Patents
Literature
299 results about "Genetic distance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
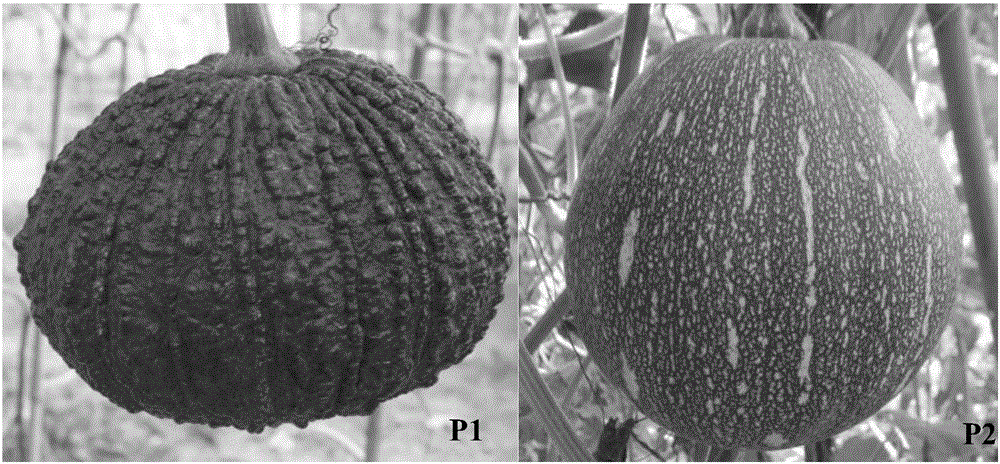
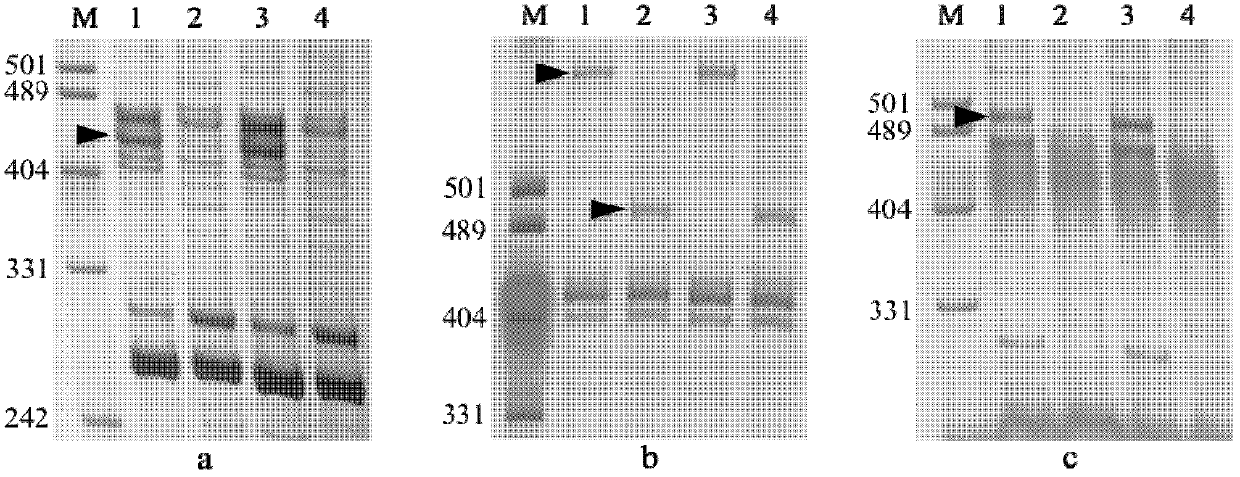
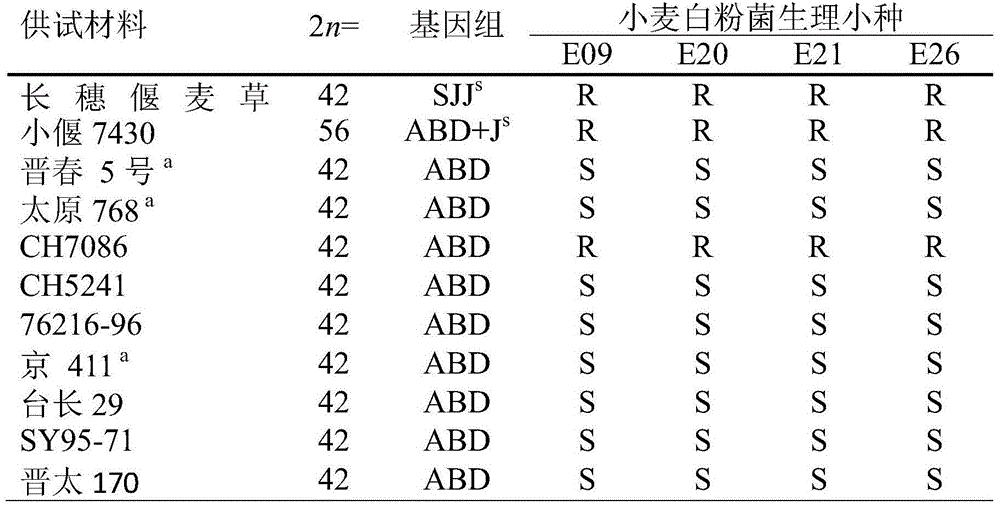
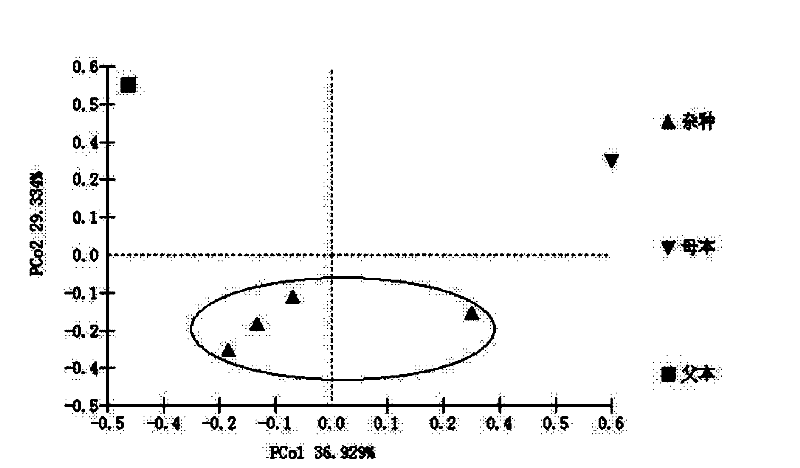
Genetic distance is a measure of the genetic divergence between species or between populations within a species, whether the distance measures time from common ancestor or degree of differentiation. Populations with many similar alleles have small genetic distances. This indicates that they are closely related and have a recent common ancestor.
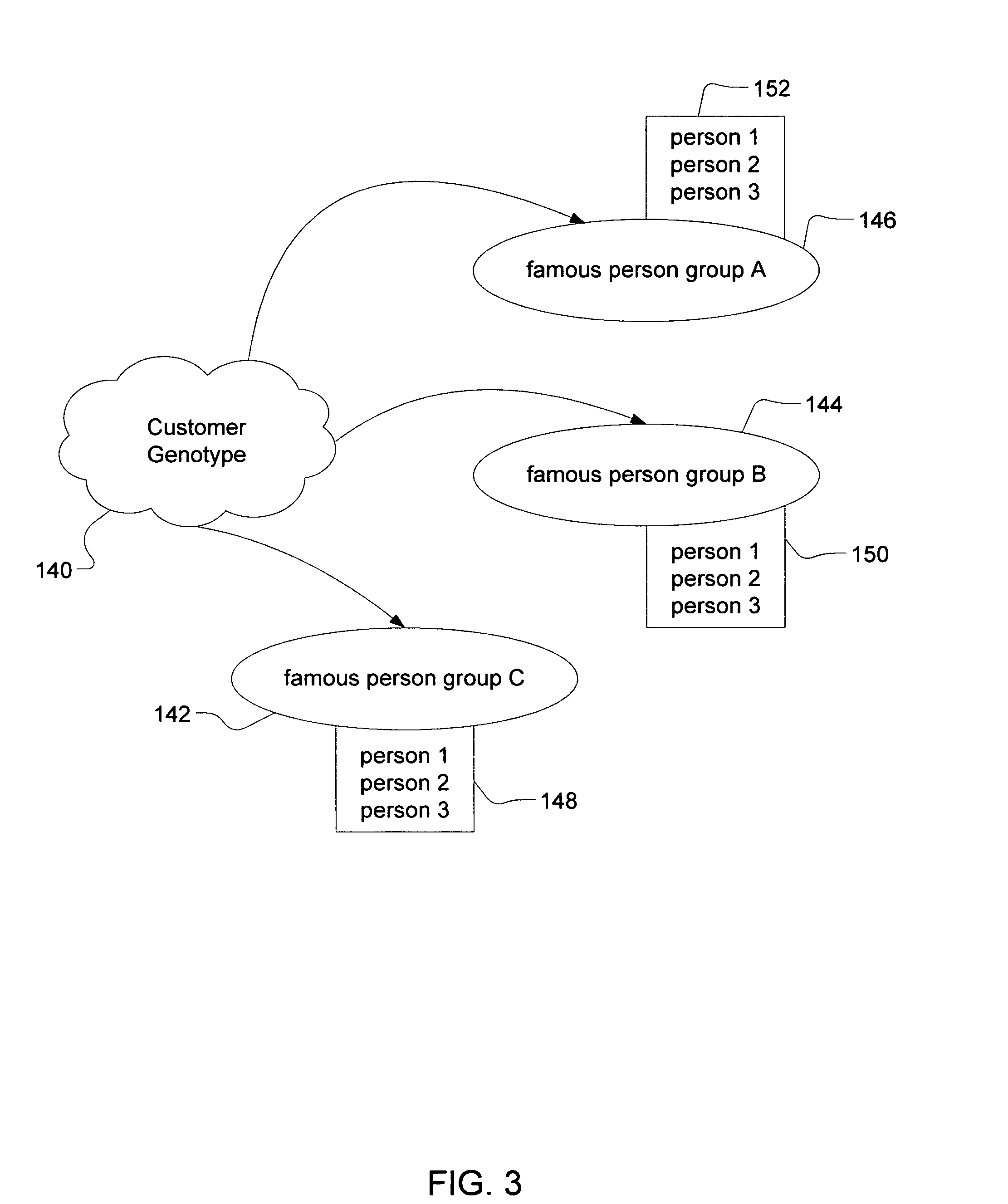
Method of determining a genetic relationship to at least one individual in a group of famous individuals using a combination of genetic markers
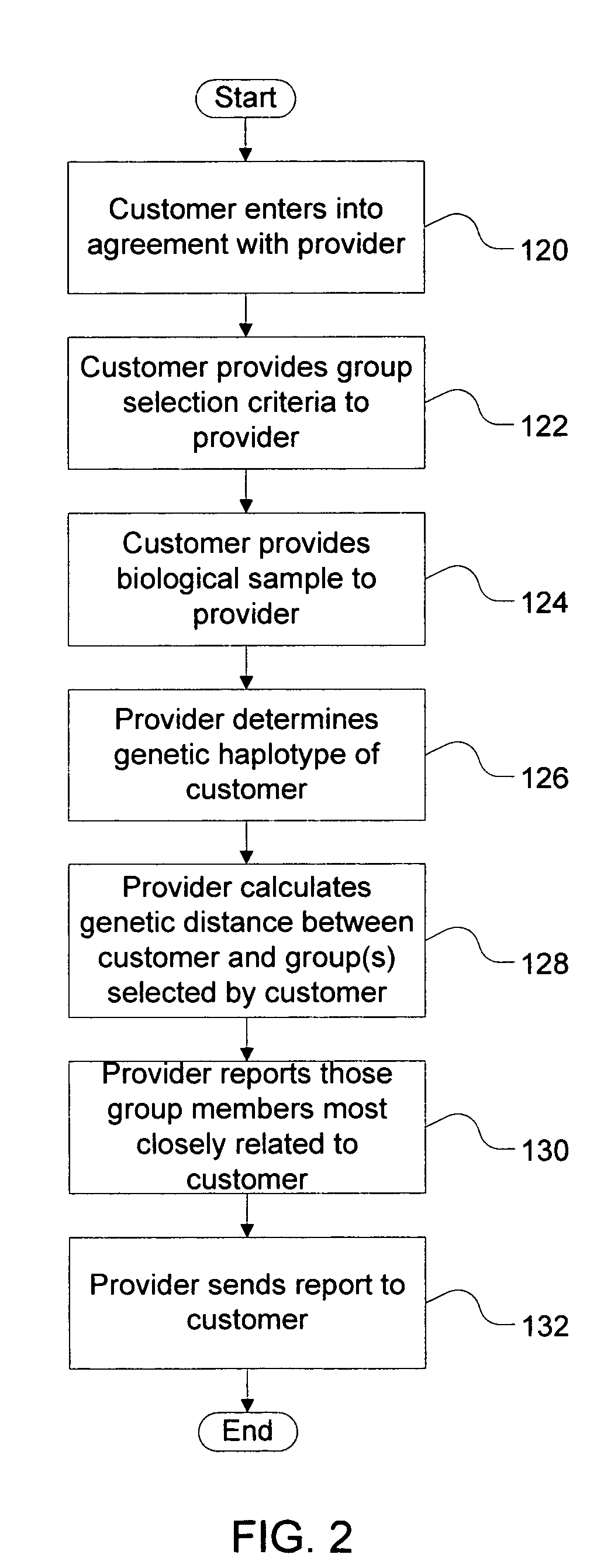
A method for quantifying the genetic relationship of a customer to at least one individual of at least one group of famous individuals, the method includes the following steps. First, receiving genetic information and famous individual group selection criteria from a customer, next, calculating the genetic distance of the customer to at least one individual within the group and finally, reporting the results to the customer.
