Linked molecular marker for powdery mildew resistant gene pm1 of cucurbita pepo L. and application of linked molecular marker
A technology of disease-resistant genes and molecular markers, which is applied in the determination/inspection of microorganisms, DNA/RNA fragments, recombinant DNA technology, etc., can solve problems such as no research reports on zucchini, and achieve convenient identification, stable amplification, and accelerated utilization Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
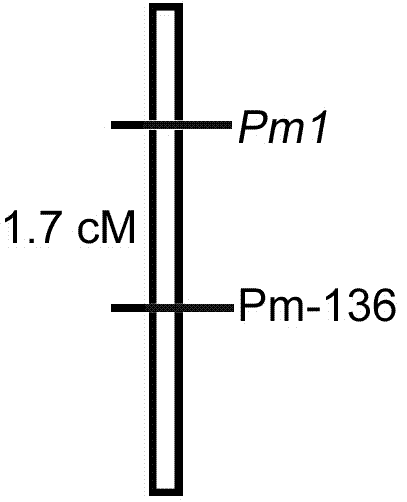
[0032] Dominant resistance gene to powdery mildew of zucchini Pm1 The linked SSR molecular marker, said molecular marker is Pm-136, which has the DNA sequence described in SEQ ID NO. 1 and SEQ ID NO. 2 in the sequence listing.
[0033] The zucchini powdery mildew dominant disease resistance gene Pm1 A method for obtaining linked SSR molecular markers, comprising the following steps:
[0034] Application of SSR-BSA technology: using zucchini inbred lines BS15 and BS9 as susceptible and resistant parents to prepare F 2 Generational segregation populations, screened with SSR primers for dominant resistance genes related to zucchini powdery mildew Pm1 Molecular markers linked to obtain a co-dominant molecular marker Pm-136, which is associated with the disease resistance gene Pm1 The genetic linkage distance of 1.7 cm.
[0035] The application of the molecular marker in the identification and transfer of powdery mildew resistance gene of zucchini germplasm resources.
[0...
Embodiment 2
[0046] This embodiment specifically describes the dominant disease resistance gene related to zucchini powdery mildew Pm1 A method for obtaining linked SSR molecular markers, comprising the following steps:
[0047] (1) Establishment and phenotypic identification of the F2 generation of zucchini inbred lines BS15 and BS9:
[0048] (1) Hybrid F1 was obtained by crossing zucchini inbred line BS15 (female parent) with BS9 (male parent), and F1 generation population was produced by selfing of F1.
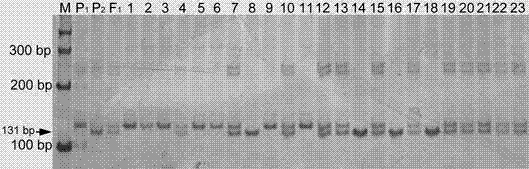
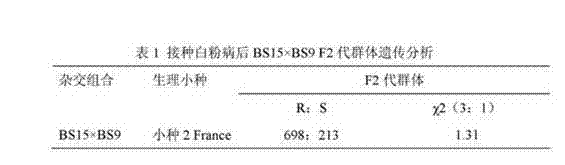
[0049] (2) The single plant of the F2 generation population was planted in a nutrient pot in a greenhouse, covered with an insect-proof net, and inoculated with powdery mildew spores after the cotyledons were fully unfolded, and the disease resistance traits were investigated 15 days after the inoculation. The identification results are shown in Table 1.
[0050]
[0051] R and S represent resistant and susceptible plants, respectively. χ2 0.05, 1 =3.84.
[0052] (3) The tra...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com