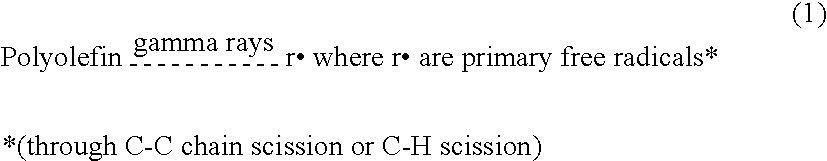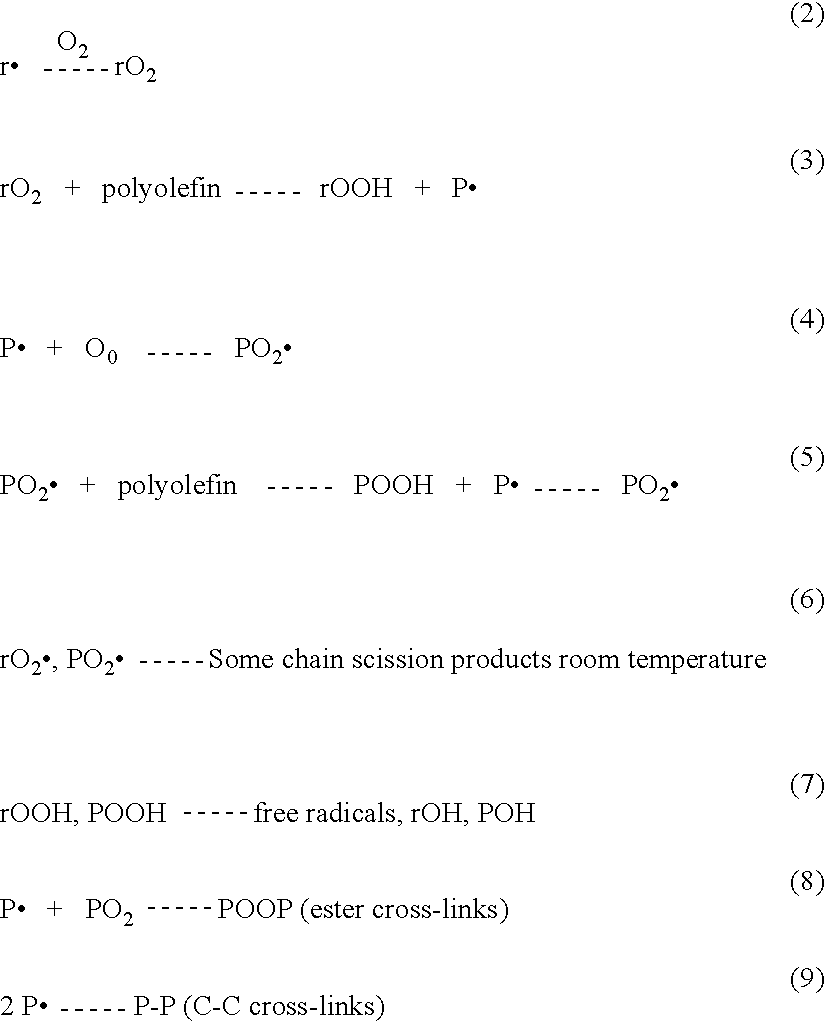Patents
Literature
1399 results about "Ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMW-PE) is a new kind of engineering thermoplastics with more than 3 million viscosity-average molecular weight.
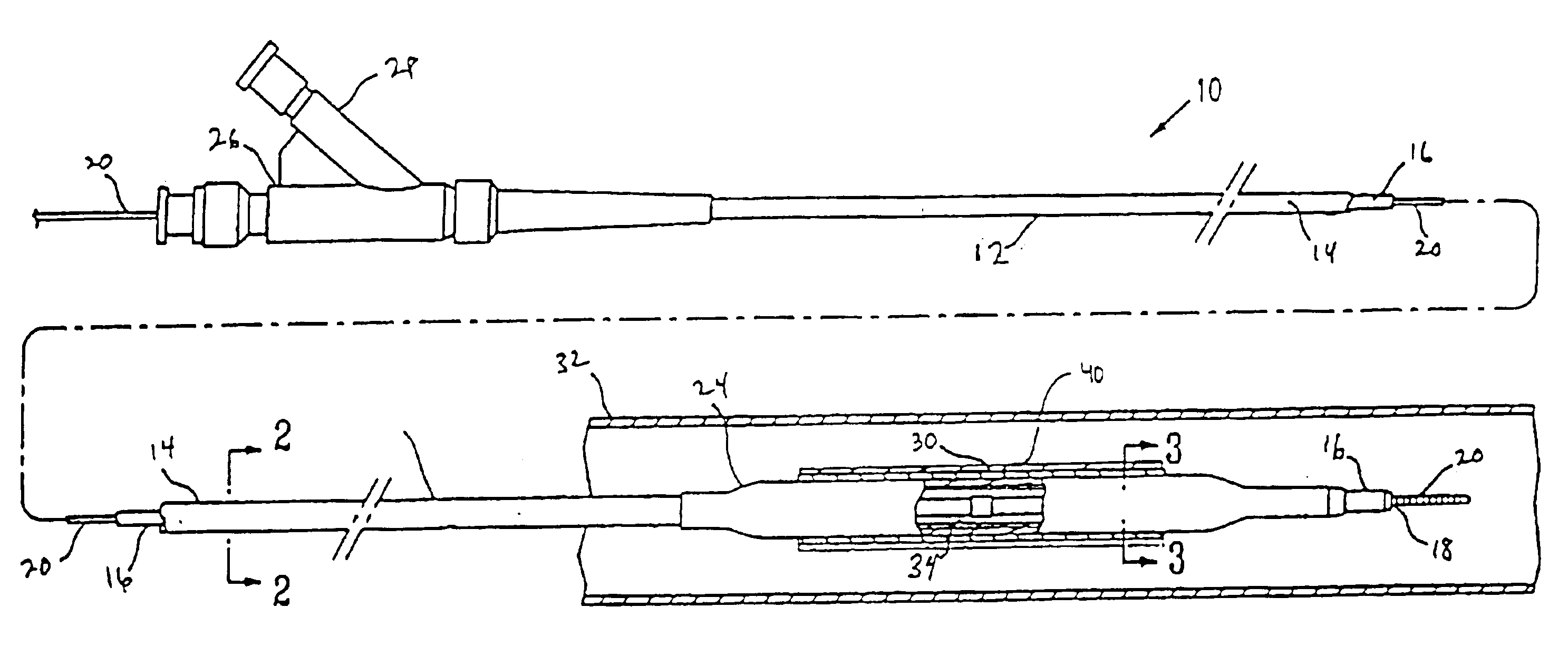
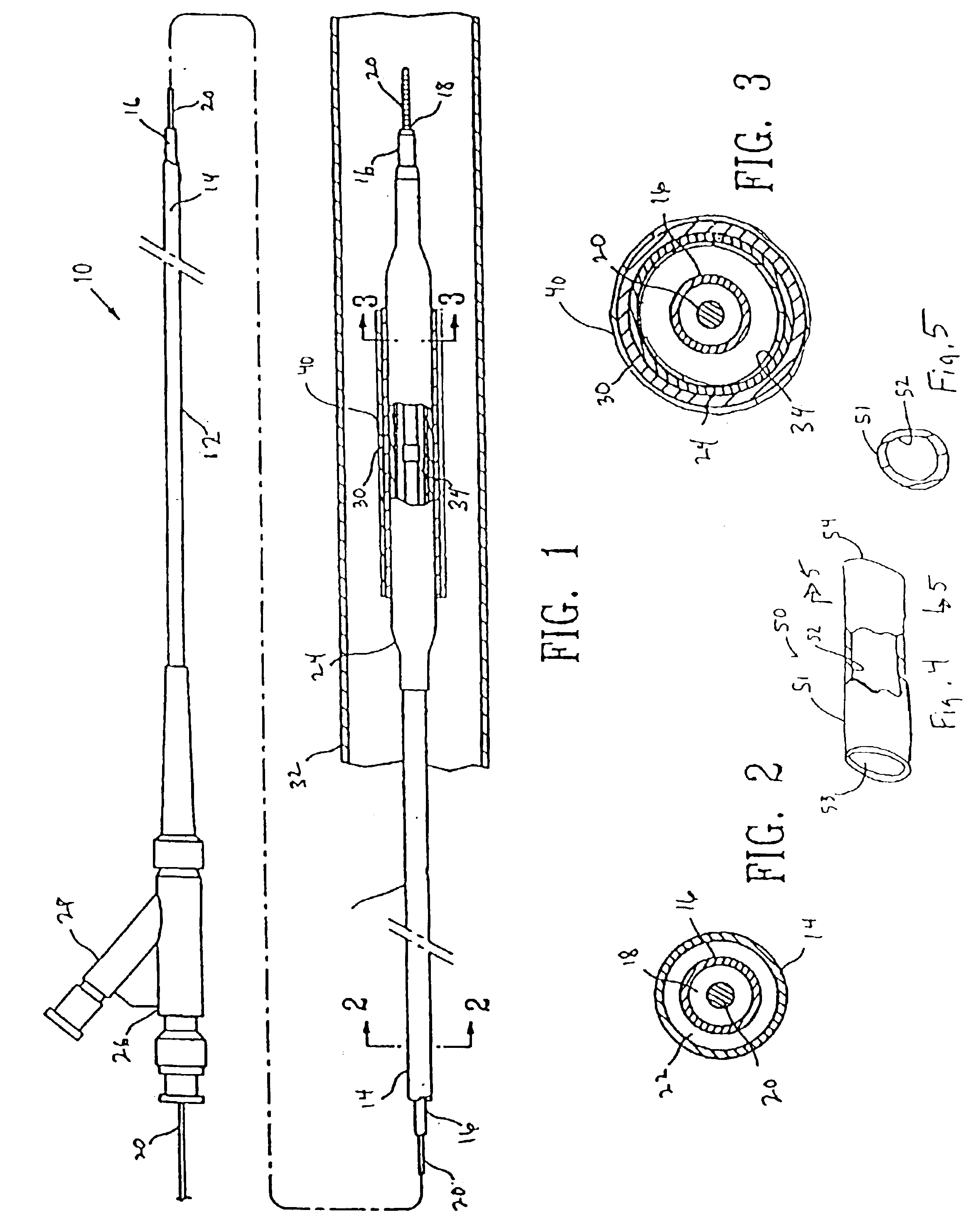
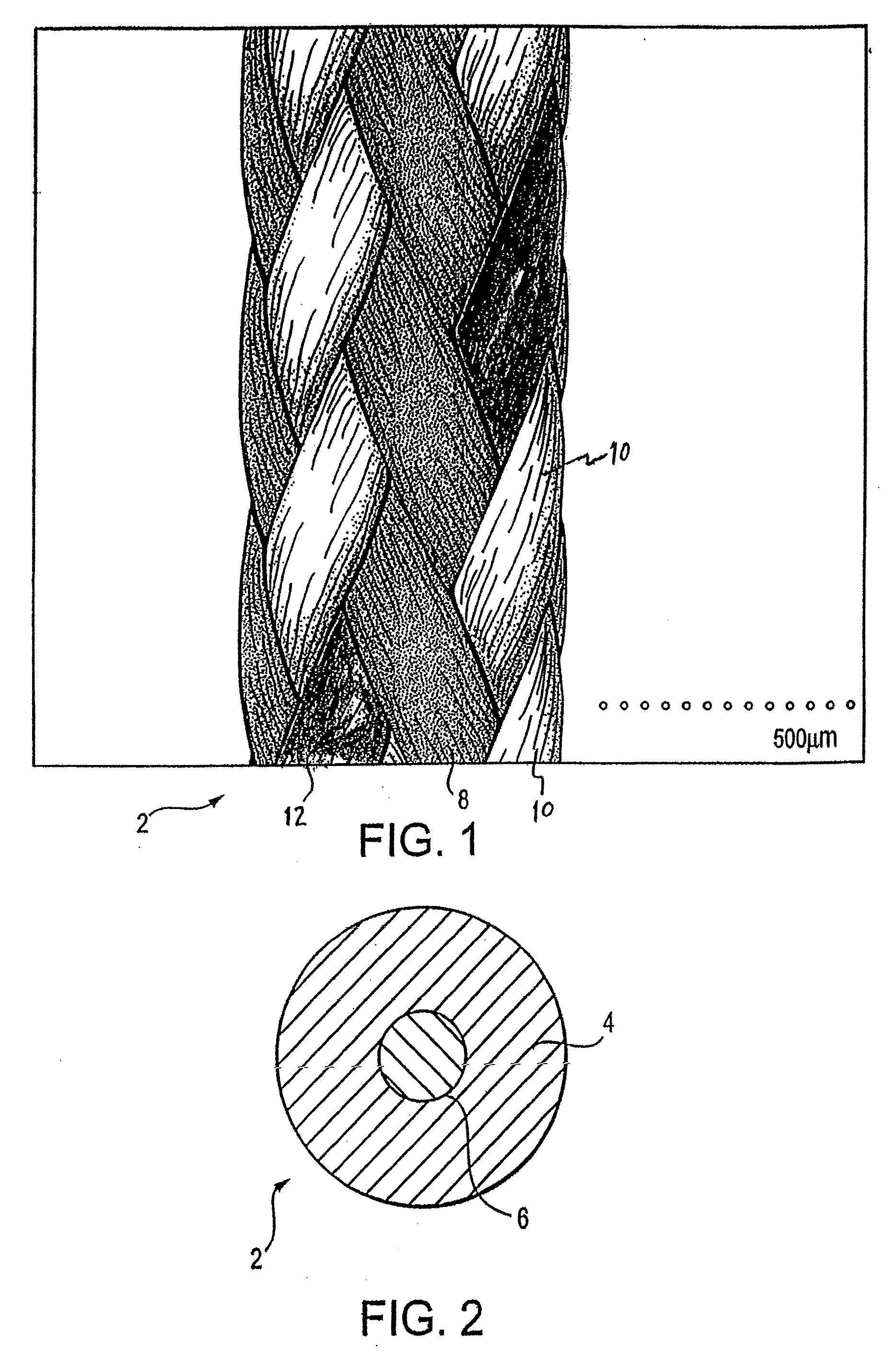
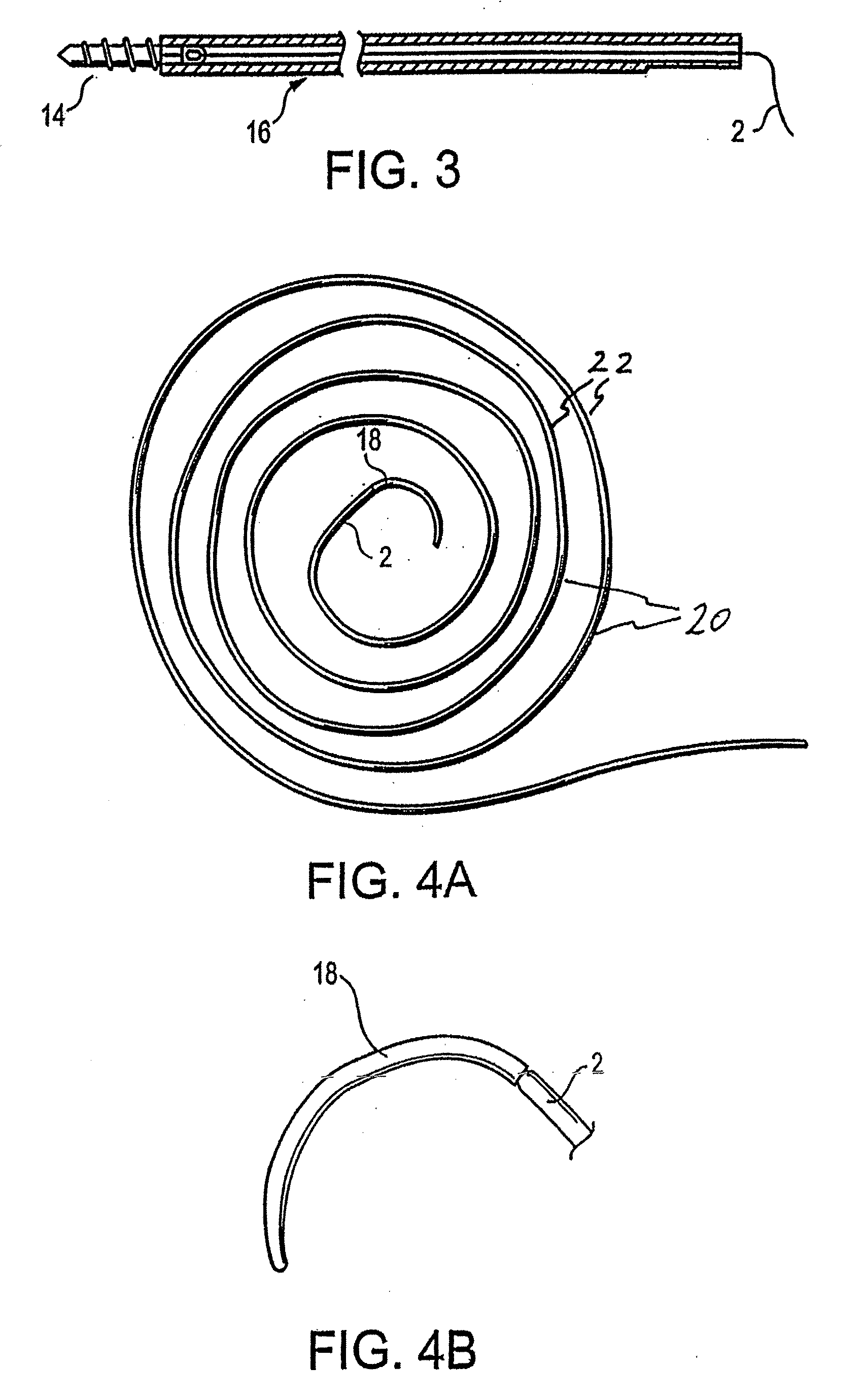
Selectively absorbable/biodegradable, fibrous composite constructs and applications thereof
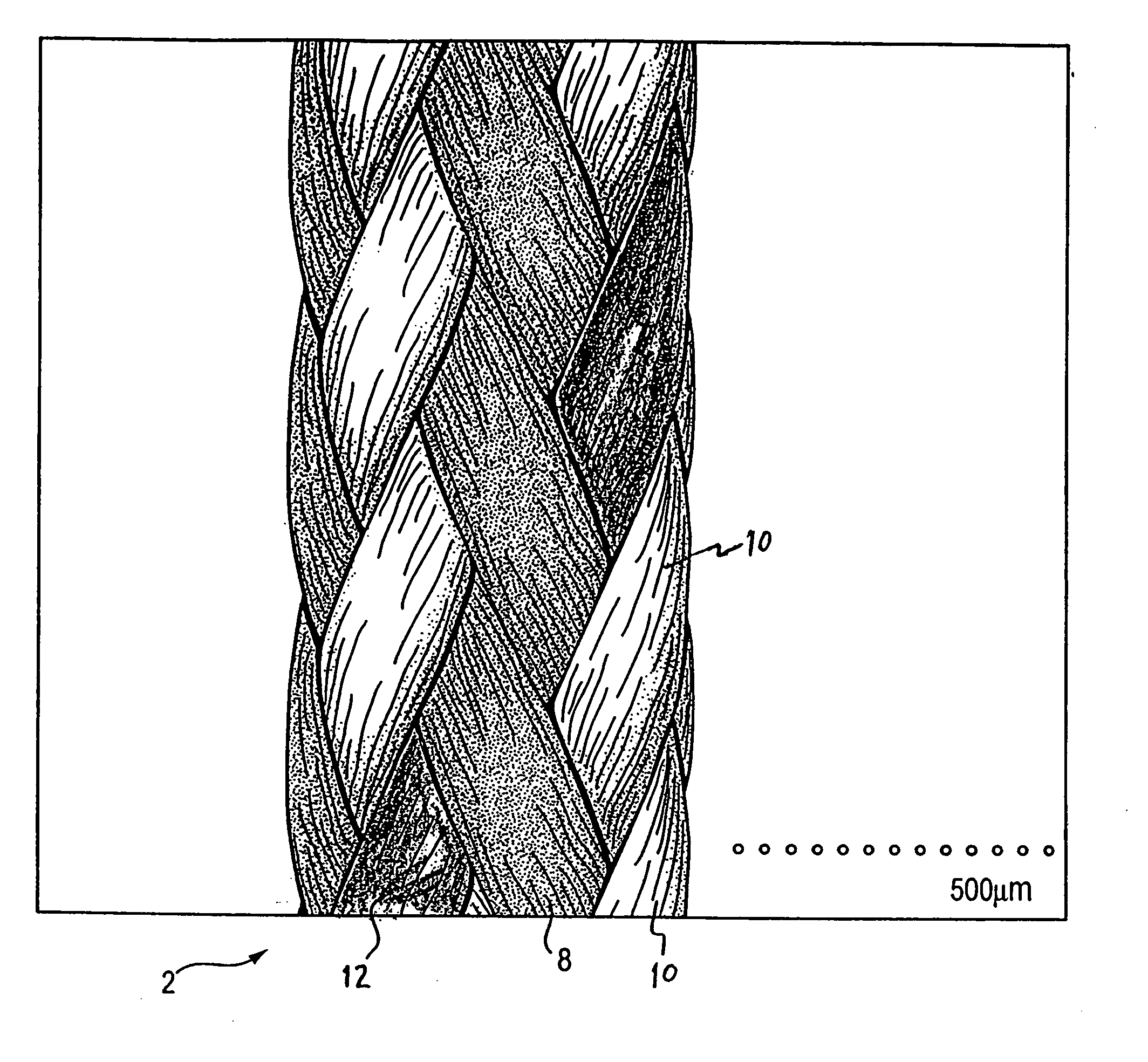
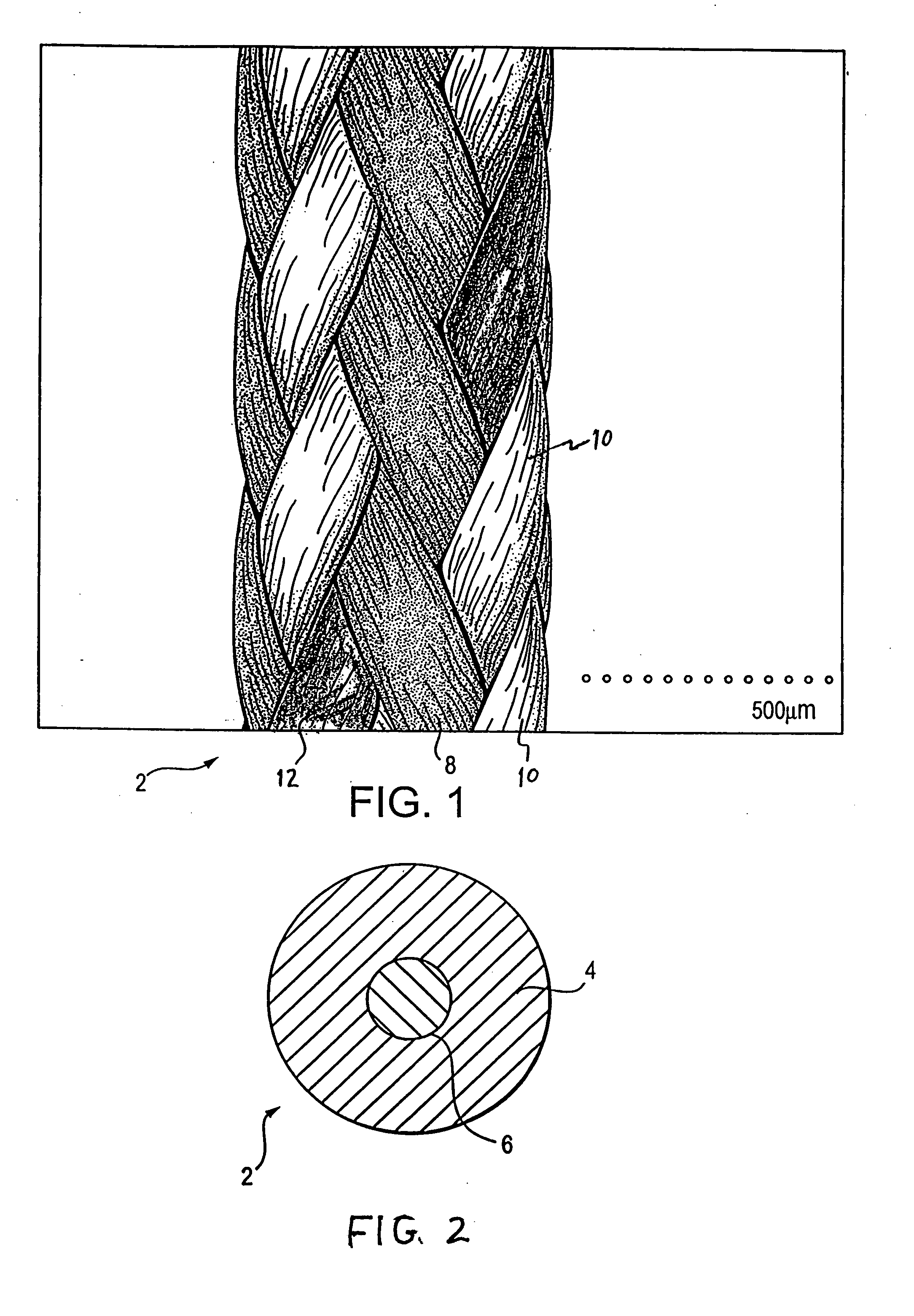
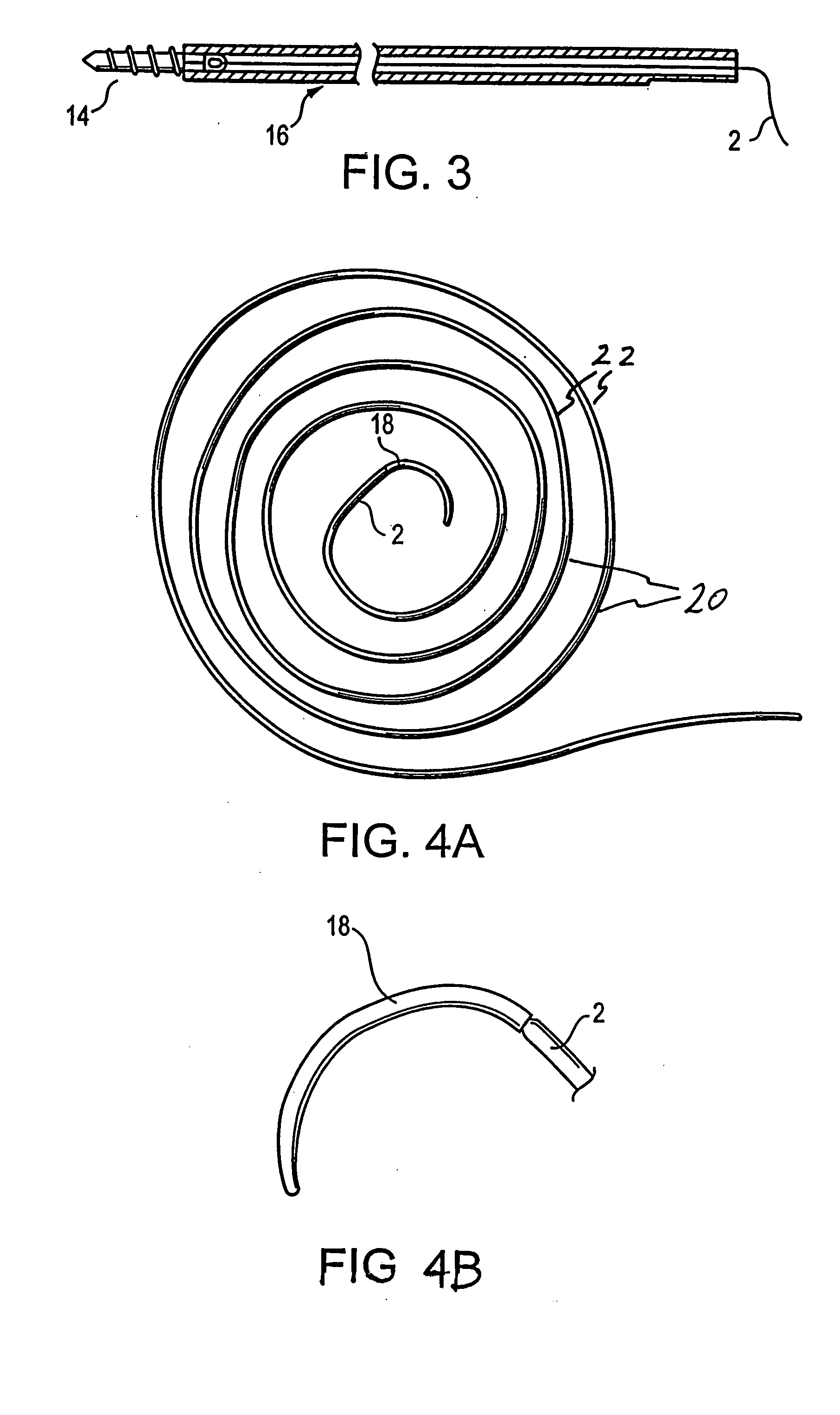
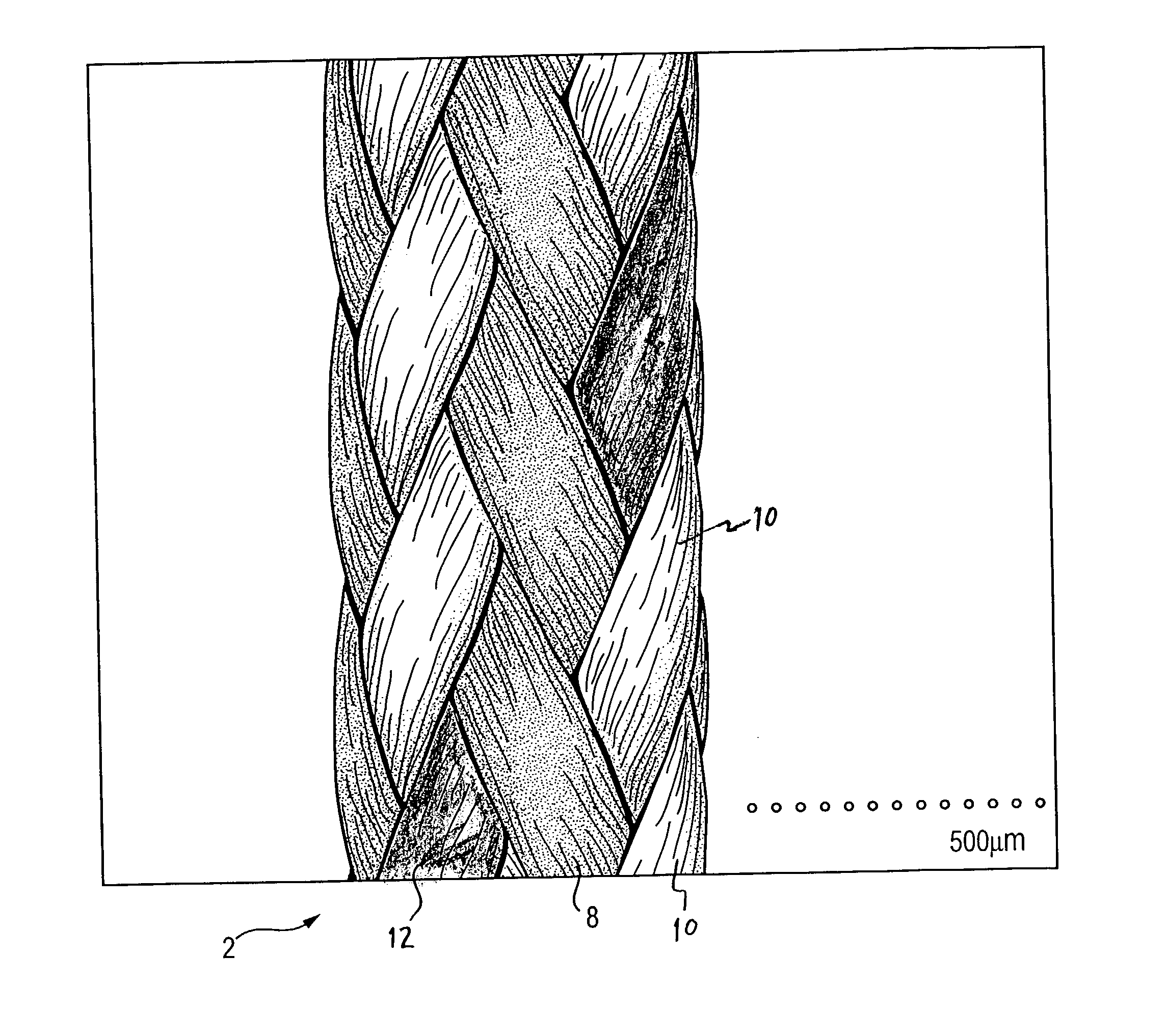
A family of selectively absorbable / biodegradable, fibrous composite constructs includes different combinations of biostable and absorbable / biodegradable yarns assembled as initially interdependent, load-bearing components, transitioning to exhibit independent functional properties during in vivo end-use. The family of constructs consists of two groups, one group is made of fiber-reinforced composites of high compliance, absorbable matrices of segmented polyaxial copolyesters reinforced with multifilament yarn constructs, which are combinations of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene fibers and at least one absorbable / biodegradable fiber selected from silk fibers and multifilament yarns made from linear segmented, l-lactide copolyesters and poly (3-hydroxyalkanoates, are useful in orthopedic, maxillofacial, urological, vascular, hernial repair and tissue engineering applications. The second group is made of coated and uncoated, warp-knitted mesh constructs for use in hernial, vascular, and urological tissue repair and tissue engineering.
