Patents
Literature
41results about How to "Passage is slowed" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
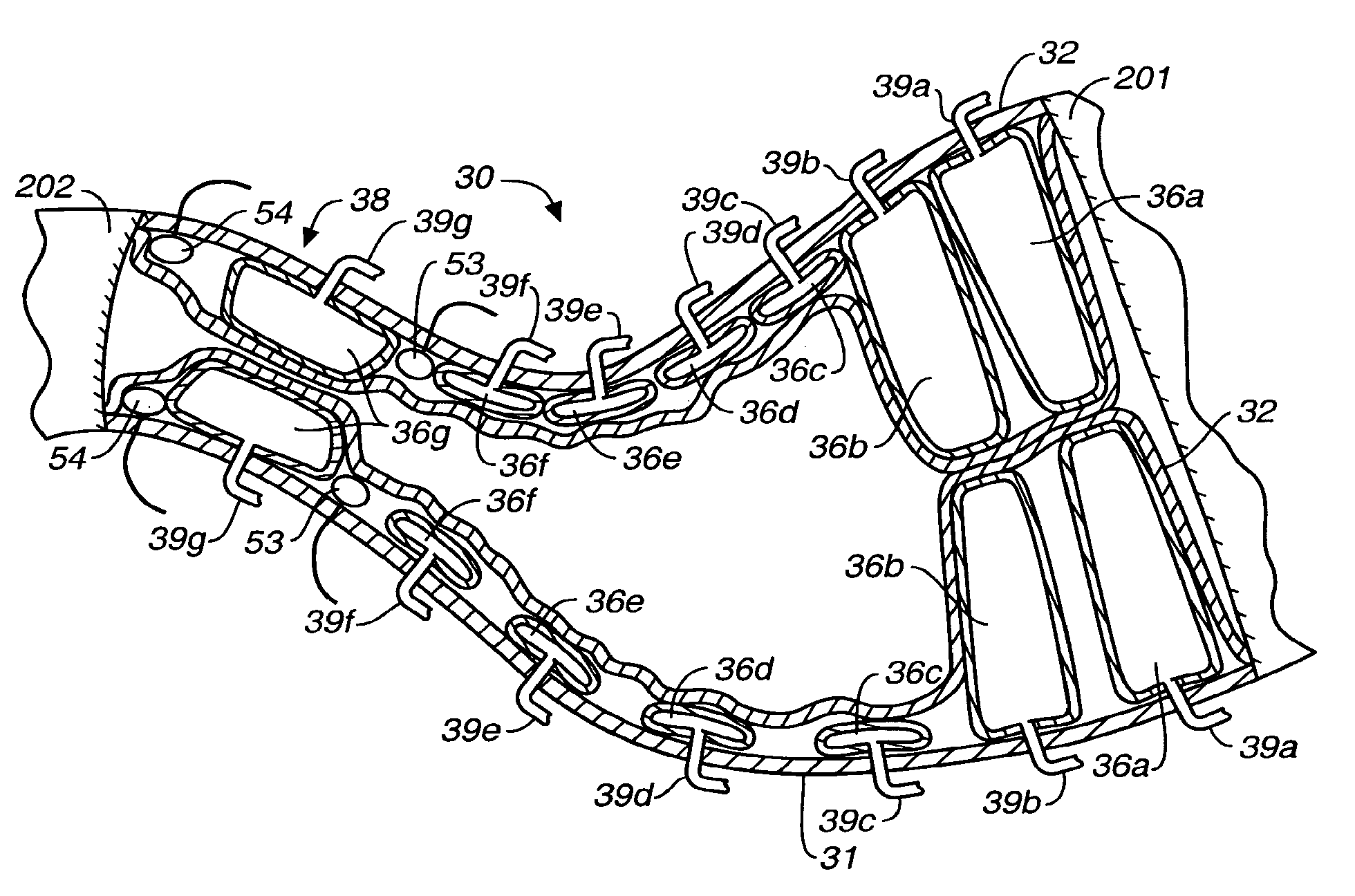
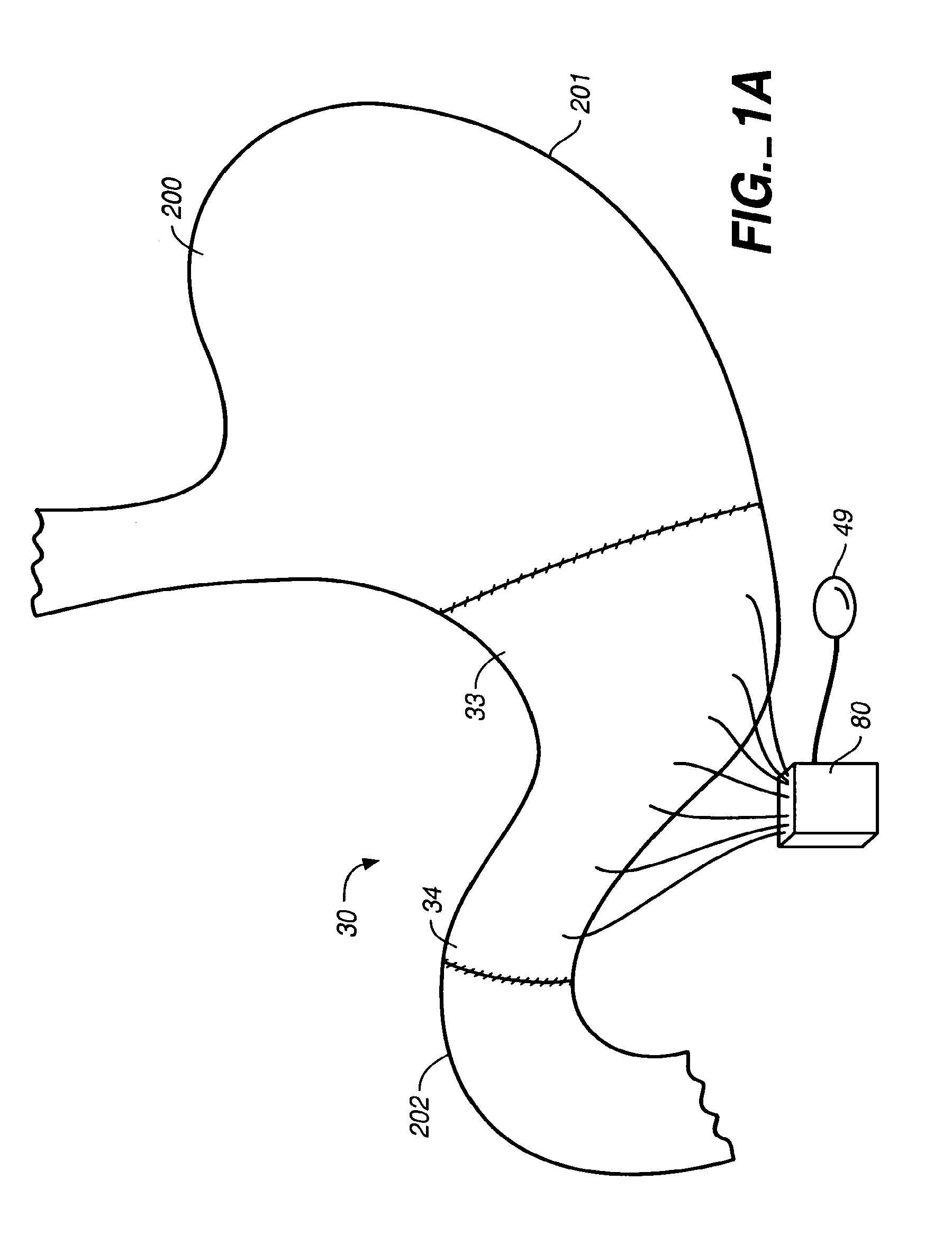
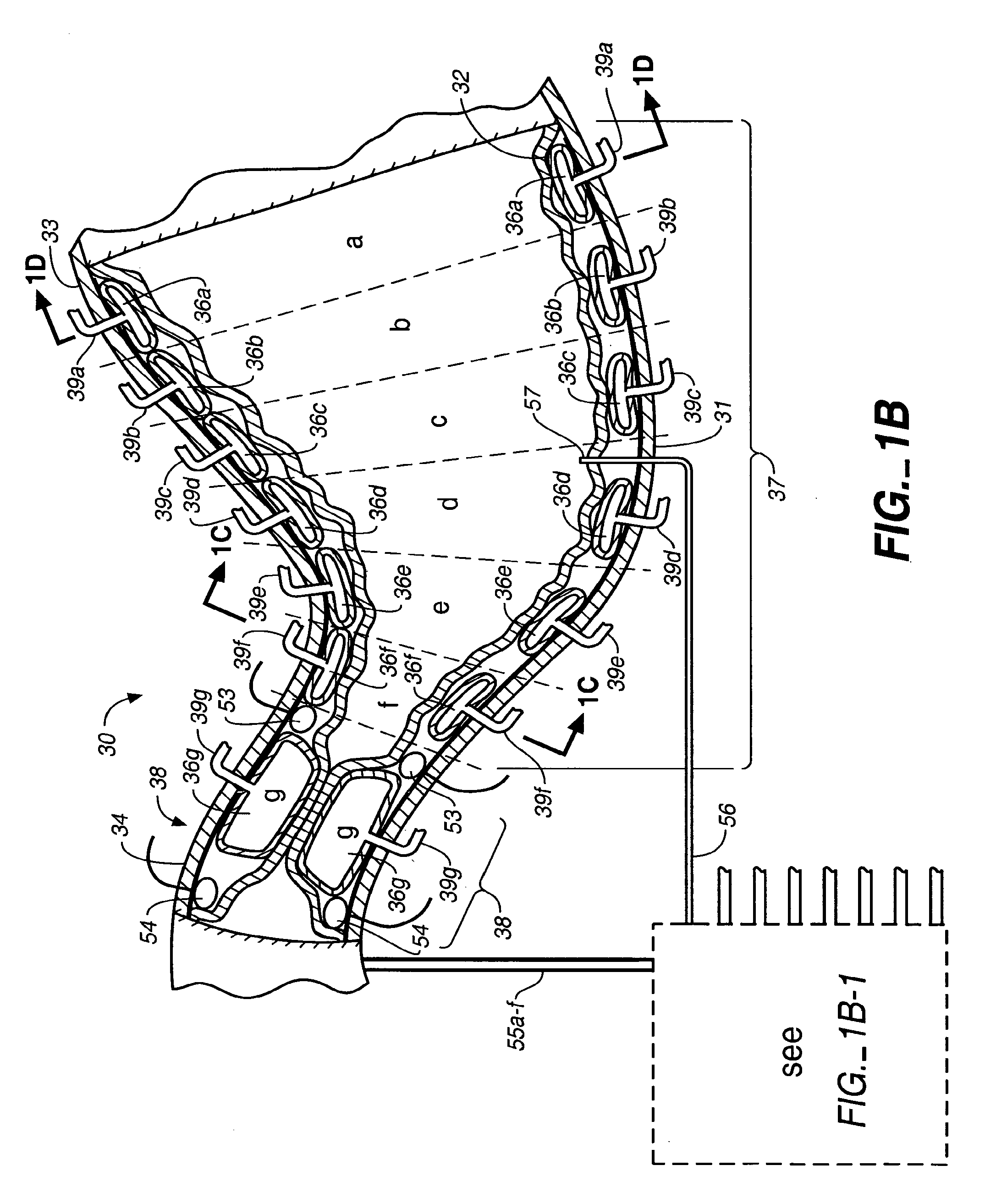
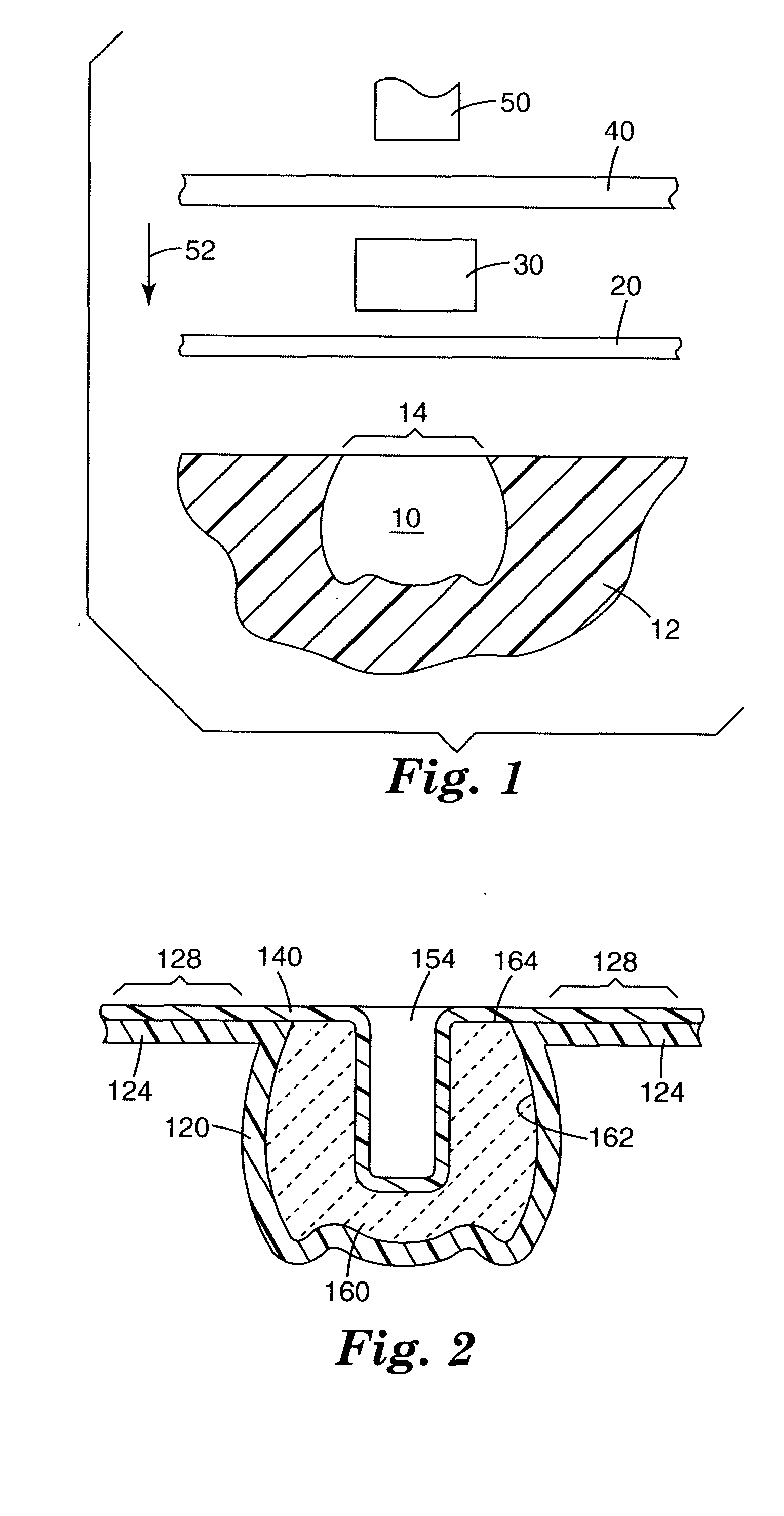
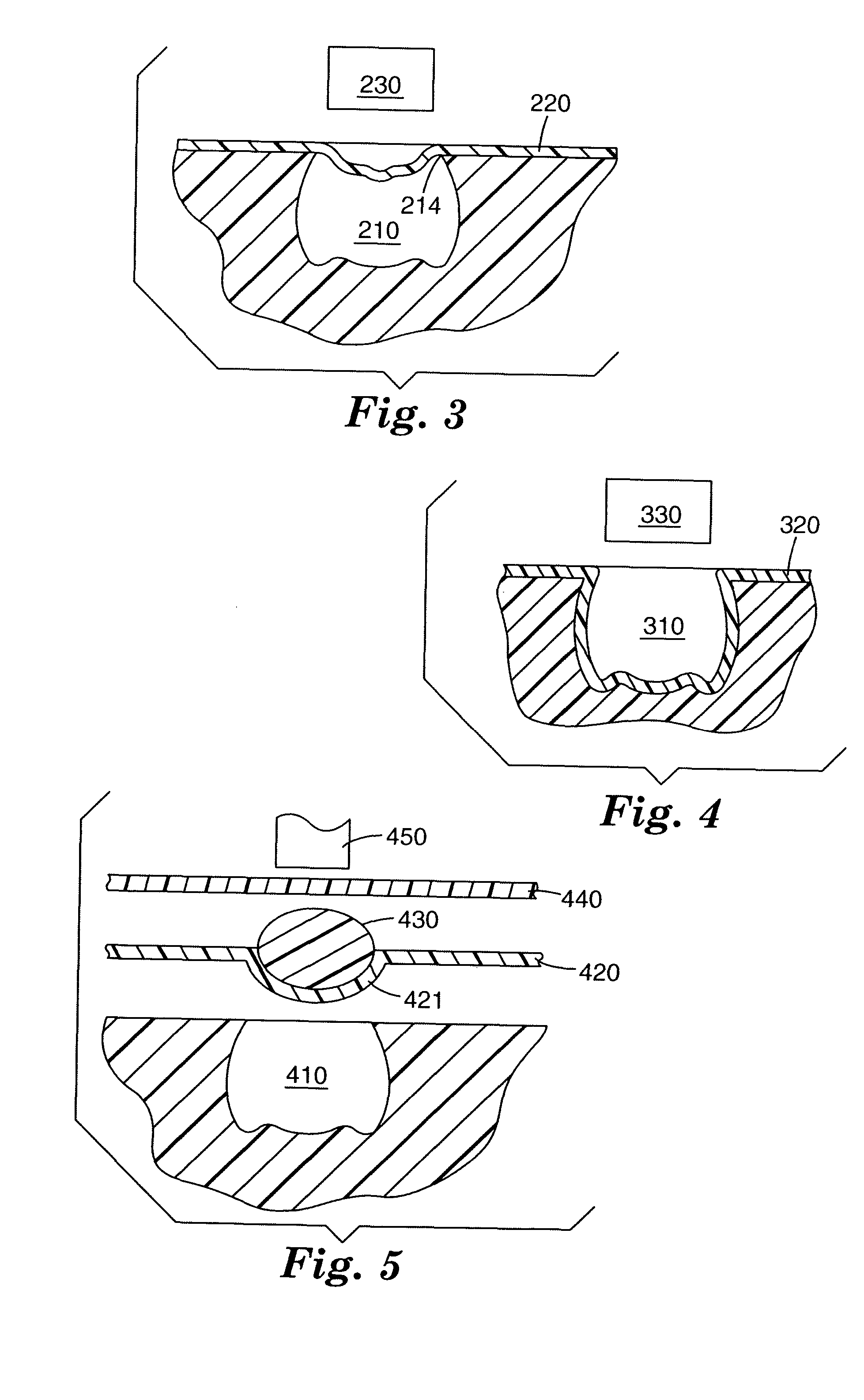
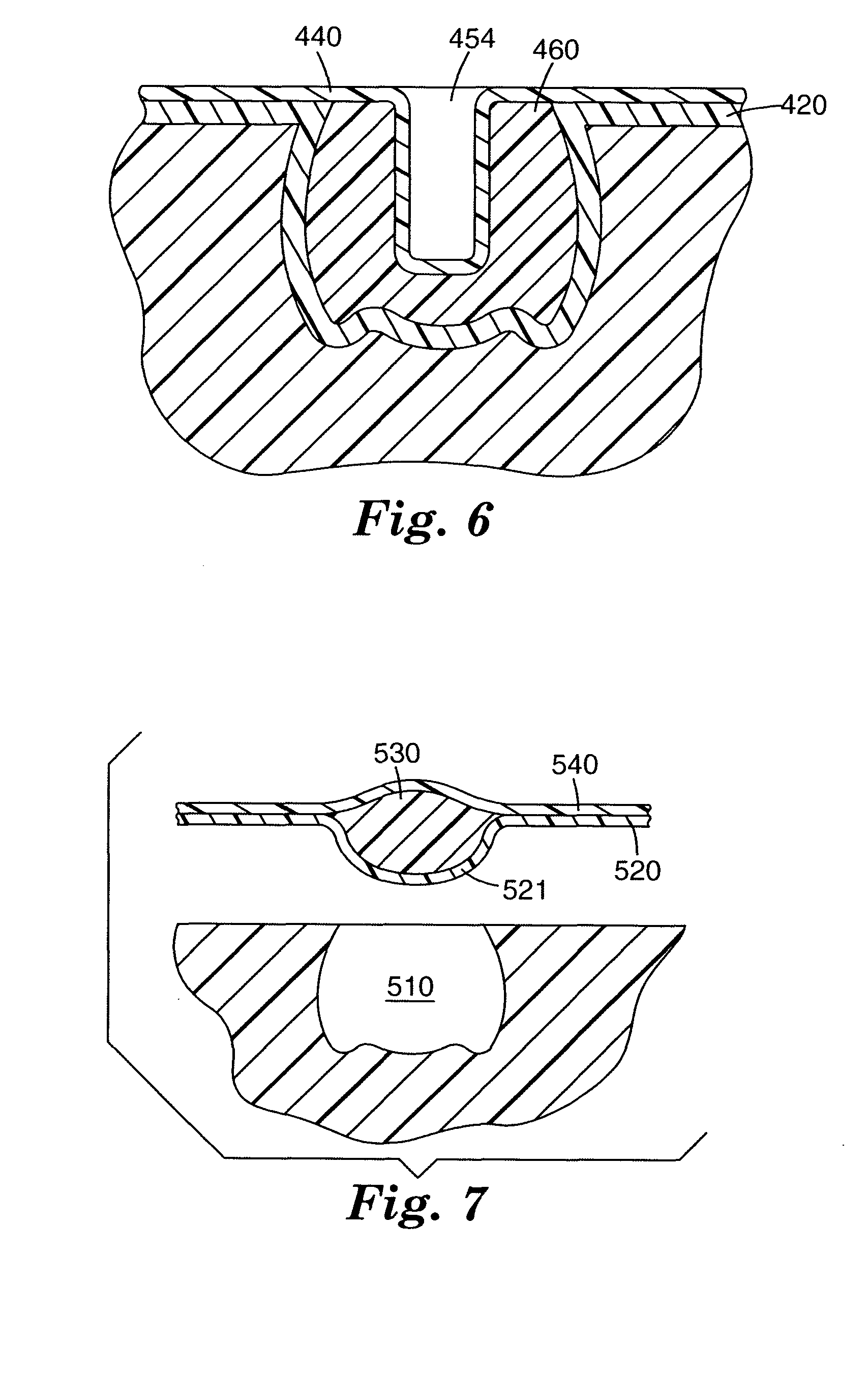
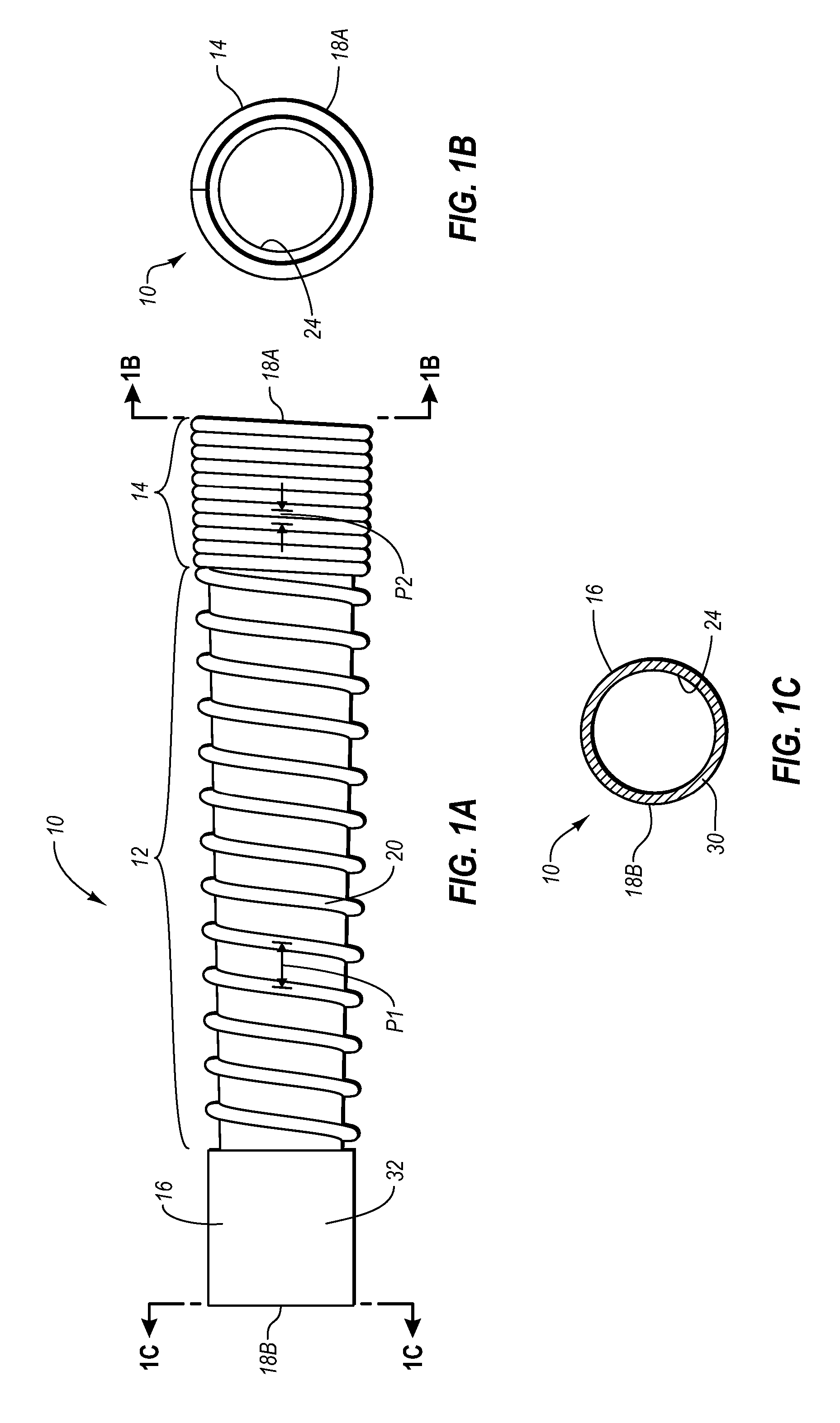
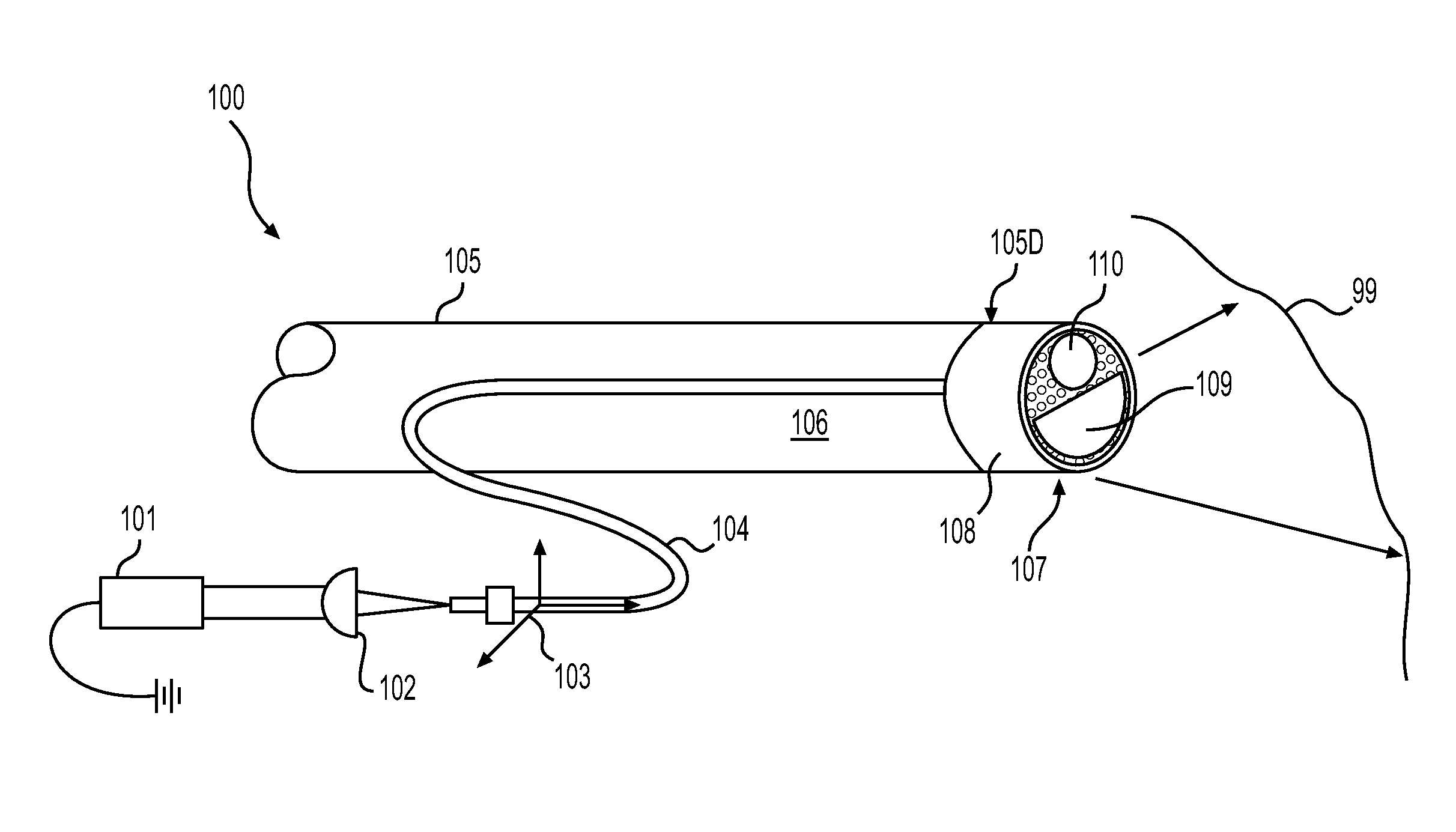
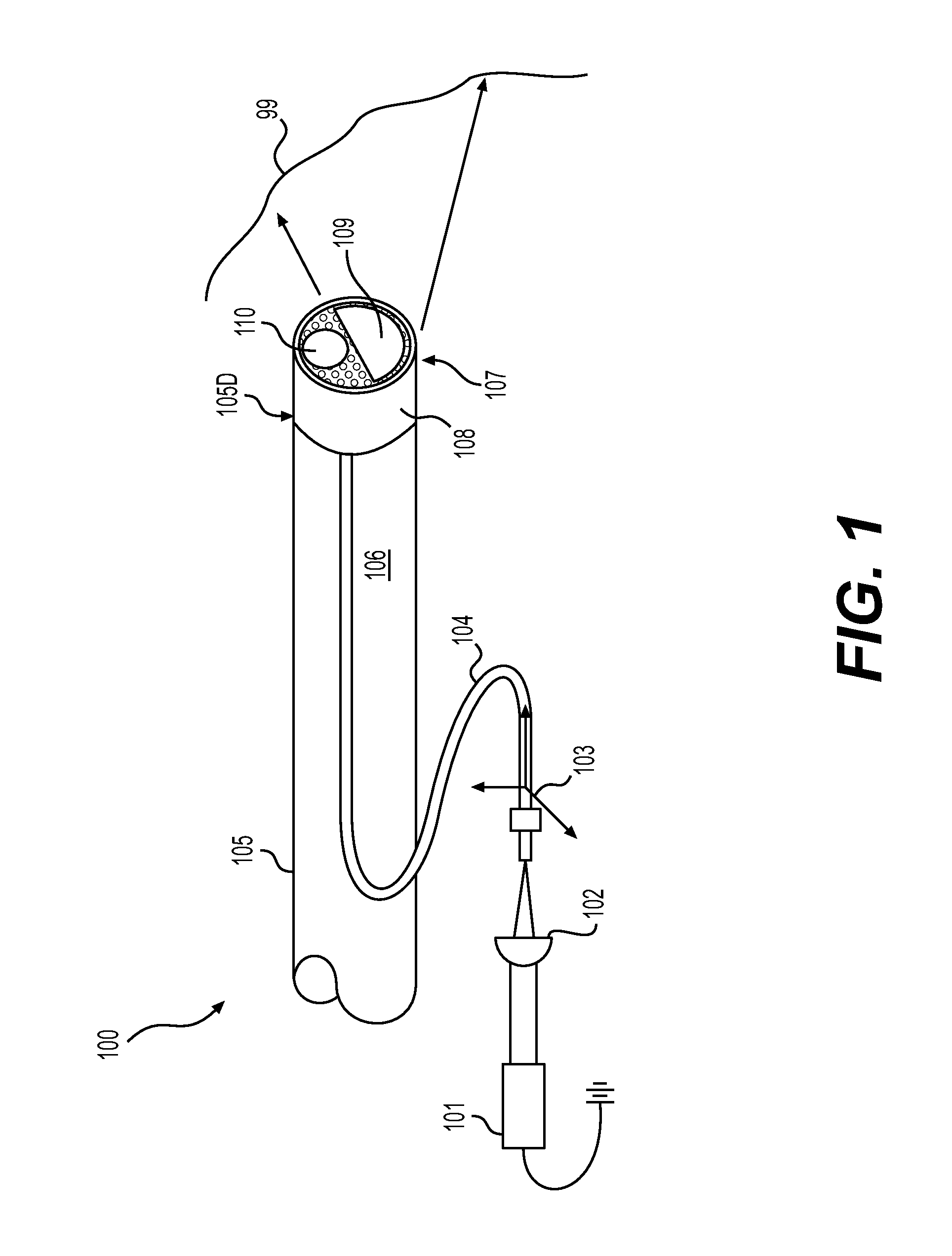
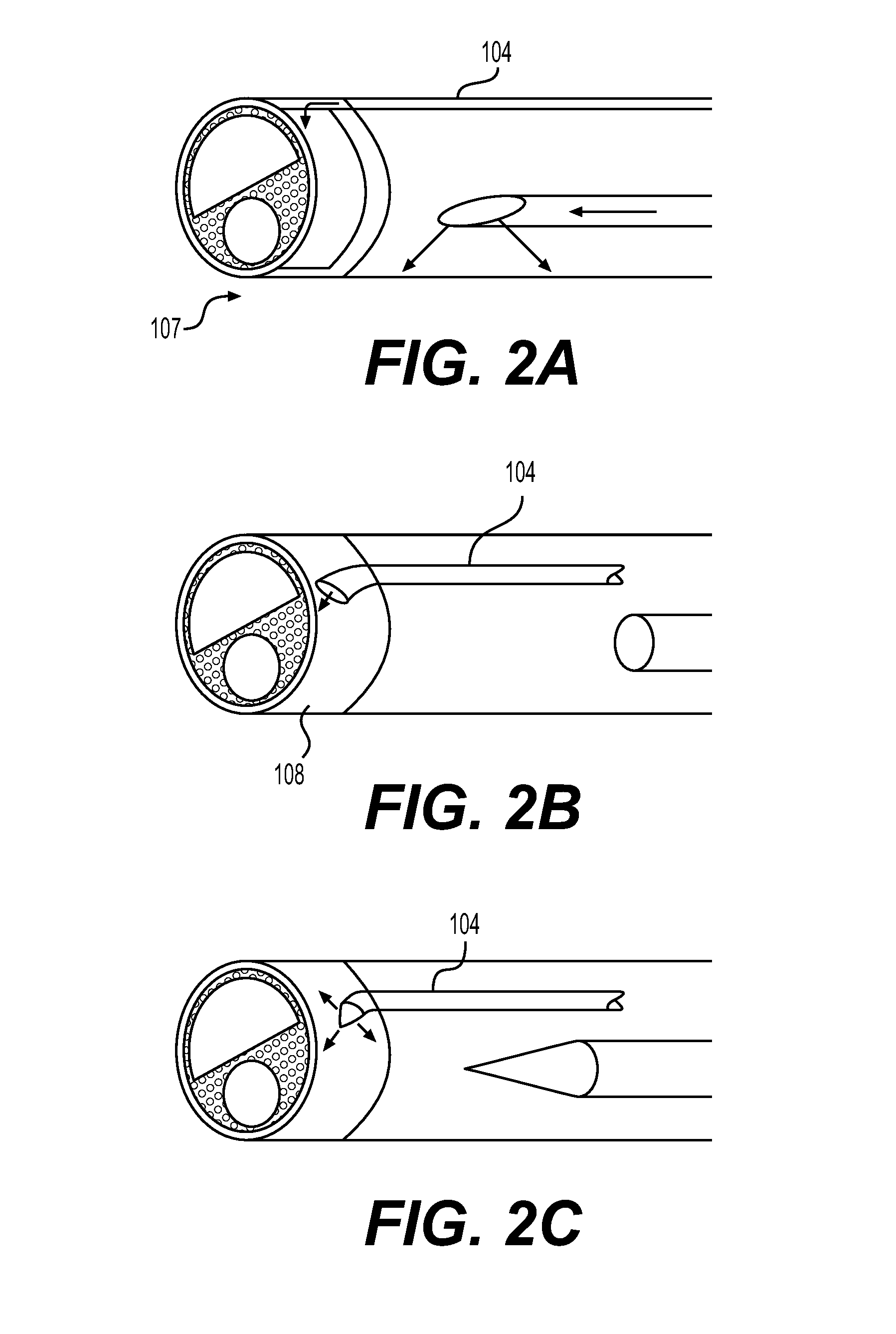
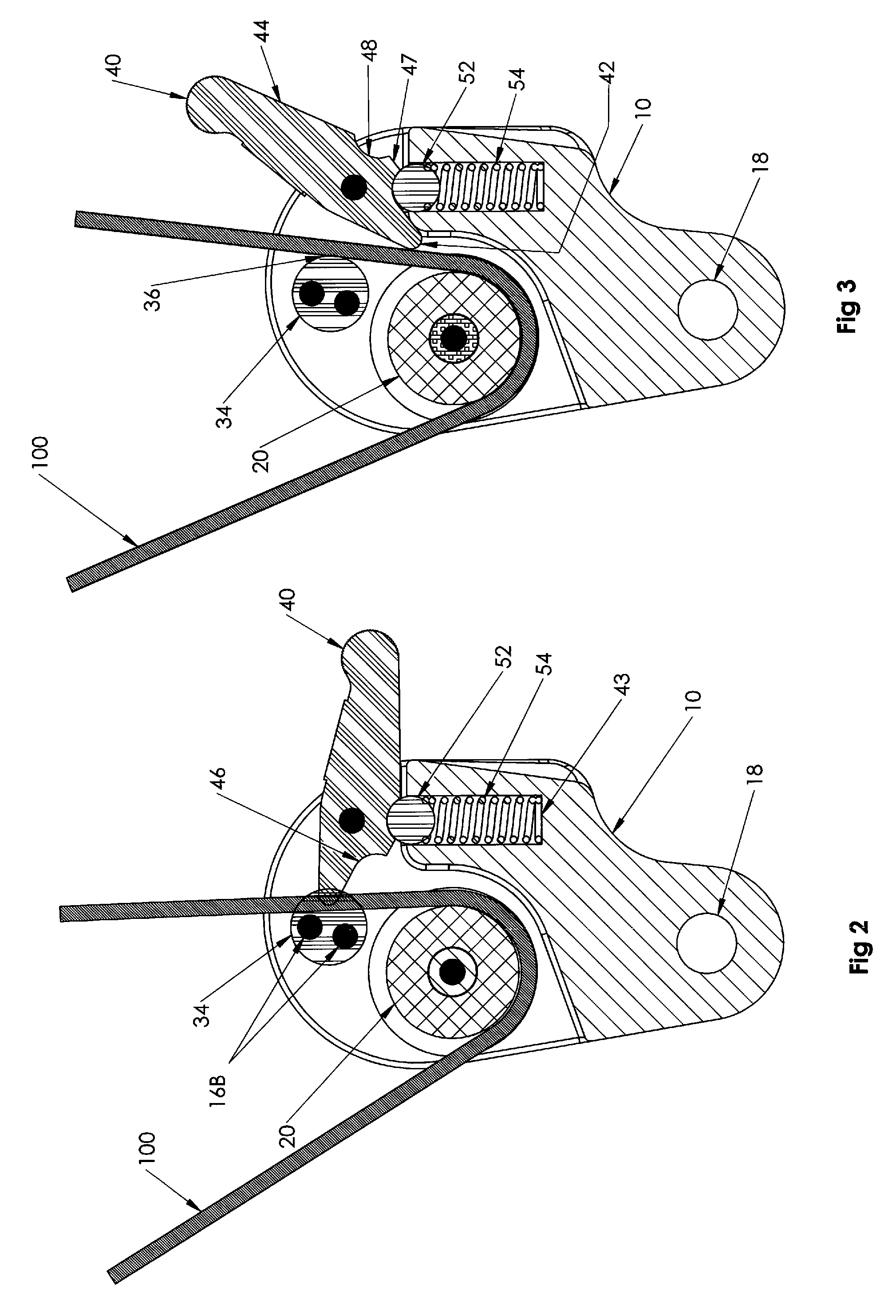
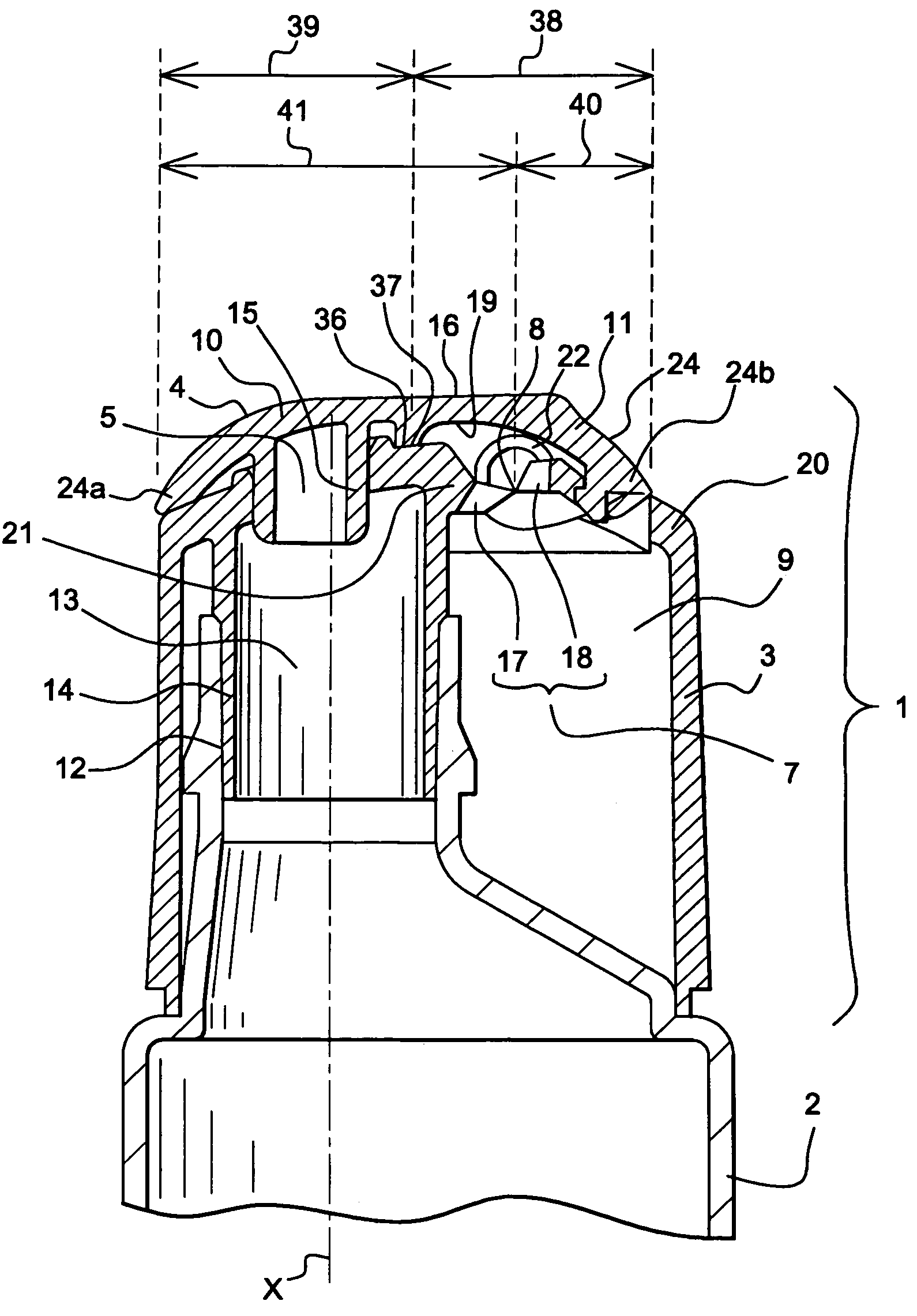
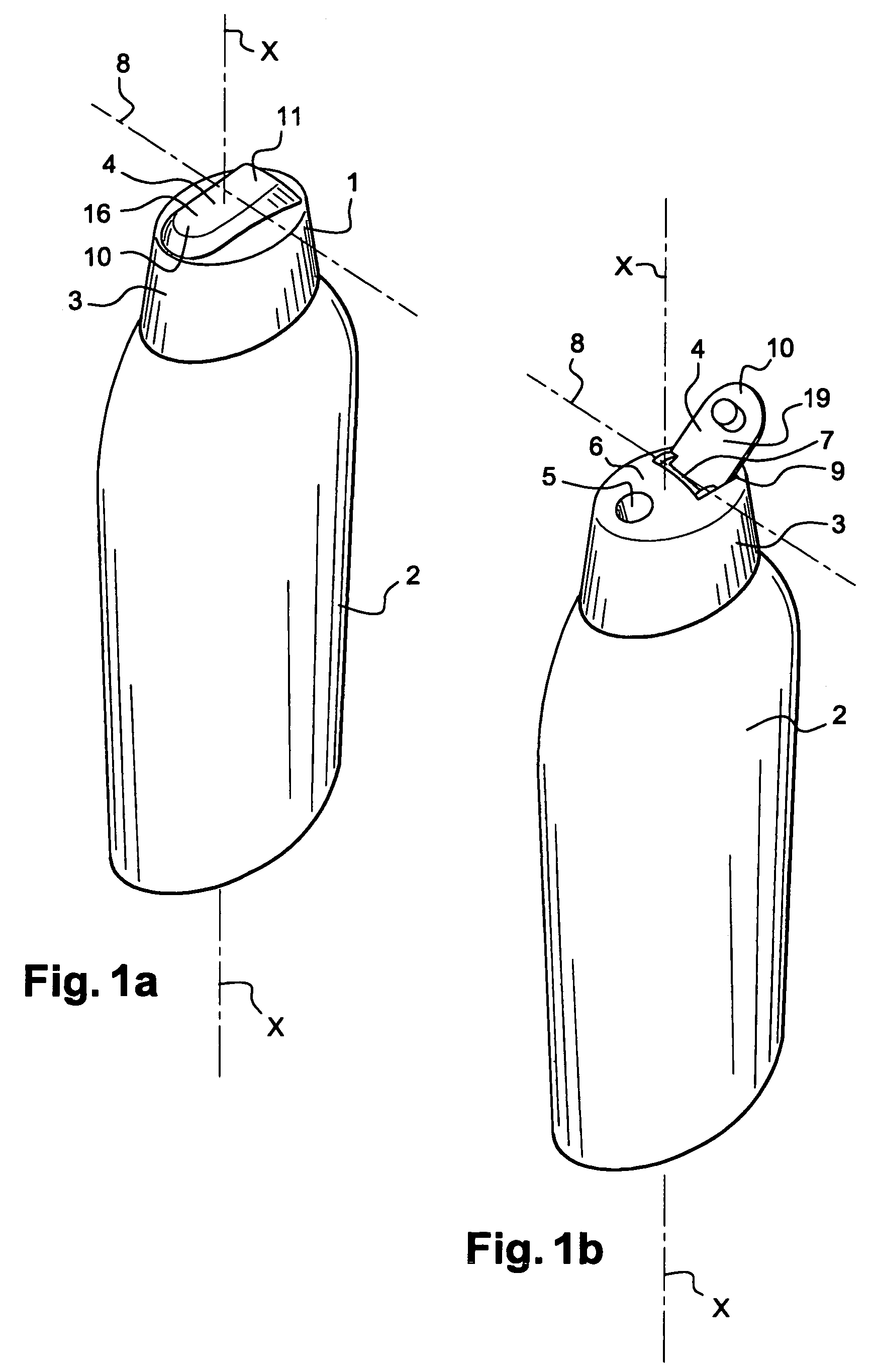
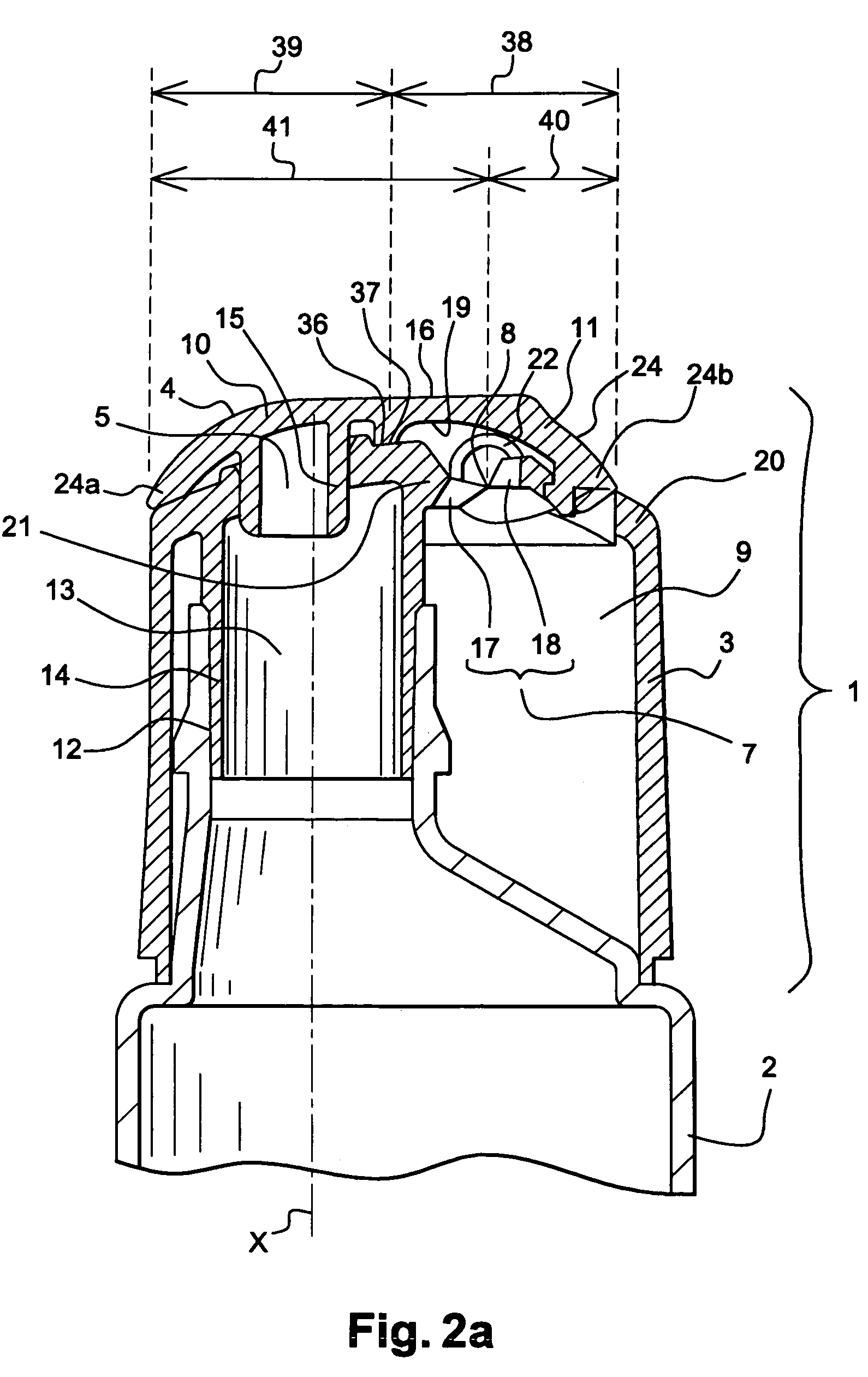
Stomach prosthesis
InactiveUS7037343B2Treating obesityFacilitate expedite mixing breaking downDiagnosticsSurgeryPylorusSmall intestine
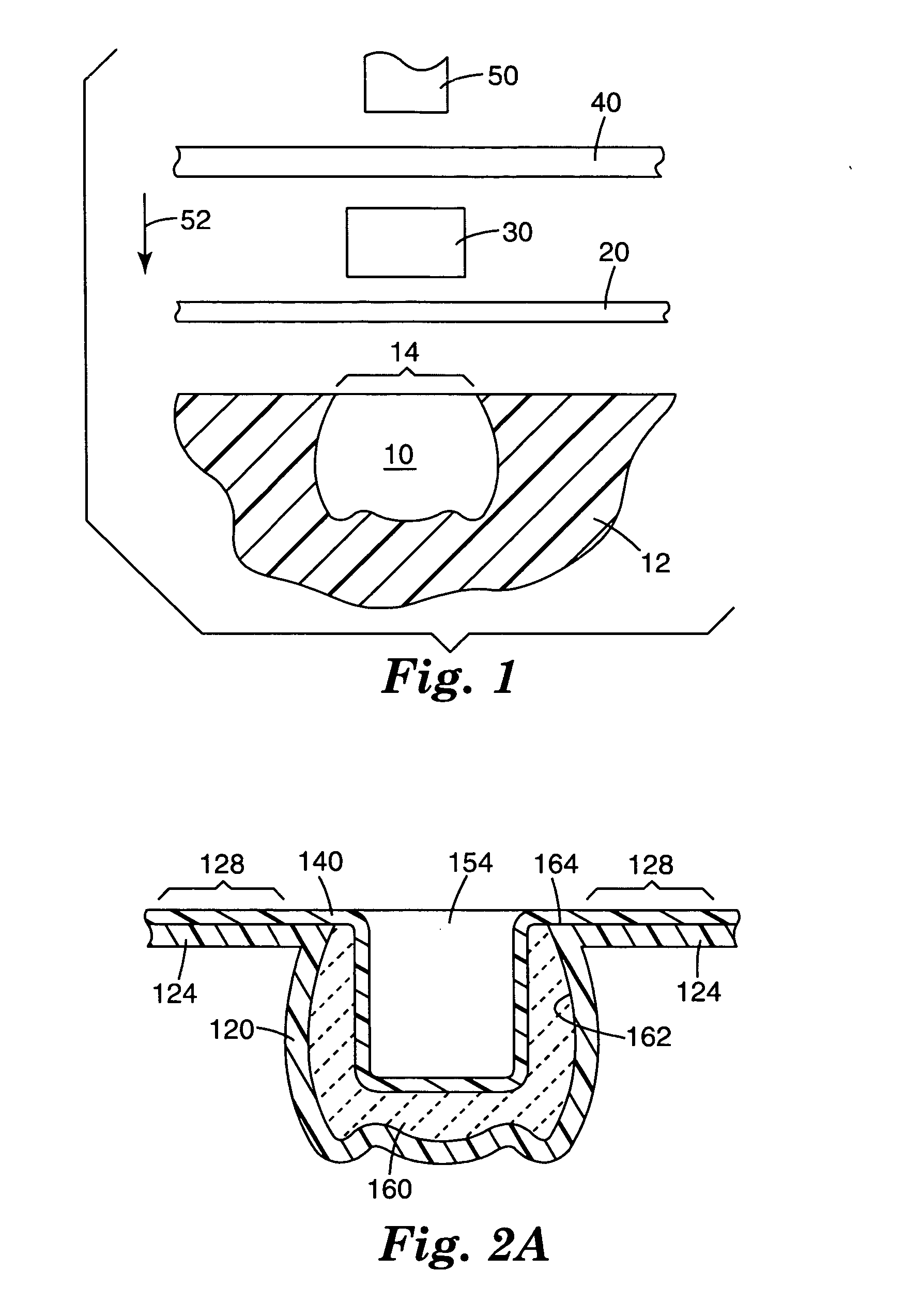
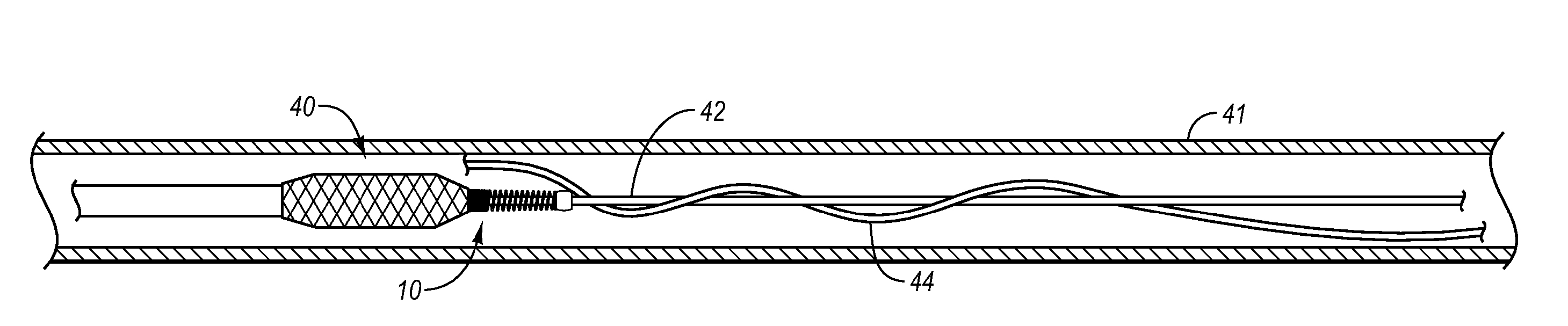
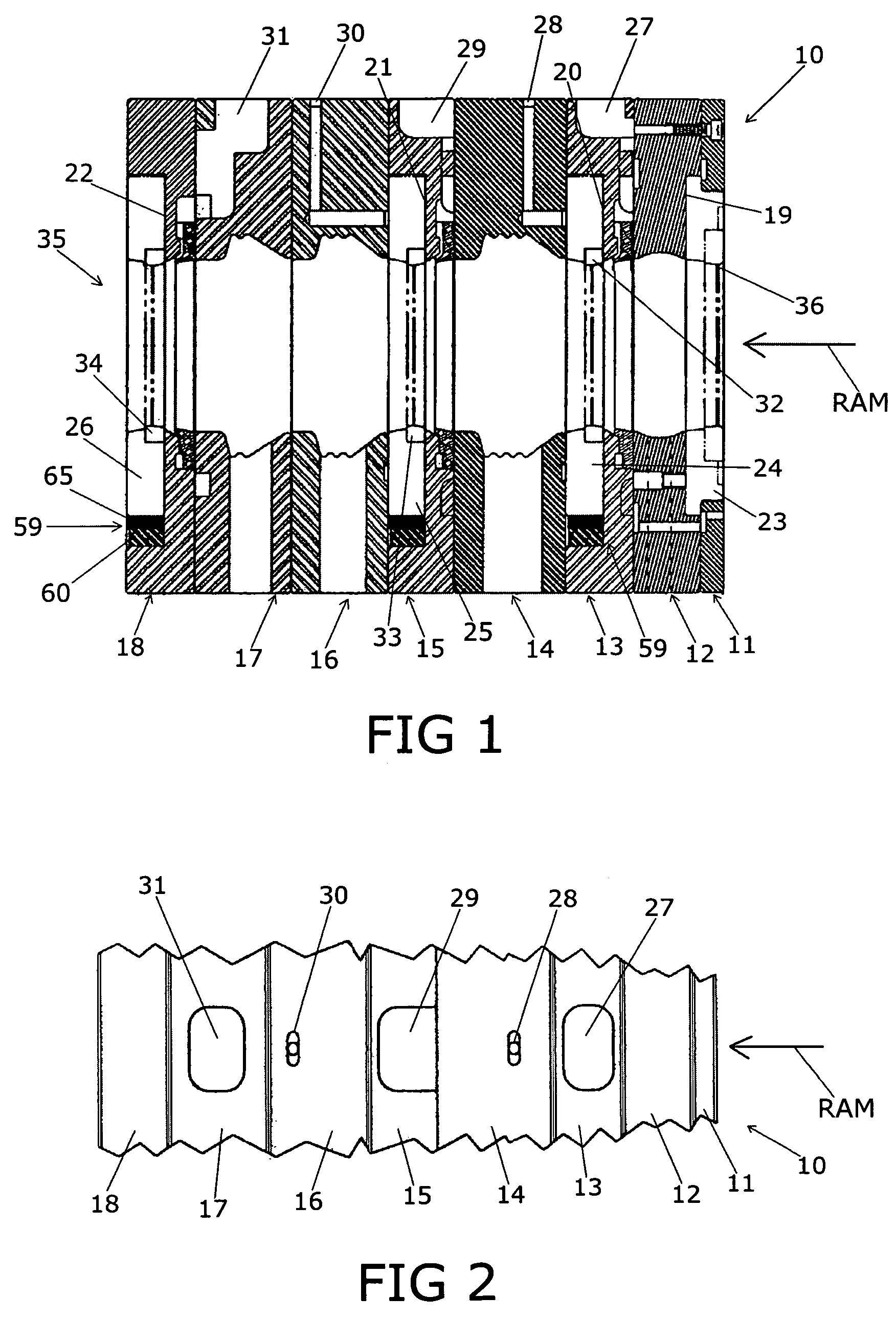
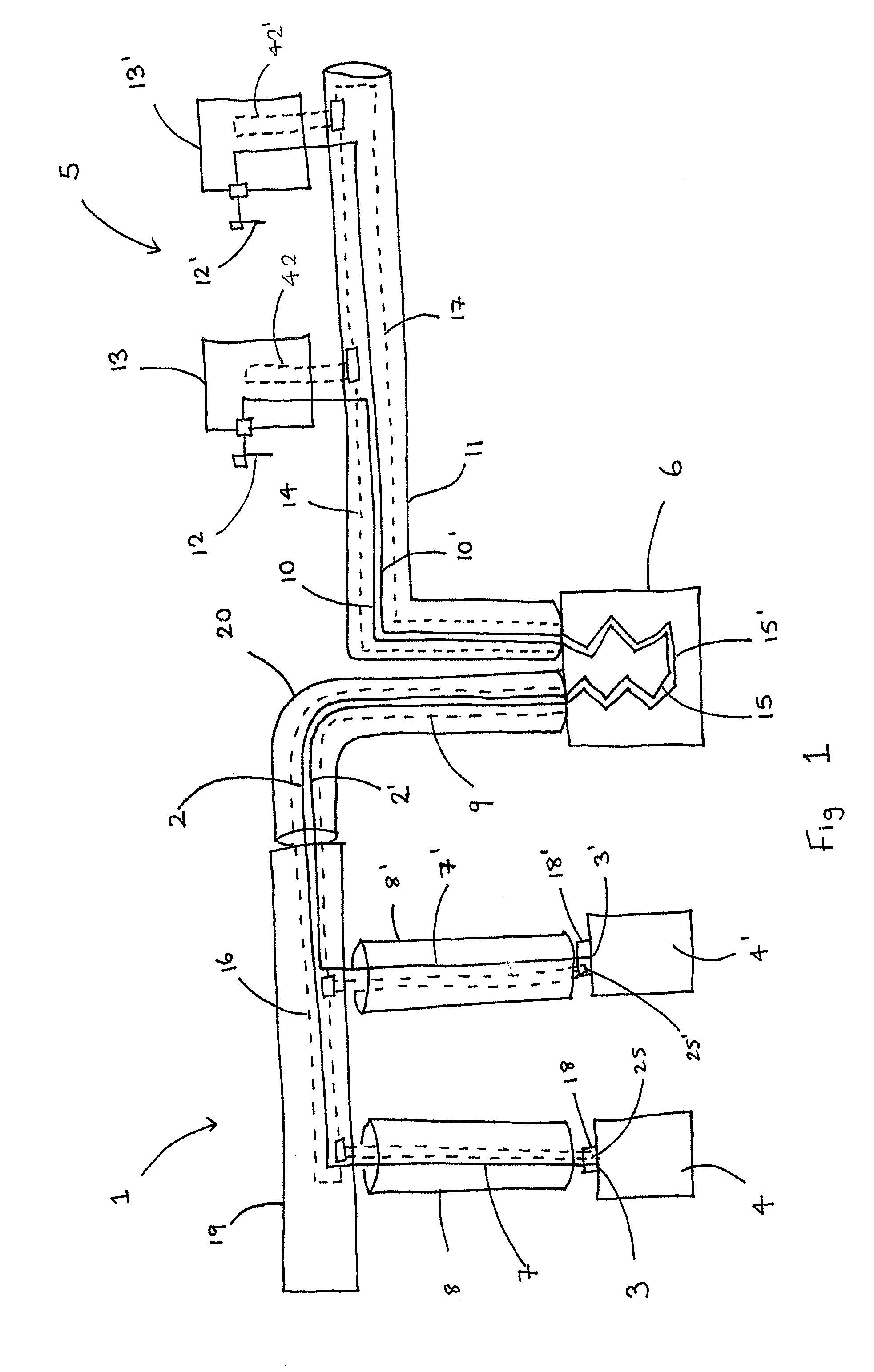
An implantable stomach prosthesis is provided for surgically replacing or augmenting all or part of the antrum and / or pylorus of a stomach. The prosthesis controls the passage of food from the stomach to the small intestine. The prosthesis may be configured to churn ingested material