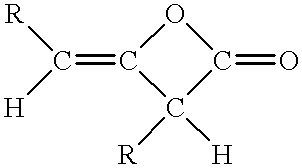
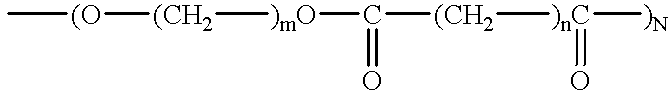
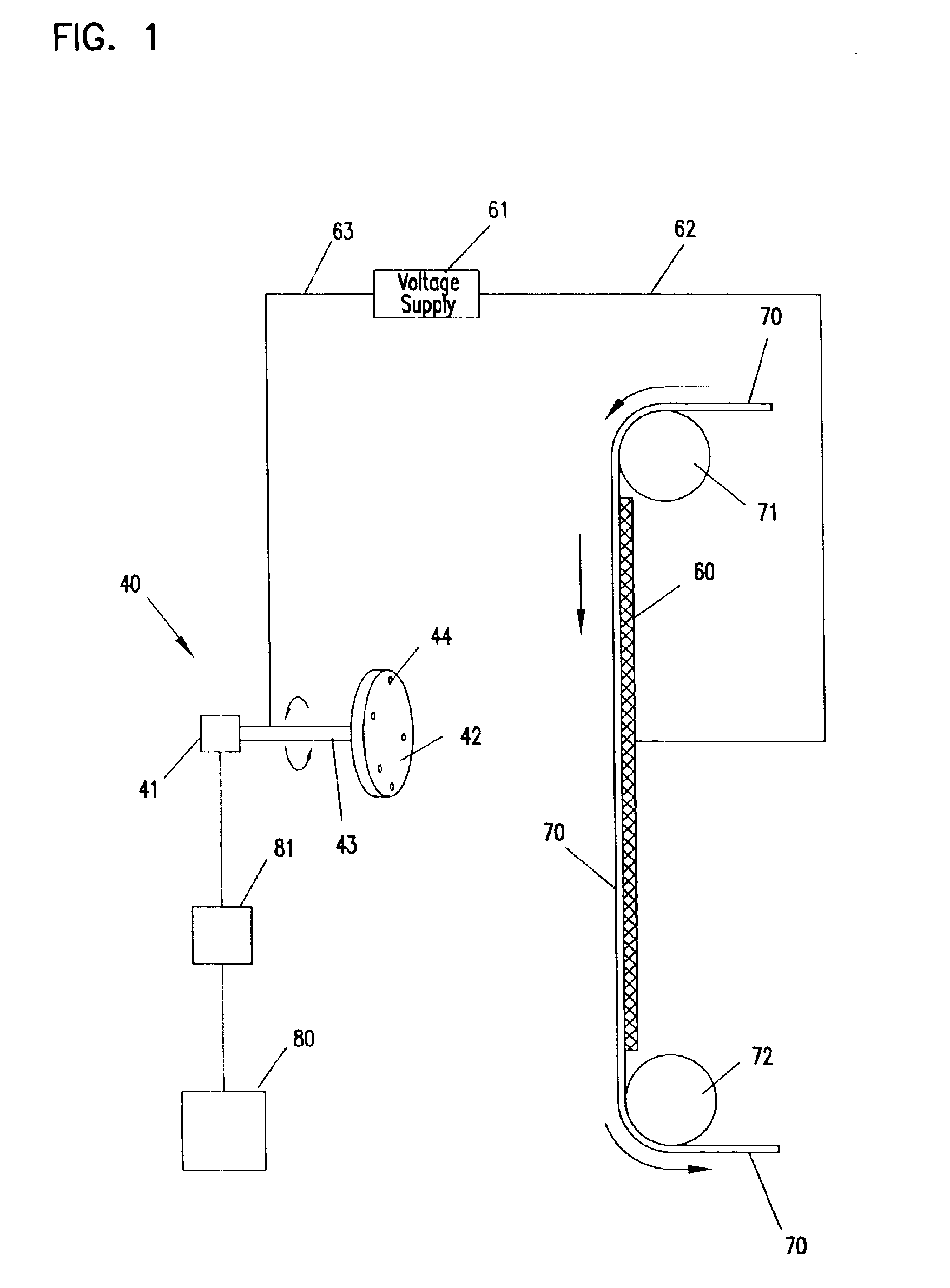
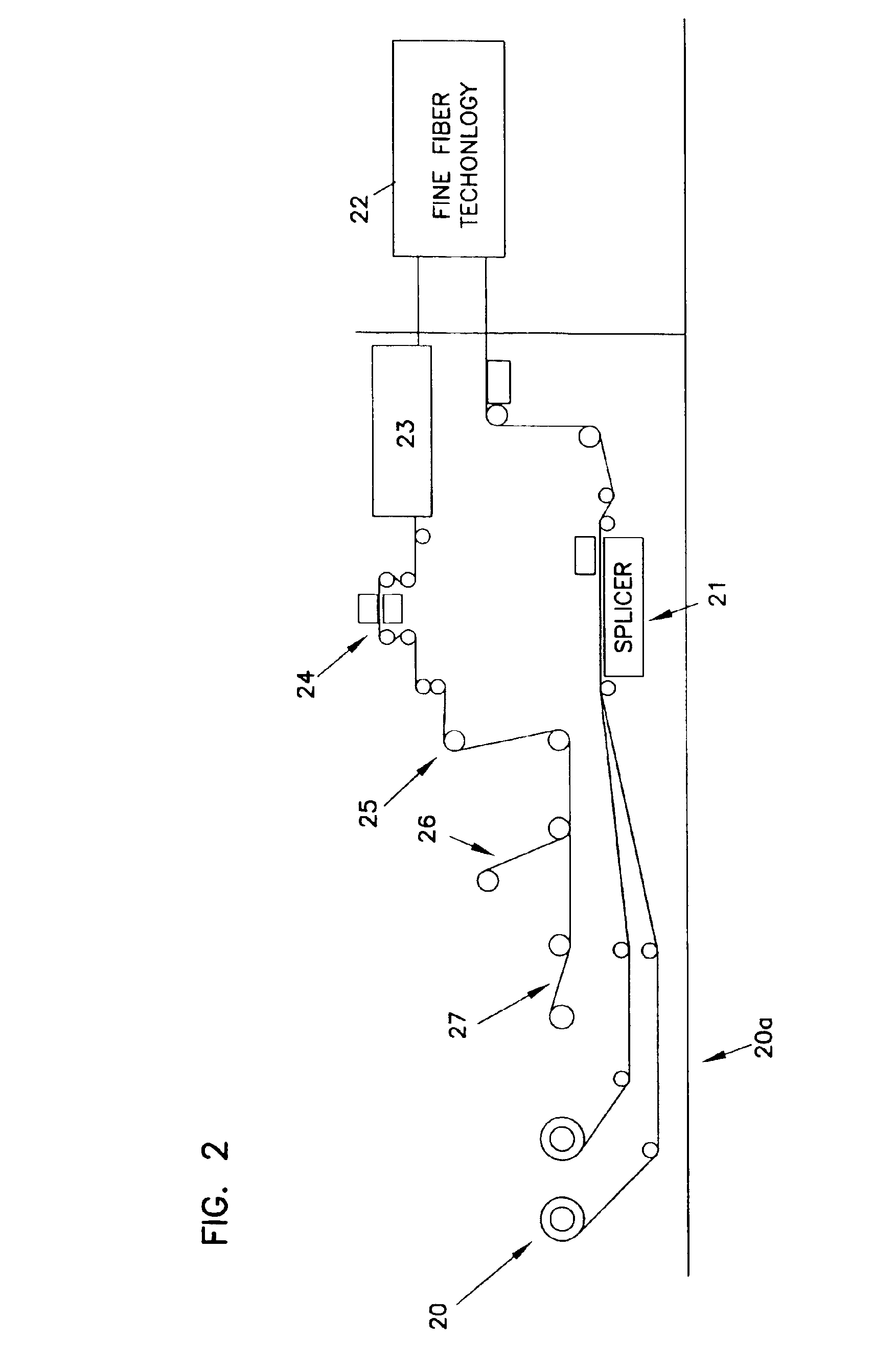
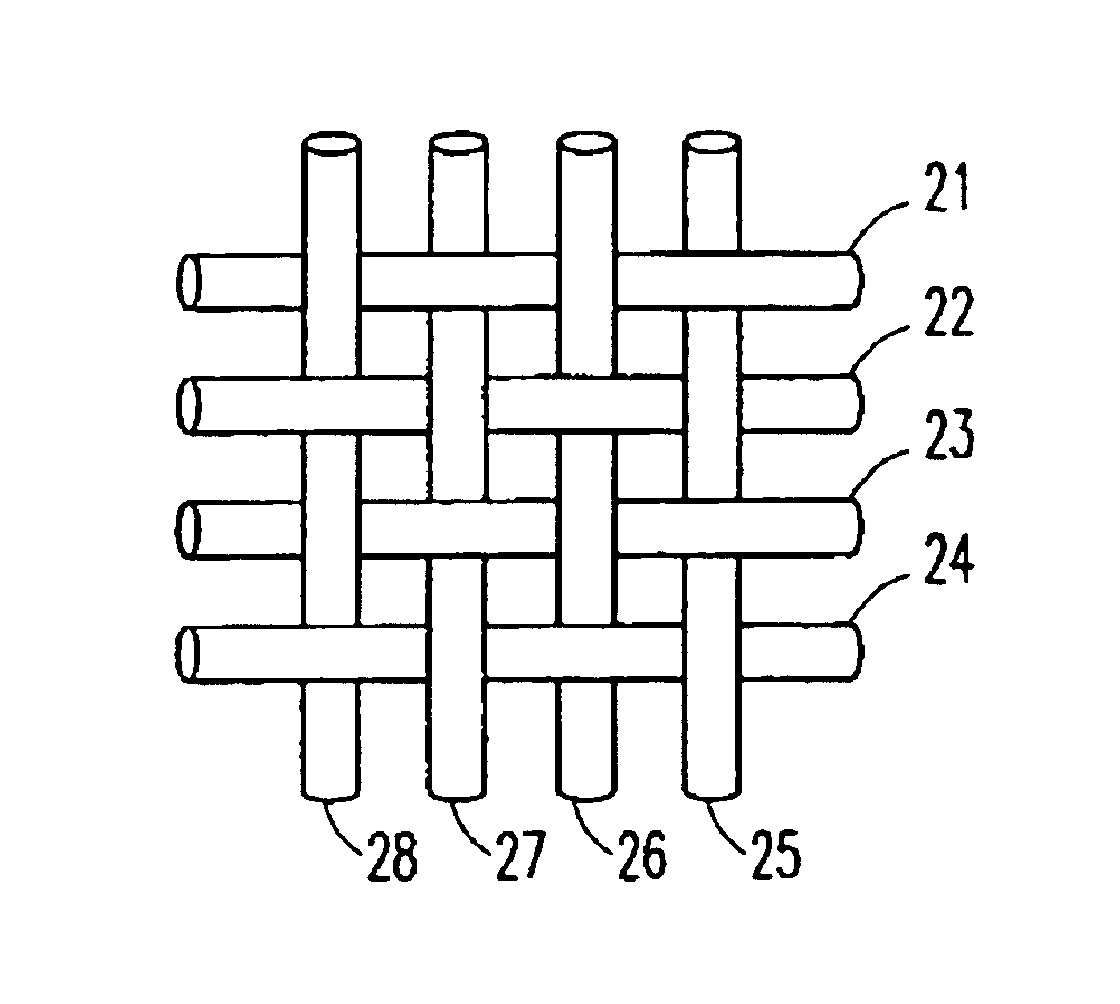
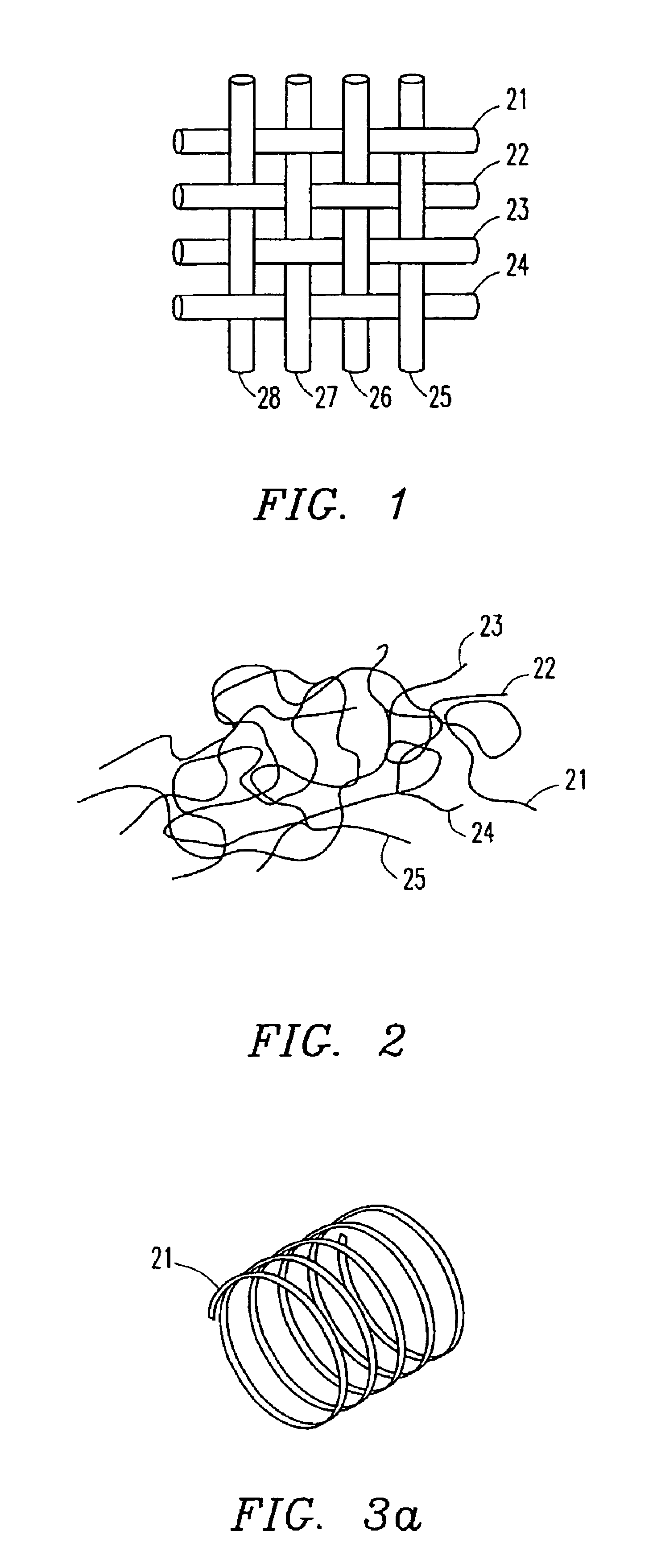
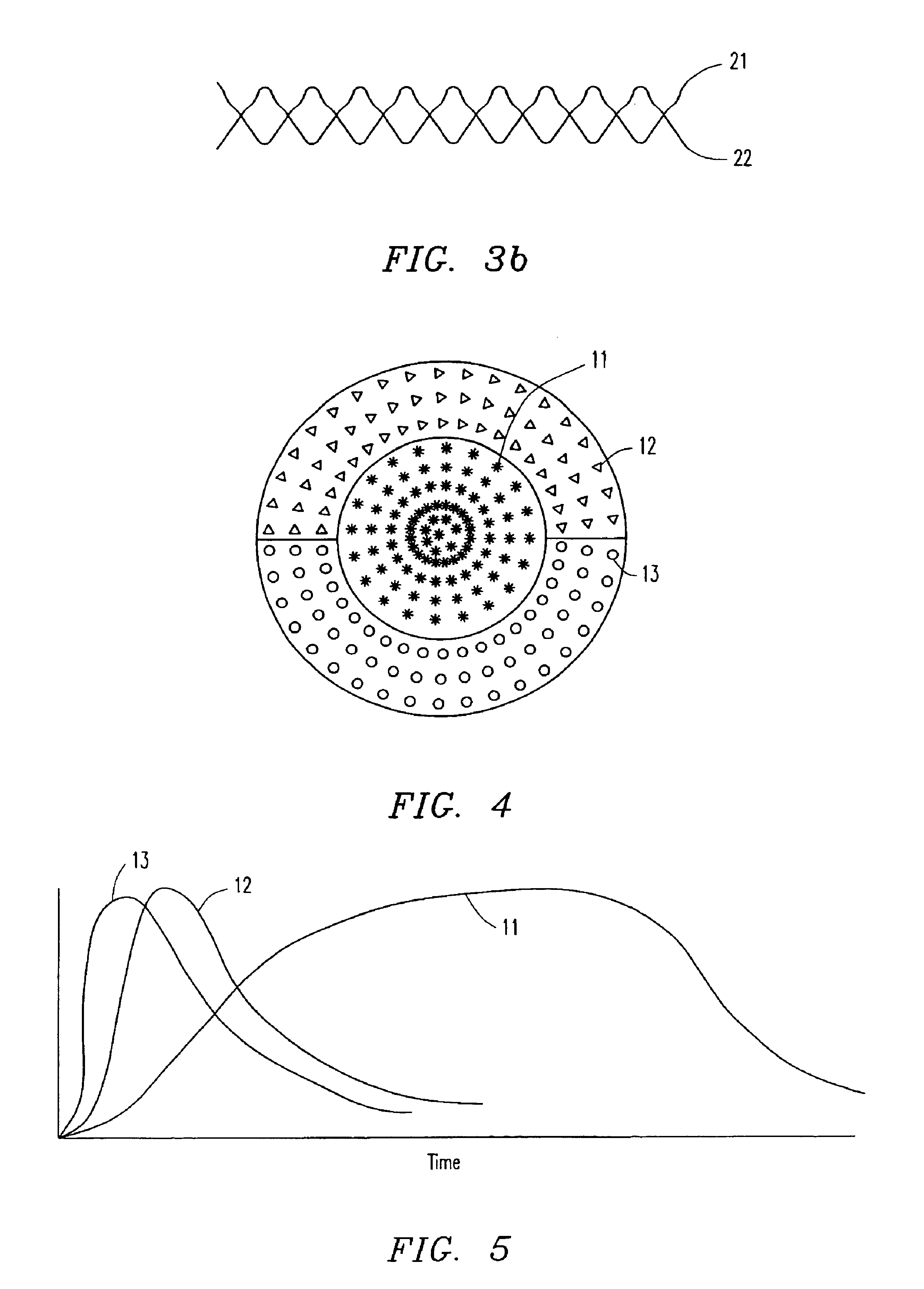
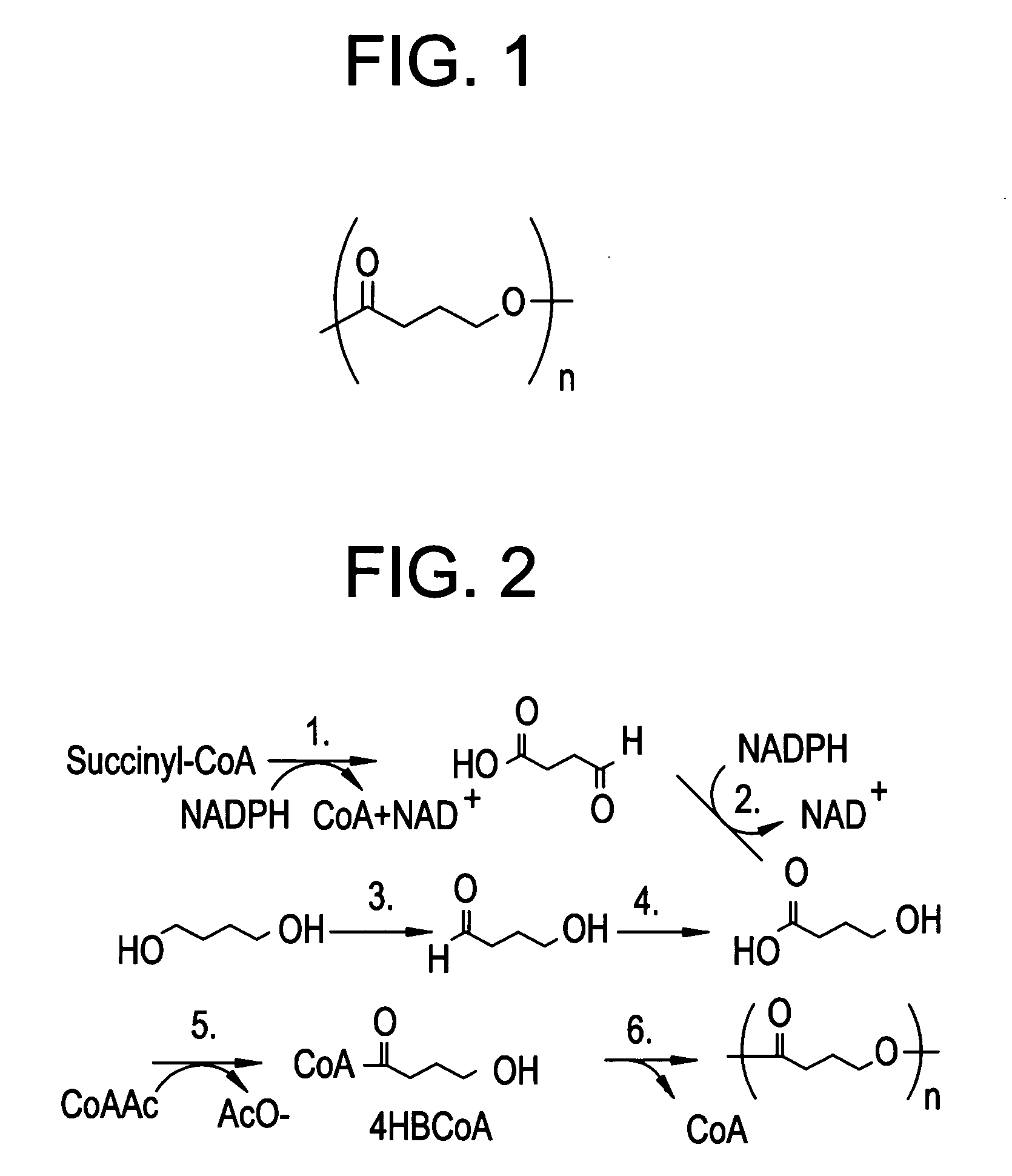
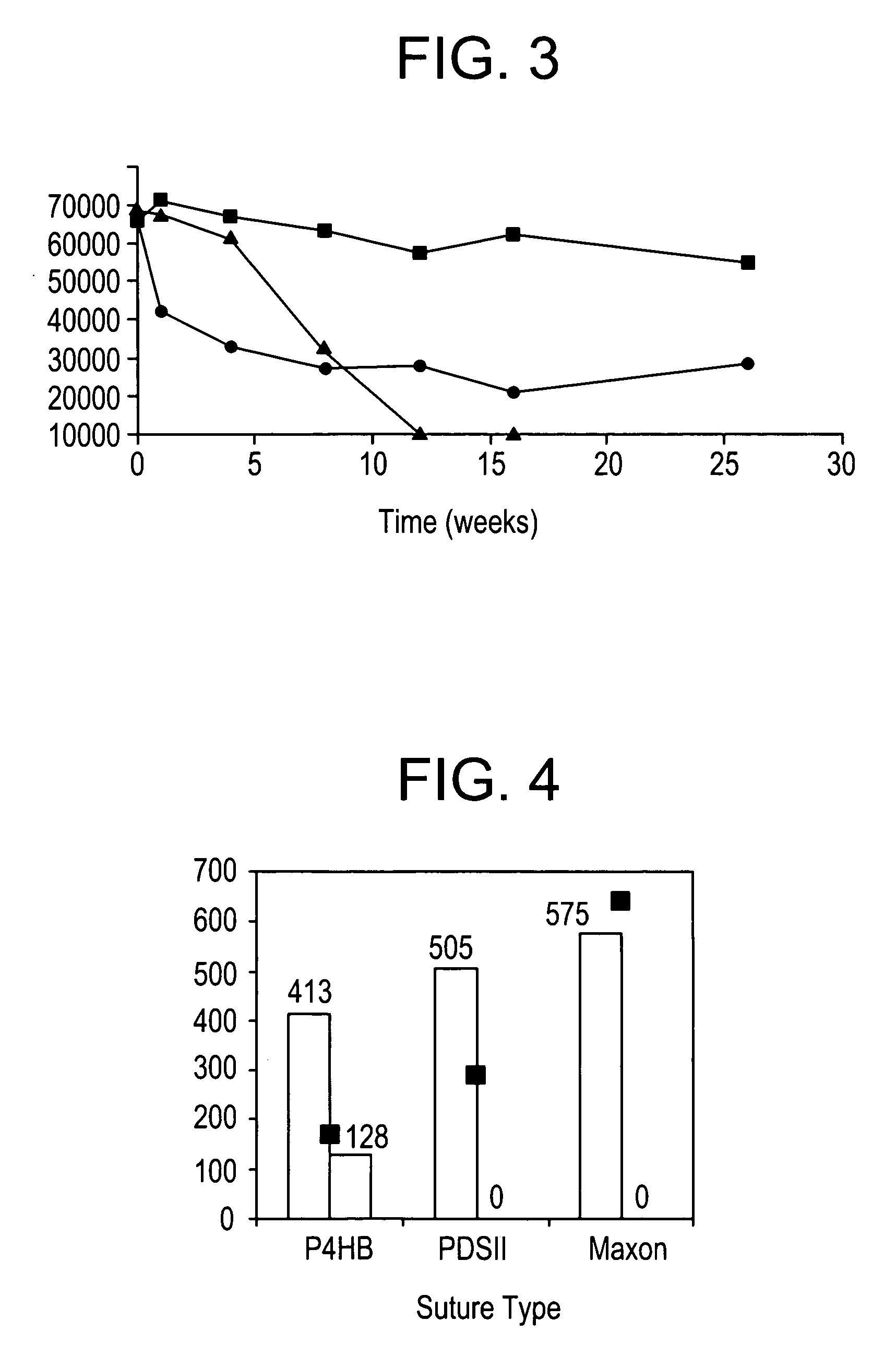
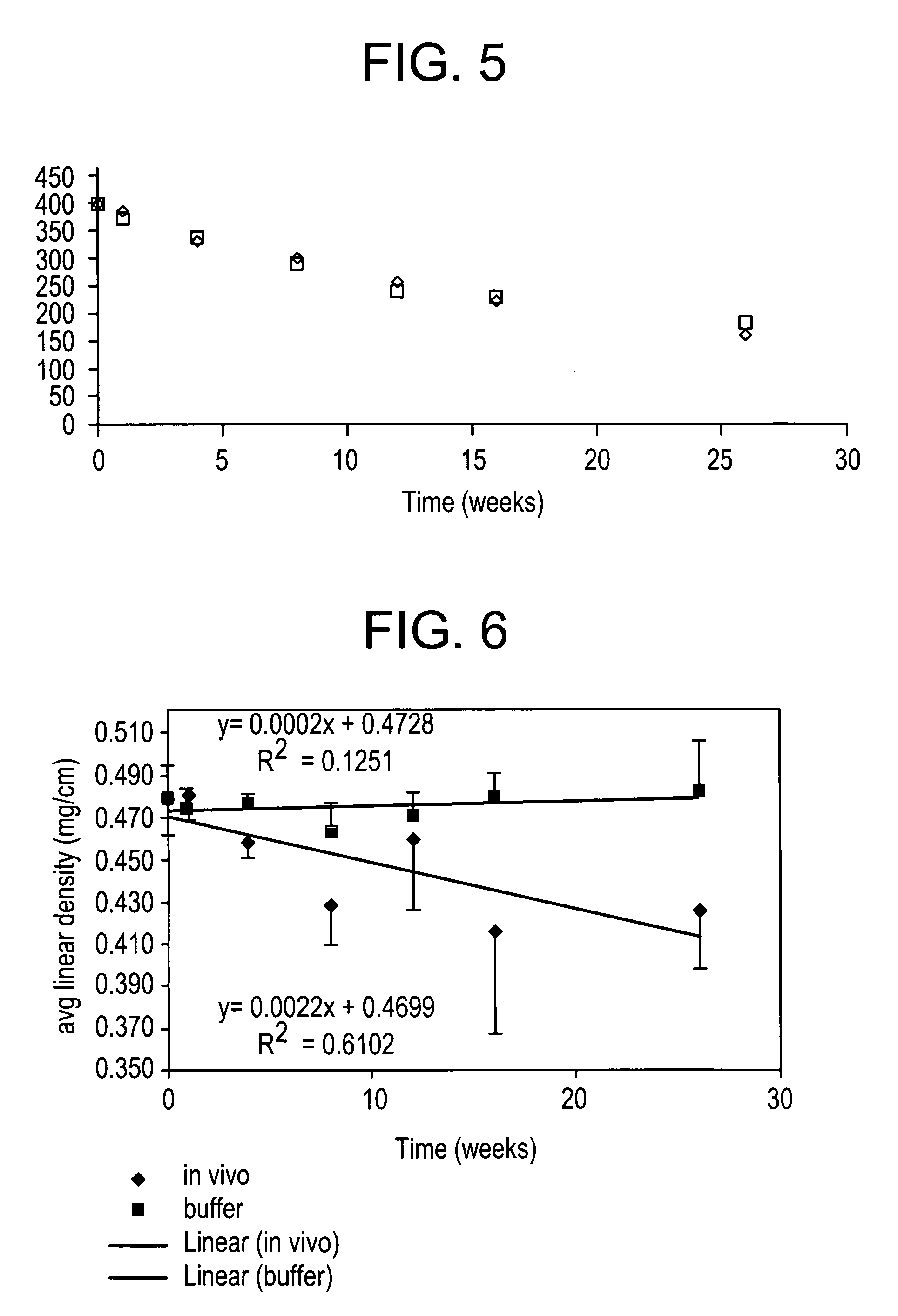
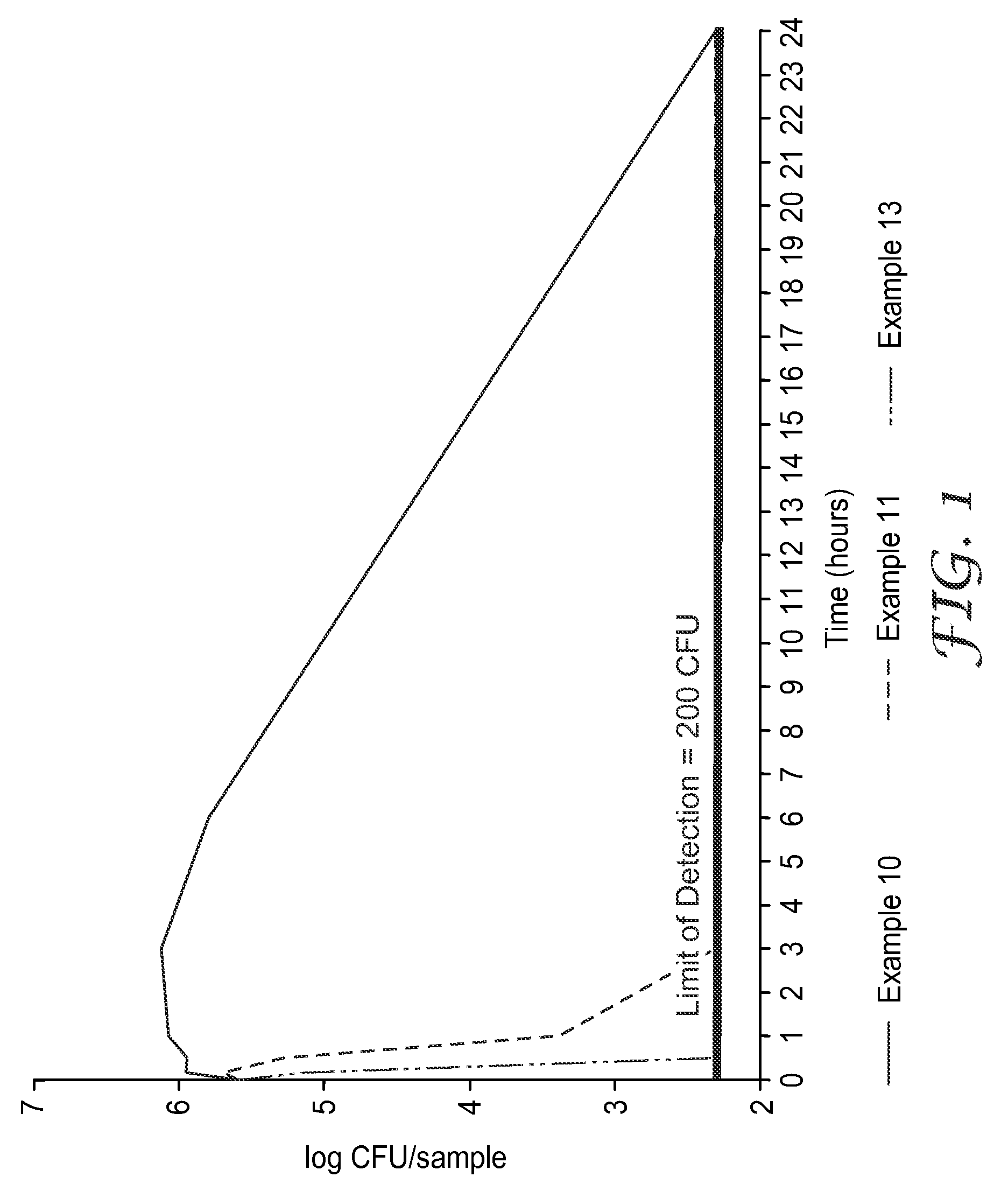
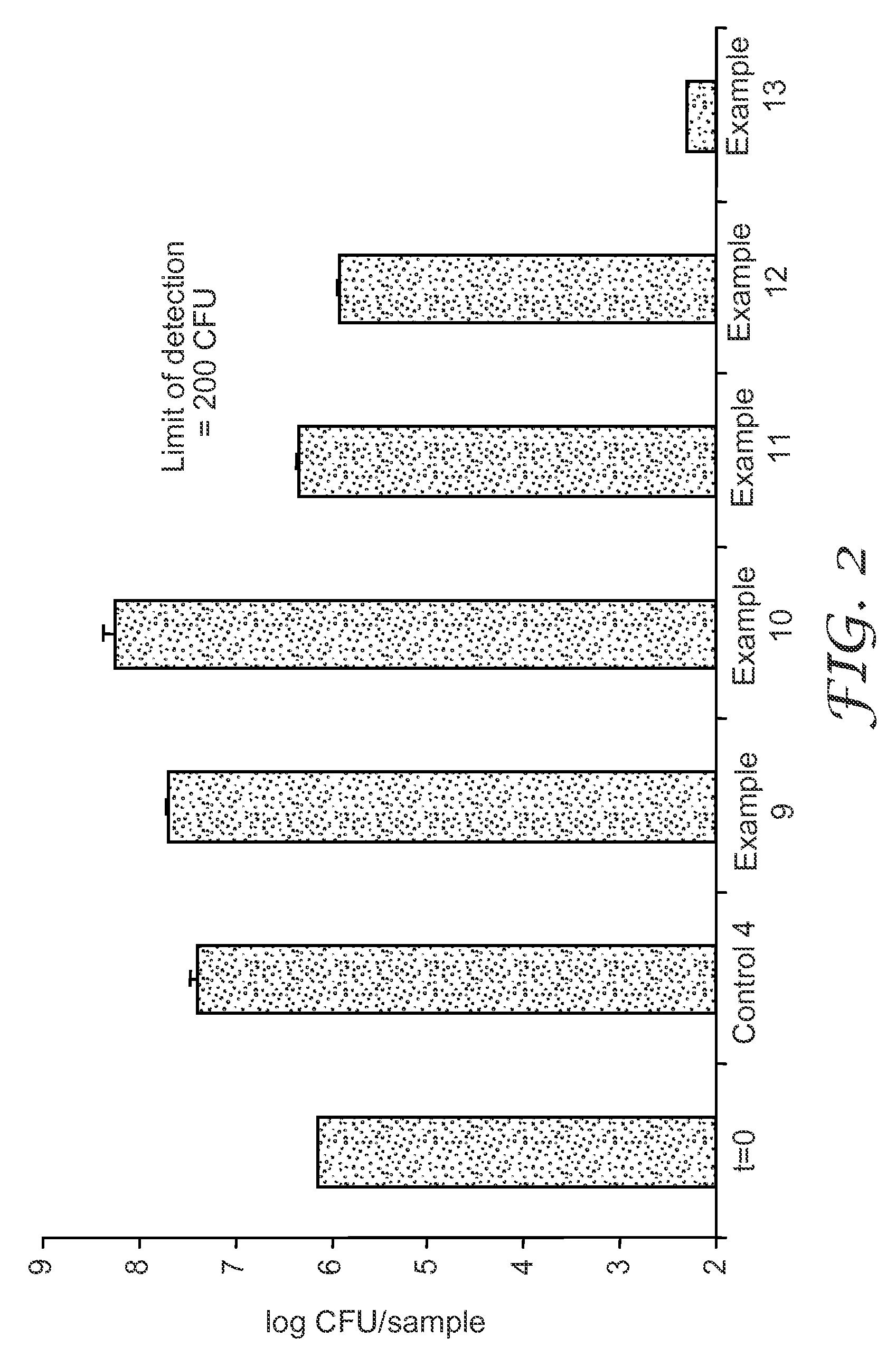
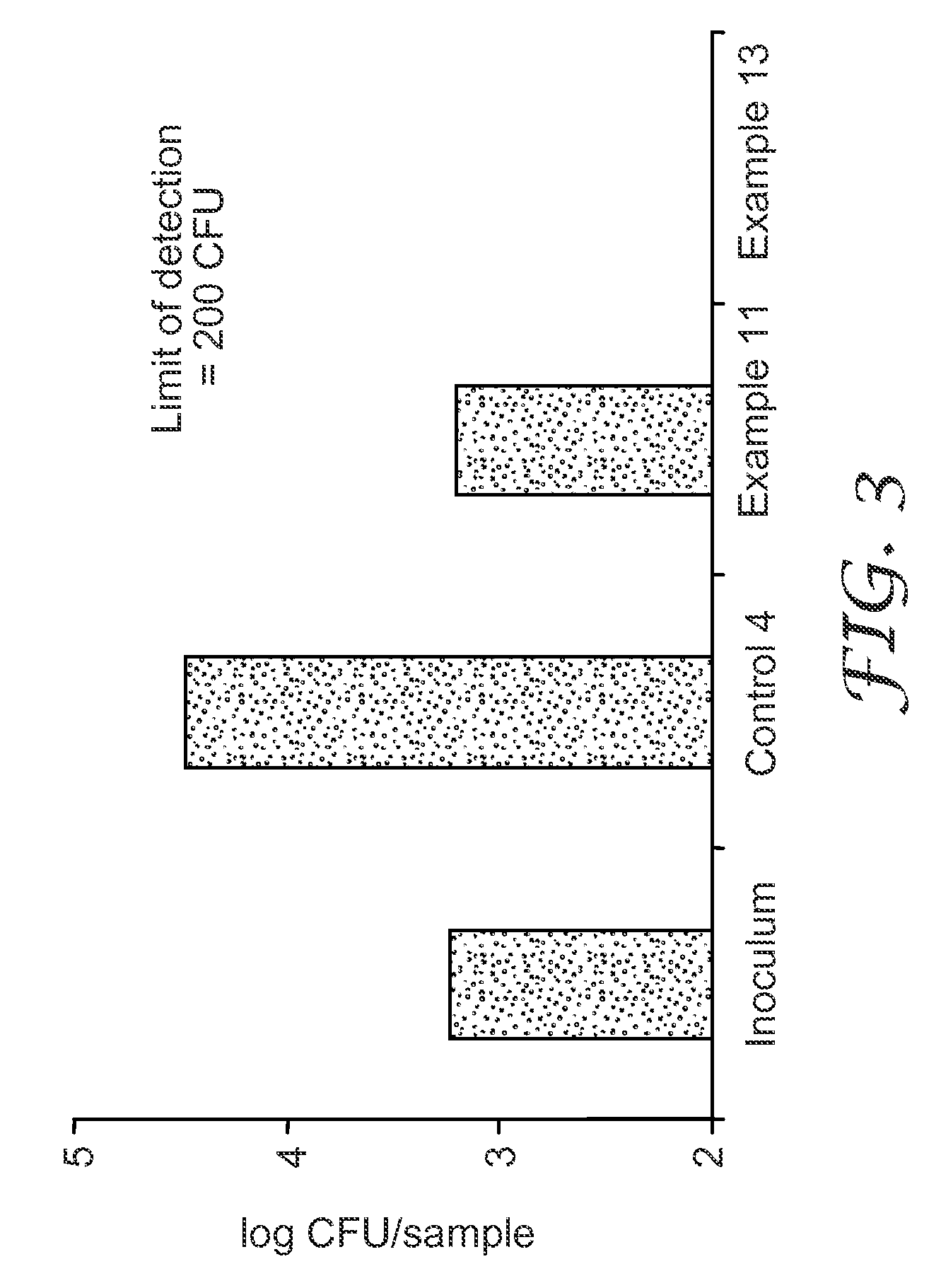
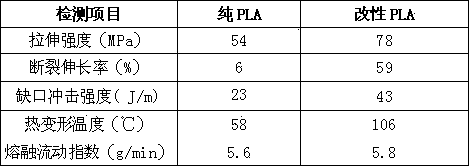
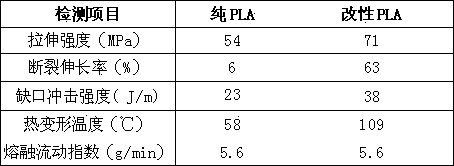
