Patents
Literature
293 results about "L lactide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
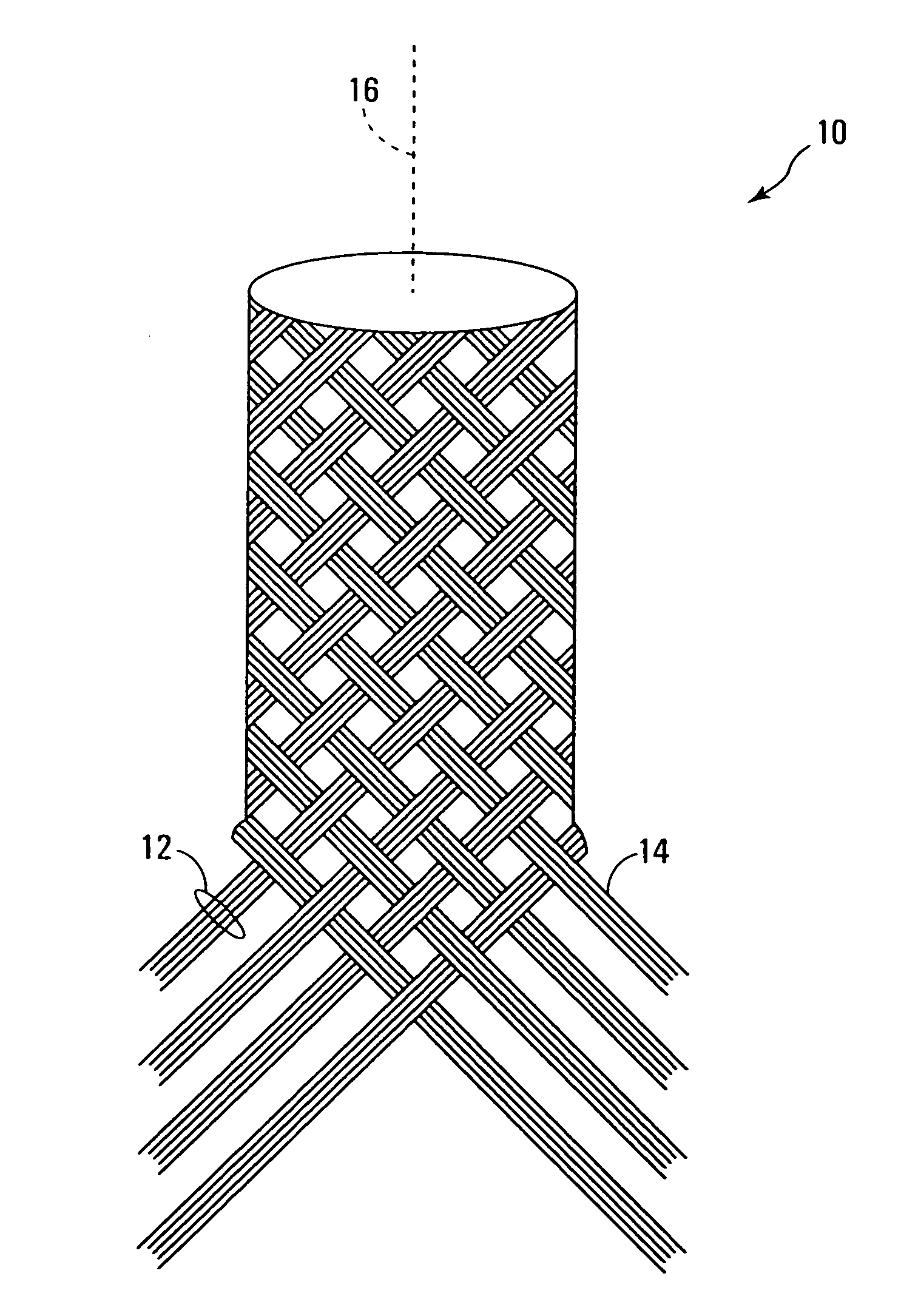
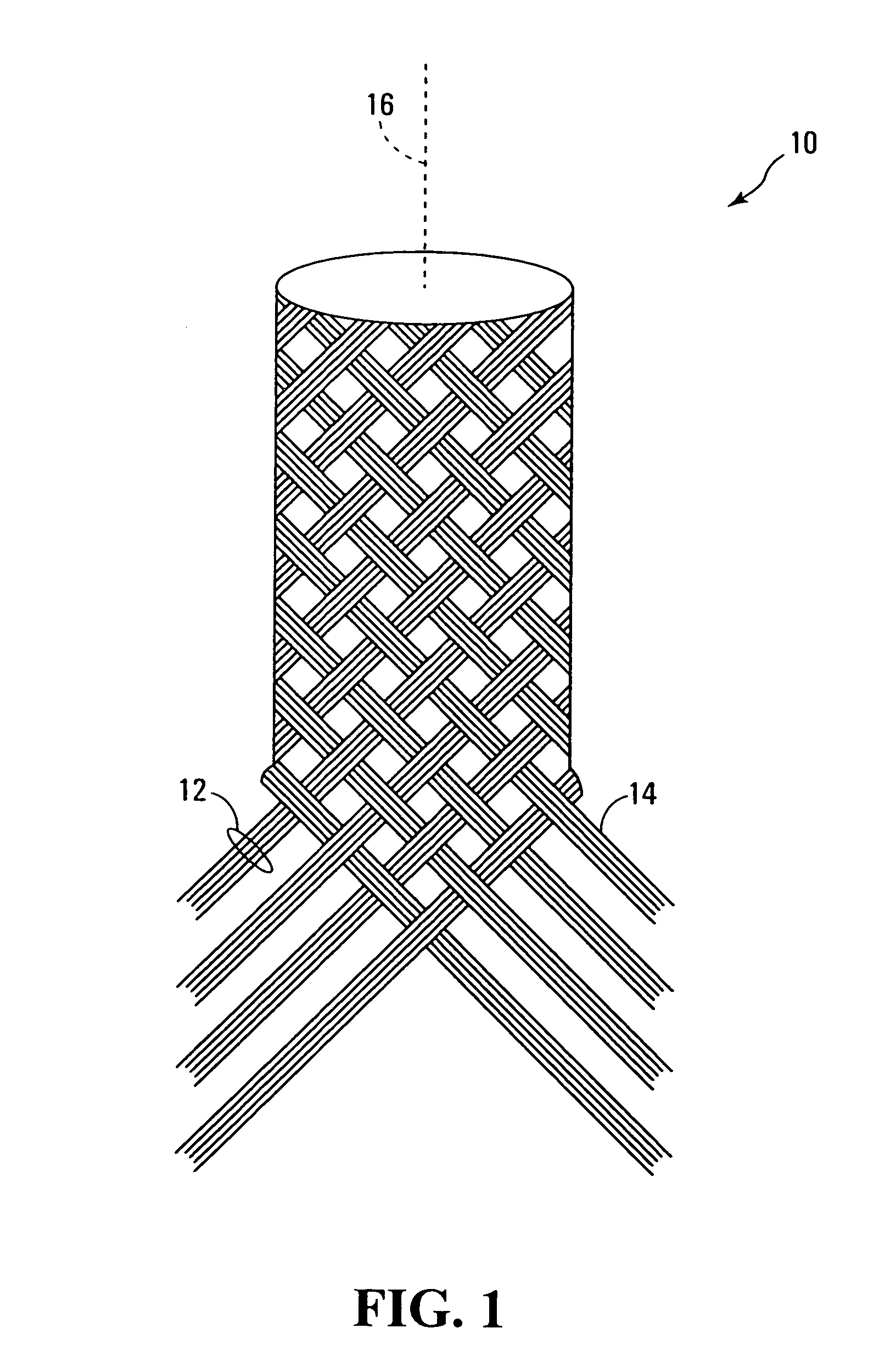
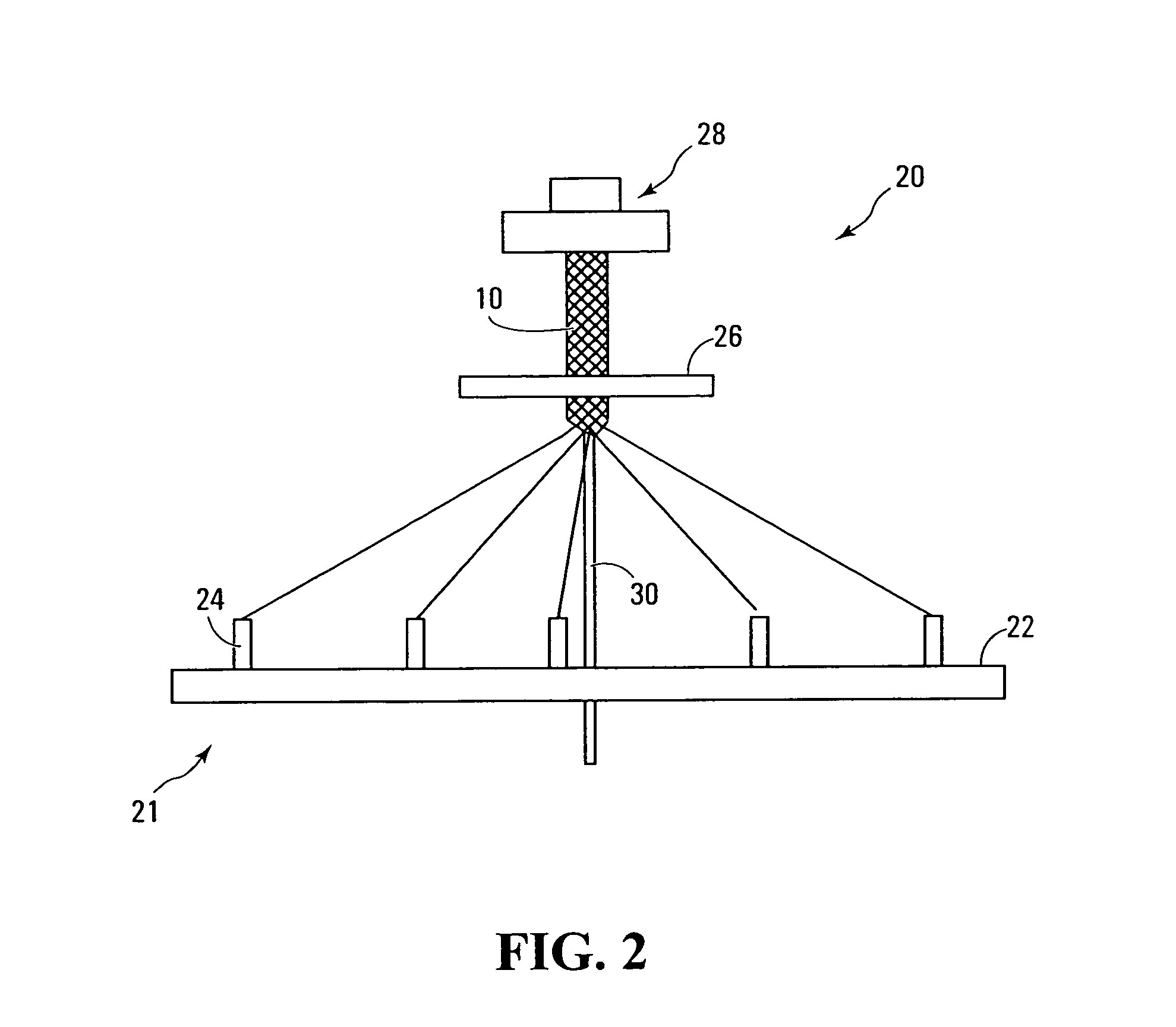
Selectively absorbable/biodegradable, fibrous composite constructs and applications thereof
A family of selectively absorbable / biodegradable, fibrous composite constructs includes different combinations of biostable and absorbable / biodegradable yarns assembled as initially interdependent, load-bearing components, transitioning to exhibit independent functional properties during in vivo end-use. The family of constructs consists of two groups, one group is made of fiber-reinforced composites of high compliance, absorbable matrices of segmented polyaxial copolyesters reinforced with multifilament yarn constructs, which are combinations of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene fibers and at least one absorbable / biodegradable fiber selected from silk fibers and multifilament yarns made from linear segmented, l-lactide copolyesters and poly (3-hydroxyalkanoates, are useful in orthopedic, maxillofacial, urological, vascular, hernial repair and tissue engineering applications. The second group is made of coated and uncoated, warp-knitted mesh constructs for use in hernial, vascular, and urological tissue repair and tissue engineering.
Owner:POLY MED
Wound healing polymer compositions and methods for use thereof
The present invention provides bioactive polymer compositions that can be formulated to release a wound healing agent at a controlled rate by adjusting the various components of the composition. The composition can be used in an external wound dressing, as a polymer implant for delivery of the wound healing agent to an internal body site, or as a coating on the surface of an implantable surgical device to deliver wound healing agents that are covalently attached to a biocompatible, biodegradable polymer and / or embedded within a hydrogel. Methods of using the invention bioactive polymer compositions to promote natural healing of wounds, especially chronic wounds, are also provided. Examples of biodegradable copolymer polyesters useful in forming the blood-compatible, hydrophilic layer or coating include copolyester amides, copolyester urethanes, glycolide-lactide copolymers, glycolide-caprolactone copolymers, poly-3-hydroxy butyrate-valerate copolymers, and copolymers of the cyclic diester monomer, 3-(S)[(alkyloxycarbonyl)methyl]-1,4-dioxane-2,5-dione, with L-lactide. The glycolide-lactide copolymers include poly(glycolide-L-lactide) copolymers formed utilizing a monomer mole ratio of glycolic acid to L-lactic acid ranging from 5:95 to 95:5 and preferably a monomer mole ratio of glycolic acid to L-lactic acid ranging from 45:65 to 95:5. The glycolide-caprolactone copolymers include glycolide and ε-caprolactone block copolymer, e.g., Monocryl or Poliglecaprone.