and release it from the stomach through a prosthetic pyloric valve. At least one expandable member is arranged to be expanded to control the passage of food and / or to mimic the churning action of a patient's stomach. The prosthesis includes an outer support structure, a flexible inner member forming a conduit for the movement of material, and at least one expandable member located between the outer support structure and inner member. An implantable pump system is provided for inflating and deflating the expandable member(s).
Owner:PYTHON MEDICAL
Hardenable dental article and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20050040551A1Improve the finishEnhancing the finish of the dental articleTooth crownsArtificial teethMaterials science
Methods of manufacturing hardenable dental articles, packaged hardenable dental articles, and methods of packaging hardenable dental articles are disclosed. In various embodiments, the manufacturing may involve molding a hardenable dental material in a mold cavity that may be lined with a mold liner. The mold body may also form the package of the hardenable dental article formed within the mold cavity. In other embodiments, the hardenable dental articles may be provided in mold cavities located in sacrificial mold bodies that may be torn, stretched, softened, dissolved, etc. to release the hardenable dental articles in the mold cavities.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
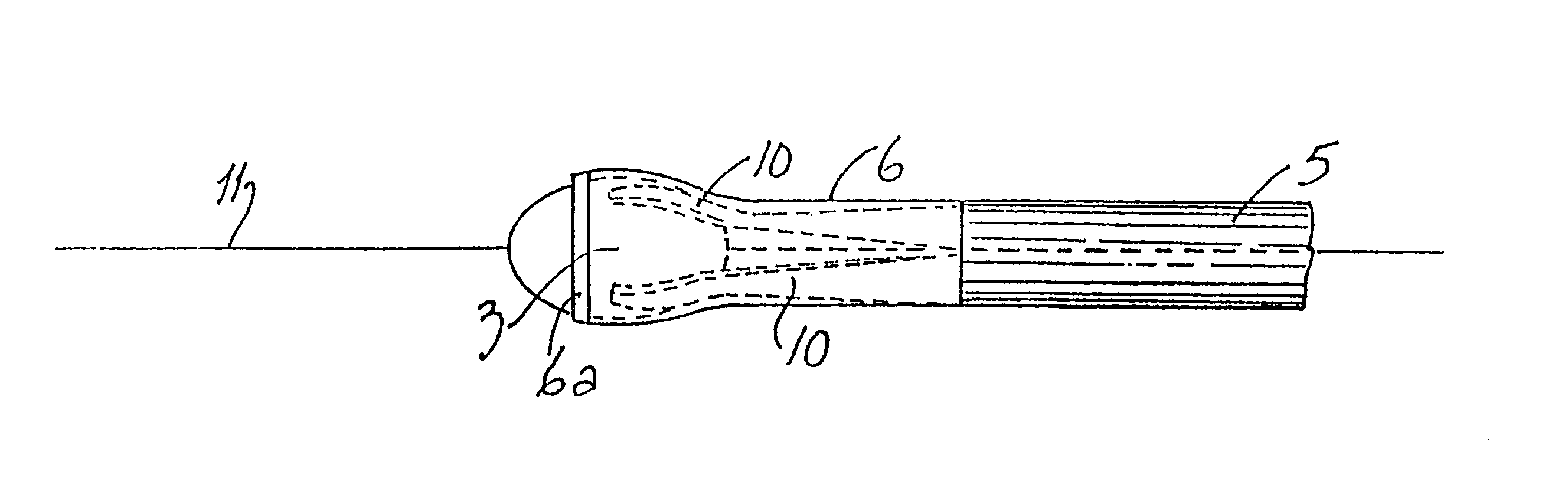
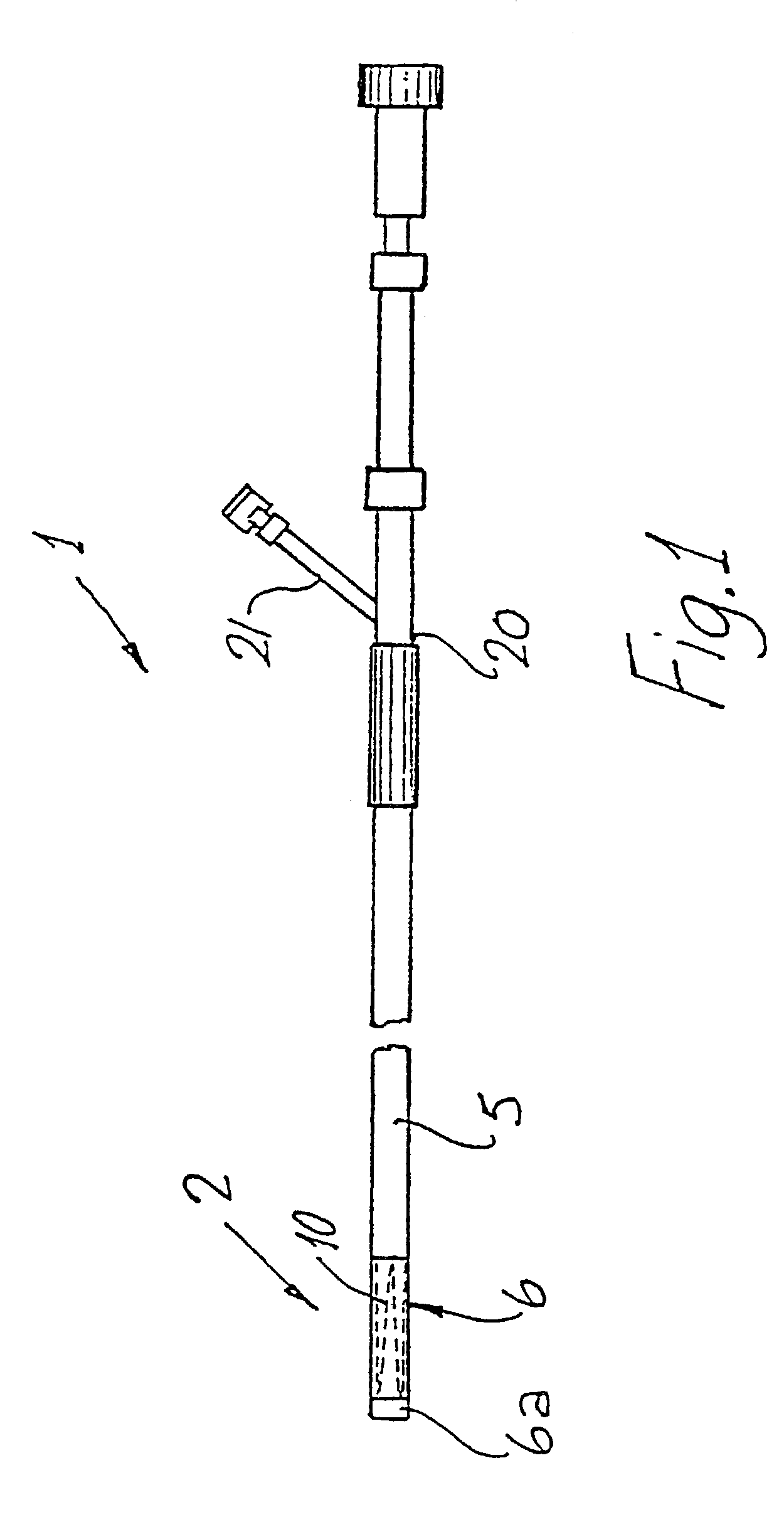
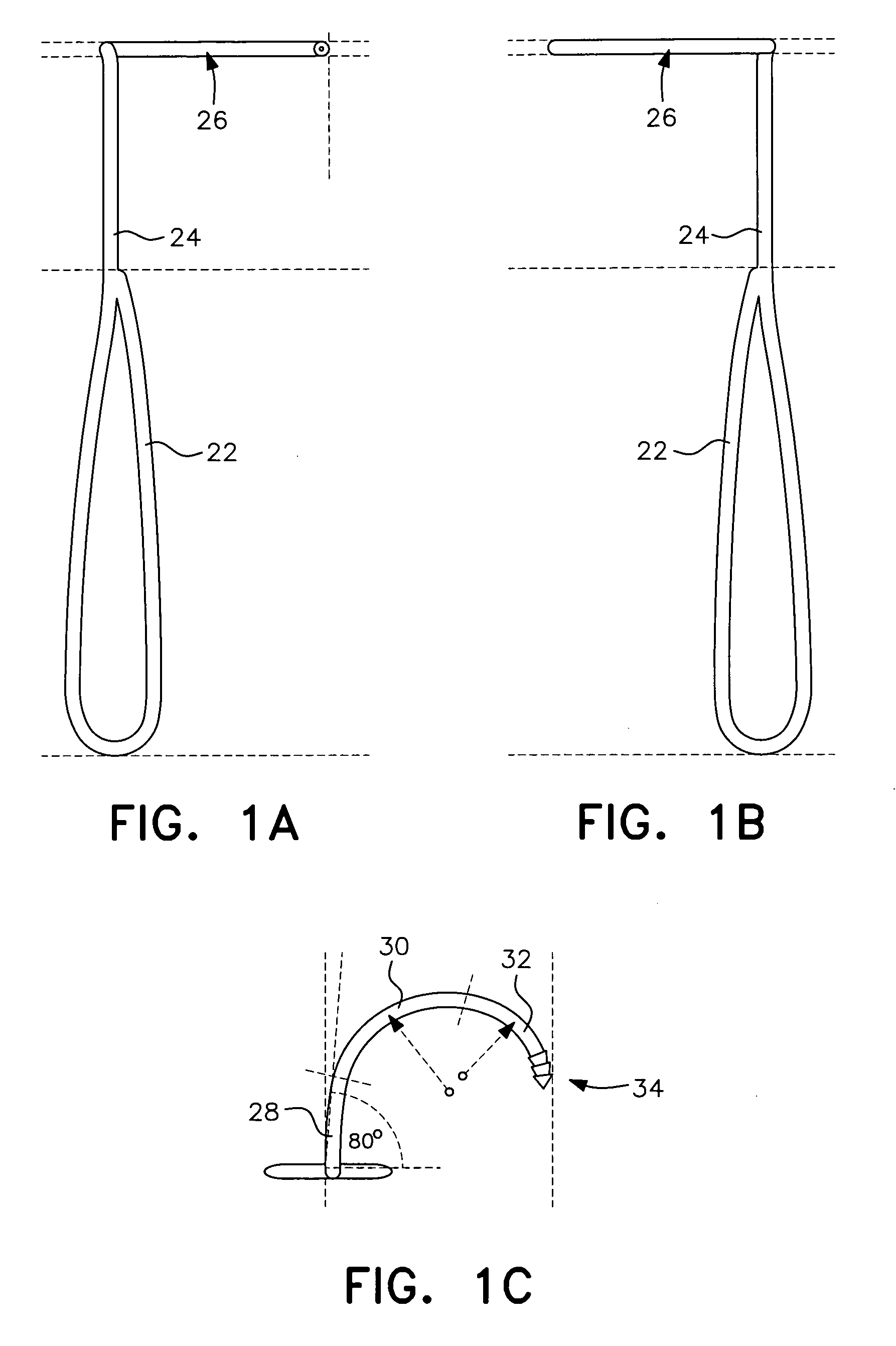
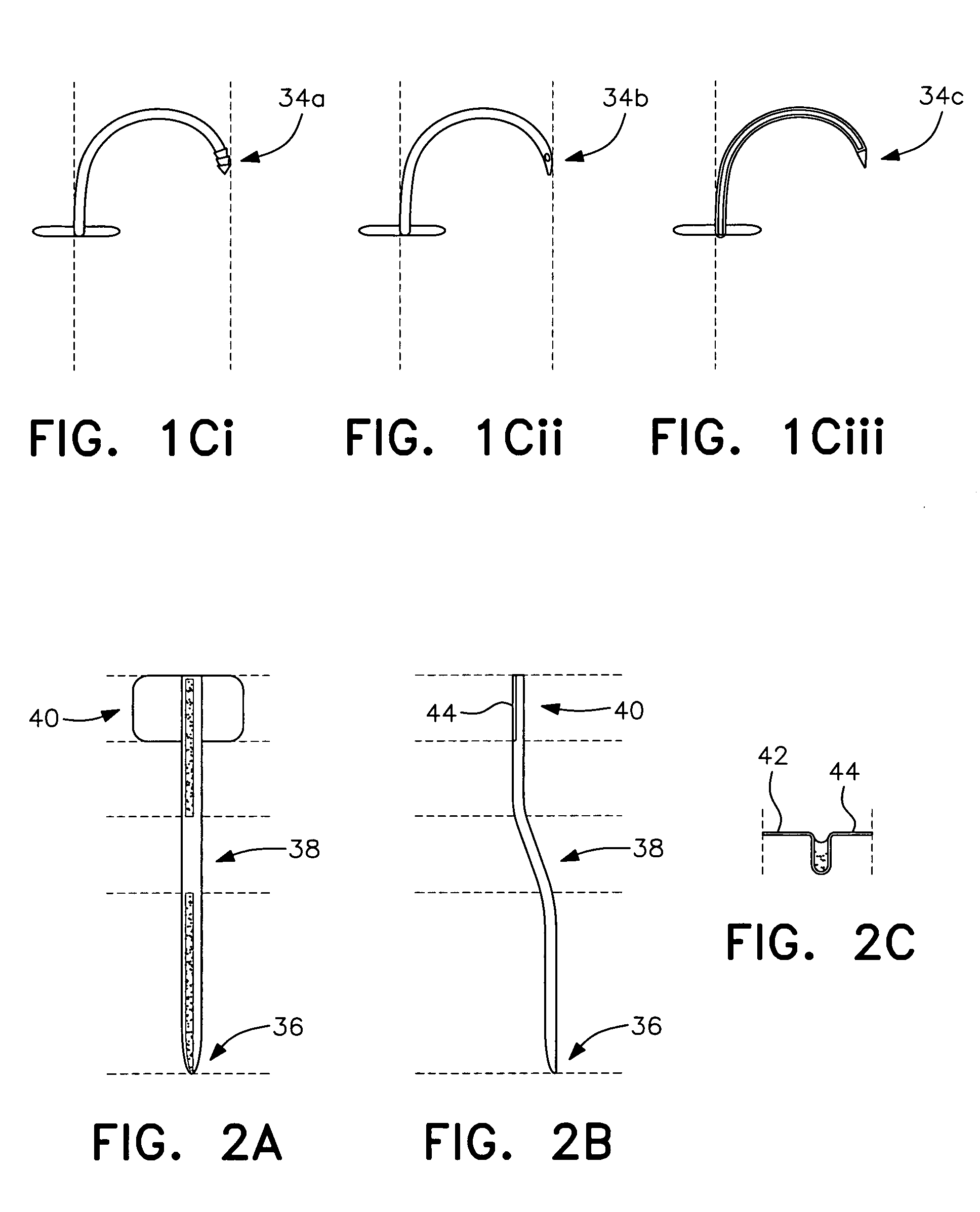
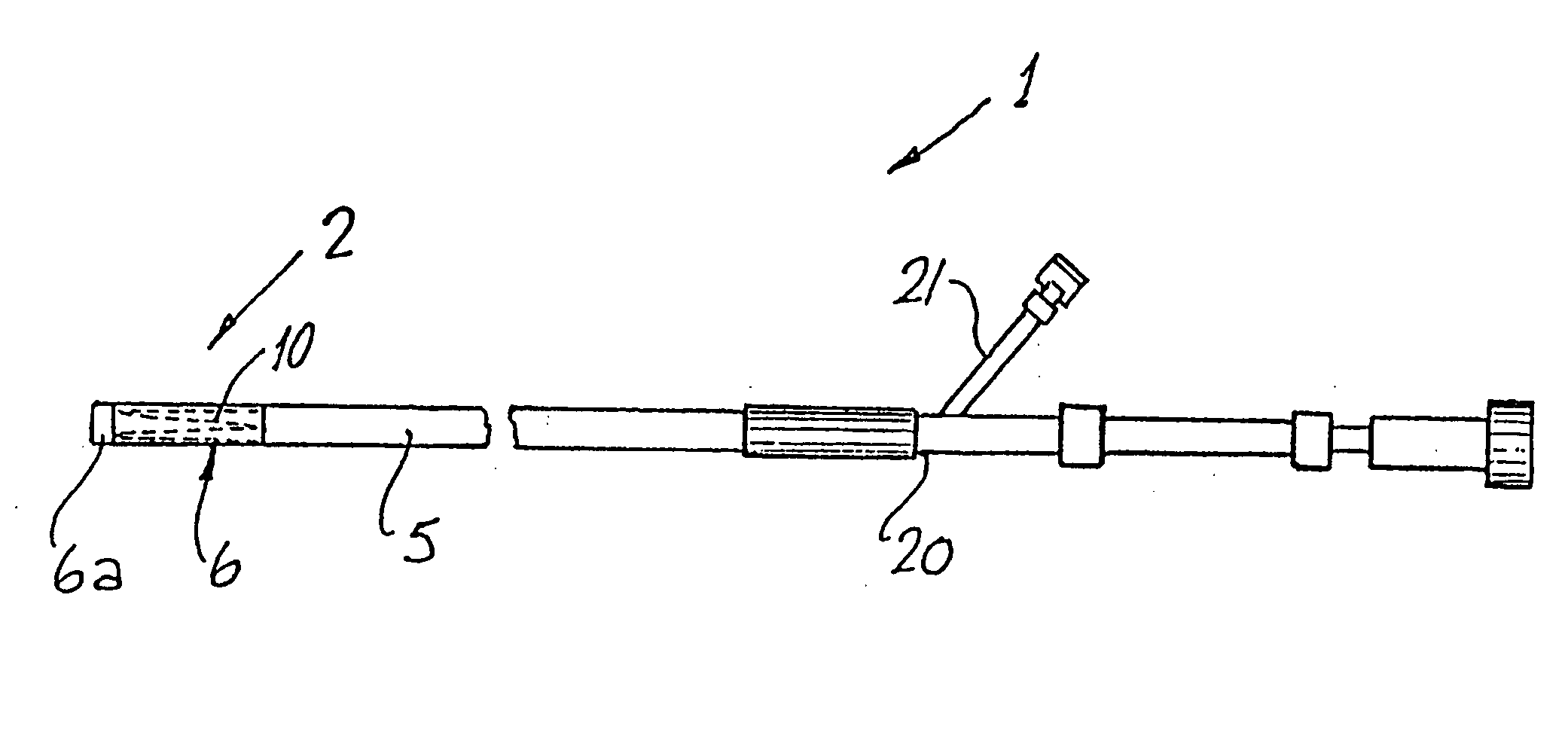
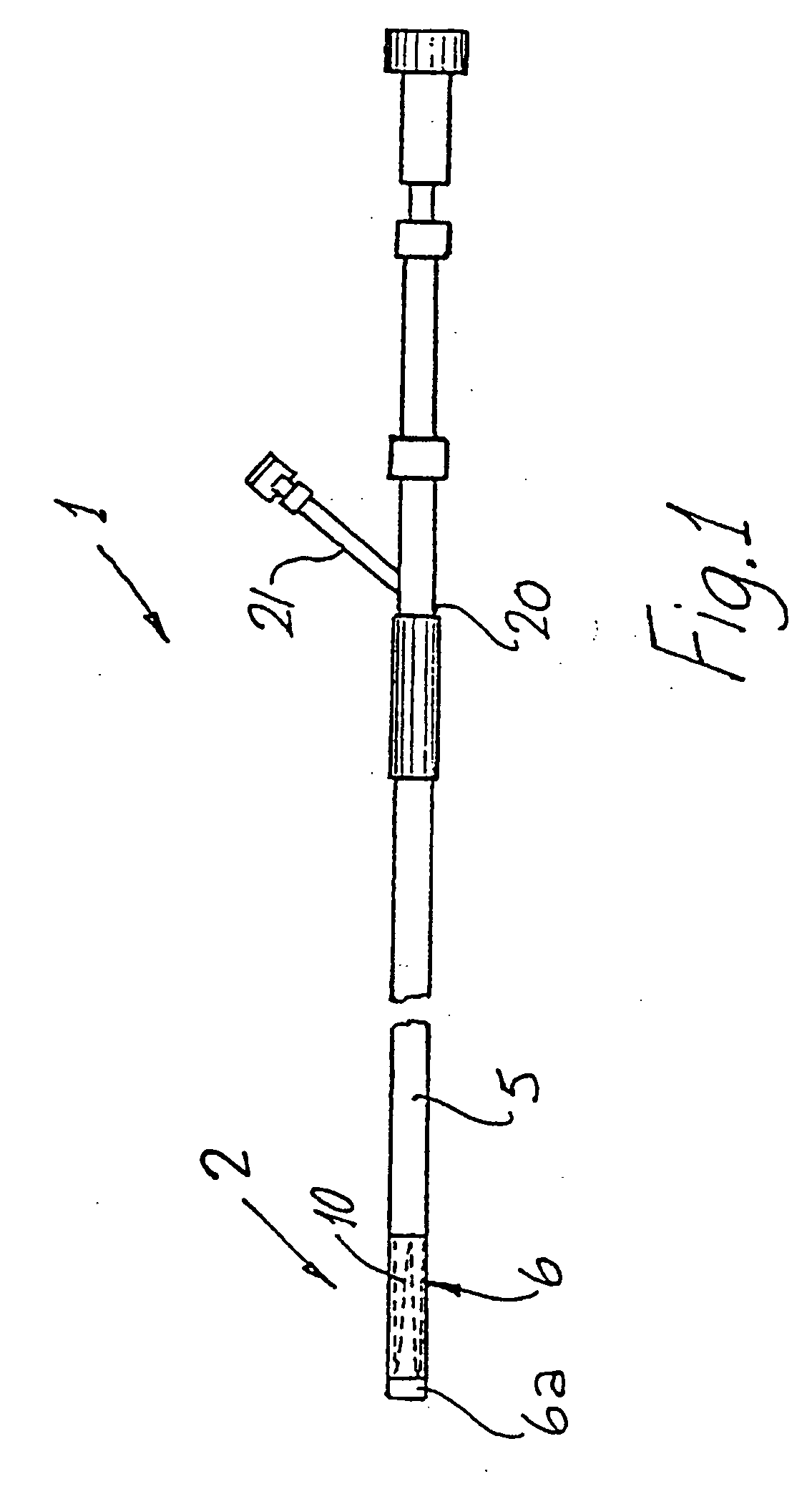
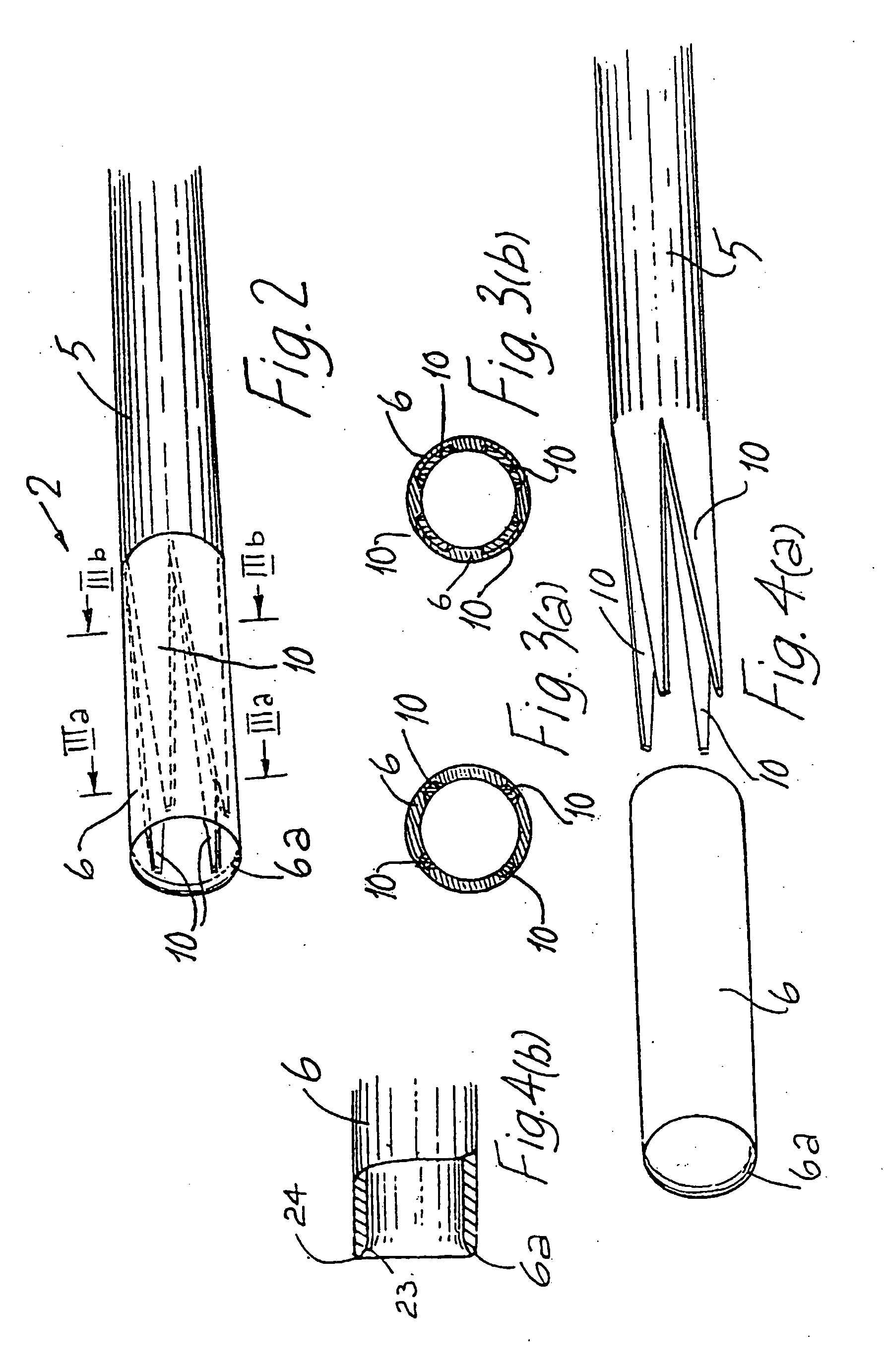
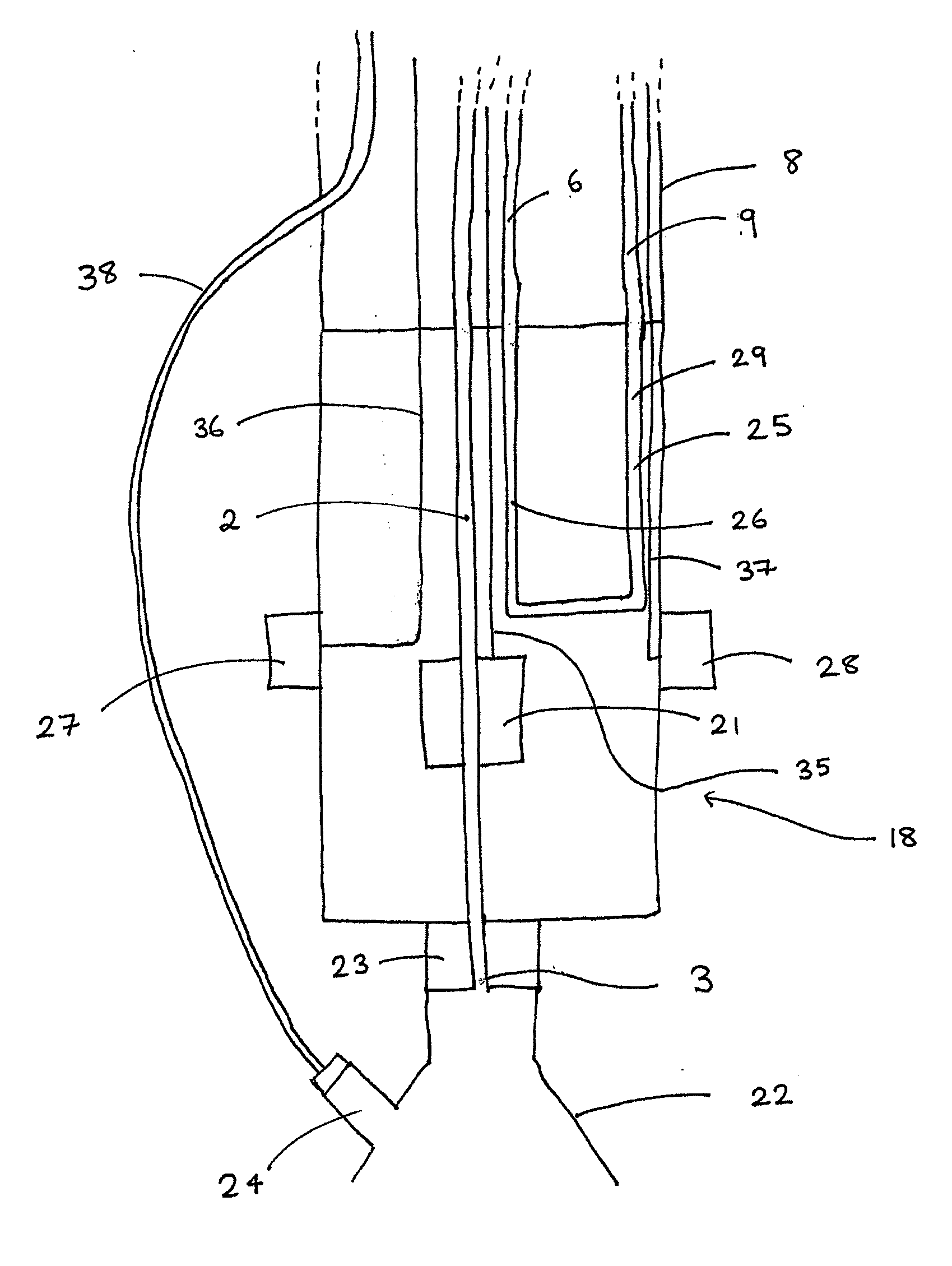
Catheter with an expandable end portion
InactiveUS7094243B2Improve axial strengthImprove scalabilityStentsEar treatmentMedical deviceBiomedical engineering
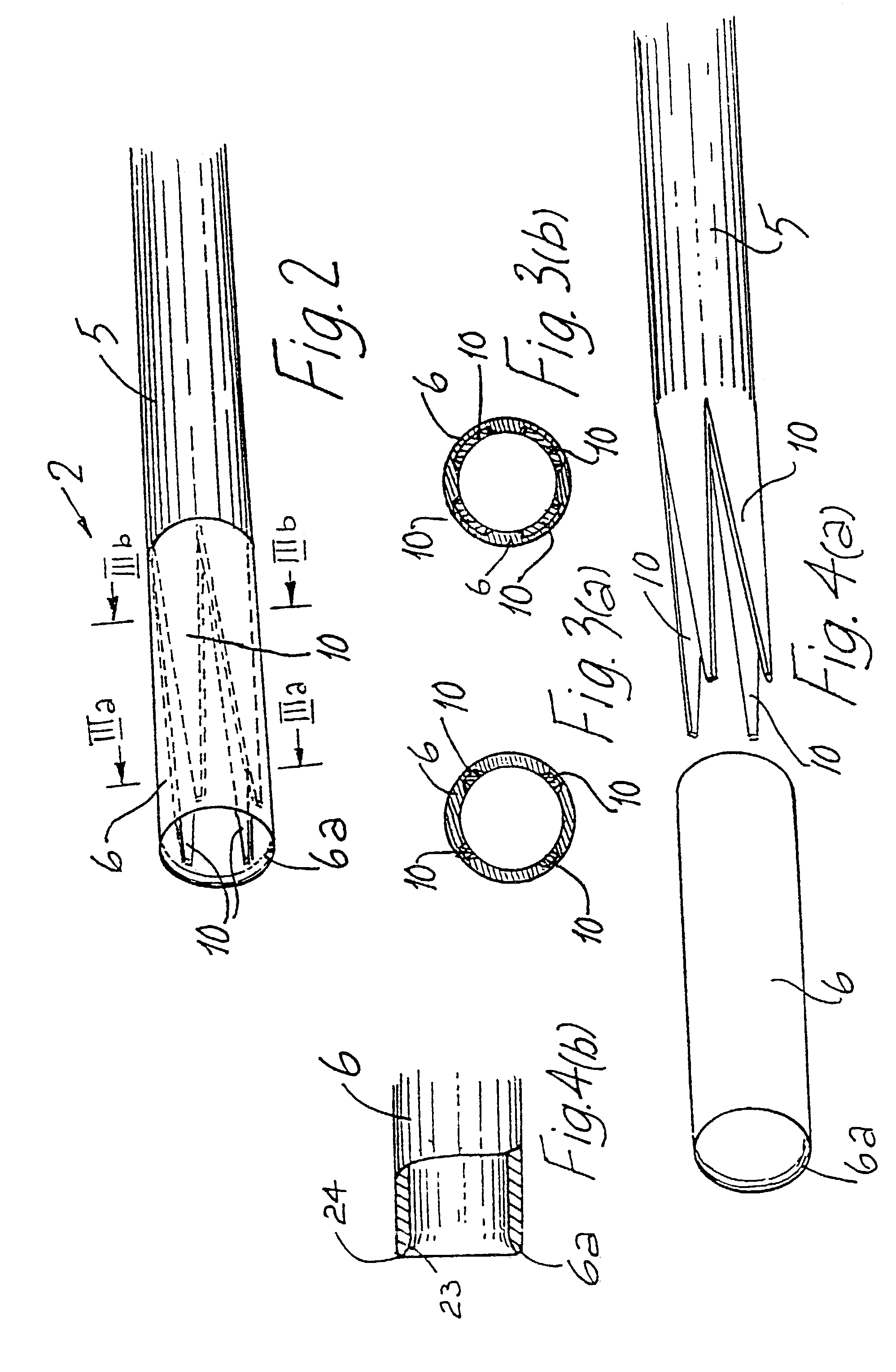
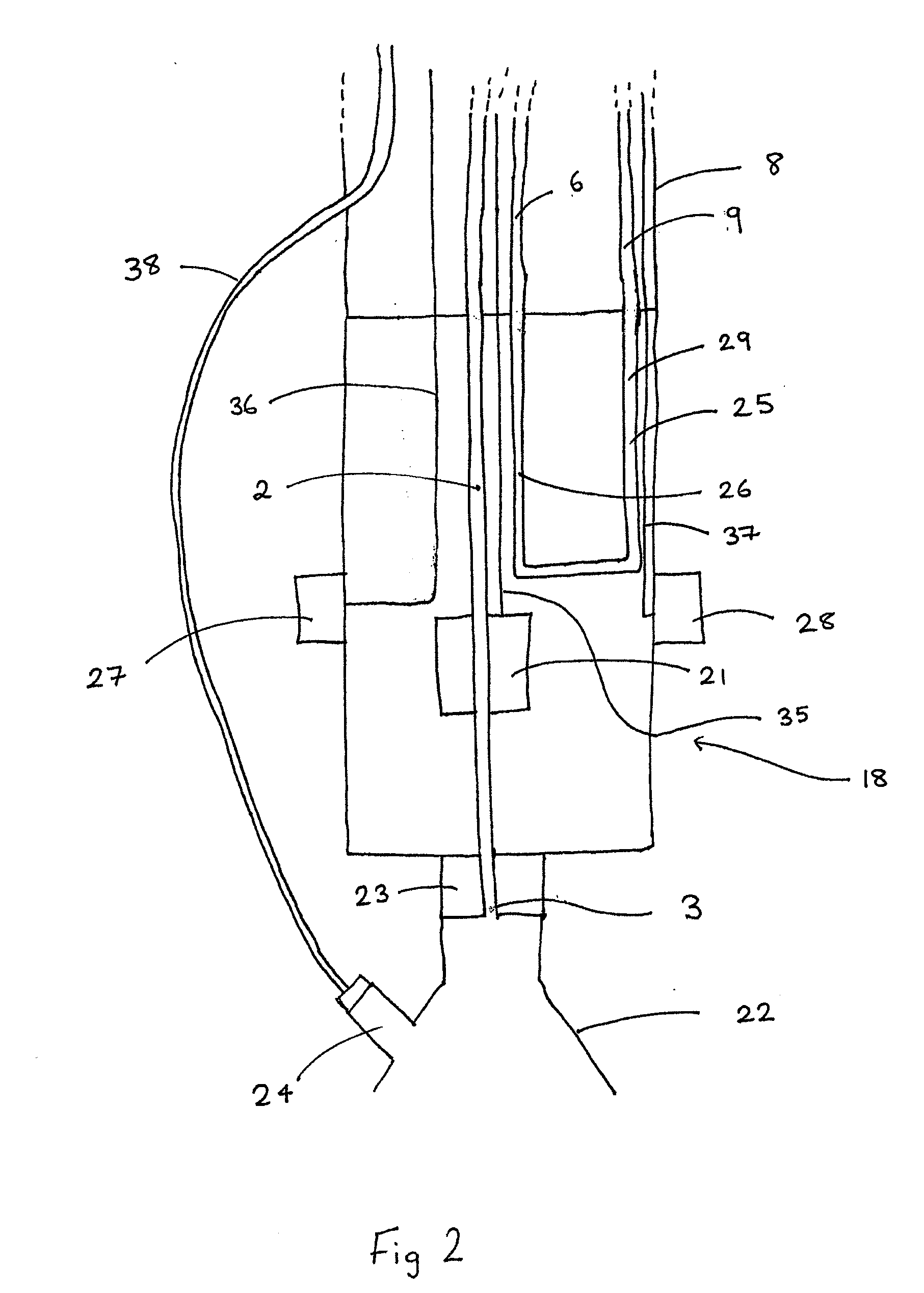
A catheter (2) is used in medical applications, for example for the retrieval of a sample from a patient or the insertion or retrieval of medical devices such as filters, stents (3) to and from the patient. The catheter (2) includes an expandable tip (6) at a leading portion of a catheter tube portion (5). This expandable tip (6) can retrieve or deliver samples, medical devices, etc. (3), which are slightly larger than the dimensions of a main catheter tube (5) inserted into the patient. The expandable tip (6) can also include extension members (10) which provide axial support to the expandable tip (6) but which still allow expansion in the radial direction.
