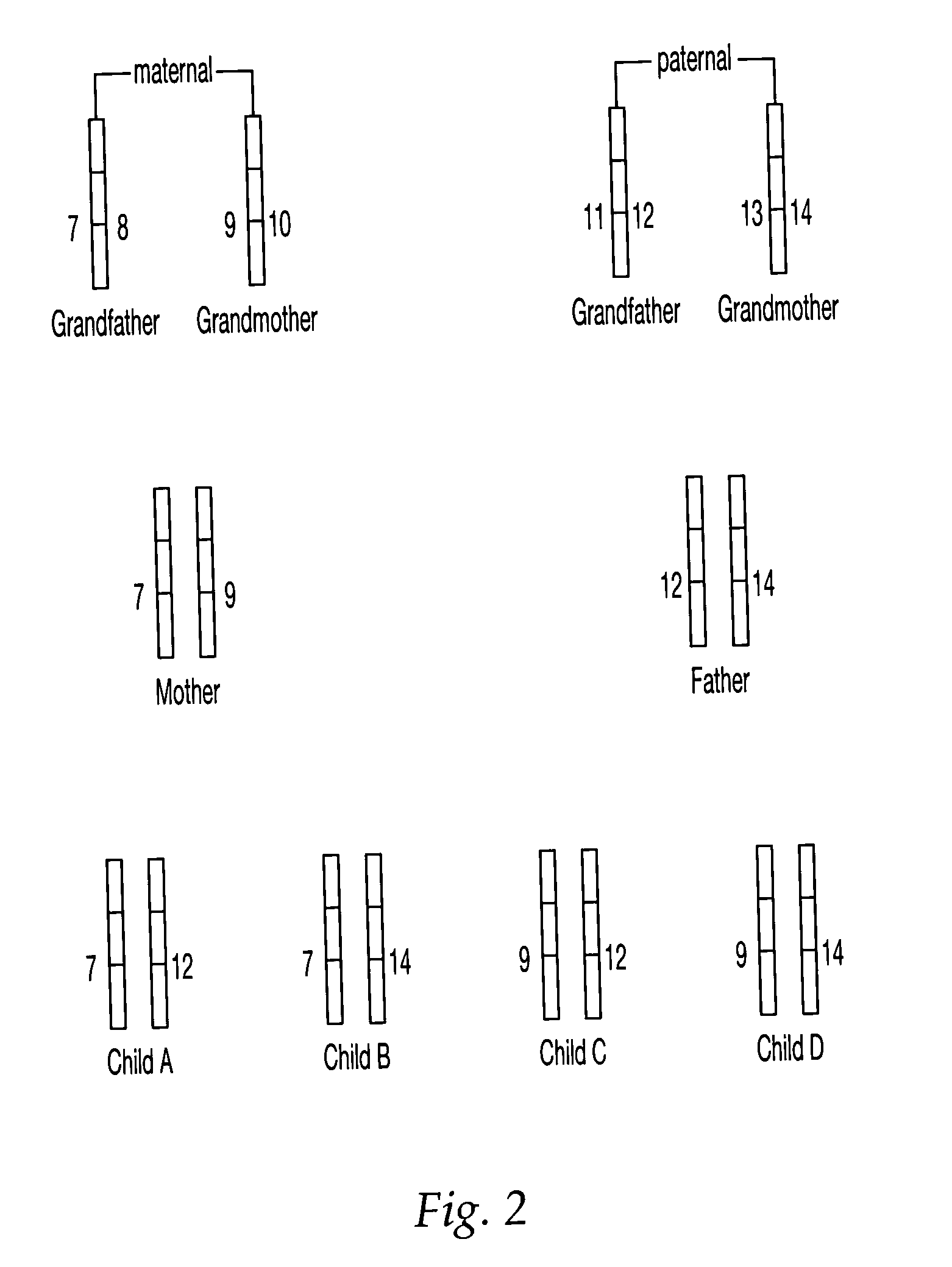Patents
Literature
5370 results about "Genotype" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The genotype is the part of the genetic makeup of a cell, and therefore of any individual, which determines one of its characteristics (phenotype). The term was coined by the Danish botanist, plant physiologist and geneticist Wilhelm Johannsen in 1903.
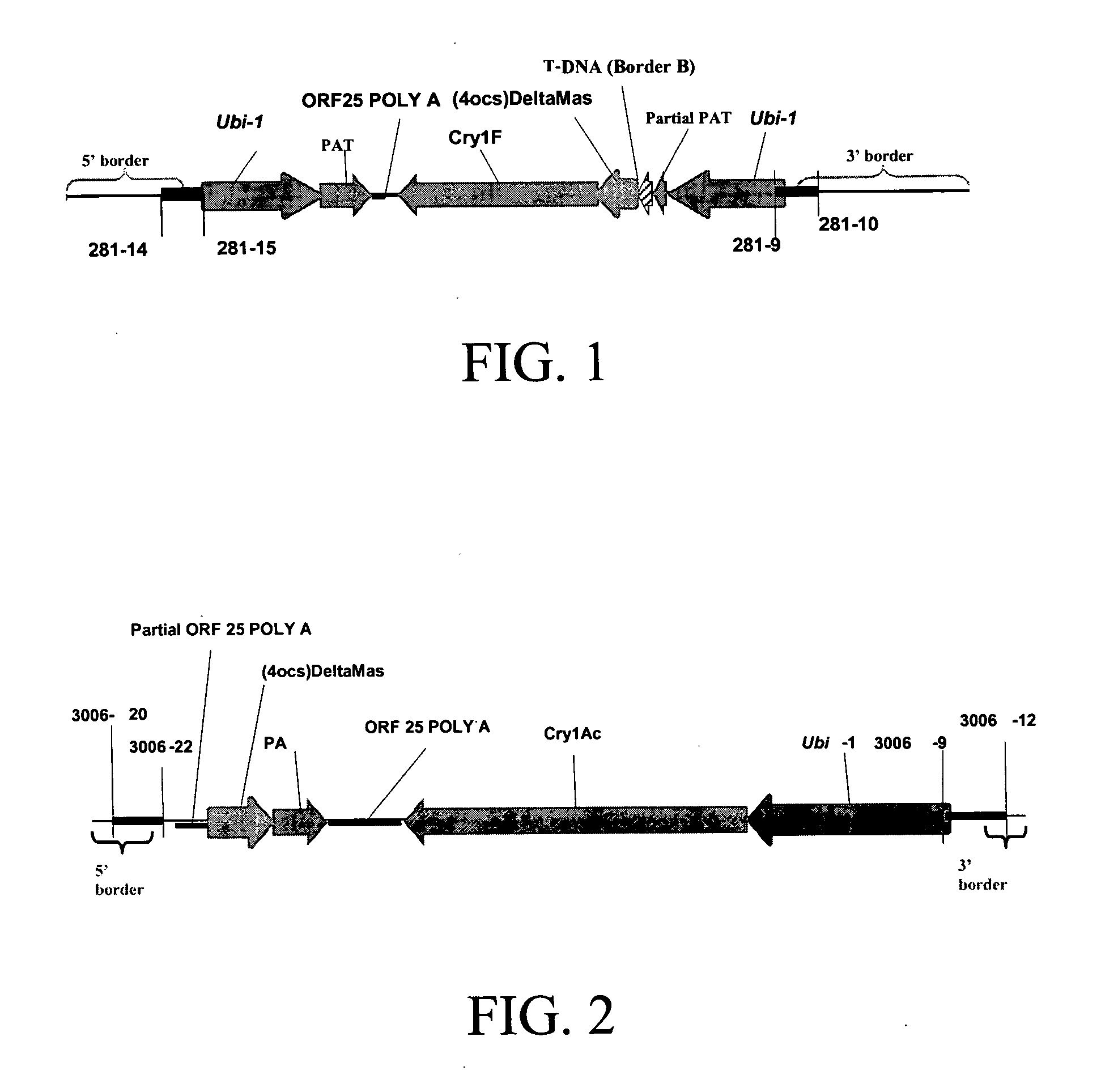
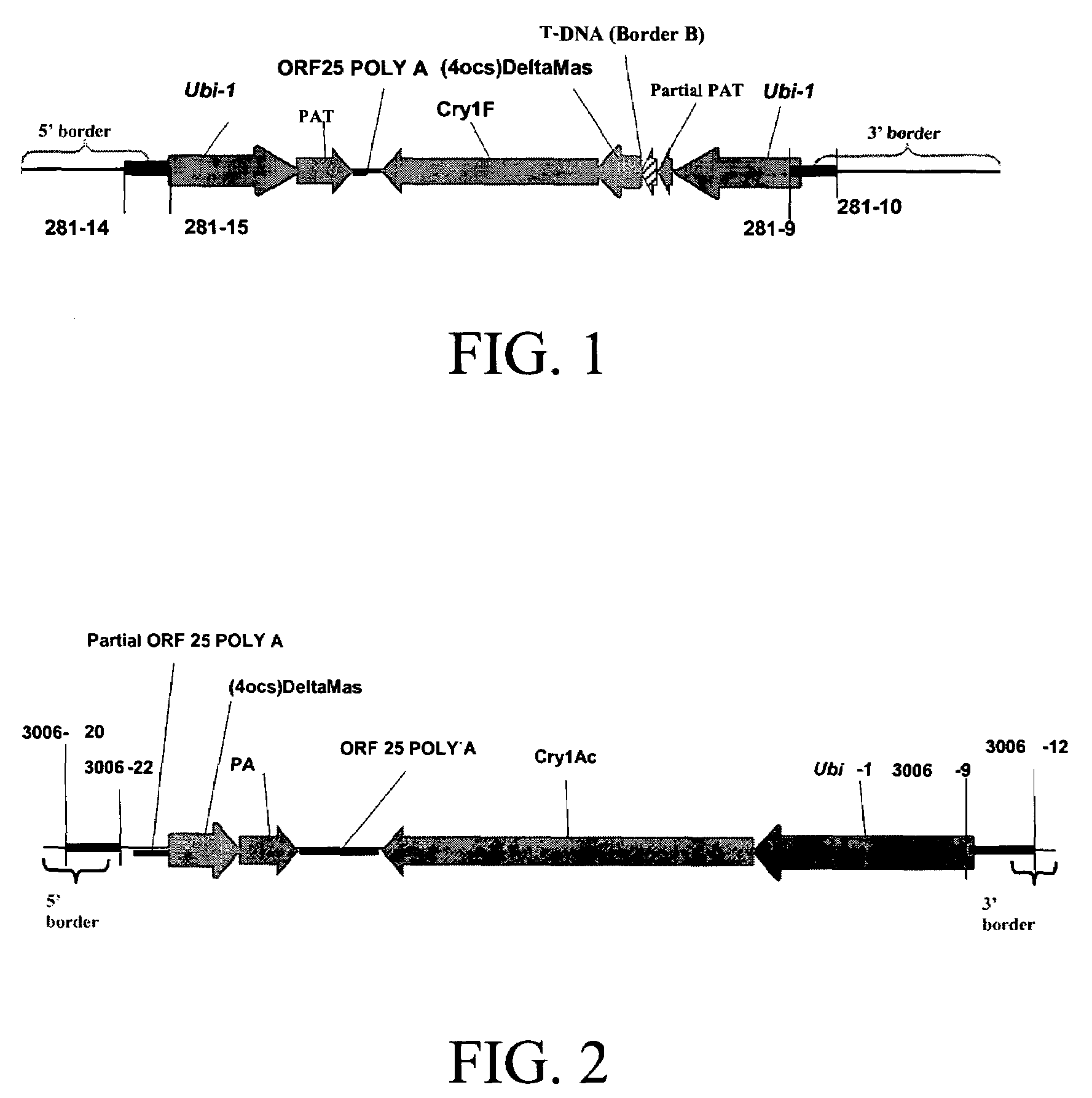
Cry1F and Cry1AC transgenic cotton lines and event-specific identification thereof
This invention relates to plant breeding and the protection of plants from insects. More specifically, this invention includes novel transformation events of cotton plants comprising one or more polynucleotide sequences, as described herein, inserted into specific site(s) within the genome of a cotton cell. In highly preferred embodiments, said polynucleotide sequences encode “stacked” Cry1F and Cry1Ac lepidopteran insect inhibitory proteins. However, the subject invention includes plants having single cry1F or cry1Ac events, as described herein. Additionally, the invention is related to cotton plants derived from that transformation event and to assays for detecting the presence of the event in a sample. More specifically, the present invention provides DNA and related assays for detecting the presence of certain insect-resistance events in cotton. The assays are based on the DNA sequences of recombinant constructs inserted into the cotton genome and of the genomic sequences flanking the insertion sites. These sequences are unique. Based on these insert and border sequences, event-specific primers were generated. PCR analysis demonstrated that these cotton lines can be identified in different cotton genotypes by analysis of the PCR amplicons generated with these event-specific primer sets. Thus, these and other related procedures can be used to uniquely identify these cotton lines. Kits and conditions useful in conducting the assays are also provided. These materials and methods can also be used to assist breeding programs to further develop traits in cotton.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Methods for Non-Invasive Prenatal Ploidy Calling
ActiveUS20120270212A1Fill in the blanksMathematical modelsMicrobiological testing/measurementDistribution patternGenotype
The present disclosure provides methods for determining the ploidy status of a chromosome in a gestating fetus from genotypic data measured from a mixed sample of DNA comprising DNA from both the mother of the fetus and from the fetus, and optionally from genotypic data from the mother and father. The ploidy state is determined by using a joint distribution model to create a plurality of expected allele distributions for different possible fetal ploidy states given the parental genotypic data, and comparing the expected allelic distributions to the pattern of measured allelic distributions measured in the mixed sample, and choosing the ploidy state whose expected allelic distribution pattern most closely matches the observed allelic distribution pattern. The mixed sample of DNA may be preferentially enriched at a plurality of polymorphic loci in a way that minimizes the allelic bias, for example using massively multiplexed targeted PCR.
Owner:NATERA
CICM cells and non-human mammalian embryos prepared by nuclear transfer of a proliferating differentiated cell or its nucleus
InactiveUS6235970B1Simple procedureSimplifying and facilitating procedureNervous disorderMuscular disorderPresent methodNuclear transfer
An improved method of nuclear transfer involving the transplantation of donor differentiated cell nuclei into enucleated oocytes of the same species as the donor cell is provided. The resultant nuclear transfer units are useful for multiplication of genotypes and transgenic genotypes by the production of fetuses and offspring, and for production of isogenic CICM cells, including human isogenic embryonic or stem cells. Production of genetically engineered or transgenic mammalian embryos, fetuses and offspring is facilitated by the present method since the differentiated cell source of the donor nuclei can be genetically modified and clonally propagated.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS AMHERST
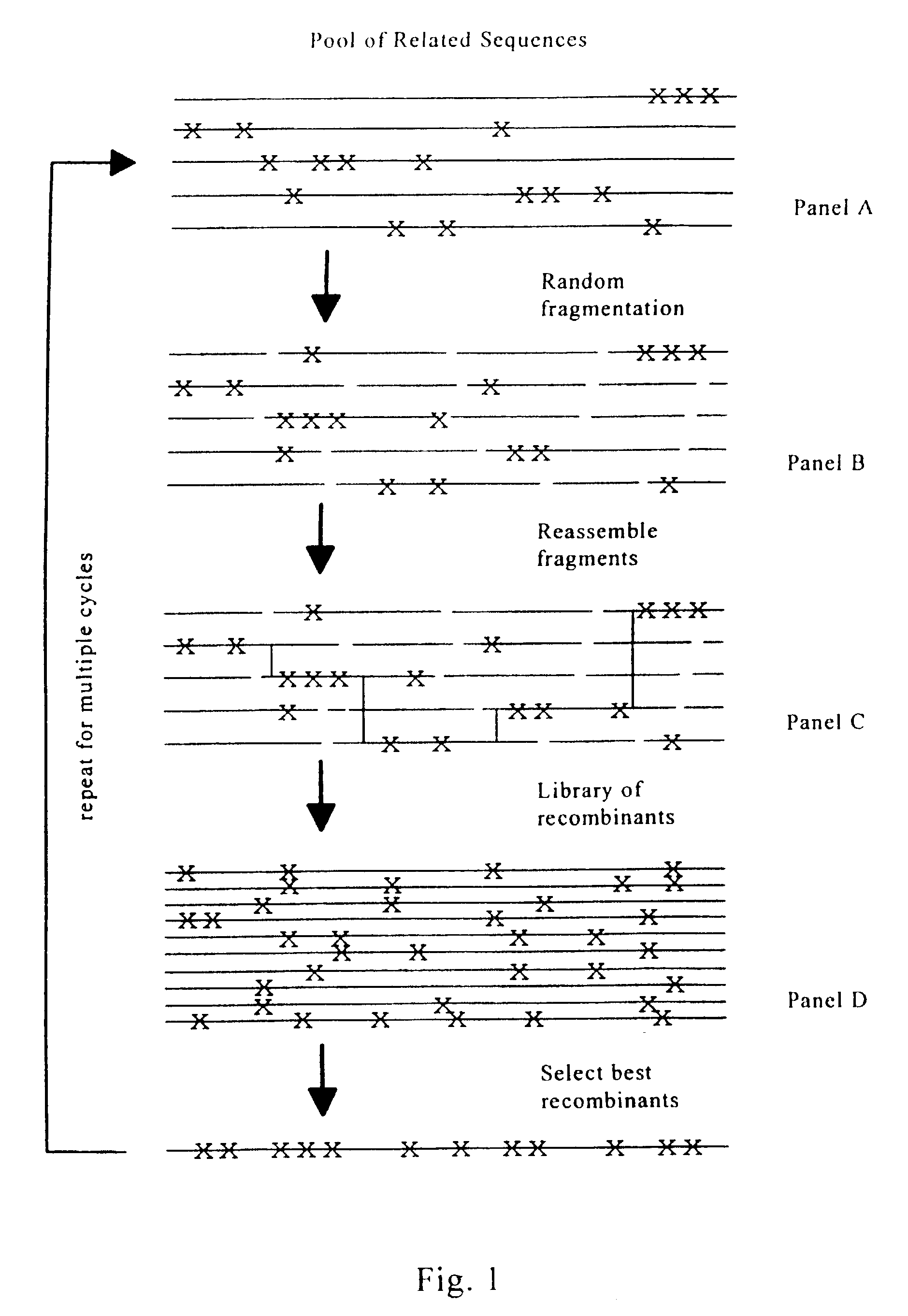
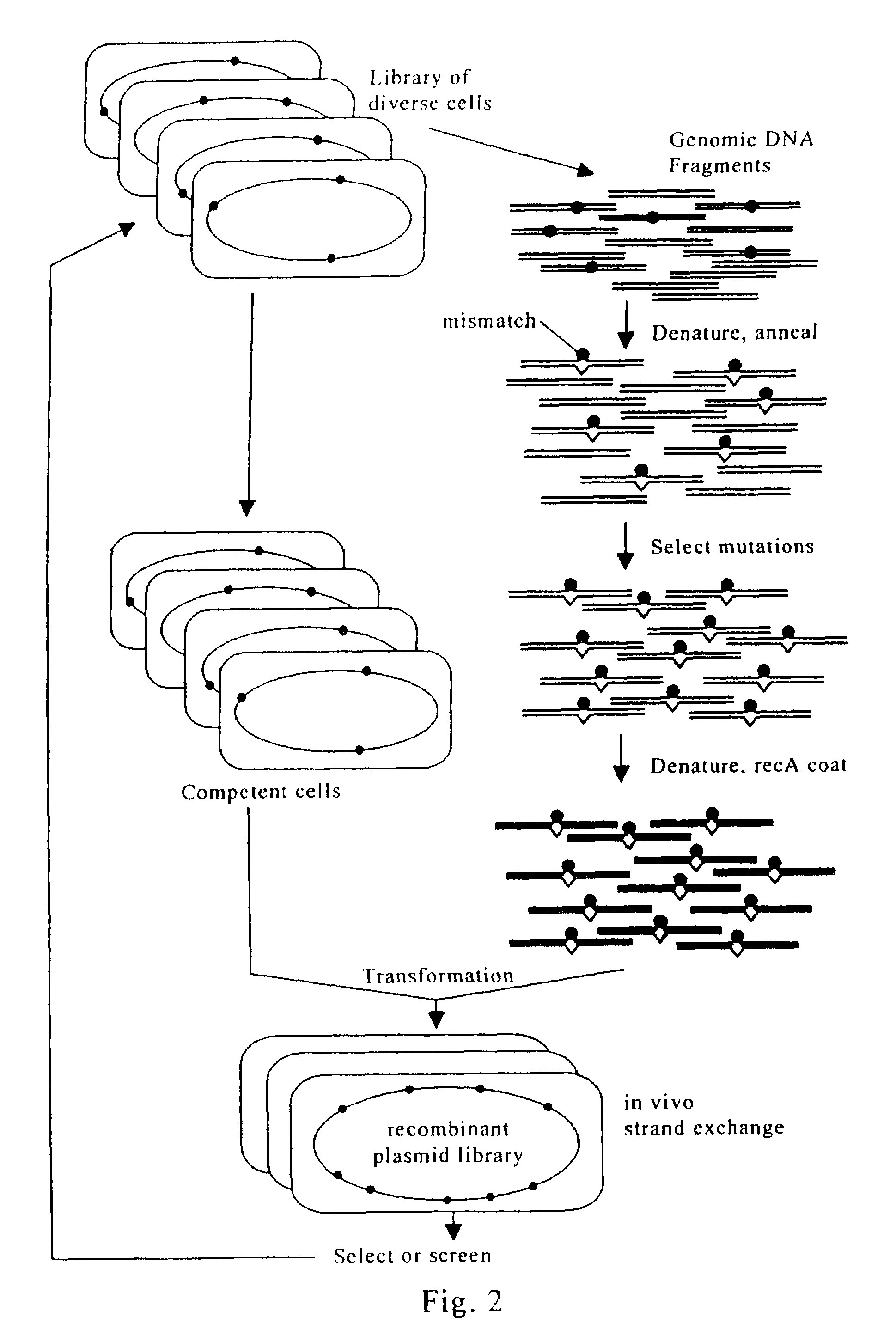
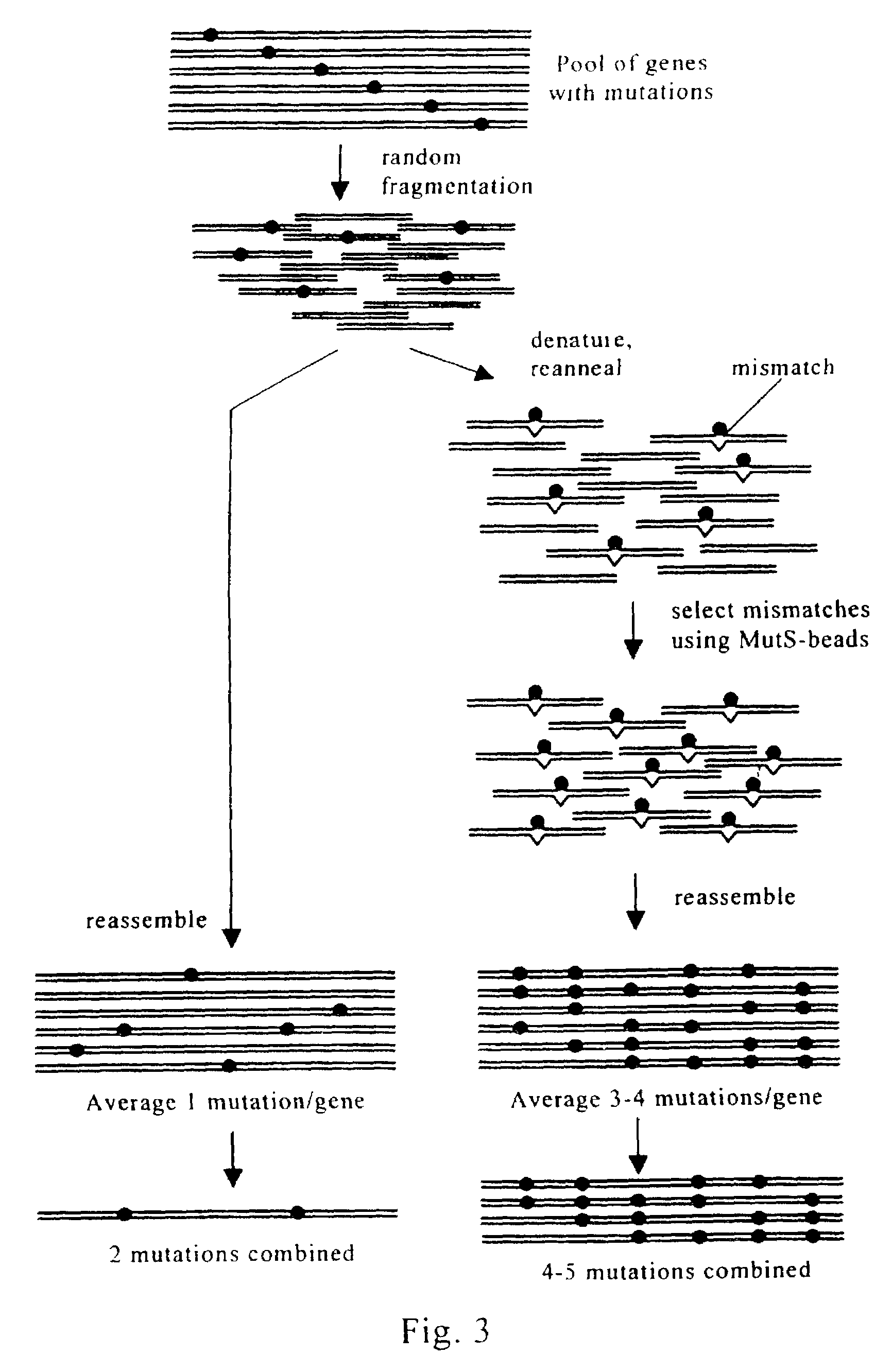
Evolution of whole cells and organisms by recursive sequence recombination
InactiveUS7148054B2Increase diversityFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementMetaboliteSecondary metabolite
The invention provides methods employing iterative cycles of recombination and selection / screening for evolution of whole cells and organisms toward acquisition of desired properties Examples of such properties include enhanced recombinogenicity, genome copy number, and capacity for expression and / or secretion of proteins and secondary metabolites.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
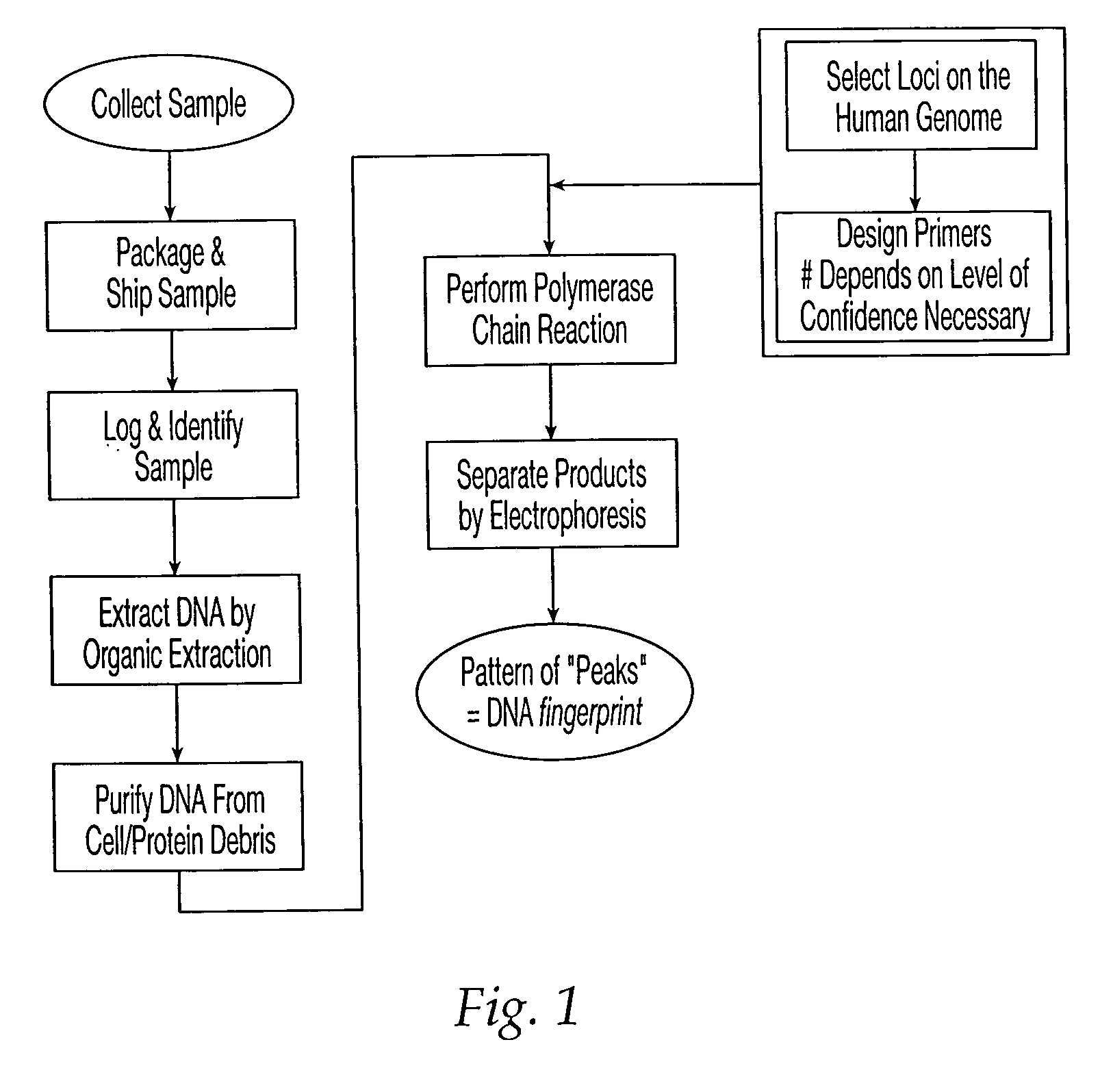
Methods and apparatus for sample tracking
InactiveUS20040157220A1Reduce chanceMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationPrenatal diagnosisGenotype
A method and apparatus are provided for identifying a biological sample obtained during either paternity screening, genetic screening, prenatal diagnosis, presymptomatic diagnosis, diagnosis to detect the presence of a target microorganism carrier detection analysis, forensic chemical analysis, or diagnosis of a subject to determine whether a subject is afflicted with a particular disease or disorder, or is at risk of developing a particular disorder, wherein the result obtained from the analysis is associated with the unique DNA fingerprint biological barcode of the genotype of the subject being analyzed. The methods and apparatus of the invention have application in the fields of diagnostic medicine, disease diagnosis in animals and plants, identification of genetically inherited diseases in humans, family relationship analysis, forensic analysis, and microbial typing.
