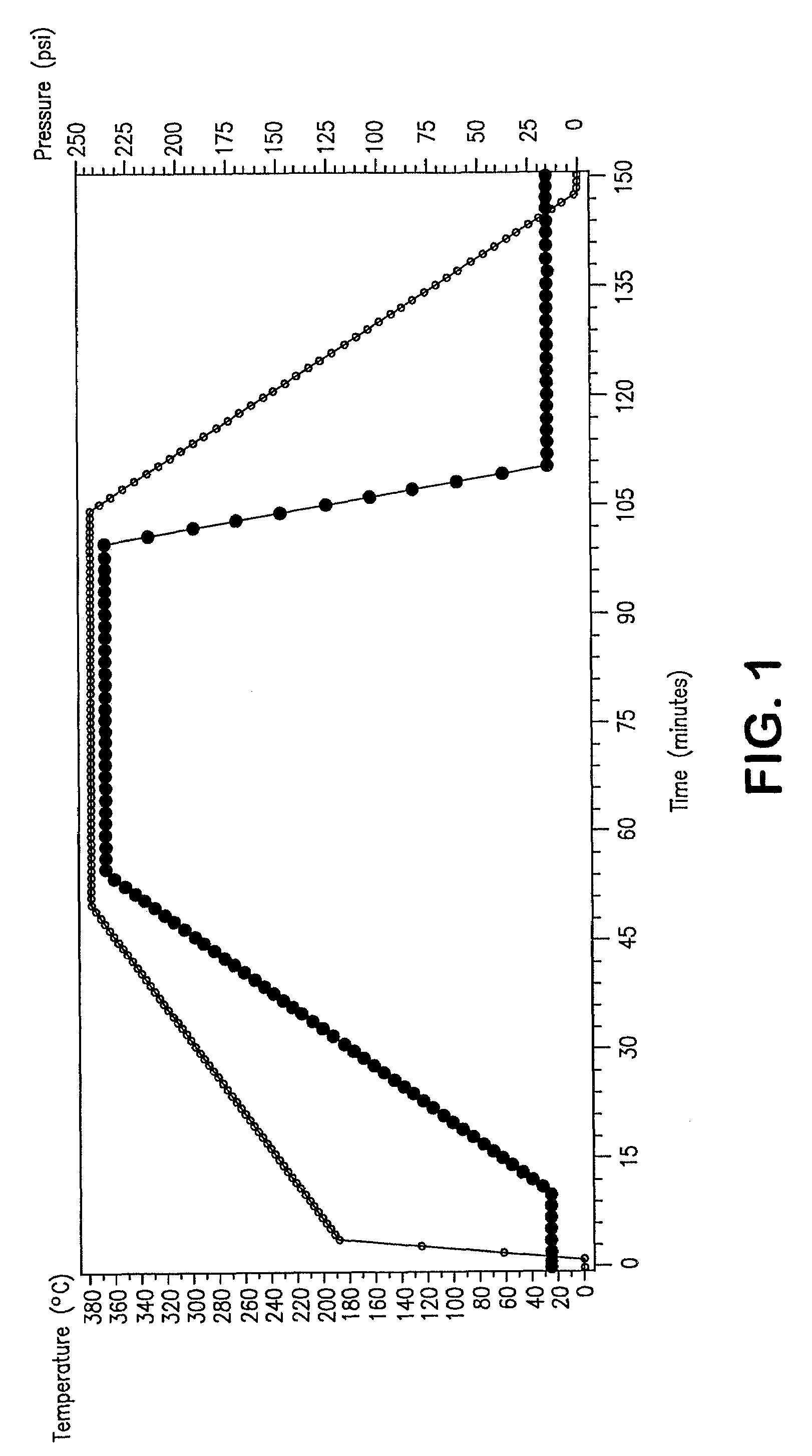
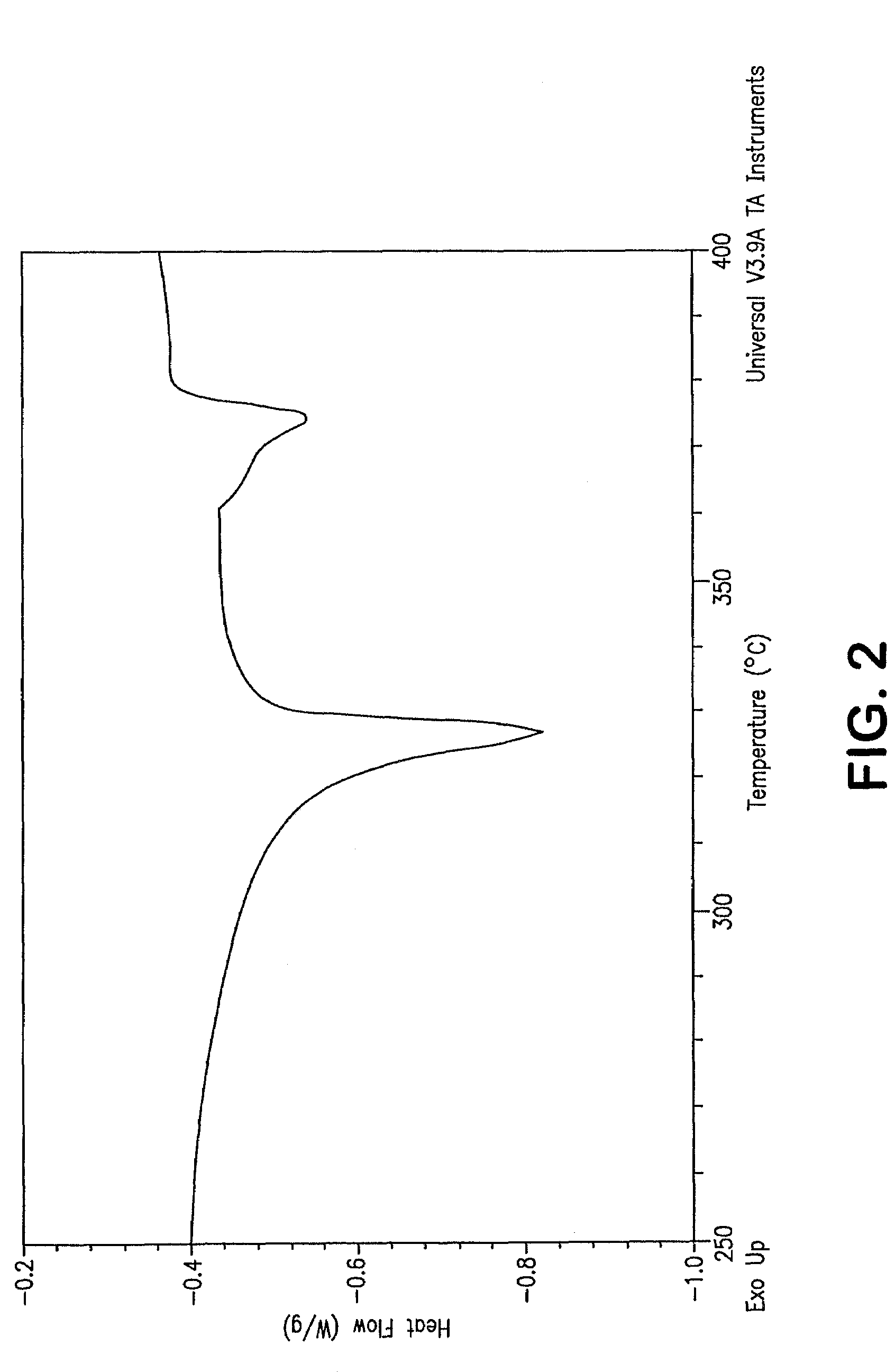
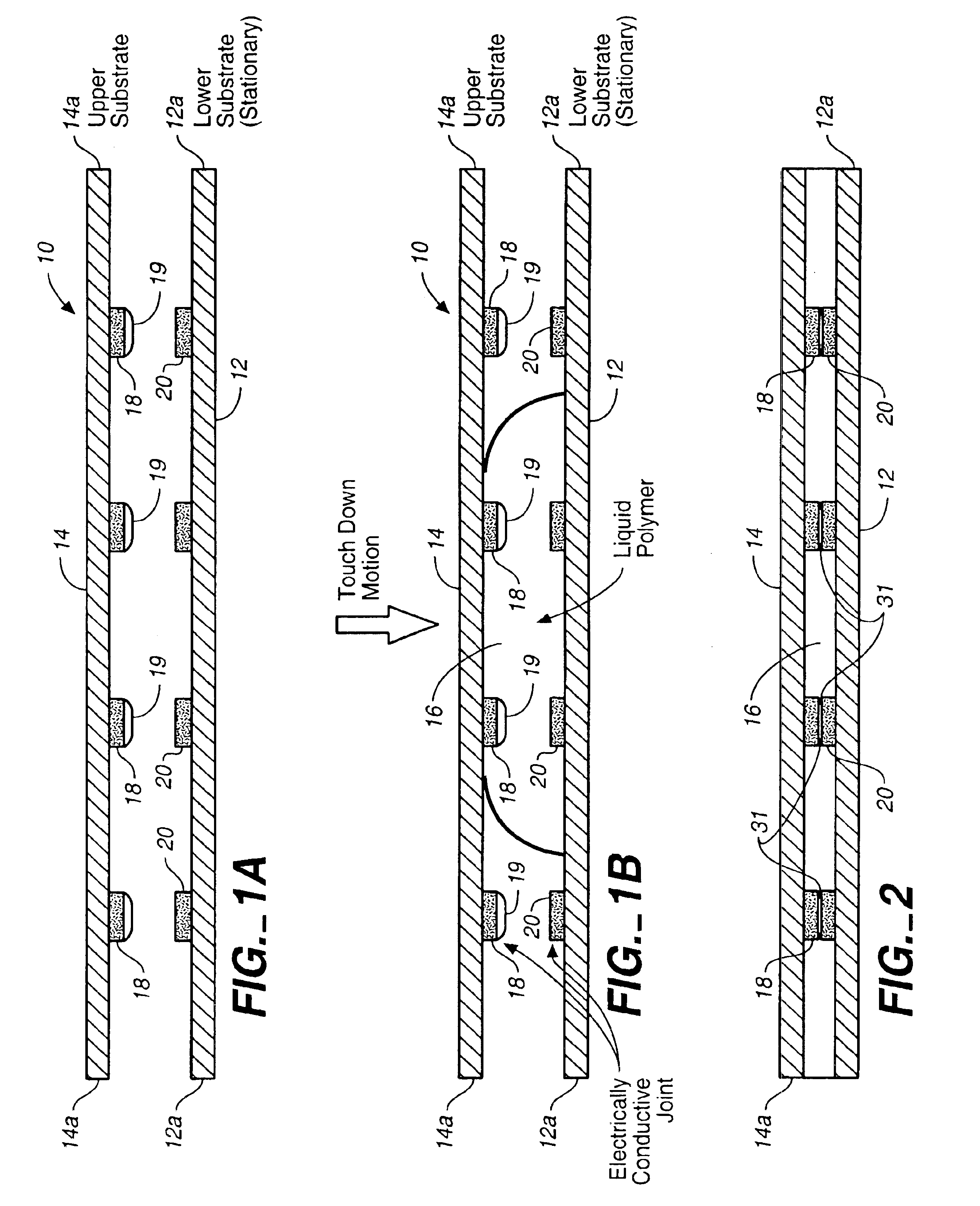
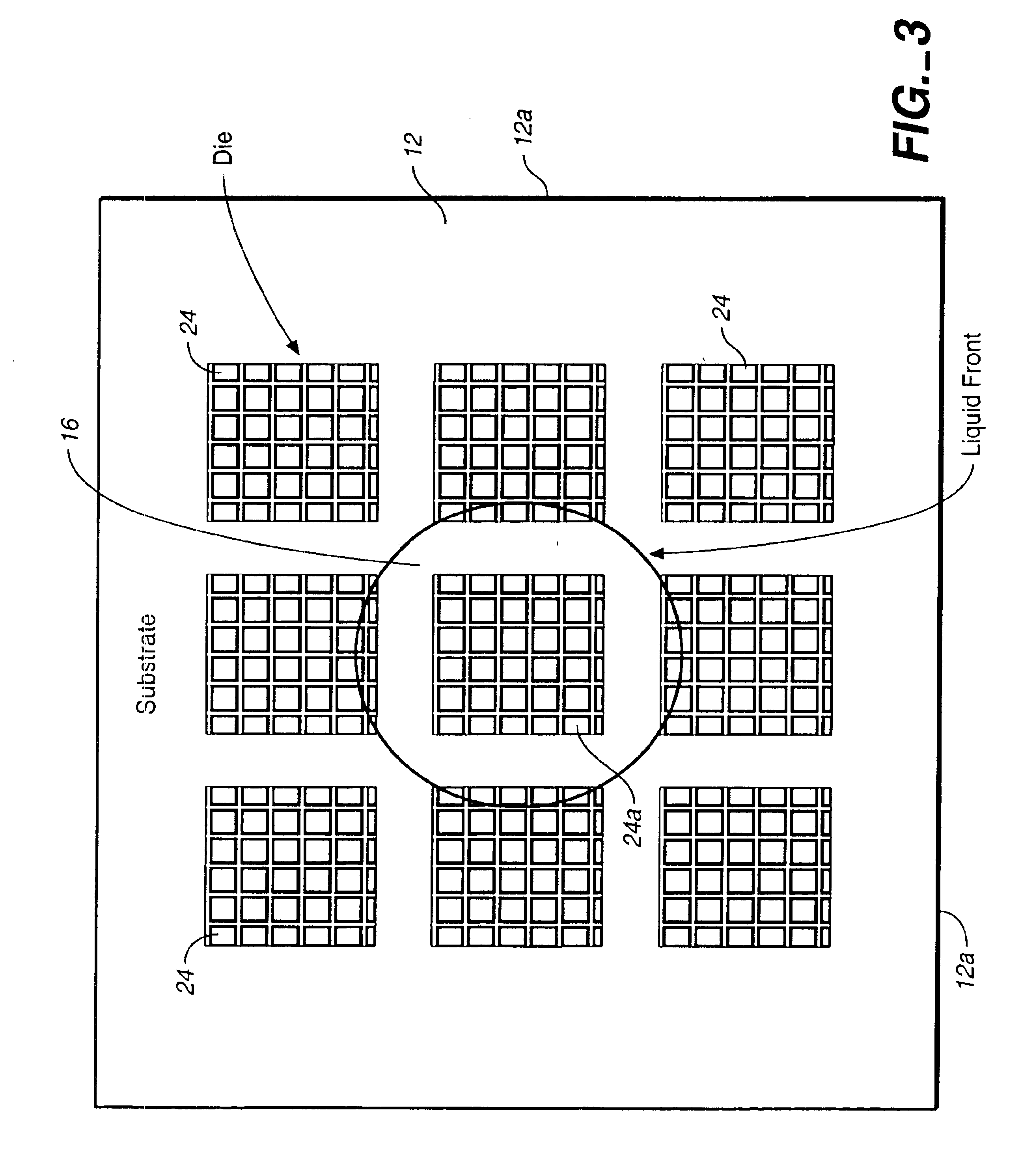
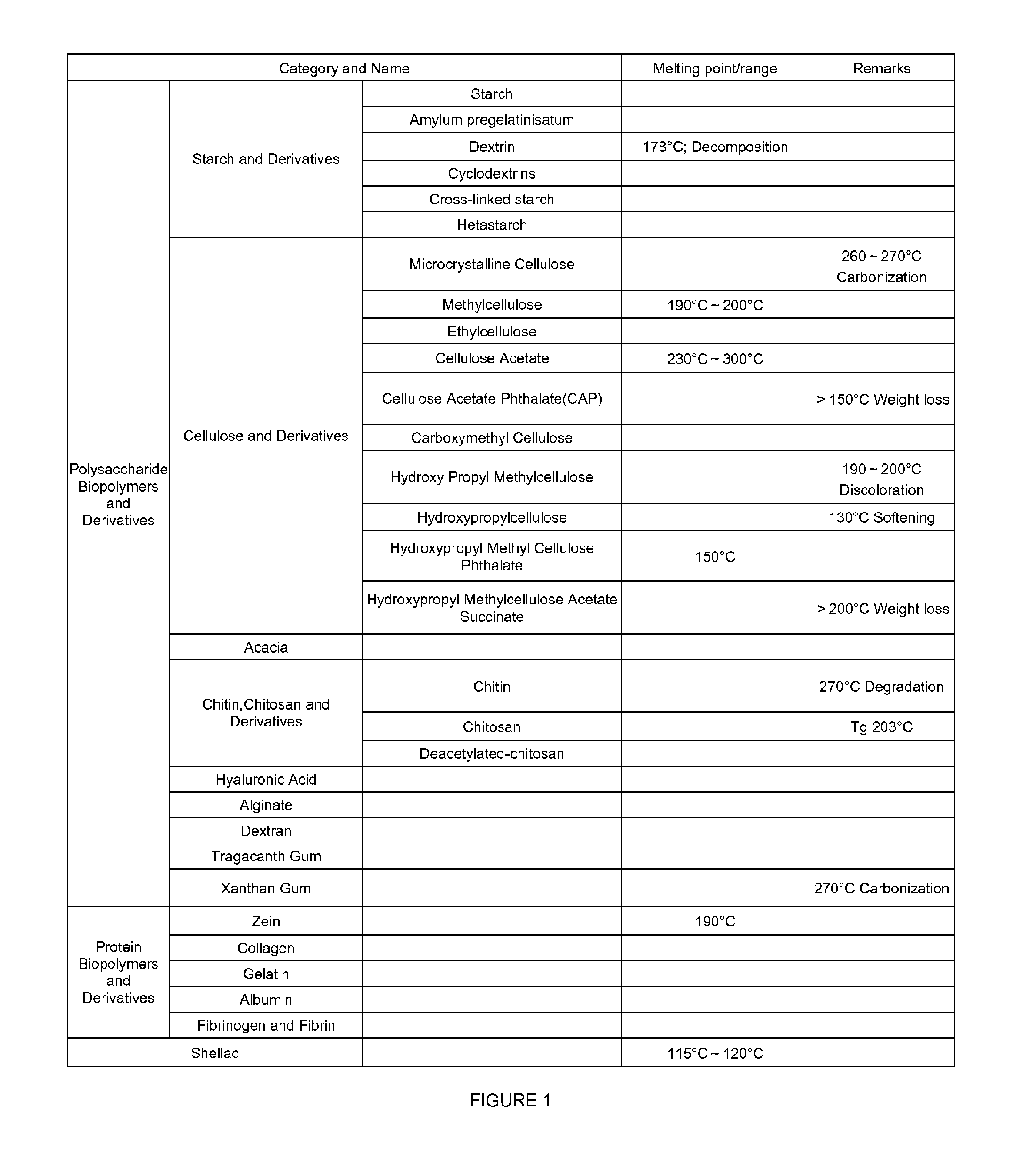
Patents
Literature
2185 results about "Melt temperature" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A melting point is essentially a set temperature that an element has where it begins to melt. Ice for example, begins to melt at 32° Fahrenheit. On the other hand, iron has a melting point of about 2,800° Fahrenheit.
