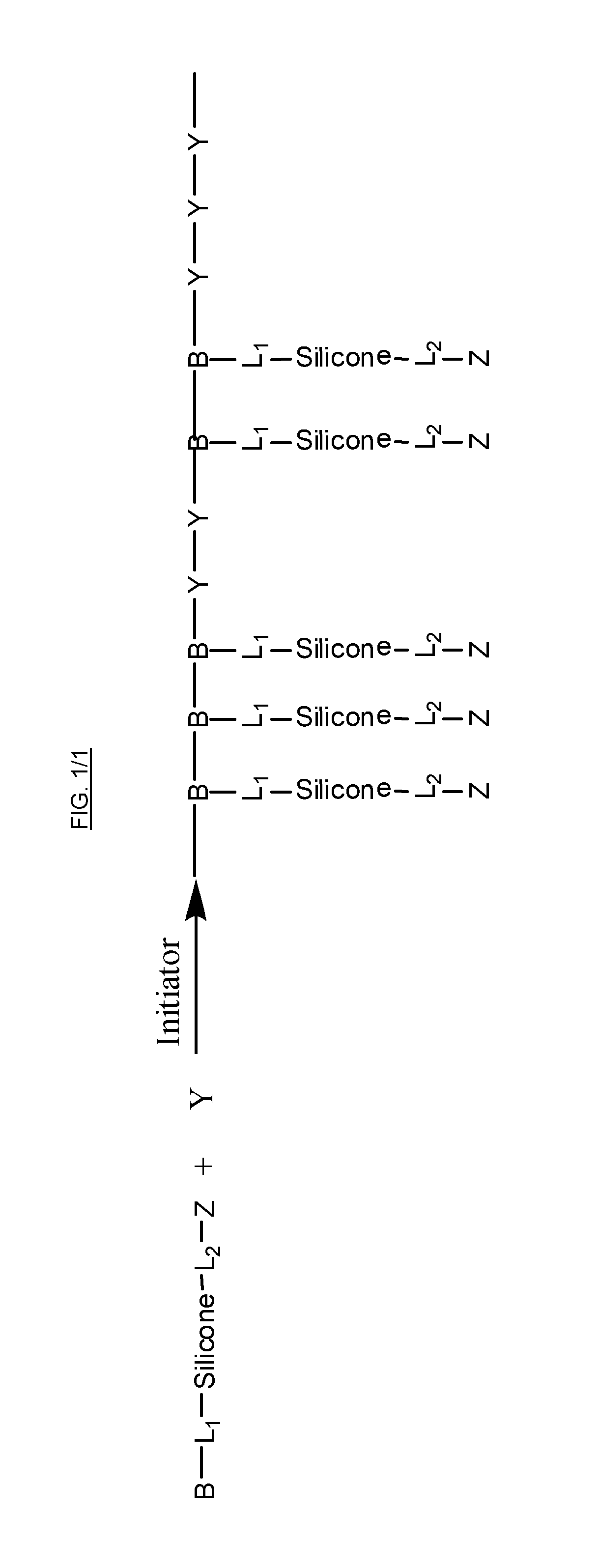
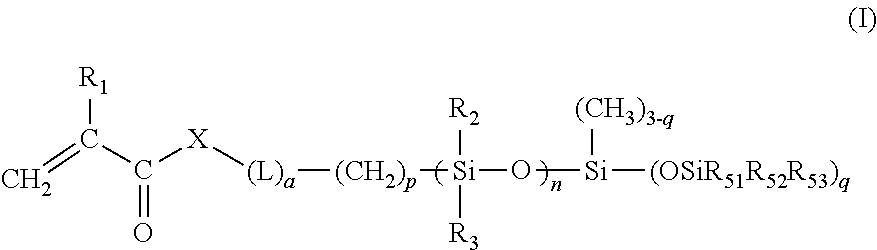Patents
Literature
31 results about "Biointerface" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
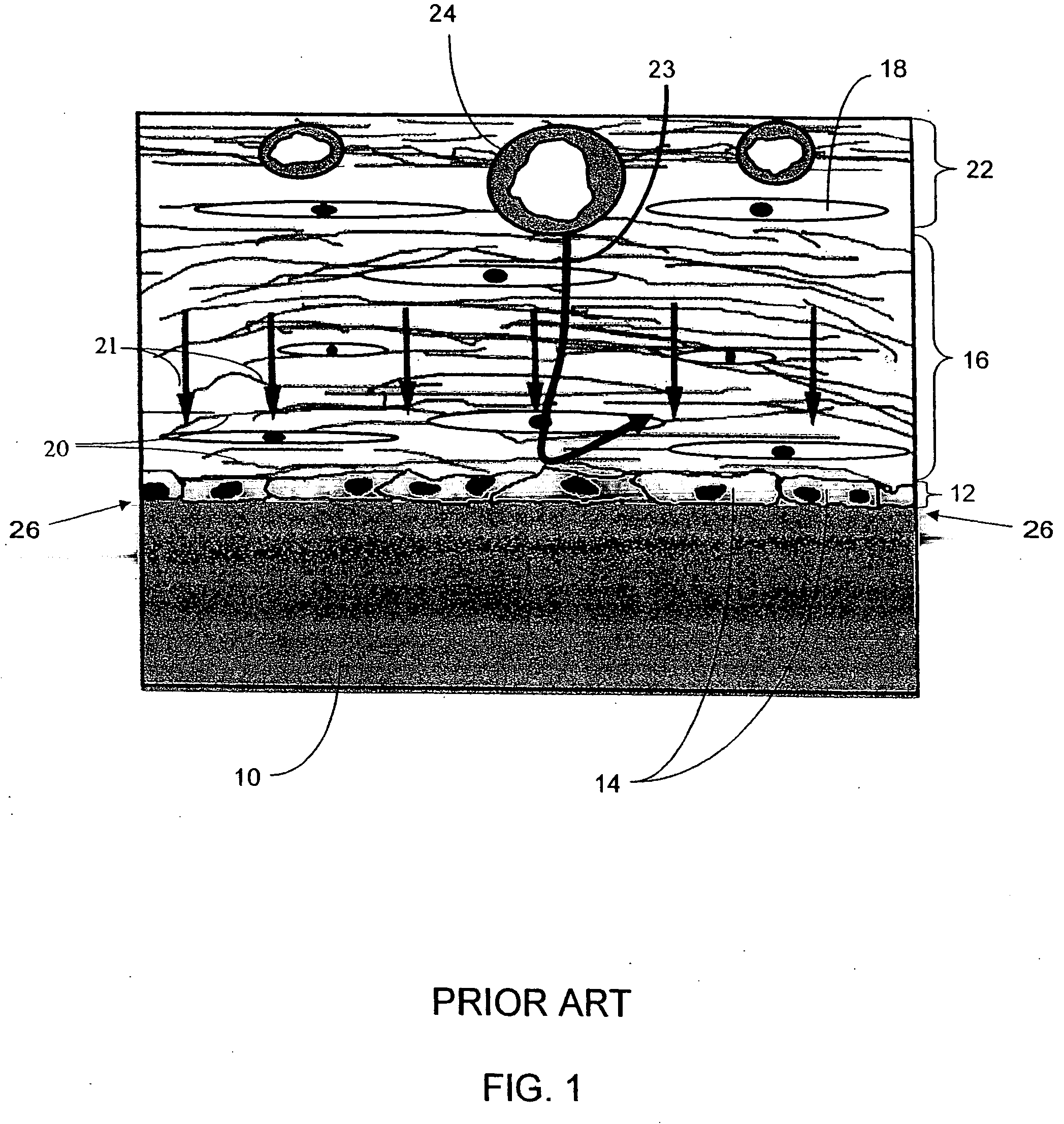
A biointerface is the region of contact between a biomolecule, cell, biological tissue or living organism or organic material considered living with another biomaterial or inorganic/organic material. The motivation for biointerface science stems from the urgent need to increase the understanding of interactions between biomolecules and surfaces. The behavior of complex macromolecular systems at materials interfaces are important in the fields of biology, biotechnology, diagnostics, and medicine. Biointerface science is a multidisciplinary field in which (bio)chemists who synthesize novel classes of biomolecules (PNA, peptidomimetics, aptamers, ribozymes, and engineered proteins) cooperate with scientists who have developed the tools to position biomolecules with molecular precision (proximal probe methods, nano-and micro contact methods, e-beam and X-ray lithography, and bottom up self-assembly methods), scientists who have developed new spectroscopic techniques to interrogate these molecules at the solid-liquid interface, and people who integrate these into functional devices (applied physicists, analytical chemists and bioengineers).
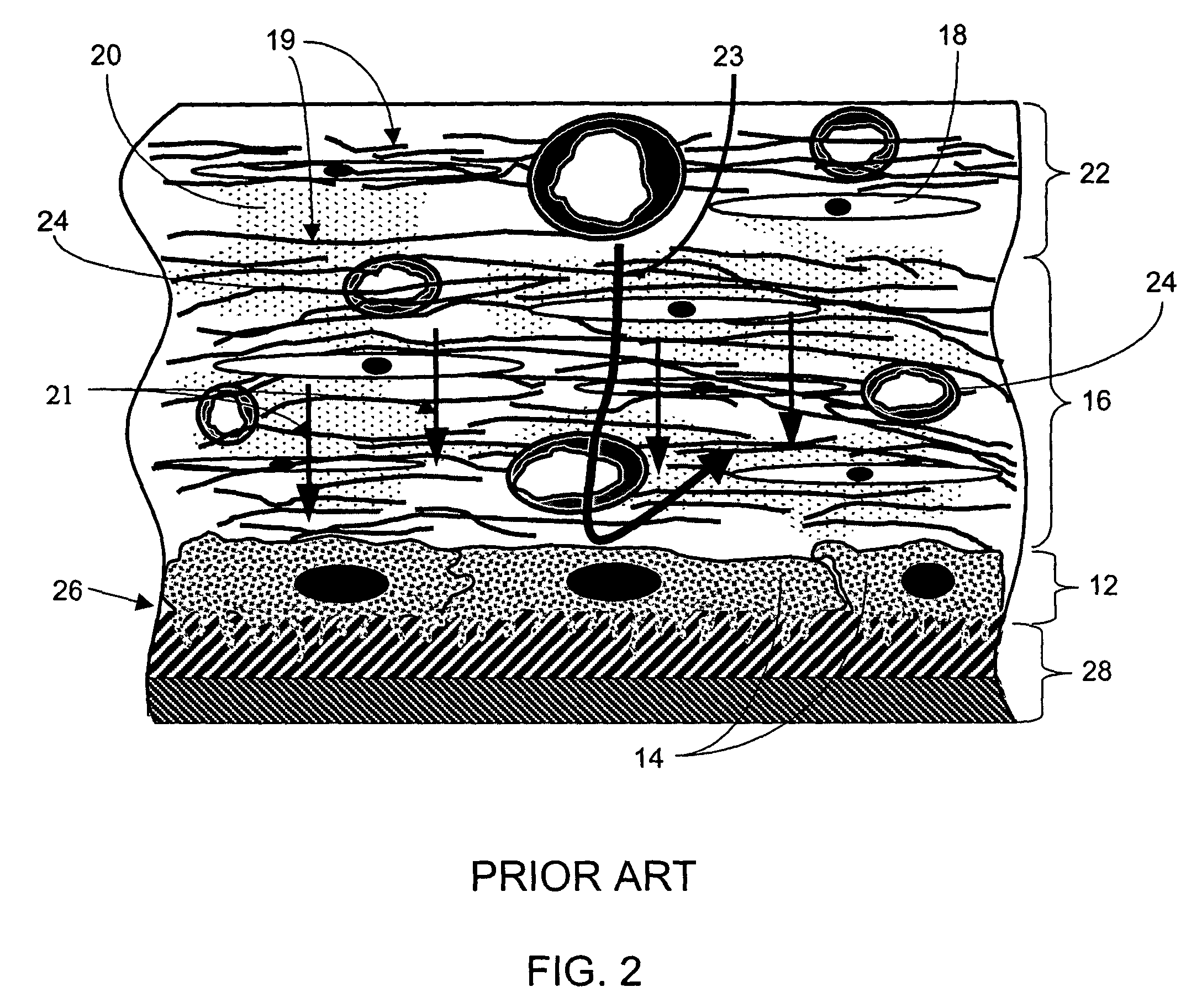
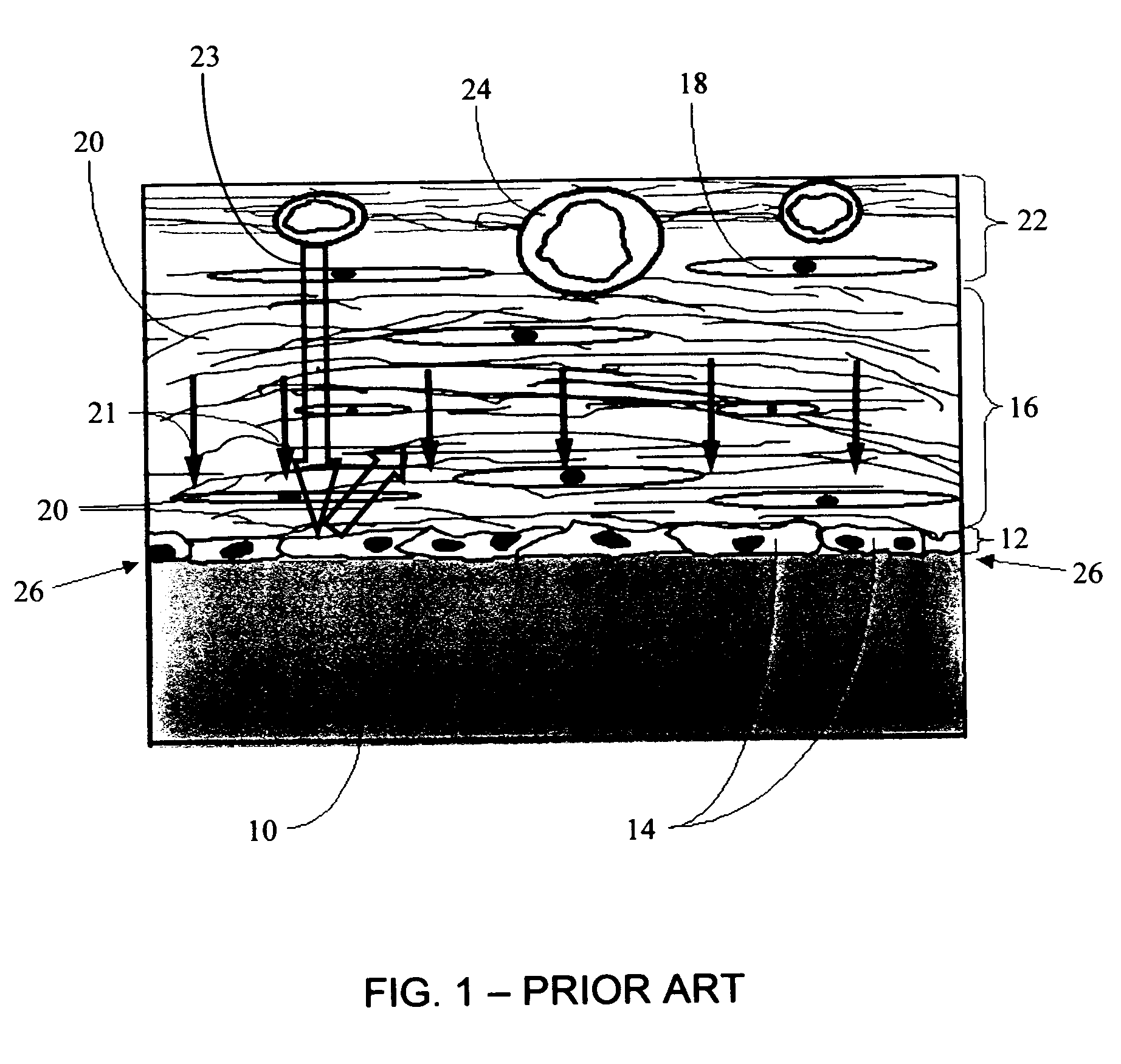
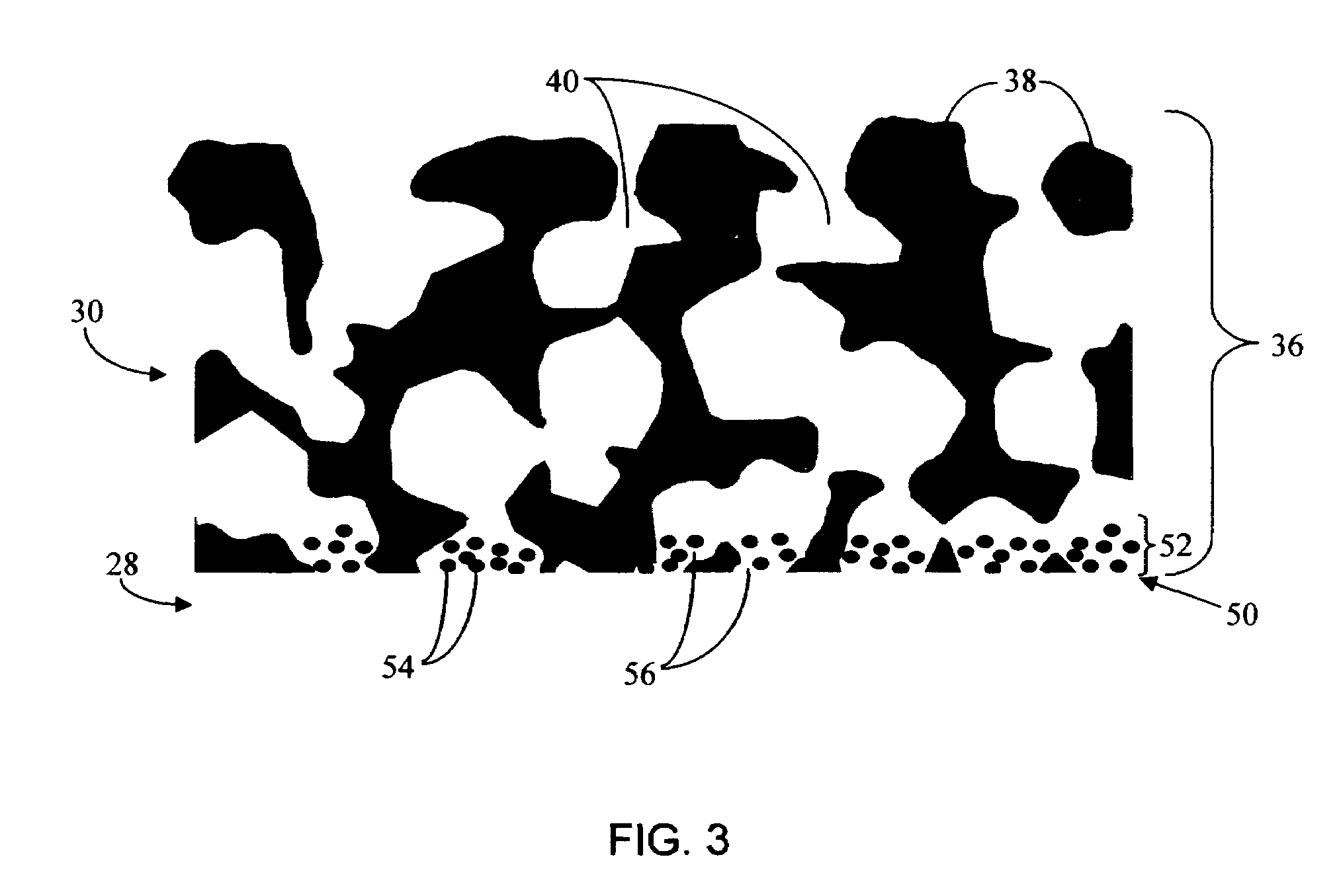
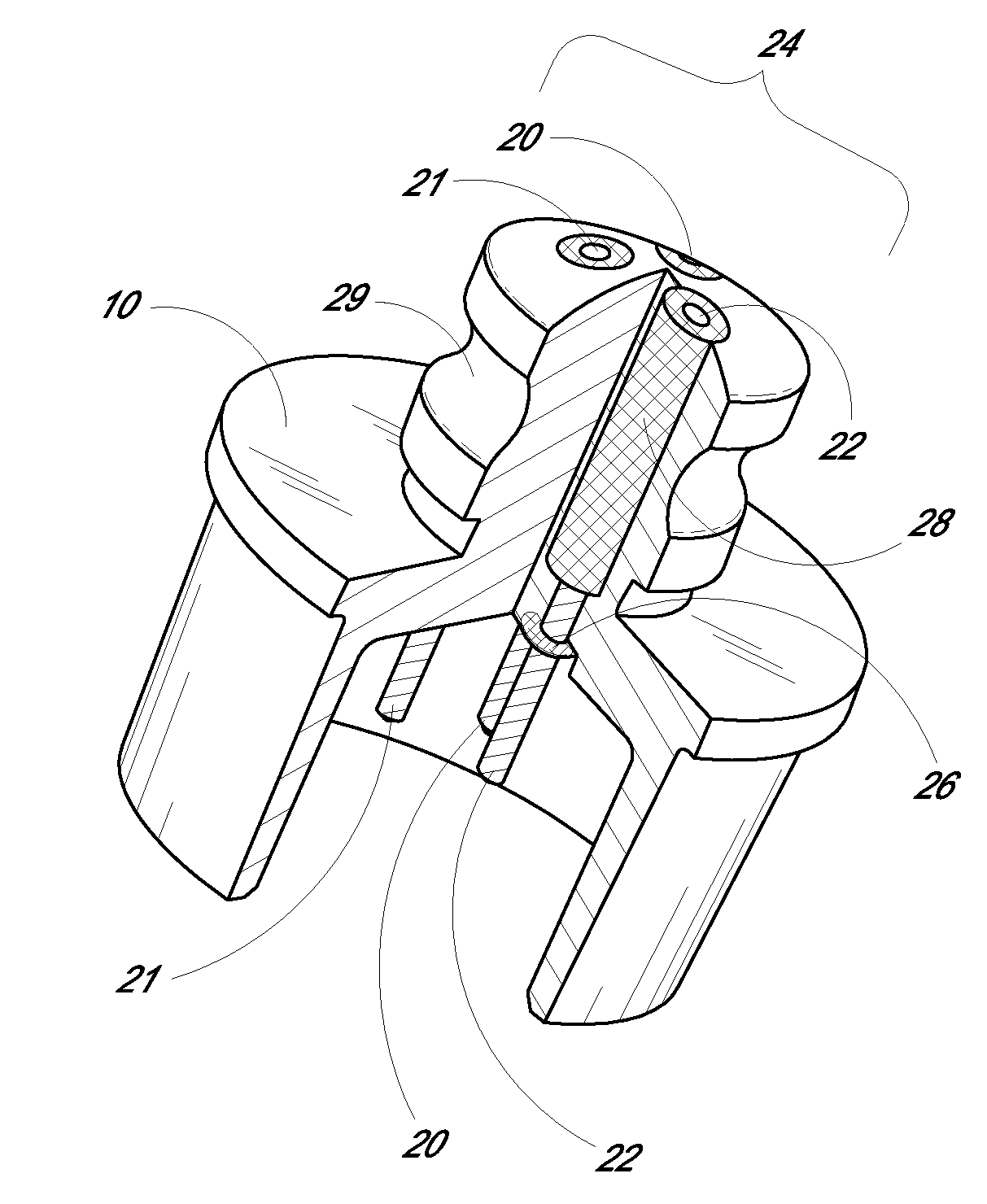
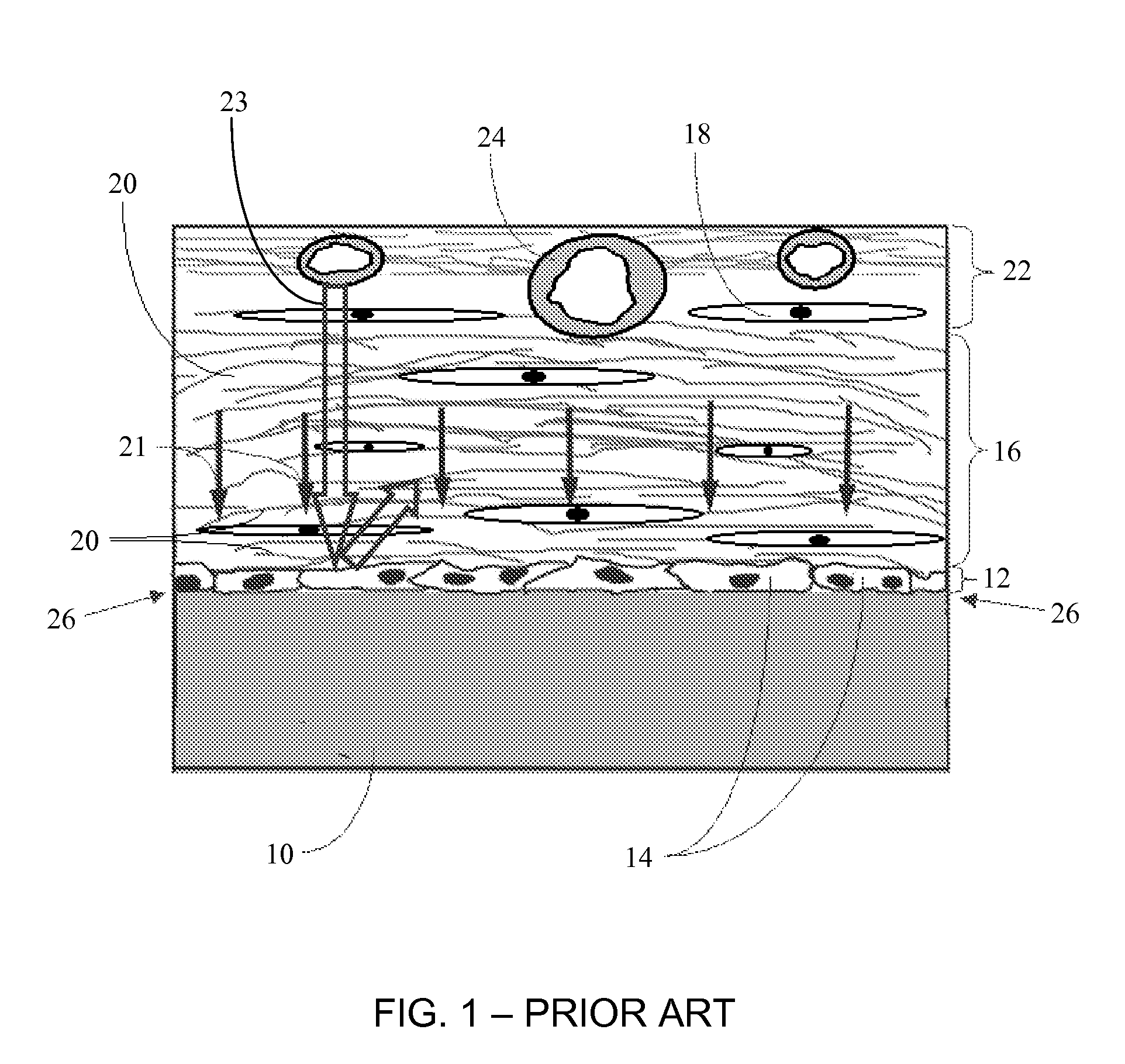
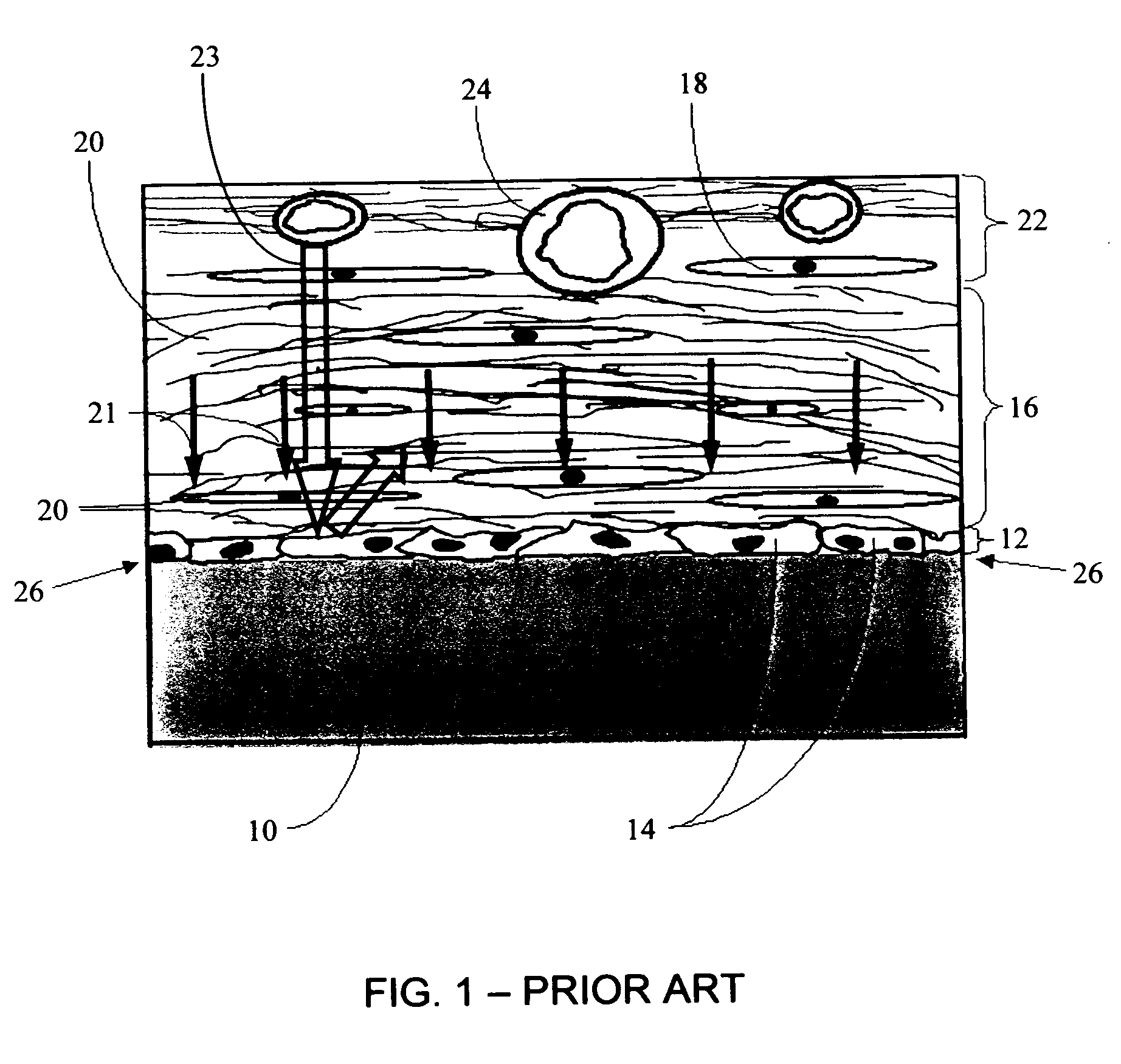
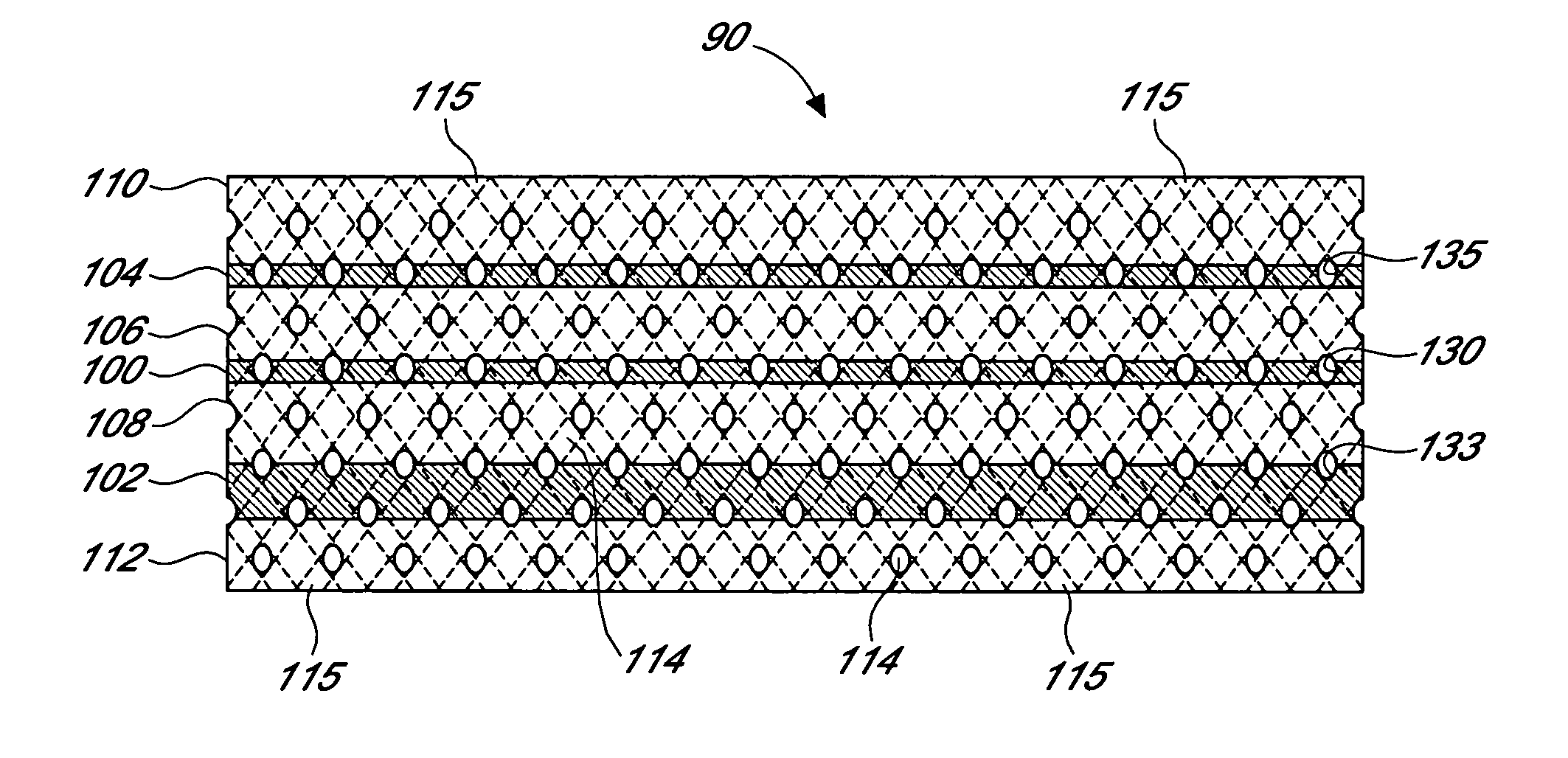
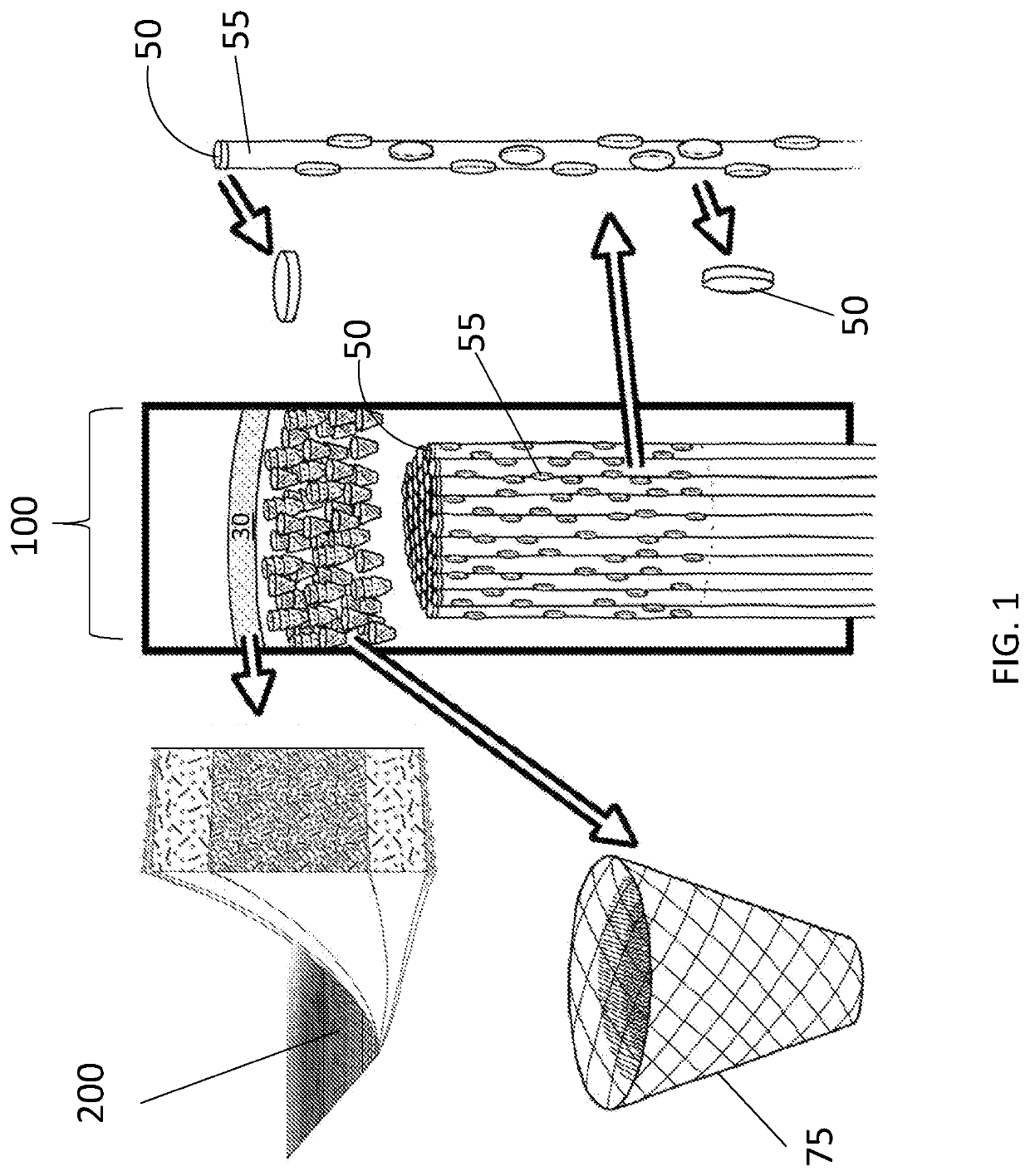
Biointerface membranes incorporating bioactive agents
