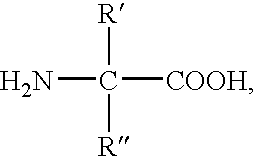Patents
Literature
251 results about "Genetic recombination" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Genetic recombination (also known as genetic reshuffling) is the exchange of genetic material between different organisms which leads to production of offspring with combinations of traits that differ from those found in either parent. In eukaryotes, genetic recombination during meiosis can lead to a novel set of genetic information that can be passed on from the parents to the offspring. Most recombination is naturally occurring.
Gene recombination and hybrid protein development
InactiveUS20020045175A1Preserve stabilityPreserve desired propertyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingBiopolymerHybrid protein
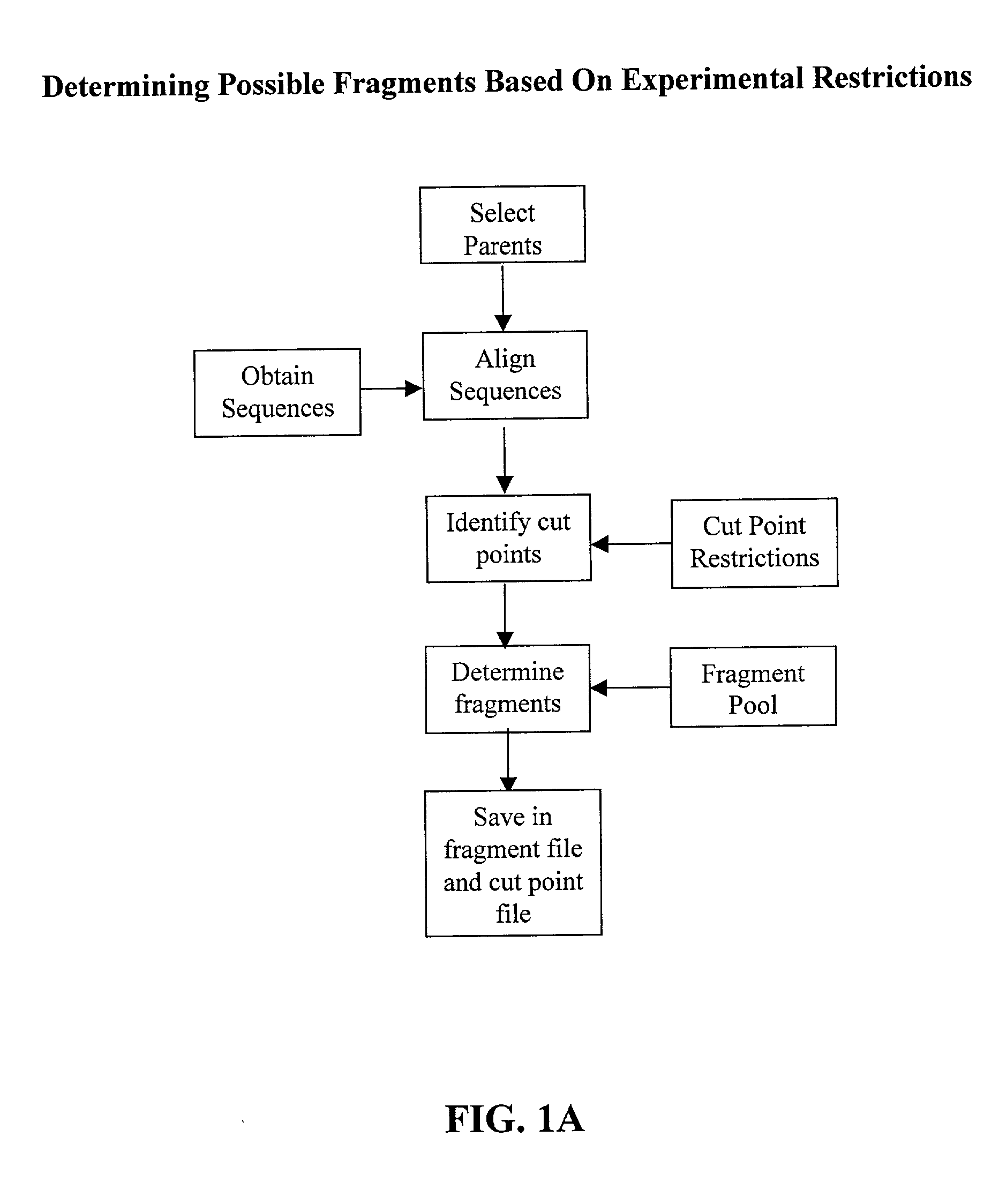
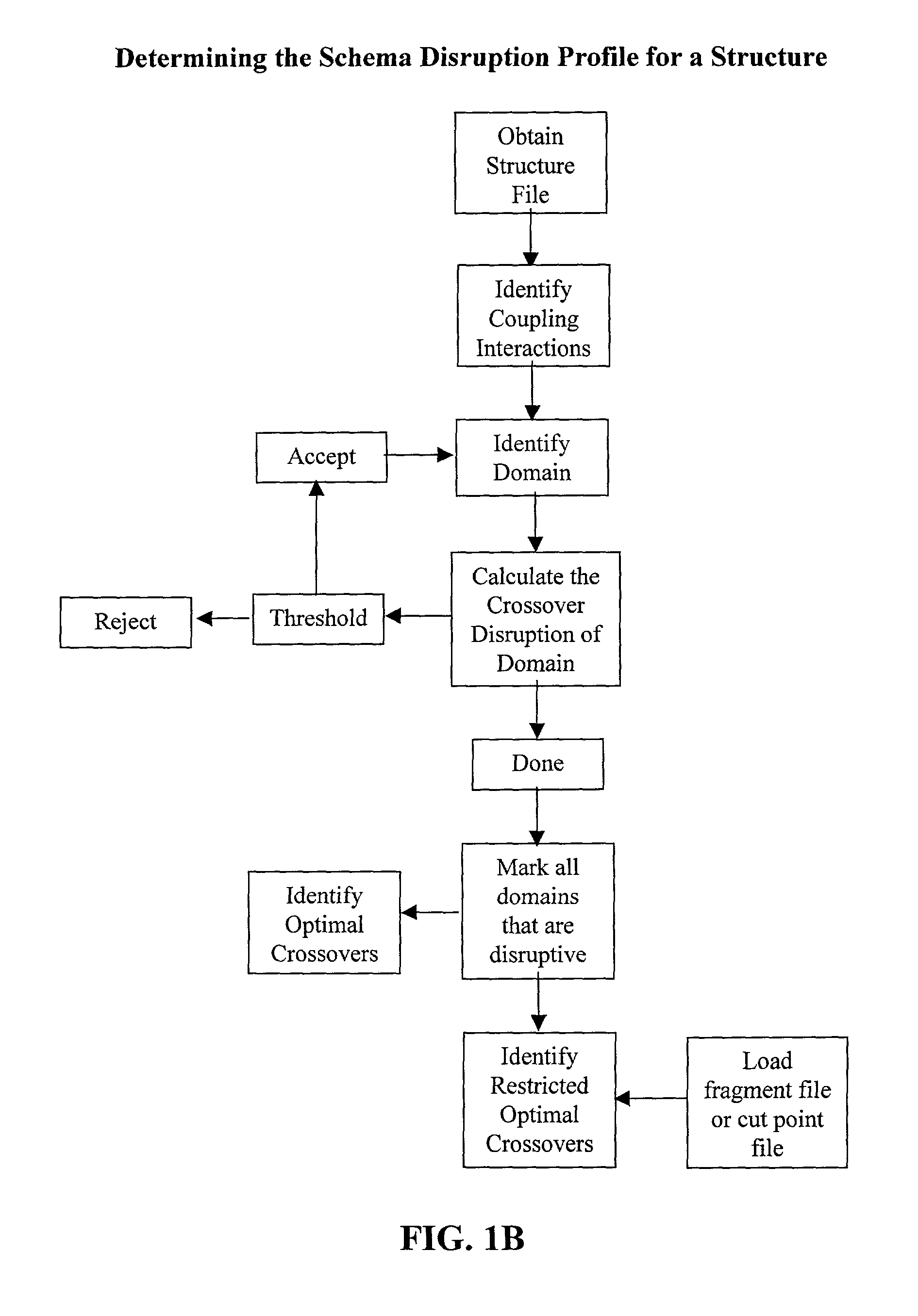
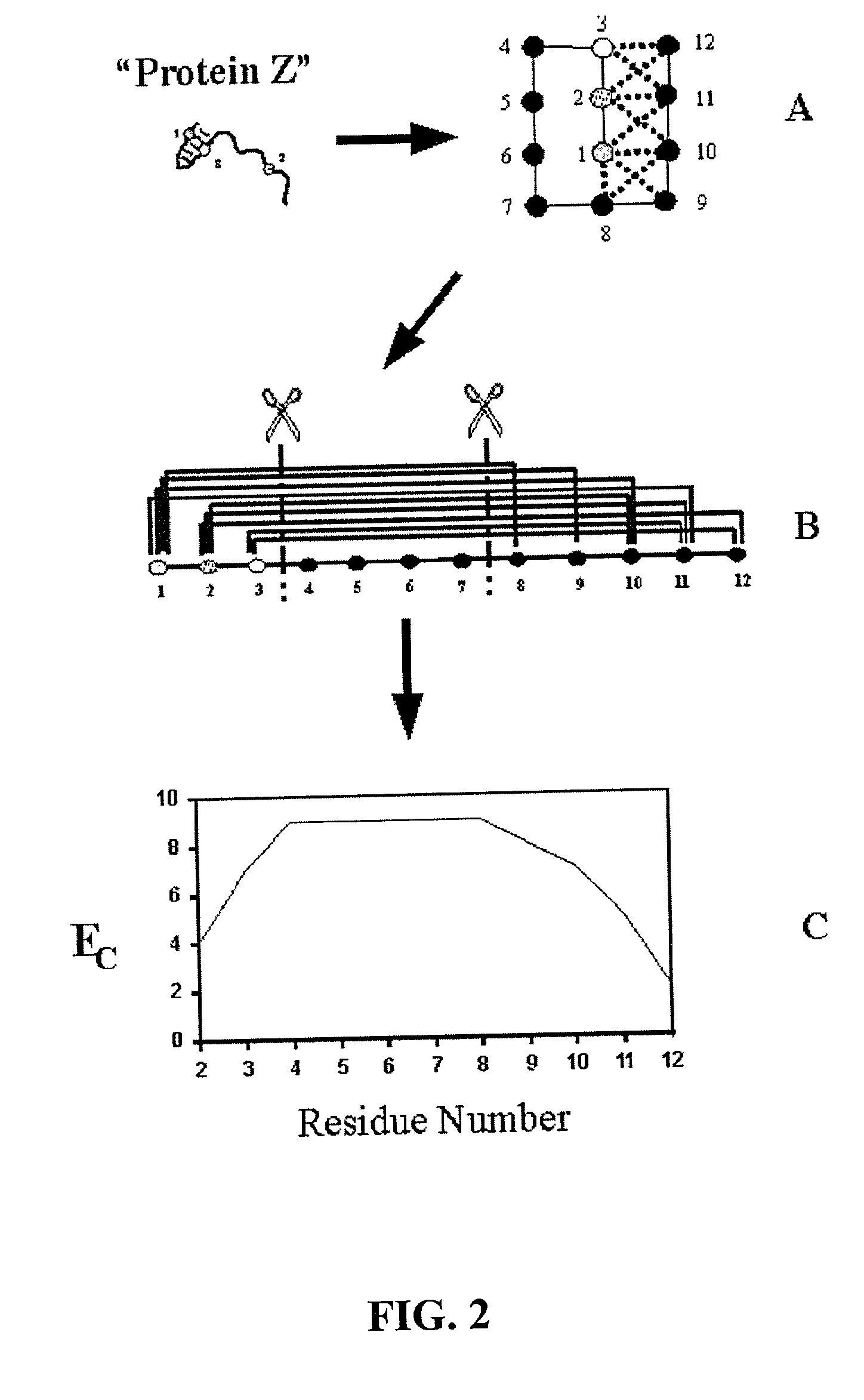
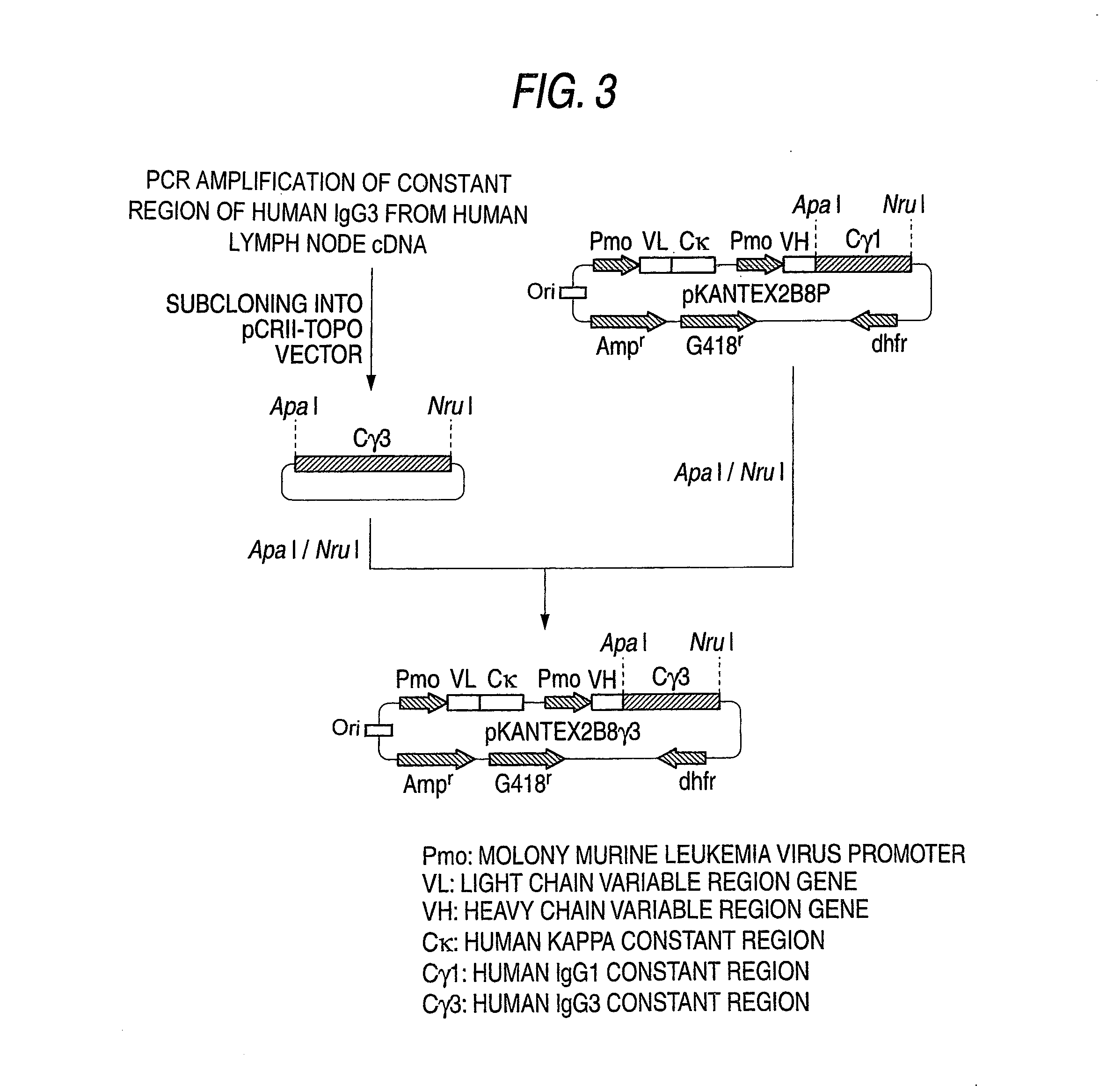
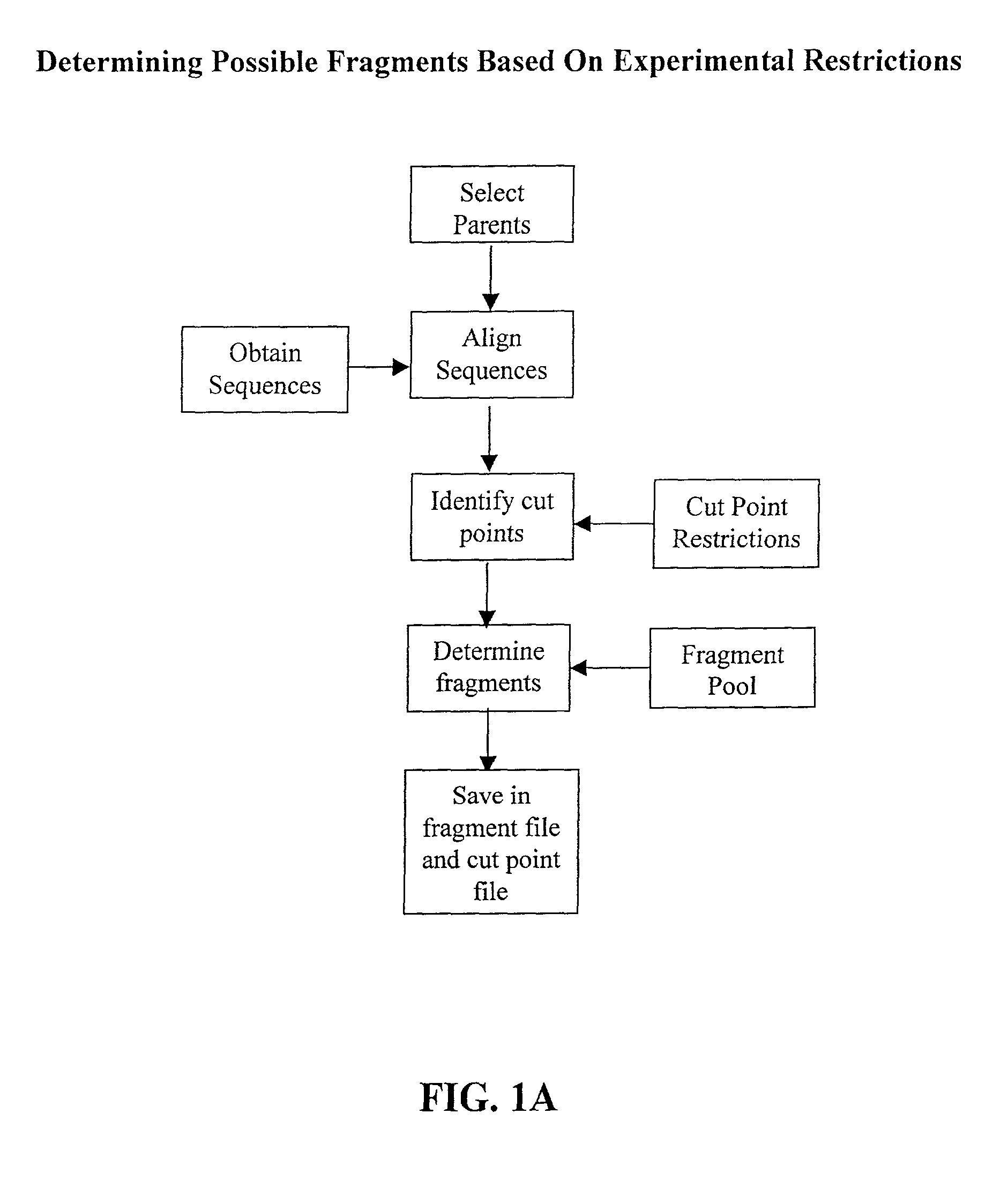
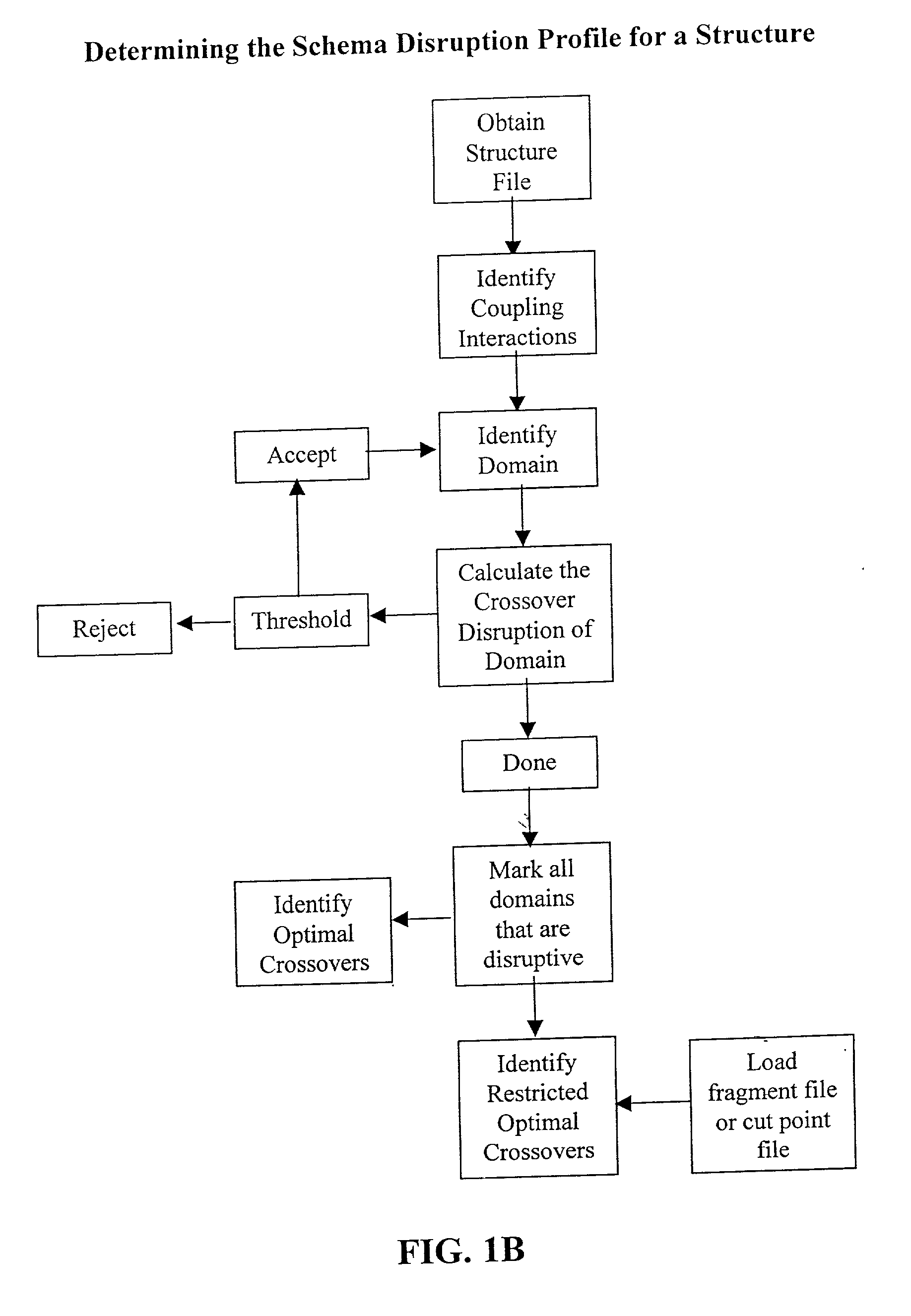
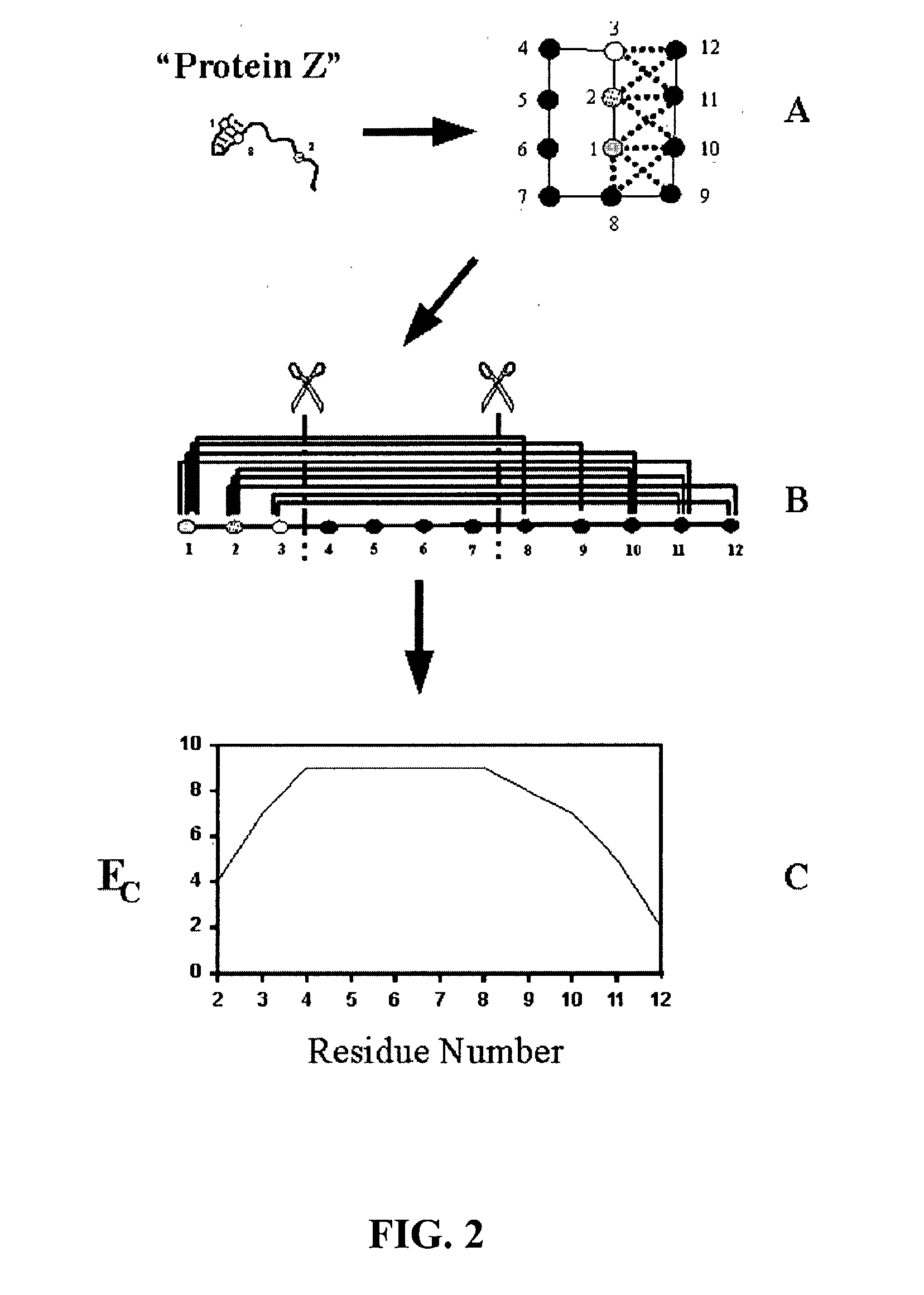
The invention relates to improved methods for directed evolution of polymers, including directed evolution of nucleic acids and proteins. Specifically, the methods of the invention include analytical methods for identifying "crossover locations" in a polymer. Crossovers at these locations are less likely to disrupt desirable properties of the protein, such as stability or functionality. The invention further provides improved methods for directed evolution wherein the polymer is selectively recombined at the identified "crossover locations". Crossover disruption profiles can be used to identify preferred crossover locations. Structural domains of a biopolymer can also be identified and analyzed, and domains can be organized into schema. Schema disruption profiles can be calculated, for example based on conformational energy or interatomic distances, and these can be used to identify preferred or candidate crossover locations. Computer systems for implementing analytical methods of the invention are also provided.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Targeted chromosomal mutagenasis using zinc finger nucleases
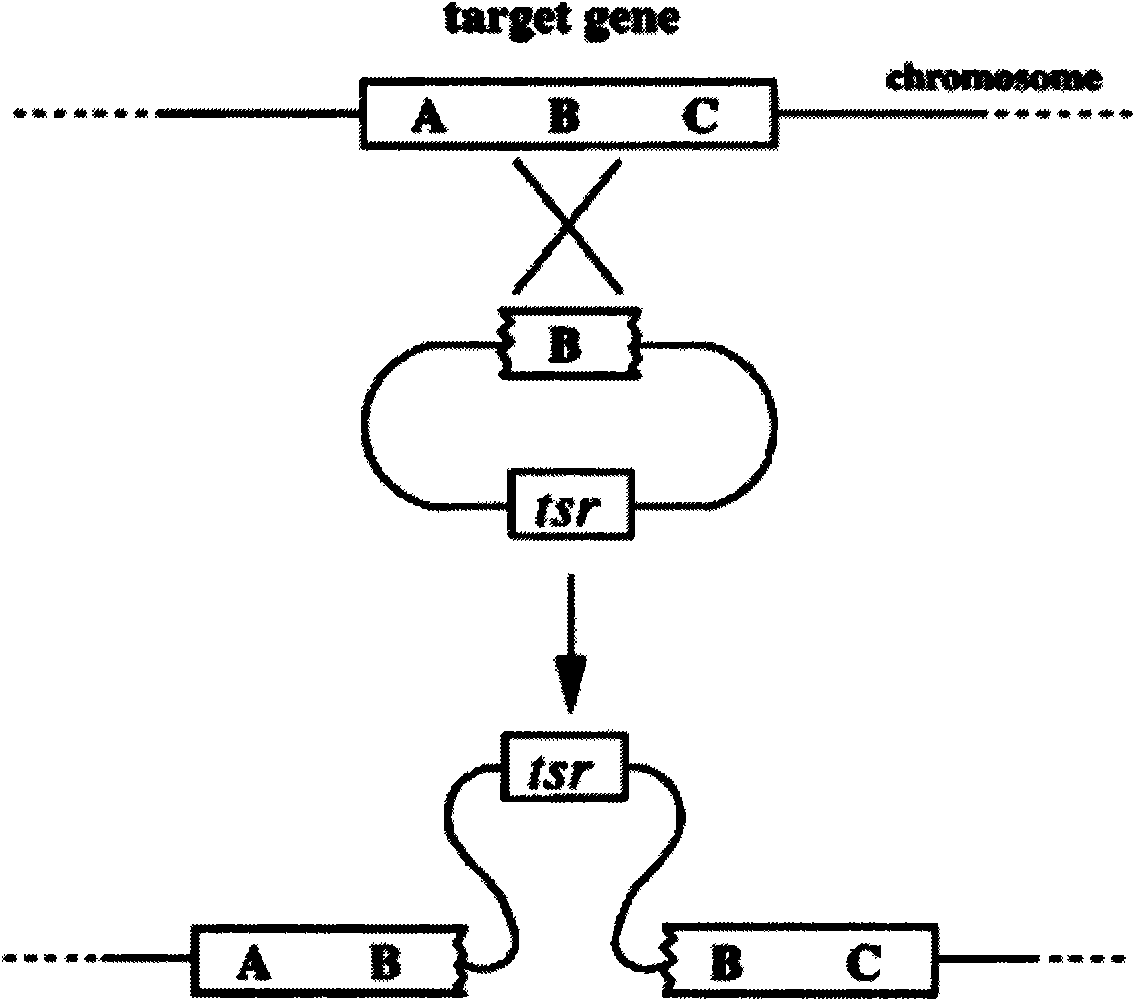
The present invention provides for a method or methods of targeted genetic recombination or mutagenesis in a host cell or organism, and compositions useful for carrying out the method. The targeting method of the present invention exploits endogenous cellular mechanisms for homologous recombination and repair of double stranded breaks in genetic material. The present invention provides numerous improvements over previous mutagenesis methods, such advantages include that the method is generally applicable to a wide variety of organisms, the method is targeted so that the disadvantages associated with random insertion of DNA in-to host genetic material are eliminated, and certain embodiments require relatively little manipulation of the host genetic material for success. Additionally, it provides a method that produces organisms with specific gene modifications in a short period of time.