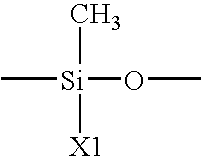Patents
Literature
1886 results about "Plant Part" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
This standard provides for all common plant parts and some fungi parts. These common plant and fungi parts are used in the CDER Special Products On-line Tracking System, and in the FDA Substance Registration System.
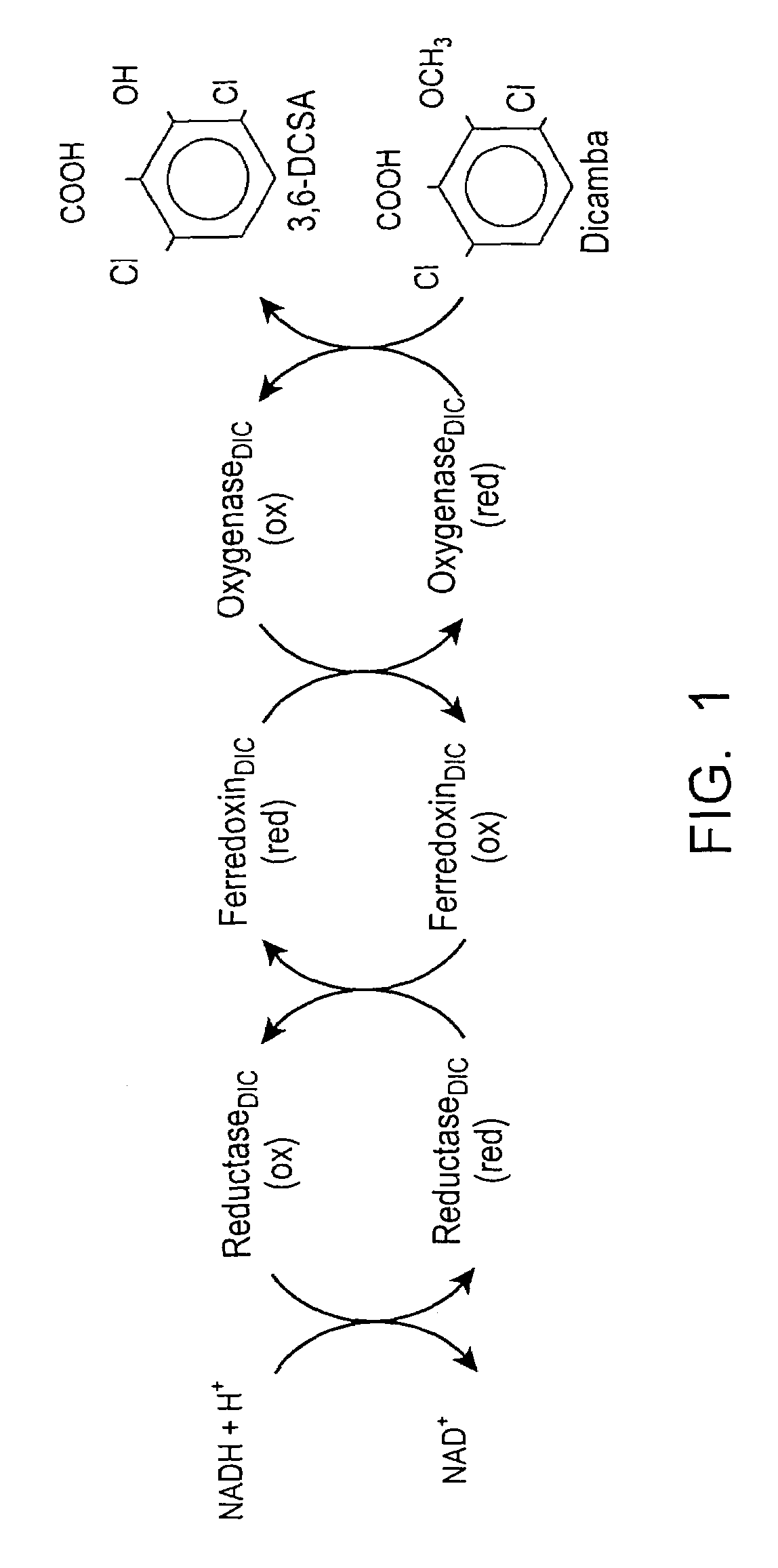
Methods and materials for making and using transgenic dicamba-degrading organisms
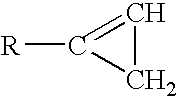
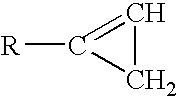
The invention provides isolated and at least partially-purified dicamba-degrading enzymes, isolated DNA molecules coding for dicamba-degrading enzymes, DNA constructs coding for dicamba-degrading enzymes, transgenic host cells comprising DNA coding for dicamba-degrading enzymes, and transgenic plants and plant parts comprising one or more cells comprising DNA coding for dicamba-degrading enzymes. Expression of the dicamba-degrading enzymes results in the production of dicamba-degrading organisms, including dicamba-tolerant plants. The invention further provides a method of controlling weeds in a field containing the transgenic dicamba-tolerant plants of the invention and a method of decontaminating a material containing dicamba comprising applying an effective amount of a transgenic microorganism or dicamba-degrading enzyme(s) of the invention to the material. Finally, the invention provides a method of selecting transformed plants and plant cells based on dicamba tolerance and a method of selecting or screening transformed host cells, intact organisms and parts of organisms based on the fluorescence of 3,6-dichlorosalicylic acid produced as a result of dicamba degradation.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF NEBRASKA
Bacillus sp. D747 strain, plant disease controlling agents and insect pest controlling agents using the same and control method using the agents
The present invention relates to a novel strain of Bacillus sp. D747 (deposited as FERM BP-8234) and methods for controlling plant diseases and insect pests, comprising administering cultures of Bacillus sp. D747 (including the viable bacteria) or viable bacteria isolated by culturing, on the plant parts such as roots, stems, leaves, seeds, and the like, or in the culture soil.
Owner:KUMIAI CHEM IND CO LTD
Compositions and Methods to Control Insect Pests
ActiveUS20140275208A1Lower Level RequirementsPest controlBiocideSugar derivativesSequence controlNucleotide
