Patents
Literature
244 results about "Surgical blade" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
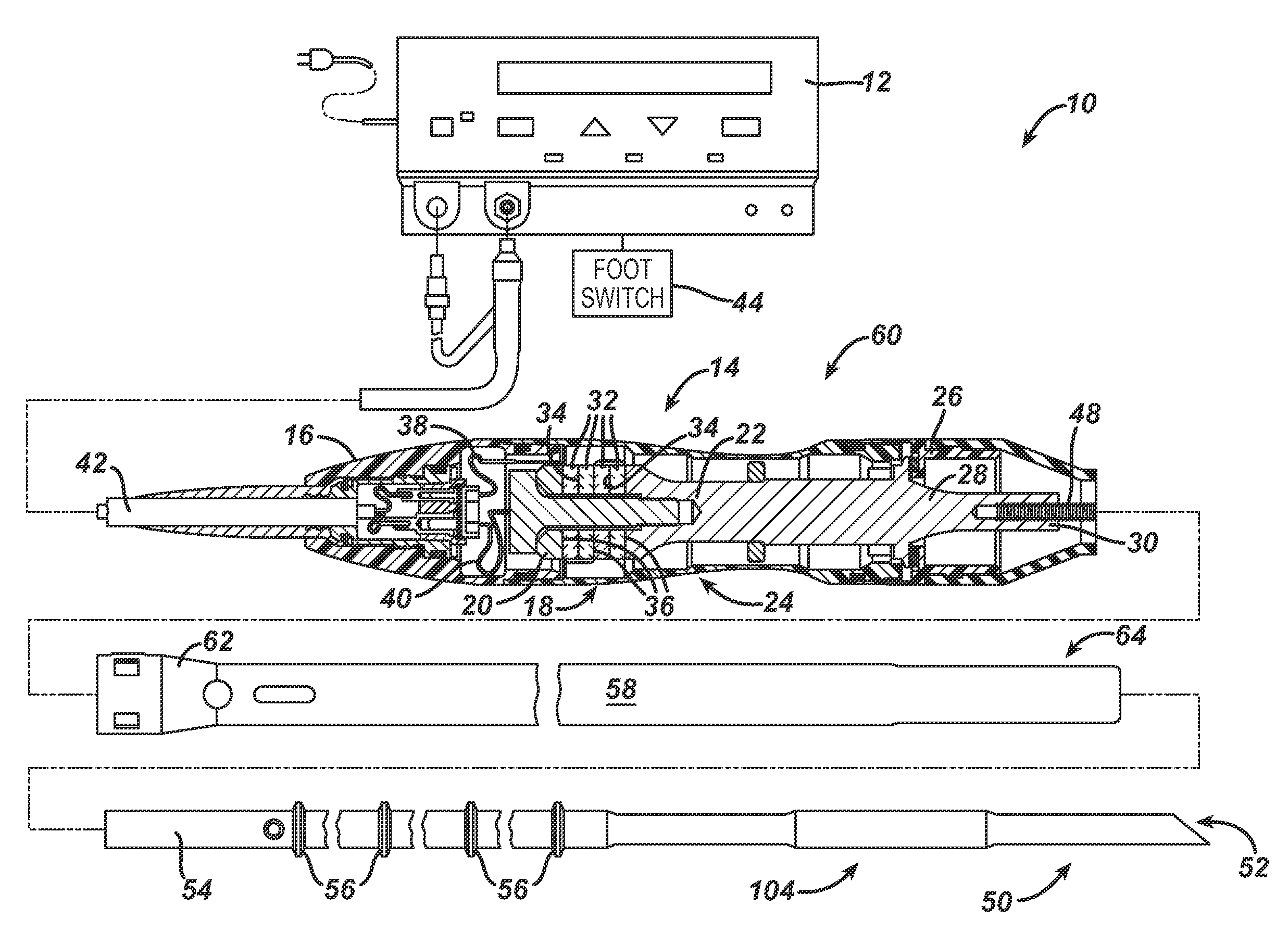
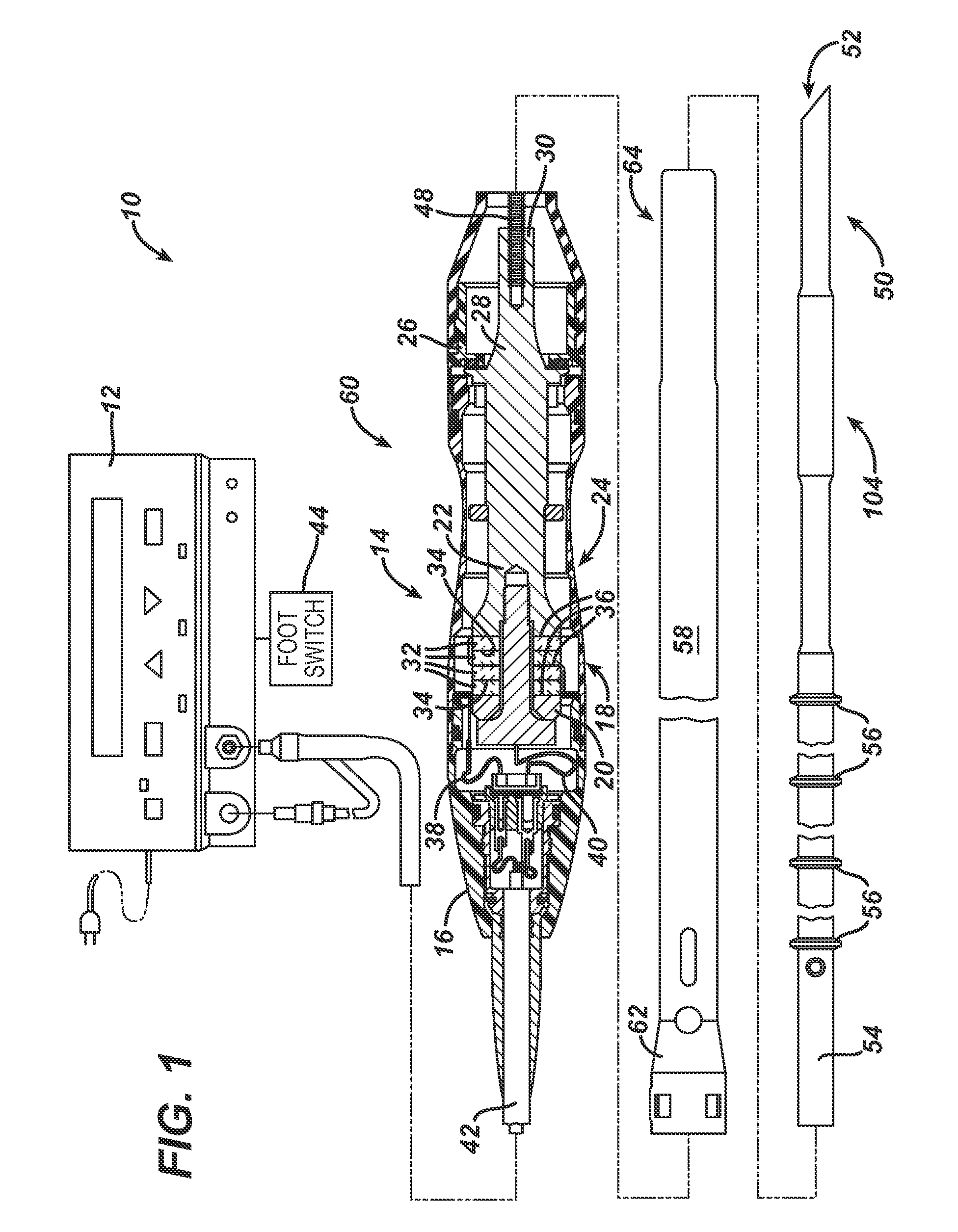
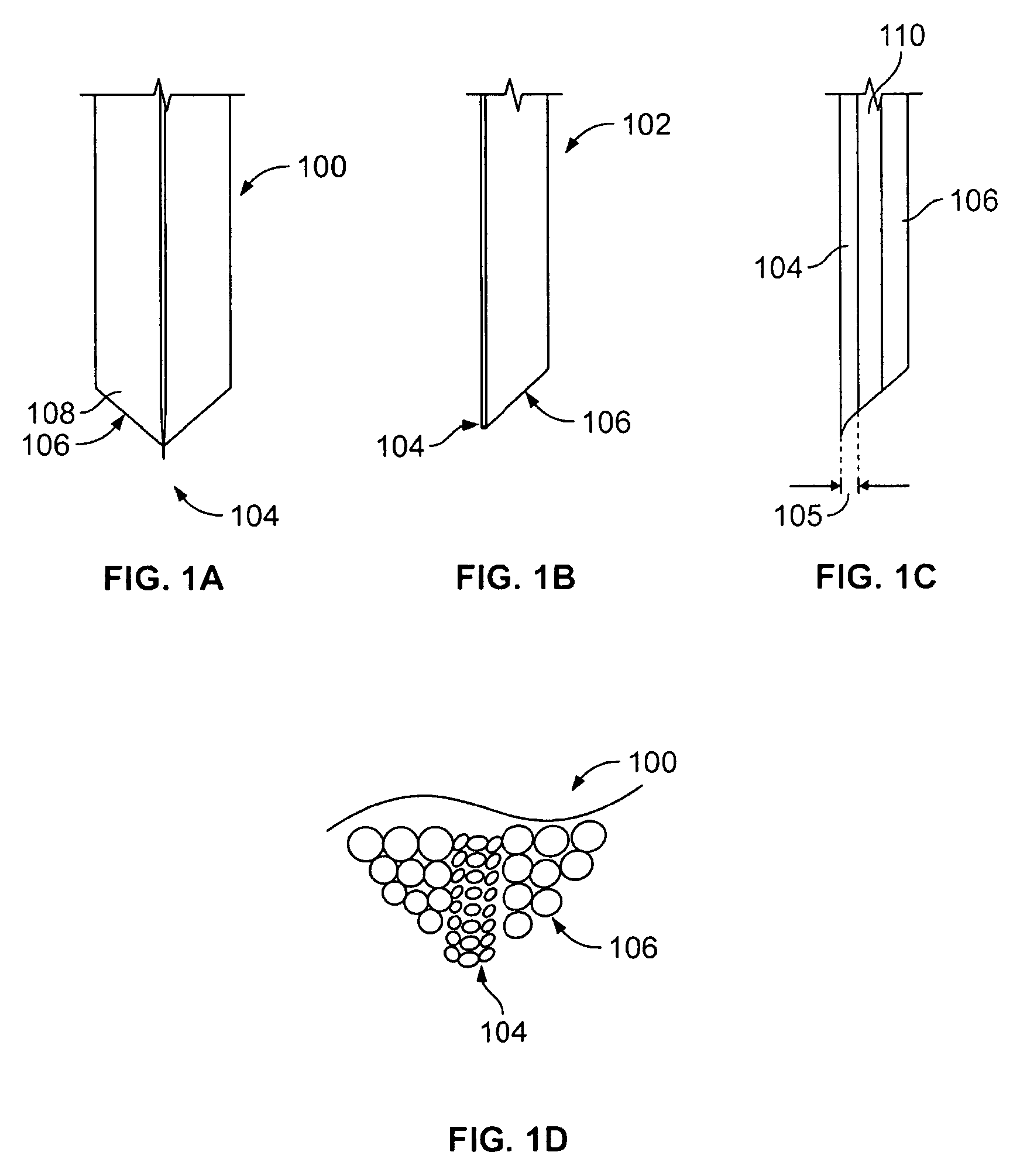
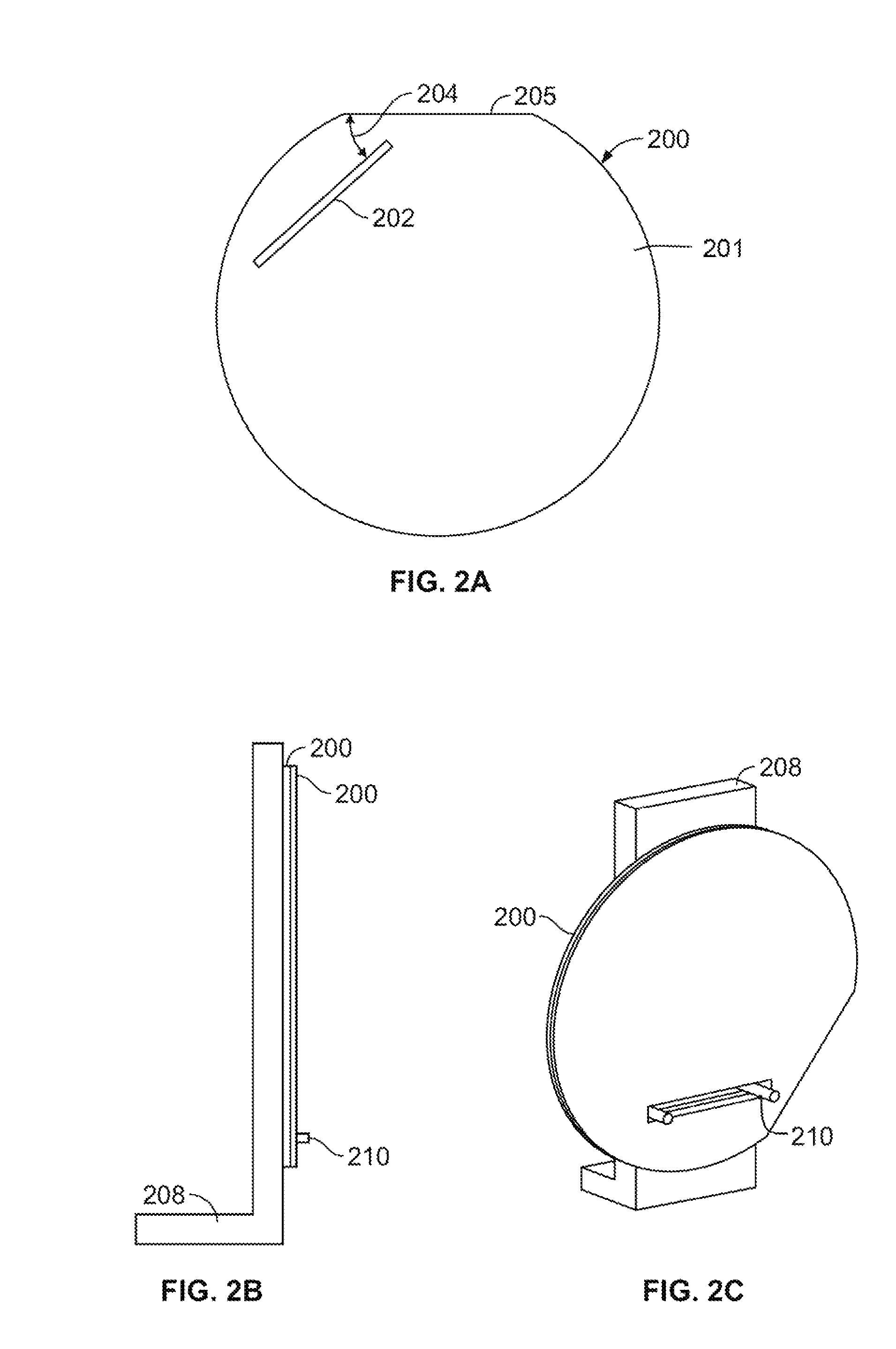
Ultrasonic surgical blade
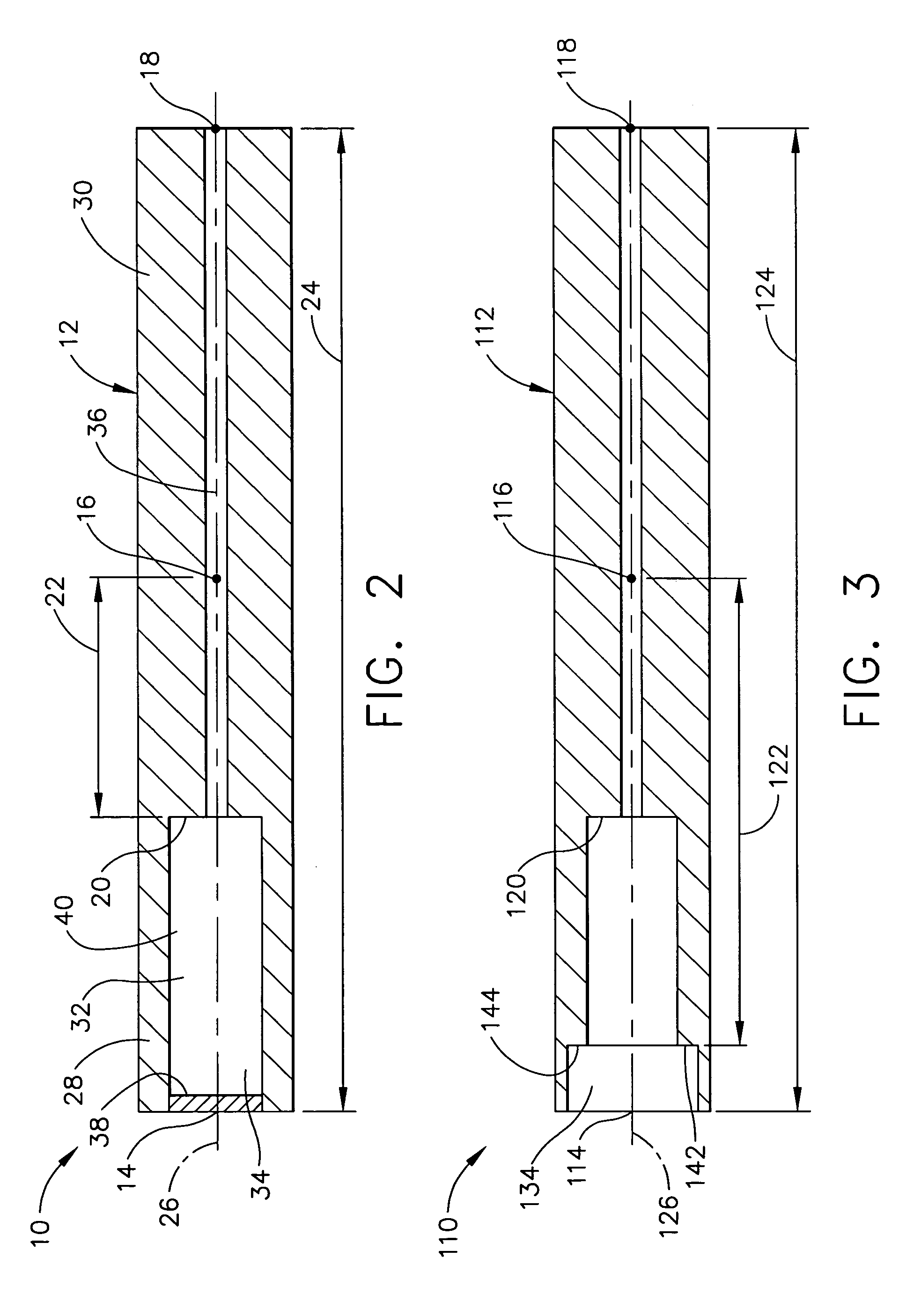
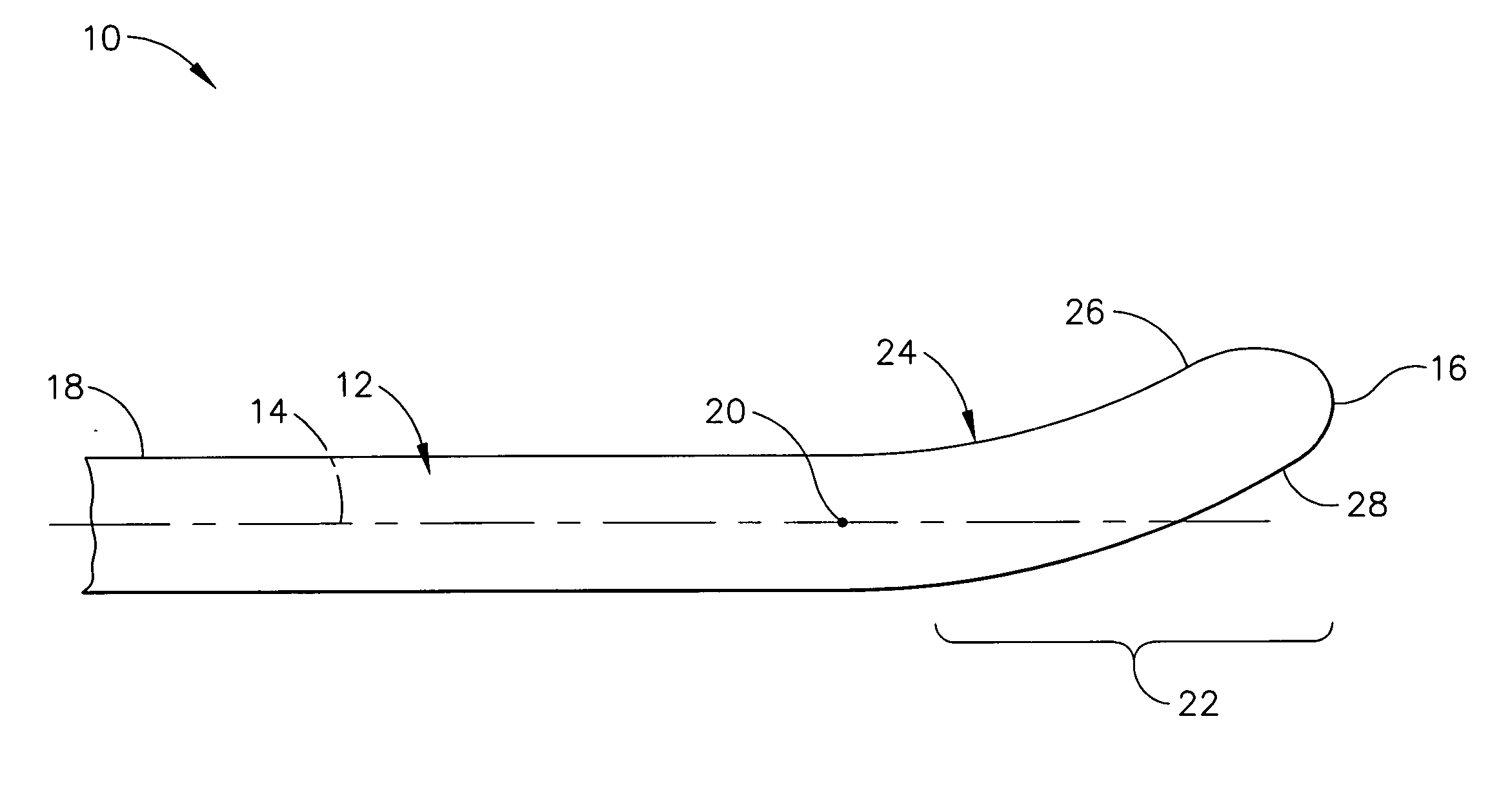
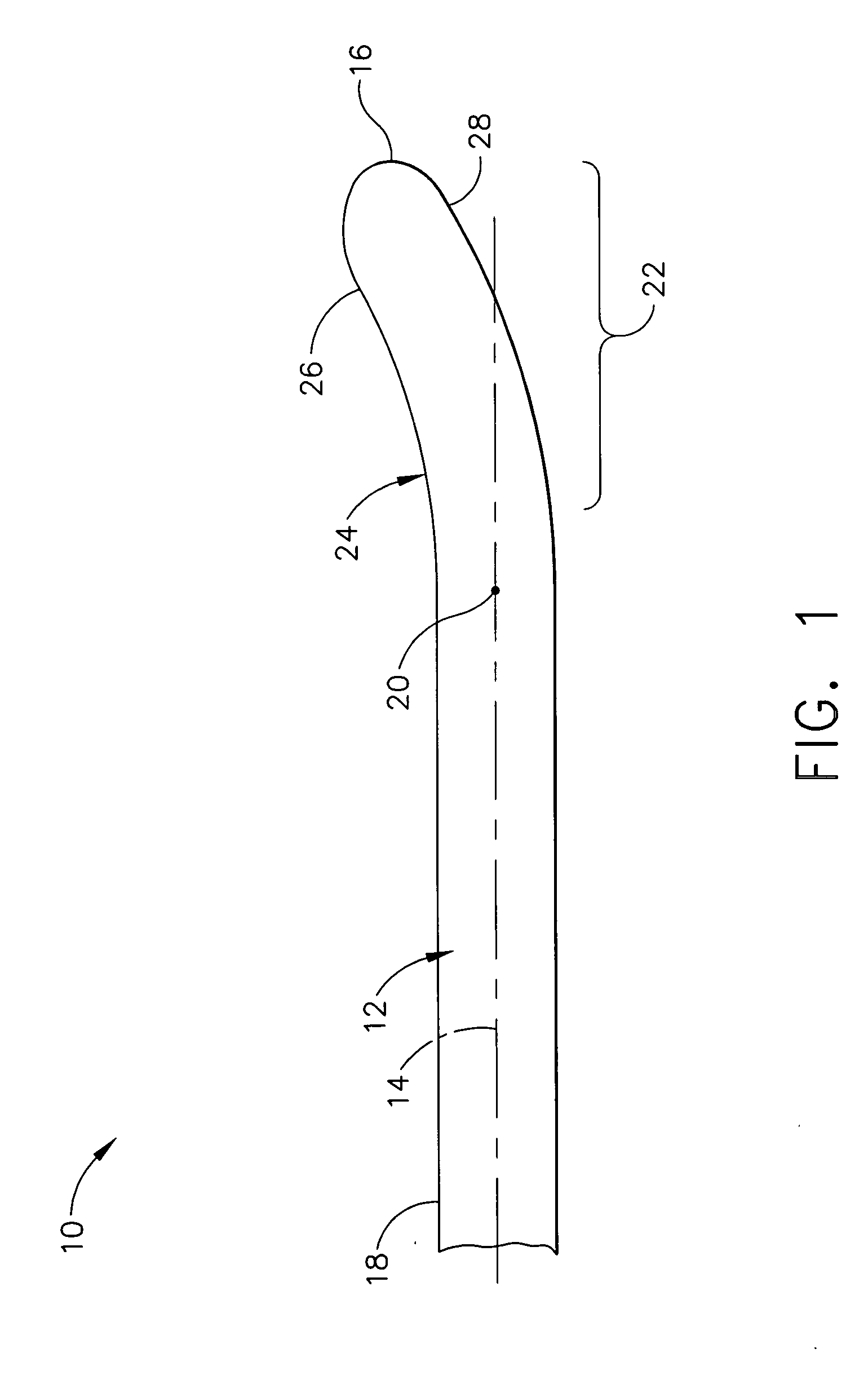
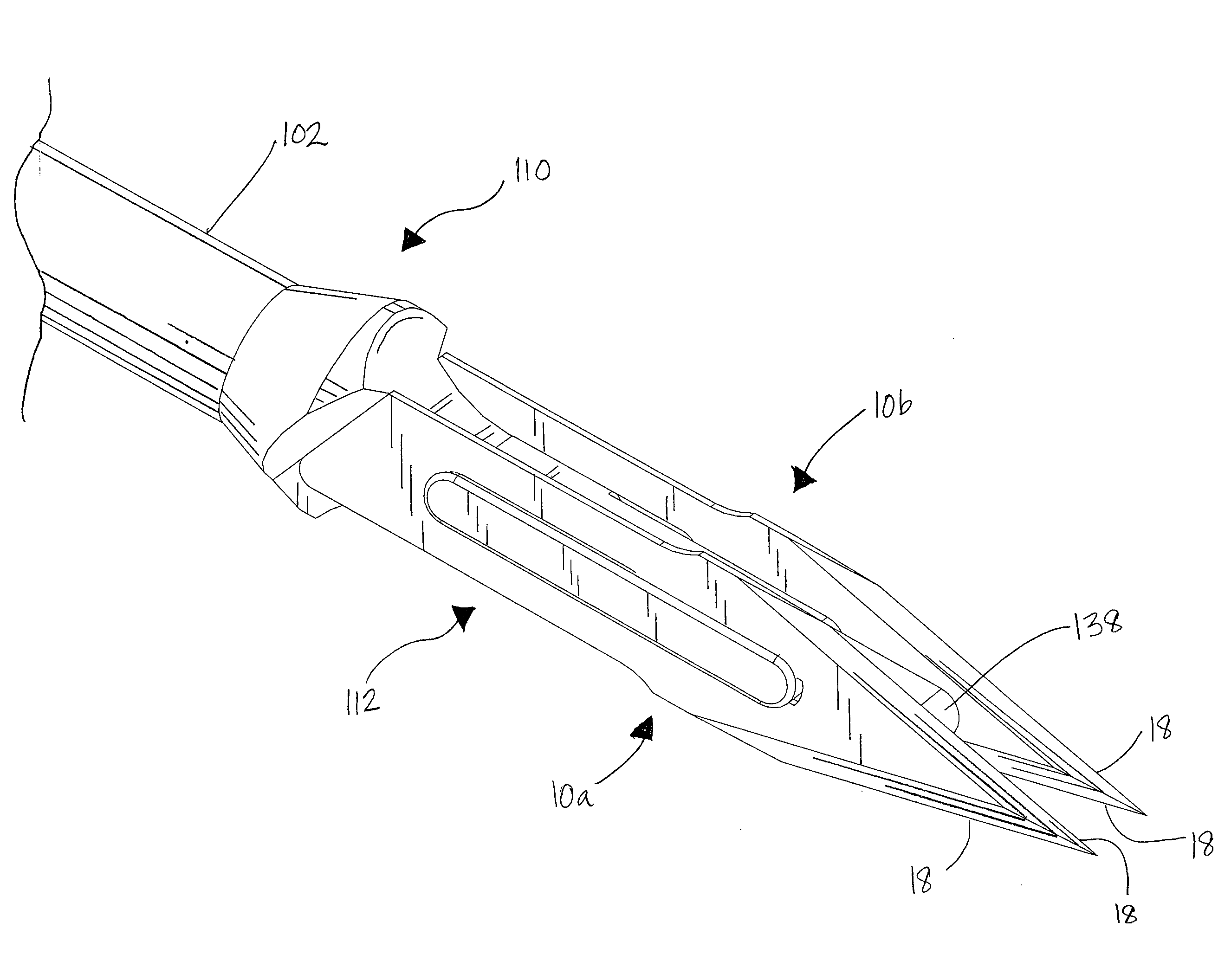
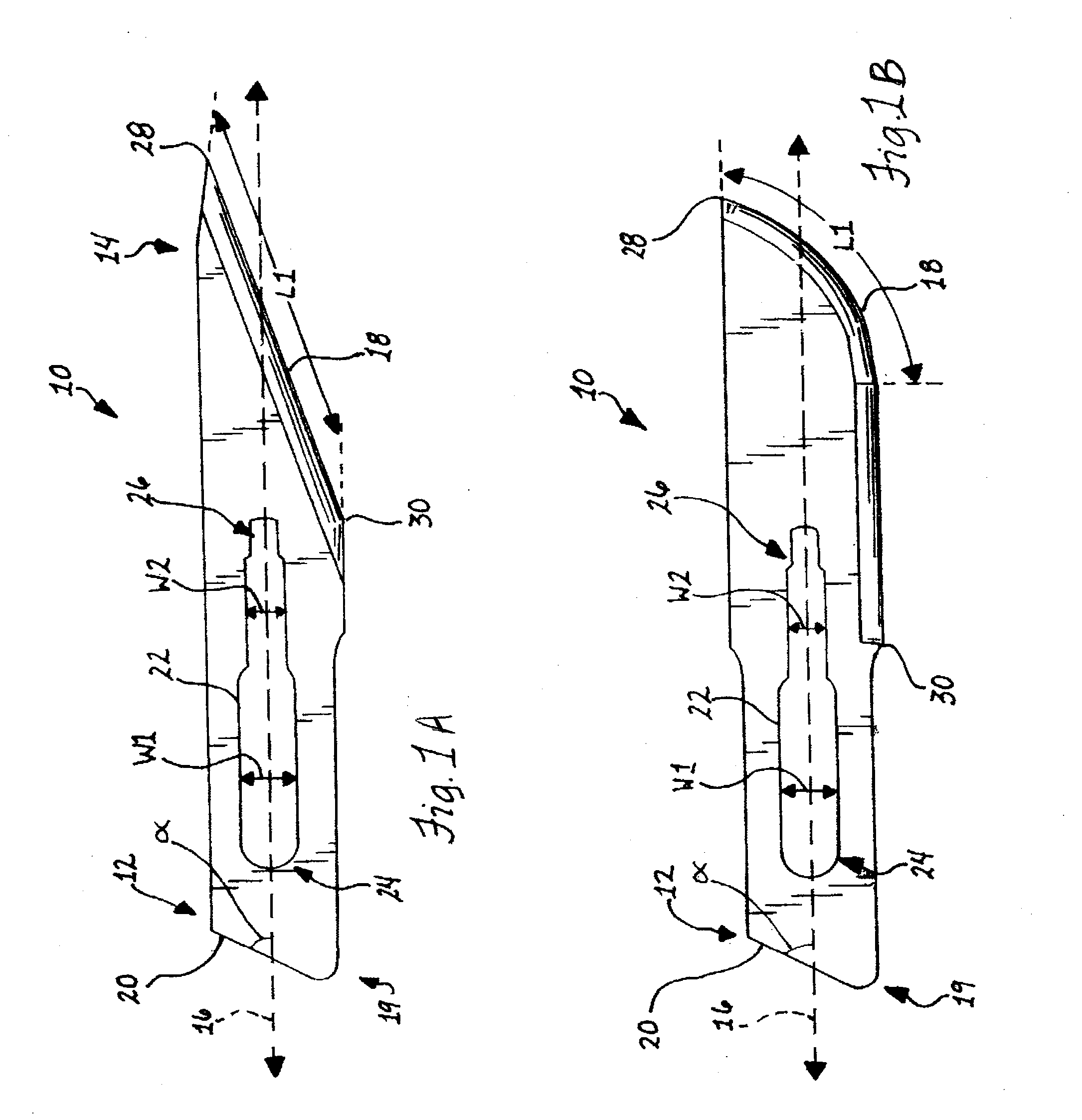
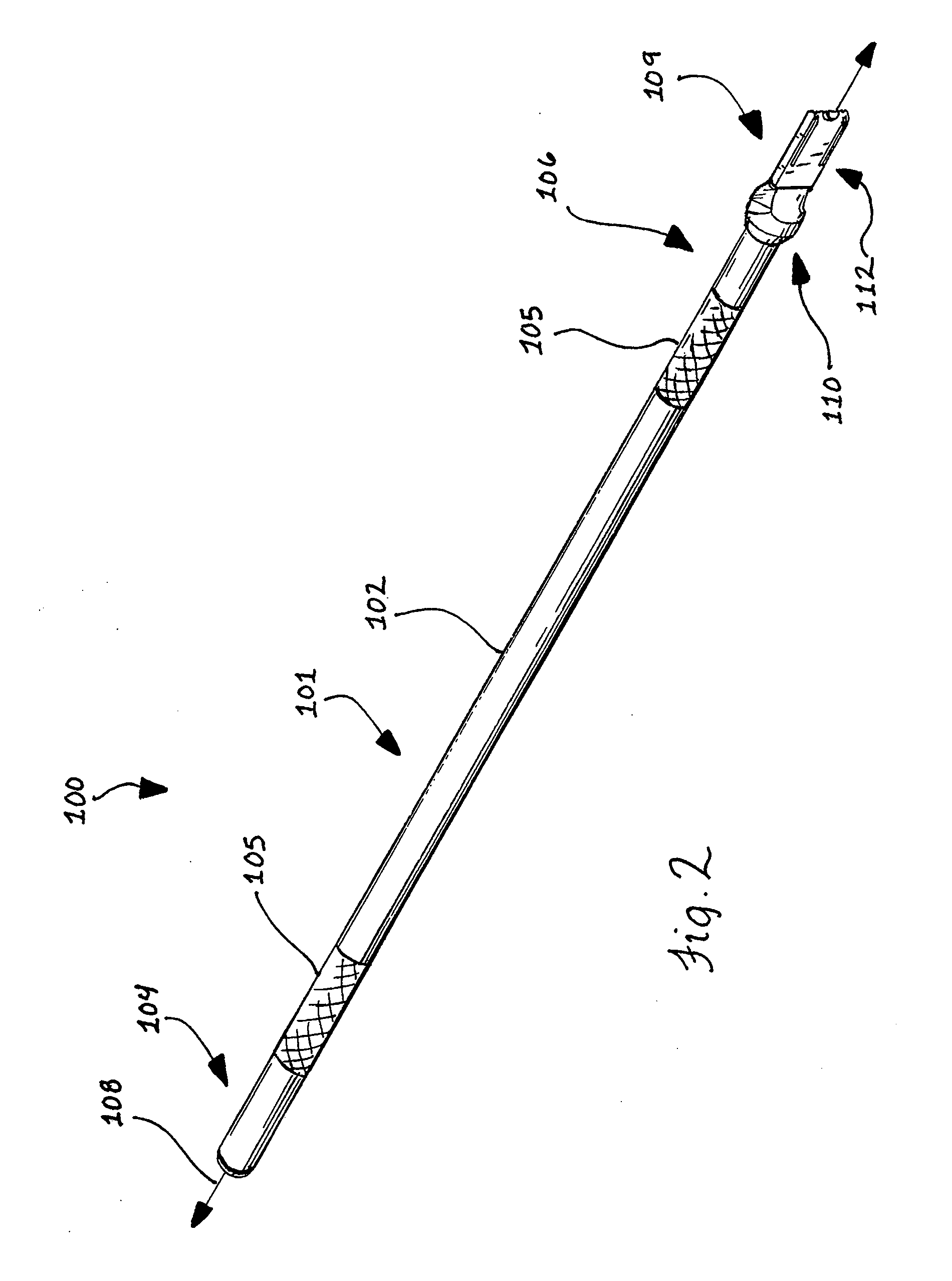
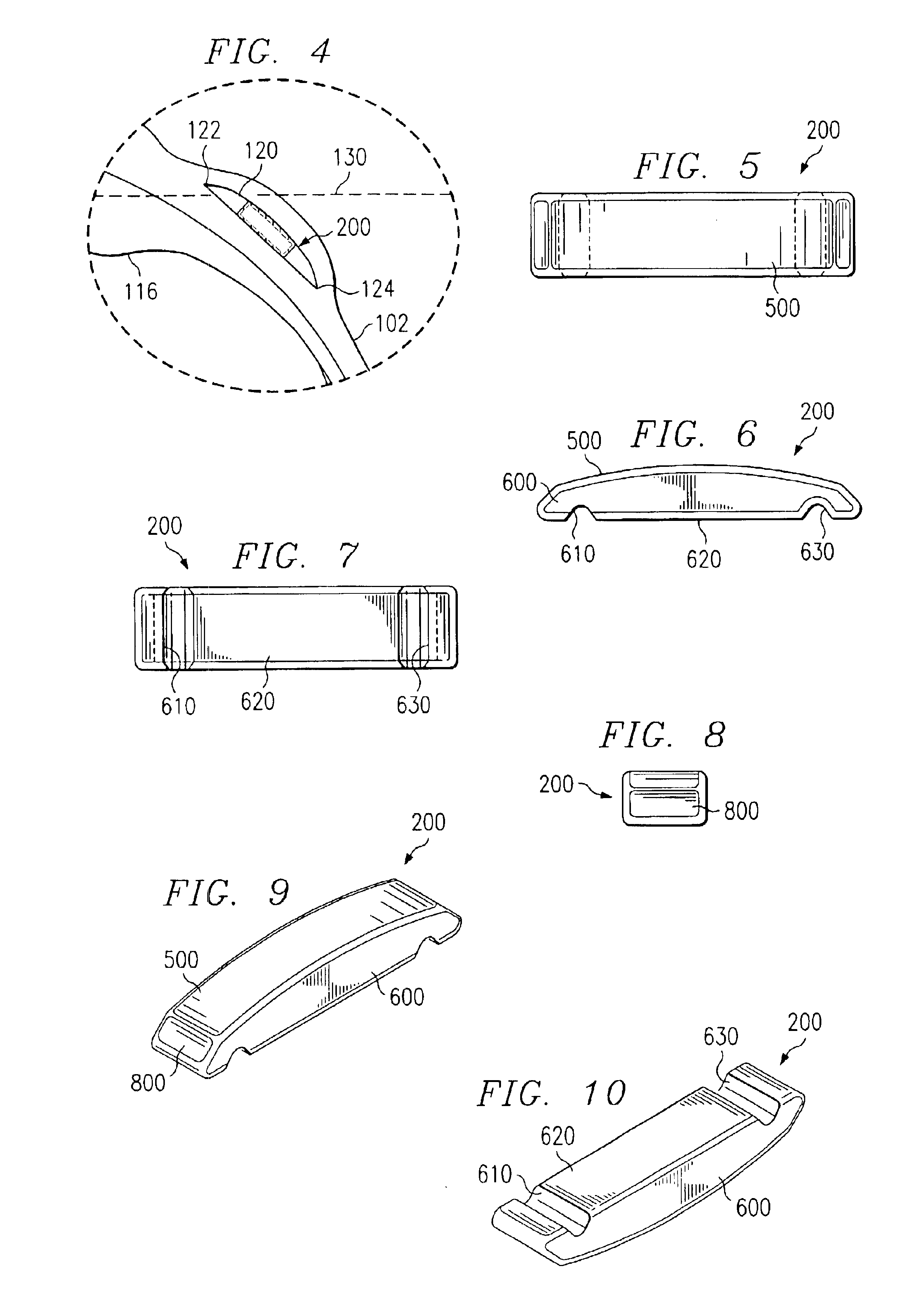
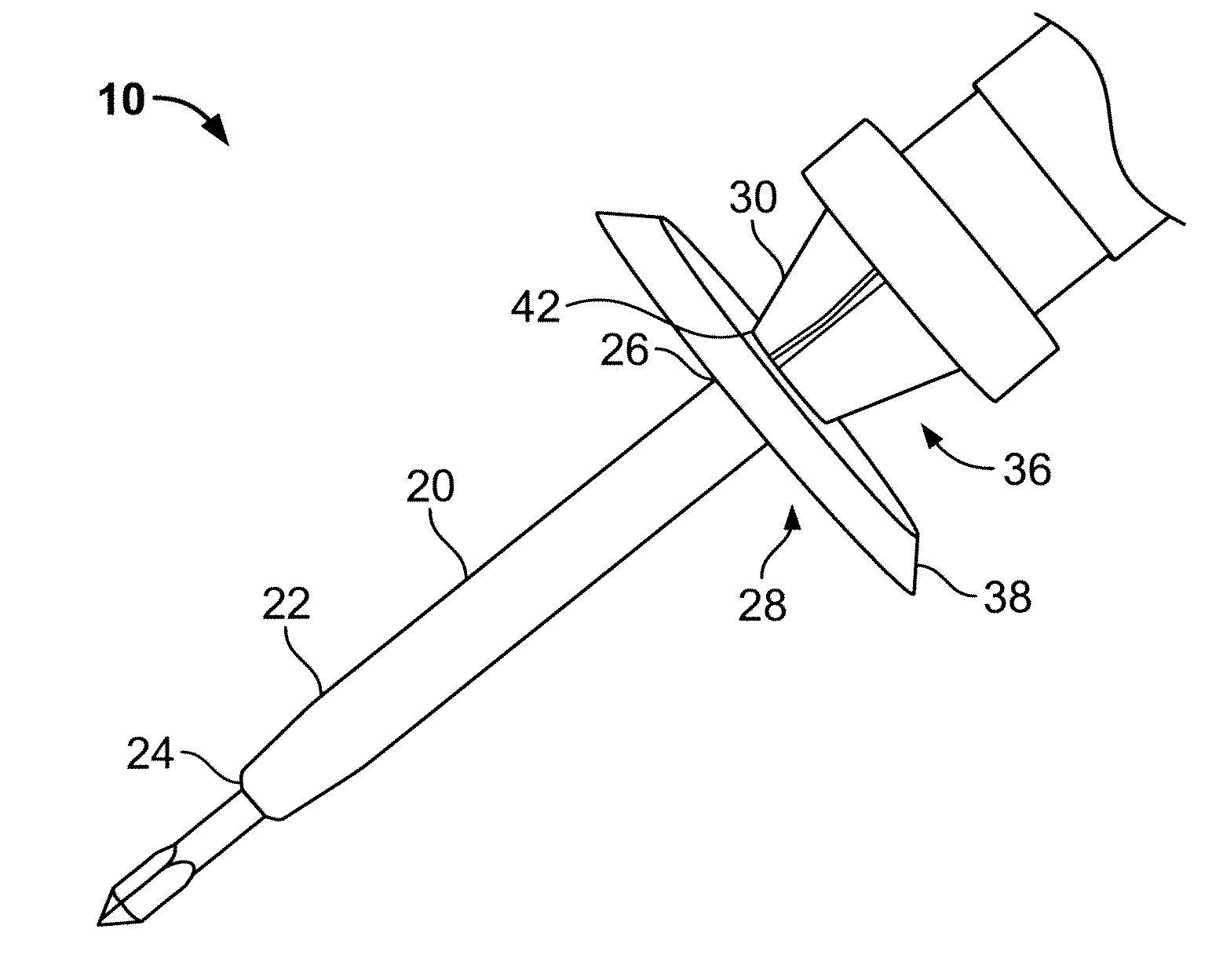
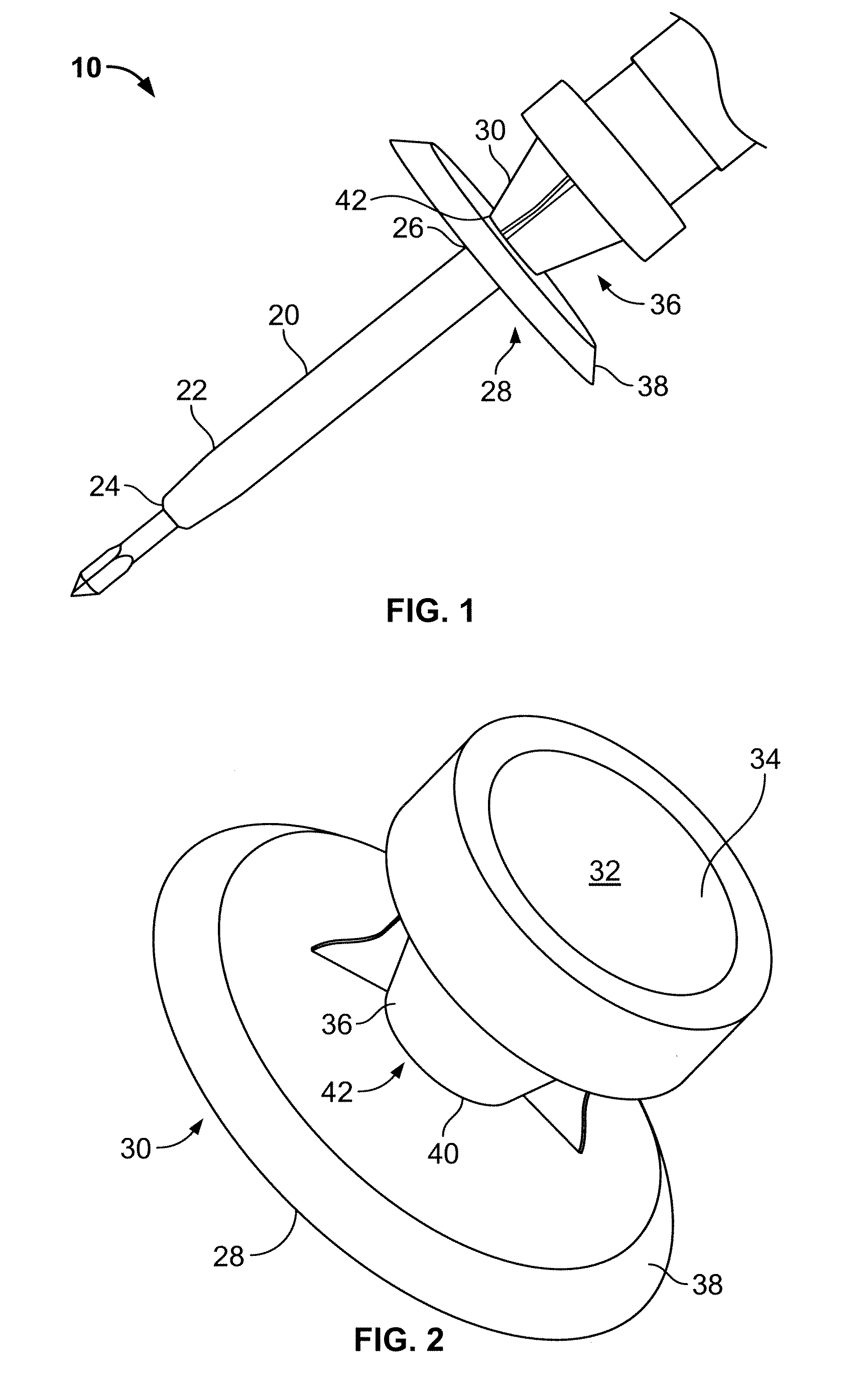
An ultrasonic surgical blade includes a body having an external surface, at least one cutting edge, and a distal end. In at least one embodiment, the cutting edge can be defined by first and second surfaces which define an angle therebetween. In various embodiments, at least a portion of the cutting edge comprises a sharp point. In other embodiments, at least a portion of the cutting edge and surface comprise a sharp point and or a beveled surface.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT +1
Microsurgical cutting instruments
InactiveUS8499673B2Reduce probabilityLow manufacturing process costIncision instrumentsLapping machinesSurgical bladeKnife blades
The present invention relates to methods and apparatus for self-sharpening micro surgical blades, knives and assemblies including those having a cutting edge that is less than 500 angstroms thick where the cutting edge is an exposed section of a thin planar layer or region that is supported on one or both sides by a material having a higher wear rate.