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Genetically recombinant antibody composition capable of binding specifically to ganglioside gm2
InactiveUS20110236374A1High cytotoxic activityAntibacterial agentsAntipyreticA-DNABULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
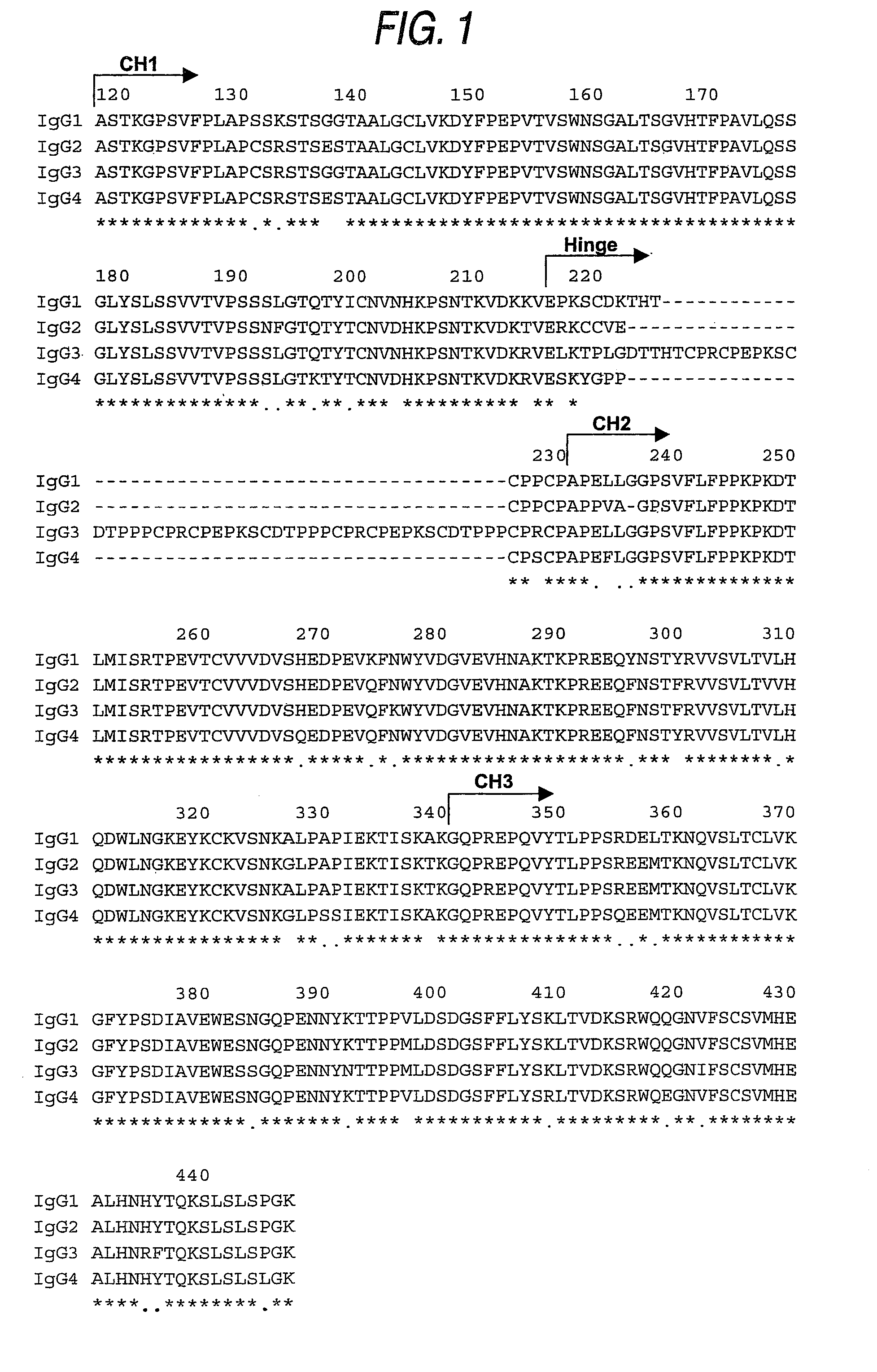
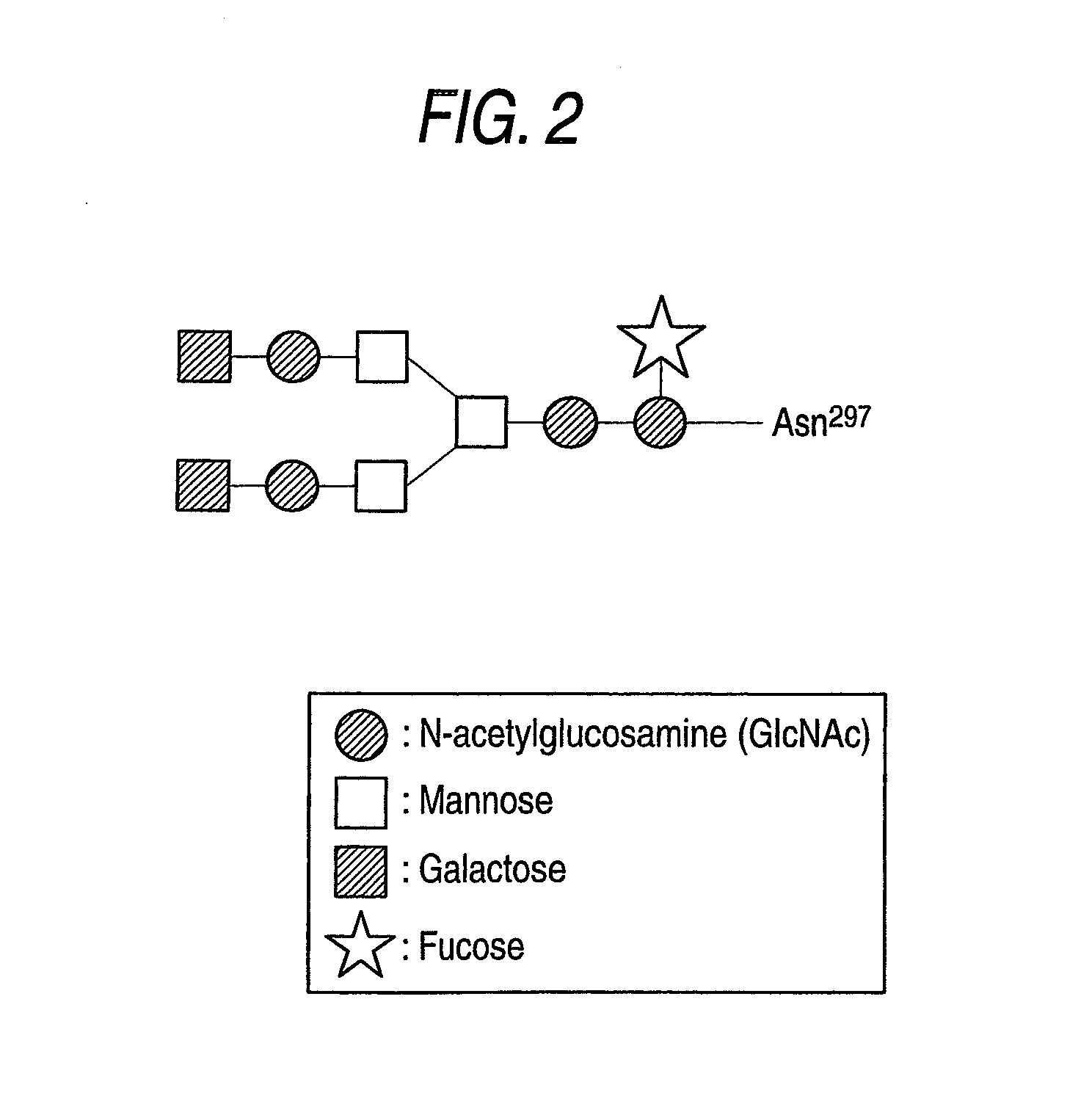
The present invention relates to a genetically recombinant antibody composition which specifically binds to ganglioside GM2, which has higher complement-dependent cytotoxic activity than a human IgG1 antibody and a human IgG3 antibody, wherein a polypeptide comprising a CH2 domain in the Fc region of a human IgG1 antibody is replaced by a polypeptide comprising an amino acid sequence which corresponds to the same position of a human IgG3 antibody indicated by the EU index as in Kabat, et al.; a DNA encoding the antibody molecule or a heavy chain constant region of the antibody molecule contained in the recombinant antibody composition; a transformant obtainable by introducing the recombinant vector into a host cell; a process for producing the recombinant antibody composition using the transformant; and a medicament comprising the recombinant antibody composition as an active ingredient.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
Gene recombination and hybrid protein development
InactiveUS20030032059A1Preserve stability and desired propertyComputationally tractableBiological testingSequence analysisBiopolymerProtein insertion
The invention relates to improved methods for directed evolution of polymers, including directed evolution of nucleic acids and proteins. Specifically, the methods of the invention include analytical methods for identifying "crossover locations" in a polymer. Crossovers at these locations are less likely to disrupt desirable properties of the protein, such as stability or functionality. The invention further provides improved methods for directed evolution wherein the polymer is selectively recombined at the identified "crossover locations". Crossover disruption profiles can be used to identify preferred crossover locations. Structural domains of a biopolymer can also be identified and analyzed, and domains can be organized into schema. Schema disruption profiles can be calculated, for example based on conformational energy or interatomic distances, and these can be used to identify preferred or candidate crossover locations. Computer systems for implementing analytical methods of the invention are also provided.