Owner:POLY MED
Process for medical implant of cross-linked ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene having improved balance of wear properties and oxidation resistance
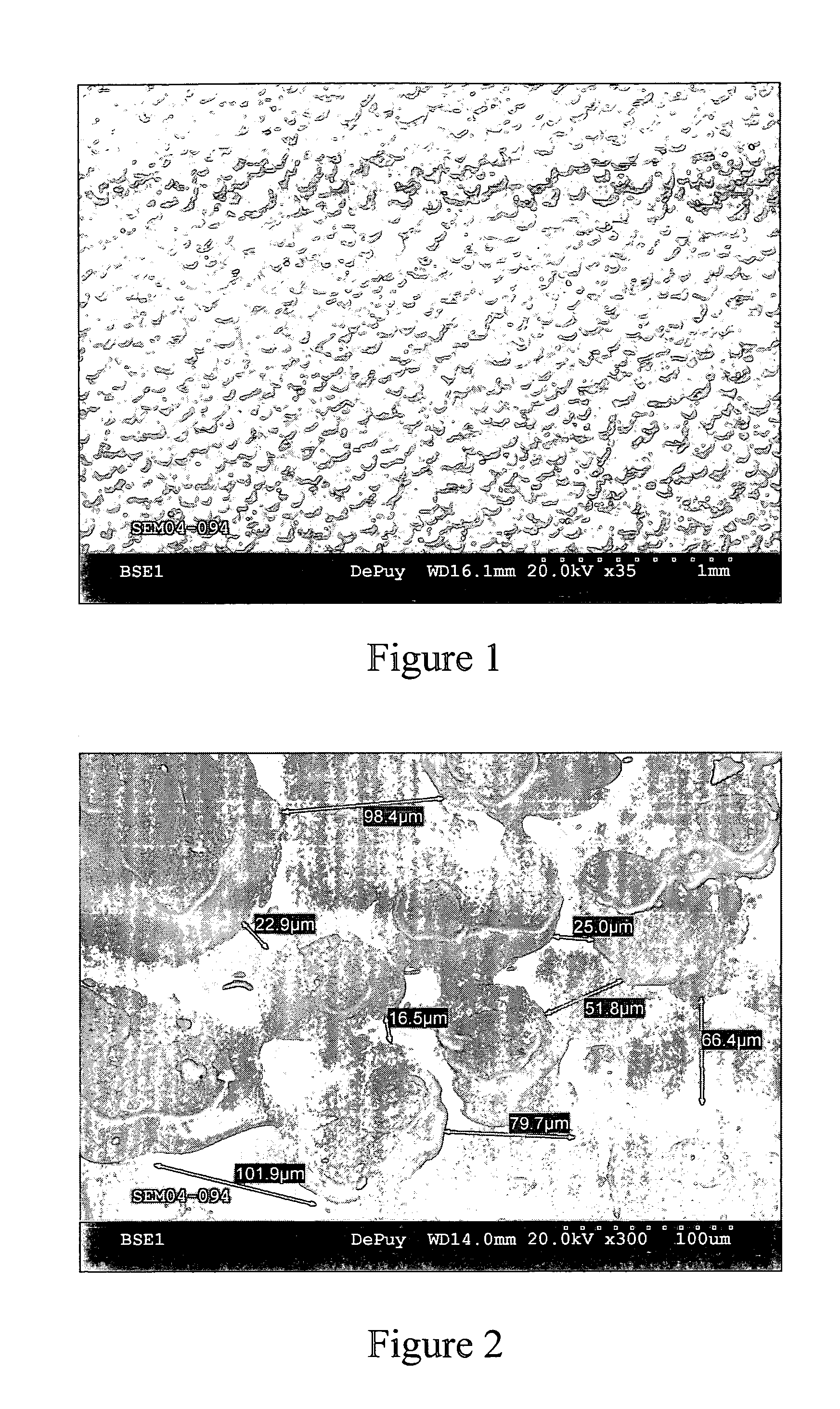
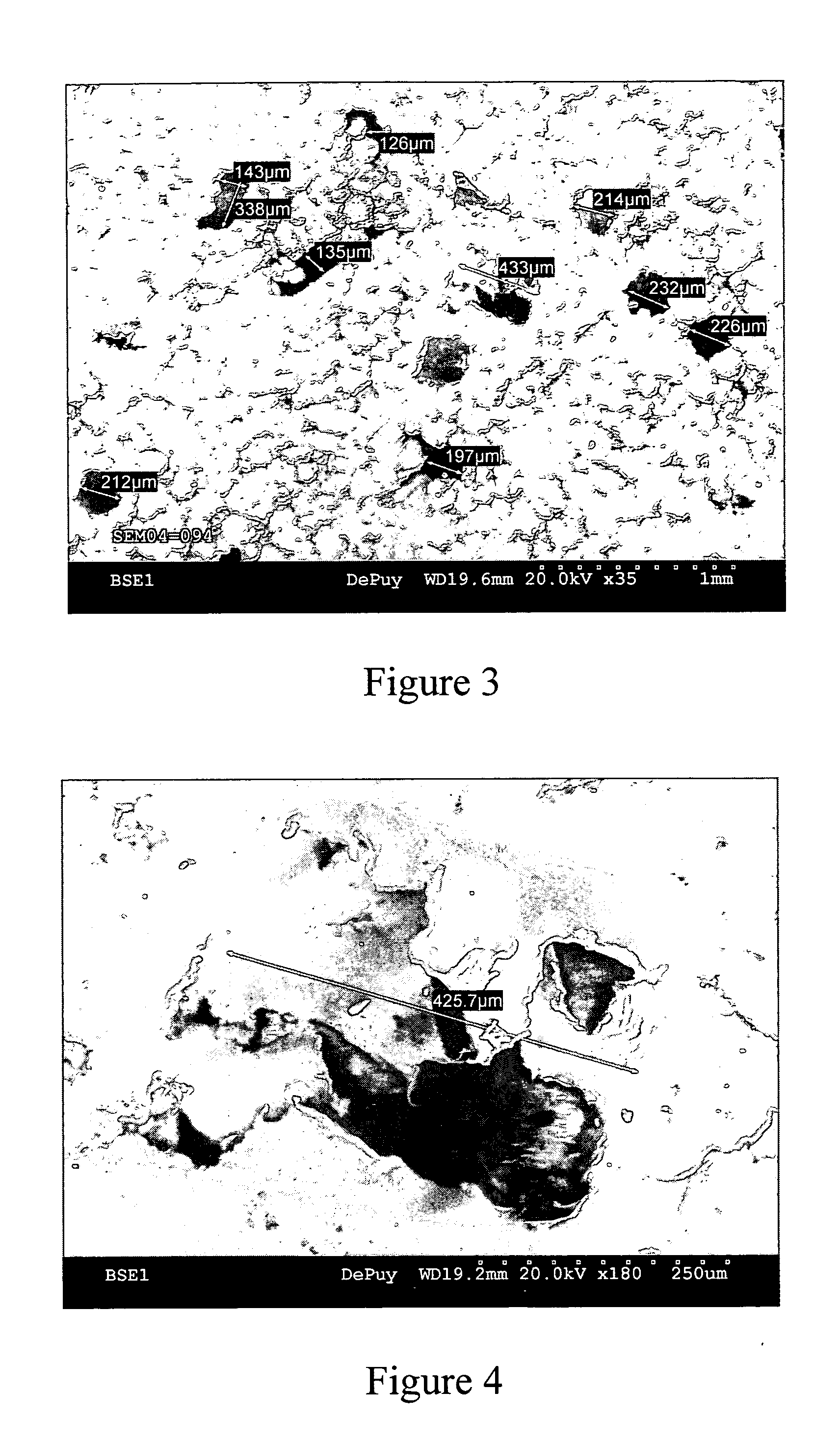
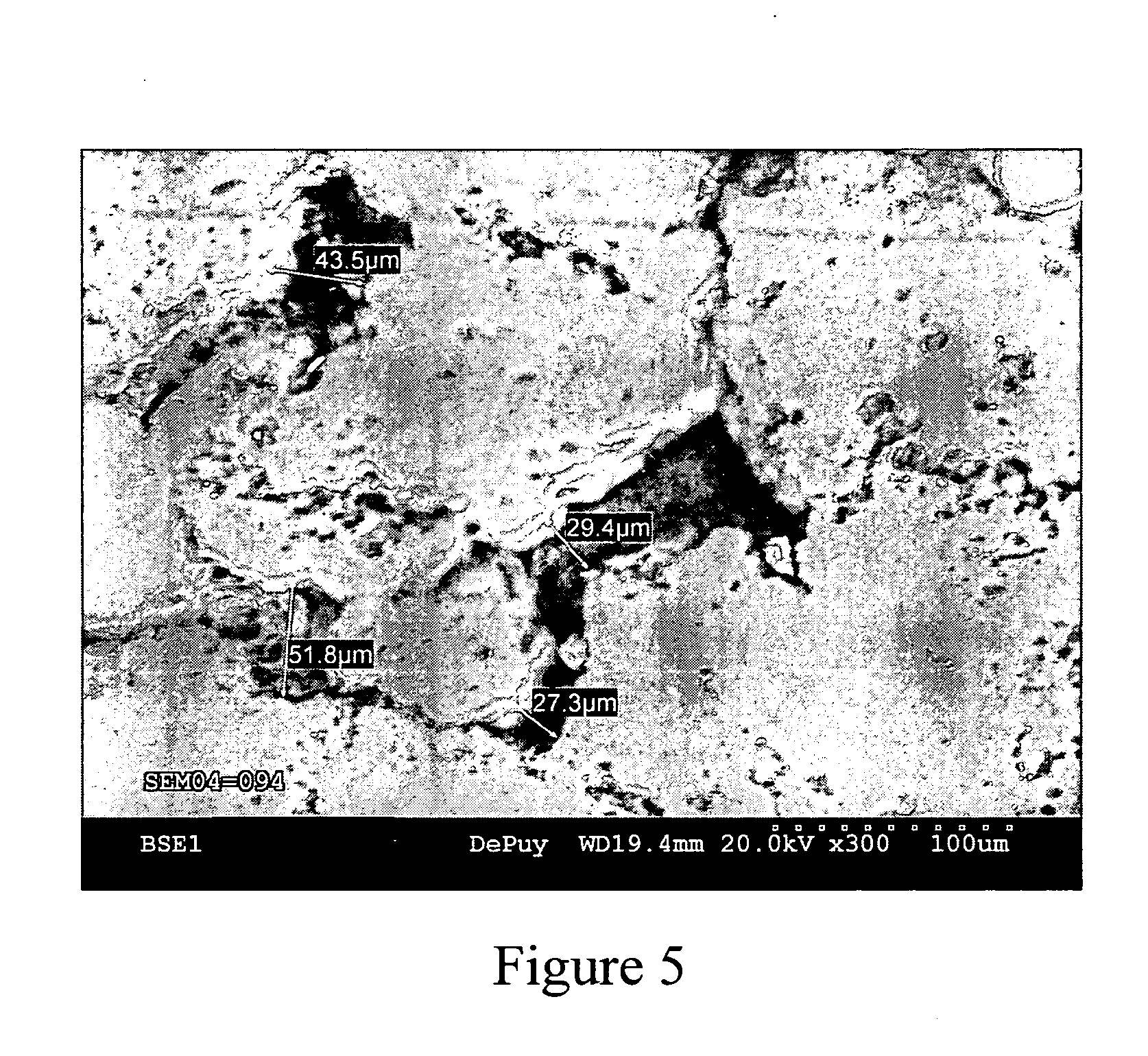
A medical implant of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene having an improved balance of wear properties and oxidation resistance is prepared by irradiating a preform of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene, annealing the irradiated preform in the absence of oxygen to a temperature at or above the onset of melting temperature, and forming an implant from the stabilized cross-linked polymer. Implants prepared according to the process of the present invention have comparable oxidation resistance and superior wear performance compared to unirradiated ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene.
Owner:DEPUY ORTHOPAEDICS INC
High strength suture with collagen fibers
InactiveUS20050033362A1High strengthGood tissue compatibilitySuture equipmentsSurgical needlesPolyesterTissue remodeling
Owner:ARTHREX
High strength suture with colored trace at one end
Owner:ARTHREX
Microporous material and a method of making same
ActiveUS20060121269A1Improved dimensional stability and physical propertyElectrolyte holding meansSemi-permeable membranesPlasticizerStretch ratio
A method for producing a microporous material comprising the steps of: providing an ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE); providing a filler; providing a processing plasticizer; adding the filler to the UHMWPE in a mixture being in the range of from about 1:9 to about 15:1 filler to UHMWPE by weight; adding