Owner:MEDIVAS LLC
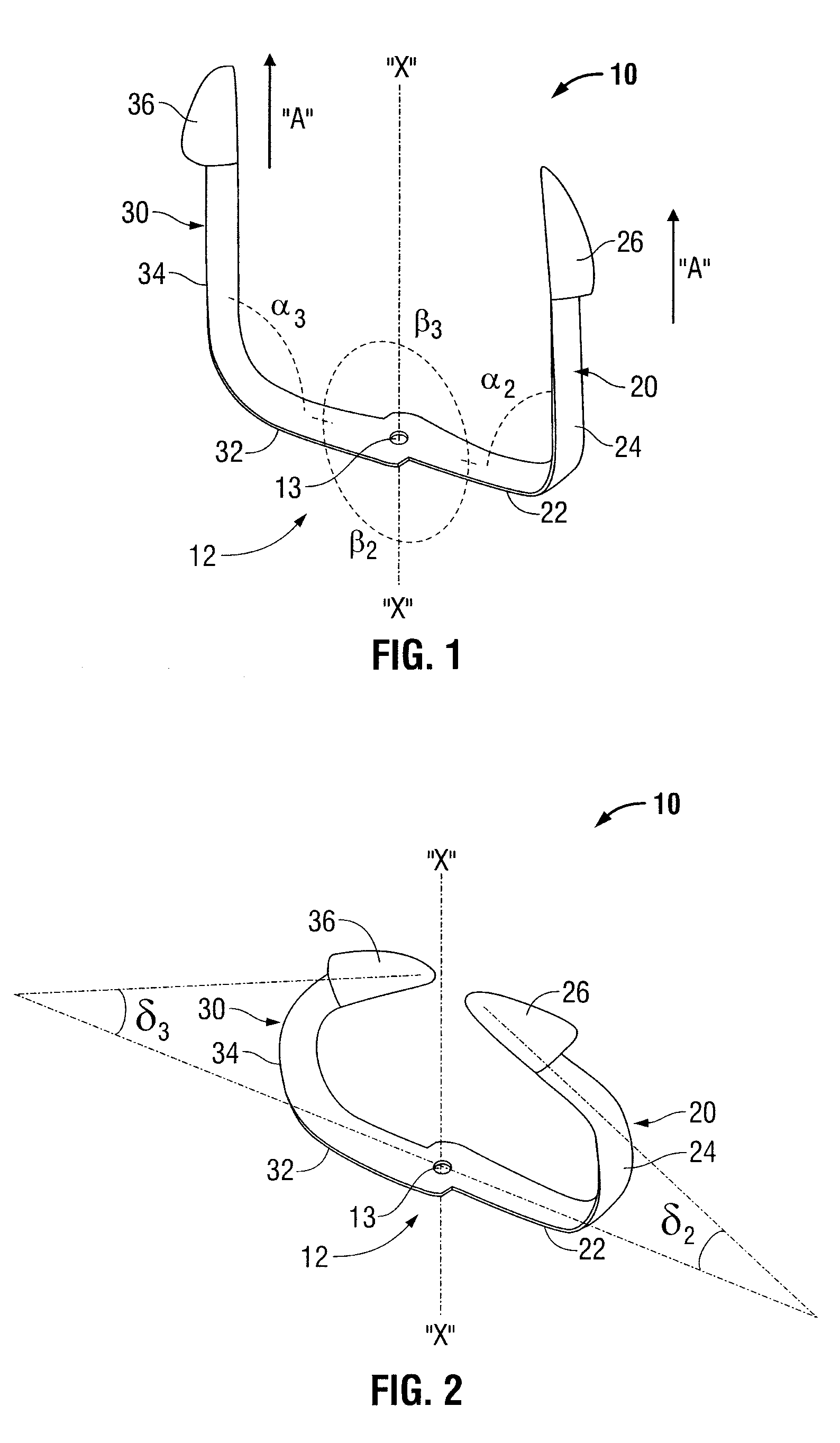
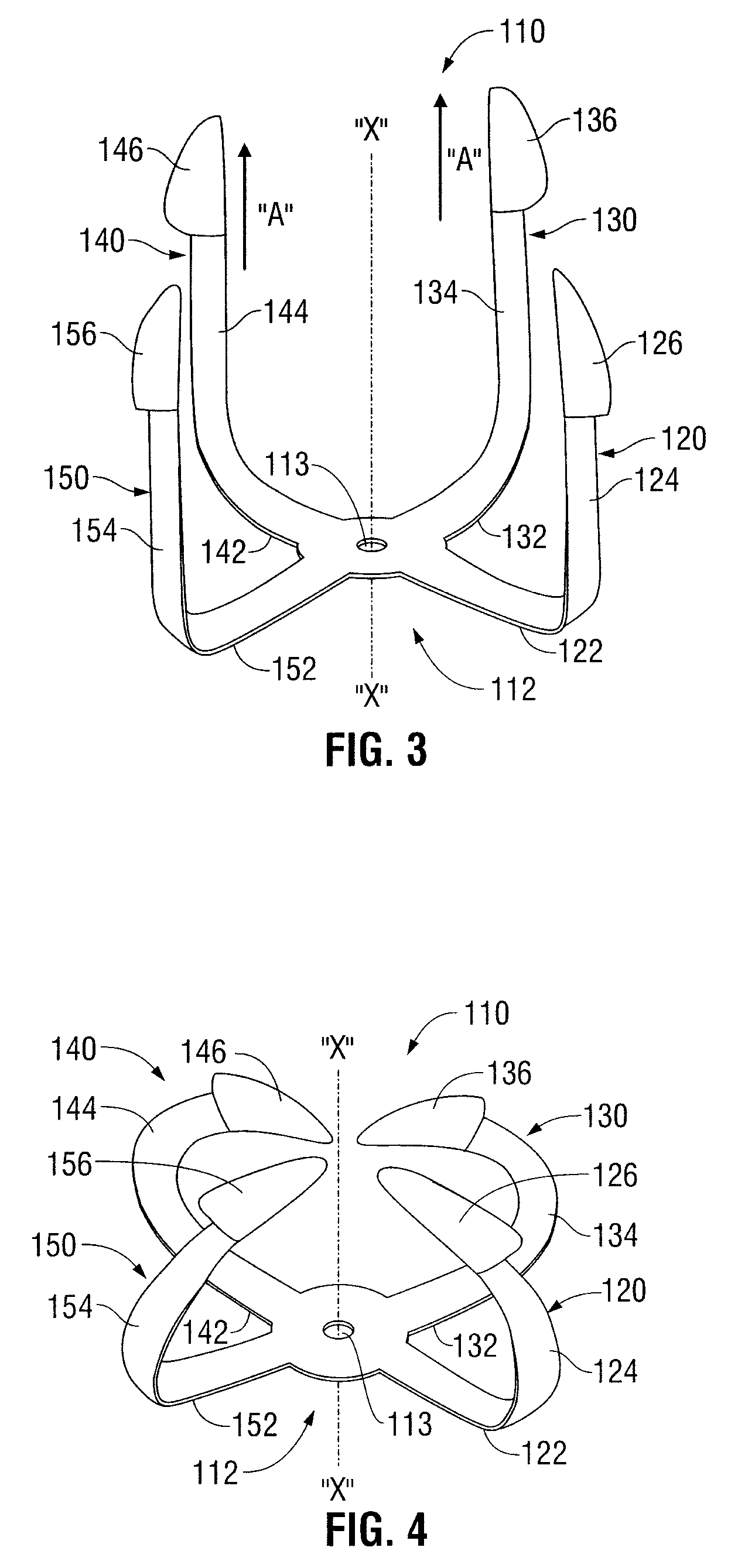
Shape memory fasteners and method of use
ActiveUS9295463B2DiagnosticsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTrimethylene carbonateBiological activation
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
Oral vaccine compositions
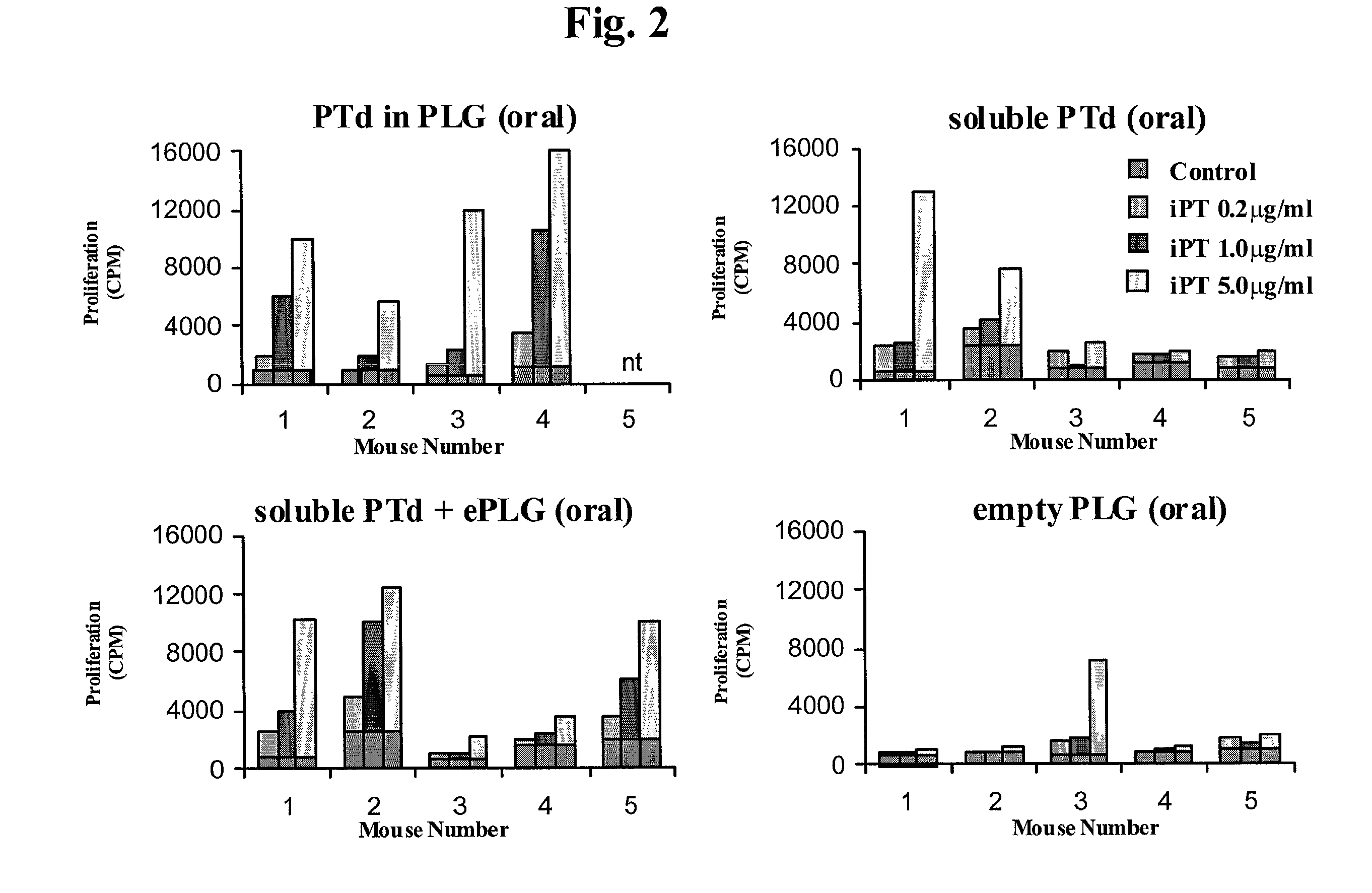
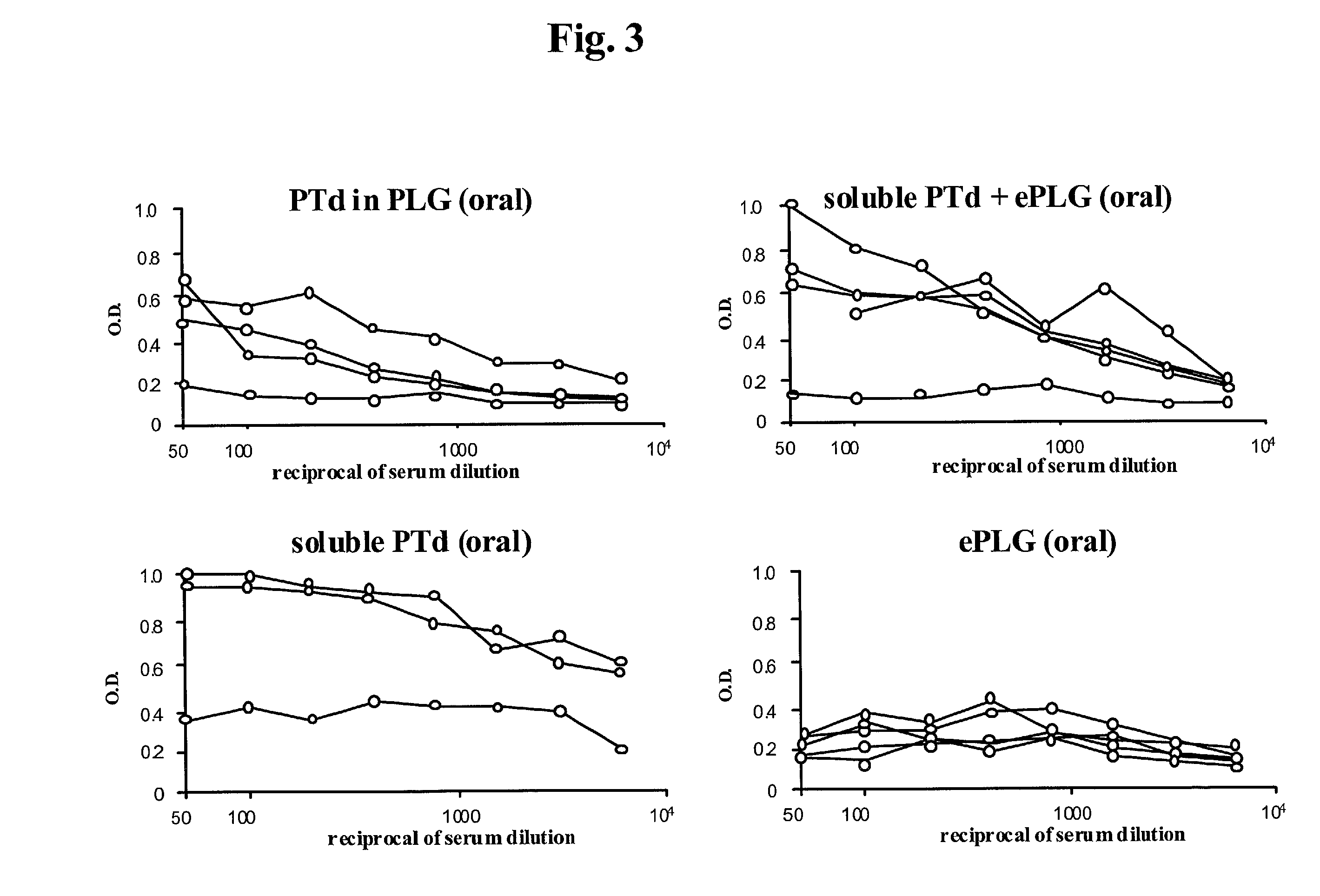
Oral vaccine formulations are disclosed having microparticles sized such that at least 50% of the microparticles are less than 5 mum, preferably less than 3 mum, the microparticles containing antigen entrapped or encapsulated, such as by a solvent evaporation method, by a biodegradable polymer, such as poly (D,L-lactide-co-glycolide). Additionally, oral vaccine formulations are disclosed having nanoparticles sized such that at least 50% of the microparticles are less than 600 nm, preferably less than 500 nm, the nanoparticles containing antigen entrapped or encapsulated, such as by a coacervation method, by a biodegradable polymer, such as poly (D,L-lactide-co-glycolide). Protective vaccine formulations containing the B. pertussis antigens PTd or a combination of PTd and FHA are provided.