Owner:WANG ZHEN GANG +3
Genetic recombinant human-like collagen
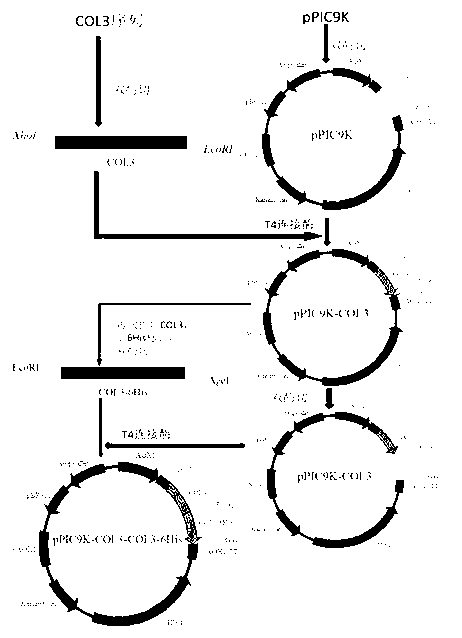
ActiveCN103102407AAvoid immune rejectionAvoid Biosafety HazardsCosmetic preparationsFungiCollagenanHistidine residue
The invention discloses humanized genetic recombinant human-like collagen produced by eukaryotic bacteria. The humanized genetic recombinant human-like collagen has amino acid with the total length of 474, and is formed by connecting two sections of completely-identical human III-type collagen sections in series; the end C is connected with six histidine residue groups serving as specificity affinity purification markers. The performance of the genetic recombination human-like collagen is superior to animal collagens and original nuclear engineering bacteria recombinant collagens; and with the specificity affinity purification markers, the high-purity product is easily acquired.
Owner:JIANGSU TRAUTEC MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) marker and its application
InactiveCN102321760AGenetic material ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementIn vivoGenetic recombination
Belonging to the field of biotechnology, the invention discloses a non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) marker, which is STAT3, and also can include CEA, CA125 and CYFRA21-1. The invention confirms the high expression of STAT3 in peripheral blood and serum, and discloses application of STAT3 in preparation of NSCLC diagnostic reagents by the inventor. Specifically, by making use of a genetic recombination technology and targeting at the gene coding region of STAT3, an eukaryotic expression vector PSUPER-STAT3 able to transcribe in vivo and generate small interference RNA (siRNA) is constructed successfully, and is transfected into an eukaryotic cell, thus laying a foundation for a further experimental study on lung cancer RNAi (RNA interference) and antitumor gene therapy. Utilization of the RNAi technology can effectively inhibit the gene expression of STAT3, induce cell apoptosis, and establish the base for molecular mechanism research and gene therapy of lung cancer, thus providing application of the marker provided in the invention in preparing related targeted medicines.
Owner:THE AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SOUTHWEST MEDICAL UNIV
Trimer of HIV env gene expression product
InactiveUS6737067B1Peptide/protein ingredientsViral antigen ingredientsAdjuvantRecombinant glycoprotein
The invention concerns a purified recombinant glycoprotein having the following properties: a) an adherence capacity to CD4; b) an affinity with a anti-gp120 antibody capable of neutralizing in vitro HIV cell infection; c) an affinity with an anti-gp41 antibody; d) a timeric form free from inter-chain disulphide bonds. The invention also concerns a vaccine comprising said purified glycoprotein and an adjuvant. The invention further concerns a method for obtaining said glycoprotein, which consists in expressing, by means of genetic recombining techniques, a glycoprotein corresponding to the properties a), b) and c) mentioned above; purifying it, and subjecting it to steps involving at least a reducing agent, an ionic detergent and / or a neutral detergent in conditions leading to a glycoprotein having said properties.
Owner:AVENTIS PASTUER LTD
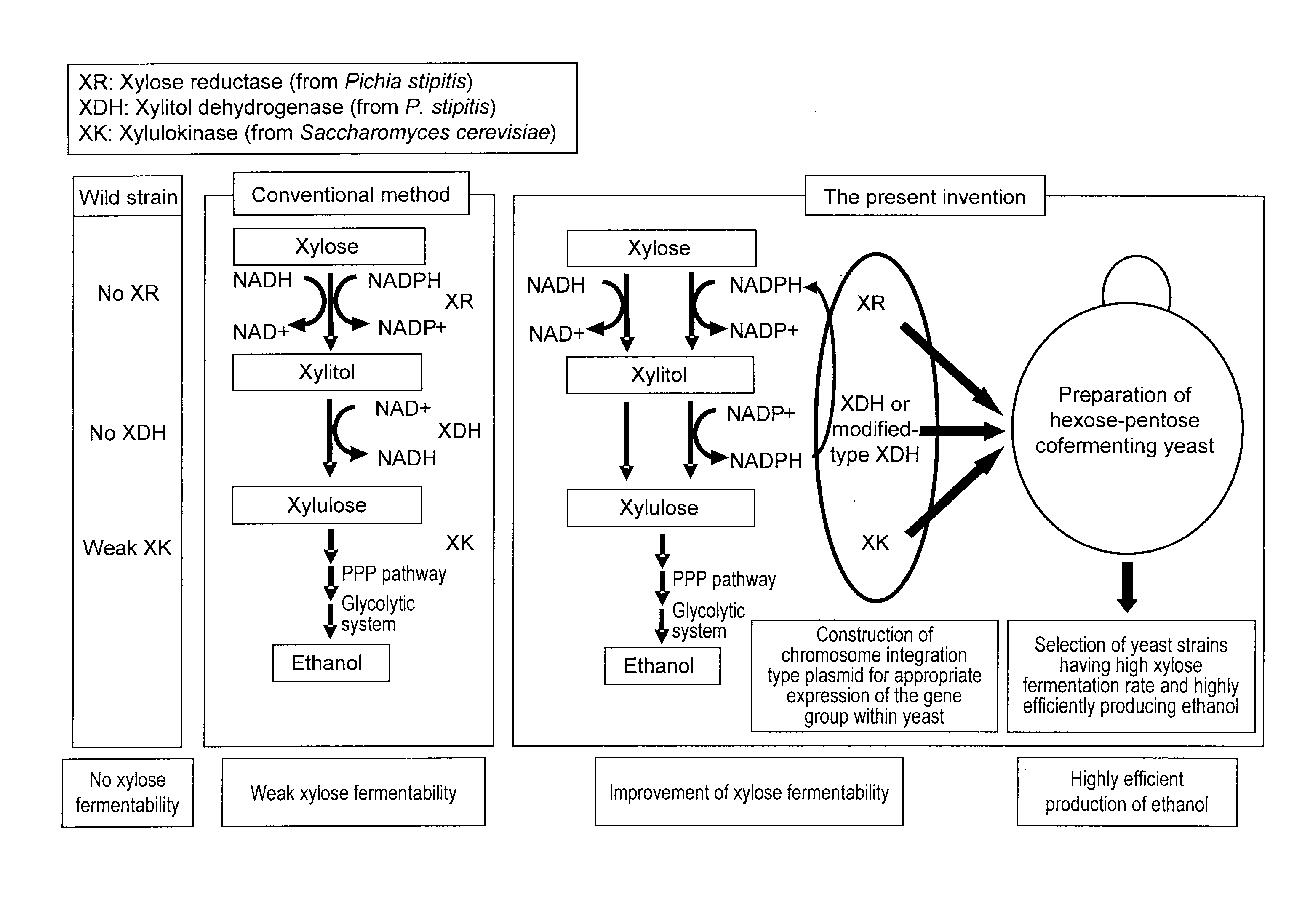
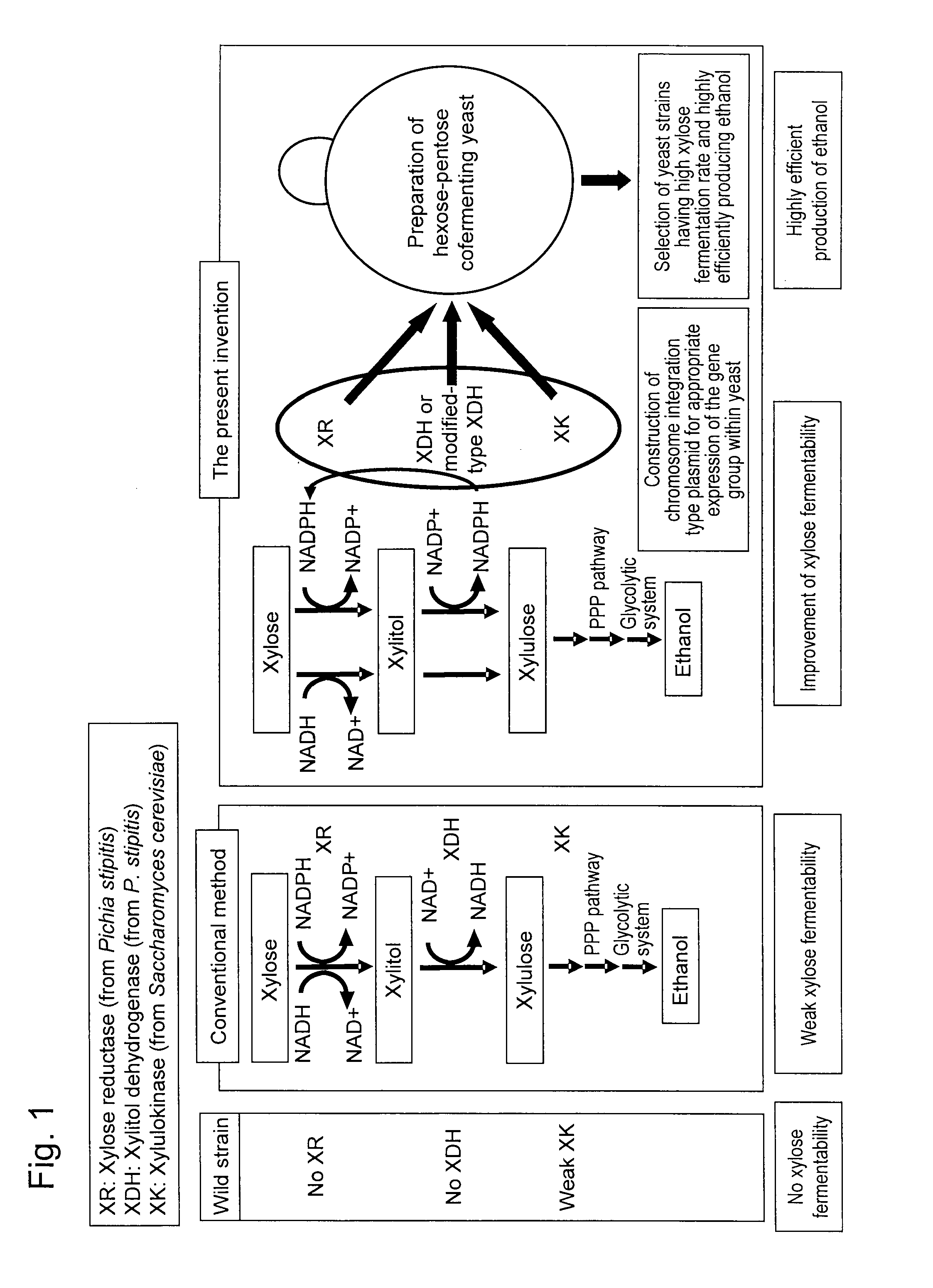
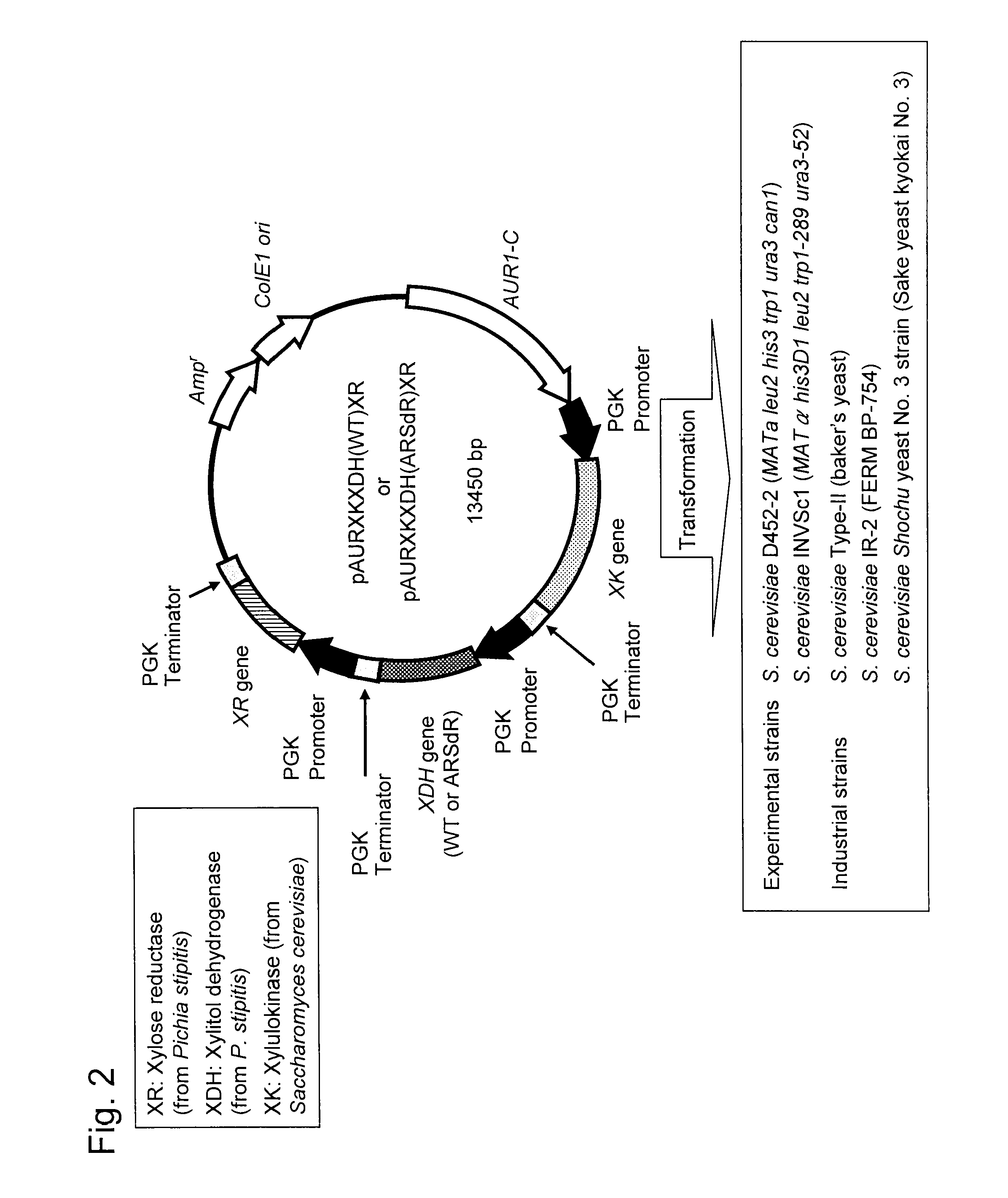
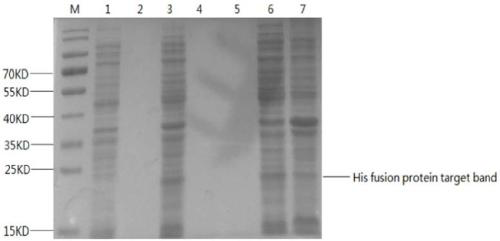
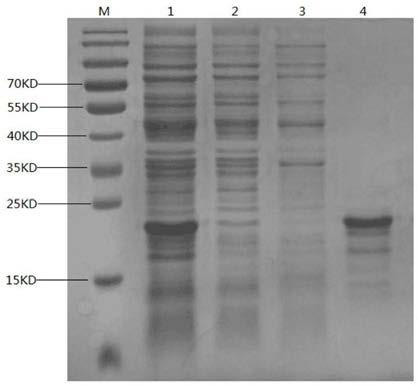
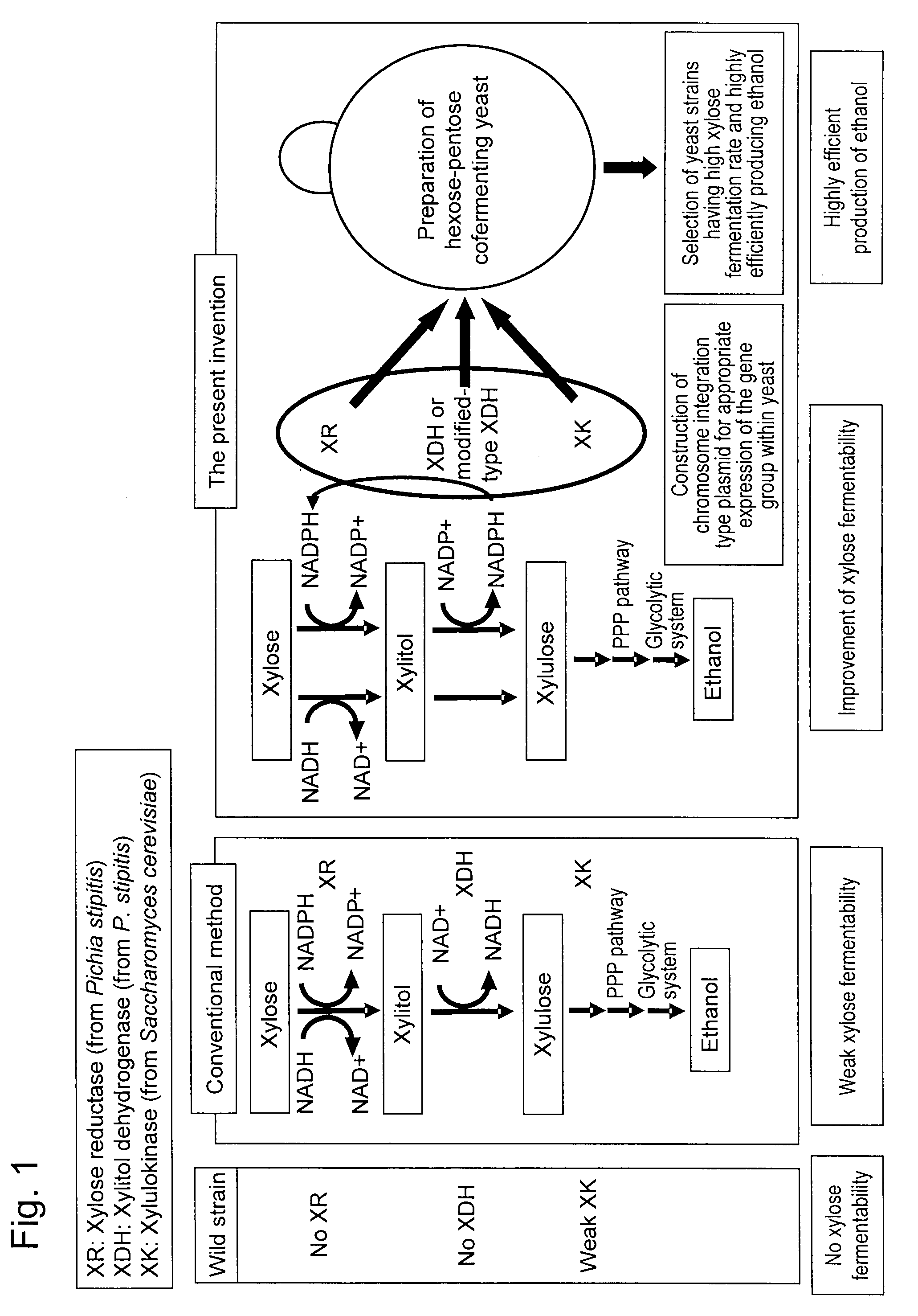
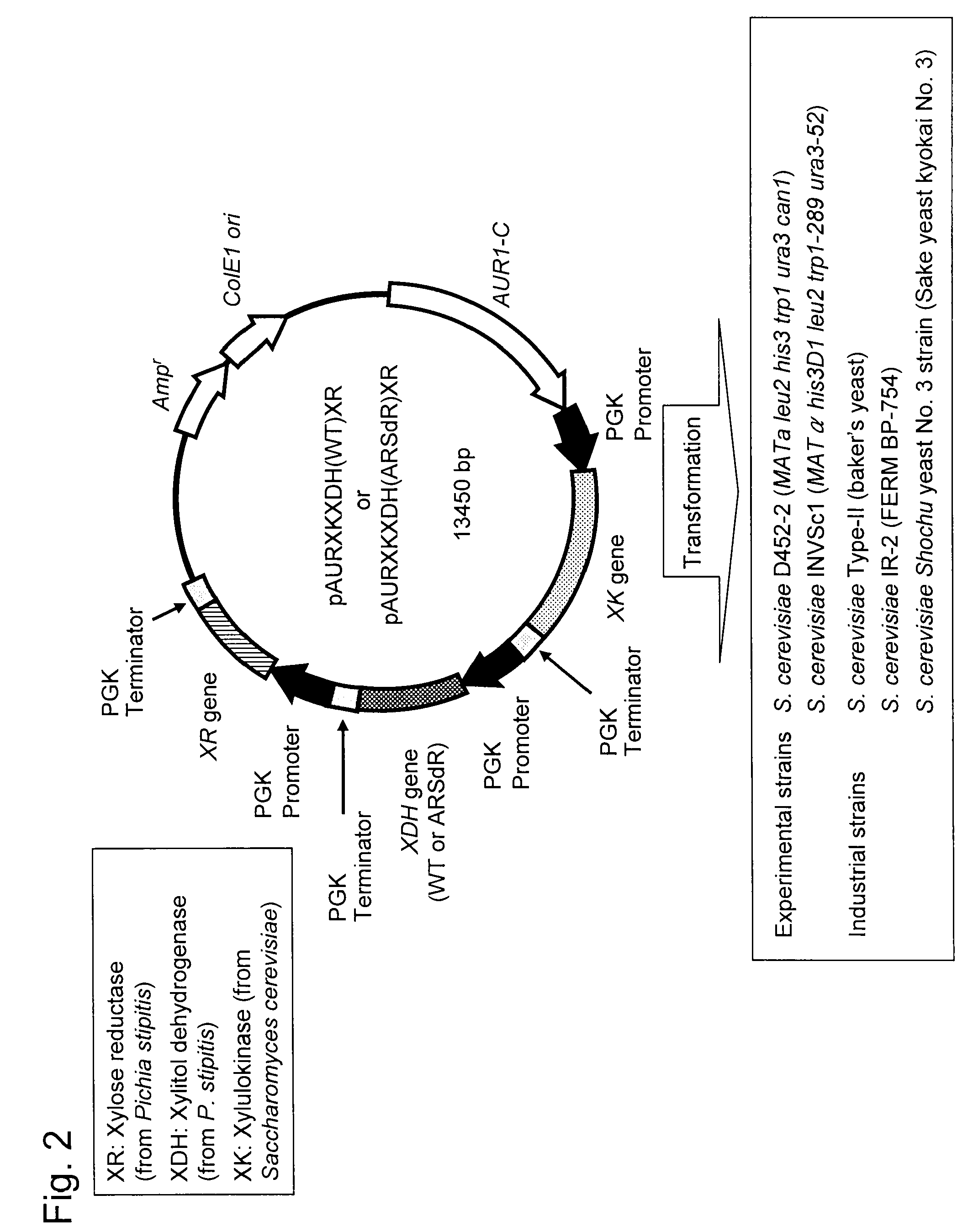