Owner:MYNOSYS CELLULAR DEVICES INC
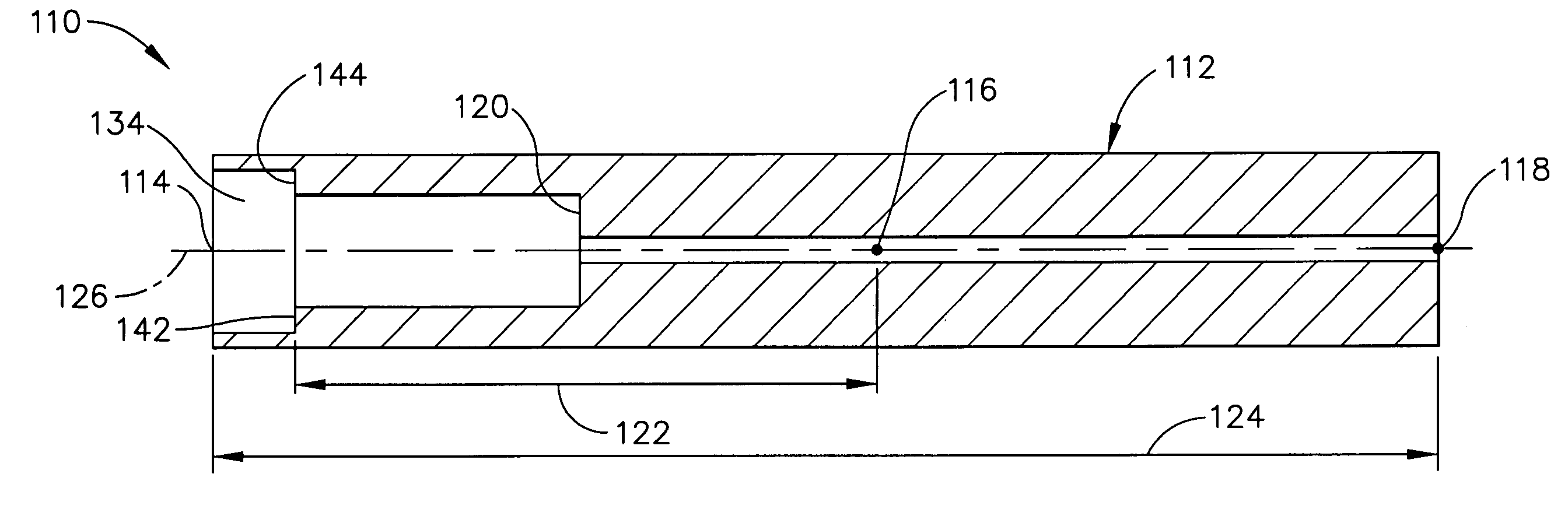
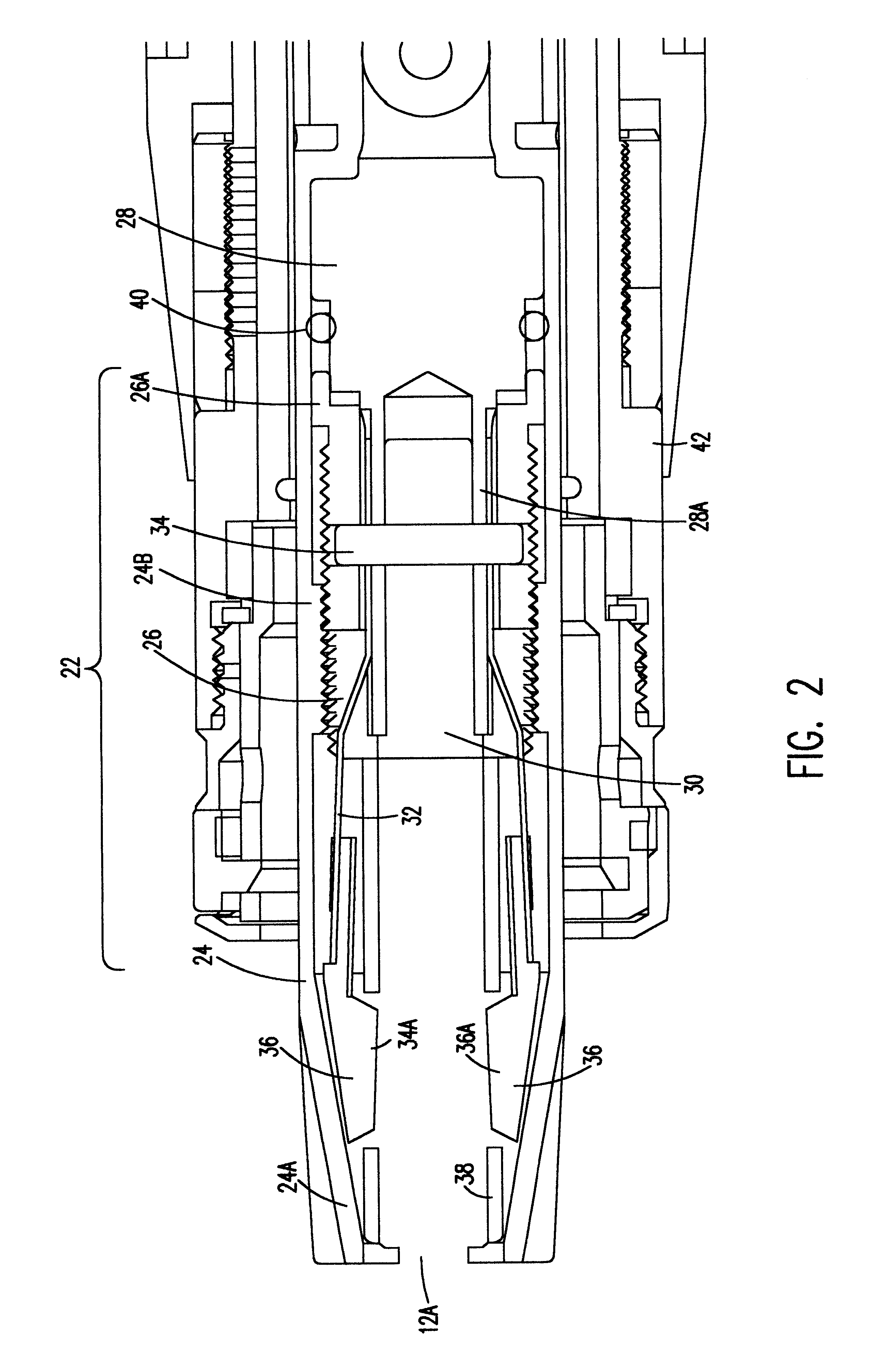
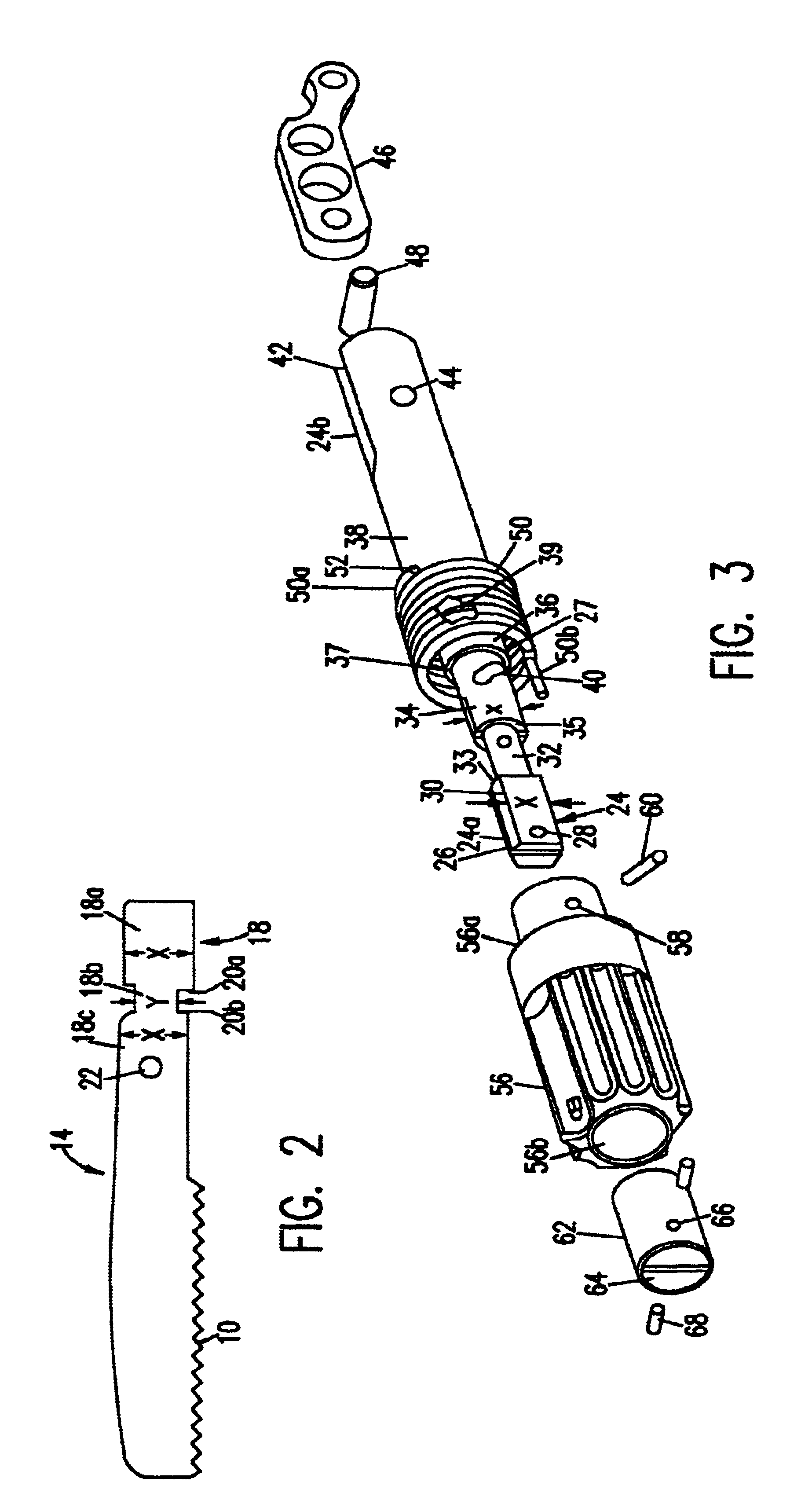
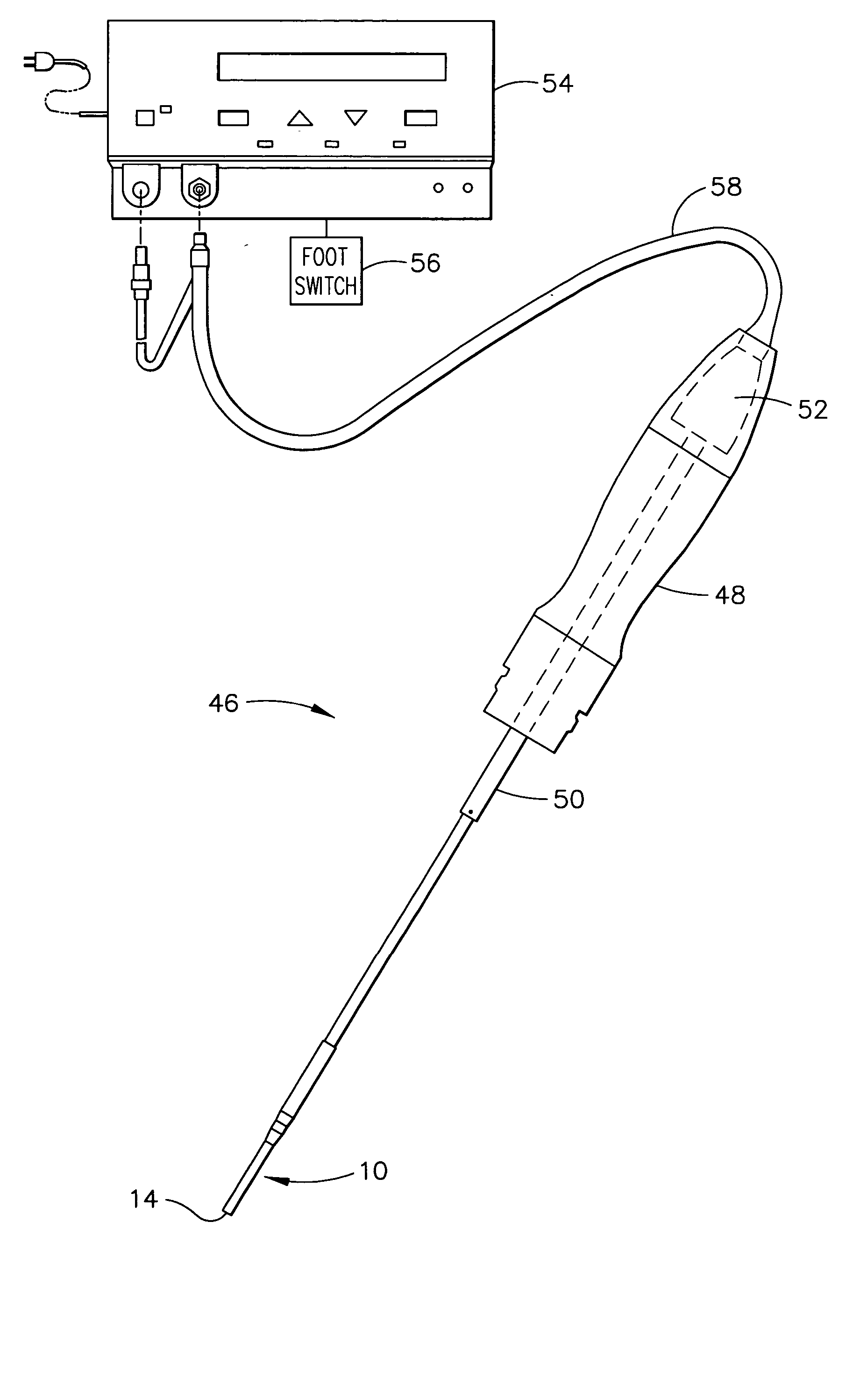
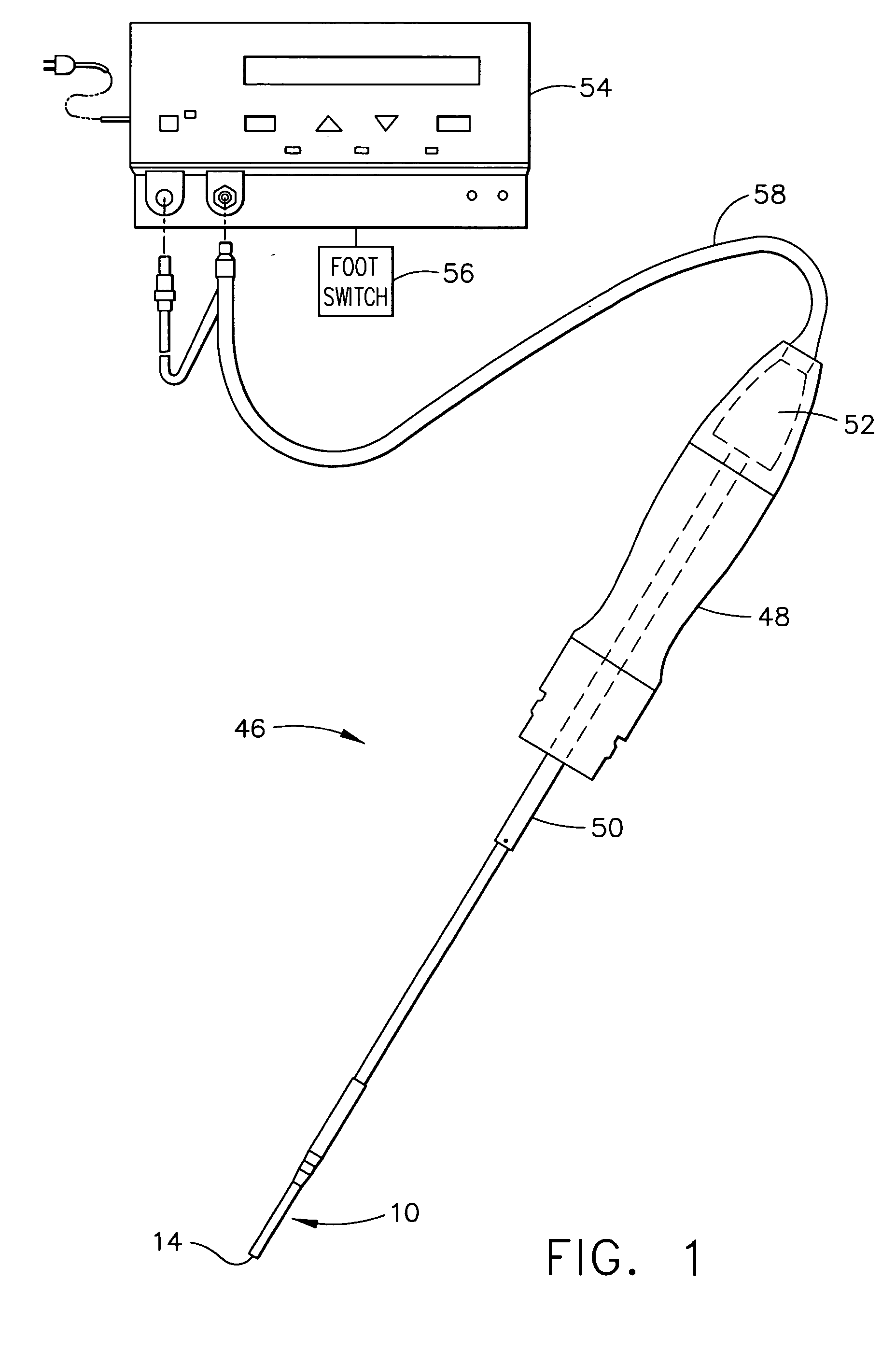
Ultrasonic surgical blade and instrument having a gain step
ActiveUS7163548B2Increase the lengthShorten half wave lengthCannulasTooth pluggers/hammersSurgical bladeWavelength
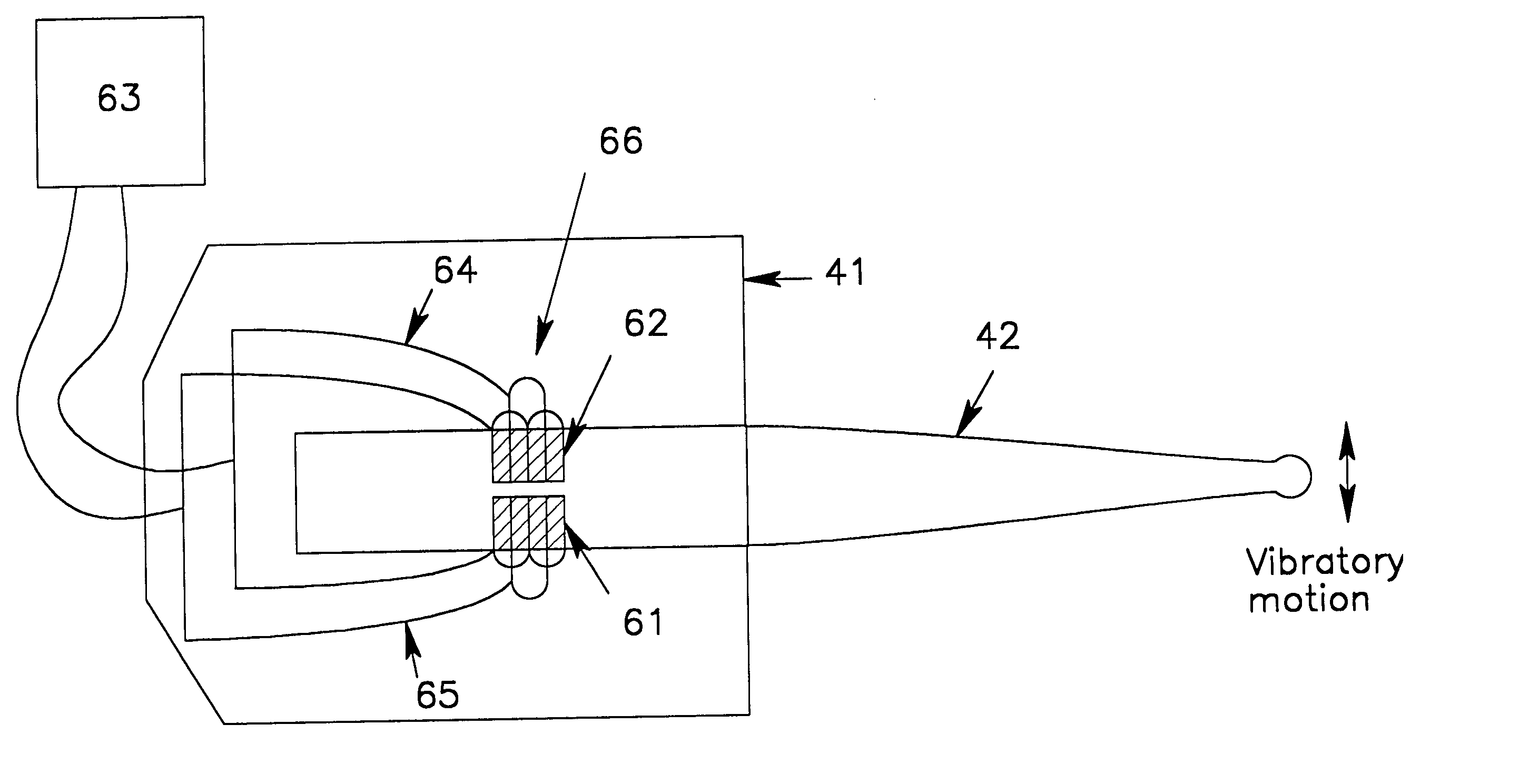
An ultrasonic surgical blade, and an instrument, having a gain step. The blade body has, in any half wave length of the ultrasonic-surgical-blade body, a first vibration antinode, a vibration node, a second vibration antinode, and a gain step. The gain step is located between the second vibration antinode and the first vibration antinode. The gain step is spaced apart from the vibration node by a gain-step distance greater than 5% of the distance between the second vibration antinode and the first vibration antinode. The instrument includes the blade, a handpiece having an ultrasonic transducer, and an ultrasonic transmission rod whose proximal end is operatively connected to the ultrasonic transducer and whose distal end activates the blade. In one option, the first vibration antinode is the distal tip, and the gain step is located between the vibration node and the distal tip, resulting in an increased active length of the blade.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Ultrasonic surgical blade having transverse and longitudinal vibration
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT +1
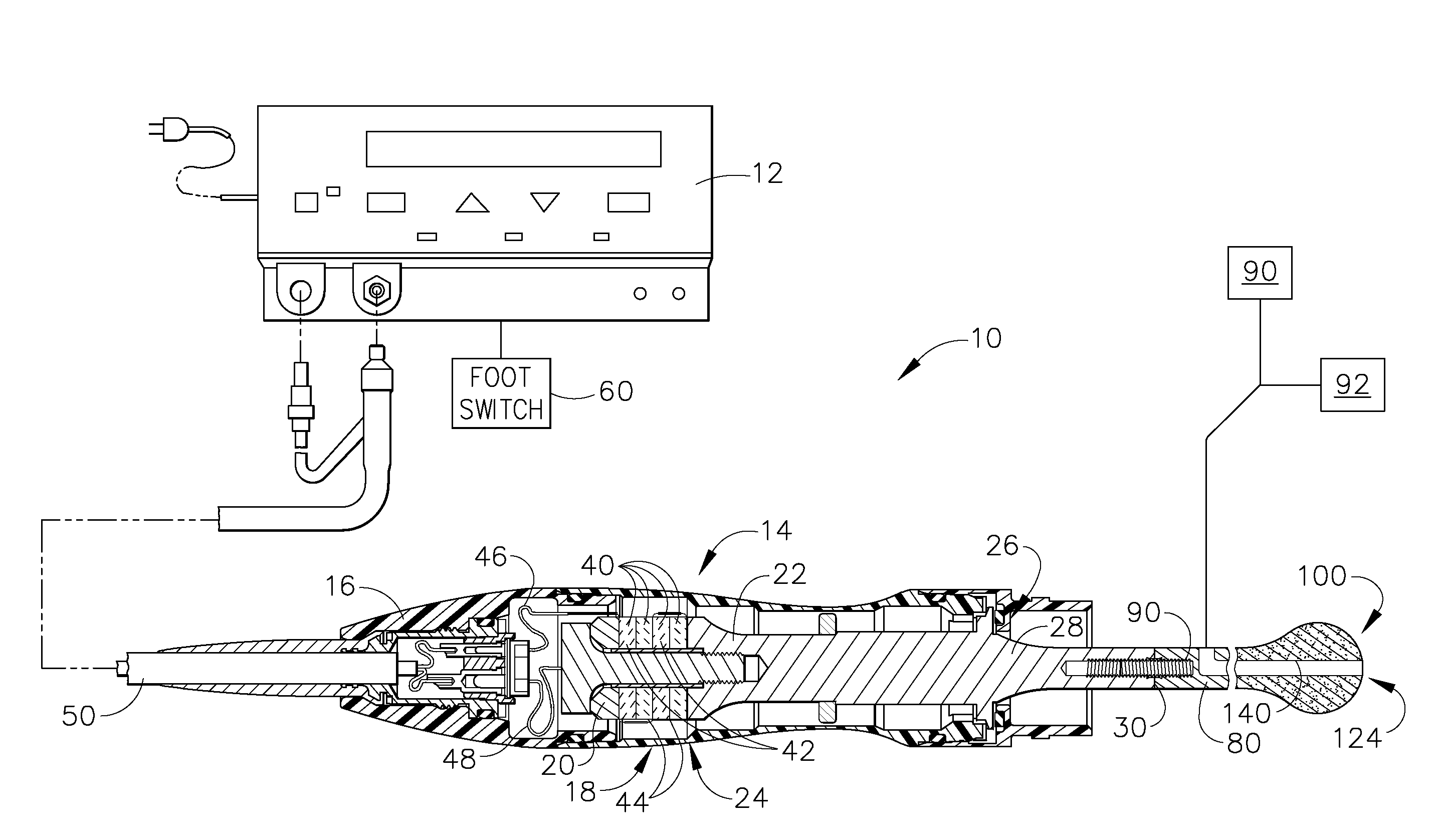
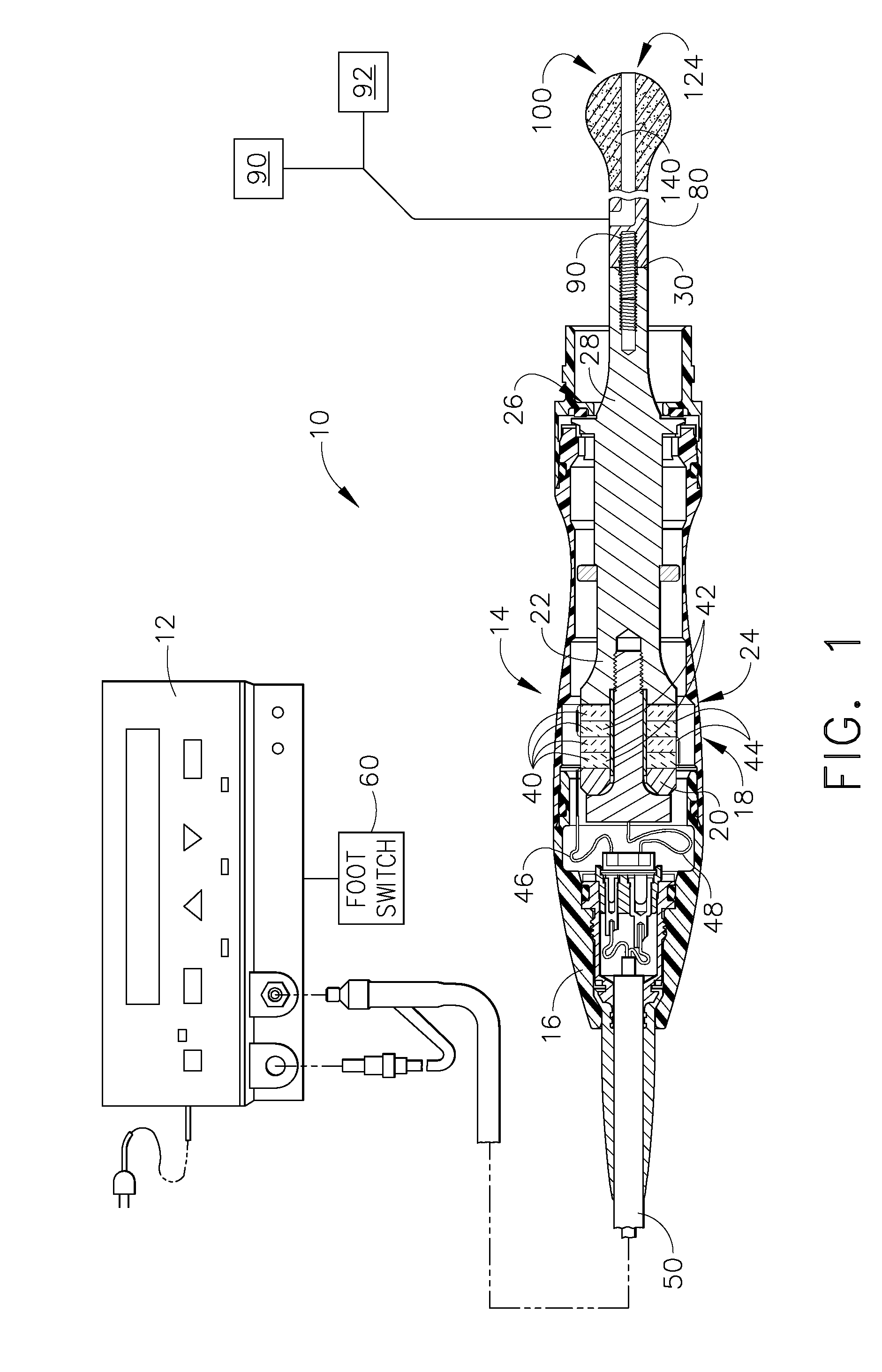
Ultrasonic surgical instrument incorporating fluid management
ActiveUS20050049546A1Load minimizationEfficient removalDiaphragm valvesEngine diaphragmsSurgical bladeSonification
Disclosed is an ultrasonic surgical device having a distally / proximally movable fluid management system consisting of single lumen or multiple lumens. The invention provides for the delivery of irrigation fluid or the removal of fluid, debris or vapor from the tissue-effecting portion of the blade while minimizing the loading on the blade. The blades of the surgical device, when excited at a natural blade system frequency, will have modal shapes characterized by longitudinal, transverse and / or