Owner:HANDYLAB
Prevention and treatment of HCV infection employing antibodies that inhibit the interaction of HCV virions with their receptor
Human monoclonal antibodies binding to epitopes common to type 1 and 2 HCV are provided, as well as conformationally conserved HCV E2 2a and 2b proteins. Compositions comprising the antibodies find use in diagnosis and therapy. The antibodies recognize conformational epitopes that are conserved across multiple genotypes of HCV. Thus the antibodies have the potential to be useful in the prevention and treatment of the majority of HCV infections. A subset of the antibodies (CBH-2, CBH-5, CBH-7, CBH-8C, CBH-8E, and CBH-11) have the ability to prevent the binding of HCV E2 proteins of multiple genotypes to human CD81, a possible co-receptor for HCV infection. A subset of the antibodies (CBH-2 and CBH-5) have been shown to inhibit the binding of HCV virions (as opposed to purified E2 protein) to human CD81. A further subset of the antibodies (CBH-4D, CBH4B, CBH-8C, and CBH-9) have been shown to prevent HCV envelope mediated fusion using an HCV psuedotype system.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
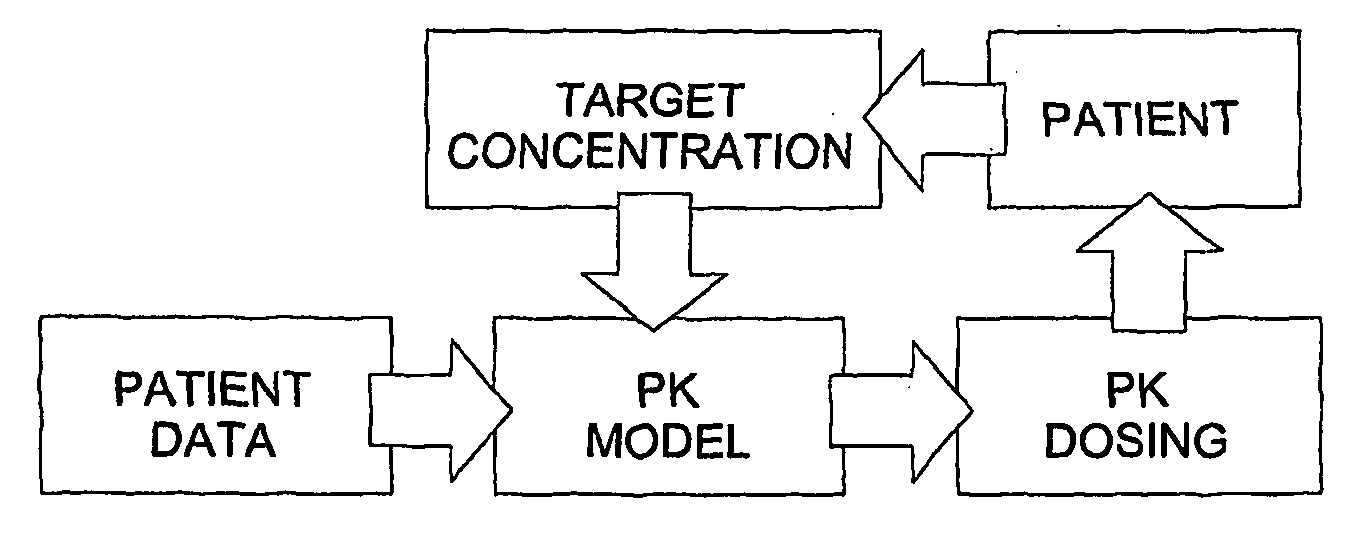
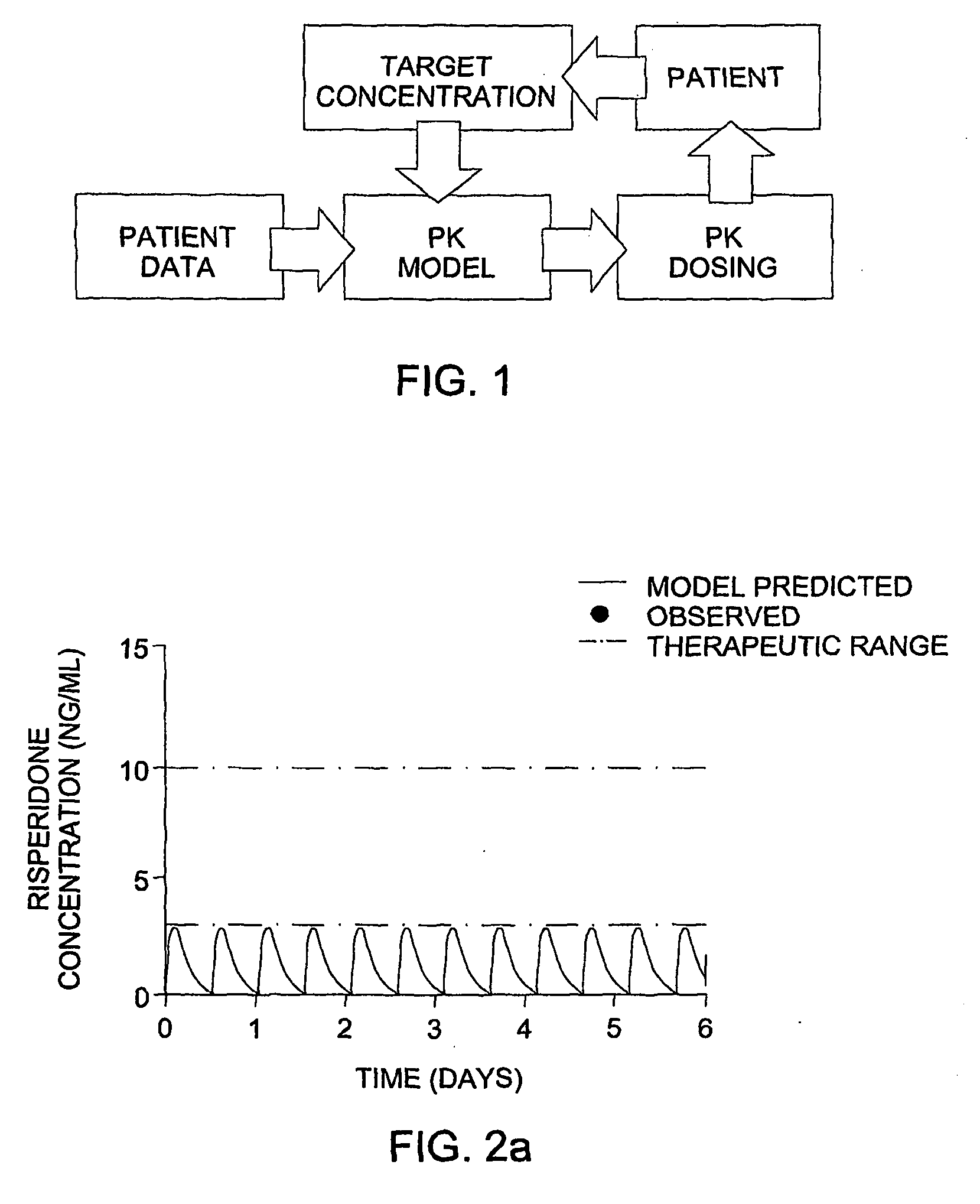
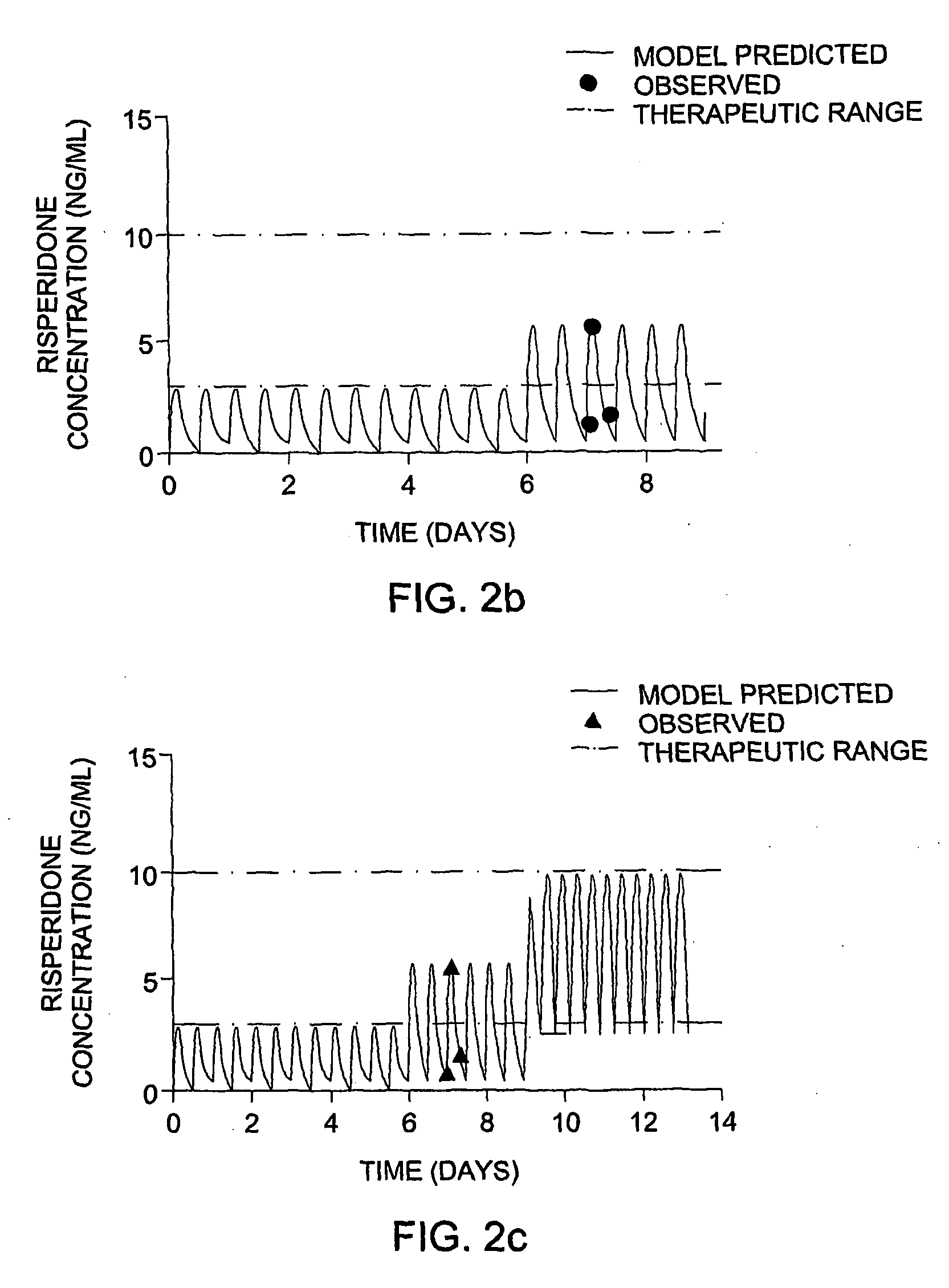
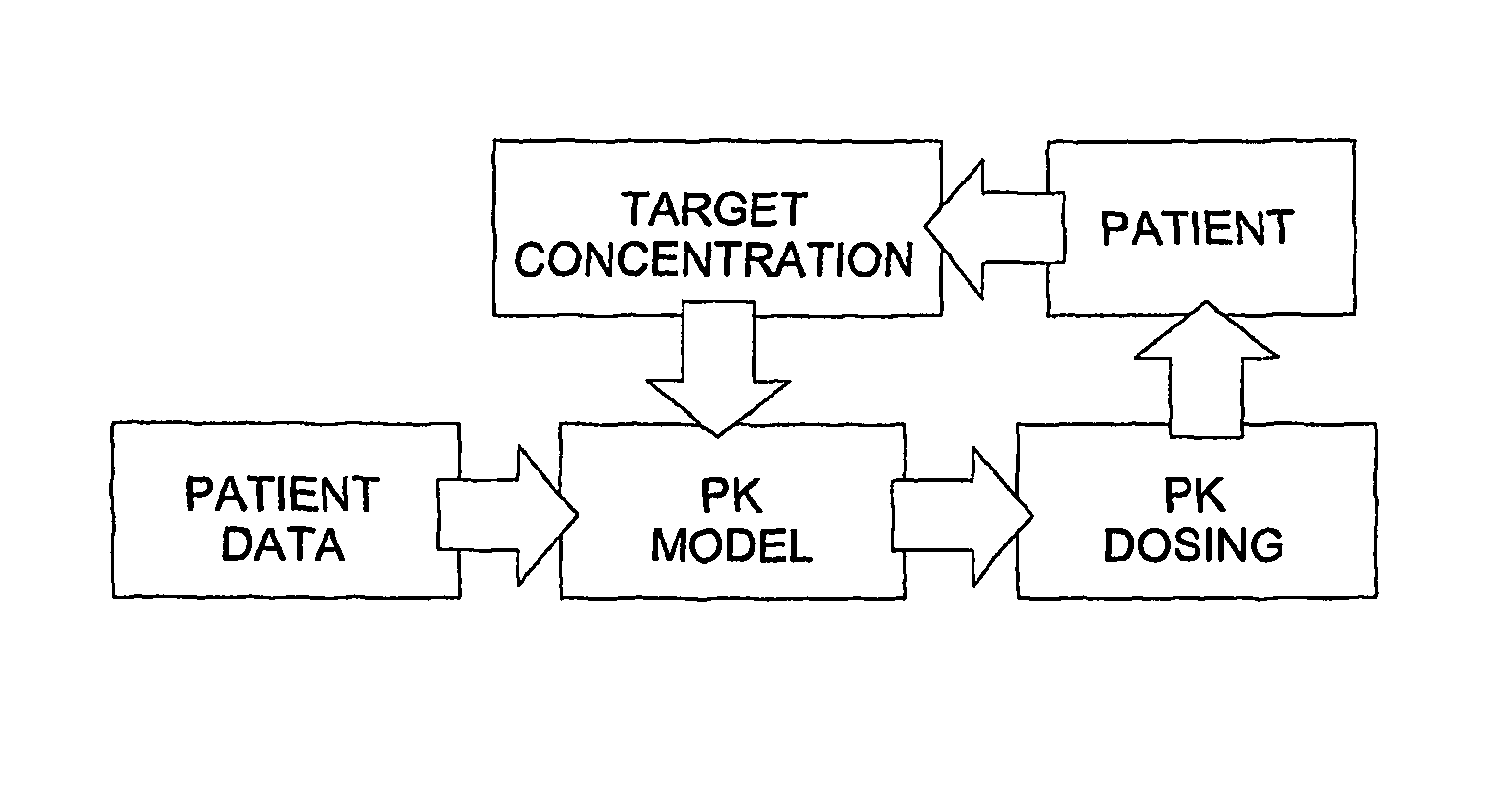
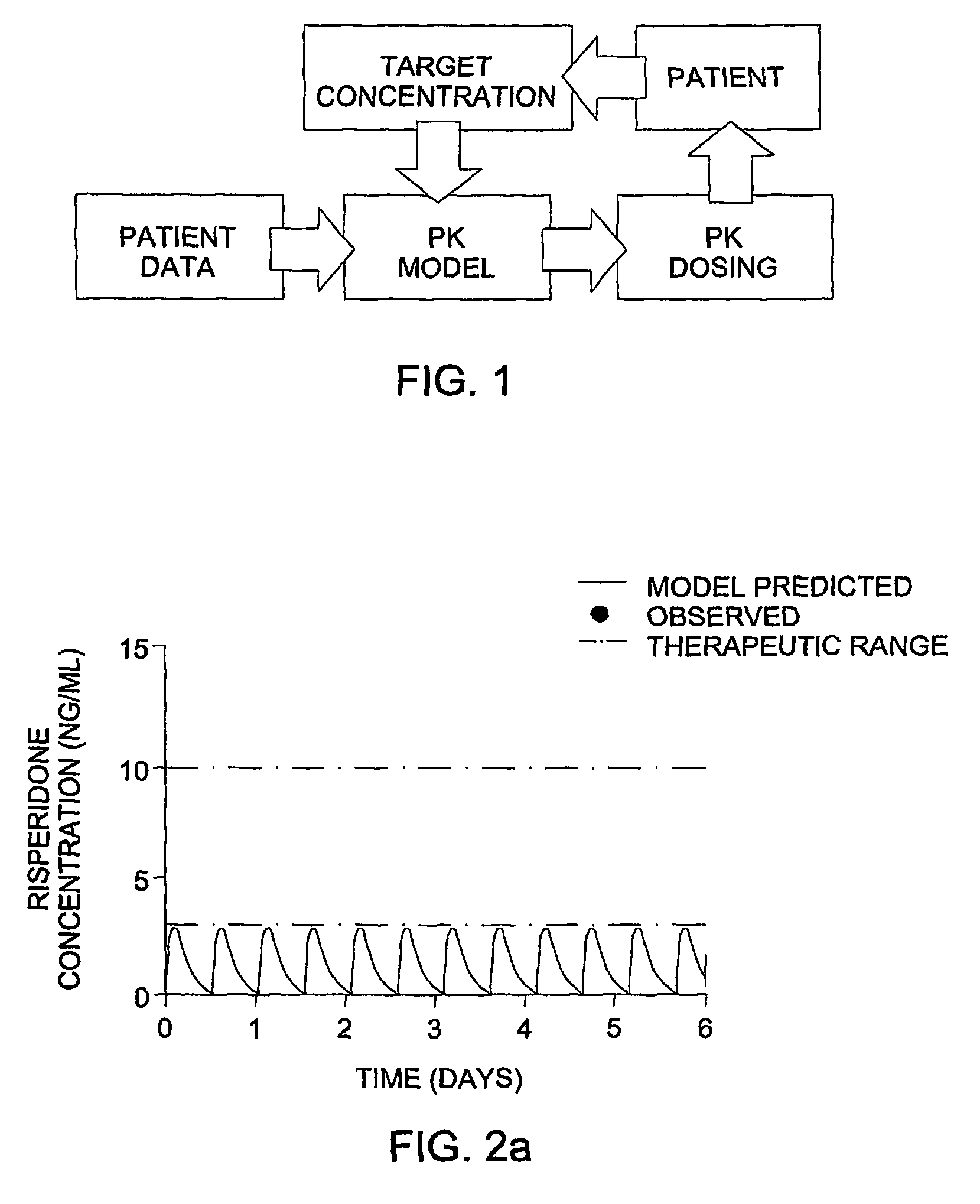
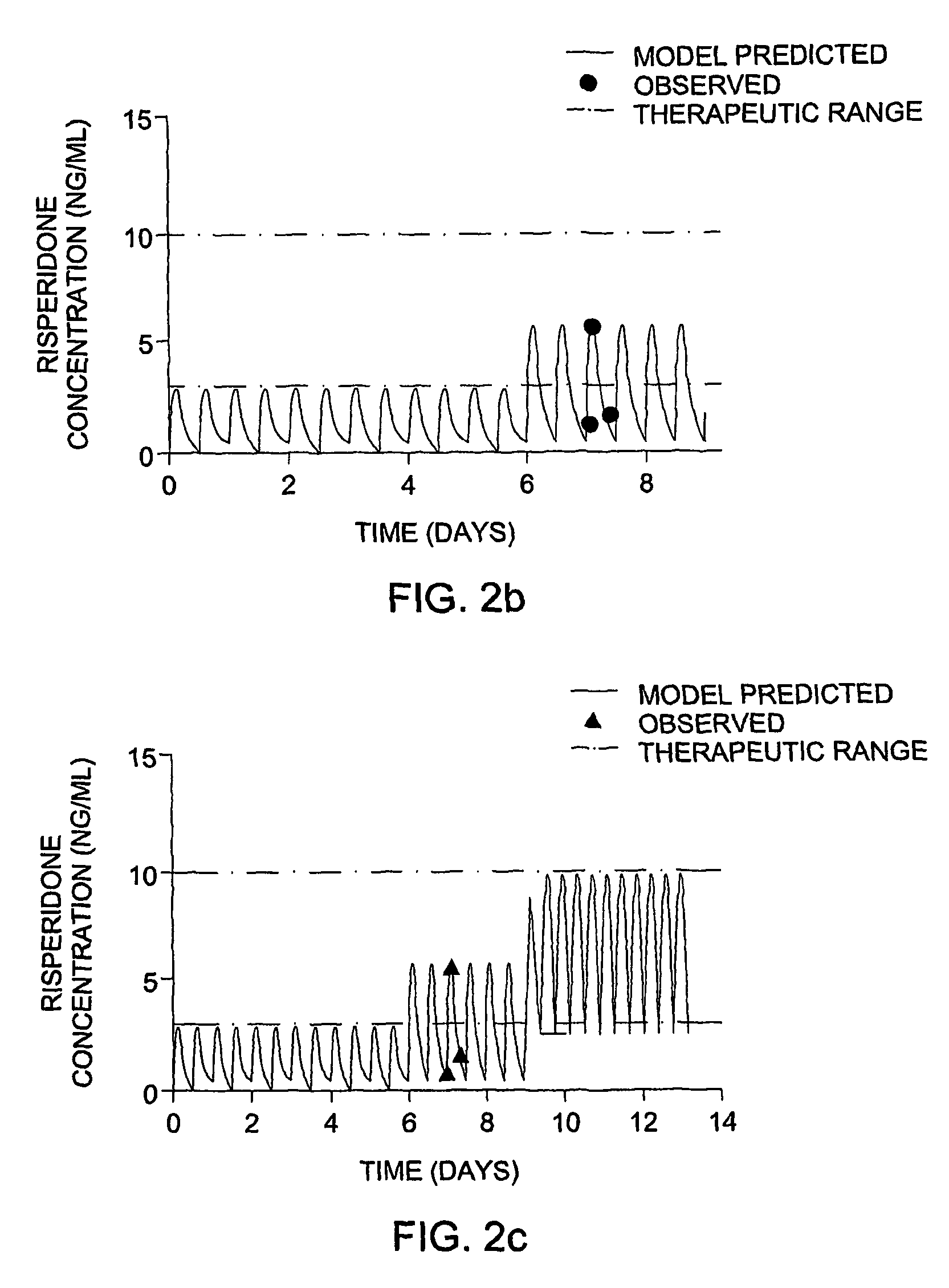
Optimization and Individualization of Medication Selection and Dosing
ActiveUS20090171697A1Easy to understandEasy to recommendationDrug and medicationsBiostatisticsPersonalizationDosing regimen
The invention provides population models, methods, and algorithms for targeting a dosing regimen or compound selection to an individual patient. The methods and algorithms of the invention utilize population models that incorporate genotype information for genes encoding drug metabolizing enzymes for one or more compounds of interest. The methods allow integration of genotype information for one or more genes encoding a drug metabolizing enzyme, particularly a cytochrome P450 gene with patient data. The methods allow integration of genotype information and the effect of one or more compounds on one or more drug metabolizing enzymes. The methods allow iterative feedback of drug metabolizing data obtained from a patient into the process of generating a dosage regimen recommendation for a compound of interest for an individual patient.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENT CINCINNATI
Cry1F and Cry1Ac transgenic cotton lines and event-specific identification thereof
This invention relates to plant breeding and the protection of plants from insects. More specifically, this invention includes novel transformation events of cotton plants comprising one or more polynucleotide sequences, as described herein, inserted into specific site(s) within the genome of a cotton cell. In highly preferred embodiments, said polynucleotide sequences encode “stacked” Cry1F and Cry1Ac lepidopteran insect inhibitory proteins. However, the subject invention includes plants having single cry1F or cry1Ac events, as described herein. Additionally, the invention is related to cotton plants derived from that transformation event and to assays for detecting the presence of the event in a sample. More specifically, the present invention provides DNA and related assays for detecting the presence of certain insect-resistance events in cotton. The assays are based on the DNA sequences of recombinant constructs inserted into the cotton genome and of the genomic sequences flanking the insertion sites. These sequences are unique. Based on these insert and border sequences, event-specific primers were generated. PCR analysis demonstrated that these cotton lines can be identified in different cotton genotypes by analysis of the PCR amplicons generated with these event-specific primer sets. Thus, these and other related procedures can be used to uniquely identify these cotton lines. Kits and conditions useful in conducting the assays are also provided. These materials and methods can also be used to assist breeding programs to further develop traits in cotton.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Immunotherapy Regimes Dependent On APOE Status
InactiveUS20090155256A1Improve securityReducing brain volume declineNervous disorderData processing applicationsDiseaseGenotype
The invention provides methods of immunotherapy of Alzheimer's and similar diseases in which the regime administered to a patient depends on the ApoE genotype of the patient.
