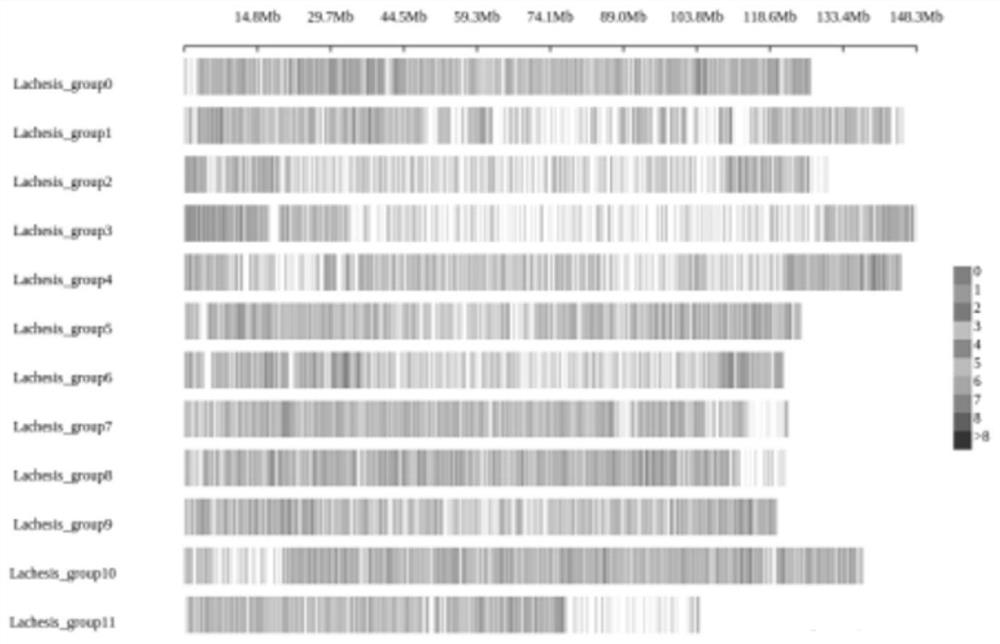
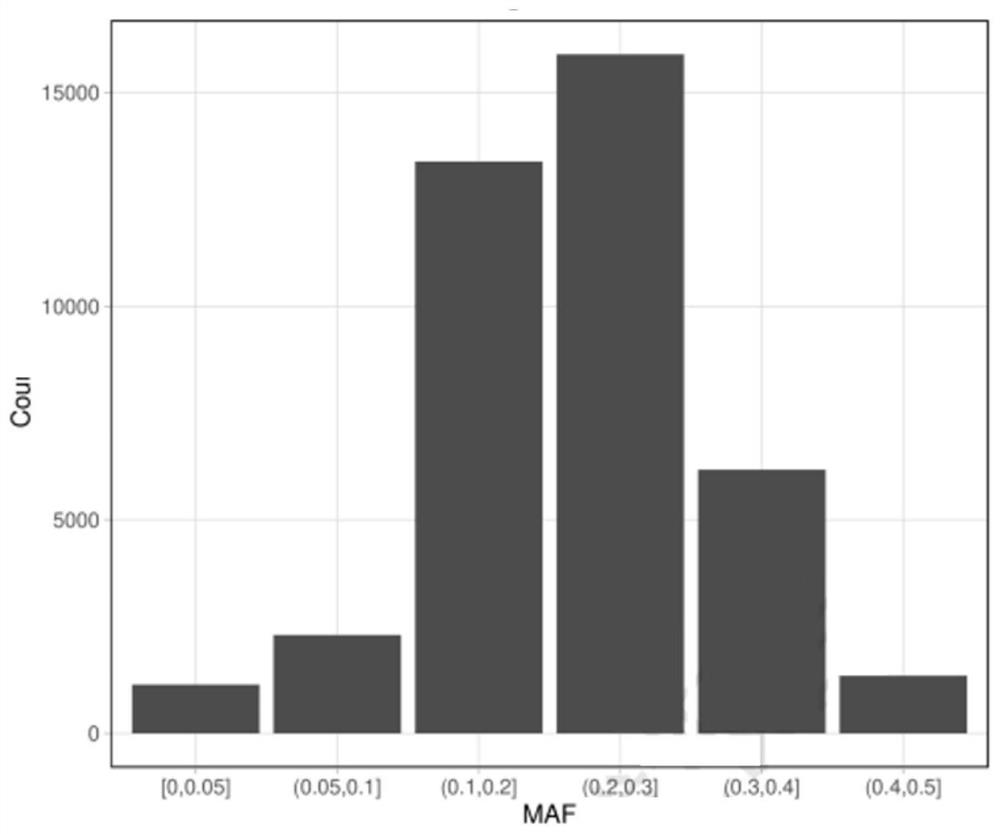
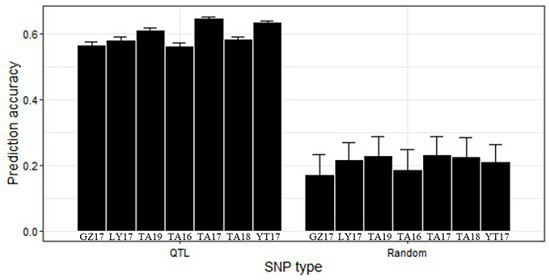
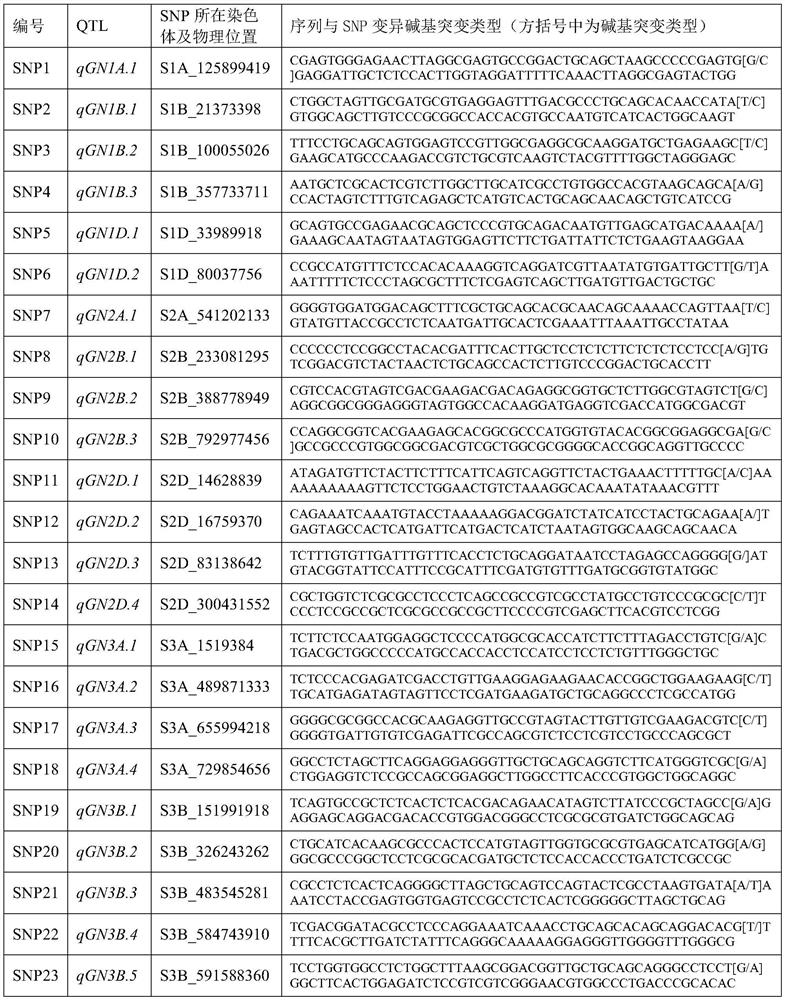
Patents
Literature
99 results about "Genomic selection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
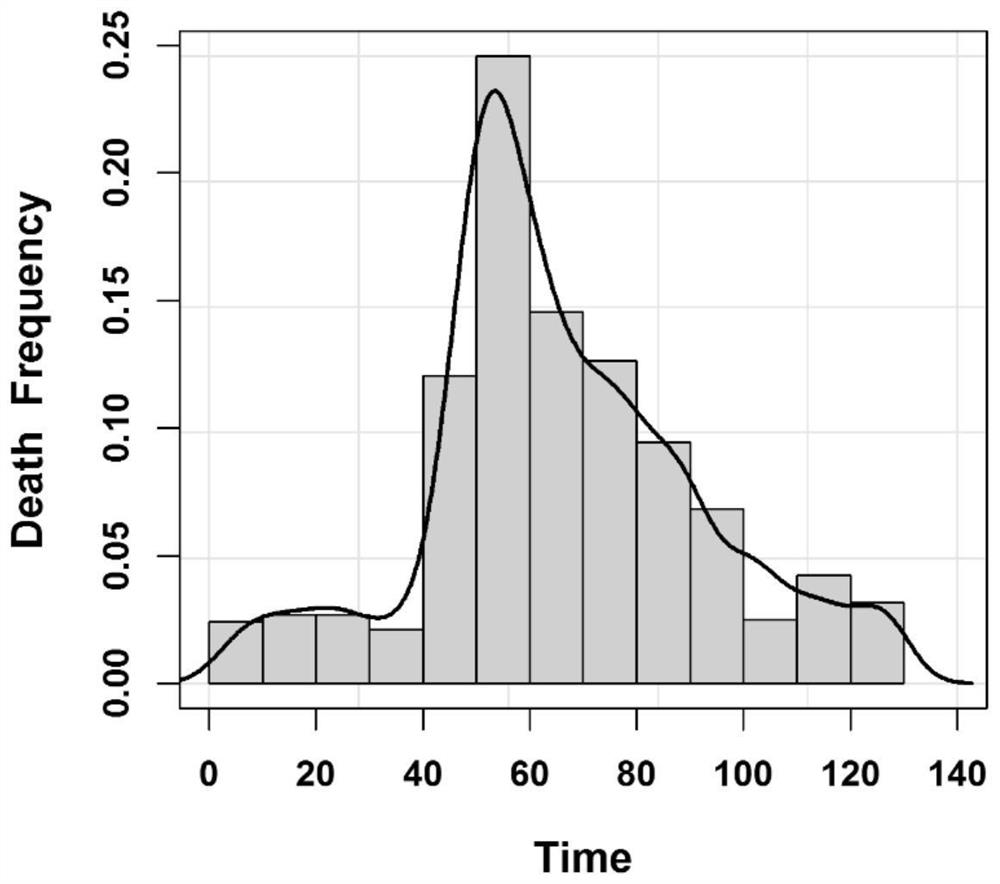
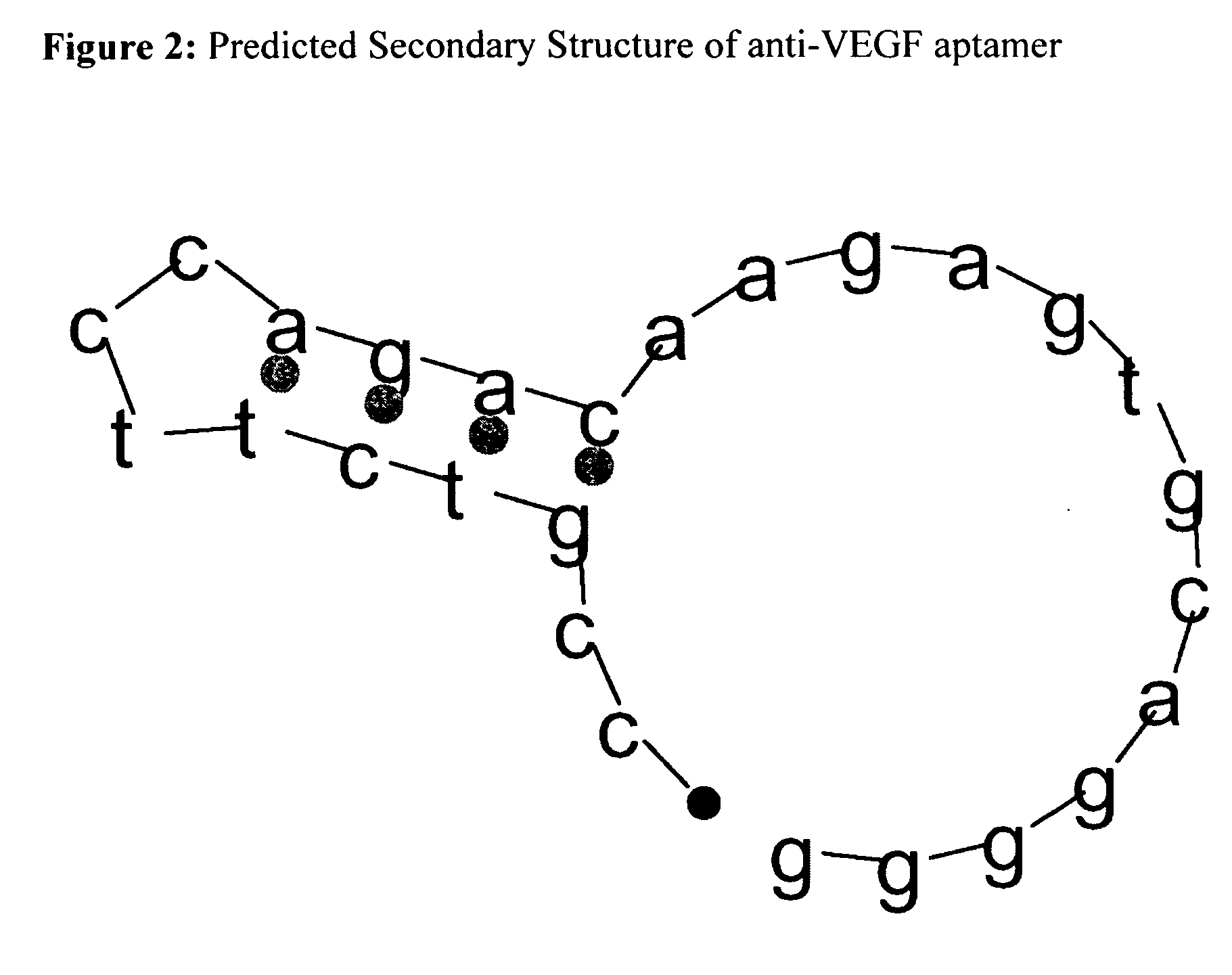
Genomic selection is a form of marker-assisted selection in which genetic markers covering the whole genome are used so that all quantitative trait loci (QTL) are in linkage disequilibrium with at least one marker. 233 views · View 1 Upvoter.
