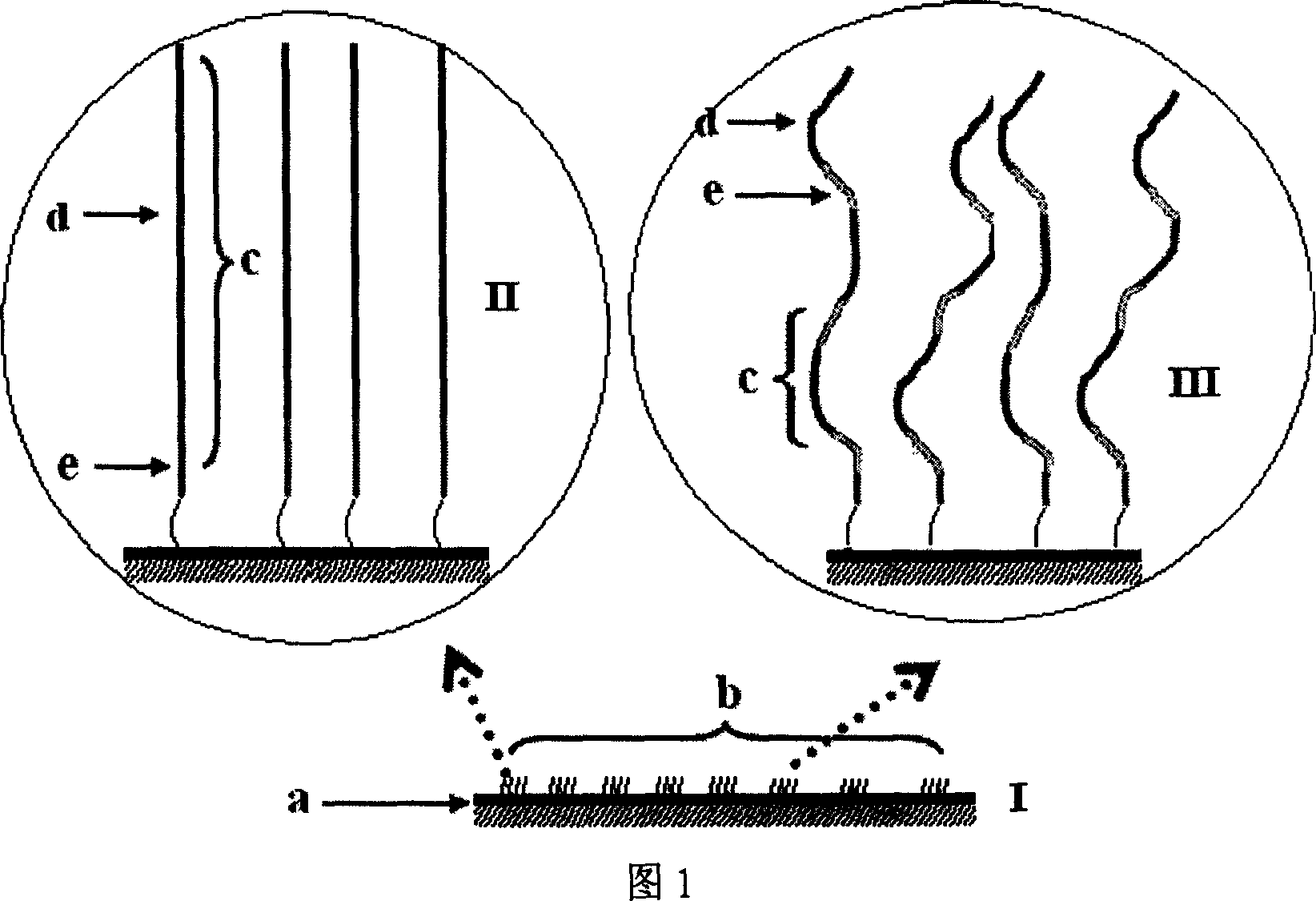
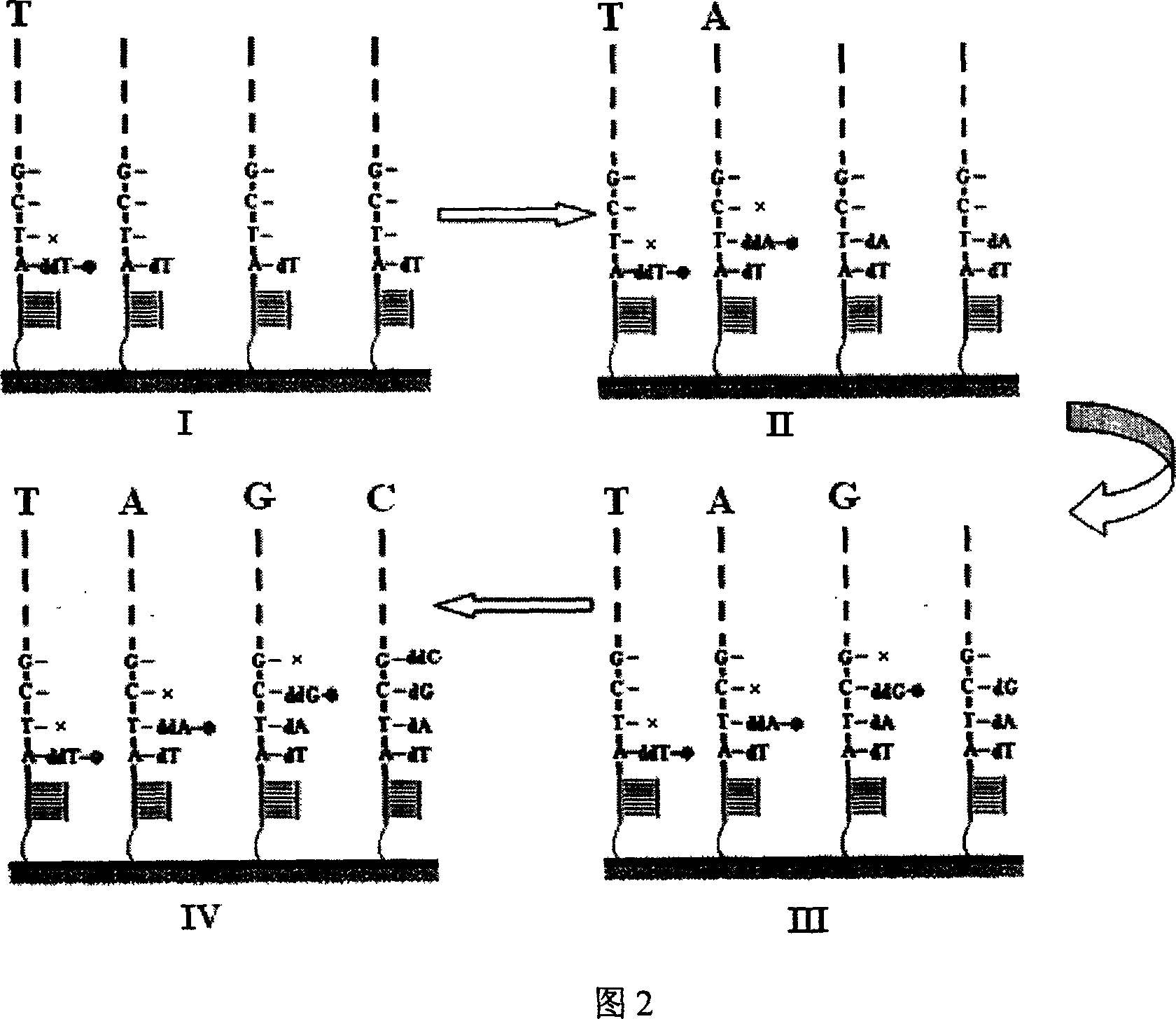
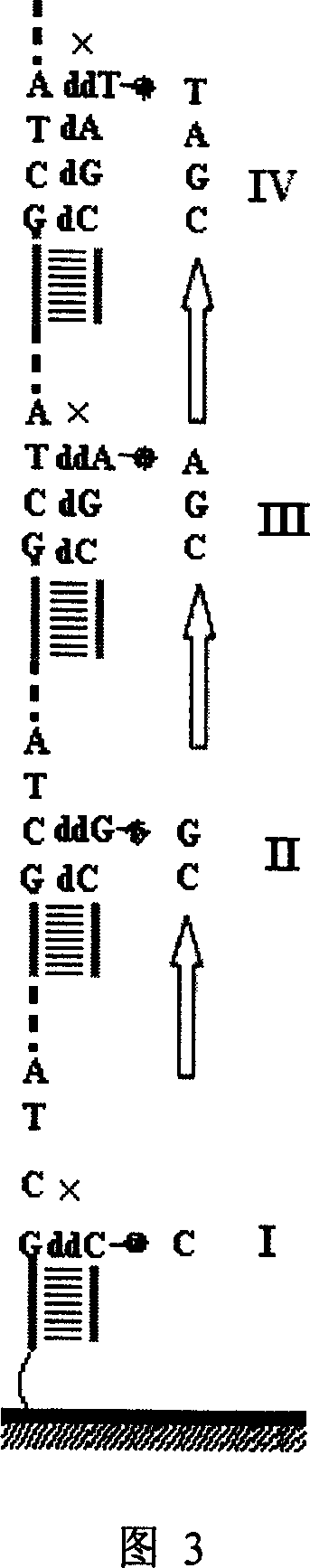
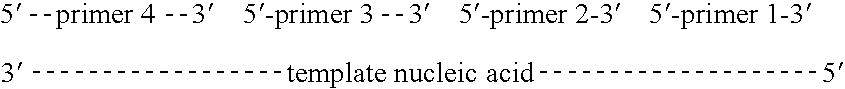Patents
Literature
529 results about "Genomic sequencing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Newborn genomic sequencing is an approach currently under study to collect and analyze large amounts of DNA sequence data in the newborn period. Genomic sequencing, a technology used to determine the order of DNA building blocks (nucleotides) in an individual's genetic code, is already available to test for genetic disorders in children and adults.
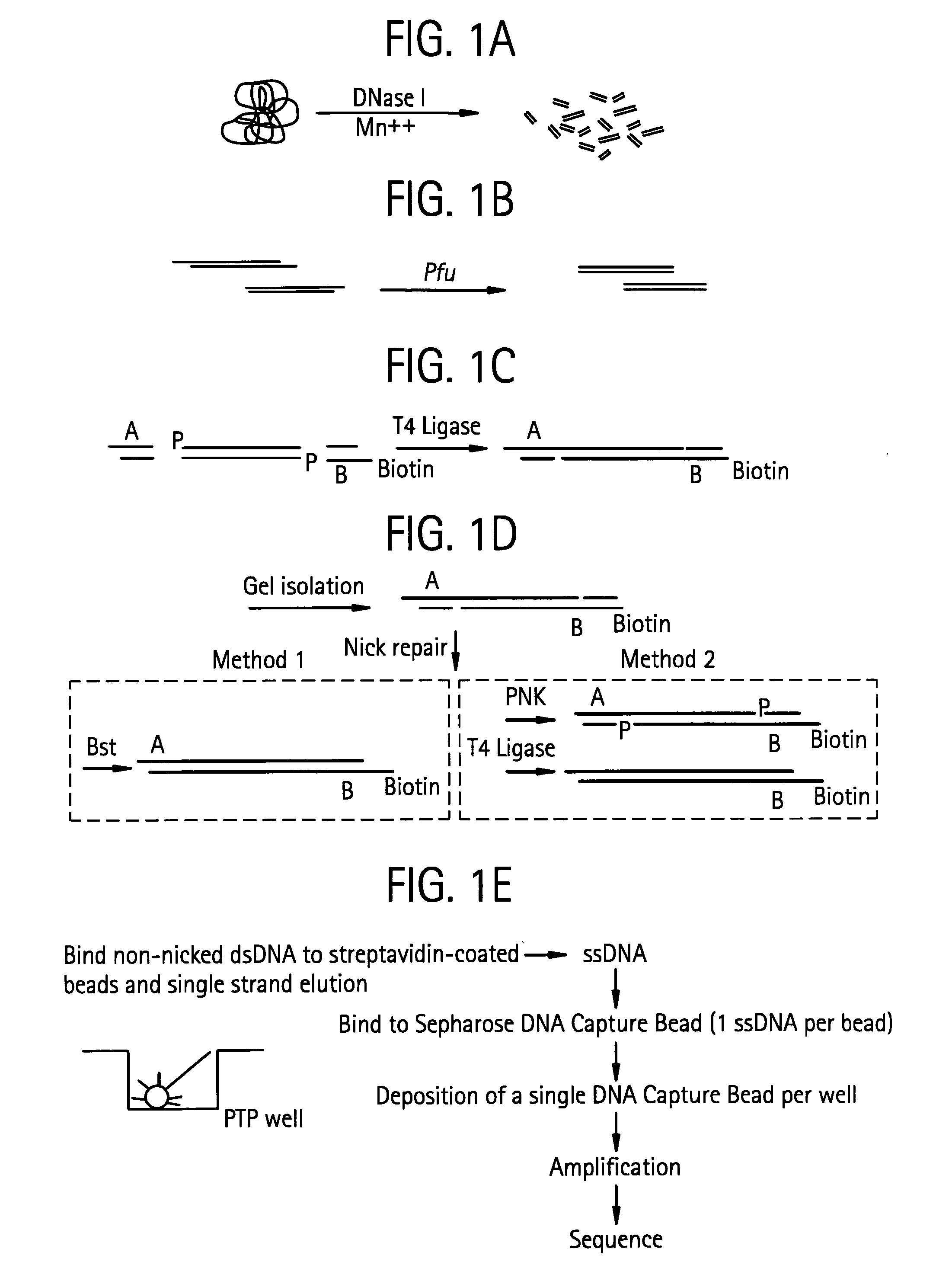
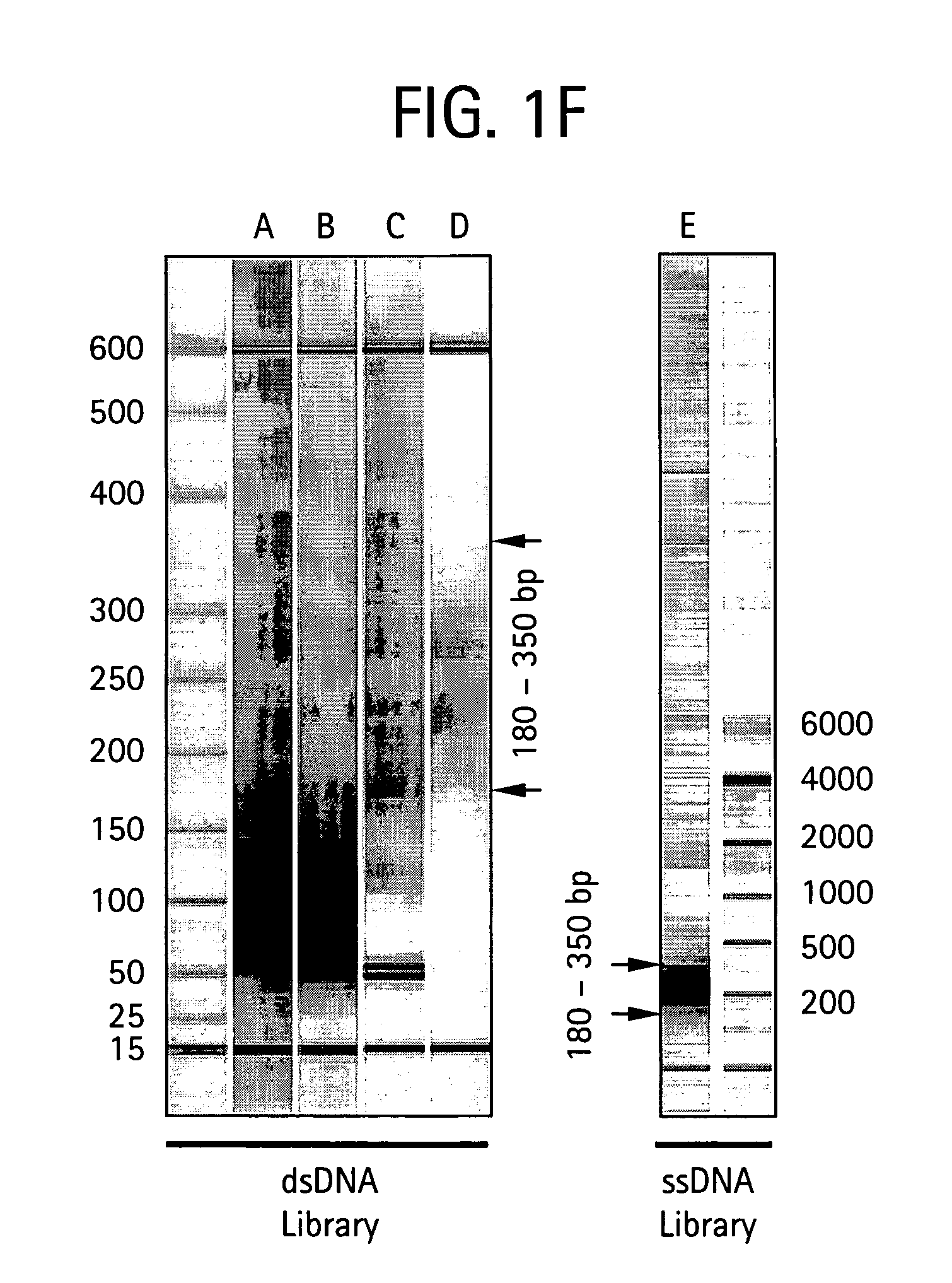
Methods of amplifying and sequencing nucleic acids
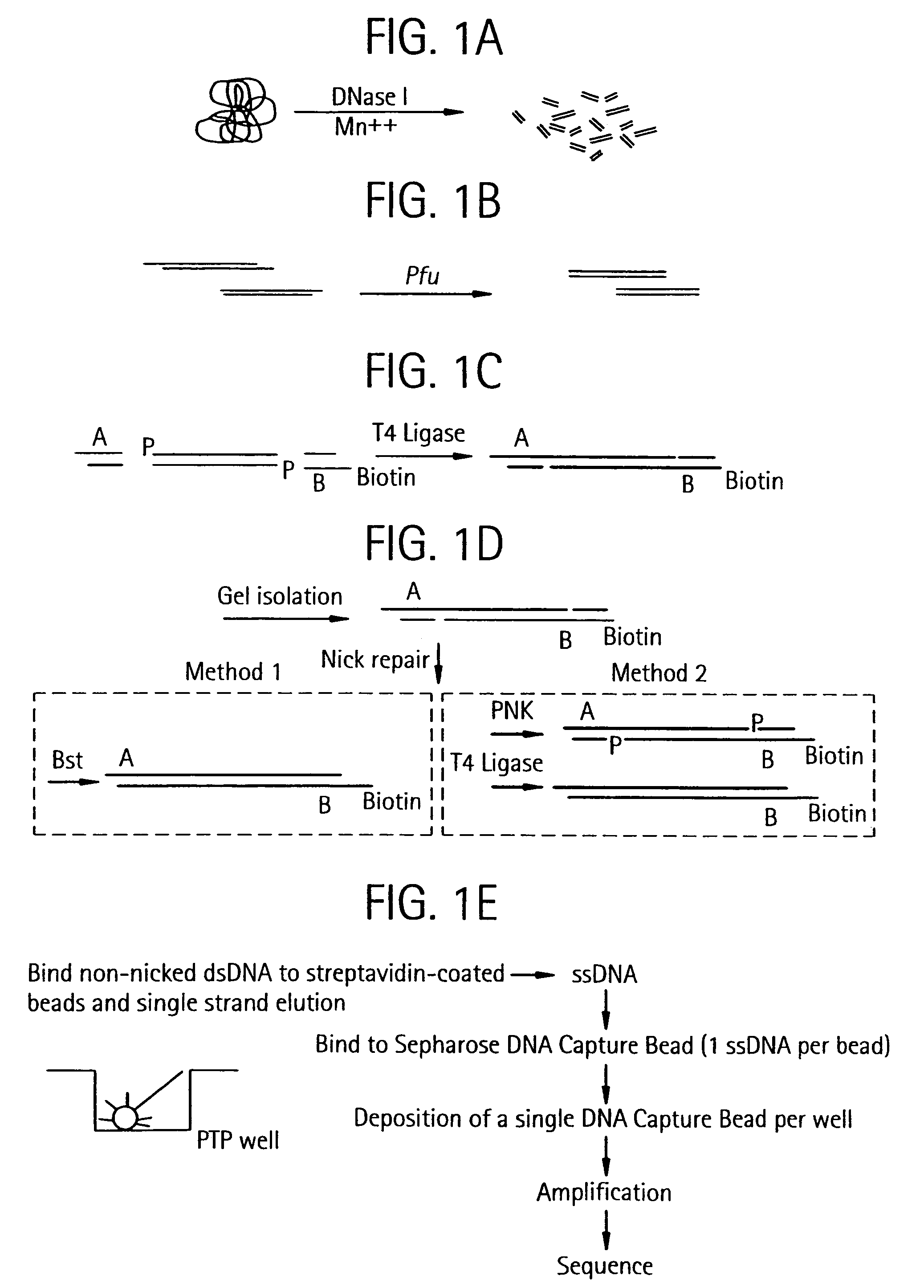
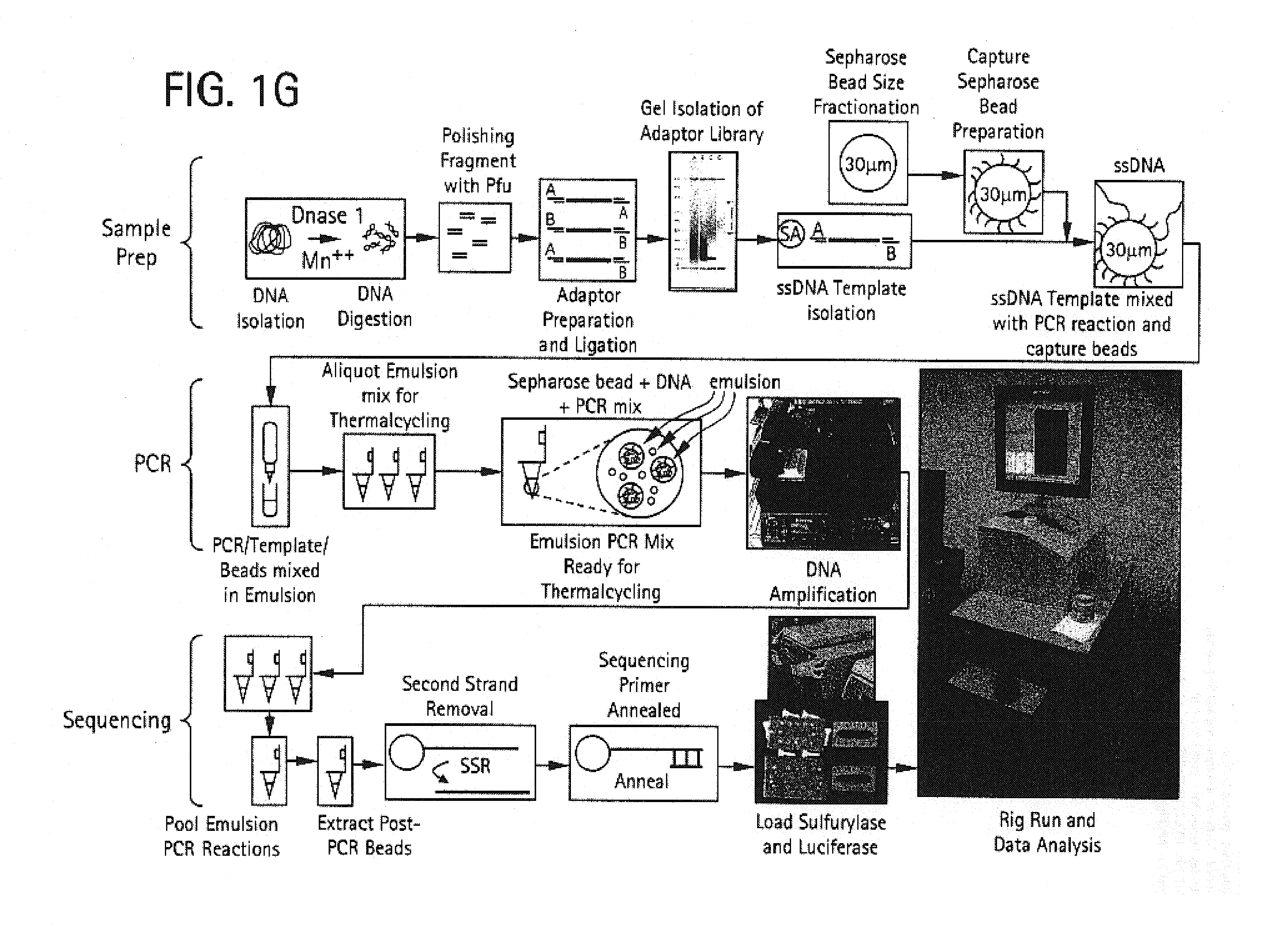
An apparatus and method for performing rapid DNA sequencing, such as genomic sequencing, is provided herein. The method includes the steps of preparing a sample DNA for genomic sequencing, amplifying the prepared DNA in a representative manner, and performing multiple sequencing reaction on the amplified DNA with only one primer hybridization step.