Owner:EGLINGTON CHRIS
Method for evaluating flooding tolerance of maize variety
The invention discloses a method for evaluating flood tolerance of the maize variety. The method comprises the following steps of 1, after a pot is drowned, performing evaluation on four indexes, such as the color of a leaf, the form of the leaf, the color of a stem and the form of a root to preliminarily determine the flooding tolerance level; 2, performing two-sample pairing statistic analysis method on 15 shapes subjected to preliminary screening in the first step, and taking the strain height, the net photosynthetic rate, the green area, the root biomass, the root growth rate, the content of chlorophyll a, the total content of chlorophyll and an SPAD (soil and plant analyzer development) value as flood tolerance degree evaluation indexes according to the waterlogging influence degree; and 3, performing clustering analysis on the authentication indexes obtained by the second step, and classifying the varieties with different flood tolerance degrees into a flood tolerance hybrid and a non flood tolerance hybrid near to 27 according to genetic distances of all property clusters. The method for quickly and easily obtaining the flood tolerance evaluation indexes in a maize seedling stage is established according to the form change of leaves and stems above the ground as well as the physiologic and morphologic expression of plants, so that a basis is supplied to correct selection of the maize variety in an easily flooding region.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
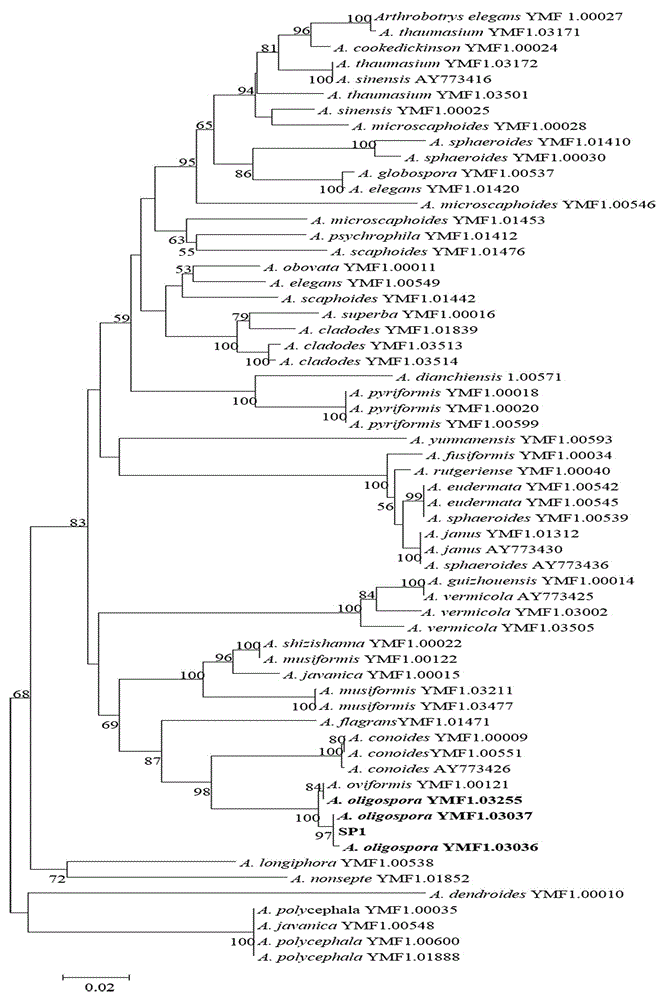
Method for identifying predator nematophagous hyphomycete arthrobotrys through DNA bar codes
InactiveCN105063761AEasy to expandEasy to compareLibrary creationSpecial data processing applicationsDNA barcodingGermplasm
The invention provides a method for identifying predator nematophagous hyphomycete arthrobotrys through DNA bar codes and belongs to the field of fungus species identification. According to the method, RPB2 genes serve as target DNA bar code genes for identifying the predator nematophagous hyphomycete arthrobotrys, combined arthrobotrys sample experiment data and target fungus data merged strategy is adopted to establish a high-cavity database, meanwhile, RPB2 genes to be identified are compared with a gene library, an identifying rule is established based on a system generation tree method of genetic distance method and clustering analysis of the Kimura-2-parameter probability to identify species. The method has the advantages that the RPB2 genes serve as the DNA bar codes most suitable for identifying the nematophagous hyphomycete arthrobotrys, and the method is universal and easy to amplify and compare. The identifying efficiency and the reliability and accuracy of the identifying method are greatly superior to those of a conventional DNA bar code method, and the method makes up for the blank of the nematophagous hyphomycete arthrobotrys DNA bar code molecular markers and the method provides a useful research tool for researches on germplasm resource excavation, biocontrol application and genetic diversity of nematophagous hyphomycete.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
High efficiency rice breeding method
InactiveCN101185420AEasy to shapeSuitable for a wide range of speciesPlant genotype modificationAngiosperms/flowering plantsDiseaseAgricultural science