torsional motion and will have nodal locations for these motions at positions along the tissue effecting length of the blade. The instrument is designed to allow for the fluid management system to be positioned at one or more motion nodes to facilitate efficient removal of tissue or fluid, which tends to accumulate at such nodes of the ultrasonic surgical blades.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Ultrasonic surgical instrument incorporating fluid management
ActiveUS8348880B2Load minimizationEfficient removalDiaphragm valvesEngine diaphragmsSurgical operationSurgical blade
Disclosed is an ultrasonic surgical device having a distally / proximally movable fluid management system consisting of single lumen or multiple lumens. The invention provides for the delivery of irrigation fluid or the removal of fluid, debris or vapor from the tissue-effecting portion of the blade while minimizing the loading on the blade. The blades of the surgical device, when excited at a natural blade system frequency, will have modal shapes characterized by longitudinal, transverse and / or torsional motion and will have nodal locations for these motions at positions along the tissue effecting length of the blade. The instrument is designed to allow for the fluid management system to be positioned at one or more motion nodes to facilitate efficient removal of tissue or fluid, which tends to accumulate at such nodes of the ultrasonic surgical blades.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Ultrasonic shears stop pad
InactiveUS20090264909A1Negative frictional effectImprove wear resistanceSurgical scissorsSurgical bladeFilling materials
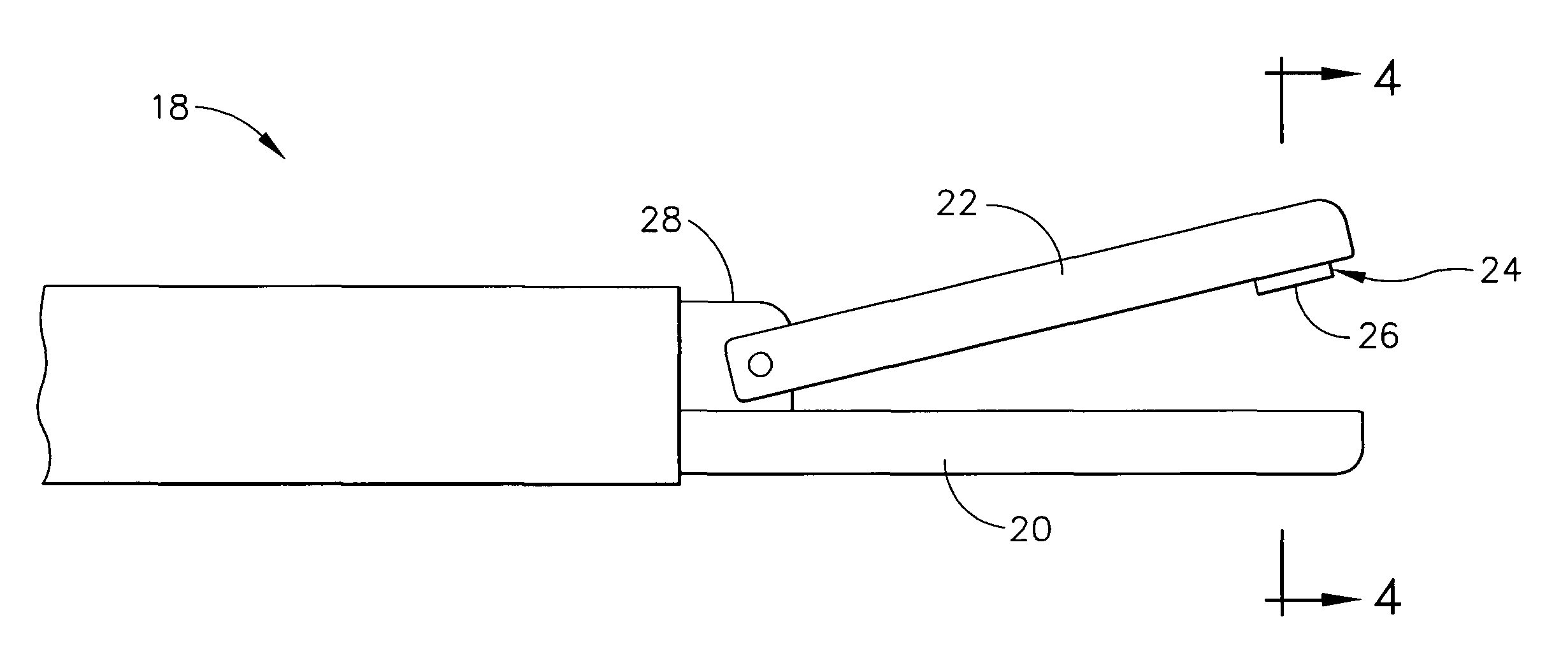
An ultrasonic-surgical-shears stop pad has a stop-pad body including a base material and at least one filler material. An alternate ultrasonic-surgical-shears stop pad has a stop-pad body adjacent to tissue pad. An ultrasonic surgical shears includes an ultrasonic surgical blade and a clamping arm which is operable to open and close toward the blade and which has a transversely and resiliently flexible distal tip. An alternate ultrasonic surgical shears includes an ultrasonic surgical blade, a clamping arm operable to open and close toward the blade, and a stop pad attached to the clamping arm and having a blade contact surface, wherein at least a portion of the stop pad is resiliently flexible in a direction substantially perpendicular to the blade contact surface.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Hook shaped ultrasonic cutting blade
