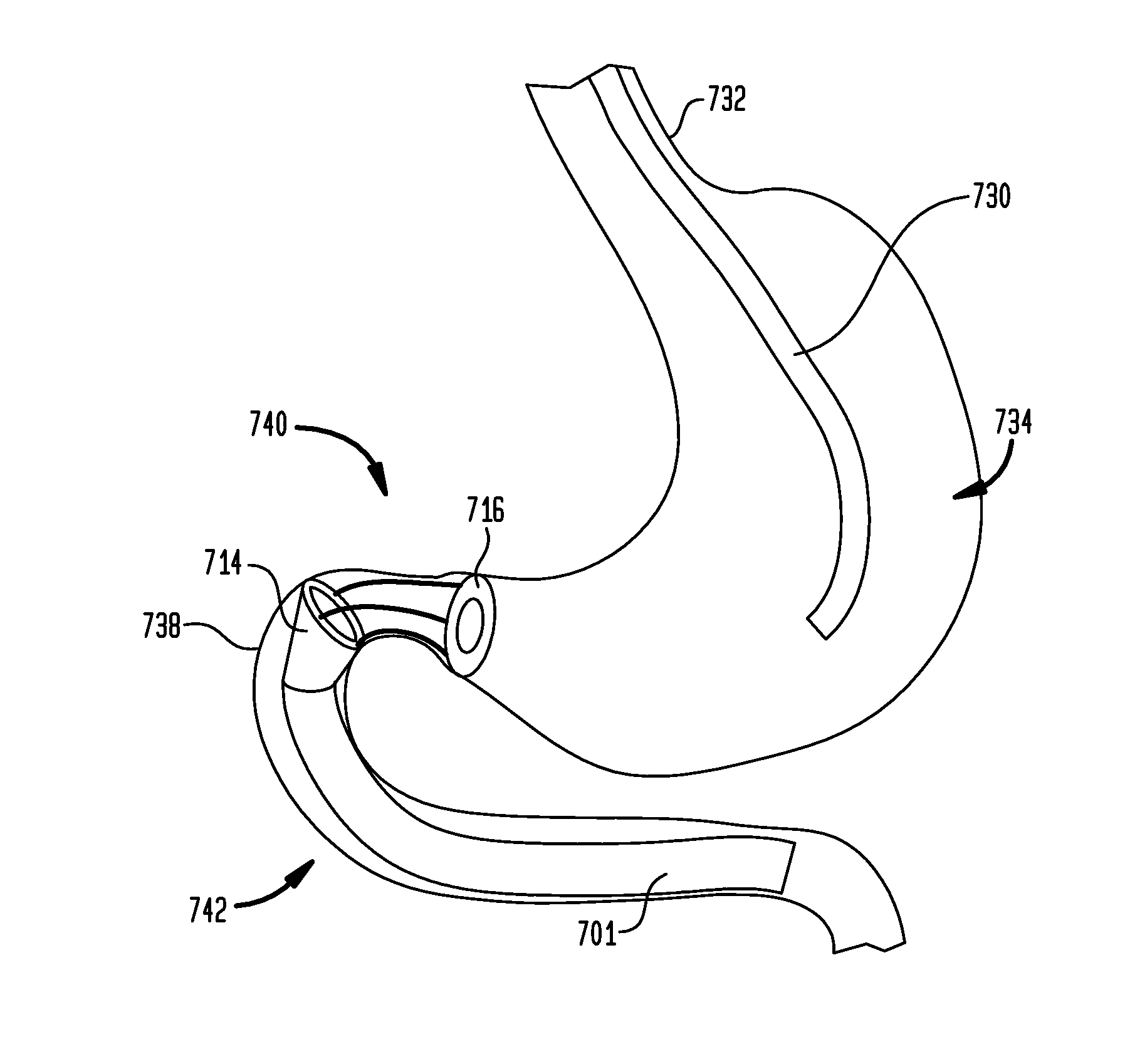
Methods of treatment using a bariatric sleeve
ActiveUS7695446B2Promote healingControlled absorptionSuture equipmentsStentsDiseaseIntestinal structure
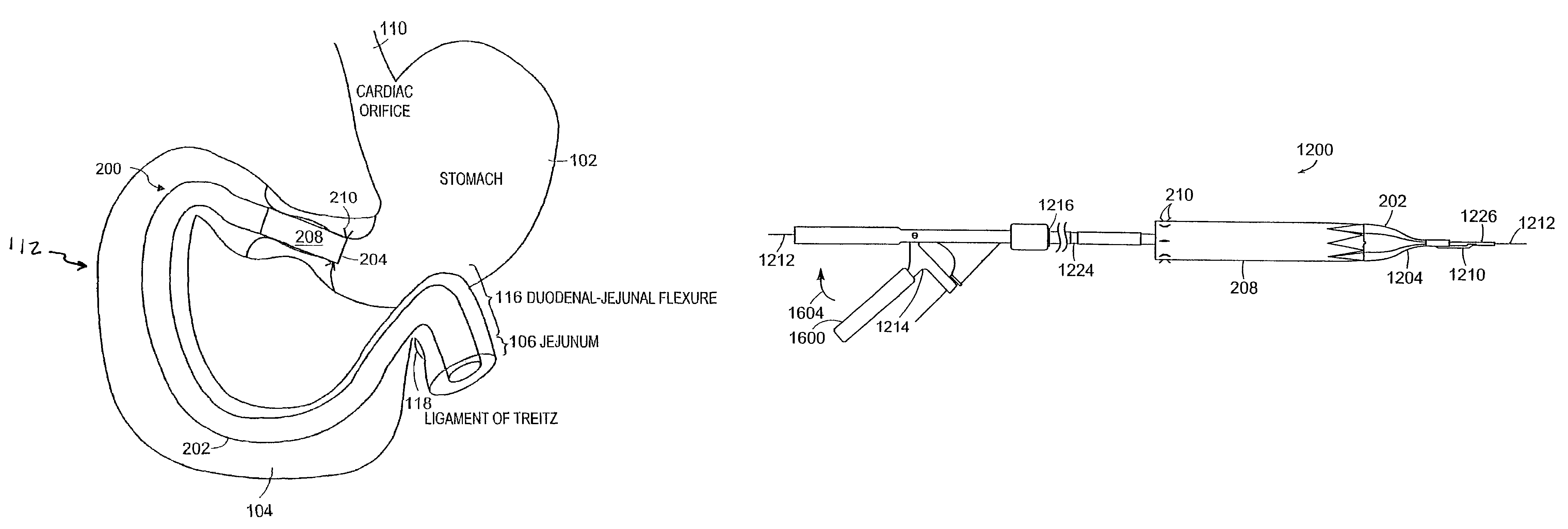
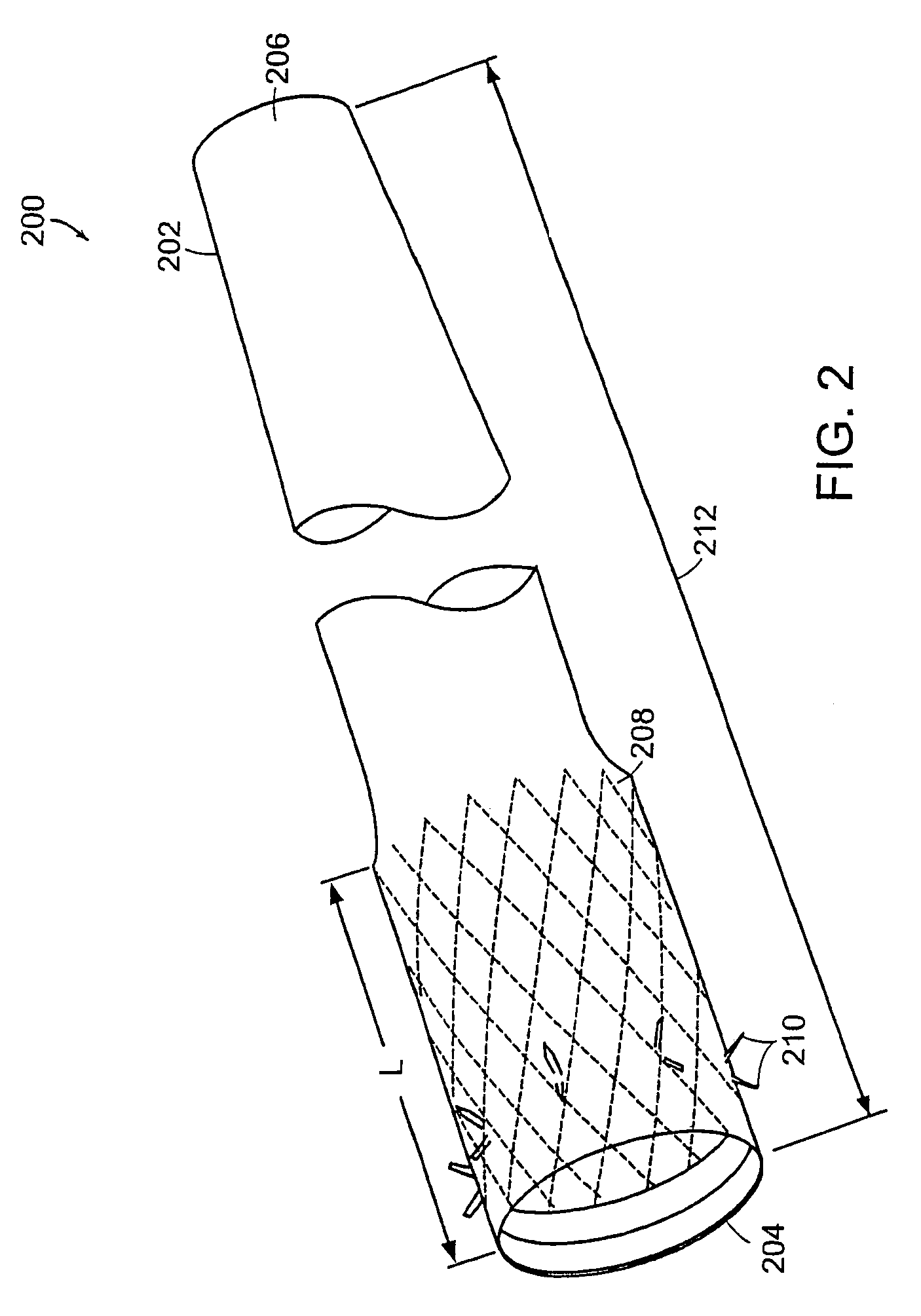
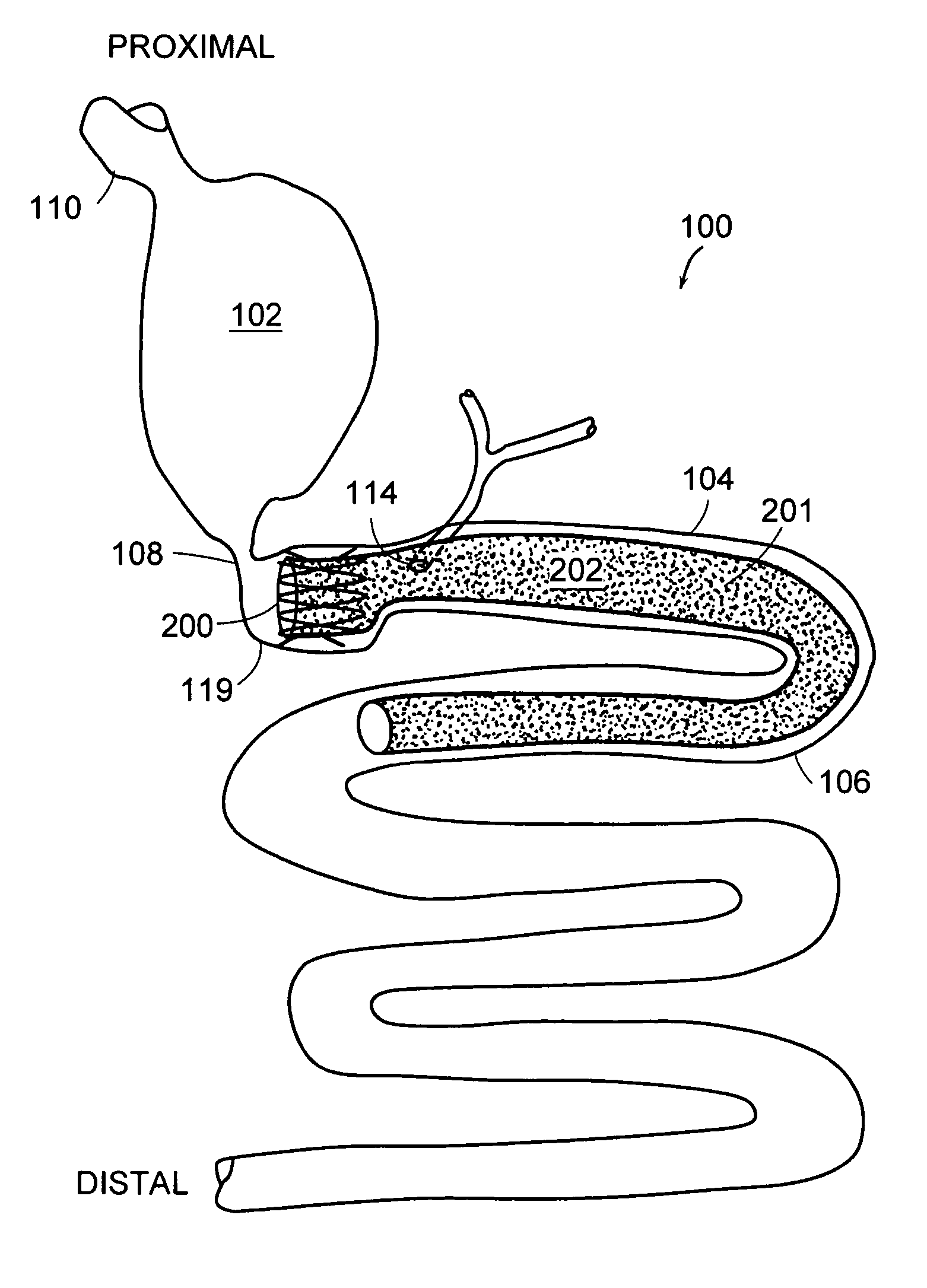
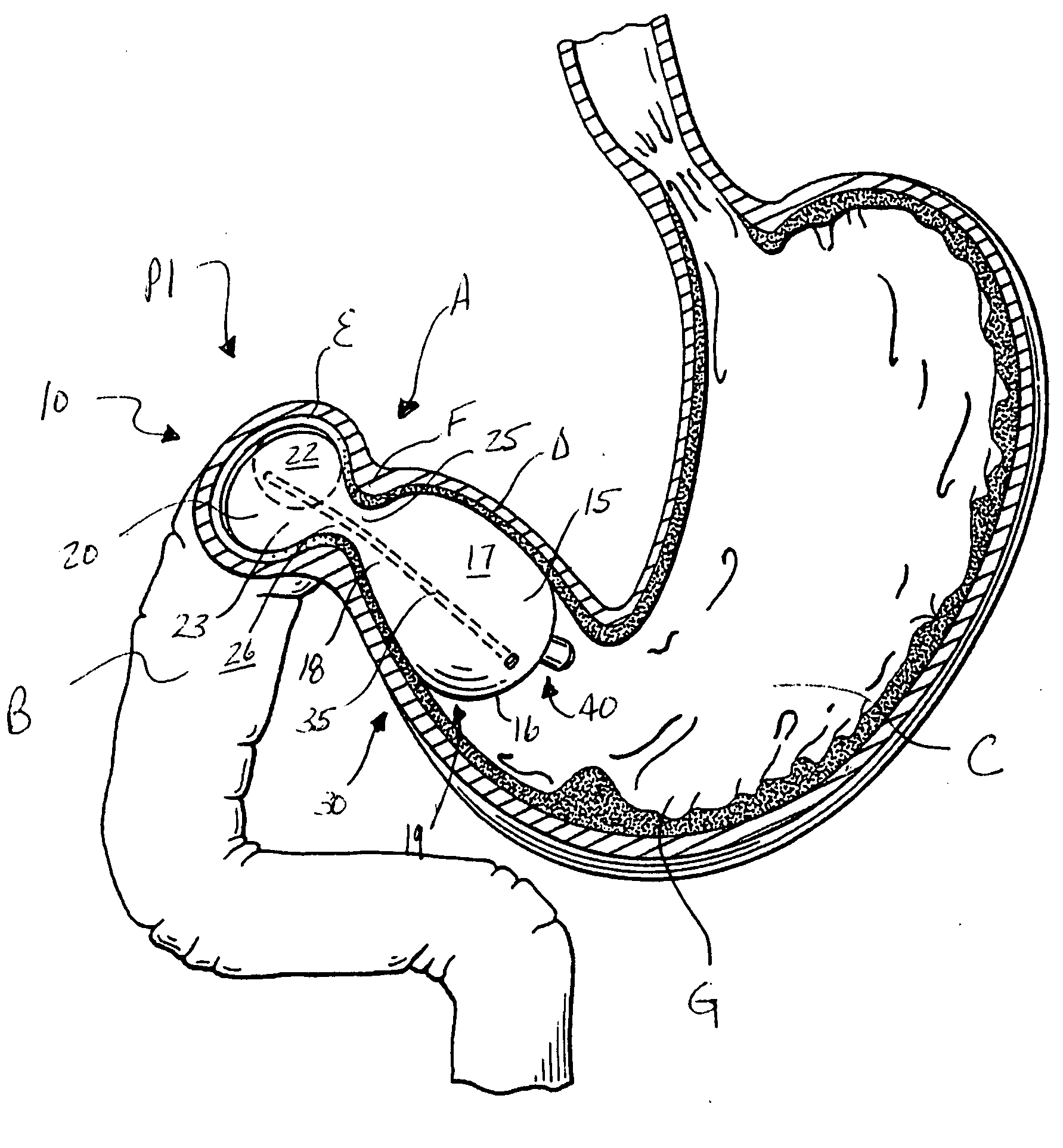
Methods of treatment using a gastrointestinal implant device removably anchored within an animal's gastrointestinal tract. For example, the implant device includes a collapsible anchor for anchoring the device coupled to a proximal end of a flexible sleeve. The implant device can be anchored within the stomach, within the pyloric orifice, and / or distal to the pylorus and extended into the duodenum. All partially-digested food, or chyme, exiting the stomach is funneled through the device. Methods of treatment include treating obesity by one or more of: limiting the absorption of nutrients within the duodenum; delaying the mixing of chyme with digestive enzymes; alter hormonal triggers; and providing negative feedback. Alternatively or in addition, the desired result includes treating a diseases, such as diabetes, or temporarily shielding a portion of the intestine to promote healing within the intestine.
Owner:GI DYNAMICS INC
Methods of treatment using a bariatric sleeve
Methods of treatment using a gastrointestinal implant device removably anchored within an animal's gastrointestinal tract. For example, the implant device includes a collapsible anchor for anchoring the device coupled to a proximal end of a flexible sleeve. The implant device can be anchored within the stomach, within the pyloric orifice, and / or distal to the pylorus and extended into the duodenum. All partially-digested food, or chyme, exiting the stomach is funneled through the device. Methods of treatment include treating obesity by one or more of: limiting the absorption of nutrients within the duodenum; delaying the mixing of chyme with digestive enzymes; alter hormonal triggers; and providing negative feedback. Alternatively or in addition, the desired result includes treating a diseases, such as diabetes, or temporarily shielding a portion of the intestine to promote healing within the intestine.