Devices and methods for microarray selection
ActiveUS20120165219A1Avoidance of long hybridization timeImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningTemperature controlTarget enrichment
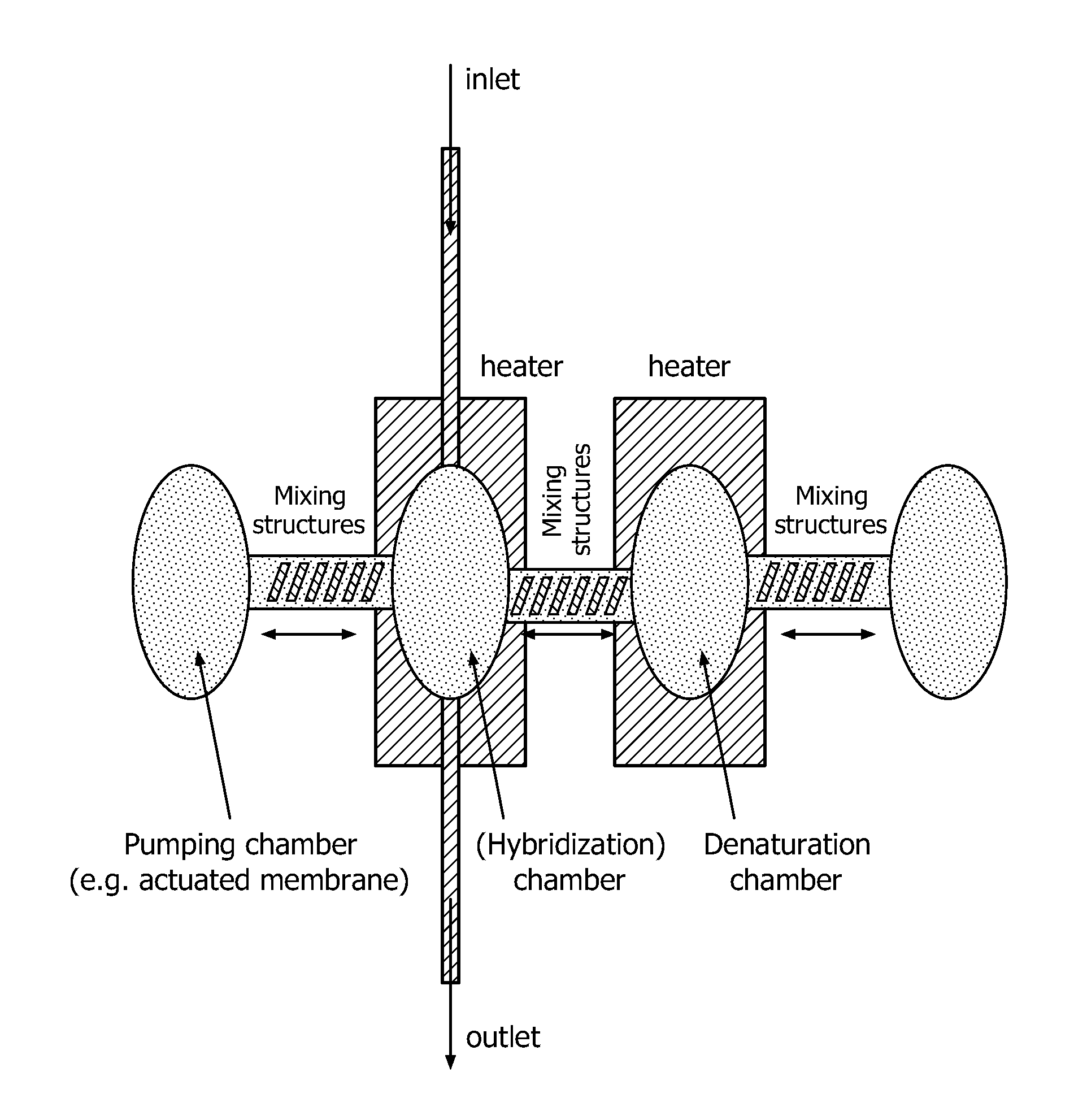
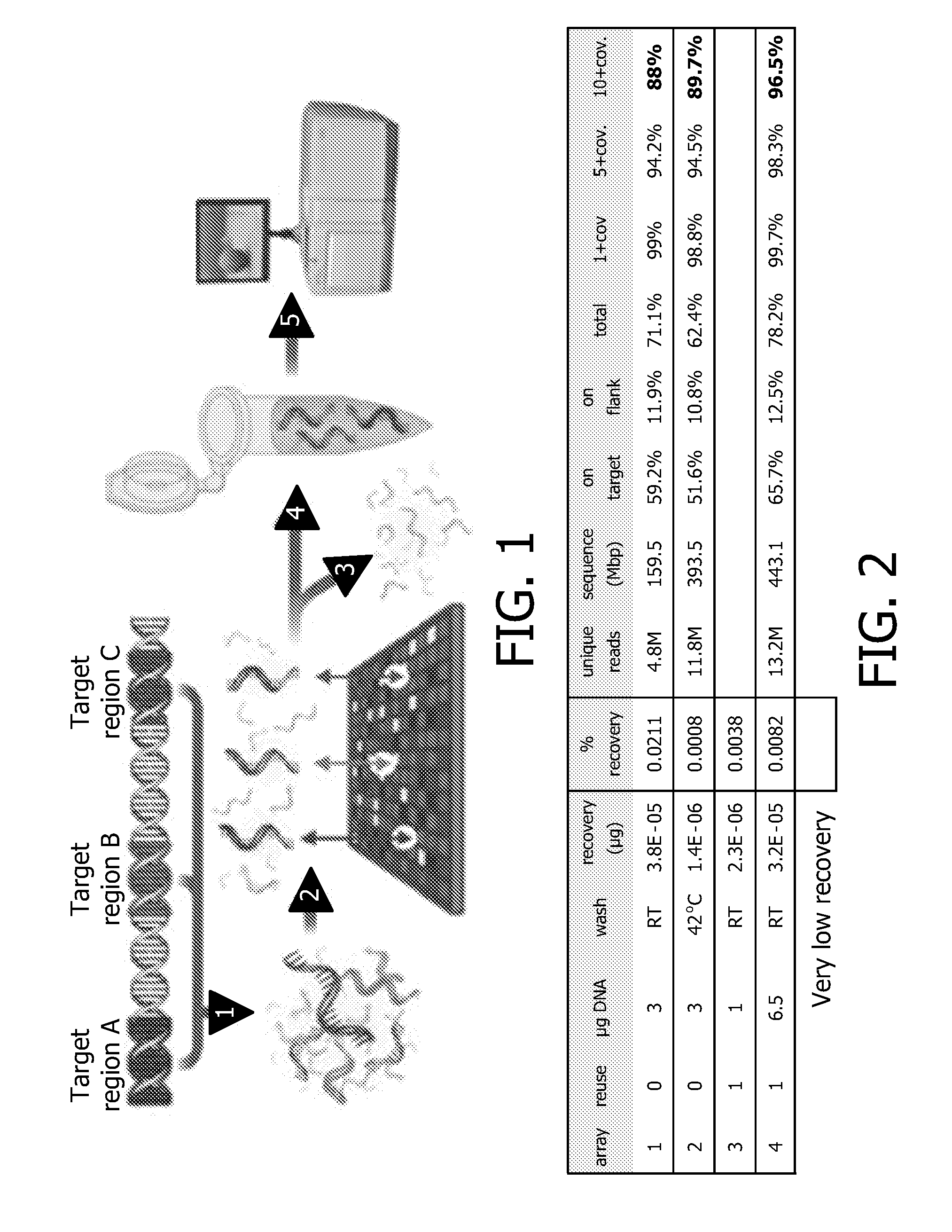
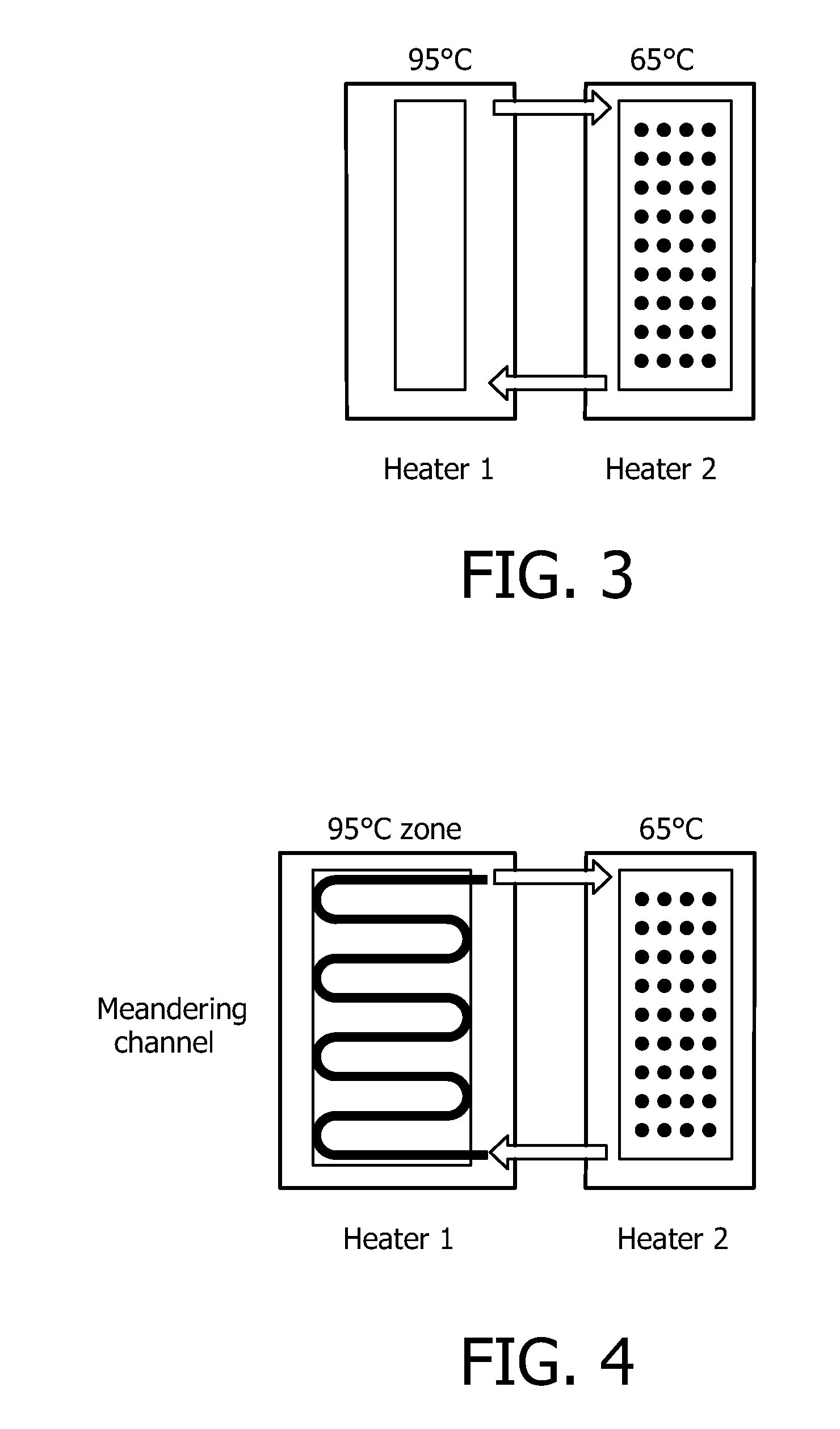
The present invention relates to a device for the specific selection of target molecules, comprising: (a) at least one reaction zone comprising a microarray, wherein the microarray comprises a substrate, on which one or more species of capture molecules are immobilized, comprising one or more temperature control and / or regulating units for controlling and / or regulating the temperature within the zone; (b) at least one non-reaction zone comprising one or more temperature control and / or regulating units for controlling and / or regulating the temperature within the zone, which is in fluid connection with the reaction zone; and (c) at least one transportation means capable of generating and / or regulating a fluid flow between said reaction zone (a) and said non-reaction zone comprising one or more temperature control and / or regulating units (b). The present invention further relates to a device for the specific selection of target molecules wherein the immobilized capture molecules are organized in the microarray in the form of spots, elongated spots and / or lines. In a further aspect the present invention relates to a method of specifically selecting target molecules, comprising the introducing a medium to such a device, performing interaction reactions in a reaction zone, transporting not interacted or not bound target molecules to a zone allowing reactivation of the target molecules and performing additional interaction reactions with the reactivated target molecules at the reaction zone, as well as the use of such a device for specifically selecting target molecules, e.g. for target enrichment also referred to as microarray based genome selection (MGS) in the literature.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
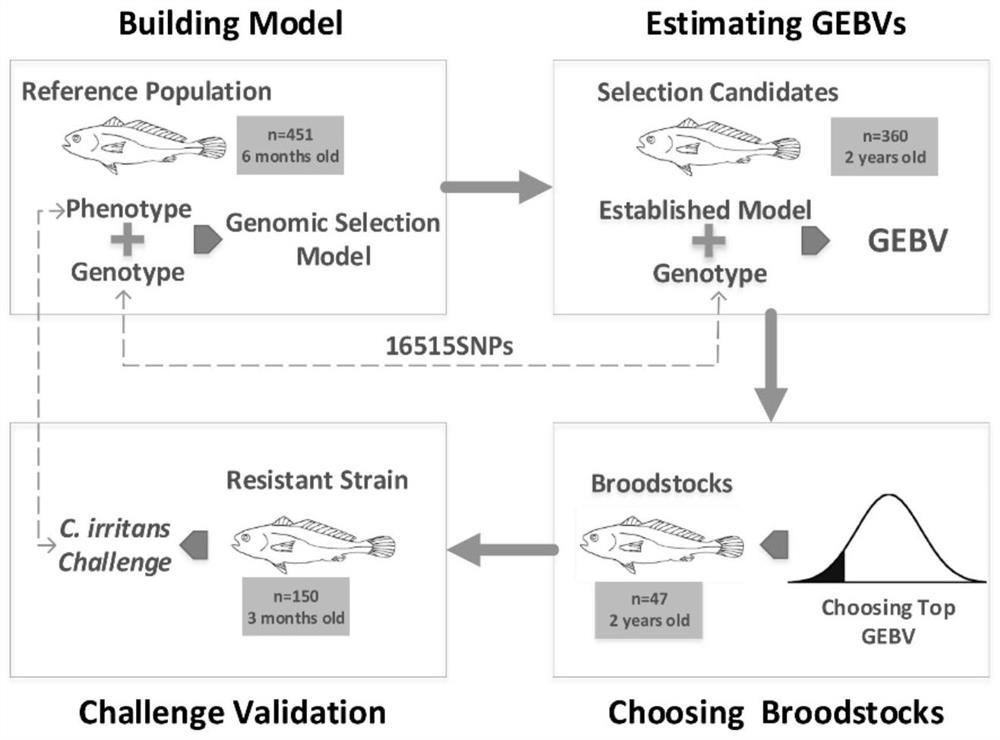
Whole-genome-selection-based method for breeding improved disease-resistant fish varieties
ActiveCN106480189ABreed fastEfficient cultivationMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationBreed typeMolecular breeding
The invention aims at providing a whole-genome-selection-based method for breeding improved disease-resistant fish varieties, thereby overcoming defects in the traditional breeding technology, providing a molecular breeding method for cultivation of improved disease-resistant high-yield fish varieties, solving a problem of lack of a whole-genome selection method in the existing fish breeding industry, providing a technical means for improved disease-resistant fish variety breeding of the fish breeding industry, realizing upgrading of the fish breeding technique, and promoting rapid development of the fish breeding industry. The disease-resistant fish offspring obtained by using the method provided by the invention has the enhanced disease-resistant capability. An experiment result demonstrates that the survival rate from infection and breeding survival rate of a disease-resistant fish offspring that is bred based on the whole genome selection method are higher than those of the control group by 20% to 30%. Using the method provided by the invention, the improved disease-resistant fish breed can be bred rapidly and efficiently; and the disease-resistant capability and breeding survival rate of fish can be enhanced. Therefore, the method provided by the invention has the great application value and broad promotion prospects in the fish breeding industry.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