InactiveUS20050031689A1Improve performancePowder deliveryAdditive manufacturing apparatusBiointerfaceActive agent
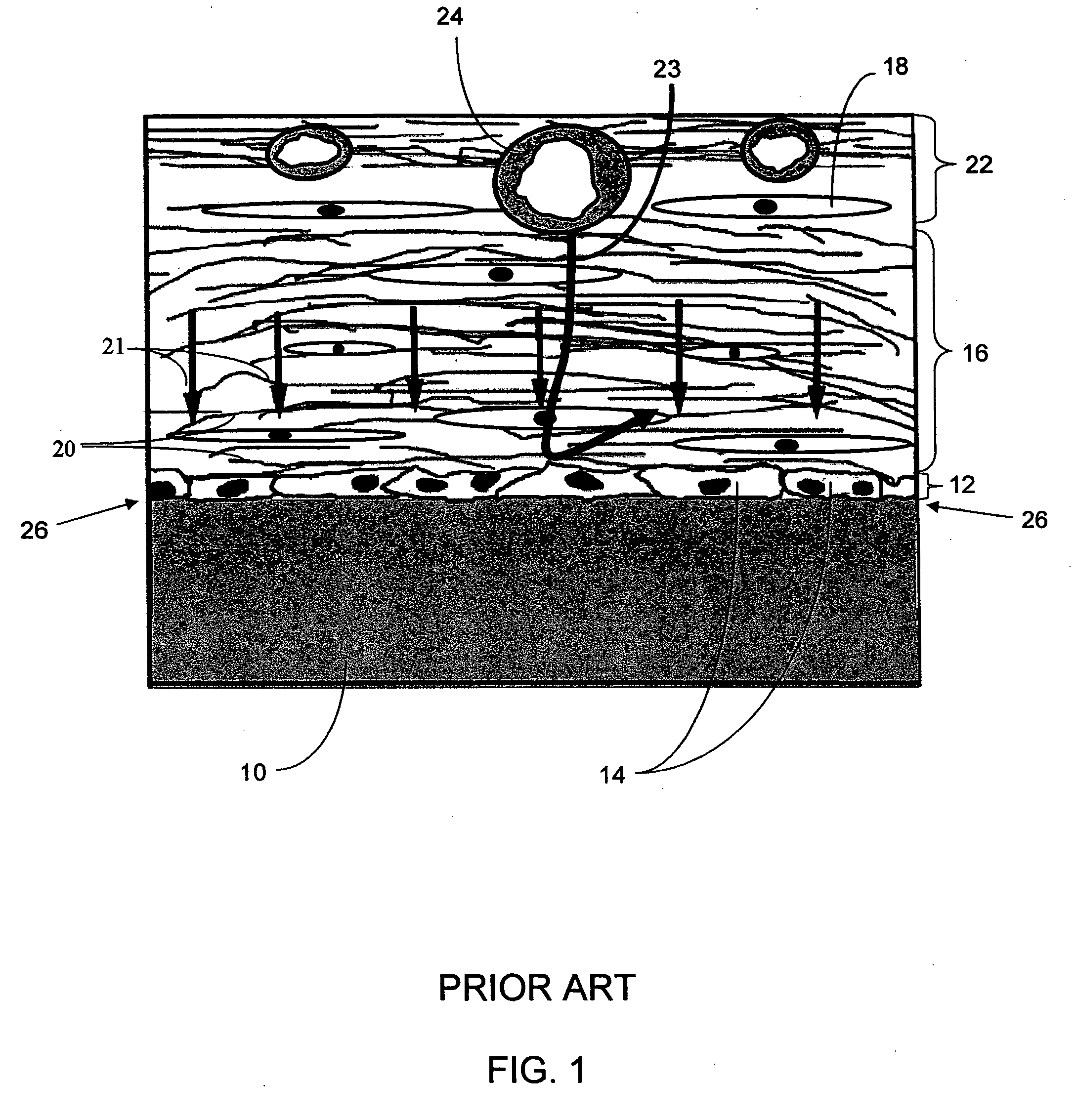
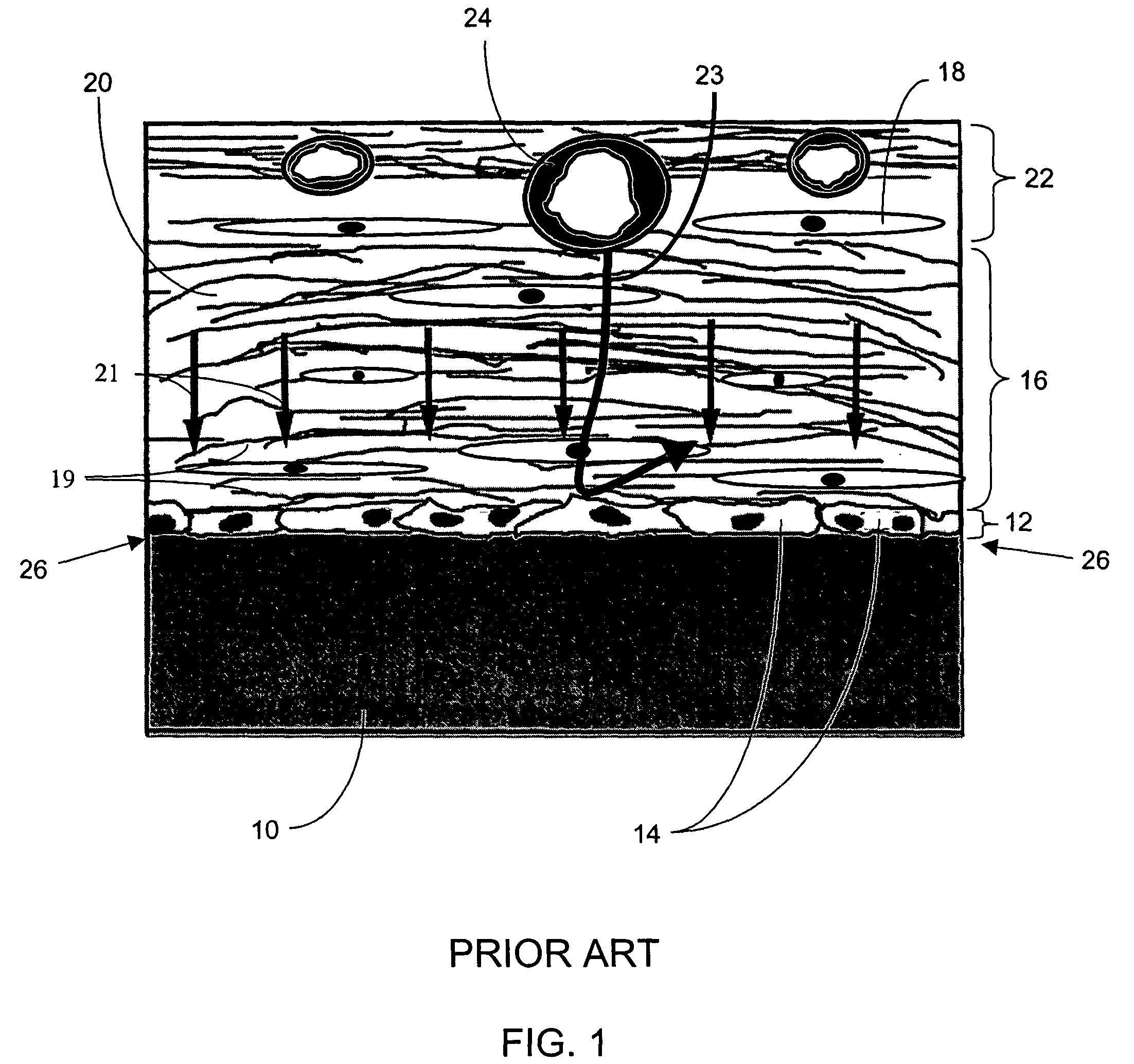
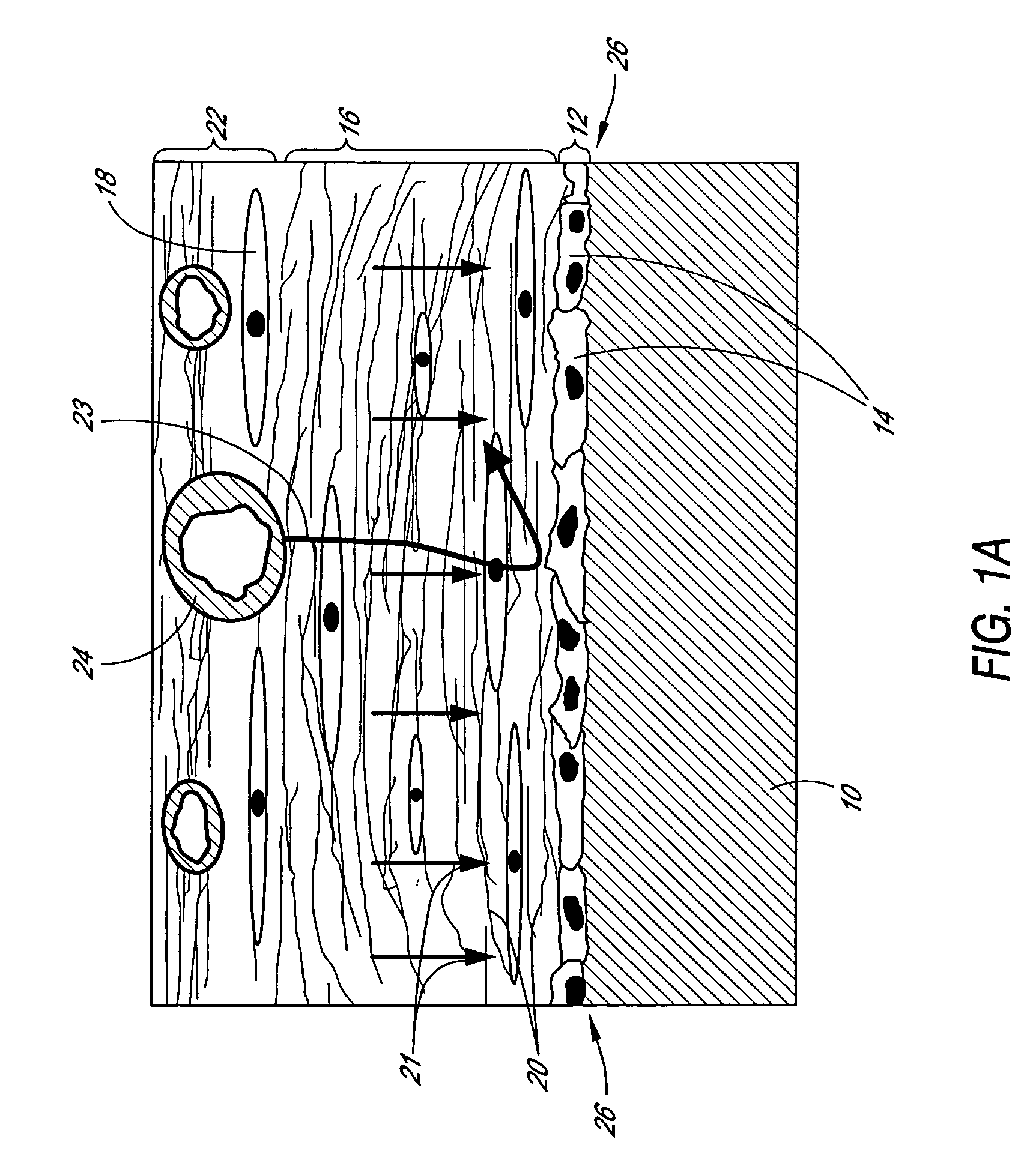
A biointerface membrane for an implantable device including a nonresorbable solid portion with a plurality of interconnected cavities therein adapted to support tissue ingrowth in vivo, and a bioactive agent incorporated into the biointerface membrane and adapted to modify the tissue response is provided. The bioactive agents can be chosen to induce vascularization and / or prevent barrier cell layer formation in vivo, and are advantageous when used with implantable devices wherein solutes are transported across the device-tissue interface.
Owner:DEXCOM
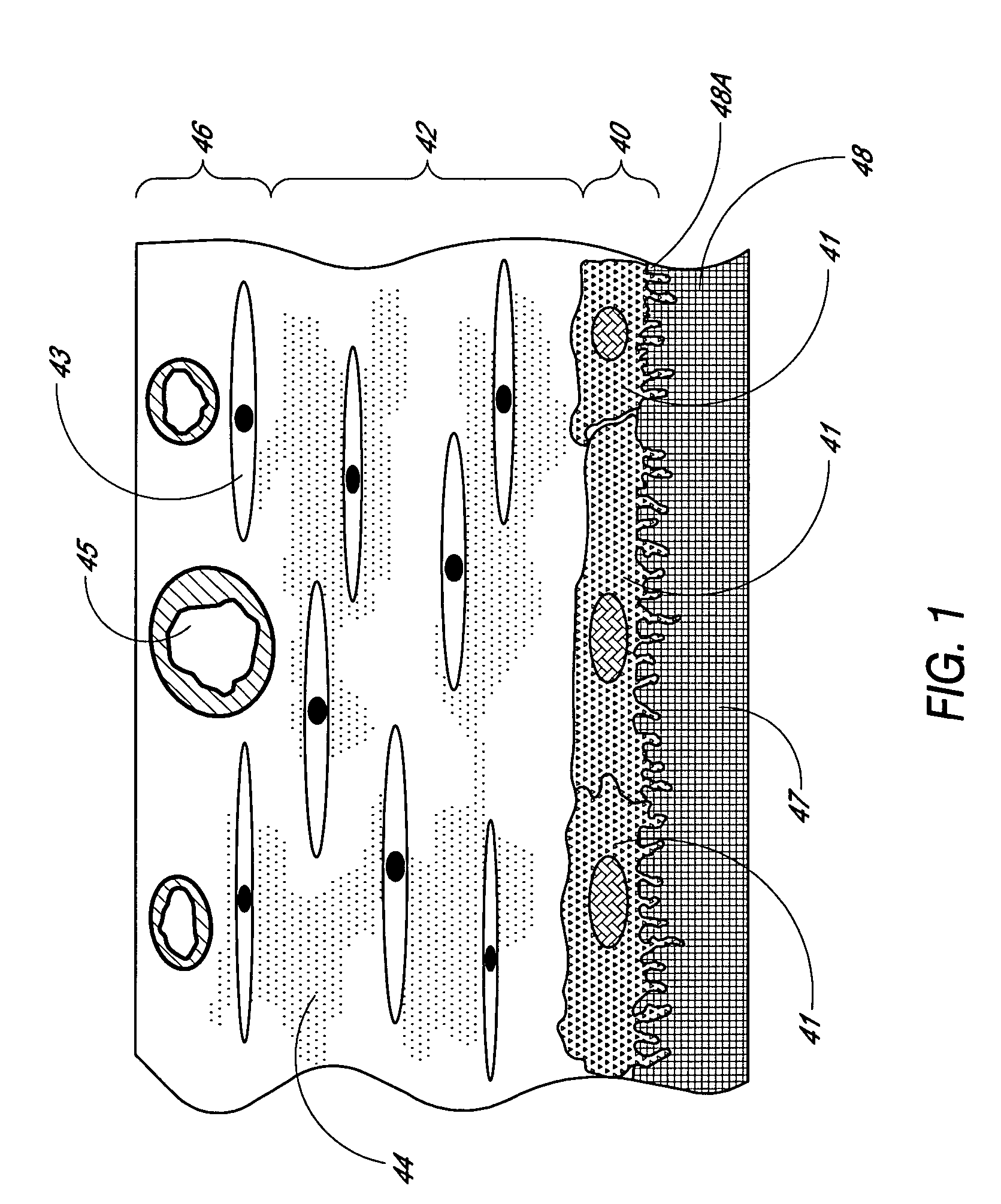
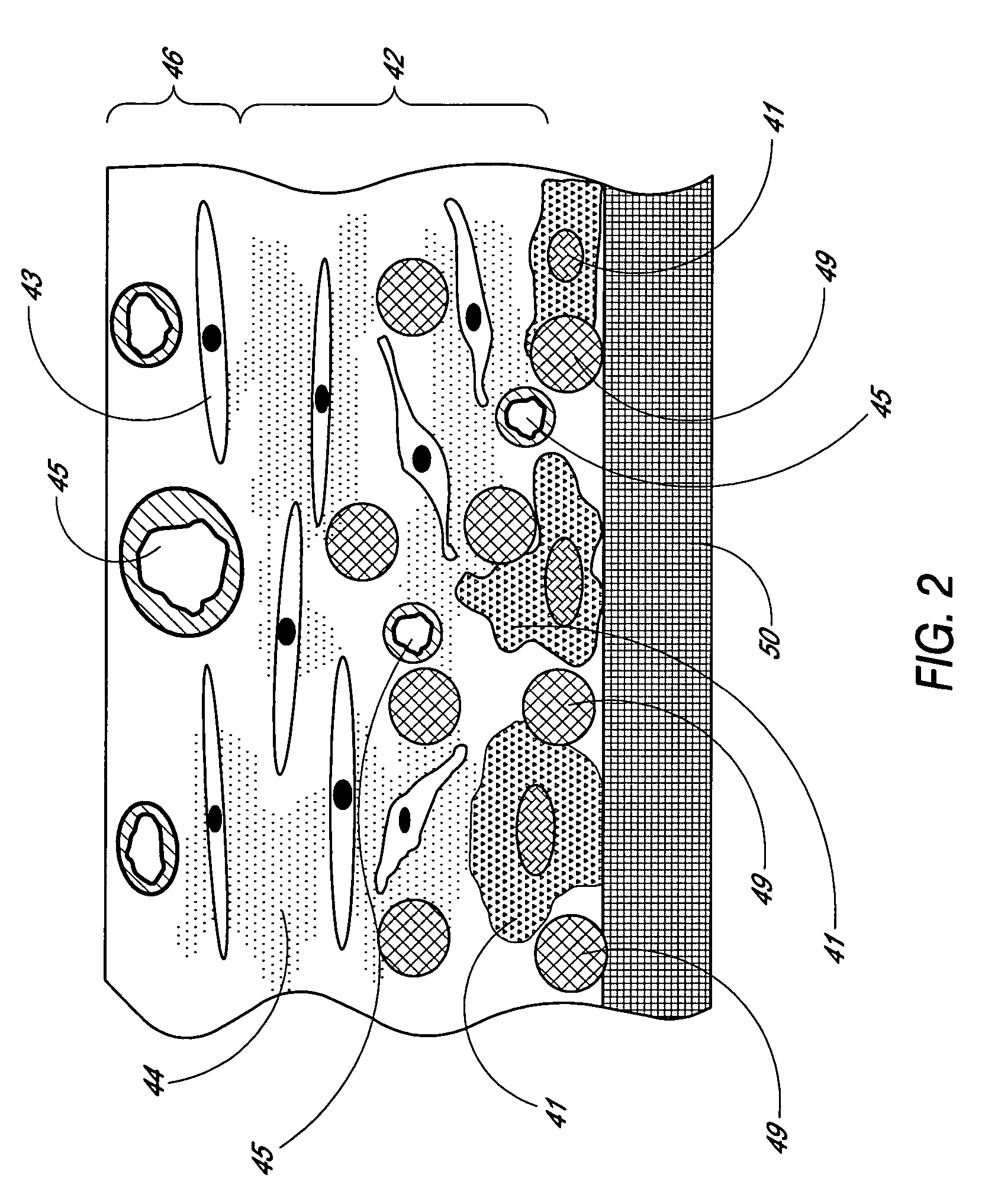
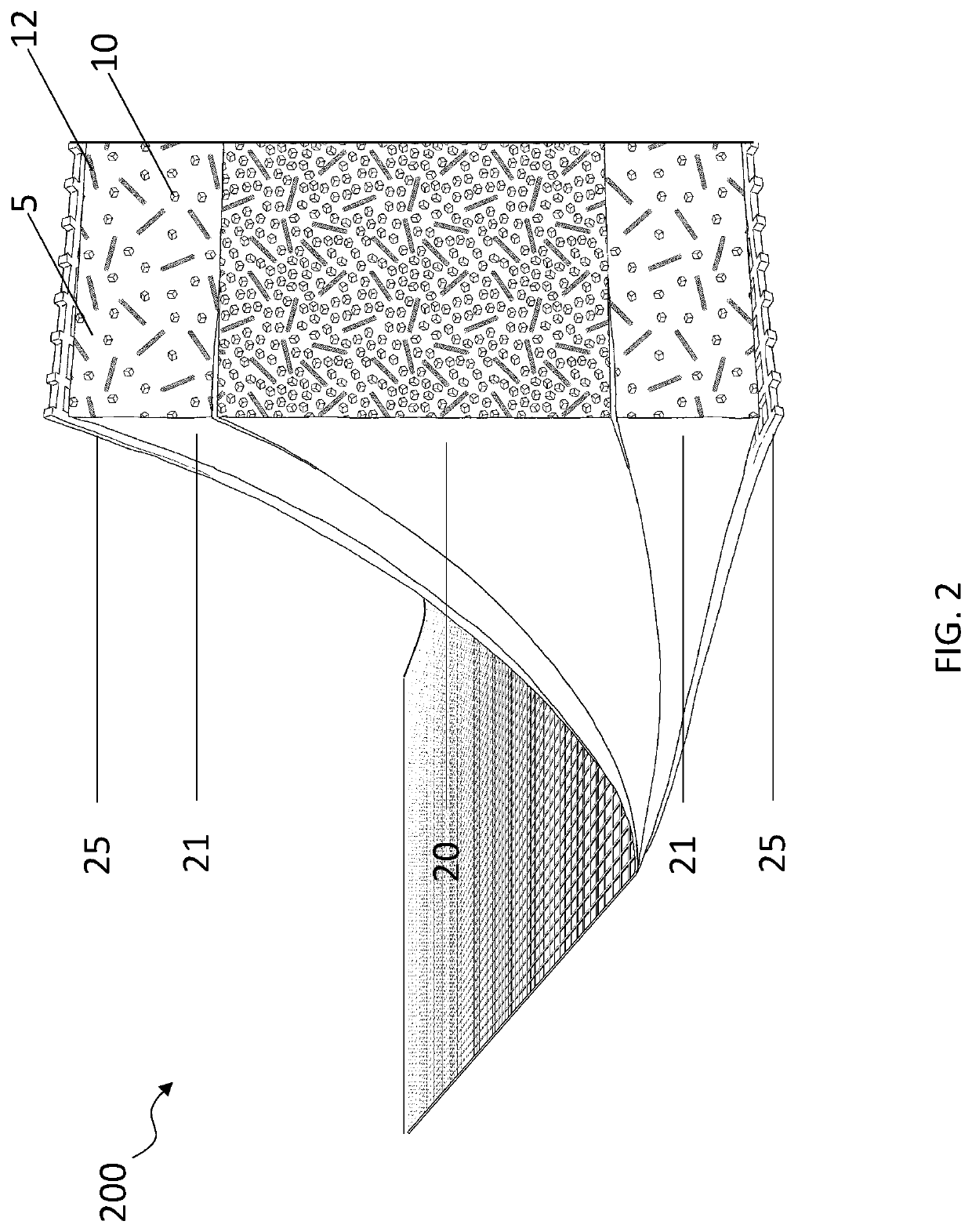
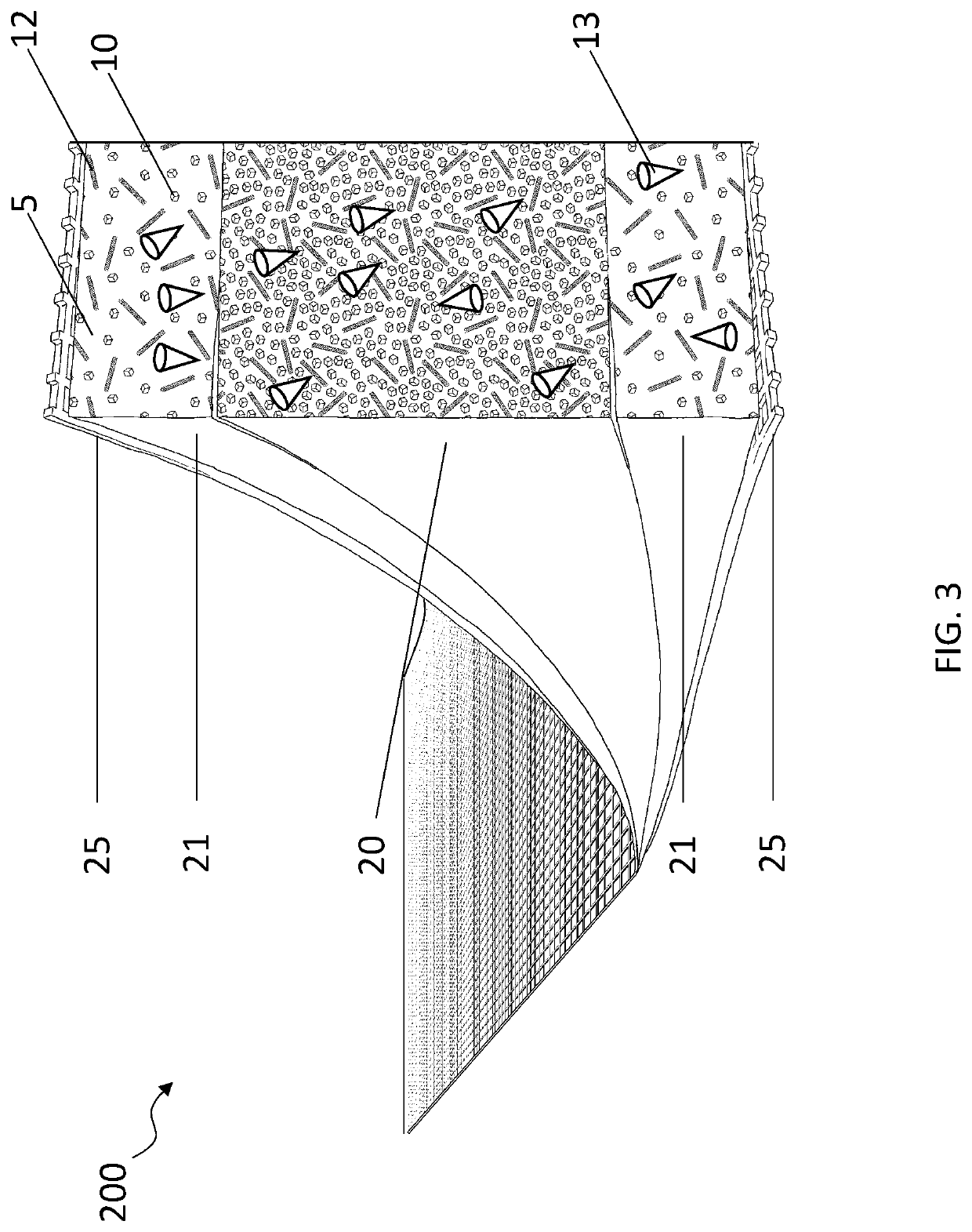
Porous membranes for use with implantable devices
A membrane for implantation in soft tissue comprising a first domain that supports tissue ingrowth, disrupts contractile forces typically found in a foreign body response, encourages vascularity, and interferes with barrier cell layer formation, and a second domain that is resistant to cellular attachment, is impermeable to cells and cell processes, and allows the passage of analytes. The membrane allows for long-term analyte transport in vivo and is suitable for use as a biointerface for implantable analyte sensors, cell transplantation devices, drug delivery devices, and / or electrical signal delivering or measuring devices. The membrane architecture, including cavity size, depth, and interconnectivity, provide long-term robust functionality of the membrane in vivo.
