Method for improving concentration of 1,3-propanediol produced by microbial fermentation
A technology for microbial fermentation and propylene glycol, applied in 1 field, can solve problems such as affecting cell growth and product synthesis, inability of extracellular nutrients to enter into cells, affecting the harvest of fermentation products, etc., and achieves a simple, effective and economical fermentation process, simple control, and ease of use. The effect of industrial application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Bacteria: Klebsiella pneumoniae (K.pneumoniae)
[0040] 400ml of fermentation medium containing 45g / L industrial glycerin was placed in a 1L shake flask, and a volume of 40ml of secondary seed solution was inserted, and the temperature was 37°C, and the shaker was cultivated at 180rpm. Add ampicillin respectively at 8 hours of fermentation, so that the content of ampicillin in the fermentation liquid is respectively 0-500 mg / L. Samples were taken at intervals, and the cell concentration was measured by spectrophotometer turbidimetry at a wavelength of 650nm. The cell concentration, that is, the amount of bacteria, was expressed as OD; the concentration of 1,3-propanediol was analyzed by gas chromatography. 24 hours to end fermentation.
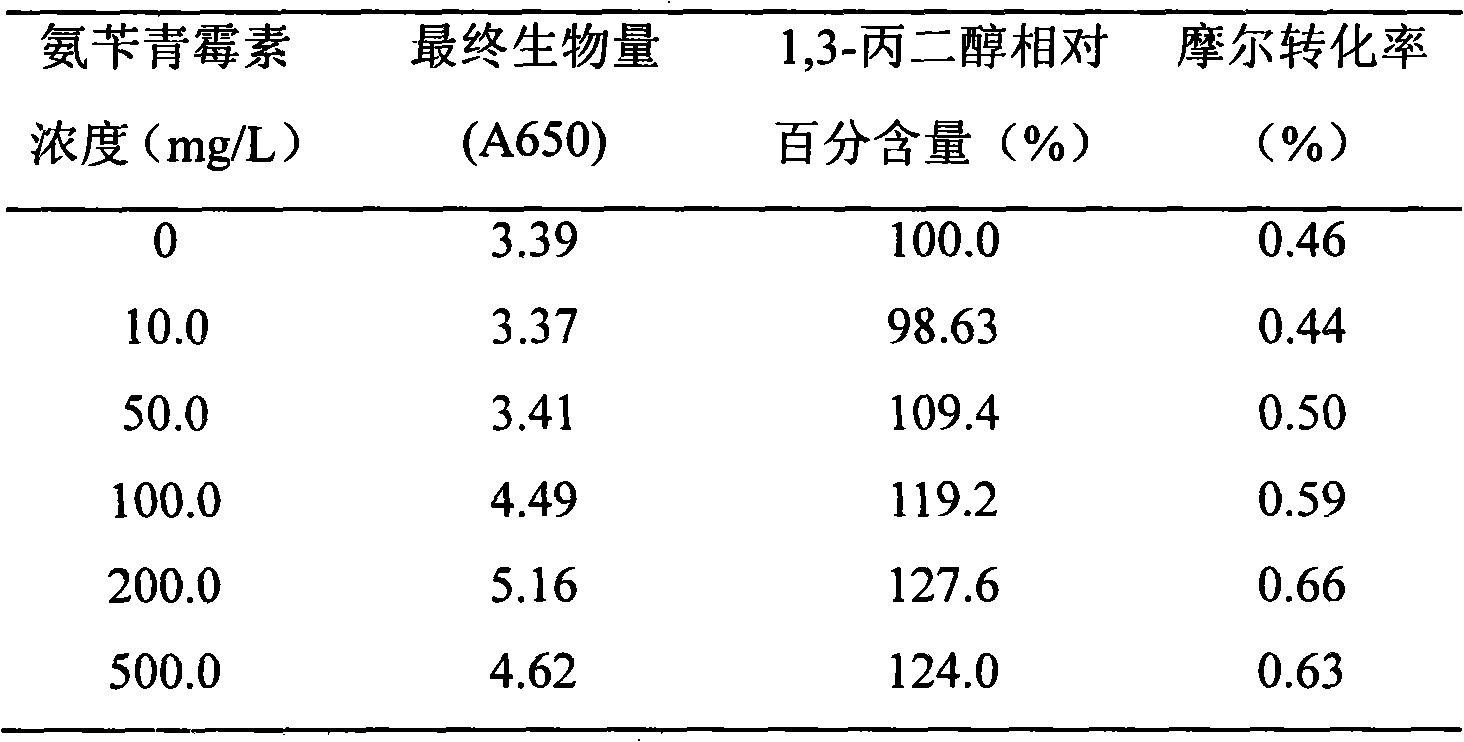
[0041] The impact of the amount of ampicillin added on the output of 1,3-propanediol in table 1
[0042]
[0043] Embodiment one has studied in fermenting glycerol production 1,3-propanediol technology, adds ampicillin, concentrati...