Owner:SALVIAC
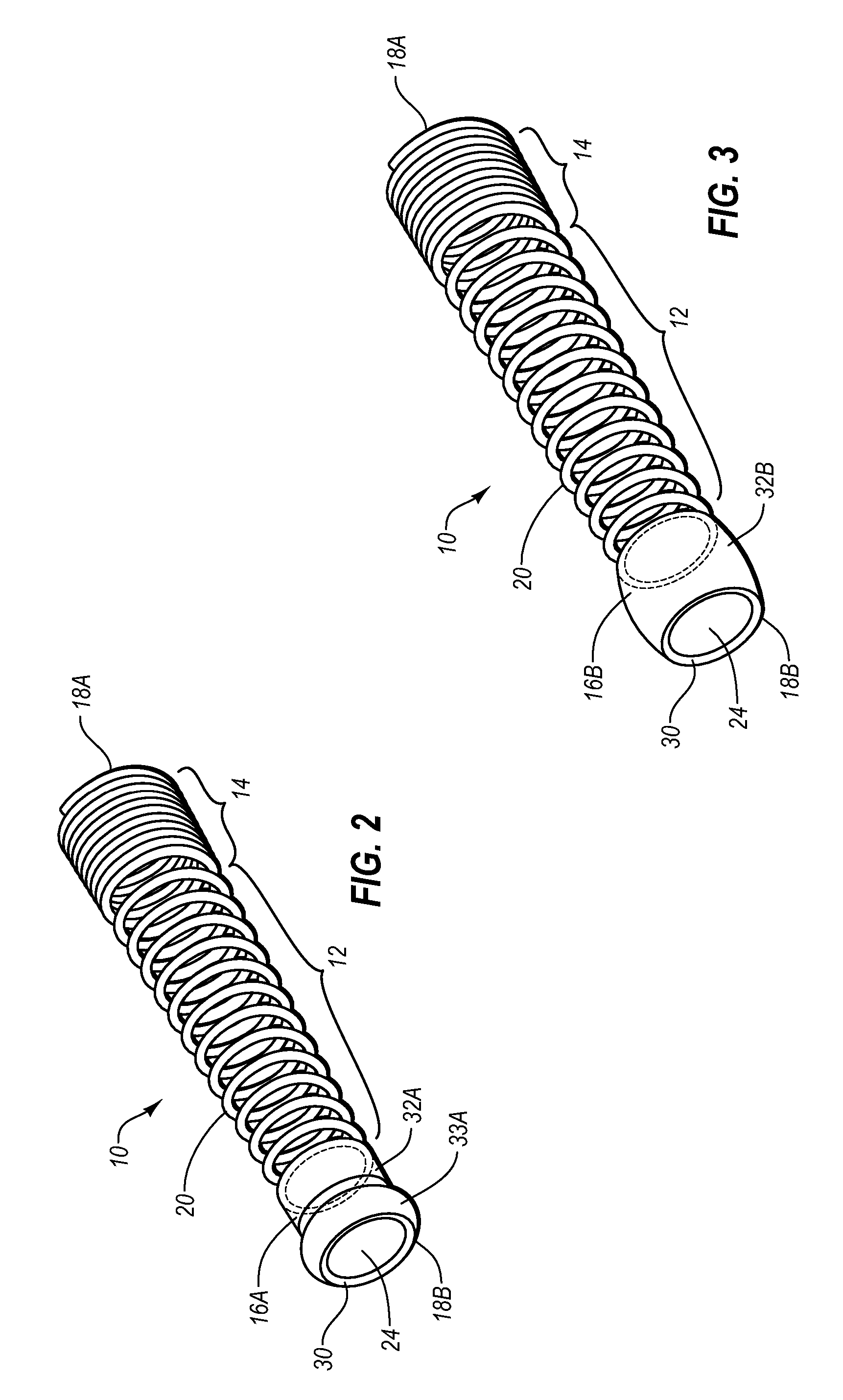
Stomach peristalsis device and method
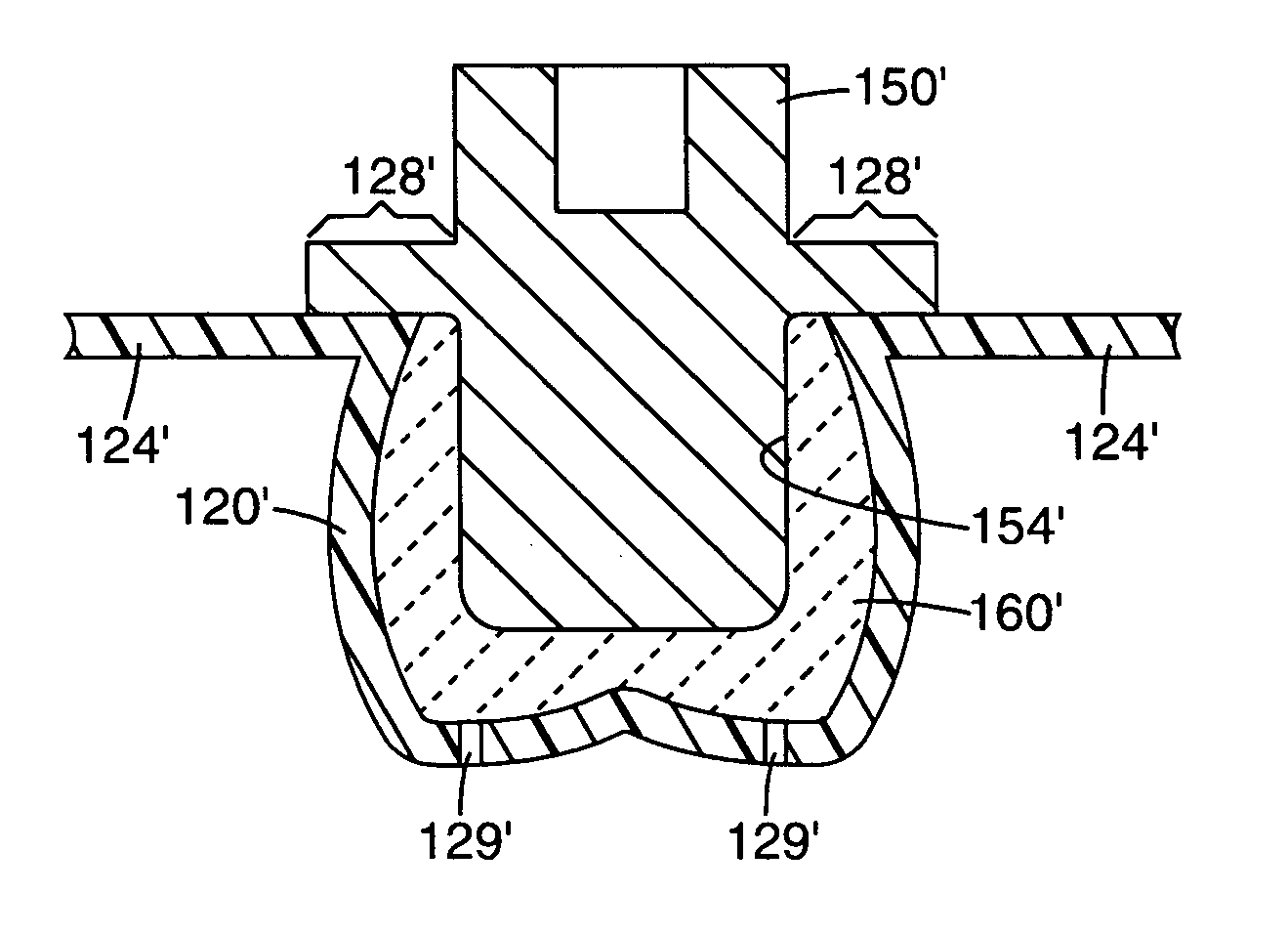
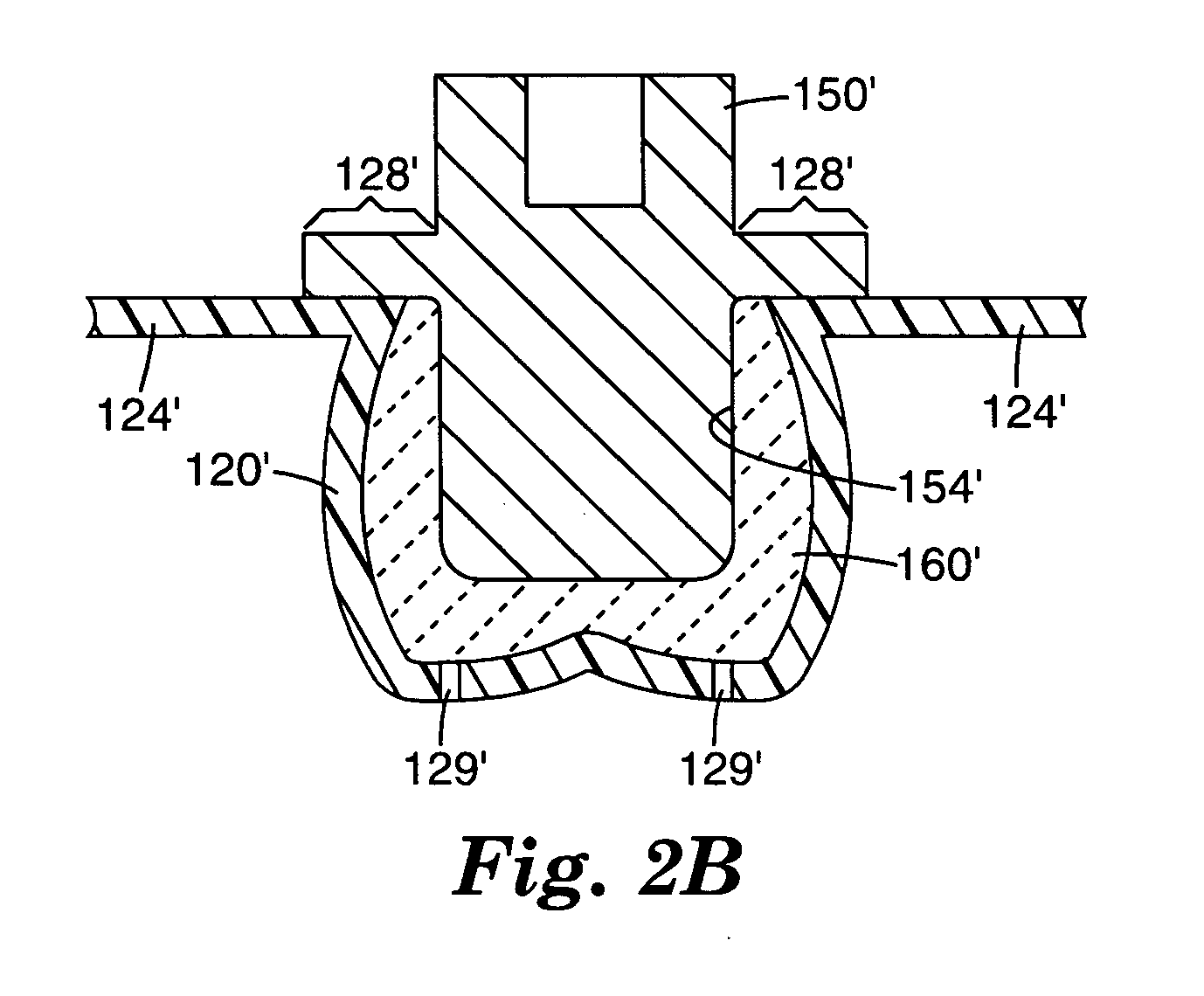
InactiveUS20060129237A1Facilitate expedite mixing breaking downPassage is slowedLigamentsMusclesPylorusPeristalsis
The invention relates to an implantable stomach prosthesis for surgically replacing or augmenting all or part of the antrum and / or pylorus of a stomach. The prosthesis controls the passage of food from the stomach to the small intestine. The prosthesis may be configured to chum ingested material and release it from the stomach through a prosthetic pyloric valve. At least one expandable member is arranged to be expanded to control the passage of food and / or to mimic the churning action of a patient's stomach. The prosthesis includes an outer support structure, a flexible inner member forming a conduit for the movement of material, and at least one expandable member located between the outer support structure and inner member. An implantable pump system is provided for inflating and deflating the expandable member(s).
