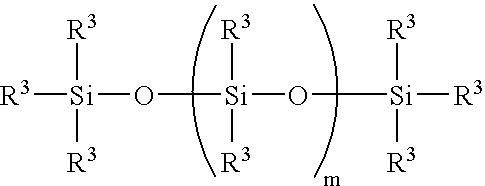Patents
Literature
112results about How to "Excellent gap filling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
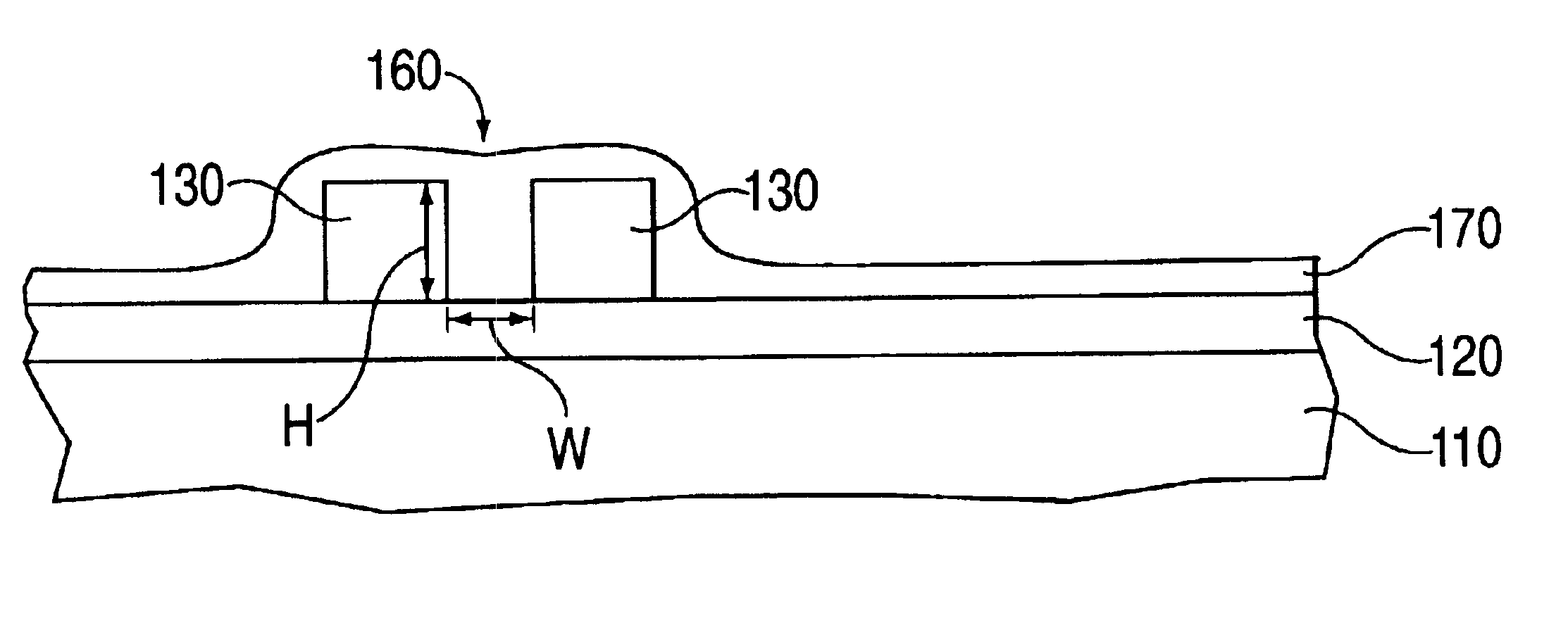
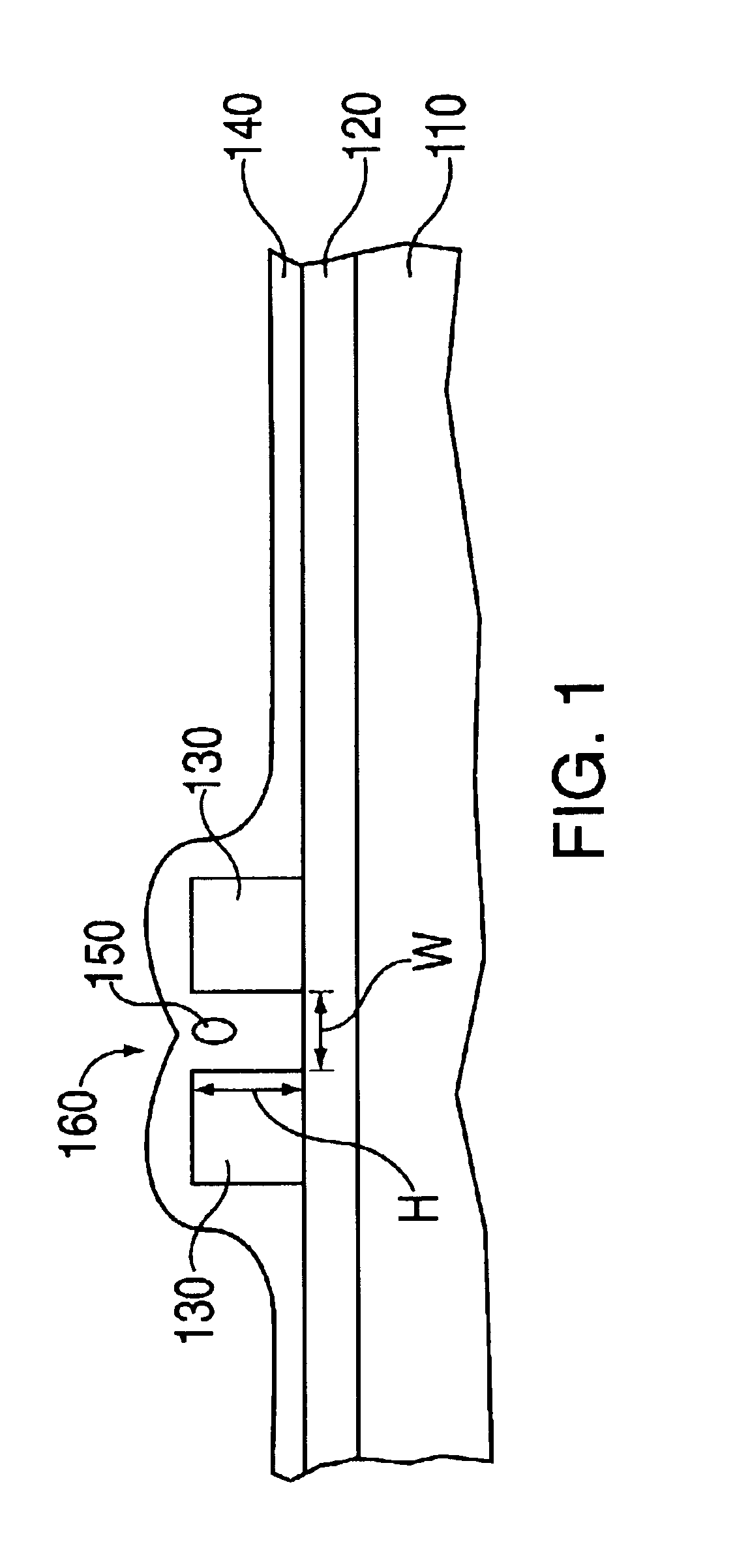
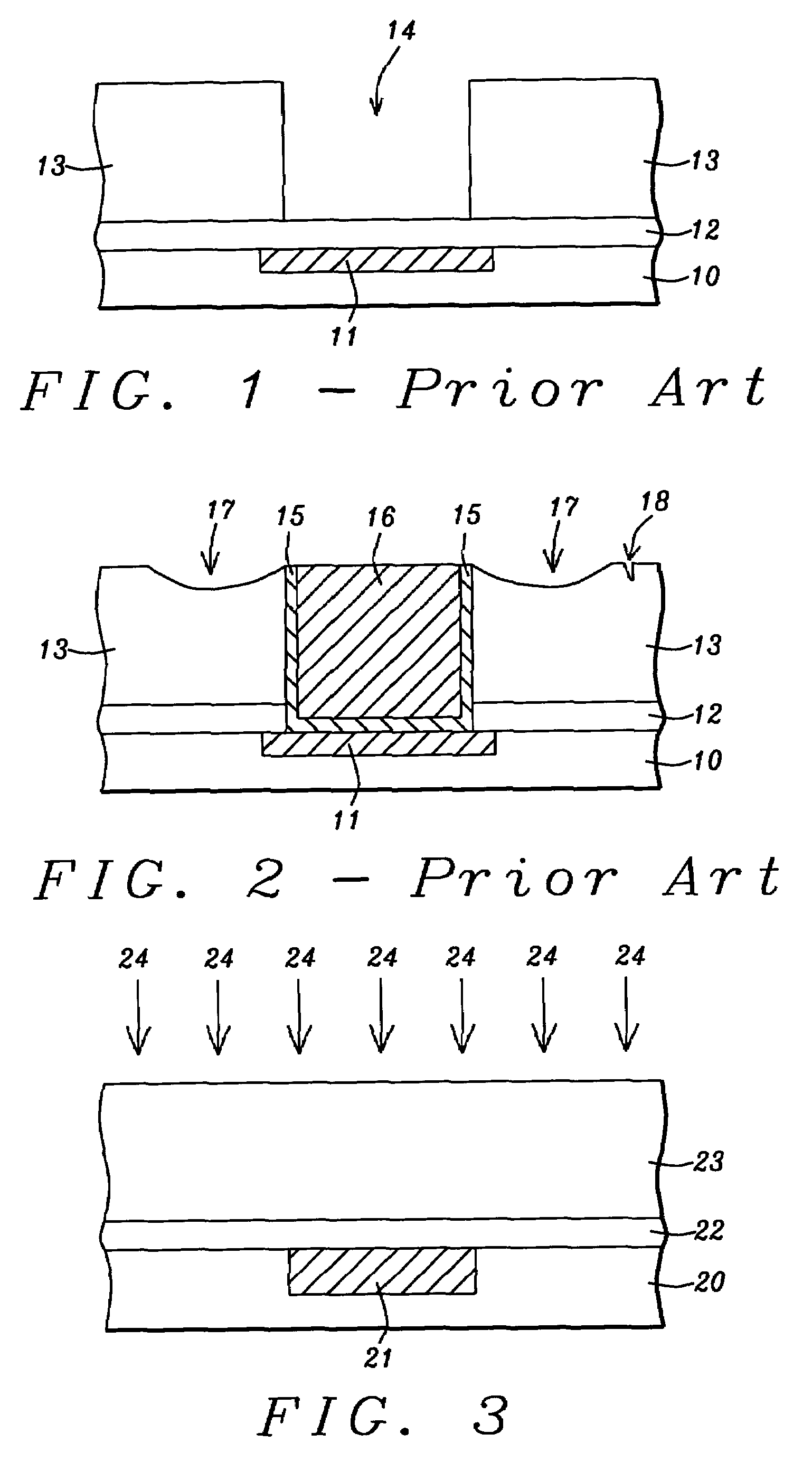
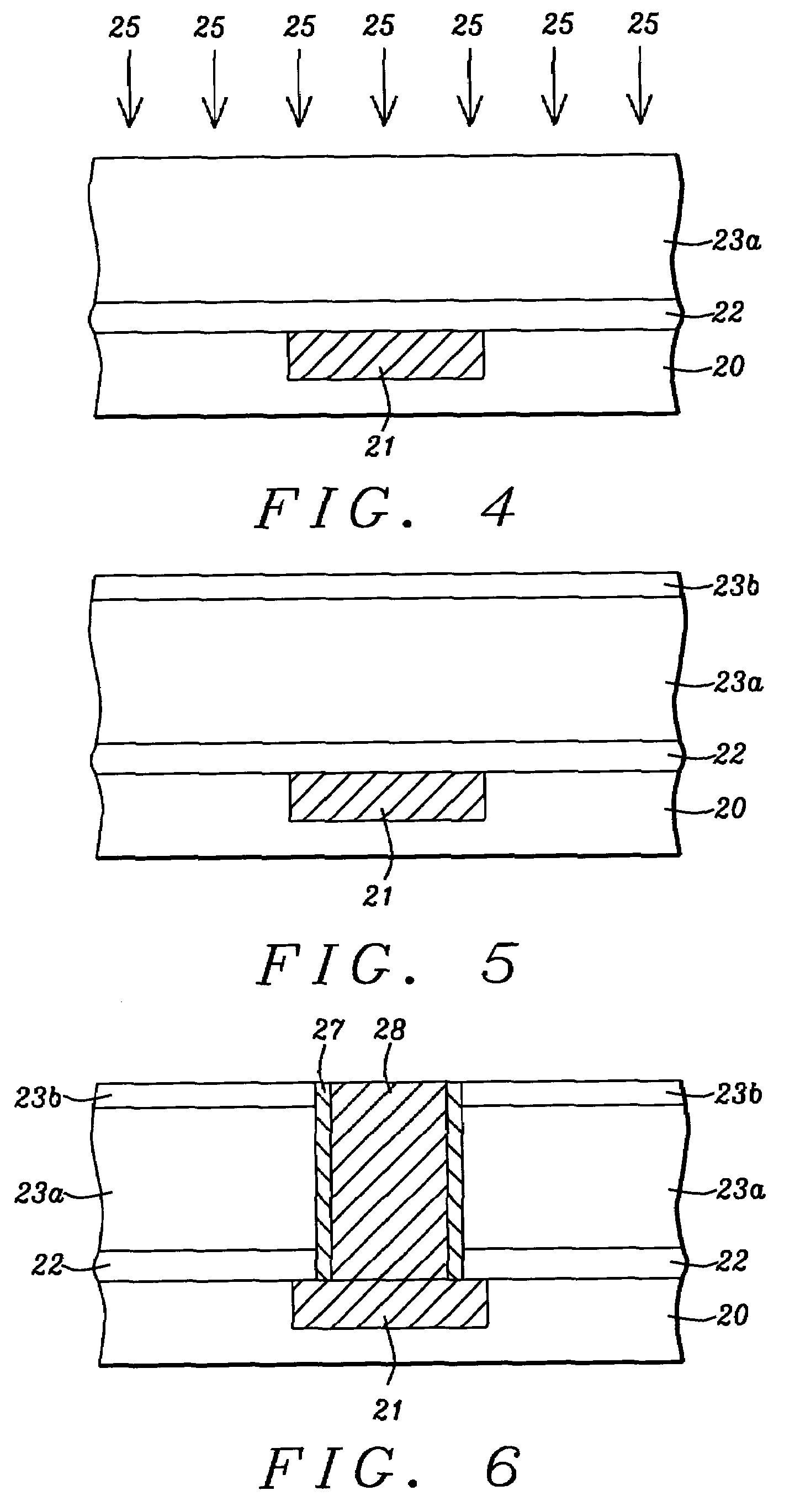
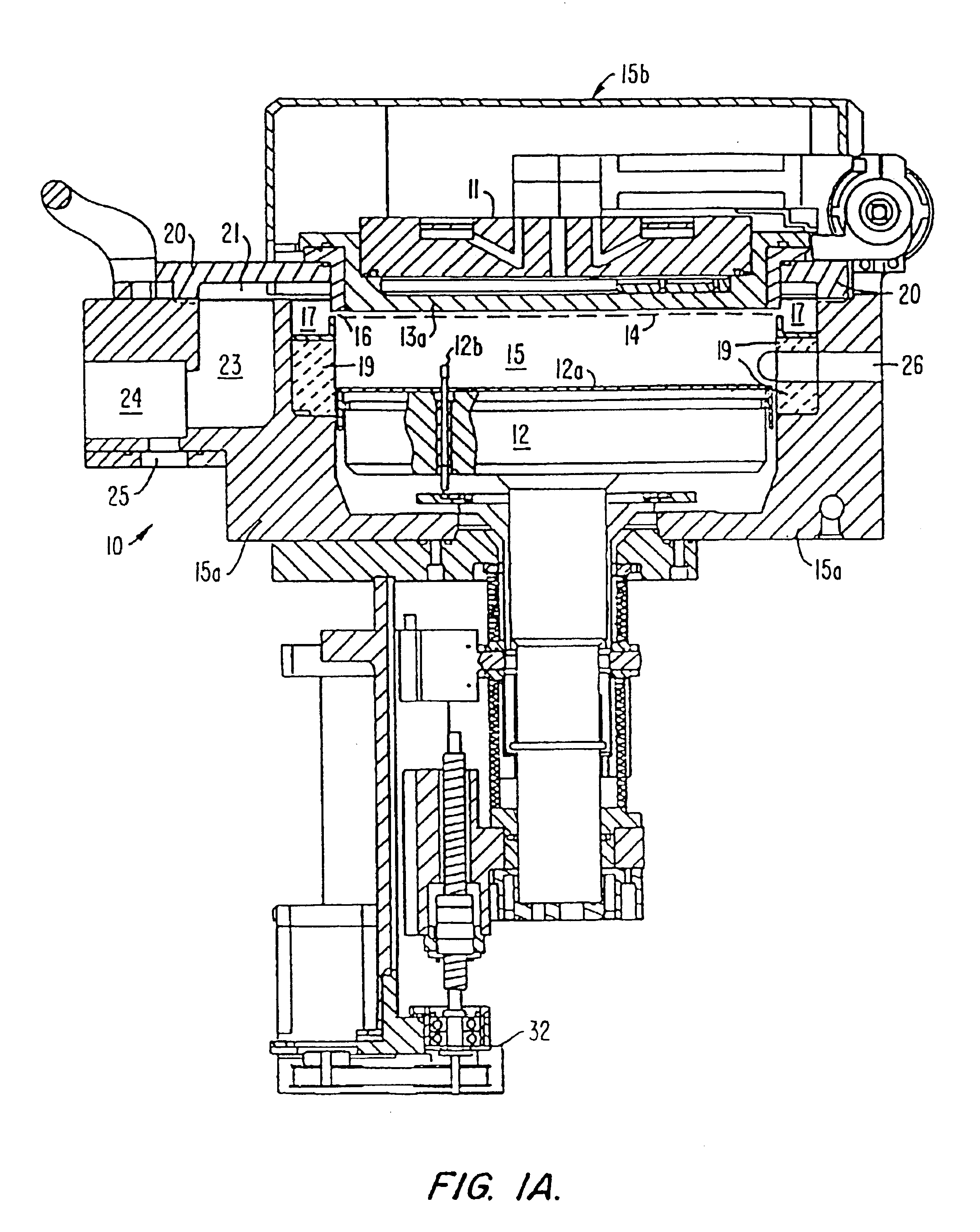
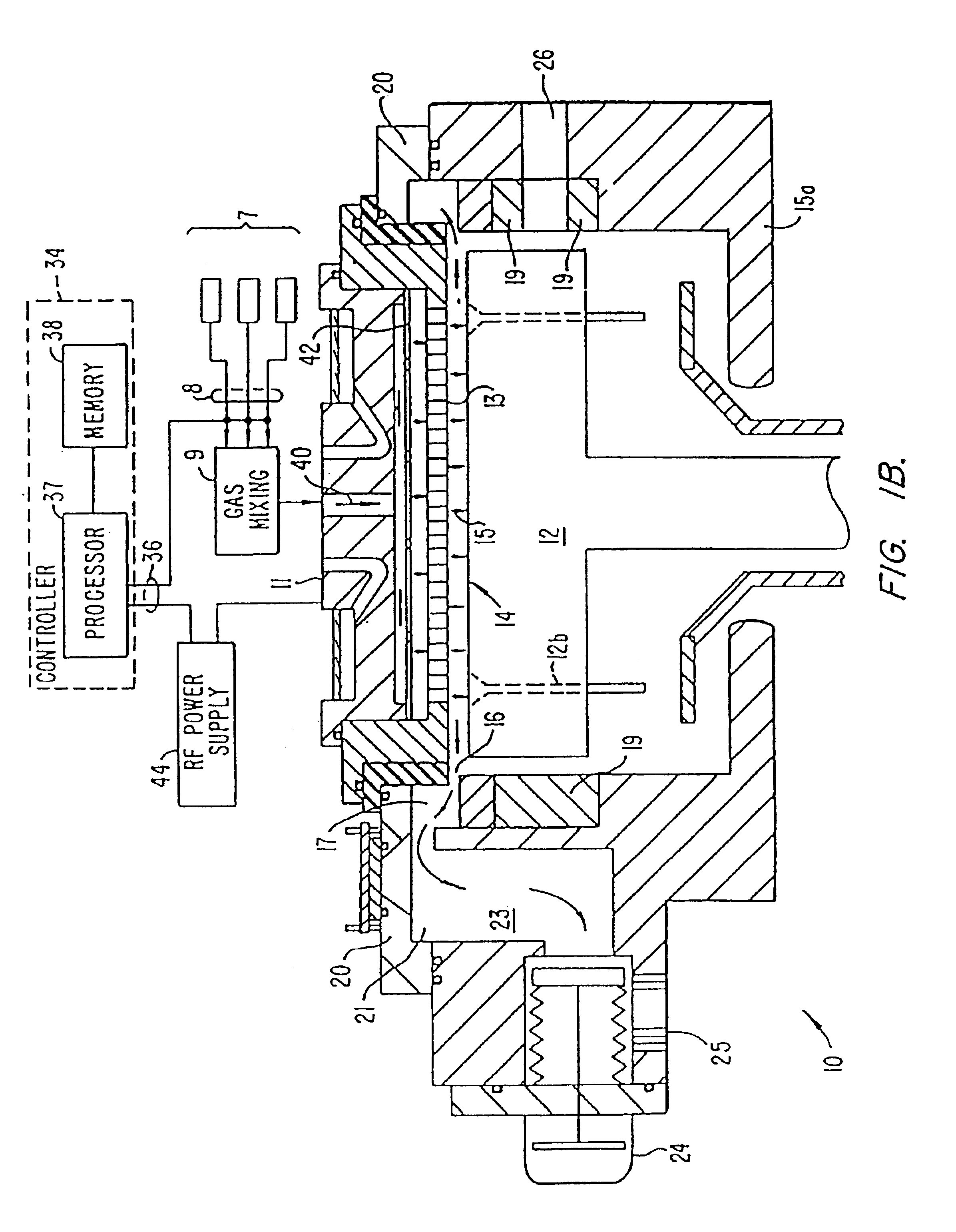
Method for low temperature chemical vapor deposition of low-k films using selected cyclosiloxane and ozone gases for semiconductor applications
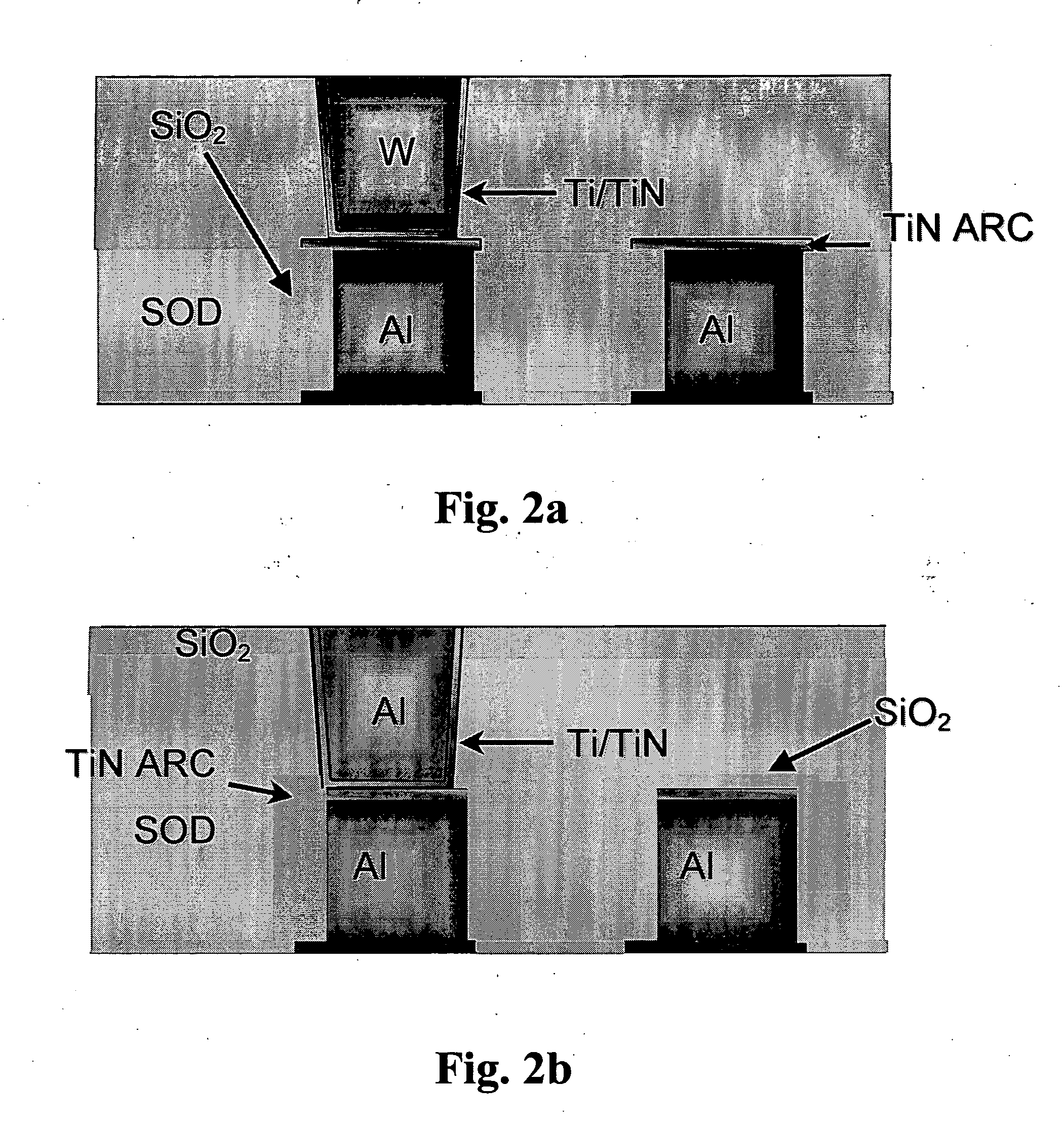
InactiveUS7084079B2Excellent gap fillingMinimize formationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductorGermanium
A method is described for forming a low-k dielectric film, in particular, a pre-metal dielectric (PMD) on a semiconductor wafer which has good gap-filling characteristics. The method uses a thermal sub-atmospheric CVD process that includes a carbon-containing organometallic precusor such as TMCTS or OMCTS, an ozone-containing gas, and a source of dopants for gettering alkali elements and for lowering the reflow temperature of the dielectric while attaining the desired low-k and gap-filling properties of the dielectric film. Phosphorous is a preferred dopant for gettering alkali elements such as sodium. Additional dopants for lowering the reflow temperature include, but are not limited to boron, germanium, arsenic, fluorine or combinations thereof.
Owner:IBM CORP
Two step post-deposition treatment of ILD layer for a lower dielectric constant and improved mechanical properties
InactiveUS20050064698A1Increase resistanceImprove the immunityDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMoistureMechanical property