Owner:MERRION RES I
Nanopatterned templates from oriented degradable diblock copolymer thin films
InactiveUS7632544B2Improve applicabilityAverage thicknessMaterial nanotechnologyDecorative surface effectsCylindrical channelPolymer science
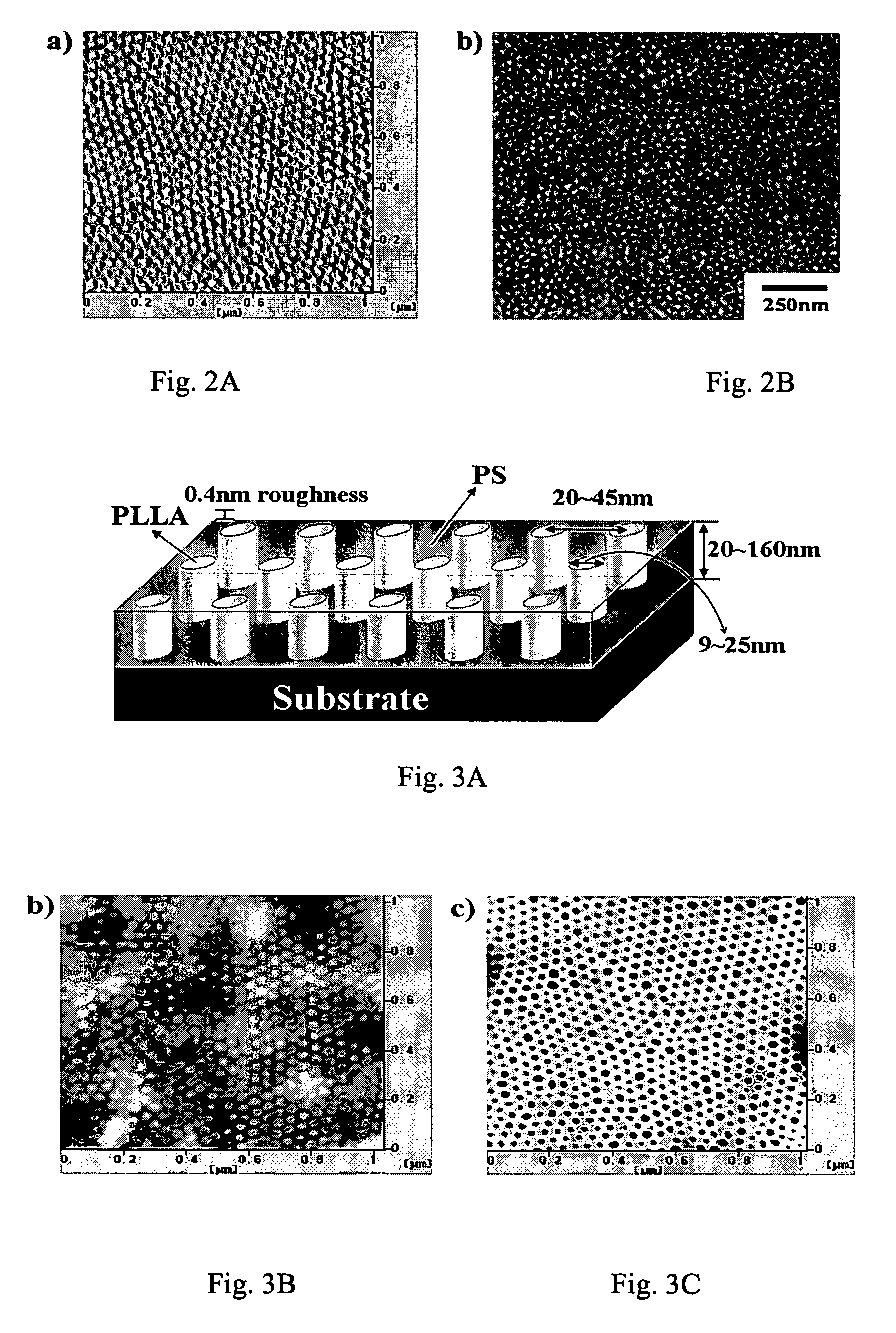
A nanopatterned template for use in manufacturing nanoscale objects. The nanopatterned template contains a nanoporous thin film with a periodically ordered porous geomorphology which is made from a process comprising the steps of: (a) using a block copolymerization process to prepare a block copolymer comprising first and second polymer blocks, the first and second polymer blocks being incompatible with each other; (b) forming a thin film under conditions such that the first polymer blocks form into a periodically ordered topology; and (c) selectively degrading the first polymer blocks to cause the thin film to become a nanoporous material with a periodically ordered porous geomorphology. In a preferred embodiment, the block copolymer is poly(styrene)-poly(L-lactide) (PS-PLLA) chiral block copolymer, the first polymer is poly(L-lactide), and the second polymer is polystyrene. Experimental results show that the first polymer blocks can be formed into a hexagonal cylindrical geomorphology with its axis perpendicular to a surface of the thin film. After hydrolysis to selectively degrade the first polymer blocks, a thin film having a series of repeated nanoscale hexagonal-cylindrical channels is obtained.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Selectively absorbable/biodegradable, fibrous composite constructs and applications thereof
A family of selectively absorbable / biodegradable, fibrous composite constructs includes different combinations of biostable and absorbable / biodegradable yarns assembled as initially interdependent, load-bearing components, transitioning to exhibit independent functional properties during in vivo end-use. The family of constructs consists of two groups, one group is made of fiber-reinforced composites of high compliance, absorbable matrices of segmented polyaxial copolyesters reinforced with multifilament yarn constructs, which are combinations of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene fibers and at least one absorbable / biodegradable fiber selected from silk fibers and multifilament yarns made from linear segmented, l-lactide copolyesters and poly (3-hydroxyalkanoates, are useful in orthopedic, maxillofacial, urological, vascular, hernial repair and tissue engineering applications. The second group is made of coated and uncoated, warp-knitted mesh constructs for use in hernial, vascular, and urological tissue repair and tissue engineering.
Owner:POLY MED
High strength fibers of L-lactide copolymers epsi-caprolactone and trimethylene carbonate and absorbable medical constructs thereof
The present invention is directed to crystalline copolymers of l-lactide and a minor portion of a cyclic monomer, preferably epsi-caprolactone or trimethylene carbonate or both. The present copolymers have a melting temperature of at least 150° C. and a crystallinity of at least 25%. Preferred are high molecular weight copolymers having an inherent viscosity of at least 1.4 dl / g. A variety of surgical constructs may be formed from the present copolymers. Surgical sutures made of mono- or multifilament yarns of the present copolymers will bioabsorb in less than three years and will maintain at least 50% of their initial strength three weeks post-operatively.
Owner:POLY MED
Medical guide tubes
Polymeric fibers were microbraided around a mandrel to make a tubular guide tube for nerve regeneration. The polymer used for the fibers was one of poly(L-lactide-co-glycolide) (10:90 PLGA) and chitosan. These polymers are biodegradable and biocompatible. The tubes were studied for their surface morphology and swelling behavior. Biological performance of the tubes was examined in the rat sciatic nerve model with a 12 mm gap. One month after implantation nine out of ten rats showed successful nerve regeneration. Morphometric analysis of regenerated nerves confirmed the quality of the regeneration compatible with those offered by other types of biodegradable nerve guide tubes. The tubes were flexible, permeable and showed no swelling.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE +1
Medicine eluted cardiovascular frame and its preparing process
InactiveCN1355005AContinuous and stable releasePromote healingStentsCoatingsCardiovascular stentEthylene Homopolymers
A medicine eluted cardiovascular frame is composed of expandible support and the medicine coated biodegradable layer coated on the said frame. The said biodegradable material contains one of the homopolymer and copolymer of glycollide, L-lactide or epsilon-caprolactone, and the copolymer of multi-group amino acids. The medicine can resist the cardiovascular narrowness. The process for preparing the said support includes such steps as preparing the said expandible support, immersing it in the mixture of the said medicine, biodegradable material and solvent, and drying. It can prevent thrombosis.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
High strength fibers of l-lactide copolymers, epsilon-caprolactone, and trimethylene carbonate and absorbable medical constructs thereof
The present invention is directed to crystalline copolymers of l-lactide and a minor portion of a cyclic monomer, preferably ε-caprolactone or trimethylene carbonate or both. The present copolymers have a melting temperature of at least 150° C. and a crystallinity of at least 20%. Preferred are high molecular weight copolymers having an inherent viscosity of at least 1.1 dl / g. A variety of surgical constructs may be formed from the present copolymers. Surgical sutures made of mono- or multifilament yams of the present copolymers will bioabsorb in less than three years and will maintain at least 50% of their initial strength three weeks post-operatively.