Owner:GI DYNAMICS
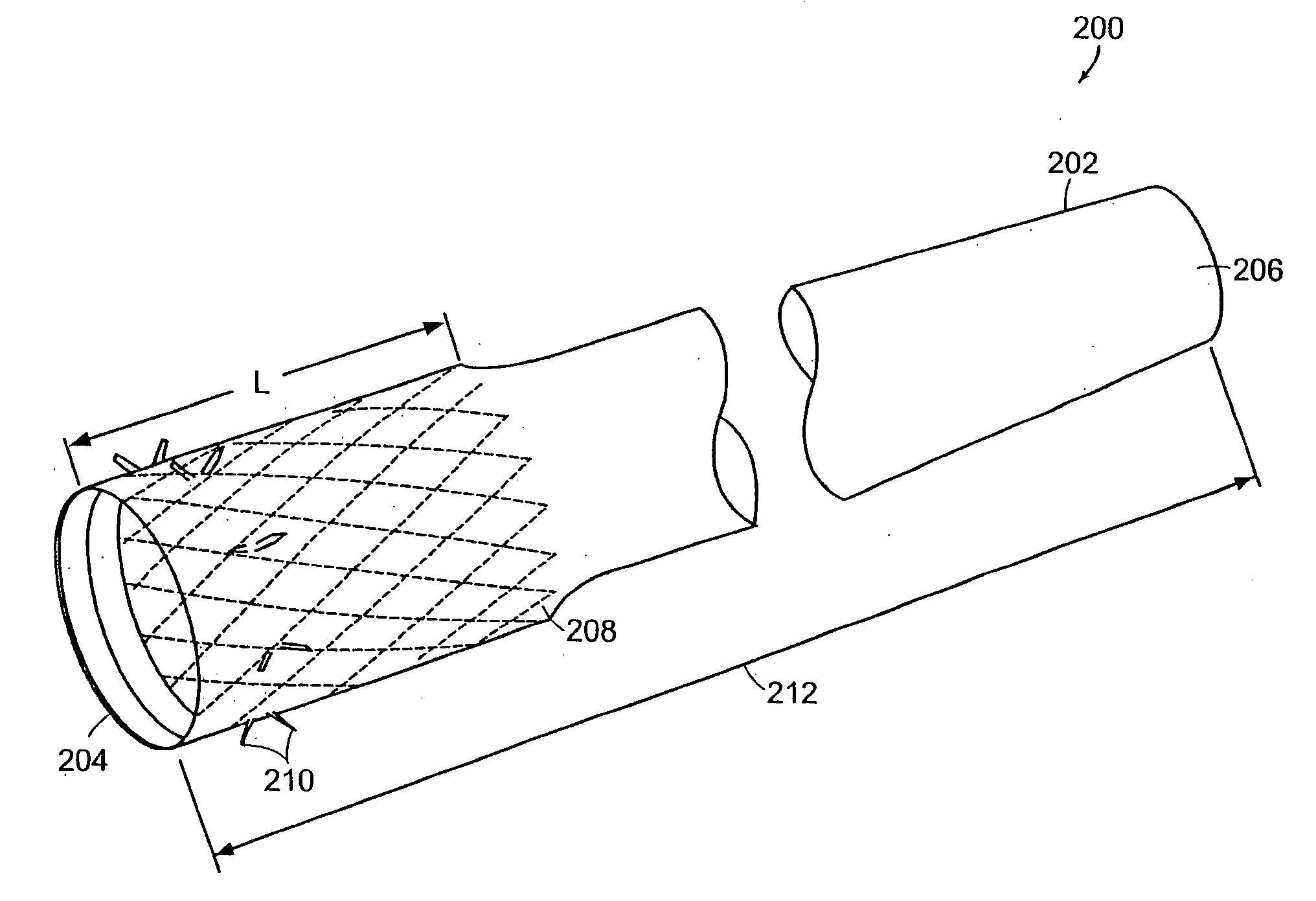
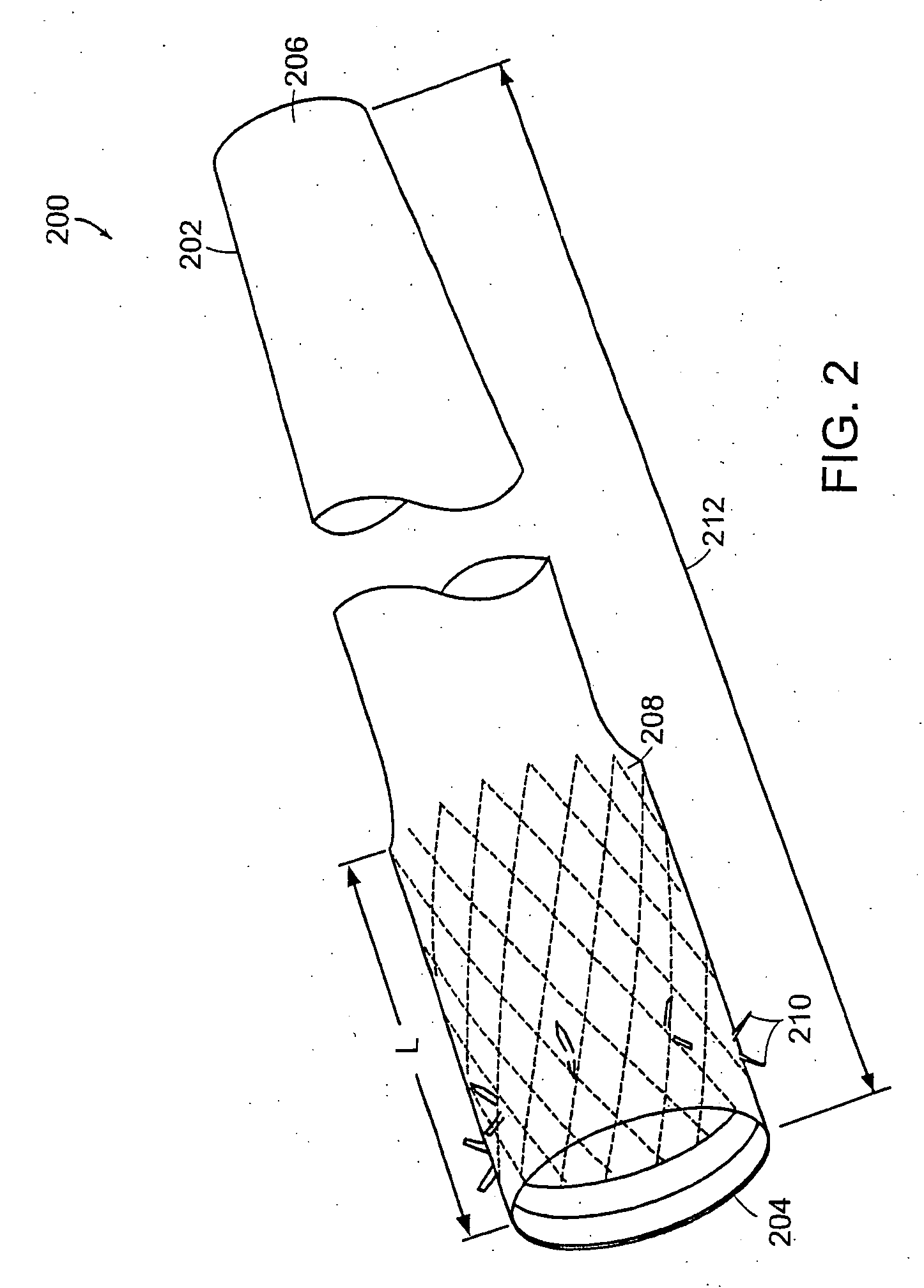
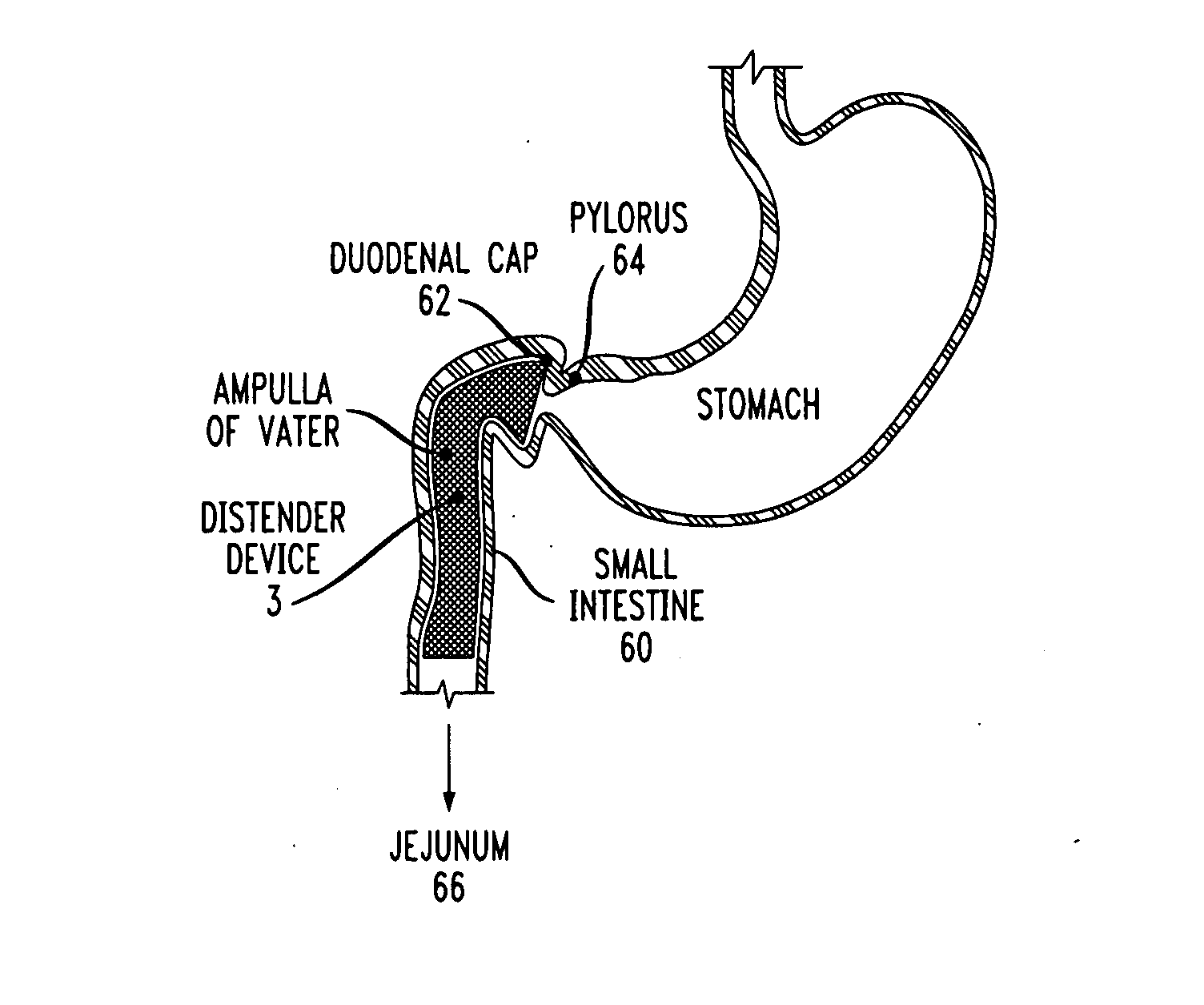
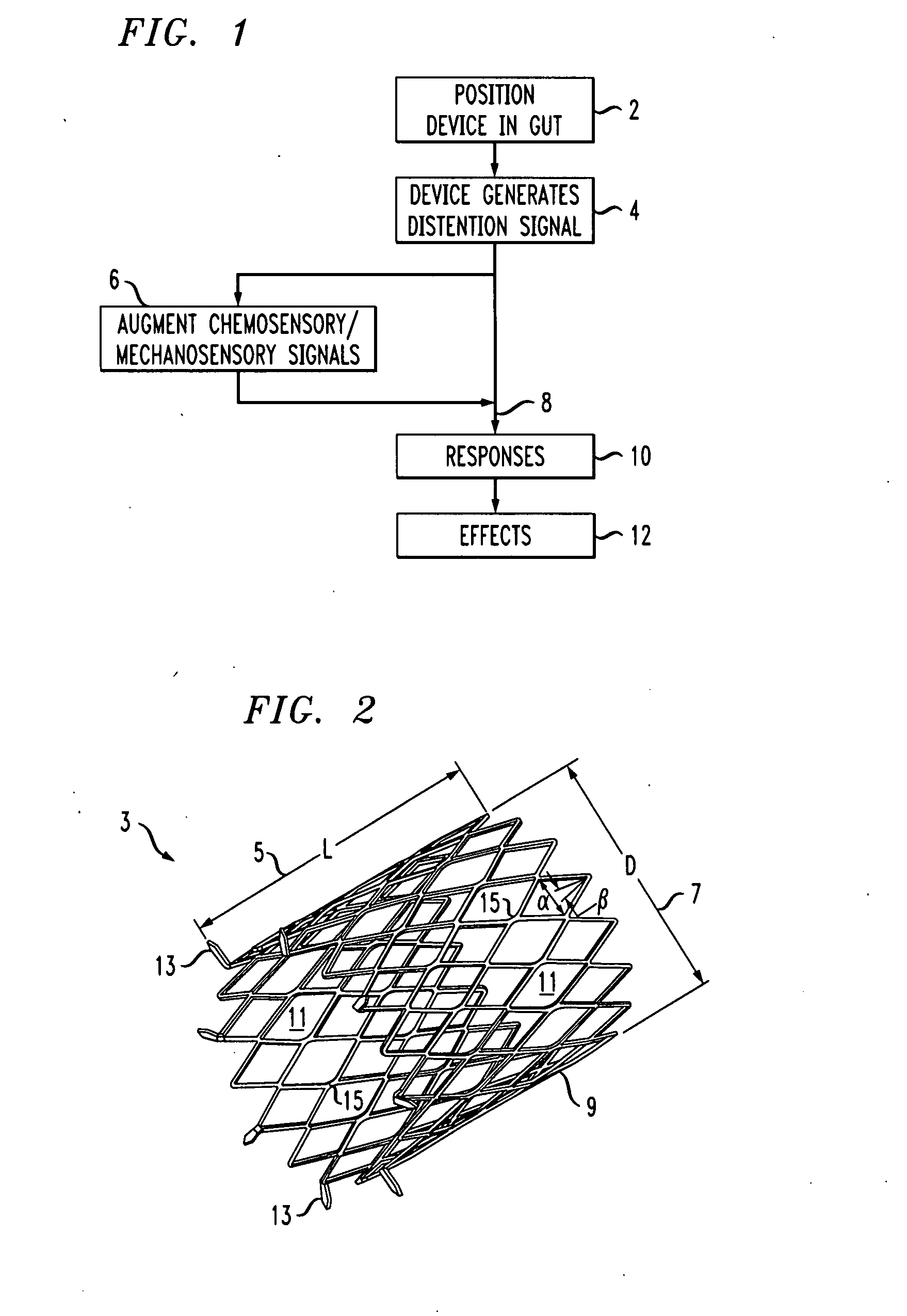
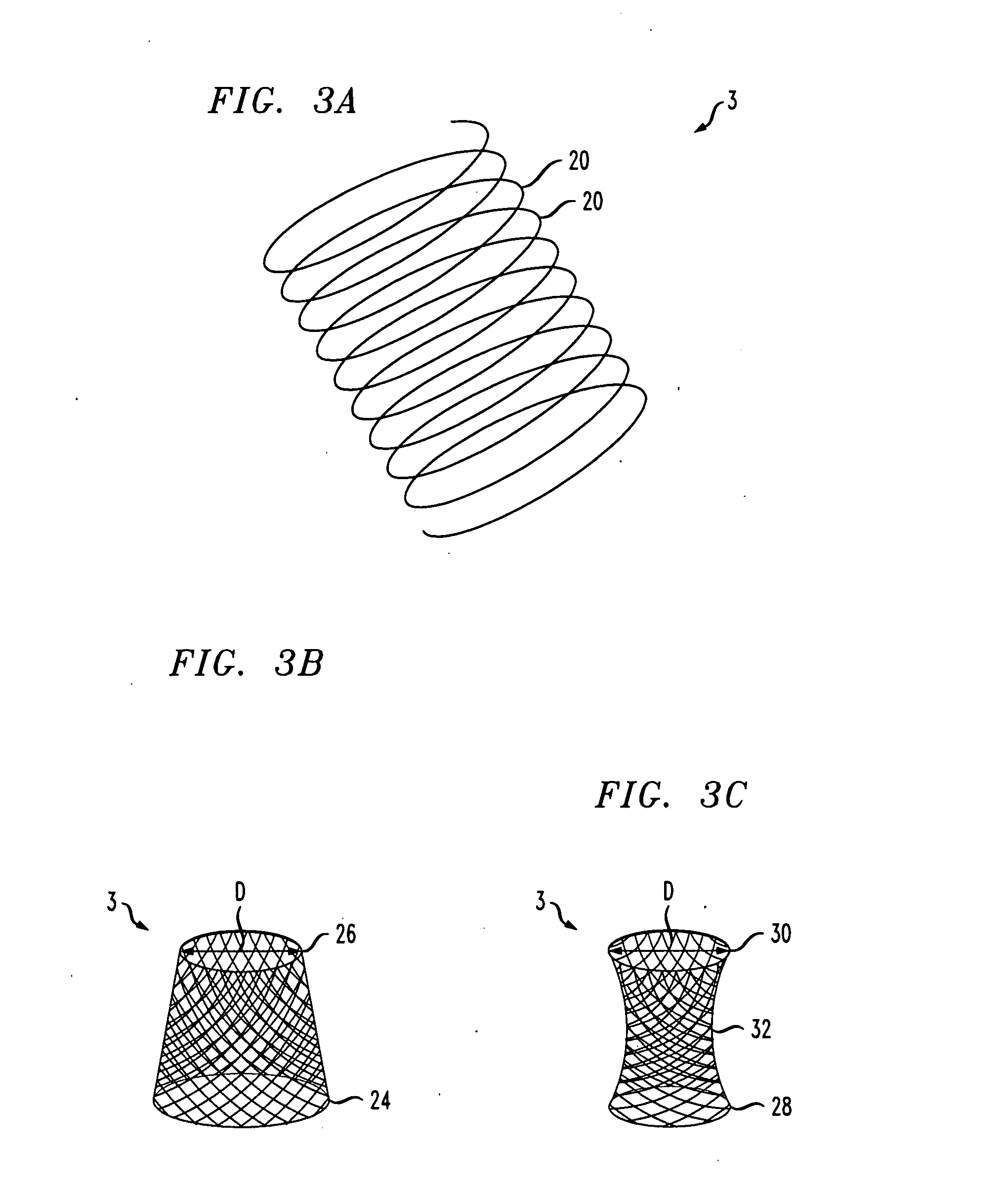
Distender device and method for treatment of obesity and metabolic and other diseases
A gastrointestinal implant device is positioned in a patient's small intestine or rectum and produces an outward force that itself produces a distension signal which is a therapeutically useful neural or humoral signal that evokes satiogenic or weight loss effects by itself. The device may advantageously be placed in the duodenum adjacent the pylorus or in the jejunum, ileum or rectum. The distension signals may amplify chemosensory or mechanosensory signals such as enteroendocrine secretions within the patient. The device may be a mesh and include a low material density that allows for unrestricted chyme absorption within the small intestine and unrestricted chyme flow through the gastrointestinal system. A method includes inserting the device into the patient