Patents
Literature
36 results about "Morphometric analysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
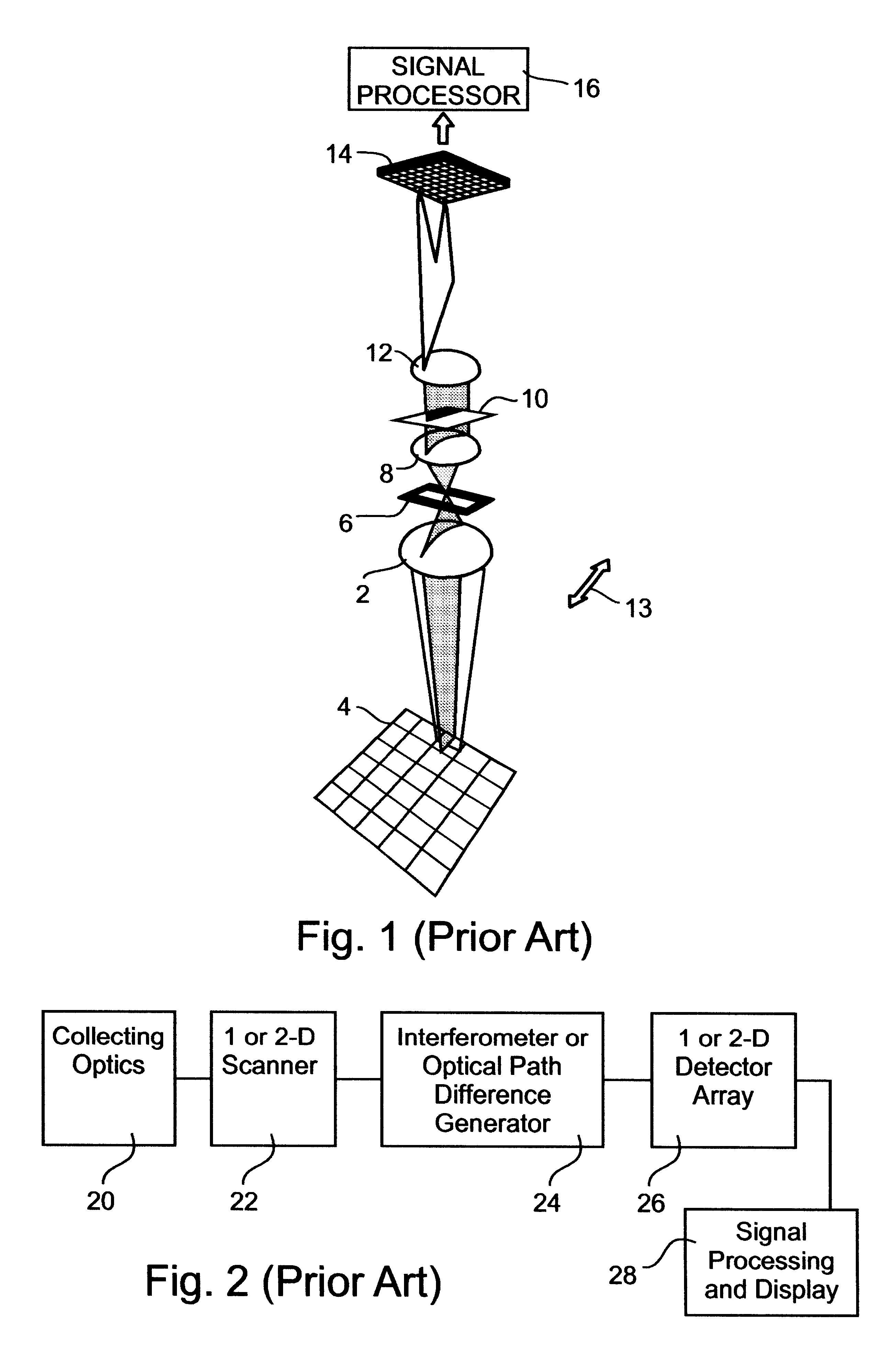
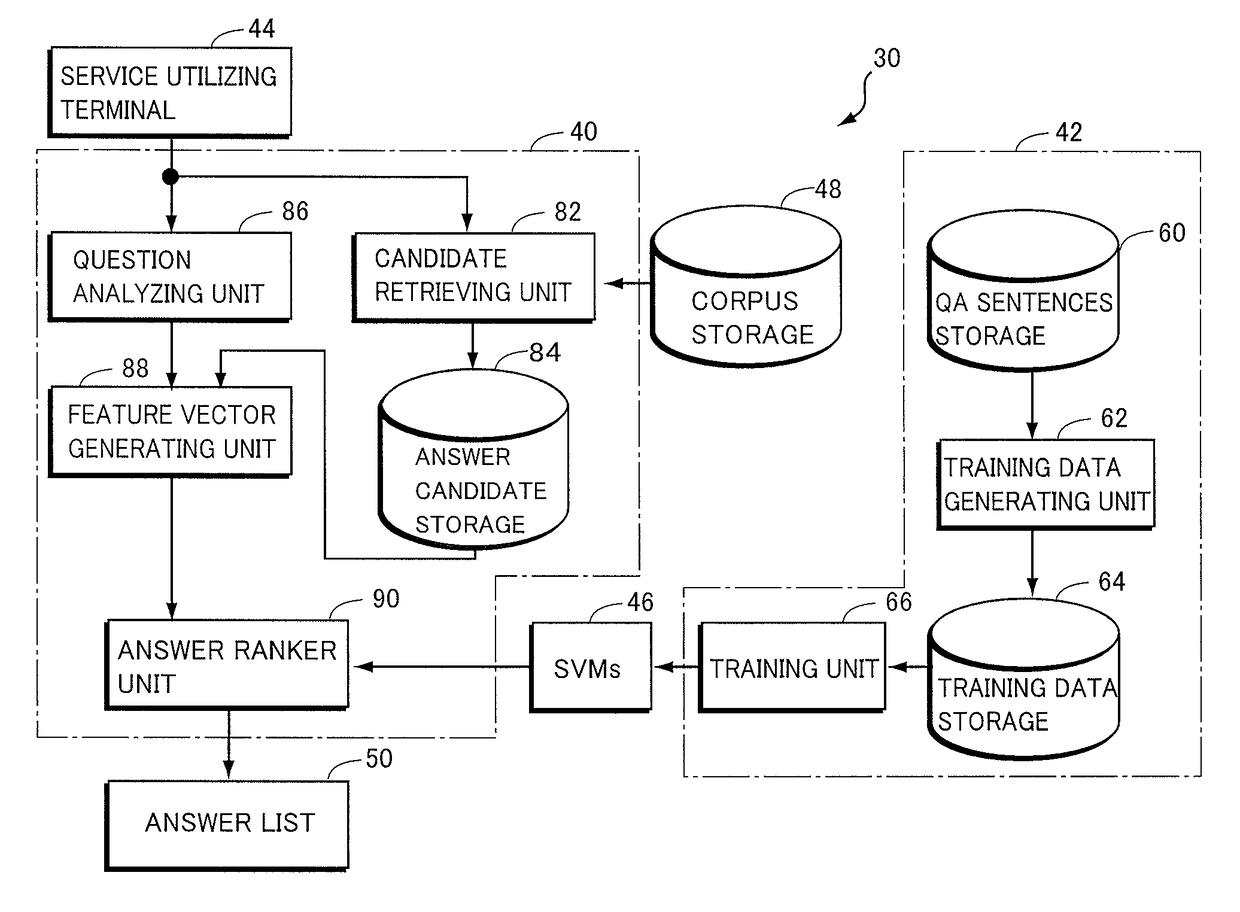
Non-factoid question-answering system and computer program
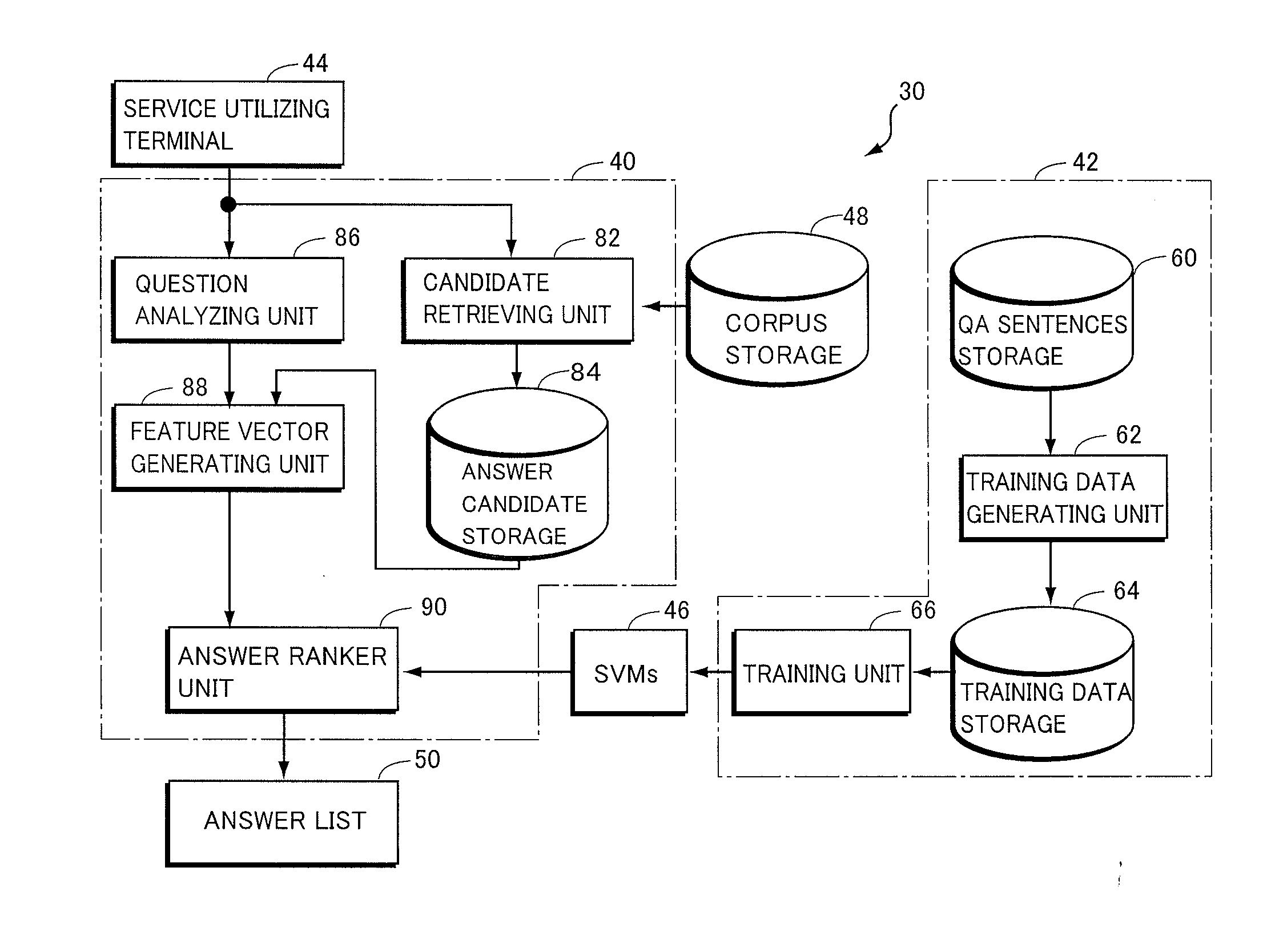
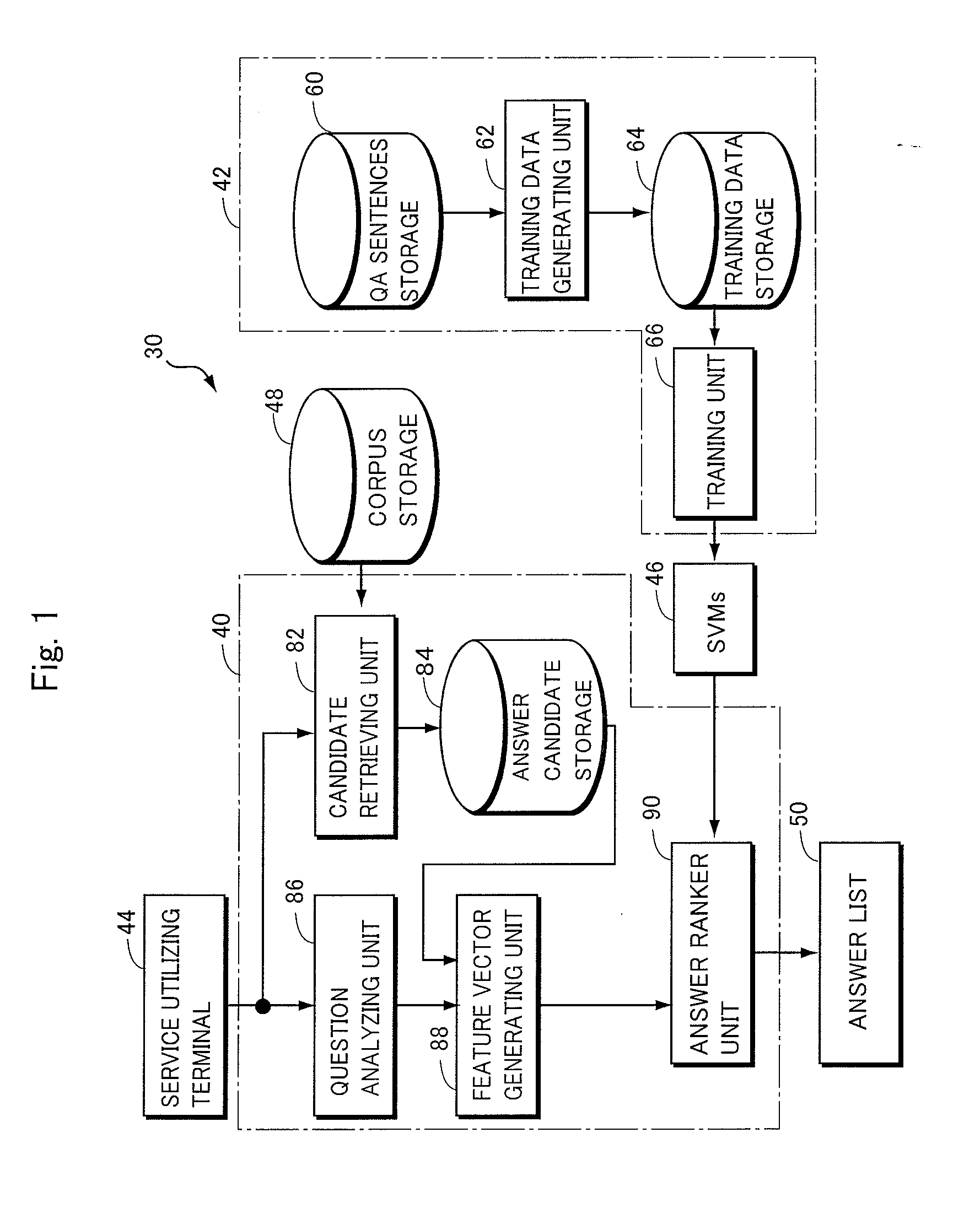
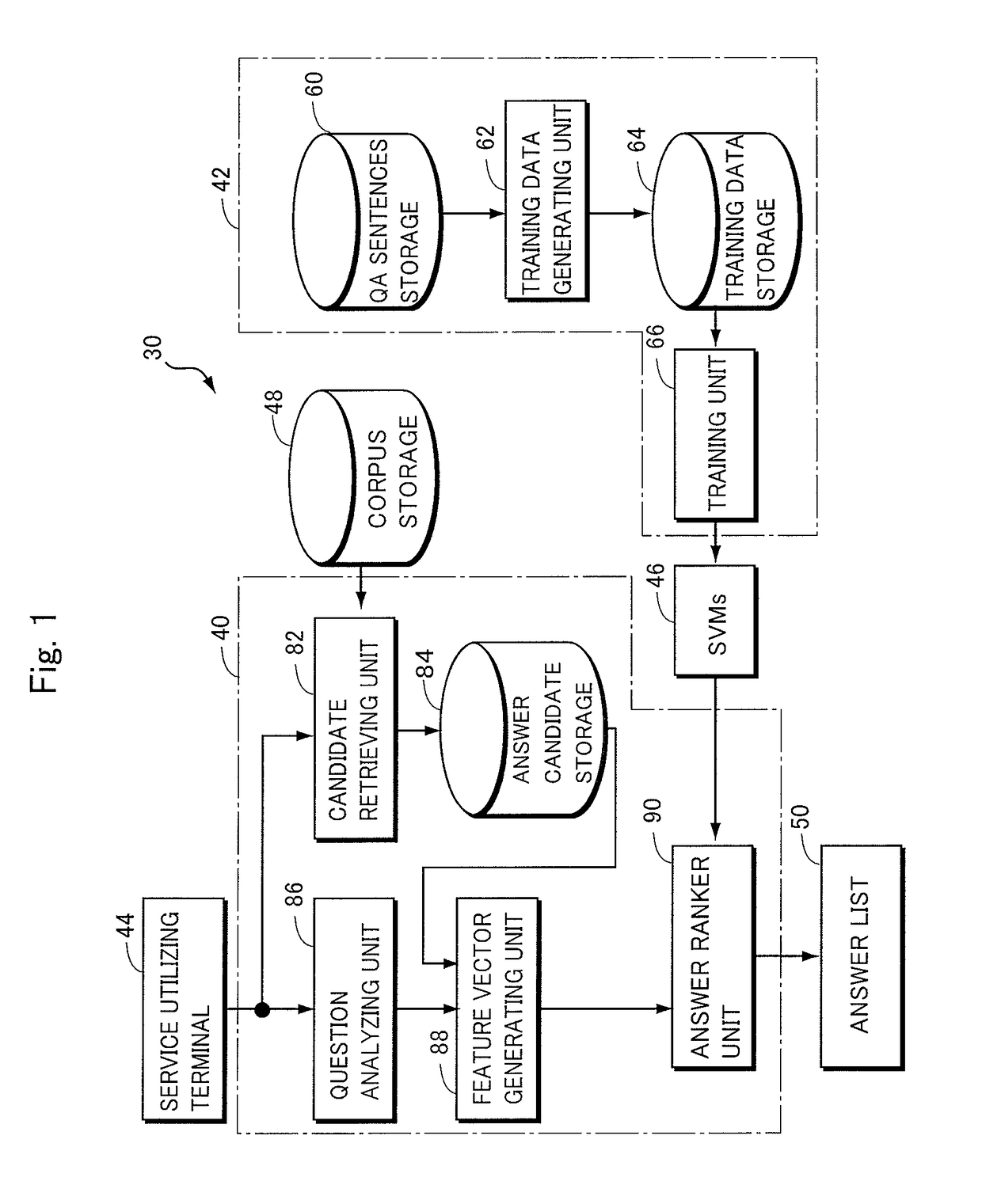
In order to provide a non-factoid question answering system with improved precision, the question answering system (160) includes: a candidate retrieving unit (222), responsive to a question, extracting answer candidates from a corpus storage (178); a feature vector generating unit (232) for generating features from combinations of a question with each of the answer candidates; SVMs (176) trained to calculate a score of how correct a combination of the question with an answer candidate is, upon receiving the feature vector therefor; and an answer ranker unit (234) outputting the answer candidate with the highest calculated score as the answer. The features are generated on the basis of the results of morphological analysis and parsing of the question, a phrase in the question evaluated as being positive or negative as well as its polarity, and the semantic classes of nouns in the features.
Owner:NAT INST OF INFORMATION & COMM TECH
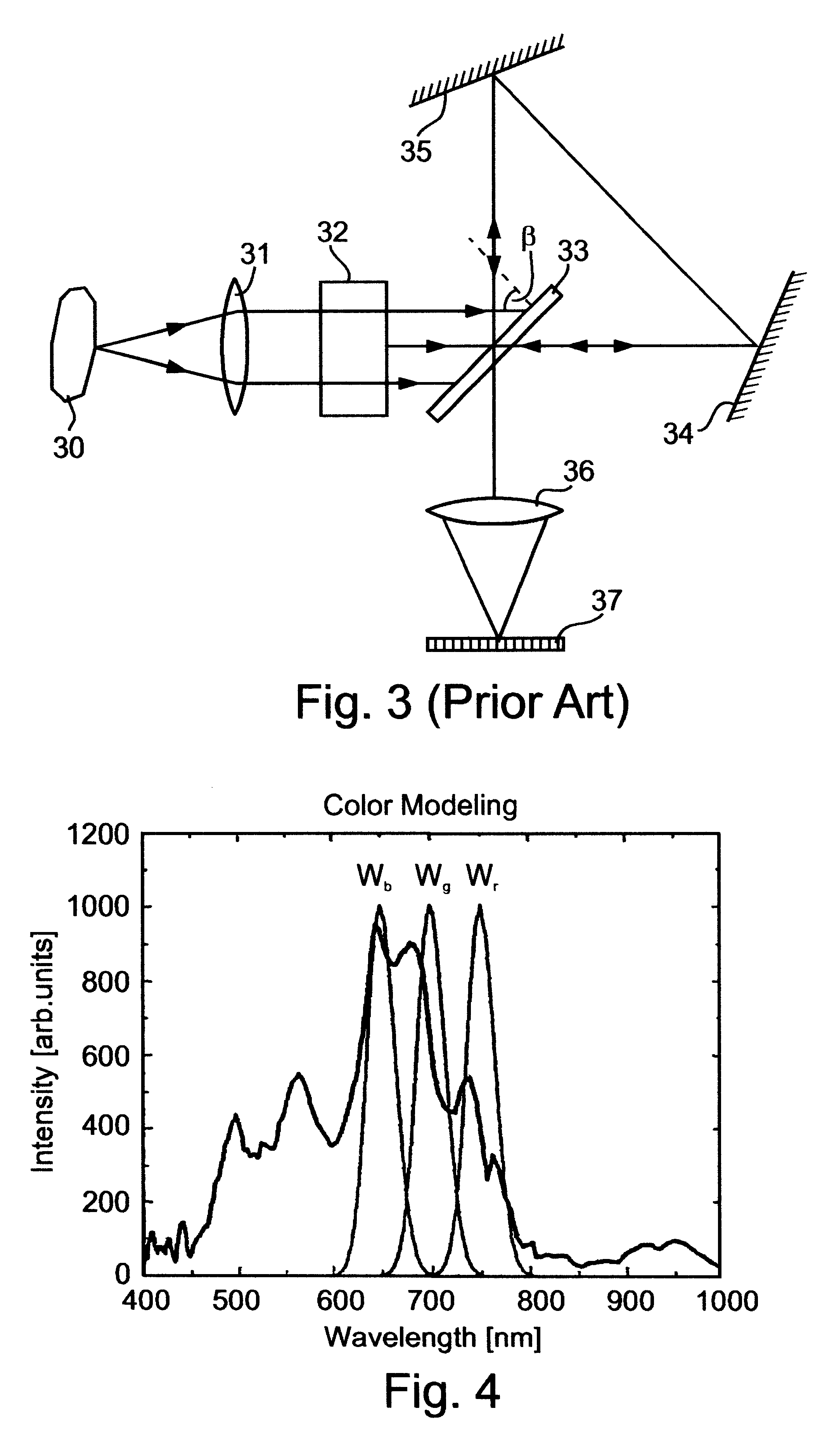
Spectral bio-imaging data for cell classification using internal reference
InactiveUS6690817B1Improve throughputReduced measurement timeRaman/scattering spectroscopyInterferometric spectrometrySpectral vectorConstant component
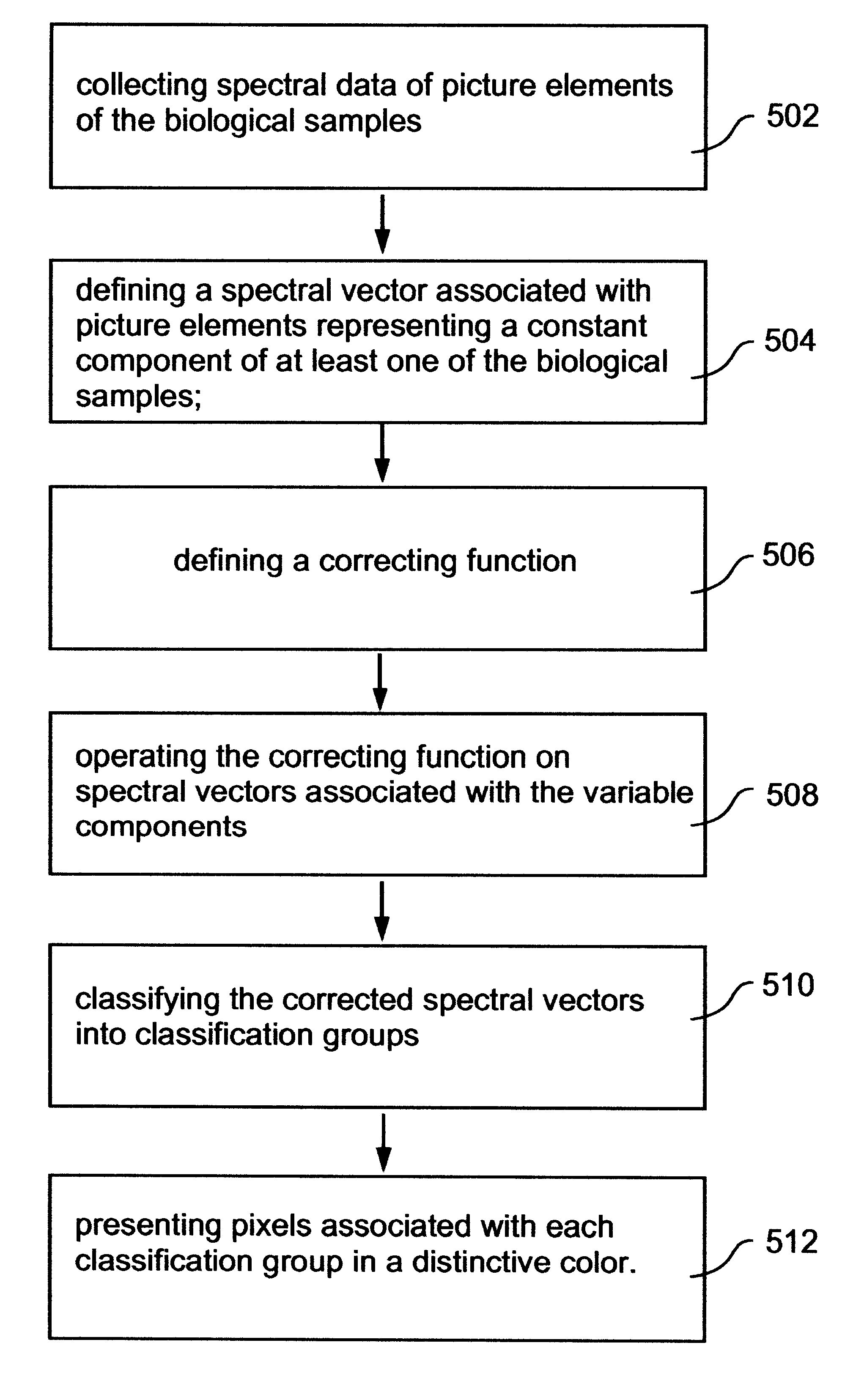
A method of spectral-morphometric analysis of biological samples, the biological samples including substantially constant components and suspected variable components, the method is effected by following the steps of (a) using a spectral data collection device for collecting spectral data of picture elements of the biological samples; (b) defining a spectral vector associated with picture elements representing a constant component of at least one of the biological samples; (c) using the spectral vector for defining a correcting function being selected such that when operated on spectral vectors associated with picture elements representing other constant components, spectral vectors of the other constant components are modified to substantially resemble the spectral vector; (d) operating the correcting function on spectral vectors associated with at least the variable components for obtaining corrected spectral vectors thereof; and (e) classifying the corrected spectral vectors into classification groups.
Owner:APPLIED SPECTRAL IMAGING
Medical guide tubes
Polymeric fibers were microbraided around a mandrel to make a tubular guide tube for nerve regeneration. The polymer used for the fibers was one of poly(L-lactide-co-glycolide) (10:90 PLGA) and chitosan. These polymers are biodegradable and biocompatible. The tubes were studied for their surface morphology and swelling behavior. Biological performance of the tubes was examined in the rat sciatic nerve model with a 12 mm gap. One month after implantation nine out of ten rats showed successful nerve regeneration. Morphometric analysis of regenerated nerves confirmed the quality of the regeneration compatible with those offered by other types of biodegradable nerve guide tubes. The tubes were flexible, permeable and showed no swelling.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE +1
Tubercle bacillus target recognizing and counting algorithm based on diverse characteristics
InactiveCN101877074AFully automatedRealize intelligenceImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionAcid-fastColor image
The invention relates to the field of medical image processing and mode recognition, in particular to a tubercle bacillus target recognizing and counting algorithm based on diverse characteristics. The algorithm comprises the following steps of: image preprocessing: carrying out image reinforcement and constructing median filter and Gaussian filter on a tubercle bacillus microimage; color image partition: carrying out fixed threshold partition based on HSV (Hue-Saturation-Value) color space on a preprocessed image and then carrying out adaptive threshold partition which is based on CIE L*a*b* color space and keeps a geometric shape of a target; communication block morphological analysis and target recognition: carrying out communication block analysis on the partitioned image; and tubercle bacillus target counting: estimating the quantity of tubercle bacillus targets in the image by utilizing a histogram statistics and multistrategy calculation method. The invention can effectively extract the bacillus targets in the tubercle bacillus microimage subjected to acid-fast stain from background and impurities and carry out accurate counting, thereby realizing the automation and the intellectualization of the detection of tubercle bacilli.