Embodiment 2
[0046] 400ml of fermentation medium containing 45g / L industrial glycerol was placed in a 1L shake flask, and a volume of 40ml of secondary seed liquid was inserted, the temperature was 37°C, and the shaker was cultivated at 180rpm. Add 200mg / L ampicillin at 4h, 8h, 12h, 16h and 20h and adjust the pH value. Two parallel samples were averaged, and the experimental results were as follows (Table 2).
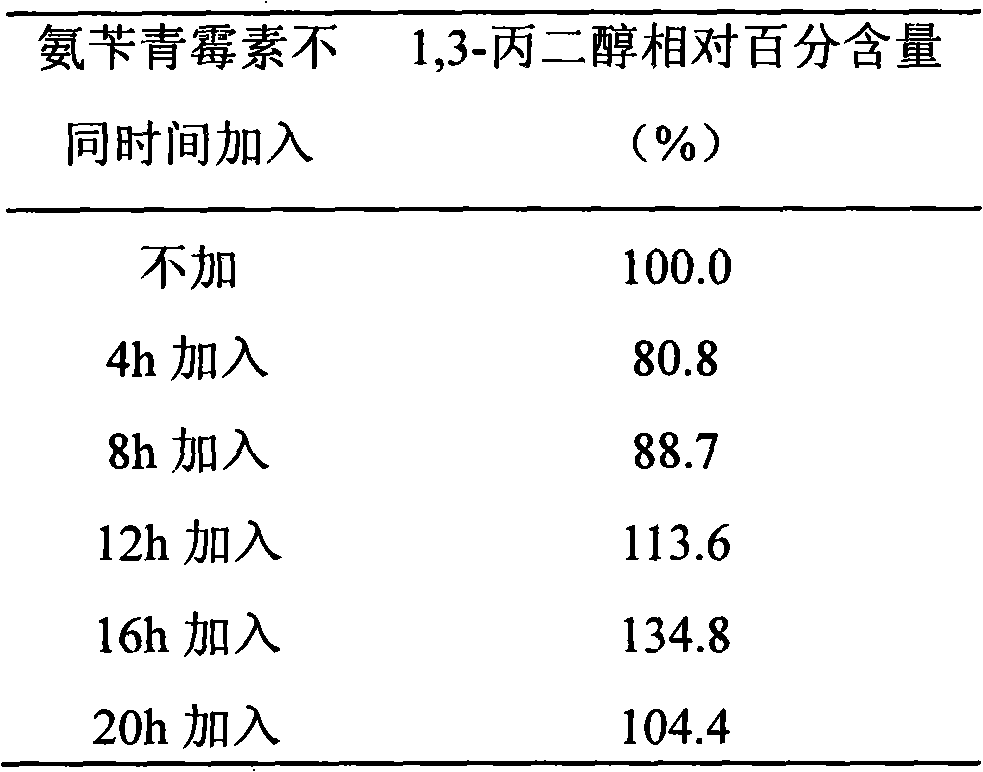
[0047] The influence of table 2 ampicillin adding time on 1,3-propanediol output
[0048]
[0049] It can be seen from the above table that the addition of ampicillin at different stages of fermentation has a greater impact on the output of 1,3-propanediol, and the addition of ampicillin in the early and middle stages of fermentation is unfavorable to the biosynthesis of 1,3-propanediol. During this period, the stable growth period has not yet been reached, and the cell wall synthesis of most proliferating cells is incomplete or even the entire cell wall synthesis is blocked, re...
Embodiment 3
[0053] 5L fermenter, liquid volume 3.8L, insert 200ml secondary seed liquid. Control the temperature at 37°C, adjust the pH with 4mol / L NaOH to maintain it at 6.8-7.0, the stirring speed at 300r / min-450r / min, the ventilation rate at 0.4vvm-2.8vvm, and add glycerin to stabilize the concentration at 20g / L- 30g / L, add ampicillin at 12h, 15h, 18h, and 21h respectively, adding 50mg / L each time, and take samples every 4h in the middle to measure the biomass, glycerol concentration and product 1,3-propanediol concentration. After 30 hours of fermentation, the concentration of 1,3-propanediol increased by 43.7% compared with that without adding ampicillin.
[0054] Through the above experiments, it can be proved that in the metabolic pathway of glycerol fermentation to produce 1,3-propanediol, adding antibiotics to increase cell permeability can effectively promote cell growth, and the process of increasing the concentration of 1,3-propanediol, the final product of fermentation, is si...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com