the processing plasticizer to the mixture; extruding the mixture to form a sheet from the mixture; calendering the sheet; extracting the processing plasticizer from the sheet to produce a matrix comprising UHMWPE and the filler distributed throughout the matrix; stretching the microporous material in at least one direction to a stretch ratio of at least about 1.5 to produce a stretched microporous matrix; and subsequently calendering the stretched microporous matrix to produce a microporous material which exhibits improved physical and dimensional stability properties over the stretched microporous matrix.
Owner:DARAMIC LLC
High strength suture coated with collagen
InactiveUS20080051834A1High strengthImproved tie down characteristicSuture equipmentsLiquid surface applicatorsYarnSuture anchors
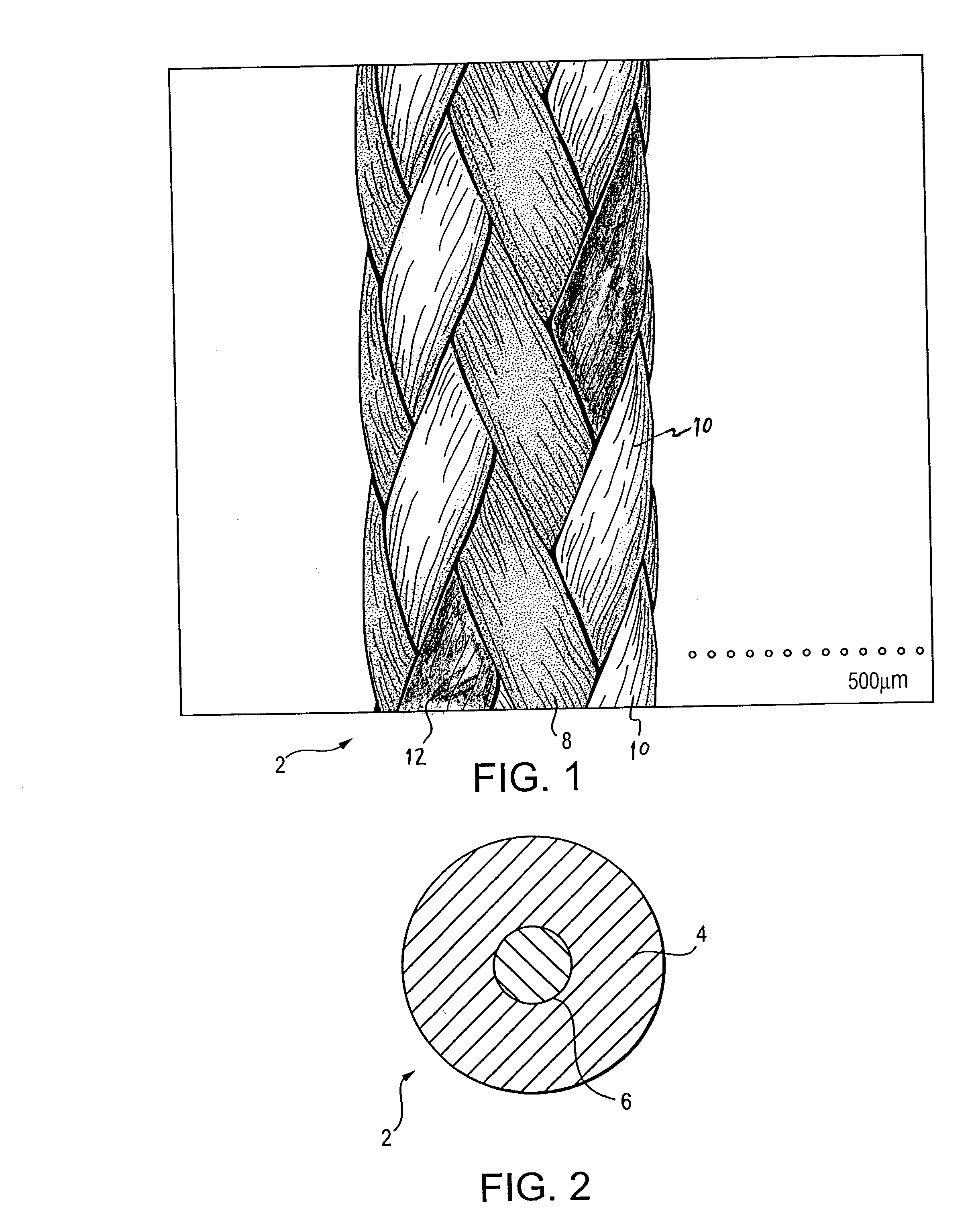
A high strength surgical suture formed of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) yarns, the suture being coated with native or denatured collagen. The braided jacket surrounds a core formed of twisted yarns of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene. The suture has exceptional strength, is ideally suited for most orthopedic procedures, and can be attached to a suture anchor or a curved needle.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
Medical device formed of ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin
Medical devices having at least a component, such as a catheter balloon, stent cover and vascular graft, formed of ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin, such as ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene. The device component is formed from ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene that has been processed so that it is microporous and has an oriented node and fibril structure. The device component expands compliantly at low strains and are substantially less compliant at higher strains. The invention also comprises methods for making such medical devices, including the steps of compacting a polyethylene powder and deforming it to impart the oriented structure.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Medical implant or medical implant part and method for producing the same
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Abrasion resistant cords and ropes
InactiveUS20150128792A1Improve wear resistanceLower the volumeAgriculture tools and machinesSynthetic resin layered productsFiberPolymer science
The abrasion resistance of organic fiber based ropes and cords is increased by a outer woven cover of tapes of high molecular weight and more preferably ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene
Owner:POLTECO
Braided filament with particularized strand compositions and methods of manufacturing and using same
In one embodiment, the present invention is a braided filament including a plurality of strands each having at least one ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene fiber and at least one polyester fiber wherein the quantity of certain types of fibers in a first strand is the same as the quantity of the same type of fibers in a second strand. In a variant, one additional strand of the braided filament is a monofilament strand. In another variant, each strand is homogeneous with respect to the other strands and is made exclusively from ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene fibers and polyester fibers such that each strand has the same distribution and quantity of fiber types.