Hexose-pentose cofermenting yeast having excellent xylose fermentability and method for highly efficiently producing ethanol using the same
InactiveUS20110027847A1Efficient conversionValid conversionFungiTransferasesXylose fermentationPichia stipitis
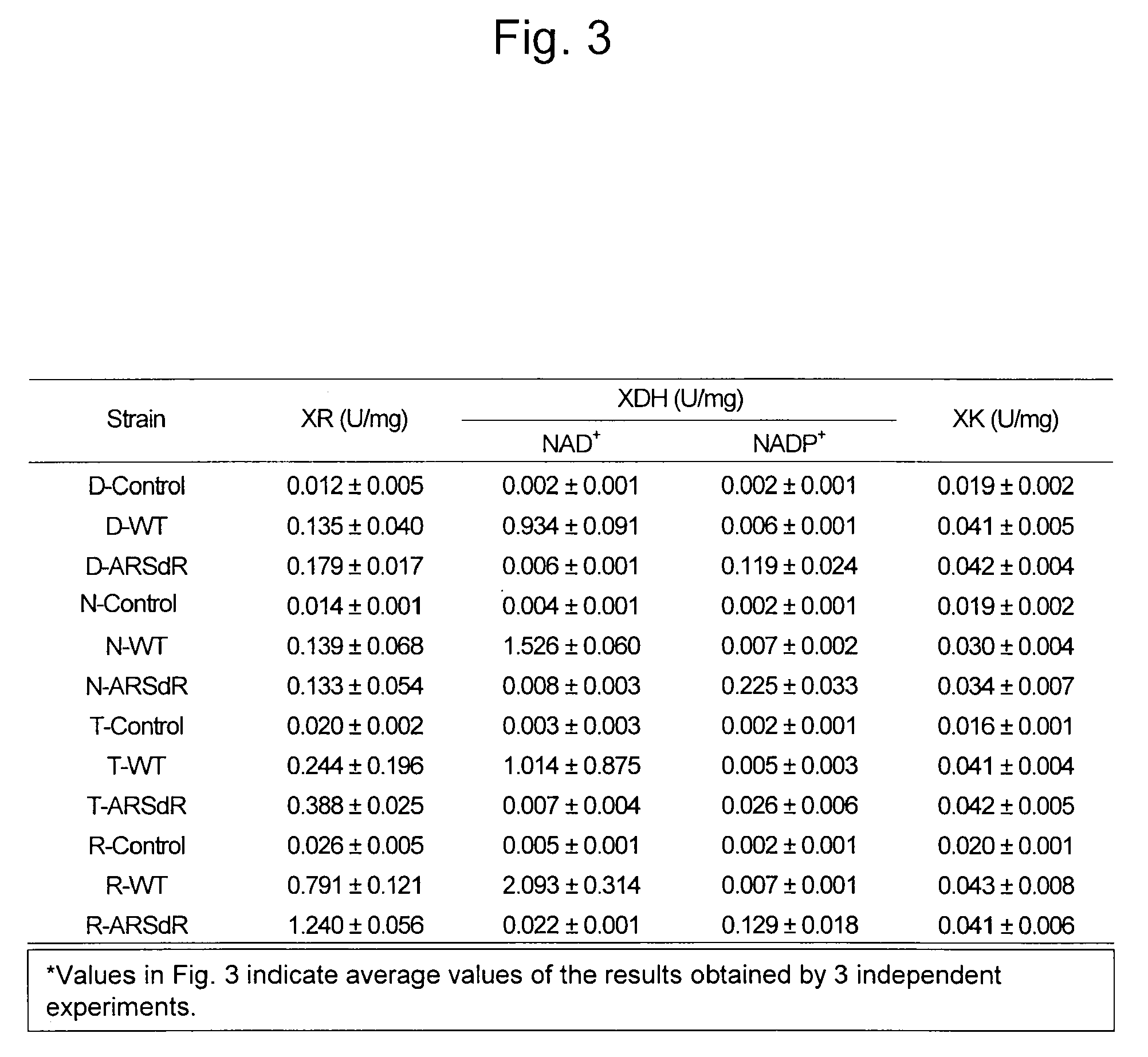
Genetic recombinant yeast expressing xylose reductase (XR), (wild-type or mutant) xylitol dehydrogenase (XDH), and xylulokinase (XK) and a method for highly efficiently producing ethanol from xylose using the yeast are provided. Pichia stipitis-derived XR and (wild-type or modified-type) XDH genes and Saccharomyces cerevisiae-derived XK gene were introduced via chromosomal integration. Thus, a genetic recombinant yeast having a high xylose fermentation rate, being capable of producing ethanol from xylose in high yields, and having high xylose fermentability in the presence of glucose, as well as a method using the recombinant yeast for highly efficiently producing ethanol from xylose or a saccharified solution from lignocellulose-based biomass are provided. Furthermore, a method for improving the xylose fermentability of the genetic recombinant yeast of the present invention via acclimatization treatment is also provided herein.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Traceless modification method of bacillus subtilis genome
ActiveCN103451224AReduce the preparation processImprove recombination efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesNucleotideLarge fragment
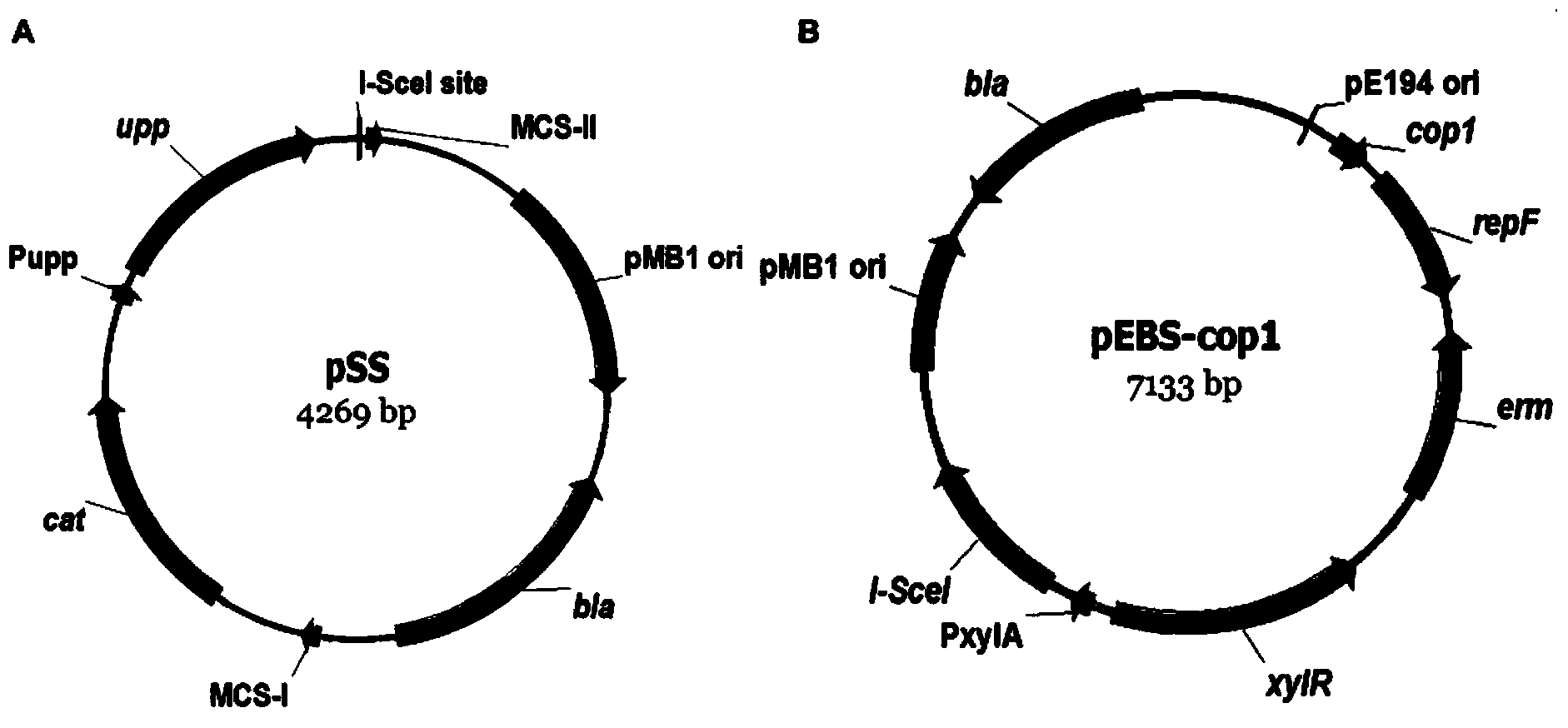
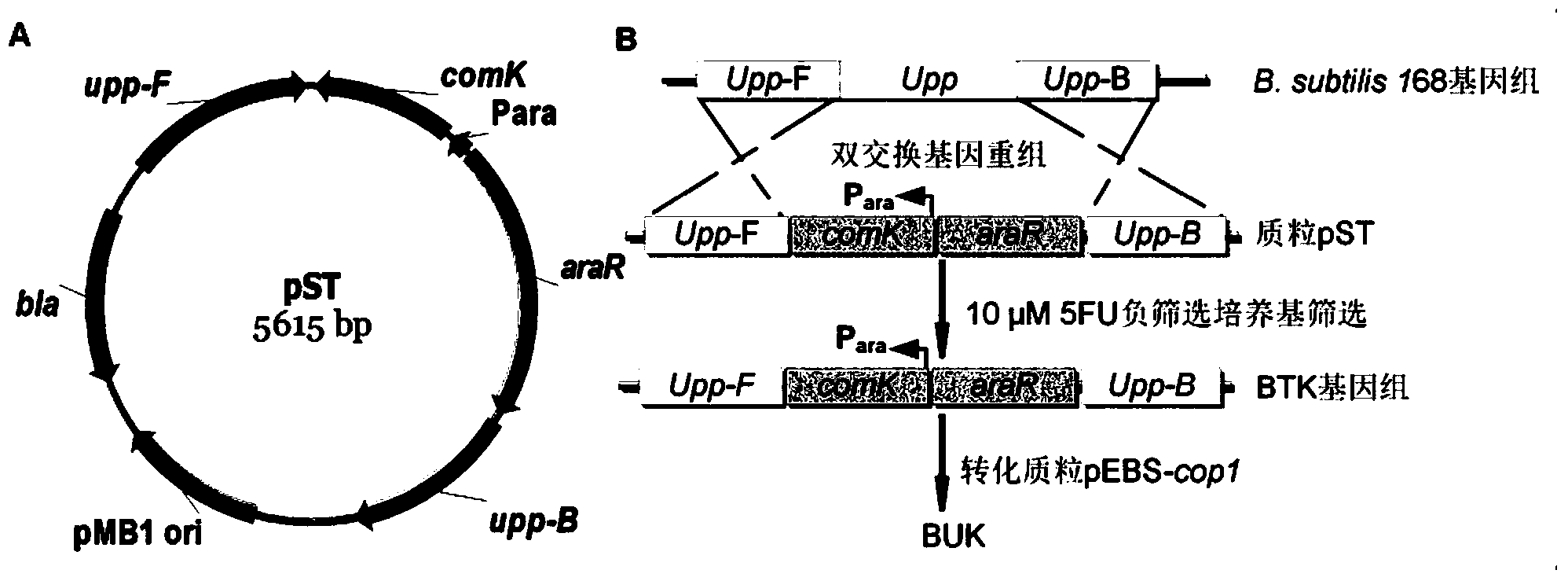
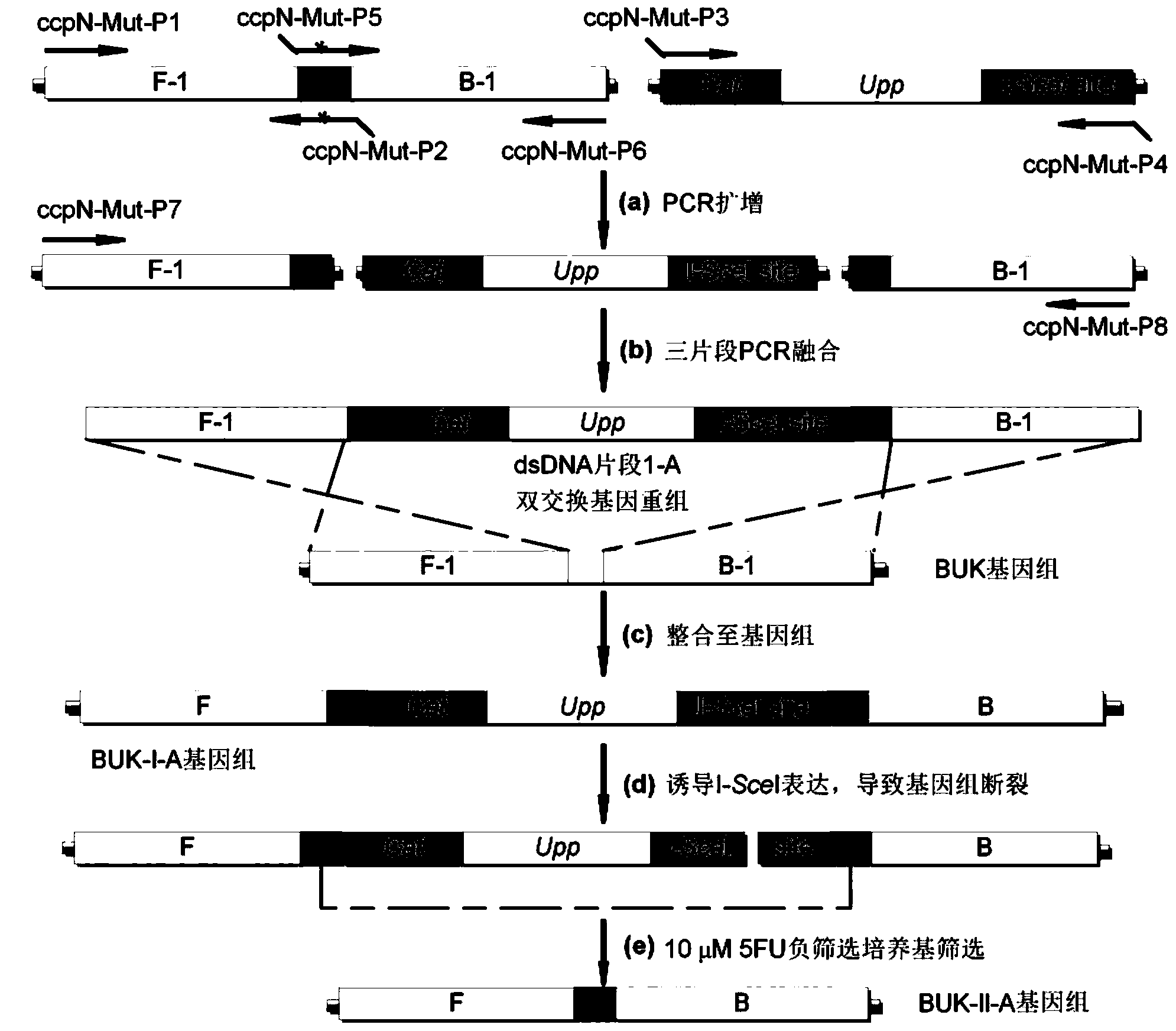
The invention discloses a traceless modification method of bacillus subtilis genome. The method disclosed by the invention is used for carrying out traceless modification on the bacillus subtilis genome by utilizing an upp positive-negative selection system. The method disclosed by the invention utilizes a ComK expression system, so that the bacillus subtilis has an excellent dsDNA (double-stranded deoxyribonucleic acid) conversion efficiency which can be up to 3-5*10<3>cfu / microgram dsDNA. Meanwhile, an exogenous endonuclease I-SceI expression system is utilized to bring double-stranded DNA breakage into the genome, so that the genetic recombination efficiency in negative selection molecules is obviously improved and can be up to 8*10<-4>. According to the method disclosed by the invention, iterative modification can be performed on a plurality of target nucleotide sequences in the bacillus subtilis genome, and the steps of introducing gene mutation to the genome, knocking out target gene sequences from the genome, deleting a large fragment of genomic sequences and the like are included.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
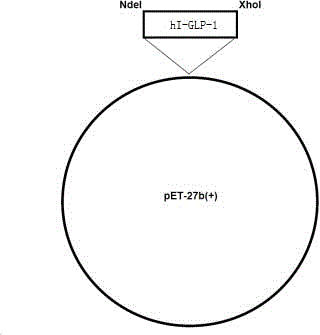
Preparation method of liraglutide intermediate polypeptide
The invention belongs to the technical field of polypeptide preparation and relates to a preparation method of a liraglutide intermediate GLP-1(7-37). The preparation method utilizes a genetic recombination technology. Compared with chemical synthesis, the preparation method reduces impurities and improves purity and a yield. The preparation method comprises the following steps of introducing plasmids with hI-GLP-1(7-37) gene sequences into cells of escherichia coli by a gene engineering method to construct recombinant engineering bacteria, carrying out fermentation induction to obtain a hI-GLP-1(7-37) expression fusion protein, and carrying out renaturation, digestion conversion and separation purification to obtain GLP-1(7-37).