Owner:PYTHON MEDICAL
Hardenable dental article and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20050100868A1Improve the finishEnhancing the finish of the dental articleTooth crownsArtificial teethMaterials science
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Flexible catheter tip having a shaped head
A catheter tip for attachment with an intravascular balloon catheter that is used within a body lumen is disclosed. The catheter tip includes a body portion having a base that is attached to the balloon catheter. The base defines a proximal end of the catheter tip. A head that is attached to the body portion defines a distal end of the catheter tip. An axial cavity, cooperatively defined by the body portion and the head, extends longitudinally from the proximal to the distal end of the catheter tip. The axial cavity receives a first guidewire along which the catheter is moved within the body lumen. An outer surface of the head is shaped in a predetermined manner to control the magnitude of deflection of a second guidewire that is often twisted about the first guidewire in the lumen so as to prevent catheter obstruction by the guidewires during catheter procedures.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Hand Held Dispenser
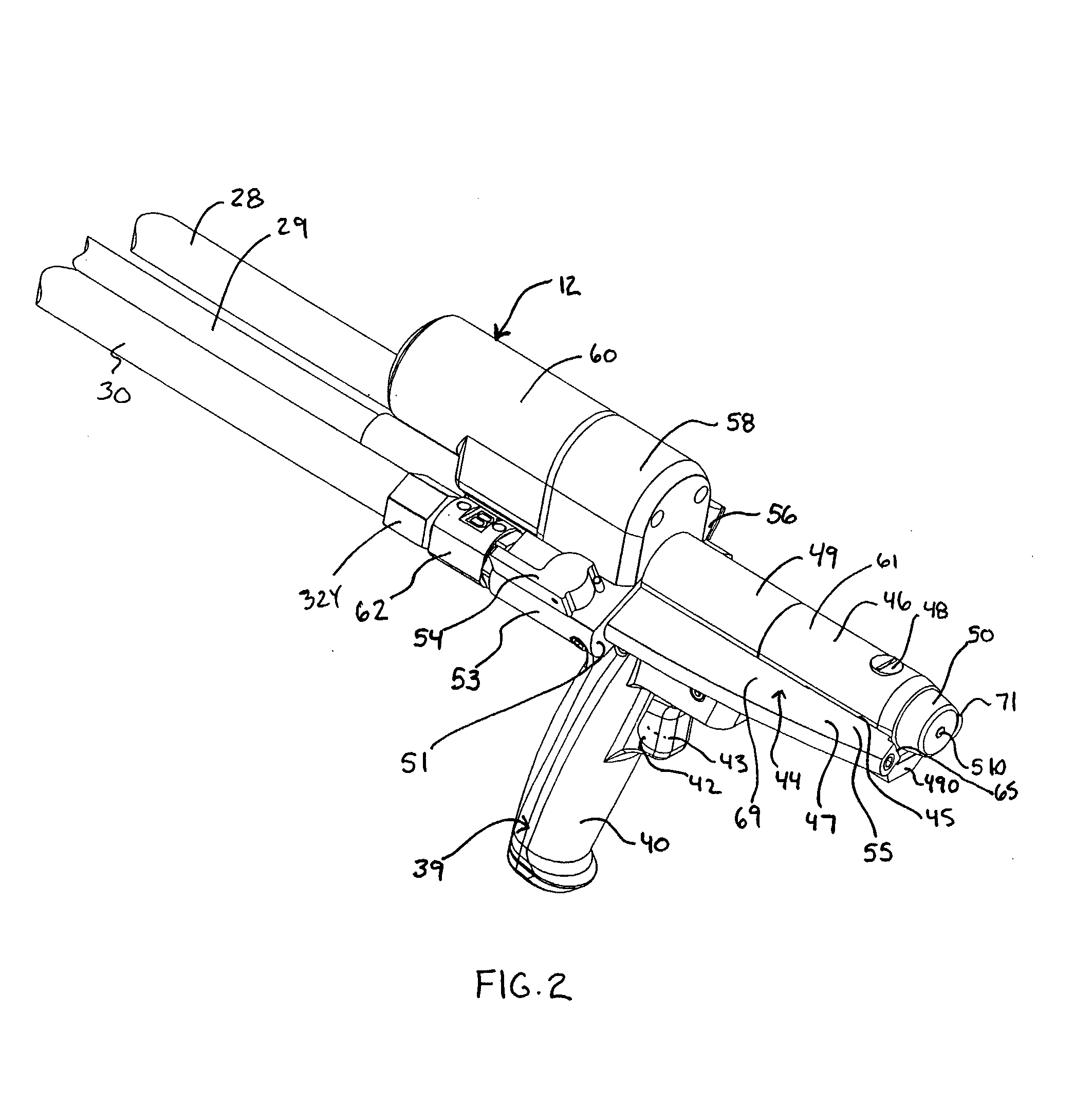
ActiveUS20080135579A1Minimize downtimeEasy to disassembleLiquid flow controllersLarge containersTemperature controlHand held
A hand held dispenser system with associated dispensed material supply assembly as in separate source chemical foam precursor feeding into, for example, streamlined chemical passageways preferably each comprised of, in series, a castellated swivel hose filter, a valve assembly housing, a wing extensions of a manifold, which manifold supports a high efficiency drive system and is supported by a handle that provides for a compact assembly and receives a rugged trigger assembly. The manifold design provides for elongated filter and, temperature controlled cartridge heater insertion. There is further provided in a preferred embodiment a readily releasable electric source feed line plug connection at the butt end of the dispenser. The dispenser is well suited for the dispensing of methane foam as in a product packaging setting.
Owner:PREGIS INTELLIPACK CORP
Stomach peristalsis device and method
InactiveUS7601178B2Facilitate expedite mixing breaking downPassage is slowedLigamentsMusclesPylorusPeristalsis
Owner:PYTHON MEDICAL
Connector with upper and lower inner housing members
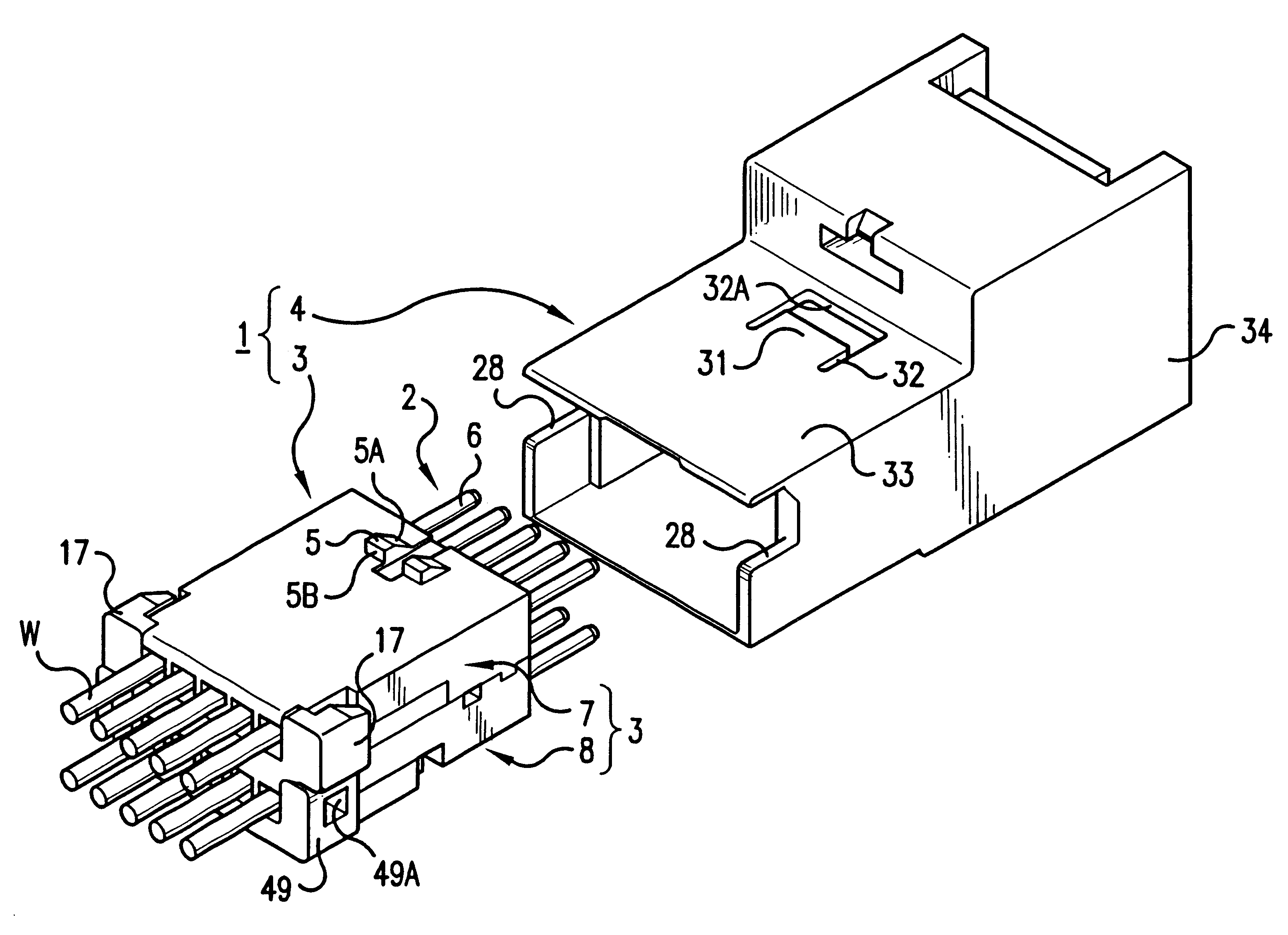
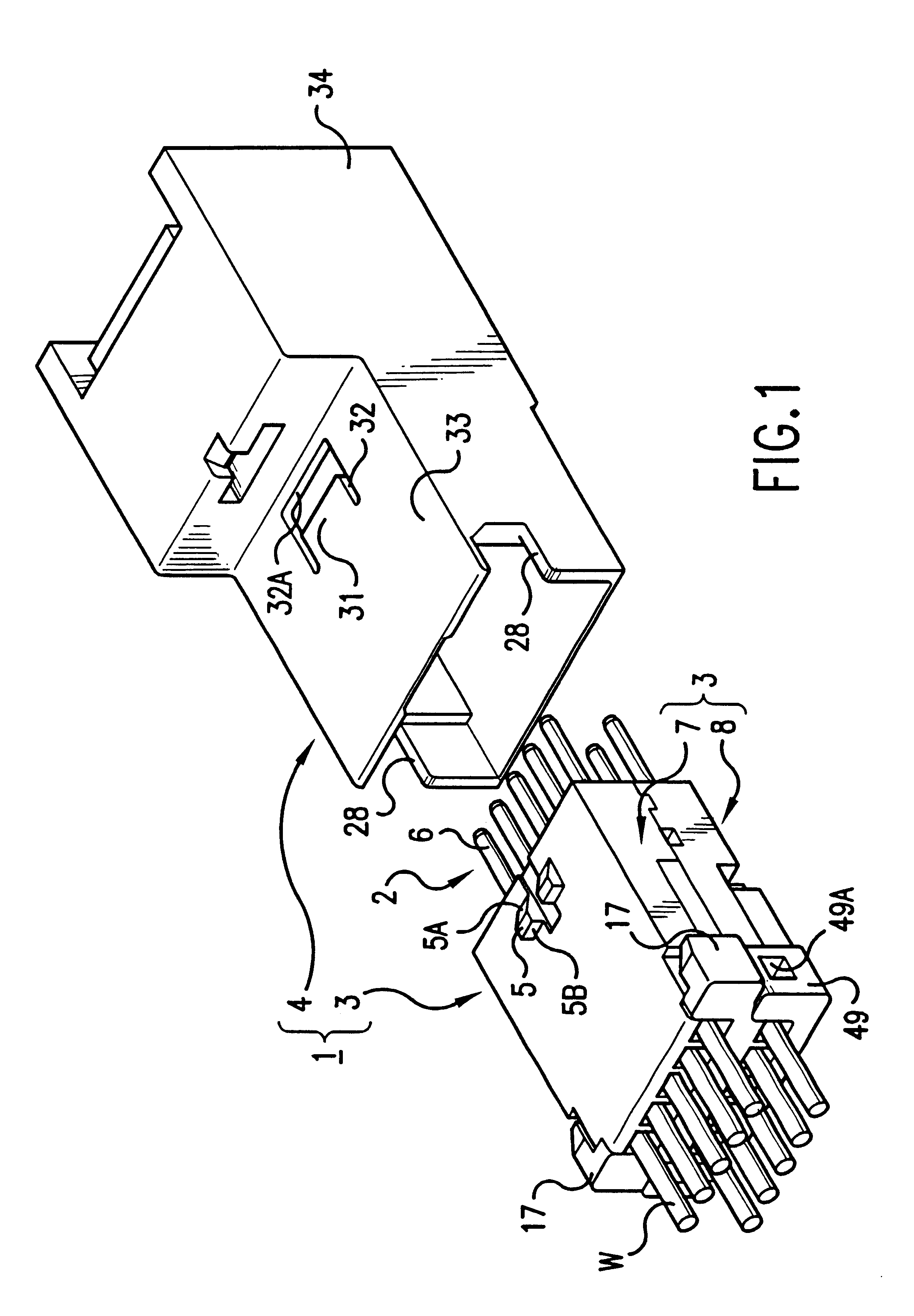
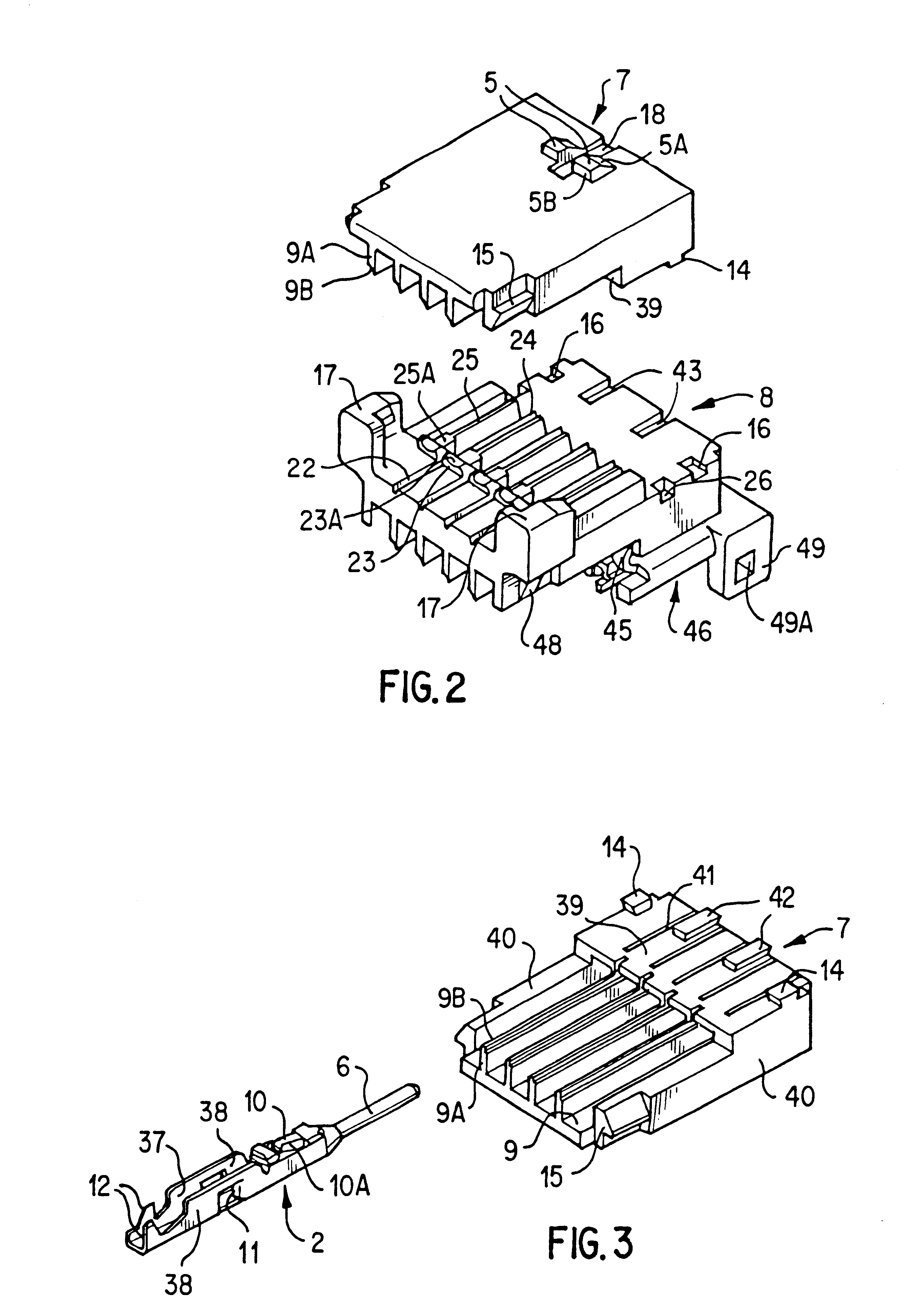
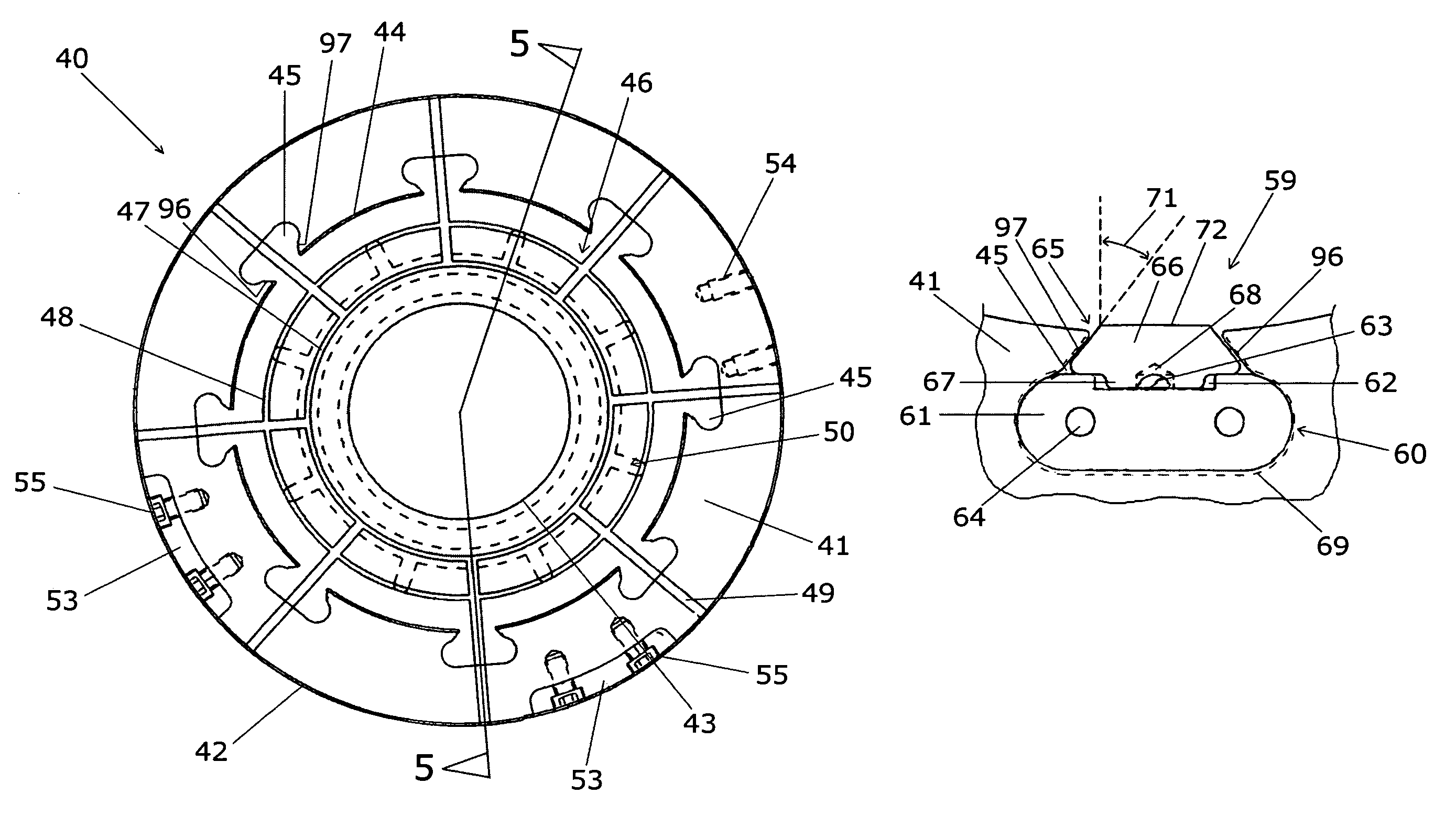
InactiveUS6231398B1Eases engagementPassage is slowedCoupling device detailsTwo-part coupling devicesMechanical engineeringEngineering
A connector including an inner housing member for housing terminal fittings and an outer member for receiving the inner housing member. The inner housing member comprises upper and lower inner members. After terminal fittings have been attached to the upper and lower inner members, these inner members are joined to one another to form the inner housing member. An angular-tubular shaped housing chamber is provided at the posterior of an outer member for housing the inner housing member. The inner housing member is pushed into the housing chamber of the outer member to complete the assembly of the connector. The connector also includes a latch that prevents the inner and outer members from being easily released, and in which rattling or vibration of the upper and lower inner members is prevented.
