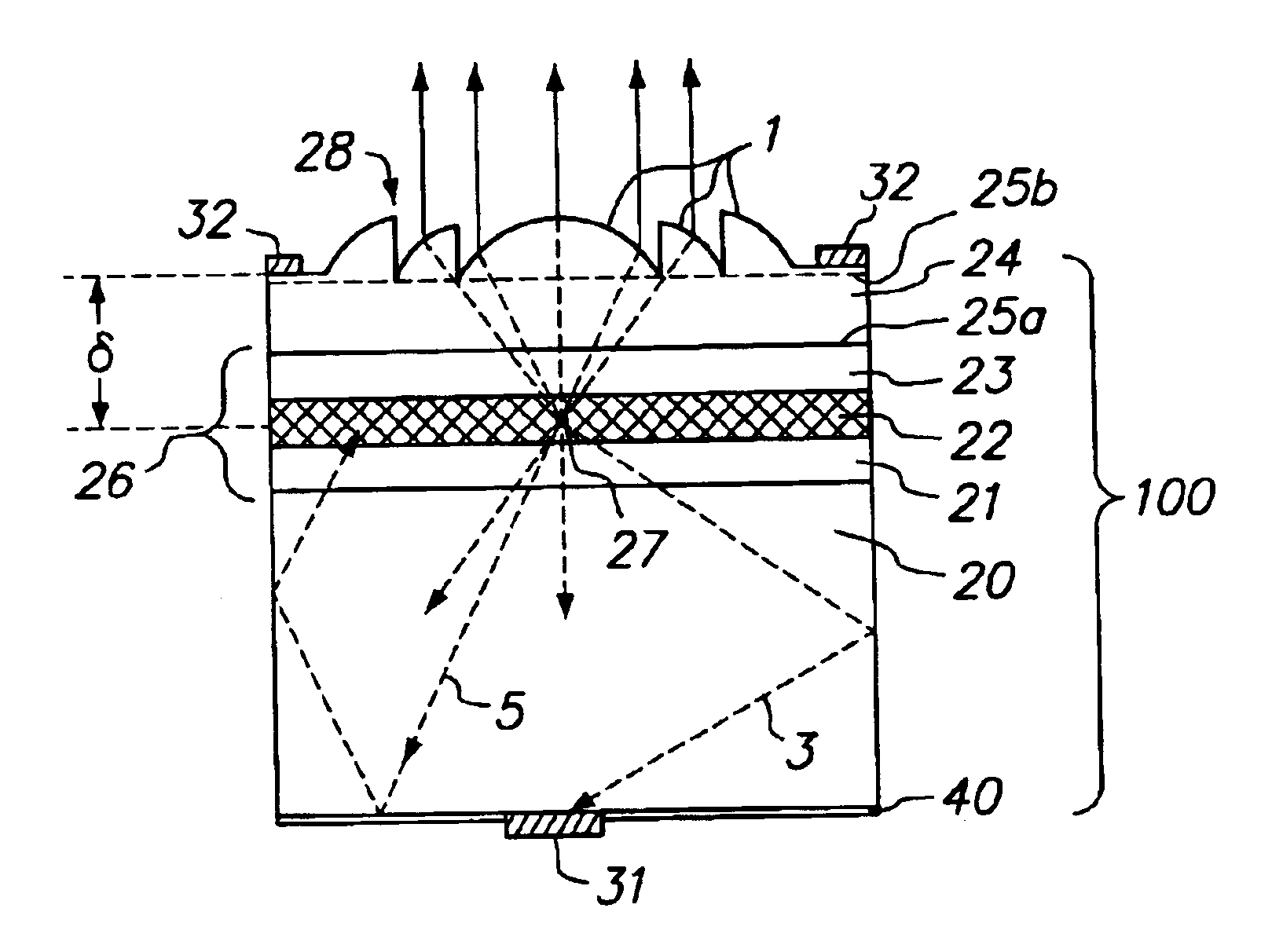
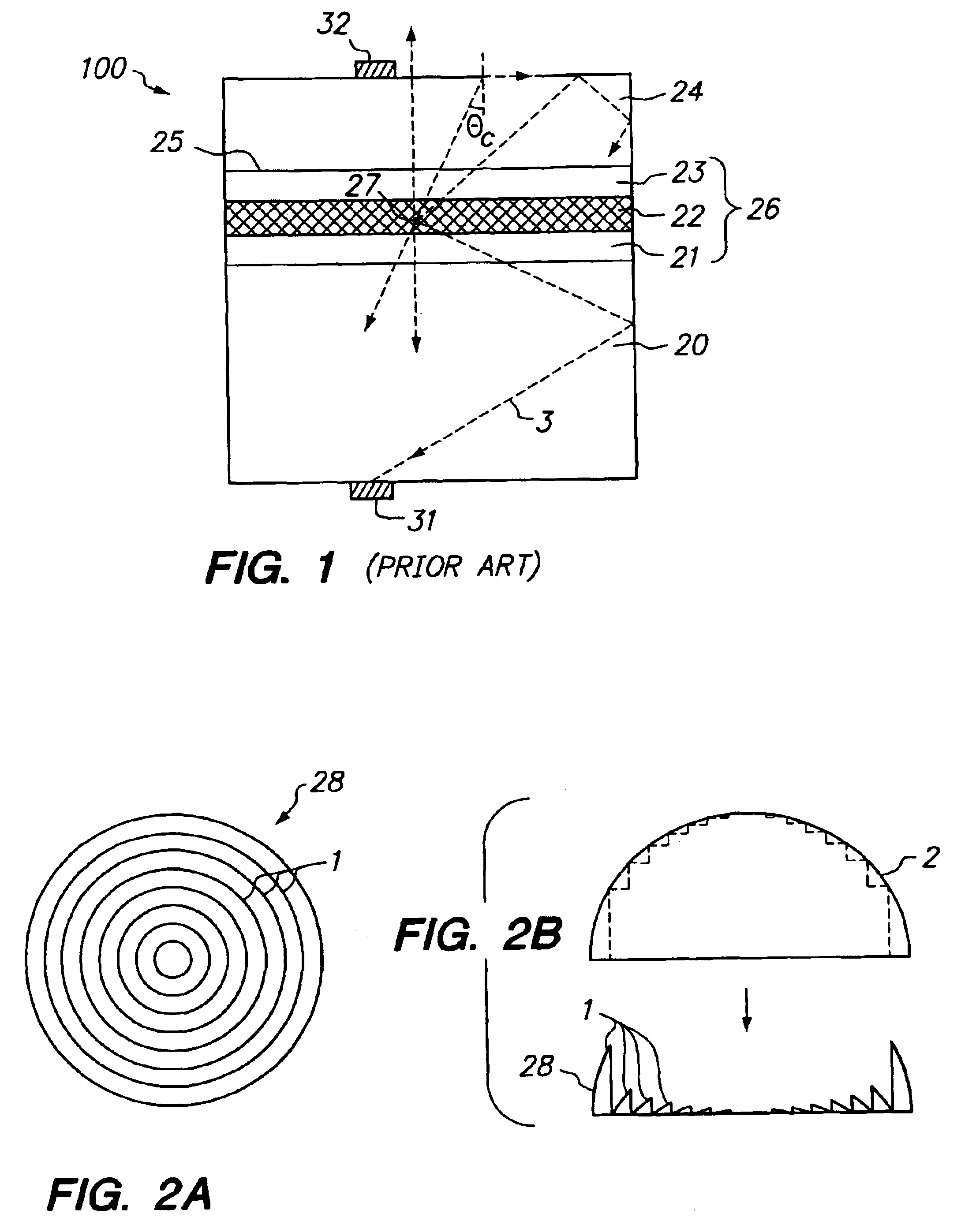
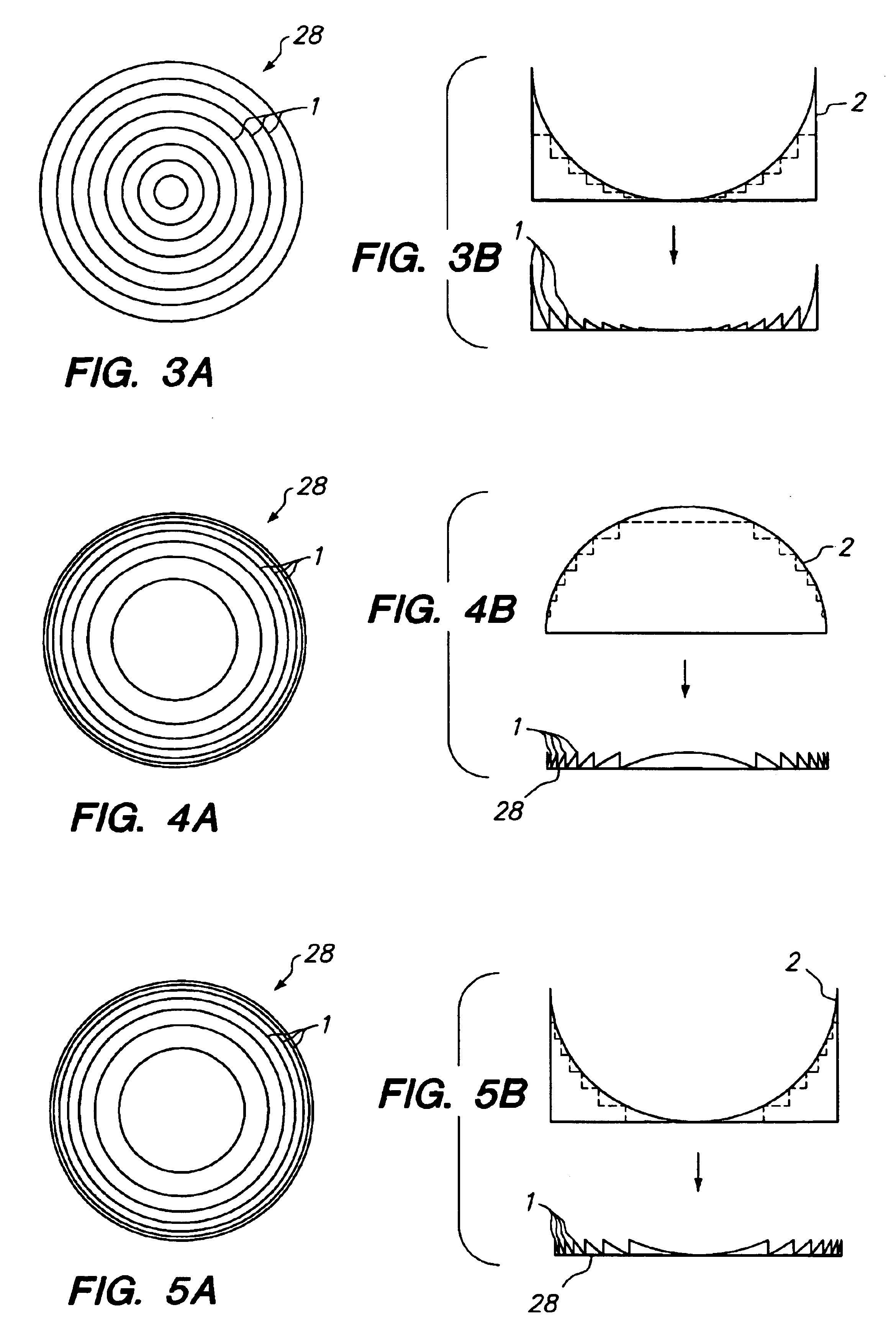
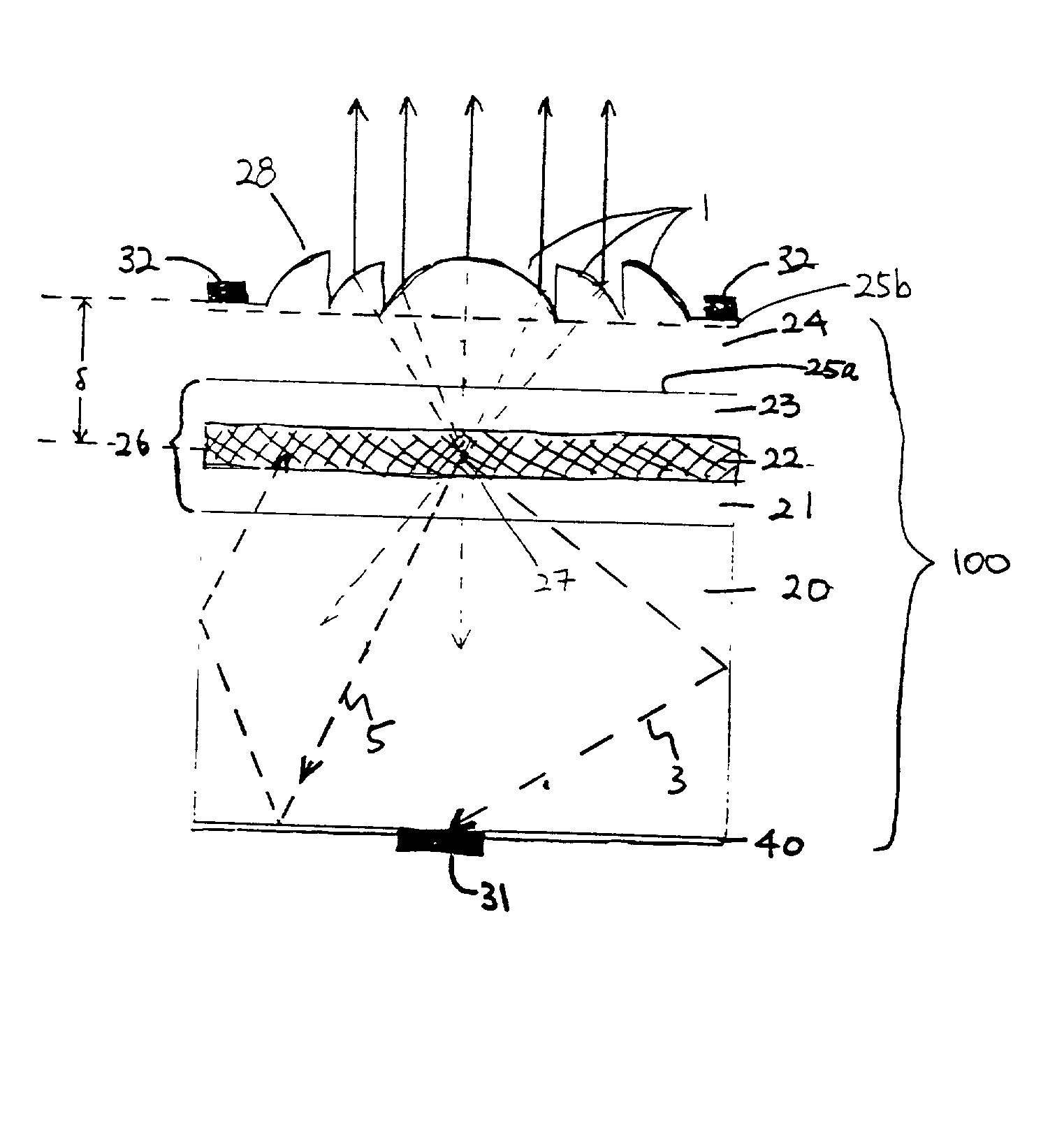
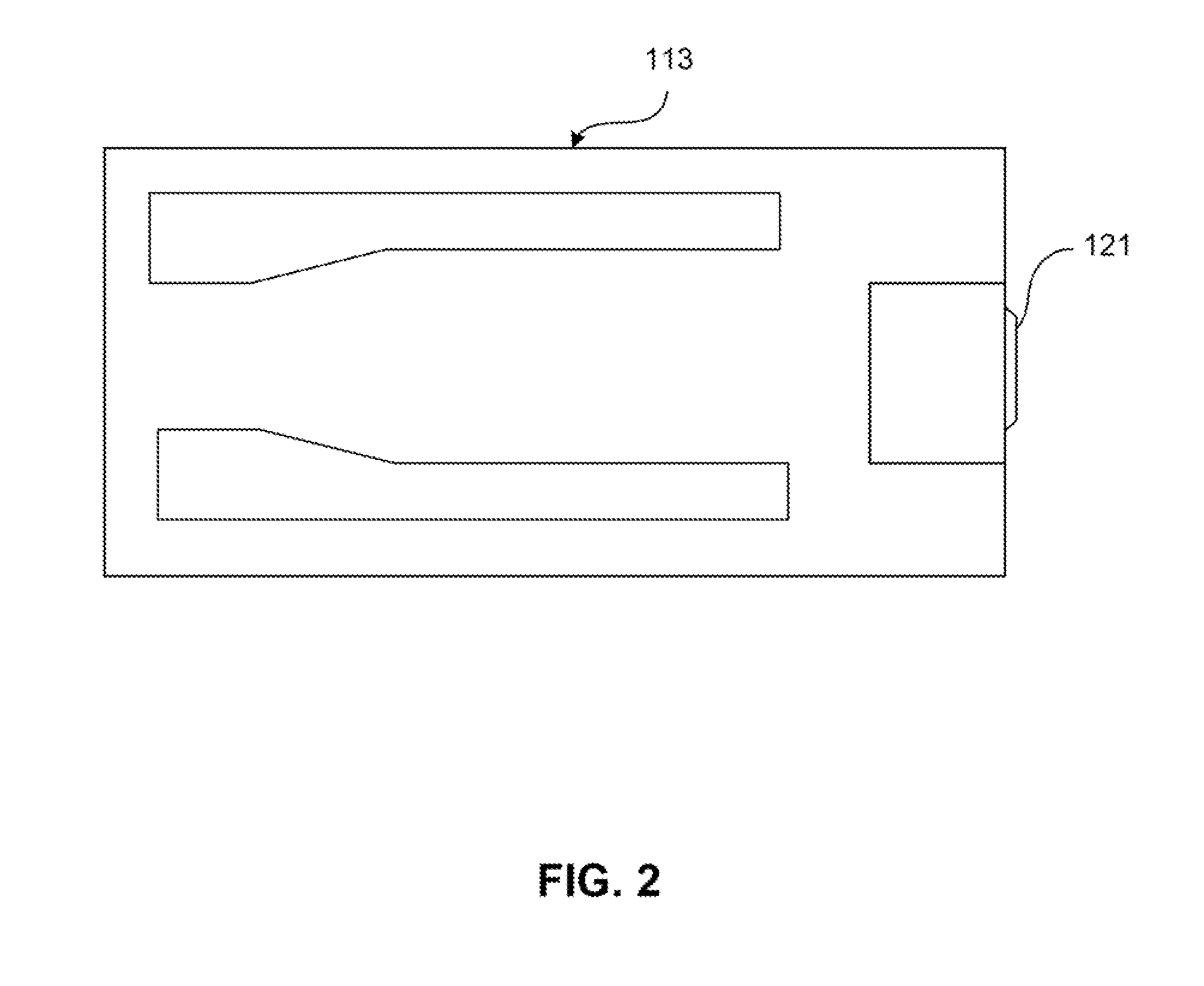
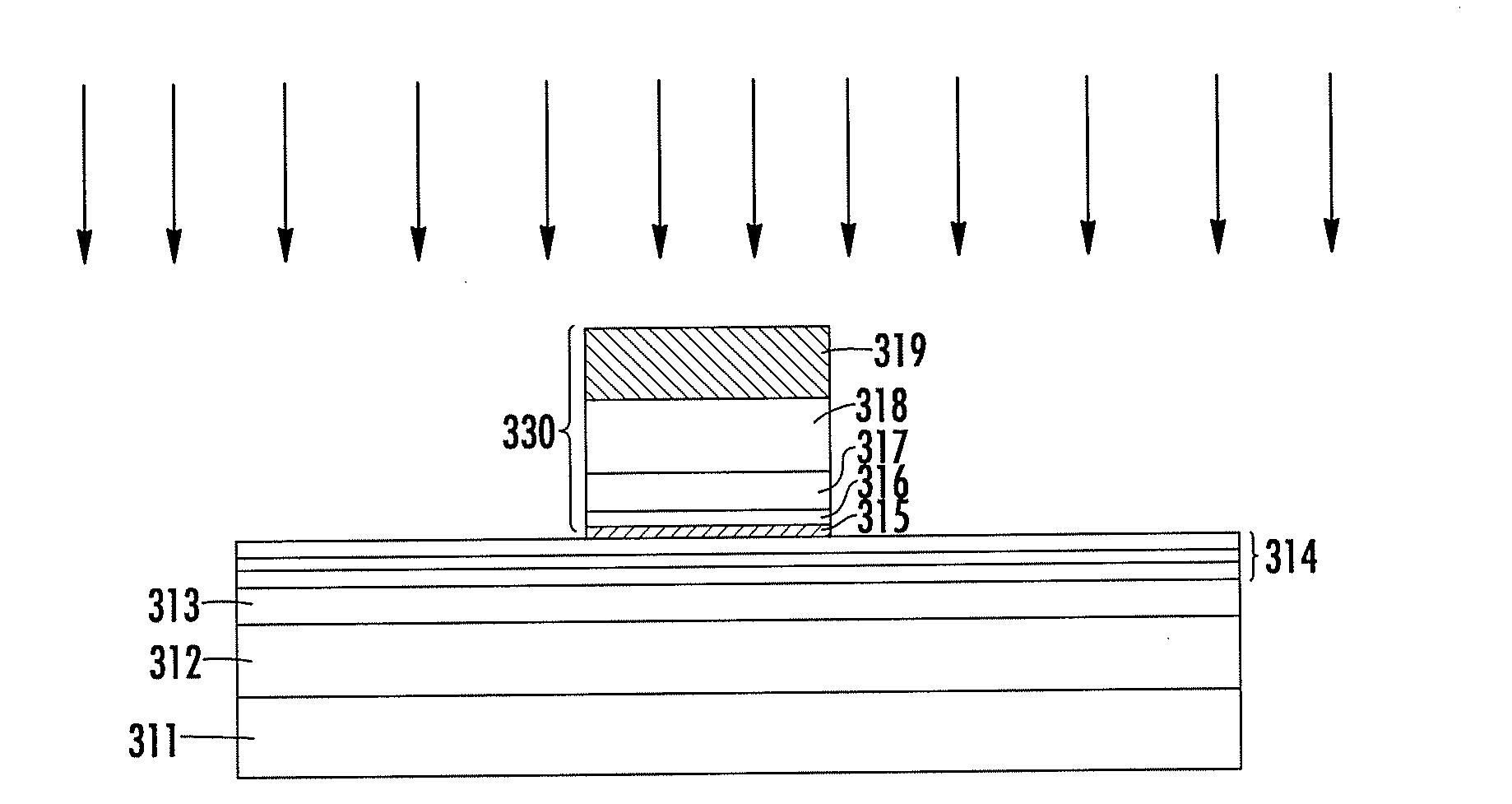
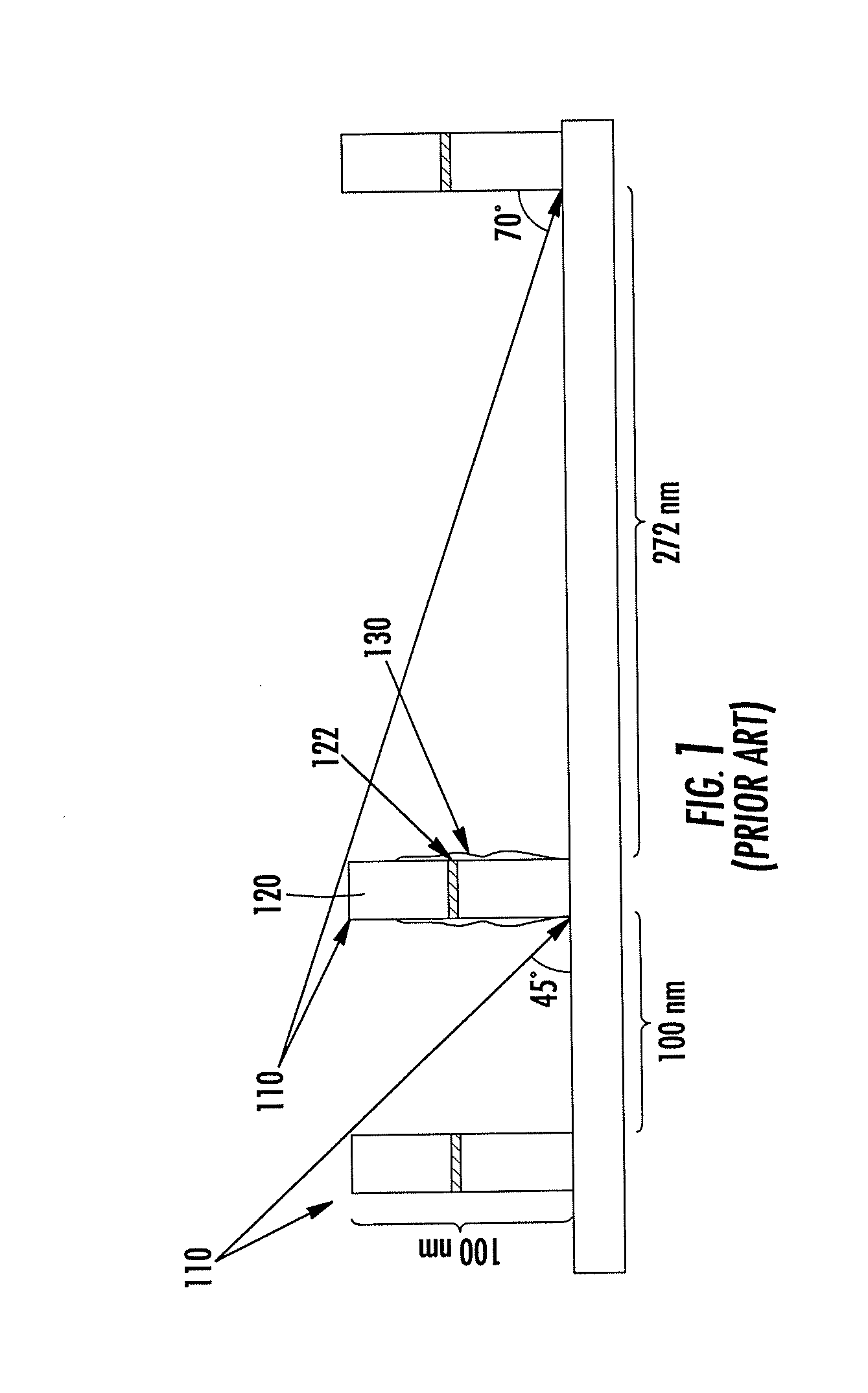
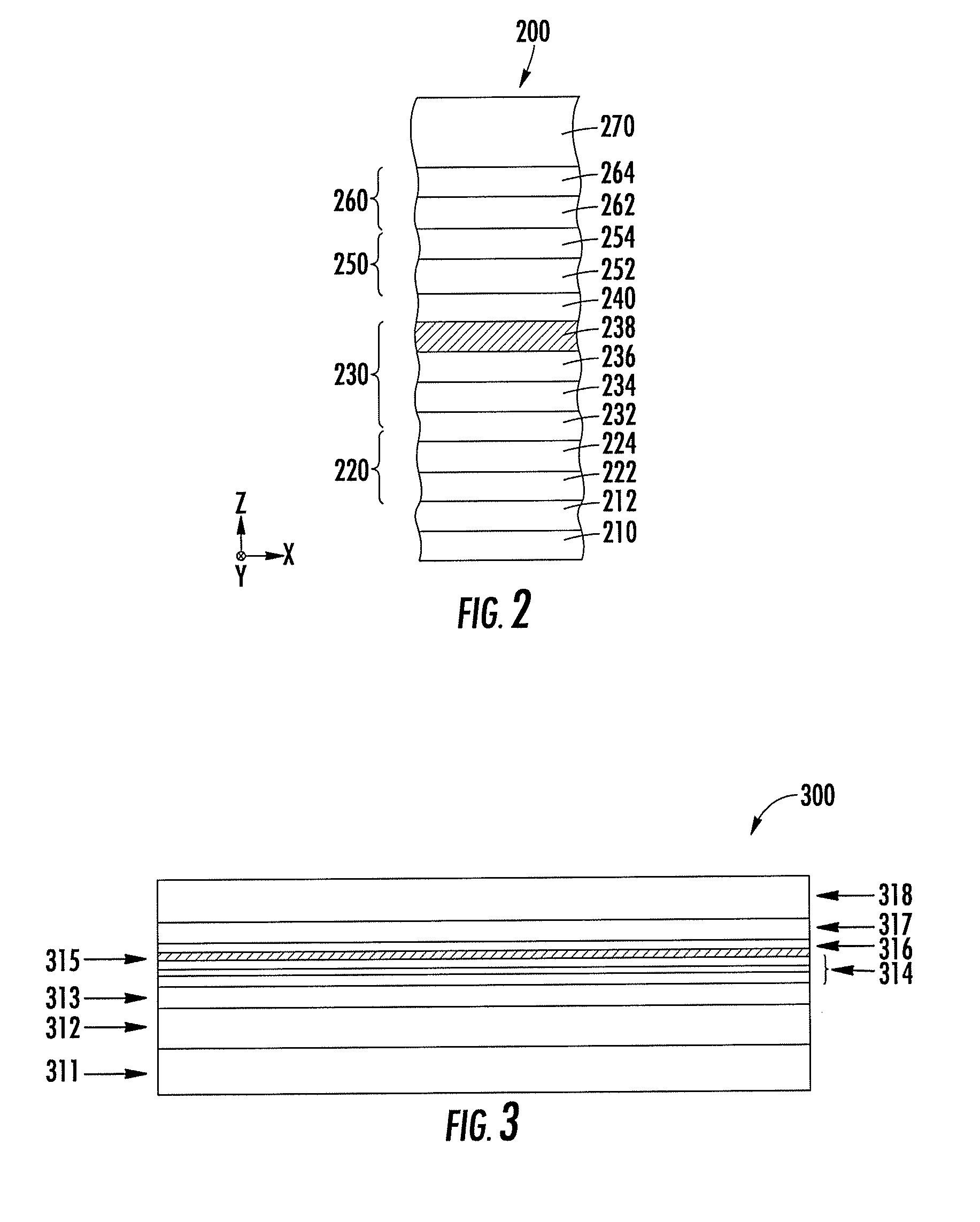
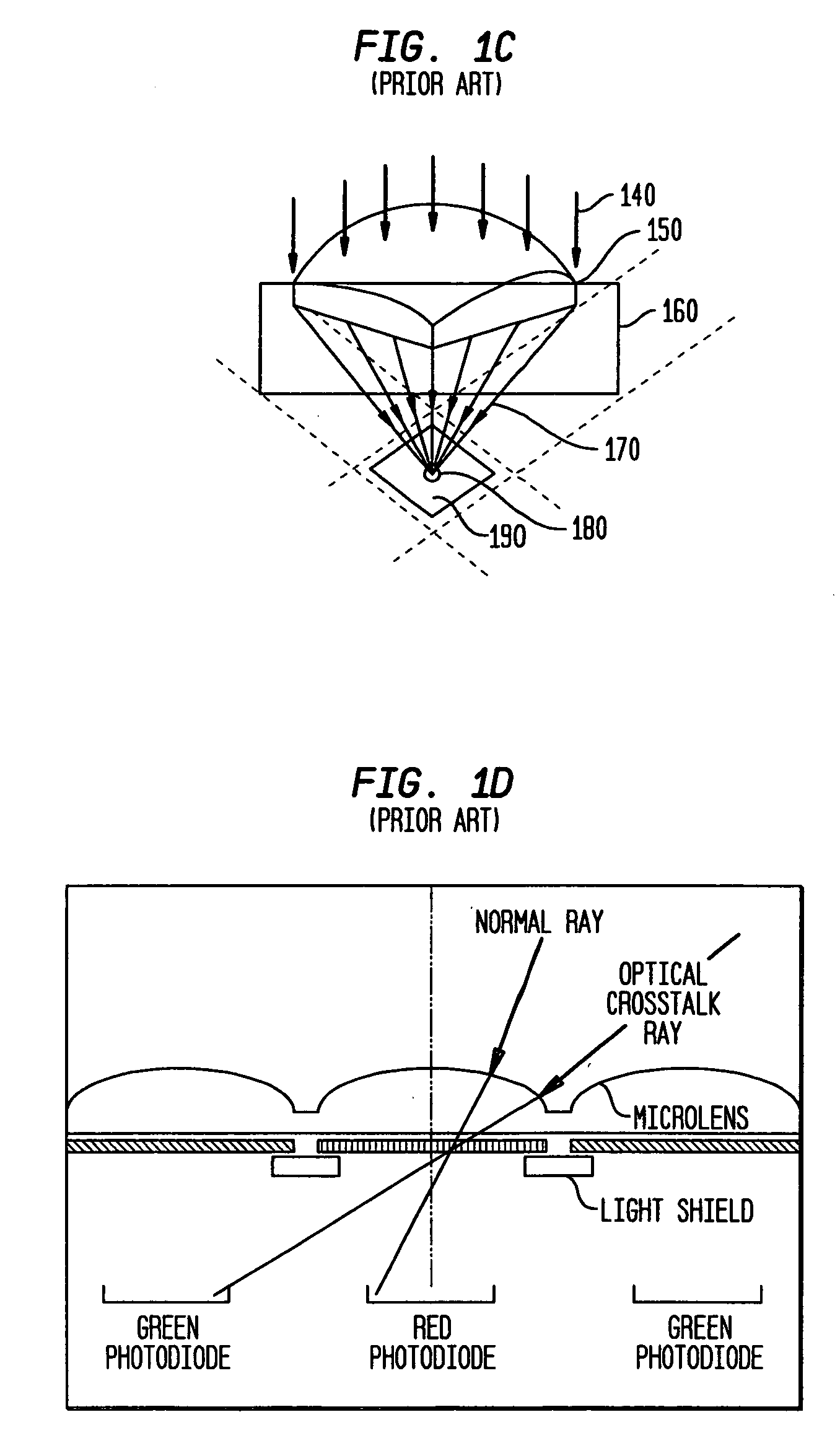
Patents
Literature
1136 results about "Reactive-ion etching" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
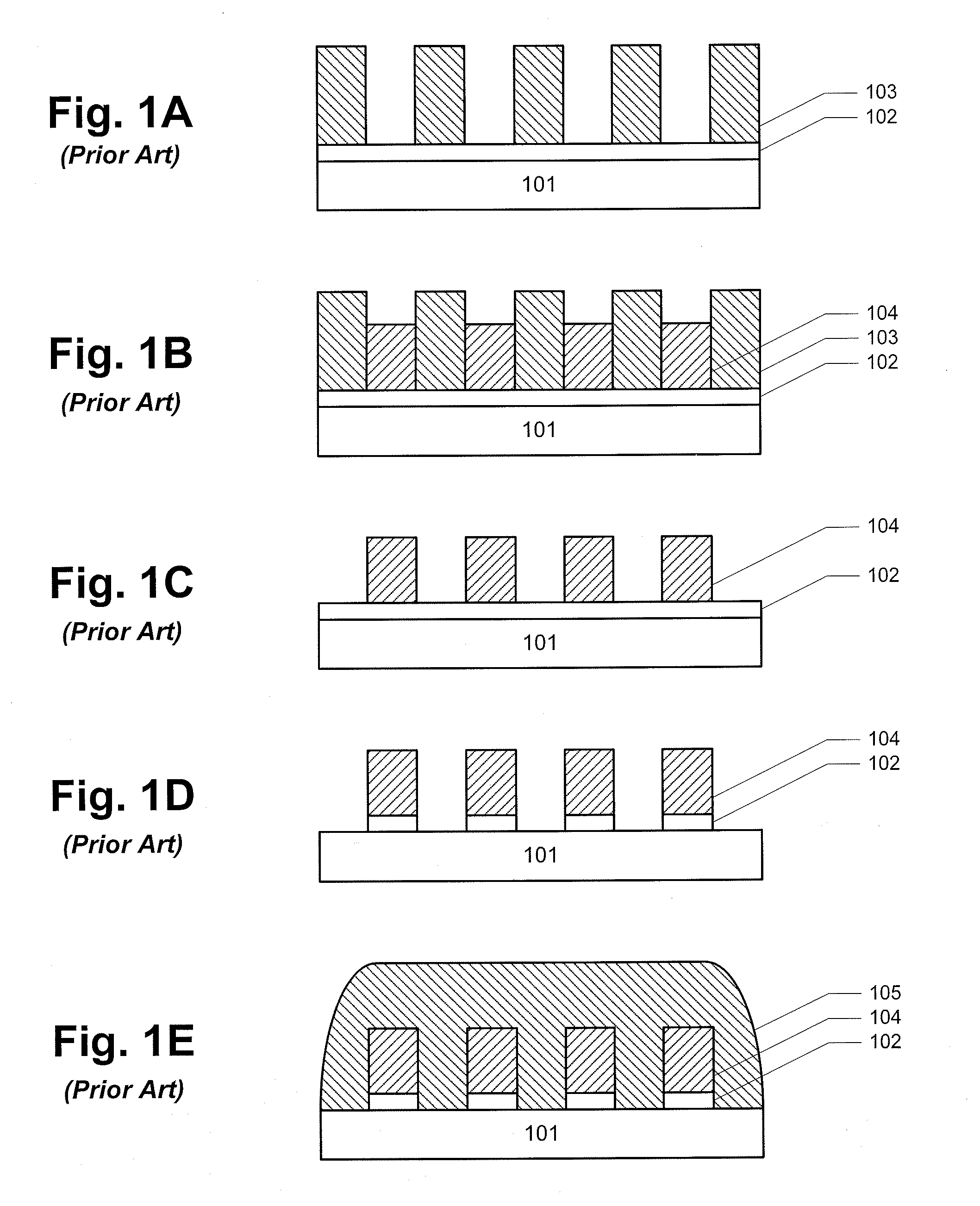
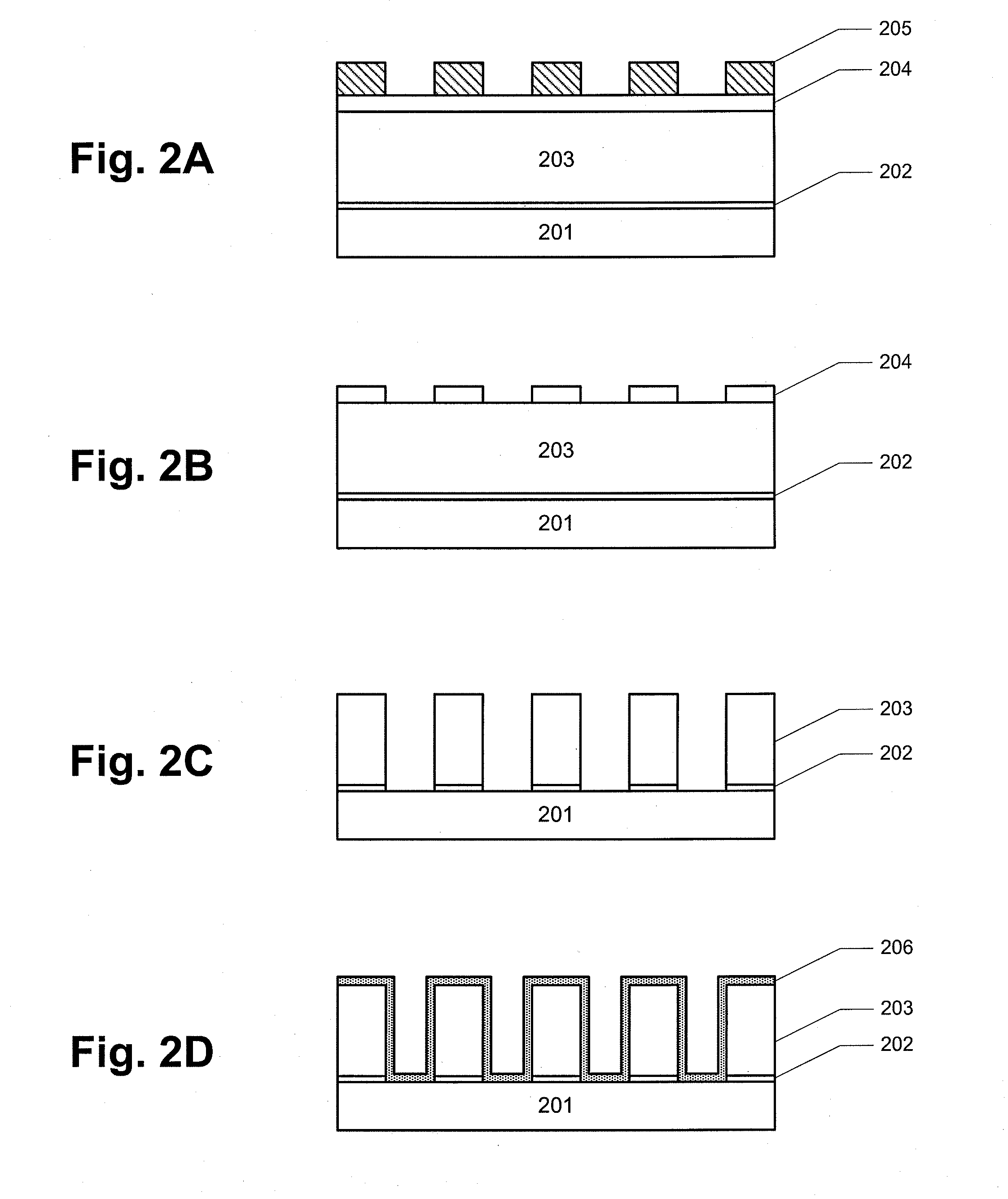
Reactive-ion etching (RIE) is an etching technology used in microfabrication. RIE is a type of dry etching which has different characteristics than wet etching. RIE uses chemically reactive plasma to remove material deposited on wafers. The plasma is generated under low pressure (vacuum) by an electromagnetic field. High-energy ions from the plasma attack the wafer surface and react with it.
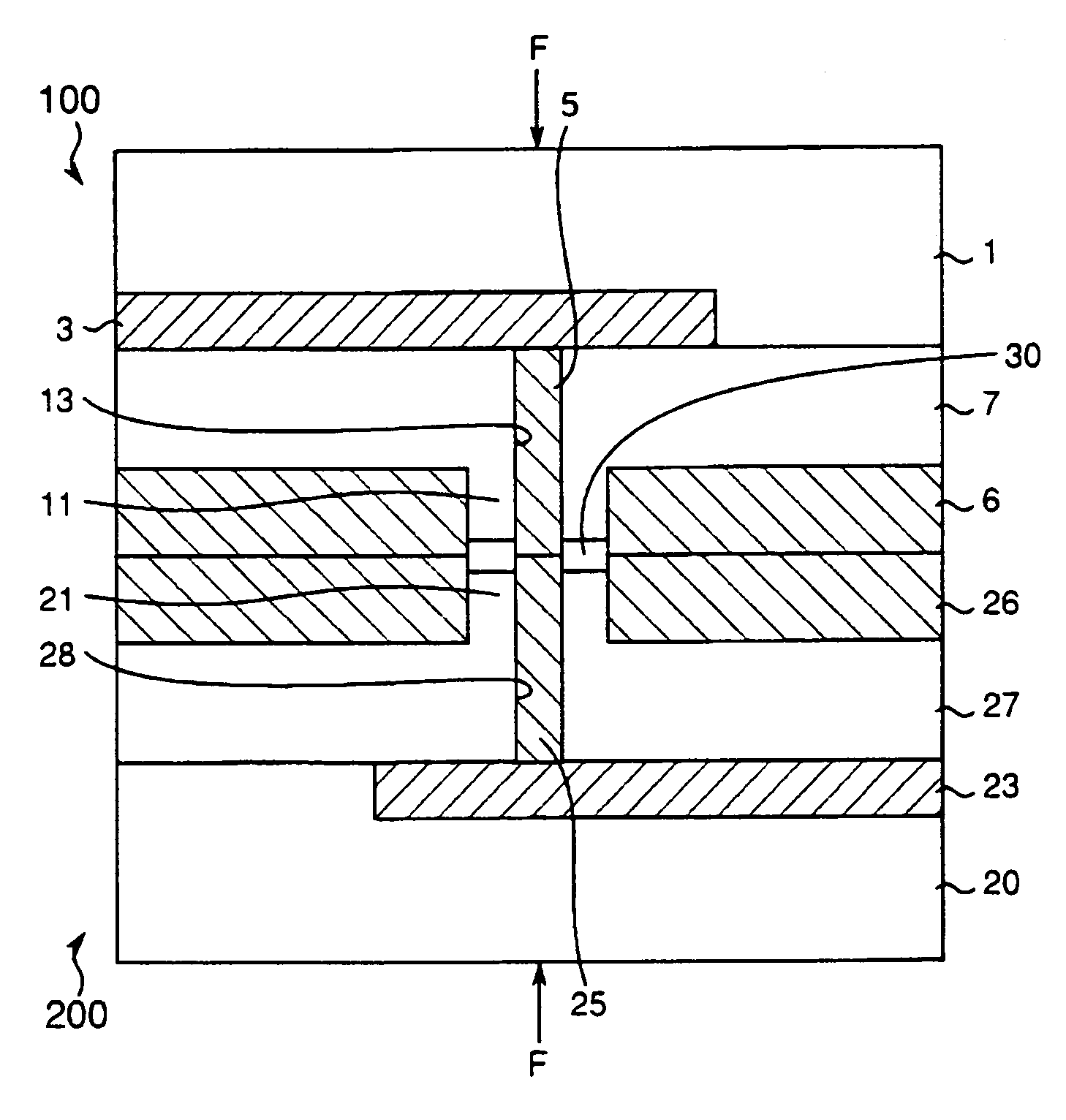
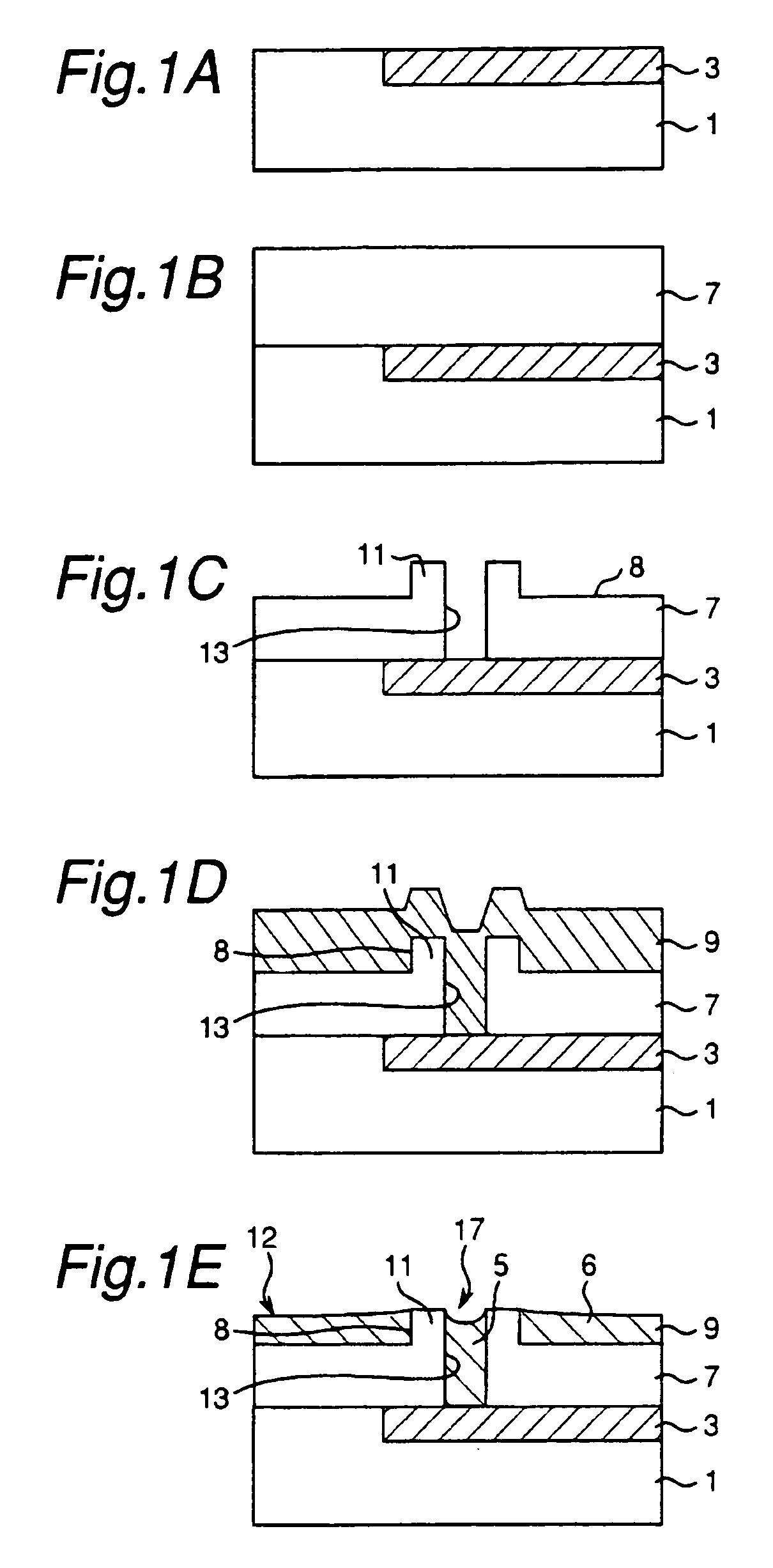
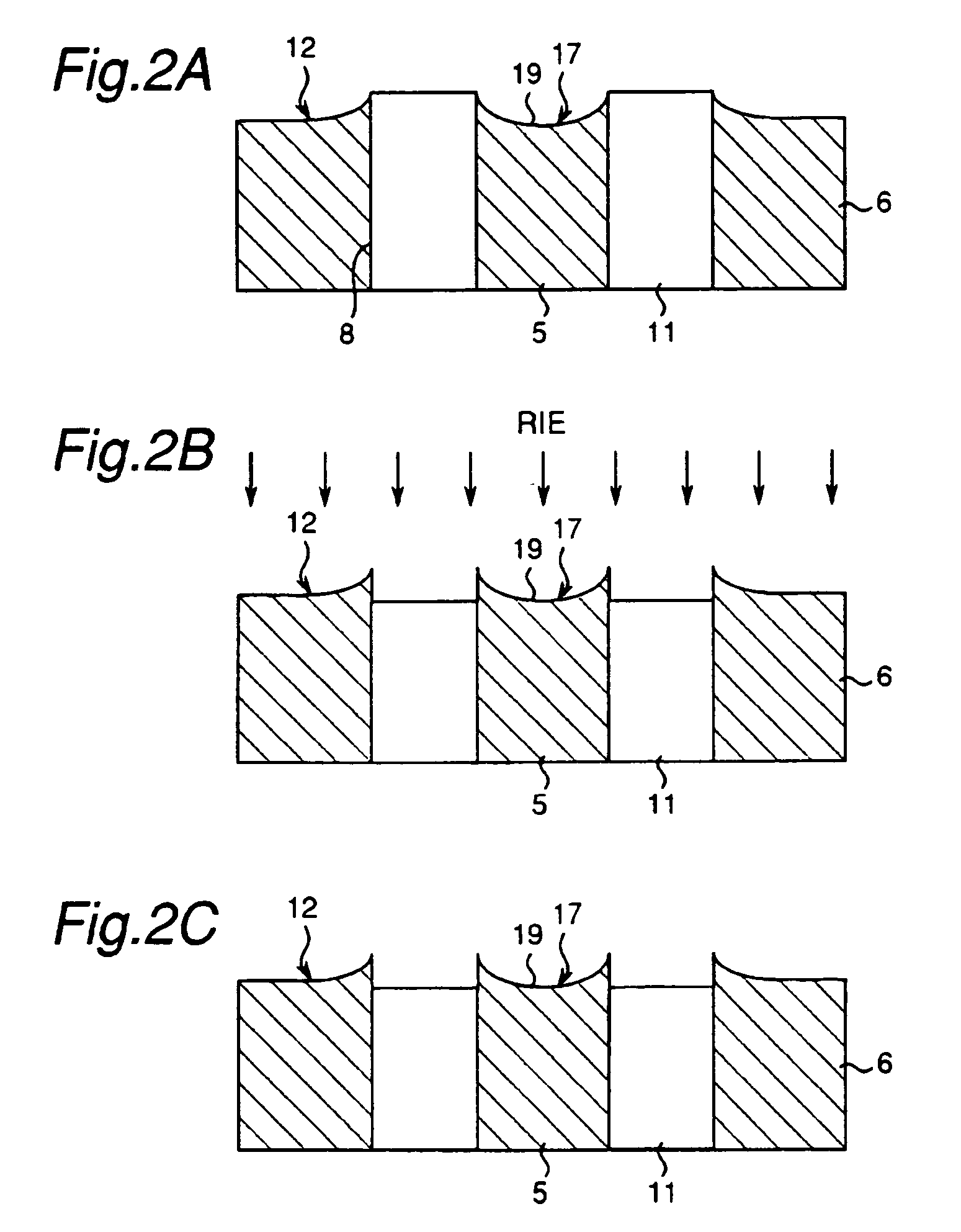
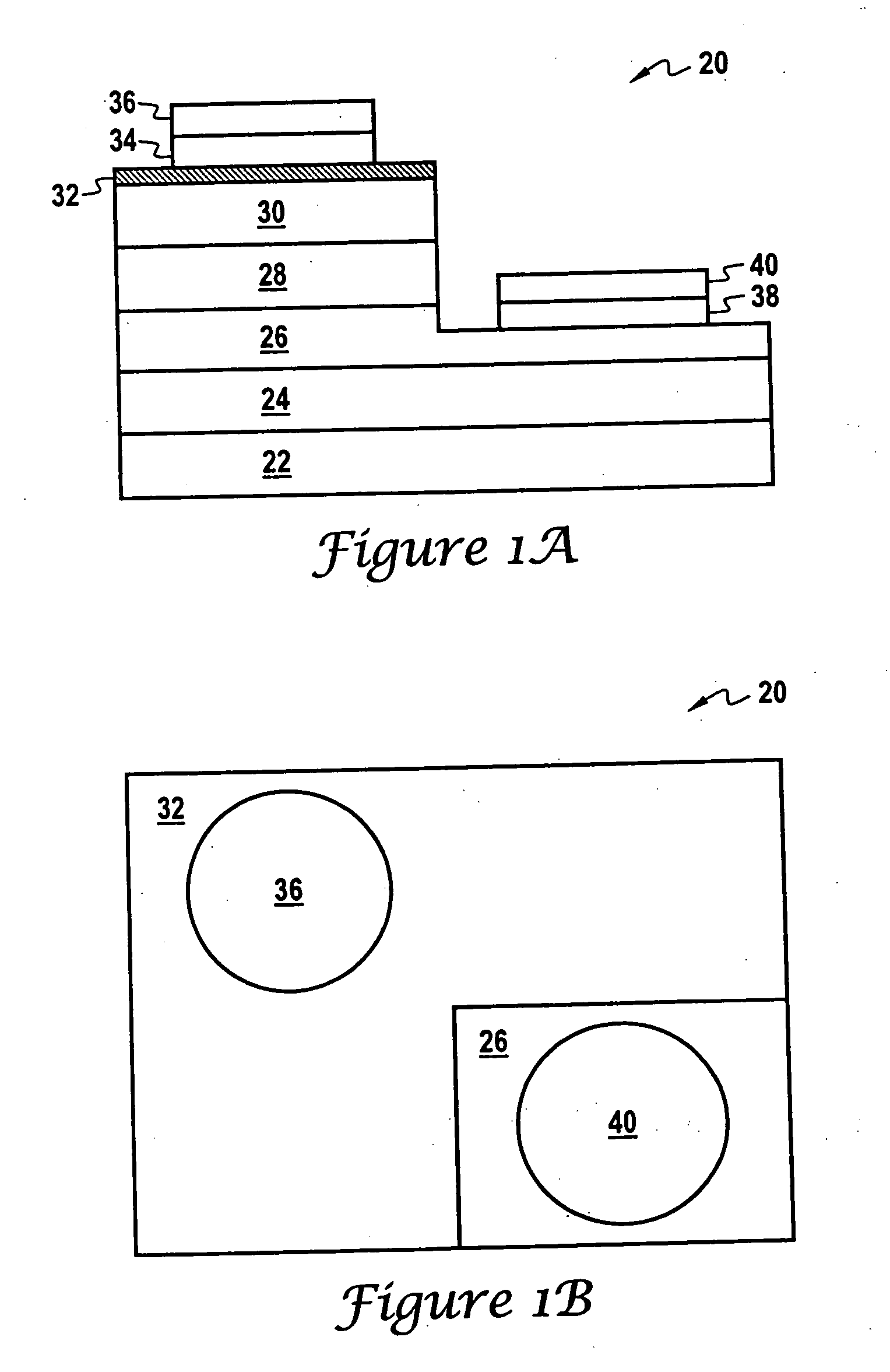