ActiveUS20080009848A1Fast cutting speedDifficult to guideSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical sawsSurgical bladeUltrasonic vibration
An ultrasonic surgical blade has a blade body and a shank. The shank is fixed at one end to the blade body and is operatively connectable at an opposite end to a source of ultrasonic vibrations. The shank has a longitudinal axis. The blade body is eccentrically disposed relative to the axis.
Owner:MISONIX INC
Hook shaped ultrasonic cutting blade
ActiveUS8814870B2Less dead boneSmall incisionSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical sawsSurgical bladeEngineering
Owner:MISONIX INC
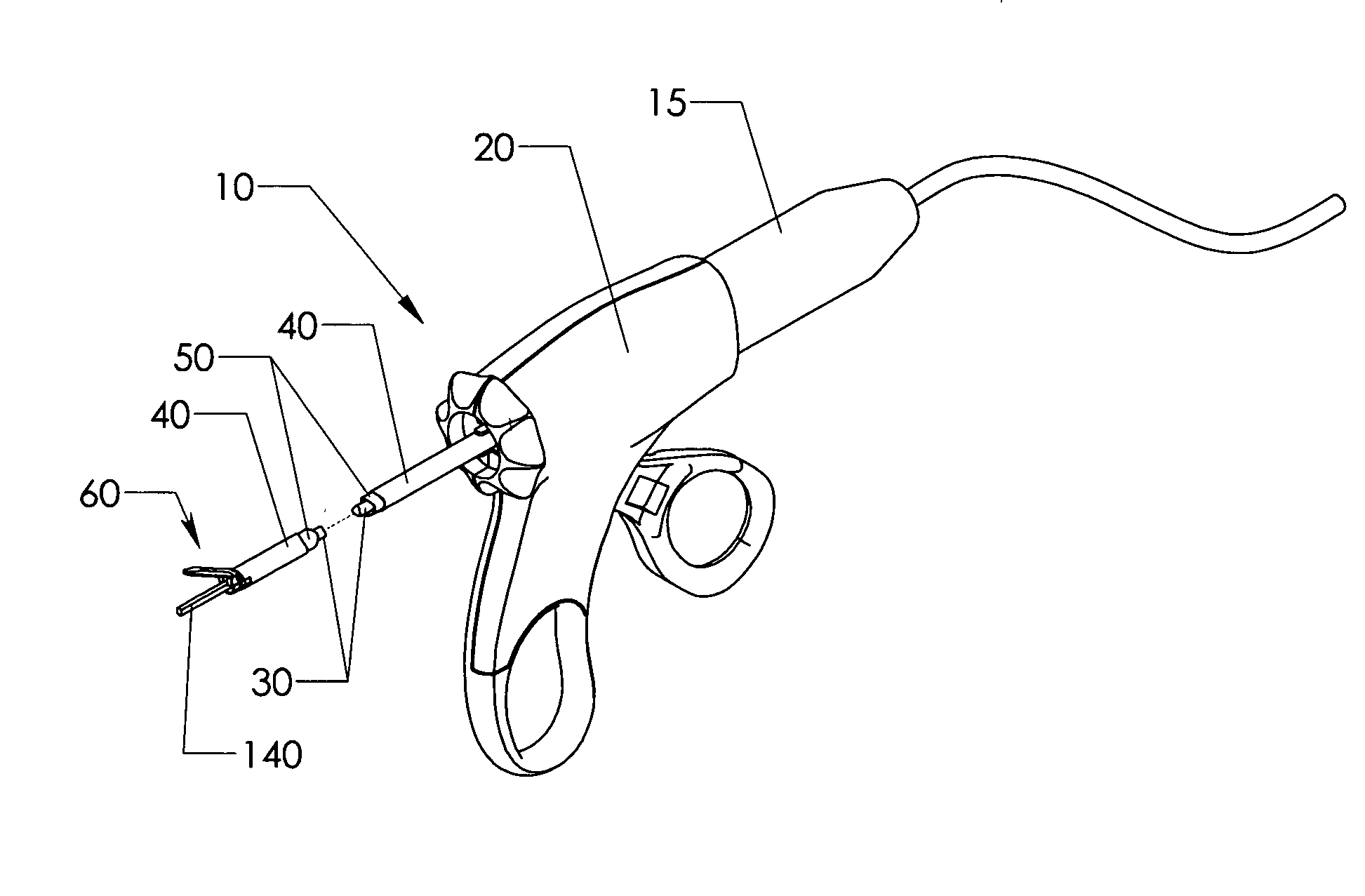
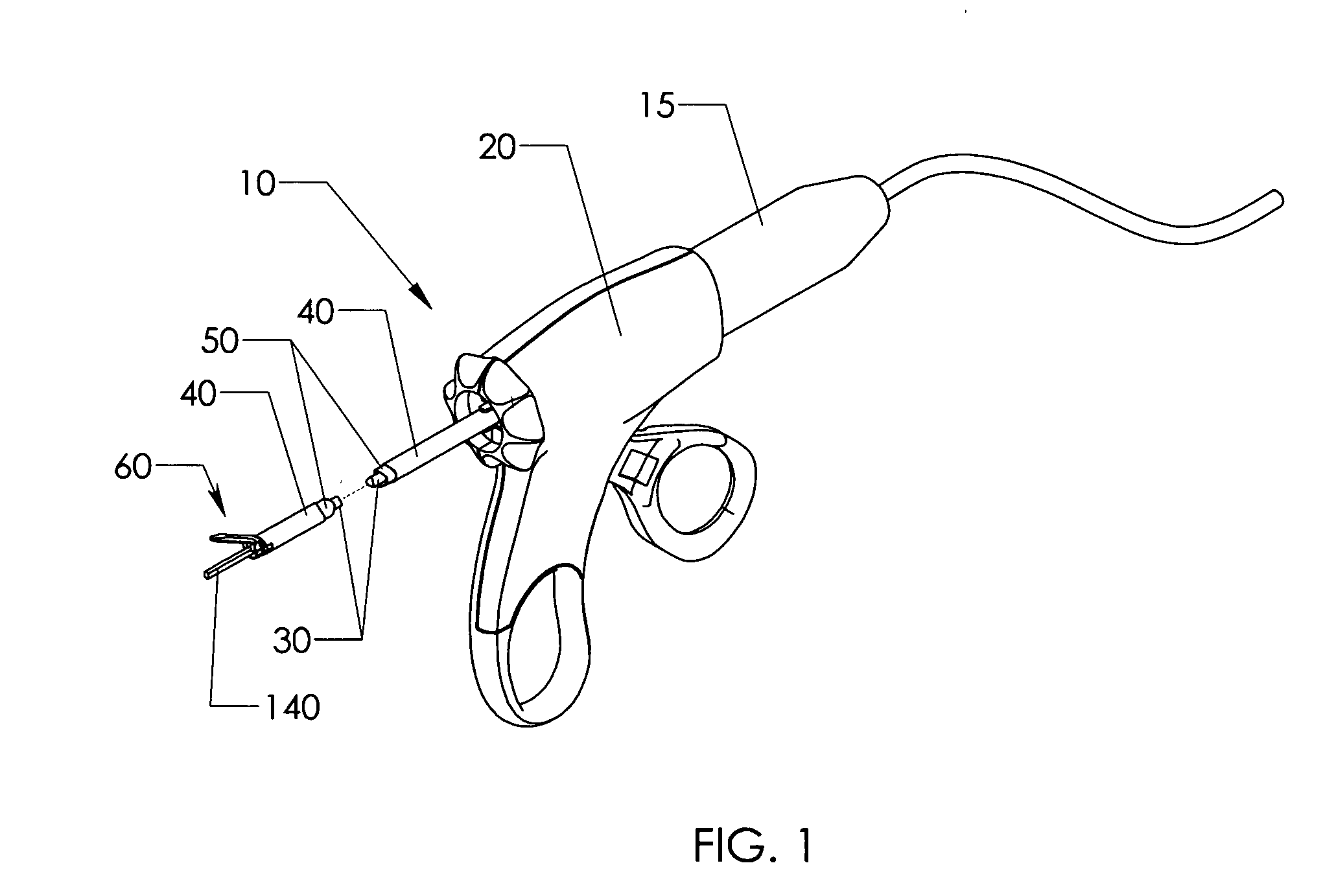
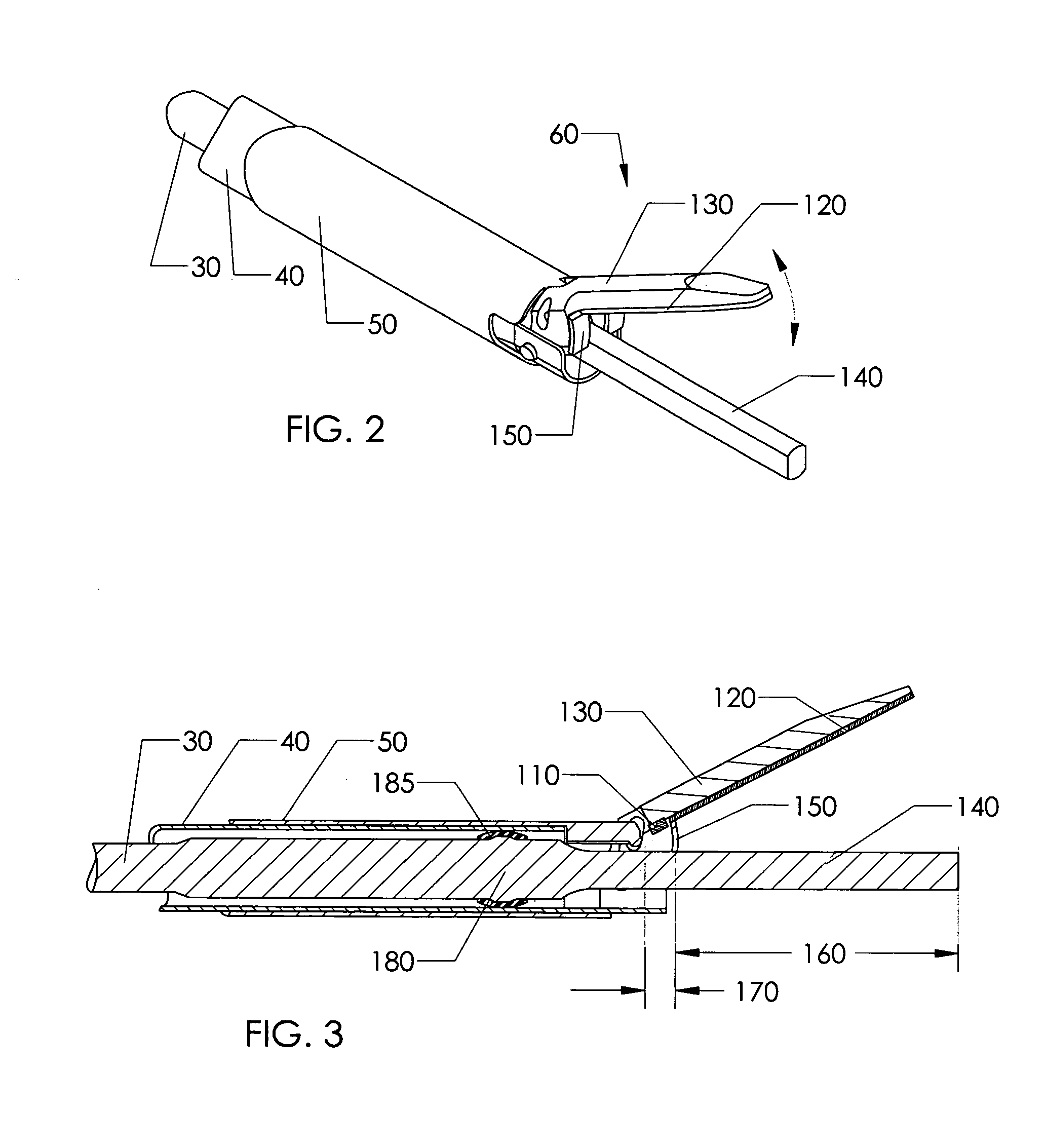
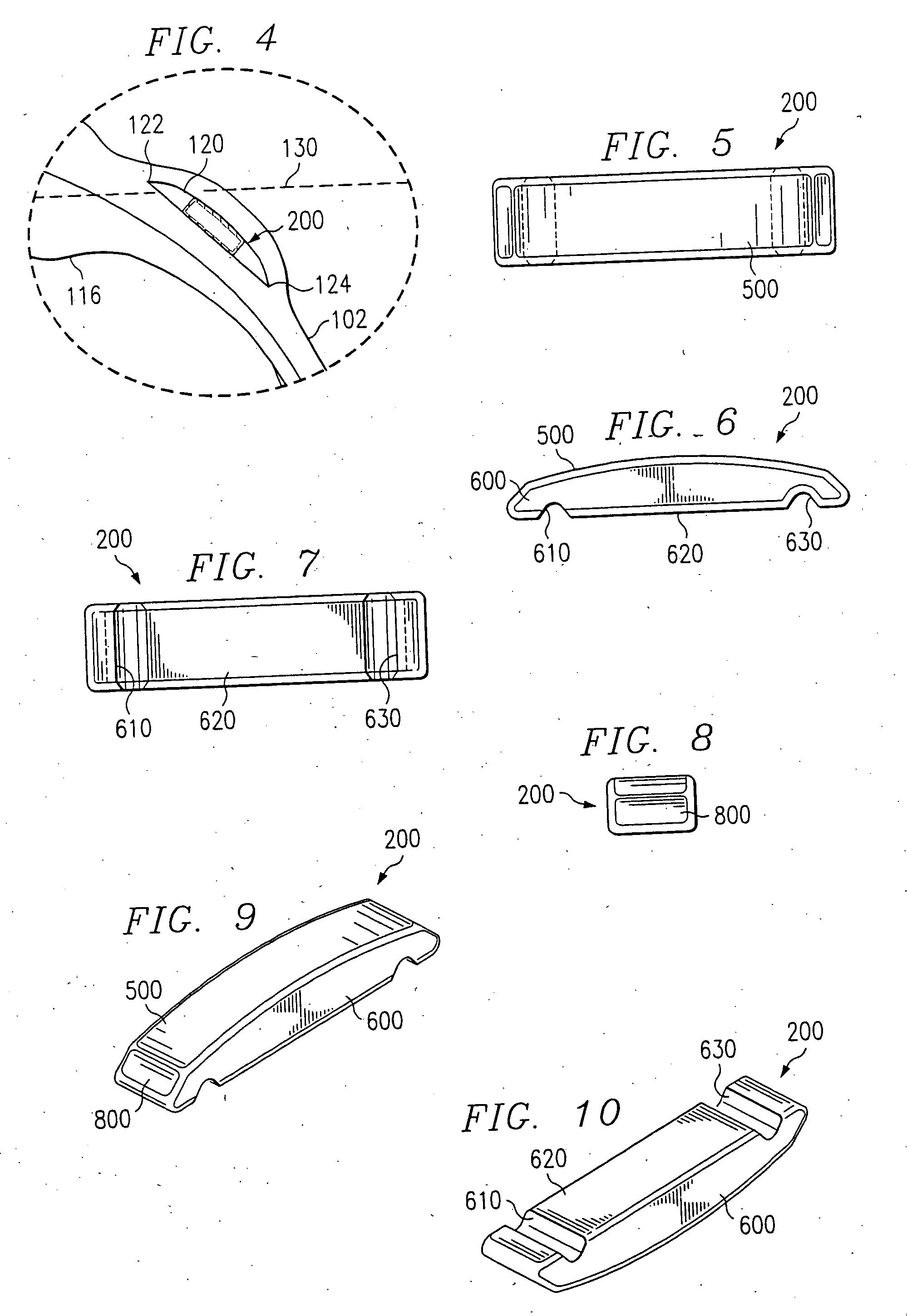
Safety Scalpel With Replaceable Blade Cartridge And Safety Brake
ActiveUS20100036404A1Easy to installPrevent movementIncision instrumentsDiagnosticsSurgical bladeEngineering
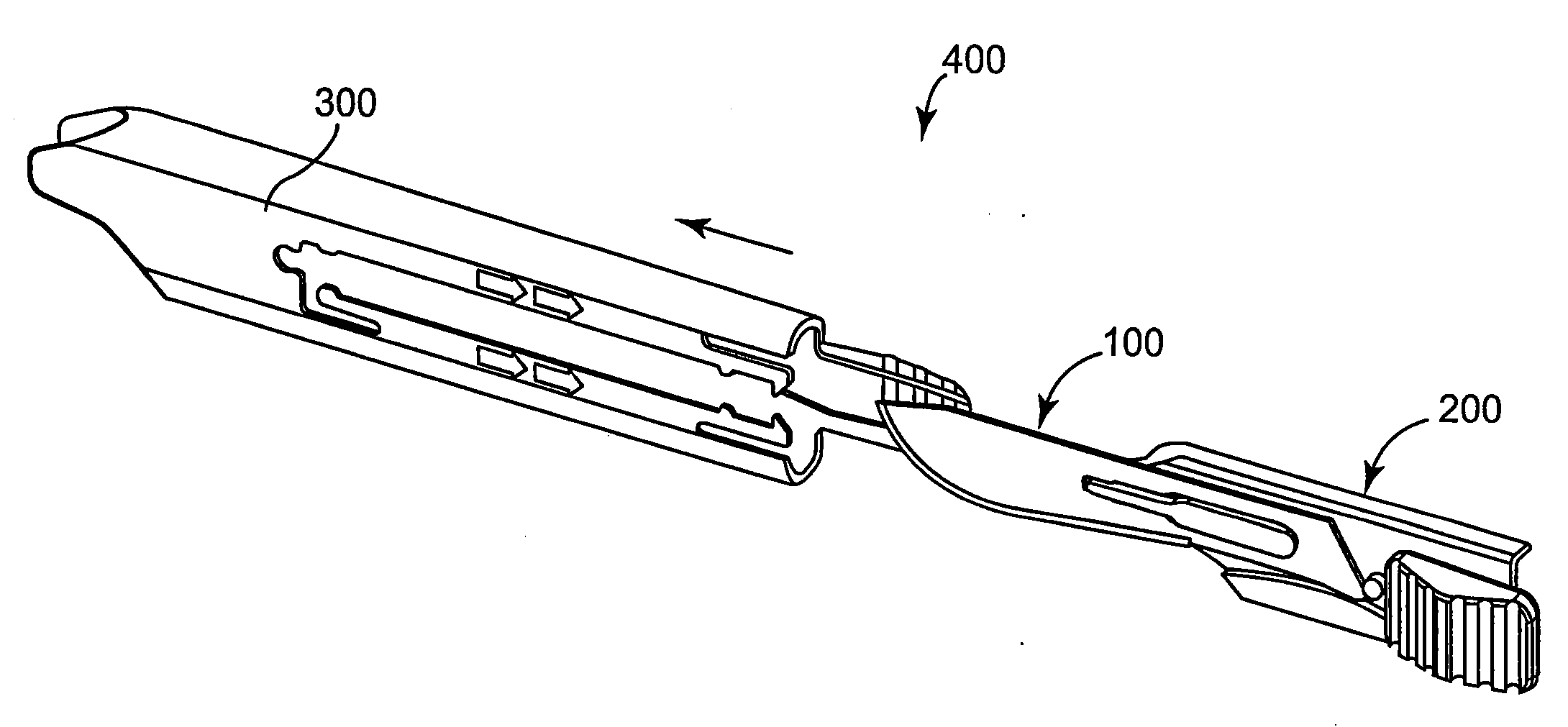
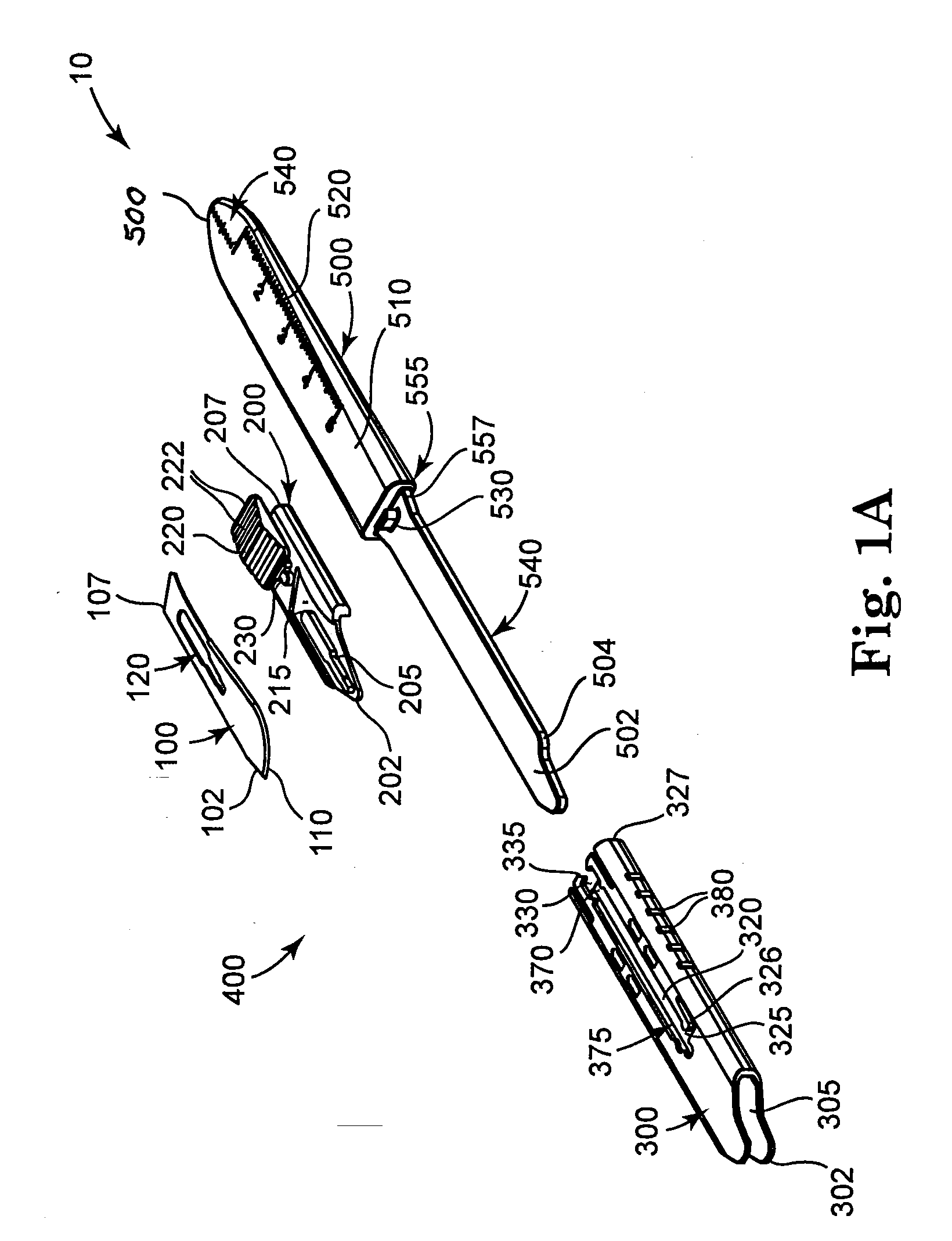
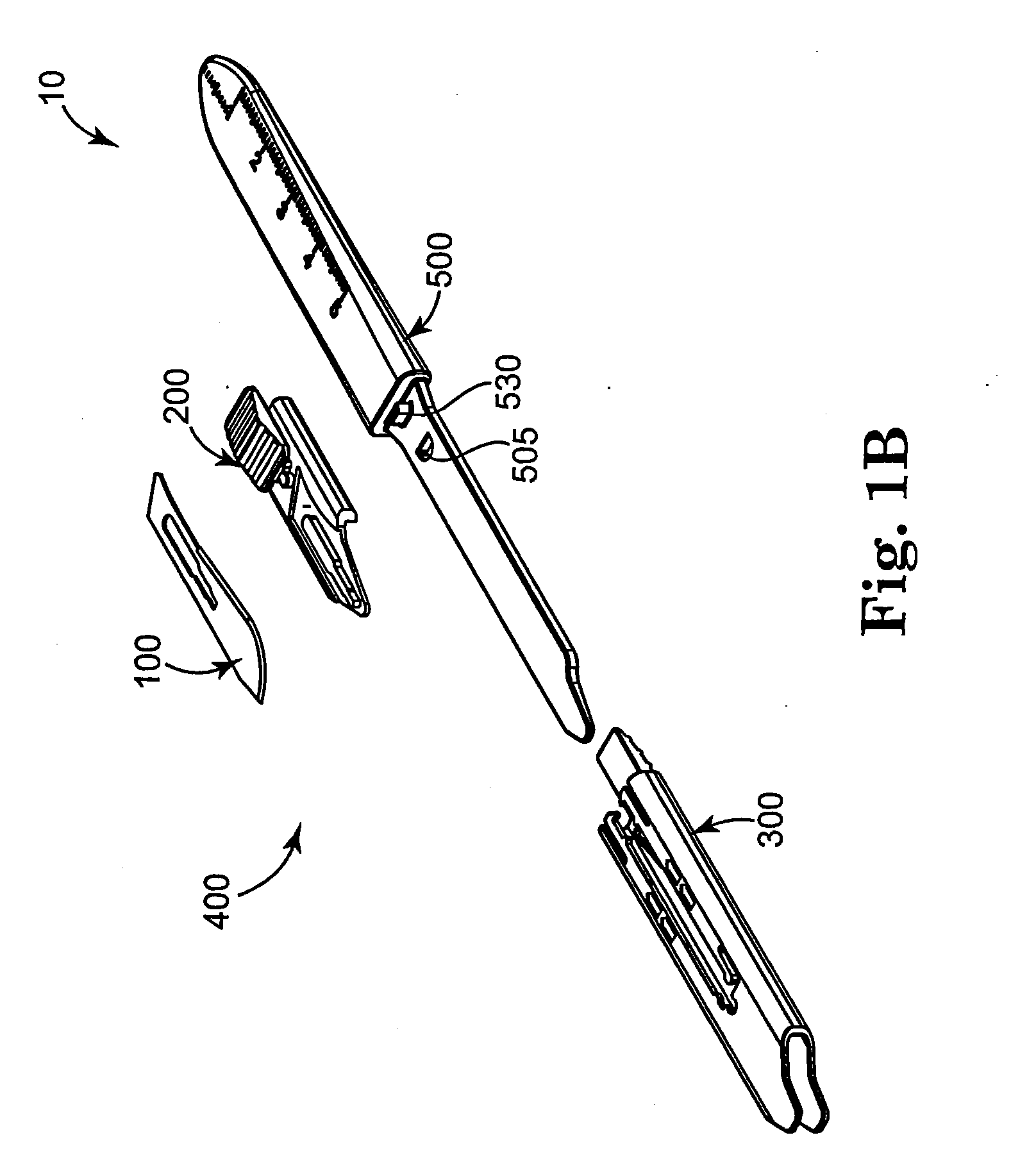
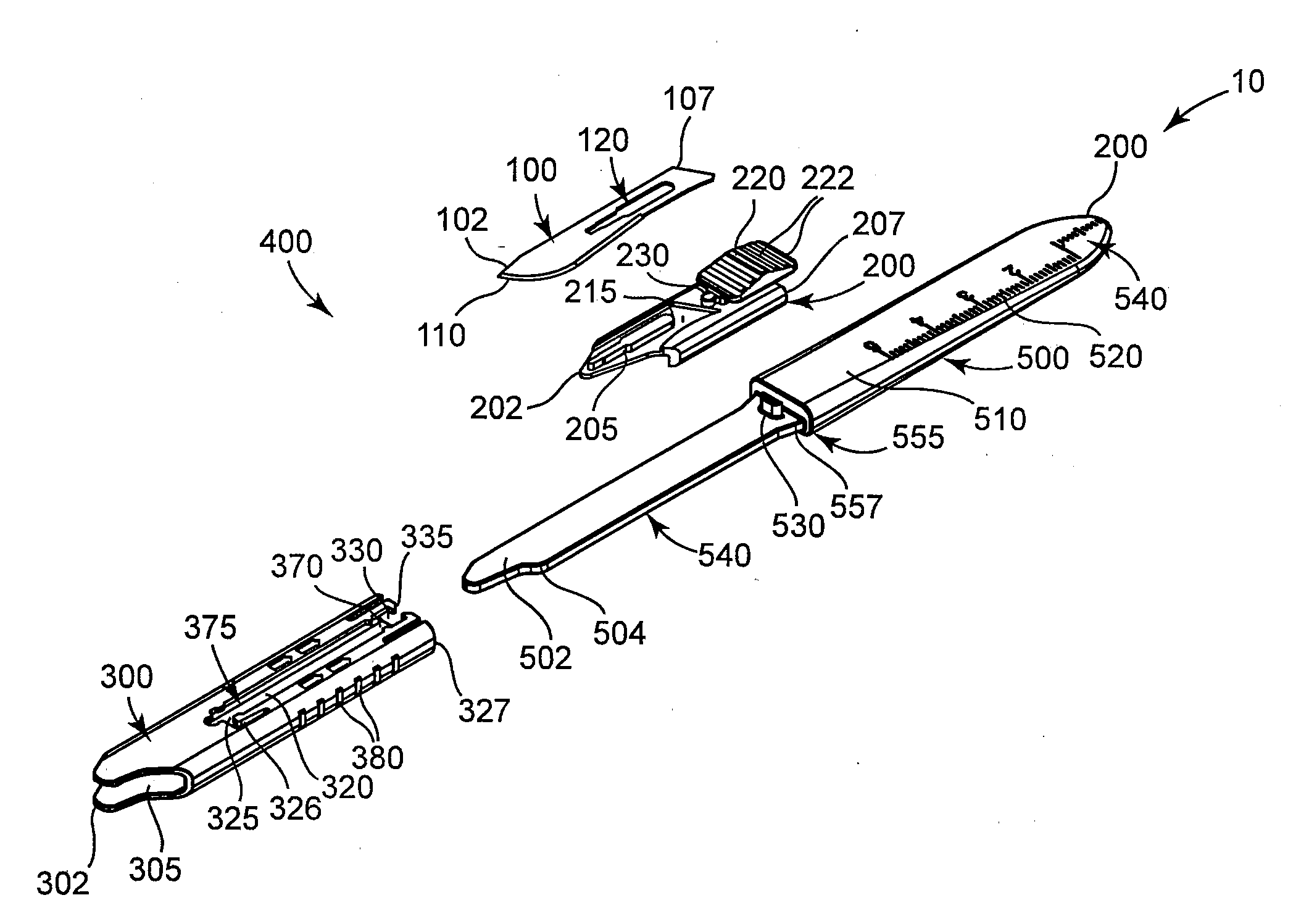
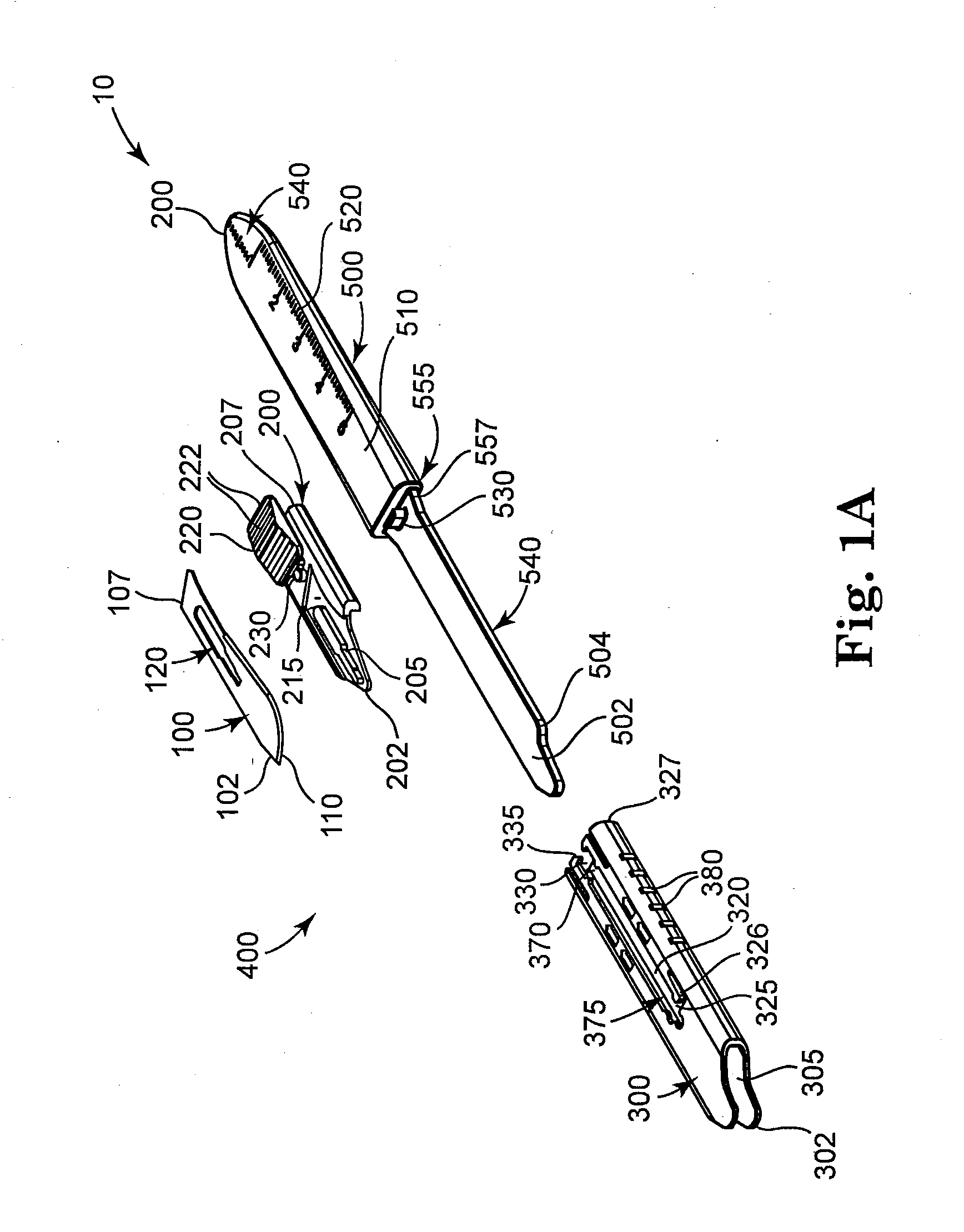
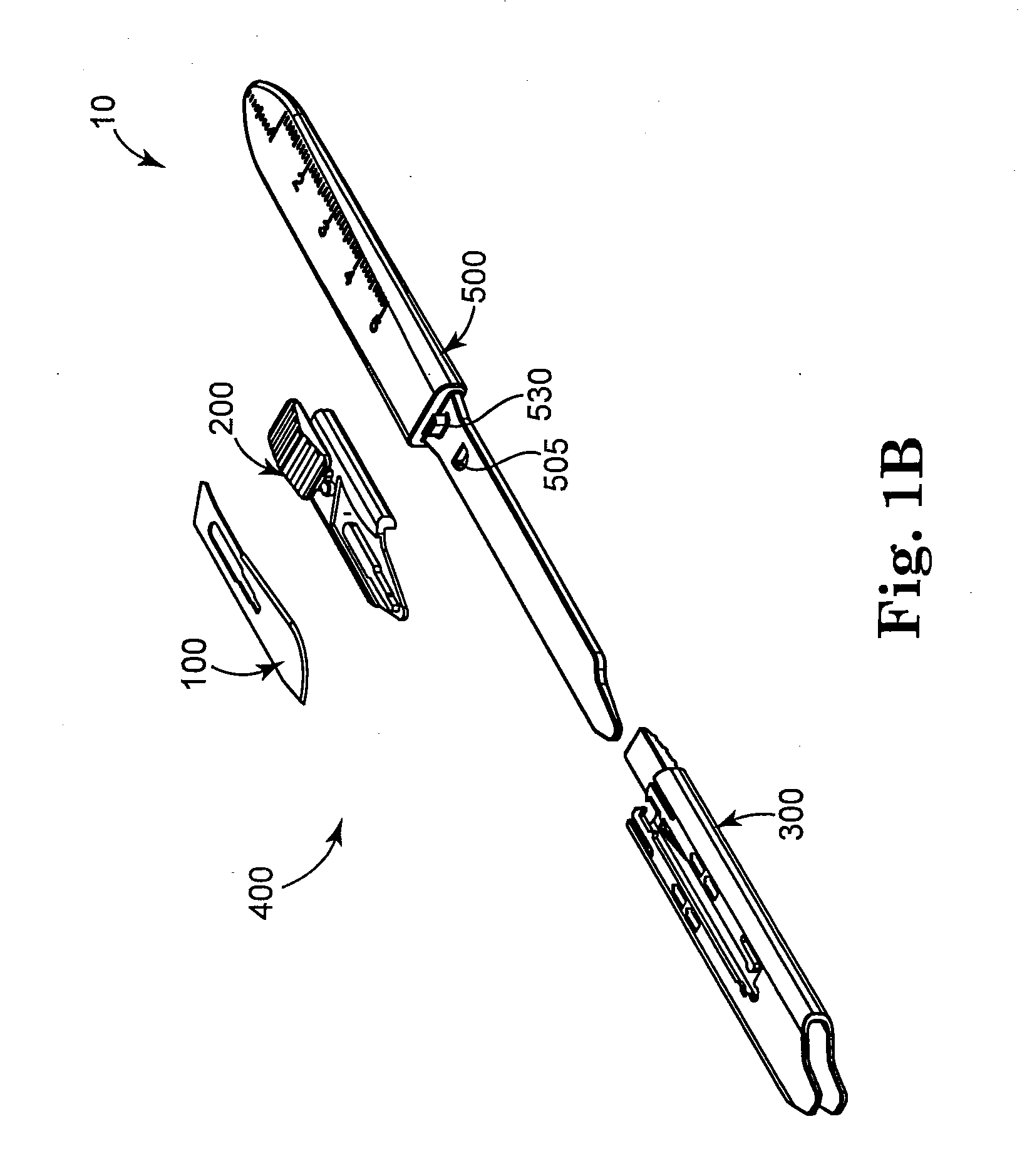
A safety scalpel that incorporates a reusable metal scalpel handle (500) similar in shape and feel to the conventional metal handle preferred by most surgeons, and a disposable blade cartridge (300) that covers the blade (100) before, during and after use, and is easily mounted and released from the scalpel handle. The blade cartridge includes a blade (100) with similar cutting profiles as standard surgical blades, a blade holder that is permanently fixed to the blade, and a blade guard (300) that covers the blade and within which the blade holder (200) is able to slide. The scalpel handle is reusable, while the blade cartridge is disposable. The blade cartridge is attachable and detachable from the scalpel handle and may include means (1301) to prevent movement of the blade except when the reusable handle is in place. A safety latch feature (2230) is provided.