then either retrieving the device after treatment is complete or allowing a device formed of a biodegradable material to degrade in time after treatment is complete.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
Intragastric Implant Devices
InactiveUS20100049224A1Avoid luminal blockageStress minimizationMedical devicesCatheterIntestinal structurePylorus
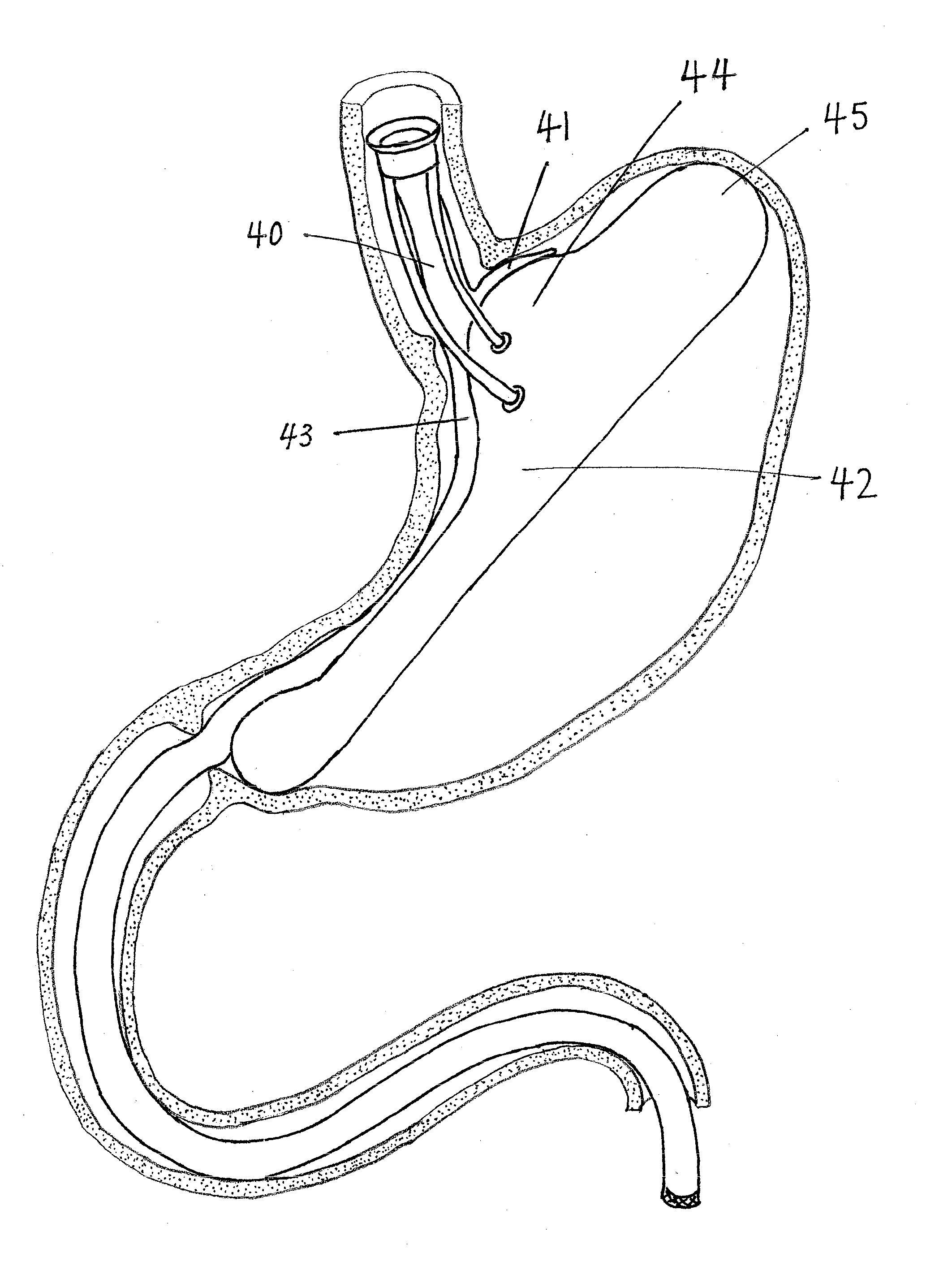
An intragastric implant comprises an anchor and a therapeutic device or a diagnostic device. The anchor is adapted to extend between the fundus and the pyloric valve of a stomach, to be retained without attachment to the stomach wall, and to anchor the device within the stomach with a relatively stable position and orientation. The therapeutic or diagnostic device is adapted to extend from the esophagus or stomach to the intestines or stomach. The therapeutic or diagnostic device, when extending into the esophagus, will be slidably received through the gastroesophageal junction and, when extending into the intestines, will be slidably received in the pyloric valve.
