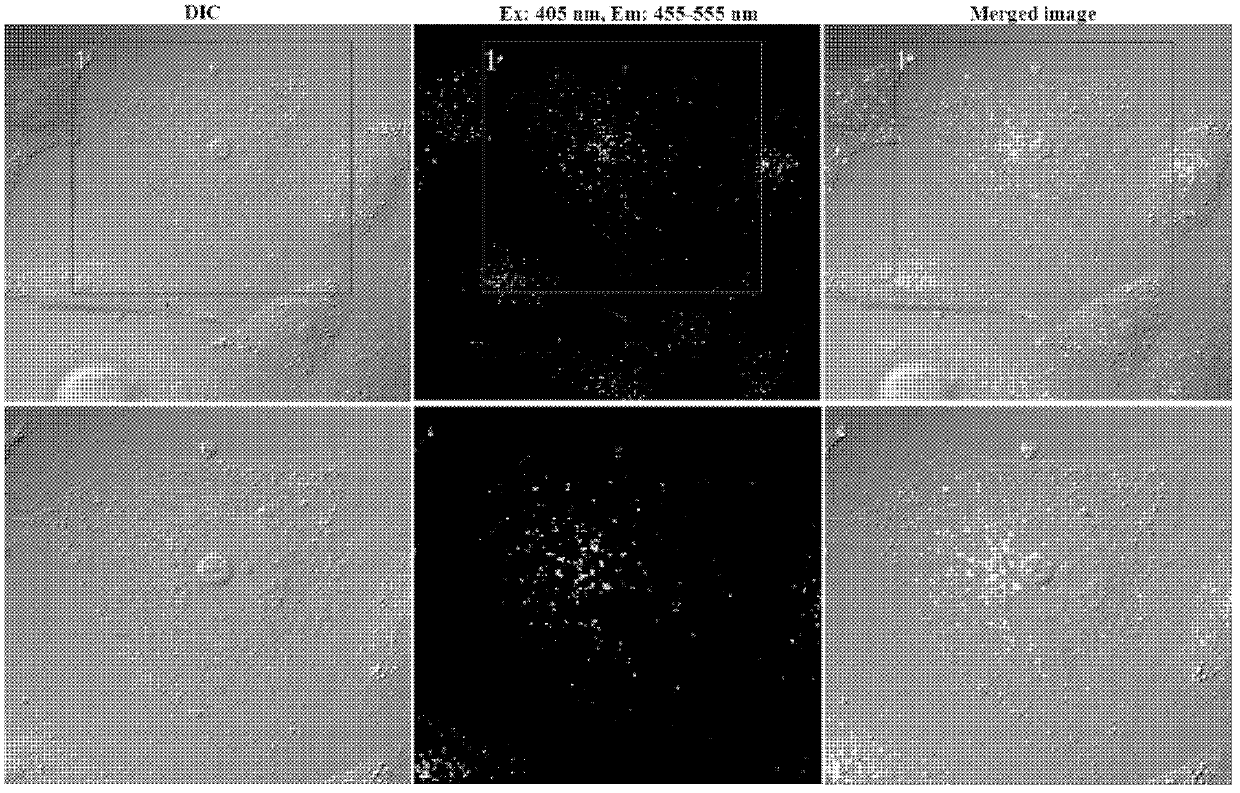
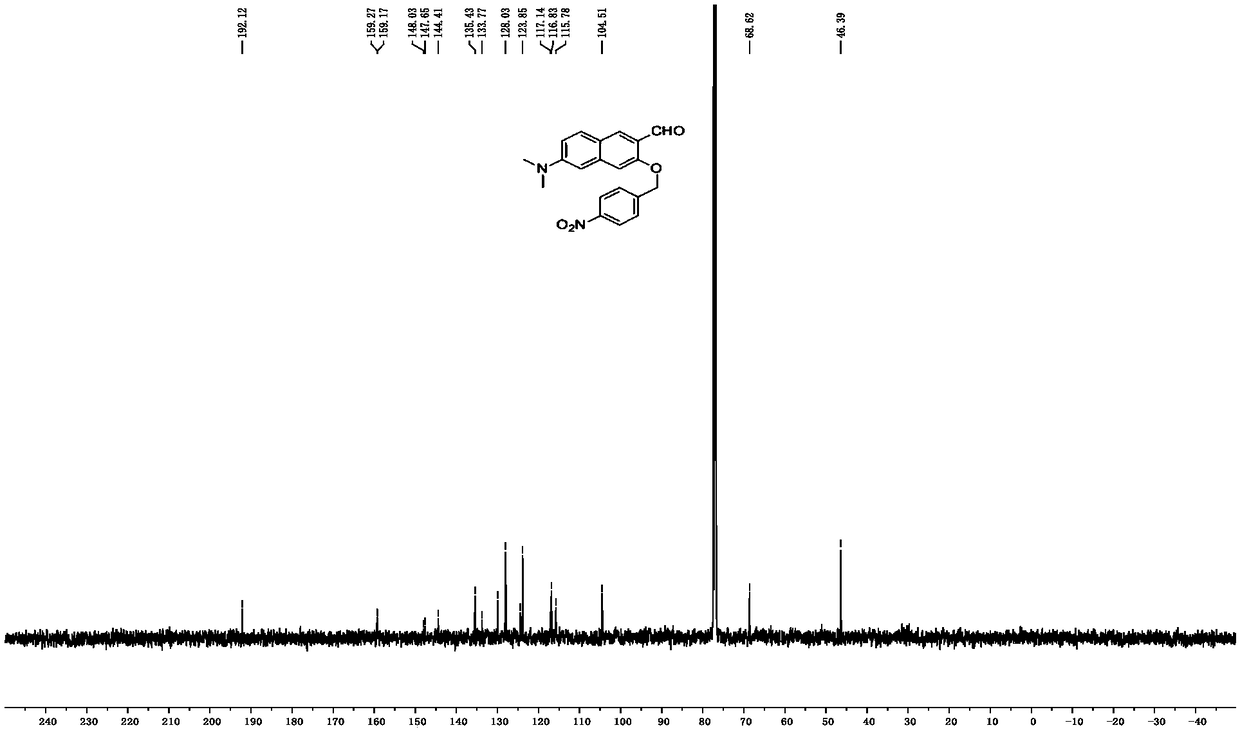
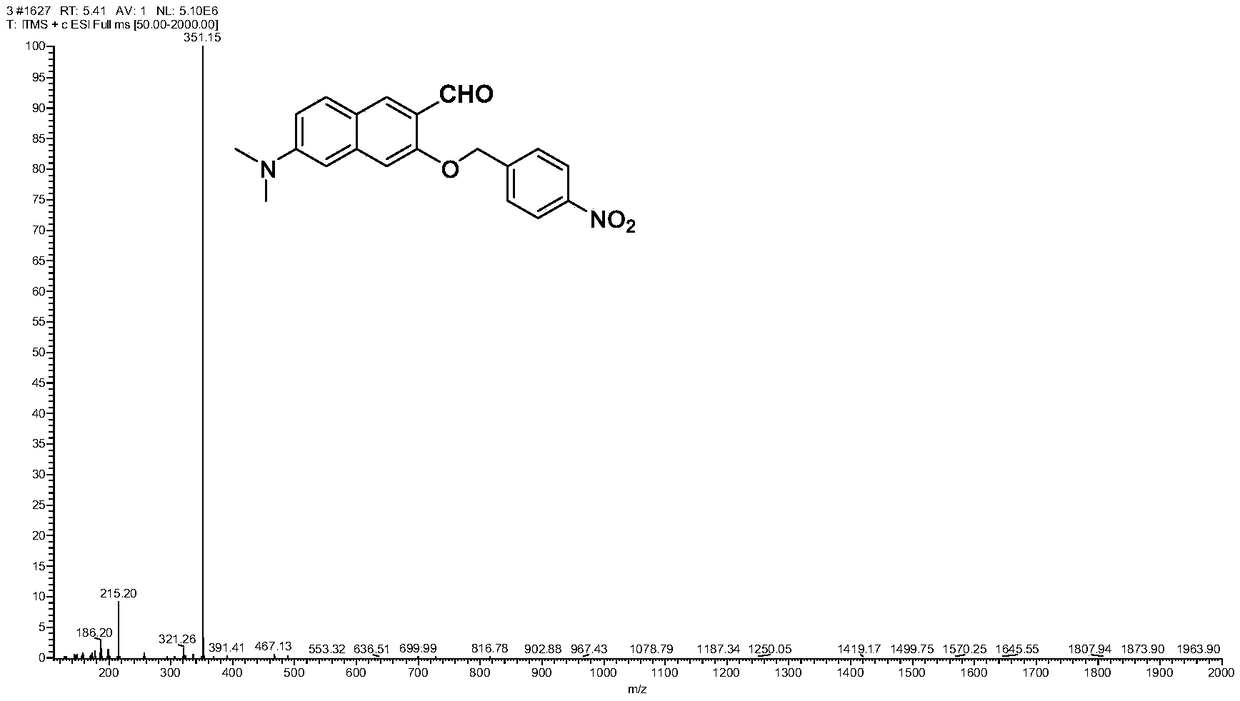
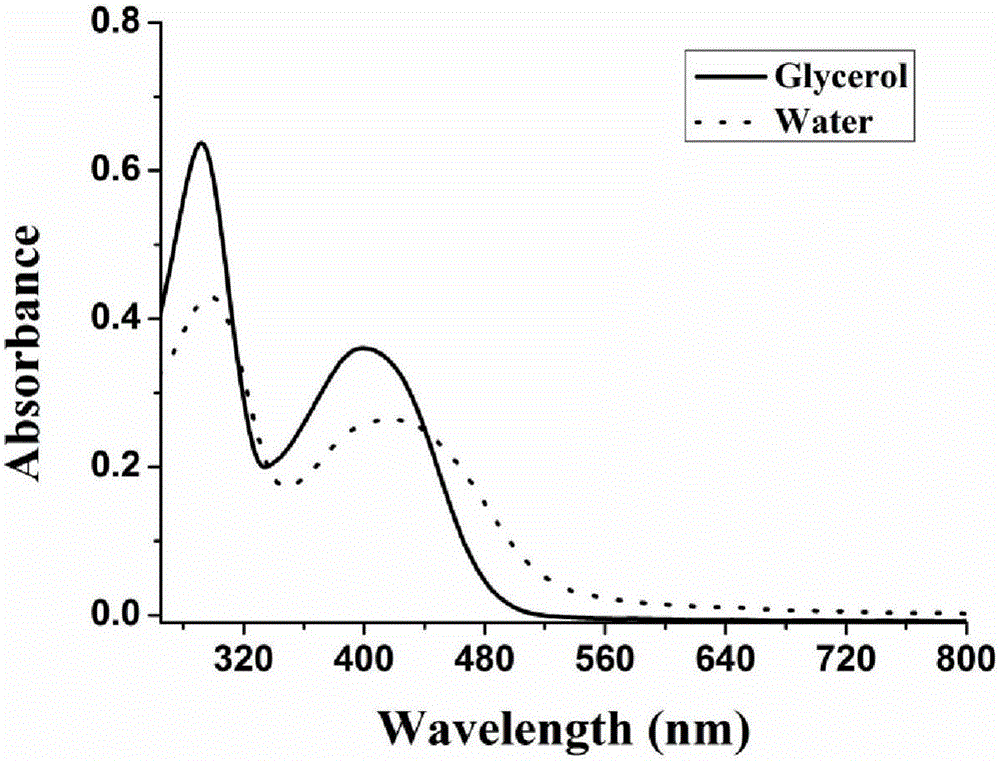
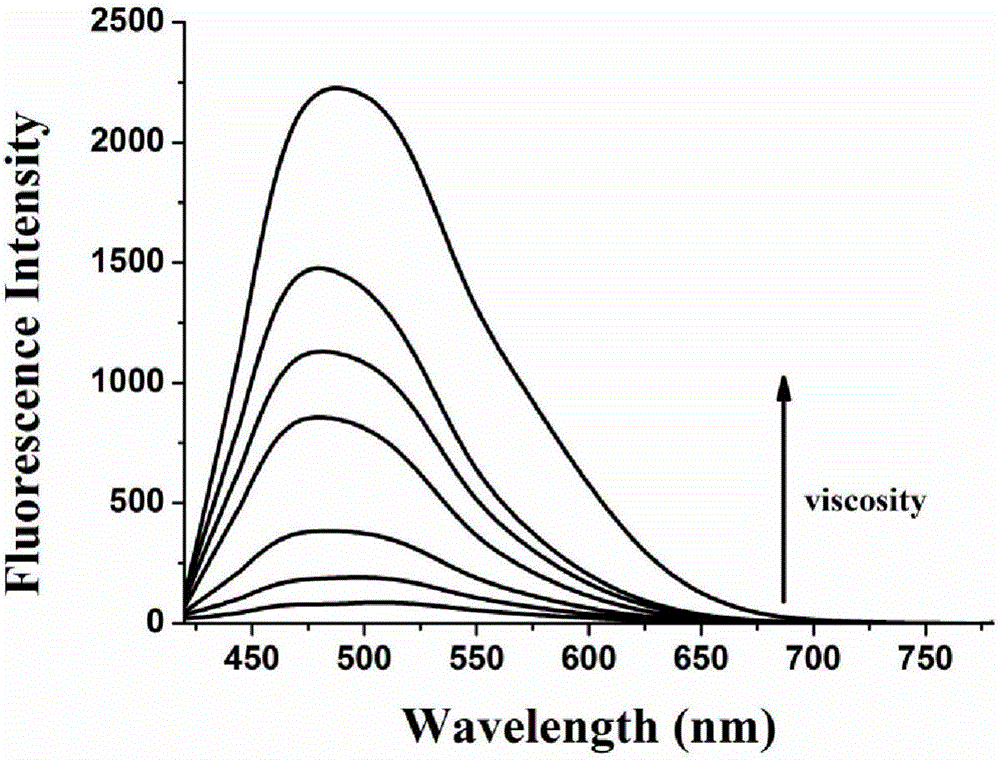
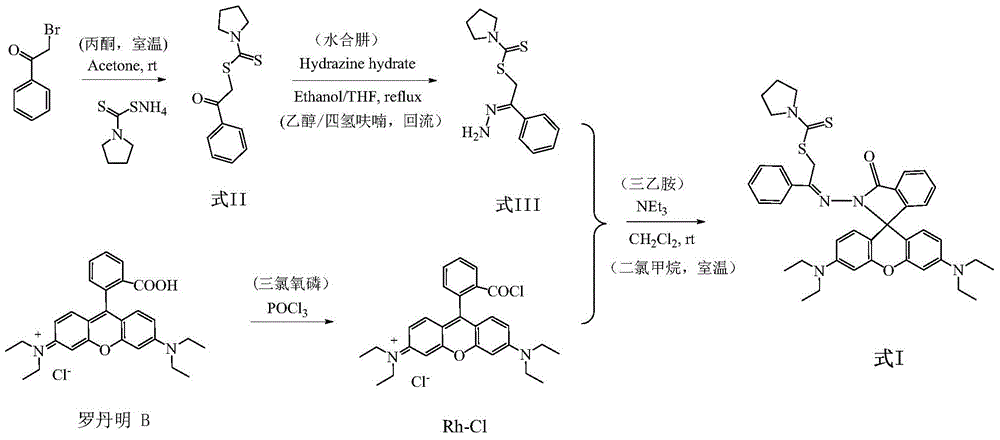
Patents
Literature
255 results about "Cell permeability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
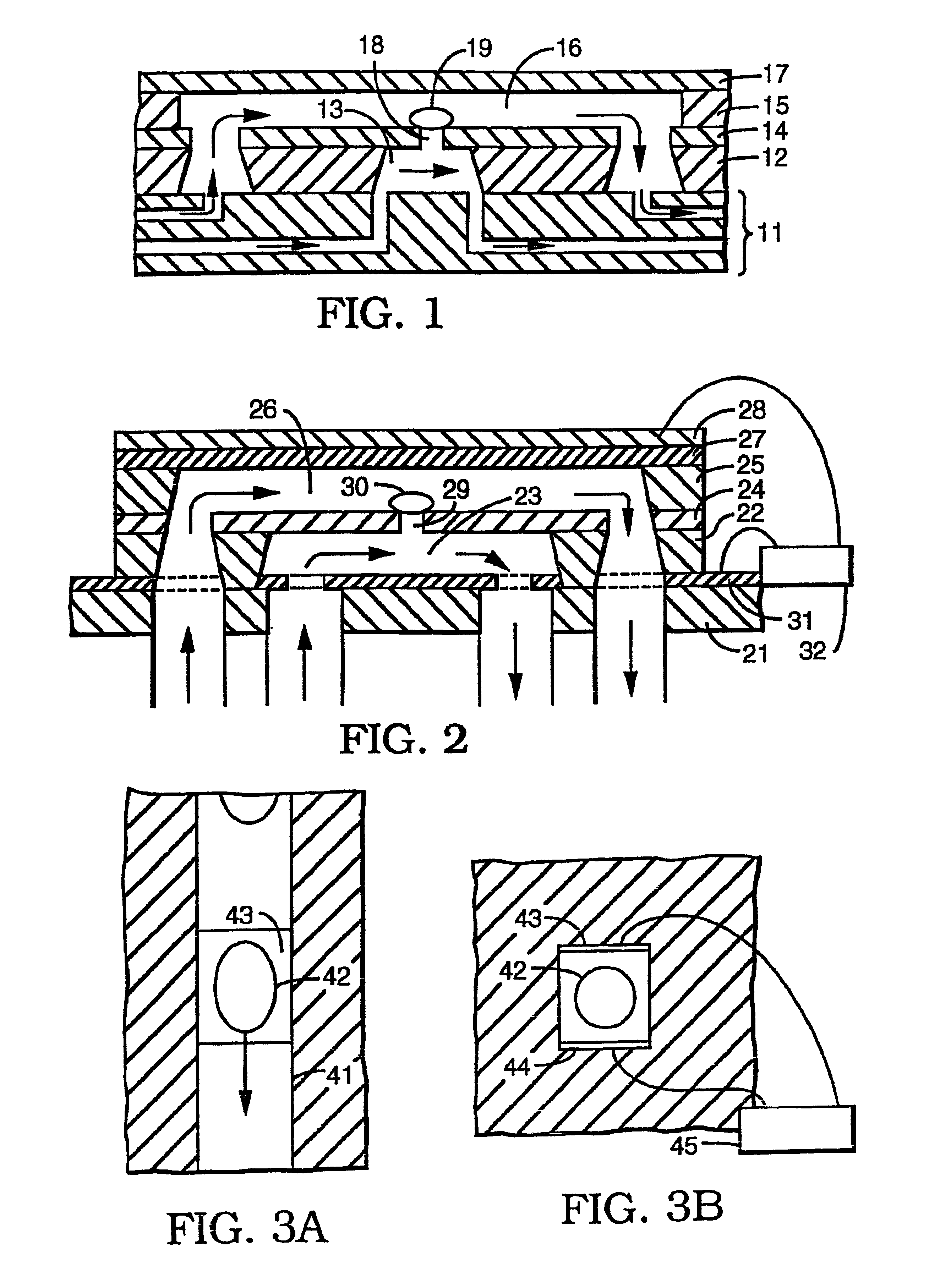
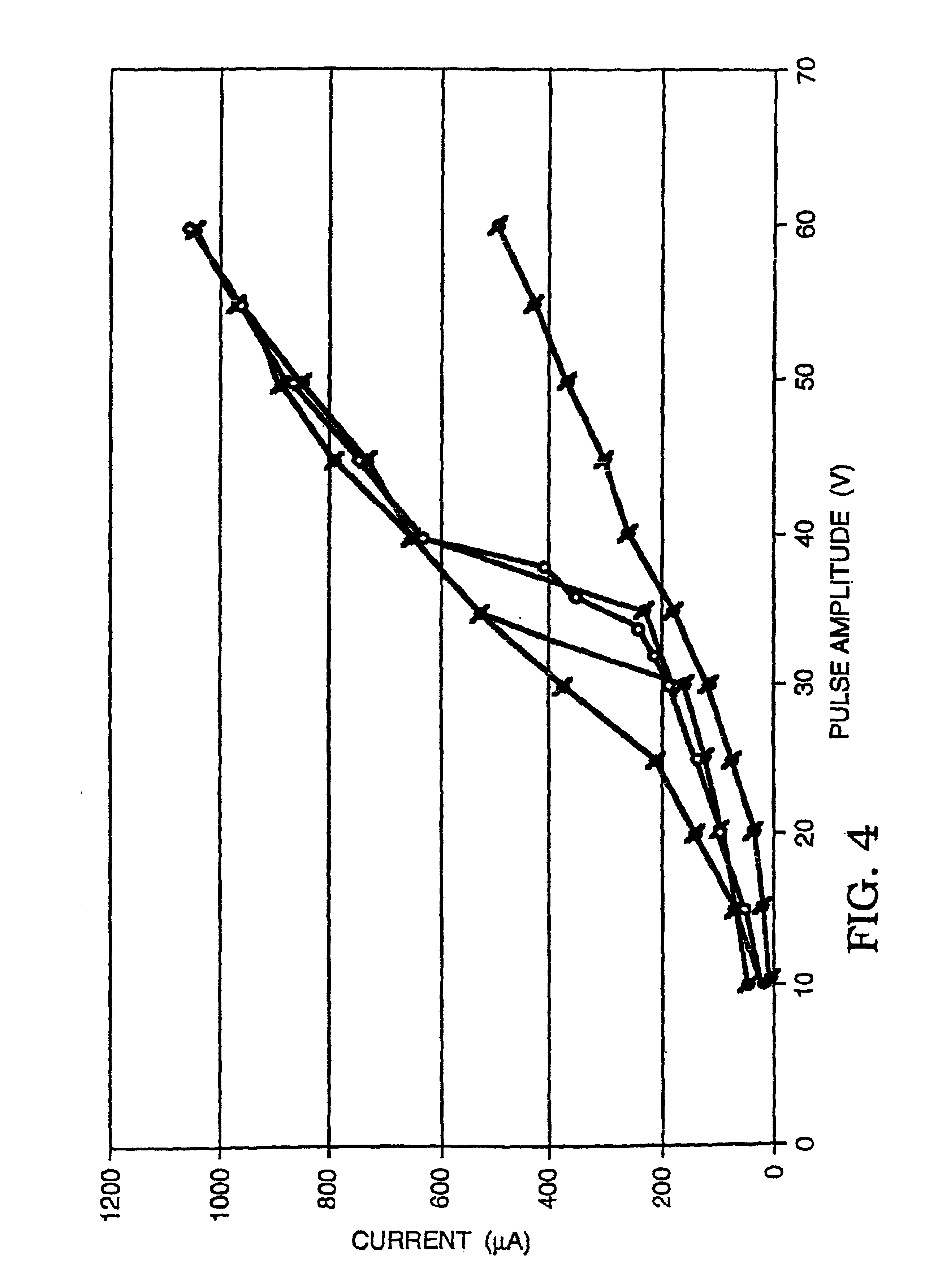
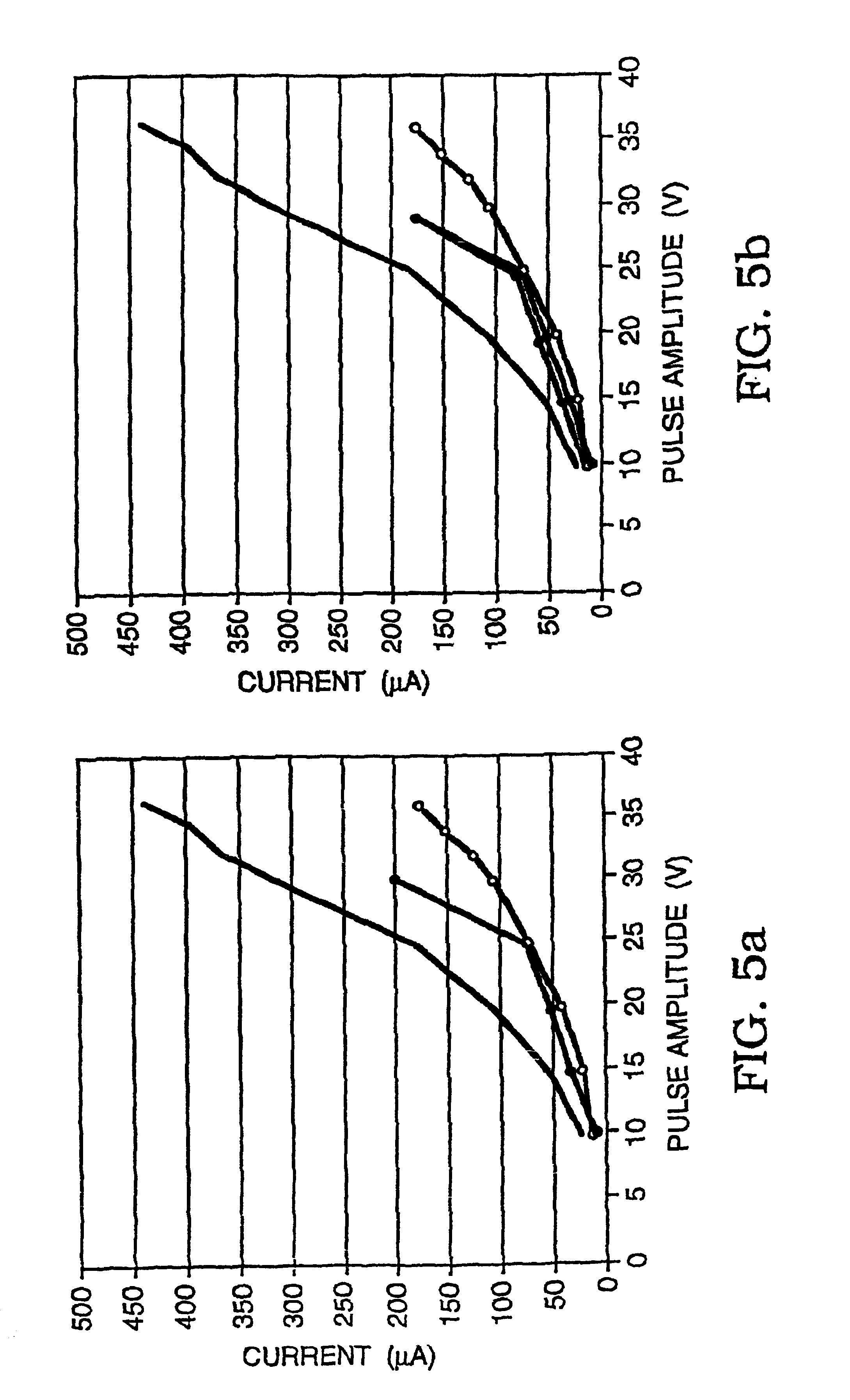
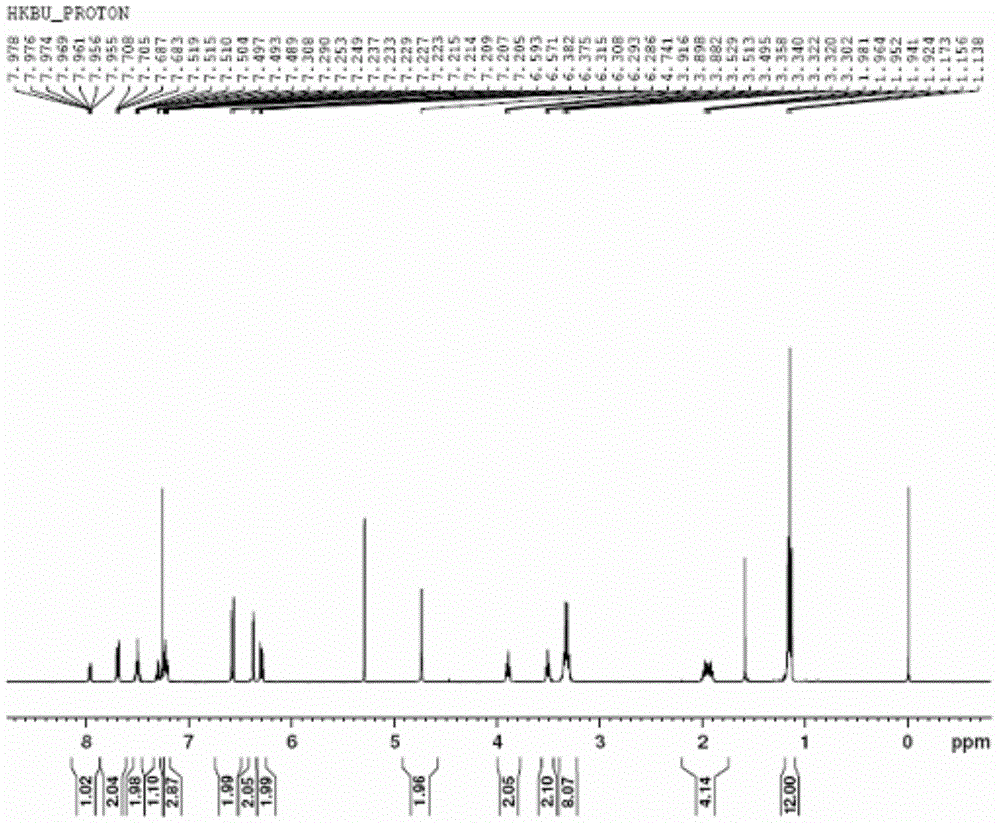
Cell viability detection using electrical measurements
InactiveUS6927049B2Quantitative measurementEnhanced informationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectricityCell membrane
A method of determining information about cell viability and other characteristics relating to cell membrane permeability is disclosed. The method involves determining the effect of a cell on current flow and relating that effect to a known standard which standard may be a known healthy cell and thereby deducing the viability of the cell being tested. The cells being tested can be subjected to different environmental conditions such as surrounding chemicals, temperature, pH and pressure to determine the effects of such conditions on cell viability and / or cell permeability. The cell being tested can be in a cell suspension, grown on s ubstarte, in tissue in vitro or in tissue in vivo. The method provides substantially instantaneous results and need not include the use of dyes or other markers.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method and system for systemic delivery of growth arresting, lipid-derived bioactive compounds
ActiveUS20050025820A1Maximizing systemic deliveryCorrection for dispersionOrganic active ingredientsMicroencapsulation basedDendrimerGene Therapy Agent
A system and method for optimizing the systemic delivery of growth-arresting lipid-derived bioactive drugs or gene therapy agents to an animal or human in need of such agents utilizing nanoscale assembly systems, such as liposomes, resorbable and non-aggregating nanoparticle dispersions, metal or semiconductor nanoparticles, or polymeric materials such as dendrimers or hydrogels, each of which exhibit improved lipid solubility, cell permeability, an increased circulation half life and pharmacokinetic profile with improved tumor or vascular targeting.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