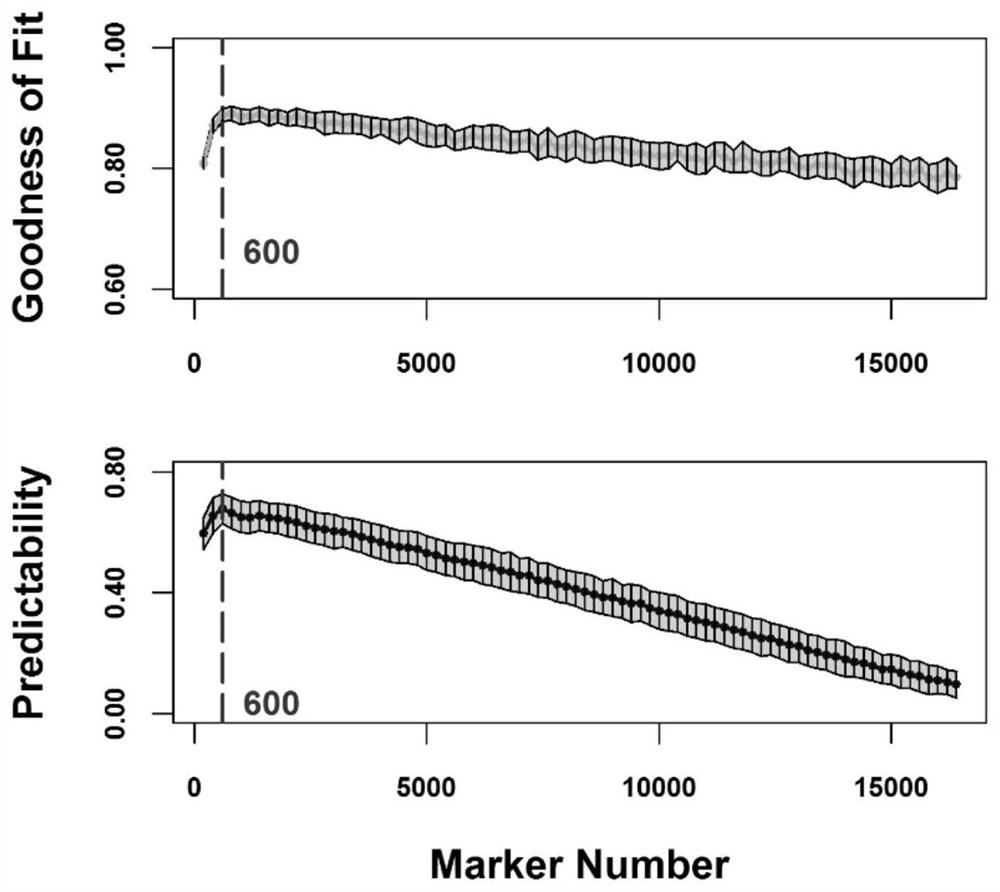
Method for determining optimal SNP quantity as well as performing genome selective breeding on production performance of large yellow croakers through selection markers
ActiveCN107338321AReduce breeding costsLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsGenomic sequencingAgricultural science
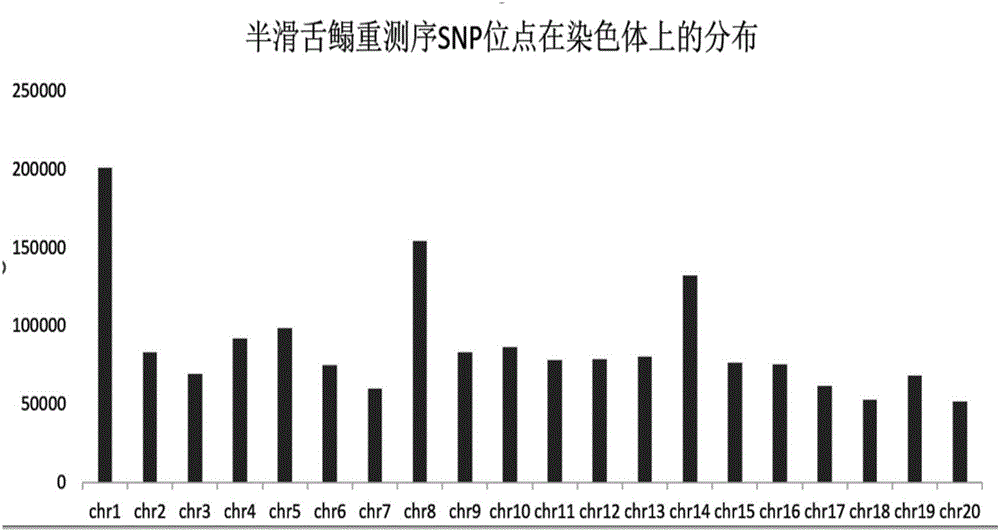
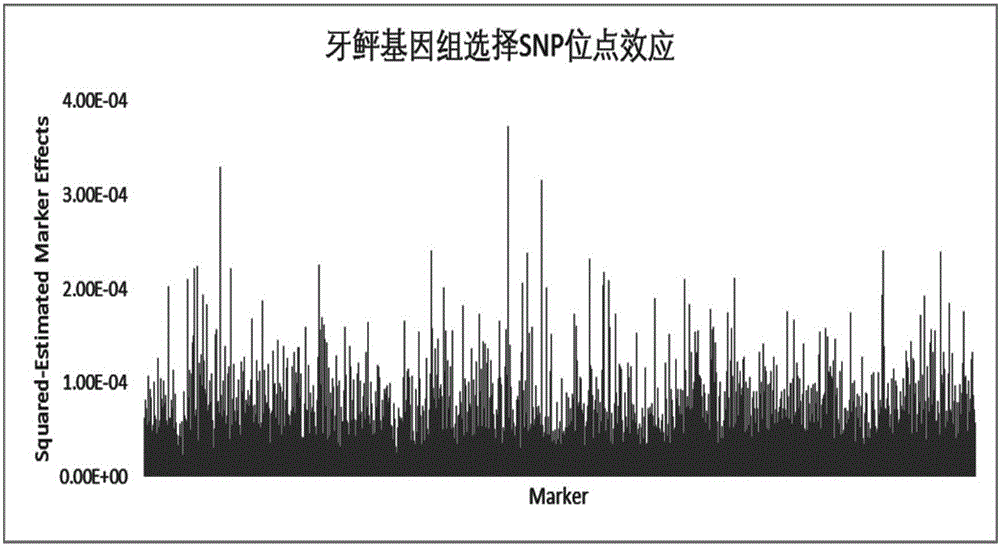
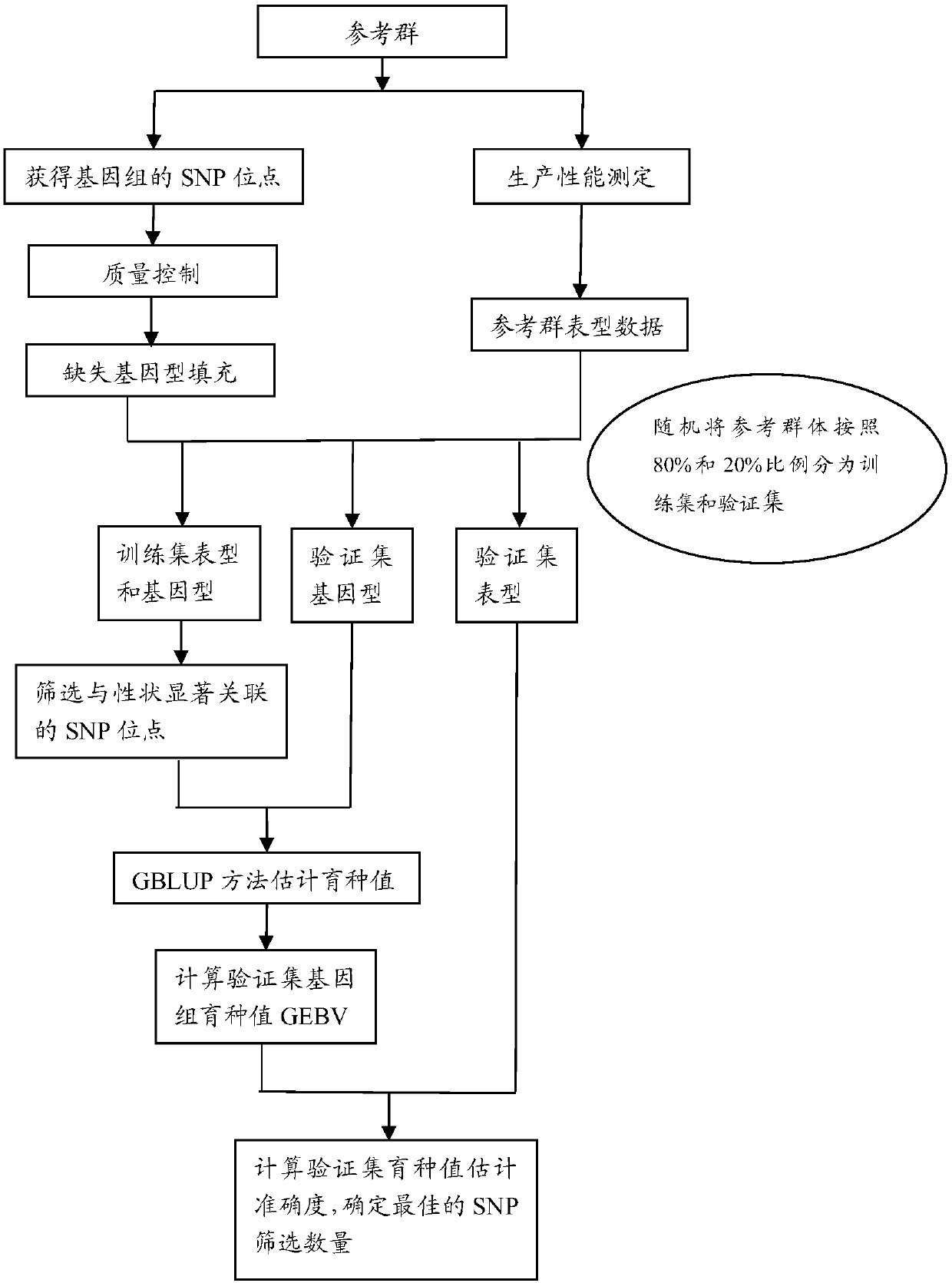
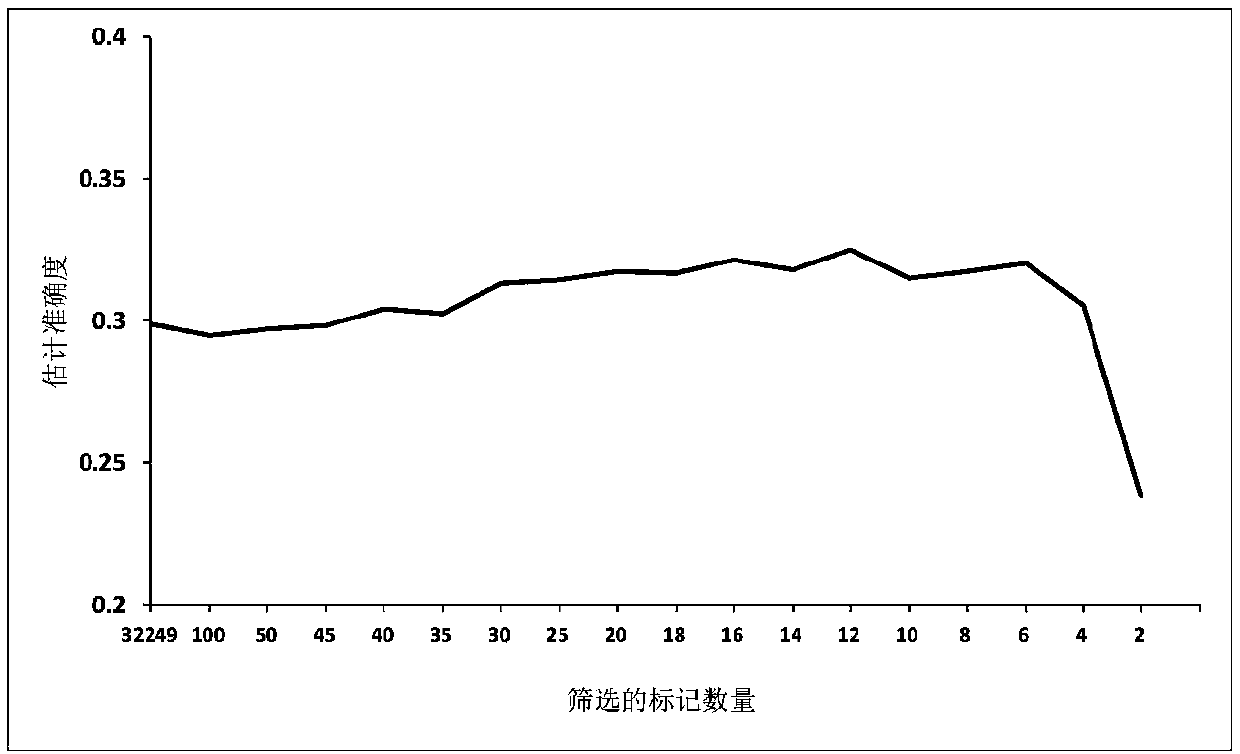
The invention discloses a method for determining optimal SNP quantity as well as performing genome selective breeding on production performance of large yellow croakers through selection markers. The method comprises the following steps: performing phenotype determination and genomic sequencing on the production performance of individuals of a reference group to obtain SNP locus; screening out the qualified SNP locus and supplementing the deleted genotype; dividing the reference group into a training set and a validation set to perform hybridization validation; screening the SNP locus most remarkably associated with the character through single marker analysis, and then calculating GEBV of individuals of the validation set only by using the locus and through a GBLUP method; further obtaining breeding value estimation accuracy under each screening SNP quantity; finally determining the optimal quantity of SNP screening; and according to the optimal quantity, calculating the GEBV by the GBLUP method, further obtaining the breeding value estimation accuracy and performing genome selective breeding according to the value size. By the method, the genomic selection cost on the production performance of the large yellow croakers can be reduced remarkably.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
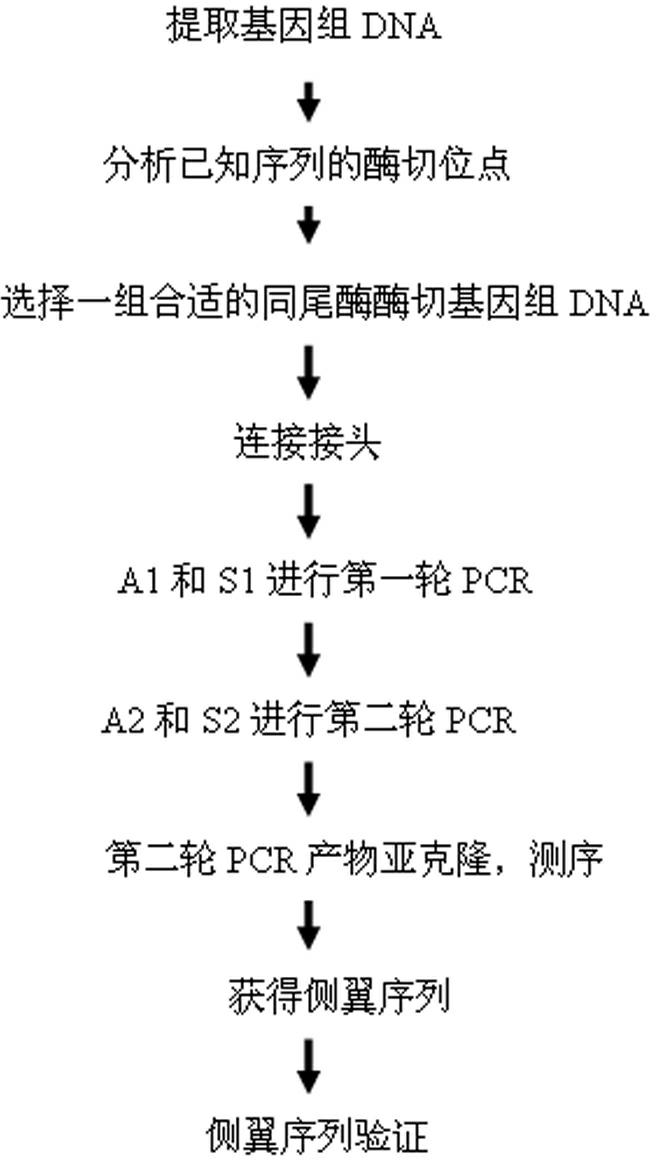
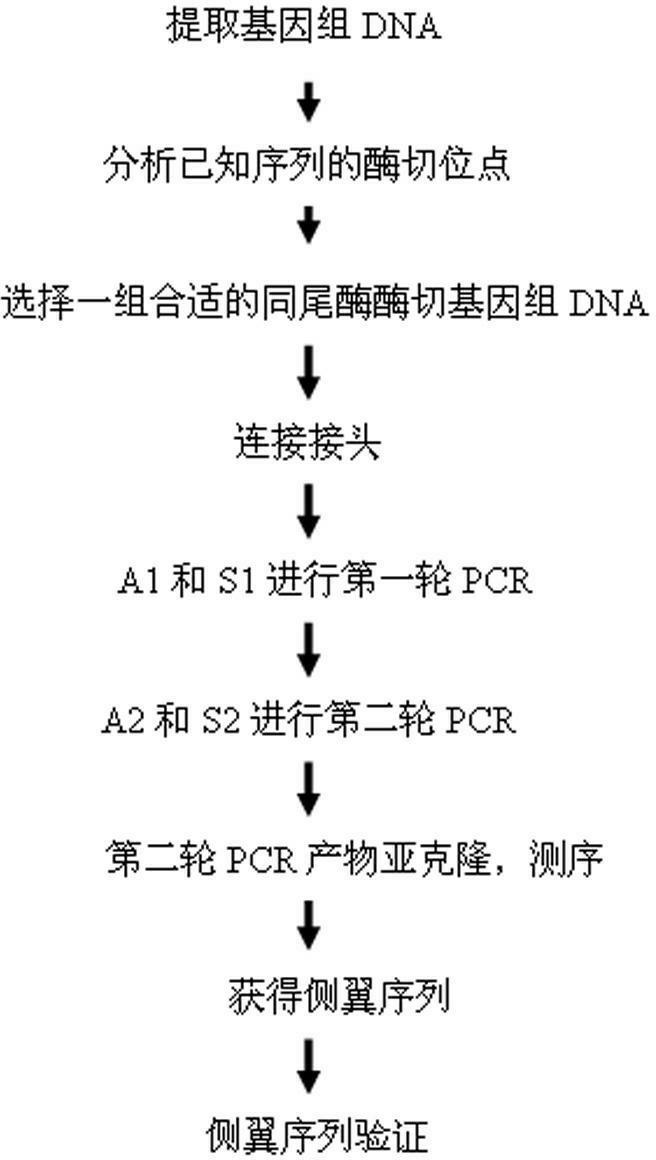
Method for applying adhesive tail end joints to flanking sequence separation
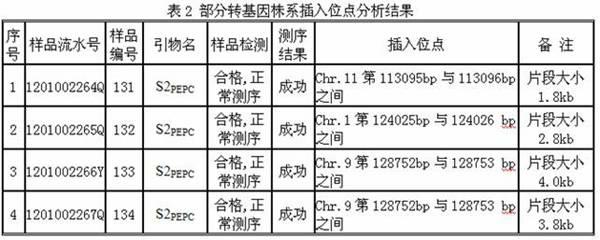
A method for applying adhesive tail end joints to flanking sequence separation includes following steps: 1) extracting a genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) to be detected; 2) selecting isocaudarner and designing and synthesizing corresponding joints; 3) digesting the genome by the isocaudarner to form DNA segments with identical adhesive tail ends; 4) detecting digestion quality in an electrophoresis manner, quantifying the concentration of the DNA segments, connecting the joints with digestion products of the genome, and forming each DNA segment with 'the joint, the digestion segment and the other joint' sequentially; 5) purifying the DNA segments with 'the joints, the digestion segments and the other joints' sequentially, and performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction); 6) recycling the segments obtained from the step 3) and sequencing; 7) analyzing a sequencing result and obtaining an unknown flanking sequence of a known sequence; and 8) checking the unknown flanking sequence. The method for flanking sequence separation is high in connection efficiency and generality and low in cost.
