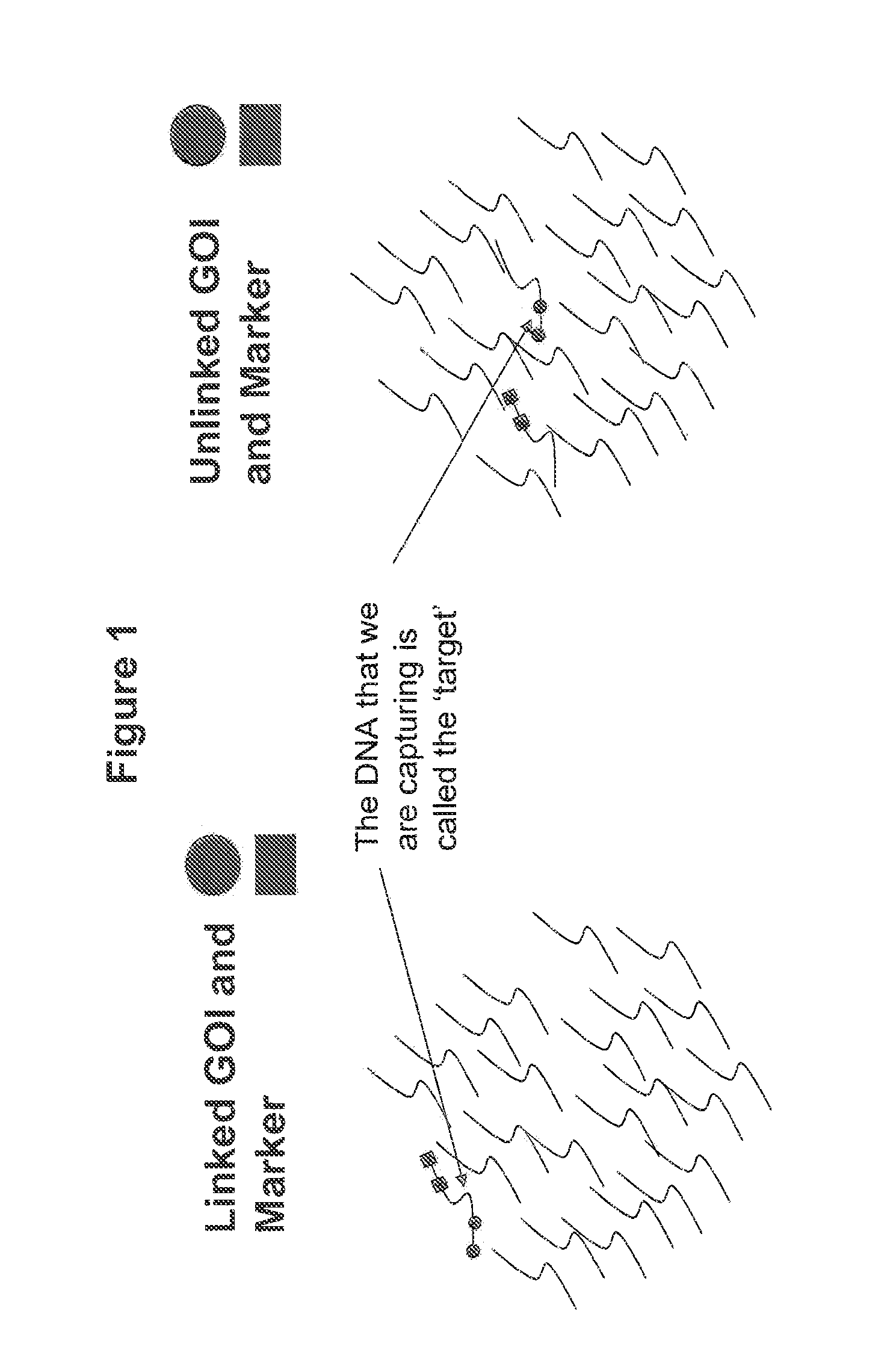
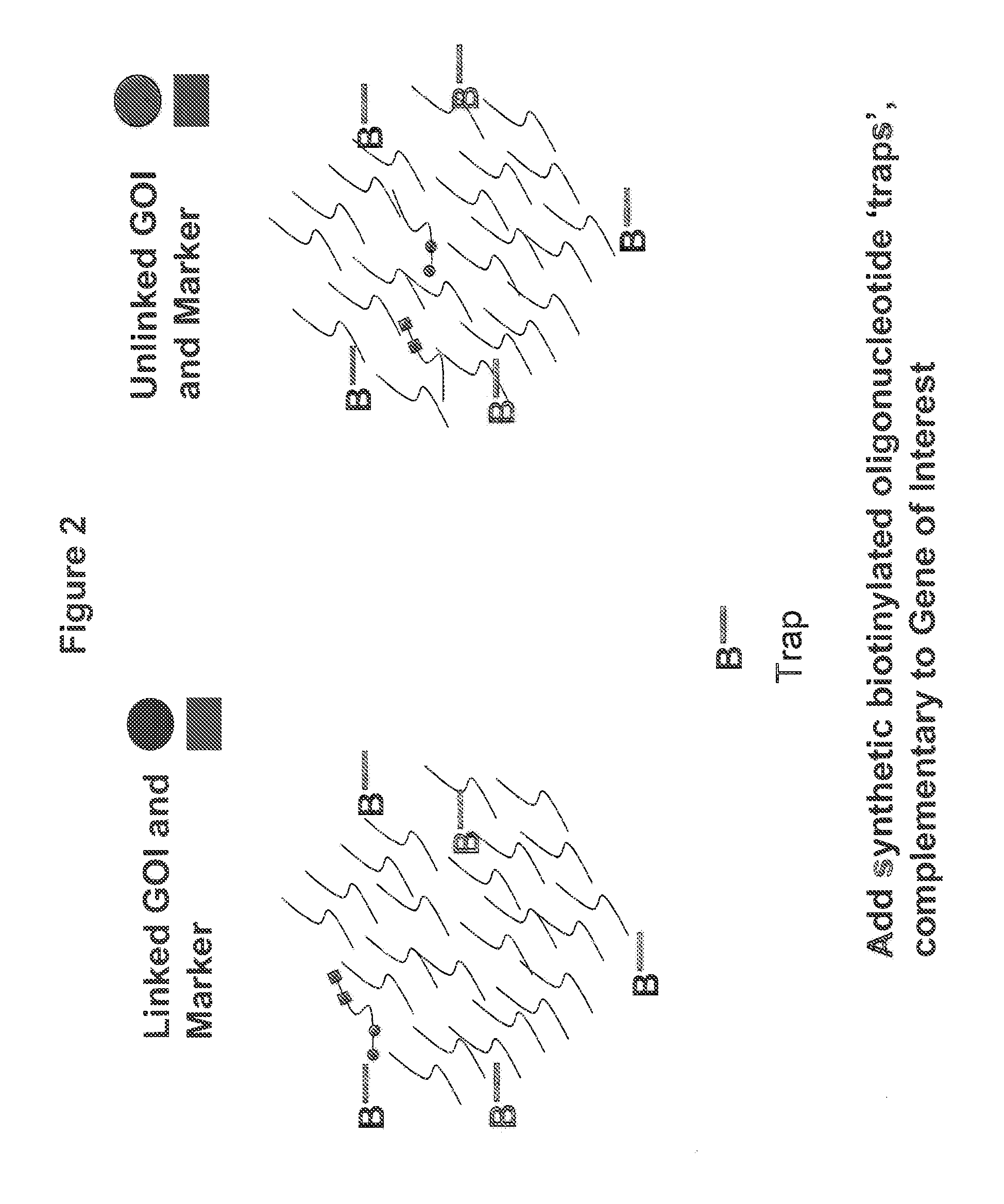
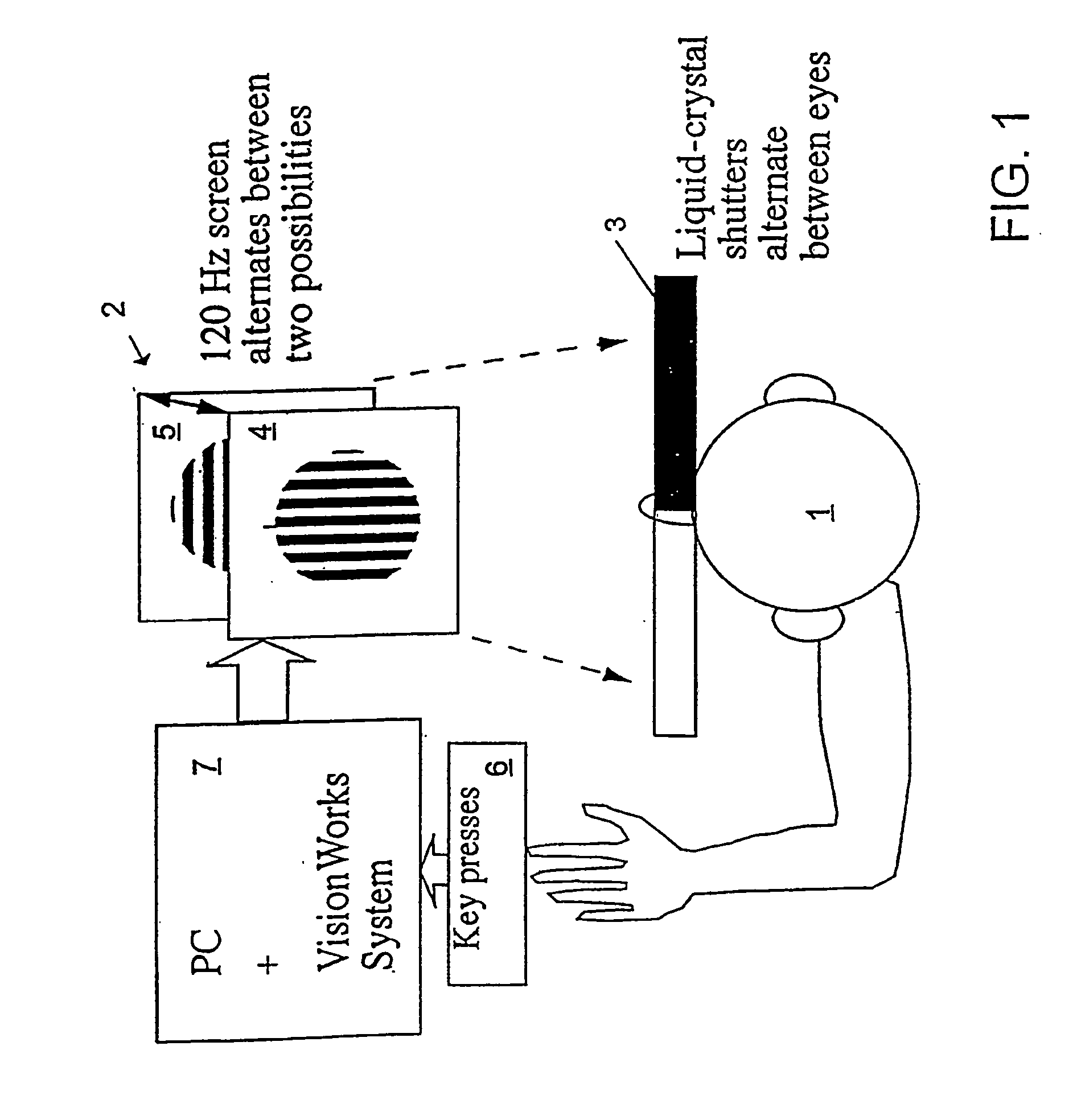
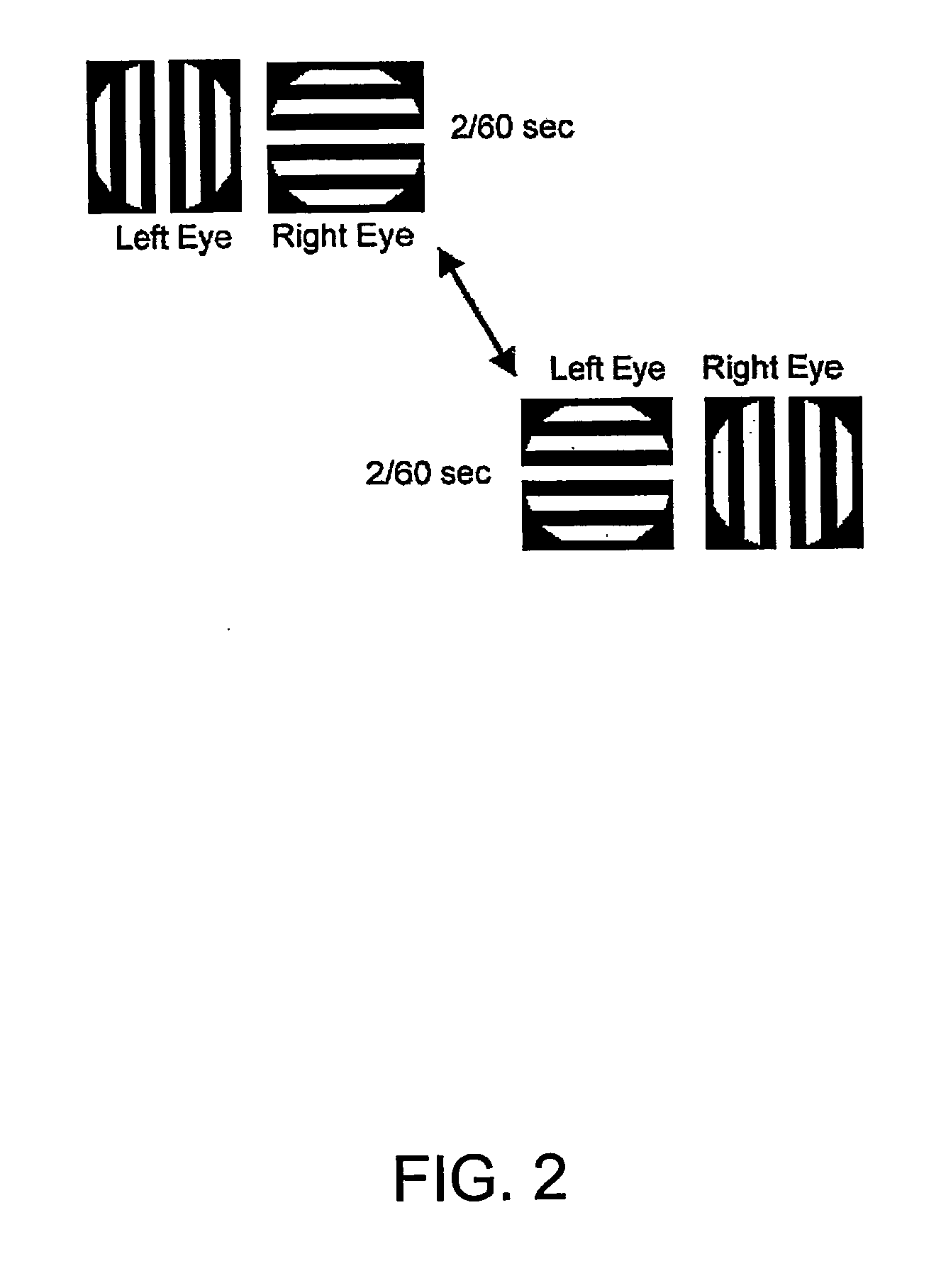
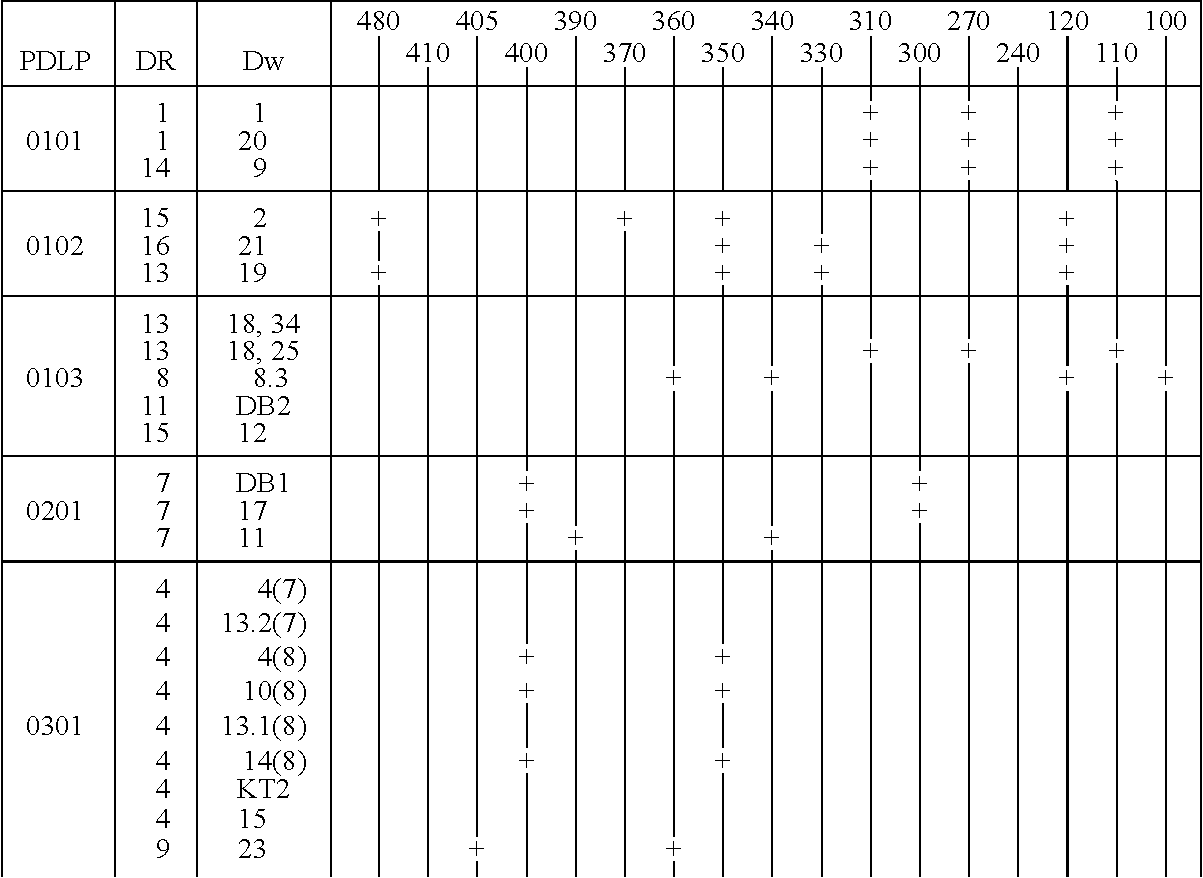
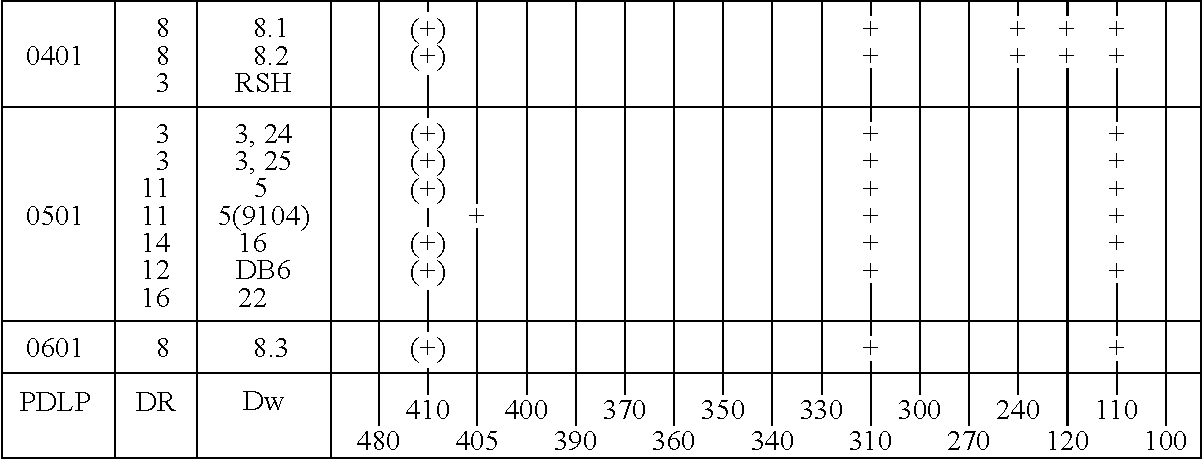
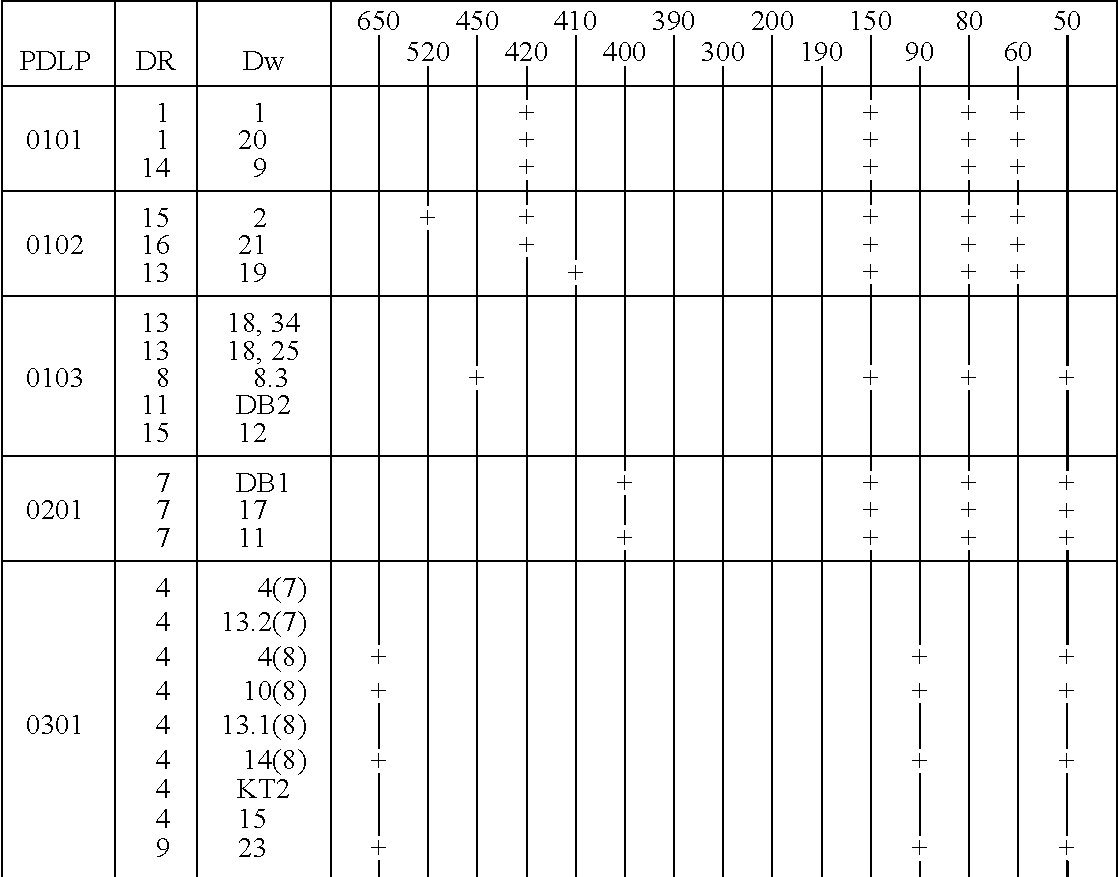
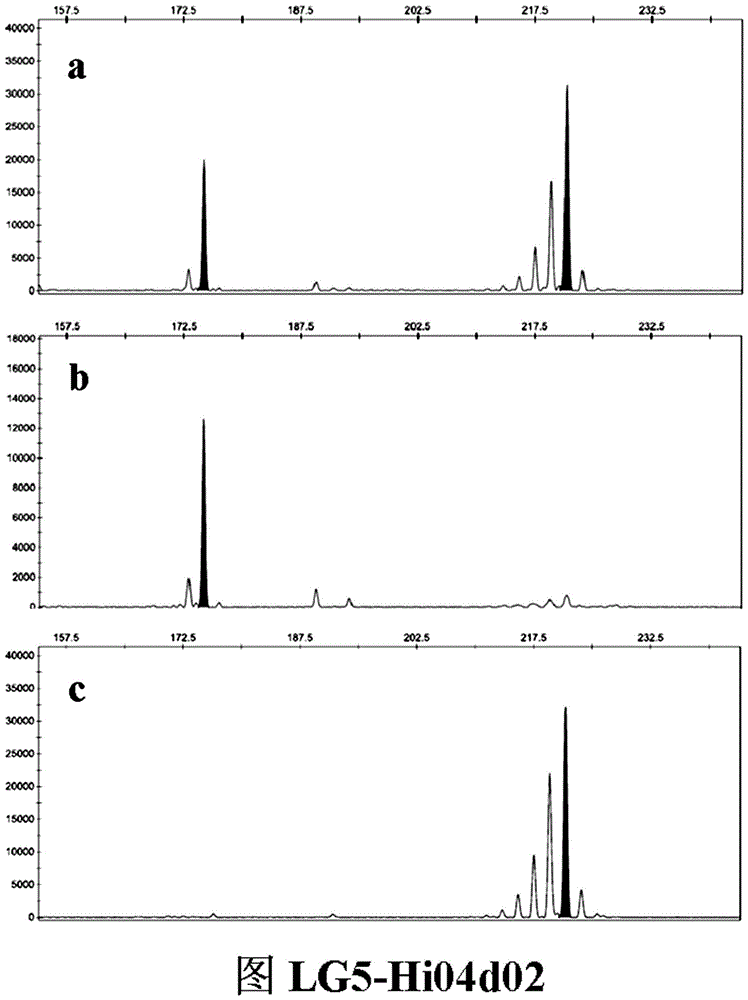
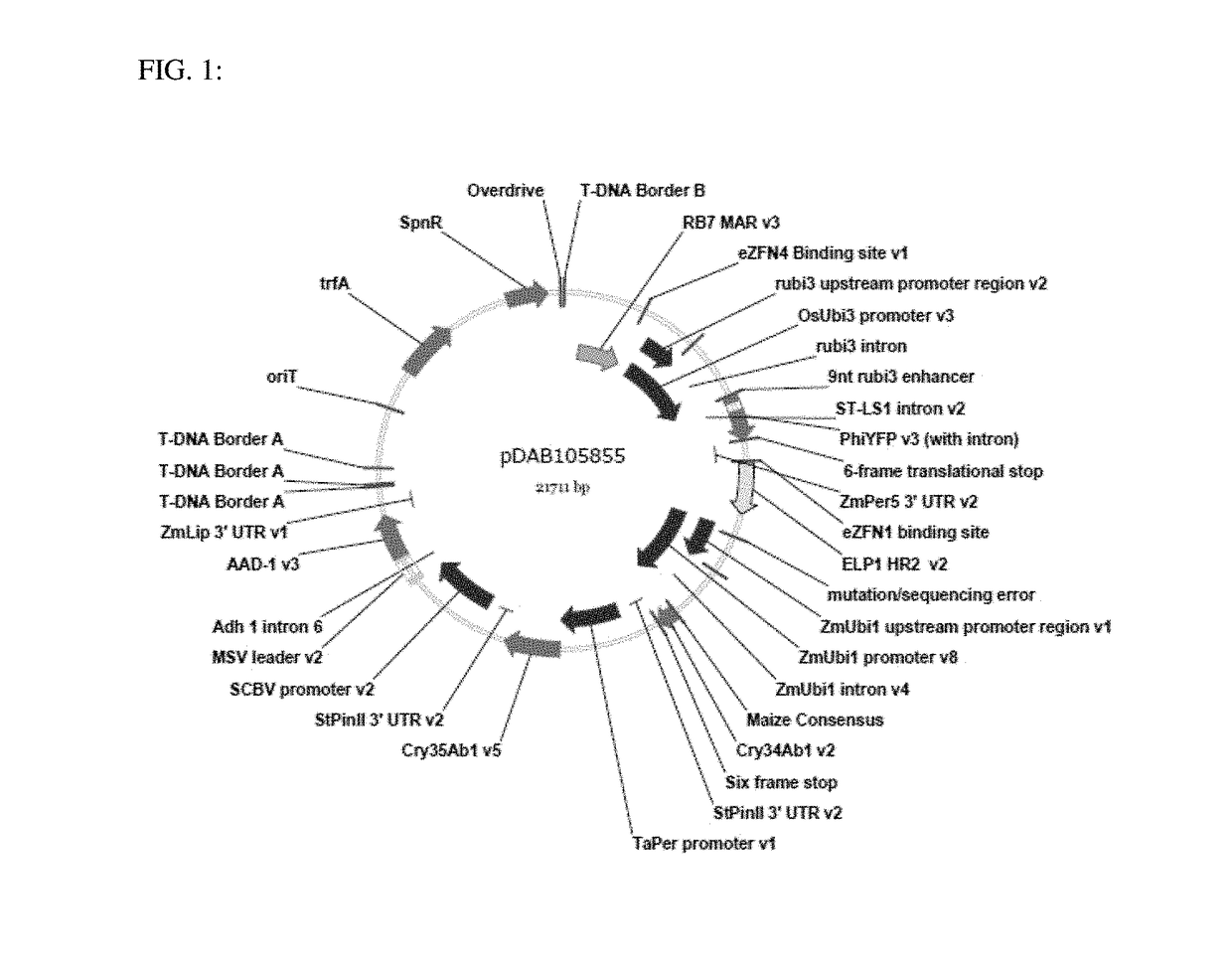
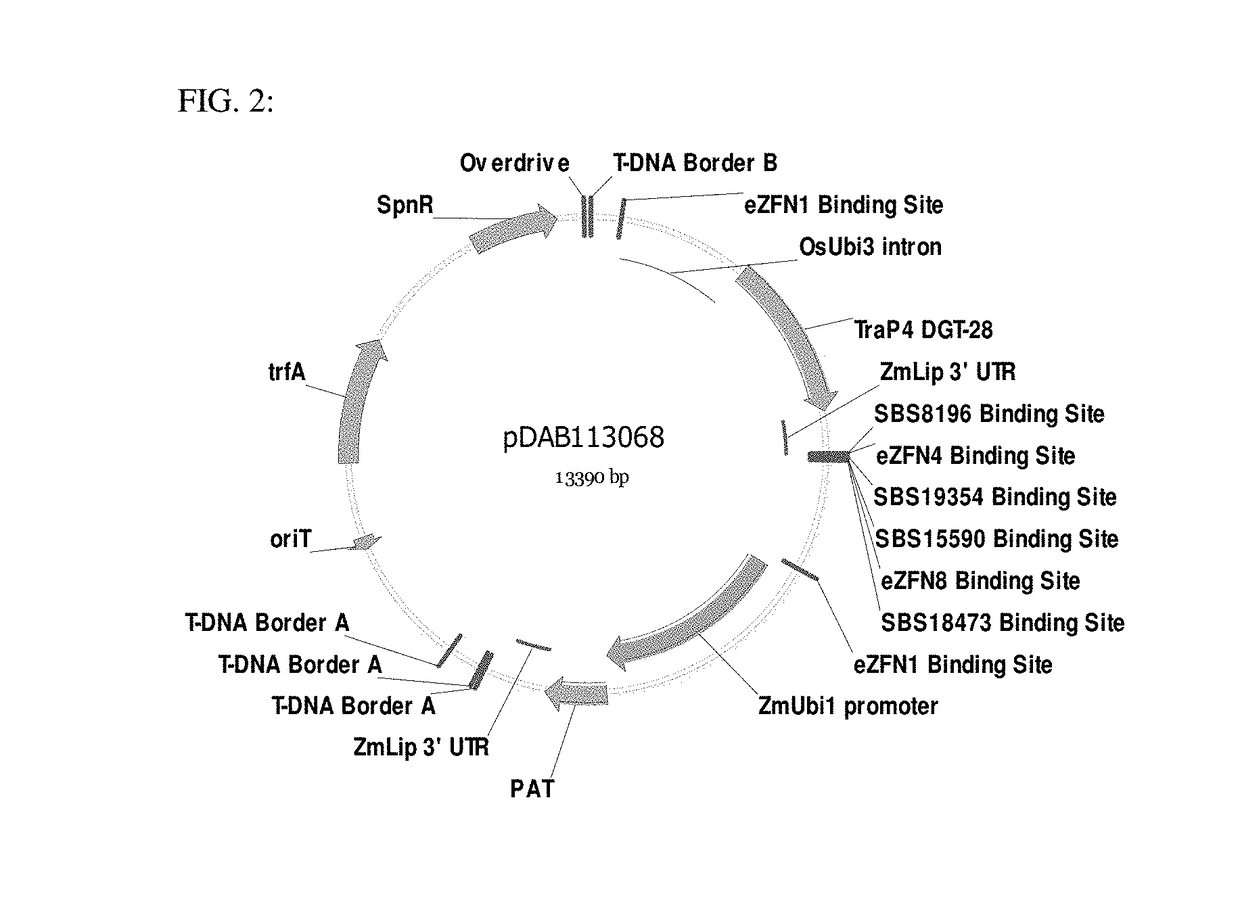
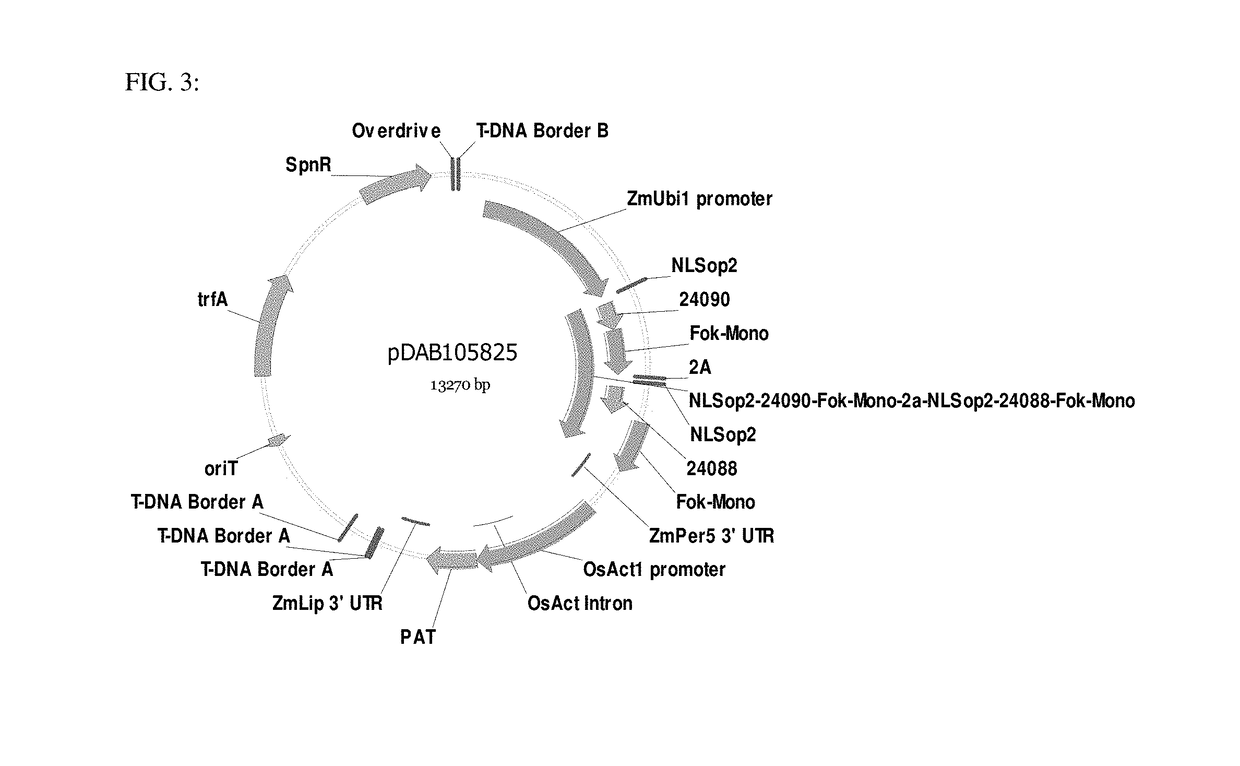
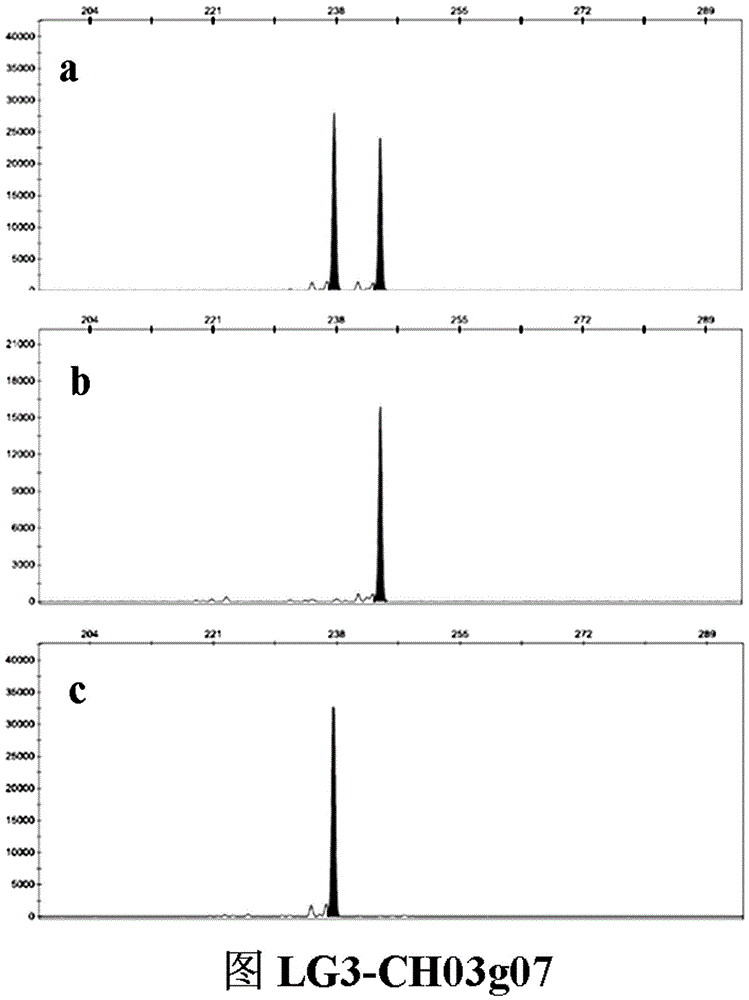
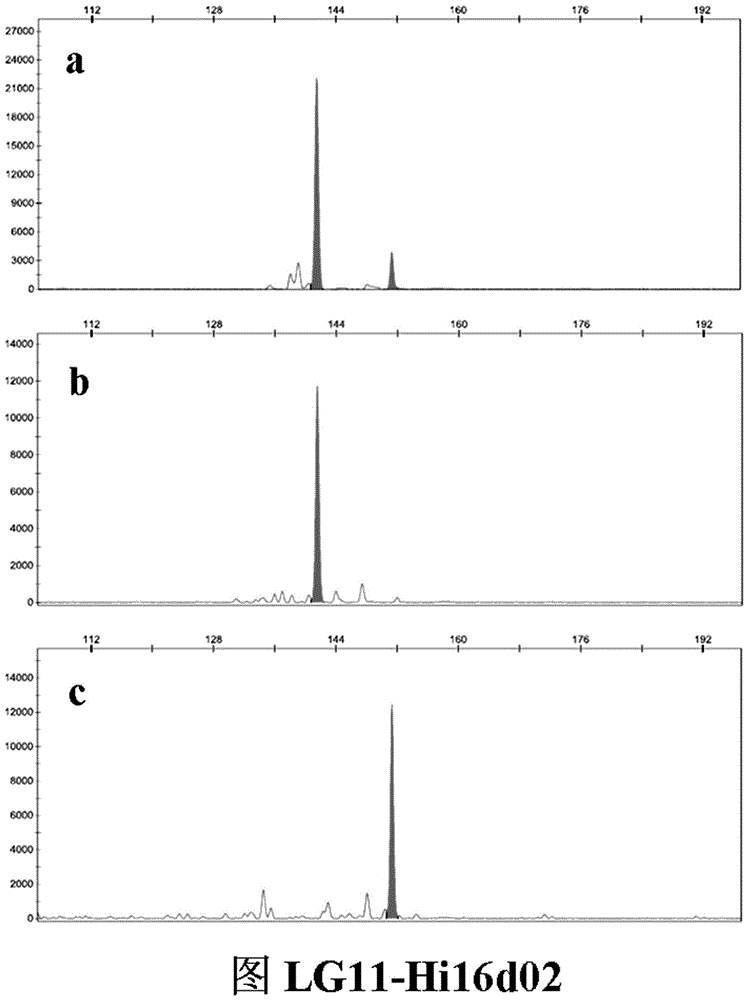
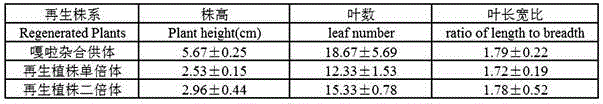
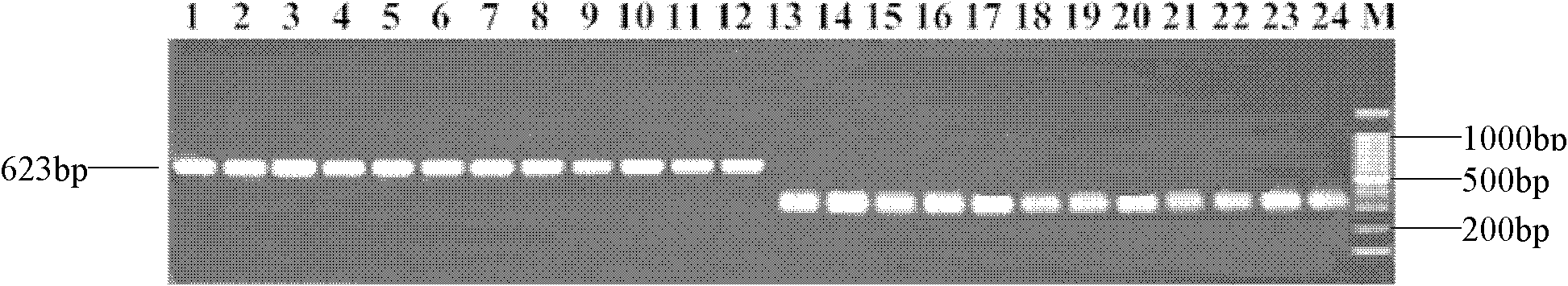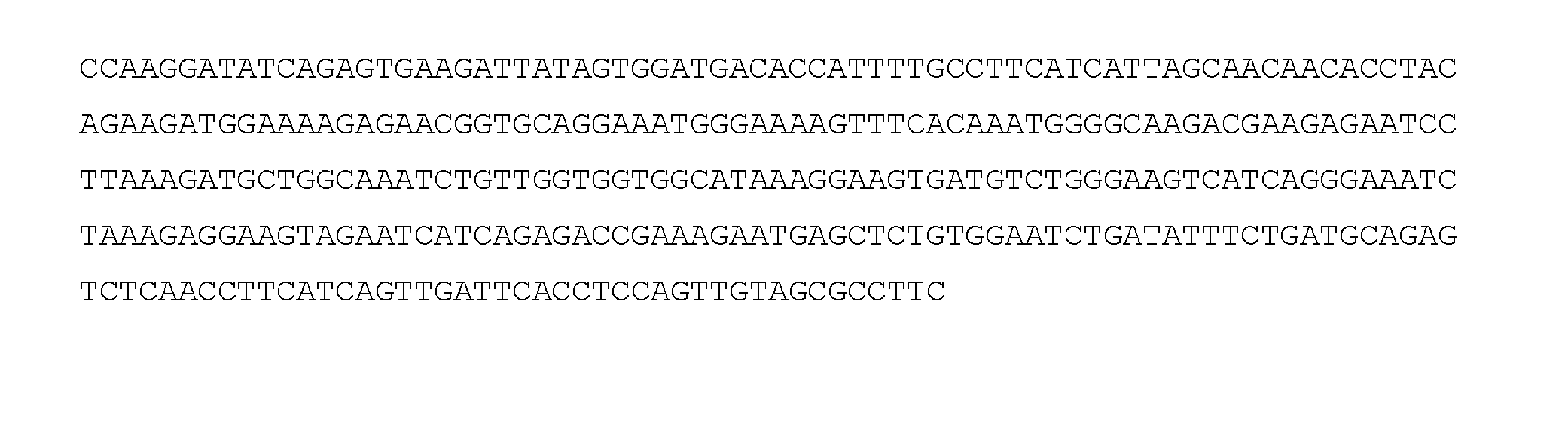Patents
Literature