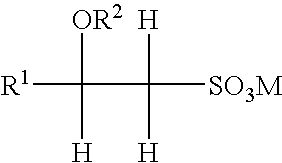
Water-dispersable materials
InactiveUS6211309B1Increase flexibilityGood dispersionMonocomponent polyesters artificial filamentMonocomponent polyamides artificial filamentThermoplasticFiber
The present invention relates to water-dispersible materials (e.g. fibers or films) and to a method of producing same. The materials of the invention comprise a water soluble component, for example, a sulfonated polycondensate thermoplastic, and a modifying auxiliary component, for example, a low melt temperature thermoplastic.
Owner:BASF CORP
Process for medical implant of cross-linked ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene having improved balance of wear properties and oxidation resistance
A medical implant of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene having an improved balance of wear properties and oxidation resistance is prepared by irradiating a preform of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene, annealing the irradiated preform in the absence of oxygen to a temperature at or above the onset of melting temperature, and forming an implant from the stabilized cross-linked polymer. Implants prepared according to the process of the present invention have comparable oxidation resistance and superior wear performance compared to unirradiated ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene.
Owner:DEPUY ORTHOPAEDICS INC
Shampoo containing a gel network
ActiveUS20060024256A1Cosmetic preparationsCationic surface-active compoundsAmphiphileSURFACTANT BLEND
Shampoo compositions comprise (a) from about 5% to about 50% of one or more detersive surfactants, by weight of the shampoo composition; (b) a dispersed gel network phase comprising, by weight of the shampoo composition, (i) at least about 0.05 % of one or more fatty amphiphiles; (ii) at least about 0.01% of one or more secondary surfactants; and (iii) water; and (c) at least about 20% of an aqueous carrier, by weight of the shampoo composition. A process for preparing a shampoo composition comprises the steps of: (a) combining a fatty amphiphile, a secondary surfactant, and water at a temperature sufficient to allow partitioning of the secondary surfactant and the water into the fatty amphiphile to form a pre-mix; (b) cooling the pre-mix below the chain melt temperature of the fatty amphiphile to form a gel network; (c) adding the gel network to one or more detersive surfactants and an aqueous carrier to form a shampoo composition.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Bandgap grading in thin-film devices via solid group IIIA particles
InactiveUS20080057616A1Efficient and simplified creationPrevent leaching and phase separationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationHigh concentrationBandgap grading
Methods and devices are provided for forming thin-films from solid group IIIA-based particles. In one embodiment, a method is provided for bandgap grading in a thin-film device using such particles. The method may be comprised of providing a bandgap grading material comprising of an alloy having: a) a IIIA material and b) a group IA-based material, wherein the alloy has a higher melting temperature than a melting temperature of the IIIA material in elemental form. A precursor material may be deposited on a substrate to form a precursor layer. The precursor material comprising group IB, IIIA, and / or VIA based particles. The bandgap grading material of the alloy may be deposited after depositing the precursor material. The alloy in the grading material may react after the precursor layer has begun to sinter and thus maintains a higher concentration of IIIA material in a portion of the compound film that forms above a portion that sinters first.
Owner:AERIS CAPITAL SUSTAINABLE IP
Metal attachment method and structure for attaching substrates at low temperatures
InactiveUS6080640ASemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesHigh densityMelt temperature
