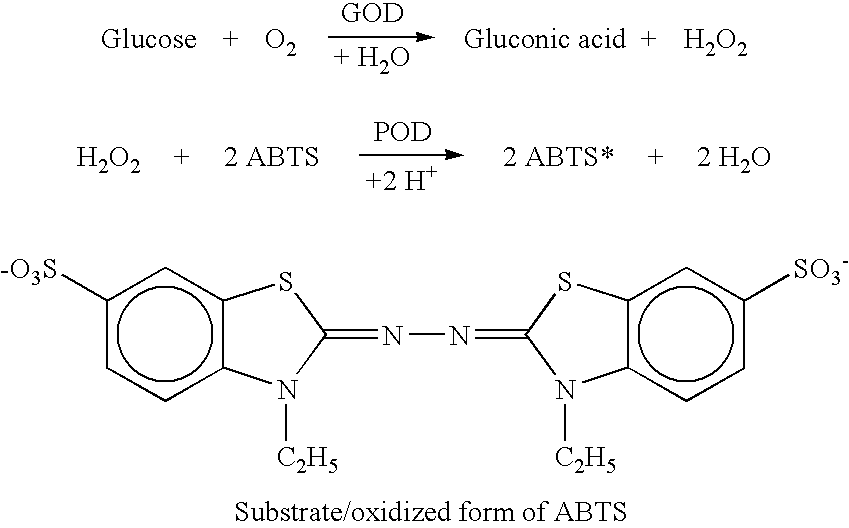
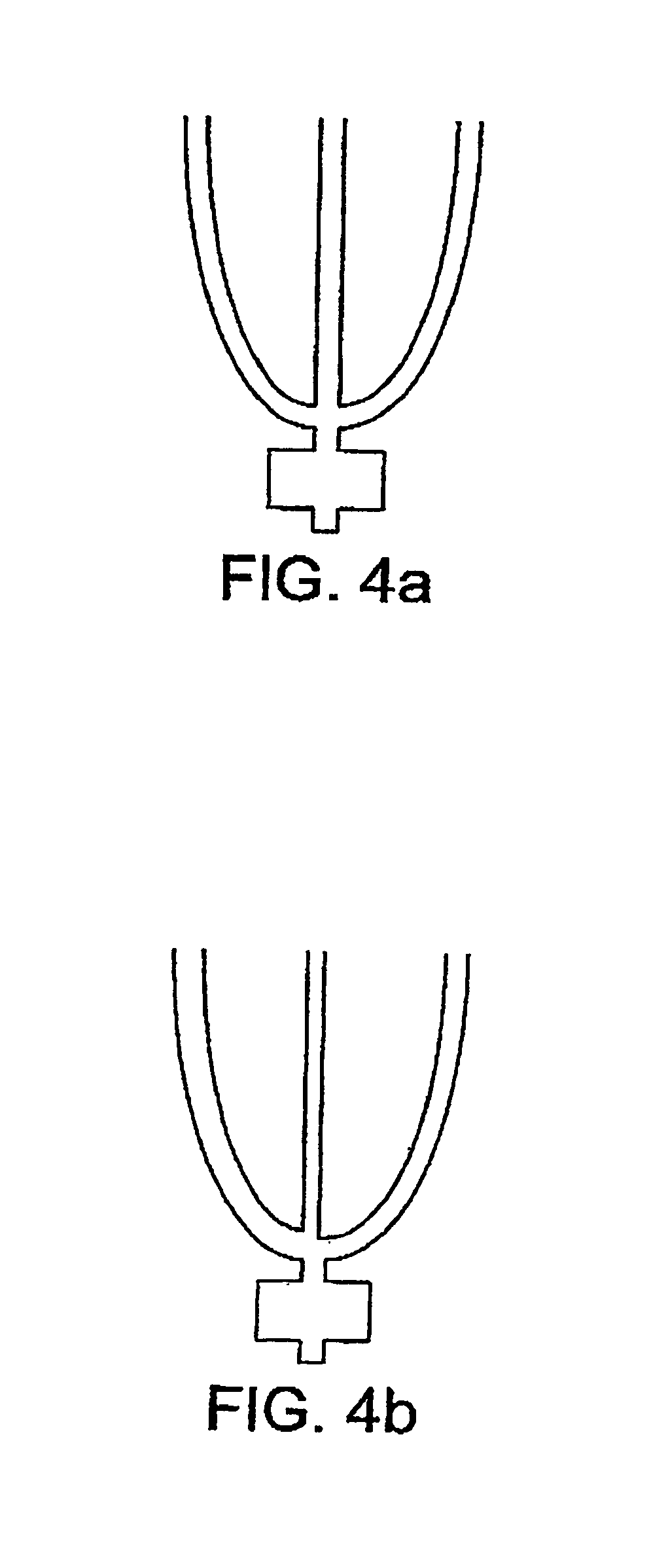
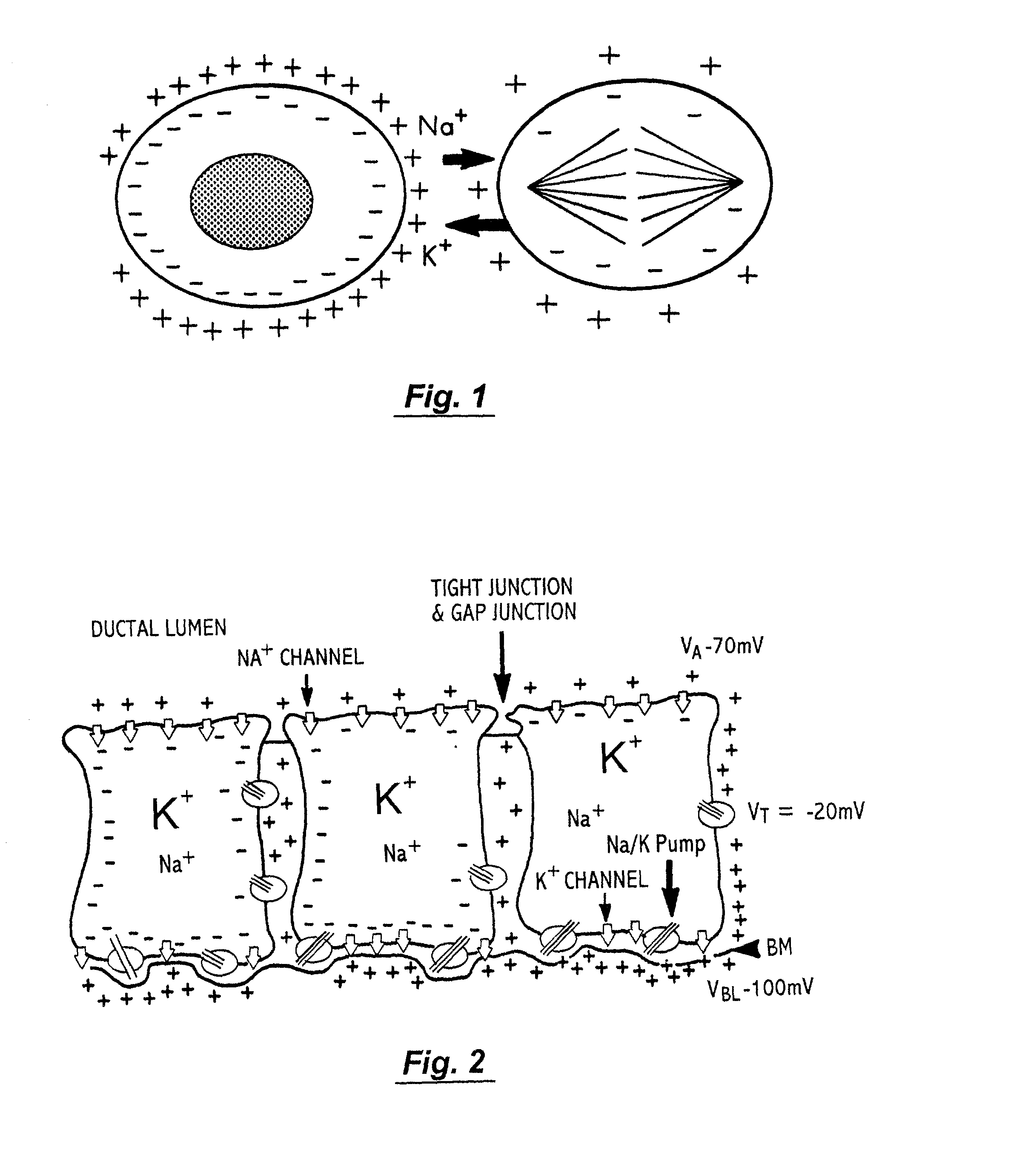
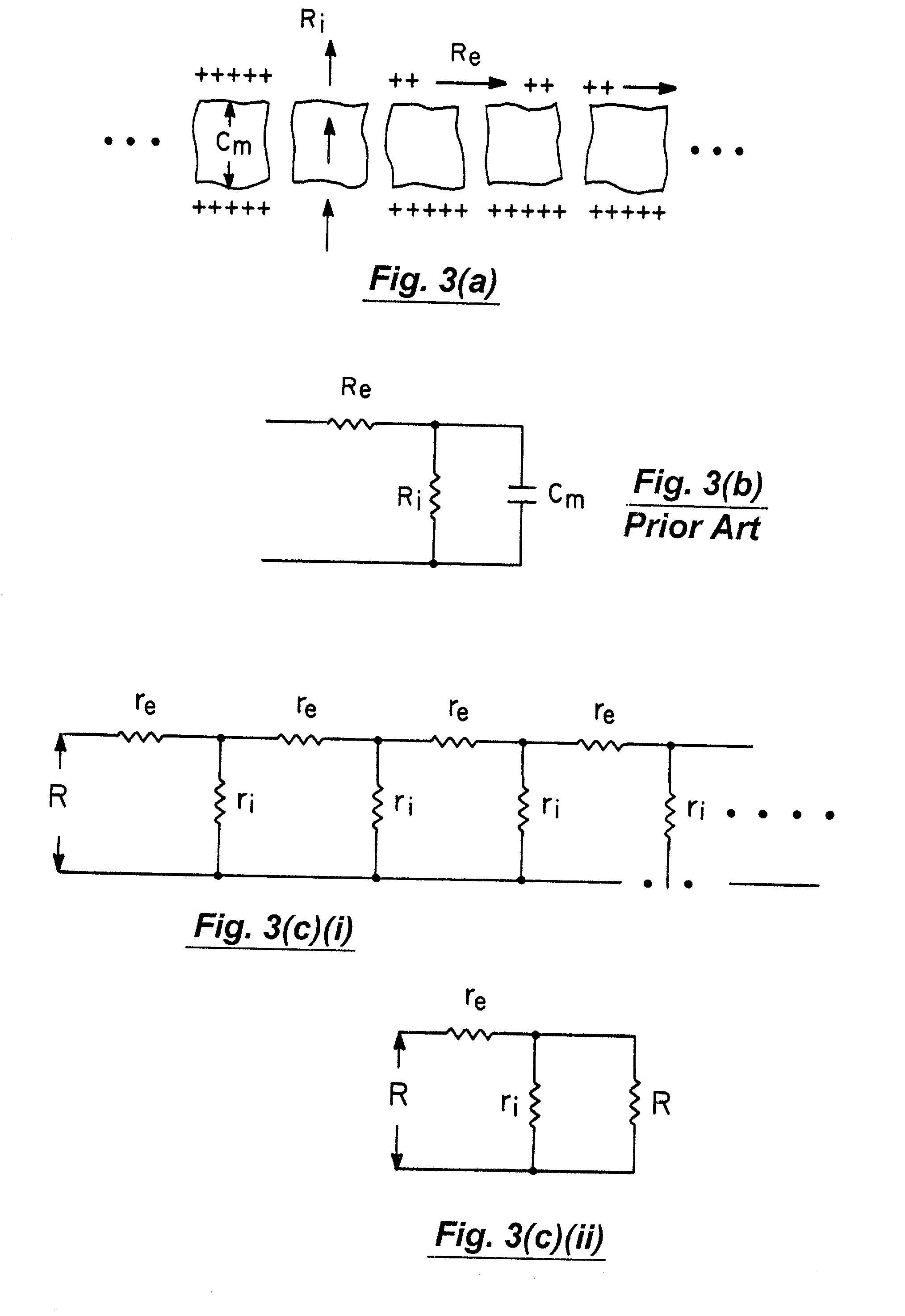
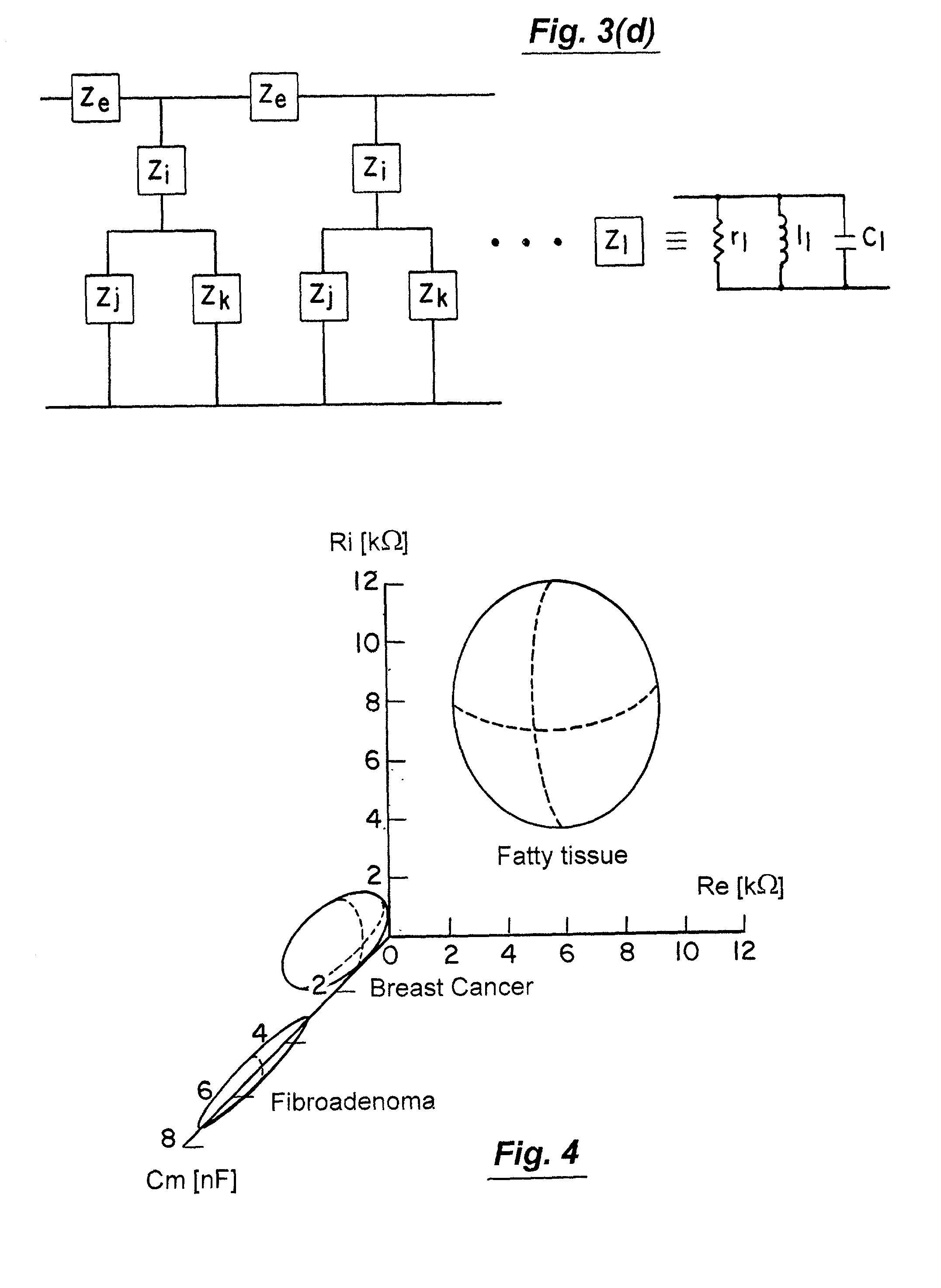
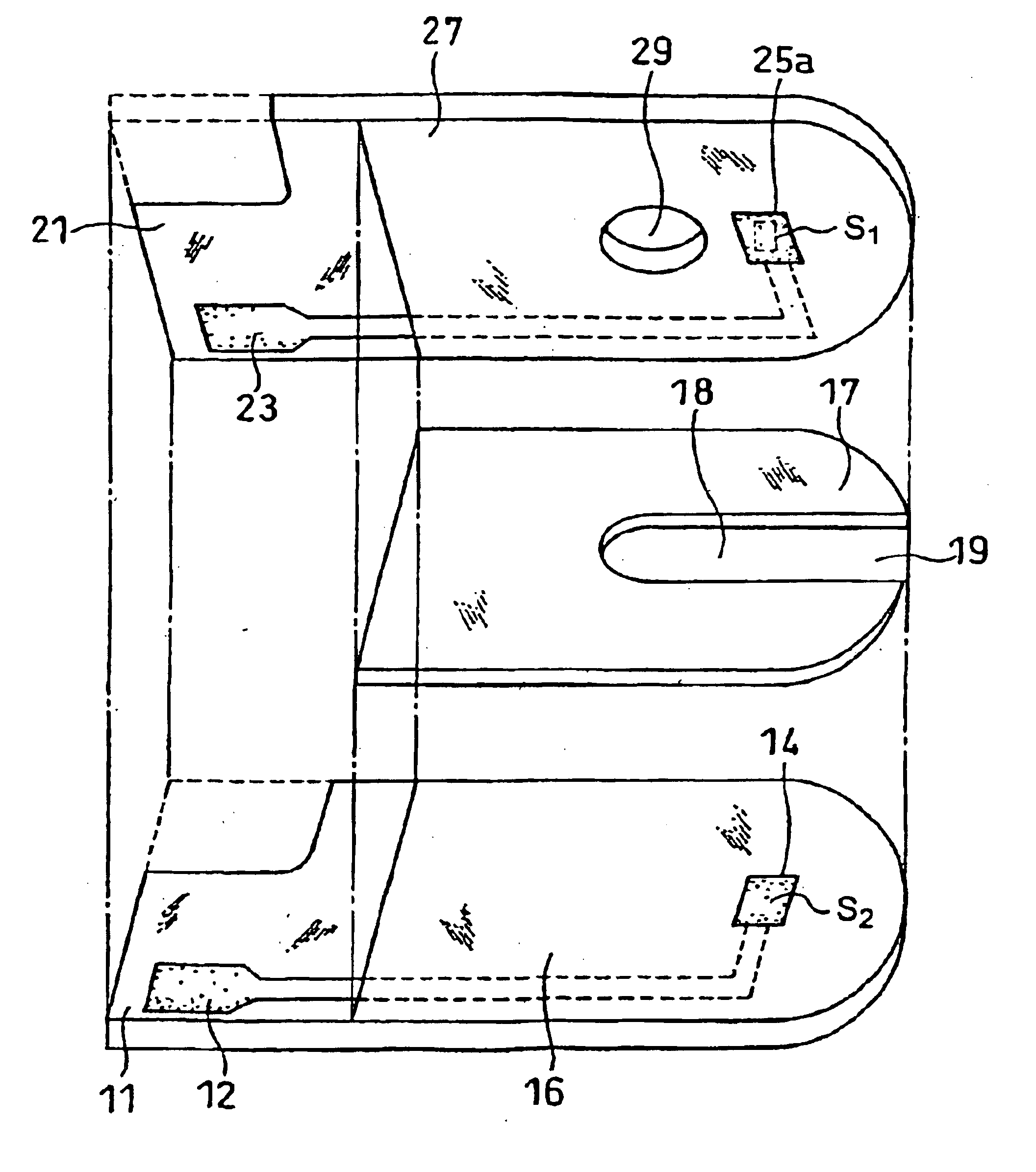
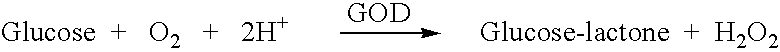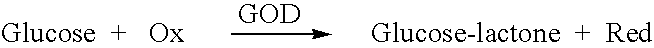Patents
Literature
2613results about "Material impedance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
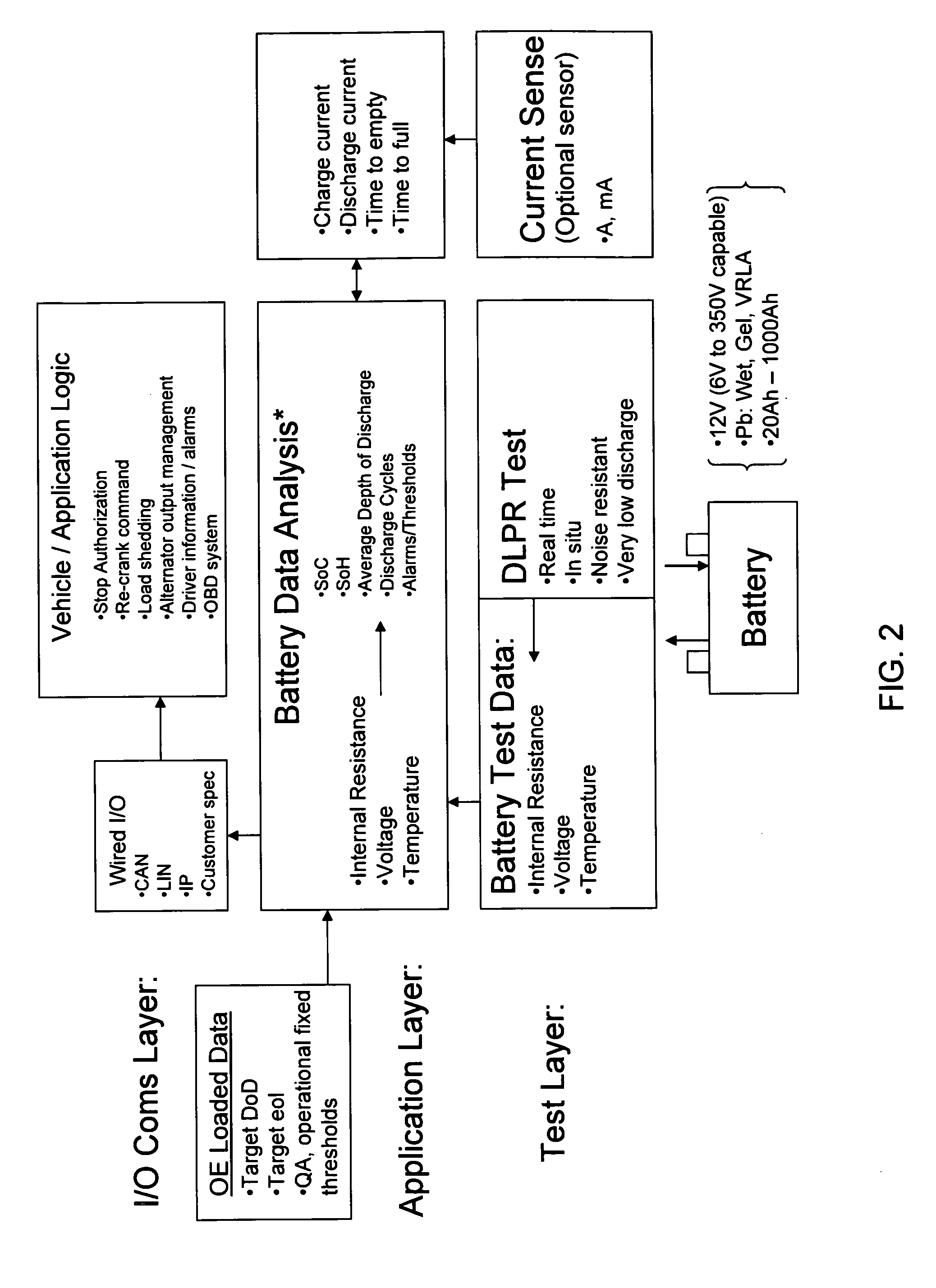
Analyte measurement
InactiveUS20040096959A1Low viscosityMore suitedBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectrochemical detectorAnalyte
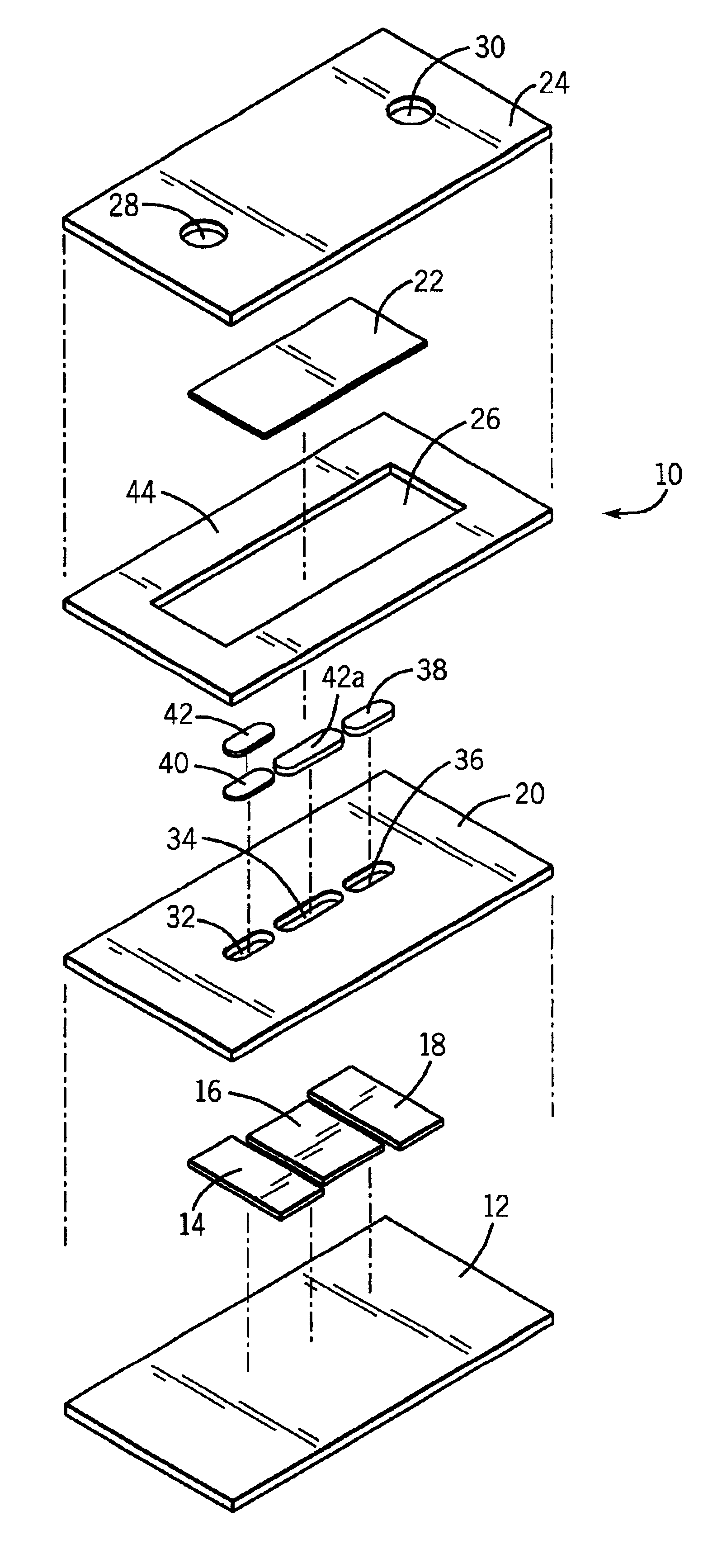
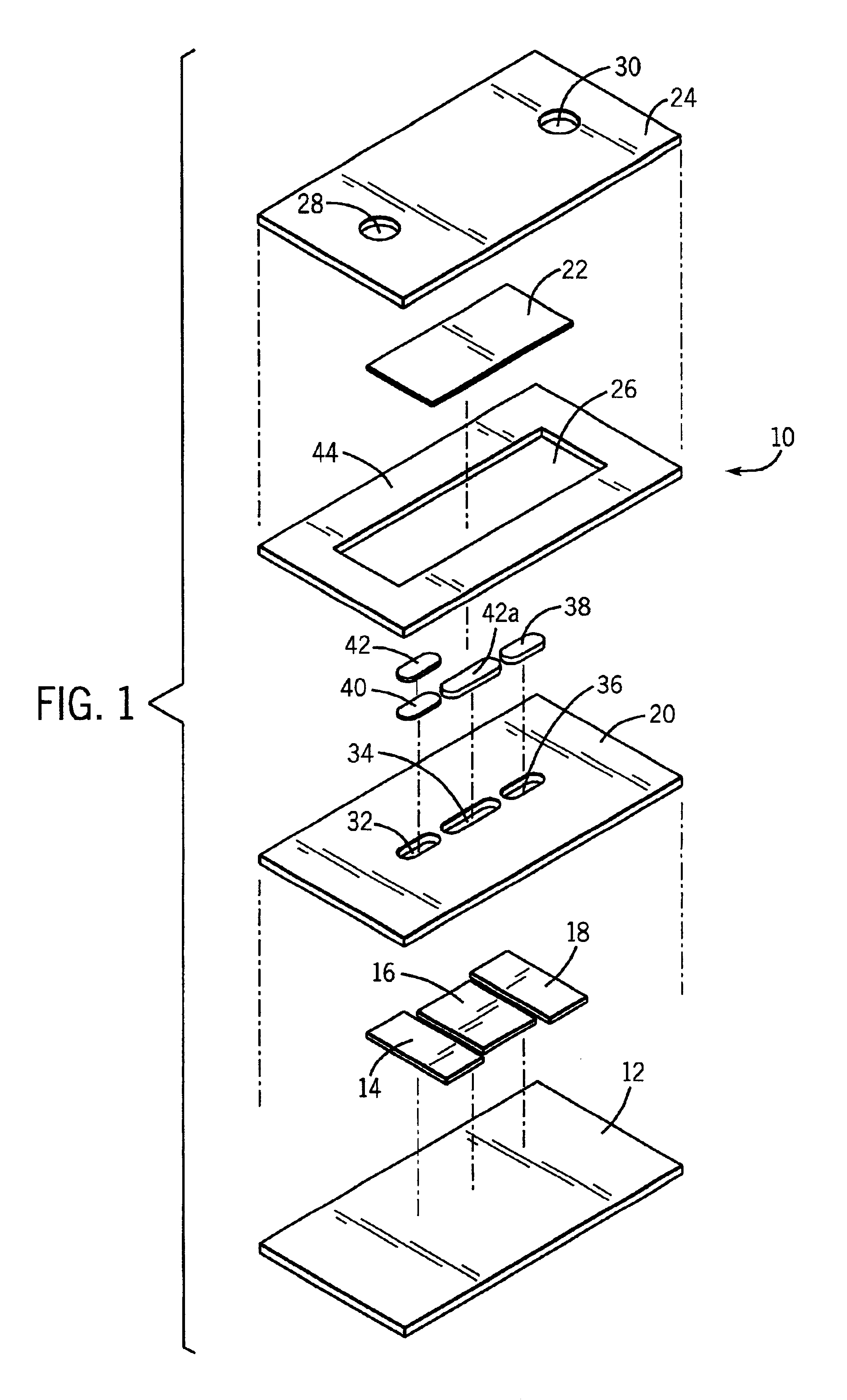
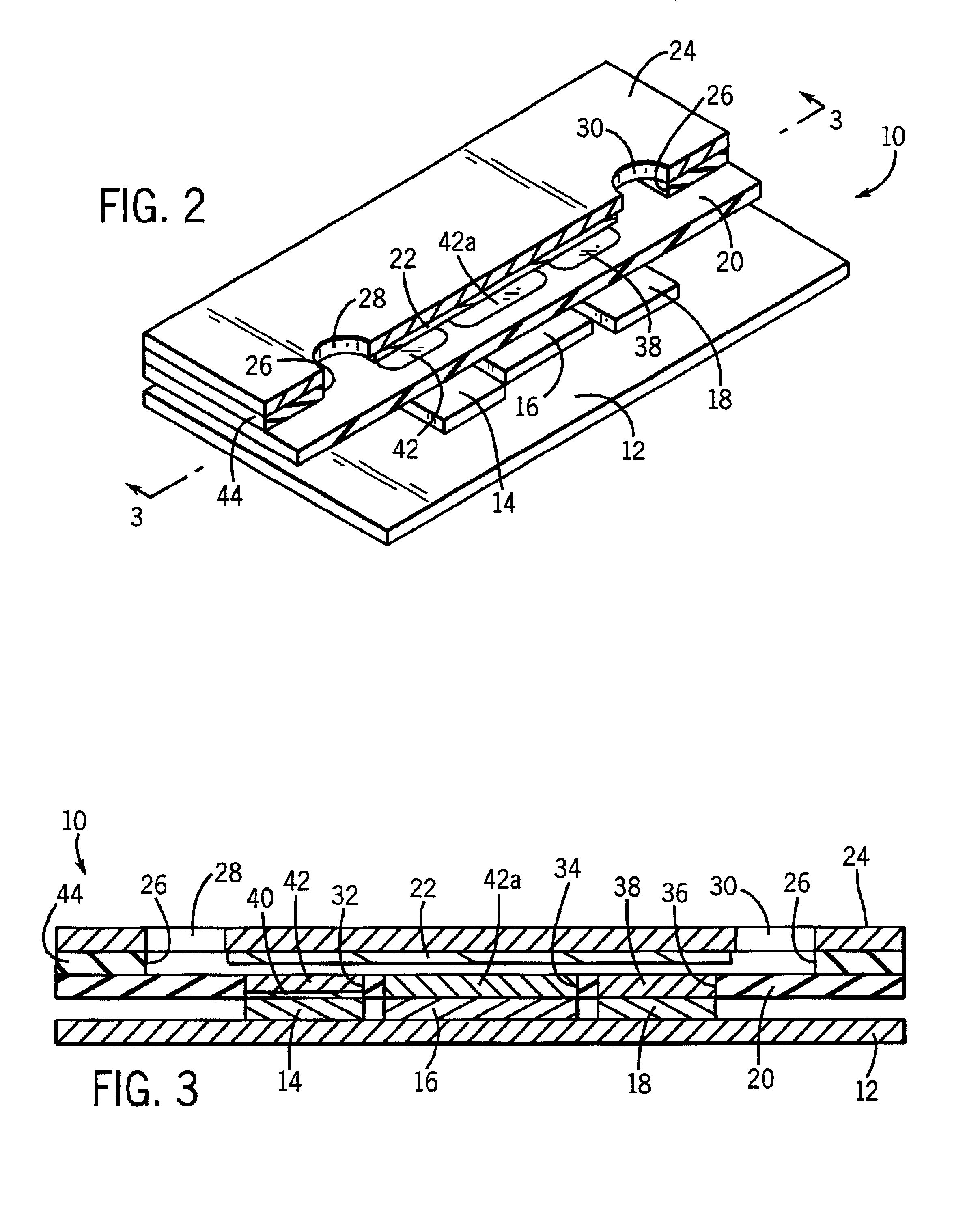
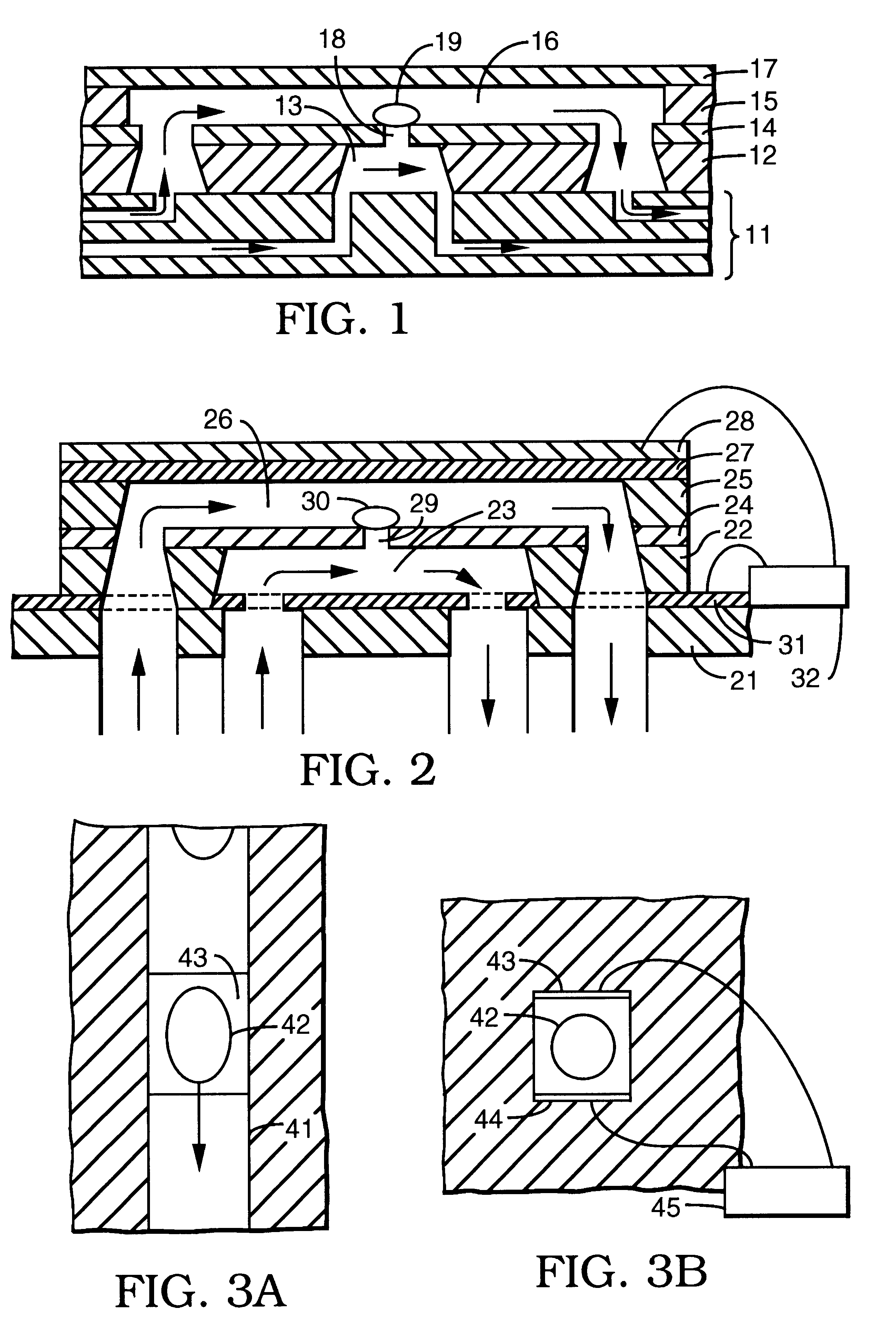
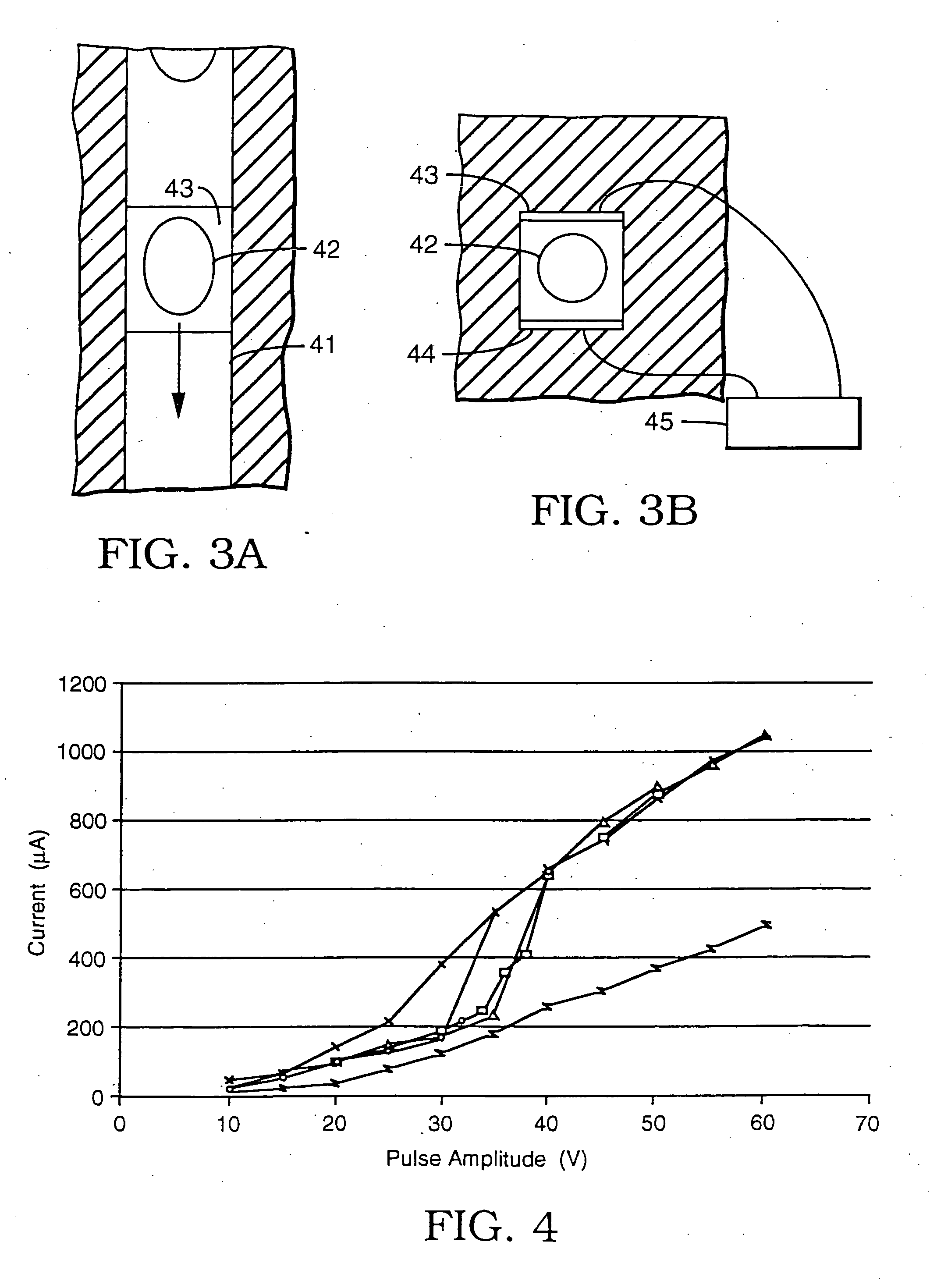
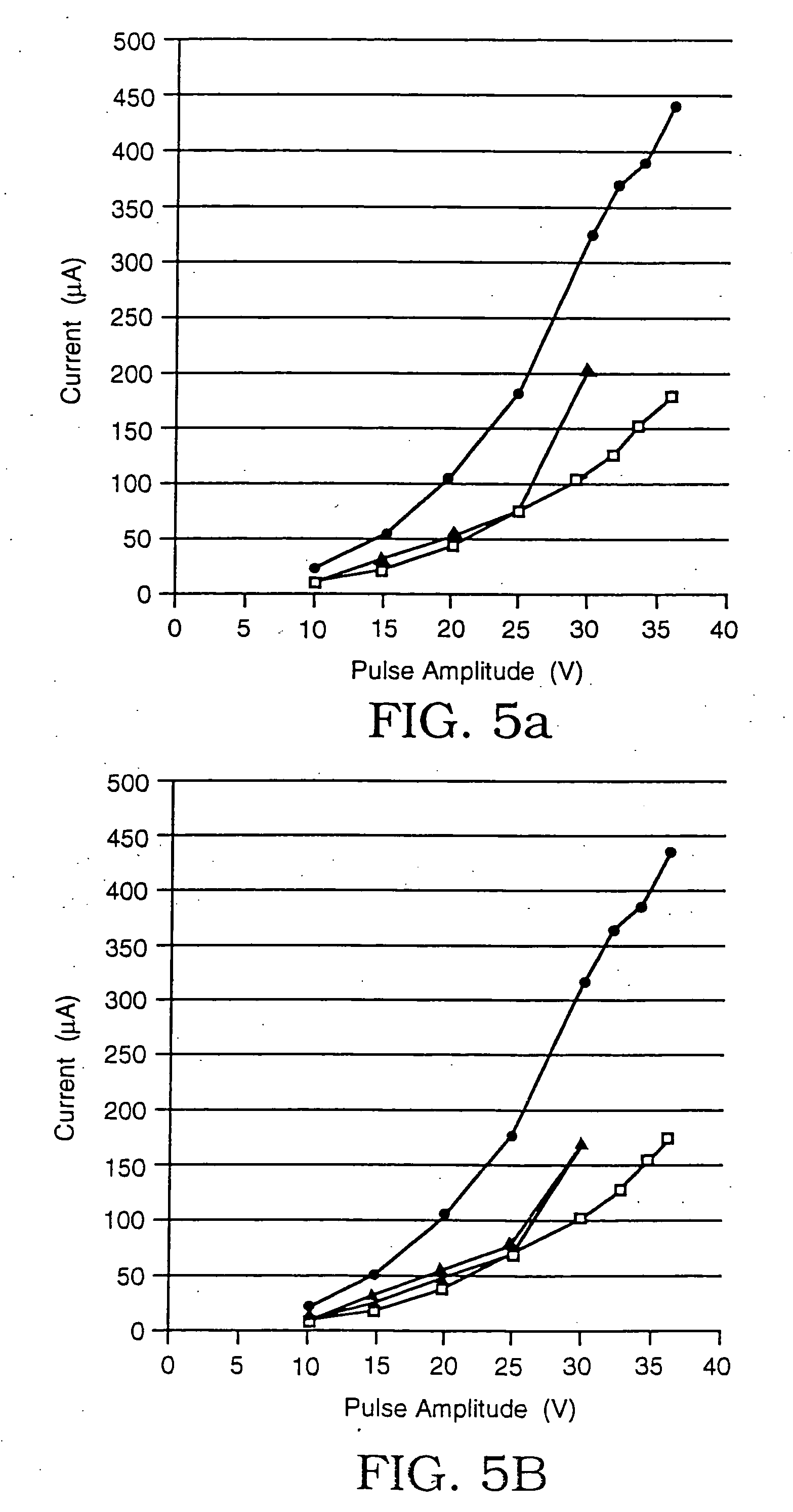
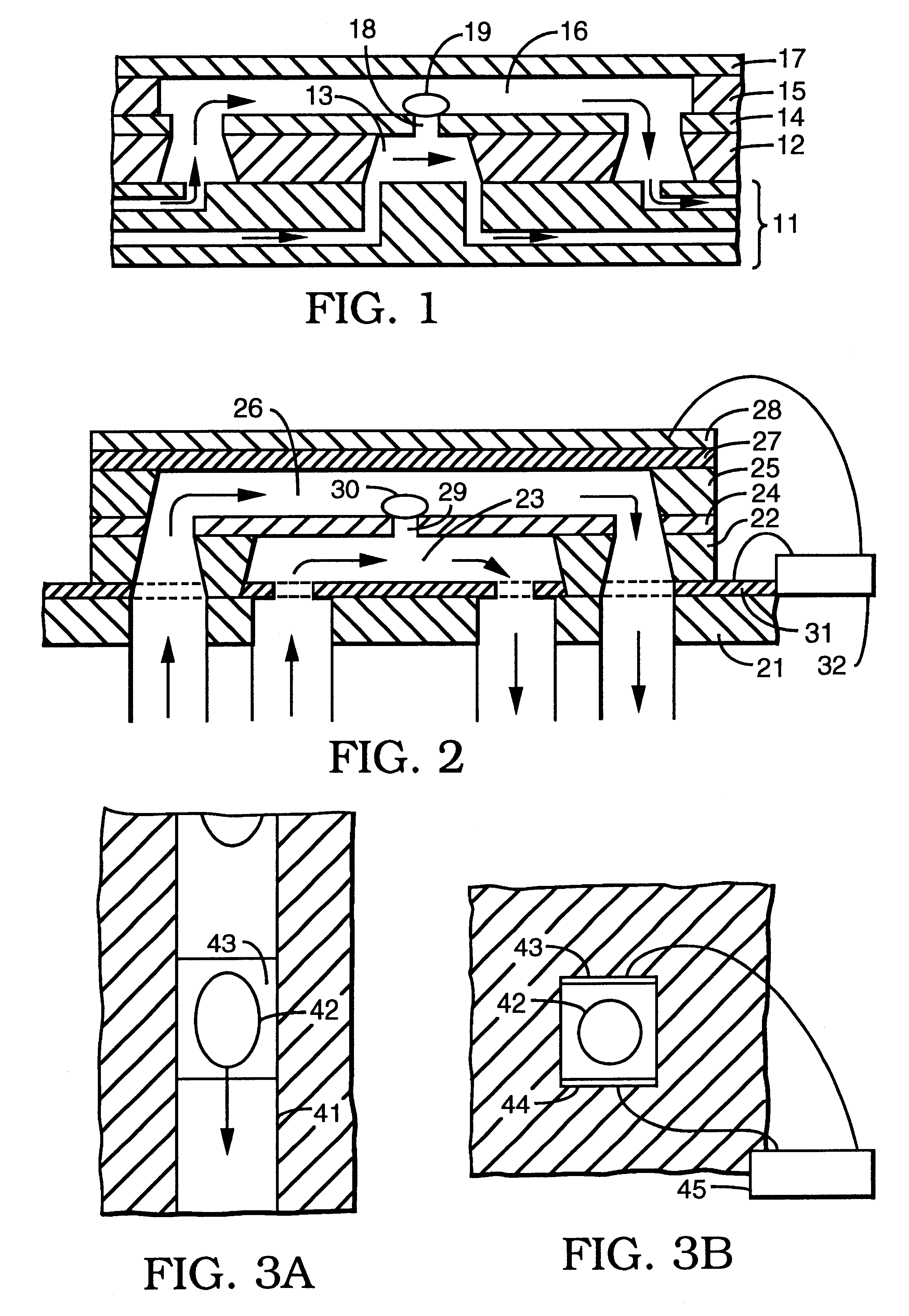
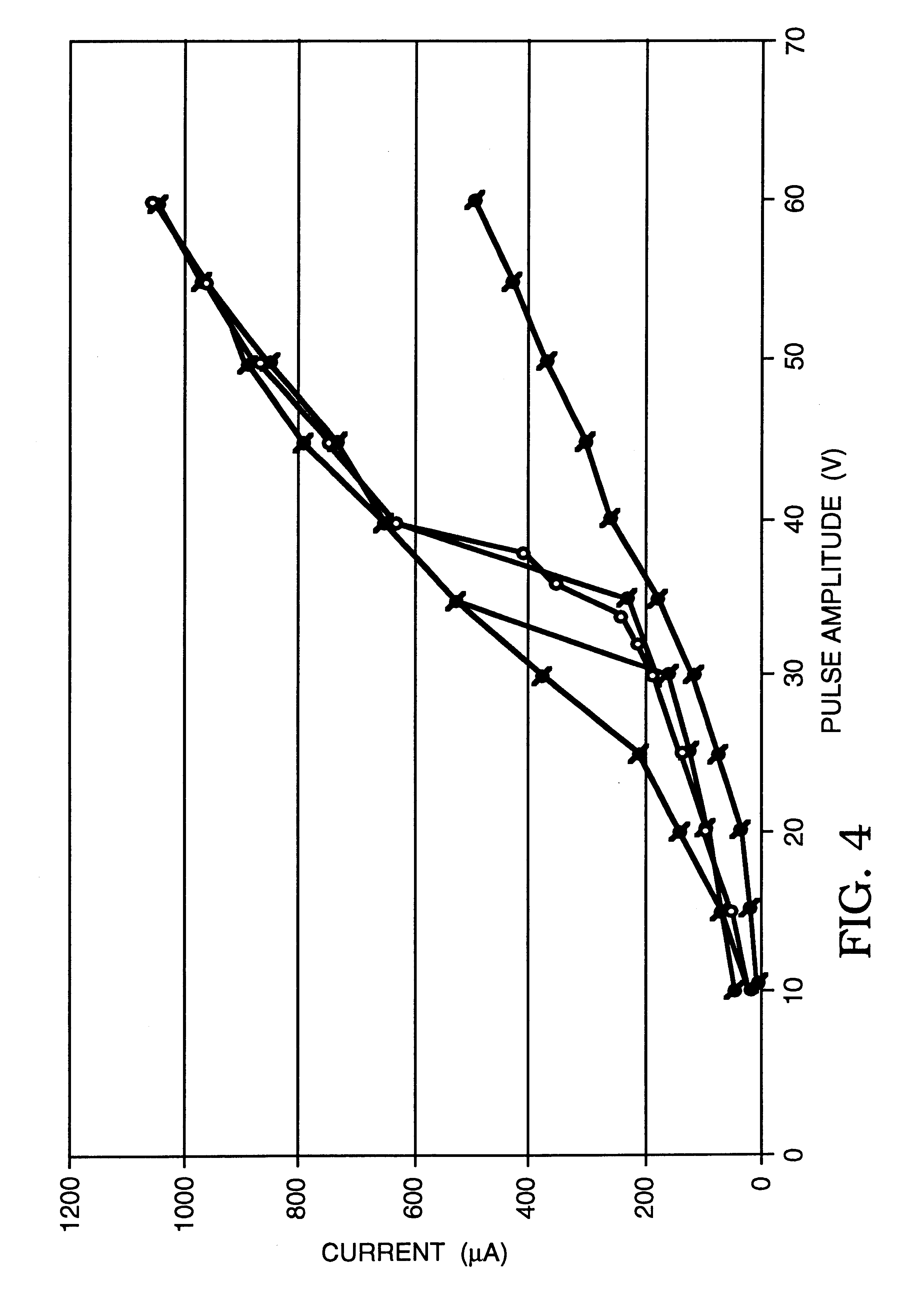
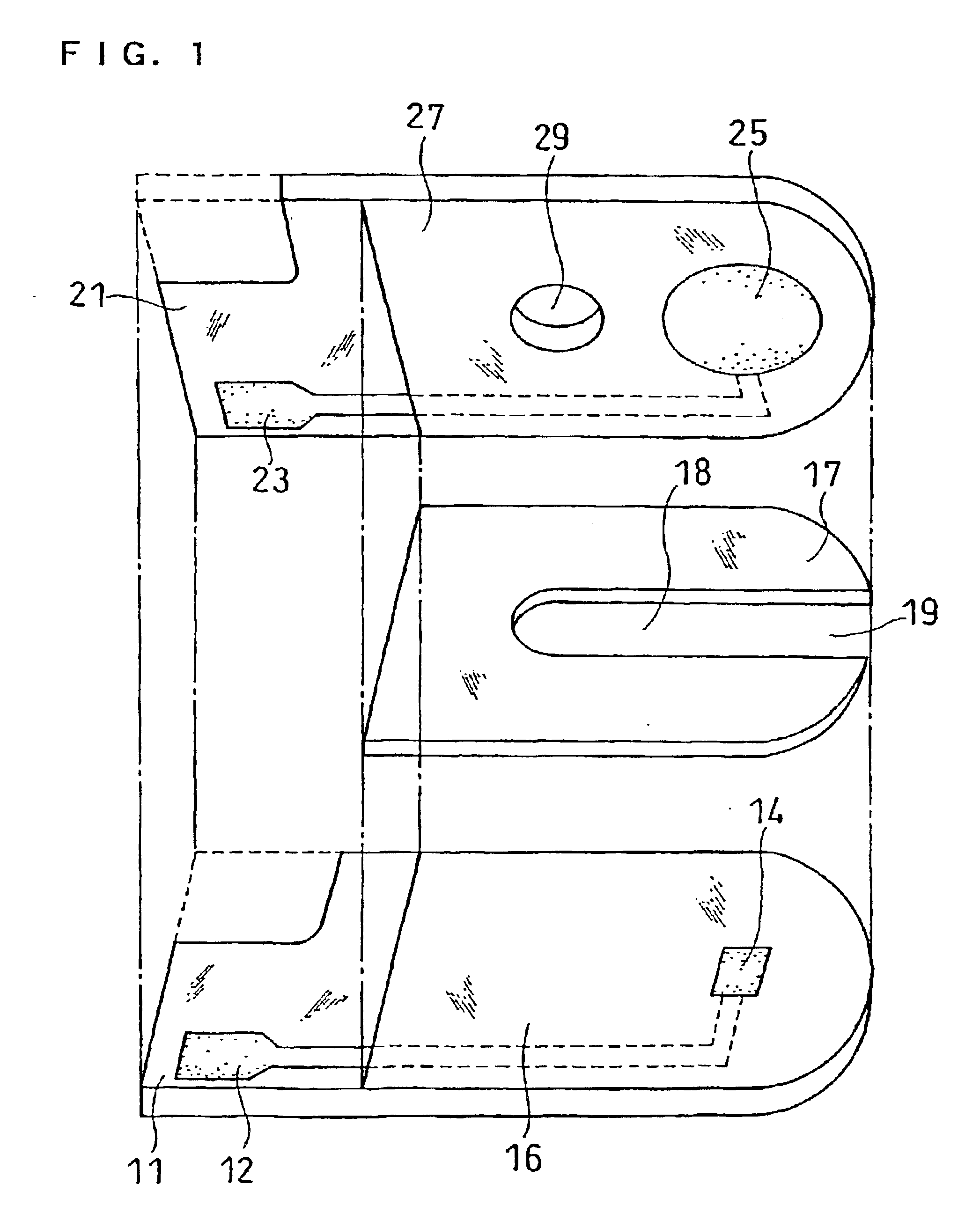
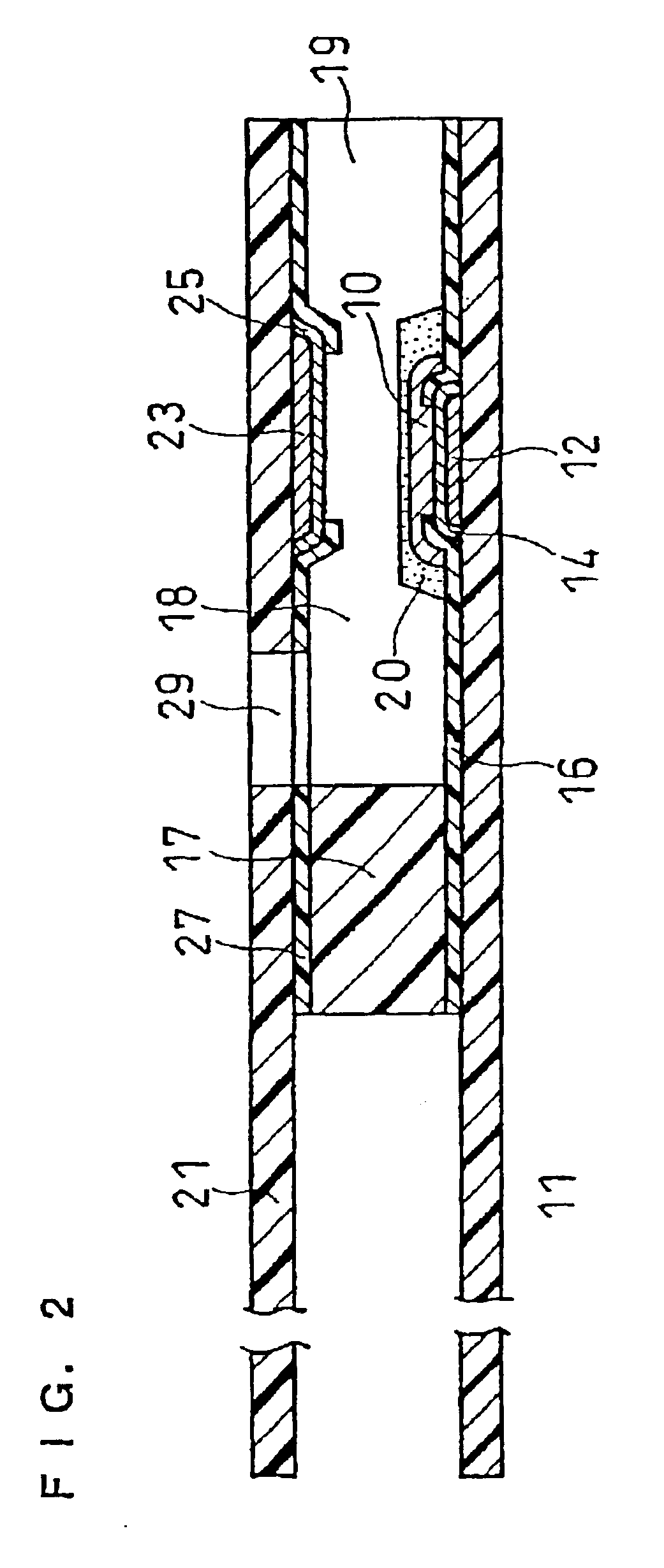
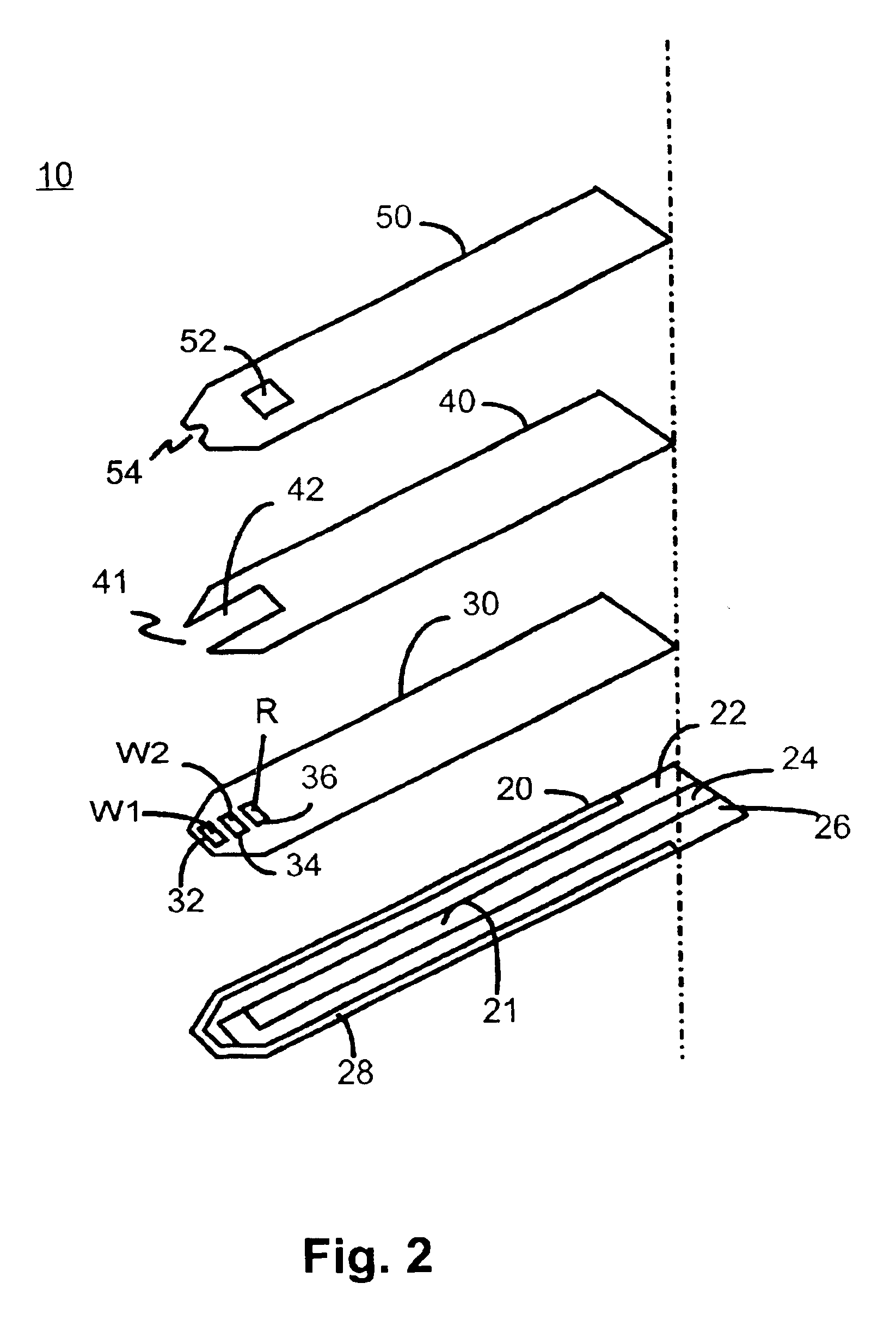
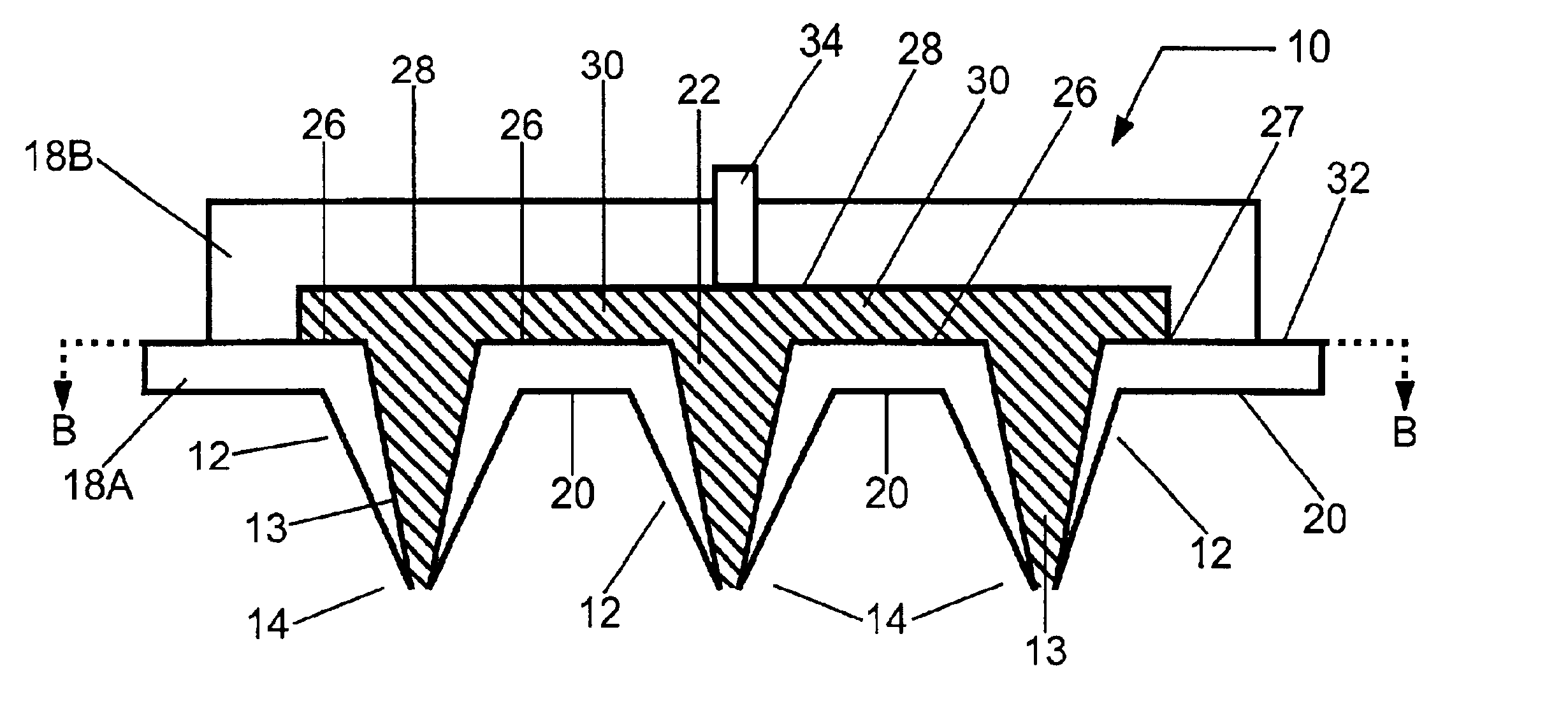
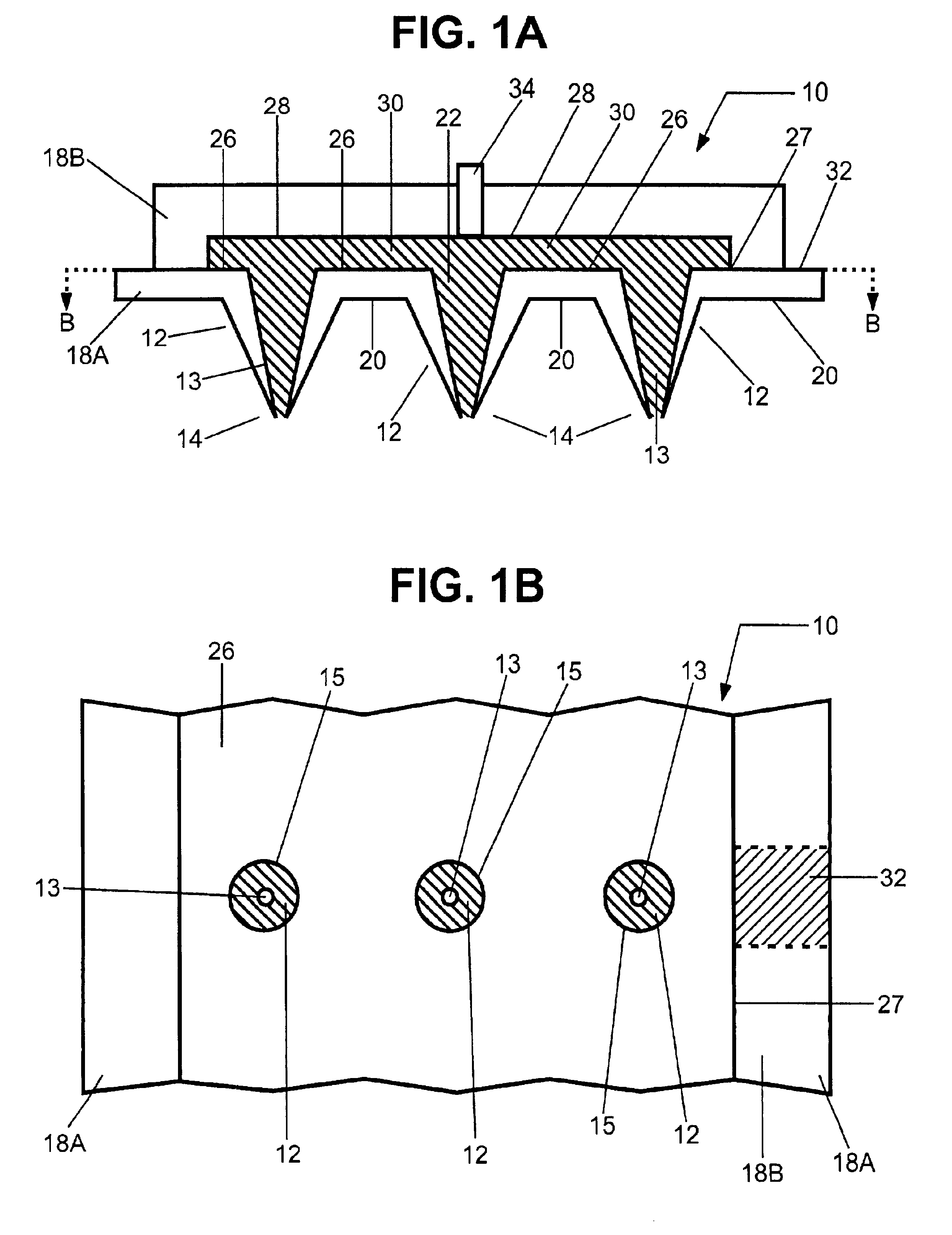
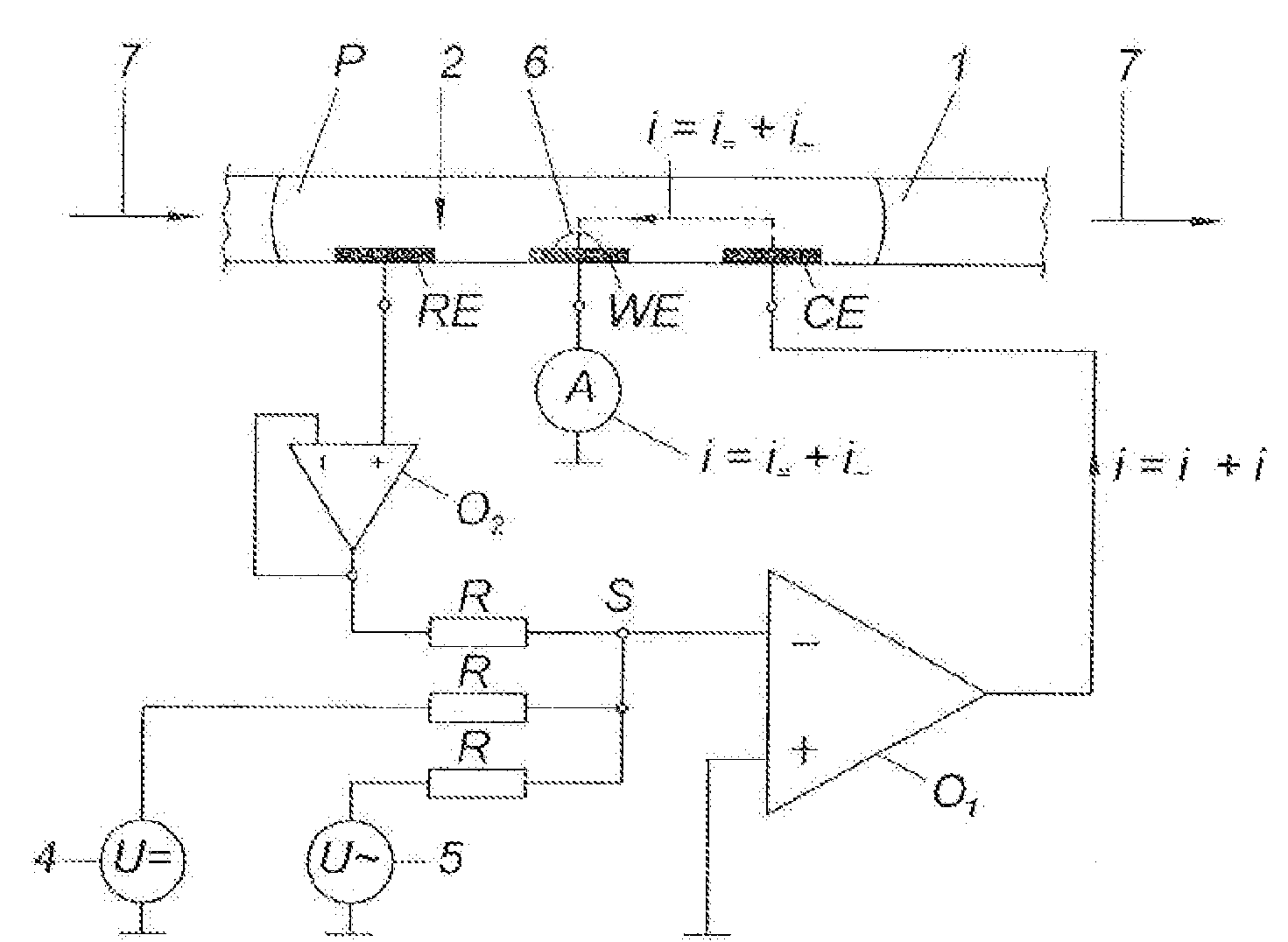
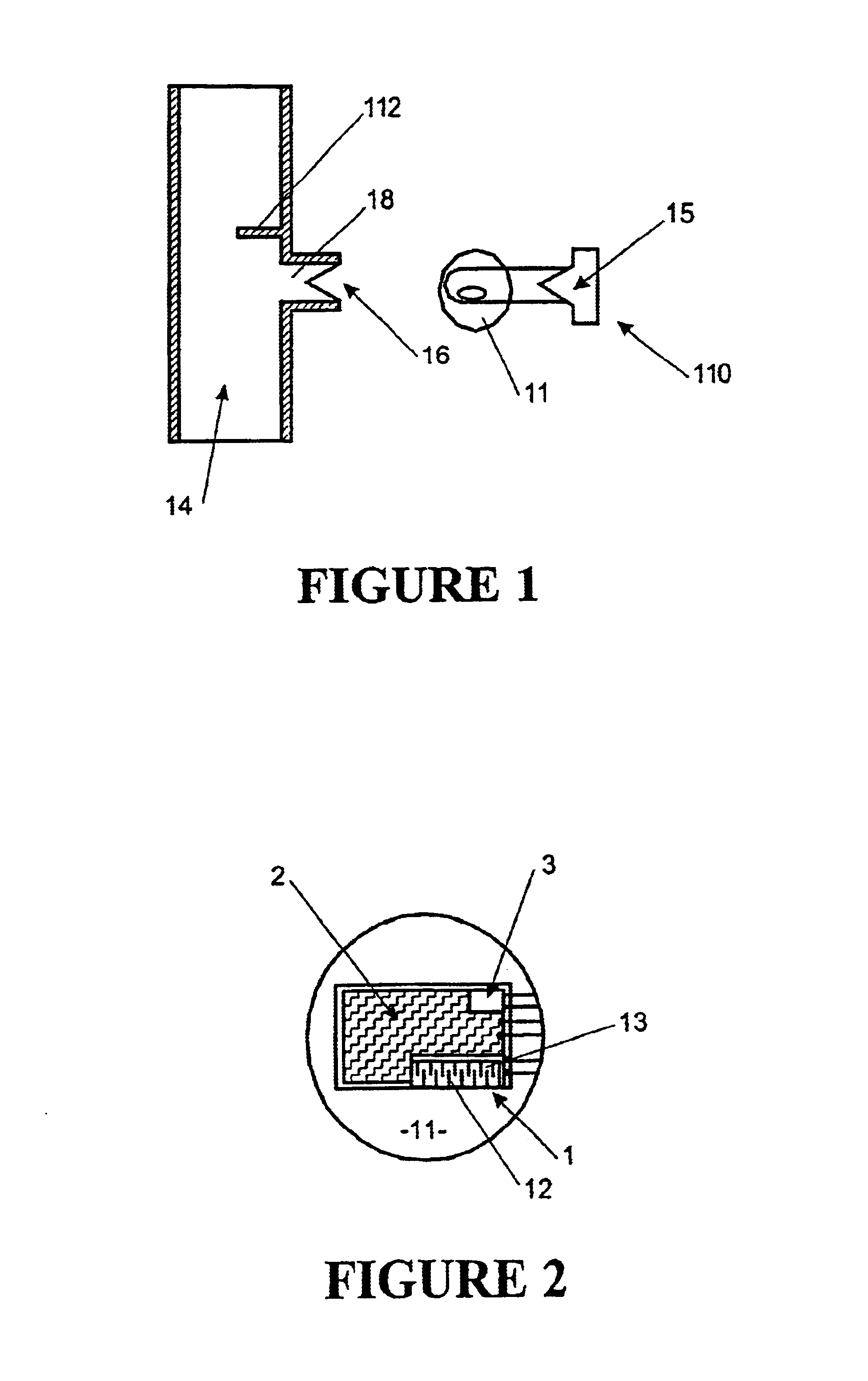
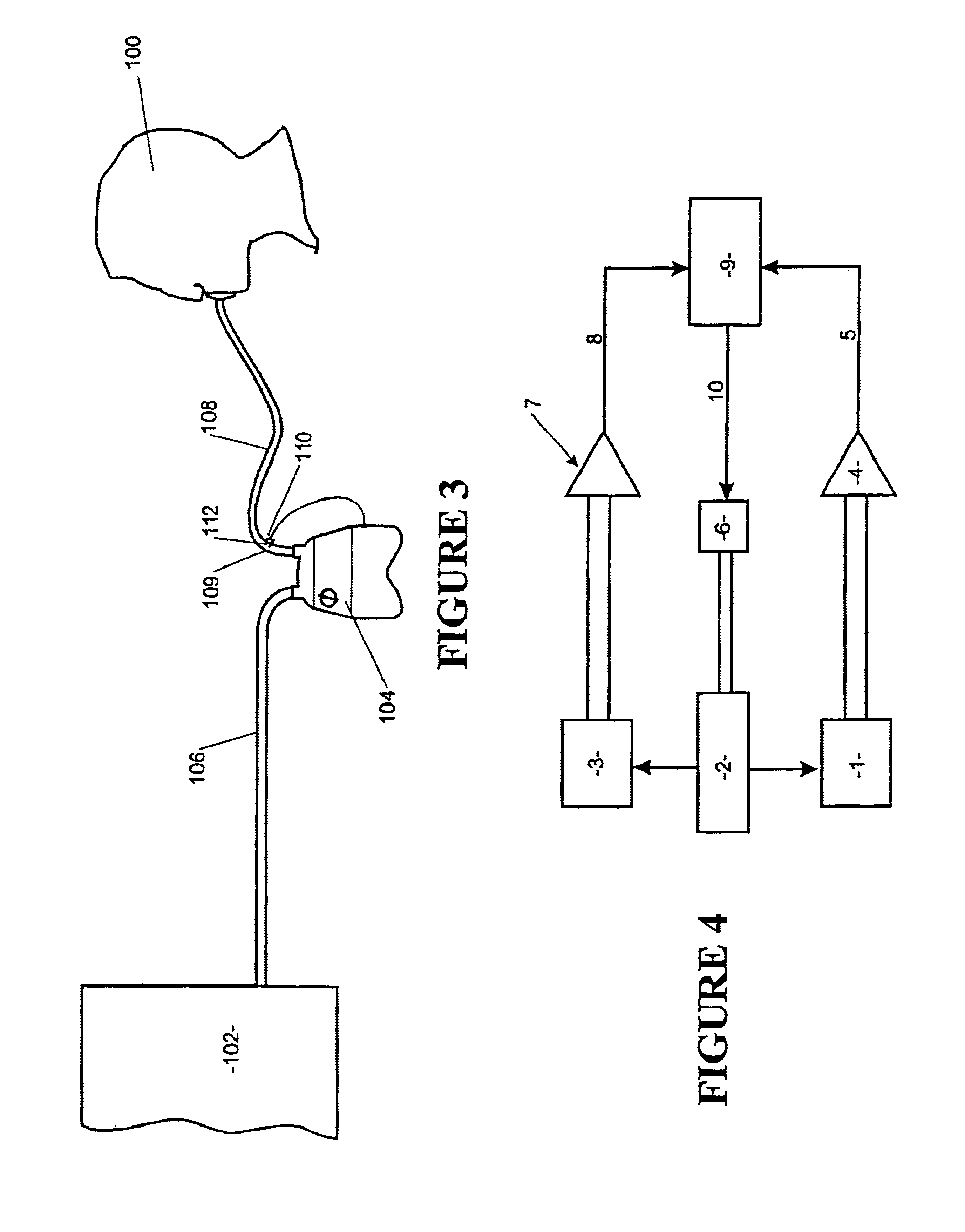
A glucose sensor in the form of a skin patch 2 has a microneedle 4 which painlessly penetrates the skin to draw out interstitial fluid. The interstitial fluid passes to a common entrance port 7. A series of microchannels 8 is provided on the skin patch. The fluid drawn onto the patch is selectively switched between a number of microchannels 8 by means of electro-osmotic pumps 10 and hydrophobic gates 12. Each microchannel 8 has an electrochemical detector 11 for sensing gluocse concentration. Also disclosed is a monlithic device with an integrated lance 83.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC +1
Sensor having electrode for determining the rate of flow of a fluid
InactiveUS6801041B2Accurate measurementMicrobiological testing/measurementVolume/mass flow by electric/magnetic effectsTarget analysisAnalyte
Sensors that are capable measuring the rate of flow of a fluid that passes over the electrodes of the sensor. In these sensors, an electrode, designated the flow rate-determining electrode, is used in conjunction with the conventional electrodes, e.g., the working electrode, the reference electrode, and the counter electrode, to determine the rate of flow of the fluid. In one aspect, this invention provides a sensor for measuring the concentration of an analyte in a sample of fluid when the sample flows continuously over the electrodes of the sensor, especially when the rate of flow of the sample is relatively low. In another aspect, this invention provides a method for measuring the concentration of an analyte in a sample of fluid, wherein the rate of flow of the sample varies during the period of time that the sensor is in place. In a preferred embodiment, the sensor employs four electrodes, namely, a working electrode, a reference electrode, a counter electrode, and a flow rate-determining electrode. Alternatively, a single electrode that performs both the function of the reference electrode and the function of the counter electrode can replace the reference electrode and the counter electrode. In addition, a dummy electrode or a blank electrode can be used to compensate for interference from electrochemically active species. The reagent(s) specific to the analyte of interest is required to be deposited on the working electrode.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Device for measuring blood coagulation and method thereof
