Seeding method of target genome DNA fragment-containing plants
A genome, whole genome technology, applied in the fields of genetics, genomics and molecular breeding, can solve the problems of offspring phenotype separation, lack of stability, judgment, etc., to speed up the breeding process and improve the breeding efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0059] Example 1 Screening of recombined single plant of rice 'Kongyu 131' introduced with DNA fragment of blast resistance gene
[0060] The materials used in this example are rice 'Kongyu 131' and 'K22'. 'K22' has been proven to have good blast resistance, and it is speculated that the gene cluster region where Pi2, Pi9 and Pigm of chromosome 6 are located may play a key role in the rice blast resistance of this material.
[0061] The inventor introduced the genomic DNA fragment where the above-mentioned gene clusters in 'K22' are located into 'Kongyu 131', the specific process is as follows:
[0062] Screening of foreground selection markers: positive selection markers are to screen polymorphic molecular markers within the range of 50kb (in rice, its genetic distance is 0.2cM) on the upper and lower reaches of the target genome DNA (rice blast resistance gene DNA) fragment, and obtain the same Tightly linked markers Pi2-4 for the target genomic DNA fragment. The negative ...
Embodiment 2
[0069] Example 2 Determination of homologous recombination fragments after 'Kongyu 131' was introduced into rice blast resistance gene
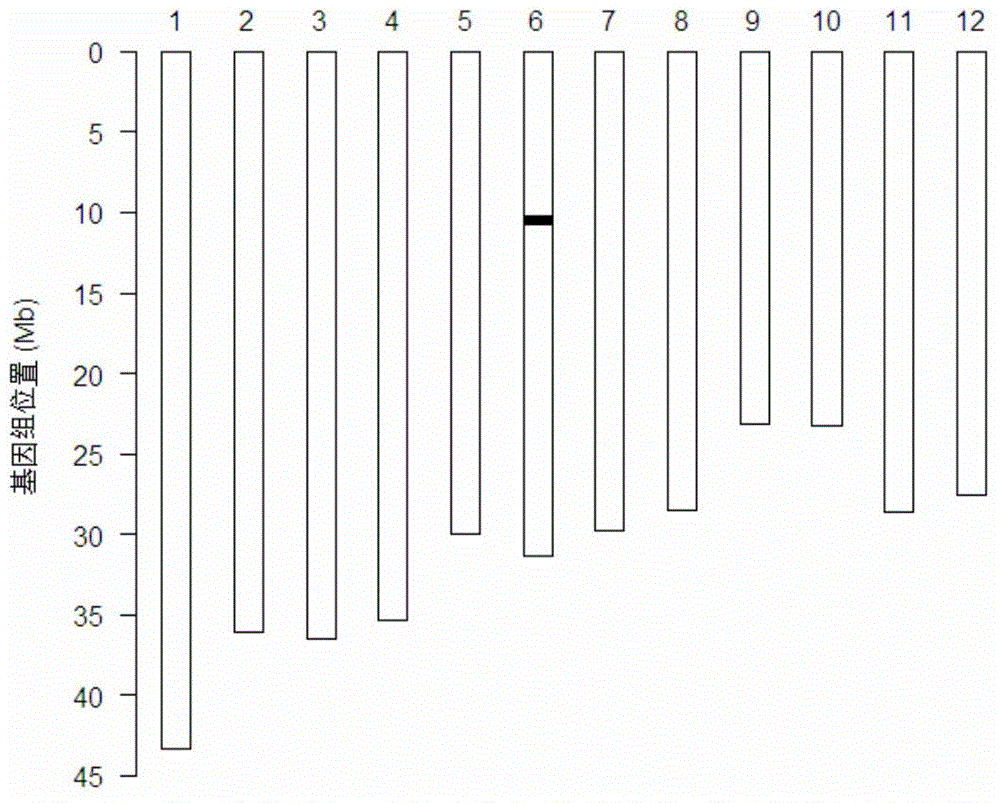
[0070] In order to determine the size of the imported rice blast resistance gene fragment and to protect the imported fragment, the inventors carried out homology of the target genome DNA fragment on both sides of the homozygous single plant of 'Kongyu 131' into which the rice blast resistance gene DNA fragment was introduced. Sequencing of recombinant fragments. First of all, it was preliminarily confirmed by the SNP chip detection results that the upstream homologous recombination fragment of the A08-1 rice blast resistance gene recombination DNA fragment segment was located in the approximately 68.2kb region between the two SNP markers R0610132417TC and R0610200630GA (10132417bp~10200630bp of chromosome 6) , the downstream homologous recombination fragment is located in the approximately 68.9kb region between the two SNP markers F061071165...
Embodiment 3
[0078] Example 3 Resistance Identification of 'Kongyu 131' After Introducing the Recombinant DNA Fragment of the Rice Blast Resistance Gene
[0079] In order to identify the resistance effect of the target individual plants, A08-1, 'Kongyu 131', Gumei No. 4 and Lijiang Xintuan Heigu were planted indoors, and they were cultivated to the 3-4 leaf stage for identification using the following method :
[0080] Ten strains of Magnaporthe oryzae isolated from diseased leaves of rice blast collected in the disease nursery of Heilongjiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences and Qixing Farm in Heilongjiang Province in 2013 were used as inoculation strains. Numbers 13-7101, 13-7102, 13-7103, 13-7104, 13-7105, 13-7201, 13-7202, 13-7203, 13-7204 and 13-7205. The strains are stored at -20°C by the paper disc method. Before use, take out the disc and activate it on PDA medium (peeled potato 200g, glucose 20g, agar powder 15g). After 5 days, take a fresh mycelium block with a size of 1 cm squa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com