The invention discloses a high-efficiency rice breeding method, pertaining to rice breeding field. Core idioplasms such as Fenghuazhan and Fengshizhan are selected by the invention as a main body parent , and crossed with those varieties with comparatively more genetic distance and complementary characters, and the agricultural characters, eating quality and content of medium linear starch of the hybrid descendents are sifted, and rice blast resistance and bacterial blight resistance are screened, to further cultivate a series of good quality, high yield and a new rice variety of rice with disease resistance. The invention has a high breeding efficiency, shortens the breeding period and saves the breeding expenses.
Owner:RICE RES INST GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
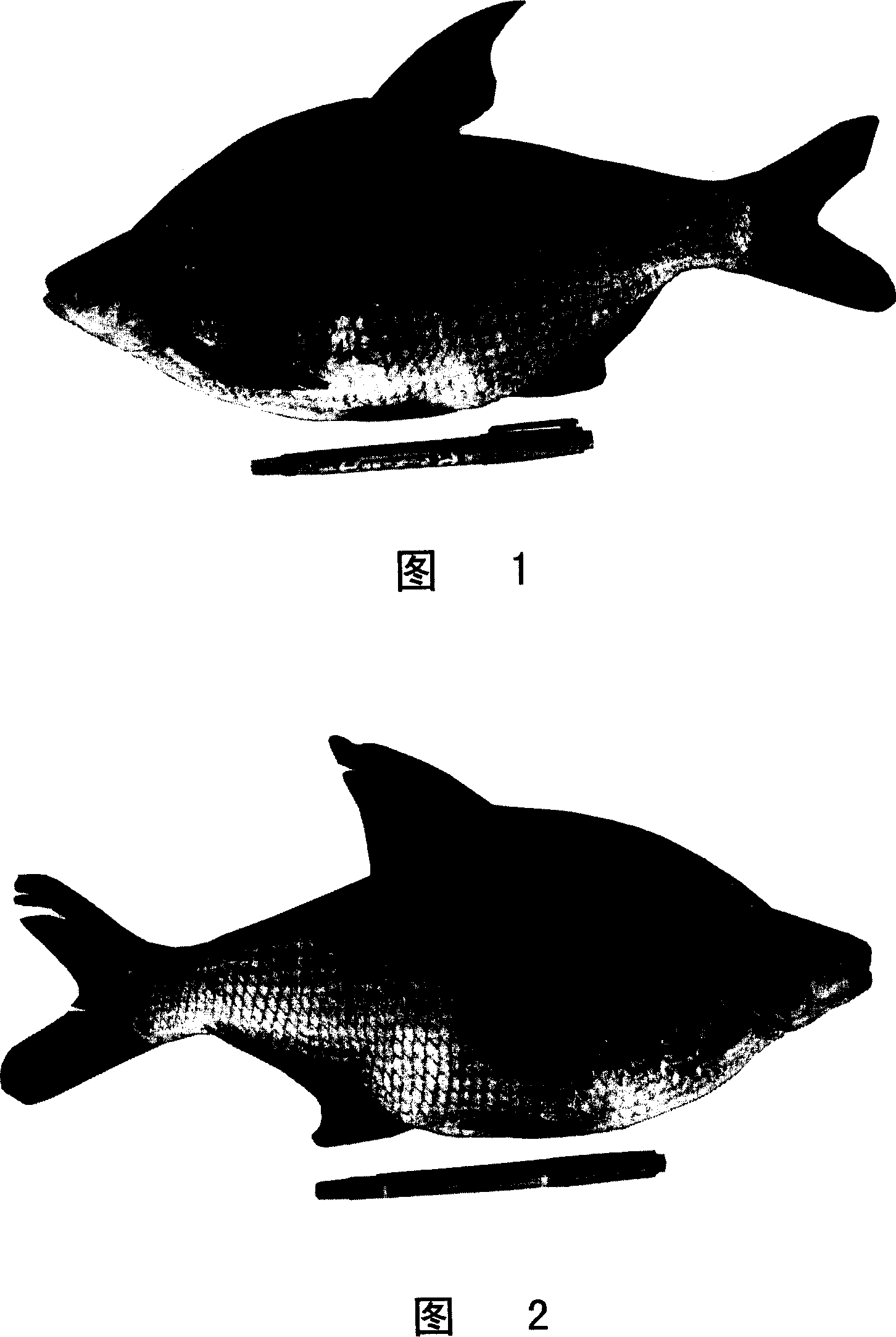
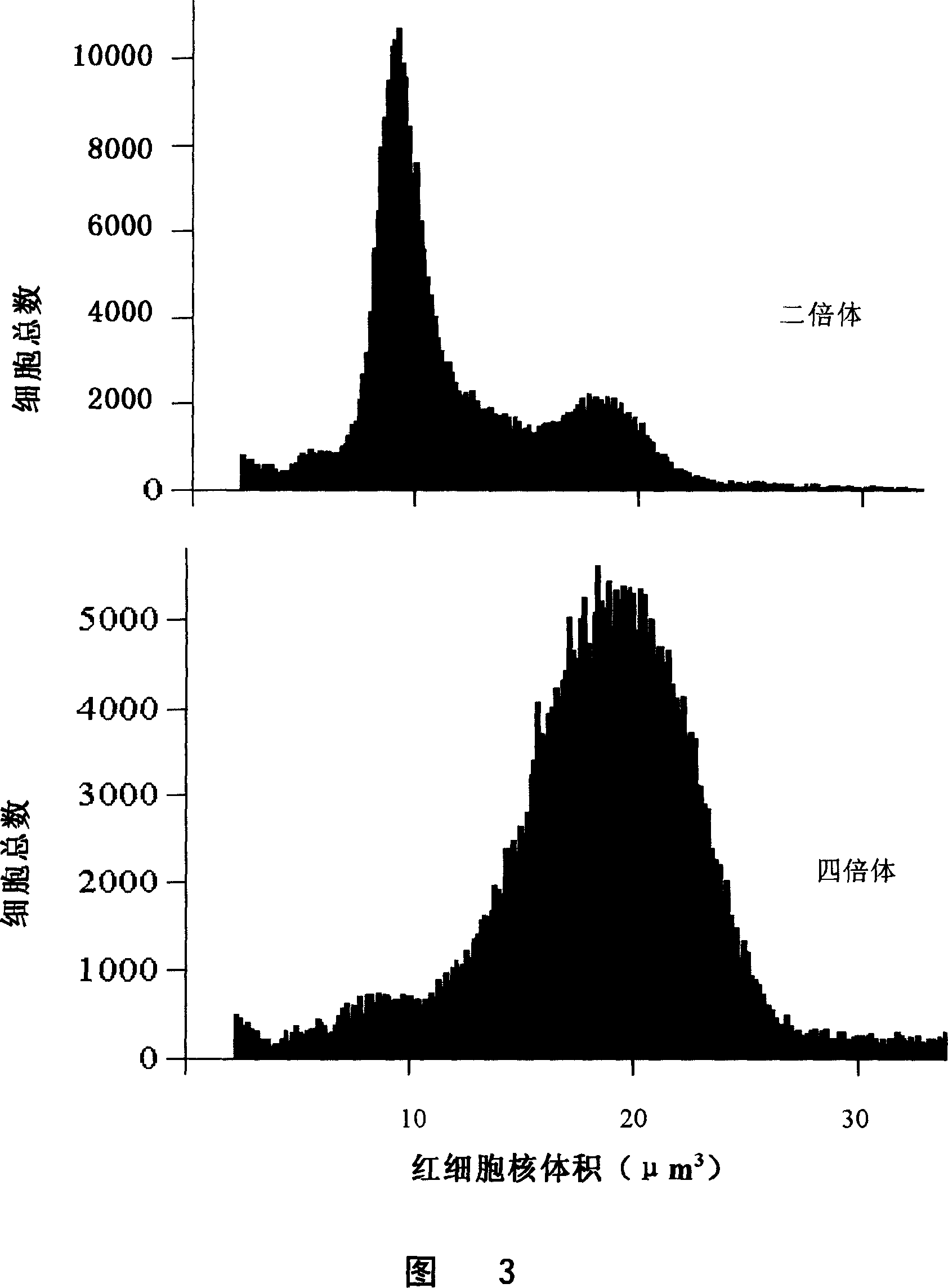
Method for constructing allotetraploid of bluntsnout bream
InactiveCN1969616AEffective establishmentAnimal reproductionPeptide/protein ingredientsFisheryGermplasm
Owner:李思发
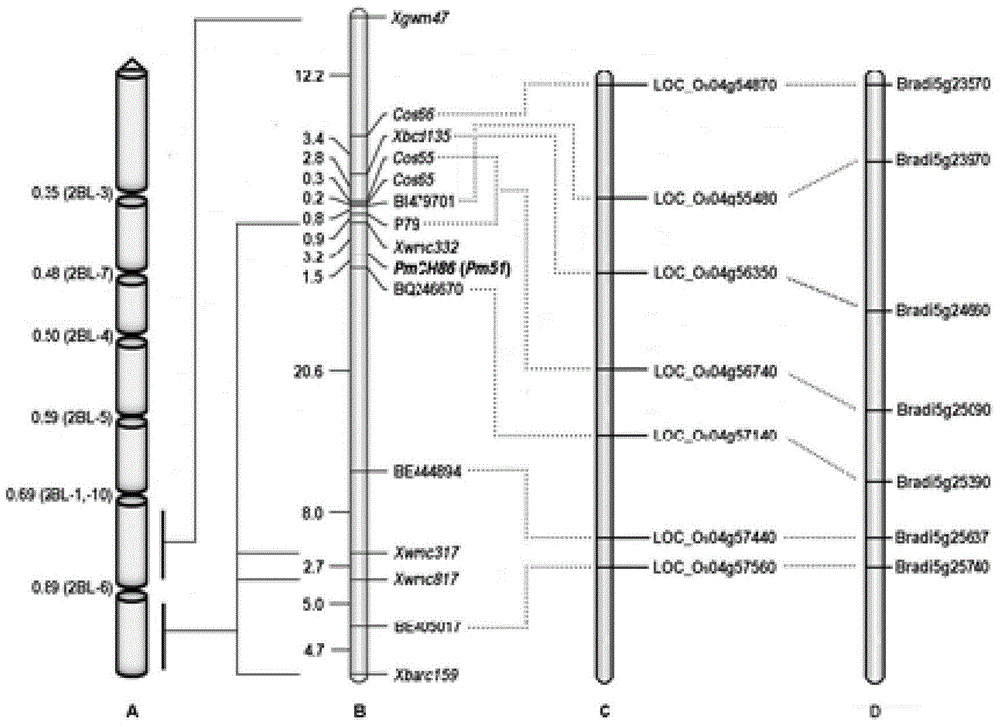
Molecular marker of wheat powdery mildew disease-resistant genes Pm51 and application of molecular marker
ActiveCN104313021AImprove utilizationRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDiseaseBiotechnology
The invention relates to plant molecular genetics and wheat breeding and in particular relates to a molecular marker of novel wheat powdery mildew disease-resistant genes Pm51 and application of the molecular marker. A functional molecular marker BQ246670 linked with powdery mildew disease-resistant genes Pm51 is obtained. The marker is a co-dominant marker, the genetic distance between the marker and the Pm51 is 1.5cM, the existence and existential state of wheat genes Pm51 can be rapidly and accurately identified, and the resistance of wheat powdery mildew disease is predicted, so that the utilization of the wheat powdery mildew disease-resistant genes Pm51 is accelerated.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
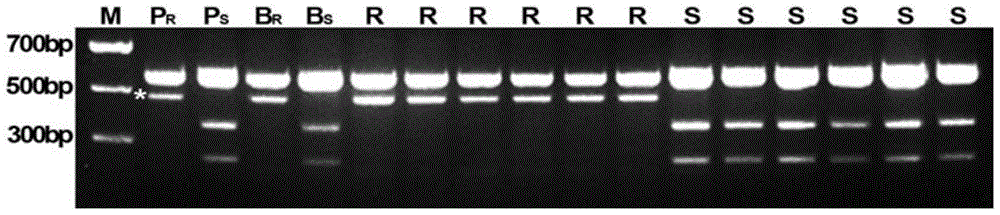
Molecular marker for assisted selection of green bean bruchid-resistant new gene Br3 and application of molecular marker
ActiveCN105368956AAccurate generation-by-generation trackingExemption from anti-bean elephant identification workMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationEarly generationAgricultural science
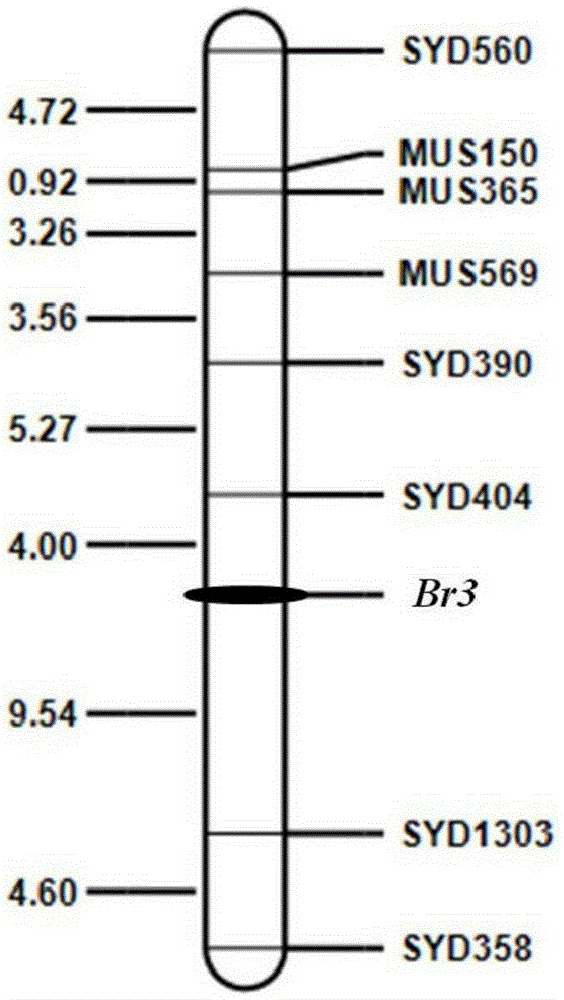
The invention discloses a molecular marker for assisted selection of a green bean bruchid-resistant new gene Br3 and application of the molecular marker. The molecular marker is named as SYD404 and obtained by using genome DNA of a green bean variety V1128 as a template and adopting a pair of SSR primers for PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification, and a genetic distance between the molecular marker and the bruchid-resistant gene Br3 is 4.0cM. The molecular marker provides a good route for bruchid-resistant breeding of the green bean variety V1128, selection can be advanced to a green bean growth seedling stage, a lot of bruchid-resistant identification work which consumes time and labor can be avoided, early generation selection of breeding materials can be realized, and accurate successive generation tracking of target genes can be realized.