Owner:DEXCOM INC
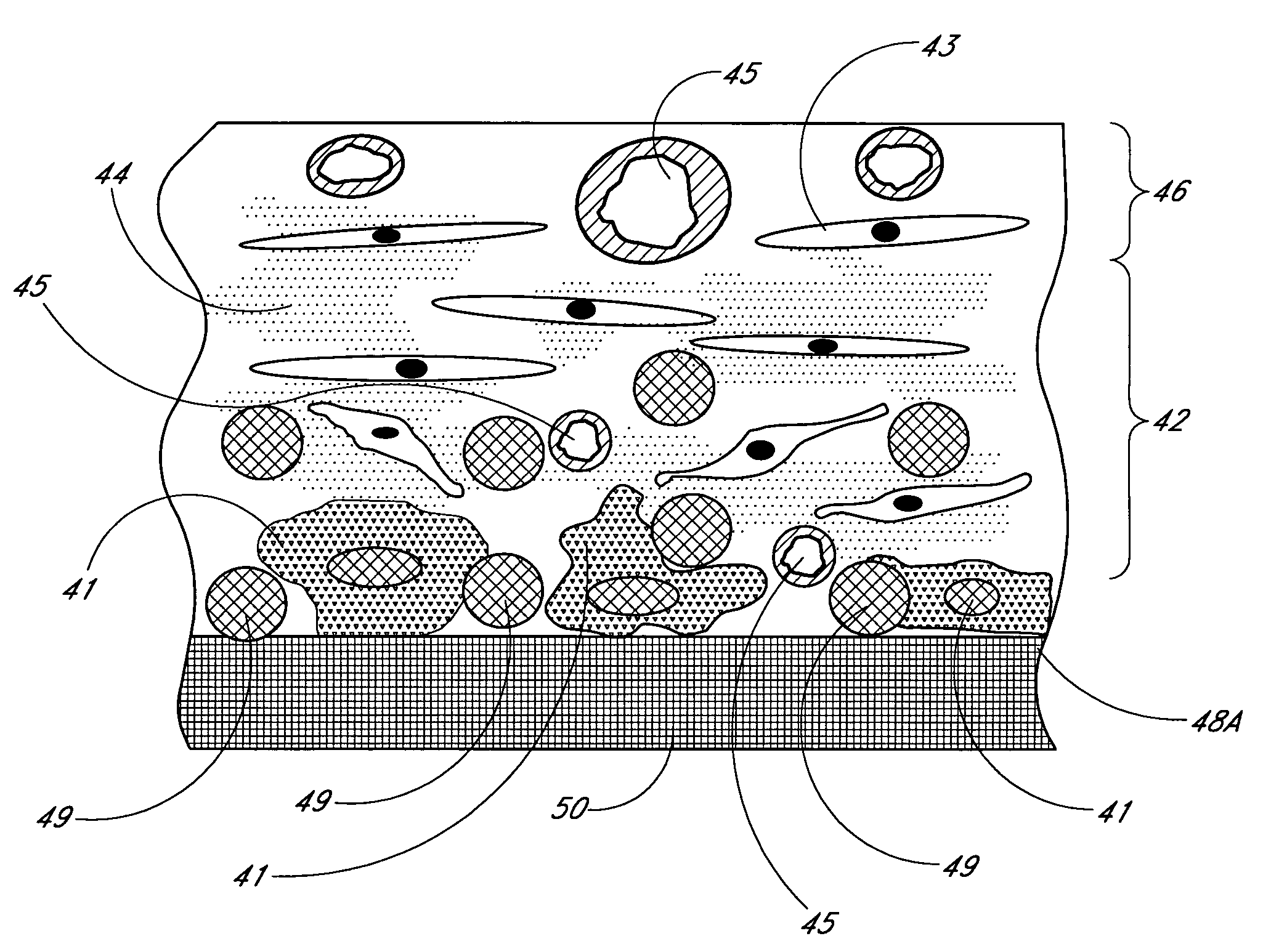
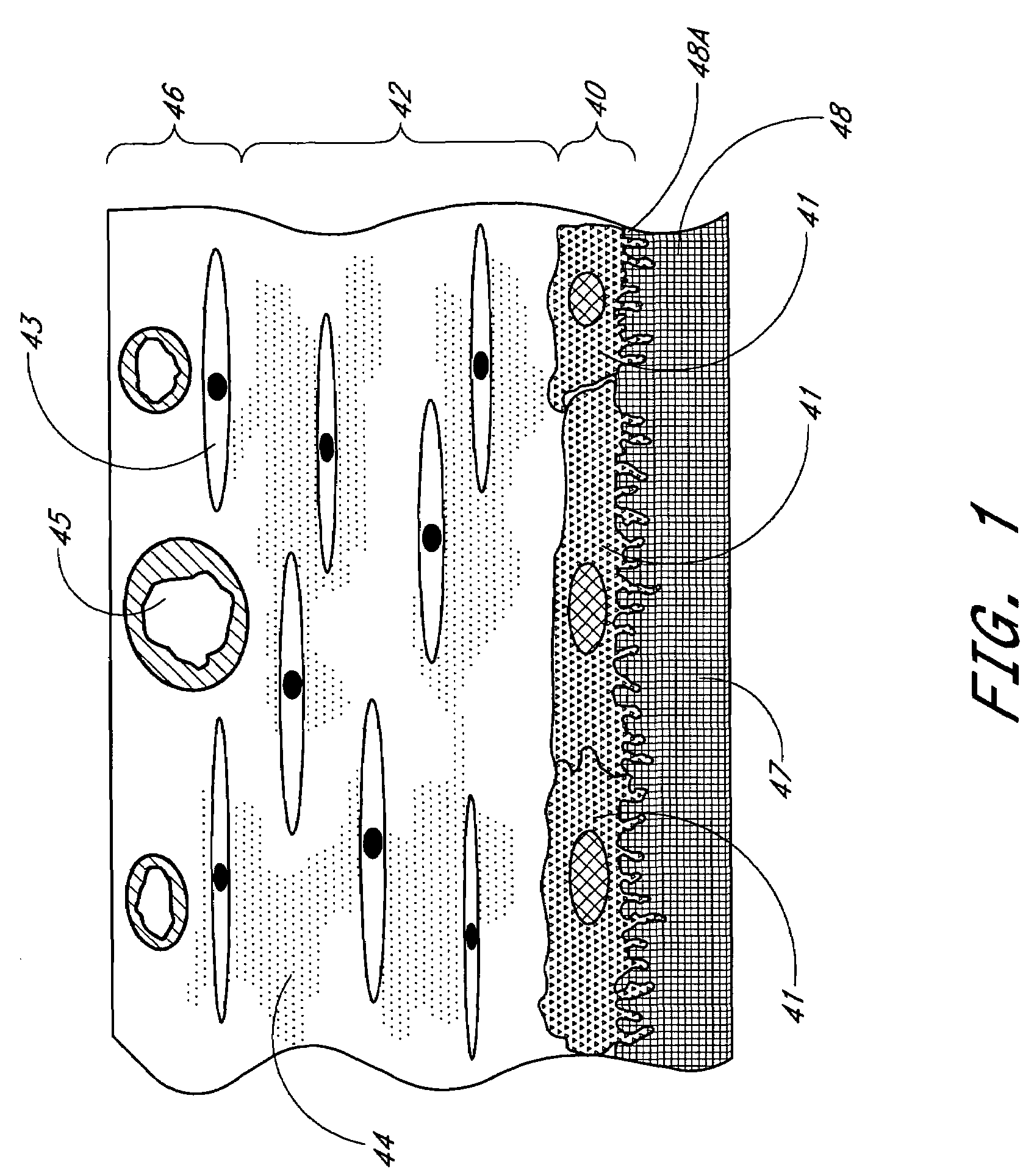
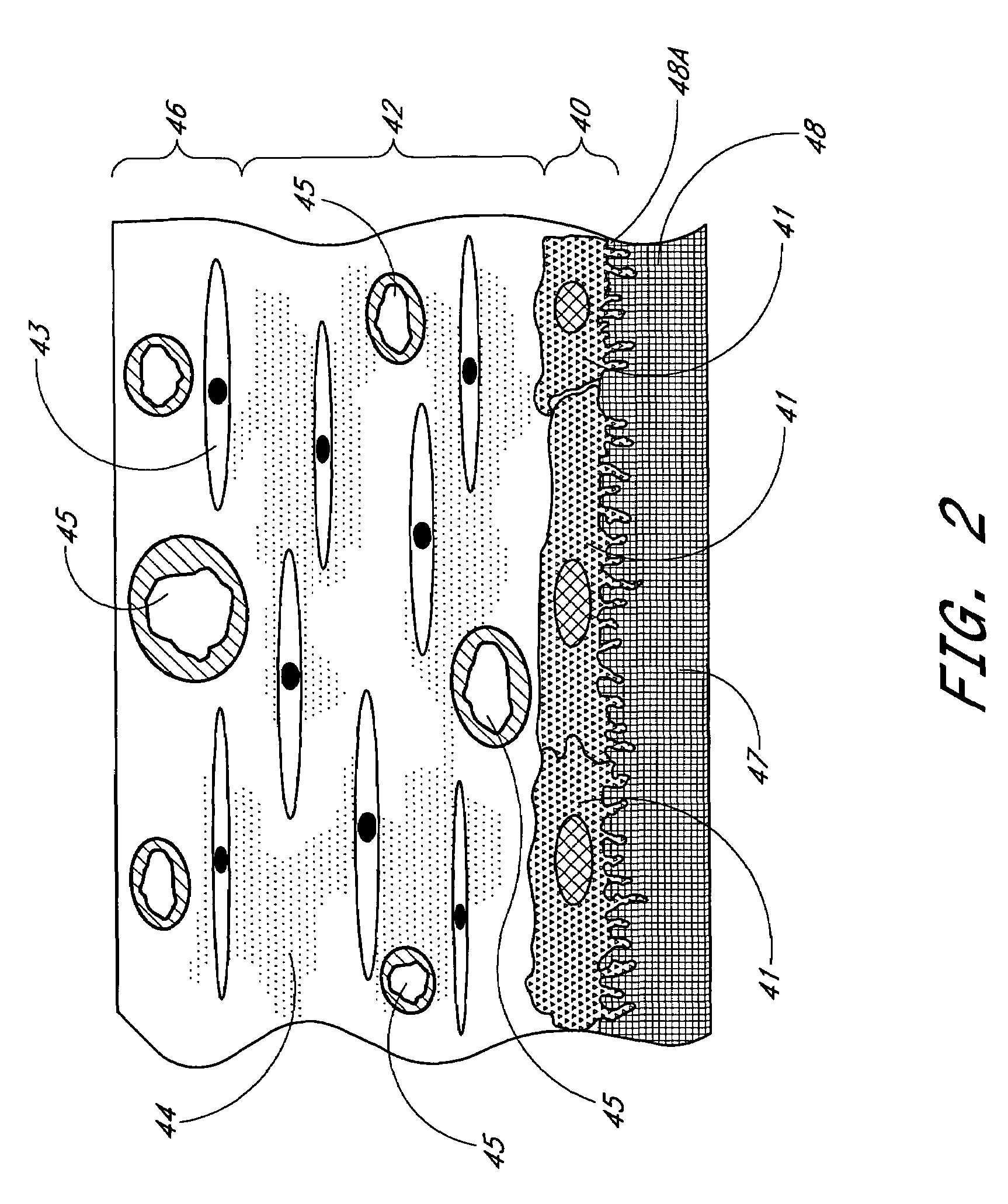
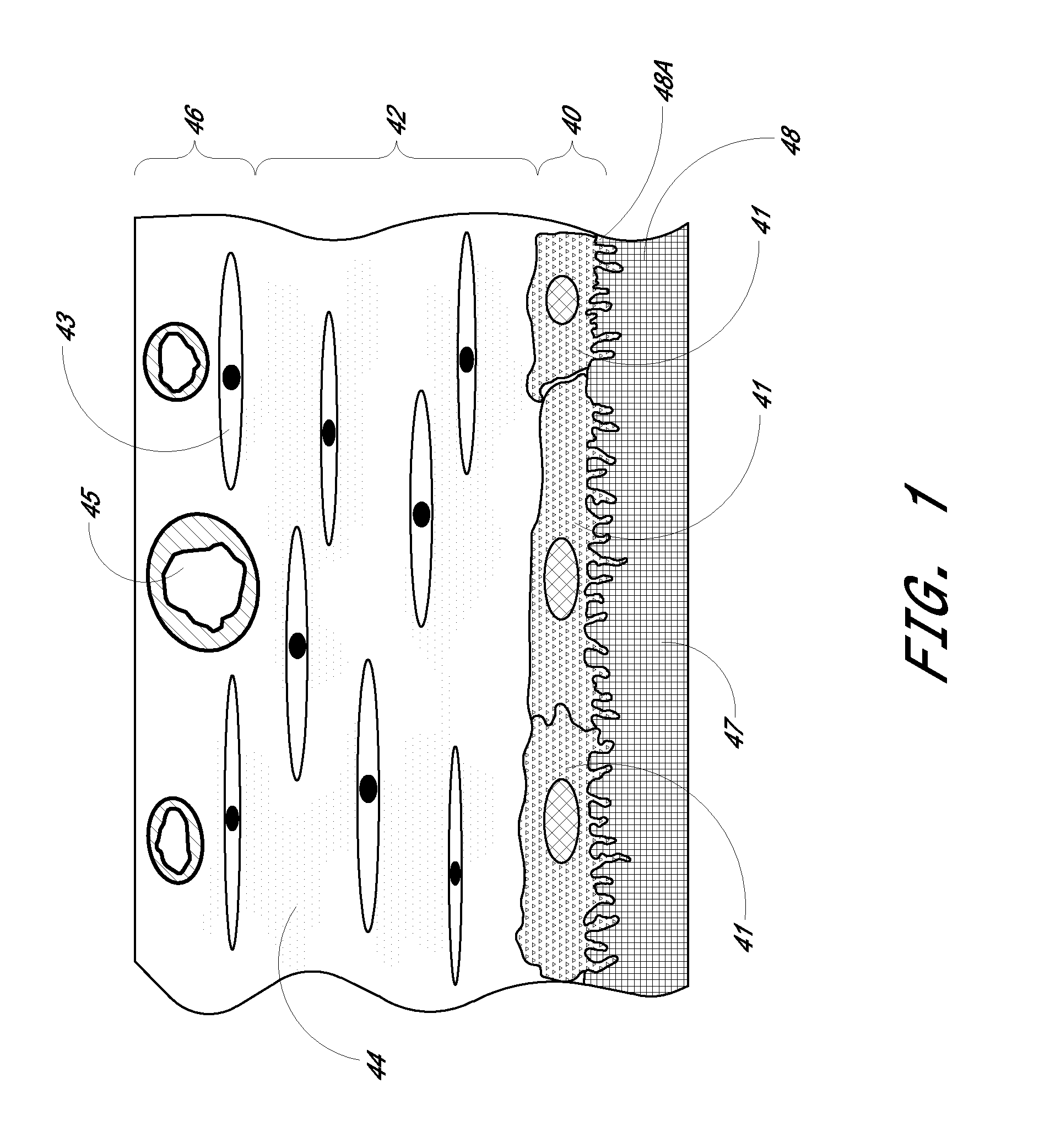
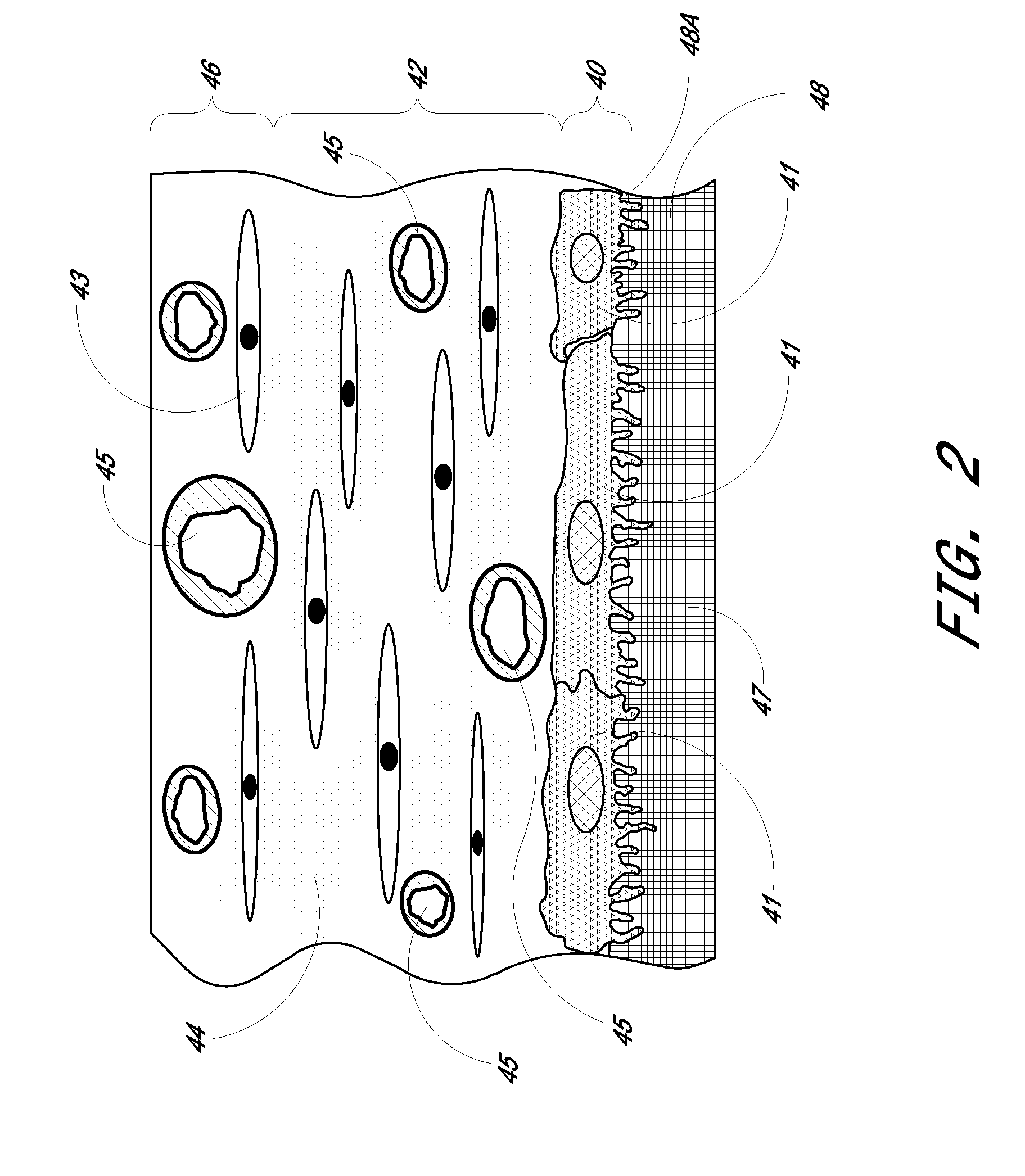
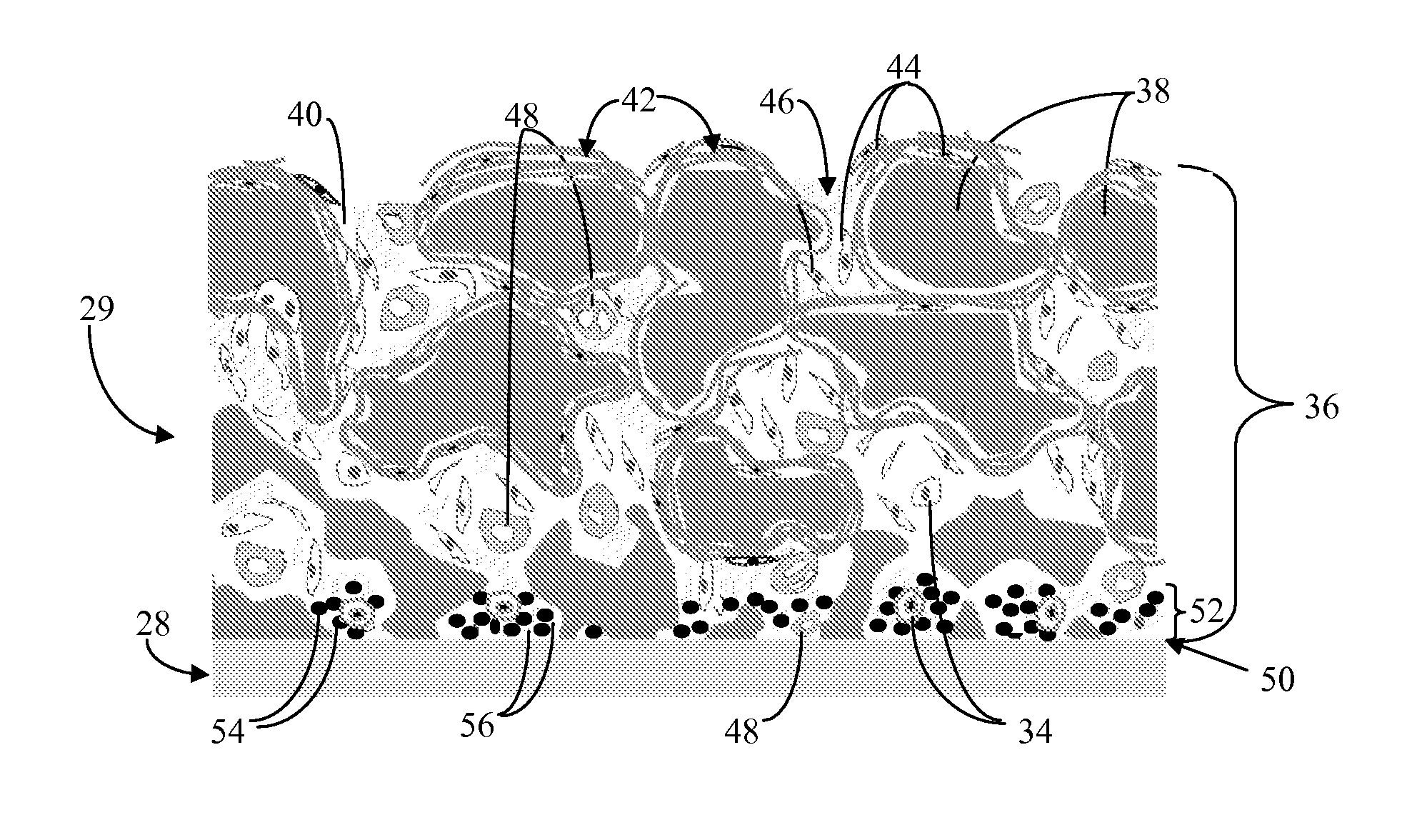
Biointerface membrane with macro-and micro-architecture
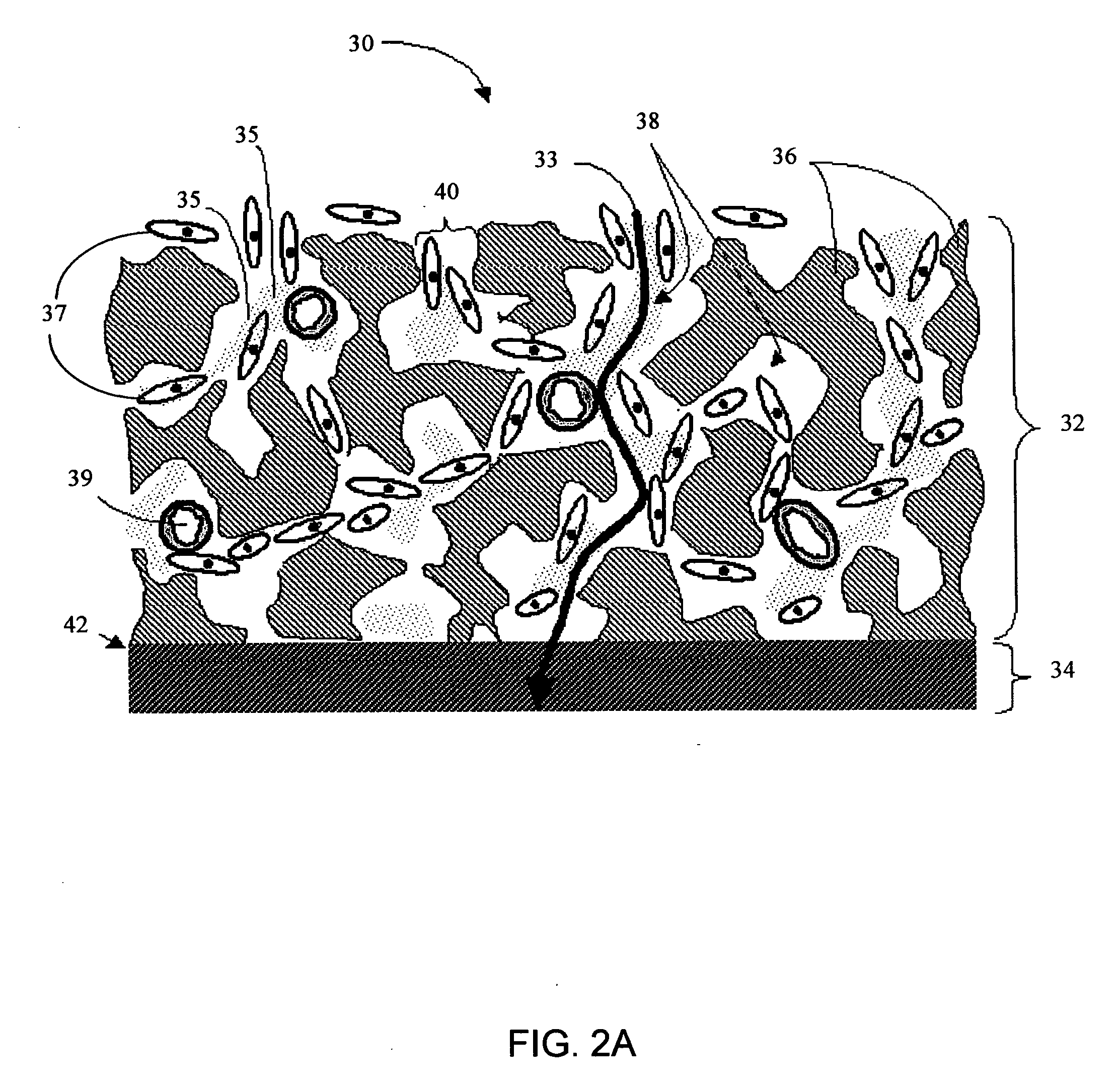
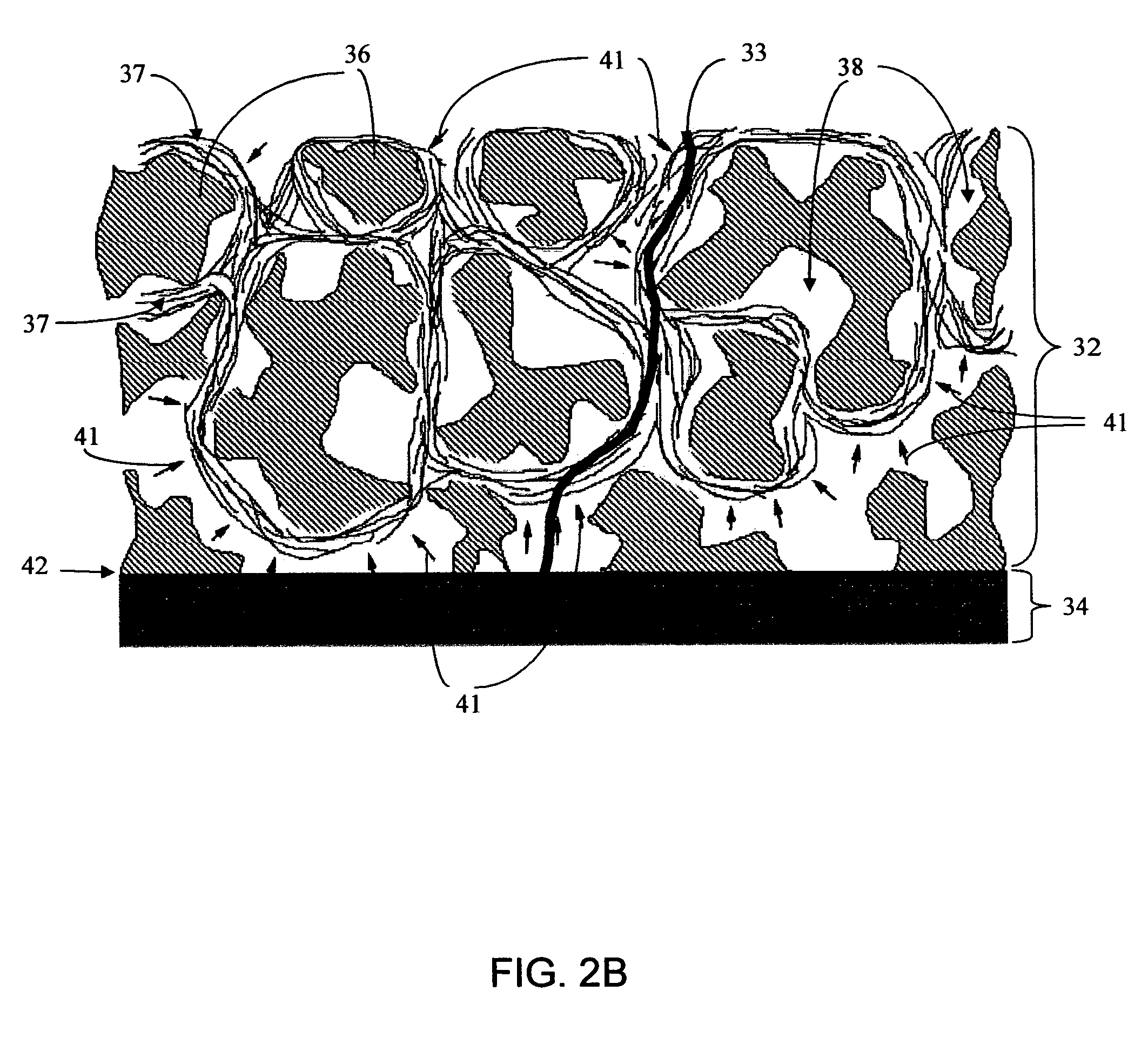
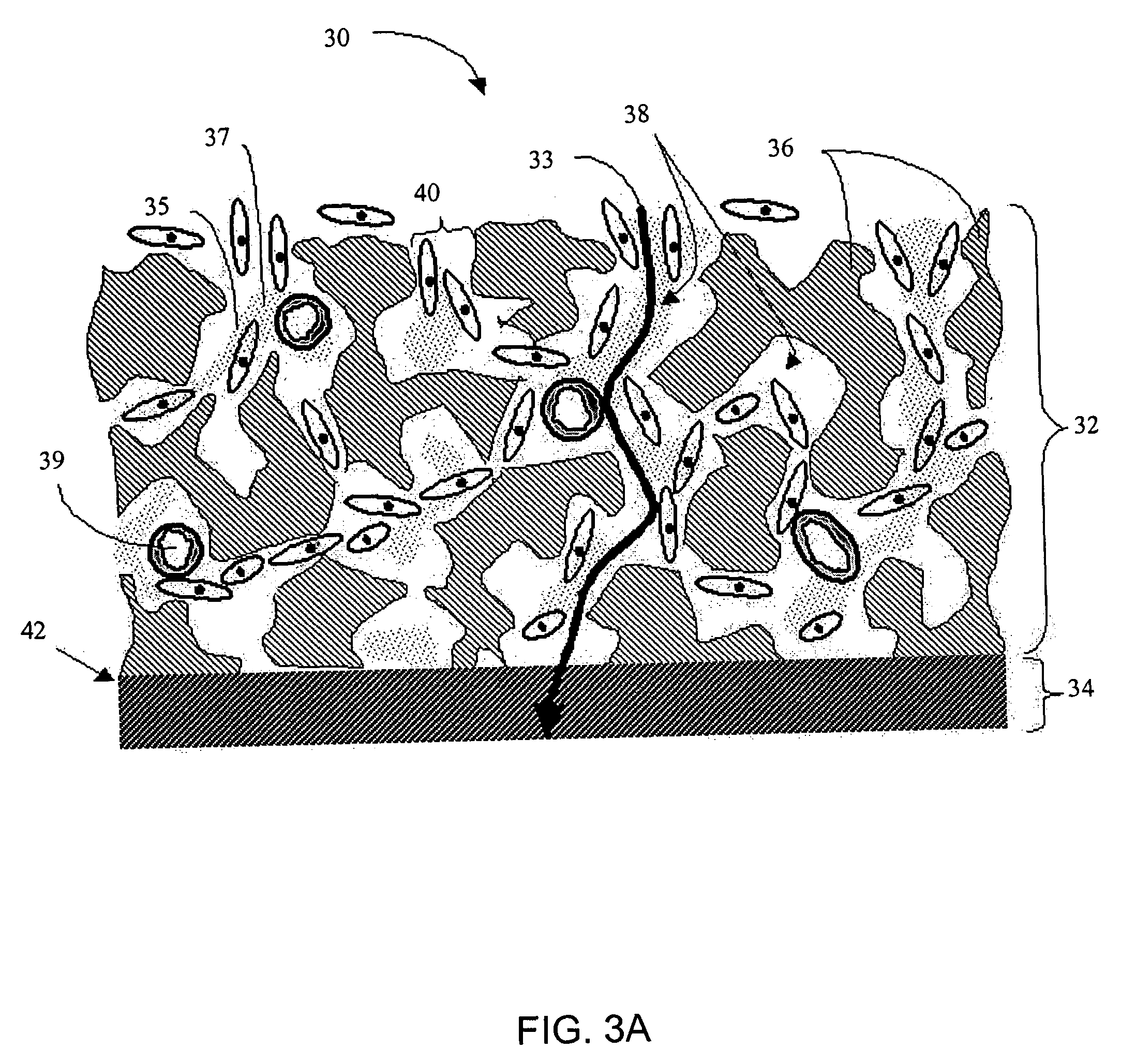
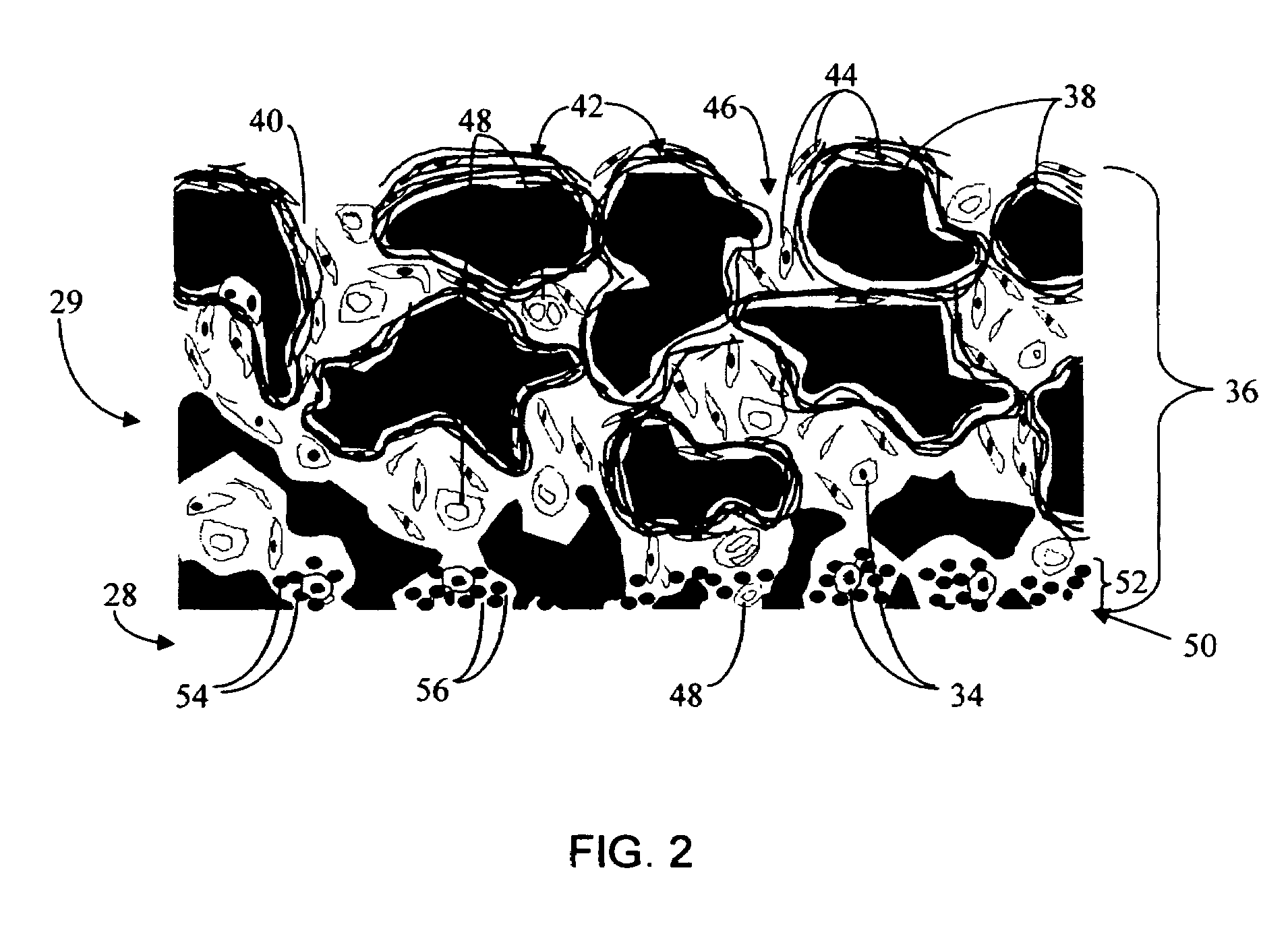
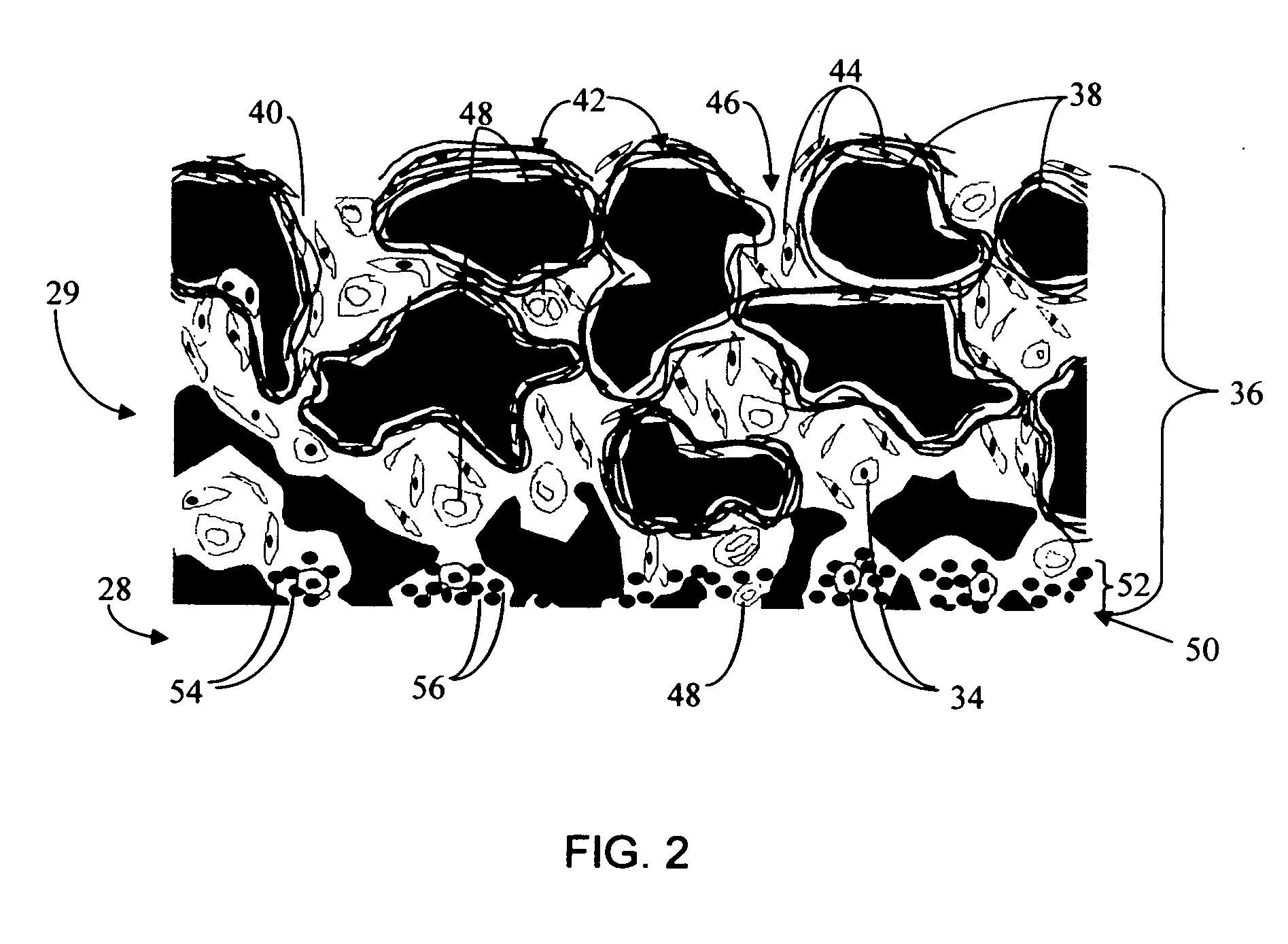
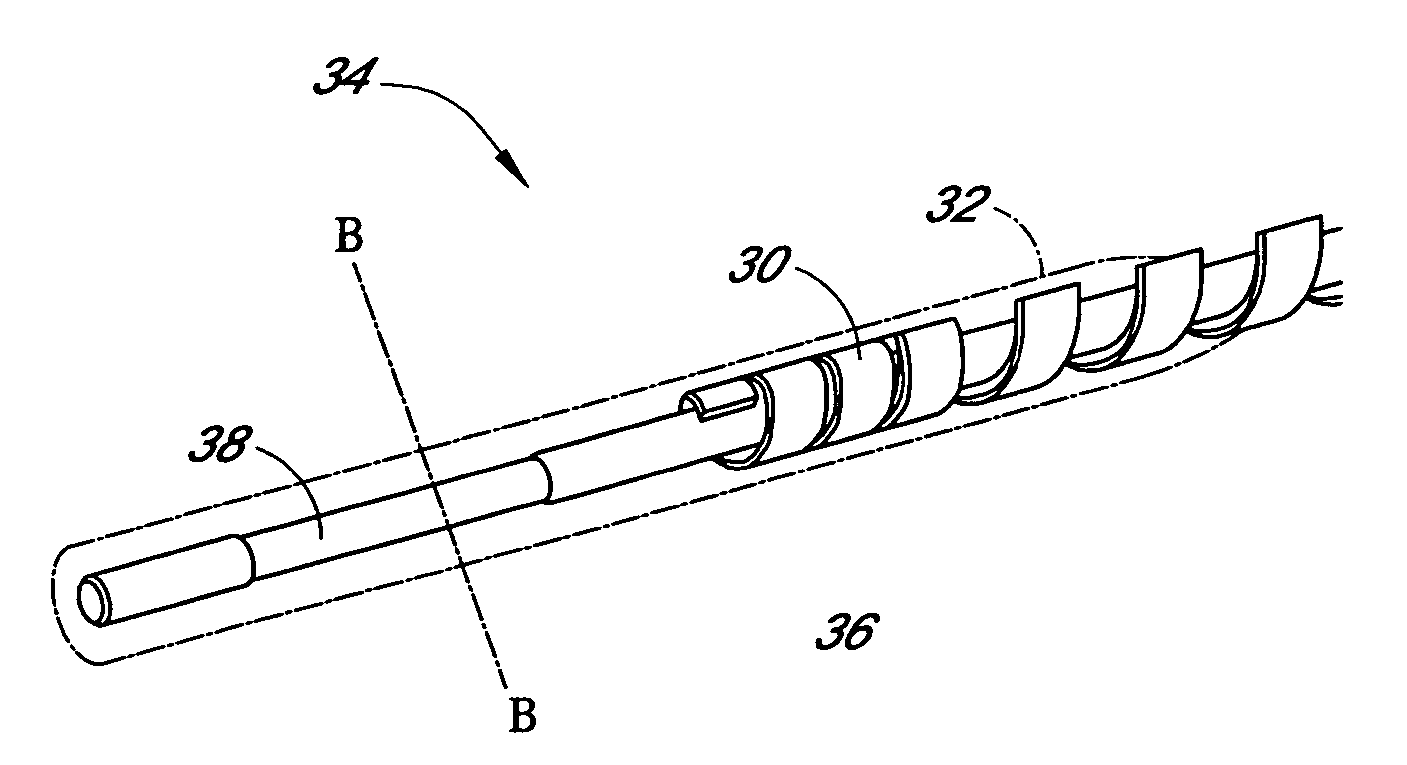
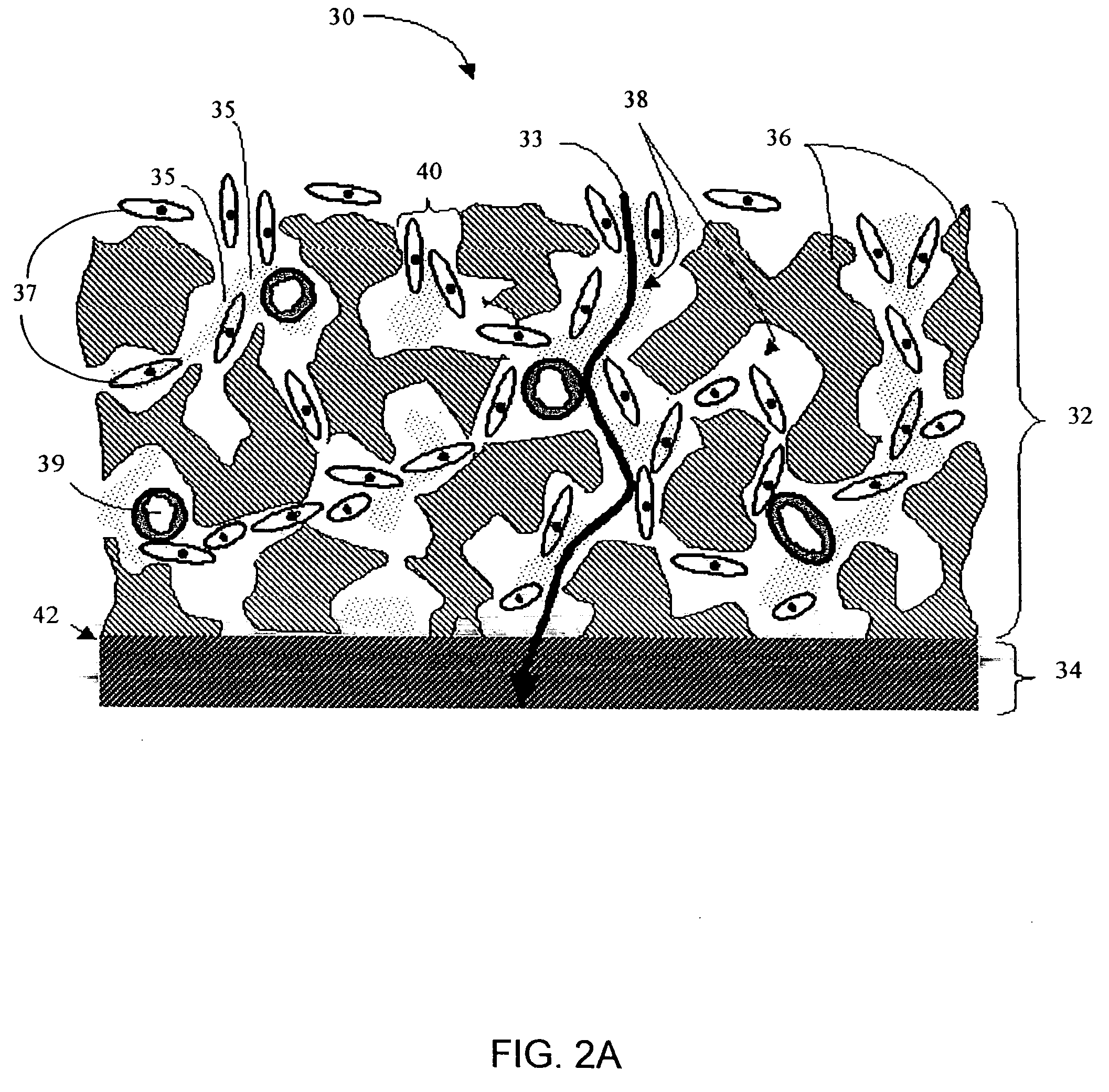
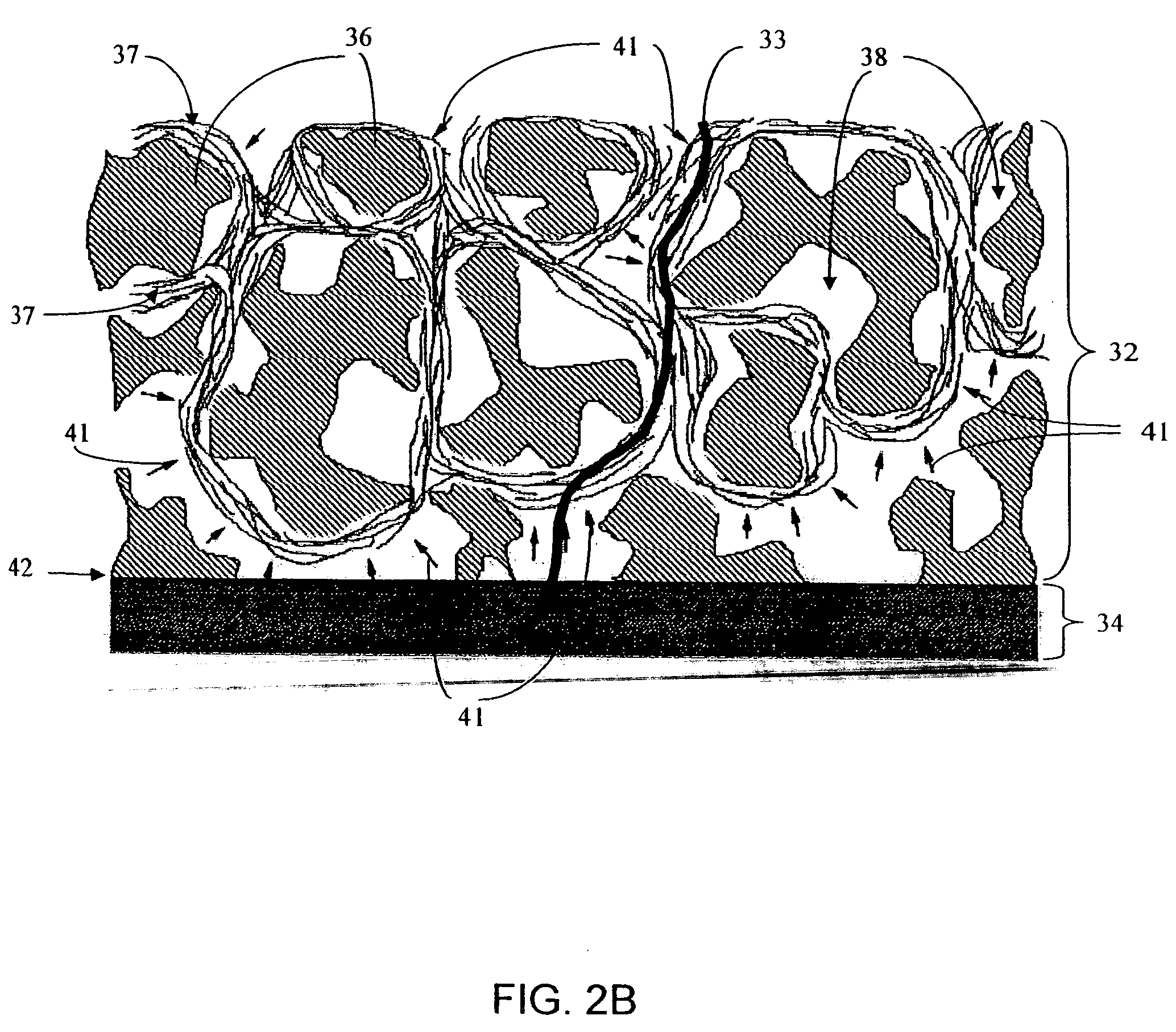
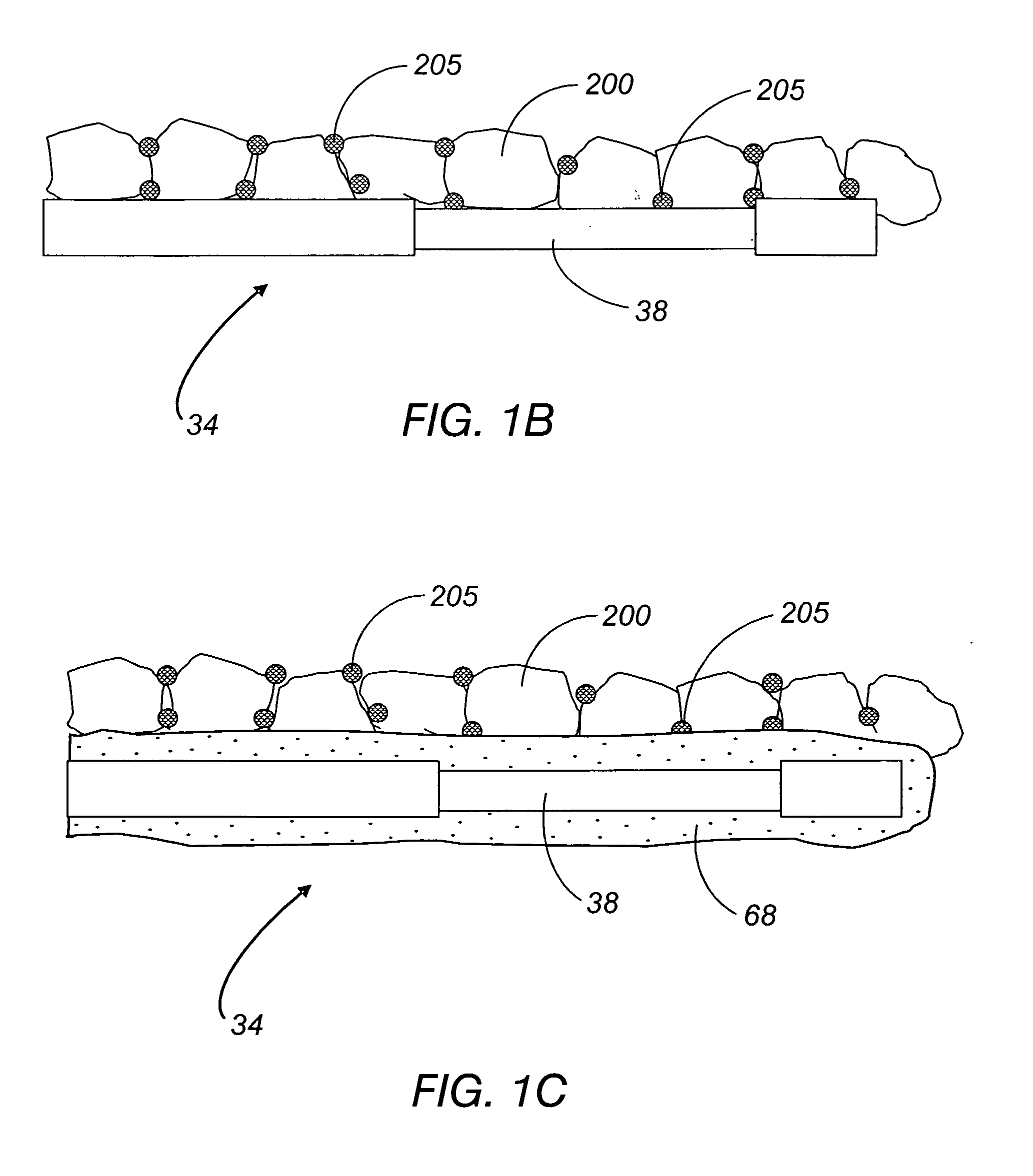
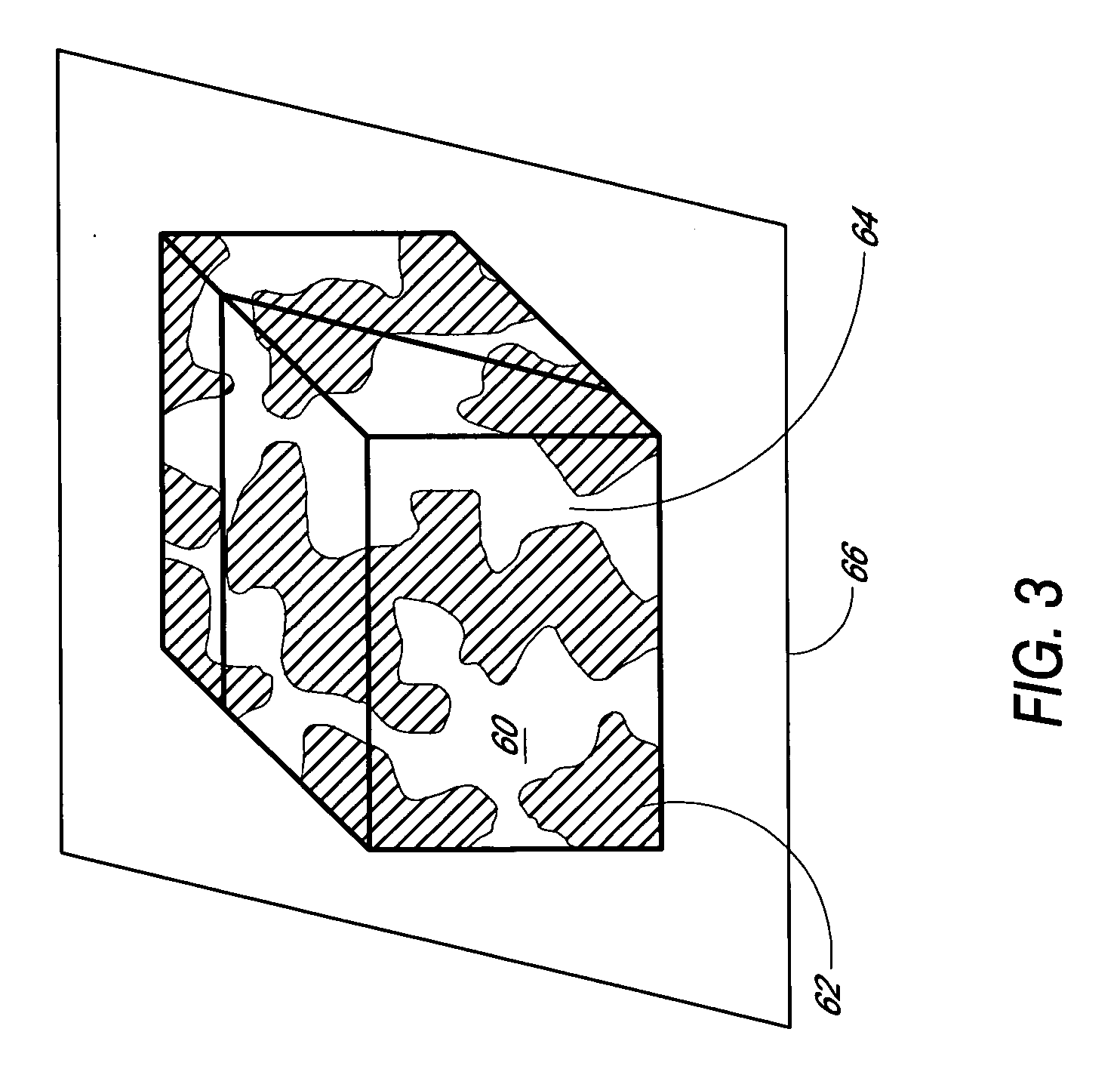
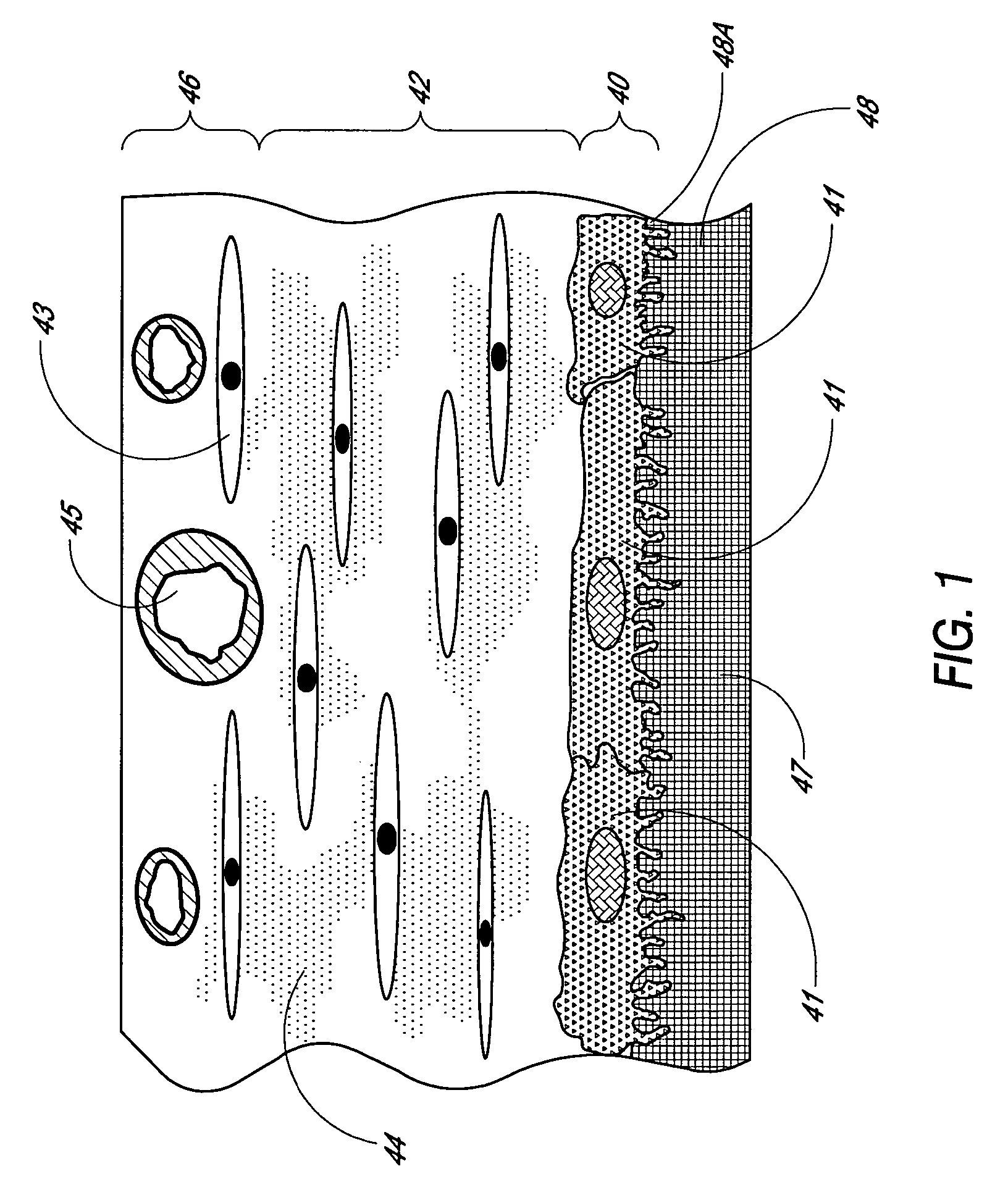
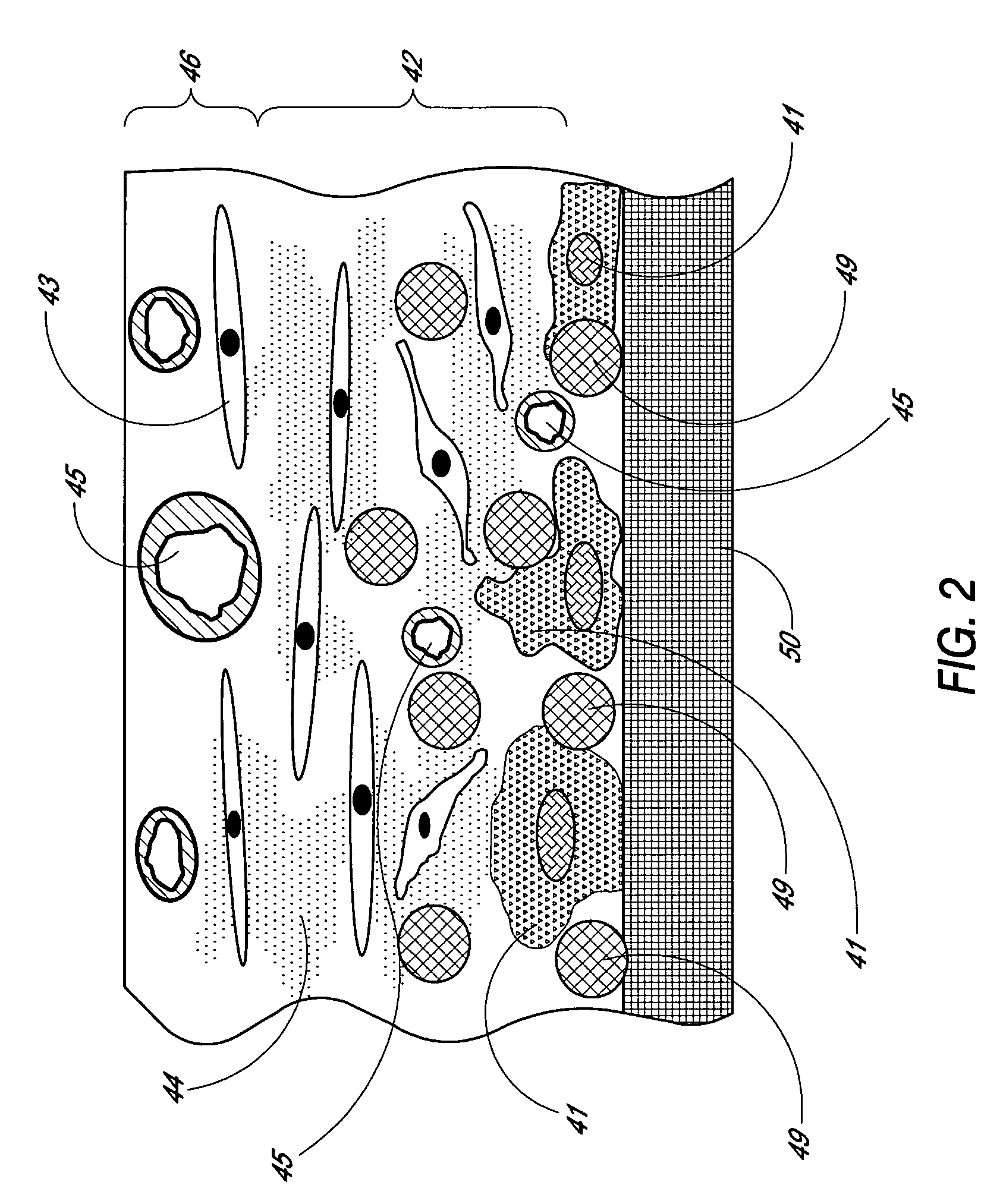
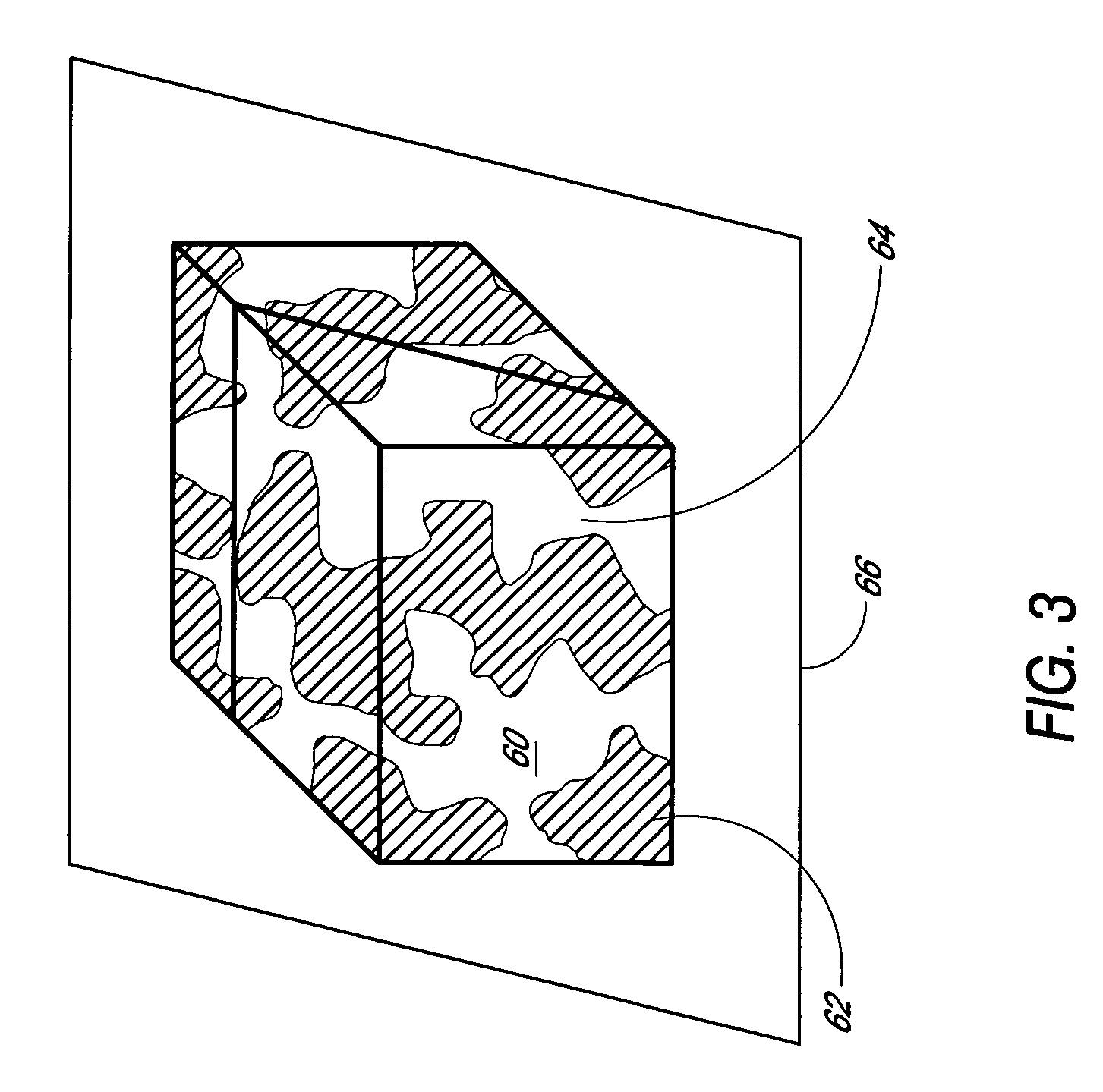
Disclosed herein are biointerface membranes including a macro-architecture and a micro-architecture co-continuous with and bonded to and / or located within at least a portion of the macro-architecture. The macro- and micro-architectures work together to manage and manipulate the high-level tissue organization and the low-level cellular organization of the foreign body response in vivo, thereby increasing neovascularization close to a device-tissue interface, interfering with barrier cell layer formation, and providing good tissue anchoring, while reducing the effects of motion artifact, and disrupting the organization and / or contracture of the FBC. The biointerface membranes of the preferred embodiments can be utilized with implantable devices such as devices for the detection of analyte concentrations in a biological sample (for example, from a body), cell transplantation devices, drug delivery devices, electrical signal delivering or measuring devices, and / or combinations thereof.