Owner:常州超媒体与感知技术研究所有限公司
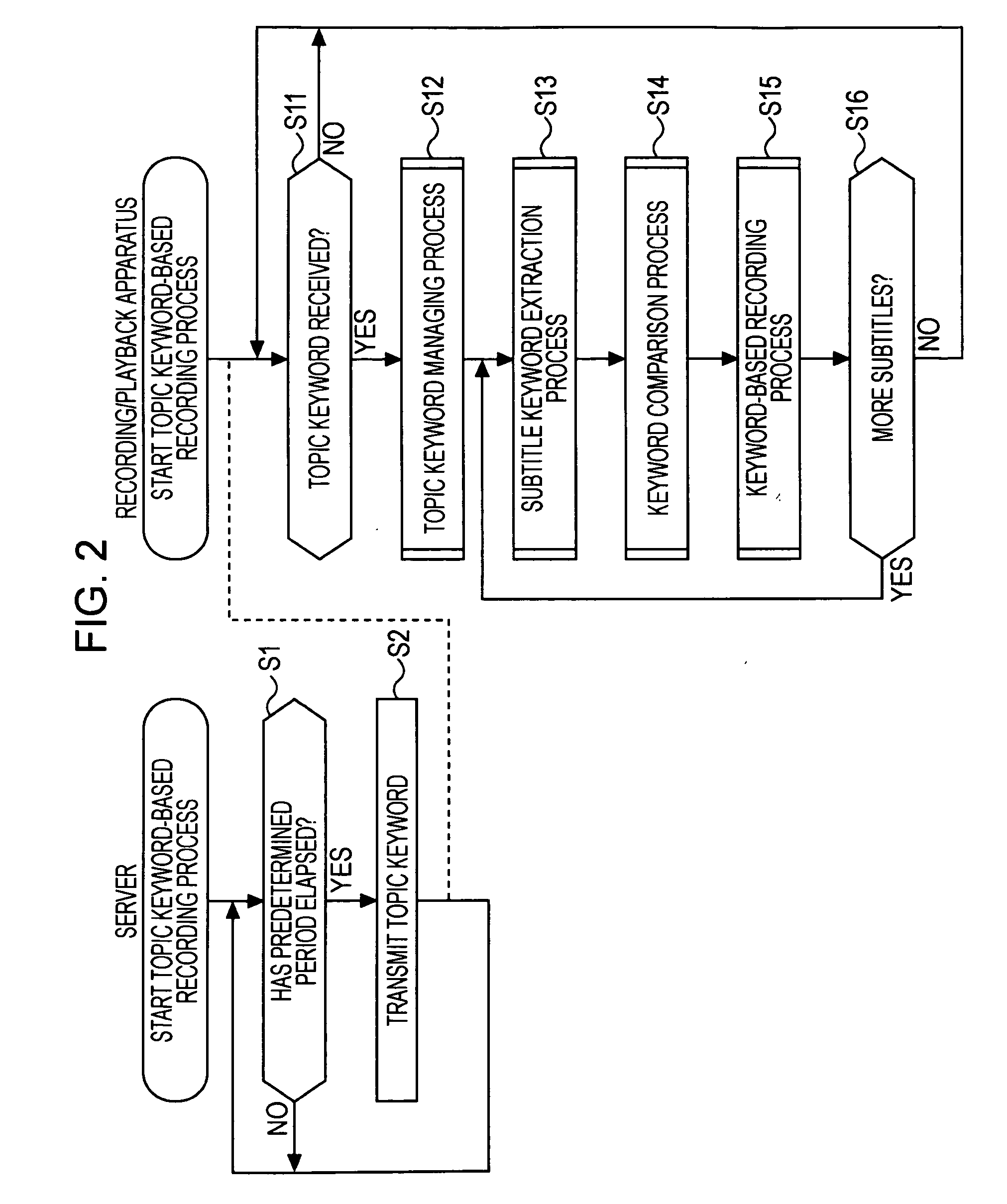
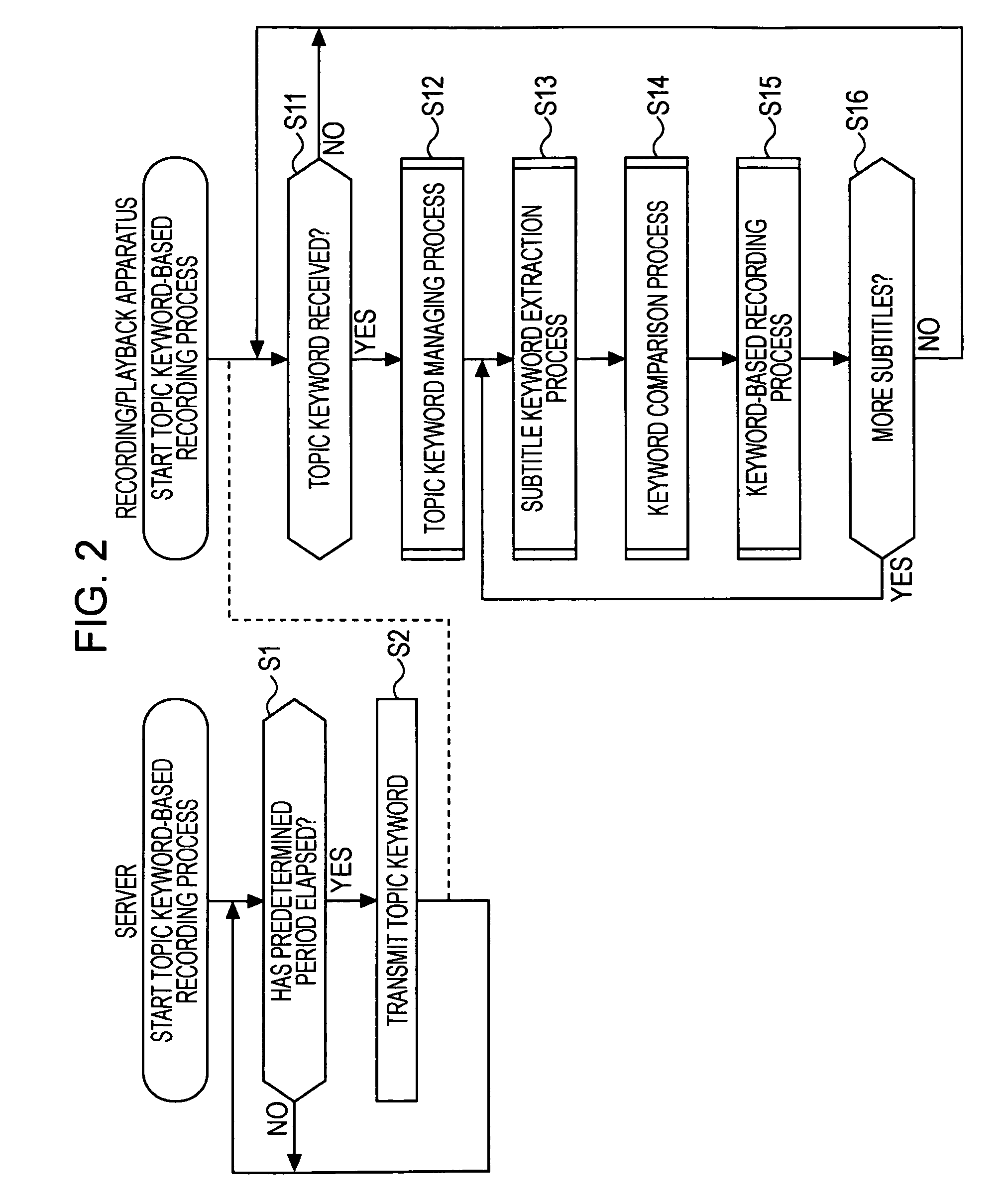
Information processing device and information processing method, information-processing system, recording medium, and program
InactiveUS20060248091A1Low similarityTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionInformation processingAlgorithm
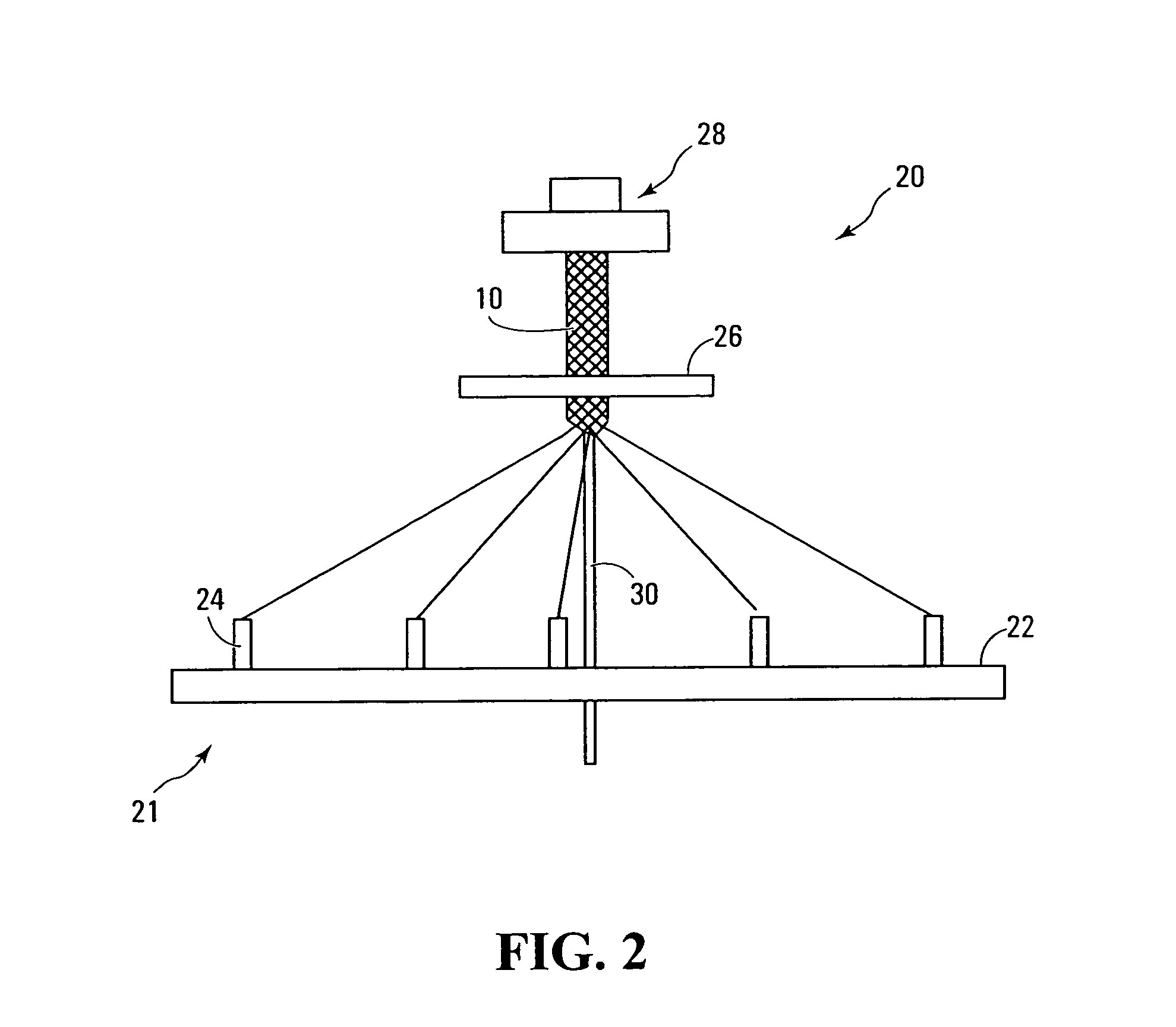
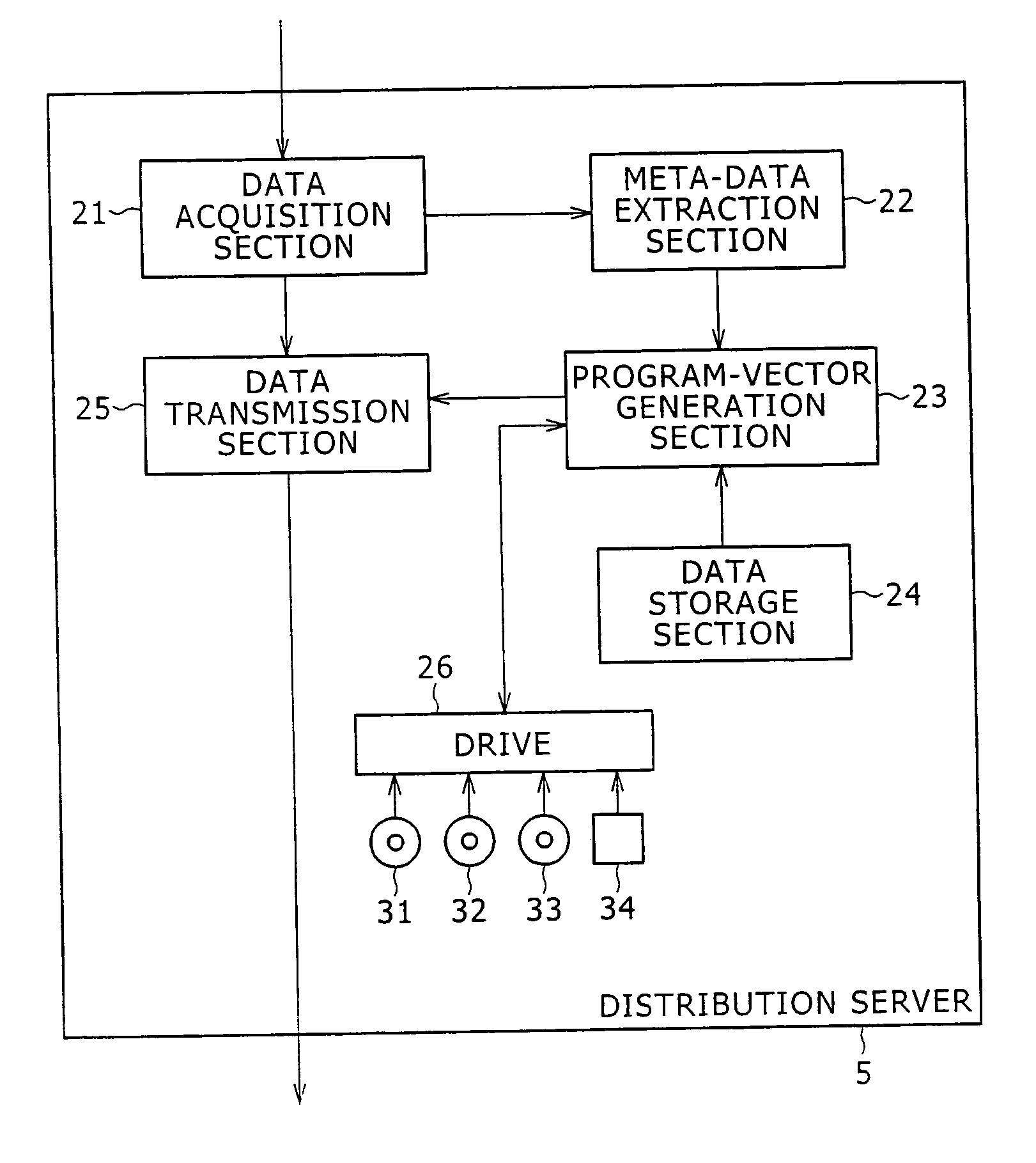
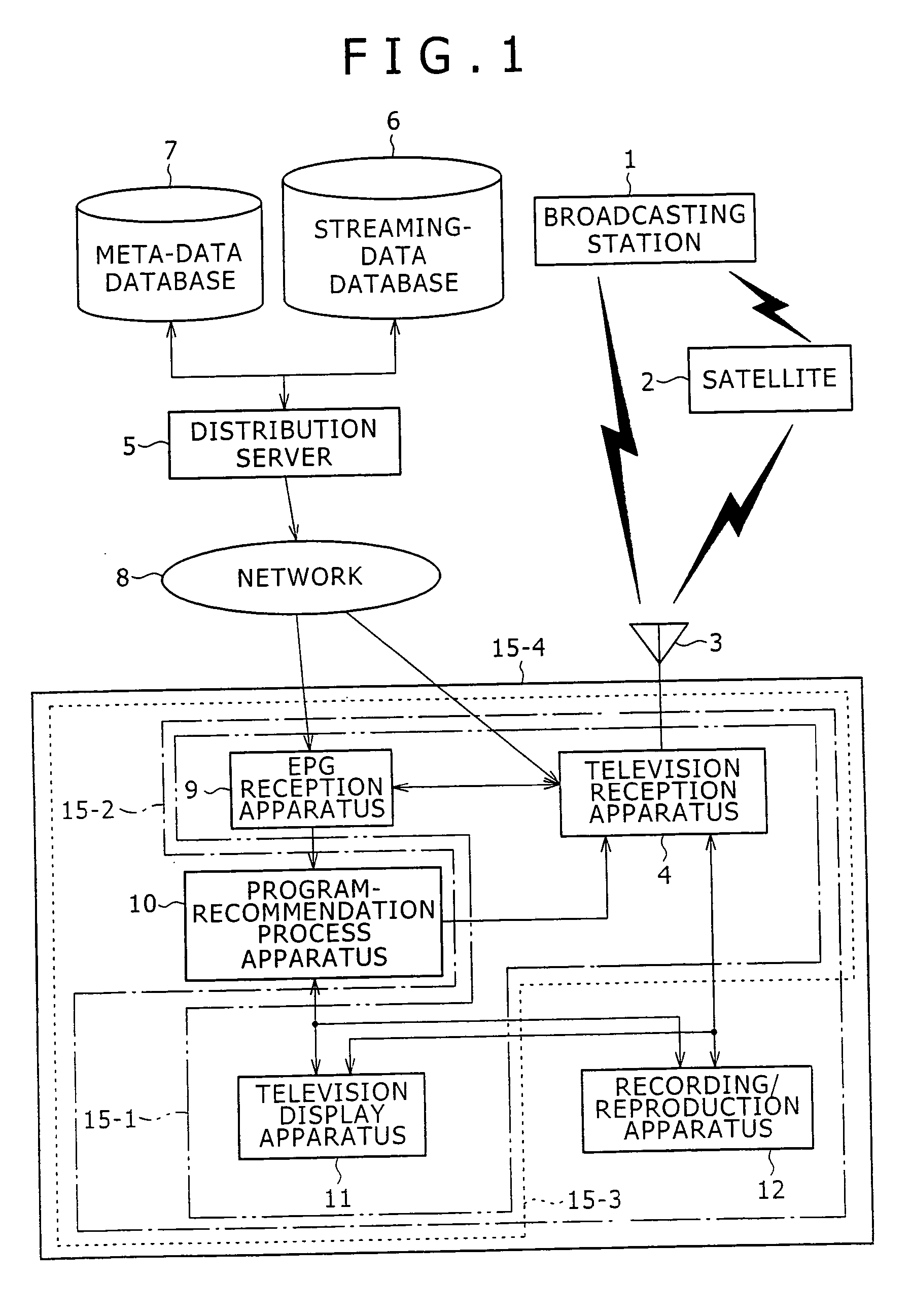
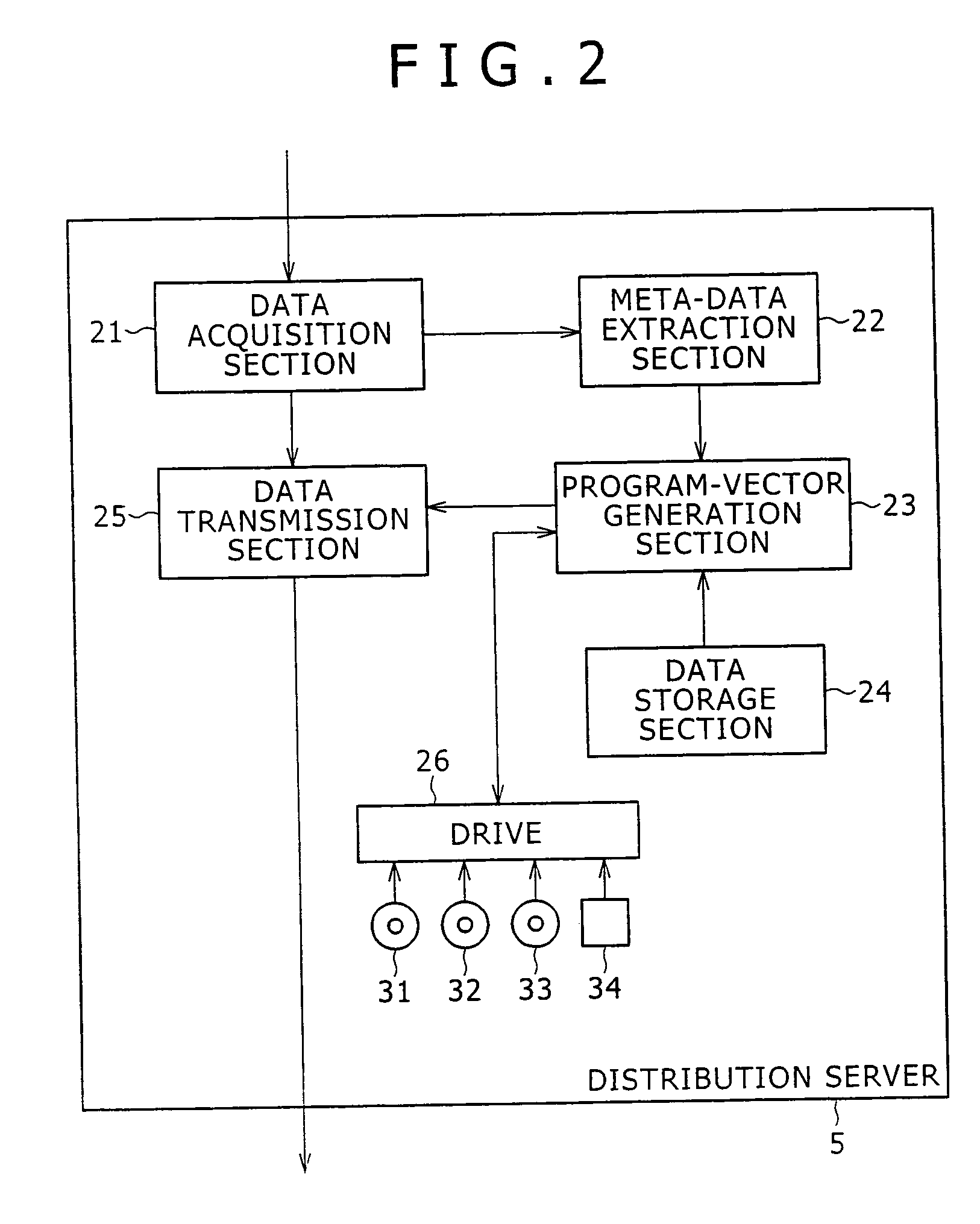
The present invention allows a program vector representing attributes of a program to be generated as follows. At a step S11, EPG data is received. At a step S12, meta data necessary for generation of a program vector PP is extracted from the EPG data. At a step S13, a morphological analysis is carried out on contents and title included in the meta data to disassemble the contents and the title into words. At a step S14, items included in the meta data are subjected to a vector creation process to generate the program vector PP. At a step S15, an effect vector is extracted on the basis of a genre of a program associated with the meta data. At a step S16, the extracted effect vector is associated with the generated program vector PP and the processing is ended. The present invention can be applied to a distribution server for distributing contents.