Owner:POLY MED
Shape Memory Fasteners And Method Of Use
ActiveUS20110087277A1DiagnosticsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTrimethylene carbonateBiological activation
A surgical fastener configured to close an opening in tissue is provided. The surgical fastener includes a base defining a central axis at least one pair of legs extending from the base. Each of the legs includes a base portion and a tissue engaging portion. When in a first position, each of the tissue engaging portions is arranged to define an insertion direction and when in a second position, each of the tissue engaging portions extends inward towards the central axis. The surgical fastener is at least partially formed from a shape memory material including a combination of Polydioxanone and Poly(L-lactide) or a combination of Trimethylene Carbonate and Poly(L-lactide). The pair of legs are configured to move from the first position to the second position upon activation of the shape memory material.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Microspheres for the sustained release of octreotide with a low initial burst
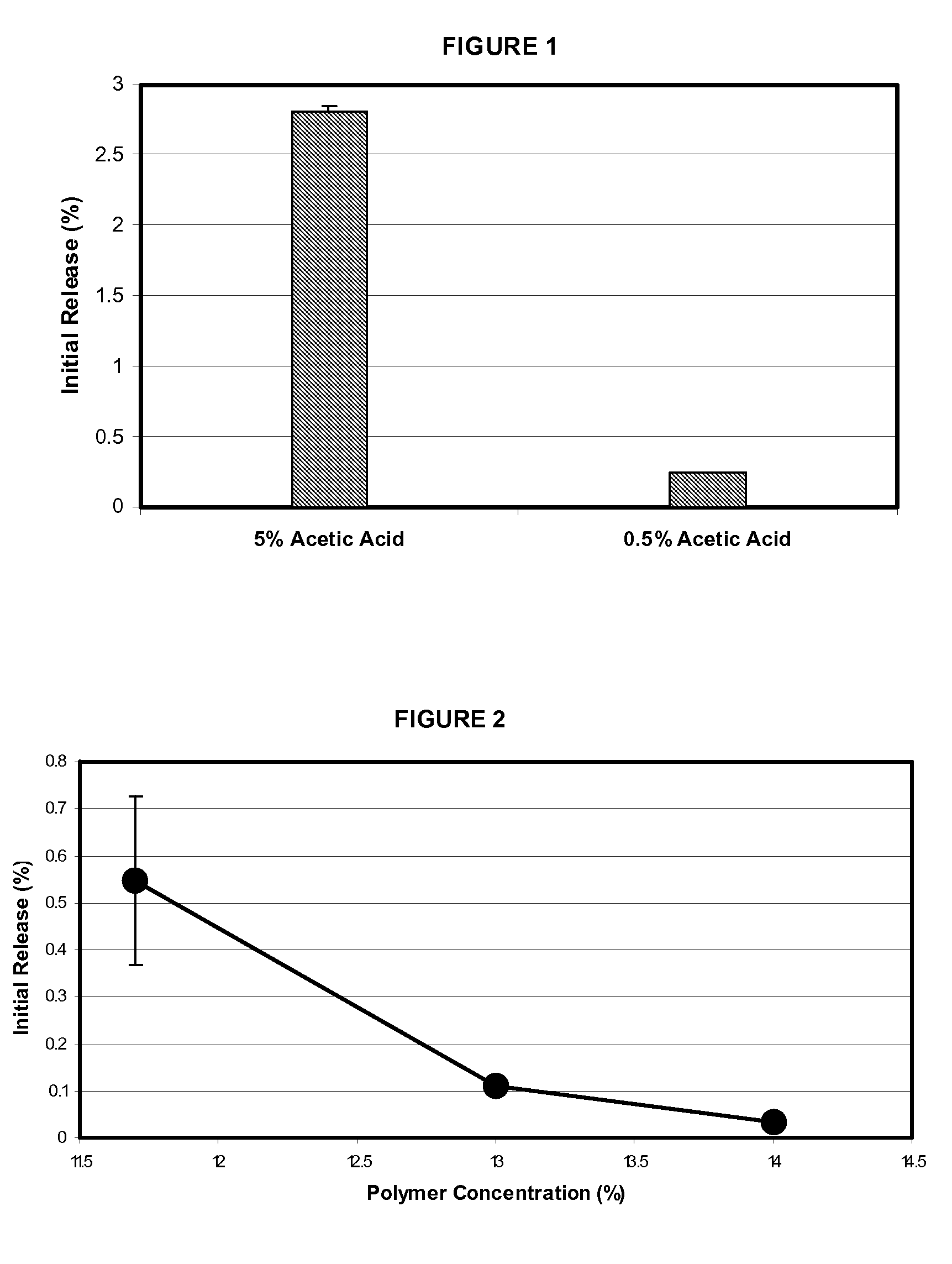
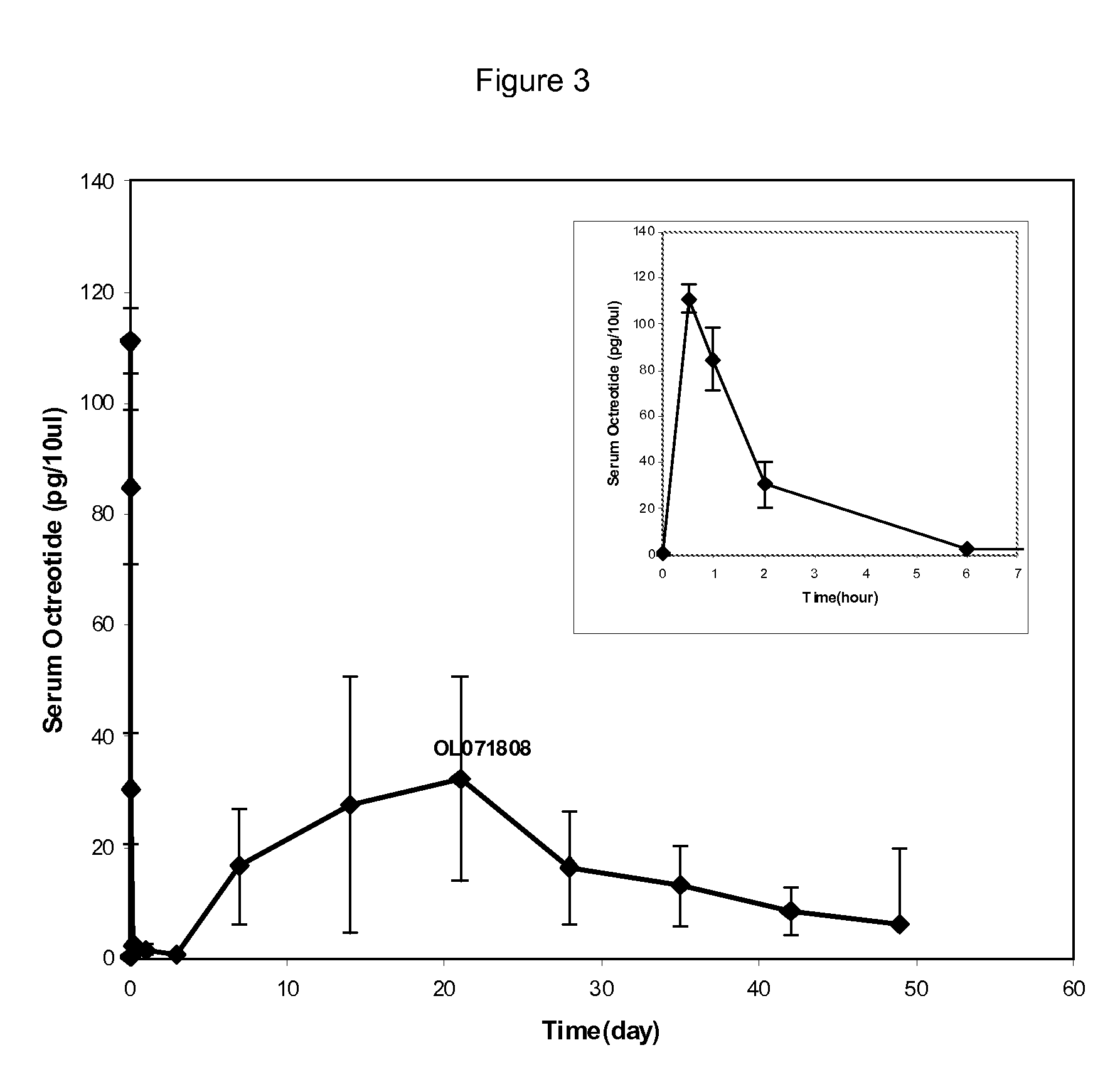
InactiveUS20100086597A1Initial burst can be loweredAvoid painPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrosphereL lactide
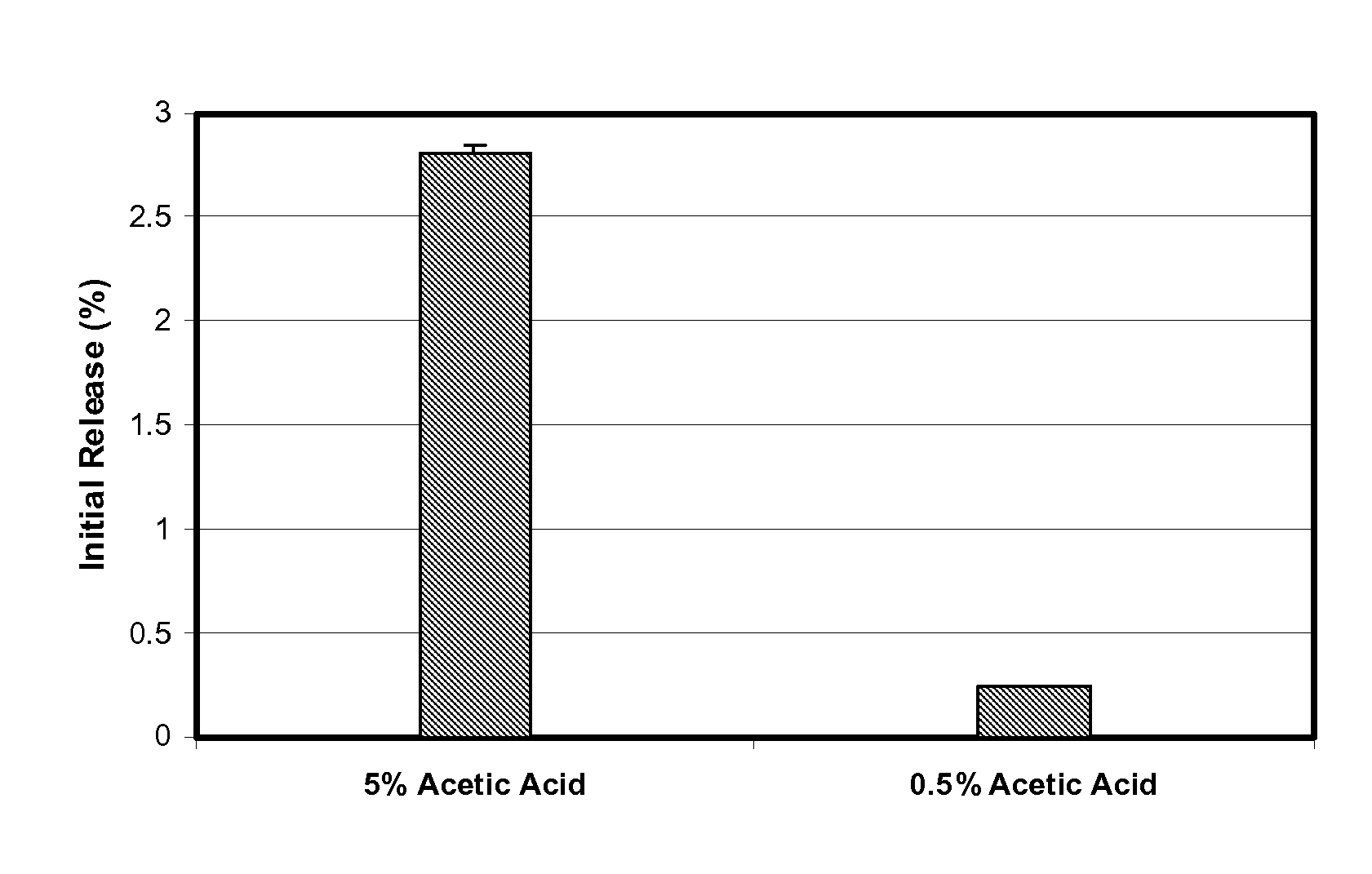
This disclosure features microspheres and a method of making them. The microspheres are for sustained release of an octreotide compound with a low initial burst, comprising a poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide) polymer matrix and an octreotide compound dispersed in the polymer matrix. The microspheres release less than 1% of a total amount of the octreotide compound within 1 hour at 37° C. and pH 7.4.
Owner:OAKWOOD LAB LLC
Coated, slow-absorbing textile constructs for sutures and tissue engineering
The present invention is directed to crystalline copolymers of l-lactide and a minor portion of a cyclic monomer, preferably epsi-caprolactone or trimethylene carbonate or both. The present copolymers have a melting temperature of at least 150° C. and a crystallinity of at least 20%. Preferred are high molecular weight copolymers having an inherent viscosity of at least 1.1 dl / g. A variety of surgical constructs may be formed from the present copolymers. Disclosed are coated surgical constructs including sutures made of multifilament yarns of the present copolymers and coated with nitrogenous copolyesters which will bioabsorb in less than three years and will maintain at least 50% of their initial strength three weeks post-operatively.