A high density integrated circuit structure and method of making the same includes providing a first silicon substrate structure having semiconductor device formations in accordance with a first circuit implementation and metal interlevel lines disposed on a top surface thereof and a second silicon substrate structure having a second circuit implementation and metal interlevel lines disposed on a top surface thereof. The first substrate structure includes a planarized low-K dielectric disposed between the metal interlevel lines and a protective coating separating the metal interlevel lines from is the low-K dielectric, the metal interlevel lines of the first silicon substrate structure have a melting temperature on the order of less than 500 DEG C. and the low-K dielectric having a dielectric K-value in the range of 2.0-3.8. The second substrate structure also includes a planarized low-K dielectric disposed between the metal interlevel lines and a protective coating separating the metal interlevel lines from the low-K dielectric, the metal interlevel lines having a melting temperature on the order of less than 500 DEG C. and the low-K dielectric having a dielectric K-value in the range of 2.0-3.8. Lastly, the first substrate structure is low temperature bonded to the second substrate structure at respective metal interlevel lines of the first and second substrate structures.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Active Thermal Runaway Mitigation System for Use Within a Battery Pack
ActiveUS20100136391A1Reduce impactHinders its propagationTemperatue controlCell temperature controlEngineeringMelt temperature
An active thermal runaway mitigation system is provided that mitigates the effects of a single cell undergoing thermal runaway, thereby preventing the propagation of the thermal runaway event to neighboring cells within the battery pack. The provided system includes at least one, fluid-containing conduit in proximity to the cells within the battery pack. The conduit includes a plurality of breach points in proximity to the subset of cells, where each breach point is configured to form a breach at a preset temperature that is lower than the melting temperature of the conduit. Once a breach is formed, the fluid contained within the conduit is discharged through the breach.
Owner:TESLA INC
Fluoropolymer barrier material
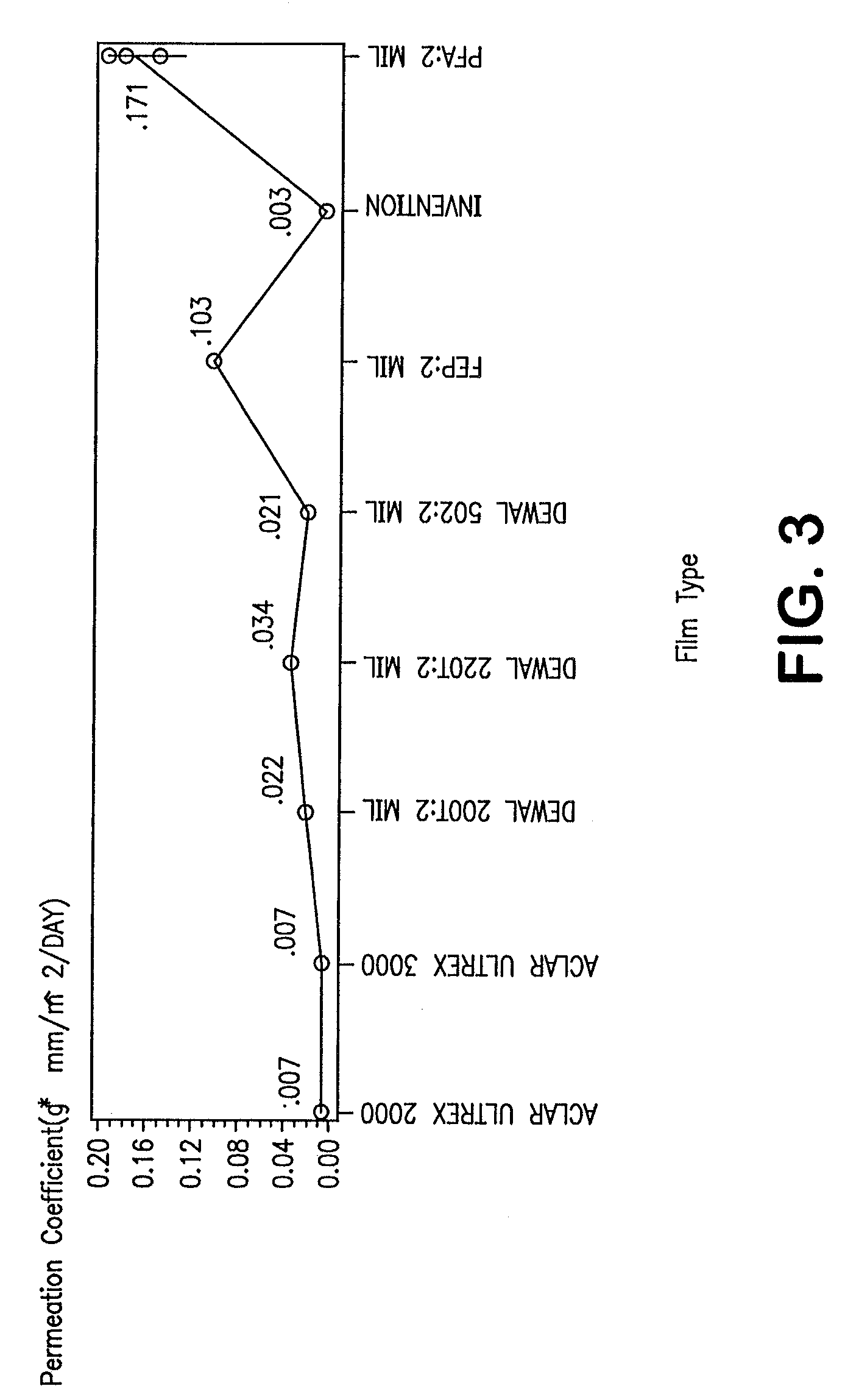
InactiveUS7521010B2Improve barrier propertiesImprove permeabilitySynthetic resin layered productsCeramic shaping apparatusPolymer scienceWater vapor permeability
A novel densified fluoropolymer article is described which has a water vapor permeation of about 0.015 g-mm / m2 / day or less, and preferably has a matrix tensile strength of at least 10,000 psi in two orthogonal directions. The articles are made by compressing expanded porous PTFE at pressures, temperatures and times which result in elimination of the pores, and subsequent stretching above the crystalline melt temperature.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
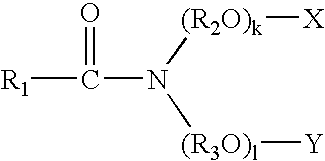
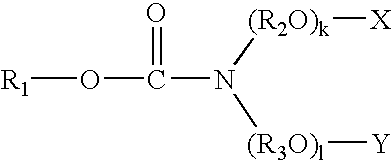
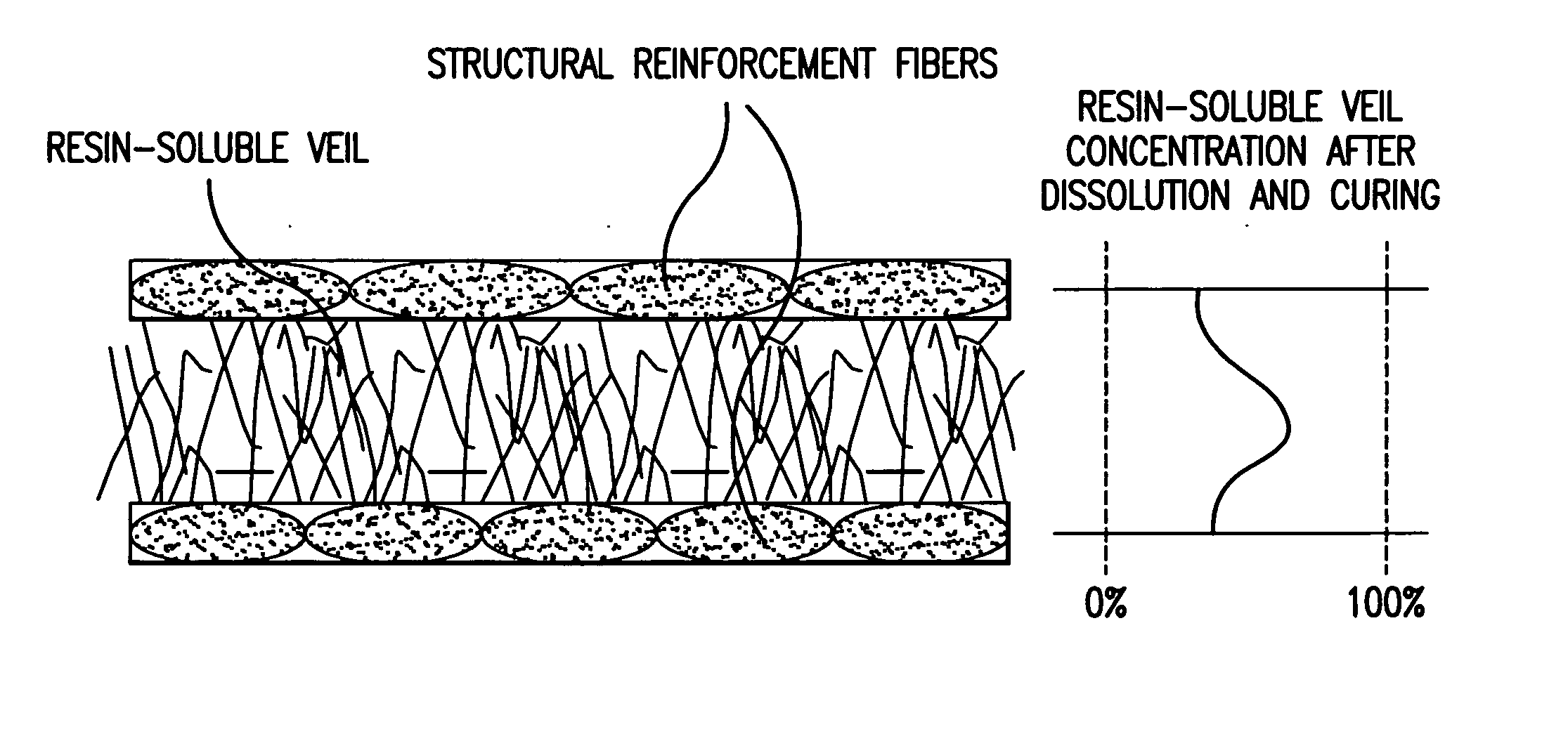
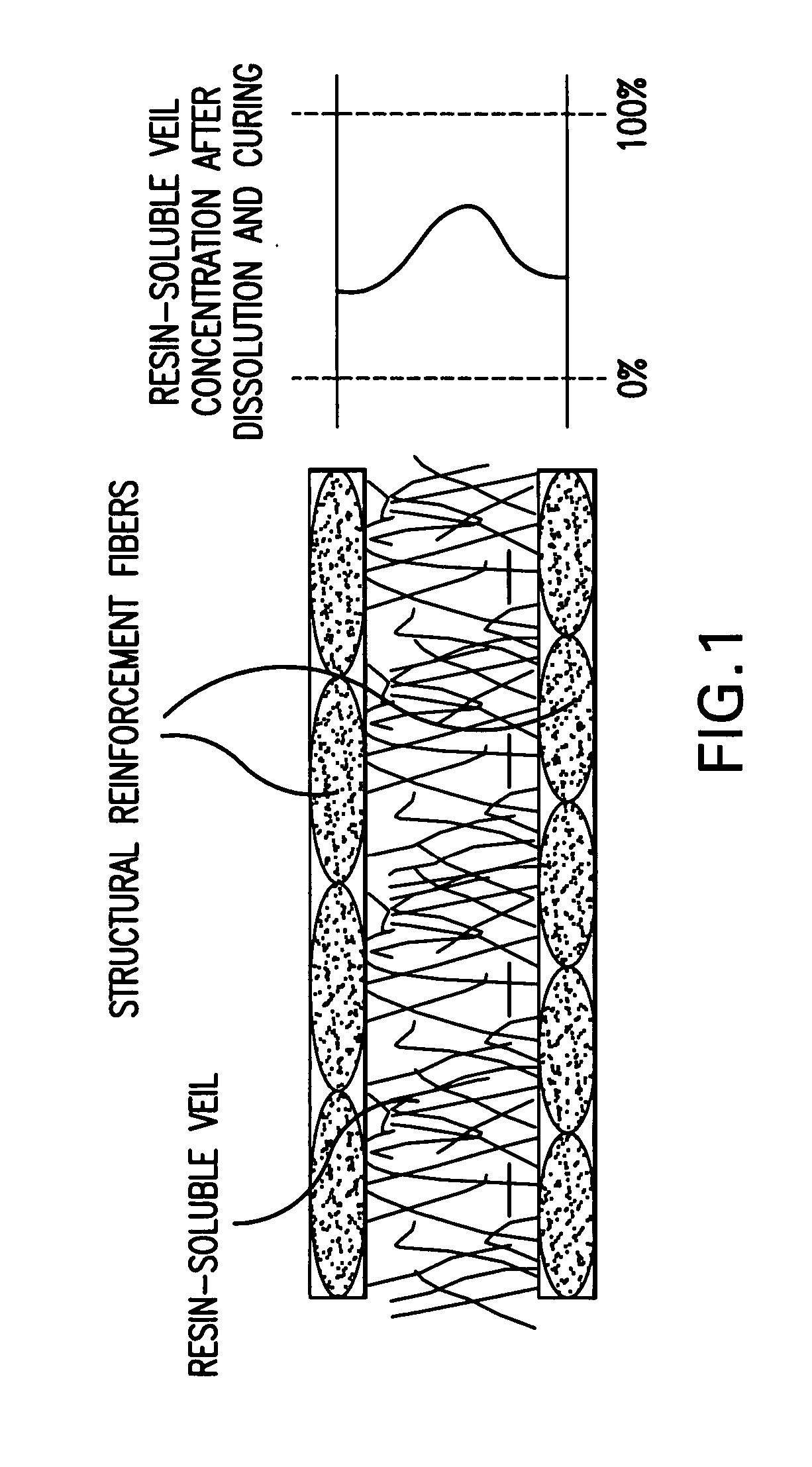
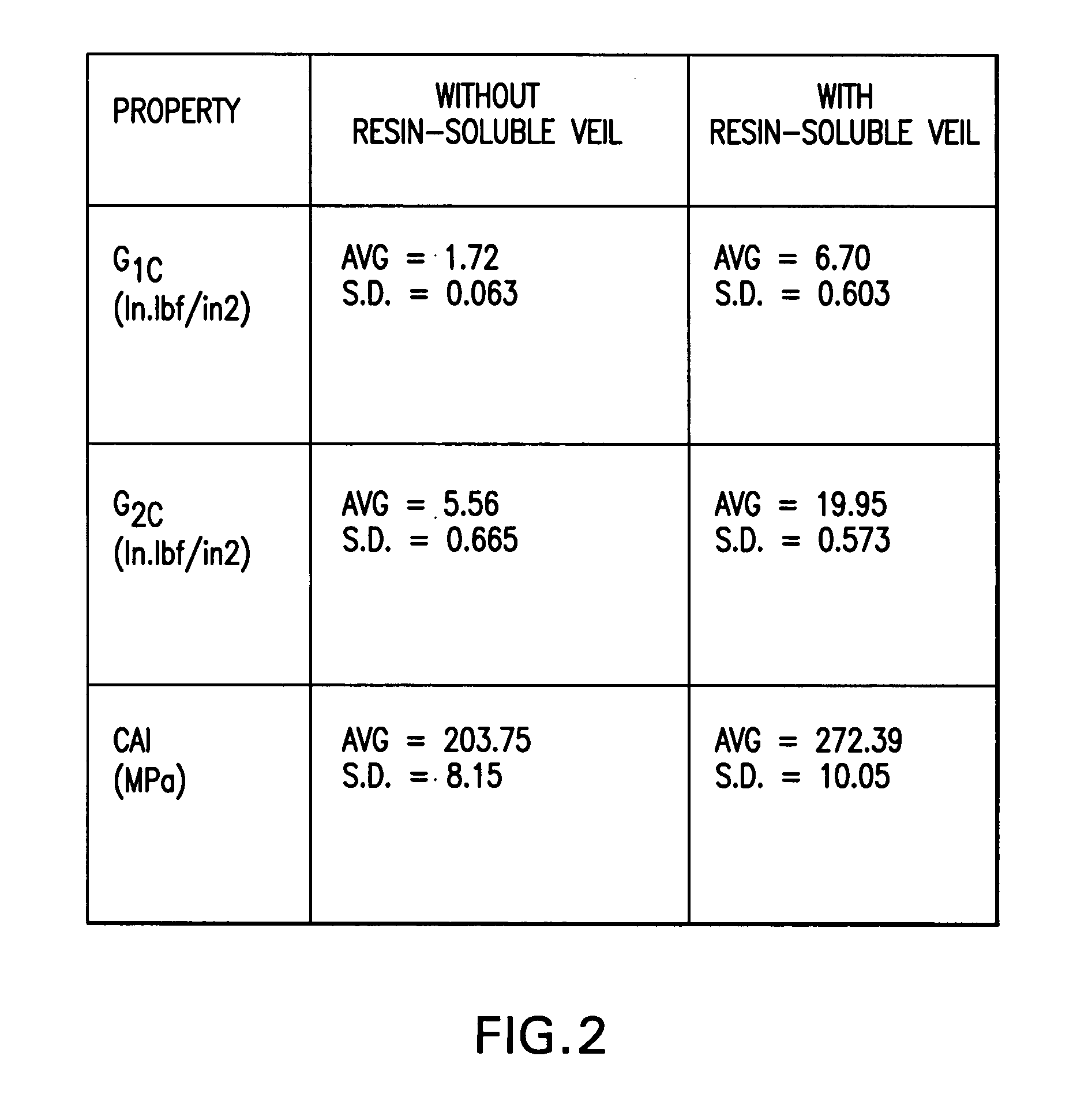
Resin-soluble thermoplastic veil for composite materials
ActiveUS20060252334A1Improve the level ofImprove toughnessWood working apparatusVehicle componentsFiberResin matrix
A resin-soluble thermoplastic polymer veil toughening element for a curable composition wherein the polymer element is a non-woven veil in solid phase adapted to undergo at least partial phase transition to fluid phase on contact with a component of the curable resin matrix composition in which it is soluble at a temperature which is less than the temperature for substantial onset of gelling and / or curing of the curable composition and which temperature is less than the polymer elements melt temperature; a method for the preparation thereof, a preform support structure for a curable composition comprising the at least one thermoplastic veil element together with structural reinforcement fibers, methods for preparation thereof, a curable composition comprising the at least one thermoplastic veil element or the support structure and a curable resin matrix composition, a method for preparation and curing thereof, and a cured composite or resin body obtained thereby, and known and novel uses thereof.
Owner:CYTEC TECH CORP
Shampoo containing a gel network
ActiveUS20070110700A1Cosmetic preparationsCationic surface-active compoundsAmphiphileSURFACTANT BLEND