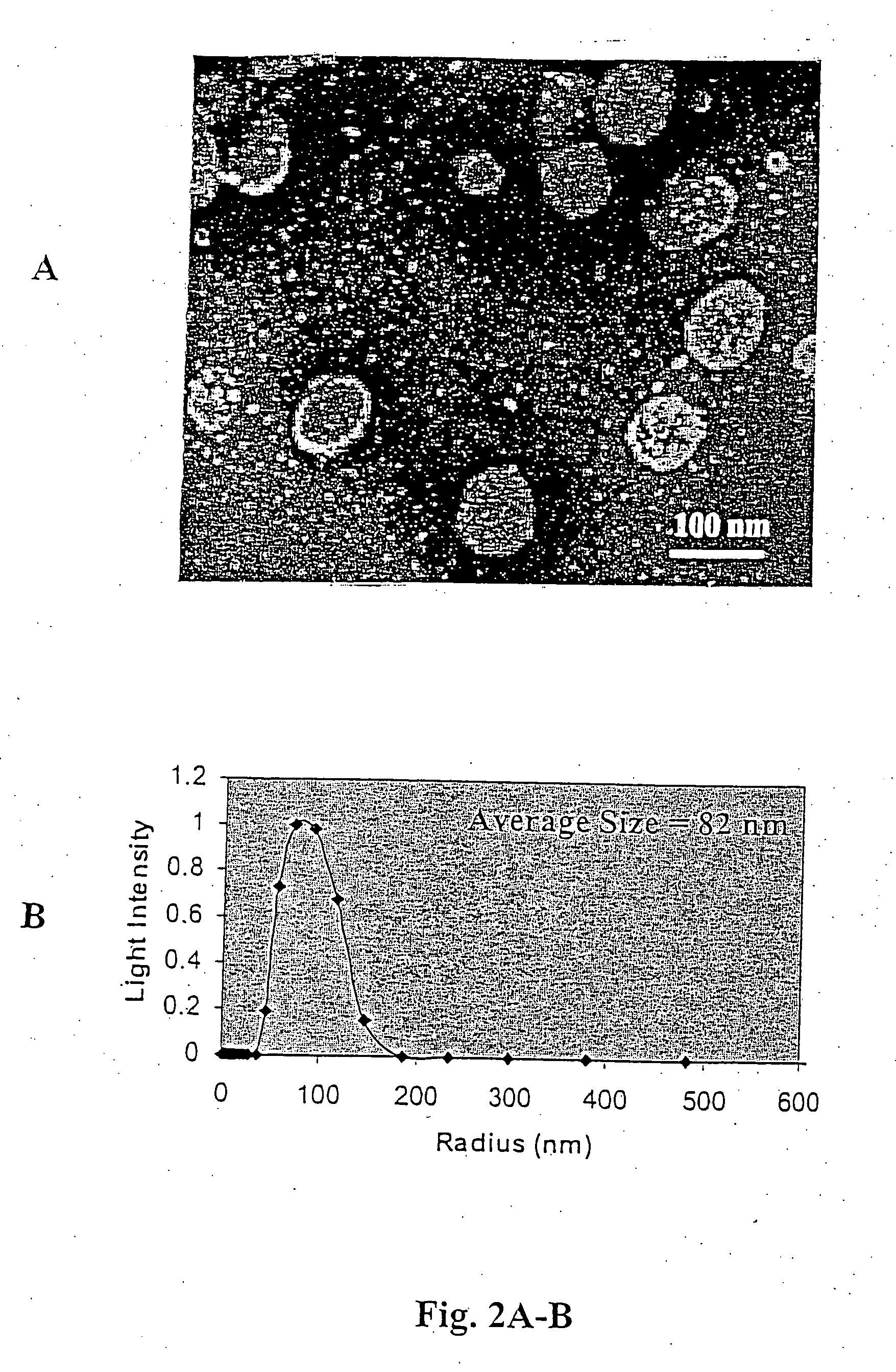
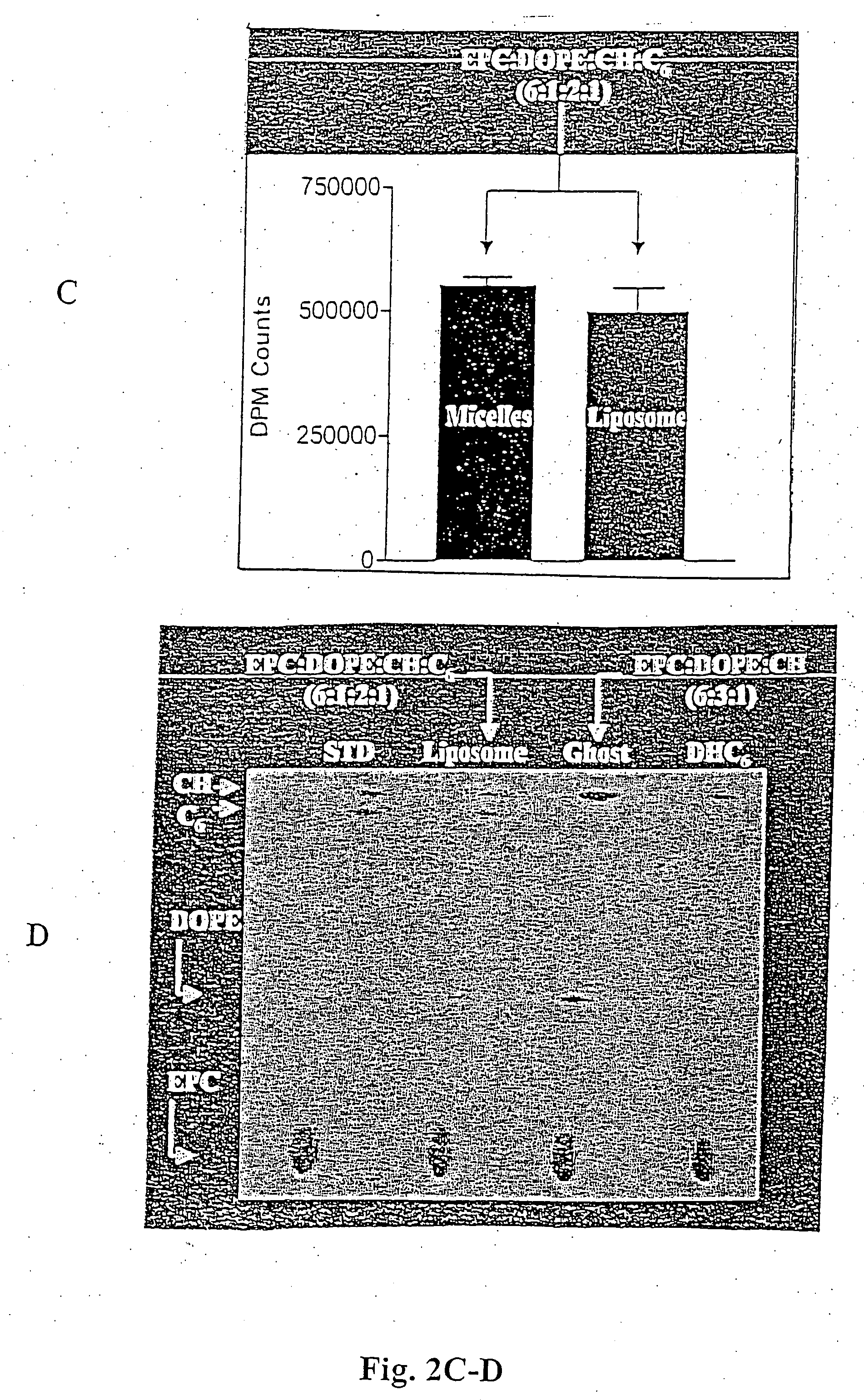
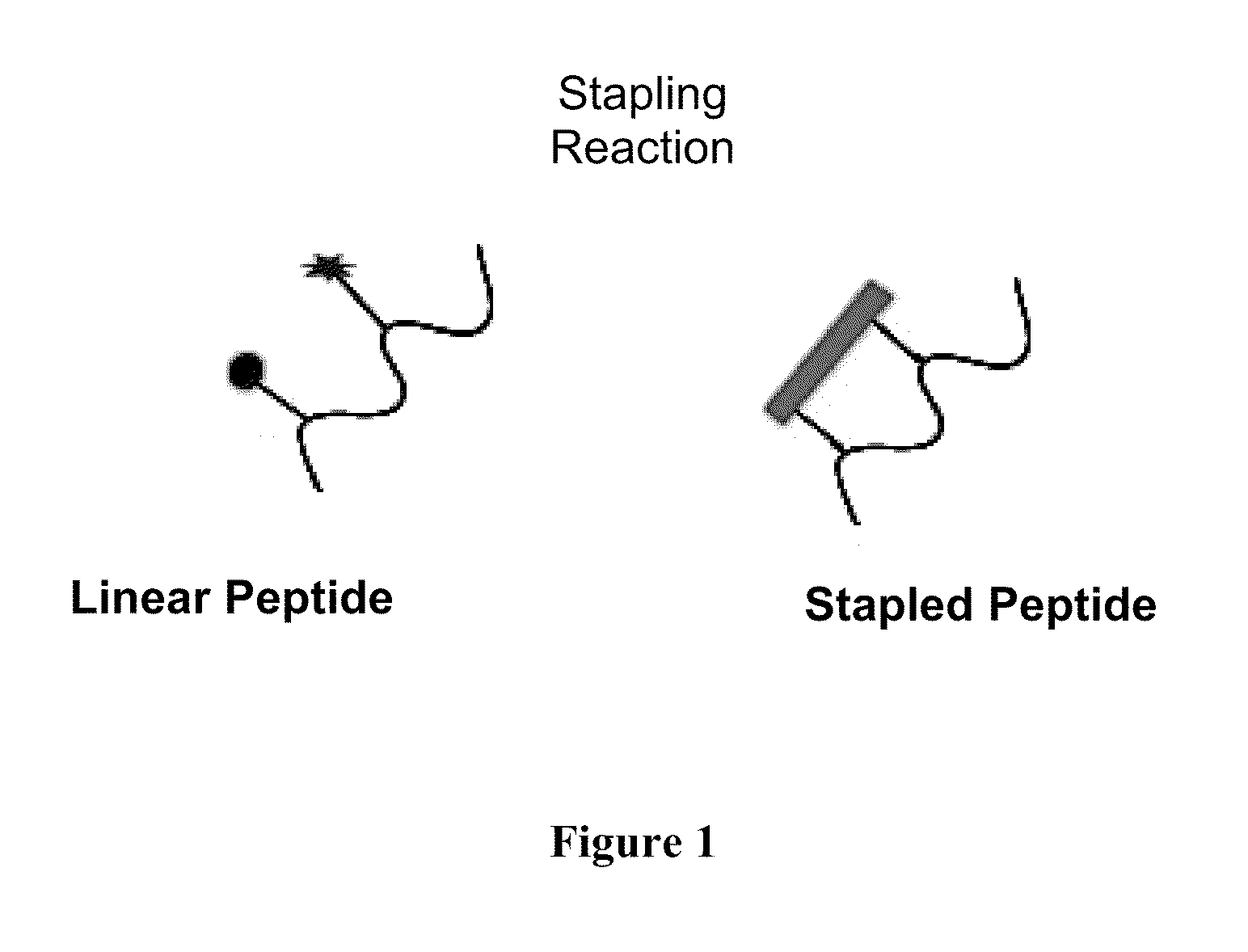
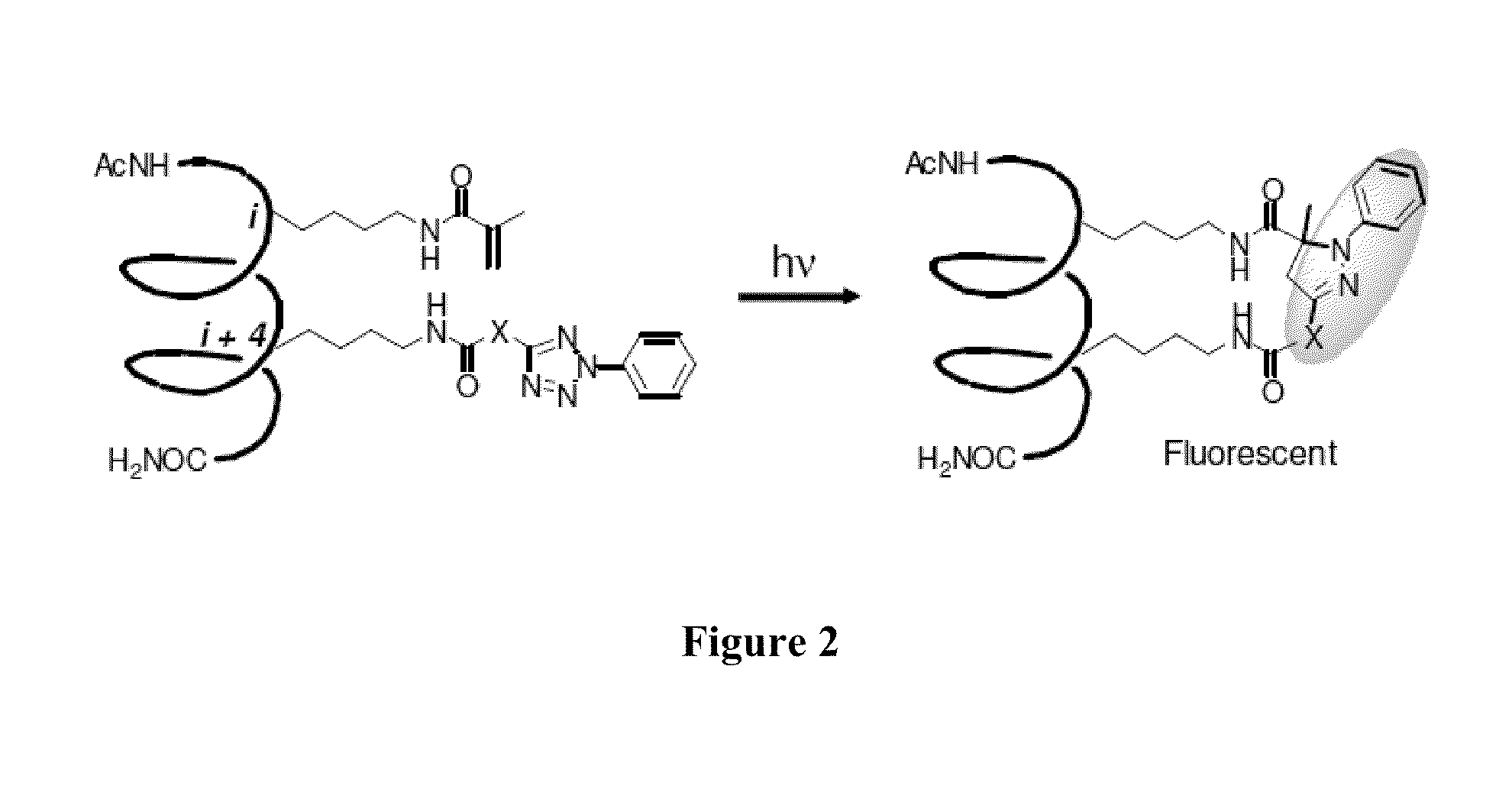
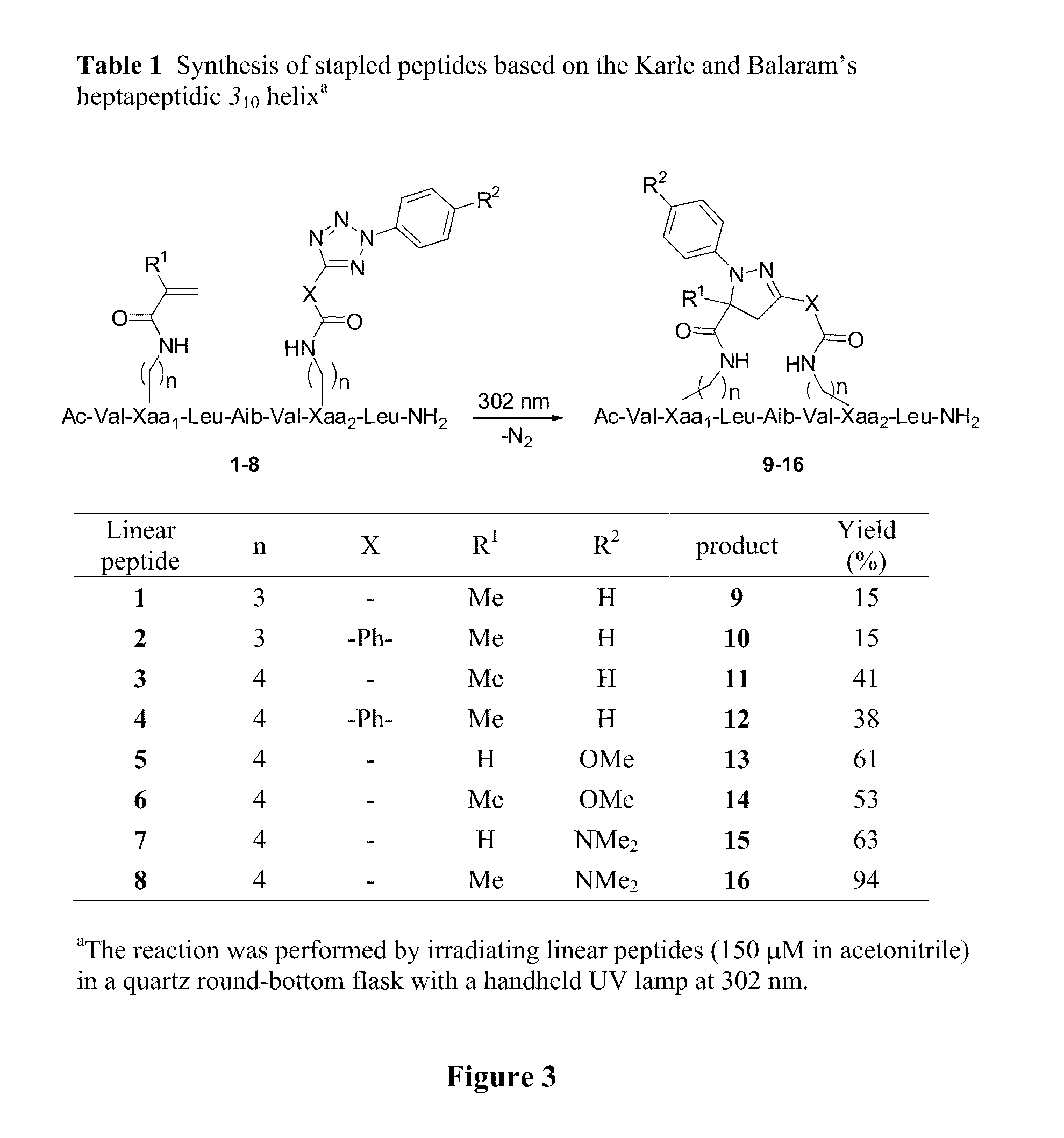
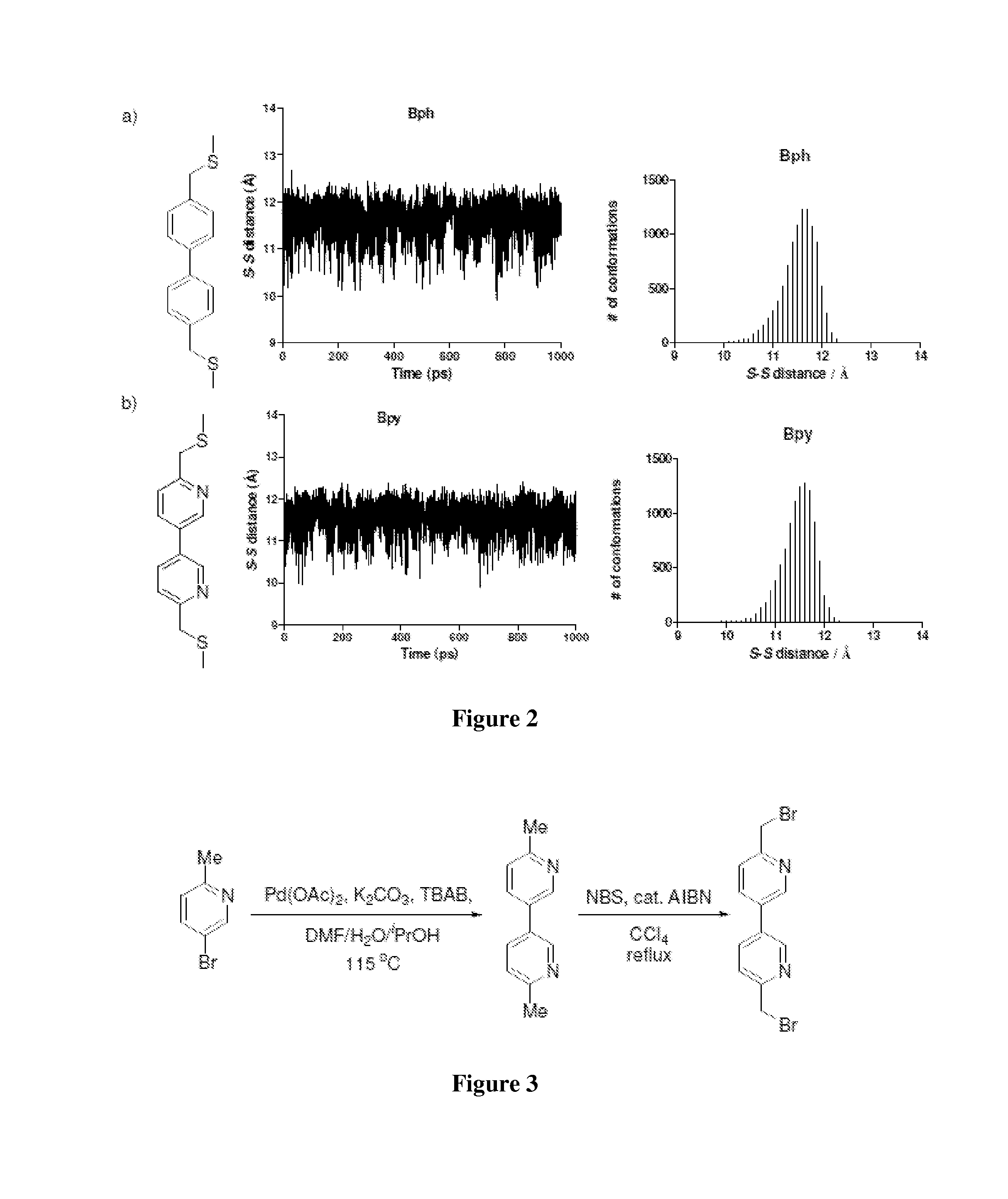
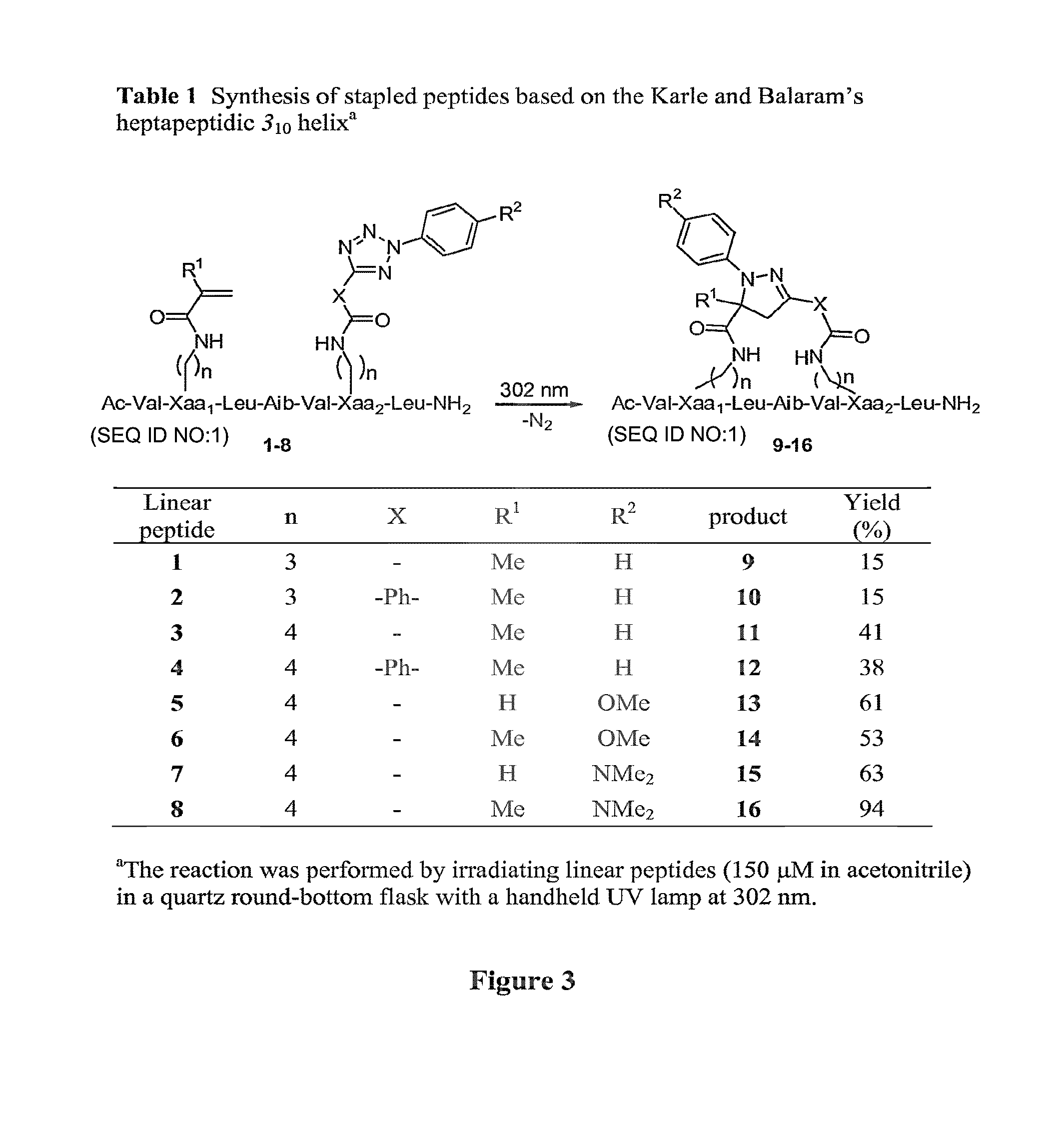
Stapled Peptides and Method of Synthesis
ActiveUS20100093086A1Reasonable reaction yieldSimple procedurePeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide sourcesCycloadditionStapled peptide
A method for preparing stapled peptides. The stapled peptides, including helical stapled peptides, are prepared according to a photochemically-based method, a [3+2] cycloaddition reaction. The helical stapled peptides exhibit increased helicity, thermal stability and cell permeability.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Ultrahigh-sensitivity fluorescent probe for detecting nitrogen monoxide
InactiveCN102617467AHigh selectivityHigh sensitivityGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsMicrobiological testing/measurementSolubilitySide effect
The invention relates to an ultrahigh-sensitivity fluorescent probe for detecting nitrogen monoxide. The ultrahigh-sensitivity fluorescent probe has the structural general formula in the original text. During preparation, firstly, 4-bromine-1, 8-anhydride naphthalene and o-nitro p-phenylenediamine with equal molar weights are used as raw materials, dissolved in ethylene glycol monomethyl ether and heated for reaction to obtain light yellow solid. Secondly, the light yellow solid is dissolved in anhydrous DMSO, primary amine is added into the anhydrous DMSO, the anhydrous DMSO is heated and refluxed, and reaction liquid is filtered in a sucking manner, depressurized and dried to obtain yellow solid. The yellow solid is dissolved in mixed liquid of tetrahydrofuran and methanol, and a yellow probe is obtained under catalysis of hydrogen and catalysts. Probe molecules have fine chemical and optical stability, good solubility and biological compatibility and high nitric oxide selectivity, and are free of interference of other active oxygen, active nitrogen and the like. Laser confocal imaging experiments indicate that the probe has fine cellular permeability, has no toxic and side effects on cells and organisms, and can be used for detecting protogenetic nitrogen monoxide in a high-sensitivity manner.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Blood cell detection reagent, blood cell processing method and blood cell identification method