Owner:SUMITOMO WIRING SYST LTD
Protective handwear
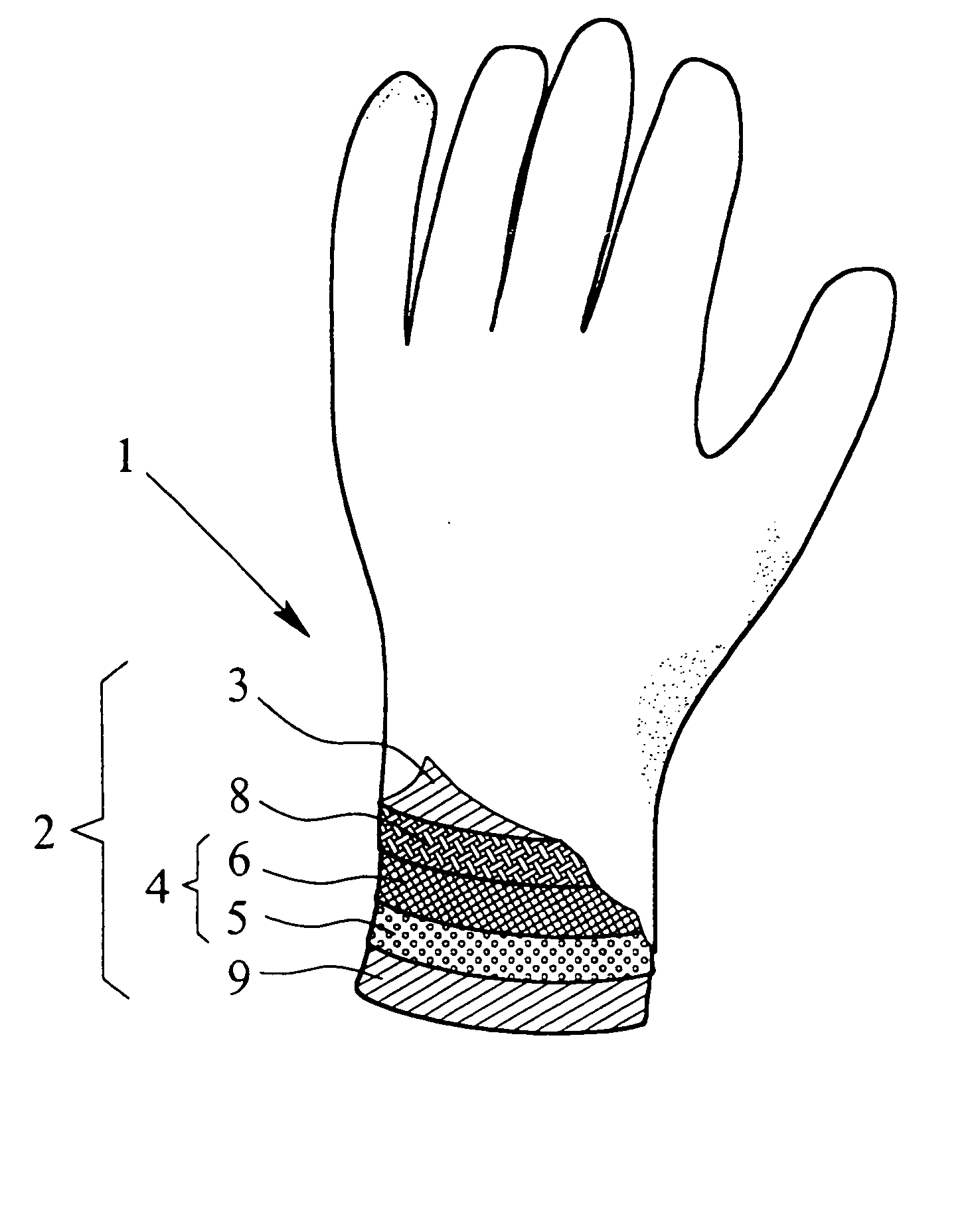
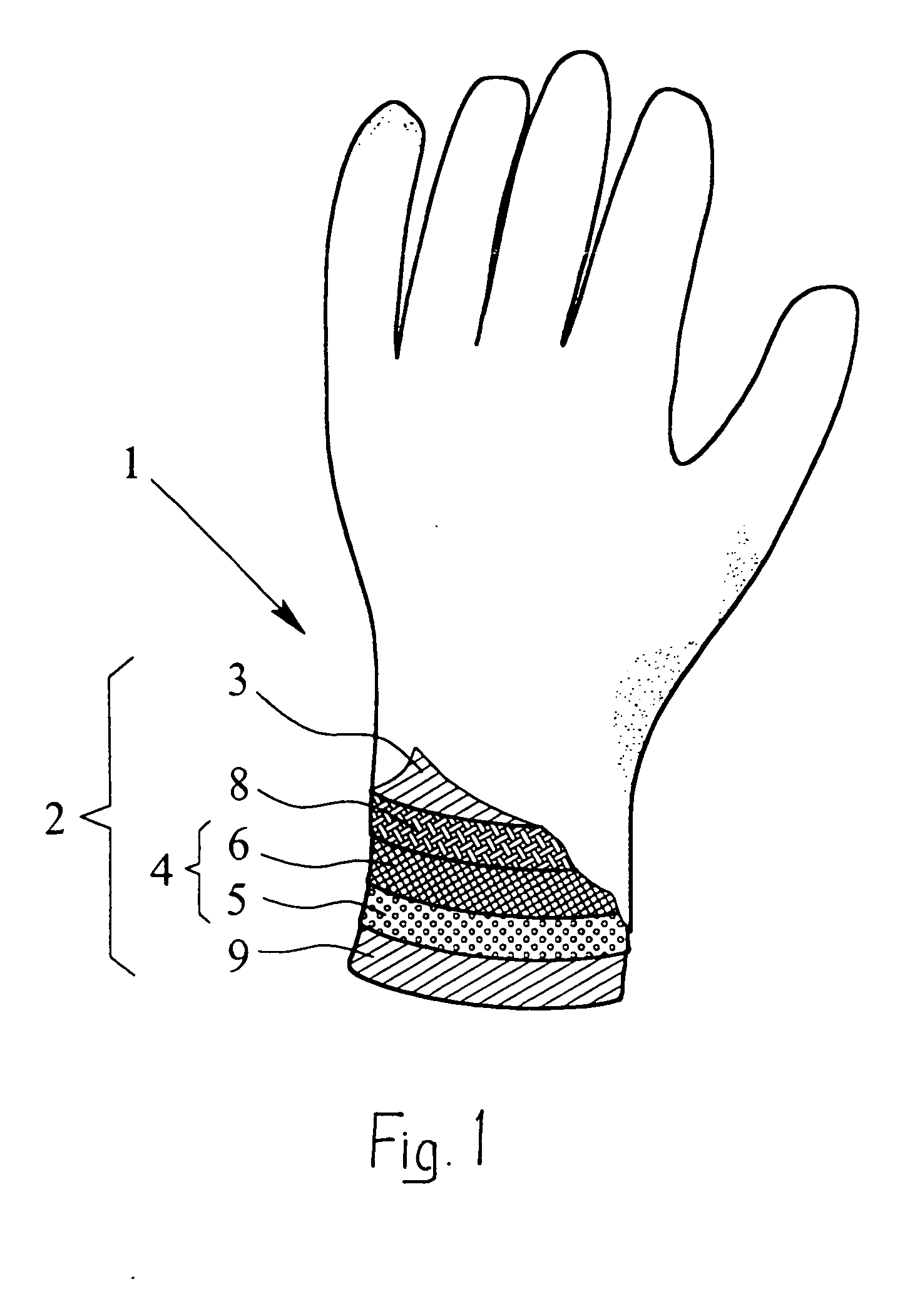
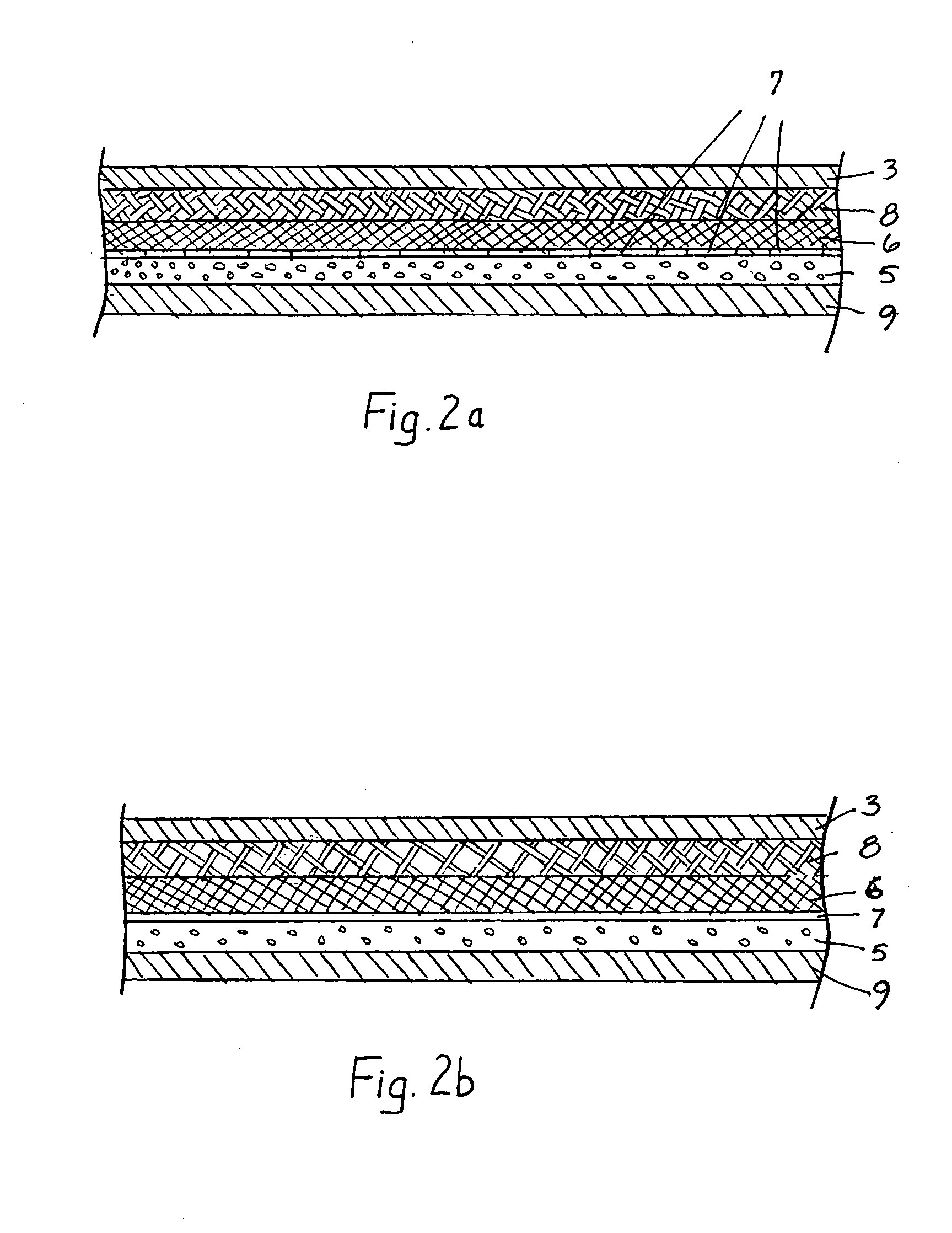
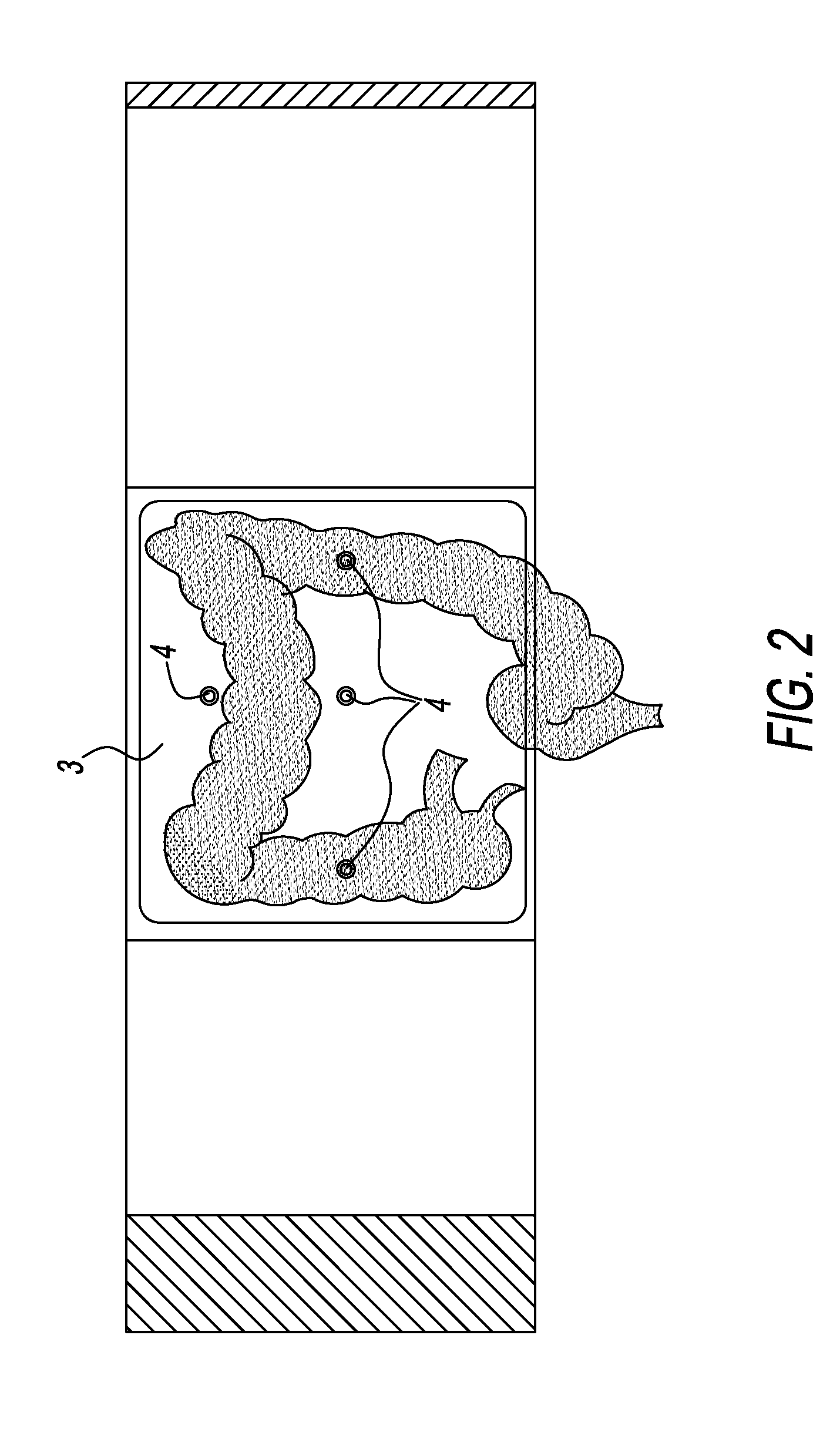
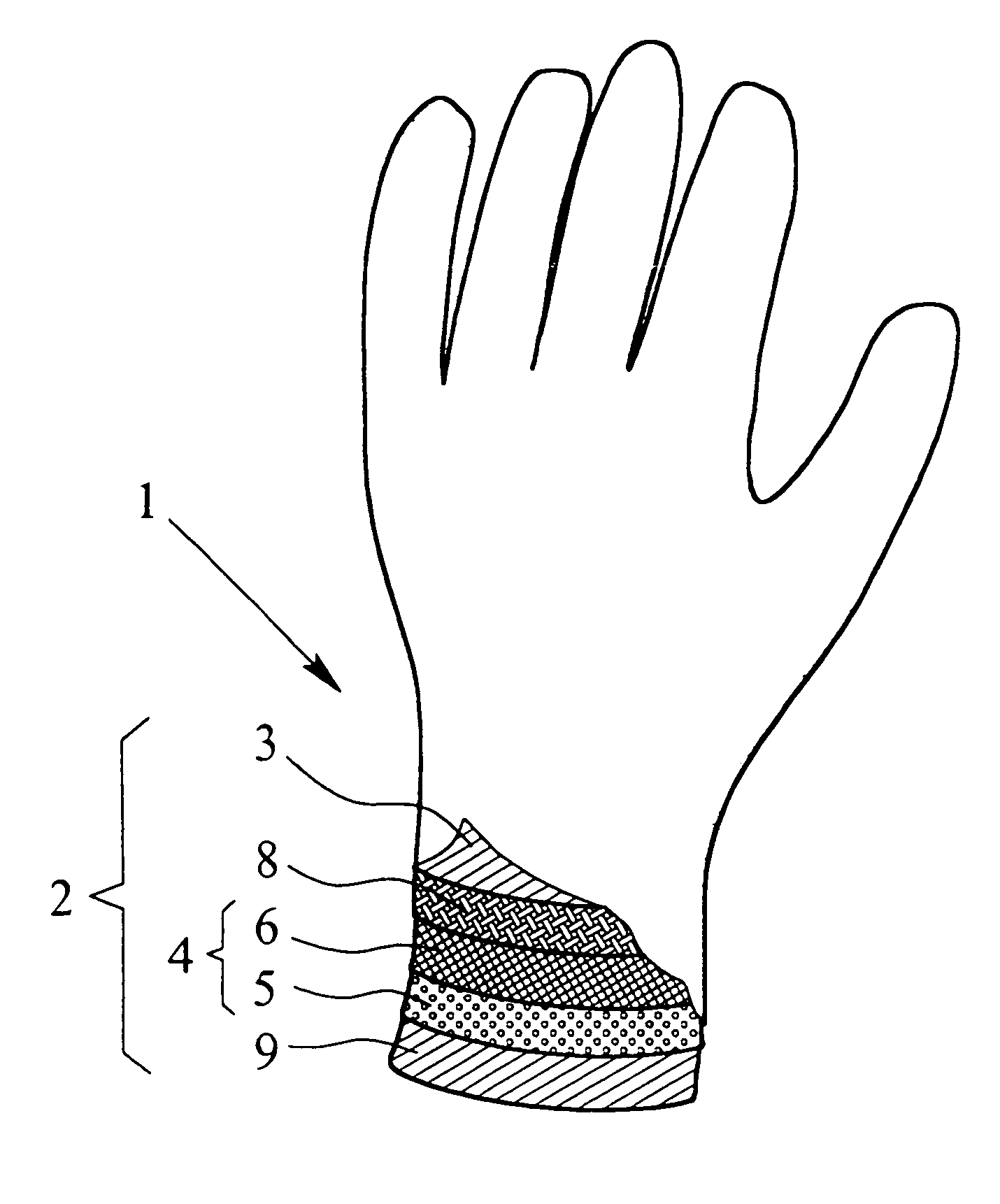
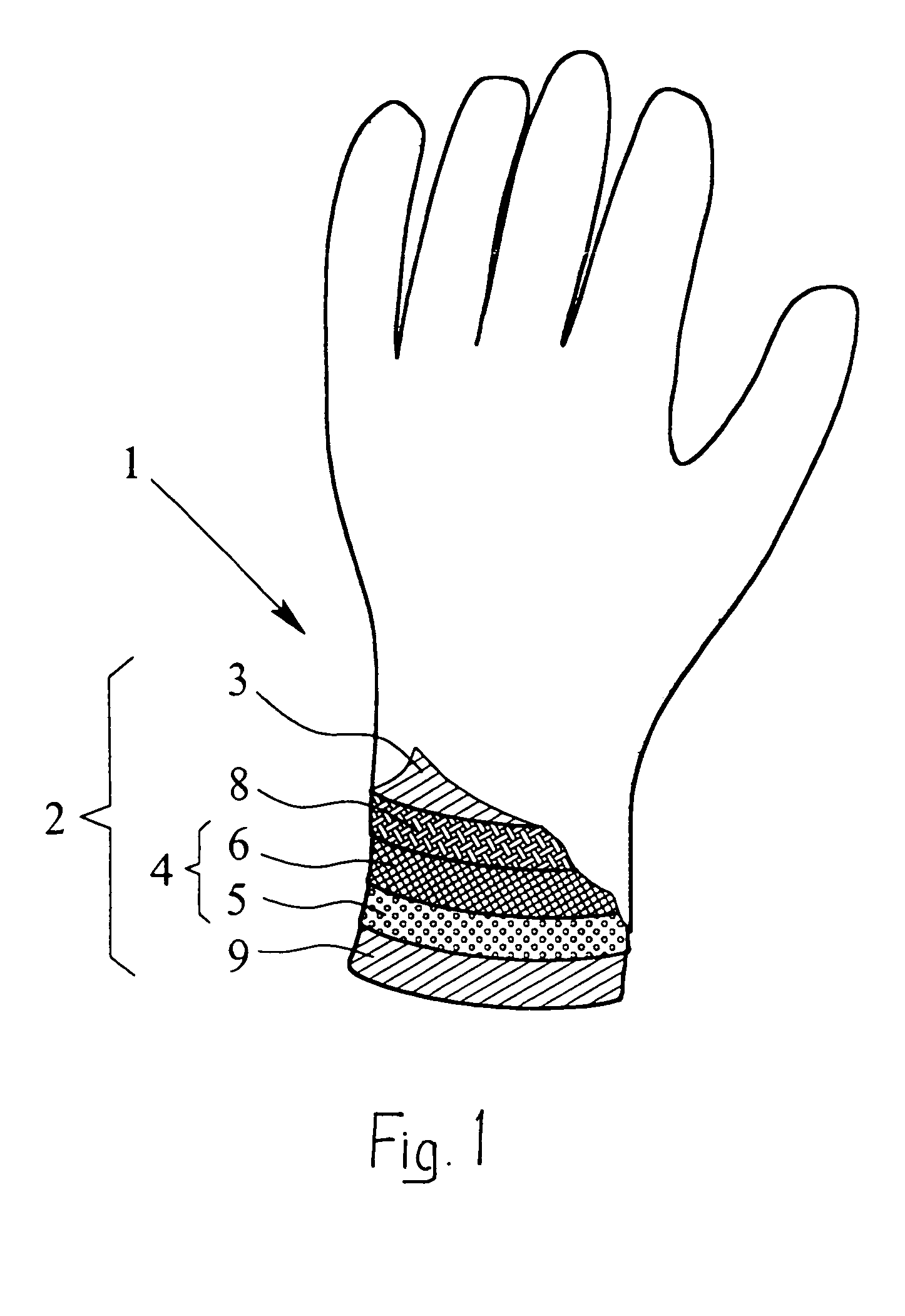
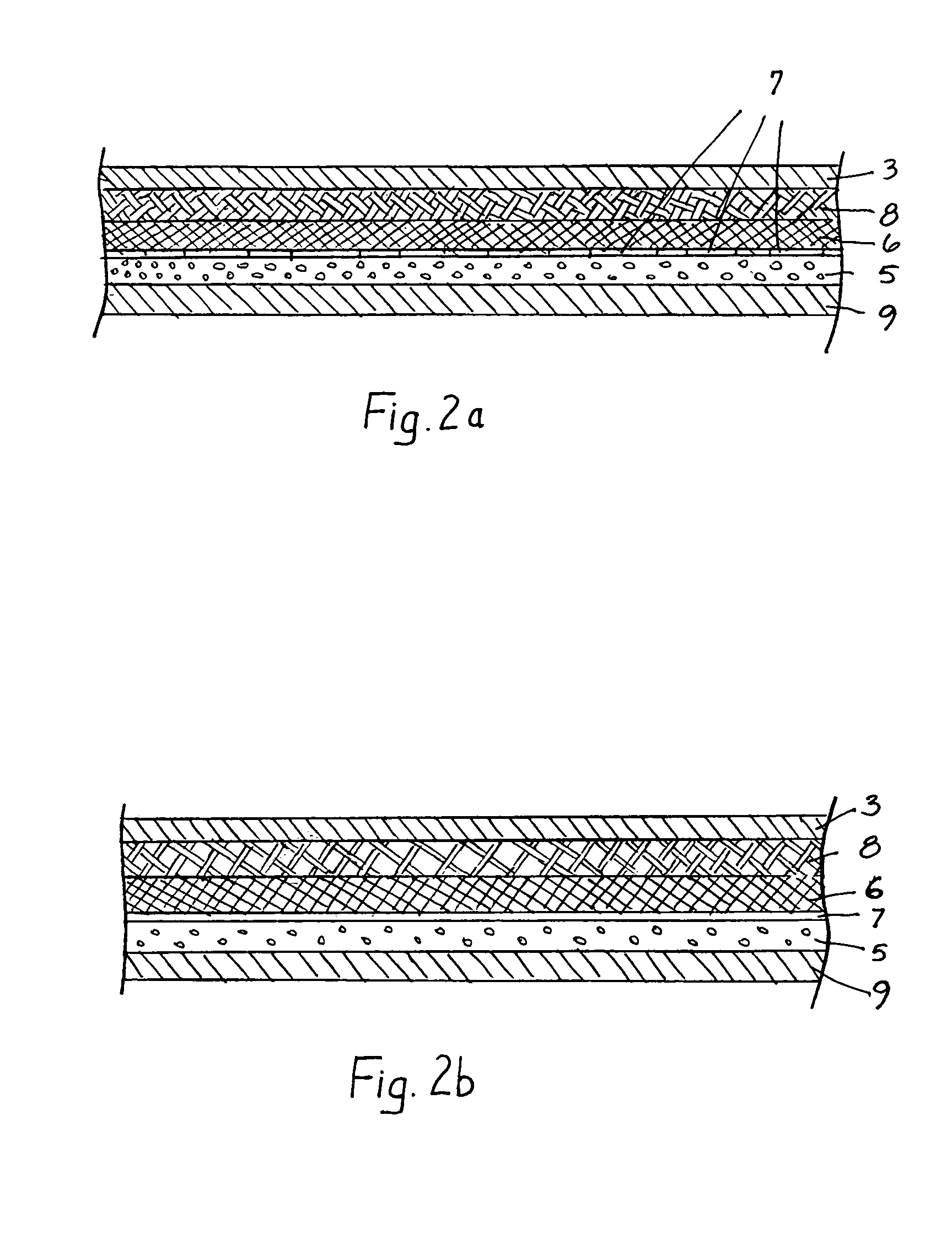
InactiveUS20050076418A1Provide protectionAvoid disadvantagesSynthetic resin layered productsGlovesActivated carbonWater vapor
A protective glove having a protective function against toxic chemical agents, especially chemical warfare agents, and a multilayer construction including a breathable layer is disclosed. The glove has a support layer and a barrier layer, which is assigned to the support layer and which faces the hand when the glove is worn, prevents or at least retards the passage of toxic chemical agents, and contains an adsorption layer based on an adsorbent material, such as activated carbon, which adsorbs toxic chemical agents. The barrier layer has, in addition to the adsorption layer, a membrane, which is at least preferably impermeable to water and air, but permeable to water vapor, and which retards the passage of toxic chemical agents or is at least essentially impermeable to toxic chemical agents. The membrane is arranged between the support layer and the adsorption layer. The protective glove has a high degree of wearing comfort with good tactility properties and at the same time provides excellent protection against toxic chemical agents.