InactiveUS7005857B2Simple and inexpensiveResistance/reactance/impedenceSurgeryCapacitanceBlood coagulations
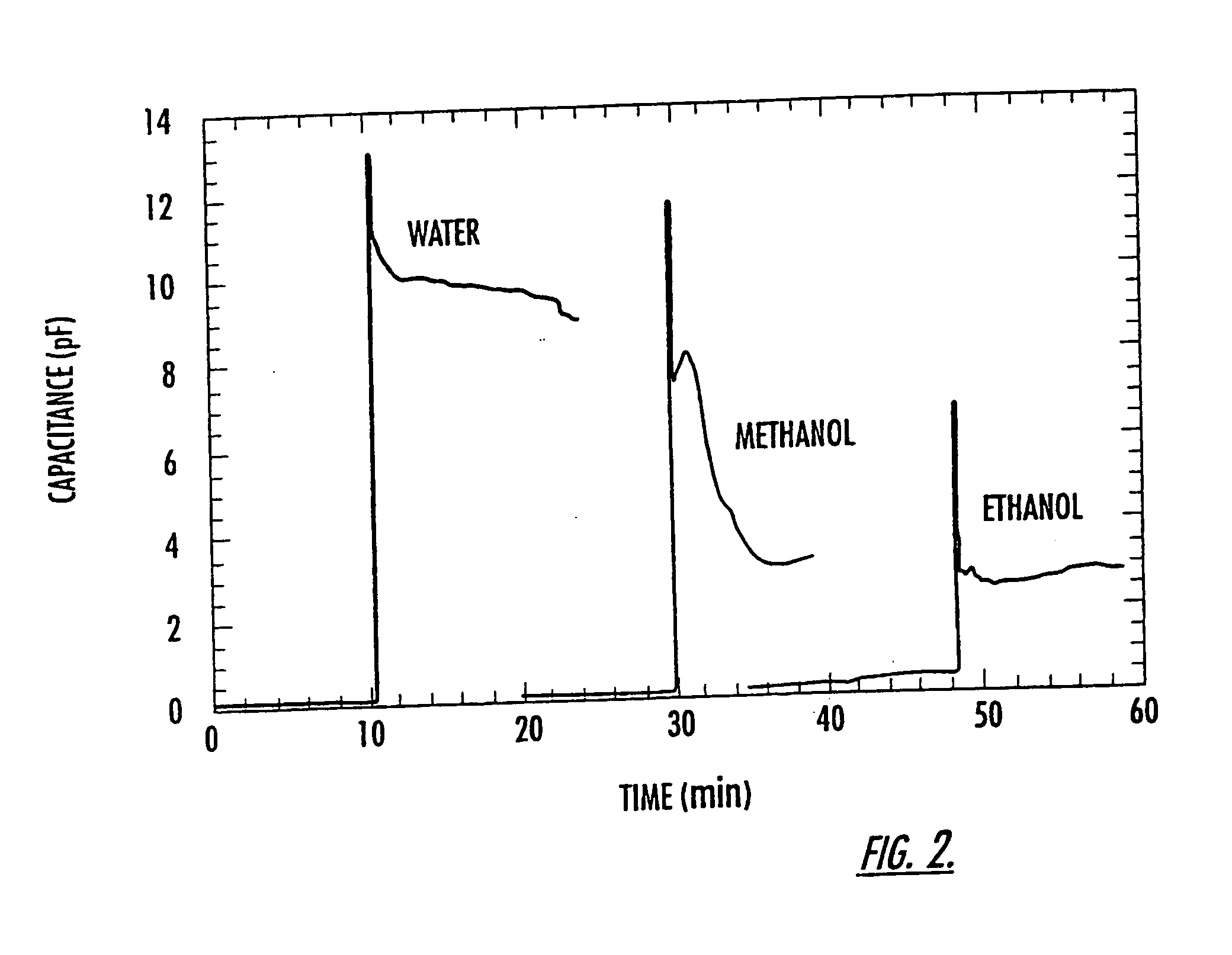
A device and method for measuring clotting times in a fluid, typically blood, within a microchannel, with the onset of clotting being determined by measurement of the rate of change, or the value, of capacitance or impedance between two electrodes situated on either side of the microchannel. The device includes an upper support member and a lower support member with a microchannel formed therein. The device also includes electrodes situated along the length of the microchannel.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
System and method for analyte measurement
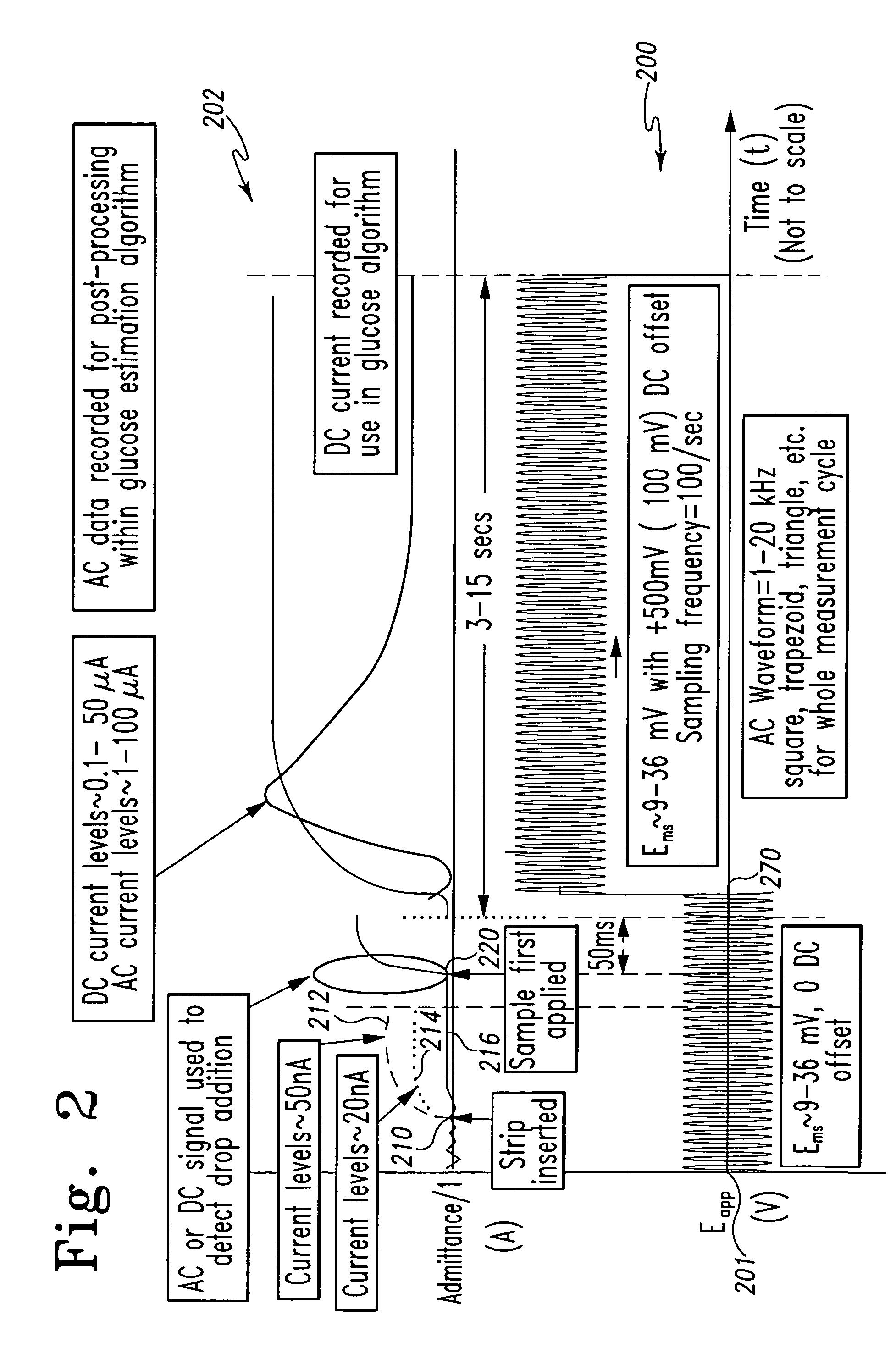
InactiveUS7338639B2Analysis using chemical indicatorsMaterial thermal conductivityAnalyteExcitation signal
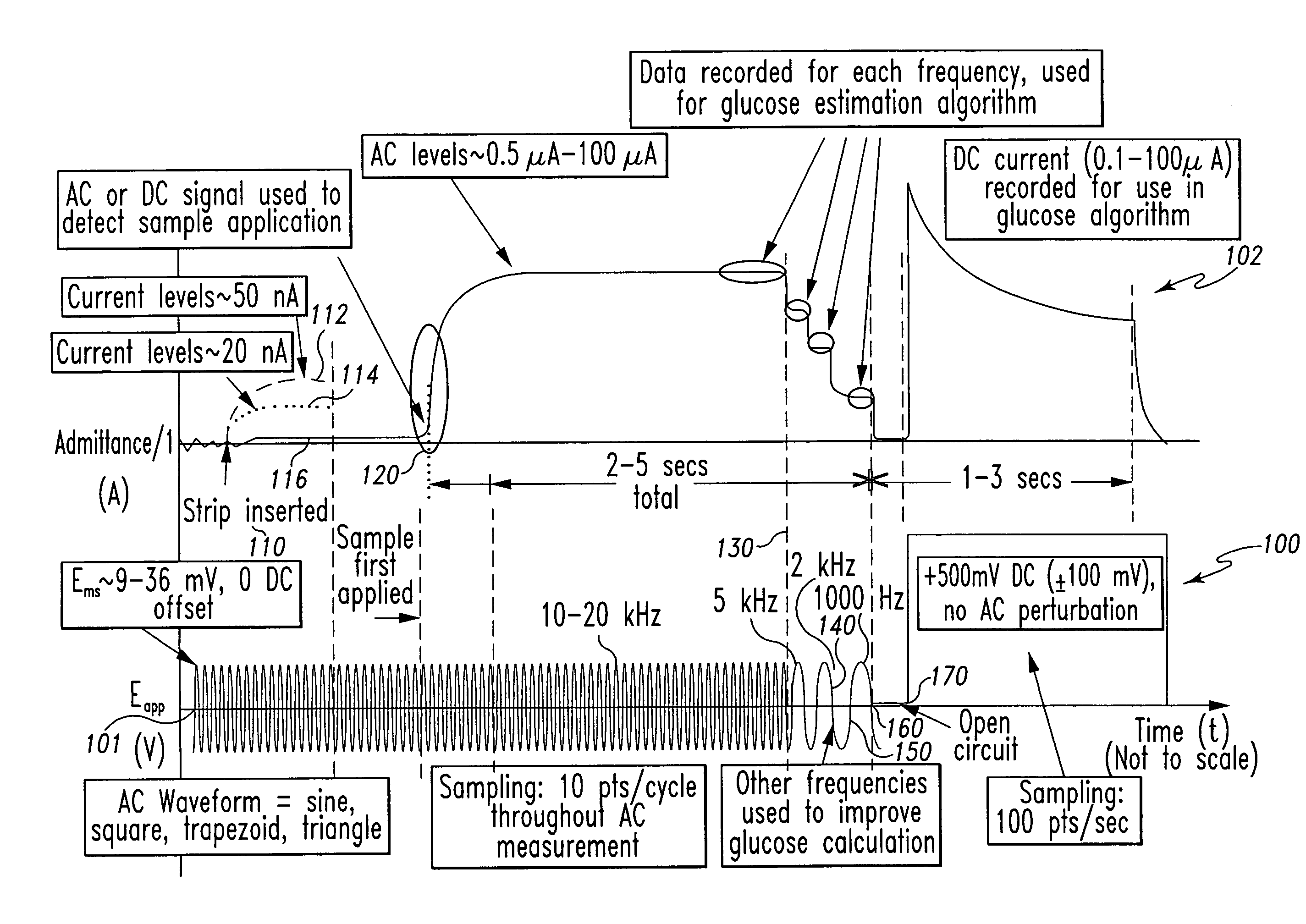
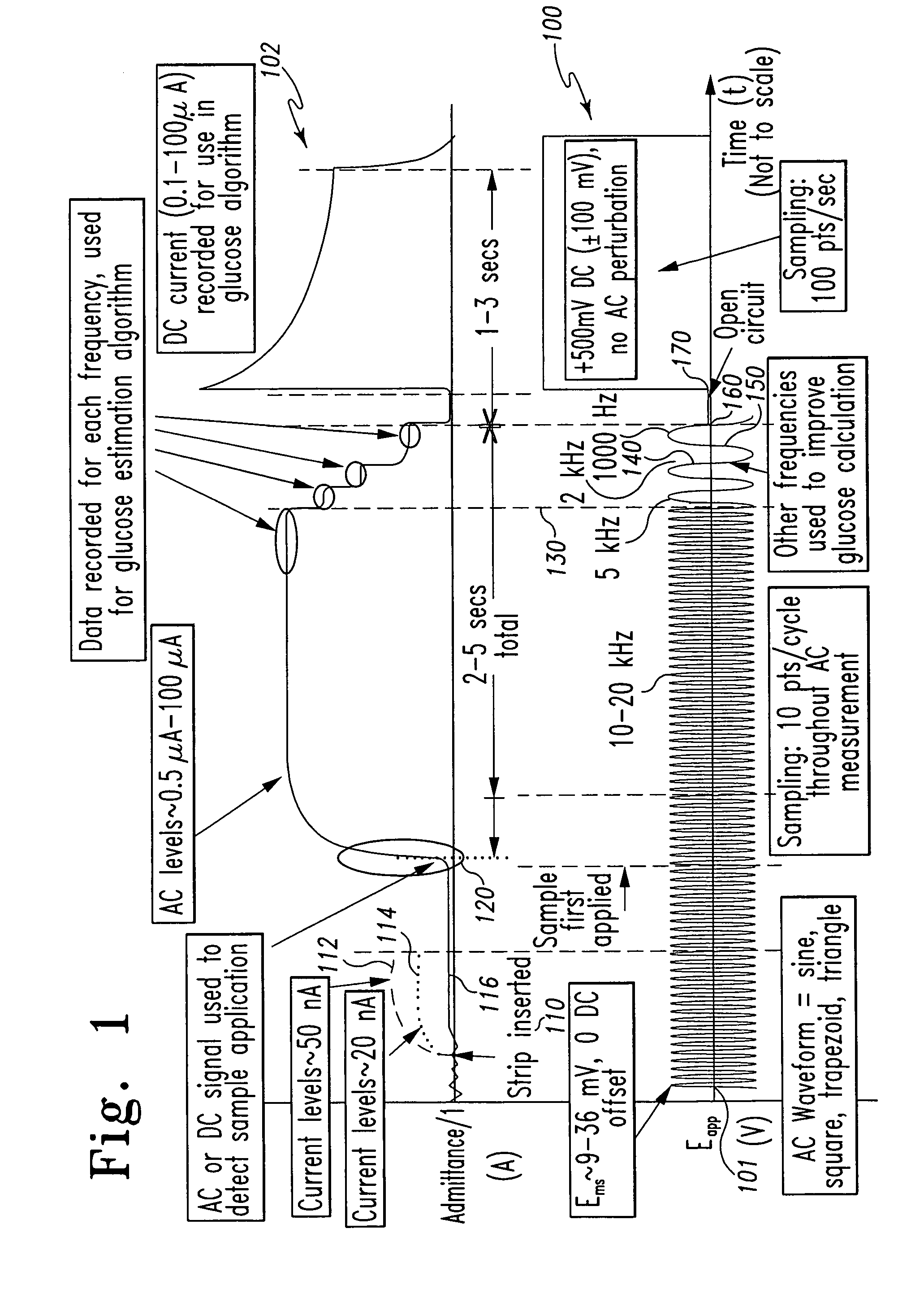
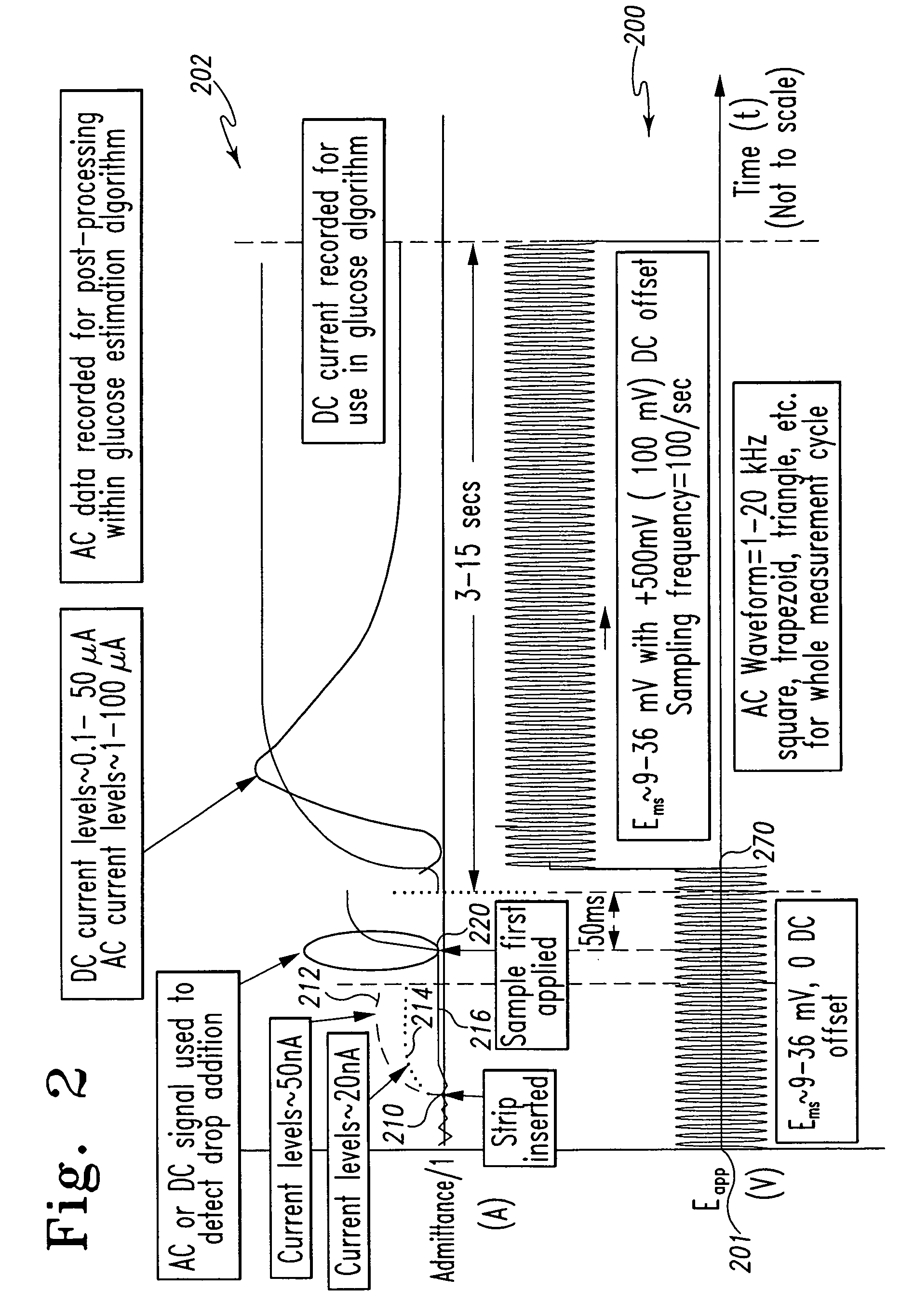
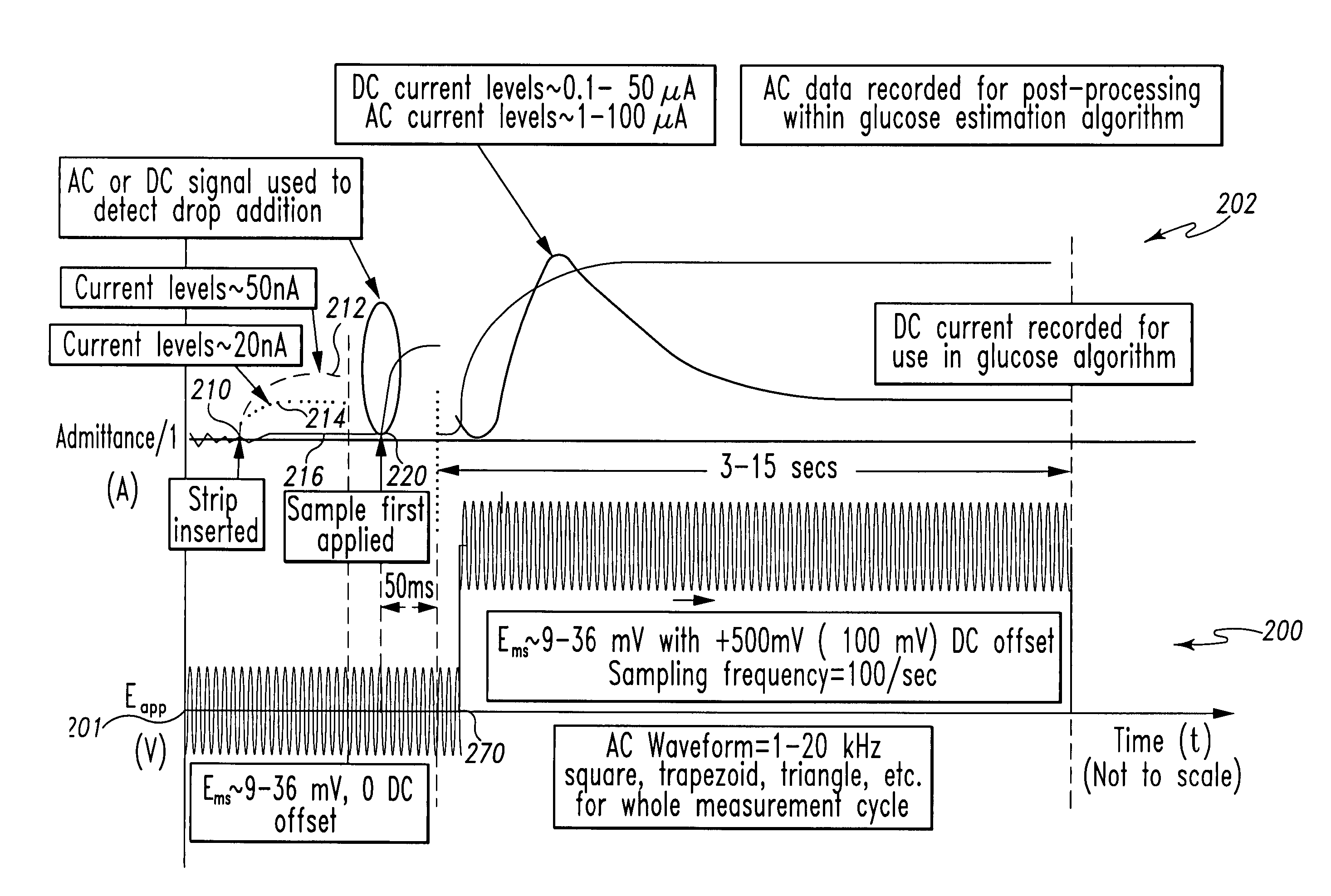
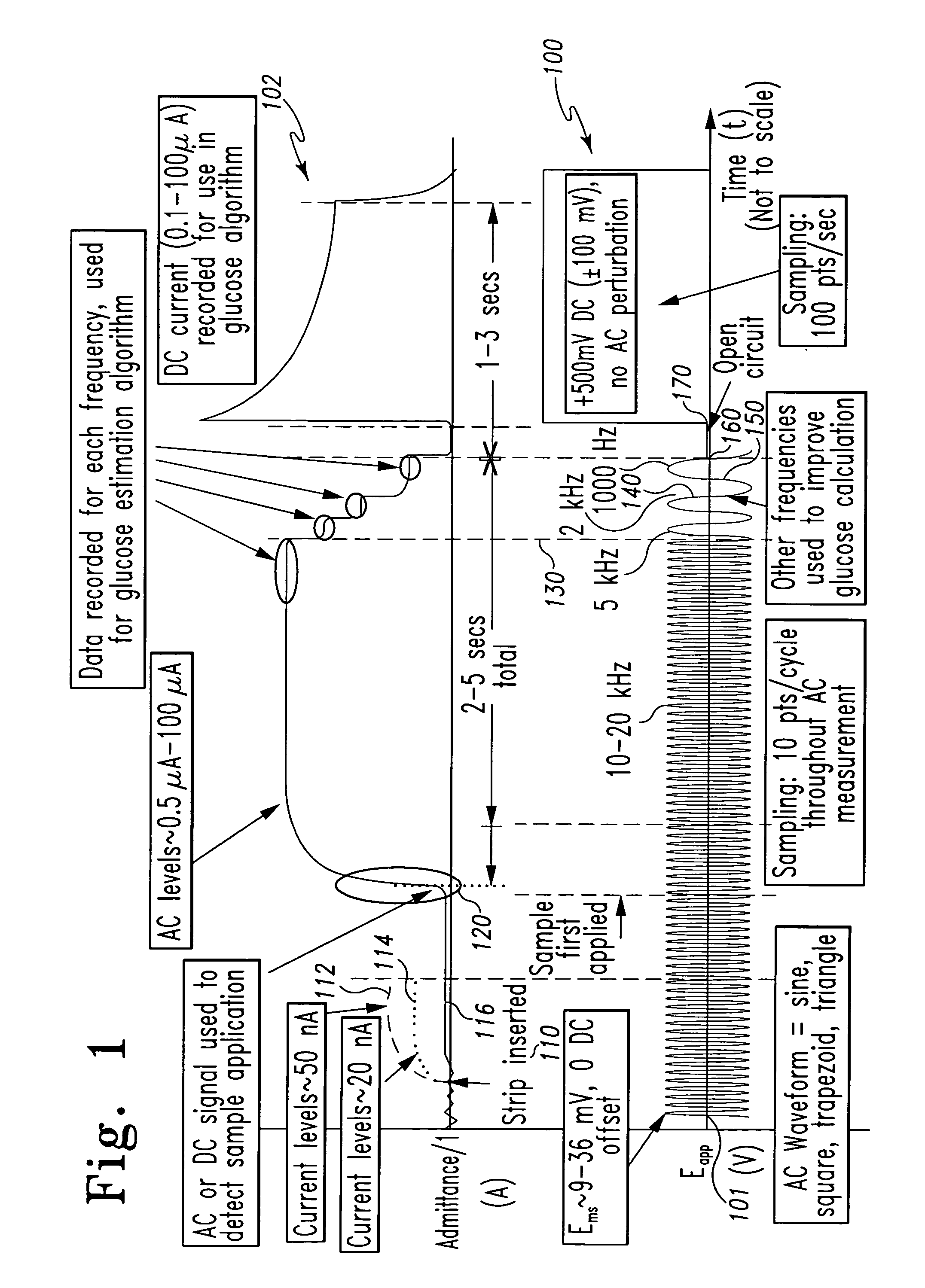
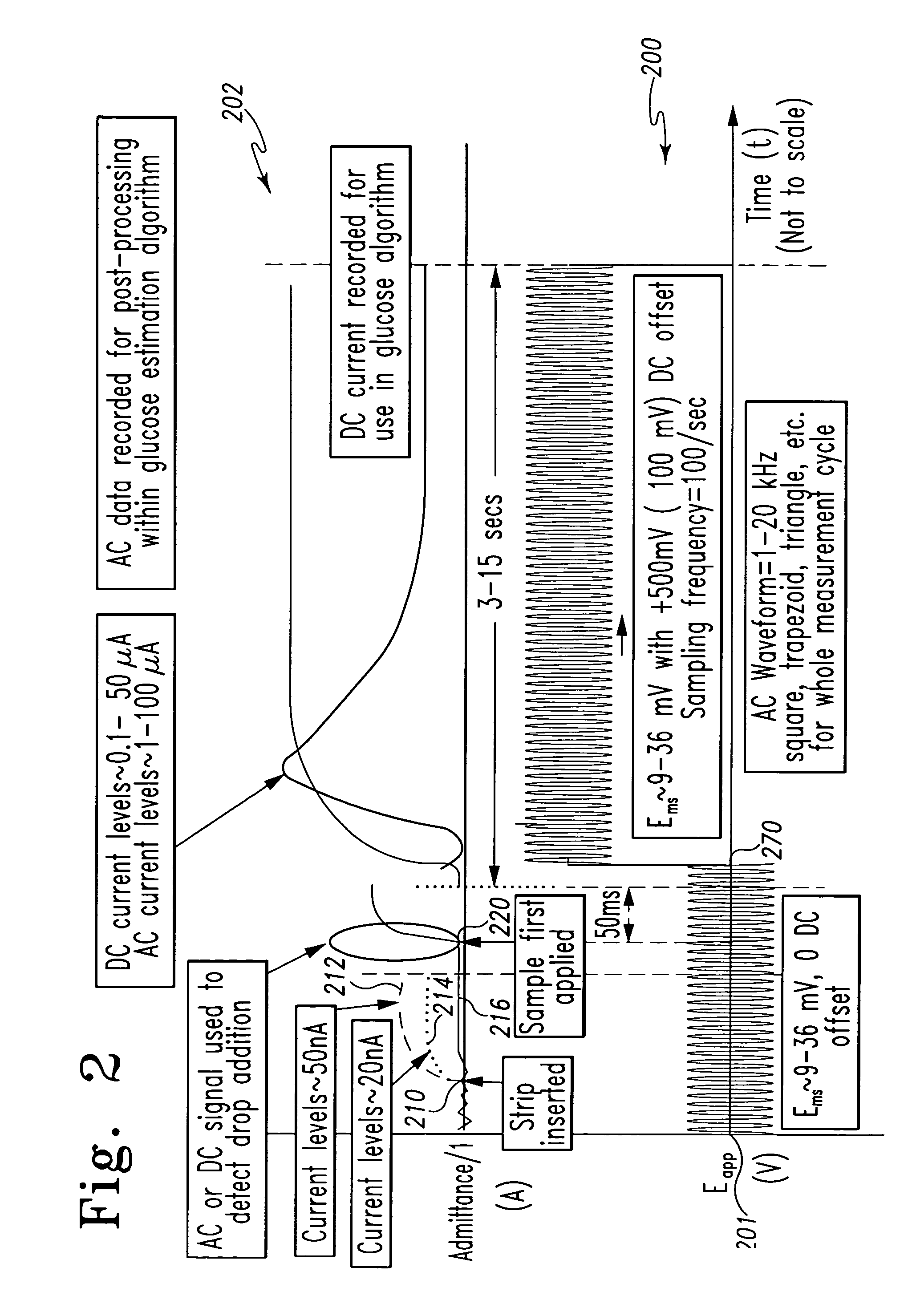
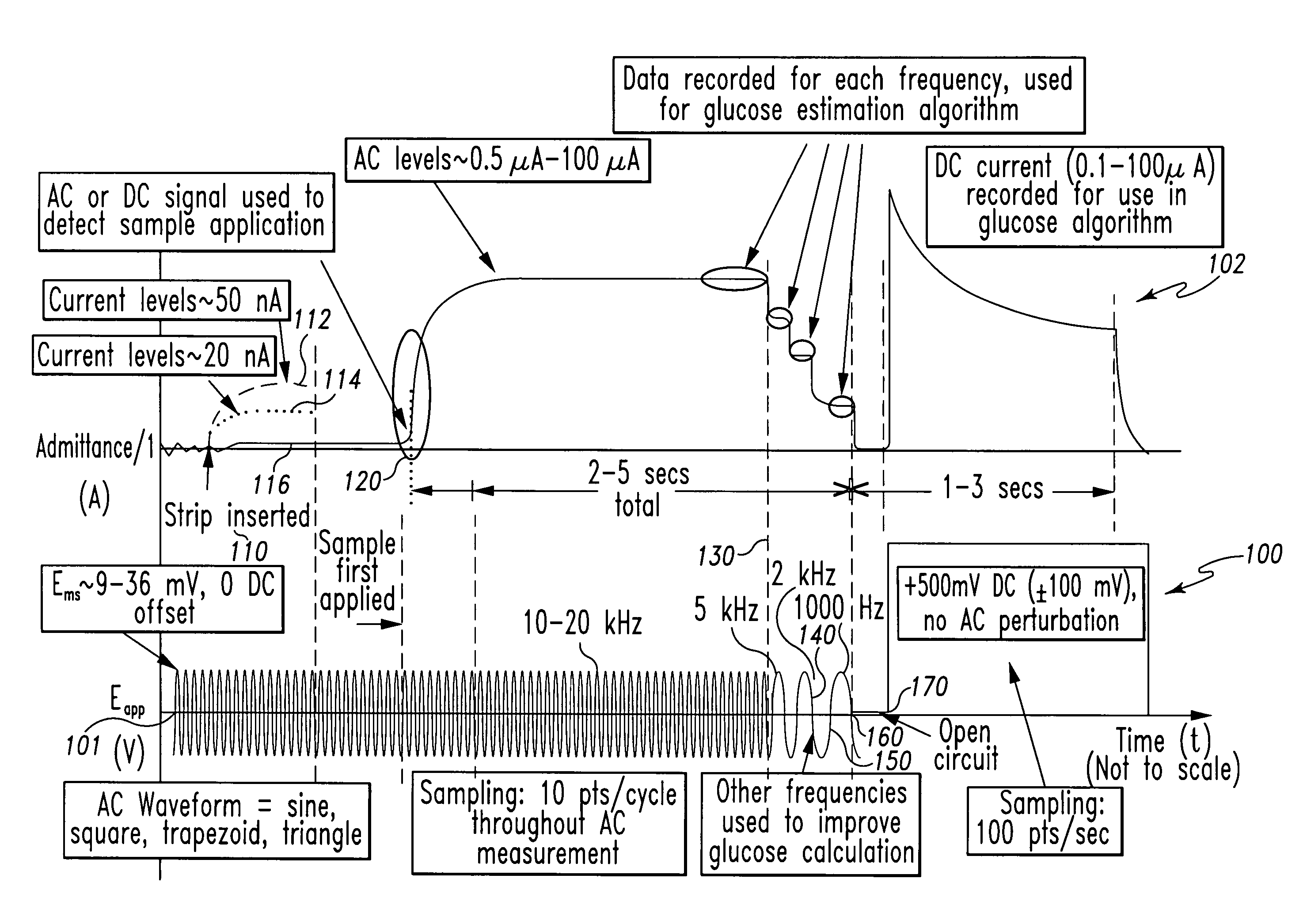
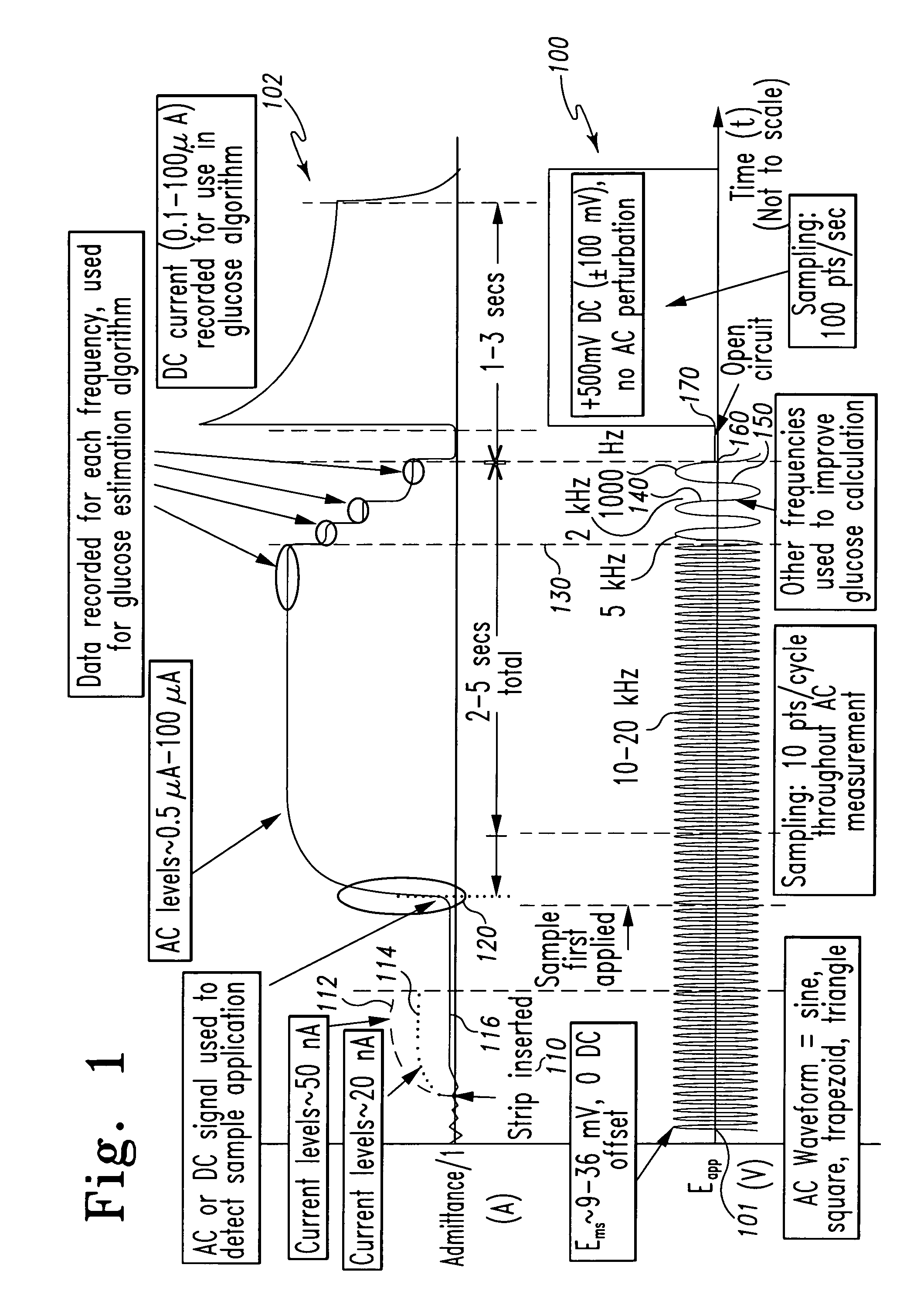
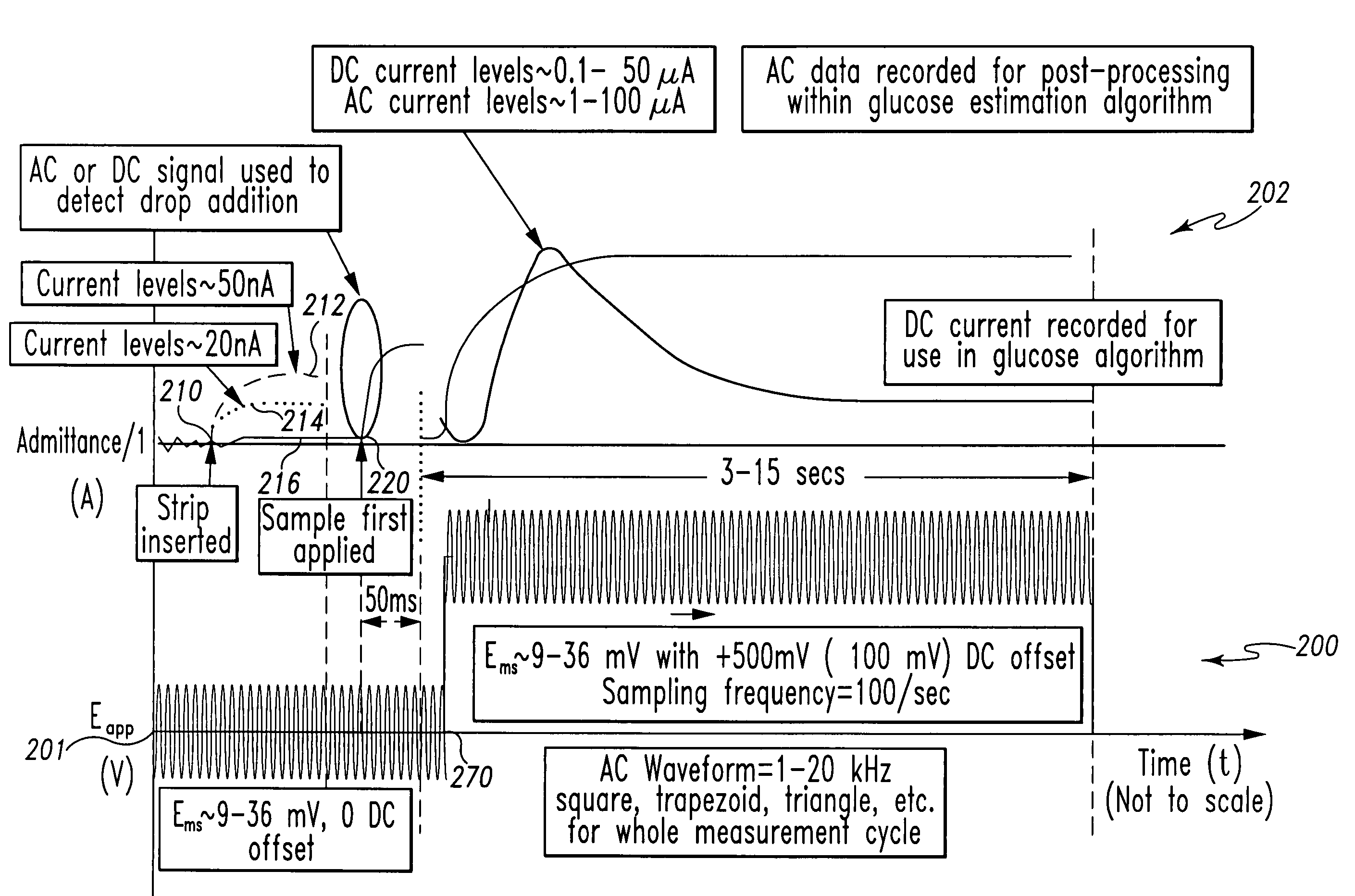
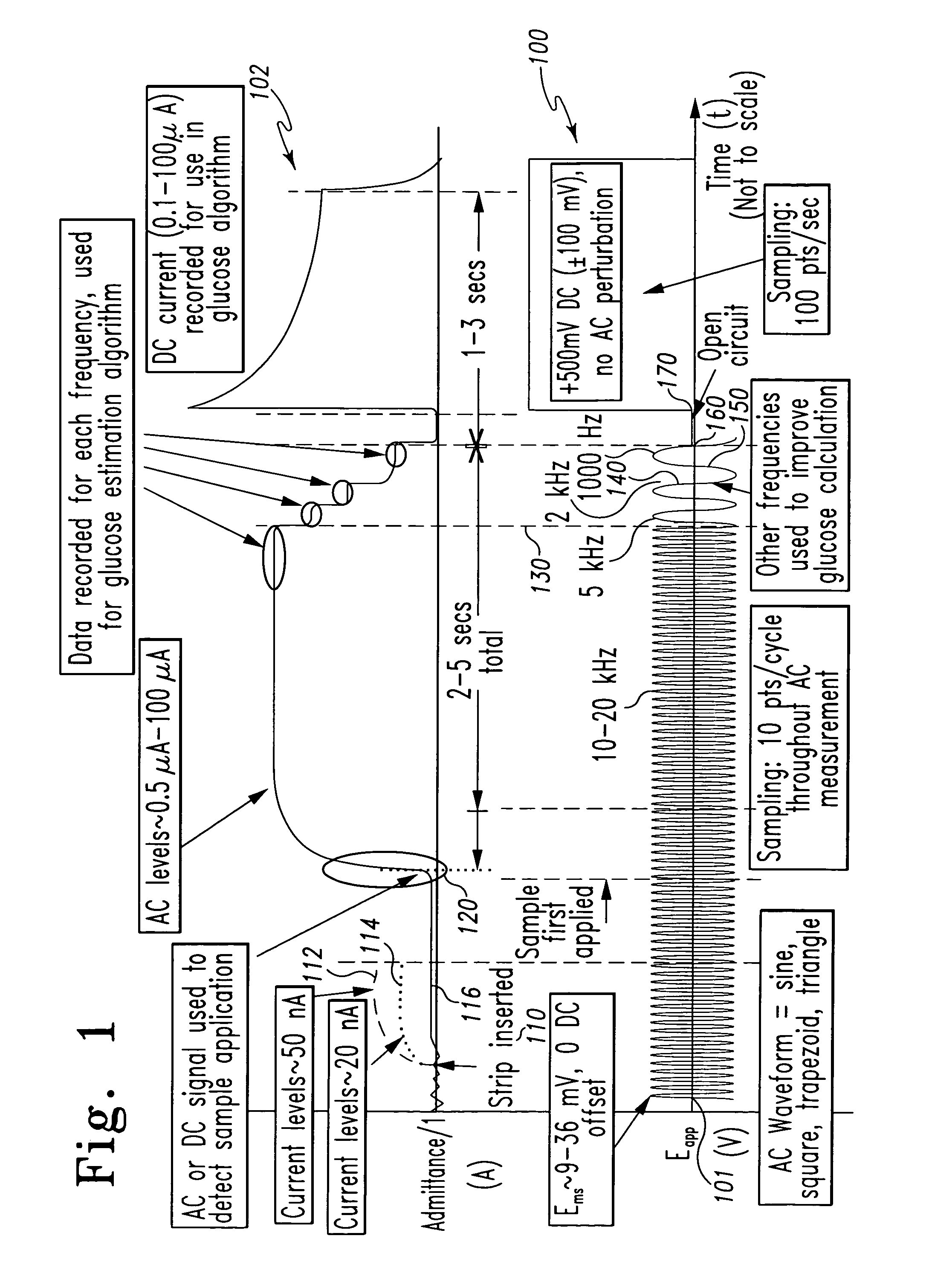
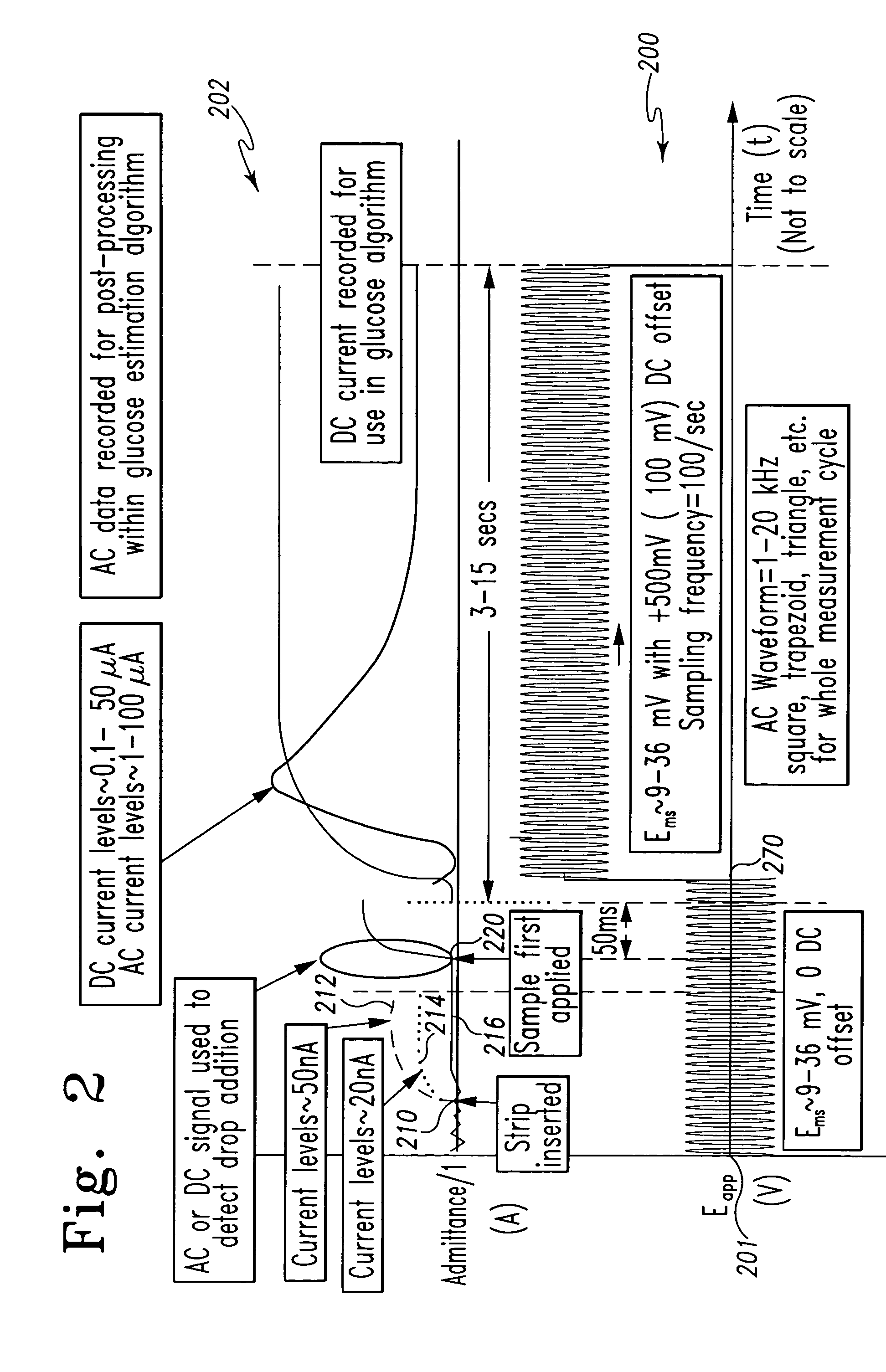
A method of measuring an analyte in a biological fluid comprises applying an excitation signal having a DC component and an AC component. The AC and DC responses are measured; a corrected DC response is determined using the AC response; and a concentration of the analyte is determined based upon the corrected DC response. Other methods and devices are disclosed.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC +1
Cell/tissue analysis via controlled electroporation
InactiveUS6482619B1The right amountAvoid cell damageBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological bodyElectrical resistance and conductance
An electrical current is created across an electrically conductive medium comprising a cell which may be part of a tissue of a living organism. A first electrical parameter which may be current, voltage, or electrical impedance is measured. A second electrical parameter which may be current, voltage or a combination of both is then adjusted and / or analyzed. Adjustments are carried out to facilitate analysis and / or obtain a desired degree of electroporation. Analysis is carried out to determine characteristics of the cell membrane and / or tissue.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Battery performance monitor
ActiveUS20090027056A1Add equipmentEasy to modifyBatteries circuit arrangementsOperating modesOperational systemInternal resistance
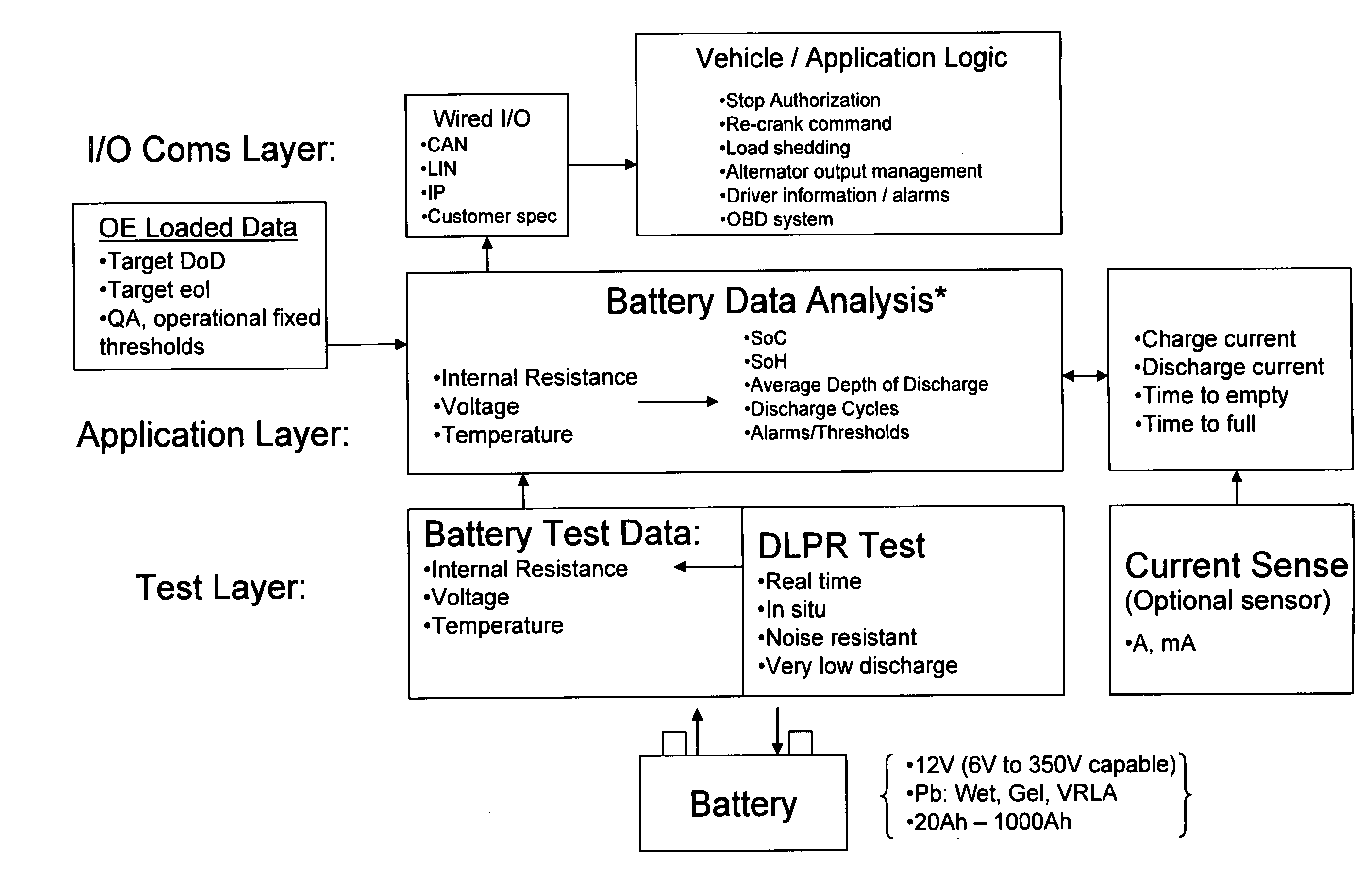
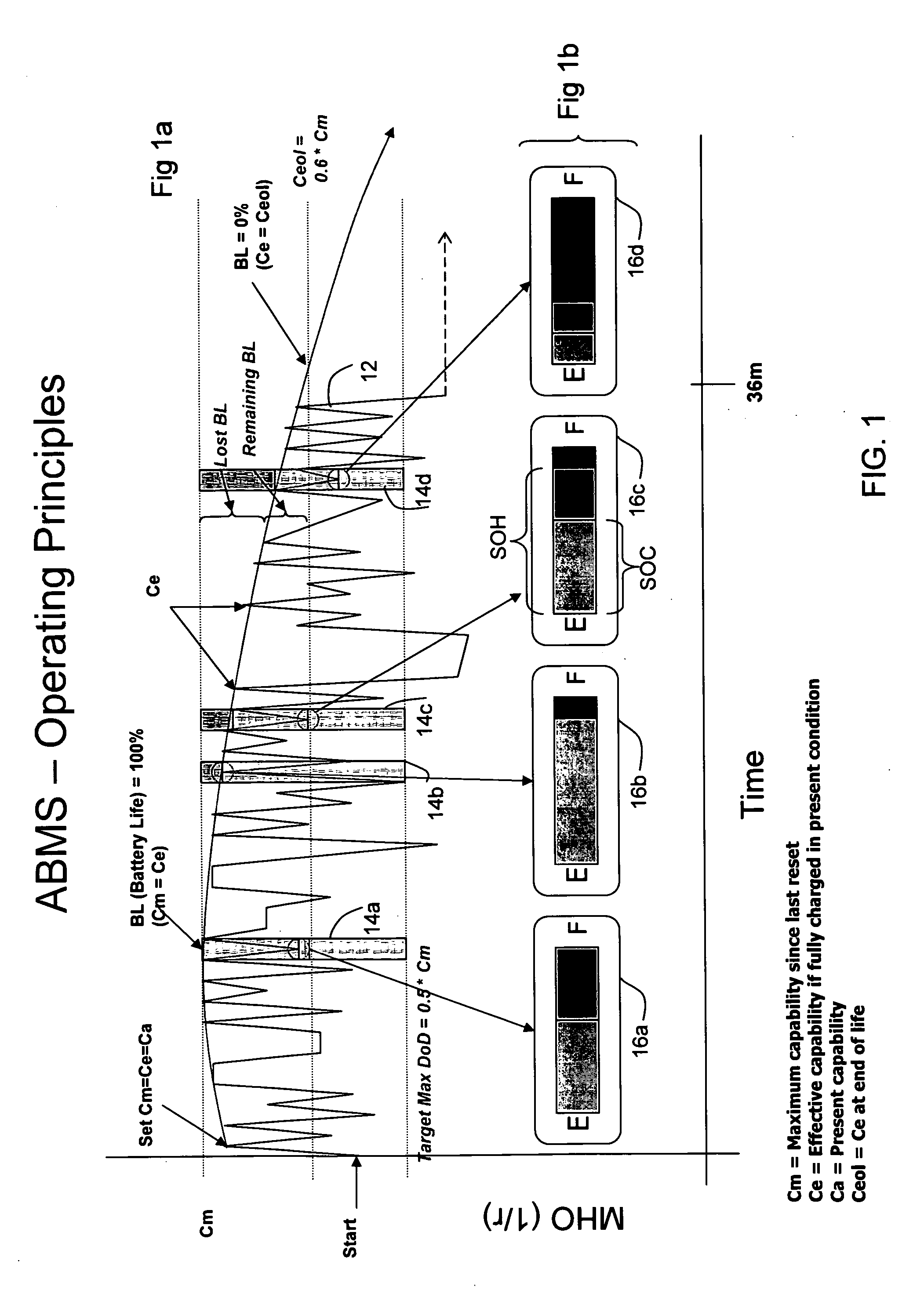