Owner:DEXCOM
Membrane for use with implantable devices
The present invention provides a biointerface membrane for use with an implantable device that interferes with the formation of a barrier cell layer including; a first domain distal to the implantable device wherein the first domain supports tissue attachment and interferes with barrier cell layer formation and a second domain proximal to the implantable device wherein the second domain is resistant to cellular attachment and is impermeable to cells. In addition, the present invention provides sensors including the biointerface membrane, implantable devices including these sensors or biointerface membranes, and methods of monitoring glucose levels in a host utilizing the analyte detection implantable device of the invention. Other implantable devices which include the biointerface membrane of the present invention, such as devices for cell transplantation, drug delivery devices, and electrical signal delivery or measuring devices are also provided.
Owner:DEXCOM
Membrane for use with implantable devices
ActiveUS20100087724A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteBiointerface
The present invention provides a biointerface membrane for use with an implantable device that interferes with the formation of a barrier cell layer including; a first domain distal to the implantable device wherein the first domain supports tissue attachment and interferes with barrier cell layer formation and a second domain proximal to the implantable device wherein the second domain is resistant to cellular attachment and is impermeable to cells. In addition, the present invention provides sensors including the biointerface membrane, implantable devices including these sensors or biointerface membranes, and methods of monitoring glucose levels in a host utilizing the analyte detection implantable device of the invention. Other implantable devices which include the biointerface membrane of the present invention, such as devices for cell transplantation, drug delivery devices, and electrical signal delivery or measuring devices are also provided.
Owner:DEXCOM INC
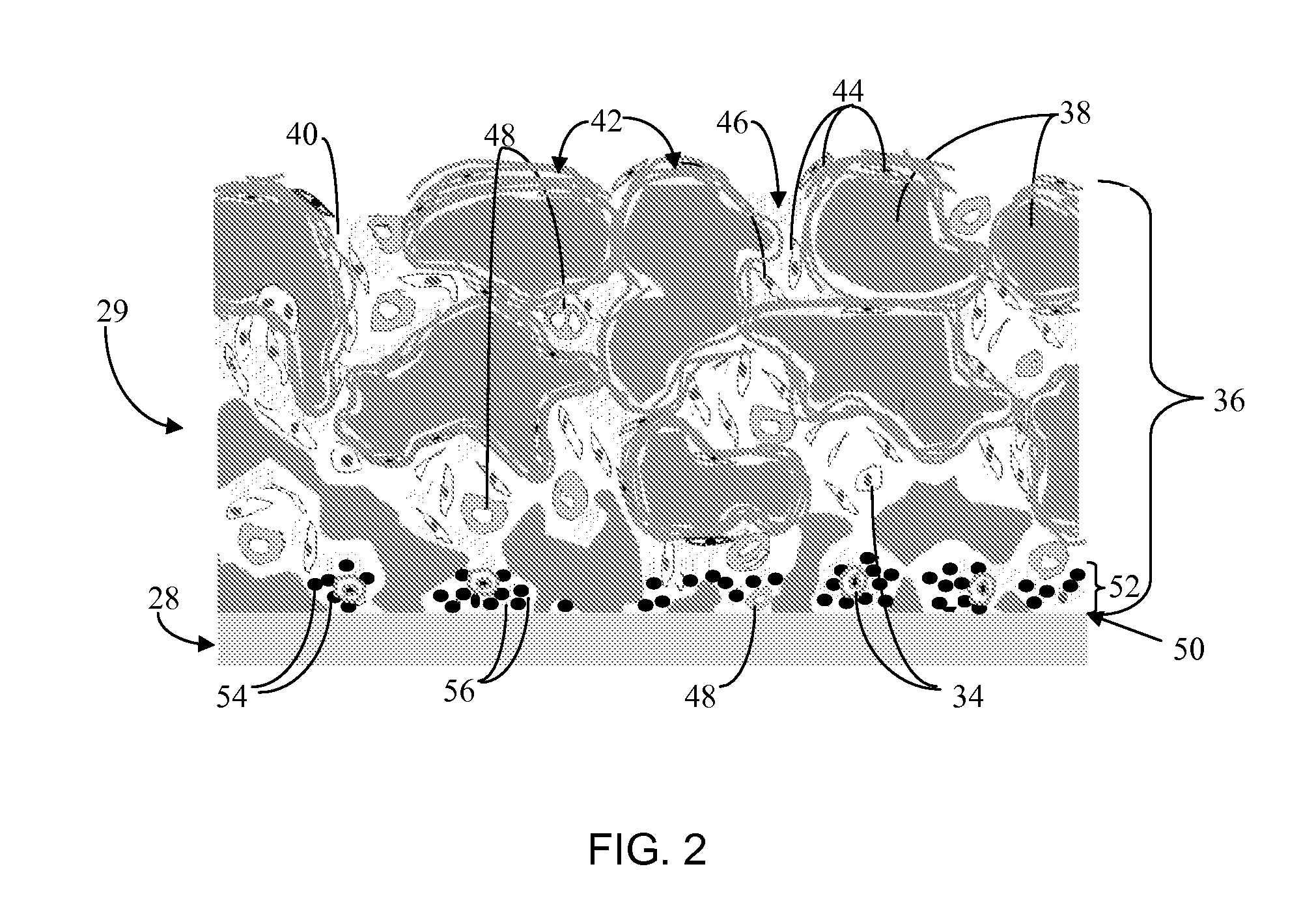
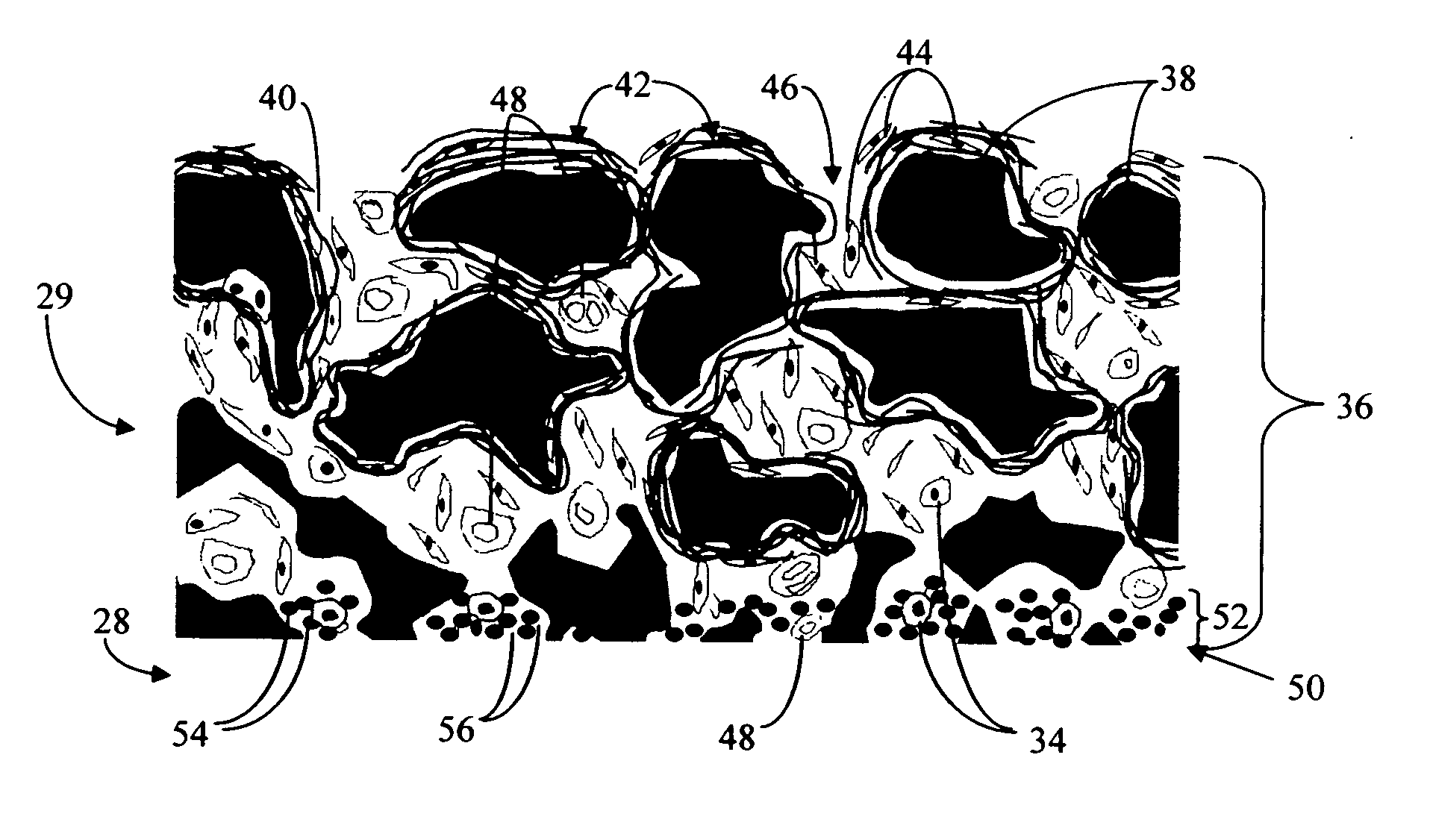
Biointerface with macro- and micro-architecture
Owner:DEXCOM INC
Biointerface with macro-and micro-architecture
Disclosed herein are biointerface membranes including a macro-architecture and a micro-architecture co-continuous with and bonded to and / or located within at least a portion of the macro-architecture. The macro- and micro-architectures work together to manage and manipulate the high-level tissue organization and the low-level cellular organization of the foreign body response in vivo, thereby increasing neovascularization close to a device-tissue interface, interfering with barrier cell layer formation, and providing good tissue anchoring, while reducing the effects of motion artifact, and disrupting the organization and / or contracture of the FBC. The biointerface membranes of the preferred embodiments can be utilized with implantable devices such as devices for the detection of analyte concentrations in a biological sample (for example, from a body), cell transplantation devices, drug delivery devices, electrical signal delivering or measuring devices, and / or combinations thereof.
Owner:DEXCOM
Analyte sensor
ActiveUS20070027370A1Increase liquid volumeLarge flowMicrobiological testing/measurementCatheterAnalyteBiointerface
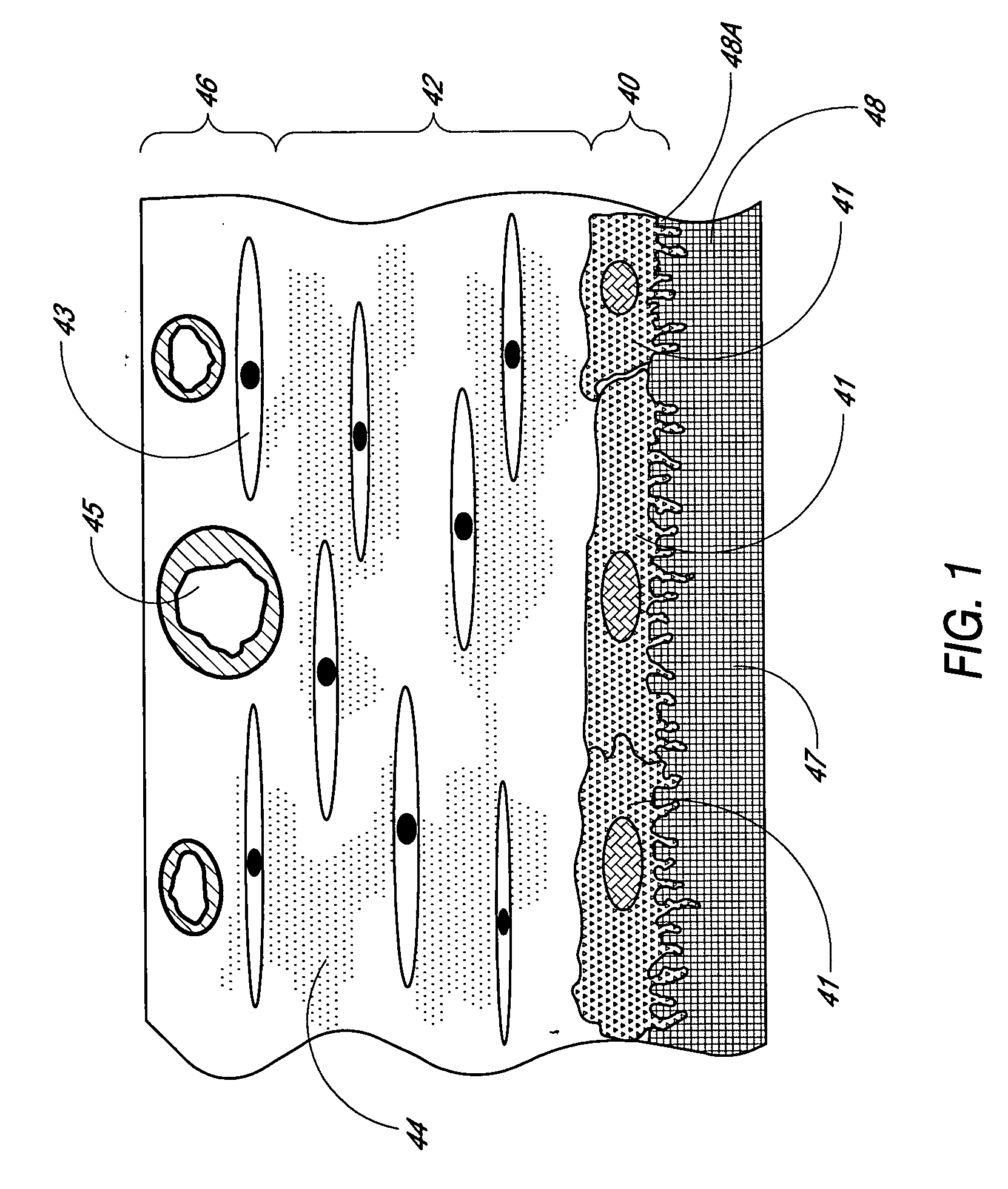
Biointerface membranes are provided which can be utilized with implantable devices, such as devices for the detection of analyte concentrations in a biological sample. More particularly, methods for monitoring glucose levels in a biological fluid sample using an implantable analyte detection device incorporating such membranes are provided.
Owner:DEXCOM
Biointerface membranes incorporating bioactive agents
InactiveUS20060198864A1Improve performanceAdditive manufacturing apparatusSurgeryBiointerfaceActive agent
A biointerface membrane for an implantable device including a nonresorbable solid portion with a plurality of interconnected cavities therein adapted to support tissue ingrowth in vivo, and a bioactive agent incorporated into the biointerface membrane and adapted to modify the tissue response is provided. The bioactive agents can be chosen to induce vascularization and / or prevent barrier cell layer formation in vivo, and are advantageous when used with implantable devices wherein solutes are transported across the device-tissue interface.
Owner:DEXCOM INC
Analyte sensor
The present invention relates generally to biointerface membranes utilized with implantable devices, such as devices for the detection of analyte concentrations in a biological sample. More particularly, the invention relates to novel biointerface membranes, to devices and implantable devices including these membranes, methods for forming the biointerface membranes on or around the implantable devices, and to methods for monitoring glucose levels in a biological fluid sample using an implantable analyte detection device.
Owner:DEXCOM
Analyte sensing biointerface
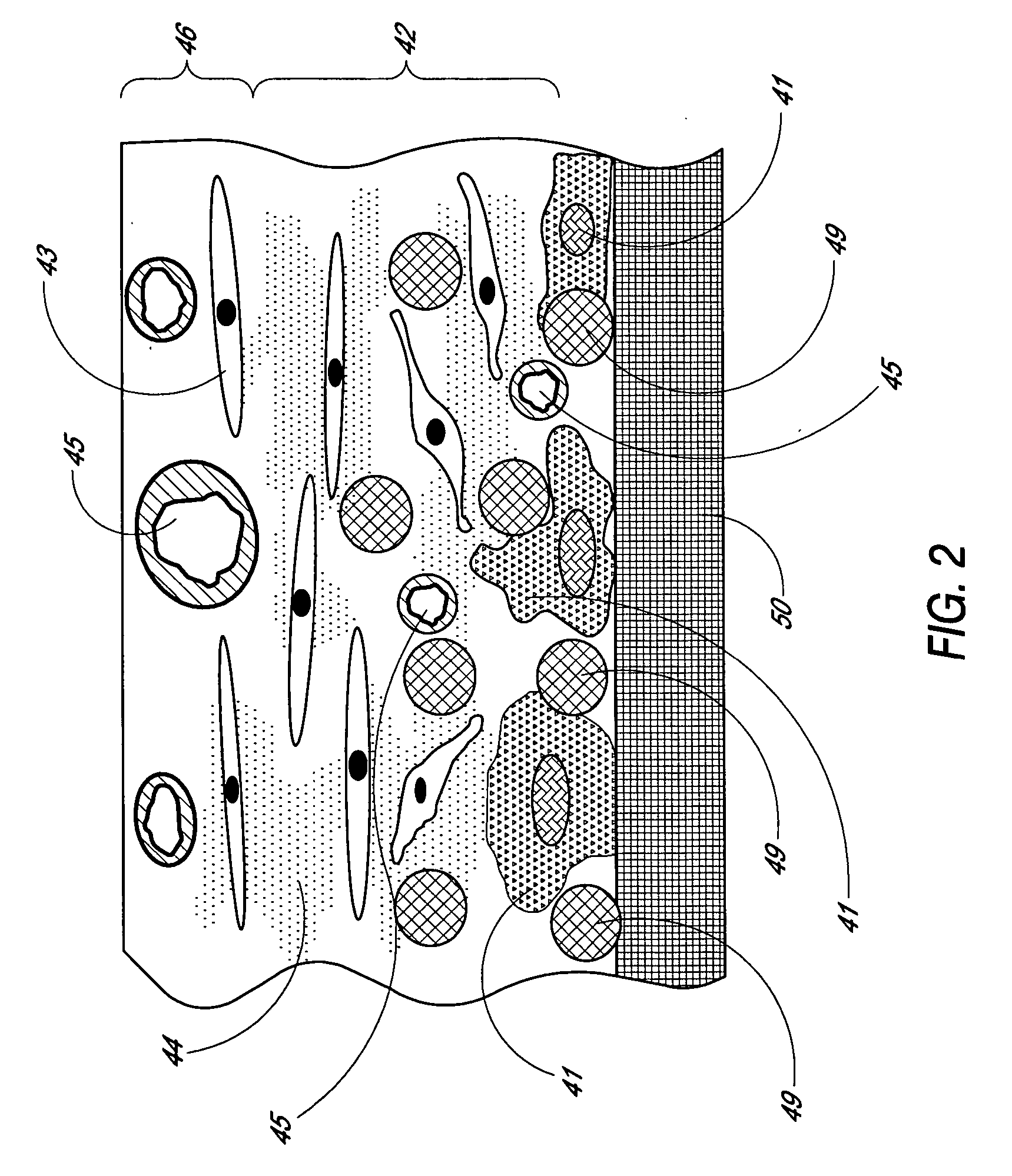
Disclosed herein is an analyte sensing biointerface that comprises a sensing electrode incorporated within a non-conductive matrix comprising a plurality of passageways extending through the matrix to the sensing electrode. Also disclosed herein are methods of manufacturing a sensing biointerface and methods of detecting an analyte within tissue of a host using an analyte sensing biointerface.
Owner:DEXCOM
Analyte sensing biointerface
InactiveUS20060257995A1Address effectBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteBiointerface
Disclosed herein is an analyte sensing biointerface that comprises a sensing electrode incorporated within a non-conductive matrix comprising a plurality of passageways extending through the matrix to the sensing electrode. Also disclosed herein are methods of manufacturing a sensing biointerface and methods of detecting an analyte within tissue of a host using an analyte sensing biointerface.
Owner:SIMPSON PETER +1
Analyte sensing biointerface
ActiveUS8060174B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsAdditive manufacturing apparatusBiointerfaceAnalyte
Disclosed herein is an analyte sensing biointerface that comprises a sensing electrode incorporated within a non-conductive matrix comprising a plurality of passageways extending through the matrix to the sensing electrode. Also disclosed herein are methods of manufacturing a sensing biointerface and methods of detecting an analyte within tissue of a host using an analyte sensing biointerface.