Owner:BLUCHER GMBH
External Pneumatic Compression Device
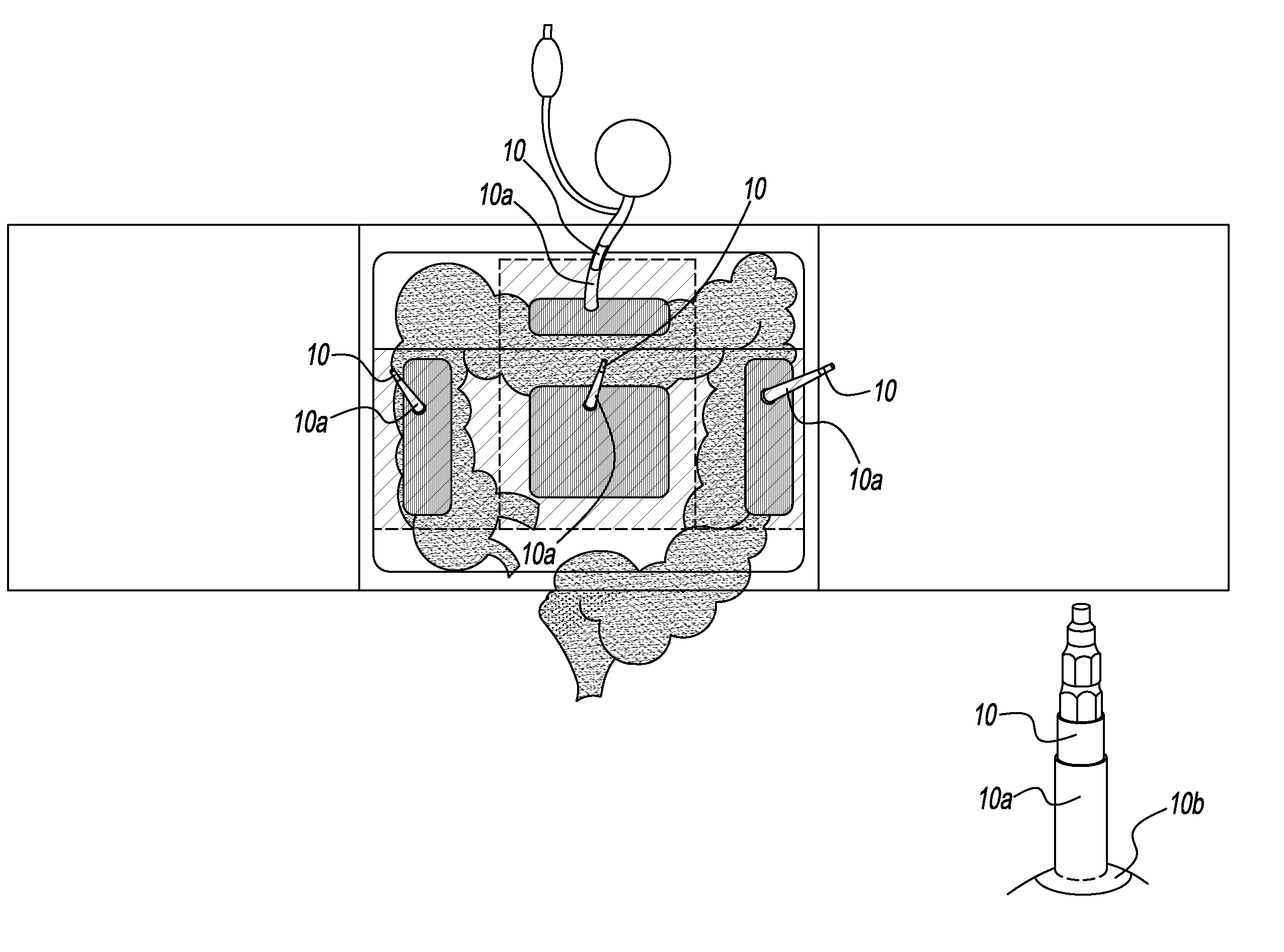
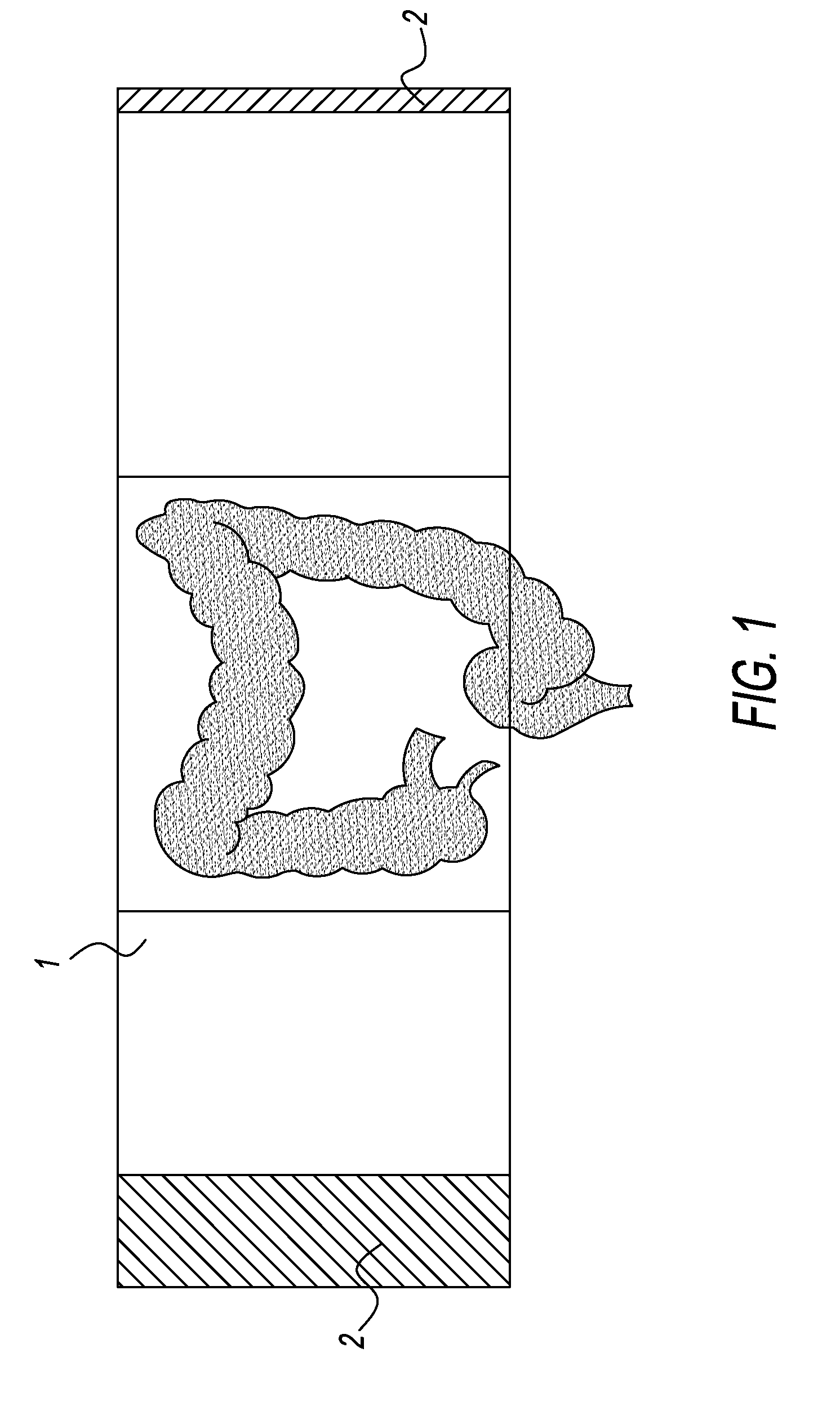
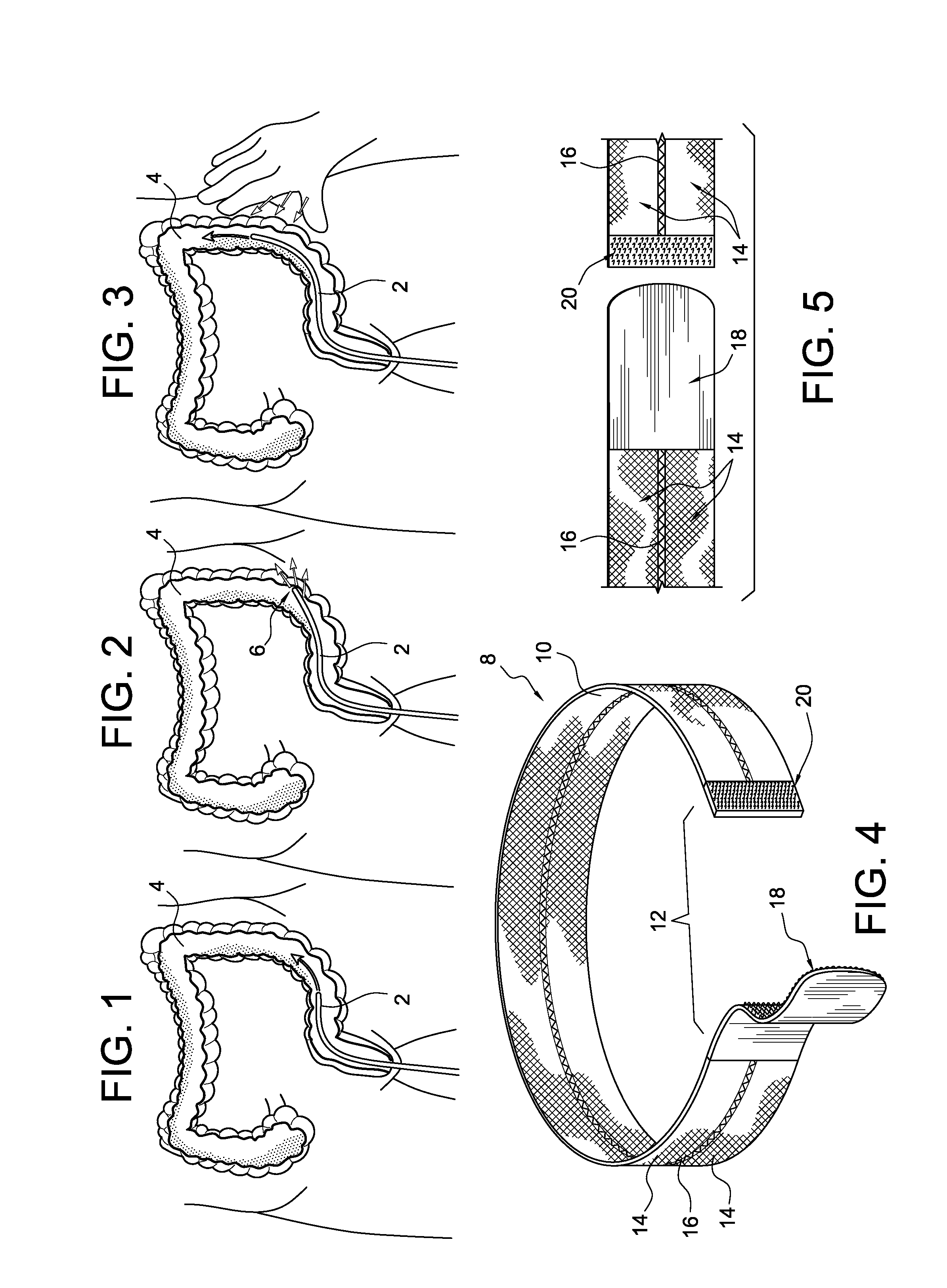
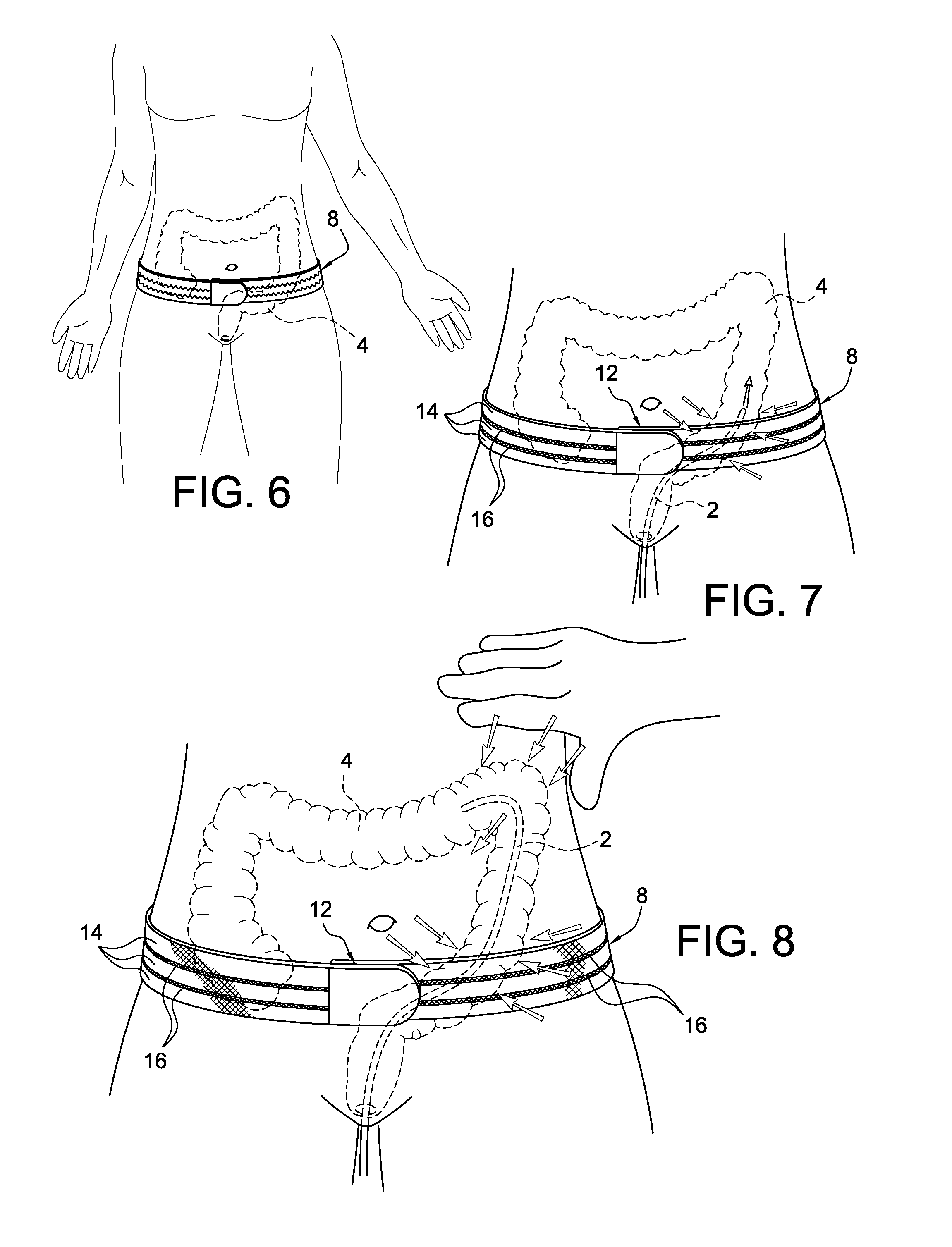
InactiveUS20110087263A1Passage is slowedReduce circulationTourniquetsCompression deviceLarge intestine
The present invention relates to a device for facilitating a colonoscopy, and more particularly to a non-invasive external pneumatic compression device that applies pressure to the abdomen of a patient in order to decrease looping of the colon during a colonoscopy and thus effectively splint a looping colon without the need for human intervention. This external pneumatic compression device comprises a flexible and breathable elastic abdominal binder for surrounding the abdomen of a patient undergoing a colonoscopy, a counter pressure plate that is secured to the middle inside of the binder for providing a counter pressure during and while the bladder or bladders are inflated, a means for supplying air and regulating the pressure in the bladders, and a plurality of inflatable bladders for applying downward pressure to specific anatomical areas of the large intestines of a patient when inflated. When the binder is secured to the abdomen of a patient, the inflatable bladders will be placed over four noted regions of the abdomen corresponding to the ascending colon, the mid-umbilical colon, the transverse colon, and the sigmoid bladder.
Owner:ARBER PATRICK THOMAS
Protective handwear
InactiveUS7451497B2Provide protectionAvoid disadvantagesSynthetic resin layered productsGlovesActivated carbonWater vapor
A protective glove having a protective function against toxic chemical agents, especially chemical warfare agents, and a multilayer construction including a breathable layer is disclosed. The glove has a support layer and a barrier layer, which is assigned to the support layer and which faces the hand when the glove is worn, prevents or at least retards the passage of toxic chemical agents, and contains an adsorption layer based on an adsorbent material, such as activated carbon, which adsorbs toxic chemical agents. The barrier layer has, in addition to the adsorption layer, a membrane, which is at least preferably impermeable to water and air, but permeable to water vapor, and which retards the passage of toxic chemical agents or is at least essentially impermeable to toxic chemical agents. The membrane is arranged between the support layer and the adsorption layer. The protective glove has a high degree of wearing comfort with good tactility properties and at the same time provides excellent protection against toxic chemical agents.
Owner:BLUCHER GMBH
Method for coating abrasives
InactiveUS20070157525A1Enhanced advantagePassage is slowedPigmenting treatmentLiquid surface applicatorsIndiumGas phase
A method of producing coated ultra-hard abrasive material, in particular coated diamond and CBN material. In a first step, an element capable of forming (singly or in combination) carbides, nitrides or borides to the surface(s) of the abrasive material is is applied using a hot coating process. At least one outer layer of a coating material selected from the group comprising transition metals, carbide, nitride, boride, oxide and carbonitride forming metals, metal carbides, metal nitrides, metal borides, metal oxides and metal carbonitrides, boronitrides and borocarbonitrides is applied over the inner layer by physical vapour deposition or chemical vapour deposition. Typically the inner layer elements come from groups IVa, Va, VIa, IIIb and IVb of the periodic table and include, for example, vanadium, molybdenum, tantalum, indium, zirconium, niobium, tungsten, aluminium, boron and silicon. The outer coating is preferably applied by reactive sputtering where a reactive gas is admitted to the sputtering chamber, resulting in the deposition of a compound of the reactive gas and the element being sputtered.
Owner:EGAN DAVID PATRICK +2
Lumen-Less Illumination System
ActiveUS20150374217A1Passage is slowedReduce the overall diameterSurgeryEndoscopesOptical radiationFiber
The present teachings relate to an endoscope (and methods of manufacturing the same) having an illumination system that utilizes small diameter fibers for delivering bright, high quality light to a target site. In accordance with one aspect, an endoscope is provided having a phosphor-loaded, light emitting distal tip that can be energized via optical radiation delivered to the light-emitting distal tip via a small-diameter optical fiber (e.g., less than about 100 μm in diameter) that extends through or along the length of the endoscope. The light-emitting distal tip can be energized by short wavelength laser light (e.g., radiation having wavelengths at 445 nm blue or 405 nm violet) coupled to the optical fiber's proximal end so as to deliver light of extremely high quality CRI (e.g., greater than 80, greater than 90, about 95).
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Method and apparatus for tensile colonoscopy compression
ActiveUS20130178893A1Eliminate riskPassage is slowedRestraining devicesSurgeryCompression devicePhysical therapy
A method and apparatus for applying pressure to the abdomen of a patient to facilitate the insertion of a colonoscope is characterized by the use of a tensile compression device in the form of an elastic band which is wrapped around the patient's abdomen and secured in place. The tension of the band is adjusted to apply a desired degree of pressure to the patient's abdomen to reduce loops in the patient's colon so that the colonoscope can be fully inserted into the colon with minimal discomfort to the patient. The ends of the device are connected together when the desired degree of tension is obtained so that constant pressure and support are provided to the patient's colon. Addition pressure can be manually applied simultaneously with the pressure from the tensile device to reduce or eliminate more distal loops in the colon.
Owner:COLOWRAP LLC
Insulated tank assembly with insulation stop and method of assembly thereof
InactiveUS20090038980A1Elongate overall stripPassage is slowedDomestic cooling apparatusLarge containersEngineeringMechanical engineering
An insulated tank assembly with insulation stop and a method of constructing such an assembly. The assembly includes an inner tank with an outer shell located in spaced relation to and surrounding the inner tank, creating at least one annular clearance space between the tank and the shell. The space is closed by a sealing device that includes a circumferential sealing strip having an unstretched strip length that is less than either the continuous outer top edge length or the continuous outer bottom edge length, or both, of the strip. Such length relationships make the sealing strip both resilient and resistant to rolling during construction of the assembly. The sealing strip may be a fibrous strip. The tank assembly may be insulated by placing insulating material within the at least one annular clearance space, which may be a foamable insulation material, foamed in place within the annular clearance space.
Owner:OWENS CORNING INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL LLC
Tool pack assembly
ActiveUS20060086170A1Improved dampening meanPassage is slowedDrawing profiling toolsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A tool pack assembly for use in the manufacture of two piece metal can bodies. The tool pack assembly of the present invention is constructed and arranged for use in a body maker assembly to form parts of metal cans. The tool pack assembly of the invention includes an improved die module structure. The improved die module includes compressible dampening structures to thereby float a die element to center and align the metal body with the die element.
Owner:PRIDE ENG LLC
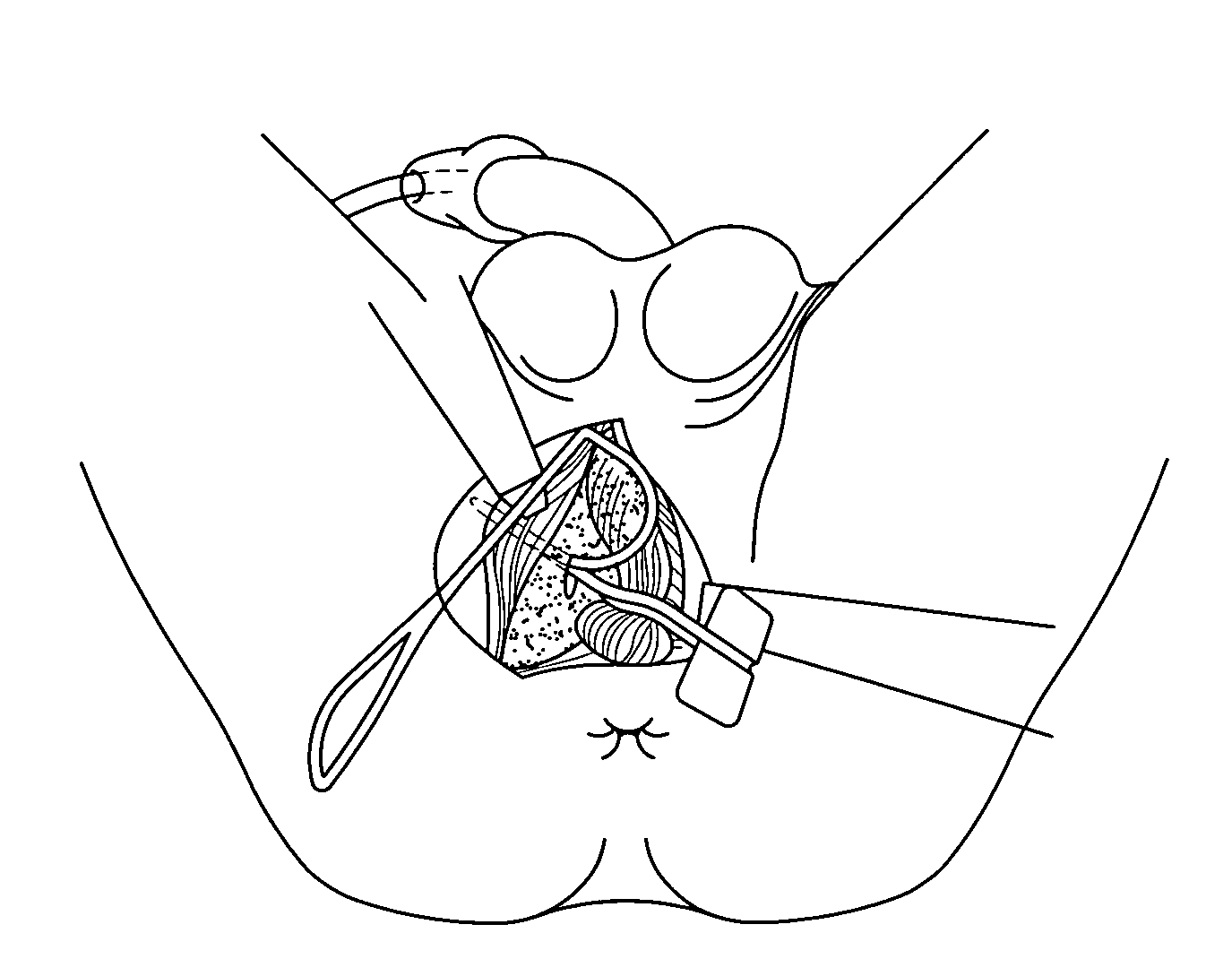
Surgical technique and tools for use in treatment of male urinary incontinence
InactiveUS20080210247A1Avoid dissectionPassage is slowedSuture equipmentsAnti-incontinence devicesTransobturator slingThigh
A transobturator technique was developed for treating male urinary incontinence. This approach helped to design specific instruments to pass around the ischio-pubic branches of the male pelvis from inside to outside (i.e from the suburethral space to the thigh fold). The inside-out transobturator sling technique uses specific instruments and a polypropylene mesh with two arms that are passed inside to outside through the obturator foramens, pulled for compressing the bulbar urethra upward, and tied to each other across the midline. The mesh passes around the ischio-pubic branch before being tied under the bulbar urethra where it brings tension and support.
Owner:UNIV LIEGE +1
Tool pack assembly
ActiveUS7107811B2Loss of production and efficiencyMinimizes productionDrawing profiling toolsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A tool pack assembly for use in the manufacture of two piece metal can bodies. The tool pack assembly of the present invention is constructed and arranged for use in a body maker assembly to form parts of metal cans. The tool pack assembly of the invention includes an improved die module structure. The improved die module includes compressible dampening structures to thereby float a die element to center and align the metal body with the die element.
Owner:PRIDE ENG LLC
Disposable absorbent article having a visibly highlighted wetness sensation member
InactiveUS20060069364A1Increase awarenessFacilitate opportunityOther accessoriesDiagnostic recording/measuringPotty trainingControl layer
A disposable absorbent article including a wetness sensation member and visible highlighting indicating the presence of the wetness sensation member to facilitate an opportunity for the toilet training of the wearer. The wetness sensation member includes a permeable layer and a flow control layer. Urine deposited on the wetness sensation member can penetrate through the permeable body-facing layer in a z direction away from the wearer to the flow control layer. The flow control layer retards the passage of the urine through the wetness sensation member in the z direction while supporting the movement of the urine in an x-y plane to increase the wetted area contacting the wearer's skin and thereby enhance the wearer's awareness that urination has occurred. The visible highlighting is visible when viewing a body-facing surface of the article and may be associatively correlated with an externally visible marking and / or with the concept of toilet training.
Owner:PROCTER & GAMBLE CO
Carotid sheath with thin-walled shaft and variable stiffness along its length
InactiveUS20120265282A1Great stiffnessMore flexibilityGuide needlesCoatingsCarotid sheathThin walled
A sheath to access a patient's vascular system where a portion of the length of the sheath is the proximal portion which has stiffer bending characteristics when taken with respect to a shorter distal section of the sheath which has increased flexibility with regard to bending characteristics.