Shampoo compositions comprise (a) from about 5% to about 50% of one or more detersive surfactants, by weight of the shampoo composition; (b) a dispersed gel network phase comprising, by weight of the shampoo composition, (i) at least about 0.05% of one or more fatty amphiphiles; (ii) at least about 0.01% of one or more secondary surfactants; and (iii) water; and (c) at least about 20% of an aqueous carrier, by weight of the shampoo composition. A process for preparing a shampoo composition comprises the steps of: (a) combining a fatty amphiphile, a secondary surfactant, and water at a temperature sufficient to allow partitioning of the secondary surfactant and the water into the fatty amphiphile to form a pre-mix; (b) cooling the pre-mix below the chain melt temperature of the fatty amphiphile to form a gel network; (c) adding the gel network to one or more detersive surfactants and an aqueous carrier to form a shampoo composition.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
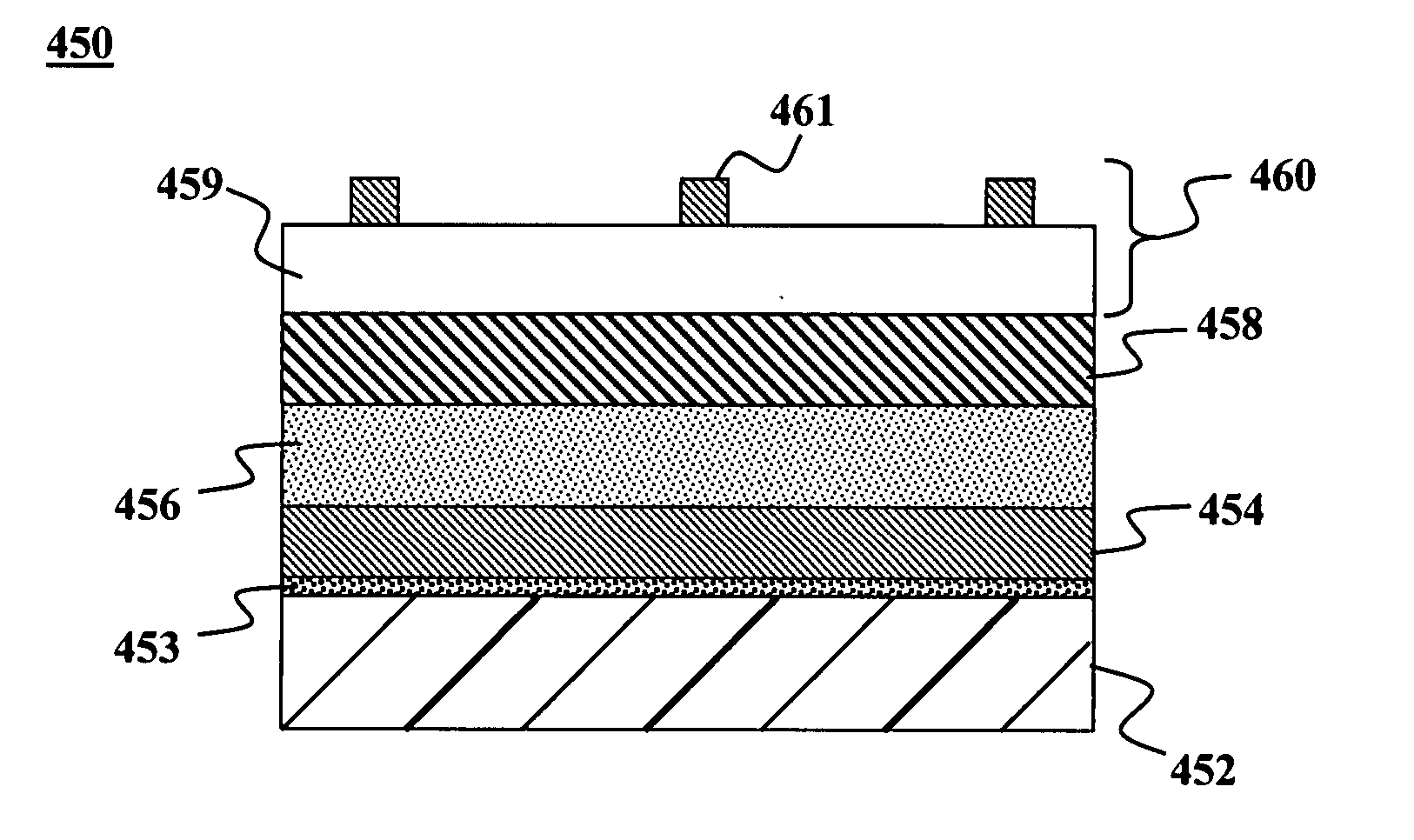
Decorative interior sound absorbing panel
A multi-layered fiber reinforced thermoplastic sound absorbing panel includes a porous fiber reinforced thermoplastic core layer having a first surface and a second surface, and includes a thermoplastic material and from about 20 weight percent to about 80 weight percent fibers, a tie layer covering the second surface of the core layer and including a thermoplastic material, and a barrier layer covering the tie layer. The barrier layer includes a thermoplastic material having a melting temperature higher than the melting temperature of the core layer thermoplastic material. The tie layer bonds the barrier layer to the core layer. The panel also includes a non-woven layer including a fabric bonded to the barrier layer. The non-woven layer forms an outer surface of the panel.
Owner:HANWA AZDEL INC
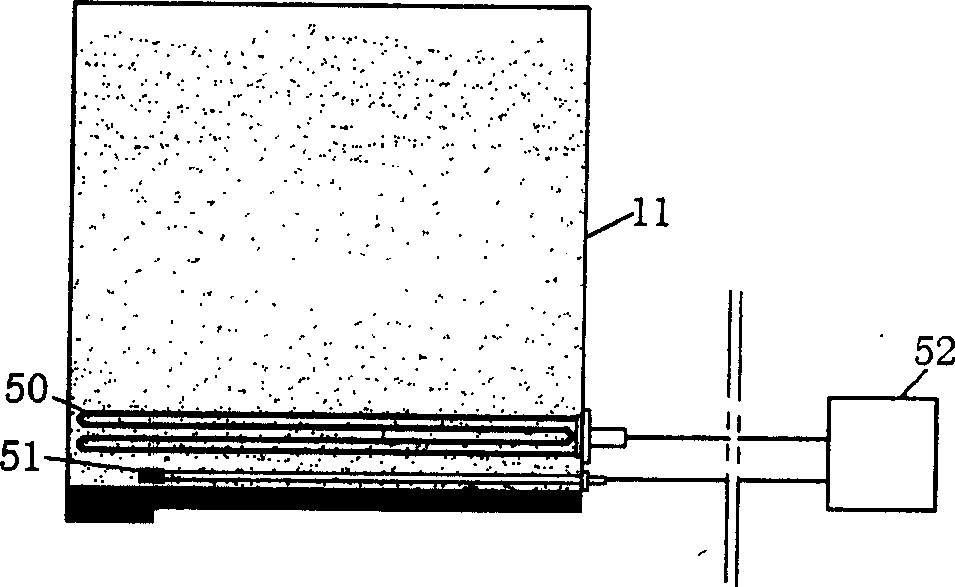
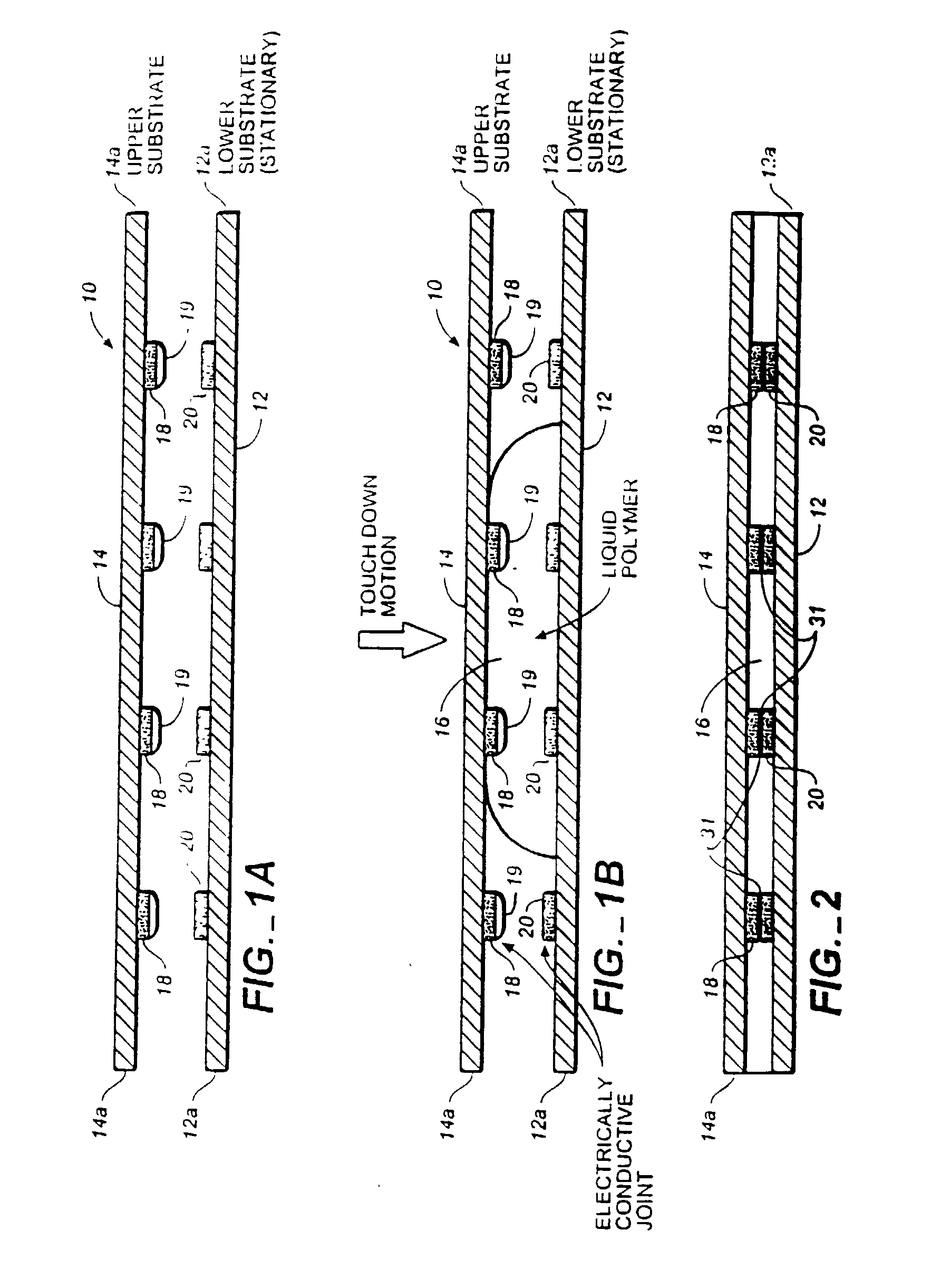
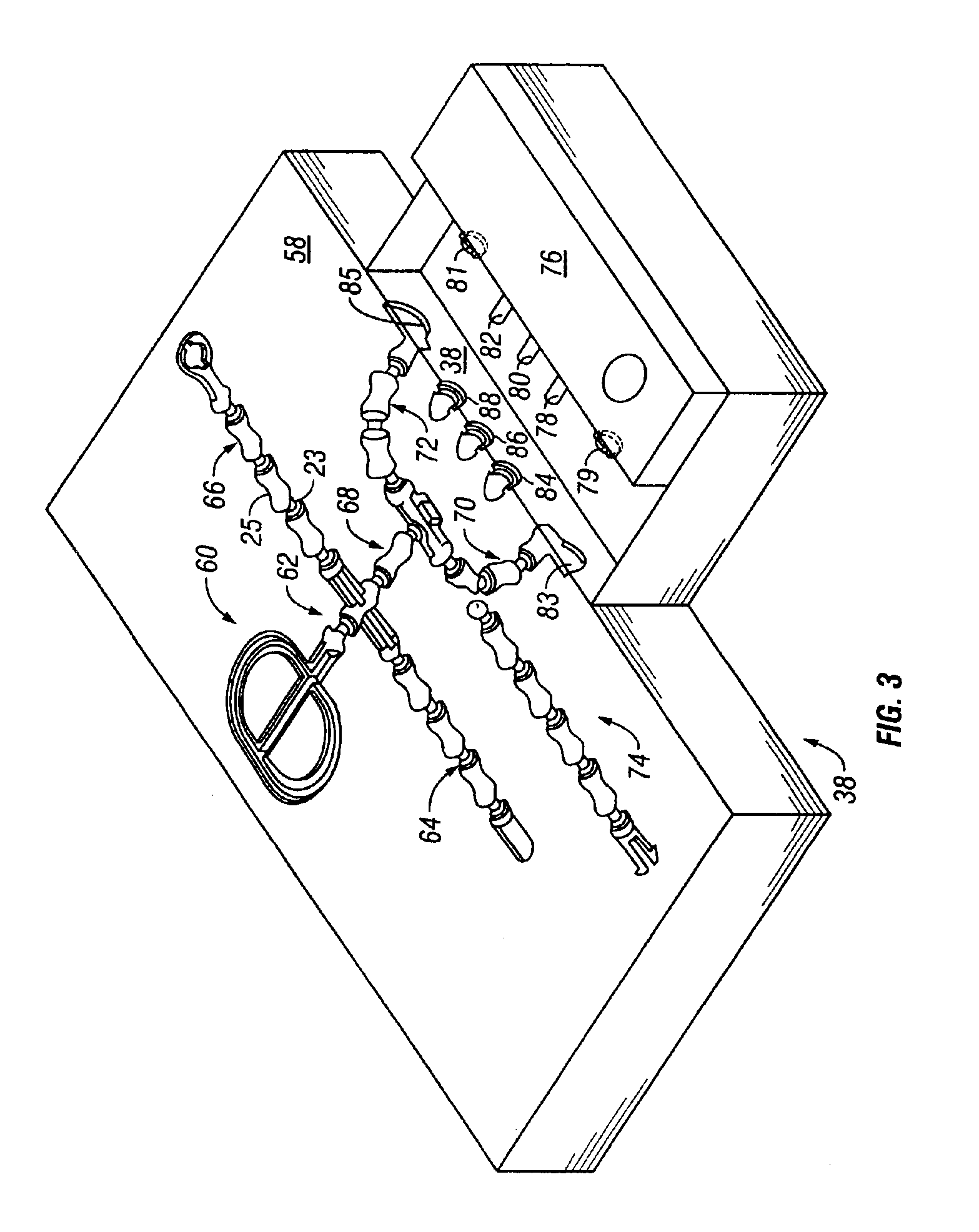
Method for joining conductive structures and an electrical conductive article
Embodiments of the invention include a method comprising disposing a thin metallic layer having a low melting temperature between one end of a conductive post on a substrate and a conducting structure on an opposing substrate. Heated platens in contact with the substrates can apply pressure and heat to the thin metallic layer and cause it to be entirely consumed and subsequently transformed into a bonding layer having a melting temperature higher than the melting temperature of the original thin metallic layer. Prior to, during, or after the conductive post is bonded to the conducting structure, the region around the conductive post and between the substrates may be filled with a dielectric material, such as polyimide.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
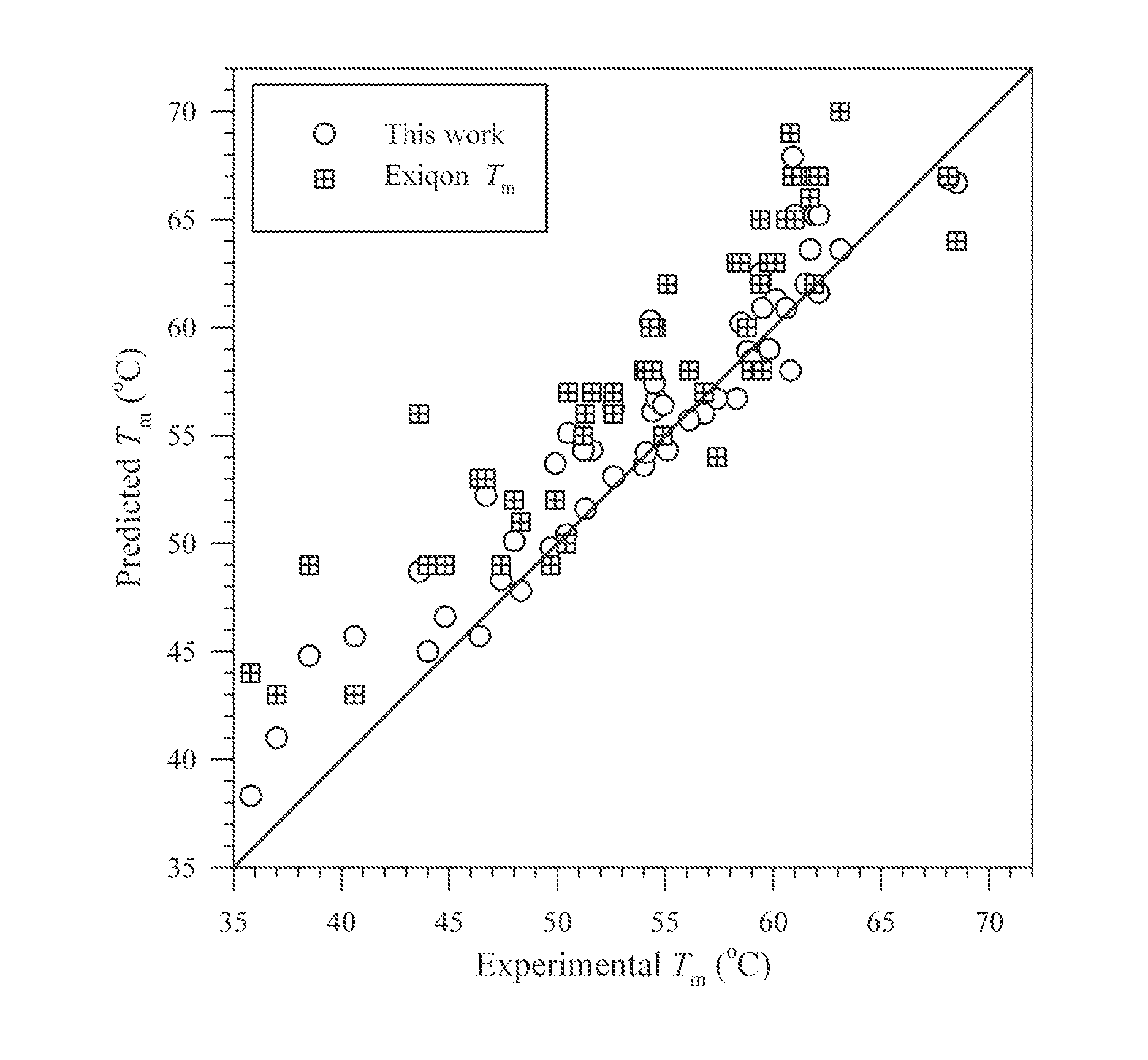
Methods for Predicting Stability and Melting Temperatures of Nucleic Acid Duplexes
ActiveUS20120029891A1Microbiological testing/measurementThermometers using physical/chemical changesOligomerLocked nucleic acid
The present invention provides methods that more accurately predict melting temperatures for duplex oligomers. The invented methods predict the Tm of chimeric duplexes containing various amounts of locked nucleic acid modifications in oligonucleotide strands.
Owner:INTEGRATED DNA TECHNOLOGIES
Method of multiple pulse laser annealing to activate ultra-shallow junctions
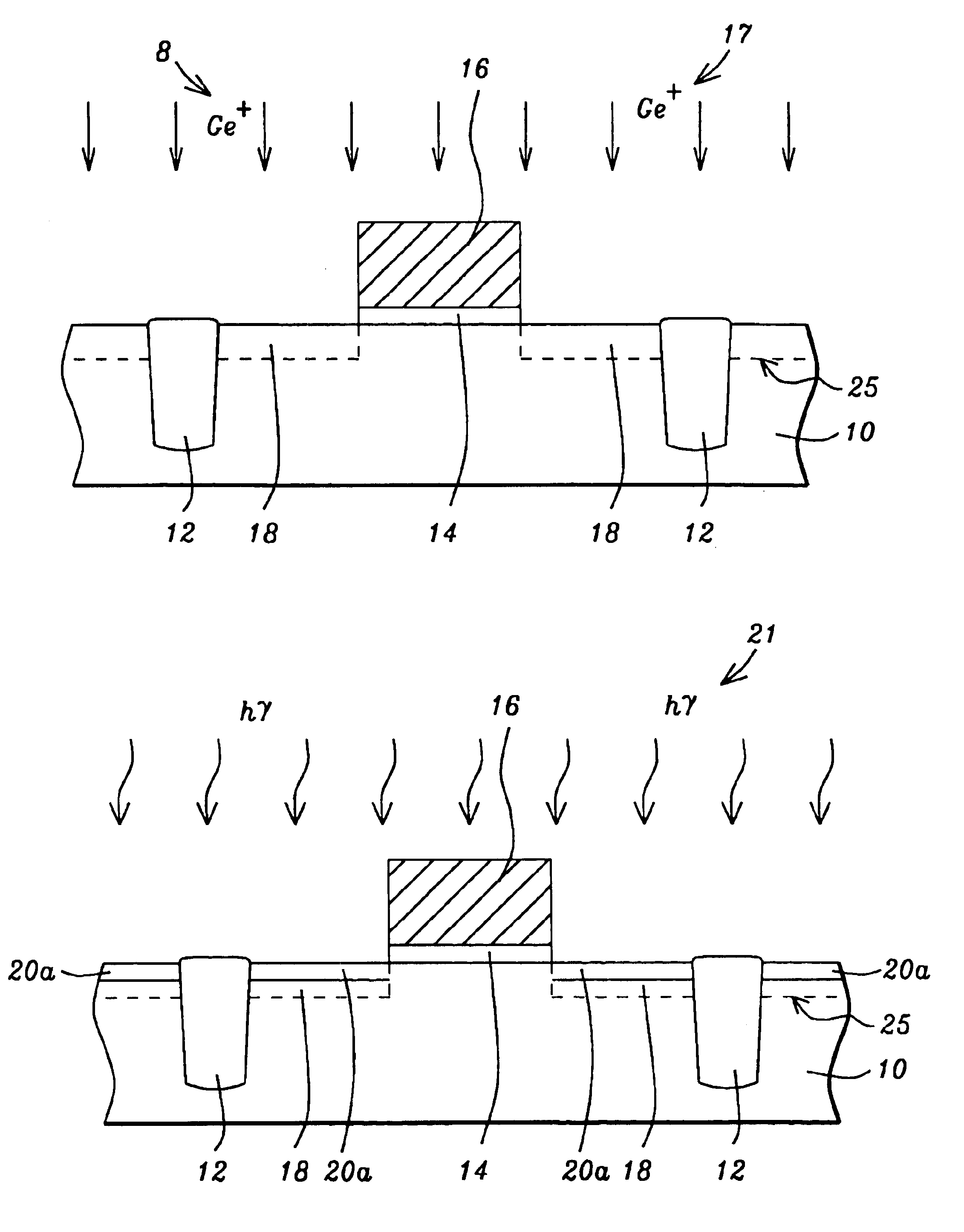
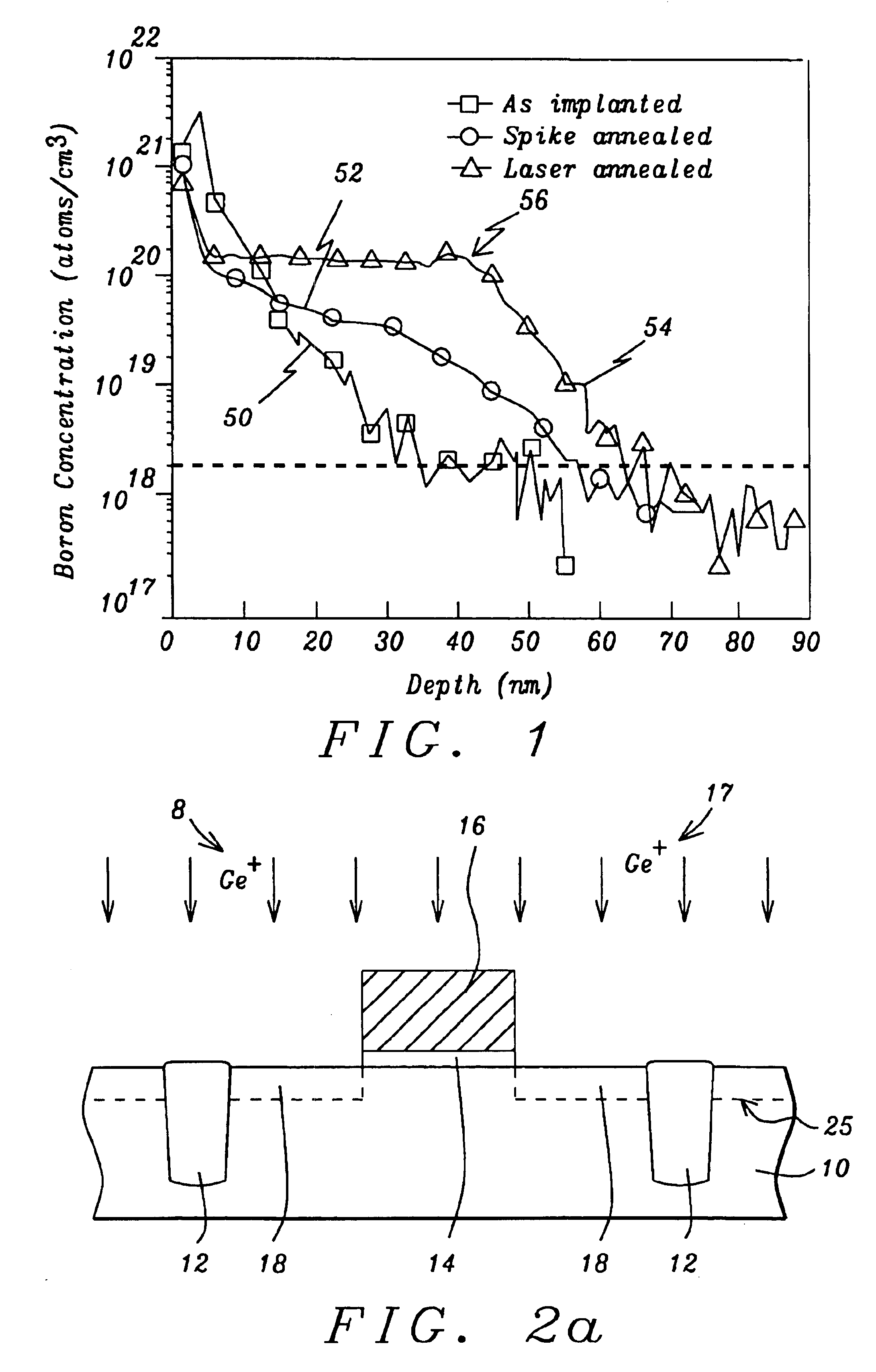
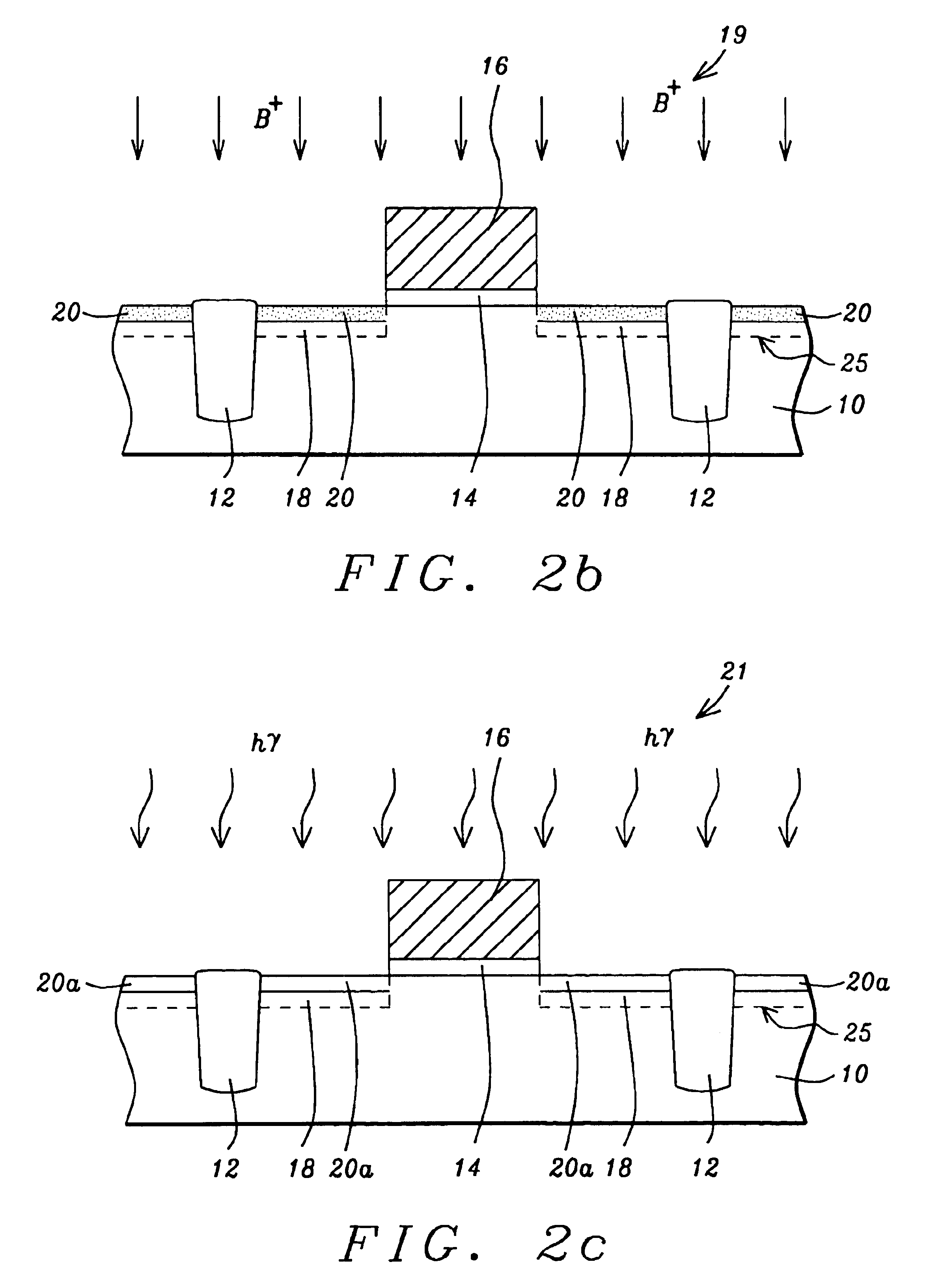
A method for forming a highly activated ultra shallow ion implanted semiconductive elements for use in sub-tenth micron MOSFET technology is described. A key feature of the method is the ability to activate the implanted impurity to a highly active state without permitting the dopant to diffuse further to deepen the junction. A selected single crystalline silicon active region is first amorphized by implanting a heavy ion such as silicon or germanium. A semiconductive impurity for example boron is then implanted and activated by pulsed laser annealing whereby the pulse fluence, frequency, and duration are chosen to maintain the amorphized region just below it's melting temperature. It is found that just below the melting temperature there is sufficient local ion mobility to secure the dopant into active positions within the silicon matrix to achieve a high degree of activation with essentially no change in concentration profile. The selection of the proper laser annealing parameters is optimized by observation of the reduction of sheet resistance and concentration profile as measured on a test site. Application of the method is applied to forming a MOS FET and a CMOS device. The additional processing steps required by the invention are applied simultaneously to both n-channel and p-channel devices of the CMOS device pair.