Owner:SONY CORP
Computer-assisted cell analysis
InactiveUS20060050946A1High throughput screeningReduce the number of cellsImage enhancementImage analysisStainingComputer-aided
The present invention provides methods and systems for automated morphological analysis of cells. The inventive methods are particularly useful in the rapid analysis of cells required in a biological screen. Agents which cause a particular phenotype in the cells can be identified using the inventive quantitative morphometric analysis of cells. The data gathered using the inventive method can also be quantified and analyzed later for various trends and classifications. Characteristics of cells which can be determined using this method include number of nuclei, size of cell, size of nuclei, number of the centrosomes, shape of cells, size of centrosomes, perimeter of nucleus, shape of nucleus, pattern of staining, and degree of staining.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
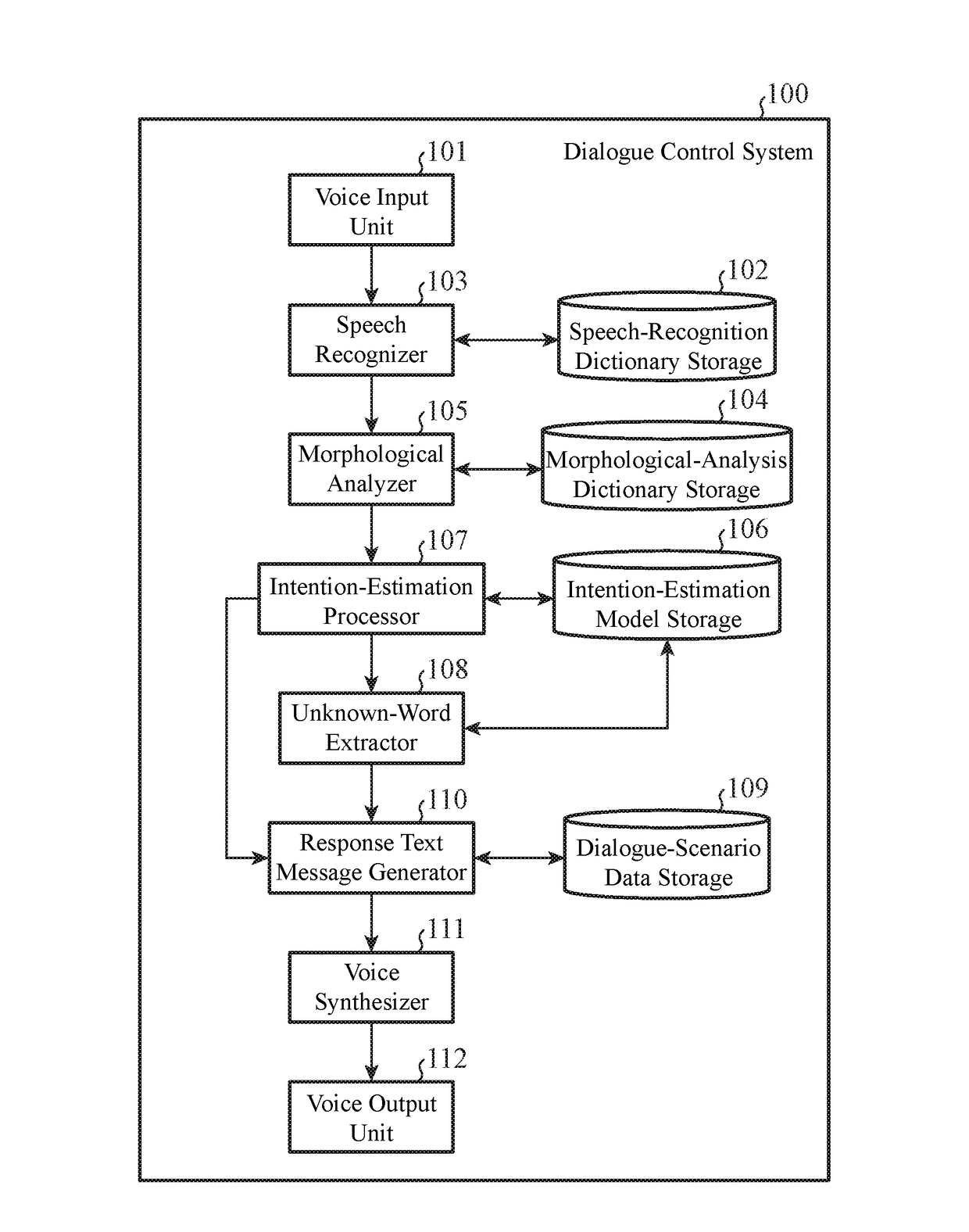
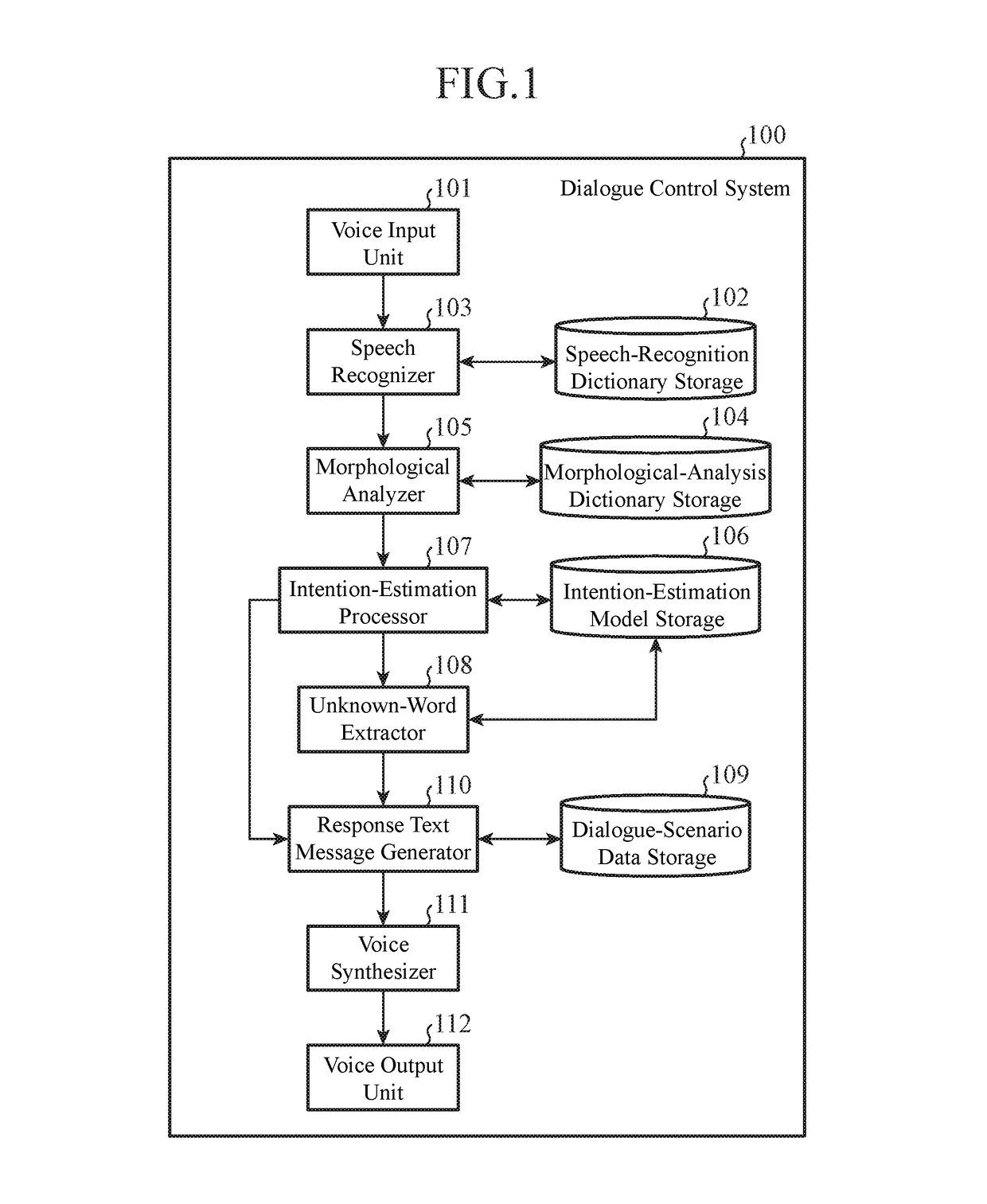
Dialogue control system and dialogue control method
InactiveUS20170199867A1Easy to identifyNatural language data processingSpeech recognitionControl systemMorphometric analysis
A configuration includes: a morphological analyzer configured to analyze a text provided as an input in a form of natural language by a user; an intention-estimation processor configured to refer to an intention estimation model in which words and corresponding user's intentions to be estimated from the words are stored, to thereby estimate an intention of the user based on the text analysis results obtained by the morphological analyzer; an unknown-word extractor configured to extract, as an unknown word, a word that is not stored in the intention estimation model from among the text analysis results when the intention of the user fails to be uniquely determined by the intention estimation processor; and a response text message generator configured to generate a response text message that includes the unknown word extracted by the unknown-word extractor.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
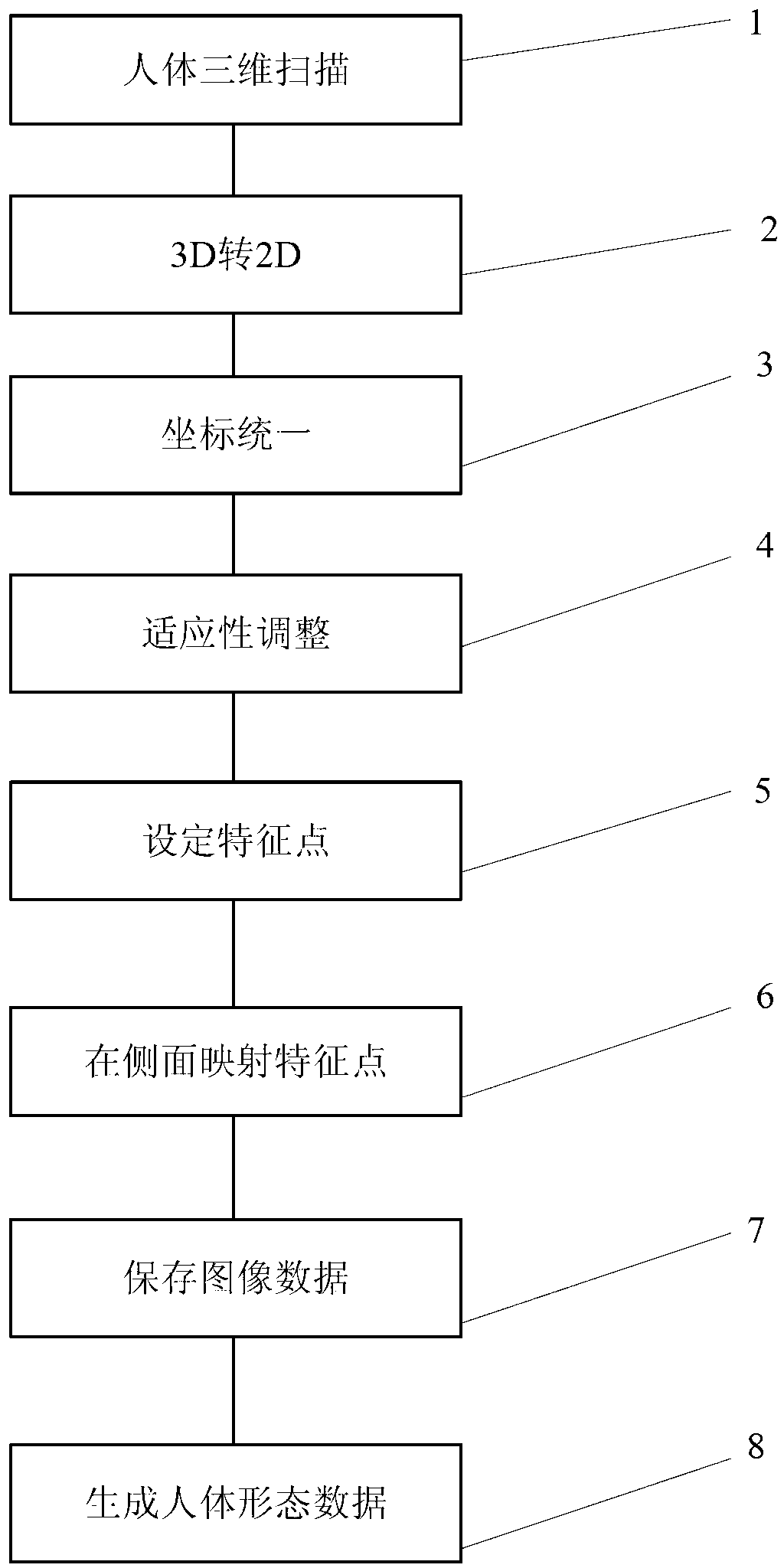
Method for measuring human body morphological characteristics
ActiveCN103006228ASimple accessEasy to operateDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsHuman bodyFast measurement
The invention relates to the field of measuring human body morphology, and in particular to a method for measuring human body morphological characteristics. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining human body morphological three-dimensional point cloud data through scanning; automatically converting the three-dimensional point cloud data into two-dimensional image data which comprises a front projection image, side projection images and a back projection image; and setting human body characteristic points on the front projection image and the back projection image respectively, mapping the human body characteristic points onto the side projection images from the front projection image and the back projection image, and thus obtaining human body morphological characteristic data. By the method, the operation for converting the three-dimensional data into the two-dimensional image data is very simple, so that a data obtaining way is simplified; the converted two-dimensional image data can be used for supplement a three-dimensional measurement project, accordingly, guarantee is provided for ensuring the accuracy of the data measurement of later human body researches; and human body detail sizes can also be obtained according to quick measurement requirements, and human body morphological analysis is carried out.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CLOTHING TECH +1
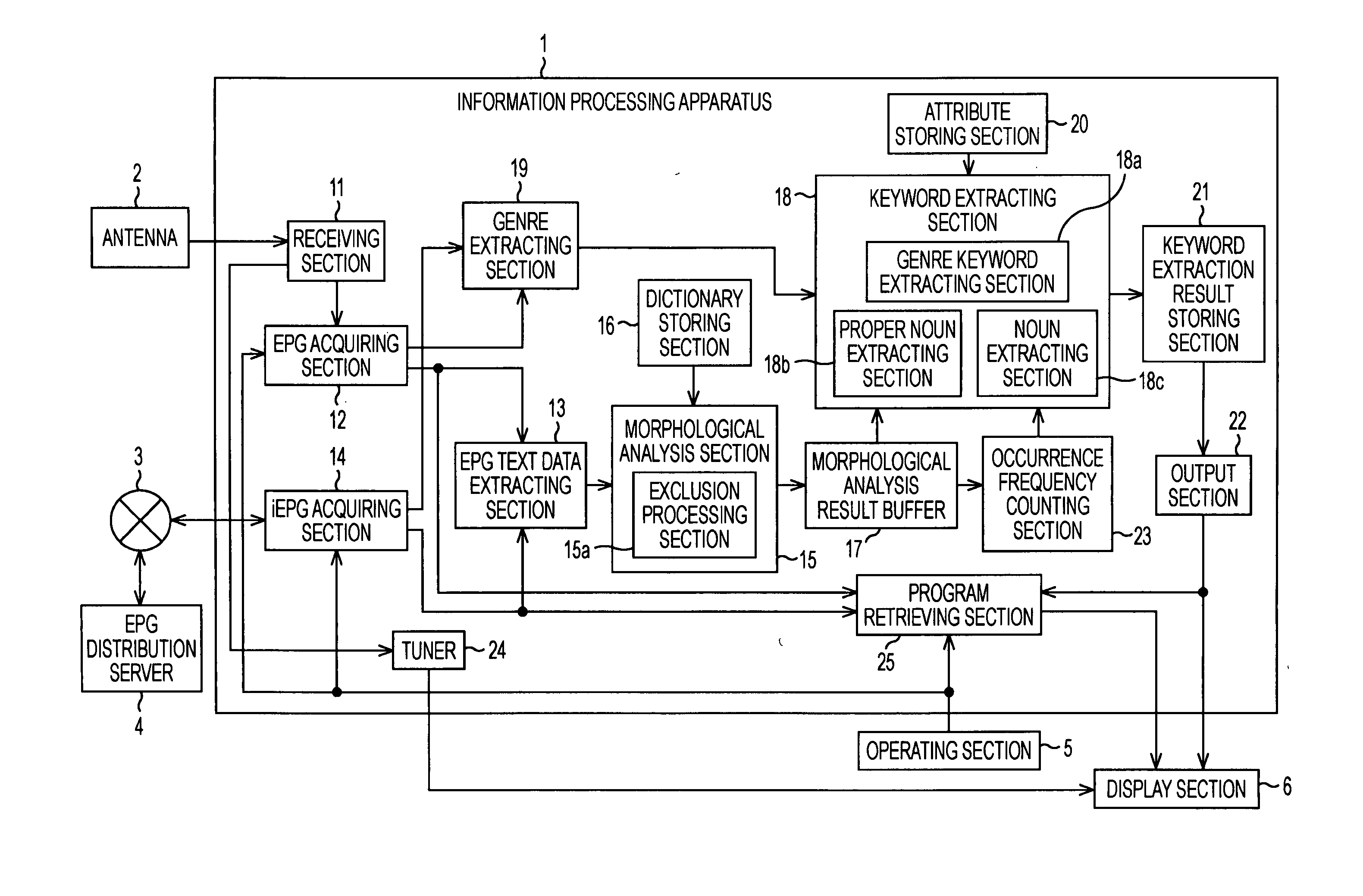
Information processing apparatus and method, program, and storage medium
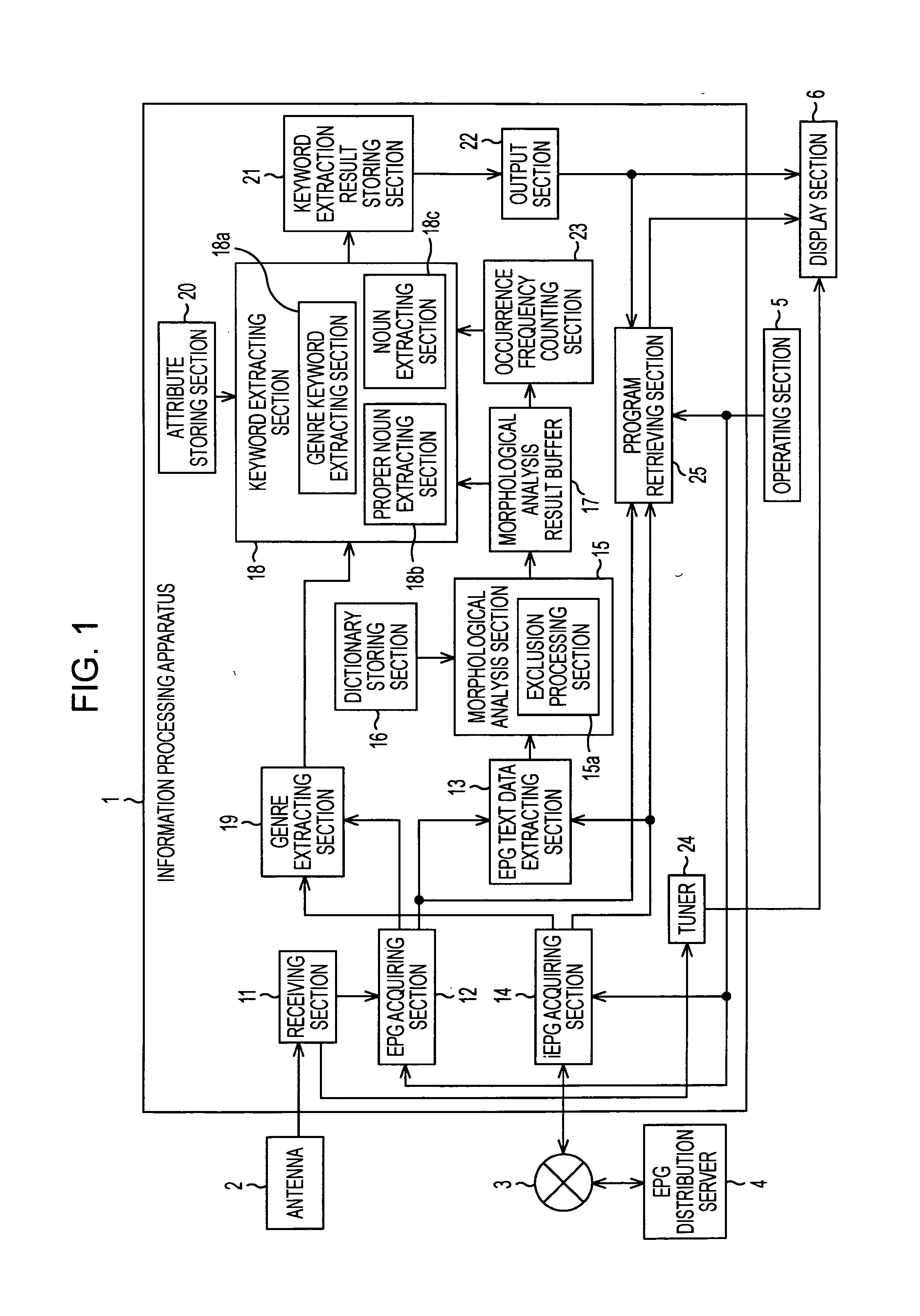
InactiveUS20080215577A1Efficient extractionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsInformation processingMorphometric analysis
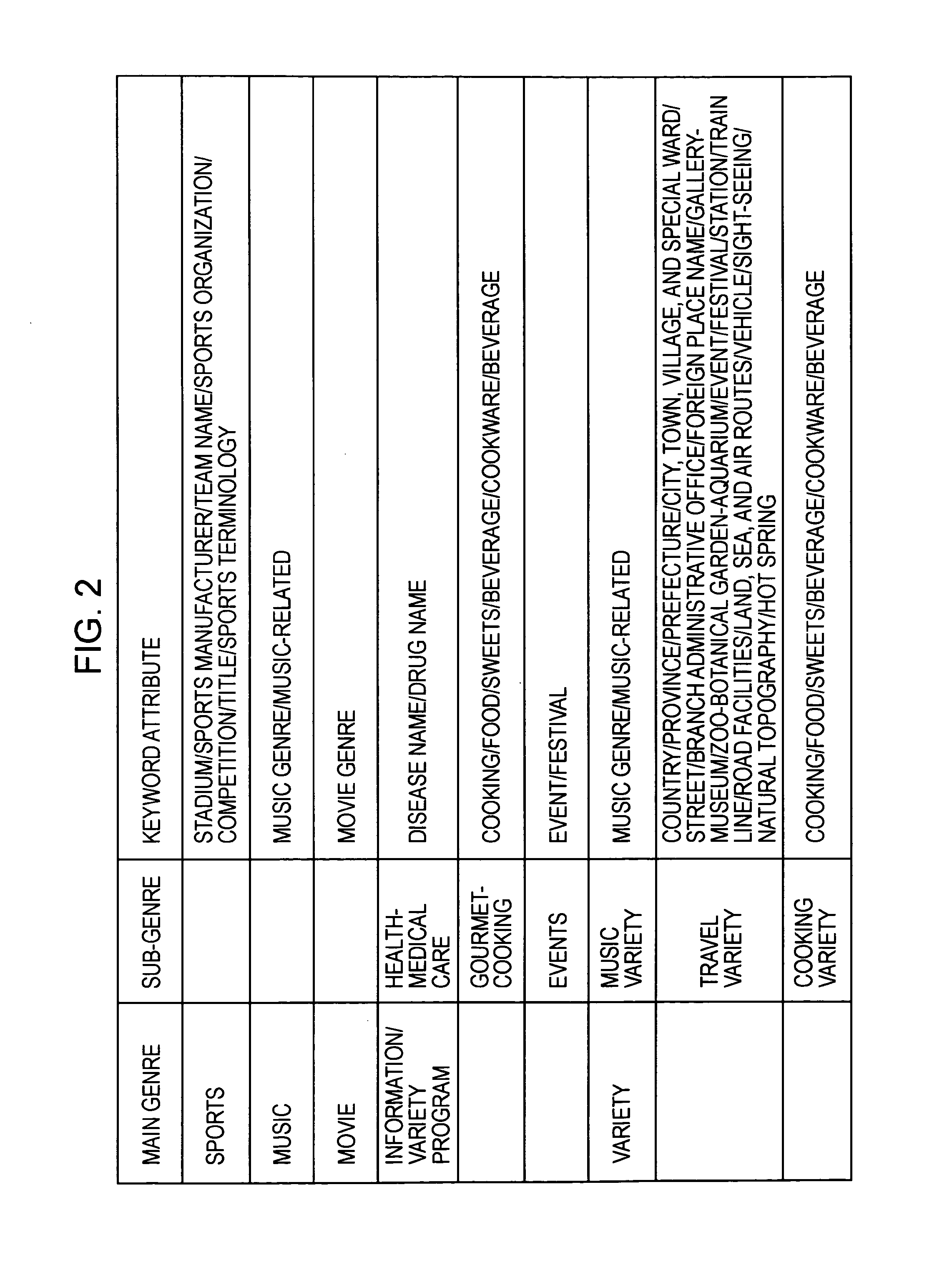
An information processing apparatus includes: an acquiring section acquiring metadata of content; a morphological analysis section performing a morphological analysis of text information included in the metadata of the content; a genre extracting section extracting genre information for each individual content in the metadata of the content; and a keyword extracting section extracting words with attributes that have relevance to the genre of predetermined content in the metadata of the content by a morphological analysis result of the morphological analysis section.
Owner:SONY CORP
Information processing apparatus, informaition processing method, and information processing program
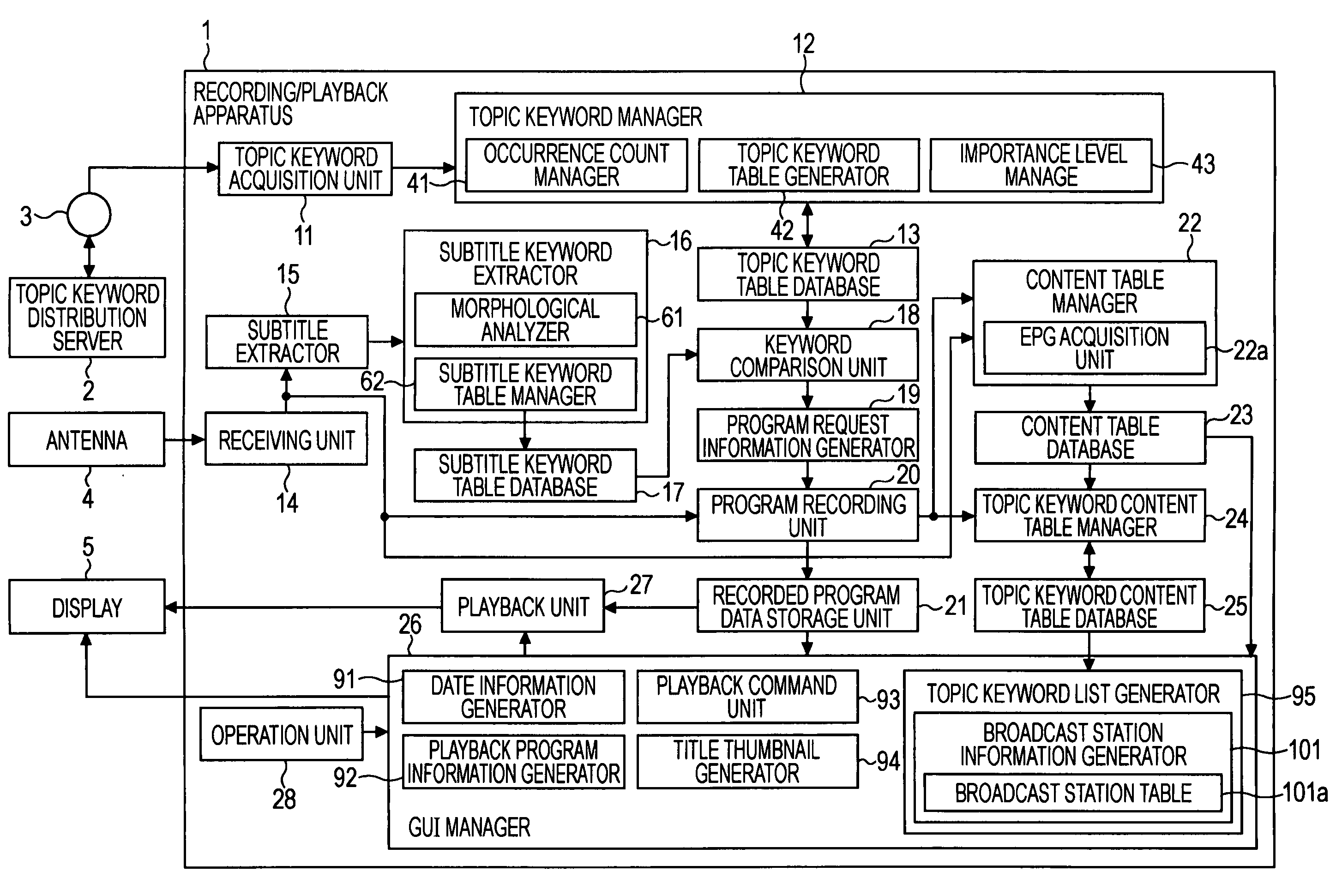
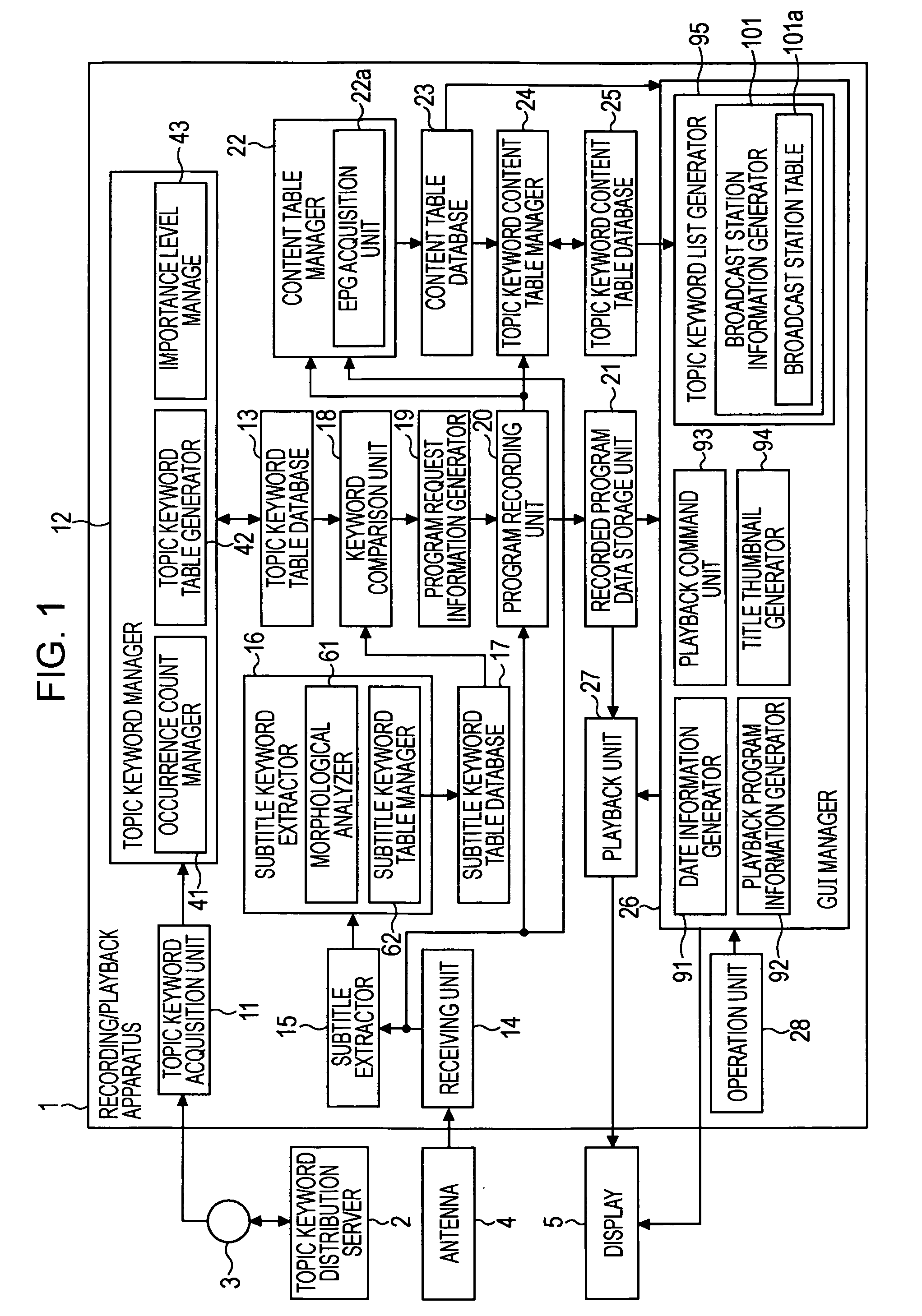
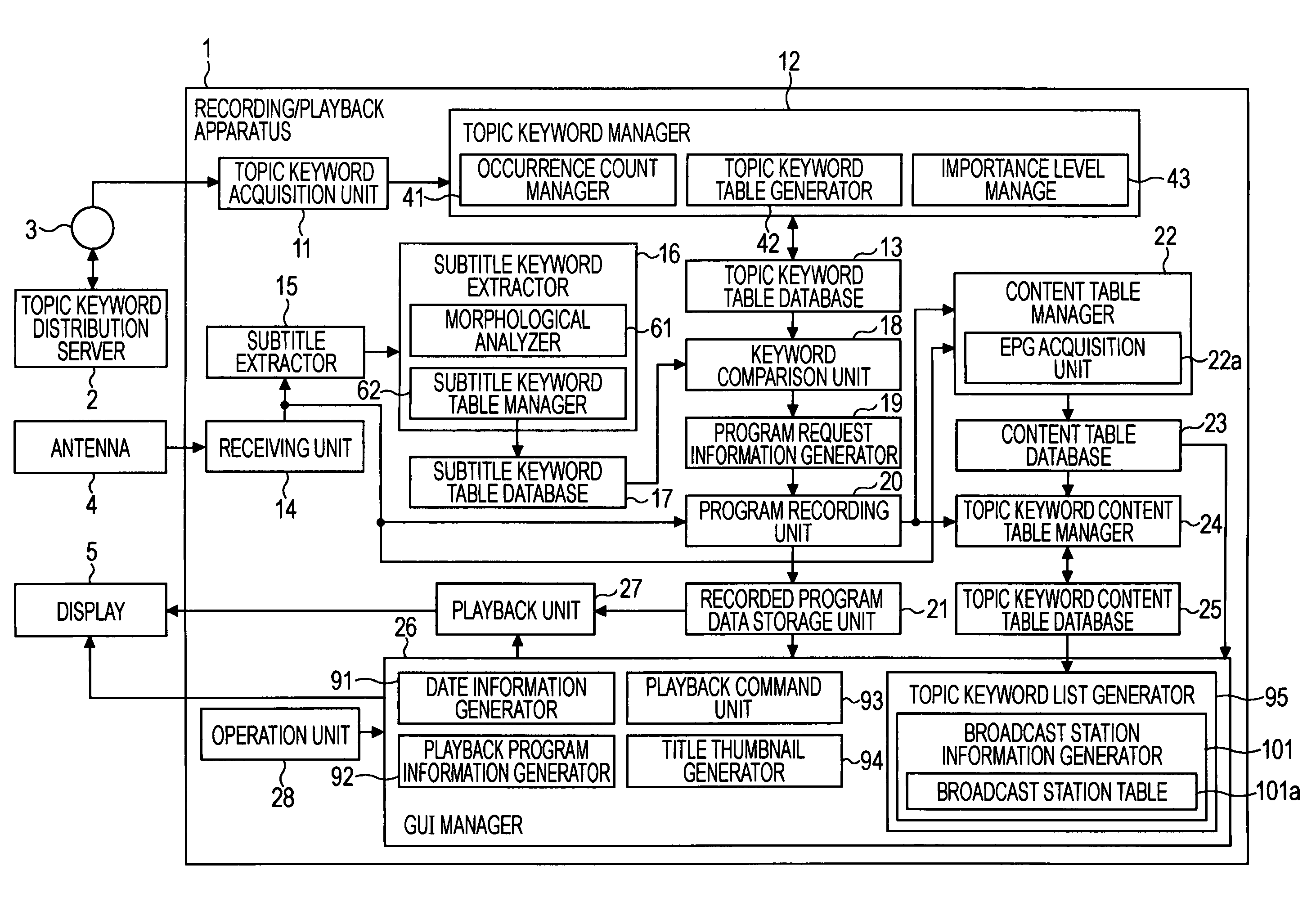
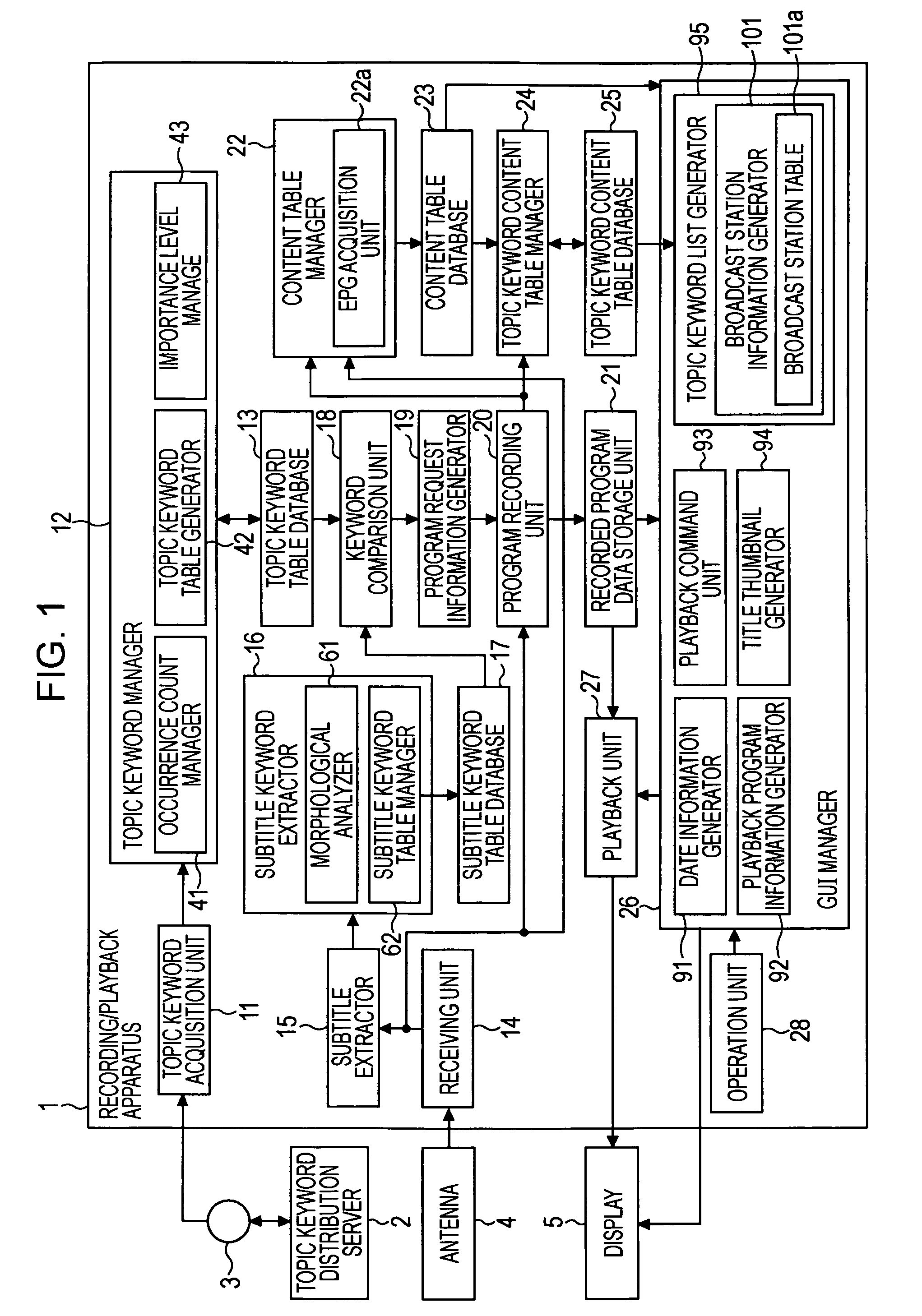
InactiveUS20080215526A1Lower Level RequirementsReduce freshnessTelevision system detailsDigital data information retrievalInformation processingAcquisition time
In an information processing apparatus, an acquisition unit acquires a keyword, and a calculation unit calculates the importance level of each keyword by adding a value determined depending on an increase in the number of occurrences to the importance level and subtracting a value determined depending on an increase in the difference between a current time and a last acquisition time to the importance level. An extraction unit extracts text information of a subtitle in a program. A subtitle morphological analysis unit morphologically analyzes the text information of the subtitle. A comparison unit compares each acquired keyword with each keyword detected via the morphological analysis. A recording unit records the program if the comparison indicates that any acquired keyword is identical to any keyword detected via the morphological analysis. A registration unit registers the recorded program and information indicating the importance level in a table in association with the keyword.