Owner:HUNAN HYBRID RICE RES CENT
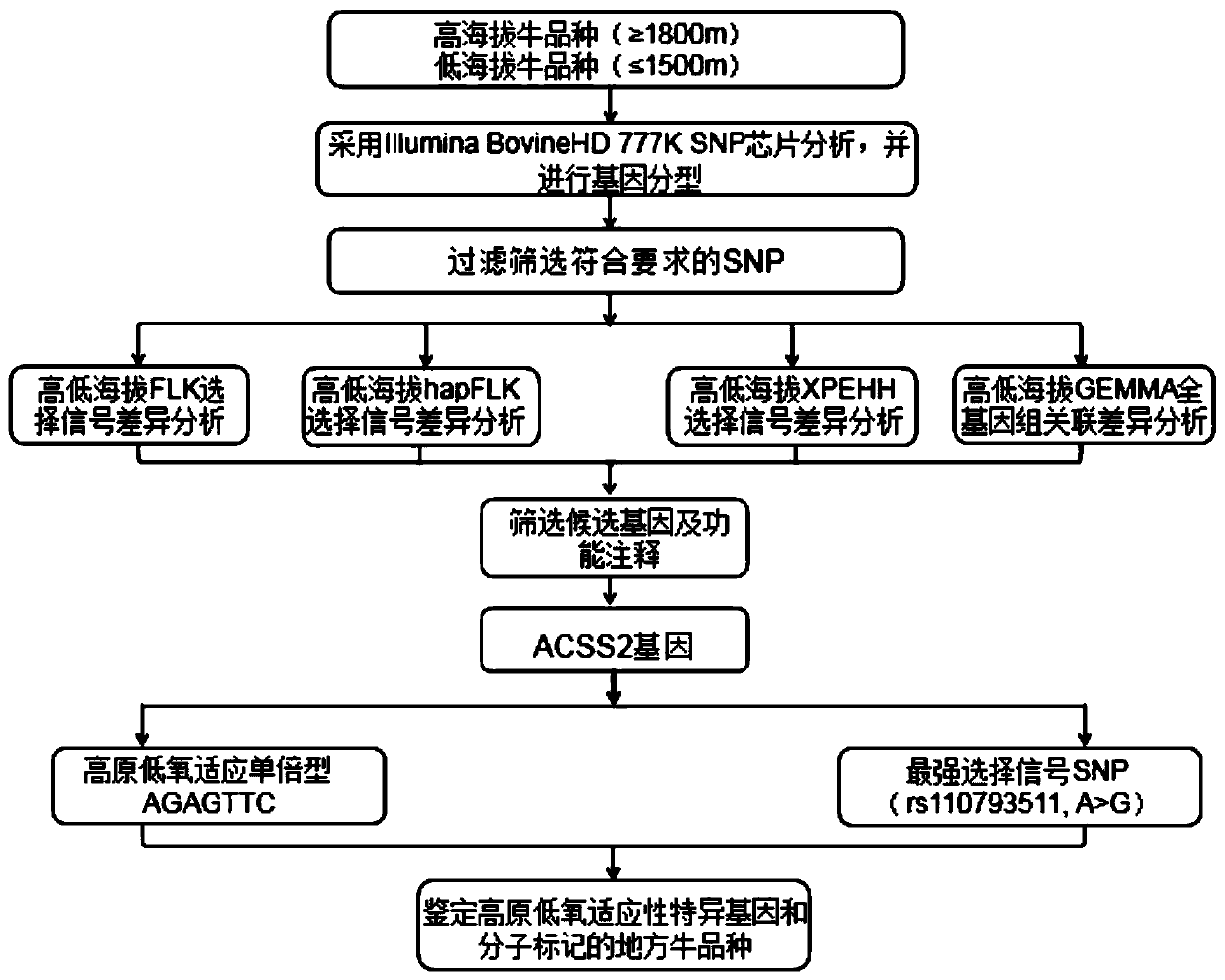
Method for screening cattle high altitude hypoxia adaptation molecular markers and application thereof
ActiveCN109994153AEfficient and accurate screeningPrecise screeningMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsHigh altitude hypoxiaGenome evolution
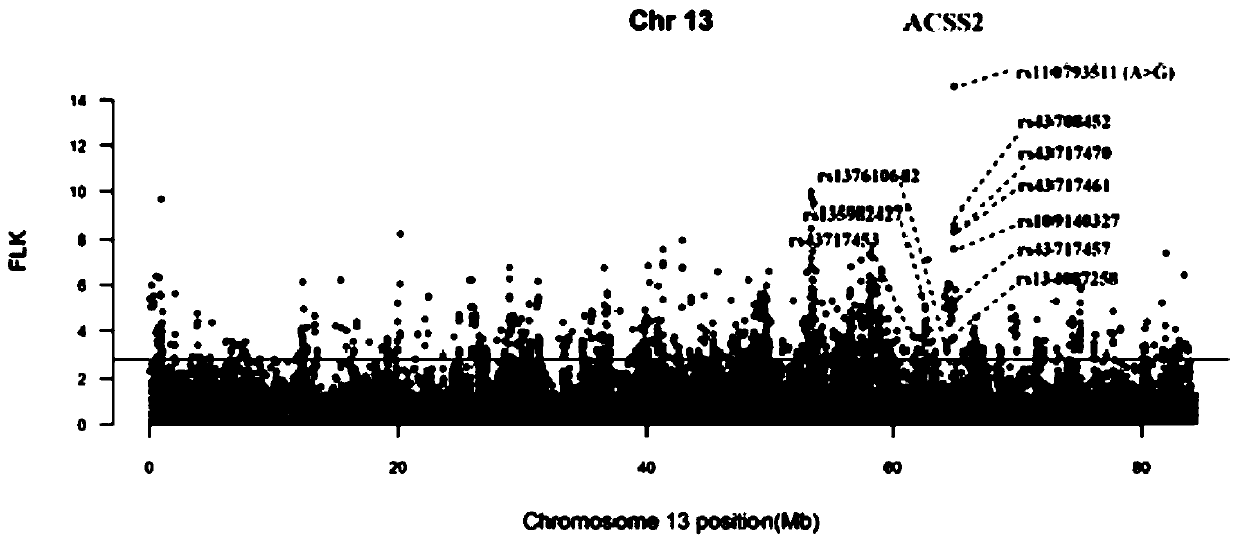
The invention provides a method for screening cattle high altitude hypoxia adaptation specific molecular marker, and furthermore a cattle kind or individual which is suitable for high altitude hypoxiasurvival is screened through the specific marker. The method aims at a high altitude hypoxia adaptation heredity characteristic of a kettle kind, and selects local cattle kinds which are distributedin high altitude regions at aspects of genome evolution, selecting and adapting. Multiple genome selecting signals, a full-genome association analysis method and a strategy are combined. Key genes andmolecular makers which are suitable for high altitude hypoxia are efficiently and accurately screened. Reasonable method designed is realized. The detecting method according to the key gene and marker designing has advantages of high accuracy, and convenient application operation. According to the method of the invention, through analyzing different altitude cattle kinds, a gene ACSS2 which is related with high altitude hypoxia adaptation and a haplotype thereof are found; and furthermore a specific SNP which bears a strongest selecting signal is positioned; and the method realizes an important meaning and a high practicability value for cattle molecule breeding operation.
Owner:DAIRY CATTLE RES CENT SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI +1
Method for performing forest tree multiple-trait pyramiding breeding based on multiple-trait genomic selection
ActiveCN106755441AReduce workloadPrecision breedingMicrobiological testing/measurementHybridisationData acquisitionMultiple traits
The invention discloses a method for performing forest tree multiple-trait pyramiding breeding based on multiple-trait genomic selection. The method sequentially comprises the following steps: clonal individual phenotypic data acquisition; clonal pedigree information and A matrix construction or SNP marker typing data and G matrix construction; multiple-trait model establishment and data analysis. The method disclosed by the invention has the benefits that the workload of forest tree trait phenotype determination can be reduced, and no lamination by the correlation degree between traits and markers exists; compared with a conventional traditional progeny determination technology, multiple-trait orientation and accurate breeding can be realized, an obtained hybrid offspring have reliable productivity and genetic background, the forest tree multiple-trait pyramiding breeding period is significantly shortened, and no specific limitation on tree species and test forest types exists; the forest tree multiple-trait pyramiding breeding purpose can be quickly achieved; therefore, the application prospect is wide.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Rapid maize breeding and population improvement method
ActiveCN109536629AAccurate phenotypeControllable genetic diversityMicrobiological testing/measurementPollinationGenotype
The invention provides a rapid maize breeding and population improvement method, wherein the method includes the following steps: carrying out genotype identification of a basic population by using ahigh-density SNP molecular marker, combining with field phenotype identification, selecting an excellent individual population, and making the excellent individual population rapidly produce a large number of DH lines by using a double-haploid technology; carrying out multi-point field phenotype identification and combining ability determination on the DH population, selecting individual plants with good performance, carrying out molecular marker identification, and analyzing and mining target trait associated marker loci; establishing a whole-genome selection model; screening a plurality of best DH lines with the established whole-genome selection model, and carrying out mixing pollination to form a new basic population; utilizing the double-haploid technology again to make the basic population rapidly produce a large number of DH lines, carrying out phenotypic prediction screening by the whole-genome selection model, carrying out multi-point field phenotype identification on the screened excellent plants, and screening good selfing lines; and circulating the steps to improve the basic population, and carrying out selected breeding of more good selfing lines.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
Tilapia genome selective breeding method
PendingCN111128306AAccelerate cultivationImprove survival rateMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsBiotechnologyDisease resistant
The invention provides a method for cultivating disease-resistant tilapia improved varieties based on a genome selection technology. The method comprises the following steps: selecting an optimal SNPmarker density by comparing the prediction accuracy of GBLUP and Bayes Cpi under different marker densities; evaluating the prediction accuracy of other genome selection methods under the selected marker density; and comprehensively considering calculation time and prediction accuracy, and selecting a genome estimation breeding value method suitable for disease-resistant breeding of tilapia. The invention provides the method for rapidly and accurately estimating the tilapia disease-resistant trait genome estimation breeding value, wherein the filial generation disease resistance obtained by using the method is higher than the filial generation disease resistance of a control group. By using the method, breeding of disease-resistant tilapia varieties can be accelerated, the tilapia breedingyield is increased, and healthy development of the tilapia breeding industry is promoted.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Method for breeding good corn germplasm high in combining ability
InactiveCN111528087AIncrease the frequency of favorable allelesIncrease productivityPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyGenetics
The invention belongs to the field of breeding techniques, and particularly relate to a method for breeding good corn germplasm high in combining ability. The method comprises the steps of firstly collecting good selfing lines for constructing an initial group, performing genotype identification and heterotic group division, selecting specific hybrids as test hybrids for assessing the combining ability expression of each material in the initial group, and establishing a complete genome selection model; then in the heterotic group, according to the combining ability assessment result, performing breeding step by step to obtain good single plants, and further obtaining homozygosis selfing lines; and finally, performing genotype identification on the homozygosis selfing lines, forecasting thecombining ability according to the complete genome selection model, and reserving the homozygosis selfing lines having high combining ability estimated value namely obtaining the good germplasm highin combining ability. The method disclosed by the invention is high in breeding efficiency and short in breeding cycle, and can accelerate the breeding process of good germplasm.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Genomic selection and sequencing using encoded microcarriers
ActiveUS20110311975A1Add information contentShorten the timeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleotideA-DNA
The present invention relates to a method for determining the sequence of a nucleic molecule. Herein a capture oligonucleotide probe is attached to an encoded microcarrier, wherein the code of said microcarrier identifies the sequence of said oligonucleotide probe. The capture oligonucleotide probe is hybridized with a sample comprising nucleic acids molecules, wherein said DNA fragment comprises a sequence which is complementary to the sequence of the capture oligonucleotide probe. The sequence of the DNA molecule is determined, wherein the capture oligonucleotide probe serves as a primer for a DNA polymerase, in the case of single molecule sequencing this is a sequencing primer. After the sequence determination, the nucleotide sequence of the capture oligonucleotide probe is identified by determining the code on the microcarrier, which corresponds with the capture oligonucleotide probe. This sequence information directly identifies the location of the sequenced DNA fragment on the genome, allowing direct comparison.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method for performing whole genome selective breeding by selecting extreme character individual
ActiveCN105868584AAchieving Genome-wide Selective BreedingLower sequencing costsBiostatisticsSpecial data processing applicationsGenomic sequencingTyping
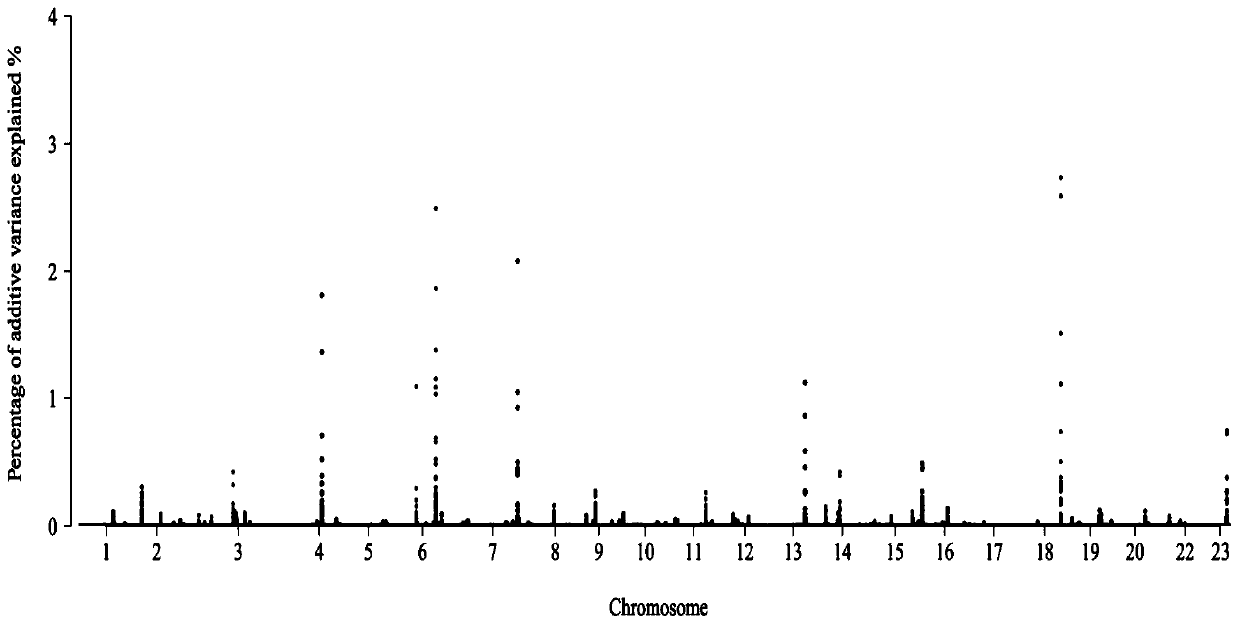
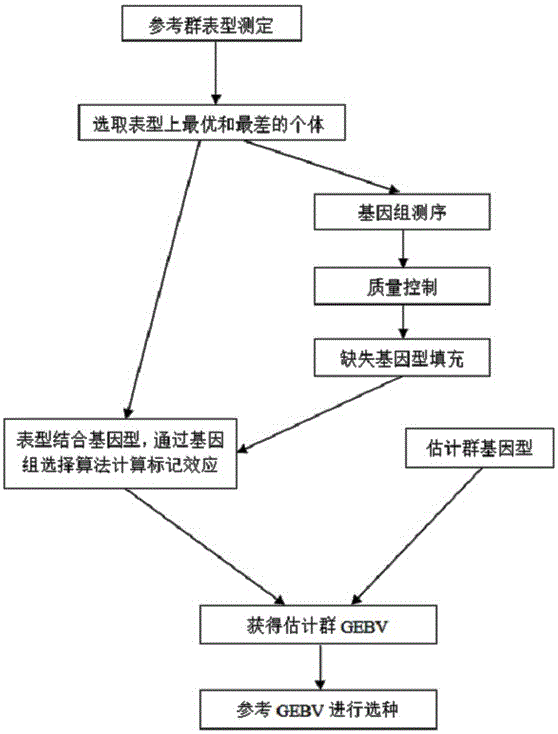
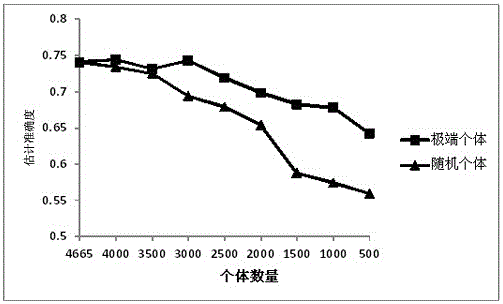
The invention discloses a method for performing whole genome selective breeding by selecting extreme character individuals. The method comprises the following steps: as for a certain amount of characters, selecting part of individuals of which the character expression is extreme, wherein the individuals of highest character expression and the individuals of lowest character expression respectively account for one half; constructing an estimation group, and performing character measurement on the estimation group; performing genome sequencing and whole genome SNP label excavation on an extreme character reference group and the estimation group; calculating the breeding effect value of each SNP label according to phenotypic values and gene type information of the extreme individuals, performing whole-genome typing on the estimation group so as to obtain the breeding values of the individuals in the estimation group, and performing final seed selection on the estimation group. According to the method, the influence on genomic estimated breeding value estimation accuracy is as less as possible, and the genome sequencing expense is greatly saved; the influence of size of a reference group on the genome selection accuracy is reduced by virtue of the extreme individuals, thereby being beneficial to relevant research on rare sample species and providing a new thought on performing genome group selection on various species.