Methods and compositions are provided which employ a silencing element that, when ingested by a pest, such as a Coleopteran plant pest or a Diabrotica plant pest, decrease the expression of a target sequence in the pest. In specific embodiments, the decrease in expression of the target sequence controls the pest and thereby the methods and compositions are capable of limiting damage to a plant. The present invention provides various target polynucleotides set forth in any one of SEQ ID NOS: disclosed herein, (but not including the forward and reverse primers.) or active variants and fragments thereof, or complements thereof, wherein a decrease in expression of one or more of the sequences in the target pest controls the pest (i.e., has insecticidal activity). Further provided are silencing elements which when ingested by the pest decrease the level of the target polypeptide and thereby control the pest. In specific embodiments, the pest is D. virgifera virgifera, D. barberi, D. virgifera zeae, D. speciosa, D. speciosa, or D. undecimpunctata howardi. Plants, plant parts, bacteria and other host cells comprising the silencing elements or an active variant or fragment thereof of the invention are also provided.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC +1
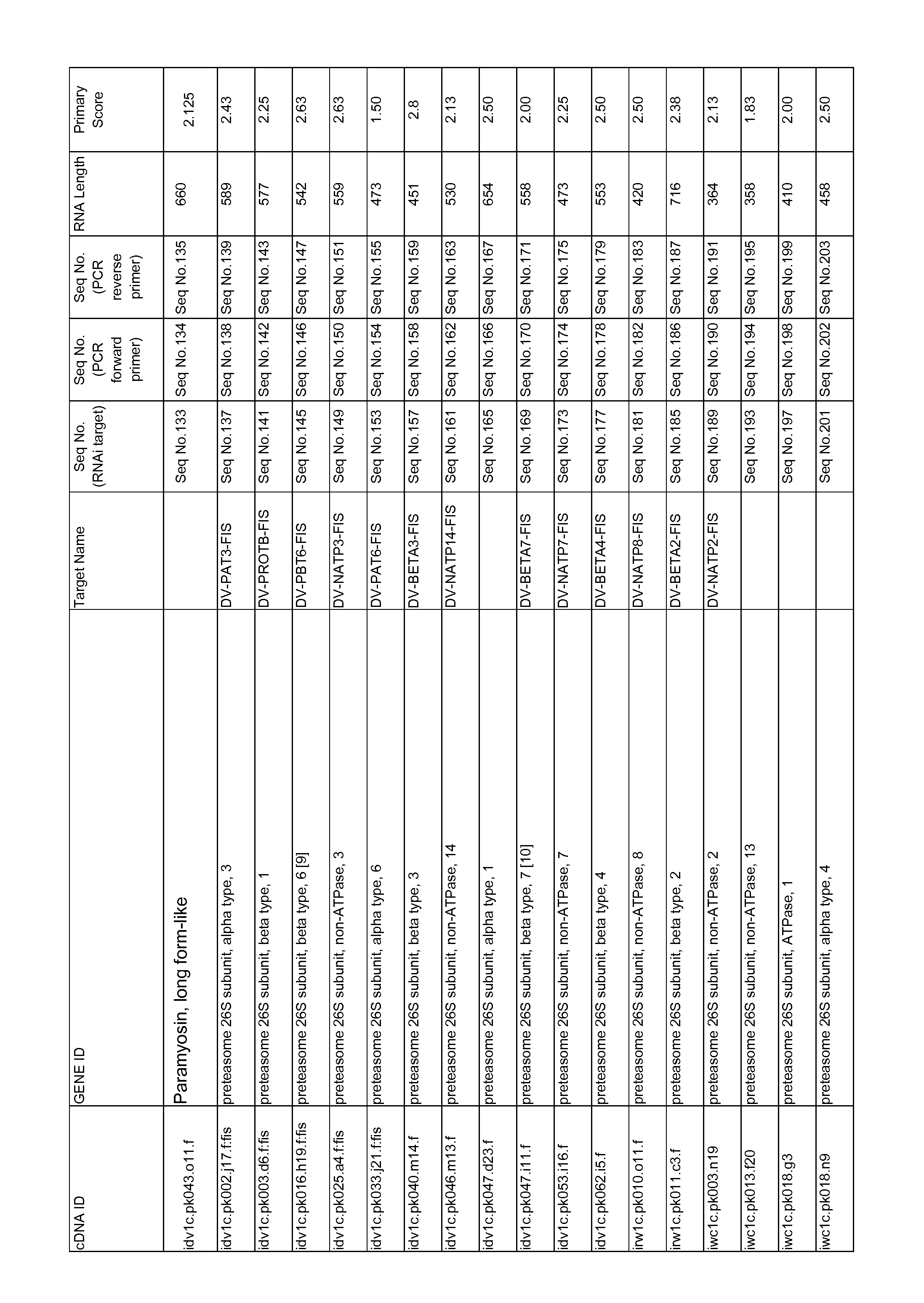
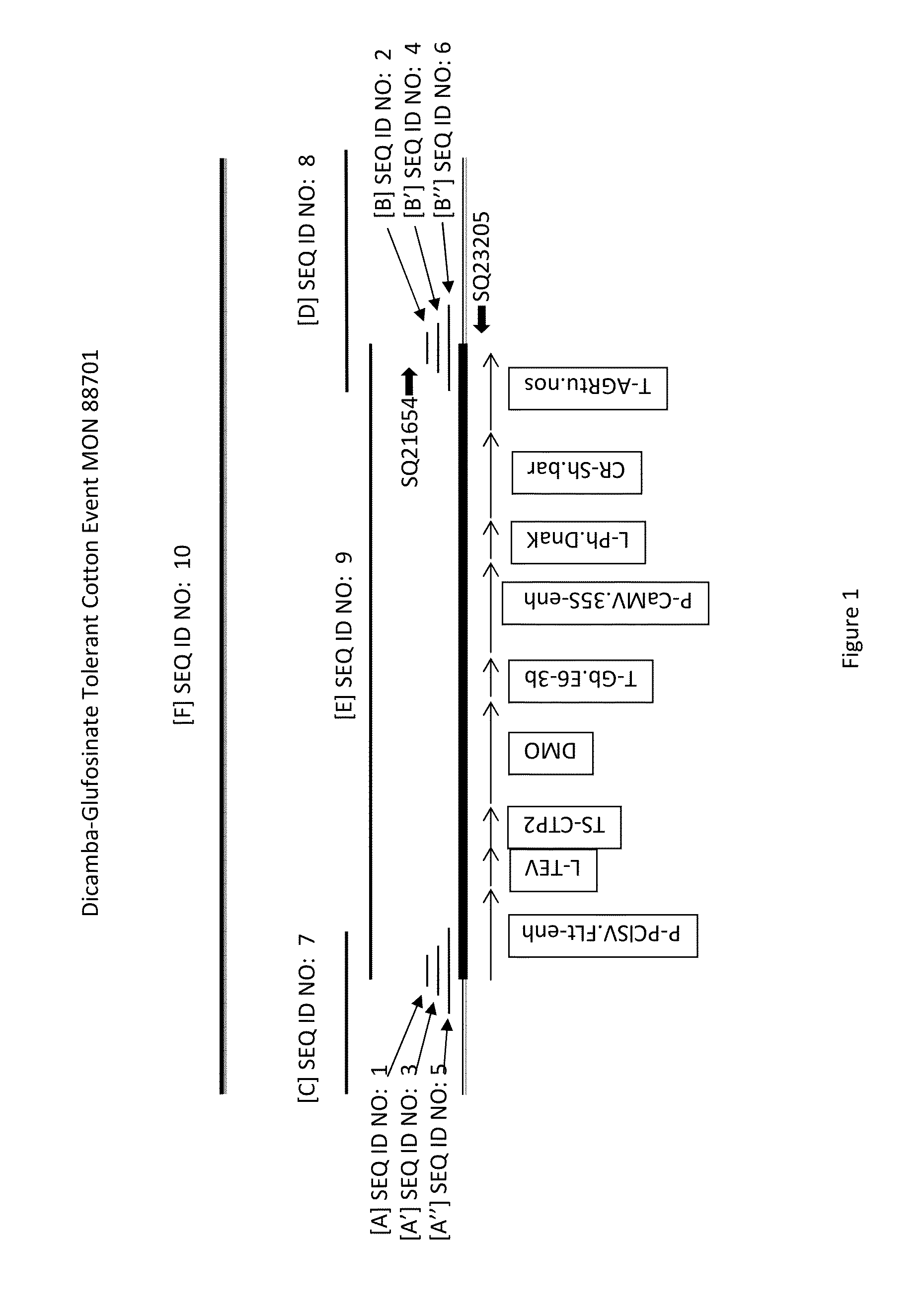
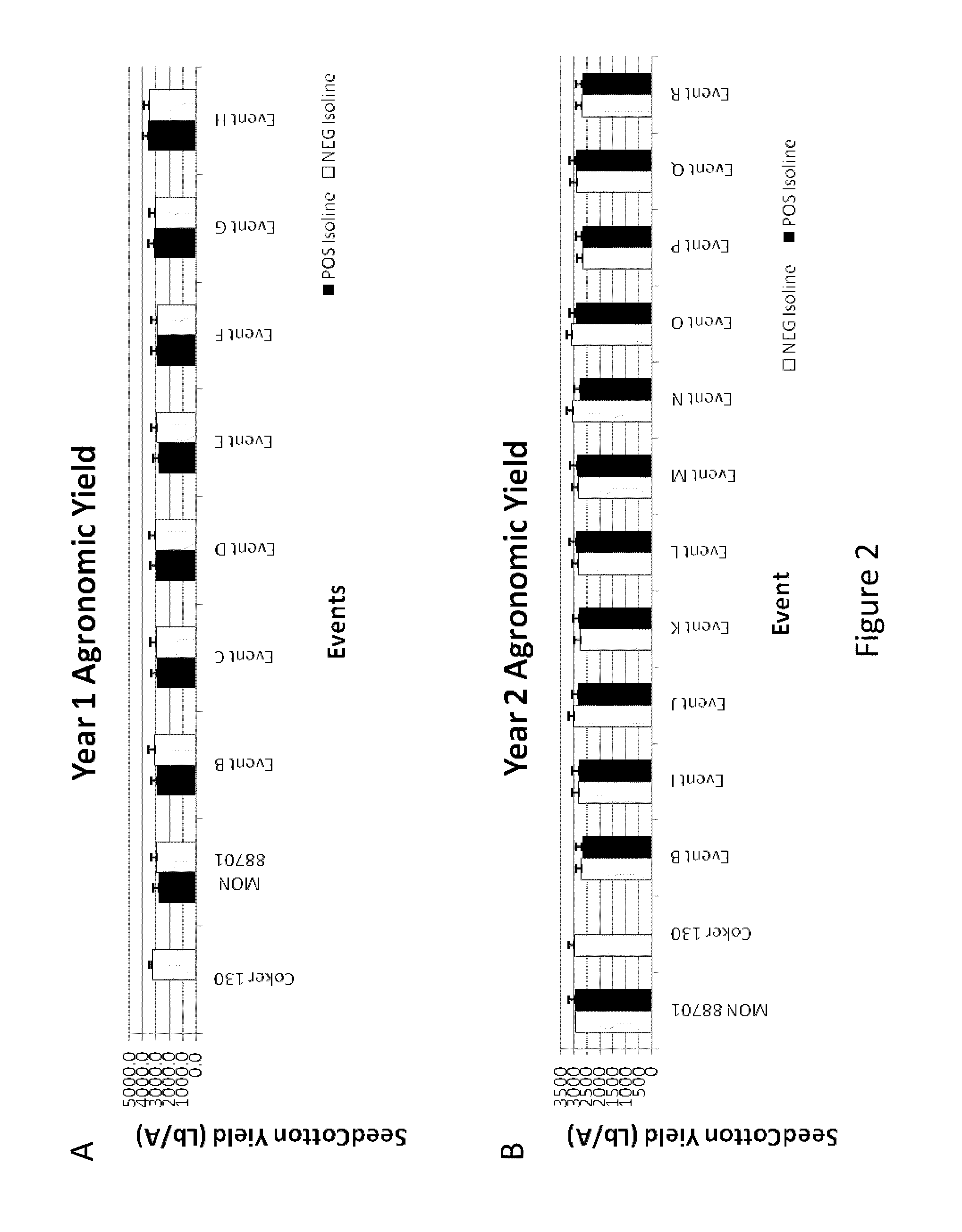
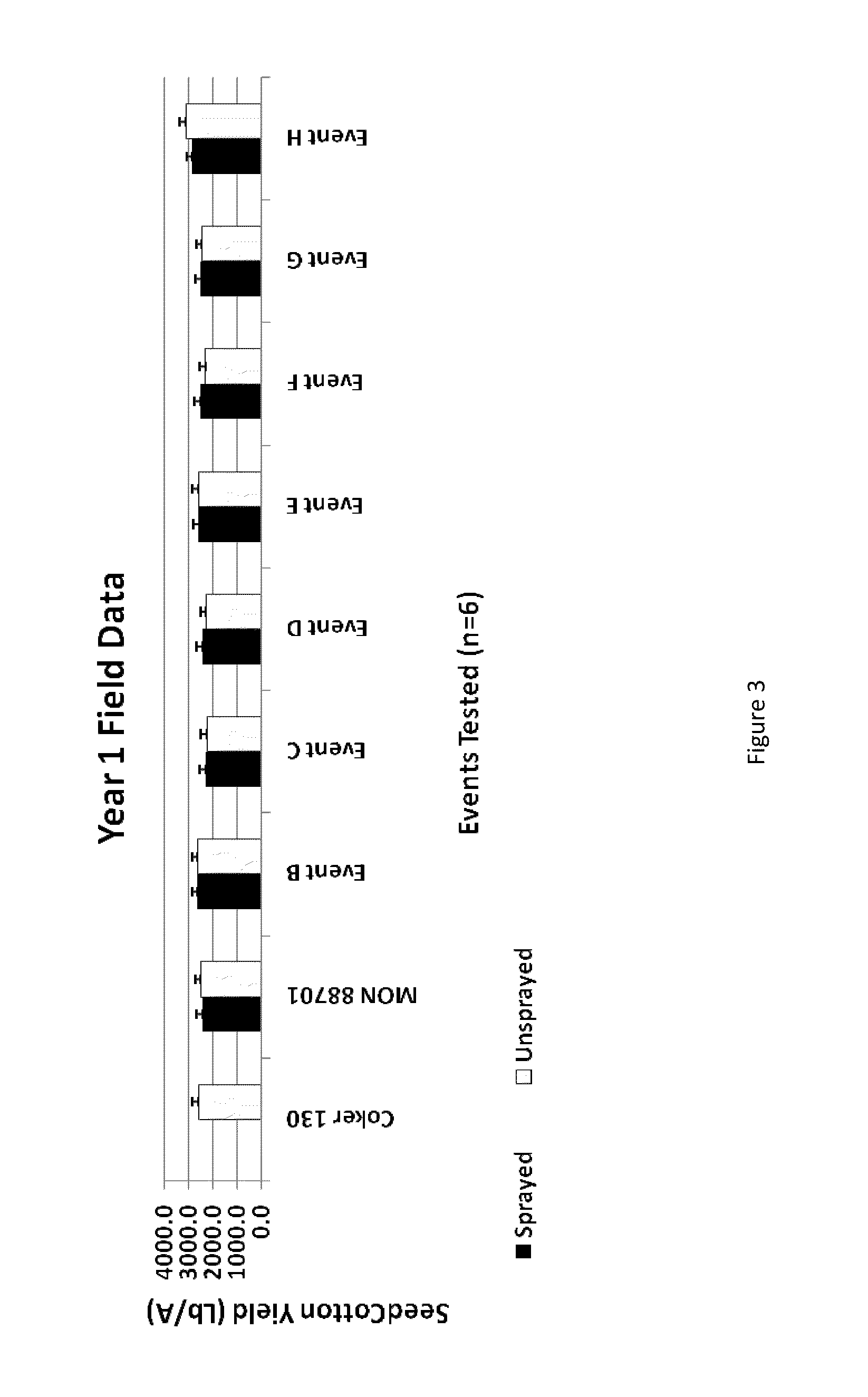
Cotton transgenic event MON 88701 and methods of use thereof
The invention provides cotton event MON 88701, and plants, plant cells, seeds, plant parts, and commodity products comprising event MON 88701. The invention also provides polynucleotides specific for event MON 88701 and plants, plant cells, seeds, plant parts, and commodity products comprising polynucleotides specific for event MON 88701. The invention also provides methods related to event MON 88701.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Canola cultivar NQC02CNX21
ActiveUS20060225146A1DegreeImprove nutritional qualityOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationBrassicaGenetic Materials
A canola cultivar designated NQC02CNX21 is disclosed. The invention relates to the seeds of canola cultivar NQC02CNX21, to the plants of canola NQC02CNX21, to plant parts of canola cultivar NQC02CNX21 and to methods for producing a canola plant produced by crossing canola cultivar NQC02CNX21 with itself or with another canola line. The invention also relates to methods for producing a canola plant containing in its genetic material one or more transgenes and to the transgenic canola plants and plant parts produced by those methods. This invention also relates to canola cultivars or breeding cultivars and plant parts derived from canola cultivar NQC02CNX21, to methods for producing other canola cultivars, lines or plant parts derived from canola cultivar NQC02CNX21 and to the canola plants, varieties, and their parts derived from use of those methods. The invention further relates to hybrid canola seeds, plants and plant parts produced by crossing the canola cultivar NQC02CNX21 with another canola cultivar.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