Owner:SONY CORP
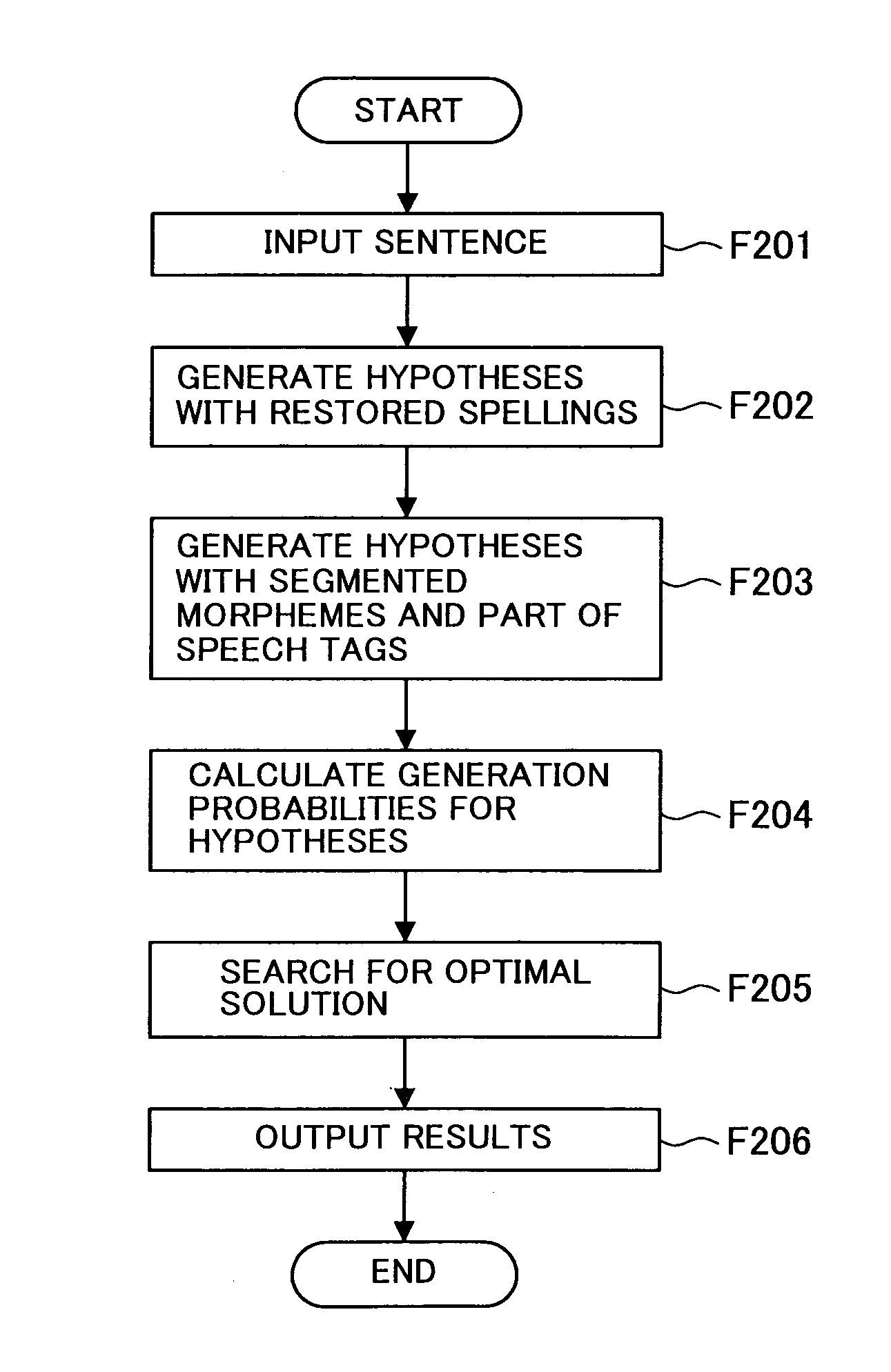
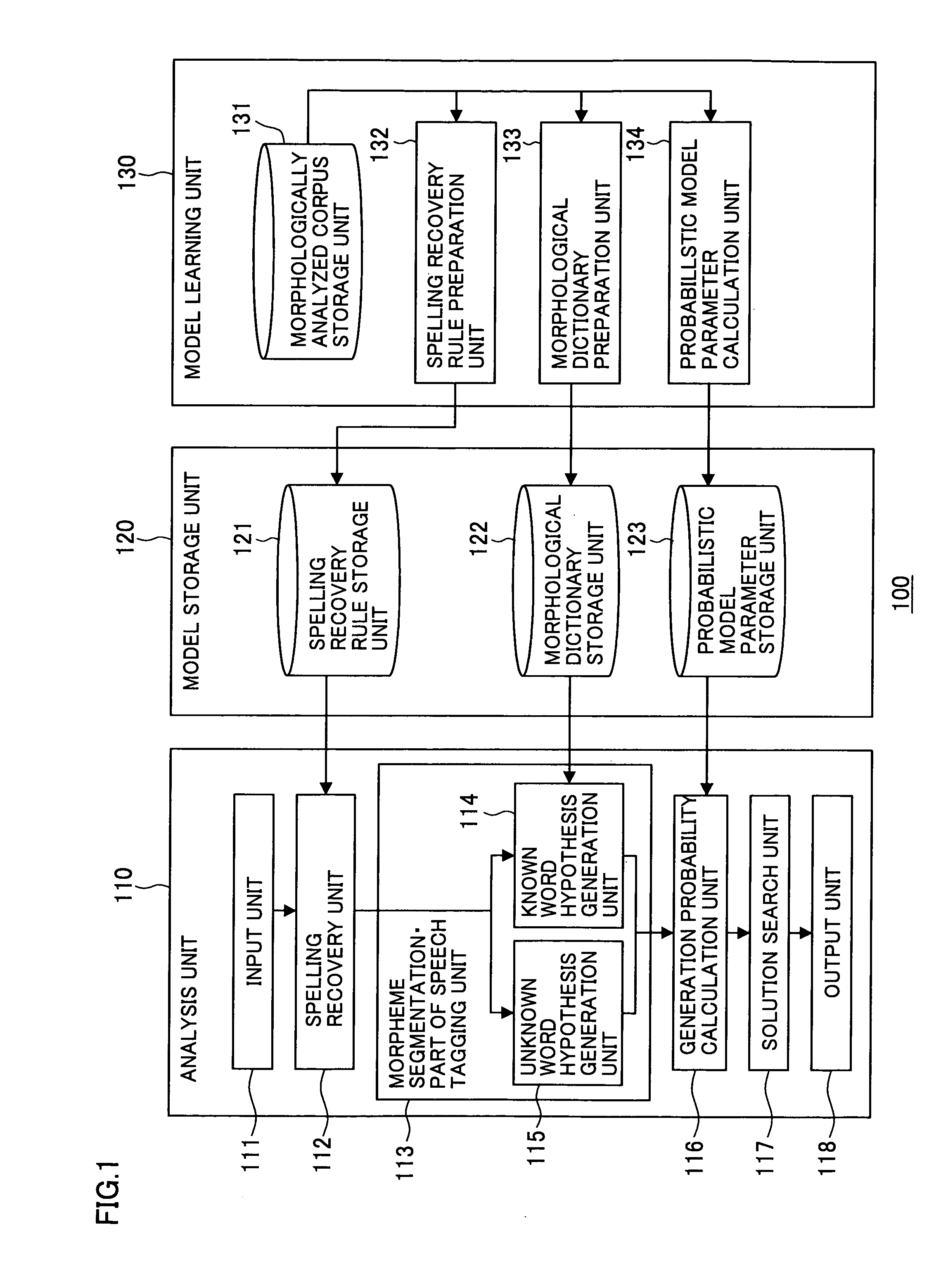
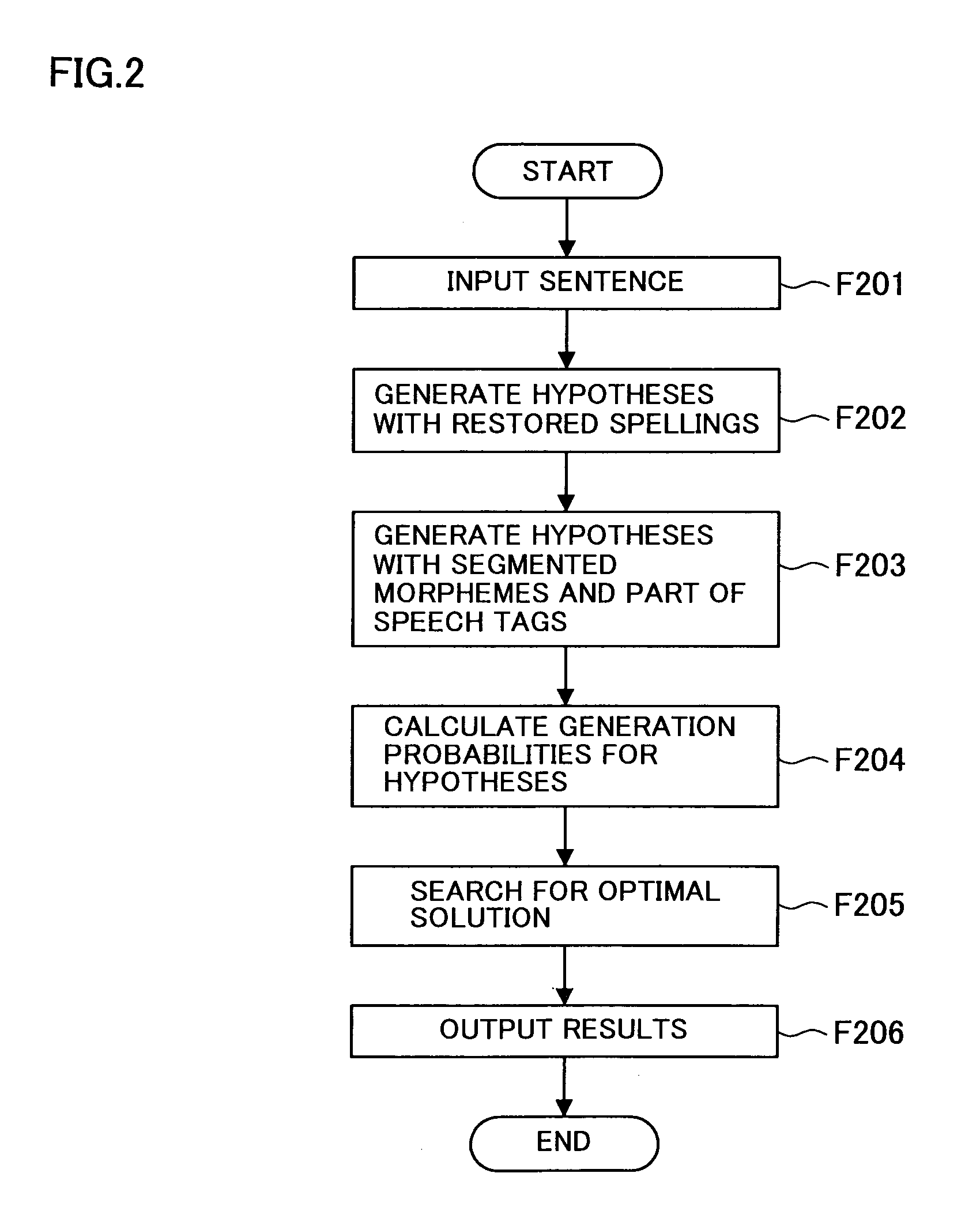
Morphological analysis apparatus, morphological analysis method and morphological analysis program
InactiveUS20070067153A1Exact searchEfficient preparationNatural language translationSpecial data processing applicationsMorphemeMorphological analysis
The morphological analysis apparatus according to the present invention, comprises a spelling recovery unit that recovers the spellings of words, a morphological analysis candidate generation unit that segments a word sequence composed of words, the spellings of which have been recovered, into morphemes, appends POS tags to the morphemes and generates a single morphological analysis candidate or a plurality of morphological analysis candidates, a generation probability calculation unit that calculates a generation probability for each morphological analysis candidate having been generated based upon the product of the probability of the pre-spelling recovery word being converted to the post-spelling recovery word and the probability of a morpheme sequence and a POS sequence being generated from the post-spelling recovery word sequence and a solution search unit that selects through a search the most likely candidate as a solution from all the morphological analysis candidates for which the generation probabilities have been calculated by the generation probability calculation unit.
Owner:OKI ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
Method for analysing images
InactiveUS20060093195A1Improve identification procedureImage enhancementImage analysisRadiologyMorphometric analysis
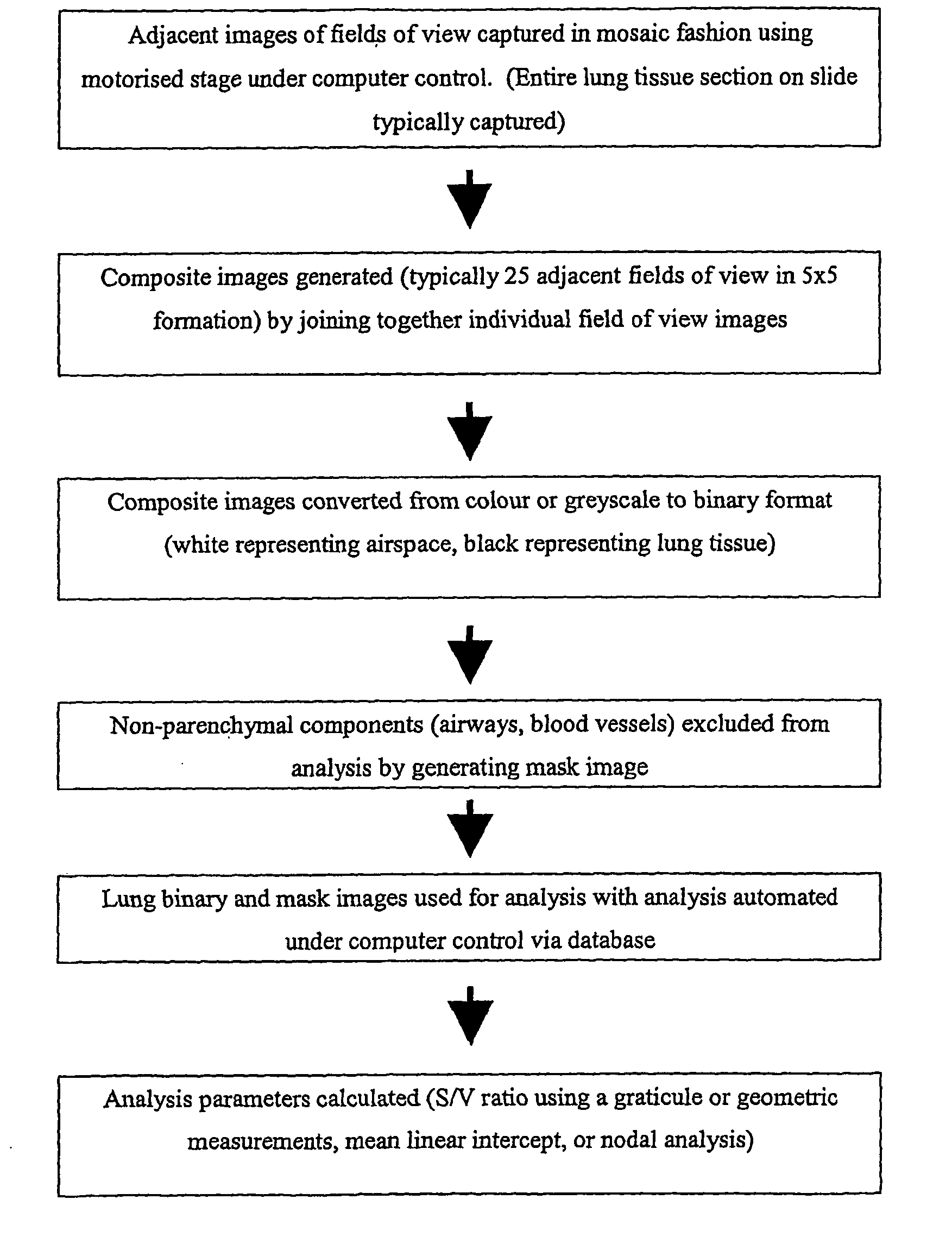
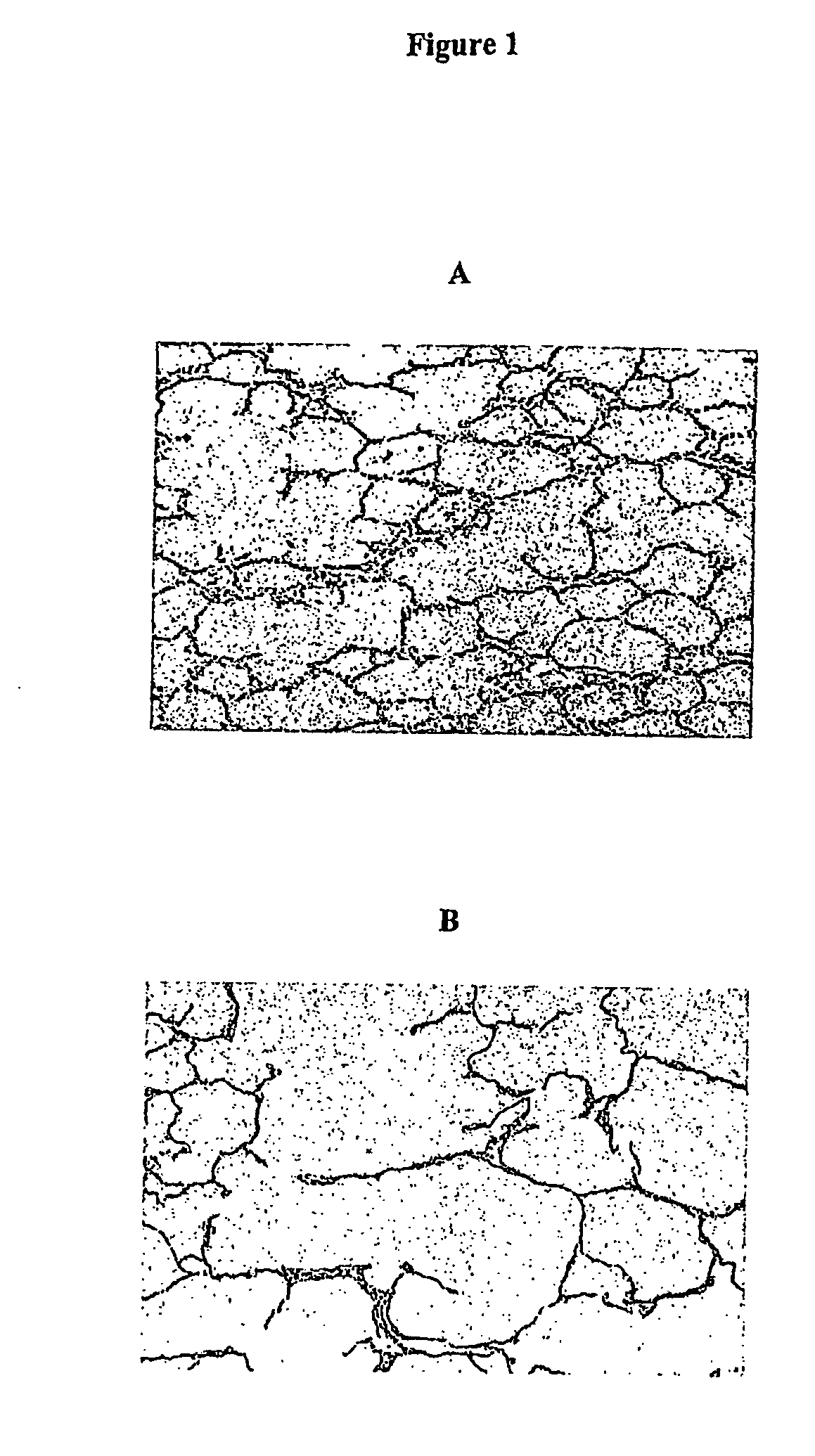
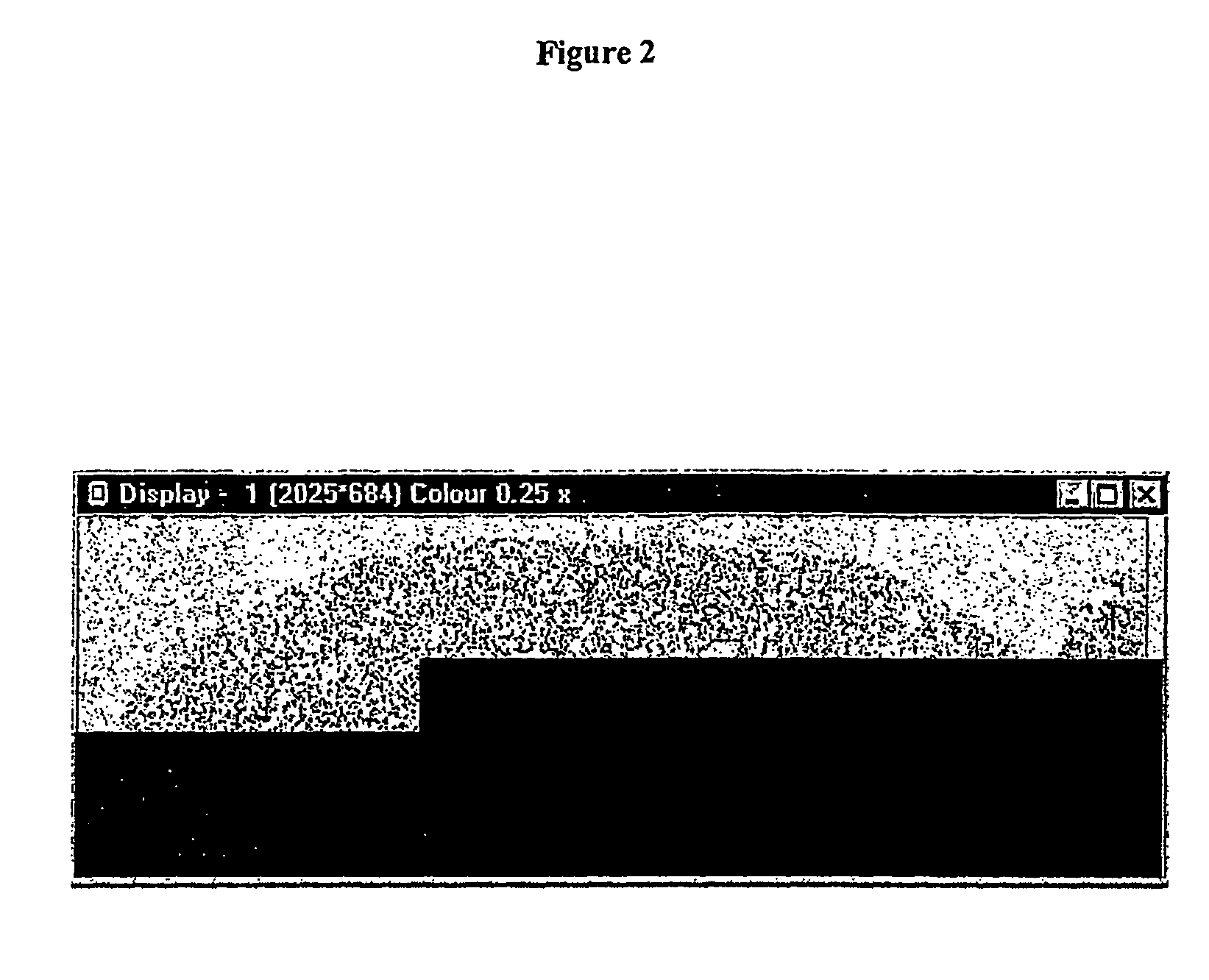
The invention relates to computer-based methods for lung morphometric analysis, employing Linear Mean Intercept (LMI), Surface Area to Volume (S / V) ratios, and mean branch length parameters to define lung emphysema.
