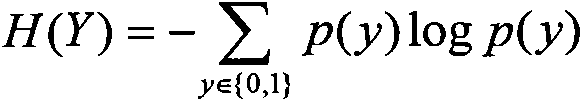Patents
Literature
58 results about "Homologous chromosome" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A couple of homologous chromosomes, or homologs, are a set of one maternal and one paternal chromosome that pair up with each other inside a cell during meiosis. Homologs have the same genes in the same loci where they provide points along each chromosome which enable a pair of chromosomes to align correctly with each other before separating during meiosis. This is the basis for Mendelian inheritance which characterizes inheritance patterns of genetic material from an organism to its offspring parent developmental cell at the given time and area.
Modulation of meiotic recombination
InactiveUS20040023388A1Inhibit cell proliferationReduced growth rateStable introduction of DNAFermentationFunctional activityMeiosis
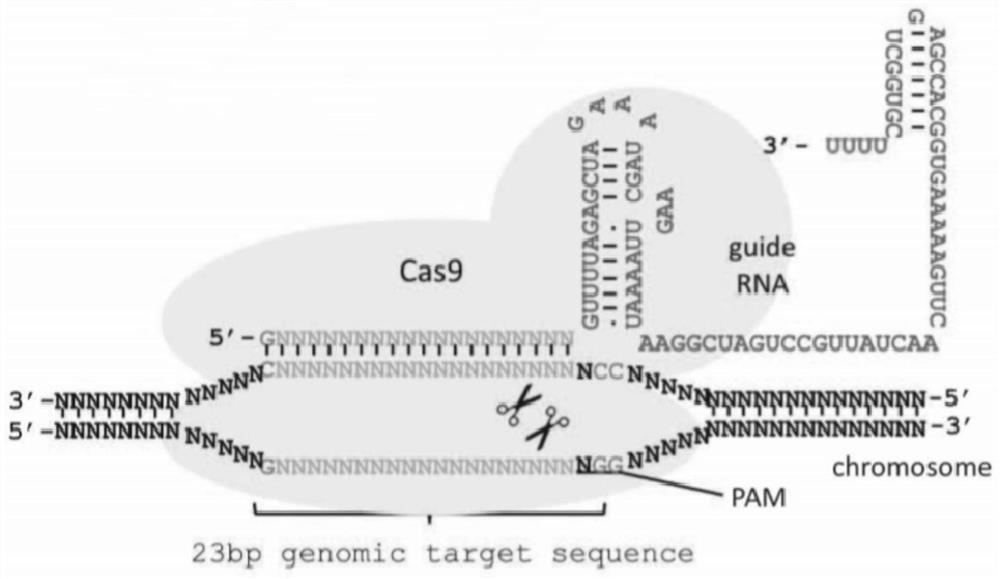
The invention provides methods of modifying the level of expression or functional activity of factors such as enzymes or other catalytic proteins or structural proteins, alone or in concert, to modify the frequency of meiotic homologous recombination involving the exchange of genetic information between non-sister chromatids from homologous maternal and paternal chromosomes. The steps at which modulation may occur include: homologous chromosome pairing, double-strand break formation; resection; strand invasion; branch migration; and resolution. Methods of plant and animal breeding are also provided that utilize the modulation of meiotic homologous recombination.
Owner:AGRI & AGRI FOOD +1
Product for diagnosing congenital scoliosis and application of product
ActiveCN104328169AEarly intervention time is goodMicrobiological testing/measurementFrameshift mutationHaplotype
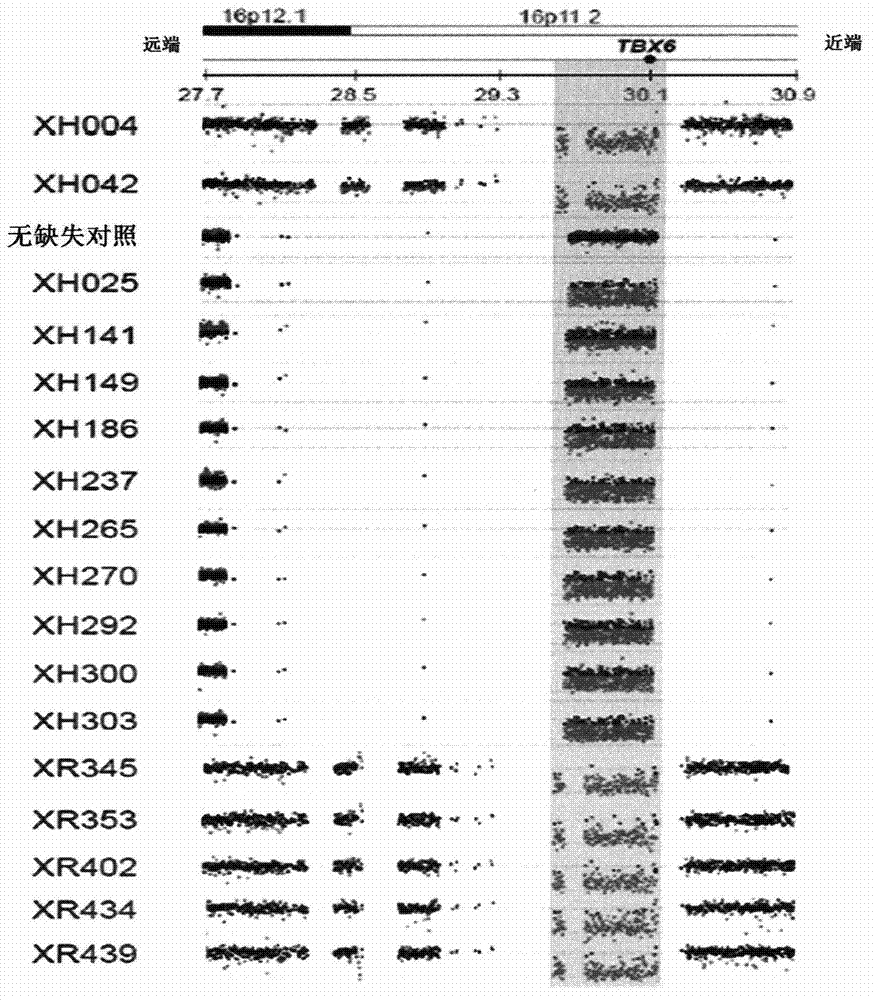
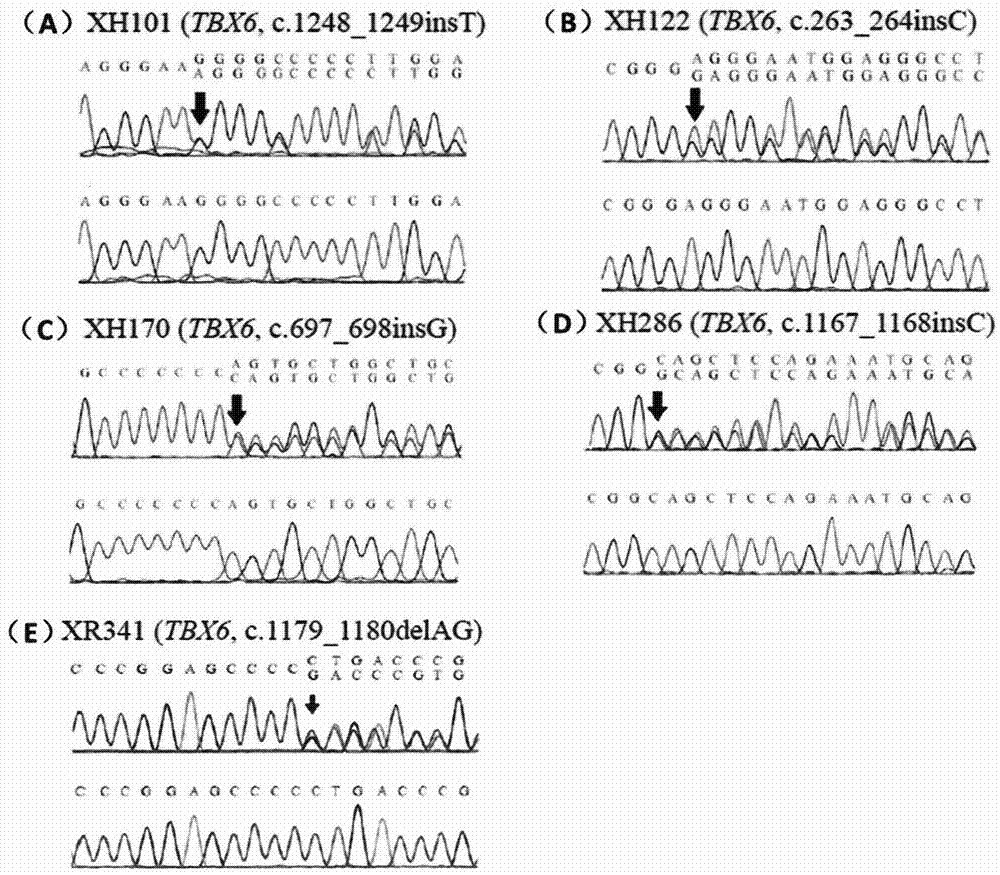
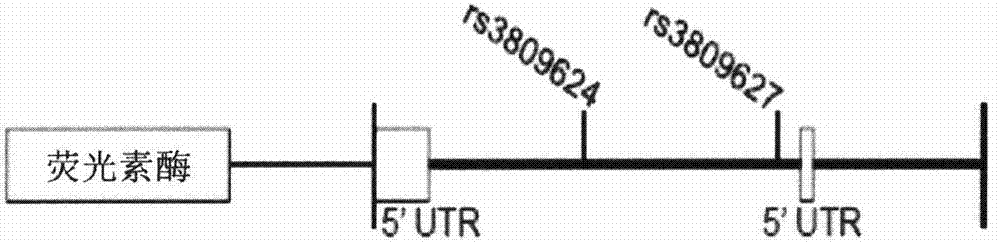
The invention discloses a product for diagnosing congenital scoliosis. According to the product, the judgment is carried by detecting whether a chromosome 16p11.2 is micro-deleted or the TBX6 gene frameshift mutation exists and according to the haplotypes of two SNP sites of rs3809624-rs3809627 in a TBX6 gene on another homologous chromosome. The diagnostic kit is sensitive and can be used for diagnosing the congenital scoliosis in early stage.