Owner:FISCHELL INNOVATIONS
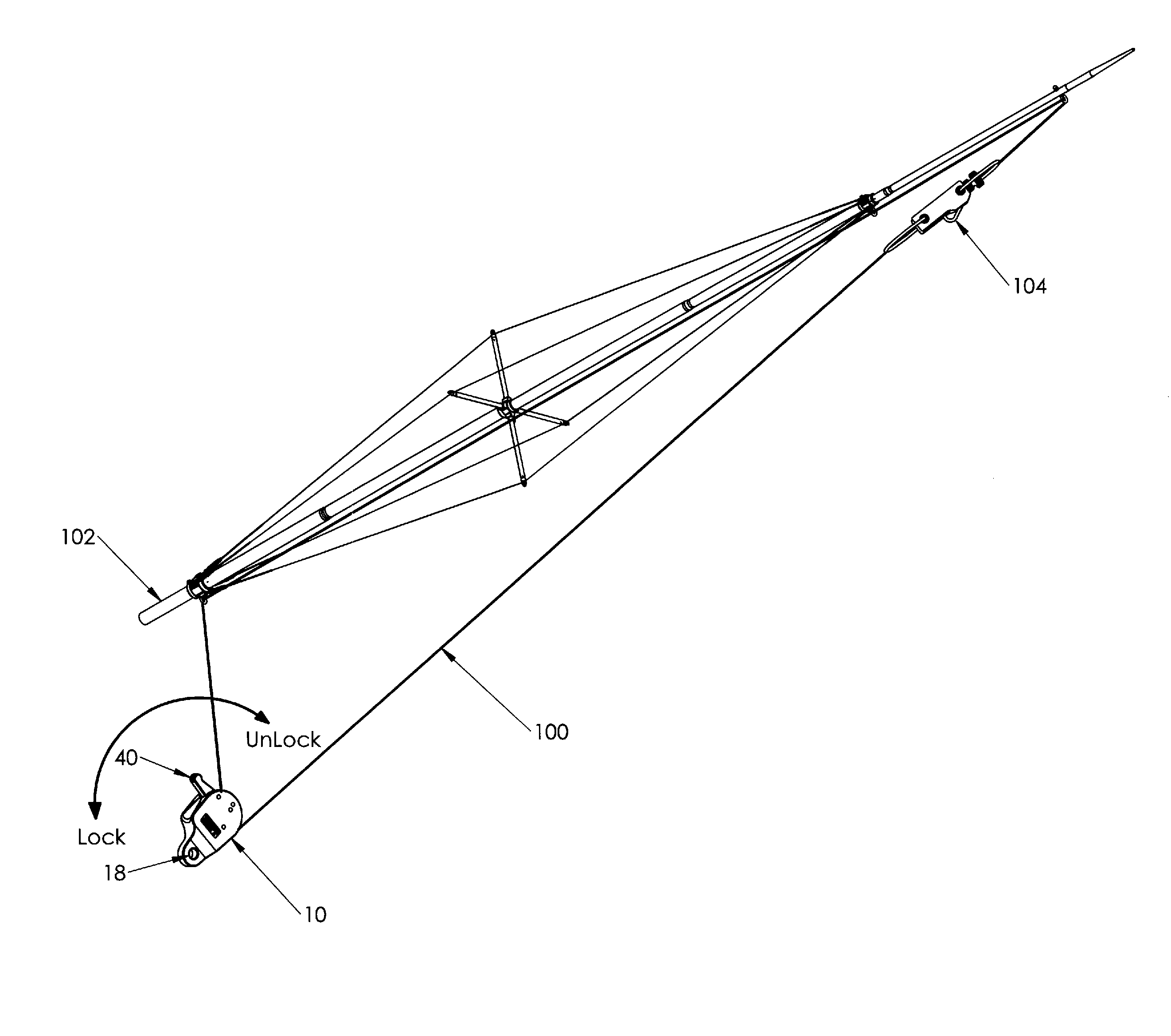
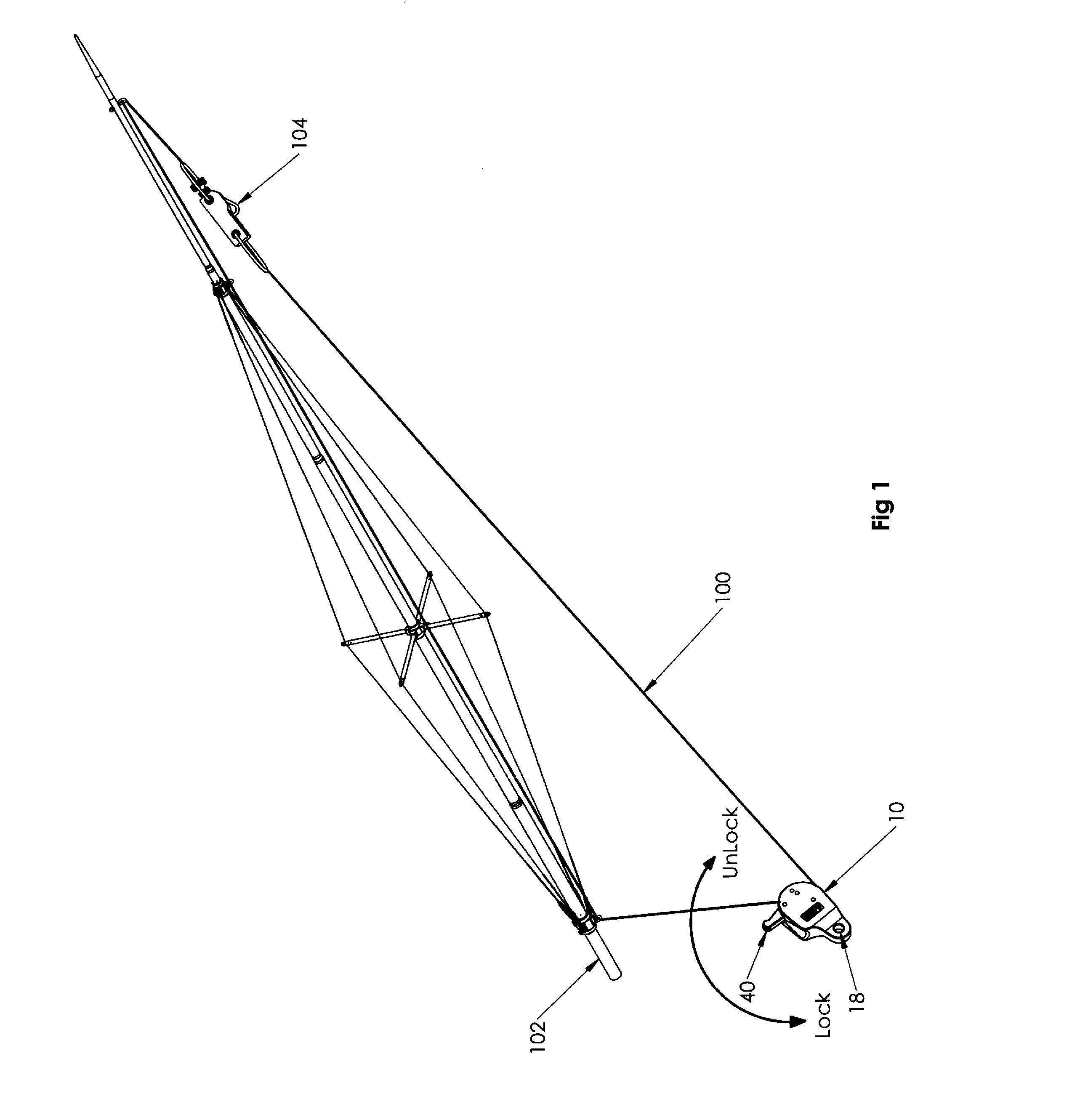
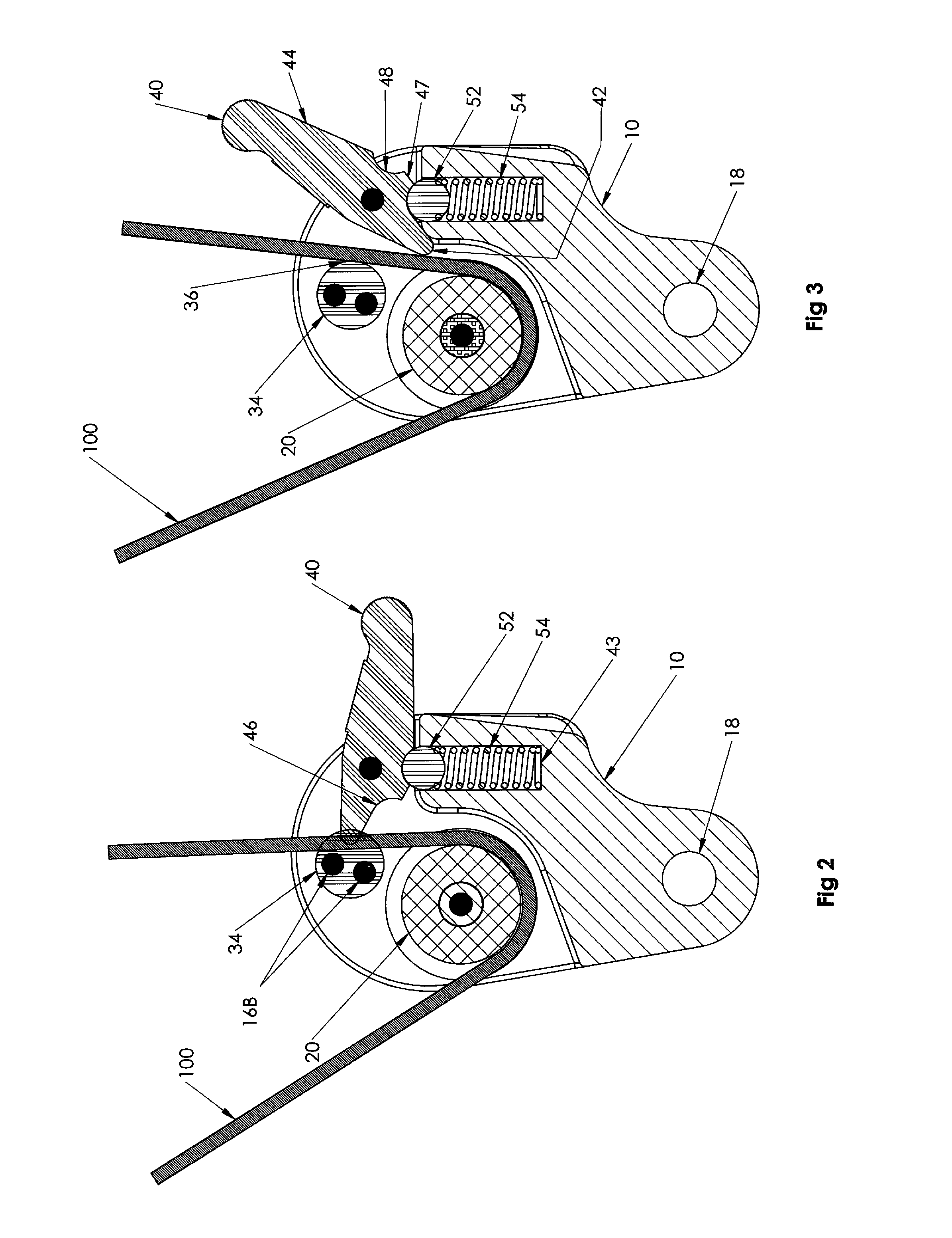
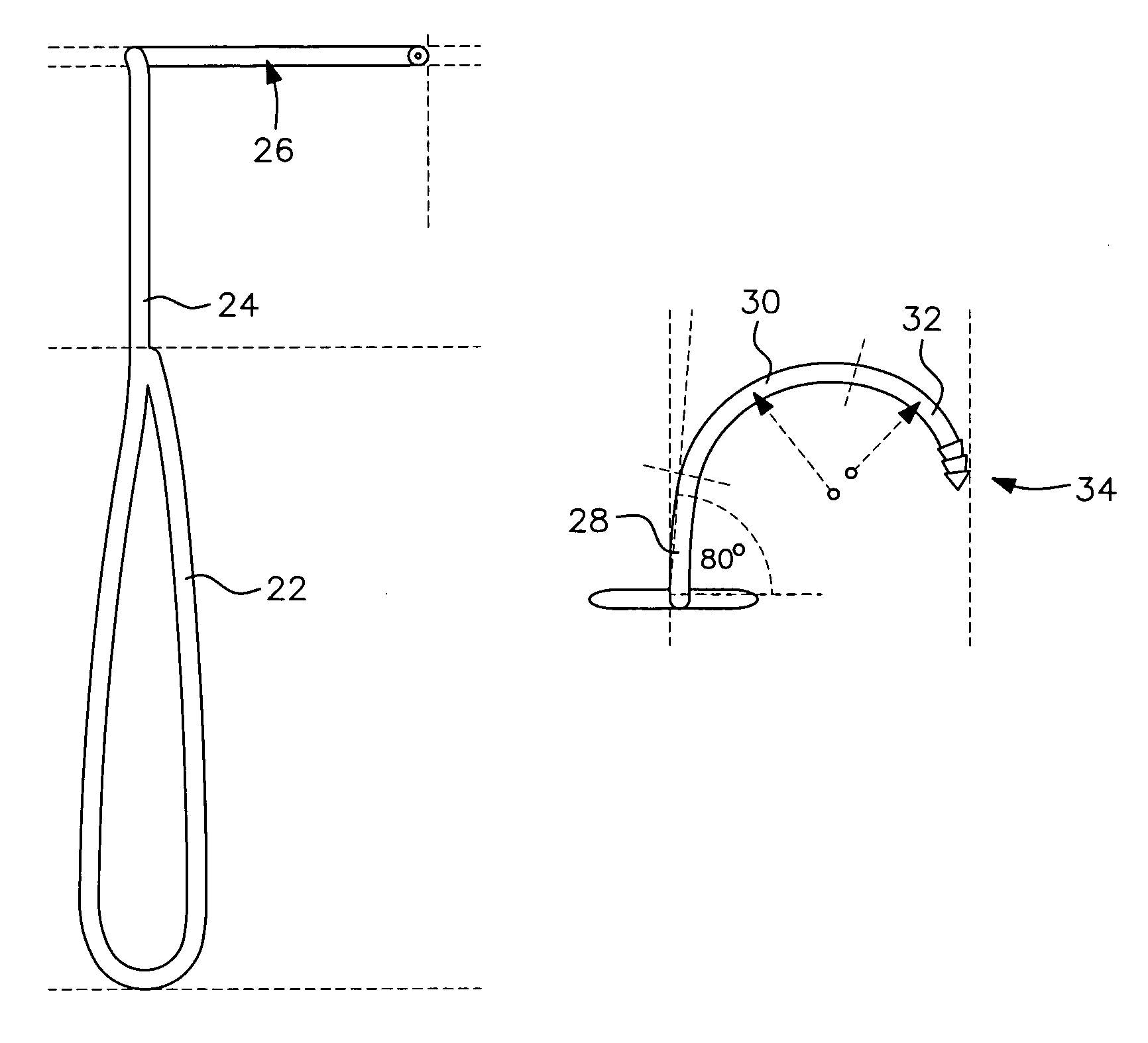
Outrigger line lock positioning device
Disclosed is a line positioning device for use with fishing vessel outriggers. The positioning device employs a housing having a pulley, a resilient bushing positioned next to the pulley, and a lever arm that is strategically positioned to engage a halyard line against the resilient bushing. A halyard line placed through the device is partially wrapped around the pulley where the line can freely move. Locking of the line requires the partial rotation of the lever arm which includes a tip end that presses the line against the resilient bushing. The lever arm includes a detent for engagement of a biased ball for use in holding the lever arm in either a locked or unlocked position.
Owner:RUPP MARINE
Surgical technique and tools for use in treatment of male urinary incontinence
InactiveUS9198747B2Avoid dissectionPassage is slowedSuture equipmentsAnti-incontinence devicesThighTransobturator sling
A transobturator technique was developed for treating male urinary incontinence. This approach helped to design specific instruments to pass around the ischio-pubic branches of the male pelvis from inside to outside (i.e from the suburethral space to the thigh fold). The inside-out transobturator sling technique uses specific instruments and a polypropylene mesh with two arms that are passed inside to outside through the obturator foramens, pulled for compressing the bulbar urethra upward, and tied to each other across the midline. The mesh passes around the ischio-pubic branch before being tied under the bulbar urethra where it brings tension and support.
Owner:UNIV LIEGE +1
Outrigger line lock positioning device
Disclosed is a line positioning device for use with fishing vessel outriggers. The positioning device employs a housing having a pulley, a resilient bushing positioned next to the pulley, and a lever arm that is strategically positioned to engage a halyard line against the resilient bushing. A halyard line placed through the device is partially wrapped around the pulley where the line can freely move. Locking of the line requires the partial rotation of the lever arm which includes a tip end that presses the line against the resilient bushing. The lever arm includes a detent for engagement of a biased ball for use in holding the lever arm in either a locked or unlocked position.
Owner:RUPP MARINE
Small flexible liquid core catheter for laser ablation in body lumens and methods for use
Embodiments relate to the design and use of a low profile ablation catheter with a liquid core for use in laser ablation removal of arterial plaque blockages to restore blood flow.
Owner:RA MEDICAL SYST
Catheter with an expandable end portion
InactiveUS20060264972A1Improve axial strengthImprove scalabilityStentsEar treatmentInsertion stentMedical device
A catheter (2) is used in medical applications, for example for the retrieval of a sample from a patient or the insertion or retrieval of medical devices such as filters, stents (3) to and from the patient. The catheter (2) includes an expandable tip (6) at a leading portion of a catheter tube portion (5). This expandable tip (6) can retrieve or deliver samples, medical devices, etc. (3), which are slightly larger than the dimensions of a main catheter tube (5) inserted into the patient. The expandable tip (6) can also include extension members (10) which provide axial support to the expandable tip (6) but which still allow expansion in the radial direction.
Owner:SALVIAC
Beverage Dispense System and Method
InactiveUS20140263433A1Improve hygieneReduced cleanlinessDomestic cooling apparatusLighting and heating apparatusEngineeringCooling medium
The present invention relates to beverage dispense systems and methods. The systems comprise a beverage line having a distal end connectable to a beverage supply for transporting beverage from the beverage supply to a dispense font at a dispensing site. They also include a cooler for cooling beverage. The beverage line comprises a first beverage line portion extending from the distal end to the cooler within a first insulated carrier. The first insulated carrier comprises a first cooling line for transporting cooling medium through the first insulated carrier so as to allow heat exchange between the cooling medium in the first cooling line and the beverage in the first beverage line portion.
Owner:HEINEKEN UK
Carotid sheath with flexible distal section
The present invention is a carotid sheath that has a proximal portion that is stiffer than the distal portion of the sheath as a result of the proximal portion having a higher durometer of the outer plastic coating of the sheath's proximal portion with a lower durometer for the plastic coating on the more flexible distal portion of the sheath. Another means to increase the flexibility of the sheath's distal portion compared to a stiffer proximal portion is by having a slightly smaller outside diameter for the outer plastic coating of the distal portion of the sheath. A more flexible distal portion of the sheath allows easier access for angiography, angioplasty or stenting when the sheath is used to access the tortuous path encountered when entering the carotid arteries.
Owner:FISCHELL INNOVATIONS
Flame gas burner diffuser for cooking equipments
InactiveUS20140345591A1Enhance heat exchange efficiencyImprove heat transfer efficiencyDomestic stoves or rangesLighting and heating apparatusGas burnerCooker
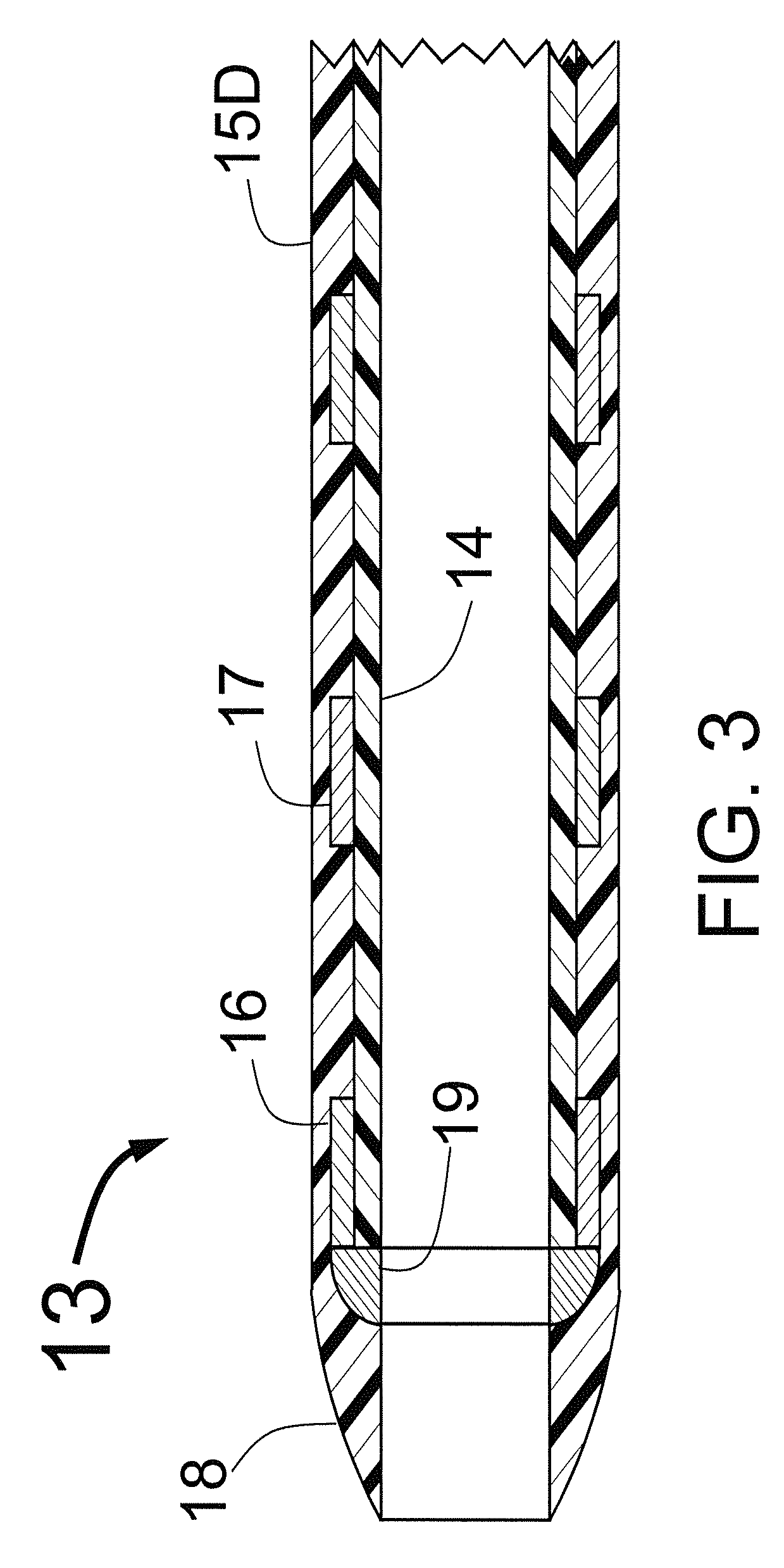
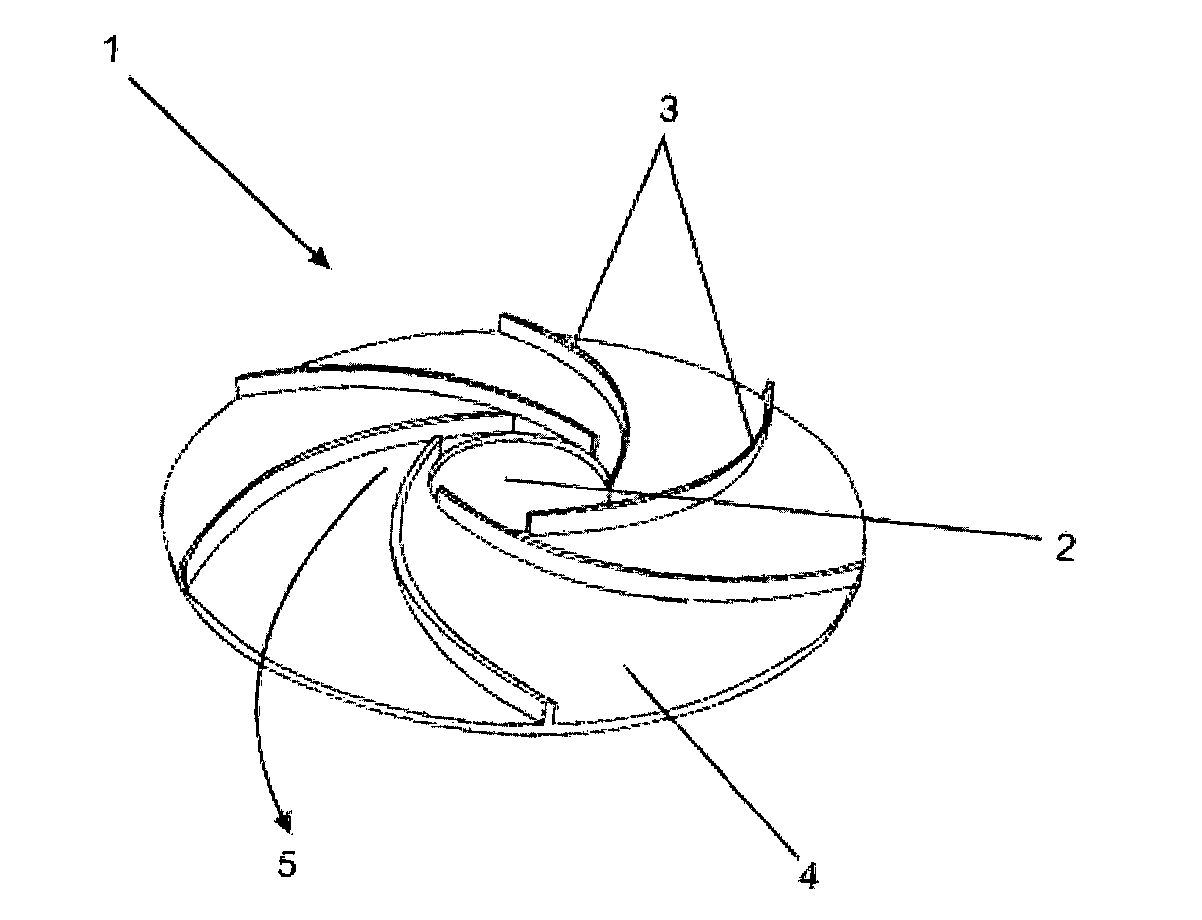
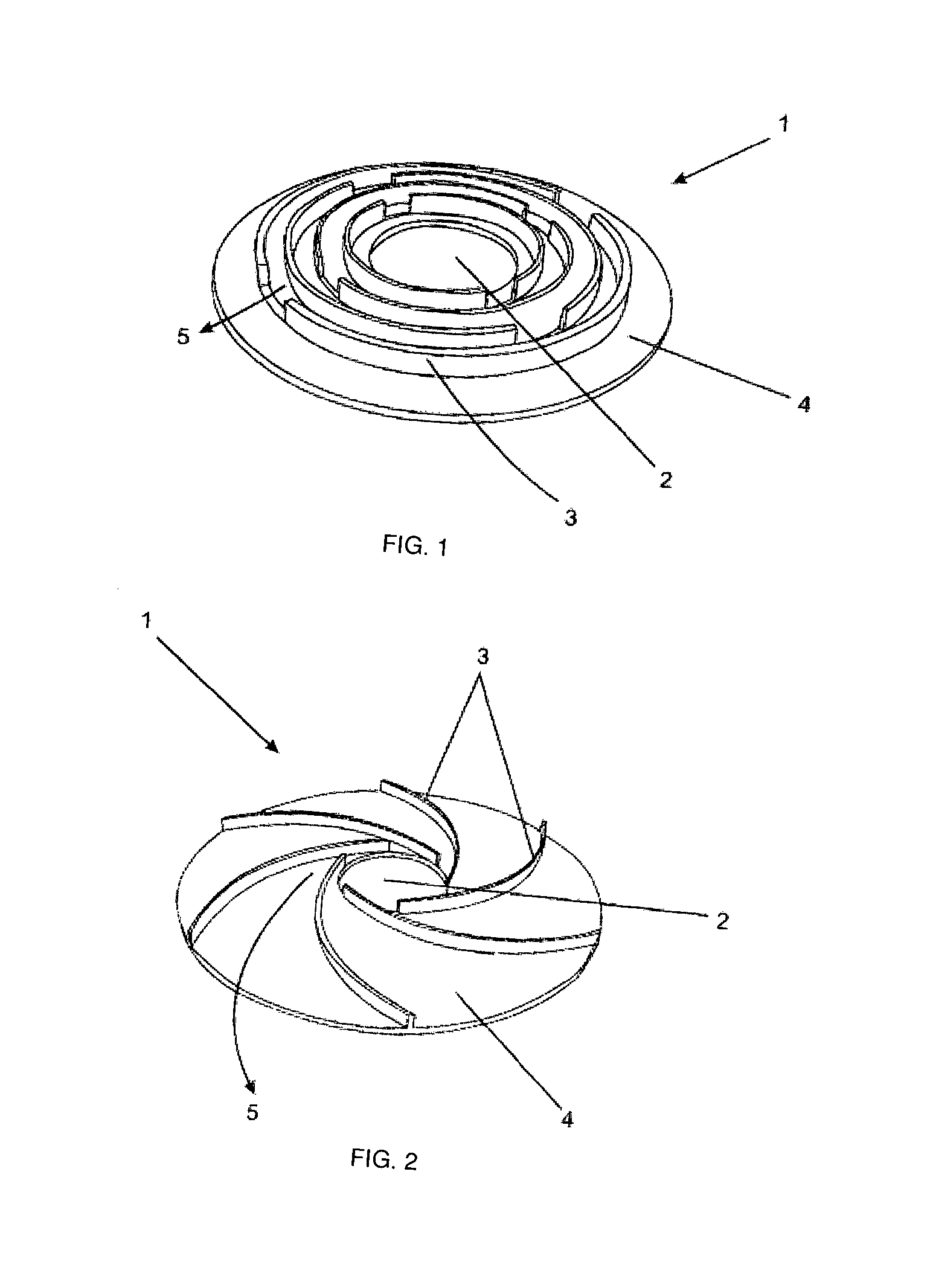
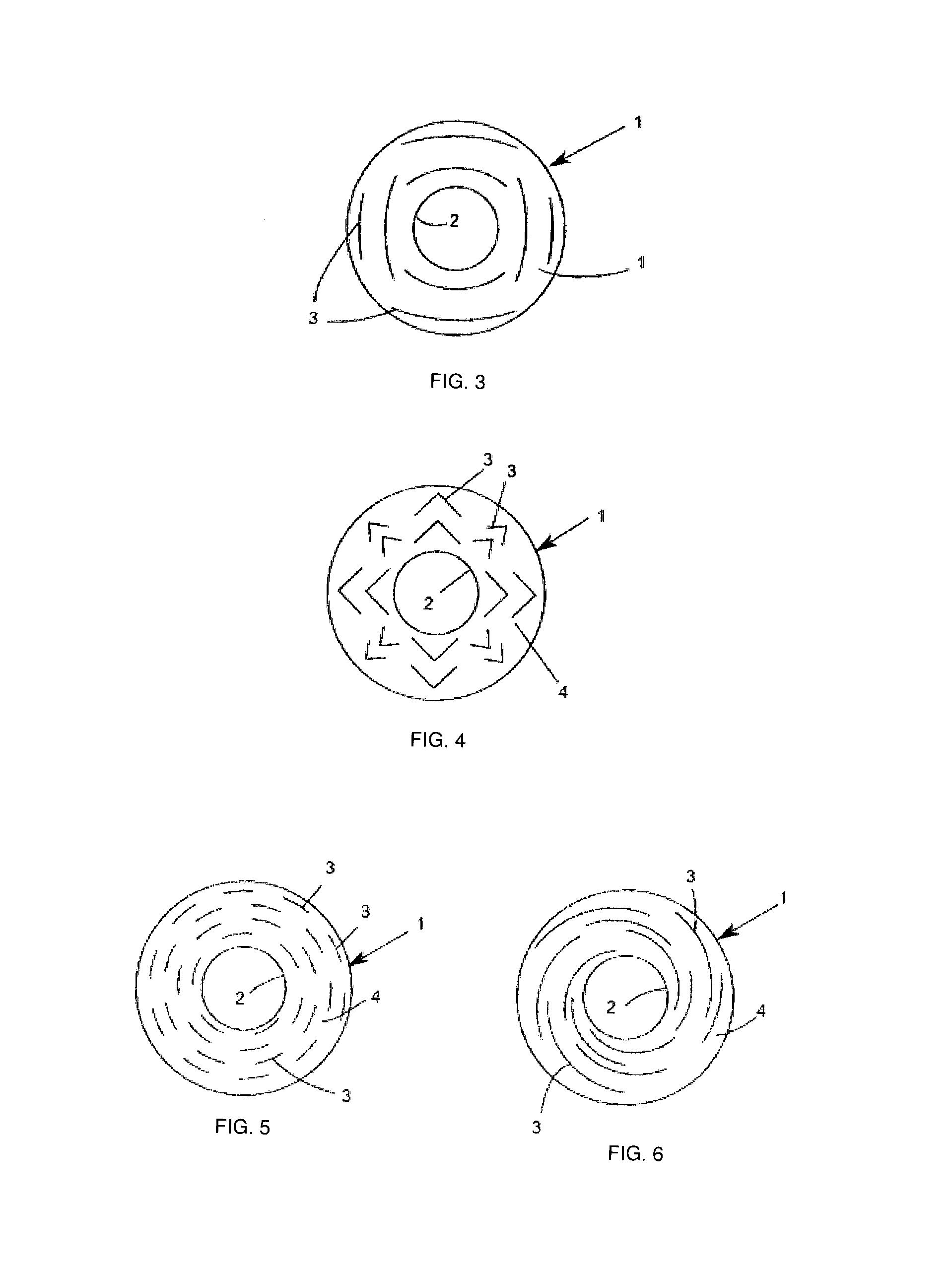
The present invention generally refers to a flame gas burner diffuser to be used in stove-type cooking equipments, more preferably in household stoves, comprising technical and functional features capable of improving the efficiency of exchanging heat with the bottom of cooking utensils. More particularly, said diffuser, according to the present invention, comprises a cup (1) provided with a surface (4) comprising an opening (2) at which a cooking equipment is accommodated, wherein over said surface (4) there is a series of barriers (3) duly arranged and positioned so as to form passage pathways and / or extended channels for allowing the hot gas flow generated by the burner flame to pass.
Owner:WHIRPOOL SA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com