Owner:POLY MED
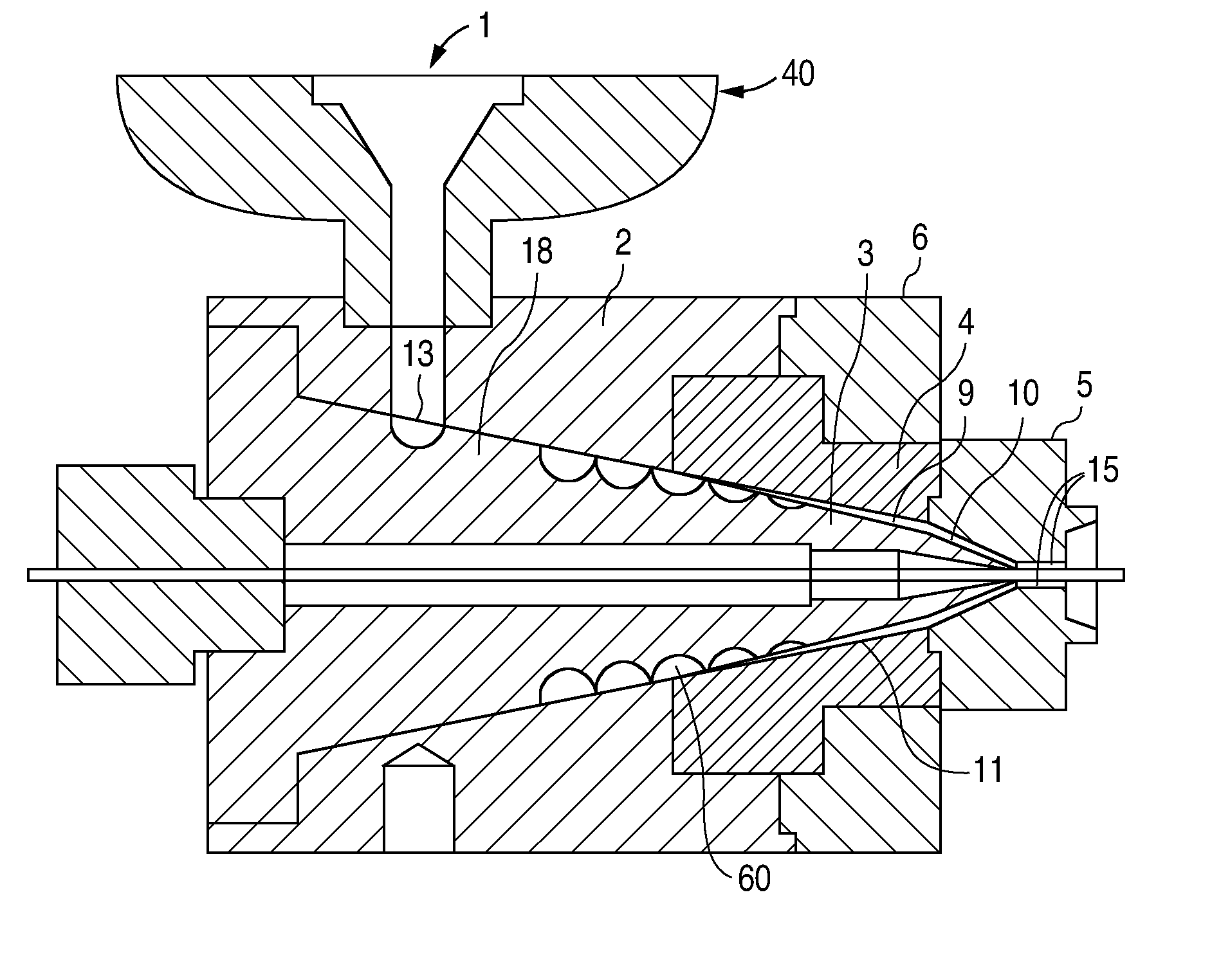
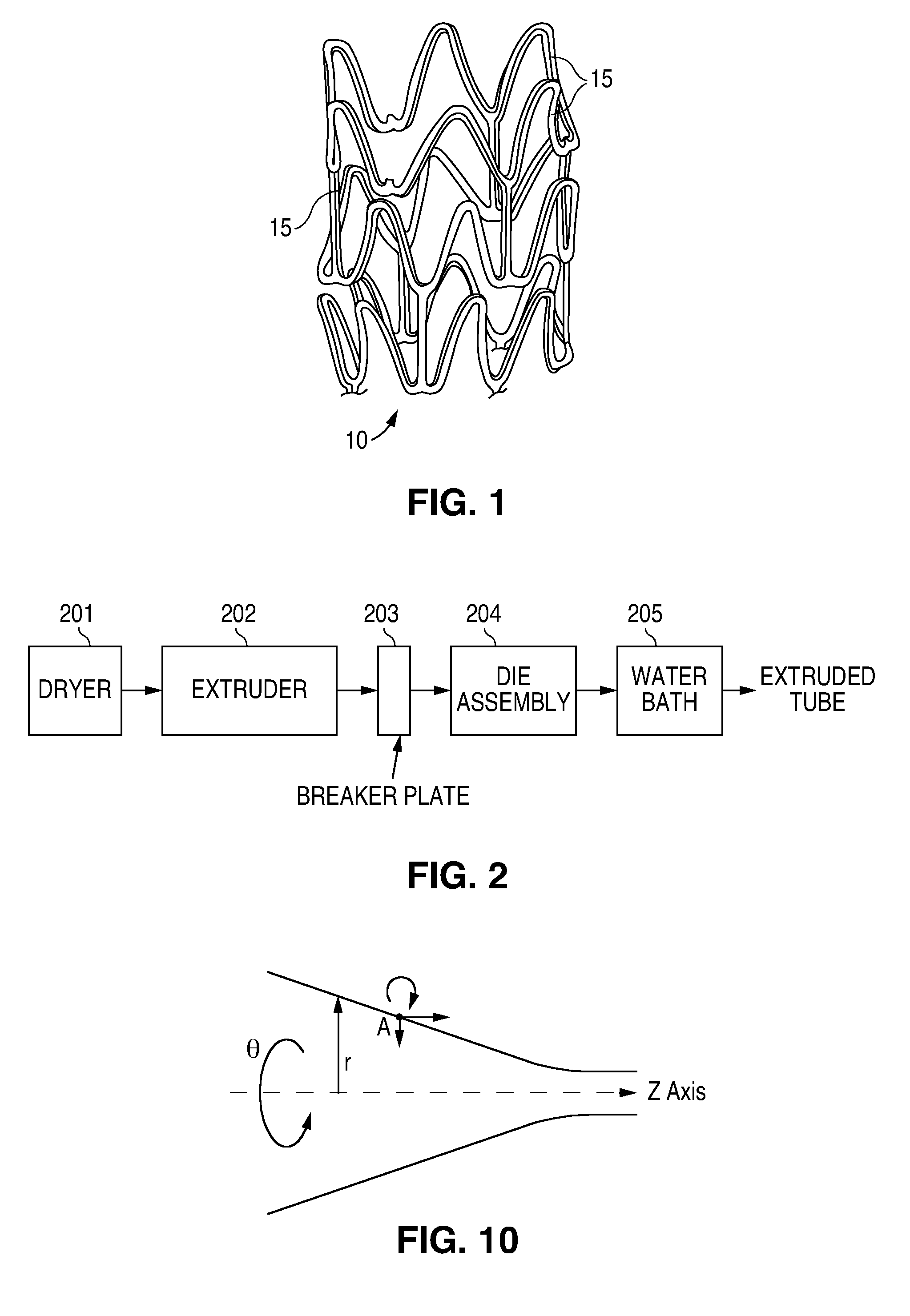
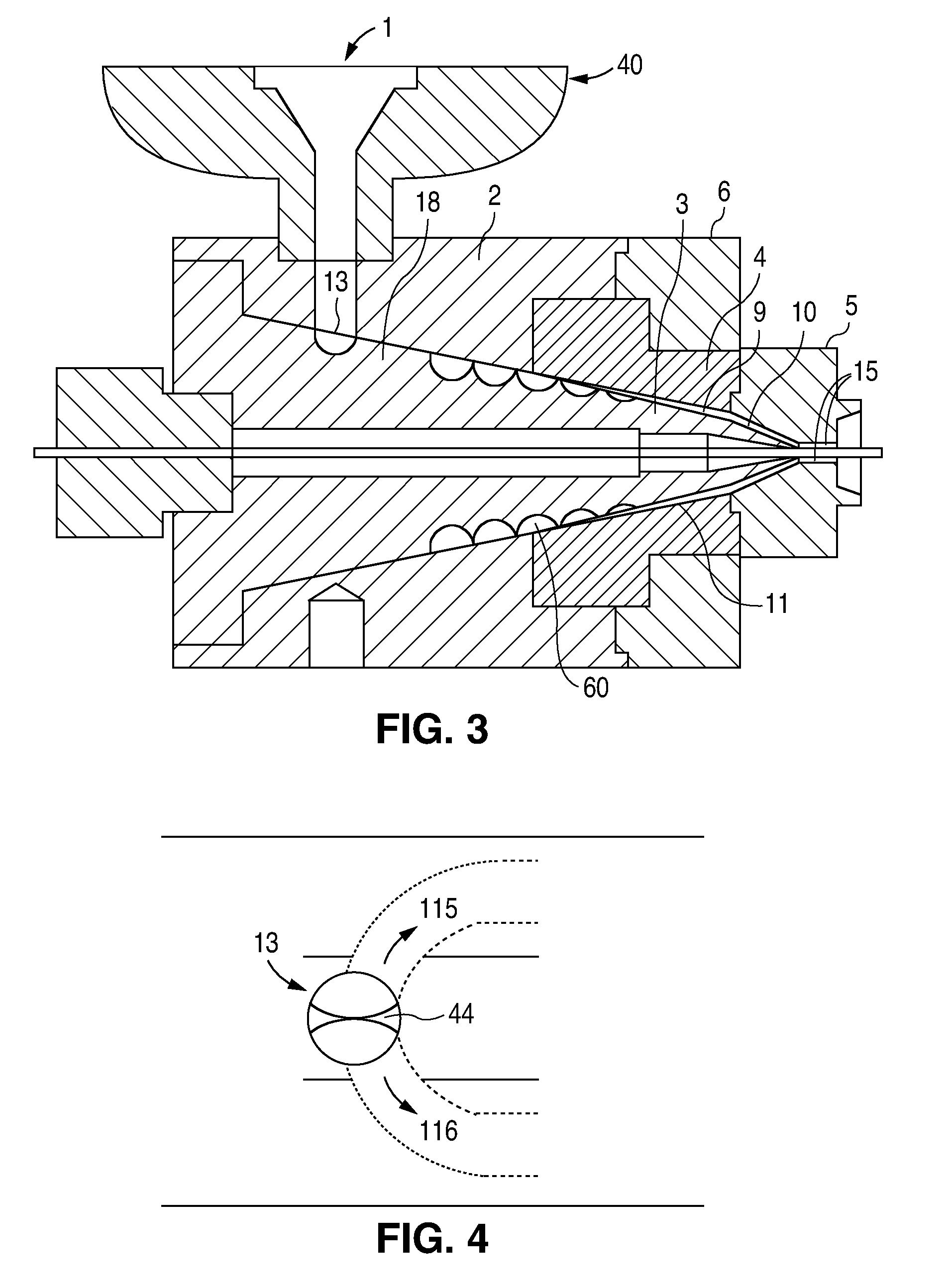
Method of fabricating a low crystallinity poly(L-lactide) tube
Methods of fabricating a low crystallinity polymer tube for polymers subject to strain-induced crystallization. The low crystallinity tube may be further processed to make an implantable medical device.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Bioabsorbable Polymeric Compositions and Medical Devices
The bioabsorbable polymers and compositions of the present invention may be formed into medical devices such as stents that can be crimped onto a catheter system for delivery into a blood vessel. The properties of the bioabsorbable polymers allow for both crimping and expansion of the stent. The crystal properties of the bioabsorbable polymers may change during crimping and / or expansion allowing for improved mechanical properties such as tensile strength and slower degradation kinetics. Typically, bioabsorbable polymers comprise aliphatic polyesters based on lactide backbone such as poly L-lactide, poly D-lactide, poly D,L-lactide, mesolactide, glycolides, lactones, as homopolymers or copolymers, as well as formed in copolymer moieties with co-monomers such as, trimethylene carbonate (TMC) or ε-caprolactone (ECL).
Owner:ORBUSNEICH MEDICAL PTE LTD
Filament bundle for degrading cigarette, preparation method thereof, and preparation method of filter stick
A filament bundle for degrading cigarette comprises raw materials including any one of the follows: poly(l-lactide) with crystallization accelerating agent, poly(r-lactide) with crystallization accelerating agent, and mixture of poly(l-lactide) and poly(r-lactide) with crystallization accelerating agent. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) drying and crystallizing at 60-120 DEG C for 10-24 hours; (2) fusing spinning at 60-120 DEG C to get protogenetic filament bundles for 10-24 hours; (3) stretching and controlling to the stretching time to be 1.5 to 3 and the trunk density of the filament bundles to be 3.0-5.0ktex; (4) crimping by a crimping machine at 40-70 DEG C, and controlling the curving number to be 18-28 / 25mm; and (5) baking for thermoforming at 60-100 DEG C within 10 min. The filament boundle is opened and cemented to produce a filter stick with the curing time within 50min.