Owner:PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Modifying DNA recombination and repair
InactiveUS7947874B2High affinityImprove stabilityOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationHeterologousNucleotide
The present invention provides methods of modifying in vivo mutagenesis or homeologous recombination in a eukaryote. The method of modifying in vivo mutagenesis involves transforming a eukaryote with a nucleotide sequence capable of expressing a wild-type prokaryotic MutS, MutL, MutH, MutU, NLS-MutS, NLS-MutL, NLS-MutH, NLS-MutU protein, or a combination thereof, and expressing the protein. A method of modifying recombination between homeologous chromosomes in an allopolyploid eukaryotic organism comprising, expressing a nucleotide sequence encoding prokaryotic NLS-MutS in combination with one or more than one of NLS-MutL, NLS-MutH, NLS-MutU, within a germ cell of the allopolyploid eukaryotic organism is also disclosed.
Owner:AGRI & AGRI FOOD
Cotton pachytene chromosome fluorescence in-situ hybridization method
InactiveCN1995396AEnhance functional geneImprove detection efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceGenomic sequencingAgricultural science
The invention discloses a fluorescent home position hybrid technique, which is characterized by the following: adopting chromosome in the pachytene as target DNA to proceed fluorescent home position hybrid; drawing high-density physical atlas; fitting for separating cloning order gene; measuring sequence of full genome of cotton; improving the locating measuring efficiency of functional gene and molecular mark for cotton effectively; adopting chromosome in the pachytene with two homologous chromosomes to avoid the identifying defect; improving distinguishing efficiency greatly.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for screening tobacco black shank resistance non-homologous chromosome plant by molecular marker
InactiveCN108754009ARealize screeningImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceNicotiana tabacum
The invention provides a method for screening a tobacco black shank resistance non-homologous chromosome plant by a molecular marker. The black shank resistance non-homologous chromosome plant is screened in Nicotiana tabcum-N.plumbaginifolia distant hybridization descendants by molecular marker tobacco. Through black shank resistance identification and genome in situ hybridization confirmation, the method disclosed by the invention can carry out screen in the backcross descendants of Nicotiana tabcum-N.plumbaginifolia sesquialter diploid plants to obtain the black shank resistance plant withan exogenous chromosome, and an accuracy rate can be 100%. The result shows that the molecular marker can be used for screening to obtain the black shank resistance plant with the Nicotiana tabcum-N.plumbaginifolia chromosome, i.e., an in situ hybridization method can be replaced for screening.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY +1
Method for filtering SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) unrelated to complex diseases from whole-genome
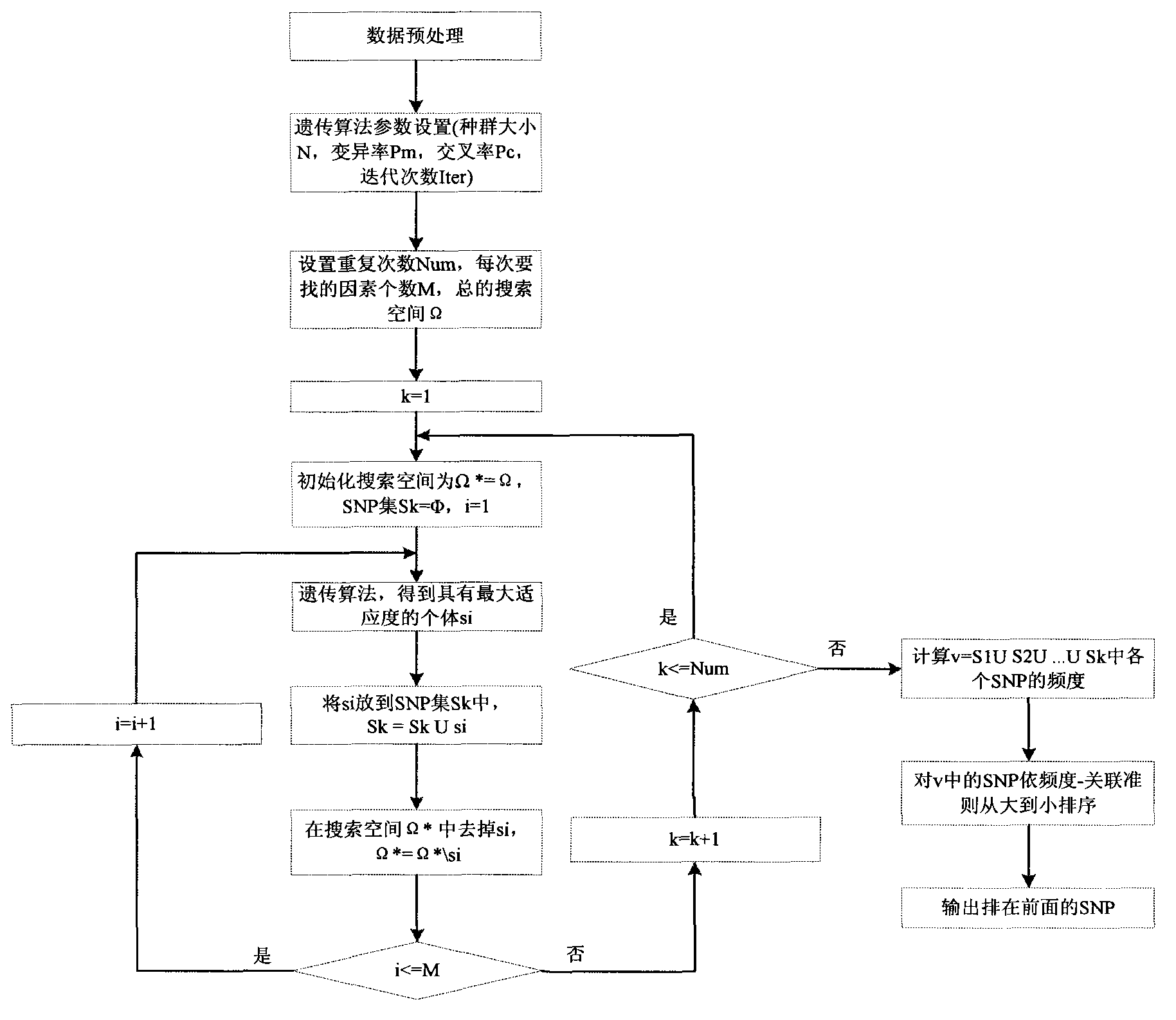
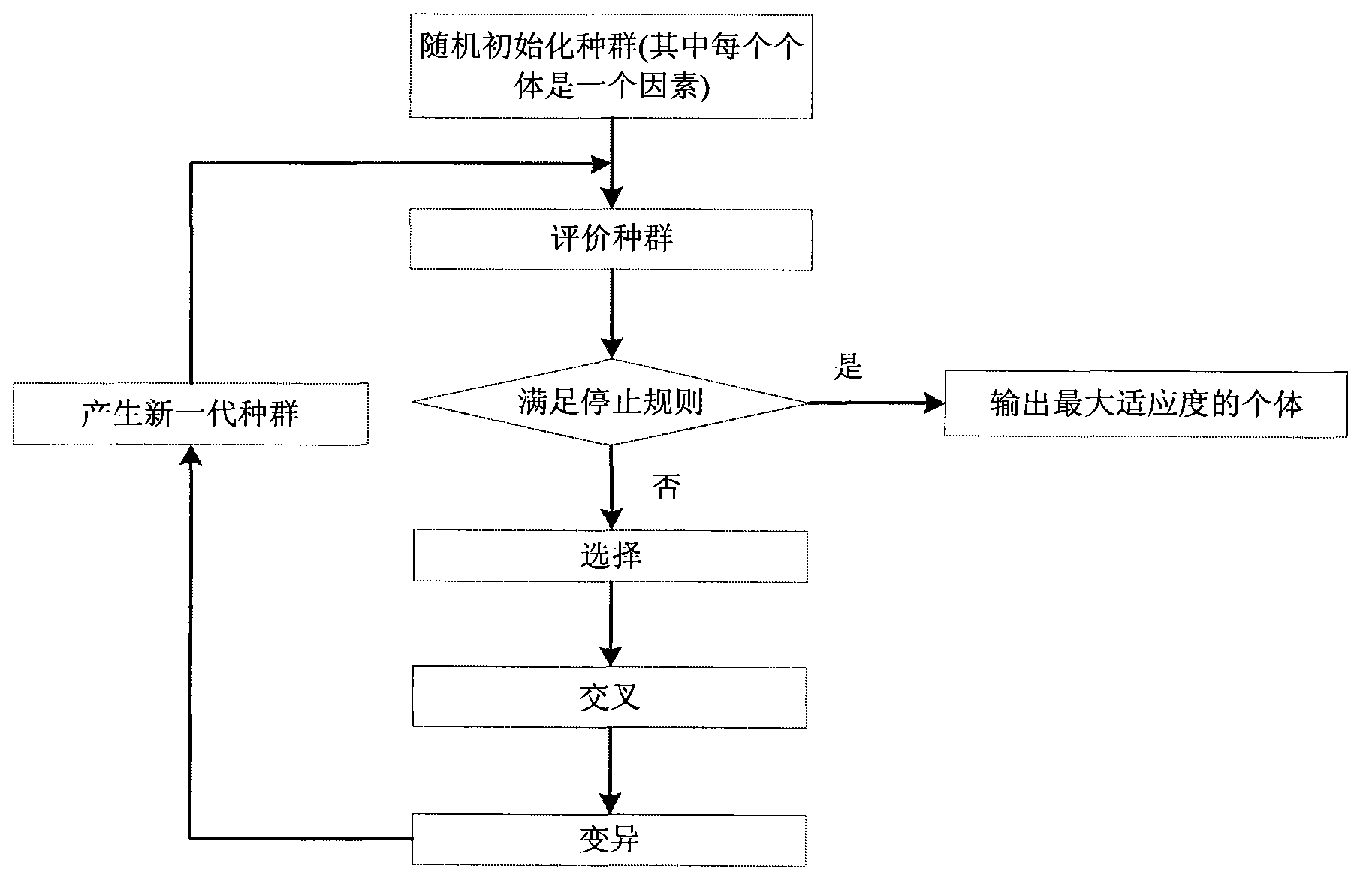
InactiveCN103366100ASearch guaranteeGuaranteed stabilitySpecial data processing applicationsFactor baseHomologous chromosome
A method for filtering SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) unrelated to complex diseases from a whole-genome is used for the pathogenetic mechanism research of complex diseases, the early diagnosis and biological medicine development. The method comprises the following steps: (1), pre-processing and initializing SNP data, and processing the SNP data into data only including 0, 1, 2, 3 as per the principle that the influence of the variation of a random gene among the alleles of homologous chromosomes on diseases can be in equal treatment; (2), defining the relevance measure, namely defining the relevance I (Y;X) between the SNP subset X and the diseases Y as mutual information MI (Y;X) between X and Y; (3), searching SNP groups of the candidate suspected pathogenesis in the SNP set by adopting an FGSA (factor based genetic search algorithm) method; (4), selecting the SNP group of which the occurrence frequency of frequentness exceeds a threshold value in the set of SNP groups of the candidate suspected pathogenesis according to the frequentness-relevance priority criterion; (5), outputting the SNP of which the frequentness is larger than the threshold value and ranking at the headmost. According to the invention, the method can reserve the SNP corresponding to the pathogenesis covered by other pathogenesis, so as to lay a foundation for the discovery of the follow-up pathogenesis.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Breeding and identifying method of soft and powdery mildew resistant triticum aestivum-Dasypyrum villosum translocation line
ActiveCN104365471AValid identificationExcellent agronomic traitsMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationAgricultural scienceTriticeae