A method of lowering the dielectric constant of an organosilicon low k dielectric layer while improving the hardness and thermal stability is provided. A deposited layer of carbon doped oxide, HSQ, or MSQ is cured and treated with a He plasma which improves hardness for a subsequent CMP step and lowers the dielectric constant. There is no loss of H2O or CH4 during the He treatment. The low k dielectric layer is then treated with a H2 plasma which converts some of the Si—O and Si—CH3 bonds near the surface to Si—H bonds, thereby further lowering the dielectric constant and increasing thermal stability that improves breakdown resistance. Moisture uptake is also reduced. The method is especially useful for interconnect schemes with deep sub-micron ground rules. Surprisingly, the k value obtained from two different plasma treatments is lower than when two He treatments or two H2 treatment are performed.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MASNUFACTURING
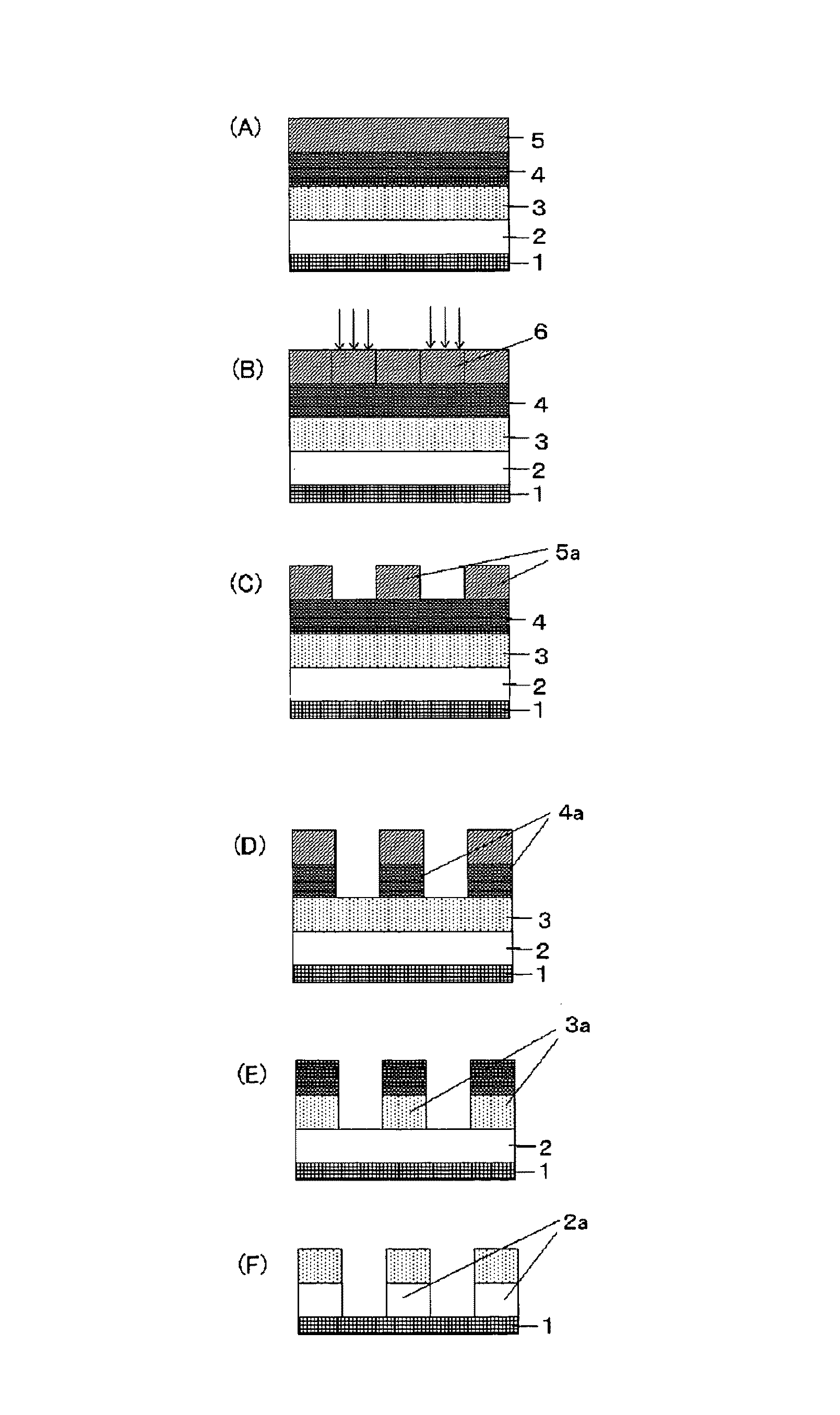
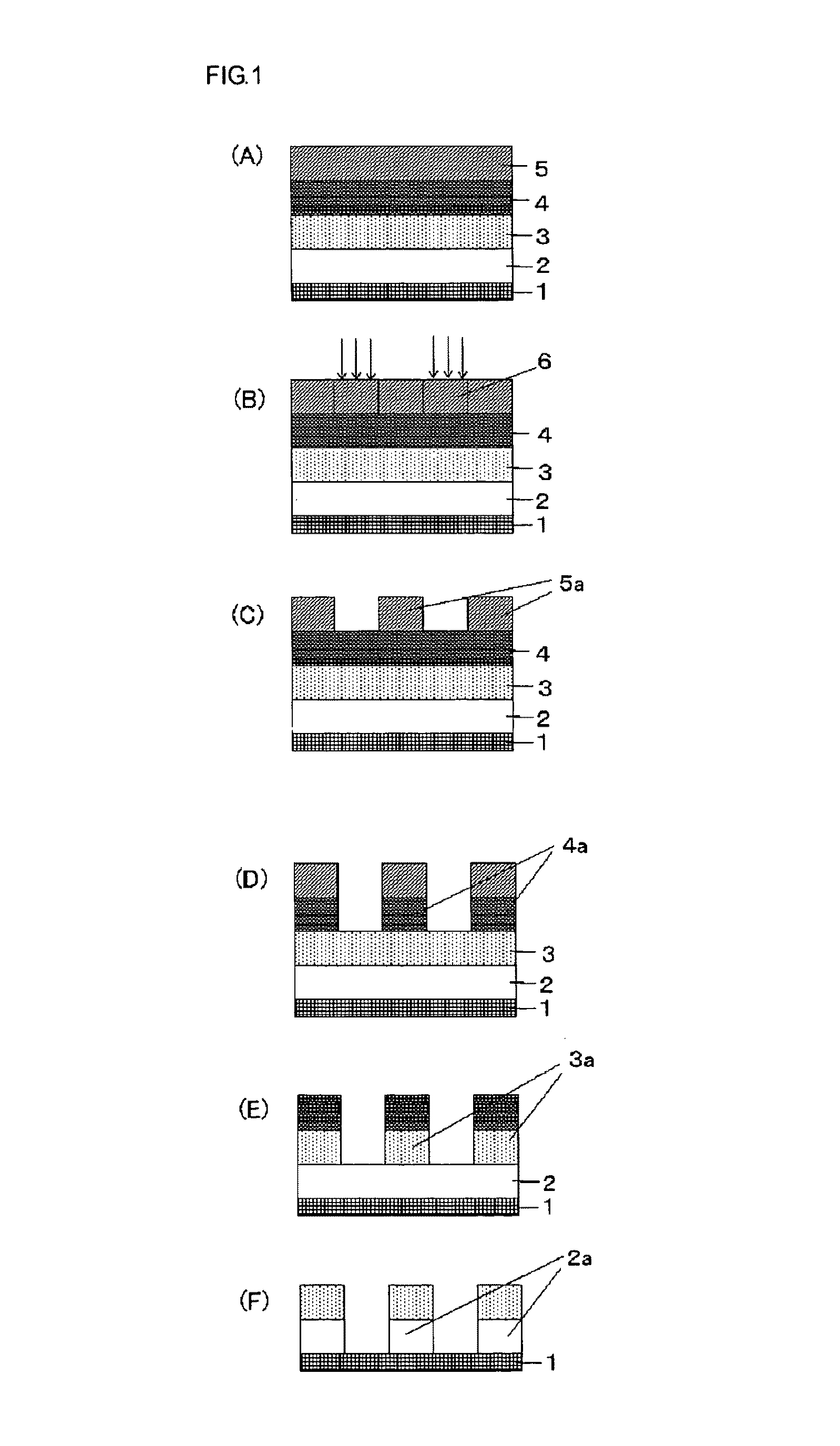
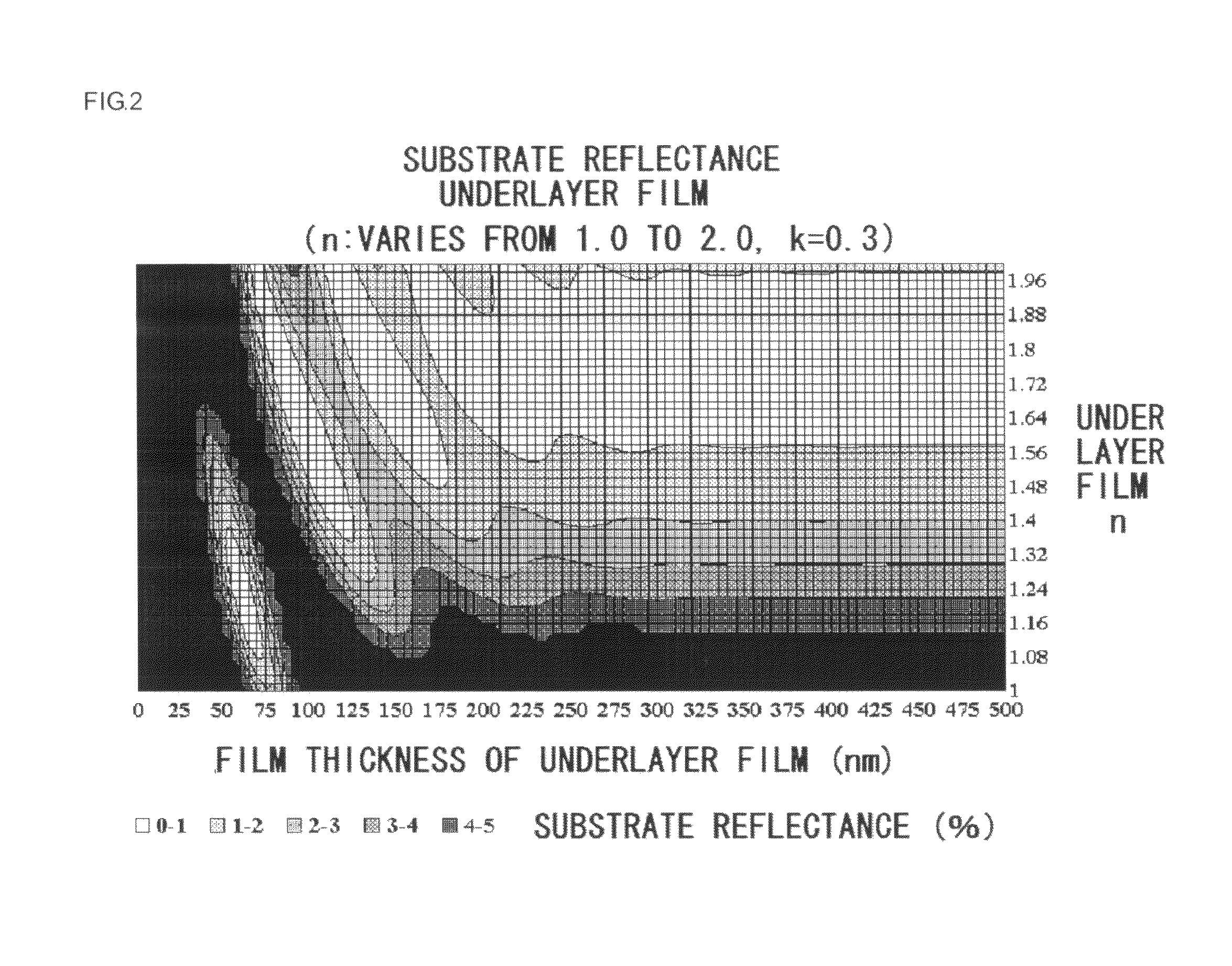
Method for forming resist underlayer film, patterning process using the same, and composition for the resist underlayer film
ActiveUS20100099044A1Reduce reflectivityIncrease resistancePhotosensitive materialsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResistEtching
There is disclosed a method for forming a resist underlayer film of a multilayer resist film having at least three layers used in a lithography, comprising at least; a step of coating a composition for resist underlayer film containing a novolak resin represented by the following general formula (1) obtained by treating a compound having a bisnaphthol group on a substrate; and