Owner:马鞍山同杰良生物材料有限公司
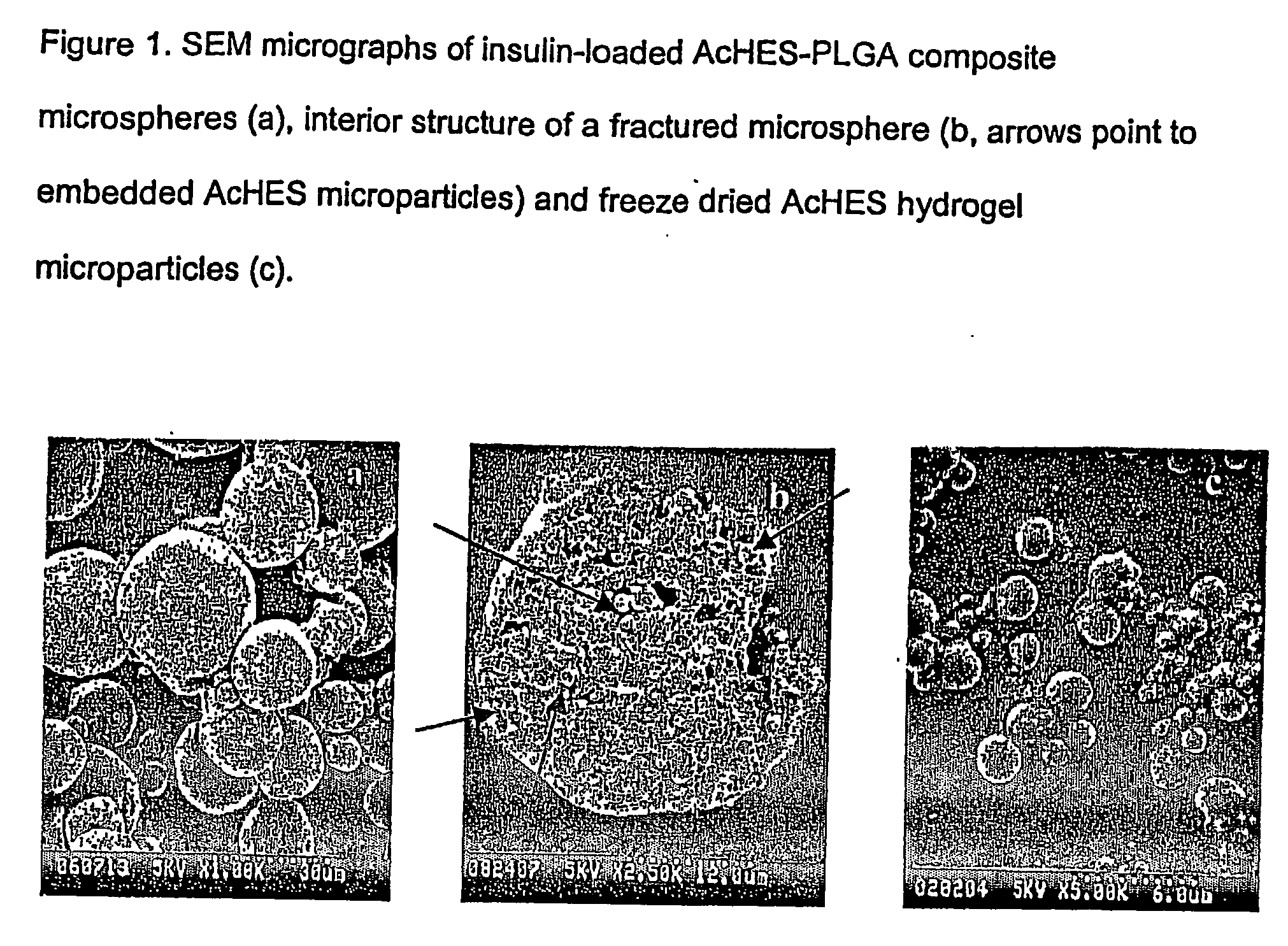
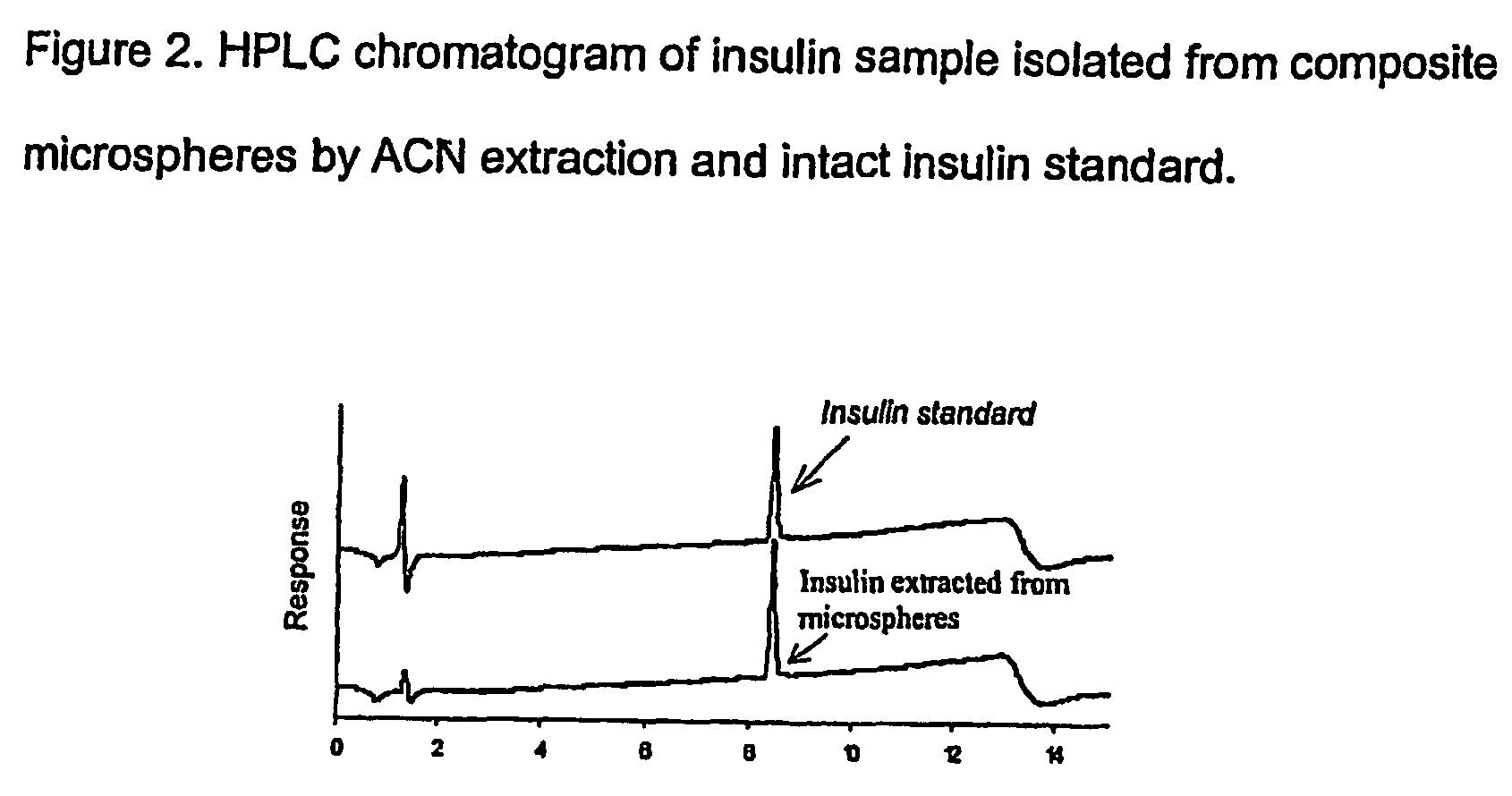
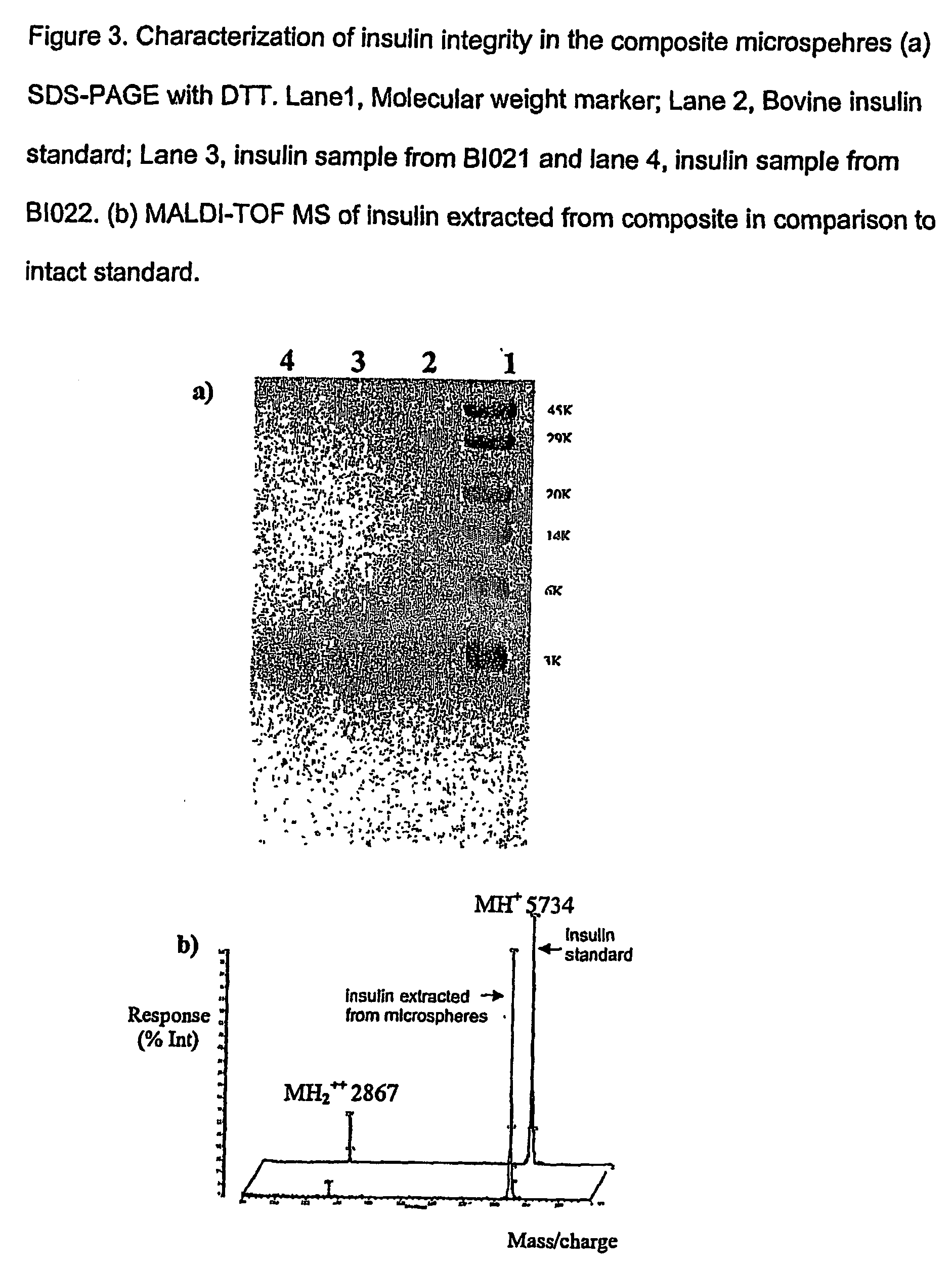
(Poly(acryloyl-hydroxyethyl starch)-plga composition microspheres
The present invention relates to a composite microsphere system comprising poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA), poly(acryloyl hydroxyethyl starch) (AcHES), and a pharmaceutically effective amount of a biologically active compound. The active compound may be, for example, an insulin, an interferon, a luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) analog, a somatostatin and / or derivatives thereof, a calicitonin, a parathyroid hormone (PTH), a bone morphogenic protein (BMP), an erythropoietin (EPO), an epidermal growth factor (EGF) or a growth hormone. This invention also relates to methods of using the composite microspheres, and methods of preparing same.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
Methods and Compositions for Tissue Augmentation
InactiveUS20080075749A1Avoid intakeInhibit migrationCosmetic preparationsPowder deliveryParticulatesPolyolefin
Methods and compositions for use in tissue volume replacement are provided. The present invention comprises compositions comprising a combination of materials, comprising preferably a solid polymer particle phase and a gel phase, and also comprises single phase compositions. More particularly, preferred embodiments comprise a solid polymer particle phase made of materials comprising Gore-Tex (micronized e-PTFE), PDS II (polydioxanone, a monofilament), NUROLON (a long chain aliphatic polymer Nylon 6 or Nylon 6,6) ETHILON (a long chain aliphatic polymer Nylon 6 and Nylon 6,6), PROLENE (Polypropylene, isotactic crystalline stereoisomer of polypropylene, a synthetic linear polyolefin.), VICRYL (copolymer made from 90% glycolide and 10% L-lactide), silk, MONACRYL (poly ε-caprolactone.), polylactide, polyglycolide, poly lactide-co-glycolide, and BIOPOL (polyhydroxyvalerate), MEDPOR (biocompatible (micronized) polyethylene), BIOGLASS (bioactive glass particulate), NOVABONE and NOVABONE-CM, and the gel phase comprises polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP). Preferred single phase compositions comprise PVP. Methods of the present invention comprising injection of such compositions for tissue augmentation.
Owner:DYER WALLACE K
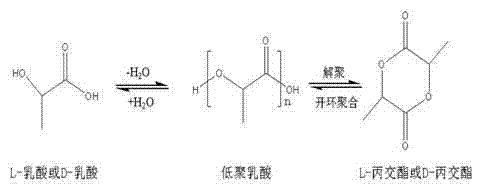
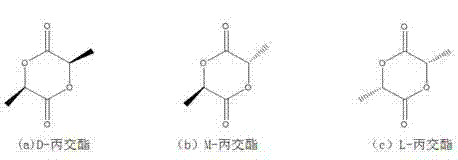
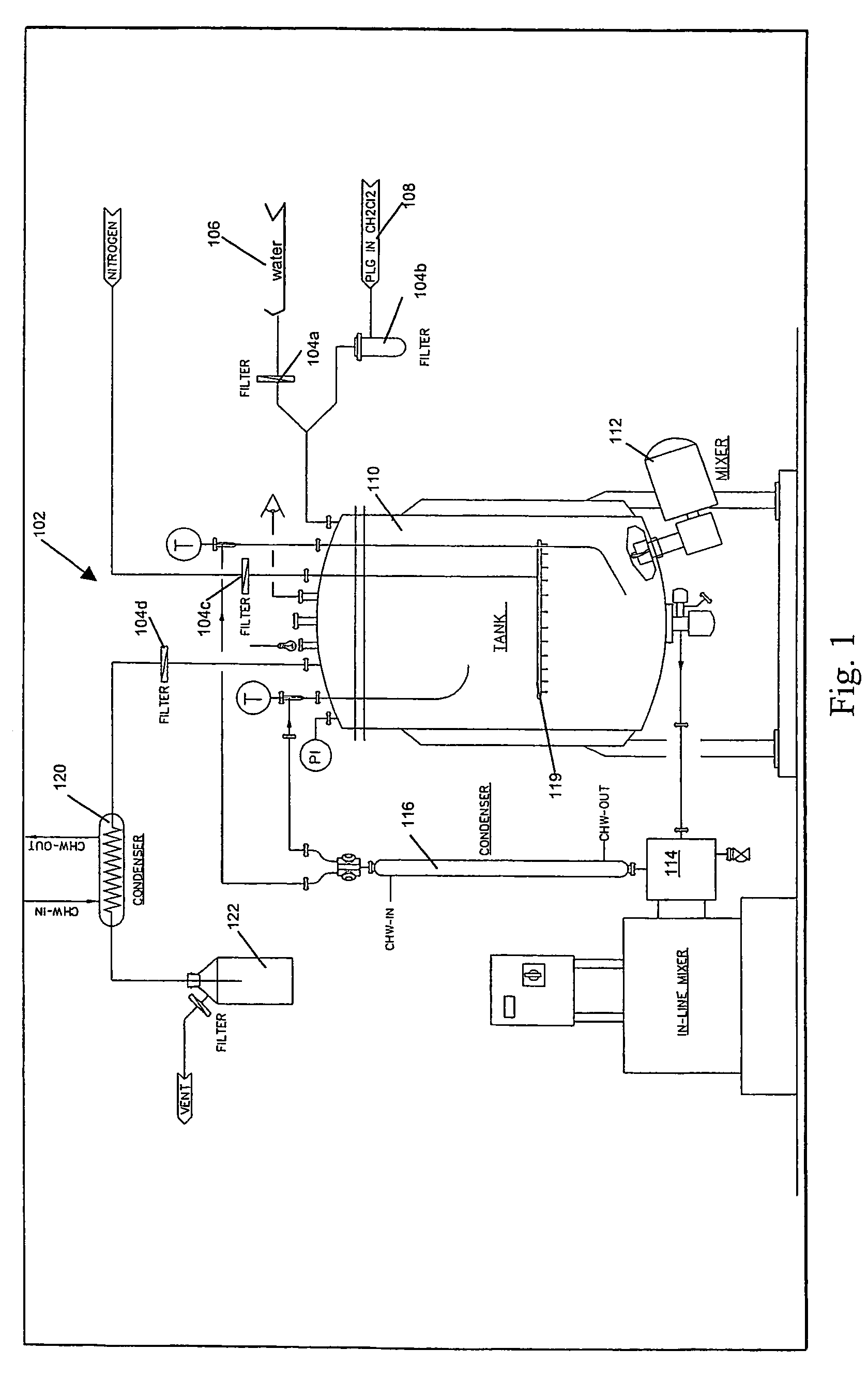
High-purity lactide and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses high-purity lactide and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps of raw material addition, free water removal, polycondensation, depolymerization, distillation and secondary distillation. The raw material addition step refers to that a catalyst is added into L-lactic acid or D-lactic acid, wherein the catalyst is one or more of zinc oxide, stannous oxide and stannous octoate. In the preparation process, the use of an organic solvent, N2 and inert gas and environmental pollution are avoided, the vacuum degree is moderate, purification loss is reduced, the production cost is reduced, and the method is suitable for industrial production. The L-lactide or D-lactide product prepared by the method is high in yield, optical purity and quality, the yield is more than or equal to 97 percent, and the optical purity of the purified lactide is 99.45 percent or above.