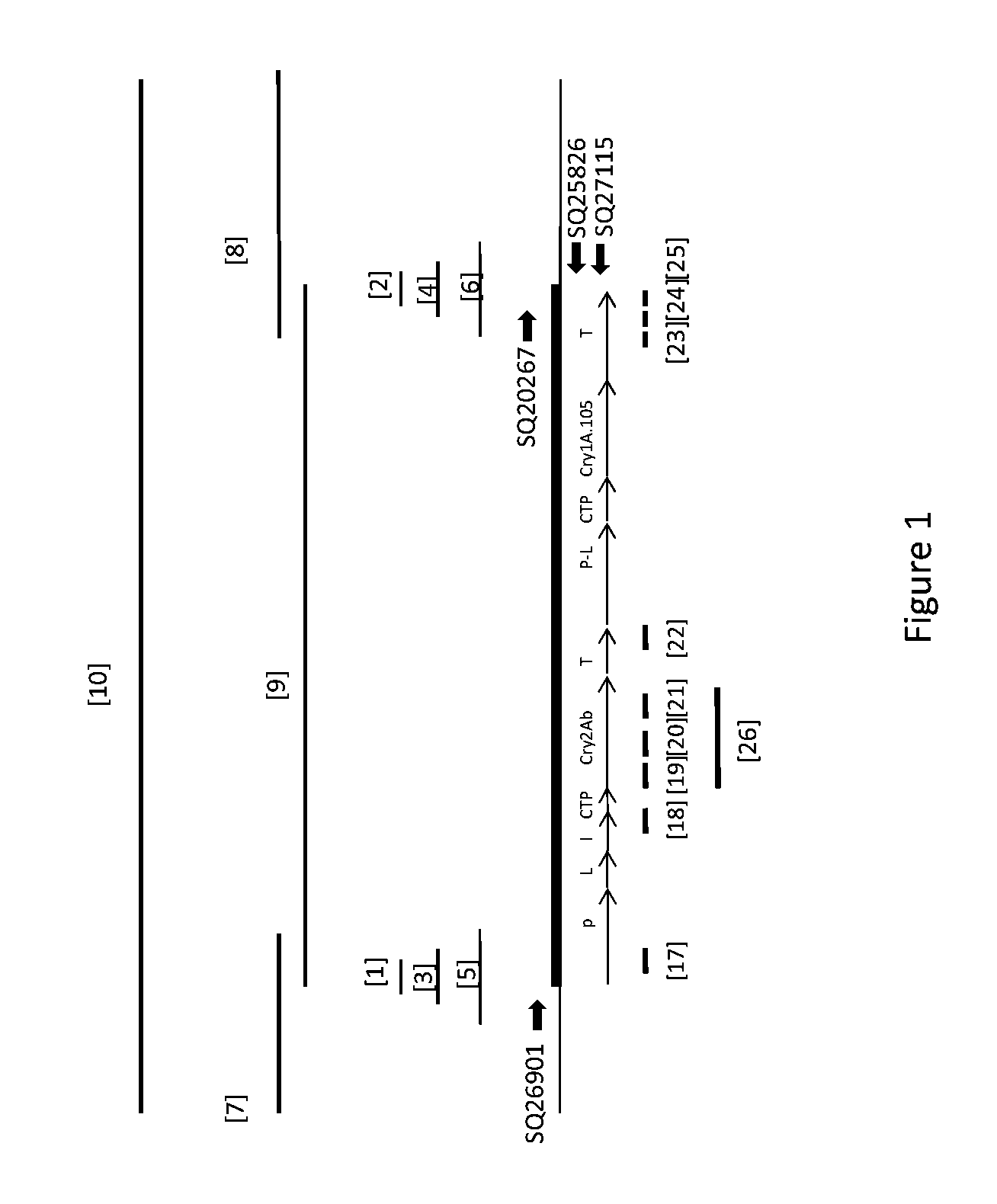
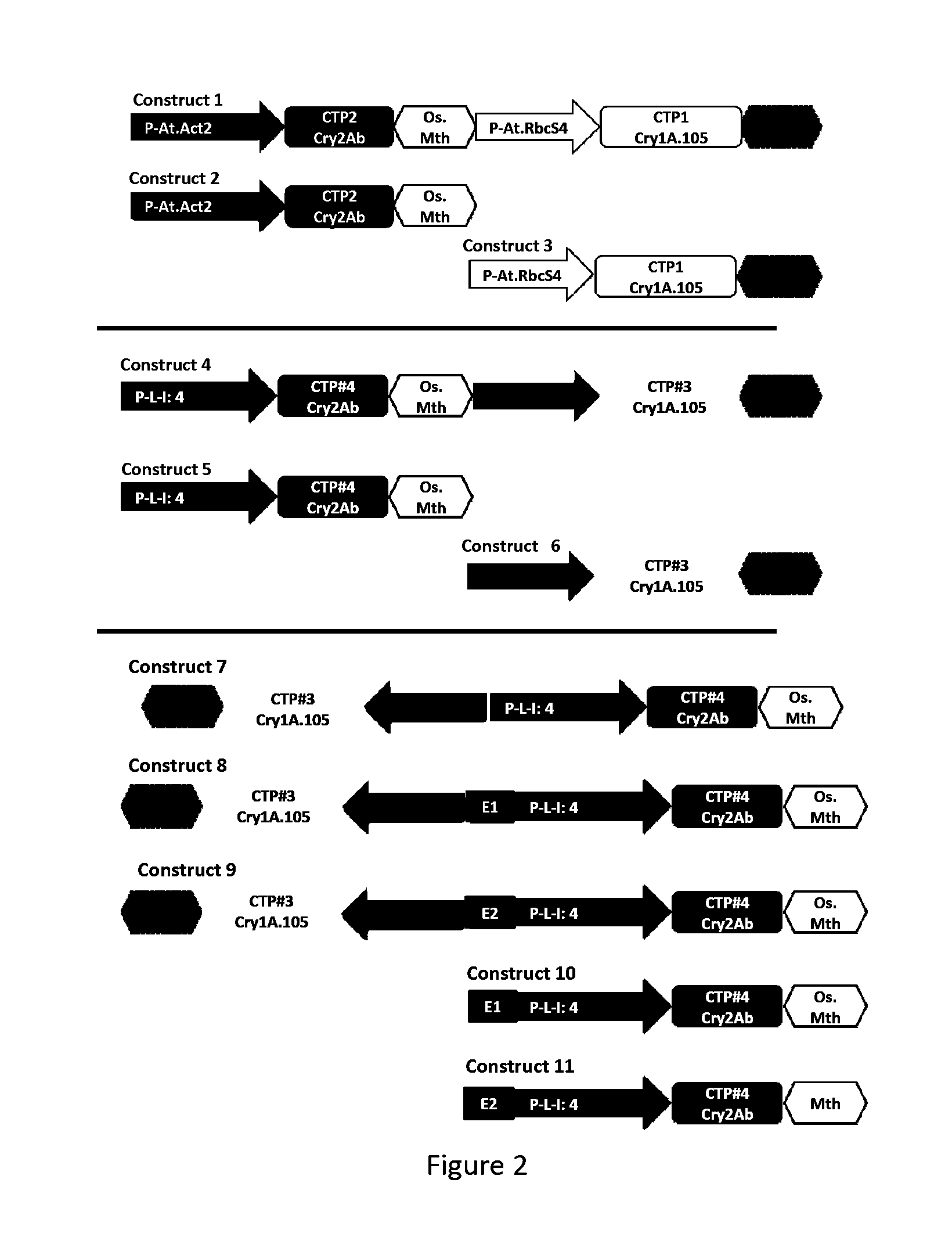
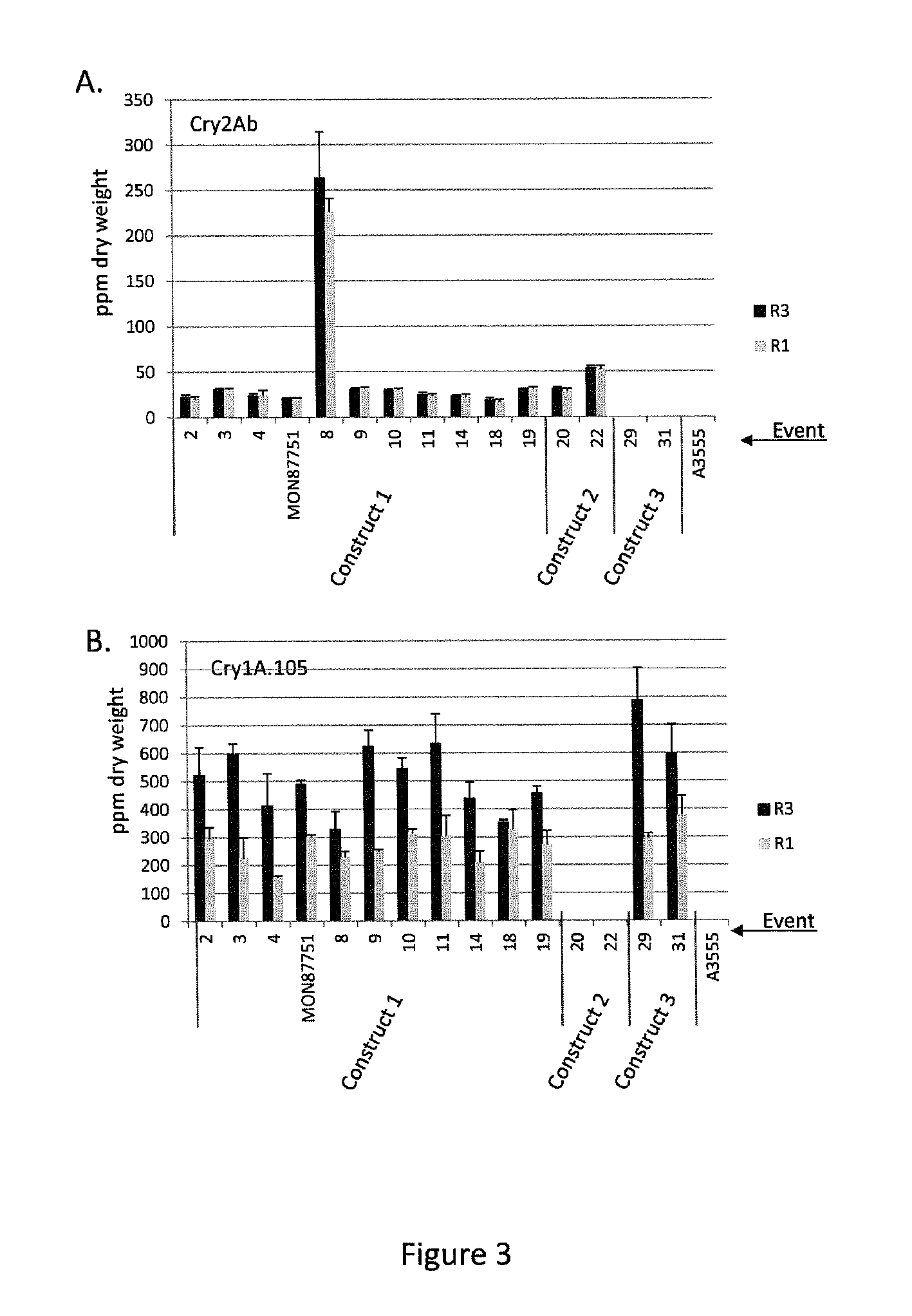
Soybean transgenic event mon87751 and methods for detection and use thereof
ActiveUS20140373191A1Maintain good propertiesImprove performanceCheese manufactureVector-based foreign material introductionGlycinePlant cell
The invention provides a transgenic Glycine max event MON87751, plants, plant cells, seeds, plant parts, progeny plants, and commodity products comprising event MON87751. The invention also provides polynucleotides specific for event MON87751, plants, plant cells, seeds, plant parts, and commodity products comprising polynucleotides for event MON87751. The invention also provides methods related to event MON87751.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Compositions and methods to control insect pests
InactiveUS20110054007A1Reduces level of targetProcess controlBiocideAnimal repellantsSequence controlSilencing Elements
Methods and compositions are provided which employ a silencing element that, when ingested by a pest, such as a Coleopteran plant pest or a Diabrotica plant pest, decrease the expression of a target sequence in the pest. In specific embodiments, the decrease in expression of the target sequence controls the pest and thereby the methods and compositions are capable of limiting damage to a plant. The present invention provides various target polynucleotides set forth in any one of SEQ ID NOS: 1-236 or active variants and fragments thereof, wherein a decrease in expression of one or more the sequences in the target pest controls the pest (i.e., has insecticidal activity). Further provided are silencing elements which when ingested by the pest decrease the level of the target polypeptide and thereby control the pest. In specific embodiment, the pest is D. virgifera virgifera, D. barberi, D. speciosa, or D. undecimpunctata howardi. Plants, plant part, bacteria and other host cells comprising the silencing elements or an active variant or fragment thereof of the invention are also provided.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Methods for Treating Live Plants or Live Plant Parts or Mushrooms with UV-C Light
InactiveUS20090272029A1Increase humidityIncrease crop yieldDead plant preservationAgricultural machinesPlant TubersMushroom
The present invention relates to a method for controlling pathogen growth on live plants and mushrooms using UV-C light and an apparatus for use in the method. Also provided are methods for removing surplus leaves and methods for destroying aerial plant parts prior to harvest of underground roots, tubers or bulbs.
