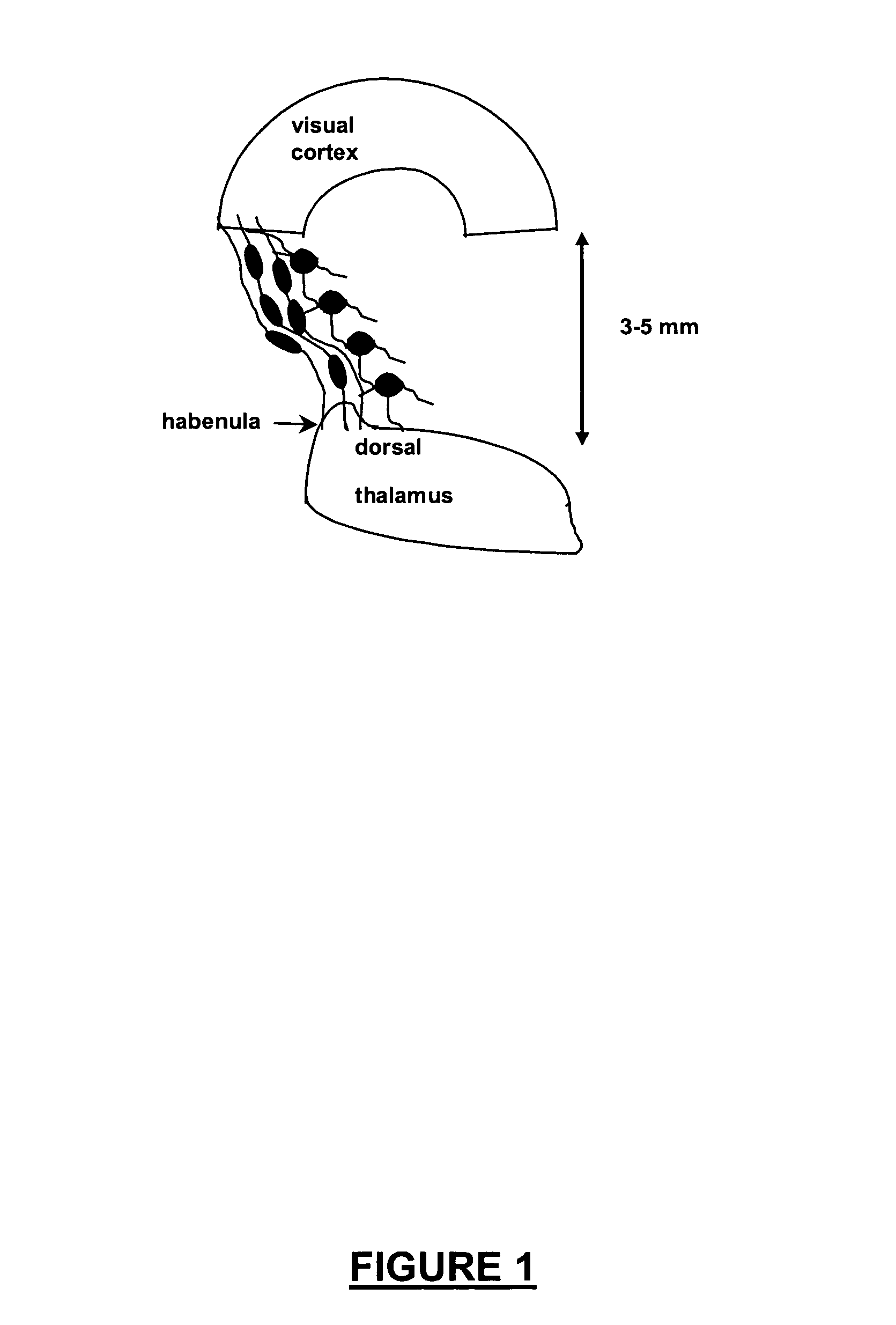
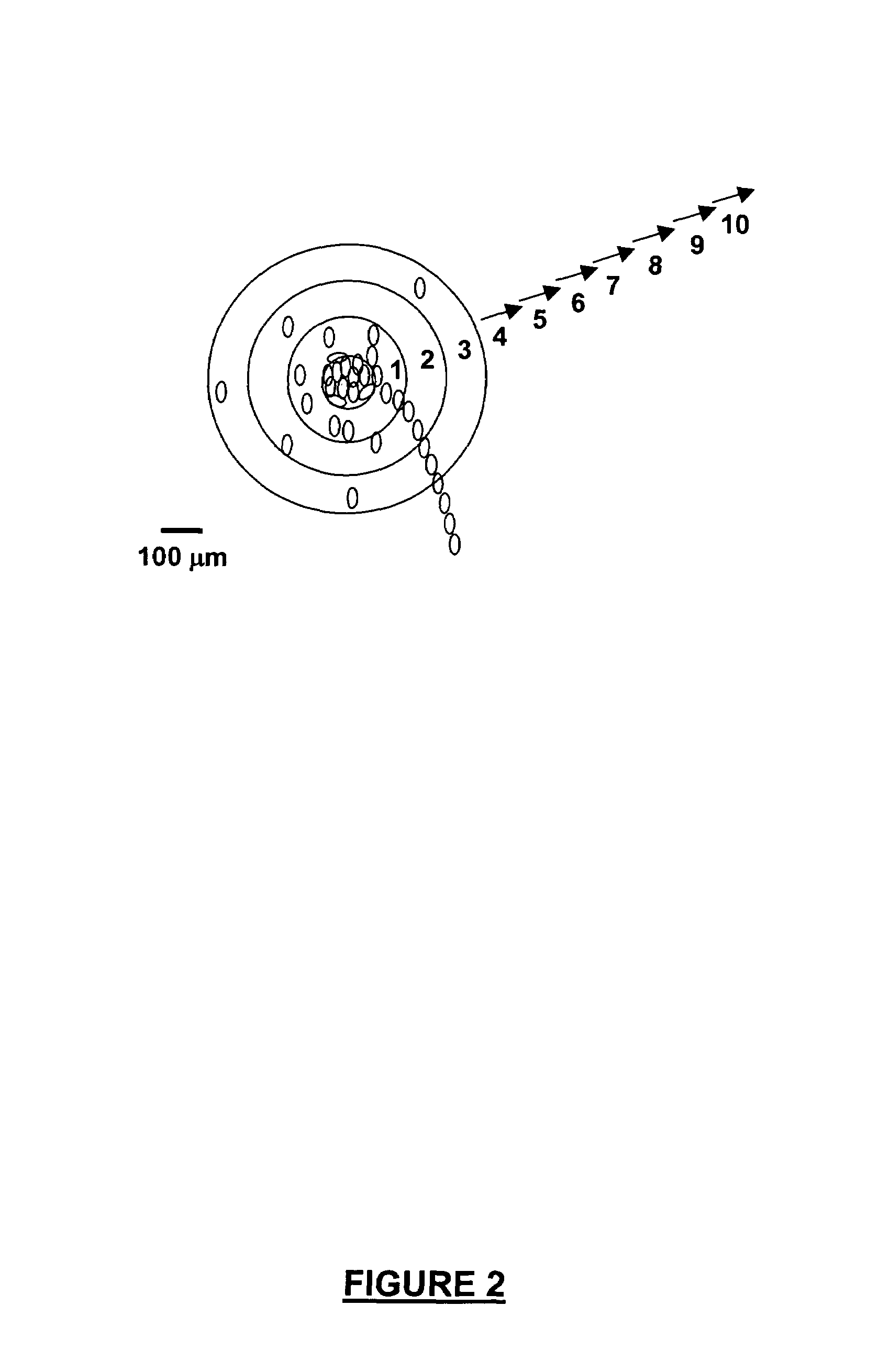
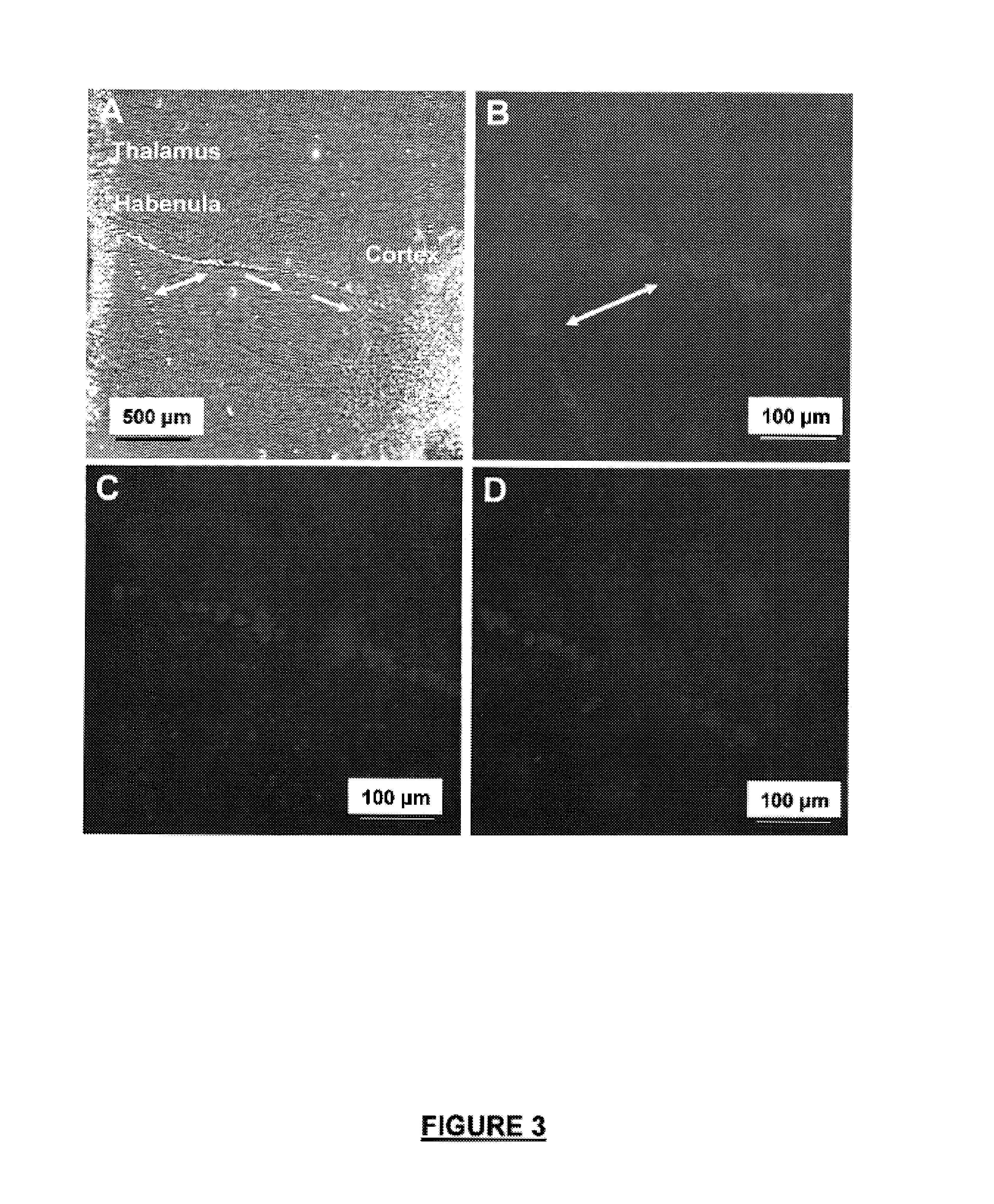
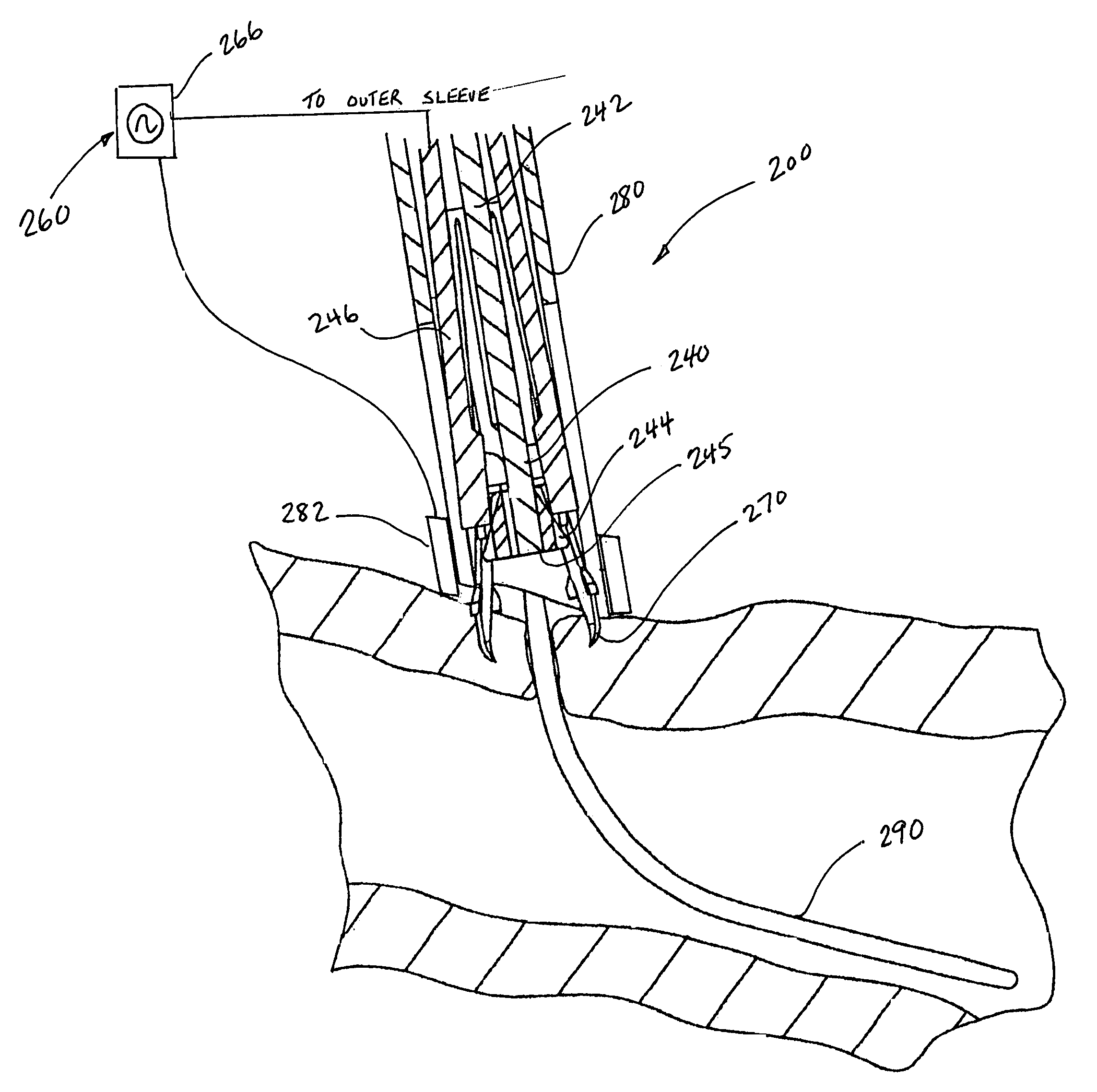
Patents
Literature
45671 results about "Blood vessel" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
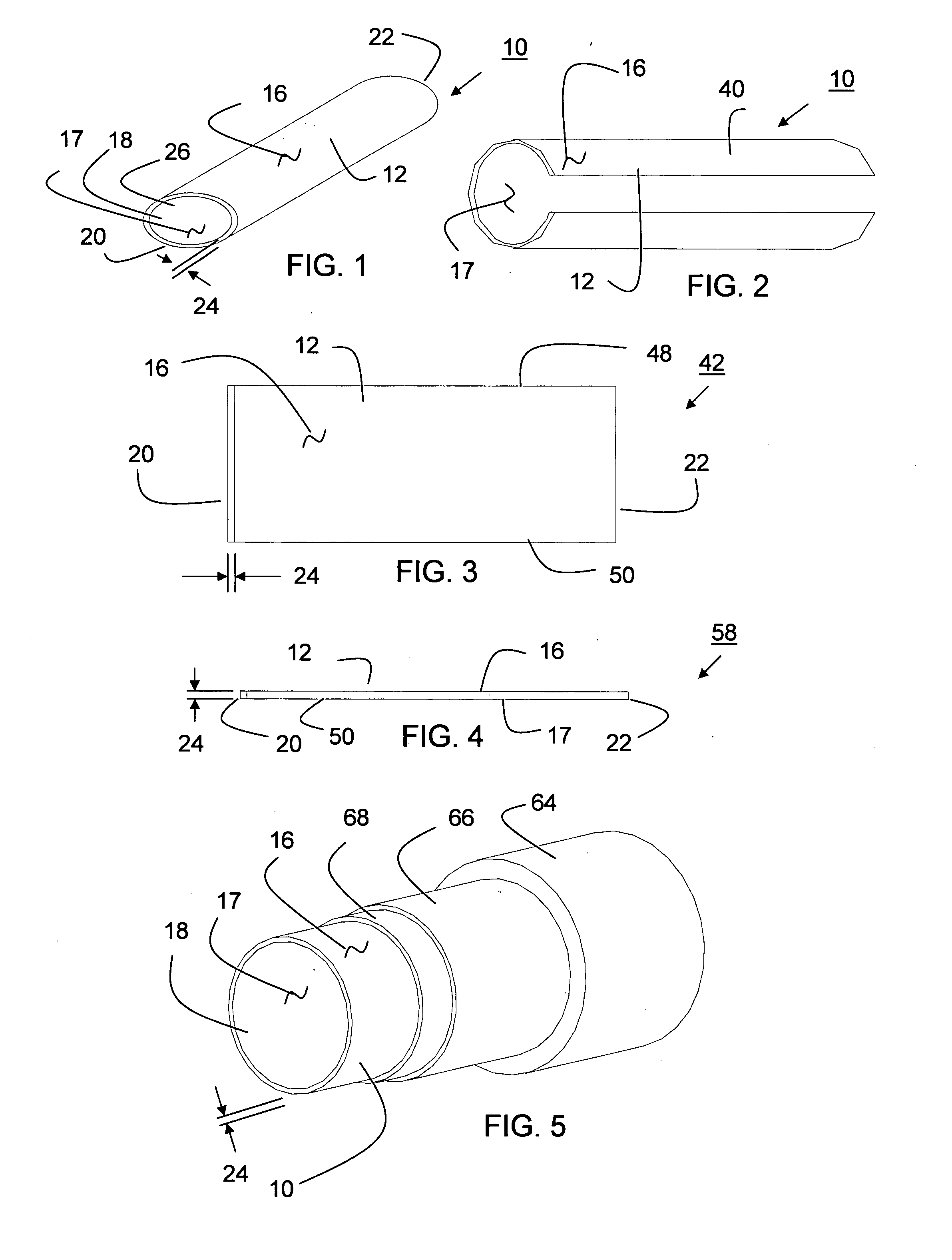
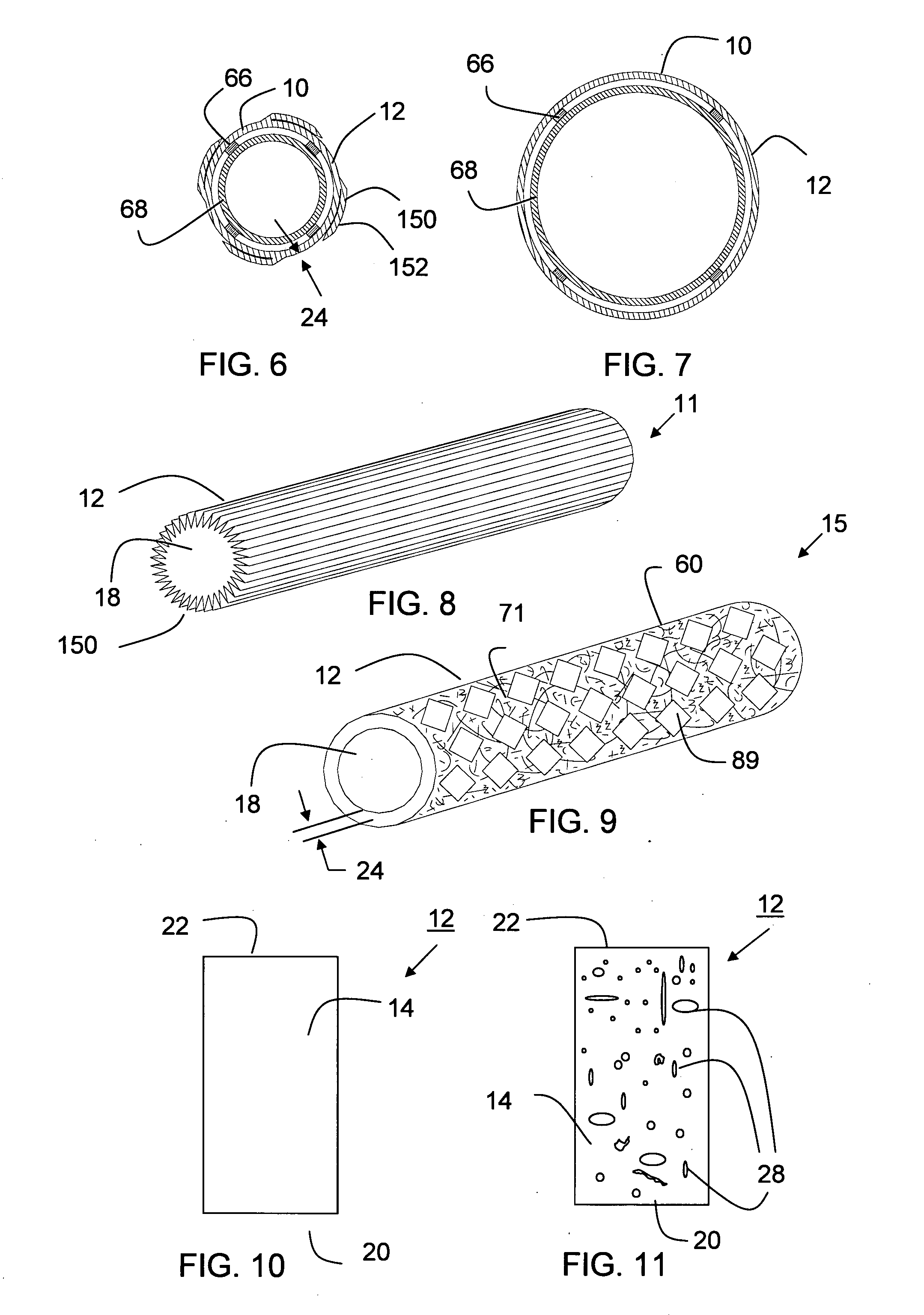
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away from the tissues. Blood vessels are needed to sustain life, because all of the body’s tissues rely on their functionality.