The invention discloses a breeding and identifying method of a soft and powdery mildew resistant triticum aestivum-Dasypyrum villosum translocation line. The method comprises the steps of hybridizing and backcrossing a triticum aestivum-Dasypyrum villosum 5V alien addition line DA5V and a Chinese spring ph1b1b mutant, identifying individual plants relevant to 5VS and ph1b1bph1b1b from BC1F1 by use of a molecular marker, identifying individual selfed seeds by use of GISH (genomic in situ hybridization) technology, and analyzing individual plants containing translocated chromosomes by use of C-zoning, GISH and molecular markers to prove that the translocated chromosome is T5VS.5AL. A PCR (polymerase chain reaction) primer is designed by use of an EST (Expressed Sequence Tag) located on the homologous chromosome group of the fifth part of triticum, a co-dominant marker capable of identifying the translocated chromosome specially can be screened, and homozygosis and heterozygosis translocations can be distinguished. The breeding utilization value of the translocation line can be disclosed through agronomic traits, kernel hardness analysis and powdery mildew resistance identification.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Use of hla-b*1301 allele
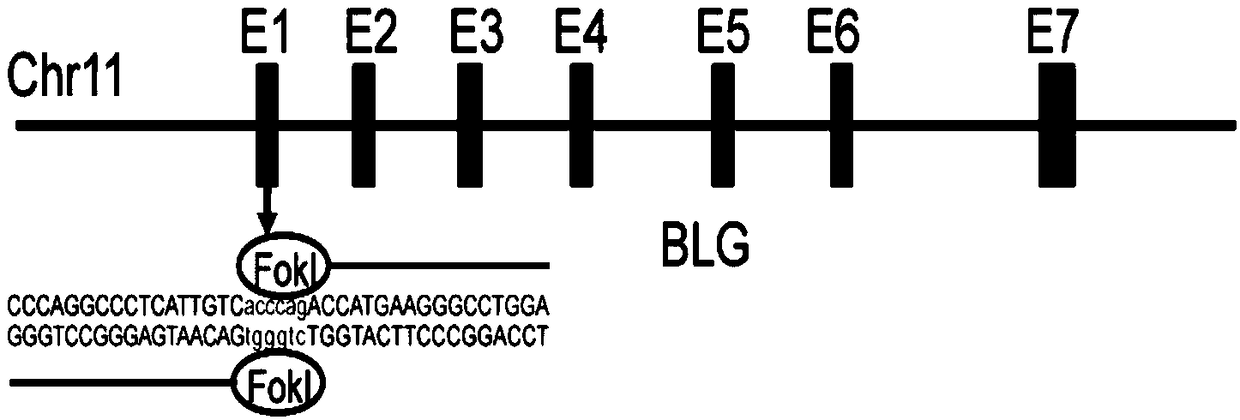
The present invention discloses uses of a HLA-B*1301 allele, comprising: 1) a use of a substance for detecting whether a person has the HLA-B*1301 allele in preparation of a product for evaluating a risk of adverse drug reactions in response to dapsone in the person; 2) a method for detecting or evaluating a risk of adverse drug reaction in response to dapsone in a person, comprising detecting whether the person has the HLA-B*1301 allele, wherein, a person with LA-B*1301 allele suffers a higher risk of adverse drug reaction upon being administered dapsone, as compared with a person without HLA-B*1301 allele, and a person with LA-B*1301 alleles at both chromosomes of a pair of homologous chromosomes suffers a higher risk of adverse drug reaction upon being administered dapsone, as compared with a person with HLA-B*1301 allele at only one of a pair of homologous chromosomes.
Owner:SHANDONG PROVINCIAL INST OF DERMATOLOGY & VENEREOLOGY
Somatic recombination
InactiveUS20050125850A1High sensitivity detectionEasily resolvedStable introduction of DNANucleic acid vectorGenes mutationCell marker
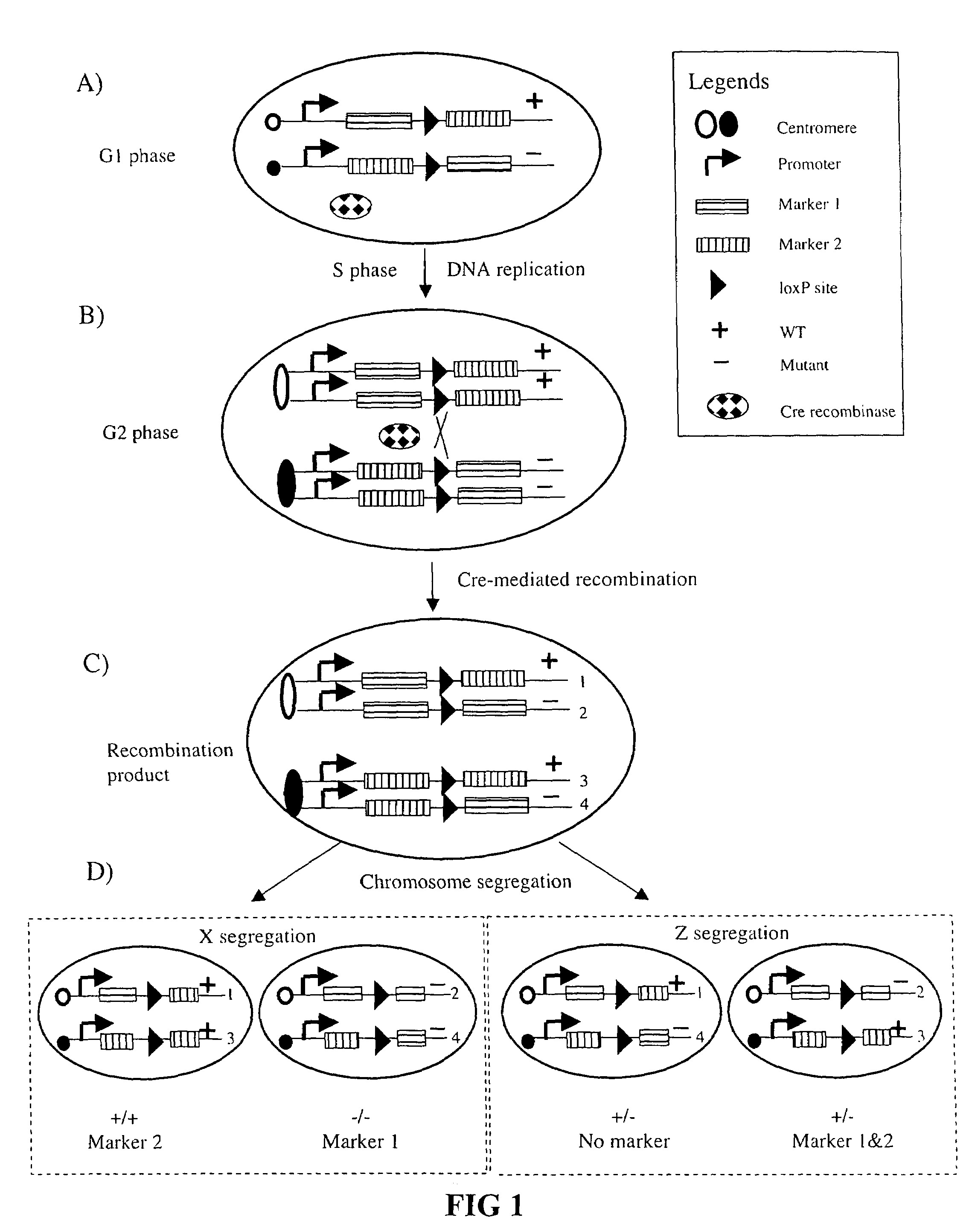
Recombination in mammalian somatic cell chromosomes is promoted and marked by a method called mosaic analysis with double marker (MADM). Mouse “knock-in” techniques are used to create pairs of chromosomes in which recombinase target sites are placed at homologous chromosomal locations. The knock-in constructs are engineered so that cellular markers, such as green or red fluorescent protein (GFP or RFP), are only expressed after recombinase-induced recombination. This system provides high-sensitivity detection of recombinase-induced mitotic recombination, even down to the single cell level. When this recombination is induced in a mouse heterozygous for a mutation in a gene distal to the “knock-in” locus on the same chromosome, it results in homozygosity of this mutation in the labeled cells. This allows the analysis in singly-labeled neurons of genes whose pleiotropic effects might otherwise result in early lethality.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Wheat TaARF12 gene and application thereof
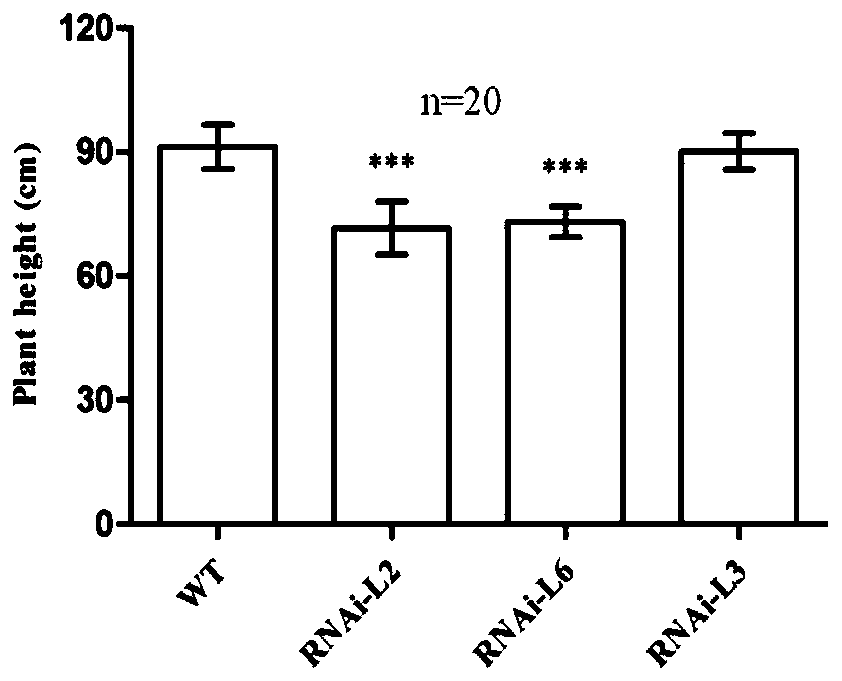
ActiveCN110846323AReduce plant heightGermplasm improvementMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesBiotechnologyWild type
The invention provides a wheat TaARF12 gene and application thereof, and belongs to the field of molecular biology of crops. A designed primer clones a coding region sequence of TaARF12 from cDNA of Chinese spring young ears, and the coding region sequence of the TaARF12 gene in homologous chromosomes A, B and D is represented as SEQ ID NO. 1-3 respectively. A TaARF12-specific RNAi fragment is selected, an RNAi vector is created, and Fierder is transformed. A CRISPR / Cas9 vector is used to create a gene editing vector containing two target sites and transform wild-type Fierder. Obtained RANi transgenic lines and gene editing lines have similar phenotypes, with plants becoming shorter and ears becoming longer. It is indicated that the wheat TaARF12 gene can regulate the plant height and theear length, and the plants become shorter and the ears become longer after the gene is interfered and expressed.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for efficiently inducing wheat-wheatgrass non-homologous chromosomes to translocate
The invention discloses a method for efficiently inducing wheat-wheatgrass non-homologous chromosomes to translocate. The method comprises the following step of irradiating wheat-wheatgrass non-homologous disome addition line plants and plants with blooming florets by means of 60 Co-gamma rays at 20 Gy of irradiation dose and 0.5 Gy / min of dose rate; and thus obtaining a wheat-wheatgrass non-homologous translocation line of which the translocation frequency is obviously improved (39.85 percent). In order to expand the genetic basis of wheat, the invention provides a high-efficiency method for transferring beneficial genes in wheatgrass chromosomes to the wheat, and the method has important significance in the aspects of basic theory research, actual application of breeding and the like.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Teaching model for demonstrating cell division