Owner:ARGENTA DISCOVERY LTD
Numerical method of calculating heat, mass, chemical and electric transport for three-dimensional porous solid
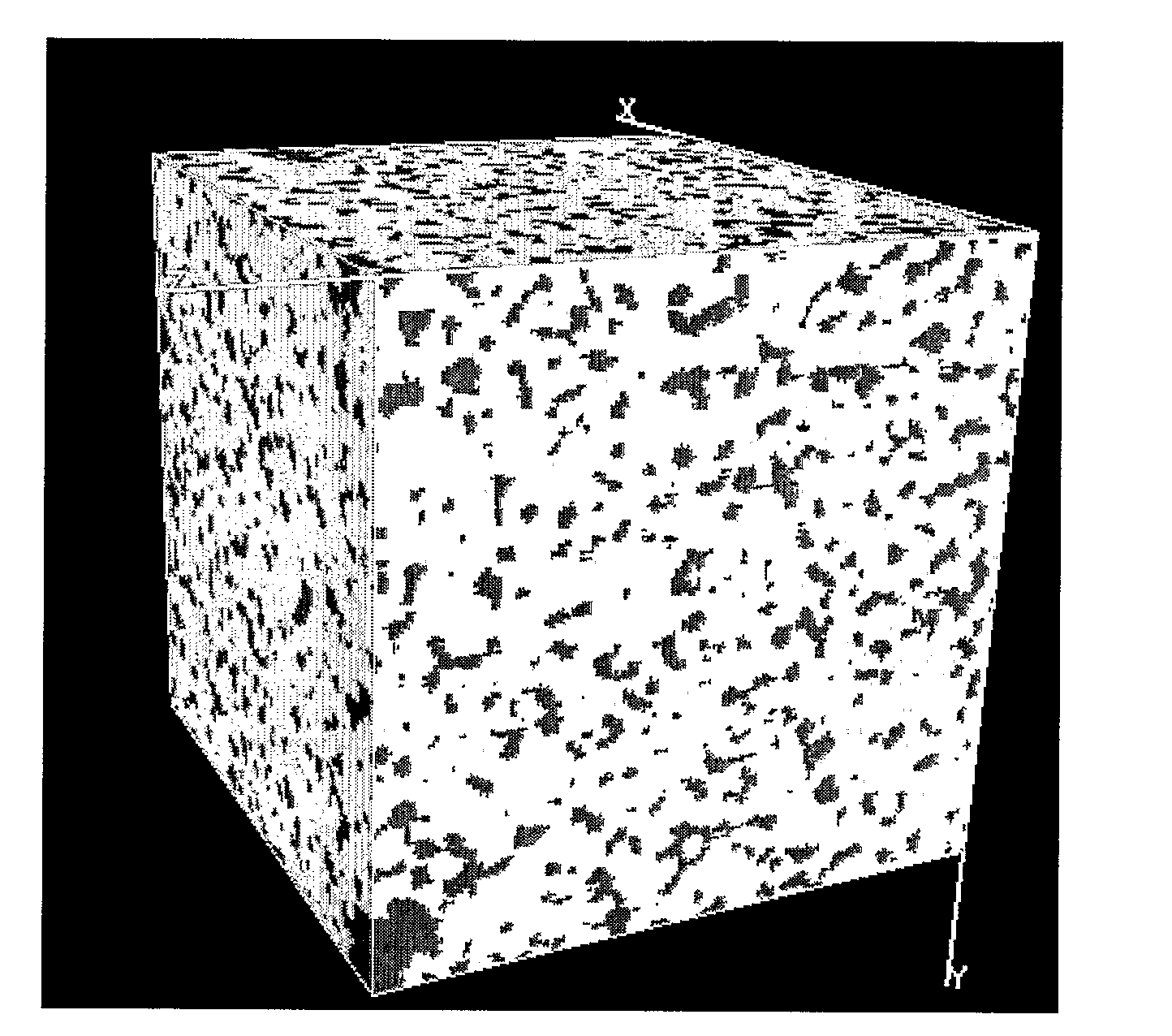
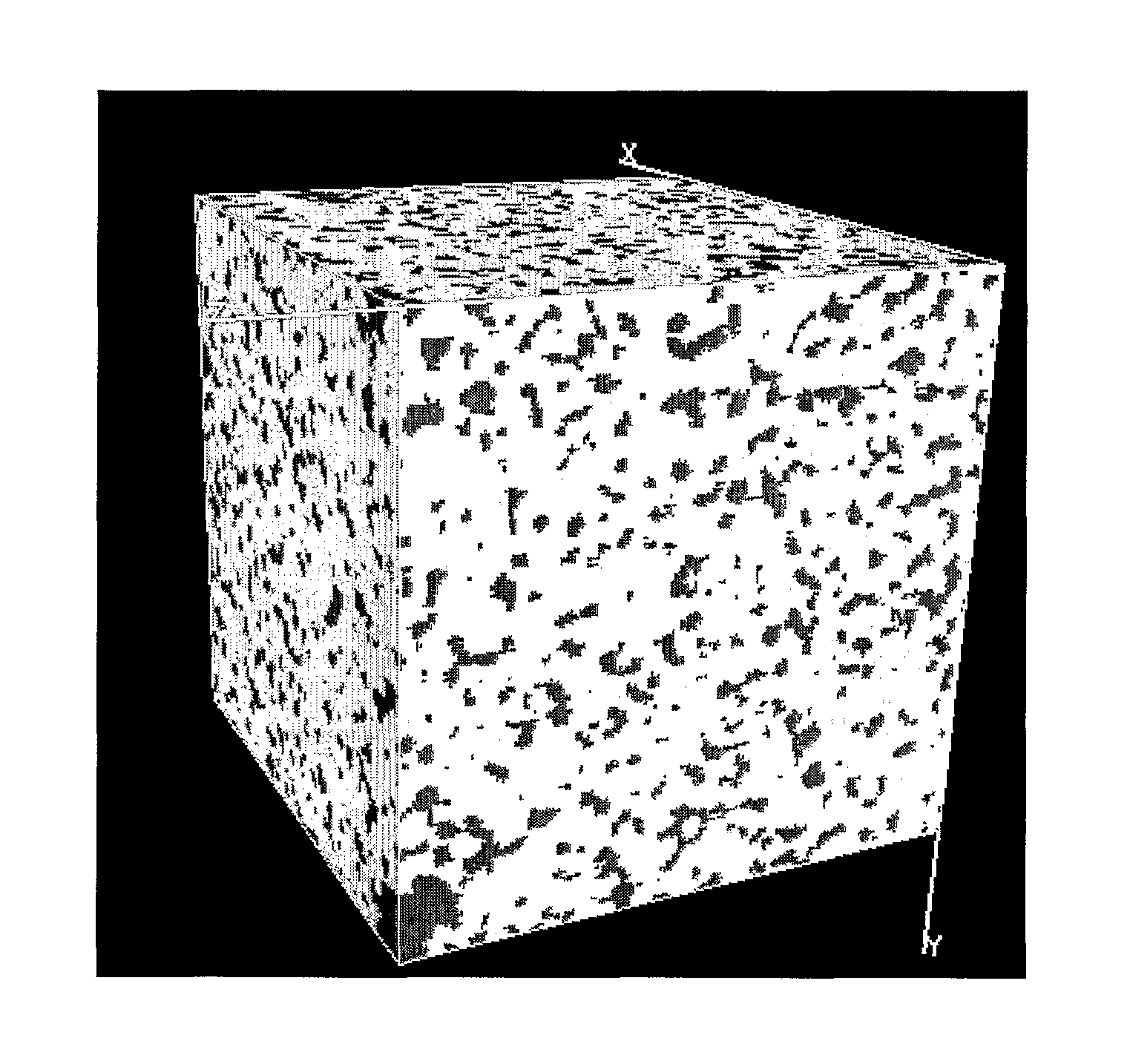
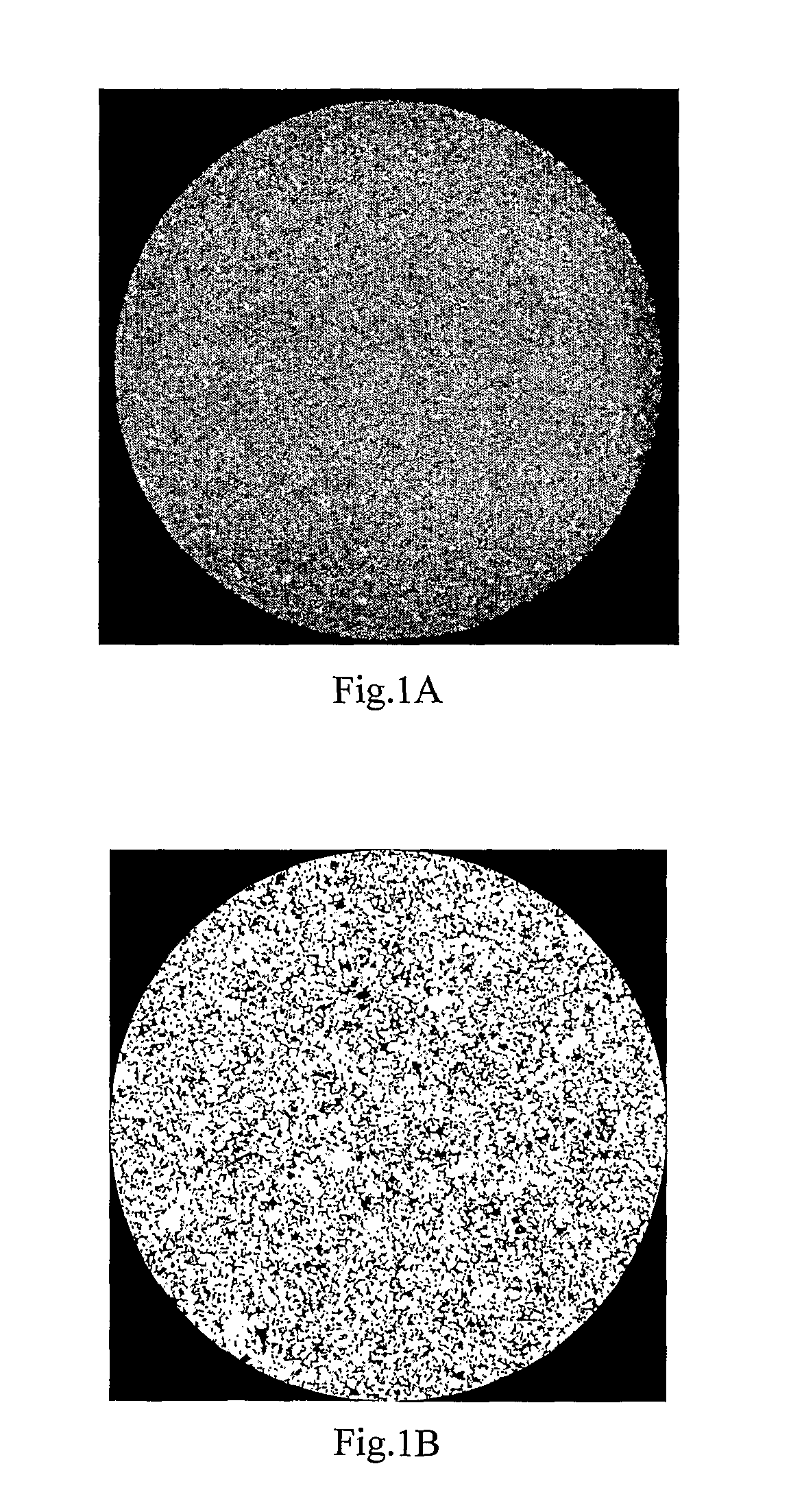
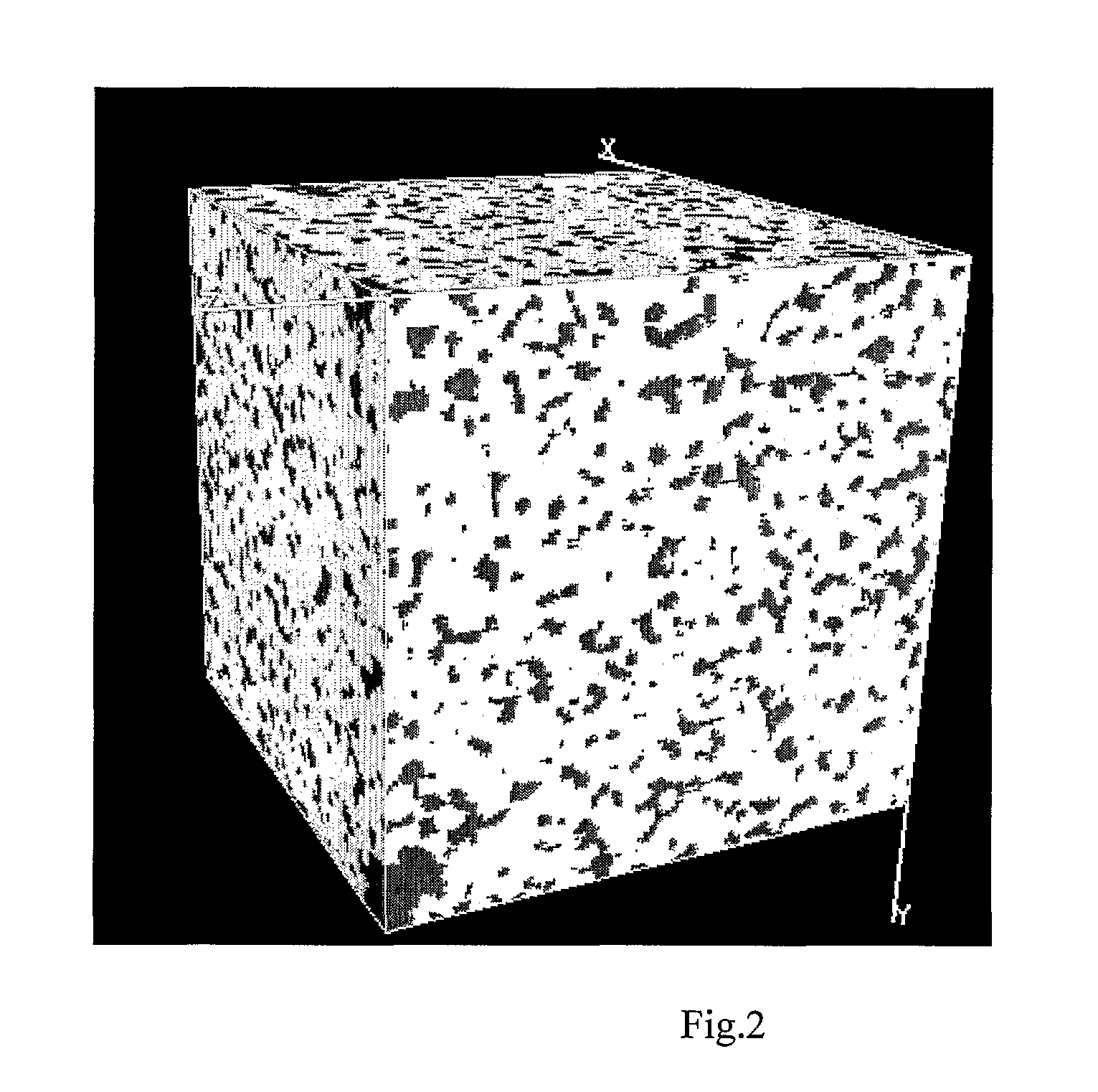
ActiveUS20120150510A1Computation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationPetrographic thin sectionMorphometric analysis
This invention relates to a method of estimating fluxes for the processes of matter and field transport through fluid-saturated or gas-saturated porous solid. The method comprises obtaining three-dimensional porous solid images by, but not limited, X-ray microtomography, 3D NMR imaging, 3D reconstruction from petrographic thin-section analysis etc., digital processing and morphological analysis of the 3D core images by consecutive application of the image filtering, segmentation and multiple property recognition for obtaining digital 3D models of porous solid samples and performing a set of morphological and geometrical statistical property analysis. For the above mentioned 3D model (models) heat, mass, chemical and electric fluxes are modeled (separately or in combination) under given boundary conditions by means of numerical solver. The new models, which are statistically equivalent to the abovementioned model (models) are generated by means of random field and stochastic geometry theory; heat, mass, chemical and electric fluxes are simulated for new models. The obtained fluxes are averaged over realizations to be used in macroscopic calculations.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
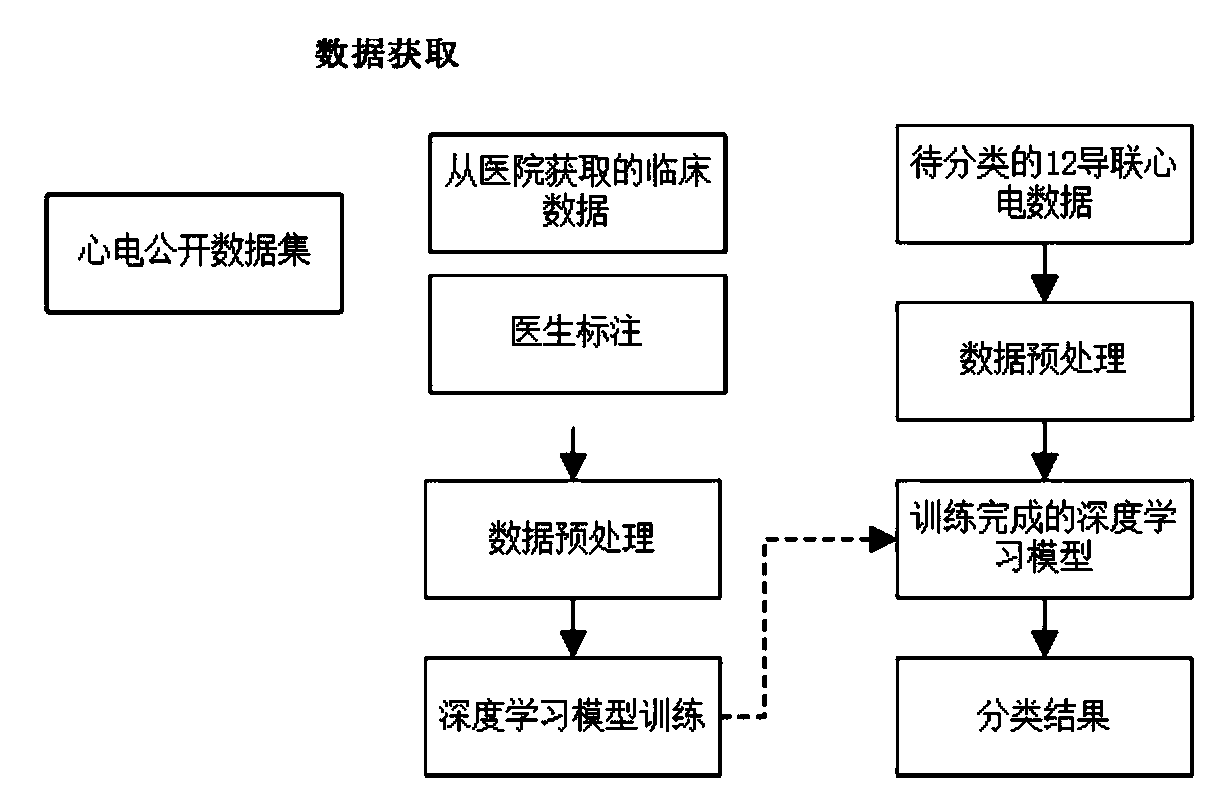
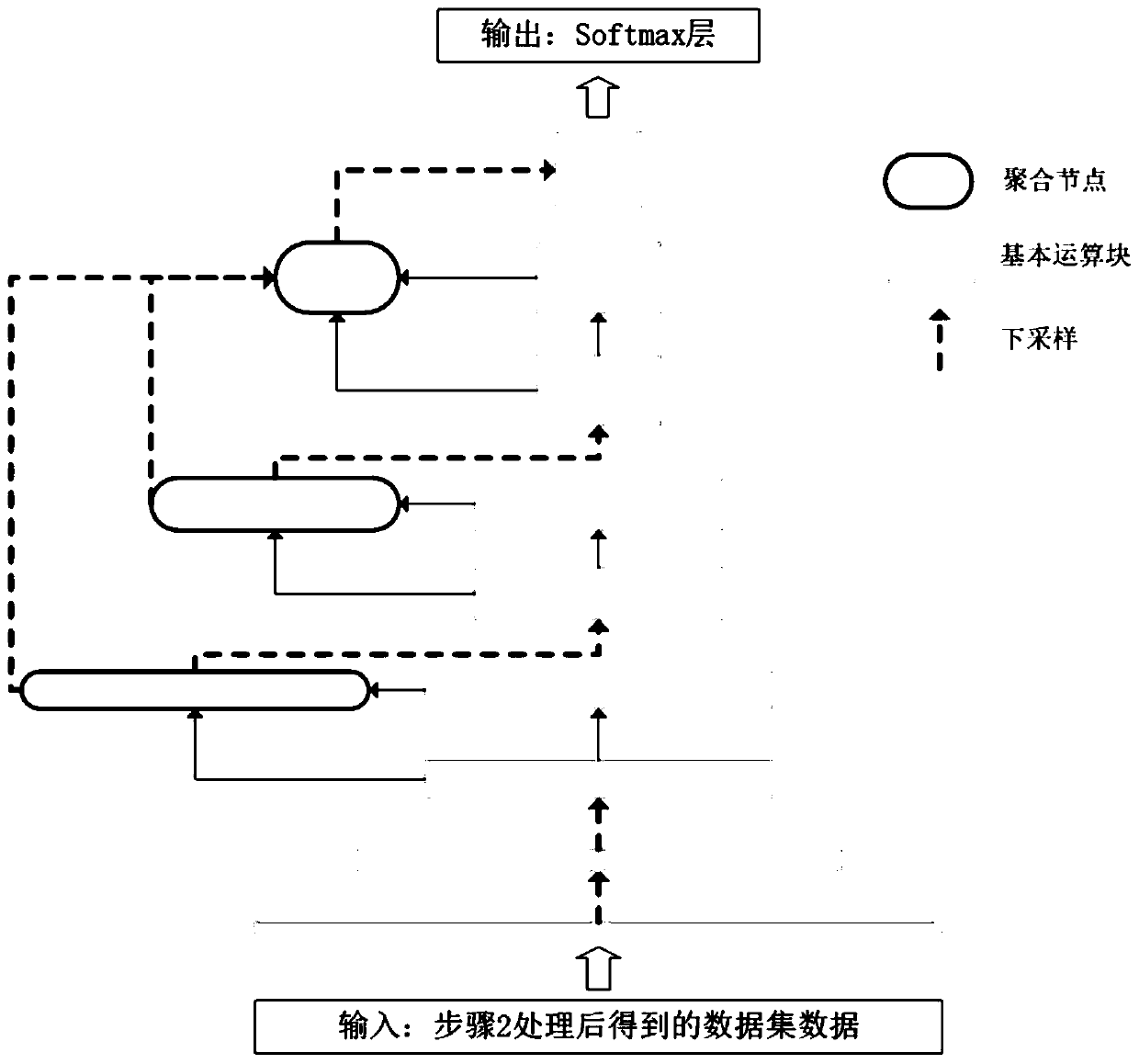
Electrocardiosignal automatic analysis method based on deep learning
PendingCN111460951AImprove accuracyImprove compatibilityCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesData setMorphological analysis
An electrocardiosignal automatic analysis method based on deep learning comprises the steps: downloading labeled electrocardiosignal data from a public data set, processing the electrocardiosignal data to obtain a data set, and dividing the data set into a training set, a verification set and a test set; constructing a deep learning model according to the DLA structure, and performing training toobtain a trained deep learning model; adjusting hyper-parameters, and selecting a model with the best classification effect on the verification set and the test set; and processing 12-lead electrocardiogram data to be classified to obtain a data set, and inputting the data of the data set into the model with the best classification effect to obtain the classification to which the electrocardiogramsignals of the electrocardiogram data belong. According to the method, low-level waveform structure features are extracted through one-dimensional convolution, shallow and deep layers are aggregated,the space and semantic features of the electrocardiosignal are obtained, morphological analysis is completed, correlation between morphologies is obtained, and the method can be applied to classification of electrocardiograms or one-dimensional time series electrocardiograms.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
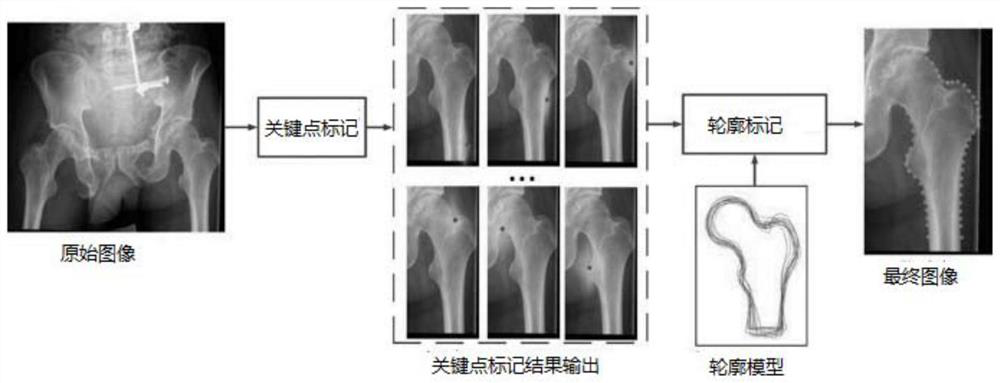
Automatic identification and model reconstruction method for anatomical features in medical image
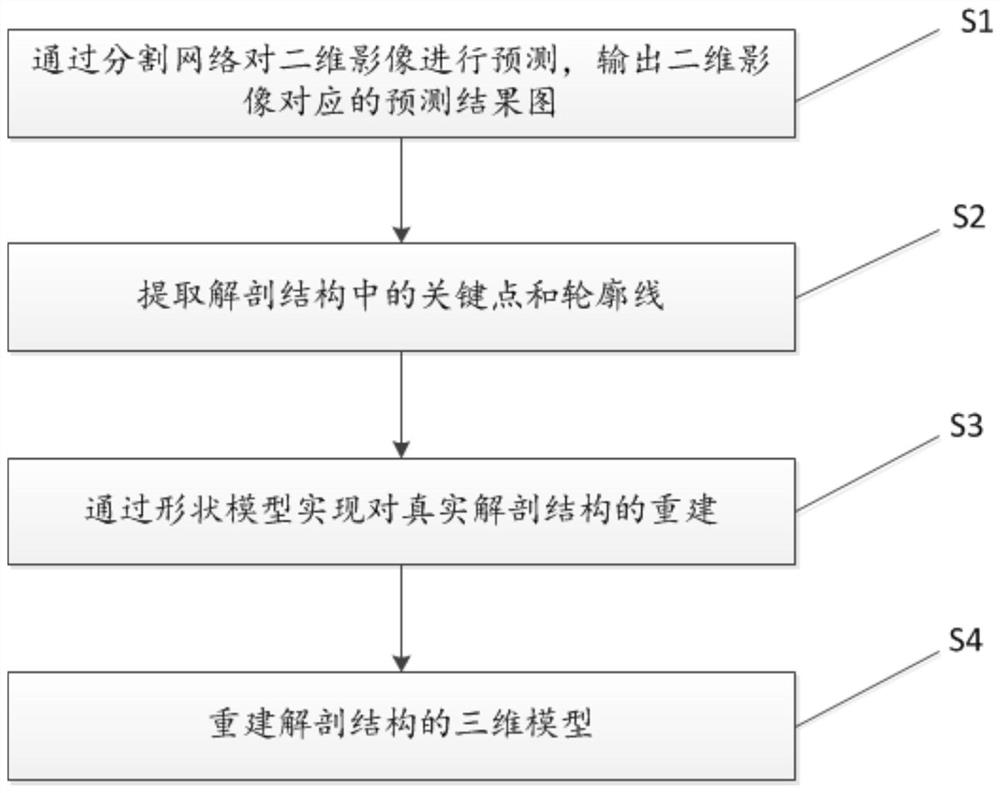
PendingCN112037200ARealize automatic identificationShorten the timeImage enhancementImage analysisAnatomical structuresModel reconstruction
The invention relates to the technical field of medical image intelligent analysis, and provides a medical image anatomical feature automatic identification and model reconstruction method comprisingthe following steps: S1, inputting a two-dimensional image into a segmentation network for prediction, and outputting a prediction result graph corresponding to the two-dimensional image; S2, performing morphological analysis on each anatomical structure segmented from the prediction result graph, and extracting positions and contour lines of key points; S3, reading the contour line and comparingthe contour line with the shape model: when the projection contour simulated by the shape model is close to the contour line, the current shape model is the reconstruction of the real anatomical structure; S4, executing the steps S1-S3 by using at least two two-dimensional images at different visual angles, so as to reconstruct the three-dimensional model of the anatomical structure. According tothe technical scheme, the anatomical feature points and the contour lines of the two-dimensional images can be automatically recognized, and the optimal three-dimensional model can be reconstructed through at least two two-dimensional images at different visual angles.