Method of cleaning substrate processing chamber, storage medium, and substrate processing chamber
ActiveUS20070186952A1Inhibition formationElectric discharge tubesHollow article cleaningElectricityReactive-ion etching
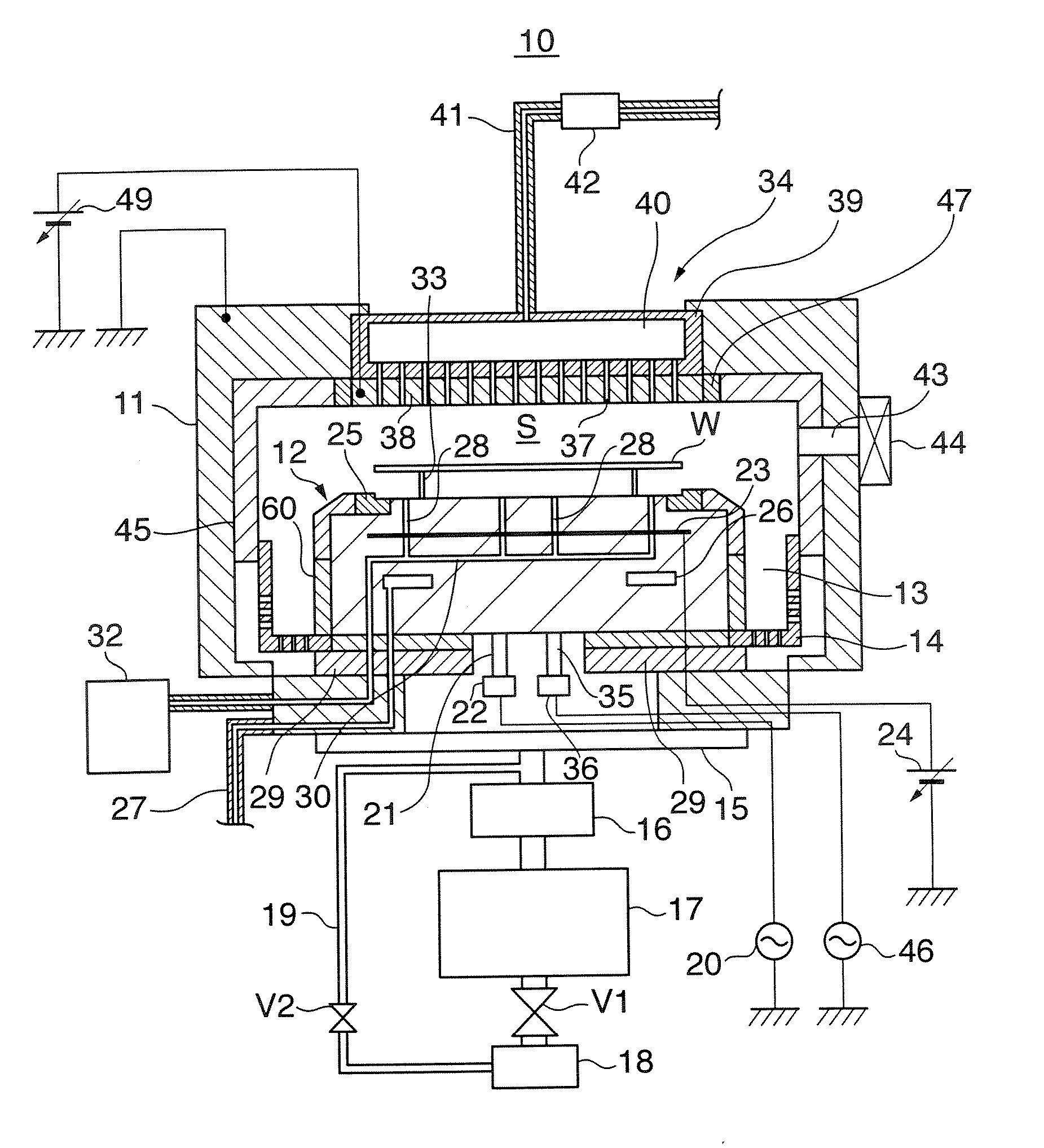
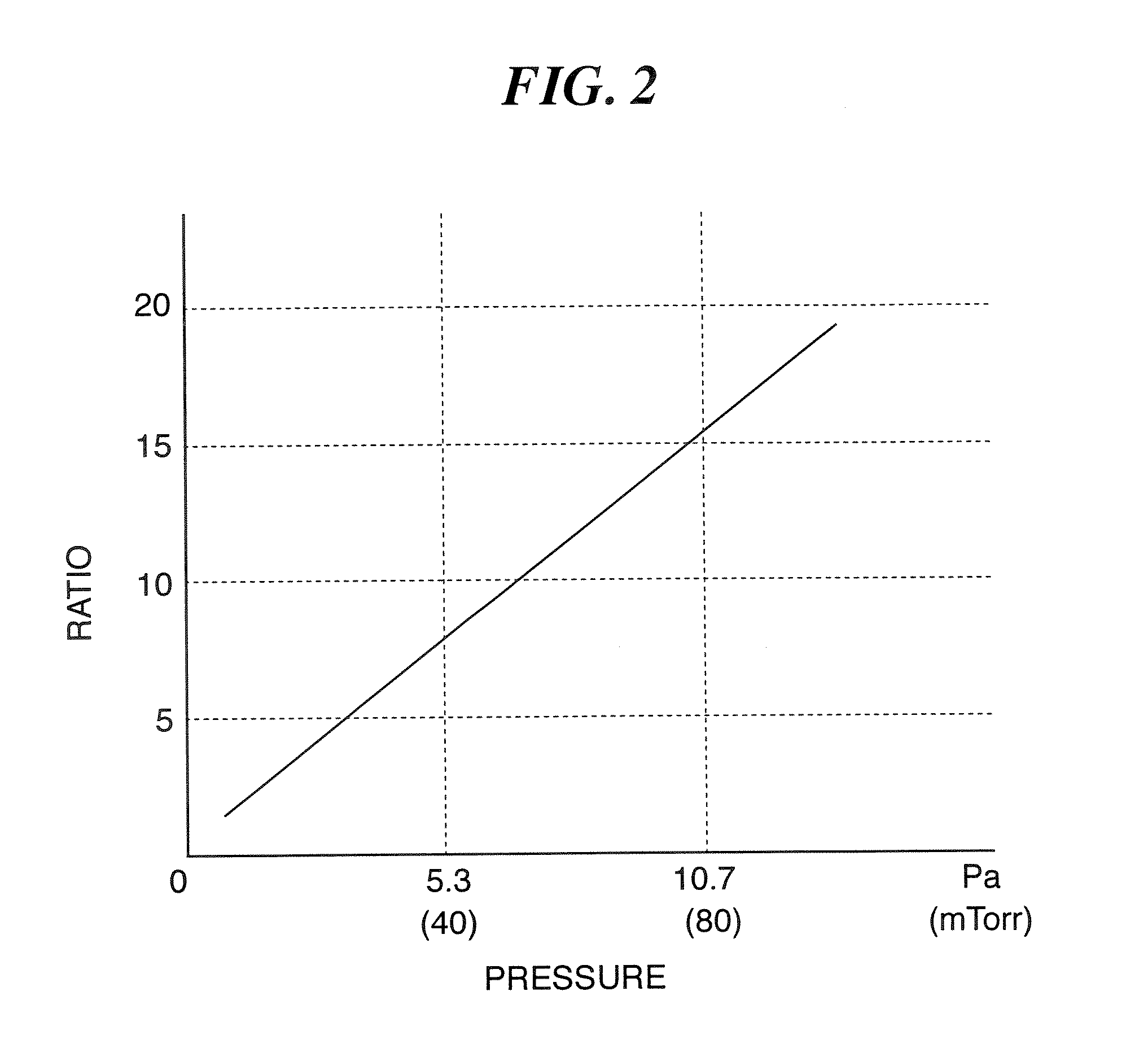
A method of cleaning a substrate processing chamber that enables formation of an oxide film on a surface of a processing chamber inside component to be prevented. A substrate processing chamber 11 has therein a processing space S into which a wafer W is transferred and carries out reactive ion etching on the wafer W in the processing space S. The substrate processing chamber 11 has an upper electrode plate 38 that comprises silicon and a lower surface of which is exposed to the processing space S. A dry cleaning is carried out on the upper electrode plate 38 using oxygen radicals produced from oxygen gas introduced into the processing space S. An oxide removal processing is carried out on the upper electrode plate 38 using fluorine ions and fluorine radicals produced from carbon tetrafluoride gas introduced into the processing space S.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
