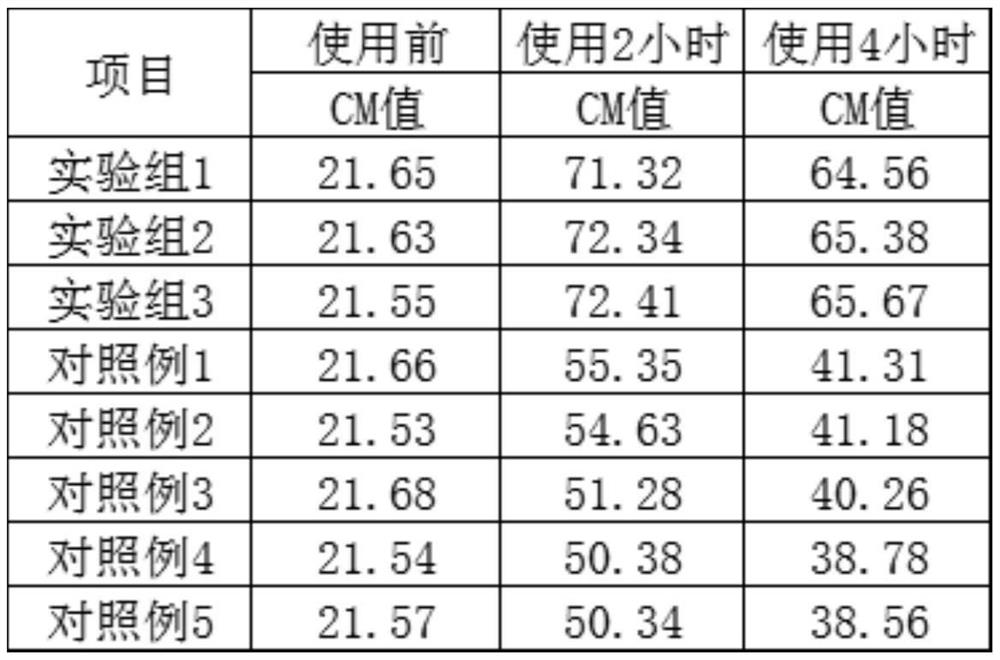
Patents
Literature
33 results about "Glycerol fermentation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
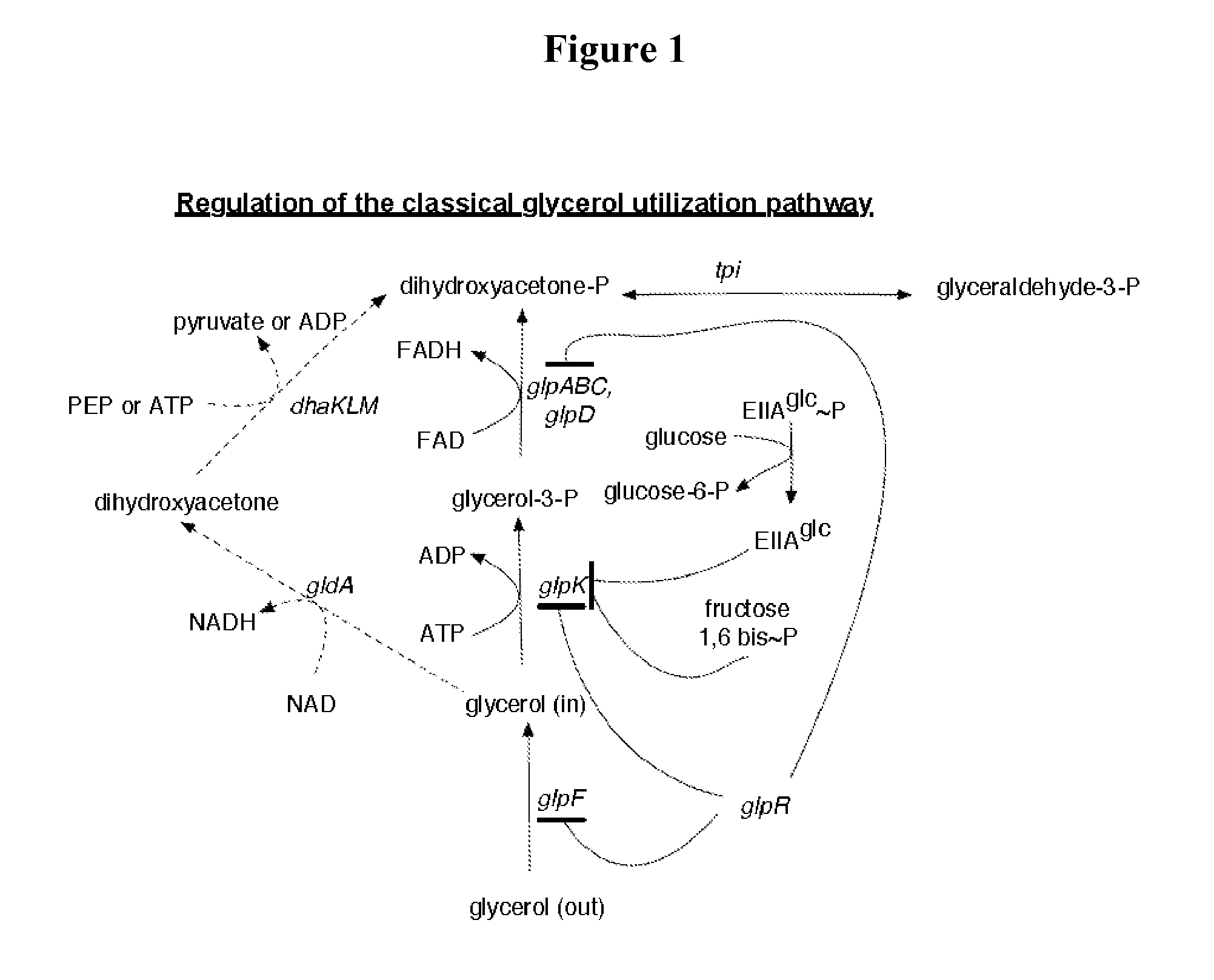
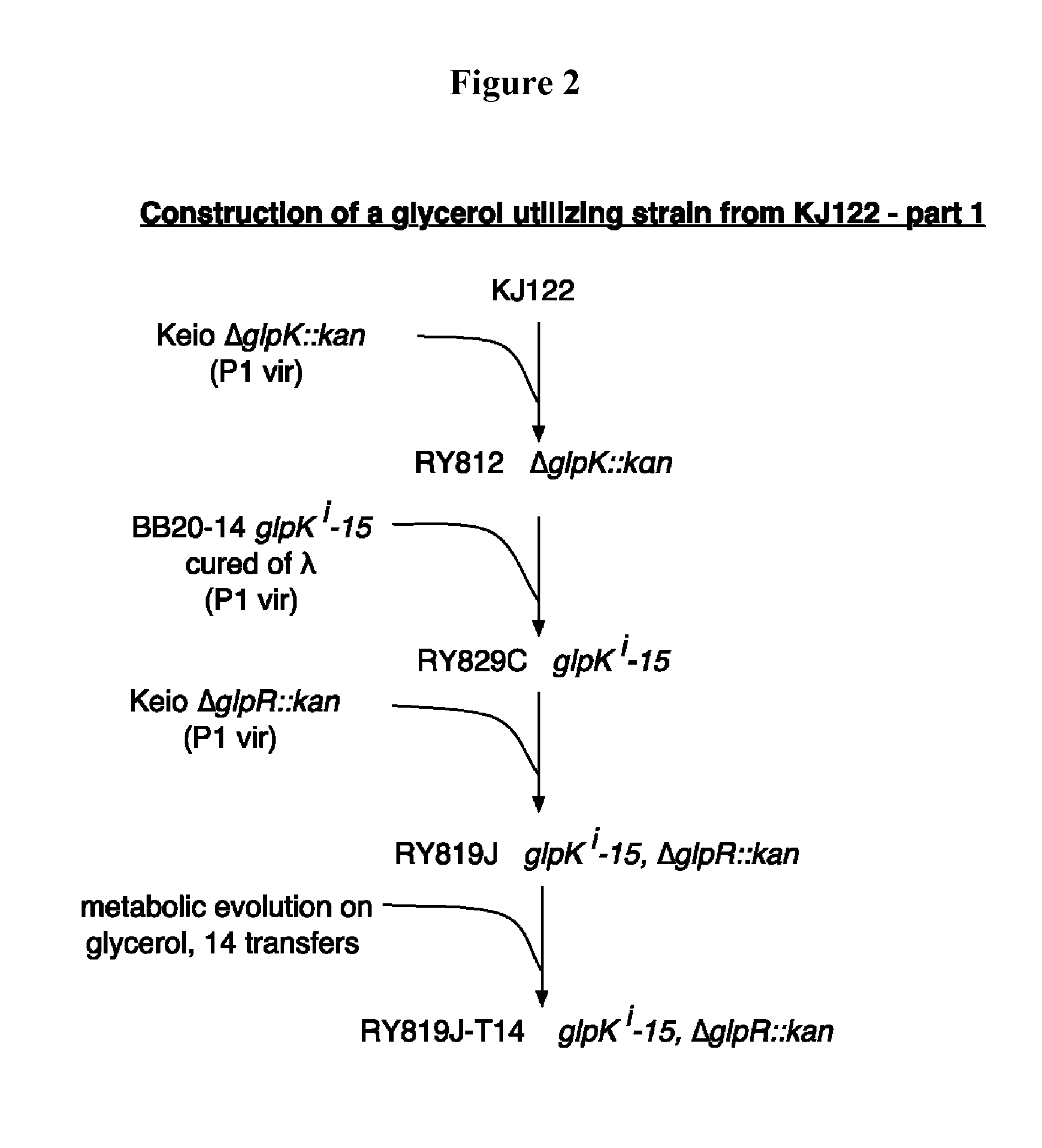
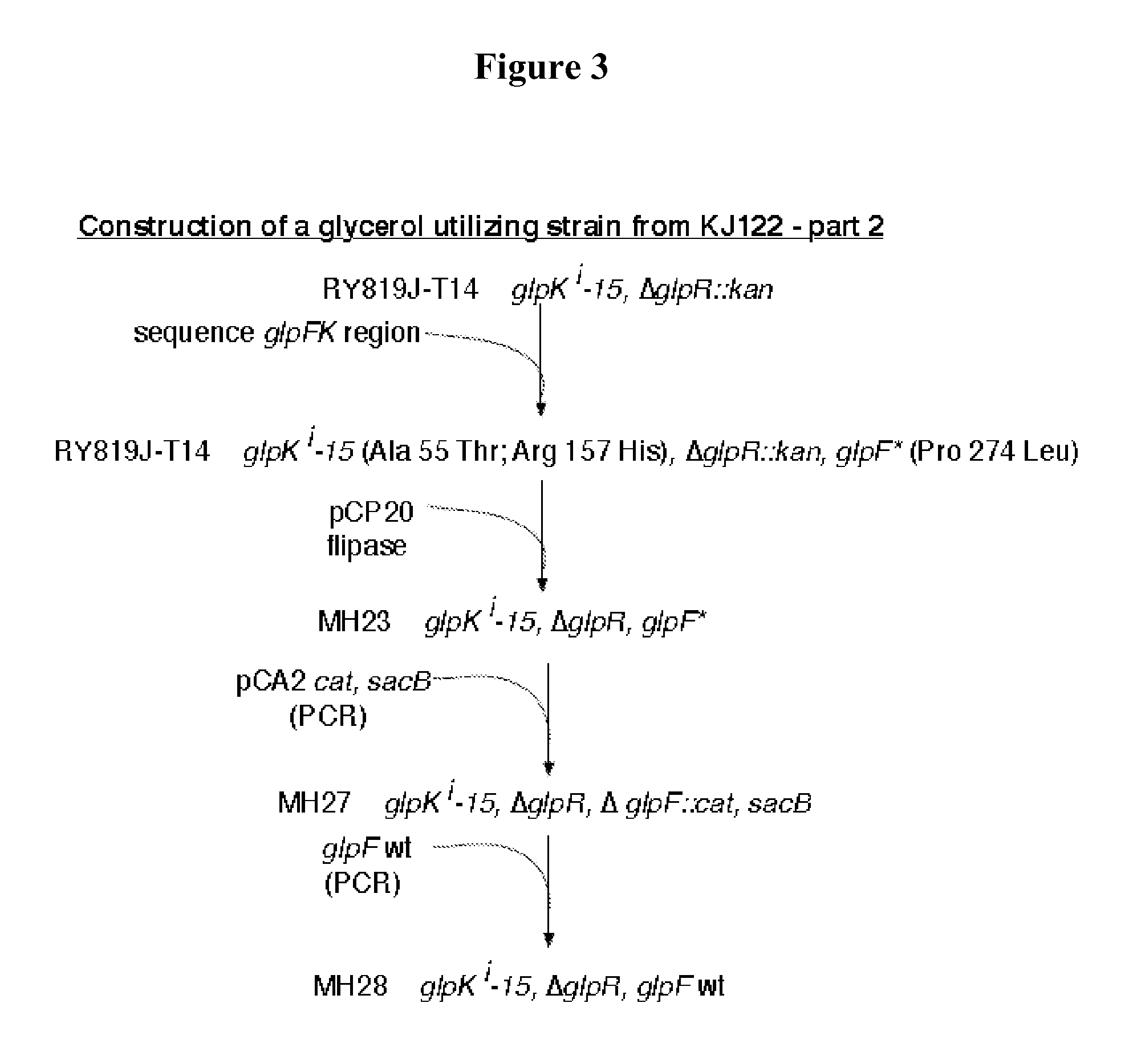
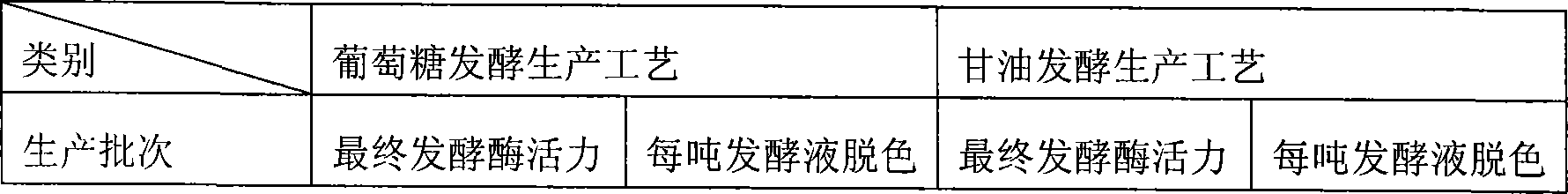
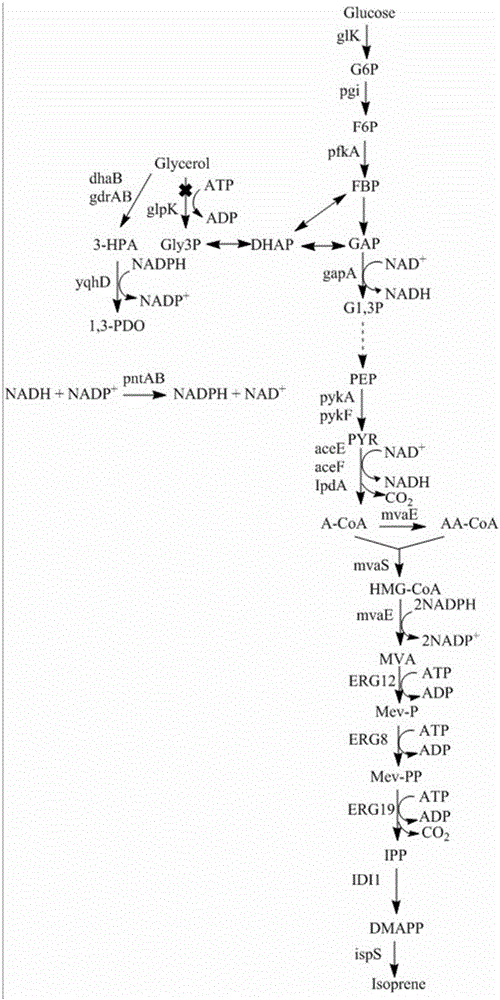
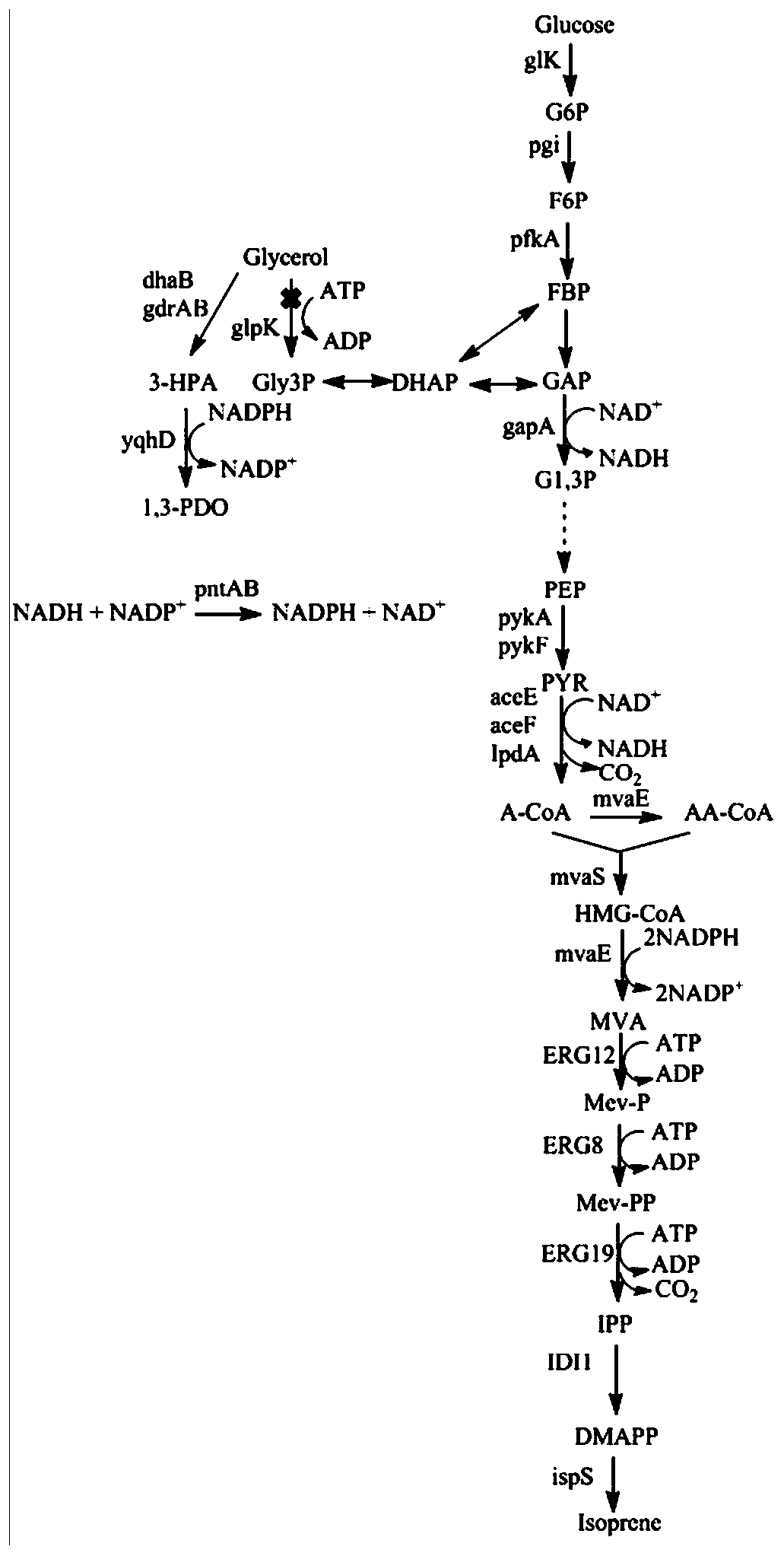
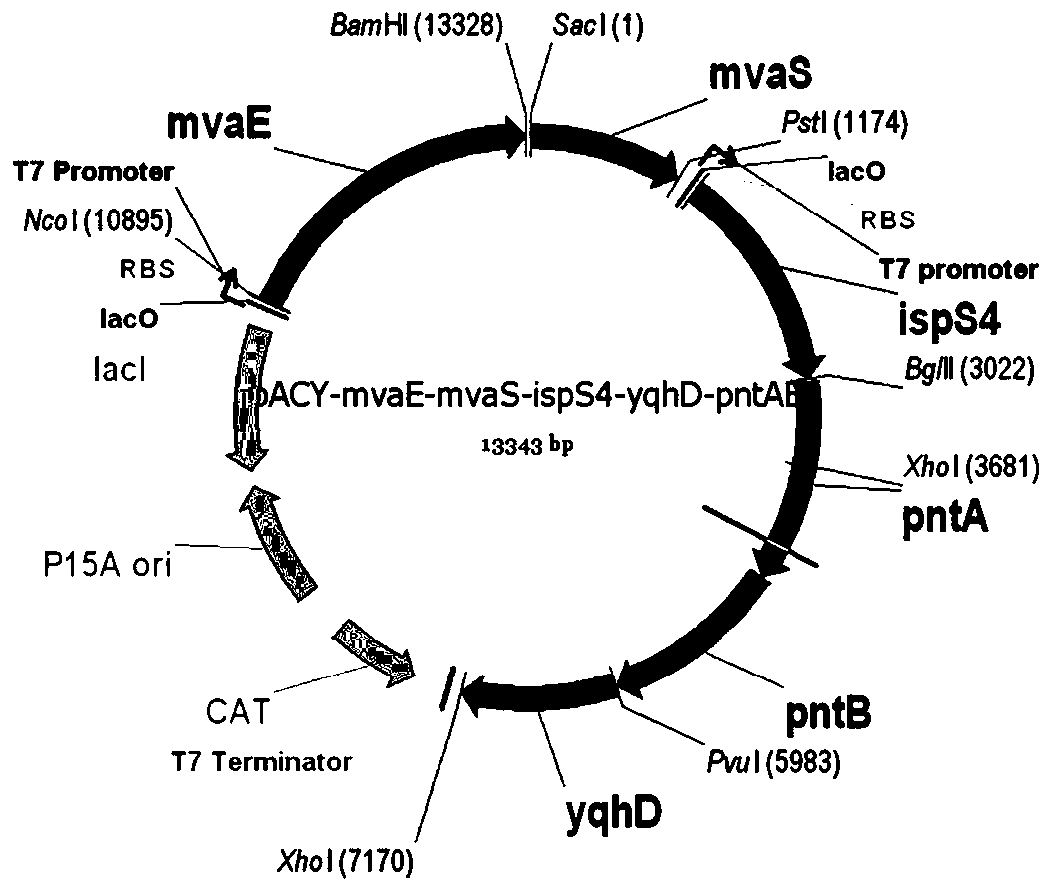
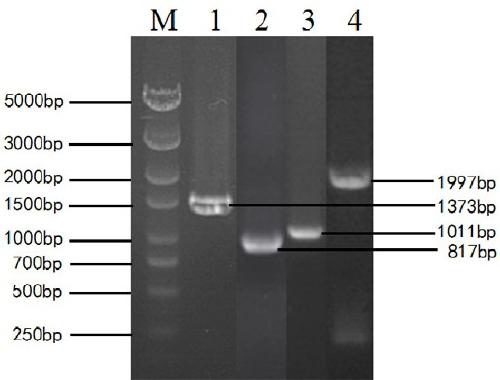
Glycerol fermentation in these organisms is mediated by a two-branch pathway, which results in the synthesis of the glycolytic intermediate dihydroxyacetone (DHA) phosphate (DHAP) and the fermentation product 1,3-propanediol (1,3-PDO) (Fig.
Mehtod for producing 1,3-propanediol and 2,3-cis-butanediol from crude starch material
This invention provides production of material 1, 3- trimethylene glycol and 2, 3- butylene-glycol by coarse starch. The coarse starch is fermented continuously by yeast cell to obtain the high concentration fermented liquid of glycerine. The fermented liquid of glycerine is filtered to obtain the cells which can be used for the next batch glycerine fermentation. The filtrate is used as the base material