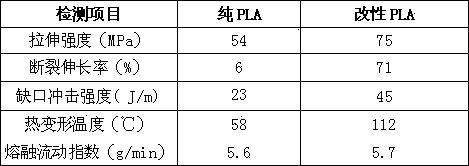
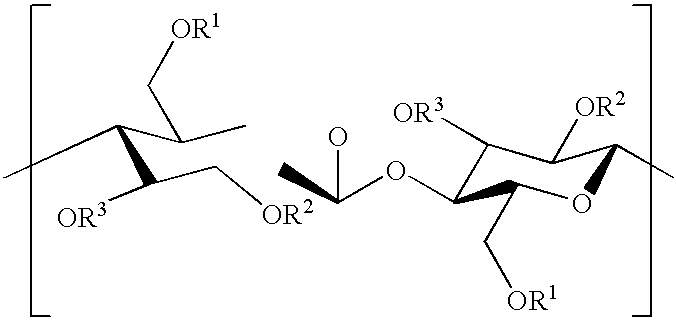
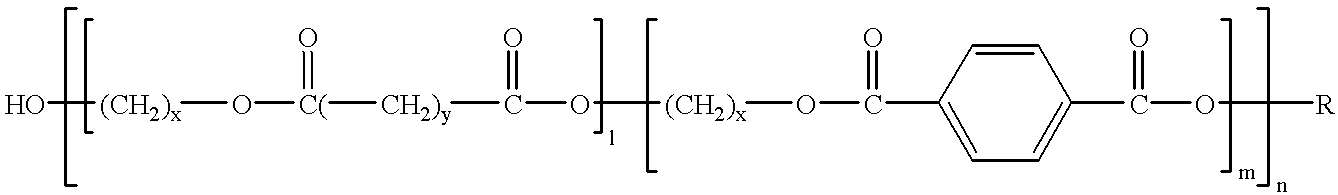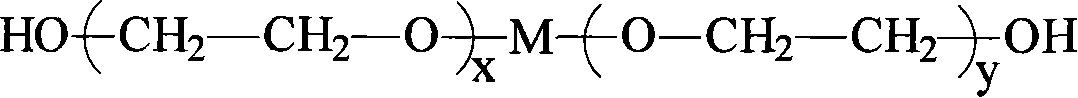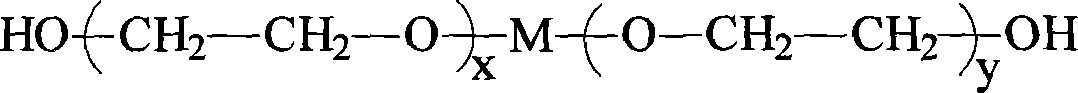Patents
Literature
7048results about "Monocomponent polyesters artificial filament" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Multilayer scaffold
InactiveUS20170182211A1Avoid disease riskAvoids the potential ethical and religious barriers to the useSkin implantsTissue regenerationMedicinePlla scaffold
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW PLC
Method of forming an implantable device
ActiveUS9352071B2Greater and beneficial tissue ingrowthLow melting pointWeft knittingMedical devicesImplanted devicePliability
Owner:ETHICON INC
Water-dispersable materials
InactiveUS6211309B1Increase flexibilityGood dispersionMonocomponent polyesters artificial filamentMonocomponent polyamides artificial filamentThermoplasticFiber
The present invention relates to water-dispersible materials (e.g. fibers or films) and to a method of producing same. The materials of the invention comprise a water soluble component, for example, a sulfonated polycondensate thermoplastic, and a modifying auxiliary component, for example, a low melt temperature thermoplastic.