Owner:XIAMEN SHENGJI TECH CO LTD
Method for improving aquatic animal whole-genome selective breeding efficiency
ActiveCN110867208AImprove accuracyLow parting costClimate change adaptationProteomicsAquatic animalZoology
The invention discloses a whole-genome selective breeding method suitable for aquatic animals. Specifically, high-density SNP typing is carried out on individuals of a breeding basic group or a core group; the phenotypic value of the target character is determined; whole-genome association analysis (GWAS) is carried out by utilizing the SNP typing data and the phenotypic data to obtain a significance P value of each SNP marker; the marks are sorted from low to high according to P values; according to different traits, different marker number combinations sorted in the top are selected according to the P values, analysis is performed by adopting methods such as GBLUP, Bayes B and the like, the prediction accuracy of the different marker numbers selected according to the P values is evaluated through cross validation, and finally, the marker combination with the highest prediction accuracy is determined. SNP typing is conducted on the candidate population or the next-generation breedingpopulation through the screened optimal marker combination, breeding value prediction is conducted on the candidate population or the next-generation breeding population through adoption of GBLUP or BayesB or ssGBLUP or other methods, and therefore, the prediction accuracy can be remarkably improved.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Whole genome selection model for predicting nicotine content of tobacco and application thereof
PendingCN111223520ALow costIdeal nicotine levelBiostatisticsProteomicsTobacco nicotineNicotiana tabacum
The invention discloses a whole genome selection model for predicting the nicotine content of tobacco and application thereof, and the whole genome selection model for predicting the nicotine contentof the tobacco is Bayes BNIC; in order that the prediction precision of the model on the phenotypic value of the nicotine content of the tobacco is optimal, core parameter values such as the number (n1) of molecular markers of the candidate prediction model Bayes B, the scale (n2) of a training group, the ratio (n3) of the training group to a test group and a model prediction precision value (n4)are clearly stipulated. The application refers to the application of the whole genome selection model Bayes BNIC to analyze the genotype data of a tobacco group so as to predict the nicotine content of the tobacco group. The tobacco nicotine content whole genome selection model Bayes BNIC provided by the invention can accurately predict the nicotine content value of each plant in a tobacco group according to the genotype of the tobacco group, so as to realize the cultivation of excellent tobacco varieties (lines) with different nicotine content levels in tobacco quality breeding.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI
Genome selection method for breeding Plectropomus leopardus disease-resistant improved variety
InactiveCN114015789AImprove survival rateMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationBiotechnologyZooid
The invention provides a genome selection method for breeding Plectropomus leopardus disease-resistant improved variety. The method comprises the following steps of: constructing a Plectropomus leopardus disease-resistant reference group by using Plectropomus leopardus young fishes from different geographical sources, and taking individuals which have disease-resistant phenotypes but are not included in the reference group as a verification group, wherein the Plectropomus leopardus young fishes used for constructing the disease-resistant reference group is obtained after disease resistance screening; and predicting a disease-resistant character genome estimation breeding value of the verification group by using the selected SNP sites and the constructed Plectropomus leopardus disease-resistant reference group, and selecting alternative parents by using the disease-resistant character genome estimation breeding value to obtain individuals with strong disease resistance for disease-resistant improved variety cultivation. According to the invention, the method for breeding the Plectropomus leopardus disease-resistant improved variety based on the whole-genome selection technology can be used for screening parents with high disease resistance, the selected parents can be directly used for breeding Plectropomus leopardus, and an efficient technical means is provided for improving the survival rate of Plectropomus leopardus breeding group.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI +1
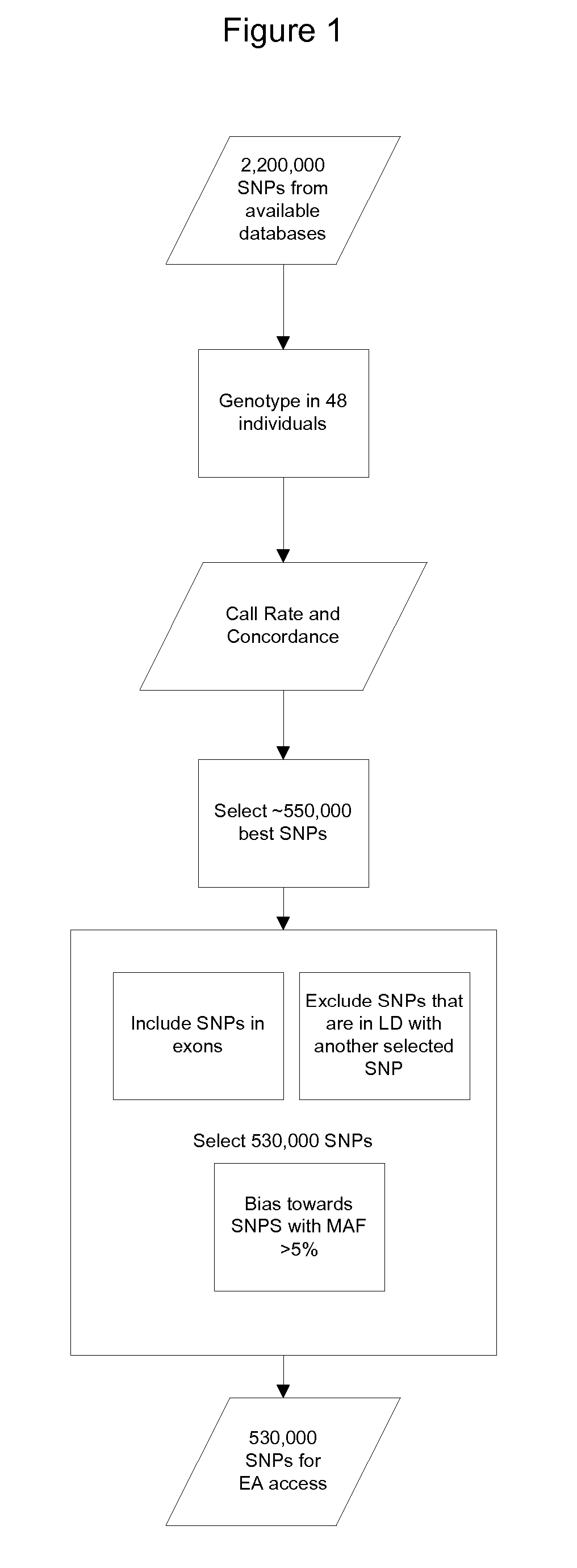
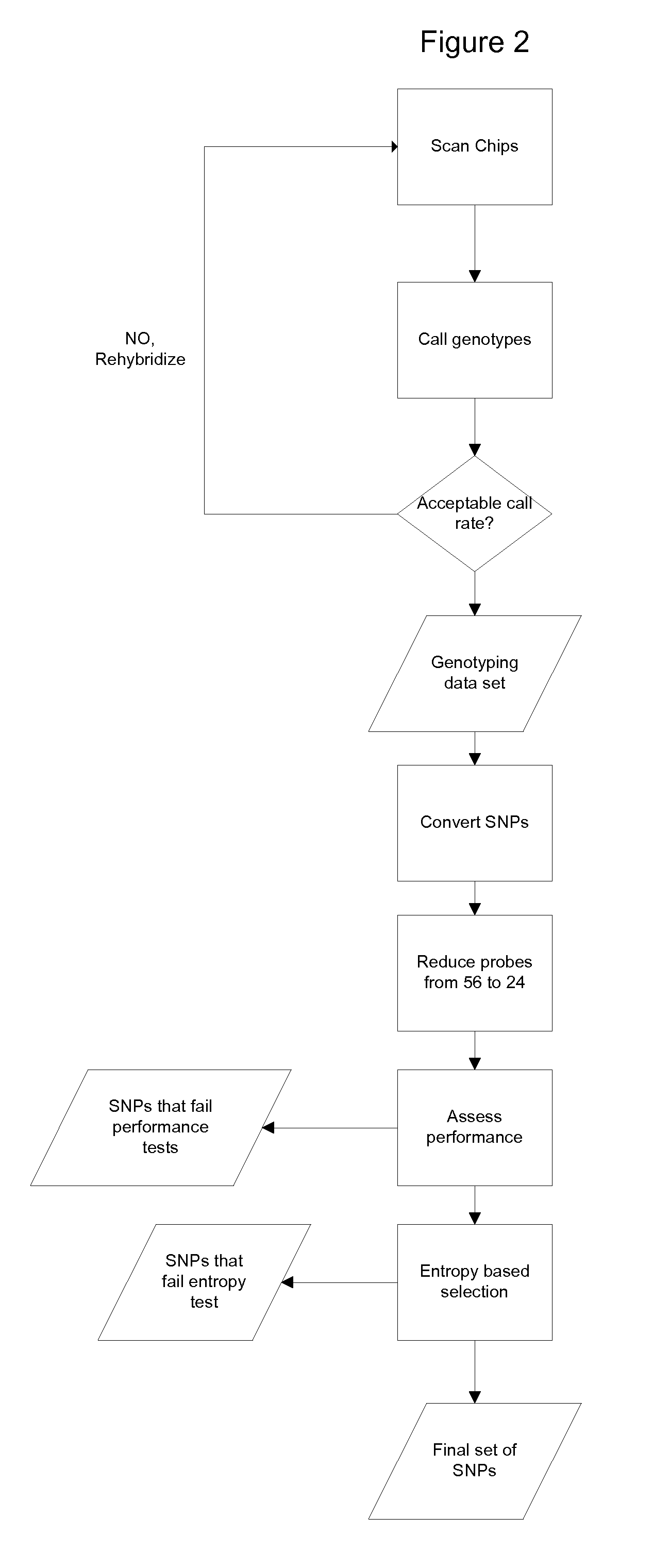
Methods for Selecting a Collection of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms
ActiveUS20070016382A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingNucleotideNucleic Acid Probes
The invention relates to the selection of a collection of relevant single nucleotide polymorphisms across a genome to design a nucleic acid probe array. As such, the invention relates to diverse fields impacted by the nature of genetics, including biology, medicine, and medical diagnostics.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Genomic selection and sequencing using encoded microcarriers
ActiveCN102333890ALarge amount of informationFacilitated sequence changeMicrobiological testing/measurementThin material handlingNucleotideA-DNA
The present invention relates to a method for determining the sequence of a nucleic molecule. Herein a capture oligonucleotide probe is attached to an encoded microcarrier, wherein the code of said microcarrier identifies the sequence of said oligonucleotide probe. The capture oligonucleotide probe is hybridized with a sample comprising nucleic acids molecules, wherein said DNA fragment comprises a sequence which is complementary to the sequence of the capture oligonucleotide probe. The sequence of the DNA molecule is determined, wherein the capture oligonucleotide probe serves as a primer for a DNA polymerase, in the case of single molecule sequencing this is a sequencing primer. After the sequence determination, the nucleotide sequence of the capture oligonucleotide probe is identified by determining the code on the microcarrier, which corresponds with the capture oligonucleotide probe. This sequence information directly identifies the location of the sequenced DNA fragment on the genome, allowing direct comparison.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Crop genetic breeding method for high-efficient utilization of heterosis
ActiveCN111771716AEfficient selectionEasy to implementPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyHeterosis
The invention relates to a crop genetic breeding method for high-efficient utilization of heterosis. Utilization of heterosis currently is that breeding of hybrid parents and extensive testcross are mainly used; reciprocal recurrent selection is also applied to hybrid breeding of crops, in particular corns, recently; with the development of a high-throughput labelling technology, whole genome selection is rapidly applied in crop heterosis utilization; effective prediction on complex quantitative traits is realized by utilization of a molecular marker covering the whole genome; but, genomic selection and reciprocal recurrent selection are not applied to crop genetic breeding at the same time currently. The invention provides that a genomic selection method and a reciprocal recurrent selection technology are applied to crop heterosis utilization at the same time, so that a heterosis utilization method, which is high-efficiency to select, easy to implement and low in material cost and manpower use cost, is provided; furthermore, the invention innovatively provides that a genomic selection technology is applied to selection of basic parents of reciprocal recurrent selection population;simultaneously, the breeding efficiency is increased by utilization of a chemical emasculation technology; and thus, the breeding accuracy and high efficiency are greatly increased.