Owner:IBIS MEDICAL
Systems and methods for treating obesity
ActiveUS7753870B2Reduce food intakeGood for weight lossIntravenous devicesTubular organ implantsPylorusGastric emptying
Methods and devices for simulating a gastric bypass and reducing the volume of the stomach involve placing a tubular liner along the lesser curve of the stomach cavity. Also, methods and devices for slowing gastric emptying involve placing valves within the stomach cavity near the gastro-intestinal junction and / or the pylorus. These methods and devices may prevent a patient from drinking and eating large volumes at one time and from eating slowly all day.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
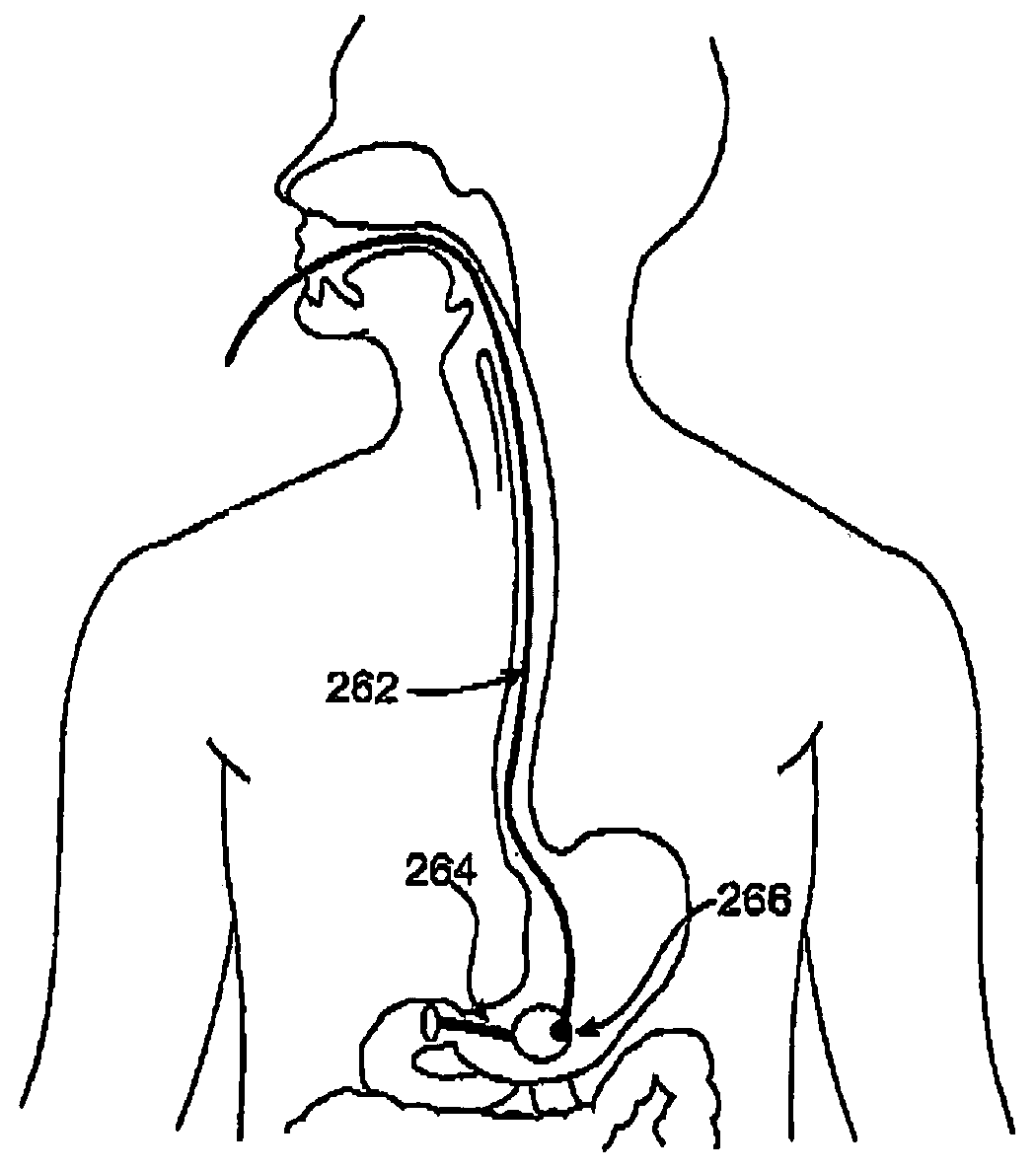
Orogastric catheter for longitudinal gastrectomy
ActiveUS20130165774A1Simple and economical to manufactureSimple and economical to and useStentsCatheterPylorusGastrectomy
The invention relates to an orogastric catheter for a longitudinal gastrectomy. The object of the invention is to make available an orogastric catheter that represents an advantageous alternative to the poorly suited catheters used today and that facilitates the work of the surgeon. This novel orogastric catheter is characterized in that this distal part carries a balloon (25) which, in the inflated state, has a shape substantially matching that of the pyloric antrum (4), in such a way as to be able to be lodged in this pyloric antrum (4), the end of the inflated balloon (25) then being in abutment against the pylorus (5), and the distal end of the body of the catheter (20) for its part being in abutment against the pyloric antrum (4), while the part of the body (21) of the catheter (20) arranged above the inflated balloon (25) is wedged against the wall of the lesser curvature (6) of the stomach (1), thus making it possible to determine the position of the start of the closure resection line in the area of the pyloric antrum (4), to define the closure resection line, and to calibrate the pyloric antrum (4) and the gastric sleeve to be preserved.
Owner:MEDICAL INNOVATION DEV
Method and apparatus for adjusting body lumens
Disclosed is a device and method for accessing the lower esophageal sphincter through the esophagus. In one embodiment, a catheter is inserted through the mouth or nose of a patient and advanced to the region of the diaphragm. Under fluoroscopy or endoscopy, a hollow needle at the distal end of the catheter punctures the wall of the esophagus from the inside so that the distal end of the needle is positioned outside the esophagus. An implant is next advanced out through the hollow needle to the region outside the sphincter where it is deflected and coerced to bluntly dissect around the circumference of the esophagus, where the implant is left in place to heal. The hollow needle is removed and the esophageal wall is allowed to heal. Subsequent diametric adjustment of the implant allows for tightening or loosening of the sphincter to minimize gastric reflux. The device and method can also be used to treat the pyloric or other body sphincters, hollow organs, or ducts.
Owner:ELLIPSE TECH
Foam filled intragastric balloon for treating obesity
An apparatus and method comprising one or more intragastric balloons comprising a foam material disposed within the gastric lumen of a mammal. When the foam material is disposed within the one or more balloons, the one or more intragastric balloons are configured to prevent the intragastric device from passing through the mammal's pylorus. The one or more intragastric balloons are loaded onto a delivery tube in a partially compacted first configuration and delivered through an overtube. The overtube includes a proximal end, a distal end and a lumen configured to receive the one or more intragastric balloons in the first configuration for delivery into the gastric lumen wherein the one or more intragastric balloons are expanded to a second configuration upon delivery of the foam material. The foam material is delivered through an inflation tube attached to an opening of the one or more intragastric balloons.