Owner:INST OF CEREAL & OIL CROPS HEBEI ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
SSR (Simples sequence repeats) and InDel (insertion/deletion) molecular marker primer linked with brassica campestris orange head gene Br-or, and application thereof
InactiveCN103103184AEasy to detectStable amplificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBrassicaAgricultural science
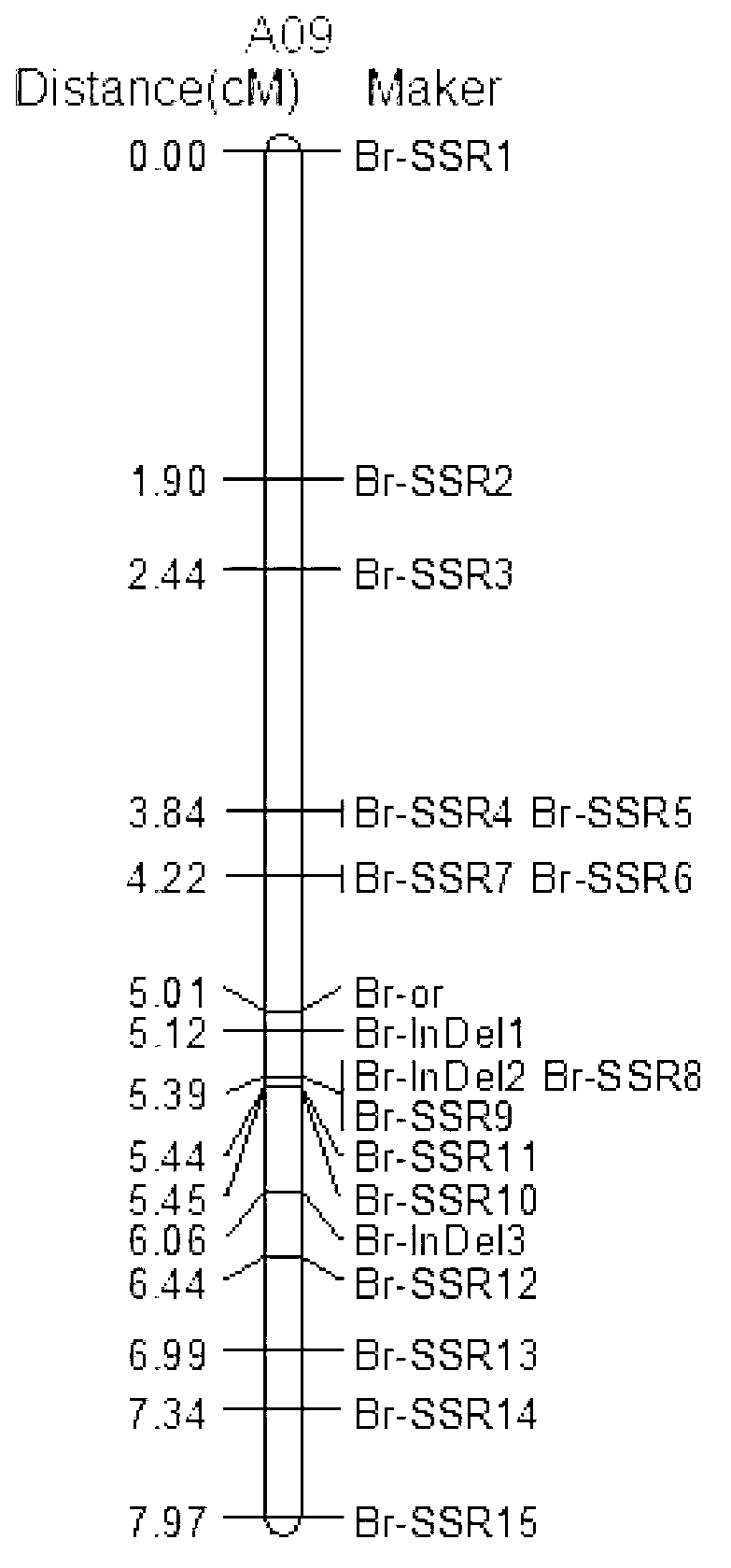
The invention discloses an SSR (simples sequence repeats) and InDel (insertion / deletion) molecular marker primer linked with brassica campestris orange head gene Br-or and an application of the molecular marker primer. The marker primer is obtained by the steps of: based on the genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of orange brassica campestris and normal white brassica campestris and F2S4 separation group as a template, carrying out polymorphism primer screening to orange head and white head single strain DNA mixed tank in F2S4 by using 480 pairs of SSR and InDel primer pairs, then analyzing single strain of F2S4 group, and screening the molecular marker linked with the brassica campestris orange head gene Br-or to finally obtain fifteen Br-SSR and three Br-InDel molecular markers linked with the Br-or gene, wherein a molecular genetic map of the brassica campestris orange head gene Br-or is created on the ninth link group (A09). According to the link analysis, the genetic distance of two markers most tightly linked with both sides of the Br-or gene are 0.11cM and 0.79cM; and the molecular marker primer has the advantages of being convenient for detection, stable in amplification, and high in repeatability and accuracy, and thus a basis is provided to the molecule assistant selective breeding of brassica campestris orange head character and the breeding process is accelerated.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
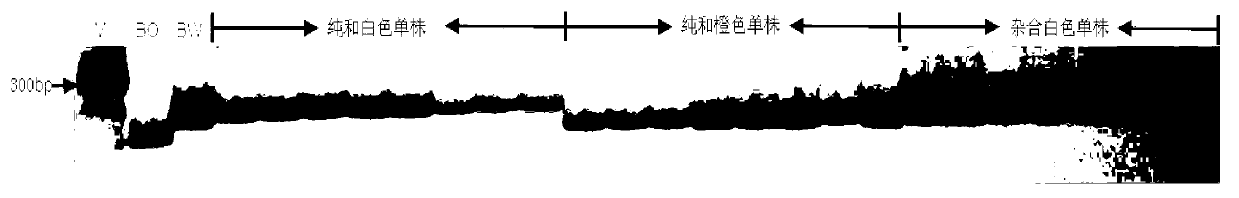
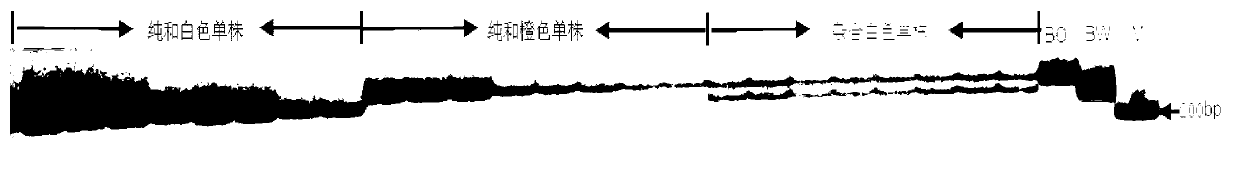
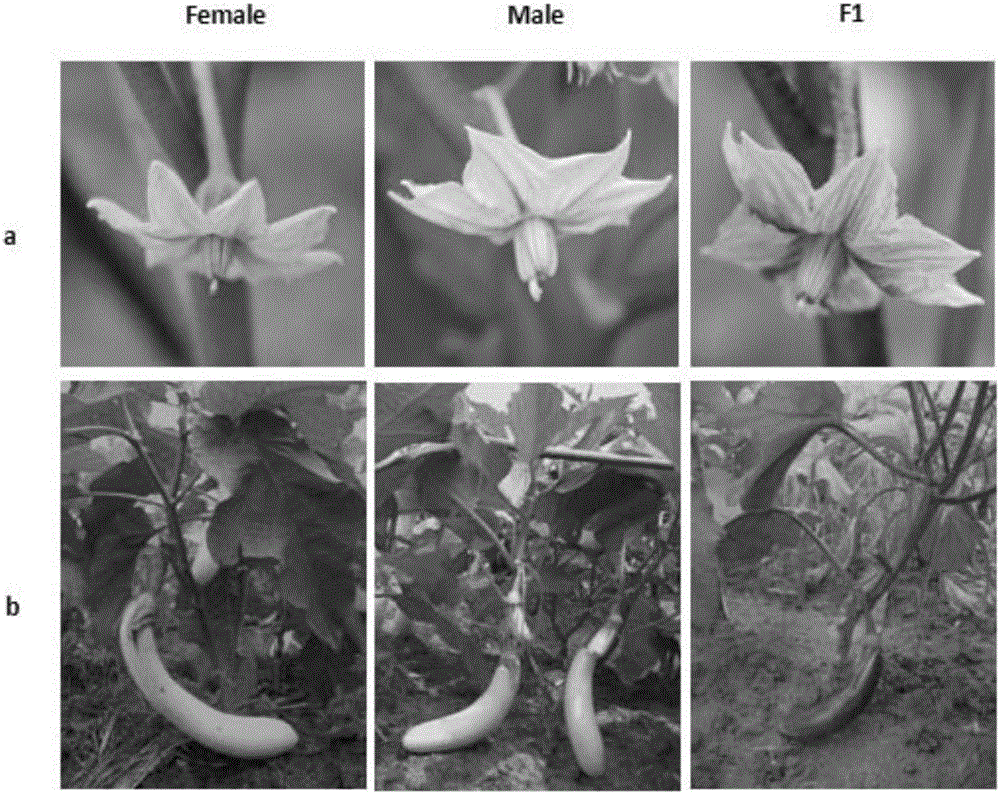
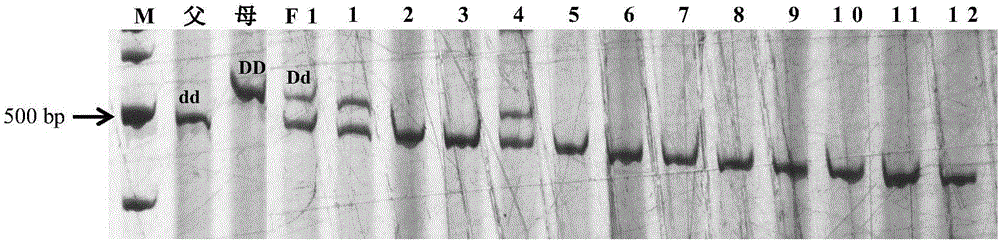
Mapping of eggplant fruit color epistatic gene D, and InDel molecular marker development and application thereof
ActiveCN106701926AImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationRe sequencingAgricultural science
The invention discloses a mapping result of an eggplant fruit color epistatic gene D. The gene D is mapped in a position near a nucleotide sequence Sme2.5_00538.1 on a No.10 chromosome of the eggplant. Based on the re-sequencing result of male and female parents, an InDel molecular marker closely linked with the eggplant fruit color epistatic gene D is obtained near the nucleotide sequence Sme2.5_00538.1 of the No.10 chromosome, and is named as InDel22522; the genetic distance of the marker from the epistatic gene D is 0.61 cM. The nucleotide sequence of the molecular marker InDel 22522 in the female parent has one 29-basic-group InDel more than that in the male parent. The mapping result on the eggplant fruit color epistatic gene D provided by the invention lays the foundation for the precise positioning and cloning of the eggplant fruit color epistatic gene; the InDel 22522 molecular marker and a molecular marker amplification primer can be applied to eggplant fruit color breeding practice in a way of simplicity, convenience, high speed and high flux; the eggplant fruit color property improving process is accelerated.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLES GUANGDONG PROV ACAD OF AGRI SCI
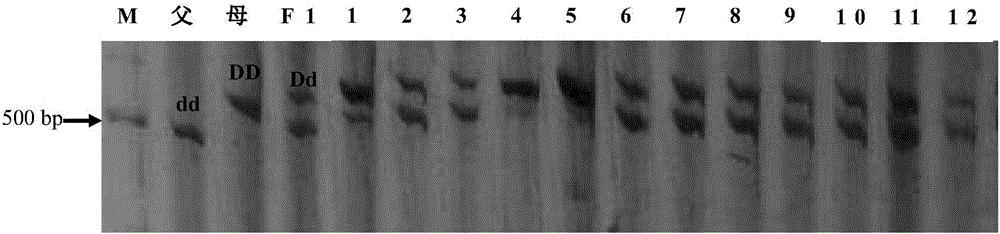
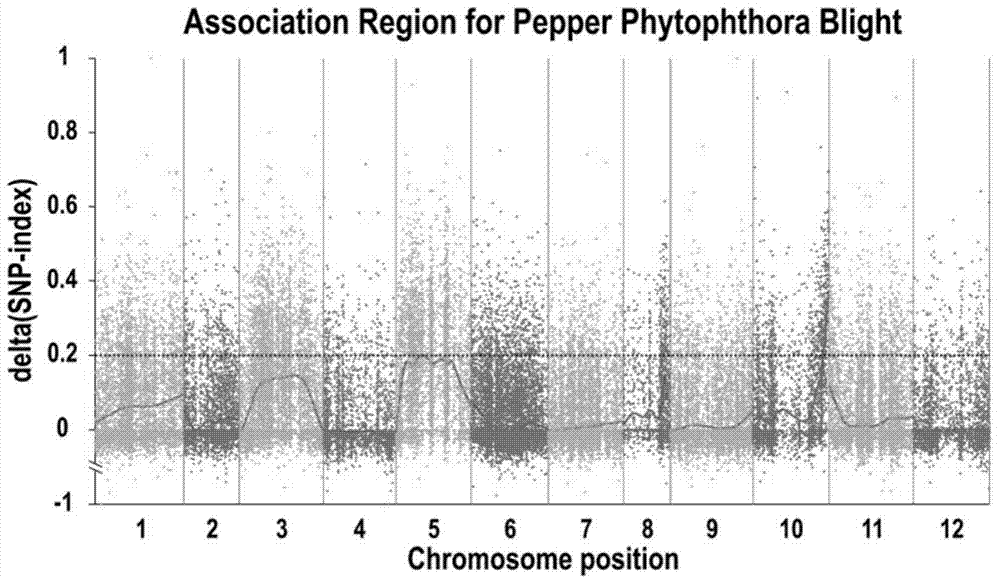
Molecular markers in close linkage with specific resistance gene for capsicum phytophthora blight of root rot and application thereof
ActiveCN104726450AImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyResistant genes