Improvements both in the methods whereby existing techniques for determining the condition of a battery are communicated to a user (for example, to the owner of a private vehicle, or to the service manager of a fleet of vehicles), or the vehicle's operating system, and in the methods for evaluating the condition of the battery are disclosed. It has been discovered by the inventors that the difference in internal resistance of a fully charged battery as measured during charging and as measured after charging is greater for a battery in poor condition than for a new battery. The invention relates in part to instruments and corresponding methods for evaluating the condition of a battery utilizing this discovery.
Owner:BATTERY TECH HLDG
Cell viability detection using electrical measurements
InactiveUS6927049B2Quantitative measurementEnhanced informationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectricityCell membrane
A method of determining information about cell viability and other characteristics relating to cell membrane permeability is disclosed. The method involves determining the effect of a cell on current flow and relating that effect to a known standard which standard may be a known healthy cell and thereby deducing the viability of the cell being tested. The cells being tested can be subjected to different environmental conditions such as surrounding chemicals, temperature, pH and pressure to determine the effects of such conditions on cell viability and / or cell permeability. The cell being tested can be in a cell suspension, grown on s ubstarte, in tissue in vitro or in tissue in vivo. The method provides substantially instantaneous results and need not include the use of dyes or other markers.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Sensor platform using a horizontally oriented nanotube element
Sensor platforms and methods of making them are described, and include platforms having horizontally oriented sensor elements comprising nanotubes or other nanostructures, such as nanowires. Under certain embodiments, a sensor element has an affinity for an analyte. Under certain embodiments, such a sensor element comprises one or more pristine nanotubes, and, under certain embodiments, it comprises derivatized or functionalized nanotubes. Under certain embodiments, a sensor is made by providing a support structure; providing a collection of nanotubes on the structure; defining a pattern within the nanotube collection; removing part of the collection so that a patterned collection remains to form a sensor element; and providing circuitry to electrically sense the sensor's electrical characterization. Under certain embodiments, the sensor element comprises pre-derivatized or pre-functionalized nanotubes. Under certain embodiments, sensor material is derivatized or functionalized after provision on the structure or after patterning. Under certain embodiments, a large-scale array includes multiple sensors.
Owner:NANTERO
Controlled electroporation and mass transfer across cell membranes
InactiveUS20060121610A1High levelImprove efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsControl mannerCell membrane