Owner:WILSONCOOK MEDICAL
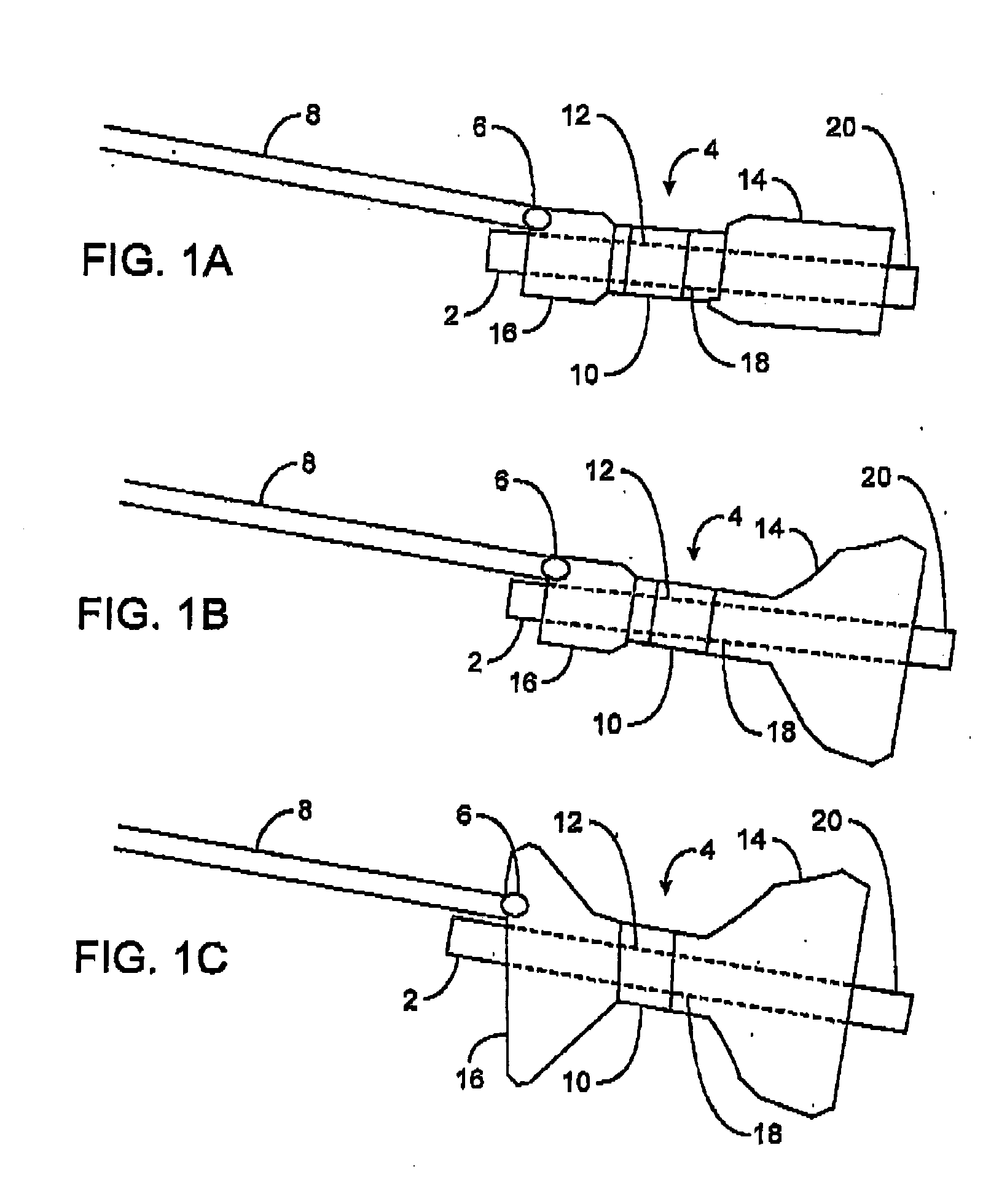
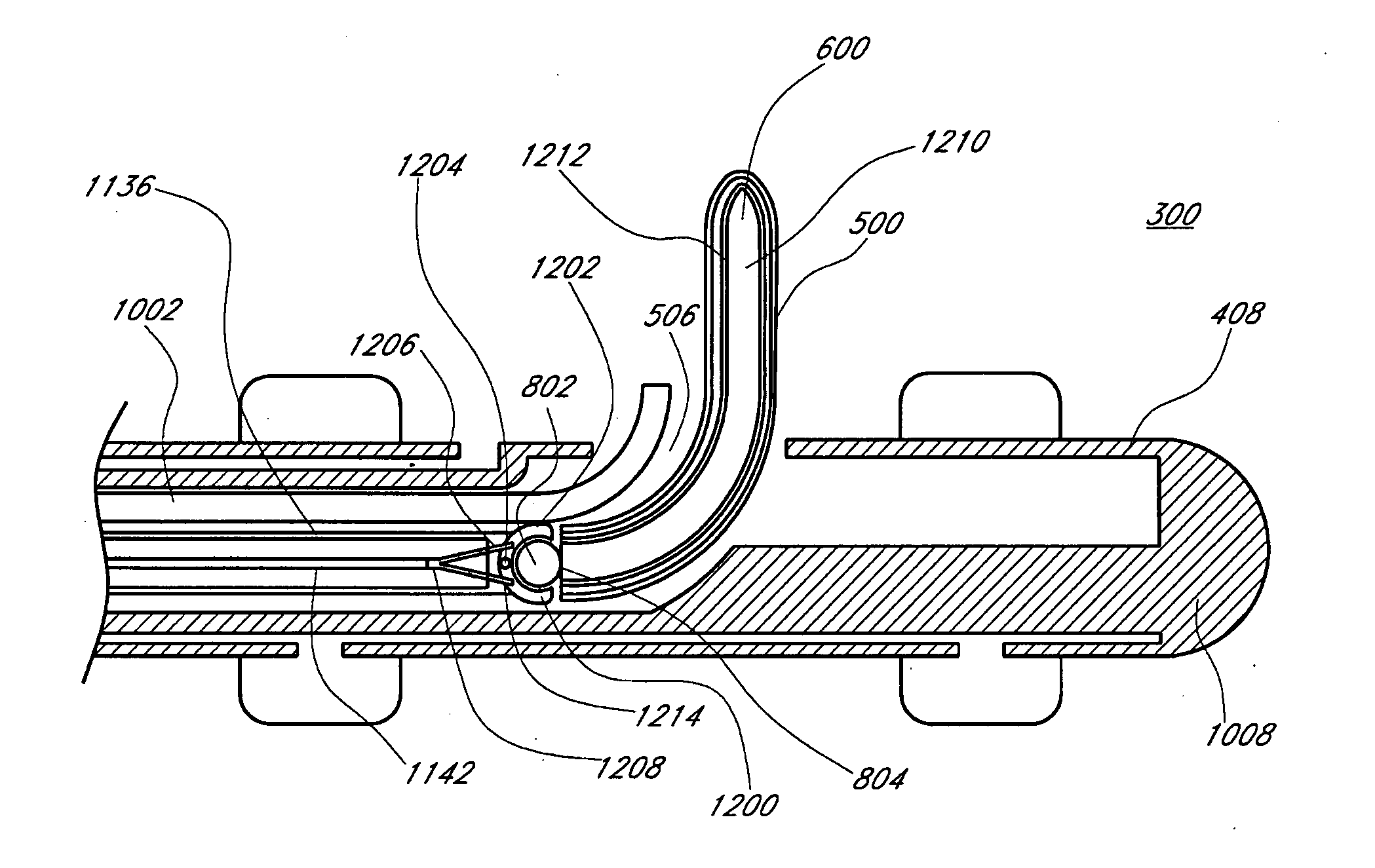
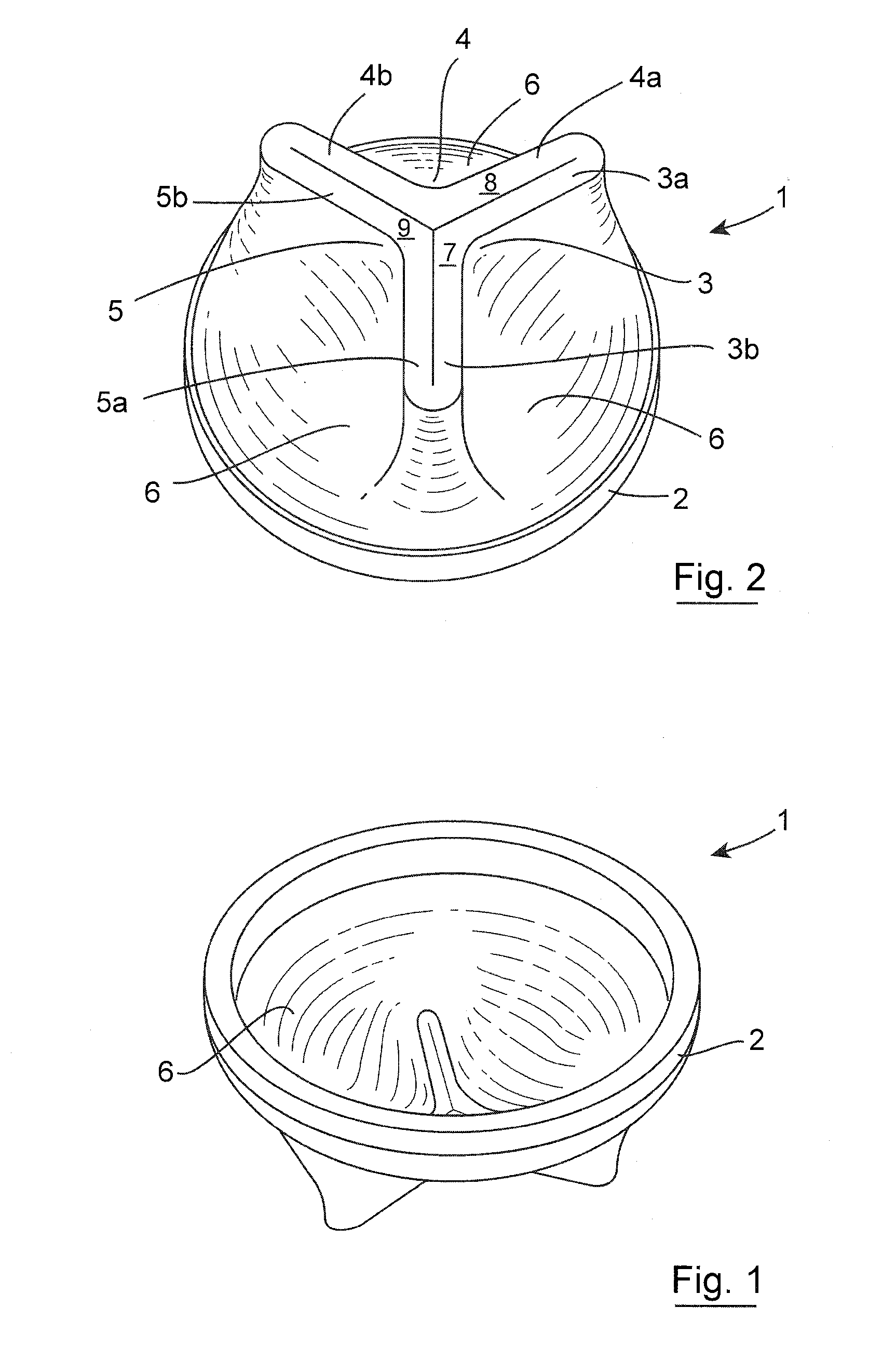
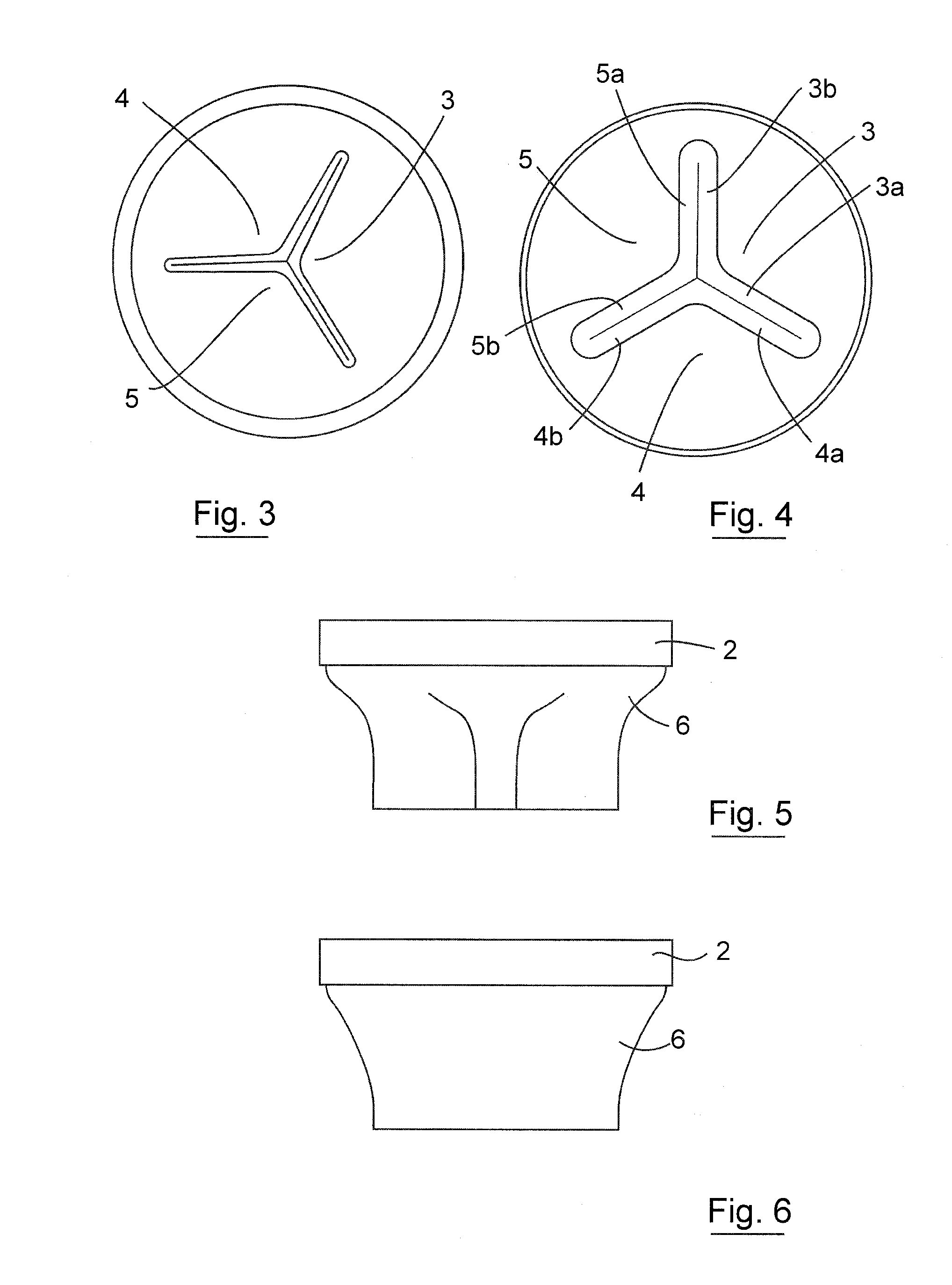
Pyloric obesity valve
The pyloric obesity valve includes a tubular valve body having proximal and distal ends. The valve body has an intermediate section which is between the proximal and distal ends. The proximal end is enlarged transversely relative to the intermediate section. The valve body has an inner surface and a lumen. The inner surface which is within the intermediate section has a cross-sectional area which is smaller than a cross-sectional area of the inner surface which coincides with the proximal end to resist a flow through the lumen of the valve body from the proximal end to the intermediate section.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Pyloric valve obstructing devices and methods
ActiveUS8048169B2Treat and ameliorate obesityReduced food intakeSuture equipmentsEndoradiosondesPylorusPartial obstruction
Owner:BARONOVA
Intragastric device for treating obesity
InactiveUS20060155311A1Small volumeEasy to placeStentsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesIntestinal structurePylorus
An apparatus and method comprising at least one intragastric member or artificial bezoar made of a digestive-resistant or substantially indigestible material that is introduced into a gastric lumen of a mammal for the treatment of obesity. The intragastric member or artificial bezoar is typically at inserted into the gastric lumen in a partially compacted configuration, whereby it is then manipulated into, or allowed to assume, a second expanded configuration sufficiently large to remain within the reservoir of the stomach during normal activities and not be passed through the pylorus into the intestines. In animals, the present invention has been found to be effective in achieving weight loss over a several month period, while being easy to place and retrieve.
Owner:HASHIBA KIYOSHI +1
Gastrointestinal anchor compliance
ActiveUS7976488B2Improve abilitiesEasy to keepOesophagiIntravenous devicesDiseaseIntestinal structure