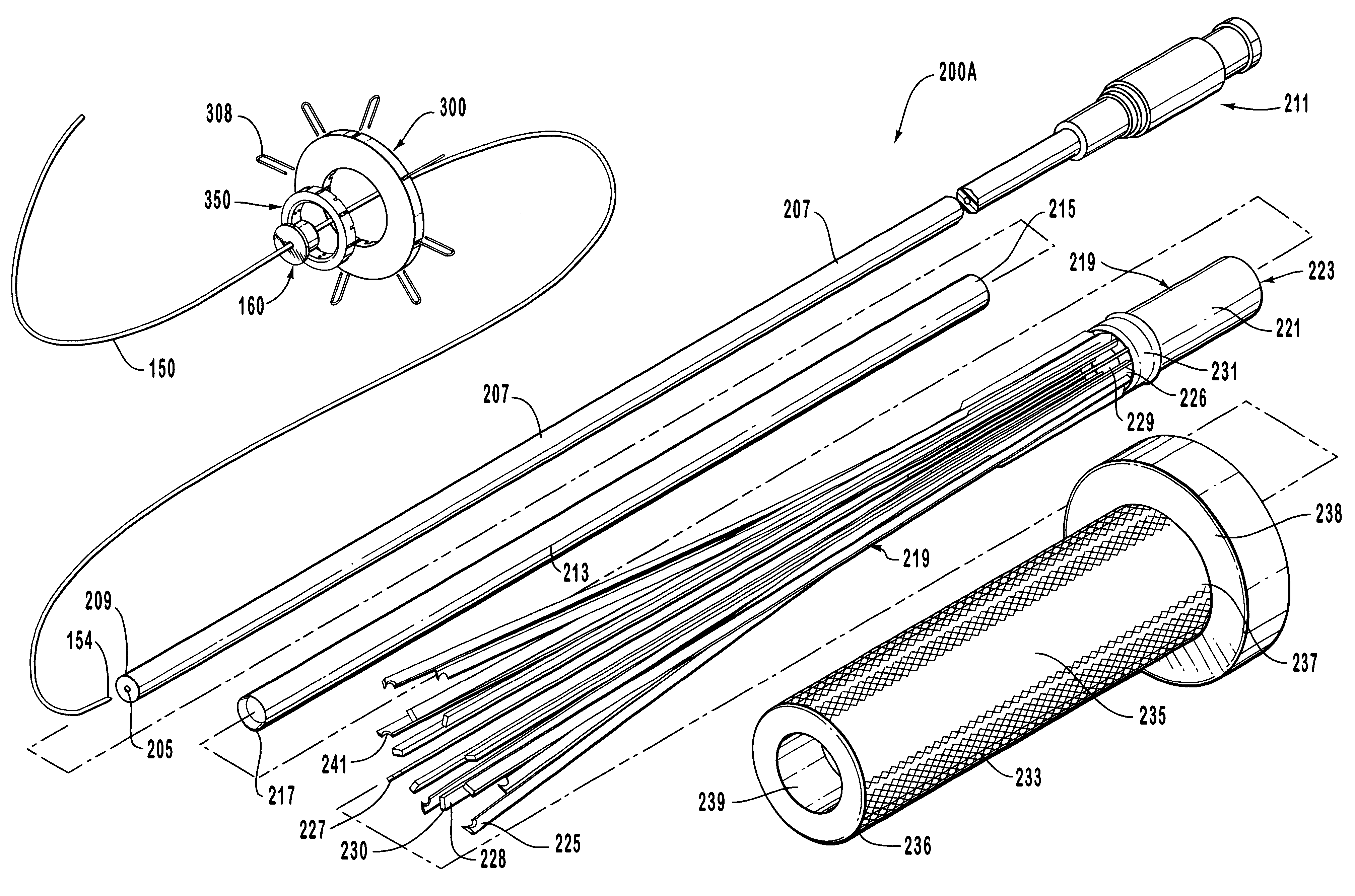
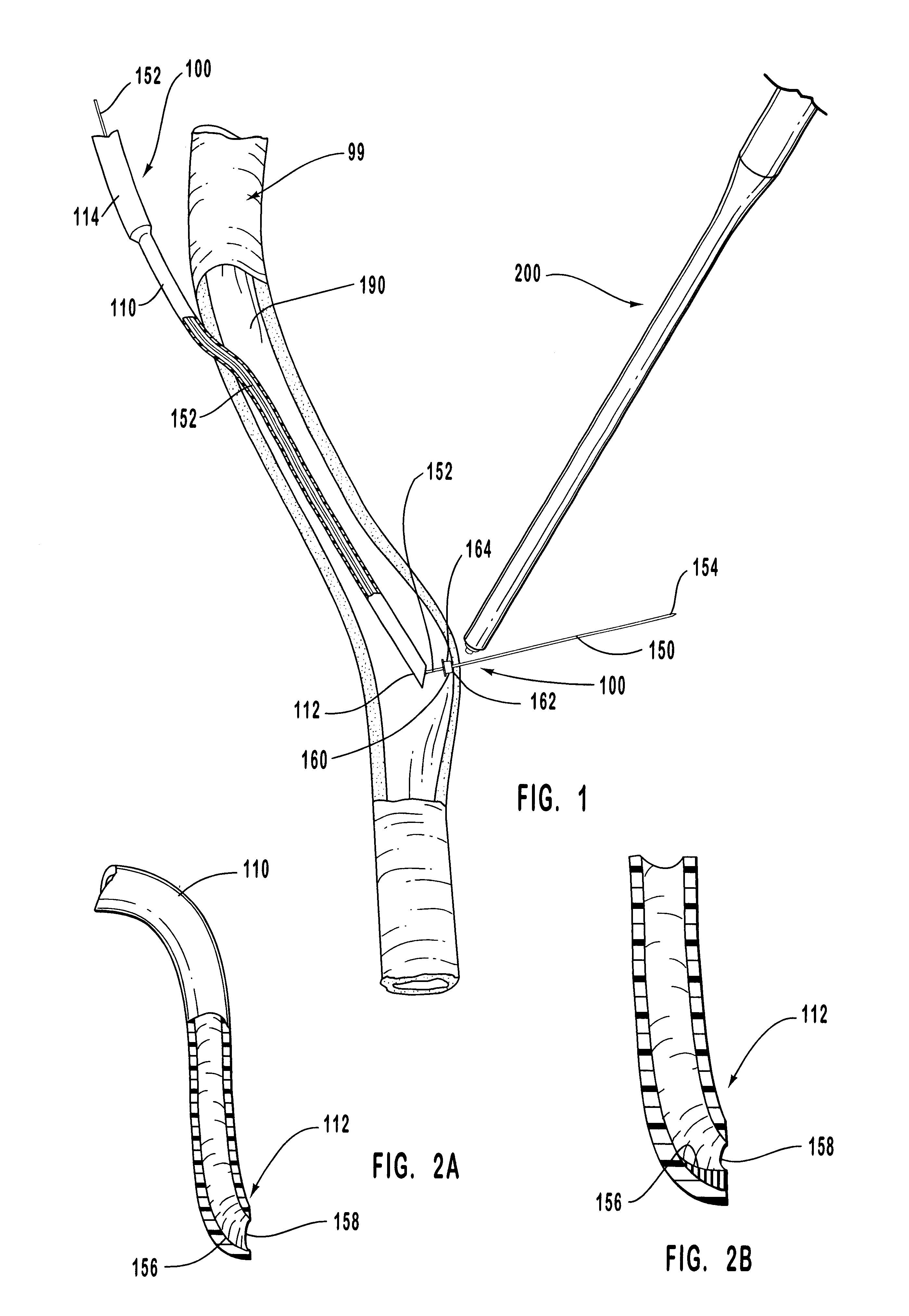
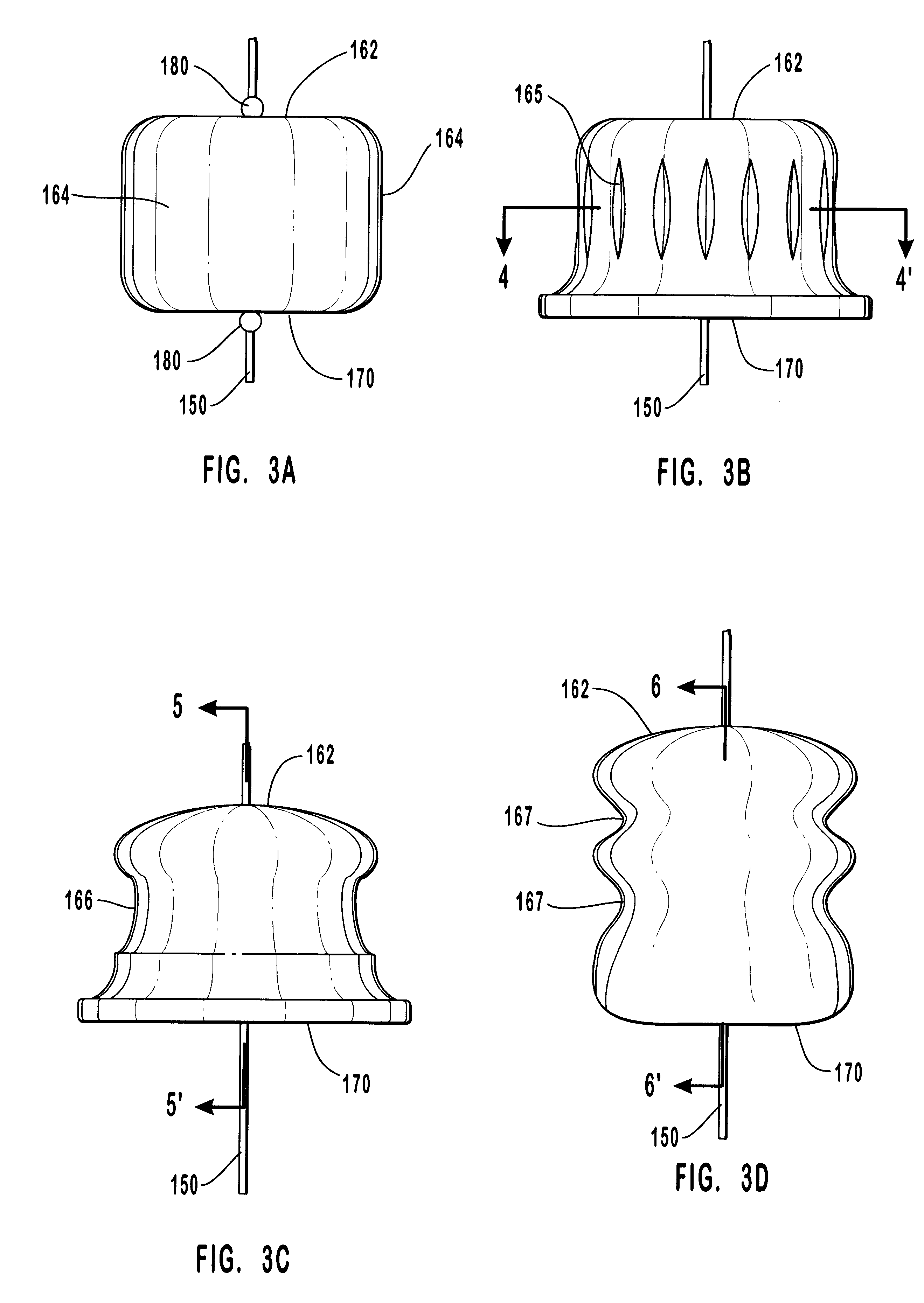
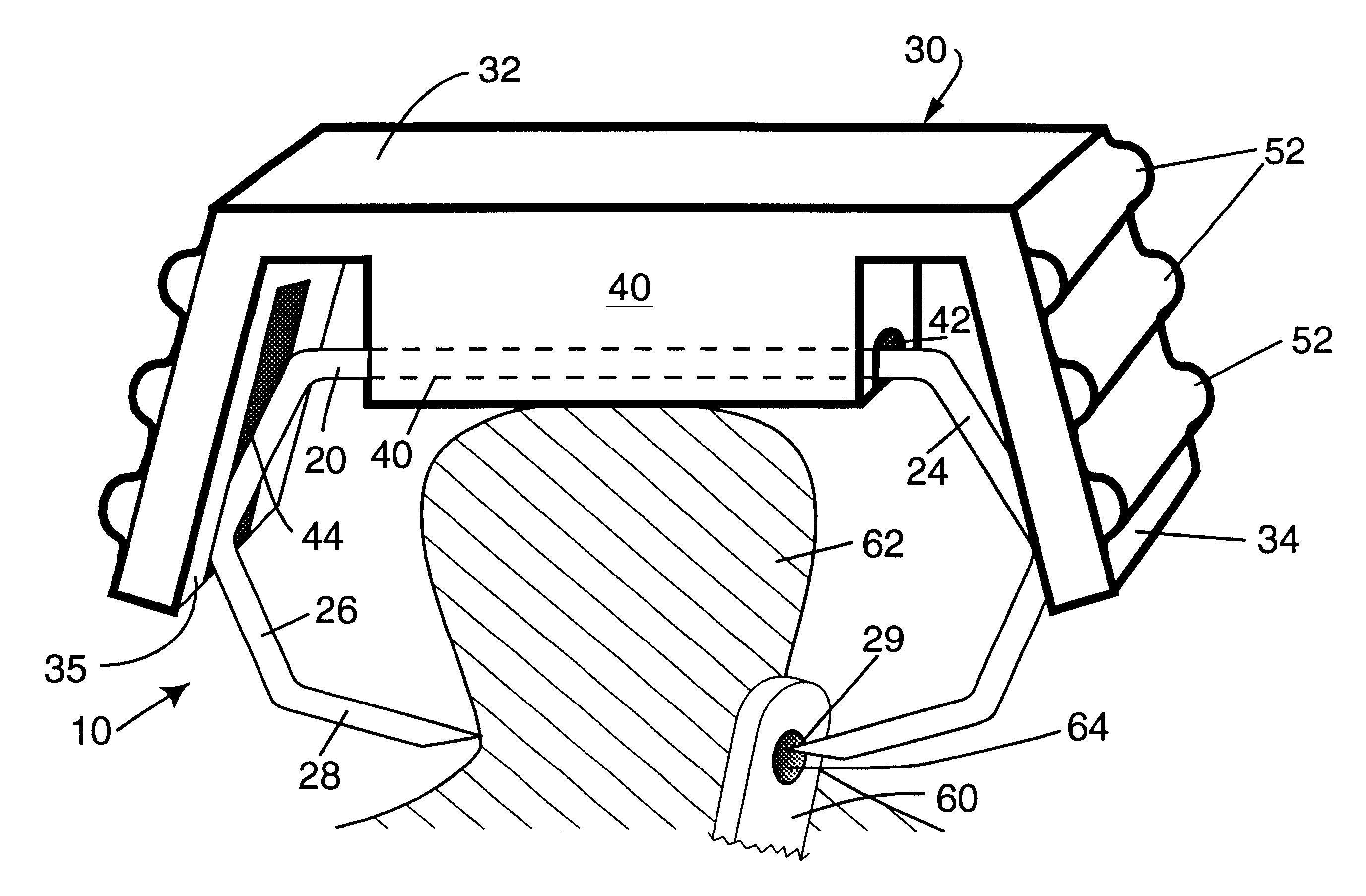
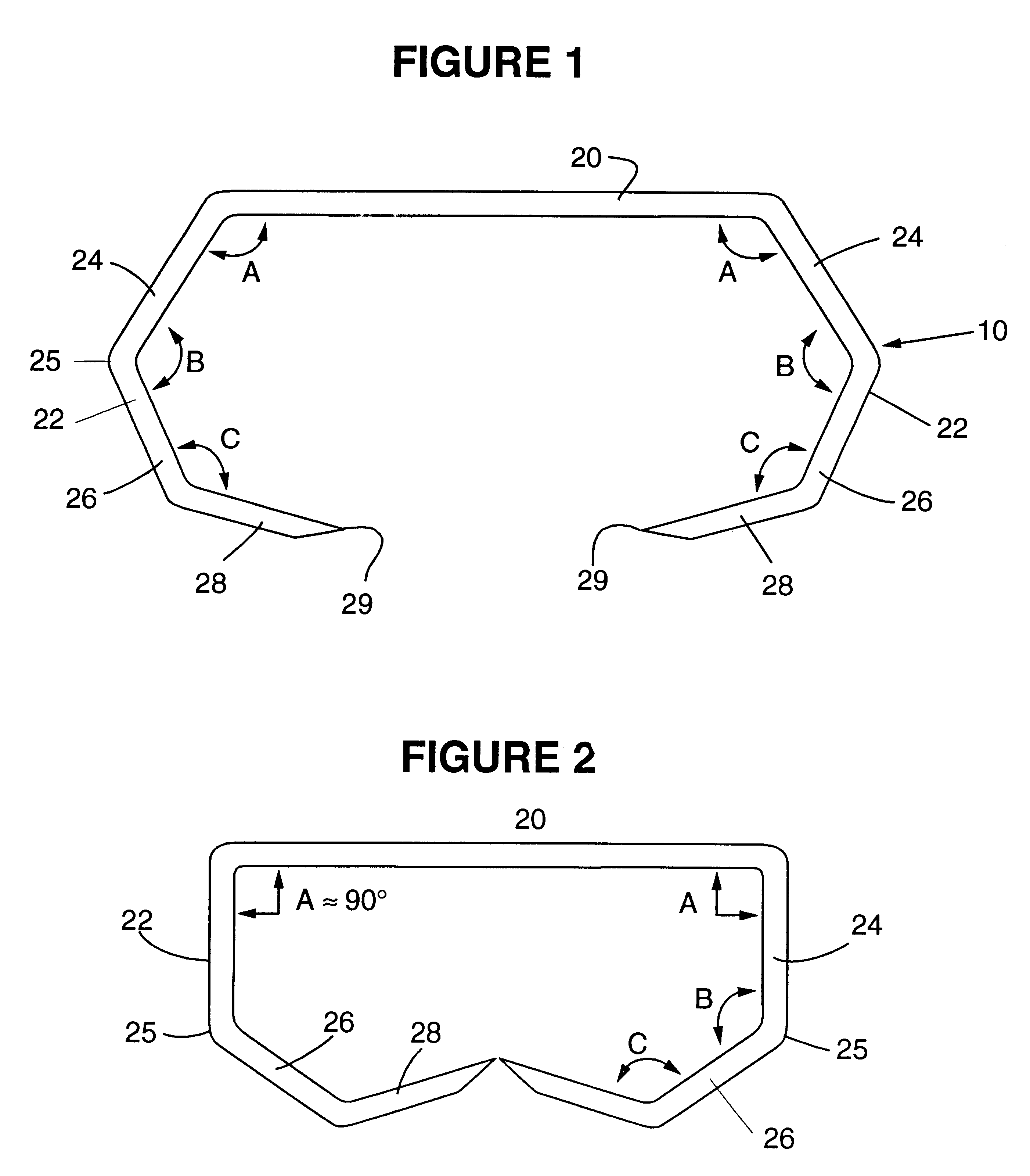
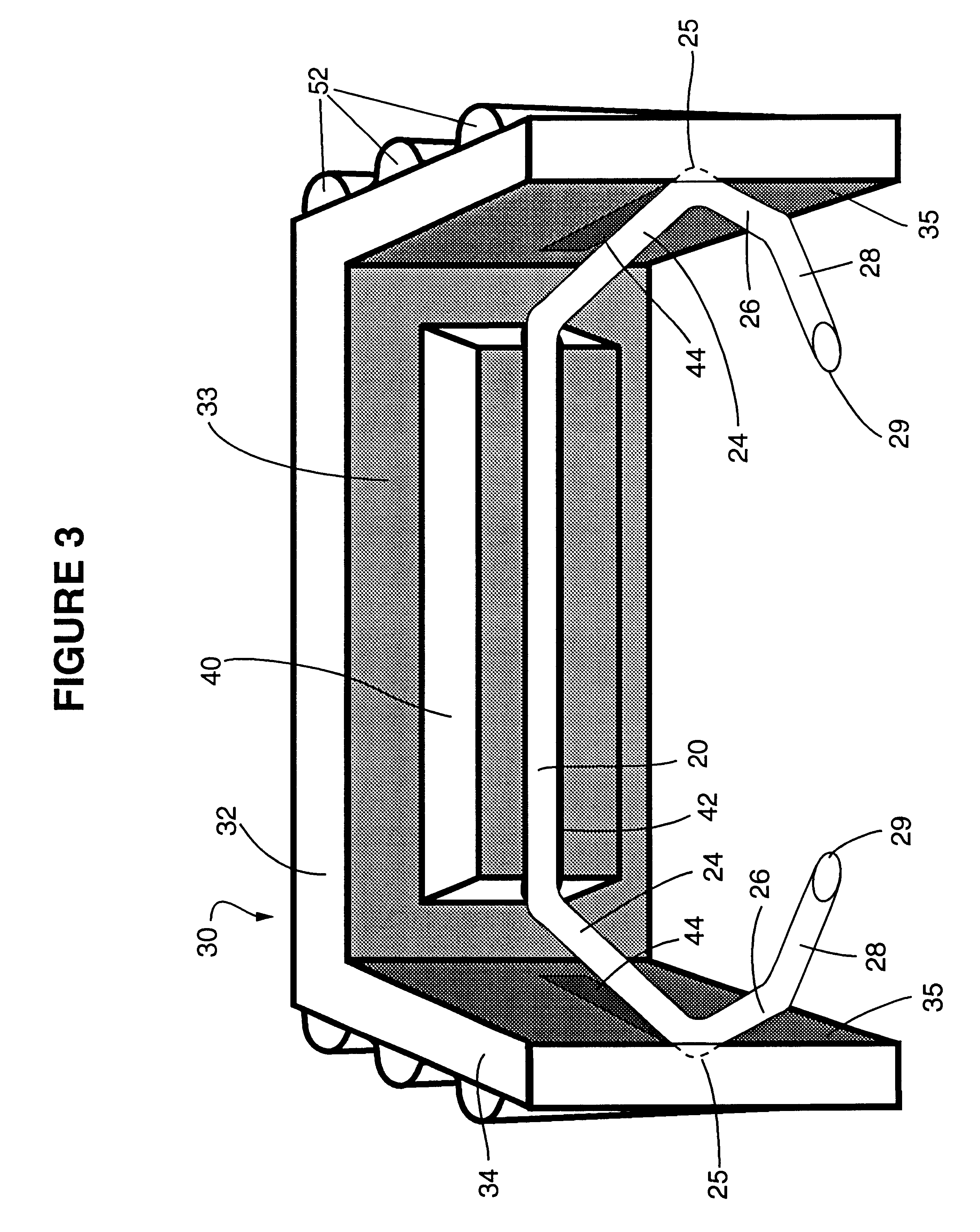
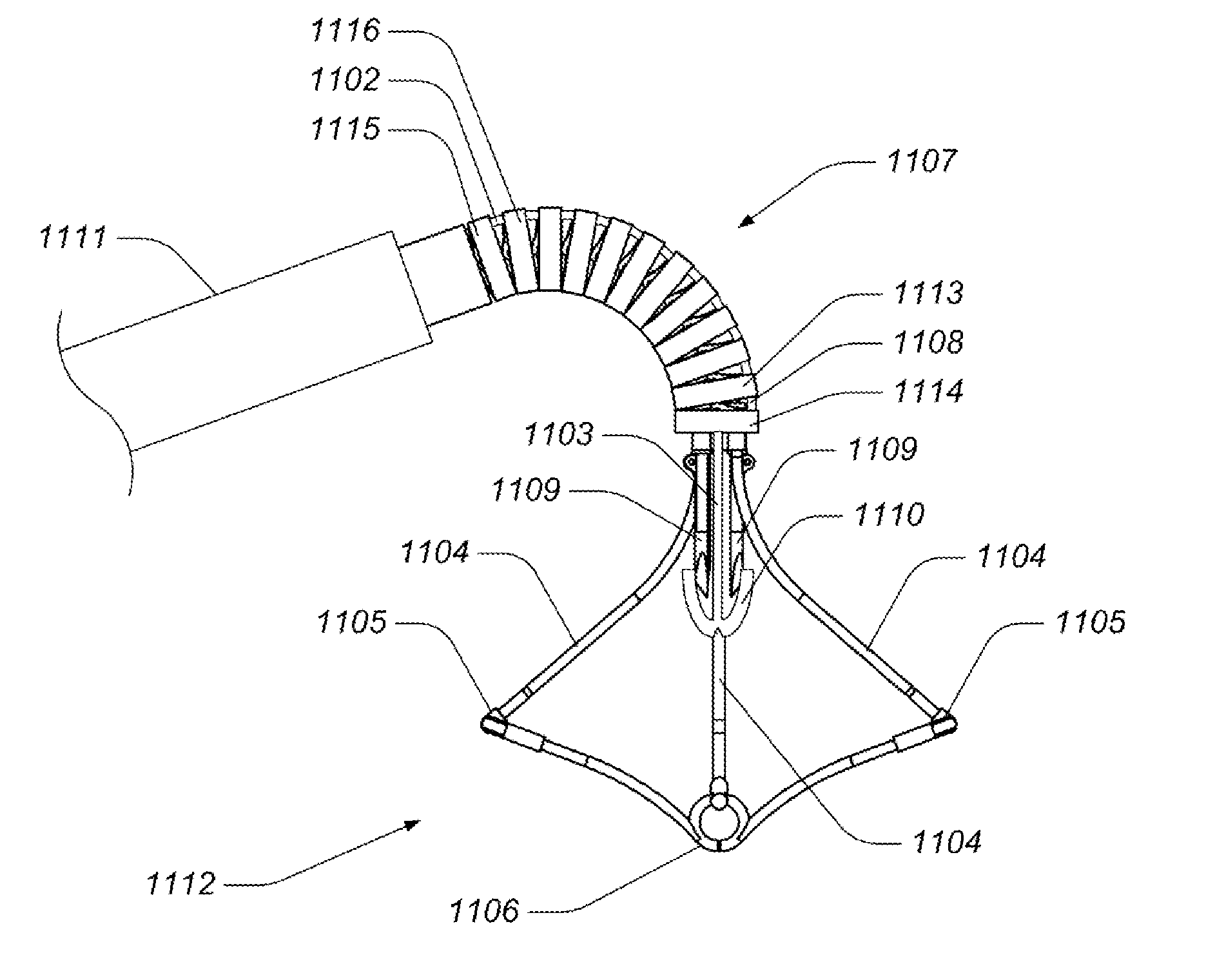
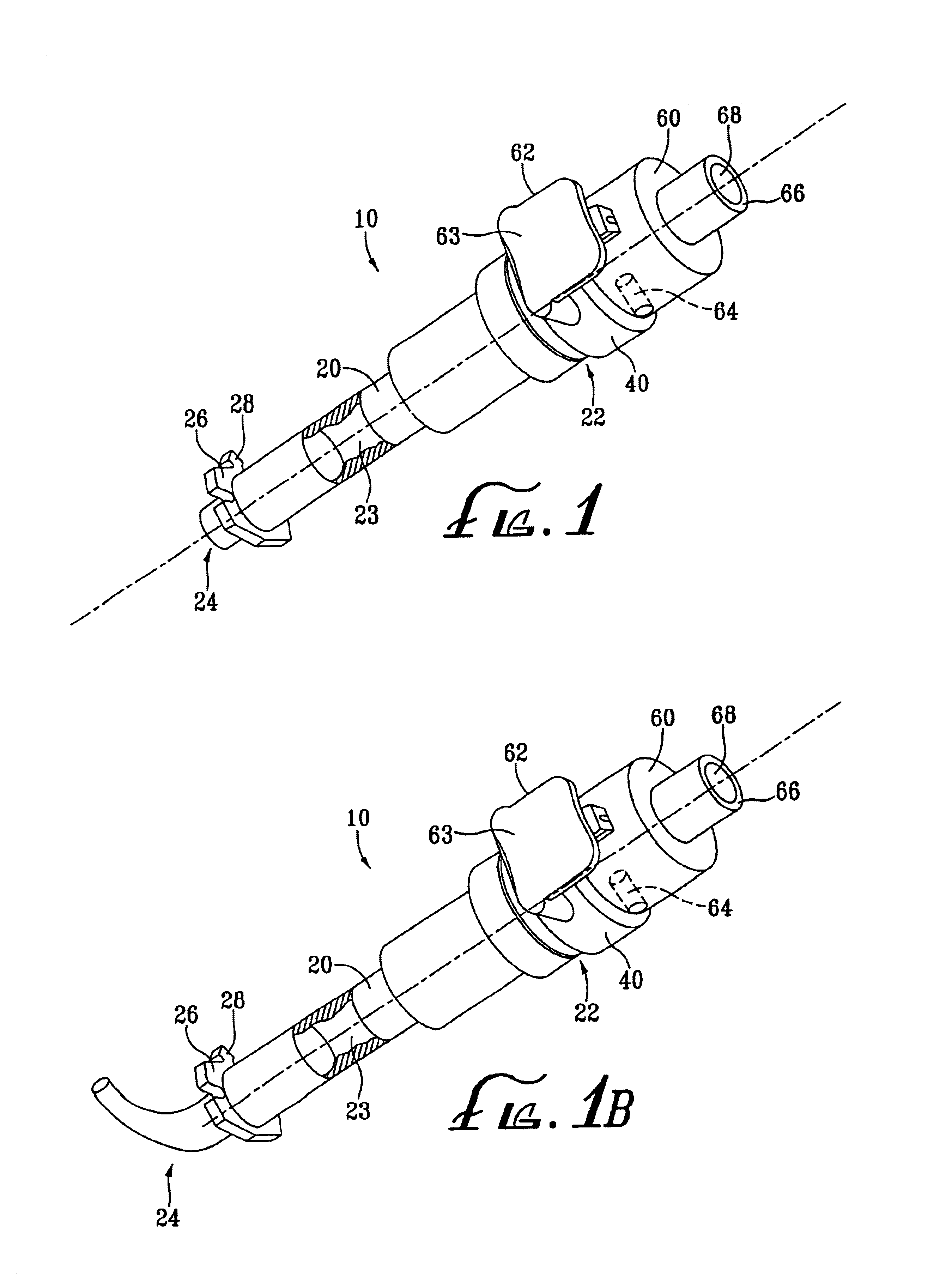
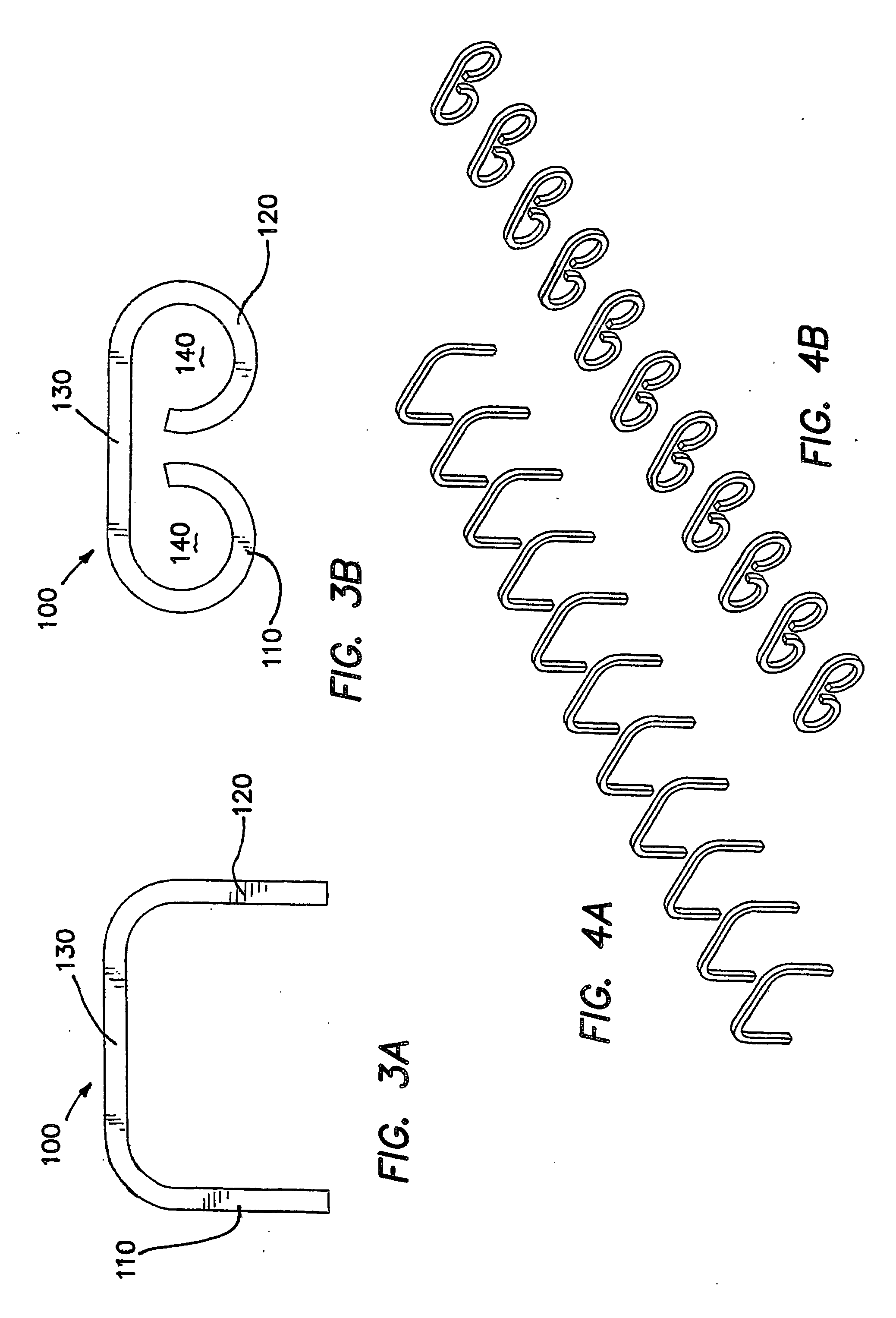
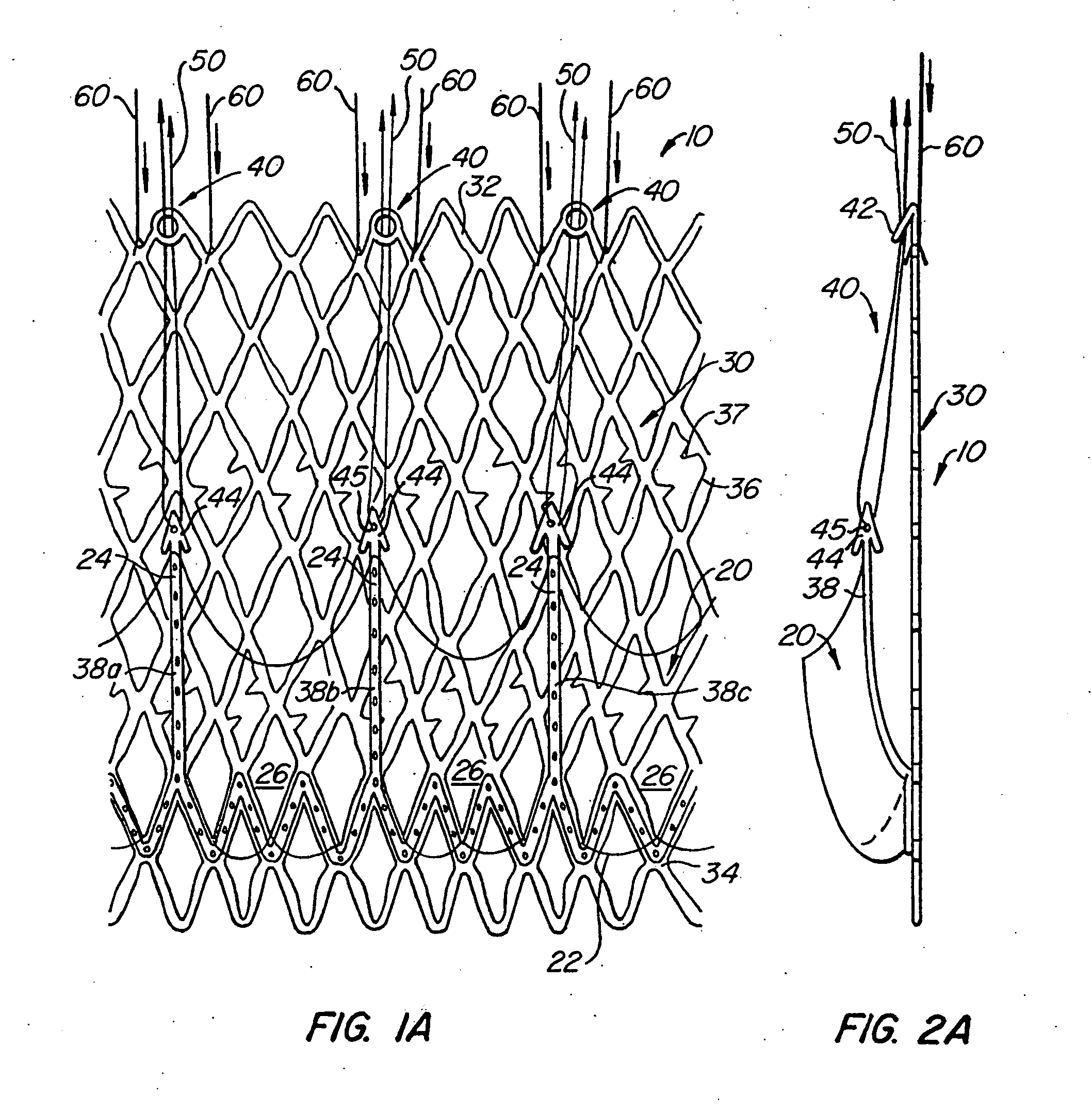
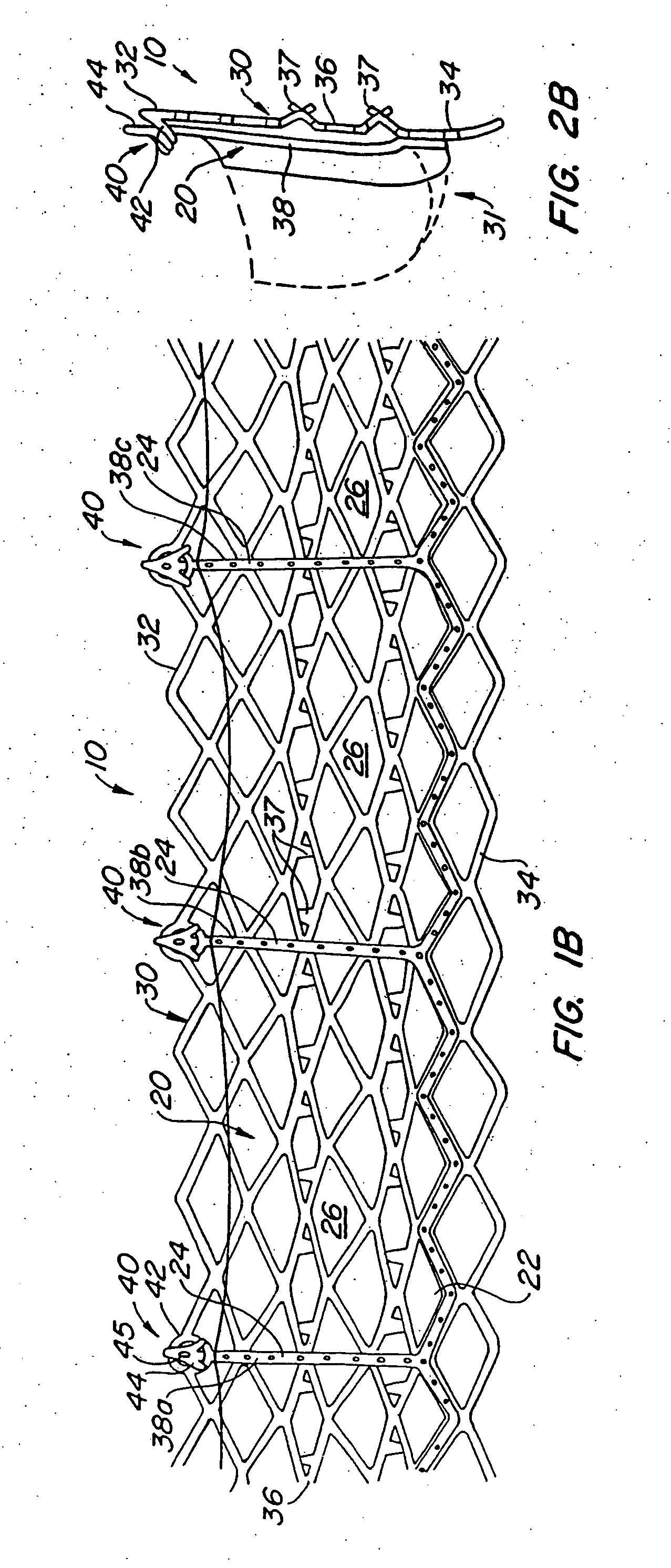
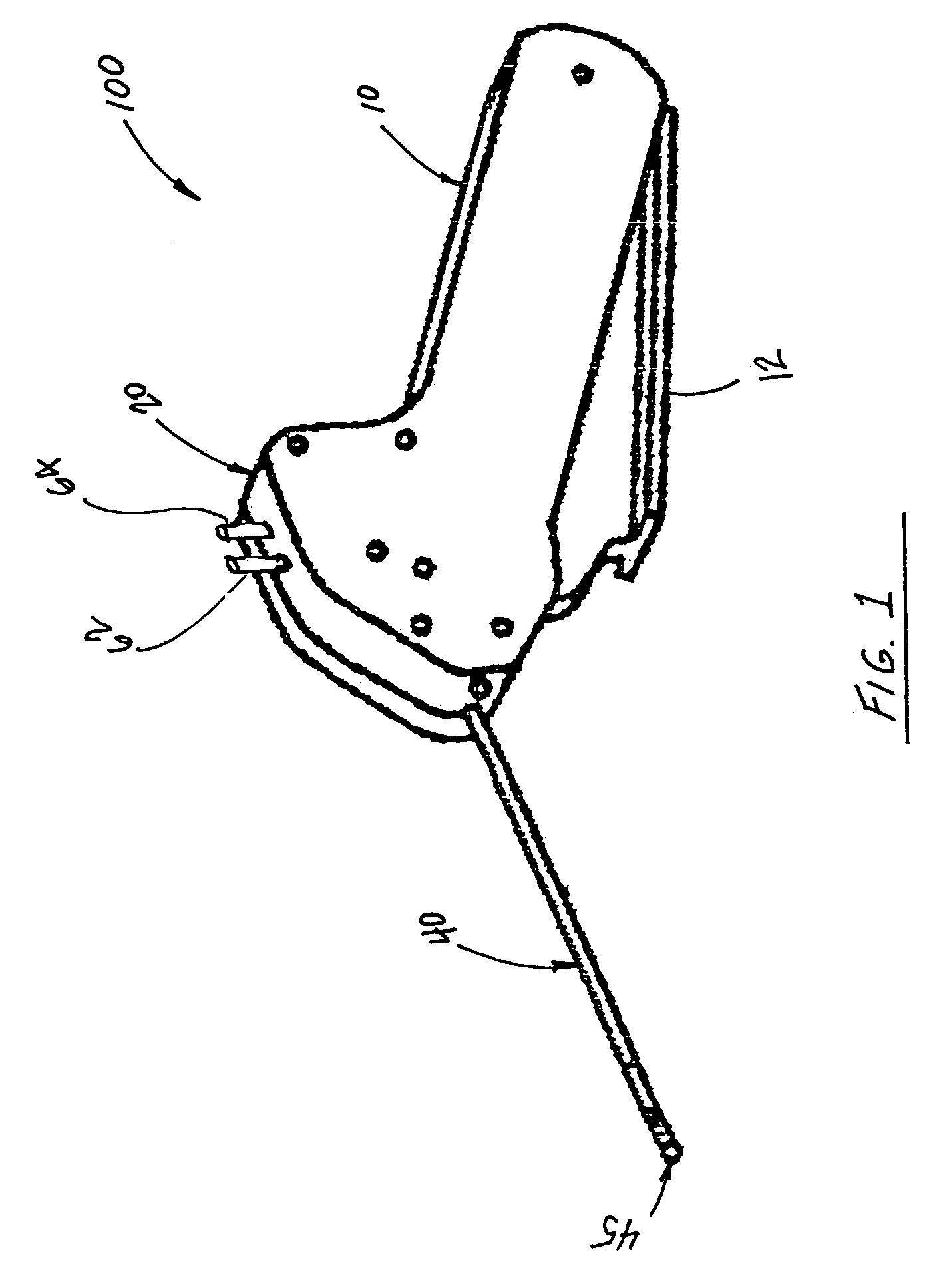
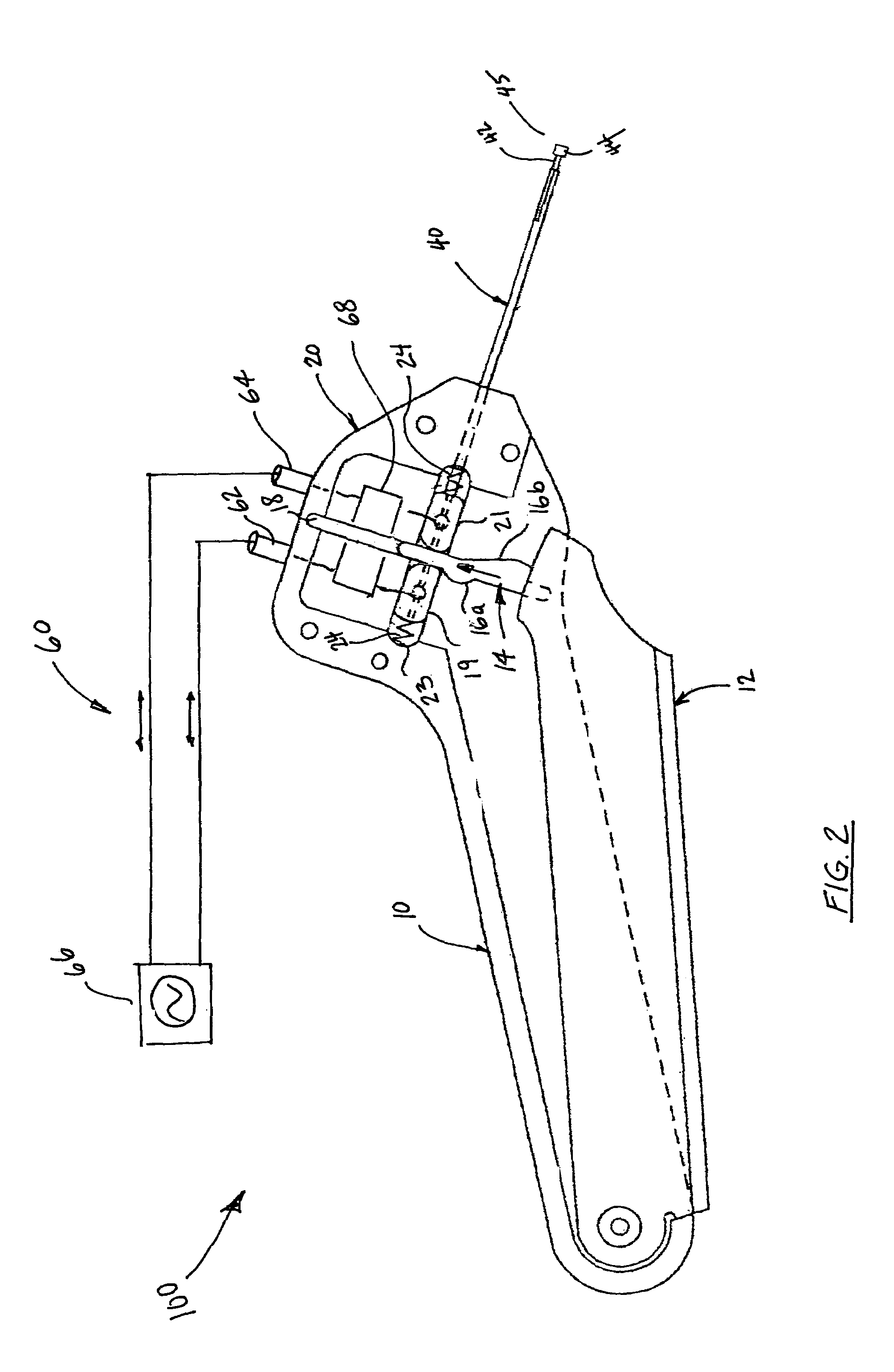
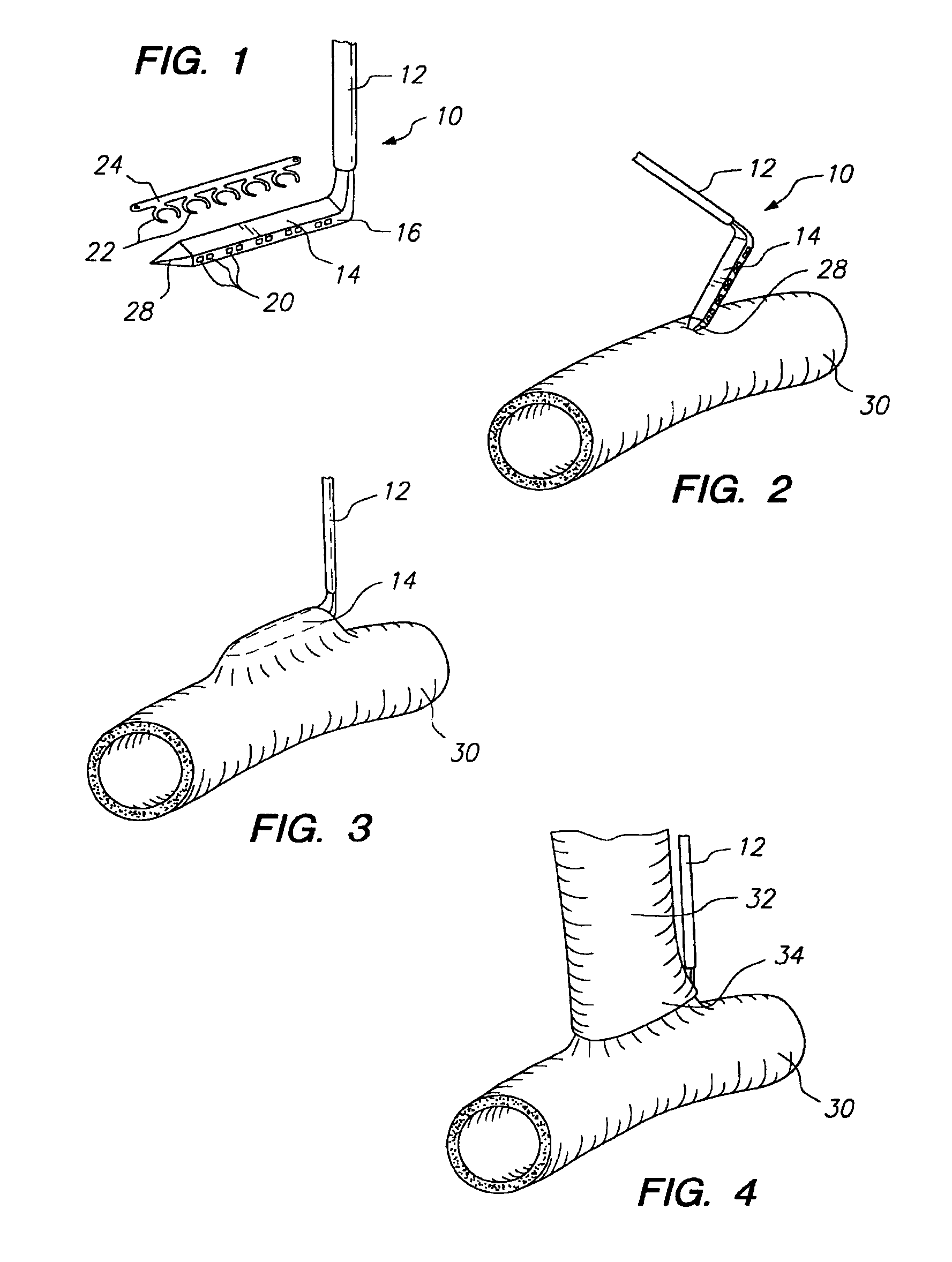
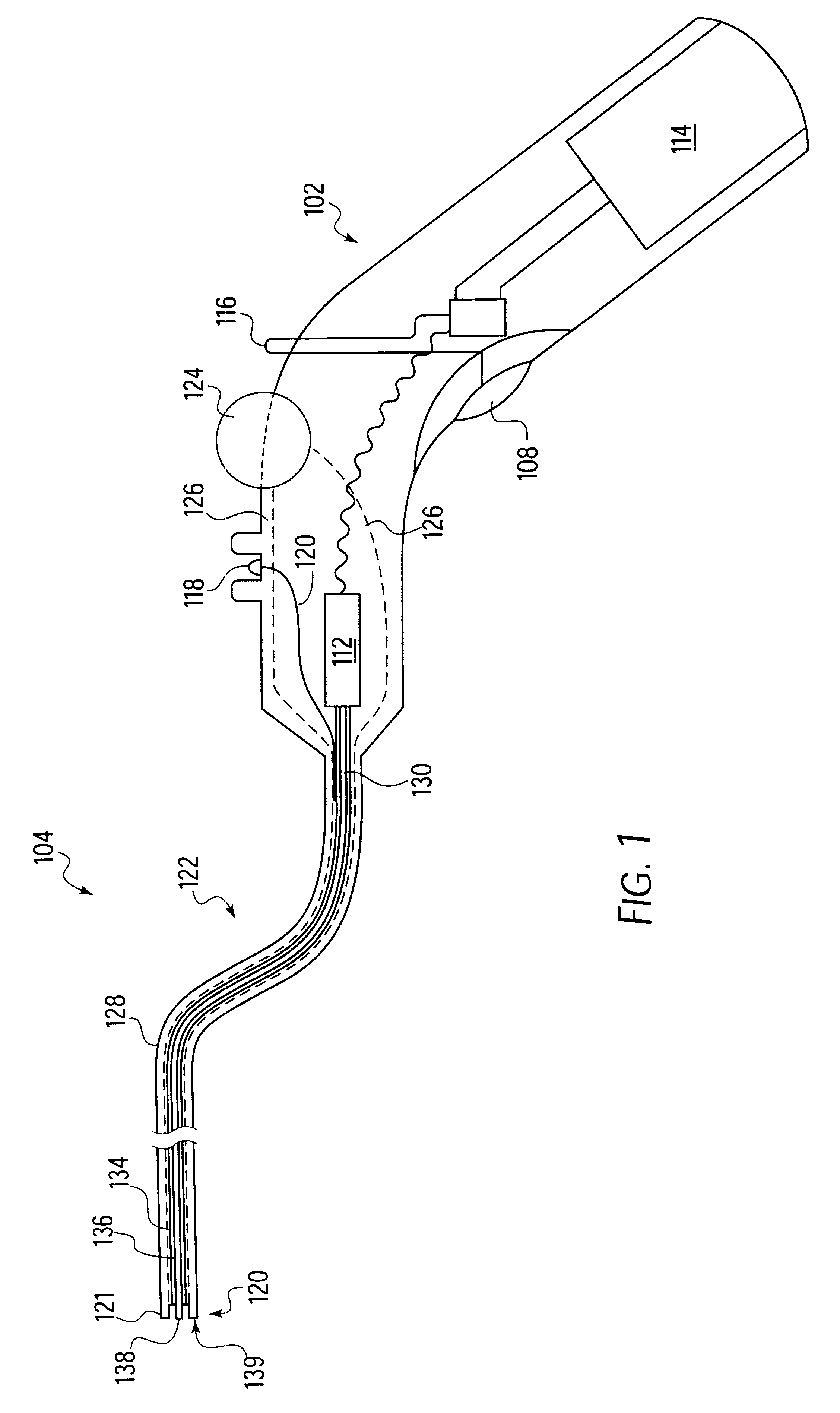
Anastomosis apparatus for use in intraluminally directed vascular anastomosis
InactiveUS6248117B1Surgical needlesSurgical staplesVascular anastomosisMinimally invasive procedures
The present invention relates to new and useful apparatus for use with an intraluminally directed anvil apparatus for intraluminally directed vascular anastomosis of an end of a graft vessel to the wall of a receiving blood vessel that is performed according to a minimally invasive procedure. The intraluminally directed vascular anastomosis does not require the interruption of blood flow in the receiving blood vessel and it is versatile enough to suitably combine a variety of cutting, welding, soldering, sealing, and joining techniques such as stapling. The