Owner:SHANGHAI TAOIMAGE MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Non-factoid question-answering system and computer program
In order to provide a non-factoid question answering system with improved precision, the question answering system (160) includes: a candidate retrieving unit (222), responsive to a question, extracting answer candidates from a corpus storage (178); a feature vector generating unit (232) for generating features from combinations of a question with each of the answer candidates; SVMs (176) trained to calculate a score of how correct a combination of the question with an answer candidate is, upon receiving the feature vector therefor; and an answer ranker unit (234) outputting the answer candidate with the highest calculated score as the answer. The features are generated on the basis of the results of morphological analysis and parsing of the question, a phrase in the question evaluated as being positive or negative as well as its polarity, and the semantic classes of nouns in the features.
Owner:NAT INST OF INFORMATION & COMM TECH
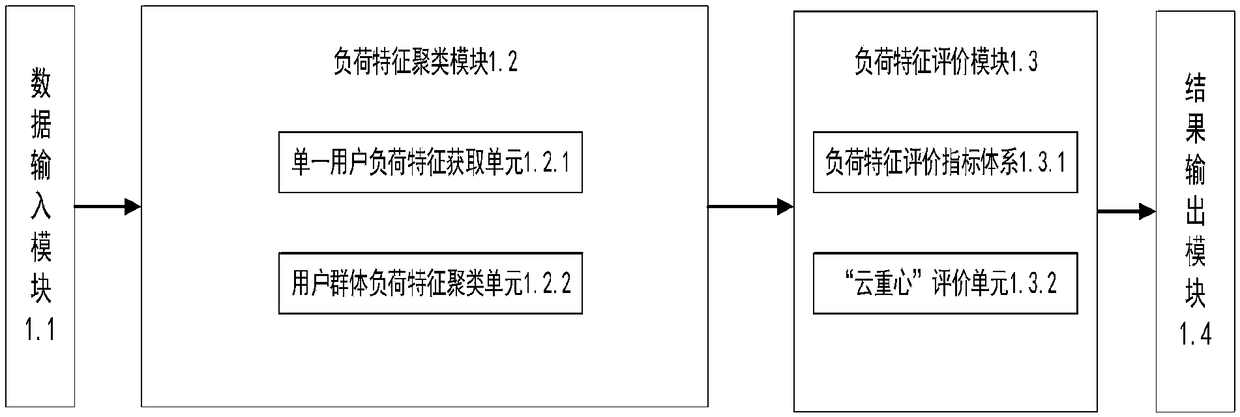
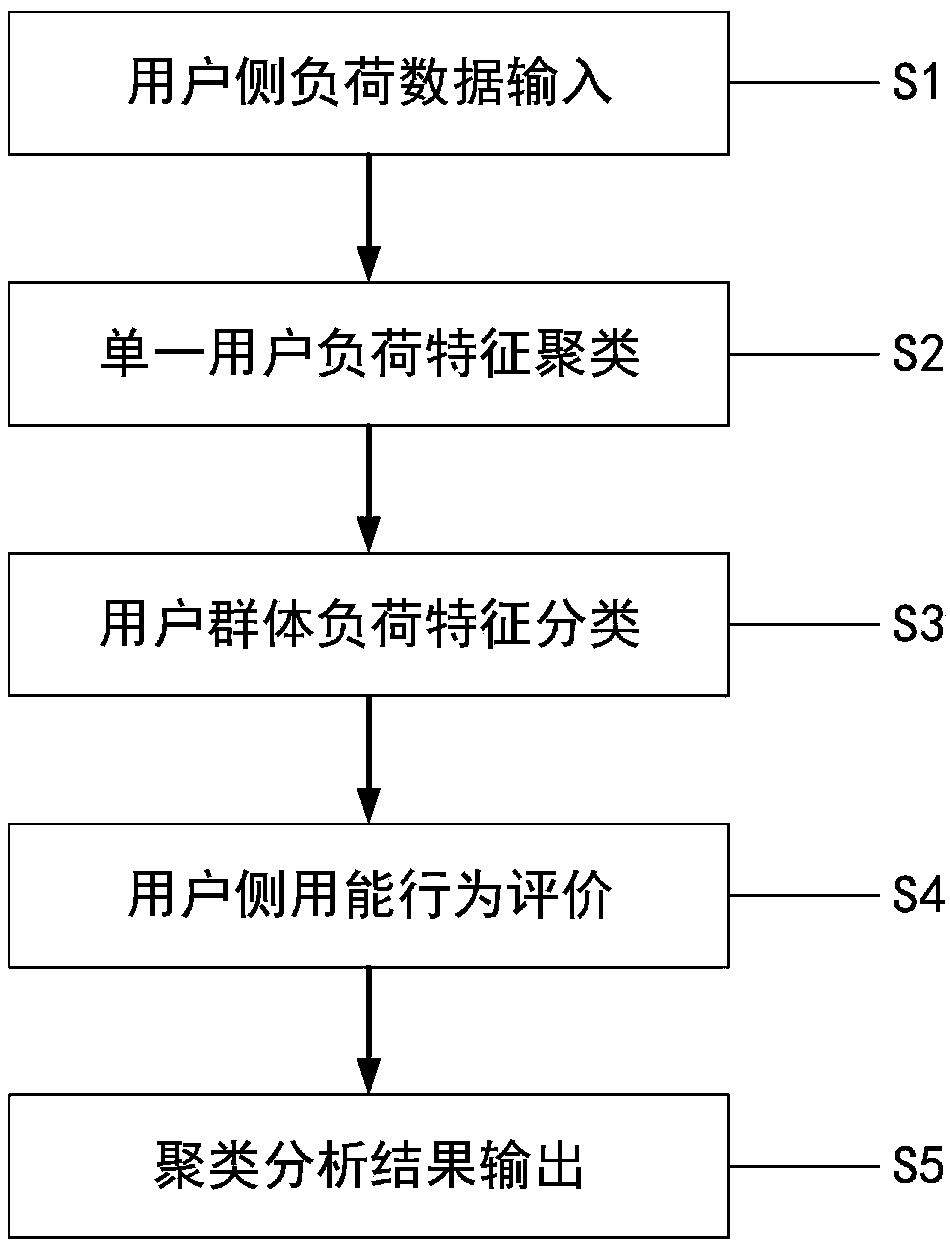
User side load feature clustering evaluation method based on morphological analysis
ActiveCN108898273AAccurate clusteringEvaluation results are intuitiveTechnology managementResourcesMorphometric analysisData mining
The invention discloses a user side load feature clustering evaluation method based on morphological analysis. The method comprises the following steps: using the data input module of the computer toinput daily load data of various types of users in a region every year; representing the typical energy consumption behavior of single user in one year; the morphological features of each curve are extracted firstly based on the typical daily load curve of each single user obtained in step S2 and the single users are classified according to the morphological features of the typical daily load curve so as to obtain the load feature curves of different types of users; the final evaluation result is generated by using the "cloud center" generator of the "cloud center" evaluation unit; and the computer result output module outputs the visual user side load feature clustering result and the "cloud center" evaluation result. The invention has the advantages of making full use of massive user side data, accurately analyzing the load data, mining the user side load features and evaluating the energy consumption behavior of the user side.
Owner:STATE GRID ENERGY RES INST +1
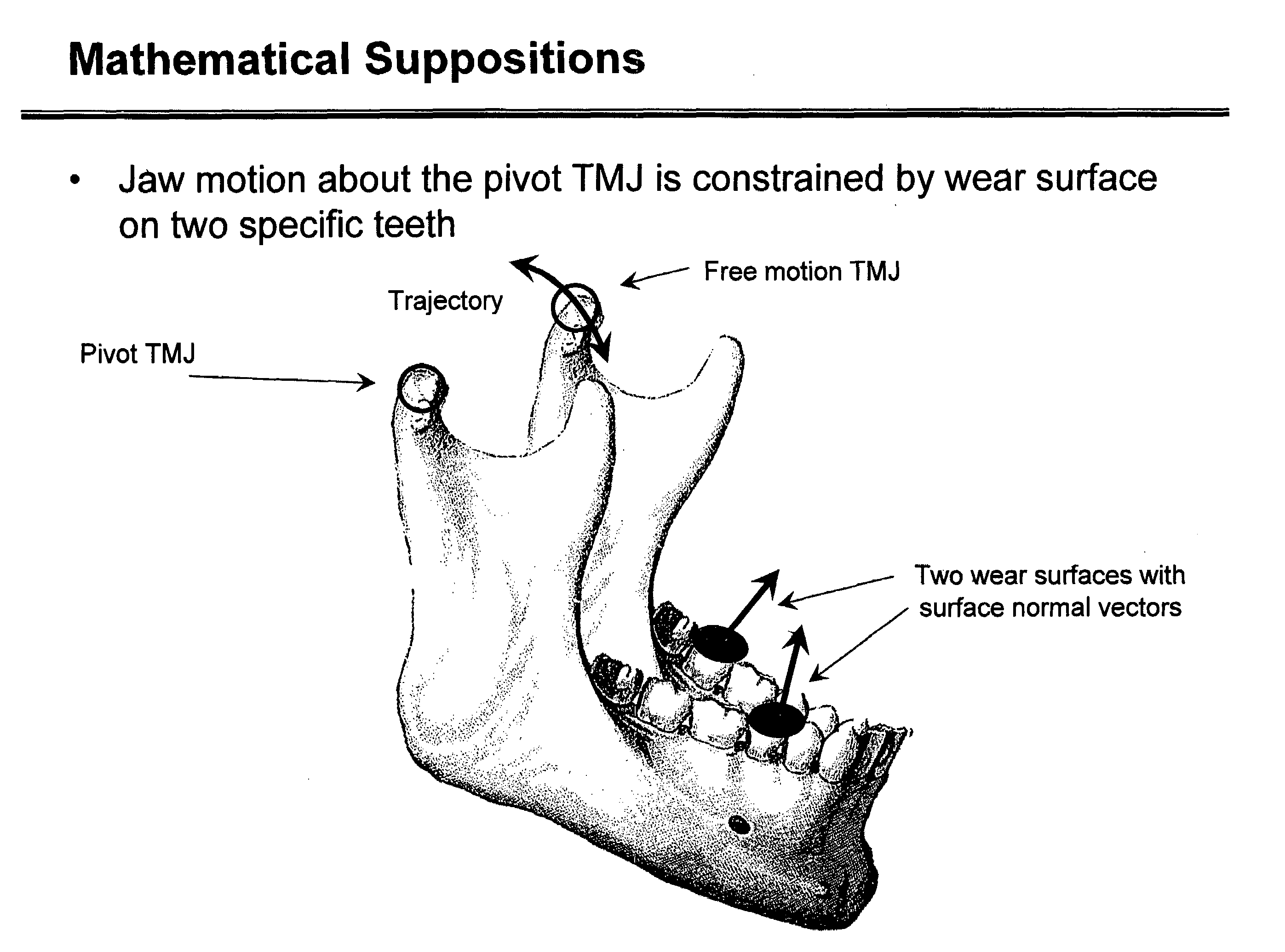
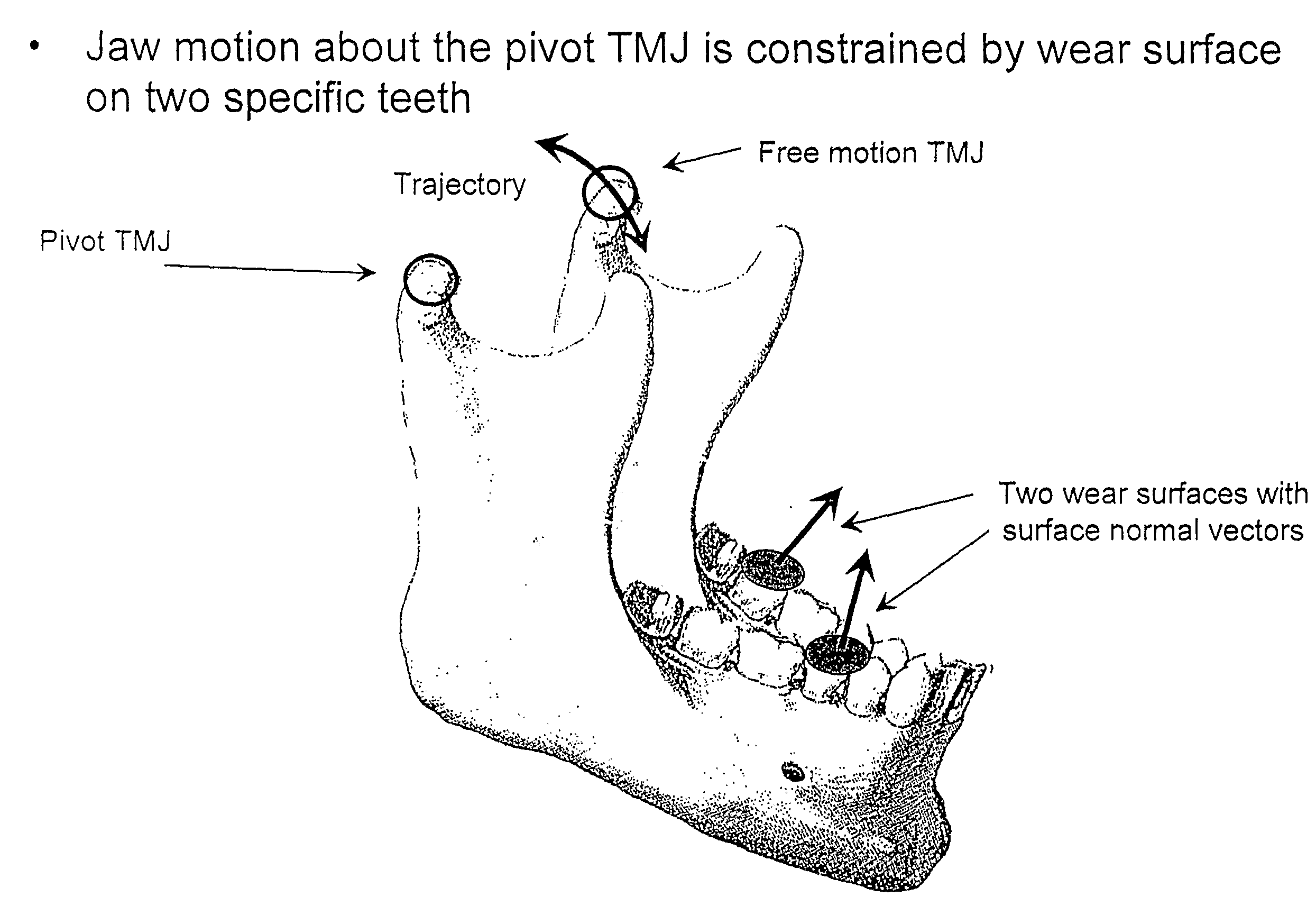
Method and system for morphometric analysis of human dental occlusal function and uses thereof
InactiveUS7412298B2Improve contourEasy to placeImpression capsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesDenturesMorphometric analysis
A method is disclosed for determining and predicting temporomandibular joint (TMJ) motion and to use the predictive model to prepare improved TMJ replacement joints, improved crown, cap or bridge contouring, improved teeth alignments and placements, and improved mouth guard and dentures.
Owner:PRESSWOOD RONALD G +1
Method and system for morphometric analysis of human dental occlusal function and uses thereof
InactiveUS20070168073A1Improved teeth alignmentSimple designImpression capsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesDenturesMorphometric analysis
A method is disclosed for determining and predicting temporomandibular joint (TMJ) motion and to use the predictive model to prepare improved TMJ replacement joints, improved crown, cap or bridge contouring, improved teeth alignments and placements, and improved mouth guard and dentures.
Owner:PRESSWOOD RONALD G +1
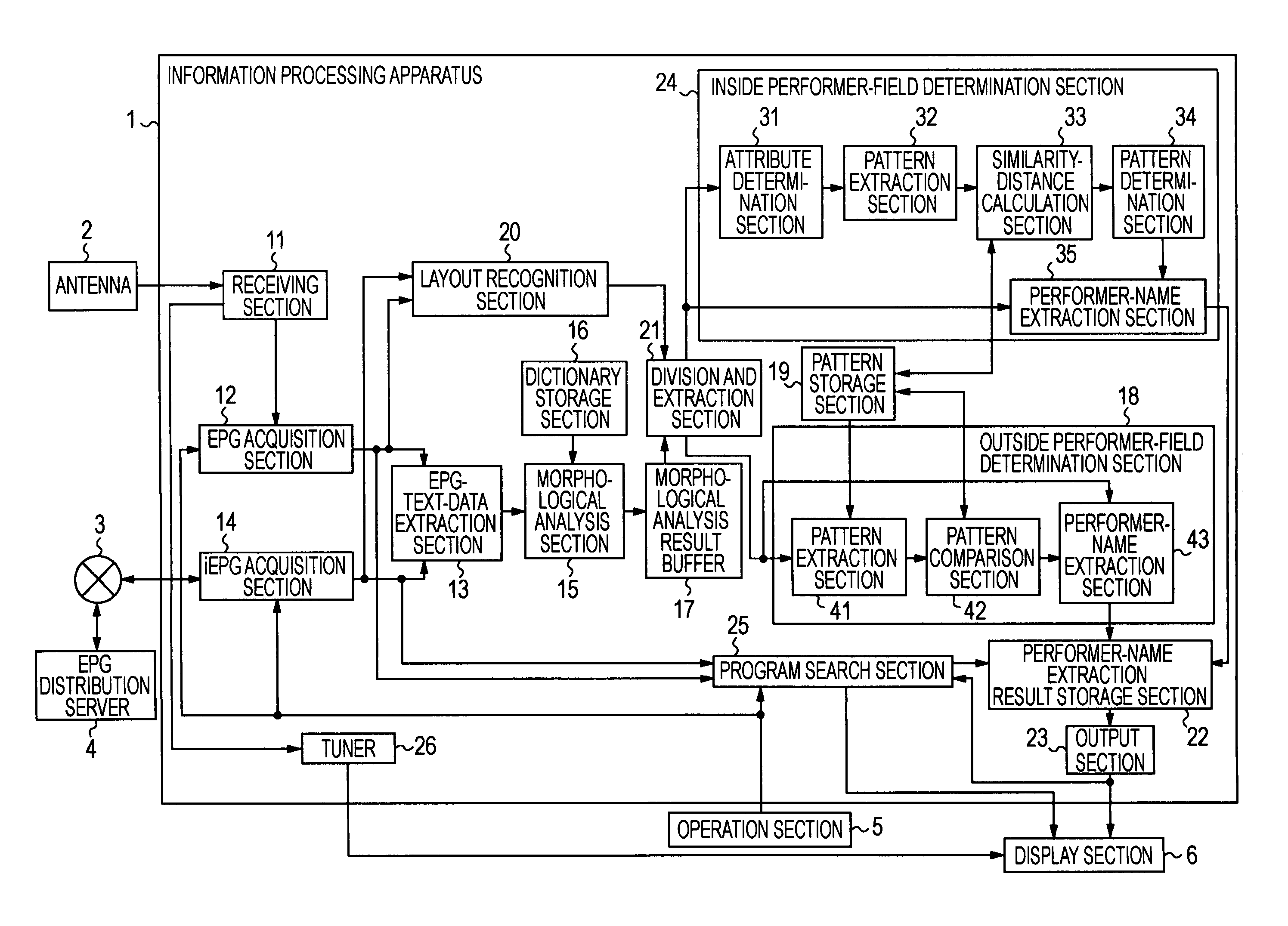
Information processing apparatus, method, and program
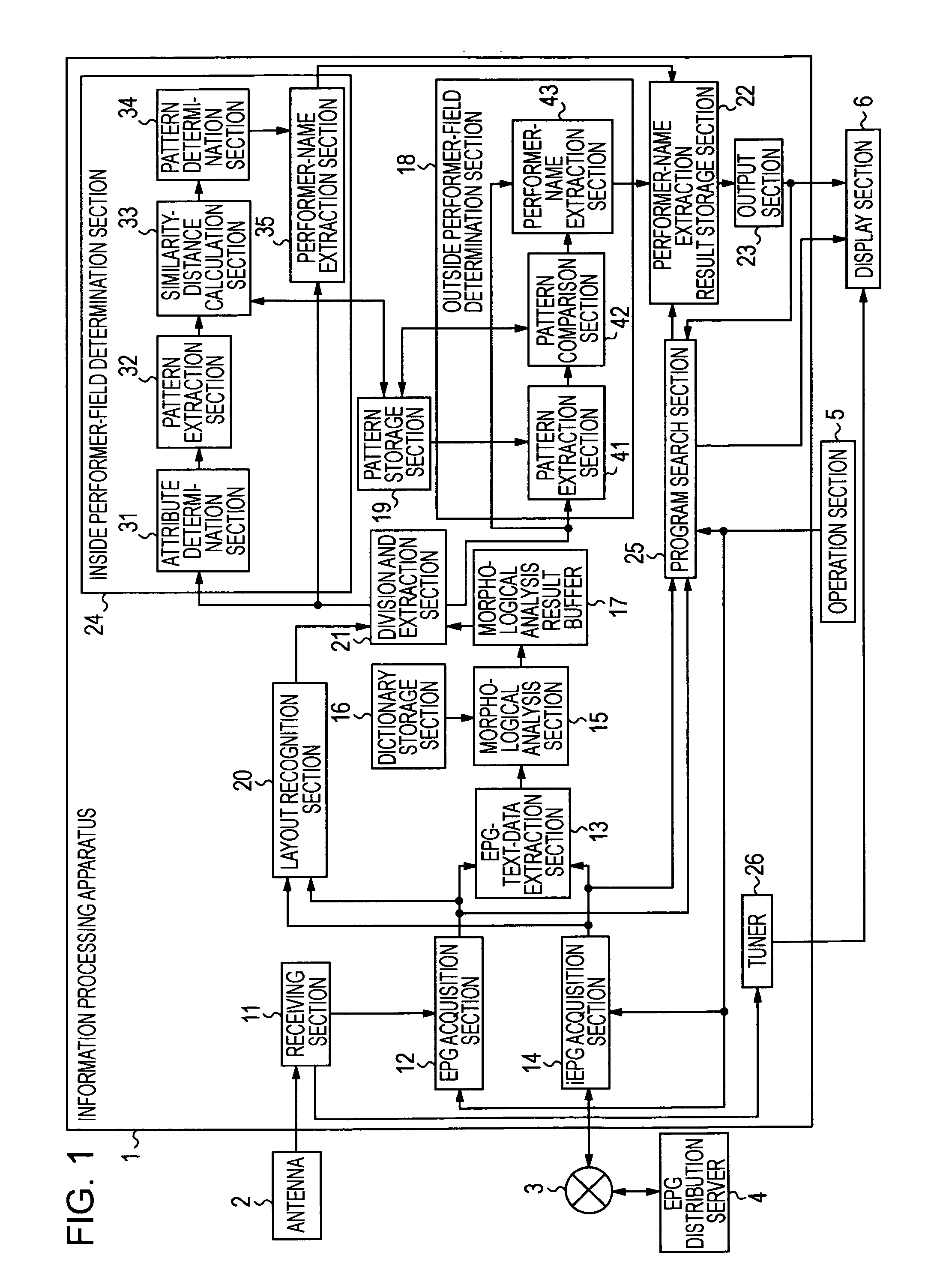
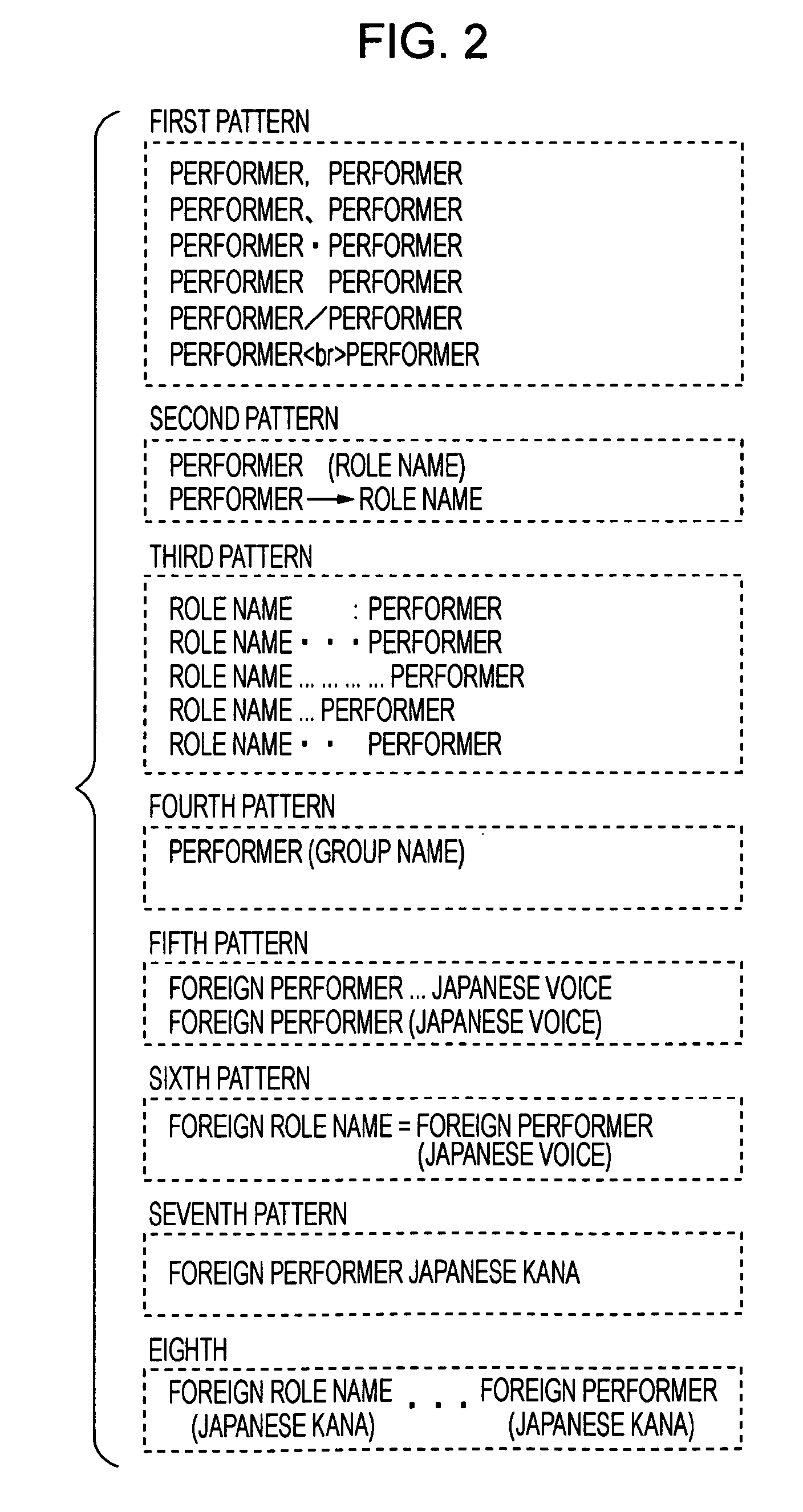
InactiveUS20090077067A1Extract information very effectivelyEfficient extractionDigital data processing detailsMetadata multimedia retrievalComputer visionMorphometric analysis
An information processing apparatus which may include acquisition means for acquiring meta-data of a content; morphological analyzing means for performing morphological analysis on text information included in the meta-data of the content; comparison means for comparing a morphological analysis result of the morphological analyzing means and a plurality of list patterns of predetermined performer names; and when there is a list pattern of predetermined performer names having matched at least one part or more out of the morphological analysis result on the basis of the comparison result of the comparison means, first extraction means for extracting a performer name with the list pattern of the matched predetermined performer name.