A teaching model for demonstrating cell division is composed of a flexible transparent chromosome magnetic model, a homologous chromosome cross exchange model, and a cell division telescopic rope model. The flexible transparent chromosome magnetic model is used for demonstrating the behavior relationship of chromosome, chromatid, DNA and gene in the processes of mitosis and meiosis, demonstrating the relationship between meiosis and the basic genetic laws and demonstrating the chromosome number and structure variation. The homologous chromosome cross exchange model is used for demonstrating cross exchange in the tetrad stage of meiosis. The cell division telescopic rope model is used for demonstrating depression and hanging division in the middle of cytomembrane in the process of animal cell division and demonstrating a dynamic change process in which a cell plate is extended to a cell wall and one cell is divided into two cells in the late stage of plant cell separation.
Owner:郭士安
Single chromosome segregation method, single chromosome high-throughput sequencing library construction method and application
InactiveCN105087484AOptimal dilution parameterSimple technical solutionMicrobiological testing/measurementBlood/immune system cellsChromosome segregationHomologous chromosome
The invention provides a single chromosome segregation method, a single chromosome high-throughput sequencing library construction method and application. According to the technical scheme, optimal dilution parameters are obtained through computer simulation experiments, chromosomes in single cell are segregated by a dilution method to obtain single chromosomes, and high-throughput sequencing and bioinformatics analysis are conducted so as to judge out that mutant genes derive from the father or the mother in homologous chromosomes. Compared with that the homologous chromosomes serve as a mixed sample for sequencing, the single chromosome segregation method has the advantages that the single chromosomes are segregated by the dilution method, and the single chromosome segregation method can be used for haplotype sequencing and has important application value in scientific research and clinical application.
Owner:SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY OF CHINA
Maize autocopulation strain assistant selection and breeding method and application thereof
InactiveCN1922982AHigh combination abilityShorten the breeding cycleMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationAgricultural scienceHomologous chromosome
The invention relates to a method for breeding corn cross system. Wherein, it comprises (1), selecting at least 20 SSR primers with polymorphism on the basic material S0 generation; each isopathic couple of chromosomes has at least two SSR primers whose genetic distance is at least 50cm; (2), using at least six couples of SSR primers, selecting single one of S1 generation that purified combined on said six SSR primers, while SSR primers are at least at six couples of isopathic chromosomes; (3), using at least 14 SSR primers expect from the ones in step (20, selecting S2 generation, to obtain the S2 single one purified combined on said 14 SSR primers, as the core cross system.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
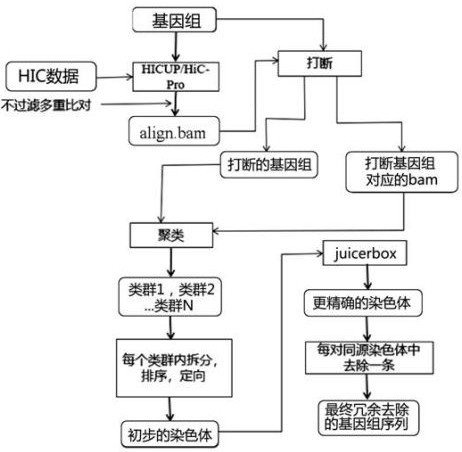
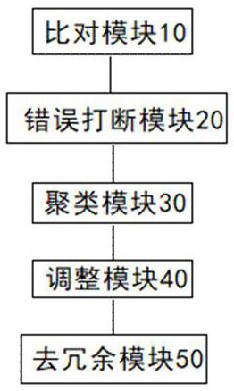
Method and device for eliminating redundancy of high-heterozygous diploid sequence assembling result and application of method and device
The invention provides a method and a device for removing redundancy of a high-heterozygous diploid sequence assembly result and application of the method and the device. The method comprises the following steps: comparing HiC data with a highly hybrid diploid sequence assembly result to obtain a comparison file of all comparison information including multiple comparison; calculating the HIC interaction intensity in contig and then interrupting the contig, which is wrongly connected, in a high-heterozygous diploid sequence assembling result; clustering contig by utilizing the broken genomes which are correctly connected, the comparison files corresponding to the broken genomes and the interaction strength between the contig to obtain a plurality of class groups; sequencing and orienting contig sequences in each class group to obtain a genome of the chromosome version; and reserving one homologous chromosome in the genome of the chromosome version, and combining with the non-mounted contig sequence to form a final genome of which the redundant sequence is removed. The problem that redundant sequences are difficult to remove is solved.
Owner:BEIJING NOVOGENE TECH CO LTD
Small-molecule fluorescent probe and application thereof in chromosome analysis and cytogenetics
ActiveCN111303145AOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementHomologous chromosomeMolecular fluorescence
The invention discloses a small-molecule fluorescent probe and an application thereof in chromosome analysis and cytogenetics, and the small-molecule fluorescent probe can be used as a universal toolfor chromosome image segmentation and is used for identifying and distinguishing overlapped, aggregated or contacted chromosomes. The small-molecule fluorescent probe is used as a reference marker forpositioning centromere positions, is used for classifying homologous chromosomes, distinguishing different forms of chromosomes and estimating chromosome arm lengths, is used in cooperation with karyotype analysis for chromosome deletion and polyploid, is used in cooperation with fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), and is used for positioning designated genes and judging chromosome abnormalities. The invention provides a rapid and reliable method for auxiliary chromosome analysis, and has great potential in conventional clinical practice.