Electroporation is performed in a controlled manner in either individual or multiple biological cells or biological tissue by monitoring the electrical impedance, defined herein as the ratio of current to voltage in the electroporation cell. The impedance detects the onset of electroporation in the biological cell(s), and this information is used to control the intensity and duration of the voltage to assure that electroporation has occurred without destroying the cell(s). This is applicable to electroporation in general. In addition, a particular method and apparatus are disclosed in which electroporation and / or mass transfer across a cell membrane are accomplished by securing a cell across an opening in a barrier between two chambers such that the cell closes the opening. The barrier is either electrically insulating, impermeable to the solute, or both, depending on whether pore formation, diffusive transport of the solute across the membrane, or both are sought. Electroporation is achieved by applying a voltage between the two chambers, and diffusive transport is achieved either by a difference in solute concentration between the liquids surrounding the cell and the cell interior or by a differential in concentration between the two chambers themselves. Electric current and diffusive transport are restricted to a flow path that passes through the opening.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Electrical impedance tomography to control electroporation
InactiveUS6387671B1The right amountAvoid cell damageBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrotherapyElectrical resistance and conductanceElectricity
Images created by electrical impedance tomography (EIT) are used to adjust one or more electrical parameters and obtain a desired degree of electroporation of cells in tissue. The parameters include current, voltage and a combination thereof. The cells are subjected to conditions such that they become permeabilized but are preferably not subjected to conditions which result in irreversible pore formation and cell death. The electroporation can analyze cell membranes, diagnose tissues and the patient as well as to move materials into and out of cells in a controlled manner.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
System and method for determining a temperature during analyte measurement
InactiveUS20060156796A1Analysis using chemical indicatorsMaterial thermal conductivityAnalyteExcitation signal
A method of measuring an analyte in a biological fluid comprises applying an excitation signal having a DC component and an AC component. The AC and DC responses are measured; a corrected DC response is determined using the AC response; and a concentration of the analyte is determined based upon the corrected DC response. Other methods and devices are disclosed.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC +1
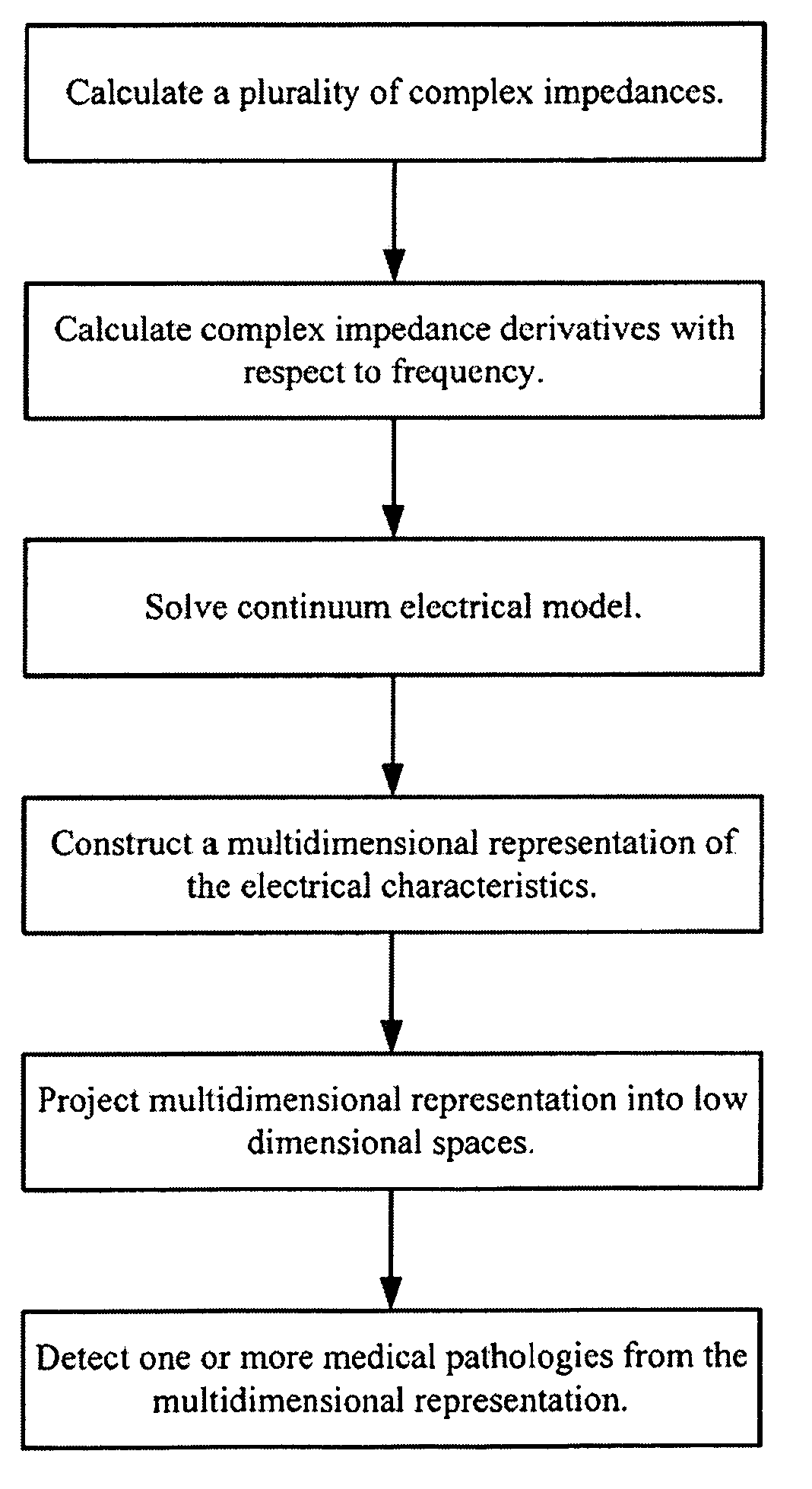
Multidimensional bioelectrical tissue analyzer