Owner:JIANGSU WANBANG BIOPHARMLS +1
Modulation of meiotic recombination
InactiveUS20040023388A1Inhibit cell proliferationReduced growth rateStable introduction of DNAFermentationFunctional activityMeiosis
The invention provides methods of modifying the level of expression or functional activity of factors such as enzymes or other catalytic proteins or structural proteins, alone or in concert, to modify the frequency of meiotic homologous recombination involving the exchange of genetic information between non-sister chromatids from homologous maternal and paternal chromosomes. The steps at which modulation may occur include: homologous chromosome pairing, double-strand break formation; resection; strand invasion; branch migration; and resolution. Methods of plant and animal breeding are also provided that utilize the modulation of meiotic homologous recombination.
Owner:AGRI & AGRI FOOD +1
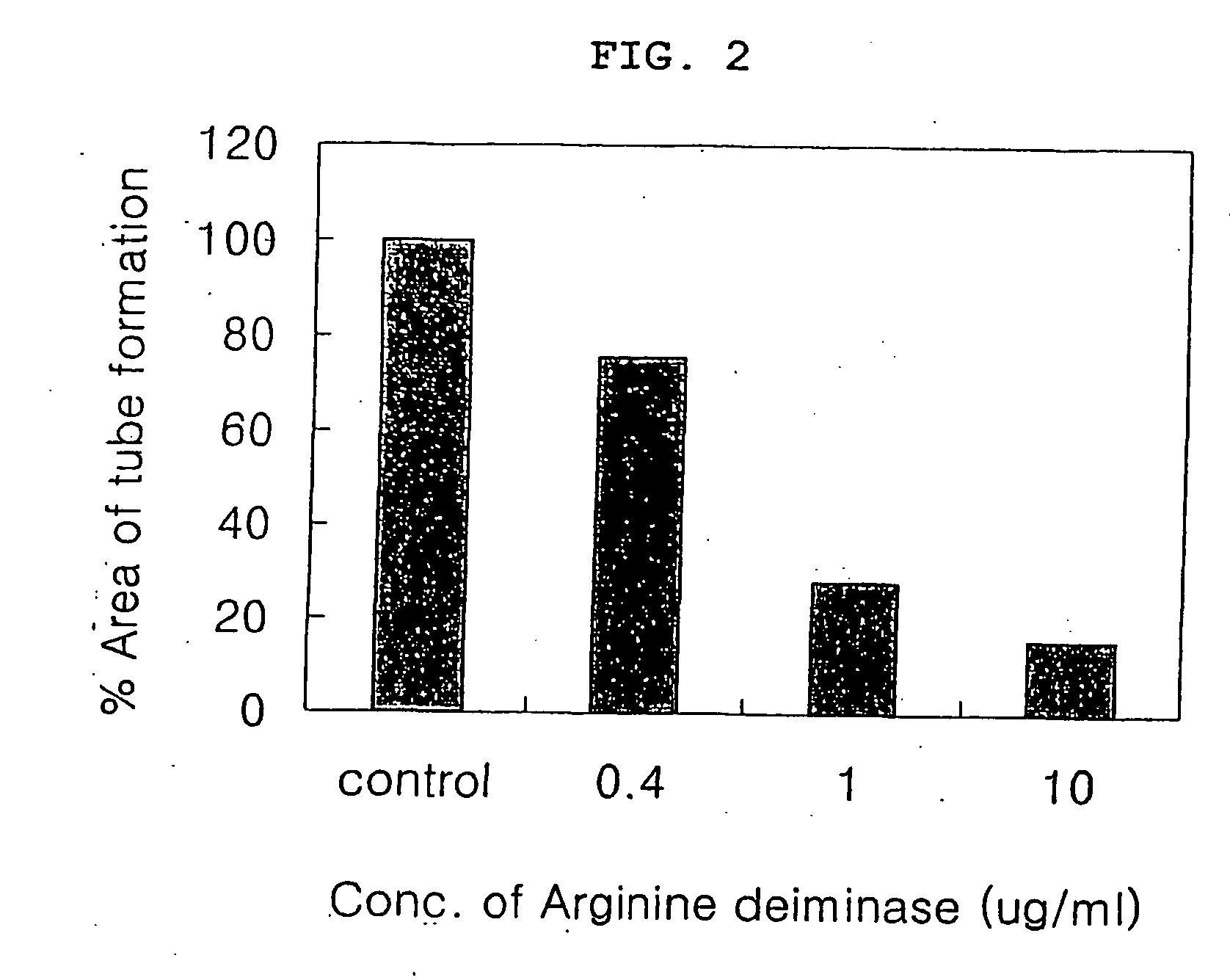
Pharmaceutical composition comprising arginine deiminase for inhibiting angiogenesis
InactiveUS20060002915A1Tube formation was suppressedInhibited tube formationSugar derivativesHydrolasesAngiogenesis growth factorBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition for inhibiting angiogenesis which comprises arginine deiminase as an active ingredient, where the arginine deiminase, obtained from Mycoplasma arginini or prepared by a genetic recombination technique, may be conjugated to an activated polymer to lower its immunogenecity and increase its life time. The pharmaceutical composition of the present invention exhibits an excellent inhibitory activity against angiogenesis.
Owner:ANGIOLAB
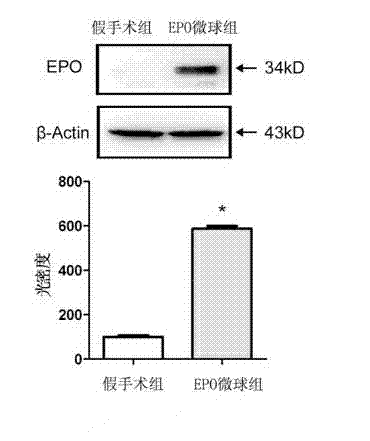
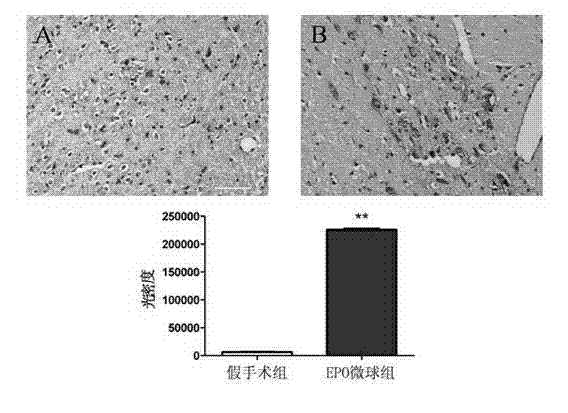
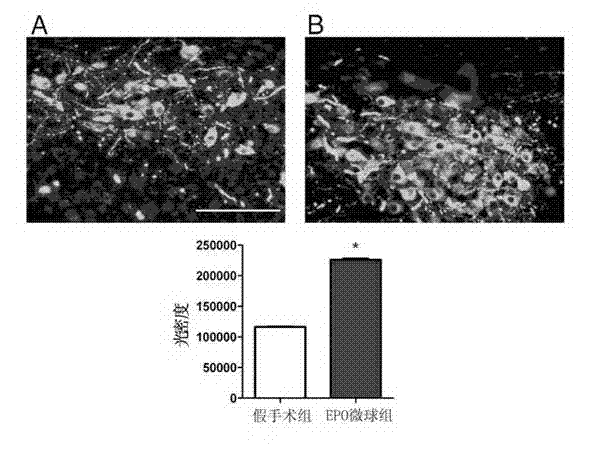
Application of erythropoietin microspheres to preparation of drugs for treating motor complications in Parkinson's disease
InactiveCN102871969ANo side effectsImprove compliancePowder deliveryNervous disorderSide effectMicrosphere
The invention discloses application of erythropoietin microspheres to preparation of drugs for treating motor complications in the Parkinson's disease. The erythropoietin microspheres are obtained by means of preparing one of naturally extracted erythropoietin, genetic recombination expression erythropoietin, polyethylene glycol modified erythropoietin, glycosylation modified erythropoietin or human serum fused erythropoietin with polysaccharides into particles, and preparing the particles with sustained-release materials into the microspheres. The application has the advantages that a novel medicinal use of the erythropoietin microspheres is cultivated, a novel application field is developed, treating and preventing the motor complications in the Parkinson's disease by the erythropoietin microspheres have the advantages of long-acting sustained release, no toxic and side effects, fine compliance, patient pain relieving, low cost and the like and are easily accepted by patients, and the erythropoietin microspheres are simple in preparation process and environment-friendly and have excellent application prospects in treating and preventing the motor complications in the Parkinson's disease.
Owner:XIN HUA HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
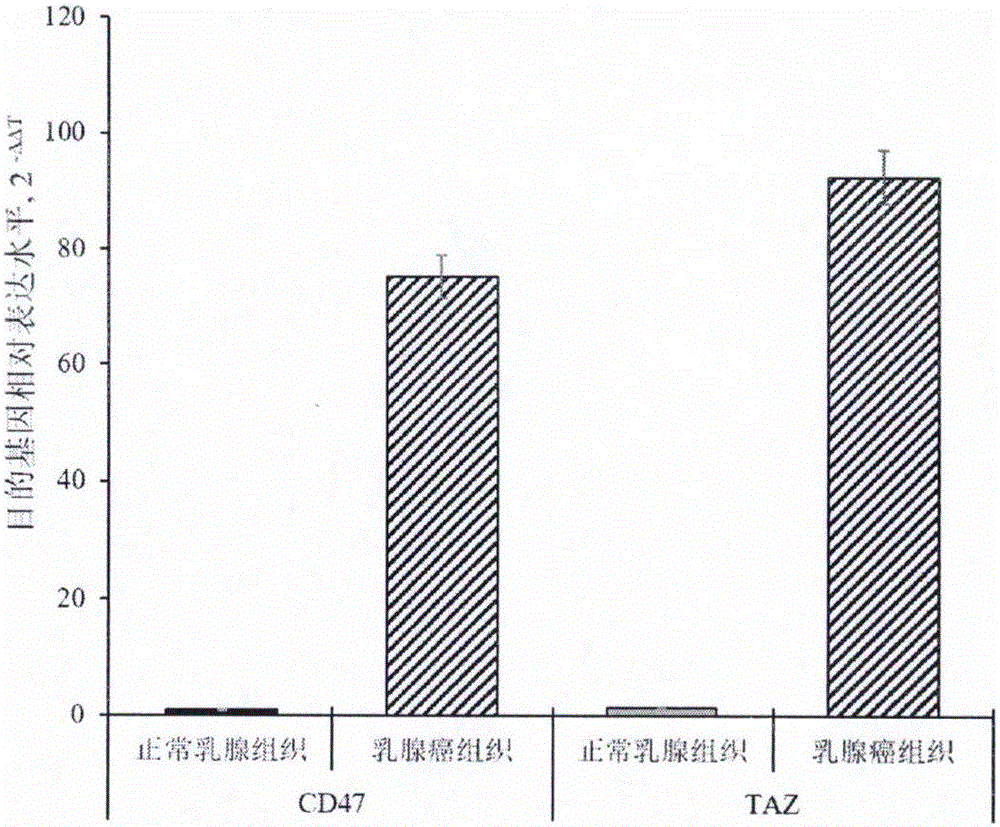
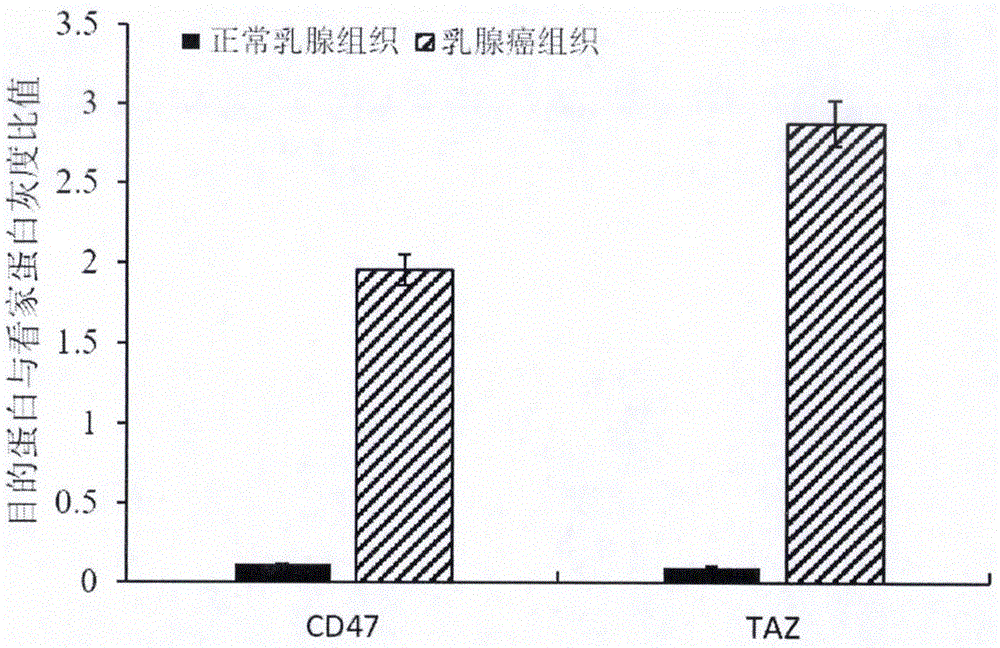
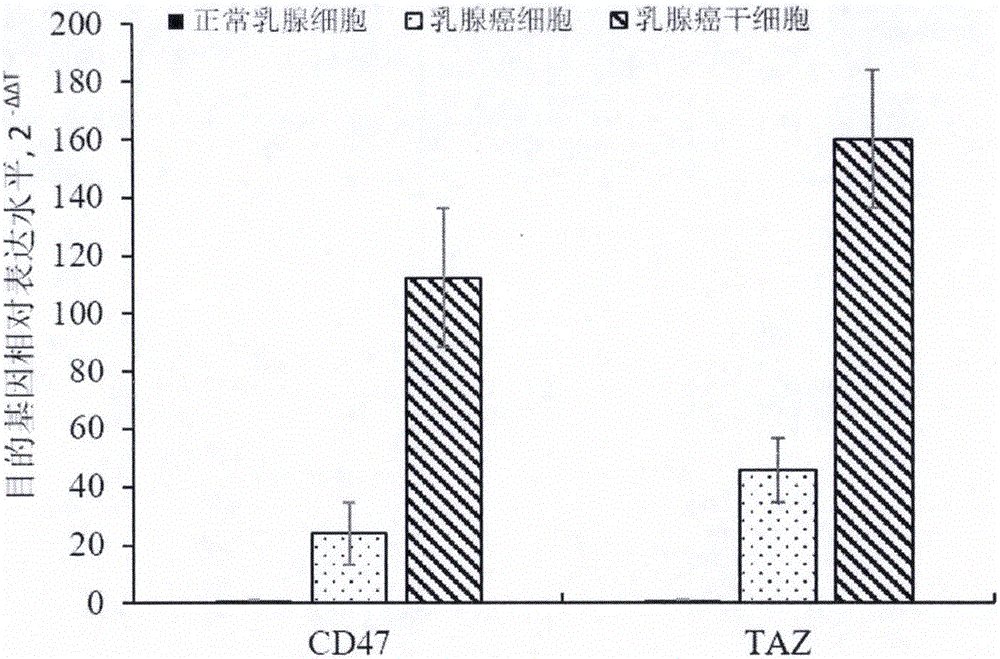
Products and preparation method of double chimeric antigen receptor gene modified T lymphocyte targeting breast cancer stem cells
InactiveCN105950561AMammal material medical ingredientsNGF-receptor/TNF-receptor superfamilySingle-Chain AntibodiesCytotoxicity
The invention provides a preparation method of a double chimeric antigen receptor gene modified T lymphocyte targeting breast cancer stem cells. The preparation method is characterized in that integrin-associated protein (CD47) and transcriptional coactivator (TAZ) are both highly expressed in breast cancer tissues, especially in the breast cancer stem cells; by established CD47 and TAZ over-expressed breast cancer cells, higher proliferation and metastasis capacity and cancer stem cell features are shown. Extracellular domain of the two breast cancer stem cell antigens CD47 and TAZ are targeted to generate monoclonal strains in specific binding under immunity action, and single-chain antibodies in specific binding with the CD47 and TAZ by genetic recombination are obtained to construct a human CD47 and TAZ containing double chimeric antigen receptor gene recombined to a virus vector to transfect human T lymphocyte. By high expression of the double chimeric antigen receptor gene in specific binding with human CD47 and TAZ expressing breast cancer stem cells, a first signal and a costimulatory signal can be activated to trigger anti-breast-cancer cytotoxicity, and high cytotoxicity in in-vivo and in-vitro anti-cancer experiments is achieved.