Owner:CLEAN LIGHT
Compositions and methods for insecticidal control of stinkbugs
InactiveUS20110301223A1Reduces level of targetProcess controlBiocideSugar derivativesSequence controlSilencing Elements
Methods and compositions are provided which employ a silencing element that, when ingested by a pest, such as a Pentatomidae plant pest or a N. viridula, Acrosternum hilare, Piezodorus guildini, and / or Halymorpha halys plant pest, decrease the expression of a target sequence in the pest. In specific embodiments, the decrease in expression of the target sequence controls the pest and thereby the methods and compositions are capable of limiting damage to a plant. The present invention provides various target polynucleotides set forth in any one of SEQ ID NOS: 1-292 or 302-304 or active variants and fragments thereof, wherein a decrease in expression of one or more the sequences in the target pest controls the pest (i.e., has insecticidal activity). Further provided are silencing elements which when ingested by the pest decrease the level of the target polypeptide and thereby control the pest. In specific embodiment, the pest is Pentatomidae. Plants, plant part, bacteria and other host cells comprising the silencing elements or an active variant or fragment thereof of the invention are also provided.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC +1
Alteration of tobacco alkaloid content through modification of specific cytochrome P450 genes
ActiveUS8124851B2Lower Level RequirementsSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNornicotineMetabolite
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV +1
Alteration of tobacco alkaloid content through modification of specific cytochrome P450 genes
ActiveUS7884263B2Decrease in levelLower Level RequirementsTobacco treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementNornicotineMetabolite
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV +1
Fungal isolates and their use to confer salinity and drought tolerance in plants
The present invention is directed to methods and compositions of endophytic fungi that confer stress tolerance to inoculated plants, including both monocots and dicots. In particular, Fusarium species, isolated from the dunegrass, Leymus mollis, growing in plant communities on Puget Sound beaches of Washington State. Upon inoculating a target plant or plant part with the endophytic fungi, the resulting plant shows stress tolerance, particularly drought and salinity tolerance.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
Compositions with cyclopropenes and adjuvants
A composition is provided that contains one or more molecular encapsulation agents within each of which is encapsulated one or more cyclopropenes and that contains one or more adjuvants selected from the group consisting of surfactants, alcohols, hydrocarbon oils, and mixtures thereof. Also provided is a method that includes the step of contacting such compositions to one or more plants or plant parts.
Owner:AGROFRESH
Method of preparation and composition of a water soluble extract of the plant species uncaria
The present invention is directed to a method of preparation and the composition of a water soluble extract of the plant species Uncaria. The present invention is also directed to the pharmaceutical use of the composition for the enhancement of the immune, anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor and DNA repair processes of warm blooded animals. The present preparation of the water soluble extract of the plant species Uncaria results in the depletion of many of the ingredients which lead to various toxic side effects associated with other extracts or compositions derived from Uncaria. Also, the present preparation leads to the depletion of many of the active ingredients commonly associated with other extracts and compositions of the plant species Uncaria. Therefore, the present invention teaches that the hot water extraction of the crude plant parts of Uncaria and the subsequent dialysis of the solubilized products yields a low molecular weight composition which maintains a high degree of the anti-tumor, inflammatory and immune stimulatory activities associated with the crude plant parts.