Owner:陈斯杰 +2
Method for identifying or assisting in identifying shapes of potatoes and special primer pair for method
ActiveCN105063217ASave manpower and material resourcesShorten the breeding cycleMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGrowth plantAgricultural science
The invention discloses a method for identifying or assisting in identifying shapes of potatoes and a special primer pair for the method. The method comprises the following steps: detecting whether the 805th deoxyribonucleotide of a target gene on a homologue of a potato to be tested is C or not, the 896th deoxyribonucleotide is T or not and the 1146th deoxyribonucleotide is A or not. The primer pair consists of DNA molecules shown in the sequence 1 of a sequence chart and DNA molecules shown in the sequence 2 of the sequence chart. Experiments show that when the primer pair is used for detecting the potato material, the fit goodness between the detection result and the phenotype identification result is 80% or above, and the fit goodness between the detection result and the round potato shape is 90% or above. The selection accuracy is high, the stability is good, the offspring can be selected in the seedling stage, influences from the plant growth stage and environmental conditions are prevented, the shape breeding process of potatoes can be effectively accelerated, and the breeding cost is lowered.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Cultivation of watermelon with few seeds
InactiveCN1778165AImprove transgenic efficiencyImprove qualityPlant genotype modificationHomologous chromosomeSelfing
A method for culturing the less-seed water melon includes such steps as determining the chromosome translocation material to obtain two non-homologous chromosome translocating bodies with different translocation sites, back crossing or selfing or test crossing to transfer them respectively to the male parent and female parent, hybridizing between said male and female parents, discriminating in field, and variety comparison. Its advantages are high transfer efficiency, and high effect to decrease the number of seeds by 45-55%.
Owner:TIANJIN KERNEL VEGETABLE RES INST
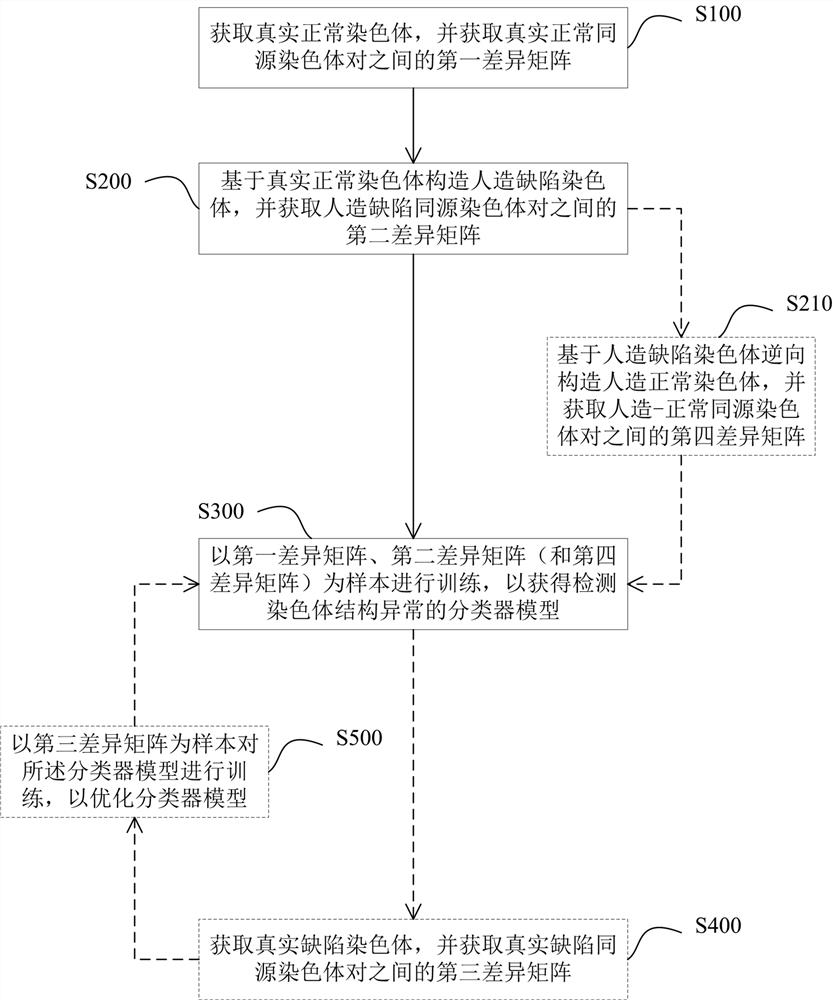
Classifier model training method and device for detecting chromosome structure abnormality
ActiveCN114841294AAutomated screeningCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionHomologous chromosome
The invention provides a classifier model training method and device for detecting chromosome structure abnormality. The training method comprises the steps that real normal chromosomes are obtained, a first difference matrix between real normal homologous chromosome pairs is obtained, and two homologous chromosomes in the real normal homologous chromosome pairs are both real normal chromosomes; artificial defect chromosomes are constructed based on the real normal chromosomes, a second difference matrix between the artificial defect homologous chromosome pairs is obtained, and at least one of two homologous chromosomes in the artificial defect homologous chromosome pairs is an artificial defect chromosome; training at least by taking the first difference matrix and the second difference matrix as samples to obtain a classifier model for detecting the chromosome structure abnormality; and judging whether the to-be-diagnosed user has chromosome abnormality based on the classifier model. According to the method, abundant structure abnormal chromosomes of different types are artificially constructed, so that sufficient and balanced samples are provided for classifier model training.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIAGENS BIOTECH CO LTD
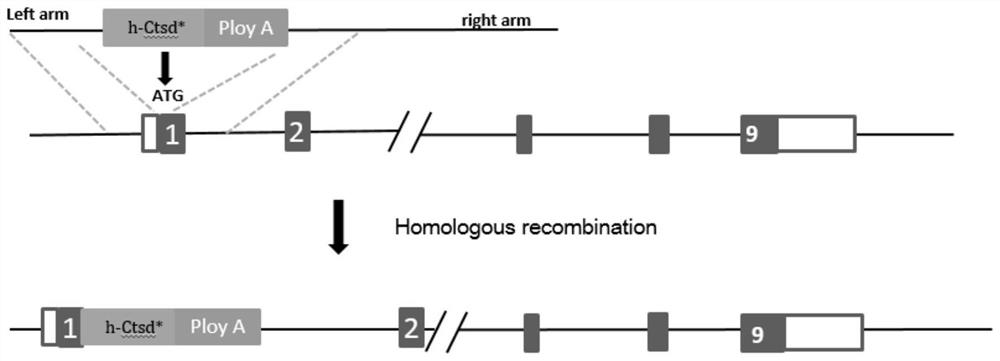
Method for preparing retinitis pigmentosa non-human mammal model
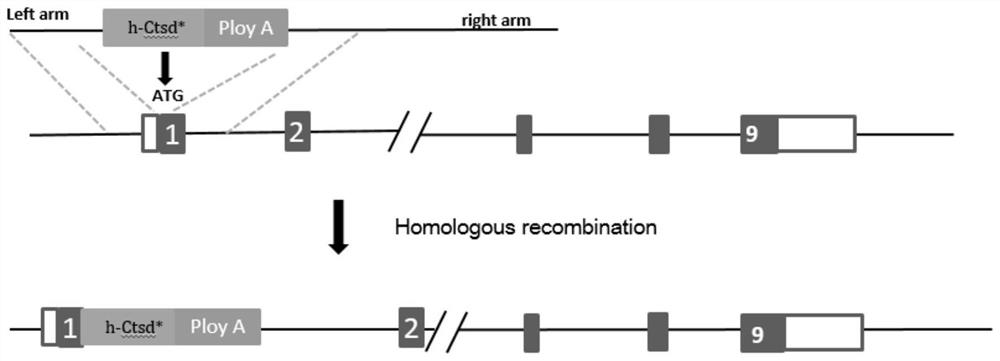
ActiveCN111979241ASimple pathological backgroundAnimal reproductionMicroinjection basedDiseaseHomologous chromosome
The invention relates to a method for preparing a retinitis pigmentosa non-human mammal model. The method comprises the following steps of replacing an endogenous ctsd gene on one of homologous chromosomes of an animal with an h-CTSD * gene, wherein the h-CTSD * gene is a humanized ctsd gene which is subjected to c.262dupC site variation. The h-CTSD * gene is discovered to be related to RP for thefirst time, and an h-CTSD * gene knocked-in mouse animal model is established. The invention provides a convenient, reliable and economic means for studying the relationship between CTSD mutation andretinitis pigmentosa and the pathogenesis of CTSD mutation and retinitis pigmentosa, and provides a reliable theoretical basis for studying CTSD mutation and retinitis pigmentosa. More importantly, besides RP, the animal does not show neurological disease symptoms such as spasm, neuron wax-like lipofuscin deposition and ataxia, the pathological background is purer, and the method is particularlysuitable for construction of an RP animal model.