52 results about "Genetic linkage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
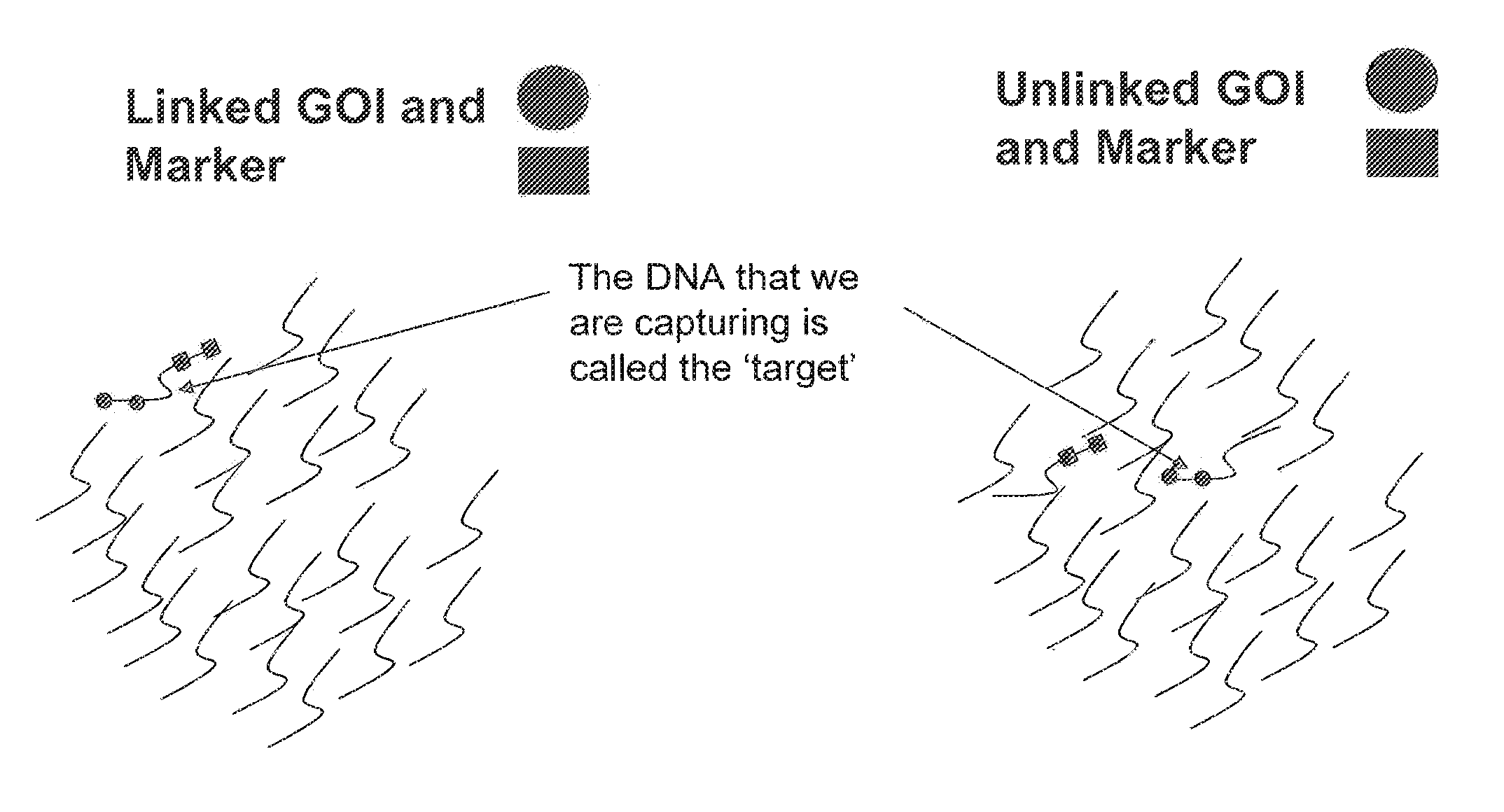
Genetic linkage is the tendency of DNA sequences that are close together on a chromosome to be inherited together during the meiosis phase of sexual reproduction. Two genetic markers that are physically near to each other are unlikely to be separated onto different chromatids during chromosomal crossover, and are therefore said to be more linked than markers that are far apart. In other words, the nearer two genes are on a chromosome, the lower the chance of recombination between them, and the more likely they are to be inherited together. Markers on different chromosomes are perfectly unlinked.