A method and apparatus that use complex impedance measurements of tissue in human or animal bodies for the detection and characterization of medical pathologies is disclosed. An analysis of the complex impedance measurements is performed by a trained evaluation system that uses a nonlinear continuum model to analyze the resistive, capacitive, and inductive measurements collected from a plurality of sensing electrodes. The analysis of the impedance measurements results in the construction of a multidimensional space that defines the tissue characteristics, which the trained evaluation system uses to detect and characterize pathologies. The method and apparatus are sufficiently general to be applied to various types of human and animal tissues for the analysis of various types of medical pathologies.
Owner:DELPHINUS MEDICAL TECH
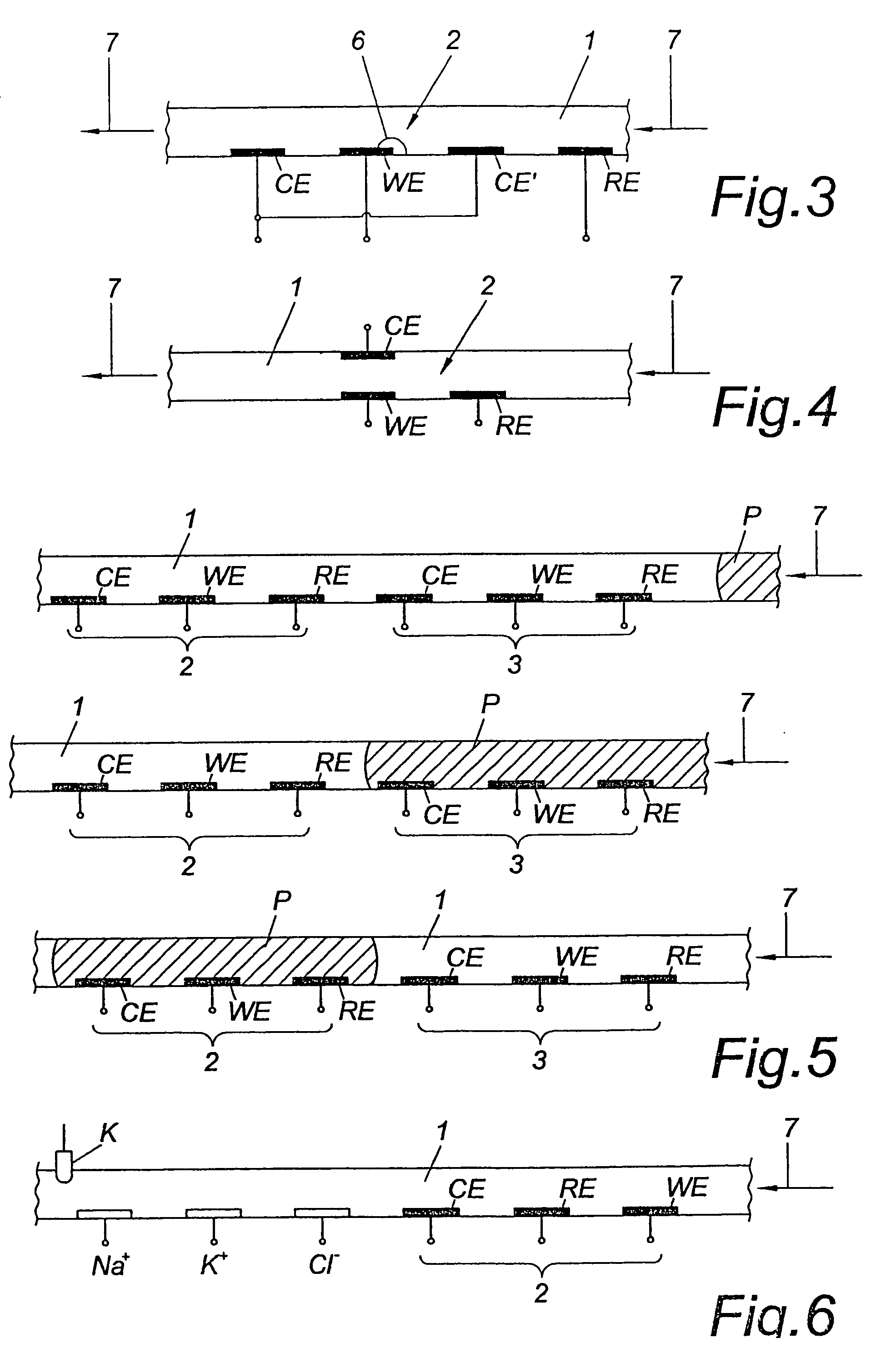
Biosensor
InactiveUS6885196B2Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsOptoelectronicsOxidoreductase
Owner:PHC HLDG CORP
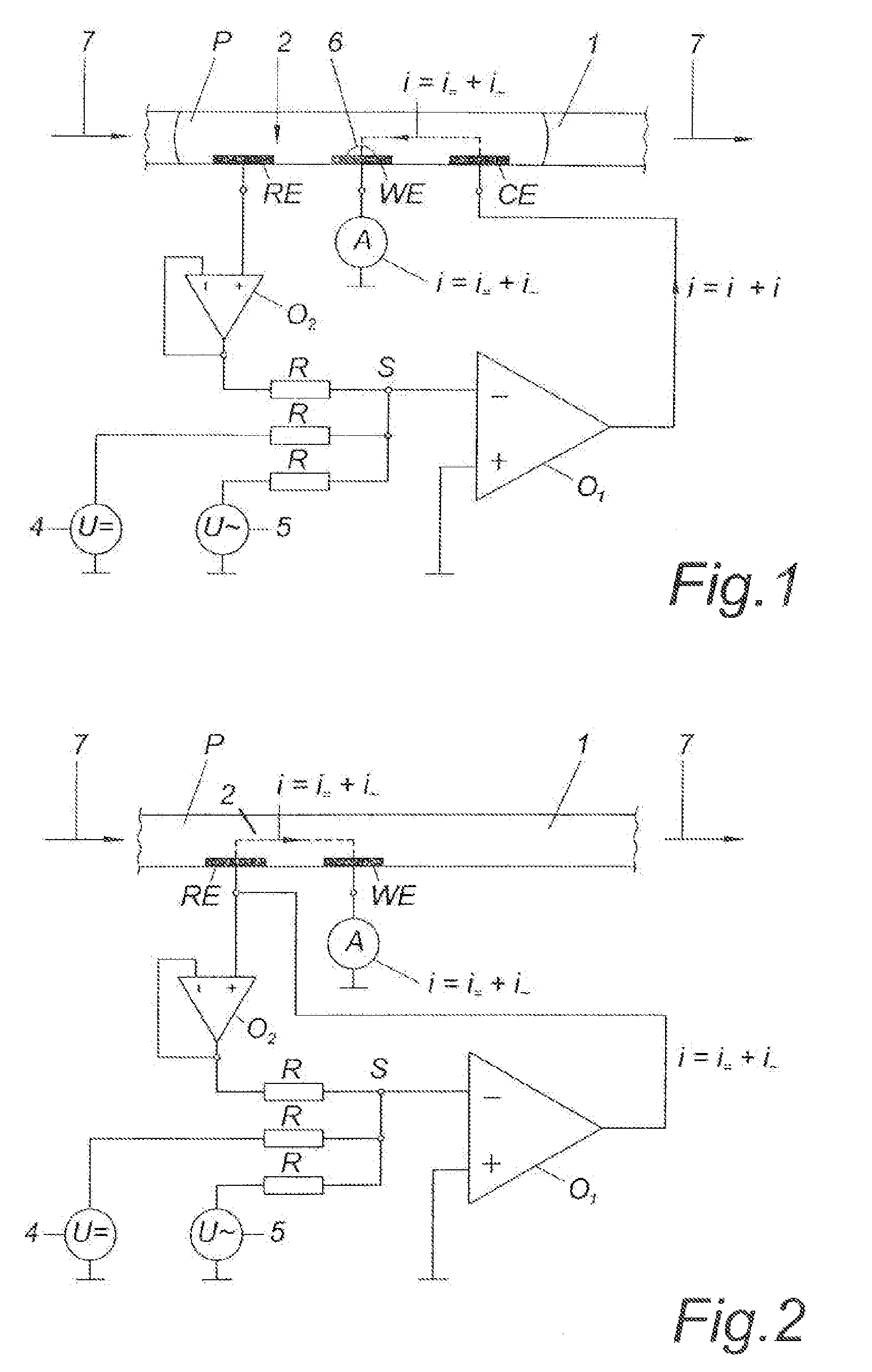
Disposable sensor with enhanced sample port inlet
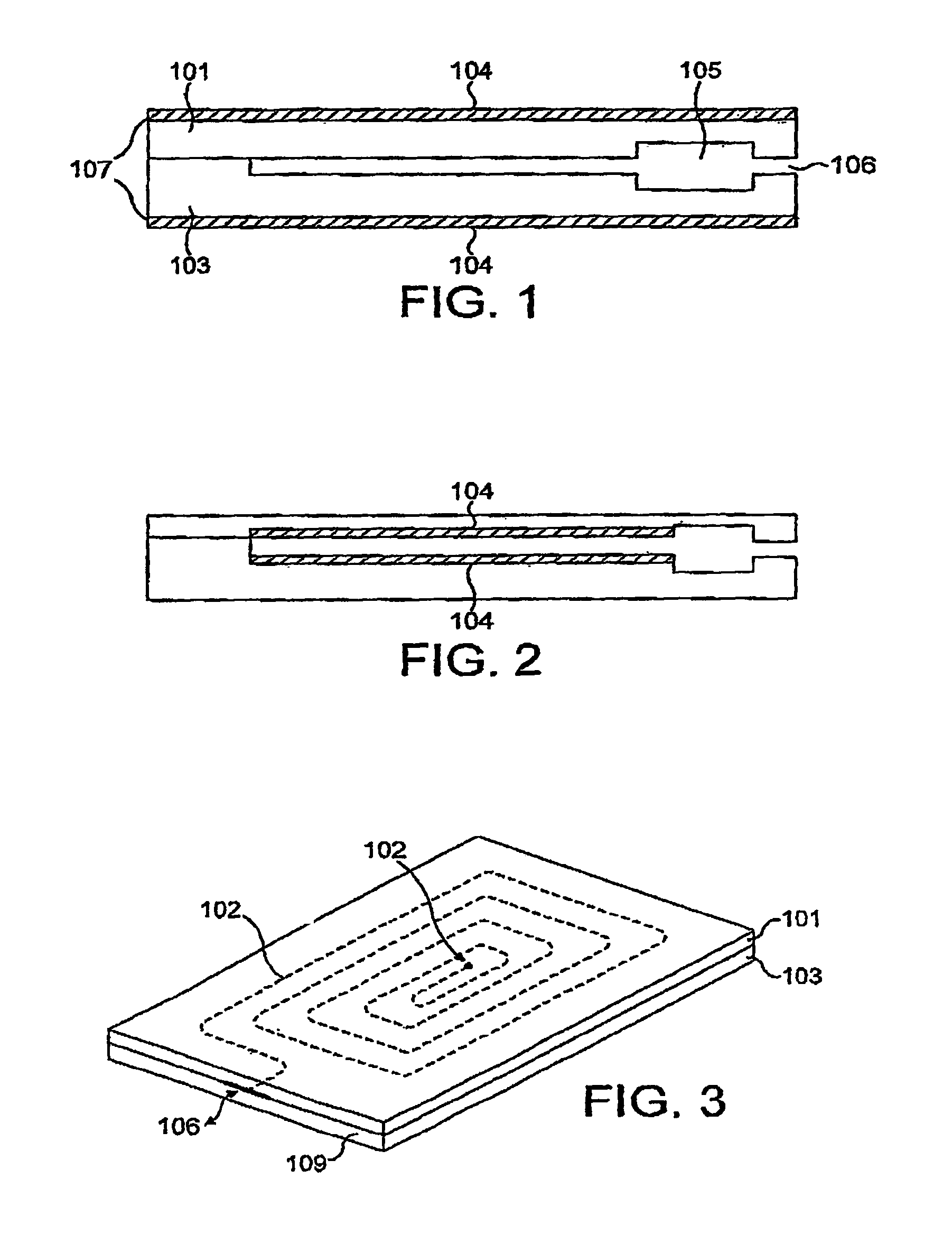
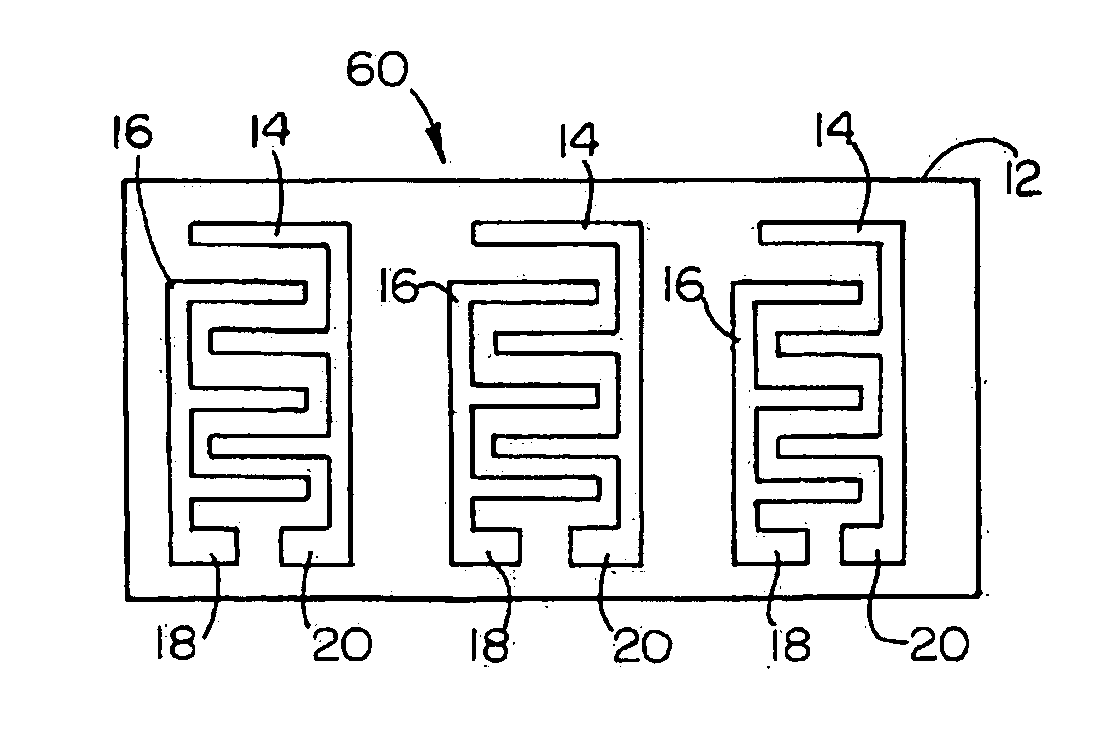
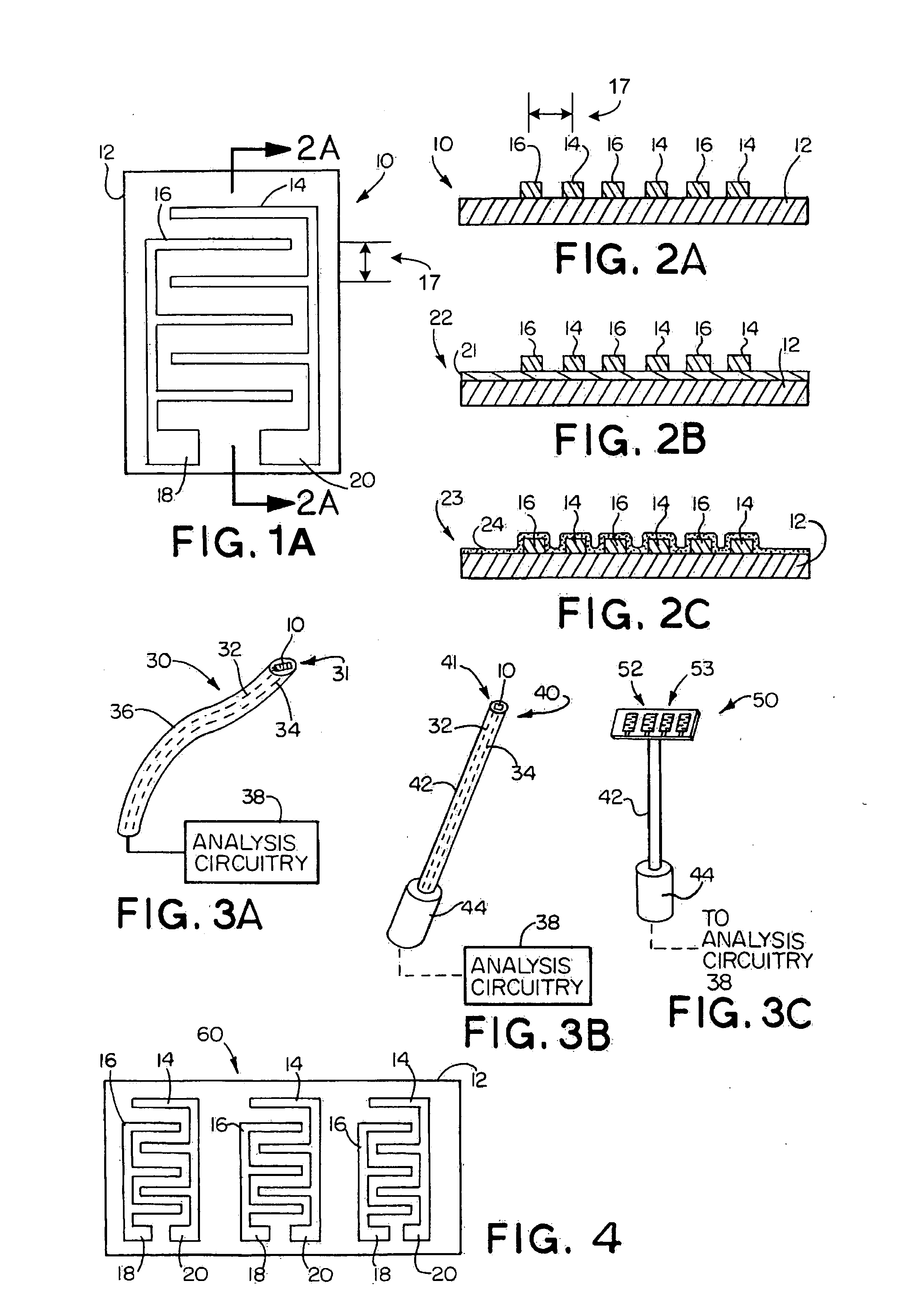
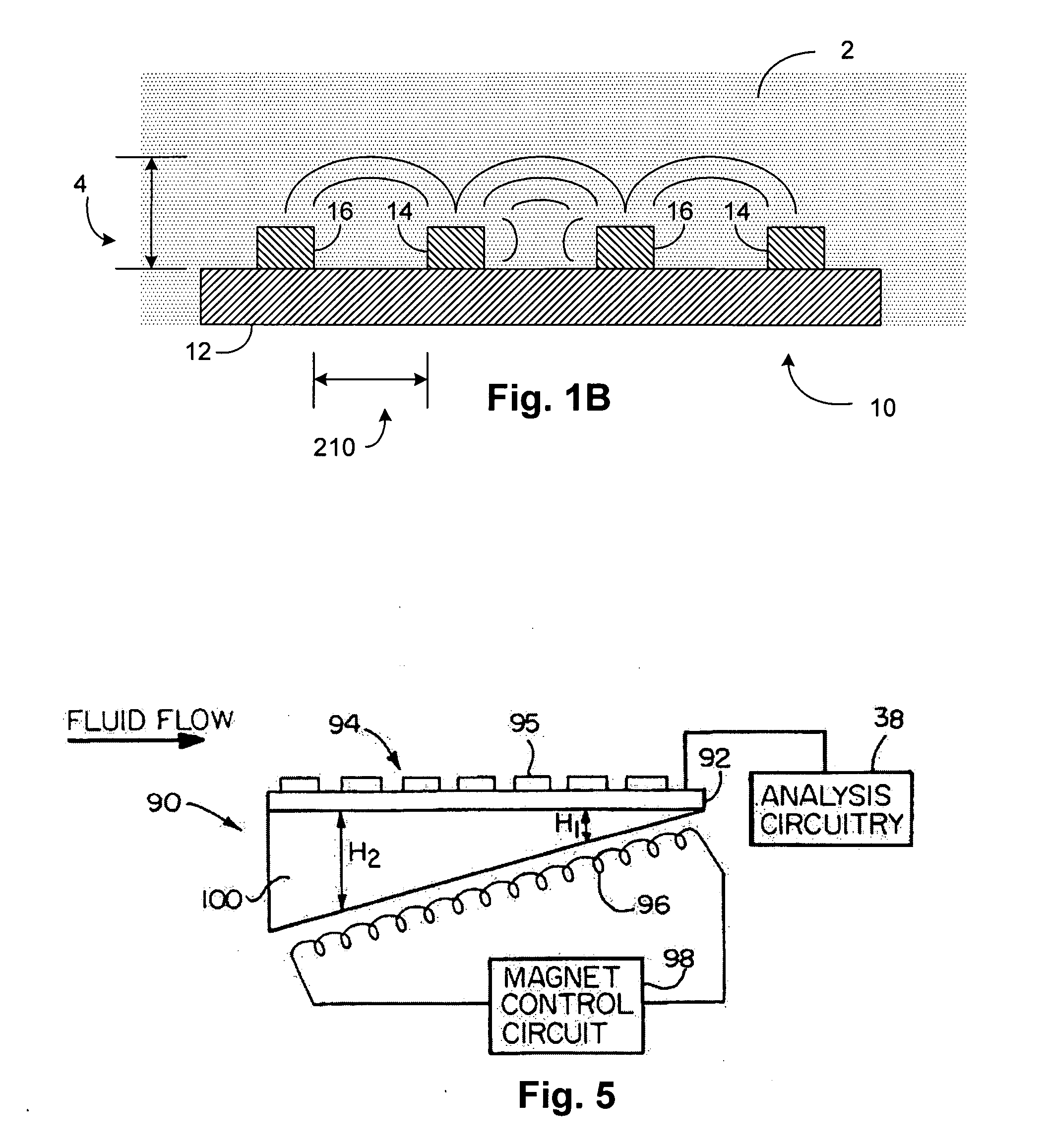
InactiveUS6837976B2Interference minimizationWide linear measurement rangeImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsProximateConductive coating
A disposable biosensor for testing a fluid sample including a laminated strip with a first and second end, a reference electrode embedded in the laminated strip proximate to the first end, at least one working electrode embedded in the laminated strip proximate to the first end and the reference electrode, an open path for receiving a fluid sample beginning from the first end and connecting to a vent spaced from the first end, the open path being sufficiently long to expose the reference electrode and the working electrode to the fluid sample, and conductive contacts located at the second end of the laminated strip. The laminated strip has a base layer with a conductive coating, a reagent holding layer, a channel forming layer and a cover having an inlet notch at the first end. The working electrode contains a reagent having an enzyme.
Owner:NOVA BIOMEDICAL
System and method for analyte measurement using AC excitation
A method of measuring an analyte in a biological fluid comprises applying an excitation signal having a DC component and an AC component. The AC and DC responses are measured; a corrected DC response is determined using the AC response; and a concentration of the analyte is determined based upon the corrected DC response. Other methods and devices are disclosed.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
Assay cartridges and methods of using the same
Assay modules, preferably assay cartridges, are described as are reader apparatuses which may be used to control aspects of module operation. The modules preferably comprise a detection chamber with integrated electrodes that may be used for carrying out electrode induced luminescence measurements. Methods are described for immobilizing assay reagents in a controlled fashion on these electrodes and other surfaces. Assay modules and cartridges are also described that have a detection chamber, preferably having integrated electrodes, and other fluidic components which may include sample chambers, waste chambers, conduits, vents, bubble traps, reagent chambers, dry reagent pill zones and the like. In certain preferred embodiments, these modules are adapted to receive and analyze a sample collected on an applicator stick.