Owner:454 LIFE SCIENCES CORP
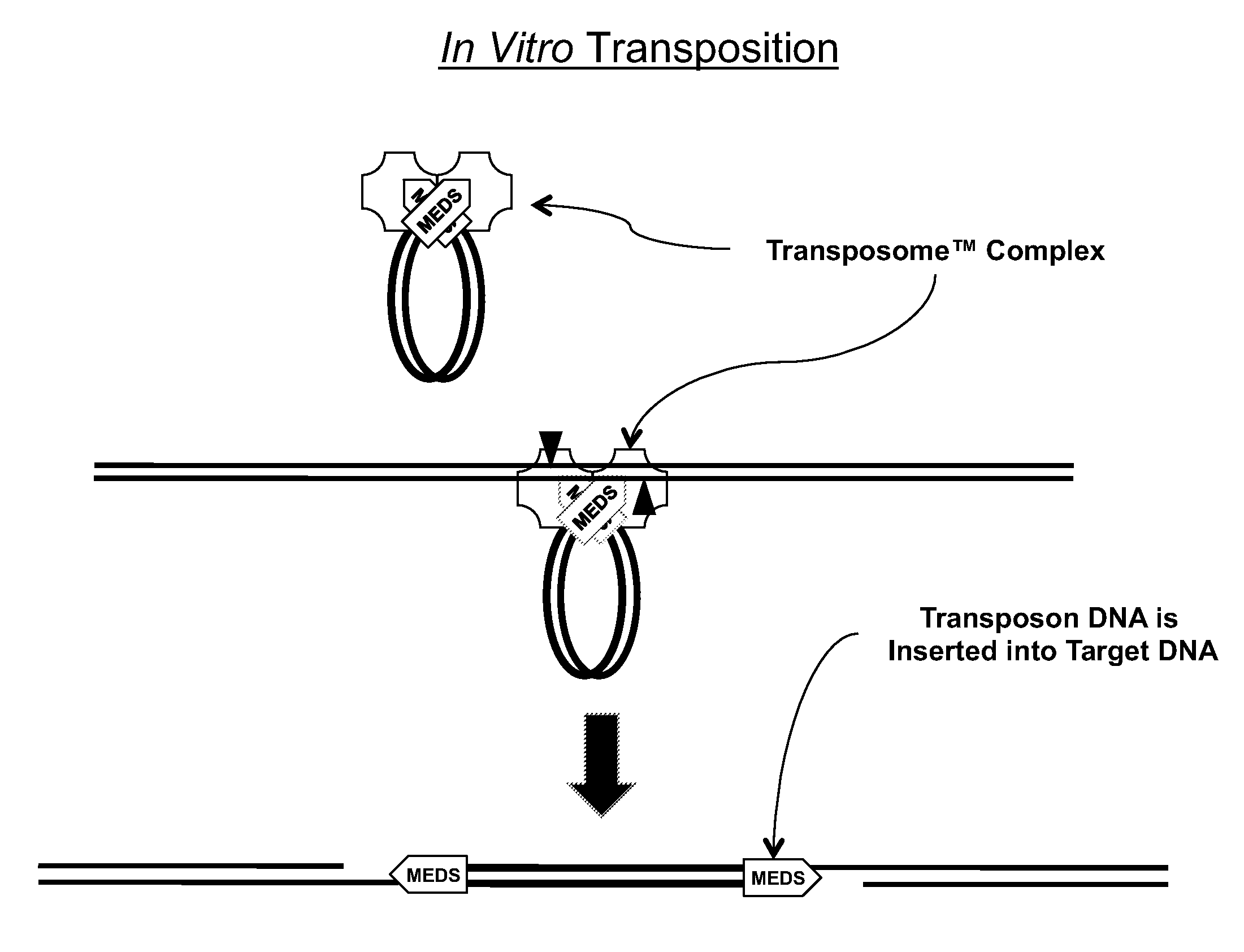
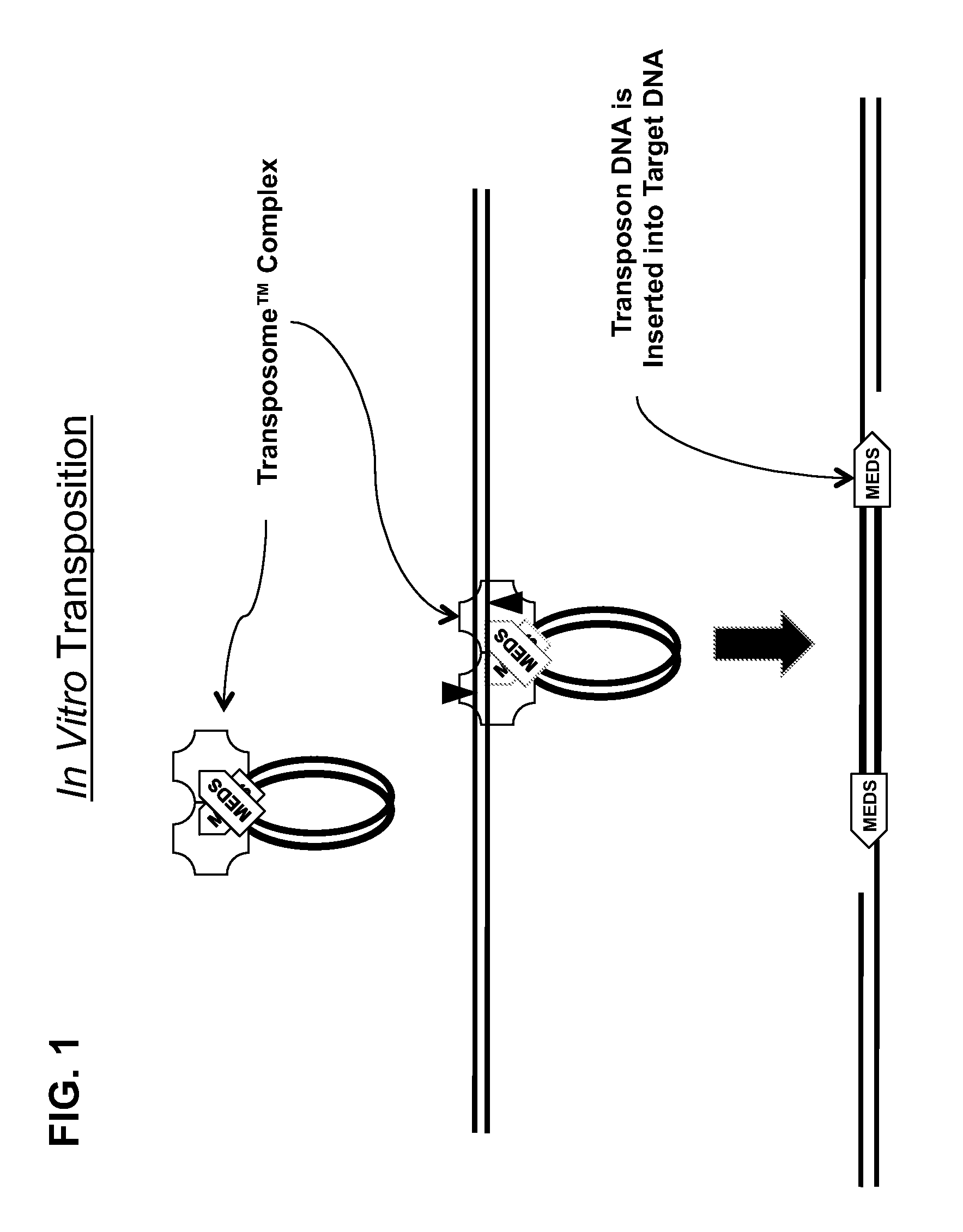
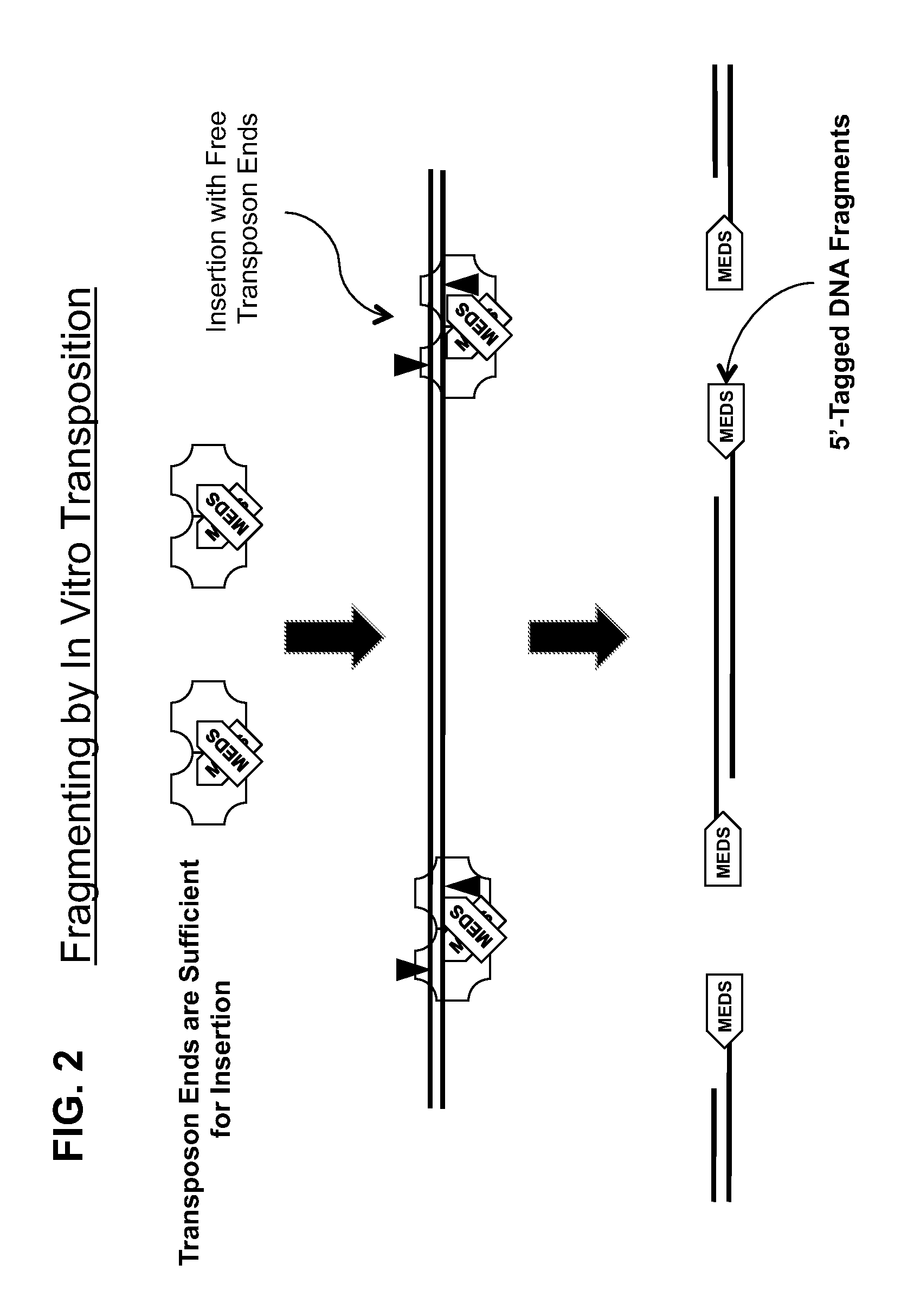
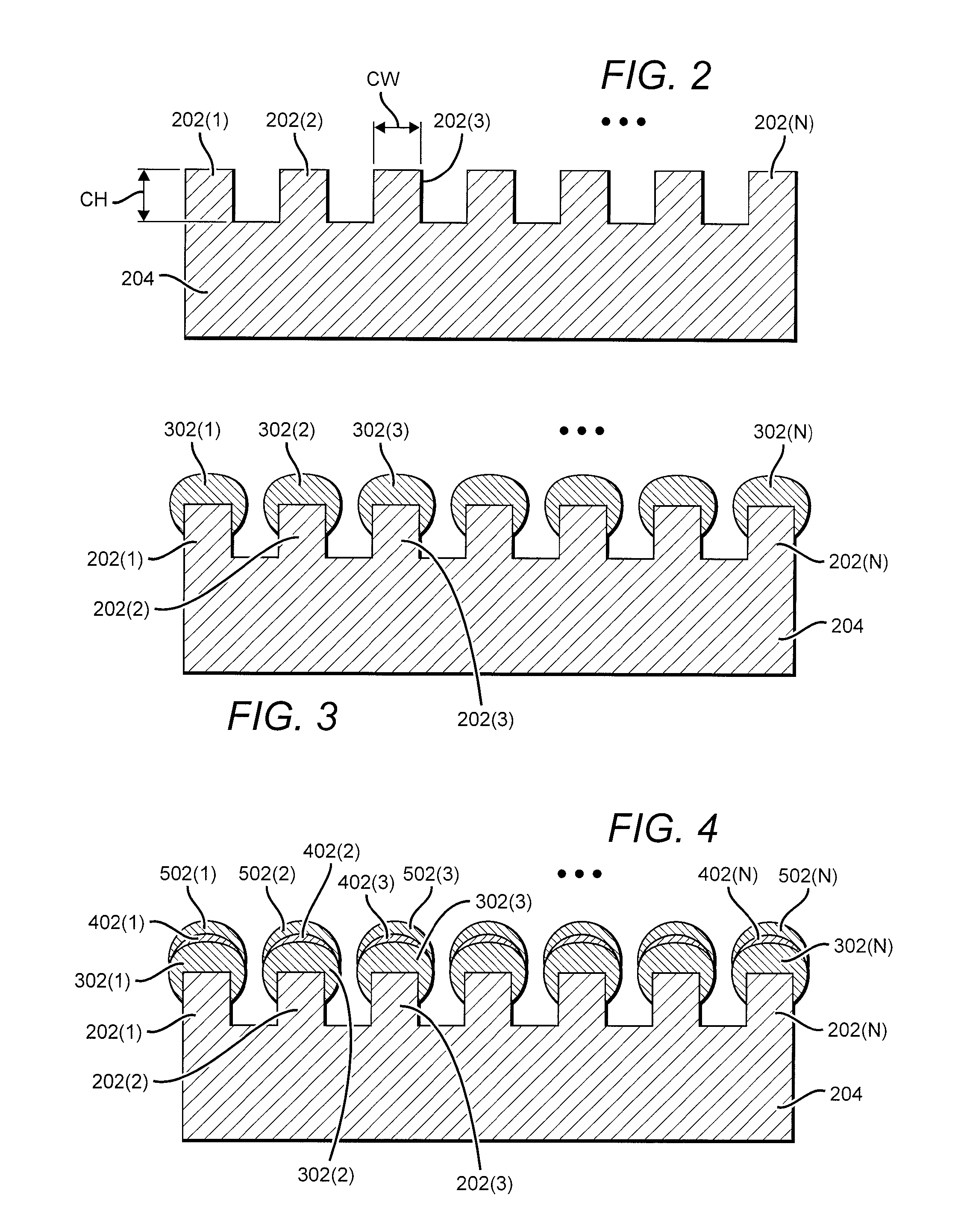
Transposon end compositions and methods for modifying nucleic acids
ActiveUS20100120098A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic sequencingPolymerase L
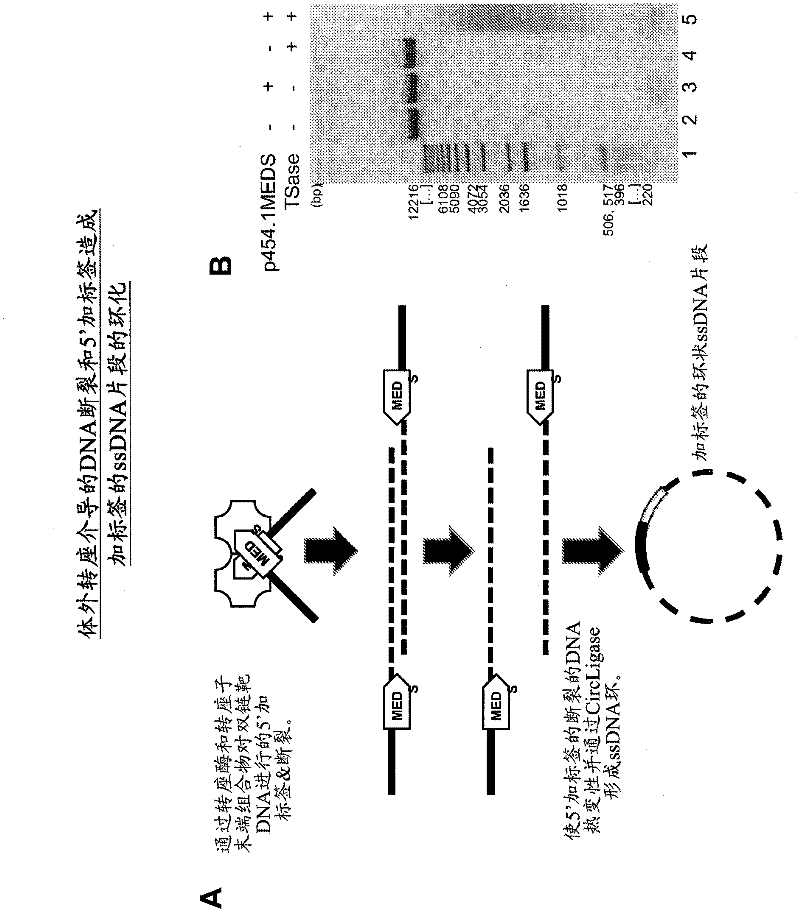
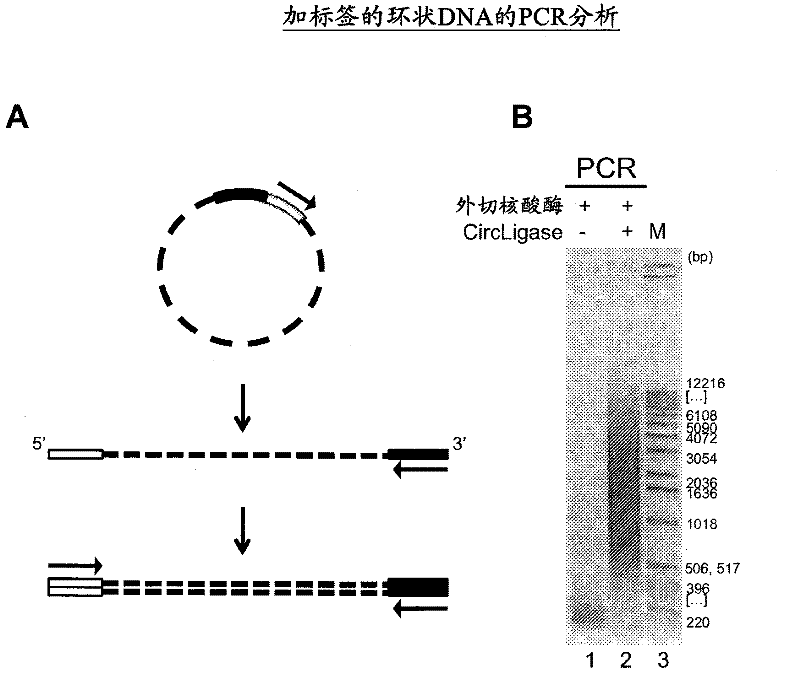
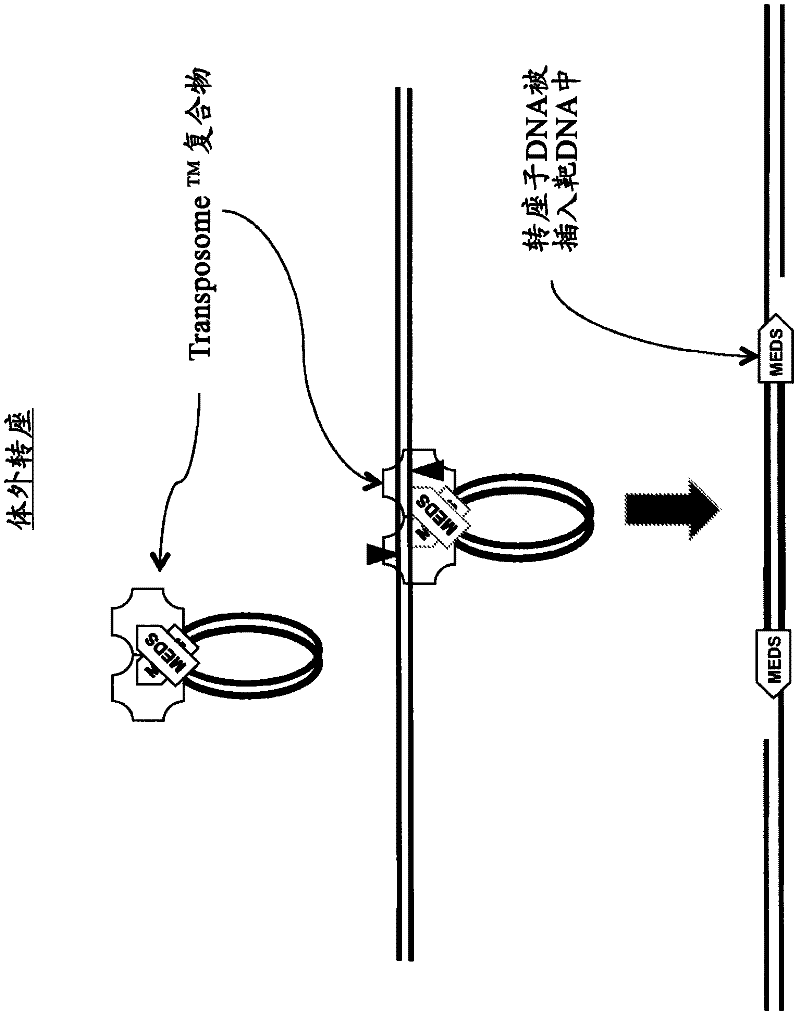
The present invention provides methods, compositions and kits for using a transposase and a transposon end for generating extensive fragmentation and 5′-tagging of double-stranded target DNA in vitro, then using a DNA polymerase for generating 5′- and 3′-tagged single-stranded DNA fragments without performing a PCR amplification reaction, wherein the first tag on the 5′-ends exhibits the sequence of the transferred transposon end and optionally, an additional arbitrary sequence, and the second tag on the 3′-ends exhibits a different sequence from the sequence exhibited by the first tag. The method is useful for generating 5′- and 3′-tagged DNA fragments for use in a variety of processes, including processes for metagenomic analysis of DNA in environmental samples, copy number variation (CNV) analysis of DNA, and comparative genomic sequencing (CGS), including massively parallel DNA sequencing (so-called “next-generation sequencing.)