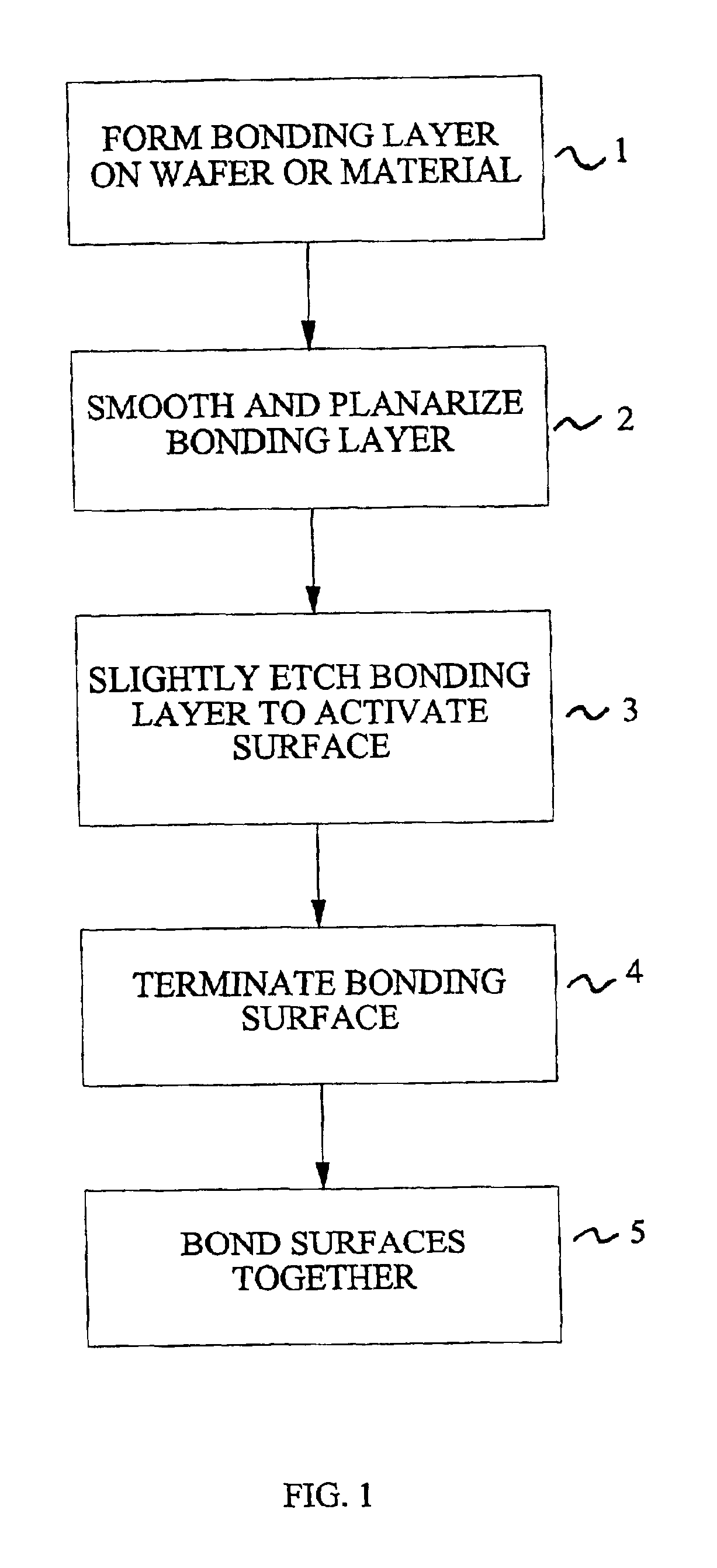
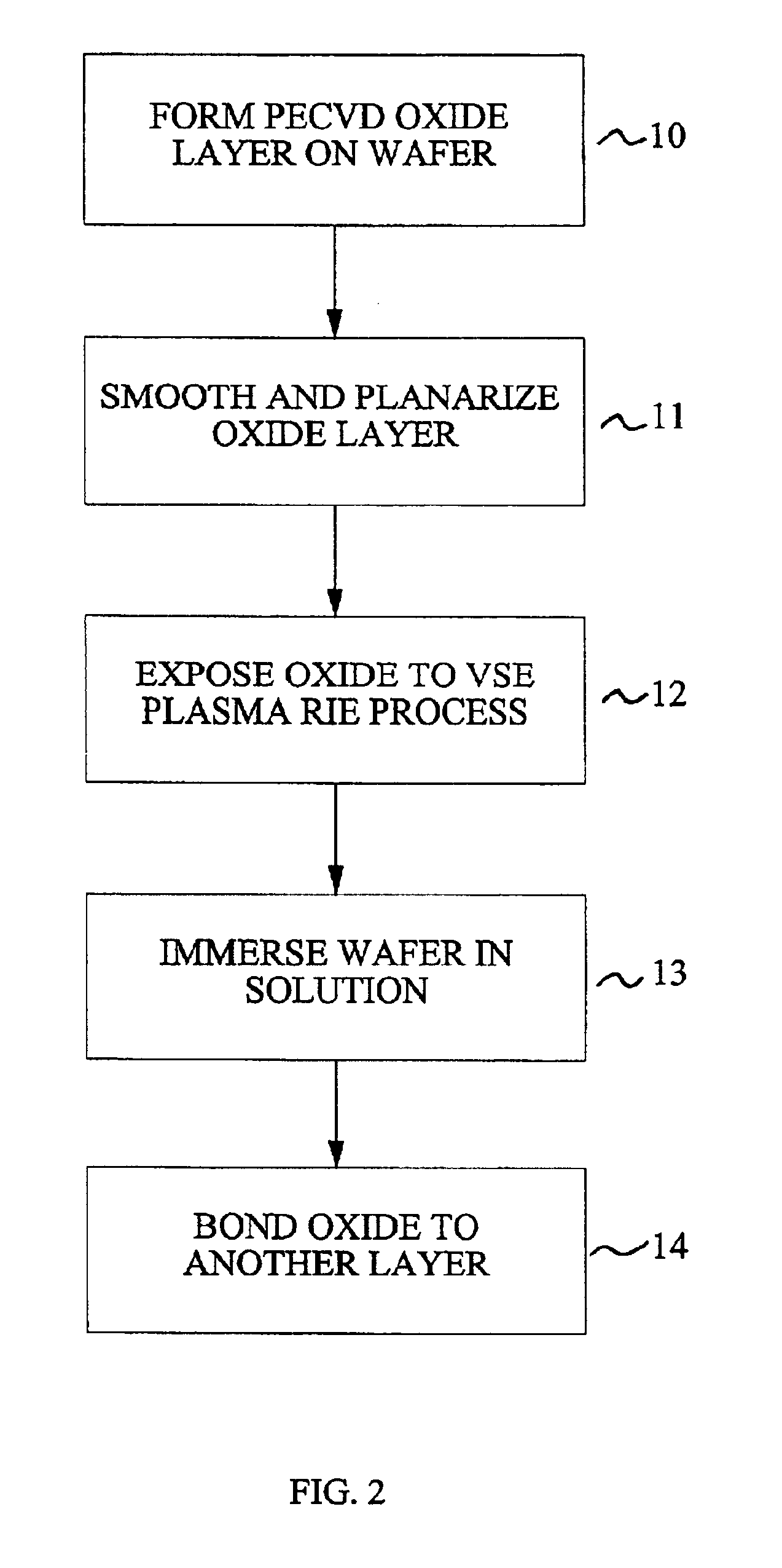
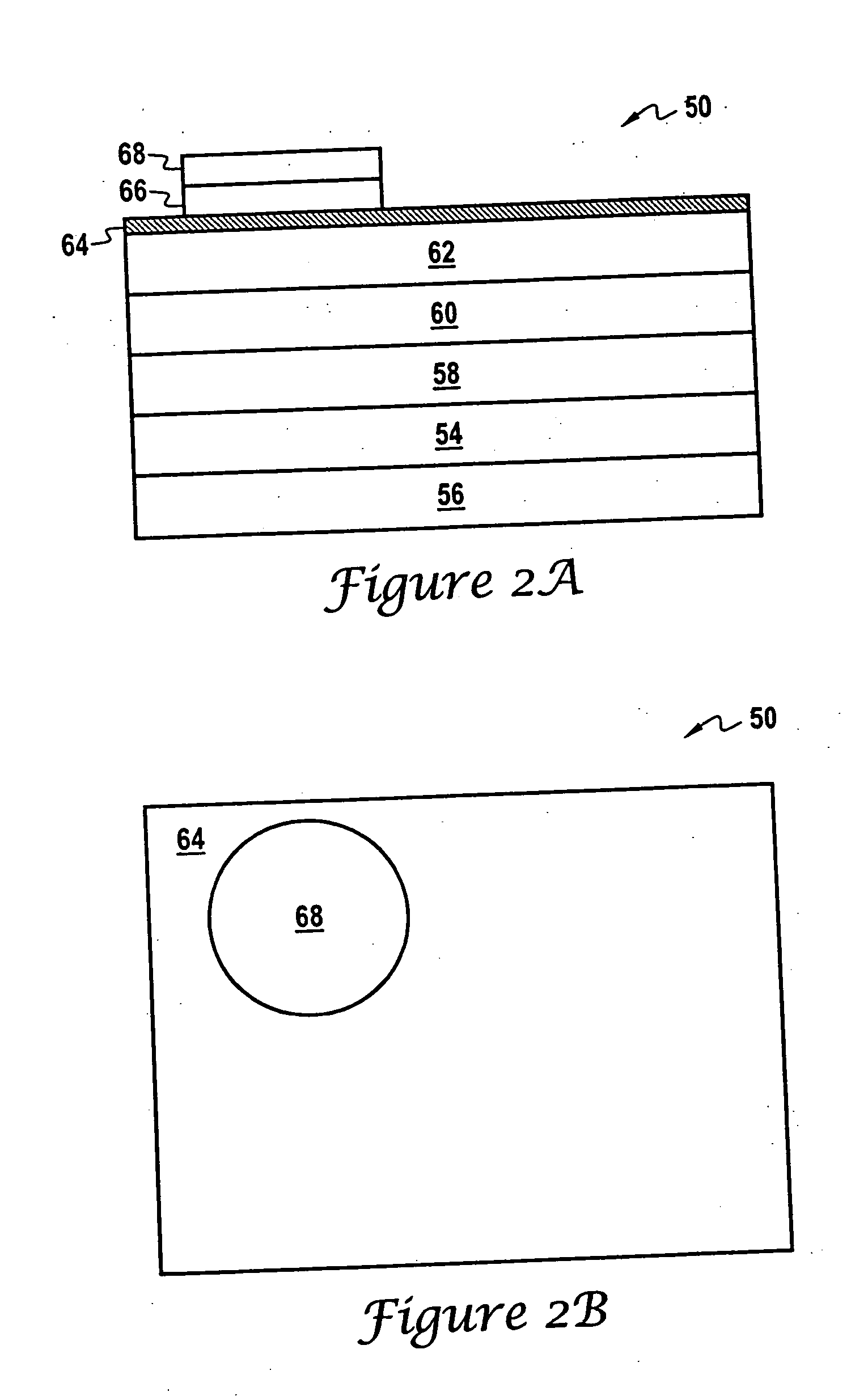
Method for low temperature bonding and bonded structure
InactiveUS6902987B1High bonding strengthSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSurface cleaningBiological activation
A method for bonding at low or room temperature includes steps of surface cleaning and activation by cleaning or etching. One etching process the method may also include removing by-products of interface polymerization to prevent a reverse polymerization reaction to allow room temperature chemical bonding of materials such as silicon, silicon nitride and SiO2. The surfaces to be bonded are polished to a high degree of smoothness and planarity. VSE may use reactive ion etching or wet etching to slightly etch the surfaces being bonded. The surface roughness and planarity are not degraded and may be enhanced by the VSE process. The etched surfaces may be rinsed in solutions such as ammonium hydroxide or ammonium fluoride to promote the formation of desired bonding species on the surfaces.