The invention discloses two molecular markers in close linkage with a specific resistance gene for capsicum phytophthora blight of root rot and application thereof. Each molecular marker contains a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO. 1 and named as P52-11-21, or contains a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO. 2 and named as P52-11-41. The molecular markers are in close linkage with the specific resistance gene for phytophthora blight of root rot, have genetic distances of 1.5cM and 1.1cM respectively, and can be directly used for establishing an assistant breeding system for the molecular markers for capsicum phytophthora blight of root rot. The molecular markers disclosed by the invention and molecular marker amplification primers can be applied to breeding practice for capsicum phytophthora blight of root rot simply and rapidly with a high flux, and lay a good foundation for the cloning and functional researches of the specific resistance gene for capsicum phytophthora blight of root rot.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLES GUANGDONG PROV ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
Molecular marker method for avirulence gene of rice blast
InactiveCN1952177AReveal Toxic ComponentsReveal featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationPyricularia griseaParental strain
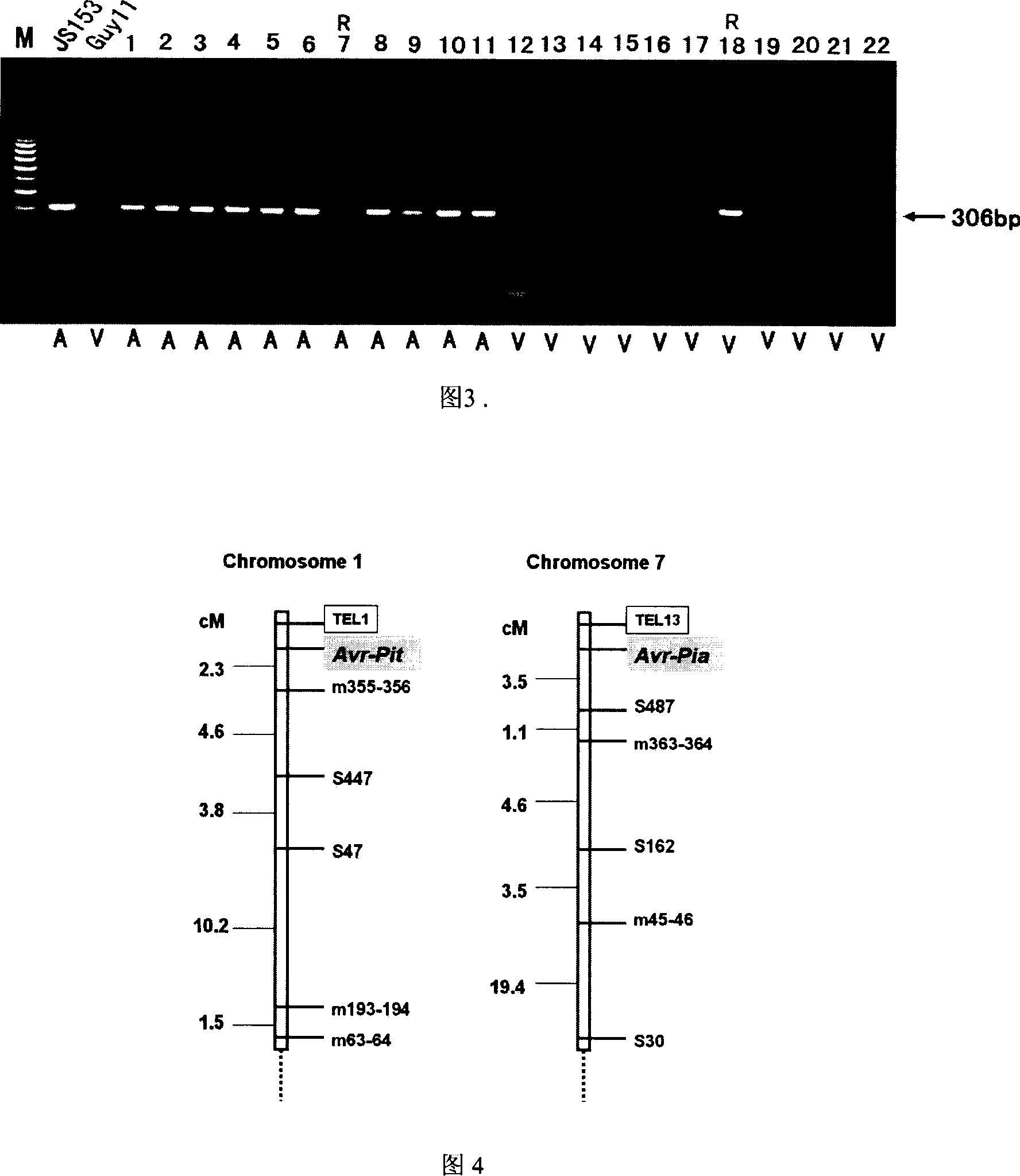
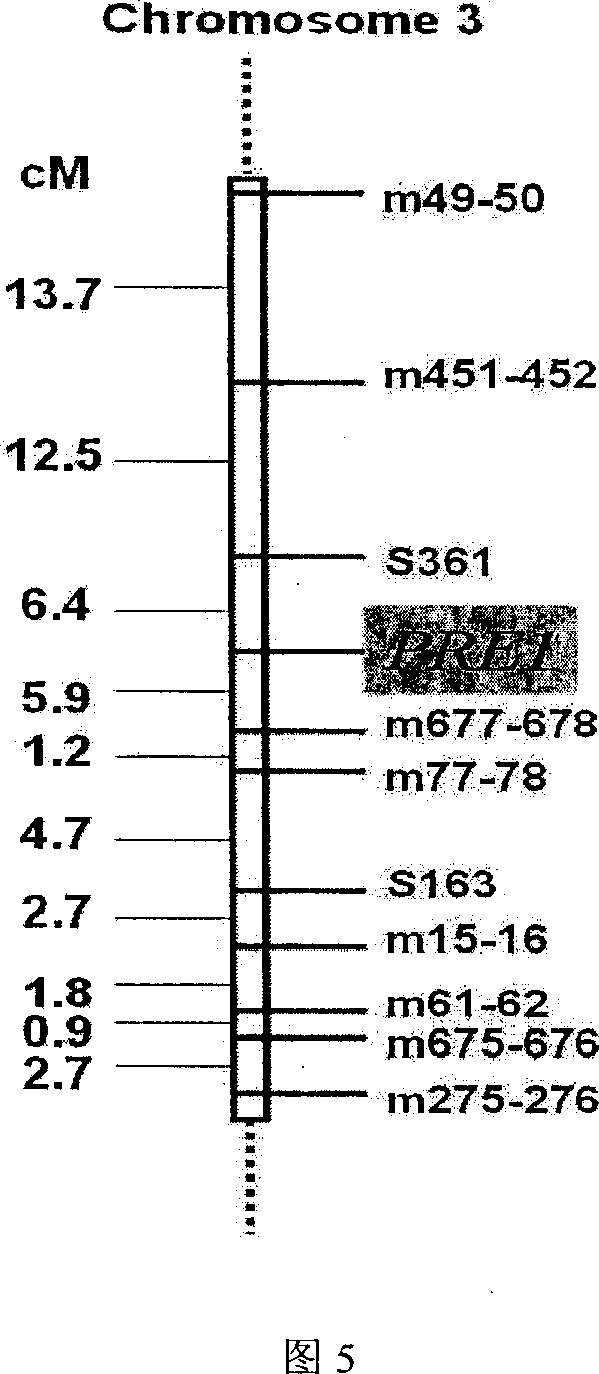
The invention of molecular labeling method of Pyricularia grisea avirulent gene belongs to the field of agricultural biotechnology. The molecular labeling technology includes performing molecular labeling to avirulent gene though assessment from two parental strains and filial generation groups of Pyricularia grisea. M355-356 labeled by SSR near NO. 1 chromosome telomere links with avirulent gene Avr-Pit with a genetic distance of 2.3cm; S487 labeled by RAPD located near NO. 7 chromosome telomere links with avirulent gene Avr-Pia with a genetic distance of 3.5cm; S361 labeled by m677-678 and RAPD located at middle of N0. 3 chromosome telomere links with Pyricularia grisea specified avirulent gene PRE1 with genetic distances of 5.9cm and 6.4. The invention can not only make use of the nontoxic gene marker as gene probe, but also set foundations for further clone of the gene through physical mapping.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
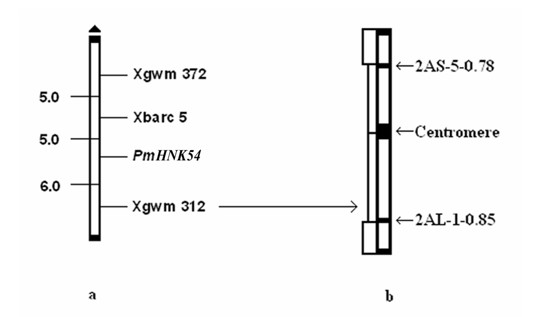
Marker primer interlocked with wheat powdery mildew resistance gene PmHNK54 and application thereof
InactiveCN101988064AReduce dosageStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationStainingGel electrophoresis
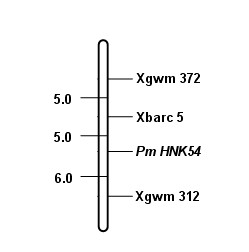
The invention relates to a marker primer interlocked with a wheat powdery mildew resistance gene PmHNK54 and application thereof in molecular marker-assisted selection. The sequence of the marker primer on a genetic map is Xbarc5, PnHNK54 and Xgwm312, and the genetic distances between Xbarc5 and PnHNK54 and between Xgwm312 and PnHNK54 are respectively 5.0cM and 6.0cM. 10 mu l of PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) reaction system during SSR (Simple Sequence Repeat) marker selection comprises 1 mu l of 10*buffer, 0.2 mu L of 10nM / mu l dNTP, 0.2 mu l of 20u M / mu L primer, 0.1 mu l of 5U / mu lTaq enzyme, 8.1 mu l of deionized water and 0.4 mu l of 20 ng / mu l genome DNA. An amplification procedure comprises the following steps of: pre-denaturing at 94 DEG C for 3 min, denaturing at 94 DEG C for 1 min, renaturing at 55 or 60 DEG C for 1 min, extending at 72 DEG C for 2 min, and repeating for 40 cycles; extending at 72 DEG C for 10 min; and performing 6% denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis or 8% nondenaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis on amplification products, observing and taking pictures after silver nitrate dyeing. The invention finds the position of the powdery mildew resistance gene PmHNK54 in wheat parent material Zheng 9754, has the advantages of strong marker specificity, high stability, cost saving and high selection efficiency and is applicable to large scale, high throughput and automation.