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
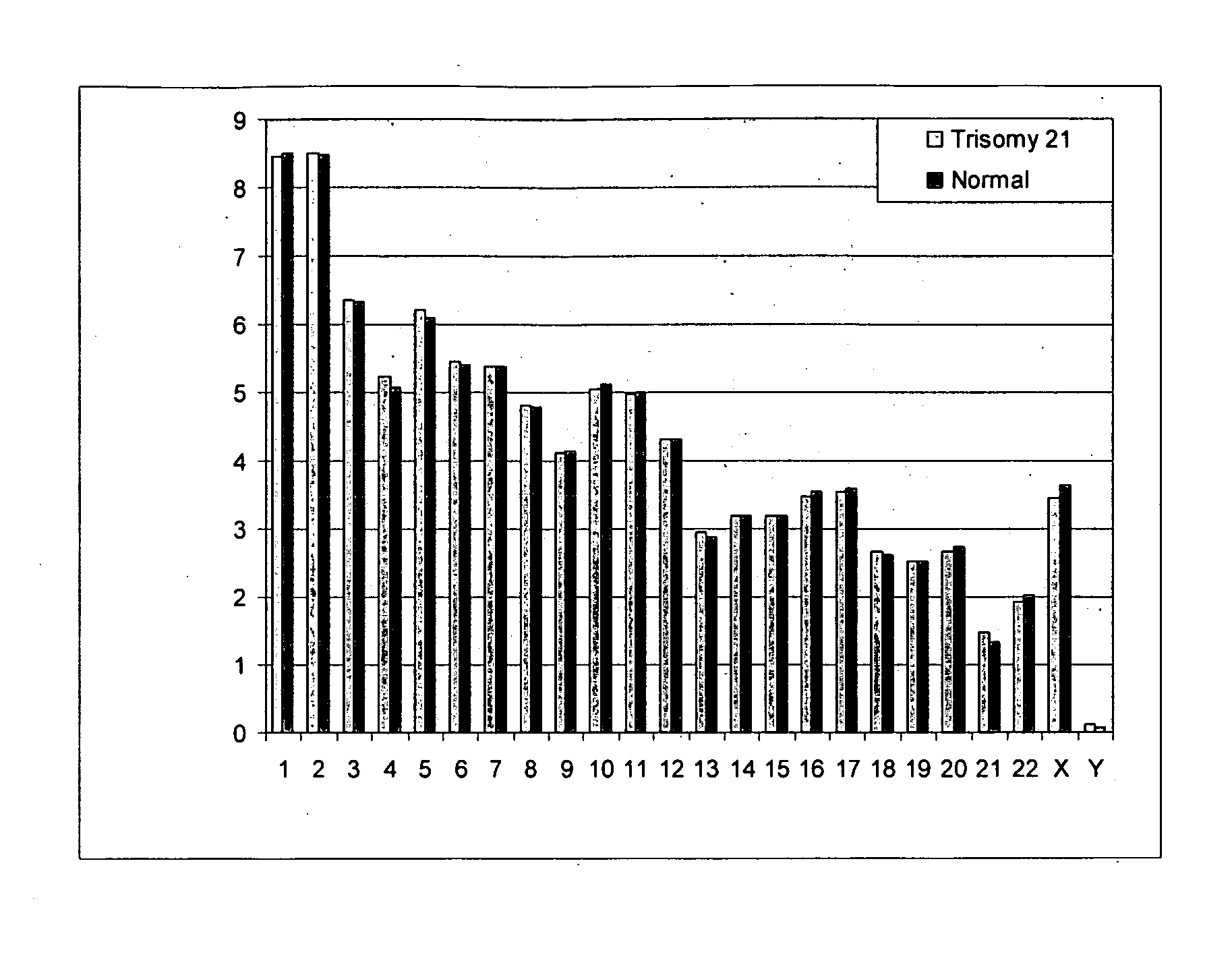
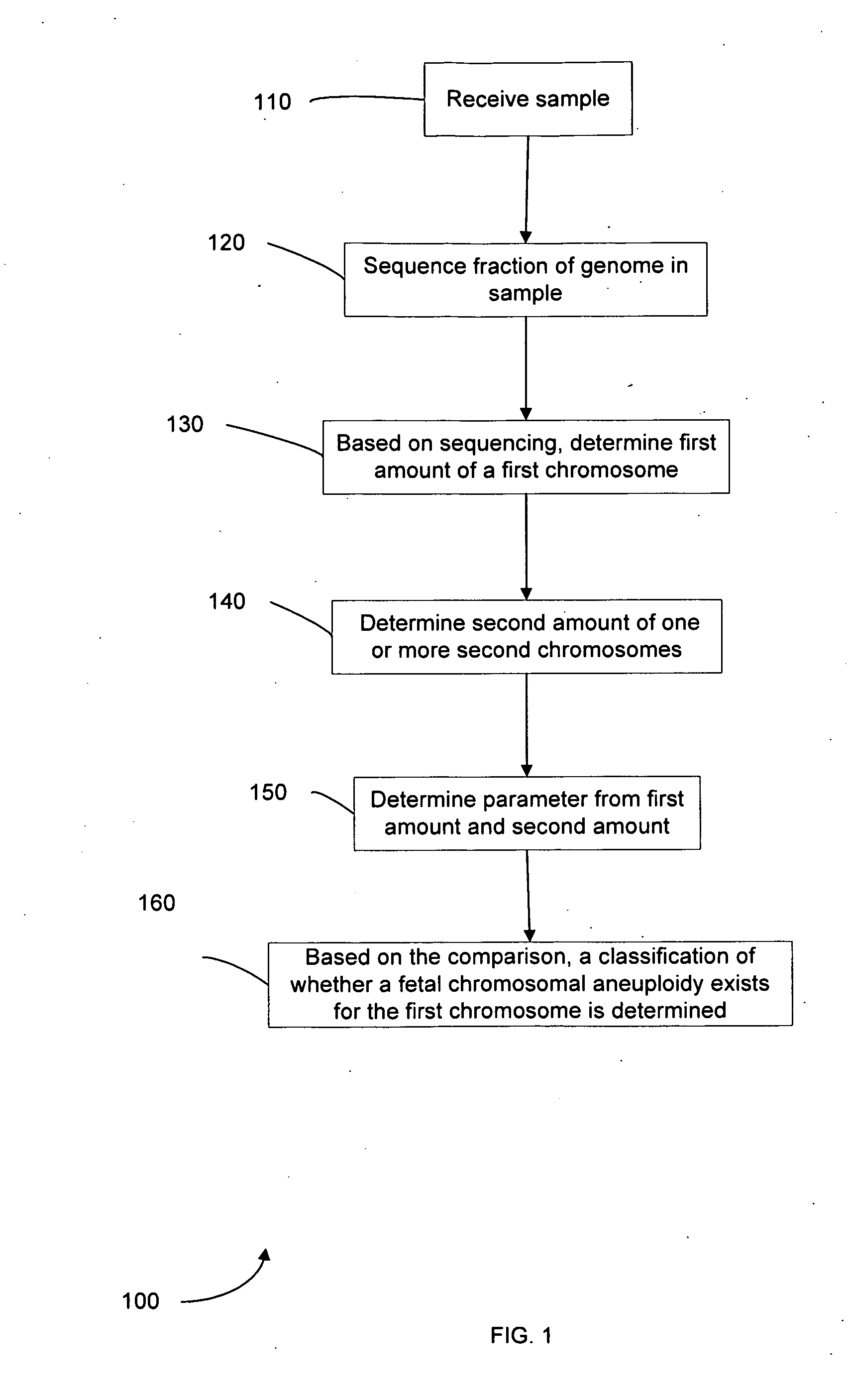
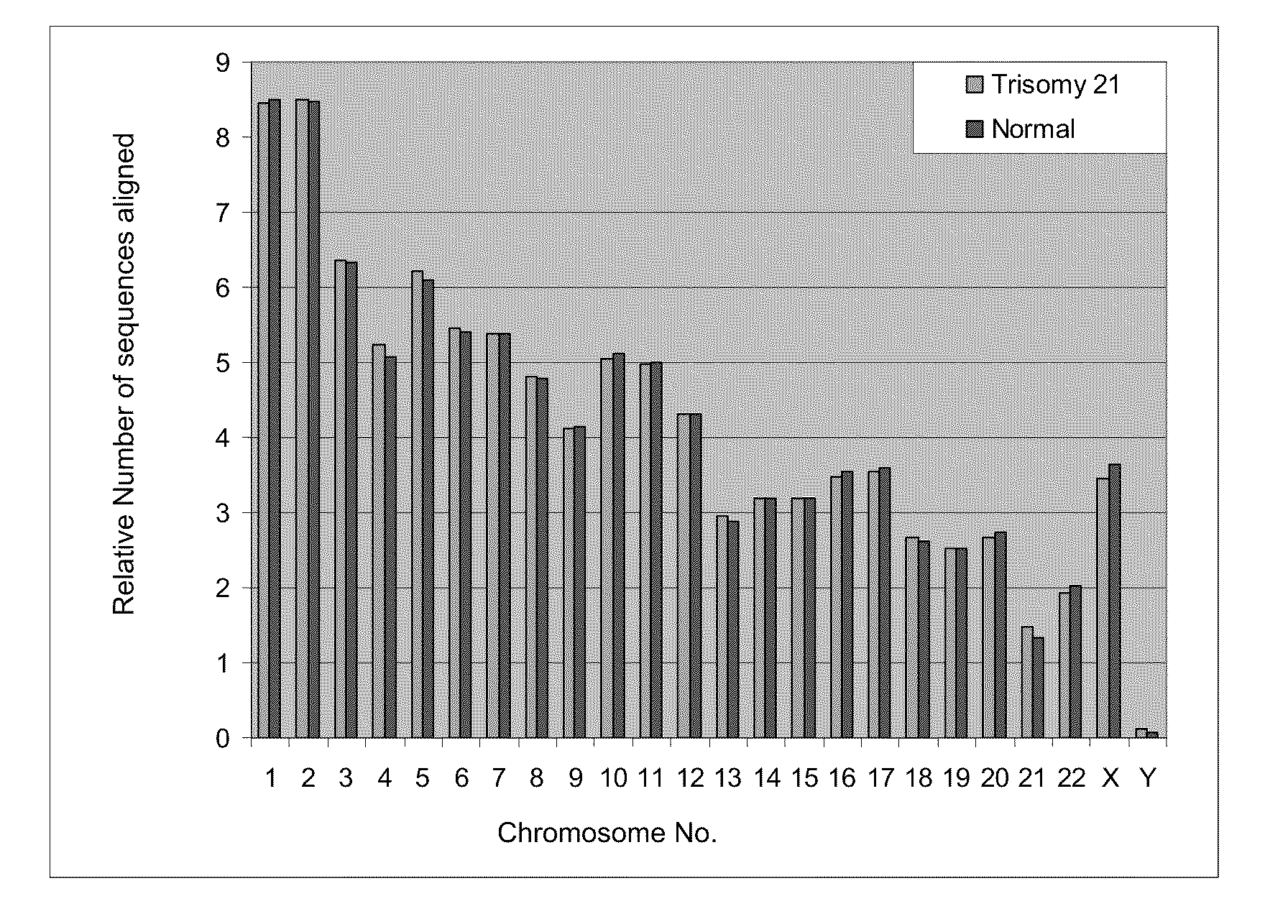
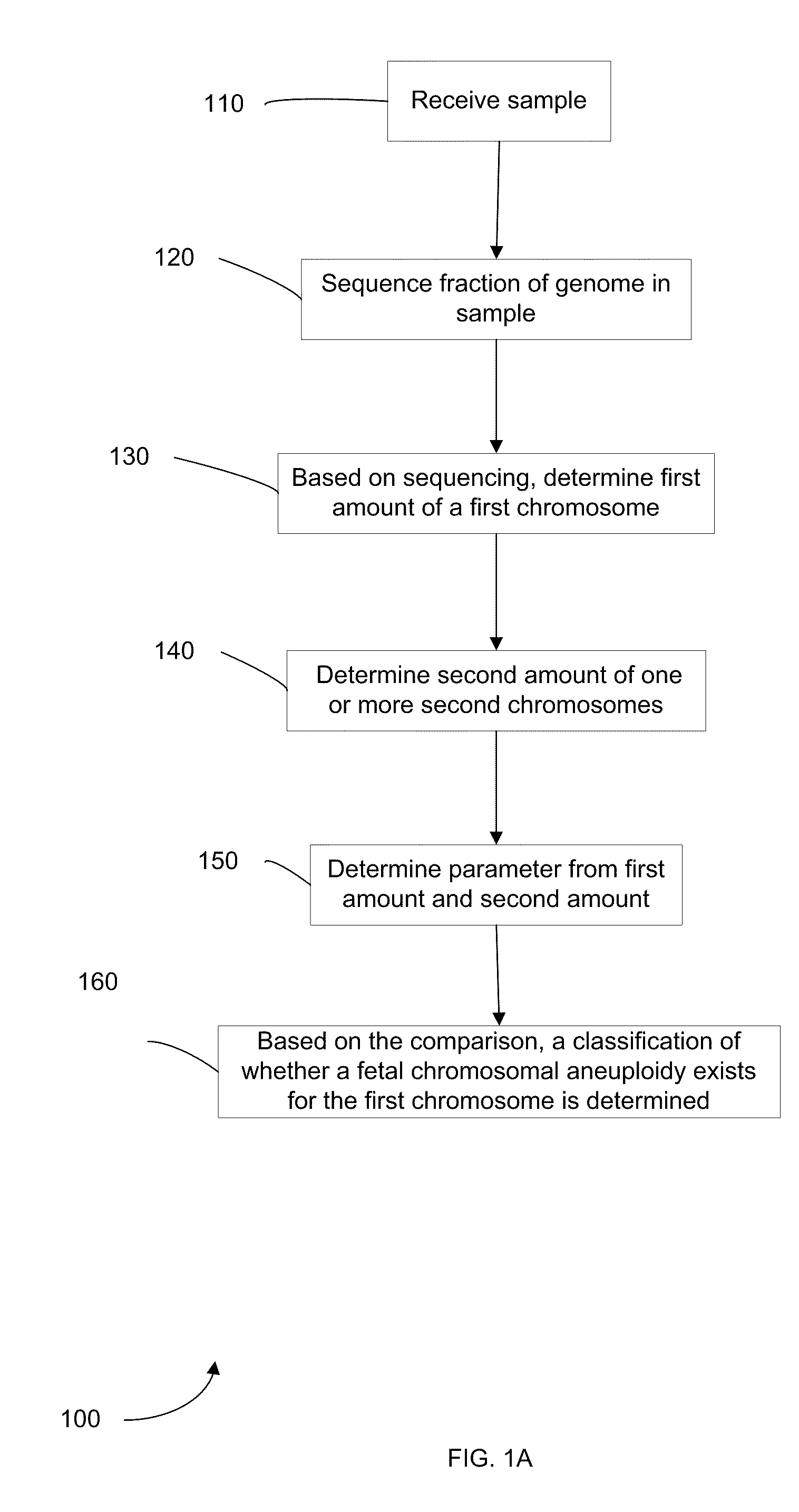
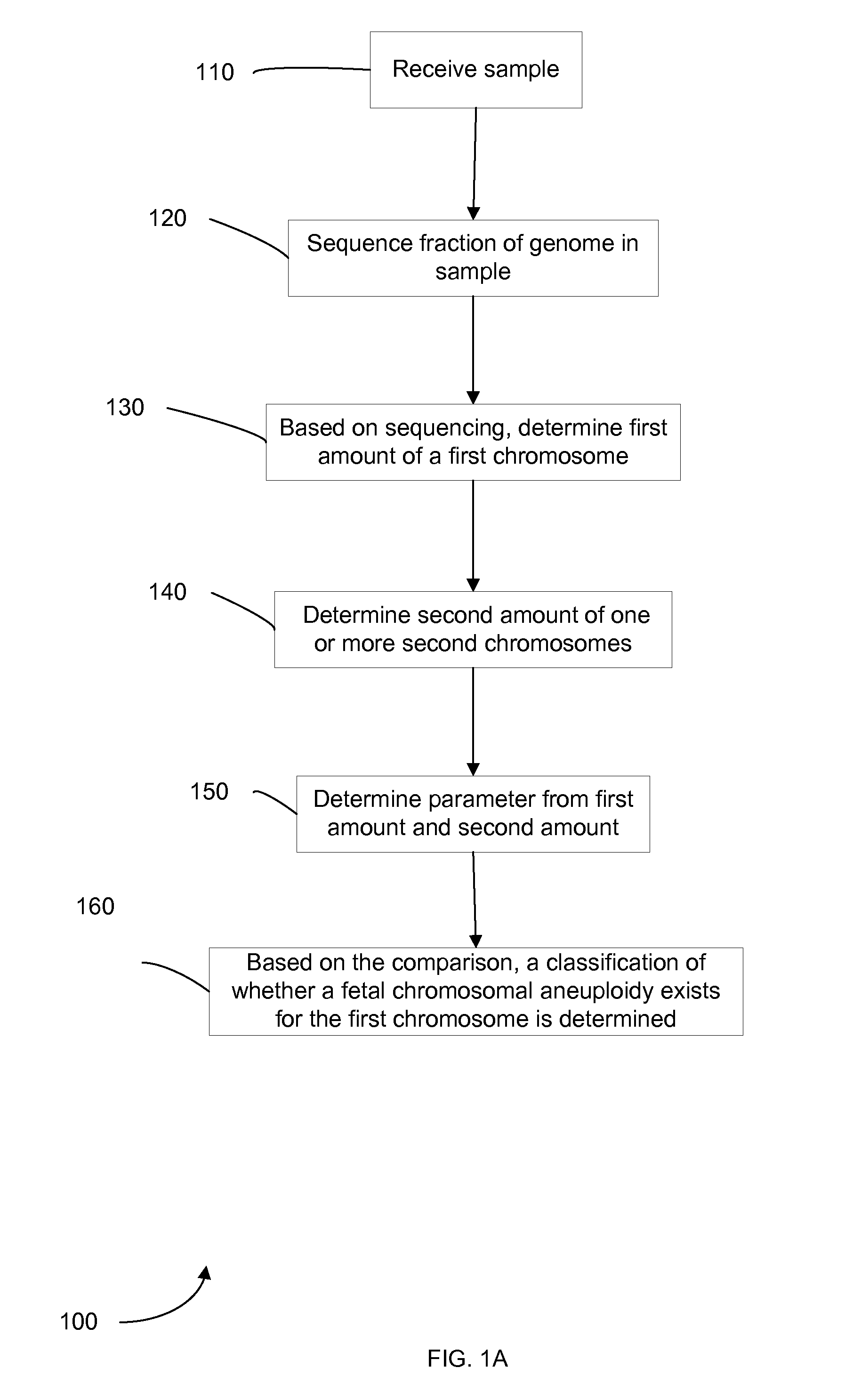
Diagnosing fetal chromosomal aneuploidy using massively parallel genomic sequencing
PendingUS20090029377A1Quantity maximizationSufficient amountMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisGenomic sequencingGenome
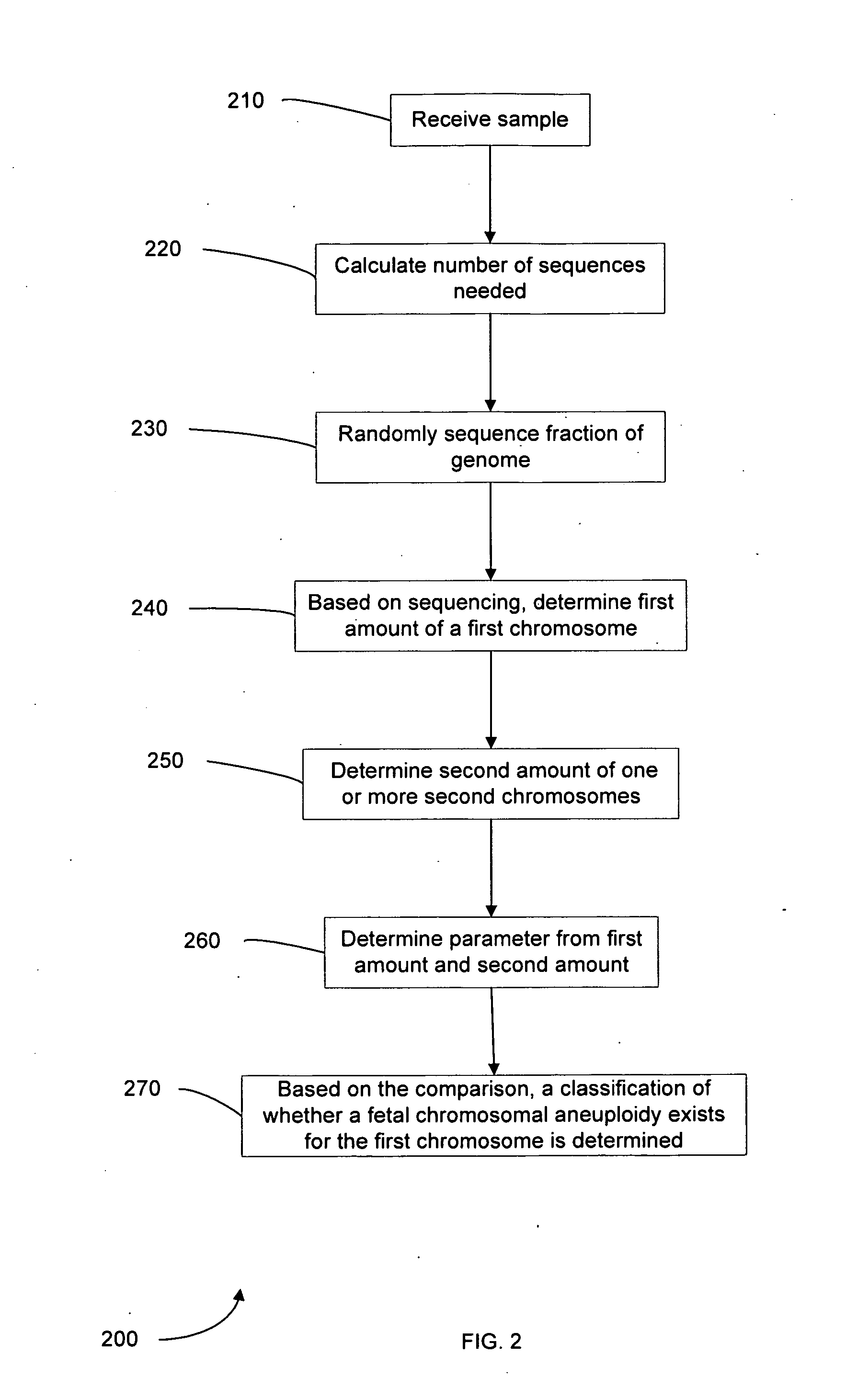
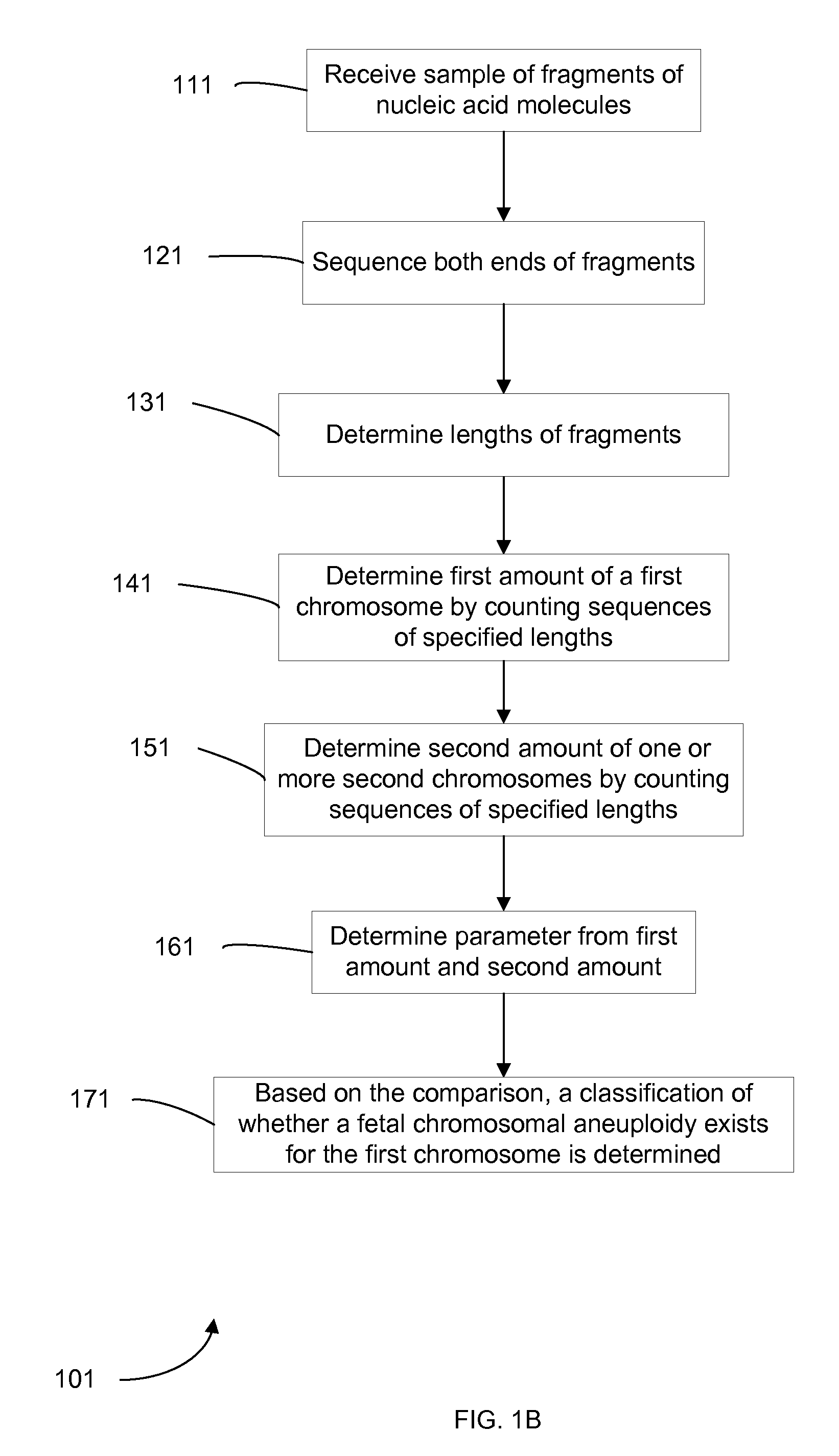
Embodiments of this invention provide methods, systems, and apparatus for determining whether a fetal chromosomal aneuploidy exists from a biological sample obtained from a pregnant female. Nucleic acid molecules of the biological sample are sequenced, such that a fraction of the genome is sequenced. Respective amounts of a clinically-relevant chromosome and of background chromosomes are determined from results of the sequencing. A parameter derived from these amounts (e.g. a ratio) is compared to one or more cutoff values, thereby determining a classification of whether a fetal chromosomal aneuploidy exists.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Methods of amplifying and sequencing nucleic acids
An apparatus and method for performing rapid DNA sequencing, such as genomic sequencing, is provided herein. The method includes the steps of preparing a sample DNA for genomic sequencing, amplifying the prepared DNA in a representative manner, and performing multiple sequencing reaction on the amplified DNA with only one primer hybridization step.