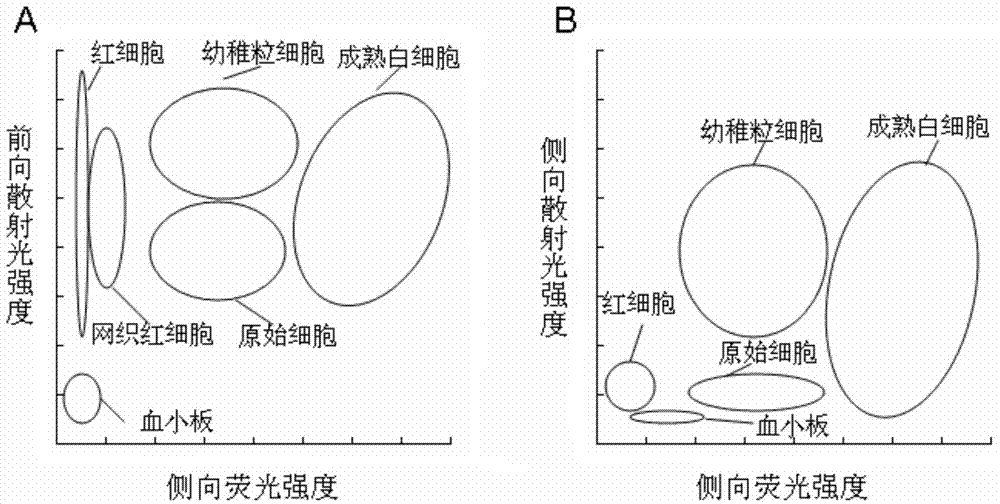
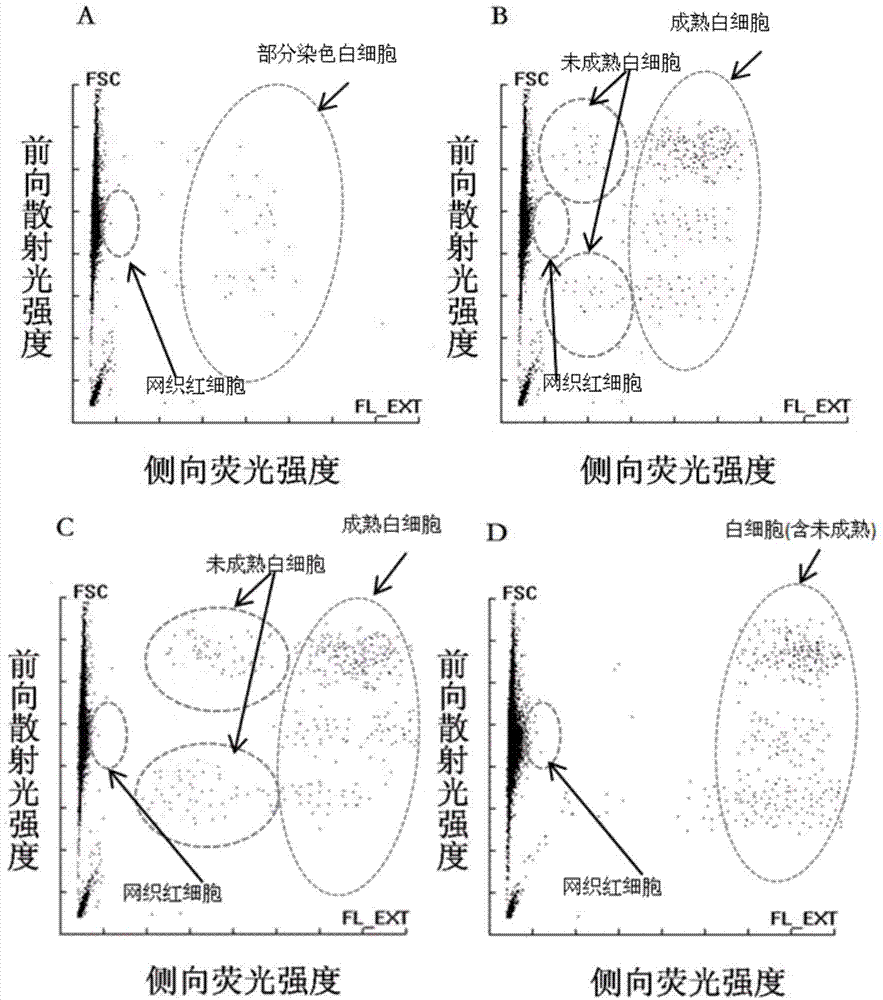
InactiveCN104749144AGood membrane permeabilityFluorescence/phosphorescenceErythrocyte membraneWhite blood cell
The invention relates to the blood cell detection field and discloses a blood cell detection reagent, a blood cell processing method and a blood cell identification method. The blood cell detection reagent comprises fluorescent dye, a sphericized component and organic alcohol, wherein the fluorescent dye has cell permeability and can specially stain the nucleic acid substance in the cell; the sphericized component can sphericize red blood cells, keep the red cell membrane to be intact and cannot damage the internal structure of the white blood cell; the organic alcohol can enhance the cell permeability and aids the fluorescent dye to enter the cells. The invention also discloses a blood cell processing method and a blood cell identification method. According to the blood cell detection reagent and the method, one kind of reagent can detect different blood cells at one time, and can particularly detect juvenile white blood cells and reticulated red blood cells simultaneously, therefore, the detection cost is greatly saved, the detection speed is increased and the instrument complexity is reduced.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Cell permeable conjugates of peptides for inhibition of protein kinases
InactiveUS20070078092A1Reduce generationAccelerated deathSenses disorderNervous disorderPTK InhibitorsDisease cause
The present invention provides inhibitors of protein kinases comprising a molecule having at least a first moiety competent for penetration of the molecule into cells, and a second moiety for having a protein kinase inhibiting effect within the cells. The first moiety is joined to the second moiety through a linker or a spacer. The complex molecules are preferably peptide conjugates having improved cell-permeability, serum stability and kinase selectivity compared to known protein kinase inhibitors. Pharmaceutical compositions that include these protein kinase inhibitors, and methods of using such compositions for treatment of cancers and other diseases associated with protein kinase activity are also disclosed.