Owner:CHARTERED SEMICONDUCTOR MANUFACTURING
Packaging of multiple active optical devices
InactiveUS20040029304A1Printed circuit assemblingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringElectron
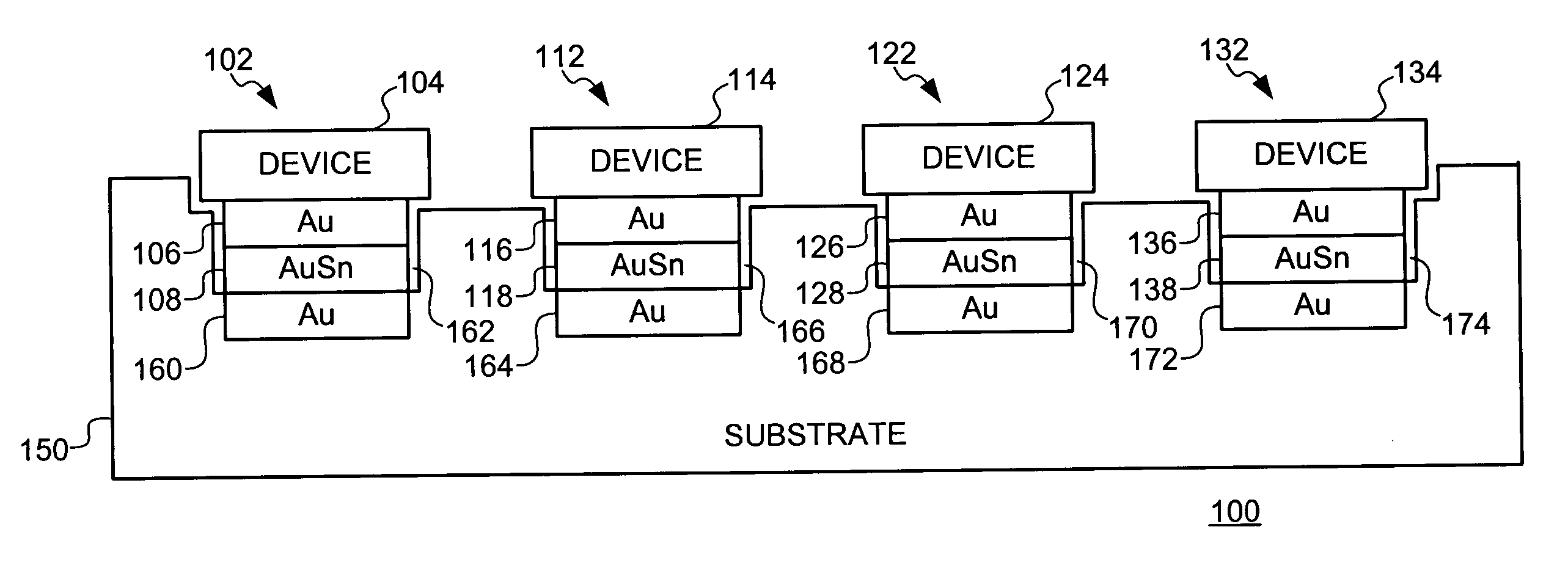
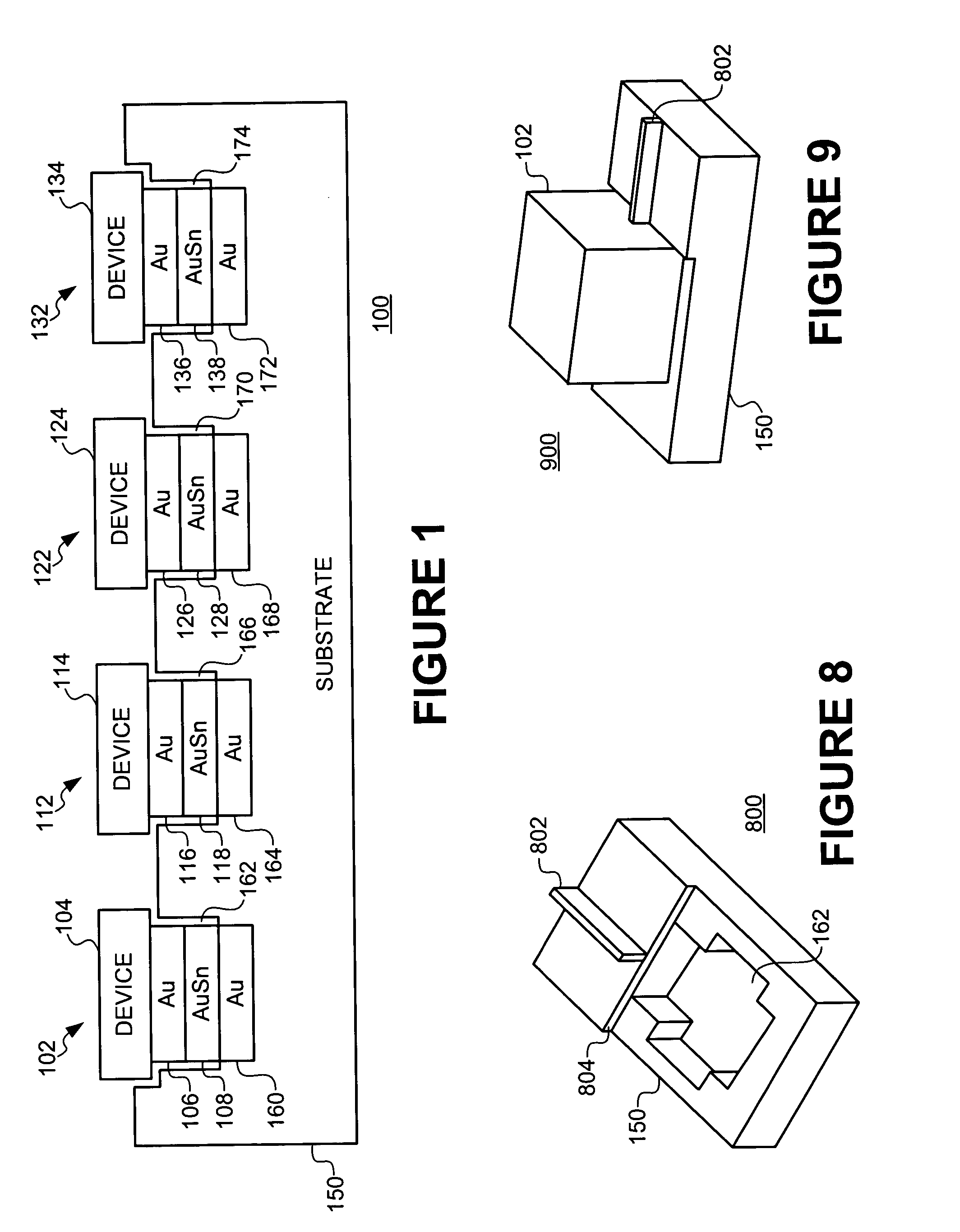
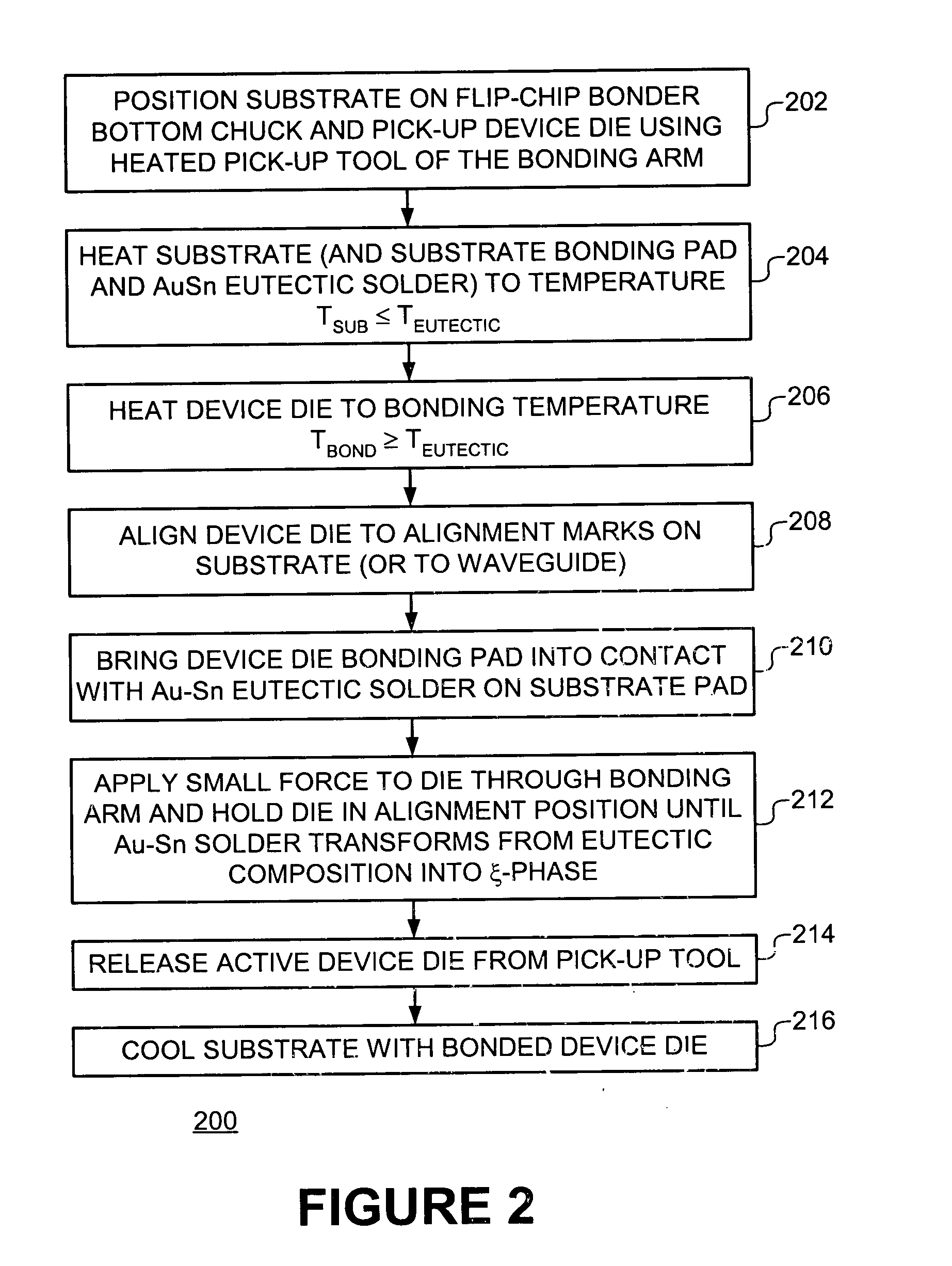
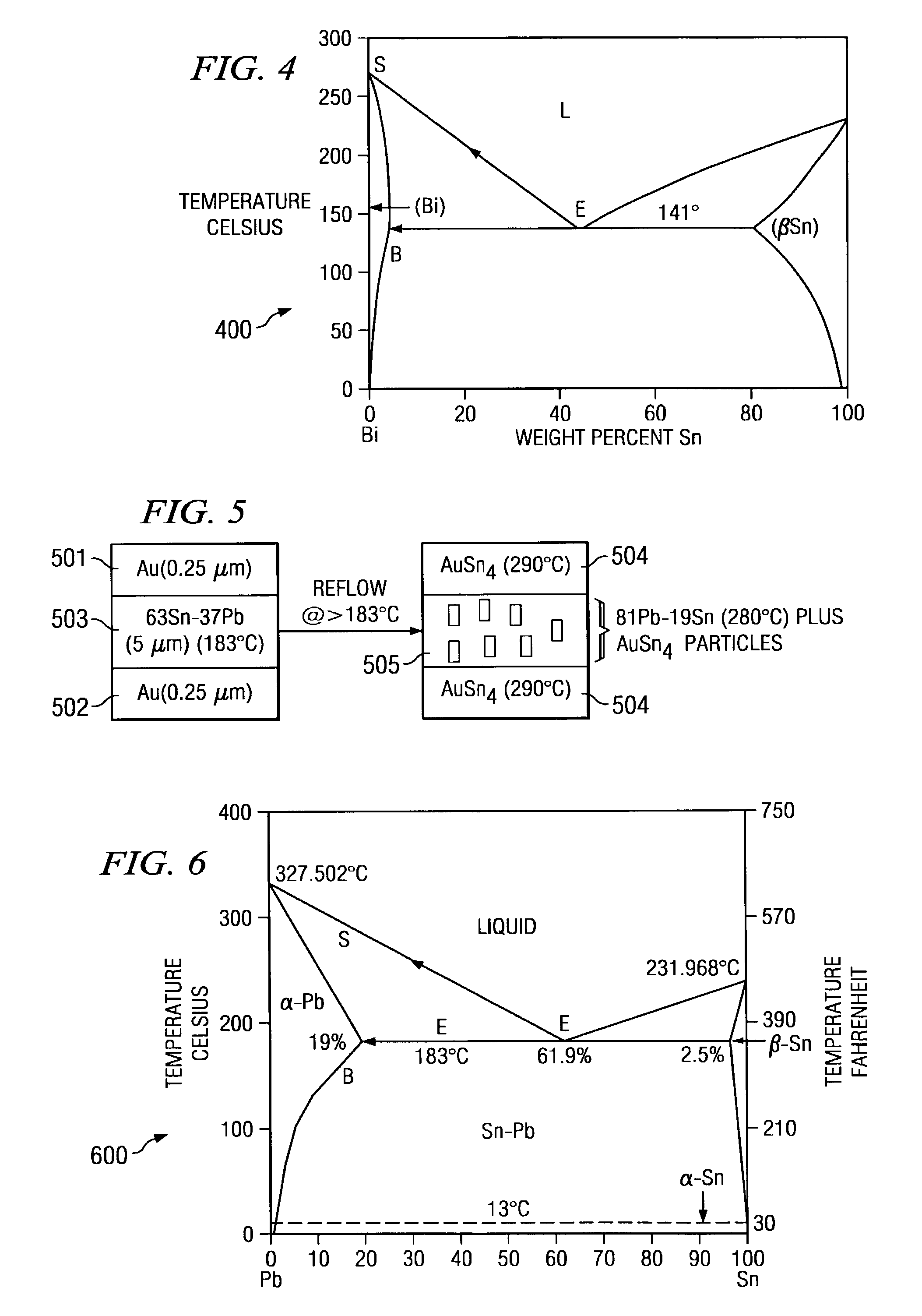
A cost effective method is provided for assembly of hybrid optoelectronic circuits requiring flip-chip bonding of multiple active optoelectronic devices onto common substrate or optical bench platform with fine pitch and high accuracy "after-bonding" alignment to the alignment features on substrate and / or to other elements of the hybrid circuit. A Flip-Chip Bonder equipped with high precision Bonding Arm and optical and mechanical system, heated substrate chuck and heated pick-up tool may be used both for alignment and thermal bonding of active component dies to corresponding bonding pads on the common substrate using gold-tin (Au-Sn) solder disposed between die bonding pad and the corresponding substrate bonding pad. During bonding of the first die, tin (Sn) diffuses from a eutectic composition of gold-tin (Au-Sn) solder to (gold (Au) on) the die-bonding pad and / or (gold (Au) on) the substrate bonding-pad resulting in transformation of the Au-Sn eutectic composition to a zeta-phase composition having much higher melting temperature as compared to that of a eutectic composition. As bonding of one or more subsequent dies is performed at temperatures equal to or slightly higher than the melting temperature of a eutectic composition and significantly lower than the melting temperature of a zeta-phase composition, the gold-tin (Au-Sn) solder at the bond of previously attached die does not melt and, consequently, the alignment is not compromised.