Owner:454 LIFE SCIENCES CORP
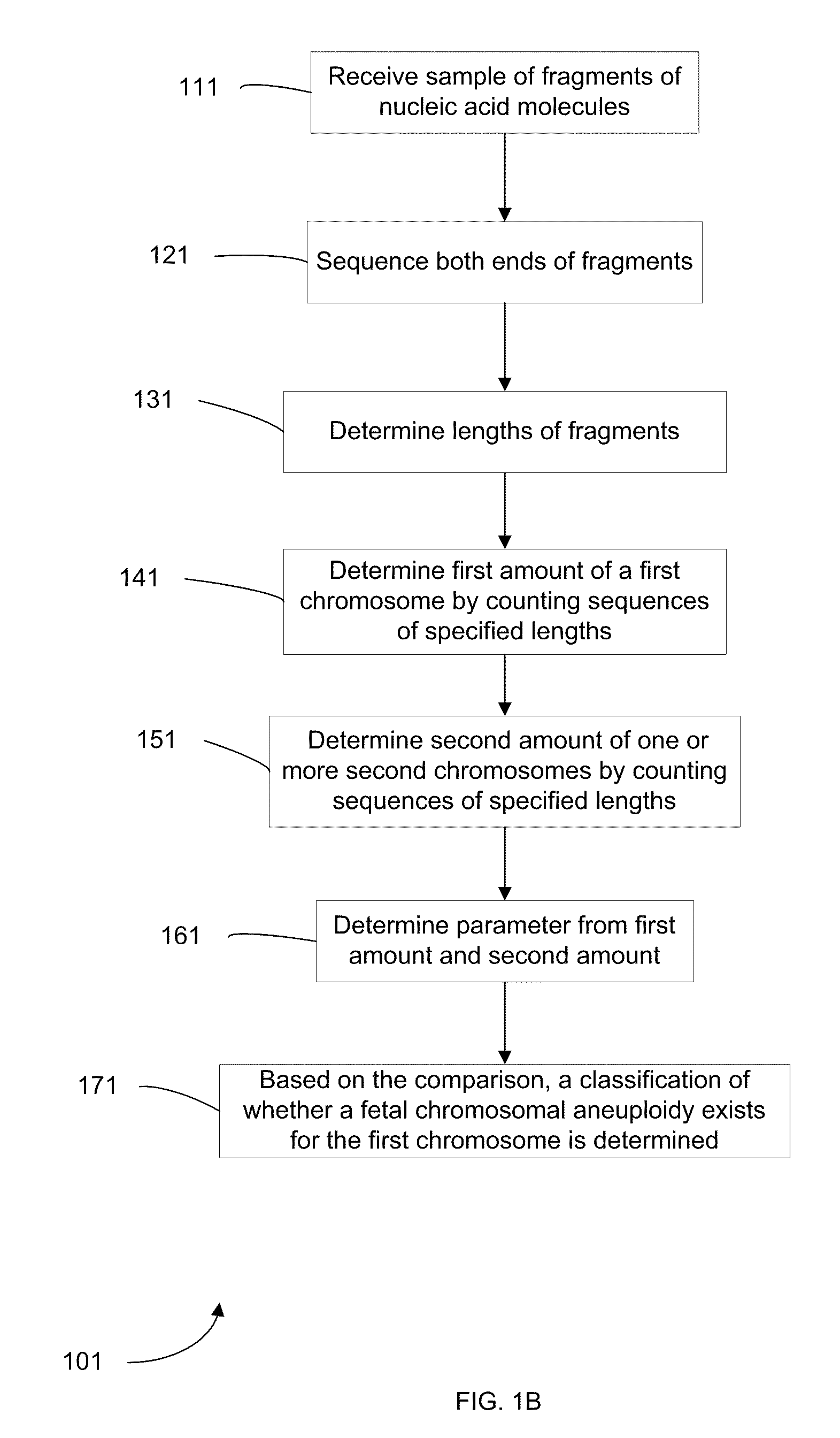
Diagnosing Fetal Chromosomal Aneuploidy Using Genomic Sequencing With Enrichment
PendingUS20100112590A1High sensitivityMore accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsGenomic sequencingDNA fragmentation
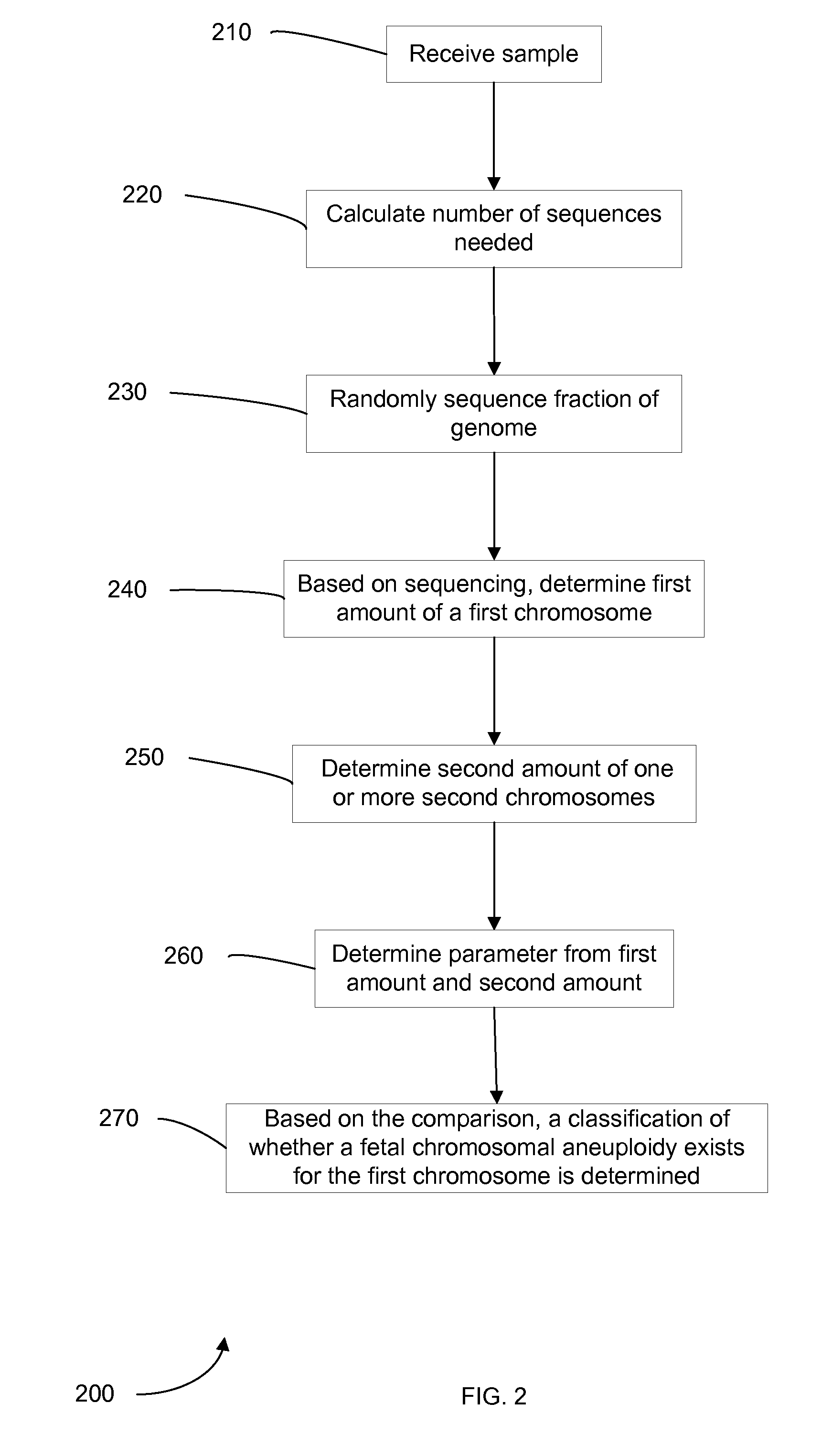
Embodiments of this invention provide methods, systems, and apparatus for determining whether a fetal chromosomal aneuploidy exists from a biological sample obtained from a pregnant female. Nucleic acid molecules of the biological sample are sequenced, such that a fraction of the genome is sequenced. Respective amounts of a clinically-relevant chromosome and of background chromosomes are determined from results of the sequencing. The determination of the relative amounts may count sequences of only certain length. A parameter derived from these amounts (e.g. a ratio) is compared to one or more cutoff values, thereby determining a classification of whether a fetal chromosomal aneuploidy exists. Prior to sequencing, the biological sample may be enriched for DNA fragments of a particular sizes.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Diagnosing fetal chromosomal aneuploidy using massively parallel genomic sequencing
PendingUS20110318734A1High sensitivityMore accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsGenomic sequencingDNA fragmentation
Embodiments of this invention provide methods, systems, and apparatus for determining whether a fetal chromosomal aneuploidy exists from a biological sample obtained from a pregnant female. Nucleic acid molecules of the biological sample are sequenced, such that a fraction of the genome is sequenced. Respective amounts of a clinically-relevant chromosome and of background chromosomes are determined from results of the sequencing. The determination of the relative amounts may count sequences of only certain length. A parameter derived from these amounts (e.g. a ratio) is compared to one or more cutoff values, thereby determining a classification of whether a fetal chromosomal aneuploidy exists. Prior to sequencing, the biological sample may be enriched for DNA fragments of a particular sizes.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Highly Efficient Plamonic Devices, Molecule Detection Systems, and Methods of Making the Same
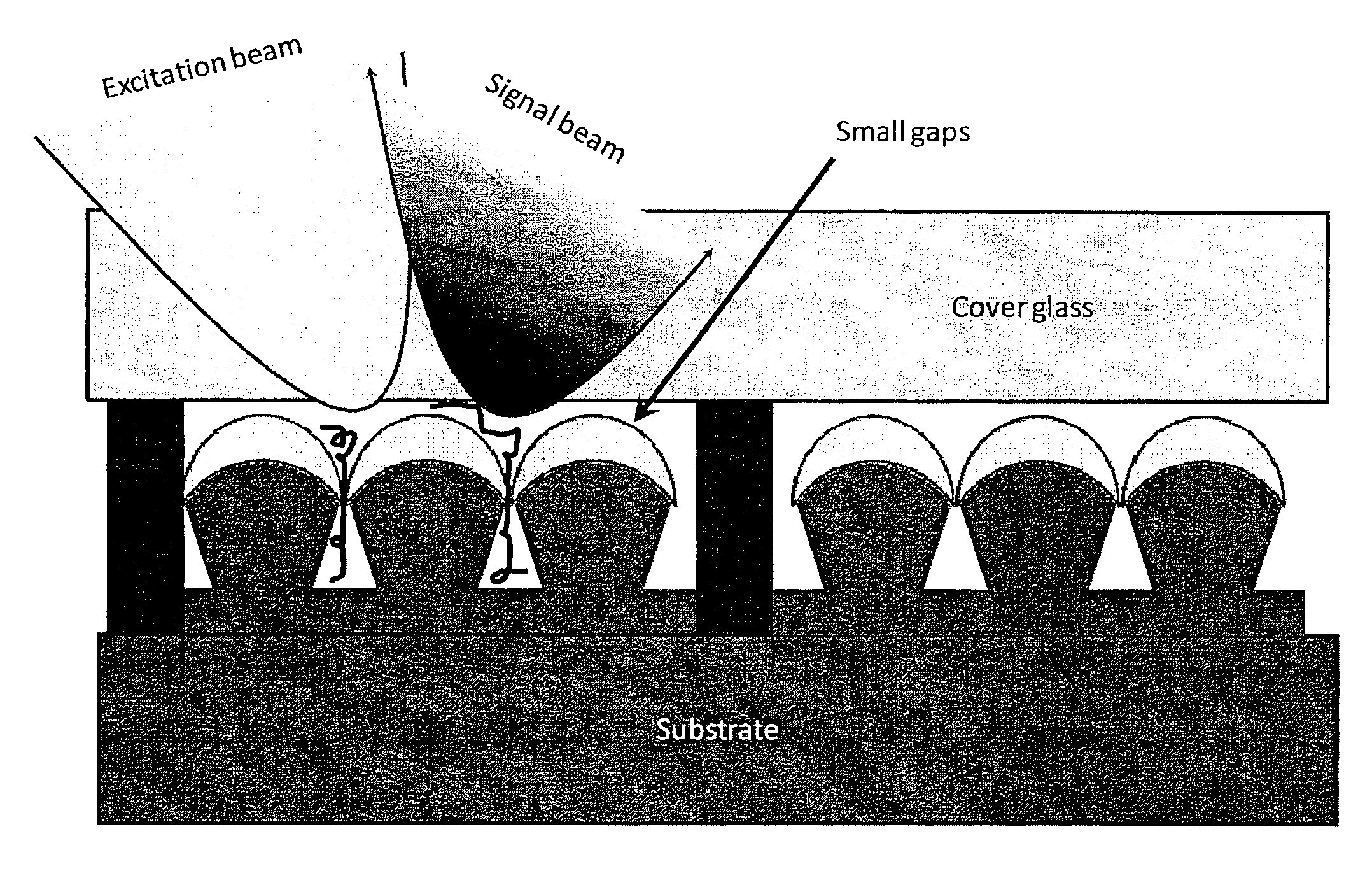
InactiveUS20120081703A1Function increaseAltering surface roughnessRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansGenomic sequencingAnalyte
Owner:NANT HLDG IP LLC
Transposon end compositions and methods for modifying nucleic acids
The present invention provides the use of transposases and transposon ends to generate extensive fragmentation and 5′-tagging of double-stranded target DNA in vitro, followed by the use of DNA polymerases to generate 5′- and 3′-tagged single DNA without PCR amplification reactions. Methods, compositions and kits for stranded DNA fragments, wherein the first label on the 5' end shows the sequence of the transferred transposon end and optionally an additional arbitrary sequence, and the second label on the 3' end shows the same The first tab shows a sequence different from the sequence. The method can be used to generate 5' and 3' tagged DNA fragments for use in a variety of processes including metagenomic analysis of DNA in environmental samples, copy number variation (CNV) analysis of DNA, and including massively parallel DNA sequencing (so-called "next generation sequencing") involves the process of comparative genome sequencing (CGS).