intraluminally directed anvil apparatus comprises an anvil and a wire used for signaling the optimal anastomosis site; this signaling can be performed when the initial exploration is performed. The intraluminally directed anvil apparatus is typically used with a catheter.
Owner:VITAL ACCESS CORP
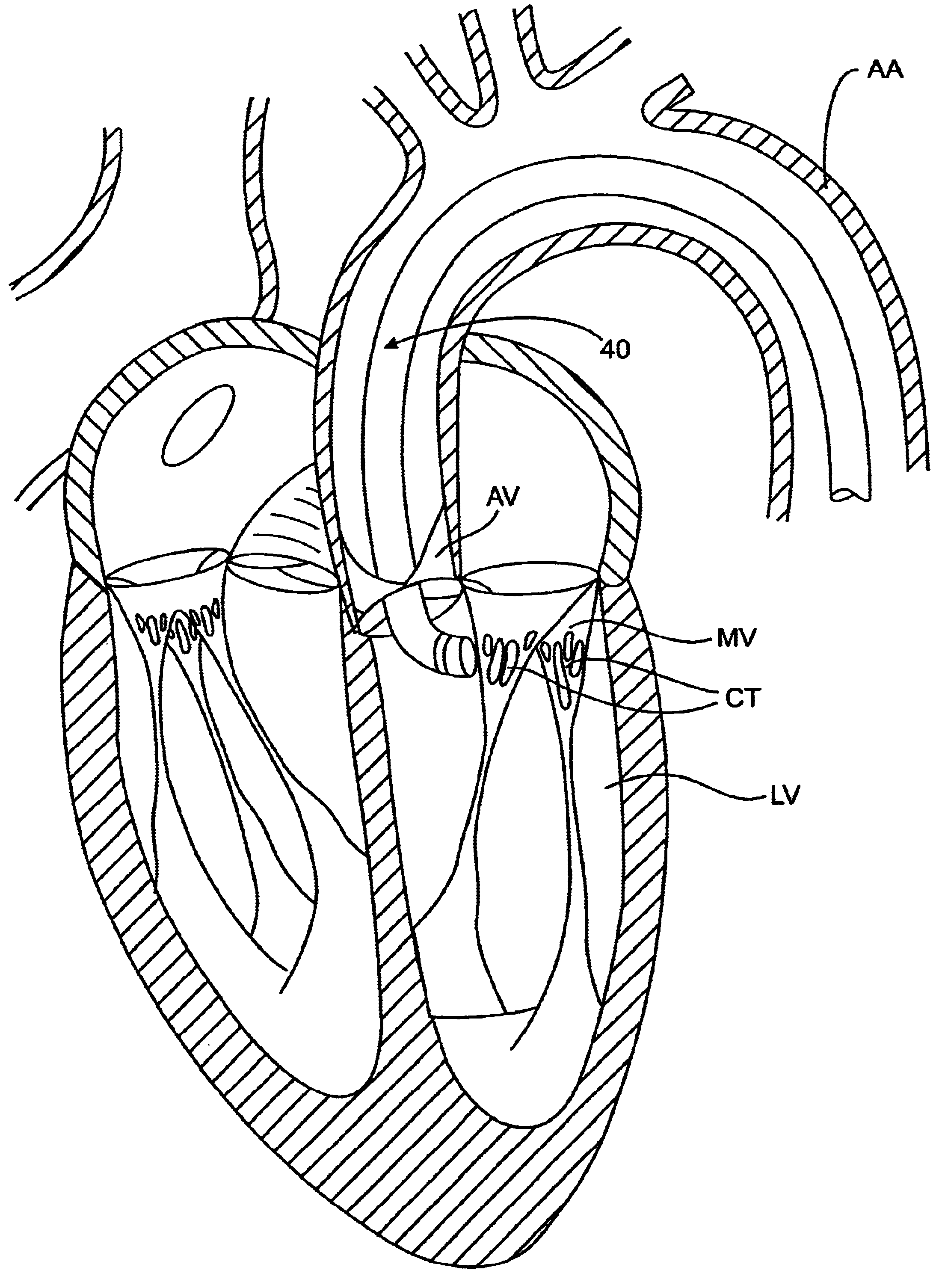
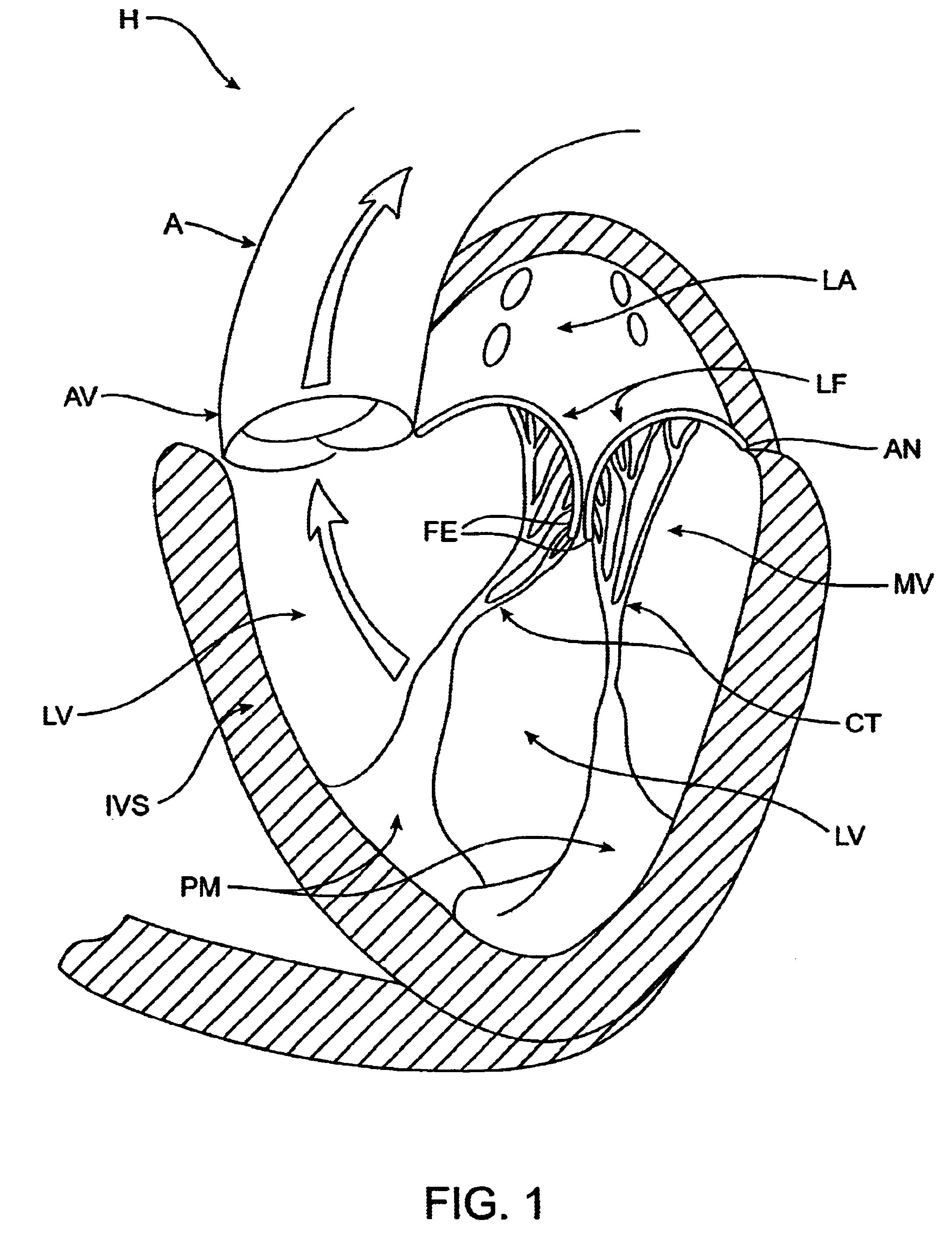
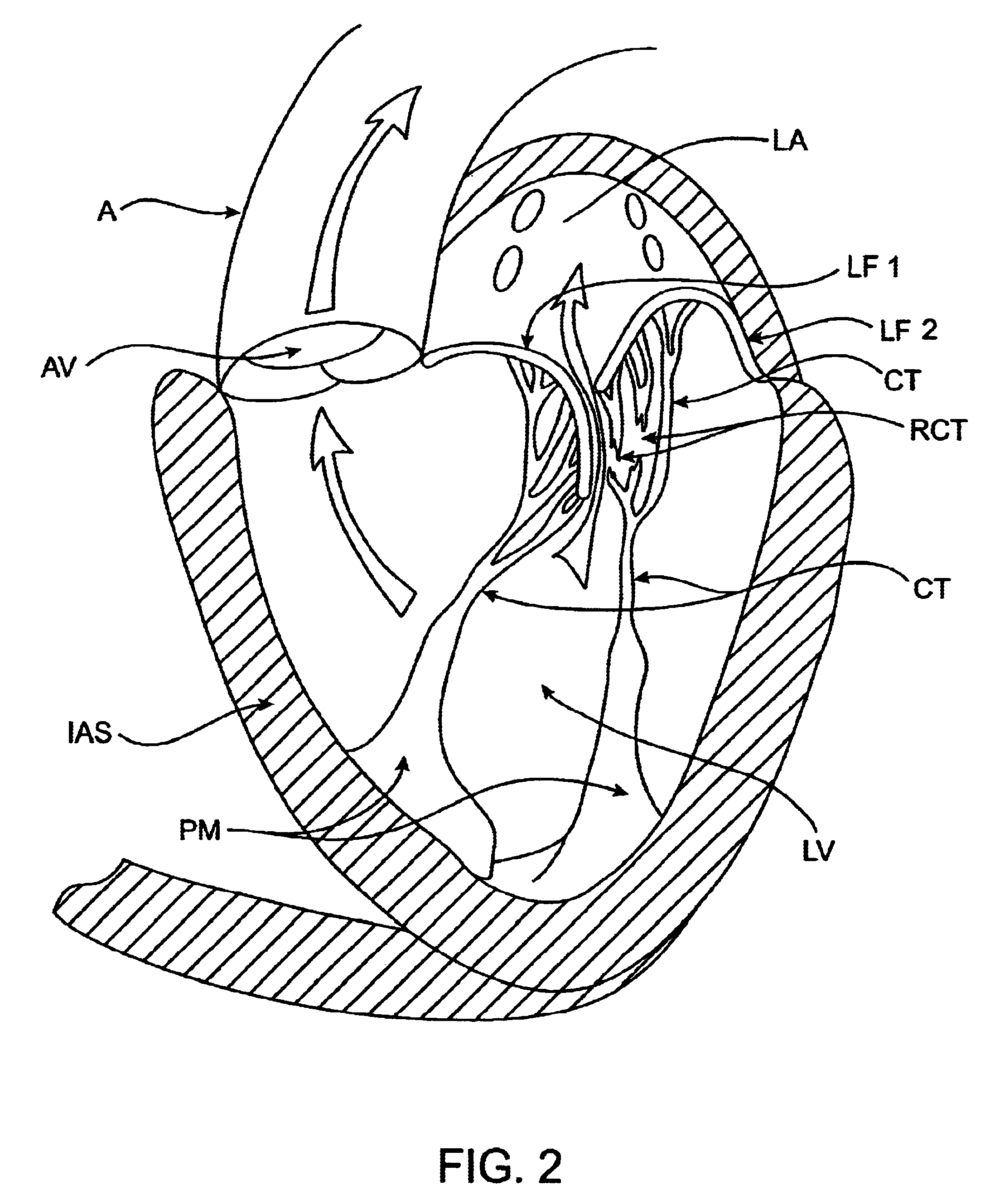
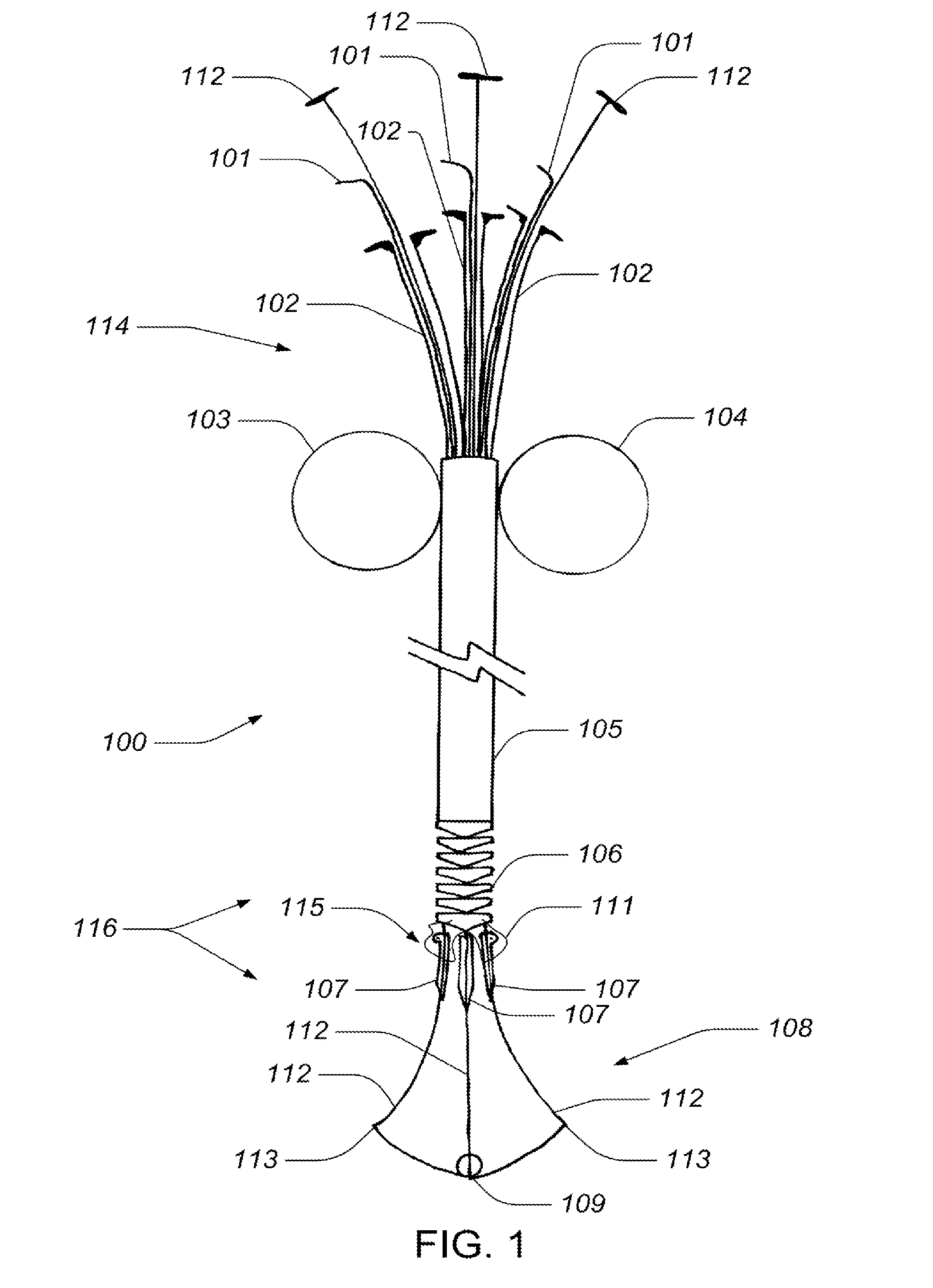
Methods and apparatus for cardiac valve repair
InactiveUS6629534B1Reduce leakageReduce regurgitationSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesHeart chamberPapillary muscle
The methods, devices, and systems are provided for performing endovascular repair of atrioventricular and other cardiac valves in the heart. Regurgitation of an atrioventricular valve, particularly a mitral valve, can be repaired by modifying a tissue structure selected from the valve leaflets, the valve annulus, the valve chordae, and the papillary muscles. These structures may be modified by suturing, stapling, snaring, or shortening, using interventional tools which are introduced to a heart chamber. Preferably, the tissue structures will be temporarily modified prior to permanent modification. For example, opposed valve leaflets may be temporarily grasped and held into position prior to permanent attachment.