A collapsible gastrointestinal anchor can be characterized in various embodiments by a radial force of about 0.1 Newtons (N) or greater at a compressed diameter of 25 millimeters (mm); by an average spring rate of about 13 Newtons / meter (N / m) or greater in a range of motion between a relaxed diameter and a compressive elastic deformation diameter; or by a radial force over the range of motion of about 0.1 N or greater. Typically, the anchor can be adapted to be retained within a subject's intestine, more typically in the duodenum, or particularly in the duodenal bulb just distal to the pylorus.A gastrointestinal implant device includes the collapsible gastrointestinal anchor and a floppy sleeve. The sleeve is open at both ends and adapted to extend into a subject's intestine, the anchor being coupled to a proximal portion of the sleeve.Also include are methods of implanting the gastrointestinal implant device in a subject, and methods of treating a subject for disease.The disclosed gastrointestinal invention leads to an improved ability to secure anchors and devices in the gastrointestinal tract while tending to minimize migration.
Owner:GI DYNAMICS
Stomach peristalsis device and method
InactiveUS20060129237A1Facilitate expedite mixing breaking downPassage is slowedLigamentsMusclesPylorusPeristalsis
The invention relates to an implantable stomach prosthesis for surgically replacing or augmenting all or part of the antrum and / or pylorus of a stomach. The prosthesis controls the passage of food from the stomach to the small intestine. The prosthesis may be configured to chum ingested material and release it from the stomach through a prosthetic pyloric valve. At least one expandable member is arranged to be expanded to control the passage of food and / or to mimic the churning action of a patient's stomach. The prosthesis includes an outer support structure, a flexible inner member forming a conduit for the movement of material, and at least one expandable member located between the outer support structure and inner member. An implantable pump system is provided for inflating and deflating the expandable member(s).
Owner:PYTHON MEDICAL
Gastrointestinal implant
A gastrointestinal implant device comprises a sleeve for extending into the duodenum and an artificial valve for placement at the pylorus to control flow from the stomach into the duodenal sleeve. The implant device also comprises a support structure for the valve.