Owner:SHANGHAI FIRST PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Method for improving polyploid poplar gamete fertility
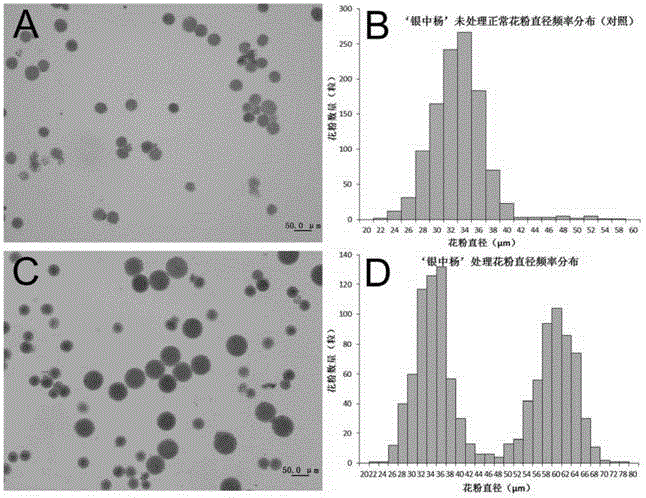
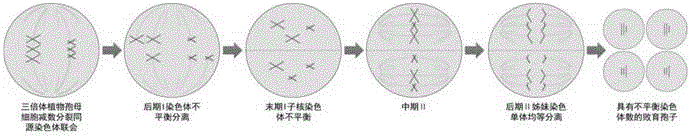
The invention discloses a method for improving polyploid poplar gamete fertility, belonging to the field of plant genetics and breeding. The method comprises the following steps: observing flower bud development situations of polyploid poplars, applying a certain concentration of chemical agents for performing induced mutation treatment when observing that spore mother cells of the polyploid poplars develop to a certain period, collecting pollen after flower buds continuously develop to reach a pollen maturation period, performing pollen germination, observing the pollen germination rate, and judging the fertility level. The method disclosed by the invention can be used for providing homologous chromosomes for each chromosome of polyploidy plants so as to help completing pairing of each chromosome, the problem of unbalanced separation of the chromosomes caused in a reduction mitosis process of a polyploidy material can be solved, the gamete fertility can be significantly improved, the fertility utilization of polyploid poplar varieties can be achieved, and the breeding efficiency of new germplasms of the poplars can be improved.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Method for breeding cattle capable of producing hypoallergenic milk and application of method
InactiveCN109321600AImprove functional propertiesMitigating Biosecurity ConcernsMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid vectorBiotechnologyEmbryo
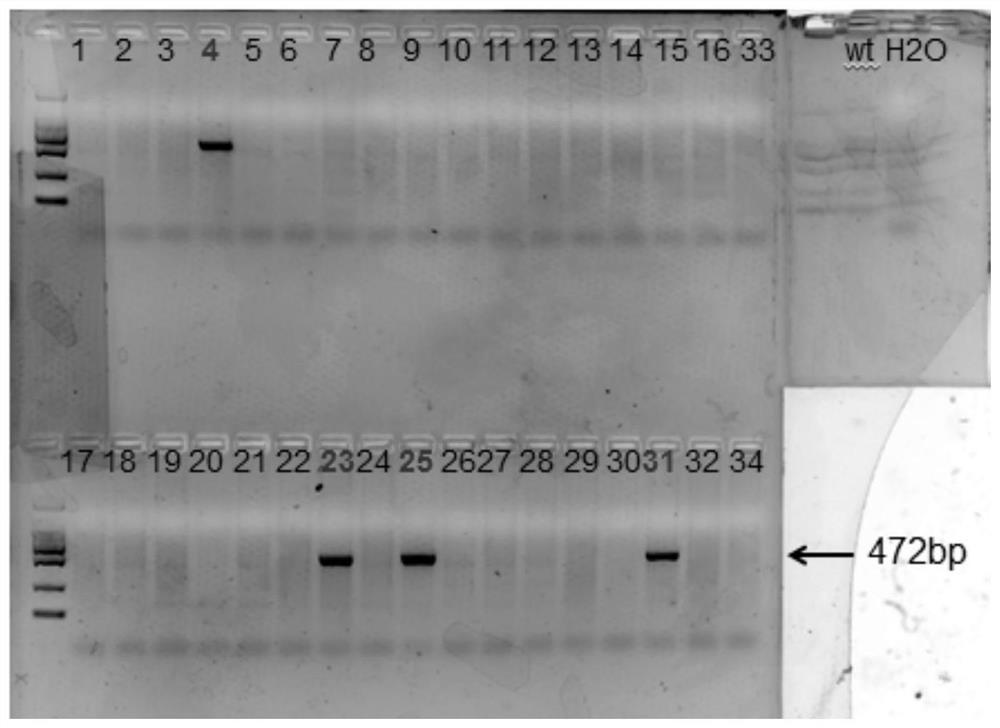
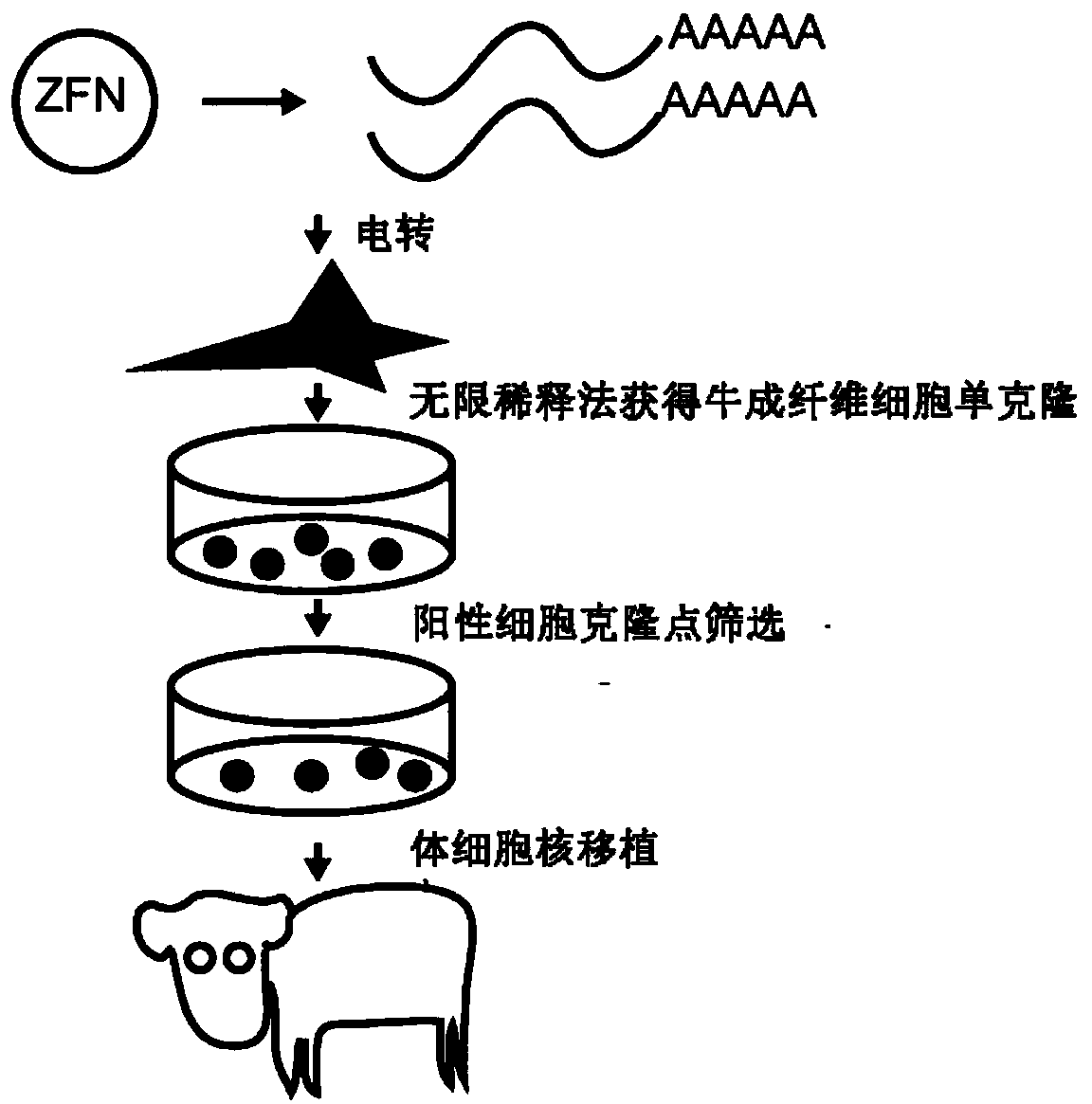
The invention discloses a method for breeding cattle capable of producing hypoallergenic milk and application of the method. The method comprises the following steps: leading a zinc finger nuclease carrier pZFN into fibroblasts of the cattle, so as to obtain donor cells with a gene type which is a biallelic mutation type, wherein the biallelic mutation type is that nucleotide molecules of beta-LGgenes on two homologous chromosomes of the cattle are subjected to frame shift mutation; transferring cell nucleuses of the donor cells into cattle oocytes without the cell nucleuses and developing toform reconstructed embryos; then transferring the reconstructed embryos into uteri of cows and delivering to obtain the cattle capable of producing the hypoallergenic milk. According to the method disclosed by the invention, beta-LG biallelic gene knockout cattle which have no exogenous DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) integration, can produce beta-lactoglobulin-free milk and deliveries mutation to the next generation through normal breeding are successfully bred. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, an important foundation is laid for allergenic problems of the milk and also provides infinite possibility for preparing humanized milk. The method has important application value.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Somatic recombination
InactiveUS7282621B2High sensitivity detectionEasily resolvedStable introduction of DNANucleic acid vectorMammalCell sensitivity
Recombination in mammalian somatic cell chromosomes is promoted and marked by a method called mosaic analysis with double marker (MADM). Mouse “knock-in” techniques are used to create pairs of chromosomes in which recombinase target sites are placed at homologous chromosomal locations. The knock-in constructs are engineered so that cellular markers, such as green or red fluorescent protein (GFP or RFP), are only expressed after recombinase-induced recombination. This system provides high-sensitivity detection of recombinase-induced mitotic recombination, even down to the single cell level. When this recombination is induced in a mouse heterozygous for a mutation in a gene distal to the “knock-in” locus on the same chromosome, it results in homozygosity of this mutation in the labeled cells. This allows the analysis in singly-labeled neurons of genes whose pleiotropic effects might otherwise result in early lethality.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Z-chromosomal markers derived from chicken (gallus domesticus) and use thereof in chromosomal mapping
