Method for specifically knocking out hepatitis B virus by CRISPR/Cas9 and gRNA applied to specific targeting HBV DNA
A hepatitis B virus, specific technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve problems such as unsatisfactory suppression effect, high HBV gene mutation rate, and low HBV gene mutation rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
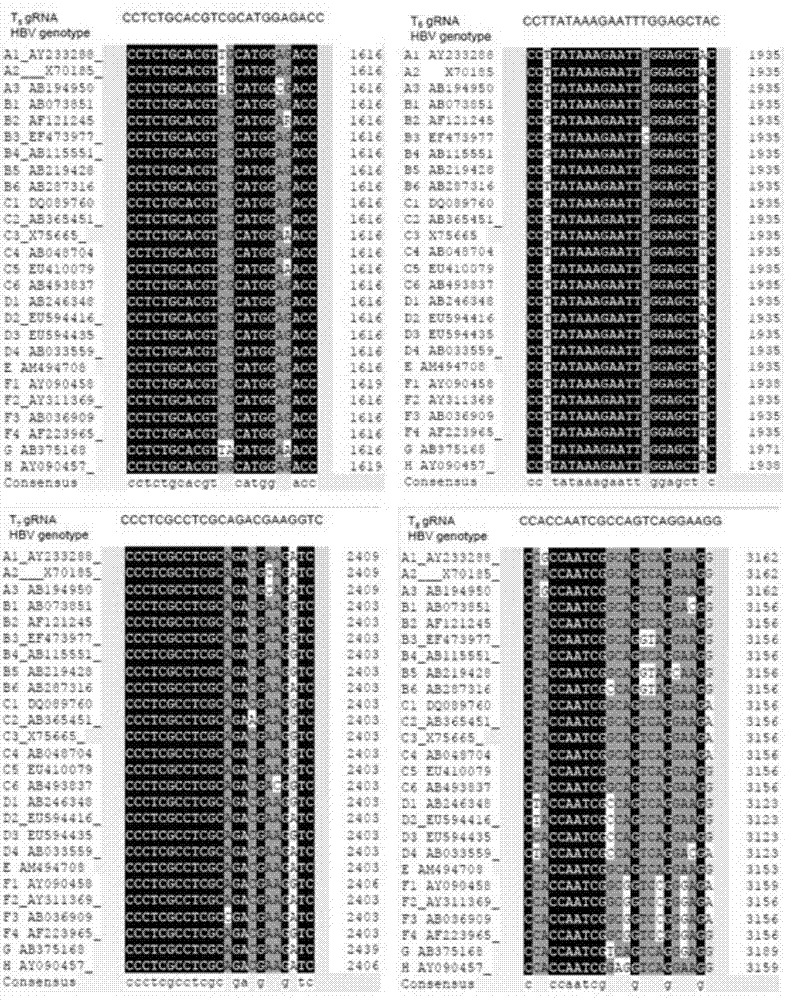
[0047] [Example 1] Design, synthesis and eukaryotic expression vector construction of gRNA sequences targeting 26 different genotypes of HBV conservative sequences
[0048] 1. Selection and design of gRNA targeting HBV DNA
[0049] Using the D-type HBV (Genebank ID: V01460.1) as the reference sequence, use the Crispr design tool on crispr.mit.edu to find the target site with a higher score on the HBV DNA. The target site sequence is in the form of 5'-N (20)-NGG3' or 5'-CCN-N(20)-3'. Different from the previous design, we compared the HBV DNA sequences of 26 different genotypes, and selected gRNA sequences located in highly conserved regions from the found target sites. These conserved regions themselves are also gene mutations during the replication process. low rate areas. At the same time, the human genome sequence was compared, gRNAs with high homology to the human genome sequence were excluded, and a series of brand new, unreported gRNA sequences and targets were fin...
Embodiment 2
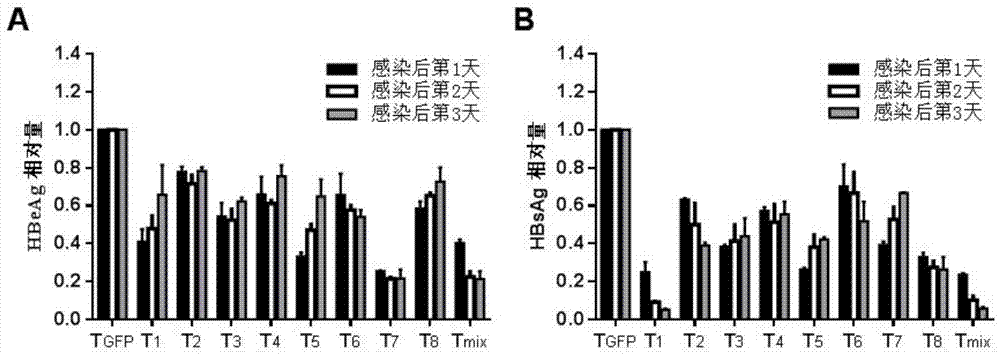
[0075] [Example 2] Verifying the inhibition of HBV replication by the gRNA-guided CRISPR / Cas9 system of the present invention at the cellular level
[0076] In order to verify whether the gRNA-guided CRISPR / Cas9 system designed in the present invention has the ability to resist HBV replication, the clone of the gRNA constructed in the present invention was combined with the replicon pHBV1.3 of hepatitis B virus (genotype D; Genebank ID: V01460.1) were co-transfected into the liver cancer cell line HepG2, and another gRNA targeting GFP (T GFP ) (SEQ ID NO. 18) was used as a control group. To normalize the transfection efficiency between different wells, each well was transfected with the same amount of β-galactosidase expression plasmid pSVβ-gal. After 24, 48, and 72 hours of transfection, the culture supernatant was taken to measure the expression levels of hepatitis B virus surface antigen (HBsAg) and hepatitis B virus e antigen (HBeAg). The results showed that 8 diffe...
Embodiment 3
[0131] [Example 3] Inhibition of HBV replication by the combined use of any two or more gRNAs
[0132] When we use multiple gRNAs in combination, the CRISPR / Cas9 system can cut two or more sites on HBV DNA at the same time, so that two or more sites can be mutated at the same time, thereby improving the inhibition efficiency of HBV. Especially when Tmix is used in combination, multiple HBV DNA breakpoints may be generated due to untimely repair, which will further degrade HBV DNA, reduce the survival rate of HBV, and greatly improve the efficiency of the CRISPR / Cas9 system to clear HBV. In the present invention, HepG2 cells were co-transfected with Tmix, pHBV1.3, and pSVβ-gal, a combination of 8 gRNAs. After 2 or 4 days of culture, ELISA, Northern blot, and qPCR were used to detect their inhibitory efficiency against HBV. From the experimental results, it can be seen that the inhibitory effect of Tmix on hepatitis B virus is significantly better than that of any gRNA alo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com