Owner:INTEL CORP
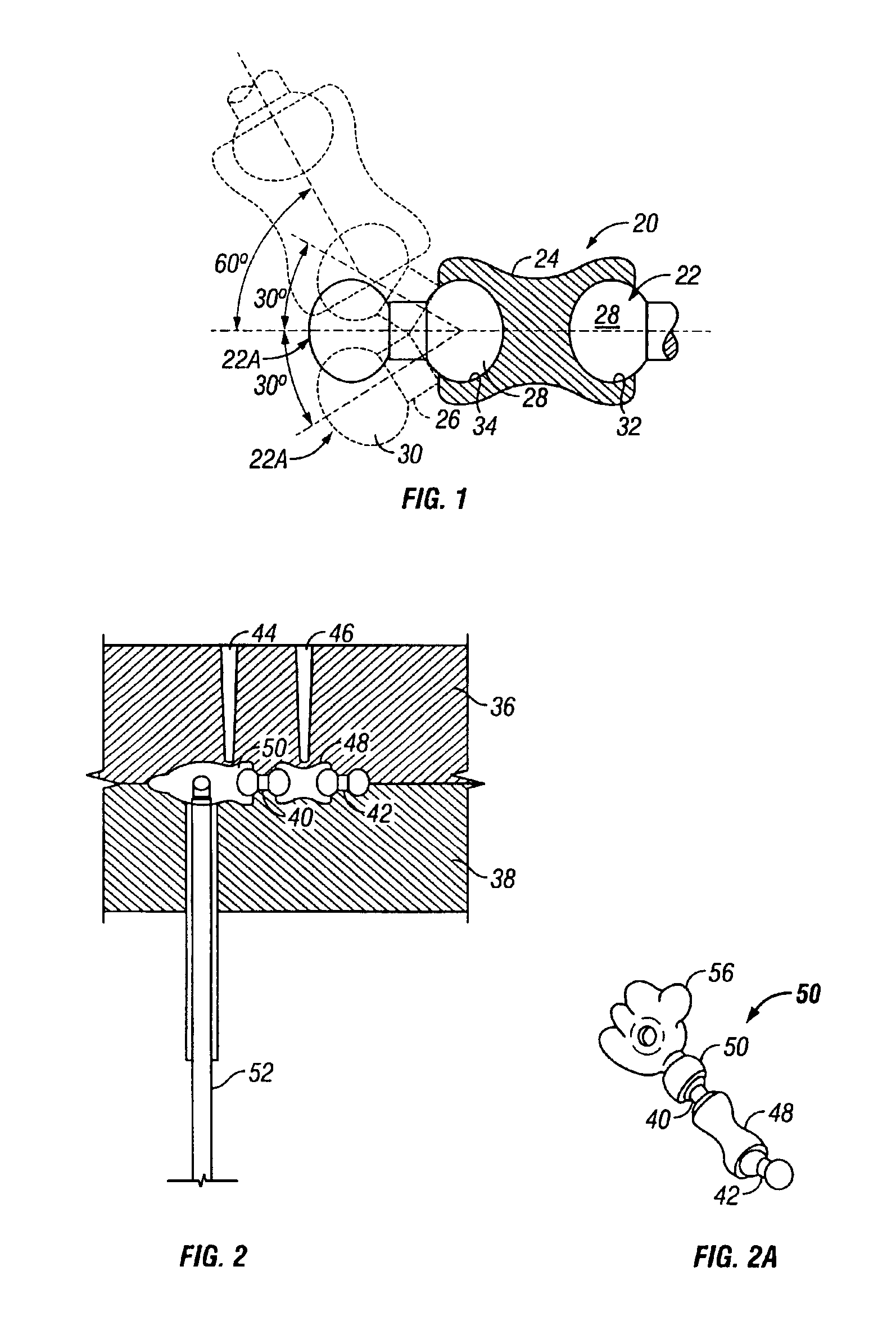
Lumen occluders made from thermodynamic materials
InactiveUS20020129819A1Regain shapeMale contraceptivesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismMelt temperatureMelting temperature
Disclosed are occluders and methods of their use. The occluders comprise shape-memory polymeric materials which, when heated above their crystalline melting temperatures, may be deformed from a first configuration into a second configuration. The occluder is then held in the deformed shape until it cools to a temperature below its crystalline melting temperature (T.sub.m) whereby it holds the deformed shape of the second configuration by virtue of the recrystallization of the polymeric occluder material. Upon reheating the occluder above its T.sub.m, the occluder will resume its original shape. In this manner, an occluder which has been deformed to reduce its diameter may be inserted into and positioned within a target lumen in the body and then allowed to warm to body temperature whereby it resumes its original diameter and results in the occlusion of the lumen. The occluders, according to preferred embodiments, may be used for reversible sterilization of mammals, among other surgical and non-surgical uses.
Owner:NUMED TECH
Metal attachment method and structure for attaching substrates at low temperatures
InactiveUS6097096ASemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesHigh densityDevice material
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Stretchable laminates of nonwoven web(s) and elastic film
A stretchable laminate, a process of making a stretchable laminate and a disposable absorbent article that includes a stretchable laminate are disclosed. The stretchable laminate includes a nonwoven web and a web of elastomeric material. The nonwoven web includes two layers of spunbond multi-component fibers and one layer of meltblown fibers. The multi-component fibers include a first polymer and a second polymer having different melt temperatures. Thermo-bonds are formed at least partially through the nonwoven web. Some of the thermo-bonds can be elongated in the cross-machine direction of the nonwoven web.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
EUV, XUV, and X-ray wavelength sources created from laser plasma produced from liquid metal solutions, and nano-size particles in solutions
InactiveUS6865255B2Efficient and inexpensiveEliminate damageX-ray tube electrodesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh power lasersUltraviolet
Special liquid droplet targets that are irradiated by a high power laser and are plasmarized to form a point source EUV, XUV and x-ray source. Various types of liquid droplet targets include metallic solutions, and nano-sized particles in solutions having a melting temperature lower than the melting temperature of some or all of the constituent metals, used a laser point source target droplets. The solutions have no damaging debris and can produce plasma emissions in the X-rays, XUV, and EUV(extreme ultra violet) spectral ranges of approximately 0.1 nm to approximately 100 nm, approximately 11.7 nm and 13 nm, approximately 0.5 nm to approximately 1.5 nm, and approximately 2.3 nm to approximately 4.5 nm. The second type of target consists of various types of liquids which contain as a miscible fluid various nano-size particles of different types of metals and non-metal materials.
Owner:CENT FLORIDA UNIV OF
Synchronous sintering process for electronic beam selection zone and three dimension layered producing device
ActiveCN1648802AHigh speedHigh precisionComputer controlElectron beam welding apparatusRapid scanHeat stress
The present invention relates to technology and apparatus with high energy beam to sinter or melt and deposit material successively to realize laminated solid manufacture. The present invention features that the electronic beam scan controller controls the electronic beam to scan fast in pattern projection mode for heating powder homogeneously. Each scanning of the electronic beam has short time in the selected area, so that the scan initiating point has no great temperature change generated during the whole scanning course. Through one or several frames of scanning, the material in the forming area has temperature synchronously raised to reach the sintering or re-melting temperature for deposition onto the forming area before synchronous cooling. The present invention has greatly reduced heat stress and raised forming precision and quality.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for joining conductive structures and an electrical conductive article
InactiveUS20030019568A1Printed circuit assemblingSolid-state devicesMelt temperatureMelting temperature
Embodiments of the invention include a method comprising disposing a thin metallic layer having a low melting temperature between one end of a conductive post on a substrate and a conducting structure on an opposing substrate. Heated platens in contact with the substrates can apply pressure and heat to the thin metallic layer and cause it to be entirely consumed and subsequently transformed into a bonding layer having a melting temperature higher than the melting temperature of the original thin metallic layer. Prior to, during, or after the conductive post is bonded to the conducting structure, the region around the conductive post and between the substrates may be filled with a dielectric material, such as polyimide.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
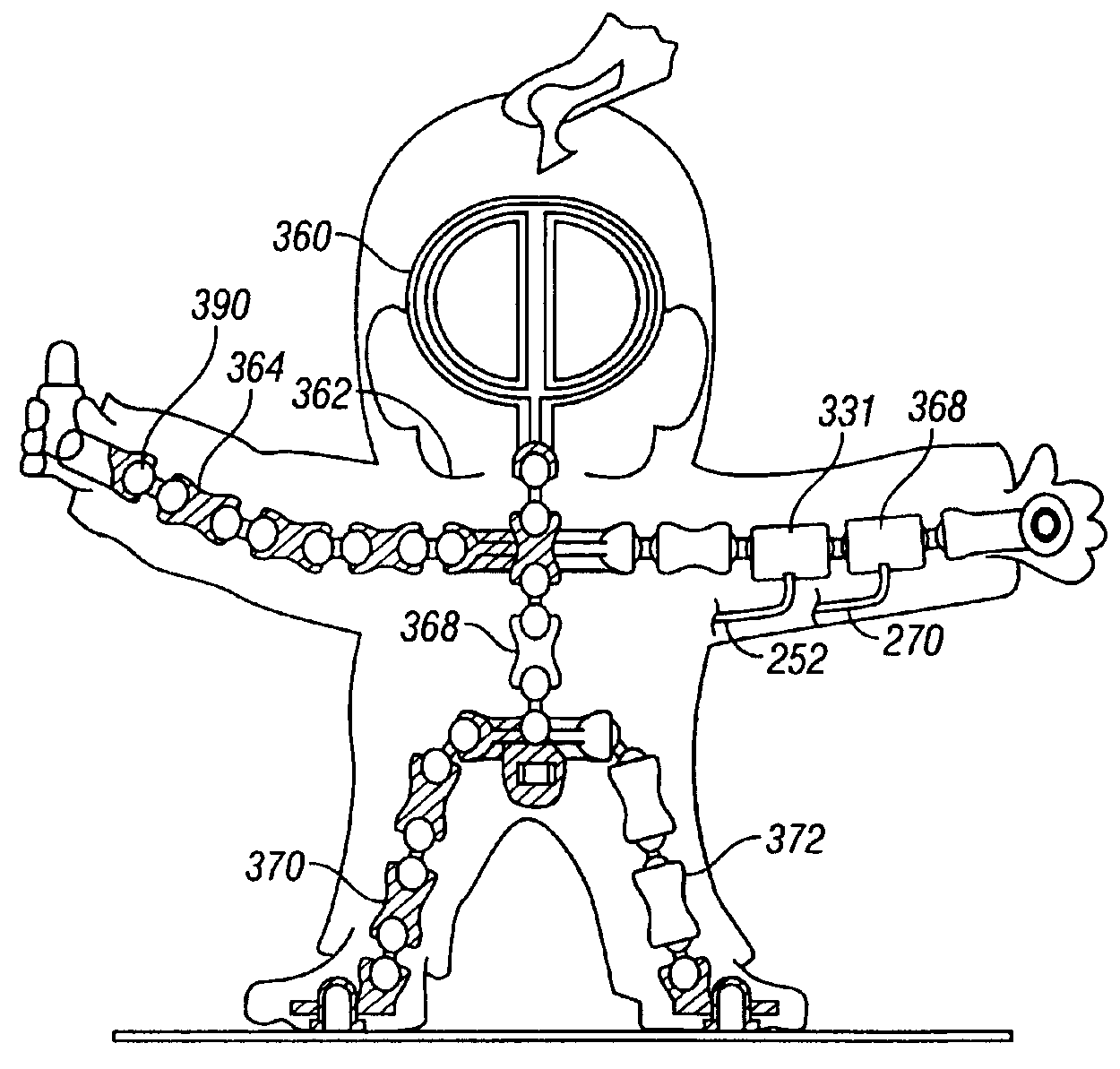
Jointed linkage system
A system for molding a jointed linkage support system with joints that allow movement and bending in many directions and degrees of freedom. A chain-like linkage system made up of a series of joints is molded in a single step from materials having different melting temperatures in a series of alternating communicating mold cavities. The jointed linkage support system emerges from the mold fully assembled. An electrical switch may be provided within one of the joints between sleeves and rods whereby movement of the rod relative to the sleeve actuates the switch.
Owner:C J ASSOCS
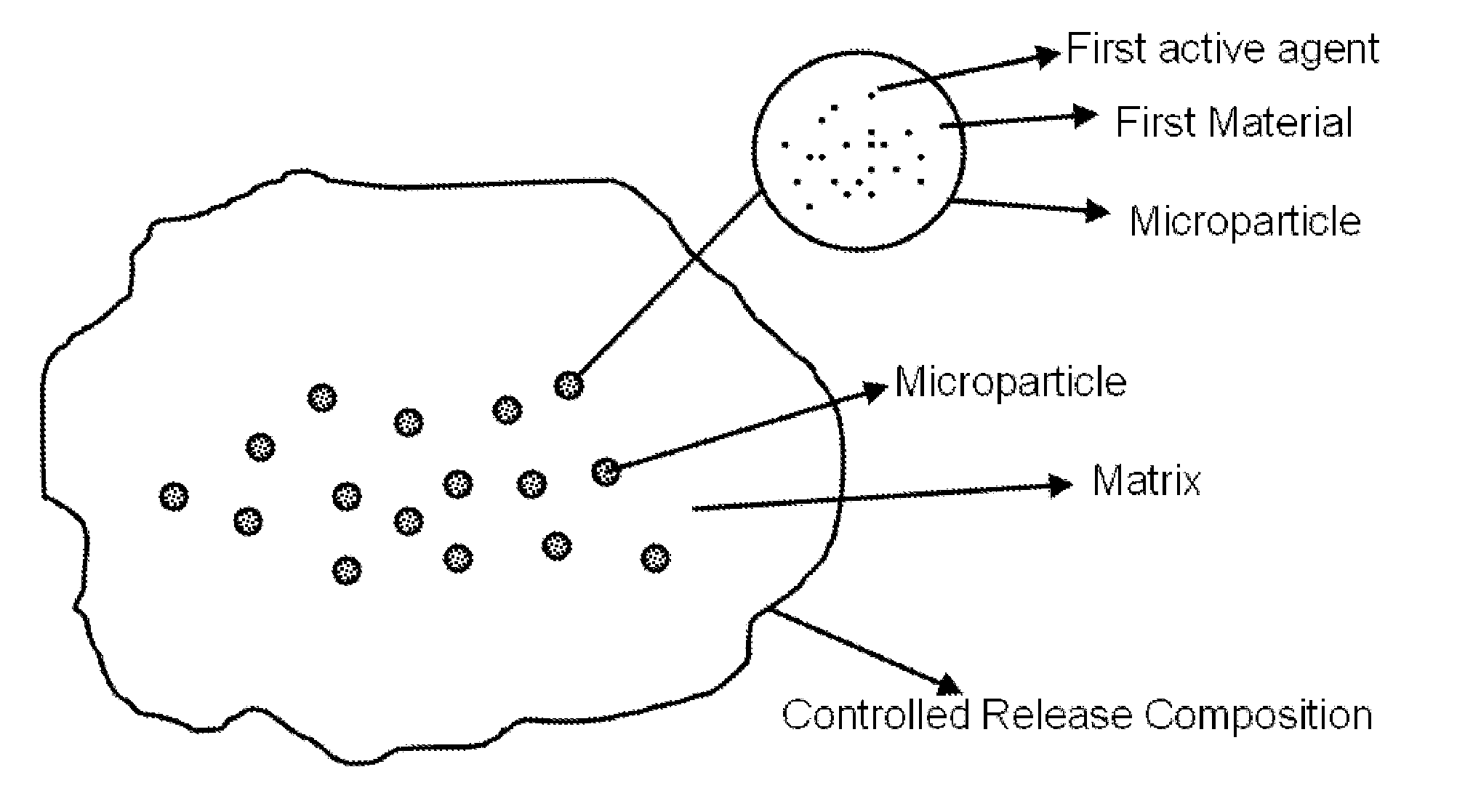
Controlled releasing composition
A controlled releasing composition comprising a plurality of microparticles and a matrix as well as the preparation method thereof is disclosed. The plurality of microparticles comprise a first material and the matrix comprises a second material. The melting temperature of the first material is higher than the melting temperature of the second material.