Owner:CUREGENICS
Method for improving cell permeability to foreign particles
ActiveUS20070042358A1Useful in detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementInorganic non-active ingredientsCellular componentNuclear membrane
The present invention provides a method for allowing foreign particles to penetrate, very efficiently, the cell wall, cell membrane, organelle membrane and / or nuclear membrane of a cell and hybridizing or binding to the complimentary target in the cell. The cells may be from a culture or from specimens obtained from a patient. The foreign particle can be a probe consisting of, for example, either individually or in any combination of two or more of the following: DNA, RNA, peptide nucleic acids (PNA), glycopeptides, lipopeptides, glycolipids or prions. The target is a cell, a cell component or, preferably, a pathogen or pathogen component. The pathogen can be, for example, bacteria, fungi, yeast or viruses.
Owner:ID FISH TECH
Fluorescent probe for detecting sulfur ions in mitochondria and application thereof
ActiveCN103937490ARapid positioningGood chemical stabilityOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceSolubilitySide effect
The invention relates to a fluorescent probe for detecting sulfur ions in mitochondria. The fluorescent probe is an RhS fluorescent probe, and the structural general formula of the RhS fluorescent probe is shown in the formula (I). The fluorescent probe can be rapidly positioned in the mitochondria and used for performing online real-time detection on the sulfur ions and hydrogen sulfide ions in the mitochondria. In addition, the probe also has relatively good chemical and optical stability, relatively good solubility and bio-compatibility and relatively high sulfur ion selectivity without interferences caused by other species such as reactive oxygen, reactive nitrogen and the like. Laser confocal imaging experiments show that the probe has relatively good cell permeability without causing toxic or side effects to cells and organisms.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY
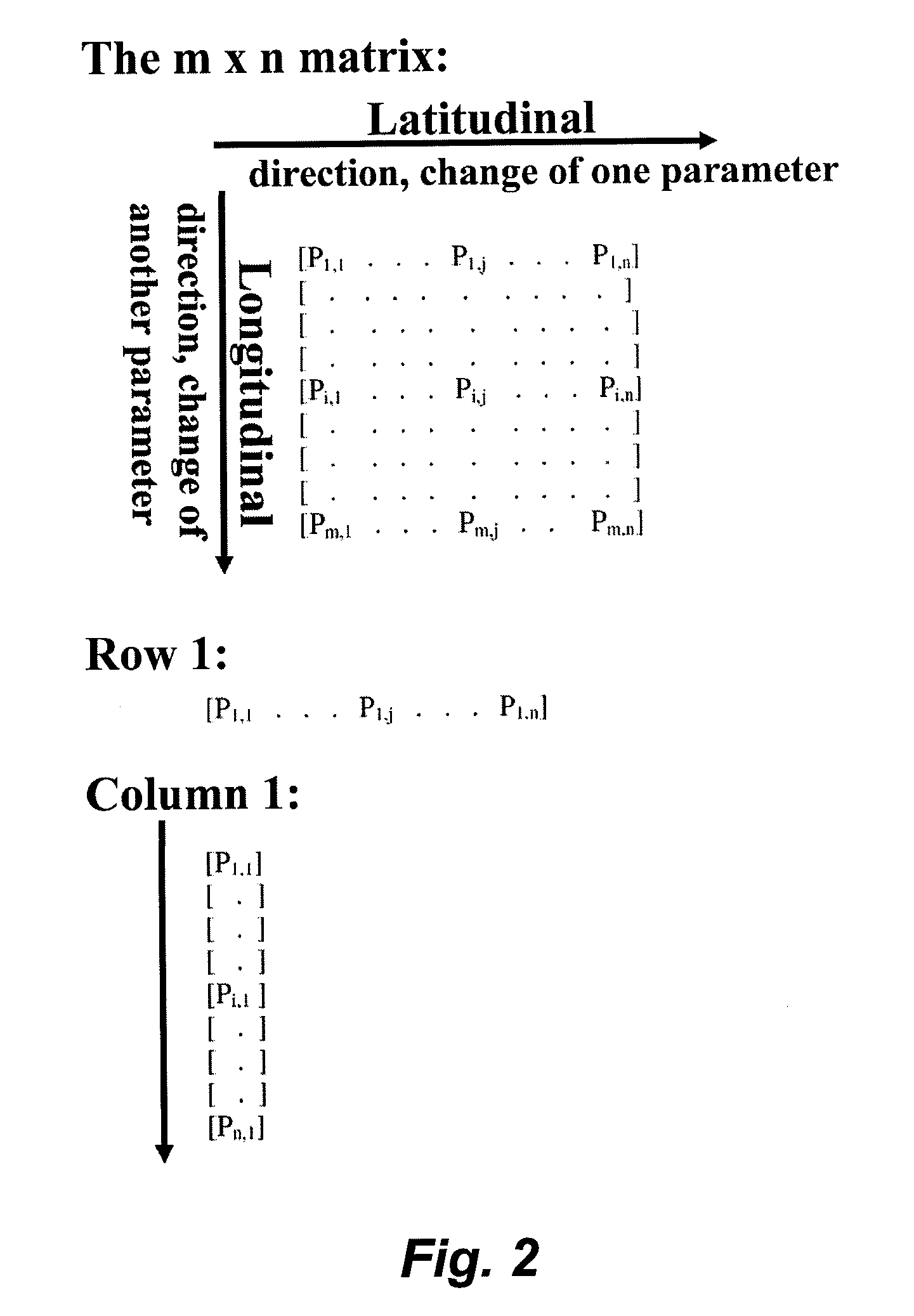
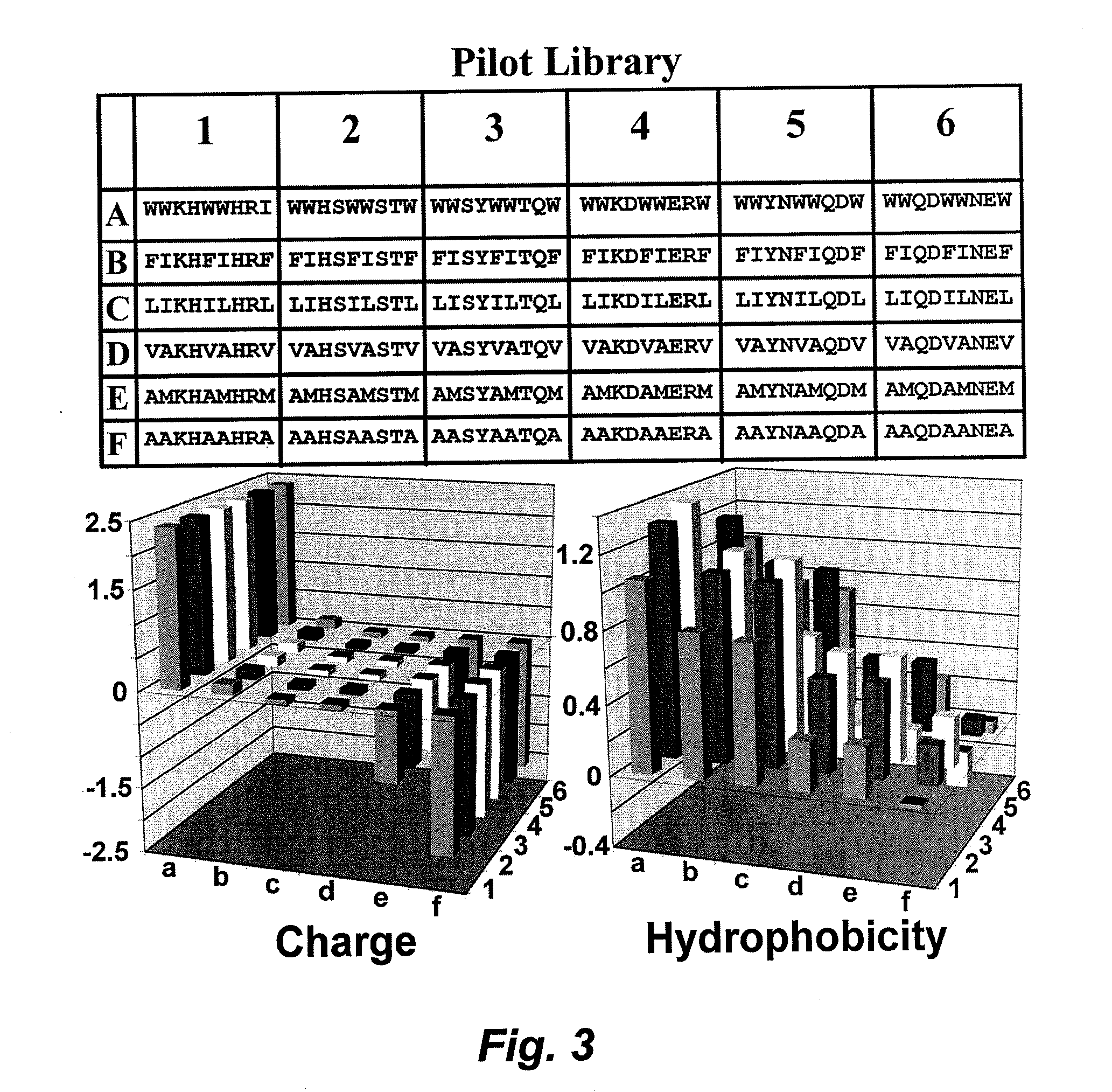
Sparse matrix system and method for identification of specific ligands or targets
InactiveUS20090298707A1Highly effective toolsManageable sizePeptide librariesPeptide/protein ingredientsSolubilityBiological property
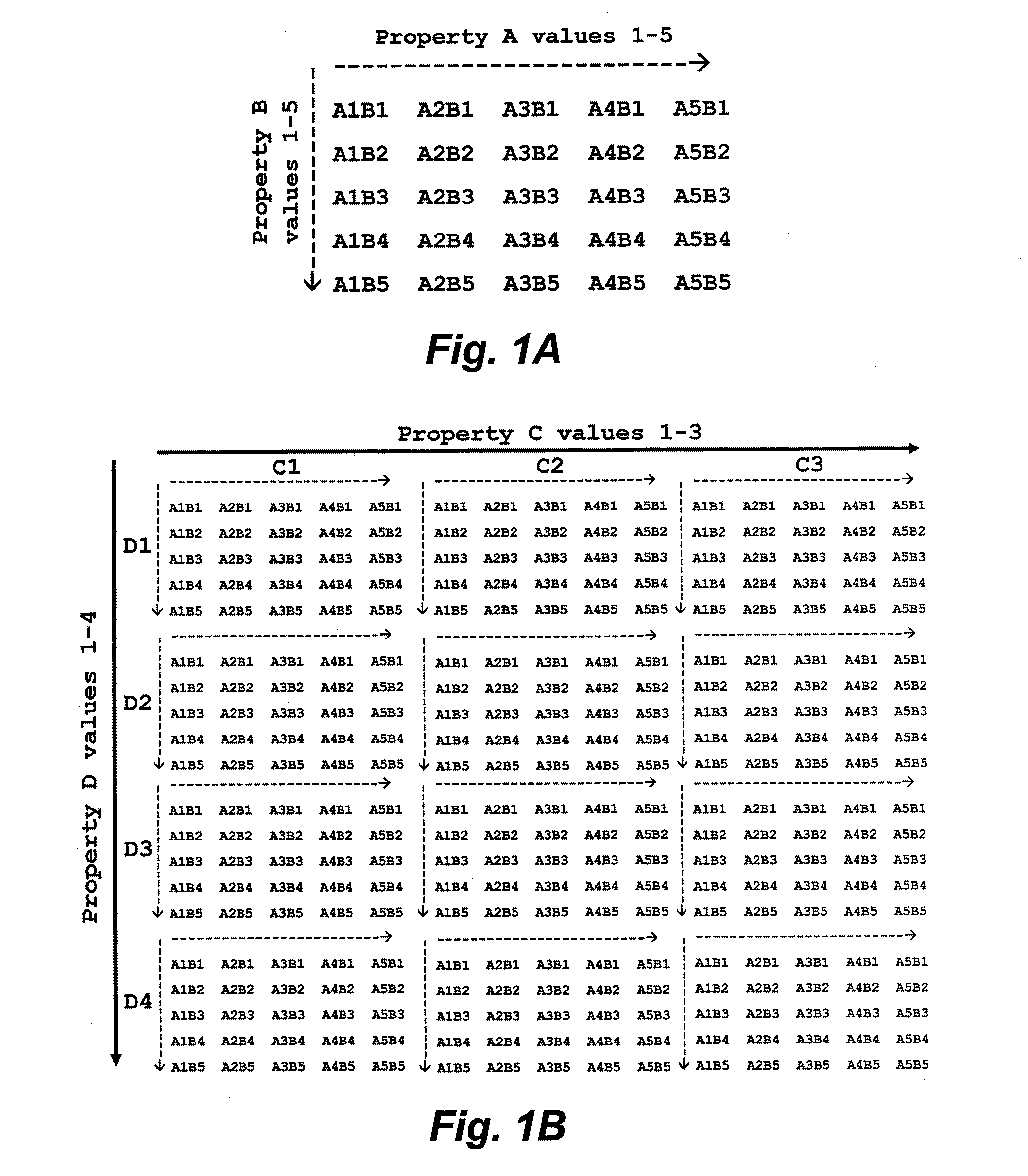
In certain embodiments, this invention pertains to the creation of “Sparse Matrix” libraries of compounds. The sparse matrix libraries of this invention typically span an n-dimensional parameter (property) space at extremely sparse intervals and thereby provide a relatively small library of compounds (e.g., a library of about 200 or fewer compounds) that can be used to quickly and efficiently screen the compound parameter space for one or more desired physical, chemical, or biological properties (e.g., binding specificity, binding avidity, γtoxicity, solubility, mobility, cell permeability, serum half-life, biocompatibility, etc.).
Owner:C3 JIAN +1
Method for improving cell permeability to foreign particles
The present invention provides a method for allowing foreign particles to penetrate, very efficiently, the cell wall, cell membrane, organelle membrane and / or nuclear membrane of a cell and hybridizing or binding to the complimentary target in the cell. The cells may be from a culture or from specimens obtained from a patient. The foreign particle can be a probe consisting of, for example, either individually or in any combination of two or more of the following: DNA, RNA, peptide nucleic acids (PNA), glycopeptides, lipopeptides, glycolipids or prions. The target is a cell, a cell component or, preferably, a pathogen or pathogen component. The pathogen can be, for example, bacteria, fungi, yeast or viruses.