Owner:DEXCOM
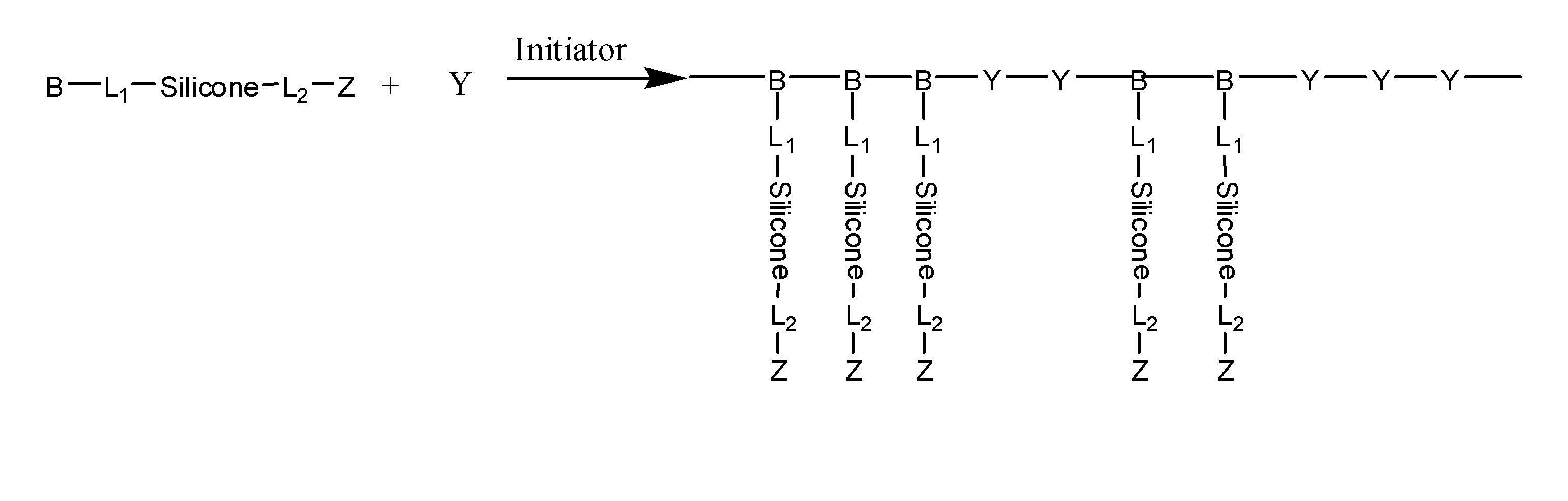
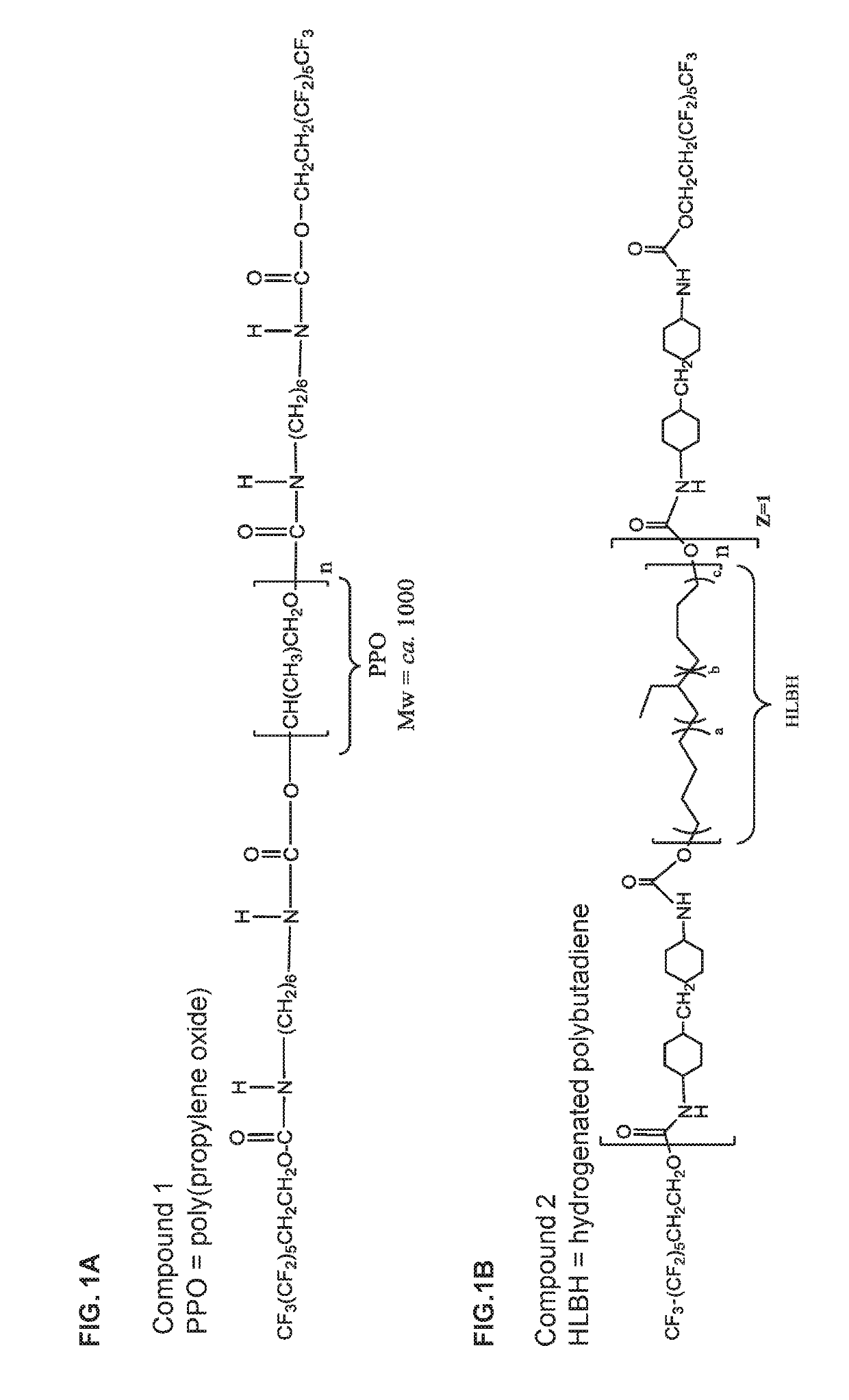
Silicone containing monomers with hydrophilic end groups
InactiveUS20140135408A1High oxygen permeabilityImprove wettabilityBiocideSilicon organic compoundsPolymer scienceOphthalmology department
Silicone containing reactive monomers with hydrophilic end-groups of formula I useful in the manufacture of biocompatible medical devices are disclosed, wherein R1 is H or CH3, a is 0 or 1, p is an integer from 1 to 6, q is an integer from 1 to 3 and for each q, the end groups R51, R52, R53 are independently an alkyl, alkyl ether, trimethylsiloxy group, or a substituted or non-substituted aromatic group and at least one of them has a hydrophilic group attached, preferably to the terminal end of R51, R52, R53, X is O or NR54, where R54 is H or a monovalent alkyl group with 1 to 4 carbons, n is an integer from 1 to 100, R2 and R3 are independently an alkyl, alkyl ether, or a substituted or non-substituted aromatic group, preferred R2 and R3 include methyl, ethyl, and phenyl, L is a divalent linker comprising substituted and unsubstituted alkylene groups having 1-14 carbon atoms, which may be straight or branched, substituted and unsubstituted alkoxy groups having 2-12 carbons, polyethers, oxazolines, and substituted and unsubstituted heterocyclic groups. Suitable substituents include aryl, amine, ether, amide, hydroxyl groups, combinations thereof and the like. In another embodiment, L comprises a straight or branched alkylene group having 2 to 12 carbons. The reactive monomers combine oxygen permeable silicone components with hydrophilic terminal groups capable of reaching to the device-bio-logic interface thus providing bulk and surface characteristics useful in the manufacture of medical devices, particularly ophthalmic devices.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Micro-reaction chamber microelectrodes especially for neural and biointerfaces
ActiveUS20130053934A1Maximize surface areaIncrease capacityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrochemical responseBiointerface
Biocompatible electrodes with smaller geometric area improve the selectivity of the neural recording and stimulation applications. A volume within the electrode back plane of a micro-reaction chamber (μRC) is used to confine and sequester an electrochemical reaction used for charge passage. The μRC electrode decreases impedance and improves charge storage capacity without altering the geometry of the active site.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Enhancing surface plasmon resonance imaging signal
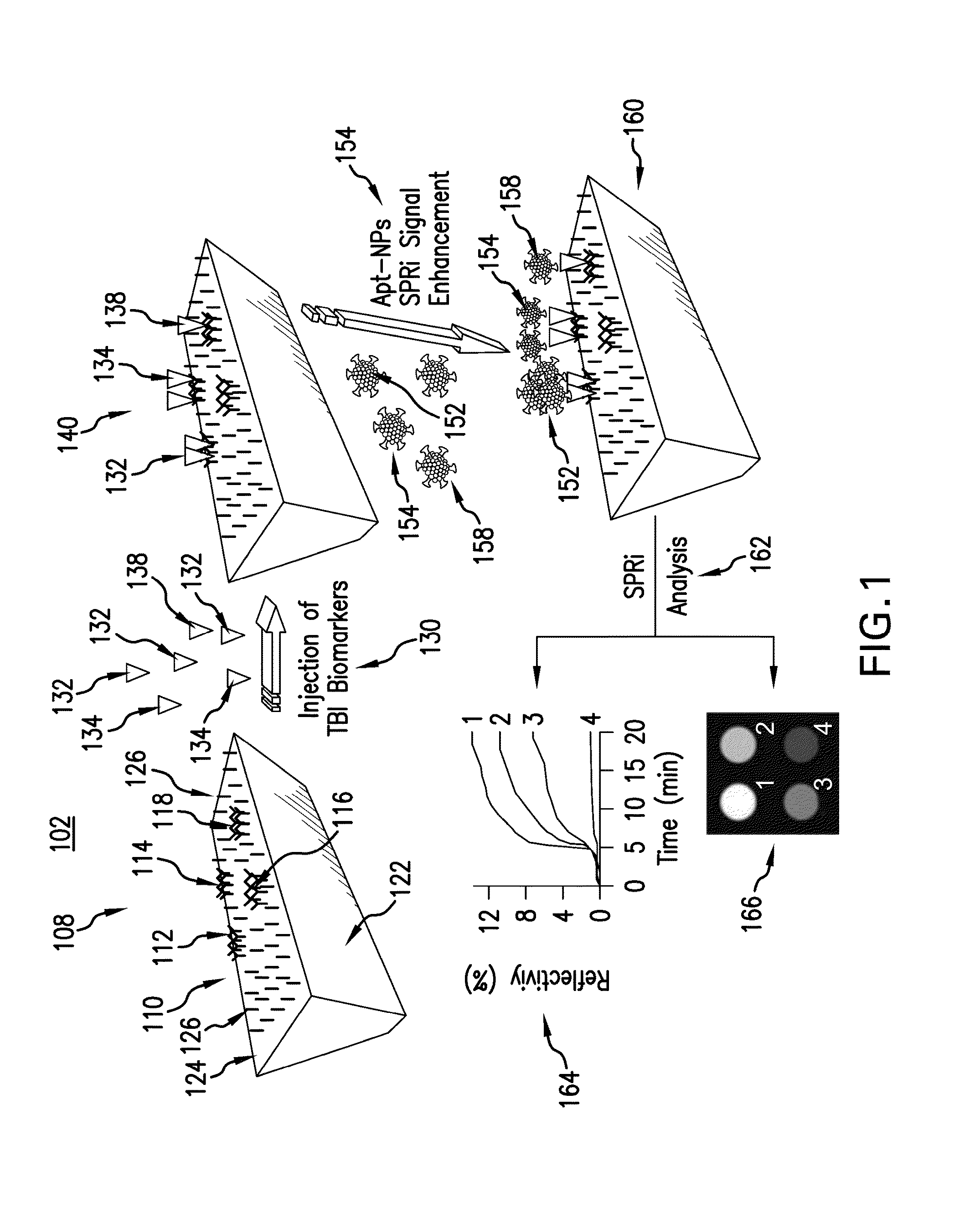
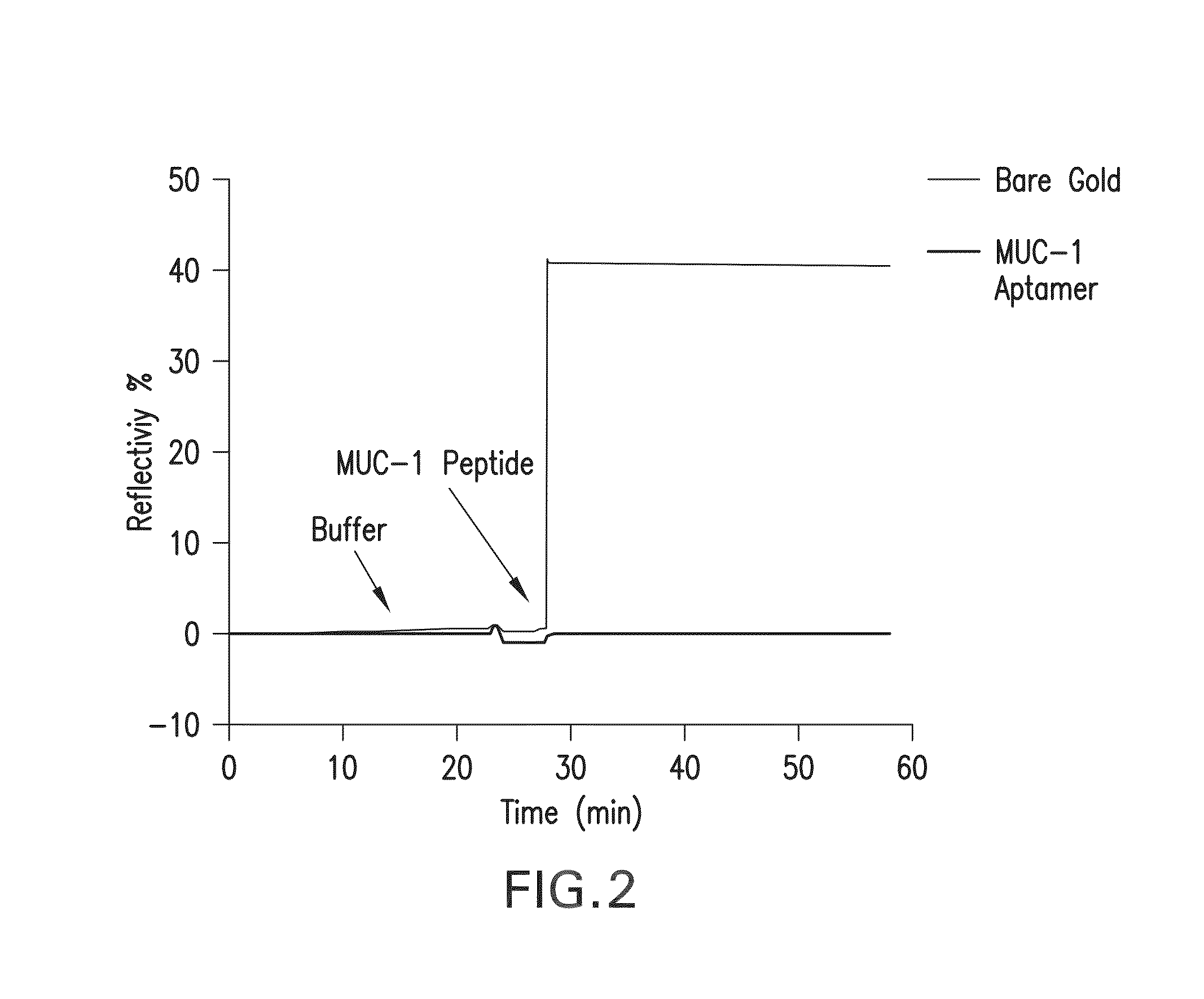
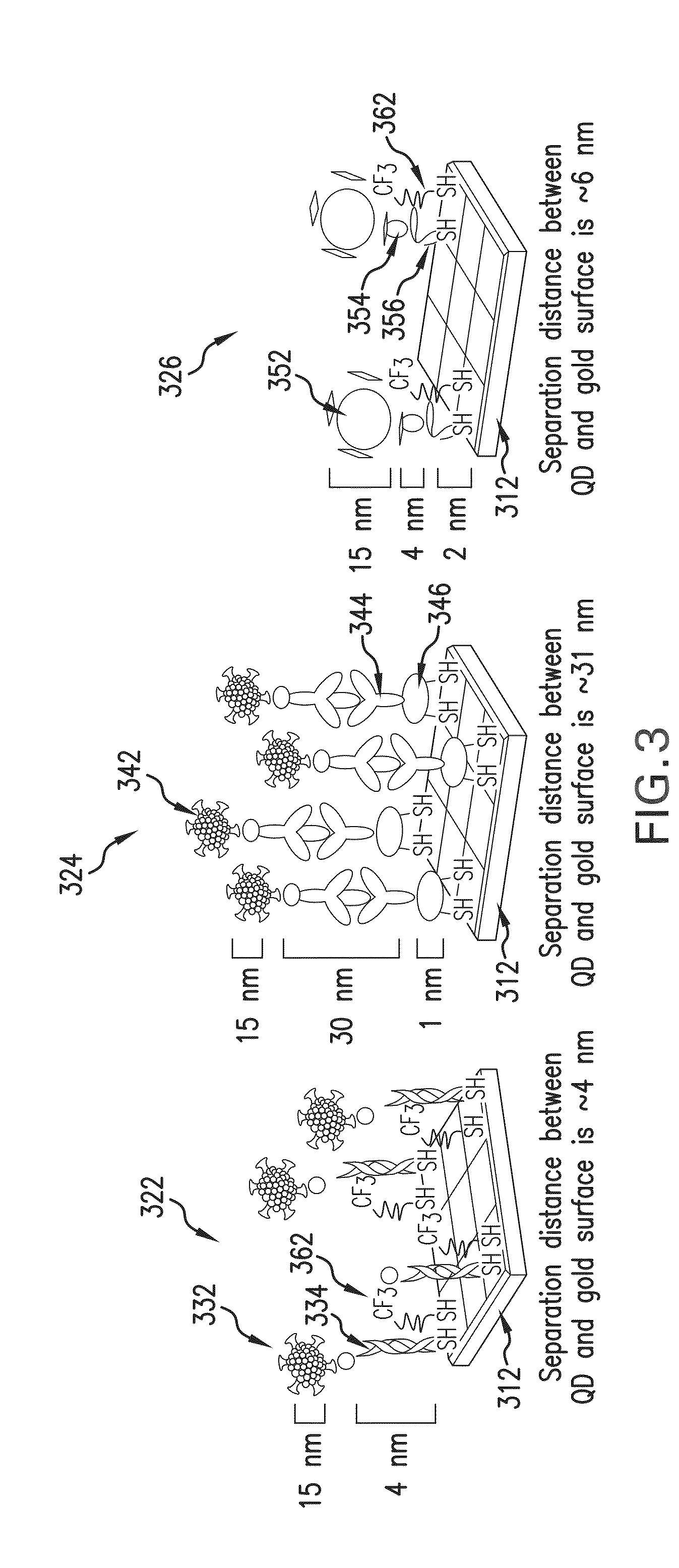
Described is a biointerface using near-infrared quantum dots for surface plasmon resonance imaging biosensors.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT GREENSBORO
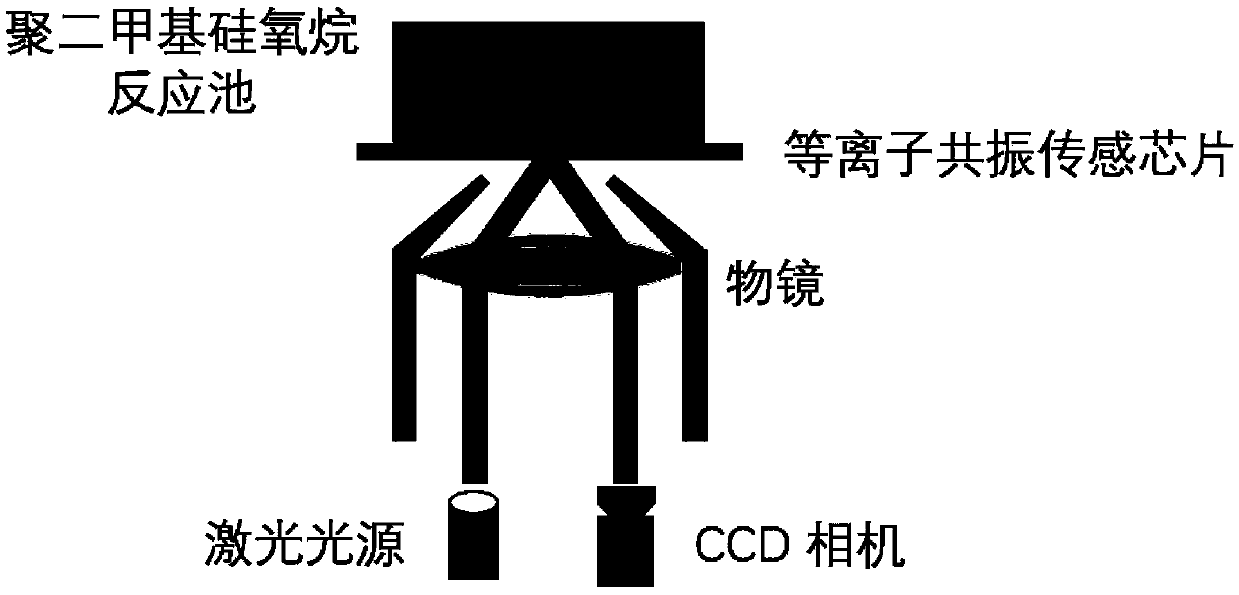
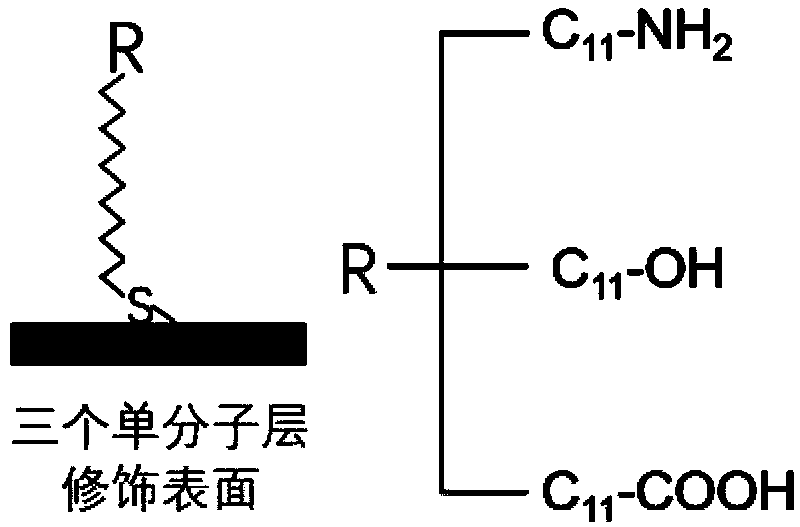
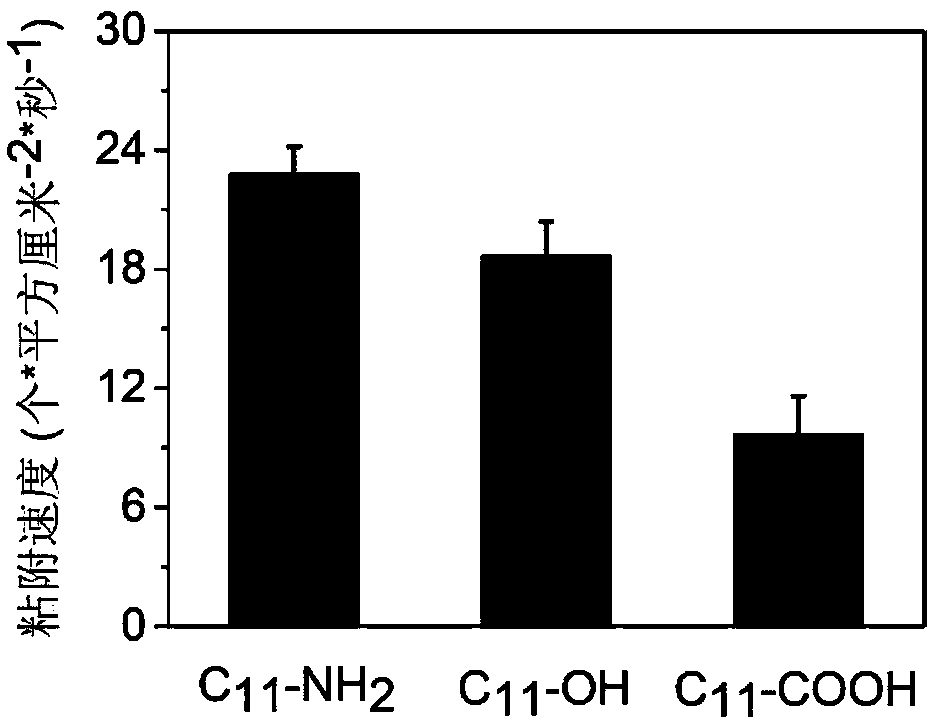
System for detecting microbial interface adhesion based on surface plasmon imaging and method
InactiveCN109632722APrecise determination of adhesion kinetic parametersImprove time resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansBiointerfaceImage resolution
The invention belongs to the field of environmental science and engineering, and discloses a system for detecting microbial interface adhesion based on surface plasmon imaging and method. The system for detecting microbial interface adhesion based on surface plasmon imaging is based on surface plasmon resonance microscopy (SPRM) and self-assembled monolayers (SAMs), advantages of being label-free,real-time in observation and high in time resolution are achieved, the adhesion kinetic parameters of bacteria on different interfaces such as an adhesion speed and a kinematic phenotype can be accurately determined by an online counting method, and the time constant of adhesion to the surface can be obtained by calculating and fitting.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Implantable glucose sensors having a biostable surface
PendingUS20190142317A1Reduce the differenceReduced protein and cell depositionSurgeryPharmaceutical delivery mechanismGlucose sensorsBiointerface
Disclosed are implantable glucose sensors having a biostable surface. The implantable glucose sensor includes a glucose detector and an enclosure defining a boundary between an internal space and an external space. The enclosure includes a semipermeable biointerface film containing a base polymer and a biostabilizing additive. The semipermeable biointerface film has a biostable surface and is permeable to glucose. The working electrode is disposed inside the internal space, and the biostable surface faces the external space or faces both the internal and the external spaces. Also disclosed are methods of preparation of the semipermeable biointerface films adapted for use in the implantable glucose sensors. Further, disclosed are methods of monitoring glucose levels in a subject through the use of an implantable glucose sensor. The implantable glucose sensor may be an implantable electrochemical glucose sensor, in which the glucose detector is a working electrode. Alternatively, the implantable glucose sensor may be an implantable optical glucose sensor, in which the glucose detector is a glucose recognition element including a glucose-binding fluorophore.