Owner:EVALVE
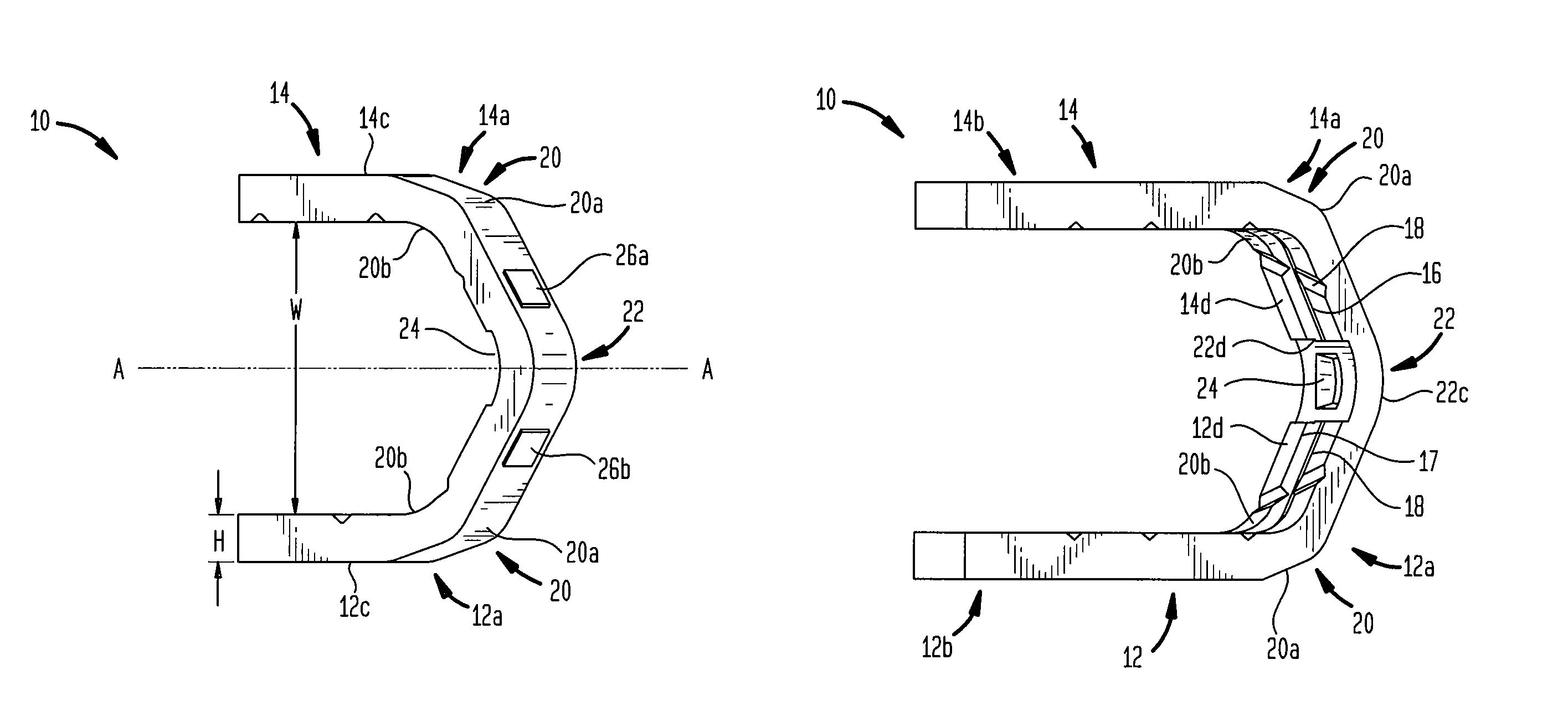
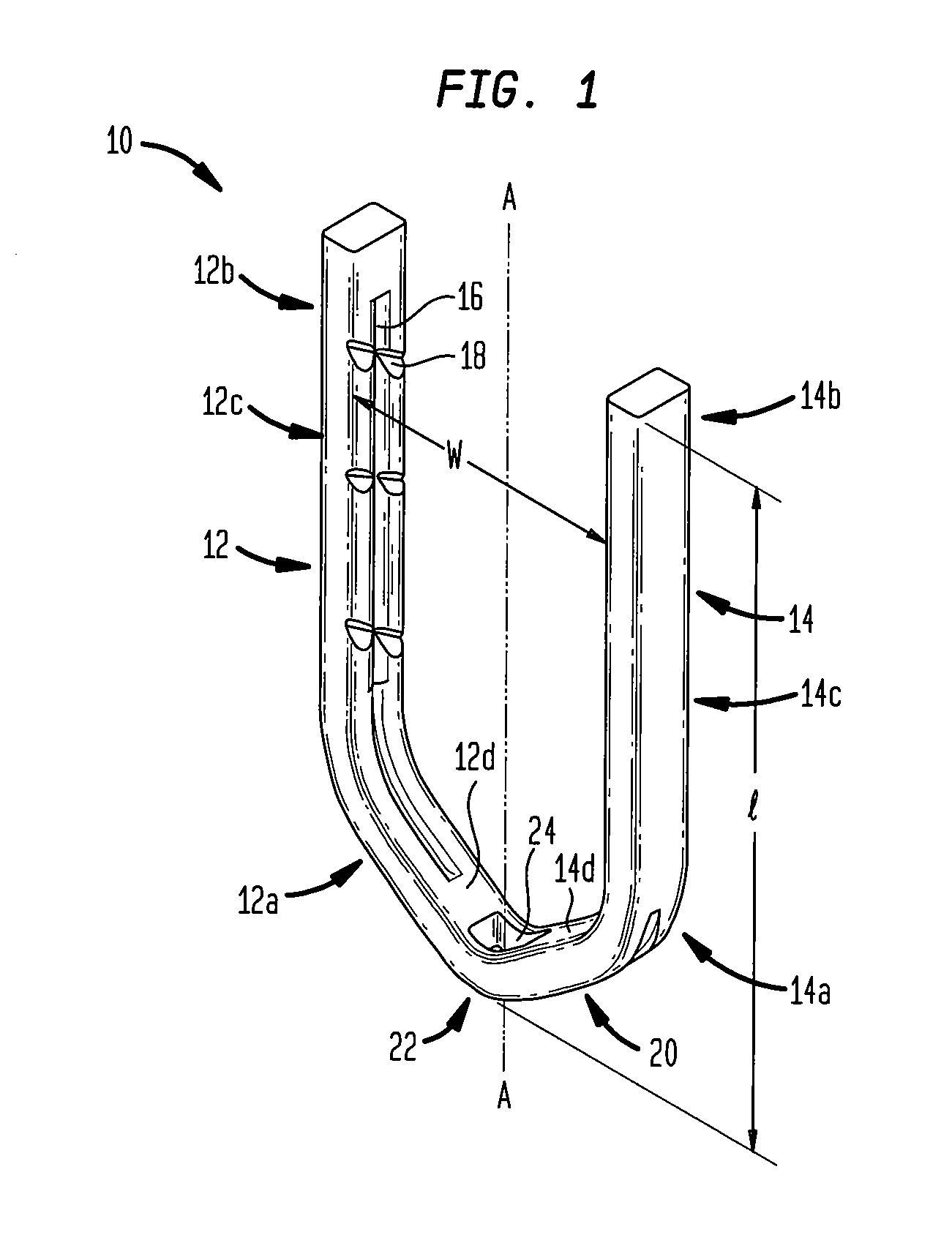
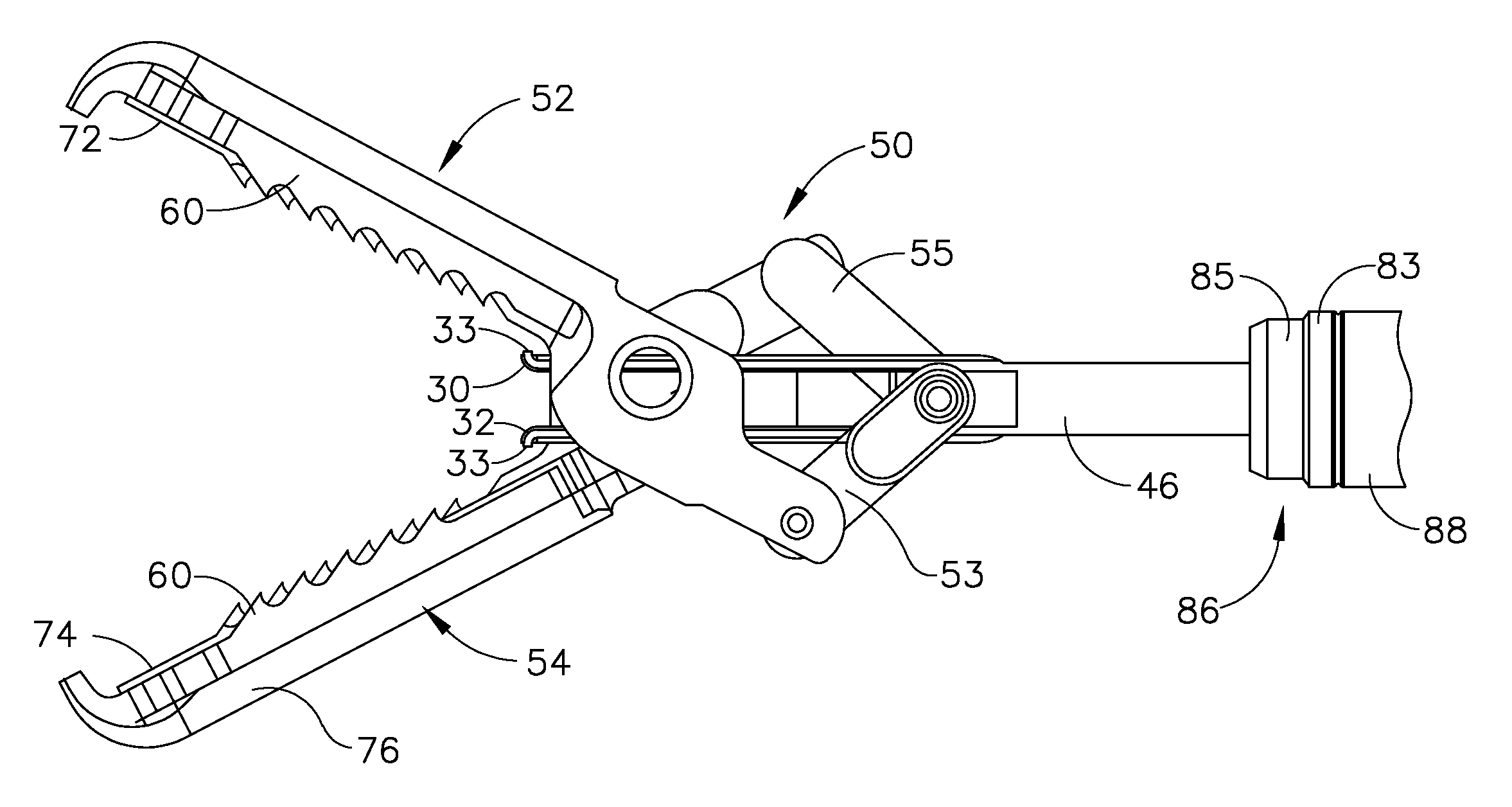
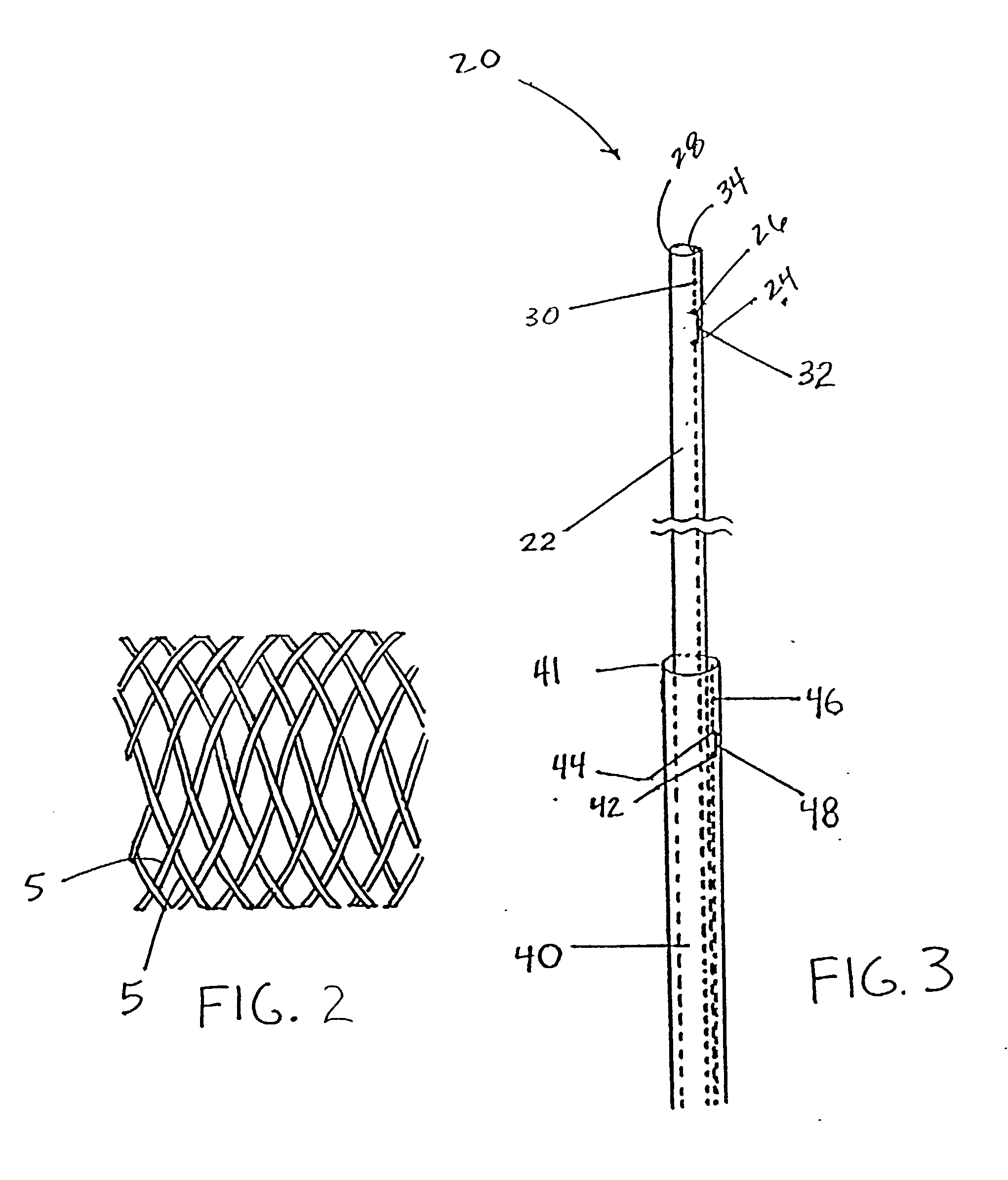
Surgical clip
ActiveUS7699860B2Less deformationElasticitySuture equipmentsSurgical veterinarySurgical ClipsBlood vessel
A clip is provided that can be used for ligating tissue, such as vessels, other tubular ducts, and the like. The clip has opposed first and second leg members having proximal and distal ends. The proximal end of each leg member is connected by an apex having a notch formed therein. Moreover, each leg member has an inner tissue-contacting surface and an outer compression-receiving surface, both of which include features to provide a more secure ligation of the vessel or duct. A method of ligating vessels is also provided.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Attachment device and methods of using the same
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
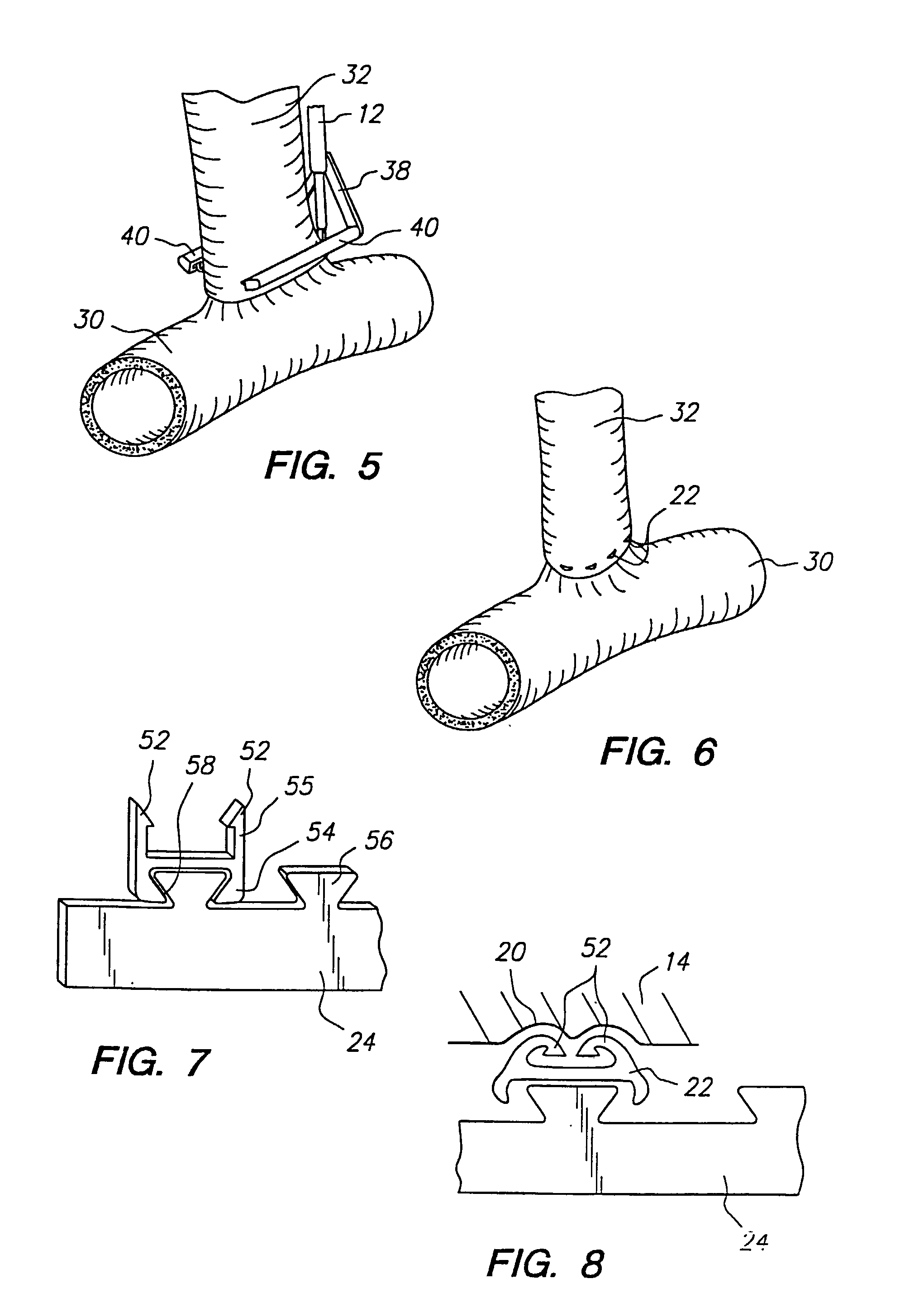
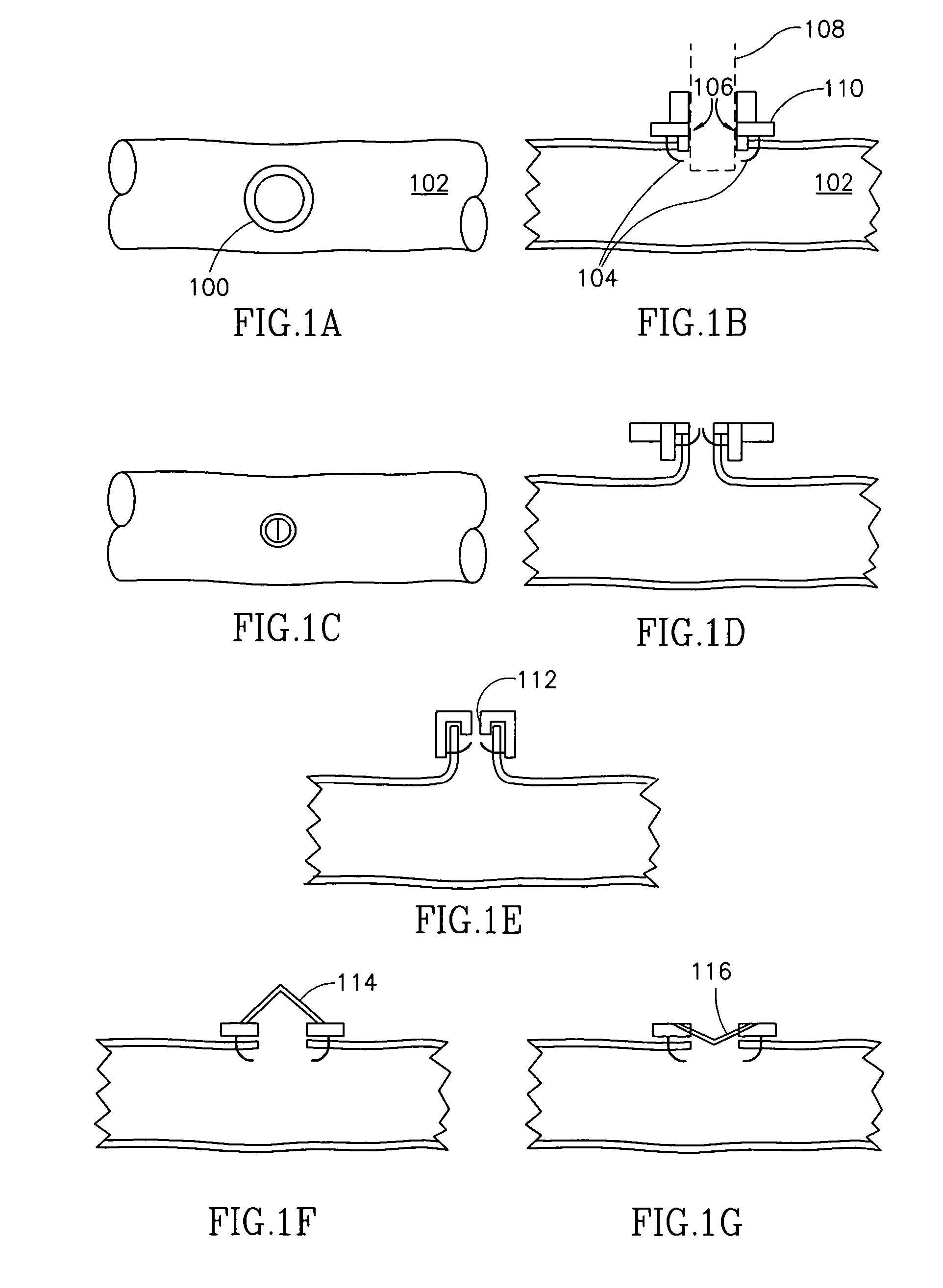
Staple and staple applicator for use in skin fixation of catheters
An inexpensive surgical stapler, such as for use in securing vascular catheters, has a plastic applicator made for use with a single staple. The applicator has a backbone and two identical arms. The inside face of the backbone has a retaining channel that secures the crown portion of the staple against movement. The inside faces of the arms have guidance grooves that direct the movement of the staple as the applicator arms are squeezed with finger pressure. The outside faces of the arms are configured to permit gripping by the operator's fingers. The stapler can be used in lieu of suturing. Other staple and applicator assemblies can include two or more of such assemblies.