a step of curing the coated composition for the resist underlayer film by a heat treatment at a temperature above 300° C. and 600° C. or lower for 10 to 600 seconds. There can be provided a method for forming a resist underlayer film, and a patterning process using the method to form a resist underlayer film in a multilayer resist film having at least three layers used in a lithography, gives a resist underlayer film having a lowered reflectance, a high etching resistance, and a high heat and solvent resistances, especially without wiggling during substrate etching.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
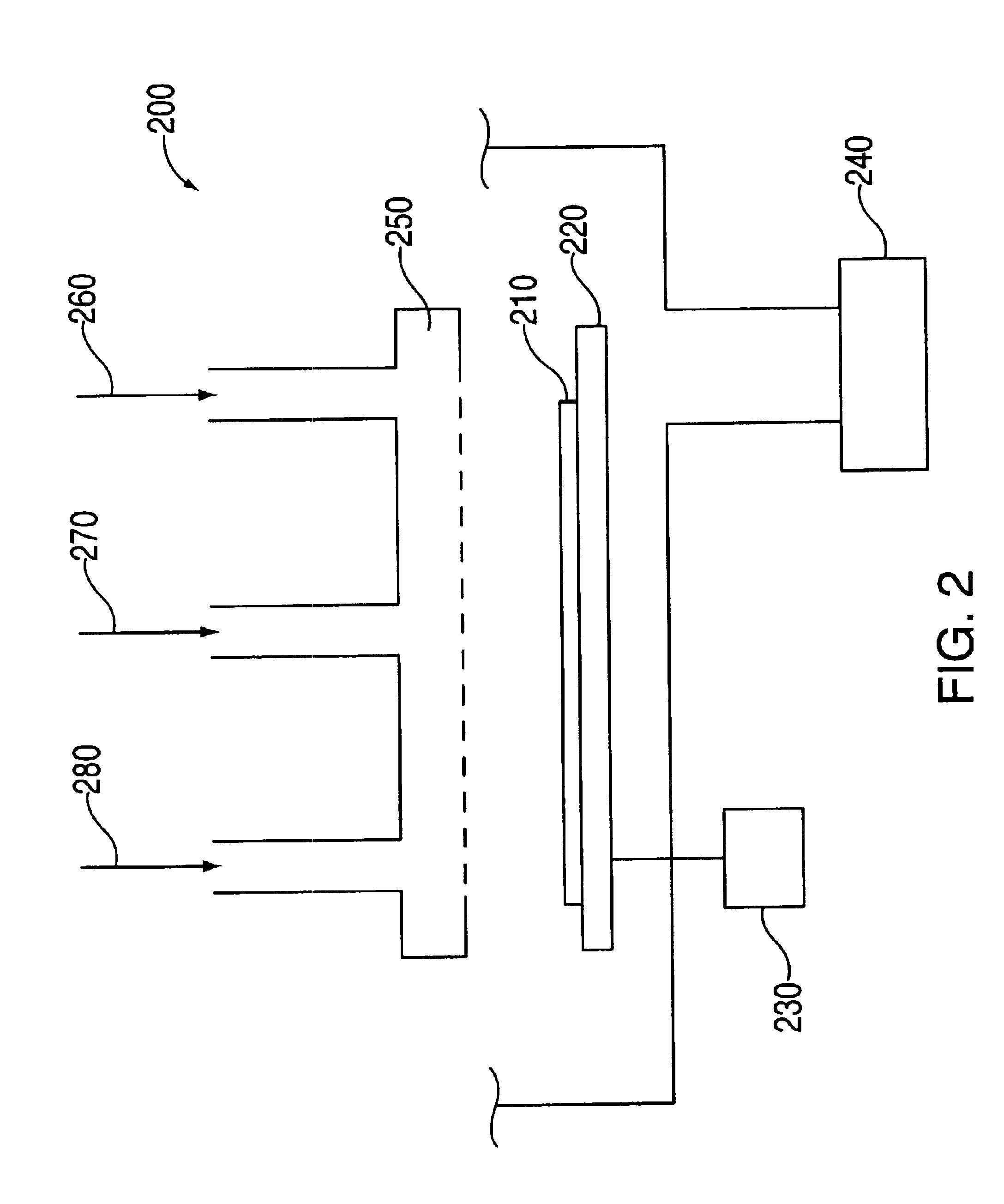
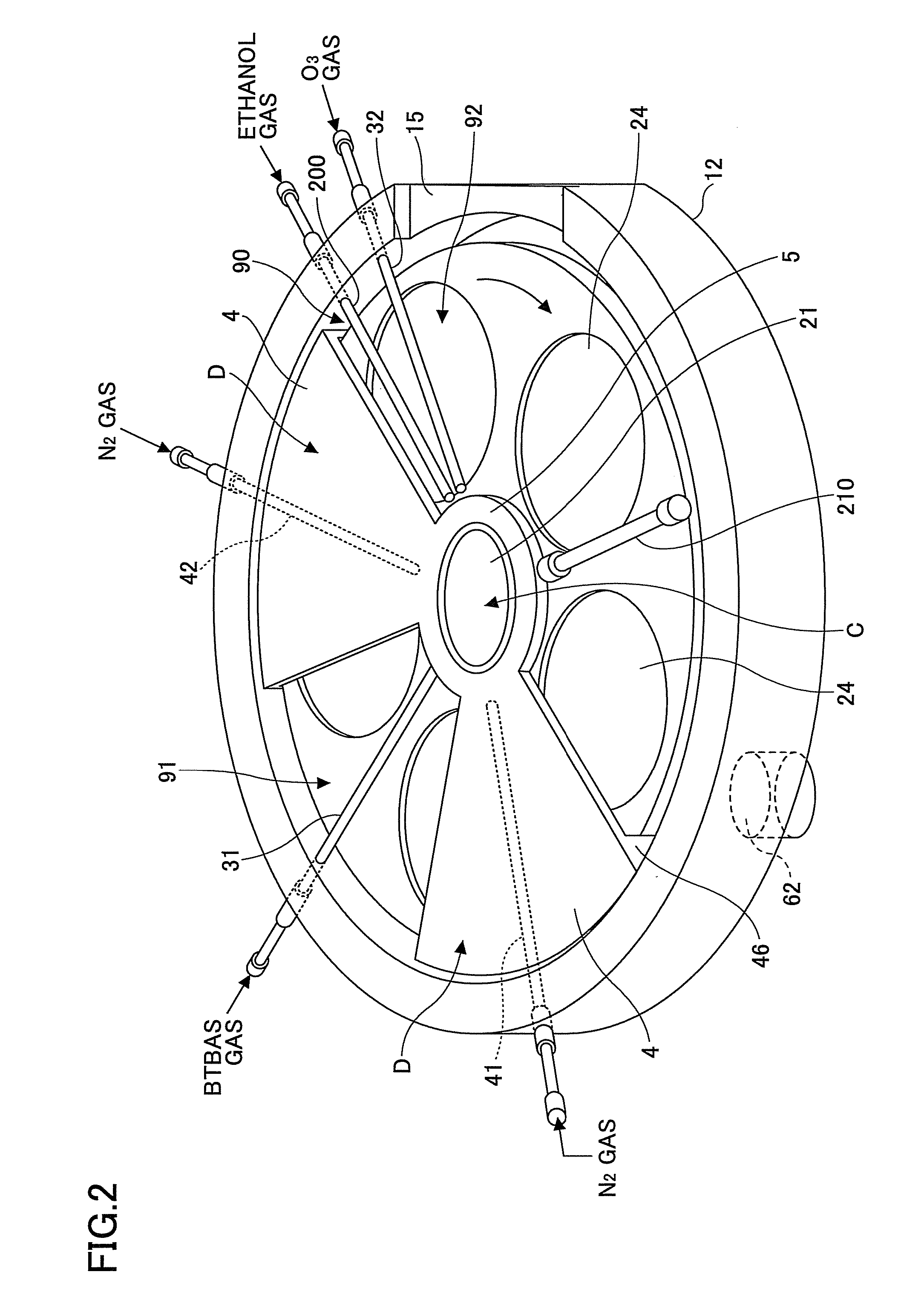
Film deposition apparatus, film deposition method, and computer readable storage medium
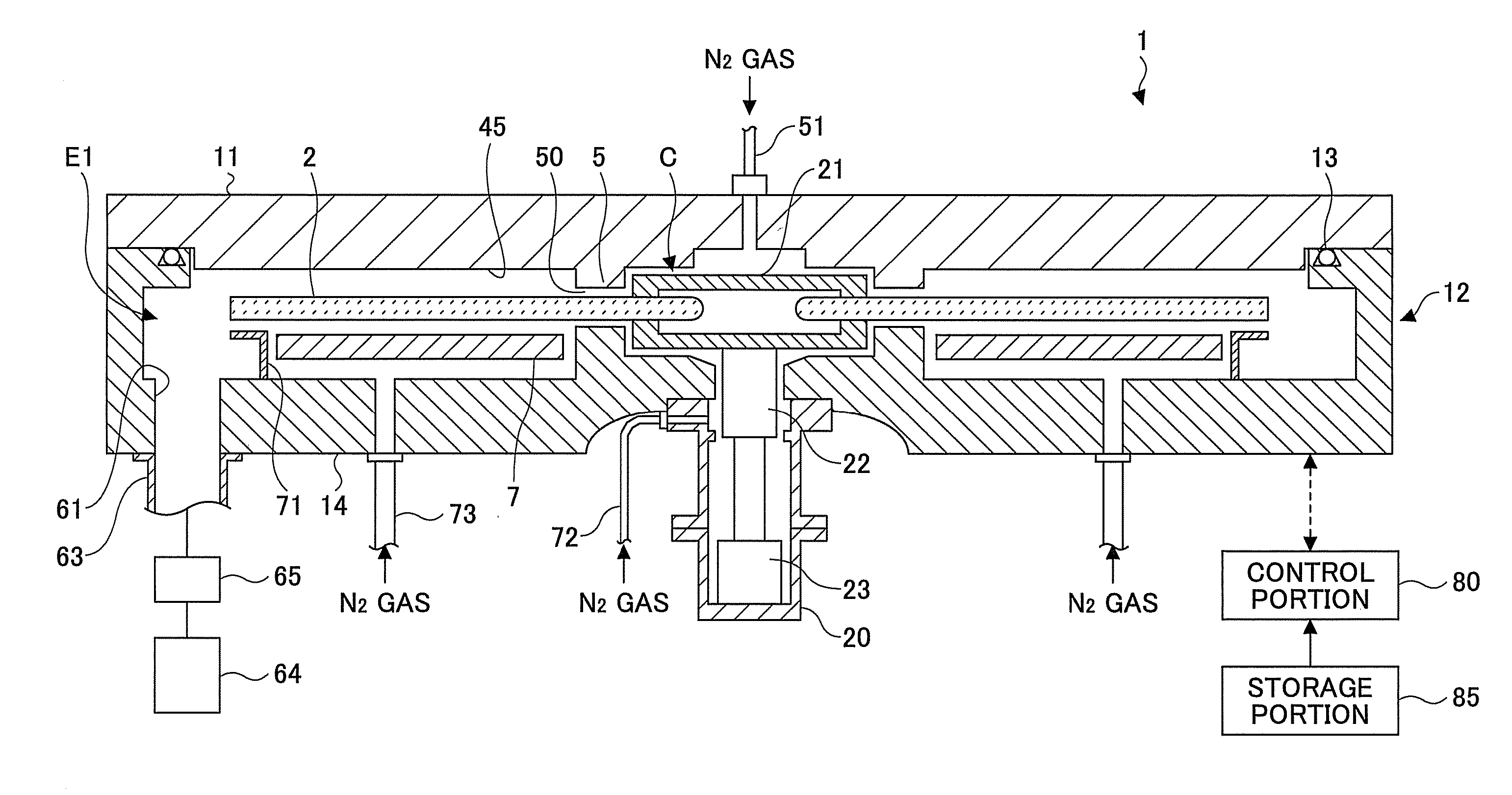
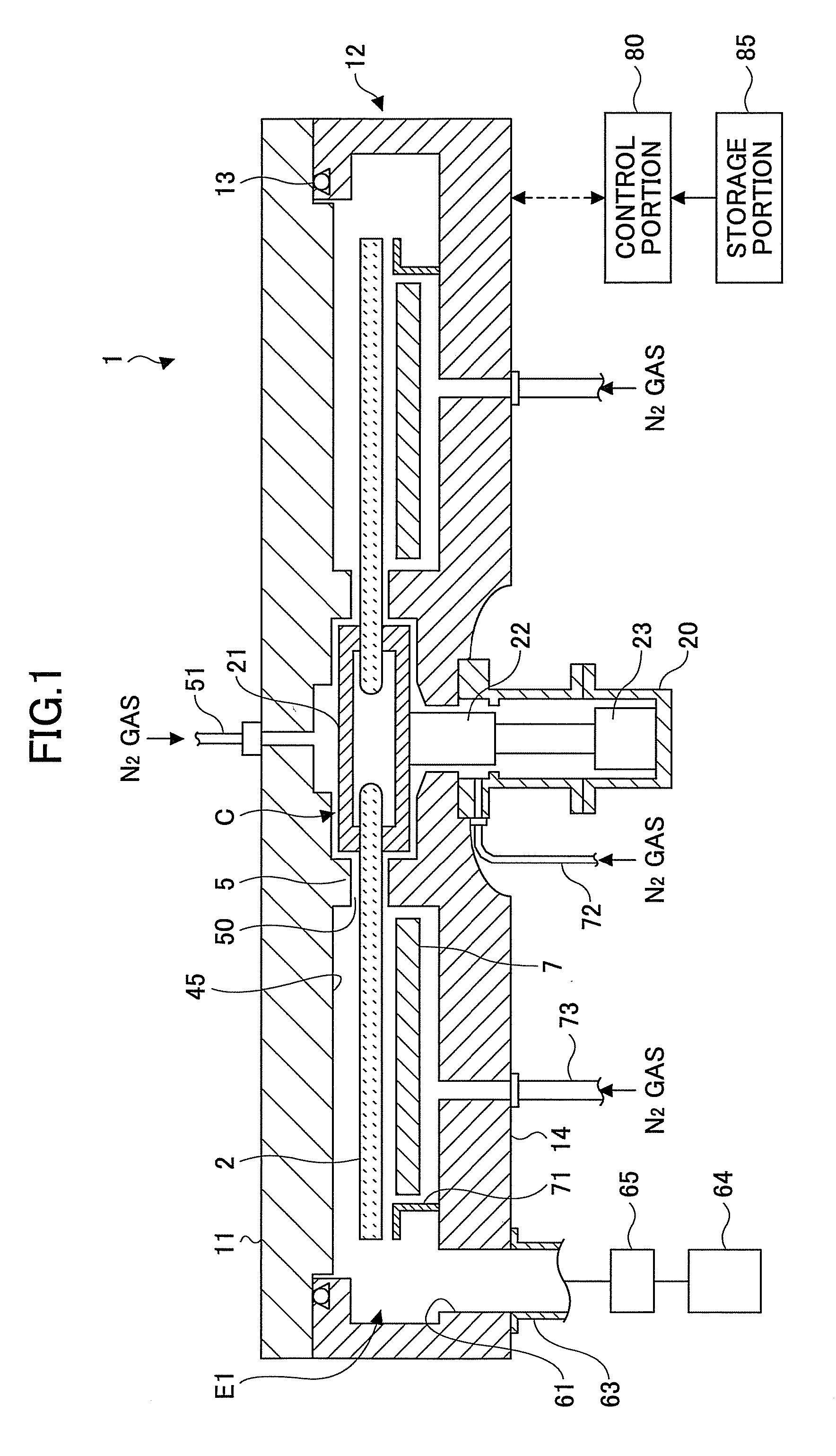
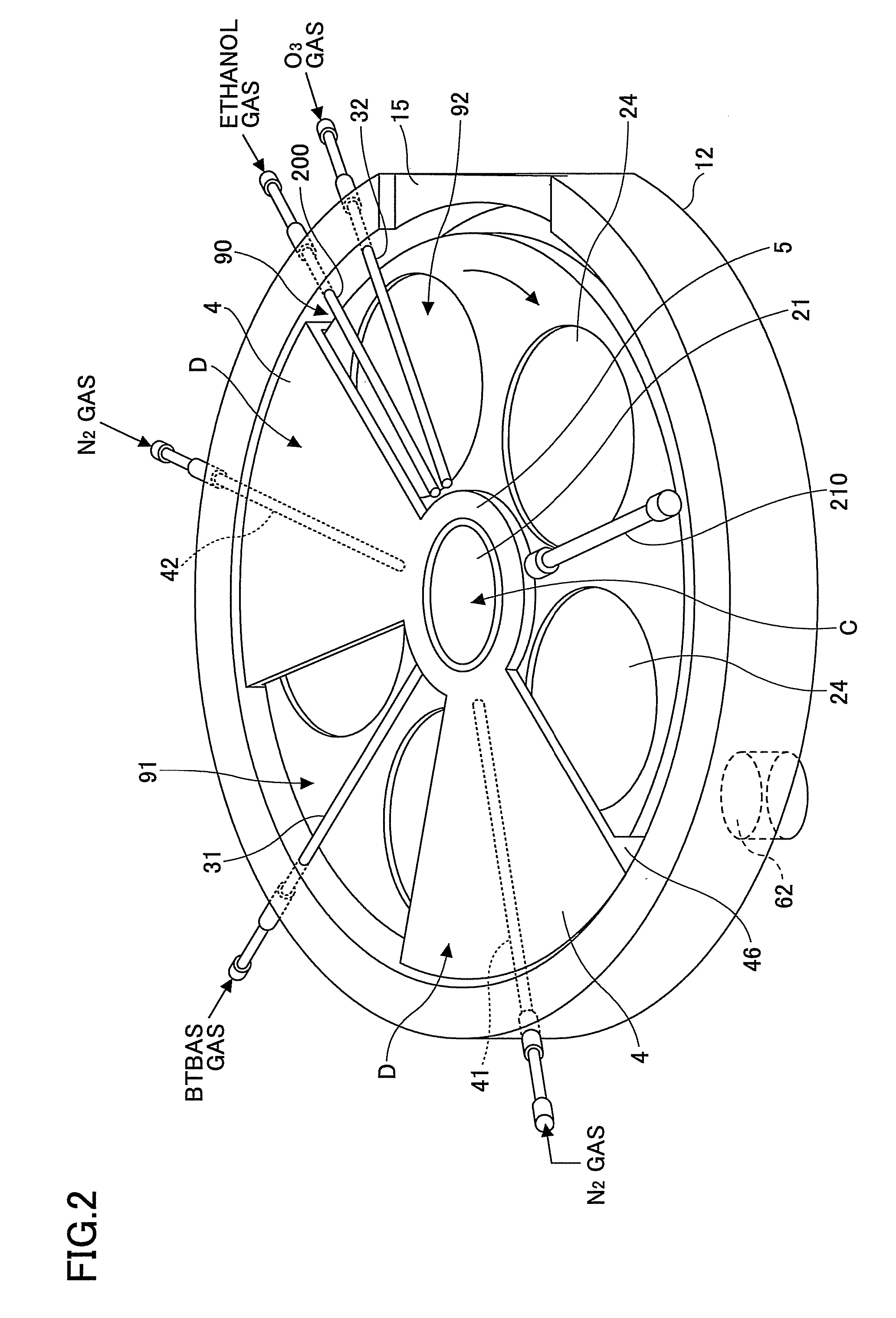
ActiveUS20100260935A1High purityExcellent gap fillingLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingVertical axisPhotochemistry
A rotation table on which a wafer is placed is rotated around a vertical axis in order to supply to an upper surface of the wafer a first reaction gas for allowing the first reaction gas to be adsorbed on the upper surface, an auxiliary gas that reacts with the first reaction gas to produce an intermediate product having reflowability, and a second reaction gas that is reacted with the intermediate product to produce a reaction product in this order; and the reaction product is heated by a heating lamp in order to densify the reaction product.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Semiconductor device having metal gate and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20160071944A1Large opening widthWell formedTransistorSolid-state devicesWork functionSemiconductor