Owner:INVENSAS BONDING TECH INC
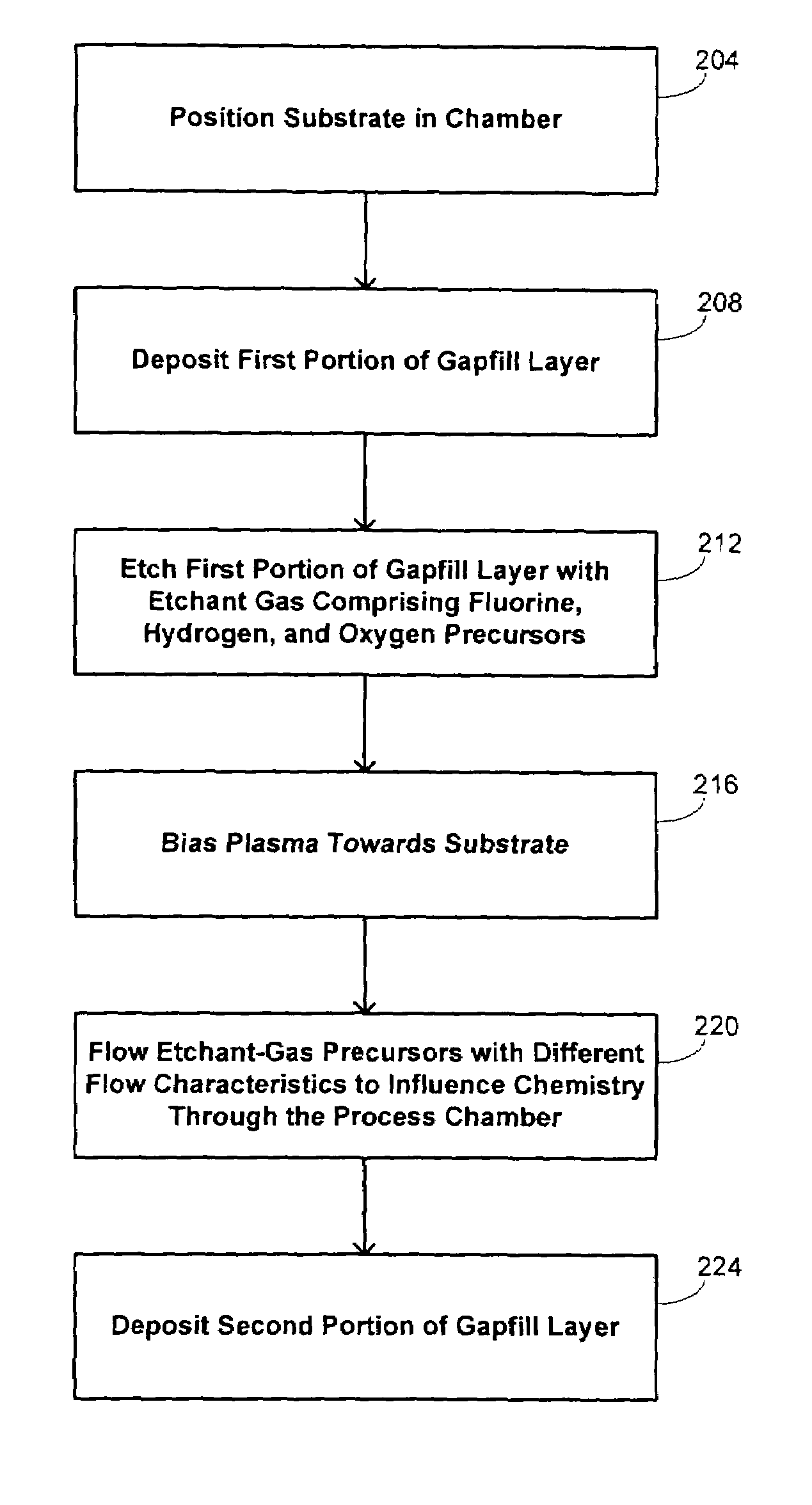
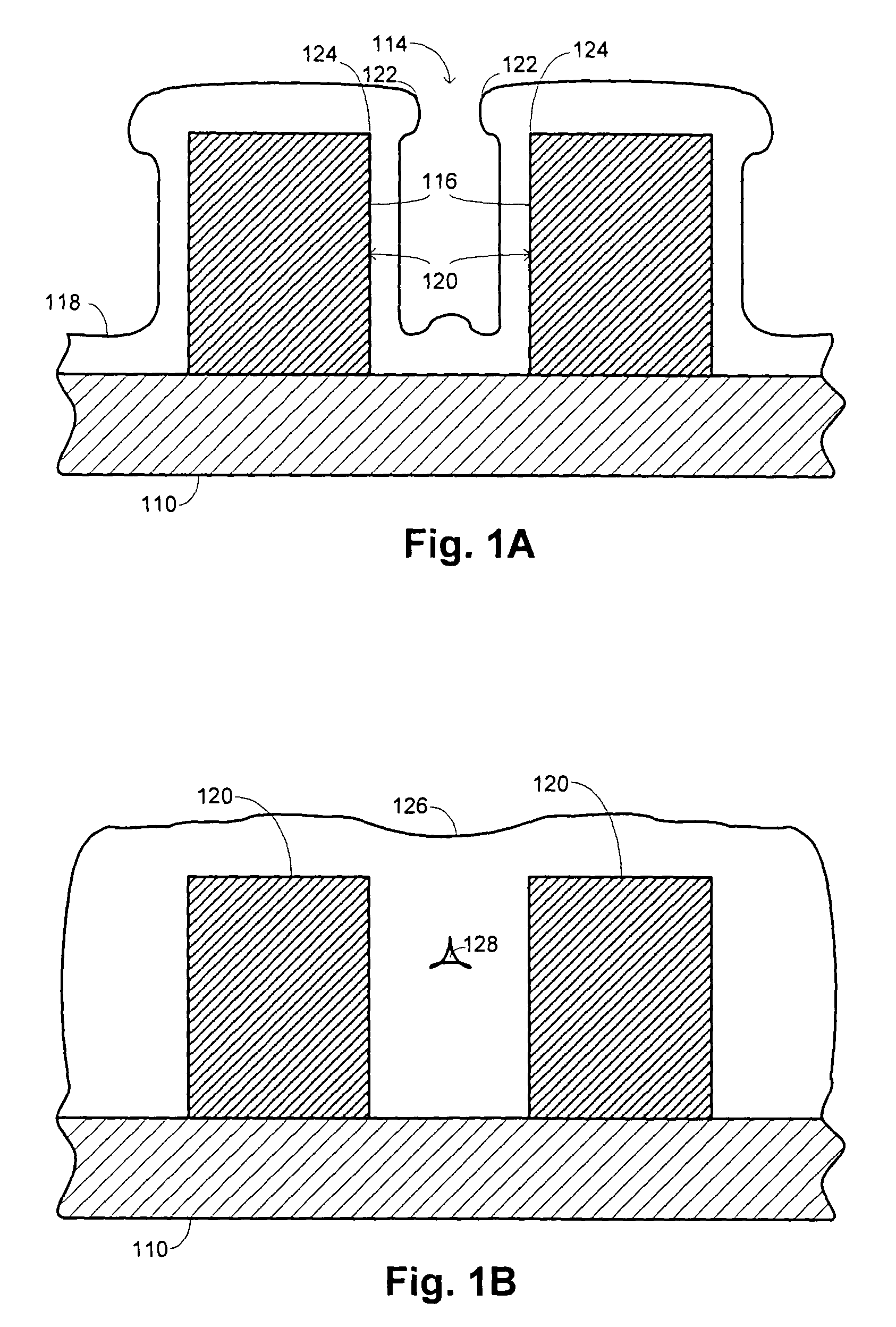
Reactive ion etching for semiconductor device feature topography modification
InactiveUS7628897B2Improvement in etch controlExcellent gap fillingDecorative surface effectsVacuum evaporation coatingHydrogenGas phase
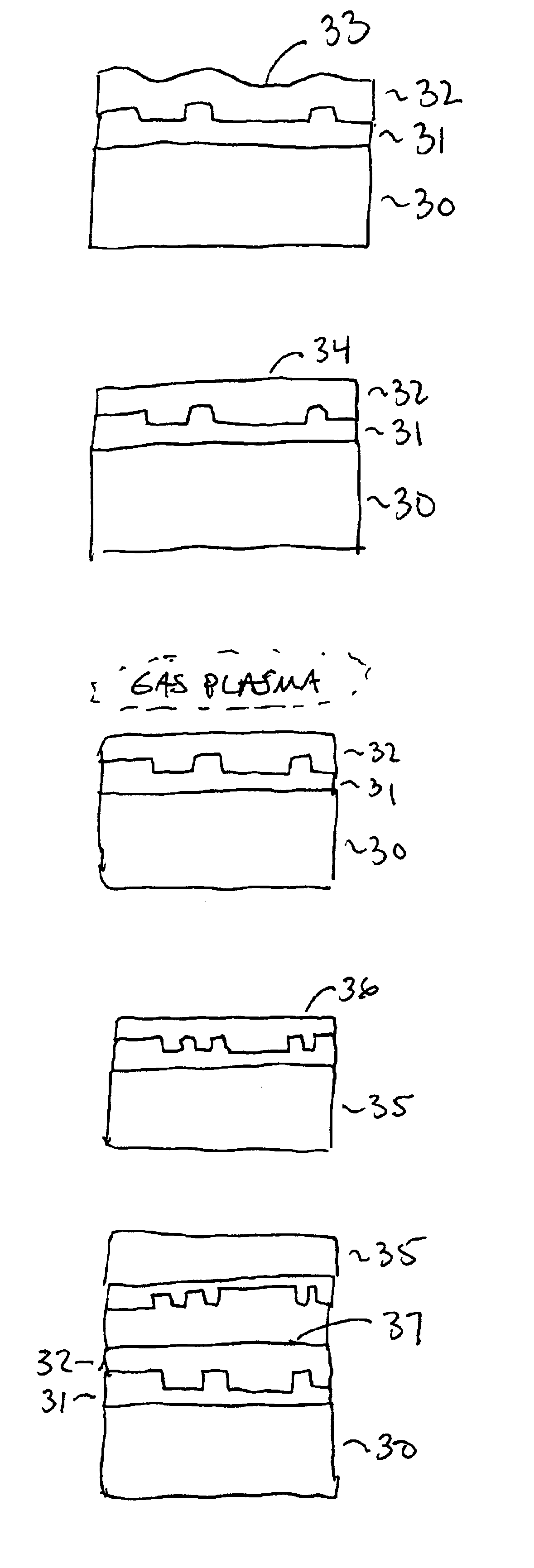
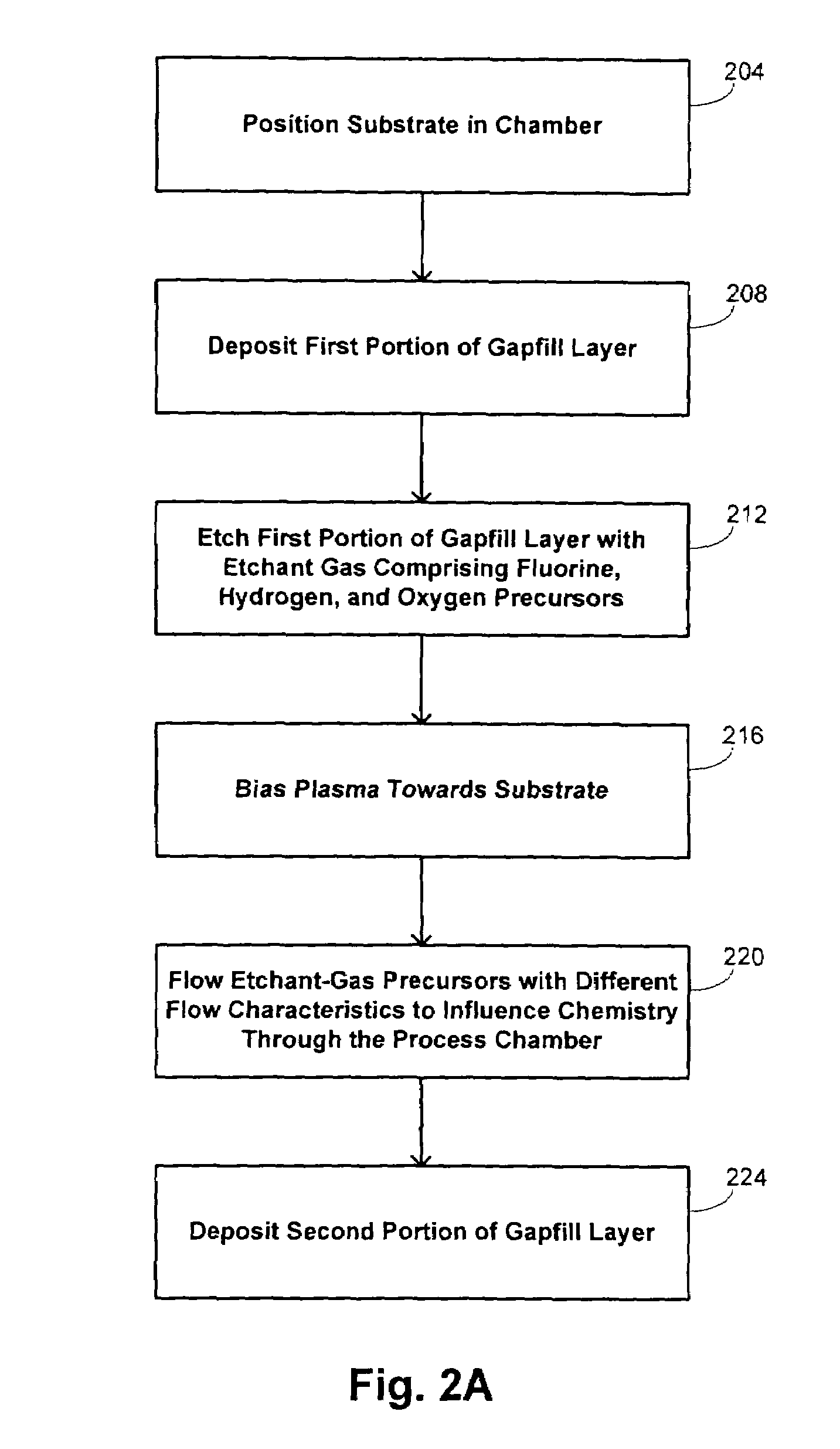
A film is deposited on a substrate disposed in a substrate processing chamber. The substrate has a trench formed between adjacent raised surfaces. A first portion of the film is deposited over the substrate from a first gaseous mixture flowed into the process chamber by chemical-vapor deposition. Thereafter, the first portion is etched by flowing an etchant gas having a halogen precursor, a hydrogen precursor, and an oxygen precursor into the process chamber. Thereafter, a second portion of the film is deposited over the substrate from a second gaseous mixture flowed into the processing chamber by chemical-vapor deposition.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Semiconductor device using element isolation region of trench isolation structure and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20090194810A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricReactive-ion etching
A stacked film including a gate dielectric film and electrode film of each memory cell of a flash memory is formed on a semiconductor substrate. The stacked film is patterned by reactive ion etching to form an isolation trench for formation of an element isolation region and the surface of the semiconductor substrate is exposed to the internal portion of the isolation trench. An O3-TEOS film exhibiting underlying material selectivity during the deposition is formed in the isolation trench as the first filling dielectric film and then the isolation trench is filled with the second filling dielectric film to form an element isolation region of an STI structure.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Forming an optical element on the surface of a light emitting device for improved light extraction
InactiveUS6987613B2Easy to integrateMaximize production efficiencyDiffraction gratingsSemiconductor devicesWafer bondingAlternative methods
Provided is a light emitting device including a Fresnel lens and / or a holographic diffuser formed on a surface of a semiconductor light emitter for improved light extraction, and a method for forming such light emitting device. Also provided is a light emitting device including an optical element stamped on a surface for improved light extraction and the stamping method used to form such device. An optical element formed on the surface of a semiconductor light emitter reduces reflective loss and loss due to total internal reflection, thereby improving light extraction efficiency. A Fresnel lens or a holographic diffuser may be formed on a surface by wet chemical etching or dry etching techniques, such as plasma etching, reactive ion etching, and chemically-assisted ion beam etching, optionally in conjunction with a lithographic technique. In addition, a Fresnel lens or a holographic diffuser may be milled, scribed, or ablated into the surface. Stamping, an alternative method for forming an optical element, can also be used to form a Fresnel lens or a holographic diffuser on the surface of a semiconductor light emitter. Stamping includes pressing a stamping block against the surface of a light emitting diode. The stamping block has a shape and pattern that are the inverse of the desired optical element. Optionally, stamping can be done before, after, or concurrently with wafer-bonding. Alternatively, a material can be stamped and later bonded to the semiconductor light emitter.
Owner:LUMILEDS
Forming an optical element on the surface of a light emitting device for improved light extraction
Provided is a light emitting device including a Fresnel lens and / or a holographic diffuser formed on a surface of a semiconductor light emitter for improved light extraction, and a method for forming such light emitting device. Also provided is a light emitting device including an optical element stamped on a surface for improved light extraction and the stamping method used to form such device. An optical element formed on the surface of a semiconductor light emitter reduces reflective loss and loss due to total internal reflection, thereby improving light extraction efficiency. A Fresnel lens or a holographic diffuser may be formed on a surface by wet chemical etching or dry etching techniques, such as plasma etching, reactive ion etching, and chemically-assisted ion beam etching, optionally in conjunction with a lithographic technique. In addition, a Fresnel lens or a holographic diffuser may be milled, scribed, or ablated into the surface. Stamping, an alternative method for forming an optical element, can also be used to form a Fresnel lens or a holographic diffuser on the surface of a semiconductor light emitter. Stamping includes pressing a stamping block against the surface of a light emitting diode. The stamping block has a shape and pattern that are the inverse of the desired optical element. Optionally, stamping can be done before, after, or concurrently with wafer-bonding. Alternatively, a material can be stamped and later bonded to the semiconductor light emitter.
Owner:LUMILEDS
Dsa grapho-epitaxy process with etch stop material
InactiveUS20140256145A1Reduce widthForming accuratelySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResistReactive-ion etching
A method for defining a template for directed self-assembly (DSA) materials includes forming an etch stop layer on a neutral material, forming a mask layer on the etch stop layer and forming an anti-reflection coating (ARC) on the mask layer. A resist layer is patterned on the ARC using optical lithography to form a template pattern. The ARC and the mask layer are reactive ion etched down to the etch stop layer in accordance with the template pattern to form a template structure. The ARC is removed from the mask layer and the template structure is trimmed to reduce a width of the template structure. A wet etch is performed to remove the etch stop layer to permit the neutral material to form an undamaged DSA template for DSA materials.
Owner:IBM CORP
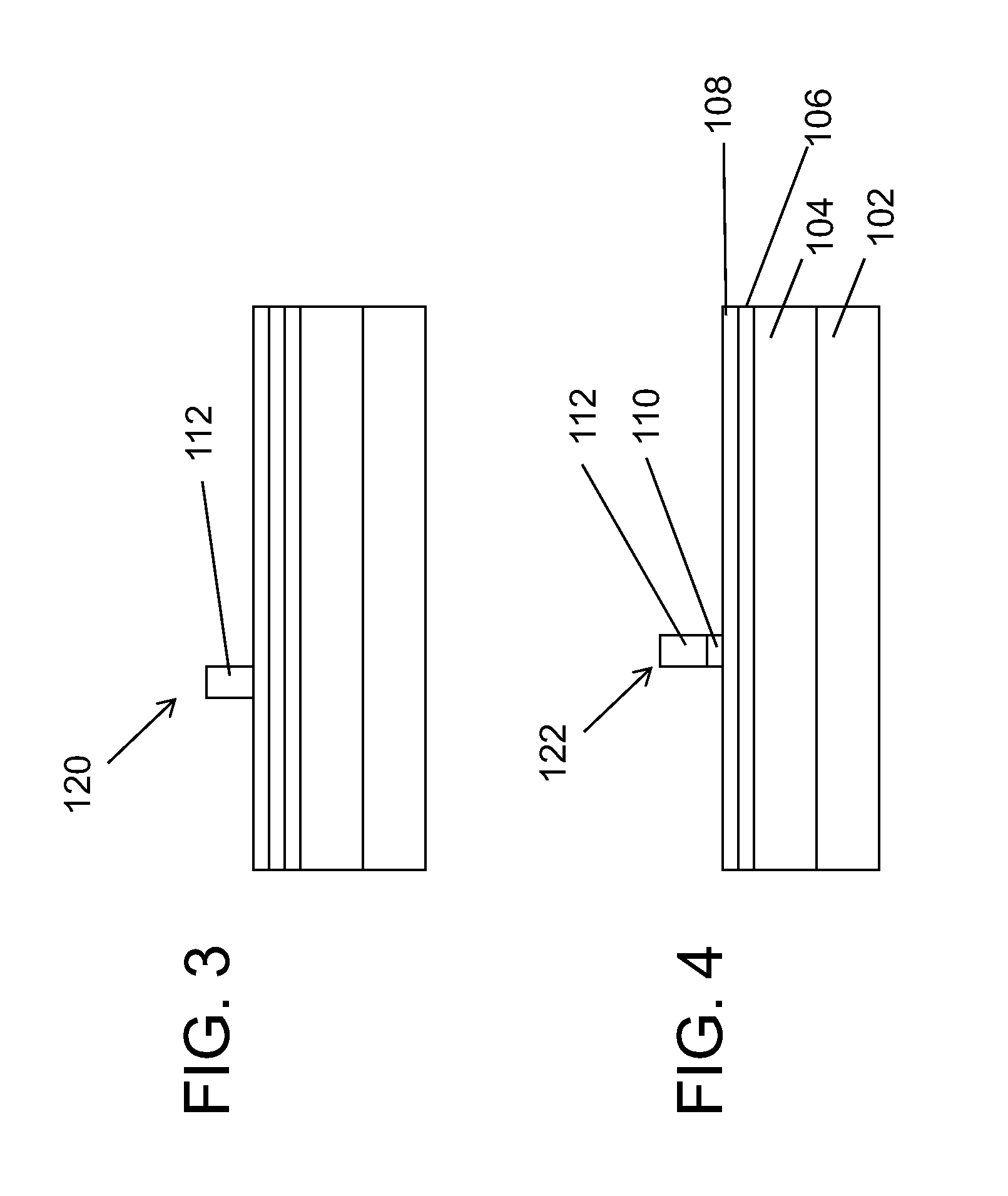
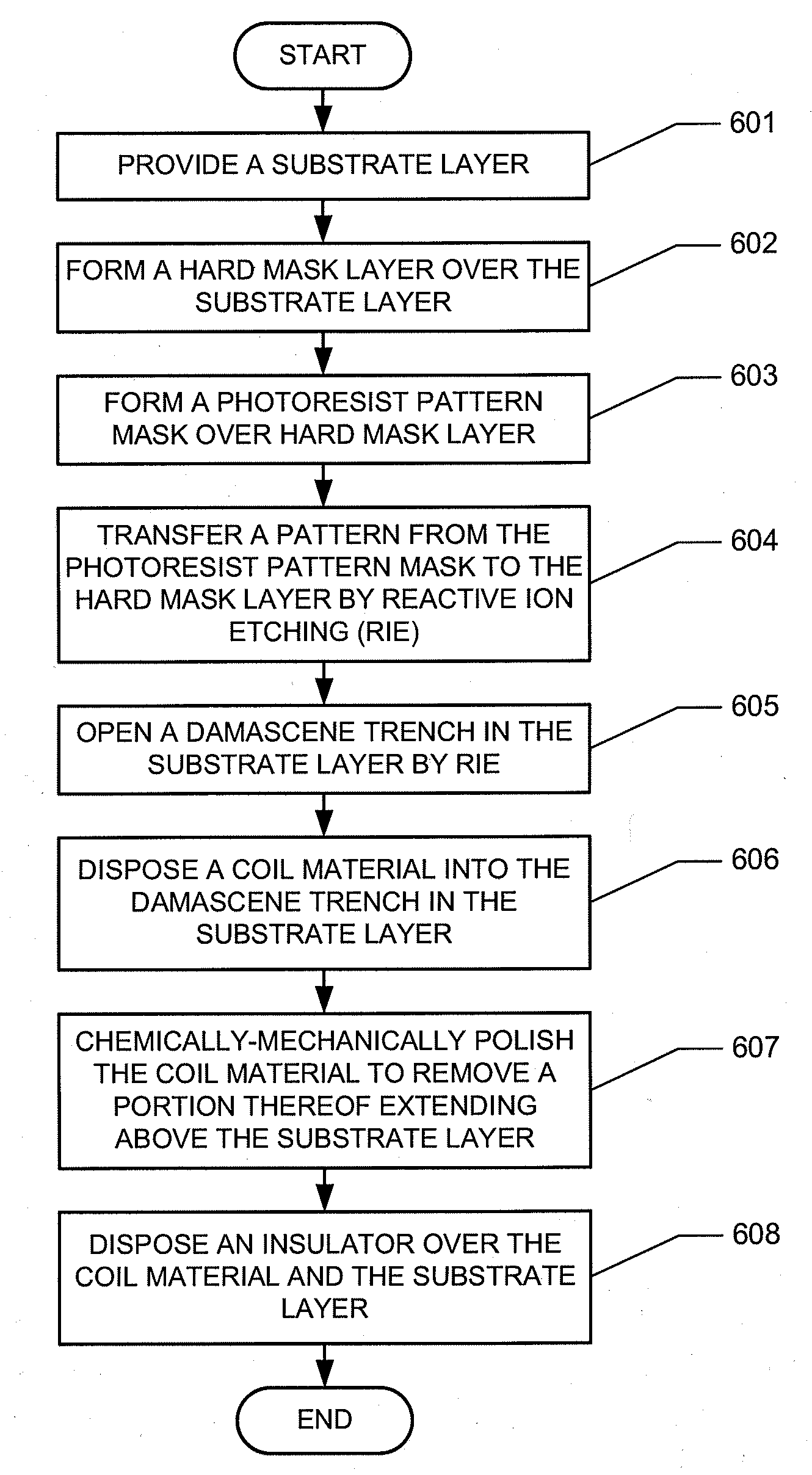
Damascene coil processes and structures
InactiveUS20100290157A1Eliminating insulation coverage problemEliminate needConstruction of head windingsDecorative surface effectsOptoelectronicsReactive-ion etching
A magnetic recording head is provided. The magnetic recording head comprises a write pole and a write coil structure configured to generate a magnetic field in the write pole. The write coil structure comprises a substrate layer and a coil material disposed within the substrate layer. The write coil structure is substantially free of photoresist. A method for forming a write coil structure is also provided. The method comprises the steps of providing a substrate layer, forming a photoresist pattern mask over the substrate layer, opening a damascene trench in the substrate layer by reactive ion etching, and disposing a coil material into the damascene trench in the substrate layer.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Method for manufacturing a field effect transistor having a field plate
InactiveUS20080283844A1Increase stickinessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesInductively coupled plasmaField-effect transistor
An opening for forming a gate electrode is provided by a first photoresist pattern formed on an insulating film. Reactive ion etching by inductively coupled plasma is applied to the insulating film through the first photoresist pattern as a mask to thereby expose the surface of a GaN semiconductor layer, evaporating thereon a gate metal such as NiAu, thereby forming the gate electrode by self-aligned process. This prevents an oxidized film from being formed on the surface of the semiconductor layer. After the gate electrode is formed, a second photoresist pattern is formed to form a field plate on the gate electrode and the insulating film through the second photoresist pattern as a mask. Thereby, Ti having a high adhesiveness with an insulating film made of SiN or the like can be used as a field plate metal.