Owner:MEDIPURPOSE PTE
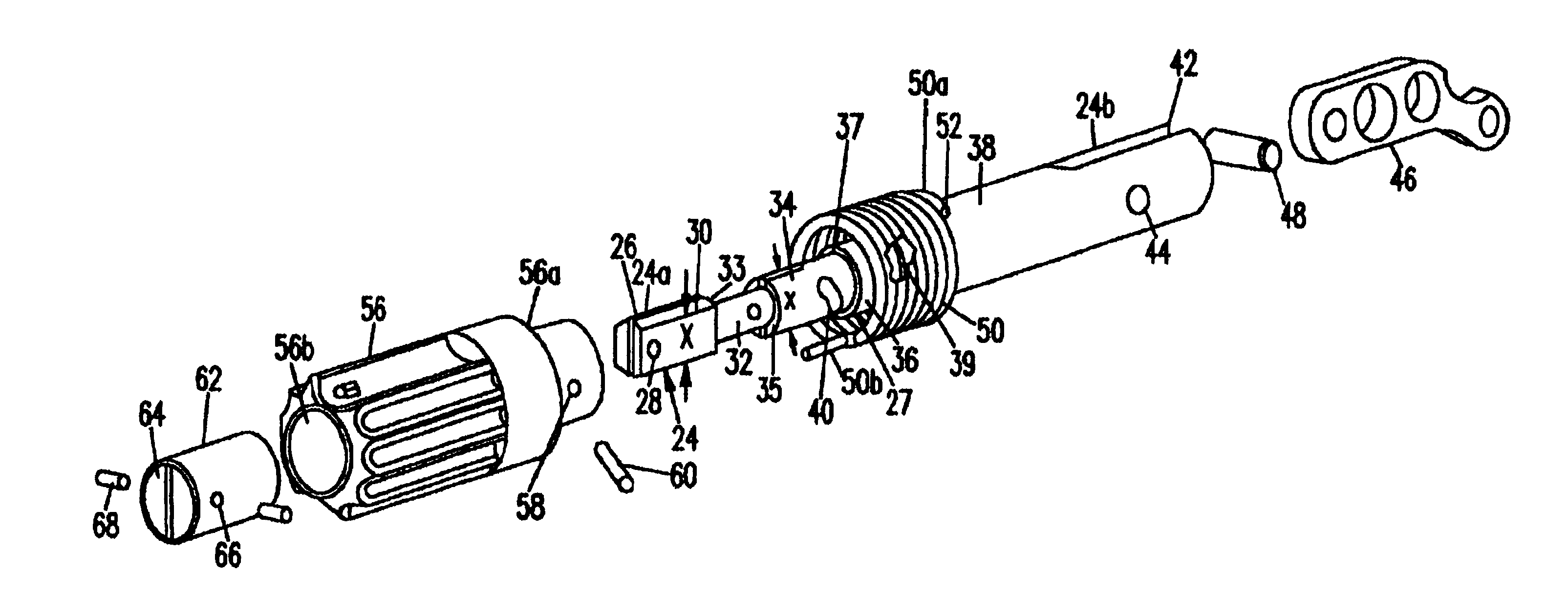
Connector assembly for a surgical tool
InactiveUS6949110B2Reliable lockingEasy to removeSuture equipmentsDrilling rodsSurgical bladeEngineering
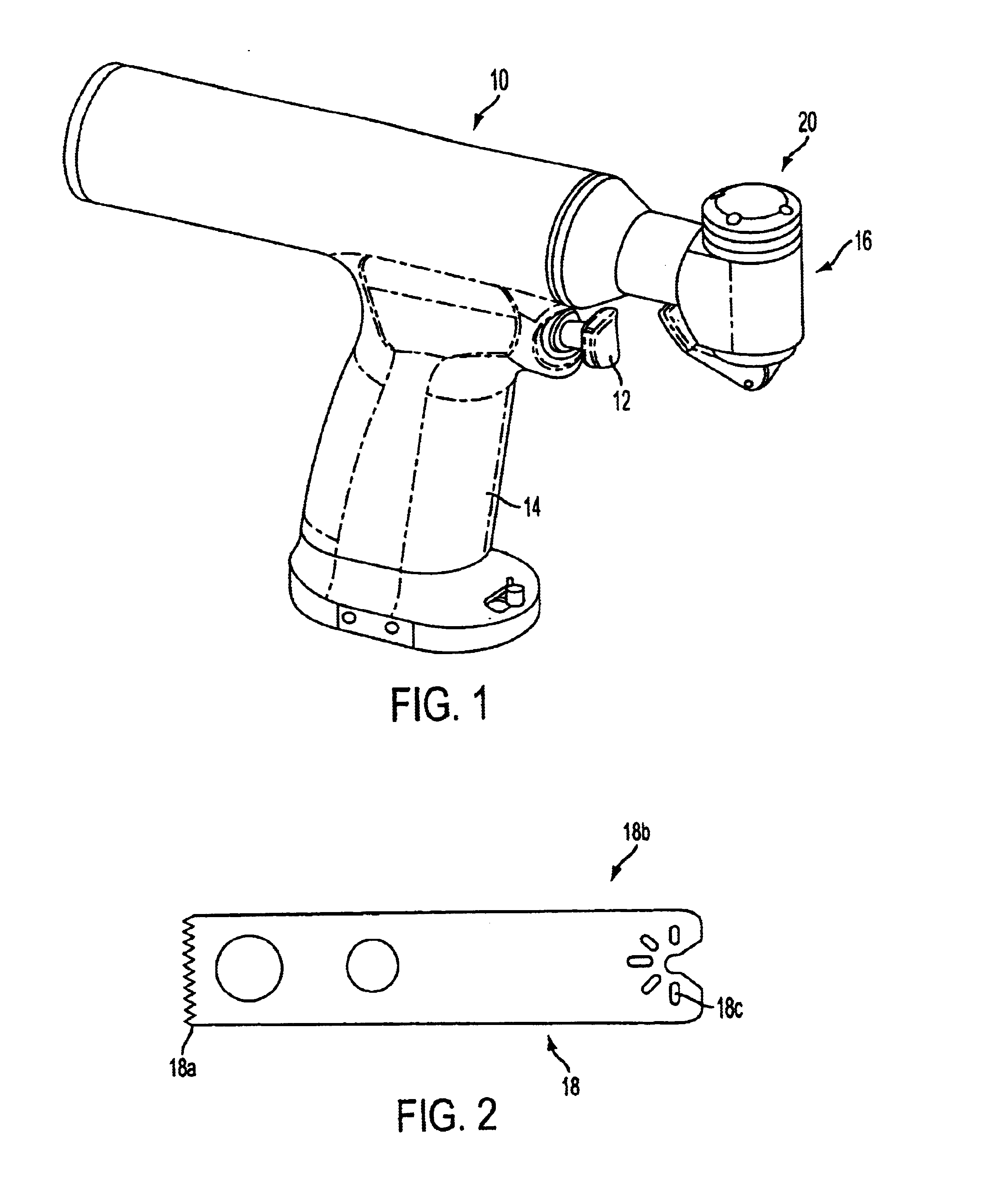
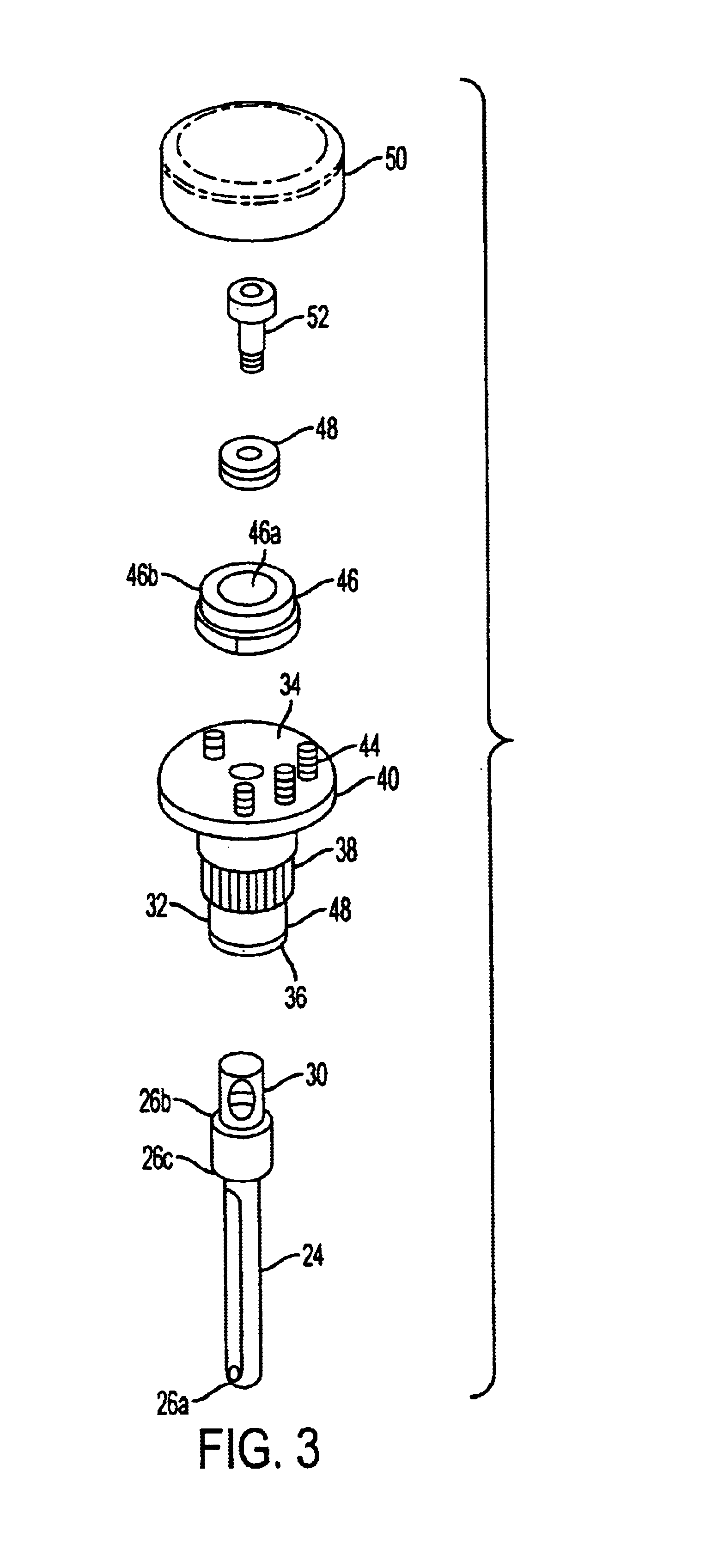
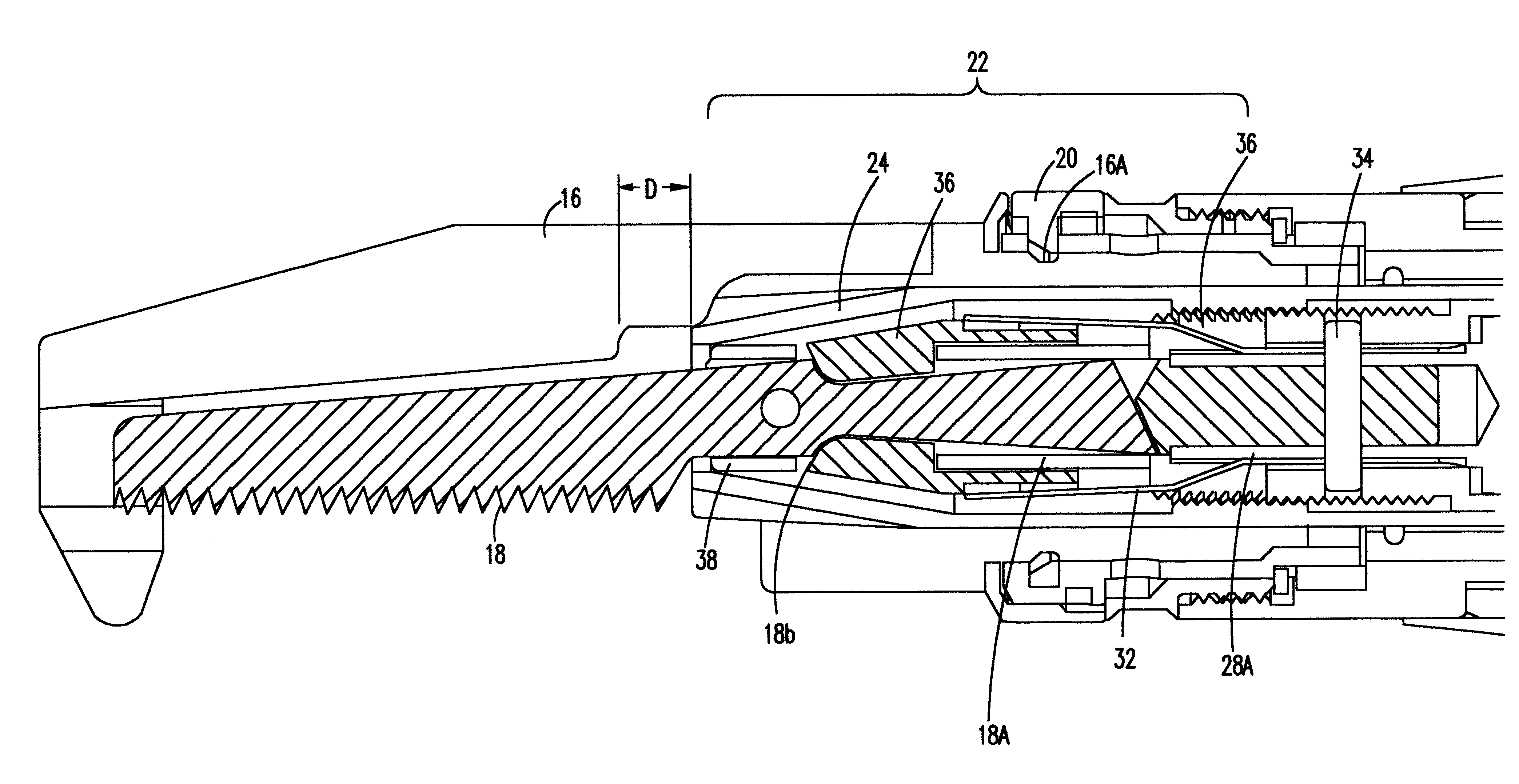
A connector assembly for connecting a surgical saw blade to a housing of a surgical instrument. The connector assembly allows a surgeon to align, insert and lock the surgical blade in the collet of the surgical instrument without any special tools, and further provides a stable and robust platform for mounting the surgical saw blade thereto. The connector assembly includes a cam lever assembly for allowing the user to apply a clamping force to the surgical saw blade with minimum actuation force.
Owner:MICROAIRE SURGICAL INSTR
Connector assembly for a surgical saw blade
InactiveUS6302406B1Precise alignmentEasy to remove and replaceMetal sawing devicesSleeve/socket jointsSurgical bladeOperative instrument
A connector assembly for connecting a surgical saw blade to a housing of a surgical instrument. The connector assembly allows a surgeon to align, insert and lock the surgical blade in the collet of the surgical instrument without any special tools, and further provides a stable and robust platform for mounting the surgical saw blade thereto. The connector assembly includes a tapered conical shaped sleeve which is positioned within the housing and rotatable in both a clockwise and counter-clock wise direction. A pair of grippers are mounted within the connector assembly and engage the surgical saw blade when the tapered conical shaped gripper sleeve is rotated in a first position. A sternum guard is also mounted to the housing.
Owner:MICROAIRE SURGICAL INSTR
Ultrasonic surgical instrument and cartilage and bone shaping blades therefor
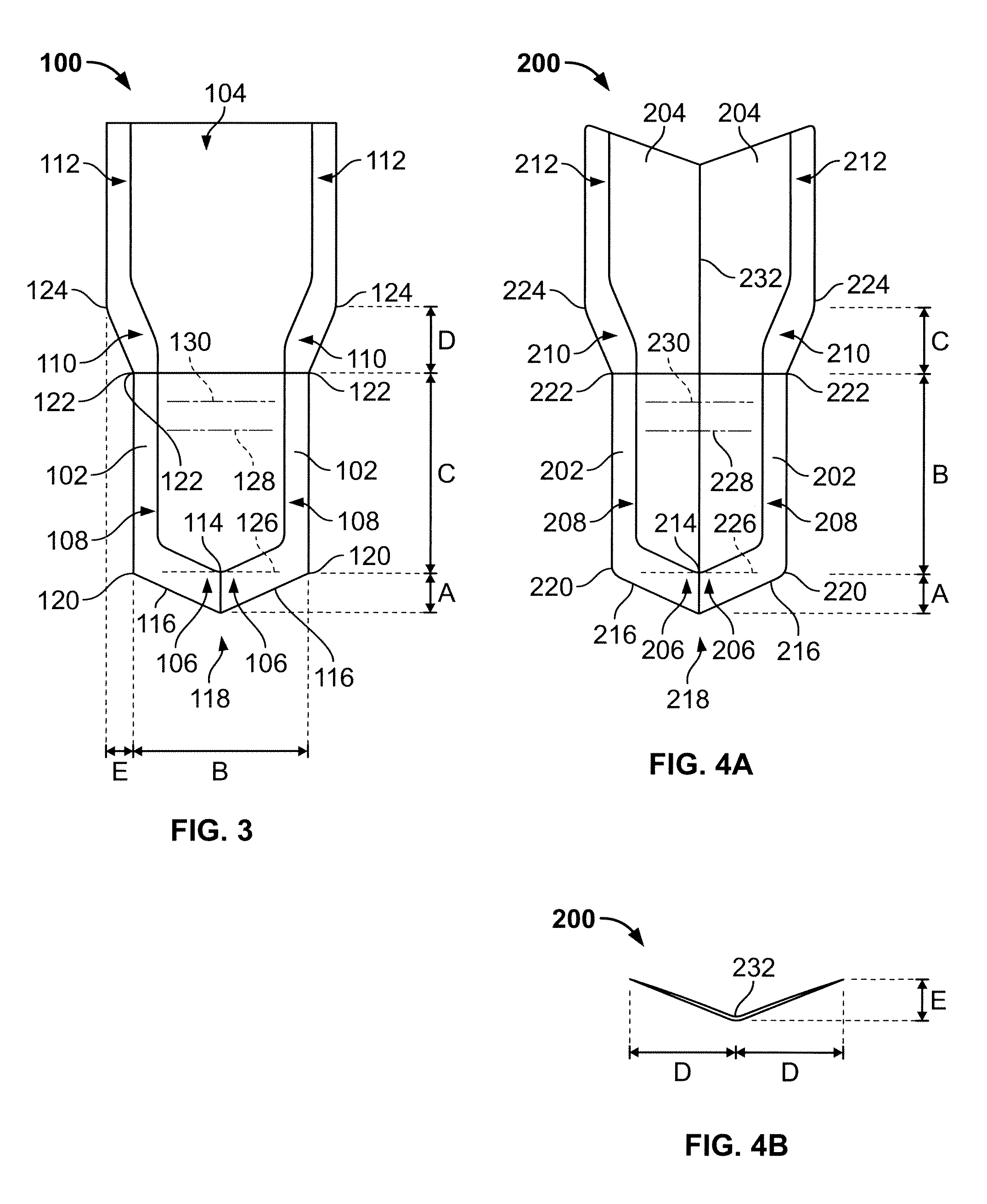
An ultrasonic surgical blade that includes a blade body that has a treatment region. At least one indentation can be formed in the treatment region of the blade body wherein each indentation forms a tissue cutting edge with an outer surface of the blade body. The indentation may comprise one or more holes, lumens, grooves or dimples or a combination of such structures. In various embodiments, one or more aspiration lumens are provided in the surgical blade which may ultimately communicate with an aspiration lumen or passage in an ultrasonic surgical instrument.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Annulus cutting tools and methods
The present invention relates to tools and methods for cutting the annulus of a spinal disc. The cutting tools of the invention may be cannulated for use in conjunction with a guide wire. A stop surface of the cutting tool is configured to contact the annulus during cutting to prevent further longitudinal movement of the surgical blade(s) into the annulus, thus limiting the size of the incision(s).
Owner:PIONEER SURGICAL TECH INC
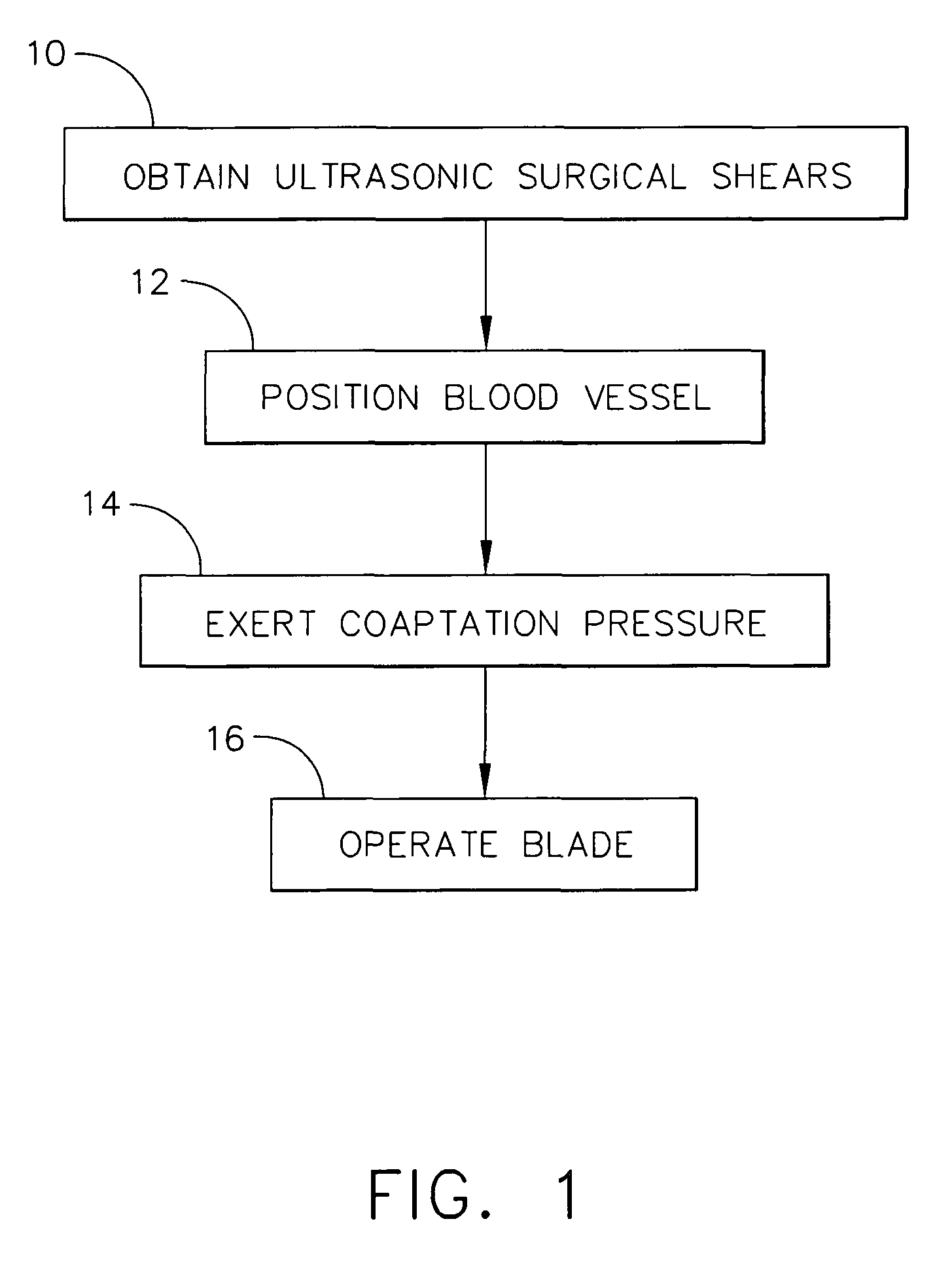
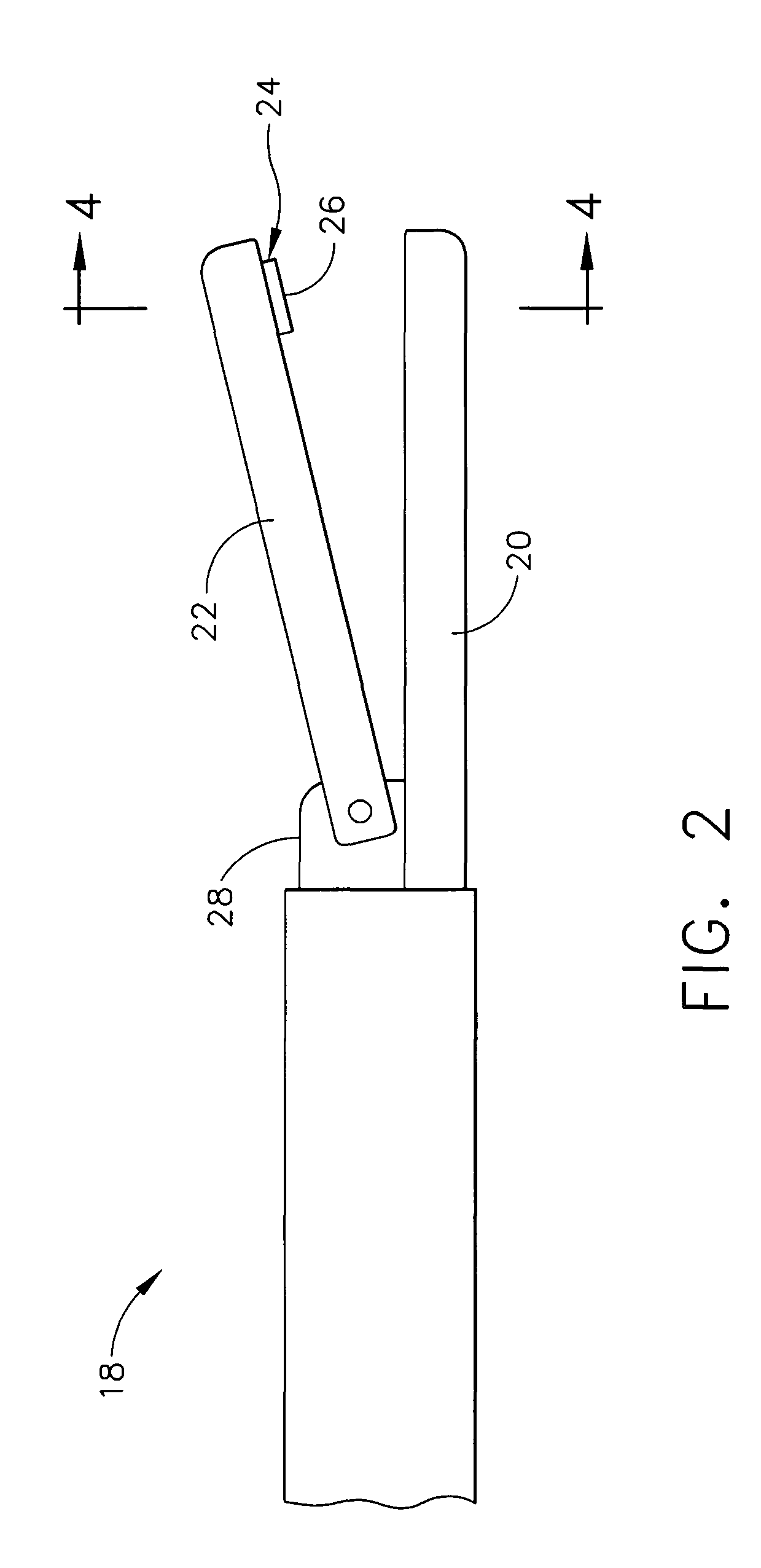
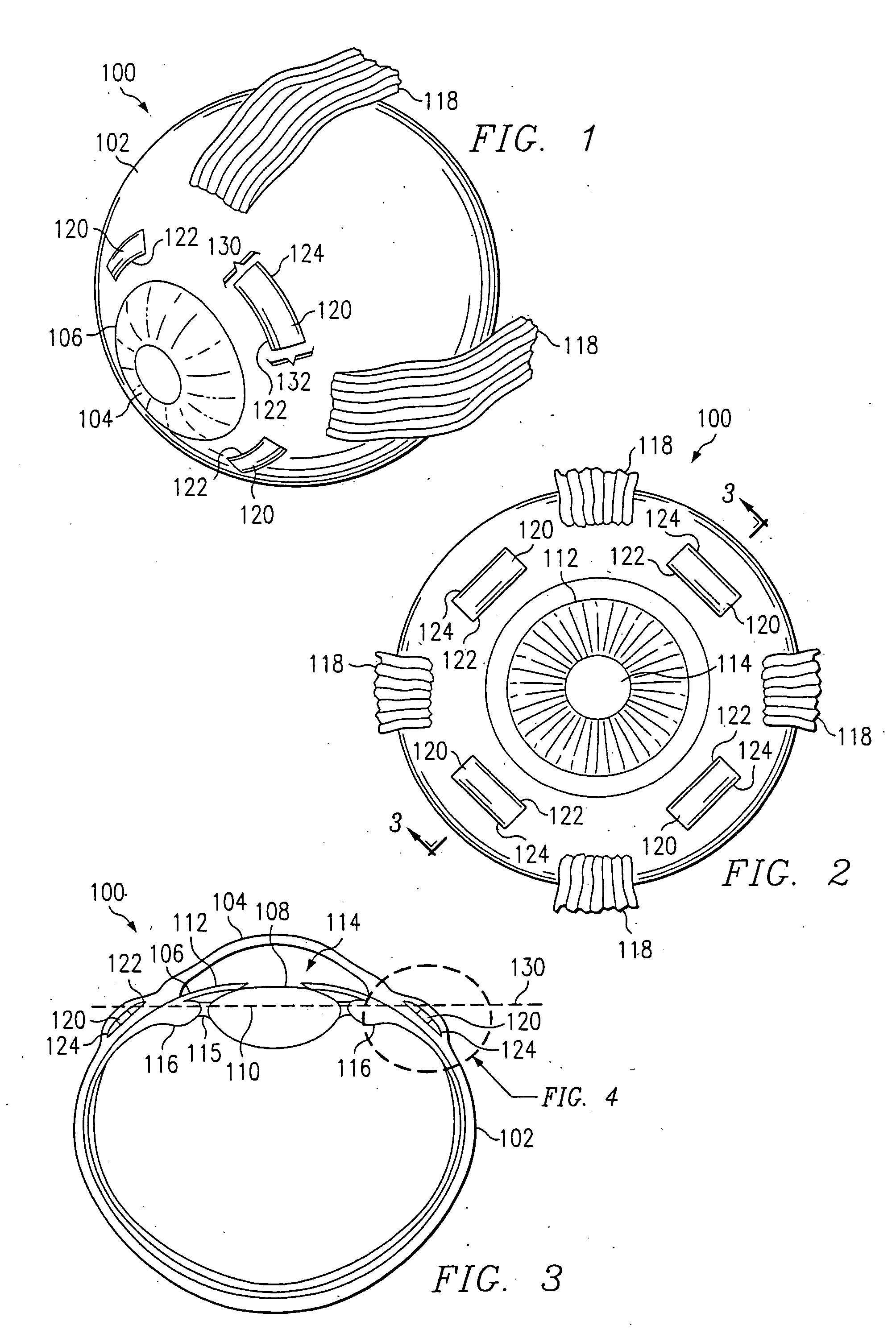
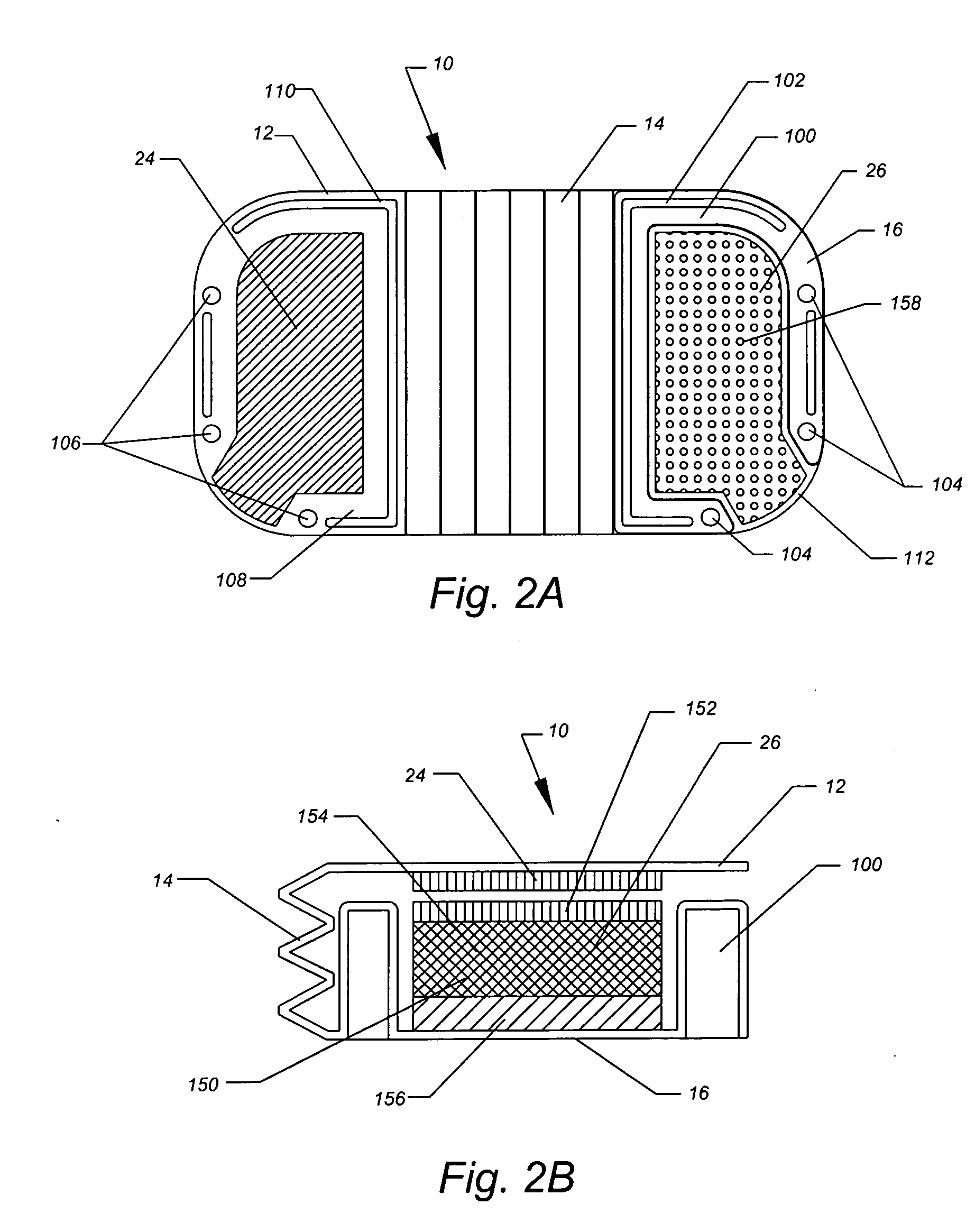
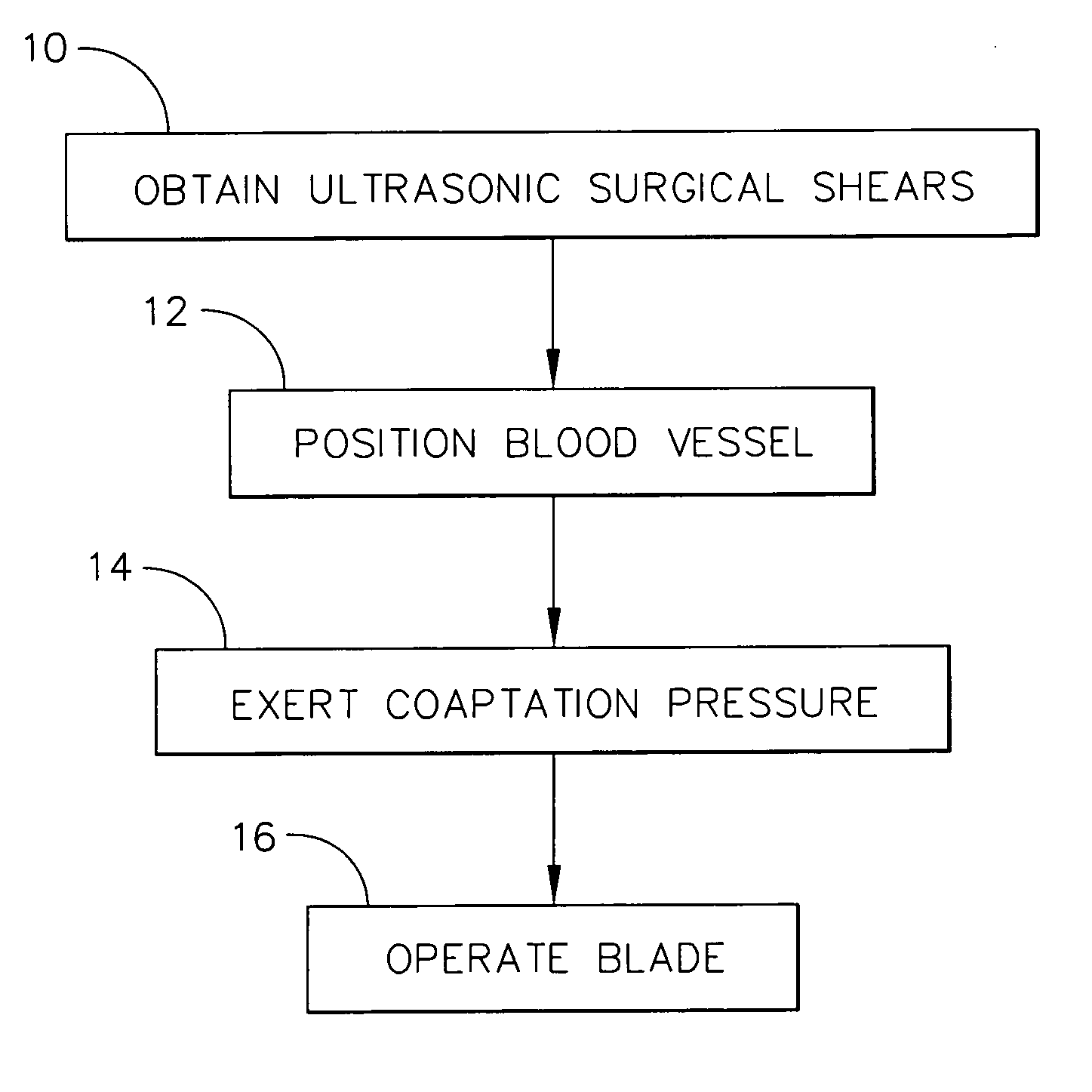
Ultrasonic surgical shears and method for sealing a blood vessel using same
An ultrasonic surgical shears includes an ultrasonic surgical blade, a clamping arm operable to open and close toward the blade, and a tissue pad attached to the clamping arm. A method for sealing a blood vessel of a patient includes obtaining an ultrasonic surgical shears and positioning the blood vessel between the blade and the tissue pad. The clamping arm is operated to exert an average coaptation pressure on the blood vessel between and including 60 psi and 210 psi. The blade is ultrasonically vibrated to transect and seal the blood vessel.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
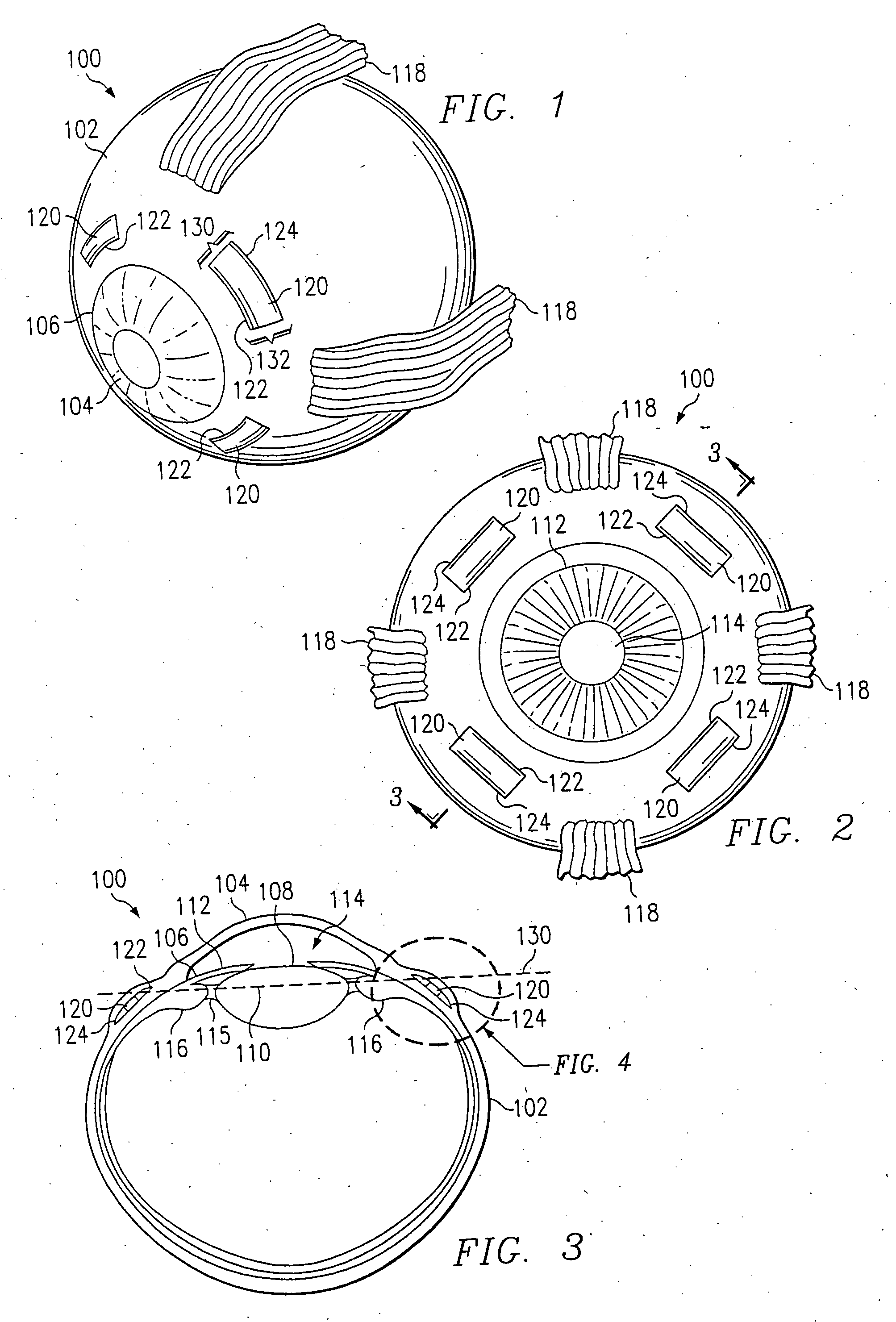
Surgical blade for use with a surgical tool for making incisions for scleral eye implants
A surgical blade is disclosed for use with a surgical tool for making incisions in the sclera of an eye to form a scleral pocket to receive a scleral prosthesis. The surgical blade comprises a rotatable support arm capable of being rotated by the surgical tool and a detachable curved cutting blade for making incisions in the sclera of an eye. The surgical tool causes the curved cutting blade to advance through the sclera to form an incision having dimensions to receive a scleral prosthesis. When the incision is complete the curved cutting blade is detached from the rotatable support arm. The curved cutting blade is then removed from the incision by pulling the curved cutting blade forward out of the incision. The incision has the exact dimensions to receive a scleral prosthesis.
Owner:REFOCUS GROUP
Ultrasonic cutting and coagulation knife using transverse vibrations
An ultrasonic frequency surgical dissecting device including a handpiece with a surgical blade that vibrates in a direction transverse to a long axis passing through the handpiece and blade for improved cutting and coagulation
Owner:SOUND SURGICAL TECH
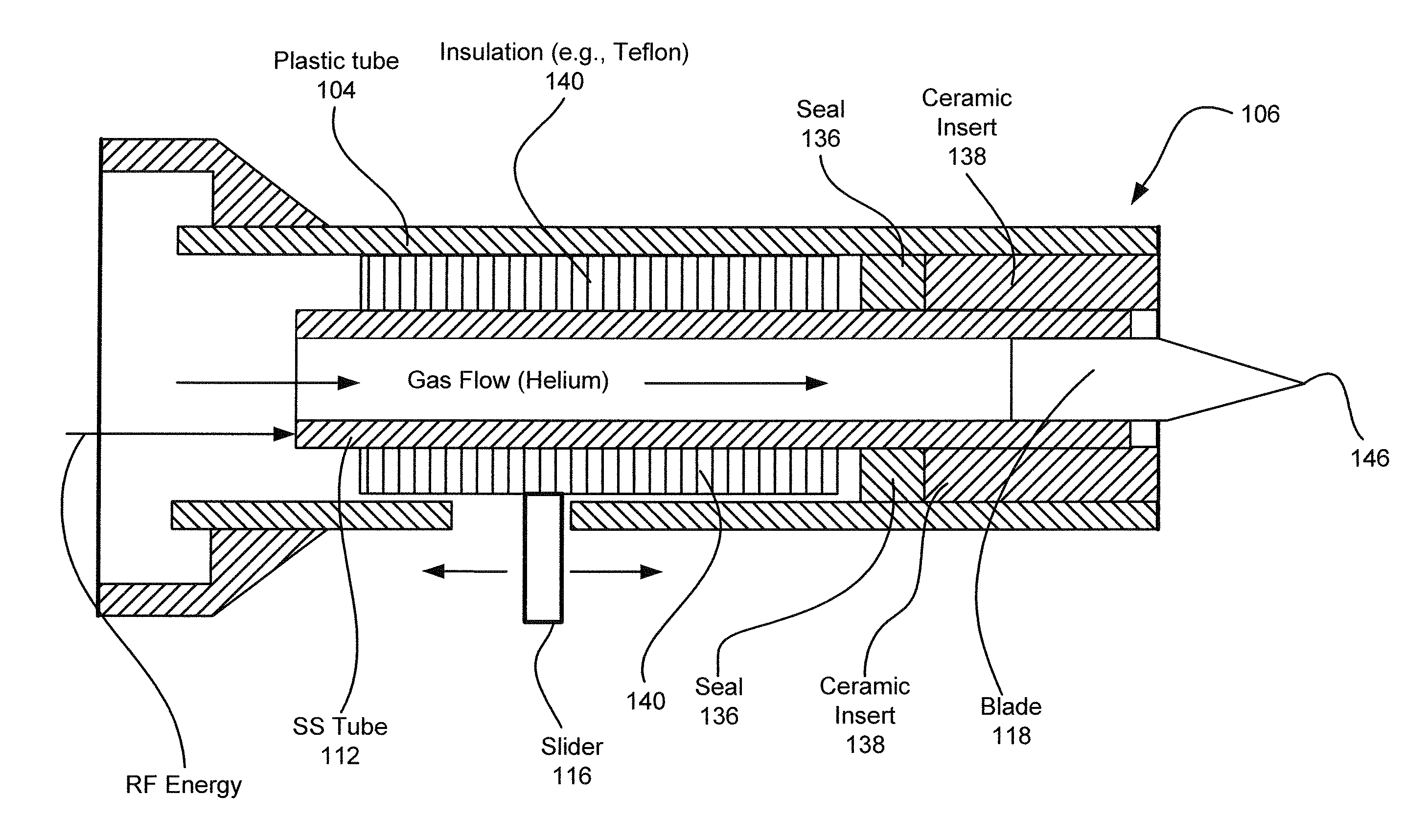
Electrosurgical apparatus with retractable blade
An electrosurgical apparatus with a retractable blade for use in cold plasma applications, electrosurgical cutting and mechanical cutting is provided. The electrosurgical apparatus employs a tip of the retractable blade as a sharp conductive point to generate a plasma beam or discharge. When the blade is retracted within the electrosurgical apparatus, it is electrically energized while an inert gas flows over it, producing a cold plasma discharge. In the de-energized state, the blade is advanced and used as a traditional, mechanical surgical blade.
Owner:BOVIE MEDICAL CORP
Surgical blade for use with a surgical tool for making incisions for scleral eye implants