Owner:WYETH LLC +1
Cloning pigs using donor nuclei from non-quiescent differentiated cells
InactiveUS6235969B1Superior genotypes of pigsSpeed up genetic progressNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsBiotechnologyPresent method
An improved method of nuclear transfer involving the transplantation of donor differentiated pig cell nuclei into enucleated pig oocytes is provided. The resultant nuclear transfer units are useful for multiplication of genotypes and transgenic genotypes by the production of fetuses and offspring. Production of genetically engineered or transgenic pig embryos, fetuses and offspring is facilitated by the present method since the differentiated cell source of the donor nuclei can be genetically modified and clonally propagated.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS UNIV OF
Method and System for Discovering Ancestors using Genomic and Genealogic Data
InactiveUS20170213127A1Reduced travel tendencyReduce in quantityData visualisationBiostatisticsCommon ancestryGenotype
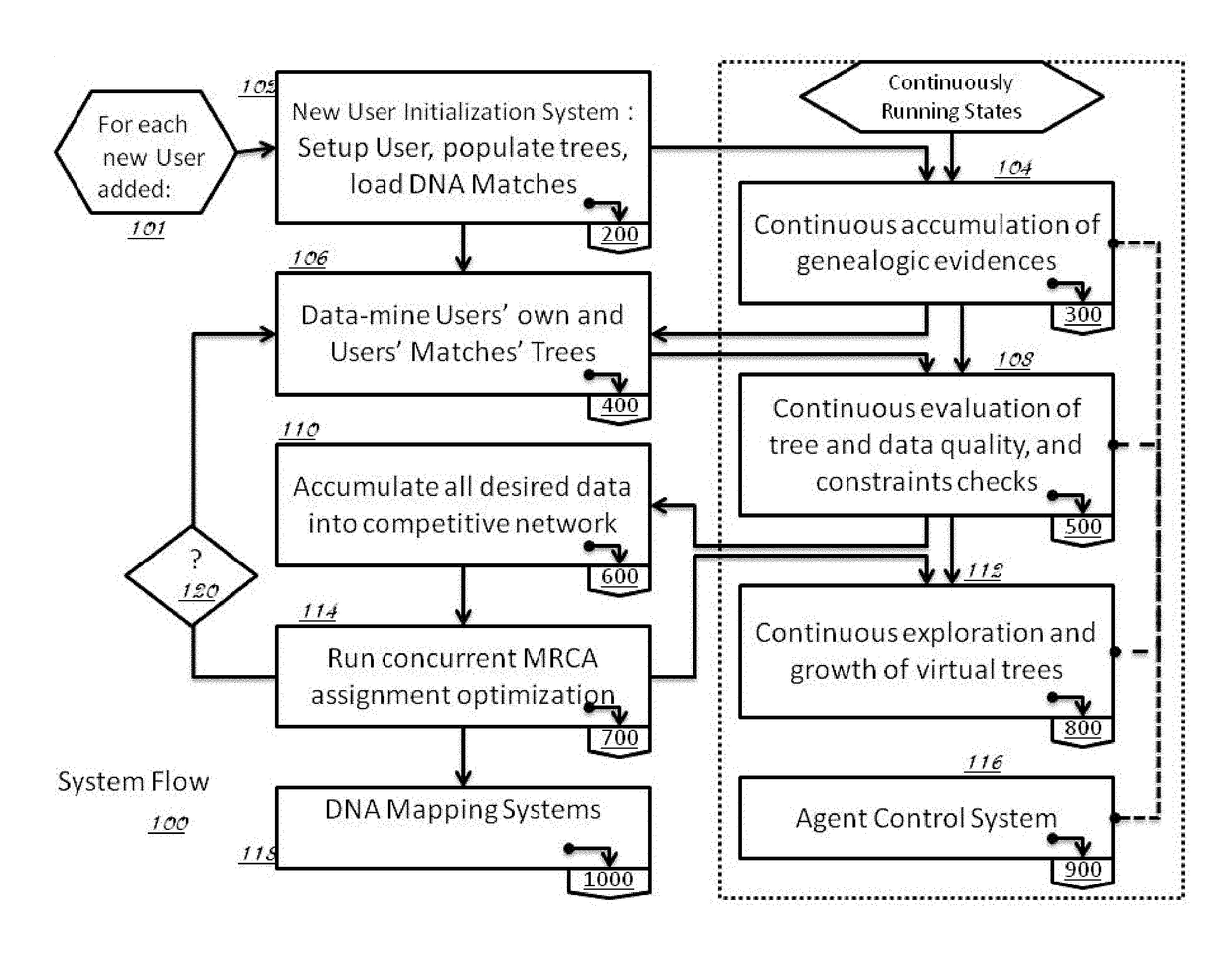
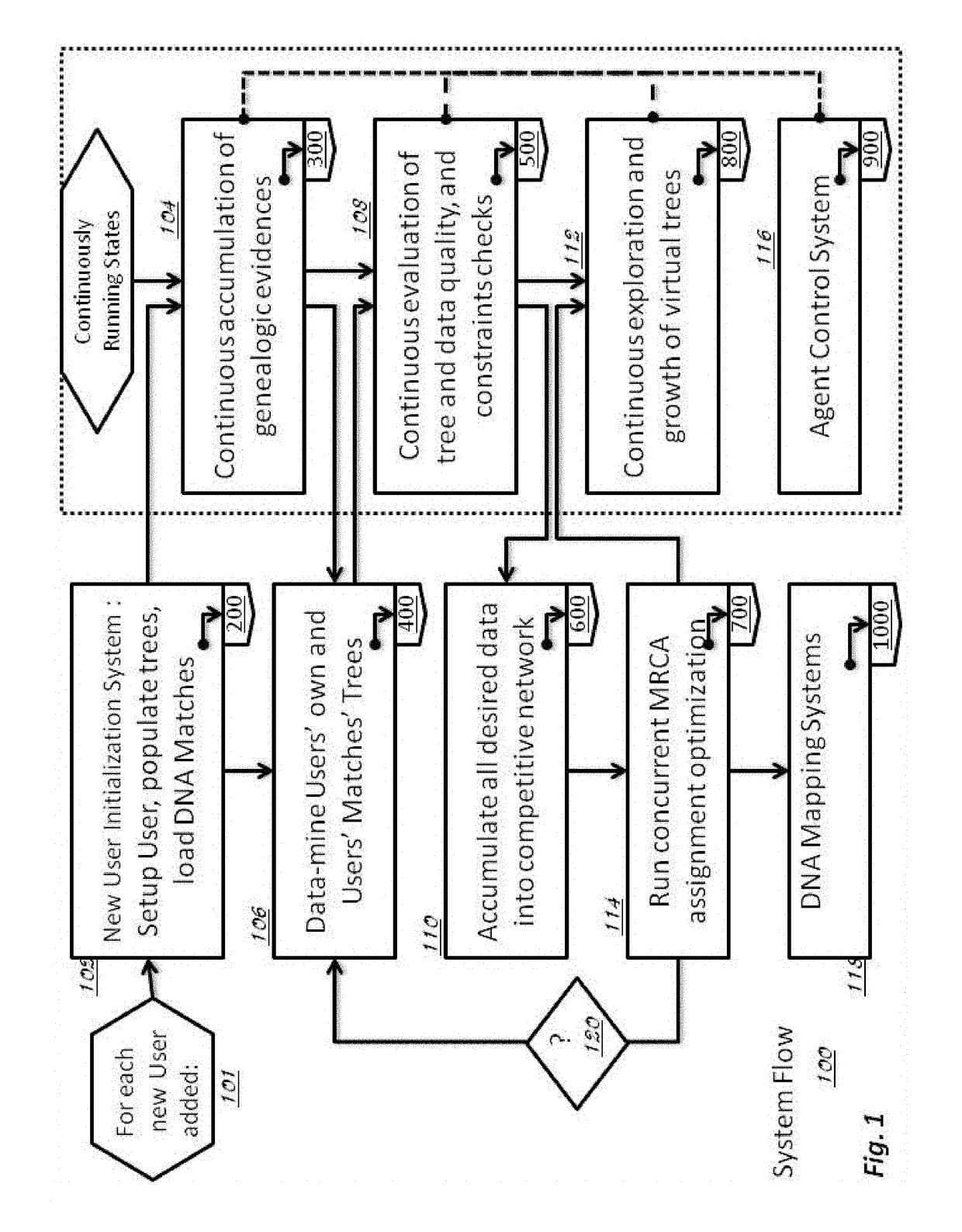
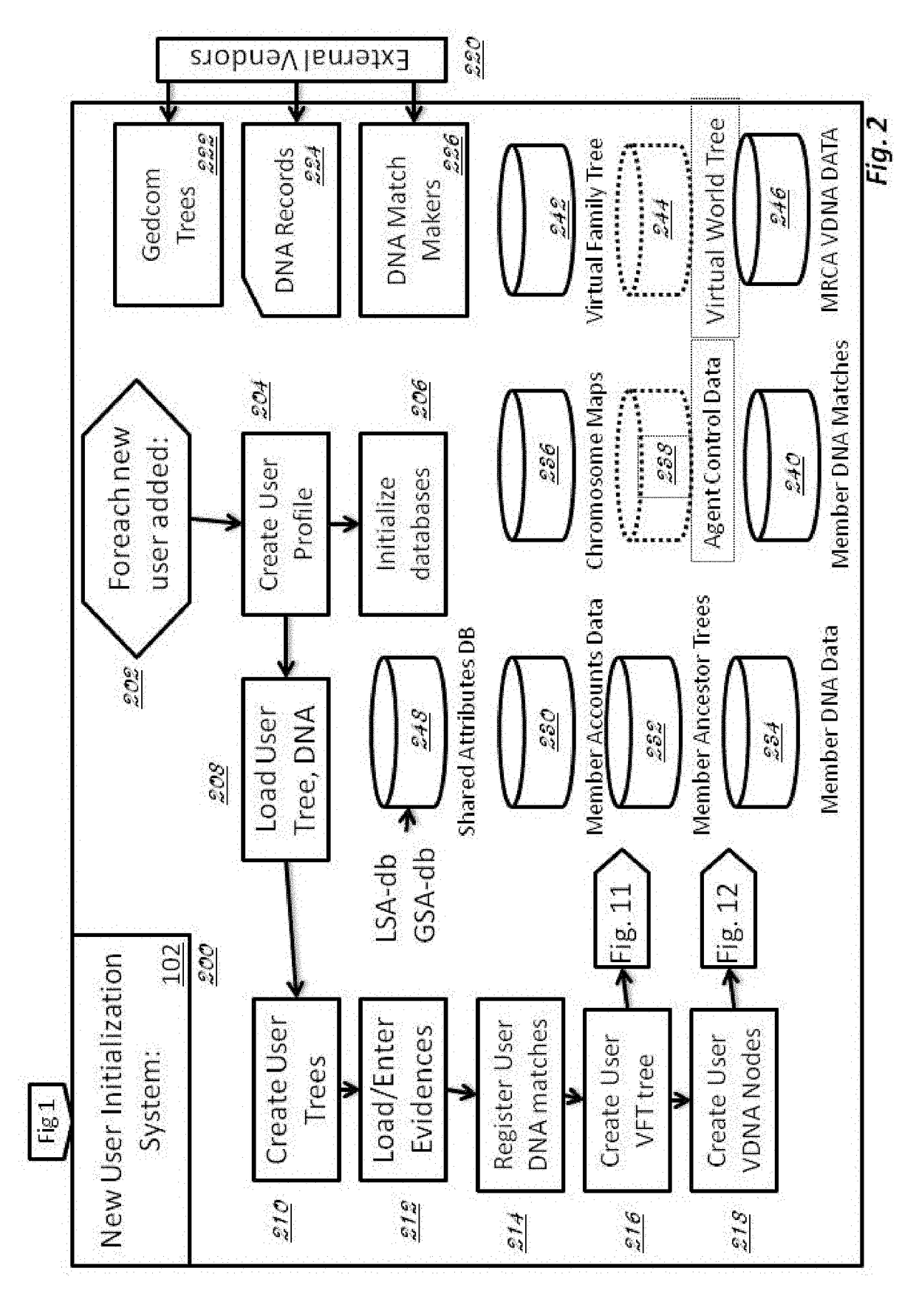
Described invention and its embodiments, in part, facilitate discovery of ‘Most Recent Common Ancestors’ in the family trees between a massive plurality of individuals who have been predicted to be related according to amount of deoxyribonucleic acids (DNA) shared as determined from a plurality of 3rd party genome sequencing and matching systems. This facilitation is enabled through a holistic set of distributed software Agents running, in part, a plurality of cooperating Machine Learning systems, such as smart evolutionary algorithms, custom classification algorithms, cluster analysis and geo-temporal proximity analysis, which in part, enable and rely on a system of Knowledge Management applied to manually input and data-mined evidences and hierarchical clusters, quality metrics, fuzzy logic constraints and Bayesian network inspired inference sharing spanning across and between all data available on personal family trees or system created virtual trees, and employing all available data regarding the genome-matching results of Users associated to those trees, and all available historical data influencing the subjects in the trees, which are represented in a form of Competitive Learning network. Derivative results of this system include, in part, automated clustering and association of phenotypes to genotypes, automated recreation of ancestor partial genomes from accumulated DNA from triangulations and the traits correlated to that DNA, and a system of cognitive computing based on distributed neural networks with mobile Agents mediating activation according to connection weights.
Owner:DUNCAN MATTHEW CHARLES
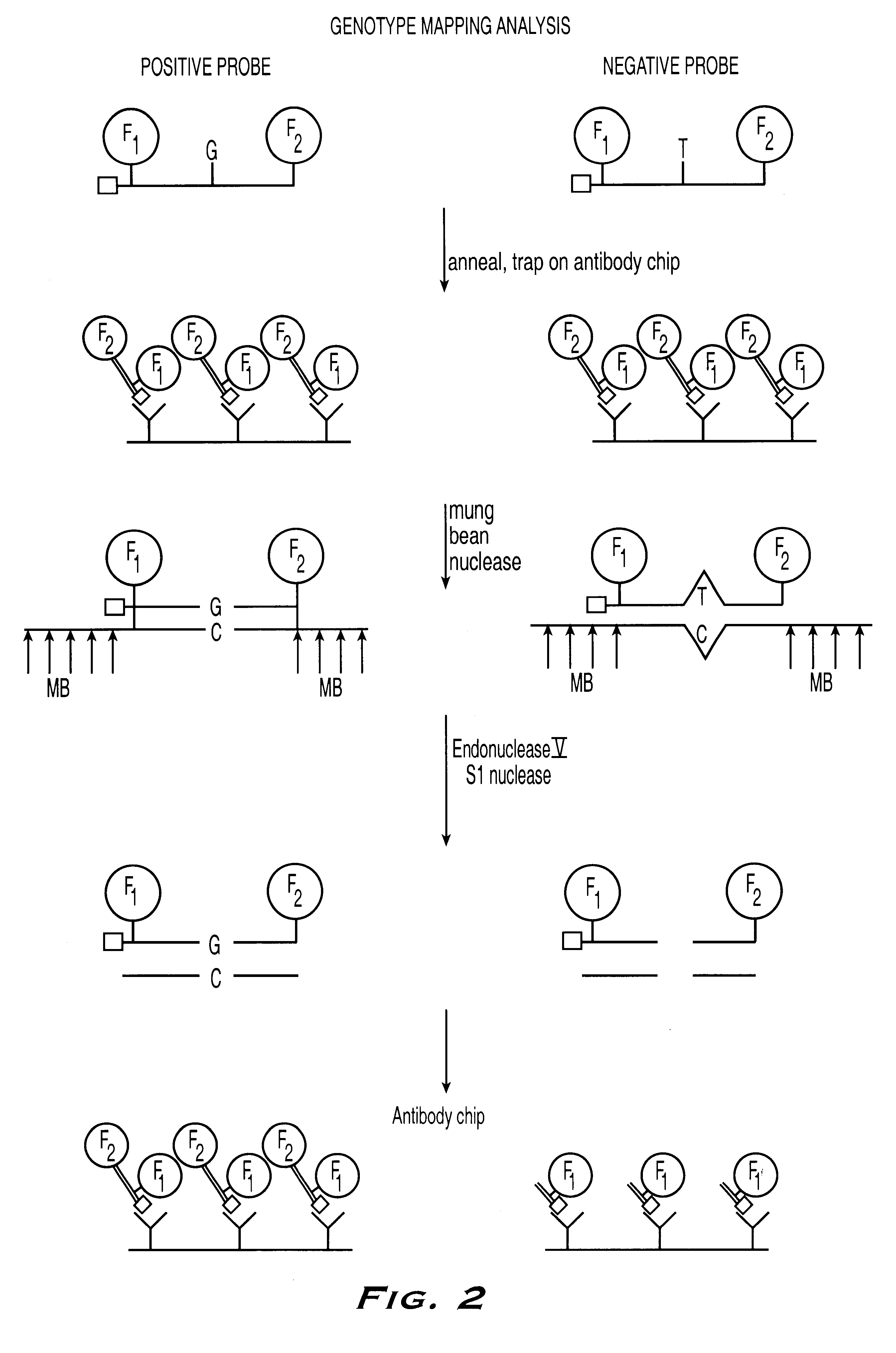
Methods for detection of nucleic acid polymorphisms using peptide-labeled oligonucleotides and antibody arrays
InactiveUS6403309B1Improve efficiencyMinimal amountBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGenotypeExpression gene
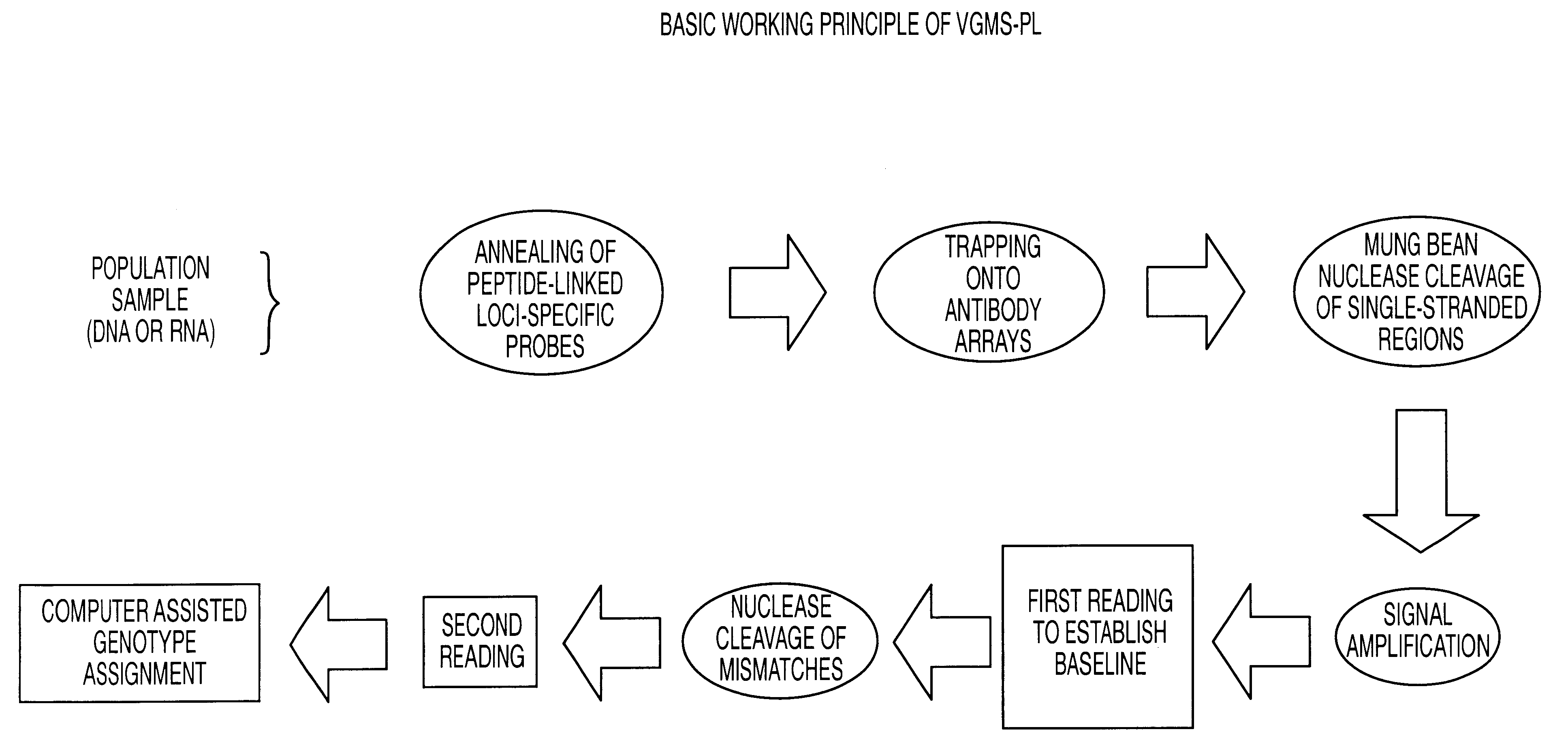
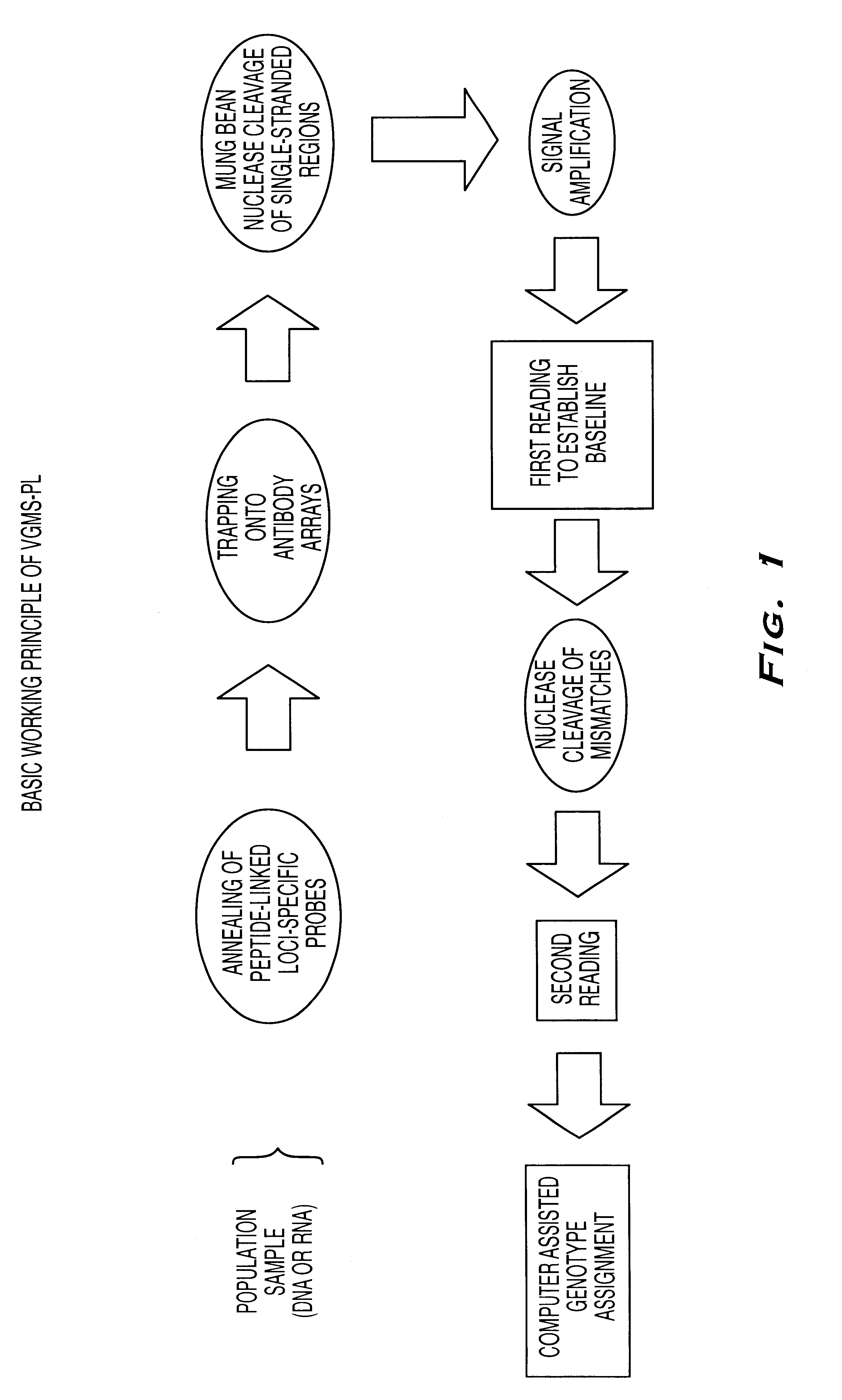
The present invention is directed to methods and compositions for use in screening nucleic acid populations for nucleic acid polymorphisms. The methods, referred to generally as ValiGeneSM Mutation Screening, Peptide-Linked (VGMS-PL) methods, are specifically designed for high-throughput genotype mapping and gene expression analysis of animal and plant nucleic acids without requiring a PCR amplification step. In particular, the methods of the invention utilize oligonucleotide probes labeled with distinguishable and identifiable peptide tags, that are captured on addressable antibody arrays.