Owner:SHANDONG SHOUGUANG JUNENG GOLDEN CORN CO LTD
Microparticles with adsorbed polypeptide-containing molecules
ActiveUS7501134B2Easy to produceSsRNA viruses negative-senseAntibacterial agentsHemagglutininLactide
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
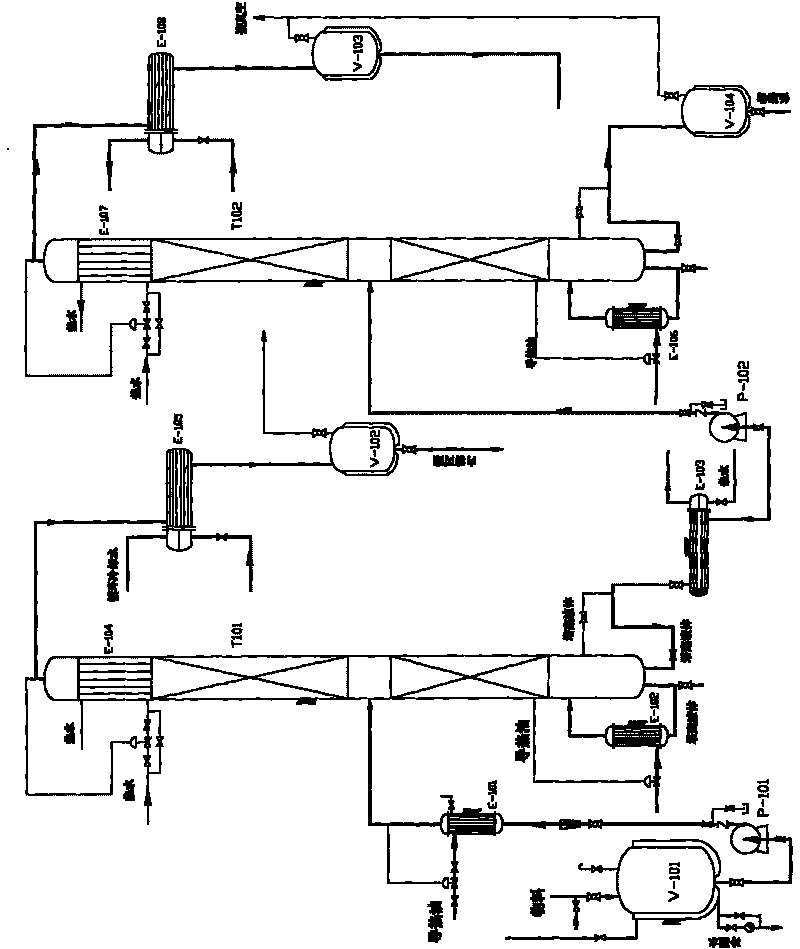
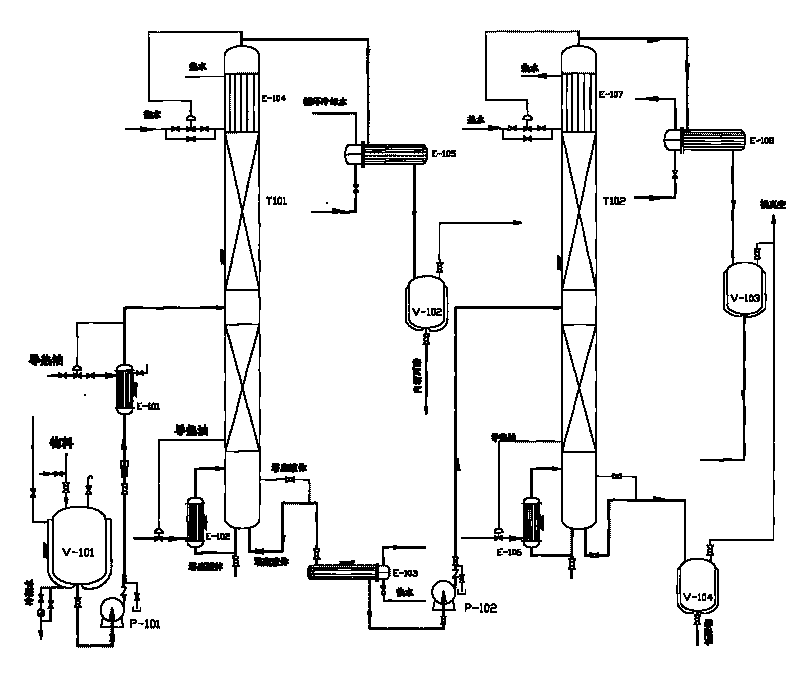
Method for continuously refining L-lactide from crude L-lactide
The invention discloses a method for continuously refining L-lactide from crude L-lactide, which comprises the following steps of: firstly, performing at least once lightness removal to the crude L-lactide by using a lightness-removing column, sending melted crude L-lactide into the middle of the lightness-removing column, refluxing and separating as well as distilling the crude L-lactide in the lightness-removing column, condensing vapor distillate at the upper end of the lightness-removing column for removing water, L-lactate and meso-lactide; secondly, enabling column bottom liquid to enter a reboiler for vaporization and then enter into the column, performing at least once rectification to the left column bottom liquid through a treating column after cooling, wherein the lower end of the lightness-removing column mainly has high-boiling point distillate liquid comprising the L-lactide and lactate oligomer; and when in rectification, refluxing and separating the column bottom liquid of the lightness-removing column to obtain a refined L-lactide; refining column bottom flow to obtain concentrated lactate oligomer. The L-lactide purified by the method can be directly used in the polymerization of poly L-lactate, thereby lowering the purifying cost of the L-lactide, increasing the yield, and being environmental friendly without organic solvents.
Owner:南京冠创生物科技有限公司
Technological method for synthesizing optical pure L-/D-lactide by using biomass organic guanidine catalyst method
ActiveCN103193759ANo metalNon-cytotoxicOrganic chemistryOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCreatinine riseDistillation
Owner:JINDAN BIOLOGICAL NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
Crystalline high-compliance glycolide copolymers and applications thereof
The present invention is directed toward an absorbable crystalline segmented copolymer comprising a polyalkylene succinate segment end-grafted in a single-step with a mixture of monomers comprising caprolactone, l-lactide, and / or glycolide. The present invention is also directed toward an absorbable crystalline segmented copolymer arising from a trihydroxy compound that is reacted in a single-step with a mixture of monomer comprising ε-caprolactone, l-lactide, and / or glycolide to produce monocentric polyaxial polymers.
Owner:POLY MED
Method Of Fabricating A Low Crystallinity Poly(L-Lactide) Tube
Methods of fabricating a low crystallinity polymer tube for polymers subject to strain-induced crystallization. The low crystallinity tube may be further processed to make an implantable medical device.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
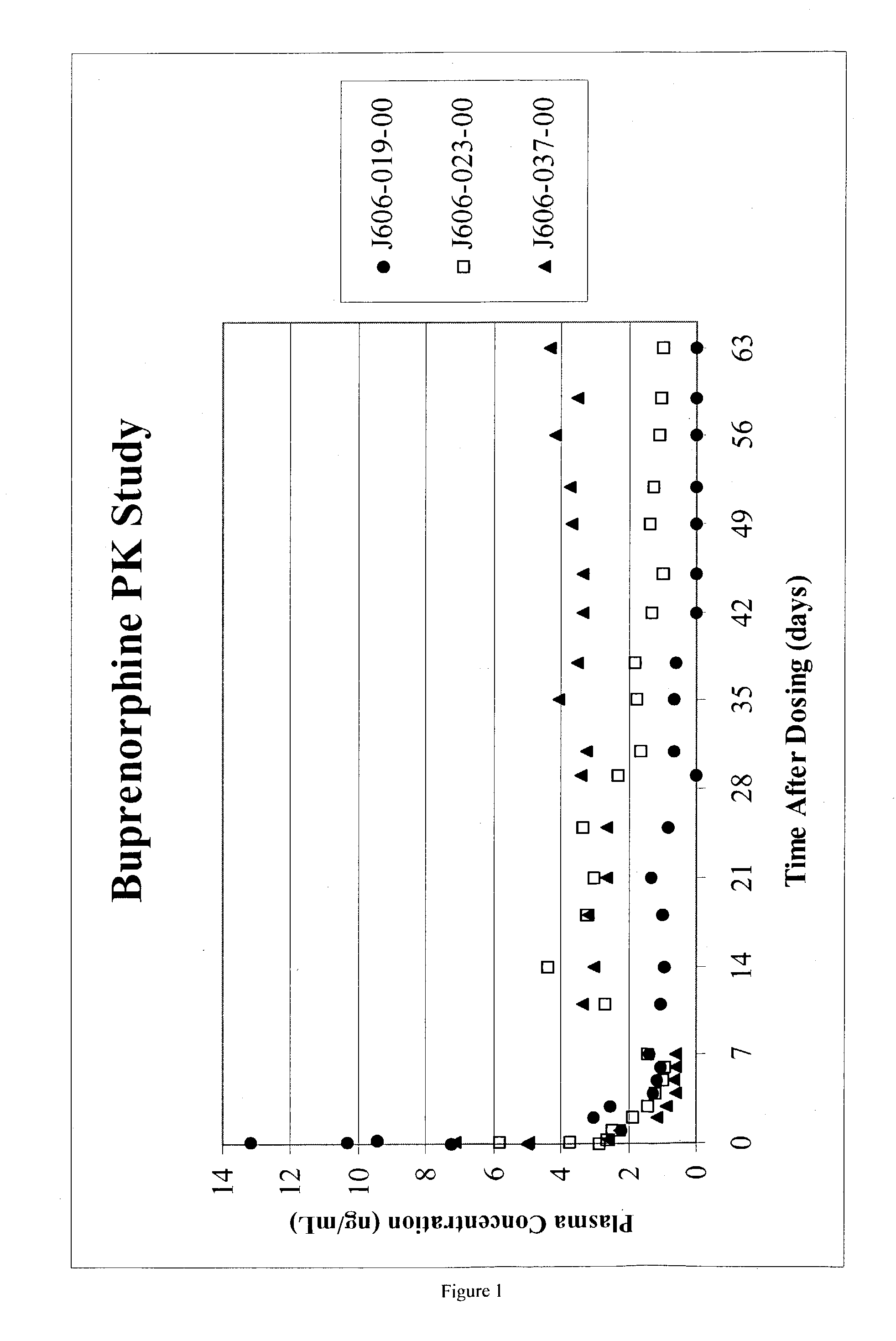
Injectable opioid partial agonist or opioid antagonist microparticle compositions and their use in reducing consumption of abused substances
InactiveUS20030152638A1Avoid prolonged useReadily injected intramuscularlyBiocidePowder deliveryOpioid antagonistControl manner
An injectable slow-release partial opioid agonist or opioid antagonist formulation is provided comprising a partial opioid agonist or opioid antagonist in a poly(D,L-lactide) excipient with a small amount of residual ethyl acetate. Upon intramuscular injection of the composition, a partial opioid agonist or opioid antagonist is released in a controlled manner over an extended period of time. The composition finds use in the treatment of heroin addicts and alcoholics to reduce consumption of the abused substances. Of particular interest are the drugs buprenorphine, methadone and naltrexone.