Owner:HENAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for constructing sweet potato core germplasm resource library based on SSR (simple sequence repeat) molecule markers
PendingCN106636377AGood repeatabilityImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementAgricultural scienceGermplasm
The invention provides a method for constructing and evaluating a sweet potato core germplasm resource library based on SSR (simple sequence repeat) molecule markers. The method includes the steps: firstly, extracting DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) from tender leaves at the top ends of stored sweet potato germplasm resources; secondly, performing PCR amplification by screened polymorphism SSR primers; thirdly, recording banding pattern data of the germplasm resources according to amplification results; analyzing obtained data with the SSR markers of '0' and '1'; constructing sweet potato core germplasm by the aid of a locus preferred sampling method and Jaccard genetic distance according to the principle that germplasm sampled in an integral clustering manner can enter core germplasm; evaluating and confirming the resource library by the aid of phenotypic data. Amplification banding patterns of the SSR markers are clear, stable and good in repeatability. Compared with a method for constructing core germplasm based on phenotypic data of agronomic characters, the method for constructing sweet potato core germplasm based on molecule marker data has the advantages that the method is good in stability, time and labor are saved and the like.
Owner:MAIZE RES INST GUANGXI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Screening method of chicken breeding materials
ActiveCN109182535AEasy to operateReduce human errorMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsAnimal scienceGenomic DNA
The invention discloses a screening method of chicken breeding materials, belonging to the field of agricultural livestock and poultry breeding. The screening method of chicken breeding materials comprises the following steps: 1) extracting genomic DNA; 2) performing microsatellite mark and PCR reaction; 3) performing mtDNA PCR reaction and sequencing; 4) performing statistical analysis; and 5) selecting breeding material. The invention adopts molecular biotechnology to analyze genetic diversity and genetic distance of breeding material, selects individuals with rich genetic diversity as breeding material, ensures rich genetic information, reduces blindness and risk of breeding, reduces breeding time, improves breeding efficiency and reduces breeding cost.
Owner:GUANGXI ZHUANG AUTONOMOUS REGION INST OF ANIMAL HUSBANDRY
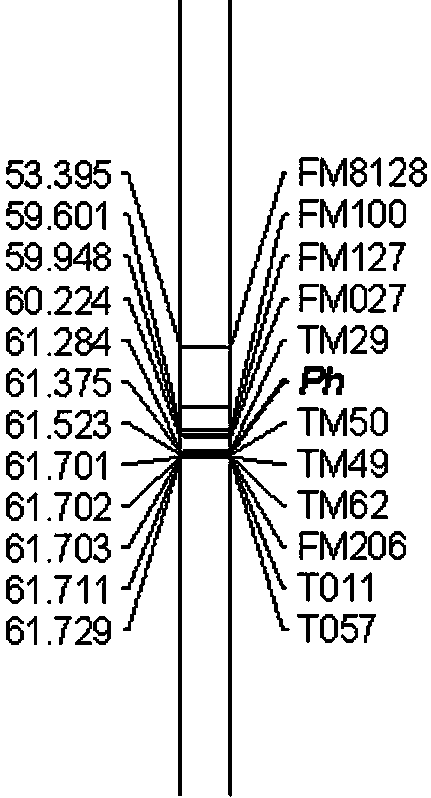
Molecular markers for assistant selection of resistance gene Ph of tobacco black shank and application thereof
ActiveCN103993013AStrong specificityImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyResistant genes
The invention provides molecular markers for assistant selection of a resistance gene (Ph) of tobacco black shank and an application thereof. The molecular markers provided by the invention are TM29 and TM50 which are respectively located on both sides of the gene (Ph) on a 20th gene linkage group and are tightly interlocked with the gene (Ph). The genetic distance from the molecular marker TM29 to the gene (Ph) is 0.091cM and that from the molecular marker TM50 to the gene (Ph) is 0.148cM. The invention further provides a molecular marking method for detecting the resistance gene (Ph) of tobacco black shank by using the molecular markers as well as the application of the molecular markers in assistant breeding of tobacco black shank and positioning of the resistance gene (Ph) of tobacco black shank. The molecular markers for assistant selection provided by the invention is clear in selection target and cost-saving, remarkably improves the selection efficiency, not only provides a resistant resource screening method to breeding of tobacco black shank, but also gets close to the gene (Ph) through a genome walking method, thereby laying a foundation for cloning of the gene (Ph).
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI
SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) molecular marker chained with pumpkin peel color gene and application thereof
ActiveCN106636393AShorten the timeImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGene mappingMolecular breeding
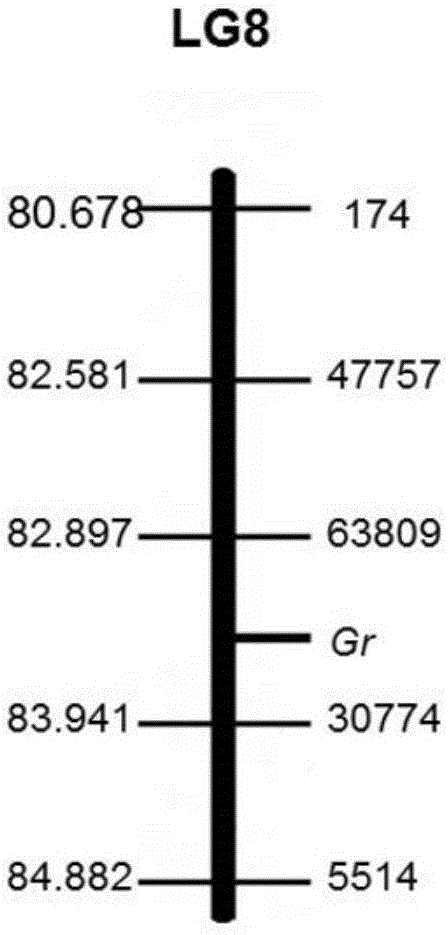
The invention discloses an SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) molecular marker chained with a pumpkin peel color gene and an application thereof. A molecular marker 63809 and a molecular marker 30774 obtained by screening are tightly chained with the pumpkin peel color gene, and the genetic distance between the two markers is 1.04cM; the SNP molecular marker can be directly applied to building of a peel color gene molecular marker assisted breeding system. A dCAPS amplification primer designed according to the two molecular markers can be used for improving molecular assisted breeding of pumpkin varieties easily, conveniently and rapidly at a high flux, technical support is provided for pumpkin appearance quality molecular breeding, and meanwhile the conventional gene mapping time is shortened greatly.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLES GUANGDONG PROV ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Multielement high flux genetic marking system and genetic analyzing method of Chinese mitten crabs
ActiveCN101613742AAvoid blindnessParsing Genetic DiversityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationPolycultureMicrosatellite
The invention relates to the field of genetic thremmatology of aquatic products, in particular to a multielement high flux genetic marking system and a genetic analyzing method of Chinese mitten crabs. The genetic marking system is a mitochondria sequence information system and a microsatellite molecule marking system, wherein the microsatellite molecule marking system comprises 7 EST-SSR systems marked 1and 6 EST-SSR marked systems 2. The method comprises the following steps: later generations produced by the same parent and different parents in a polyculture family are separated according to hereditary constitution and genetic diversity through information of sequences of three pairs of primer amplifications COI, Cytb and CR of mitochondria, and male parent discrimination is performed on later generations of the discriminated parents according to genetic distance and genetic diversity through the EST-SSR microsatellite molecule marking system, thereby completing the genealogy authentication during the genetic breeding of the Chinese mitten crabs and determining the inbreeding coefficients. The invention discriminates the genetic relationship among filial generations by using the multielement high flux genetic marking system on the basis of effectively utilizing species genetic information, and effectively avoids the inbreeding recession.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
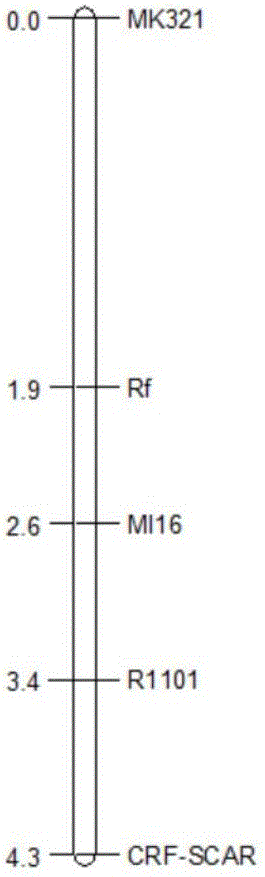
Molecular marker for aiding selection of Rf (fertility restorer) gene, specific primers and application
ActiveCN106048012ASupplementary researchSave manpower and material resourcesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSweet PeppersAgricultural science
This invention relates to the field of molecular markers, in particular to a molecular marker for aiding selection of a Rf (fertility restorer) gene, specific primers and an application. The genetic distance between the molecular marker and the Rf gene is 0.7cM, and the molecular marker is closely linked with the gene. Specific upstream and downstream primers of the molecular marker are as follows: the sequence of the upstream primer of MI16 is CCTCGAATATAAACTTATGGTGTCC, and the sequence of the downstream primer of MI16 is GCTTGGCAACCTATTCTTAGAAGTT. The M16 marker can quickly identify the Rf gene in a sweet pepper, and better complement the study of the sweet pepper in the direction of male sterility.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