for producing 1, 3- trimethylene glycol. Add the nitrogen source in the fermented course. When finishing the fermentation conduct the processes of desalting, distillation, vacuum rectification etc. step to the 3- Trimethylene glycol and 2, 3- Butylene-glycol to obtain the products. At the same time the concention of 1, 3- Trimethylene glycol and 2, 3- Butylene-glycol with high added value is increased through cell back-use and mending material craft. Its advantage lies in: reduced the production cost effectively, raised production efficiency.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Fermentation of glycerol to organic acids
The present invention is in the field of producing organic acids and other useful chemicals via biological fermentation using glycerol as a source of carbon. Novel microorganisms and fermentation processes are described that are capable of converting glycerol to useful organic acids in high yield and high purity.
Owner:PTT GLOBAL CHEMICAL PUBLIC COMPANY LIMITED
Method for preparing phytase taking glycerol as carbon source
InactiveCN101182499AReduce generationIncrease enzyme activityHydrolasesMicrobiology processesBiotechnologyYeast
A method for preparing phytase using glycerol as a carbon source, adopting the fermentation production process of phytase-producing genetically engineered bacteria using Pichia pastoris as a carrier, characterized in that glycerol is used as a carbon source, and an appropriate amount of bacterial strains for production is used , cultured in a shake flask in a seed medium, and then through the first-level seed culture, second-level seed culture, and fermentation culture processes, the only carbon source in the growth stage of the bacteria before the seed culture and fermentation enzyme production is glycerol; during fermentation, After the glycerol in the basic fermentation medium is completely consumed, start to feed 50% glycerol solution into the medium. After the glycerol is exhausted, start to feed methanol to induce phytase production. Methanol also acts as a carbon source in the production stage. The positive effect is: Glycerin as a carbon source increases the final phytase production by 20-30%, increases the enzyme activity by 20-30%, the color of the fermentation liquid is light and does not require decolorization treatment, and reduces production costs. This method reduces costs compared with traditional processes About 1 / 3.