Owner:江西省农业科学院作物研究所
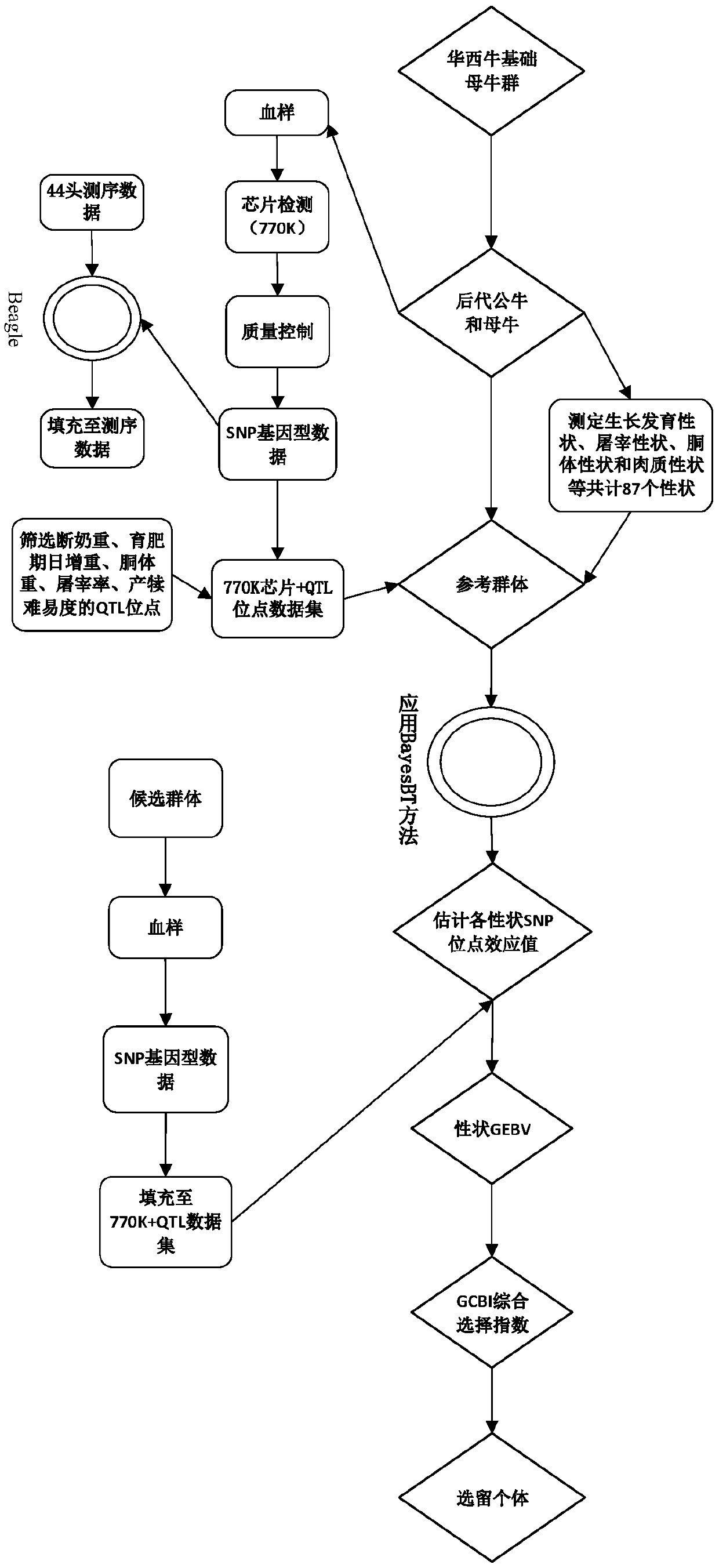
Western China cattle genome selection method
ActiveCN111243667AImprove selection efficiencyReduce breeding costsMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsBiotechnologyMolecular breeding
The invention discloses a Western China cattle genome selection method, and aims to solve the problem of insufficient seed production and supply capacity of existing beef cattle breeding groups. The method comprises the following specific steps: 1, constructing a reference population and determining economic traits; 2, performing genotyping on the reference population, and performing processing and quality control on data; 3, performing genotype data filling to obtain sequencing data, and then performing QTL locus screening; 4, calculating effect values of all SNP markers of each character inthe reference population; and 5, obtaining a candidate population genome breeding value, and calculating the comprehensive selection index of individuals according to the genome estimated breeding value of each character. The invention aims to establish the efficient and high-quality breeding method for the Chinese western cattle based on the genome selection technology, comprehensively improve the beef cattle population selection efficiency in China, greatly save the breeding cost, provide a molecular breeding method for the breeding of the high-quality Chinese western cattle, and promote therapid development of the beef cattle breeding industry.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Breeding method of pseudosciaena crocea resisting cryptocaryon irritans based on whole genome selection
ActiveCN112273291ASolve the problem that the parents cannot carry out the resistance testSolve the problem that the resistance test cannot be performedMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationZooidAnimal science
The invention discloses a breeding method of pseudosciaena crocea resisting cryptocaryon irritans based on whole genome selection, and belongs to the field of animal disease resistance breeding. The method comprises the steps of establishing a reference group; performing resistance trait measurement on the reference group; establishing a breeding group; carrying out genotyping on the reference group and the breeding group; establishing an optimal whole genome selection model; estimating a genomic breeding value GEBV of the breeding group; selecting individuals, with the GEBV ranked in the front, of the breeding group as parent fishes according to a certain selection intensity, and propagating to generate a first filial generation resisting the cryptocaryon irritans; and conducting cryptocaryon irritans toxicity attack verification on the first filial generation with resistance. The insect resistance is obviously improved; and the estimation accuracy of the genomic breeding value of thebreeding group is improved, the breeding period is greatly shortened, high-resistance offspring can be obtained within one generation, the economic loss of the cryptocaryon irritans to the pseudosciaena crocea breeding industry is reduced, reference and basis are provided for disease-resistant breeding of other fishes, and the method has a wide application prospect.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
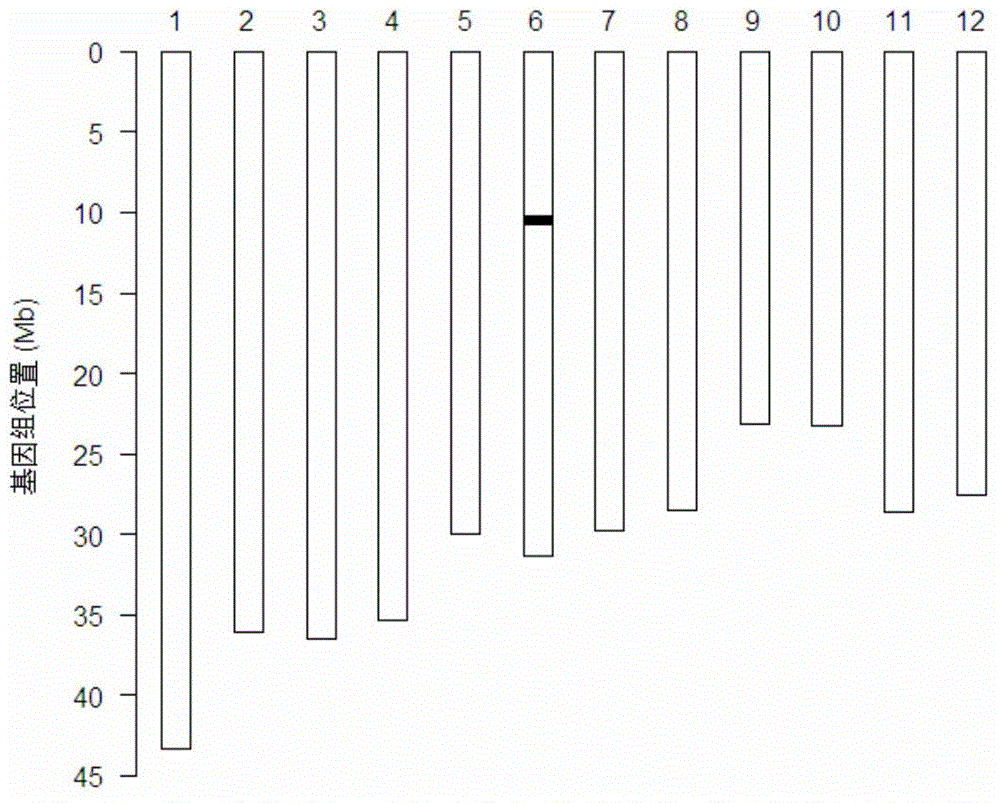
Seeding method of target genome DNA fragment-containing plants
ActiveCN105567790AImprove breeding efficiencySpeed up the breeding processMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationHigh densityResistant genes
The invention provides a method for rapidly and accurately seeding target genome DNA fragment-containing plants on the basis of a whole-genome seeding technology. The method comprises the following steps: 1, hybridizing, backcrossing and selfing a donor plant parent containing the fragment and a recurrent parent which is a receptor plant parent free from the target genome DNA fragment; 2, using a foreground selection marker in the breeding process to carry out foreground selection; 3, using a high density molecular marker detection technology in the breeding process to carry out whole genome background selection; and 4, using above steps until the target plants with homologous recombination of two sides of the target genome DNA fragment, target genome DNA fragment homozygosis and complete background return. The invention also provides a seeding method of blast-resistant gene recombinant DNA fragment-containing plants. The stable plants having background being completely consistent with that of the receptor parent and only containing the donor parent target genome DNA fragment can be rapidly obtained through accurate foreground selection and high density molecular marker whole genome background selection.
Owner:CHINA NAT SEED GRP
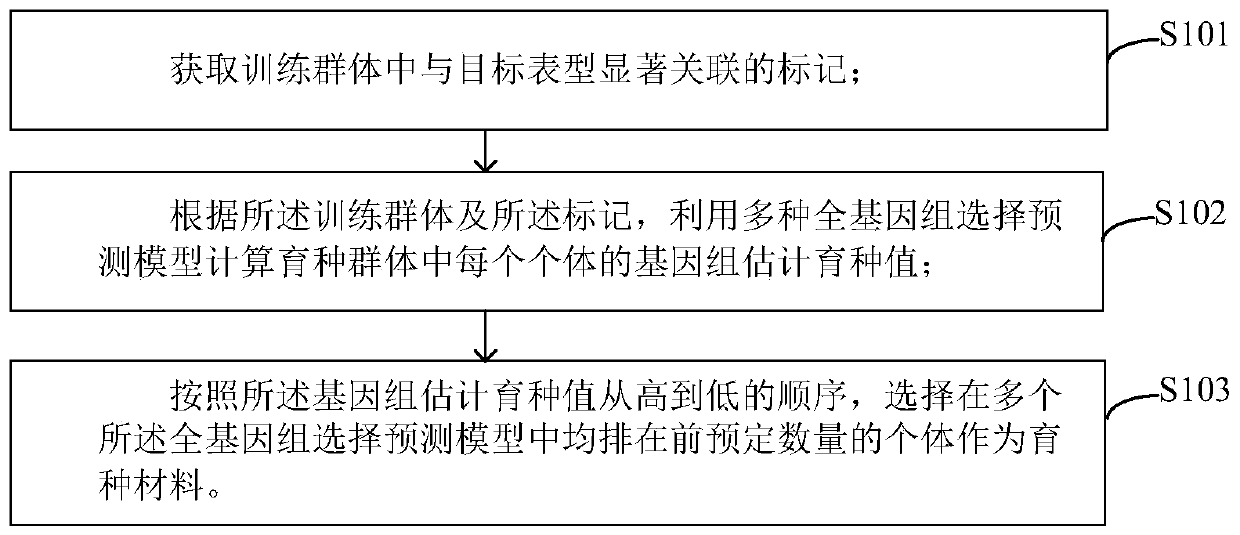
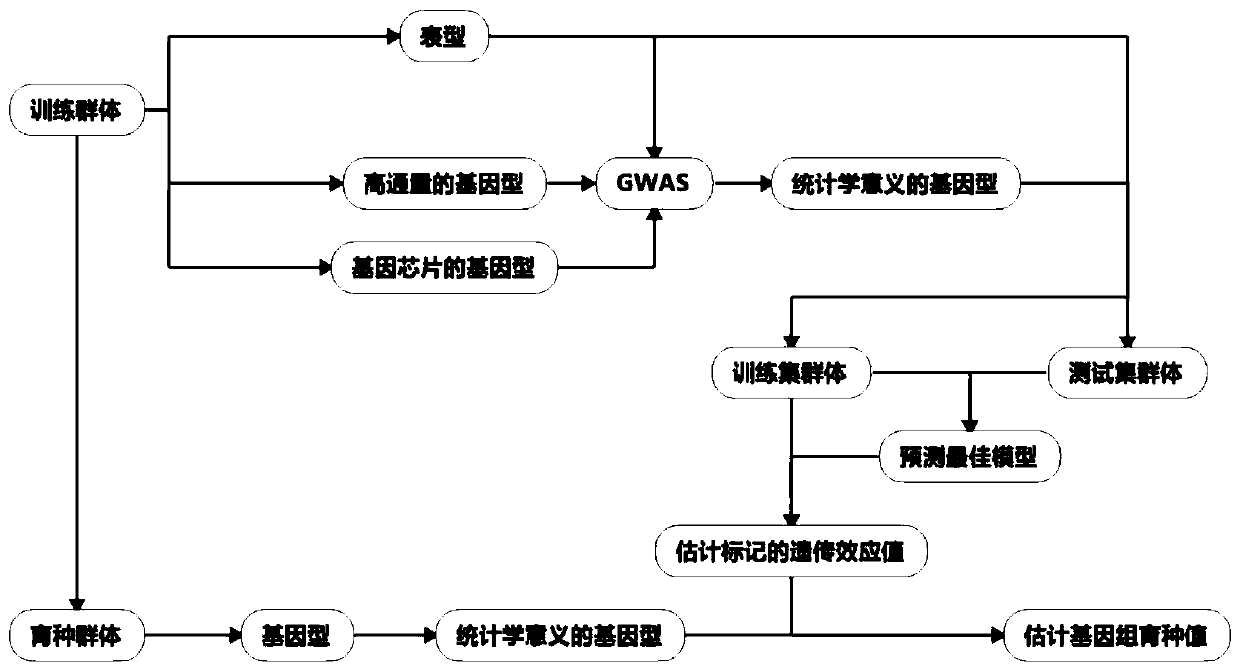
Whole-genome selective breeding method and apparatus
The invention provides a whole-genome selective breeding method and apparatus. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring markers significantly associated with a target phenotype in a training group; calculating a genome estimated breeding value of each individual in a breeding population by utilizing a plurality of whole-genome selection prediction models according to a training population and the markers; and according to the sequence that the genome estimated breeding values gradually decreases, selecting a predetermined number of individuals which are ranked ahead in the plurality of whole-genome selection prediction models as breeding materials. According to the invention, genome estimated breeding value calculation is carried out based on the plurality of models, multiplemodel results are used for co-localization, and the individuals with high breeding values in all the models are selected as the breeding materials, so the accuracy of results is greatly improved. Themethod can adapt to most of material backgrounds, fills the blank of genome selection analysis in a super computer, improves the effect of breeding selection, and promotes the progress of breeding.
Owner:天津诺禾致源生物信息科技有限公司
Wolfberry 40K liquid phase chip and application thereof
ActiveCN114657238AOvercoming diversityOvercoming positioningMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsGenetic diversityGene Microarray
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene chips, relates to a Chinese wolfberry 40K liquid phase chip and application, and in particular relates to a Chinese wolfberry 40K liquid phase chip which is developed by utilizing a targeted capture sequencing technology and is used for genotyping a Chinese wolfberry genome. The lycium barbarum 40K liquid phase chip comprises a lycium barbarum 40K site probe mixed solution and a hybridization capture reagent, the Chinese wolfberry 40K site probe mixed solution comprises a Chinese wolfberry 40K SNP site probe and 165 Chinese wolfberry SNP functional site probes, and two capture probes are arranged at each site on average. The Chinese wolfberry 40K liquid phase chip overcomes the defect of high application cost of genetic diversity analysis, QTL positioning and GWAS analysis of Chinese wolfberry in scientific research, solves the problem that no applicable product exists in Chinese wolfberry molecular assisted breeding and whole genome selective breeding, and accelerates the Chinese wolfberry research and breeding process.