Owner:DEAN ALLGEYER M D
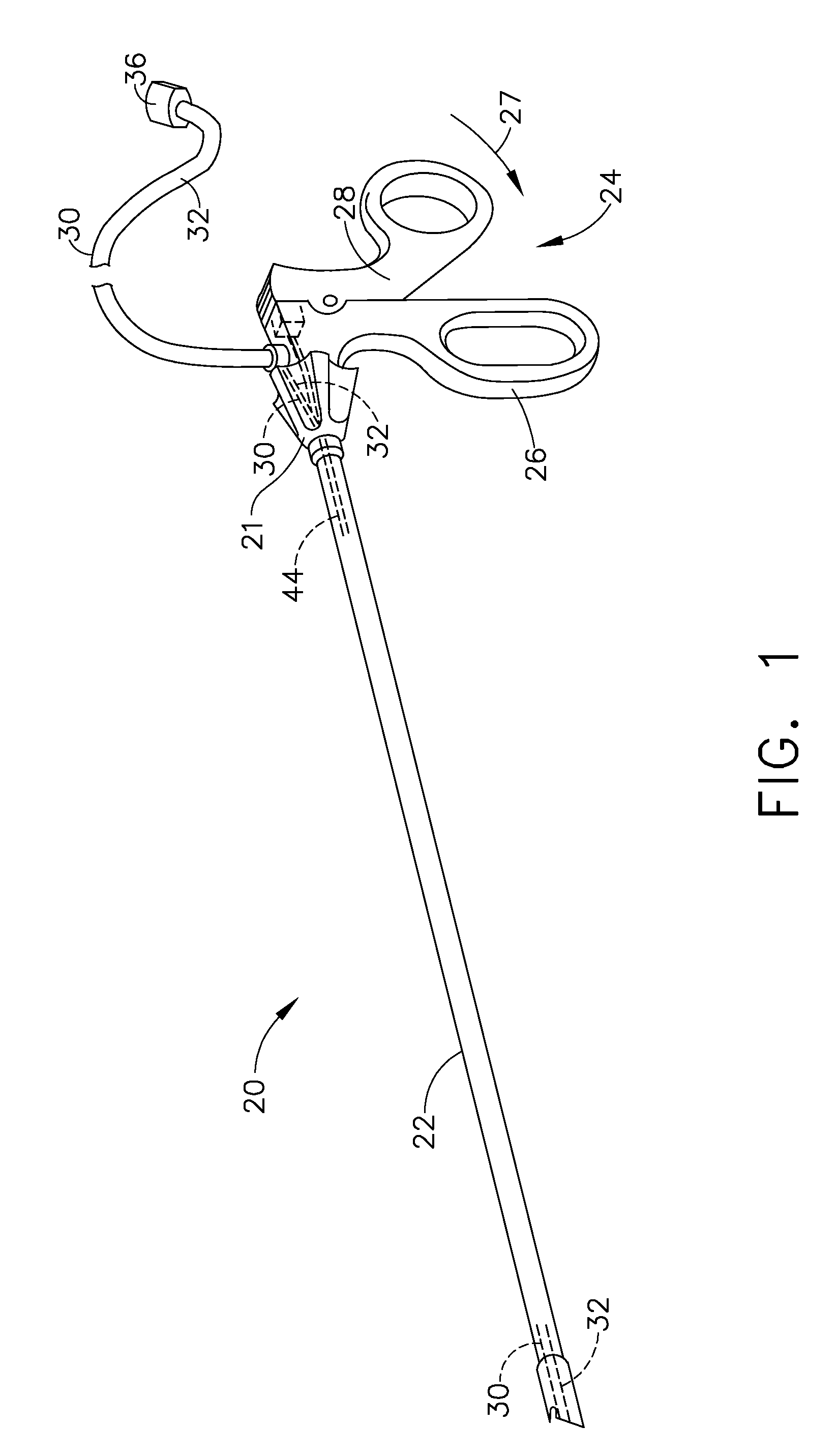
Anastomosis instrument and method for performing same
InactiveUS7438718B2Promote sportsPromote activationSuture equipmentsStapling toolsEngineeringActuator
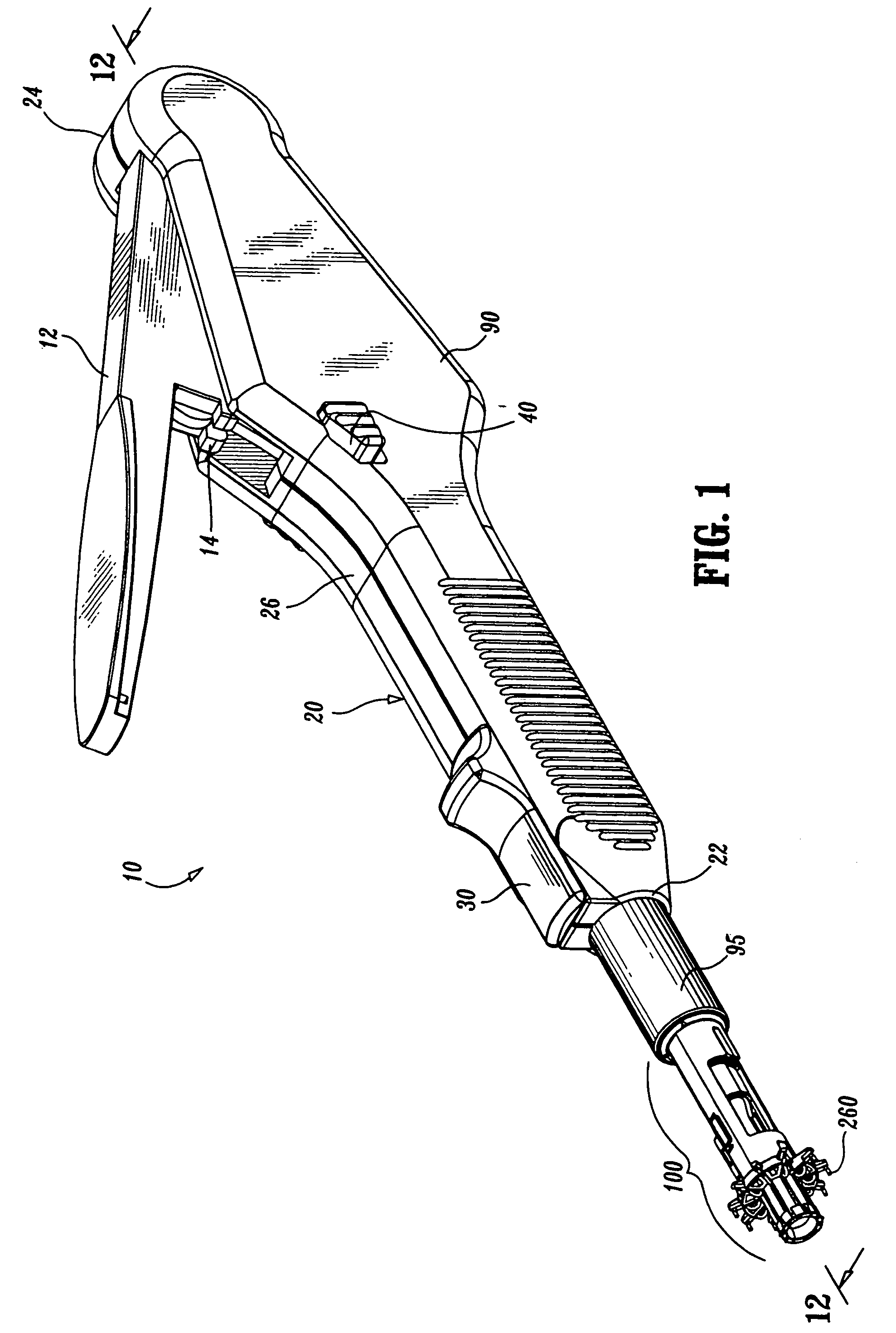
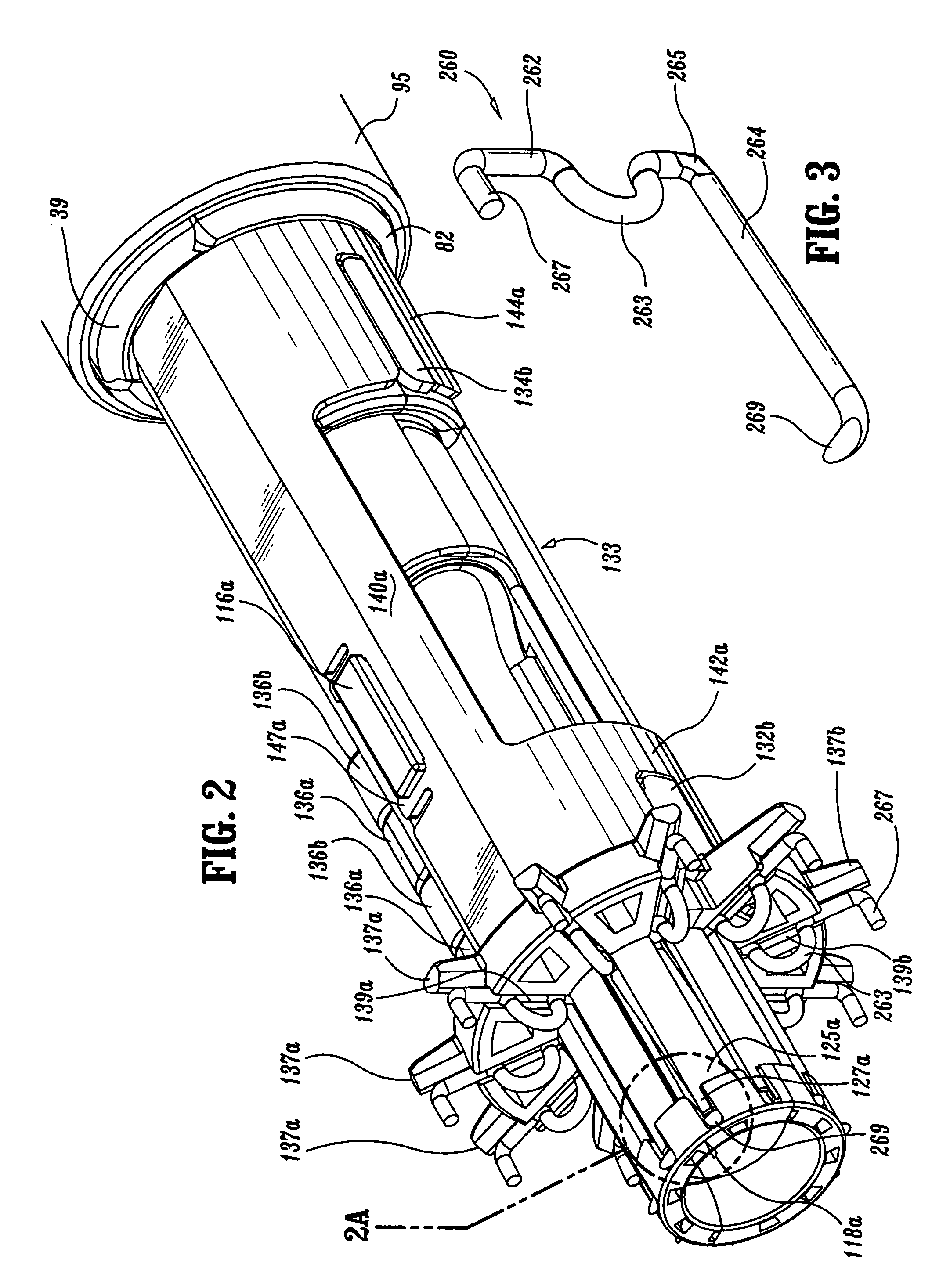
A surgical instrument for anastomosis of first and second blood vessels includes a housing having distal and proximal ends and an actuator disposed therebetween. The actuator includes a handle and a link assembly, the link assembly being movable through a firing stroke in response to movement of the handle. The instrument also includes a disposable loading unit releasably attached to the distal end of the housing in mechanical cooperation with the actuator. The disposable loading unit supports a plurality of surgical fasteners, which deform upon movement of the actuator and the link assembly through the firing stroke.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
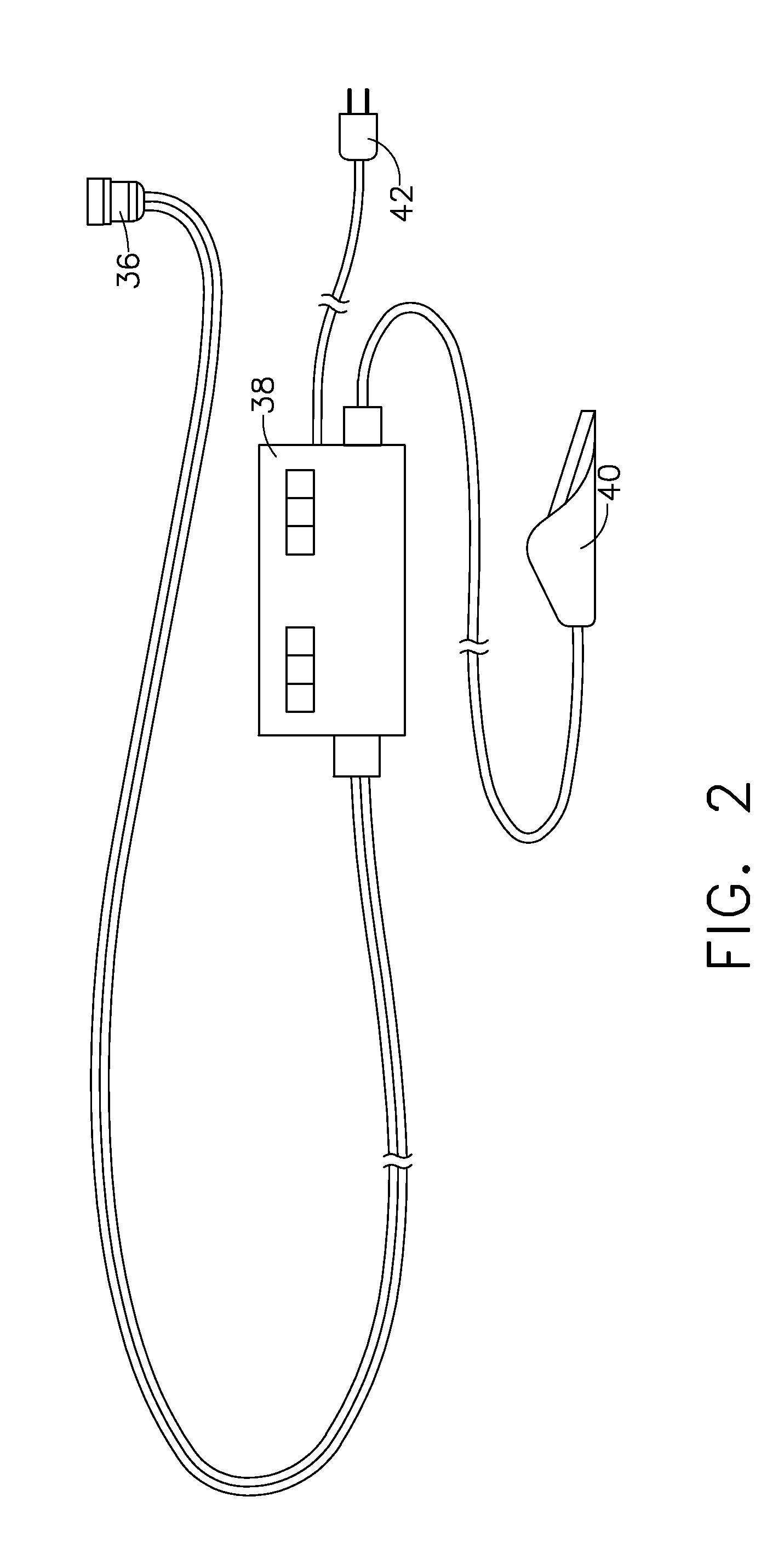
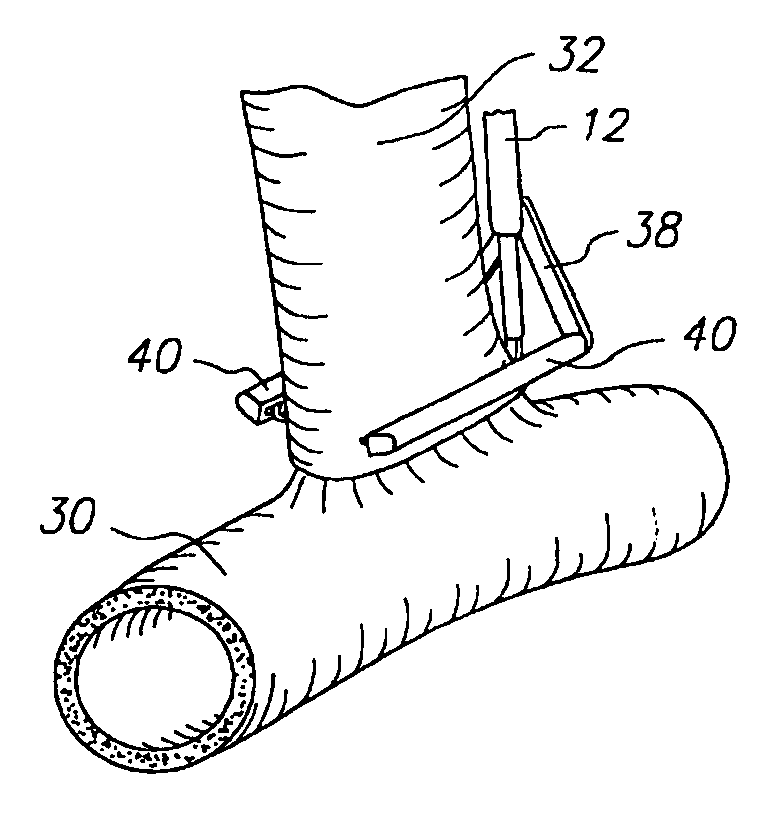
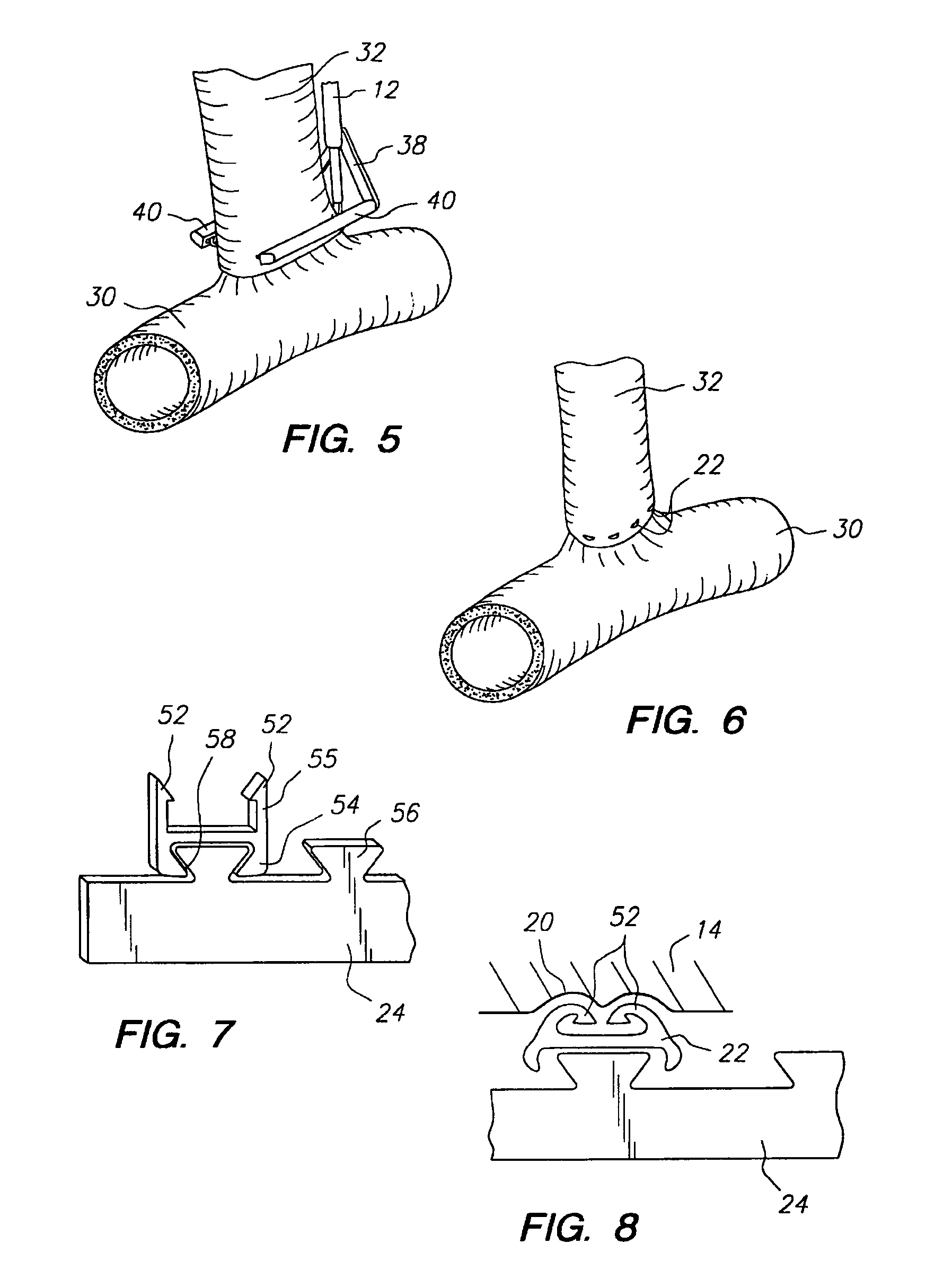
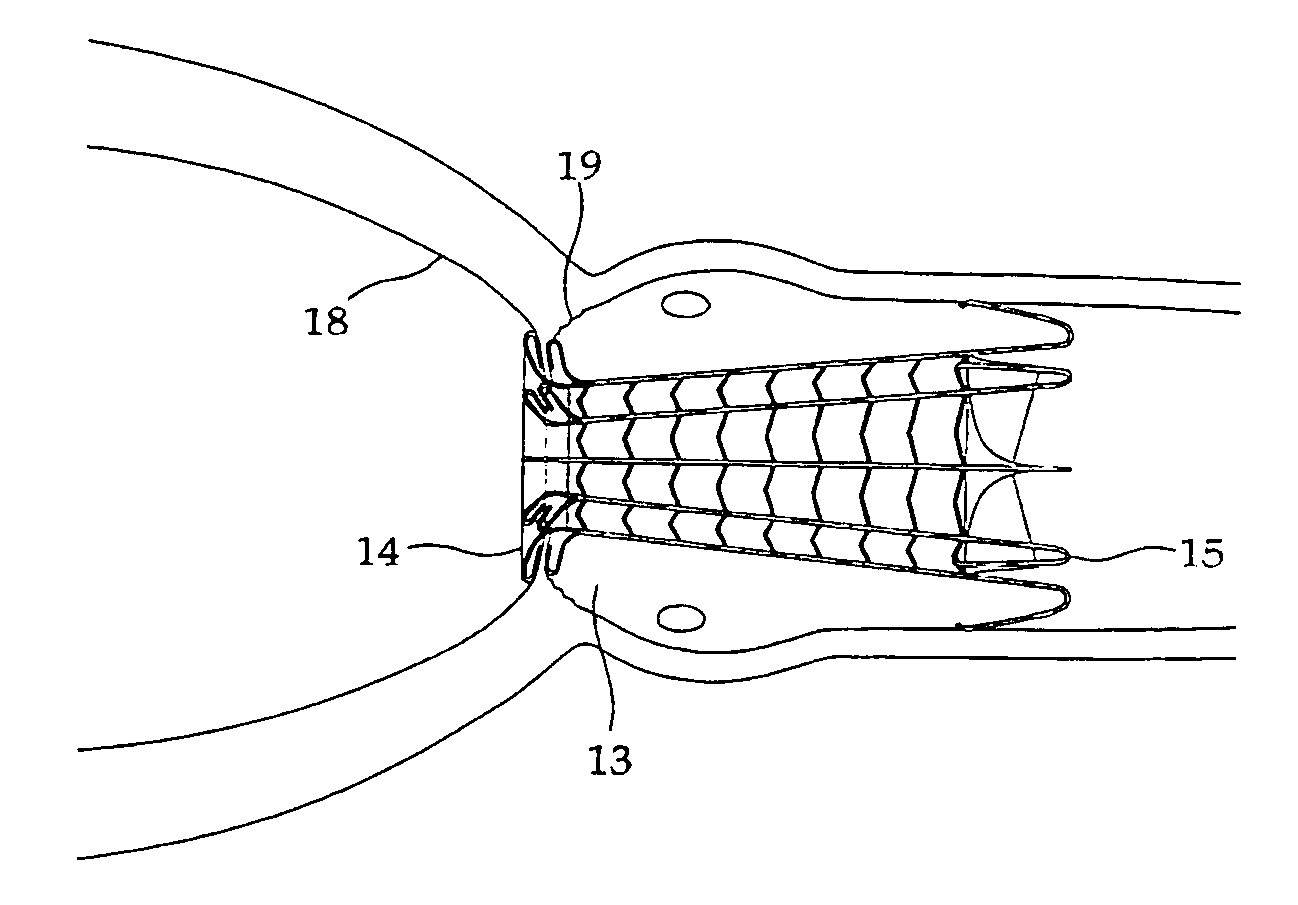
Anastomosis method
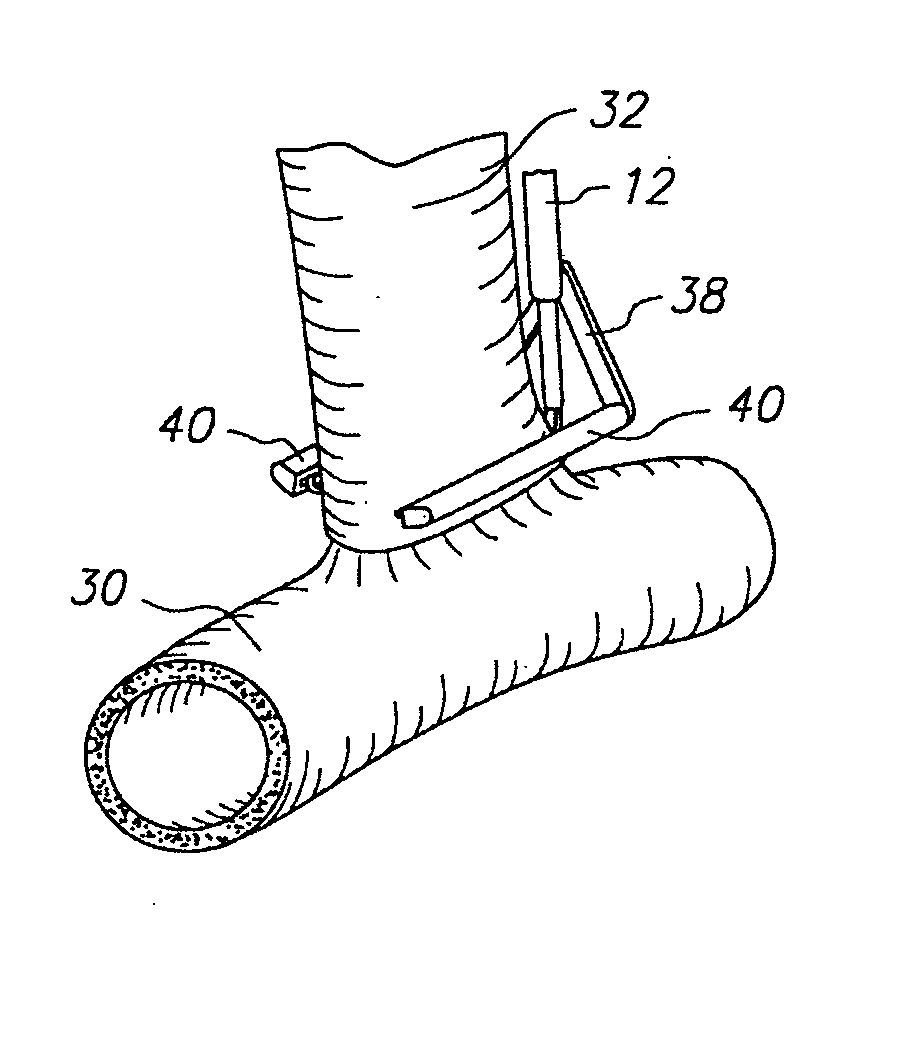
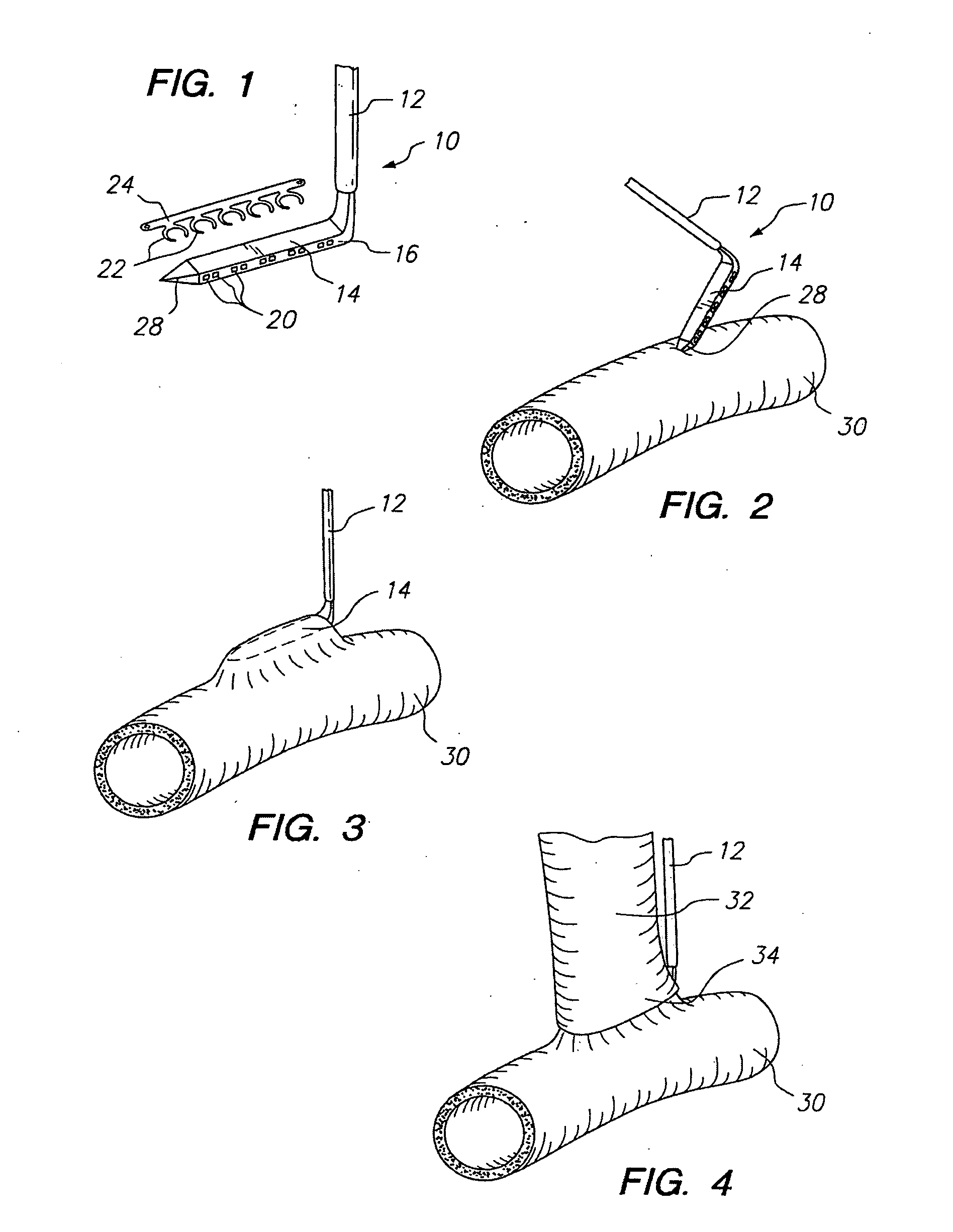
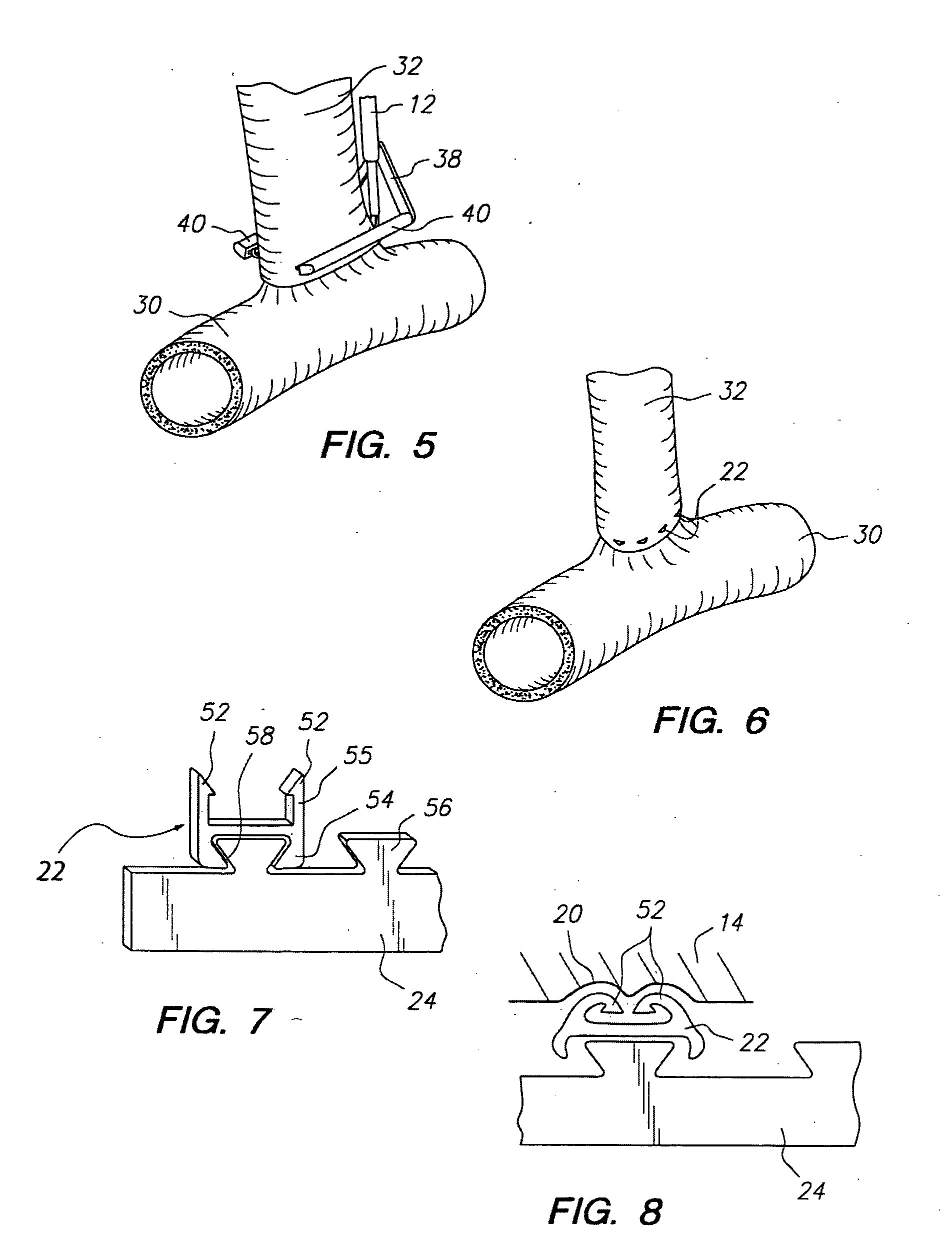
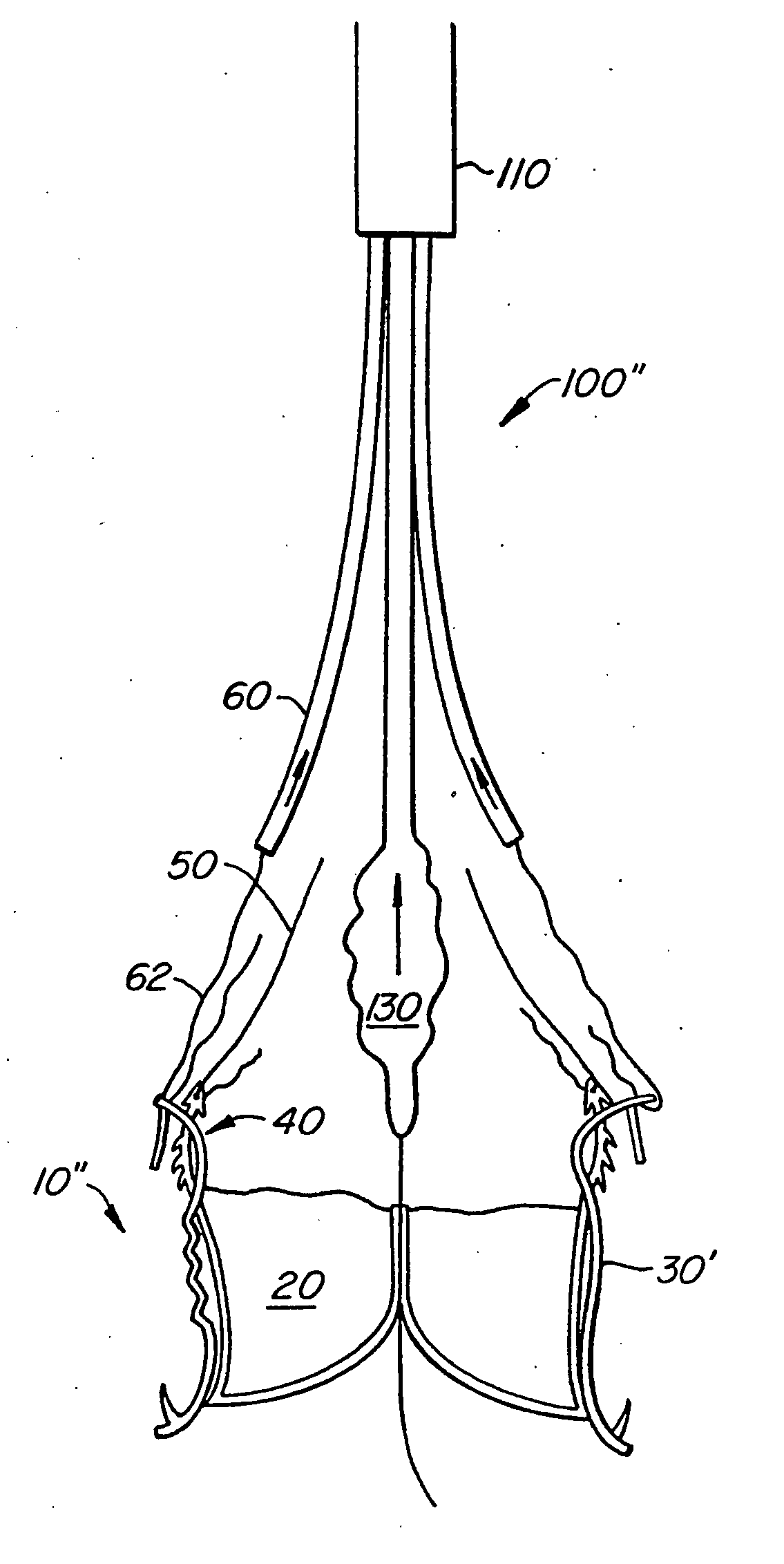
An anastomosis system and method uses an anvil to control and support a tissue site during an anastomosis procedure. The anvil is particularly useful for supporting a wall of a coronary artery during attachment of a graft vessel to the coronary artery because the wall of the coronary artery is very thin, difficult to grasp, and susceptible to tearing. In one method, the anvil is inserted into a pressurized or unpressurized target vessel and is pulled against an inner wall of the target vessel causing tenting of the thin tissue of the vessel wall. A graft vessel is then advanced to the anastomosis site and an end of the graft vessel is positioned adjacent and exterior of the target vessel. Staples are inserted through the tissue of the graft vessel and the target vessel by pivoting the arms of a staple holder towards the anvil. When the ends of the staples engage staple bending features on the anvil, the ends of the staples bend over securing the graft vessel and target vessel together. After stapling is complete, an incision is formed in the wall of the target vessel to allow blood flow between the target vessel and the graft vessel.