Owner:OKI ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
Method for manufacturing MTJ memory device
ActiveUS9263667B1Reduce materialReduce harmMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionReactive-ion etchingPhotoresist
A method for manufacturing MTJ pillars for a MTJ memory device. The method includes depositing multiple MTJ layers on a substrate, depositing a hard mask on the substrate and coating a photoresist on the hard mask. Further, alternating steps of reactive ion etching and ion beam etching are performed to isolate MTJ pillars and expose side surfaces of the MTJ layers. An insulating layer is the applied to protect the side surfaces of the MTJ layers. A second insulating layer is deposited before the device is planarized using chemical mechanical polishing.
Owner:INTEGRATED SILICON SOLUTION CAYMAN INC
Method for manufacturing a magnetic read sensor with narrow track width using amorphous carbon as a hard mask and localized CMP
ActiveUS8617408B2Narrow widthTrack-width can be very smallElectrical transducersMagnetic measurementsCarbon layerInsulation layer
A method for manufacturing a magnetic read sensor at very narrow track widths. The method uses an amorphous carbon mask layer to pattern the sensor by ion milling, rather than a mask constructed of a material such as photoresist or DURIMIDE® which can bend over during ion milling at very narrow track widths. By using the amorphous carbon layer as the masking layer, the trackwidth can be very small, while avoiding this bending over of the mask that has been experienced with prior art methods. In addition, the track-width can be further reduced by using a reactive ion etching to further reduce the width of the amorphous carbon mask prior to patterning the sensor. The method also allows extraneous portions of the side insulation layer and hard bias layer to be removed above the sensor by a light CMP process.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Method for manufacturing mtj memory device
ActiveUS20160163973A1Reduce materialReduce harmGalvano-magnetic material selectionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringReactive-ion etching
A method for manufacturing MTJ pillars for a MTJ memory device. The method includes depositing multiple MTJ layers on a substrate, depositing a hard mask on the substrate and coating a photoresist on the hard mask. Further, alternating steps of reactive ion etching and ion beam etching are performed to isolate MTJ pillars and expose side surfaces of the MTJ layers. An insulating layer is the applied to protect the side surfaces of the MTJ layers. A second insulating layer is deposited before the device is planarized using chemical mechanical polishing.
Owner:INTEGRATED SILICON SOLUTION CAYMAN INC
Semiconductor device and method for fabricating the device
InactiveUS7078811B2Firmly connectedSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorElectrical connection
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP +10
Data protection by detection of intrusion into electronic assemblies
InactiveUS7901977B1Improve adhesionImprove thermal stabilityPig casting plantsPrinted electric component incorporationResistFilling materials
Electronic assemblies, especially one containing volatile memory, used a flexible membrane with conducting lines which acts as an intrusion sensor against chemical and mechanical attacks. The lines are fabricated from inherently conducting polymers which are solution processed and directly patterned. The material was applied to a flexible polymer film by spin coating and patterned by application of a resist, followed by exposure / development of the resist and transferring the image into the polyaniline by reactive ion etching techniques. The conducting lines have high conductivity, tranparency properties which made them difficult to detect and possess excellent adhesion to the substrate film, as well as to the potting material which enclosed the structure. They also offered lightweight advantages over conventionally filled materials. These materials can also be used in conjunction with conventional conductor materials to further enhance protection against intrusion by sophisticated mechanical means.
Owner:IBM CORP
Injection molded microoptics
ActiveUS20070029277A1Minimizes number and task-timesReduces of semiconductor arraysMaterial nanotechnologySolid-state devicesFiberTransformer
A wafer-scale apparatus and method is described for the automation of forming, aligning and attaching two-dimensional arrays of microoptic elements on semiconductor and other image display devices, backplanes, optoelectronic boards, and integrated optical systems. In an ordered fabrication sequence, a mold plate comprised of optically designed cavities is formed by reactive ion etching or alternative processes, optionally coated with a release material layer and filled with optically specified materials by an automated fluid-injection and defect-inspection subsystem. Optical alignment fiducials guide the disclosed transfer and attachment processes to achieve specified tolerances between the microoptic elements and corresponding optoelectronic devices and circuits. The present invention applies to spectral filters, waveguides, fiber-optic mode-transformers, diffraction gratings, refractive lenses, diffractive lens / Fresnel zone plates, reflectors, and to combinations of elements and devices, including microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) and liquid crystal device (LCD) matrices for adaptive, tunable elements. Preparation of interfacial layer properties and attachment process embodiments are taught.
Owner:IBM CORP
Through-wafer contact to bonding pad
InactiveUS20050156330A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringConductive materials
An integrated circuit with conductive channels connecting the bonding pads to alternative surfaces of the IC chip is disclosed. Typically the channels would be formed by reactive ion etching, passivated and then filled with copper or other conductive material. The channels may be formed at alternative points in the wafer processing flow depending on the requirements of the IC. Alternatively the channels may be used for heat sinks; in this case the channel would connect a chip “hot spot” with a conductive package member.
Owner:HARRIS JAMES M
Method for manufacturing mtj memory device
ActiveUS20160027999A1Reduce materialReduce harmMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionReactive-ion etchingPhotoresist
A method for manufacturing MTJ pillars for a MTJ memory device. The method includes depositing multiple MTJ layers on a substrate, depositing a hard mask on the substrate and coating a photoresist on the hard mask. Further, alternating steps of reactive ion etching and ion beam etching are performed to isolate MTJ pillars and expose side surfaces of the MTJ layers. An insulating layer is the applied to protect the side surfaces of the MTJ layers. A second insulating layer is deposited before the device is planarized using chemical mechanical polishing.
Owner:INTEGRATED SILICON SOLUTION CAYMAN INC
Structure and method for simultaneously forming a through silicon via and a deep trench structure
ActiveUS20120091593A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesOptoelectronicsReactive-ion etching
A through silicon via (TSV) and a deep trench capacitor (DTCap) or a deep trench isolation (DTI) are simultaneously formed on the same substrate by a single mask and a single reactive ion etching (RIE). The TSV trench is wider and deeper that the DTCap or DTI trench. The TSV and DTCap or DTI are formed with different dielectric materials on the trench sidewalls. The TSV and DTCap or DTI are perfectly aligned.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
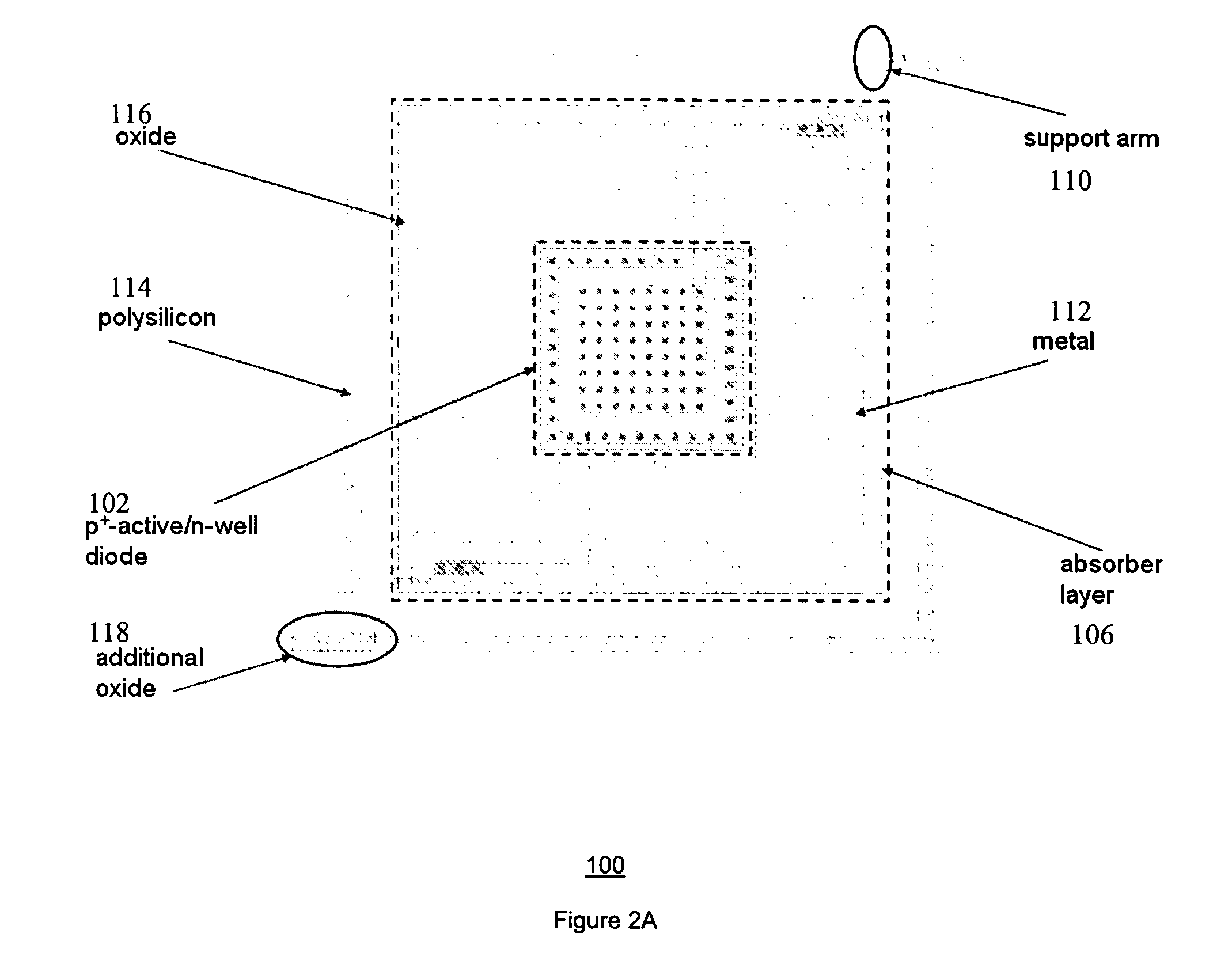
Ultra low-cost uncooled infrared detector arrays in CMOS
InactiveUS20050224714A1Low costImprove insulation performanceSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansDetector arrayReactive-ion etching
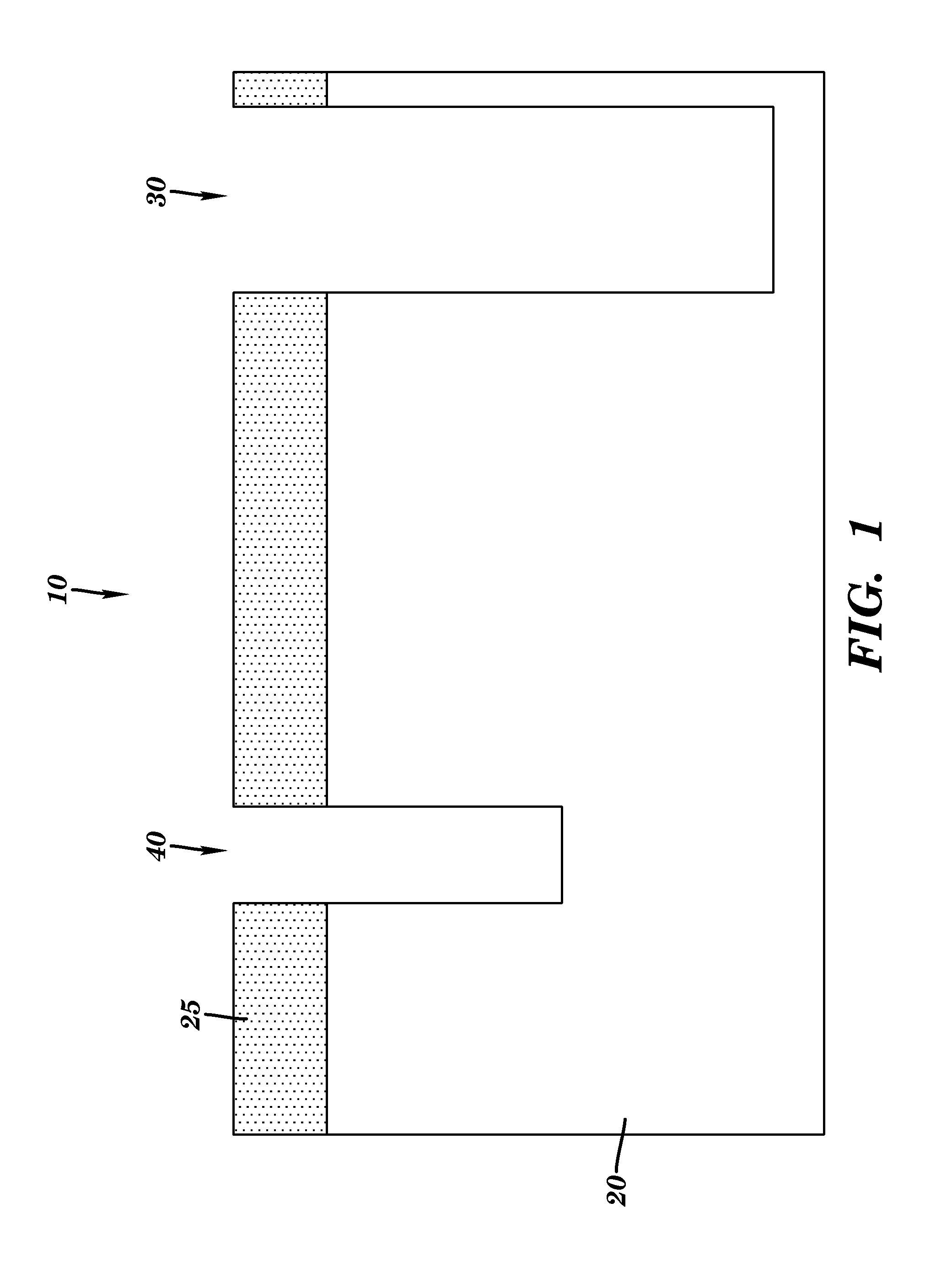
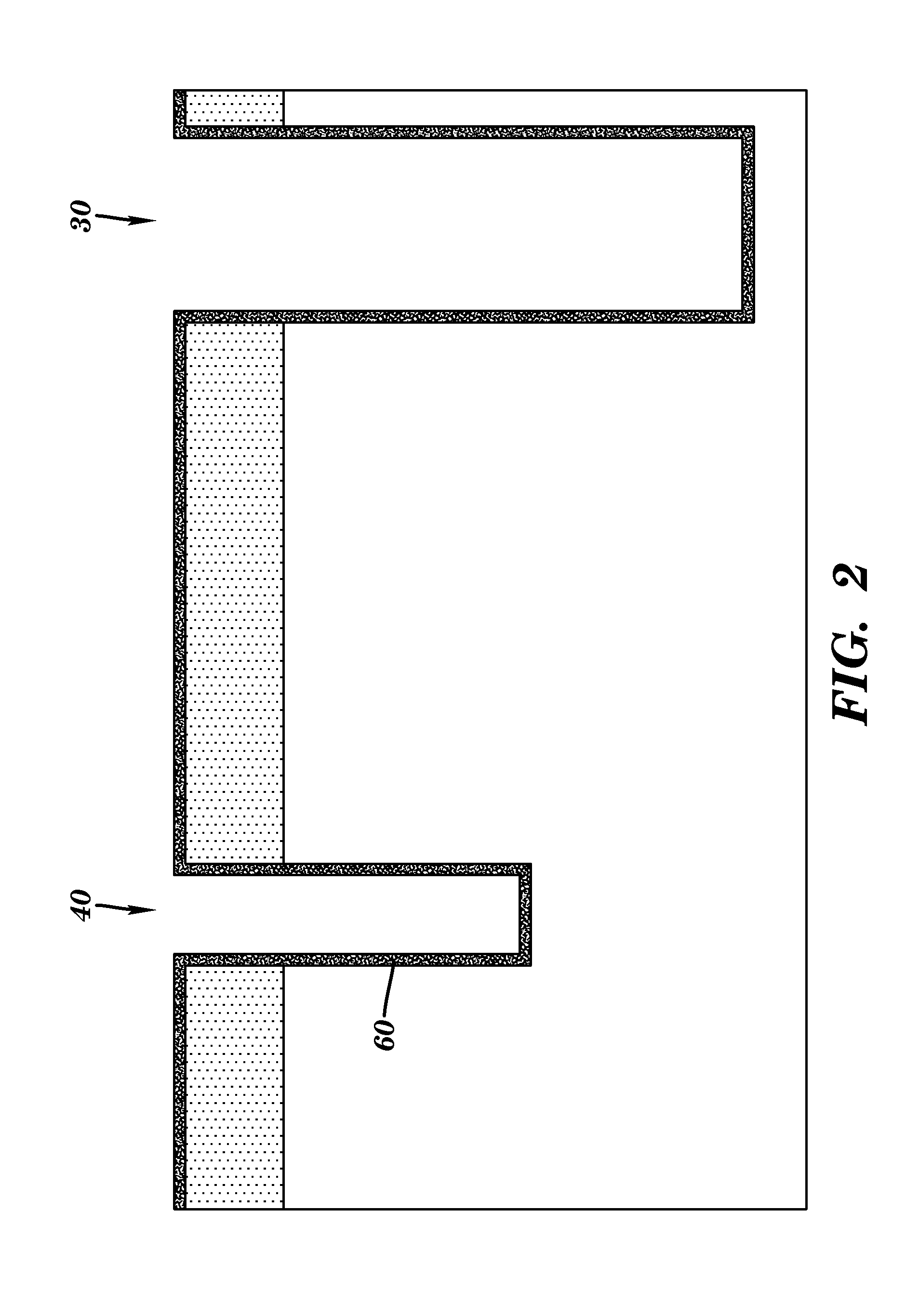
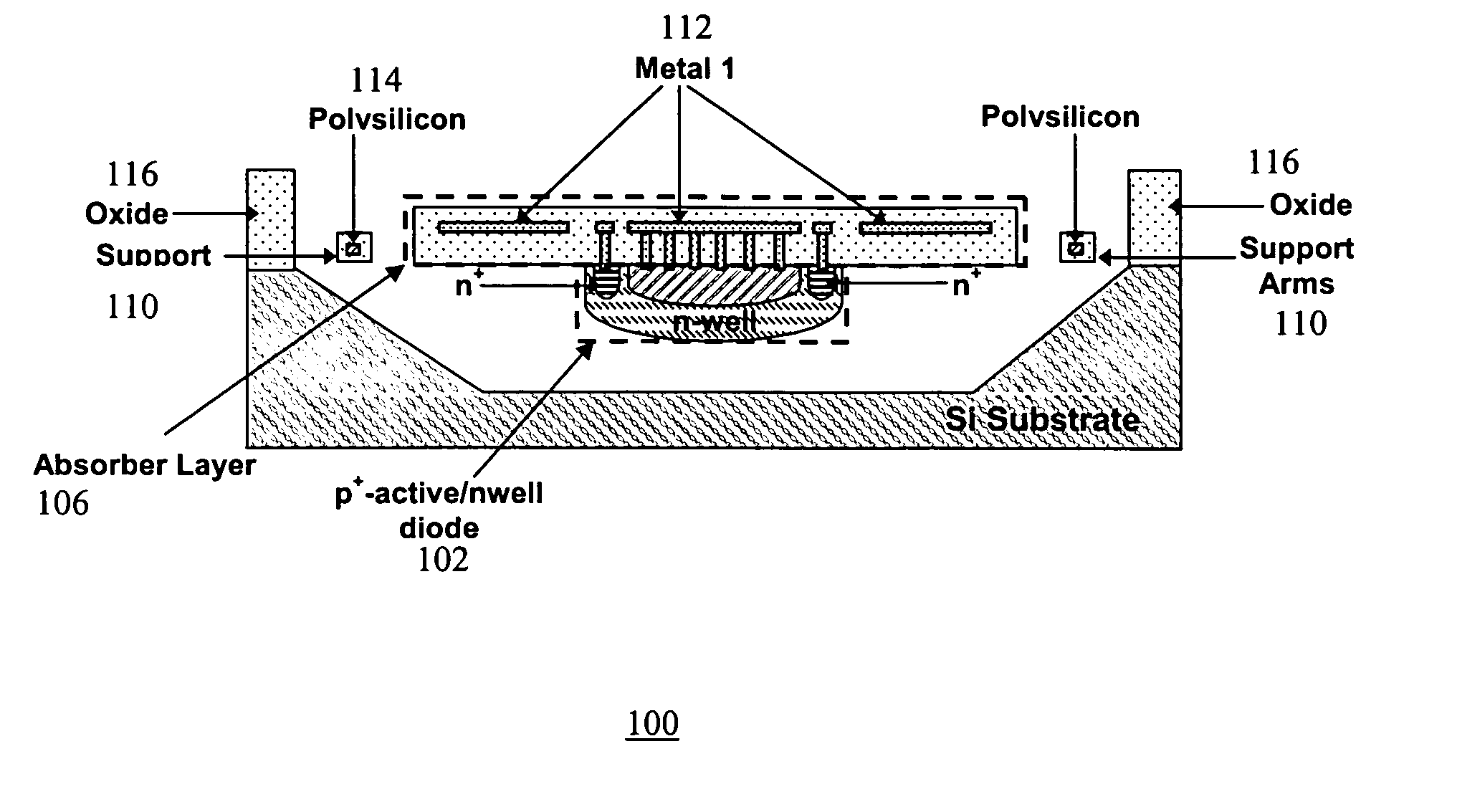
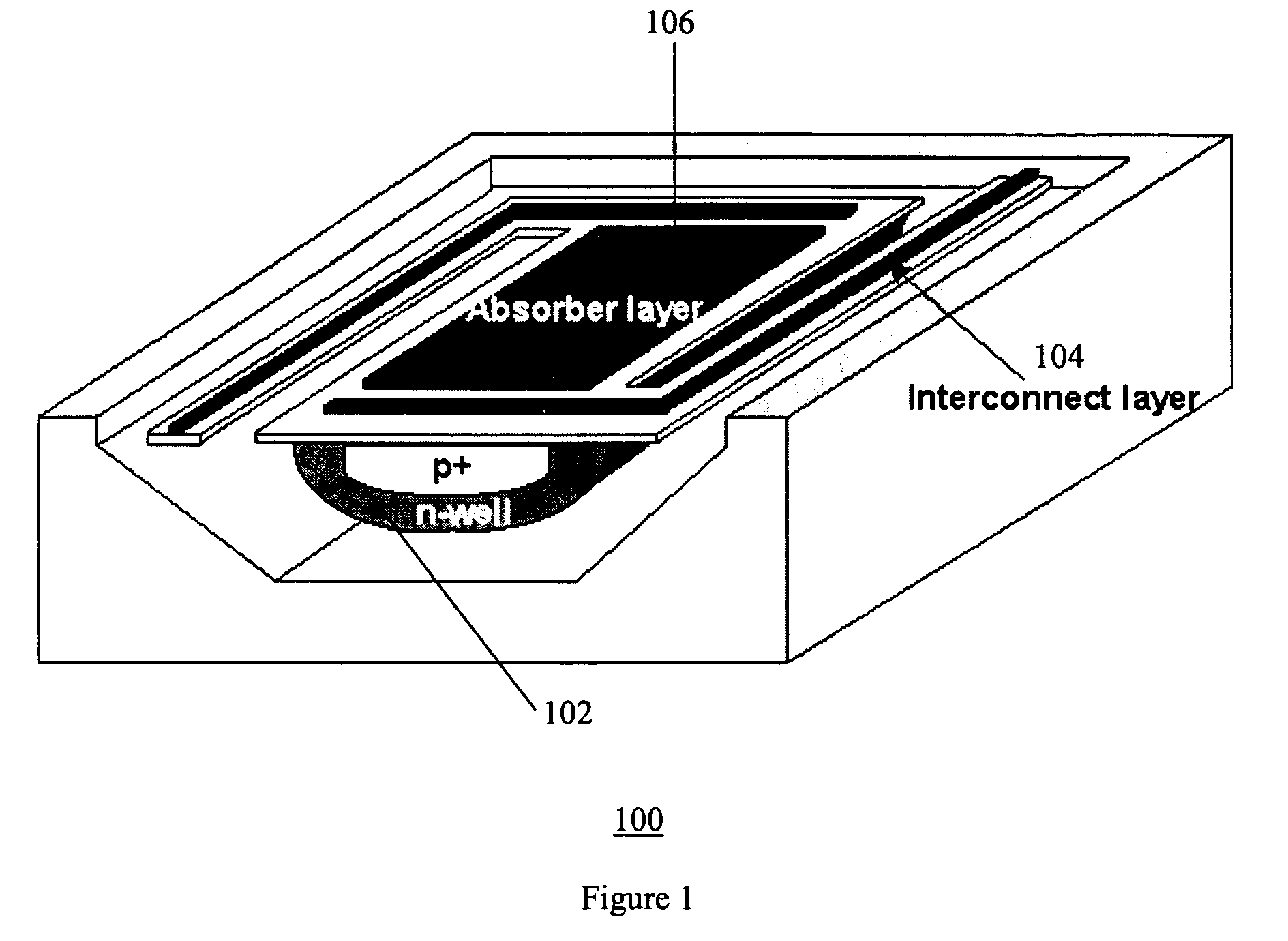
Micromachined, CMOS p+-active / n-well diodes are used as infrared sensing elements in uncooled Focal Plane Arrays (FPA). The FPAs are fabricated using a standard CMOS process followed by post-CMOS bulk-micromachining steps without any critical lithography or complicated deposition processes. Micromachining steps include Reactive Ion Etching (RIE) to reach the bulk silicon and anisotropic silicon wet etching together with electrochemical etch-stop technique to obtain thermally isolated p+-active / n-well diodes. The FPAs are monolithically integrated with their readout circuit since they are fabricated in any standard CMOS technology.