Owner:STRYKER CORP +1
Free radical quench process for irradiated ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene
The invention provides a process for quenching free radicals present in irradiated ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene comprising the steps of (a) providing a mass of irradiated ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene, wherein the mass comprises free radicals, (b) immersing at least a portion of the mass of irradiated ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene in a non-polar solvent having a temperature for a time and under conditions sufficient to quench a substantial portion of the free radicals contained therein, wherein the temperature of the non-polar solvent is maintained below the melting point of the ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene, (c) removing the mass of irradiated ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene from the non-polar solvent, and (d) removing any non-polar solvent from the mass of irradiated ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Preparation method and application of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene/graphene composite fiber
ActiveCN102618955AHigh strengthImprove mechanical propertiesFilament/thread formingPersonal protection gearFiberPolymer science
The invention discloses an ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene / graphene composite fiber and a preparation method as well as application thereof. The composite fiber consists of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) and graphene; the weight-average molecular weight of the ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene is 1*10<6>-4*10<6>, particularly 1*10<6>-3*10<6>; the diameter of the graphene is 0.6-1.8 mum; and the thickness of the graphene is 0.5-5 nm. The graphene is a material which has the maximum strength in the world up to now. According to the invention, the graphene powder is introduced into the ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene fiber, so that the ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene / graphene composite fiber has excellent mechanical property. Preliminary research shows that the tensile strength of the ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene / graphene composite fiber prepared by the method can reach 2.5 GPa, the tensile modulus is 130 GPa, and the thermal decomposition temperature in nitrogen gas can reach up to over 390 DEG C.
Owner:THE QUARTERMASTER EQUIPMENT RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF THE GENERAL LOGISITIC DEPARTME +1
Selectively absorbable/biodegradable, fibrous composite constructs and applications thereof
A family of selectively absorbable / biodegradable, fibrous composite constructs includes different combinations of biostable and absorbable / biodegradable yarns assembled as initially interdependent, load-bearing components, transitioning to exhibit independent functional properties during in vivo end-use. The family of constructs consists of two groups, one group is made of fiber-reinforced composites of high compliance, absorbable matrices of segmented polyaxial copolyesters reinforced with multifilament yarn constructs, which are combinations of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene fibers and at least one absorbable / biodegradable fiber selected from silk fibers and multifilament yarns made from linear segmented, l-lactide copolyesters and poly (3-hydroxyalkanoates, are useful in orthopedic, maxillofacial, urological, vascular, hernial repair and tissue engineering applications. The second group is made of coated and uncoated, warp-knitted mesh constructs for use in hernial, vascular, and urological tissue repair and tissue engineering.
Owner:POLY MED
Method for preparing conductive ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene fiber
The invention relates to a method for preparing a conductive ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene fiber. The conventional method is complicated in process and causes environmental pollution. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, immersing the ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene fiber into acetone, ethanol or a tetrahydrofuran solution, performing ultrasonic washing on the fiber and airing; secondly, dissolving a dopamine substance into a buffer solution to prepare an activation solution, placing the ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene fiber into the activation solution and activating the ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene fiber under stirring; and finally, immersing the activated ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene fiber in a plating solution at temperature of 10 to 60 DEG C for 0.5 to 10 hours so as to finish silver plating. By the method, the surface of the ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene fiber is activated by using dopamine polymer and metallized by using chemical plating, so that the ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene fiber with extremely high conductivity can be obtained; and the whole process is environment-friendly and pollution-free.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Support for solar energy collectors
ActiveUS9035168B2Reduce laborLow costPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyCollection systemOpen bite
A solar energy collection system can include support devices made with bearings formed from sheet material. These bearings can be optionally formed so as to provide tool-less connections to their associated bearing housings. The bearings can be formed with an open configuration allowing a shaft to be inserted into an open bite of the bearing. Optionally, the bearing can be made from an ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene plastic material. Additionally, two open-type bearing assemblies can be mounted axially offset and opposed to one another.
Owner:SUNPOWER CORPORATION
Method of making microporous material
ActiveUS7445735B2Improved dimensional stability and physical propertyElectrolyte holding meansSemi-permeable membranesPlasticizerStretch ratio
Owner:DARAMIC LLC
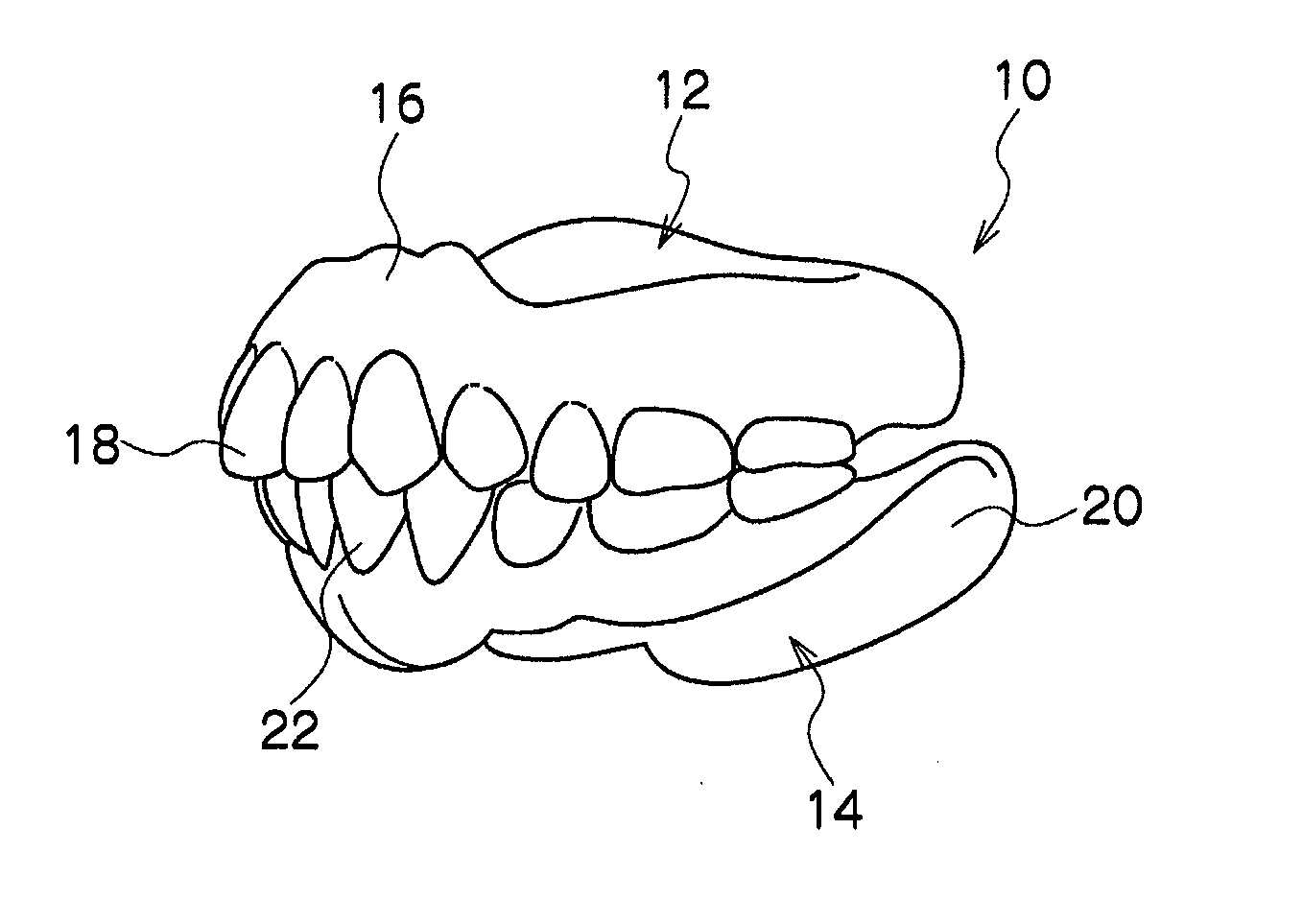
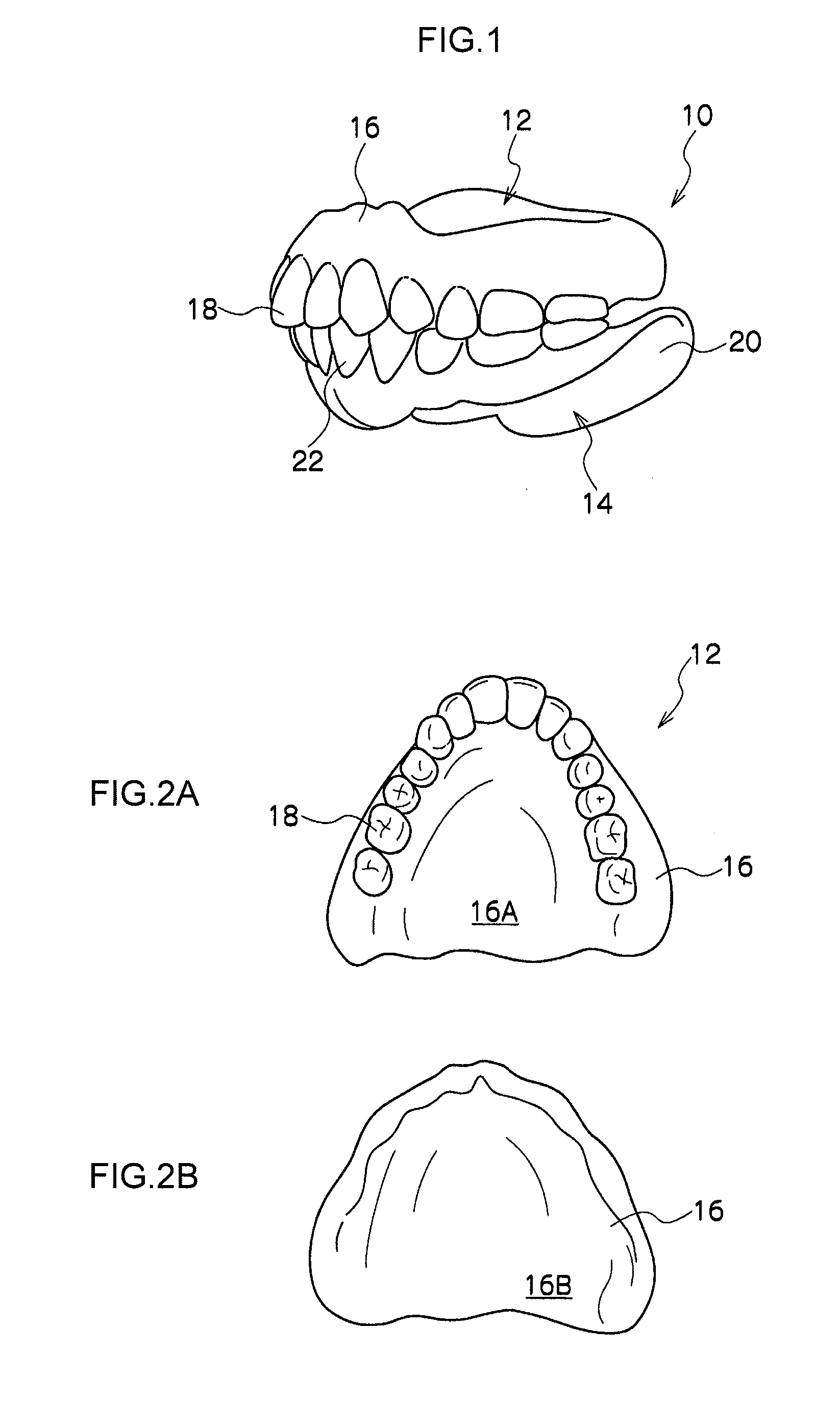
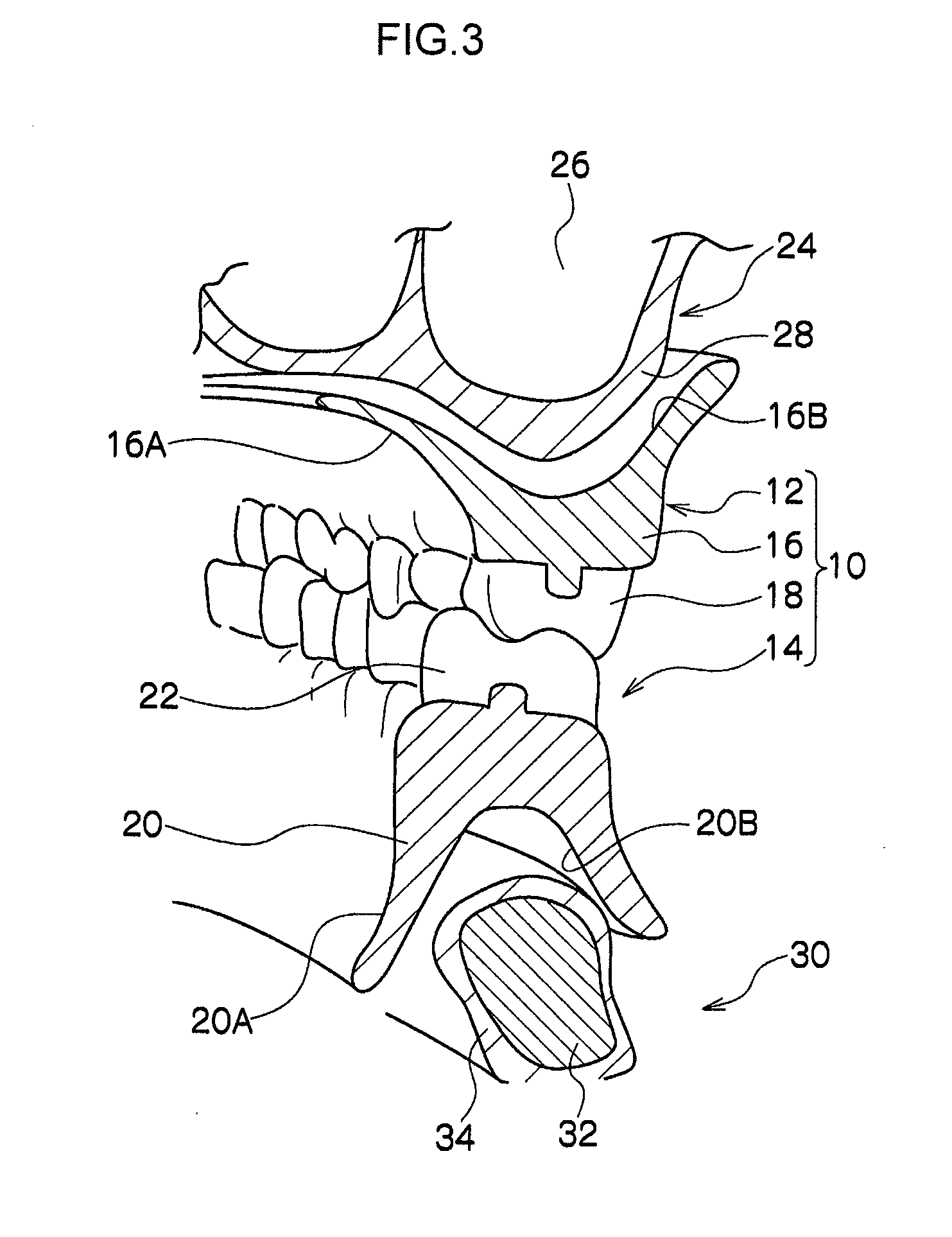
Removable denture and method of producing the same
InactiveUS20110236856A1Easy to disassembleIncreased durabilityDental prostheticsDentistryDenture base
A removable denture includes a denture base that is made of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene and is formed in a predetermined shape by a molded object of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene being cut; and artificial teeth that are arrayed at the denture base.