Method and apparatus for diagnosis of a mood disorder or predisposition therefor
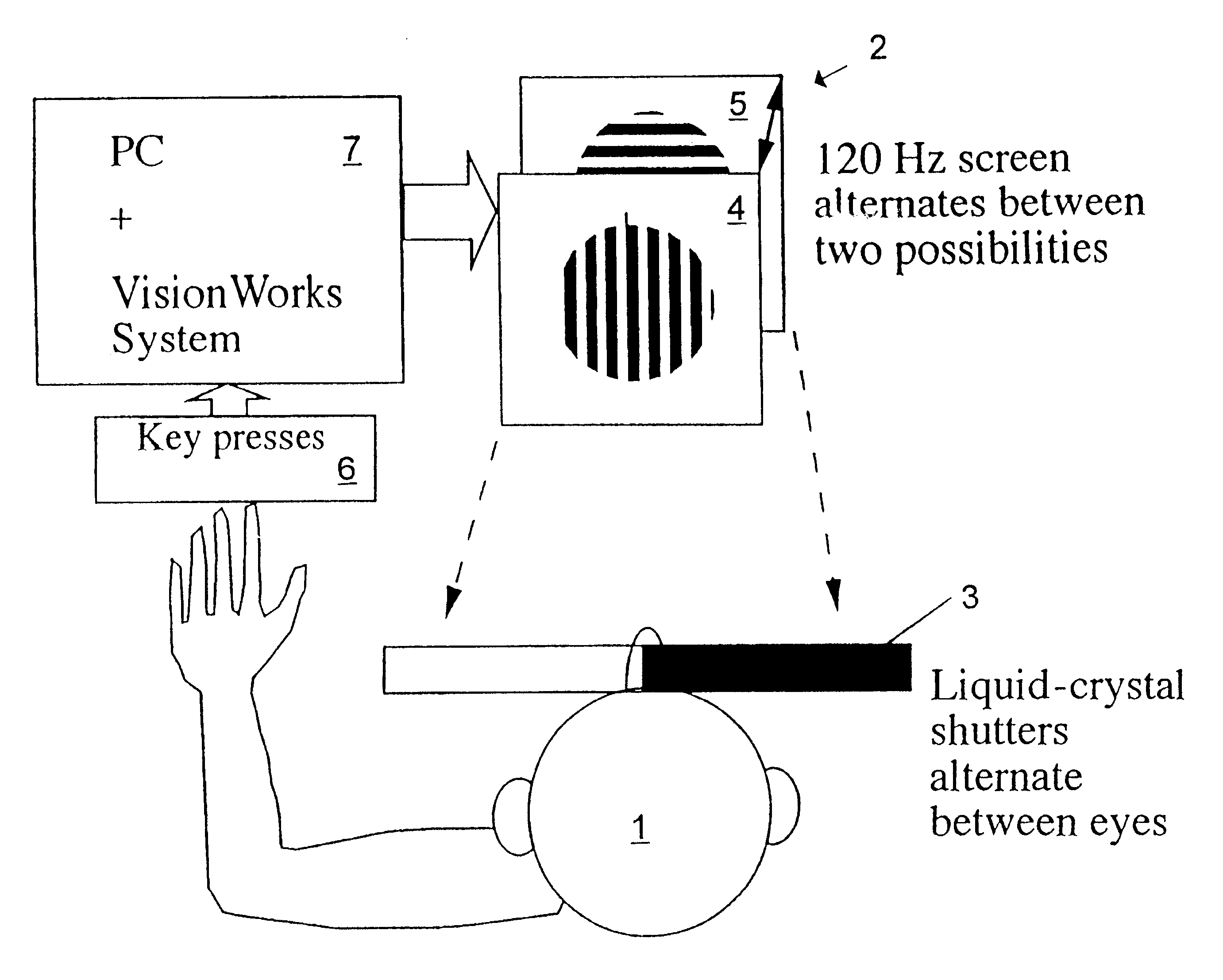
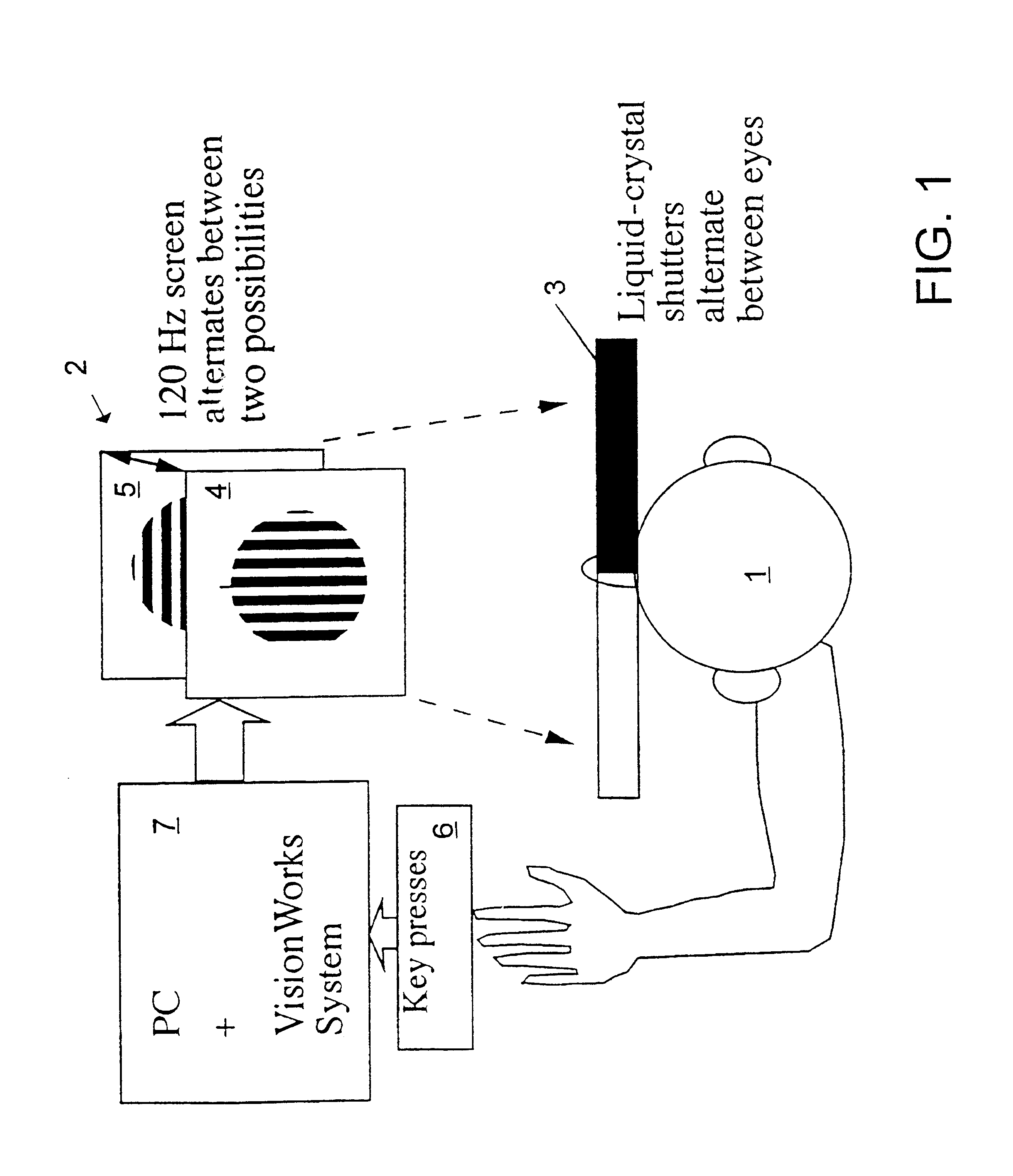
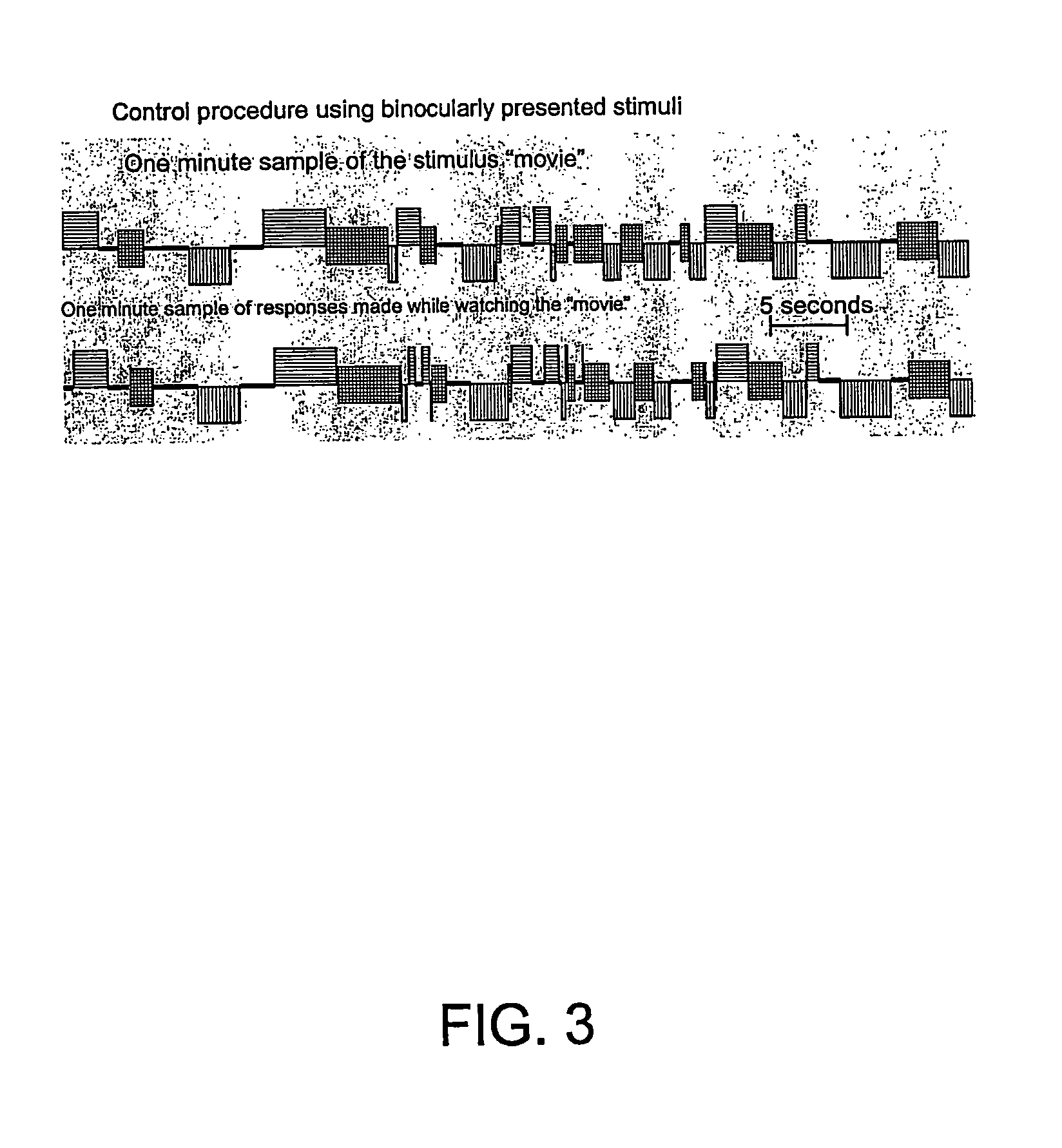
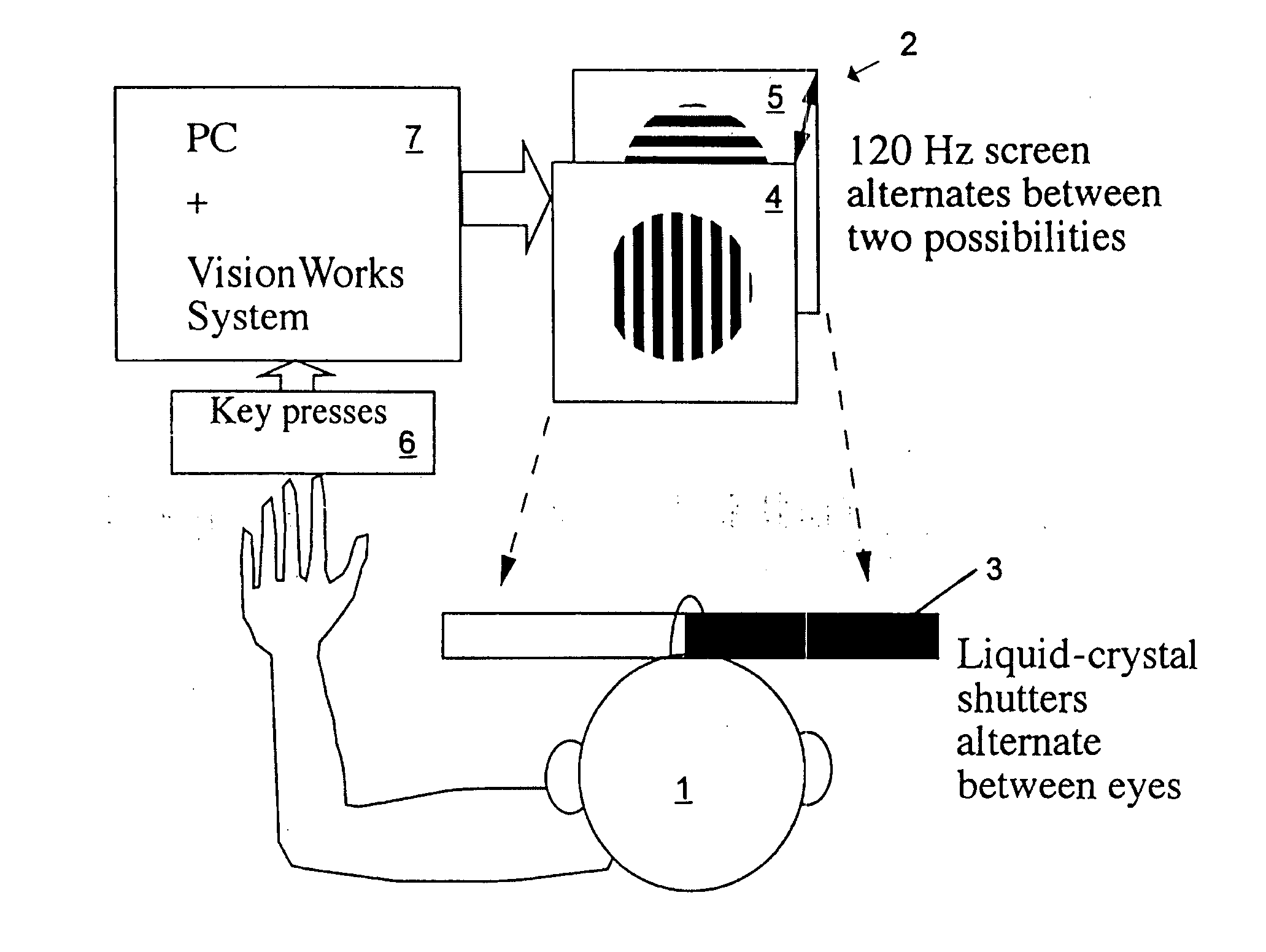
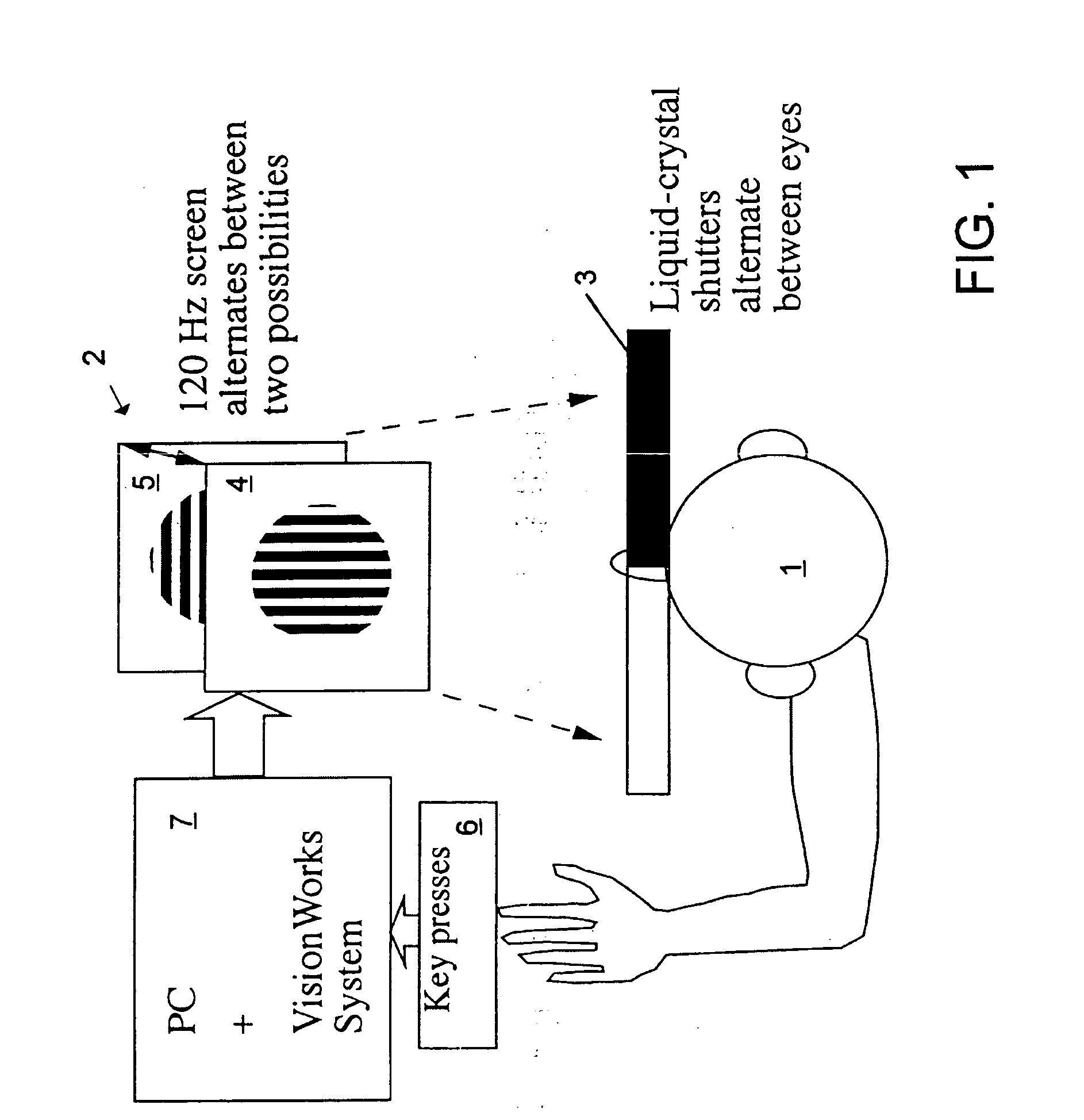
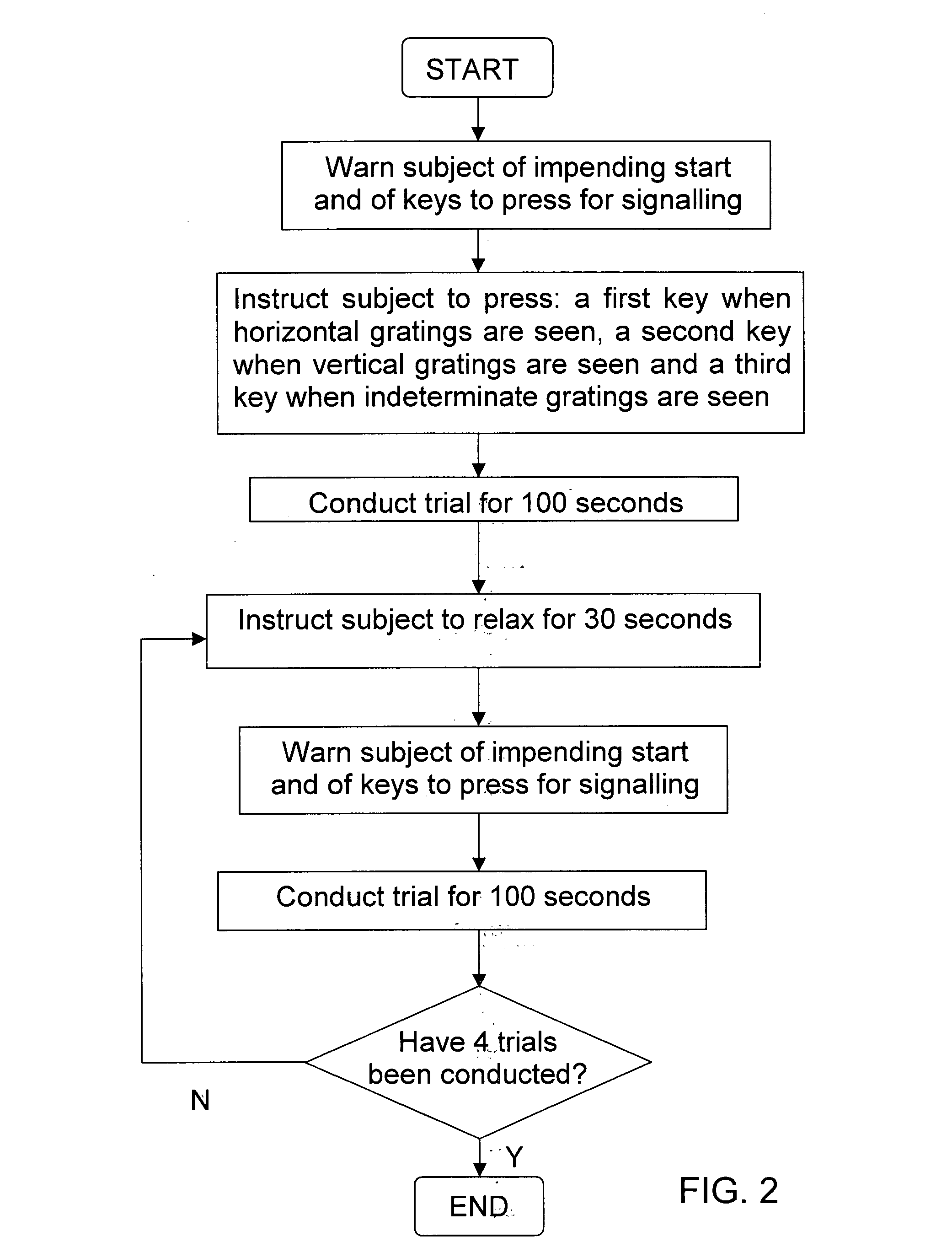
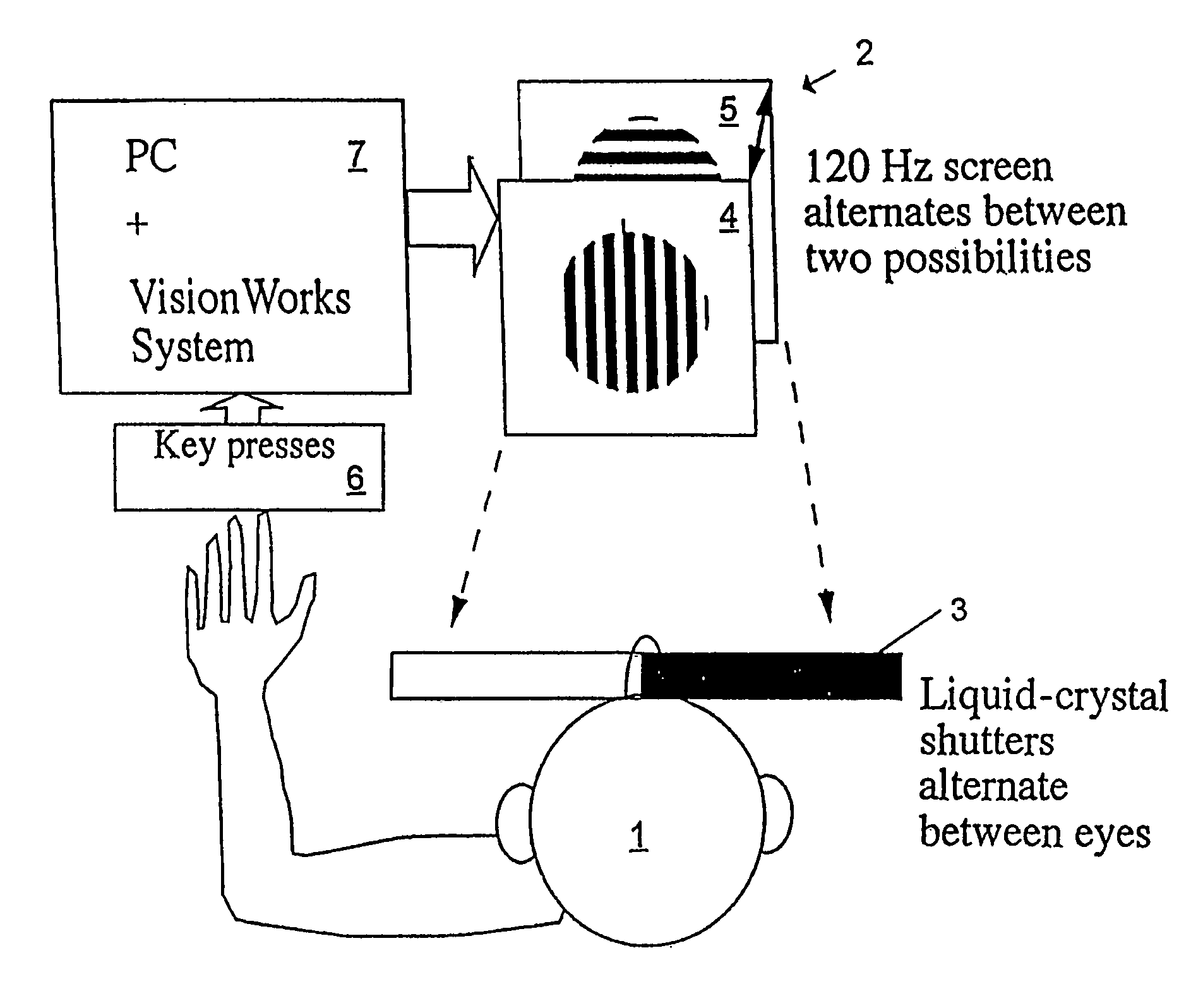
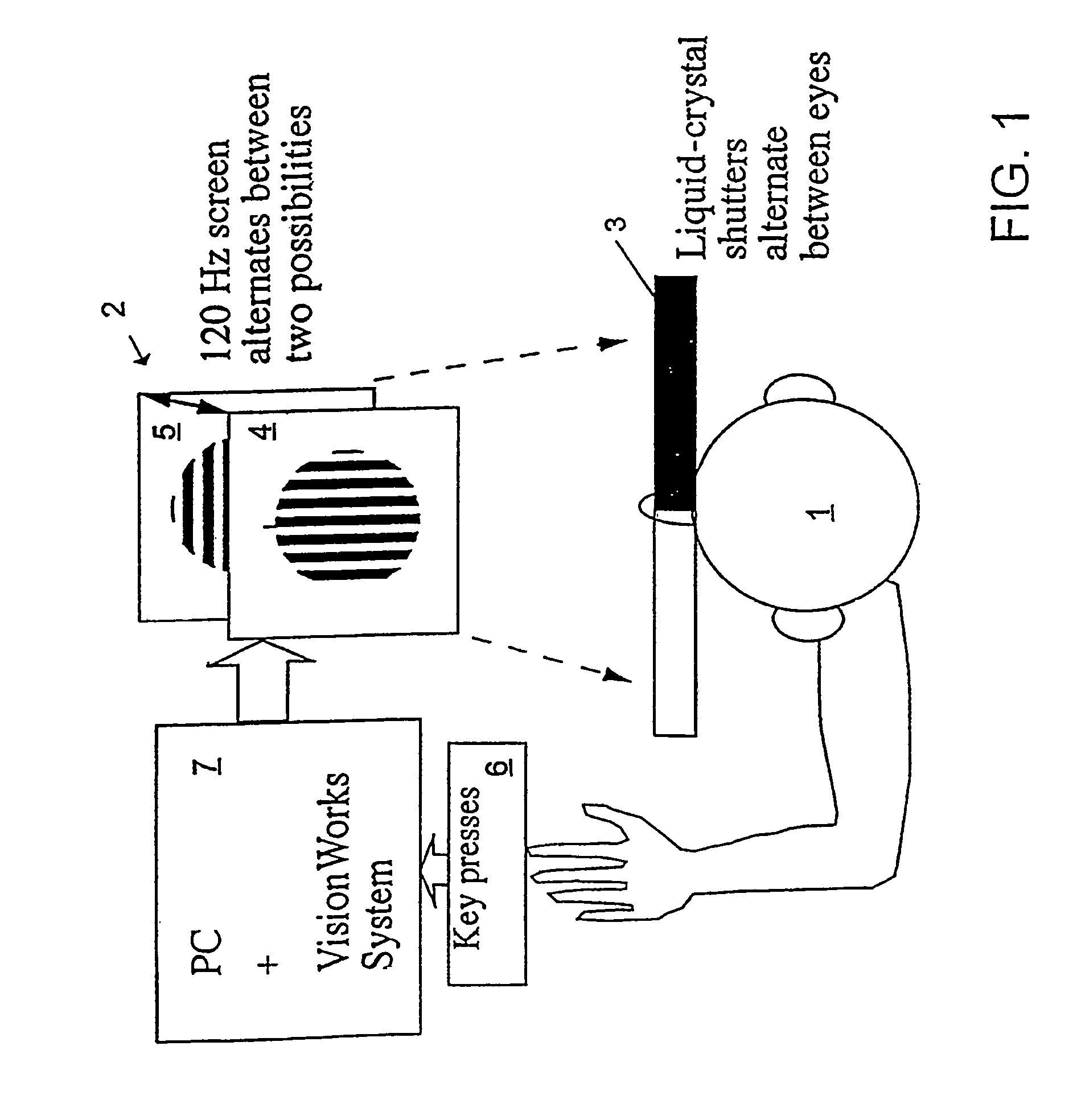
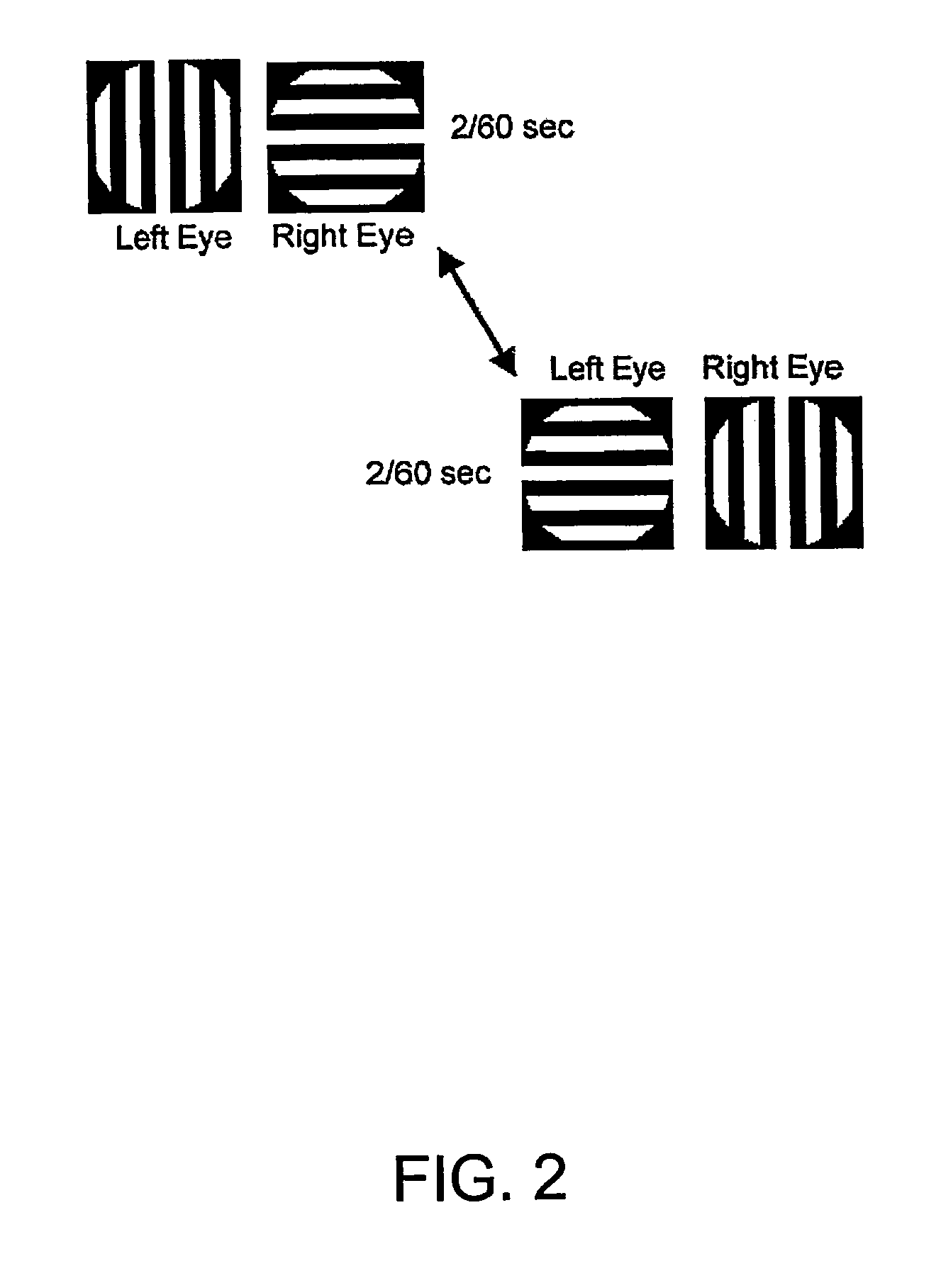
InactiveUS6629935B1Great absolute magnitude of changeEasy to changeIndividual molecule manipulationSensorsDiseaseBinocular rivalry
A method for diagnosis of a mood disorder or predisposition therefor in a test subject is disclosed. The method includes the steps of determining an interhemispheric switch rate of the test subject, and comparing the switch rate with a corresponding reference switch rate to diagnose presence or absence of the mood disorder or predisposition therefor. In a preferred embodiment, the interhemispheric switch rate is determined by measuring the rate of binocular rivalry in the test subject. Also disclosed is an apparatus for diagnosis of a mood disorder or predisposition therefor, use of the diagnostic method in genetic linkage studies for the identification of the molecular defect(s) underlying these disorders, and for the identification of compounds which may alleviate such disorders.
Owner:QUEENSLAND UNIV OF THE
Methods for Identifying Genetic Linkage
InactiveUS20110015084A1Suppress expression of endogenousMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningHomopolynucleotideNucleotide
The present invention provides a high-throughput system for determining linkage of distinct polynucleotides and determining the sequence of polynucleotides that are linked to the distinct polynucleotides. The methods are particularly useful for analyzing transgenes in a transformed host organism. The disclosed methods provide for the detection of linkage between distinct transgenic polynucleotides in transformed hosts and sequencing of DNA regions linked to the distinct transgenic polynucleotides. Methods for identifying a transgenic plant containing a transgene insertion in an undesirable genomic location are also disclosed.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Method and apparatus for diagnosing schizophrenia and schizophrenia subtype
InactiveUS20050079636A1Reduce misdiagnosisIncrease chanceEye diagnosticsSensorsMedicineBinocular rivalry
A method and apparatus for diagnosing schizophrenia, schizophrenia disorder subgroup, or predisposition thereto in a test subject is disclosed. The method includes the steps of determining an interhemispheric switch rate of the test subject. In one embodiment, the interhemispheric switch rate of the test subject is under conditions of increasing rate of dichoptic reveral, and comparing the switch rate with a corresponding reference switch rate to diagnose presence or absence of schizophrenia, a schizophrenic disorder subgroup, or predisposition thereto. In a preferred embodiment, the interhemispheric switch rate is determined by measuring the rate of binocular rivalry in the test subject. Also disclosed is use of a diagnostic method in genetic linkage studies for the identification of the molecular defect(s) underlying schizophrenia, and for the identification of compounds which may alleviate the disorder.