InactiveUS20020018993A1High saturationReduce gapSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementZ chromosomeFowl
We have developed a chicken (Gallus domesticus) Z-chromosome-specific DNA library in a phage vector, by means of chromosome microisolation and microcloning. The chromosomal origin, specificity and purity was evaluated by fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) on chicken metaphases. Heterologous chromosome painting, using this Z-chromosome-specific probe on turkey (Meleagris gallopavo) metaphases identified its homologous Z-chromosome, under the same stringent conditions as that used in the chicken, indicating a high degree of Z-chromosome sequence homology among these two species. This chicken Z-chromosome library will facilitate the development of Z-chromosome-specific DNA markers that will be useful for genetic mapping in the domestic chicken and related avian species. The Z-chromosome-specific DNA probe will also be useful for studies pertaining to the sex chromosome evolution in avian species.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS A PUBLIC INSTION OF HIGHER EDUCATION OF THE COMMONWEALTY OF AMSSACHUSETTS AS REPRESENTED BY ITS AMHERST COMPUS
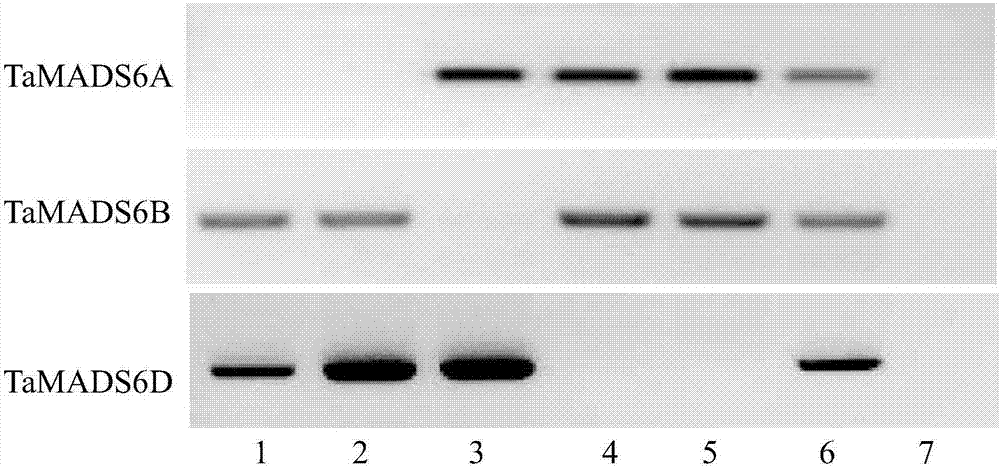
Wheat TaMADS6 gene and application thereof
InactiveCN106906222AImproving and improving germplasm resourcesIncrease biological functionMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesBrachypodiumNullisomic
The invention provides a wheat TaMADS6 gene and an application thereof, and belongs to the field of crop molecular biology. Primers are designed, TaMADS6 encoding region sequences are cloned from China spring young spike cDNA, TaMADS6 is located in a wheat sixth homologous group by using a China spring nullisomic-tetrasome, and the TaMADS6 gene encoding region sequences in sequences of A, B and D homologous chromosomes are shown in SEQ ID NO.1-3 respectively. The encoding region sequence of the D homologous chromosome of the TaMADS6 gene transforms Brachypodium Bd21-3, the gene can make nrachypodium significantly flower in advance, and flowering is promoted by increasing expression of BdFT1, BdFT2 and BdVRN1.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
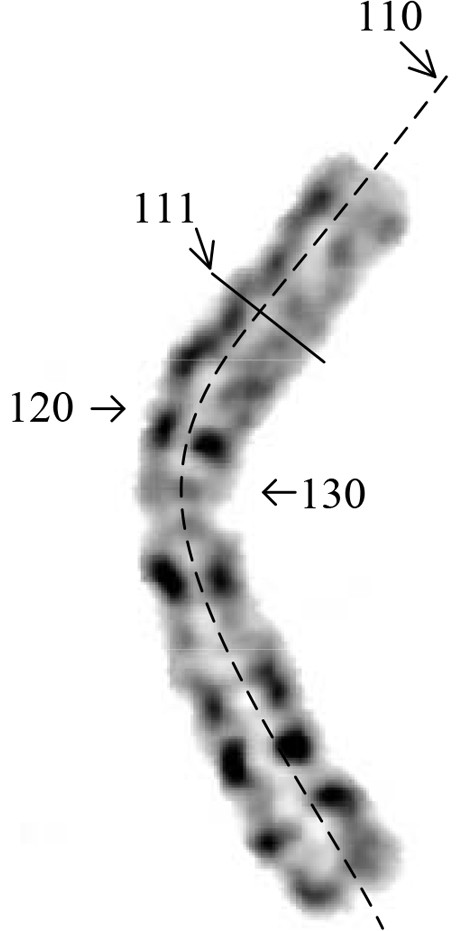
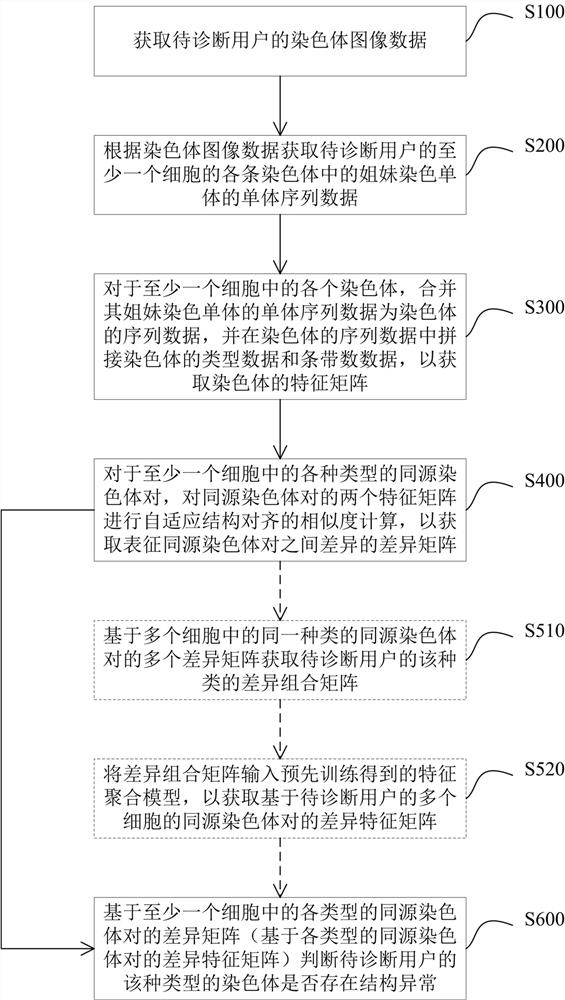
Method and device for detecting chromosome structure abnormality based on deep learning
ActiveCN114842472AImprove screening efficiencyGet detailed and accurateAcquiring/recognising microscopic objectsRecognition of DNA microarray patternStainingAlgorithm
The invention provides a chromosome structure anomaly detection method and device based on deep learning. The detection method comprises the following steps: acquiring chromosome image data of a to-be-diagnosed user; according to the chromosome image data, obtaining a feature matrix of each chromosome through monomer sequence data, type data and stripe number data of sister dyeing monomers of each chromosome; obtaining a difference matrix representing the difference between the homologous chromosome pairs based on the two feature matrixes of the homologous chromosomes; and at least based on the difference matrix of the homologous chromosome pairs of various types in the at least one cell, judging whether the chromosome of the type of the user to be diagnosed has structural abnormality or not. According to the method, the chromosomes are represented through the feature matrix, and the difference between the homologous chromosome pairs is represented through the difference matrix, so that whether the chromosome structure abnormality exists in the user or not can be judged according to the difference matrix through deep learning, and the screening efficiency of the chromosome structure abnormality can be greatly improved.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIAGENS BIOTECH CO LTD
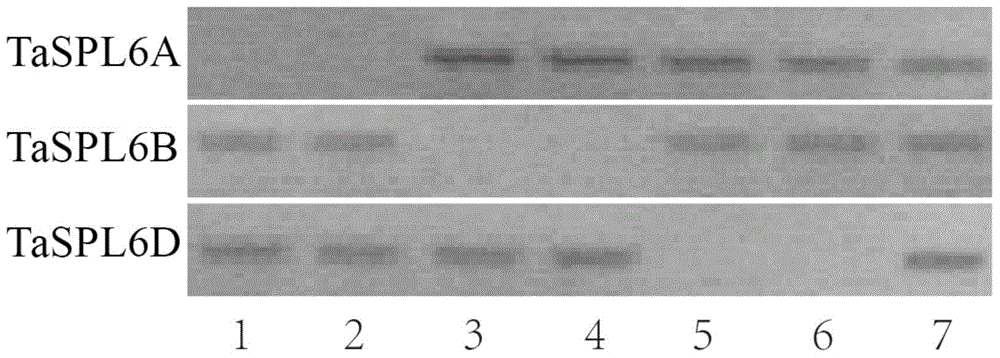
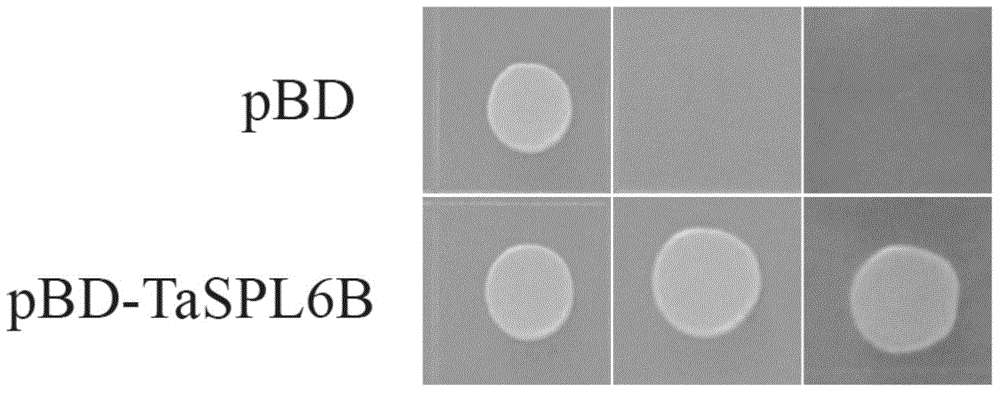
Wheat TaSPL6 gene and application thereof
ActiveCN104789574AGermplasm improvementImproving and improving germplasm resourcesMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationBiomassArabidopsis
The invention provides a wheat TaSPL6 gene and application thereof, and belongs to the field of crop molecular biology. According to the wheat TaSPL6 gene and the application thereof, the specific primers are used for cloning the coding region sequences of the TaSPL6 from cDNA of leaves of Triticum aestivum L.; nulli-tetrasome is utilized to position TaSPL6 on the wheat fifth homologous group; the sequences of the coding region sequences of the TaSPL6 gene are respectively as shown in SEQ ID NO.1-3. Through transforming arabidopsis by the TaSPL6 gene, the result proves that the gene is capable of enlarging the Arabidopsis leaves and increasing the biomass.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
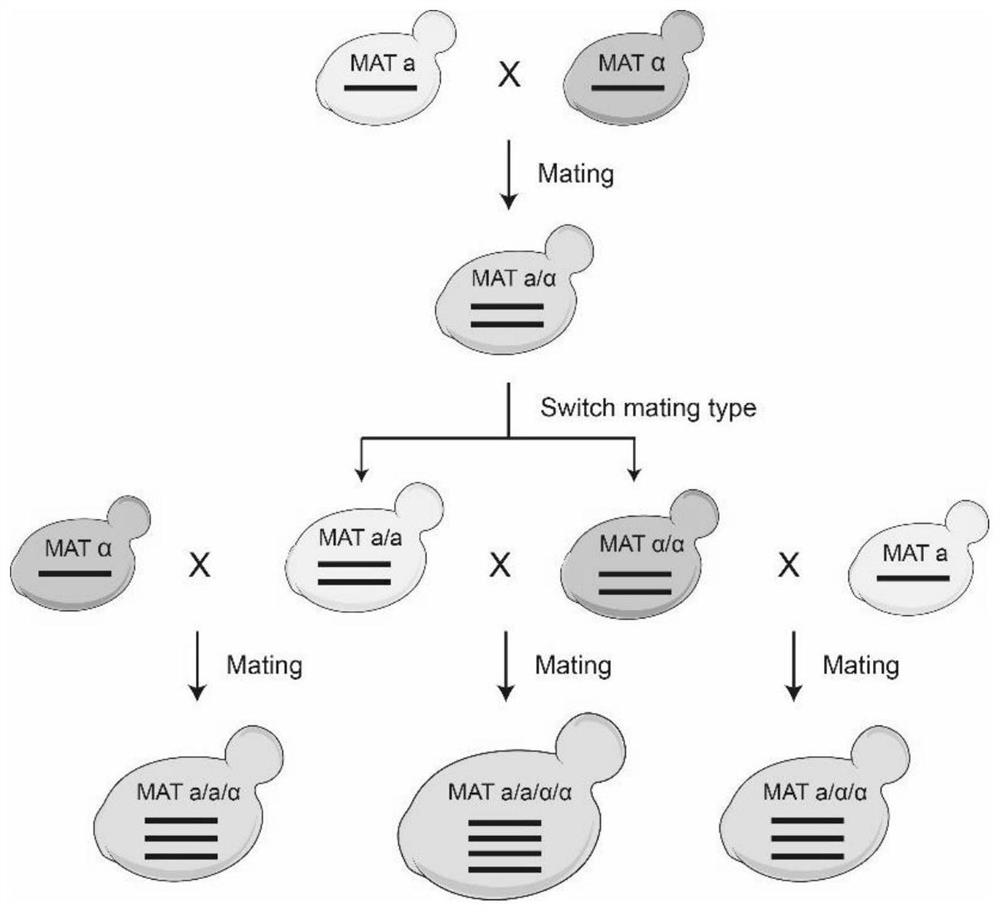
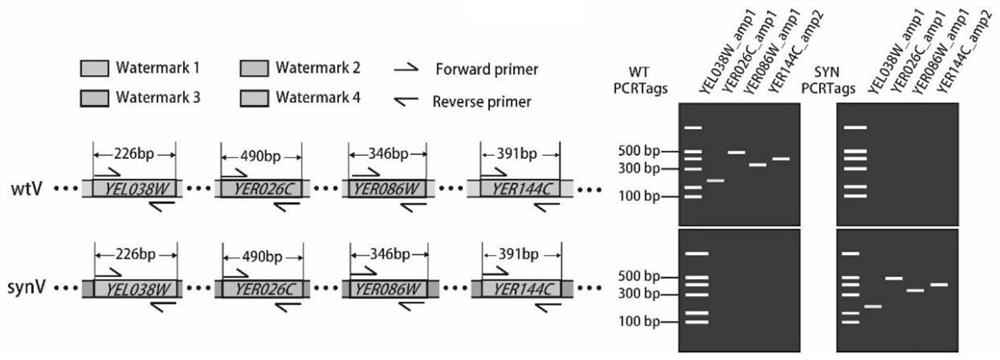
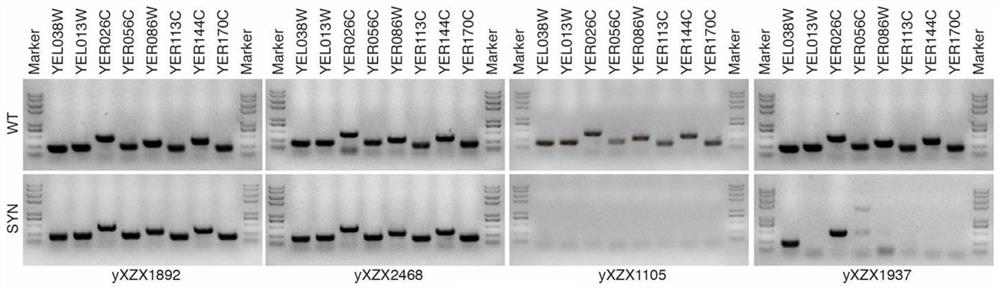
Detection method of yeast mitosis recombination hotspot
ActiveCN113549682AMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationSynthetic biologyRapid identification
The invention relates to the technical field of synthetic biology, in particular to a detection method of yeast mitosis recombination hotspot. A PCRTag tag combination provided by the invention can be used for rapidly detecting eukaryotic genome mitosis recombination hotspots. By utilizing the tag combination, the mitosis recombination hotspot of the homologous chromosome can be quickly identified through a specific watermark tag, and a convenient method is provided for researching the eukaryotic mitosis recombination event.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Breeding method using tetraploid recombination inbred lines hybridized/doubled between rice indica japonica subspecies
InactiveCN111543310AAvoid mutationMuch variationPlant genotype modificationAngiosperms/flowering plantsBiotechnologyGenomic mutation
The invention discloses a breeding method using a tetraploid recombination inbred lines hybridized / doubled between rice indica japonica subspecies. The breeding method includes the steps that indica rice is hybridized with japonica rice; doubling is carried out to obtain a tetraploid; the tetraploid is inbred, and tetraploid with target traits is selected for recombinant inbred lines; and a diploid with target traits is obtained by means of chromosome set ploidy reduction, that is, a rice breeding material with the targeted traits. The sterility of indica japonica F1 hybrids is overcome, the high tolerance of the tetraploid to the instability of a chromosome set is used to take the tetraploid as a platform that can quickly induce a large number of genomic mutations, the tetraploid recombination inbred lines with chromosome set variation such as part of homologous chromosome fragment exchange in the chromosome set and diverse phenotypes are quickly obtained from inbred progeny, and a diploid restorer induced by the chromosome set ploidy reduction method can mostly inherit the phenotype and resistance characteristics of their parental tetraploid. The breeding method has important significance for rice breeding.
Owner:NORTHEAST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing retinitis pigmentosa non-human mammal model
ActiveCN111979241BSimple pathological backgroundAnimal reproductionMicroinjection basedRetinal pigmentationDisease
The invention relates to a method for preparing a non-human mammalian model of retinitis pigmentosa. The method comprises replacing the endogenous ctsd gene on one of the homologous chromosomes of the animal with the h-CTSD* gene; the h-CTSD* gene is a human ctsd gene with a c.262dupC site mutation. This application first discovered that the h-CTSD* gene is related to RP, and established a mouse animal model in which the h-CTSD* gene was knocked in. The invention provides a convenient, reliable and economical means for studying the relationship between CTSD mutation and retinitis pigmentosa and its pathogenic mechanism, and provides a reliable theoretical basis for the research. More importantly, the animal does not show symptoms of neurological diseases such as spasms, neuronal ceroid lipofuscin deposition, ataxia, etc., except for RP, and the pathological background is simpler, which is very suitable for the construction of RP animal models .
Owner:SHANGHAI FIRST PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com