Owner:EPICENT TECH CORP
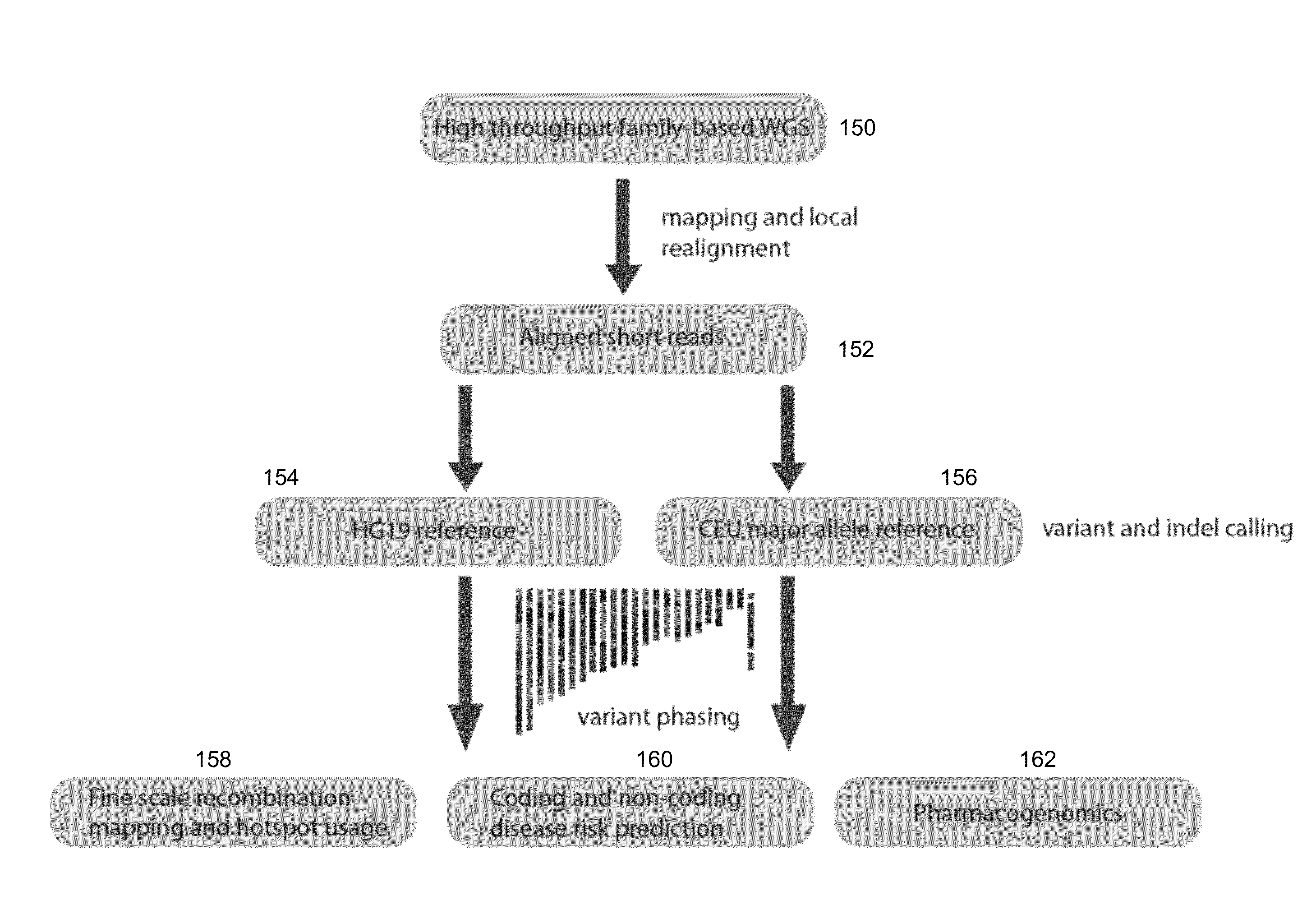
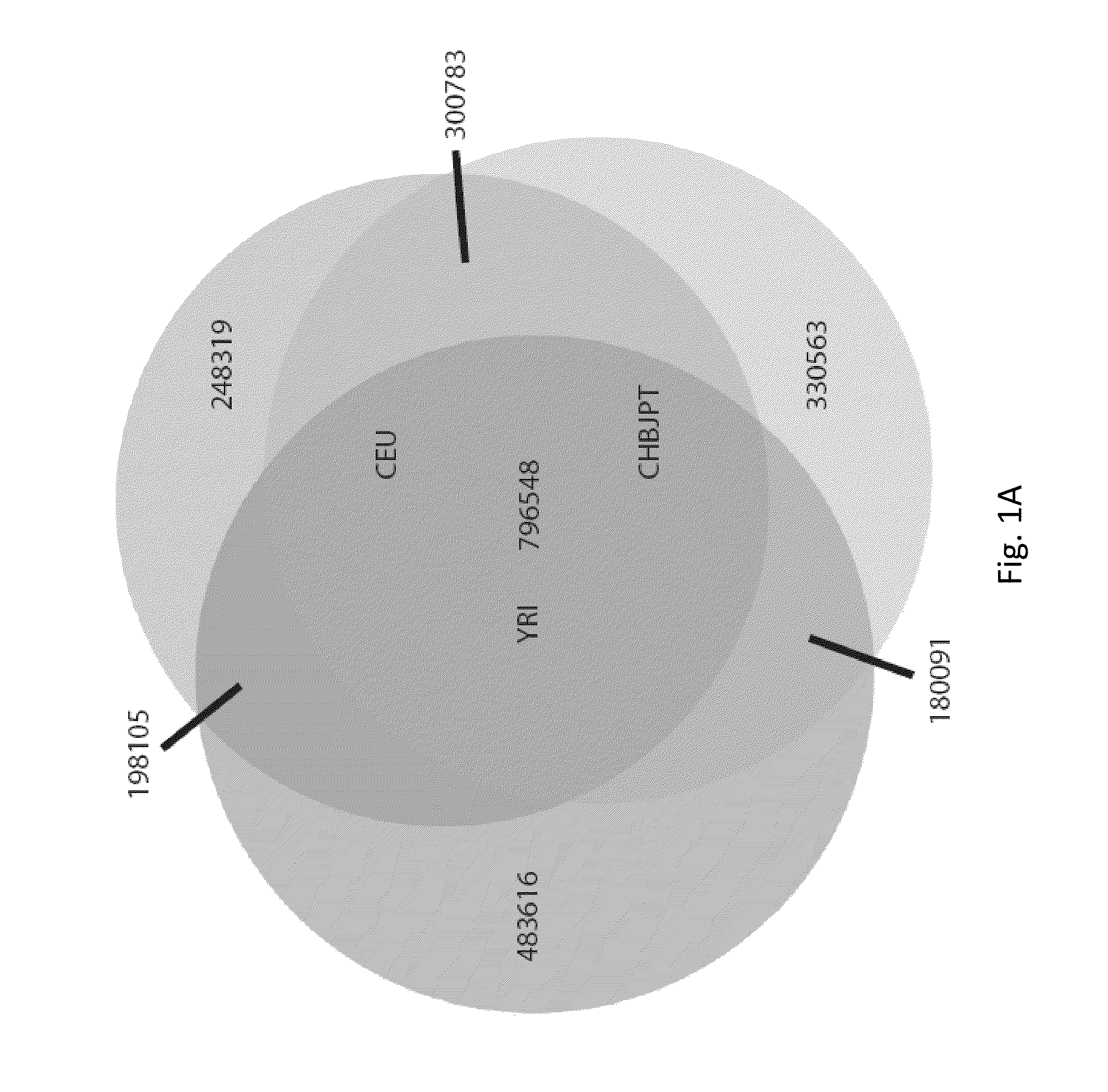
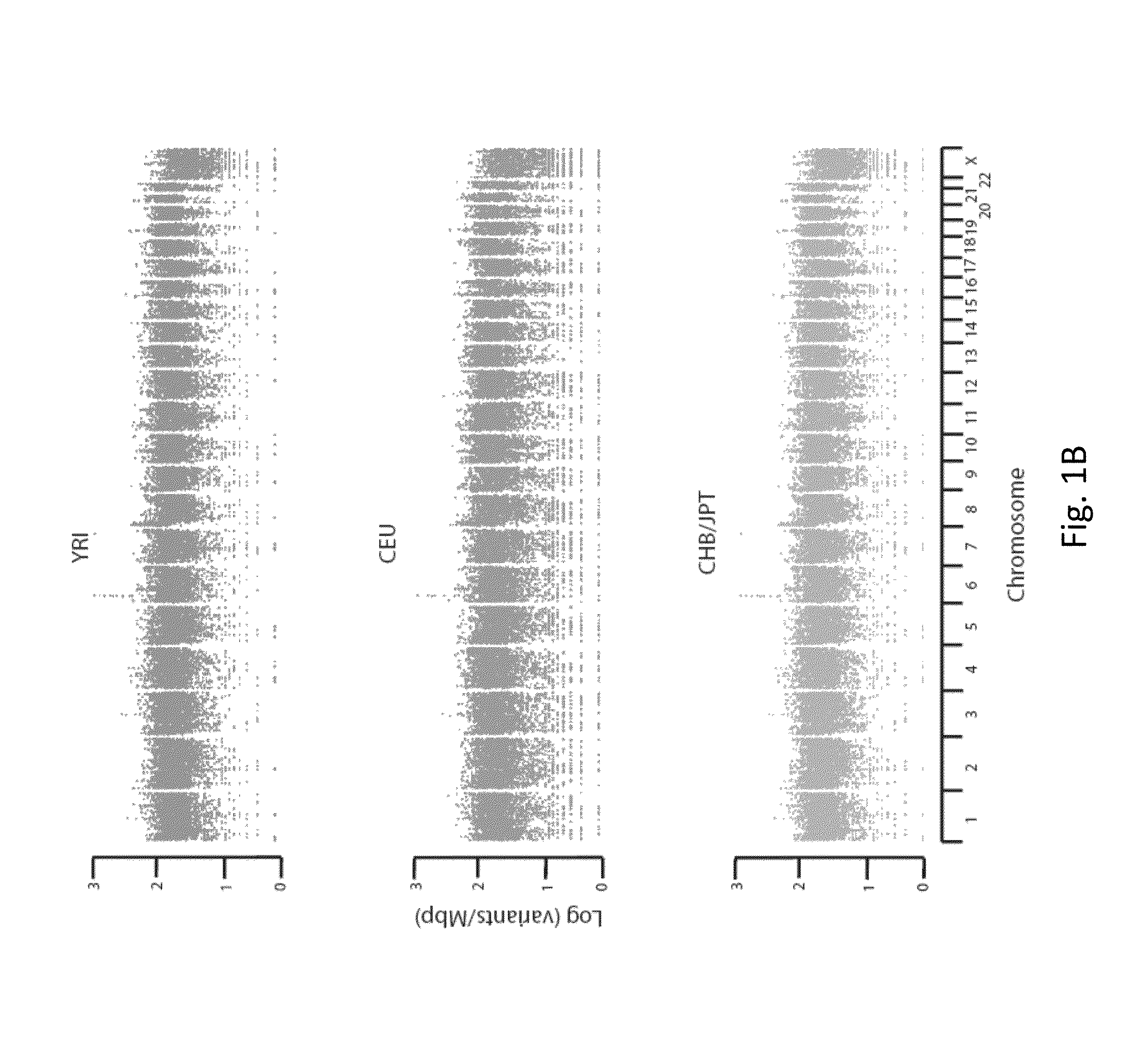
Phased Whole Genome Genetic Risk In A Family Quartet
In an embodiment of the present invention, three novel human reference genome sequences were developed based on the most common population-specific DNA sequence (“major allele”). Methods were developed for their integration into interpretation pipelines for highthroughput whole genome sequencing.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
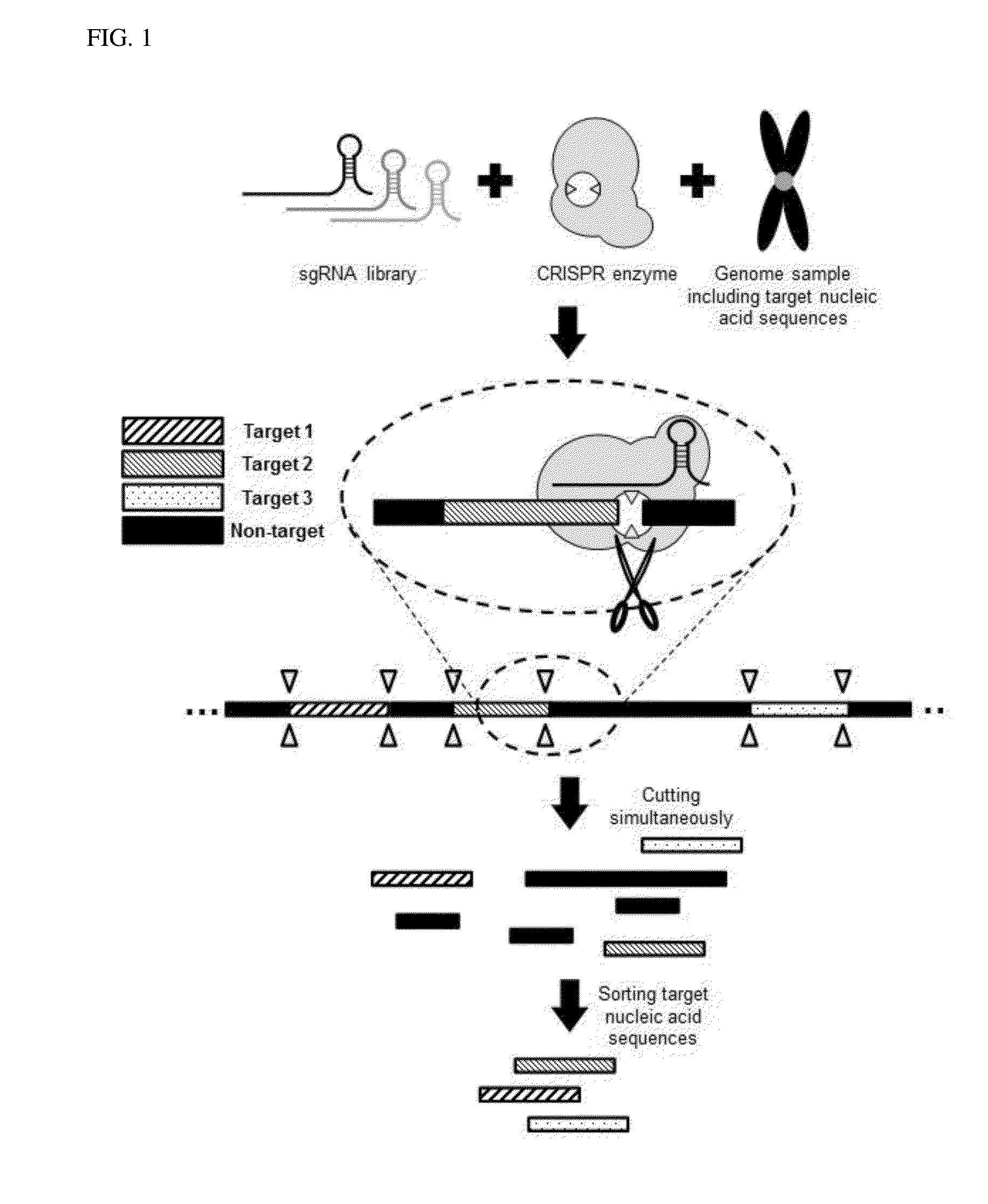
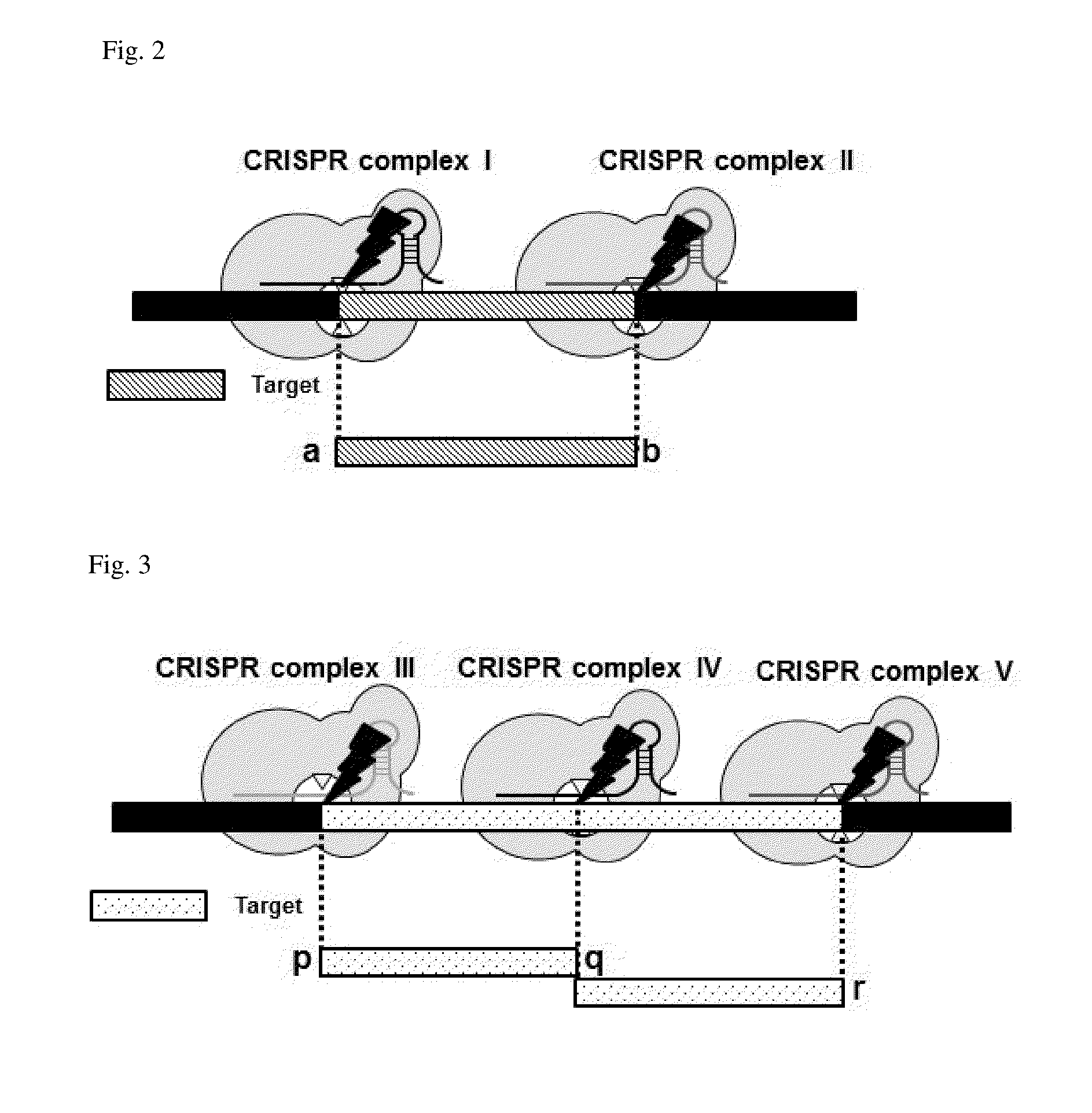
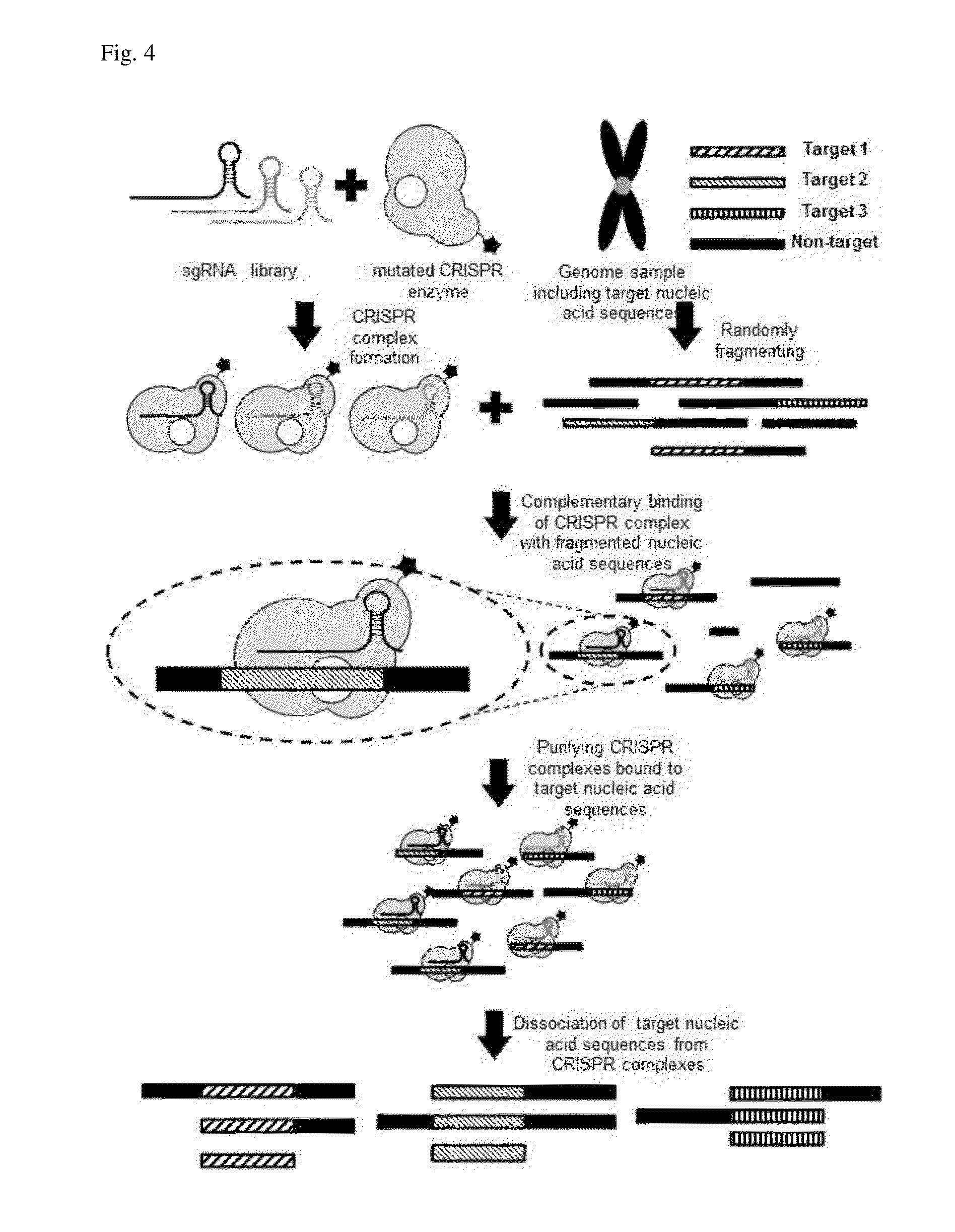
Method for target DNA enrichment using crispr system
The present invention relates to a method of capturing a target nucleic acid sequence in genome sequencing, e using a CRISPR system. According to the present invention, the use of a plurality of CRIPSR systems enables capturing a plurality of target nucleic acids within genome simultaneously.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC CORP FOUND YONSEI UNIV
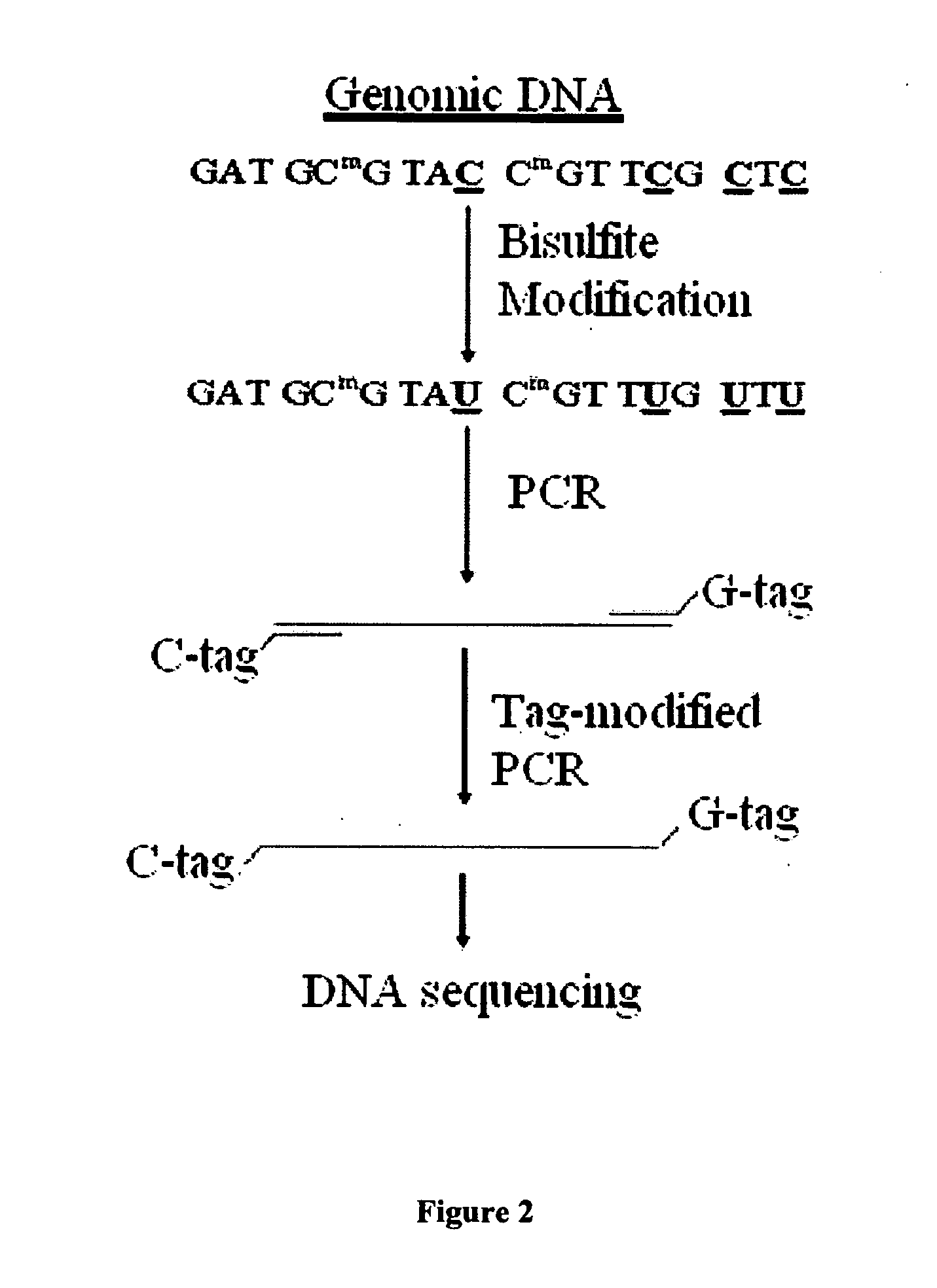
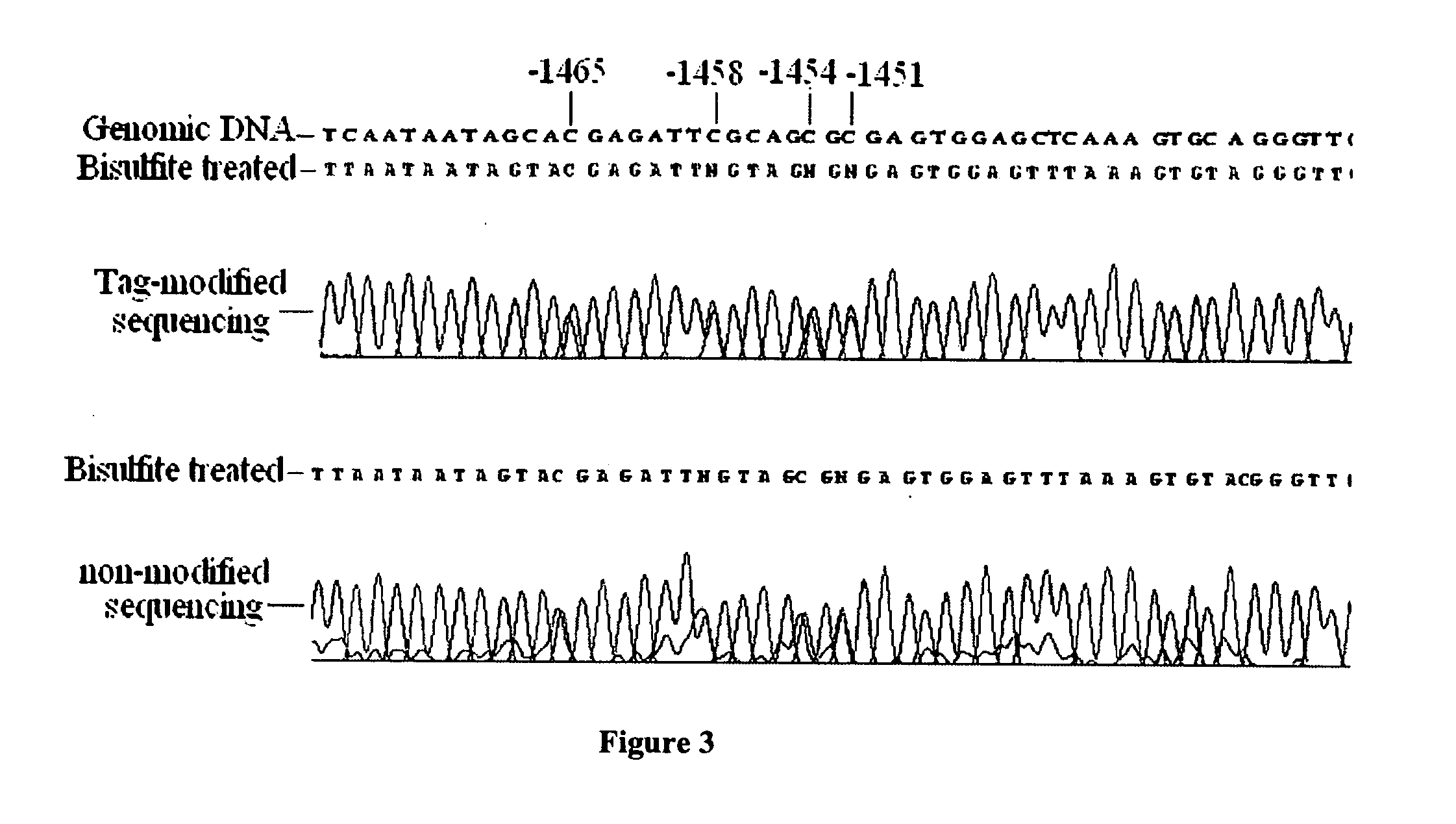
GC tag-modified bisulfite genomic DNA sequencing for continuous methylation spectra
InactiveUS20070054295A1Avoid the needMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationGenomic sequencingCycle sequencing
The present invention relates to a tag-modified bisulfite genomic sequencing (tBGS) method developed for simplified evaluation of DNA methylation sites. The method employs direct cycle sequencing of PCR products at kilobase scale, without conventional DNA fragment cloning. The method entails subjecting bisulfite-modified genomic DNA to a second-round PCR amplification employing GC-tagged primers. The invention also relates to a method for identifying a patient at risk for lung cancer using the tBGS technique disclosed.
Owner:SPIVACK SIMON DANIEL +2
Method and system for accurate alignment and registration of array for DNA sequencing
ActiveUS20110268347A1High precisionImprove trustImage enhancementImage analysisGenomic sequencingPattern matching
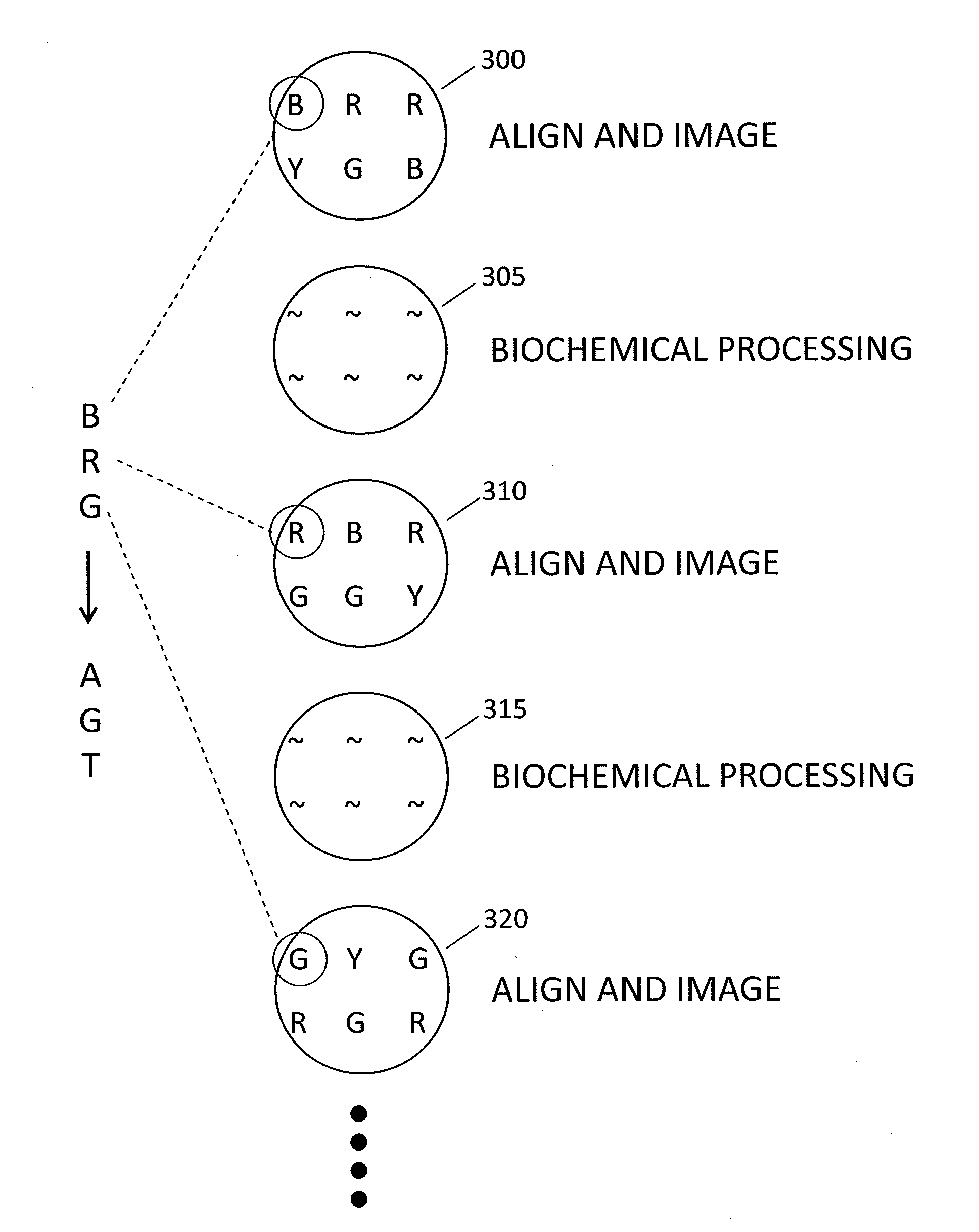
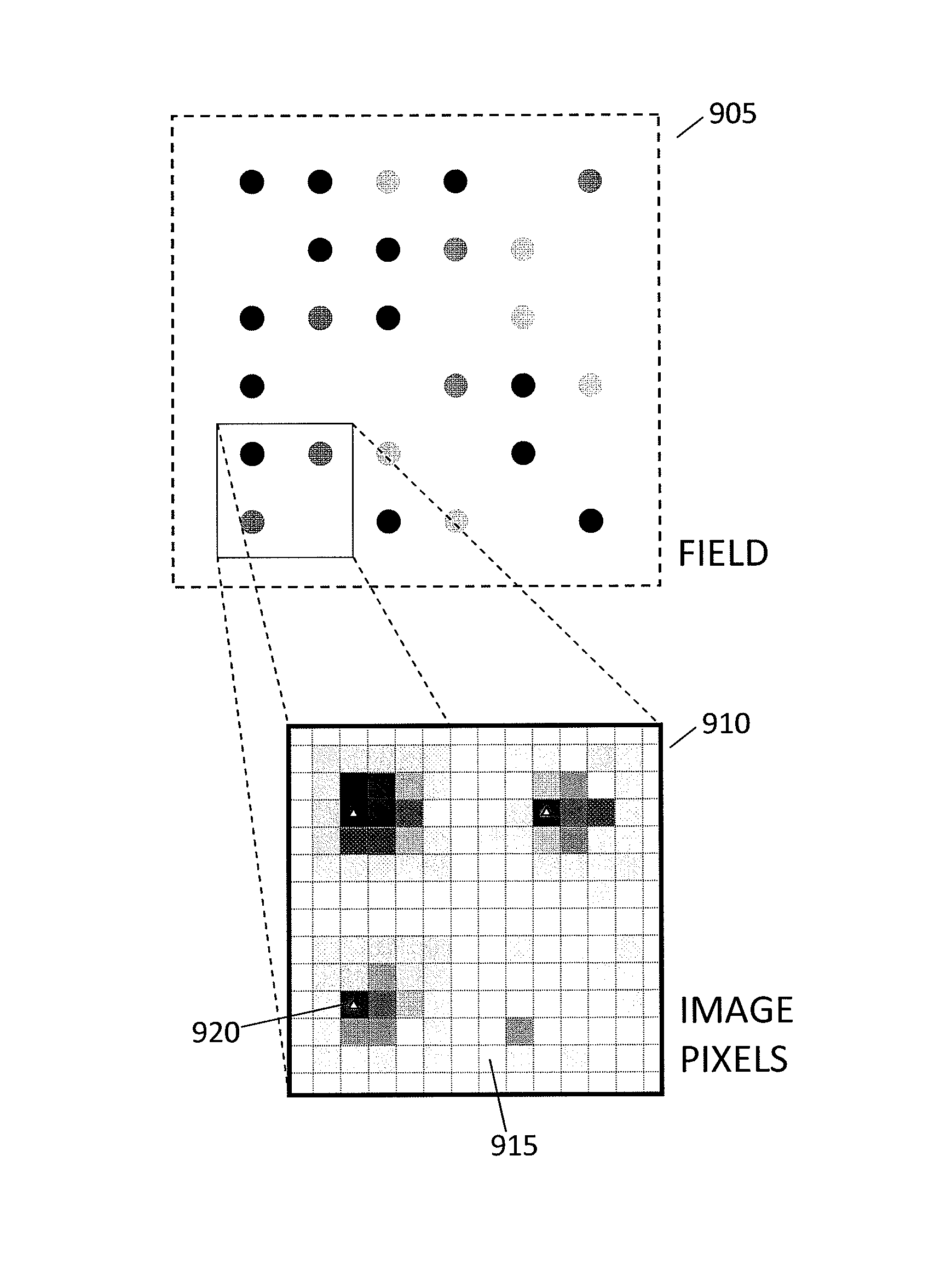
In a genome sequencing system and methodology, a protocol is provided to achieve precise alignment and accurate registration of an image of a planar array of nanoballs subject to optical analysis. Precise alignment correcting for fractional offsets is achieved by correcting for errors in subperiod x-y offset, scale and rotation by use of minimization techniques and Moiré averaging. In Moiré averaging, magnification is intentionally set so that the pixel period of the imaging element is a noninteger multiple of the site period. Accurate registration is achieved by providing for pre-defined pseudo-random sets of sites, herein deletion or reserved sites, where nanoballs are prevented from attachment to the substrate so that the sites of the array can be used in a pattern matching scheme as registration markers for absolute location identification. Information can be extracted with a high degree of confidence that it is correlated to a known location, while at the same time the amount of information that can be packed on a chip is maximized.