Owner:MESO SCALE TECH LLC
Multidimensional bioelectrical tissue analyzer
Owner:DELPHINUS MEDICAL TECH
Sensor platform using a non-horizontally oriented nanotube element
Sensor platforms and methods of making them are described. A platform having a non-horizontally oriented sensor element comprising one or more nanostructures such as nanotubes is described. Under certain embodiments, a sensor element has or is made to have an affinity for an analyte. Under certain embodiments, such a sensor element comprises one or more pristine nanotubes. Under certain embodiments, the sensor element comprises derivatized or functionalized nanotubes. Under certain embodiments, a sensor is made by providing a support structure; providing one or more nanotubes on the structure to provide material for a sensor element; and providing circuitry to electrically sense the sensor element's electrical characterization. Under certain embodiments, the sensor element comprises pre-derivatized or pre-functionalized nanotubes. Under other embodiments, sensor material is derivatized or functionalized after provision on the structure or after patterning. Under certain embodiments, a large-scale array of sensor platforms includes a plurality of sensor elements.
Owner:NANTERO
Impedance based devices and methods for use in assays
ActiveUS7470533B2Easy to adaptNoise minimizationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectricityConductive materials
A device for detecting cells and / or molecules on an electrode surface is disclosed. The device detects cells and / or molecules through measurement of impedence changes resulting from the cells and / or molecules. A disclosed embodiment of the device includes a substrate having two opposing ends along a longitudinal axis. A plurality of electrode arrays are positioned on the substrate. Each electrode array includes at least two electrodes, and each electrode is separated from at least one adjacent electrode in the electrode array by an expanse of non-conductive material. The electrode has a width at its widest point of more than about 1.5 and less than about 10 times the width of the expanse of non-conductive material. The device also includes electrically conductive traces extending substantially longitudinally to one of the two opposing ends of the substrate without intersecting another trace. Each trace is in electrical communication with at least one of the electrode arrays.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Biological fluid constituent sampling and measurement devices and methods
A device for accessing biological fluid, sampling biological fluid constituents and determining the concentration of at least one target constituent within the accessed biological fluid is provided. The device has at least one micro-piercing member used to penetrate the skin to a selected depth and to access biological fluid, a constituent sampling means and a constituent measuring means. The constituent sampling means comprises a constituent transfer medium, such as a hydrophilic gel material, by which sampled constituents are transferred from the micro-piercing member to the measuring means. The measuring means includes an electrochemical cell having at least one porous electrode through which at least one sampled constituent is caused to enter into the electrochemical cell. Methods of sampling constituents within the skin and measuring the sampled constituents, as well as kits for practicing the invention are provided.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