Owner:EVONIK CORP
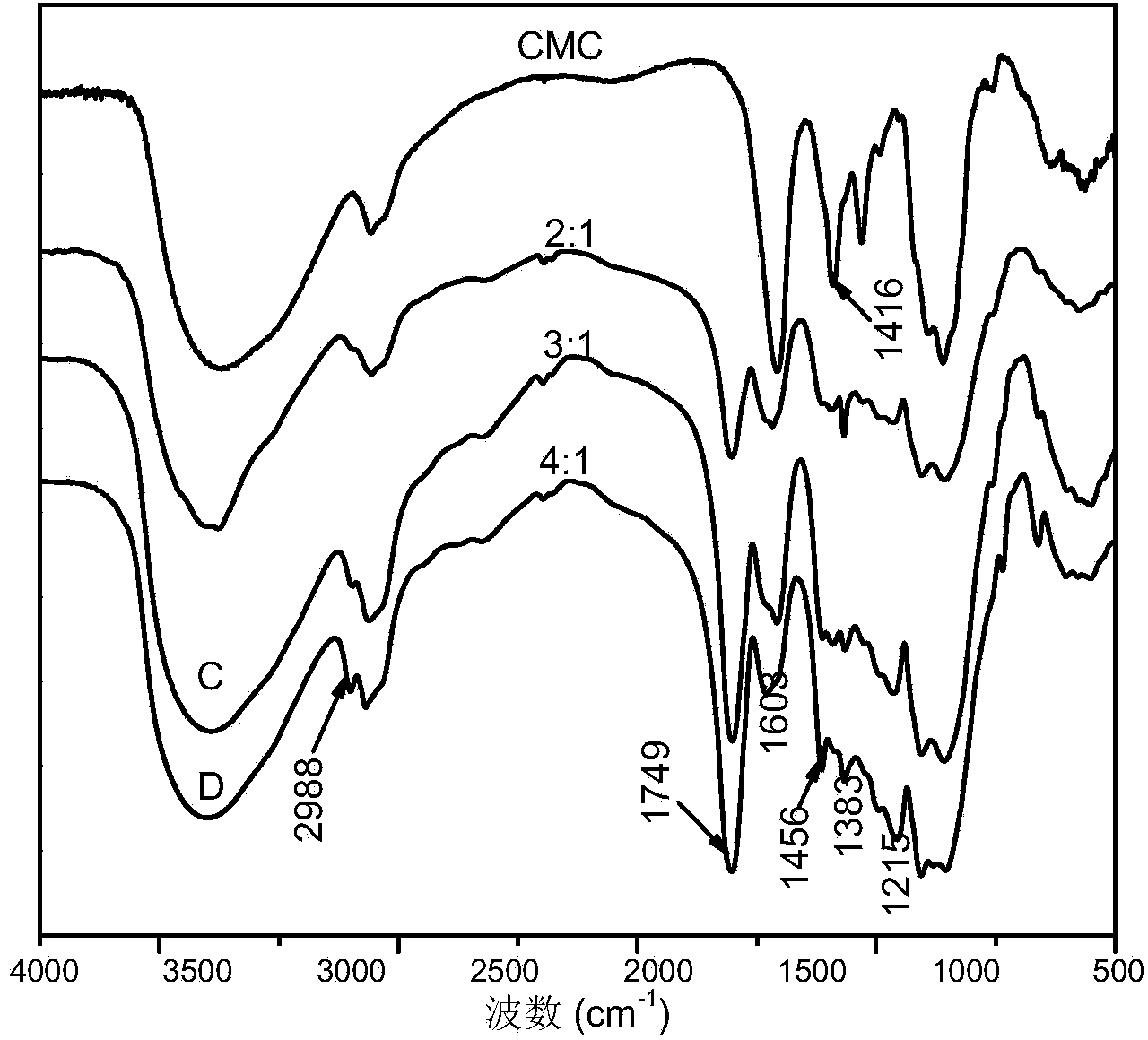
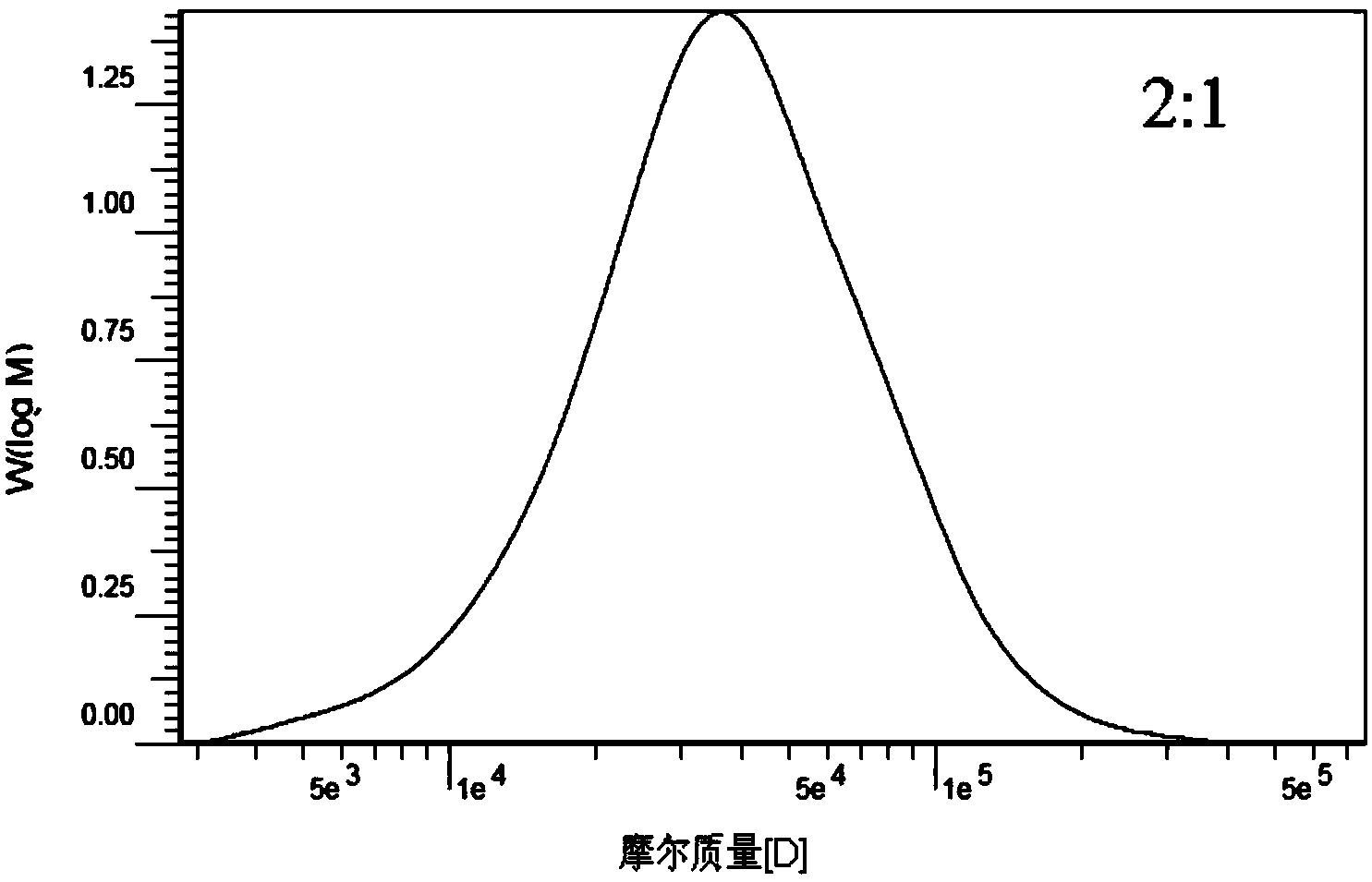
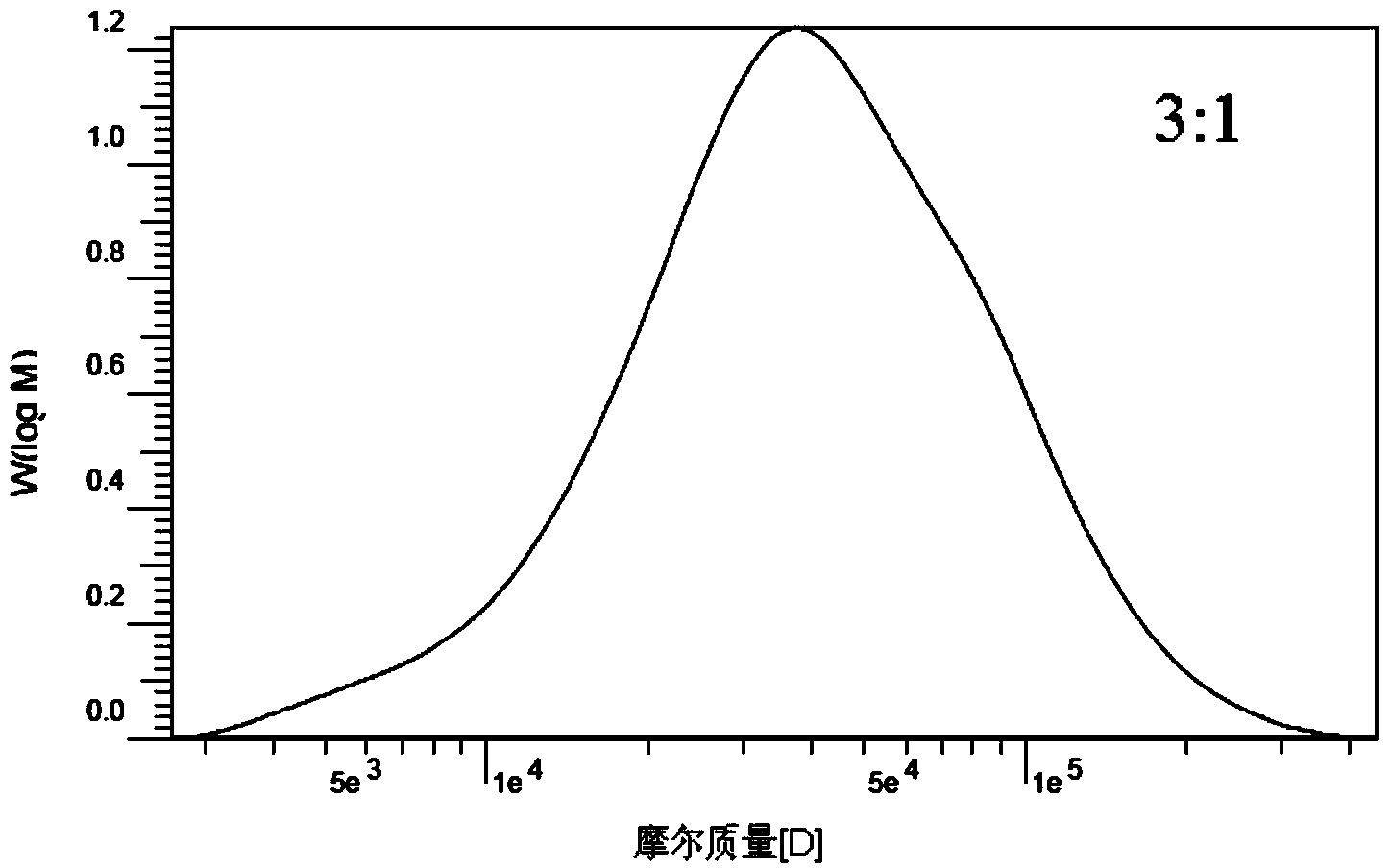
Carboxymethyl cellulose grafted polylactic acid amphiphilic polymer, as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103450361AControllable molecular structureImprove control effectOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsNitrogen gasIonic liquid
The invention discloses a carboxymethyl cellulose grafted polylactic acid amphiphilic polymer, as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: dissolving carboxymethyl cellulose in an ionic liquid to form a homogeneous solution; adding grafting monomers, namely L-lactide monomers and a catalyst, namely stannous octoate into the homogeneous solution; controlling the temperature at 100 DEG C-130 DEG C, performing magnetic stirring, reacting for 18-24 hours in the presence of nitrogen, stopping the reaction and reducing the temperature of a system to room temperature; pouring the reaction system into ethanol to produce a precipitate, filtering and separating the precipitate, and washing with anhydrous ethanol; performing extraction on an obtained product in acetone, and performing vacuum drying to get the purified carboxymethyl cellulose grafted polylactic acid amphiphilic polymer. A dialysis method is utilized for forming self-assembled nanosphere-like micelles of the carboxymethyl cellulose grafted polylactic acid amphiphilic polymer, the particle size is 30-150nm, the critical micelle concentration is 0.01-0.1g / L and the anti-dilution stability is good.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Coupling refining method of high-purity L-lactide
The invention provides a method for refining high-purity L-lactide by way of liquid crystallization and melt crystallization. The method comprises the following steps of: based on 80% L-lactide crude product as a raw material, initially purifying the L-lactide crude product by way of liquid crystallization; and then secondarily purifying the L-lactide by way of melt crystallization. The method specifically comprises cooling and crystallizing, melt crystallization, sweating, and melting. L-lactide with purity over 99.5% can be prepared by applying the method.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Degradable double-layer compound ureteral stent tube
The invention discloses a ureteral stent tube made of a degradable material. The stent tube is a double-layer compound tube, the inner layer is constituted by a L-lactide / epsilon-caprolactone copolymer (PLLCA) elastomer material, and the weight average molecular weight of an L-lactide / epsilon-caprolactone copolymer is 0.1-0.8 million, wherein an epsilon-caprolactone unit accounts for 15%-25% in the copolymer, an L-lactide unit accounts for 75%-85%, and a layer of poly-1,4-dioxanone (PPDO) is uniformly covered on the outer layer of the ureteral stent tube. The viscosity average molecular weight is 0.1-0.5 million. The ureteral stent tube has the advantages of being good in biocompatibility, being capable of realizing self-degradation, being capable of being degraded and excreted from a body without drawing the tube, and reducing suffering and economic burden of a patient.
Owner:ZHEJIANG APELOA JIAYUAN BIOMEDICAL MATERIAL +1
Biodegradability hydrogel controlled-release preparation and its preparation method and application
InactiveCN101283966ASimple manufacturing methodControl release speedPharmaceutical delivery mechanismLactidePLA-PEG-PLA
The invention relates to a biodegradable hydrogel controlled release preparation and a preparation and an application thereof, belonging to the technology field of medicines. The preparation method comprises the steps of: synthesizing poly(lactic acid)-polyethylene glycol-poly(lactic acid) (PLA-PEG-PLA) triblock copolymer by inducing L-lactide and D-lactide to respectively conduct ring-expansion polymerization by using zinc powder, zinc lactate or stannous octoate as catalyst and polyethylene glycol (PEG) 2,000-20,000; respectively dissolving poly-L-lactic acid-polyethylene glycol-poly-L-lactic acid and poly-D-lactic acid-polyethylene glycol-poly-D-lactic acid in water to obtain solutions with concentration of 0.05-0.5g / mL, swelling, mixing, and allowing gelatinization under constant temperature to obtain PLA-PEG-PLA triblock copolymer hydrogel for injection by complexing reaction. The hydrogel has good biological compatibility and biodegradability, can be used for embedding water-soluble drugs, and is an ideal drug controlled release carrier.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Ureter rack tube made of absorbable material
InactiveCN1672739AIncrease elasticitySolve the defects of low molecular weight and poor elasticitySurgeryDilatorsMedicineLactide
The present invention discloses one kind of medical ureter rack tube made of absorbable material. The absorbable material is epsilon-caprolactone-lactide copolymer or the copolymer of epsilon-caprolactone and lactide and / or diglycolide of molecular weight 50-800 KD, where epsilon-caprolactone accounts for 10-80 wt% of the copolymer and the lactide is DL-lactide or L-lactide. The absorbable material for ureter rack tube has excellent biocompatibility, can degrade automatically and may be exhausted out after degrading with less pain and burden.
Owner:CHENGDU ORGANIC CHEM CO LTD CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com