Owner:CAMPAMED +2
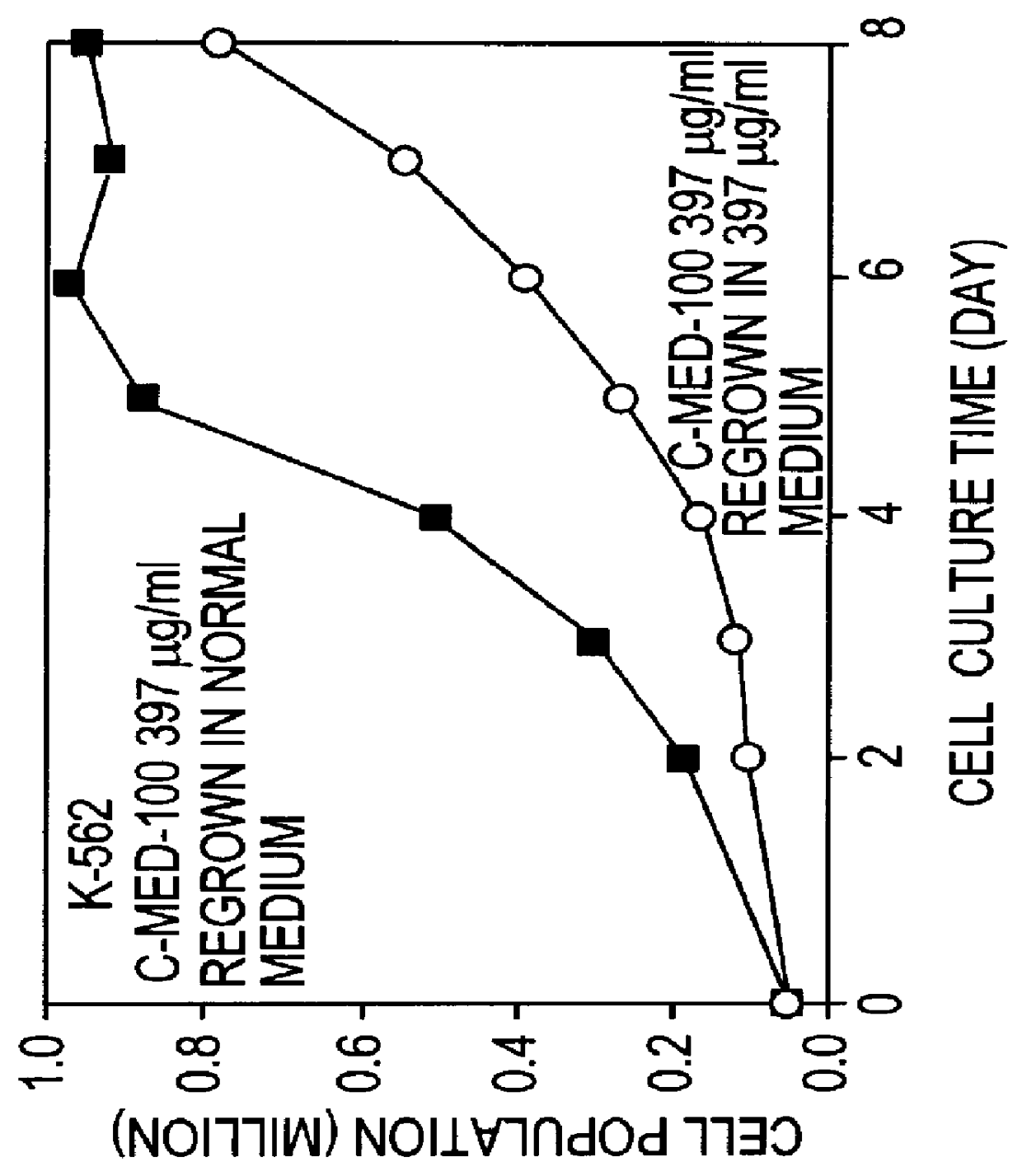
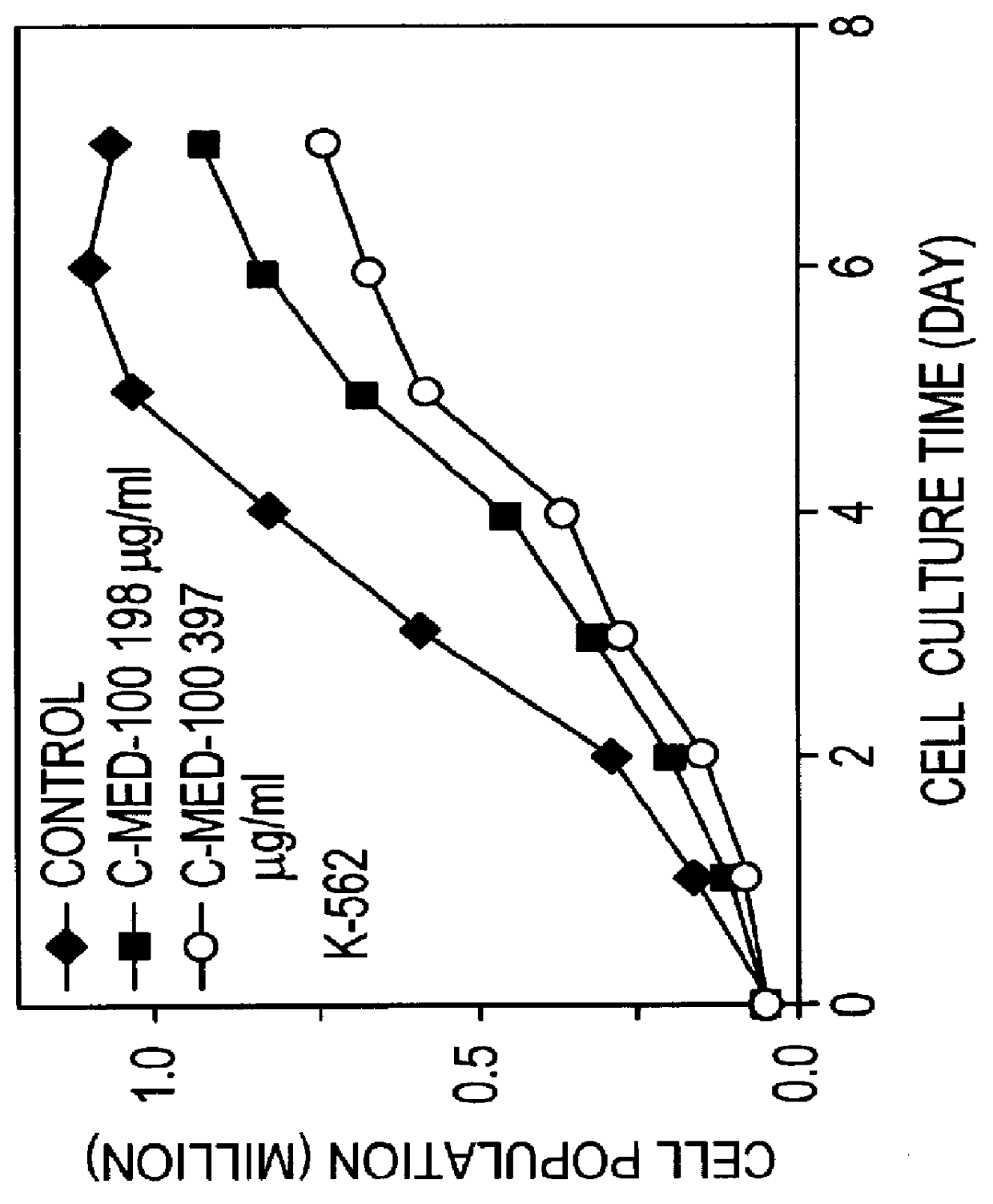
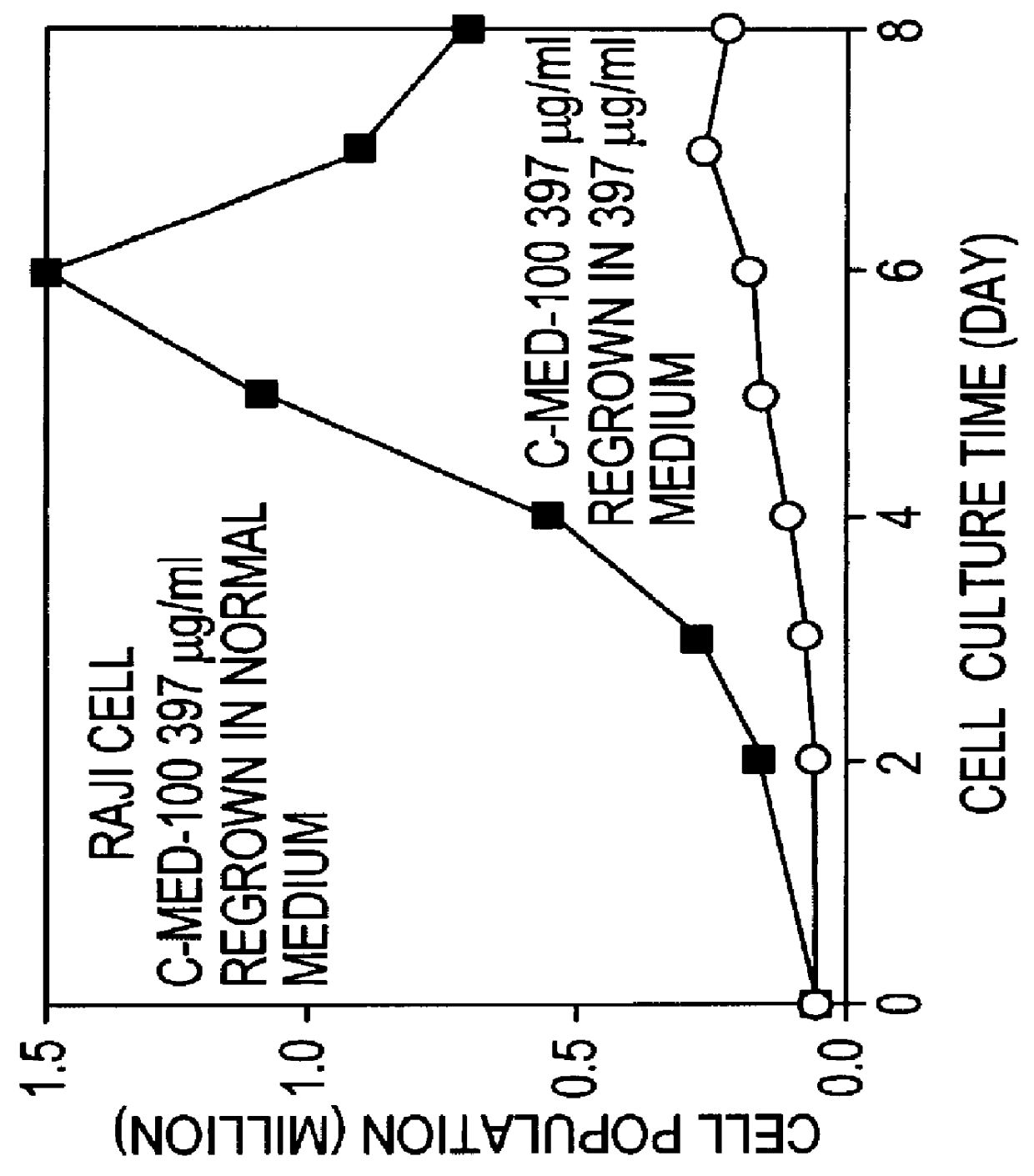
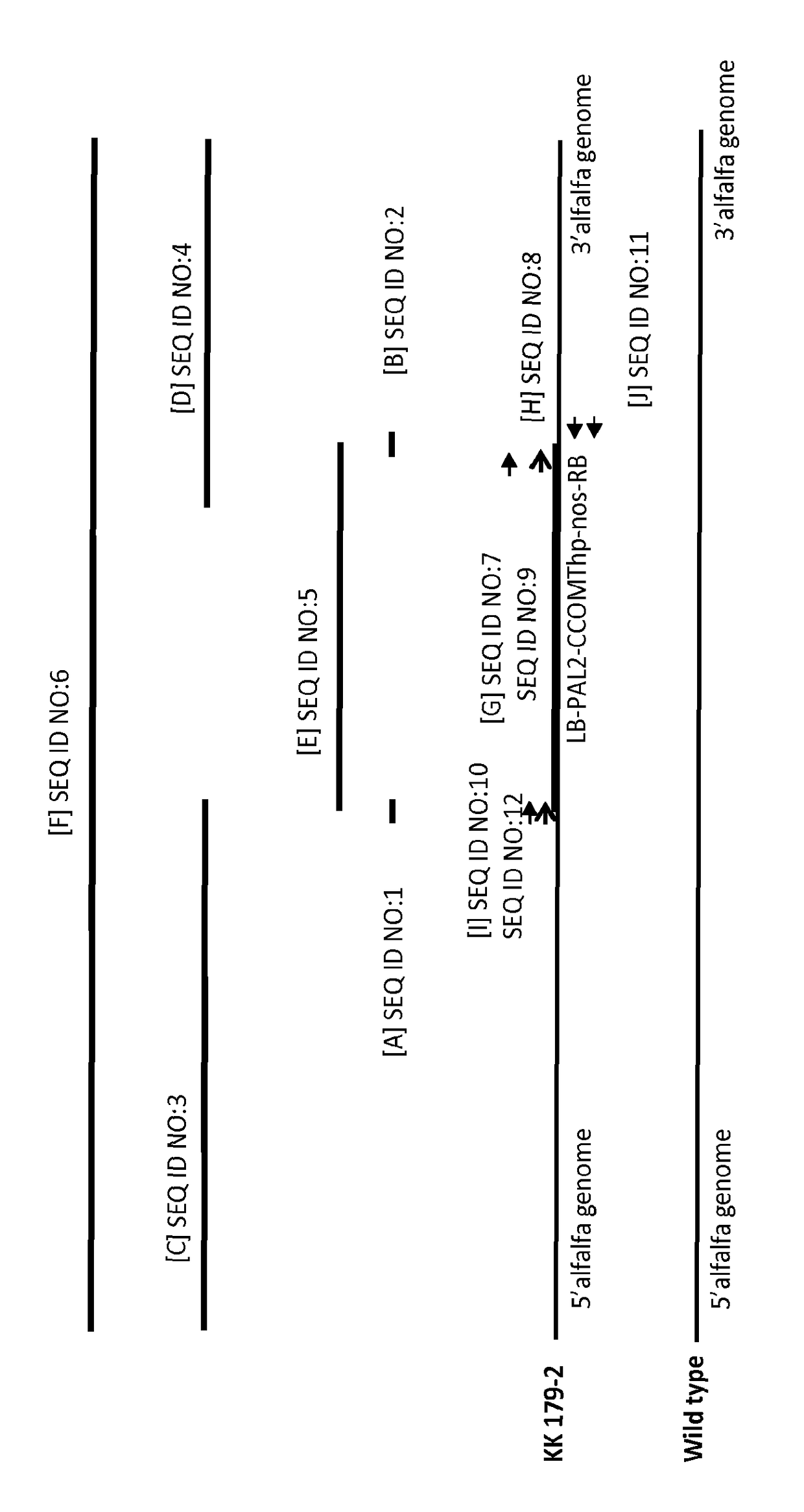
Alfalfa plant and seed corresponding to transgenic event KK 179-2 and methods for detection thereof
The present invention provides a transgenic alfalfa event KK179-2. The invention also provides cells, plant parts, seeds, plants, commodity products related to the event, and DNA molecules that are unique to the event and were created by the insertion of transgenic DNA into the genome of a alfalfa plant. The current invention also provides anti-sense-oriented RNA gene suppression agents in the form of a loop of anti-sense-oriented RNA that is produced in the cells of transgenic alfalfa. In addition, the invention also provides methods for detecting the presence of said alfalfa event nucleotide sequences in a sample, probes and primers for use in detecting nucleotide sequences that are diagnostic for the presence of said alfalfa event.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC +1
Canola cultivar dn040845
ActiveUS20080263717A1Improve nutritional qualityPlant genotype modificationAngiosperms/flowering plantsBiotechnologyCultivar
The present invention relates to a new and distinctive canola cultivar, designated DN040845. Also included are seeds of canola cultivar DN040845, to the plants, or plant parts, of canola DN040845 and to methods for producing a canola plant produced by crossing the canola DN040845 with itself or another canola cultivar, and the creation of variants by mutagenesis or transformation of canola DN040845.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
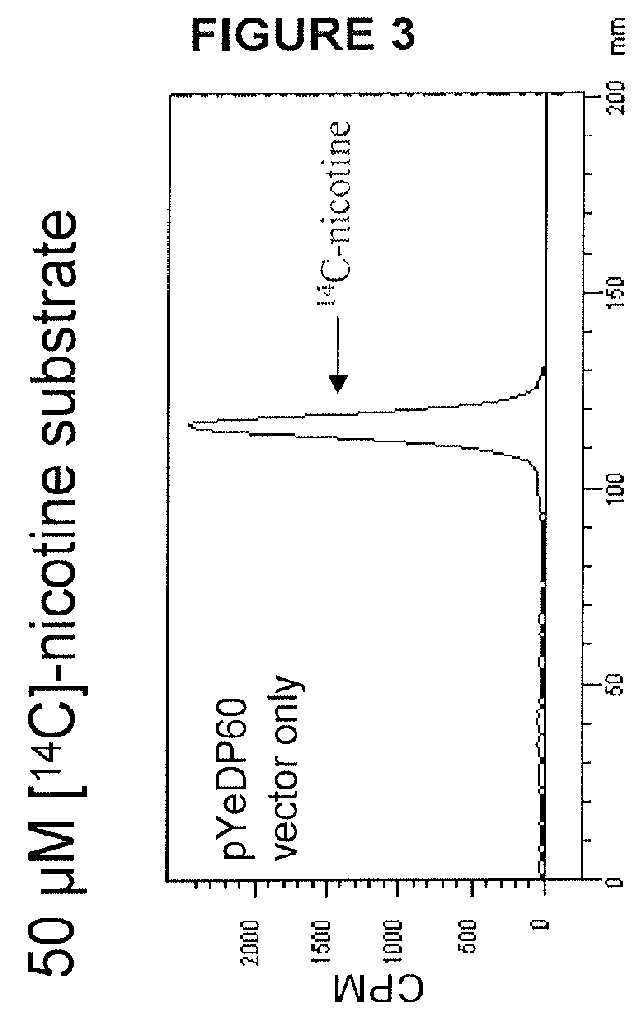
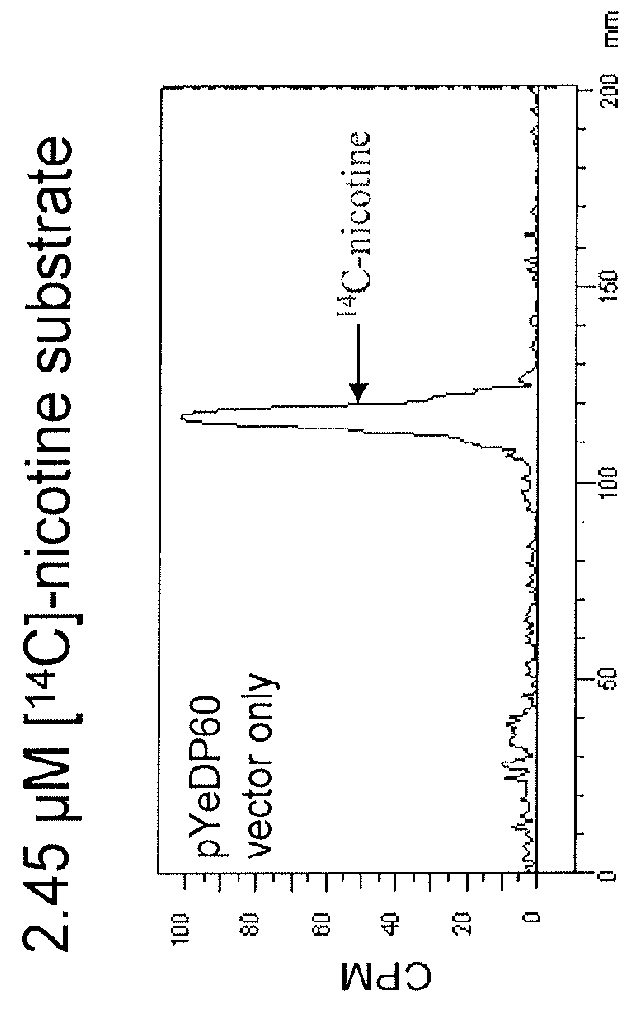
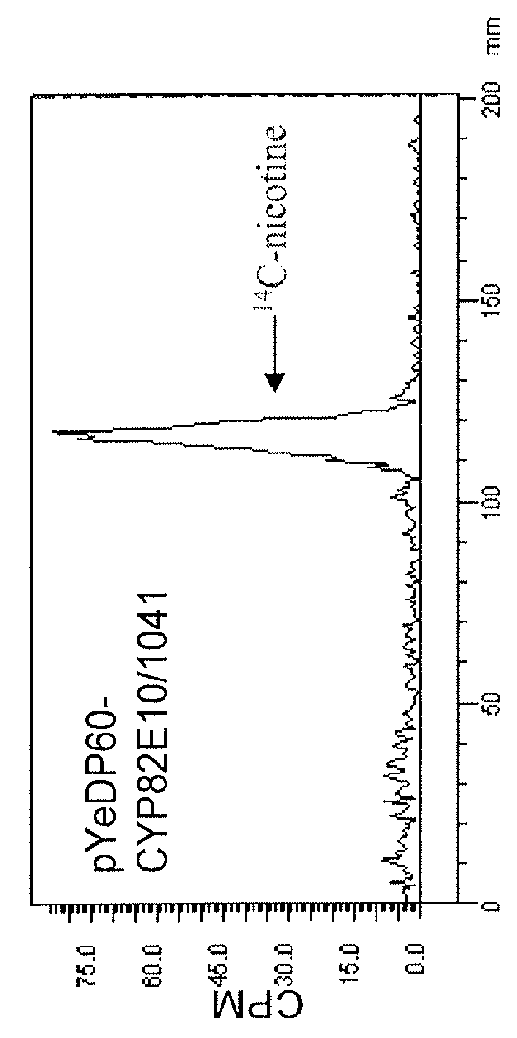
Compositions and methods for minimizing nornicotine synthesis in tobacco
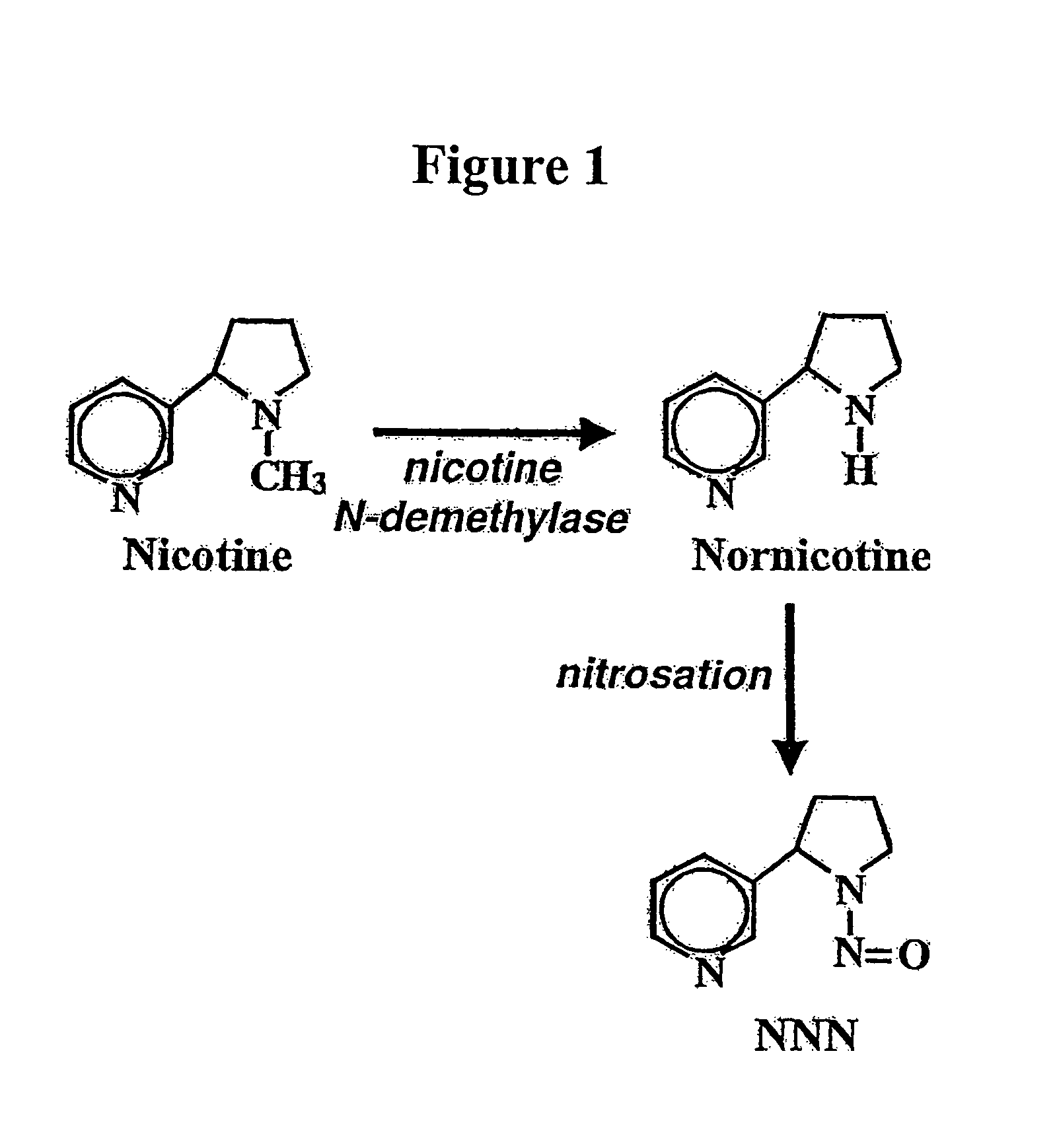
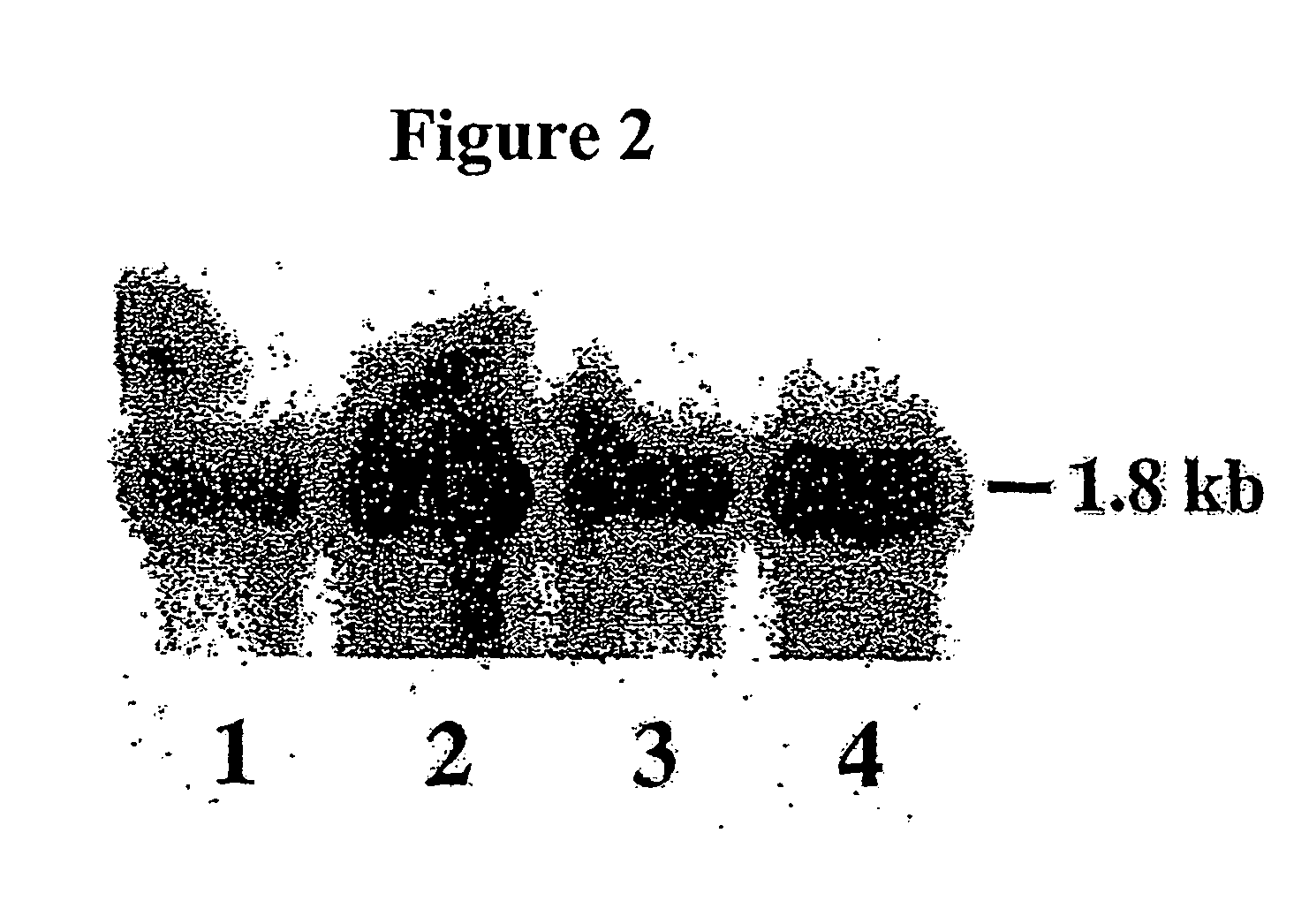
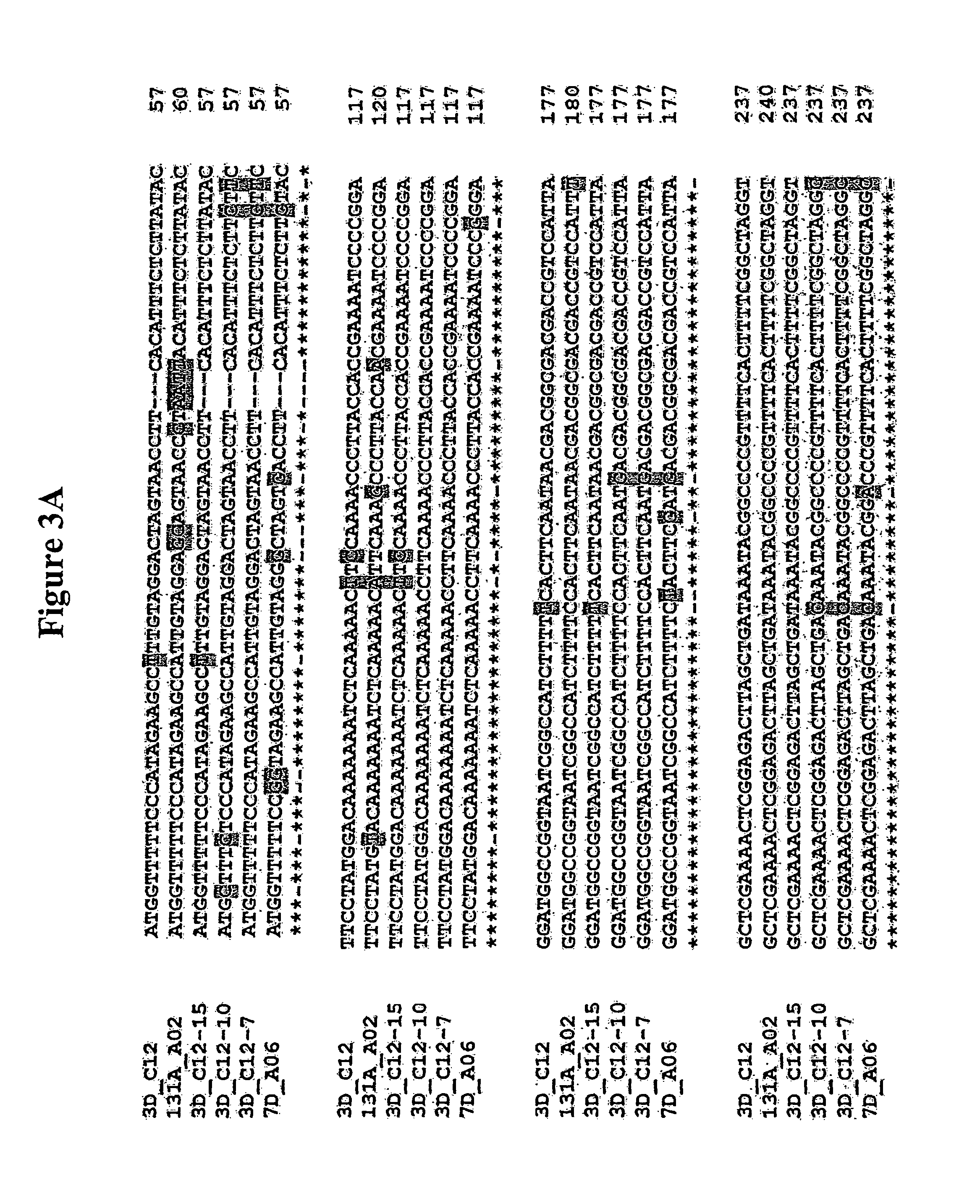
Compositions and methods for reducing the level of nornicotine and N′-nitrosonornicotine (NNN) in tobacco plants and plant parts thereof are provided. The compositions comprise isolated polynucleotides and polypeptides for a root-specific nicotine demethylases, CYP82E10, and variants thereof, that are involved in the metabolic conversion of nicotine to nornicotine in these plants. Compositions of the invention also include tobacco plants, or plant parts thereof, comprising a mutation in a gene encoding a CYP82E10 nicotine demethylase, wherein the mutation results in reduced expression or function of the CYP82E10 nicotine demethylase. Seed of these tobacco plants, or progeny thereof, and tobacco products prepared from the tobacco plants of the invention, or from plant parts or progeny thereof, are also provided. Methods for reducing the level of nornicotine, or reducing the rate of conversion of nicotine to nornicotine, in a tobacco plant, or plant part thereof are also provided. The methods comprise introducing into the genome of a tobacco plant a mutation within at least one allele of each of at least three nicotine demethylase genes, wherein the mutation reduces expression of the nicotine demethylase gene, and wherein a first of these nicotine demethylase genes encodes a root-specific nicotine demethylase involved in the metabolic conversion of nicotine to nornicotine in a tobacco plant or a plant part thereof. The methods find use in the production of tobacco products that have reduced levels of nornicotine and its carcinogenic metabolite, NNN, and thus reduced carcinogenic potential for individuals consuming these tobacco products or exposed to secondary smoke derived from these products.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Hybrid maize 36W66