A method for identification of distant hybrid offspring of peony and peony
InactiveCN102260736AEffective selection processMicrobiological testing/measurementMolecular identificationMolecular genetics
The invention relates to a method for identifying plant hybrid progeny, in particular to a method for identifying distant hybrid progeny of peony and peony. The identification method provided by the invention comprises: identification and screening of hybrid seedling early form, identification of female parent by chloroplast DNA, identification of male parent by SSR molecular marker. Through the combination of morphology and molecules, identify hybrid offspring, identify true and false hybrids, study and summarize the relationship between true hybrid seedlings and parents, determine the heritable external morphological indicators, and obtain a reasonable hybrid at the molecular genetic level The genetic distance between the species and the parent, the degree of kinship, and finally a reasonable identification standard system is established on the basis of morphological and molecular genetics, so that the later selection process can be carried out effectively.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Method for screening wheat approximate variety by virtue of SSR molecular marker
InactiveCN105132551AError allowedWill not increase the quantity significantlyMicrobiological testing/measurementElectrophoresisFluorescence
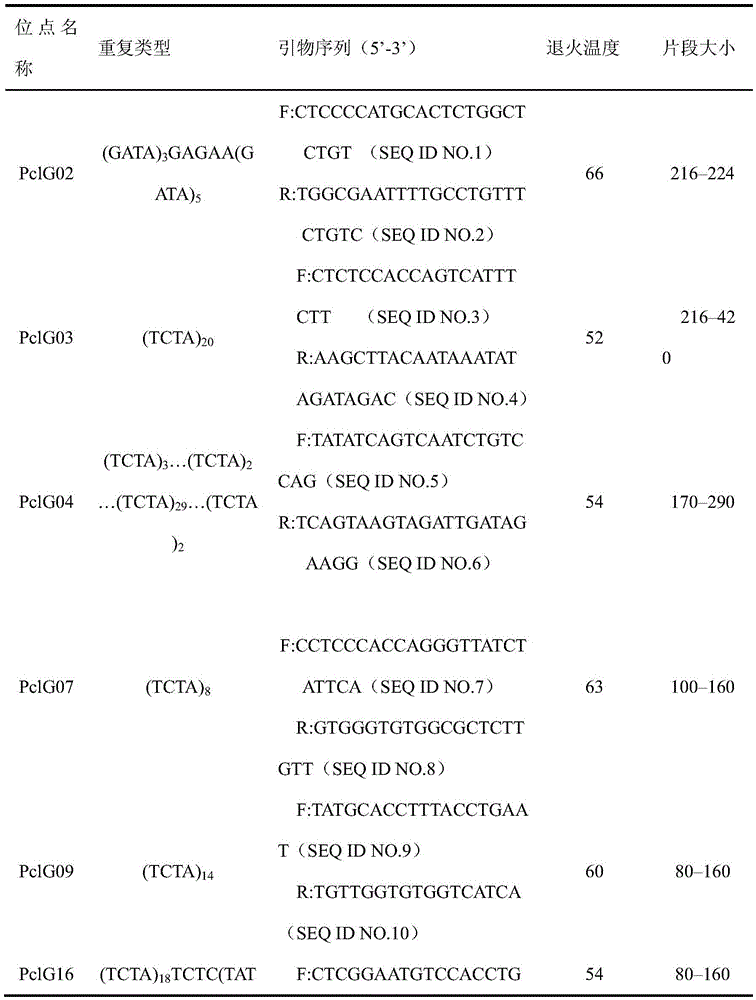
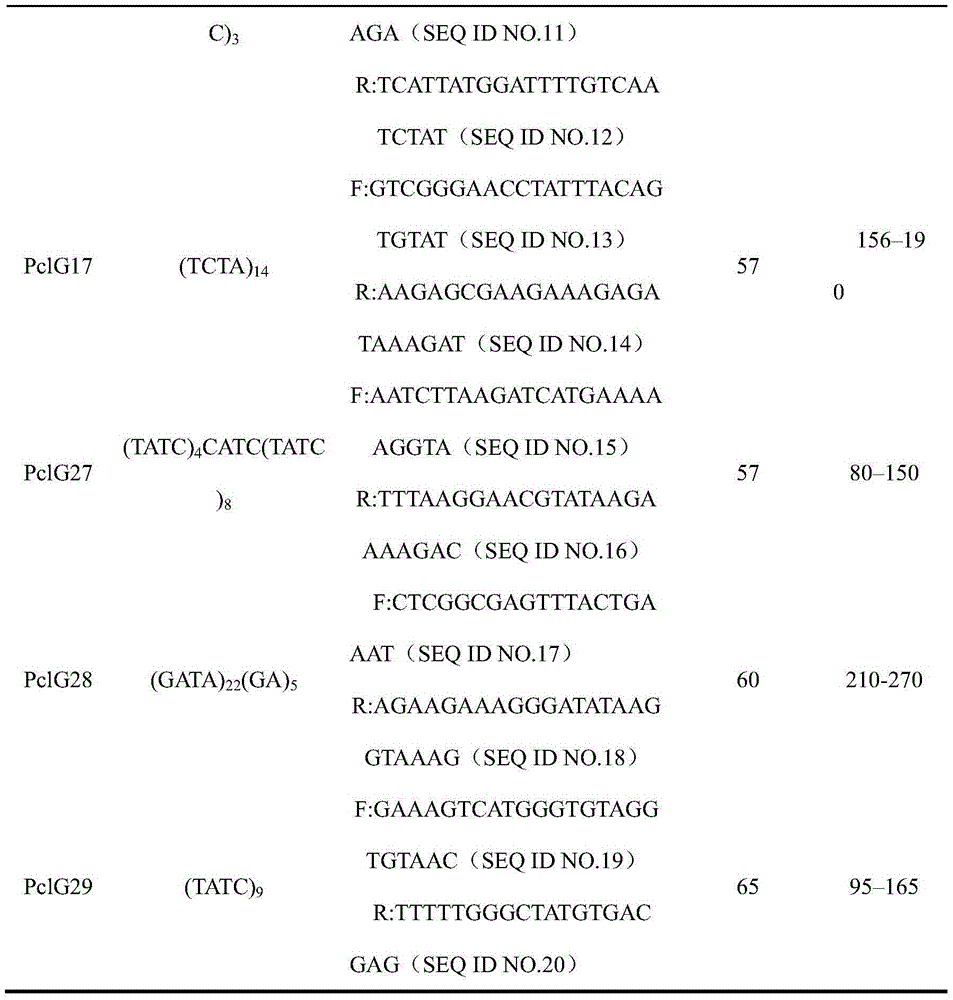
The invention discloses a method for screening a wheat approximate variety by virtue of an SSR molecular marker. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, extracting DNA of an experimental variety; then, respectively implementing PCR amplification on template DNA of the experimental variety by virtue of 21 pairs of basic core SSR fluorescently-labeled primers as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1-42 in a sequence list and 21 pairs of extended core SSR fluorescently-labeled primers as shown in SEQ ID NO. 43-84 in the sequence list; acquiring data of a PCR product through electrophoresis detection; and then, analyzing the acquired data through PowerMarker so as to obtain a genetic distance between varieties, and judging the variety that genetic distance is less than 0.2 as an approximate variety. The method can be used for improving test precision and reducing test cost.
Owner:CROP RES INST SHANDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
DNA bar code technology for identifying rosewood and rosewood product, and application method thereof
InactiveCN104404131ALarge capacityReduce dependenceMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA barcodingPhylogenetic tree
The invention discloses a DNA bar code technology for identifying rosewood and rosewood products and an application method thereof. The technology is as below: constructing a high capacity database through a strategy by merging database of rosewood samples experiment data and a target plant; sequencing a DNA bar code sequence of the rosewood samples; merging the sequencing sequences with homologous sequences published in the Genbank database to construct a rosewood DNA bar code gene database with wide range of data sources; and establishing an algorithm and decision rules for the identification database by using matK+rbcL genes as the target DNA bar code gene for rosewood identification, and using a search tool method of a local alignment algorithm based on frequency, a genetic distance method based on Kimura-2-parameter probability and a phylogenetic tree method based on clustering analysis. The DNA bar code technology for identifying rosewood and rosewood products and the application method thereof establish an accurate and quick rosewood DNA bar code identification technology.
Owner:NANJING INST OF PROD QUALITY INSPECTION
Molecular marker of wheat powdery mildew-resistant gene Pm45 and application of molecular marker
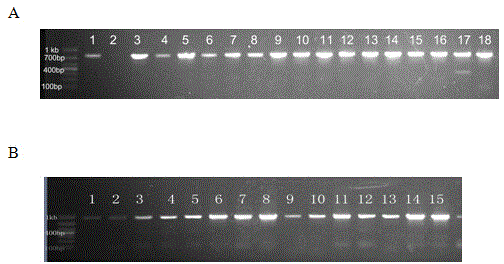
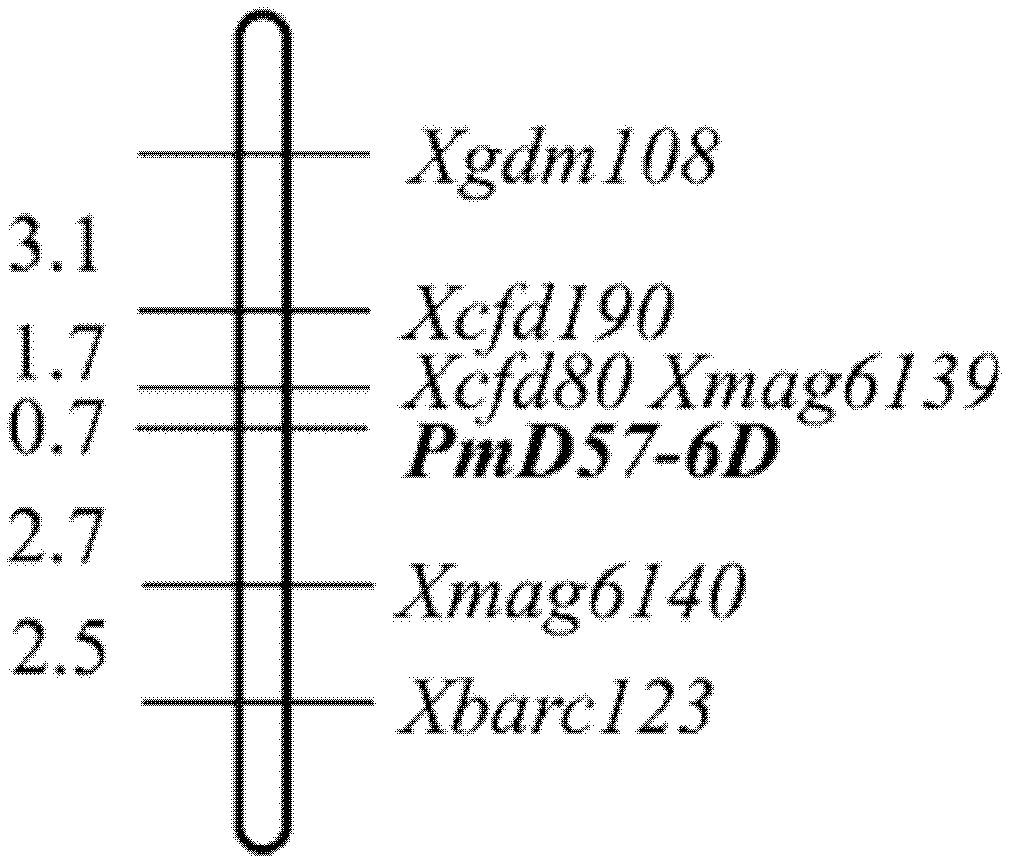
InactiveCN102604942AIncrease diversityExcellent disease resistance performanceMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationResistant genesDisease resistant
The invention belongs to the field of molecular genetics and relates to a molecular marker of a wheat powdery mildew-resistant gene Pm45 and application of molecular marker. The molecular marker is selected from any one of MAG6139, MAG6140 and BARC123, and the genetic distance from the MAG6139, MAG6140 and BARC123 to the Pm45 is 0.7cm, 2.7cm and 5.2cm respectively. A Pm45-containing single plant is selected according to the molecular marker MAG6139, the molecular marker MAG6140 and the molecular marker BARC123, and then Pm45-containing disease-resistant varieties with different genetic backgrounds can be selected and cultivated. The Pm45-containing plants can be simply, conveniently and quickly selected by using the molecular marker tightly linked with the Pm45. Due to the application of the molecular marker MAG6139, the molecular marker MAG6140 and the molecular marker BARC123, the time and the labor for selecting a disease-resistant material can be greatly saved, and the accuracy of pre-detection can be improved.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method used for identifying different families of procambarus clarkii
InactiveCN105602946AAvoid inbreedingPrevent breedingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationStainingProcambarus clarkii
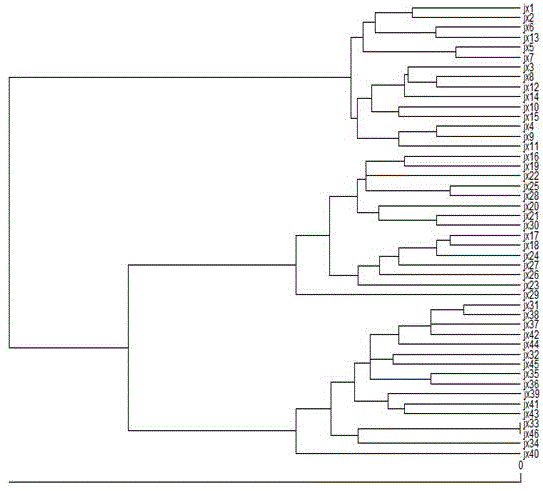
The invention discloses a method used for identifying different families of procambarus clarkii. The method comprises following steps: half-sib families are established artificially; DNA is extracted from the tail muscle of procambarus clarkii; 10 pairs of selected microsatellite primers are used for PCR amplification of the extracted DNA; obtained PCR products are subjected to electrophoretic analysis and silver staining; silver staining results are subjected to digital analysis; genetic distances of individuals are measured using a genetic software, a UPGMA cluster analysis diagram is drawn based on the genetic distances, and the individuals from different families can be distinguished based on cluster analysis results. The method can be used for distinguishing the families of procambarus clarkii quickly and accurately, and preventing inbreeding effectively, and possesses high application value in breeding of procambarus clarkii families.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Molecular marker and specific primers for assisting in test of wilt disease resistance in brassica oleracea and use thereof
InactiveCN102108407AAchieve early selectionMicrobiological testing/measurementAgricultural scienceSheath blight
The invention discloses a molecular marker and specific primers for assisting in test of wilt disease resistance in brassica oleracea and use thereof. The invention provides a reagent for assisting in the test of wilt disease resistance in brassica oleracea and / or assisting in screening brassica oleracea with wilt disease resistance, which is a specific primer pair formed by nucleotides represented by a sequence 2 and a sequence 3 in a sequence table. The invention also provides a specific gene fragment which is at a genetic distance about 2.87cM to the wilt disease resistance gene in brassica oleracea and is formed by nucleotides represented by a sequence 1 in a sequence table. The result of the identification of wilt disease resistance in brassica oleracea and / or screening of the brassica oleracea with wilt disease resistance with assistance from the reagent (primer pair) or sequence characterized amplified region (SCAR) marker, which are provided by the invention, is 97 percent consistent with that of field identification. When used in breeding, the reagent, molecular marker or method has the advantages of accuracy, quickness, capability of realizing early breeding and the like and has a bright application prospect.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES +1