Owner:VALIGEN US
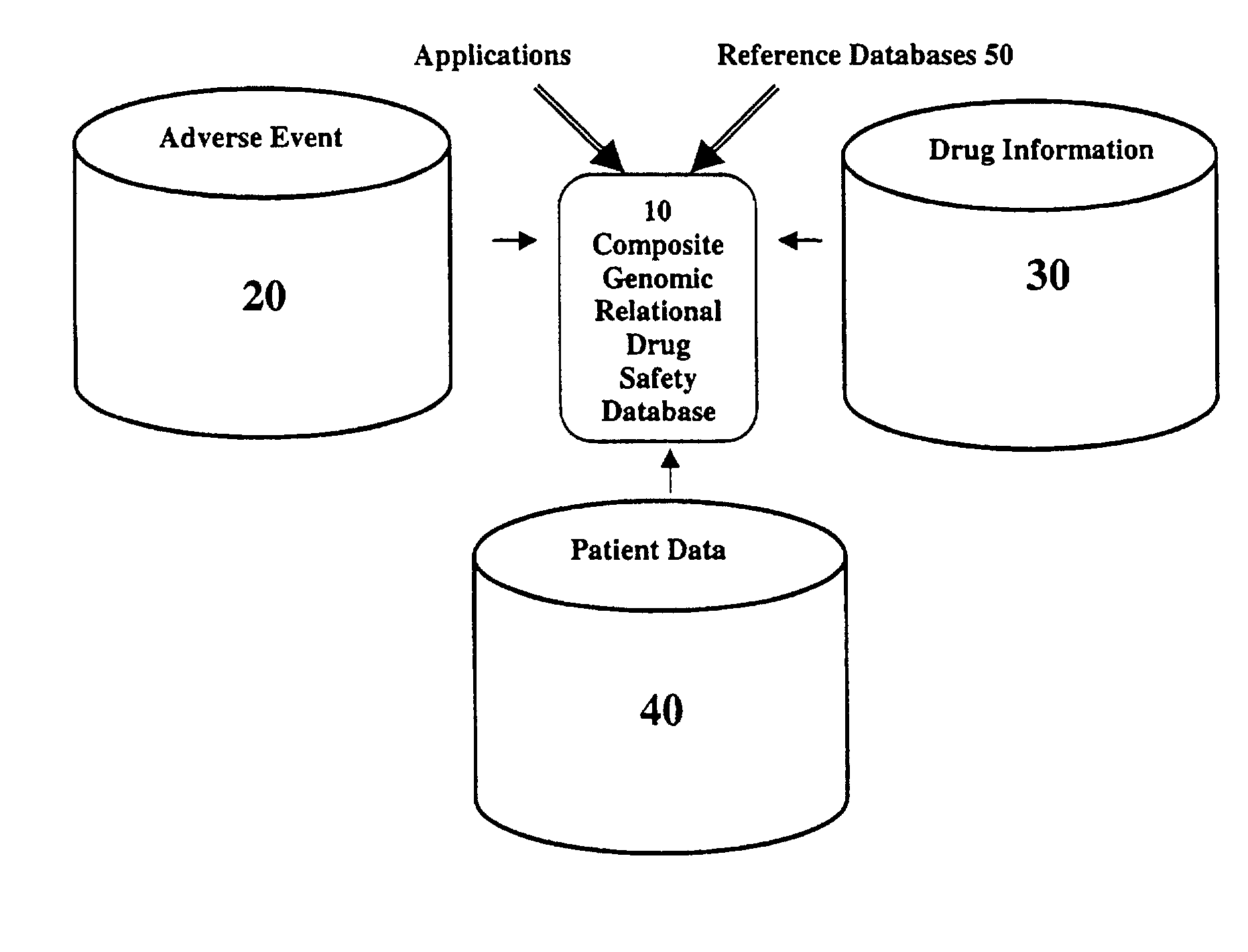
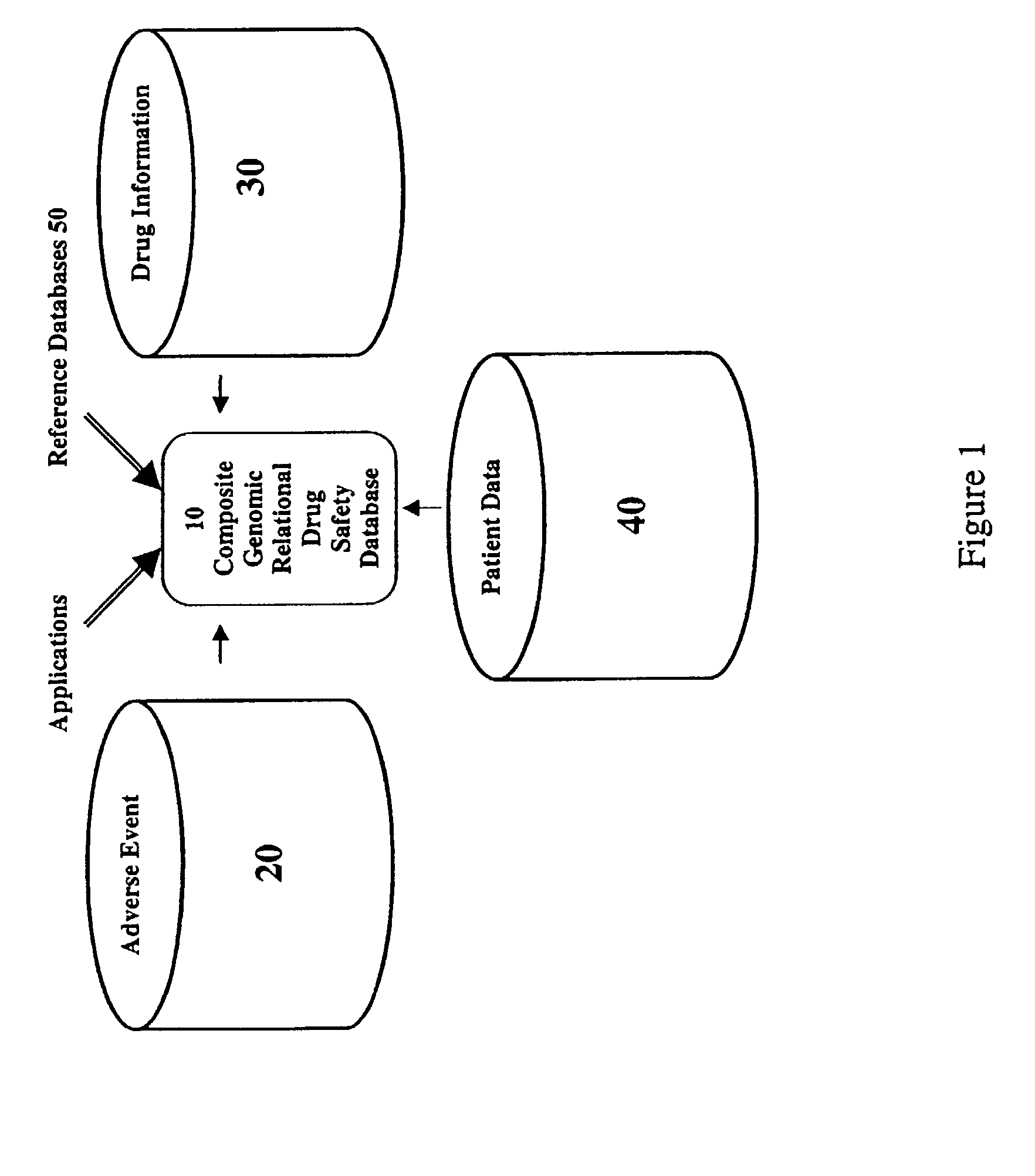
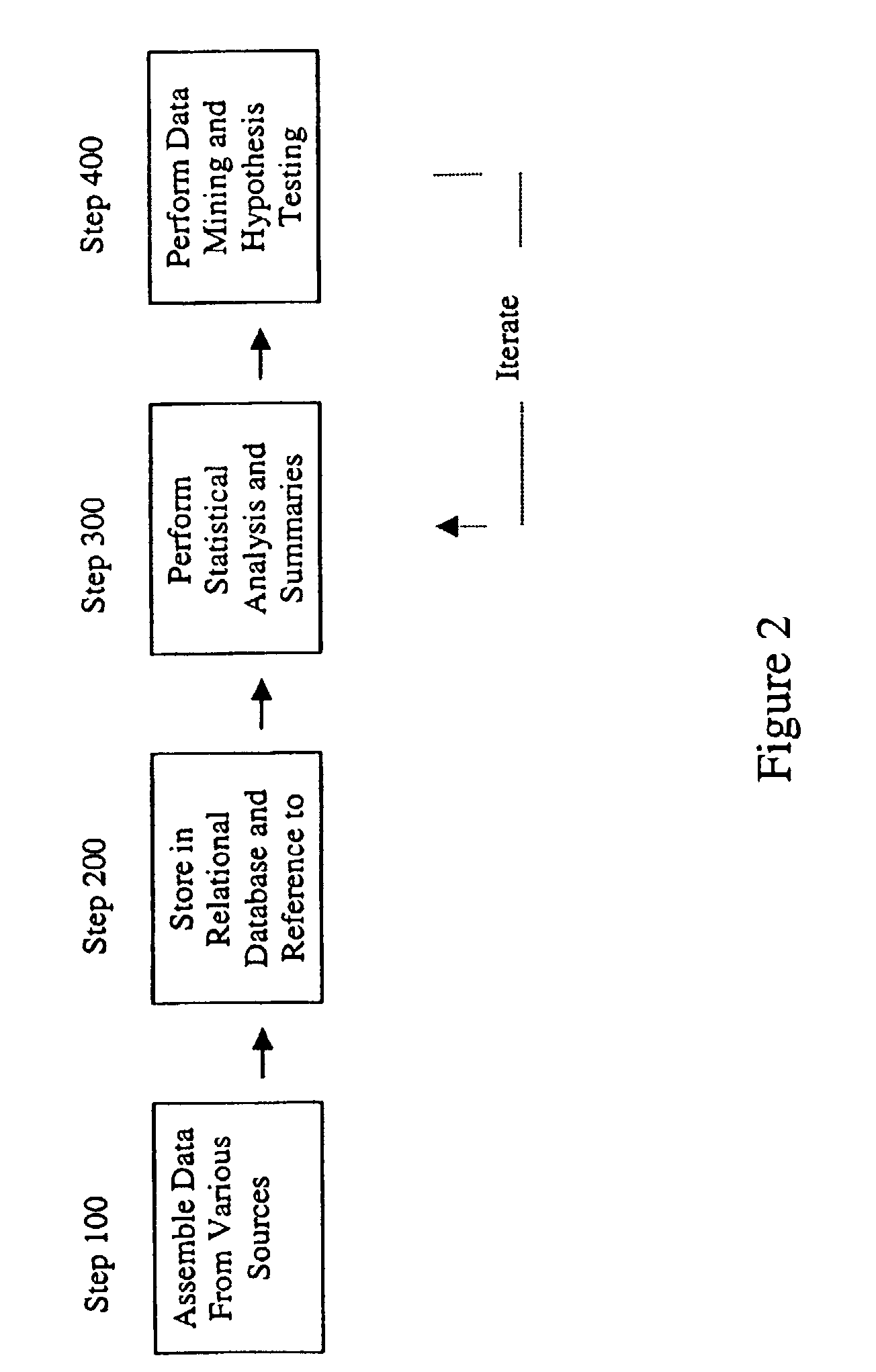
Method and system for the analysis and association of patient-specific and population-based genomic data with drug safety adverse event data
ActiveUS7461006B2Risk of adverse drug reactionIncreased and decreased chanceBiostatisticsComputer-assisted medical data acquisitionPatient characteristicsGenomic DNA
A method for assessing and analyzing one or more drugs, adverse effects and associated risks, and patient characteristics resulting from the use of at least drug of interest is disclosed. The method comprises the steps of selecting one or more cases for analysis, said cases describing the behavior between at least one drug of interest and a patient genotype; profiling statistically derived values from multiple cases related to the safety of the at least one drug, wherein at least one filter is employed for deriving said values; at least one data mining engine; and an output device for displaying the analytic results from the data mining engine. A system for performing the method is likewise disclosed.
Owner:DRUGLOGIC
Method for identifying polymorphic markers in a population
InactiveUS6799122B2Microbiological testing/measurementCharacter and pattern recognitionGenomic DNAGenotype
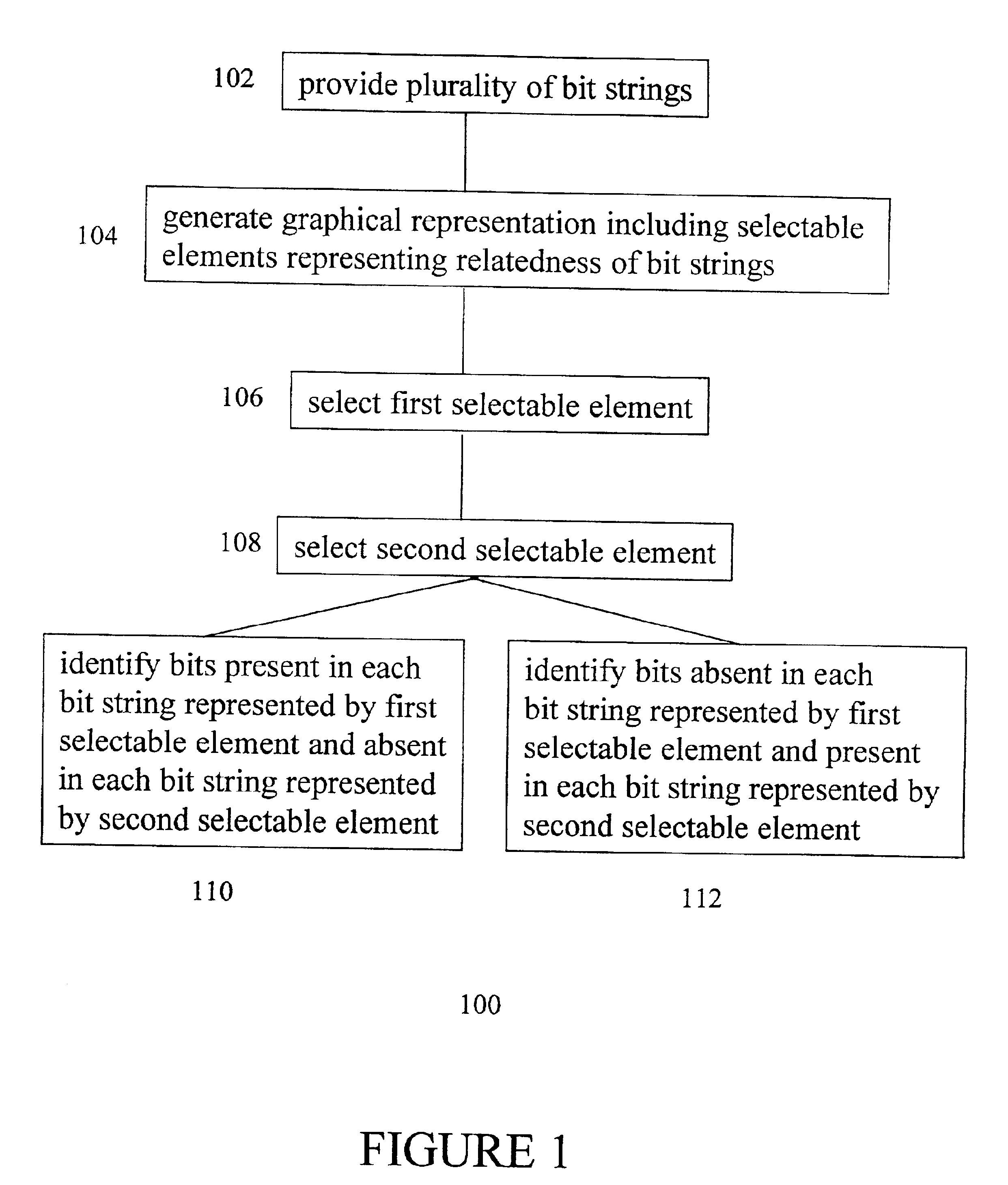
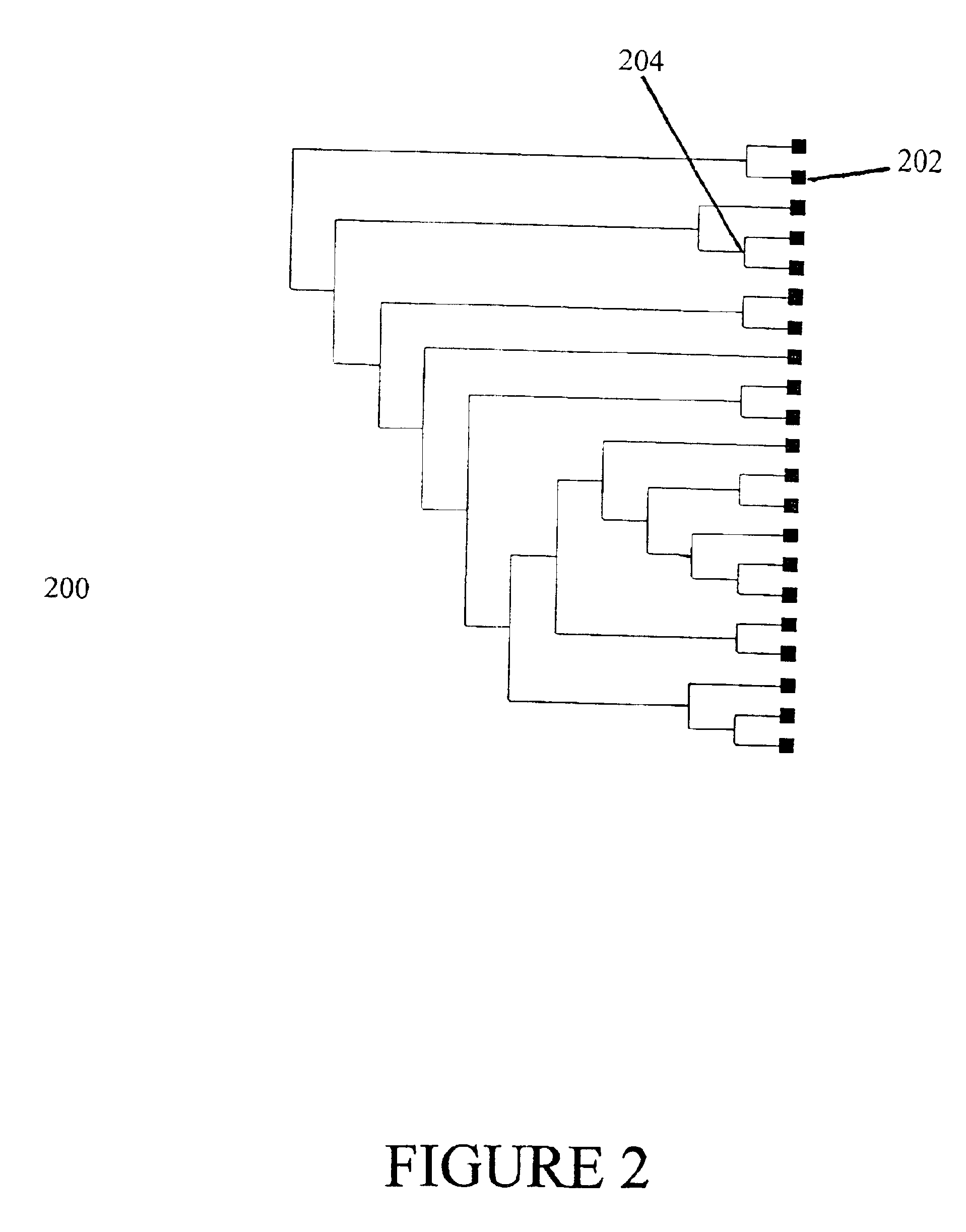
A method is provided for the identification of polymorphic markers in a population. The method includes genotypically characterizing a first sample of a population, selecting one or more individuals of the first sample based upon the genotypic characterization, fabricating a microarray with genomic DNA from each individual selected, and genotyping a second sample of the population using each fabricated microarray as a reference, thereby identifying the polymorphic markers in the population. Also provided is a method for the identification of polymorphic markers in a bacterial population. The method includes phenotypically characterizing a first sample of a population, selecting one or more individuals of the first sample based upon the phenotypic characterization, fabricating a microarray with genomic DNA from each individual selected, and genotyping a second sample of the population using each fabricated microarray as a reference, thereby identifying the polymorphic markers in the population. Also provided is a method for identifying unique bits among a plurality of bit strings including providing a plurality of bit strings, wherein each string has the same number and position of bits, and each bit has a value of 0 or 1, generating a graphical representation-including selectable elements-representing the relatedness of the bit strings, making a selection of a first selectable element, making a selection of a second selectable element, and identifying bits that are present in each bit string represented by the first selectable element and absent in each bit string represented by the second selectable element, or vice-versa.