Owner:QUEENSLAND UNIV OF THE +1
Method and apparatus for diagnosis of a mood disorder or predisposition therefor
Owner:THE UNIV OF QUEENSLAND
Method and apparatus for diagnosing schizophrenia and schizophrenia subtype
InactiveUS7338455B2Reduce misdiagnosisIncrease chanceSensorsEye diagnosticsMedicineBinocular rivalry
Owner:QUEENSLAND UNIV OF THE +1
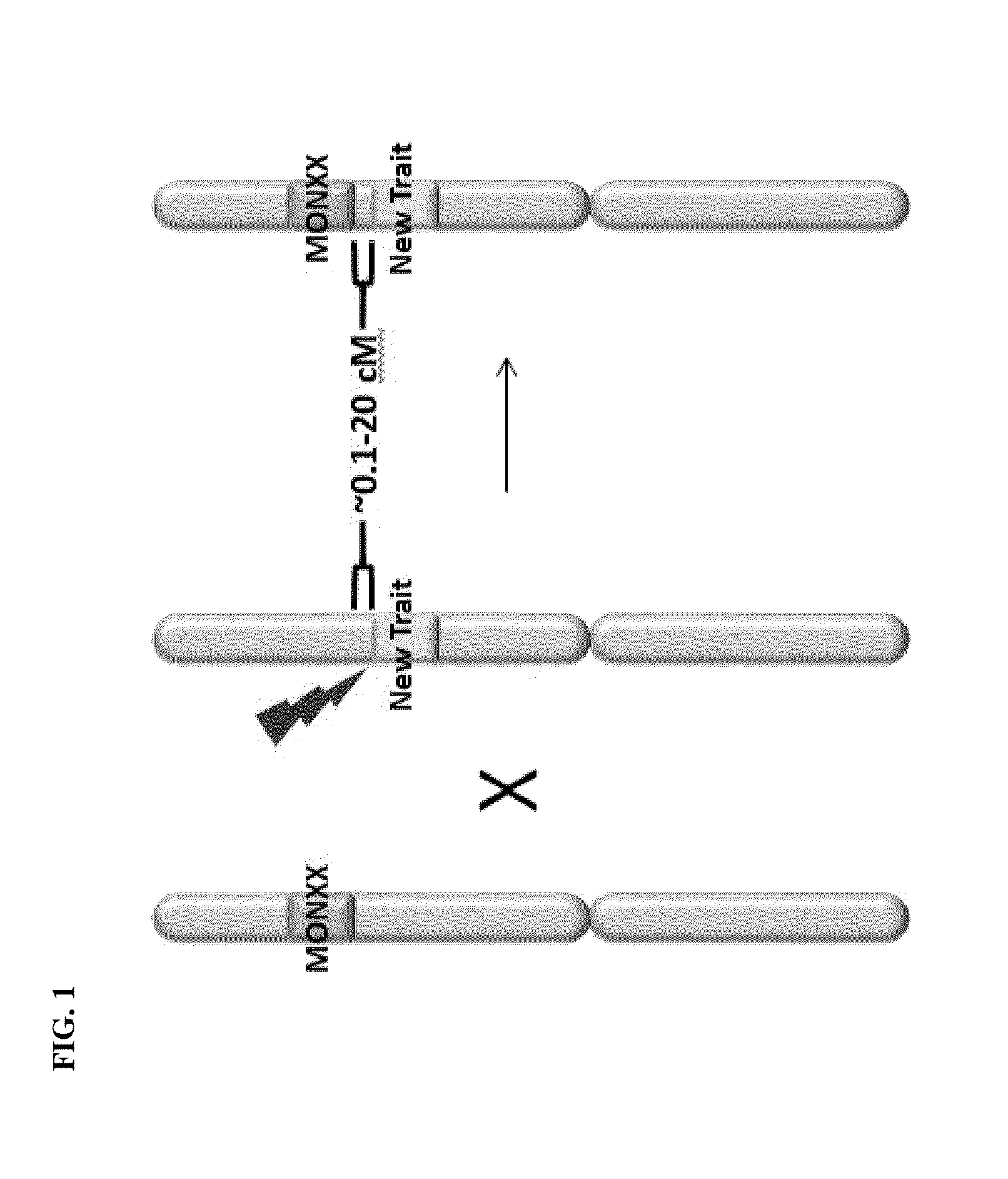
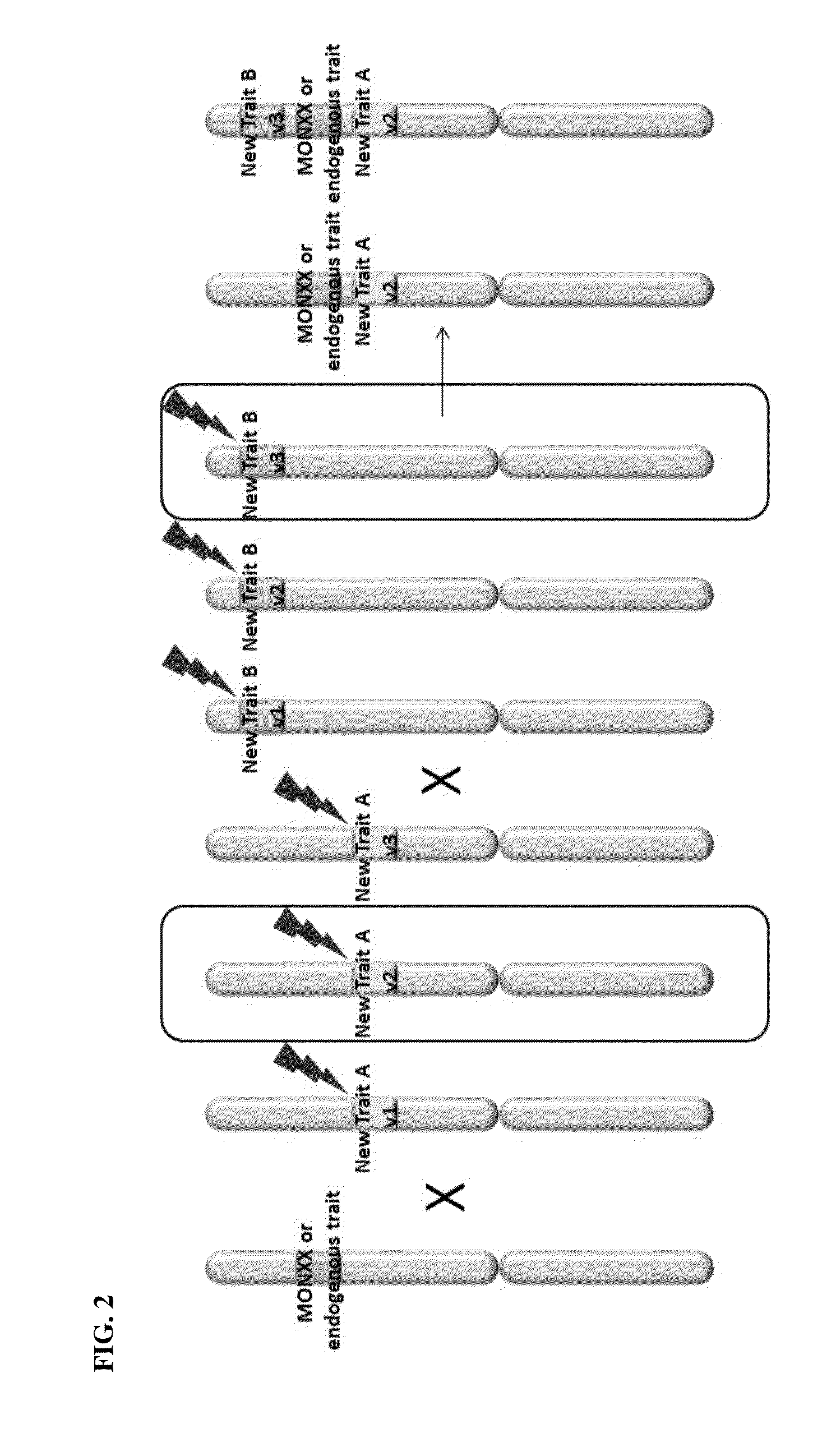
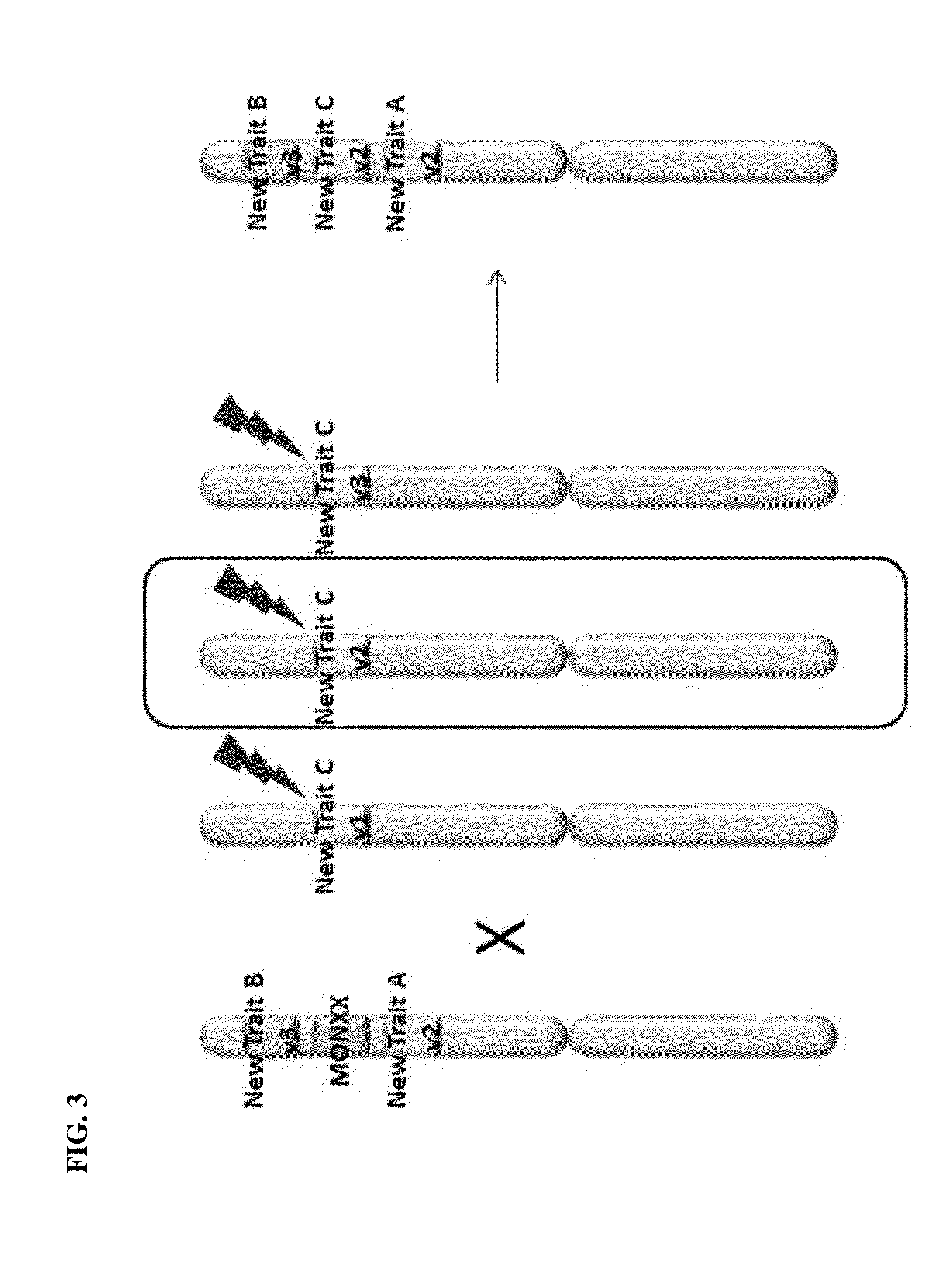
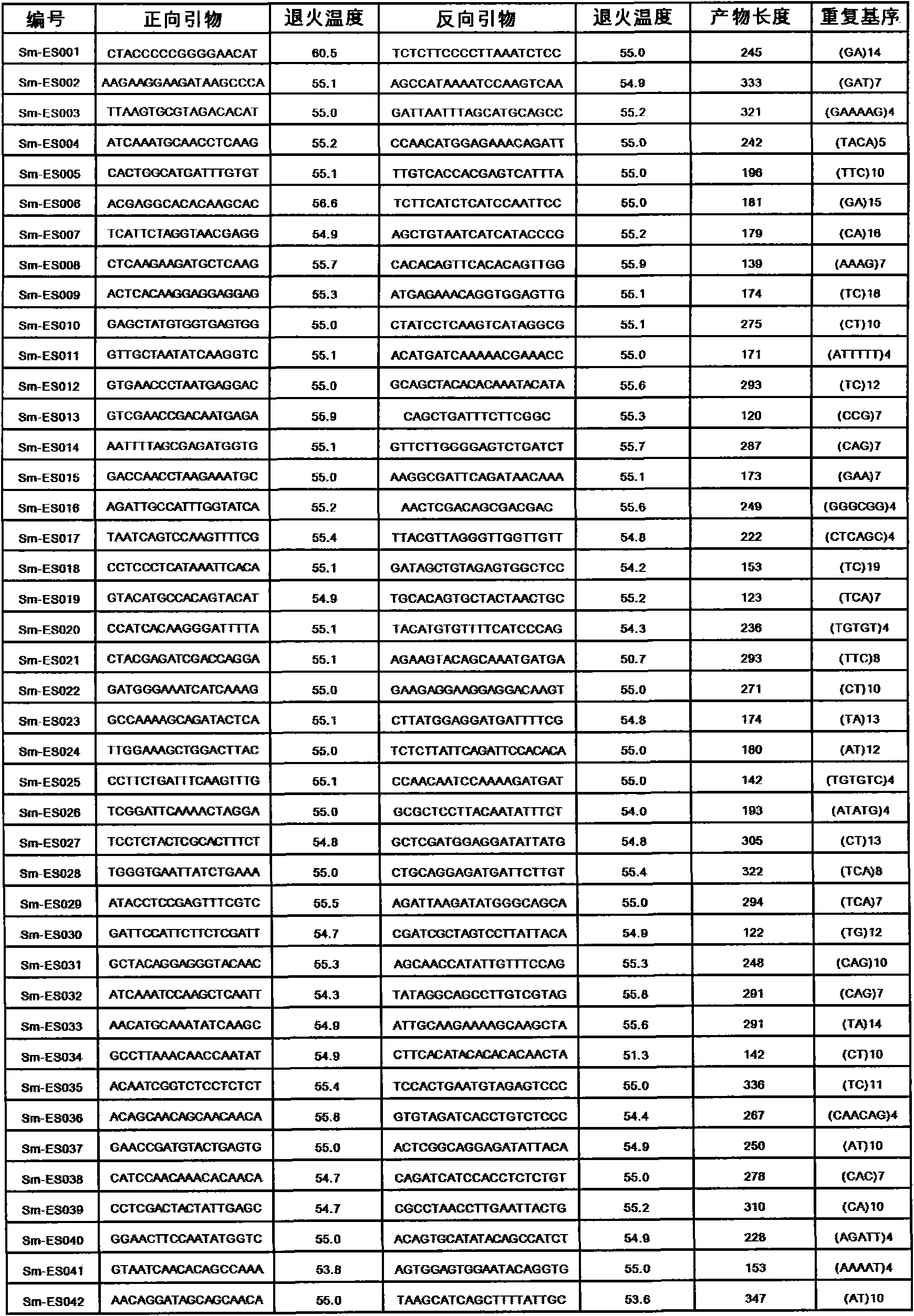
Creation and transmission of megaloci
The current invention provides methods for creating a block of genetically linked transgenic traits or a megalocus that can be transmitted as a single genetic unit. The present invention further provides methods for trait introgression to other plants, varieties or species using the megaloci of the invention. Also provided are plants, seeds, and plant parts comprising the megaloci.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
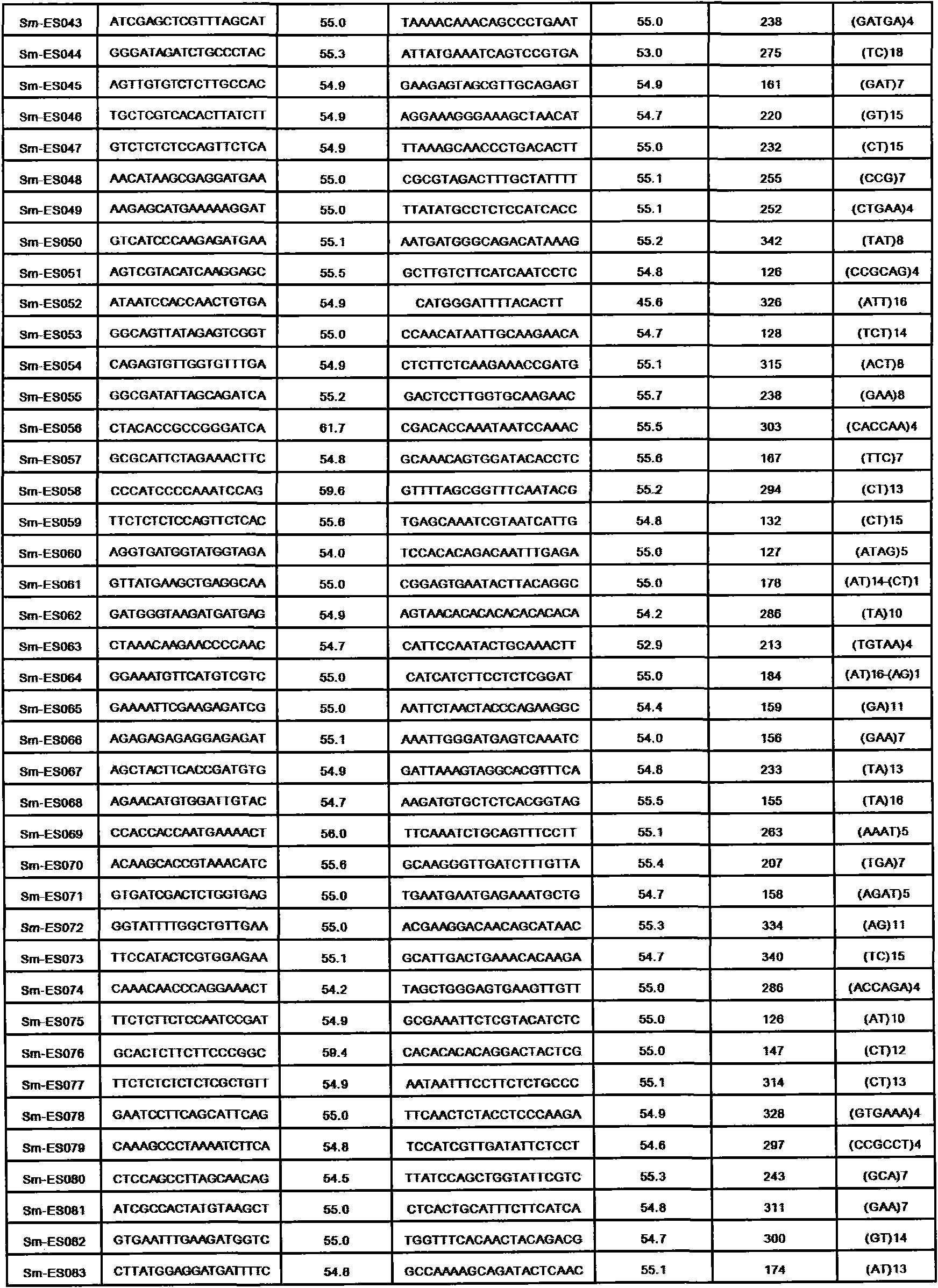
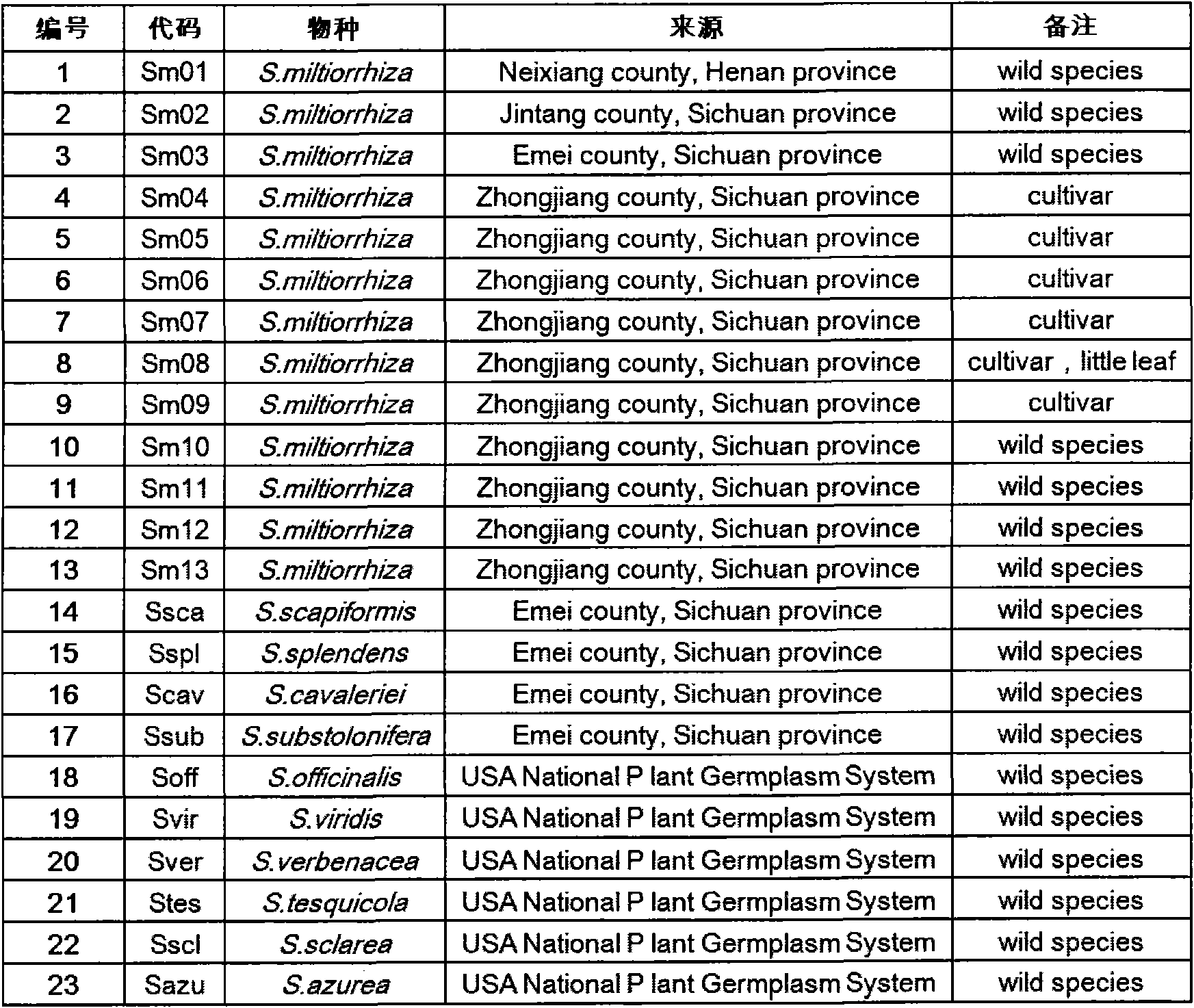
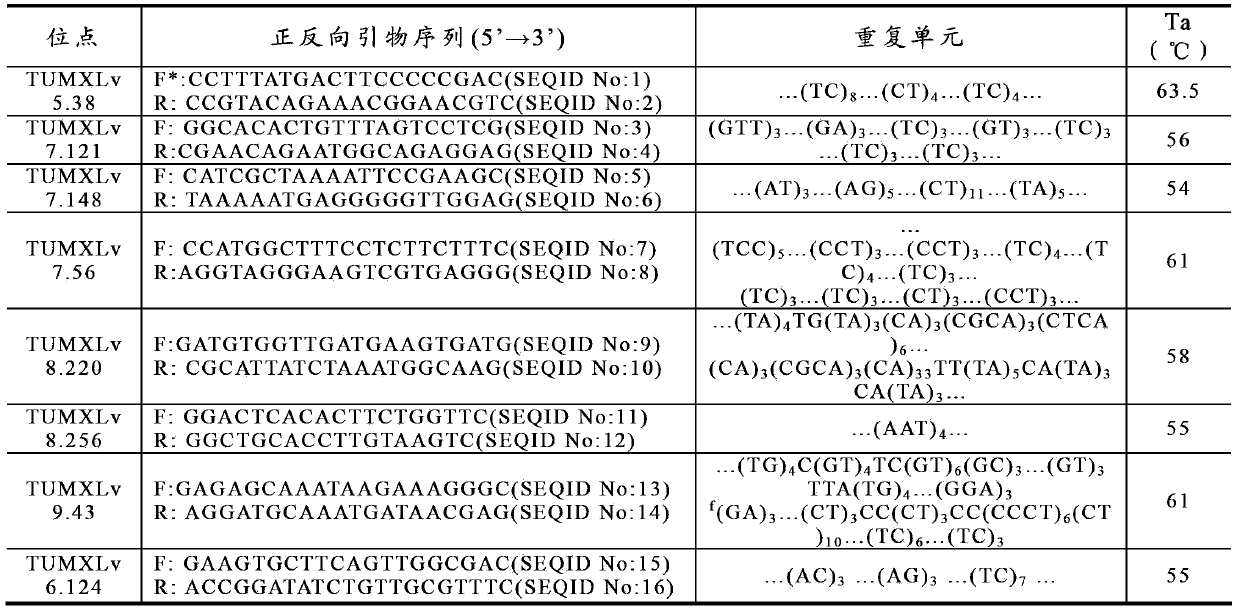
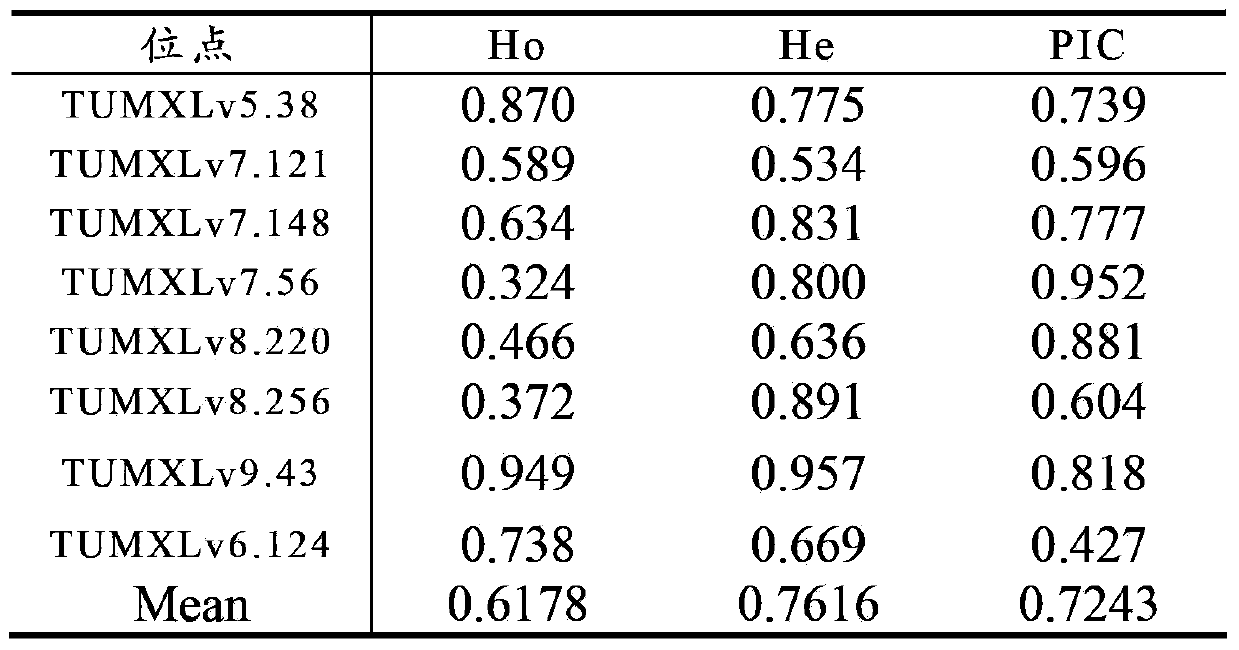
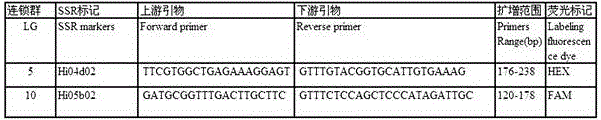
Method for preparing salvia miltiorrhiza EST-SSR molecular mark, specific primer and application thereof
The invention discloses a method for preparing a salvia miltiorrhiza EST-SSR molecular mark. The method mainly comprises the following steps of obtaining and pre-processing a salvia miltiorrhiza EST sequence, screening a SSR locus in the salvia miltiorrhiza EST sequence, designing and synthesizing the salvia miltiorrhiza EST-SSR primer, screening the salvia miltiorrhiza EST-SSR primer and the like. The method excavates the SSR locus aiming at the salvia miltiorrhiza EST and designs the PCR primer according to the flanking sequence of the SSR locus, and on the basis of this, the salvia specificEST-SSR mark system is established; and the method lays a solid foundation for genetic diversity evaluation, genetic relationship or idioplasmatic identification, genetic linkage description, molecular mark auxiliary selection, gene mapping cloning, functional genome analysis, related researches and the like of related species of the salvia miltiorrhiza and the salvia. The invention also discloses the EST-SSR locus specific primer obtained by the method for preparing the salvia miltiorrhiza EST-SSR molecular mark and the application thereof.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Litopenaeus vannamei base population establishing method based on genetic information and excellent properties