A semiconductor device having metal gate includes a substrate, a first metal gate positioned on the substrate, and a second metal gate positioned on the substrate. The first metal gate includes a first work function metal layer, and the first work function metal layer includes a taper top. The second metal gate includes a second work function metal layer. The first work function metal layer and the second work function metal layer are complementary to each other.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Method for forming an L-shaped spacer using a disposable polysilicon spacer
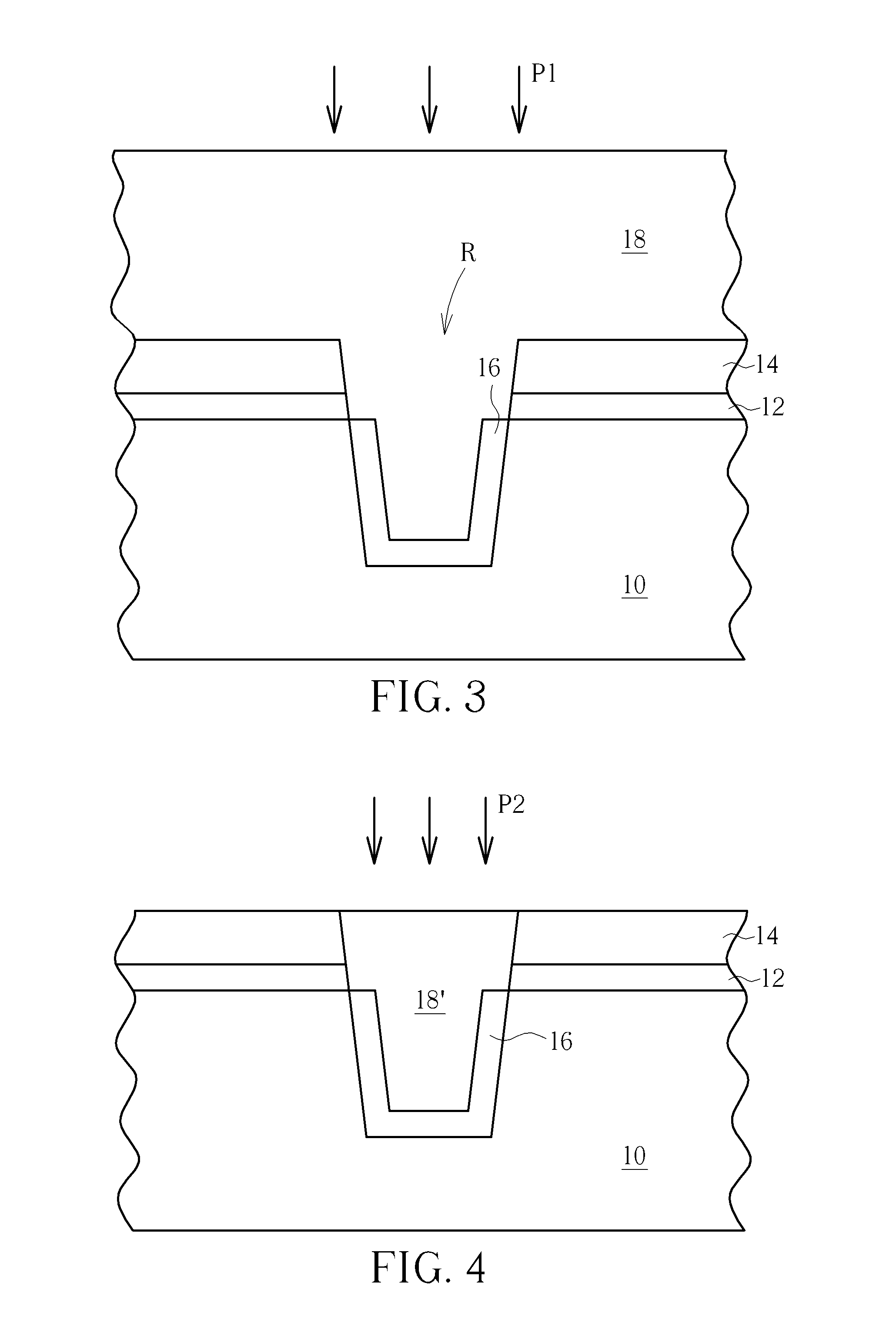
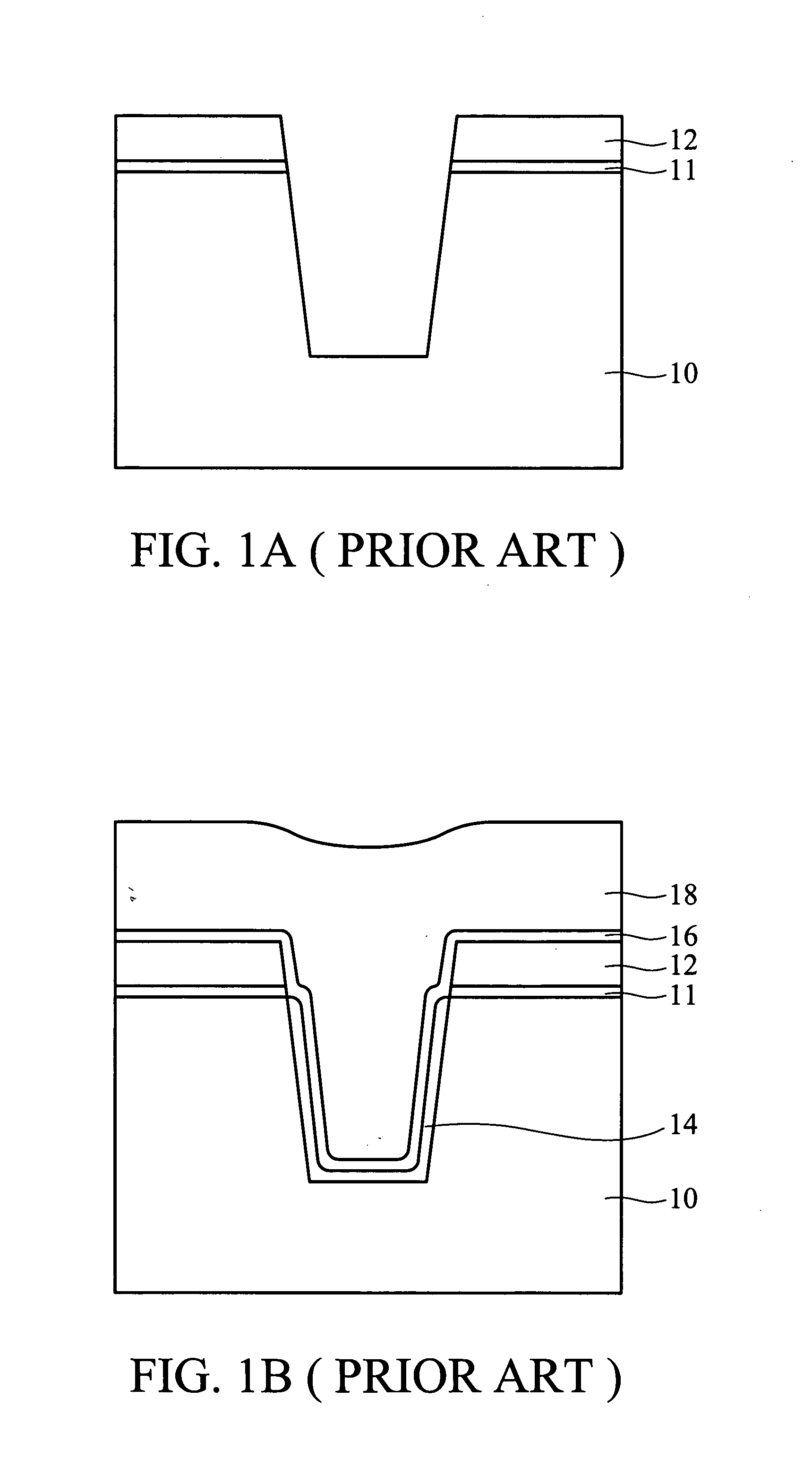
InactiveUS6346468B1Excellent gap fillingAvoid large gapsTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor structurePolycrystalline silicon
A method for forming an L-shaped spacer using disposable polysilicon top spacers. A semiconductor structure is provided having a gate structure thereon. A liner oxide layer is formed on the gate structure. A dielectric spacer layer is formed on the liner oxide layer. A disposable polysilicon top spacer layer is formed on the dielectric spacer layer. The disposable polysilicon top spacer layer is anisotropically etched to form disposable polysilicon top spacers. The dielectric spacer layer is etched to form L-shaped dielectric spacers, using the disposable polysilicon top spacers as an etch mask. The disposable polysilicon top spacers are removed leaving an L-shaped dielectric spacer. In one embodiment, lightly doped source and drain regions are formed prior to forming the liner oxide layer and the L-shaped spacers.