A surgical blade is disclosed for use with a surgical tool for making incisions in the sclera of an eye to form a scleral pocket to receive a scleral prosthesis. The surgical blade comprises a rotatable support arm capable of being rotated by the surgical tool and a detachable curved cutting blade for making incisions in the sclera of an eye. The surgical tool causes the curved cutting blade to advance through the sclera to form an incision having dimensions to receive a scleral prosthesis. When the incision is complete the curved cutting blade is detached from the rotatable support arm. The curved cutting blade is then removed from the incision by pulling the curved cutting blade forward out of the incision. The incision has the exact dimensions to receive a scleral prosthesis.
Owner:REFOCUS GROUP
Connector assembly for a surgical tool
InactiveUS6638290B2Precise alignmentReliable lockingMetal sawing devicesSleeve/socket jointsSurgical bladeOperative instrument
A connector assembly for connecting a surgical saw blade to a housing of a surgical instrument. The connector assembly allows a surgeon to align, insert and lock the surgical blade in the collect of the surgical instrument without any special tools, and further provides a stable and robust platform for mounting the surgical saw blade thereto. The connector assembly includes a gripper having a centrally located bore and a pair of opposing shelves. A shaft having shoulders is slidably fitted within the bore of the gripper. The shoulders communicate with ledges of the shelves to prohibit movement of the finger gripper. This same mechanism also prevents movement of a surgical saw blade, once inserted within the slot of the shaft, from becoming dislodged or ejected from the connector assembly. A biasing spring biases the gripper in a first position, but the gripper can move between the first position and a second position.
Owner:MICROAIRE SURGICAL INSTR
System and method for making incisions for scleral eye implants
A system and method is disclosed for making incisions in the sclera of an eye to form a scleral pocket to receive a scleral prosthesis. The system and method comprises a surgical tool comprising a surgical blade for making incisions in the sclera of an eye. When a surgeon places the surgical blade on the sclera of the eye a pressure sensor in the surgical tool determines whether there is sufficient pressure between the surgical tool and the sclera of the eye for the surgical tool to operate properly. The surgeon activates the surgical tool to cause the surgical blade to advance through the sclera to form an incision having dimensions to receive a scleral prosthesis. When the incision is complete the surgical blade is rotated back out of the incision. The incision has the exact dimensions to receive a scleral prosthesis.
Owner:REFOCUS GROUP
Surgical blade and trocar system
InactiveUS20080215078A1Minimize bendingEasily and rapidly removedEye surgeryCannulasEye SurgeonSurgical blade
The present invention provides an improved surgical blade and trocar system for accessing the retina and other parts of the eye while doing vitreo-retinal and cataract surgeries, including surgeries for macular degeneration. The eye surgeon uses an improved surgical blade for vitreo-retinal and cataract surgeries having a generally flat, V-shaped, W-shaped, or “extended W” shaped cross-section. Using the improved surgical blade, the surgeon creates a multi-planar, self-sealing surgical wound, first by directing the surgical blade substantially perpendicular to the eye surface, then redirecting the blade to follow the general curvature of the eye globe, and finally redirecting the blade to enter the interior of the eye. The improved surgical blade is used with an improved trocar system having two main parts-a relatively rigid, wide-mouthed outer segment and a generally thin-walled, collapsible plastic polymer or metal mesh sleeve that spans the surgical wound and substantially molds to its contour. The improved surgical blade and trocar system can be adapted for use in either vitreo-retinal or cataract surgeries.
Owner:BENNETT MICHAEL D
Safety scalpel
A safety scalpel that incorporates a reusable metal scalpel handle similar in shape and feel to the conventional metal handle preferred by most surgeons, and a disposable blade cartridge that covers the blade before, during and after use, and is easily mounted and released from the scalpel handle. The blade cartridge includes a blade with similar cutting profiles as standard surgical blades, a blade holder that is permanently fixed to the blade, and a blade guard that covers the blade and within which the blade holder is able to slide. The scalpel handle is reusable, while the blade cartridge is disposable. The blade cartridge is attachable and detachable from the scalpel handle.
Owner:MEDIPURPOSE PTE
Method and apparatus for sharps protection
ActiveUS20090266729A1Risk minimizationSuture equipmentsIncision instrumentsHypodermic needleSurgical blade
Devices and methods are disclosed for protecting individuals from the sharp ends of medical objects following use on a patient. Such sharp objects include hypodermic needles, scalpel blades, cannulae, trocars, and the like. The invention utilizes a disposable protective cover for the used sharp. The protective cover is designed to surround and embed the sharp in a permanent cover that is blunt and will not permit further puncture or cutting with the sharp. In an embodiment, the protective cover also absorbs any fluids on or in the used sharp and prevents any fluids from escaping the protective cover. The sharp cover is configured to irreversibly lock, once closed. A refillable or replaceable dispenser dispenses the protective covers at points of use. A disposable receptacle receives the used sharp embedded in the protective cover. When the receptacle is full, the entire receptacle may be discarded in a medical waste container.