InactiveCN103416333AOvercoming diversityOvercome the loss of some good traitsMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationEconomic benefitsInformation design
The invention provides a Litopenaeus vannamei base population establishing method based on genetic information and excellent properties. The method comprises the following detail steps that multiple Litopenaeus vannamei populations with different excellent properties are selected, the genetic relationship among introduced individuals is analyzed by using molecular markers, a hybridization scheme is designed based on the genetic relationship information and excellent property information, and a great numbers of families are established to form a Litopenaeus vannamei base population with relative abundant heritable variation and excellent properties. According to the method, in the establishing process of the Litopenaeus vannamei base population, the molecular markers are used for detecting the genetic relationship among different individuals and designing the hybridization scheme, inbreeding can be avoided, genetic linkages can be broken through, sufficient recombination and orientated mating can be acquired, continuity and scientificity of breeding work are guaranteed, thus the acquisition of Litopenaeus vannamei base populations with the relative abundant heritable variation and excellent properties can be facilitated, therefore, genetic improvement and production performance improvement can be further carried out on the later generations of the Litopenaeus vannamei to a large extent, and better economic benefit is brought.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Molecular marker SIsv0010 closely linked with heading-date gene of millet
InactiveCN102154281AImprove throughputEasy to set upMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionAgricultural scienceSequence identity
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology, and relates to a molecular marker, in particular to a molecular marker closely linked with a heading-date gene of millet. The molecular marker comprises a sequence shown as Seq ID No. 1 (Sequence Identity Number 1). The invention also relates to a primer for amplifying the molecular marker, application of the molecular marker and the primer to heading date gene location of the millet or genetic-breeding of the millet, and a millet breeding method. Through the molecular marker provided by the invention, a genome DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) sequence is linked with the heading-date gene of the millet, so that the establishment of a millet molecular marker assisted breeding system is facilitated; and close genetic linkage distance between the molecular marker and the heading-date gene of the millet is 3.2cM. The molecular marker and the molecular marker amplification primer provided by the invention can be easily, conveniently and rapidly applied to millet breeding practices as well as resource and variety identification at high throughput.