Genome information assisted breeding method-breeding parent selection based on SNP clustering information and PAV variation information
InactiveCN106169034AAccurately and effectively obtainReduce workloadBiostatisticsSpecial data processing applicationsGenomicsGenomic sequencing
The invention relates to a genome information assisted breeding method for parent selection by means of SNP clustering and PAV variation. The essence of the genome information assisted breeding method is to obtain genome sequencing information of candidate parents with the help of genomic and bioinformatics methods; on one hand, a high-quality SNP data set is obtained through sequence alignment, a genetic distance matrix of the candidate parents is calculated, and the affinity between the candidate parents is judged with the help of a clustering tree; on the other hand, a Denovo assembled candidate parent contig is positioned to a reference genome, and the PAV variation of candidate parent target trait related genes is obtained according to the physical location. By combining the PAV variation and affinity information based on SNP, a parent subset is screened out from a large number of candidate parents for phenotype identification; finally, a selected breeding parent is determined by combining the phenotype identification result of the parent subset. The genome information assisted breeding method belongs to the field of rice molecular breeding, the range of the materials for phenotype identification can be effectively narrowed from the large number of the candidate parents, the workload of phenotype identification is reduced, and the breeding work efficiency is improved.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
SSR (Simple Sequence Repeats) marker of gummy stem blight resistant gene Gsb-4 of melon
InactiveCN102199598ASite detection is convenient and fastNot limited by environmental conditionsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationResistant genesAgricultural science
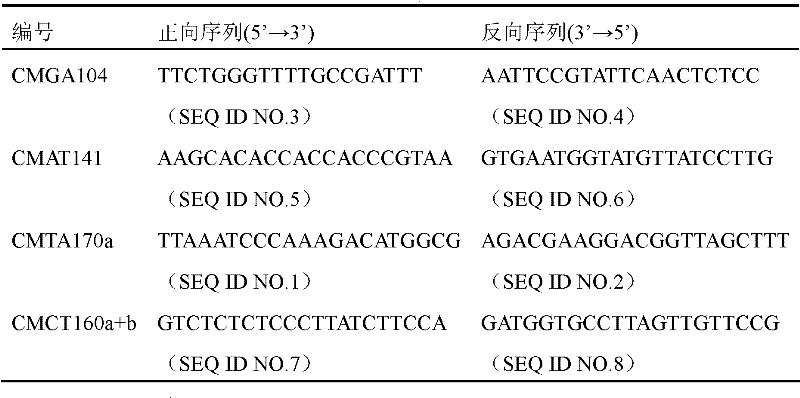
The invention belongs to the technical field of crop genetic and breeding and biology and relates to an SSR (Simple Sequence Repeats) marker of a gummy stem blight resistant gene Gsb-4 of a melon resource PI482398; an SSR primer marker CMAT170a is utilized to amplify a breeding material or a variety DNA of the gummy stem blight resistant gene Gsb-4 of the melon resource PI482398 to obtain a 120 bp amplified fragment which is the SSR marker of the gummy stem blight resistant gene Gsb-4 of the melon resource PI482398; and the genetic distance from the SSR marker to a resistant gene is 5.14cM. In the invention, an SSR molecular marker tightly linked with the gummy stem blight resistant gene Gsb-4 of the melon is internationally obtained for the first time. The gummy stem blight resistance of the melon can be predicted by detecting the molecular marker and further a disease-resistant variety or a strain is quickly screened out for breeding the melons. The disease-resistant gene locus is convenient and quick to detect without being limited by environmental conditions.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Molecule making method for gene locus for preventing mycosphaerella melonis of muskmelon
InactiveCN101173311AClear locationEasy to identifyMicrobiological testing/measurementMelon (food)Cultivar
The invention relates to a molecular marker method for a melon blight resistance gene, belonging to the field of biotechnology. There are four AFLP molecular markers that are linked to the gene for resistance to blight blight, the marker EcoRI-TG / MseI-CTC200 is a 200bp band; the marker EcoRI-AT / MseI-CTG90 is a 90bp band; the EcoRI-TC / MseI-CAG60 is a 60bp band band; the marker EcoRI-TG / MseI-CTA70 is a 70bp band; the linkage distances are 2.0, 6.0, 5.4 and 6.0cM, respectively. Detect whether PI 420145 and its derivative varieties (lines) contain the gene through the molecular marker method provided by the present invention, predict its resistance level to vine blight, improve the selection efficiency, and help to accelerate the selection of excellent vine blight-resistant melon varieties in my country It is used in the production process to identify the purity of muskmelon varieties resistant to vine blight.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
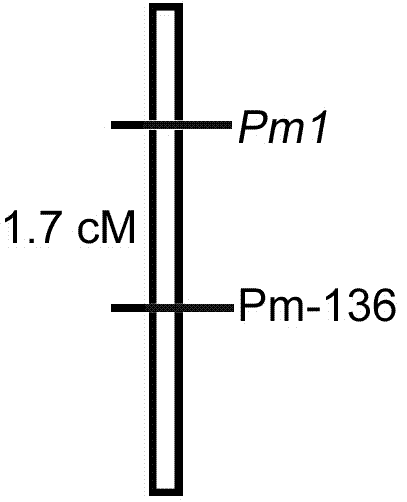
Linked molecular marker for powdery mildew resistant gene pm1 of cucurbita pepo L. and application of linked molecular marker
ActiveCN104498484AExcellent disease resistance performanceImprove use valueMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyDisease
The invention discloses an SSR molecular marker (Pm-136) linked with a powdery mildew resistant gene pm1 of cucurbita pepo L., belongs to the technical field of breeding of vegetable molecules for disease resistance, and relates to an SSR molecular marker linked with the powdery mildew resistant gene, and an application of the SSR molecular marker. The genetic linkage distance between the molecular marker Pm-136 and the resistance gene is 1.7cm. Whether a disease resistance character transfer offspring plant carries with the resistance gene Pm1 or not can be rapidly and accurately detected by virtue of the molecular marker Pm-136, thus the disease-resistant breeding efficiency is significantly improved; and the breeding cycle is shortened. The obtained marker Pm-136 has the advantages of being stable, reliable, simple to operate, good in repeatability and the like, and has high utilization value in identification of resistant and susceptible varieties and a disease-resistant transfer single offspring plant.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Molecular marker of wheat scab resistance expansion gene Fhbl and application thereof
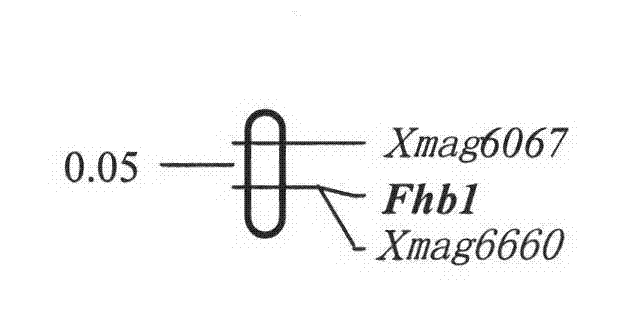
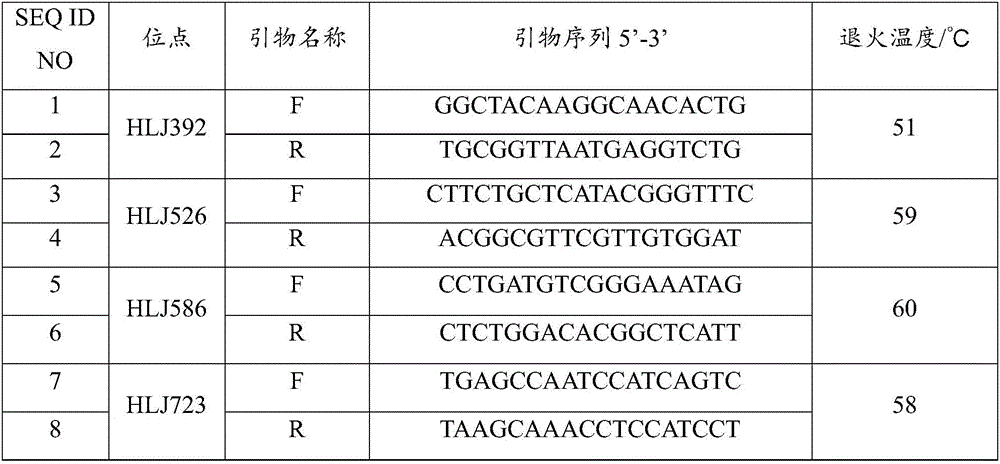
InactiveCN102653759AEasy to detectStable amplificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationAgricultural sciencePhenotype
The invention belongs to the field of crop breeding, and relates to a molecular marker of wheat scab resistance expansion gene Fhbl and application thereof. The molecular marker is one of MAG6067 and MAG6660 with a genetic distance to an Fhbl gene being respectively 0.05cM and 0cM. A molecular marker which is closest linked to the Fhbl for the first time internationally by utilizing the invention. The Fhbl gene can be detected by marking the MAG6660 to determine whether the Fhbl exists or not and the existing state of the Fhbl, and the scab resistance of wheat can be predicted, so that a plant carrying the Fhbl can be quickly screened; and the molecular marker can be used for breeding a scab-resistance variety. Furthermore, laboratory detection can be carried out by utilizing the molecular marker to avoid the influence of the environment to the phenotype. According to the molecular marker closely linked with the Fhbl, time and labor for screening scab resistance materials can be greatly saved, the prediction accuracy can be enhanced, and clone of the Fhbl gene can be accelerated.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for keeping genetic diversity of Jian carps
InactiveCN106480192AAvoid inbreedingAvoid matingMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationMatingGermplasm
The invention discloses a method for keeping the genetic diversity of Jian carps. The method comprises the steps of individual tagging, template creating, genetic typing, family building, breeding file establishing and parent updating. Compared with the prior art, inbreeding of the Jian carps can be effectively avoided, the genetic diversity of Jian carp groups is kept and increased, and genetical characterization decline of the Jian carps is slowed down; in addition, breeding is assisted through molecular markers, a breeding file is established, genetic distances of the groups are analyzed by combining all parameters in the file, and therefore dominant groups are selectively reserved, and descendants excellent in genetic characterization are obtained through mating.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com