Owner:NAT UNIV CORP TOKYO MEDICAL & DENTAL UNIV
Suture with filaments formed of polyether-ketone variant
A high strength abrasion resistant surgical suture material with improved tie down characteristics and tissue compliance with braided yarns formed of ether-ketone variant. The suture features a multifilament jacket formed of braided yarns of ether-ketone variant, optionally braided with yarns of polyester, silk, nylon, ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene or aramid fibers. The braided jacket surrounds a core formed of twisted yarns of ether-ketone variant or ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene. The suture has exceptional strength, is ideally suited for most orthopedic procedures, and can be attached to a suture anchor or a curved needle.
Owner:ARTHREX
Extra high-molecular polythene catalyst and its production
Ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene catalyst and its production are disclosed. The catalyst consists of main components of catalyst and catalyst accessory. The process is carried out by reacting halide magnesium compound with alcohol compound and organic titanate compound to obtain magnesium compound solution, reacting with alkyl chlorine aluminum compound to obtain intermediate product, reacting with titanium compound and electron-donating to obtain final product. It has higher activity and better stacking density.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES INST OF CHEM IND +1
Rotational molding wear-resistant polyolefin resin and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101735505AImprove wear resistanceImprove friction and wear propertiesLow-density polyethyleneLinear low-density polyethylene
The invention discloses a rotational molding wear-resistant polyolefin resin and a preparation method thereof. In the rotational molding wear-resistant polyolefin resin, raw materials commonly used in the rotational molding process, namely linear low-density polyethylene, high-density polyethylene or polypropylene is taken as a matrix material; and by adding components of an inorganic filler, ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene and a lubricant, the wear resistance of the matrix resin is improved. The rotational molding wear-resistant polyolefin resin consists of the following components in percentage by mass: 70 to 80 percent of matrix resin, 10 to 15 percent of inorganic filler subjected to surface treatment, 4 to 13 percent of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene and 1.5 to 2 percent of lubricant, wherein the matrix resin is the linear low-density polyethylene, the high-density polyethylene or the polypropylene; and a range of a melt flow rate of the matrix resin is between 2g / 10min and 15g / 10min.
Owner:江苏吉星管业科技有限公司
Ultrahigh wear-resistant thermoplastic elastomer material for shoe-sole
The present invention relates to a sole material, in particular it is a thermoplastic rubber sole material to which a high-molecular wear-resisting modifier ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene is added, its composition comprises SBS, PS, filler, softening oil, UHMWPE, demoulding agent, antioxidant, thermal stabilizing agent, light stabilizer and foaming agent. On the basis of SBS, PS, softening oil, filler and colour powder a high-molecular wear-resisting modifier ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) is added, its molecular chain has carbon-carbon long-chain structure, and its number-average molecular weight is 1000000-8000000. In the mixture formula other components and contents are regulated, so that the abrasion-resistance of the sole can be greatly raised (the length of abrasive crack is less than 7 mm).
Owner:FUJIAN HONGWEI SHOES PLASTIC CO LTD
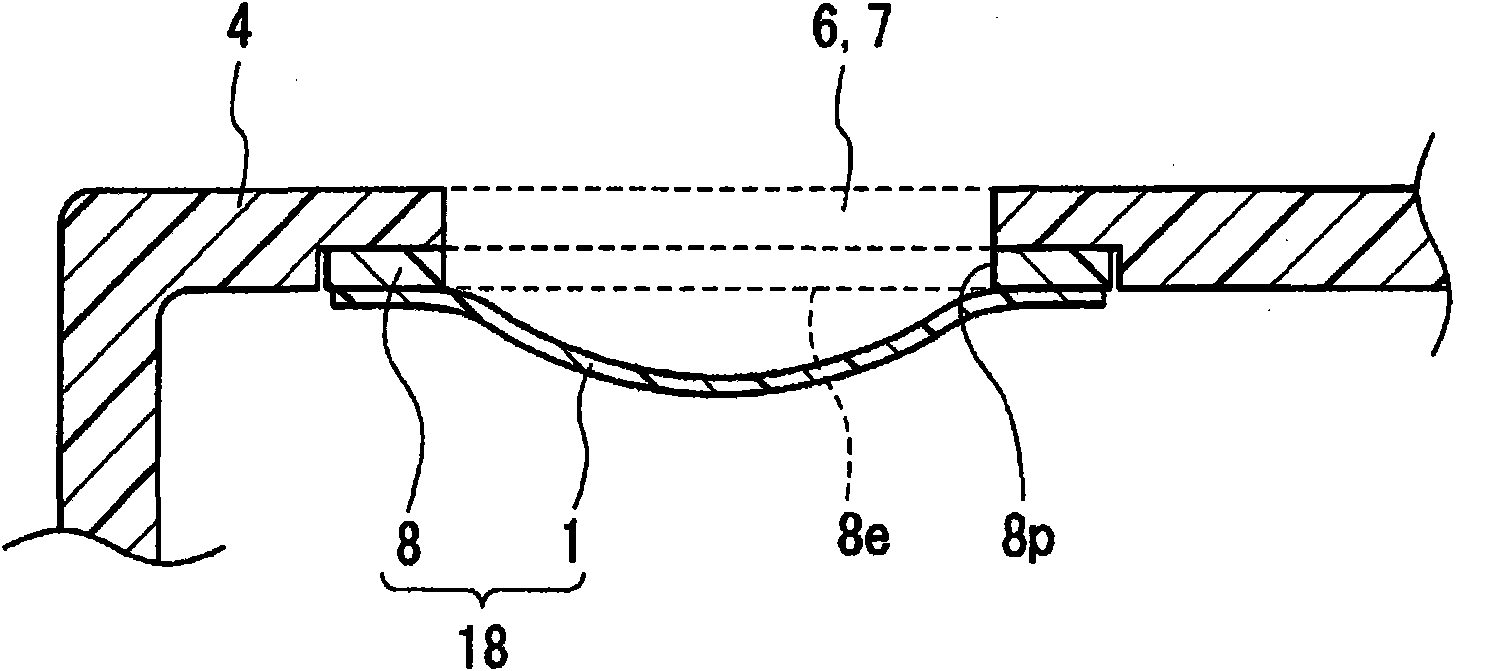
Sound passing member utilizing waterproof sound passing membrane and process for manufacturing the same
ActiveCN101816187AEfficient manufacturingEffective relaxationTransducers for subaqueous useThin material handlingPorous membraneEngineering
A sound passing member (18) comprising a waterproof sound passing membrane (1) adapted to allow the passage of sound but block the passage of liquid and a main body part (8) having an opening (8p) for the passage of sound, the opening (8p) covered by the waterproof sound passing membrane (1). The waterproof sound passing membrane (1) in a slack state is fixed to the main body part (8). A polytetrafluoroethylene porous membrane or ultrahigh-molecular-weight polyethylene porous membrane can appropriately be used as the waterproof sound passing membrane (1).
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Chemically crosslinked ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene for artificial human joints
InactiveUS20080133018A1Withstand wearReduce crystallinityJoint implantsFemoral headsIn vivoIrradiation
The present invention discloses a method for enhancing the wear-resistance of polymers by crosslinking them, especially before irradiation sterilization. In particular, this invention presents the use of chemically crosslinked ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene in in vivo implants.
Owner:SALOVEY RONALD +2
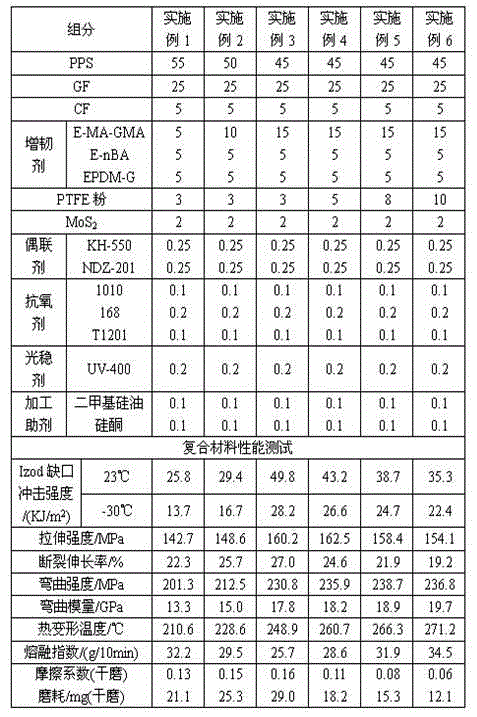
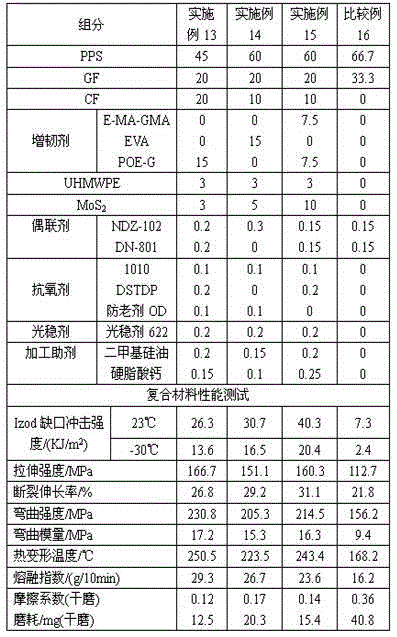
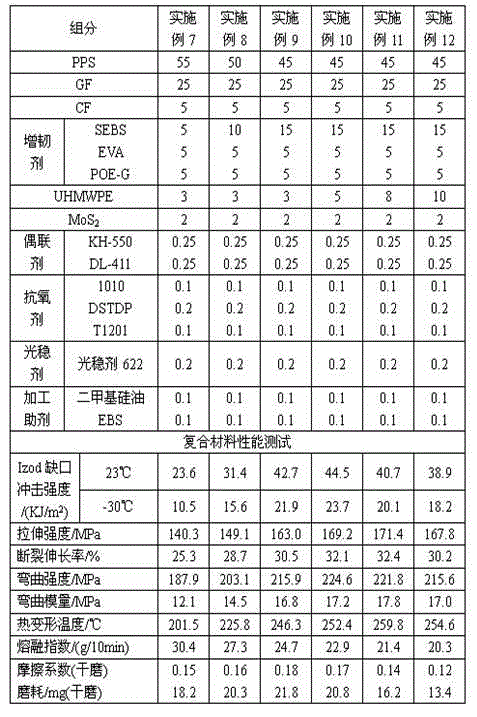
Wear-resistant and high-toughness polyphenylene sulfide composite material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a wear-resistant and high-toughness polyphenylene sulfide composite material and a preparation method thereof. The composite material is composed of the following components of, by weight, 30-75 parts of polyphenylene sulfide, 20-50 parts of glass fibre, 5-20 parts of carbon fiber, 5-30 parts of a toughening agent, 0-20 parts of polytetrafluoroethylene, 0-20 parts of an ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene, 2-10 parts of molybdenum disulfide, 0.2-1.5 parts of a coupling agent, 0.2-1 part of an antioxidant, 0.1-0.5 part of a light stability agent and 0.2-2 parts of a processing auxiliary agent. The composite material has a series of outstanding advantages of excellent low-temperature impact performance, high strength, high modulus, high heat stability, easy processing and molding, and the like, and has wide application fields such as automobiles, aeronautics and astronautics, etc.