Owner:BASF CORP
Synthetic fiber
InactiveUS6135987AFormed easily and efficientlyCeramic shaping apparatusBaby linensPolyesterVitrification
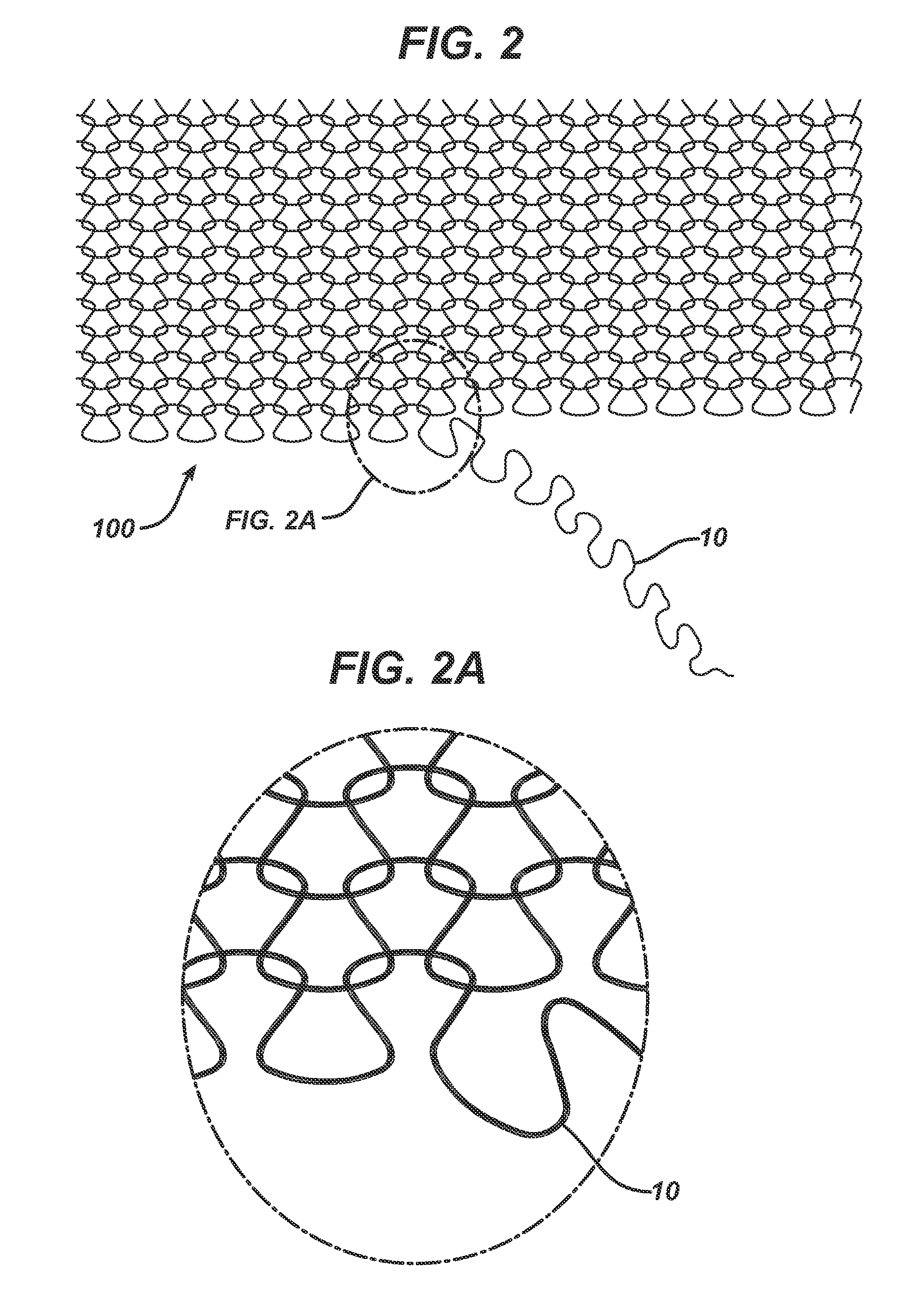
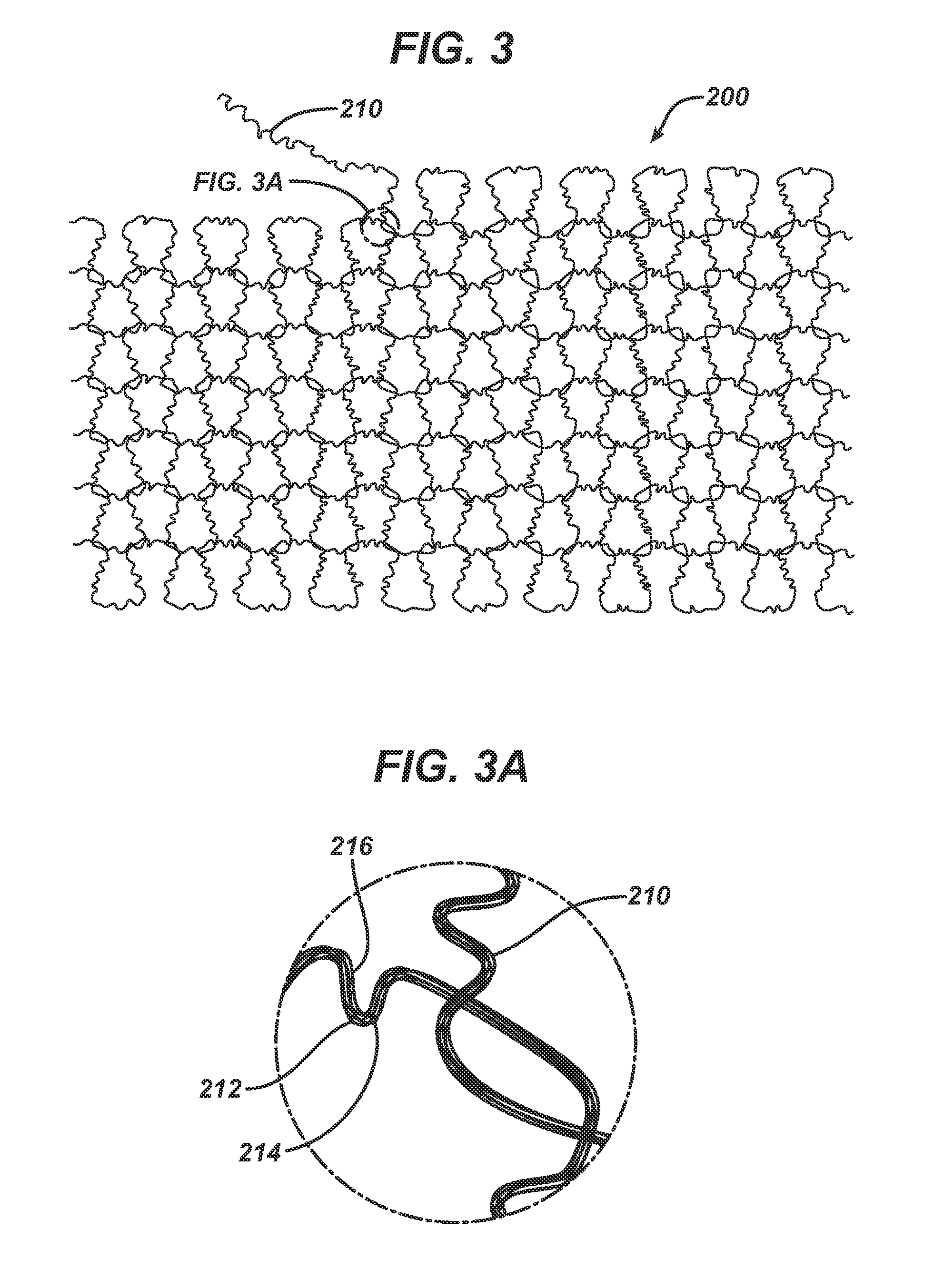
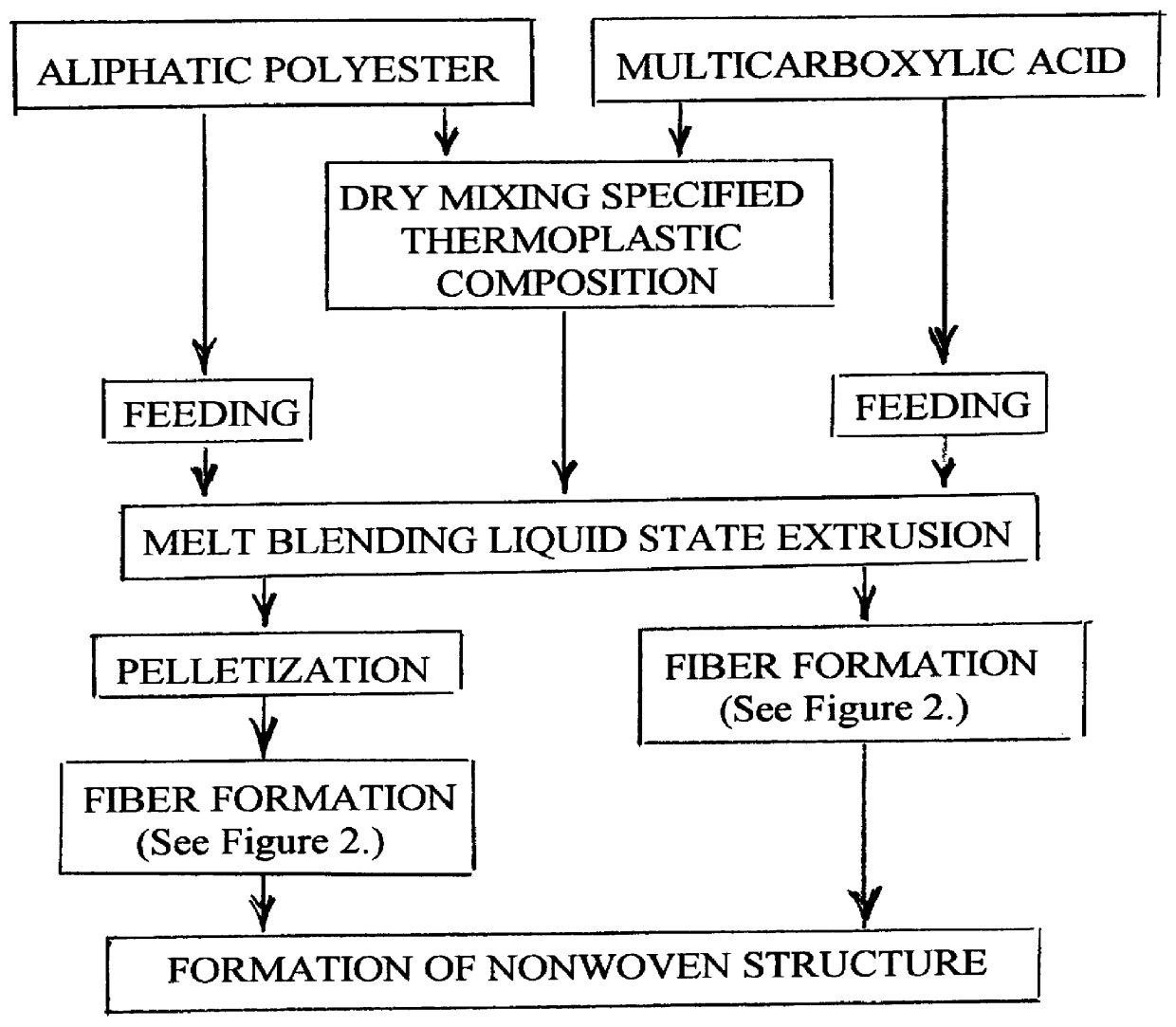
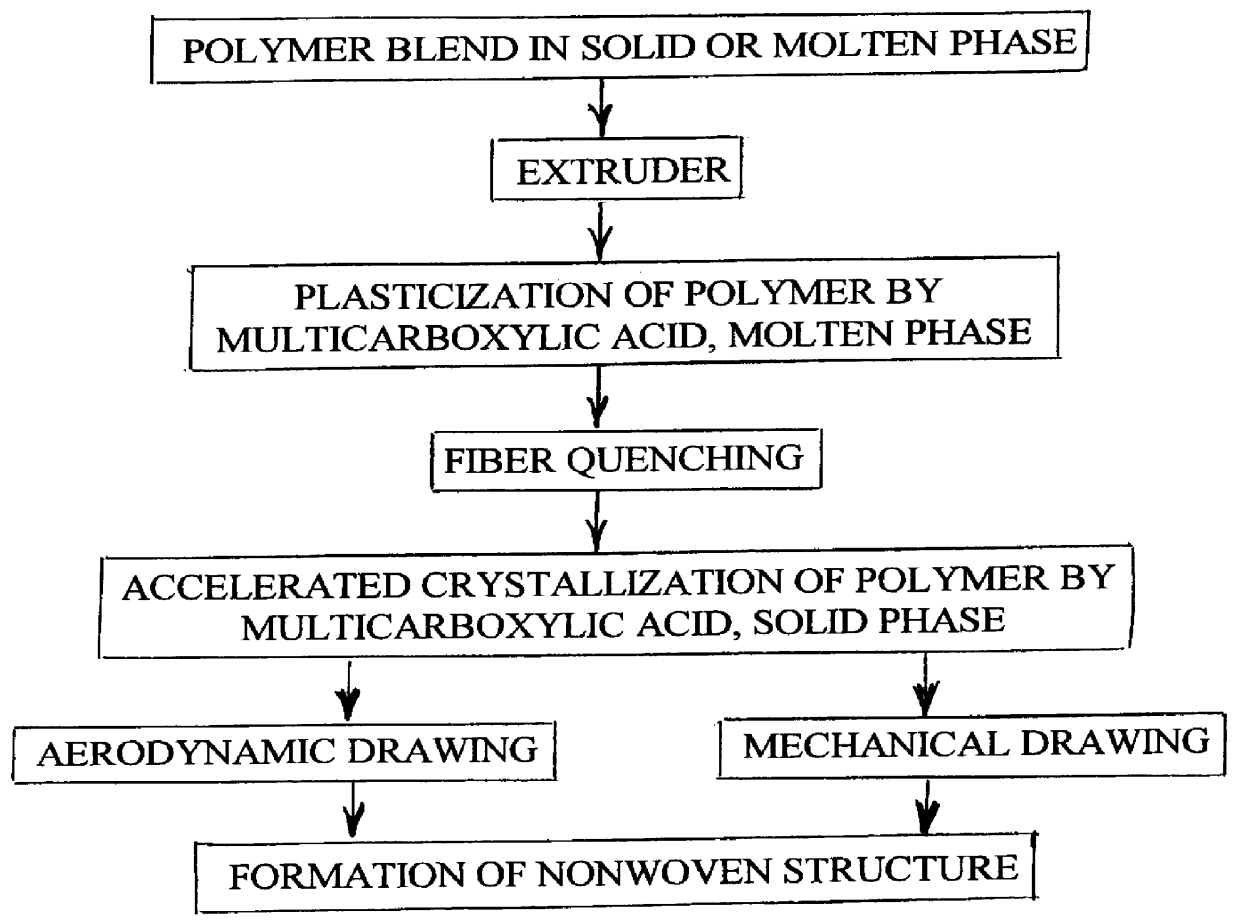
A process is disclosed for forming a synthetic fiber including providing a first component of an aliphatic polyester polymer a second component of a multicarboxylic acid, mixing the first component aliphatic polyester polymer and the second component multicarboxylic acid to form an unreacted specified thermoplastic composition, and melt blending the unreacted specified thermoplastic composition in an extruder or a mixer. The second component multicarboxylic acid lubricates the extruder and provides a nucleating agent for crystallizing the specified thermoplastic composition to form a mean crystal size less than about 120 Angstroms. Fiber composed of the specified thermoplastic composition has a mean crystal size less than about 120 Angstroms. The fiber has a glass transition temperature (Tg) less than about 55 DEG C. In one aspect, a first component of polylactic acid and a second component of adipic acid provide synthetic fibers in a nonwoven structure used in a biodegradable and compostable disposable absorbent product for the absorption and removal of body fluids.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
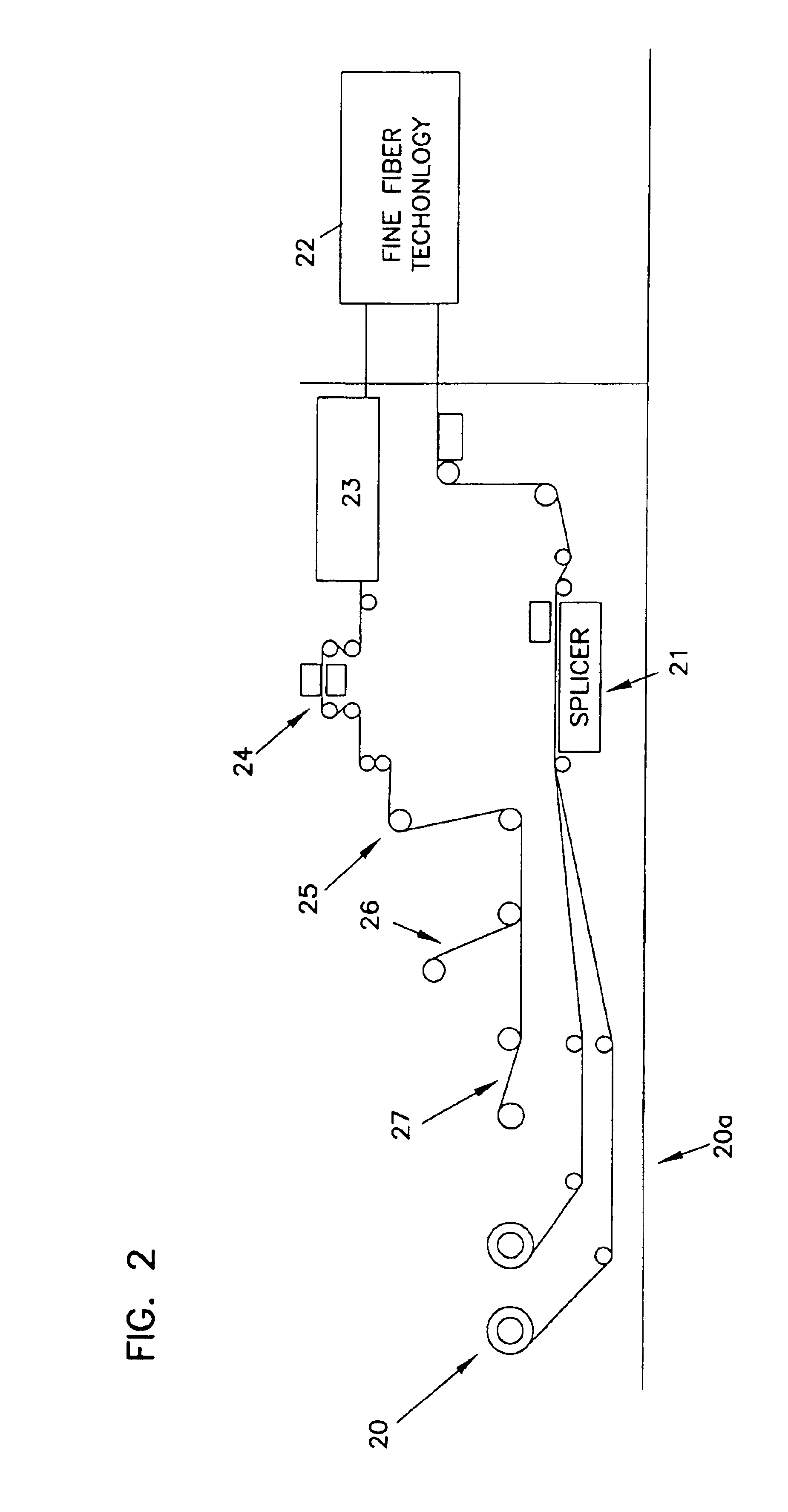
Process if making fine fiber material
Improved polymer materials and fine fiber materials can be made from the improved polymeric materials in the form of microfiber and nanofiber structures. The microfiber and nanofiber structures can be used in a variety of useful applications including the formation of filter materials.
Owner:DONALDSON CO INC
Compositions and methods for manufacturing thermoplastic starch blends
InactiveUS6235816B1Improved chemical and physical propertyPromote degradationFireproof paintsPaper coatingPolyesterPolymer science
A biologically degradable polymer mixture containing at least one biopolymer made from renewable raw materials and a polymer selected from the following materials: an aromatic polyester; a polyester-copolymer with both aliphatic and aromatic blocks; a polyesteramide; a polyglycol; a polyester urethane; and / or mixtures of these components. The preferred renewable raw material is starch, more preferably native starch, most preferably native starch that has been predried.
Owner:BIO TEC BIOLOGISCHE NATURVERPACKUNGEN
Nanofibrillar structure and applications including cell and tissue culture
ActiveUS20050095695A1Reduce usageBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNanostructure manufactureLipid formationNanofiber
A nanofibrillar structure for cell culture and tissue engineering is disclosed. The nanofibrillar structure can be used in a variety of applications including methods for proliferating and / or differentiating cells and manufacturing a tissue. Also disclosed is an improved nanofiber comprising a lipid, lipophilic molecule, or chemically modified surface. The nanofibers can be used in a variety of applications including the formation of nanofibrillar structures for cell culture and tissue engineering.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Polymer, polymer microfiber, polymer nanofiber and applications including filter structures
InactiveUS6924028B2Simple materialSubstantial surface loadingCombination devicesMaterial nanotechnologyPolymer scienceNanofiber
Disclosed are improved polymer materials. Also disclosed are fine fiber materials that can be made from the improved polymeric materials in the form of microfiber and nanofiber structures. The microfiber and nanofiber structures can be used in a variety of useful applications including the formation of filter materials.