Owner:WOLFBERRY SCI INST NINGXIA ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
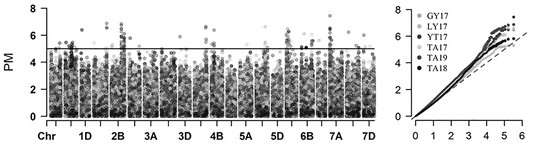
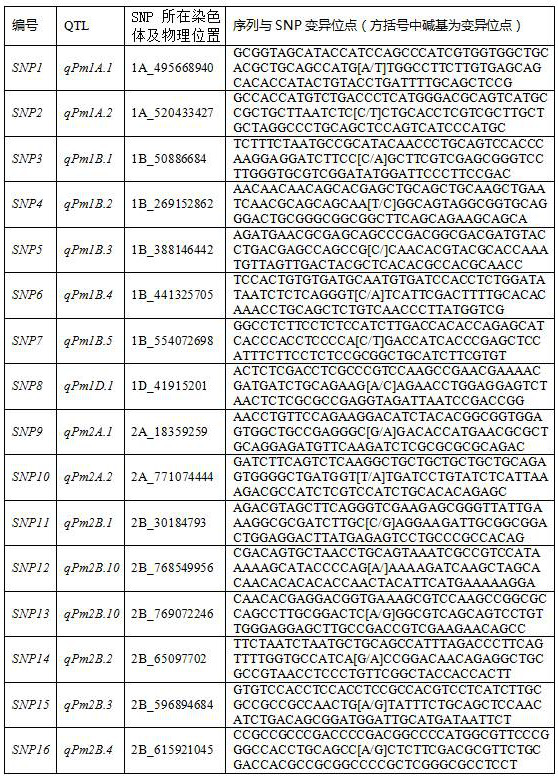
Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) sites remarkably associated with grain number per ear of wheat and application of SNP sites in genetic breeding of wheat
PendingCN113684300AImprove breeding efficiencyImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyReference genome sequence
The invention discloses a group (50) of SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) loci obviously associated with the grain number per ear of wheat and an application method of the SNP loci in inheritance and breeding. The SNPs are identified by performing simplified genome sequencing (GBS) on 768 wheat varieties and excellent strains from main wheat producing areas in China, comparing reference genome sequences to explore single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and then performing whole genome association analysis. The SNP site is high in accuracy, can be used for being converted into a KASP marker and an SNP chip, and is widely applied to positioning of related genes of the grain number per ear of wheat, fine mapping and candidate gene identification as well as marker-assisted selective breeding and whole-genome selective breeding of the grain number per ear of wheat, new germplasm and new species of wheat with increased grain number per ear of wheat are bred, and the yield of wheat is increased.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
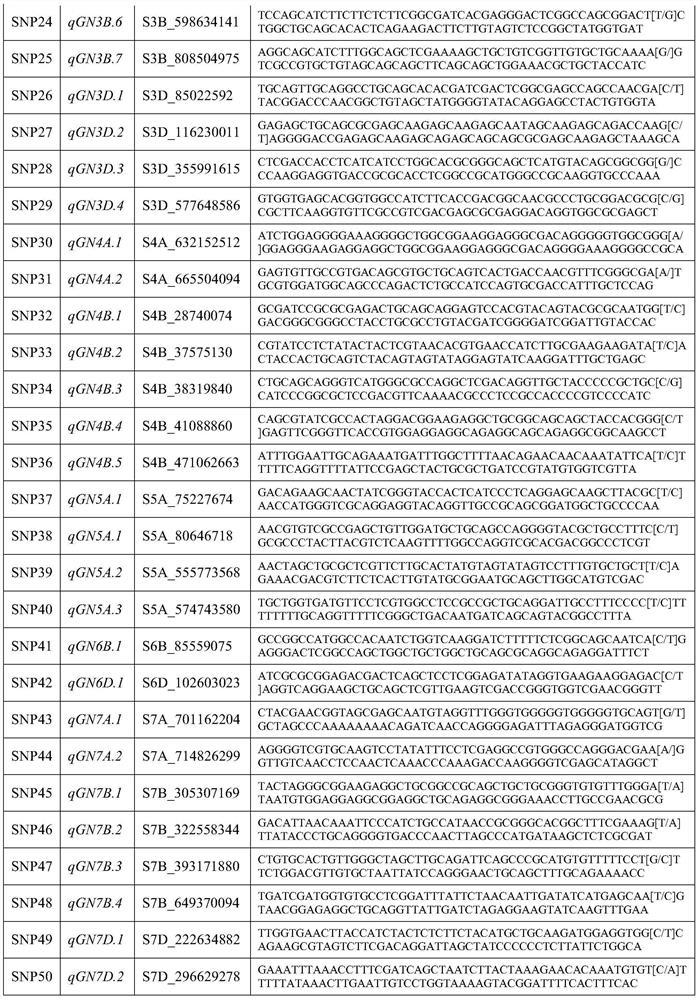
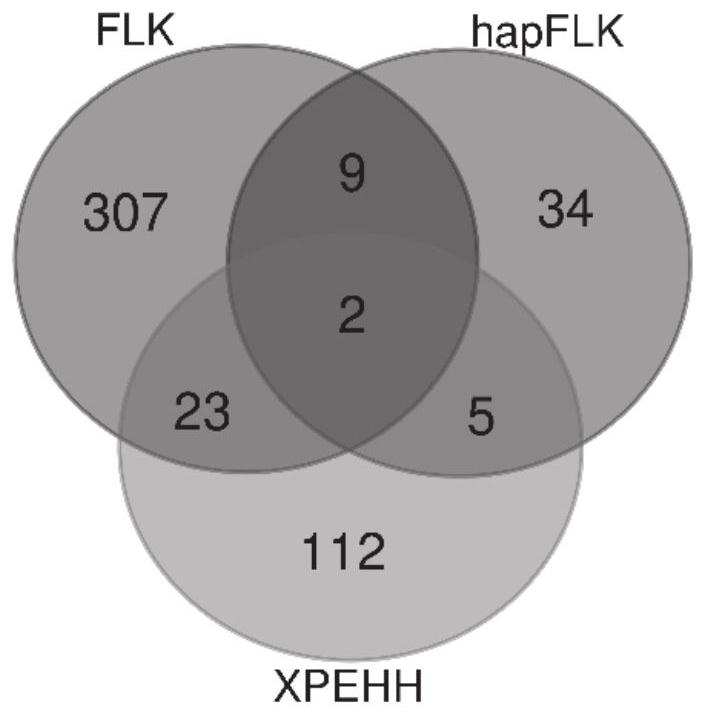
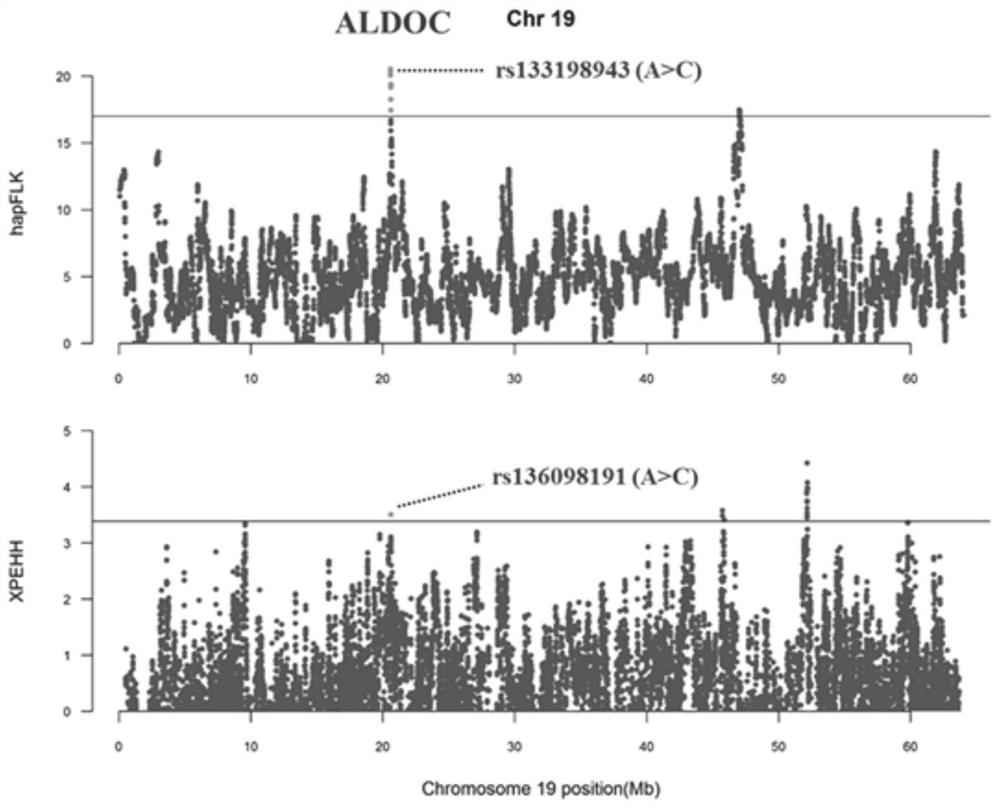
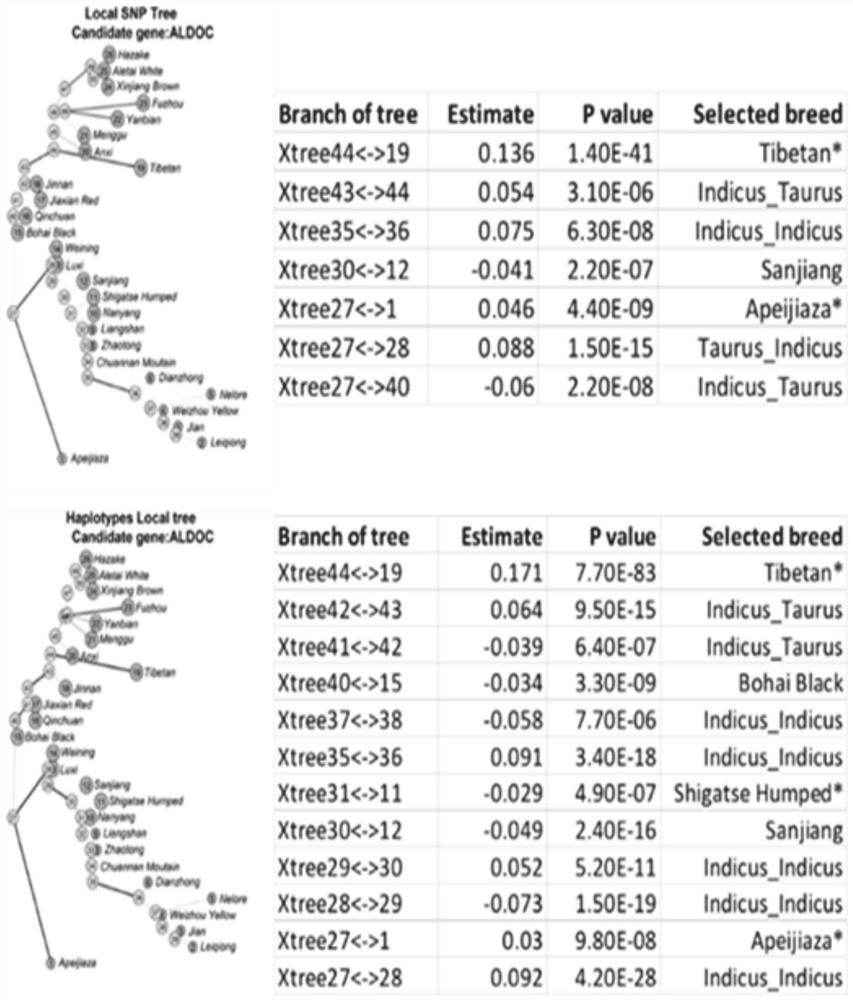
Method for screening bovine plateau hypoxia-adapted gene ALDOC and functional molecular markers and application of bovine plateau hypoxia-adapted genes ALDOC and functional molecular markers
ActiveCN112652362AReduce incubation timeStrong adaptability to plateau hypoxiaMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsBiotechnologyCandidate Gene Association Study
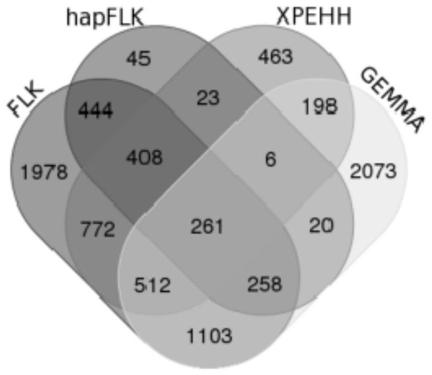
The invention provides a method for screening a bovine plateau hypoxia-adapted gene ALDOC and a functional molecular marker and application of the bovine plateau hypoxia-adapted gene ALDOC and functional molecular markers, and belongs to the technical field of animal molecular breeding. According to the invention, cattle varieties distributed at high altitude and low altitude are selected from the perspectives of cattle genome selection, genetic adaptation and the like, and genome selection signals between cattle at high altitude and cattle at low altitude and in the cattle varieties are compared by adopting an SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) chip and integrating three genome selection signal analysis methods of FLK, hapFLK and XPEHH; candidate genes adapting to the plateau hypoxic extreme environment are identified through a combined screening strategy and bioinformatics analysis, potential functional molecular markers are further mined through selection signal verification and re-sequencing data analysis, and a corresponding detection method is established. A scientific basis and a simple and feasible detection technology are provided for molecular breeding such as cultivation of plateau hypoxic characteristic cattle varieties; meanwhile, the method has important significance and value for protection, evaluation and utilization of genetic resources of local cattle varieties.