System and method for analyte measurement using a nonlinear sample response
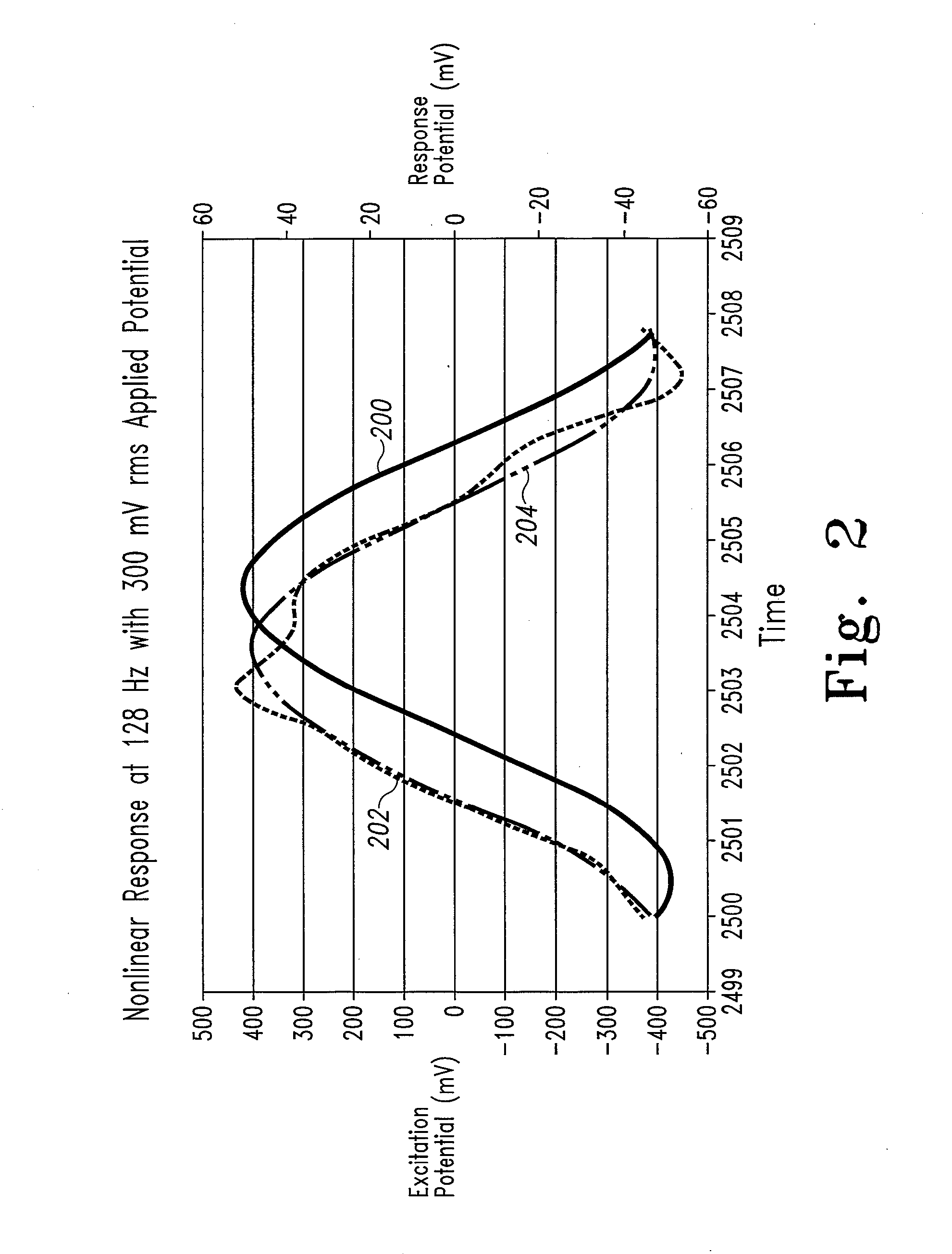
InactiveUS20070264721A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingLinear componentApplied potential
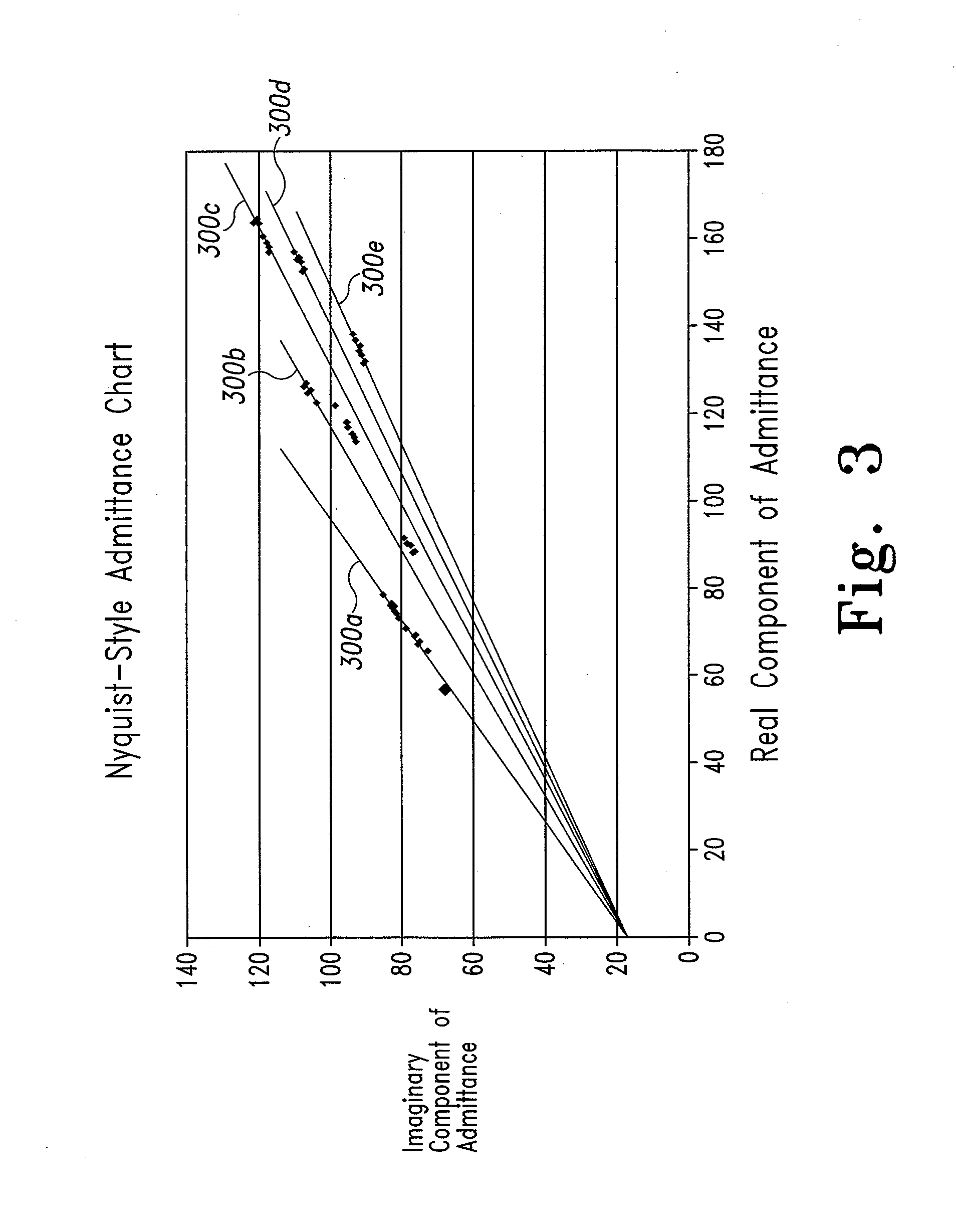
The systems and methods of the present invention utilize a linear component of a non-linear, faradaic current response generated by a biological fluid sample when an AC excitation potential sufficient to produce such a faradaic current response is applied to the sample, in order to calculate the concentration of a medically significant component in the biological fluid sample. The current response is created by the excitation of electrochemical processes within the sample by the applied potential. Typically, the linear component of the current response to an applied AC potential contains phase angle and / or admittance information that may be correlated to the concentration of the medically significant component. Also typically, the fundamental linear component of the current response is utilized in the disclosed systems and methods. Harmonics of the fundamental linear component may also be used. Other methods and devices are disclosed.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
System and method for analyte measurement using AC phase angle measurements
A method of measuring an analyte in a biological fluid comprises applying an excitation signal having a DC component and an AC component. The AC and DC responses are measured; a corrected DC response is determined using the AC response; and a concentration of the analyte is determined based upon the corrected DC response. Other methods and devices are disclosed.
Owner:ROCHE OPERATIONS +1
MEMS-based sensor for lubricant analysis
A fluid contamination analyzer employs one or more MEMS-based sensors. The sensors are incorporated into probes or alternatively may be employed in an in-line analyzer residing in the fluid. The sensors, which can be selective to detect a distinct contaminant within the fluid, sense an impedance of the fluid, which is a function of its contamination and communicates the impedance to analysis circuitry.
Owner:PREDICT
Method and apparatus for providing stable voltage to analytical system
An electrochemical cell has two terminals. One of the terminals is connected to a pulse-width-modulated (PWM) power supply and to a voltmeter. The other terminal is connected to circuitry capable of switching between amperometric and potentiometric measurement modes. A sequence of successive approximations permits selection of a PWM duty cycle giving rise to a desired voltage at the terminal connected with the power supply. In this way a stable excitation voltage is supplied to the cell even in the face of supply voltage instability or drift or instability in electronics coupled with the cell.