Owner:泰州市数康生物科技有限公司
Strain and method for producing glucosamine through microorganism fermentation
ActiveCN105039193ASportyPromote safe productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacillus licheniformisMicroorganism
The invention relates to a non-genetic recombinant strain for producing N-acetyl-D-glucosamine and D-glucosamine through microorganism fermentation, wherein the strain has been preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center. A bacillus subtilis strain NJ090259 is assigned the accession number of CGMCC10257. A bacillus licheniformis strain NJ091195 is assigned the accession number of CGMCC10258. The two strains are both preserved at 29th, December, 2014. The invention provides the novel strain for producing N-acetyl-D-glucosamine and D-glucosamine and the production method thereof. By means of the method, stable production and supplement of the N-acetyl-D-glucosamine can be achieved. The invention also achieves non-animal-sourced and safe production of the N-acetyl-D-glucosamine and the D-glucosamine. The method is short in production period, is low in cost and is more environment-friendly.
Owner:安徽福方高科生物科技有限公司
Infectious clone vector of pepper mild mottle virus, agrobacterium tumefaciens strain, method for preparing same and application of infectious clone vector
InactiveCN105219800AInvasive cloneEfficient infectionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPlant virusTobacco mosaic virus
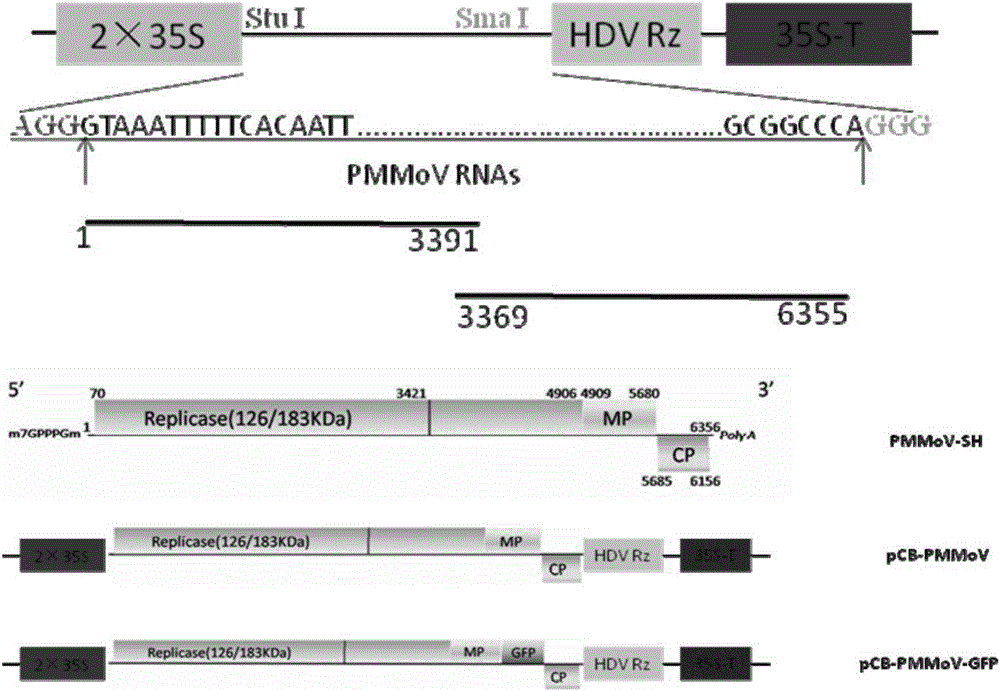
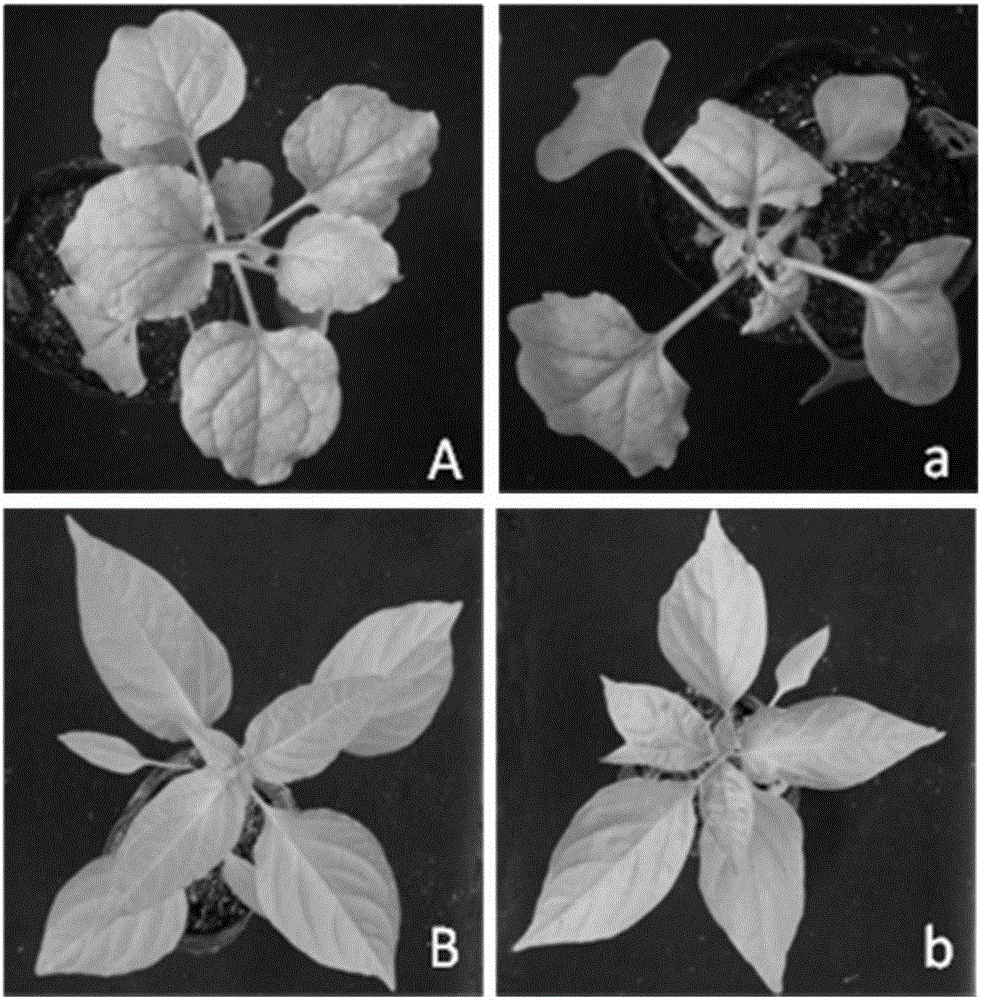
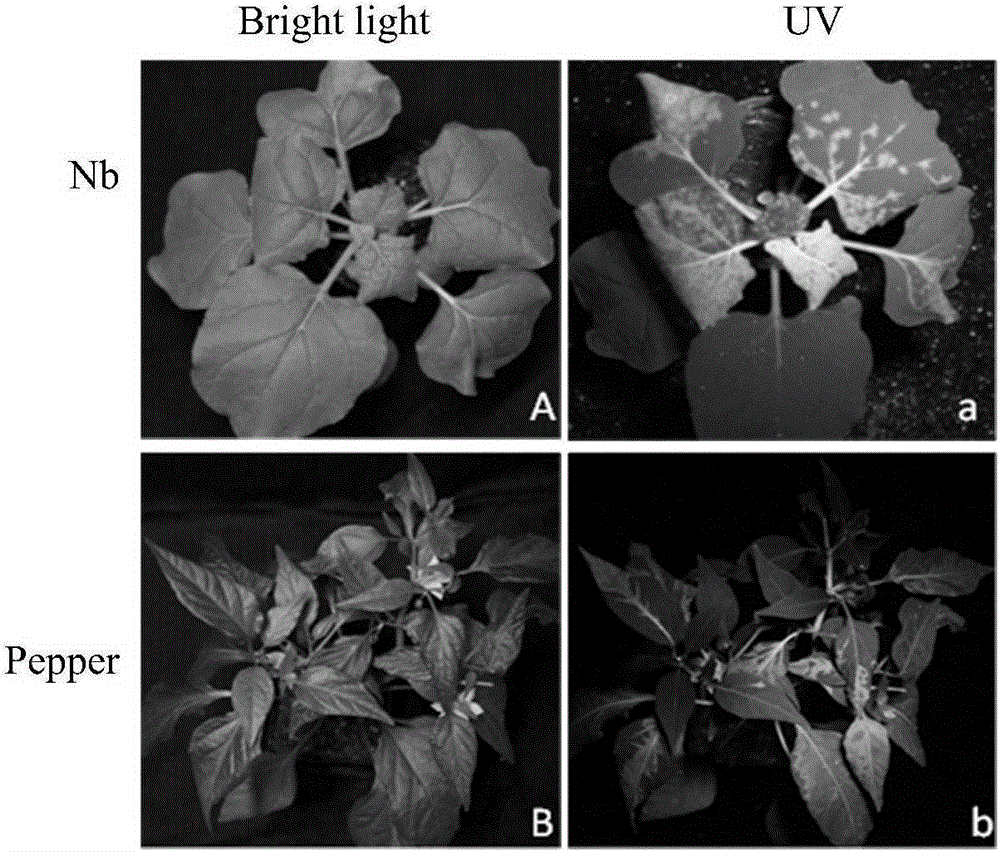
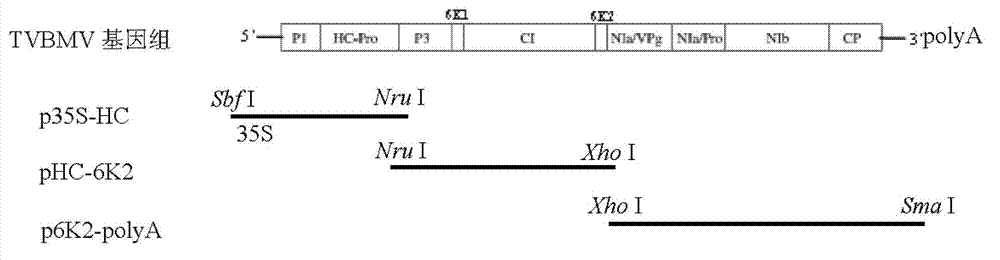
The invention relates to the field of genetic engineering, in particular to preparation of an infectious clone vector of a Pepper mild mottle virus (PMMoV) of RNA (ribonucleic acid) plant viruses and tobacco mosaic viruses, pathogenesis analysis on an infectiously cloned agrobacterium tumefaciens strain with the pepper mild mottle virus and exogenous proteins infectiously cloned and expressed by the aid of the PMMoV. The preparation, the pathogenesis analysis and exogenous proteins have the advantages that genomes of Shanghai bay isolate of the pepper mild mottle virus are constructed onto efficient plant expression vectors pCB301-CH by the aid of a genetic recombination process, the recombinant vectors are transferred into the agrobacterium tumefaciens strain by means of electroporation, and accordingly the virus vector with infection ability can be obtained; the plant expression vectors can be constructed by means of infectious cloning, and the exogenous proteins can be efficiently and stably expressed in host plants; mature systems can be provided for studying structures and functions of the virus genomes and studying interaction between the virus and hosts.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Construction and application of tobacco vein banding mosaic virus infectious clone
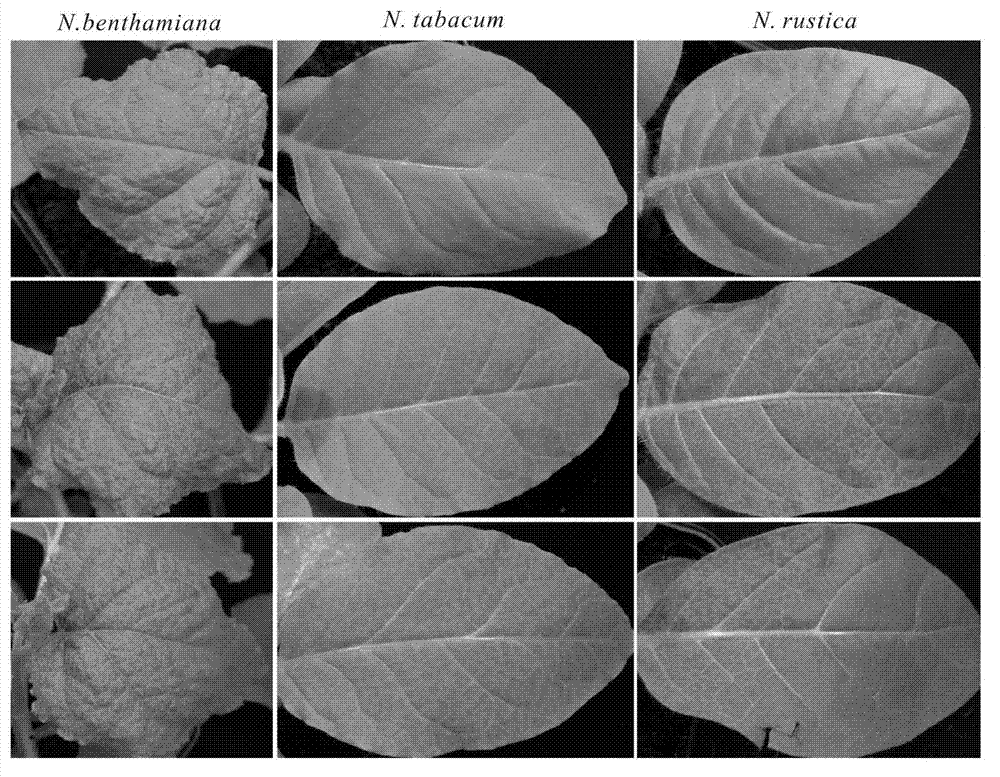
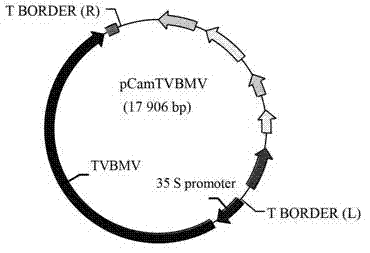
InactiveCN103031325AOvercome the effects of degradationStable storageVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsNicotiana tabacumGene engineering
The invention relates to the field of plant virus gene engineering and provides a construction and an application of a tobacco vein banding mosaic virus infectious clone. A genome of a tobacco vein banding mosaic virus HN39 isolate is cloned to the downstream part of a 35S promoter in a genetic recombination mode, and the infectious clone with strong infectivity is obtained. A plant expression vector can be constructed by utilizing the infectious clone and used for stably and efficiently expressing extrinsic protein in a host plant body, and the infectious clone can be also modified into a low virulent strain for protecting a plant from being infected with a high virulent strain.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Mutant plant, a method for producing thereof and a method of increasing frequency of a genetic recombination
ActiveUS20110277189A1Reduce restrictionsReduce the ratioOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationGenomic DNAPlant cell
According to the present invention, a technique of increasing the frequency of genetic recombination in genomic DNA of a plant is established. Such technique comprises: introducing a restriction enzyme gene that can be expressed in a target plant cell into the plant cell and causing the restriction enzyme gene to be transiently expressed so as to induce genetic recombination of genomic DNA; or introducing a promoter and a restriction enzyme gene using the Agrobacterium method so as to induce genetic recombination of genomic DNA.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
Targeted Chromosomal Mutagenesis Using Zinc Finger Nucleases
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
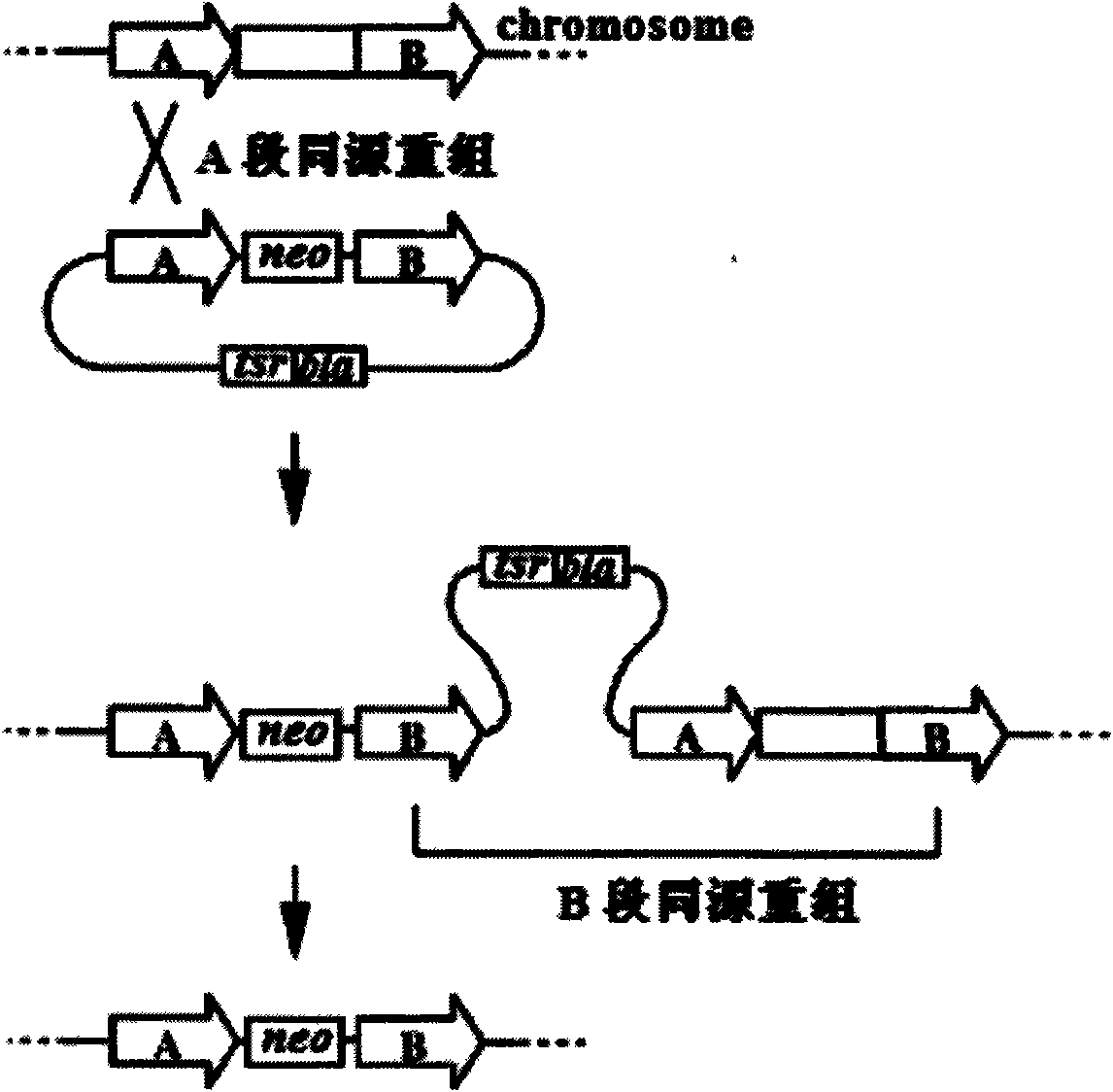
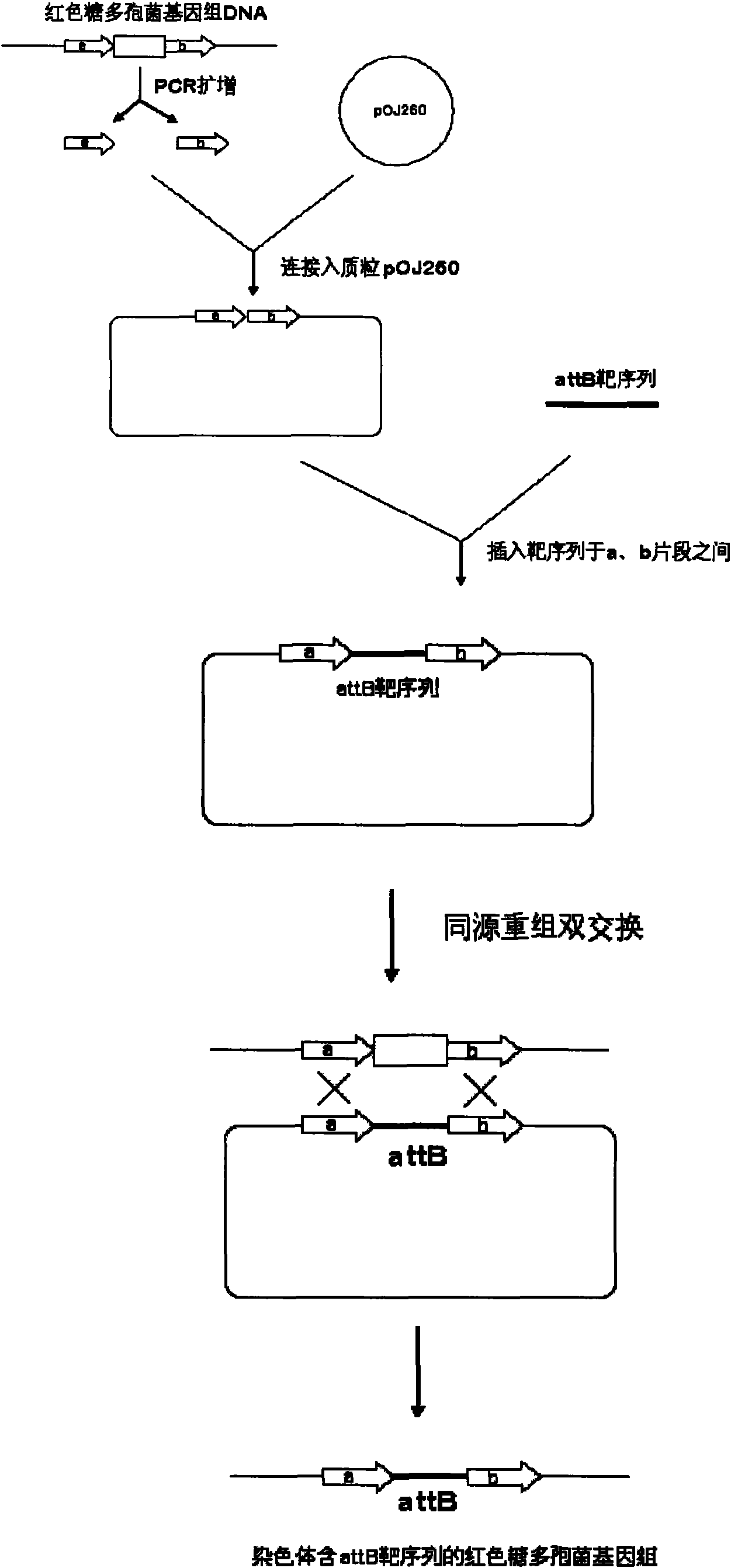
Gene recombination mediated by phiC312 and inheritance reformation for erythrocin producing bacterium
ActiveCN101649326AFacile genetic recombinationMicroorganism based processesFermentationGenomeGenetic recombination
The invention discloses gene recombination mediated on the basis of phiC312 and inheritance reformation for an erythrocin producing bacterium. A target gene can be stably integrated on a locus pre-constructed by a host cell genome by a method of gene recombination mediated by a phiC312 locus specificity integration mechanism. The invention also relates to an application of the method on the inheritance reformation of the erythrocin producing bacterium.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Genetic recombination escherichia coli and method for efficiently producing pullulanase