Owner:EVONIK CANADA INC
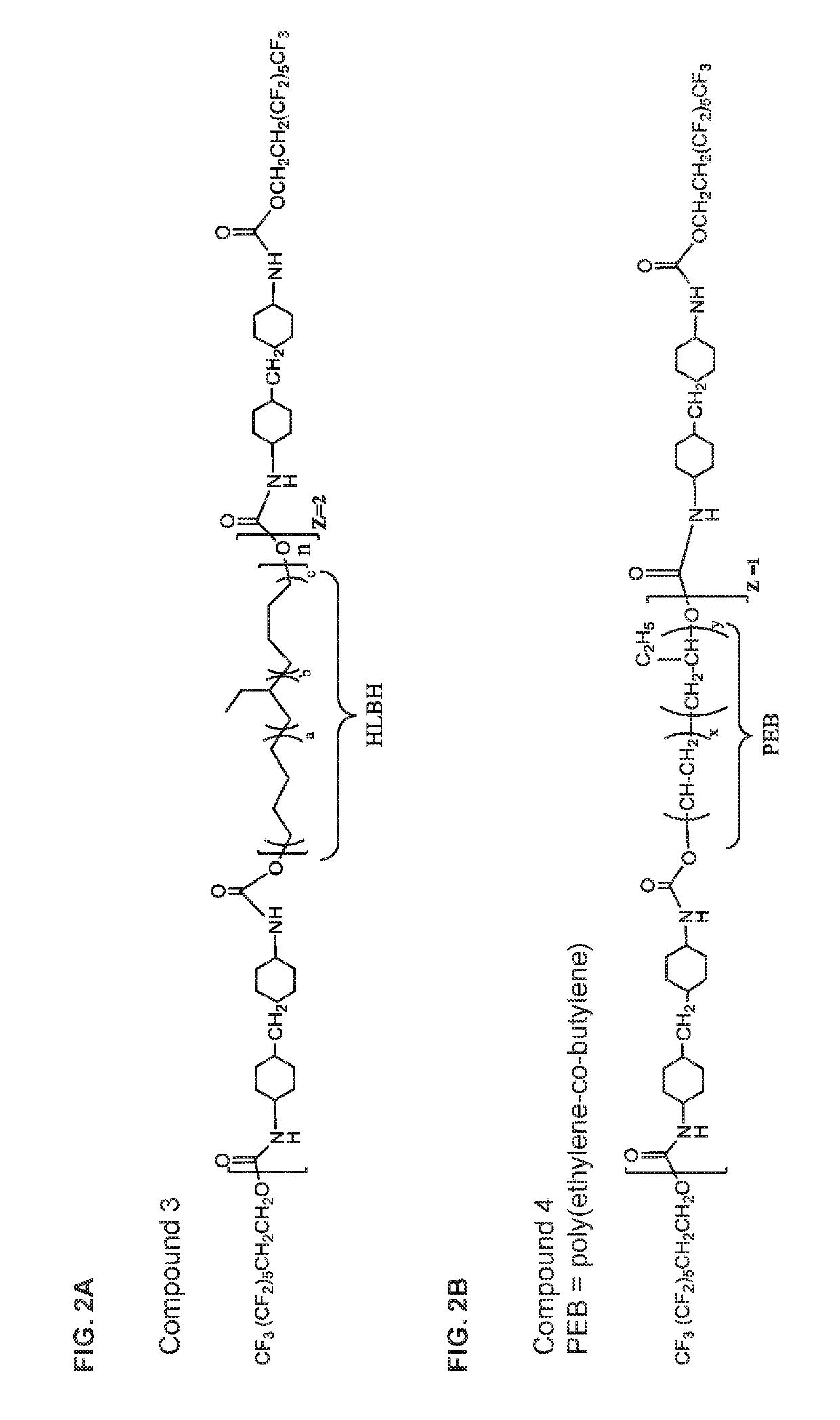
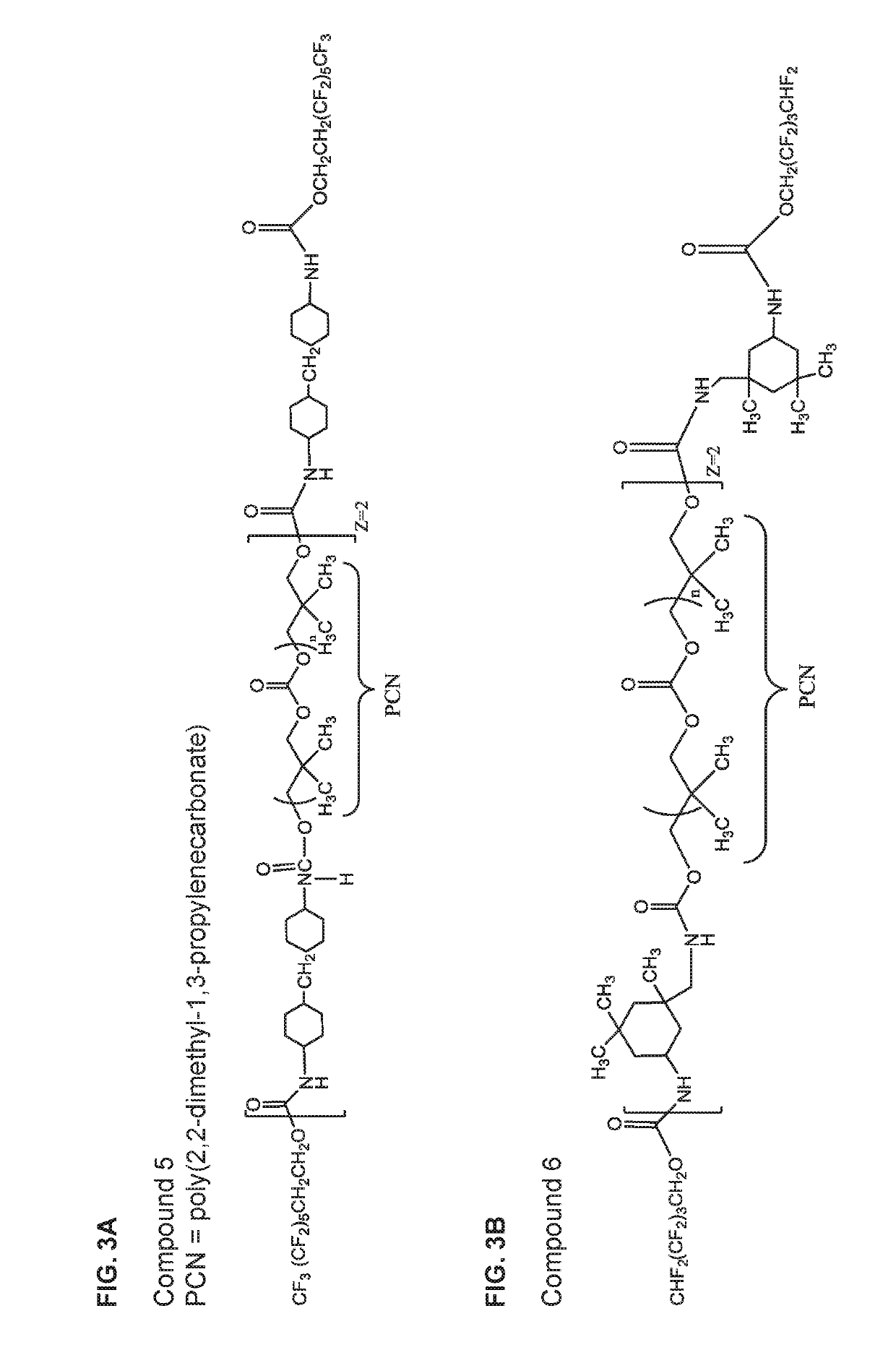
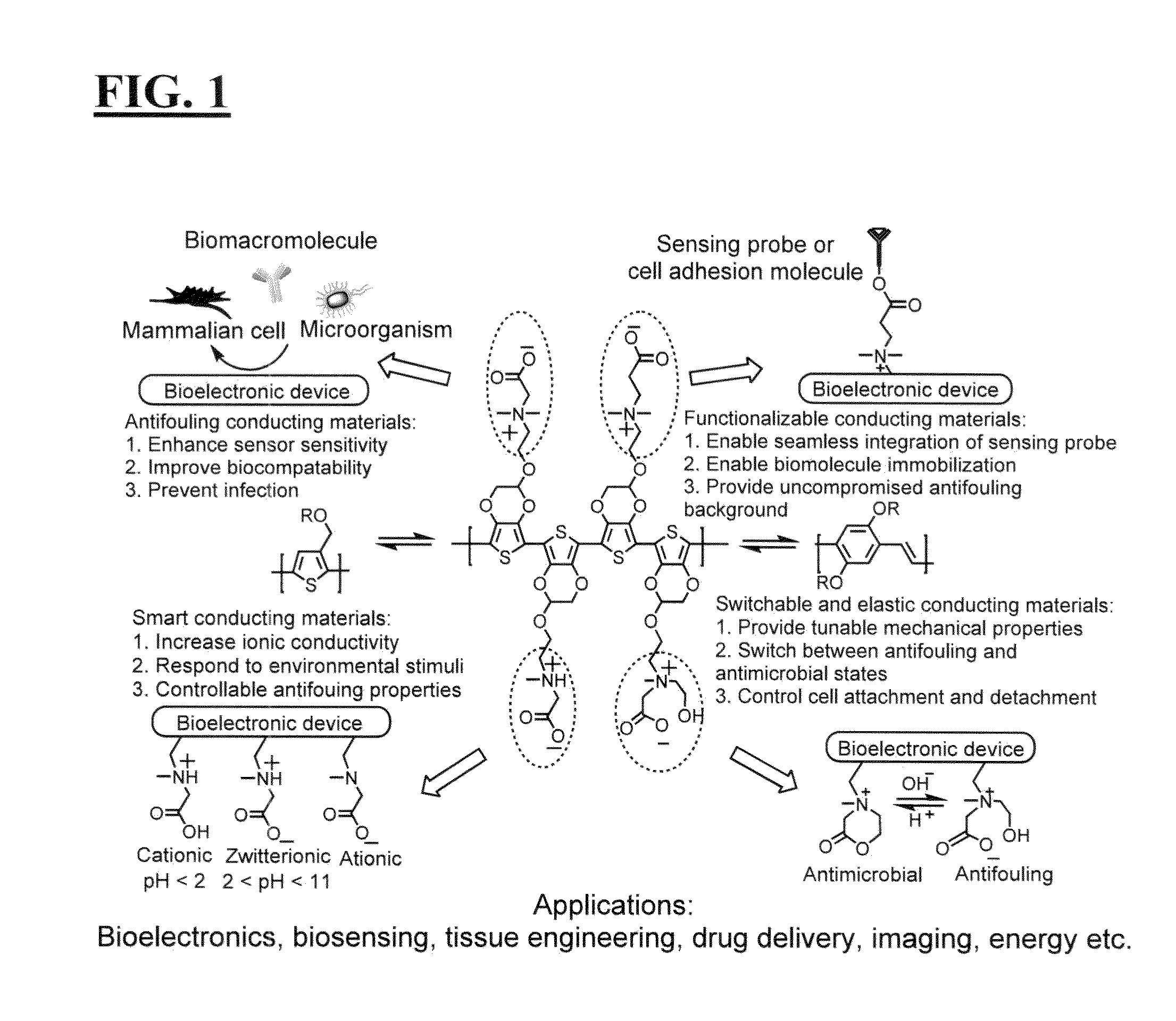
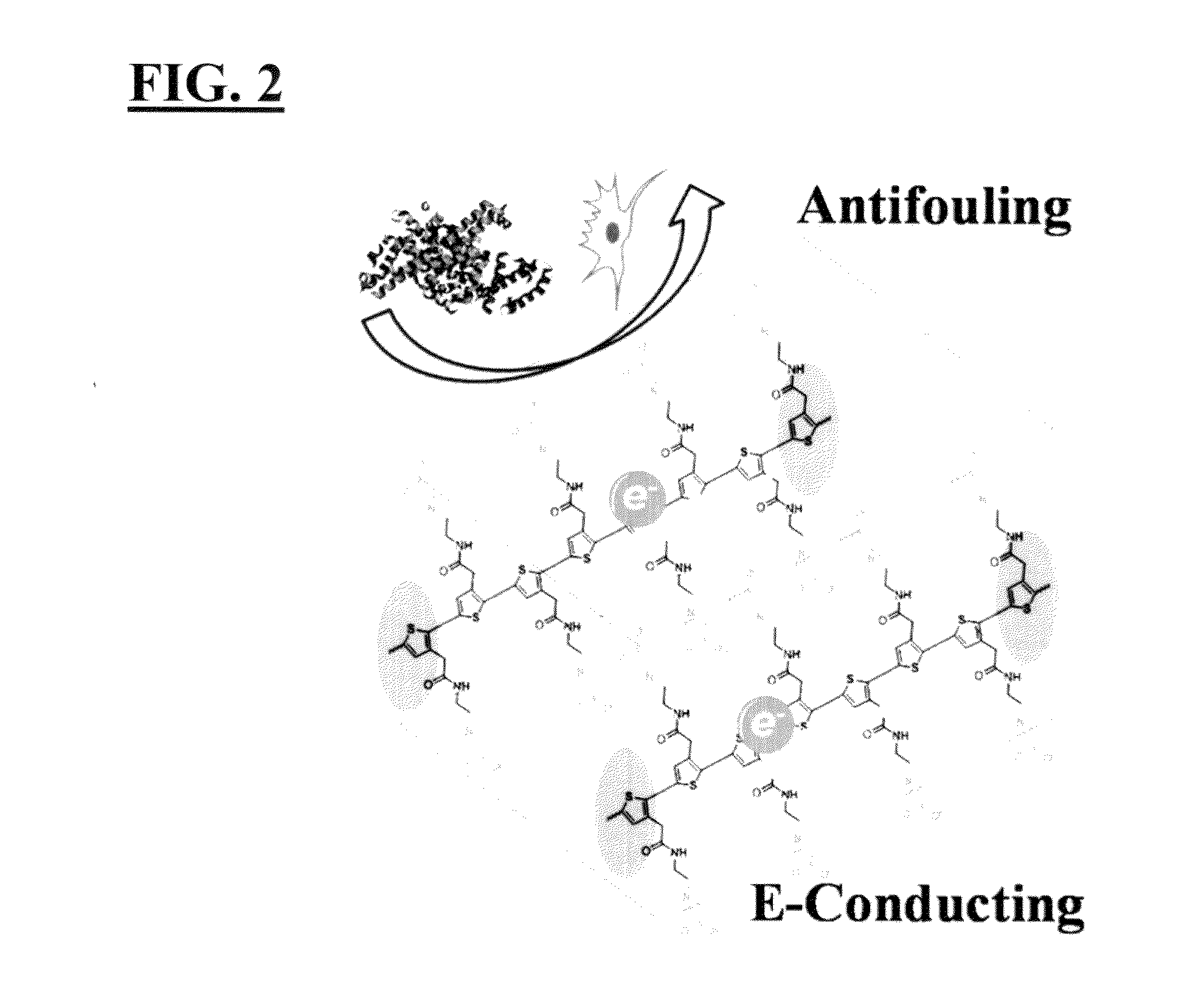
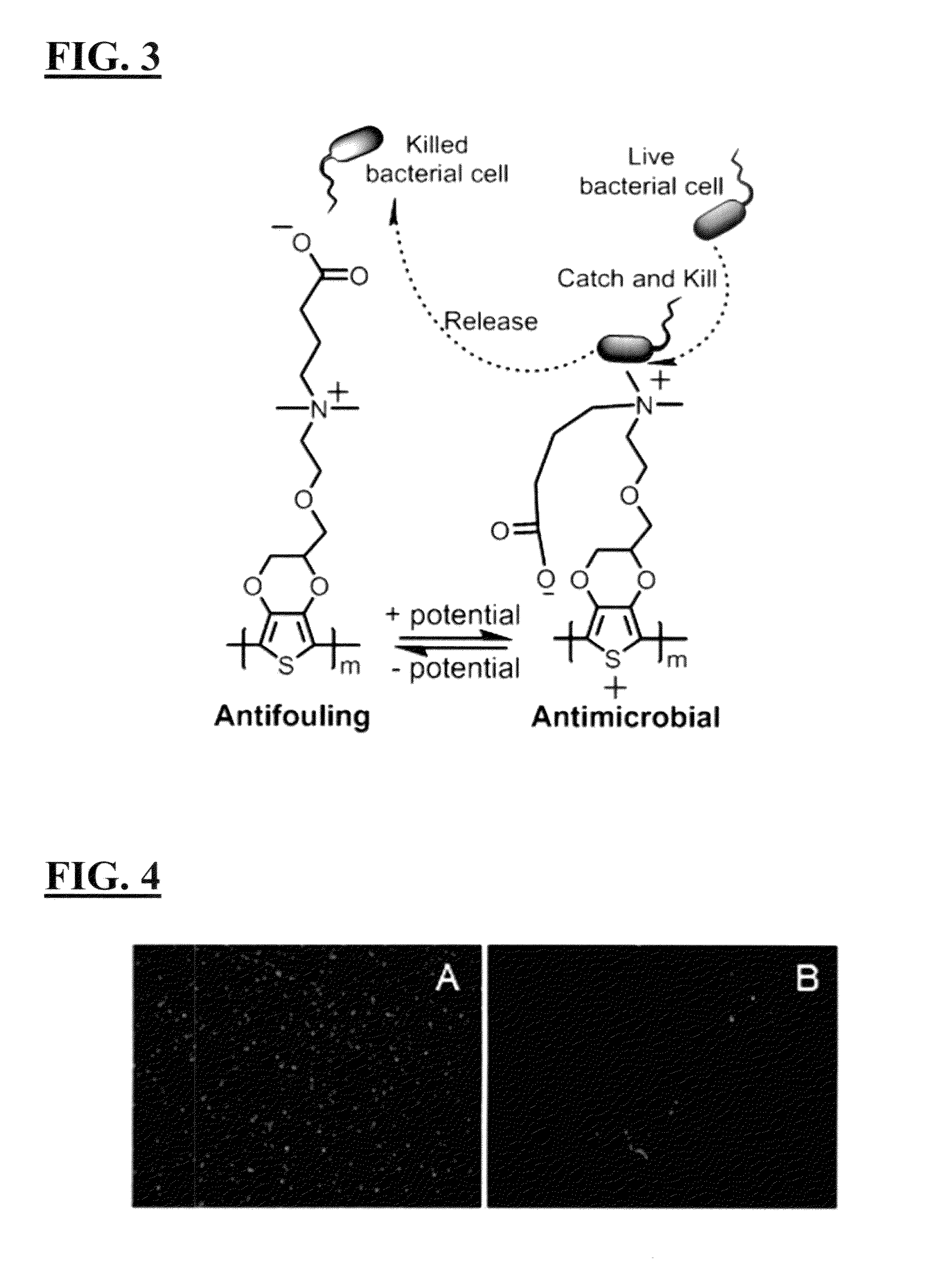
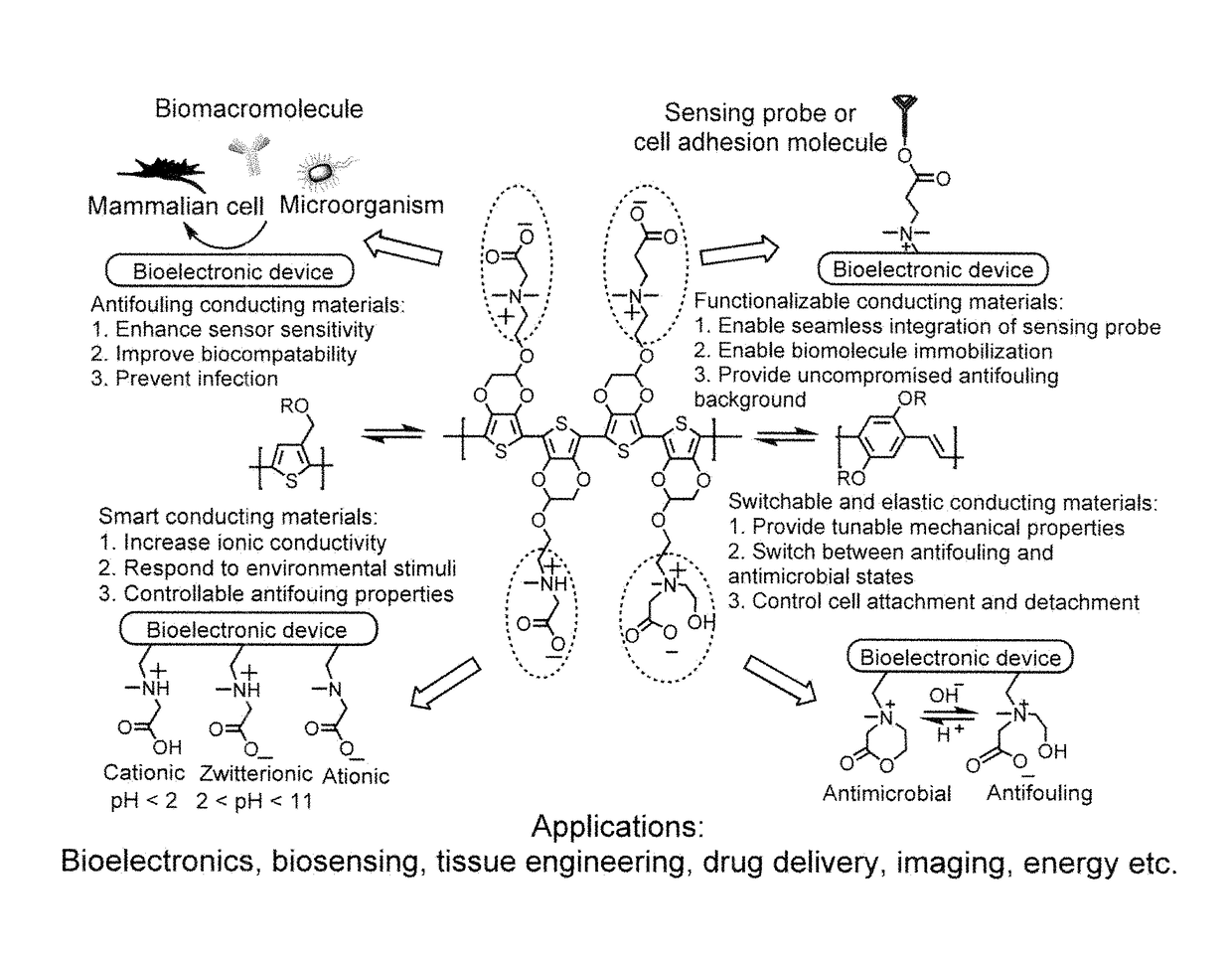
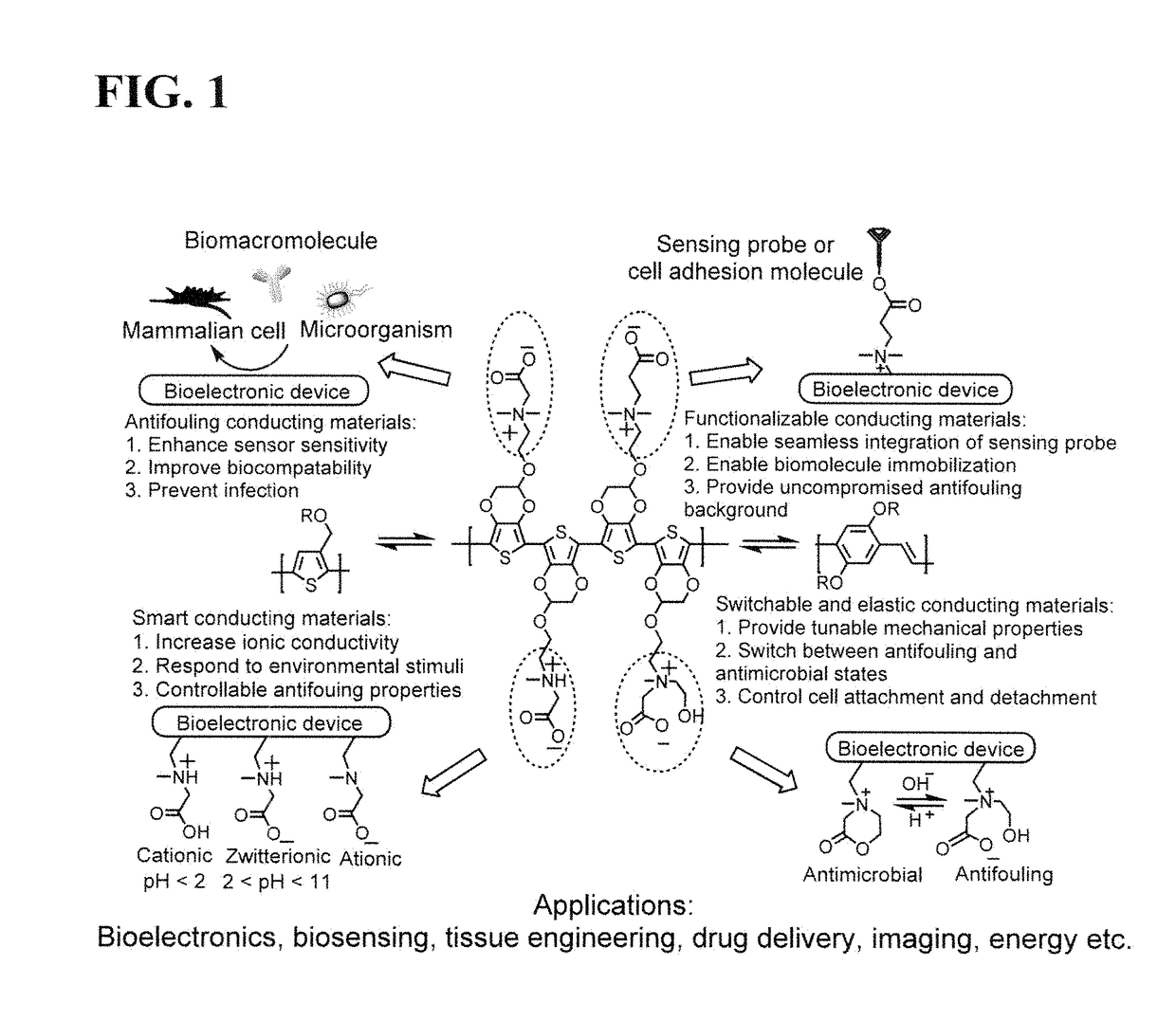
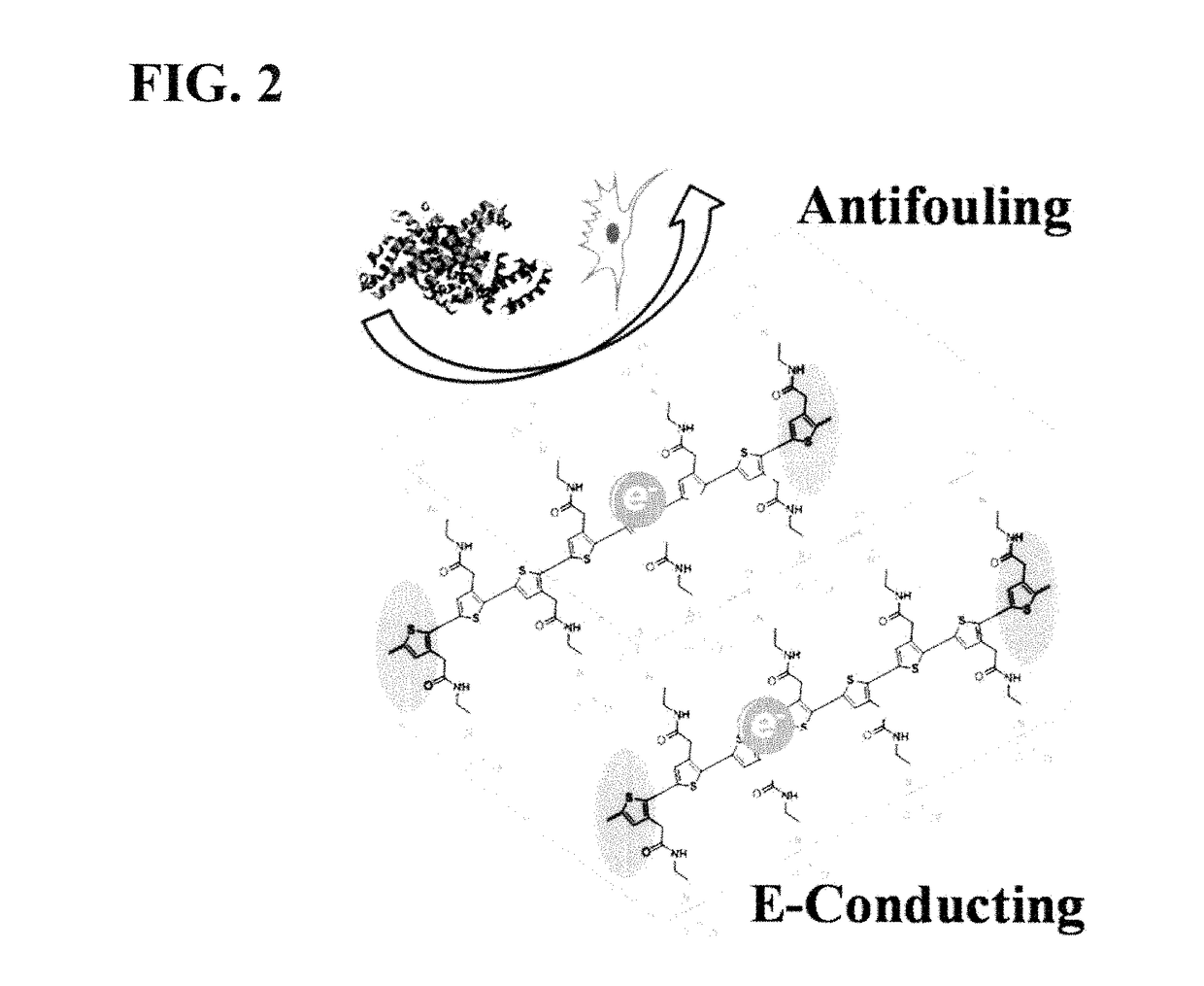
Integrated zwitterionic conjugated polymers for bioelectronics, biosensing, regenerative medicine, and energy applications
ActiveUS20160244554A1Improve antifouling performanceImprove conductivitySurgeryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsConductive polymerSide chain
The present invention is directed to a versatile and high performance zwitterionic CP platform, which integrates all desired functions into one material. This zwitterionic CP consists of the conducting backbone and multifunctional zwitterionic side chains. Non-conducting zwitterionic materials gain electronic conductivity through the conducting backbone and CPs obtain excellent biocompatibility, sensitivity to environmental stimuli and controllable antifouling properties via multifunctional zwitterionic side chains. Unique properties from two distinct materials (conducting materials and zwitterionic materials) are integrated into one material without sacrificing any properties. This platform can potentially be adapted for a range of applications (e.g. bioelectronics, tissue engineering, wound healing, robotic prostheses, biofuel cell, etc.), which all require high performance conducting materials with excellent antifouling / biocompatibility at complex biointerfaces. This conducting material platform will significantly advance the development of conducting polymers in the field of biomedicine and biotechnology.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF AKRON
Micro-reaction chamber microelectrodes especially for neural and biointerfaces
ActiveUS9592378B2Increase capacityLower impedanceImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrochemical responseBiointerface
Biocompatible electrodes with smaller geometric area improve the selectivity of the neural recording and stimulation applications. A volume within the electrode back plane of a micro-reaction chamber (μRC) is used to confine and sequester an electrochemical reaction used for charge passage. The μRC electrode decreases impedance and improves charge storage capacity without altering the geometry of the active site.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
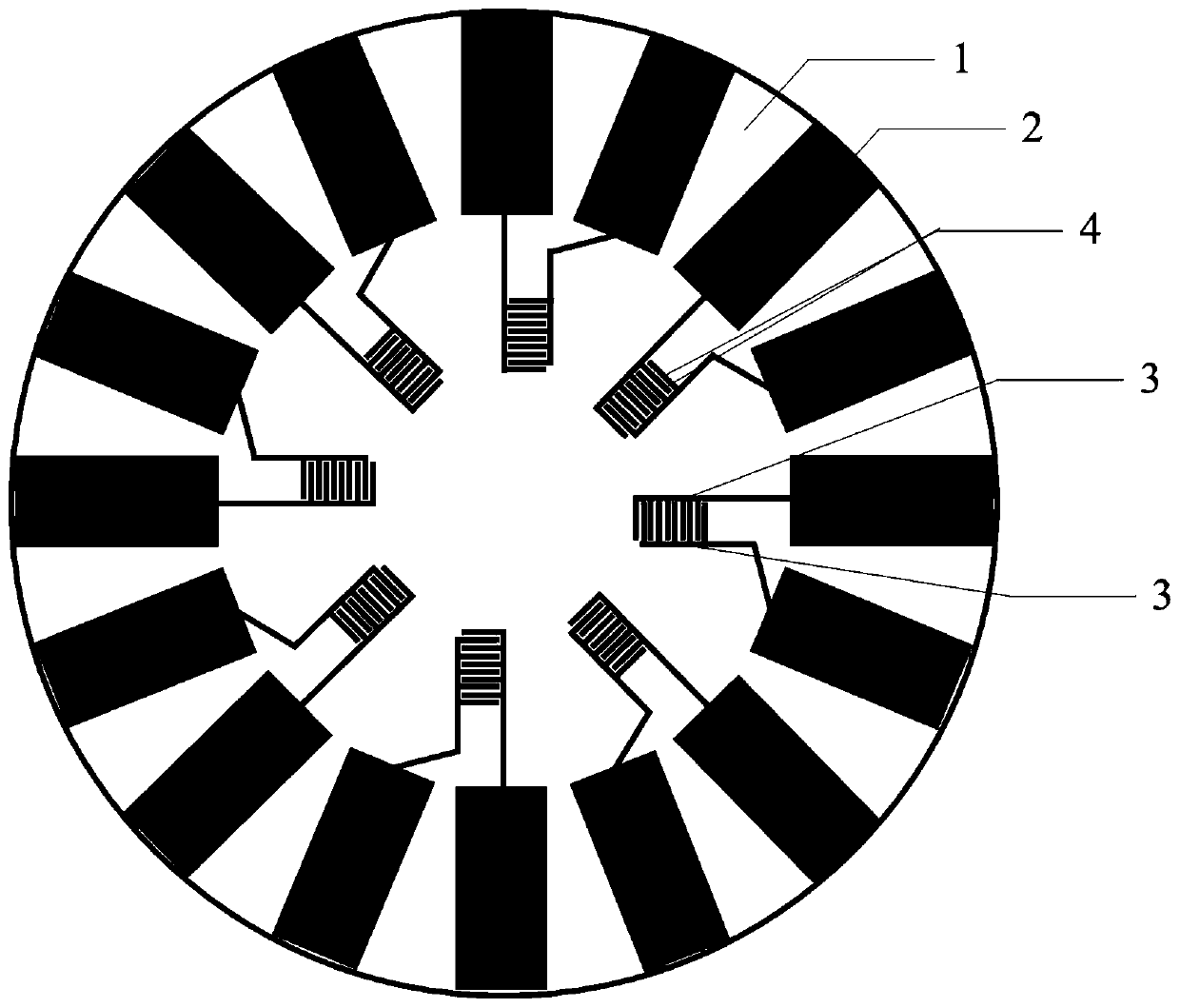
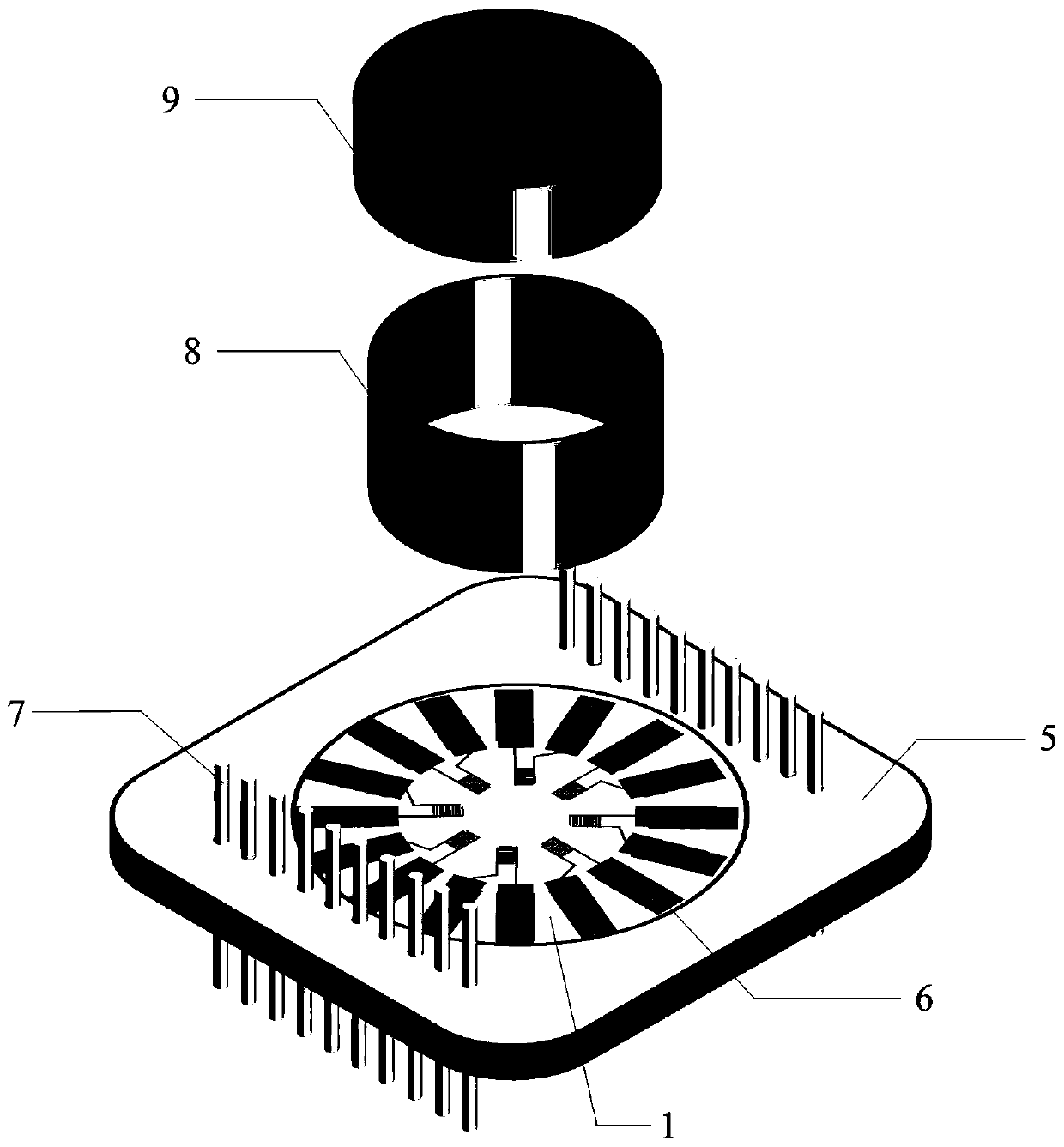
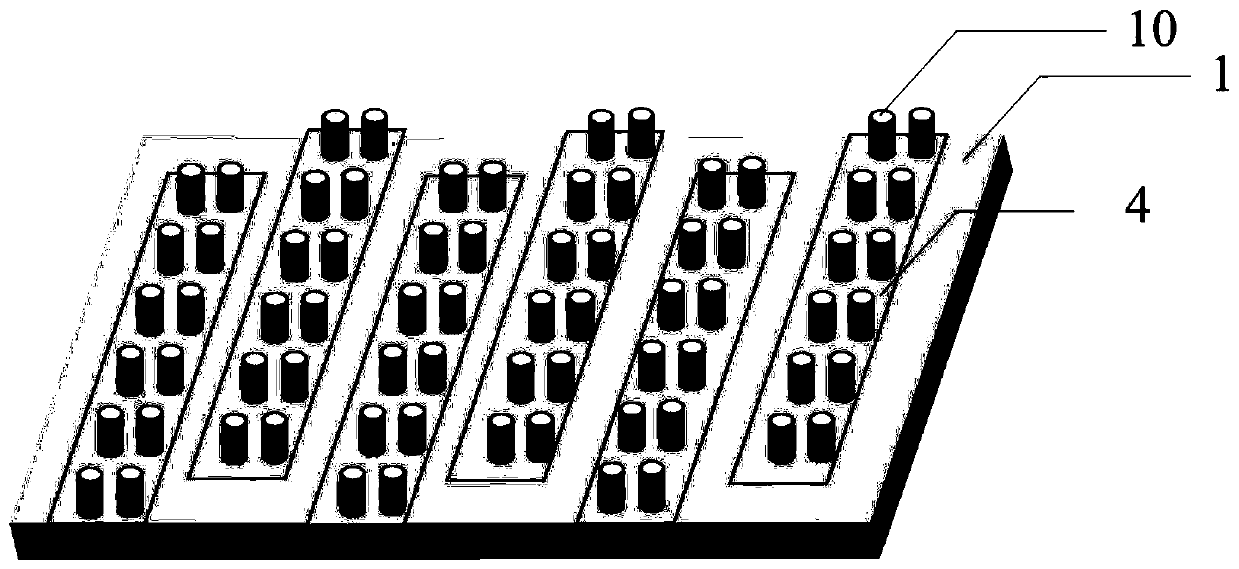
Interdigital arrangement conductive nanotube sensing device for cardiac muscle cell multi-element activity detection
ActiveCN111272819AGood biocompatibilityLarge specific surface areaMaterial impedanceCultured cellBiocompatibility
The invention discloses a sensing device for cardiac muscle cell multi-element activity detection. The device comprises a PCB and multiple groups of interdigital electrodes, the plurality of groups ofinterdigital electrodes are distributed in a central symmetry manner. Each interdigital electrode comprises a bus and an interdigital electrode array, a plurality of interdigital electrode pairs is vertically distributed at one end of each bus to form the interdigital electrode array, and interdigital electrode arrays of every two buses are oppositely arranged in a staggered mode to form the interdigital electrode. The other end of each bus is connected with a bonding pad on PCB. A culture cavity for culturing cells is fixed on the surface of the interdigital electrode. The interdigital electrode is composed of a conductive nano hollow tube deposited on the PET porous membrane. According to the invention, the platinum hollow nanotube array is used as a three-dimensional biological interface; the prepared sensor has the advantages of good biocompatibility, large specific surface area and better coupling with cells, so that the prepared sensor can greatly improve the detection sensitivity of various signals while realizing the multi-element activity synchronous detection of electrophysiology, growth and mechanical pulsation signals and metabolic signals of myocardial cells.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Integrated zwitterionic conjugated polymers for bioelectronics, biosensing, regenerative medicine, and energy applications
ActiveUS9695275B2Improve antifouling performanceGood biocompatibilitySurgeryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsConductive polymerSide chain
The present invention is directed to a versatile and high performance zwitterionic CP platform, which integrates all desired functions into one material. This zwitterionic CP consists of the conducting backbone and multifunctional zwitterionic side chains. Non-conducting zwitterionic materials gain electronic conductivity through the conducting backbone and CPs obtain excellent biocompatibility, sensitivity to environmental stimuli and controllable antifouling properties via multifunctional zwitterionic side chains. Unique properties from two distinct materials (conducting materials and zwitterionic materials) are integrated into one material without sacrificing any properties. This platform can potentially be adapted for a range of applications (e.g. bioelectronics, tissue engineering, wound healing, robotic prostheses, biofuel cell, etc.), which all require high performance conducting materials with excellent antifouling / biocompatibility at complex biointerfaces. This conducting material platform will significantly advance the development of conducting polymers in the field of biomedicine and biotechnology.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF AKRON
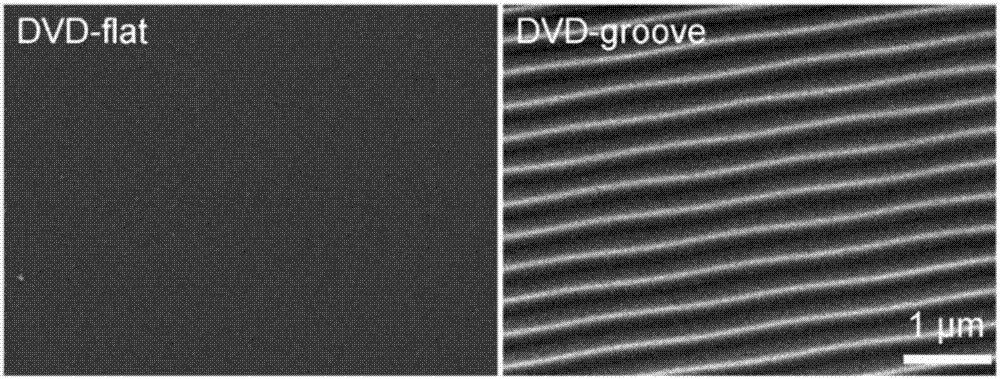
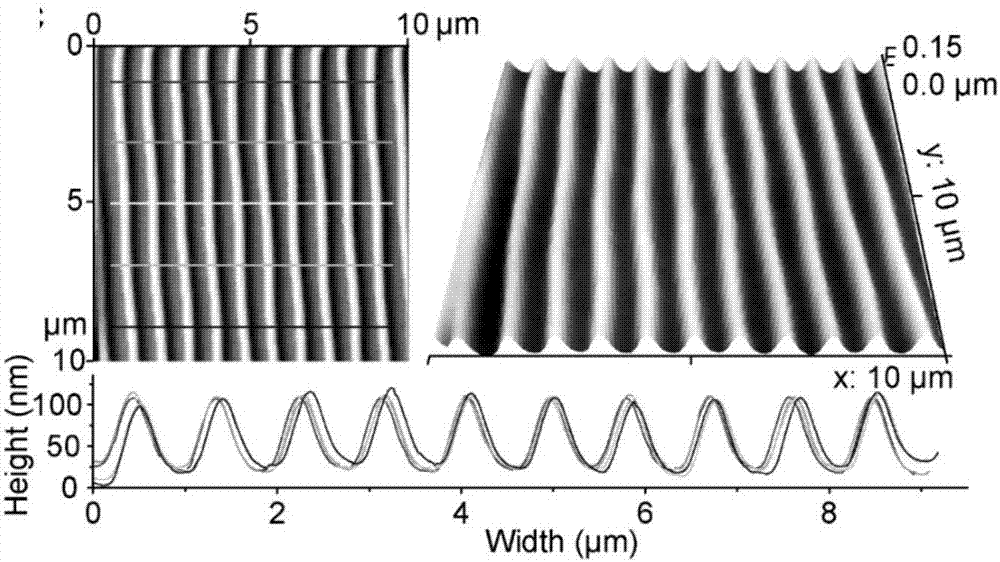
Method for recycling waste light disk and method for culturing PC12 cells by virtue of recycled light disk
The invention discloses a method for recycling waste light disk and a method for culturing PC12 cells by virtue of the recycled light disk. According to the methods, electronic waste is directly utilized and is applied to nervous tissue engineering, so that ready-made waste materials with various micron / nanometer structures can be provided so as to solve problems in the supplying and manufacturing of micron / nanometer patterns, and a new hopeful environmental protection manner can be provided; the application proves that wasted electronic products can be directly and repeated used as highly anisotropic substrates in the in vitro study of cell behaviors; PC12 cells cultured on the two substrates with different morphologies present different cell morphologies; and more chances are provided for the combination of theories and advantages of the information technique field and other fields, and a novel biological interface is hopefully constructed and designed by combining methods of biochemical building blocks, projects, materials and the like and is applied to the fields of biomedicines, biosensors, energy and the like.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Biosensor and method
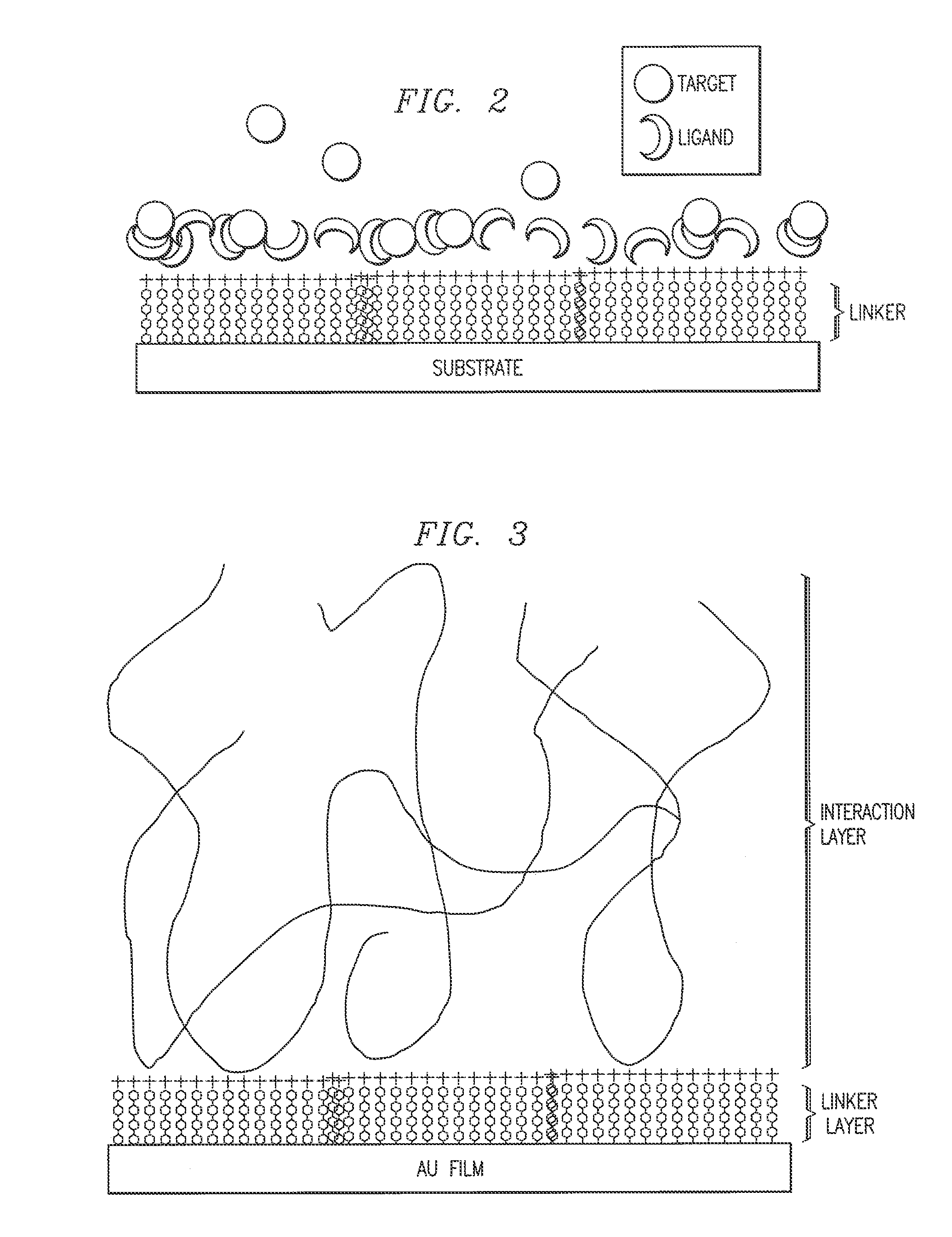
ActiveUS8785179B2Detection easeEase sensitivityMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsInteraction layerThiol
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Novel multilayered composite material utilizing quantum dot based photovoltaic effect for bi-directional brain-computer interface
A photovoltaic unit that includes a biological interface for sensing an electrical signal from the biological tissue, the biological interface including a multilayered piezoelectric amplifier including a composite impulse generating layer including a matrix of a piezo polymeric material and dispersed phases including piezo nanocrystals and carbon nanotubes. The photovoltaic unit also includes a transducer structure comprising a fiber substrate having quantum dots present on a receiving end of the fiber. The receiving end of the fiber receiving the electrical signal. The quantum dots converts the electrical signal to a light signal.