Owner:AESCULAP AG
Vascular hole closure device
Owner:REX MEDICAL LP
Medical device, kit and method for constricting tissue or a bodily orifice, for example, a mitral valve
InactiveUS20110082538A1Prevent retreatSuture equipmentsBone implantPosterior leafletAnnuloplasty rings
A device, kit and method may include or employ an implantable device (e.g., annuloplasty implant) and a tool operable to implant such. The implantable device is positionable in a cavity of a bodily organ (e.g., a heart) and operable to constrict a bodily orifice (e.g., a mitral valve). The tissue anchors may be guided into precise position by an intravascularly or percutaneously deployed anchor guide frame of the tool and embedded in an annulus of the orifice. Constriction of the orifice may be accomplished via a variety of structures, for example by cinching a flexible cable or via a anchored annuloplasty ring, the cable or ring attached to the tissue anchors. The annuloplasty ring may be delivered in an unanchored, generally elongated configuration, and implanted in an anchored generally arch, arcuate or annular configuration. Such may approximate the septal and lateral (clinically referred to as anterior and posterior) annulus of the mitral valve, to move the posterior leaflet anteriorly and the anterior leaflet posteriorly, thereby improving leaflet coaptation to eliminate mitral regurgitation.
Owner:KARDIUM
Biointerface membranes incorporating bioactive agents
InactiveUS20050031689A1Improve performancePowder deliveryAdditive manufacturing apparatusBiointerfaceActive agent
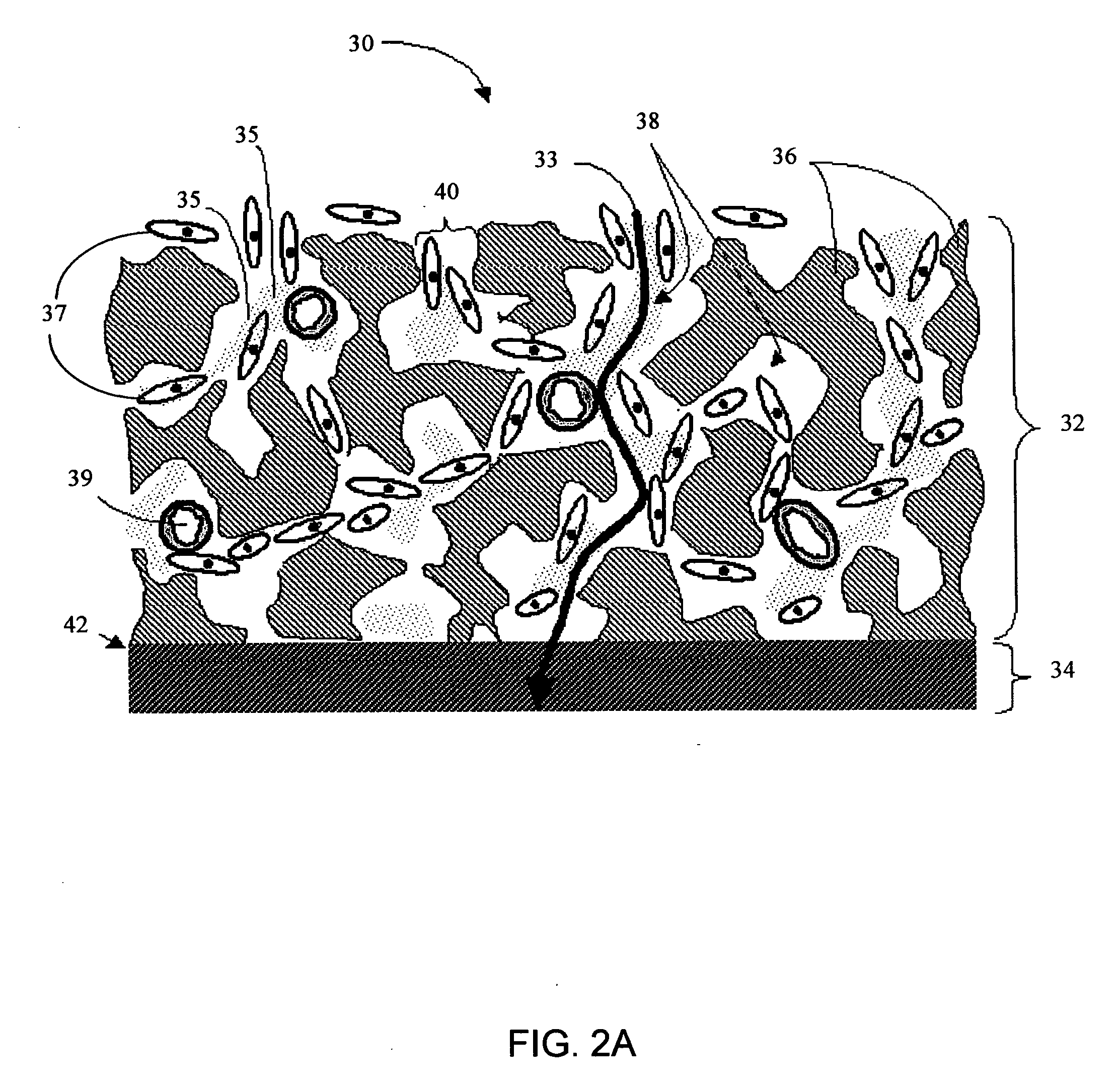
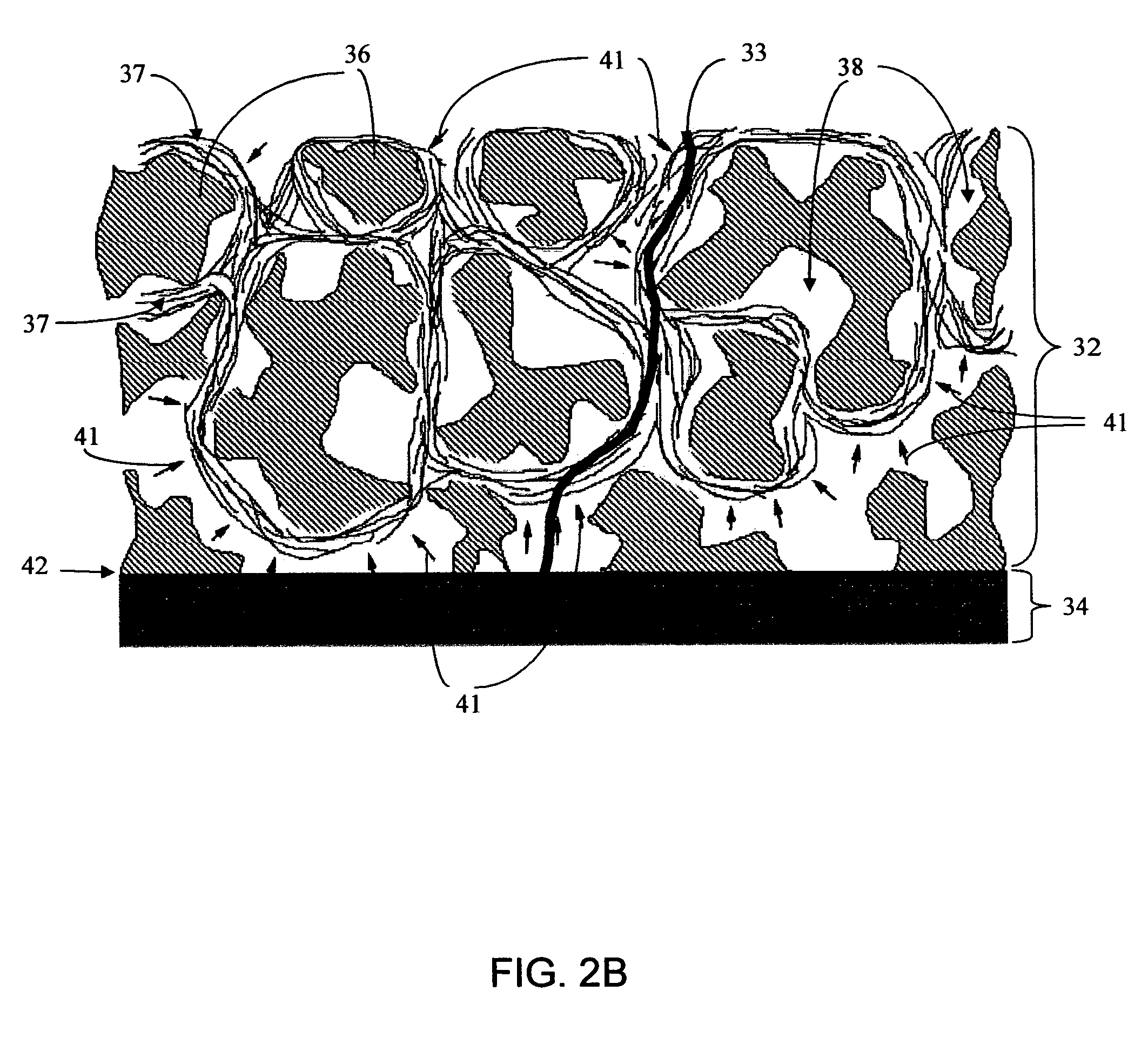
A biointerface membrane for an implantable device including a nonresorbable solid portion with a plurality of interconnected cavities therein adapted to support tissue ingrowth in vivo, and a bioactive agent incorporated into the biointerface membrane and adapted to modify the tissue response is provided. The bioactive agents can be chosen to induce vascularization and / or prevent barrier cell layer formation in vivo, and are advantageous when used with implantable devices wherein solutes are transported across the device-tissue interface.
Owner:DEXCOM
Vascular closure device
InactiveUS20050283188A1Avoid blood leakagePrevent leakageExcision instrumentsSurgical veterinaryVascular closure deviceVascular device
A method of accessing a blood vessel, comprising: forming a hole in the blood vessel; mounting a hole closure device onto the blood vessel; accessing the blood vessel through the hole, while the hole closure device is mounted on the blood vessel; and closing the hole by the hole closure device, after accessing the blood vessel through the hole.
Owner:BY PASS
Vascular hole closure device
Owner:REX MEDICAL LP
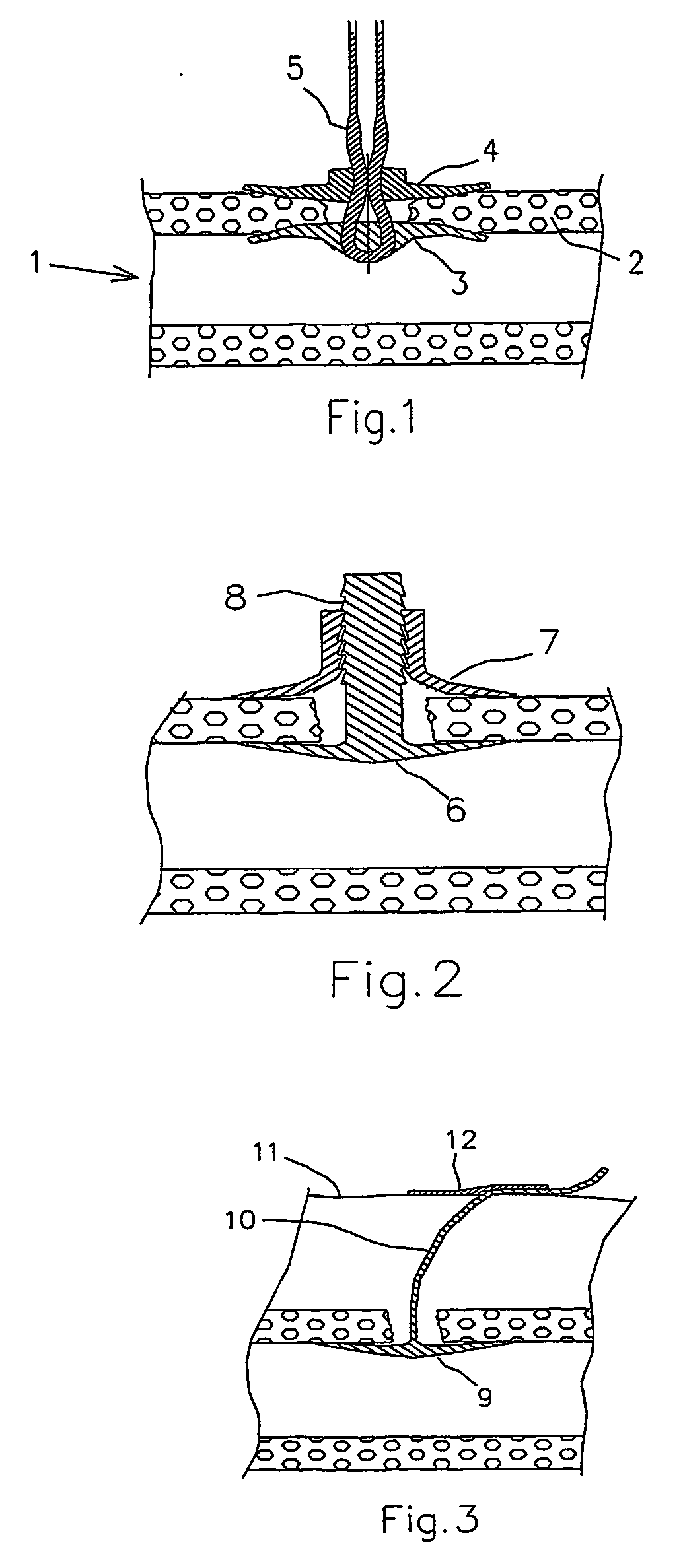
Dissolvable medical sealing device
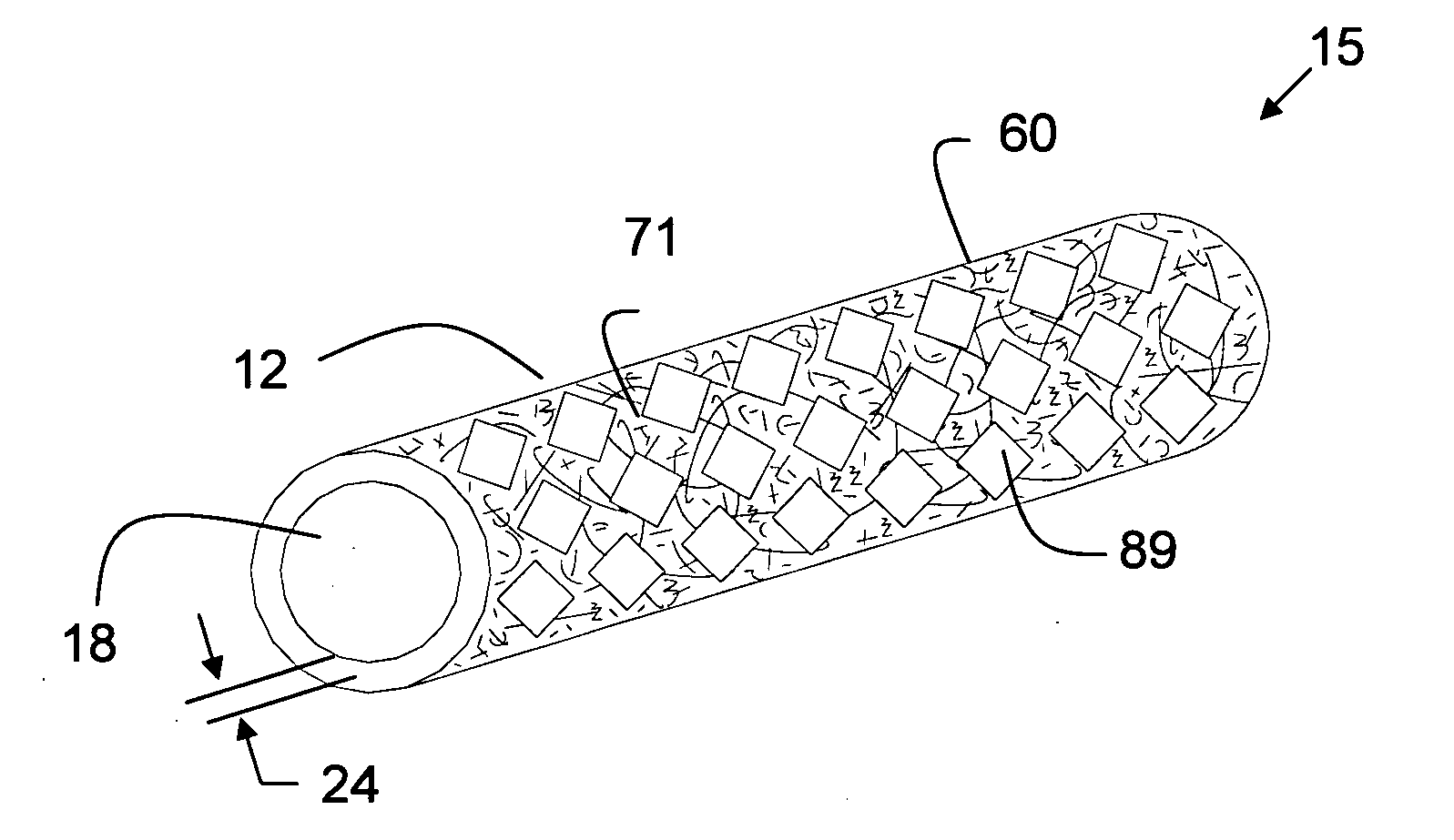
ActiveUS20050169974A1Shorten the timeSuture equipmentsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismOrganismal ProcessPolyvinyl alcohol
The present invention provides a dissolvable medical sealing device (3, 4; 6, 7; 9) for closing a wound in vessel. A sealing device (3, 4, 6, 7, 9) according to the invention is made of a material that dissolves by means of physical processes, rather than by means of chemical or biological processes. Such a sealing device (3, 4; 6, 7; 9) can be made of polyethylene glycol, polypropylene glycol, copolymers containing ethylene glycol and propylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol or polyvinyl pyrolidone, or any combinations thereof.
Owner:TERUMO MEDICAL CORP
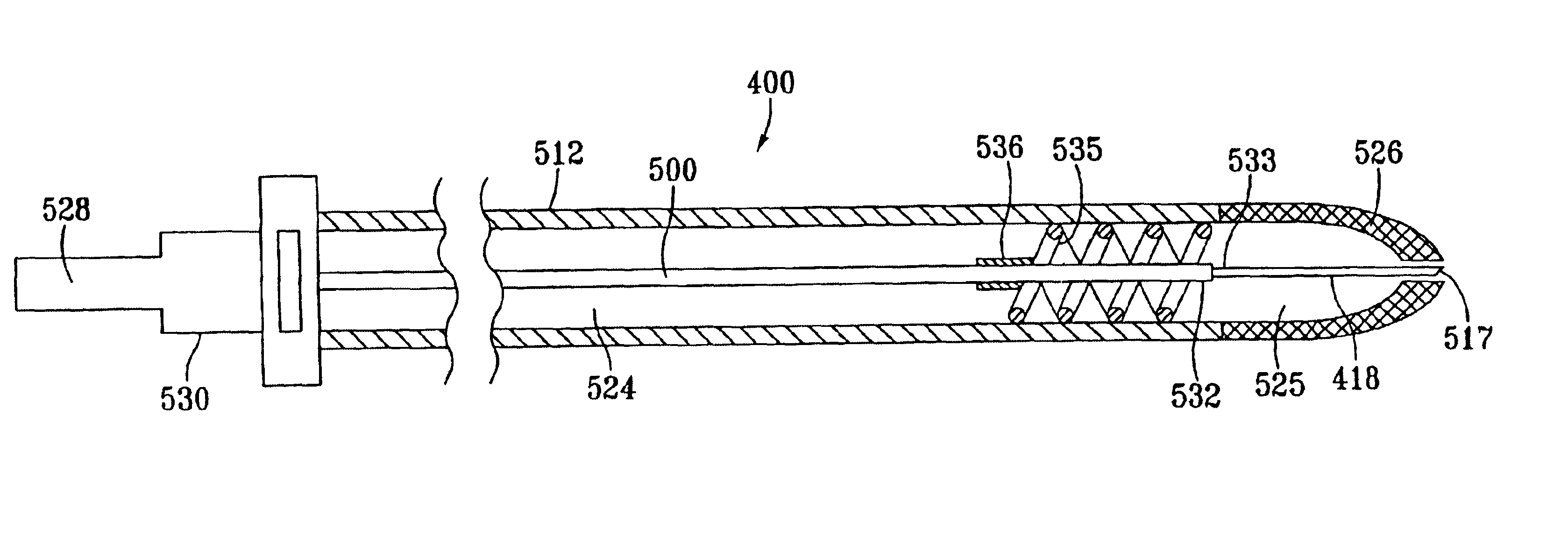
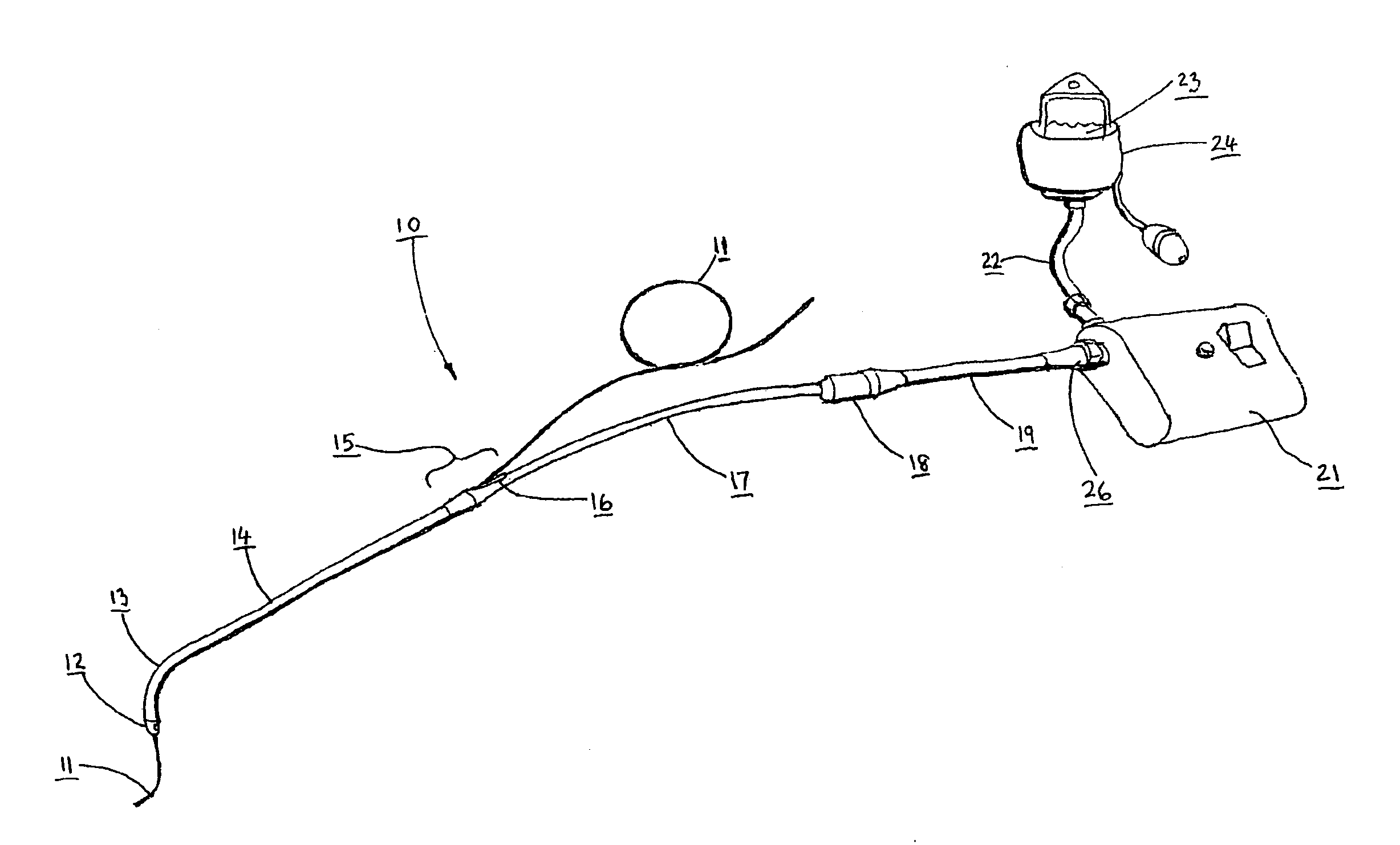
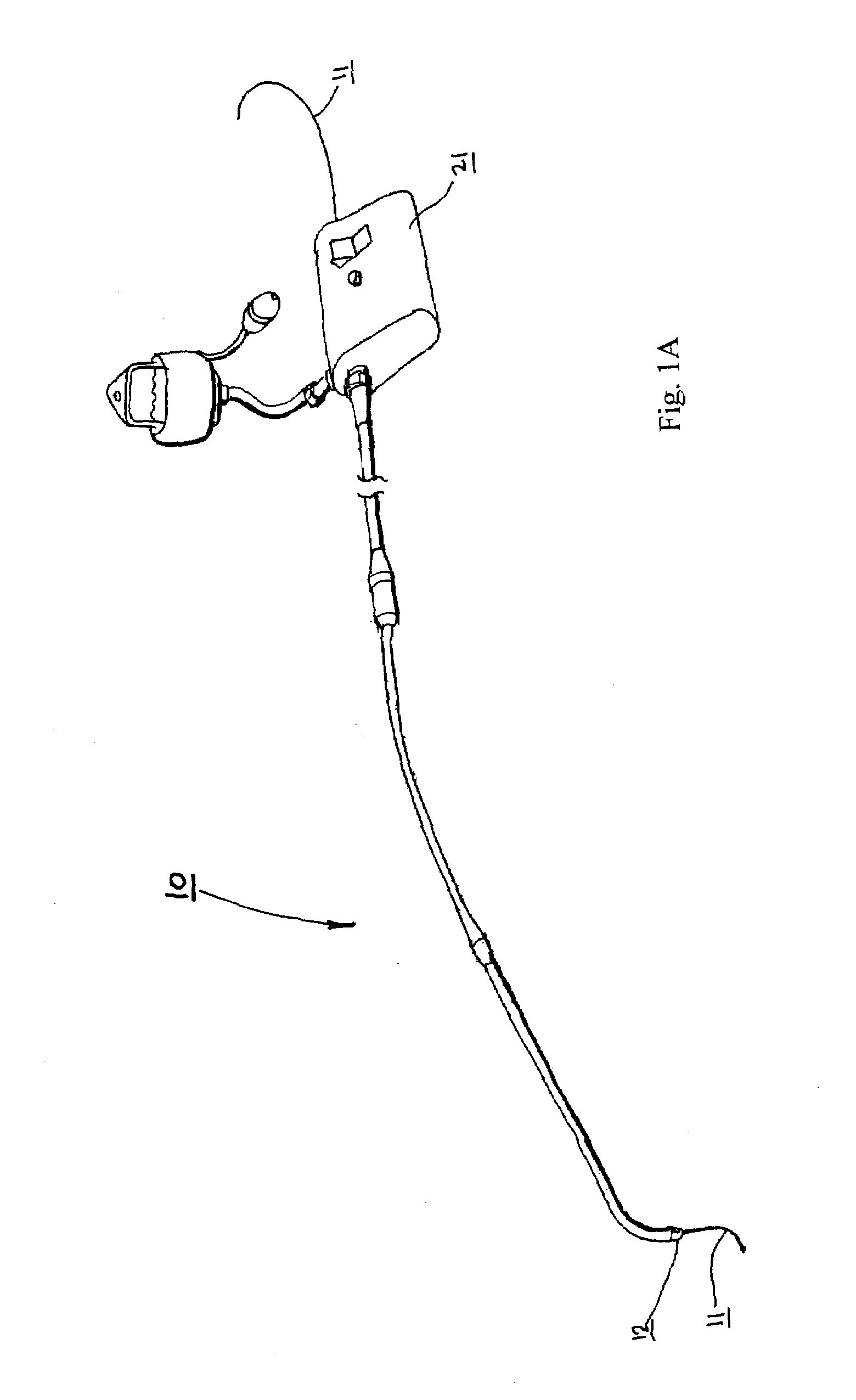
Medical device introducer and obturator
An introducer having an elongate tubular member and a device connector releasably attached to a proximal end of the tubular member. The introducer allows exchange of medical instruments, such as a blood filter and cardioplegia catheter, through a single lumen. An obturator having a retractable blade for making incision on a tissue is insertable through the lumen of the introducer. Methods of using the obturator and the introducer for introducing medical device(s) into body cavity, such as a vessel or cardiac tissue, are also disclosed.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Electroactive polymer actuated medical devices
ActiveUS6969395B2High degreeLimited accessSuture equipmentsDilatorsBiomedical engineeringMedical procedure
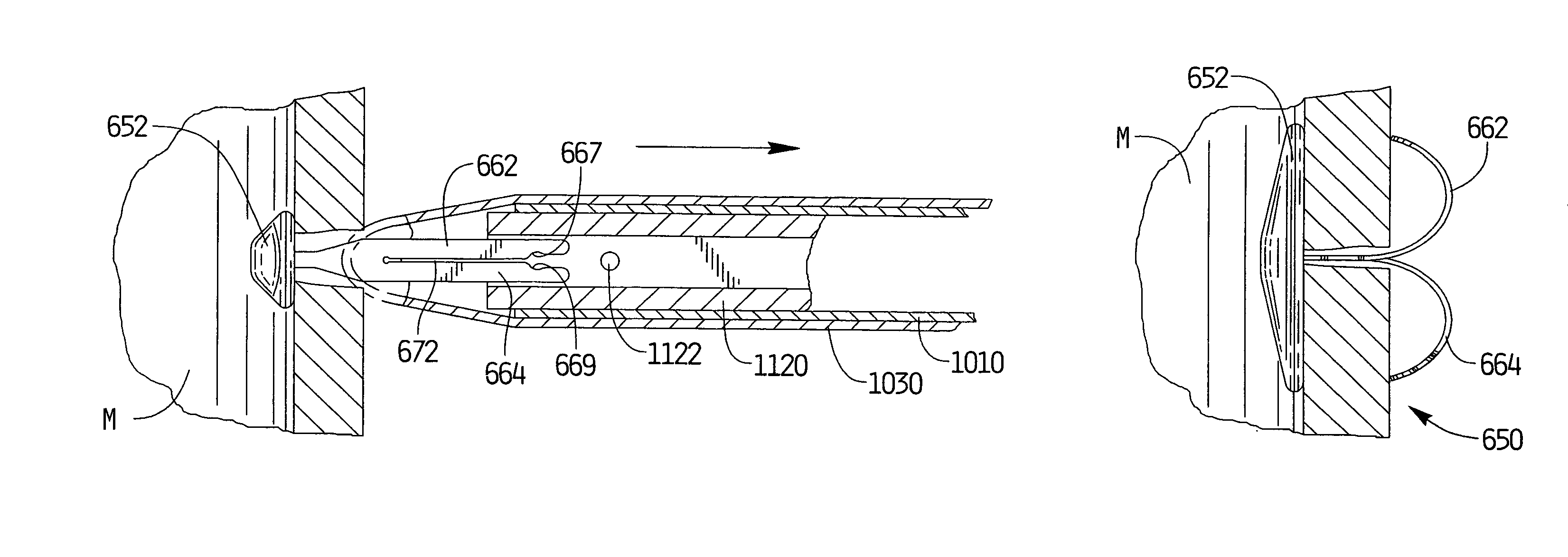
The present invention is directed to novel apparatus for use in medical procedures relating to tubular body fluid conduits. According to a first aspect of the invention, a filter apparatus is provided for delivery over a guidewire within a tubular body conduit, such as a blood vessel. The filter apparatus comprises: (a) a filter element transformable between a collapsed state and a deployed state, wherein the filter element is adapted to filter particulate matter from fluid within the tubular body conduit while in the deployed state; and (b) a locking member comprising one or more electroactive polymer actuators which switch the locking member between (i) a locking state wherein the locking member securely engages the guidewire and (ii) a release state wherein the locking member is movable along the length of the guidewire. According to a second aspect of the invention, a connector apparatus is provided for use in making an anastomotic connection between first and second tubular fluid conduits in a patient. The connector apparatus comprises: (a) a locking member, which further comprises one or more electroactive polymer actuators that switch the locking member between a locking state and a release state; and (b) a connector body that is configured to permit flow of bodily fluid between the first and second tubular fluid conduits. The connector body has a first portion configured for insertion into an axial end of the first tubular fluid conduit and a second portion configured for insertion through a sidewall of the second tubular fluid conduit. The second portion of the connector body is further configured to securely engage the locking member when the locking member is in the locking state.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Surgical staple-clip and applier
InactiveUS20060100649A1Constrict or occludeNourishment to the body tissue is maintainedStaplesNailsSurgical stapleSurgical site
A surgical staple-clip including a clip component and a securing member is used in a wide range of surgical procedures. The staple-clip may be introduced to a surgical site in an un-assembled condition through a small port or trocar. An applier for the staple-clip comprising a pair of opposed jaw-like channels is provided to position and apply the clip component and the securing member. The clip component is positioned around a target tissue and is compressed or clamped upon the tissue using only the force required for a specific surgical procedure such as occlusion, ligation or fixation. When the clip component is properly applied, the securing member is urged forward and over the clip component to secure the staple-clip. The clip component may include traction enhancement features such as surface interruptions, bumps, valleys and ridges. With the staple-clip of the invention, the force required to constrict or occlude the tissue is separate from the force required to secure and maintain the staple-clip in position and, as a result, the body tissue is not over-compressed and nourishment to the body tissue is maintained. Other aspects of the invention include thumb actuated clip appliers for use in hand assisted laparoscopy (HAL). In one embodiment, a clip applier includes a handle and a thumb actuated mechanism that is used to slidably release clips onto a body tissue or vessel by sliding the thumb actuated mechanism forward and backward using only one hand. In another aspect of the invention, a two-stage clip is disclosed having a clip component and a staple component for securing the clip after it has been properly positioned.