Owner:COMPLETE GENOMICS INC
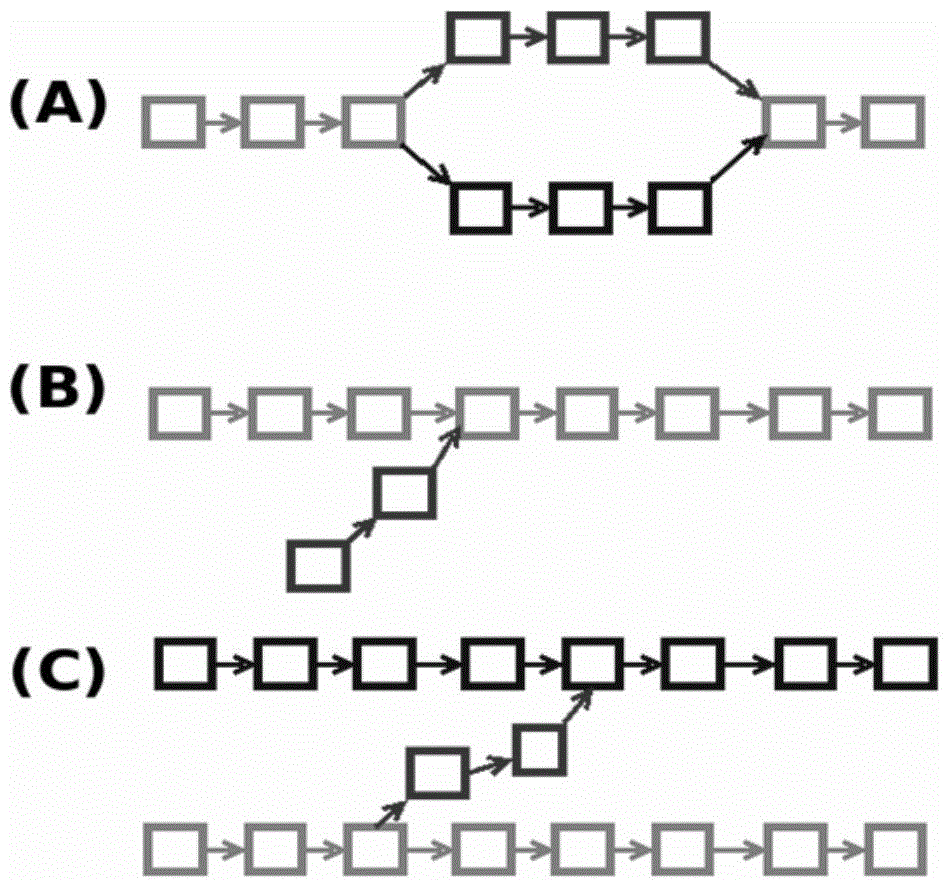
Splicing method and system of second generation and third generation genomic sequencing data combination
The invention relates to the field of biology information technology and computational biology, in particular to a splicing method and system of second generation and third generation genomic sequencing data combination. The splicing method of the second generation and third generation genomic sequencing data combination comprises the steps that second generation genomic sequencing data are obtained, preprocessing is performed on the second generation genomic sequencing data through quality information of part base sequence reads in the second generation genomic sequencing data, and a de Brui jn graph is built; sequencing error processing is performed on the de Brui jn graph to generate a new de Brui jn graph, compression is performed on the new de Brui jn graph to generate a compressed de Brui jn graph, and sequence multiplicity of a compressed edge of the compressed de Brui jn graph is obtained; third generation genomic sequencing data are obtained, the third generation genomic sequencing data are posted onto a single molecule graph gapped fragments of the second generation genomic sequencing data, the compressed de Brui jn graph is dismantled through the optimal configuration, and gaps in optimal configuration are filled to complete the splicing of the genomic sequencing data.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Blood metagenome sequencing data analysis method and device and application thereof
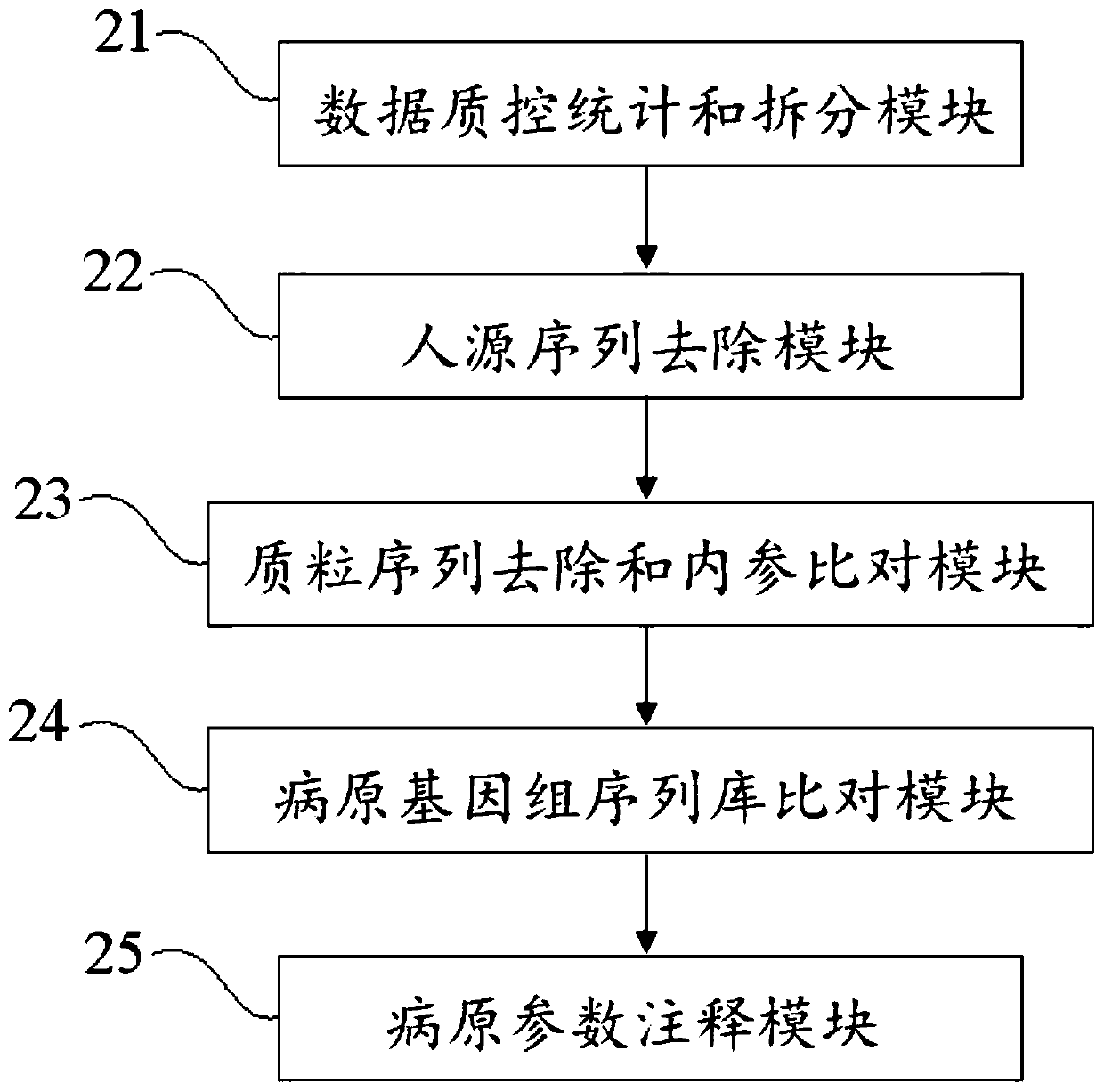
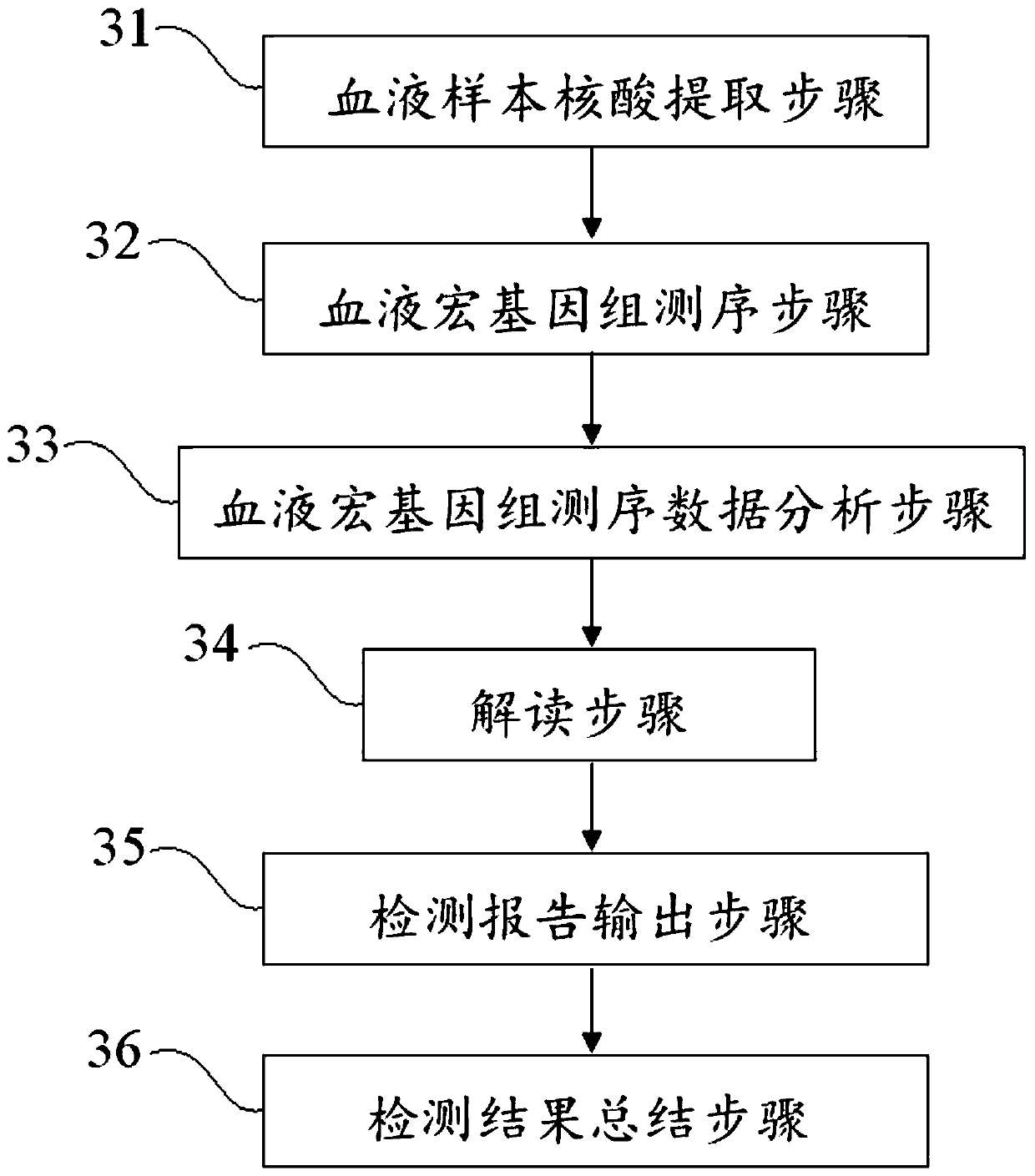
ActiveCN110349630AEffective deep diggingRealize Interpretation AnalysisMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsGenomic sequencingData quality
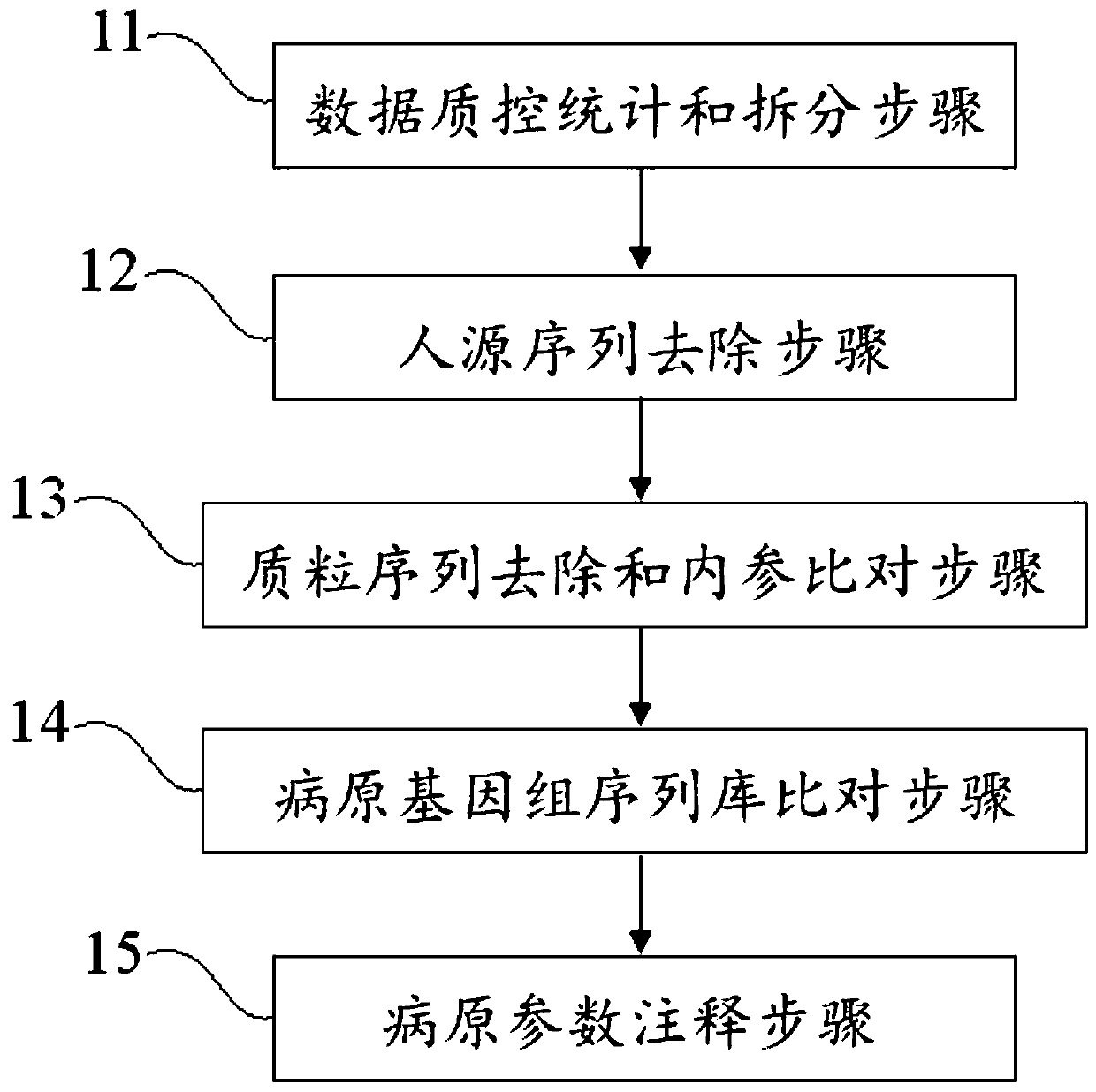
The invention discloses a blood metagenome sequencing data analysis method and device and an application thereof. The blood metagenome sequencing data analysis method comprises a data quality controlstatistics and splitting step, a humanized sequence removal step, a plasmid sequence removal and internal reference comparison step, a pathogen genome sequence library comparison step and a pathogen parameter annotation step. The invention provides a blood flow infection detection device based on a blood metagenome sequencing data analysis method. According to the method and device provided by theinvention, the free nucleic acid sequences in blood are detected through a metagenome sequencing method, a bioinformatics analysis method is combined, more than 8,000 pathogenic microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites possibly existing in a blood flow infection patient body are detected at a time, and a detection result can be obtained within 24 hours at the soonest. The speed, the sensitivity, the accuracy and the efficiency of blood flow infection detection are greatly improved.
Owner:深圳华大因源医药科技有限公司 +1
Genomic DNA sequencing methods and kits
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
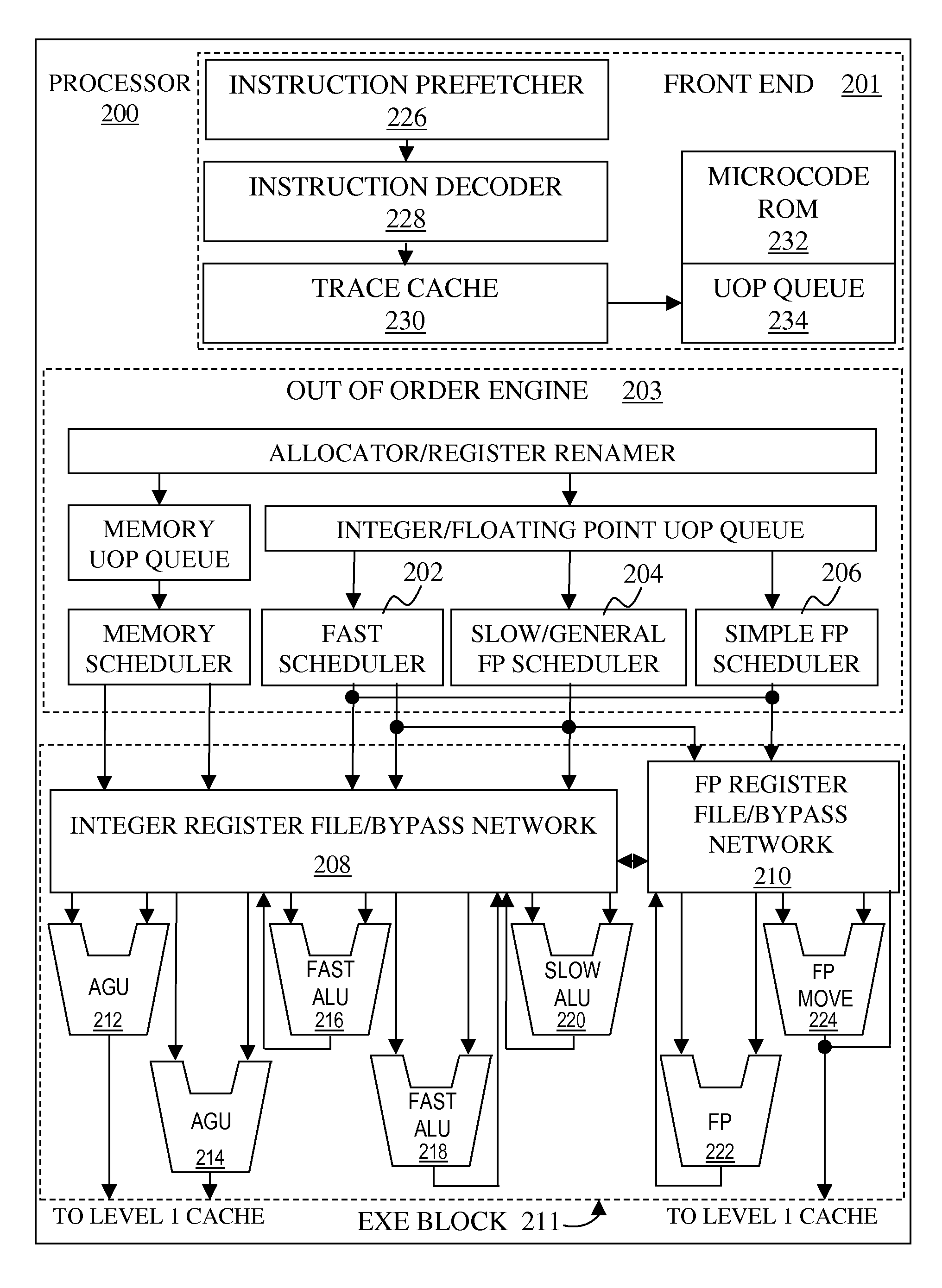
Methods, apparatus, instructions and logic to provide population count functionality for genome sequencing and alignment
ActiveUS20150046672A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationInstruction analysisGenomic sequencingProcessor register
Instructions and logic provide SIMD vector population count functionality. Some embodiments store in each data field of a portion of n data fields of a vector register or memory vector, at least two bits of data. In a processor, a SIMD instruction for a vector population count is executed, such that for that portion of the n data fields in the vector register or memory vector, the occurrences of binary values equal to each of a first one or more predetermined binary values, are counted and the counted occurrences are stored, in a portion of a destination register corresponding to the portion of the n data fields in the vector register or memory vector, as a first one or more counts corresponding to the first one or more predetermined binary values.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Selection of embryo of test tube baby through sequencing by single cell genome of polar body or embryo
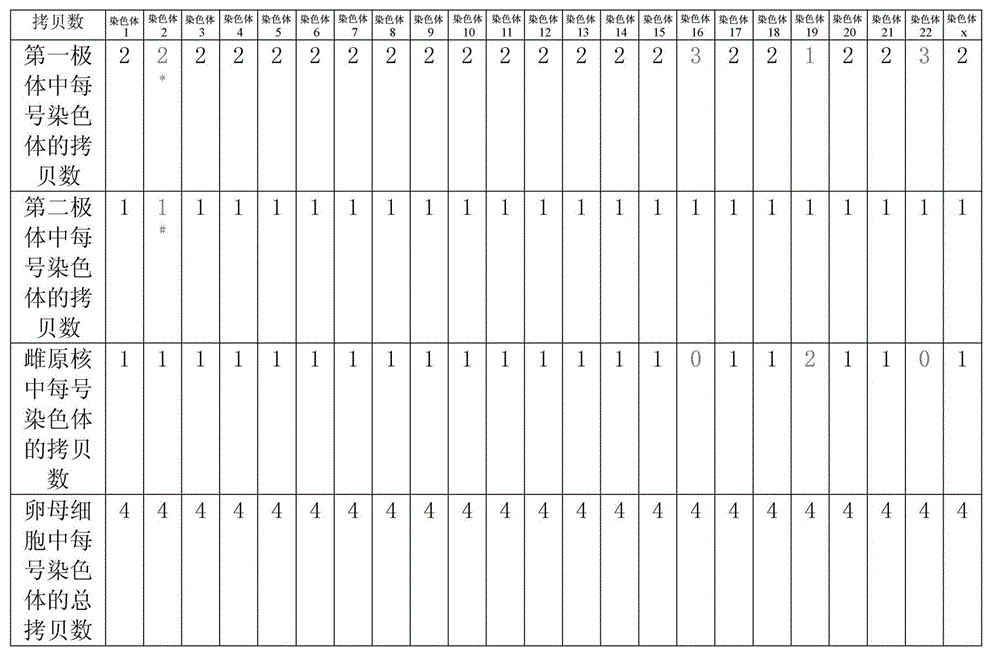
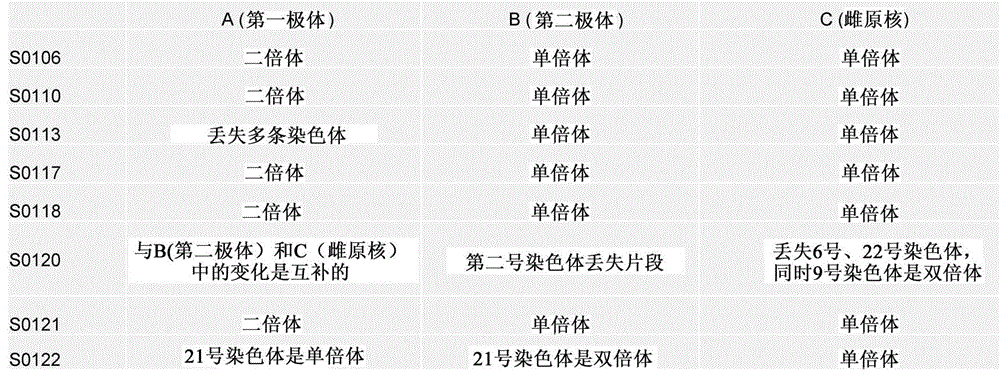
Disclosed is a method for using a first polar body and a second polar body as well as a single-cell embryo to carry out whole-genome non-exponential amplification and high-throughput genome sequencing, so as to perform preimplantation genetic diagnosis for genetic disease and testing for pathogenic genes causing repeated miscarriages. The method of the present invention comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining oocytes and embryos, and carrying out separation and genome amplification of first and second polar bodies and single-cell embryos; (2) establishing a genome sequencing library and sequencing, and carrying out bioinformatic analysis of the genome to obtain a gene spectrum and information concerning the number of copies of chromosomes and fragments thereof; (3) determining the chromosome ploidy of the polar bodies and embryos as well as information concerning defects, replication and point mutation in the chromosome fragments; (4) selecting normal or suitable embryos for implantation.