A novel hybrid maize variety designated 36W66 and seed, plants and plant parts thereof, produced by crossing two Pioneer Hi-Bred International, Inc. proprietary inbred maize lines. Methods for producing a maize plant that comprises crossing hybrid maize variety 36W66 with another maize plant. Methods for producing a maize plant containing in its genetic material one or more traits introgressed into 36W66 through backcross conversion and / or transformation, and to the maize seed, plant and plant part produced thereby. This invention relates to the hybrid seed 36W66, the hybrid plant produced from the seed, and variants, mutants, and trivial modifications of hybrid 36W66. This invention further relates to methods for producing maize lines derived from hybrid maize variety 36W66 and to the maize lines derived by the use of those methods.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Pathogen-inducible promoters and their use in enhancing the disease resistance of plants
Methods for producing pathogen-inducible promoters for the expression of genes in plants are provided. The pathogen-inducible promoters are inducible by one, two, three, or more plant pathogens. Methods for producing R genes that are inducible in a plant by more than one plant pathogen are further provided. Additionally, provided are R genes and other nucleic acid molecules comprising the pathogen-inducible promoters and that are made by such methods as well as plants, plant parts, plant cells, seeds, and non-human host cells comprising the R genes and other nucleic acid molecules
Owner:TWO BLADES FOUND
Methods and compositions for producing male sterile plants
Methods of making a targeted modification in a male fertility gene in the genome of a plant are disclosed. The methods involve contacting a plant cell with an engineered double-strand-break-inducing agent capable of inducing a double-strand break in a target sequence in the male fertility gene and identifying a cell comprising an alteration in the target sequence. Also disclosed are plants, plant cells, plant parts, and seeds comprising a male fertility gene with an alteration in a male fertility gene. Nucleic acid molecules comprising male fertility genes with at least one targeted modification therein, optimized nucleic acid molecules encoding endonucleases that are engineered double-strand-break-inducing agents and expression cassettes, host cells, and plants comprising one or more of the nucleic acid molecules are further disclosed.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Nucleotide sequences and polypeptides encoded thereby useful for modifying nitrogen use efficiency characteristics in plants
ActiveUS20070044172A1Improve scalabilityPromote recoverySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementLow nitrogenNitrogen assimilation
Isolated polynucleotides and polypeptides encoded thereby are described, together with the use of those products for making transgenic plants with increased nitrogen use efficiency. The present invention further relates to nucleotide sequences and the use of those nucleotide sequences in the genetic-engineering of plants to display enhanced nitrogen assimilatory and utilization capacities, grow larger, more efficiently or rapidly, and / or have enriched nitrogen contents in vegetative and / or reproductive plant parts and / or increased biomass. More particularly, this invention relates to producing transgenic plants engineered to have altered expression of key components in the nitrogen assimilation and utilization pathways. The engineered plants may be productively cultivated under conditions of low nitrogen fertilizer input or in nitrogen poor soils. Alternatively, the engineered plants may be used to achieve faster growing or maturing crops, higher crop yields and / or more nutritious products under ideal cultivation conditions.