Owner:SONY CORP
Information processing apparatus, information processing method, and information processing program
InactiveUS8209348B2Lower Level RequirementsReduce freshnessTelevision system detailsDigital data information retrievalInformation processingAcquisition time
Owner:SONY CORP
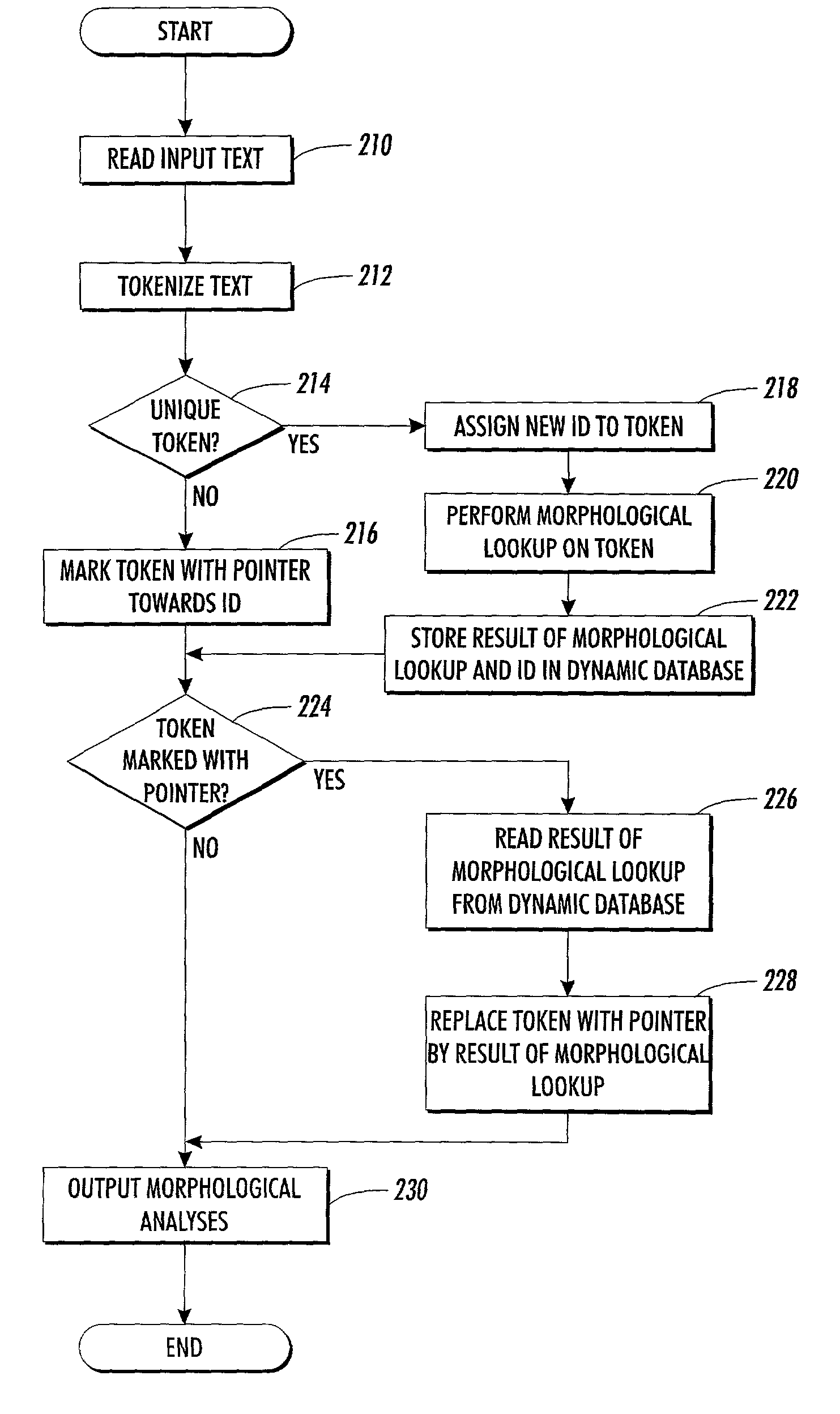
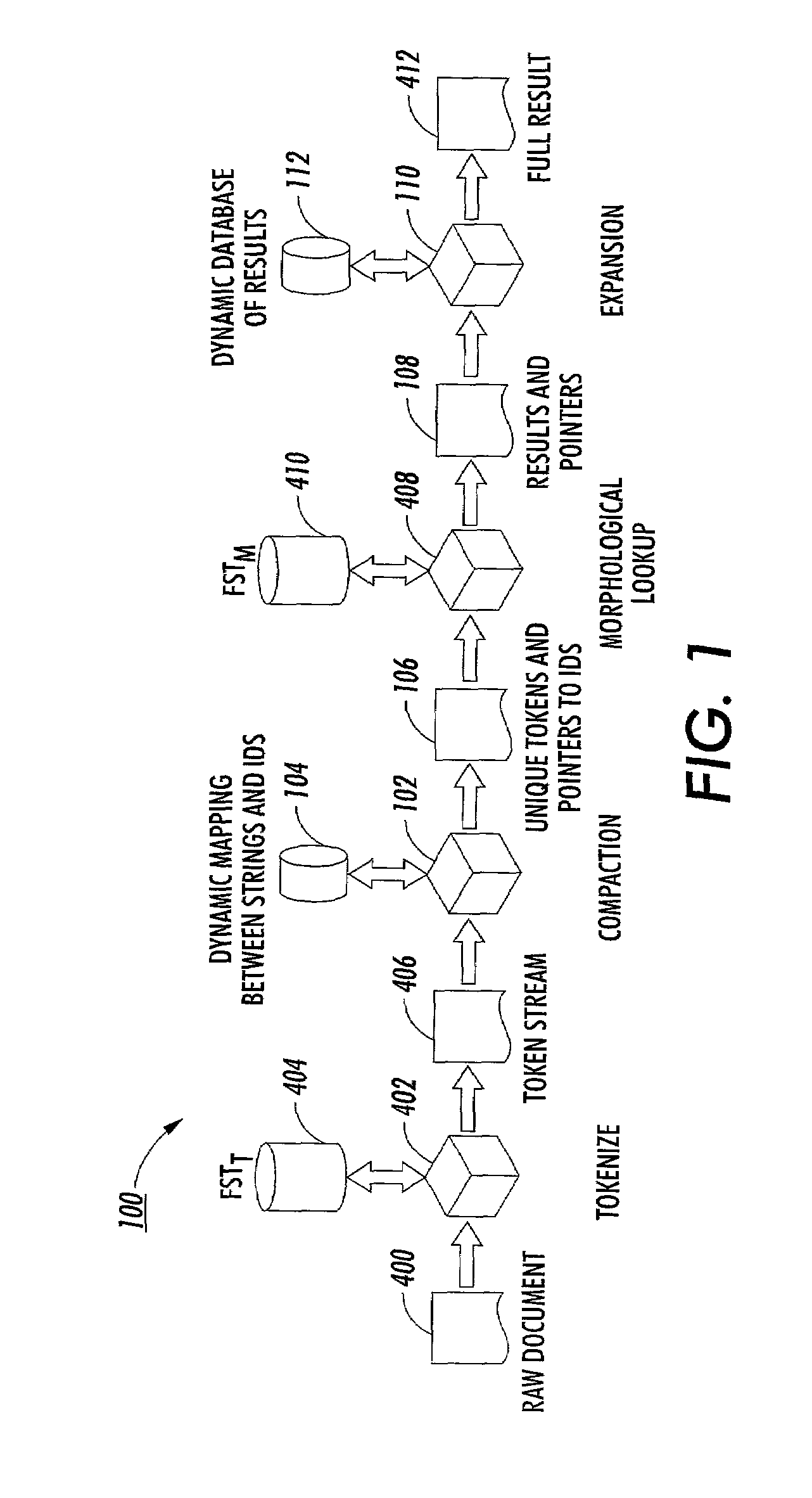
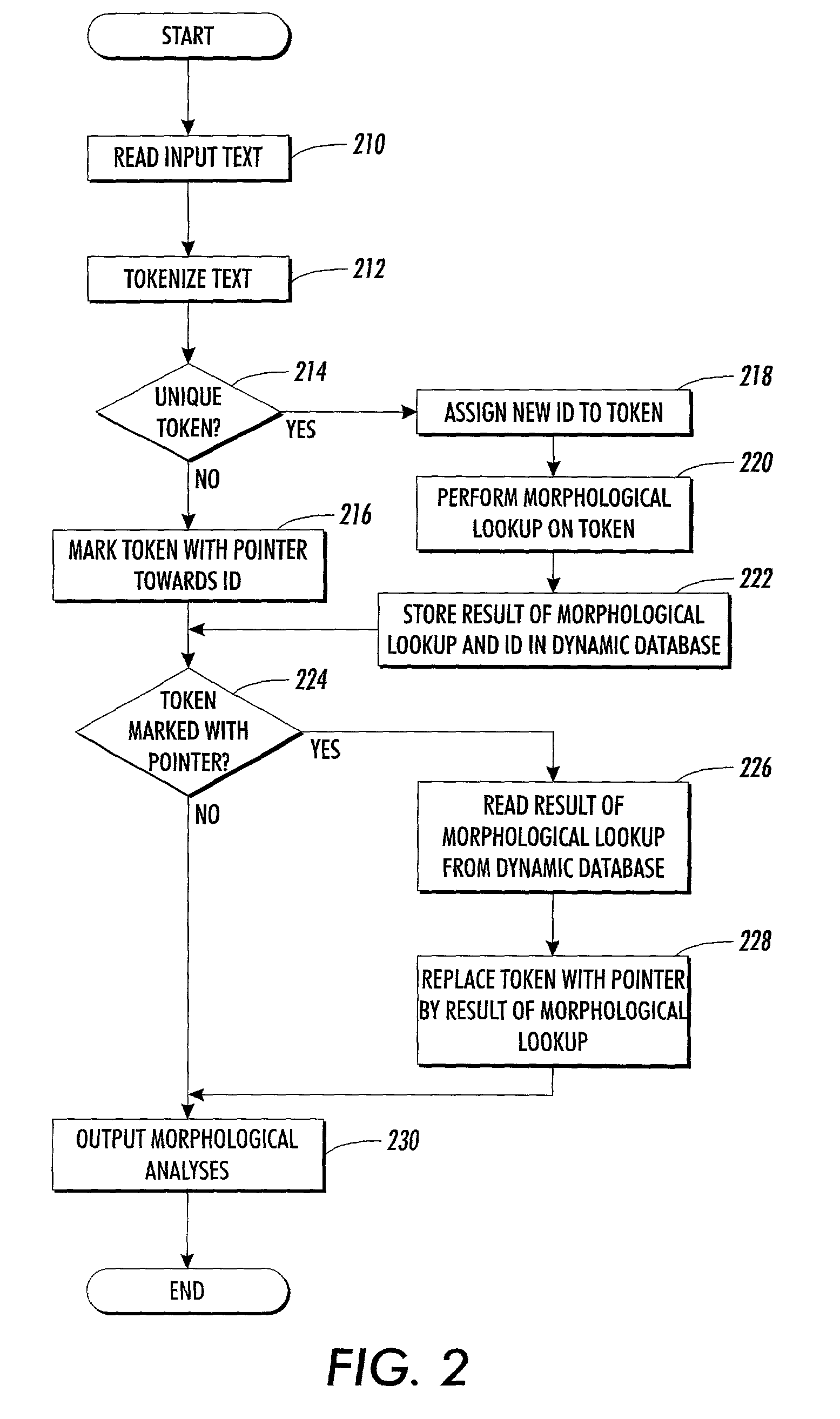
Method and system for accelerated morphological analysis
InactiveUS7013261B2Reduce processing timeShorten the timeSpeech analysisNatural language data processingMorphometric analysisComputer science
A system provides accelerated morphological analysis and in particular a speed-up of morphological look-up via a caching mechanism. The system determines whether each incoming token in a token stream is unique or recurring. Unique tokens, which occur for the first time in the token stream, are marked with a unique numerical identification (ID). A pointer is added to recurring tokens, which already occurred in the token stream, and directed towards the unique numerical ID which was defined for the respective token when occurring for the first time. A morphological look-up is performed on the unique tokens. Subsequently, the tokens carrying the pointer are detected and replaced with the results of morphological look-up stored under the unique numerical ID of the respective unique token.
Owner:XEROX CORP
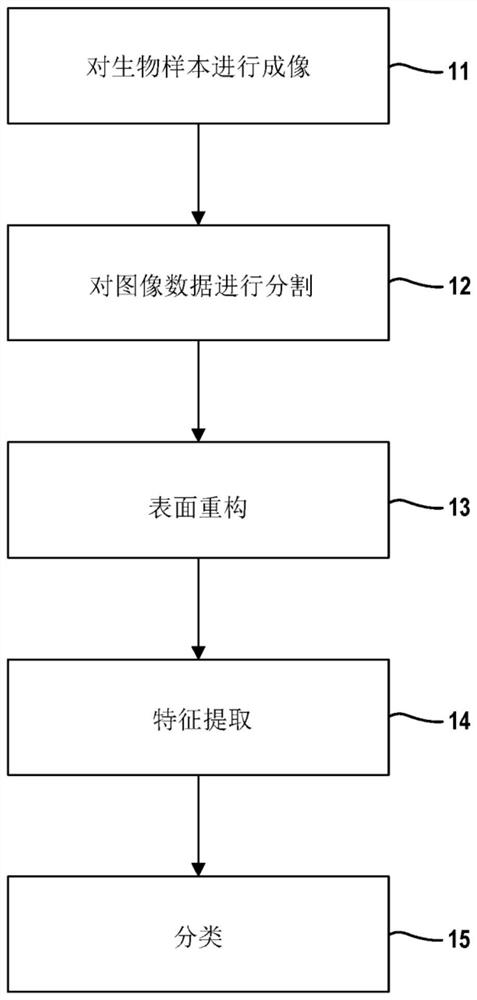
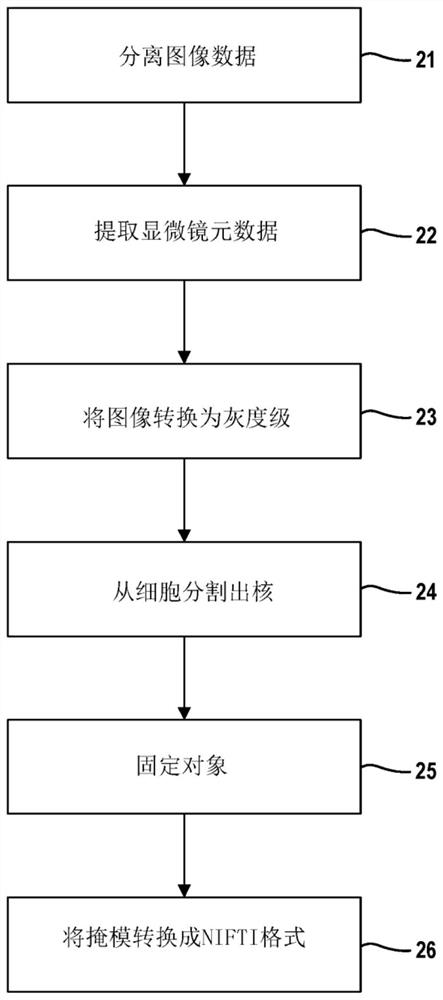
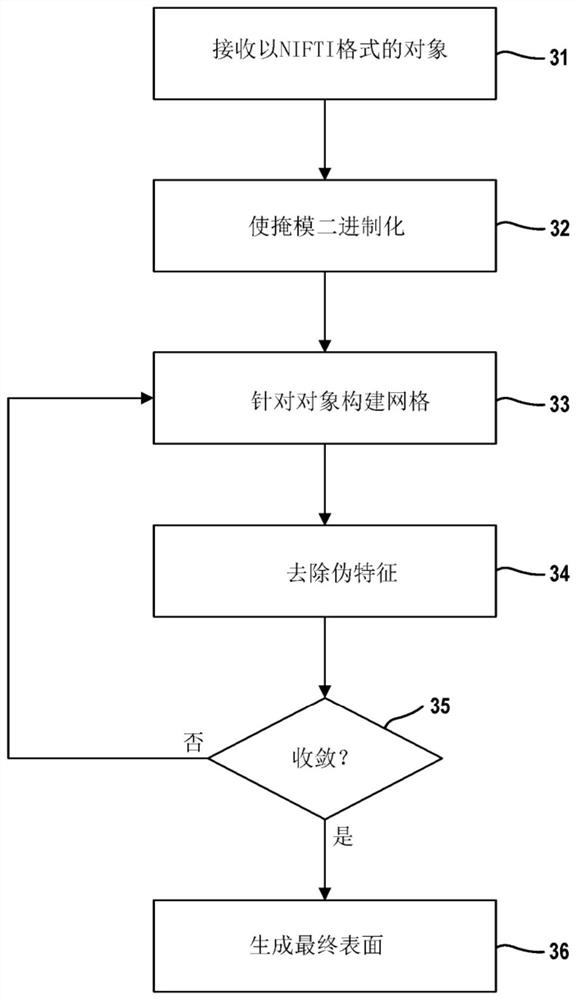
Three-dimensional cell and tissue image analysis for cellular and sub-cellular morphological modeling and classification
The ability to automate the processes of specimen collection, image acquisition, data pre-processing, computation of derived biomarkers, modeling, classification and analysis can significantly impactclinical decision-making and fundamental investigation of cell deformation. This disclosure combine 3D cell nuclear shape modeling by robust smooth surface reconstruction and extraction of shape morphometry measure into a highly parallel pipeline workflow protocol for end-to-end morphological analysis of thousands of nuclei and nucleoli in 3D. This approach allows efficient and informative evaluation of cell shapes in the imaging data and represents a reproducible technique that can be validated, modified, and repurposed by the biomedical community. This facilitates result reproducibility, collaborative method validation, and broad knowledge dissemination.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
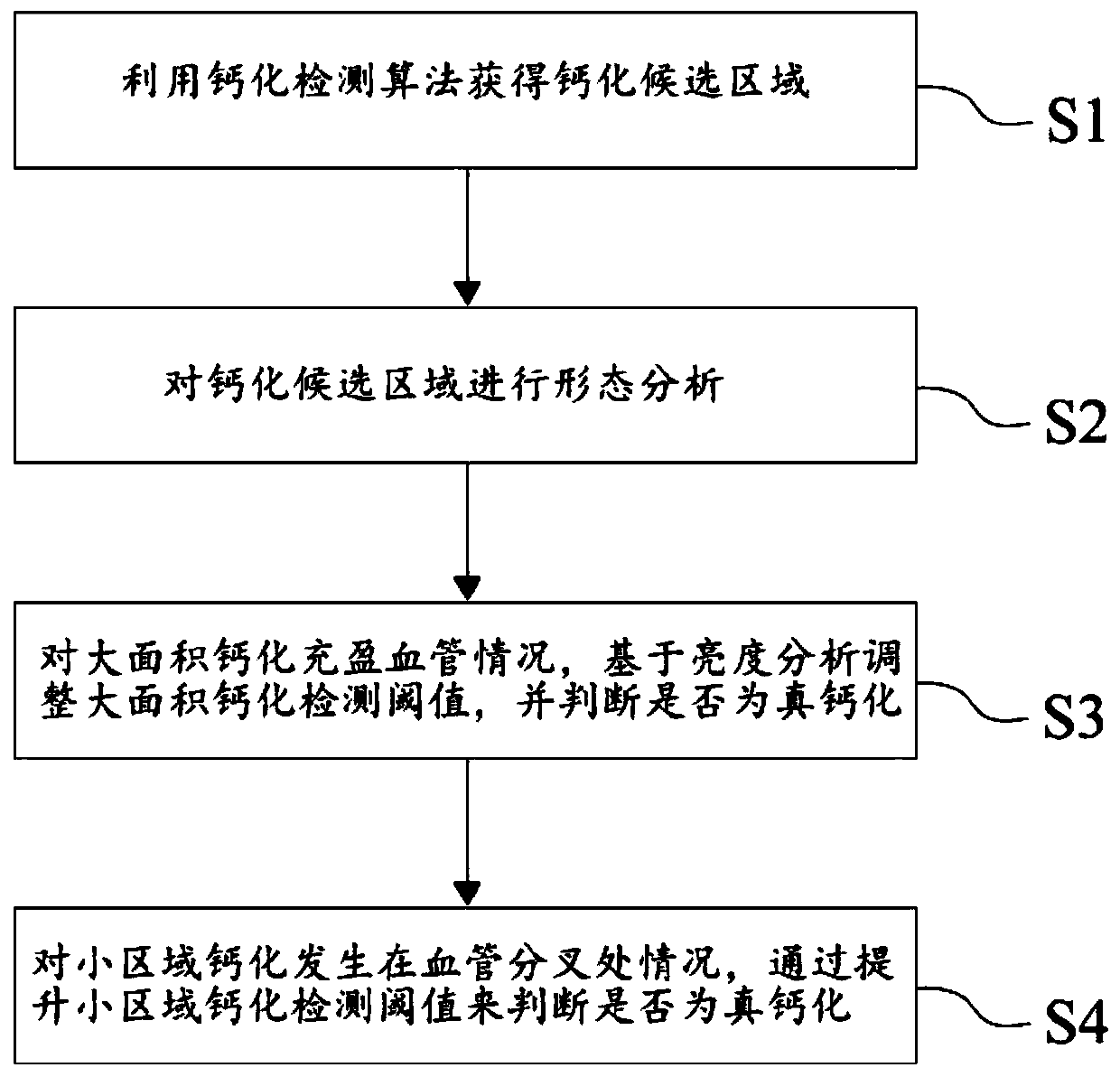
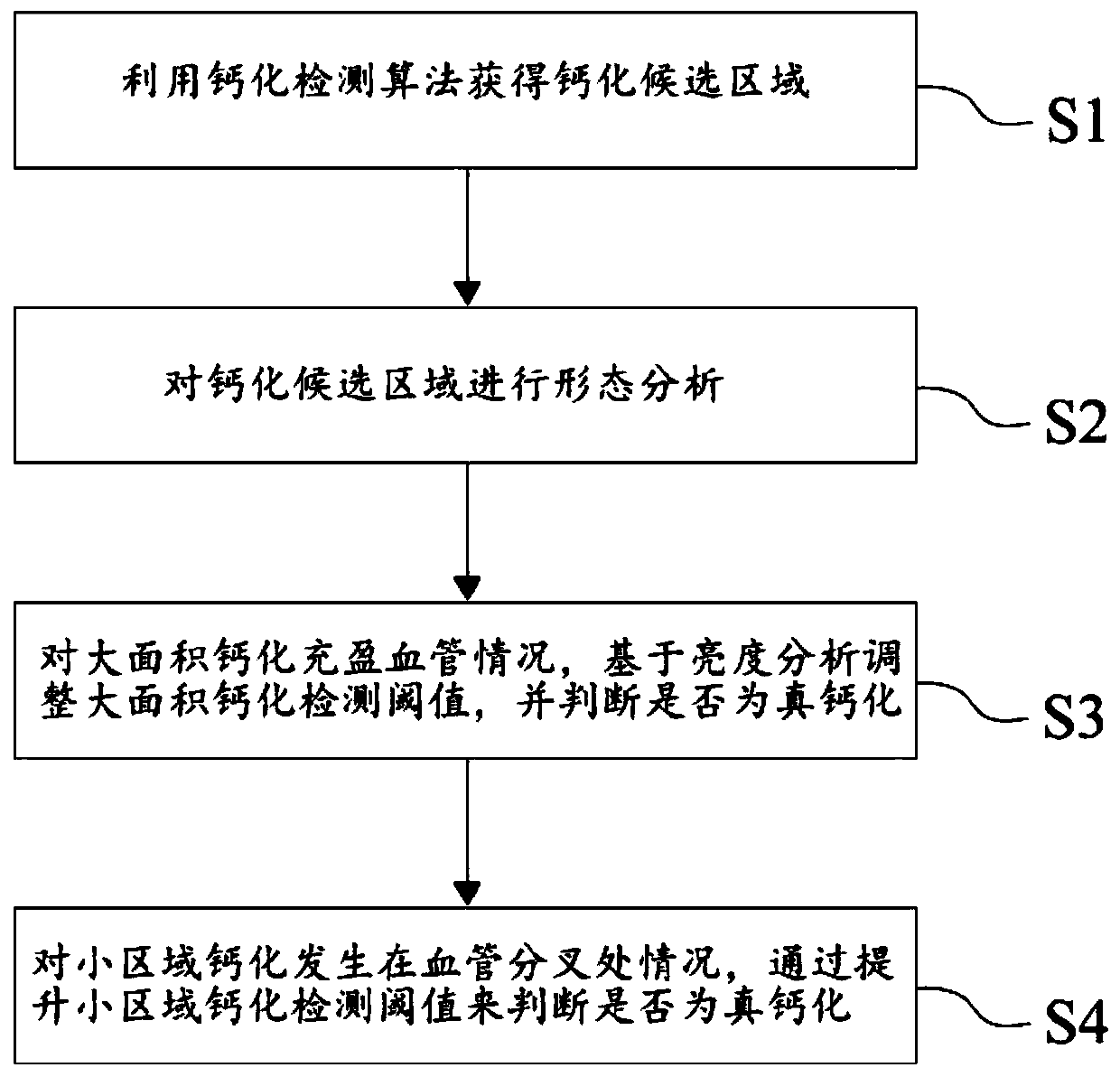
Blood vessel calcification false alarm detection method based on brightness analysis
ActiveCN109846465AAvoid False Positive SituationsImage analysisCatheterVascular calcificationMorphometric analysis
The invention discloses a blood vessel calcification false alarm detection method based on brightness analysis. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining a calcification candidate area by utilizing a calcification detection algorithm aiming at a blood vessel image; performing morphological analysis on the calcification candidate area, and detecting whether a large-area calcification fills blood vessels or not and whether a small-area calcification occurs at a blood vessel bifurcation or not; for the condition that the large-area calcification fills blood vessels, adjusting a large-area calcification detection threshold value based on brightness analysis, and judging whether the calcification is true or not by using the large-area calcification detection threshold value; and for the condition that the small-area calcification occurs at the blood vessel bifurcation, judging whether the calcification is true or not by raising the detection threshold value of the small-area calcification. The method firstly performs morphological analysis on the calcification candidate area to find out the candidate area where false alarm condition easily occurs, then, adjusts the detection threshold value based on brightness analysis, and discriminates and eliminates false calcification so as to effectively avoid the occurrence of false alarm condition.