Owner:DAIRY CATTLE RES CENT SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI +1
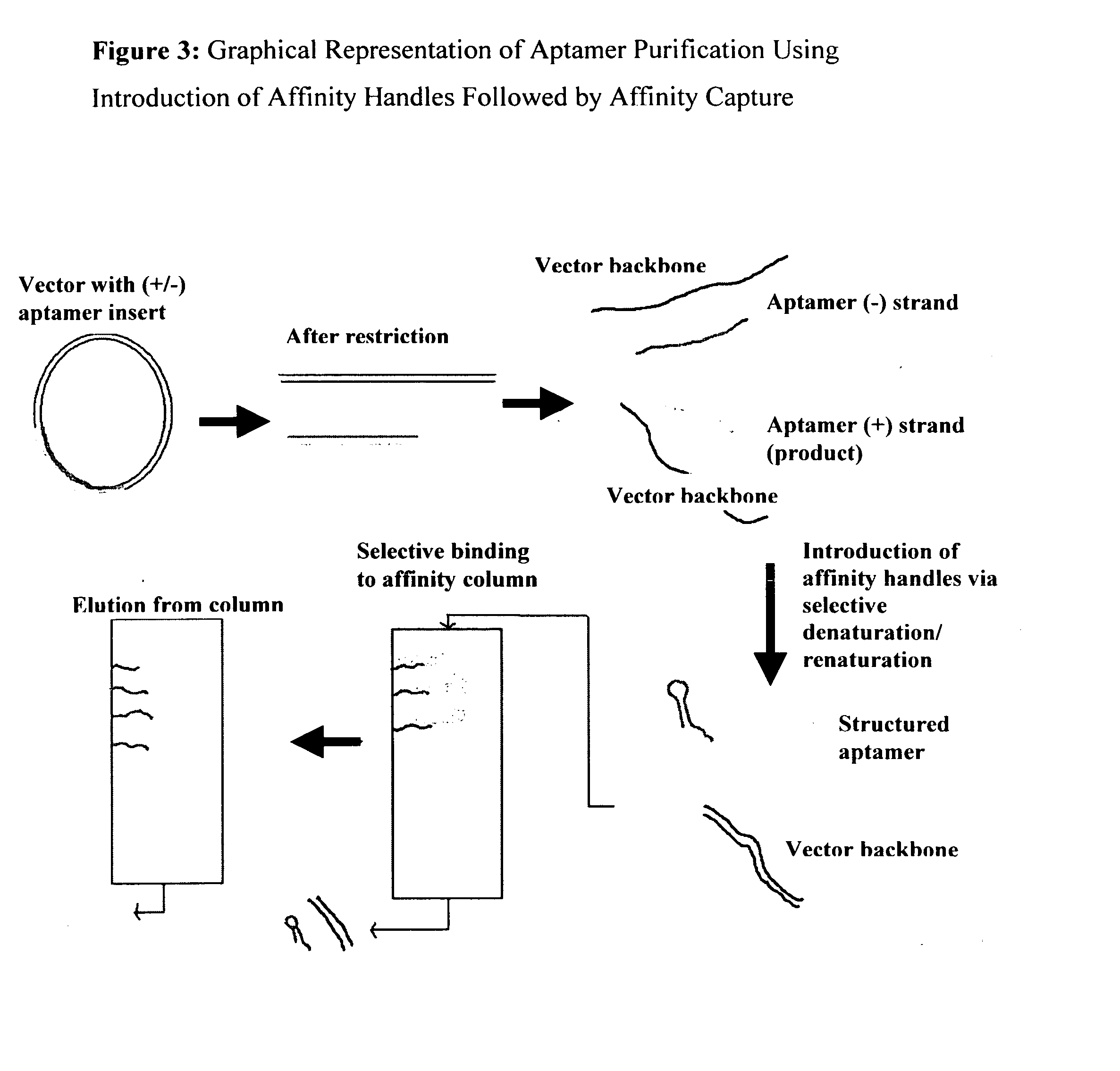
Introduction of structural affinity handles as a tool in selective nucleic acid separations
InactiveUS20060160093A1Remove pollutantsIncrease effective capacitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic DNAEukaryotic plasmids
The method is used for separating nucleic acids and other similar constructs. It involves selective introduction, enhancement, or stabilization of affinity handles such as single-strandedness in the undesired (or desired) nucleic acids as compared to the usual structure (e.g., double-strandedness) of the desired (or undesired) nucleic acids. The undesired (or desired) nucleic acids are separated from the desired (or undesired) nucleic acids due to capture by methods including but not limited to immobilized metal affinity chromatography, immobilized single-stranded DNA binding (SSB) protein, and immobilized oligonucleotides. The invention is useful to: remove contaminating genomic DNA from plasmid DNA; remove genomic DNA from plasmids, BACs, and similar constructs; selectively separate oligonucleotides and similar DNA fragments from their partner strands; purification of aptamers, (deoxy)-ribozymes and other highly structured nucleic acids; Separation of restriction fragments without using agarose gels; manufacture recombinant Taq polymerase or similar products that are sensitive to host genomic DNA contamination; and other applications
Owner:UNIV HOUSTON SYST +1
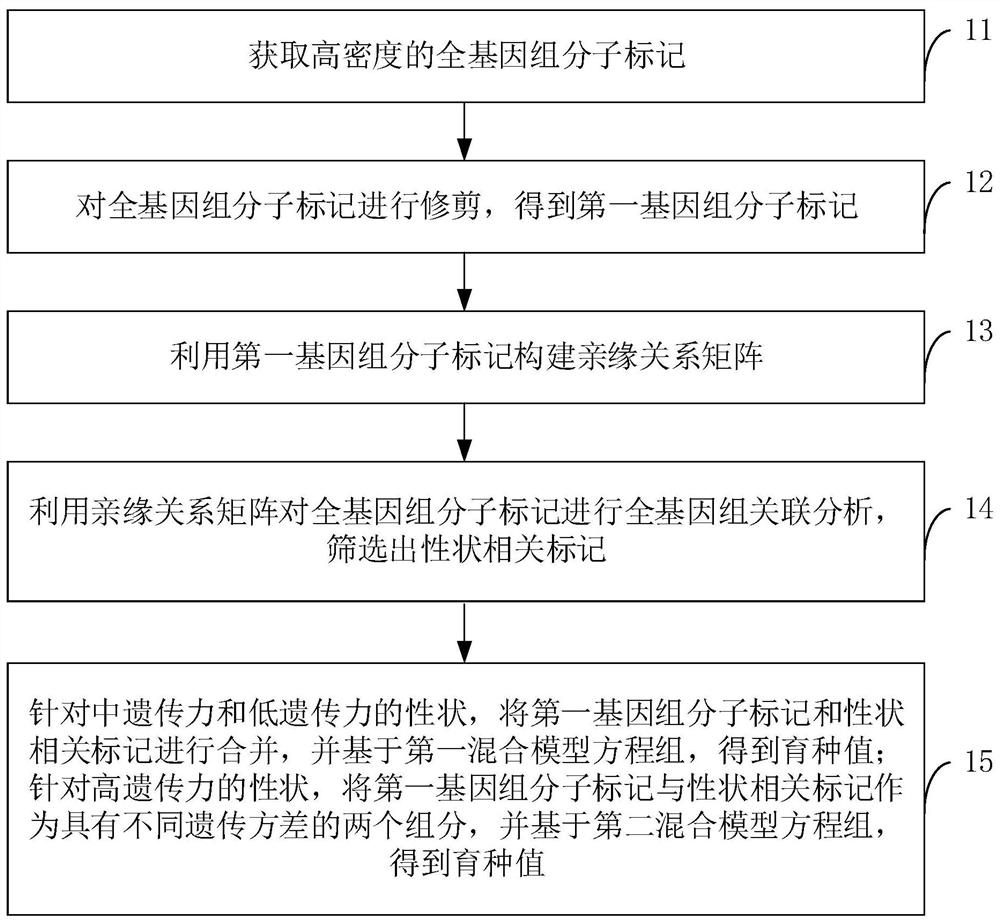
Method, device and system for estimating genome breeding value
PendingCN112712852AReduce redundancyReduce consumptionBiostatisticsHybridisationGenomeGenomewide association
The invention relates to a method, device and system for estimating a genome breeding value. The method for estimating the genome breeding value comprises the following steps: acquiring a high-density whole genome molecular marker; trimming the whole genome molecular marker to obtain a first genome molecular marker; constructing a genetic relationship matrix by utilizing the first genome molecular marker; performing whole-genome association analysis on the whole-genome molecular markers by utilizing the genetic relationship matrix, and screening out character-related markers; combining the first genome molecular marker and the trait related marker aiming at the middle genetic ability and low genetic ability traits, and obtaining a breeding value based on a first mixed model equation set; and aiming at the character with high heredity, taking the first genome molecular marker and the character related marker as two components with different heredity variances, and obtaining a breeding value based on a second mixed model equation set. Therefore, the calculation efficiency is improved, the consumption of calculation resources is reduced, the genome selection accuracy is improved, and the genetic improvement of animals and plants can be accelerated.
Owner:BGI INST OF APPLIED AGRI
Genome selection method of residual feed intake of white feather broilers
PendingCN112002371AImprove accuracyAccelerating progress in genetic selectionProteomicsGenomicsBiotechnologyZoology
The invention provides a genome selection method of residual feed intake of white feather broilers. GEBV estimation is carried out on the residual feed intake (RFI) of an important feed conversion character index by utilizing a one-step whole-genome breeding value (GEBV) estimation method integrating a remarkable SNP marker effect. The invention further provides an SNP marker remarkably related tothe residual feed intake character of the white feather broiler chicken and application of the SNP marker. The SNP marker comprises the marker rs13649171, the marker rs740268684, the marker rs312607889, the marker rs314437326 and the marker rs313748618. Compared with a conventional one-step GEBV estimation result, the selection accuracy of the breeding method of the white feather broiler chickenline with the low residual feed intake character can be improved by 15.44%. The method can shorten the new strain breeding time, save the breeding cost, improve the breeding efficiency and acceleratethe white feather broiler chicken autonomous strain breeding process in China.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
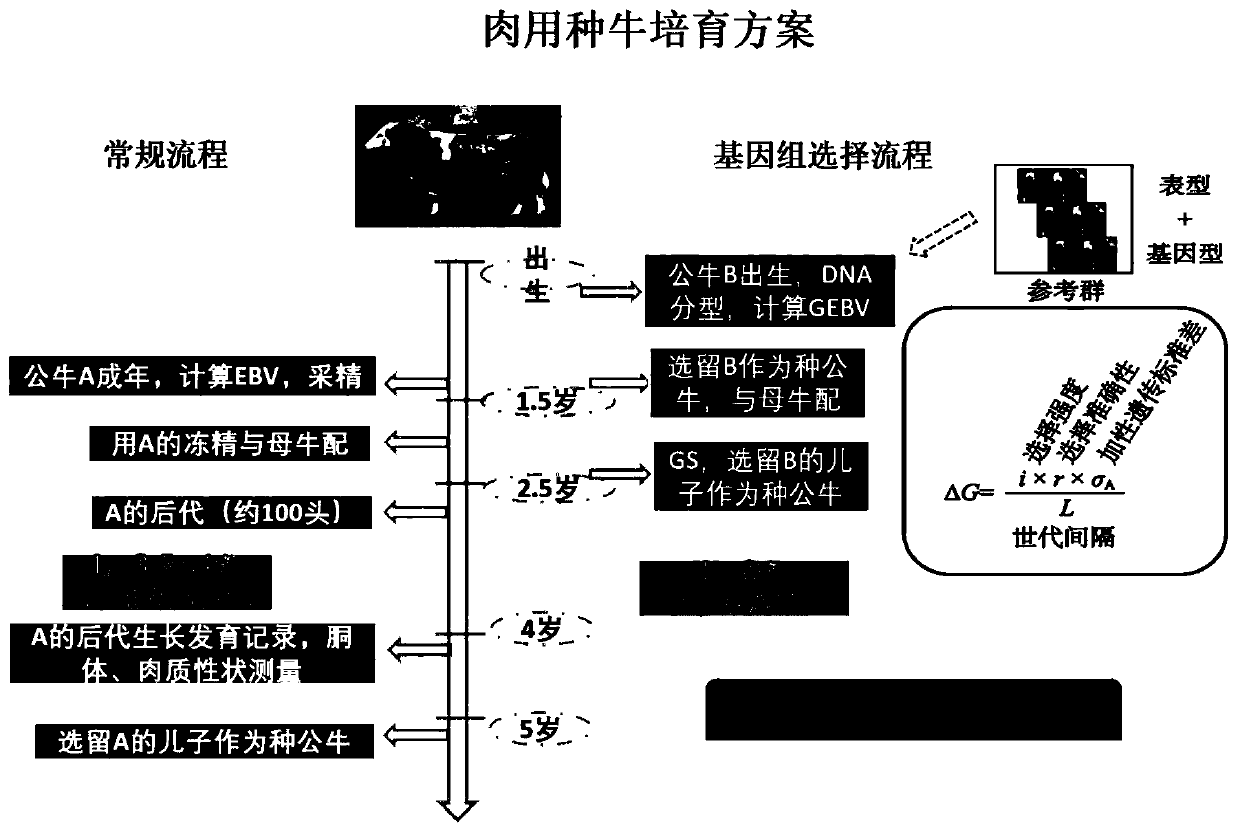
A method for cultivating elite bulls using genome-wide selection and sex-controlled embryo technology
InactiveCN103598146BBreed fastImprove stabilityAnimal reproductionMicrobiological testing/measurementSemenSexual characteristics
The present invention provides a method for rapid and directional breeding of superior breeding bulls by using whole-genome selection and sex-controlled embryo technology, which is to select excellent cows and bulls as oocytes and semen respectively by using whole-genome selection, DHI measurement technology and descendant measurement technology Through the process of superovulation, artificial insemination and embryo collection, a large number of excellent embryos with similar genetic backgrounds are obtained, and then the sex characteristics of the embryos are obtained through in vitro embryo sex identification technology, and male embryos are selected for embryo transfer and genome breeding value determination , CPI comprehensive breeding value measurement and trait correlation analysis to realize rapid breeding and directional breeding of bulls.
Owner:天津市奶牛发展中心
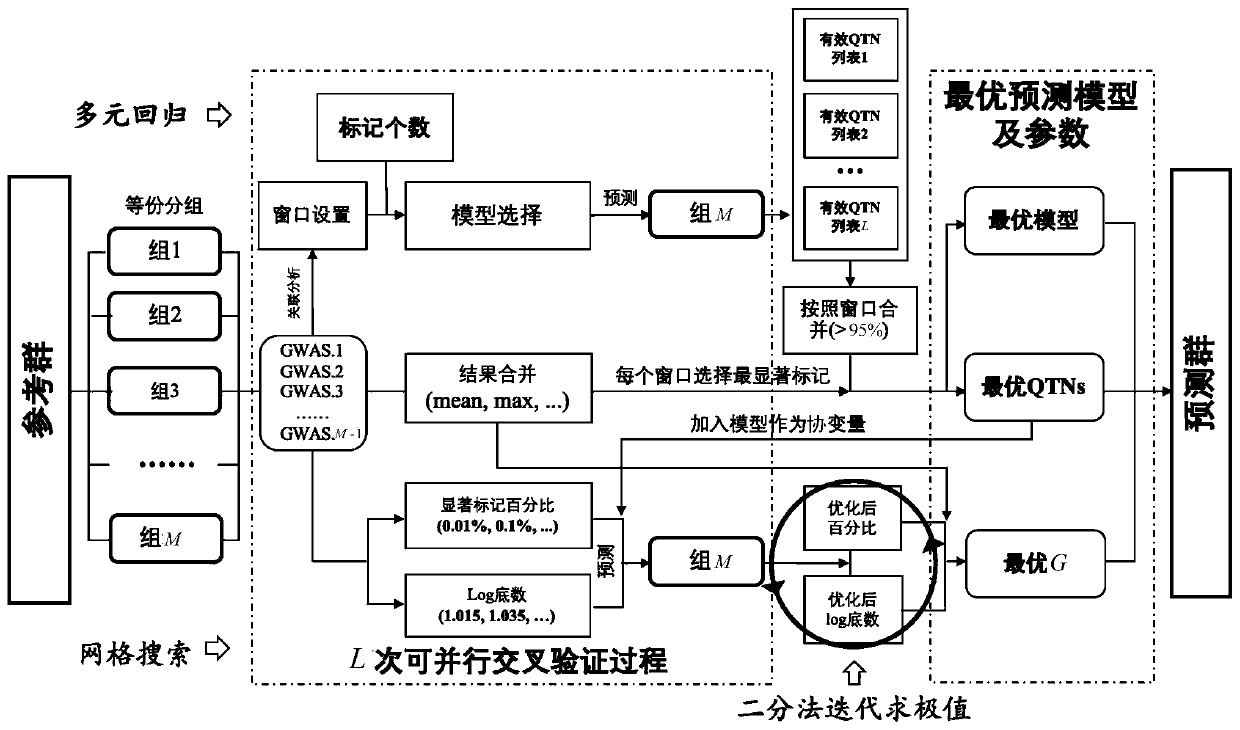
Efficient high-accuracy whole-genome selection method capable of performing parallel operation
ActiveCN110610744AImprove accuracyImprove computing efficiencyProteomicsGenomicsWhole Genome Association AnalysisAlgorithm
The invention relates to the technical field of animal and plant breeding and human disease prediction, and provides an efficient high-accuracy whole-genome selection method capable of performing parallel operation. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, reading an original genotype file and a phenotype file, constructing a new genotype file and a new phenotype file, and calculating agenetic relationship matrix of all individuals; then, extracting all individuals in the new phenotypic file as a reference group, and extracting all individuals without phenotypic data in the originalgenotypic file as a prediction group; carrying out whole genome association analysis by utilizing the reference group data, and extracting result characteristics of the whole genome association analysis; constructing a model library with specific characters, sequentially optimizing an optimal fixed effect and an optimal random effect by adopting a cross validation strategy, and selecting an optimal prediction model from the model library; and finally, calculating genome estimated breeding values of the prediction group by utilizing the optimal prediction model. The method can quickly, accurately and stably predict individual genome breeding values, and thus the accuracy and efficiency of whole genome selection are improved.
Owner:武汉影子基因科技有限公司
SNP sites remarkably associated with wheat powdery mildew resistance and application thereof in genetic breeding
InactiveCN112501345AReduce in quantityQuantitatively lowMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyWhole Genome Association Analysis
The invention discloses a group (58 wheat varieties) of SNP sites remarkably associated with wheat powdery mildew resistance and an application method thereof in genetic breeding. The SNP sites are identified by performing simplified genome sequencing (GBS) on 768 wheat varieties and excellent strains to explore SNP sites and then performing disease resistance identification and whole genome association analysis. The group of SNP sites are high in accuracy, can be converted into KASP markers and SNP chips, and are used for positioning, fine mapping and candidate gene identification of wheat powdery mildew resistance genes and wheat powdery mildew resistance whole genome selective breeding.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com