Owner:CERES INC
Inbred corn line BB46
ActiveUS8026432B2Improve nutritional qualityModified waxy contentBryophytesPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyGenetic Materials
An inbred corn line, designated BB46, is disclosed. The invention relates to the seeds of inbred corn line BB46, to the plants and plant parts of inbred corn line BB46 and to methods for producing a corn plant, either inbred or hybrid, by crossing inbred corn line BB46 with itself or another corn line. The invention further relates to methods for producing a corn plant containing in its genetic material one or more transgenes and to the transgenic plants produced by that method and to methods for producing other inbred corn lines derived from inbred corn line BB46.
Owner:KWS SAAT SE +1
Inbred corn line BB59
ActiveUS7989682B2Improve nutritional qualityModified waxy contentBryophytesPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyGenetic Materials
An inbred corn line, designated BB59, is disclosed. The invention relates to the seeds of inbred corn line BB59, to the plants and plant parts of inbred corn line BB59 and to methods for producing a corn plant, either inbred or hybrid, by crossing inbred corn line BB59 with itself or another corn line. The invention further relates to methods for producing a corn plant containing in its genetic material one or more transgenes and to the transgenic plants produced by that method and to methods for producing other inbred corn lines derived from inbred corn line BB59.
Owner:LIMAGRAIN EURO +1
Compositions with cyclopropenes and non-hydrocarbon oils
A composition is provided that contains one or more molecular encapsulation agents within each of which is encapsulated one or more cyclopropenes and that contains one or more non-hydrocarbon oils. Also provided is a method that includes the step of contacting such compositions to one or more plants or plant parts.
Owner:BASEL RICHARD M +2
Canola hybrid cultivar G152936H
ActiveUS8664477B2Improve nutritional qualityTissue cultureVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyGenetics
The present invention relates to a new and distinctive canola, designated G152936H. Also included are seeds of canola G152936H, to the plants, or plant parts, of canola G152936H and to methods for producing a canola plant produced by crossing the canola G152936H with itself or another canola genotype, and the creation of variants by mutagenesis or transformation of canola G152936H.
Owner:AGRI GENETICS
Canola cultivar G2X0023
ActiveUS8304611B2Improve nutritional qualityTissue cultureVector-based foreign material introductionCultivarCanola
The present invention relates to a new and distinctive canola cultivar, designated G2X0023. Also included are seeds of canola cultivar G2X0023, to the plants, or plant parts, of canola G2X0023 and to methods for producing a canola plant produced by crossing the canola G2X0023 with itself or another canola cultivar, and the creation of variants by mutagenesis or transformation of canola G2X0023.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Canola cultivar G31064
ActiveUS8558065B2Improve nutritional qualityTissue cultureVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyRapeseed
The present invention relates to a new and distinctive canola cultivar, designated G31064. Also included are seeds of canola cultivar G31064, to the plants, or plant parts, of canola G 31064 and to methods for producing a canola plant produced by crossing the canola G31064 with itself or another canola cultivar, and the creation of variants by mutagenesis or transformation of canola G31064.