Owner:BEACON VENTURE MANAGEMENT +1
Method for specifically knocking out hepatitis B virus by CRISPR/Cas9 and gRNA applied to specific targeting HBV DNA
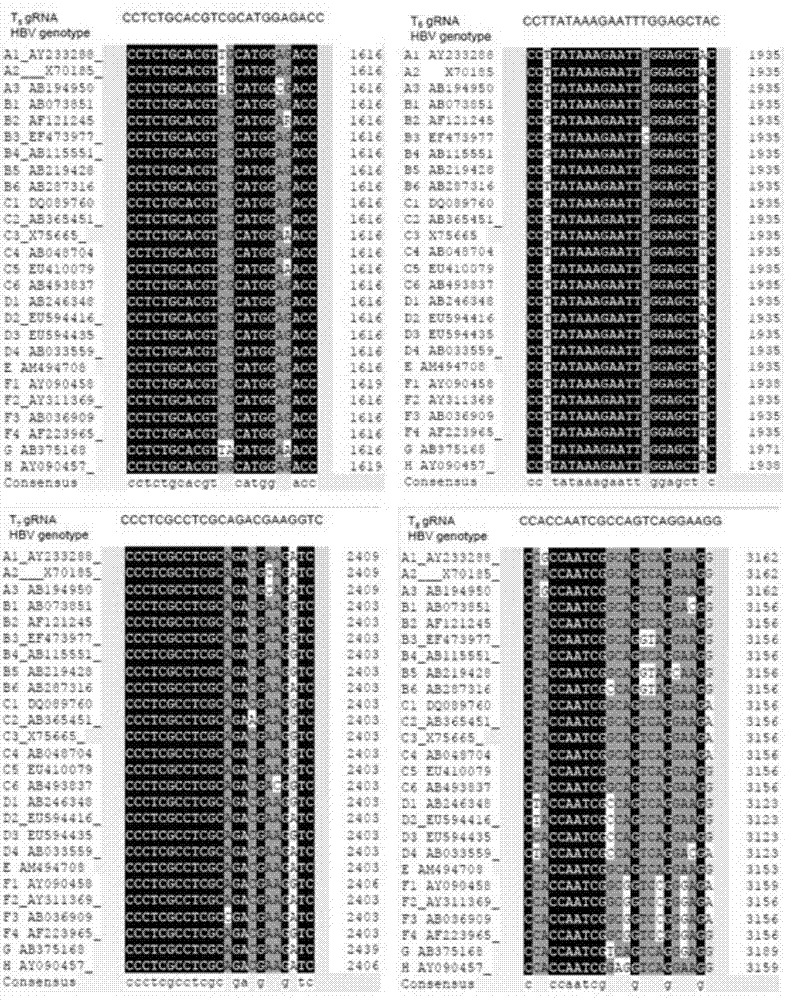
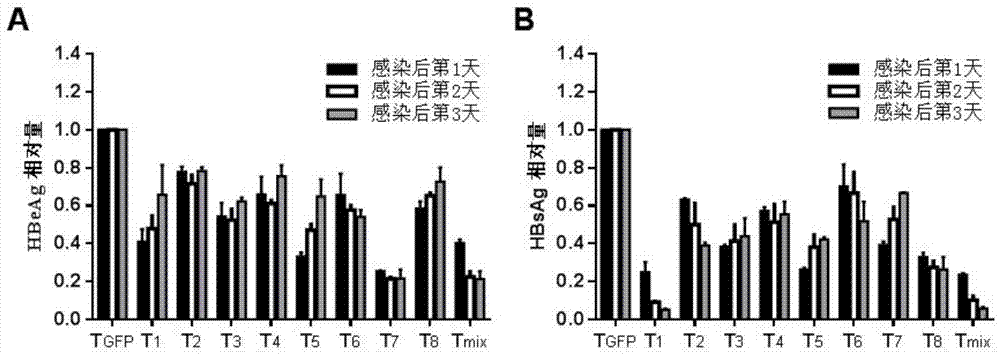
ActiveCN104498493AEfficient removalReduce escape from treatmentGenetic material ingredientsAntiviralsDrugRNA
The invention relates to the technical field of molecular biology and biological medicines, and particularly relates to application of gRNA sequences and combination thereof based on a CRISPR system in treatment on hepatitis B virus. According to the method disclosed by the invention, eight types of guidance RNAs (gRNA) are designed according to design rules of CRISPR gRNA and a conservative region of different genotypes of HBV sequences, and the eight types of guidance RNAs are structured on a PX330 expression vector. By utilizing the eight gRNAs in a cell model, a mouse model and a CRISPR / Cas9 system guided by combination of the cell model and the mouse model, the expression and replication of the hepatitis B virus can be effectively inhibited. By united application of a plurality of gRNAs, a better effect can be achieved, and different genotypes of HBV replication can be better inhibited. The system has the characteristics of being easy to operate, high in inhibition efficiency on HBV replication and applicable to various genotypes. Therefore, the gRNA and the combination thereof related to the invention are expected to be applied in preparation of a novel drug for treating the hepatitis B virus.
Owner:浙江安维珞诊断技术有限公司
Methods and systems for designing animal food compositions
InactiveUS20060200320A1Good for healthPrevent and treat diseaseData processing applicationsAccessory food factorsAnimal foodData set
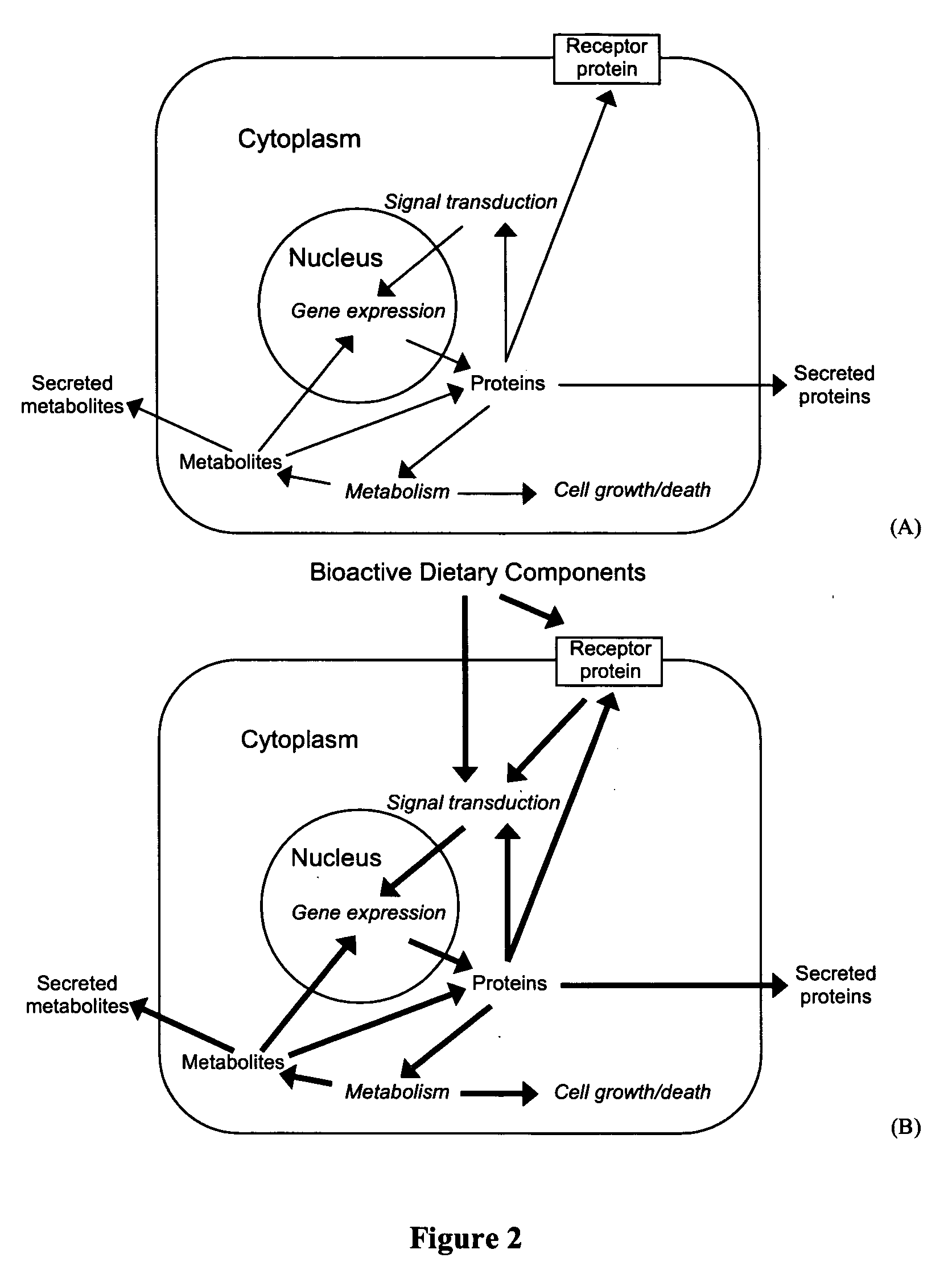
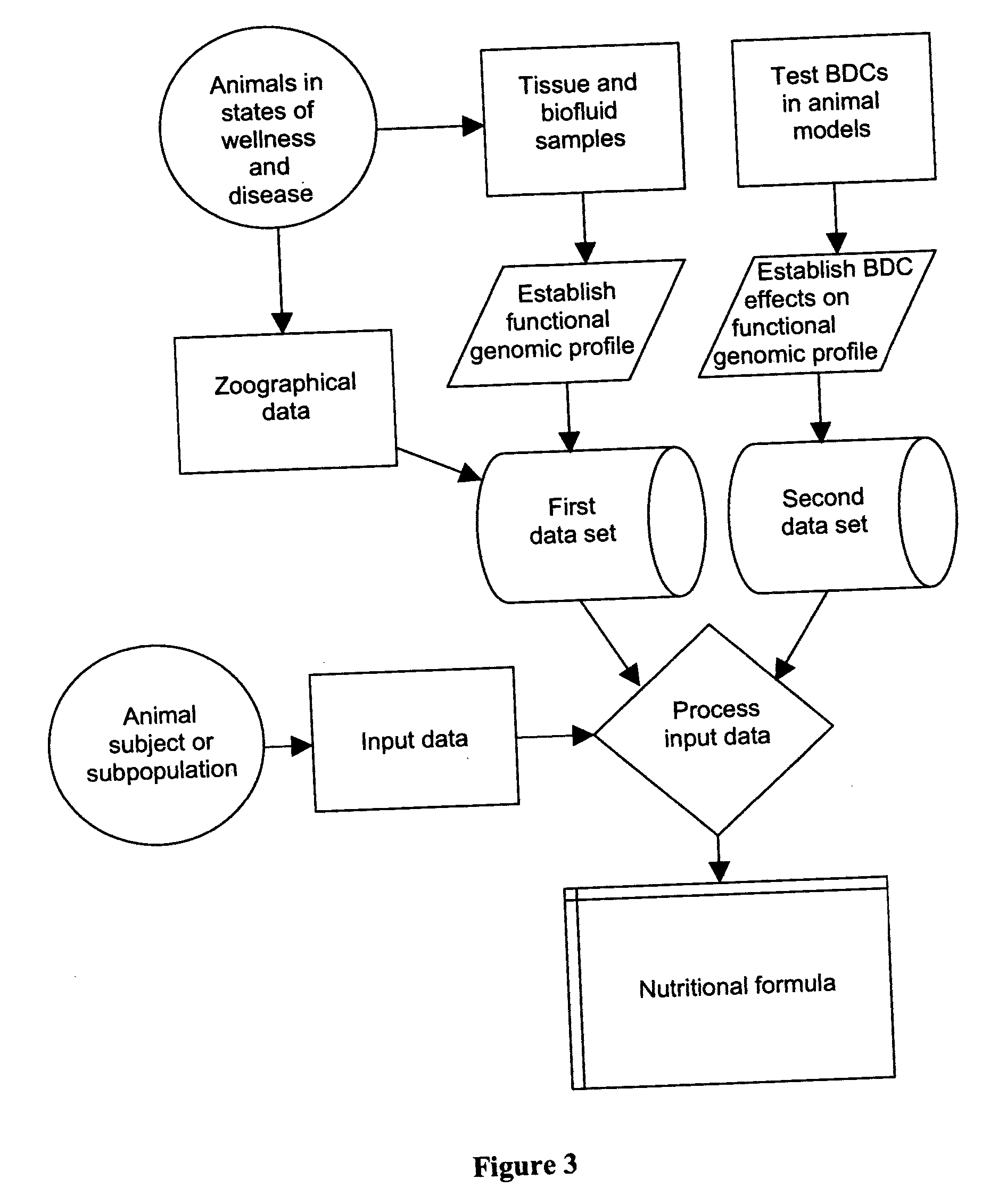
A method for preparing a food composition for animals comprising (a) accessing at least one database that comprises a first data set relating functional genomic profile of a biofluid or tissue sample from an animal to physiological condition and optionally genotype of the animal; (b) accessing at least one database that comprises a second data set relating to effects of bioactive dietary components on functional genomic profile; (c) by use of an algorithm drawing on these data sets, processing input data defining physiological condition and optionally genotype of a subpopulation of animals to derive a nutritional formula promoting wellness of one or more animals of the subpopulation; and (d) preparing a food composition based on the nutritional formula.
Owner:HILLS PET NUTRITION INC
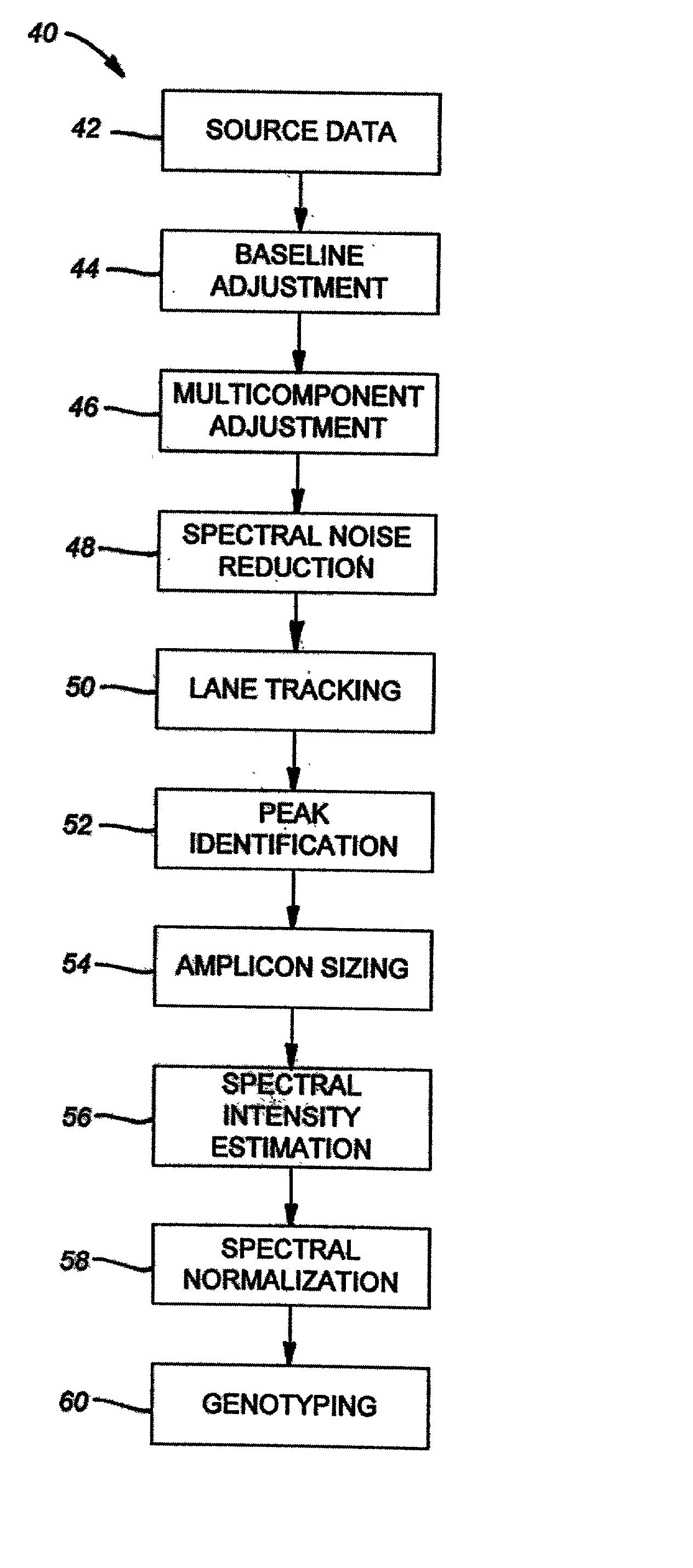
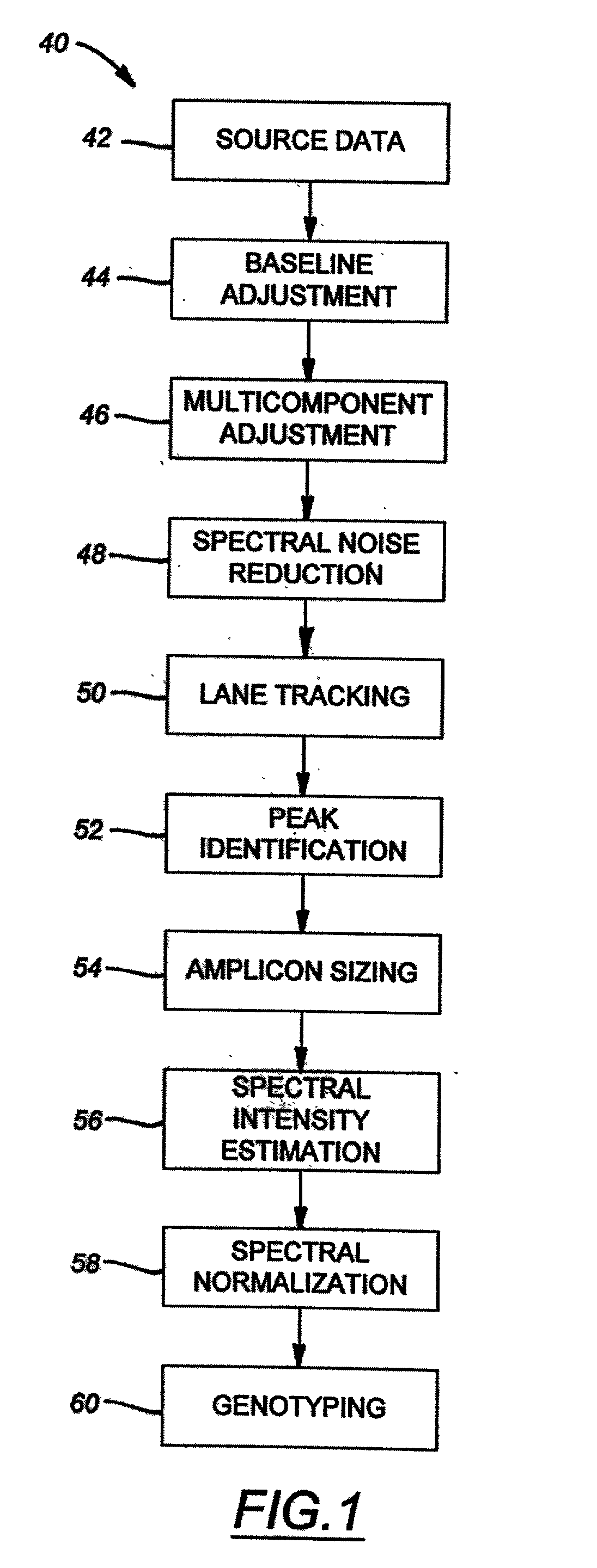
Method, system, and computer software for the presentation and storage of analysis results
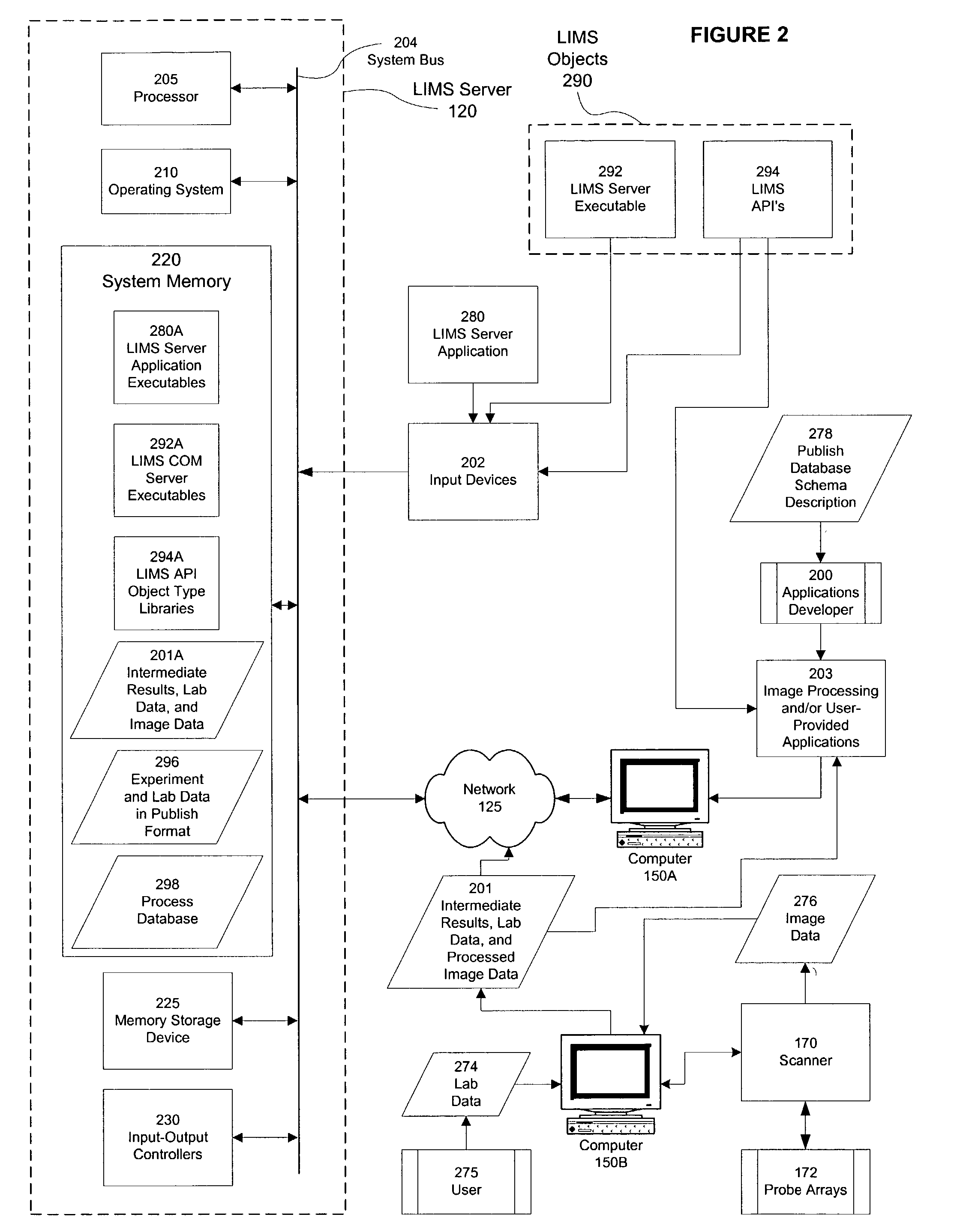
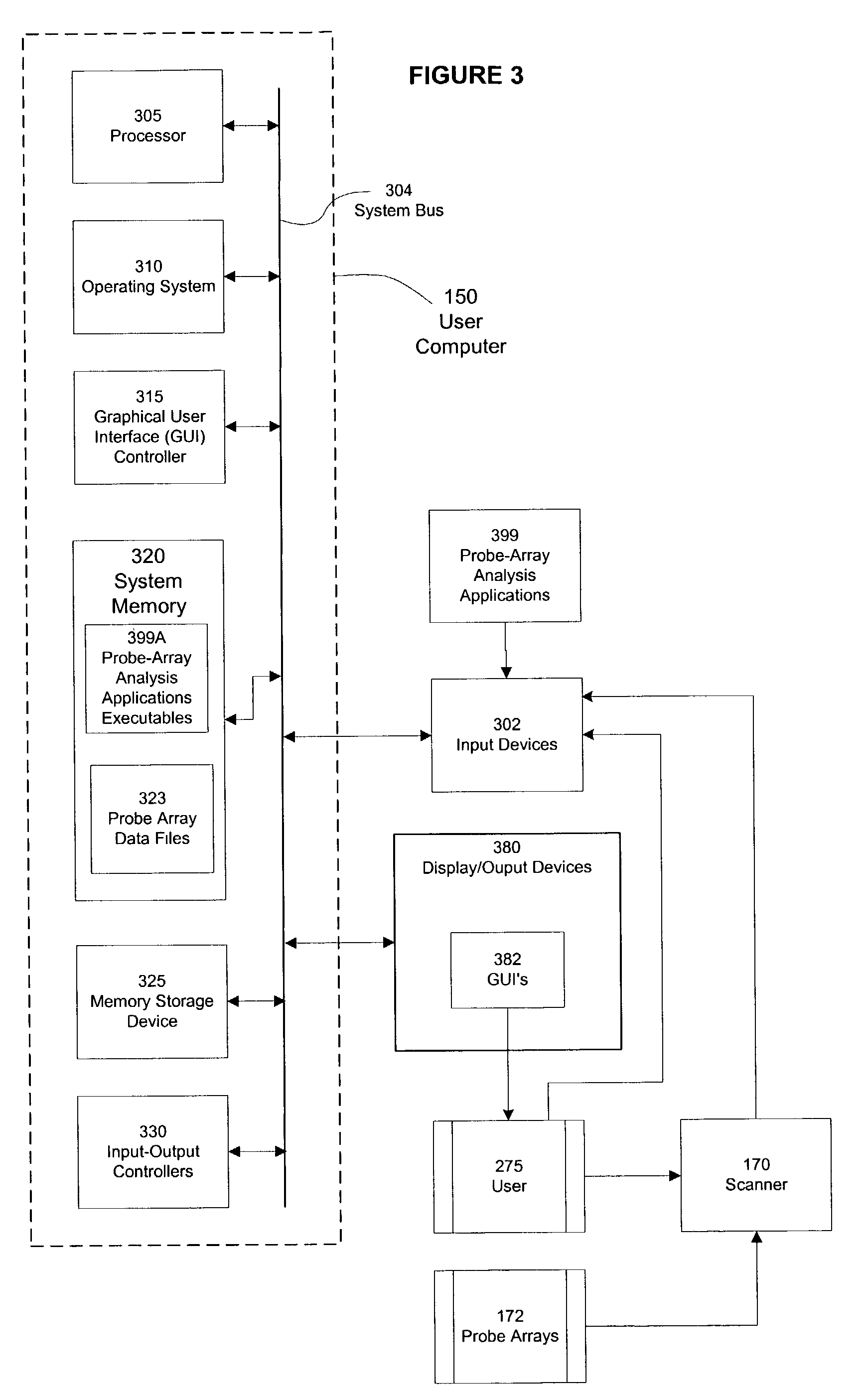