Owner:HARVARD UNIV +2
Method for constructing high-flux simplified genome sequencing library
ActiveCN104694635AReduce the impact of quantitative accuracy before mixingImprove uniformityMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationGenomic sequencingPhosphorylation
The invention provides a method for constructing a high-flux simplified genome sequencing library. The method comprises the following steps: digesting genome DNA of different samples by using restriction enzymes, thereby obtaining blunt-end DNA fragments with phosphorylation modification at the 5' end; adding the base A at the 3' end, connecting the DNA fragments of different samples with 5' phosphorylation and 3' cohesive ends A with joints containing different bar code sequences, connecting the products PCR, purifying and mixing the amplification products, performing low-cycle PCR amplification, thereby obtaining a target fragment amplification product of which the ratio of the joints to joint dimers is greatly reduced; and separating, purifying, and forming the high-flux simplified genome sequencing library from the purified products. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the flux is high, the cost is low, and the generated library is high in sequencing quality and has very wide application prospects in researches such as high-flux SNP detection and marker development, genetic map drawing and functional gene location.
Owner:BIOMARKER TECH
CNV detection method and CNV detection apparatus
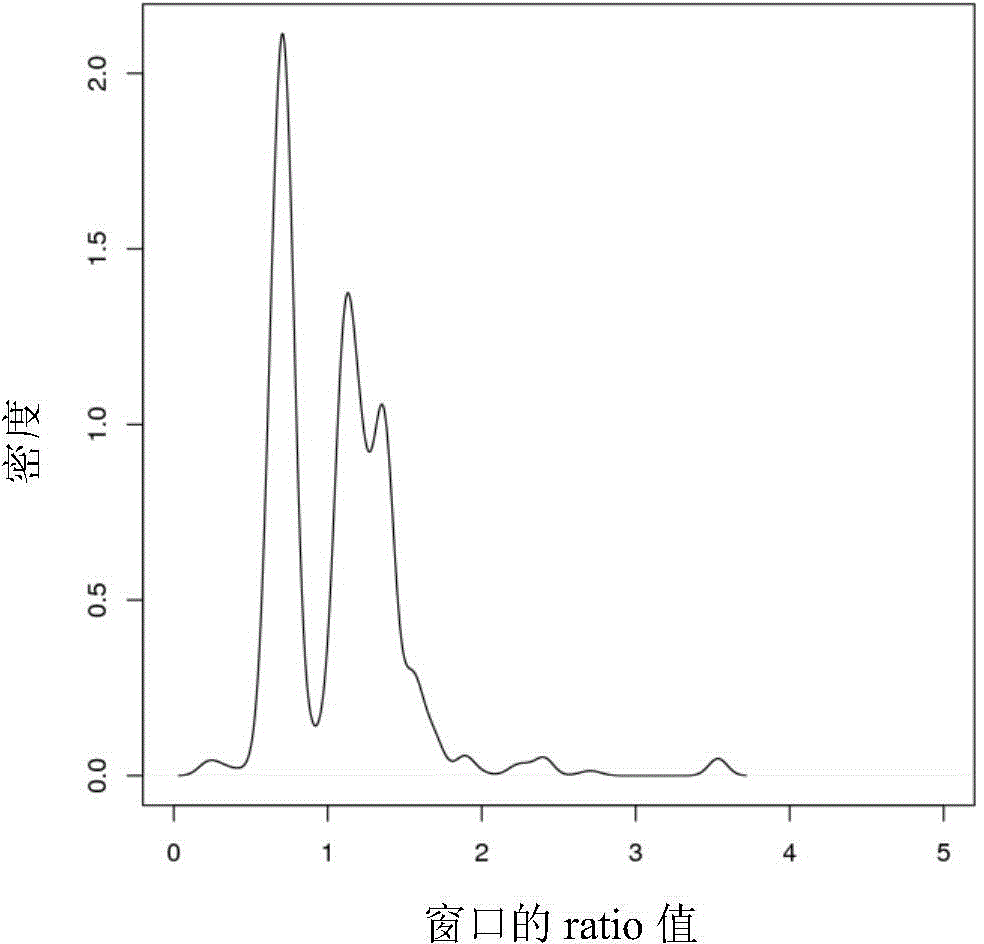
The invention provides a CNV detection method which including the steps of: 1) acquiring a genome sequencing result of a target individual; 2) comparing the sequencing result with a reference sequence to obtain a comparison result, wherein the reference sequence comprises a plurality of windows; 3) on the basis of the comparison result, calculating initial comparison ratio of each window, which is the number of reads in the windows on the comparison dividing the average value of the number of the reads in the windows on the comparison, wherein the average value of the number of the reads in the windows on the comparison is the total number of reads in all windows on the comparison dividing the number of the windows; 4) combining a plurality of adjacent windows of which the initial comparison ratios have no significant difference, and defining the combined adjacent windows as a primary zone, and the rest individual windows are respectively called the primary zones; and 5) if the comparison ratio of the primary zone is not equal to a preset comparison ratio, determining existence of CNV in the primary zone.
Owner:BGI SHENZHEN CO LTD
Detection device for instability of genome copy number
InactiveCN104560697ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGenomic sequencingInformation analysis
The invention relates to the technical field of medical detection and discloses a detection device for the instability of the genome copy number. The detection device comprises a sequencing unit, a calculation unit and a statistical analysis unit, wherein the sequencing unit is used for sequencing of free DNAs in a plasma sample of a person to be detected and obtaining the sequencing number of each genome window of the sample to be detected; the calculating unit is used for calculating the variance value of the copy number of each genome window; and the statistical analysis unit is used for carrying out statistics on the variance value of the copy number of each genome window and analyzing whether the instability of the genome copy number exists. The detected instability of the genome copy number can be further used for judging the risk of the person to be detected suffered from the cancers. The detection device disclosed by the invention has the advantages that a molecular biological sequencing technology and a biological information analysis technology are combined, the recognition for the abnormal condition of the copy number of chromosome is achieved by detecting free DNAs in blood, so that whether the person to be detected is suffered from cancers is judged, and further early-stage non-invasive screening for the cancers is realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI MAJORBIO BIO PHARM TECH
Method and system for accurate alignment and registration of array for DNA sequencing
ActiveUS8774494B2High precisionImprove trustImage enhancementImage analysisGenomic sequencingPattern matching
In a genome sequencing system and methodology, a protocol is provided to achieve precise alignment and accurate registration of an image of a planar array of nanoballs subject to optical analysis. Precise alignment correcting for fractional offsets is achieved by correcting for errors in subperiod x-y offset, scale and rotation by use of minimization techniques and Moiré averaging. In Moiré averaging, magnification is intentionally set so that the pixel period of the imaging element is a noninteger multiple of the site period. Accurate registration is achieved by providing for pre-defined pseudo-random sets of sites, herein deletion or reserved sites, where nanoballs are prevented from attachment to the substrate so that the sites of the array can be used in a pattern matching scheme as registration markers for absolute location identification. Information can be extracted with a high degree of confidence that it is correlated to a known location, while at the same time the amount of information that can be packed on a chip is maximized.
Owner:COMPLETE GENOMICS INC
Paired-end library construction method and method for sequencing genome by using library
InactiveCN102181943AReduce workloadLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionGenomic sequencingDNA fragmentation
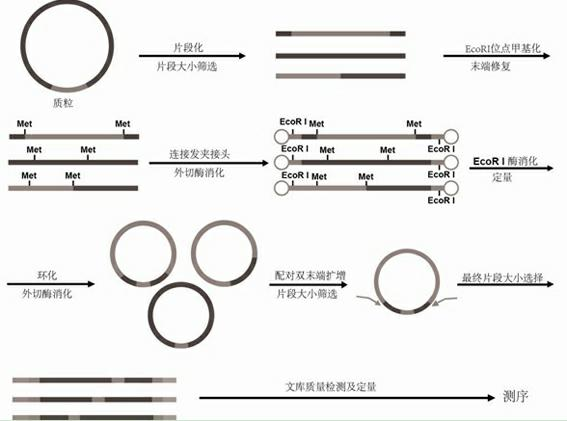
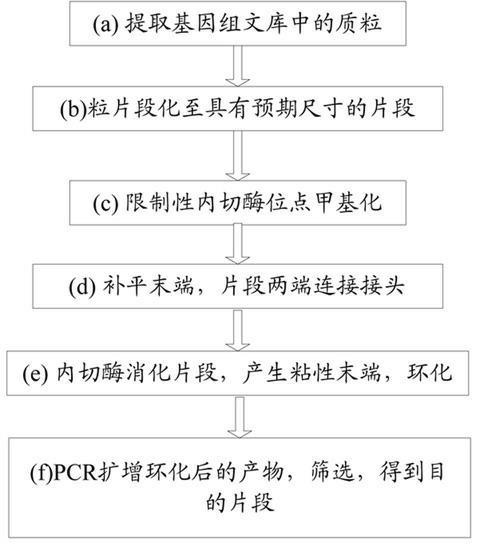
The invention relates to a paired-end library construction method and a method for sequencing a genome by using the library. The paired-end library construction method comprises the following steps of: performing plasmid extraction on clone in a constructed genome DNA library, fragmenting the extracted plasmid DNA, performing methyl protection on the restriction endonuclease site on the fragmented DNA, adding a hairclip type joint, performing enzyme cutting and cyclization to obtain circular DNA, then amplifying the genome library paired-end fragment in the circular DNA through a pair of composite primers to obtain a paired-end sequence of ultra-long span, and finally performing high flux sequencing. The paired-end sequence obtained by using the method can be applied to splicing of a new species genome sequence so as to further improve the splicing quality.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Genetic map construction method and device, haplotype analytical method and device
ActiveCN102952855AHigh resolutionUnderstand the genetic laws of reproductionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGenomic sequencingTyping Classification
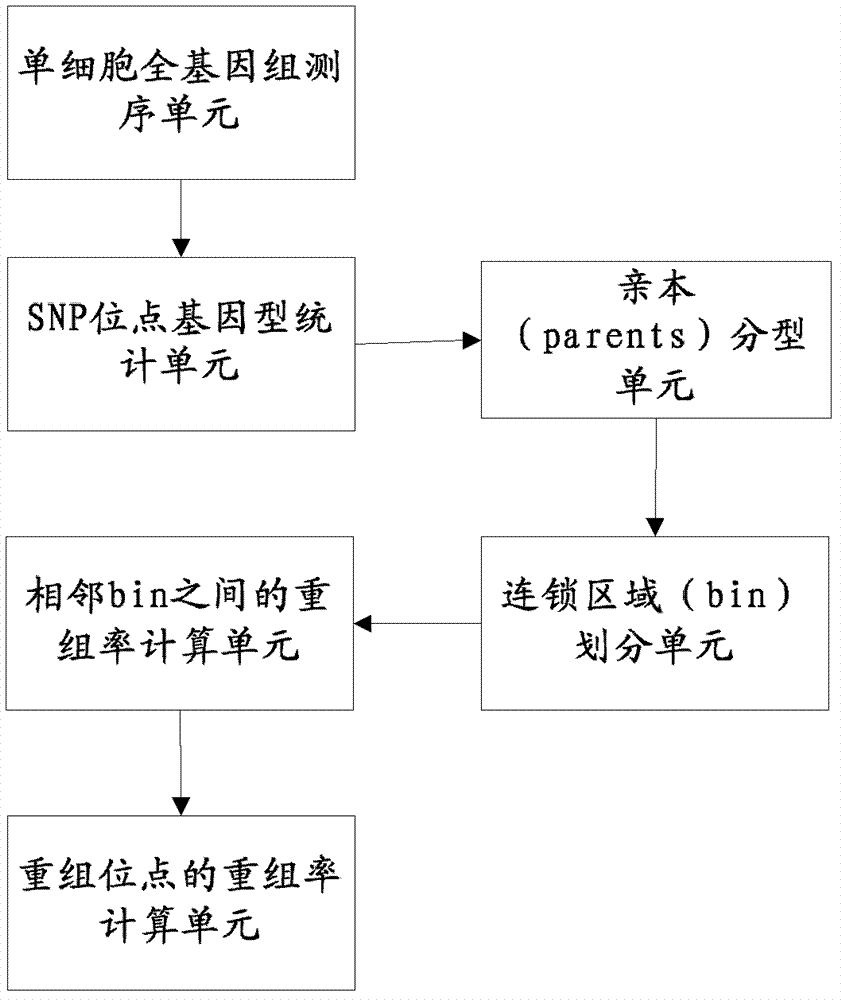
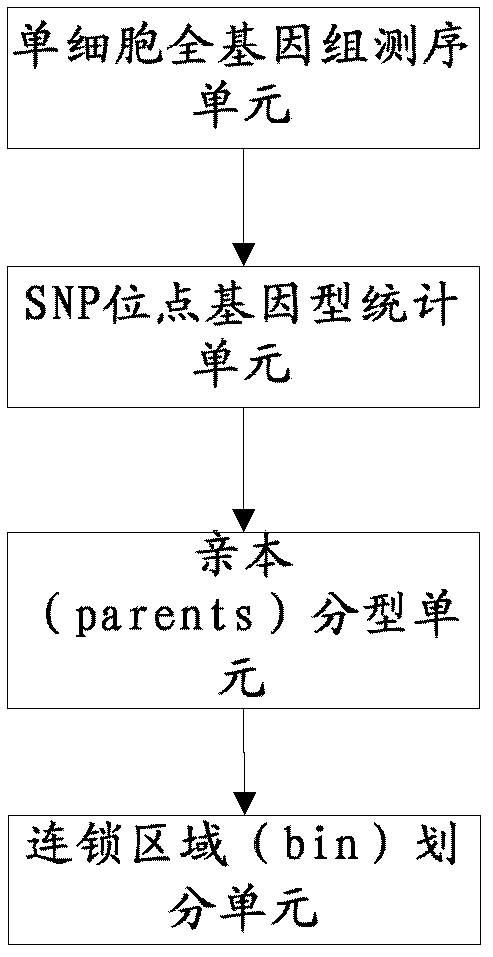
The invention relates to a genetic map construction and haplotype analytical method based on single-cell whole genome sequencing, and a device used for the method. The genetic map construction method comprises the following steps: comparing a whole genome sequence of a single cell of a species with a reference sequence to obtain a statistic result of a single nucleotide polymorphic site genotype; performing parent type classification of the genotype result to obtain a most appropriate male parent / female parent (a / b) result, so as to obtain a minimum recombination frequency of all the cells in the statistic result; according to the type classification result, dividing a linkage area (bin); calculating a change ratio of a / b to obtain recombination rates between all adjacent bins; and finally obtaining the genetic map according to the recombination rate of each recombinant site. The method of the invention can obtain a genetic map with high resolution by using a single cell, can not only applicable to human, but also applicable to some higher organisms with limited fertility, especially to endangered species.
Owner:TIANJIN MEDICAL LAB BGI
Method for determining optimal SNP quantity as well as performing genome selective breeding on production performance of large yellow croakers through selection markers
ActiveCN107338321AReduce breeding costsLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsGenomic sequencingAgricultural science
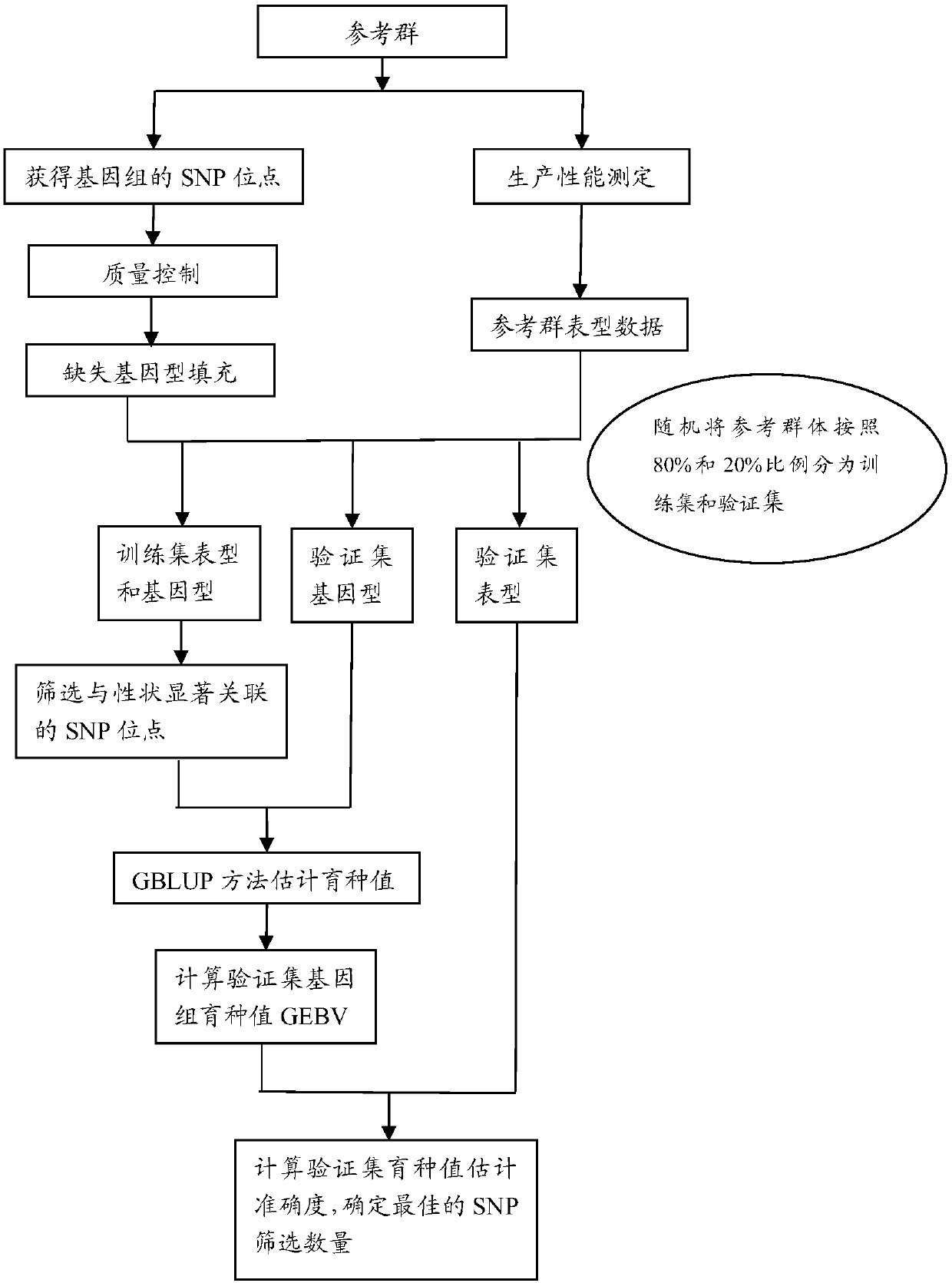
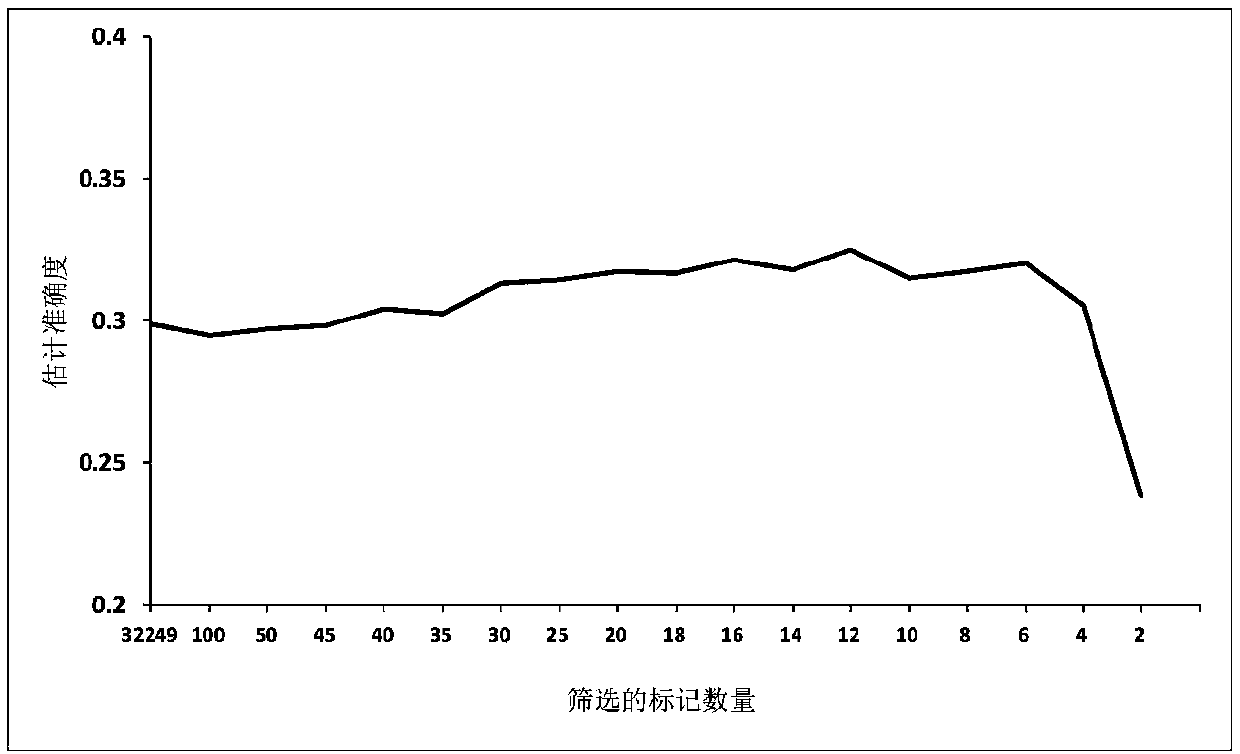
The invention discloses a method for determining optimal SNP quantity as well as performing genome selective breeding on production performance of large yellow croakers through selection markers. The method comprises the following steps: performing phenotype determination and genomic sequencing on the production performance of individuals of a reference group to obtain SNP locus; screening out the qualified SNP locus and supplementing the deleted genotype; dividing the reference group into a training set and a validation set to perform hybridization validation; screening the SNP locus most remarkably associated with the character through single marker analysis, and then calculating GEBV of individuals of the validation set only by using the locus and through a GBLUP method; further obtaining breeding value estimation accuracy under each screening SNP quantity; finally determining the optimal quantity of SNP screening; and according to the optimal quantity, calculating the GEBV by the GBLUP method, further obtaining the breeding value estimation accuracy and performing genome selective breeding according to the value size. By the method, the genomic selection cost on the production performance of the large yellow croakers can be reduced remarkably.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
Nucleic acid sequencing process based on micro array chip
InactiveCN1932033AMature technologyEasy to implementMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic sequencingNucleotide
The nucleic acid sequencing process based on nucleic acid micro array chip is for sequencing genome and detecting gene transcription and expression spectrum of some specific species, and detecting various genome DNA modifying spectrum. Different DNA segments to be sequenced are fixed onto one solid chip to form nucleic acid micro array, and each of the DNA segments is made to contain the same common sequence as the complementary sequence of the sequencing primer. After crossing the common sequencing primer and the chip, some mixed nucleotide solution with certain ratio of fluorescent marker ddNTP and dNTP is injected to the chip to terminate on-chip base reaction with a micro flow controller by means of Sanger end terminating process. Once the termination is finished, one fluorescent signal is obtained through scanning to obtain the base extending information in different sample points on the chip. All the sequencing maps are finally superposed to obtain the complete nucleic acid segment information.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
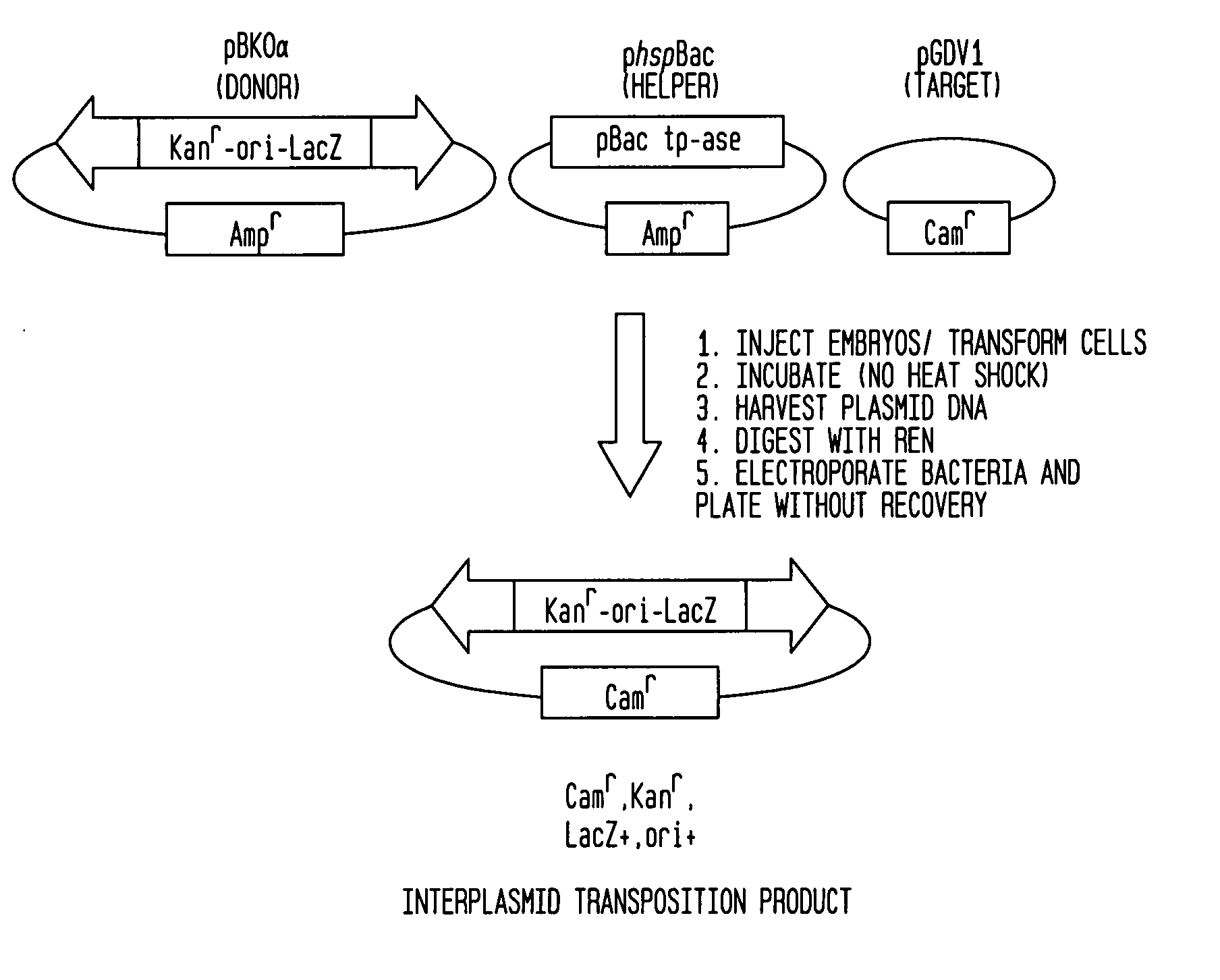
PiggyBac constructs in vertebrates
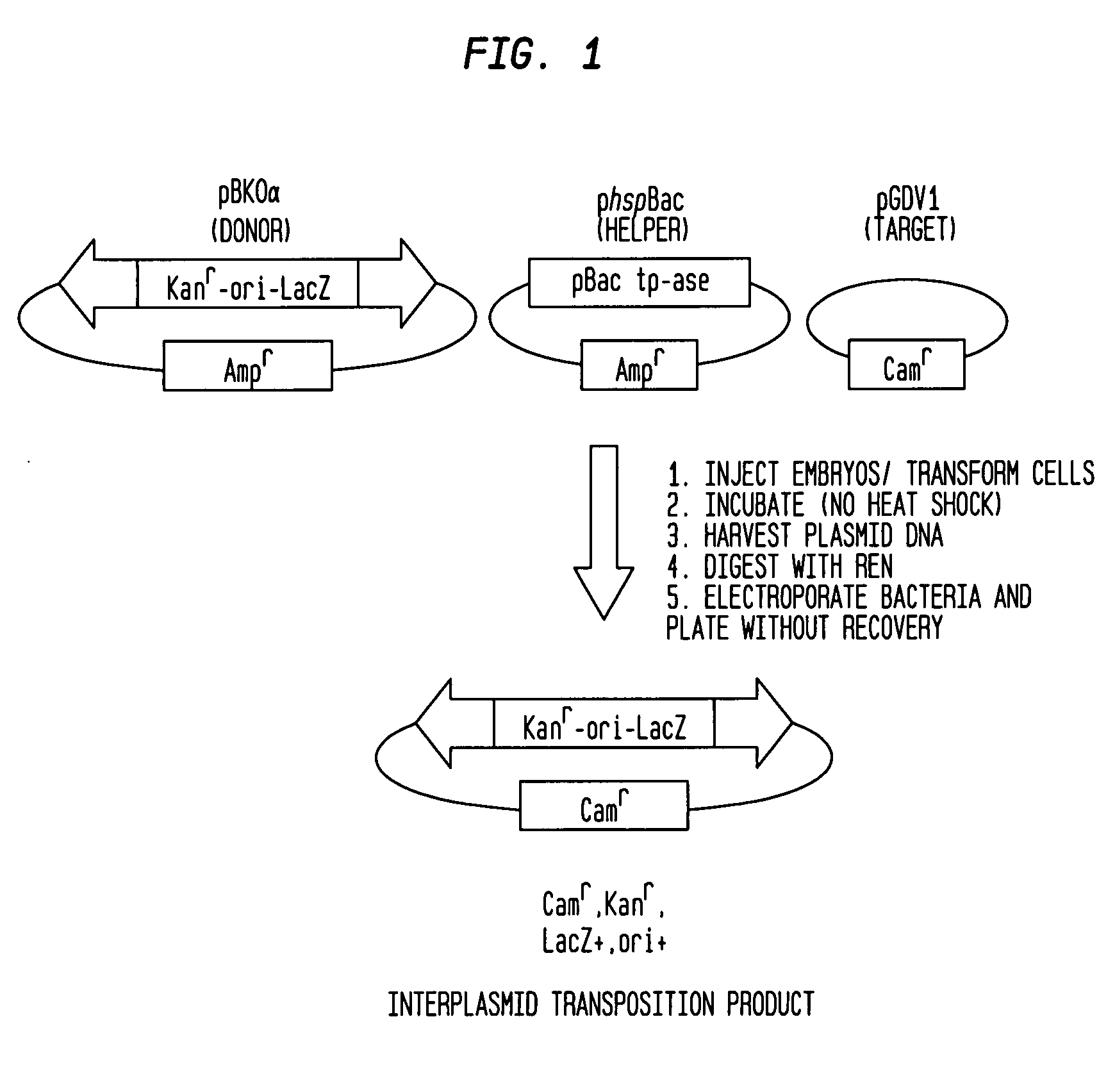
The piggyBac transposon is disclosed herein as an extremely versatile helper-dependent vector for gene transfer and germ line transformation in a wide range of vertebrate species. Presented are methods wherein genome sequencing databases may be examined using piggyBac, as homologues of piggyBac have been found among several sequenced animal genomes, including the human genome. This transposon is demonstrated to provide transposition in primate cells and embryos of the zebra fish, Danio rerio. PiggyBac mobility is demonstrated using an interplasmid transposition assay that consistently predicts the germ line transformation capabilities of this mobile element in several species. Both transfected COS-7 primate cells and injected zebrafish embryos supported the helper-dependent movement of tagged piggyBac element between plasmids in a cut-and-paste, TTAA target-site specific manner. The present invention discloses the use of piggyBac as a tool for genetic analysis of vertebrates.