Owner:PROVIDENCE ST JOSEPH HEALTH
Ultrasonic surgical shears and method for sealing a blood vessel using same
ActiveUS20050192612A1Improved blood vessel sealingShort transection timeSurgical forcepsSurgical bladeSurgical department
An ultrasonic surgical shears includes an ultrasonic surgical blade, a clamping arm operable to open and close toward the blade, and a tissue pad attached to the clamping arm. A method for sealing a blood vessel of a patient includes obtaining an ultrasonic surgical shears and positioning the blood vessel between the blade and the tissue pad. The clamping arm is operated to exert an average coaptation pressure on the blood vessel between and including 60 psi and 210 psi. The blade is ultrasonically vibrated to transect and seal the blood vessel.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INTERNATIONAL
Ultrasonic surgical blade and instrument having a gain step
ActiveUS20050096679A1Increase in active lengthShorten half wave lengthTooth pluggers/hammersCannulasSurgical bladeWavelength
An ultrasonic surgical blade, and an instrument, having a gain step. The blade body has, in any half wave length of the ultrasonic-surgical-blade body, a first vibration antinode, a vibration node, a second vibration antinode, and a gain step. The gain step is located between the second vibration antinode and the first vibration antinode. The gain step is spaced apart from the vibration node by a gain-step distance greater than 5% of the distance between the second vibration antinode and the first vibration antinode. The instrument includes the blade, a handpiece having an ultrasonic transducer, and an ultrasonic transmission rod whose proximal end is operatively connected to the ultrasonic transducer and whose distal end activates the blade. In one option, the first vibration antinode is the distal tip, and the gain step is located between the vibration node and the distal tip, resulting in an increased active length of the blade.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
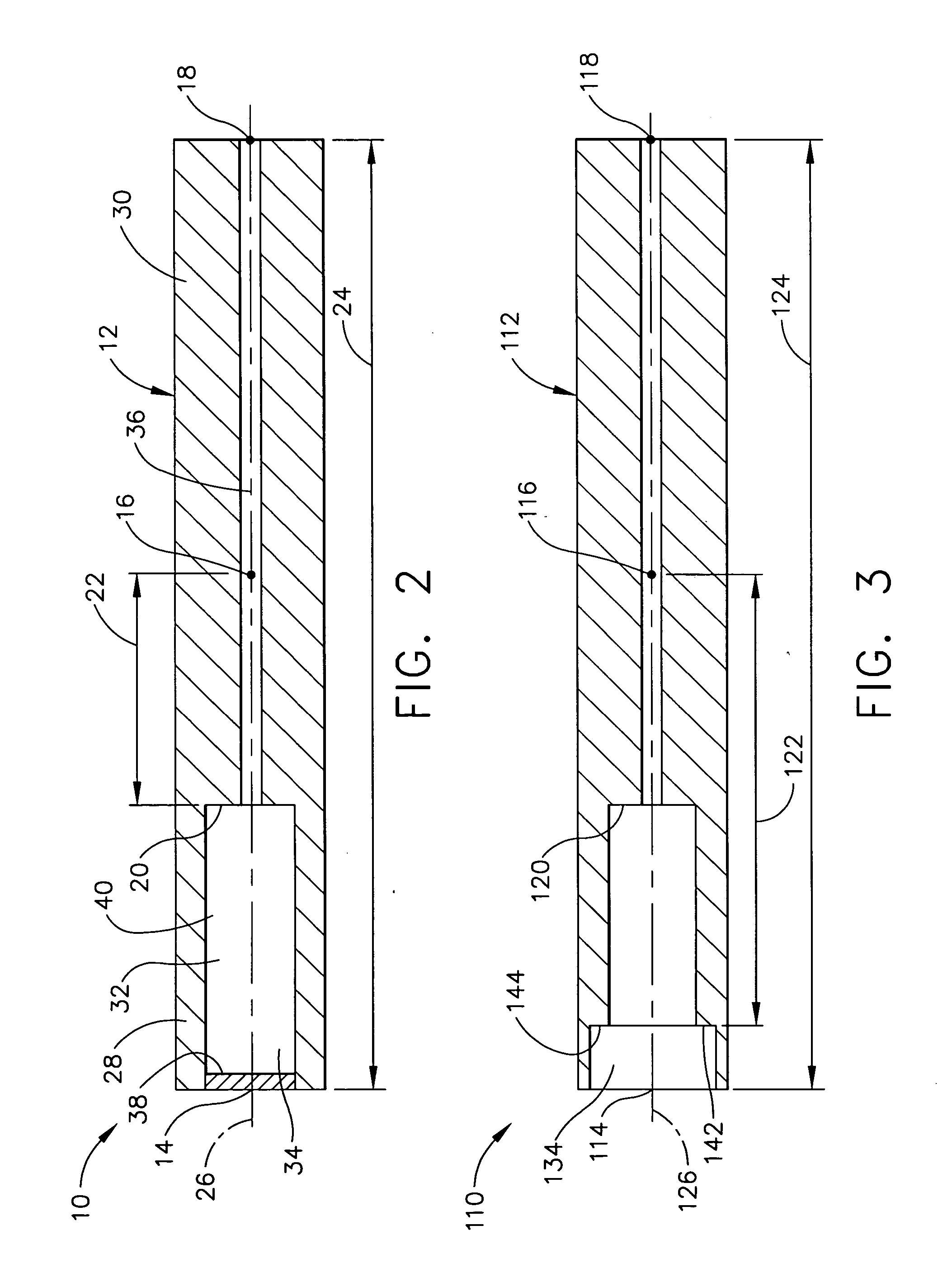
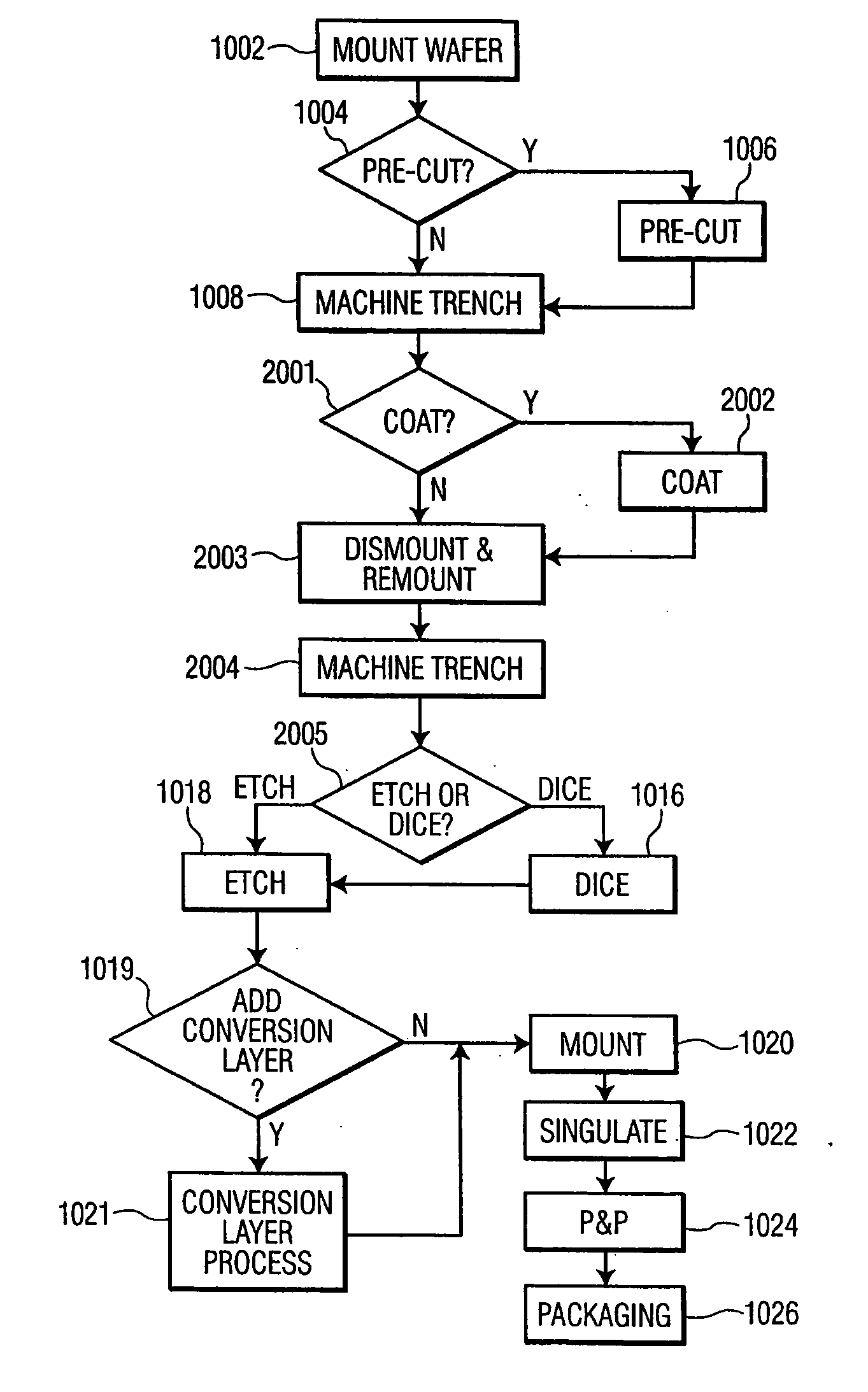
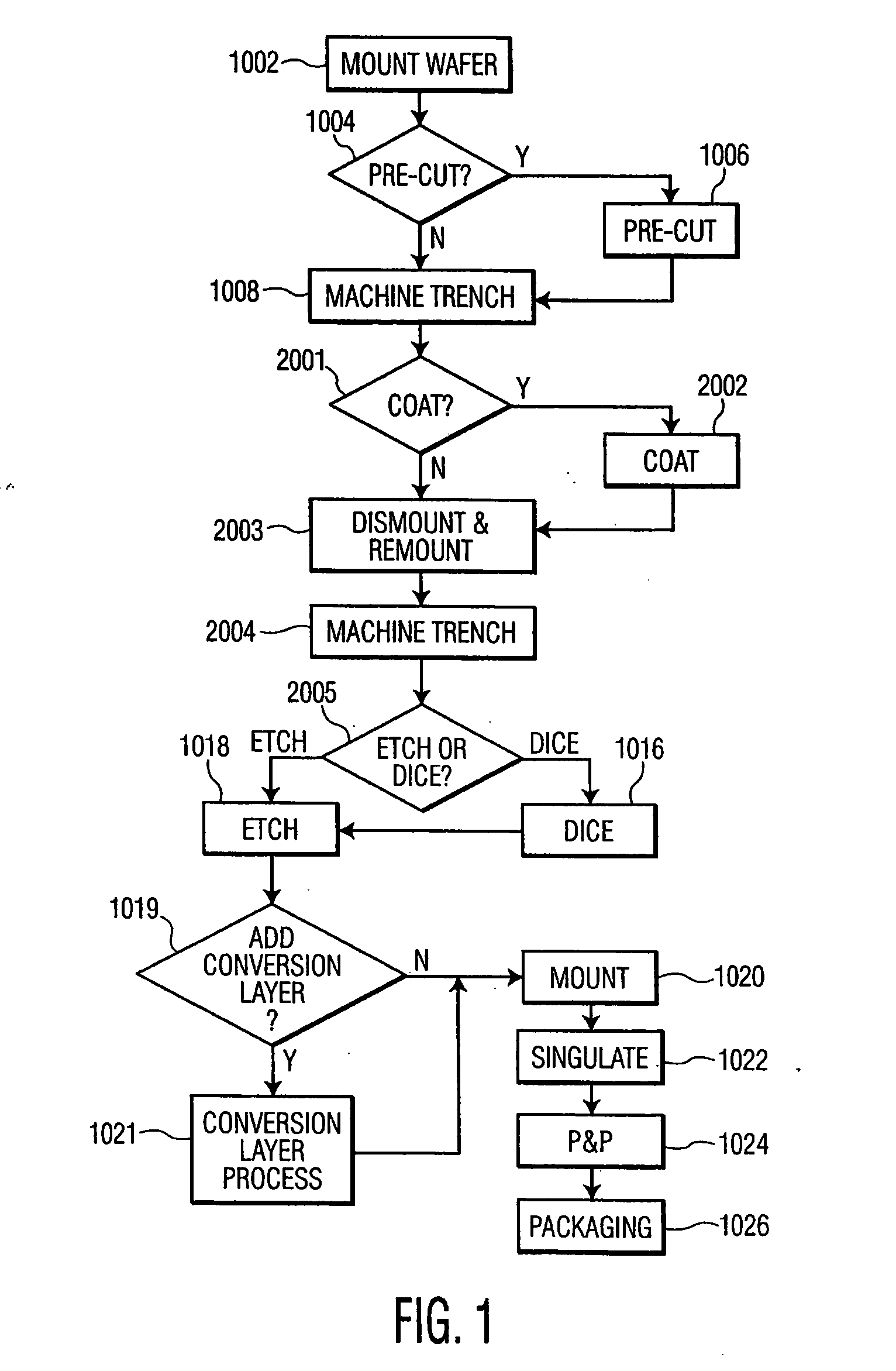
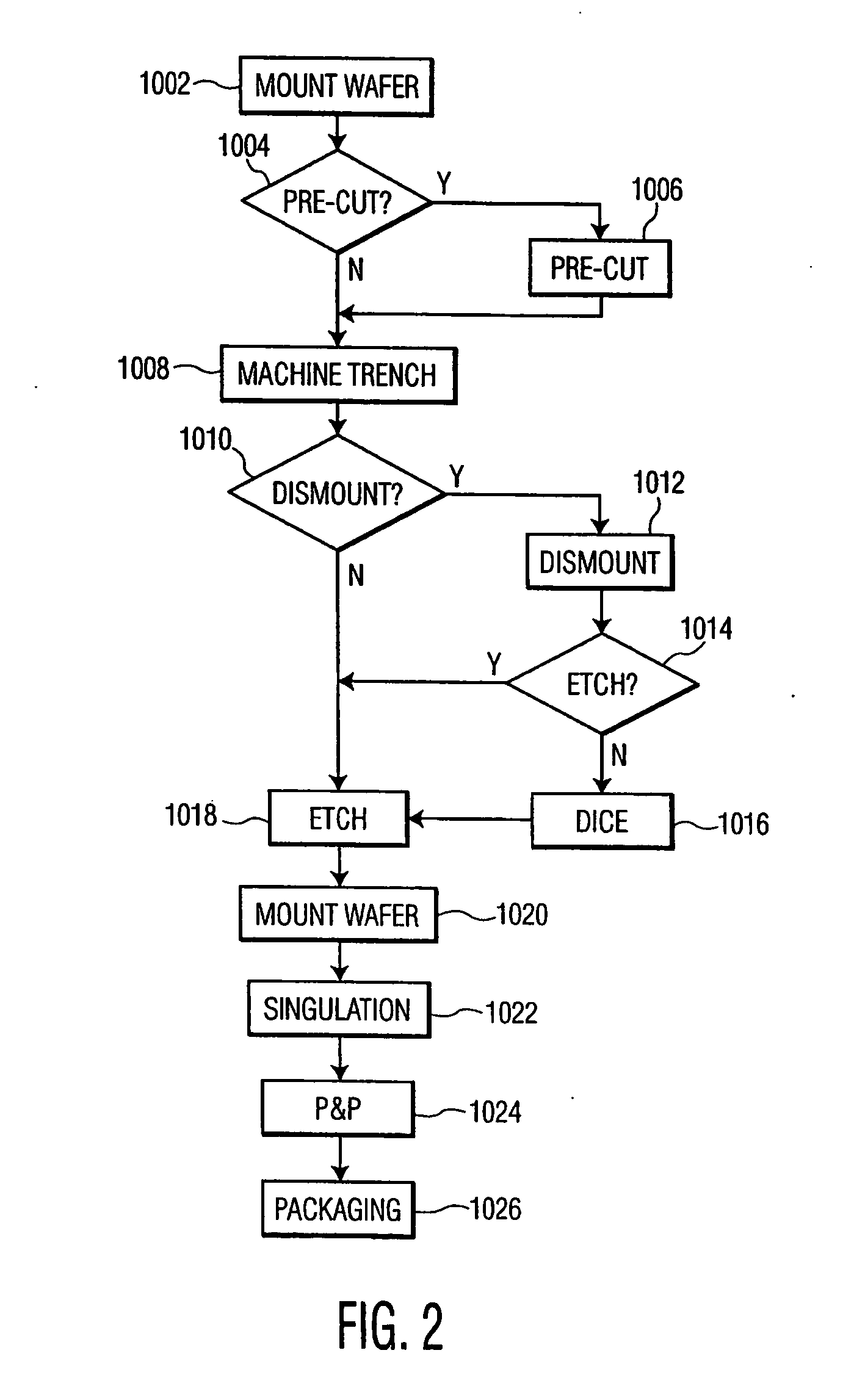
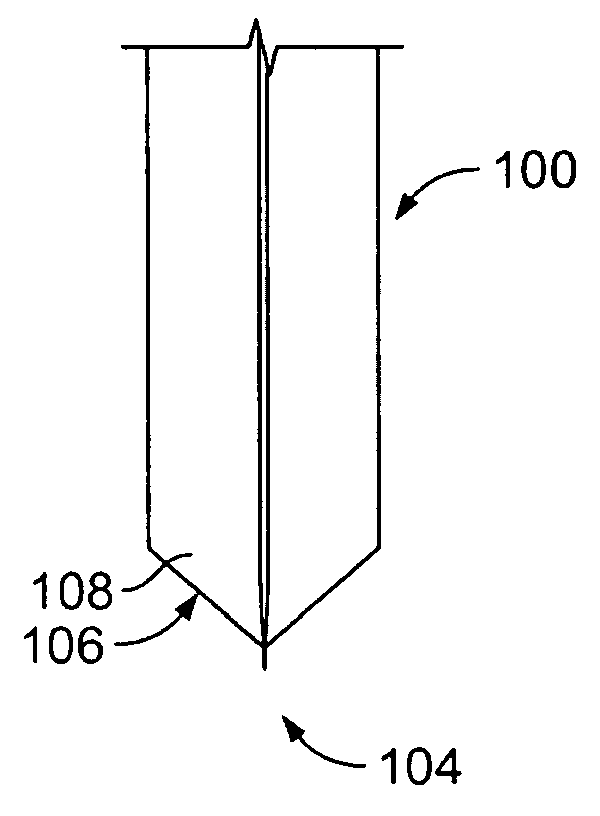
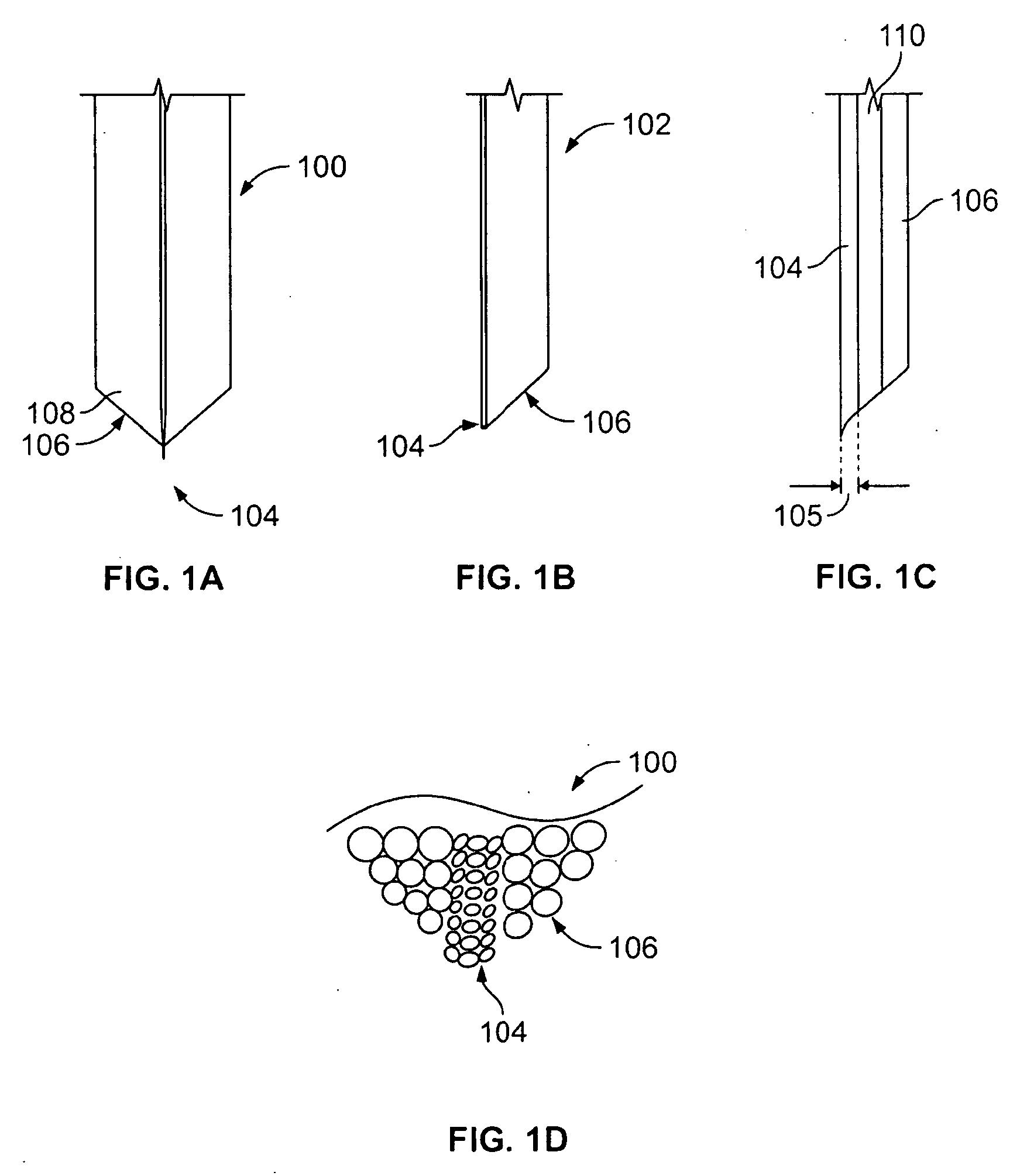
Methods of fabricating complex blade geometries from silicon wafers and strengthening blade geometries
ActiveUS20050266680A1High strengthEasy to controlIncision instrumentsDecorative surface effectsSurgical bladeEngineering
Ophthalmic surgical blades are manufactured from either a single crystal or poly-crystalline material, preferably in the form of a wafer. The method comprises preparing the single crystal or poly-crystalline wafers by mounting them and etching trenches into the wafers using one of several processes. Methods for machining the trenches, which form the bevel blade surfaces, include a diamond blade saw, laser system, ultrasonic machine, a hot forge press and a router. Other processes include wet etching (isotropic and anisotropic) and dry etching (isotropic and anisotropic, including reactive ion etching), and combinations of these etching steps. The wafers are then placed in an etchant solution which isotropically etches the wafers in a uniform manner, such that layers of crystalline or poly-crystalline material are removed uniformly, producing single, double or multiple bevel blades. Nearly any angle can be machined into the wafer, and the machined angle remains after etching. The resulting radii of the blade edges is 5-500 nm, which is the same caliber as a diamond edged blade, but manufactured at a fraction of the cost. A range of radii may be 30 to 60 nm, with a specific implementation being about 40 nm. The blade profile may have an angle of, for example, about 60°. The ophthalmic surgical blades can be used for cataract and refractive surgical procedures, as well as microsurgical, biological and non-medical, non-biological purposes. Surgical and non-surgical blades and mechanical devices manufactured as described herein can also exhibit substantially smoother surfaces than metal blades.
Owner:BEAVER VISITEC INT US
Microsurgical cutting instruments
InactiveUS20090177217A1Low manufacturing process costLow costIncision instrumentsLapping machinesSurgical bladeKnife blades
The present invention relates to methods and apparatus for self-sharpening micro surgical blades, knives and assemblies.
Owner:MYNOSYS CELLULAR DEVICES INC
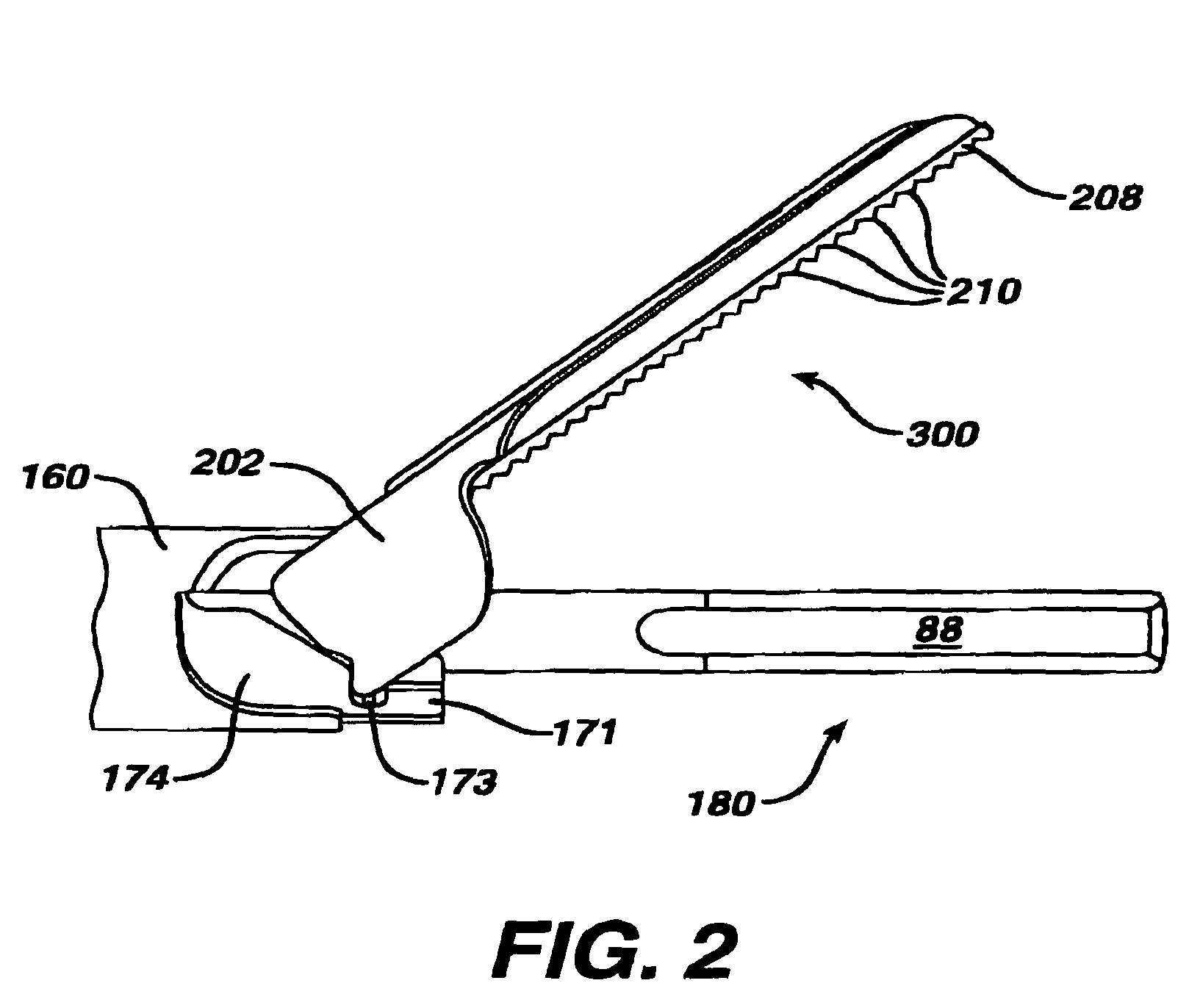
Handle with removable disposable surgical blade and blade removal system including disposal container
InactiveUS20070156160A1Easy to disassembleEasy to unlockIncision instrumentsSurgical furnitureInterference fitSurgical blade
A surgical blade includes a handle with a recess sized to receive the proximal end of a blade assembly. The recess includes a notch as well as opposed facing distal ridges designed to engage elevated surfaces in the blade assembly to maintain the blade assembly and handle assembled. The blade assembly includes a blade portion and a fitting having a protrusion sized to be received in the proximal notch of the recess in the handle when the blade portion is assembled to the handle. The fitting also includes side faces having opposed elevated surfaces obliquely disposed so that they are engaged by the distal ridges within the handle recess. The fitting also includes an upwardly extending catch that engages a distal surface on the handle to assist in locking the blade assembly to the handle. The recess of the handle includes inner tapered surfaces. The side faces of the fitting are tapered to the same degree so that as the fitting is pushed upwardly within the recess, the side faces of the fitting engage the lateral inner surfaces of the recess to provide an interference fit therebetween. A blade removal system permits the blade assembly to be removed from the handle without any danger of cutting or puncturing the fingers or hands of the surgeon. The system includes a container having a removable lid, with the lid having an opening leading to a short passageway receiving the blade assembly. The blade assembly may be inserted into the recess until the fitting engages within a rectangular opening therein. In that orientation, the handle may be pivoted to unlock the blade assembly from the handle.
Owner:PETERSEN THOMAS D
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com