A computer program product, and related systems and methods, are described that processes emission intensity data corresponding to probes of a biological probe array. The computer program includes a genotype and statistical analysis manager that determines absolute or relative expression values based, at least in part, on a statistical measure of the emission intensity data and at least one user-selectable statistical parameter. The analysis manager may also determine genotype calls for one or more probes based, at least in part, on the emission intensity data, The analysis manager may further display the absolute or relative expression values based, at least in part, on at least one user-selectable display parameter and / or a measure of normalized change between genotype calls. The measure of normalized change may be based, at least in part, on a comparison of genotype calls and a reference value.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
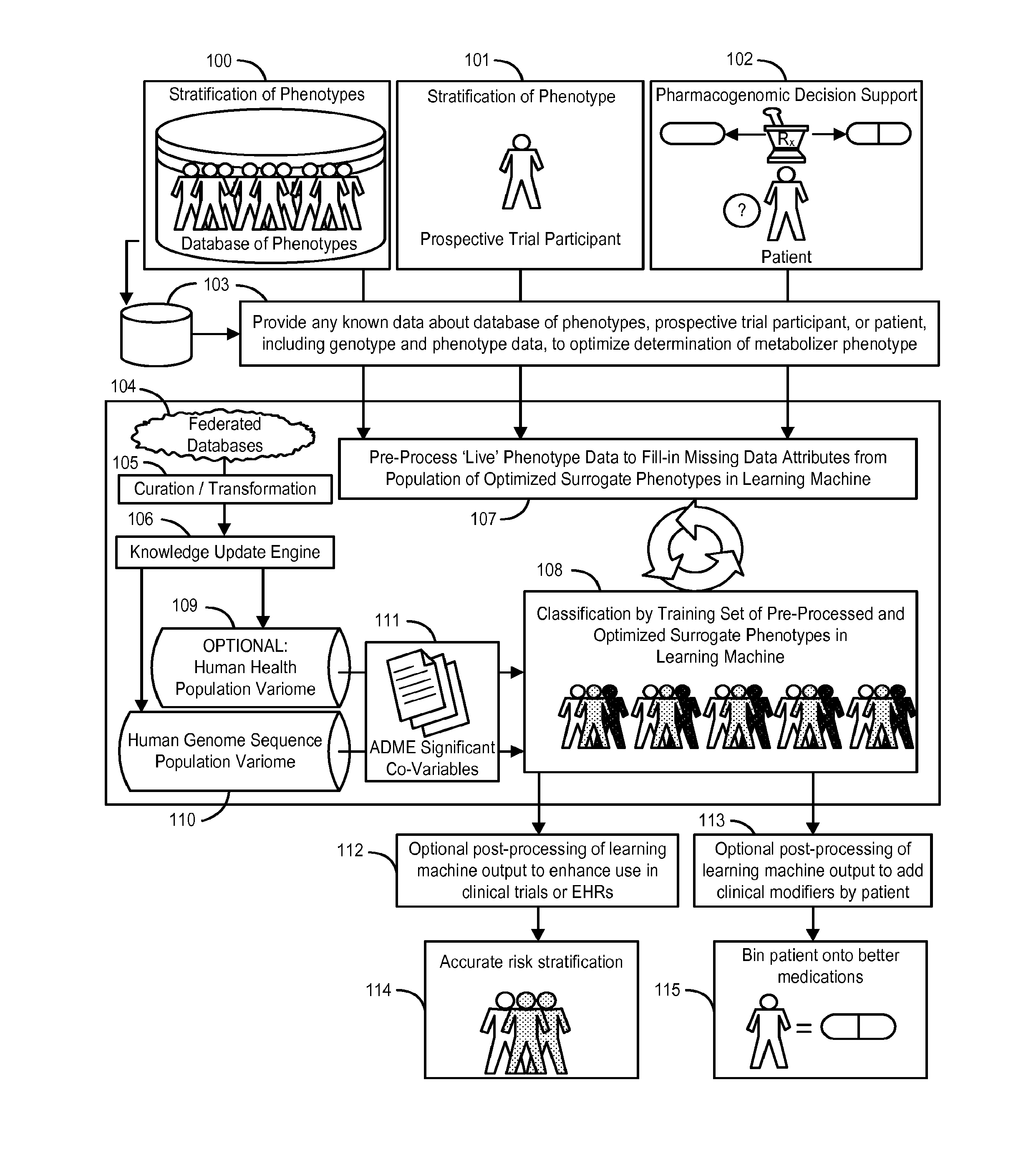
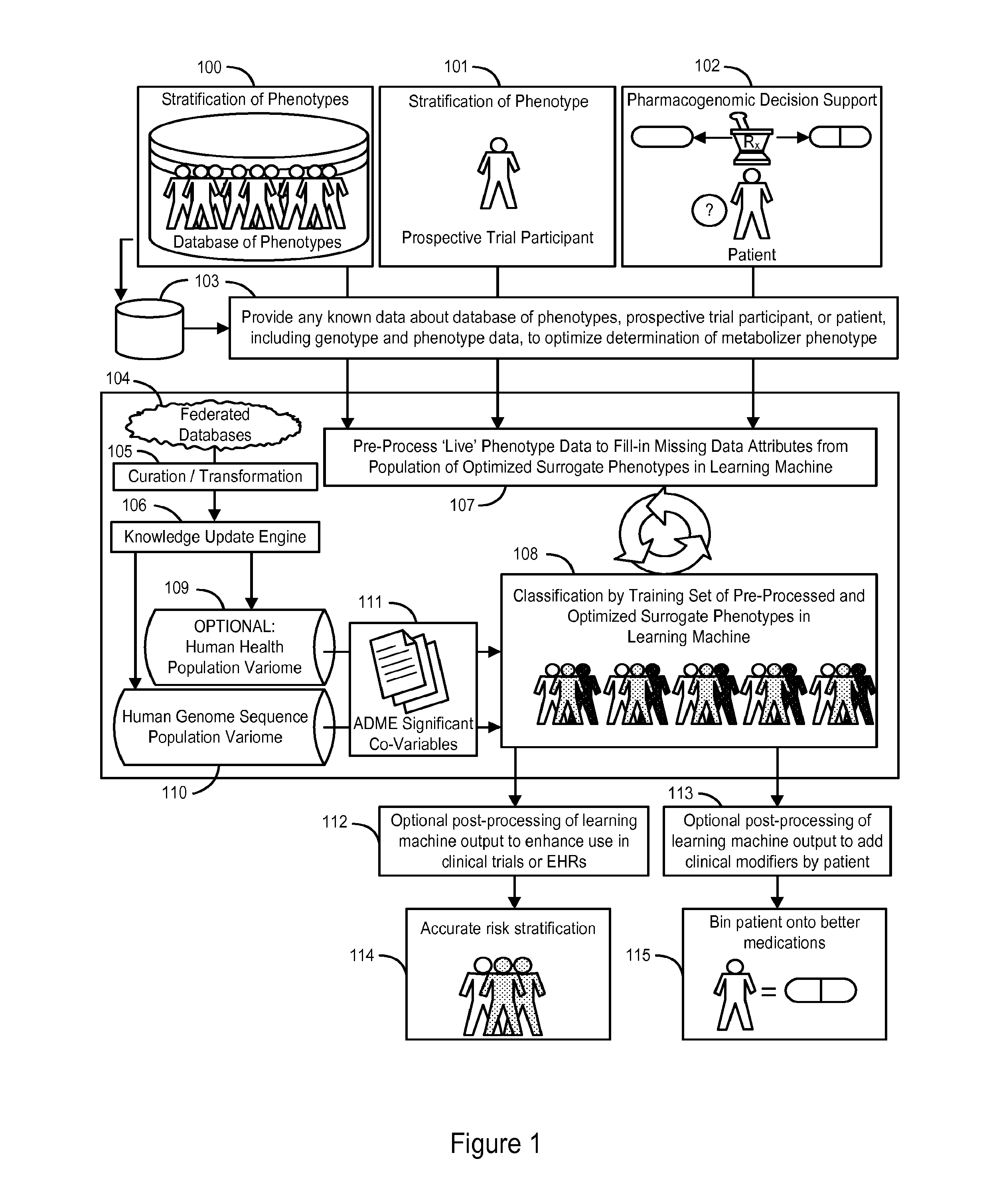
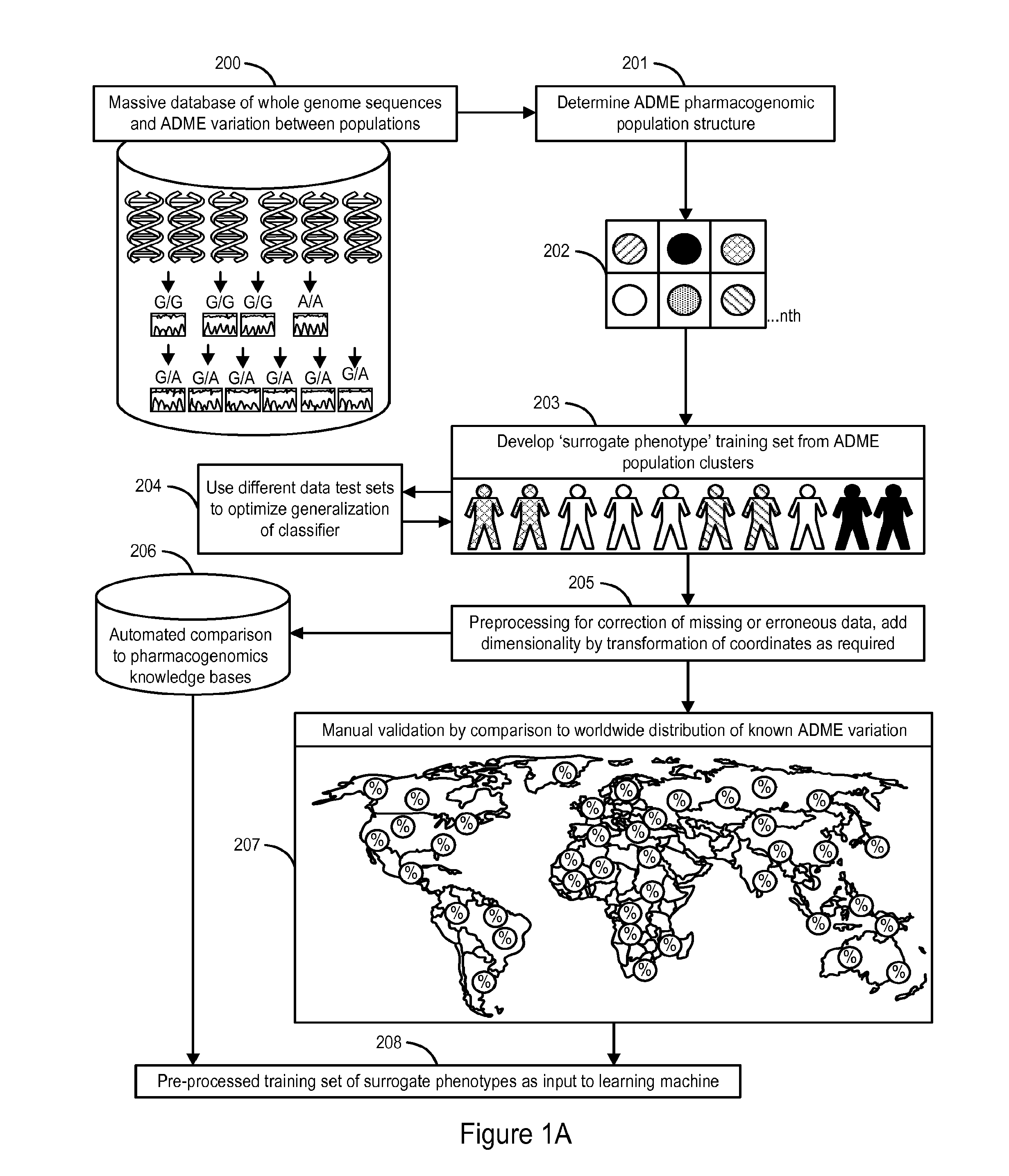
System and Methods for Pharmacogenomic Classification
InactiveUS20140222349A1Good statistical effectDataset can also become very largeBiostatisticsProteomicsGenomicsLearning machine
The invention provides a system and methods for the determination of the pharmacogenomic phenotype of any individual or group of individuals, ideally classified to a discrete, specific and defined pharmacogenomic population(s) using machine learning and population structure. Specifically, the invention provides a system that integrates several subsystems, including (1) a system to classify an individual as to pharmacogenomic cohort status using properties of underlying structural elements of the human population based on differences in the variations of specific genes that encode proteins and enzymes involved in the absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion (ADME) of drugs and xenobiotics, (2) the use of a pre-trained learning machine for classification of a set of electronic health records (EHRs) as to pharmacogenomic phenotype in lieu of genotype data contained in the set of EHRs, (3) a system for prediction of pharmacological risk within an inpatient setting using the system of the invention, (4) a method of drug discovery and development using pattern-matching of previous drugs based on pharmacogenomic phenotype population clusters, and (5) a method to build an optimal pharmacogenomics knowledge base through derivatives of private databases contained in pharmaceutical companies, biotechnology companies and academic research centers without the risk of exposing raw data contained in such databases. Embodiments include pharmacogenomic decision support for an individual patient in an inpatient setting, and optimization of clinical cohorts based on pharmacogenomic phenotype for clinical trials in drug development.
Owner:ASSUREX HEALTH INC
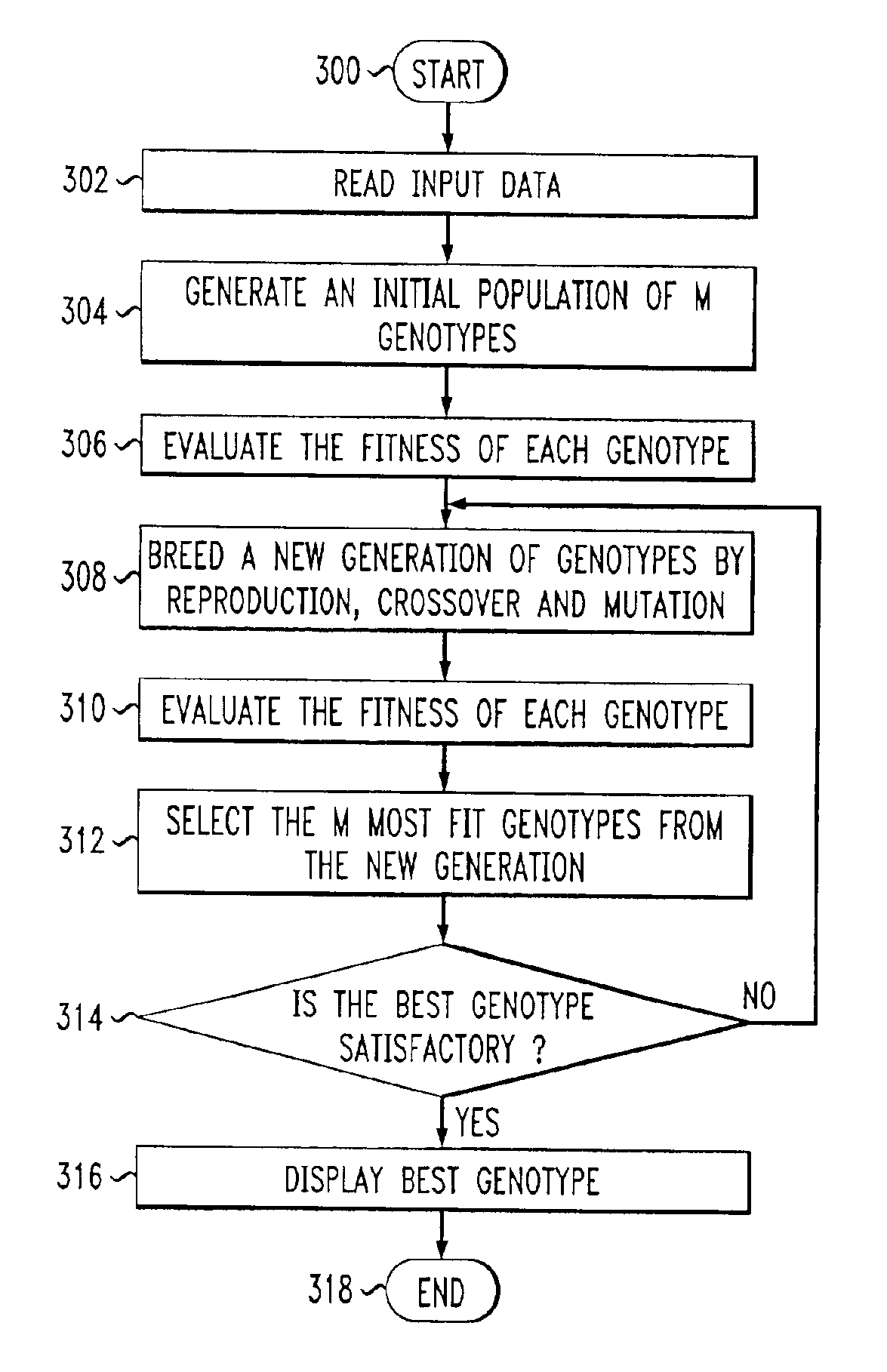
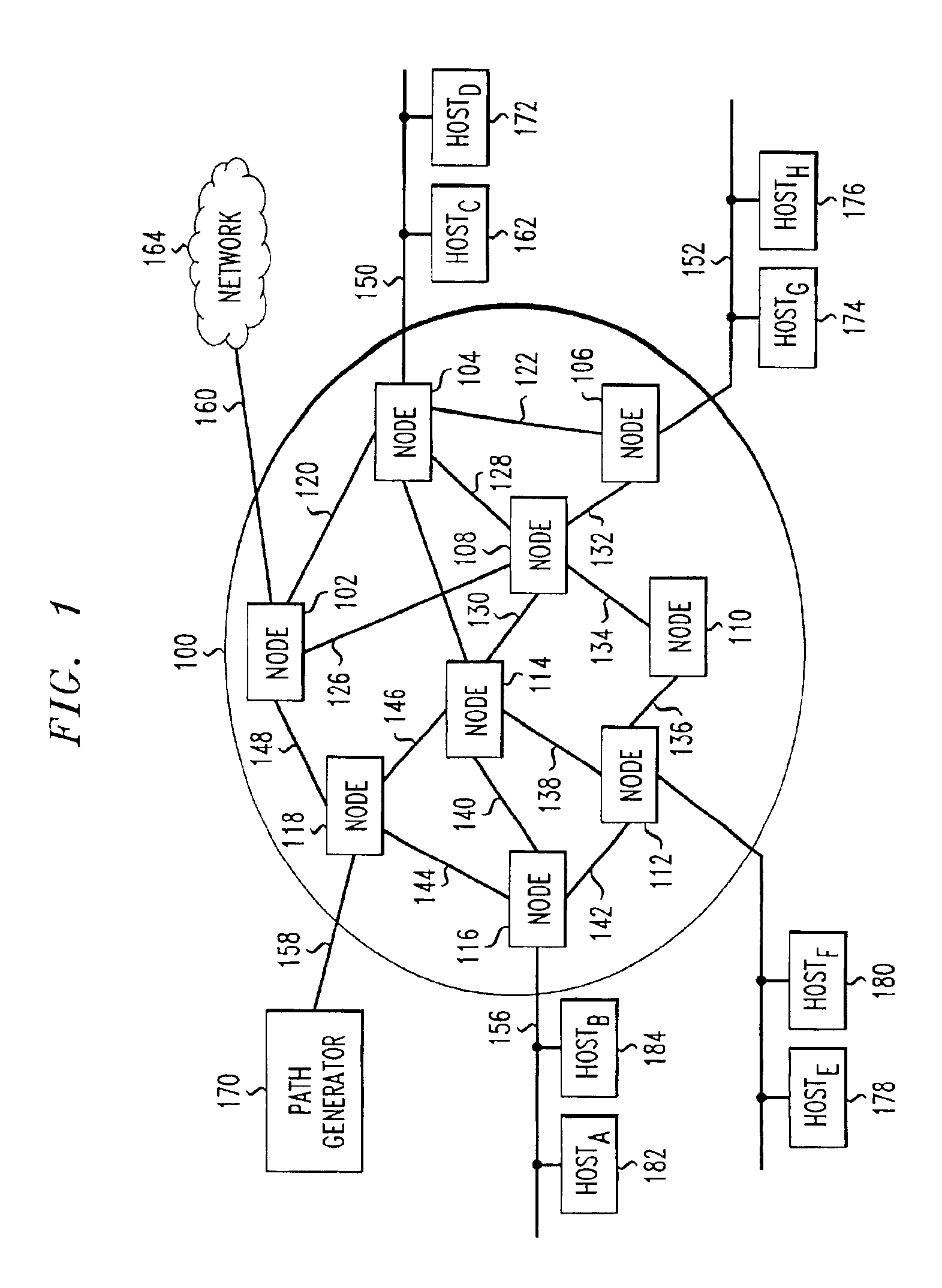
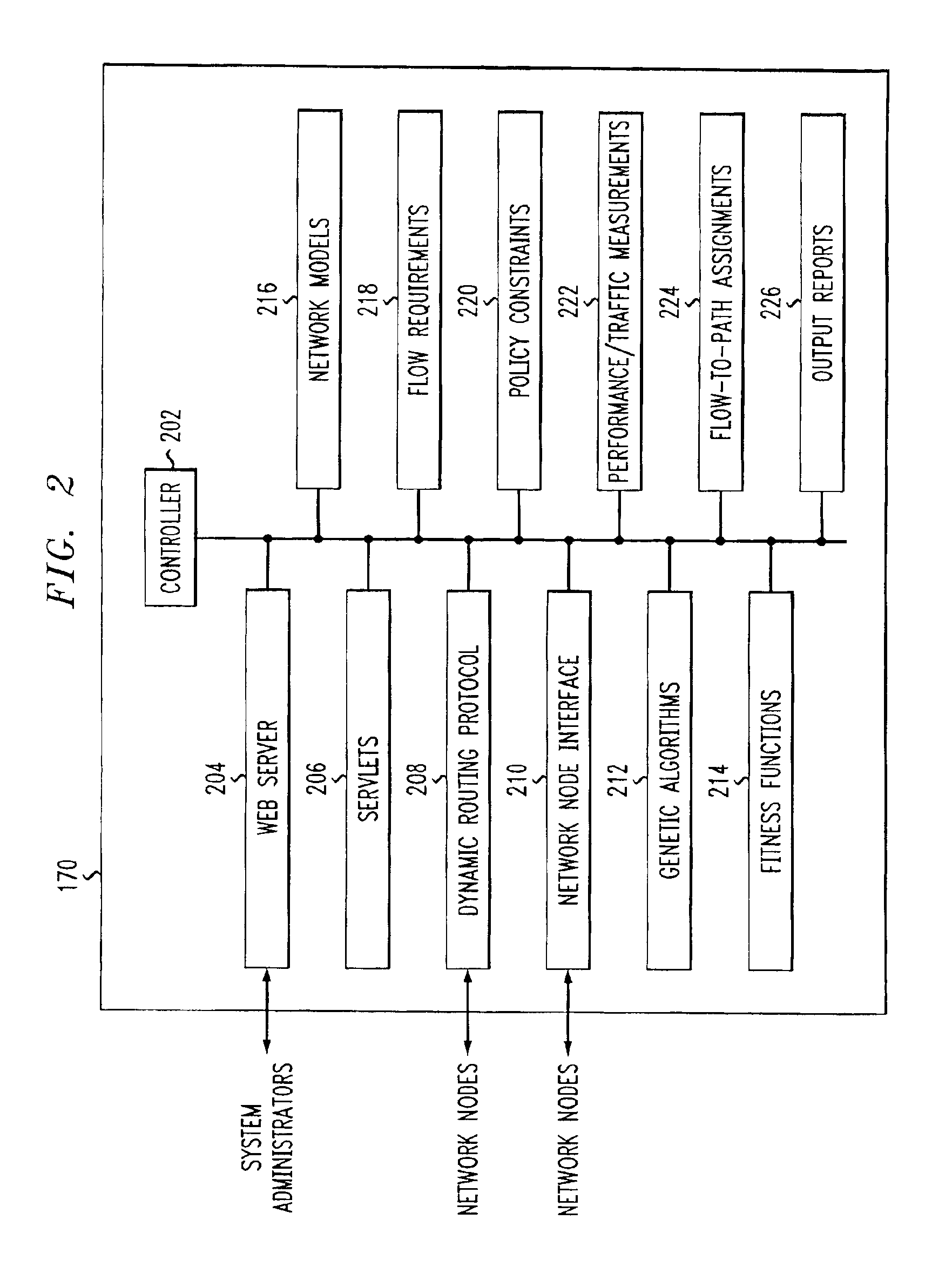
Method for utilizing a generic algorithm to provide constraint-based routing of packets in a communication network
ActiveUS6912587B1Consider flexibilitySatisfactory solutionMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksTraffic capacityPath generation