Owner:DONALDSON CO INC
Fibers comprising starch and biodegradable polymers
Owner:PROCTER & GAMBLE CO
Reinforced polymers
InactiveUS6331265B1Less tangleImprove mechanical propertiesMaterial nanotechnologyWood working apparatusPolymer scienceNanotube
Provided is a method for the production of a reinforced polymer, which method comprises:(a) introducing carbon nanotubes into a polymer to provide a mixture of the polymer and the nanotubes;(b) stretching the mixture at or above the melting temperature (Tm) of the polymer to orient the carbon nanotubes; and(c) stretching the mixture in the solid state to further orient the carbon nanotubes.
Owner:FINA RES SA
Fibers comprising polyhydroxyalkanoate copolymer/polylactic acid polymer or copolymer blends
InactiveUS6905987B2Improve material performancePersonal careSynthetic resin layered productsFiberPolymer chemistry
Environmentally degradable melt spun fibers comprising a polyhydroxyalkanoate copolymer and a polylactic acid polymer or copolymer are disclosed. A preferred configuration of the present invention is directed to environmentally degradable fibers comprising a sheath / core structure where the core comprises a biodegradable polyhydroxyalkanoate copolymer and the sheath comprises a polymer or copolymer of polylactic acid. Nonwoven webs and disposable articles comprising the environmentally degradable fibers are also disclosed.
Owner:DANIMER IPCO LLC
Polymer, polymer microfiber, polymer nanofiber and applications including filter structures
Disclosed are improved polymer materials. Also disclosed are fine fiber materials that can be made from the improved polymeric materials in the form of microfiber and nanofiber structures. The microfiber and nanofiber structures can be used in a variety of useful applications including the formation of filter materials.
Owner:DONALDSON CO INC
Electrospun blends of natural and synthetic polymer fibers as tissue engineering scaffolds
InactiveUS20060263417A1Facilitate cell penetrationFacilitate proliferationBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsFiberPolymer science
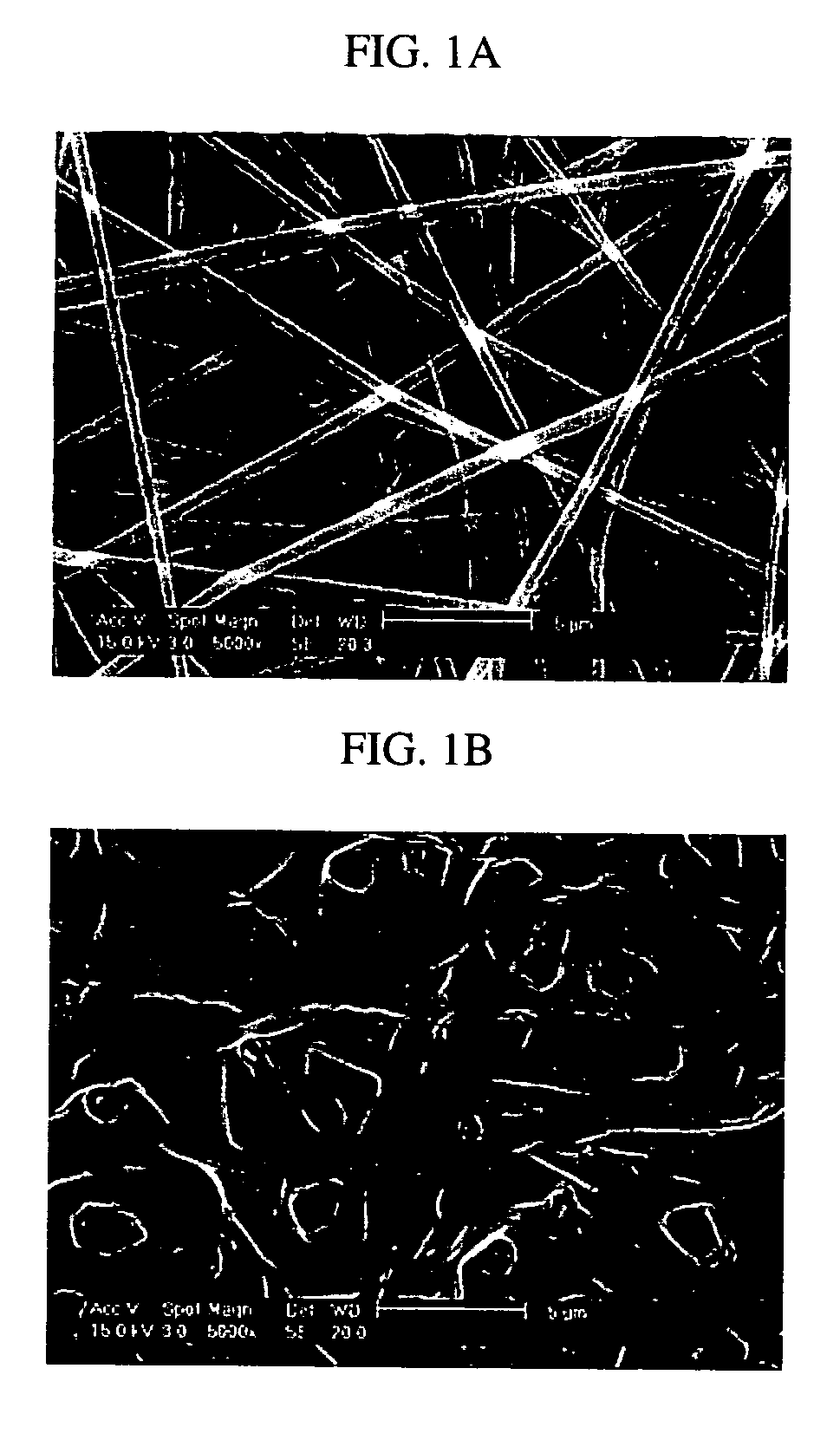
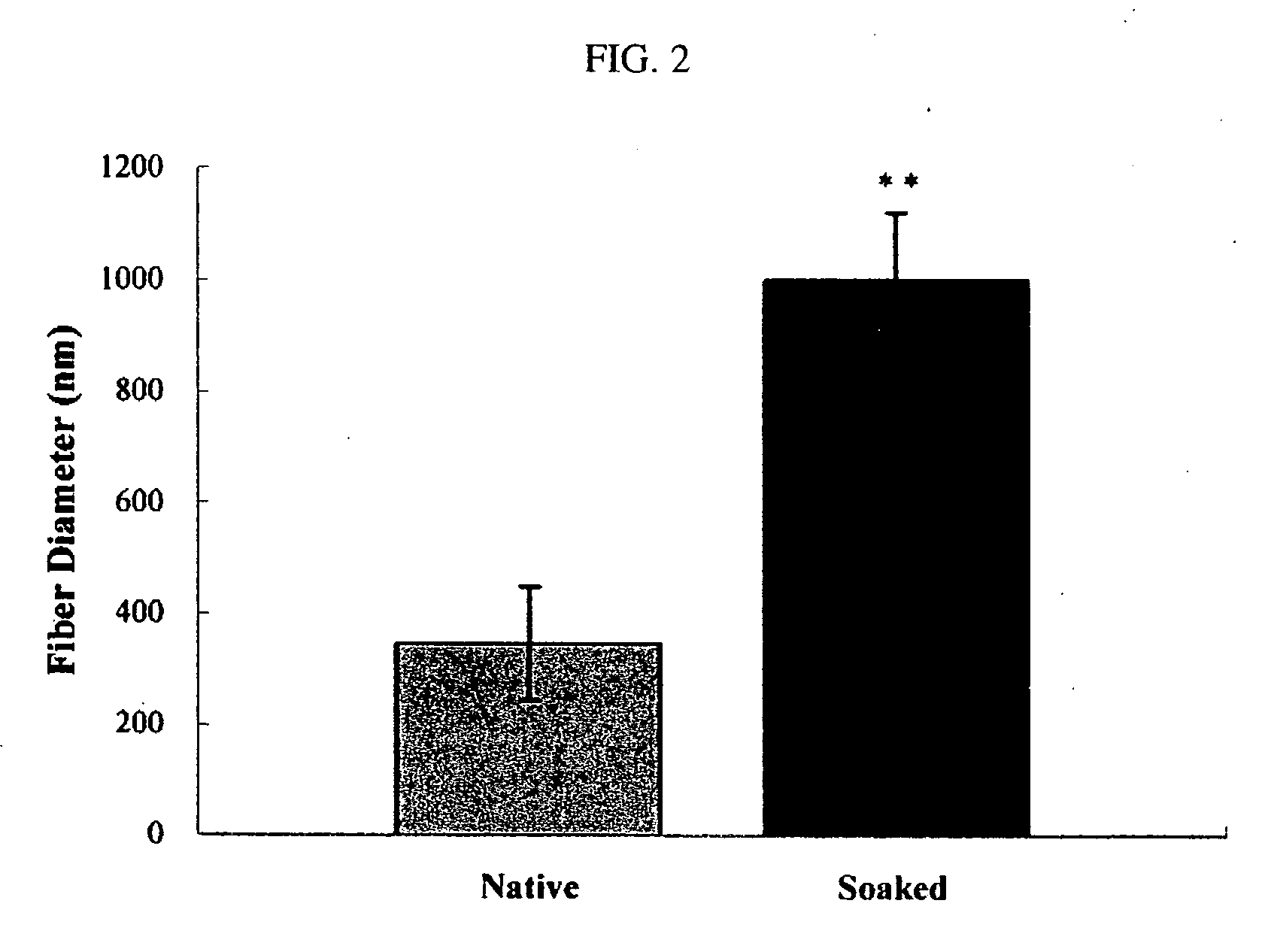
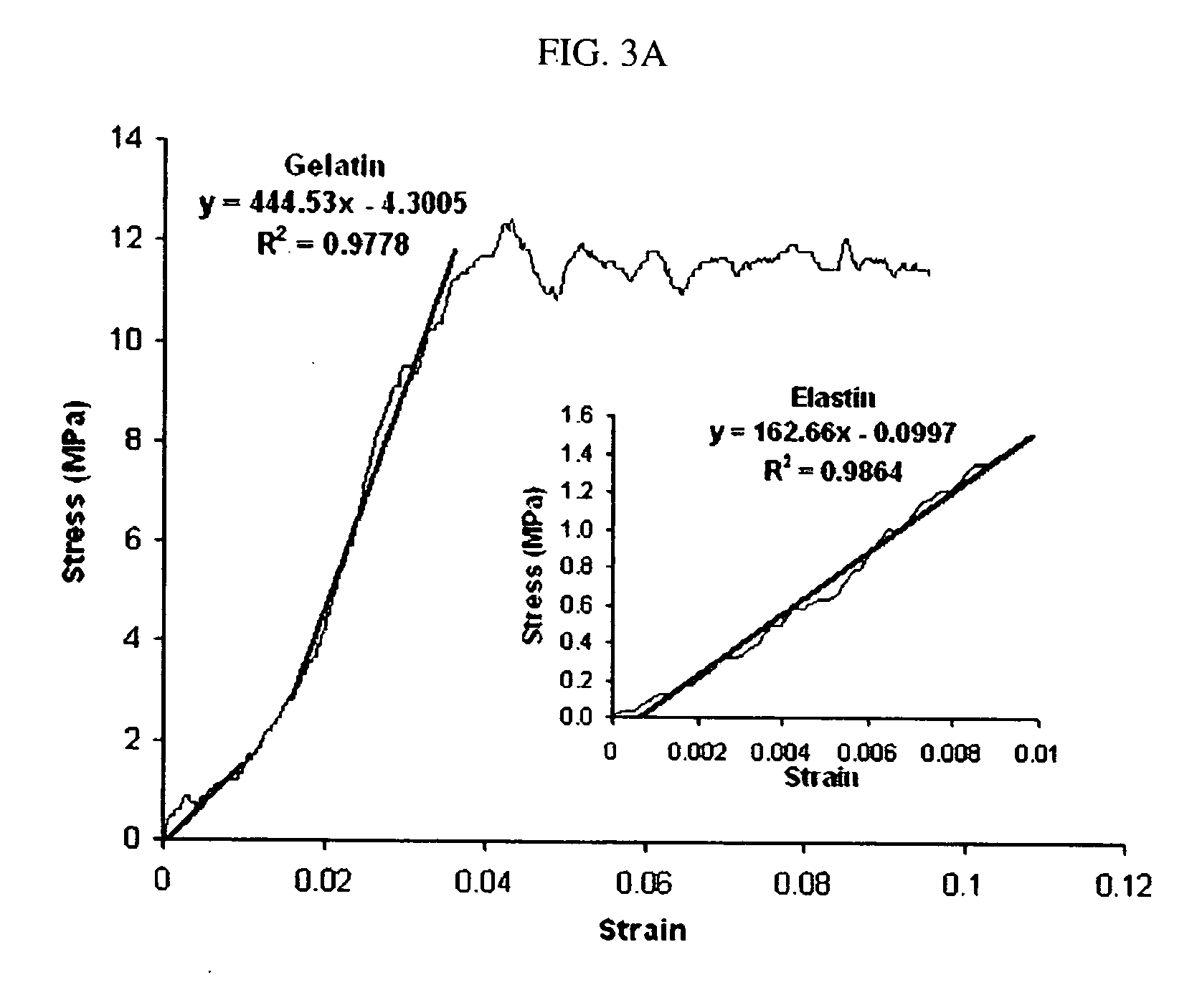
Non-woven fibrous scaffolds made by electrospinning from the synthetic biodegradable polymer such as, for example, poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) and natural proteins, such as, for example, gelatin (denatured collagen) and elastin and a method of making thereof.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
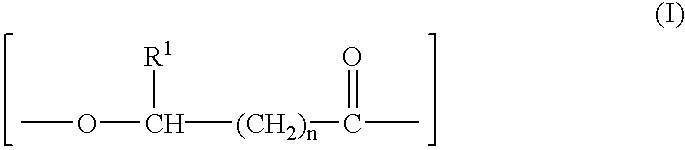
Aliphatic polyester microfibers, microfibrillated articles and use thereof
InactiveUS6890649B2Increase surface areaUseful applicationEngine sealsFilament/thread formingPolyesterParticulates
The present invention relates to aliphatic polyester microfibers, films having a microfibrillated surface, and methods of making the same. Microfibers of the invention can be prepared by imparting fluid energy, typically in the form of high-pressure water jets, to a highly oriented, highly crystalline, aliphatic polyester film to liberate microfibers therefrom. Microfibrillated films of the invention find use as tape backings, filters for particulate contaminants, such as face masks and water or air filters, fibrous mats, such as those used for removal of oil from water and those used as wipes, and thermal and acoustical insulation. Microfibers of the invention, when removed from the film matrix may be used in the preparation of woven or nonwoven articles and used as wipes for the removal of debris or dust from a surface. The microfibers and microfibrillated articles of the invention may be biodegradable, rendering them useful for geotextiles.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Industrial bag house elements
InactiveUS6740142B2Low efficiencyShort lifeCombination devicesMaterial nanotechnologyAir filterFilter media
The filter structures commonly known as a bag house or a filter bag or an air filter with a bag construction can be made by preparing the bag assembly, either in a tubular or a bi-fold construction by placing a layer of fine fiber on the upstream surface of the filter media structure. The filter assembly includes a filter cabinet with an interior component. The filter component is suspended within the filter cabinet interior. The filter component includes a frame or support for the filter media. The frame or support holds the filter bags such that the filter bags are suspended from the frame in the cabinet interior. The intake air enters the cabinet, passes through the filter assembly and exits the cabinet. The air must pass first into the fine fiber layer, the filter media and then the exterior of the cabinet.