Owner:ID FISH TECH
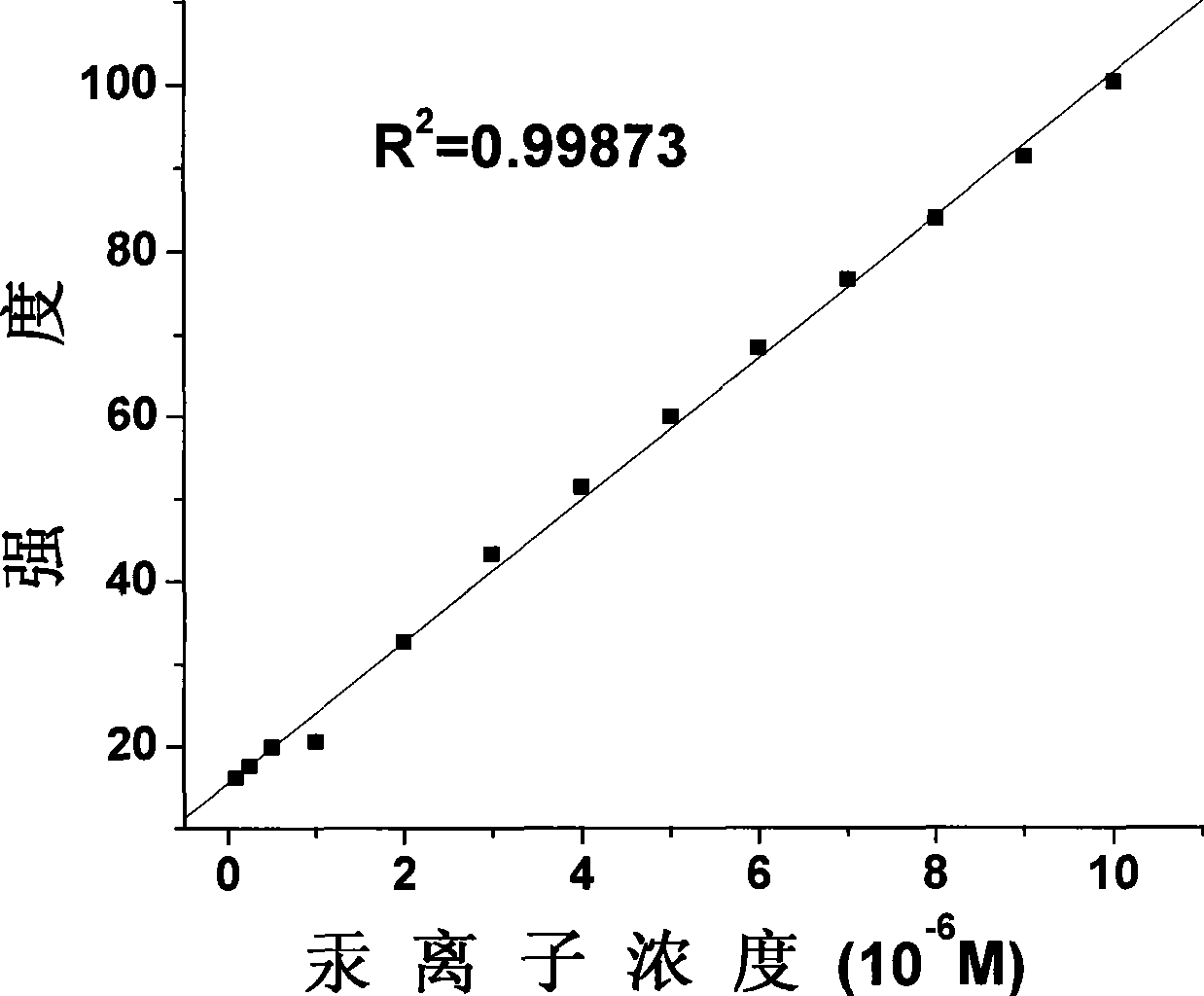
Fluorescent probe for detecting mercury ion in cell, and synthesizing method and usage
InactiveCN101368945ANo side effectsGood choiceBiological testingLuminescent compositionsSide effectIon
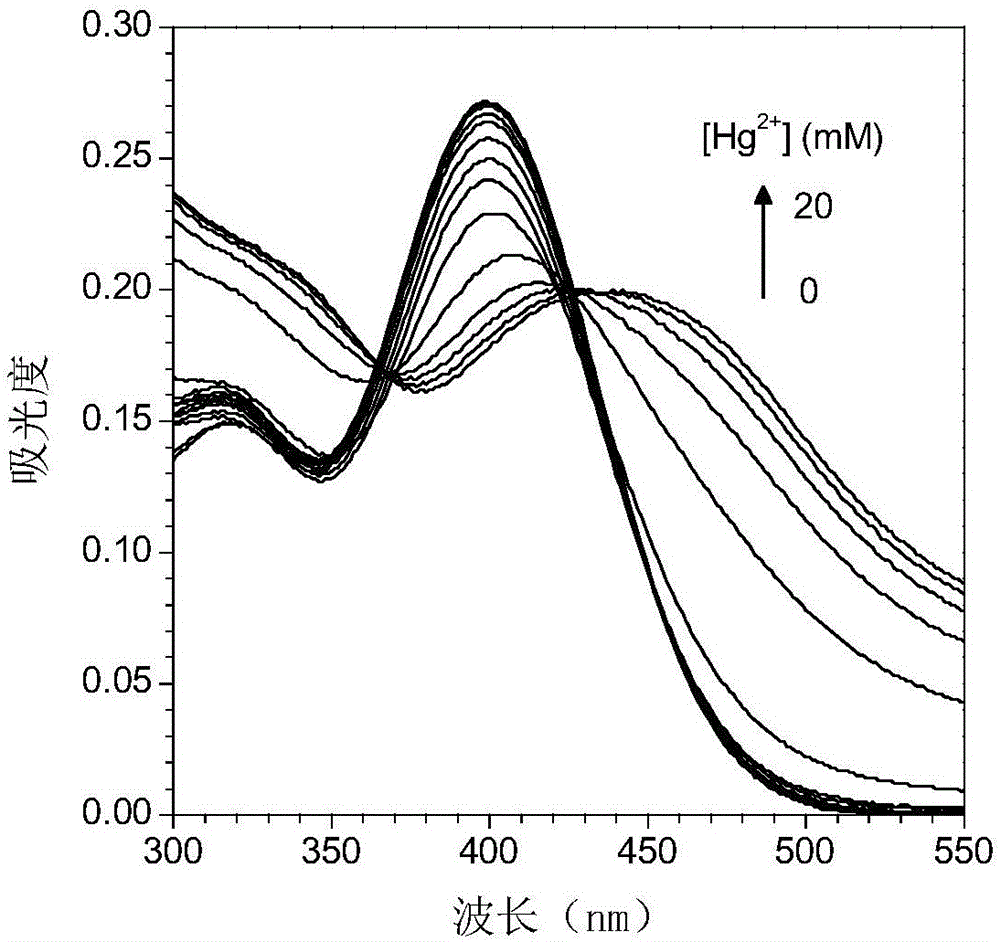
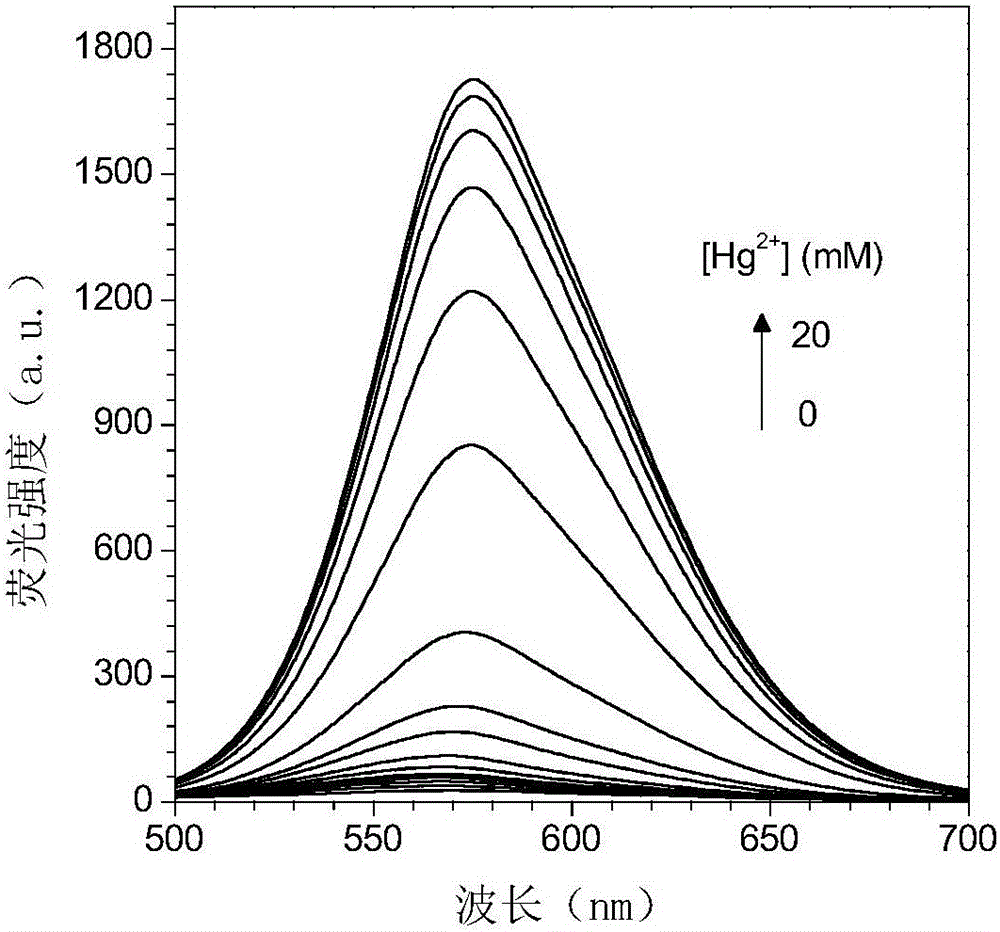
The invention relates to a fluorescent probe for detecting the intracellular mercury ions, a synthesizing method thereof and the purposes. The fluorescent probe has a good selectivity on the mercury ions and also has good cell permeability; and the probe has no toxic side effects and is applied to the intracellular mercury ion detection. The method comprises the following steps: dissolving 1 mol of 3-carboxyl rhodamine into a dry organic solvent, slowly dripping 1-2 mol of POCl3 under stirring, heating, refluxing, removing the organic solvent and obtaining the crude rhodamine chloride; dissolving 1 mol of 2-aminoethanethiol hydrochloride or cystamine dihydrochloride in a dry organic solvent, adding 4-8 mol of acid binding agent, slowing dripping the obtained rhodamine chloride in ice bath, removing the organic solvent and obtaining the target product of the formula (I) or the formula (II), wherein, X is O; and dissolving the equivalent mol of the target product and the Lawson reagent in a dry organic solvent, heating and refluxing under the protection of inert gas, and finally obtaining the target product of the formula (I) or the formula (II) through column chromatography separation , wherein, X is S.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
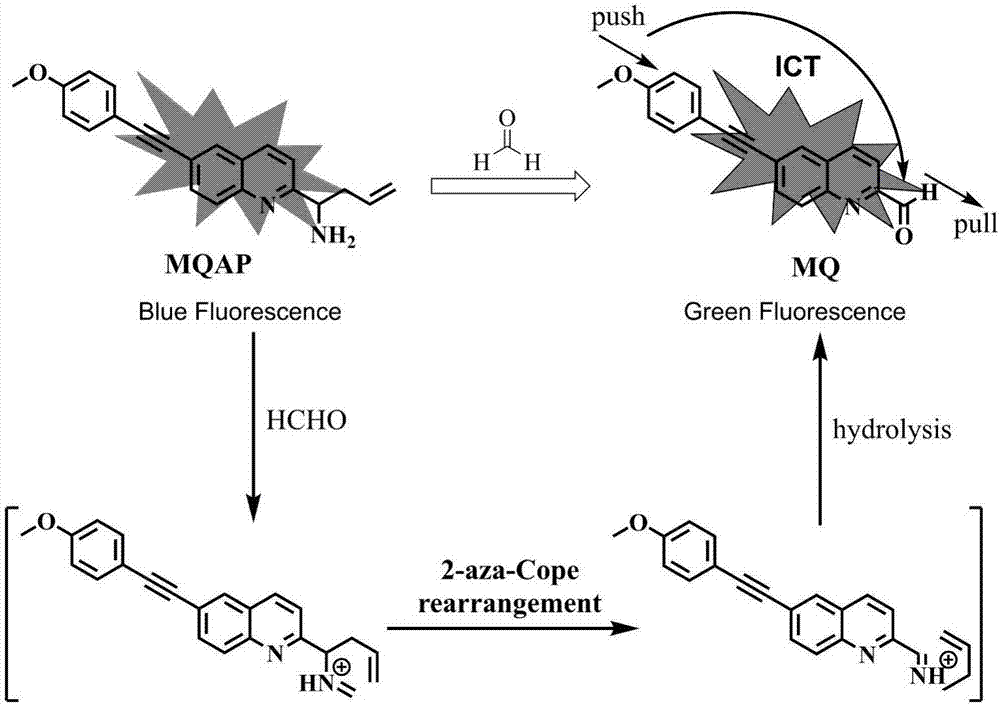
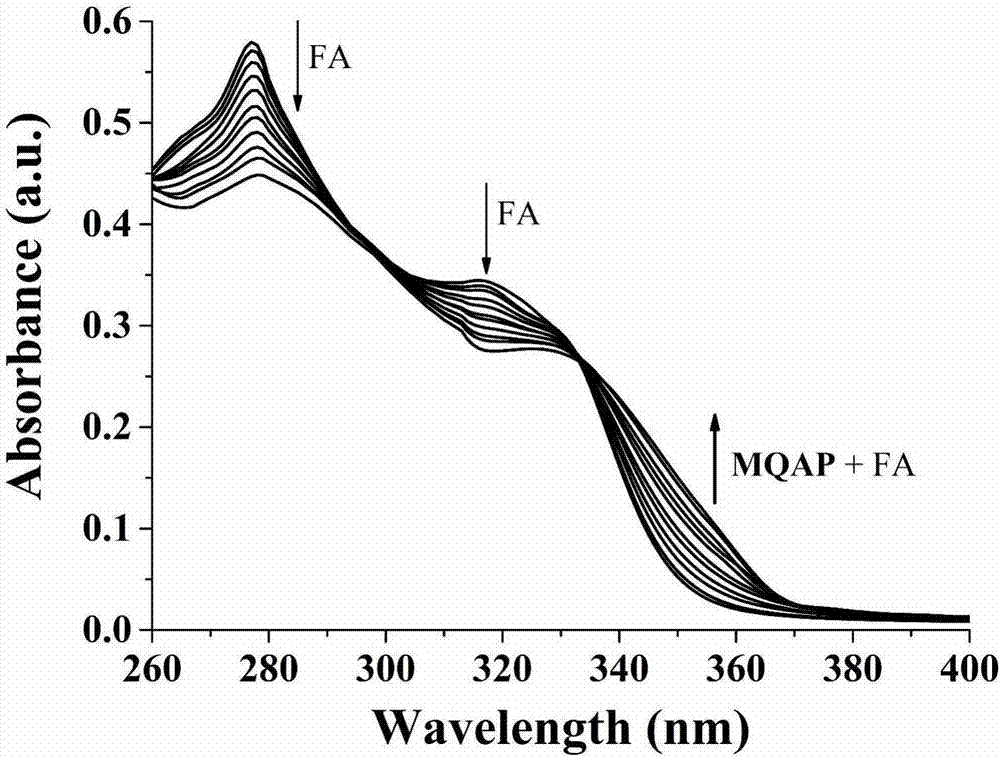
Ratio-type two-photon formaldehyde fluorescent probe, preparation method therefor and use of ratio-type two-photon formaldehyde fluorescent probe
ActiveCN106946773ALow fluorescence quantum yieldSimple structureOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicro imagingCytotoxicity testing
The invention discloses a ratio-type two-photon formaldehyde fluorescent probe, a preparation method therefor and use of the ratio-type two-photon formaldehyde fluorescent probe. The ratio-type two-photon formaldehyde fluorescent probe has a structure as follows shown in the description. Molecules of the fluorescent probe disclosed by the invention show relatively high selectivity and sensitivity to formaldehyde in a coexisting system of molecules of the formaldehyde and other aldehydes, amino acids and the like. Proven by cytotoxicity tests, the molecules of the fluorescent probe disclosed by the invention are almost free of toxic action on cells; and shown by two-photon fluorescence microscopy imaging experiments, the molecules of the fluorescent probe disclosed by the invention have good cell permeability to MCF-7 cells, so that the fluorescent probe is applicable to the detection of presence of formaldehyde molecules in the cells.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
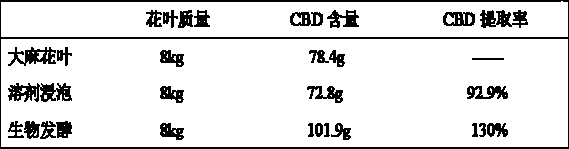
Process for improving extraction rate of cannabidiol by treating flowers and leaves of Cannabis sativa by using microorganisms
InactiveCN110041172AImprove permeabilityEasy extractionOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationCannabis sativa plantPlant cell
The invention belongs to the field of plant extraction, and particularly relates to a method for treating industrial flowers and leaves of Cannabis sativa by using microorganisms and improving the extraction rate of cannabidiol. The method comprises the following steps: 1) separating one or more fungi by using the industrial Cannabis sativa plants, and culturing and propagating the fungi, then fermenting the industrial flowers and leaves of Cannabis sativa by using the fungi to effectively destroy cell walls, so that the cell permeability of the flowers and leaves of Cannabis sativa is improved; 2) extracting and filtering the fermented flowers and leaves of Cannabis sativa by using organic solvents such as ethanol and n-hexane, and concentrating the obtained filtrate under reduced pressure in vacuum to obtain crude extract containing cannabidiol; 3) separating and purifying the cannabidiol from the extract by silica gel column chromatography; and 4) further purifying cannabidiol through crystallization to obtain the high-purity CBD crystal with the liquid phase content of 99.2%. According to the method, the enzymatic reaction of microorganisms is fully utilized to destroy plant cell walls, the extraction efficiency of a target object reaches 110-130%, the production cost is effectively reduced, and the method is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:YUNNAN LVXIN BIOLOGICAL PHARMA CO LTD
Probe capable of realizing two-photon fluorescence detection of nitroreductase (NTR) and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108727223AGood chemical stabilityGood biocompatibilityCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationNitroreductaseSide effect