A Path Generator connects to a communication network and uses genetic algorithms to assign flows to paths. Genotypes encode flow to path assignments for working and protection paths. Genotype fitness functions are computed as a weighted sum of constraint fitness functions. Each constraint fitness function evaluates the degrees to which the genotype is a satisfactory solution. The system can be used for network modeling. It can also receive requests for on-demand assignment of flows and on-demand rerouting of flows.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
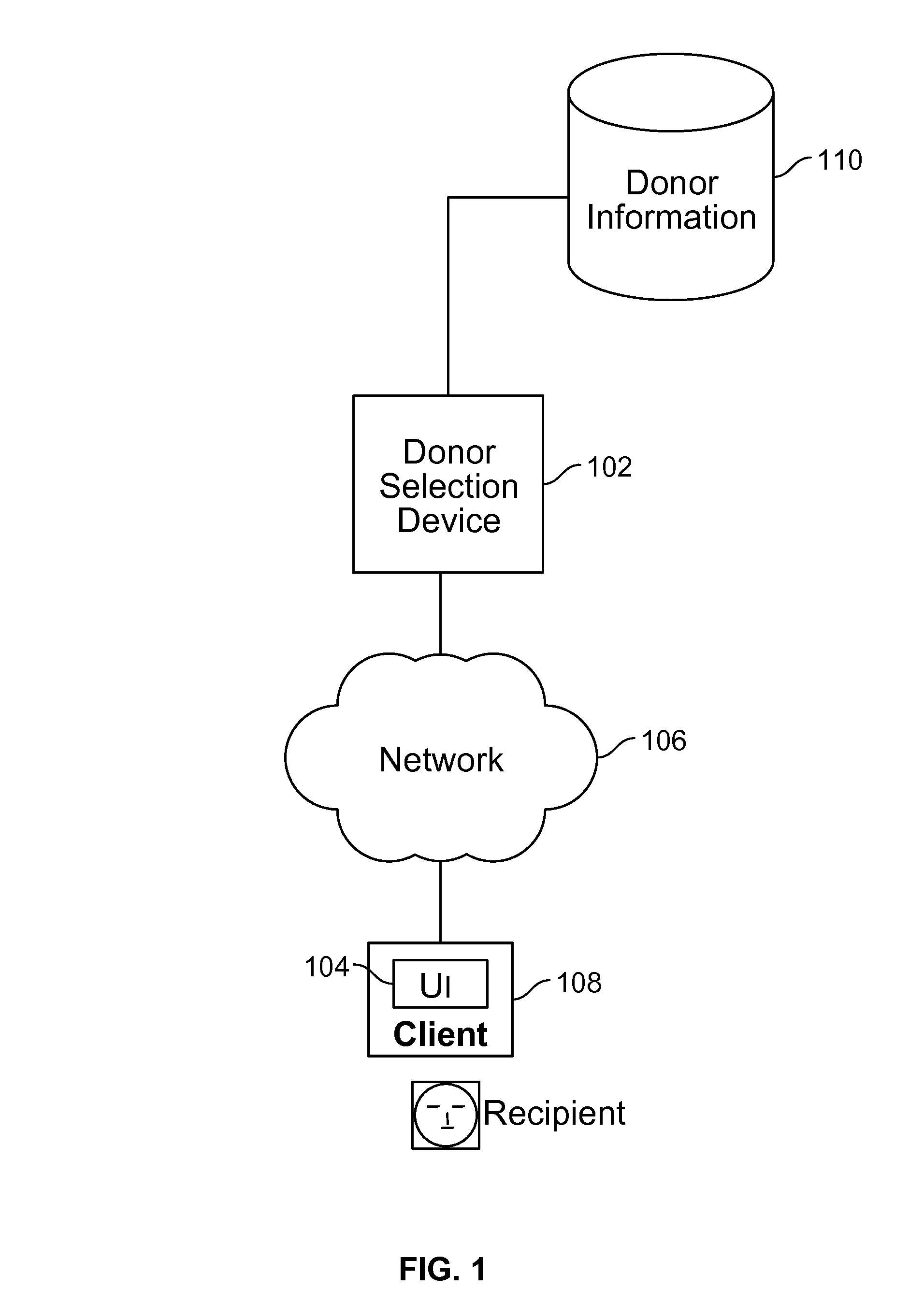
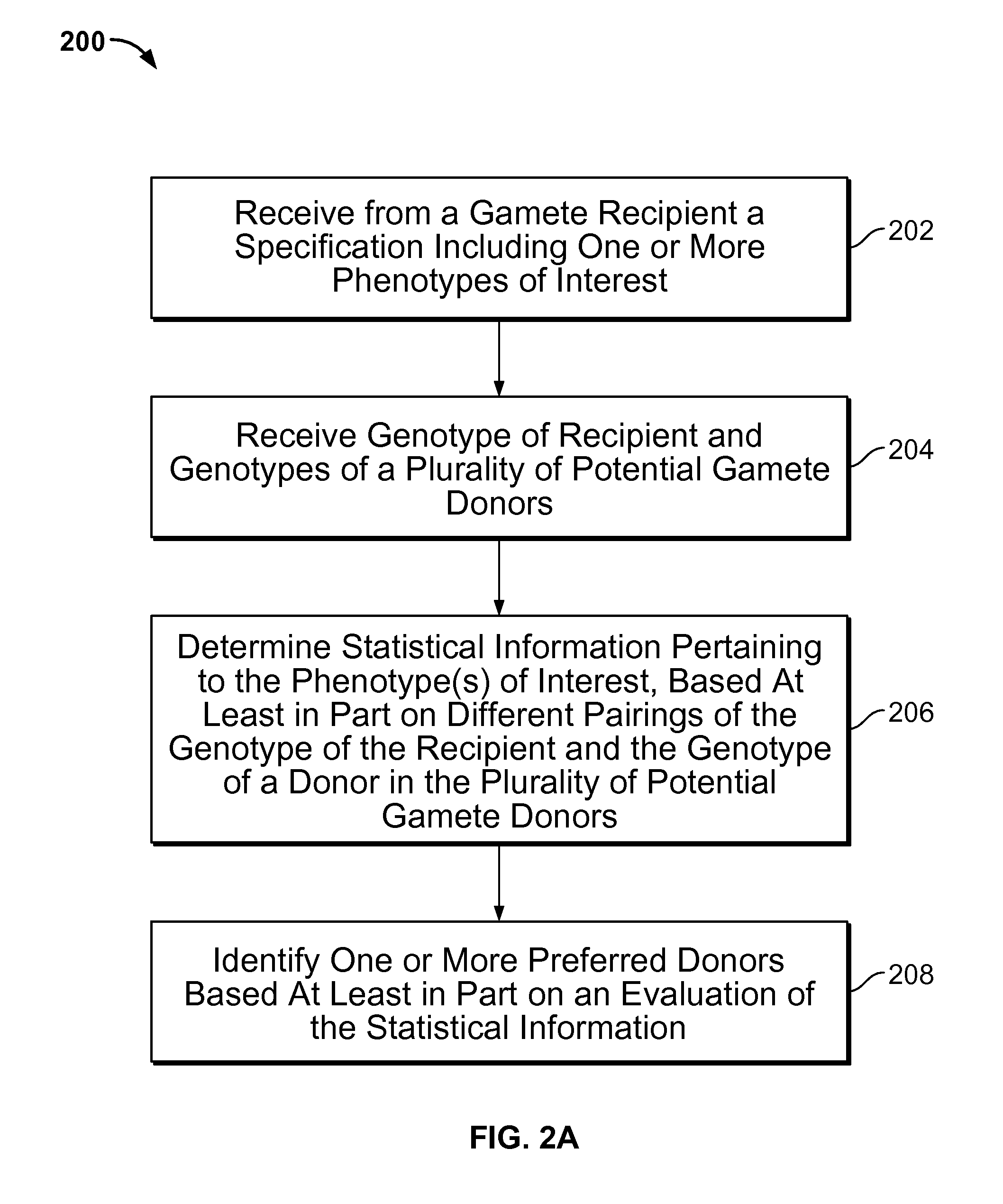
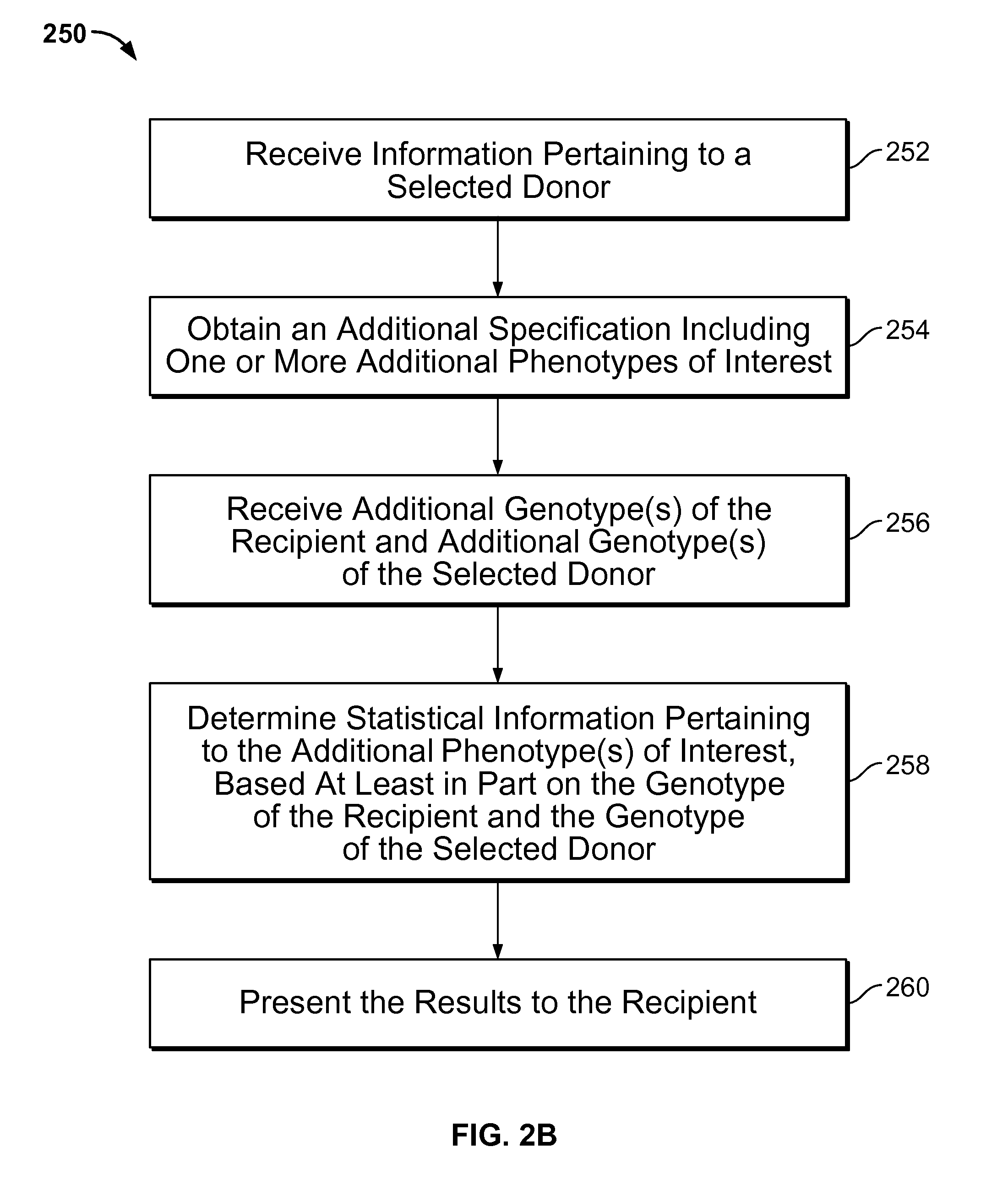
Gamete donor selection based on genetic calculations
ActiveUS8543339B2Digital data processing detailsAnalogue computers for electric apparatusGenotypePairing
Owner:23ANDME
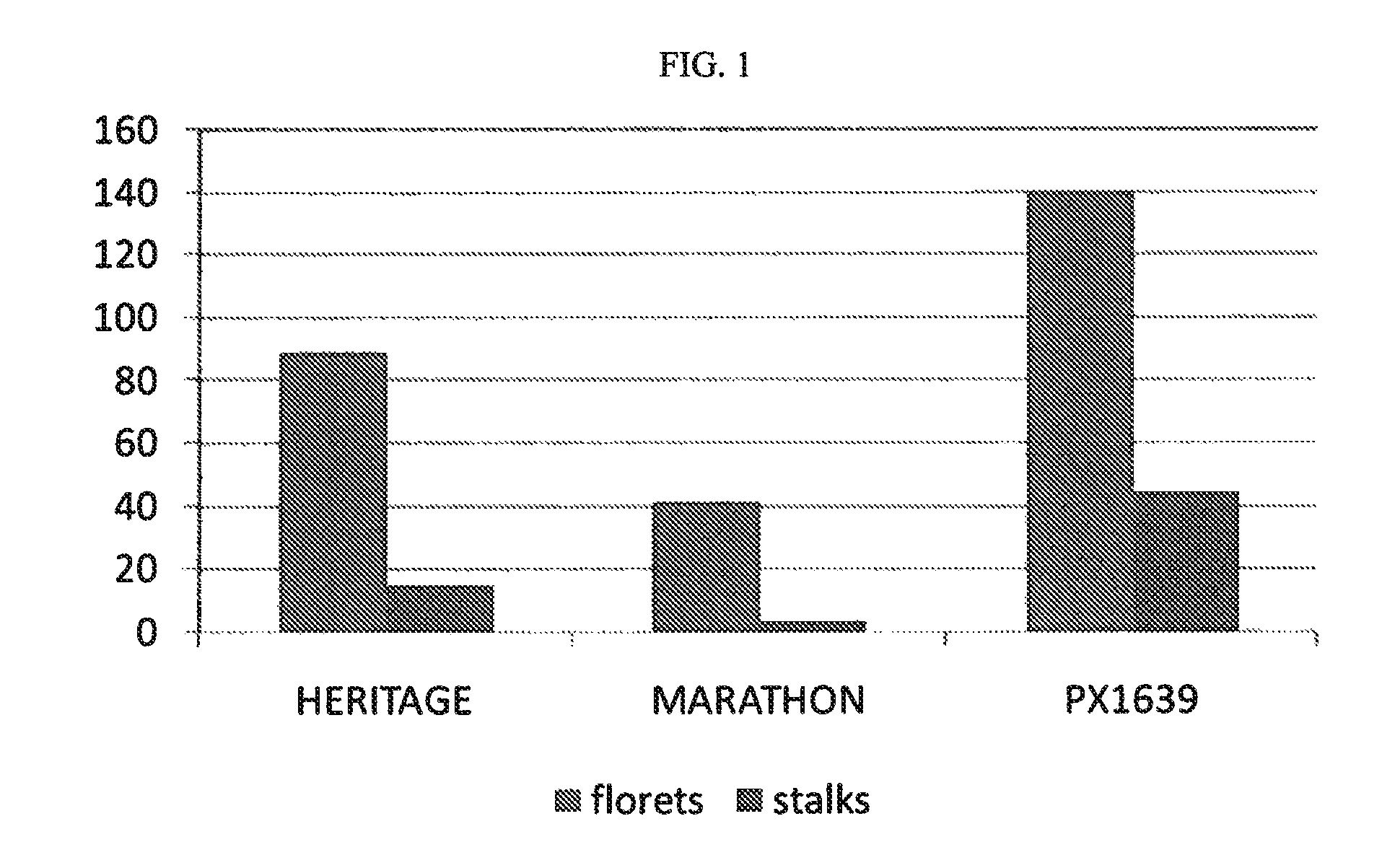
Broccoli hybrid PS05151639
The invention provides seed and plants of broccoli hybrid PS05151639 and the parent lines thereof. The invention thus relates to the plants, seeds and tissue cultures of broccoli hybrid PS05151639 and the parent lines thereof, and to methods for producing a broccoli plant produced by crossing such plants with themselves or with another broccoli plant, such as a plant of another genotype. The invention further relates to seeds and plants produced by such crossing. The invention further relates to parts of such plants.
Owner:SEMINIS VEGETABLE SEEDS
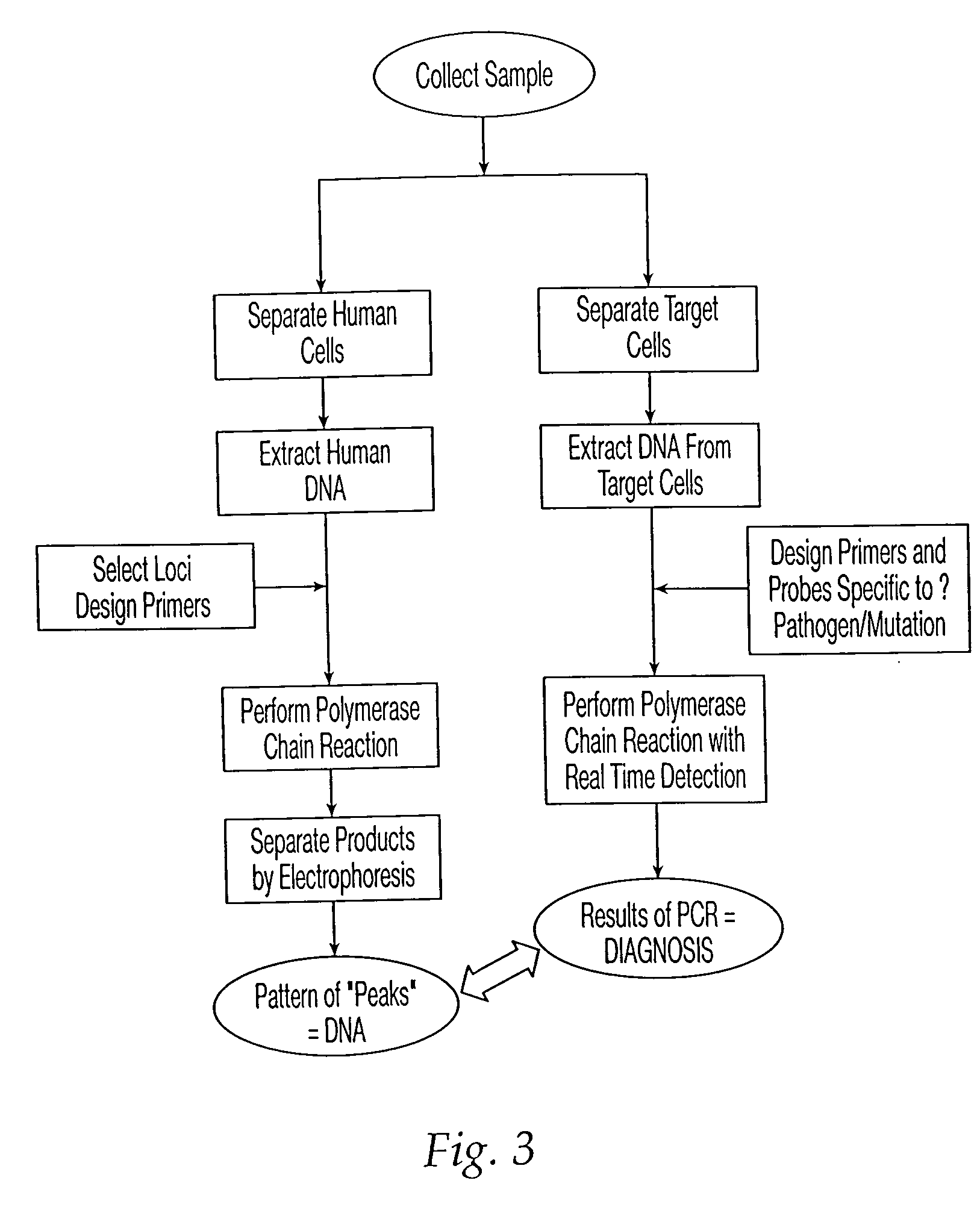
Assays for the detection of genotype, mutations, and/or aneuploidy
InactiveUS20140186827A1Increase percentageMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisAssayGenotype
The present invention provides amplification-based methods for detection of genotype, mutations, and / or aneuploidy. These methods have broad applicability, but are particularly well-suited to detecting and quantifying target nucleic acids in free fetal DNA present in a maternal bodily fluid sample.
Owner:FLUIDIGM INC
Method for improved plant breeding
InactiveUS20110167721A1Quick analysisAvoid prolonged exposureGrain huskingGrain polishingGenotypeBreeding program
The invention relates generally to an improved plant breeding system. More particularly, this invention relates to a method for automated, high throughput analysis of plant phenotype and plant genotype in a breeding program.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI
Broccoli hybrid PX 05181808 and parents thereof
Owner:SEMINIS VEGETABLE SEEDS
Method for genotype determination
InactiveUS20040115684A1Enabling detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationReference genesMedicine
The present invention is directed to a new method for genotype determination at a specific gene locus of an individual or a fetus comprising (i) amplifying a first sequence of said gene locus and a second sequence of a second reference gene locus from DNA originating from a sample containing biological material of said individual or fetus (ii) Monitoring both amplifications preferably in real time and determining the amount of amplification products after each cycle, and (iii) Calculating the ratio between the amount of DNA from the first gene locus and the amount of DNA from the second gene locus. The new method is useful for a variety of applications, especially for detection of chromosomal abnormalities in fetal cells.