Owner:LIAONING HUAXING BIOTECHOLOGY
Method for producing sophorose ester through fermenting waste molasses and waste glycerin
InactiveCN102329833ASolve the problem of difficult storage and large emission pollutionReduce manufacturing costFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologySporeling
The invention relates to a method for producing sophorose ester through fermenting waste molasses and waste glycerin, which comprises the following implementation steps that: (1) spore suspension preparation: torulopsis utilis TJZKBA 10326 is inoculated on the inclined surface of a culture medium and is cultured for 2 to 4 days at the constant temperature being 30 DEG C, and normal saline with the mass concentration being 0.75 percent is added for washing mycelia, and the bacterial suspension is obtained; (2) the bacterial suspension is used for being inoculated into the sterilized liquid seed culture medium, the spore suspension is inoculated into the cooled liquid seed culture medium according to the inoculation quantity with the volume percentage being 2 to 5, and liquid seeds are obtained; (3) the liquid seed culture medium is used for being inoculated into a sterilized 5L fermentation tank, then, the liquid culture medium is inoculated into the cooled fermentation tank culture medium according to the inoculation quantity with the volume percentage being 2 to 5, the fermentation temperature is 30 to 34 DEG C, the dissolved oxygen is controlled to be 30 to 40 percent, and the fermentation time is 48 to 72h; and (4) after the fermentation is completed, the mixed organic solvent of organic solvent ethyl acetate / isopropanol with the same volume as the fermentation liquid is used for extracting the sophorose ester. The method has the advantages that the process is simple, the cost is low, and the effect is obvious.
Owner:天津实发中科百奥工业生物技术有限公司
Method for producing 1,3-propanediol and 2,3-butanediol from raw starch material
The invention discloses a method for producing 1,3-propanediol and 2,3-butanediol from raw starch materials, including the following steps: 1) Candida krusei or Hansenula Arabitolgens Fang are inoculated into a fermentation medium with the saccharifying liquid of the raw starches as a carbon source; the yeast cells are cultured on an aerobic condition until glucose-consuming-rate is significantly reduced, and then fermented anaerobically to a glucose concentration from 5 to 10 g / L; the fermentation broth is collected and filtered to remove the yeast cells in the broth, and the resultant filtrate is glycerin fermentation broth; 2) Klebsiella, Clostridium butyricum, or Clostridium pasteurianum are inoculated into a fermentation medium in which the glycerin fermentation broth obtained from step 1) serves as a carbon source; the bacteria are fermented anaerobically for 30-32 hours, and then fermented aerobically when the production rate of 1,3-propanediol decreased obviously, and the fermentation was stopped when the concentration of glycerin is reduced to a level below 10 g / L, and finally 1,3-propanediol and 2,3-butanediol are obtained. The method of the present invention can effectively reduce production cost and increase productivity.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for synthesizing 1,3-dioxyacetone by glycerol fermentation
The invention relates to the synthesis of a 1,3-dioxyacetone. A method for synthesizing 1,3-dioxyacetone by glycerol fermentation comprises the following steps: performing the gene recombination and DNA rearrangement technology on bacillus licheniformis B-05571 separated and screened from acid soil, integrating a dehydrogenase gene into an Escherichia coli JM109, constructing industrial engineering bacteria of 1,3-dioxyacetone synthesized by glycerol dehydrogenization, immobilizing by using a supermolecule self-assembly template, then fermenting in a culture medium containing glycerol to synthesize 1,3-dioxyacetone. The product 1,3-dioxyacetone can be obtained by the steps of filtering fermentation liquor, extracting with an organic solvent and recrystallizing with a combined solvent. The synthesis process route is simple and convenient, the product is high in quality and low in cost, and the total mass yield is higher than 75%.
Owner:XUZHOU HENGYUAN BIOENG
Genetic engineering strain capable of coproducing isoprene and 1,3-propylene glycol and establishment method and application thereof
ActiveCN106350476AReduce consumptionBalance metabolismBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyHMG-CoA reductase
The invention discloses a genetic engineering strain capable of coproducing isoprene and 1,3-propylene glycol and an establishment method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. In the genetic engineering strain, a glycerol dehydratase gene and a glycerol dehydratase gene reactivating enzyme gene are integrated, a glycerol kinase gene is knocked out, and HMG-CoA reductase, HMG-CoA synthetase, mevalonate kinase, phosphomevalonate kinase, pyrophosphomevalonate decarboxylase, IPP isomerase, isoprene synthetase, aldehyde reductase and transhydrogenase are overexpressed. According to the invention, through genetic engineering, a metabolic way capable of coproducing the isoprene and the 1,3-propylene glycol is successfully established in escherichia coli; by the establishment method, redox cofactors in cells of the genetic engineering strain are metabolized in a balanced way, and the yield in coproducing the isoprene and the 1,3-propylene glycol through glucose and glycerol fermentation is increased.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Clostridium butyricum strain with high yield of 1,3-propanediol and sequential inoculation fermentation process
ActiveCN110438052AIncrease productionLess investmentBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementContinuous fermentationMicroorganism
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering, and particularly relates to a clostridium butyricum strain with high yield of 1,3-propanediol and a sequential inoculation fermentationprocess thereof. The strain is named as clostridium butyricum DL07 and a preservation number is CGMCCCNO. 17934. The strain of the present invention can produce 104.78 g / L and 94.23 g / L of 1,3-propanediol by fermentation with pure glycerin and crude glycerin respectively, and the currently reported natural microorganisms uses the pure glycerin and crude glycerin to ferment and produce the highestyield of 1,3-propanediol. The invention also provides a sequential inoculation fermentation process and an automatic fed-substrate fermentation control method, which saves seed cultivation time and realizes multi-stage continuous fermentation, and provides a new fermentation control mode with high degree of automation and excellent economy for the production of 1,3-propanediol by microbial fermentation, and the process has the good industrial application prospect.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Clostridium butyricum and application of clostridium butyricum in immobilized fermentation production of 1, 3-propylene glycol
ActiveCN112358986AStrong toleranceReduce manufacturing costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
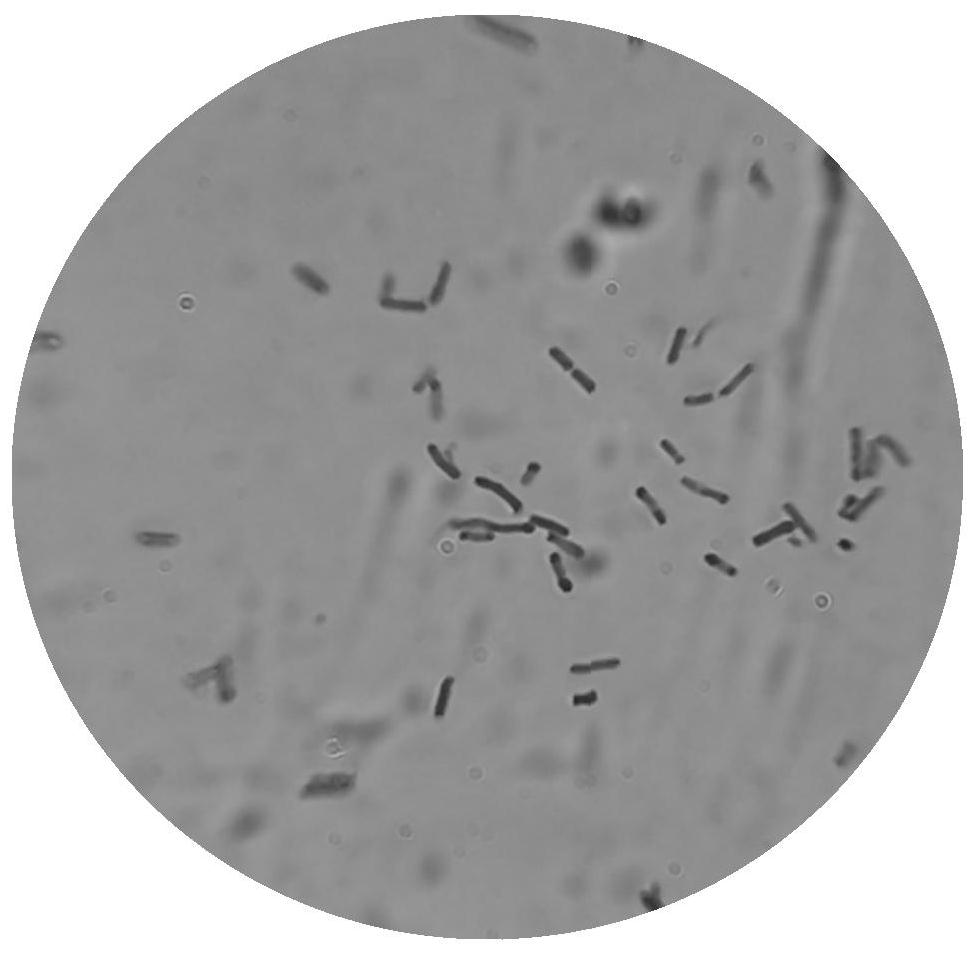
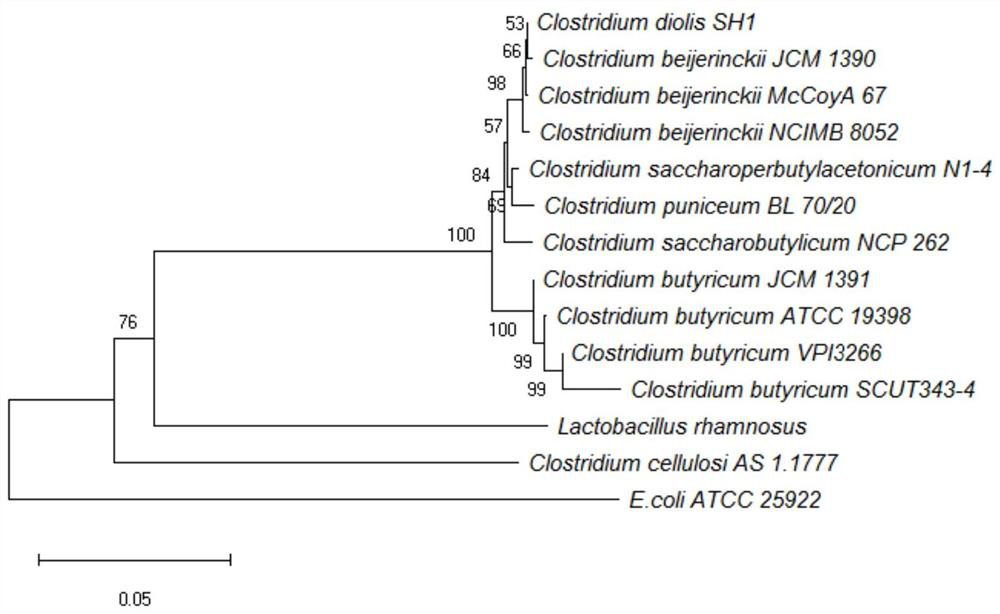