Owner:UNIV OF NOTRE DAME DU LAC
Specific molecular marker for acquiring genders of bighead carps and screening method and application thereof
ActiveCN106947827AOvercome operabilityTo overcome the disadvantages such as time-consumingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenomic sequencingScreening method
The invention discloses a specific molecular marker for acquiring the genders of bighead carps and a screening method and application thereof. The screening method comprises the following steps: firstly, performing reduced-representation sequencing on 5 female bighead carps and 5 male bighead carps by using a 2b-RAD technology to identify a male specific sequence; then, performing genome resequencing and genome assembly on one of the male bighead carps, comparatively searching 2b-RAD specific sequences of the male bighead carps in a male bighead carp genome to obtain a long-fragment male bighead carp specific sequence, and designing a male specific primer. By adopting the screening method, a male specific sequence and a gender specific primer of the bighead carps are screened for the first time, and a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) technology for generic gender determination is built. The method has the advantages of low cost, easiness, rapidness and accuracy in operation, and the like, and a reliable technical measure is provided for the development of a gender marker and gender determination of the bighead carps. The method can be popularized and applied in gender marker development and gender determination research of other fishes.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
Targeted-panel tumor mutational burden calculation systems and methods
PendingUS20200258601A1Adapt quicklyLarge adaptabilityBiostatisticsMedical automated diagnosisGenomic sequencingCell Fraction
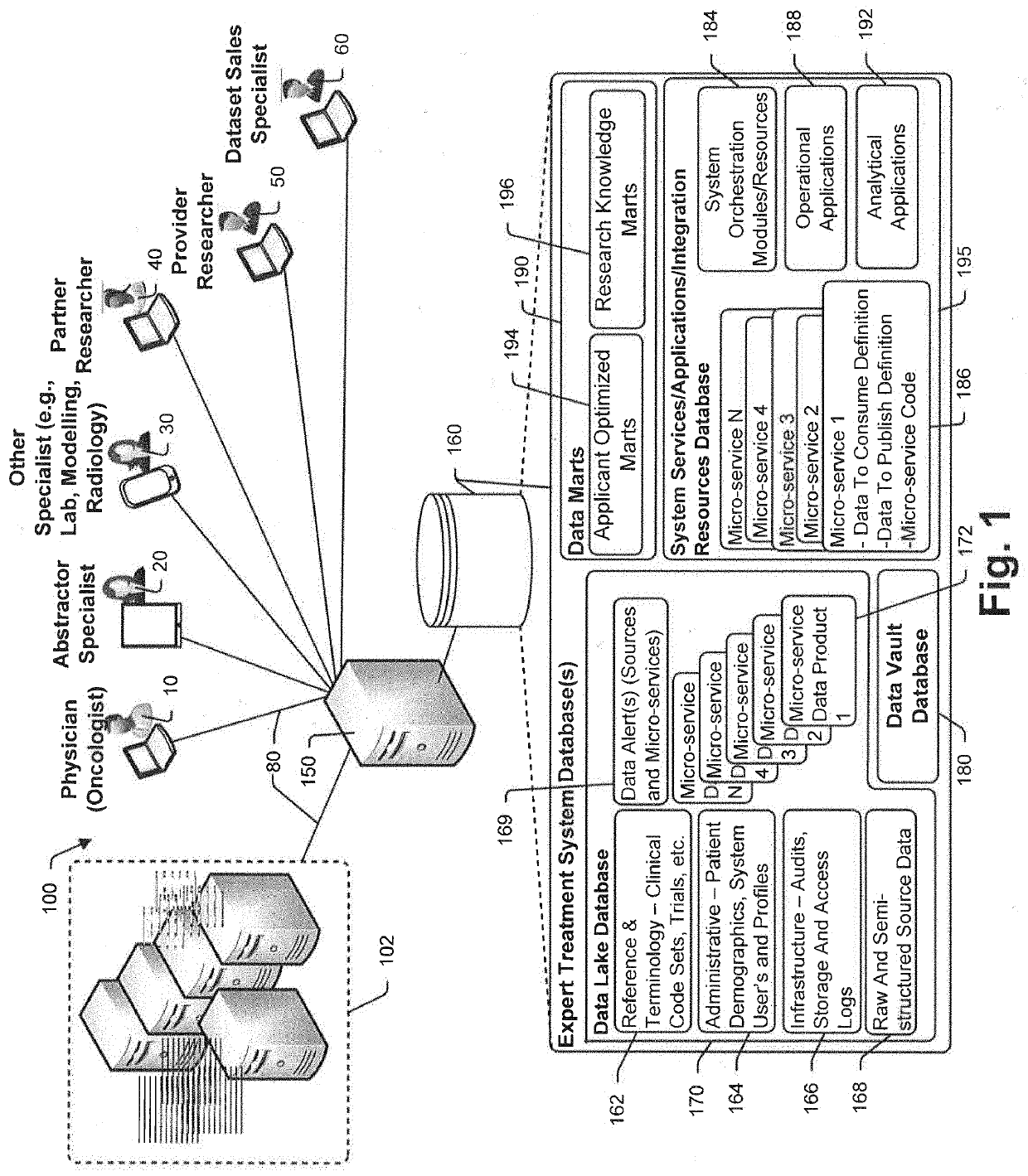
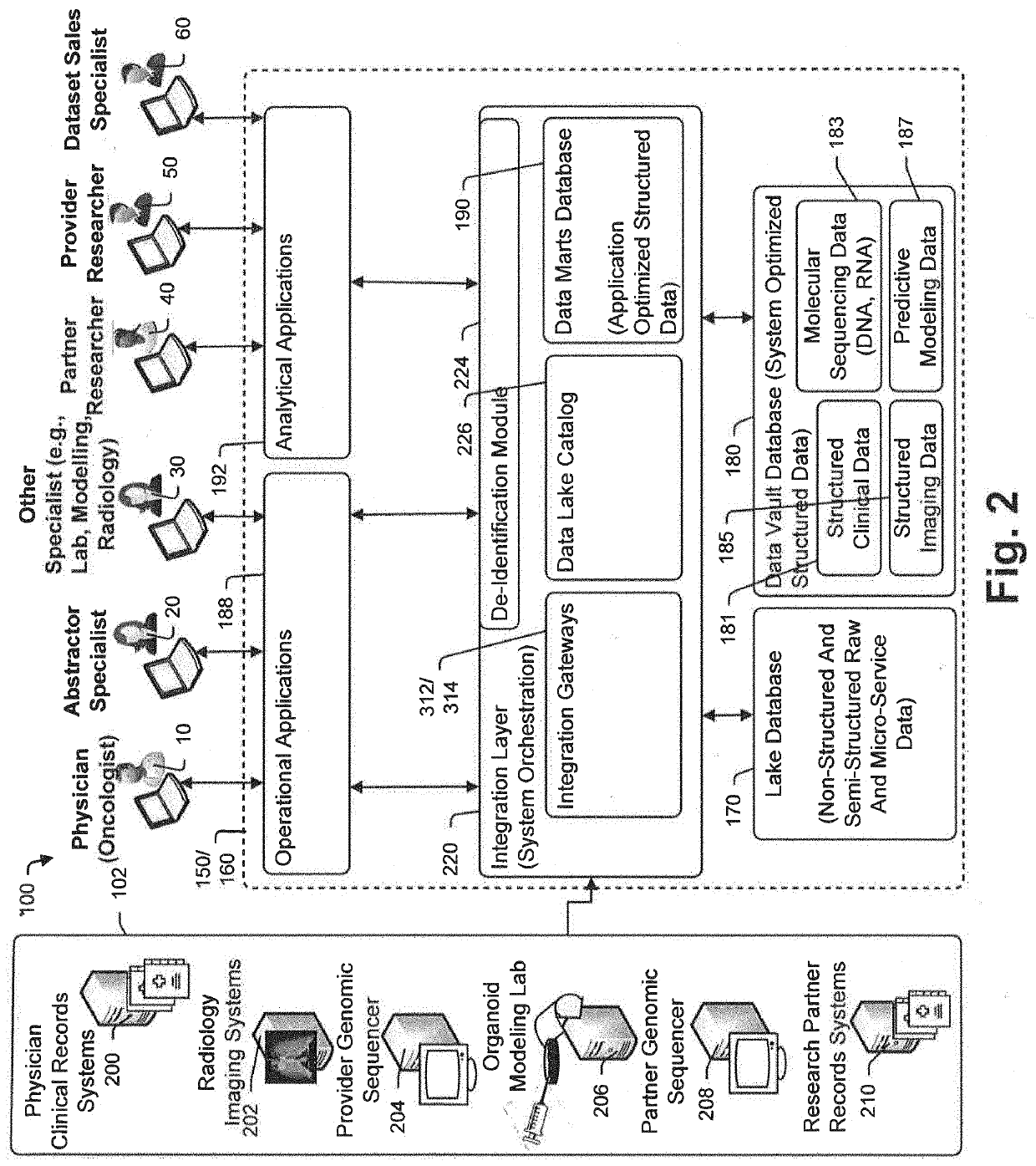
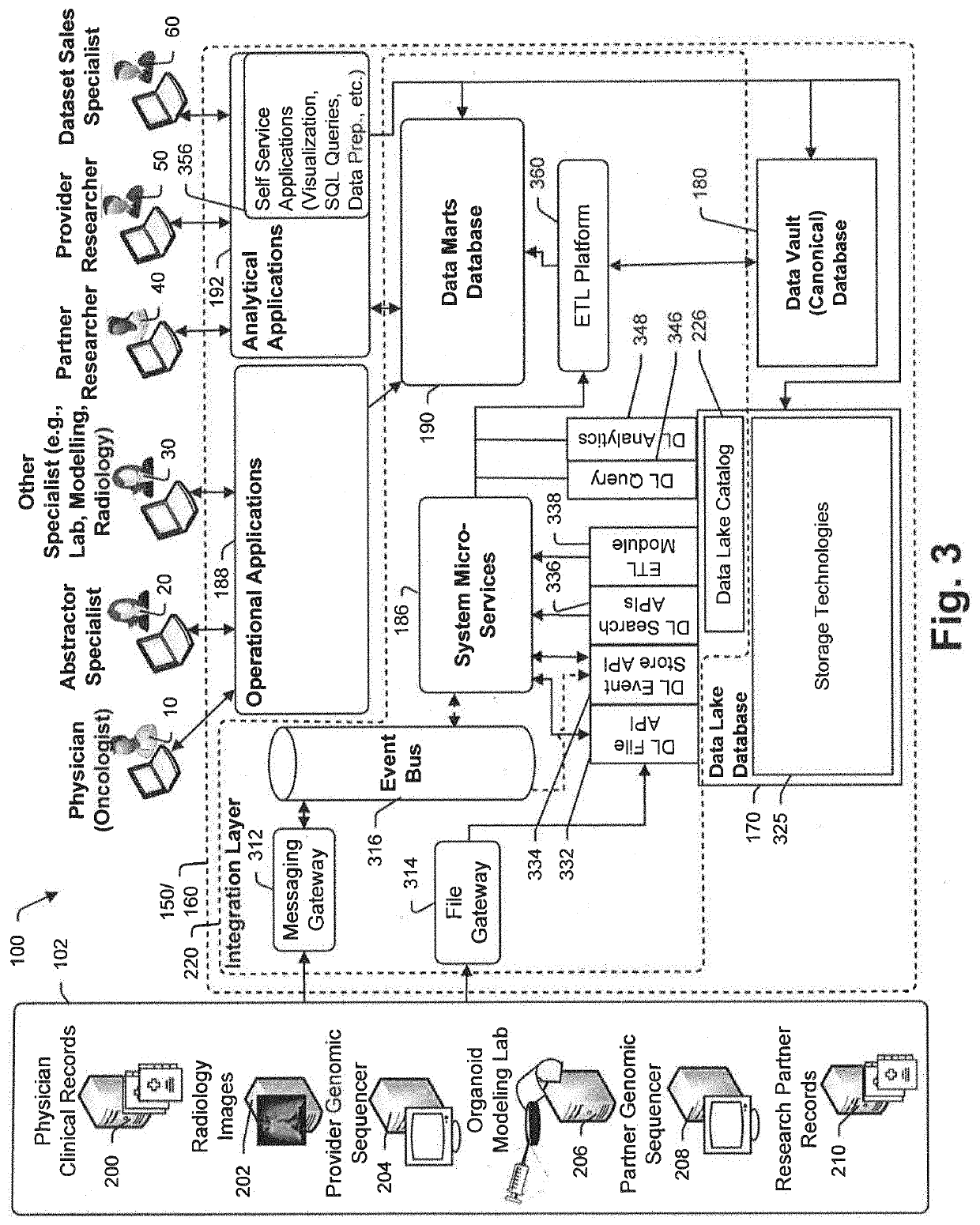
A method and system for conducting genomic sequencing, the system comprising a first microservice for receiving an order from a physician, the order to initiate an NGS of a patient's germline specimen and somatic specimen using a targeted-panel, a second microservice for executing an NGS of the patient's germline specimen to identify sequences of nucleotides in the germline specimen using the targeted-panel to generate germline sequencing results, a third microservice for executing an NGS of the patient's somatic specimen to identify sequences of nucleotides in the somatic specimen using the targeted-panel to generate somatic sequencing results, a fourth microservice for executing quality control (QC) testing on the germline sequencing results to generate a germline QC score and on the somatic sequencing results to generate a somatic QC score, a fifth microservice for generating at least one clinical report, and a sixth microservice for providing the at least one clinical report to the physician, the at least on clinical report comprising the patient's TMB status.
Owner:TEMPUS LABS
Method for acquiring chicken whole genome high-density SNP marker sites
ActiveCN105238859ALow costGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic sequencingGenetic engineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering, and provides a method for acquiring chicken whole genome high-density SNP marker sites. The method comprises the following steps: (1) predicting distribution of restriction fragments acquired from double-restriction chicken genomes of EcoRI and MseI; (2) designing a universal joint, a barcode joint and a PCR amplification primer according to the distribution characteristics of the restriction fragments of EcoRI and MseI; (3) constructing a simplified genome sequencing library; (4) sequencing by virtue of the library constructed in the step (3) through a computer; and (5) according to a sequencing result, acquiring SNP marker sites. The method disclosed by the invention provides a universal strategy for the construction of a whole genome high-density SNP map by virtue of double-restriction GBS for different varieties of chickens, so that the cost on acquiring every SNP marker site is reduced by an order of magnitude compared with a conventional chip technology; and the method is stable in technology and high in repeatability.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
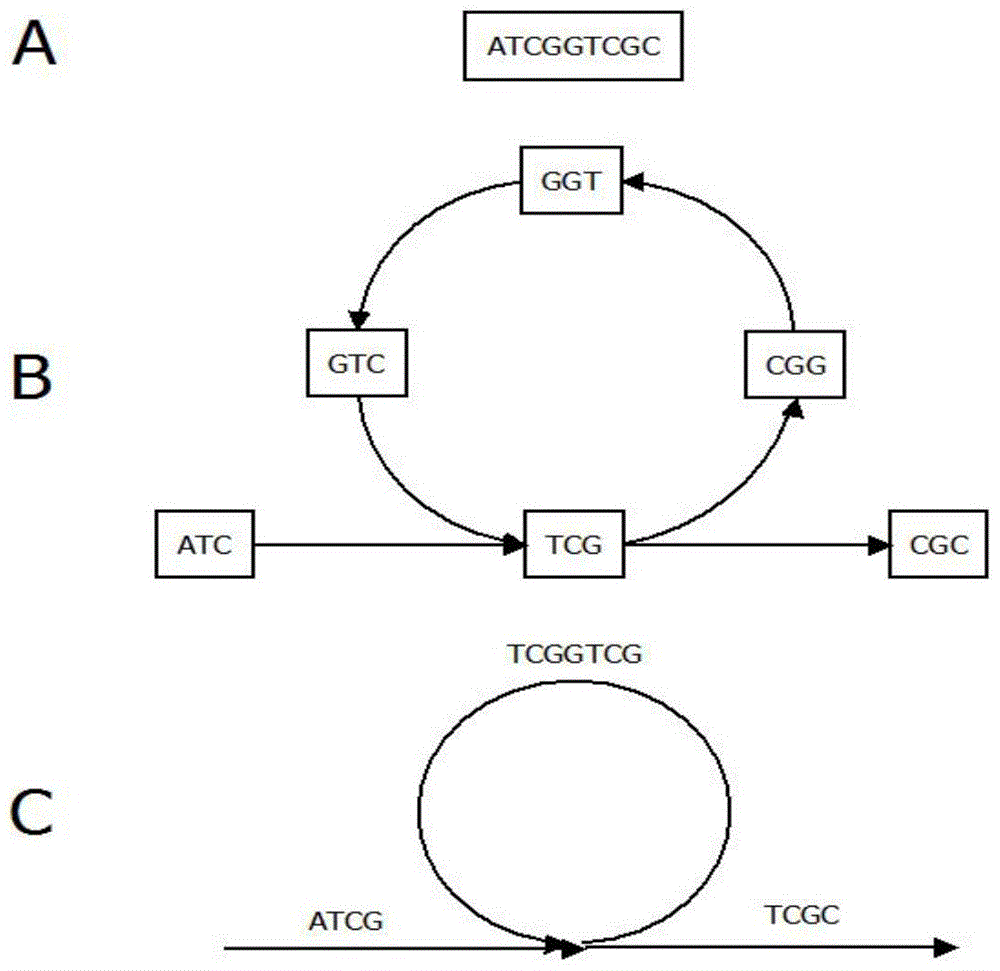
Circular 'connection-extension' genome sequencing method
The invention relates to a circular 'connection-extension' DNA sequencing method. The method comprises the following steps: based on the sequencing principle of an SOLiD sequencing technology, adopting a sequencing primer to connect a section of universal oligonucleotide, detecting the base information of a corresponding position of a DNA template by extending a base, then cutting a marking object from a certain position in the oligonucleotide connected with the sequencing primer, and according the same method, extending one marking monomer after reconnecting the same oligonucleotide, and then sequentially determining the base information of a plurality of spacing positions on the DNA template; eliminating the sequencing primer finishing the determination of the base sequences of a plurality of spacing positions by a denaturation method or a digestion method, changing a new sequencing primer, and determining the base information of a plurality of other spacing positions on the DNA template by the 'connection-extension' method in the same way; circularly changing sequencing primers, and finally combining the base information of the spacing positions determined by these sequencing primers to obtain arrangement information of all bases of certain fragment of the DNA template so as to realize the DNA sequence detection.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com