Owner:VYSERA BIOMEDICAL
Method for treating obesity using an implantable weight loss device
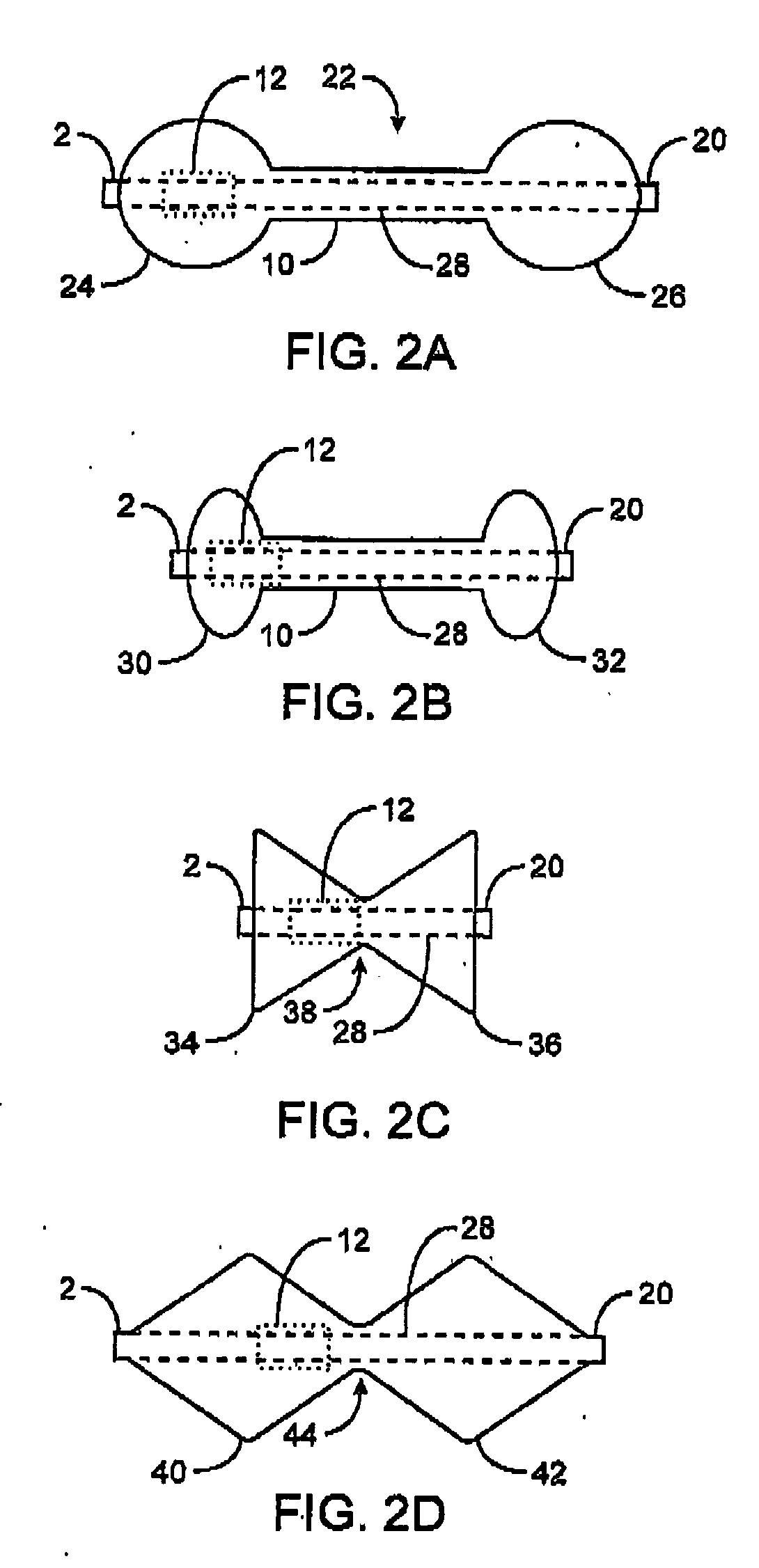
InactiveUS20080208239A1Reduce the overall diameterAccelerate the accumulation processSurgeryDilatorsPylorusProximate
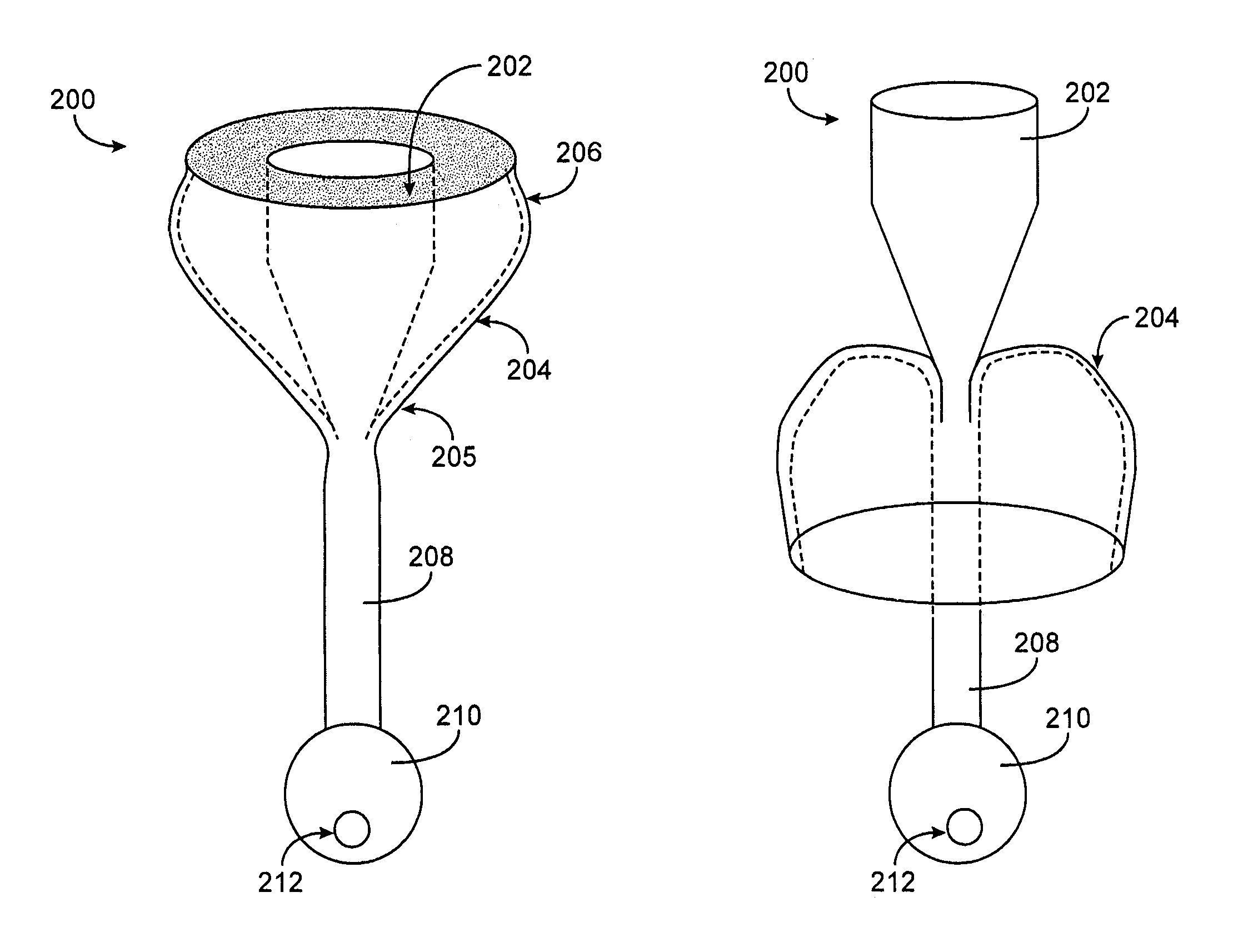
The present invention provides methods of treating overweight or obese patients with an inflatable weight control device that is implanted in the patient's digestive tract. A first method comprises the steps of providing the weight control device which includes an inflatable body having a first bulb, a second bulb, an intermediate portion, and an internal passageway extending from the first bulb through the intermediate portion and to the second bulb. The inflatable body includes a valve assembly that is grasped by the endoscope during insertion of the weight control device in the patient's pylorus. Next, the endoscope is used to position the weight control device within the pylorus such that the intermediate portion resides within the pyloric valve and the first bulb resides within the pyloric antrum. The weight control device is then inflated with the endoscope such that the first bulb engages an inner surface of the pyloric antrum to form an outlet obstruction within the pyloric antrum. This obstruction causes chyme to accumulate proximate the first bulb prior to entering the internal passageway where it is then transported through the body and discharged from the second bulb into the patient's duodenum. The accumulation of chyme in pyloric antrum and the stomach causes the patient to feel full and stop eating. Thus, the treatment method provides a gastric outlet obstruction that slows the passage of chyme into the duodenum and as a result, the patient feels full and stops eating after consuming relatively small portions.
Owner:AGT INC (US)
Systems and Methods for Treatment of Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes
InactiveUS20110046537A1Reducing collateral tissue damageMinimize impactWound drainsOesophagiPylorusIt impact
The present invention provides systems and methods for treating and controlling obesity and / or type II diabetes. In one aspect of the invention, a device comprises a hollow sleeve sized and shaped for positioning within a duodenum of the patient, an anchor coupled to the proximal end of the sleeve and being sized and shaped to inhibit distal migration of the sleeve and a plurality of elastomeric objects coupled to the distal end of the sleeve and being sized and shaped to inhibit proximal migration of the sleeve through a pylorus of the patient. The bypass device can be placed and removed endoscopically through the patient's esophagus in a minimally invasive outpatient procedure and it is “self-anchoring” and does not require invasive tissue fixation within the patient's GI tract, thereby reducing collateral tissue damage and minimizing its impact on the digestive process.
Owner:E2 LLC DENTONS
Intragastric device for treating obesity
An apparatus comprising an intragastric member re-configurable from a first configuration to a second configuration, the first configuration being sufficiently small to permit introduction of said intragastric member into a gastric lumen of a mammal, the second configuration being sufficiently large to prevent said intragastric device from passing through the mammal's pylorus, wherein said intragastric member comprises a plurality of spaced apart openings. The intragastric member comprises an elongate member having a proximal end and a distal end, wherein the elongate member is threaded through the openings of the intragastric member, and the intragastric member is disposed between the proximal end and the distal end of the elongate member. The apparatus also comprises a proximal stopper engaged to the distal end of the elongate member and a proximal stopper engaged to the proximal end of the elongate member for securing the intragastric member upon delivery into the gastric lumen of the patient. The elongate member can also comprise a cinching member to facilitate delivery of the intragastric member into the gastric lumen of the patient.
Owner:WILSONCOOK MEDICAL
Implantable weight control device
ActiveUS20080208135A1Reduce the overall diameterAccelerate the accumulation processSurgeryObesity treatmentPylorusImplanted device
The present invention provides an endoscopically implantable weight control device that forms a gastric outlet obstruction in a patient's digestive tract. The weight control device includes an inflatable body residing within the patient's pylorus and between the stomach and duodenum. The body features a first bulbous portion and a second bulbous portion, the exterior dimensions of the first bulbous portion exceeding the exterior dimension of the second bulbous portion. The body also includes an intermediate portion with exterior dimensions that are less than the exterior dimensions of both the first and second bulbous portions, wherein the intermediate portion resides within the patient's pyloric valve when the device is implanted. An internal passageway extends through the body, wherein the passageway receives and allows for the passage of chyme from the stomach to the duodenum. A method of treating obese patients with the inflatable weight control device utilizing a sequence of different-sized devices is also provided.
Owner:AGT INC (US)
Process and electrostimulation device for treating obesity and/or gastroesophageal reflux disease
InactiveUS20060206160A1Prevent and slow down stomach emptyingTransit delayElectrotherapyRefluxPylorus
An improved process using electrostimulation for treating obesity and / or related motor disorders is provided. The improved method of this invention provides electrostimulation on the lesser curvature of the stomach. Preferably, the electrostimulation or pacemaker device provides electrostimulation to the lower or distal end of the lesser curvature (i.e., towards the pylorus) for the treatment or control of obesity. Preferably, the electrostimulation or pacemaker device provides electrostimulation to the upper or proximal end of the lesser curvature for the treatment or control of gastroesophageal reflux disease. In one embodiment, the process employs stimulation of the lesser curvature at a rate of about 2 to about 14 pulses / minute with each pulse lasting about 0.5 to about 4 seconds such that there is a pause of about 3 to about 30 seconds between the pulses.
Owner:MEDTRONIC TRANSNEURONIX
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com