The invention relates to preparation of a probe capable of realizing two-photon fluorescence detection of nitroreductase (NTR) as shown in the figure (I) and belongs to the field of organic fluorescent probes. The structural formula of the probe capable of realizing two-photon fluorescence detection of the NTR is as shown in the description. The fluorescent probe provided by the invention can accurately detect the content of the NTR in cells and avoid the interference of other reducing agents in cells. In addition, the probe has the characteristics of better chemical stability, biological compatibility and selectively and the like. A laser confocal imaging experiment shows that the probe has better cell permeability, has no toxic and side effects on cells and organisms, can realize detection of content of cell level NTR and indicate the cell hypoxia condition, and can be further applied to research of precancerous detection.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
Two-photon viscosity fluorescence probe as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105801479ASimple structureEasy to synthesizeOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceSignal responseQuinoline
The invention discloses a two-photon viscosity fluorescence probe as well as a preparation method and application thereof. With quinoline as parent, the two-photon viscosity fluorescence probe has a structure shown in the specification. The two-photon viscosity fluorescence probe disclosed by the invention realizes specific fluorescence signal response to viscosity. Cell toxicity tests indicate that the two-photon viscosity fluorescence probe rarely causes toxic and side effects on cells; and two-photon confocal fluorescence microscopy imaging experiments show that the two-photon viscosity fluorescence probe has good cell permeability to HeLa cells and can be adapted to intracellular viscosity detection.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
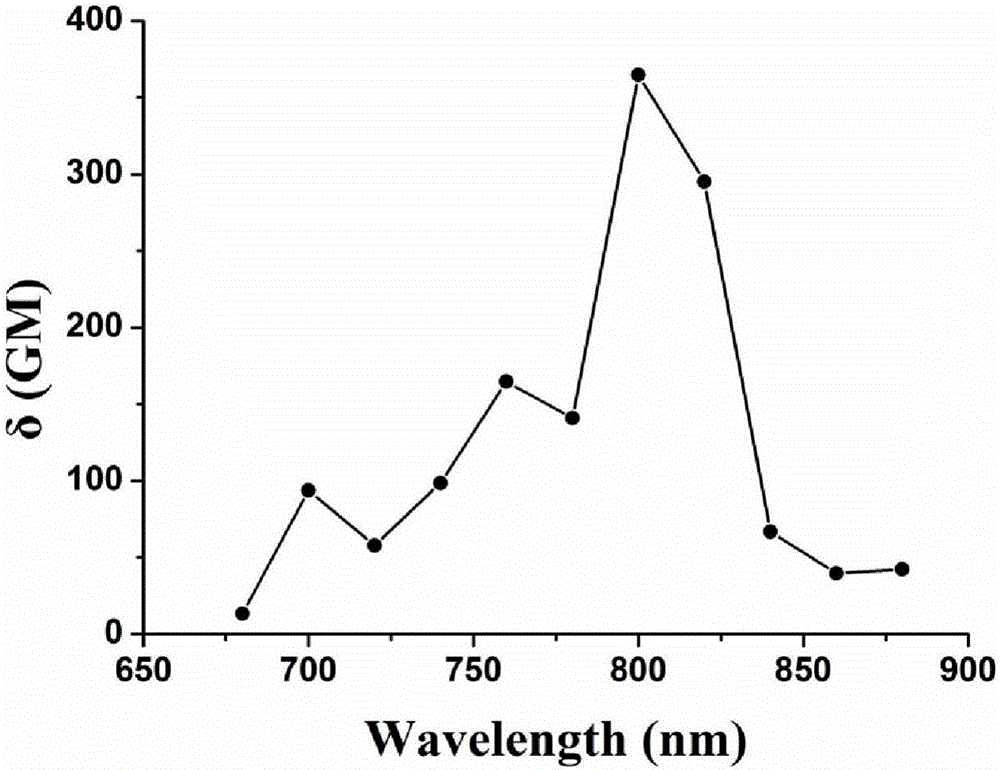
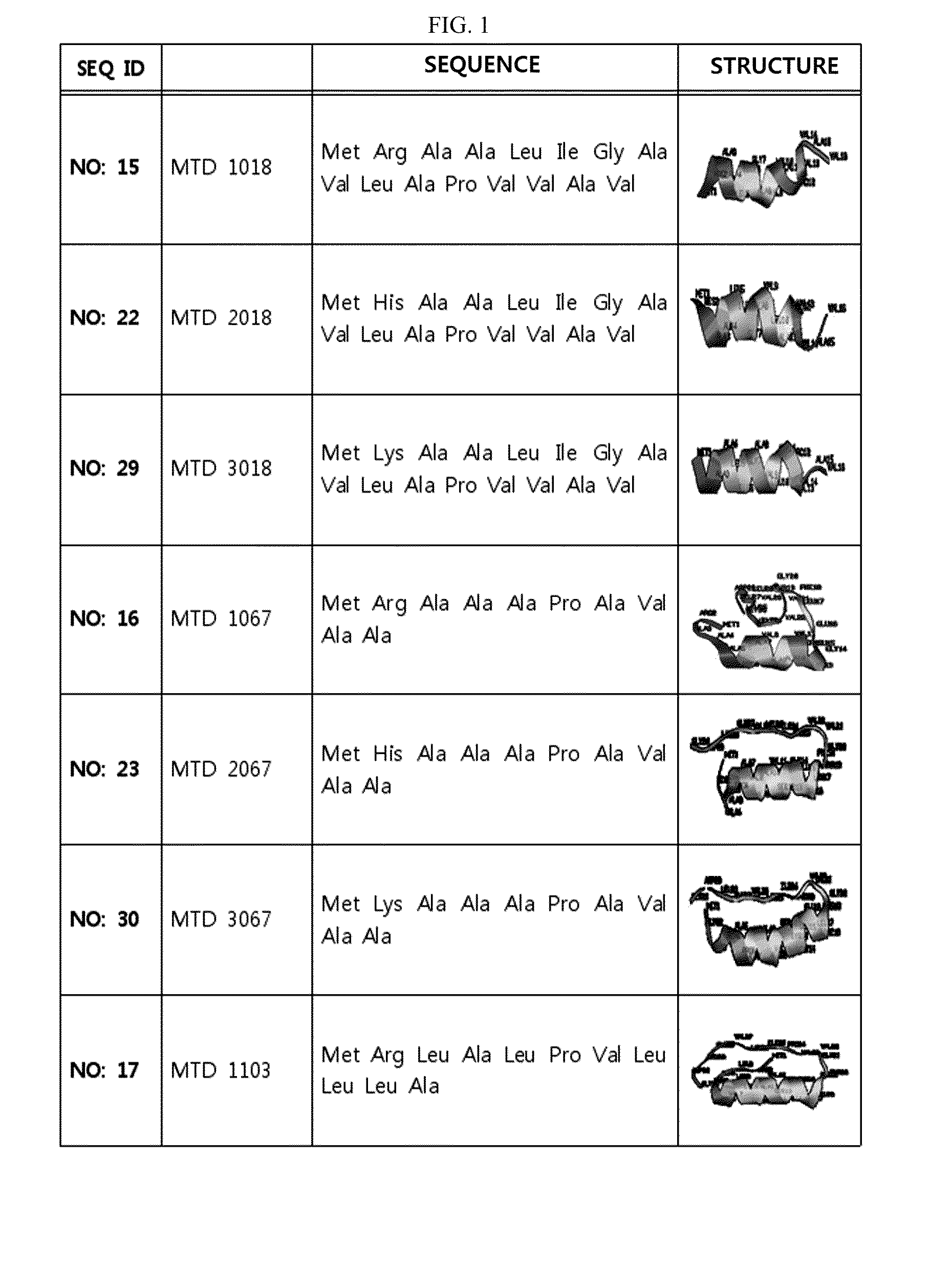
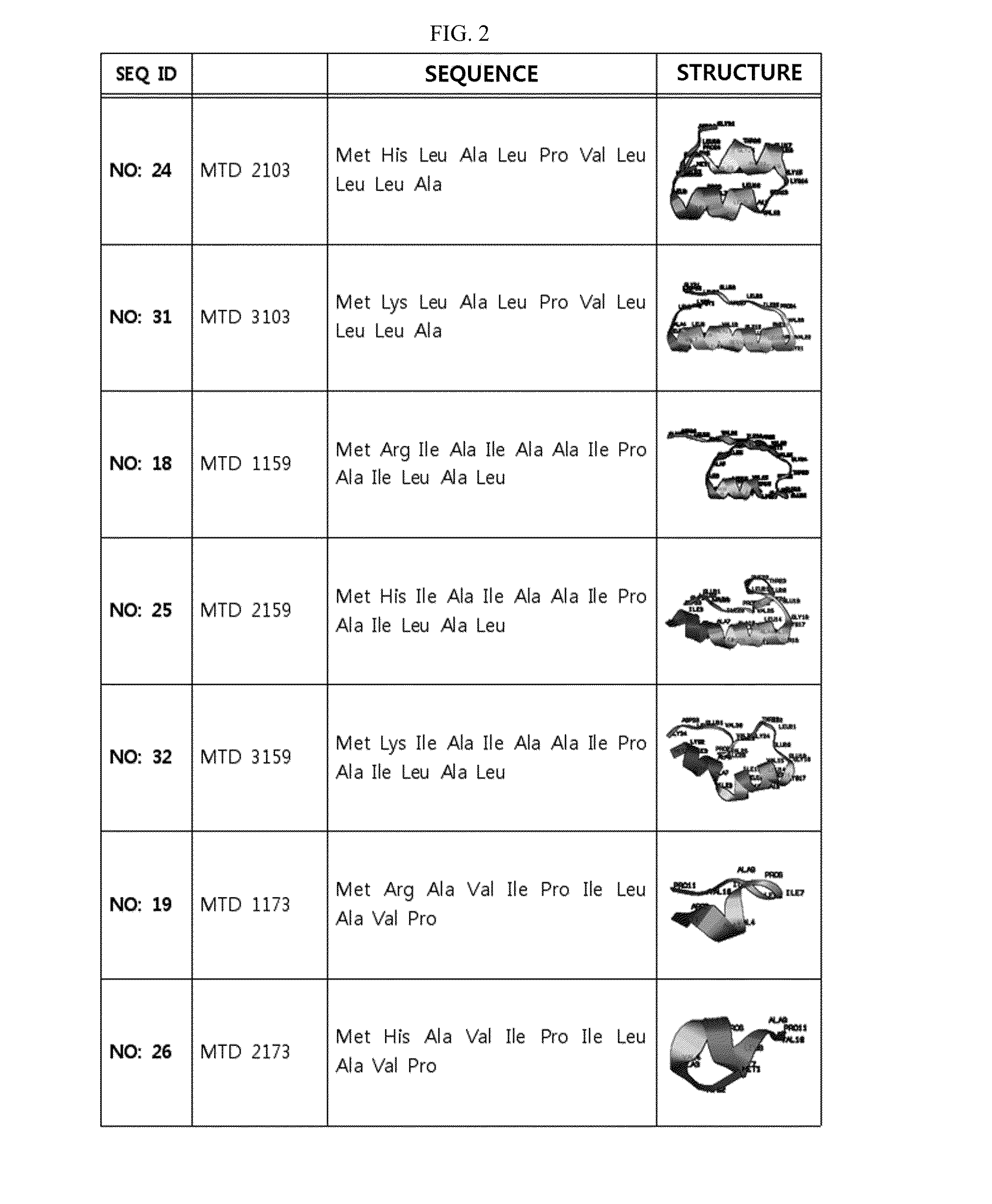
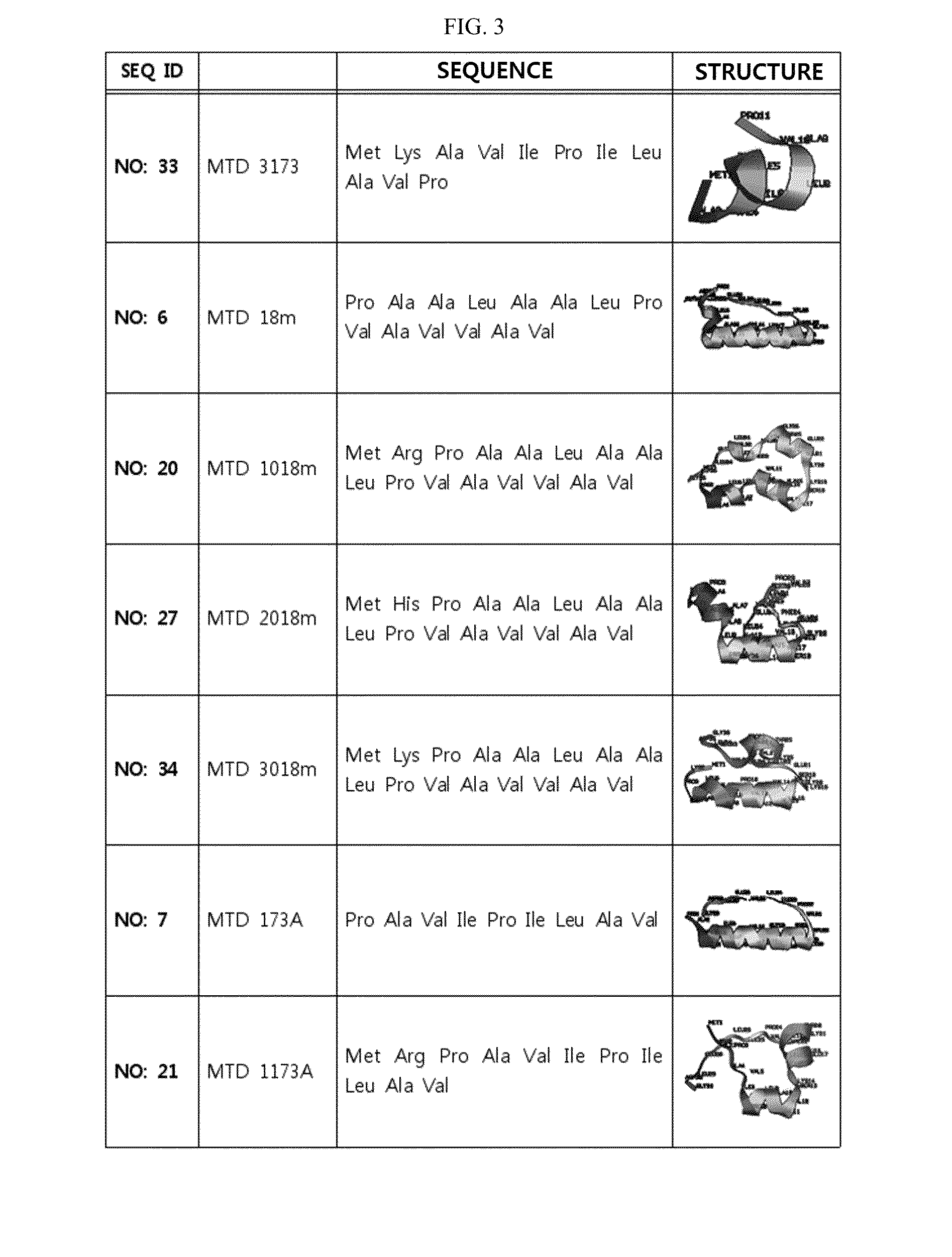
Development of Novel Macromolecule Transduction Domain with Improved Cell Permeability and Method for Using Same
ActiveUS20140329737A1Good cell permeabilityMaintain activityCosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsCell membraneOrganism
The present invention relates to an improved macromolecule transduction domain (MTD), which facilitates permeating the cell membrane of a biologically active molecule, having enhanced cell permeability. Specifically, an improved MTD according to the present invention, compared to an existing MTD, can transmit various types of biologically active molecule from inside the body and inside a test tube more effectively, and thus can be effectively used in a method to genetically alter a biologically active molecule so as to have cell permeability or in a method to transport a biologically active molecule into a cell, or the like. Additionally, the improved MTD can be very useful in development of new drugs and incrementally modified drugs as uses of the improved MTD are possible in drug delivery systems, recombinant protein vaccines or DNA / RNA therapeutic agents, gene or protein therapies, and pharmacologically or medically useful protein production or medical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical compositions.
Owner:PROCELL THERAPEUTICS
Genetic recombination escherichia coli and method for efficiently producing pullulanase
InactiveCN102994425AIncrease enzyme activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliFermentation
The invention discloses a genetic recombination escherichia coli and a method for efficiently producing pullulanase, belonging to the technical field of microbial fermentation. The method comprises the following steps of: connecting a signal peptide PelB of a plasmid pET20b(+) and bacillus naganoensis CCTCC NO:M2012388 pullulanase genes, and commonly inserting the signal peptide and the bacillus naganoensis into an expression vector pET28a(+) to construct a recombination strain E.coliBL21(DE3) / pET28a(+)-PelB-pul with the signal peptide and target genes; and using the strategies of auto-induction culturing and adding glycine to control the cell permeability in the fermentation and production of extracellular pullulanase, using an auto-induction culture medium with lactose in a concentration of 10g / L, shaking and culturing for about 2 hours under the conditions of a temperature of 37 DEG C and a speed of 200rpm, then adding the glycine with a final concentration of 6g / L and transferring to culturing for 70 hours at a temperature of 20 DEG C. The enzyme activity of the extracellular pullulanase reaches 505U / mL and is enhanced by 1260 times to the enzyme activity of the original strains of the wild fungus. The application of the invention is of great significance.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Application of thiospirolactone in intracellular hypochloric acid detection
InactiveCN101870864AHigh sensitivityImprove permeabilityOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceCytotoxicity
The invention relates to a fluorescence detection method and provides a fluorescent probe which has high sensitivity and high selectivity and is used for detecting intracellular hypochloric acid and an application of thiospirolactone in intracellular hypochloric acid detection. The structure of the fluorescent probe for detecting the intracellular hypochloric acid is a triphenylmethane fluorescent probe with a Xanthone ring parent structure; and the fluorescent probes of the thiospirolactone all adopt corresponding spirolactones as raw materials. The thiospirolactone has high-sensitivity fluorescent response characteristics on hypochloric acid, and when being used in the fluorescent probe for detecting the intracellular hypochloric acid, the selectivity is high. The probe has strong lightstability, no illumination self oxidation, rapid response to an aimed compound, good cell permeability and no strong cytotoxicity, and a product formed by combining the fluorescent probe and the aimed compound has strong photobleaching resistance. The thiospirolactone used for detecting the hypochloric acid of the aimed compound has high sensitivity and strong specificity and other active oxygen in cells has no interference on the detection.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
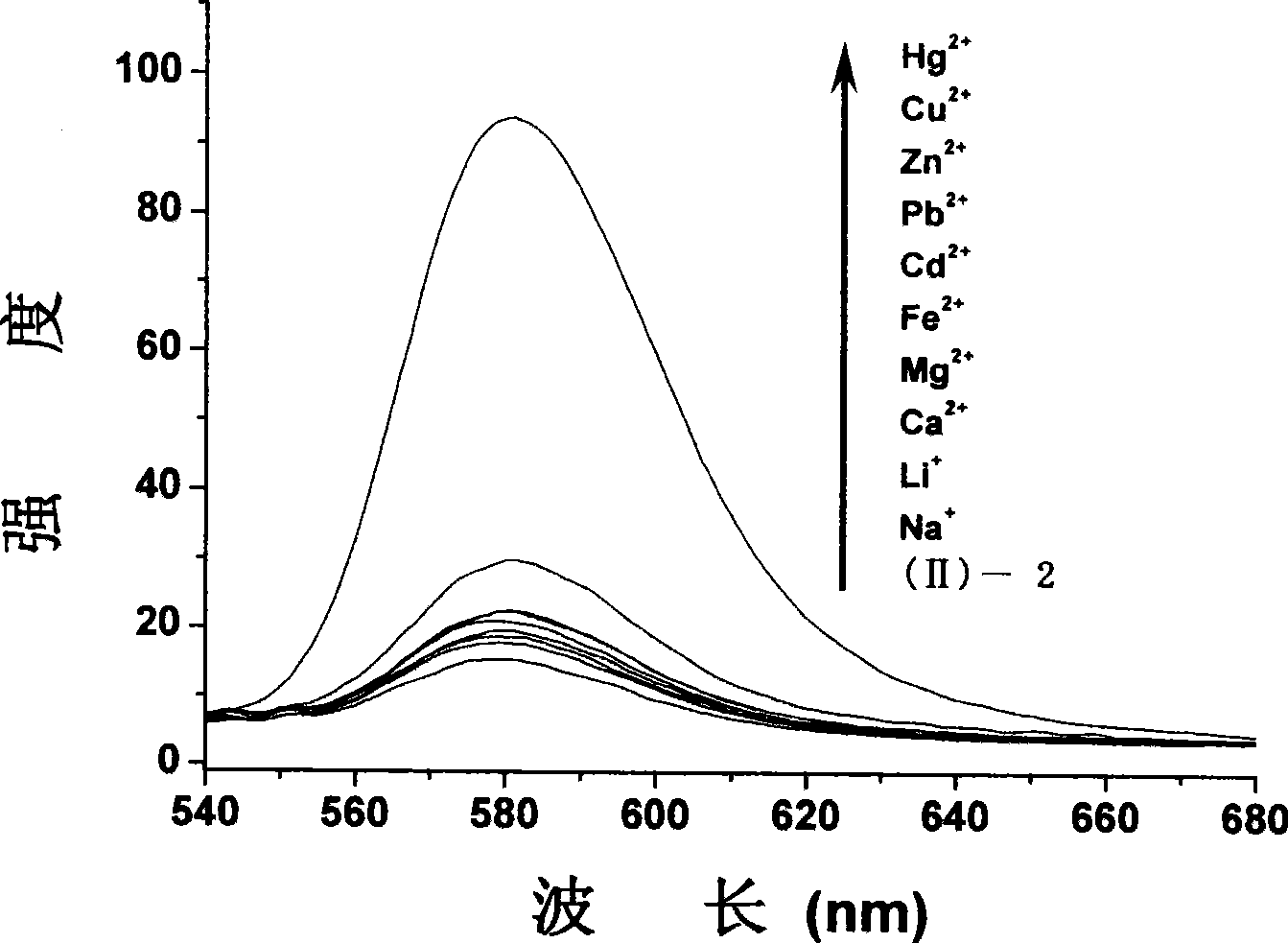
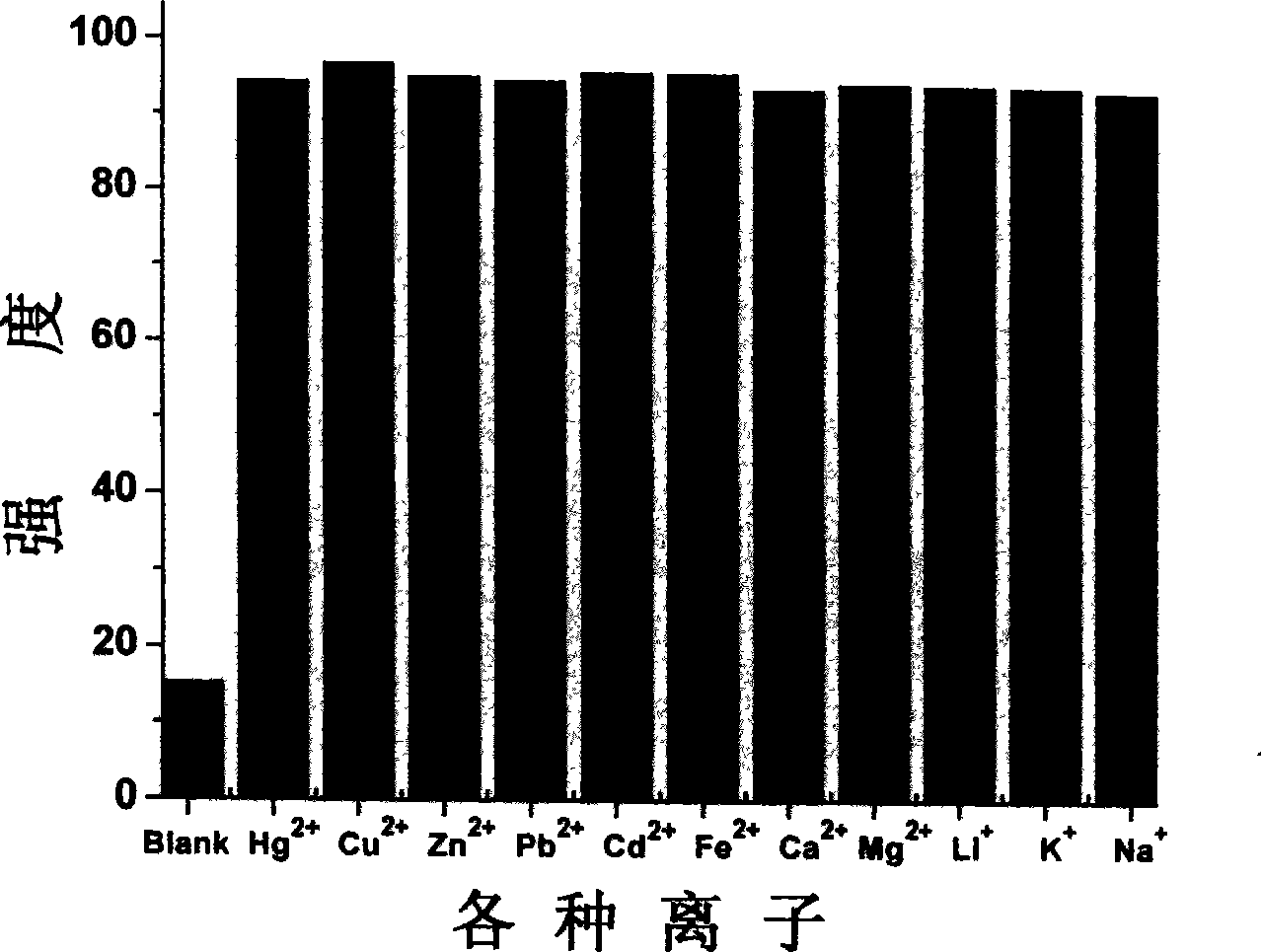
Rhodamin B double-sulfur fluorescence probe for detecting aqueous mediums and intracellular mercury ions, preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN104479671AHigh selectivityNo obvious toxic effectOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceCytotoxicityBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a rhodamin B double-sulfur fluorescence probe for detecting aqueous mediums and intracellular mercury ions, preparation and application thereof. According to rhodamin B double-sulfur fluorescence probe, molecular closed loops in the rhodamin fluorescence probe are opened in the aqueous mediums by chelating and coordinating the mercury ions, so that fluorescence is generated; the fluorescence intensity is in a good linear relation with the initial concentration of the mercury ions; the color change can be seen by naked eyes when a probe solution is changed from colorless to pink; meanwhile, the fluorescence probe is high in specific selectivity on the mercury ions; in addition, the fluorescence probe is high in biocompatibility and cell permeability and low in cytotoxicity, can be used for detecting the intracellular mercury ions and is high in detection sensitivity of the mercury ions. The preparation of the rhodamin B double-sulfur fluorescence probe is characterized by taking the rhodamin B as the raw material, and enabling the rhodamin B to react with phosphorus oxychloride to prepare a rhodamin B acyl chloride intermediate; the acyl chloride intermediate is further condensed with a double-sulfur intermediate to obtain a mercury ion probe with high sensitivity and high selectivity.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Methods and apparatus for improving in vitro measurements using boyden chambers
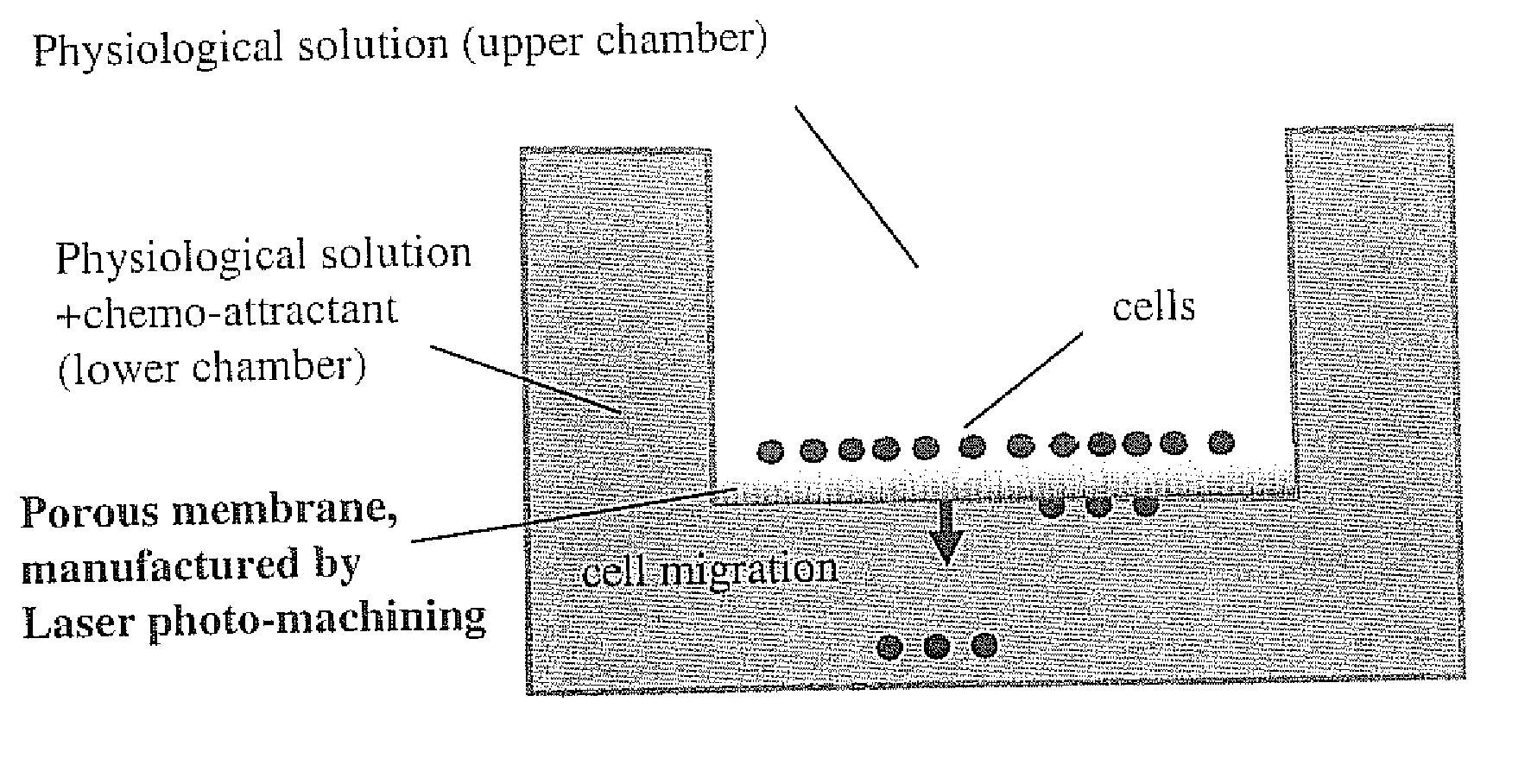
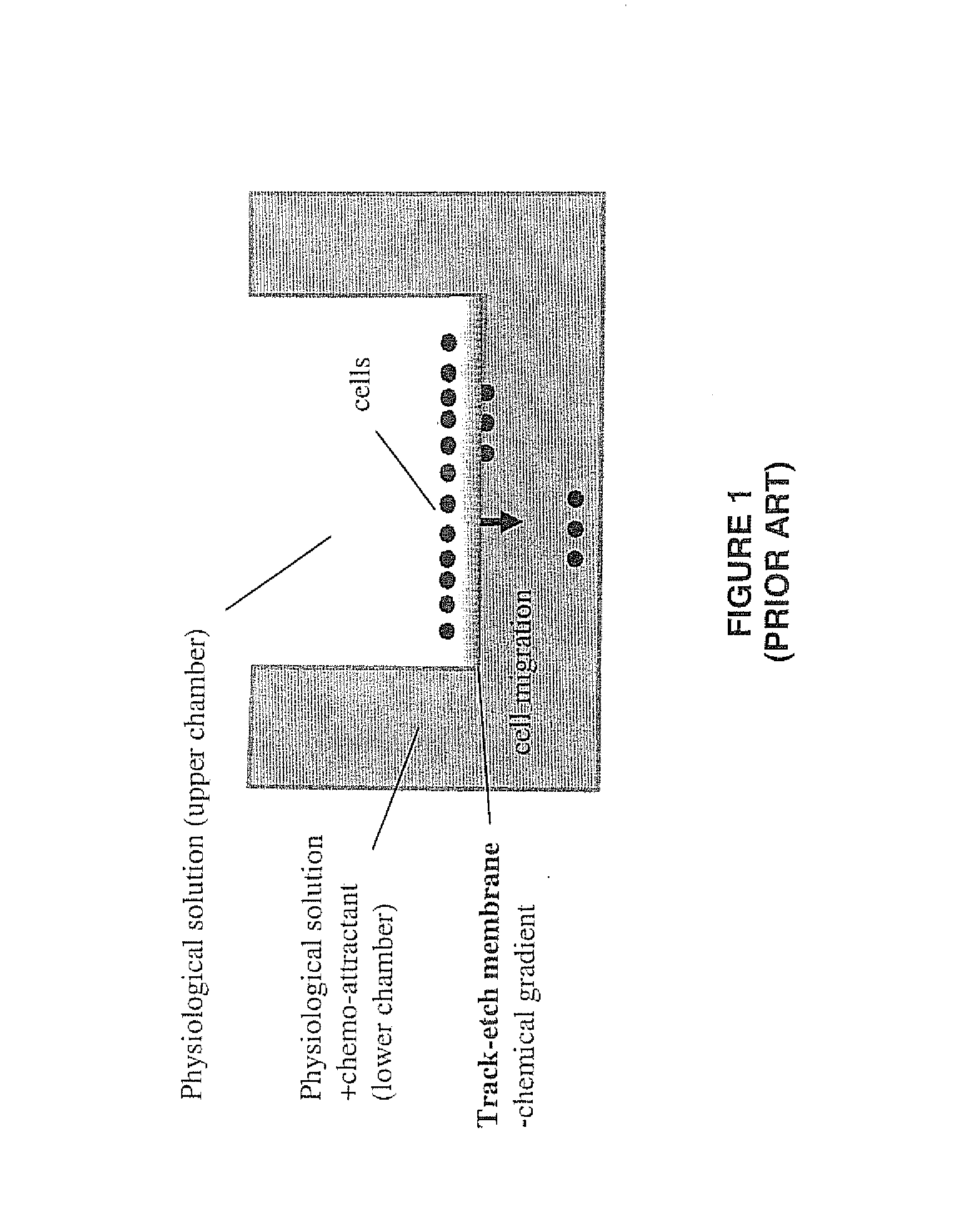
ActiveUS20120315660A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCell invasionStaining
Apparatus and methods to improve the Boyden chamber used in cellular biological measurements, allowing quantitative optical microscopy of biological cells in situ without using fluorescent probes or optical staining. In the preferred embodiment, a thin porous membrane separating top and bottom reservoirs includes an array of precisely positioned micropores pores manufactured using a laser-based photo-machining (ablation) process. The membrane may be composed of polyethylene terephthalate (PET), polycarbonate, polyimide, polyether ether ketone (PEEK) or other appropriate material. The pores formed in the membrane may have diameters in the range of 1 to 15 microns and spaced apart at a distance ranging from 10 to 200 microns. A plurality of upper and lower reservoirs may be provided to form a multi-well plate. The invention finds application in a wide range of potential biological applications where Boyden chamber geometries are currently used including co-culture studies, tissue remodeling studies, cell polarity determinations, endocrine signaling, cell transport, cell permeability, cell invasion and chemotaxis assays.
Owner:U S BANK NAT ASSOC FOR ITSELF & AS ADMINISTATIVE AGENT FOR THE LENDERS
Novel macromolecule transduction domains and methods for identification and uses thereof
ActiveCN101616928AEasy to transportAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsGenetic material ingredientsPeptideCell permeability
The present invention discloses novel macromolecule transduction domain (MTD) peptides which facilitate the traverse of a biologically active molecule across the cell membrane. Also disclosed are polynucleotides encoding the MTD peptides, methods of identifying the MTD peptides; methods of genetically engineering a biologically active molecule to have cell permeability by using the MTD peptides, methods of importing a biologically active molecule into a cell by using the MTD peptides, and uses thereof.
Owner:PROCELL THERAPEUTICS
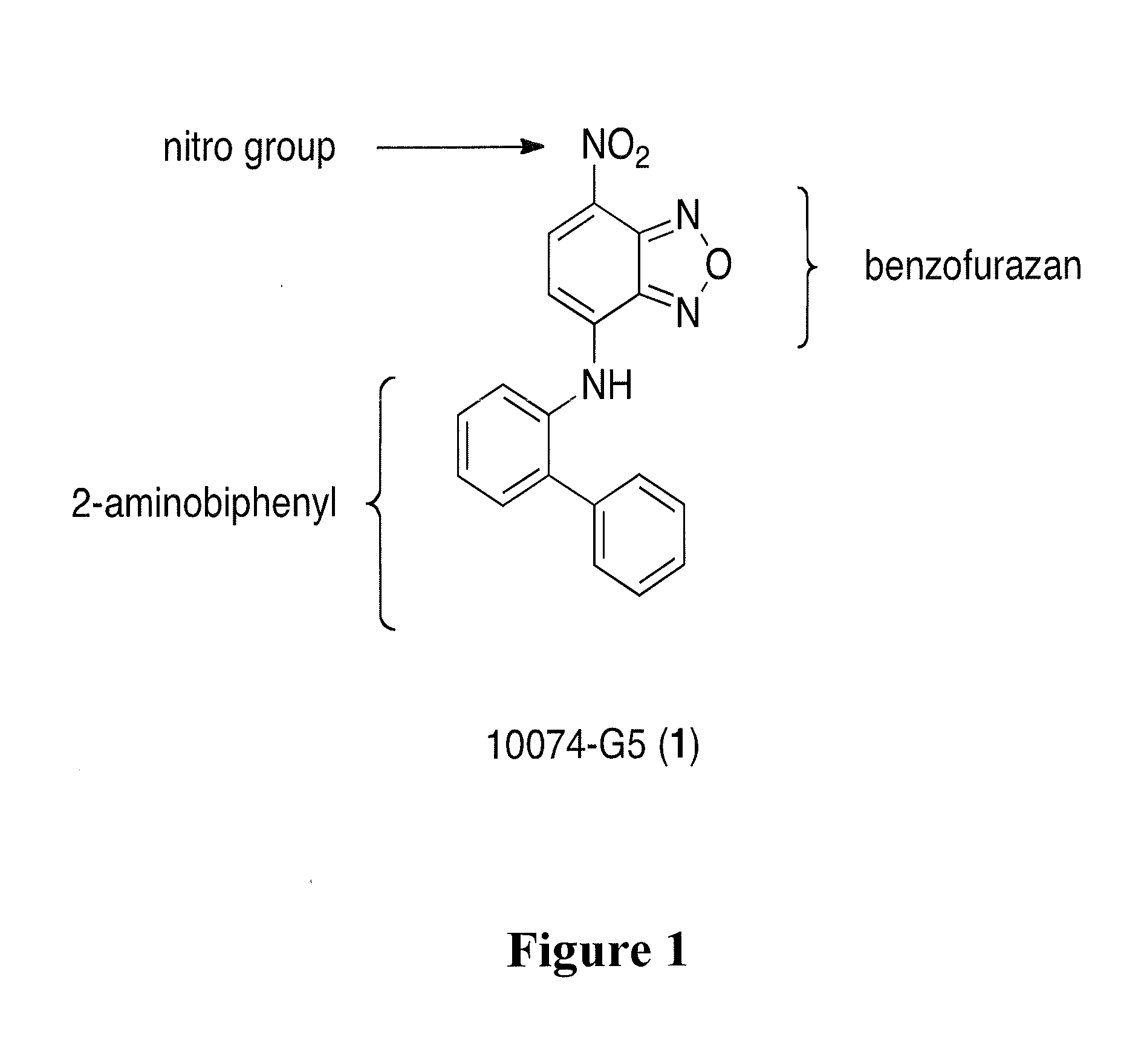
Potent analogues of the c-myc inhibitor 10074-g5 with improved cell permeability
The present invention relates compounds and compositions for interfering with the association of Myc and Max. These compounds and compositions are useful in methods for inhibiting growth or proliferation of a cell. Methods of inhibiting growth or proliferation of a cell comprise contacting the cell with an amount of a compound that interferes with Myc and Max association effective to inhibit growth or proliferation of the cell. The compounds exhibit increased inhibitory activity against c-Myc relative to the known c-Myc inhibitor small-molecule benzofurazan N-([1,1′-biphenyl]-2-yl)-7-nitrobenzo[c][1,2,5]oxadiazol-4-amine (10074-G5).