Owner:深圳华大基因农业控股有限公司
Method for breeding high-yield high-oil peanut species
InactiveCN102067816ADeep leaf colorBig fruitPlant genotype modificationAngiosperms/flowering plantsHeterosisOperability
The invention discloses a method for breeding high-yield high-oil peanut species. In the method, a genetic relationship of the selected high-yield high-oil peanut species is found out by an SSR (Simple Sequence Repeat) molecule marker technology; the species with distant hybrid advantages and larger selection difference is used as a parent for preparing cross combination; the variation frequency is expanded by radiation effect, and the selecting range of a high-yield high-oil gene is expanded; the genetic linkage of an adverse gene is broken down by applying hybridization, and the recombination, polymerization and complementation of high yield, high oil and resistance are realized; an individual plant is directionally selected by using ideal characters as a target in stable generation; and the individual plant is inbred for one generation, a plant system with complete and ideal characters is further selected, and the high-yield high-oil plant system is obtained. The invention has the characteristics of rapidly breeding the high-yield high-oil peanut new species and having simple method and high operability.
Owner:山东鲁花农业科技推广有限公司
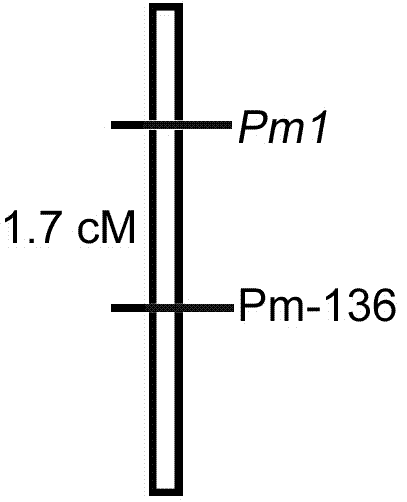
Linked molecular marker for powdery mildew resistant gene pm1 of cucurbita pepo L. and application of linked molecular marker
ActiveCN104498484AExcellent disease resistance performanceImprove use valueMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyDisease
The invention discloses an SSR molecular marker (Pm-136) linked with a powdery mildew resistant gene pm1 of cucurbita pepo L., belongs to the technical field of breeding of vegetable molecules for disease resistance, and relates to an SSR molecular marker linked with the powdery mildew resistant gene, and an application of the SSR molecular marker. The genetic linkage distance between the molecular marker Pm-136 and the resistance gene is 1.7cm. Whether a disease resistance character transfer offspring plant carries with the resistance gene Pm1 or not can be rapidly and accurately detected by virtue of the molecular marker Pm-136, thus the disease-resistant breeding efficiency is significantly improved; and the breeding cycle is shortened. The obtained marker Pm-136 has the advantages of being stable, reliable, simple to operate, good in repeatability and the like, and has high utilization value in identification of resistant and susceptible varieties and a disease-resistant transfer single offspring plant.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Molecular marker of high erucic acid gene in Brassica napus L. and breeding method thereof
PendingCN109234428AImprove breeding efficiencyShorten the breeding processMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationDiseaseGenomic DNA
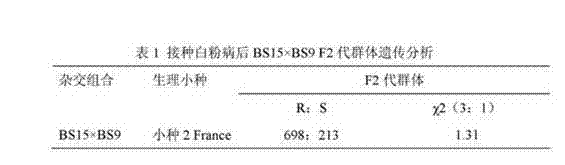
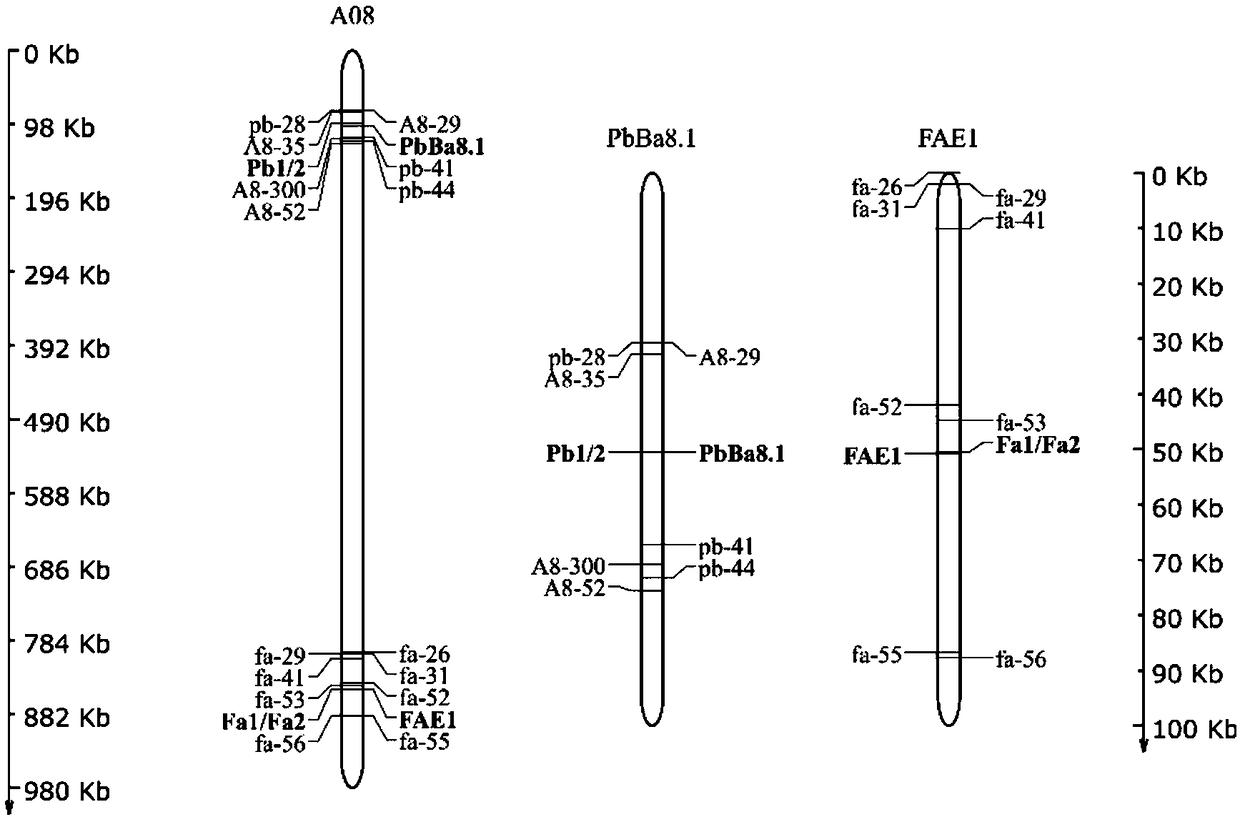
The invention discloses a molecular marker of a high erucic acid gene in Brassica napus L. and a breeding method thereof and relates to the biological breeding field. The method comprises the following steps of: S1, constructing a segregating population; 2, extract that genomic DNA of the material to be tested by the CTAB method; 3, carry out PCR amplification; S4, using marker primer pairs Pb1, Pb2, Fa1, Fa2 to detect whether a single plant in the segregated population contains root swelling resistance site PbBa8.1 or low erucic acid gene fae1 and classify; S5, a new rapeseed variety with high erucic acid and root swelling resistance locus PbBa 8.1 and low erucic acid and low erucic acid and low erucic acid and low erucic acid and low erucic acid and low erucic acid and low erucic acid and low erucic acid and low erucic acid and low erucic acid and low erucic acid and low erucic acid and high erucic acid and low erucic acid were selected. The method for selecting and breeding rapeseedwith root swelling disease resistance and low erucic acid in grain can be used for auxiliary selection of root swelling disease resistance site PbBa8.1 and low erucic acid gene fae1 with genetic linkage at seedling stage, The theoretical accuracy of gene-specific markers reached 100%, which improved the breeding efficiency of rapeseed resistant to root swelling and low erucic acid, and shortenedthe breeding process.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Method for improving biomass yield
InactiveUS20120054917A1Increased biomass productionMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationBiotechnologyHaplotype
A method for predicting harvestable biomass yield in a crop comprising: genotyping a sample obtained from a crop plant for one or more markers genetically linked to a polynucleotide sequence having at least 50, 55, 60, 65, 70, 75, 80, 85, 90, 95, 97, 98, 99 or 100% identity to SEQ BD NO 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24 or 25, whereby the markers individually or collectively identify a haplotype associated with yield in a plurality of crop plants and correlating the haplotype with the harvested biomass yield.
Owner:ROTHAMSTED RES LTD
SSR (simple sequence repeat) molecular marker V for identifying descendant plants of Gala apple and application thereof
InactiveCN106755479ARapid identificationAccurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceCO-DOMINANT
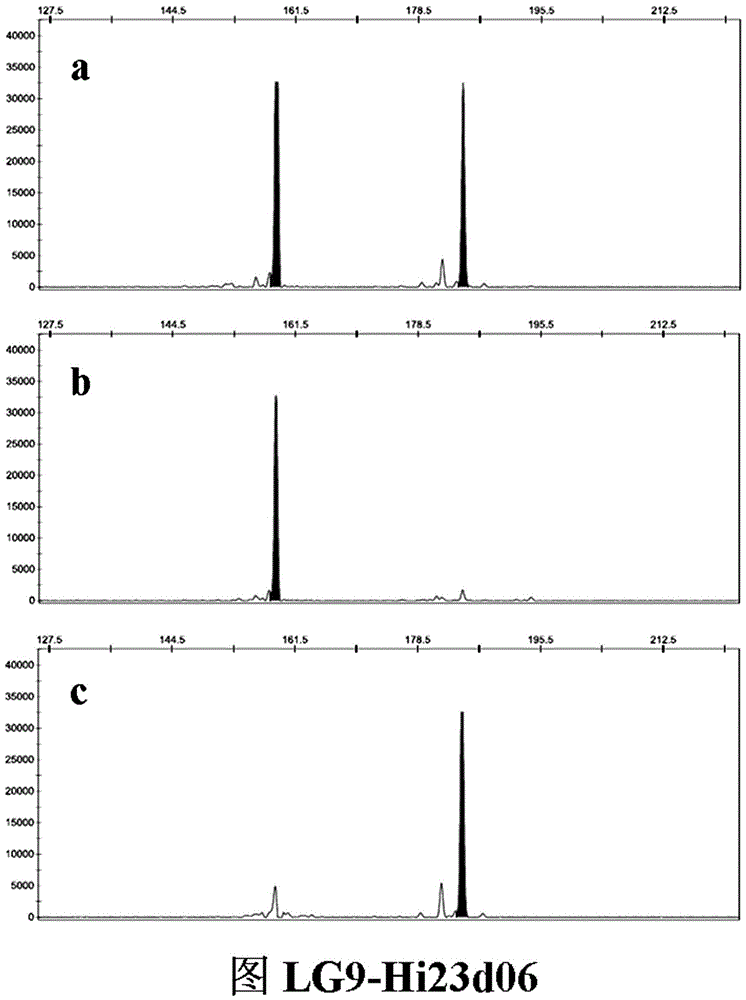
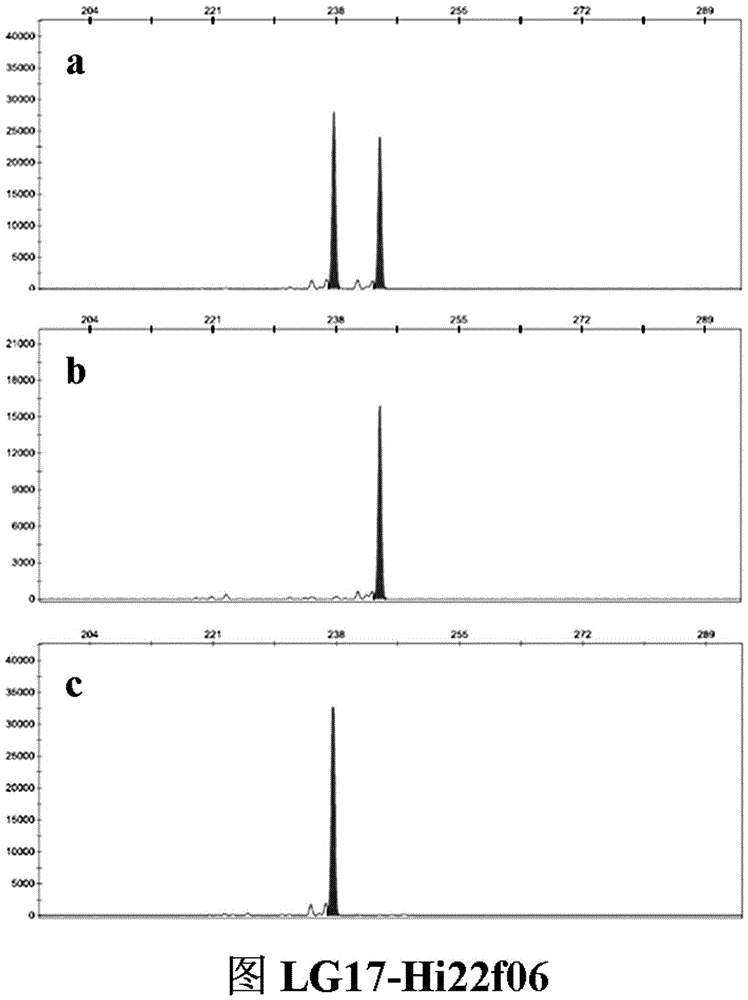
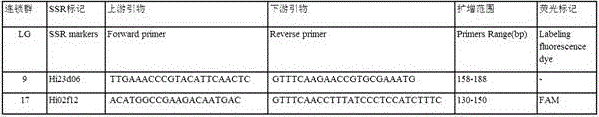
The invention belongs to the field of innovation and research of plant genetics breeding and apple germplasm, in particular to an SSR (simple sequence repeat) molecular marker V for identifying descendant plants of Gala apple and application thereof. The SSR molecular marker V is characterized in that in the detection process, the SSR molecular markers linked with No.9 and No.17 chromosomes are simultaneously used, DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of an apple gene group is used as a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification template, the SSR molecular markers are respectively used as primer pairs, and the PCR amplification and product detection are performed, so as to identify the genetics linkage, anther culture plants and variety sources. The SSR molecular marker V has the advantages that the SSR molecular marker is used for identifying the apple linkage group of the identifying material for the first time, and the SSR molecular markers linked with No.9 and No.17 chromosomes of the apple are disclosed; the molecular marker is a co-dominant marker, so that the Gala apple genetic linkage group, the anther culture plant and the Gala source plant are quickly and accurately identified; the molecular level support is provided for further accelerating the utilization of the Gala apple and important agronomic trait linkage gene, and the genetic breeding of apple homozygous plants.
Owner:AGRI BIOTECH RES CENT OF SHANXI PROVINCE +2
Method for removing genetic linkage in a plant
The current disclosure relates to the field of plants, in particular to the fields of plant breeding and plant genetics. More particular, the disclosure concerns inventive methodology that may be useful in improving plant properties. In particular the invention may be useful in removing linkage drag. Also provided are plant and plant parts obtained with the method disclosed herein.
Owner:KEYGENE NV
SSR (simple sequence repeat) molecular marker III for identifying descendant plants of Gala apple and application thereof
InactiveCN106755482ARapid identificationAccurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceGermplasm
The invention belongs to the field of innovation and research of plant genetics breeding and apple germplasm, in particular to an SSR (simple sequence repeat) molecular marker III for identifying descendant plants of Gala apple and application thereof. The SSR molecular marker III is characterized in that in the detection process, the SSR molecular markers linked with No.4, No.6, No.12 and No.14 chromosomes are simultaneously used, DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of an apple gene group is used as a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification template, the SSR molecular markers are respectively used as primer pairs, and the PCR amplification and product detection are performed, so as to identify the genetics linkage, anther culture plants and variety sources. The SSR molecular marker III has the advantages that the SSR molecular marker is used for identifying the apple linkage group of the identifying material for the first time, and the SSR molecular markers linked with No.4, No.6, No.12 and No.14 chromosomes of the apple are disclosed; the molecular marker is a co-dominant marker, so that the Gala apple genetic linkage group, the anther culture plant and the Gala source plant are quickly and accurately identified; the molecular level support is provided for further accelerating the utilization of the Gala apple and important agronomic trait linkage gene, and the genetic breeding of apple homozygous plants.
Owner:POMOLOGY INST SHANXI ACAD OF AGRI SCI +2
Intron sequence analysis method for detection of adjacent and remote locus alleles as haplotypes
InactiveUS20040197775A1Small sizeSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisIntein
The present invention provides a method for detection of at least one allele of a genetic locus and can be used to provide direct determination of the haplotype. The method comprises amplifying genomic DNA with a primer pair that spans an intron sequence and defines a DNA sequence in genetic linkage with an allele to be detected. The primer-defined DNA sequence contains a sufficient number of intron sequence nucleotides to characterize the allele. Genomic DNA is amplified to produce an amplified DNA sequence characteristic of the allele. The amplified DNA sequence is analyzed to detect the presence of a genetic variation in the amplified DNA sequence such as a change in the length of the sequence, gain or loss of a restriction site or substitution of a nucleotide. The variation is characteristic of the allele to be detected and can be used to detect remote alleles. Kits comprising one or more of the reagents used in the method are also described.
Owner:GENETIC TECHNOLOGIES LIMTIED
SSR (simple sequence repeat) molecular marker IV for identifying descendant plants of Gala apple and application thereof
InactiveCN106755478ARapid identificationAccurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceGermplasm
The invention belongs to the field of innovation and research of plant genetics breeding and apple germplasm, in particular to an SSR (simple sequence repeat) molecular marker IV for identifying descendant plants of Gala apple and application thereof. The SSR molecular marker IV is characterized in that in the detection process, the SSR molecular markers linked with No.5 and No.10 chromosomes are simultaneously used, DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of an apple gene group is used as a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification template, the SSR molecular markers are respectively used as primer pairs, and the PCR amplification and product detection are performed, so as to identify the genetics linkage, anther culture plants and variety sources. The SSR molecular marker IV has the advantages that the SSR molecular marker is used for identifying the apple linkage group of the identifying material for the first time, and the SSR molecular markers linked with No.5 and No.10 chromosomes of the apple are disclosed; the molecular marker is a co-dominant marker, so that the Gala apple genetic linkage group, the anther culture plant and the Gala source plant are quickly and accurately identified; the molecular level support is provided for further accelerating the utilization of the Gala apple and important agronomic trait linkage gene, and the genetic breeding of apple homozygous plants.