Owner:AGRI GENETICS
Canola cultivar G030994
ActiveUS8530726B2Improve nutritional qualityTissue cultureVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyCultivar
The present invention relates to a new and distinctive canola cultivar, designated G030994. Also included are seeds of canola cultivar G030994, to the plants, or plant parts, of canola G030994 and to methods for producing a canola plant produced by crossing the canola G030994 with itself or another canola cultivar, and the creation of variants by mutagenesis or transformation of canola G030994.
Owner:AGRI GENETICS
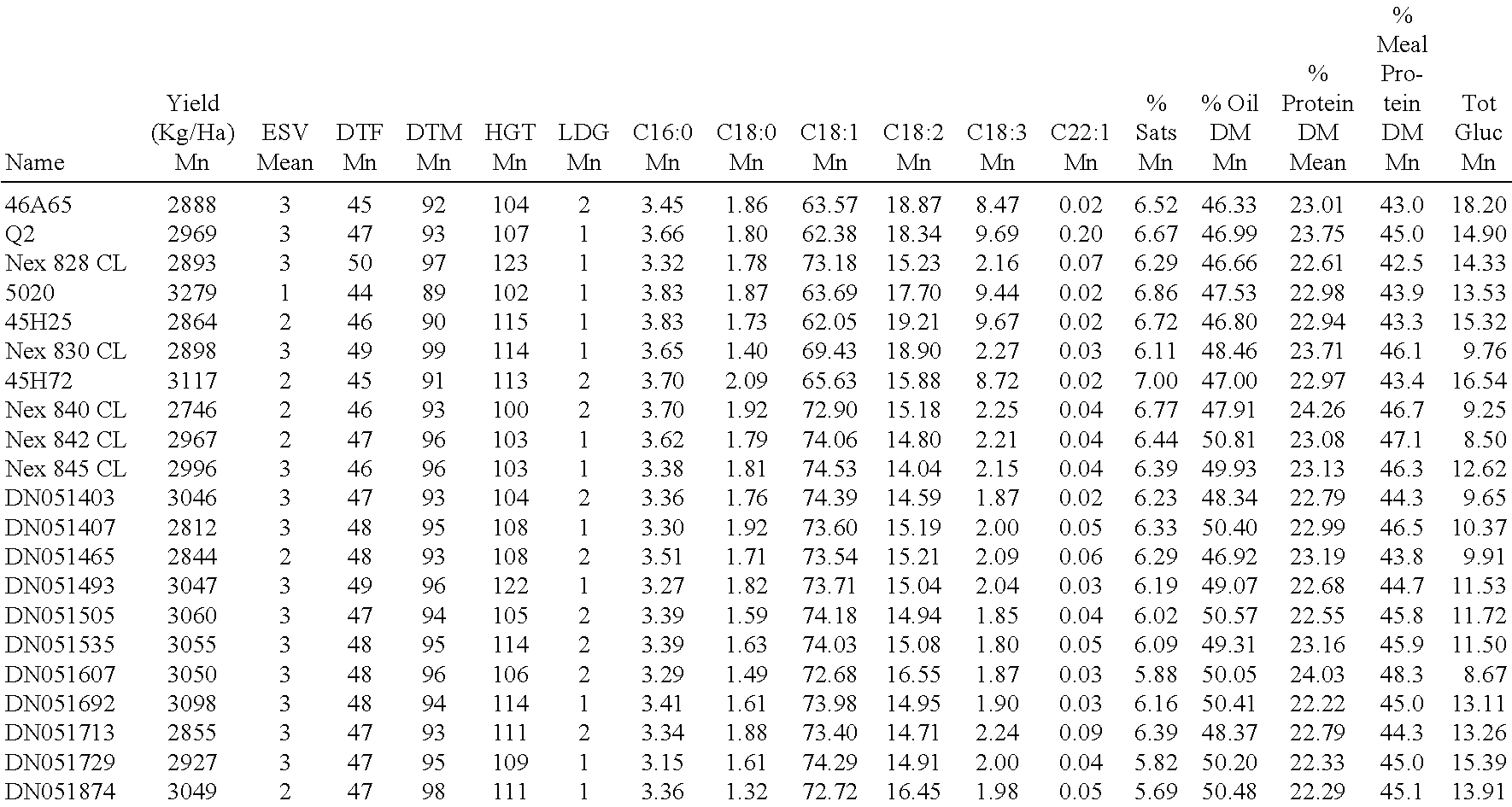
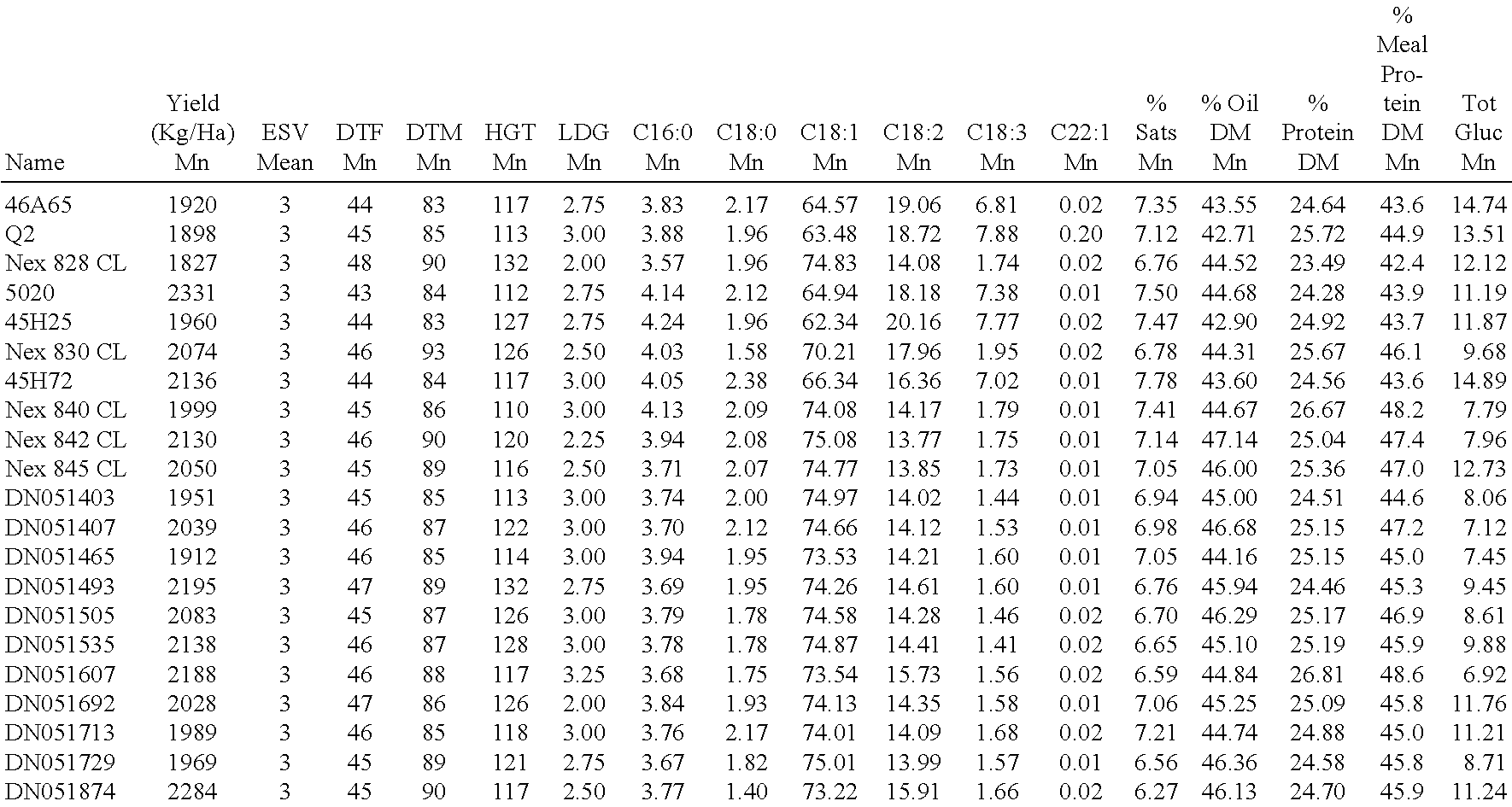
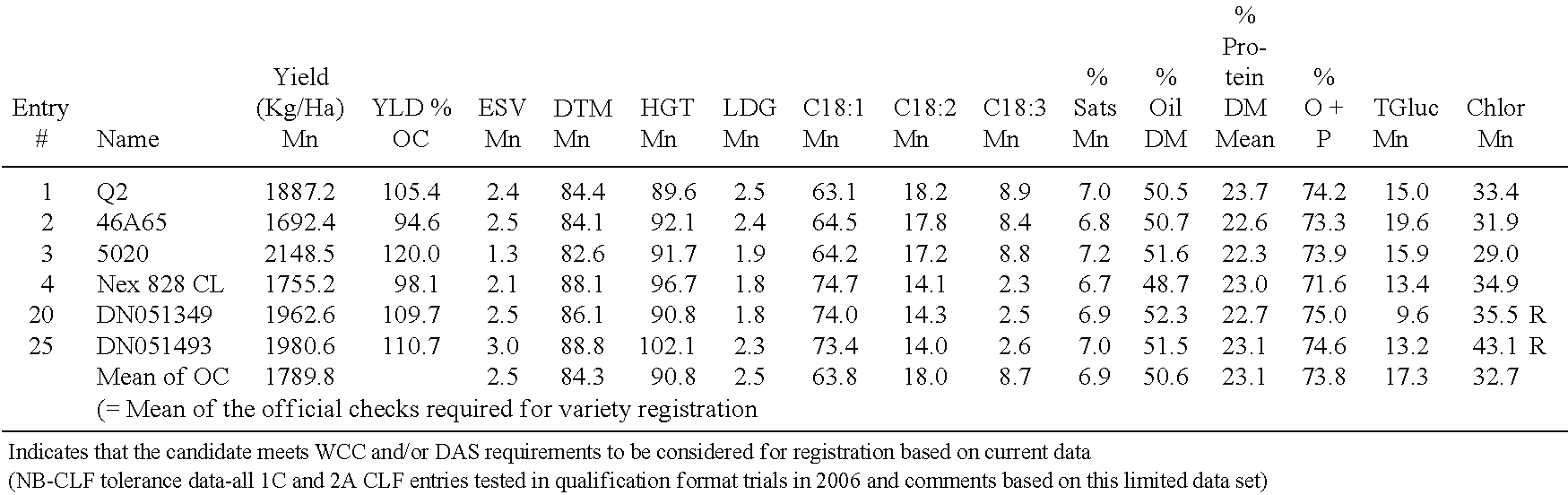
Canola cultivar DN051493
ActiveUS8378177B2Improve nutritional qualityTissue cultureVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyCultivar
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Hybrid maize 34P88
ActiveUS7084332B2Good yieldImprove the immunityImmunoglobulinsFermentationHybrid seedGenetic Materials
A novel hybrid maize variety designated 34P88 and seed, plants and plant parts thereof, produced by crossing two Pioneer Hi-Bred International, Inc. proprietary inbred maize lines. Methods for producing a maize plant that comprises crossing hybrid maize variety 34P88 with another maize plant. Methods for producing a maize plant containing in its genetic material one or more traits introgressed into 34P88 through backcross conversion and / or transformation, and to the maize seed, plant and plant part produced thereby. This invention relates to the hybrid seed 34P88, the hybrid plant produced from the seed, and variants, mutants, and trivial modifications of hybrid 34P88. This invention further relates to methods for producing maize lines derived from hybrid maize variety 34P88 and to the maize lines derived by the use of those methods.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com