Owner:XU JIANJIAN +2
Polymeric encapsulation of nanoparticles
Polymeric nanoencapsulation methods, which combine sonication and nonsolvent temperature induced crystallization, are provided. The steps include (a) providing active agent nanoparticles having an average diameter between about 5 and about 100 nm; (b) treating said active agent nanoparticles (e.g., a superparamagnetic material) with an anionic surfactant to form modified active agent nanoparticles; (c) mixing the modified active agent nanoparticles with a solution of a polymer in a solvent at a first temperature, which is greater than the melting temperature of the polymer and less than the boiling point of the solvent to form a first mixture, said mixing comprising the use of sonication; (d) mixing a non-solvent with the first mixture to form a second mixture, the non-solvent being a non-solvent for the solvent and for the polymer and having a boiling point greater than the melting temperature of the polymer; (e) sonicating the second mixture to form an emulsion; and (f) cooling the emulsion to a second temperature and at a rate effective to precipitate polymeric nanoparticles comprising the polymer with the modified active agent nanoparticles dispersed therein.
Owner:SUTHERLAND ASBILL BRENNAN LLP +2
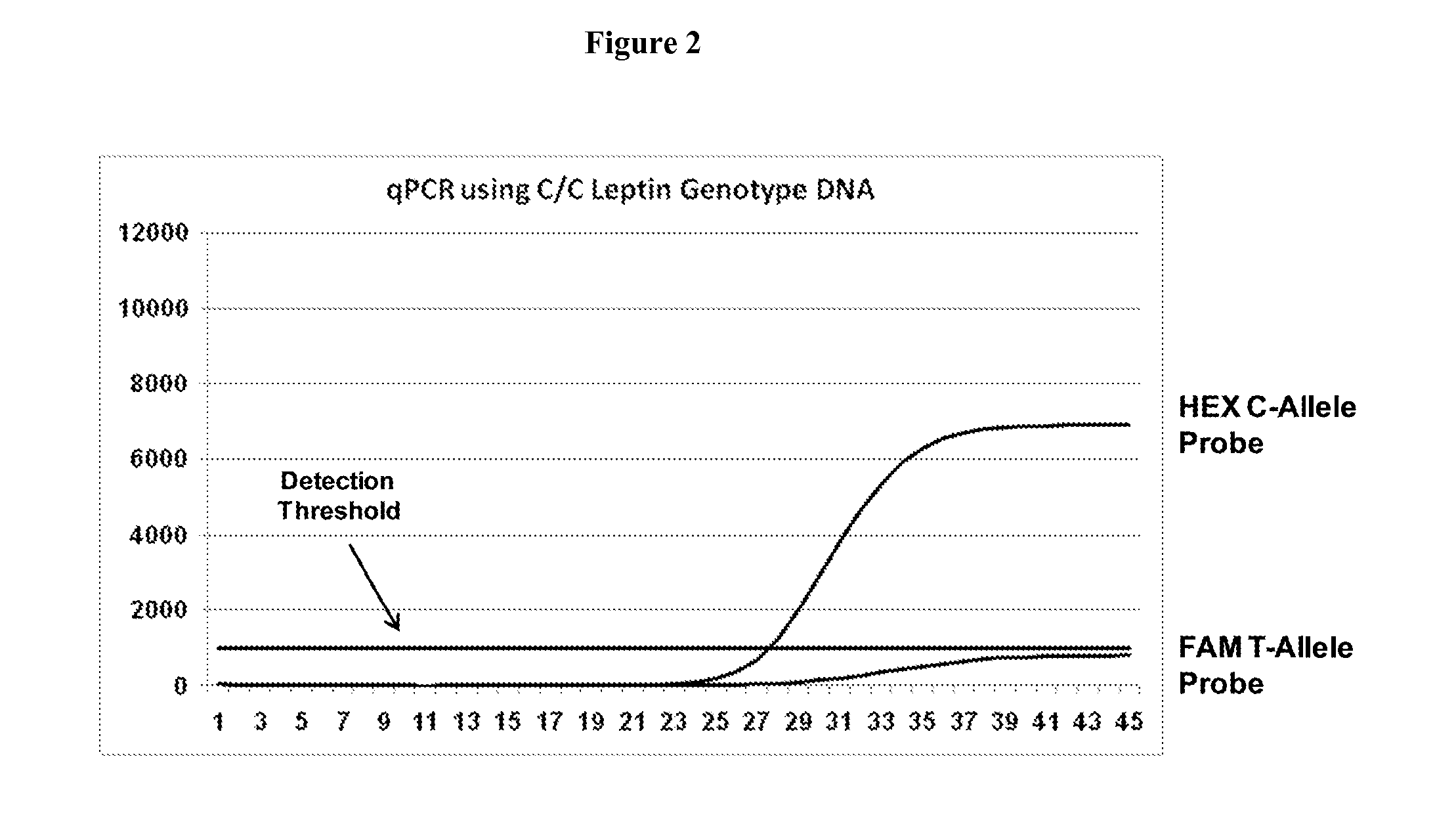
Methods of genotyping using differences in melting temperature
InactiveUS20060172324A1Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationOligonucleotide primersGenotyping
The present invention relates to the identification of a particular nucleotide polymorphism in a nucleic acid sample in a single reaction utilizing oligonucleotide primers with different melting temperature characteristics.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Thermoplastic component repair
Thermoplastic components may experience local damage, including cracks and decohesion of fiber reinforcements, among others. Such thermoplastics may be repaired by heating them to a suitable softening / melting temperature under pressure and maintaining them under pressure and at elevated temperature until the damage is healed. This may be done in-place using custom-fabricated, suitably-shaped die portions maintained under pressure by magnetic attraction. Various heating methods and die portion fabrication methods are described.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
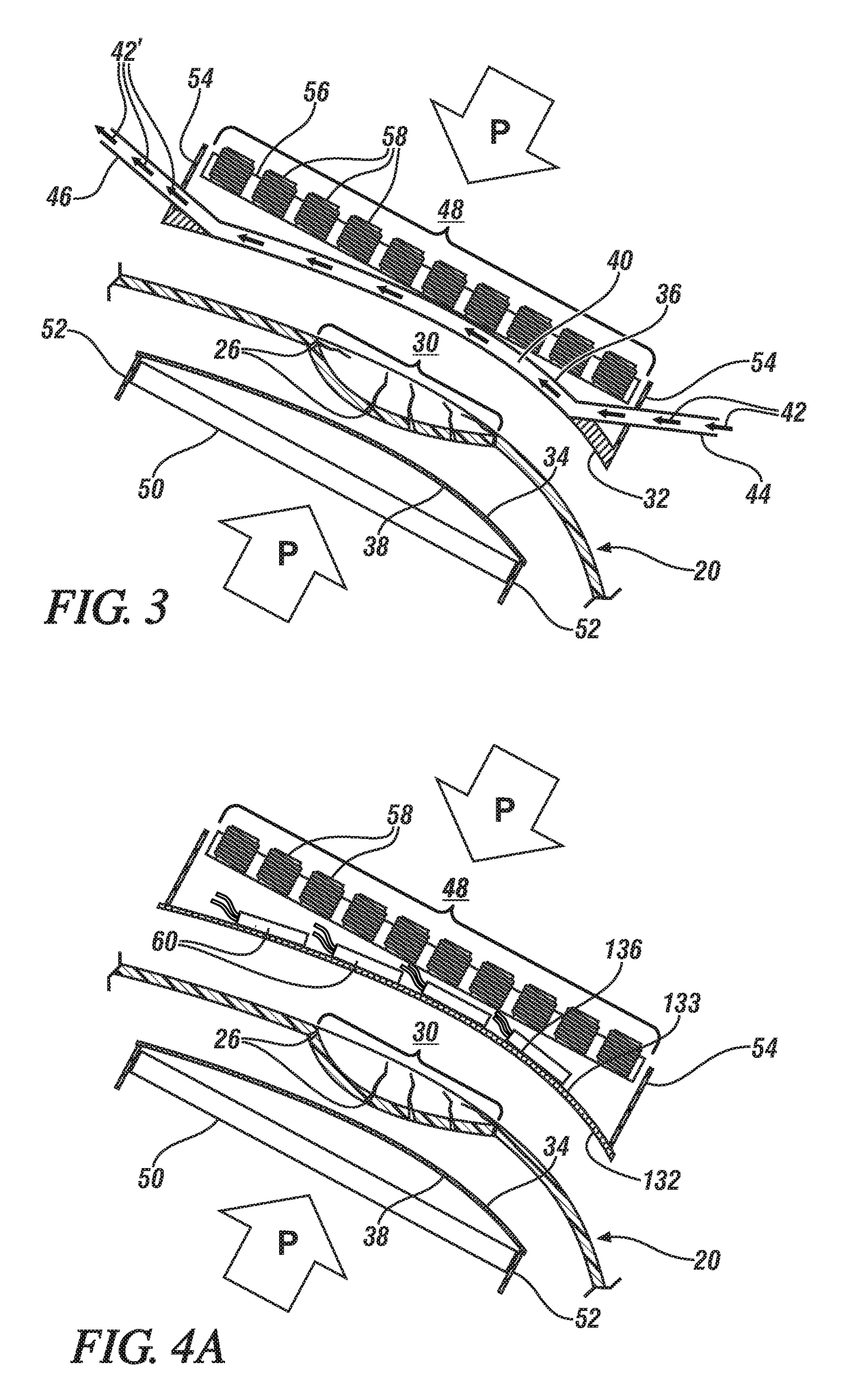
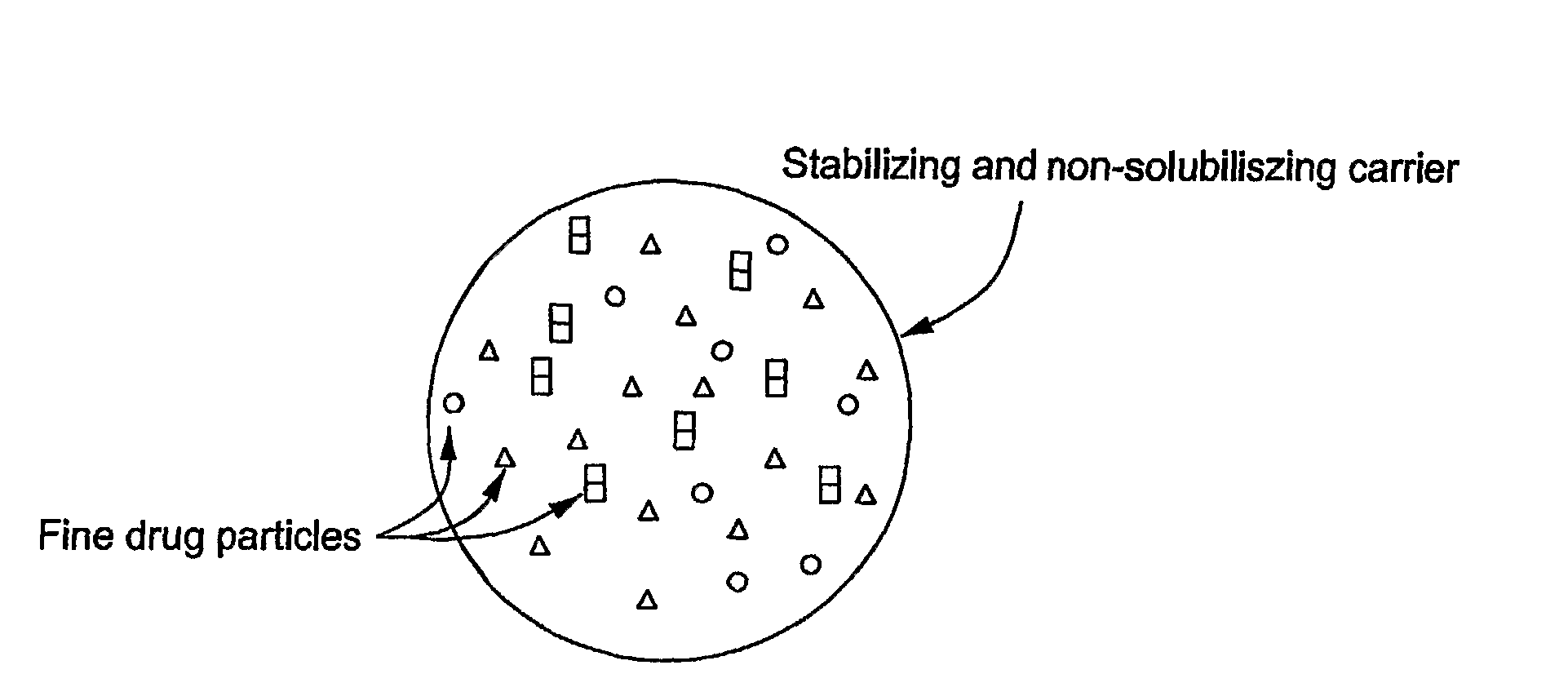
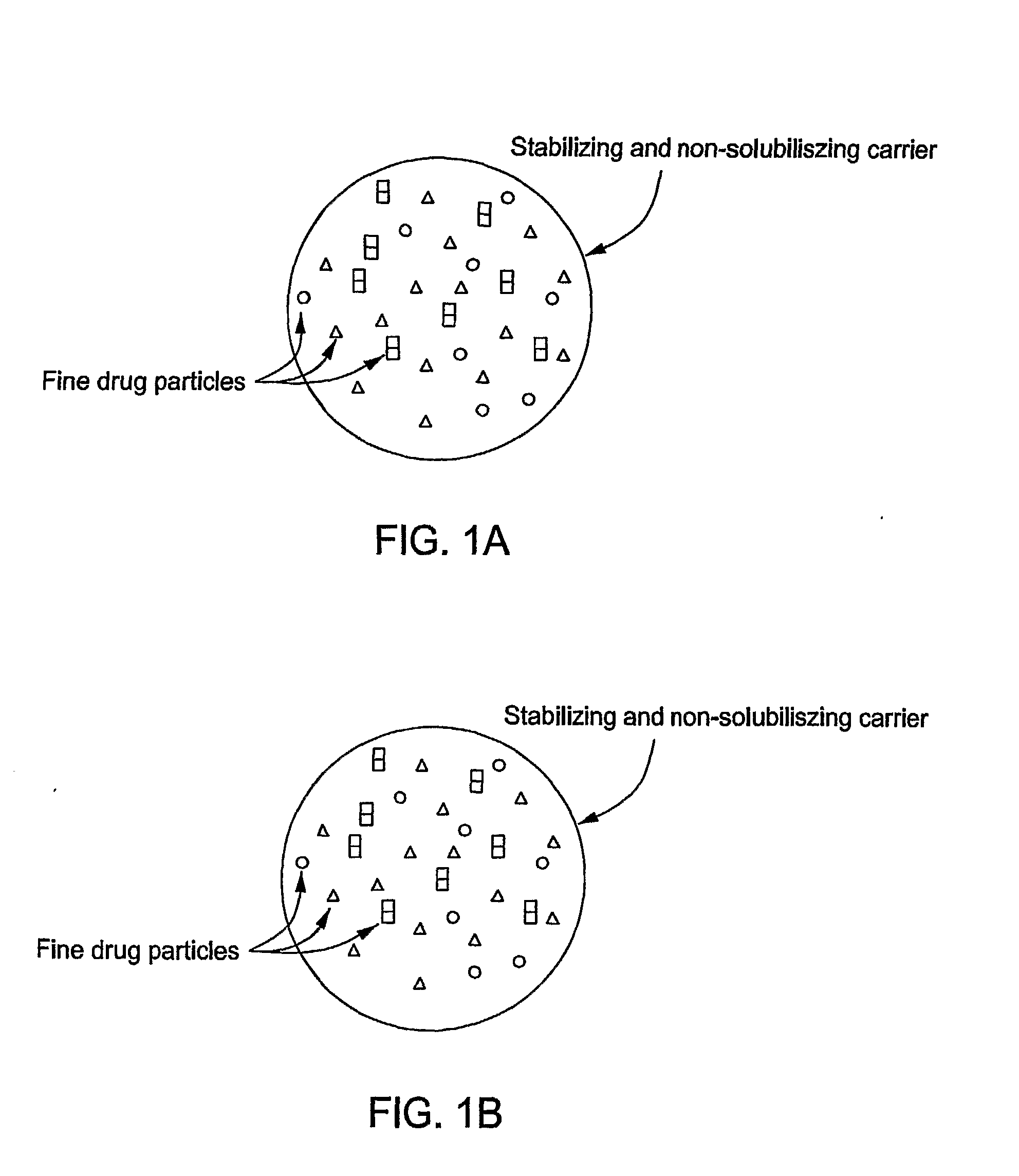
Stabilized Hme Composition With Small Drug Particles
ActiveUS20080274194A1Facilitated releaseReduce releasePowder deliveryCyclic peptide ingredientsAntioxidantCarrier system
A hot-melt extruded composition having finely divided drug-containing particles dispersed within a polymeric and / or lipophyllic carrier matrix is provided. The carrier softens or melts during hot-melt extrusion but it does not dissolve the drug-containing particles during extrusion. As a result, a majority or at least 90% wt. of the drug-containing particles in the extrudate are deaggregated during extrusion into essentially primary crystalline and / or amorphous particles. PEO is a suitable carrier material for drugs insoluble in the solid state in this carrier. Various functional excipients can be included in the carrier system to stabilize the particle size and physical state of the drug substance in either a crystalline and / or amorphous state. The carrier system is comprised of at least one thermal binder, and may also contain various functional excipients, such as: super-disintegrants, antioxidants, surfactants, wetting agents, stabilizing agents, retardants, or similar functional excipients. A hydrophilic polymer, such as hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC E15), polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), or poloxamer, and / or a surfactant, such as sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS), can be included in the composition. A process for preparing the extrudate is conducted at a temperature approximating or above the softening or melting temperature of the matrix and below the point of solubilization of drug-containing particles in the carrier system, and below the recrystallization point in the case of amorphous fine drug particles.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Three dimensional printing
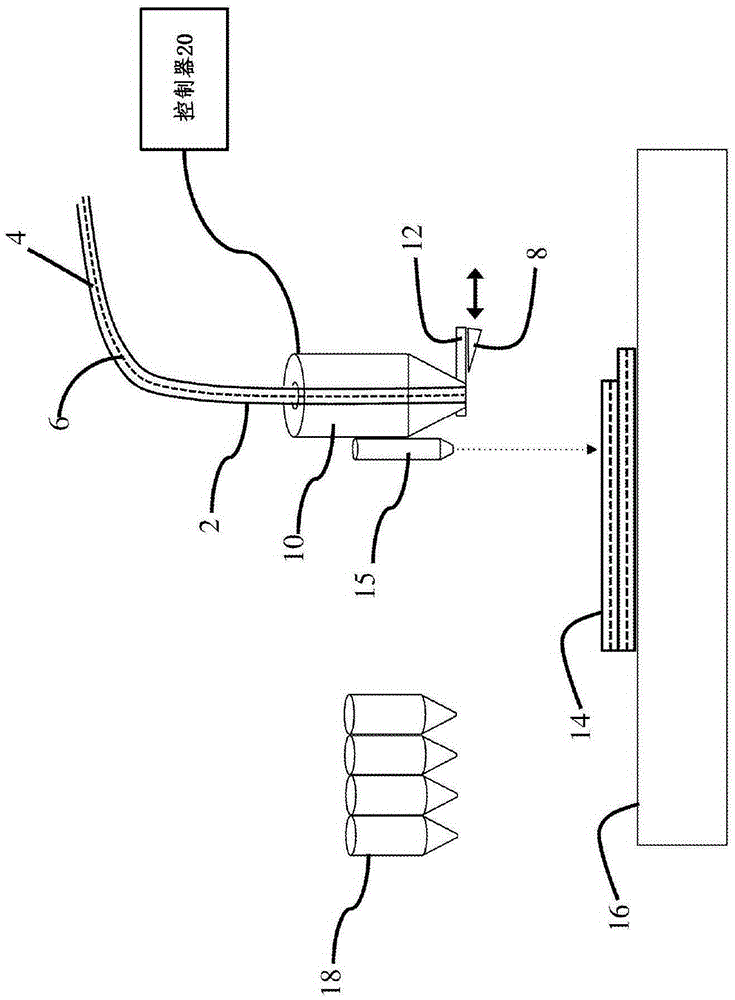
ActiveCN105339154AHigh strengthStrength is easy to customizeLamination ancillary operationsLaminationPolymer scienceMelt temperature
Three dimensional printers, and reinforced filaments, and their methods of use are described. A void free reinforced filament is fed into an extrusion nozzle. The reinforced filament includes a core, which may be continuous or semi-continuous, and a matrix material surrounding the core. The reinforced filament is heated to a temperature greater than a melting temperature of the matrix material and less than a melting temperature of the core prior to extruding the filament from the extrusion nozzle.