Owner:CHARTERED SEMICONDUCTOR MANUFACTURING
Sti of a semiconductor device and fabrication method thereof
ActiveUS20080166888A1Preferable qualityExcellent gap fillingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetallurgyDeposition process
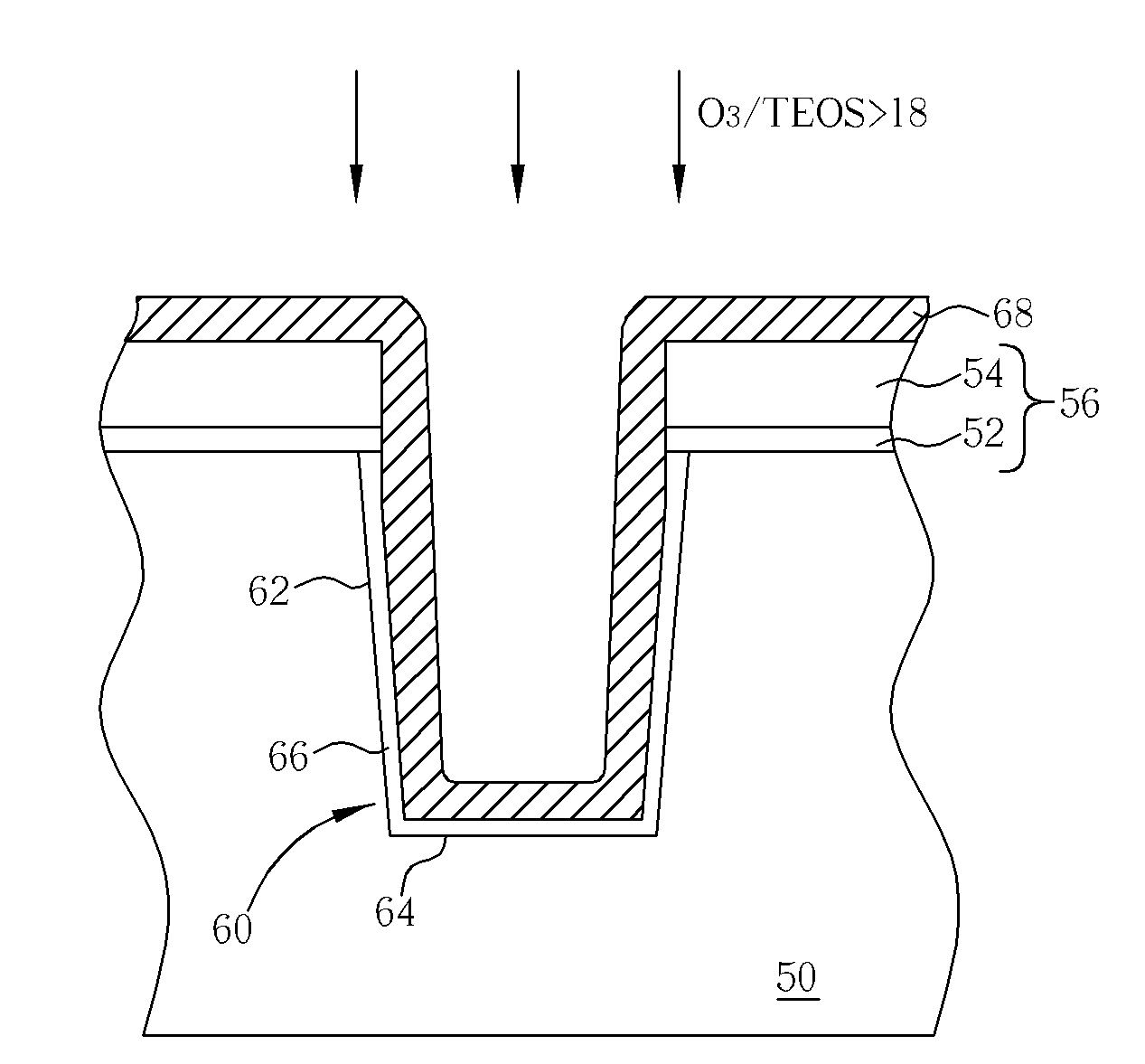
A method for filling silicon nitride materials into a trench includes providing a substrate having a plurality of trenches, performing a first deposition process to form a first silicon nitride layer in the trenches, and performing a second deposition process to form a second silicon nitride layer in the trenches. The reactant gas of the first deposition process has a first O3 / TEOS flow ratio larger than a second O3 / TEOS flow ratio of the reactant gas of the second deposition process.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Method for fabricating semiconductor device with fine patterns
InactiveUS7037850B2Excellent gap fillingMinimizing linewidthTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotoresistResist
The present invention relates to a method for fabricating a semiconductor device with realizable advanced fine patterns. The method includes the steps of: forming a hard mask insulation layer on an etch target layer; forming a hard mask sacrificial layer on the hard mask insulation layer; coating a photoresist on the hard mask insulation layer; performing selectively a photo-exposure process and a developing process to form a photoresist pattern having a first width for forming a line pattern; etching selectively the hard mask sacrificial layer by using the photoresist pattern as an etch mask to form a sacrificial hard mask having a second width; removing the photoresist pattern; etching the hard mask insulation layer by controlling excessive etching conditions with use of the sacrificial hard mask as an etch mask to form a hard mask having a third width; and etching the etch target layer by using the sacrificial hard mask and the hard mask as an etch mask to form the line pattern having a fourth width, wherein the first width is wider than the fourth width.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Method using TEOS ramp-up during TEOS/ozone CVD for improved gap-fill
InactiveUS6905940B2Excellent gap fillingImprove throughputSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingGas phaseSilicon oxide
Embodiments of the present invention provide methods, apparatuses, and devices related to chemical vapor deposition of silicon oxide. In one embodiment, a single-step deposition process is used to efficiently form a silicon oxide layer exhibiting high conformality and favorable gap-filling properties. During a pre-deposition gas flow stabilization phase and an initial deposition stage, a relatively low ratio of silicon-containing gas:oxidant deposition gas is flowed, resulting in formation of highly conformal silicon oxide at relatively slow rates. Over the course of the deposition process step, the ratio of silicon-containing gas:oxidant gas is increased, resulting in formation of less-conformal oxide material at relatively rapid rates during later stages of the deposition process step.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method for fabricating trench isolations with high aspect ratio
InactiveUS6946359B2Excellent gap fillingQuicker procedureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCable/conductor manufactureHigh densityCompound (substance)
A method of fabricating a trench isolation with high aspect ratio. The method comprises the steps of: providing a substrate with a trench; depositing a first isolation layer filling the trench by low pressure chemical vapor deposition; etching the first isolation layer so that its surface is lowered to the opening of the trench; depositing a second isolation layer to fill the trench without voids by high density plasma chemical vapor deposition and achieving global planarization by chemical-mechanical polishing then providing a rapidly annealing procedure. Accordingly, the present invention achieves void-free trench isolation with high aspect ratio.
Owner:NAN YA TECH
Solution for FSG induced metal corrosion & metal peeling defects with extra bias liner and smooth RF bias ramp up
ActiveUS6953608B2No damageSimple methodSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSpecial surfacesCorrosionDeposition process
A HDP CVD process for depositing a USG liner followed by a FSG dielectric layer on a metal line pattern is described. The substrate is heated in a chamber with a plasma comprised of Ar and O2. A USG liner is deposited in two steps wherein the first step is without an RF bias and the second step is with a moderate RF bias that does not damage the metal lines or an anti-reflective coating on the metal. The moderate RF bias is critical in forming a sputtering component that redeposits USG to form more uniform sidewalls and better coverage at top corners of metal lines. The USG deposition process has a good gap filling capability and significantly reduces device failure rate by preventing corrosion of metal lines during subsequent thermal process cycles. The method also includes a PECVD deposited FSG layer that is planarized to complete an IMD layer.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Method for forming an L-shaped spacer with a disposable organic top coating
InactiveUS6294480B1Reduce sensitivityExcellent gap fillingTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOrganic structureDielectric
A method for forming an L-shaped spacer using a sacrificial organic top coating. A semiconductor structure is provided having a gate structure thereon. A liner oxide layer is formed on the gate structure. A dielectric spacer layer is formed on the liner oxide layer. In the preferred embodiment, the dielectric spacer layer comprises a silicon nitride layer or a silicon oxynitride layer. A sacrificial organic layer is formed on the dielectric spacer layer. The sacrificial organic layer and the dielectric spacer layer are anisotropically etched to form spacers comprising a triangle-shaped sacrificial organic structure and an L-shaped dielectric spacer. The triangle-shaped sacrificial organic structure is removed leaving an L-shaped dielectric spacer.
Owner:CHARTERED SEMICONDUCTOR MANUFACTURING
Method of fabricating dielectric layer and shallow trench isolation
ActiveUS20140134824A1Excellent gap fillingNot to damageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOxygen plasmaCompound (substance)
A method of fabricating a dielectric layer includes the following steps. At first, a dielectric layer is formed on a substrate, and a chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) process is performed on the dielectric layer. Subsequently, a surface treatment process is performed on the dielectric layer after the chemical mechanical polishing process, and the surface treatment process includes introducing an oxygen plasma.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Zn-Mg-Al magnesium alloy solder
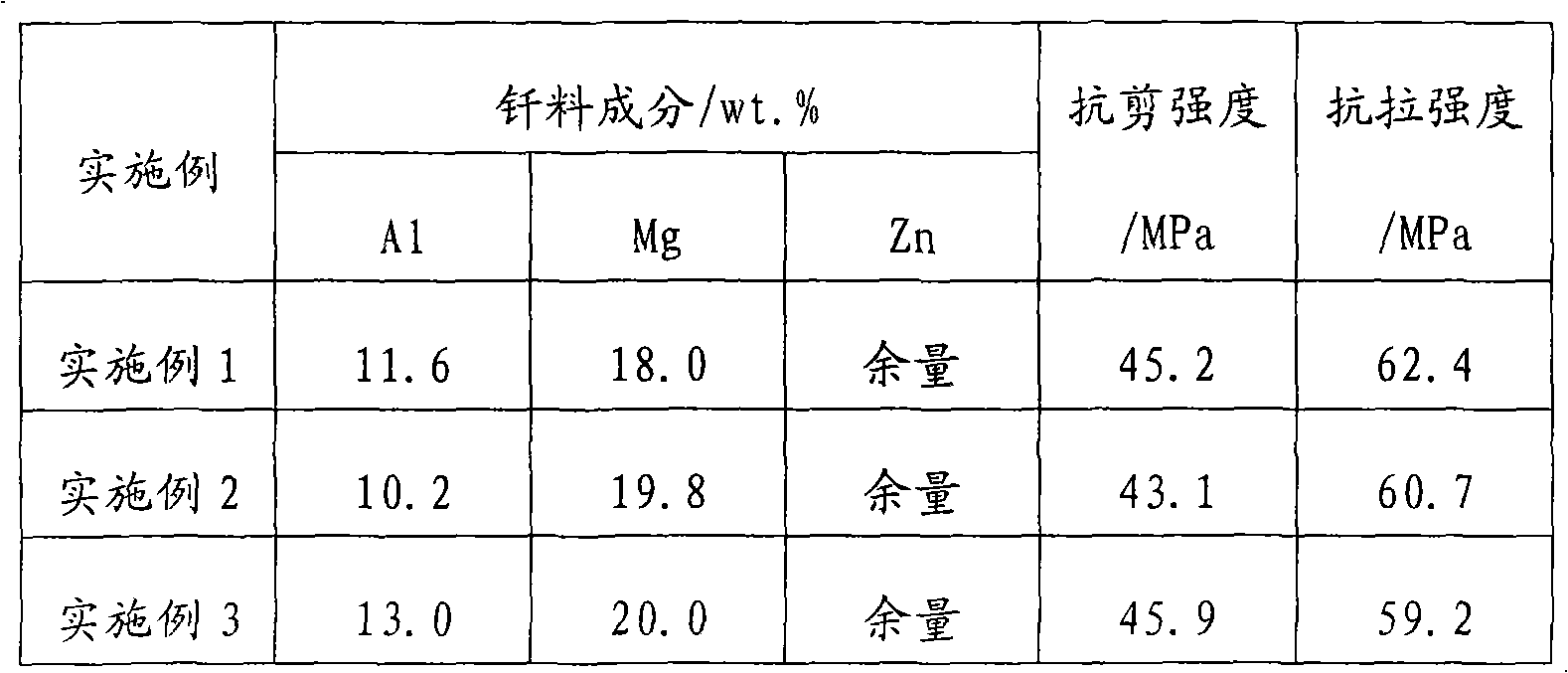
InactiveCN101653879AGood spreadabilityExcellent gap fillingWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaButt jointSoldering
The invention provides a Zn-Mg-Al magnesium alloy solder, belonging to the technical field of magnesium alloy welded joint. The components of the provided Zn-Mg-Al magnesium alloy solder contain 10% to 13% of Al, 18% to 20% of Mg and the remains are Zn. The melt temperature of the Zn-Mg-Al magnesium alloy solder is ranged from 379 DEG C to 488 DEG C and the soldering temperature is ranged from 500DEG C to 510 DEG C. The solder can be applied to the magnesium alloy solder with solidus temperature above 510 DEG C. The AZ31B magnesium can be soldered in the manner of high frequency induction welding. The slip resistance of the solder overlap joint is ranged from 43MPa to 45 MPa and the tensile strength of the butt joint is ranged from 59MPa to 62MPa.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for fabricating trench isolations with high aspect ratio
ActiveUS20050016948A1Excellent gap fillingRapid thermal annealing procedureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCable/conductor manufactureAspect ratioHigh density
A method of fabricating a trench isolation with high aspect ratio. The method comprises the steps of: providing a substrate with a trench; depositing a first isolation layer filling the trench by low pressure chemical vapor deposition; etching the first isolation layer so that its surface is lowered to the opening of the trench; depositing a second isolation layer to fill the trench without voids by high density plasma chemical vapor deposition and achieving global planarization by chemical-mechanical polishing then providing a rapidly annealing procedure. Accordingly, the present invention achieves void-free trench isolation with high aspect ratio.
Owner:NAN YA TECH
Semiconductor device having metal gate and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20120139042A1Well formedExcellent gap fillingTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringDielectric layer
A method of manufacturing a semiconductor device having metal gate includes providing a substrate having at least a dummy gate, a sacrificial layer covering sidewalls of the dummy gate and a dielectric layer exposing a top of the dummy gate formed thereon, forming a sacrificial layer covering sidewalls of the dummy gate on the substrate, forming a dielectric layer exposing a top of the dummy gate on the substrate, performing a first etching process to remove a portion of the sacrificial layer surrounding the top of the dummy gate to form at least a first recess, and performing a second etching process to remove the dummy gate to form a second recess. The first recess and the second recess construct a T-shaped gate trench.