Owner:山西省农业科学院农业资源与经济研究所 +2
Method to predict iris color
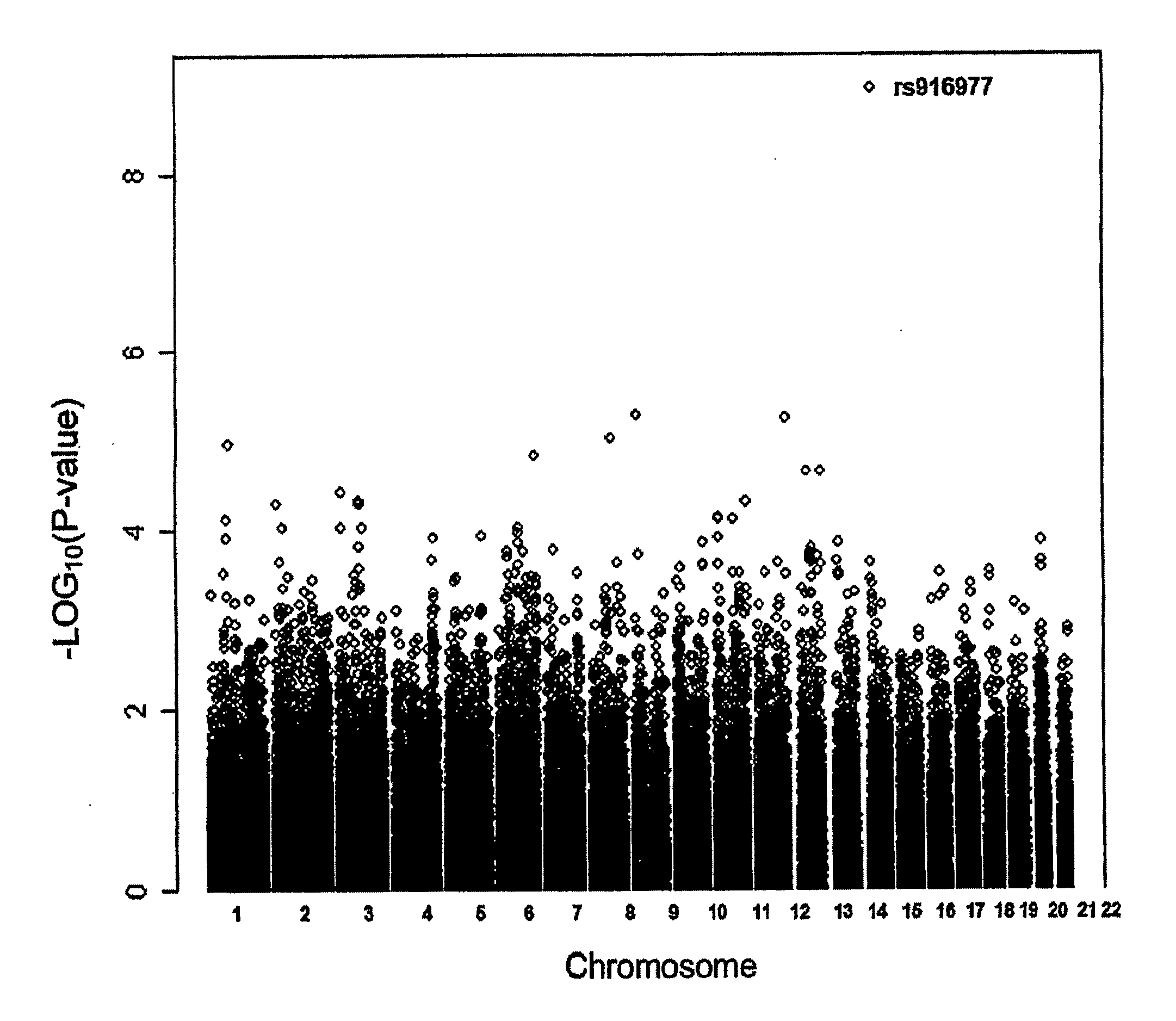
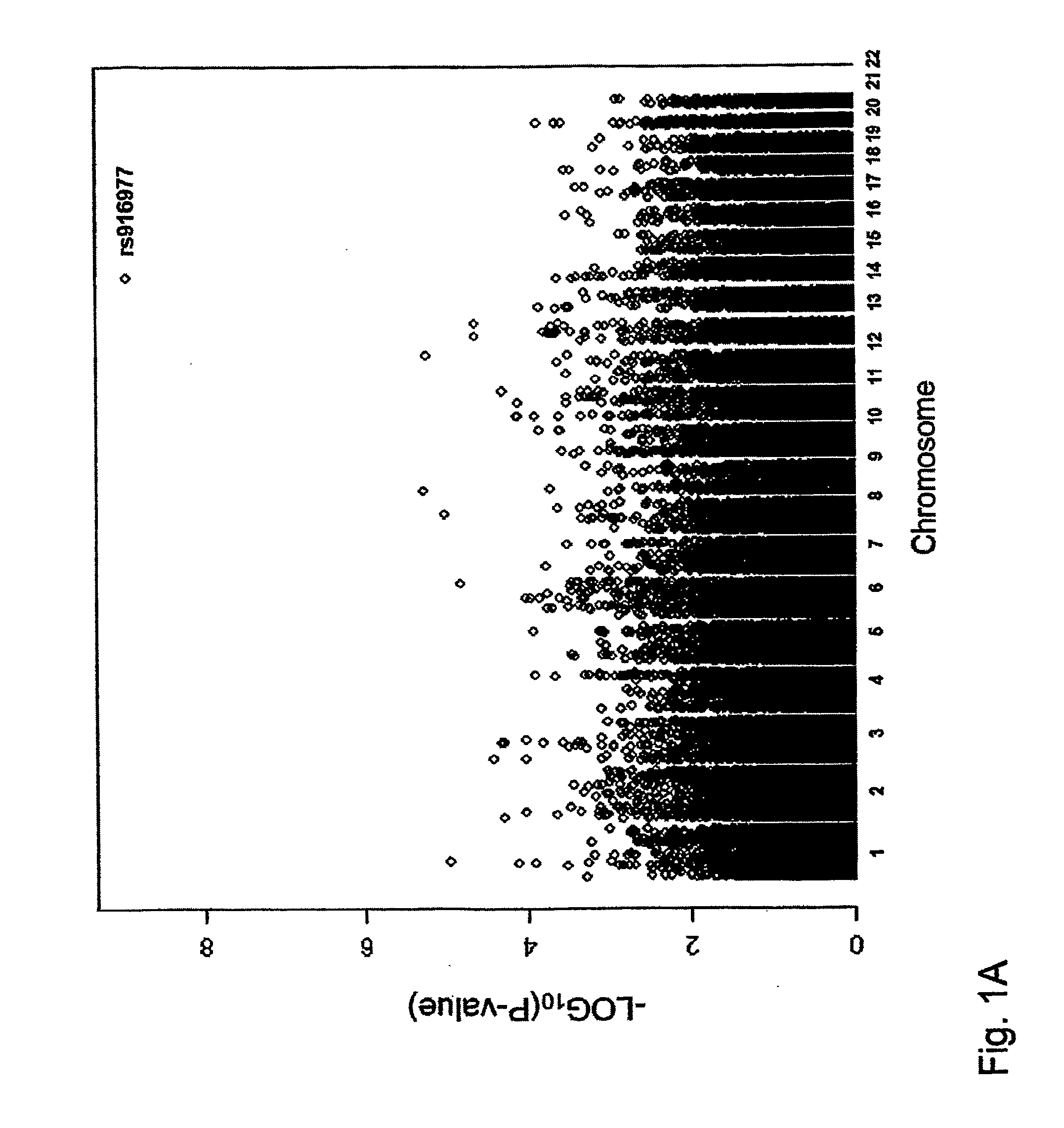
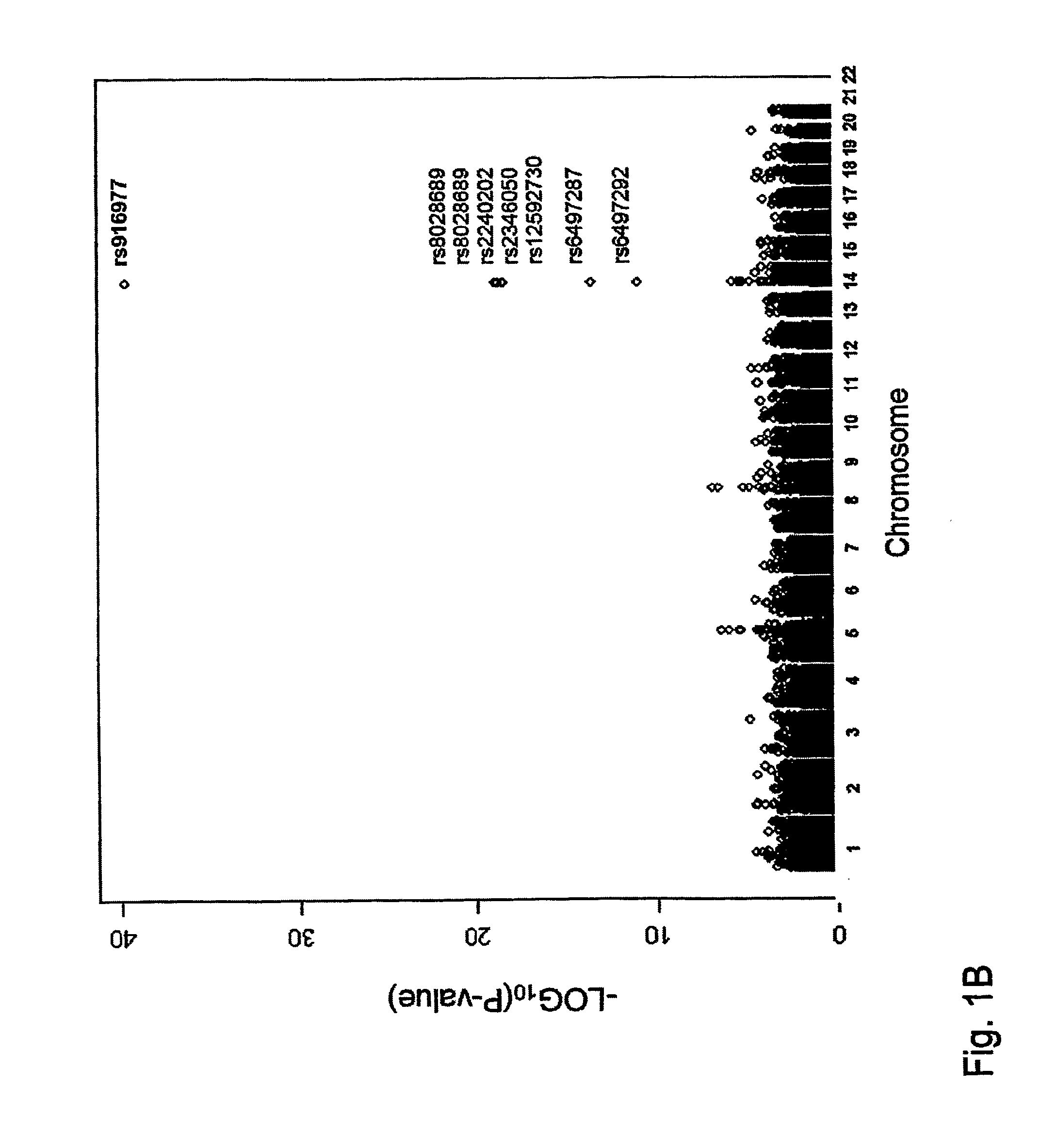
The invention comprises a method to predict iris color of a human from a nucleic acid / protein sample comprising assaying for one or more polymorphisms in the region 5′ proximal of the OCA2 gene up to and including the HERC2 gene on chromosome 15 between basepairs 26018062 and 26240890 according to NCBI build 36 or Ensemble Homo sapiens version 46.36h and on basis of the results from the assay predicting the eye color of a human e.g. an unknown person (such as perpetrators and / or victims of crime, missing persons etc.) in forensic and other applications of human identification. Said polymorphisms preferably are selected from the group consisting of rs916977, rs8028689, rs6497287, rs8041209, rs6497292, rs2240202, rs2346050, rs12592730, rs7183877, rs2240204, rs8039195, rs16950979, rs16950987, rs1667394, and rs1635168 or any marker in close physical distance to said markers and consequently in genetic linkage in the region of chromosome 15 between basepairs 26018062 and 26240890 according to NCBI build 36 or Ensemble Homo sapiens version 46.36h. Said polymorphisms are analysed from human material such as human body fluids (e.g. blood, saliva, semen etc.) or other human body parts (e.g. hairs, organs, etc) or from material obtained from whole bodies. The invention further comprises primers and probes, and a kit for the assay. The invention includes application of the genetic eye color prediction using said markers or their combinations (haplotypes) for forensic and other purposes of human identification such as to identify or trace unknown persons e.g. perpetrators and / or victims of crime, missing persons etc.
Owner:ERASMUS UNIV MEDICAL CENT ROTTERDAM ERASMUS MC
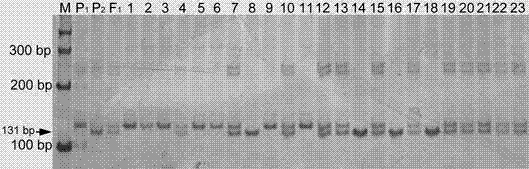
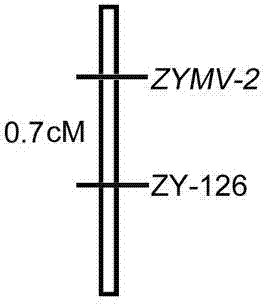
Linked molecular marker for dominant resistance gene ZYMV-2 of cucurbita pepo L. ZYMV and application of linked molecular marker
InactiveCN104498485AExcellent disease resistance performanceEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyDisease
The invention discloses an SSR molecular marker (ZY-126) linked with a dominant resistance gene ZYMV-2 of a zucchini yellow mosaic virus (ZYMV) of cucurbita pepo L., belongs to the technical field of breeding of vegetable molecules for disease resistance, and relates to an SSR molecular marker linked with the dominant resistance gene of ZYMV, and an application of the SSR molecular marker. The genetic linkage distance between the molecular marker ZY-126 and the resistance gene is 0.7cm. Whether a disease resistance character transfer offspring plant carries with the resistance gene ZYMV-2 or not can be rapidly and accurately detected by virtue of the molecular marker ZY-126, thus the disease-resistant breeding efficiency is significantly improved; the breeding cycle is shortened; and a solid foundation is laid for breeding of disease-resistant varieties of the ZYMV. The obtained molecular marker ZY-126 has the advantages of being stable, reliable, simple to operate, good in repeatability and the like, and has high utilization value in identification of resistant and susceptible varieties and a disease-resistant transfer single offspring plant.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Use of male sterility to prevent transgene spread in plants
InactiveUS7112719B2Avoid spreadingPrevent the transgene being disseminatedBacteriaClimate change adaptationPollenGastric lipase
The invention relates to a method for preventing the spread via pollen of a transgene encoding dog gastric lipase or collagen from transgenic plants comprising said transgene. In this method plants are transformed with a construct comprising the transgene genetically linked to a second construct conferring male sterility on the plant. Plants produced by the method are male sterile, and thus cannot spread the transgene via their pollen.
Owner:BIOGEMMA SAS
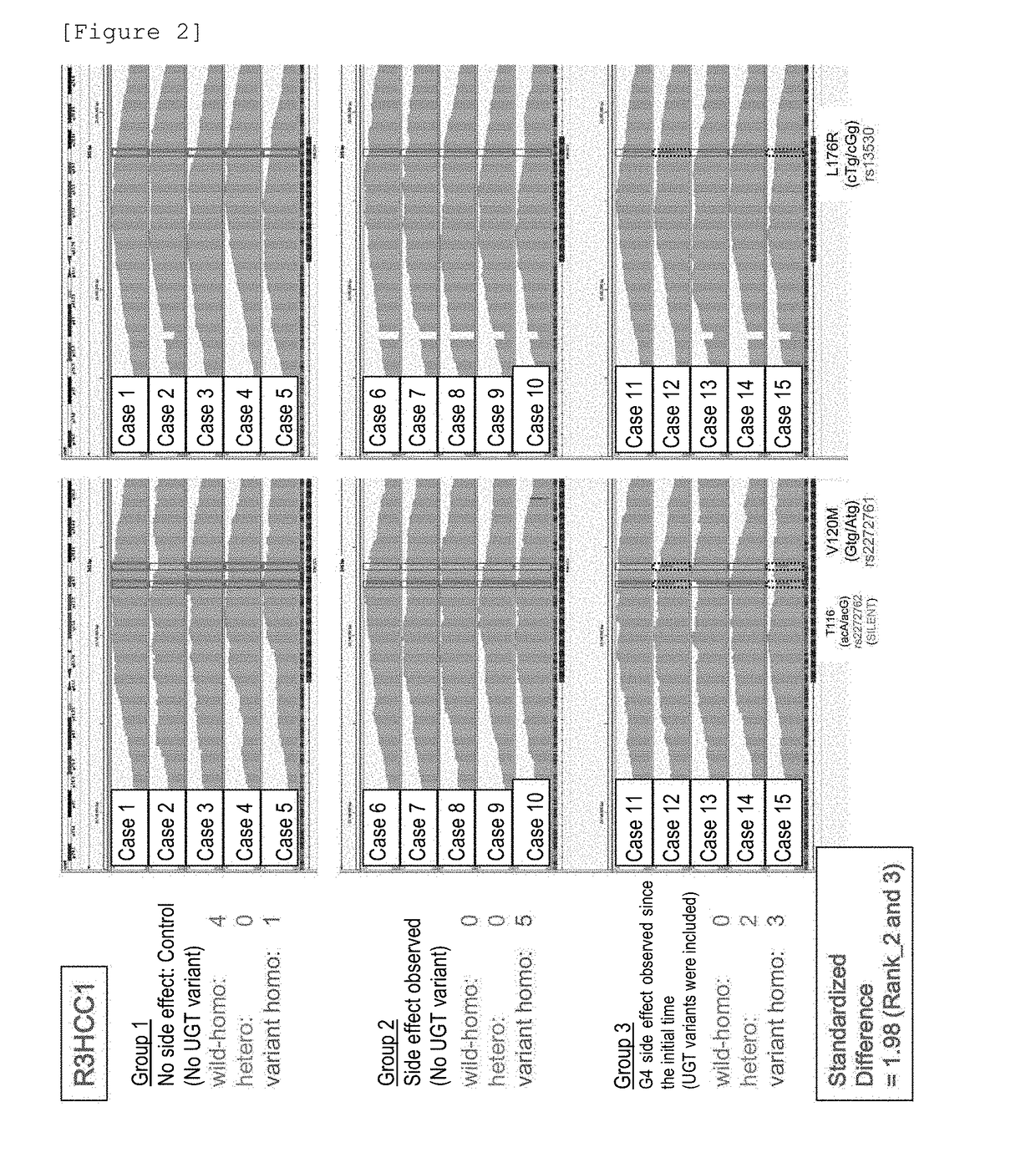
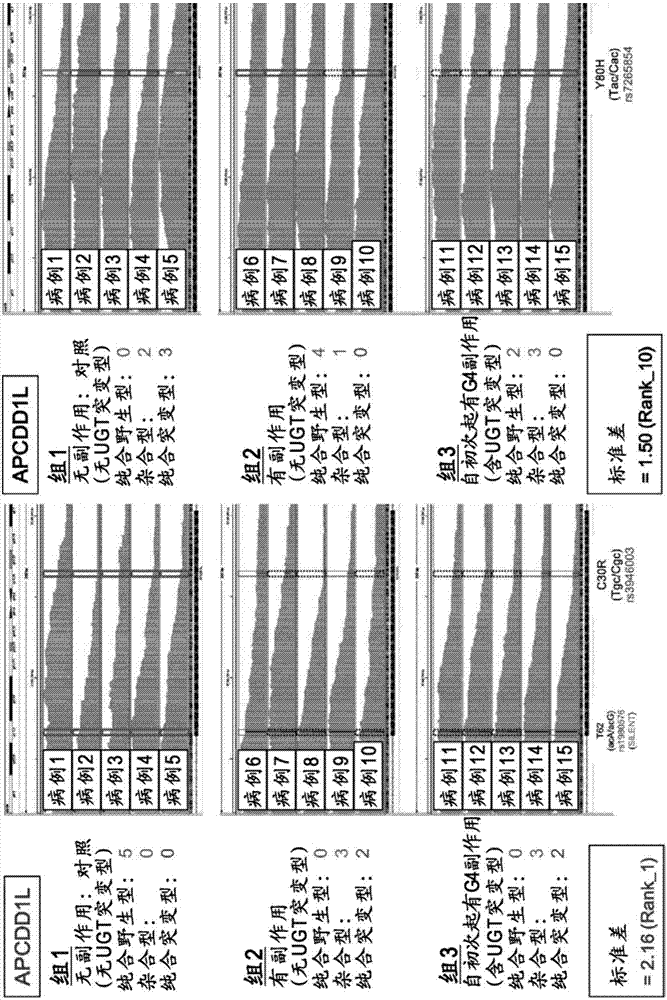
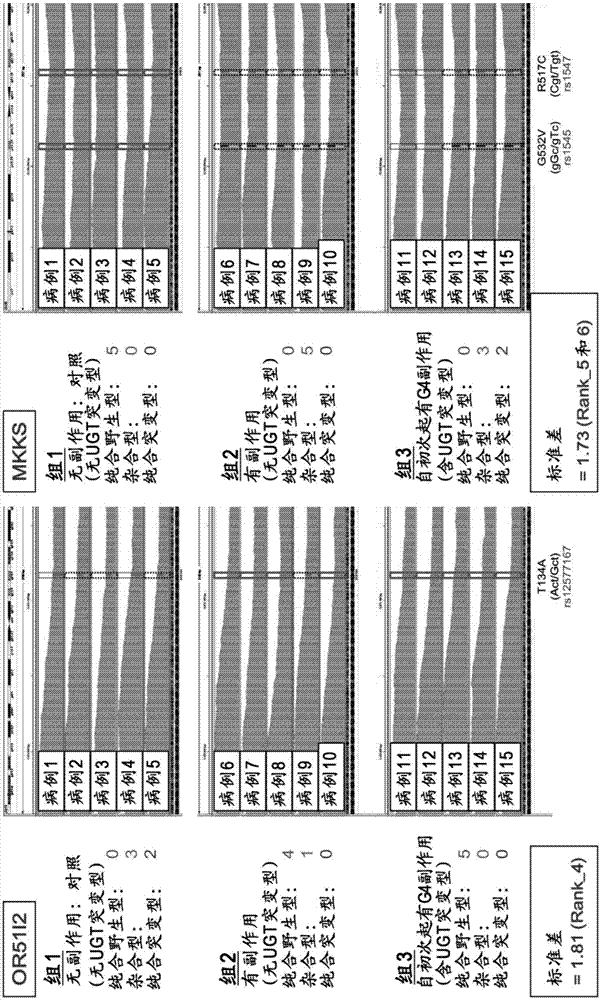
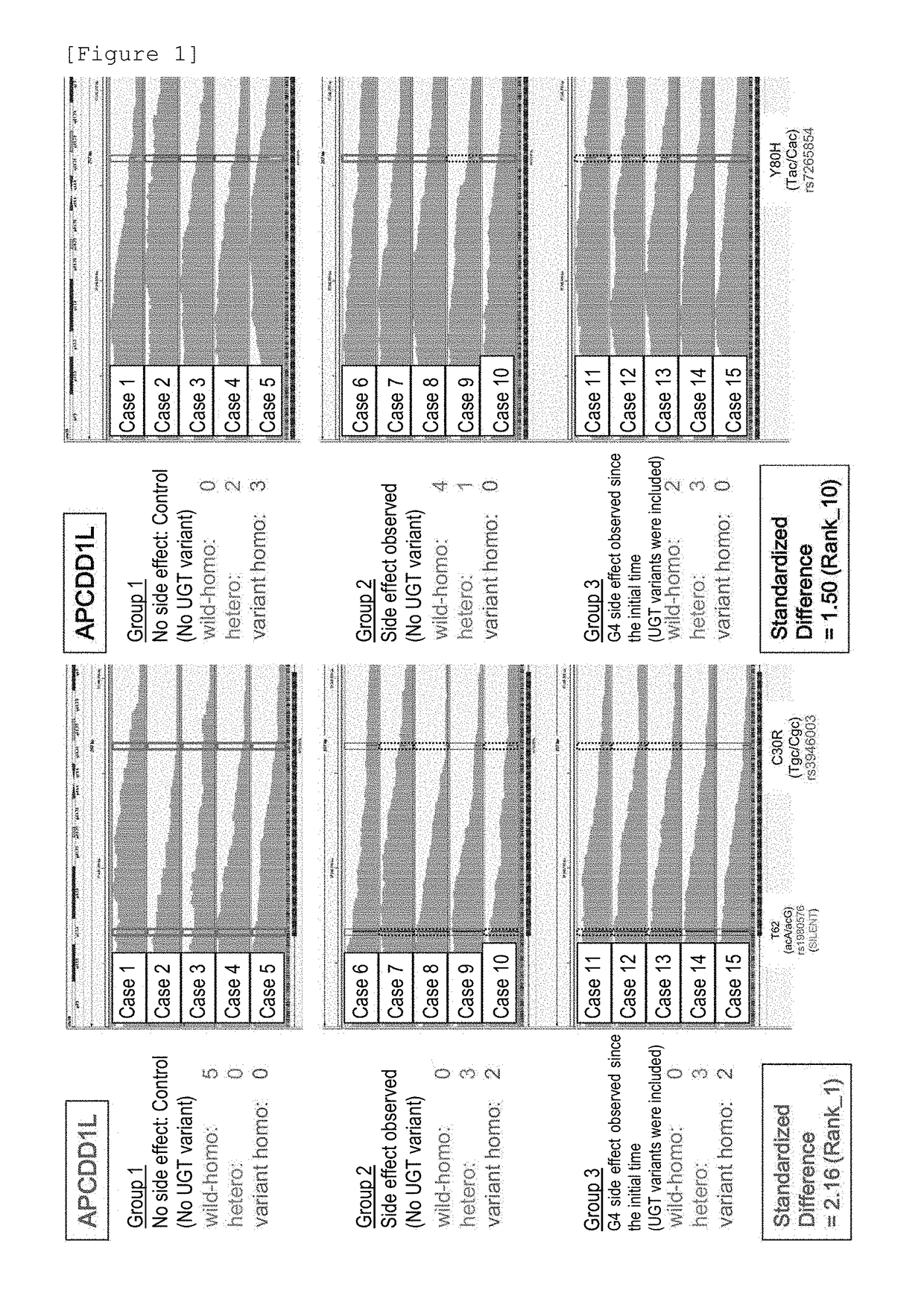
Method for assisting prediction of risk of occurrence of side effect of irinotecan
ActiveCN107208163AMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologySide effectGenetic linkage disequilibrium
The present invention addresses the problem of providing a simple and efficient means for predicting the risk of occurrence of a side effect of irinotecan by analyzing a single nucleotide polymorphism in a region encoding a specific gene. The prediction of the risk of occurrence of a side effect of irinotecan is assisted by analyzing: a single nucleotide polymorphism in a region encoding the APCDD1L gene, the R3HCC1 gene, the OR51I2 gene, the MKKS gene, the EDEM3 gene, or the ACOX1 gene which are present on genomic DNA in a biological sample collected from a subject; or a single nucleotide polymorphism which is in linkage disequilibrium with or genetically linked to the single nucleotide polymorphism, thereby determining whether the single nucleotide polymorphism is homozygous or heterozygous for a variant-type, or homozygous for a wild-type and assisting prediction of the risk of occurrence of a side effect of irinotecan.