The invention discloses clostridium butyricum and an application thereof in immobilized fermentation production of 1, 3-propylene glycol, the clostridium butyricum is clostridium butyricum SCUT343-4 and is preserved in Guangdong province microbial strain preservation center on October 12, 2019, and the preservation number is GDMCC NO: 60805. The strain can be used for directly converting pure glycerol or crude glycerol into 1, 3-propylene glycol, has higher substrate conversion rate and substrate tolerance, has few types and contents of byproducts, and is beneficial to separation and purification of subsequent products; the strain has the most outstanding tolerance to a substrate crude glycerol, and the conversion rate and the production efficiency are not reduced during crude glycerol fermentation, so that the processing and utilization of the crude glycerol are facilitated, and the production cost of the 1, 3-propylene glycol is remarkably reduced. The strain is applied to immobilized fermentation production of 1, 3-propylene glycol, the production efficiency can be remarkably improved and reaches 4.20 g / L.h.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
A kind of treatment method of biodiesel by-product glycerin
ActiveCN105585449BThe method steps are simpleReduce energy consumptionOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound separation/purificationBiodieselAlcohol
The invention discloses a treatment method for biodiesel by-product glycerol. The method includes the following contents: (1) acidifying the biodiesel by-product glycerin, standing for stratification, and taking the lower clear liquid; (2) adding organic alcohol to the lower clear liquid obtained in step (1), mixing evenly, and solidifying After liquid separation, glycerin clear liquid is obtained; (3) The glycerin clear liquid obtained in step (2) is added for dilution, electrodialysis is performed for desalination, and then rectification, and the residue is collected as the product. The glycerin product obtained by the method can be used for microbial fermentation, has a simple process and is easy to realize industrial application.
Owner:SINOPEC DALIAN RES INST OF PETROLEUM & PETROCHEMICALS CO LTD +1
Production technology of 1,3-propylene glycol by using glycerol fermentation method
InactiveCN103146766AImprove conversion rateShorten fermentation timeBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyHeterologous
The invention discloses a production technology of 1,3-propylene glycol (PDO) by using a biological fermentation method, belonging to the technical field of biochemical engineering. The production technology comprises the following steps of: preparing 2'-dehydroxylase gene (sisII) from 3',4'-double dehydroxylase gene of sisI in micromonospora inyoensis through genetic recombination, DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) rearrangement and the like; cloning to obtain sisII; constructing the sisII to a pET30a expression vector, and performing heterologous expression in E.coli BL21 to construct engineering bacteria BL21-sis for synthesizing 1,3-propylene glycol through glycerol dehydration; performing immobilization by a supramolecular self-assembly template method; fermenting to synthesize 1,3-propylene glycol in a glycerol-containing culture medium; and obtaining the product 1,3-propylene glycol through fermentation liquid filtration, organic solvent extraction and the like. The method for preparing 1,3-propylene glycol has the advantages of short production period, simple equipment, environmental friendliness, easiness in operation and control, cheap raw materials and the like, facilitates industrial production and has great practical value.
Owner:XUZHOU KAIMIKE NEW MATERIALS
Method for producing ethanol by adopting mixed culture organism by means of glycerol fermentation
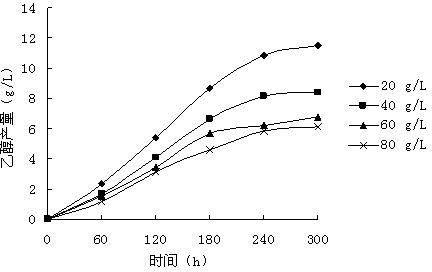
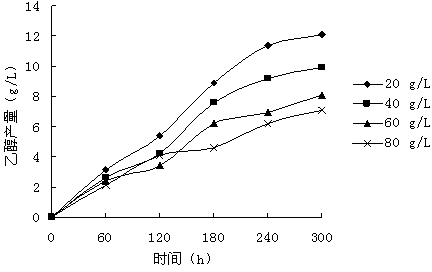
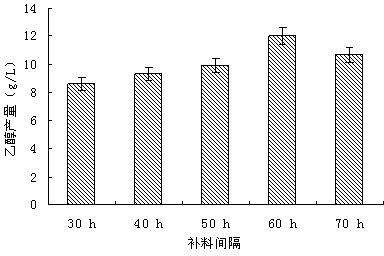
The invention provides a method for producing ethanol by adopting paenibacillus macerans and monasucs by means of glycerol mixed culture fermentation. According to the invention, the paenibacillus macerans and monasucs are taken as original strains and glycerol as raw materials, researches are carried out on initial glycerol concentration, glycerol concentration in feeding supplement, feeding supplement time interval, fermentation time and slurry quantity that influence the ethanol yield.
Owner:TAICANG ZHOUSHI CHEM PROD
Gene producing glycerin candida NAD+ depending- glycerin3- glycerophosphate dehydrogenase and clone thereof
InactiveCN101157931AExpand genetic resourcesImprove stress resistanceOxidoreductasesGenetic engineeringOpen reading framePhosphate
Glycerol fermentation by candida glycerinogenes NAD+ depends on glycerine-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene and clone thereof and pertains to the microorganism molecular biology field. The invention relates to a new gene order SEQID NO.1. a degenerate primer PCR method and a reverse PCR method are adopted to clone rate-limiting enzyme NAD+ depending glycerine-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene and lateral regulation sequence thereof from genome DNA of glycerine-producing candida mycoderma WL2002-5-59 which is produced by glycerine. The total length of the gene is 4900bp and a start codon ATG is at 2082bp while a stop codon TAA is at 3246bp. The sequence has no intron but has an 1167bp complete open reading frame which encodes 388 amino acids. The gene has homology as high as 60 percent with saccharomyces cerevisia GPD1 gene and 70 percent with Angus pichia yeast GPD gene. The clone of the gene expands gene resource of microorganism anti-osmotic pressure stress research and lays a foundation for research on molecular mechanism of glycerine-producing candida mycoderma producing glycerine with high yield.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Genetically engineered bacteria for co-production of isoprene and 1,3-propanediol and its construction method and application
ActiveCN106350476BRealize joint productionHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliBiotechnology
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
A method for producing 1,3-propanediol by fermentation of glycerol by microorganisms
ActiveCN111394396BReduce manufacturing costImprove conversion rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
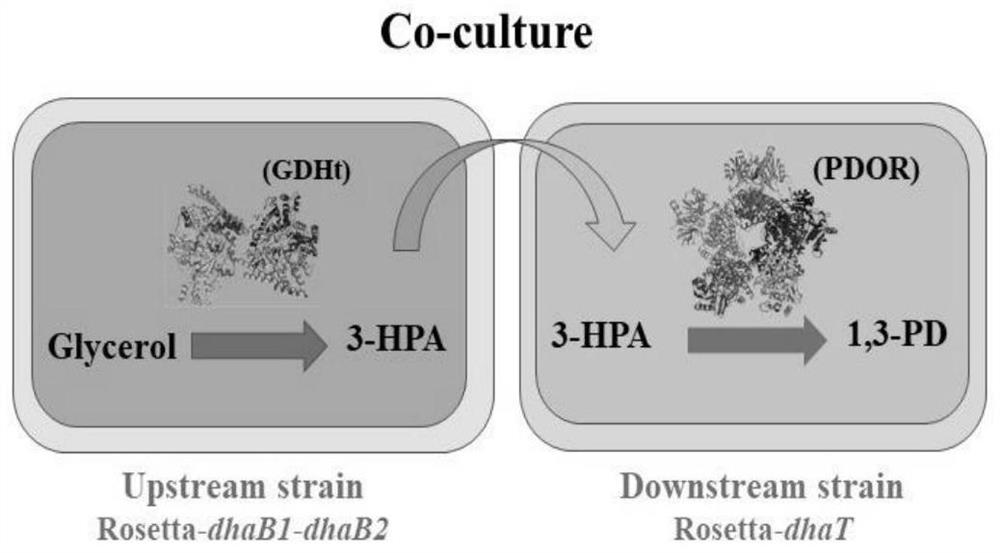
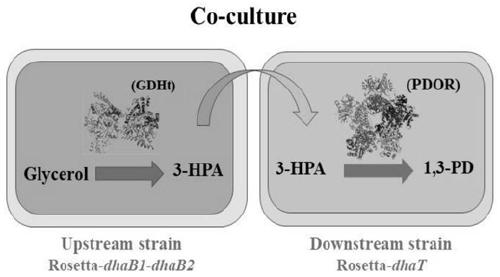
The invention provides a method for producing 1,3-propanediol by fermentation of glycerol in a microbial co-cultivation system, by successfully constructing recombinant Escherichia coli Rosseta-dhaB1dhaB2 and Rosseta-dhaT, co-cultivating the above-mentioned recombinant Escherichia coli for seed culture and fermentation culture , wherein the recombinant Escherichia coli Rosseta-dhaB1dhaB2 realizes the utilization of glycerol to produce the intermediate metabolite 3-hydroxypropionaldehyde (3-HPA), and the recombinant Escherichia coli Rosseta-dhaT catalyzes 3-HPA to produce 1,3-propanediol. During the fermentation process, press Inoculate in the fermentation medium at a ratio of 1:1.5, add 60g / L substrate glycerol and 10g / L cosubstrate glucose. The method of the present invention improves the conversion rate of glycerol and the output of 1,3-propanediol, and the present invention adopts Clostridium butyricum containing independent coenzyme B 12 Glycerol dehydratase, which reduces the production cost.