Owner:AKIN TAYFUN
Metal catalyst technique for texturing silicon solar cells
InactiveUS6329296B1Improve throughputDiminish current extractionDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingManufacturing technologySilicon solar cell
Textured silicon solar cells and techniques for their manufacture utilizing metal sources to catalyze formation of randomly distributed surface features such as nanoscale pyramidal and columnar structures. These structures include dimensions smaller than the wavelength of incident light, thereby resulting in a highly effective anti-reflective surface. According to the invention, metal sources present in a reactive ion etching chamber permit impurities (e.g. metal particles) to be introduced into a reactive ion etch plasma resulting in deposition of micro-masks on the surface of a substrate to be etched. Separate embodiments are disclosed including one in which the metal source includes one or more metal-coated substrates strategically positioned relative to the surface to be textured, and another in which the walls of the reaction chamber are pre-conditioned with a thin coating of metal catalyst material.
Owner:SANDIA NAT LAB
Fast x-ray lenses and fabrication method therefor
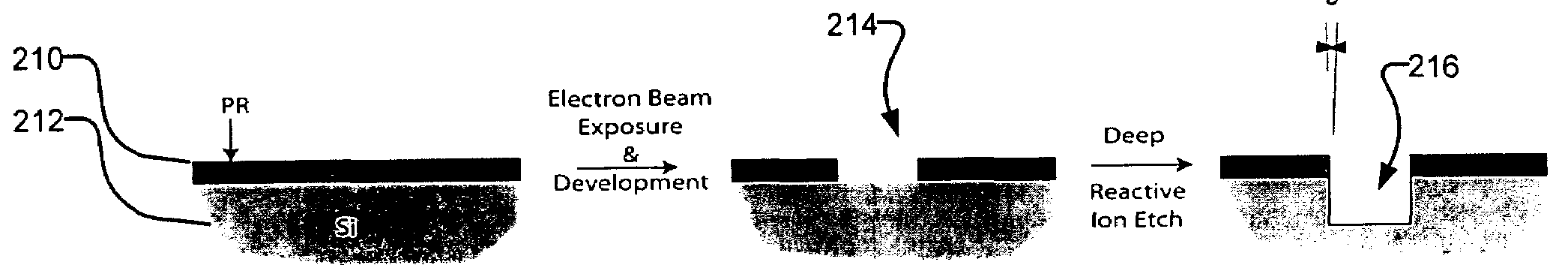
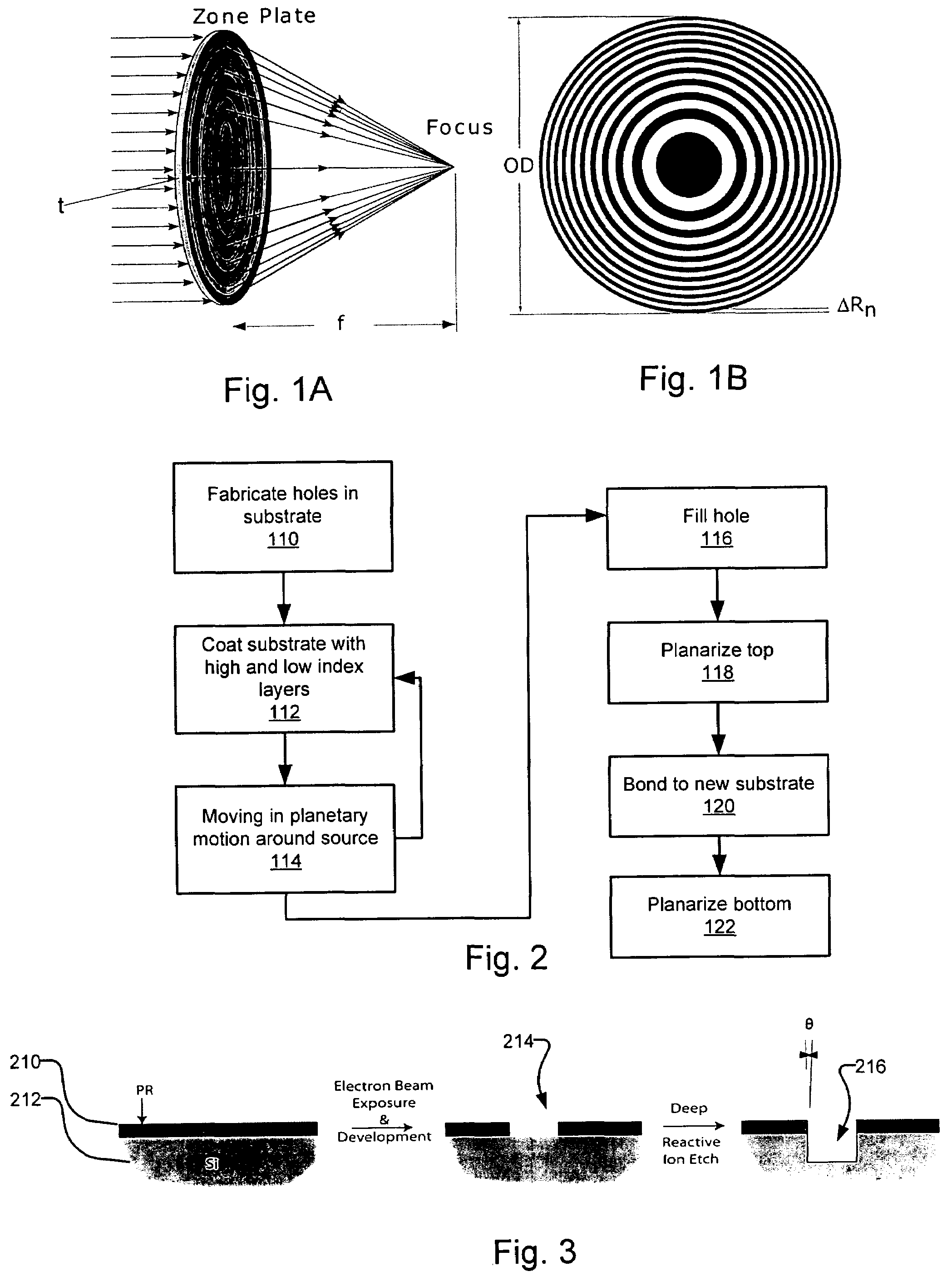
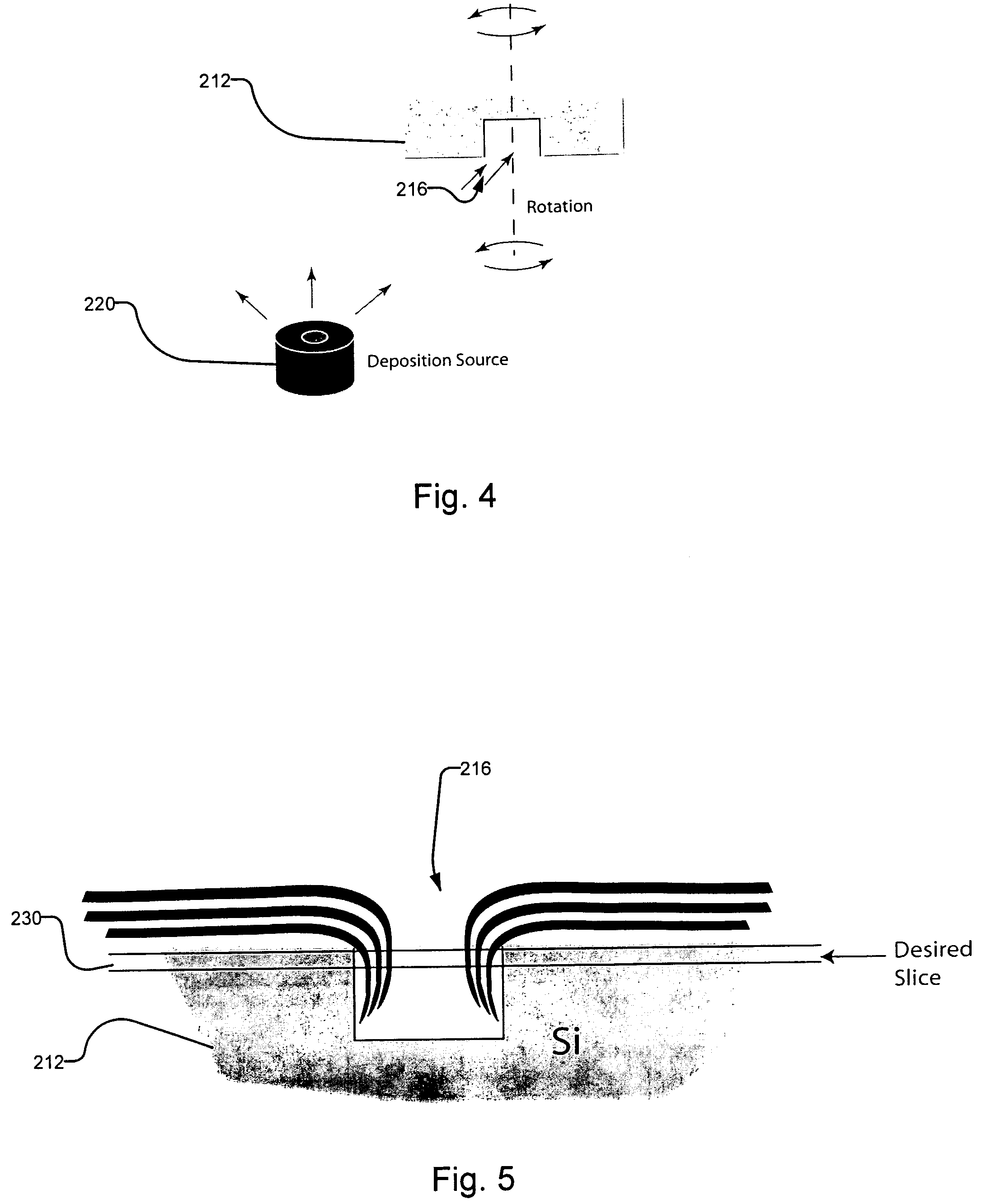
A fabrication process for zone plate lenses is based on controlled thin layer deposition for fabricating structures as small as 2 nanometers (nm) in width, and potentially smaller. The substrate for deposition will take the form of a precision hole, fabricated in a substrate, such as silicon by electron beam lithography and subsequent reactive ion etching. A controlled layer deposition is then used to form the required zone plate structure. A subsequent thinning process is used to section the hole and produce a zone plate with the required layer thicknesses.
Owner:CARL ZEISS X RAY MICROSCOPY
Method of fabricating vertical structure LEDs
InactiveUS20050098792A1Avoid damageSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialReactive-ion etching
A method of fabricating semiconductor devices, such as GaN LEDs, on insulating substrates, such as sapphire. Semiconductor layers are produced on the insulating substrate using normal semiconductor processing techniques. Trenches that define the boundaries of the individual devices are then formed through the semiconductor layers and into the insulating substrate, beneficially by using inductive coupled plasma reactive ion etching. The trenches are then filled with an easily removed layer. A metal support structure is then formed on the semiconductor layers (such as by plating or by deposition) and the insulating substrate is removed. Electrical contacts, a passivation layer, and metallic pads are then added to the individual devices, and the individual devices are then diced out.
Owner:SUZHOU LEKIN SEMICON CO LTD
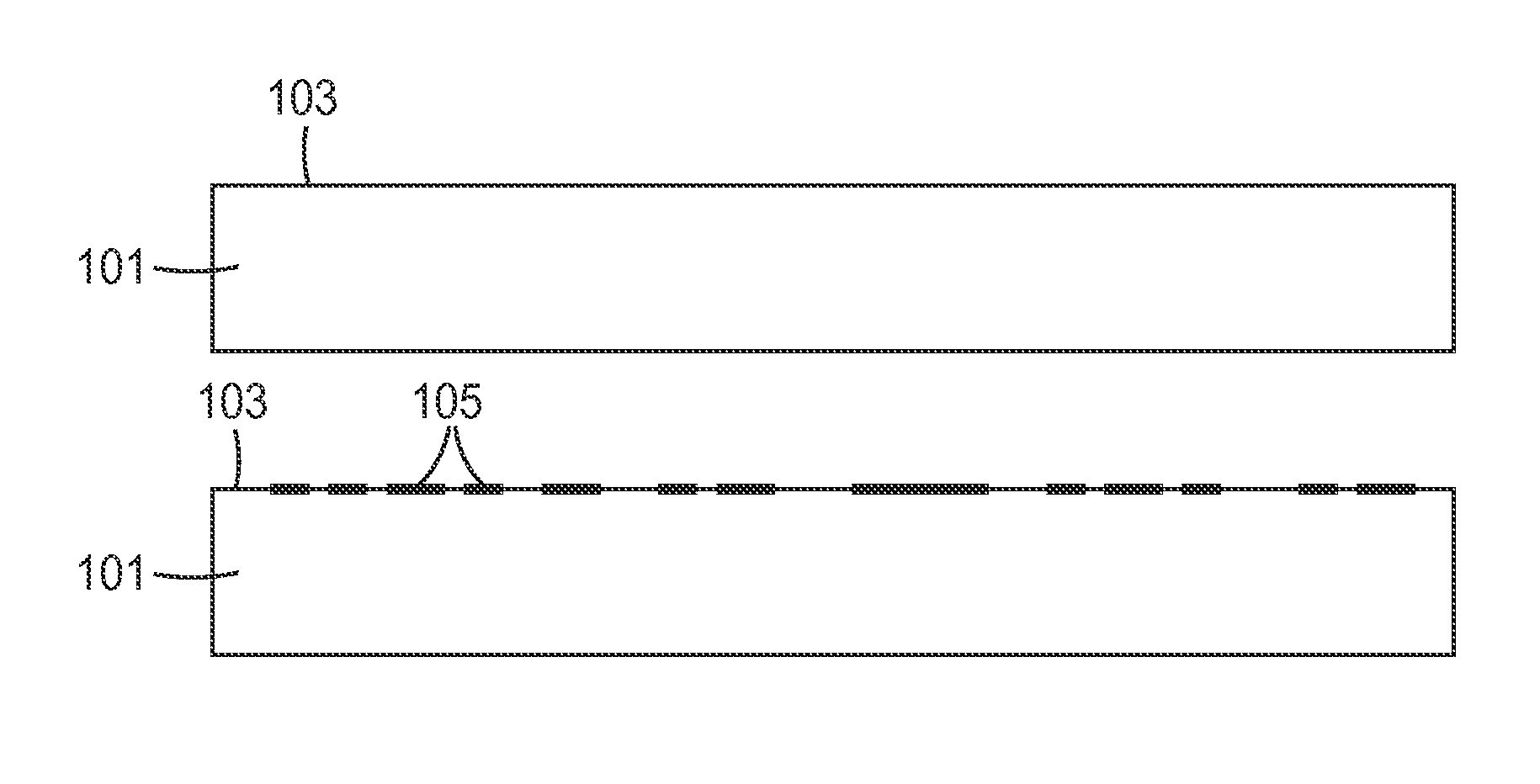
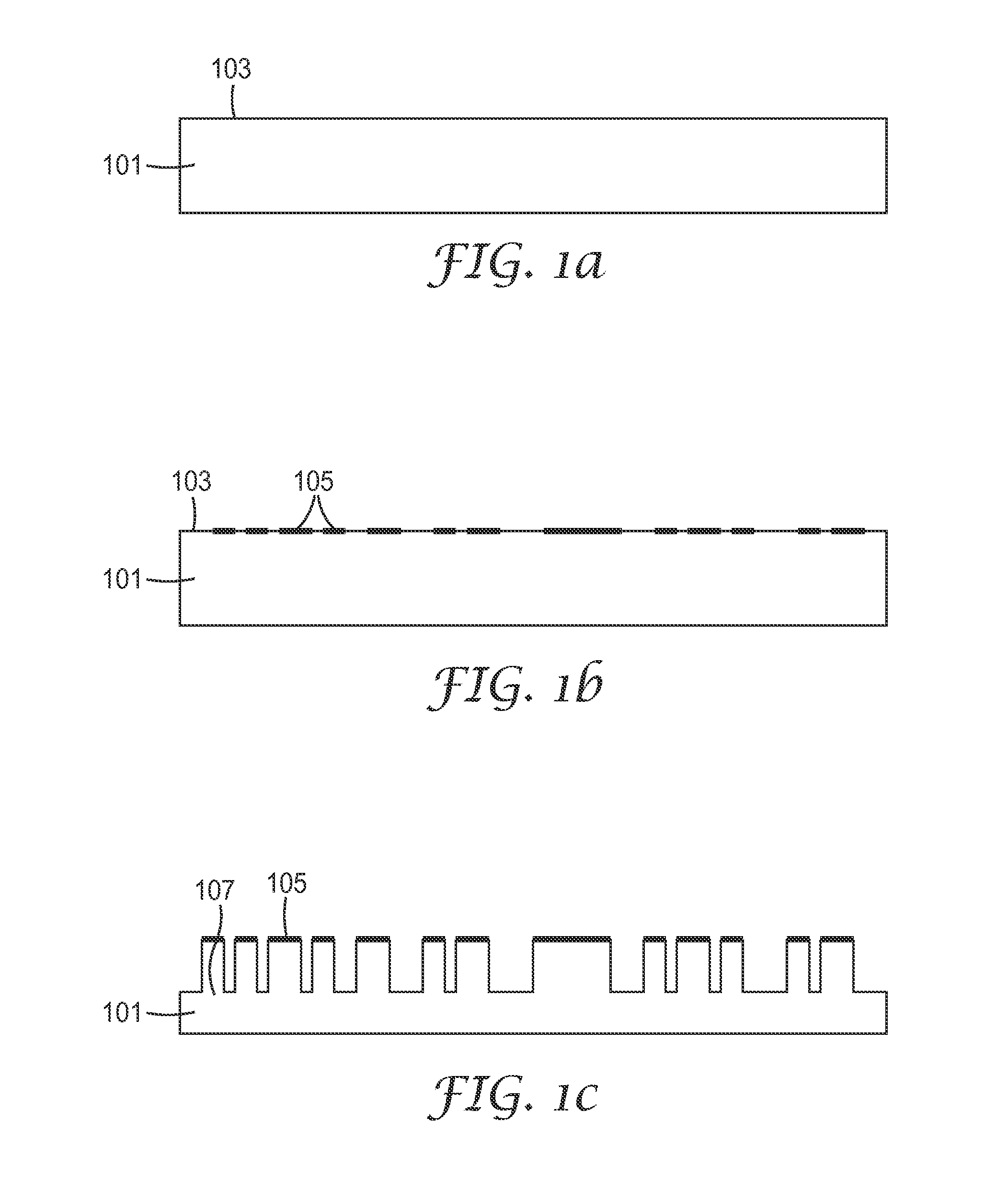
Method of making a nanostructure
ActiveUS8634146B2Reduce reflectivityScratch resistantMaterial nanotechnologyLayered productsMetal acetylacetonatesAlloy
A method of making a nanostructure is provided that includes applying a thin, random discontinuous masking layer (105) to a major surface (103) of a substrate (101) by plasma chemical vapor deposition. The substrate (101) can be a polymer, an inorganic material, an alloy, or a solid solution. The masking layer (105) can include the reaction product of plasma chemical vapor deposition using a reactant gas comprising a compound selected from the group consisting of organosilicon compounds, metal alkyls, metal isopropoxides, metal acetylacetonates, and metal halides. Portions (107) of the substrate (101) not protected by the masking layer (105) are then etched away by reactive ion etching to make the nanostructures.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Method of fabricating vertical structure LEDs
InactiveUS20060071230A1Avoid damageSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialReactive-ion etching
A method of fabricating semiconductor devices, such as GaN LEDs, on insulating substrates, such as sapphire. Semiconductor layers are produced on the insulating substrate using normal semiconductor processing techniques. Trenches that define the boundaries of the individual devices are then formed through the semiconductor layers and into the insulating substrate, beneficially by using inductive coupled plasma reactive ion etching. The trenches are then filled with an easily removed layer. A metal support structure is then formed on the semiconductor layers (such as by plating or by deposition) and the insulating substrate is removed. Electrical contacts, a passivation layer, and metallic pads are then added to the individual devices, and the individual devices are then diced out.