Owner:数坤(北京)网络科技股份有限公司
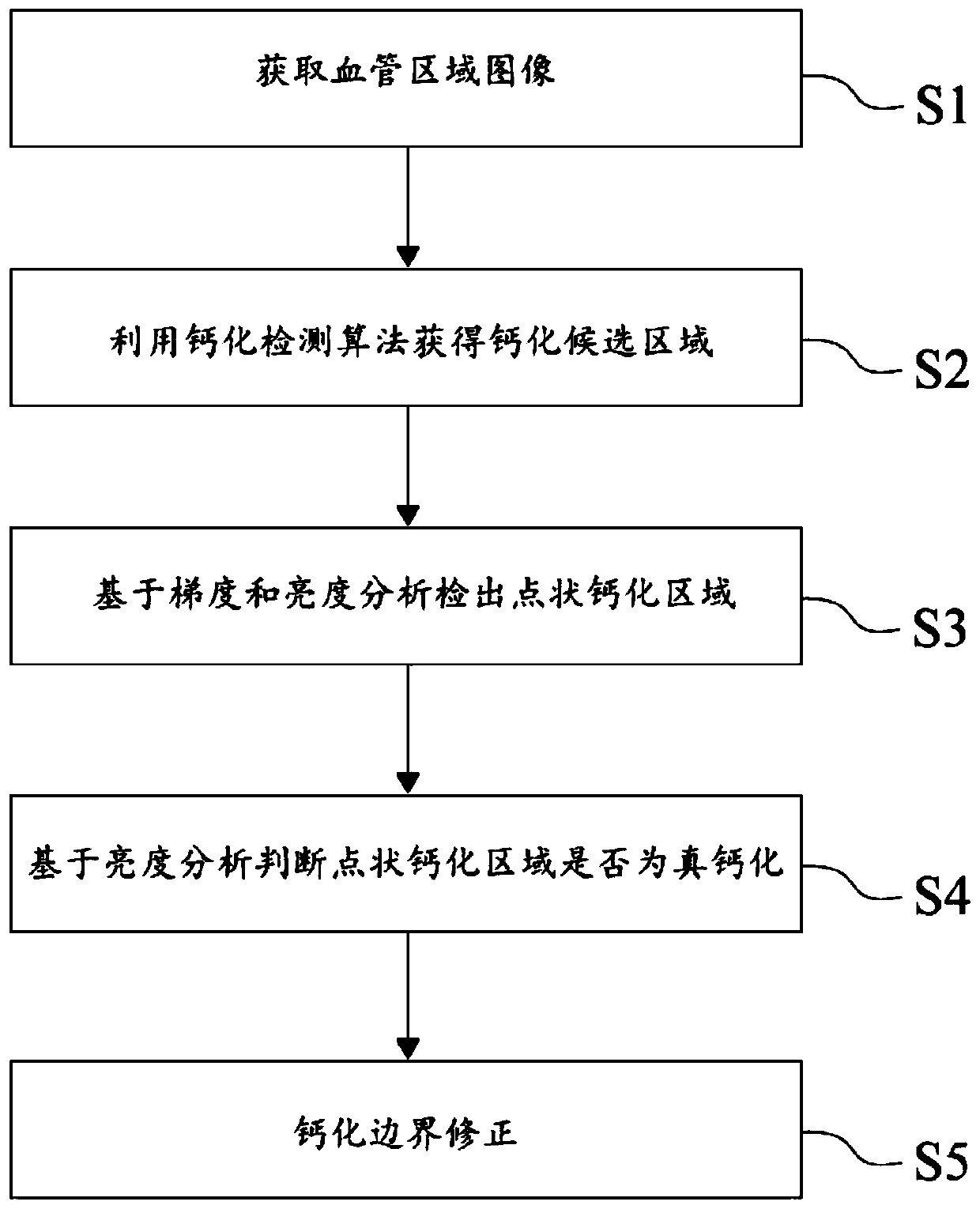
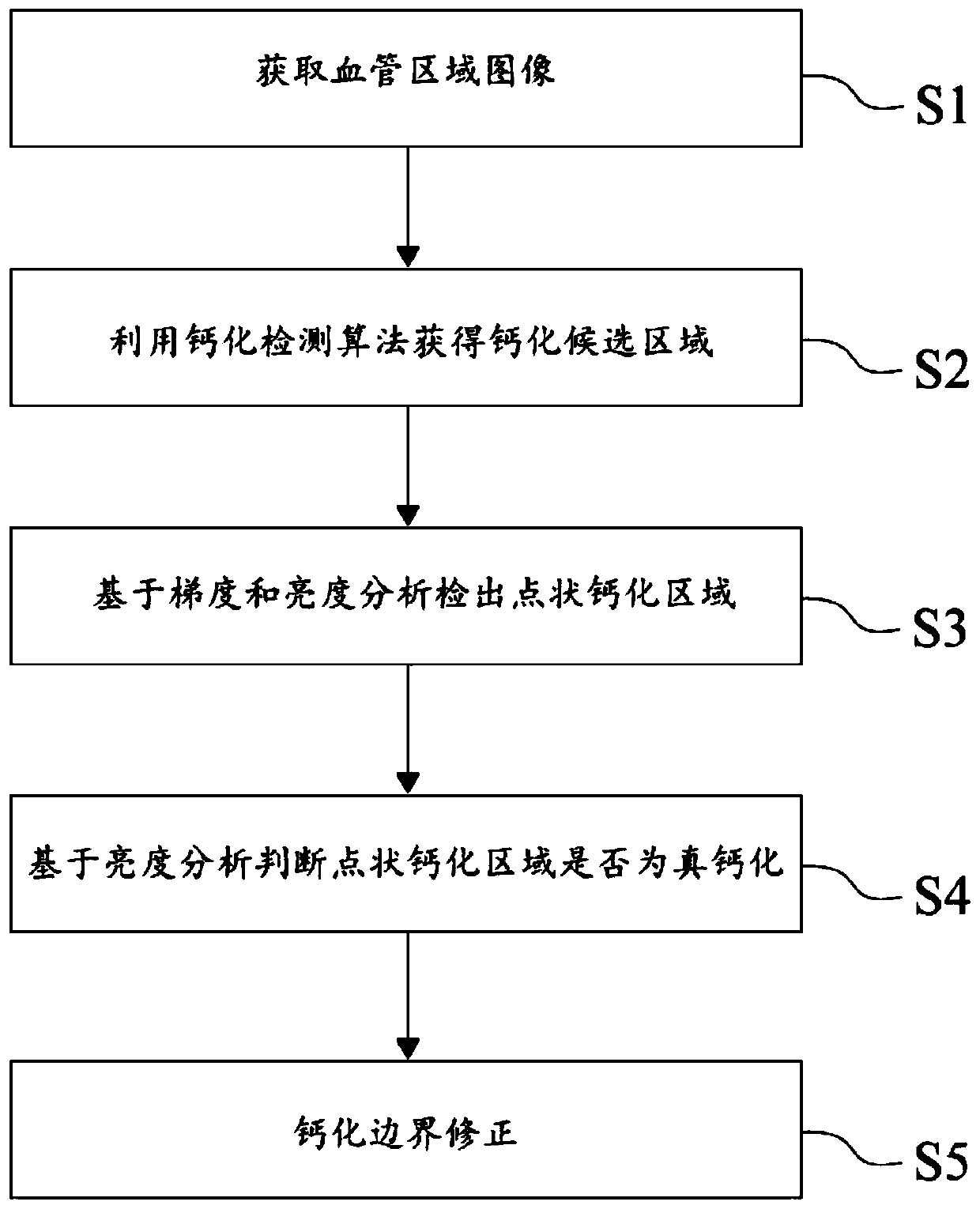
Calcification detection method
ActiveCN110021016AImprove accuracyAvoid missing detectionImage enhancementImage analysisCalcificationMorphometric analysis
The invention discloses a calcification detection method. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a blood vessel region image; obtaining a calcification candidate region by using a calcification detection algorithm; on the basis of gradient and brightness analysis, detecting a dotted calcified region; judging whether the dotted calcified area is true calcified or not based on brightness analysis; and carrying out calcified boundary correction. The method can effectively detect the punctiform calcification area on the blood vessel image, eliminates the false alarm area through morphological analysis, and effectively avoids missed detection and false alarm.
Owner:数坤(深圳)智能网络科技有限公司
Human organ surface mapization method based on sectional image reconstruction
InactiveCN104680479AWatch intuitivelyGeometric image transformation2D-image generationHuman bodyPrime meridian
The invention discloses a human organ surface mapization method based on sectional image reconstruction. For a human organ based on sectional image reconstruction, drawing factors such as the prime meridian and the contour line of an organ map are determined according to the inertia principal axis of the organ, and organ surface mapization is achieved by using methods such as sectional image reconstruction and sectional boundary development. Quantitative study can be provided for morphological analysis on the organ surface.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
Filtering method based on iteration self-adaption multiscale morphological analysis
InactiveCN103716012AFully reflectShock components stand outAdaptive networkPattern recognitionHarmonic
The invention discloses a filtering method based on iteration self-adaption multiscale morphological analysis. The content includes: after performing self-adaption multiscale morphological analysis filtering once, applying a self-adaption method to a filtering result of the last time to determine a new structural element scale range, using the newly determined scale range to perform multiscale morphological filtering on an original signal, iterating the abovementioned processes till the structural element scale range determined by the self-adaption method is stable, and finally averaging the scale results as a final result. The filtering method based on iteration self-adaption multiscale morphological analysis in the invention, a self-adaption multiscale morphological analysis method is used iteratively, and thus in the circumstance of a strong noise background and relatively high sampling frequency, interference of noise and harmonic can still be effective suppressed, fault features can be clearly extracted, and an ideal filtering result can be obtained. The filtering method overcomes the defects of self-adaption multiscale morphological analysis, and enriches a theoretical method of morphological filtering.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Computer-aided morphological analysis of data items
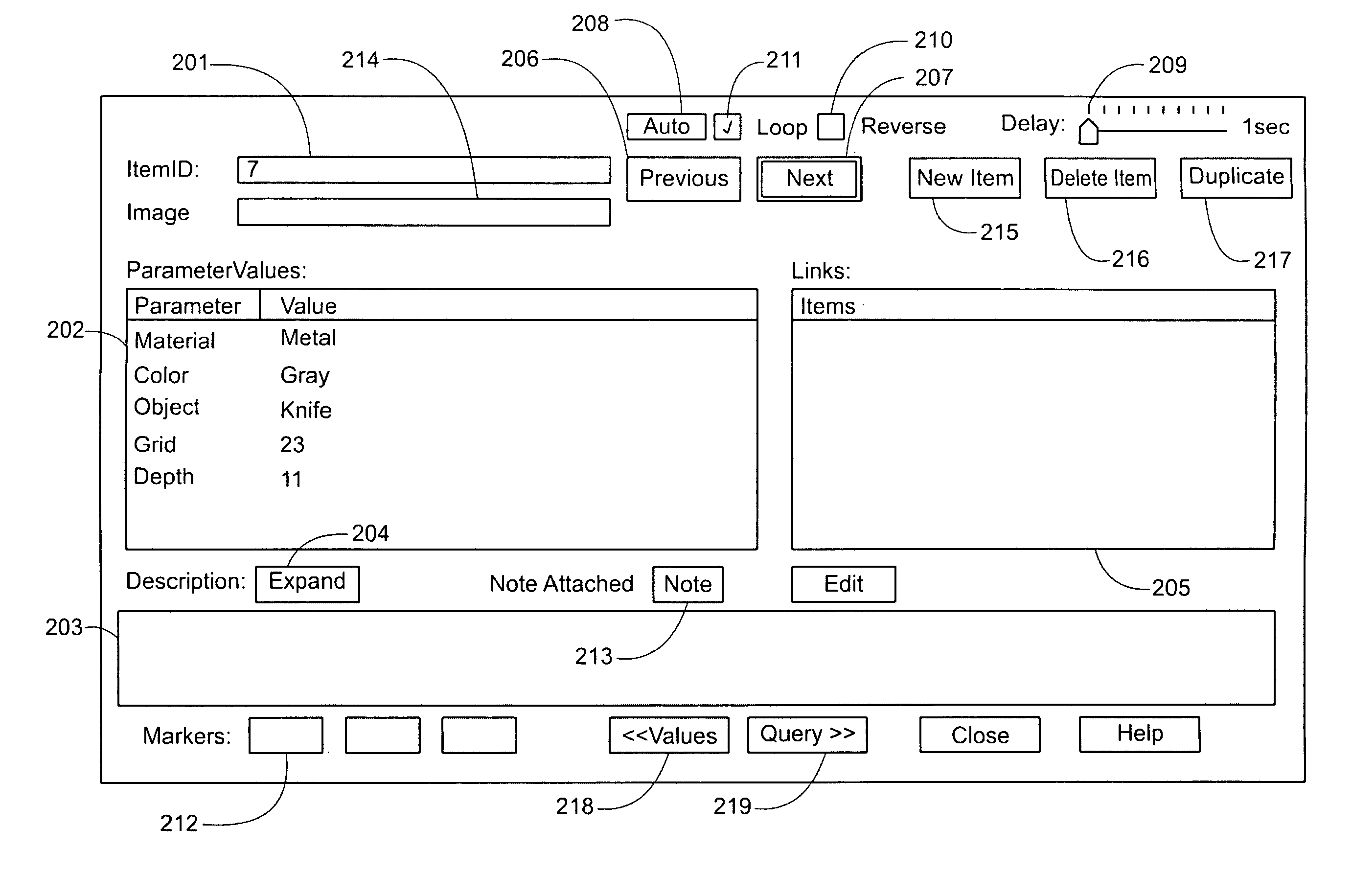
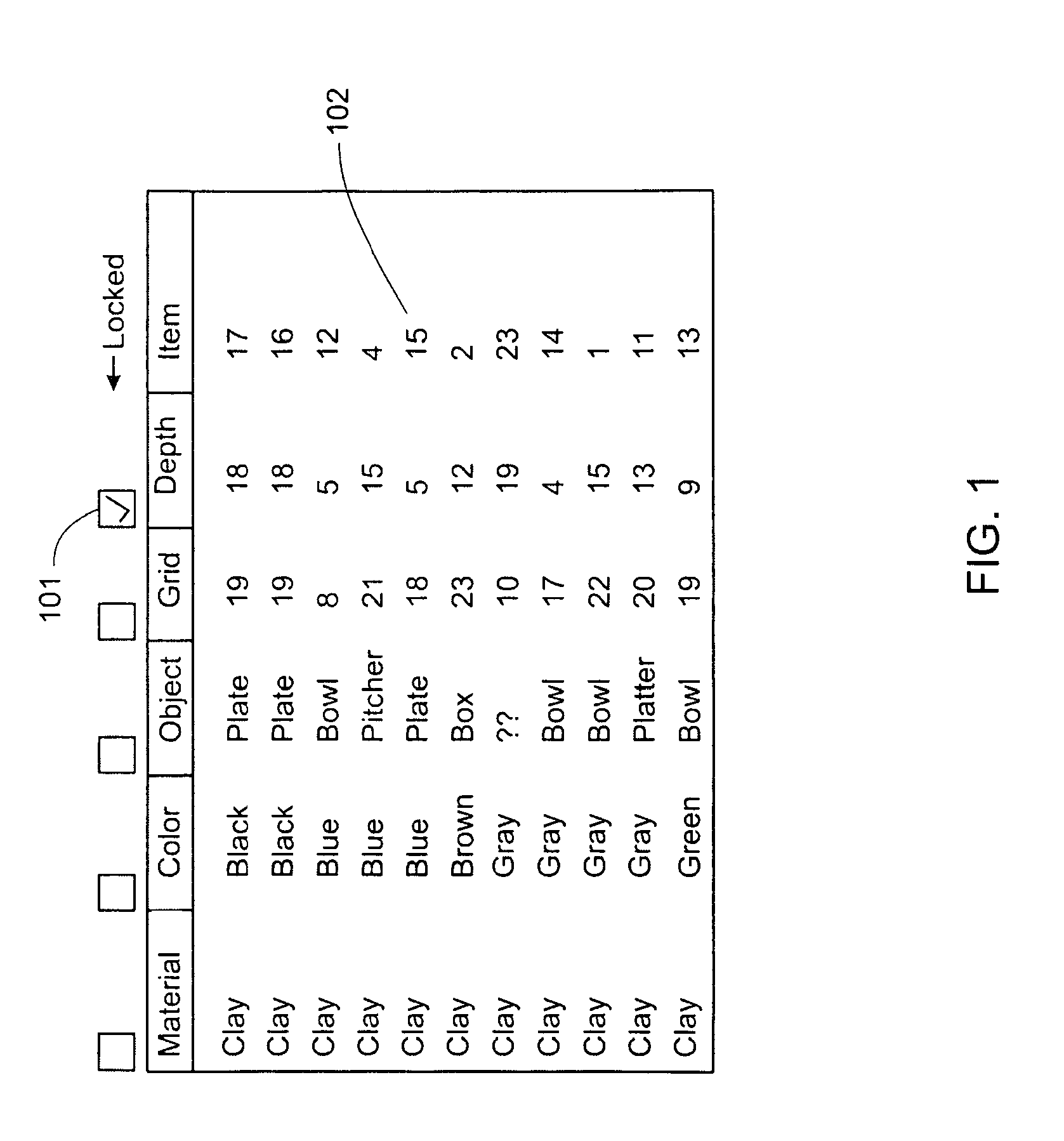
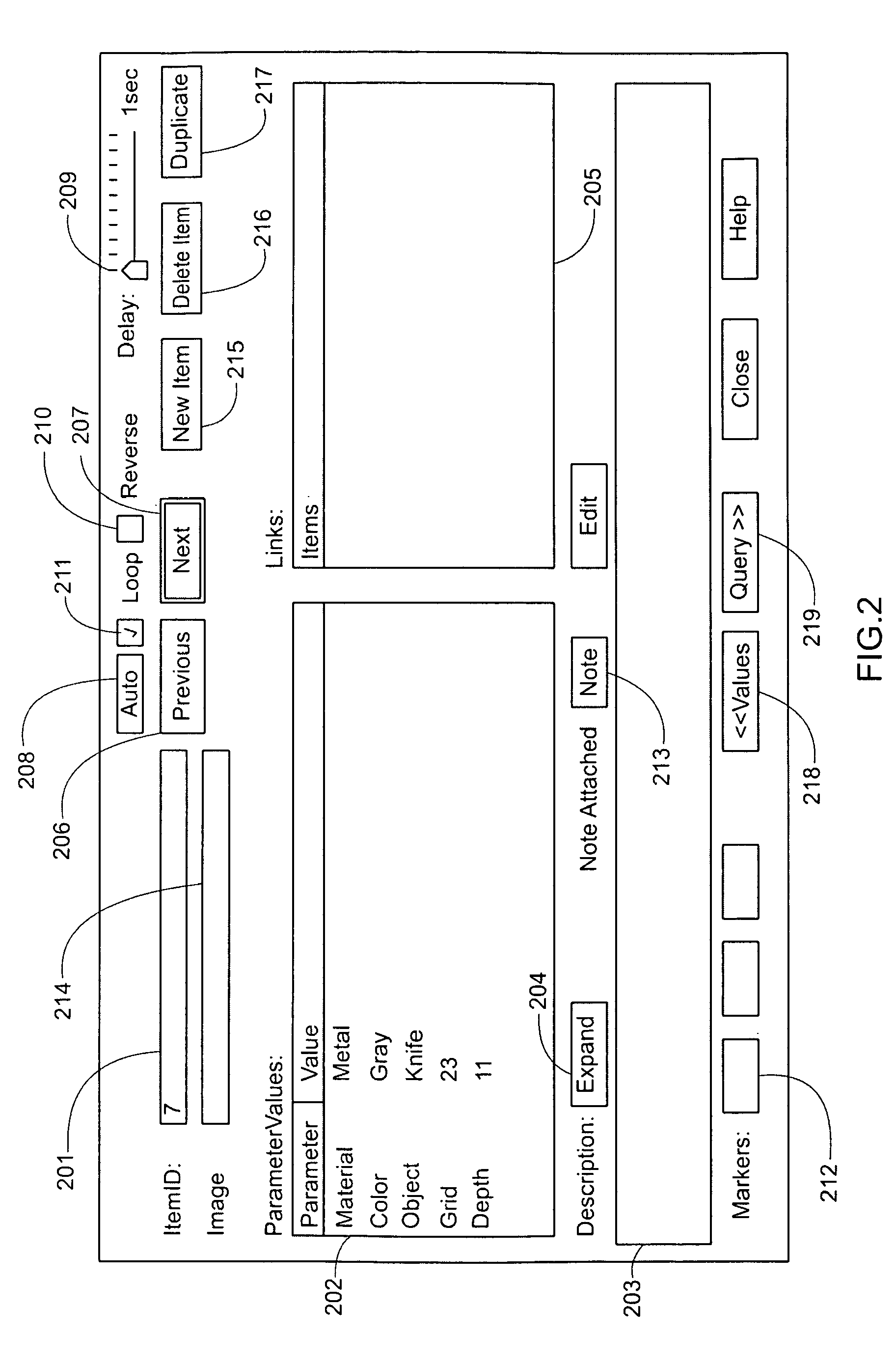
ActiveUS8266160B2Digital data processing detailsSpecial data processing applicationsComputer usersAlgorithm
Improvements to computer-aided methodology of morphological analysis of a set of text data objects and associated graphic images. The methodology, named contextual data modeling (CDM), involves personal discovery of meaningful interrelations of parametric values and names of text data objects using automated permutation of a data table; plus viewing for each item listed on the table an integrated dialog box (item screen), containing the item's parametric data and other data; plus concurrent and coordinated display of the data table and graphic images associated with items on the data table. Near real time operation optimizes retention of perceived data in the computer user's short term working memory as reasoning leads to modeling (manipulating) the data, including editing and colorization, until the user's reasoning is reflected in the displayed data.
Owner:EXECWARE
Numerical method of calculating heat, mass, chemical and electric transport for three-dimensional porous solid
ActiveUS8965740B2Computation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationPetrographic thin sectionMorphometric analysis
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Three-dimensional shape-based particle analysis method and particle placement bracket
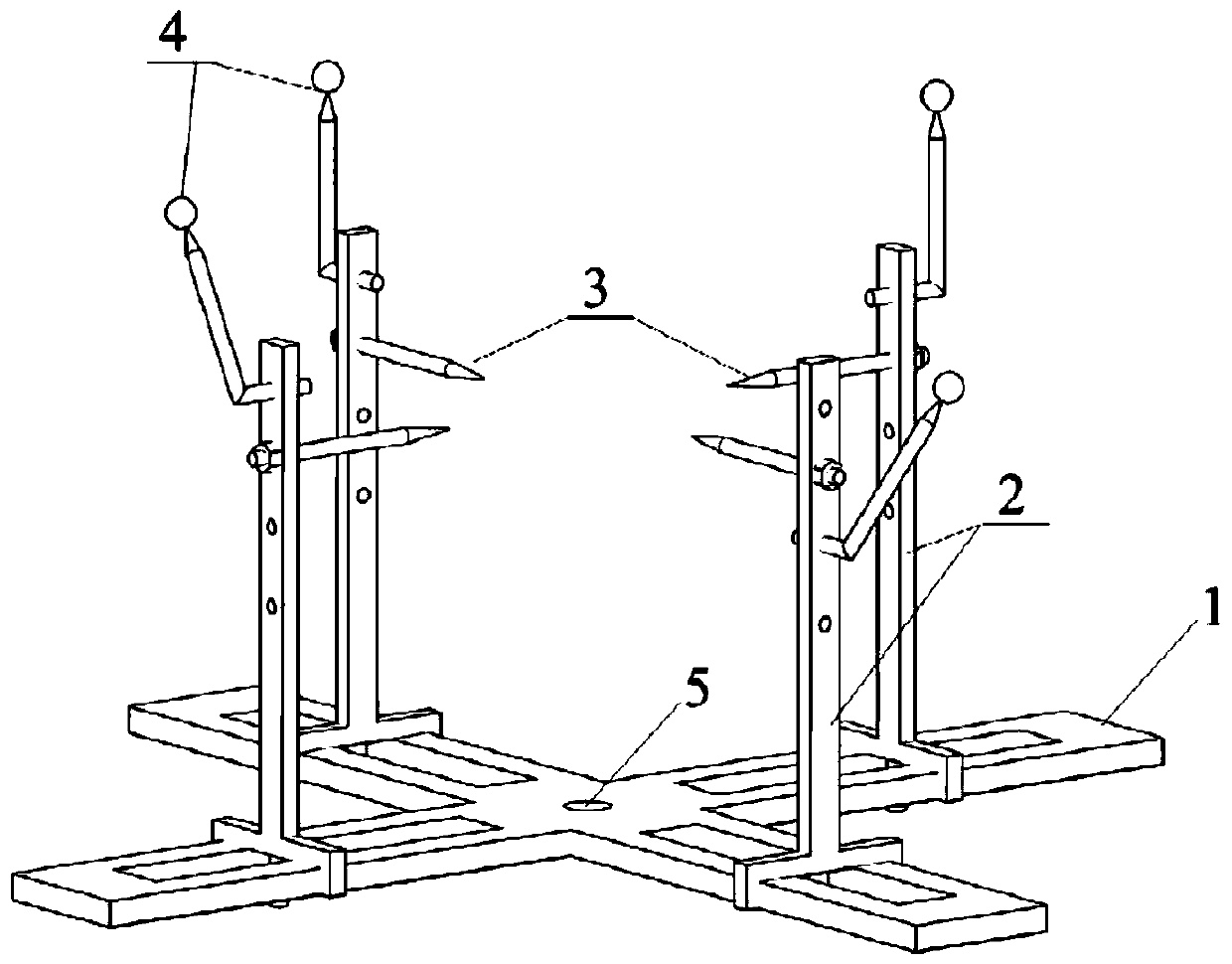
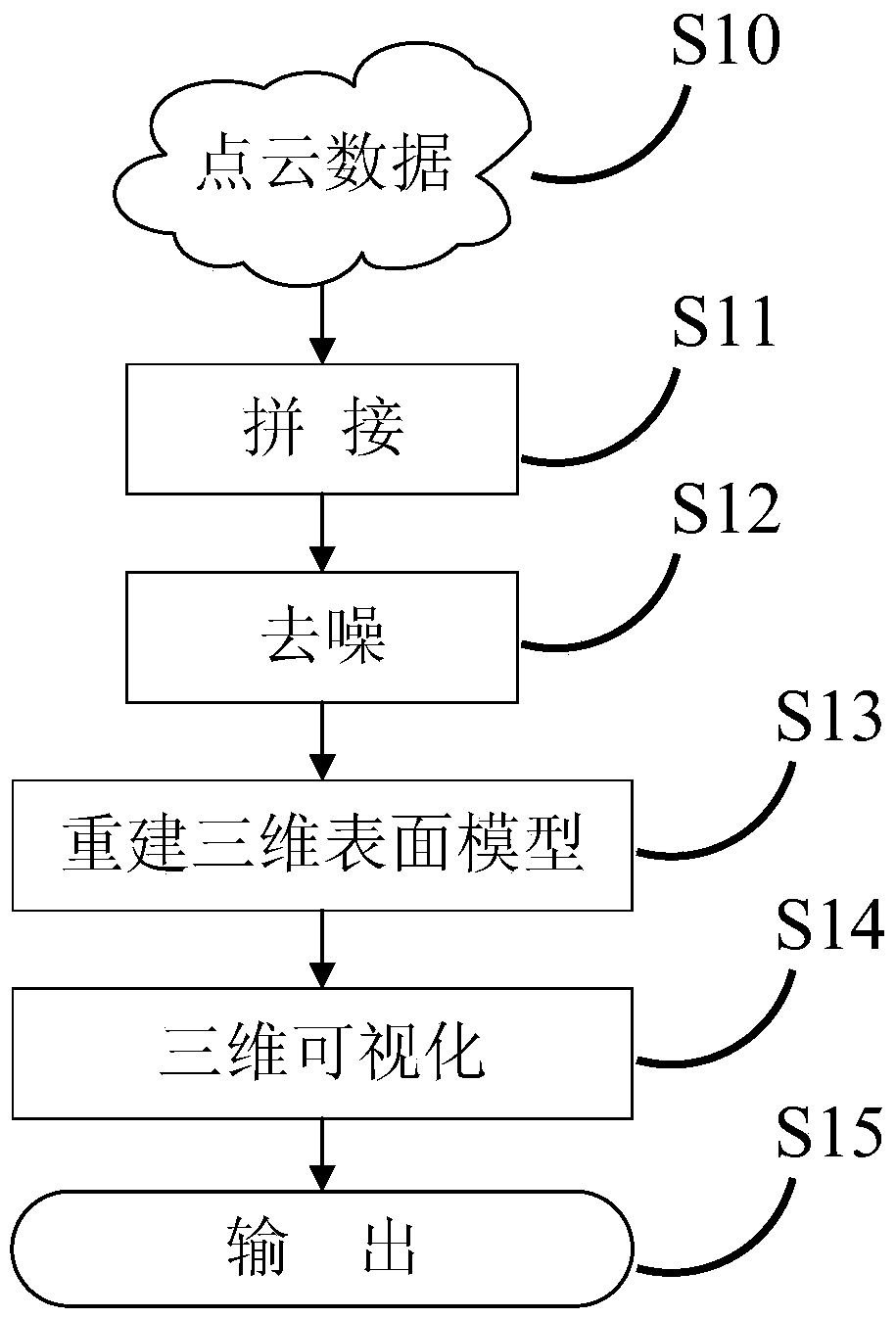
InactiveCN104008573BIncrease the use of functionsMultipurposeParticle size analysisStands/trestlesParticulatesPoint cloud
The present invention proposes a particle analysis method based on three-dimensional morphology, which includes the following steps: scanning the particles with multiple viewing angles to obtain point cloud data of the particles under multiple viewing angles; splicing the point cloud data under multiple viewing angles; Denoise the spliced point cloud data to obtain the final point cloud data; construct the mesh model of the three-dimensional surface morphology of the particles according to the final point cloud data; render and display the mesh model of the three-dimensional surface morphology to obtain the final point cloud data according to the display results Analyze and count the geometric and morphological properties of particles. The method according to the embodiment of the present invention can conveniently realize three-dimensional fine measurement, reconstruction, three-dimensional visualization and quantitative analysis of particle morphology. The invention also provides a particle placing bracket.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com