Owner:DONALDSON CO INC
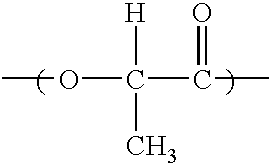
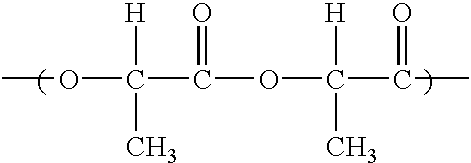
Biodegradable polyesters
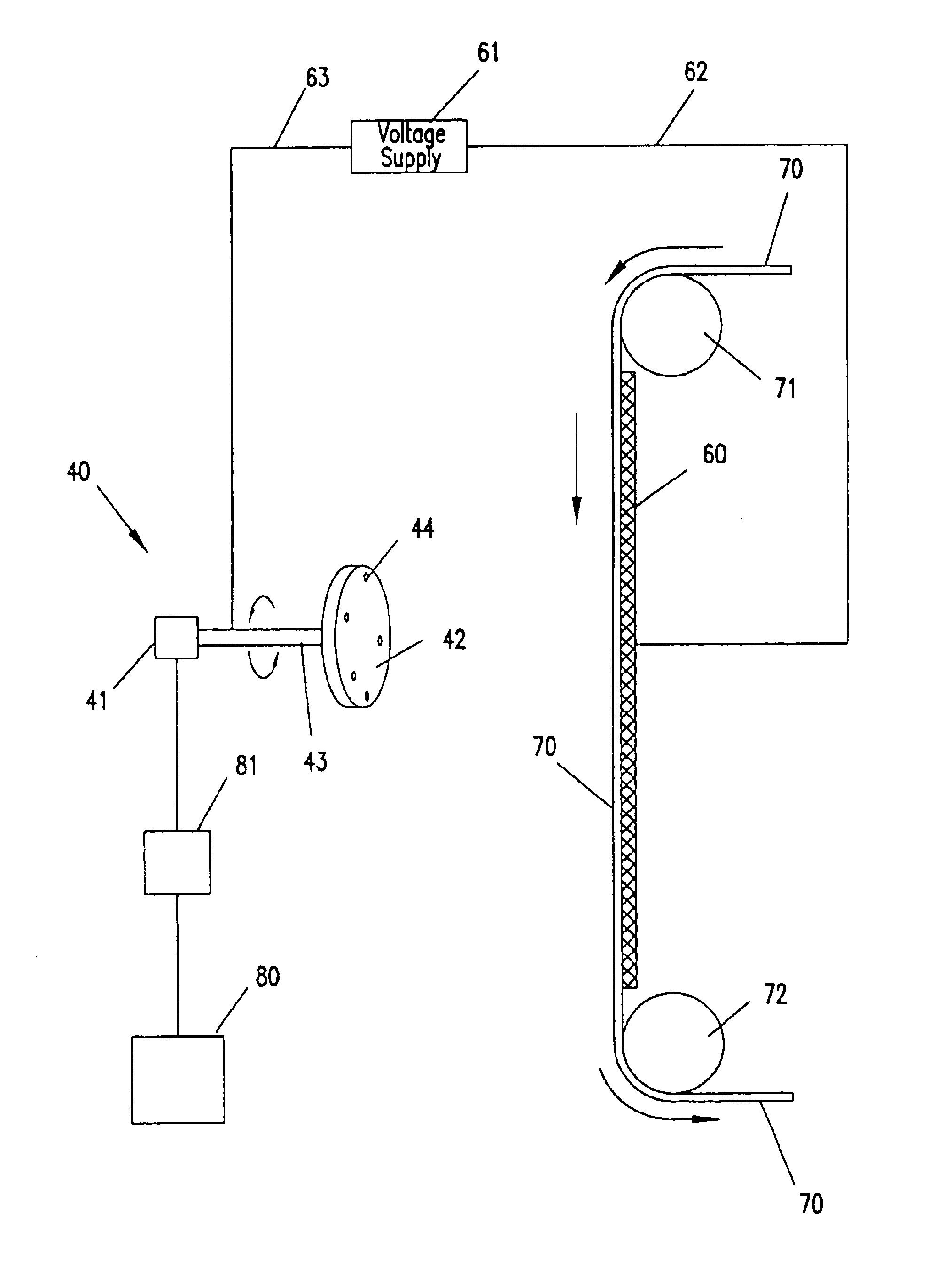
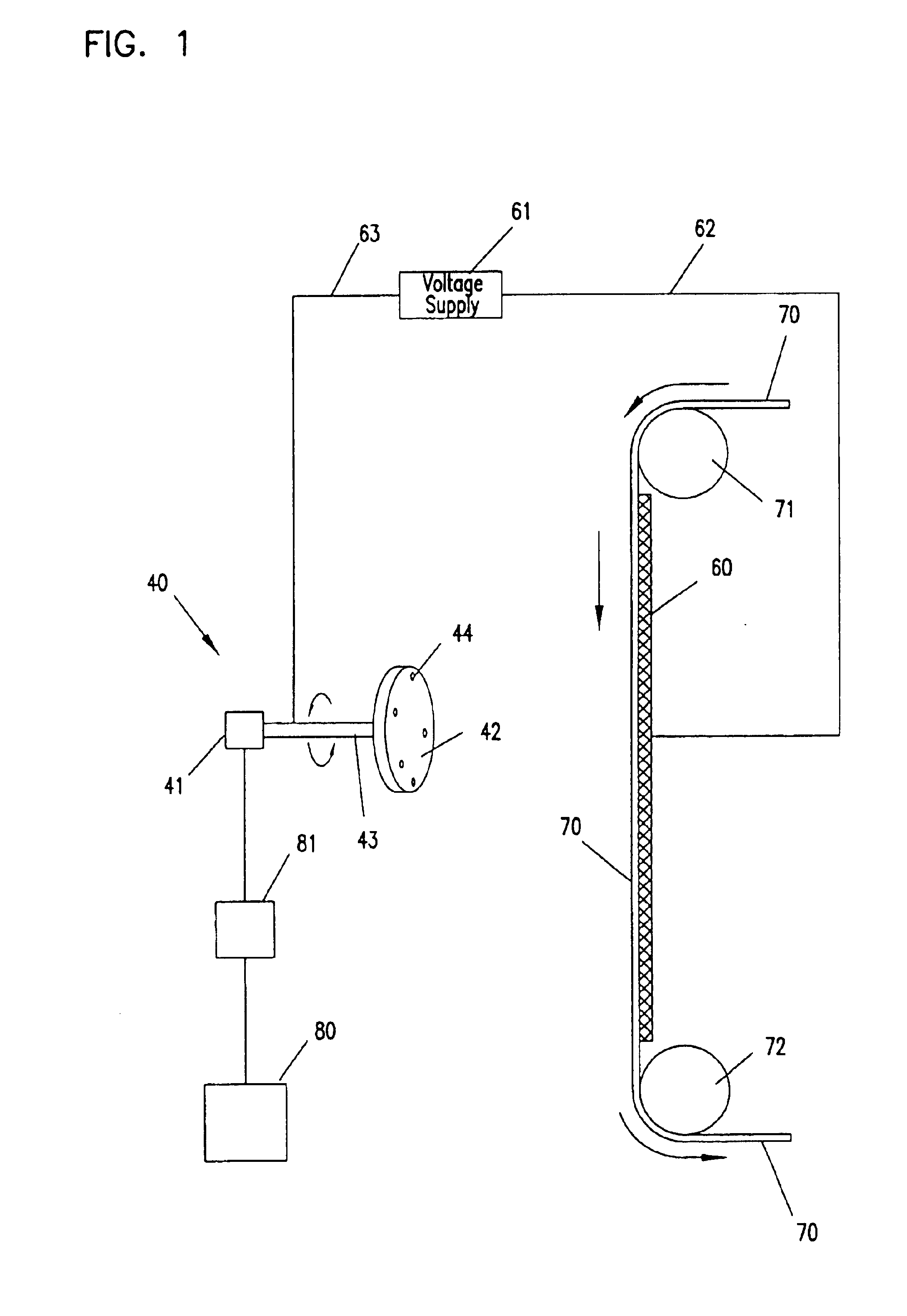
InactiveUS6120895AMonocomponent copolyesters artificial filamentPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsFiberPolymer science
PCT No. PCT / EP97 / 04908 Sec. 371 Date Mar. 17, 1999 Sec. 102(e) Date Mar. 17, 1999 PCT Filed Sep. 19, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 12242 PCT Pub. Date Mar. 20, 1998Biodegradable polyesters based on A) 95-99.99 mol % of at least one polyester A containing as monomeric building blocks of an acid component comprising a11) 20-95 mol % of at least one aliphatic or cycloaliphatic dicarboxylic acid or its ester-forming derivative and a12) 5-80 mol % of at least one aromatic dicarboxylic acid or its ester-forming derivative and at least one dihydroxy compound or at least one amino alcohol or their mixtures, and B) 0.01-5 mol % of a mixture comprising mono-, bi-, tri-, tetra- and higher-nuclear isocyanurates or corresponding compounds containing two, three or four functional groups capable of reacting with the end groups of polyester A, or mixtures of the isocyanurates and the corresponding compounds, as well as molding compositions comprising said polyesters, their manufacture and their use in the manufacture of moldings, filsm, fibers and coatings.
Owner:BASF AG
Water-dispersible and multicomponent fibers from sulfopolyesters
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Fabrication of drug loaded biodegradable polymer fibers
InactiveUS20050106211A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsFiberThree dimensional matrix
The invention provides tissue engineering compositions and methods wherein three-dimensional matrices for growing cells are prepared for in vitro and in vivo use. The matrices comprise biodegradable polymer fibers capable of the controlled delivery of therapeutic agents. The spatial and temporal distribution of released therapeutic agents is controlled by use of defined nonhomogeneous patterns of therapeutic agents in the matrices.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Electrospun cell matrices
InactiveUS20060204539A1Function increaseFiber sizeMonocomponent protein artificial filamentElectro-spinningElectrospinningUltimate tensile strength
The invention is directed to compositions and methods for preparing electrospun matrices comprising at least one natural biological material component and at least one synthetic polymer material. The natural component makes the matrices highly biocompatible while the molecular weight polymer component can impart additional strength mechanical strength to the scaffold and / or improve ease of manufacture by increasing viscosity and spinning characteristics of the solution during electrospining.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV
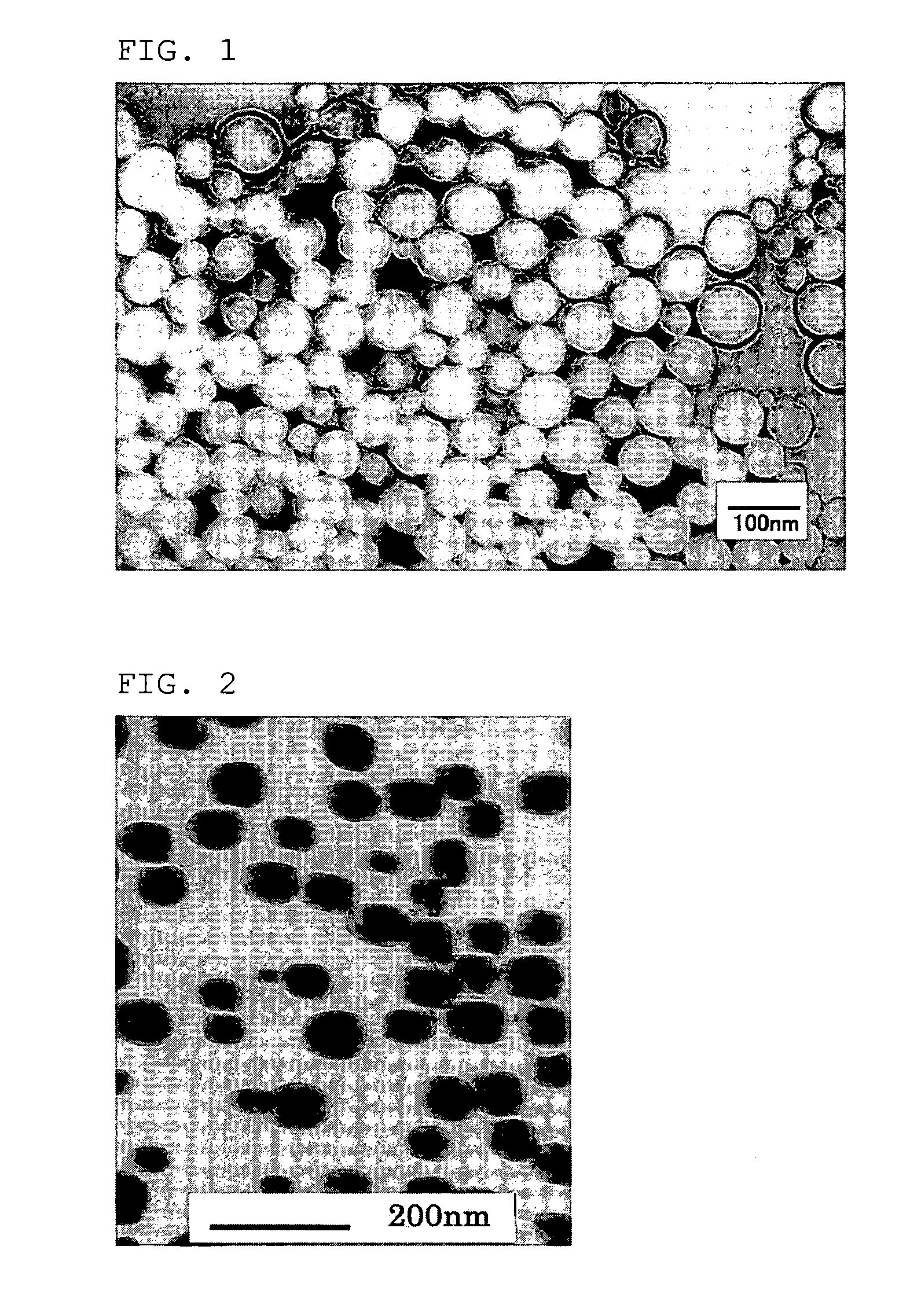
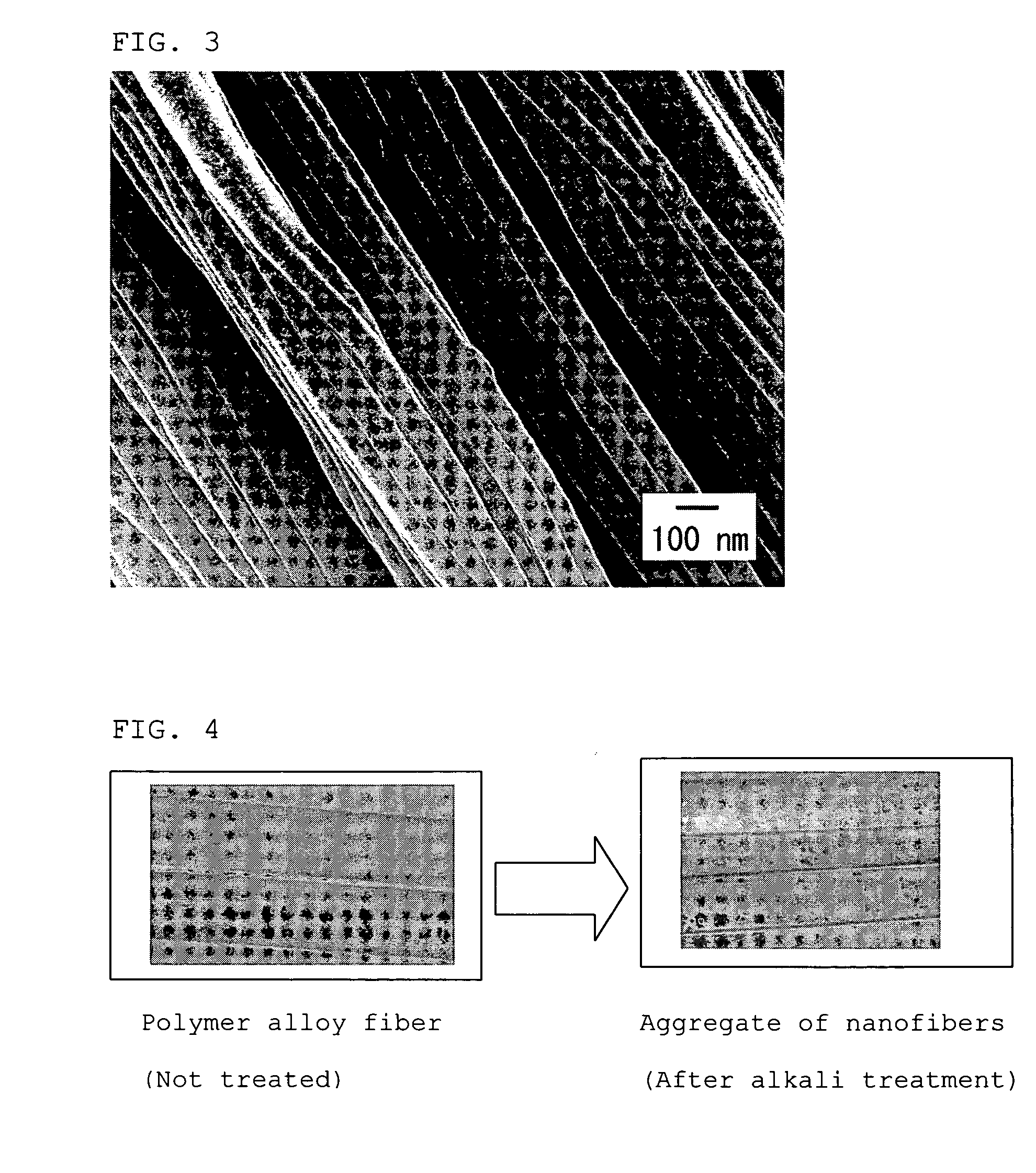
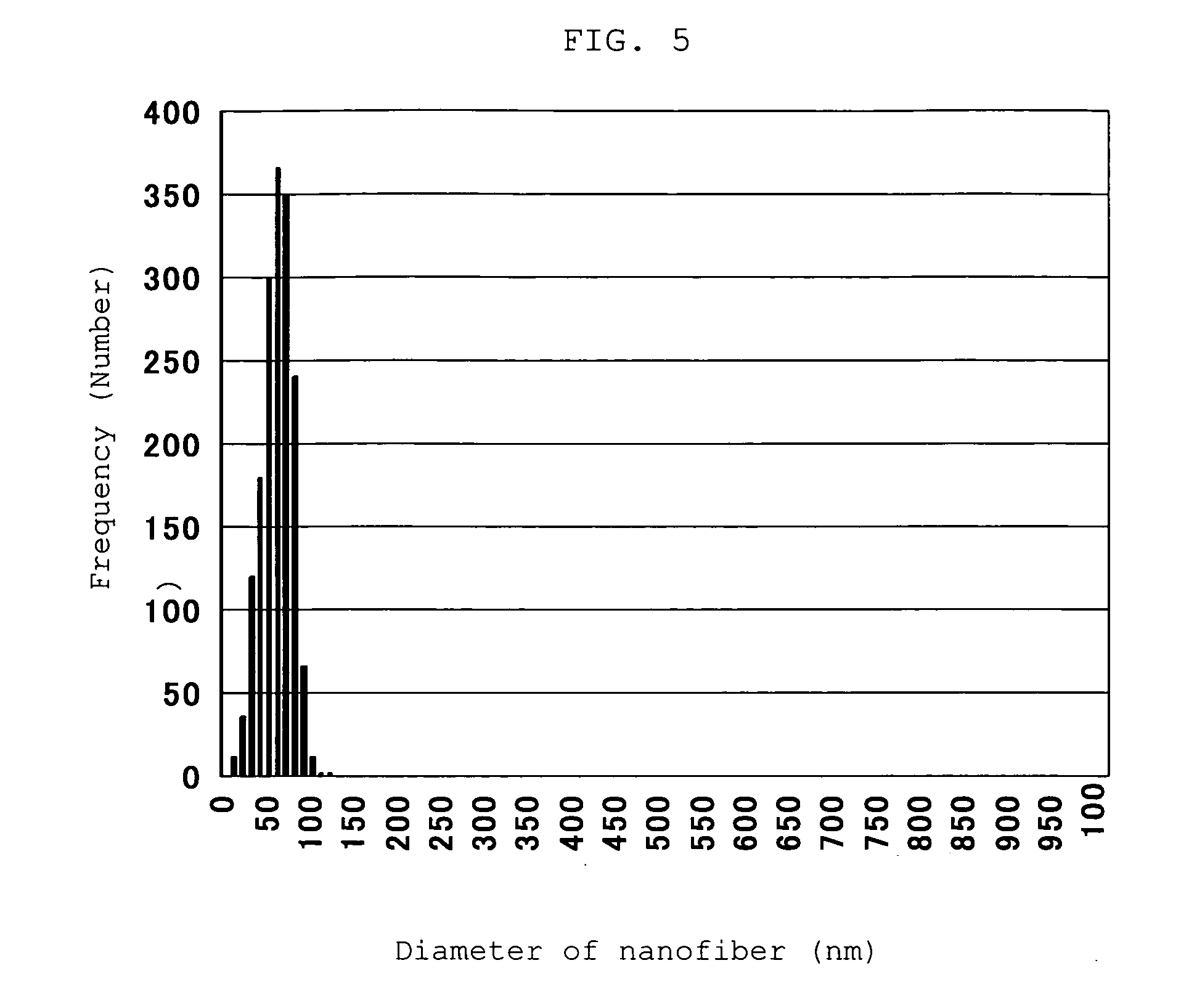
Nanofiber aggregate, polymer alloy fiber, hybrid fiber, fibrous structures, and processes for production of them
InactiveUS20060057350A1Less spreadingWide applicationSynthetic resin layered productsFilament/thread formingPolymer sciencePolymer alloy
The present invention provides an aggregate of nanofibers having less spread of single fiber fineness values that can be used in wide applications without limitation to the shape and the kind of the polymer, and a method for manufacturing the same. The present invention is an aggregate of nanofibers made of a thermoplastic polymer having single fiber fineness by number average in a range from 1×10−7 to 2×10−4 dtex and single fibers of 60% or more in fineness ratio have single fiber fineness in a range from 1×10−7 to 2×10−4 dtex.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Air filtration arrangements having fluted media constructions and methods
Filter arrangements include a barrier media in the form of fluted media treated with a deposit of fine fibers. The media is particularly advantageous in high temperature (greater than 140 to 240° F.) systems. Such systems may include engine systems, gas turbine systems, and fuel cell systems. Filter arrangements may take the form of media packs having a circular cross-section or a racetrack shaped cross-section, or media packs formed in a panel configuration.