Owner:MARLIN SEMICON LTD
Two step post-deposition treatment of ILD layer for a lower dielectric constant and improved mechanical properties
InactiveUS7250370B2Increase resistanceImprove the immunityDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMechanical propertyMoisture
A method of lowering the dielectric constant of an organosilicon low k dielectric layer while improving the hardness and thermal stability is provided. A deposited layer of carbon doped oxide, HSQ, or MSQ is cured and treated with a He plasma which improves hardness for a subsequent CMP step and lowers the dielectric constant. There is no loss of H2O or CH4 during the He treatment. The low k dielectric layer is then treated with a H2 plasma which converts some of the Si—O and Si—CH3 bonds near the surface to Si—H bonds, thereby further lowering the dielectric constant and increasing thermal stability that improves breakdown resistance. Moisture uptake is also reduced. The method is especially useful for interconnect schemes with deep sub-micron ground rules. Surprisingly, the k value obtained from two different plasma treatments is lower than when two He treatments or two H2 treatment are performed.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MASNUFACTURING
Post-deposition treatment to enhance properties of Si-O-C low films
InactiveUS6858923B2Reduce Shrinkage ProblemsHigh film stabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSilicon oxygenReducing atmosphere
A method for providing a dielectric film having enhanced adhesion and stability. The method includes a post deposition treatment that densifies the film in a reducing atmosphere to enhance stability if the film is to be cured ex-situ. The densification generally takes place in a reducing environment while heating the substrate. The densification treatment is particularly suitable for silicon-oxygen-carbon low dielectric constant films that have been deposited at low temperature.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Film deposition apparatus, film deposition method, and computer readable storage medium
ActiveUS8882915B2High purityExcellent gap fillingLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProduct gasVertical axis
A rotation table on which a wafer is placed is rotated around a vertical axis in order to supply to an upper surface of the wafer a first reaction gas for allowing the first reaction gas to be adsorbed on the upper surface, an auxiliary gas that reacts with the first reaction gas to produce an intermediate product having reflowability, and a second reaction gas that is reacted with the intermediate product to produce a reaction product in this order; and the reaction product is heated by a heating lamp in order to densify the reaction product.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
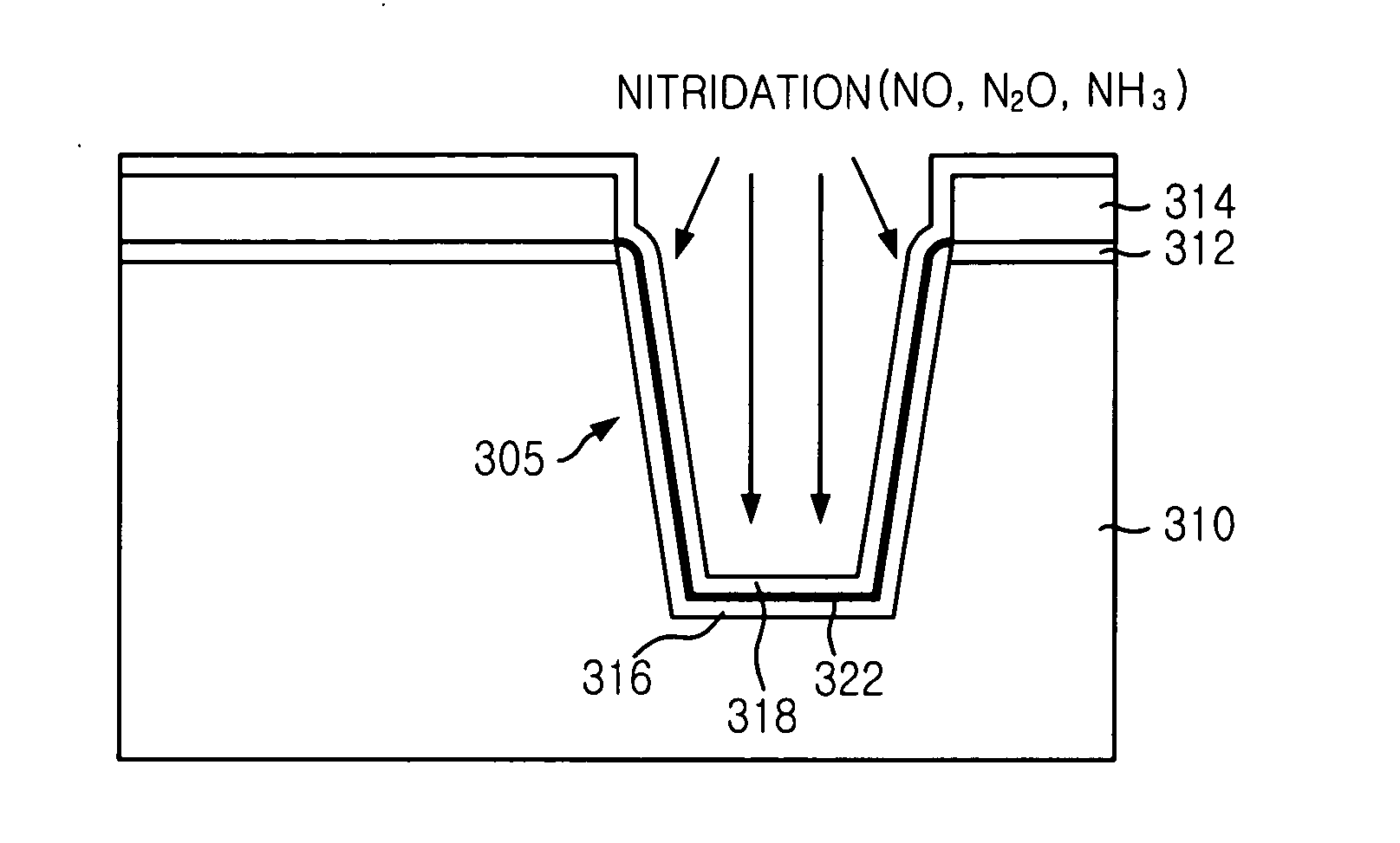
Method for manufacturing shallow trench isolation in semiconductor device
ActiveUS20050020027A1Excellent gap fillingPrevent punchthrough phenomenonSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialEngineering
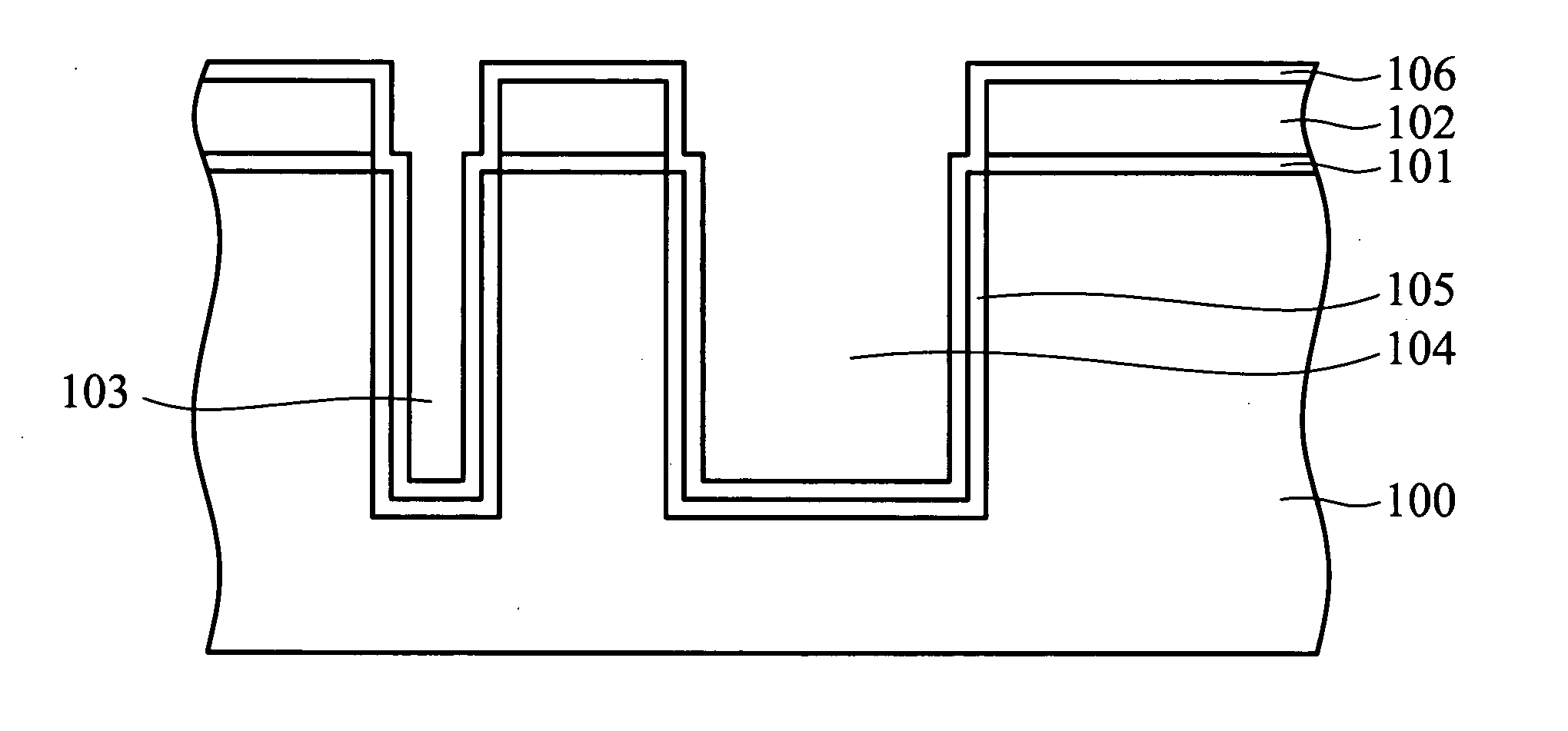
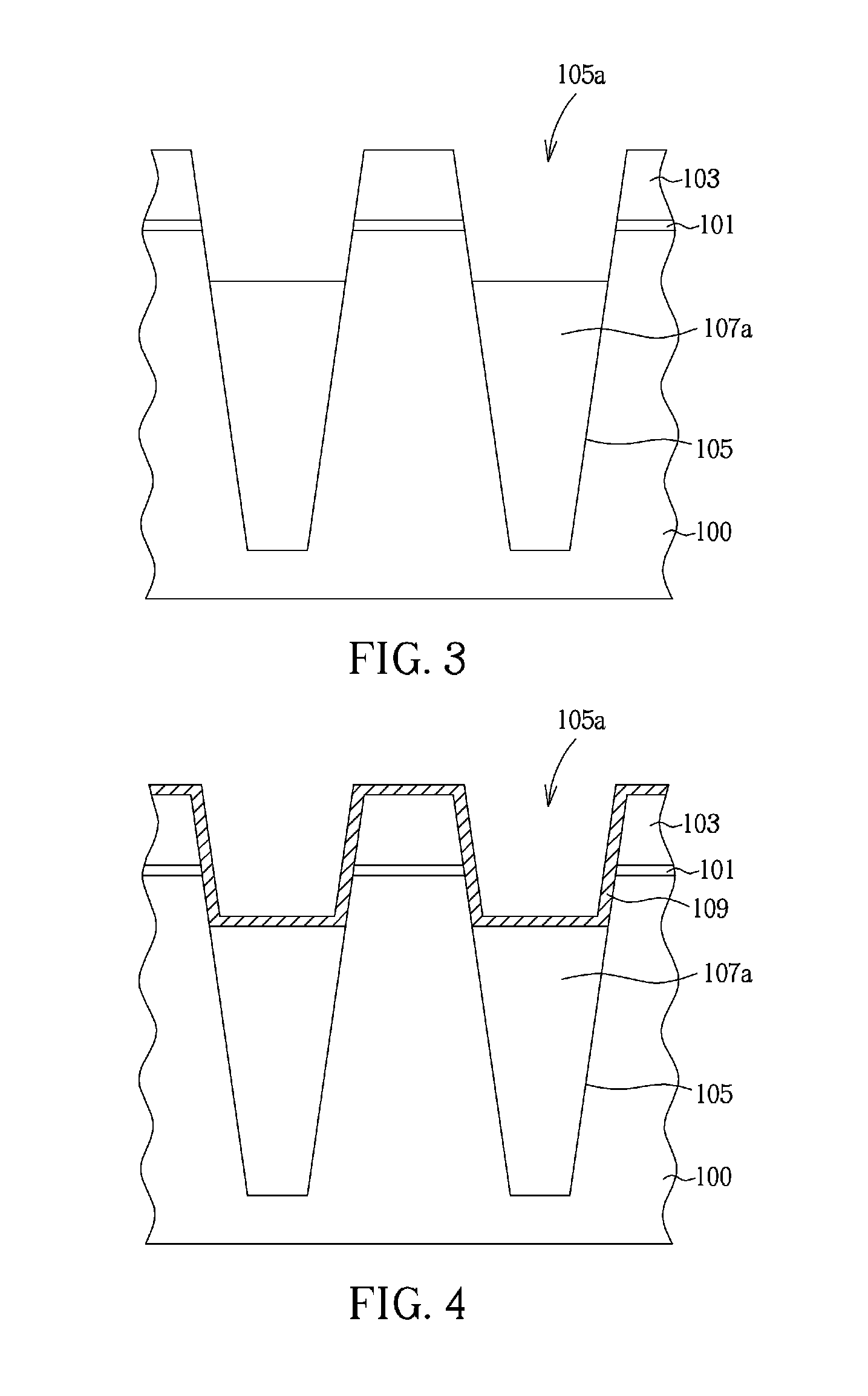
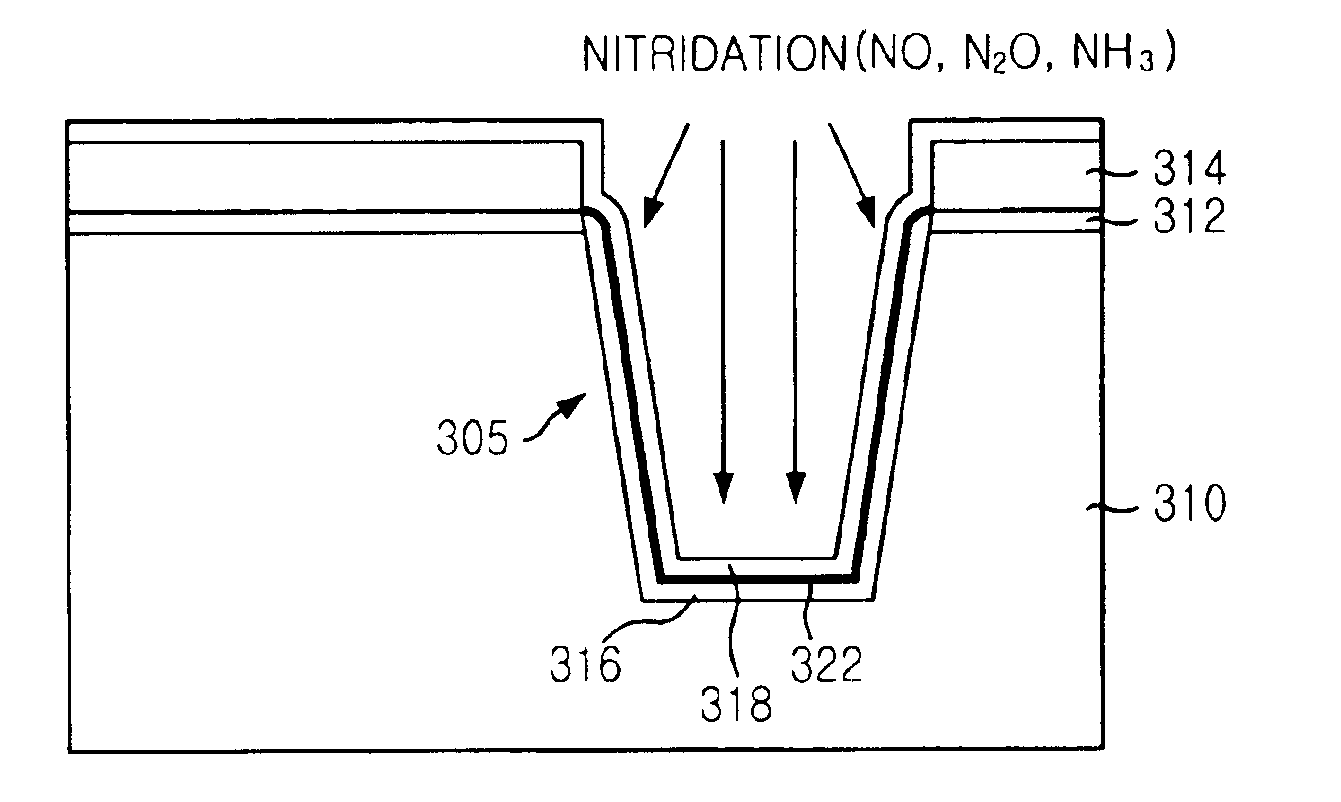
The method for manufacturing an STI in a semiconductor device with an enhanced gap-fill property and leakage property is disclosed by introducing a nitridation process instead of forming a liner nitride. The method includes steps of: preparing a semiconductor substrate obtained by a predetermined process on which a pad oxide and a pad nitride are formed on predetermined locations thereof; forming an isolation trench with a predetermined depth in the semiconductor substrate; forming a wall oxide on the trench; forming a liner oxide on the wall oxide and an exposed surface of the pad nitride; carrying out a nitridation process for forming a nitrided oxide; forming an insulating layer over the resultant structure, wherein the isolation trench is filled with the insulating layer; and planarizing a top face of the insulating layer.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Method using TEOS ramp-up during TEOS/ozone CVD for improved gap-fill
InactiveUS20050064730A1Excellent gap fillingImprove throughputSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingGas phaseSilicon oxide
Embodiments of the present invention provide methods, apparatuses, and devices related to chemical vapor deposition of silicon oxide. In one embodiment, a single-step deposition process is used to efficiently form a silicon oxide layer exhibiting high conformality and favorable gap-filling properties. During a predeposition gas flow stabilization phase and an initial deposition stage, a relatively low ratio of silicon-containing gas:oxidant deposition gas is flowed, resulting in formation of highly conformal silicon oxide at relatively slow rates. Over the course of the deposition process step, the ratio of silicon-containing gas:oxidant gas is increased, resulting in formation of less-conformal oxide material at relatively rapid rates during later stages of the deposition process step.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