Owner:镇江百泰生物科技有限公司
Construction method and application of engineered strain for producing phenol through glycerol fermentation
ActiveCN105112351AReduce manufacturing costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliGlycerol
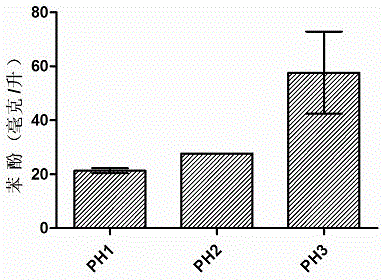
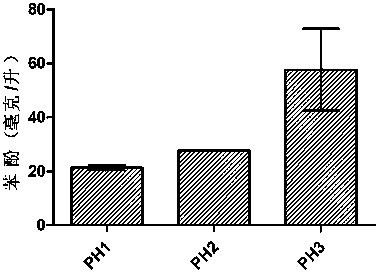
The invention relates to the technical field of engineered strain construction, in particular to a construction method of an engineered strain for producing phenol through glycerol fermentation. The second base sequence and the third base sequence in a sequence list are inserted in a pTrc99a carrier to obtain recombinant plasmid; the recombinant plasmid is electrically transformed into an ATC31884 strain, the engineered strain for producing the phenol through glycerol fermentation is obtained. The constructed engineered strain efficiently presents tyrosine phenol lyase and phenylalanine4-monooxygenase, and content of the obtained escherichia coli engineered strain for producing the phenol through glycerol is 21.30-57.66 mg / L, so that the phenol is produced through glycerol fermentation through the biological method, production cost of the phenol is reduced, and economic benefits are improved.
Owner:QUFU NORMAL UNIV
Method for producing 1,3-propylene glycol through glycerol fermentation via microorganisms
ActiveCN111394396AReduce manufacturing costImprove conversion rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliMetabolite
The invention provides a method for producing 1,3-butanediol through glycerol fermentation via a microbial co-culture system. The method comprises the following steps: successfully constructing recombinant escherichia coli Rosseta-dhaB1dhaB2 and Rosseta-dhaT, co-culturing the recombinant escherichia coli, and carrying out seed culture and fermentation culture, wherein the recombinant escherichia coli Rosseta-dhaB1dhaB2 is used for realizing the production of the intermediate metabolite 3-hydroxypropionaldehyde (3-HPA) from glycerol, the recombinant escherichia coli Rosseta-dhaT catalyzes 3-HPAto produce 1,3-propanediol, and in the process of fermentation, a fermentation medium is inoculated with the recombinant escherichia coli in a ratio of 1: 1.5, and a substrate glycerinum with a concentration of 60 g / L of and an auxiliary substrate glucose with a concentration of 10 g / L of are added. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the conversion rate of glycerol and the yieldof 1,3-propylene glycol are increased; and the adopted clostridium butyricum contains glycerol dehydratase which does not depend on coenzyme B12, so the production cost is reduced.
Owner:镇江百泰生物科技有限公司
Method for producing 1,3-propylene glycol by glycerol fermentation
ActiveCN111100901AAddressing Cytotoxicity IssuesReduce ion concentrationMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyPhosphorylation
The invention relates to a method for producing 1,3-propylene glycol by glycerol fermentation. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, culturing fermentation strains under a microaerobic condition to obtain a fermentation seed liquid; then, culturing microalgae under an autotrophic condition to obtain a microalgae seed liquid; then, inoculating a fermentation culture medium with the fermentation seed liquid to carry out microaerobic fermentation, adding the microalgae seed liquid when the acetic acid concentration is more than 3g / L, and performing culturing until fermentation is finished; and finally, adjusting the pH value to be alkaline, and performing standing for layering to obtain fermentation clear liquid containing 1,3-propylene glycol. According to the method provided bythe invention, through combination of microalgae cell metabolism and a fermentation system, oxidative phosphorylation of the substrate level in glycerol metabolism is strengthened, and the fermentation level is improved.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
A kind of bacterial strain used for producing succinic acid by fermentation of biodiesel by-product crude glycerol and production method thereof
ActiveCN106701637BIncrease profitReduce manufacturing costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiodieselButanedioic acid
The invention discloses a bacterial strain used to produce succinic acid by fermenting crude glycerol, a by-product of biodiesel, and a production method thereof. The bacterial strain Actinobacillus succinoproducens ( Actinobacillus succinogenes ) XT, deposit number CCTCC NO: M2016397, can use biodiesel by-product crude glycerol as raw material to ferment and produce succinic acid, the yield of succinic acid can reach up to 72 g / L, and the yield can reach up to 95%. The production method of the present invention is simple, efficient, and low in cost, realizes the efficient resource utilization of industrial waste crude glycerin, solves the environmental problems caused by the discharge of biodiesel by-product glycerin, extends the biodiesel industry chain, and improves the biodiesel industry. Overall technical level and circular benefits.
Owner:GUANGXI ACAD OF SCI
Pseudomonas aeruginosa as well as construction method and application thereof
PendingCN114438000AIncrease productionImprove glycerin utilizationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention discloses pseudomonas aeruginosa as well as a construction method and application thereof. The invention discloses a pseudomonas aeruginosa recombinant bacterium which is used for overexpressing NAD (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) + synthetase. The invention provides a new development strategy for producing rhamnolipid by using microorganisms through glycerol fermentation.
Owner:WANHUA CHEM (SICHUAN) CO LTD +1
A strain for enhancing glycerol metabolism and its application
ActiveCN105838652BPromote accumulationReduce the level of reducing powerBacteriaMicroorganism based processesOrganic acidNormal growth
The invention discloses a bacterial strain that strengthens glycerol metabolism, and the bacterial strain is classified and named as Actinobacillus succinate ( Actinobacillus succinogenes ) JF1315, which was deposited in China Center for Type Culture Collection on March 31, 2016, and its deposit number is: CCTCC NO: M 2016160. The present invention also relates to the application of the Actinobacillus succinogenes JF1315 in fermentative production of organic acids. Under the anaerobic condition, compared with the control strain, the strain can grow and metabolize at a lower pH condition, and can efficiently utilize glycerol to ferment and synthesize reduced organic acids. Under the condition of pH 4.8-6.8, the strain can grow normally, and metabolize glucose to synthesize organic acids such as succinic acid; in addition, under this condition, the strain can efficiently use glycerol for anaerobic fermentation, synthesize and accumulate organic acids. acid.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
A kind of construction method and application of engineering strain for producing phenol by fermentation of glycerol
ActiveCN105112351BReduce manufacturing costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliGlycerol
The invention relates to the technical field of engineered strain construction, in particular to a construction method of an engineered strain for producing phenol through glycerol fermentation. The second base sequence and the third base sequence in a sequence list are inserted in a pTrc99a carrier to obtain recombinant plasmid; the recombinant plasmid is electrically transformed into an ATC31884 strain, the engineered strain for producing the phenol through glycerol fermentation is obtained. The constructed engineered strain efficiently presents tyrosine phenol lyase and phenylalanine4-monooxygenase, and content of the obtained escherichia coli engineered strain for producing the phenol through glycerol is 21.30-57.66 mg / L, so that the phenol is produced through glycerol fermentation through the biological method, production cost of the phenol is reduced, and economic benefits are improved.