Owner:COSTA JEAN MARC
Method for single cell classification and screening and device therefor
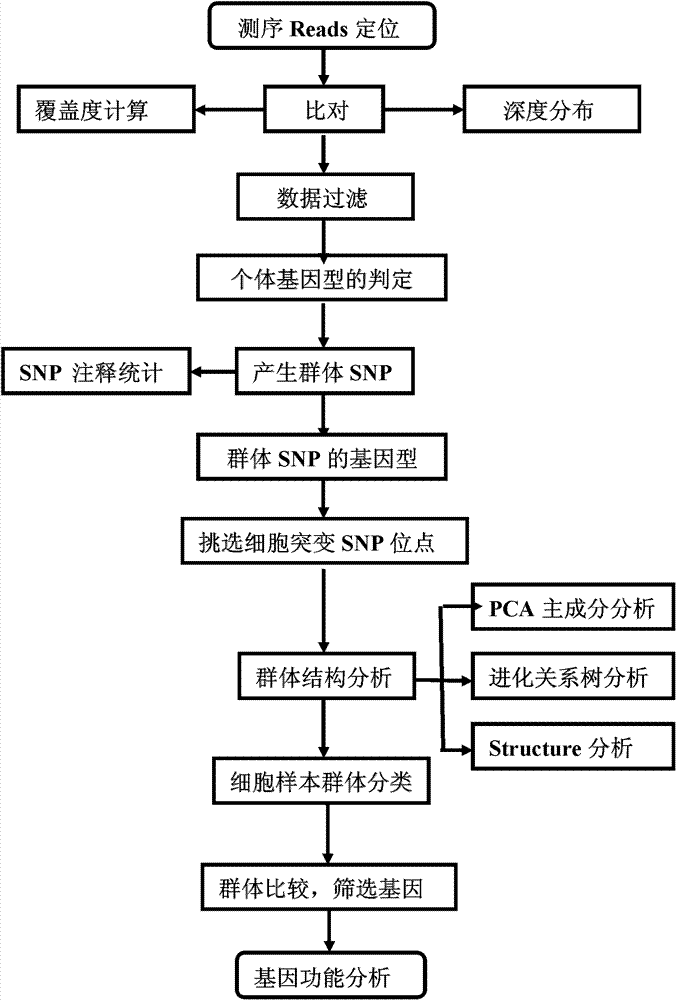
ActiveCN102952854AAvoid marked actionsImprove accuracyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsReference genesData set
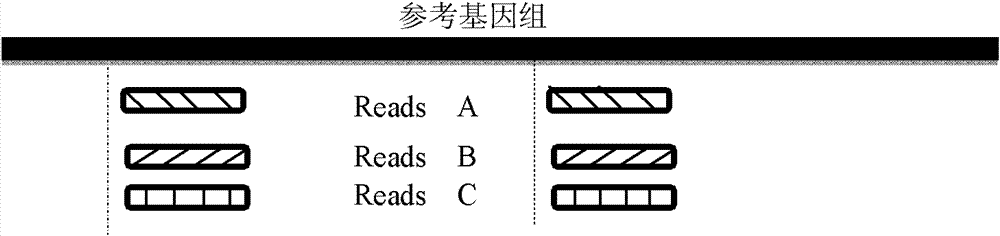
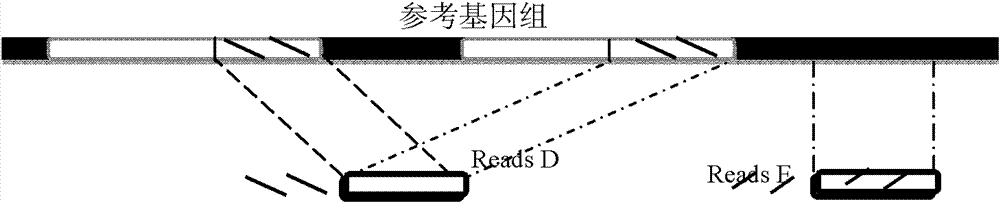
The invention provides a method for single cell classification and screening and a device therefor. The method comprises the following steps of carrying out comparison of reads obtained by sample sequencing and a reference genome, carrying out data filtration of a comparison result, determining a consistent genotype of all single cell samples according to filtered data, saving the consistent genotype of the all single cell samples into a SNP data set, extracting genotype files of loci corresponding to reference genome SNP data set positions from the saved SNP data set, selecting a cell mutation SNP locus, and carrying out cell classification and functional gene screening according to a genotype file of the cell mutation SNP locus. The method and the device avoid cell marking, solve the problem that the traditional single cell classification method can not realize classification of a certain cell subset having no corresponding specific markers, realize complete analysis of genetic variation information of a single cell genome, and greatly improve the accuracy of cell subset classification.
Owner:BGI SHENZHEN CO LTD +1
Method of genotyping by determination of allele copy number
The majority of PCR-based fingerprinting technologies generate dominant genetic markers; homozygote present and heterozygote genotypes cannot be distinguished using conventional detection methods. In contrast, codominant genetic markers provide an unambiguous distinction among each genotype. A genotyping method is described that includes procedures implemented in software. This method quantifies allele copy number and enables recovery of codominant genotypes from markers expressing ostensibly dominant phenotypes. These procedures are designed and implemented to (1) greatly reduce variability attributable to sample assay and detector noise, (2) accurately estimate allele size and copy number, (3) provide normalization criteria for intra- and inter-marker comparisons, and (4) scale the resulting data to determine the genotype of individual markers.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
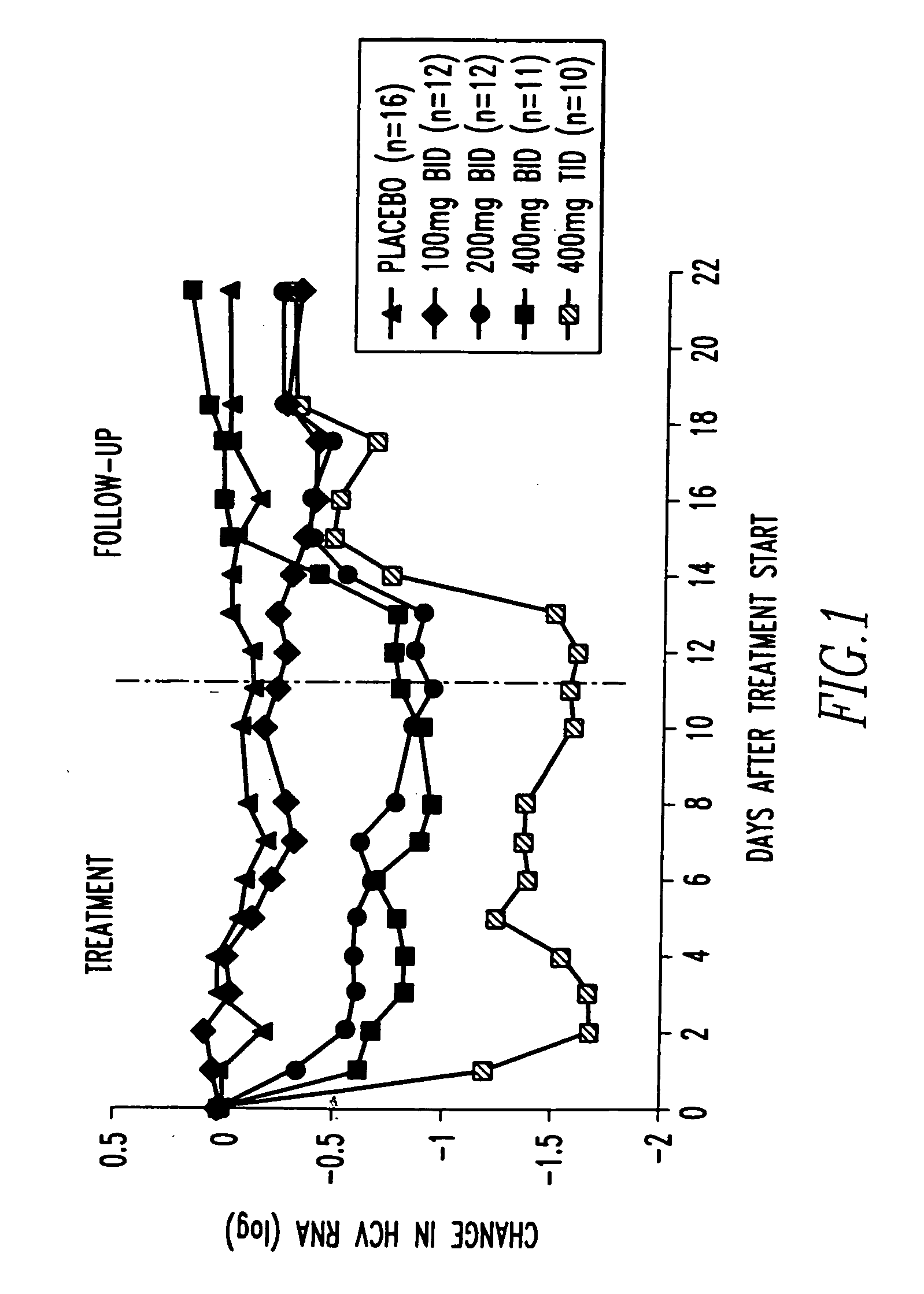
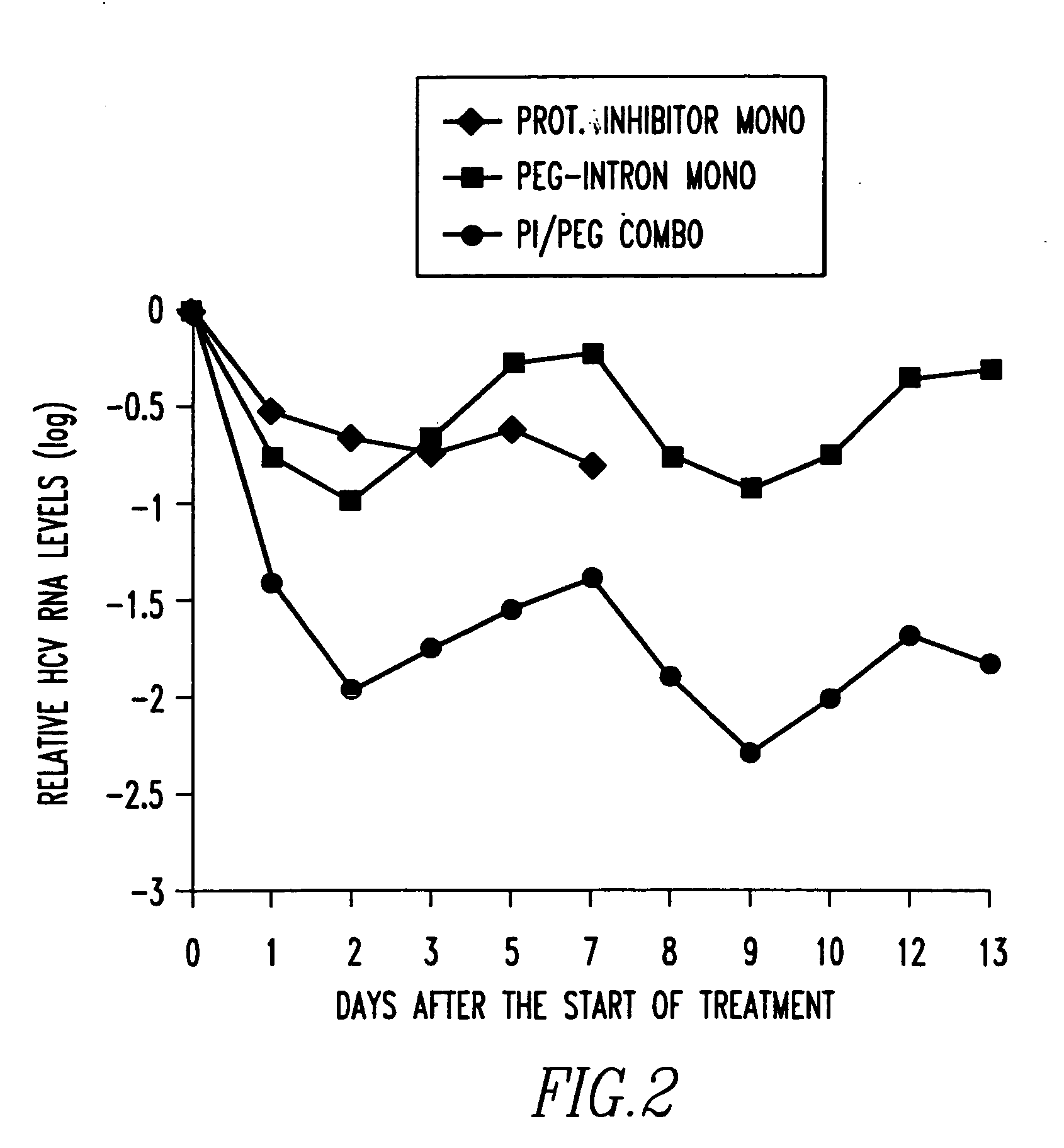
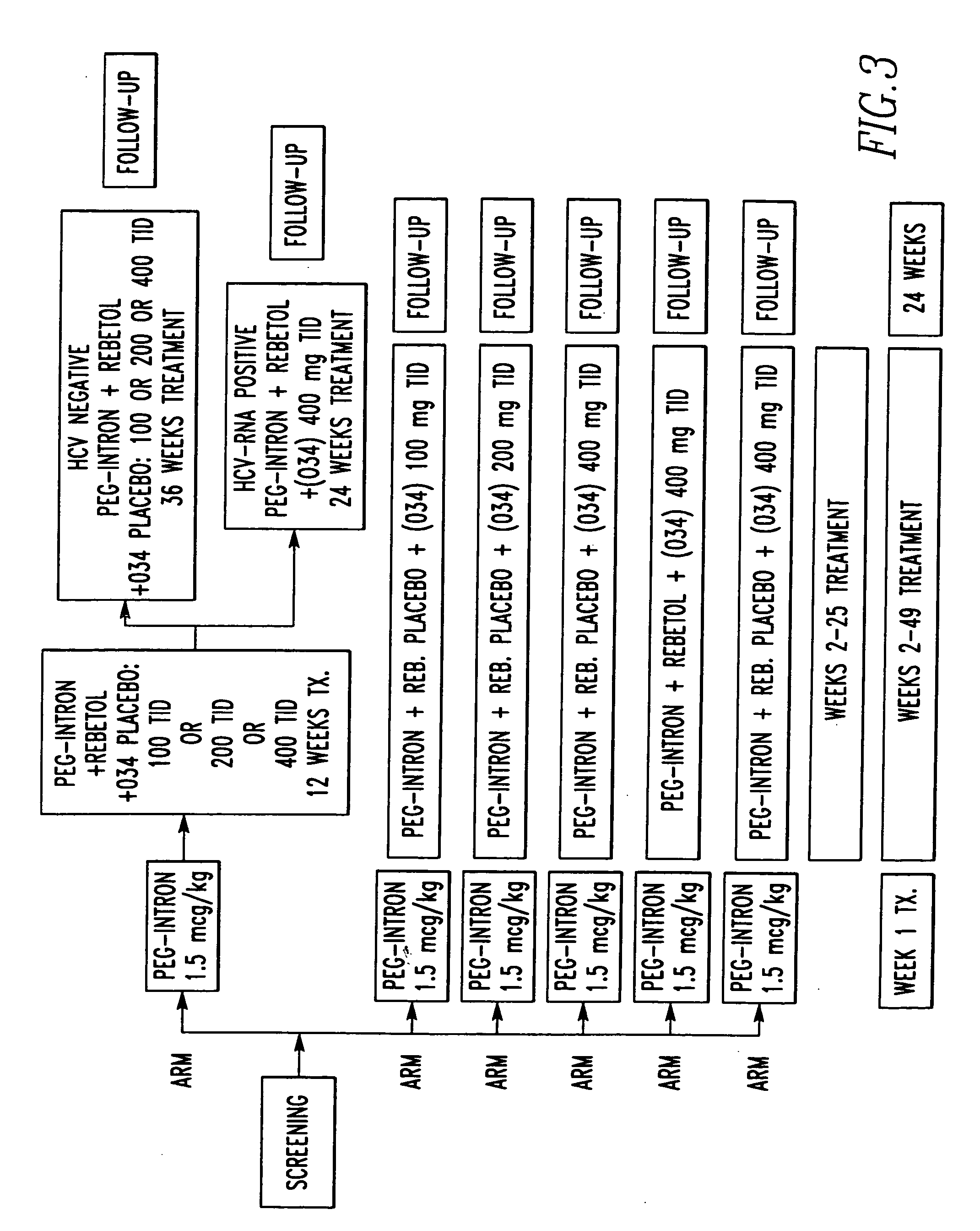
Method of treating interferon non-responders using HCV protease inhibitor
A method of treating, preventing or ameliorating one or more symptoms associated with hepatitis C virus (HCV) in a patient in whom either the HCV is of Genotype 1 and / or the patient was previously treated with interferon and the previous interferon therapy was ineffective to treat the one or more symptoms associated with HCV, comprising administering to such a patient an effective amount of at least one compound of formulae I-XXVI of which the following structural formula is exemplary or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, solvate or ester thereof. Optional combined administration of said at least one compound with an interferon or pegylated interferon and / or ribaviron is also contemplated.
Owner:SCHERING CORP
Optimization and individualization of medication selection and dosing
ActiveUS8589175B2Easy to understandEasy to recommendationDrug and medicationsBiostatisticsPersonalizationDosing regimen
The invention provides population models, methods, and algorithms for targeting a dosing regimen or compound selection to an individual patient. The methods and algorithms of the invention utilize population models that incorporate genotype information for genes encoding drug metabolizing enzymes for one or more compounds of interest. The methods allow integration of genotype information for one or more genes encoding a drug metabolizing enzyme, particularly a cytochrome P450 gene with patient data. The methods allow integration of genotype information and the effect of one or more compounds on one or more drug metabolizing enzymes. The methods allow iterative feedback of drug metabolizing data obtained from a patient into the process of generating a dosage regimen recommendation for a compound of interest for an individual patient.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENT CINCINNATI
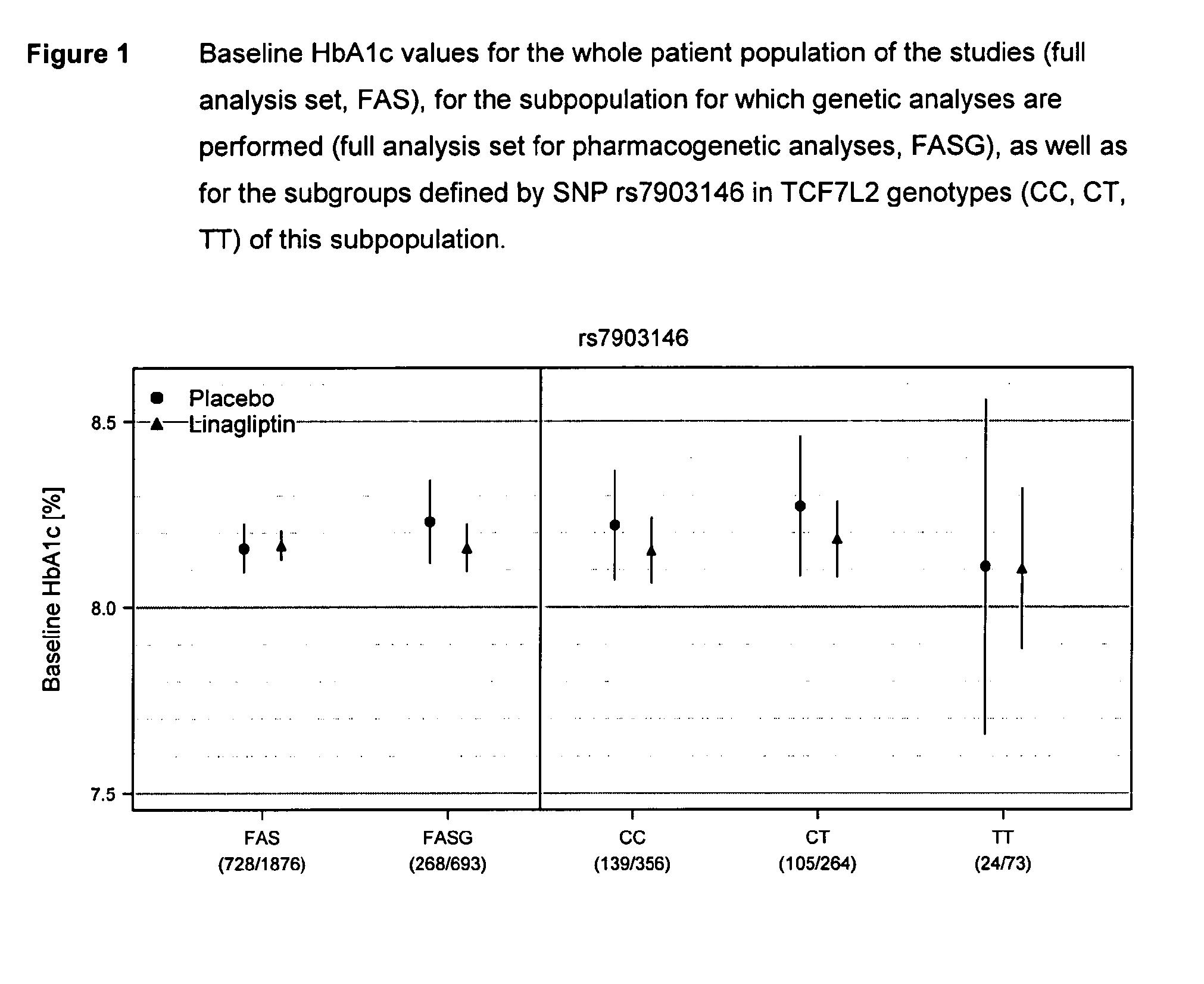
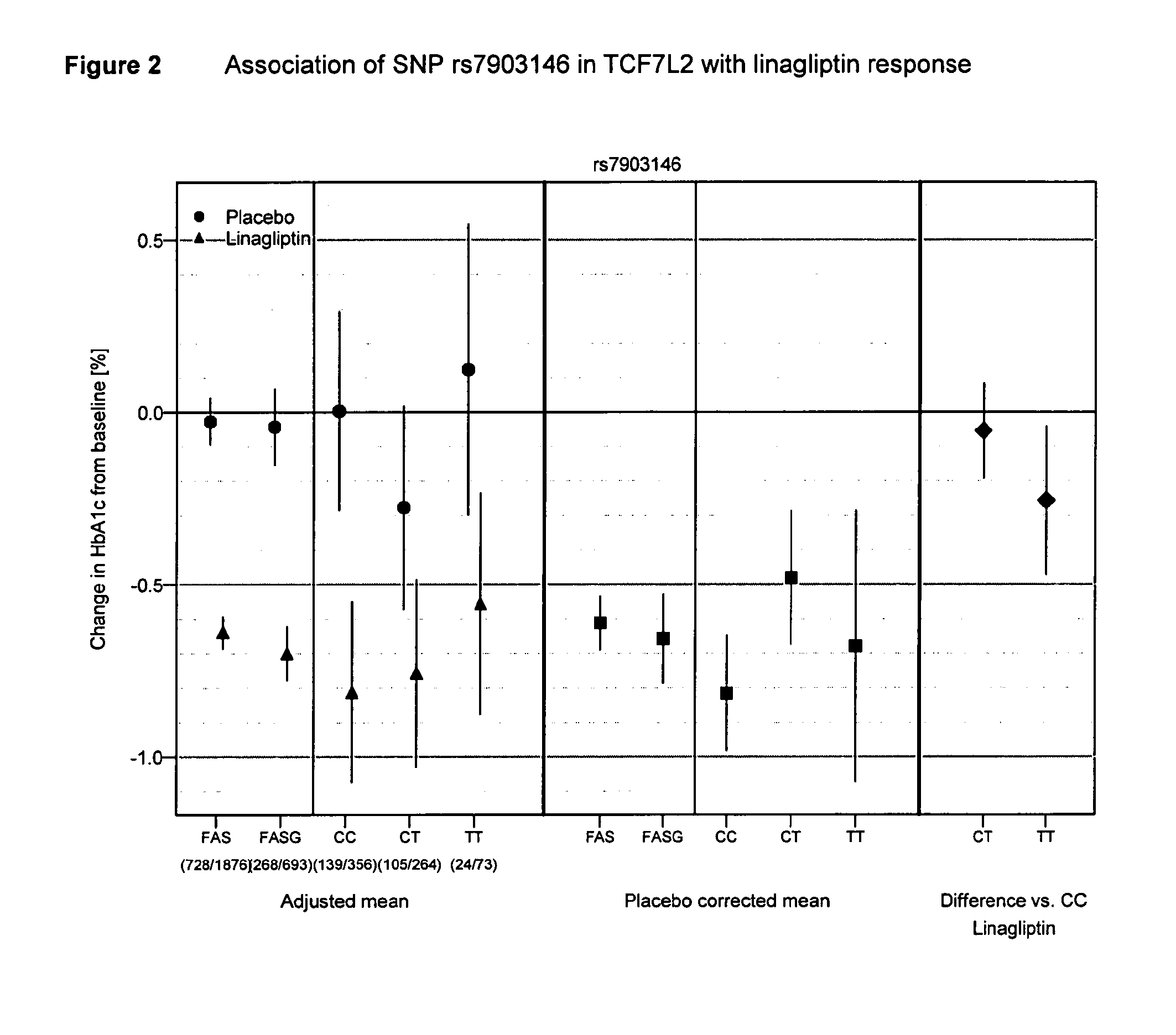
Treatment of genotyped diabetic patients with dpp-iv inhibitors such as linagliptin
ActiveUS20130196898A1Weight increaseLose weightBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsPatient groupGenotype
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com