Owner:NEUROSILICA INC
Method for detecting environmental behaviors and biological effects of nanoparticle pollutants
PendingCN113654953AHelp study migration and transformationAids in the study of biological toxicityNanoparticle analysisFluorescence/phosphorescencePhospholipidFluorochrome Dye
The invention discloses a method for detecting environmental behaviors and biological effects of nanoparticle pollutants. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a micro-model and a vesicle suspension dyed by a fluorescent dye; injecting the vesicle suspension into the micro-model from a sample inlet; introducing a background solution into the micro-model from the sample inlet, and flushing unloaded vesicles; and introducing a suspension sample of nanoparticle pollutants into the micro-model from the sample inlet, connecting a microscope with a CCD, taking pictures at fixed time, observing the fluorescence intensity in the micro-model and the distribution change of the nanoparticle pollutants, collecting effluent from a sample outlet, measuring the fluorescence intensity at fixed time by using a fluorospectro photometer, and judging whether the nanoparticle pollutants interact with the phospholipid layer or not. According to the method disclosed by the invention, environmental behaviors such as flowing, migration and the like of the nanoparticle pollutants in an environmental medium can be monitored when the biological interface exists; and the interaction between the nanoparticle pollutants and cell membranes can be detected, and the biological effect of the nanoparticle pollutants can be evaluated.
Owner:山东大学深圳研究院
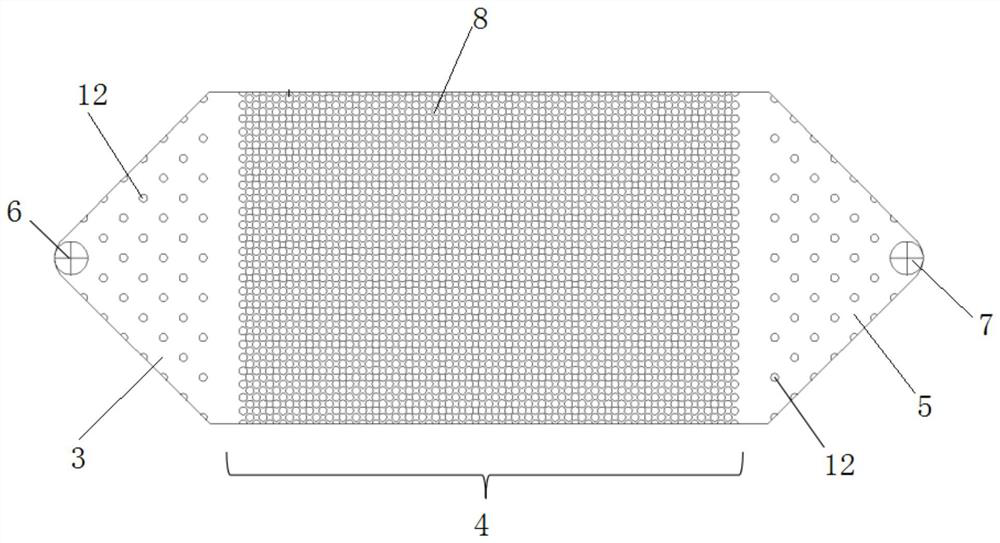
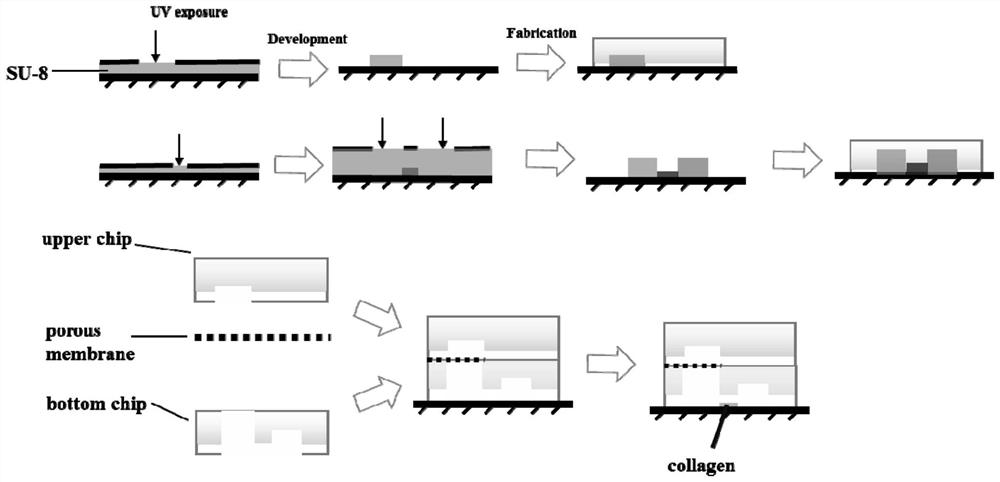
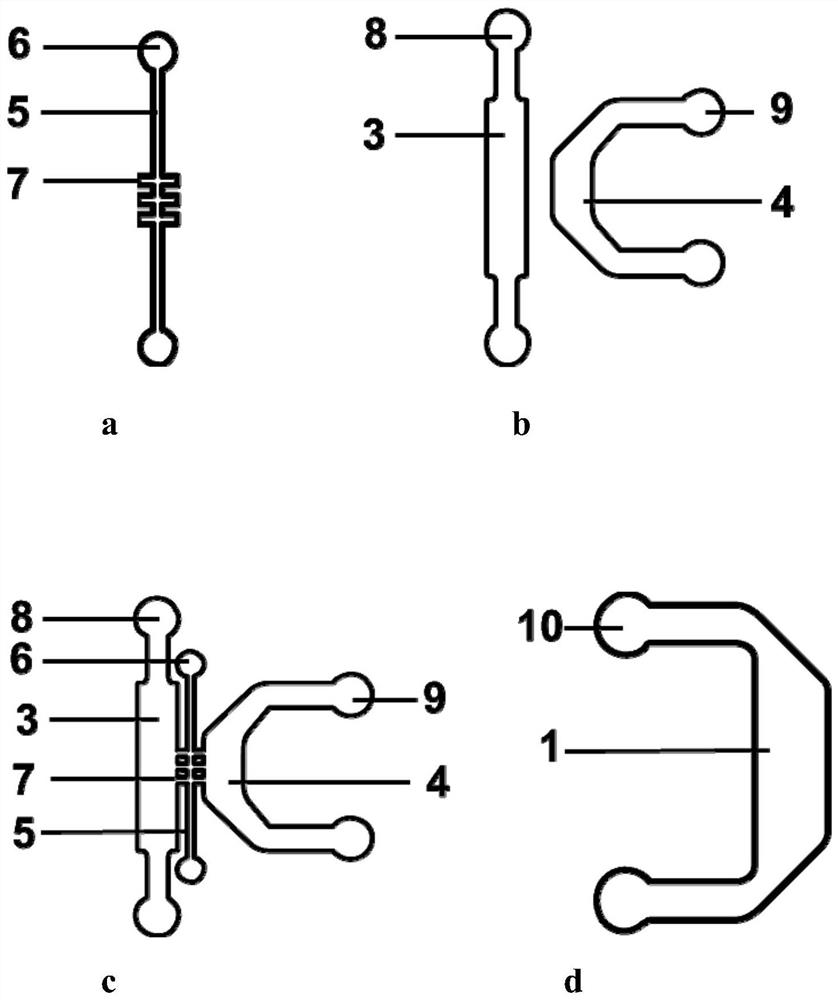
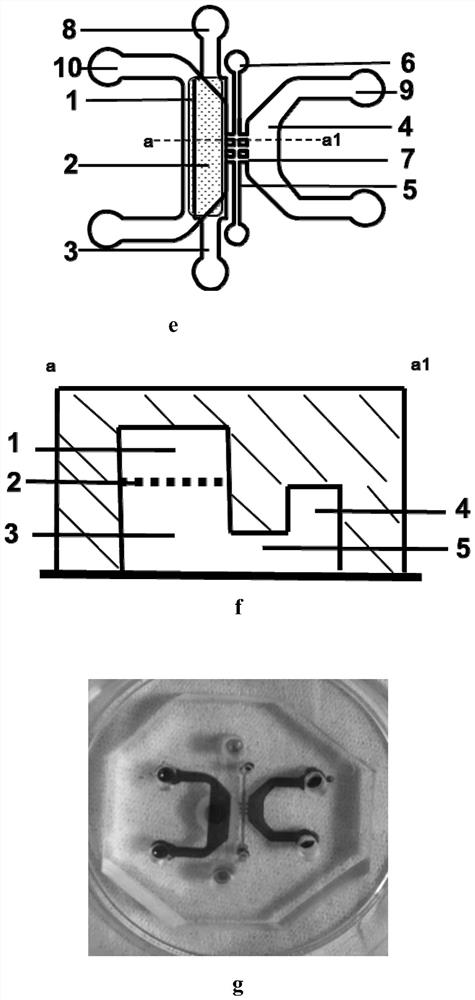
A microfluidic chip of a bionic multi-energy biological interface system and its preparation method
ActiveCN107955775BBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiointerfacePharmaceutical drug
The invention provides a microfluidic chip of a bionic multi-energy biological interface system and a preparation method thereof. The microfluidic chip is mainly composed of a top chip, a porous filter membrane and a bottom chip. On the surface, the lower surface of the porous filter membrane sealed with the top chip is bonded and sealed with the upper surface of the bottom chip through PDMS; the microfluidic chip prepared by this preparation method has a multi-interface structure, which can simulate the construction of various biological interfaces, and can be applied For cell co-culture, cell barrier construction, ADME research of drugs, cell migration and other research.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
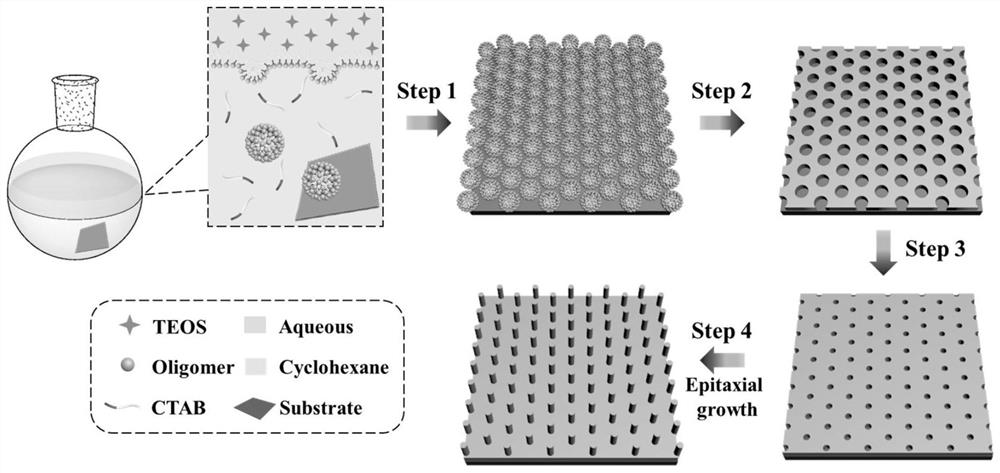
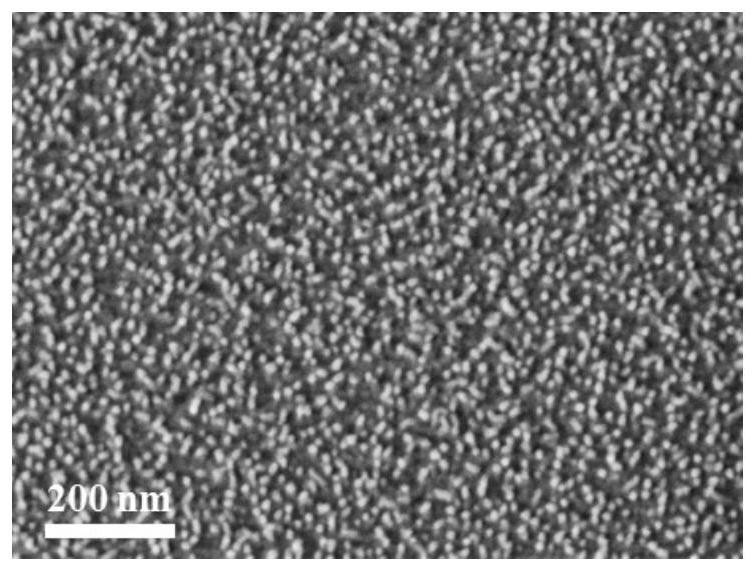
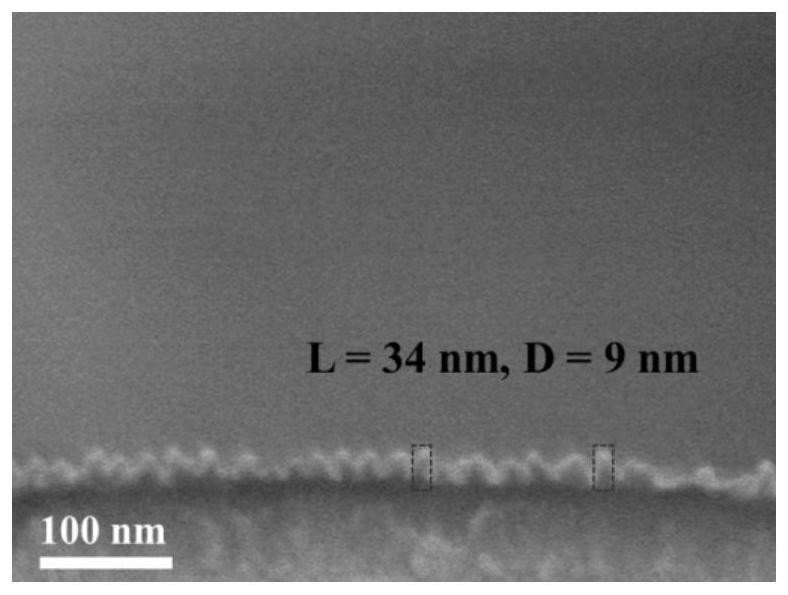
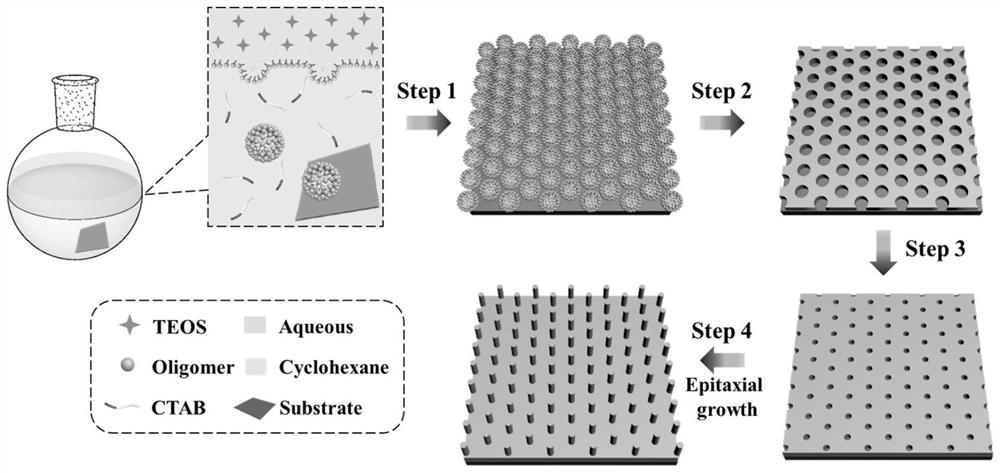
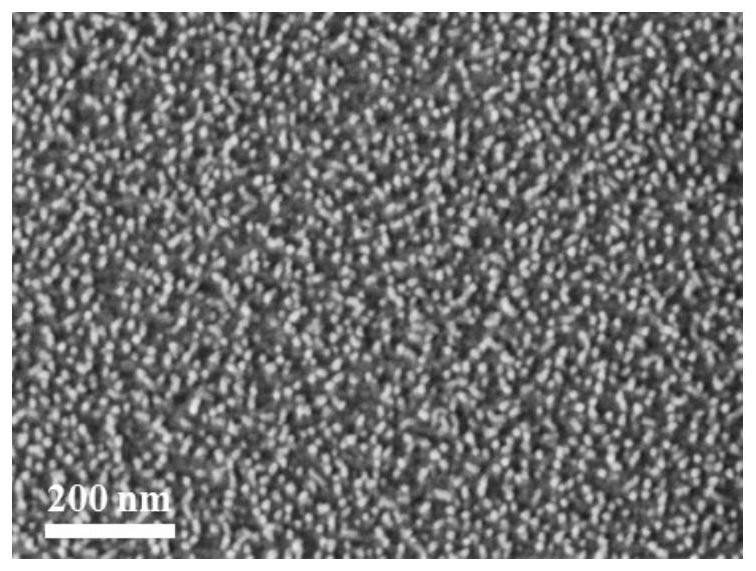
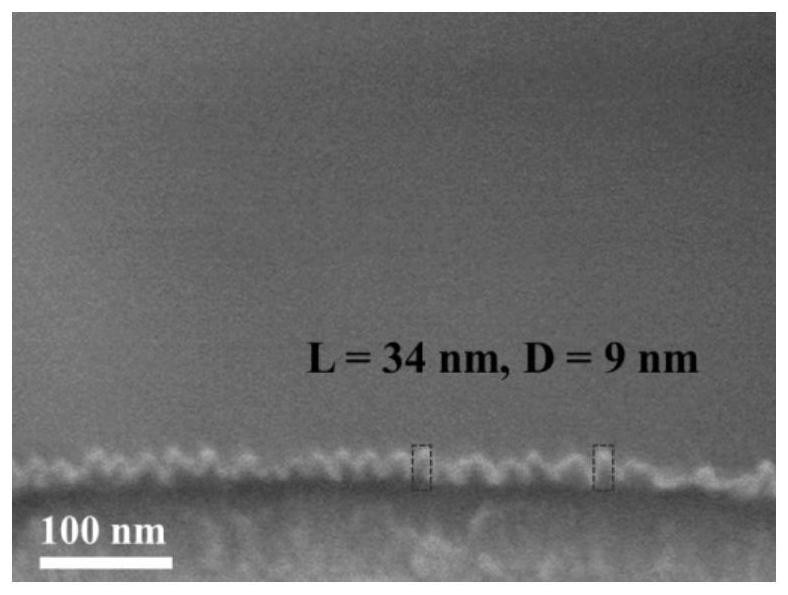
Silica nanoarray with controllable morphology, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN112939626BImprove capture efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCell adhesionPtru catalyst
The invention belongs to the technical field of nanomaterials, in particular to a silicon dioxide nanoarray with controllable morphology, a preparation method and application thereof. The silicon dioxide nano-array provided by the present invention has an array height of 8-46 nm and a distribution density of 210-3100 / μm 2 . The nano-array is prepared by adopting an oil / water dual-phase single micelle epitaxy growth method, using CTAB as a structure-directing agent, TEOS as a precursor, and NaOH as a catalyst to form a silicon nano-array on the surface of the substrate; the substrate can be glass Chips, silicon wafers, glass rods, glass tubes, microfluidic chips, etc. Silica nanoarrays can impart a rough surface structure to the substrate and enhance the interaction between the substrate and tumor cells and this biological interface. Compared with the substrate modified by the smooth silicon layer, the cell adhesion ability is significantly improved. A device consisting of a nest of glass rods and glass tubes with surface-grown silica nanoarrays can be used to isolate tumor cells from whole blood.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method for improving electron transfer efficiency of flora in situ
PendingCN114835243AImprove conductivityGood biocompatibilityTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesWater contaminantsCell membraneElectron transfer
The invention provides a method for improving the electron transfer efficiency of a flora in situ, which is suitable for wastewater treatment of a three-dimensional electro-catalysis biological membrane system. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, constructing a three-dimensional electro-catalysis biological membrane system to culture an electro-active microbial membrane with target pollutant degradation capacity, then periodically regulating and controlling the electric field intensity to selectively enrich the electro-active microbial membrane, and finally, introducing low-concentration metal ion wastewater according to a certain flow ratio and controlling the current density. And nano-particles are synthesized in situ inside or on the surfaces of the microorganisms on the main electrode and the particle electrode. The biomineralization synthesized nanoparticles are tightly combined with cell membranes and periplasmic space, idle and dead electron conduits are connected, the electron transfer efficiency between organisms and electron acceptors and between organisms and non-biological interfaces is improved, the electron transfer process is improved, the current utilization efficiency of a three-dimensional electro-catalysis biological membrane system is further improved, and the service life of the three-dimensional electro-catalysis biological membrane system is prolonged. The treatment energy consumption is reduced; and pollutants can be efficiently degraded.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Shape-controllable silicon dioxide nano array and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN112939626AImprove capture efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCell adhesionPtru catalyst
The invention belongs to the technical field of nano materials, and particularly relates to a shape-controllable silicon dioxide nano array and a preparation method and application thereof. According to the silicon dioxide nano array, the array height is 8-46 nm, and the distribution density is 210-3100 / mu m < 2 >. The preparation method of the nano array comprises the following steps: forming a silicon nano array on the surface of a substrate by adopting an oil / water double-phase single micelle epitaxial growth method and taking CTAB as a structure-directing agent, TEOS as a precursor and NaOH as a catalyst; the substrate can be a glass sheet, a silicon wafer, a glass rod, a glass tube, a micro-fluidic chip and the like. The silicon dioxide nano array can endow the substrate with a rough surface structure, and the interaction between the substrate and tumor cells and the biological interface is enhanced. Compared with a substrate modified by a smooth silicon layer, the cell adhesion capacity is remarkably improved. The device formed by nesting the glass rod with the silicon dioxide nano array growing on the surface and the glass tube can be used for separating tumor cells from whole blood.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com