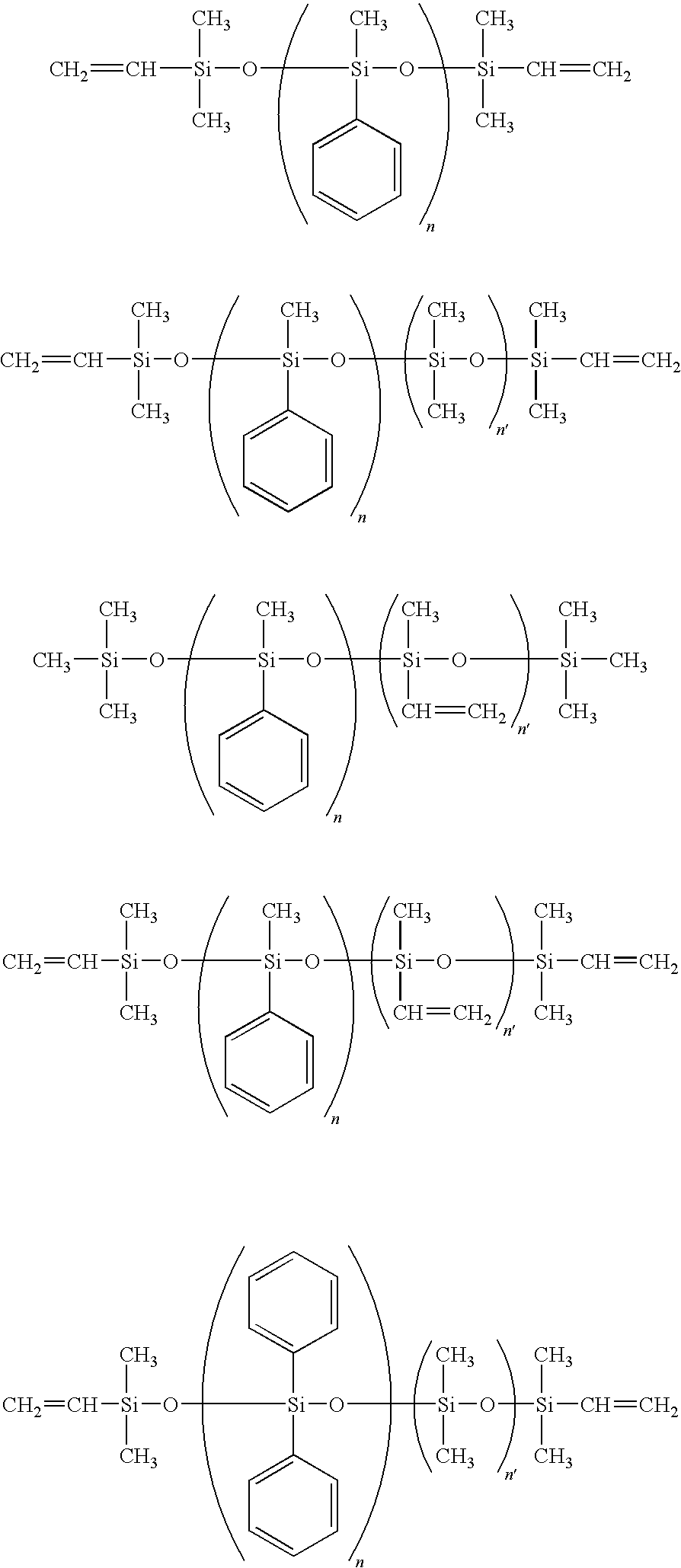
Novel polyorganosiloxane dielectric materials
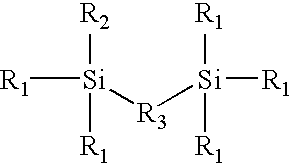
ActiveUS20060058487A1Good chemical resistanceFacilitate cross-linkingSilicon organic compoundsPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsOrganic groupPolarizability
A thin film comprising a composition obtained by polymerizing a monomer having the formula I: wherein: R1 is a hydrolysable group, R2 is a polarizability reducing organic group, and R3 is a bridging hydrocarbon group, to form a siloxane material. The invention also concerns methods for producing the thin films. The thin film can be used a low k dielectric in integrated circuit devices. The novel dielectric materials have excellent properties of planarization resulting in good local and global planarity on top a semiconductor substrate topography, which reduces or eliminates the need for chemical mechanical planarization after dielectric and oxide liner deposition.
Owner:SILECS OY
Copper-based solder and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103358051ALower melting temperatureImprove wettabilityWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaCorrosionSmelting process
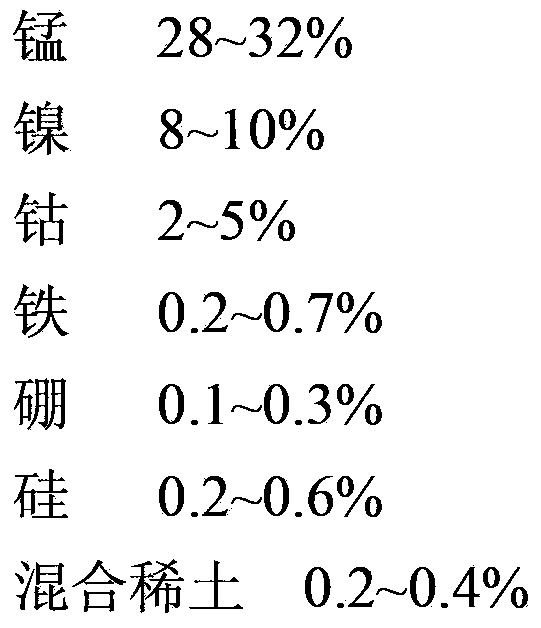
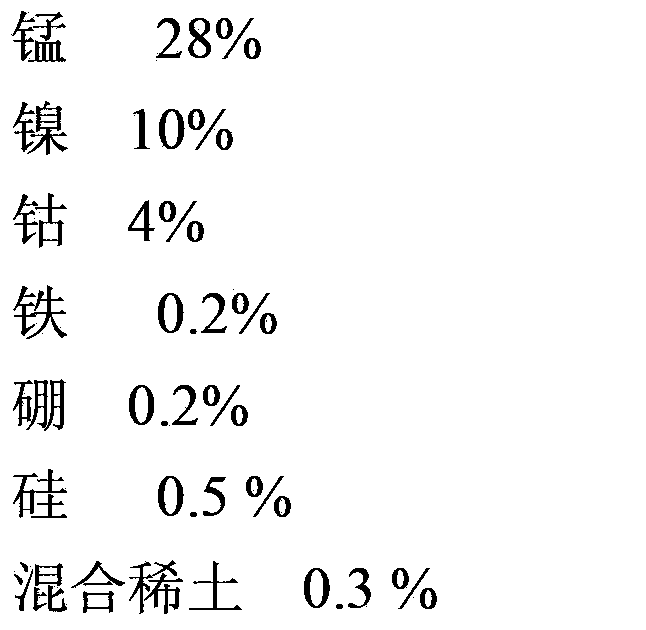
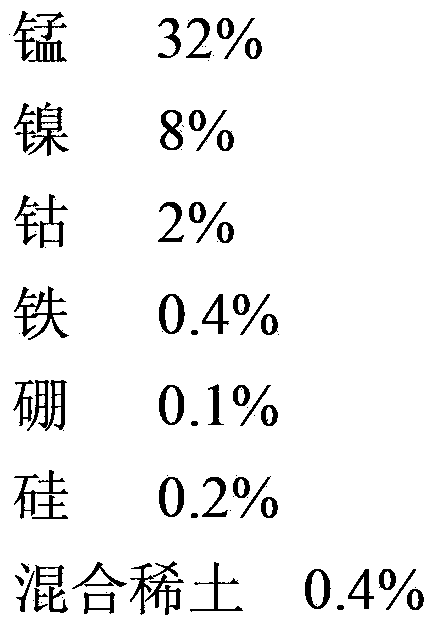
The invention discloses a method for preparing a copper-based solder. The method comprises the following steps: (1) burdening: preparing a furnace burden from copper, manganese, nickel, cobalt, silicon, a copper-ferrous intermediate alloy, a copper-boron intermediate alloy and a copper-mixed rare earth intermediate alloy serving as raw materials; (2) casting: putting the prepared furnace burden into the a corundum crucible according to the sequence of manganese, copper, nickel, cobalt, silicon, copper-boron intermediate alloy, copper-mixed rare earth intermediate alloy and copper-ferrous intermediate alloy, smelting by adopting medium-frequency induction, and cooling along with the furnace to obtain an alloy blank, wherein the smelting process is performed under the protection of argon gas; and (3) rolling: rolling the alloy blank with a cold-rolling mill to obtain the copper-based solder. The copper-based solder provided by the invention can be applied to an ODS (Oxide Dispersion Strengthened) high-temperature alloy welding joint, has high brazing process performance, heat resistance, corrosion resistance and machining process, and is low in cost.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Collecting pipe material for micro-channel heat exchanger and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a collecting pipe material for a micro-channel heat exchanger, which consists of a layer of brazing layer alloy and a layer of matrix alloy, wherein the brazing layer alloy comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 9-11% of Si, 0.2-0.4% of Fe, 0.005-0.05% of Cu, 0.005-0.05% of Mn, 0.005-0.05% of Mg, 0.005-0.05% of Cr, 0.3-0.7% of Zn, 0.005-0.05% of Zr, 0.005-0.10% of Ti and the balance of A1; the preparation method of the brazing layer alloy comprises the processes of casting, modifying and founding; the preparation method of the matrix alloy comprises the processes of casting, founding and homogenizing; processes of compositing, hot rolling, cold rolling and intermediate annealing are carried out on the brazing layer alloy and the matrix alloy to obtain the collecting pipe material; the brazing layer alloy has favorable grain refining effect so that favorable fluidity, wettability and gap filling capability are provided during the brazing of the material; cold machining is carried out on the material with a machining rate of 25-35% after the intermediate annealing treatment; and the machining rate can ensure that the forming property is favorable during the pipe making of the material and the fluidity of the brazing layer is favorable during the brazing of the collecting pipe.
Owner:潍坊三源铝业有限公司
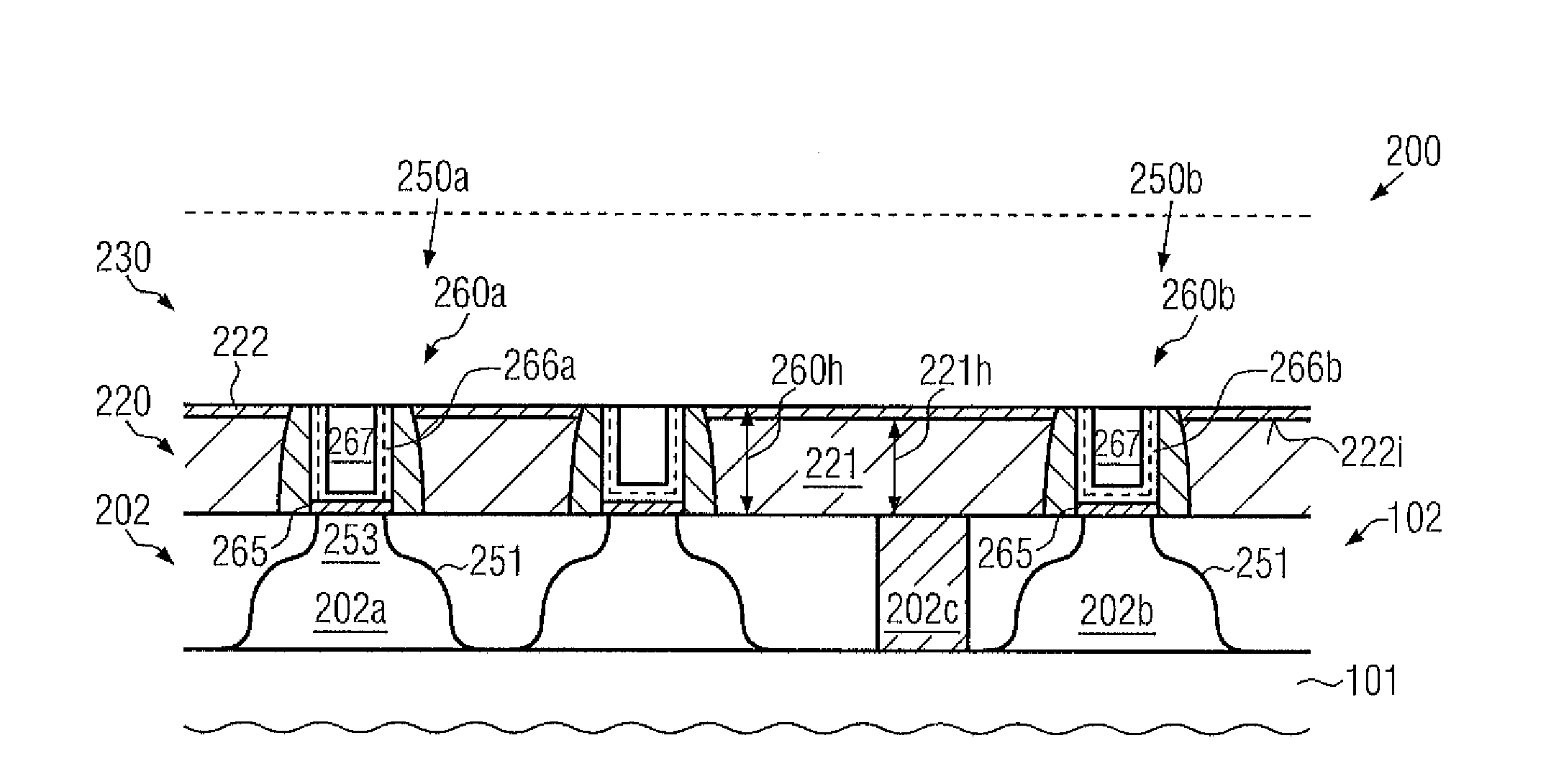
Replacement Gate Approach for High-K Metal Gate Stacks by Using a Multi-Layer Contact Level
ActiveUS20130214335A1Efficient reductionExcellent gap fillingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesElectricityMaterial Erosion
In a replacement gate approach, the dielectric material for laterally encapsulating the gate electrode structures may be provided in the form of a first interlayer dielectric material having superior gap filling capabilities and a second interlayer dielectric material that provides high etch resistivity and robustness during a planarization process. In this manner, undue material erosion upon replacing the placeholder material may be avoided, which results in reduced yield loss and superior device uniformity.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Two-portion shallow-trench isolation