Owner:APPL MEDICAL RESOURCES CORP
Tear and abrasion resistant expanded material and reinforcement
InactiveUS20070207186A1Increase flexibilityLess complex manufacturing processStentsSurgeryDiseaseEngineering
The present invention is a more durable expanded material that enables thinner wall thicknesses and a more flexible reinforcement suitable for stenting. The present invention is especially useful in the construction of grafts, stents, and stent-grafts which are used, for example, in repairing or replacing blood vessels that are narrowed or occluded by disease, aneurismal blood vessels, or other medical treatments. The inventive material and configurations allow expansion or contraction in size or adjustment in size in an incremental manner so that the optimum size, shape, and fit with other objects can be obtained. The present invention is also optionally capable of more accurately delivering one or more active ingredients such as drugs over longer periods of time. The present invention optionally includes surface modifications and additives that increase the surface adhesion of active ingredients, coatings, or combinations thereof. Finally, the present invention optionally includes growing cells on the inventive material so that the expanded material, reinforcement, or combinations thereof are useful, for example, in producing lab-grown blood vessels or organs.
Owner:SCANLON JOHN JAMES +1
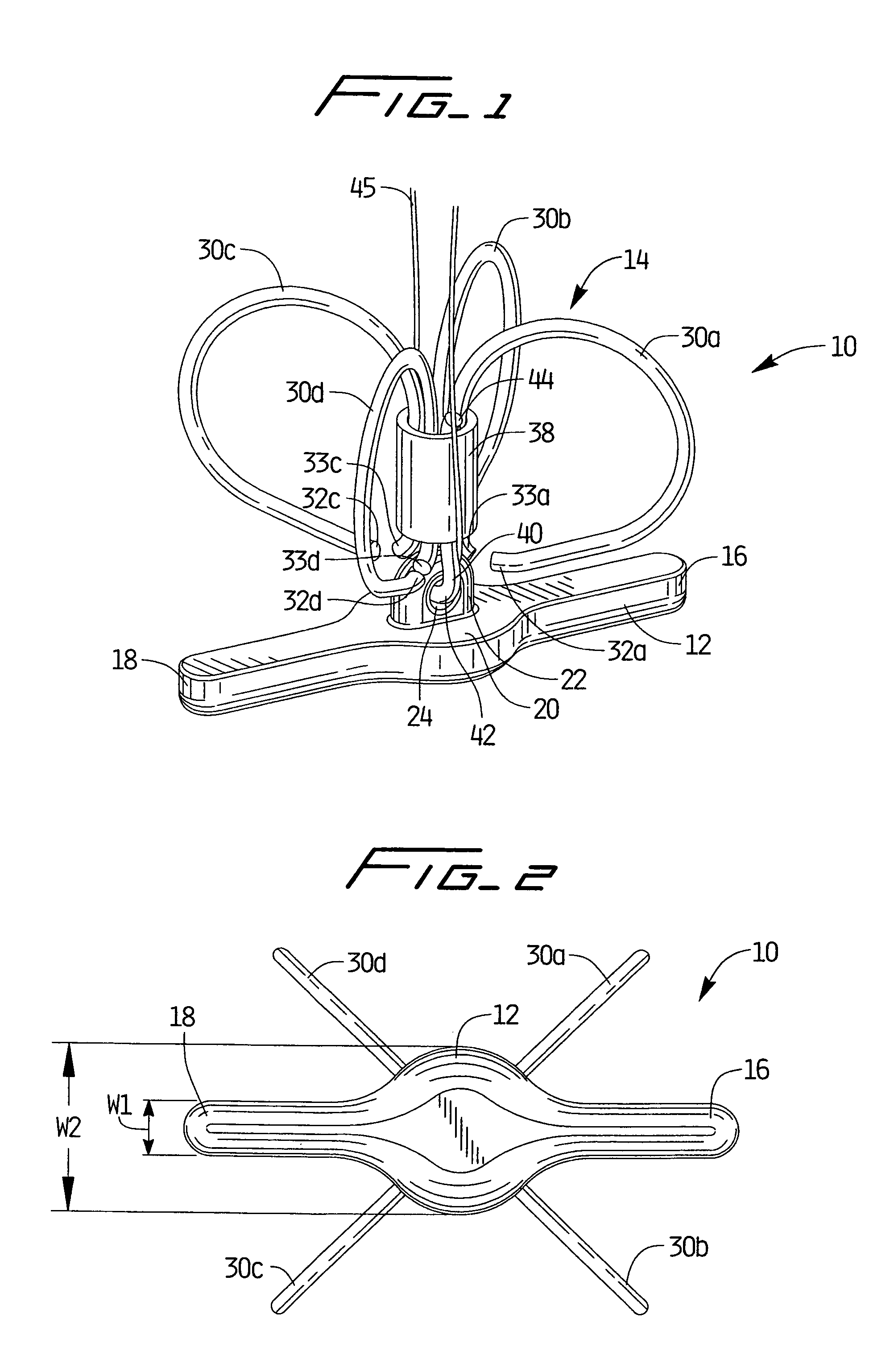
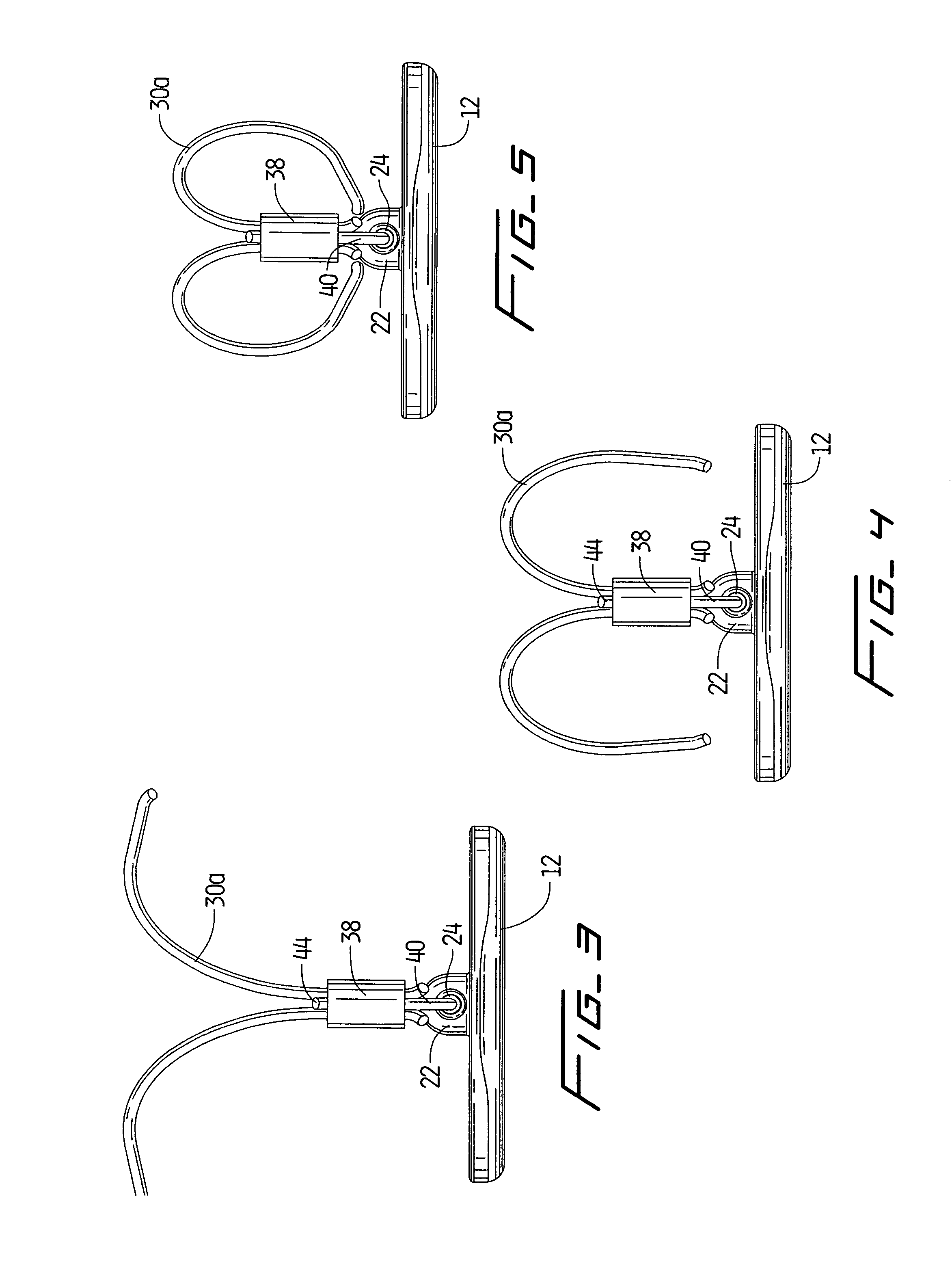
Method for anastomosing vessels
InactiveUS20050154406A1Precise positioningSecurely holdSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsSurgeryBlood vessel
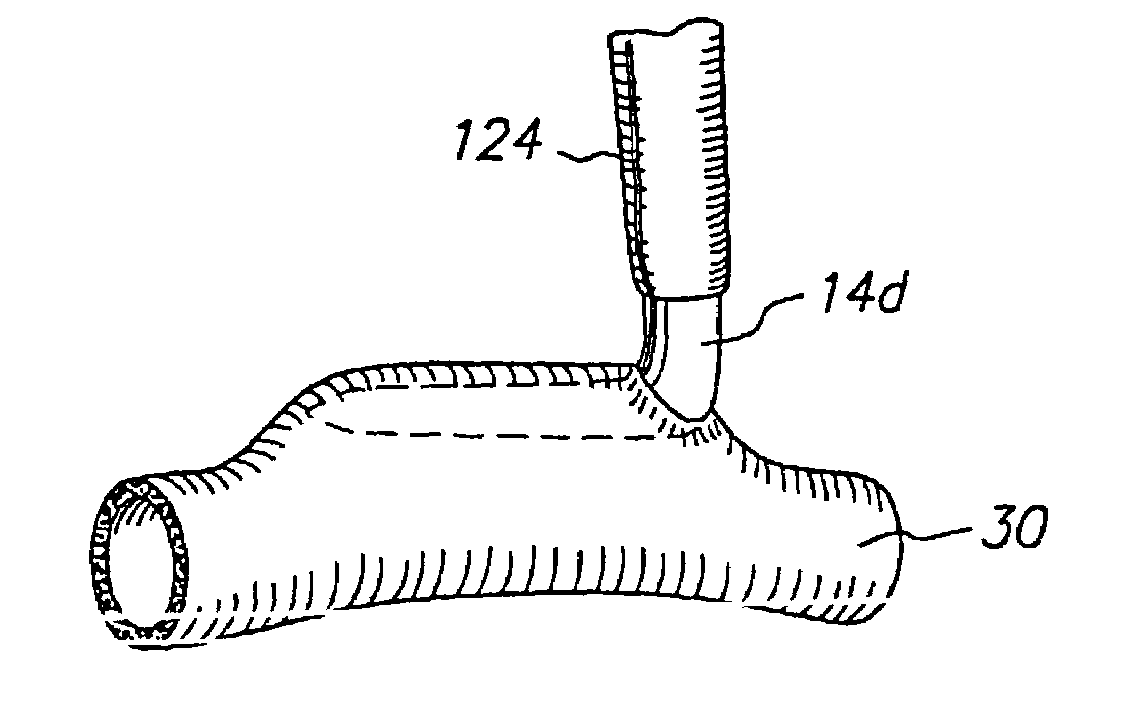
A method for connecting a graft vessel to a target vessel, each vessel having a wall surrounding a lumen, may include providing a connector holder, associating an end of the graft vessel with the connector holder, positioning the connector holder outside of the lumen of the target vessel, outside the lumen of the graft vessel, and in proximity to the outer surface of the wall of the target vessel, and actuating the connector holder to secure the end of the graft vessel to the side of the target vessel.
Owner:AESCULAP AG
Externally expandable heart valve anchor and method
InactiveUS20050137686A1Reduce paravalvular leakageReduce regurgitationStentsBalloon catheterBlood vesselVALVE PORT
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Catheter for conducting a procedure within a lumen, duct or organ of a living being
In an embodiment, the invention provides a catheter suitable for use in performing a procedure within a vessel, lumen or organ of a living having a distal end which is steerable, such as upon the application of compression. The catheter may be of the over the wire type, or alternatively may be a rapid exchange catheter. The catheter may provide for a rotating element which may be used to open a clogged vessel, or alternatively to provide information about adjacent tissues, such as may be generated by imaging or guiding arrangements using tissue detection systems known in the art, e.g., ultrasound, optical coherence reflectometry, etc. For rapid exchange catheters having a rotating element, there is provided an offset drive assembly to allow the rotary force to be directed from alongside the guidewire to a location coaxial to and over the guidewire.
Owner:KENSEY NASH CORP
Surgical clip and applier device and method of use
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Neural regeneration peptides and methods for their use in treatment of brain damage
InactiveUS7563862B2High expressionEasy SurvivalPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsNervous systemInjury brain
The invention discloses a family of peptides termed NRP compounds or NRPs that can promote neuronal migration, neurite outgrowth, neuronal proliferation, neural differentiation and / or neuronal survival, and provides compositions and methods for the use of NRPs in the treatment of brain injury and neurodegenerative disease. NRP compounds can induce neurons and neuroblasts to proliferate and migrate into areas of damage caused by acute brain injury or chronic neurodegenerative disease, such as exposure to toxins, stroke, trauma, nervous system infections, demyelinating diseases, dementias, and metabolic disorders. NRP compounds may be administered directly to a subject or to a subject's cells by a variety of means including orally, intraperitoneally, intravascularly, and directly into the nervous system of a patient. NRP compounds can be formulated into pharmaceutically acceptable dose forms for therapeutic use. Methods for detecting neural regeneration, neural proliferation, neural differentiation, neurite outgrowth and neural survival can be used to develop other neurally active agents.
Owner:CURONZ HLDG
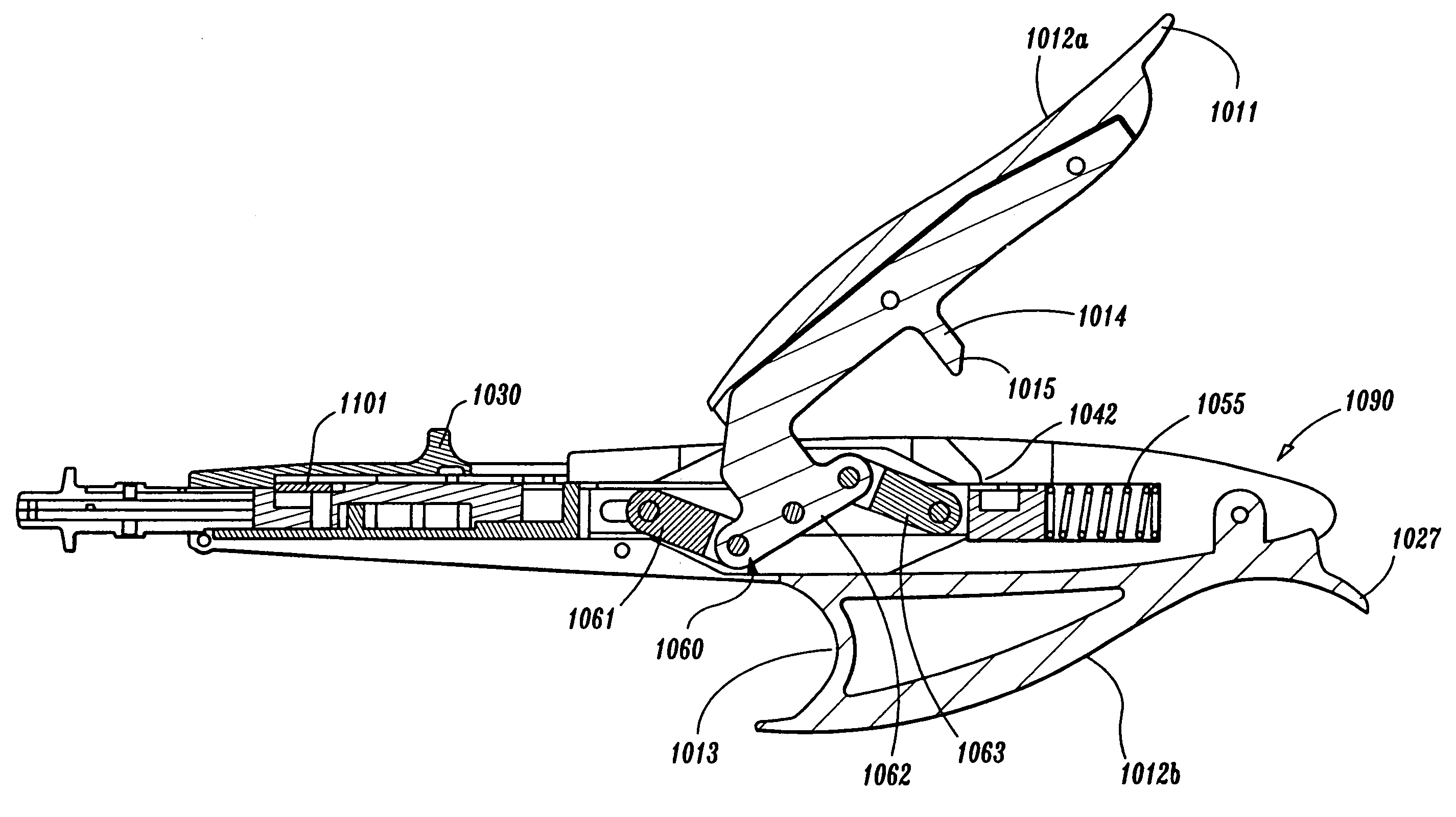
Wound closure device
Disclosed is a wound closure device and method for using the same. The wound closure device includes a handle, a body portion extending distally from the handle, a stapling mechanism extending distally from the body portion and a mechanism for supplying electrical energy from an RF power supply to a fastener (e.g. staple) which is associated with the stapling mechanism. In a representative embodiment, the stapling mechanism includes an inner rod member disposed within an elongated outer sleeve and slidably movable therein. The rod member has an enlarged tip for deploying the fastener that is supported adjacent to the tip into body tissue. The wound closure device further includes an actuator mechanism associated with the handle and body portion and configured to facilitate relative movement of the inner rod and the outer sleeve so as to deploy the fastener into body tissue. In alternative embodiments, a second pole of the RF power supply is connected to a conductive ring associated with a vascular introducer.
Owner:INSTRASURGICAL
Bipolar forceps
ActiveUS8579897B2Likelihood that the wire may become damaged or broken can be reducedReduce the possibilityLavatory sanitorySurgical instruments for heatingEngineeringSurgical technical
In various surgical techniques, a bipolar forceps can be used to seal a vessel in two locations such that the vessel can be incised at a location positioned intermediate the two seal locations. The bipolar forceps can include a cutting element which can be configured to incise the vessel. In various embodiments, the cutting element can include a sharp edge which can be moved relative to the vessel. In at least one embodiment, the cutting element can be electrically connected to a source of energy. The bipolar forceps can include first and second electrodes positioned within first and second jaw members, respectively, wherein at least one of the jaw members can include a substantially tapered profile and can be configured to pull the vessel away from the surrounding soft tissue. Such jaw members can include ridges, teeth, and / or a textured outer surface configured to grip the soft tissue and / or vessel.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Apparatus for performing anastomosis
An apparatus for performing anastomosis between a graft vessel and a target vessel may include a connector holder having spaced-apart arms, and a member connected to the connector holder, where the member is insertable through an opening in a wall of the target vessel at least partially into the lumen of the target vessel. One or more connectors, such as staples, may be deployed from each arm to connect the graft vessel to the target vessel. One or more connectors may be deformable against the member.
Owner:AESCULAP AG
Devices and methods for treating pain associated with tonsillectomies
Described here are devices and methods for treating one or more conditions or symptoms associated with a tonsil procedure. In some variations, a drug-releasing device may be at least partially delivered to one or more tonsillar tissues before, during, or after a tonsil procedure. In some variations, the drug-releasing device may be configured to be biodegradable. In other variations, the drug-releasing device may comprise one or more hemostatic materials or one or more adhesives. The drug-releasing device may be configured to release one or more drugs or agents, such as, for example, one or more analgesics, local anesthetics, vasoconstrictors, antibiotics, combinations thereof and the like.
Owner:INTERSECT ENT INC
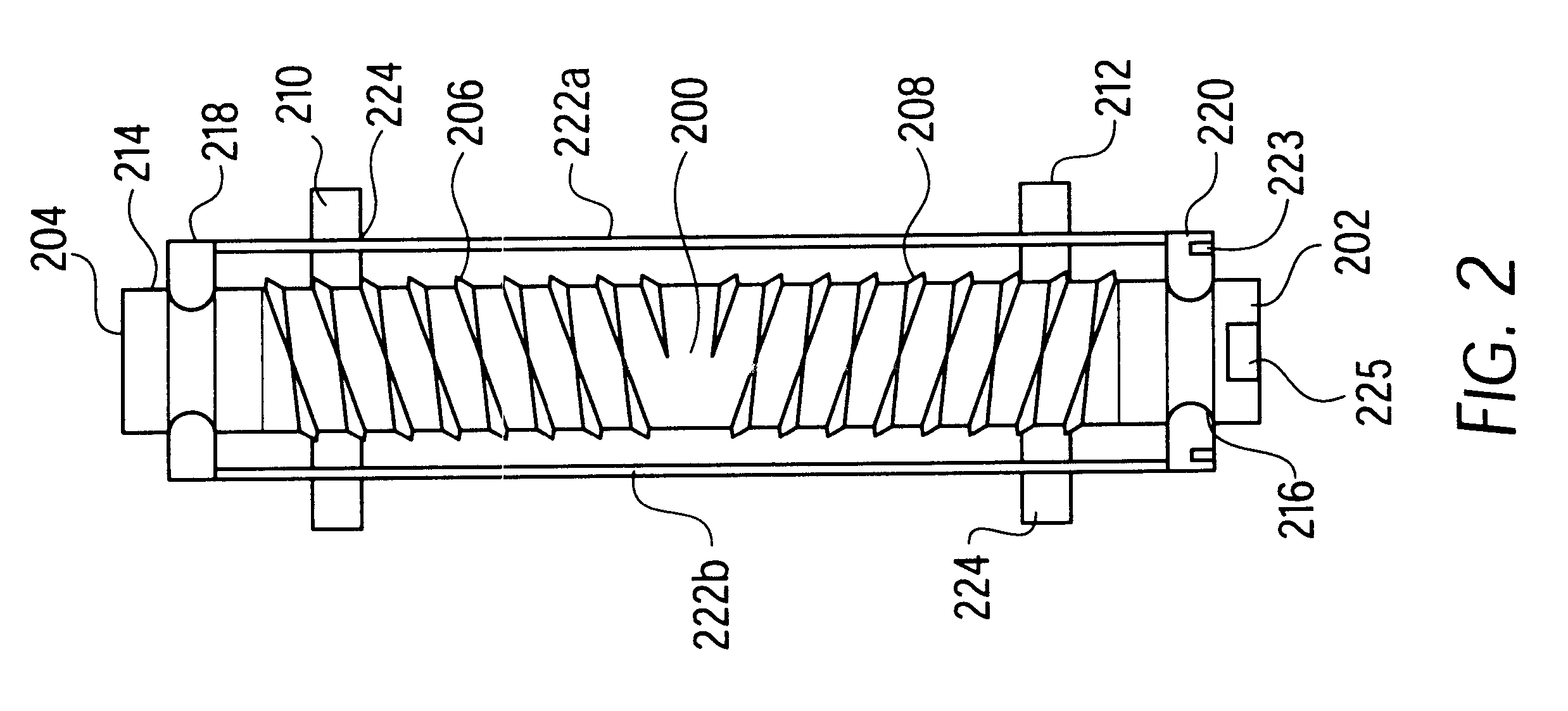
Vessel and lumen expander attachment for use with an electromechanical driver device
A selectively coupleable and remotely actuateable surgical attachment for use with an electromechanical driver device for use in expanding occluded vessels and lumens. The attachment includes an axial rod which is coupleable to the electromechanical driver device, and which is selectively rotateable in accordance with the action of the electromechanical driver device. The rod is also threaded in opposing orientations at either end thereof. A pair of nuts are mounted to the rod, and specifically on the opposing threads. The rod and nuts are disposed within an axial track which permits the rod to turn, but constrains the rotational motion of the nuts, thereby permitting the nuts to move axially along the threadings of the rod when the rod turns. Attached to the nuts are a series of jointed spokes which are coupled to a flexible tubular shroud which surrounds the entire assembly. The jointed spokes are radially extended and retracted in accordance with the motion of the nuts in an umbrella-like fashion in accordance with the actuation of the electromechanical driver device. The radial expansion of the flexible tubular shroud provides the necessary force to expand an occluded vessel or lumen.