Owner:DONALDSON CO INC
Fabrication of drug loaded biodegradable polymer fibers
InactiveUS6858222B2Limit maximum numberOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsFiberControlled release
The invention provides tissue engineering compositions and methods wherein three-dimensional matrices for growing cells are prepared for in vitro and in vivo use. The matrices comprise biodegradable polymer fibers capable of the controlled delivery of therapeutic agents. The spatial and temporal distribution of released therapeutic agents is controlled by use of defined nonhomogeneous patterns of therapeutic agents in the matrices.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Polyhydroxyalkanoate medical textiles and fibers
ActiveUS8034270B2Easy to operateProlonged strength retentionSurgerySynthetic resin layered productsPolyesterFiber
Absorbable polyester fibers, braids, and surgical meshes with prolonged strength retention have been developed. These devices are preferably derived from biocompatible copolymers or homopolymers of 4-hydroxybutyrate. These devices provide a wider range of in vivo strength retention properties than are currently available, and could offer additional benefits such as anti-adhesion properties, reduced risks of infection or other post-operative problems resulting from absorption and eventual elimination of the device, and competitive cost. The devices may also be particularly suitable for use in pediatric populations where their absorption should not hinder growth, and provide in all patient populations wound healing with long-term mechanical stability. The devices may additionally be combined with autologous, allogenic and / or xenogenic tissues to provide implants with improved mechanical, biological and handling properties.
Owner:TEPHA INC
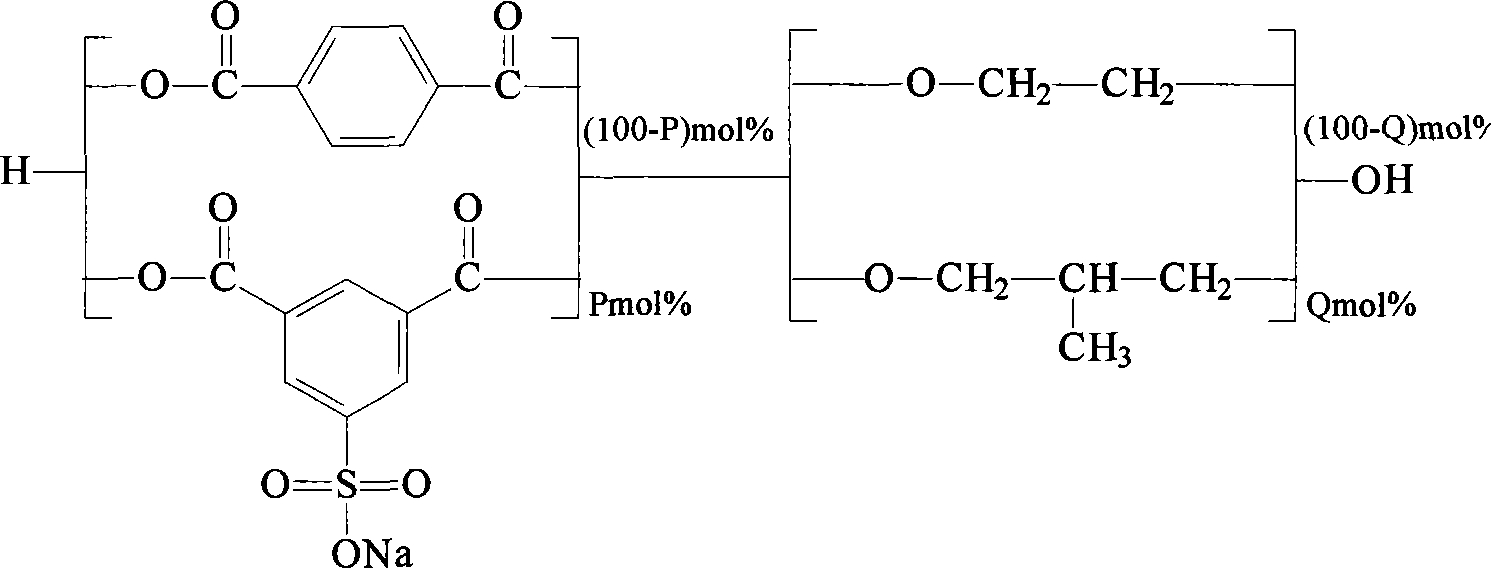
Modified copolyester slicer or fabric and method for making same
InactiveCN101063236ASoft lusterImprove shrinkageMonocomponent polyesters artificial filamentFiberAlcohol
The invention relates to a modified copolyester slice or fiber and a relative preparation, wherein the slice is copolymerized from terephthalic acid, ethandiol, isophthalate esters of sulfonic acid sodium (or potassium), and fatty group dibasic alcohol (or relative alkylate) with side chain. And the preparation comprises that (1), mixing the ethandiol and the fatty group dibasic alcohol (or relative alkylate) into a mixed alcohol, adding catalyzer and stabilizer to esterify the terephthalic acid under 220-260Deg. C, (2), adding 1-9%mol isophthalate esters of sulfonic acid sodium (or potassium) relative to the terephthalic acid for polycondensation at 250-300Deg. C, (3), drying, fusing, spinning, and drawing to obtain the modified copolyester filament. The inventive product can dye anion paint and disperse paint into deep color at normal pressure, with better feeling, high contraction, hidden micro coiled property, simple preparation, low cost and batch production support.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
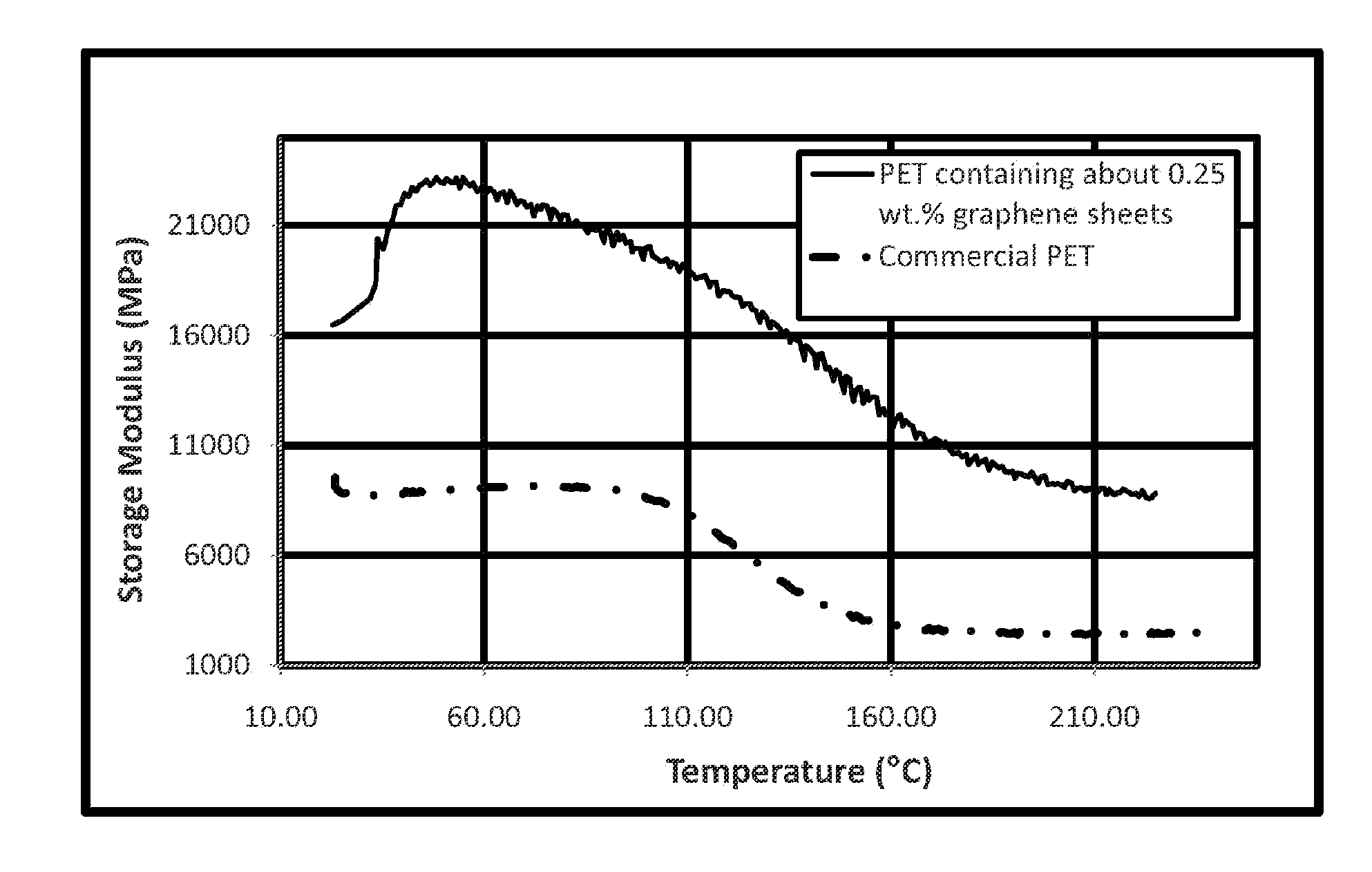
Polymeric fibers and articles made therefrom
InactiveUS20120244333A1Electric discharge heatingMonocomponent cellulose artificial filamentPolyesterYarn
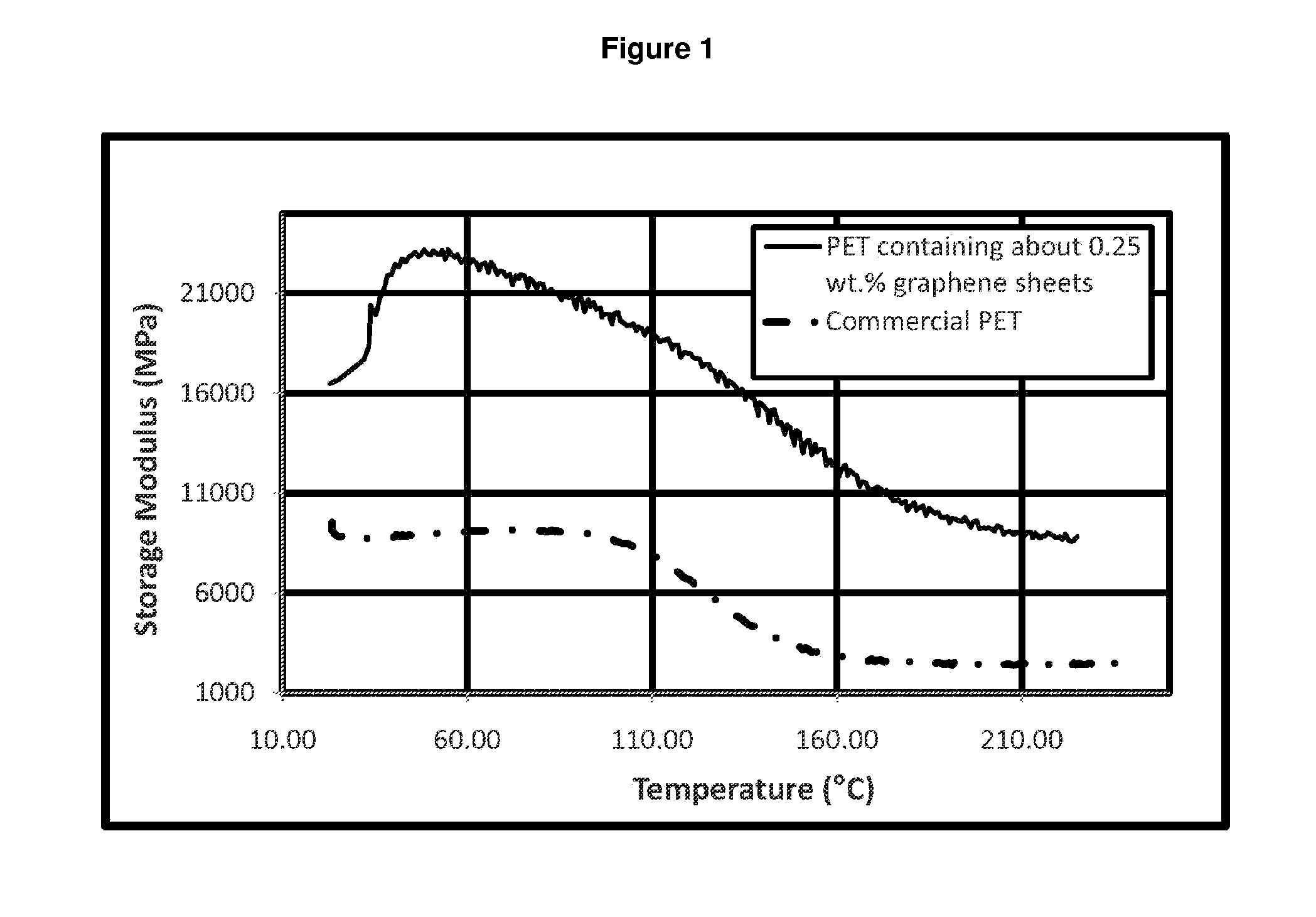
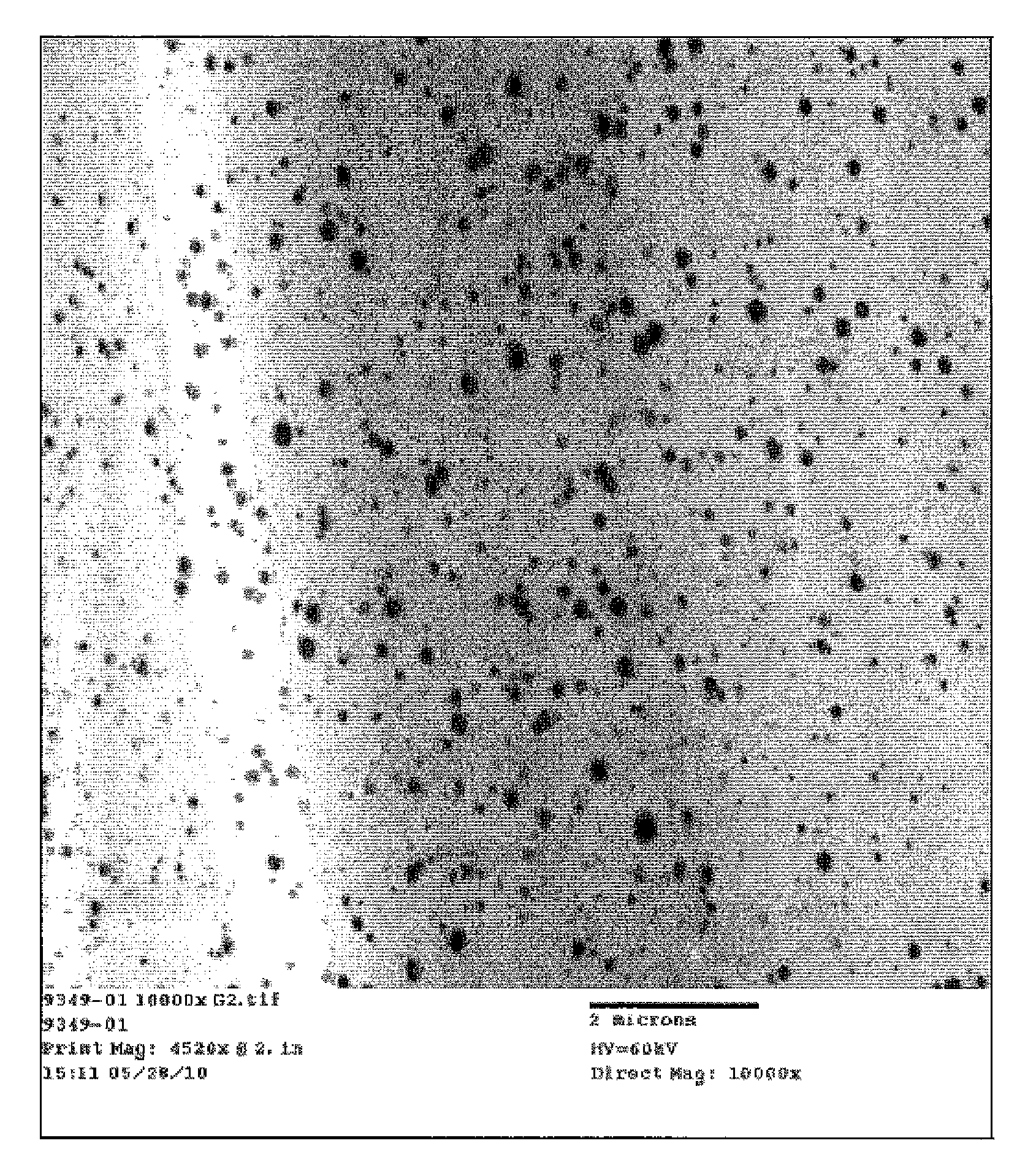
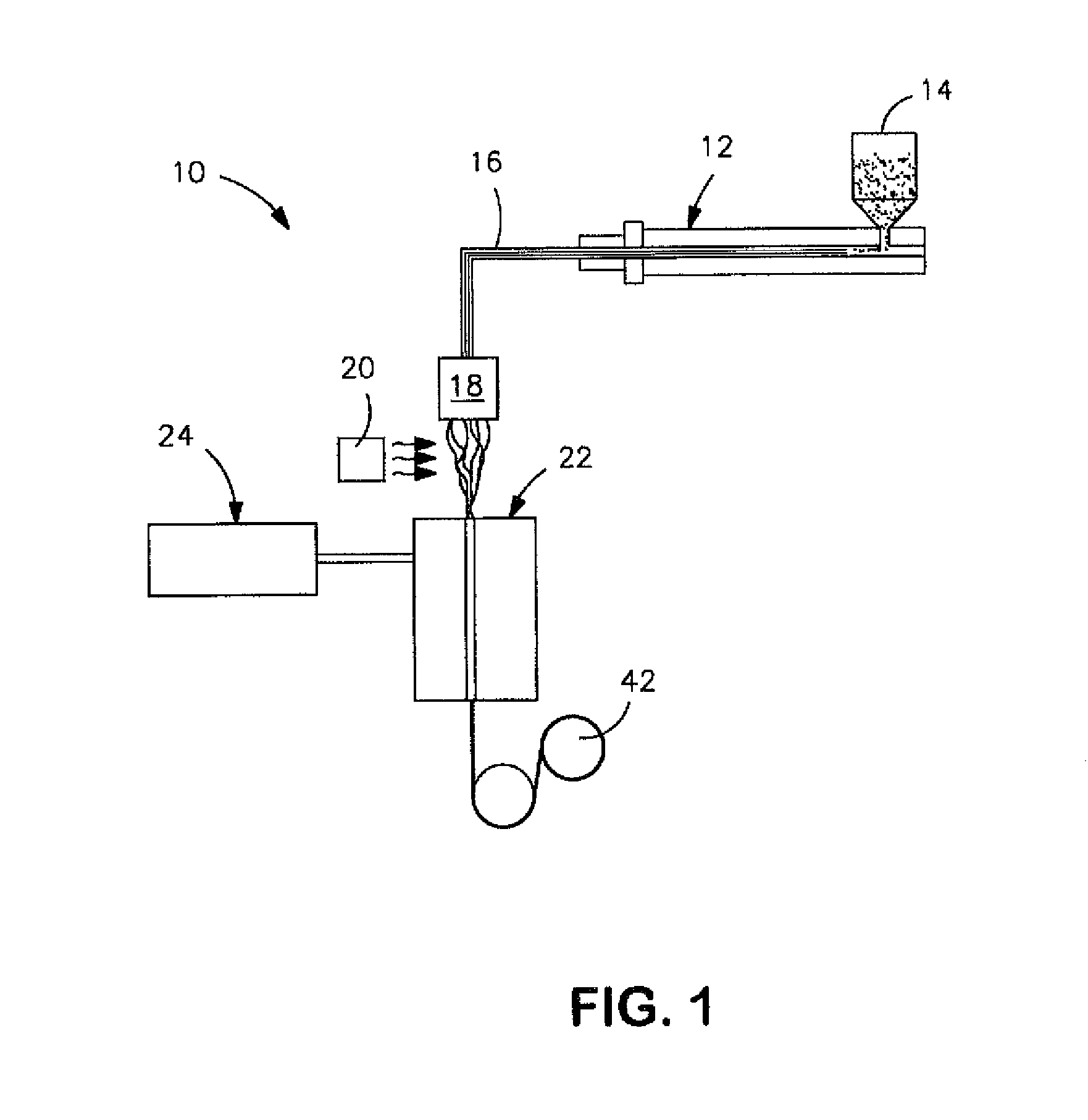
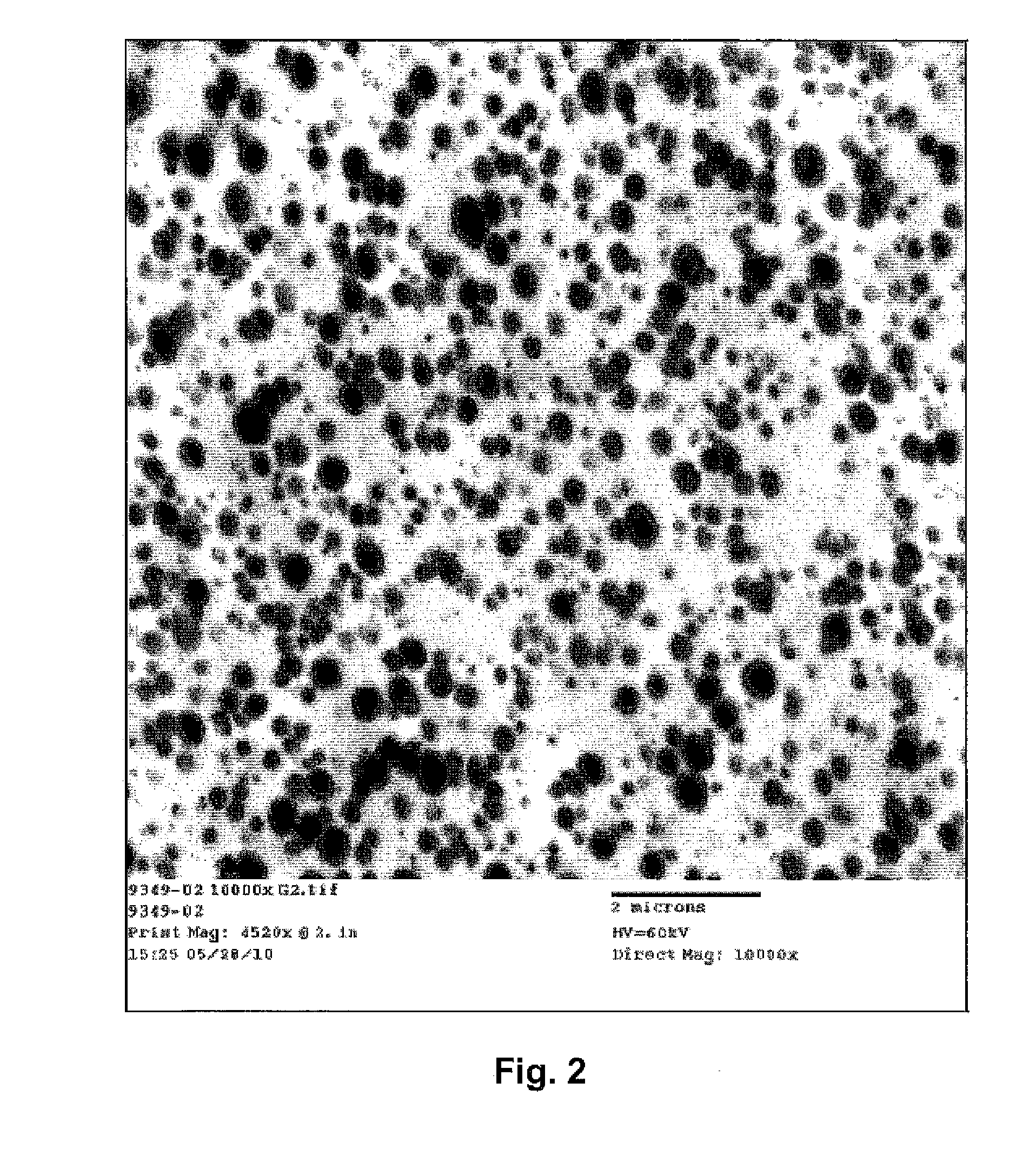
Fibers described herein comprise a composition including a polymer and graphene sheets. The fibers can be further formed into yarns, cords, and fabrics. The fibers can be in the form of polyamide, polyester, acrylic, acetate, modacrylic, spandex, lyocell fibers, and the like. Such fibers can take on a variety of forms, including, staple fibers, spun fibers, monofilaments, multifilaments, and the like.
Owner:VORBECK MATERIALS CORP +1
Modified Polylactic Acid Fibers
ActiveUS20120040582A1Improve responseMelt spinning methodsWoven fabricsChain scissionGlass transition