Owner:SUZHOU LEKIN SEMICON CO LTD
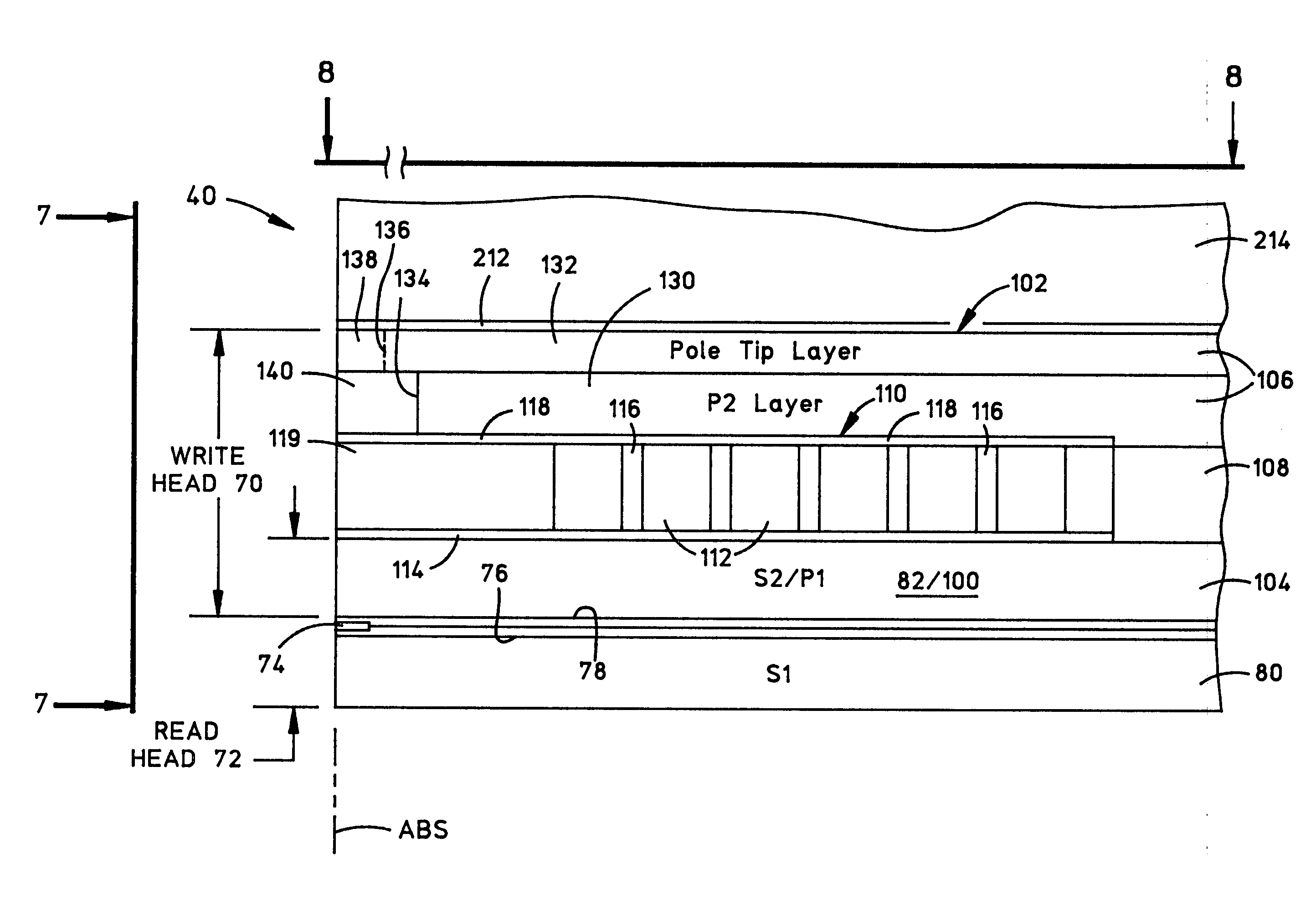
Thin film piezoelectric resonator, thin film piezoelectric device, and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS7388318B2Large electromechanical coupling coefficientSuperior acoustic quality factorPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesInsulation layerThin membrane
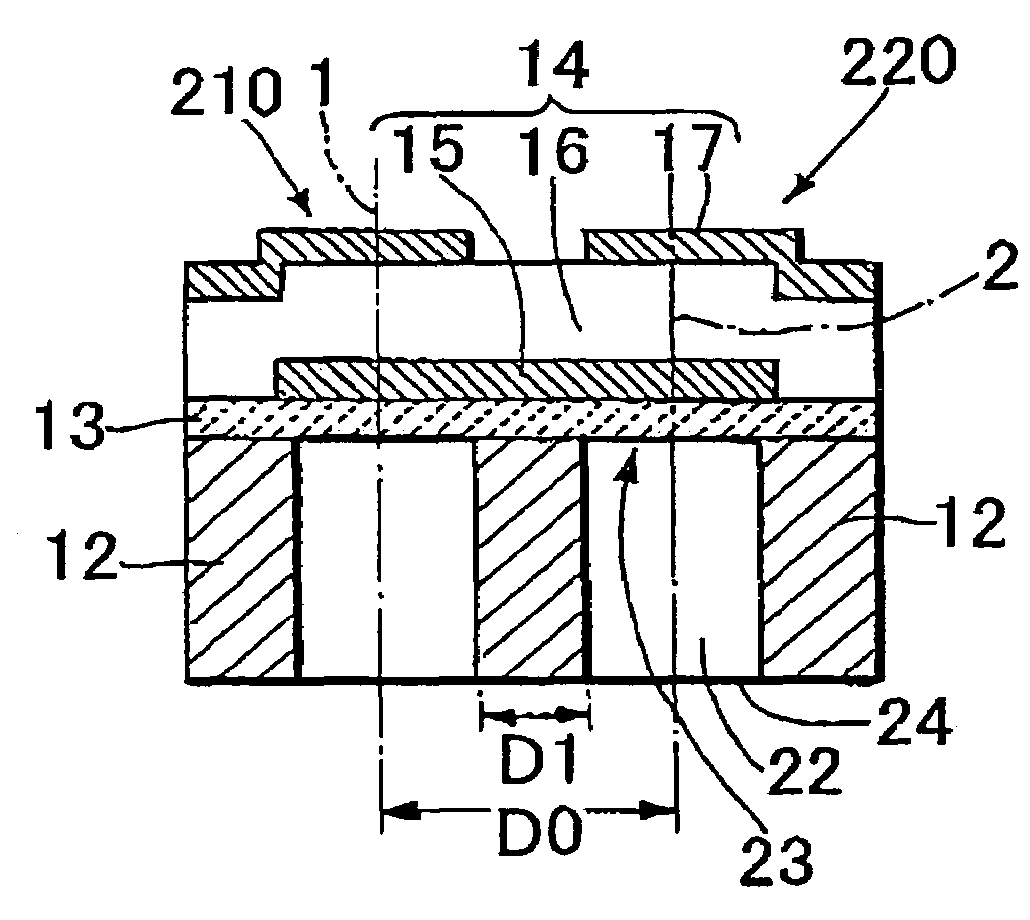
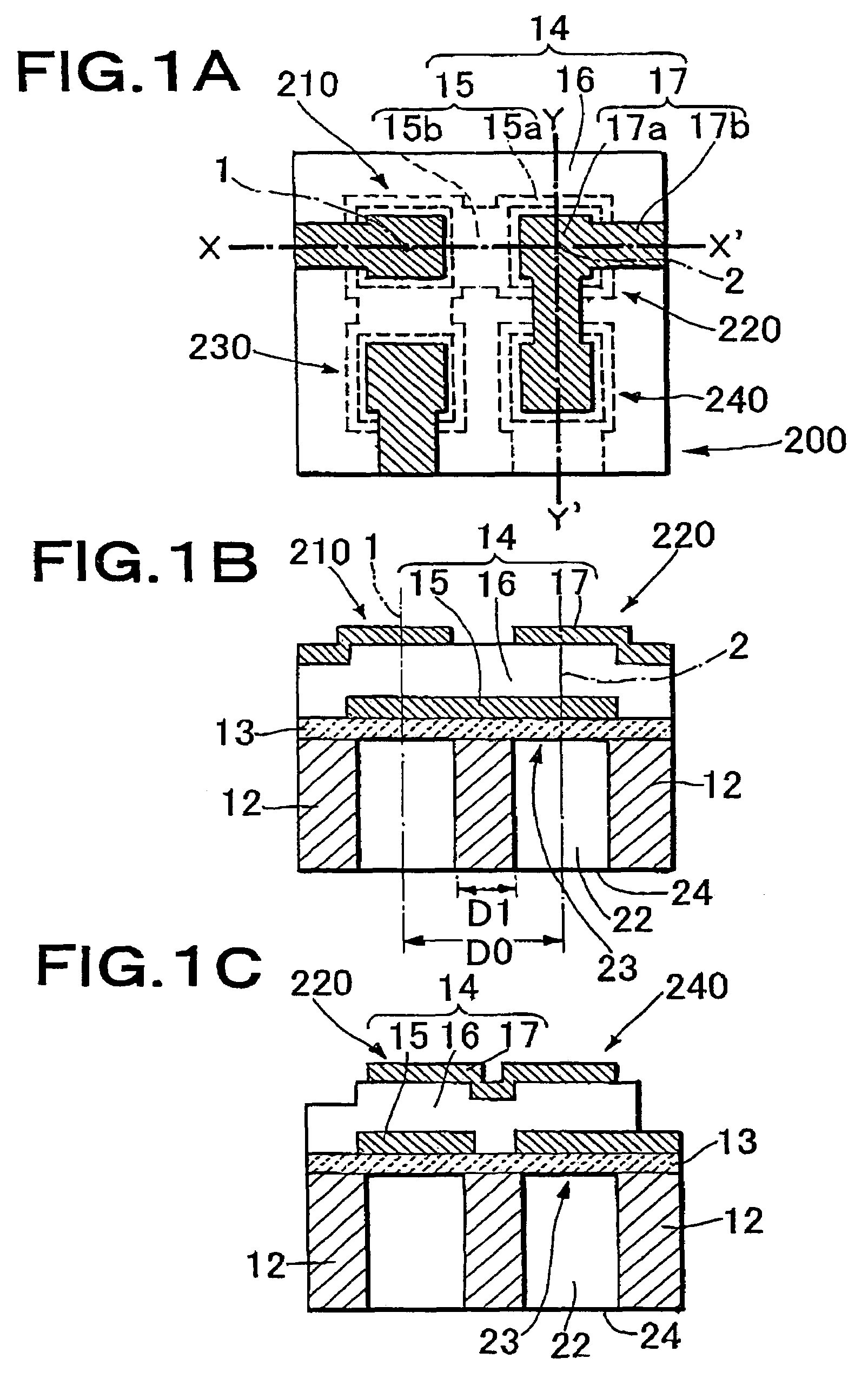
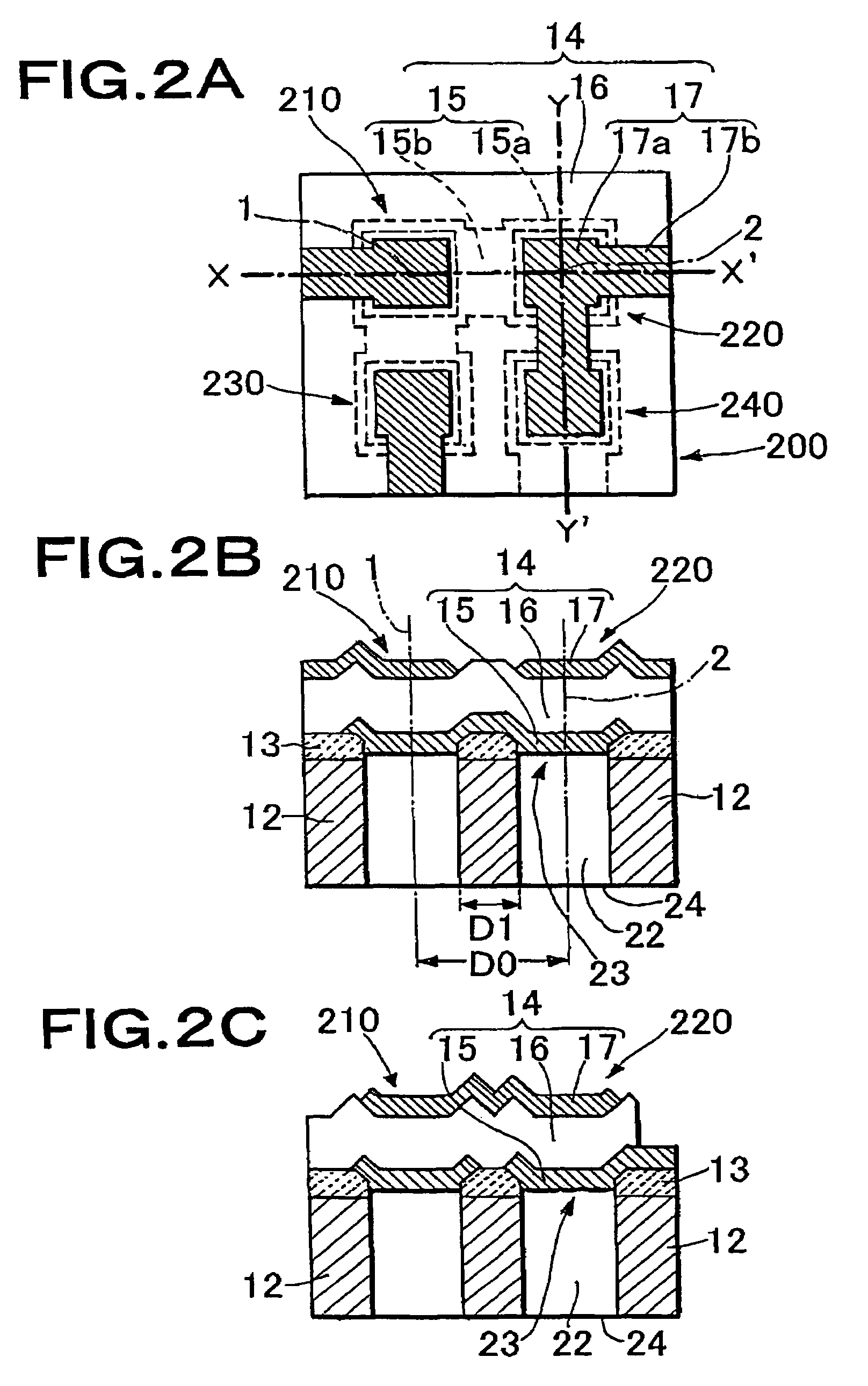
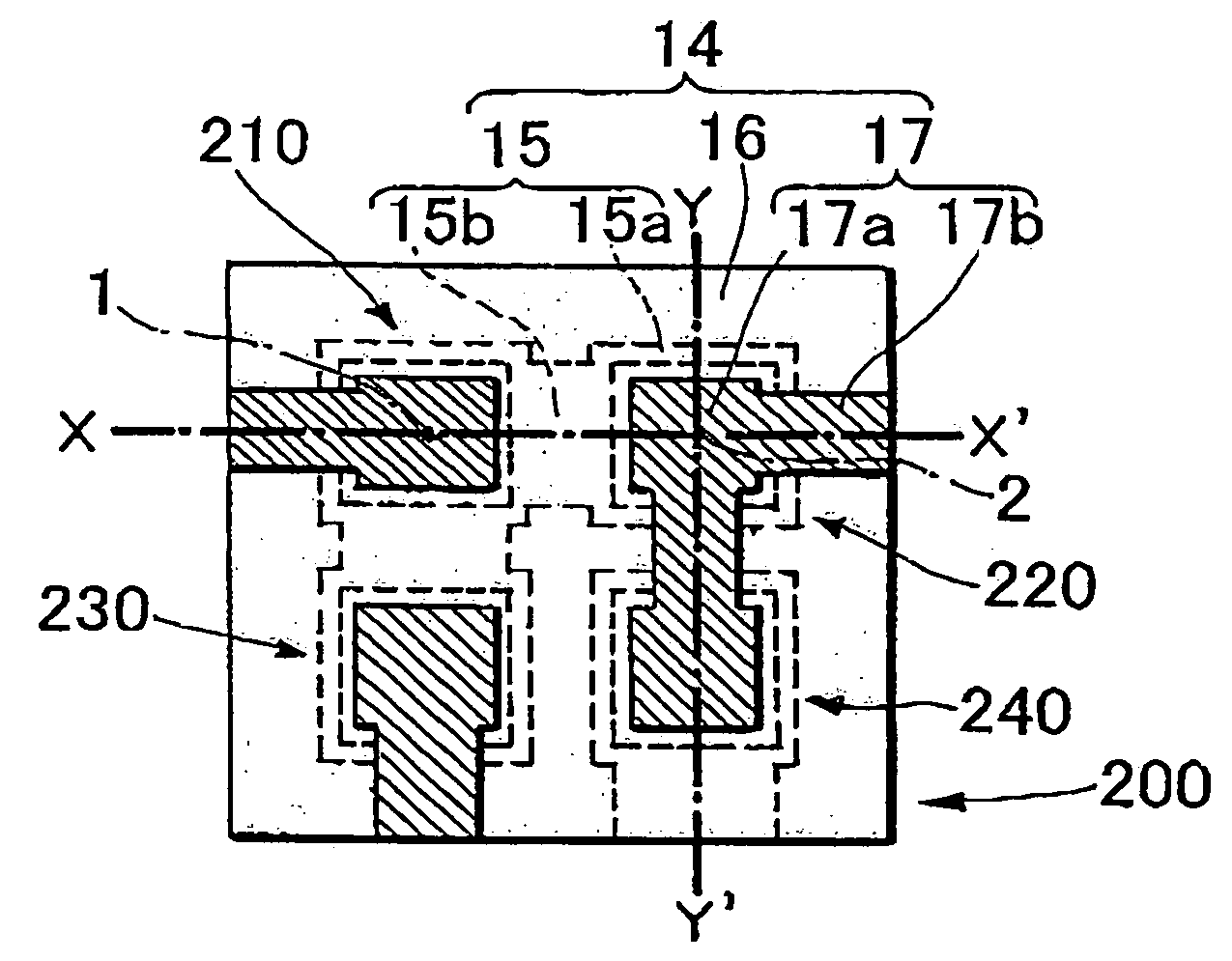
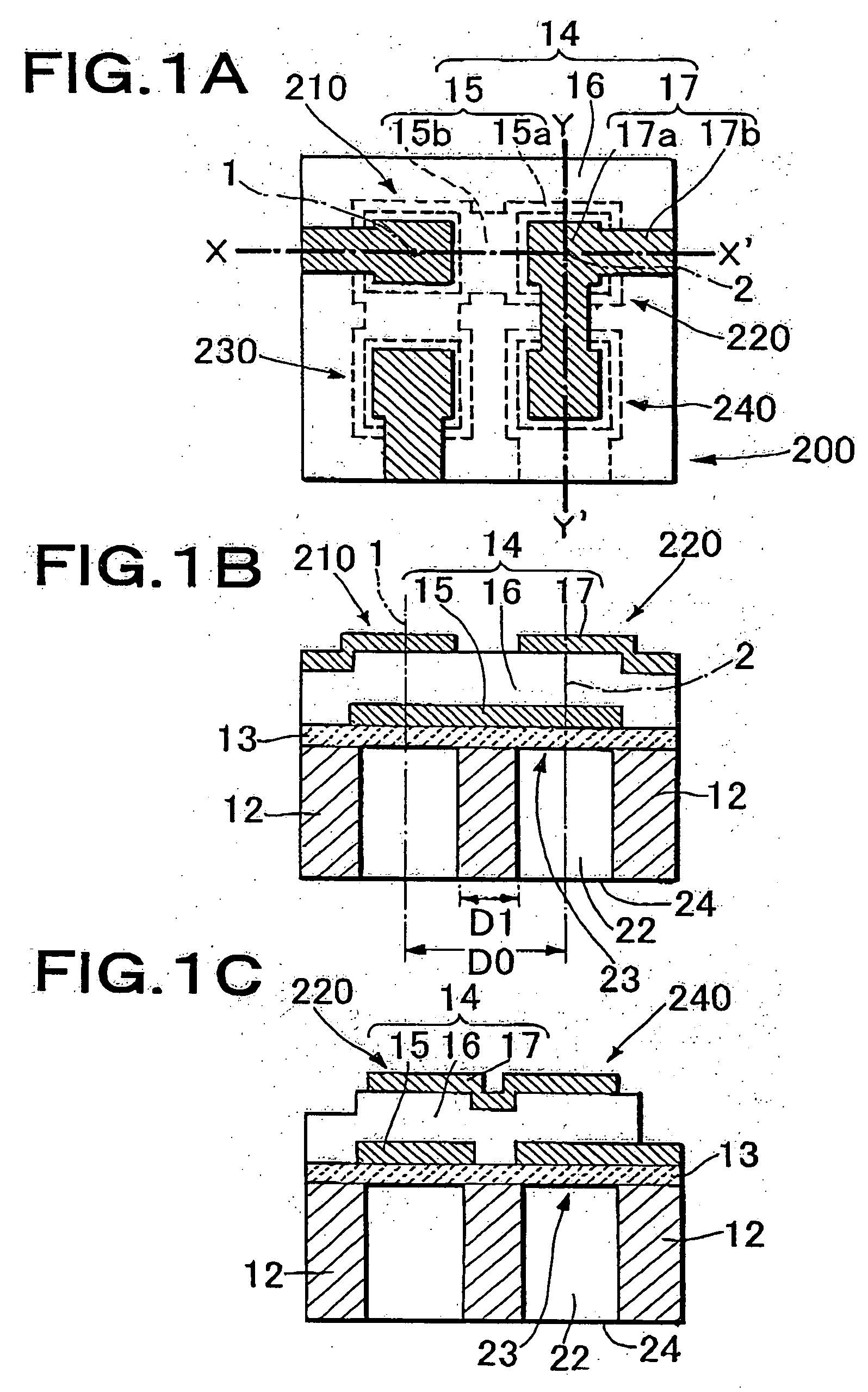
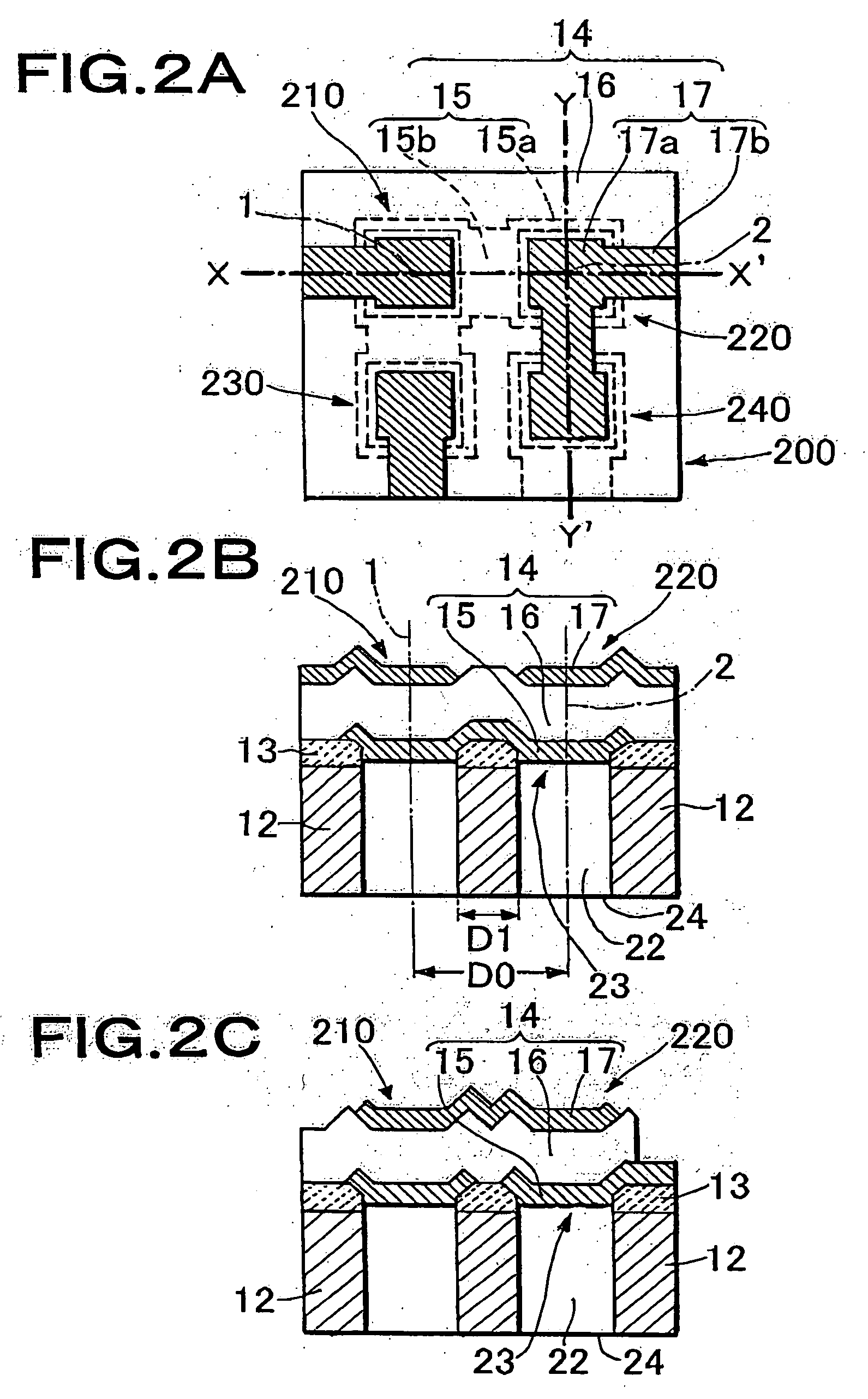
A thin film piezoelectric device includes a substrate (12) having via holes (22) and a piezoelectric laminated structure (14) consisting of a lower electrode (15), a piezoelectric film (16), and an upper electrode (17) formed on the substrate (12) via an insulation layer (13). A plurality of thin film piezoelectric resonators (210, 220) are formed for the via holes (22). The piezoelectric laminated structure (14) includes diaphragms (23) located to face the via holes (22) and a support area other than those. The thin film piezoelectric resonators (210, 220) are electrically connected by the lower electrode (15). When the straight line in the substrate plane passing through the centers (1, 2) of the diaphragms (23) of the thin film piezoelectric resonators (210, 220) has the length D1 of the segment passing through the support area and the distance between the centers of the diaphragms of the thin film piezoelectric resonators (210, 220) is D0,the ratio D1 / D0 is 0.1 to 0.5. The via hole (22) is fabricated by the deep graving type reactive ion etching method.