Owner:AGAMATRIX INC
System and method for determining an abused sensor during analyte measurement
ActiveUS7488601B2Measurement arrangements for variableCounting objects with random distributionAnalyteExcitation signal
A method of measuring an analyte in a biological fluid comprises applying an excitation signal having a DC component and an AC component. The AC and DC responses are measured; a corrected DC response is determined using the AC response; and a concentration of the analyte is determined based upon the corrected DC response. Other methods and devices are disclosed.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC +1
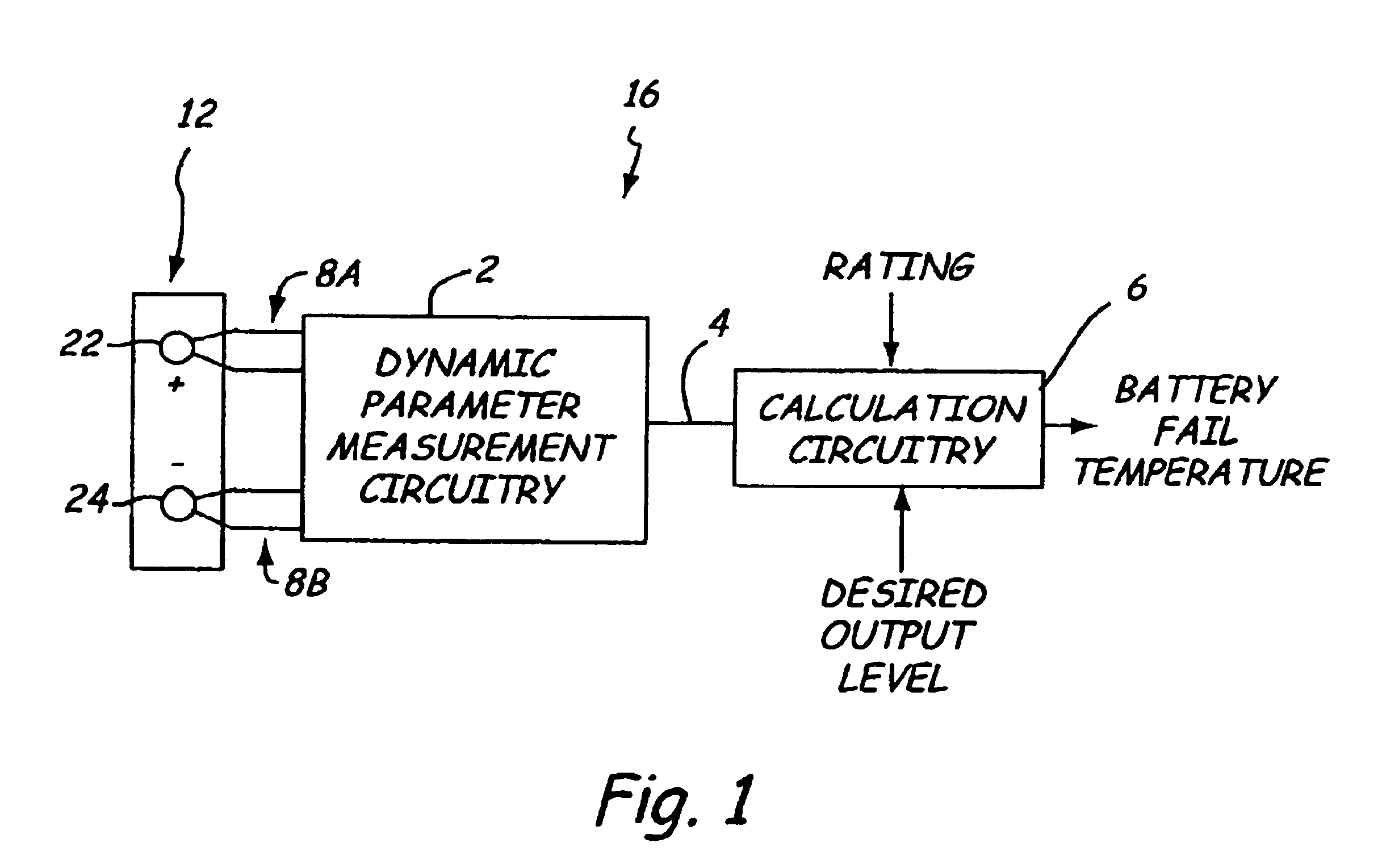
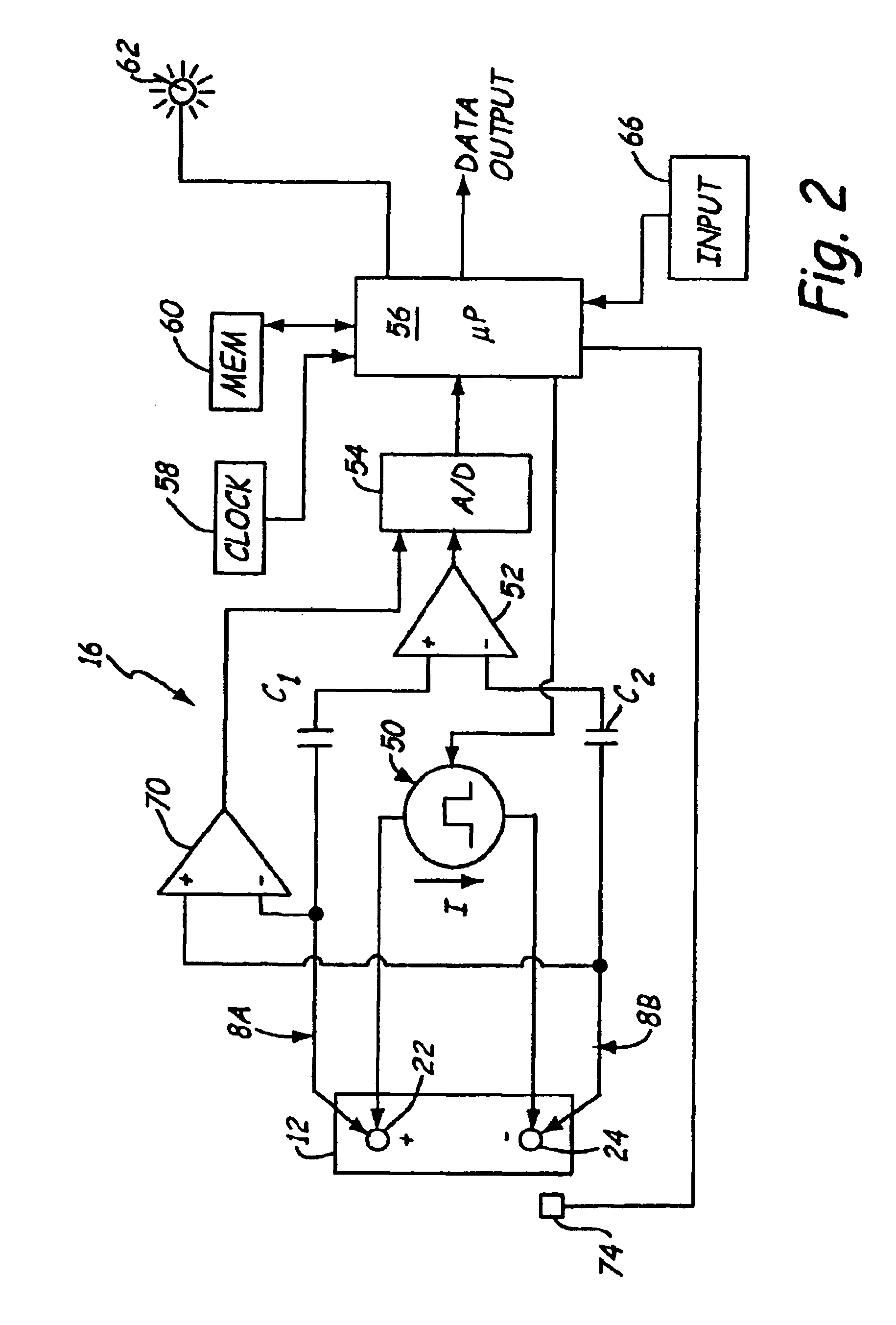
Electronic battery tester with battery failure temperature determination
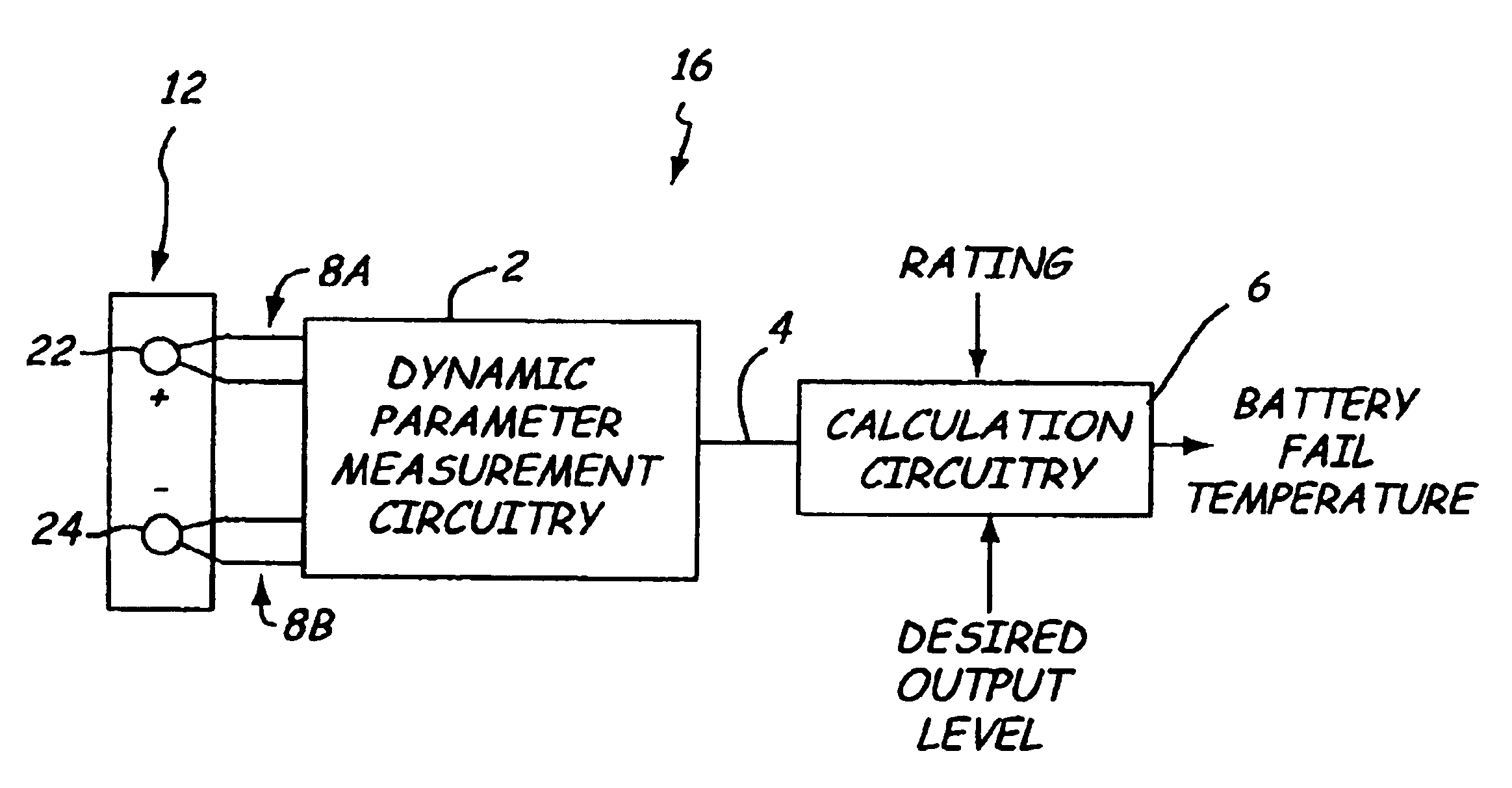
InactiveUS6930485B2Electrical testingMaterial impedanceElectrical resistance and conductanceTester device
A method and apparatus for testing a storage battery is provided that generates a temperature at which the battery will fail to meet performance criteria. The use of a temperature-based system to rate battery performance provides a clearer understanding to those not skilled in the art of battery testing. The critical failure temperature is obtained using the battery parameters of open circuit voltage, temperature and a dynamic parameter such as conductance or resistance.
Owner:MIDTRONICS +1
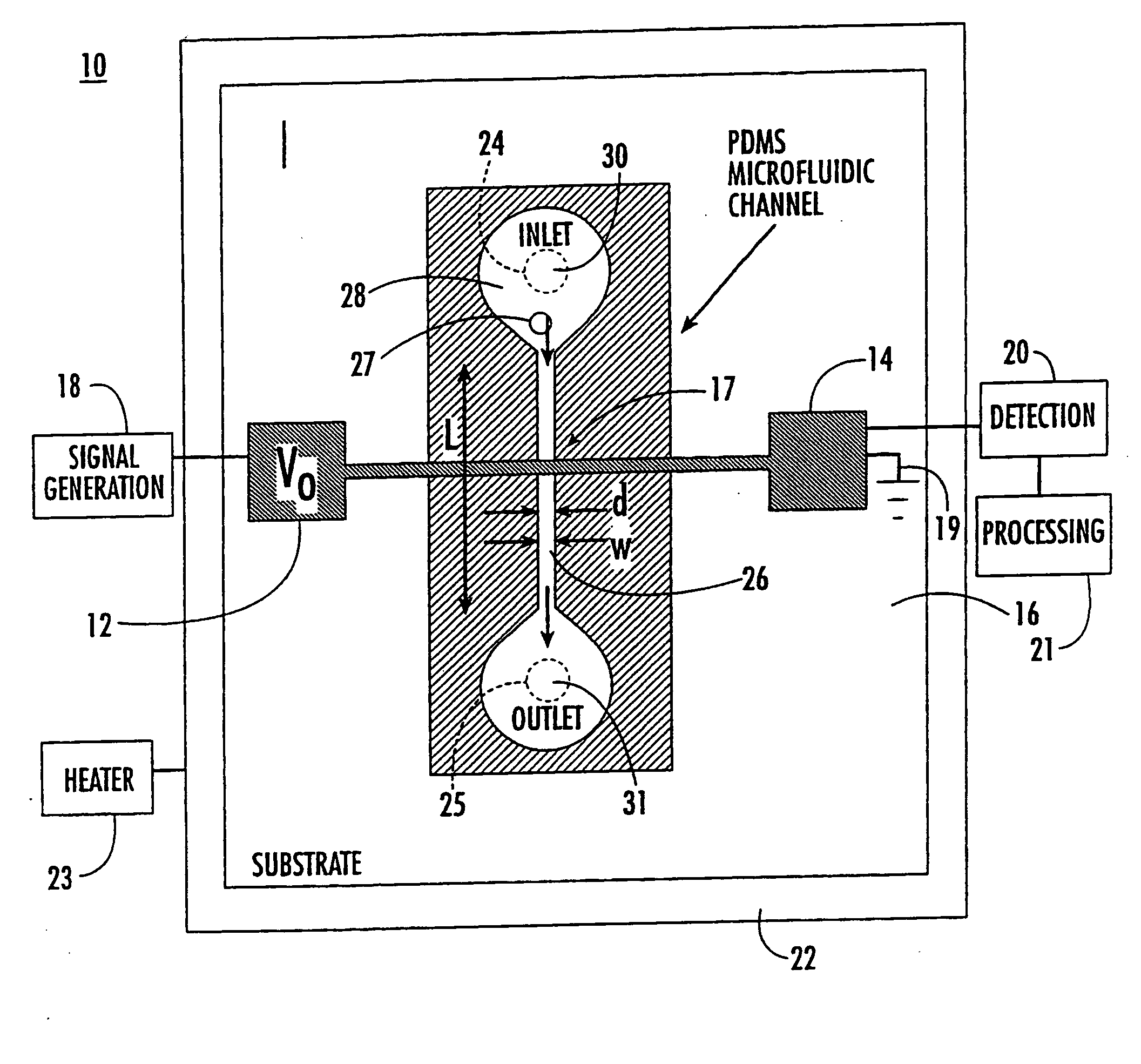
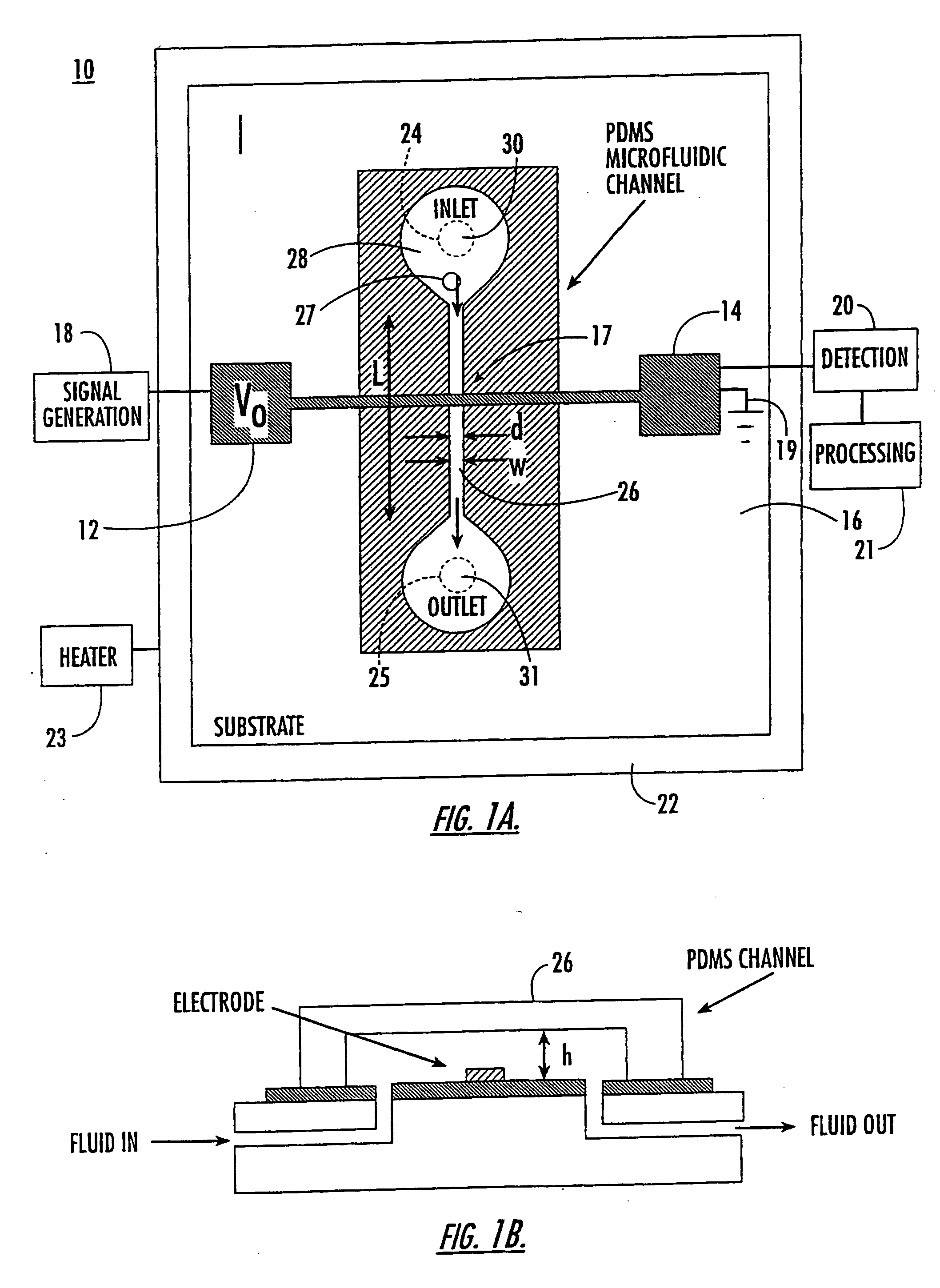
Microfluidic and nanofluidic electronic devices for detecting changes in capacitance of fluids and methods of using
InactiveUS20070238112A1Simpler and faster and less-expensiveMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCapacitanceCell Cycle Kinetics
The present invention (also identified as “Capacitance cytometry”) relates to microfluidic and nanofluidic devices for detecting or measuring an electrical property of a fluid (liquid or aerosol), a single molecule, particle, or cell in fluid. In a particular embodiment, the devices detect or measure changes in capacitance of a fluid, molecule, particle or cell as it passes through the device. The invention relates to detection and measurement of single molecules, particularly biological molecules, and to methods of sequencing polynucleotide molecules (RNA or DNA) by detecting differentially labeled single nucleotides. Single molecule detection applications include DNA or RNA sequencing, detection of SNPs, protoemics, and particle sizing. The device can be used to determine cell DNA content, to analyze cell-cycle kinetics of cell populations, and to assay for abnormal changes in cell DNA content. Nano-microfluidic devices of this invention also have utility as detectors in molecular sorting systems and for detecting pathogens.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Fusible conductive ink for use in manufacturing microfluidic analytical systems
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
Method and a device for monitoring a medical microsample in the flow measuring cell of an analyzer
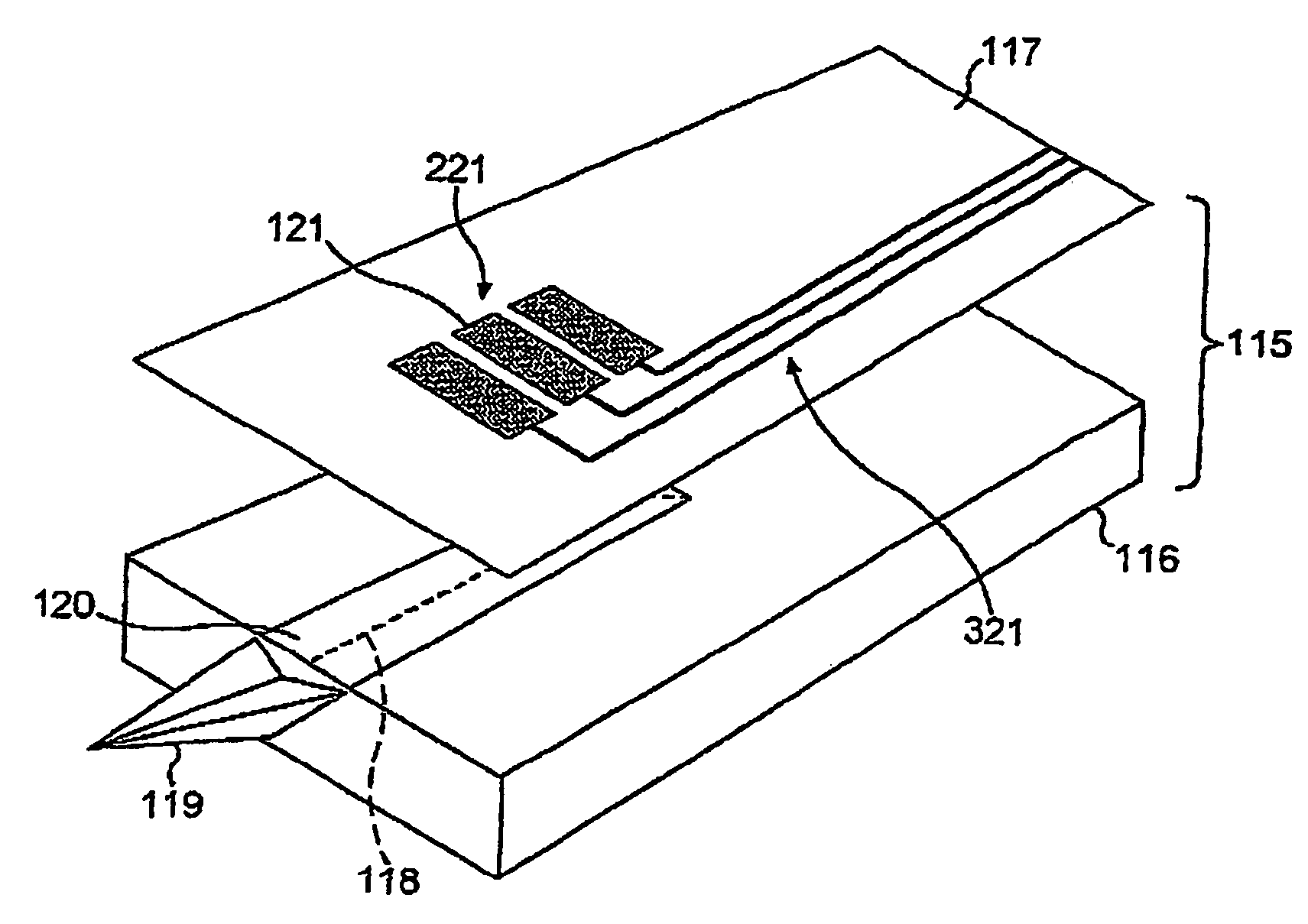
ActiveUS7297241B2Reliable measurement resultsSimple designImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrical impedanceSingle electrode
The invention relates to a method and device for the monitoring of a medical microsample in the flow measuring cell of an analyzer with regard to position and absence of bubbles by means of an alternating voltage applied to the measuring cell, the measuring cell being provided with a multitude of electrode systems placed one behind the other, each system comprising a number of single electrodes for measuring a substance contained in the microsample by means of a measurement voltage which essentially is a DC voltage. To monitor the exact position of the microsample and / or to detect air bubbles in the area of each electrode system, the alternating voltage and the measurement voltage are simultaneously and directly applied to the single electrodes of the corresponding electrode system, and the measured AC component respectively the measured impedance gives a measure for the position of the microsample and the absence of bubbles.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
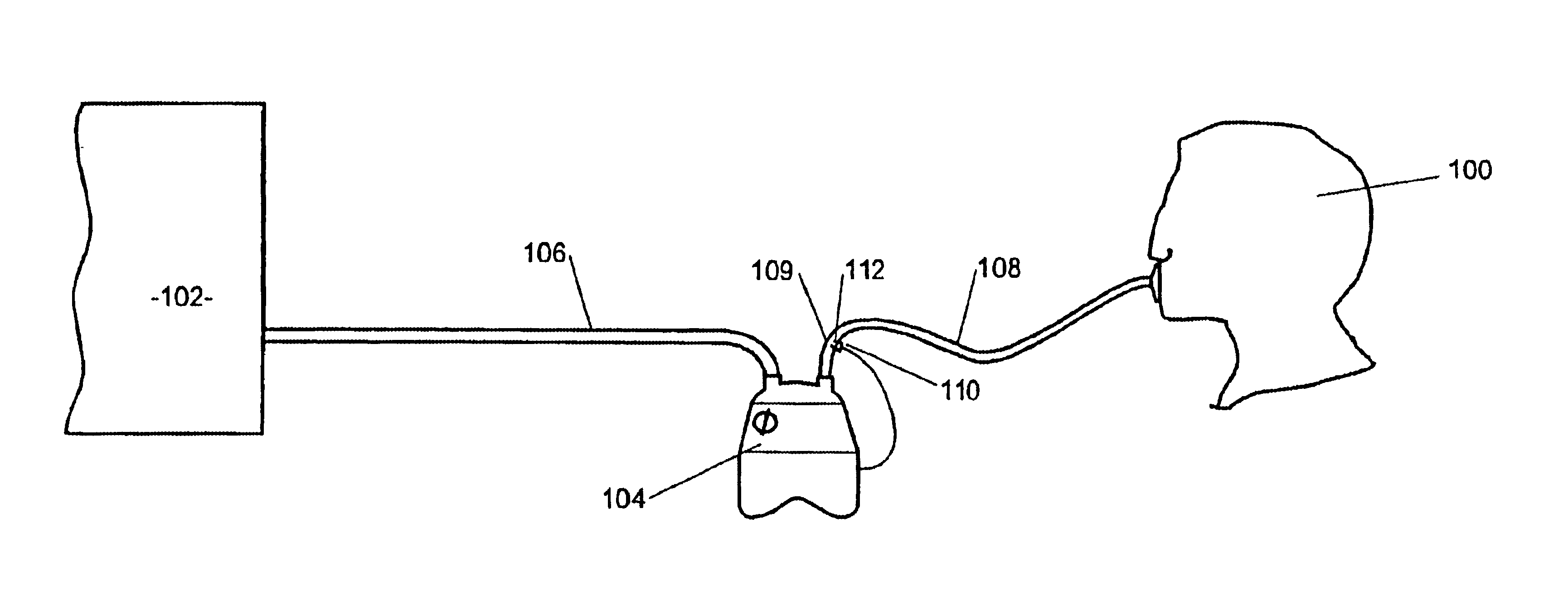
Humidity sensor
InactiveUS6895803B2RespiratorsAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesTransducerMoisture sensor
A method and apparatus are described for sensing the absolute humidity of gases where the relative humidity of gases are measured, the humidity transducer is heated, the resulting temperature measured and the absolute humidity calculated (based on the power to heat said transducer, the temperature of said transducer and the relative humidity).In further embodiments the humidity transducer may be heated to a pasteurisation temperature, to substantially kill any common pathogens present on the humidity transducer. The flow rate may be determined to estimate a more instantaneous valve of humidity. The operation of the sensor may be continually monitored for correct operation and various constructions disclosed for improving the efficiency of operation.
Owner:FISHER & PAYKEL HEALTHCARE LTD
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com