Owner:QUFU NORMAL UNIV
A method for producing 1,3-propanediol by fermentation of glycerol
ActiveCN111100901BAddressing Cytotoxicity IssuesReduce ion concentrationMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyPhosphorylation
The invention relates to a method for producing 1,3-propanediol by fermentation of glycerin. Firstly, the fermentation strain is cultivated under microaerobic conditions to obtain a fermented seed liquid; then microalgae are cultured under autotrophic conditions to obtain a microalgae seed liquid Then, insert the fermented seed liquid in the fermentation medium to carry out micro-aerobic fermentation, add the microalgae seed liquid when the acetic acid concentration is greater than 3g / L, and cultivate until the end of fermentation; finally adjust the pH to alkaline, and let it stand for stratification A fermentation broth containing 1,3-propanediol is obtained. The method of the invention utilizes the combination of microalgae cell metabolism and fermentation system to strengthen the oxidative phosphorylation at the substrate level in glycerin metabolism and improve the fermentation level.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for increasing hyperosmotic-resistant yeast-fermented glycerol concentration by adding amphotericin fermented broth
InactiveCN1230549CIncrease concentrationSimple processFermentationBiotechnologyMembrane permeability
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Method for mixed culture of R.salina
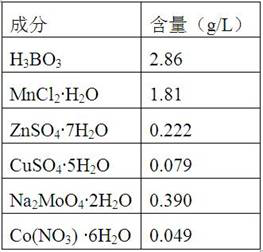
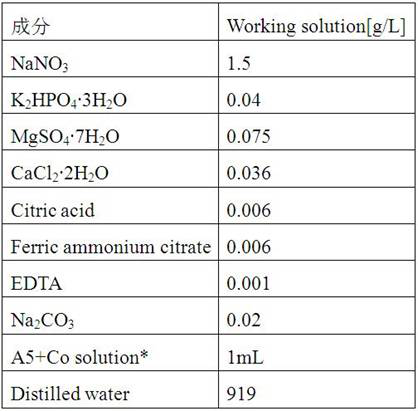
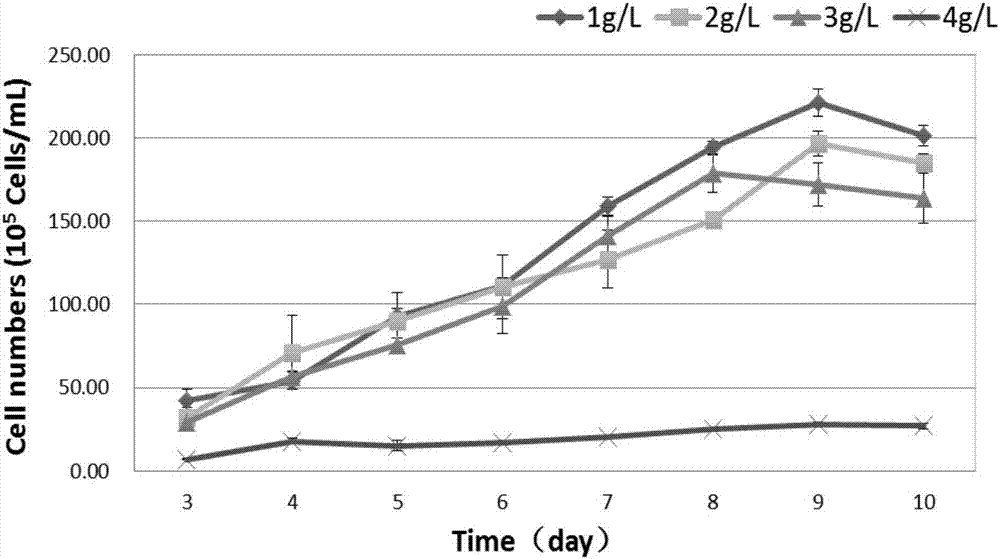
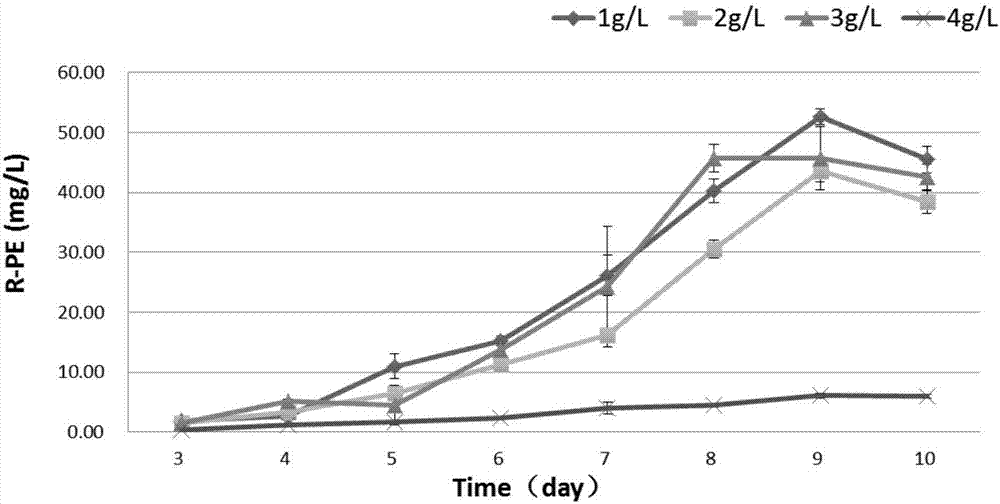
ActiveCN106916751AImprove substrate utilizationFast growthUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesPhycoerythrinGlycerol
The invention provides a method for mixed culture of R.salina; the method includes the steps: culturing R.salina with a seed culture medium; carrying out domestication culture by using glycerol; inoculating a glycerol fermentation culture medium with the R.salina after domestication; and culturing the R.salina by using light with different wavelengths and intensities. The thallus substrate utilization rate, growth rate, living weight, and phycoerythrin, total protein, polyunsaturated fatty acid and total lipid contents during R.salina fermentation are improved, the problems of harvest of the R.salina are reduced, the biomass concentration and the pre-processing cost of target product extraction are reduced.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
A kind of production method and application of thermophilic fungus mannanase
ActiveCN112029751BRich varietyHas acid and alkali resistanceAnimal feeding stuffMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMalbranchea cinnamomea
The invention discloses a production method and application of mannanase. The method for producing mannanase provided by the present invention comprises: introducing the mannanase gene derived from Cladosporium camphoropsis S168 into recipient yeast to obtain recombinant yeast; performing basic fermentation culture, glycerol In the fed-feed fermentation stage and the methanol-feed-induced expression stage, the mannanase was obtained from the fermentation product. The mannanase expression level of the engineering bacteria of the present invention reaches 42200U / mL through high-density fermentation, and the optimal pH of the obtained enzyme is 7.5, and the optimal temperature is 75°C. It has acid and alkali resistance, good thermal stability, and excellent hydrolysis properties. Features, in addition, the present invention broadens the scope of application of mannanase, and the partially hydrolyzed konjac gum prepared by using this enzyme has great application value in industries such as food and feed, enriches the types of prebiotic products, and promotes the development of prebiotic products in my country. The development of yuan industry has great social and economic benefits.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
1,3-propylene glycol and 2,3-butanediol production method using glecerol by microorganism two-step fermentation method
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously preparing 1,3-propylene glycol and 2,3-butylene glycol from glycerol by using microbe employing prior-stage anaerobic and later-stage aerobic two-stage fermentation process, which belongs to the field of the bio-chemical engineering technology. In the fermentation process, the seed liquid is added in the primary fermentation medium containing industrial glycerol or glycerol fermentation liquid, after 3-5 hours, the mixed liquid of glycerol and glucose is added in the form of the flow. The product concentrations of 1,3-propylene glycol and 2,3-butylene glycol are controlled by adjusting the air flow in the two-stage fermentation process and controlling the fermentation temperature. When the fermentation process is over, 1,3-propylene glycol and 2,3-butylene glycol are separated and purified by desalting, distilling, and vacuum rectification. The preparing method can improve the fermentation concentration and the yield of 1,3-propylene glycol and the production intensity, at the same time, 2,3-butylene glycol with higher concentration can be obtained with high raw material availability and low cost.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
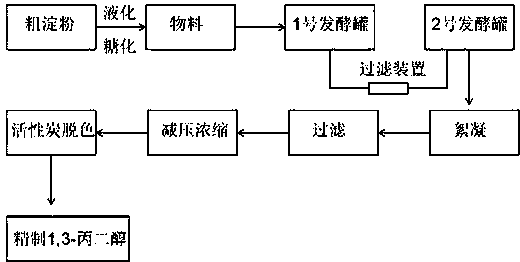
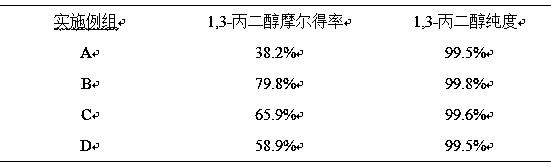
Bio-fermentation method for preparing 1,3-propanediol
InactiveCN108070622AImprove reuseReduce manufacturing costMicroorganism based processesFermentationDistillationGlycerol fermentation
The invention discloses a bio-fermentation method for preparing 1,3-propanediol. The method comprises the following steps: performing aerobic and anaerobic fermentation on crude starch as a raw material in a No. 1 fermentation tank by adopting pressure-resistant yeast to obtain glycerol fermentation broth, filtering the fermentation broth, recovering thalli for next fermentation, transferring a filtrate into a No. 2 fermentation tank accommodating Klebsiella pneumoniae for anaerobic fermentation, performing flocculating, filtering, evaporating and concentrating, reduced pressure distillation and decolorization on the fermentation broth to obtain the finished product 1,3-propanediol. With application of the method, the technical level of bio-fermentation in China is greatly improved, raw materials can be used to the greatest extent, the production cost is effectively reduced, productivity of 1,3-propanediol is improved, and the method is more suitable for industrial production.