A method for forming biodegradable fibers is provided. The method includes blending polylactic acid with a polyepoxide modifier to form a thermoplastic composition, extruding the thermoplastic composition through a die, and thereafter passing the extruded composition through a die to form a fiber. Without intending to be limited by theory, it is believed that the polyepoxide modifier reacts with the polylactic acid and results in branching of its polymer backbone, thereby improving its melt strength and stability during fiber spinning without significantly reducing glass transition temperature. The reaction-induced branching can also increase molecular weight, which may lead to improved fiber ductility and the ability to better dissipate energy when subjected to an elongation force. To minimize premature reaction, the polylactic acid and polyepoxide modifier are first blended together at a relatively low temperature(s). Nevertheless, a relatively high shear rate may be employed during blending to induce chain scission of the polylactic acid backbone, thereby making more hydroxyl and / or carboxyl groups available for subsequent reaction with the polyepoxide modifier. Once blended, the temperature(s) employed during extrusion of the blended composition can be selected to both melt the composition and initiate a reaction of the polyepoxide modifier with hydroxyl and / or carboxyl groups of the polylactic acid. Through selective control over this method, the present inventors have discovered that the resulting fibers may exhibit good mechanical properties, both during and after melt spinning.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Antimicrobial disposable absorbent articles
InactiveUS20080200890A1Small amountImprove mechanical propertiesBiocideSurgeryPolyesterPersonal care
Disposable absorbent articles comprising an absorbent material and a degradable thermoplastic polymer composition comprising an aliphatic polyester and an antimicrobial composition. The antimicrobial composition includes an antimicrobial component and an enhancer component. The aliphatic polyester and antimicrobial composition are formed into webs by melt extrusion, such as nonwovens and films, that are incorporated into disposable absorbent articles, such as disposable infant diapers, adult incontinence articles, feminine hygiene articles such as sanitary napkins, panty liners and tampons, personal care wipes and household wipes to provide odor control, control of microbial growth, and control of microbial toxin production.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
3D printing modified polylactic acid material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103467950AIncrease profitSelf-performance has not declinedMonocomponent polyesters artificial filamentArtifical filament manufactureHeat deflection temperaturePolymer science
A 3D printing modified polylactic acid material comprises, by weight, 70-85 parts of polylactic acid, 1-5 parts of chain extenders, 1-5 parts of cross-linking agents, 0.5-1 part of nucleating agents, 5-10 parts of polymers with low molecular weights, 5-10 parts of flexibilizers, 1-5 parts of fortifiers and 0.3-0.8 part of antioxidants. According to the 3D printing modified polylactic acid material, a low-temperature smashing hybrid reaction technology is utilized, modified processing is carried out on polylactic acid, toughness, impact strength and the heat distortion temperature for the polylactic acid are improved to a large extent, and the polylactic acid can have wider application prospects in 3D printing materials.
Owner:佛山市斯太克科技有限公司
Water stable fibers and articles comprising starch, and methods of making the same
Water stable fibers and articles made therefrom are formed from a thermoplastic composition comprising destructured starch, polyhydric alcohol, triglyceride, and optionally acid. Processes for making water stable compositions may comprise melt extruding a mixture of destructured starch, polyhydric alcohol, triglyceride, and optionally acid, to form an extrudate, and heating the mixture, extrudate, or both to provide a water stable article.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Copolyesters and fibrous materials formed therefrom
InactiveUS20020132960A1Deep dyeabilityGood printabilityMonocomponent copolyesters artificial filamentArtificial filaments from cellulose derivativesCelluloseFiber
This invention relates to binary blends of cellulose esters and aliphatic-aromatic copolyesters, cellulose esters and aliphatic polyesters as well as ternary blends of cellulose esters and / or aliphatic polyesters and / or aliphatic-aromatic copolyesters and / or polymeric compounds as well as fibers, nonwovens, molded objects, and films prepared therefrom.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com