InactiveCN102994425AIncrease enzyme activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliFermentation
The invention discloses a genetic recombination escherichia coli and a method for efficiently producing pullulanase, belonging to the technical field of microbial fermentation. The method comprises the following steps of: connecting a signal peptide PelB of a plasmid pET20b(+) and bacillus naganoensis CCTCC NO:M2012388 pullulanase genes, and commonly inserting the signal peptide and the bacillus naganoensis into an expression vector pET28a(+) to construct a recombination strain E.coliBL21(DE3) / pET28a(+)-PelB-pul with the signal peptide and target genes; and using the strategies of auto-induction culturing and adding glycine to control the cell permeability in the fermentation and production of extracellular pullulanase, using an auto-induction culture medium with lactose in a concentration of 10g / L, shaking and culturing for about 2 hours under the conditions of a temperature of 37 DEG C and a speed of 200rpm, then adding the glycine with a final concentration of 6g / L and transferring to culturing for 70 hours at a temperature of 20 DEG C. The enzyme activity of the extracellular pullulanase reaches 505U / mL and is enhanced by 1260 times to the enzyme activity of the original strains of the wild fungus. The application of the invention is of great significance.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
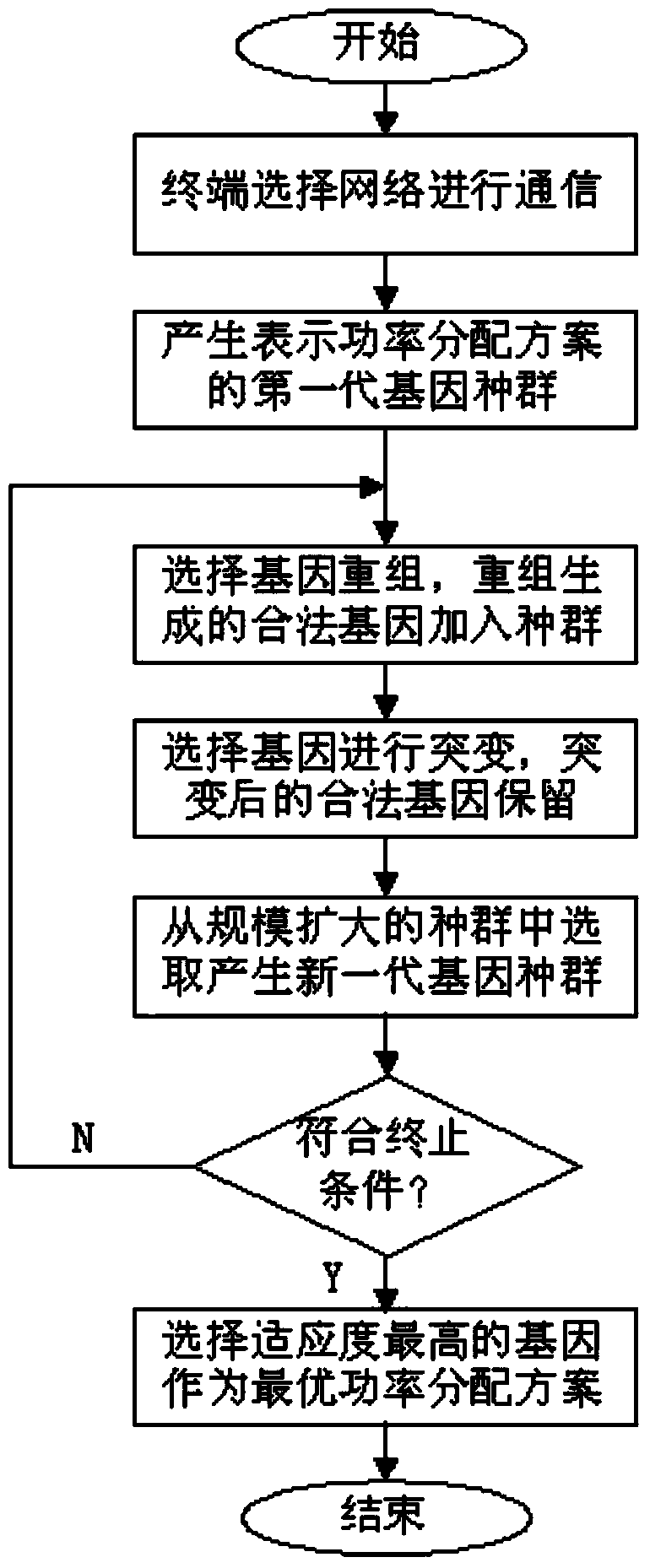
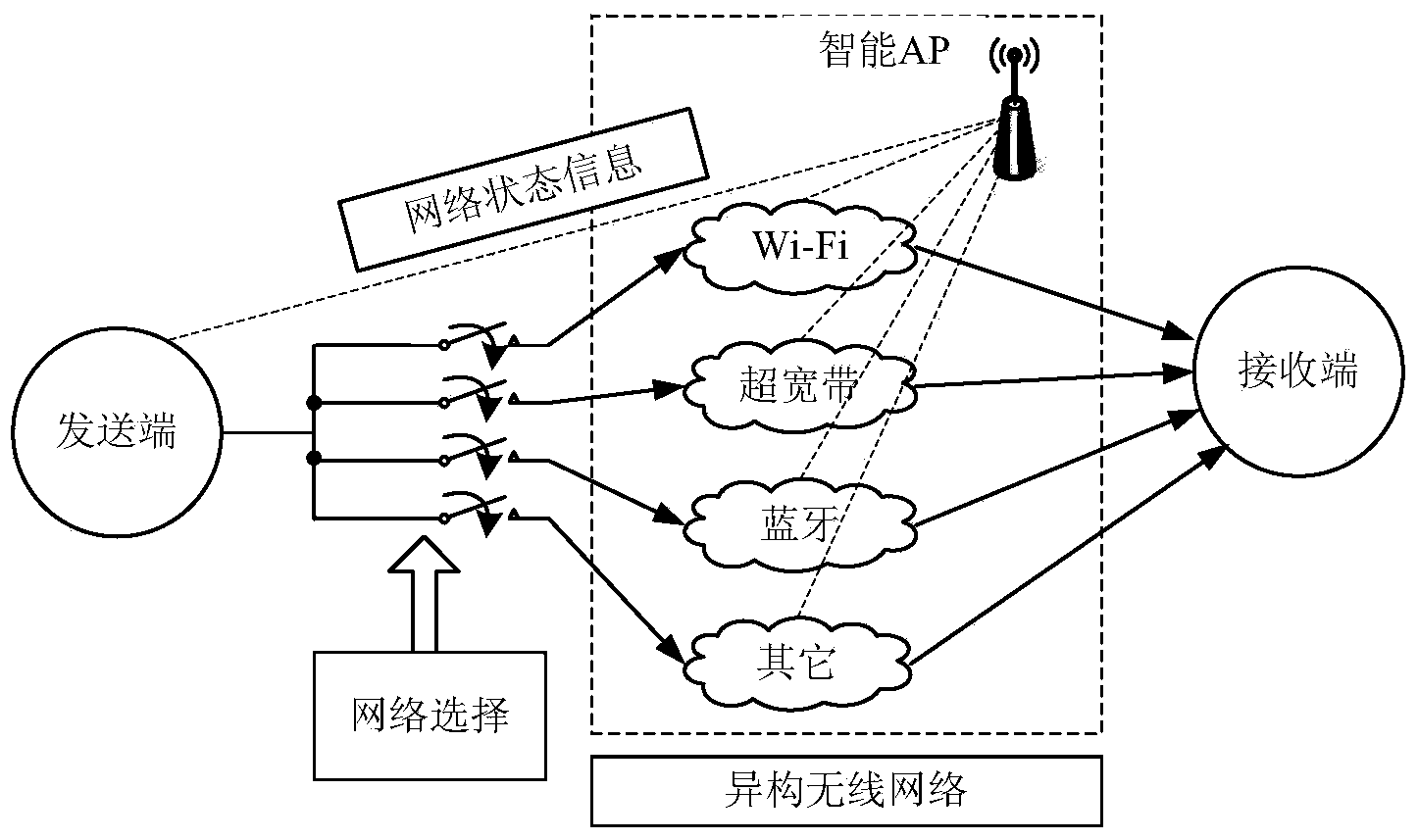
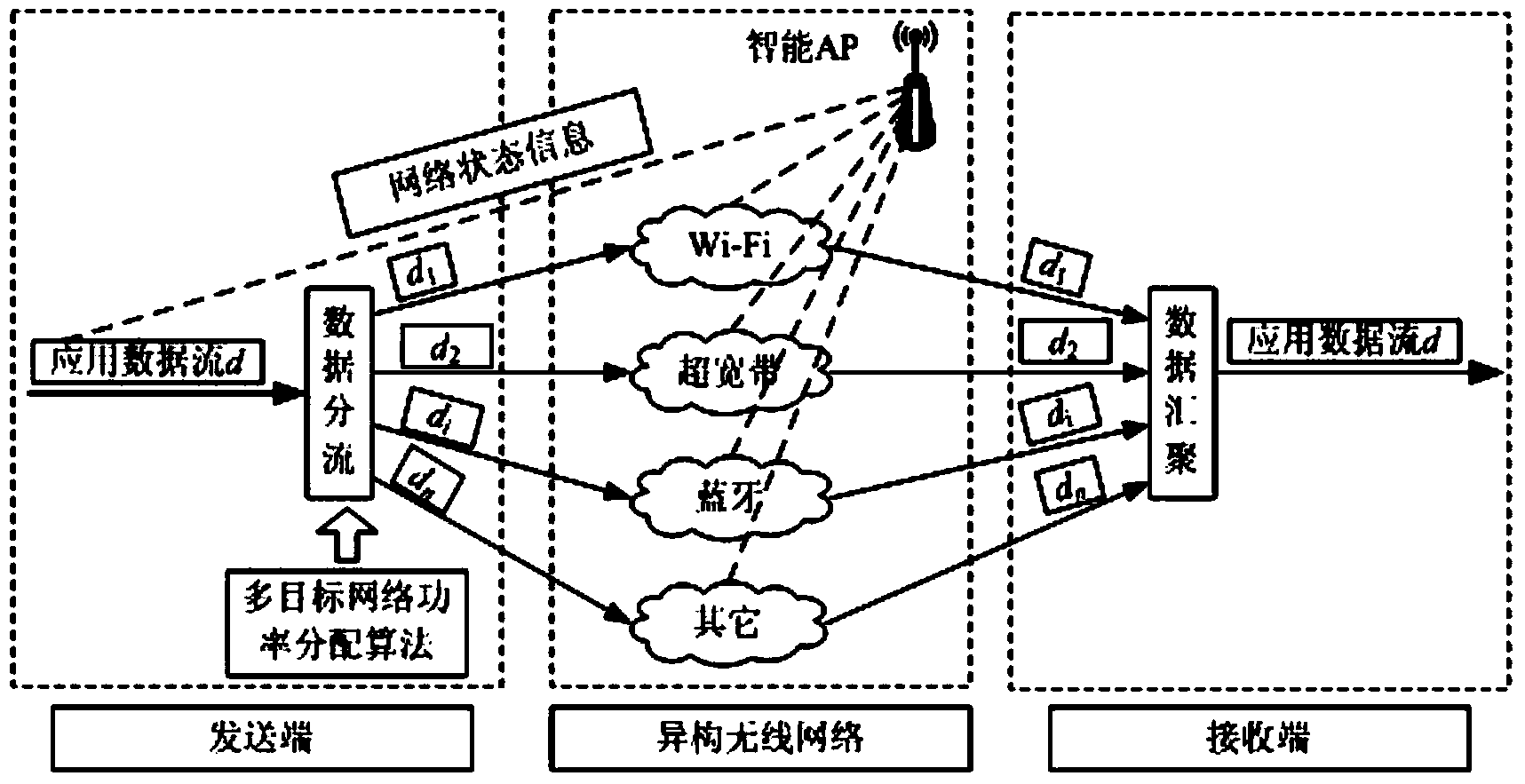
Multi-target-network power distribution method in heterogeneous wireless network cooperative communication
InactiveCN103561457AIncrease transfer rateReduce consumptionPower managementArray data structureDistribution method
The invention discloses a multi-target-network power distribution method in heterogeneous wireless network cooperative communication. The multi-target-network power distribution method comprises the following steps that firstly, a mobile intelligent terminable detects wireless networks which are capable of being accessed and provided with vacant service channels, N wireless networks with good channel conditions are selected by the mobile intelligent terminal from the networks which are capable of being accessed, and the mobile intelligent terminal has access to the N wireless networks; secondly, a heredity expression of a power distribution scheme is defined; thirdly, an adaptation function of the power distribution scheme is defined; fourthly, M arrays are generated; fifthly, according to the method that a high-fitness value is preferential, genetic recombination is conducted through m2 genes randomly selected from a population; sixthly, mutation is conducted on m1 genes randomly selected from low-fitness genes of a population generated after genetic recombination according to the probability; seventhly, a new generation of population is selected and generated; eighthly, the fifth step, the sixth step and the seventh step are executed repeatedly, and when increase of the highest-fitness value of the population genes is smaller than a given threshold value successive l times and continuously, the optimal power distribution scheme is obtained. The multi-target-network power distribution method in heterogeneous wireless network cooperative communication has the advantages of being flexible in algorithm.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
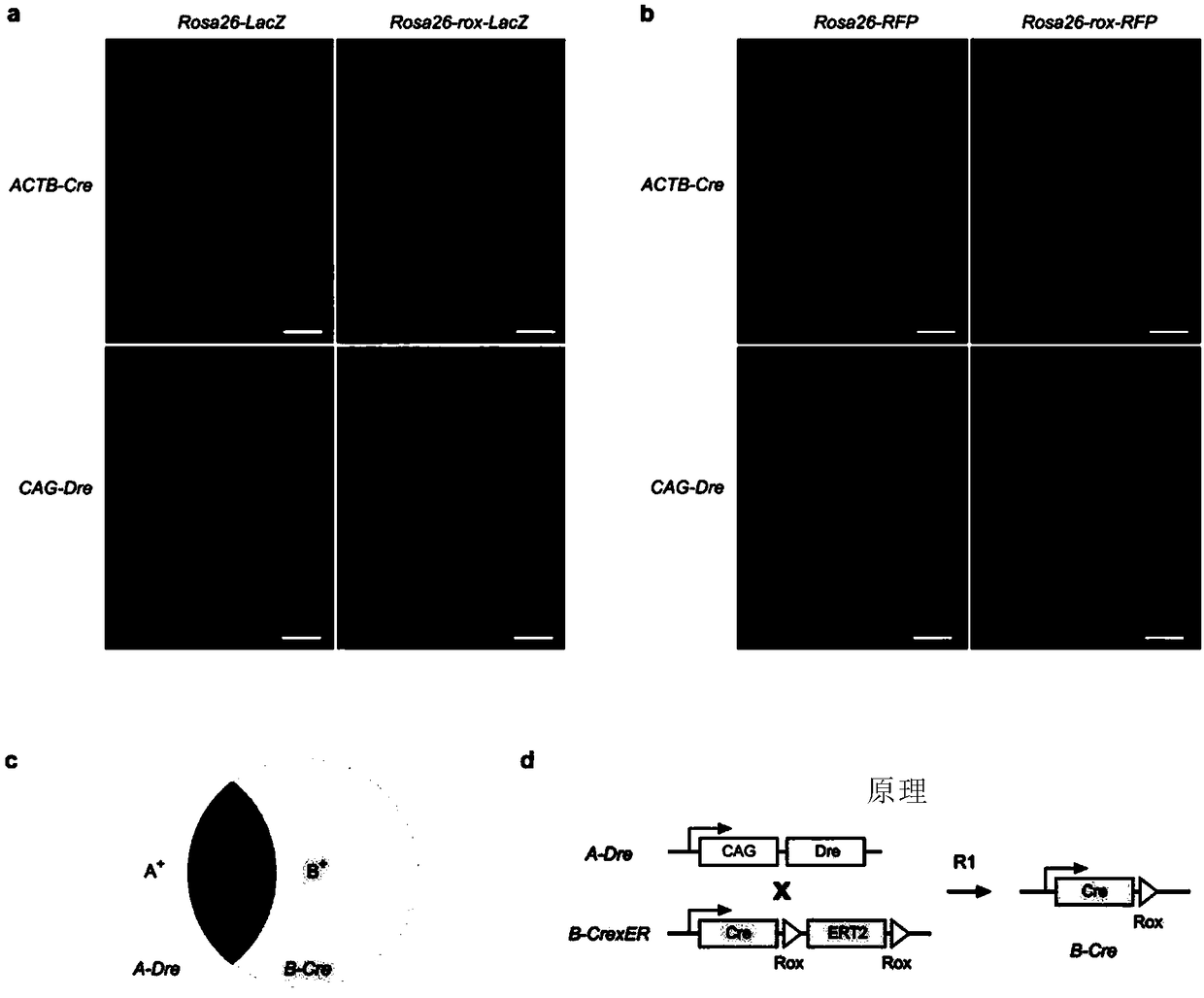
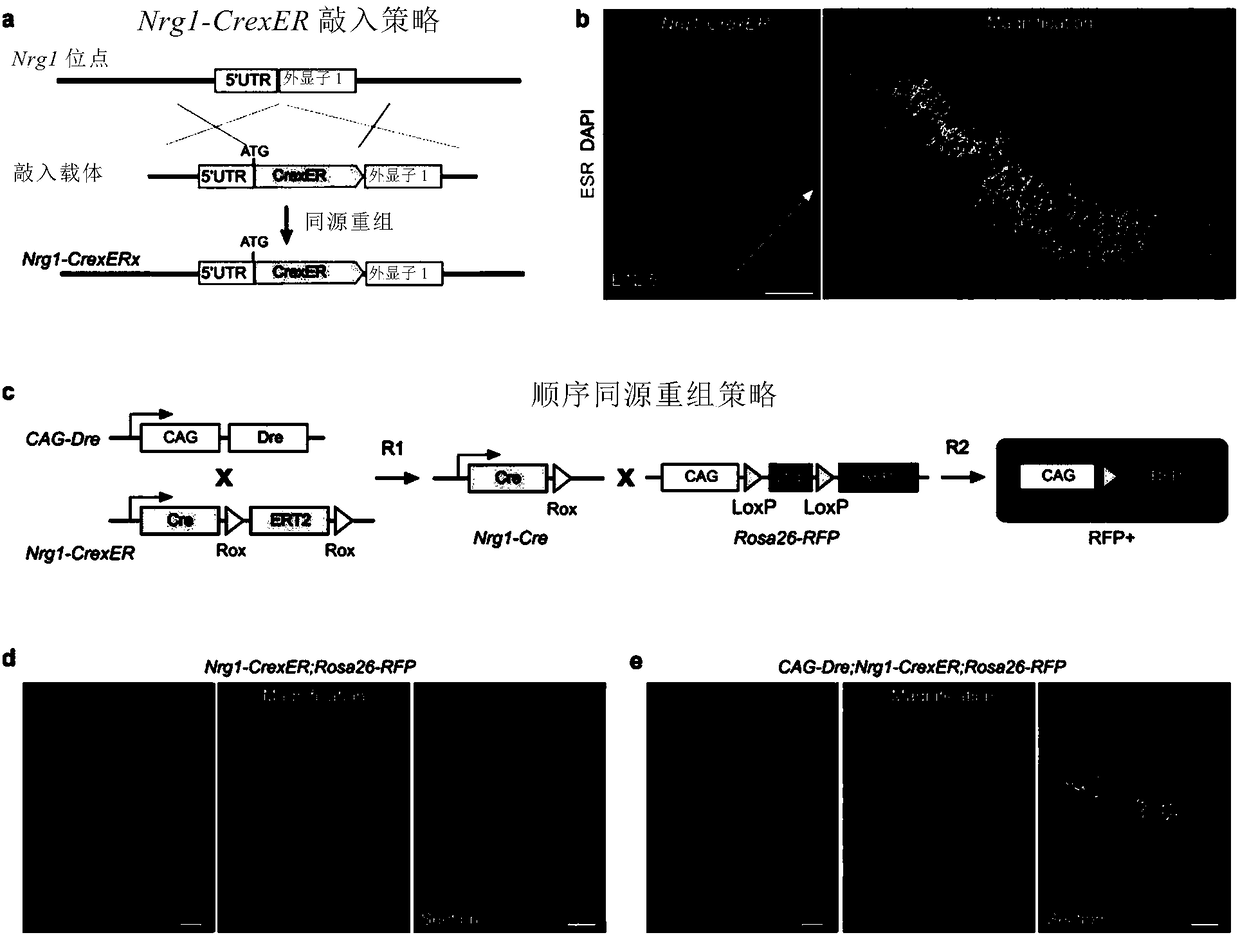
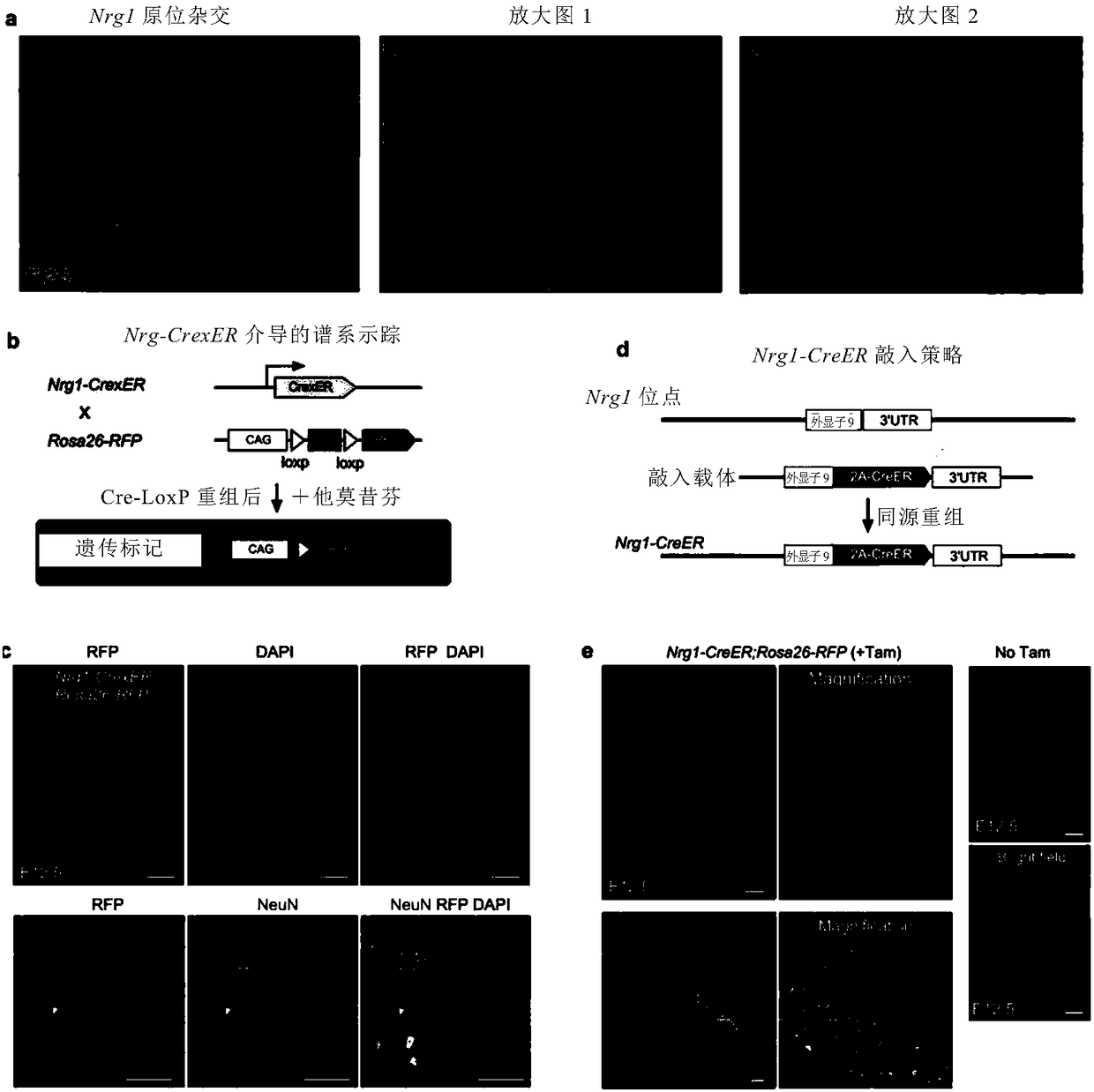
Inducible inheritance recombinase system CrexER
The invention relates to an inducible inheritance recombinase system CrexER. The CrexER is a fusion protein; the fusion protein is a protein formed by fusing recombinase Cre, estrogen receptors ER andrecombination sites rox specifically recognized by recombinase Dre. The invention also provides a coding sequence of the fusion protein, a nucleic acid construct containing the coding sequence, a host cell and the like. The ahead occurrence of Dre-rox homologous recombination is used for inducing the subsequent occurrence of Cre-loxP homologous recombination; the targeted operation of the A-Dre and B-Cre mark cell intersection (A+B+) is realized. The application range of the inheritance targeted operation is greatly expanded; a precious strategy is provided for the precise inheritance targeted operation and biomedical research.
Owner:CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR CELL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of Inducing Genome Reorganization Via Intracellular Activation of Thermostable Multifrequency Dna-Cleaving Enzyme
InactiveUS20080166809A1Easy to implementThe process is simple and convenientHydrolasesMicroorganismsGenomic DNABiological activation
The present invention relates to a method for increasing genetic recombination frequency in a genomic DNA and a method for inducing genome rearrangement. Specifically, according to the present invention there are provided: the method for increasing genetic recombination frequency in a cell in which genetic recombination takes place at any sites in the genome, comprising causing a restriction enzyme to be expressed in the cell, inducing transient activation of the restriction enzyme, and then introducing 2 or more double strand cleavages into any genomic DNA of the cell, so as to increase the genetic recombination frequency; the method for inducing genome rearrangement through the use of the above method; and cells each prepared through the use of the above 2 methods.