Owner:HUNAN ER KANG PHARMA
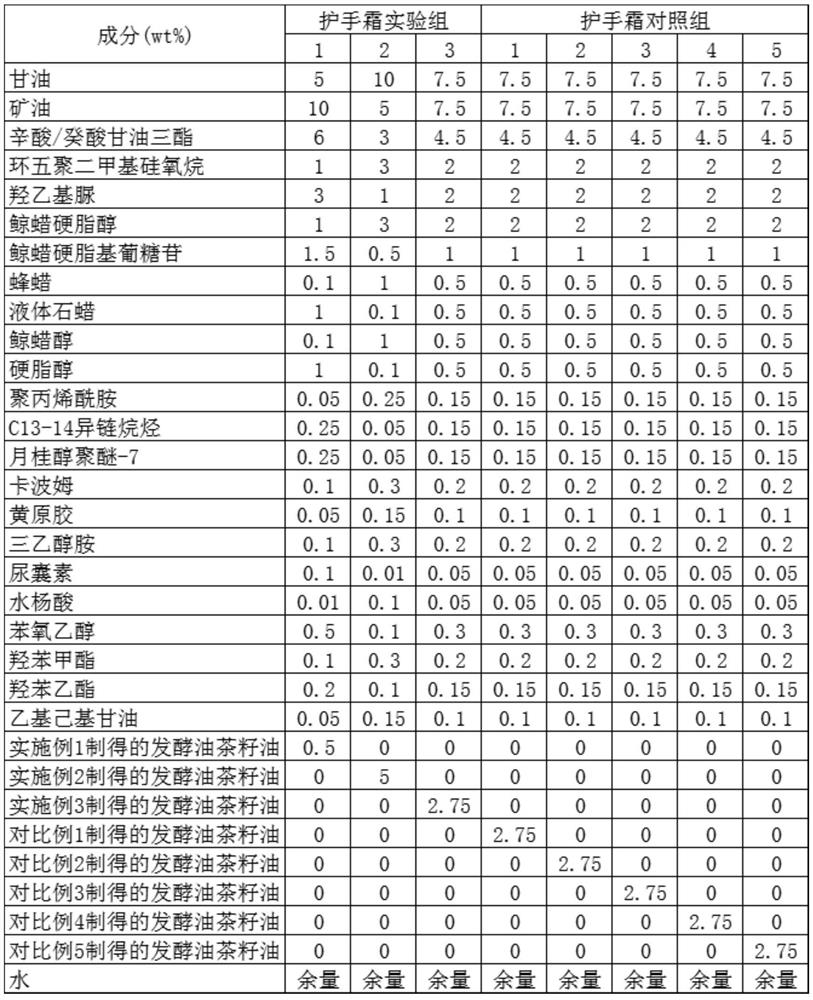
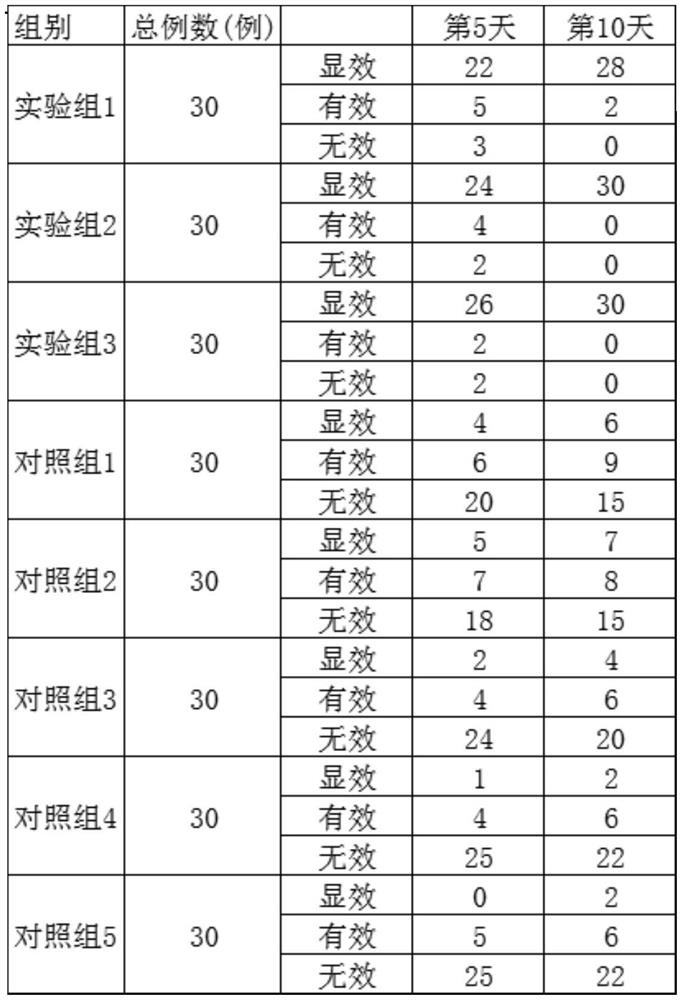
A tea oil hand cream
InactiveCN109568181BPromote energy saving and emission reductionGood skin careCosmetic preparationsAntipyreticBiotechnologyAlkane
The invention provides a tea oil hand cream, which is mainly composed of the following components in mass percent: 5-10% of glycerin, 5-10% of mineral oil, 3-6% of caprylic / capric triglyceride, cyclic Pentamethicone 1‑3%, Hydroxyethyl Urea 1‑3%, Cetearyl Alcohol 1‑3%, Cetearyl Glucoside 0.5‑1.5%, Beeswax 0.1‑1%, Liquid Paraffin 0.1‑1%, Cetyl Alcohol 0.1‑1%, Stearyl Alcohol 0.1‑1%, Polyacrylamide 0.05‑0.25%, C13‑14 Isoparaffin 0.05‑0.25%, Laureth‑7 0.05‑ 0.25%, Carbomer 0.1‑0.3%, Xanthan Gum 0.05‑0.15%, Triethanolamine 0.1‑0.3%, Allantoin 0.01‑0.1%, Salicylic Acid 0.01‑0.1%, Phenoxyethanol 0.1‑0.5%, 0.1-0.3% of methylparaben, 0.1-0.2% of ethylparaben, 0.05-0.15% of ethylhexylglycerin, 0.5-5% of fermented camellia oleifera seed oil, 53-80% of water; wherein the fermented camellia oleifera seed oil is composed of It is prepared from the following raw materials: camellia oleifera seed cake, camellia oleifera root, and camellia oleifera. The hand cream of the invention is easy to be absorbed through the skin, and can play a good skin care effect of preventing frost cracking, preventing skin roughness, preventing chapping, moisturizing and rejuvenating the skin, and relieving itching and pain.
Owner:JIANGXI GREEN SEA OIL FAT CO LTD
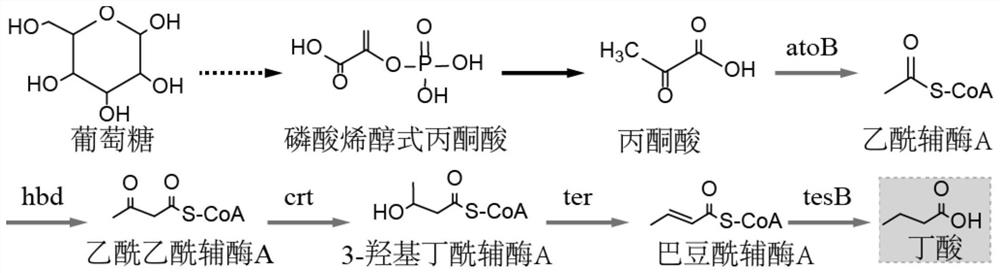
Construction and application of an engineered strain of Escherichia coli producing n-butyric acid
The invention discloses the construction and application of an Escherichia coli engineering bacterium producing n-butyric acid, and belongs to the technical field of fermentation engineering. The present invention takes Escherichia coli ATCC 8739 as the starting strain, utilizes metabolic engineering means, constructs butyric acid-producing Escherichia coli genetically engineered bacteria by constructing a butyric acid synthesis path and cutting off redundant metabolic branches. After 72 hours of fermentation, the production of butyric acid reached 15g / L. The fermentation process is an aerobic fermentation, the bacteria grow fast, the fermentation period is short, and the acid production rate is high. At present, there is no report of directly using glycerol to ferment and produce butyric acid. The method adopts a simple fermentation process, is easy to control, has low production cost, and is beneficial to popularization and application of industrial production.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com