Owner:格雷戈里·托马斯·马克
System and method for hermetic seal formation
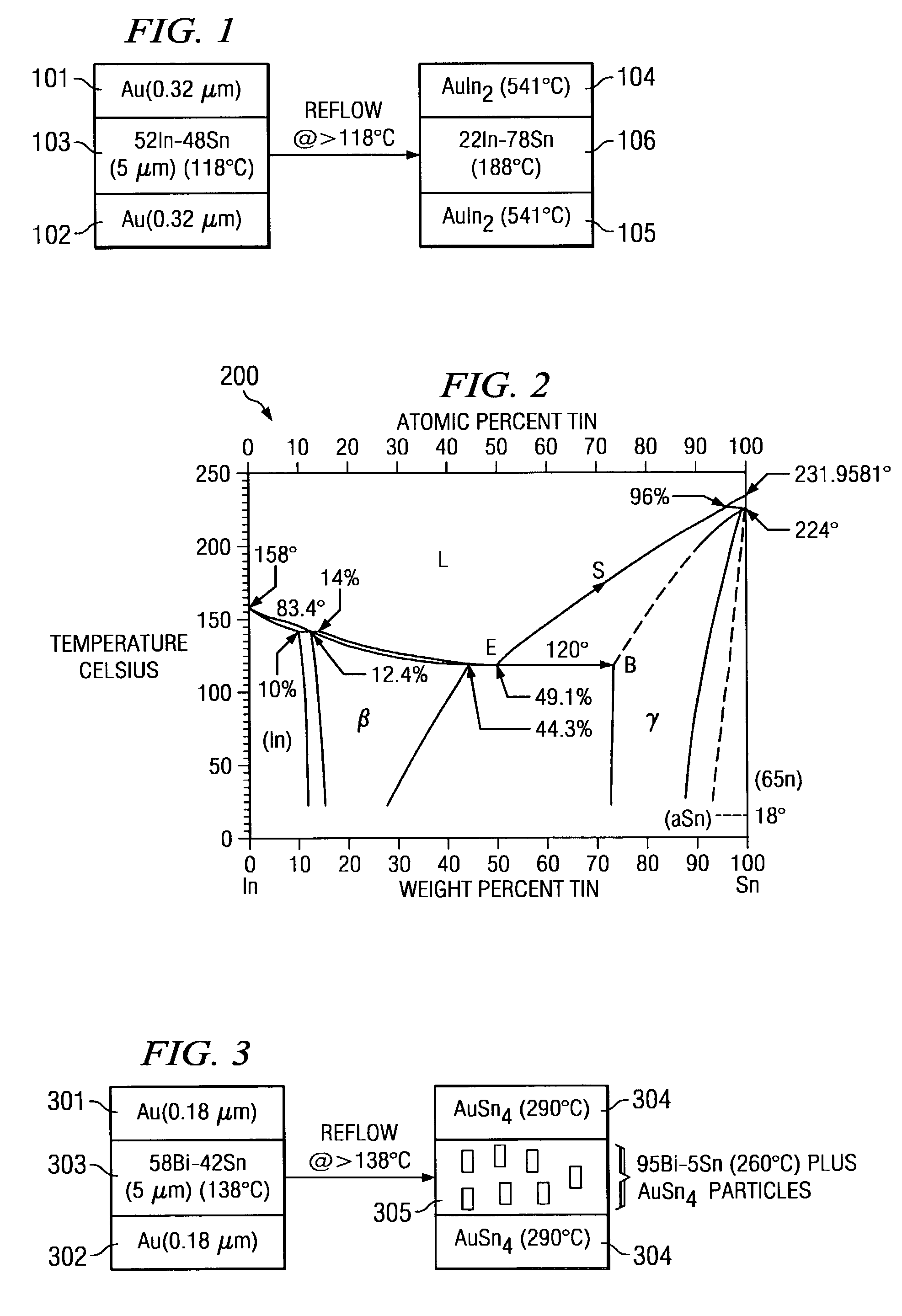
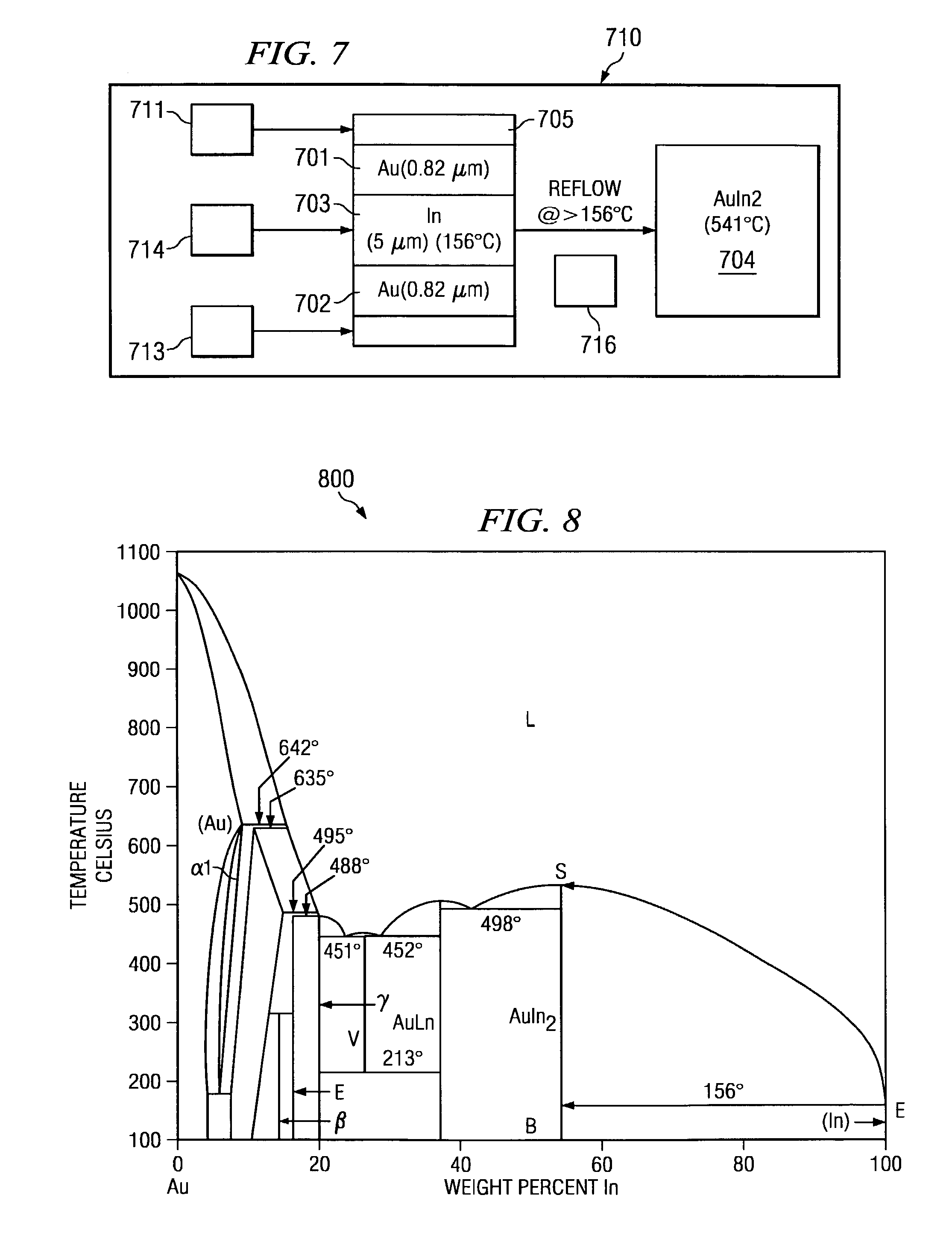
InactiveUS7168608B2High melting temperatureMinimize thermal induced warpageEngine sealsSolid-state devicesMetallurgyHermetic seal
System and method for formation of a hermetic seal with an significantly greater melting temperature than the melting temperature of the solder employed. The hermetic seal is formed from a solder with a low melting point and a metal having a predetermined thickness that corresponds to the solder. The solder and metal combination undergoes reflow for a period of time relative to the solder thickness. The resultant seal has a melting point at a temperature significantly greater than the melting temperature of the solder.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
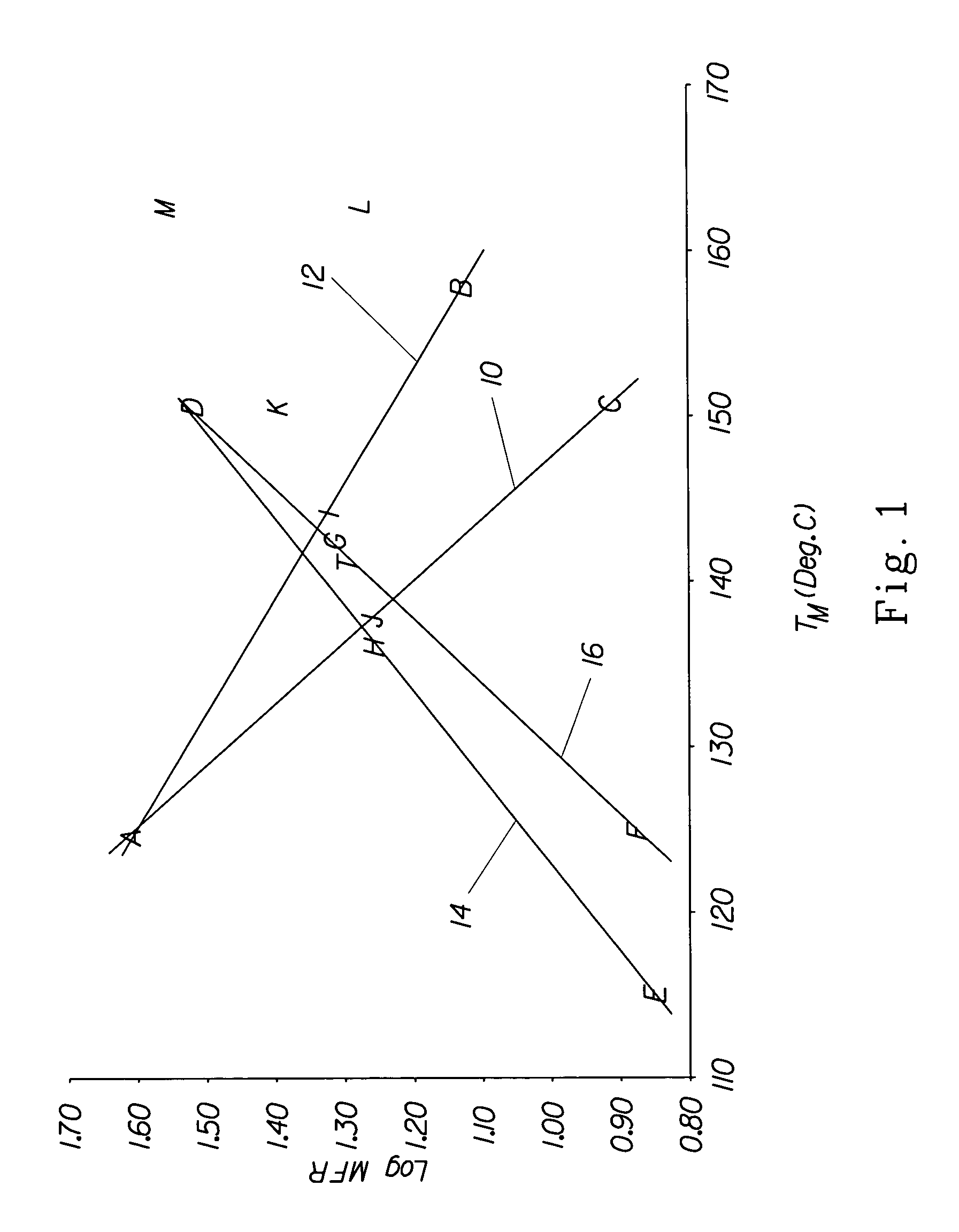
Flexible poly(arylene ether) composition and articles thereof
A thermoplastic composition comprises poly(arylene ether) having an initial intrinsic viscosity greater than 0.25 dl / g as measured in chloroform at 25° C.; a polyolefin having a melt temperature greater than or equal to 120° C. and a melt flow rate of 0.3 to 15; a first block copolymer having a aryl alkylene content greater than or equal to 50 weight percent based on the total weight of the first block copolymer; a second block copolymer having an aryl alkylene content less than 50 weight percent based on the total weight of the second block copolymer; and a flame retardant, wherein the poly(arylene ether) is present in an amount greater than the amount of polyolefin. The composition is useful in the production of covered wire.
Owner:SHPP GLOBAL TECH BV
Fibers and nonwovens comprising polypropylene blends and mixtures
InactiveUS7491770B2Conjugated synthetic polymer artificial filamentsNon-woven fabricsFiberPolymer science
Fibers and nonwoven materials comprising polymeric blends and polymeric mixtures that incorporate a blend of a first metallocene polypropylene and a second polypropylene are described. The first and second polypropylenes have a predetermined relationship for the melt temperature and the melt flow rate of the individual polypropylenes. Also described are fibers (including bicomponent fibers) and nonwoven materials made from the fibers where the fibers are extruded using the polymeric blends, and / or the polymeric mixtures.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com