Owner:HEFEI GENIUS NEW MATERIALS
Method for preparing super high molecular polythene porous membrane by thermally phase separation method
InactiveCN101164677ANarrow pore size distributionHigh porositySemi-permeable membranesPolymer sciencePhase separation process
The present invention relates to a preparation method of ultrahigh molecutar weight polyethylene porous membrane, specially, it relates to a method for preparing high-performance ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) porous membrane by adopting thermal phase separation process. It is characterized by that it uses a high-temperature-resistant solvent-resistant high-strength ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene resin as membrane material, under the action of diluting agent said invention makes the polyethylene resin membrane material undergo the processes of solution preparation, extrusion, drawing, cooling extraction and recovering extracting agent so as to obtain the invented ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene porous membrane. The described diluting agent can be selected from white camphor oil, paraffin and paraffin oil.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Polyethylene cross-linked with an anthocyanin
ActiveUS20100036491A1Improve wear resistanceReduced chain-scissionLavatory sanitoryMedical waste disposalCross-linkUltimate tensile strength
A method for manufacturing of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) for implants, where the implants have been machined out of UHMWPE blocks or extruded rods, has anthocyanin dispersely imbedded in the polyethylene. The implant is then exposed to γ ray or electron beam irradiation in an amount of at least 2.5 Mrad followed by a heat treatment to prevent the implant from becoming brittle in the long term as well as to improve strength and wear. The method includes mixing a powder or granulate resin of UHMWPE with an aqueous liquid that contains anthocyanin in a predetermined amount. The water is then evaporated in order to deposit the anthocyanin in a predetermined concentration on the polyethylene particles. The doped UHMWPE particles are compressed into blocks at temperatures in a range of approximately 135° C.-250° C. and pressures in a range of approximately 2-70 MPa. Medical implants are made from the blocks.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Medical implant or medical implant part comprising porous UHMWPE and process for producing the same
The invention provides a medical implant or medical implant part comprising porous ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene having a weight average molecular weight of about 400,000 atomic mass units or more and a porosity of about 15% to about 65%. The invention further provides a process for producing a medical implant or medical implant part.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
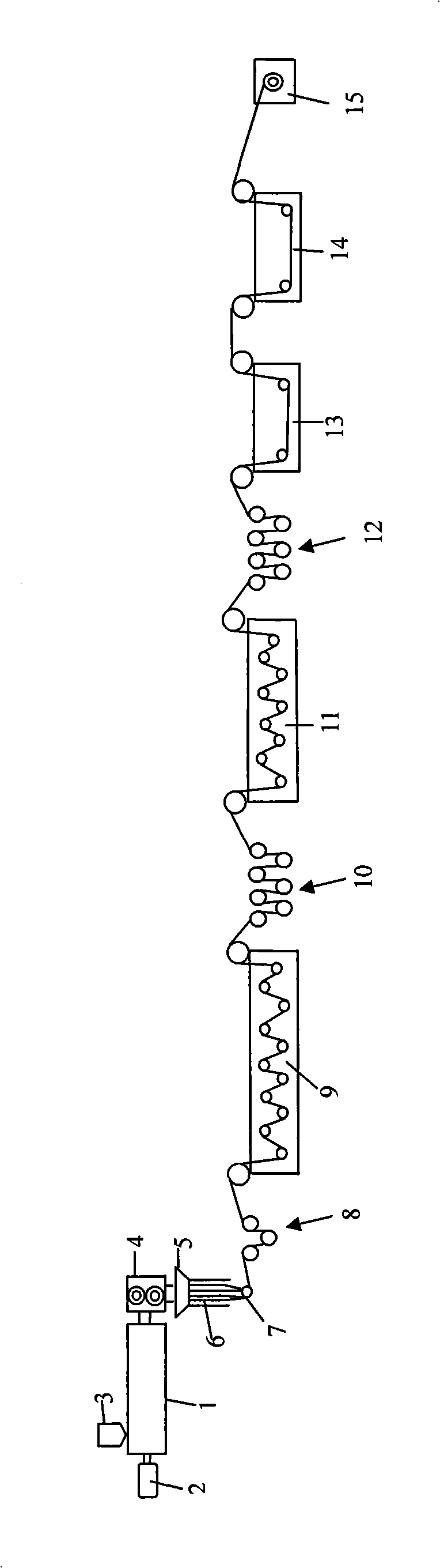
Method and equipment for preparing ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene fibers