ActiveUS8823132B2High aspect ratioExcellent gap fillingSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLayer interfaceElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Method for manufacturing shallow trench isolation in semiconductor device
ActiveUS6953734B2Excellent gap fillingPrevent a punchthrough phenomenonSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringNitride
The method for manufacturing an STI in a semiconductor device with an enhanced gap-fill property and leakage property is disclosed by introducing a nitridation process instead of forming a liner nitride. The method includes steps of: preparing a semiconductor substrate obtained by a predetermined process on which a pad oxide and a pad nitride are formed on predetermined locations thereof; forming an isolation trench with a predetermined depth in the semiconductor substrate; forming a wall oxide on the trench; forming a liner oxide on the wall oxide and an exposed surface of the pad nitride; carrying out a nitridation process for forming a nitrided oxide; forming an insulating layer over the resultant structure, wherein the isolation trench is filled with the insulating layer; and planarizing a top face of the insulating layer.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Method for forming resist underlayer film, patterning process using the same, and composition for the resist underlayer film
ActiveUS8450048B2Reduce reflectivityIncrease resistancePhotosensitive materialsPretreated surfacesEtchingVarnish
There is disclosed a method for forming a resist underlayer film of a multilayer resist film having at least three layers used in a lithography, comprising at least; a step of coating a composition for resist underlayer film containing a novolak resin represented by the following general formula (1) obtained by treating a compound having a bisnaphthol group on a substrate; and a step of curing the coated composition for the resist underlayer film by a heat treatment at a temperature above 300° C. and 600° C. or lower for 10 to 600 seconds. There can be provided a method for forming a resist underlayer film, and a patterning process using the method to form a resist underlayer film in a multilayer resist film having at least three layers used in a lithography, gives a resist underlayer film having a lowered reflectance, a high etching resistance, and a high heat and solvent resistances, especially without wiggling during substrate etching.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM CO LTD
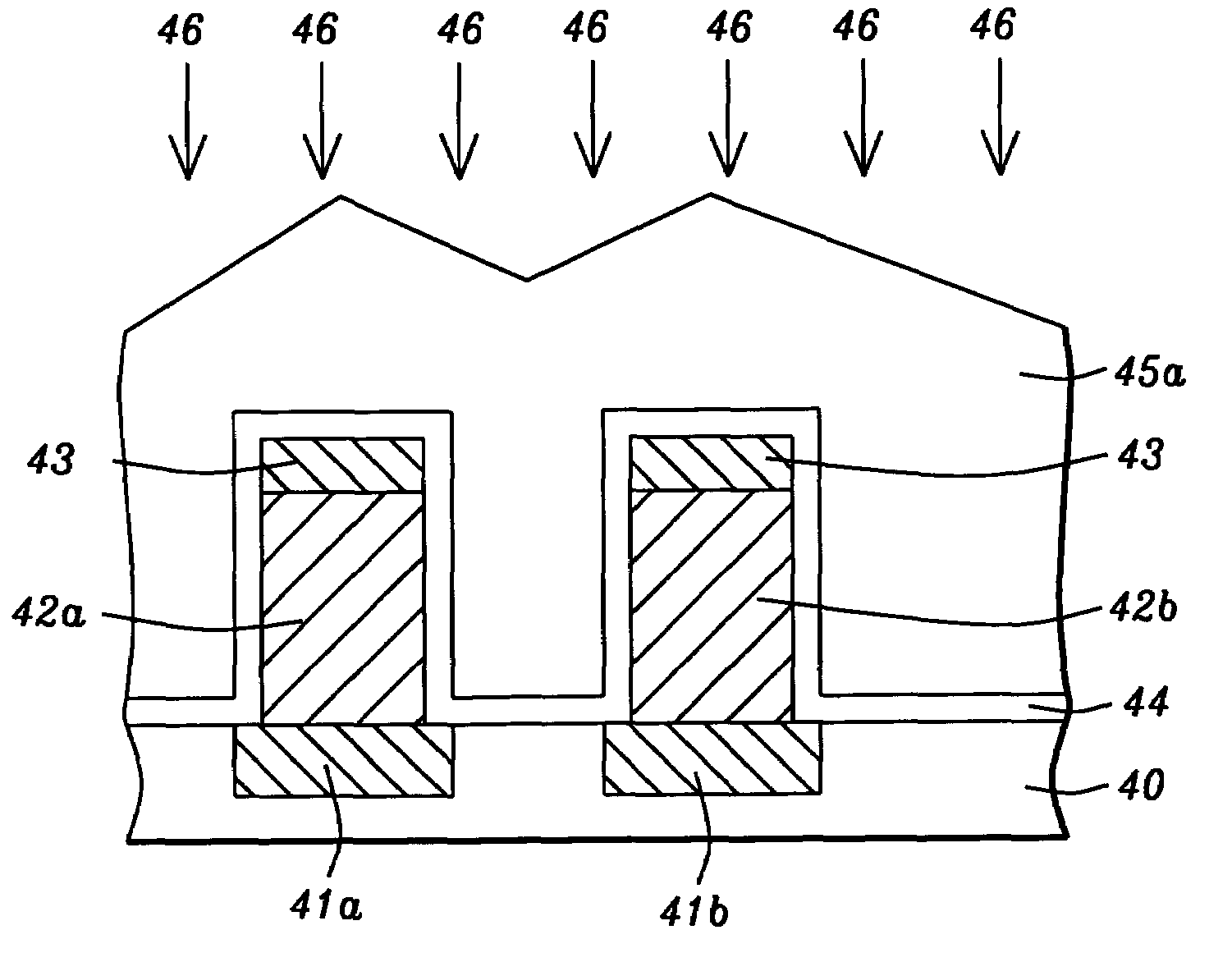
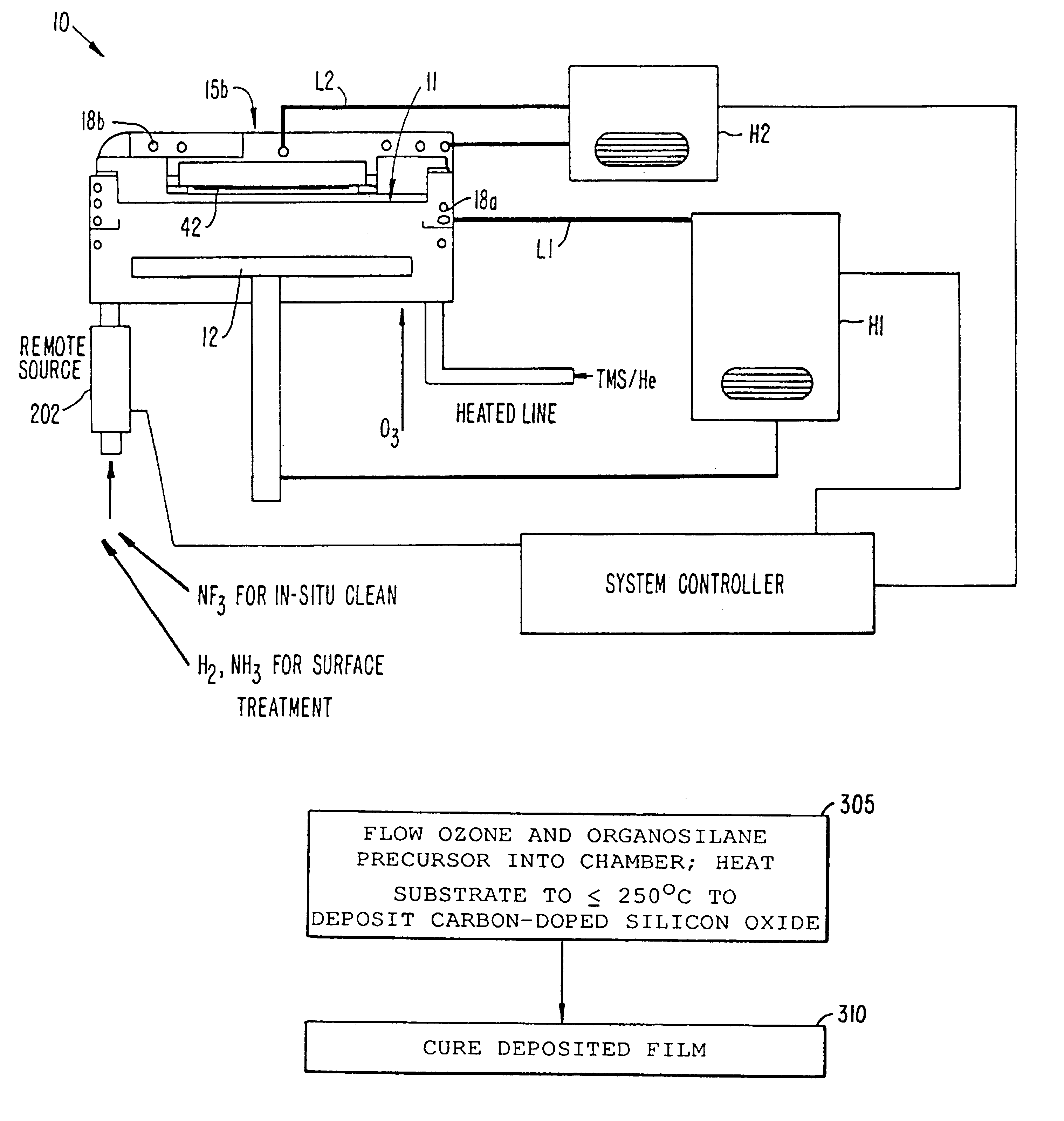
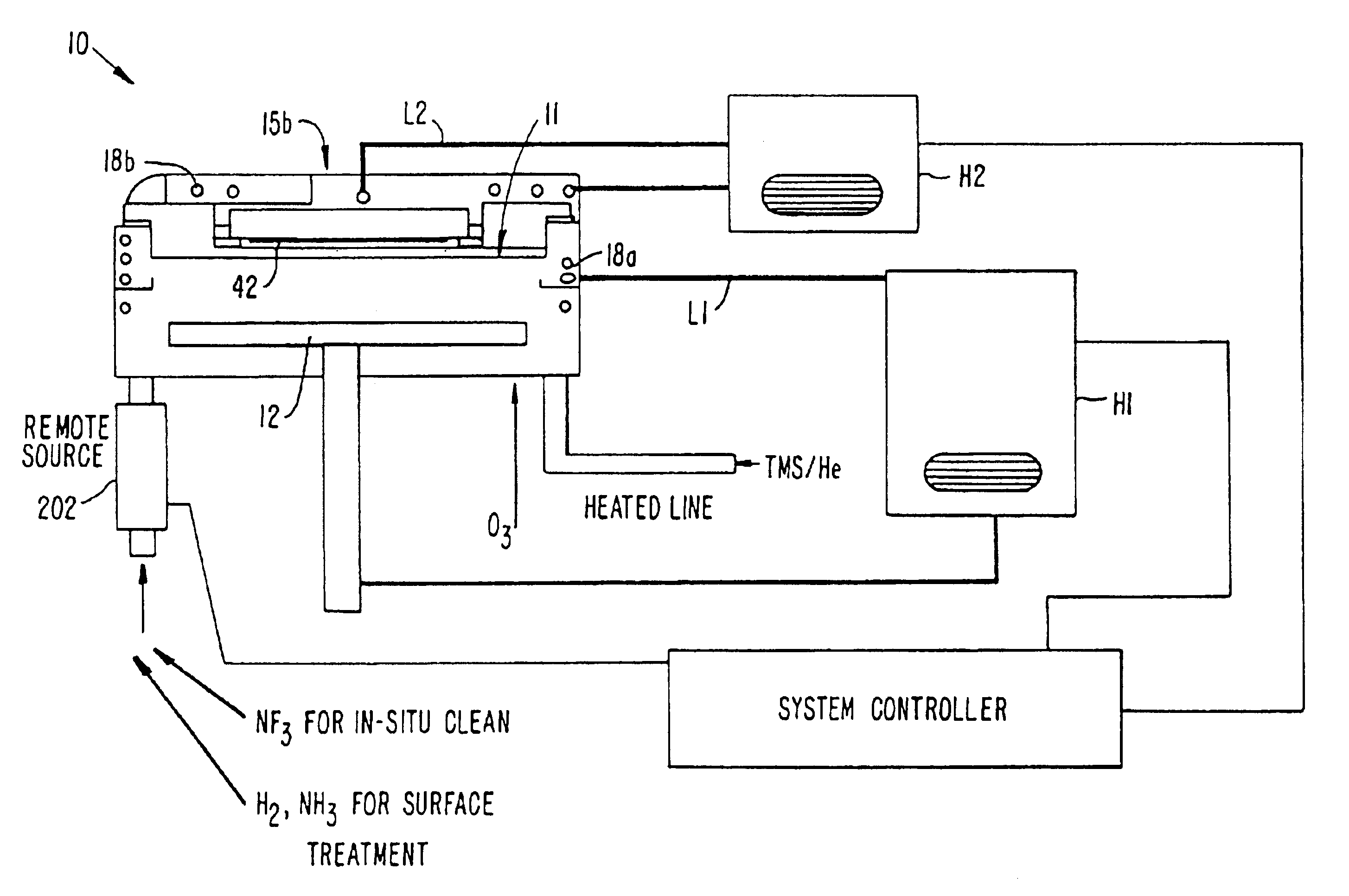
Lid cooling mechanism and method for optimized deposition of low-K dielectric using TR methylsilane-ozone based processes
InactiveUS6899763B2Good gap fill capabilityHigh film stabilityLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCarbon dopedLow-k dielectric
An apparatus and method for depositing thin films. The apparatus generally comprises a process chamber having one or more walls and a lid and two heat exchangers. A first heat exchanger is coupled to the walls and a second heat exchanger is coupled to the lid. The two heat exchangers are configured to provide separate temperature control of the walls and lid. Separate control of the lid and wall temperatures inhibits reaction of the organosilane within the lid while optimizing a reaction within the chamber. The apparatus implements a method, in which a process gas comprising ozone and an organosilane are admitted through the into a processing while a substrate is heated to form a carbon-doped silicon oxide layer over the substrate. During deposition, the lid is kept cooler than the walls.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Hot-Melt Silicone Adhesive
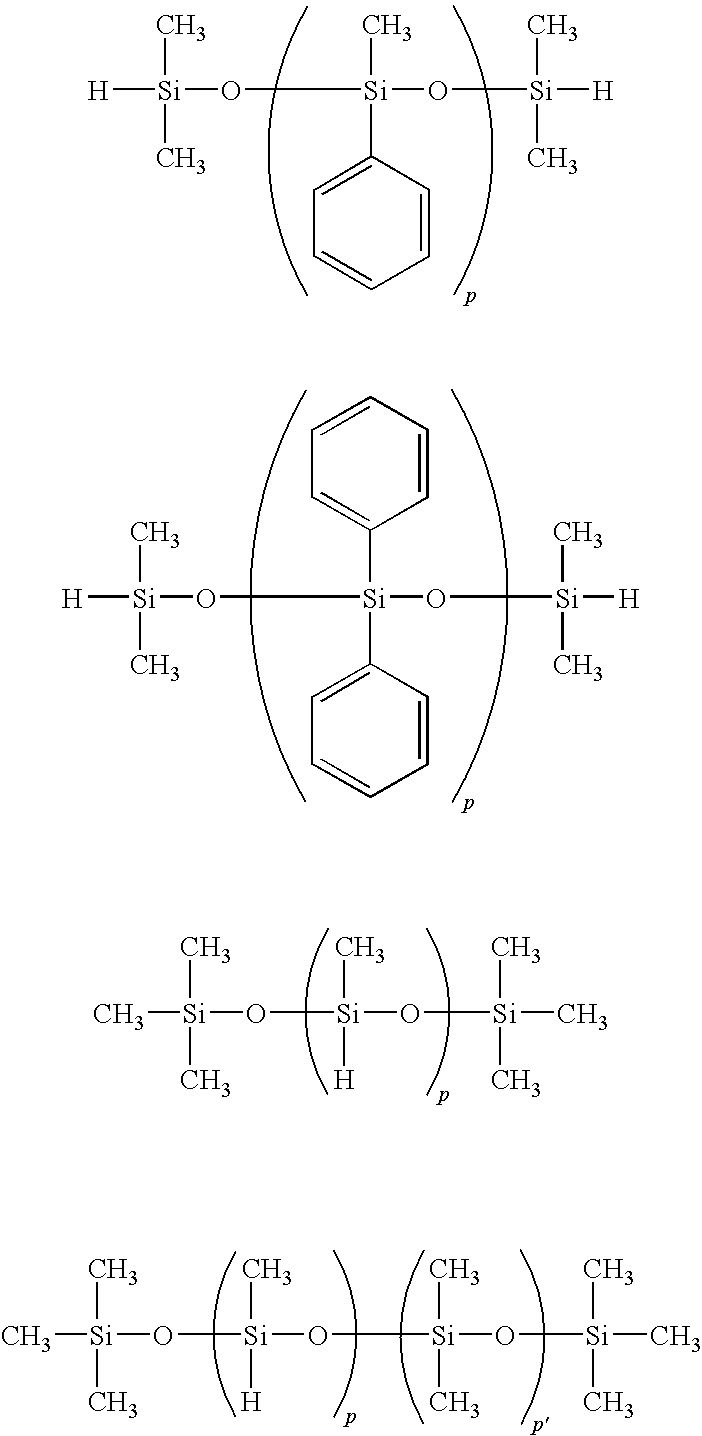
ActiveUS20090075009A1Excellent gap fillingImprove surface roughnessLayered productsAdhesivesHydrosilylationHigh surface
A hot-melt silicone adhesive comprising: (A) an organopolysiloxane resin with a softening point in the range of 40 to 250° C.; (B) an organopolysiloxane that at 25° C. is liquid or in the state of a crude rubber, which contains in one molecule at least two alkenyl groups; (C) a composition selected from a mixture of (i) an organopolysiloxane that contains silicon-bonded hydrogen atoms and (ii) an organic silicon compound that contains a silicon-bonded alkoxy group; or (iii) an organopolysiloxane that contains silicon-bonded hydrogen atoms and a silicon-bonded alkoxy group; (D) a hydrosilylation catalyst; and (E) a hydrosilylation-reaction inhibitor, demonstrates good gap-filling ability during thermo-compressive bonding to adherends with high surface roughness, even at low pressures, and that provides strong adhesion to the adherend after cross-linking.
Owner:DOW TORAY CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com