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE
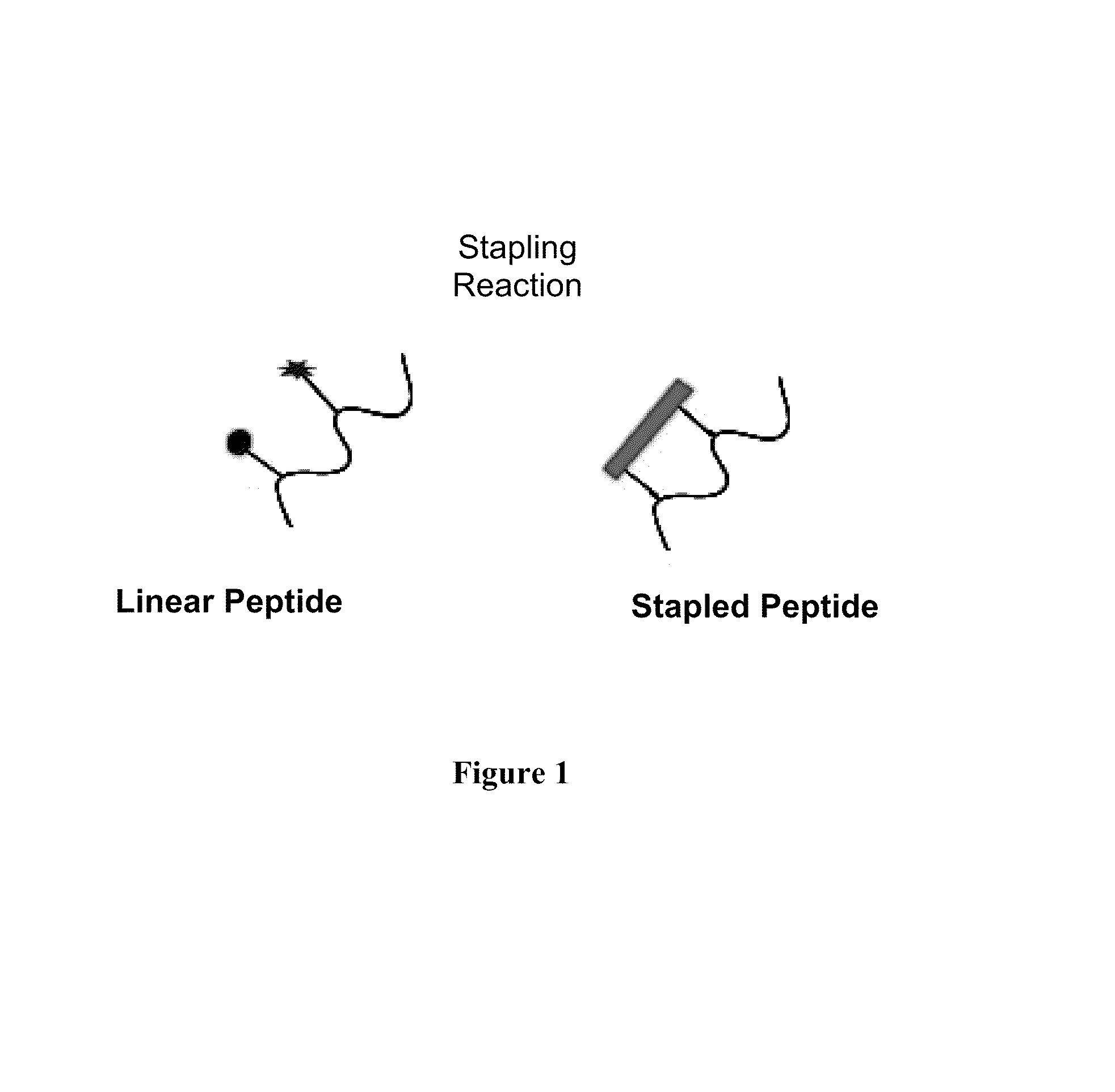
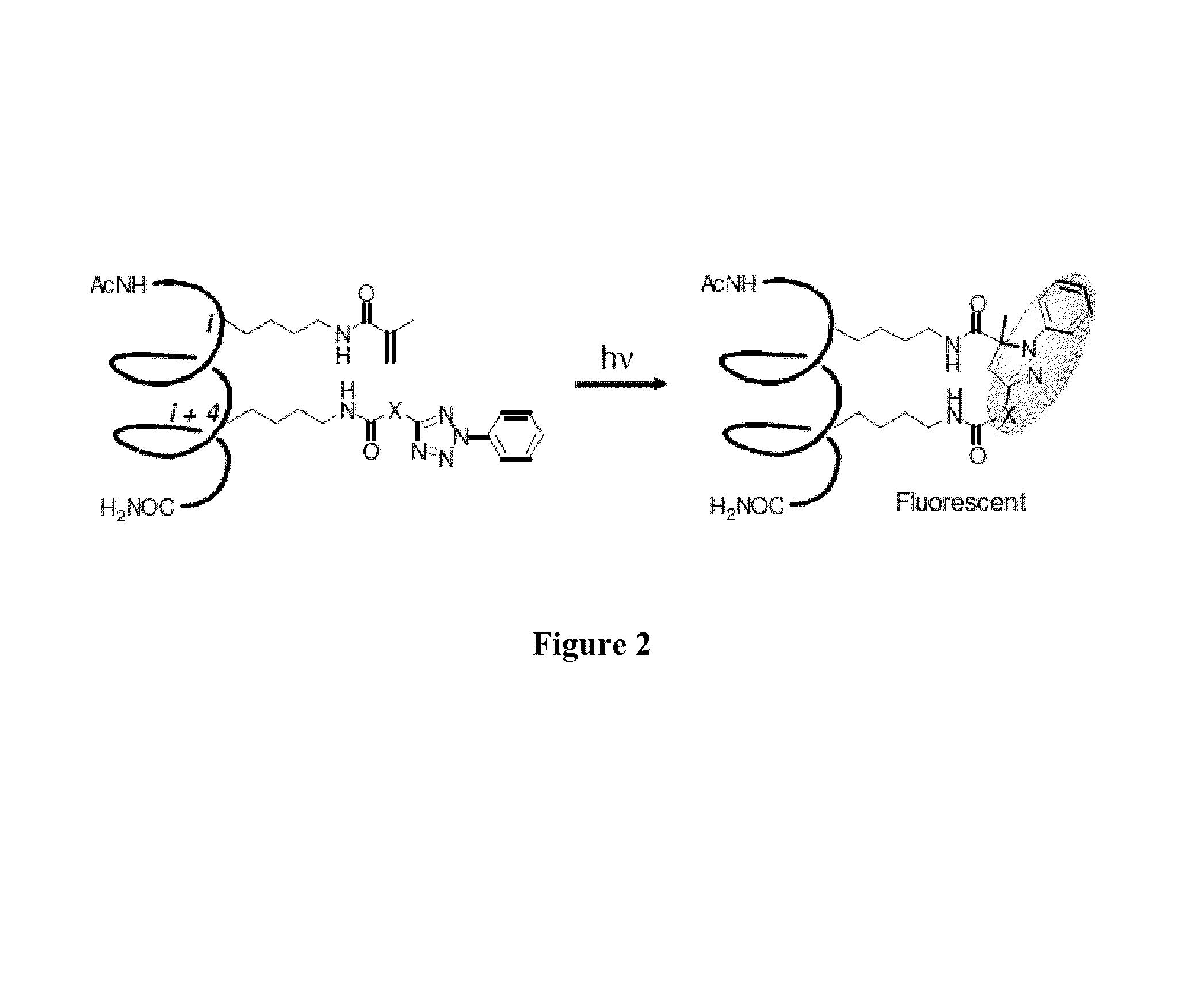
Cross-Linked Peptides and Proteins, Methods of Making Same, and Uses Thereof
ActiveUS20140057857A1Improve propertiesImprove enzyme stabilityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsFusion with degradation motifCross-linkCrystallography
Cross-linked proteins and peptides, and methods of making and uses of such cross-linked proteins and peptides. The cross-linked proteins and peptides have rigid, distance-matching bismethylene aryl cross-linking moieties. Compositions comprising the cross-linked proteins and peptides can be used as pharmaceutical delivery formulations. The cross-linked proteins and peptides can have improved properties, such as cell permeability, as compared to the parent protein or peptide.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Stapled peptides and method of synthesis
ActiveUS8586707B2Reasonable reaction yieldsImprove stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide sourcesCycloadditionStapled peptide
A method for preparing stapled peptides. The stapled peptides, including helical stapled peptides, are prepared according to a photochemically-based method, a [3+2] cycloaddition reaction. The helical stapled peptides exhibit increased helicity, thermal stability and cell permeability.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
A strain of Issakia orientalis and its whole cell transformation method for producing citicoline
InactiveCN102286386AEfficient preparationIncrease regeneration rateFungiMicroorganism based processesCholine PhosphateManganese
The invention relates to Issatchenkia orientalis and a method for producing citicoline by whole cell conversion of Issatchenkia orientalis, belonging to the technical field of biological pharmacy. In the method provided by the invention, the whole cells of Issatchenkia orientalis Z1, namely CCTCC (China Center for Type Culture Collection) NO: M2011272 are utilized to prepare citicoline, choline phosphate and 5'-cytidylic acid are used as substrates, glucose is used as an energy donor, and the ATP (adenosine triphosphate) regeneration efficiency is improved by adding inorganic ions; glucose is used as the energy donor, so that the energy requirement of the strain is provided and ATP is provided for a citicoline synthesis enzyme system; one or more of potassium ion, magnesium ion and manganese ion are added to change the metabolism flow direction and improve the ATP regeneration rate, so that the ATP regeneration rate is matched with the rate of the citicoline enzyme synthesis system and the high-efficiency preparation of citicoline is achieved; and the whole cells of Issatchenkia orientalis are used, and toluene is added to an aqueous solution during the preparation process so as to improve the cell permeability, so that the rate of the citicoline enzyme synthesis system is improved.
Owner:江苏华晟知识产权运营有限公司
Carrier protein, recombinant expression vector, exosome and preparation method and application of exosome
InactiveCN109293745AEfficient entryEfficient expressionAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDepsipeptidesSterol carrier proteinForeign protein
The invention provides carrier protein, recombinant expression vector, an exosome and a preparation method and application of the exosome. Foreign protein can be carried into the exosome efficiently through fusion of the carrier protein with the foreign protein. Through the recombinant expression vector, a to-be-expressed foreign protein peptide fragment gene sequence is inserted into polyclonal sites of the recombinant expression vector, so that efficient and directed expression of the foreign protein in the cell exosome is achieved; meanwhile, the invention also provides the preparation method of the exosome for carrying the foreign protein, foreign gene can be brought into the exosome effectively, and simple and easy operation, a stable process and good applicability are achieved; and the exosome prepared by using the preparation method contains the foreign protein, has good cell permeability and highly efficiency of cell transfection, the activity and efficacy of the foreign protein can be developed at the same time, and a broad application prospect is achieved.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Hg2+ detecting aggregation-induced emission type fluorescent sensor and production method and application thereof
InactiveCN106008510AHas aggregation-induced luminescent propertiesGood cell permeabilityOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceAggregation-induced emissionBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses an Hg2+ detecting aggregation-induced emission type fluorescent sensor and a production method and application thereof. The structural formula of the fluorescent sensor is as shown in specification. The fluorescent sensor is of aggregation-induced emission property and is nonluminous in solution, and its fluorescent light is enhanced in an aggregation state, accordingly, the fluorescent sensor can be applied to recognition of highly specific selectivity and anti-interference performance of Hg2+. Besides, the fluorescent sensor has high biocompatibility and cellular permeability, can target mitochondria in cells and light the Hg2+ in mitochondria by fluorescent light, and accordingly can realize detection of Hg2+ in the mitochondria.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Method for improving concentration of 1,3-propanediol produced by microbial fermentation
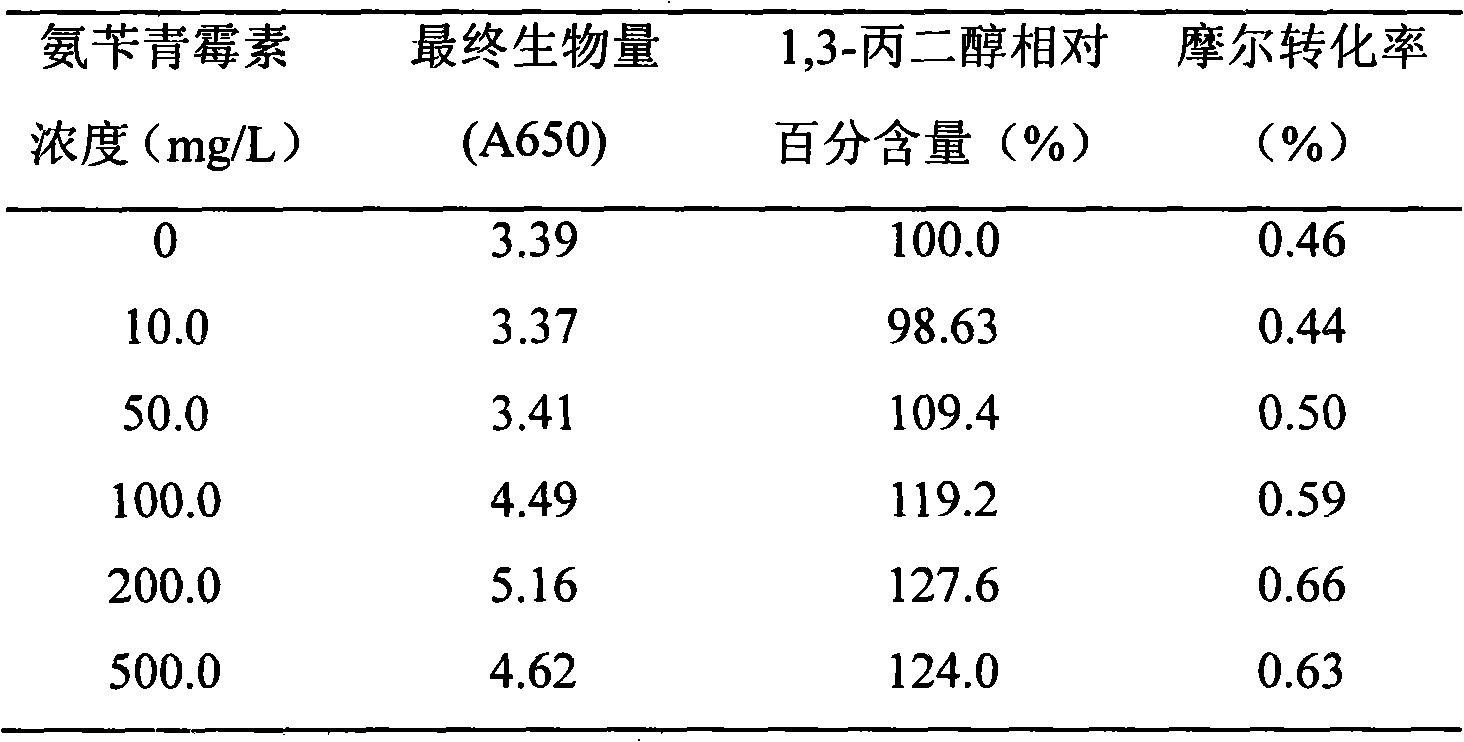
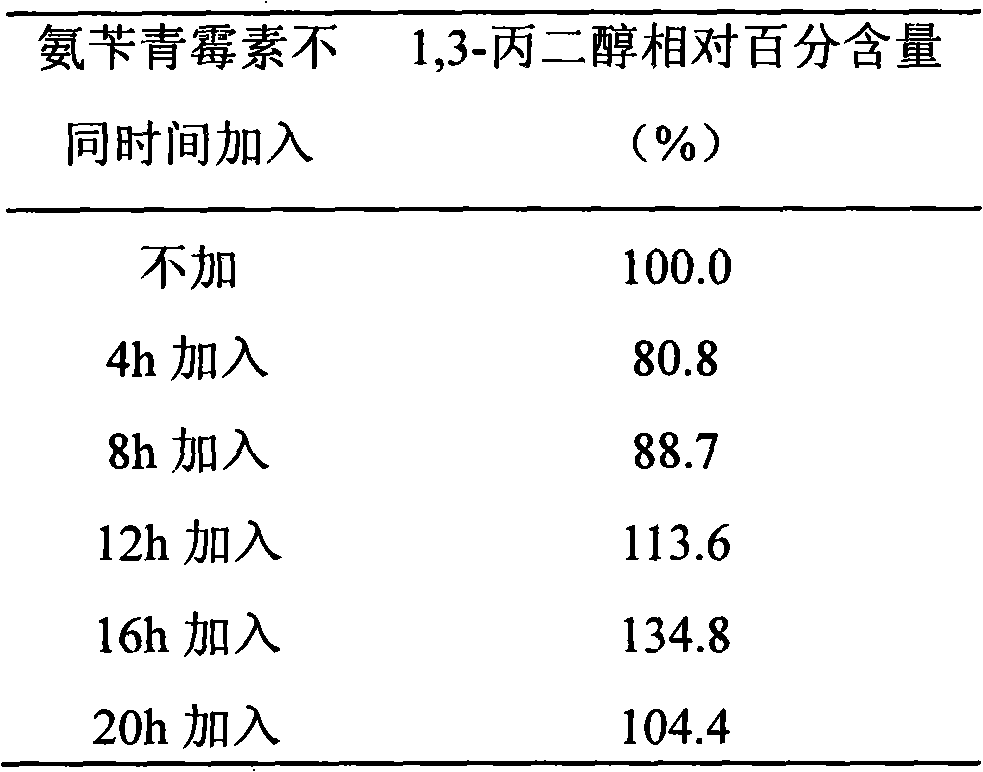
InactiveCN101323863AIncrease concentrationEasy to controlMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention provides a method for increasing the concentration of 1, 3-propanediol in biological fermentation production, particularly relating to a method for adding an antibiotic, reducing transfer resistance when nutrition and metabolites enter or exit a cell, effectively promoting cell growth and increasing the concentration of the 1, 3-propanediol in the biological fermentation production. The technical process includes the steps that: a secondary seed culture solution is fed into a fermentation culture solution, meanwhile, the antibiotic which can improve cell permeability is added into the fermentation liquor, and the antibiotic is added to change the cell permeability so as to reduce the transfer resistance when the nutrition and the metabolites enter or exit the cell, thus improving the growth capability and the productivity of the thalli and increasing the concentration of the product, 1, 3-propanediol; furthermore, microbes are impelled to excrete the metabolites outside the cells, which decreases the accumulation of the metabolites in the cells, is favorable to eliminate the inhibition of products and by-products, especially reduces the inhibition of the 1, 3-propanediol to cell growth and cell catalytic activity, and at last, the concentration of the fermentation product, 1, 3-propanedio, is improved by 10 percent to 70 percent. The technical process is easy and simple, with low production cost.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Cell three-dimensional culture scaffold, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104830774AEvenly distributedPromote growthArtificial cell constructsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsBiocompatibility TestingUltimate tensile strength
The invention belongs to the fields of biological tissue engineering and biological medicines and relates to a cell three-dimensional culture scaffold, a preparation method and an application thereof. In particular, one or more pores are distributed in the cell three-dimensional culture scaffold, wherein each pore can accommodate at least one cell; in addition, the pores have openings, through which at least one cell can enter the pores. The cell three-dimensional culture scaffold is compact in pore size, is excellent in biocompatibility and cell permeability, is good in strength and is free of collapse, separation and the like defects.
Owner:TIANJIN WEIKAI BIOENG
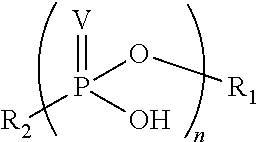
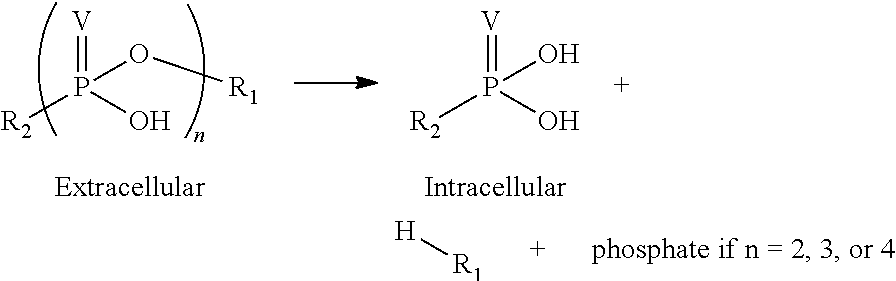
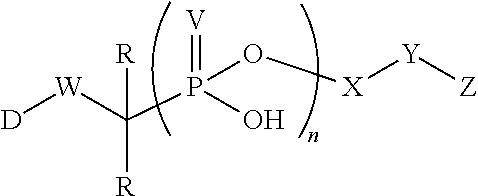
Phosponate linkers and their use to facilitate cellular retention of compounds
ActiveUS20190030171A1Facilitates intracellular retentionPhosphonate group is stableAntipyreticGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsCellular retentionCell permeability
Phosphonate linkers and their use for delivering compounds with passive cell permeability into a cell wherein the phosphonate group facilitates cellular retention of the compound are described.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com