Owner:DORROS GERALD M D
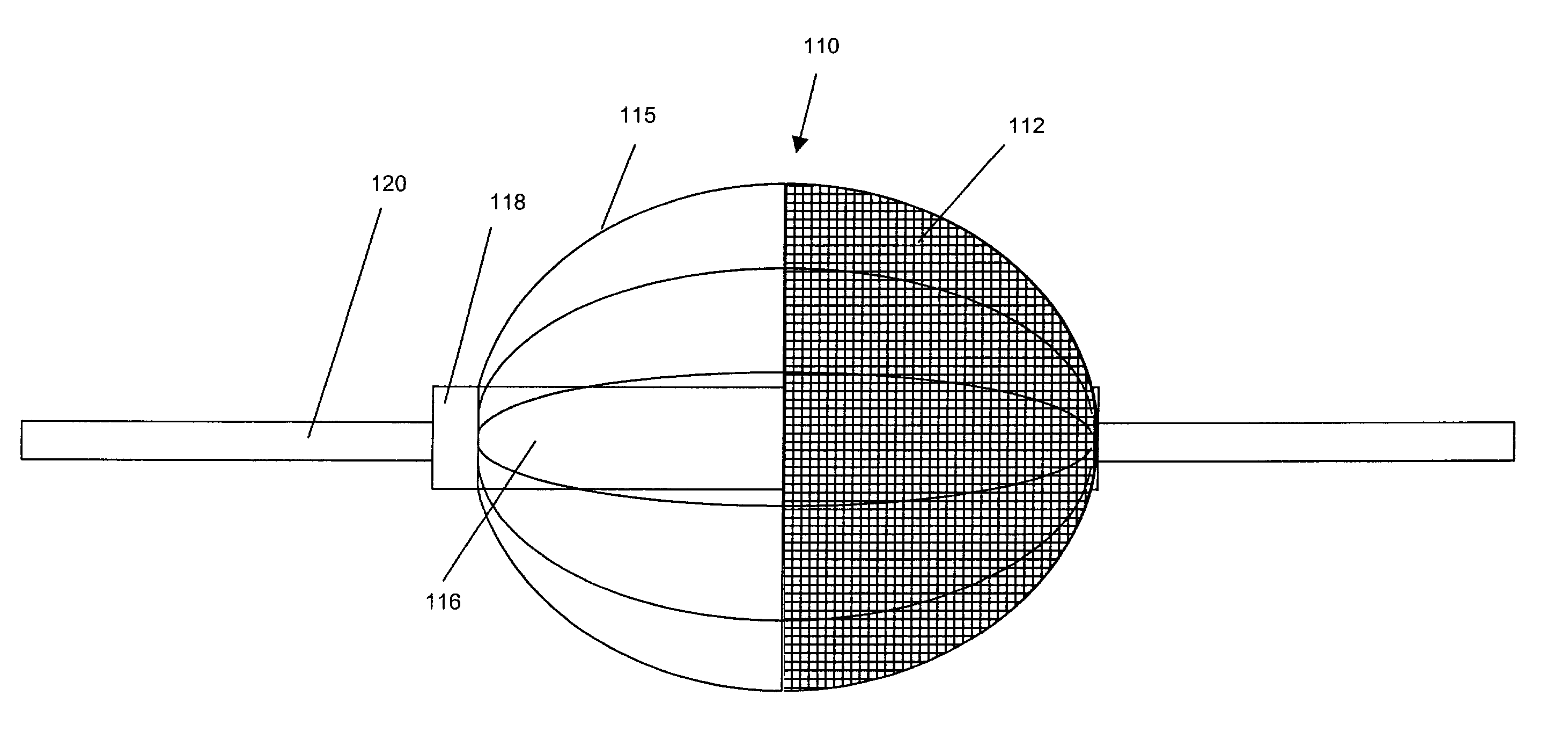
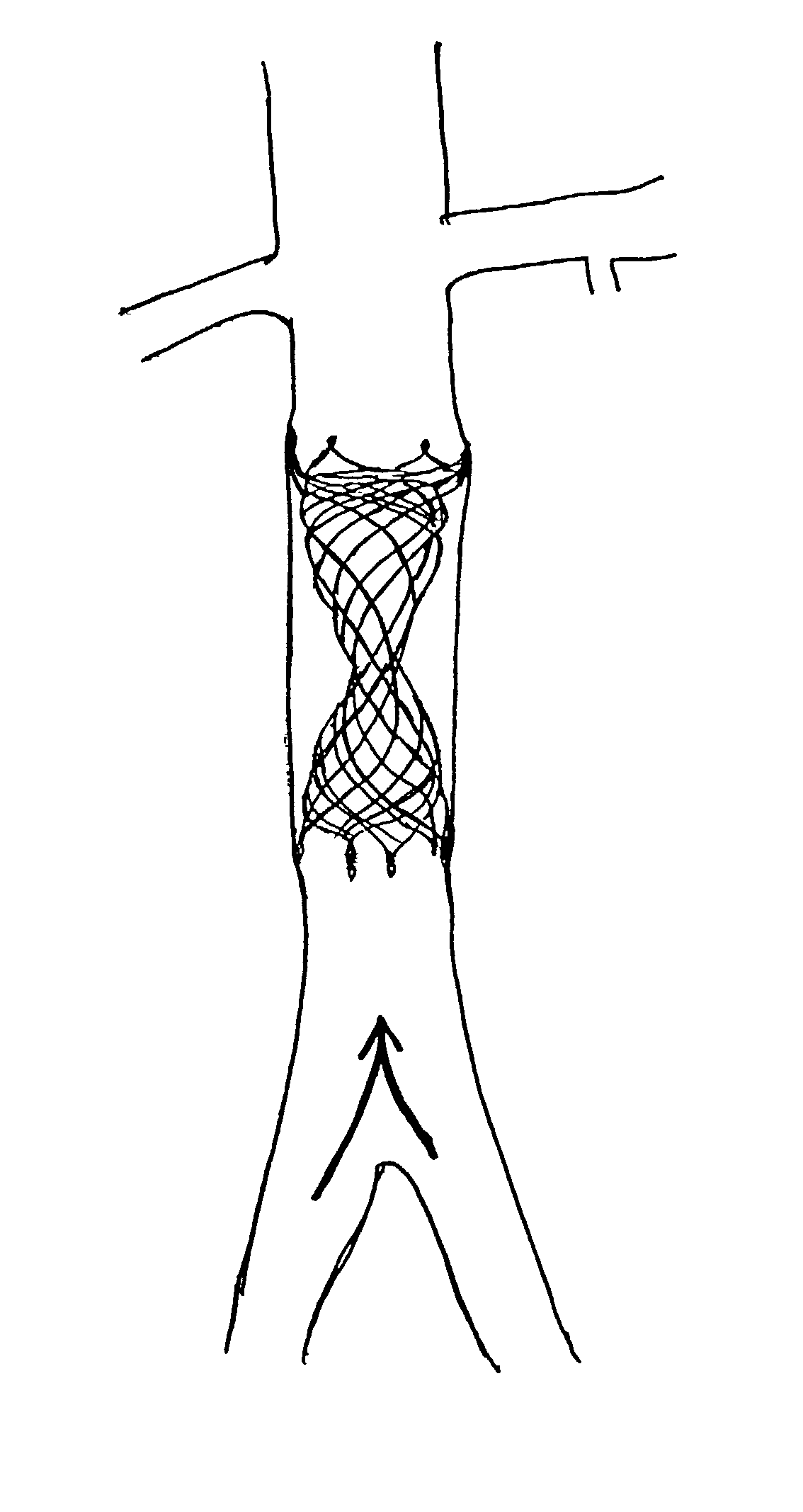
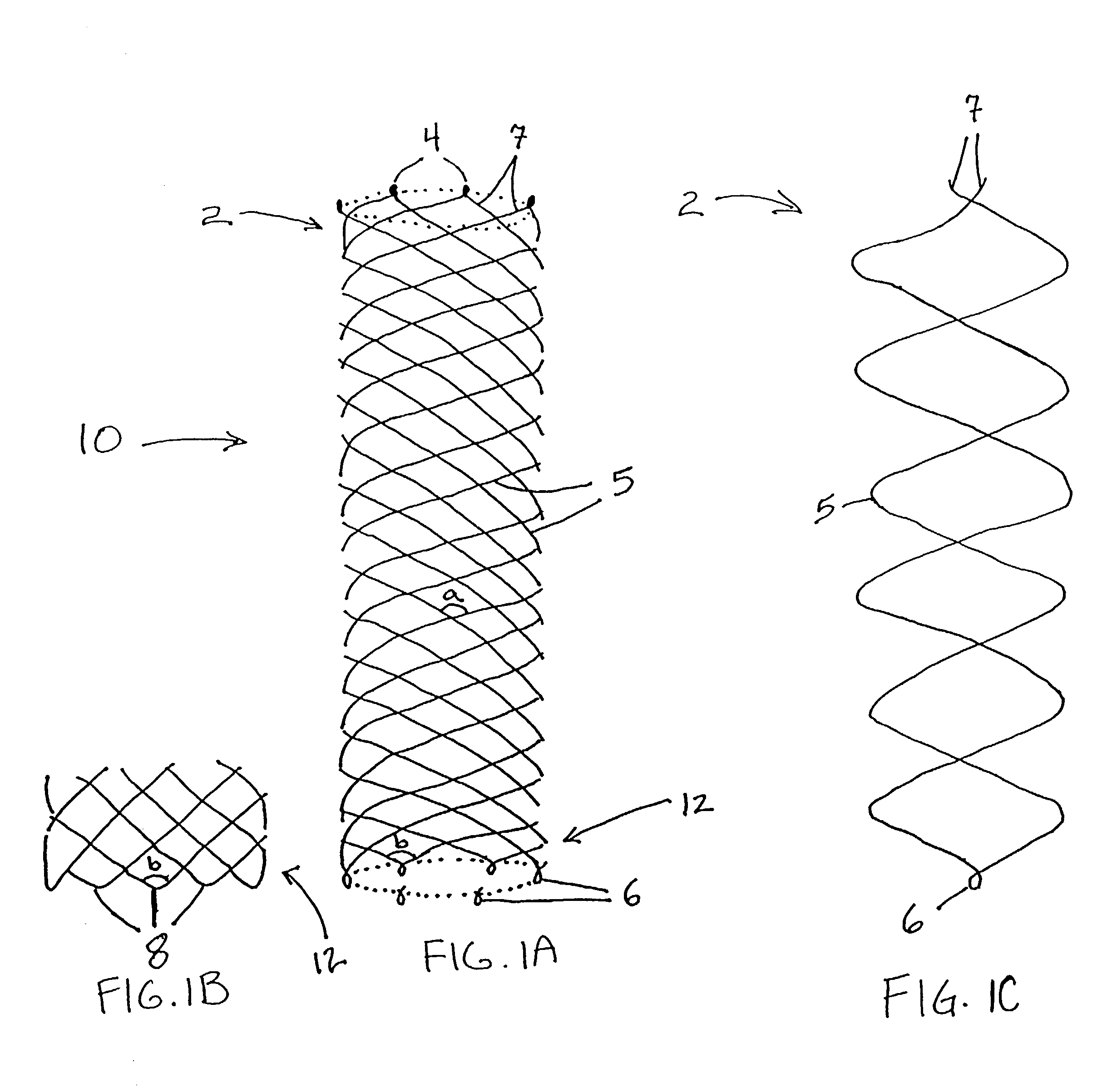
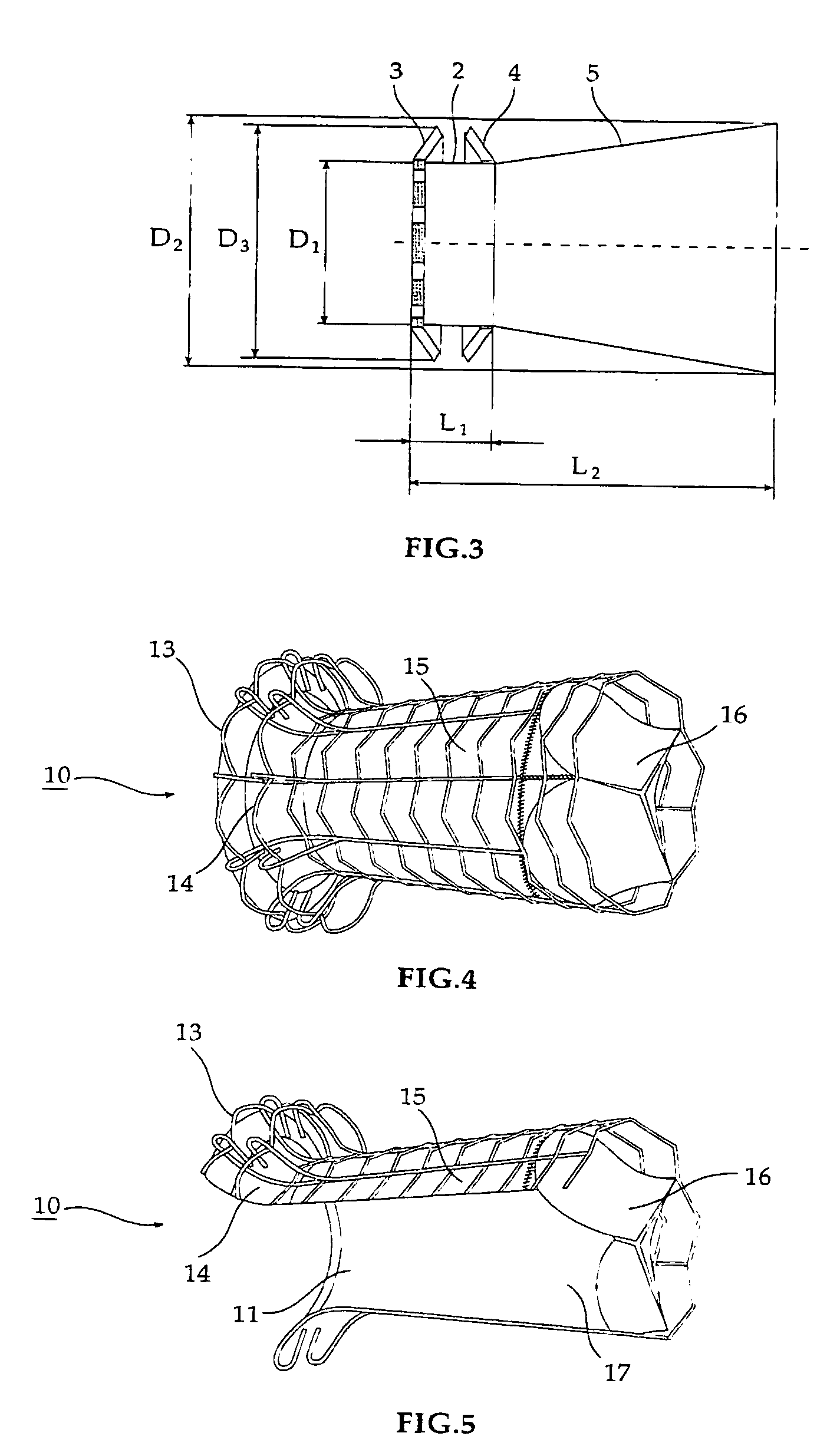
Delivery devices
Self-expandable, woven intravascular devices for use as stents (both straight and tapered), filters (both temporary and permanent) and occluders for insertion and implantation into a variety of anatomical structures. The devices may be formed from shape memory metals such as nitinol. The devices may also be formed from biodegradable materials. Delivery systems for the devices include two hollow tubes that operate coaxially. A device is secured to the tubes prior to the implantation and delivery of the device by securing one end of the device to the outside of the inner tube and by securing the other end of the device to the outside of the outer tube. The stents may be partially or completely covered by graft materials, but may also be bare. The devices may be formed from a single wire. The devices may be formed by either hand or machine weaving. The devices may be created by bending shape memory wires around tabs projecting from a template, and weaving the ends of the wires to create the body of the device such that the wires cross each other to form a plurality of angles, at least one of the angles being obtuse. The value of the obtuse angle may be increased by axially compressing the body.
Owner:HYODOH HIDEKI +2
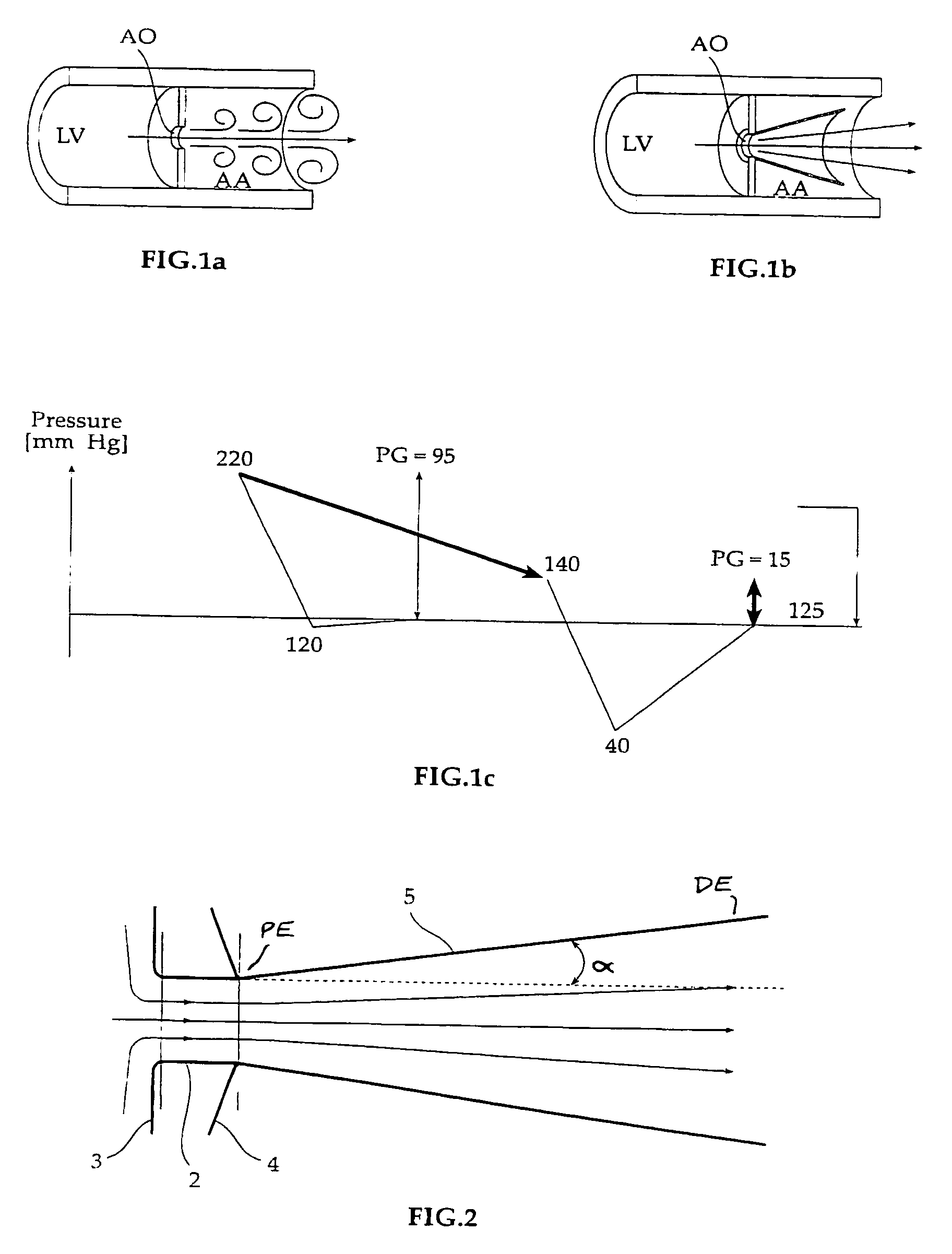
Fluid flow prosthetic device
A prosthetic device including a valve-orifice attachment member attachable to a valve in a blood vessel and including a fluid inlet, and a diverging member that extends from the fluid inlet, the diverging member including a proximal end near the fluid inlet and a distal end distanced from the proximal end, wherein a distal portion of the diverging member has a larger cross-sectional area for fluid flow therethrough than a proximal portion thereof. The diverging member may have a diverging taper that causes fluid to flow therethrough with pressure recovery at the distal end thereof.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VENTOR TECH
Analyte sensor
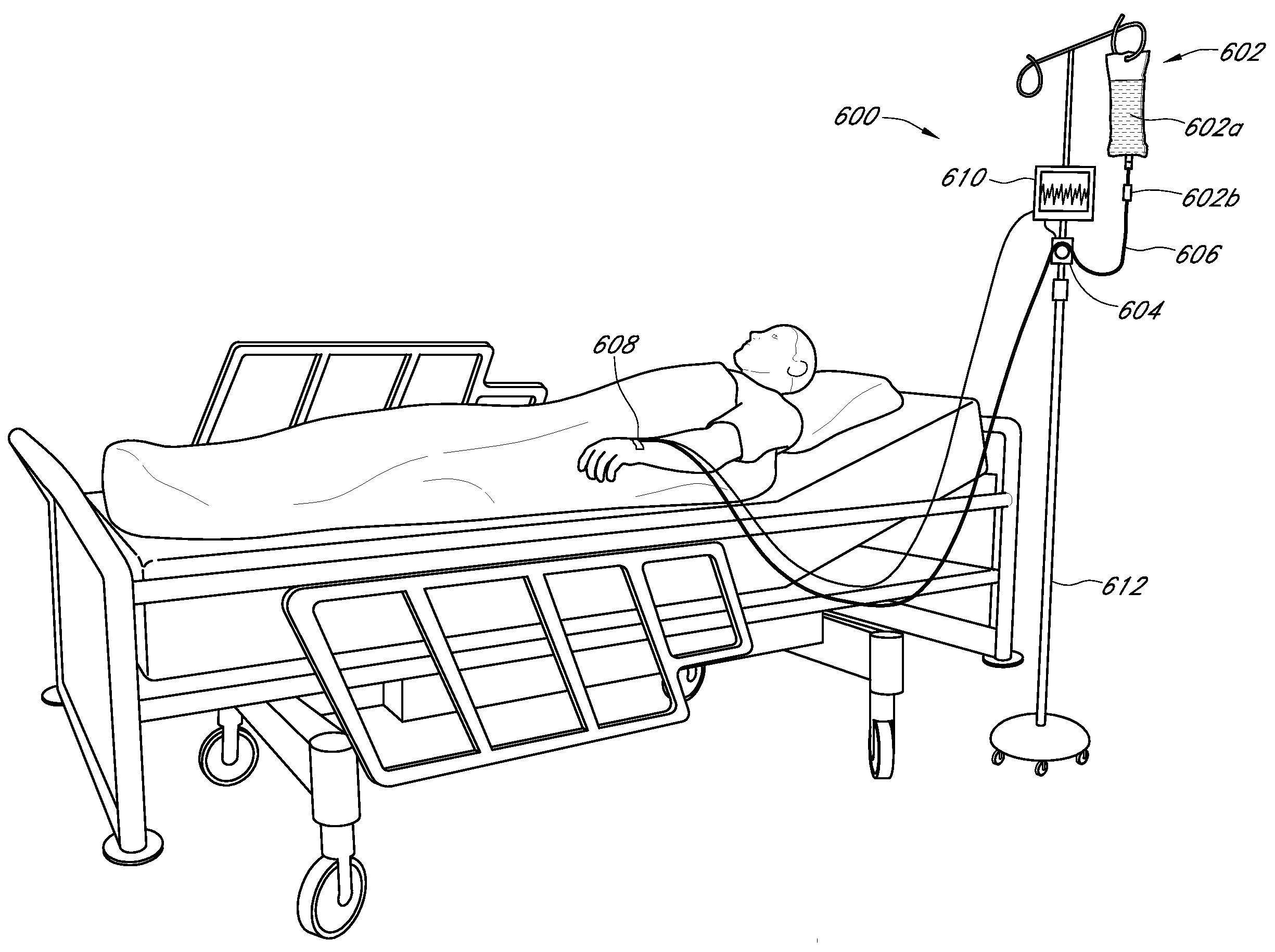
Systems and methods of use for continuous analyte measurement of a host's vascular system are provided. In some embodiments, a continuous glucose measurement system includes a vascular access device, a sensor and sensor electronics, the system being configured for insertion into communication with a host's circulatory system.
Owner:DEXCOM INC
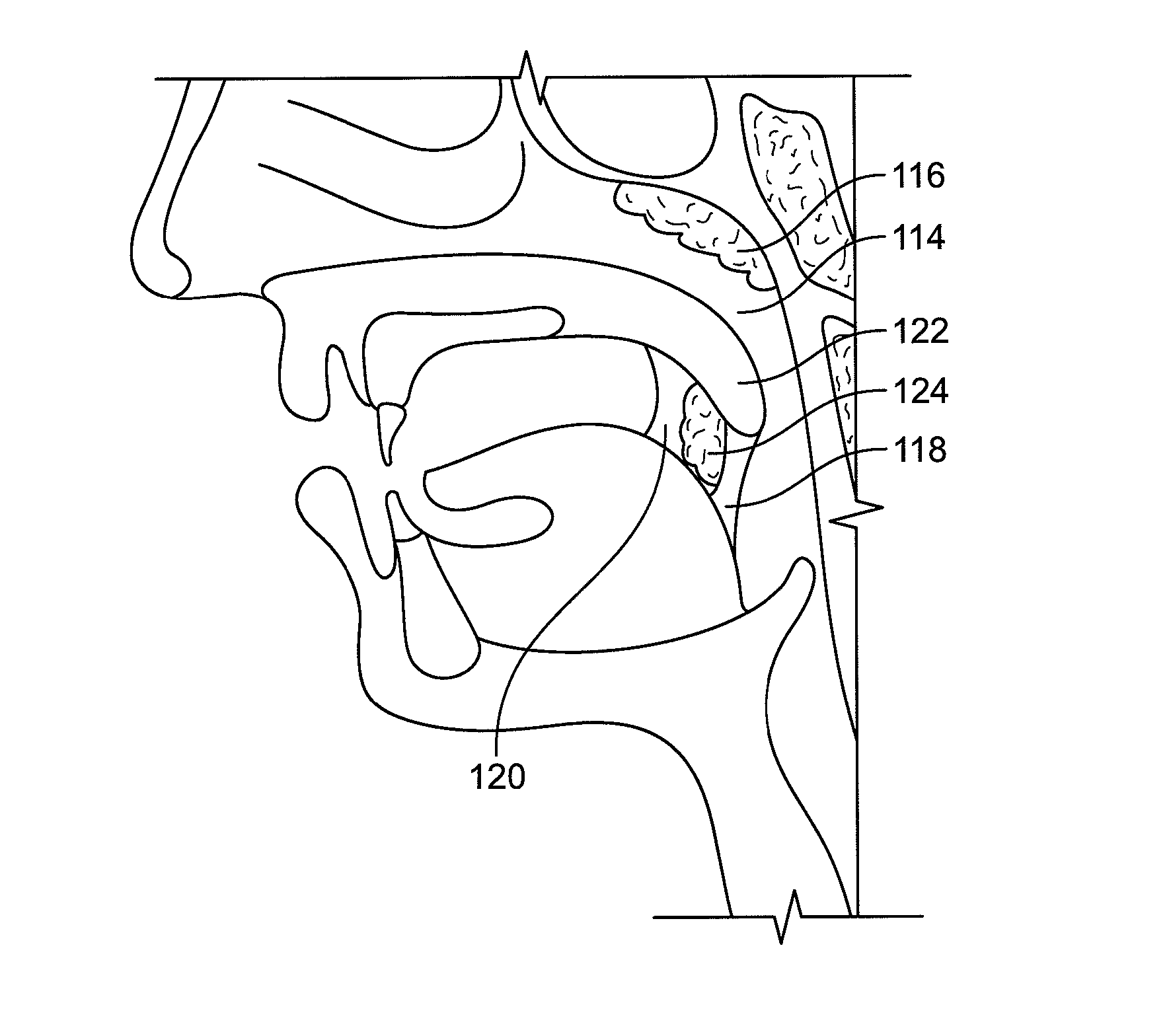
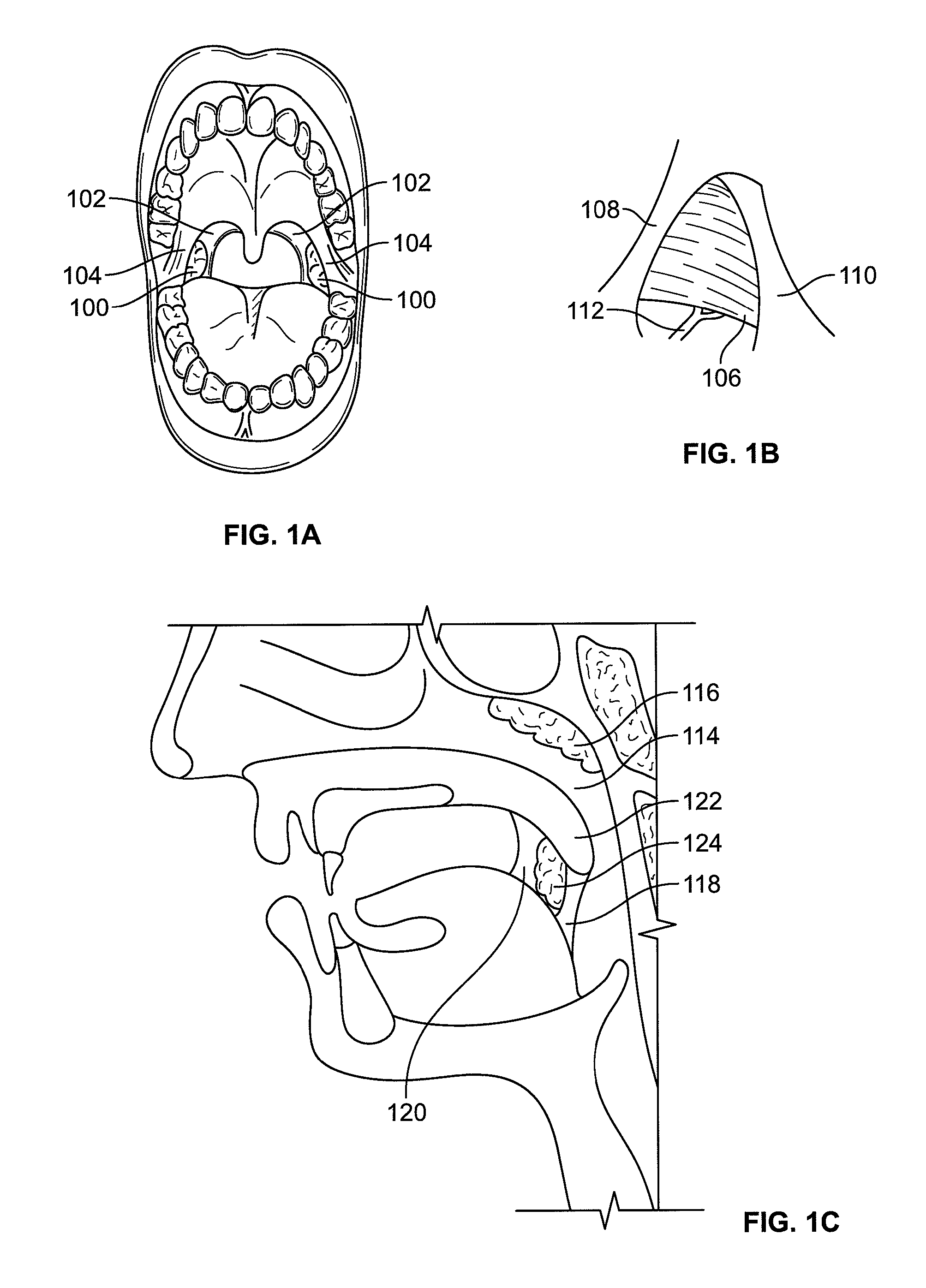
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com