Owner:YAMAGUCHI UNIV +1
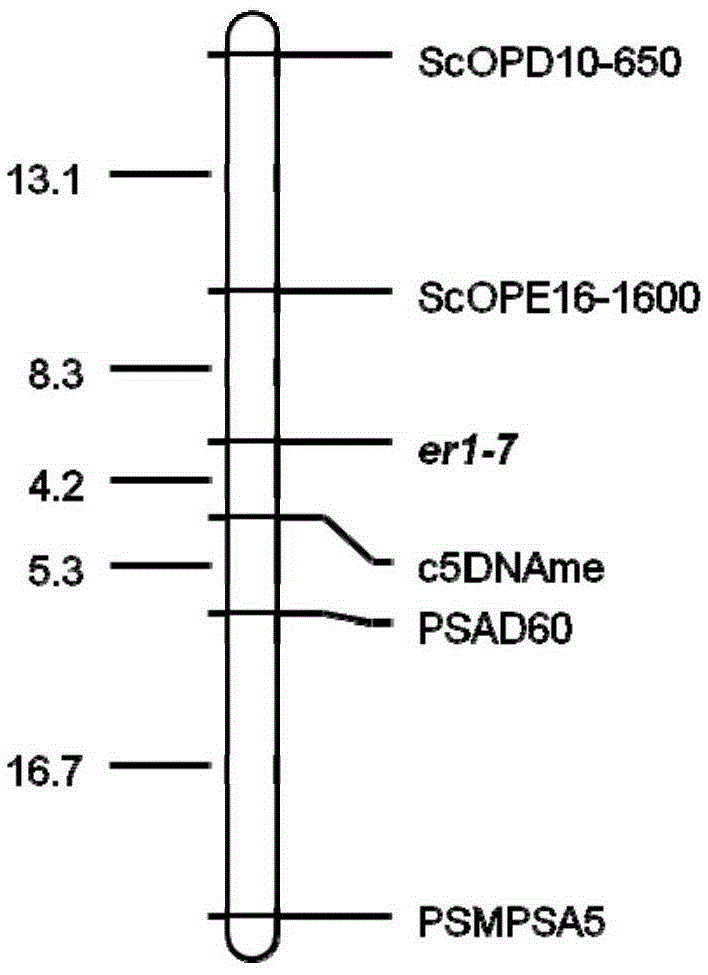
Pea anti-powdery mildew er1 allele er1-7 and gene er1-7 linked-molecular marker
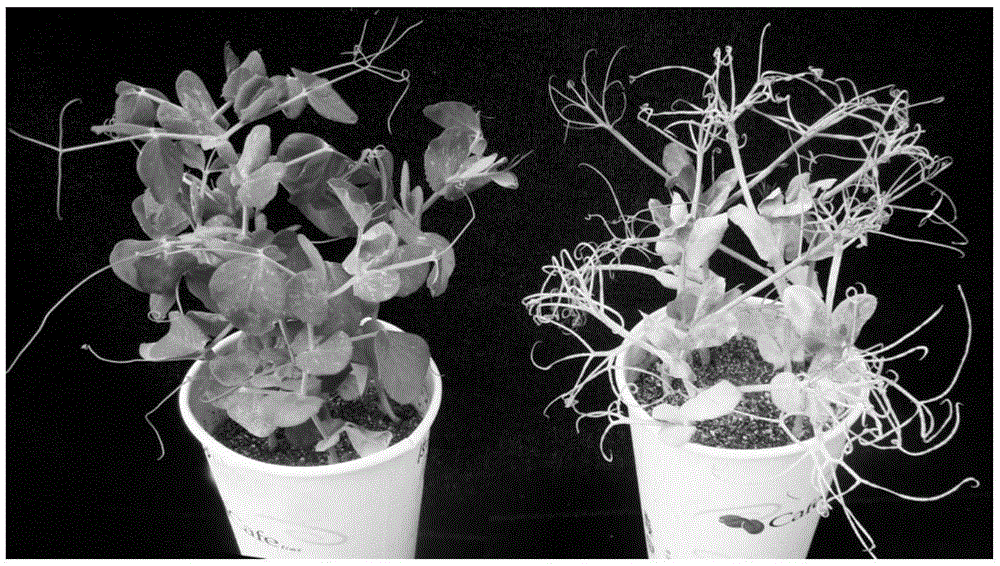
The invention relates to a pea anti-powdery mildew er1 new allele er1-7 and a gene er1-7 linked-molecular marker, wherein the allele is positioned on an er1 gene locus of the VI linkage group of a pea genetic map. A pea resource G0003967 is immune to China powdery mildew isolate EPYN and EPBJ. Through a genetical analysis of resistance, genetic linkage mapping and determining on a candidate gene PsMLO1cDNA sequence of er1, an anti-disease gene of G0003967 is authenticated, and it is found that compared with a wild type susceptible gene PsMLO1cDNA sequence, the 111-120 base groups of an open reading frame of the PsMLO1cDNA sequence of the G0003967 are deleted, thus causing change of protein functions of PsMLO1. Such small fragment deletion mutation is a new PsMLO1 deviant form, and shows that the anti-powdery mildew gene contained in the G0003967 is a new er1 allele and is named as er1-7, thus providing a new gene resource for molecular breeding of powdery mildew resistance of pea resource.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
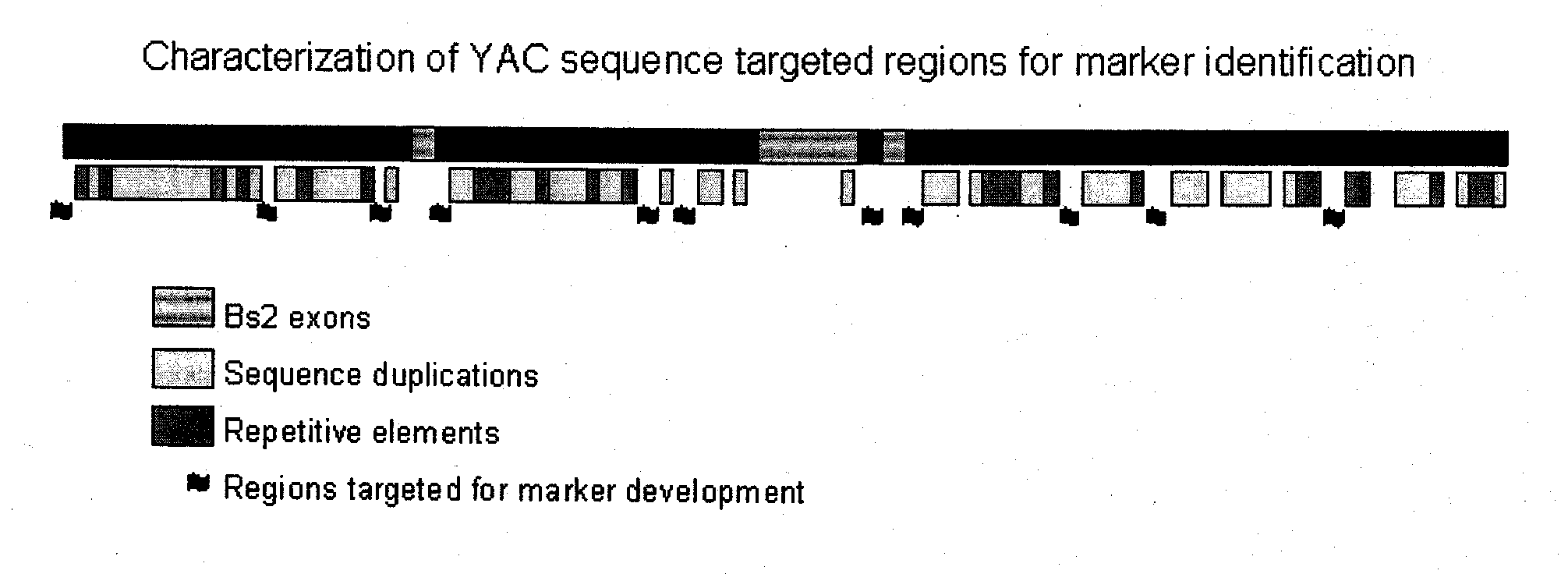
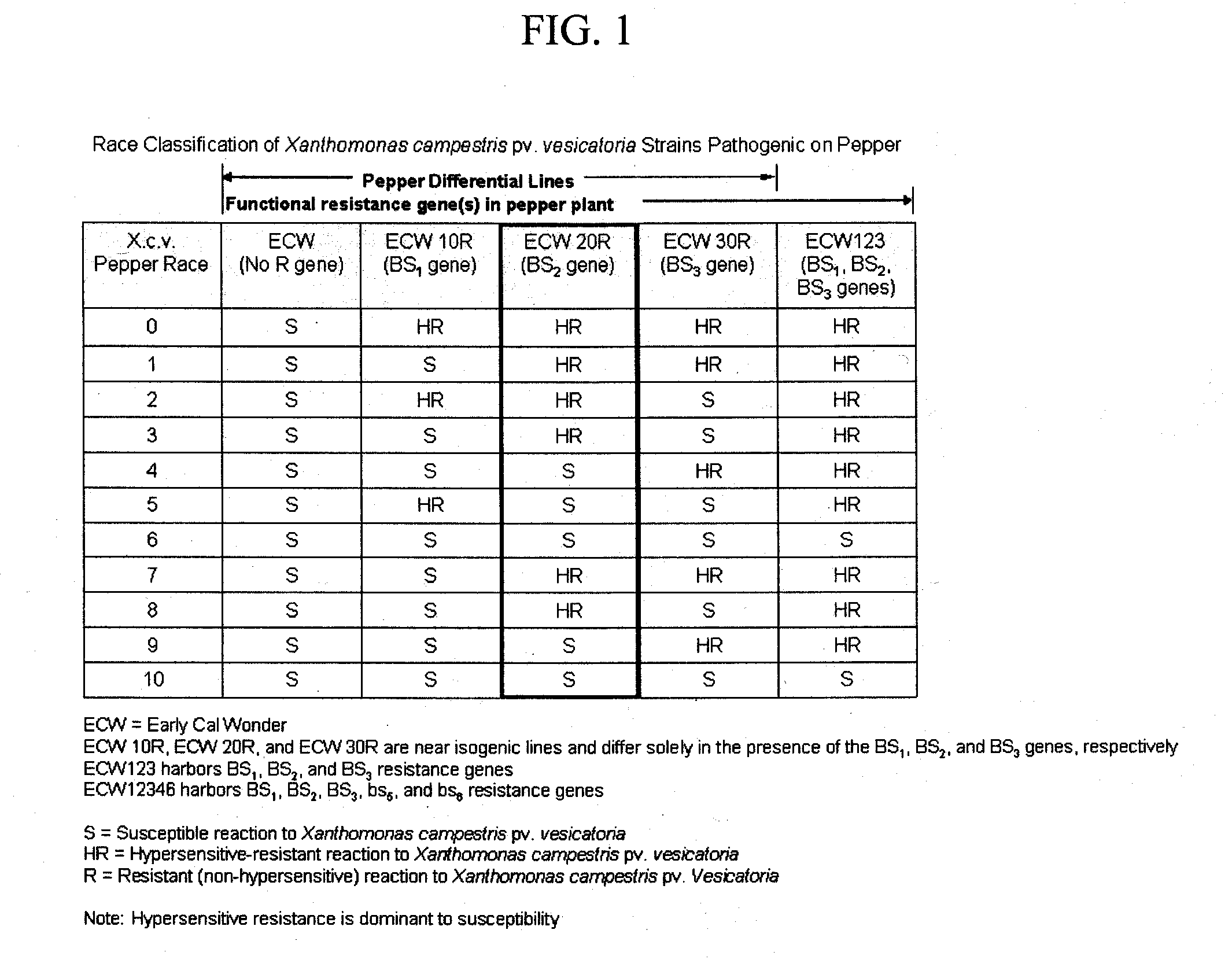
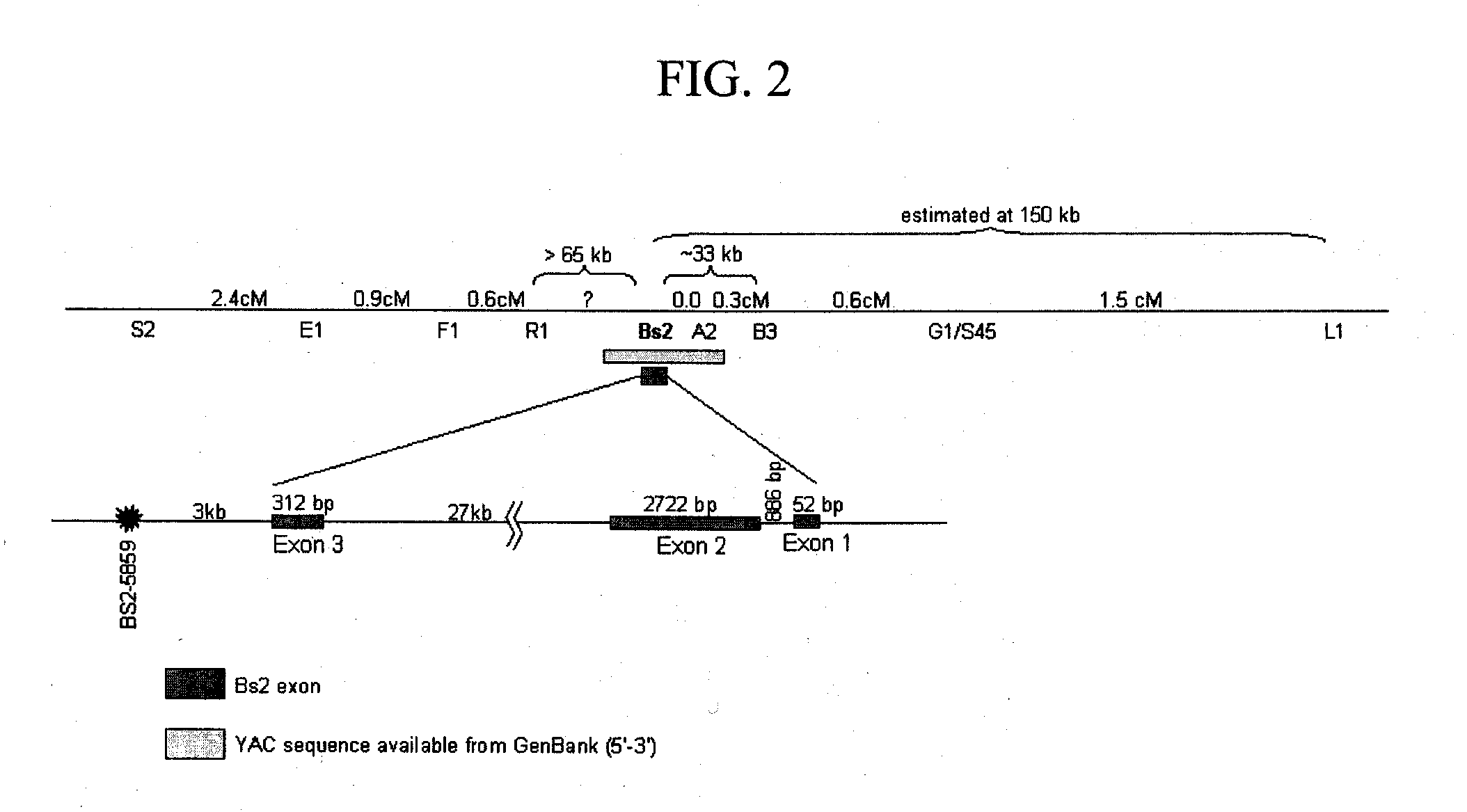
COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS FOR ASSAYING MARKERS TIGHTLY LINKED TO RESISTANCE LOCUS Bs2 OF PEPPER
ActiveUS20100083399A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementXanthomonas campestrisGenotype
The invention relates to compositions and methods for genotypically screening pepper lines for the presence of a polymorphism at the Bs2_5859 locus genetically linked to the Bs2 gene conferring resistance to Bacterial Spot caused by Xanthomonas campestris. Further provided are methods for producing plants displaying Bs2-mediated resistance, and fruit and seeds therefrom.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Method for assisting prediction of risk of occurrence of side effect of irinotecan
InactiveUS20180237833A1Predict riskMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingVariant typeSide effect
An object of the present invention is to provide a simple and efficient device for predicting a risk of occurrence of a side effect of irinotecan by analyzing a single nucleotide polymorphism in a region encoding a specific gene. The prediction of the risk of the occurrence of a side effect of irinotecan is assisted by analyzing a single nucleotide polymorphism in a region encoding the APCDD1L gene, the R3HCC1 gene, the OR5112 gene, the MKKS gene, the EDEM3 gene, or the ACOX1 gene which are present on genomic DNA in a biological sample collected from a test subject; or a single nucleotide polymorphism which is in linkage disequilibrium with or genetically linked to the single nucleotide polymorphism, and determining whether the single nucleotide polymorphism is homozygous for a variant type, heterozygous, or homozygous for a wild-type.
Owner:YAMAGUCHI UNIV +1
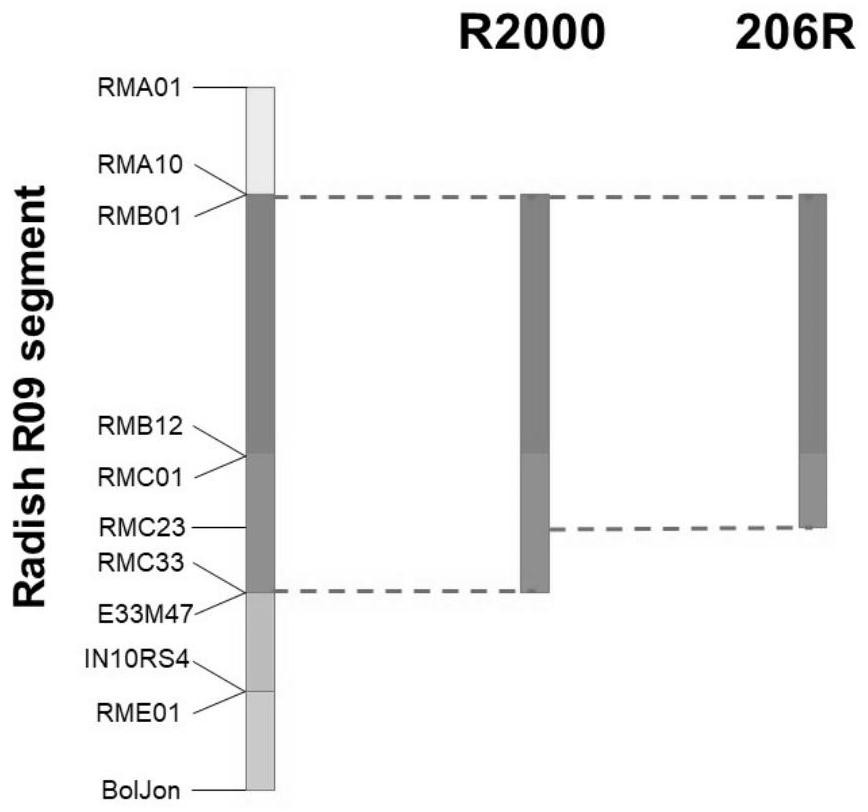
Breeding method of brassica napus radish cytoplasm restorer line
The invention discloses a breeding method of a brassica napus radish cytoplasm restoring line. The breeding method comprises the following steps: by taking a mustard type rape radish cytoplasm restorer line RLM198 as a female parent and brassica napus Yu7-120 as a male parent, introducing a restoring gene of mustard type rape cytoplasm into a brassica napus genome through continuous backcross, and conducting selfing to obtain a homozygous stable restorer line. With adoption of genetic linkage and whole genome re-sequencing analysis method, it is proved that the radish section of the obtained restorer line is short and located at the tail end of the A10 chromosome, and the obtained novel restorer line is sufficient in pollen amount, good in restoring rate, normal in seed setting and free of linkage burdens and can be directly applied to production of rape hybrids in China.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Intron sequence analysis method for detection of adjacent and remote locus alleles as haplotypes
InactiveUS20030119003A1Small sizeGenetic material ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisIntein
The present invention provides a method for detection of at least one allele of a genetic locus and can be used to provide direct determination of the haplotype. The method comprises amplifying genomic DNA with a primer pair that spans an intron sequence and defines a DNA sequence in genetic linkage with an allele to be detected. The primer-defined DNA sequence contains a sufficient number of intron sequence nucleotides to characterize the allele. Genomic DNA is amplified to produce an amplified DNA sequence characteristic of the allele. The amplified DNA sequence is analyzed to detect the presence of a genetic variation in the amplified DNA sequence such as a change in the length of the sequence, gain or loss of a restriction site or substitution of a nucleotide. The variation is characteristic of the allele to be detected and can be used to detect remote alleles. Kits comprising one or more of the reagents used in the method are also described.
Owner:GENETIC TECHNOLOGIES LIMTIED
Construction and evaluation of parting High Map on basis of high throughput
ActiveCN103525917BEliminate build effectsImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementData visualisationBiologyVisualization methods
The invention provides a construction method of a parting High Map on the basis of high throughput. The construction method comprises the steps as follows: 1), genetic segregation population markers subjected to development and parting with a high-throughput sequencing method; 2), every two markers are subjected to genetic linkage test, and linkage groups are divided; 3), linear ordering is performed and the genetic distance is calculated with an SGS algorithm, and parting errors and parting loss in sample parting data are subjected to error correction and loss compensation with a KNN algorithm; and 4), the constructed map is subjected to accuracy evaluation, and the map quality is directly displayed with a visual method. According to the construction method of the parting High Map, the parting errors and the parting loss caused by high-throughput sequencing parting are effectively eliminated through parting error correction, and the accuracy of the constructed map is improved remarkably; the SGS sequencing algorithm is used, so that the sequencing speed is high, a High Map with more than one thousand markers in a single linkage group can be constructed, and the map drawing efficiency is improved remarkably; and the requirement for original parting data is reduced, and the parting error tolerance is improved greatly.
Owner:BIOMARKER TECH
Methodologies and Compositions for Creating Targeted Recombination and Breaking Linkage Between Traits
ActiveUS20170362600A1High frequencyFrequencyHydrolasesVector-based foreign material introductionAllelePlant variety
The current disclosure relates to methods and compositions for improving plant varieties through plant breeding and plant genetics. For instance, the disclosure concerns increasing the recombination frequency of a heterozygous trait genetically linked to a second trait within plants. Further, the disclosure concerns breaking the genetic linkage between a first allele and a second allele.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
SSR (simple sequence repeat) molecular marker II for identifying descendant plants of Gala apple and application thereof
InactiveCN106755483ARapid identificationAccurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceCO-DOMINANT
The invention belongs to the field of innovation and research of plant genetics breeding and apple germplasm, in particular to an SSR (simple sequence repeat) molecular marker II for identifying descendant plants of Gala apple and application thereof. The SSR molecular marker II is characterized in that in the detection process, the SSR molecular markers linked with No.3 and No.11 chromosomes are simultaneously used, DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of an apple gene group is used as a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification template, the SSR molecular markers are respectively used as primer pairs, and the PCR amplification and product detection are performed, so as to identify the genetics linkage, anther culture plants and variety sources. The SSR molecular marker II has the advantages that the SSR molecular marker is used for identifying the apple linkage group of the identifying material for the first time, and the SSR molecular markers linked with No.3 and No.11 chromosomes of the apple are disclosed; the molecular marker is a co-dominant marker, so that the Gala apple genetic linkage group, the anther culture plant and the Gala source plant are quickly and accurately identified; the molecular level support is provided for further accelerating the utilization of the Gala apple and important agronomic trait linkage gene, and the genetic breeding of apple homozygous plants.
Owner:POMOLOGY INST SHANXI ACAD OF AGRI SCI +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com