Owner:MEMS SOLUTIONS INC
Sensor and polarimetric filters for real-time extraction of polarimetric information at the focal plane
ActiveUS7582857B2Material analysis by optical meansPhotoelectric discharge tubesMetallic materialsReactive-ion etching
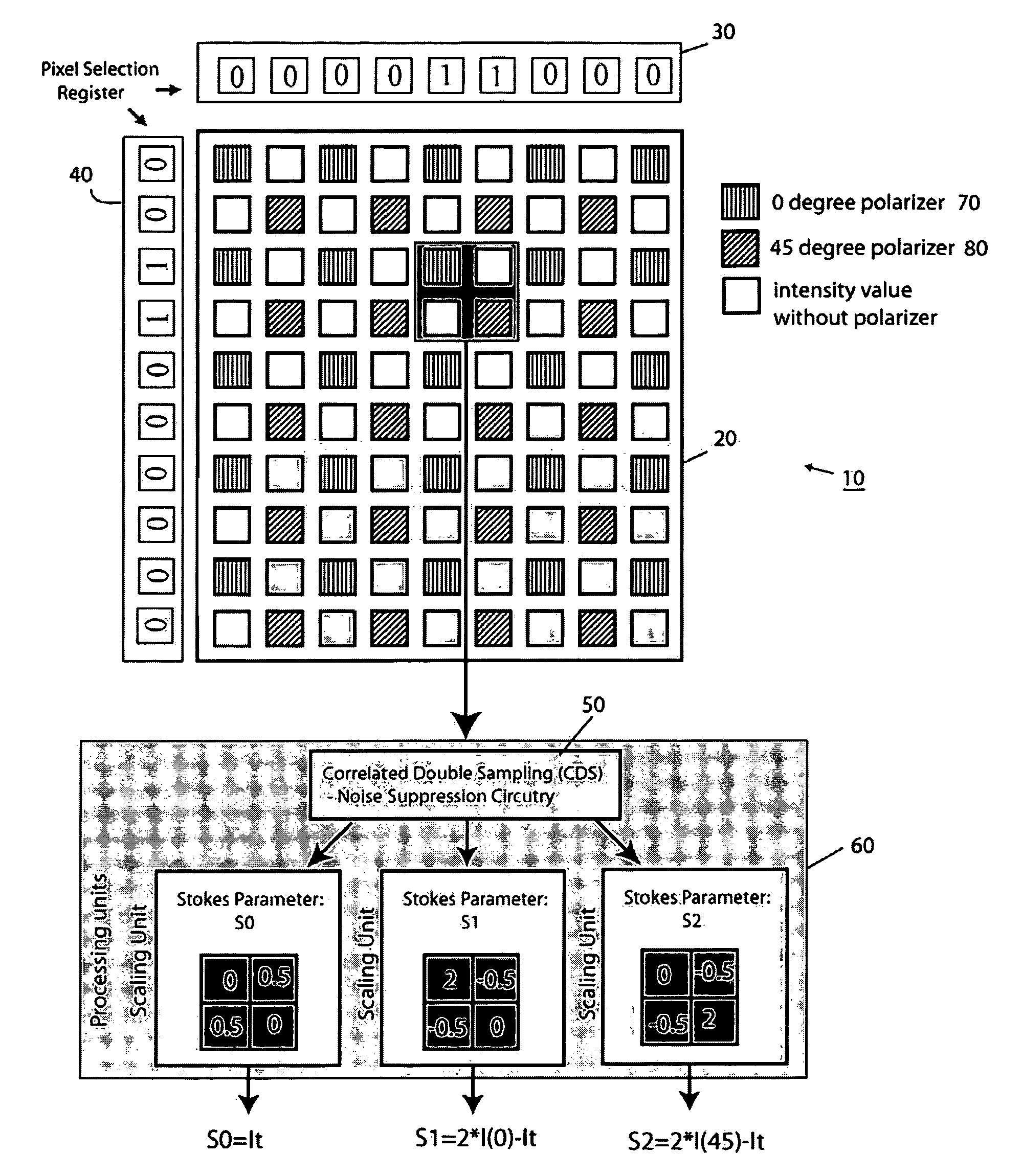
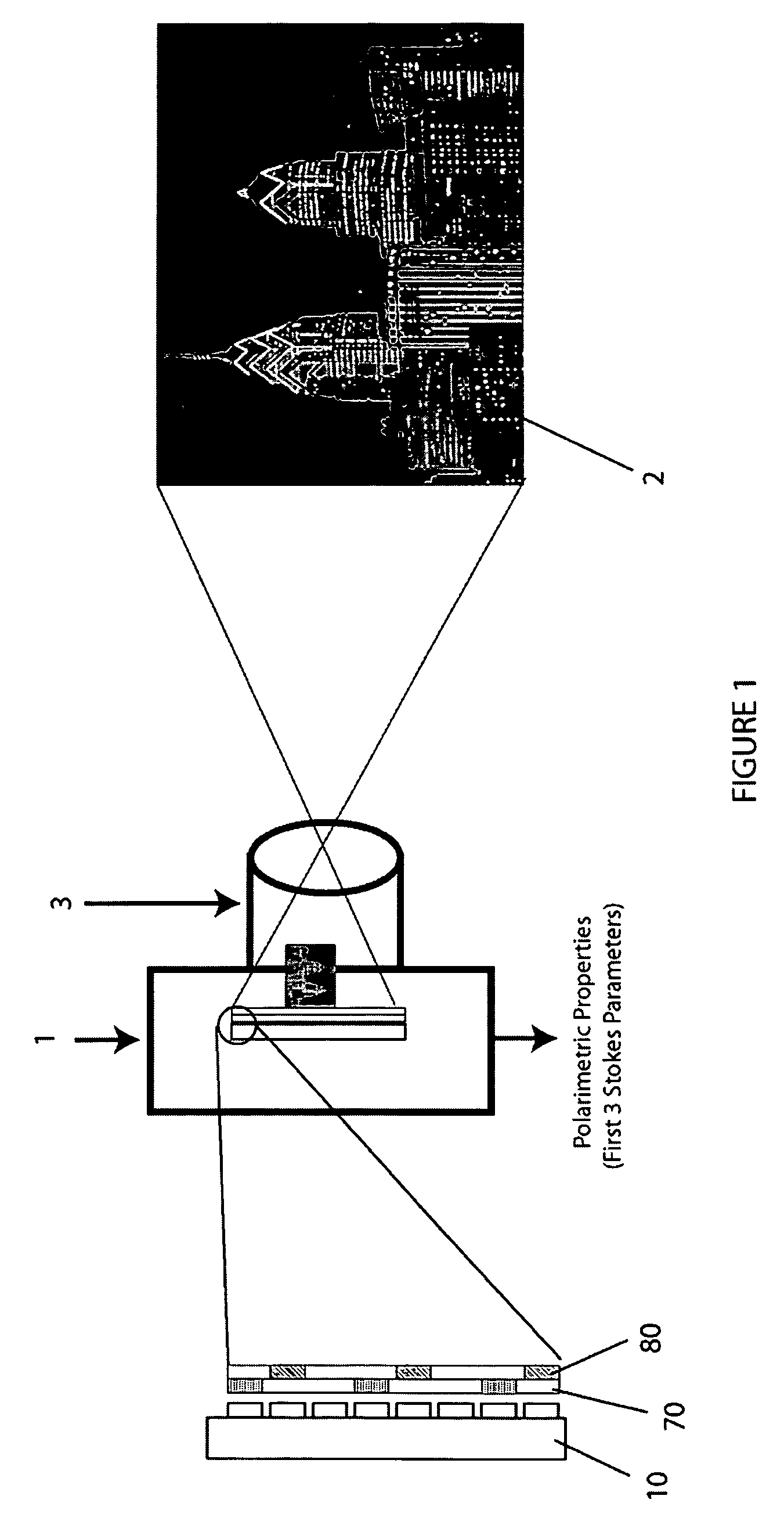
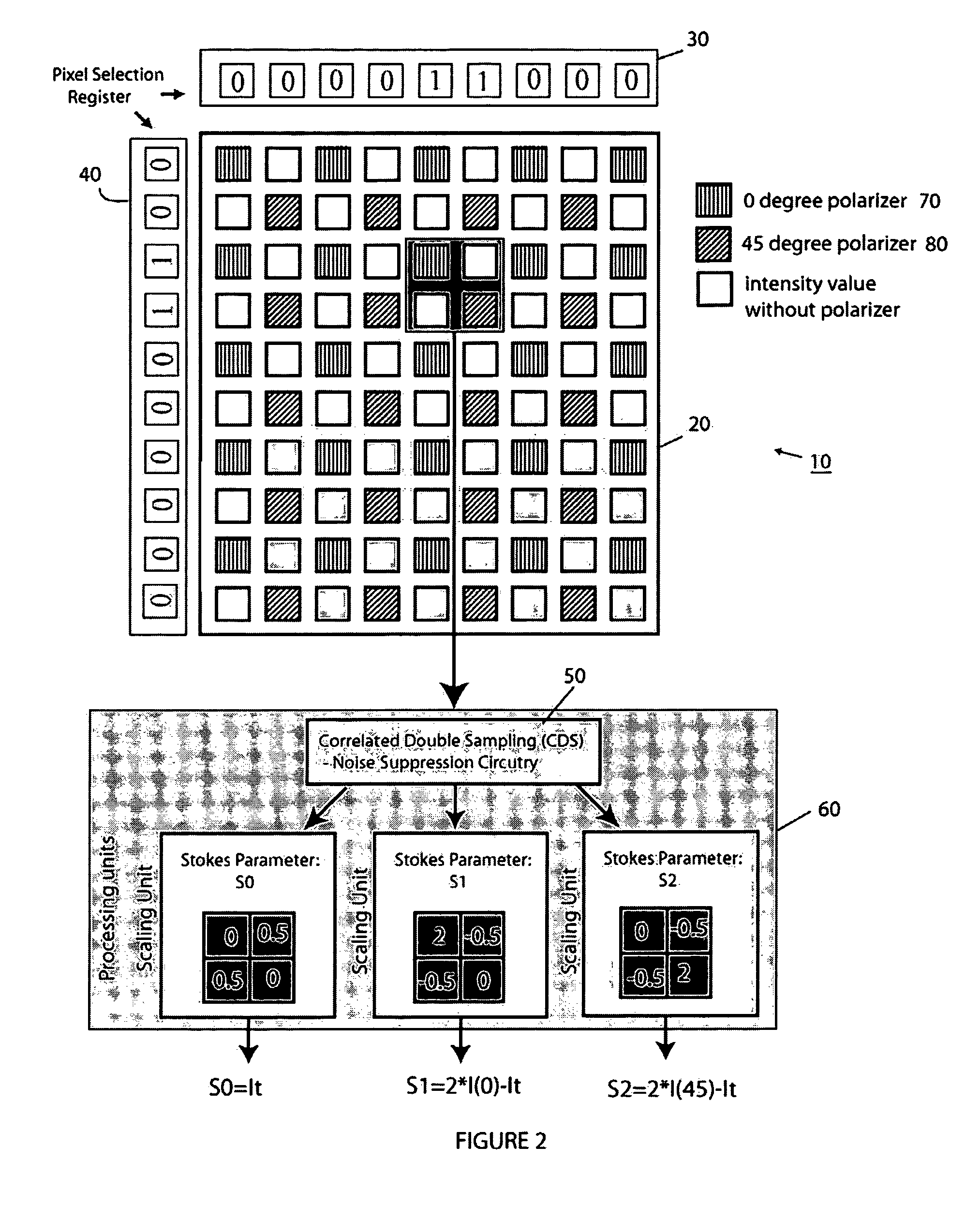
A polarimetric imaging system employs a pixel pitch matched filter for use within, for example, a 2 by 2 pixel neighborhood, in which one pixel samples the scene via a 0 degree polarization filter and a second pixel samples the scene via a 45 degree polarization filter. The remaining two pixels record the intensity of the light within the 2 by 2 neighborhoods. The polarization filters employ organic materials such as polymers or metallic materials that are patterned and etched using reactive ion etching (RIE) or other appropriate etching technique in order to create 14 micron or smaller circular (or square) periodic structures that are patterned into polarization thin films that are deposited on an imaging sensor that includes a processor that computes from the polarization-filtered inputs the first three Stokes parameters in real-time.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Method for producing a grid structure, an optical element, an evanescence field sensor plate, microtitre plate and an optical communication engineering coupler as well as a device for monitoring a wavelength
InactiveUS6873764B2Improve accuracyLow effortCladded optical fibreMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorGratingPulsed DC
Owner:OERLIKON TRADING AG TRUEBBACH
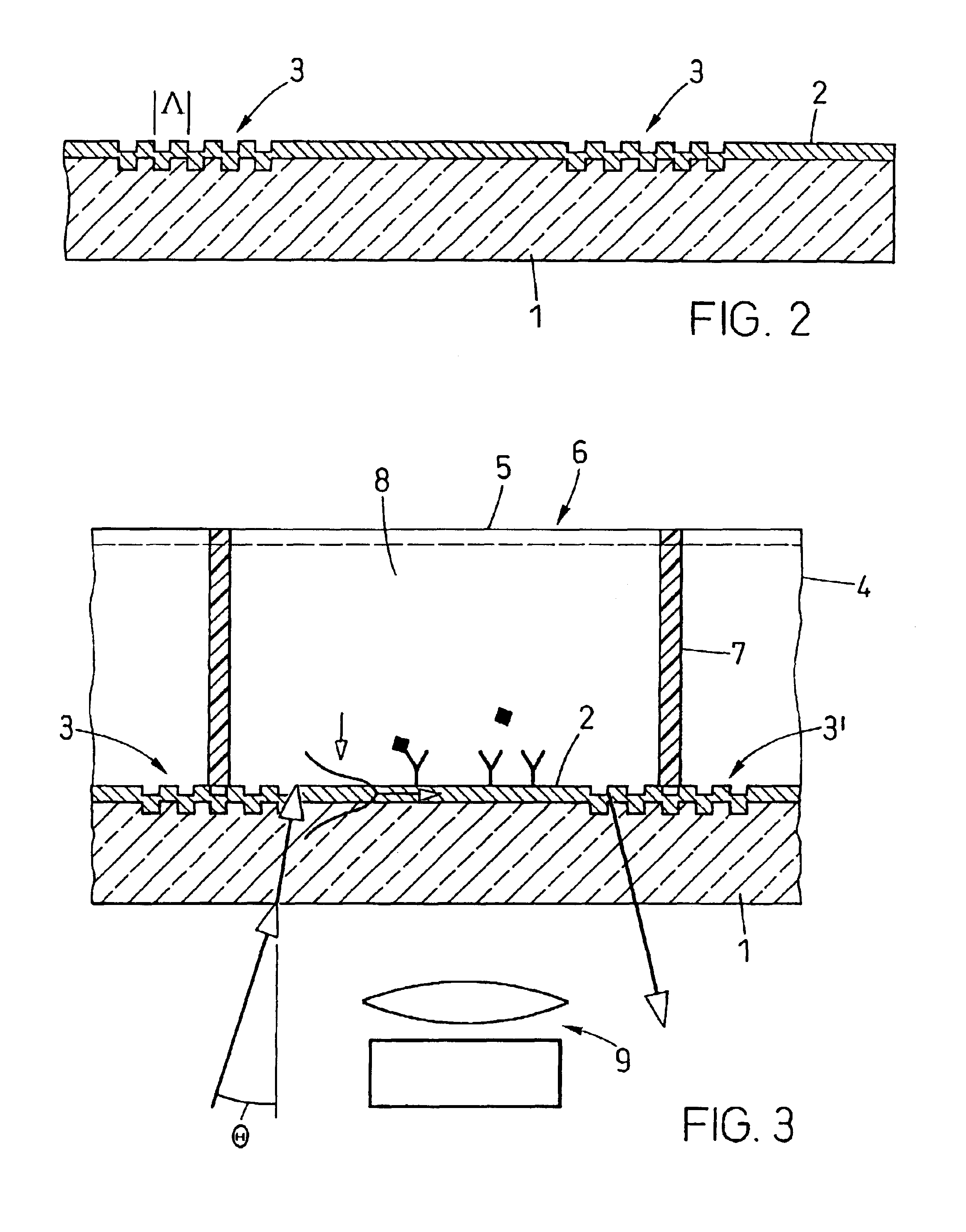
Method of making a perpendicular recording magnetic head pole tip with an etchable adhesion CMP stop layer
InactiveUS20050024779A1Increasing number of processing stepHigh momentElectrical transducersDecorative surface effectsCompound (substance)Pole piece
The method of making a magnetic head assembly includes forming a second pole piece layer that is recessed from a head surface, forming a reactive ion etchable (RIEable) pole tip forming layer on the second pole piece layer, forming an adhesion / stop layer of tantalum (Ta) on the pole tip forming layer, forming a photoresist mask on the adhesion / stop layer with an opening for patterning the adhesion / stop layer and the pole tip forming layer with another opening, reactive ion etching (RIE) through the opening to form the other opening, forming the second pole piece pole tip in the other opening with a top which is above a top of the adhesion / stop layer and chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) the top of the second pole piece pole tip until the CMP contacts the adhesion / stop layer. The invention also includes the magnetic head made by such a process.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Thin film piezoelectric resonator, thin film piezoelectric device, and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20050248238A1Planar shape is optimizedReduced insertion lossPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyImpedence networksInsulation layerEngineering
A thin film piezoelectric device includes a substrate (12) having via holes (22) and a piezoelectric laminated structure (14) consisting of a lower electrode (15), a piezoelectric film (16), and an upper electrode (17) formed on the substrate (12) via an insulation layer (13). A plurality of thin film piezoelectric resonators (210, 220) are formed for the via holes (22). The piezoelectric laminated structure (14) includes diaphragms (23) located to face the via holes (22) and a support area other than those. The thin film piezoelectric resonators (210, 220) are electrically connected by the lower electrode (15). When the straight line in the substrate plane passing through the centers (1, 2) of the diaphragms (23) of the thin film piezoelectric resonators (210, 220) has the length D1 of the segment passing through the support area and the distance between the centers of the diaphragms of the thin film piezoelectric resonators (210, 220) is D0,the ratio D1 / D0 is 0.1 to 0.5. The via hole (22) is fabricated by the deep graving type reactive ion etching method.
Owner:MEMS SOLUTIONS INC
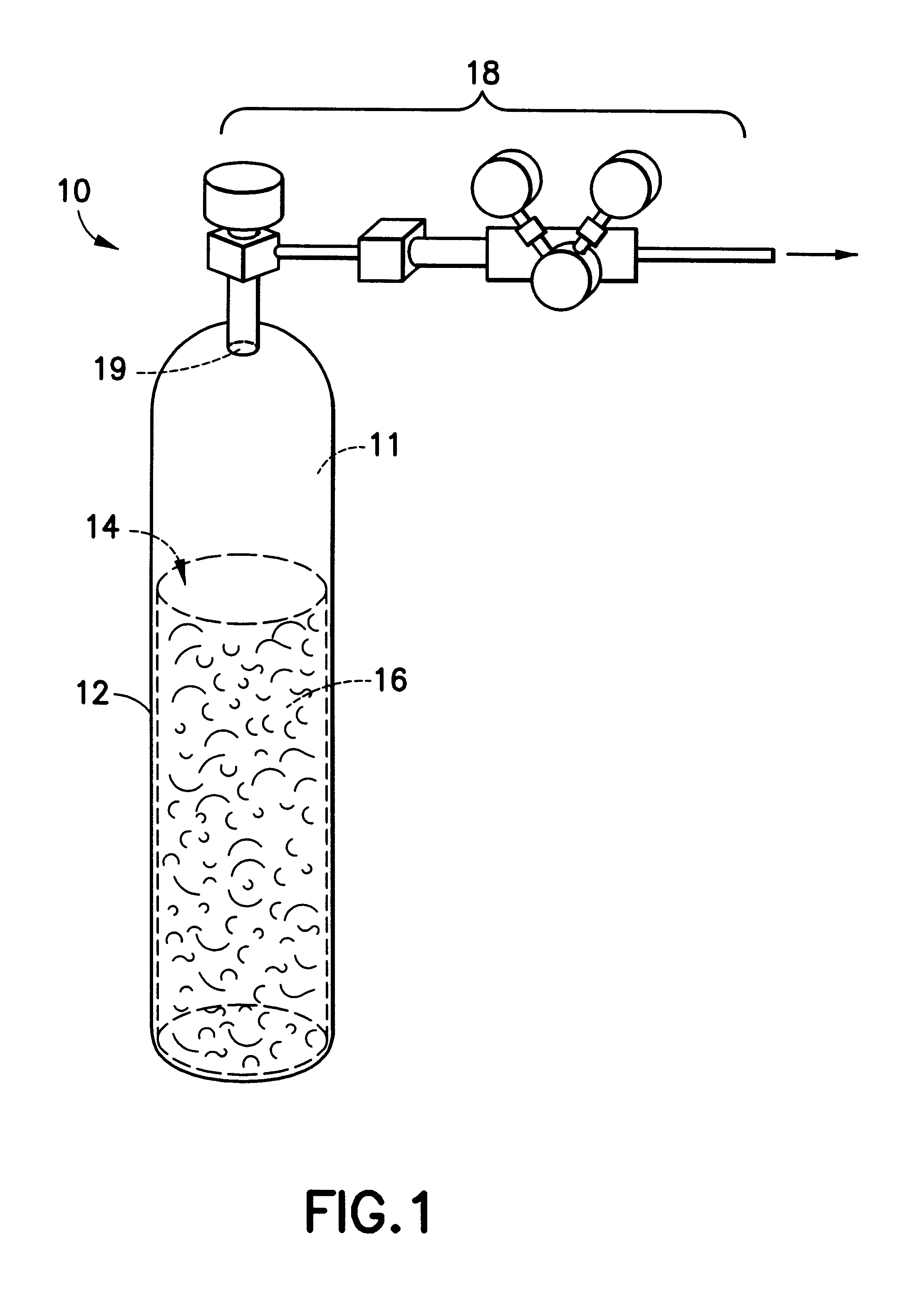
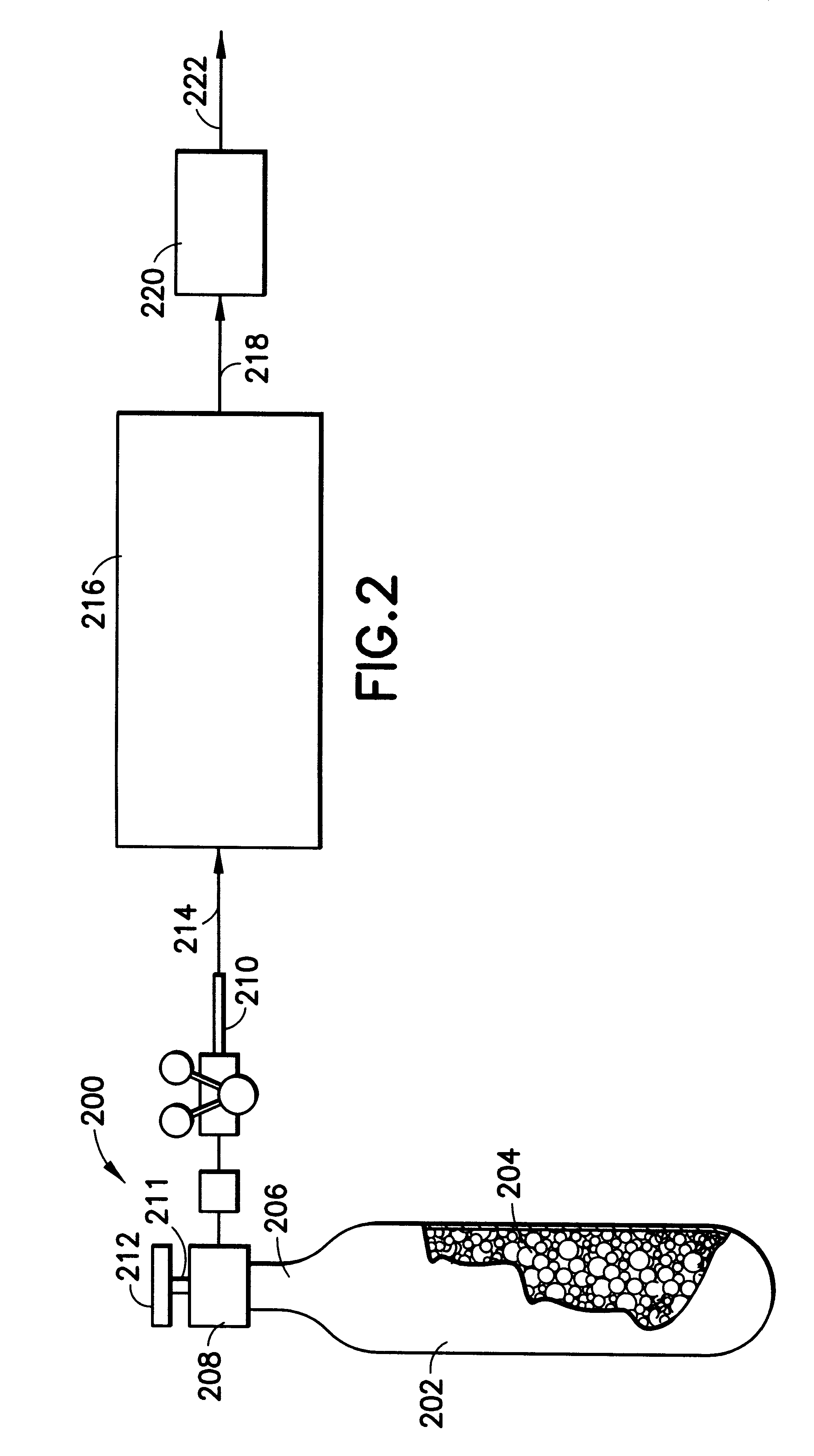
Apparatus and process for manufacturing semiconductor devices, products and precursor structures utilizing sorbent-based fluid storage and dispensing system for reagent delivery
InactiveUS6204180B1Vessel mounting detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGas phaseSorbent
A process for fabricating an electronic device structure on or in a substrate. A storage and dispensing vessel is provided, containing a solid-phase physical sorbent medium having physically adsorbed thereon a fluid for fabrication of the electronic device structure, e.g., a source fluid for a material constituent of the electronic device structure, or a reagent such as an etchant or mask material which is utilized in the fabrication of the electronic device structure but does not compose or form a material constituent of the electronic device structure. In the process, the source fluid is desorbed from the physical sorbent medium and dispensing source fluid from the storage and dispensing vessel, and contacted with the substrate, under conditions effective to utilize the material constituent on or in the substrate. The contacting step of the process may include process steps such as ion implantation; epitaxial growth; plasma etching; reactive ion etching; metallization; physical vapor deposition; chemical vapor deposition; cleaning; doping; etc. The process of the invention may be employed to fabricate electronic device structures such as transistors; capacitors; resistors; memory cells; dielectric material; buried doped substrate regions; metallization layers; channel stop layers; source layers; gate layers; drain layers; oxide layers; field emitter elements; passivation layers; interconnects; polycides; electrodes; trench structures; ion implanted material layers; via plugs; precursor structures for the foregoing electronic device structures; and device assemblies comprising more than one of the foregoing electronic device structures. The electronic device structure fabricated by such process may in turn may be employed as a component of an electronic product such as a telecommunications device or electronic appliance.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com