InactiveCN101935894AContinuous productionShort processArtificial thread manufacturing machinesMelt spinning methodsFiberYarn
The invention discloses a method and equipment for preparing ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene fibers. The method comprises the following steps of: blending and melting ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene and a modifier to prepare a granular or powdery modified ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene raw material; melting and extruding the raw material by using an extruder to form melt of which a flow rate is 0.01 to 0.2 grams per 10 minutes, feeding the melt to a spinning mould by using a melt pump to form melt strips, and cooling and pre-stretching the melt strips to obtain primary yarns; and stretching the primary yarns in a plurality of stages to obtain the ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene fibers. The equipment comprises the extruder, the melt pump, the spinning mould, a cooling channel, a three-roller tractor, a primary hot-stretching box, a first seven-roller tractor, a secondary hot-stretching box, a second seven-roller tractor, a rinsing trough, a drying box and a winder which are arranged sequentially. The method and the equipment have the characteristics of continuous production capability, relatively shorter process flow, relatively fewer equipment components, no need of solvent, low production cost and the like.
Owner:王庆昭
Abrasion resistant cords and ropes
ActiveUS20110197564A1Improve wear resistanceLower the volumeSynthetic resin layered productsYarnFiberPolymer science
The abrasion resistance of organic fiber based ropes and cords is increased by a outer woven cover of tapes of high molecular weight and more preferably ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene
Owner:POLTECO
Gas-permeable membrane
InactiveUS7169451B2Suppress mutationEffective blockingWrappersPreformed elementsSide chainBiological materials
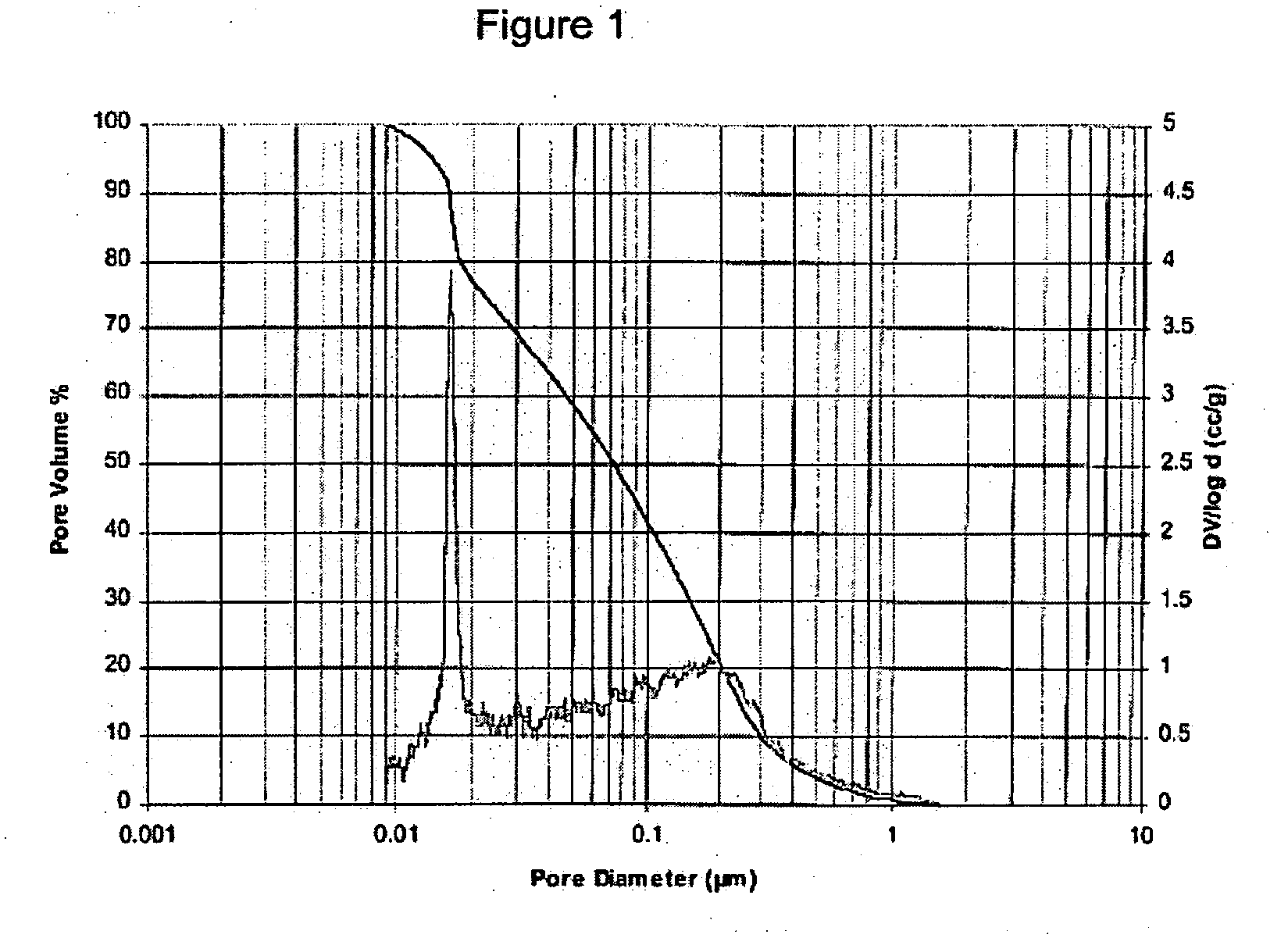
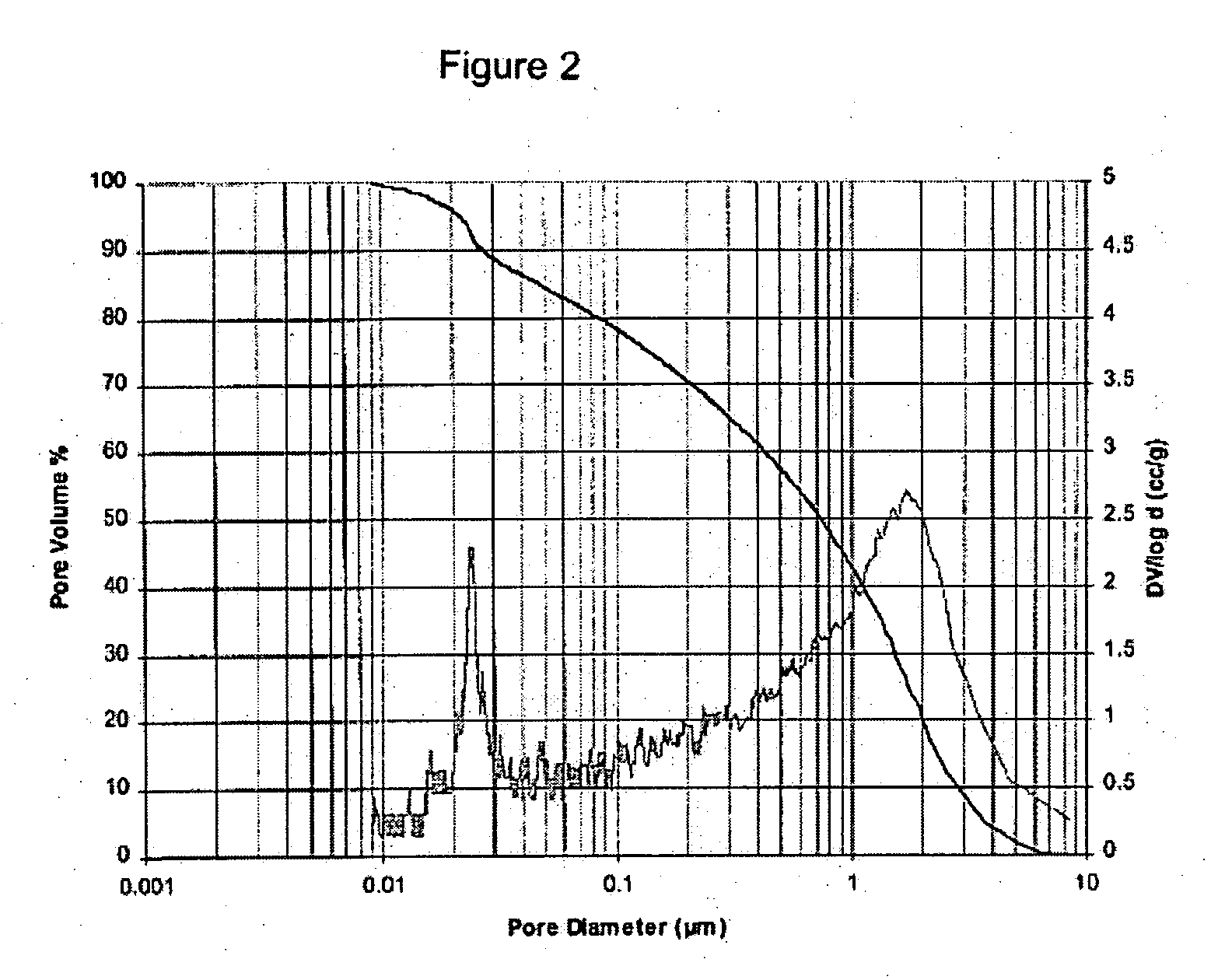
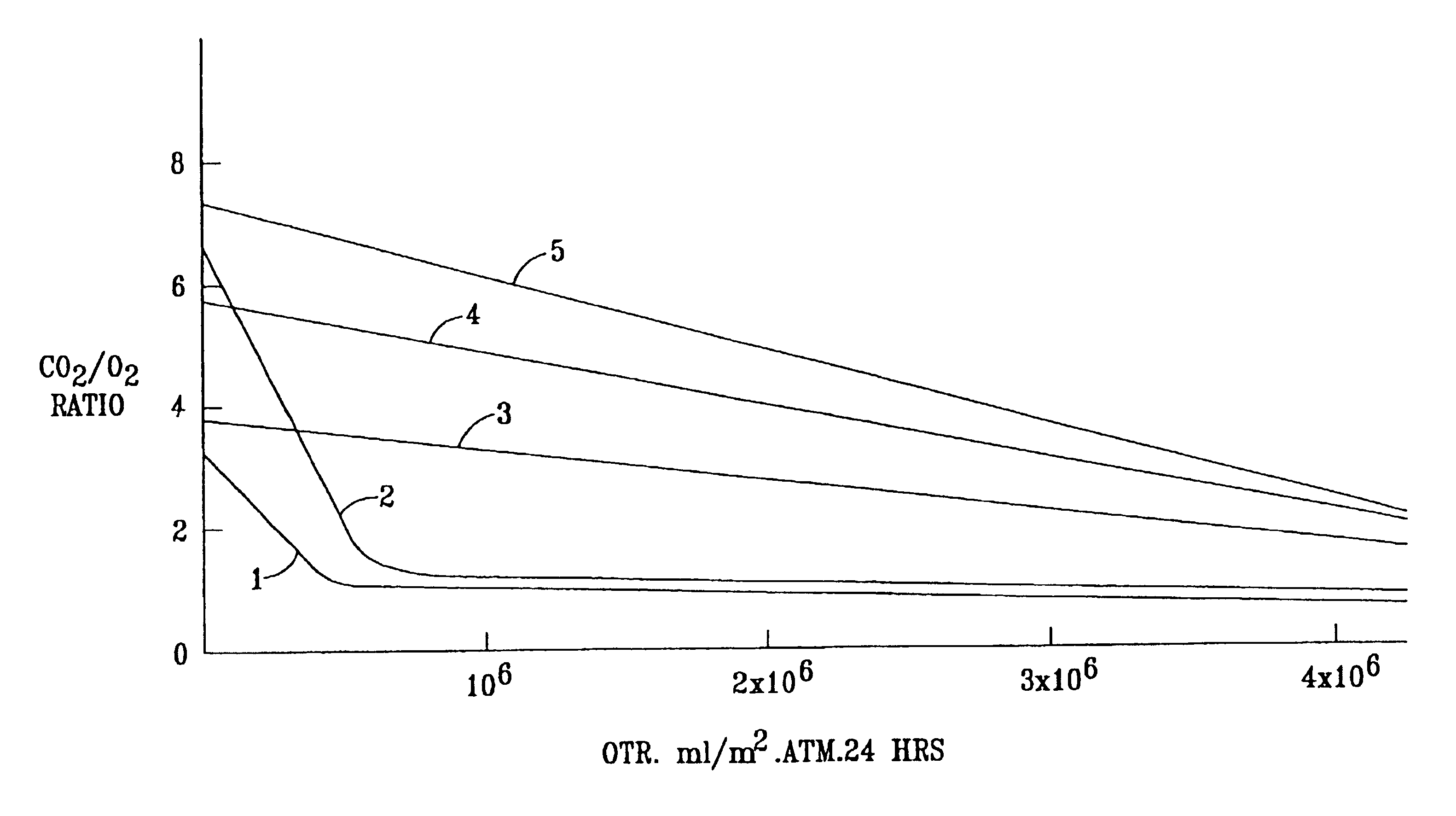
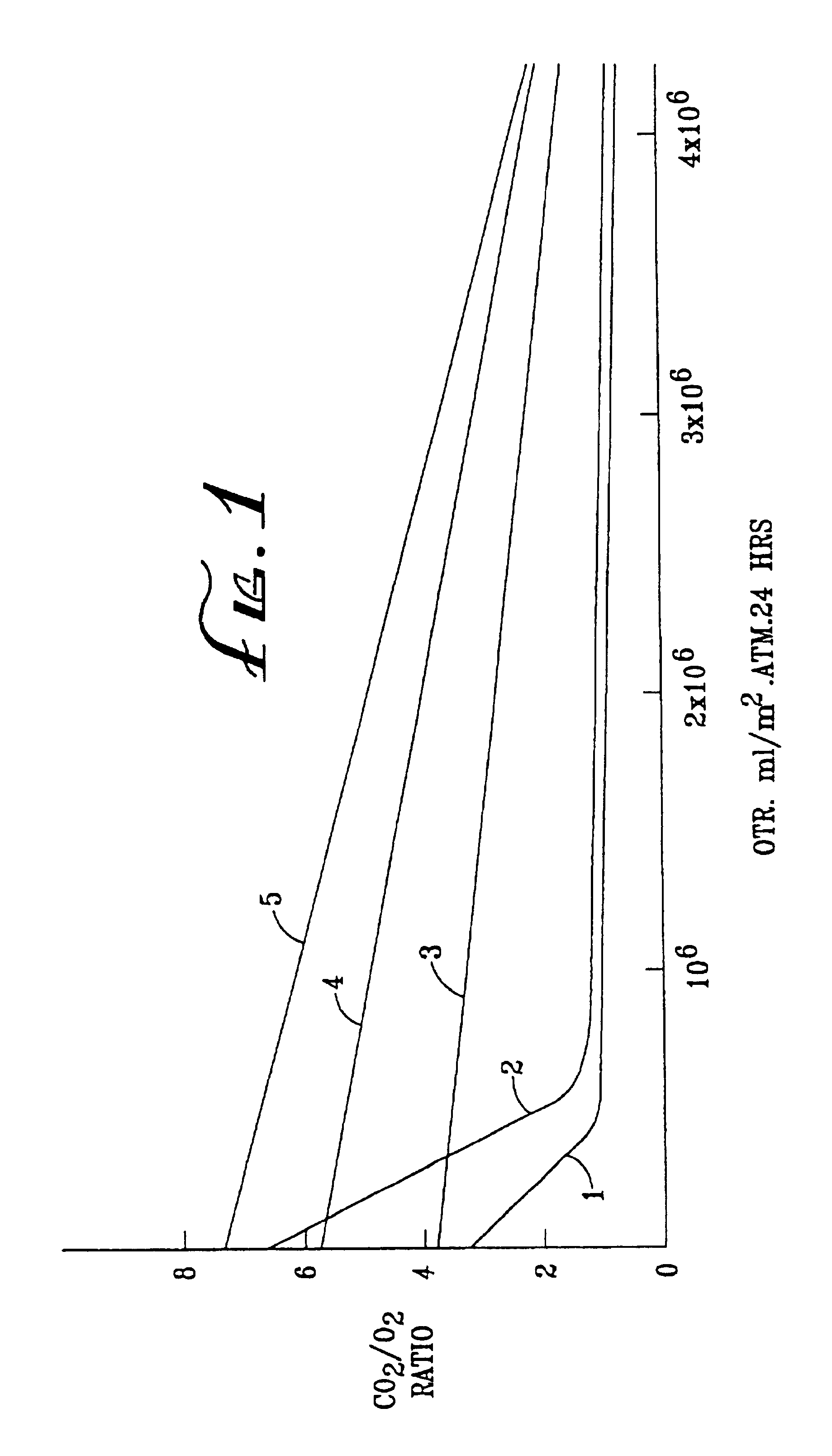
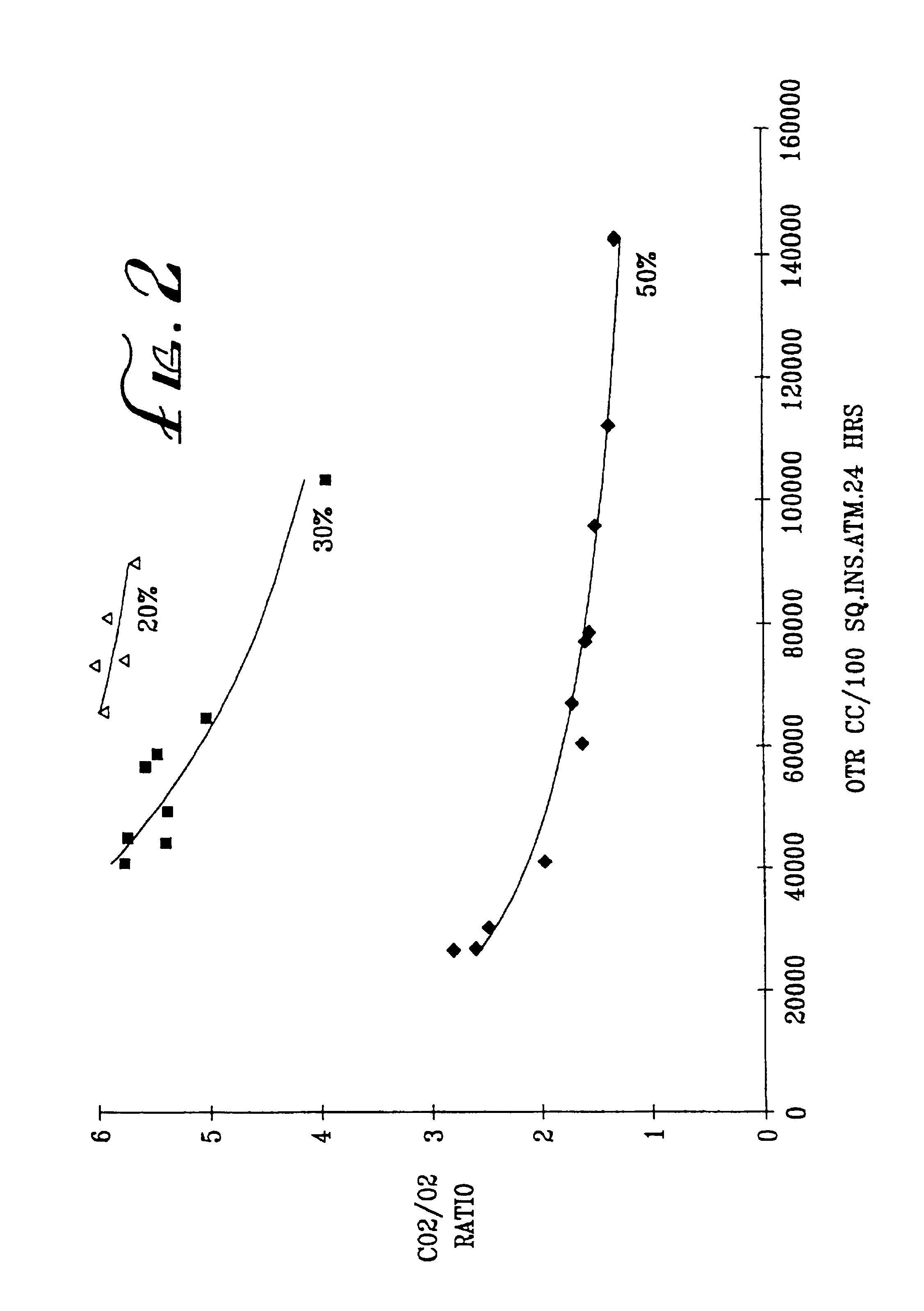
Novel gas-permeable membranes which are particularly useful in the packaging of fresh cut fruit and vegetables, and other respiring biological materials. The membranes have an O2 permeability of at least 775,000 ml / m2.atm.24 hrs, a P10 ratio of at least 1.3, and a ratio of CO2 permeability to O2 permeability (R) of at least 1.5, and are made by forming thin polymeric coatings on microporous polymeric films. Preferred coating polymers are side chain crystalline polymers. Preferred microporous films contain inorganic fillers, particularly such films based on ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene or polypropylene. FIG. 1 illustrates how O2 permeability and R ratio vary for different coating polymers and microporous films.
Owner:LANDEC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com