Owner:RIKEN
Genetic recombinant collagen-like peptide MJLGG-34 as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109593127ASmall molecular weightPromote absorptionCosmetic preparationsConnective tissue peptidesBiotechnologySide effect
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Hexose-pentose cofermenting yeast having excellent xylose fermentability and method for highly efficiently producing ethanol using the same
InactiveUS8445243B2Efficient conversionValid conversionFungiTransferasesXylose fermentationPichia stipitis
Genetic recombinant yeast expressing xylose reductase (XR), (wild-type or mutant) xylitol dehydrogenase (XDH), and xylulokinase (XK) and a method for highly efficiently producing ethanol from xylose using the yeast are provided. Pichia stipitis-derived XR and (wild-type or modified-type) XDH genes and Saccharomyces cerevisiae-derived XK gene were introduced via chromosomal integration. Thus, a genetic recombinant yeast having a high xylose fermentation rate, being capable of producing ethanol from xylose in high yields, and having high xylose fermentability in the presence of glucose, as well as a method using the recombinant yeast for highly efficiently producing ethanol from xylose or a saccharified solution from lignocellulose-based biomass are provided. Furthermore, a method for improving the xylose fermentability of the genetic recombinant yeast of the present invention via acclimatization treatment is also provided herein.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Anti-ageing gene oligopeptide-containing preparation and application of preparation to cosmetics
The invention provides an anti-ageing gene oligopeptide-containing preparation and an application of the preparation to cosmetics. The preparation is prepared by compounding gene oligopeptide key components, auxiliary materials and preparation raw materials. Gene oligopeptide is selected from one or a combination of genetic recombination hydrolyzed collagen dipeptide, genetic recombination hydrolyzed collagen tripeptide, genetic recombination hydrolyzed collagen tetrapeptide, genetic recombination hydrolyzed collagen pentapeptide, genetic recombination hydrolyzed collagen hexapeptide, first genetic recombination hydrolyzed collagen, second genetic recombination hydrolyzed collagen, third genetic recombination hydrolyzed collagen, genetic recombination gene protein, first genetic recombination hydrolyzed hyaluronic acid and second genetic recombination hydrolyzed hyaluronic acid.
Owner:SHAANXI HUIKANG BIO TECH CO LTD
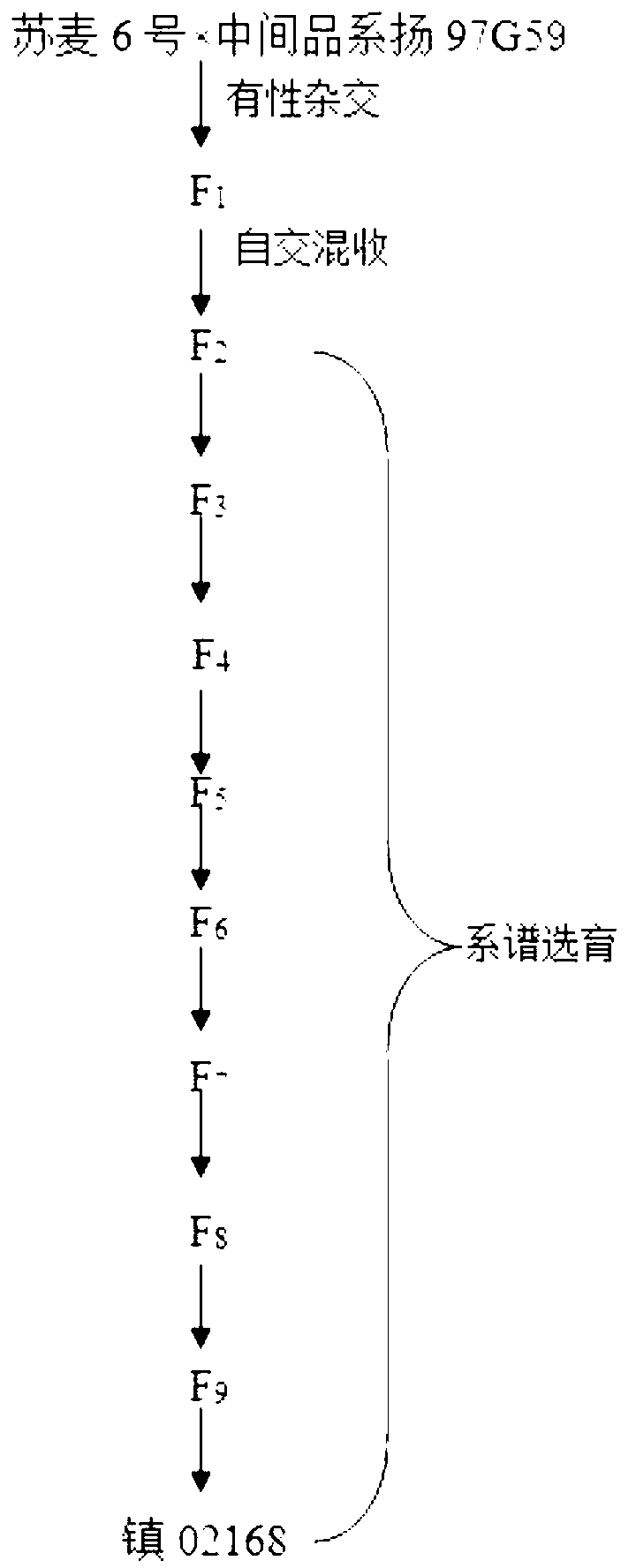
Cultivating and planting method of strong gluten wheat
InactiveCN103340148AGood acquaintanceImprove fullnessPlant genotype modificationHorticultureTriticeaeTriticum turgidum
The invention discloses a cultivating and planting method of strong gluten wheat. The cultivating and planting method comprises the following steps of: selecting biparental Suzhou wheat VI and intermediate strain yang 97G59 with excellent characters; and creating transgression descendant by utilizing genetic recombination and an additive effect, so that the novel wheat strain zhen 02168 which is excellent in gluten, large in grain, good in comprehensive resistance, stalked and lodging-resistant, delicately grown, good in later-stage coloring and good in ripe phase. The novel wheat strain cultivated by the cultivating and planting method disclosed by the invention is full in seed and red in skin, hard and good in fullness, and is the novel wheat strain with the seed quality reaching the quality gluten standards, which firstly passes examination and approval of China and Jiangsu province in Huainan wheat region of Jiangsu. Moreover, the strong gluten wheat has the advantages of being good in ripe phase, high in yield and strong in stress resistance. Besides, the wheat strain is invented for solving a big problem in the Huainan wheat region of Jiangsu, and strong in practical value.
Owner:ZHENJIANG AGRI SCI INST JIANGSU HILLY AREAS
Method for producing a modified peptide
InactiveUS7138489B2Simple methodQuality improvementPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsPhosphorylationSide chain
Owner:DAIICHI SANKYO CO LTD +1
Application of HBcAg (hepatitis B core antigen) virus-like particle serving as cancer therapeutic vaccine carrier
InactiveCN105497886AImprove the level ofViral antigen ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsHepatitis B virus core AntigenEscherichia coli
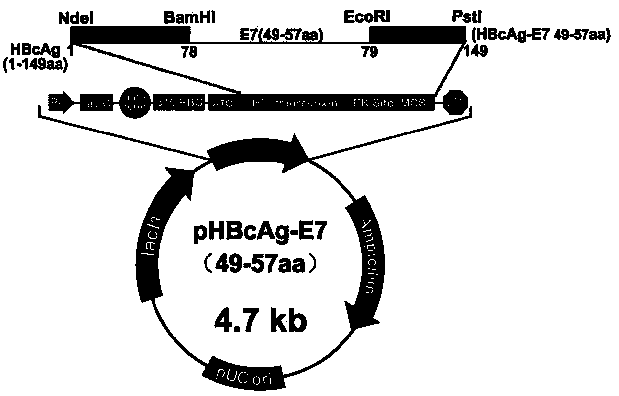
The invention relates to the field of molecular biology and immunology, in particular to an application of an HBcAg (hepatitis B core antigen) virus-like particle serving as a cervical cancer therapeutic vaccine carrier. A preparation method comprises steps as follows: an HPV16 E749-57CTLs epitope peptide fragment is selected, a DNA (deoxyribose nucleic acid ) fragment of the HPV16 E749-57CTLs epitope peptide fragment is inserted between 78 and 79 amino acids of the HBcAg through genetic recombination, an obtained recombinant plasmid pHBcAg-E749-57 is converted into Escherichia coli DH5alpha, and an HBcAg virus-like particle vaccine presenting E749-57 is obtained after induction expression and purification. After a tumor-bearing mouse is immunized with the virus-like particle vaccine, the body of the mouse can be induced to generate a higher HPV16E7 specific cellular immunologic response, and growth of tumors is remarkably inhibited.
Owner:INST OF MEDICAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com