Patents
Literature
1081results about "Adaptive network" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
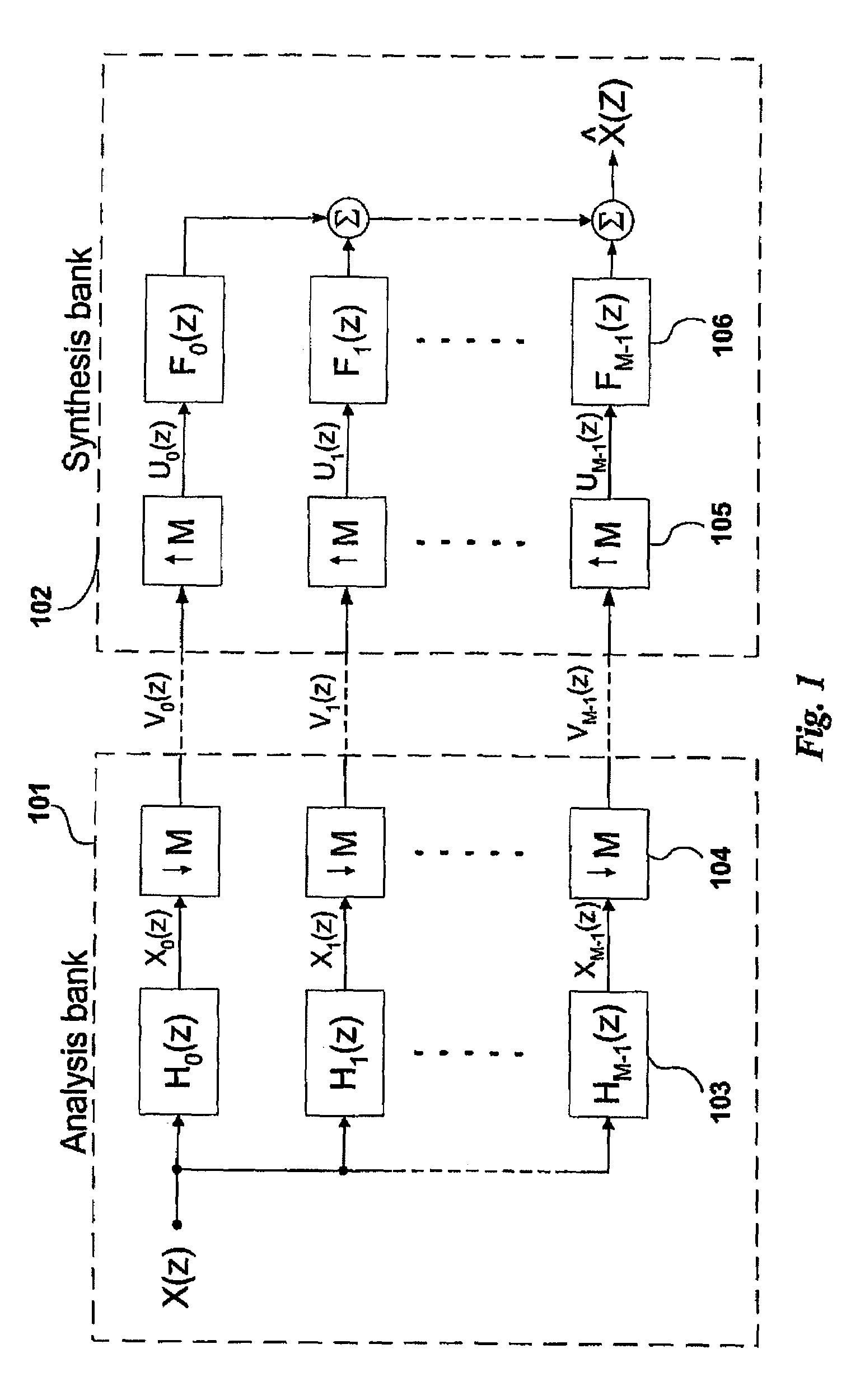
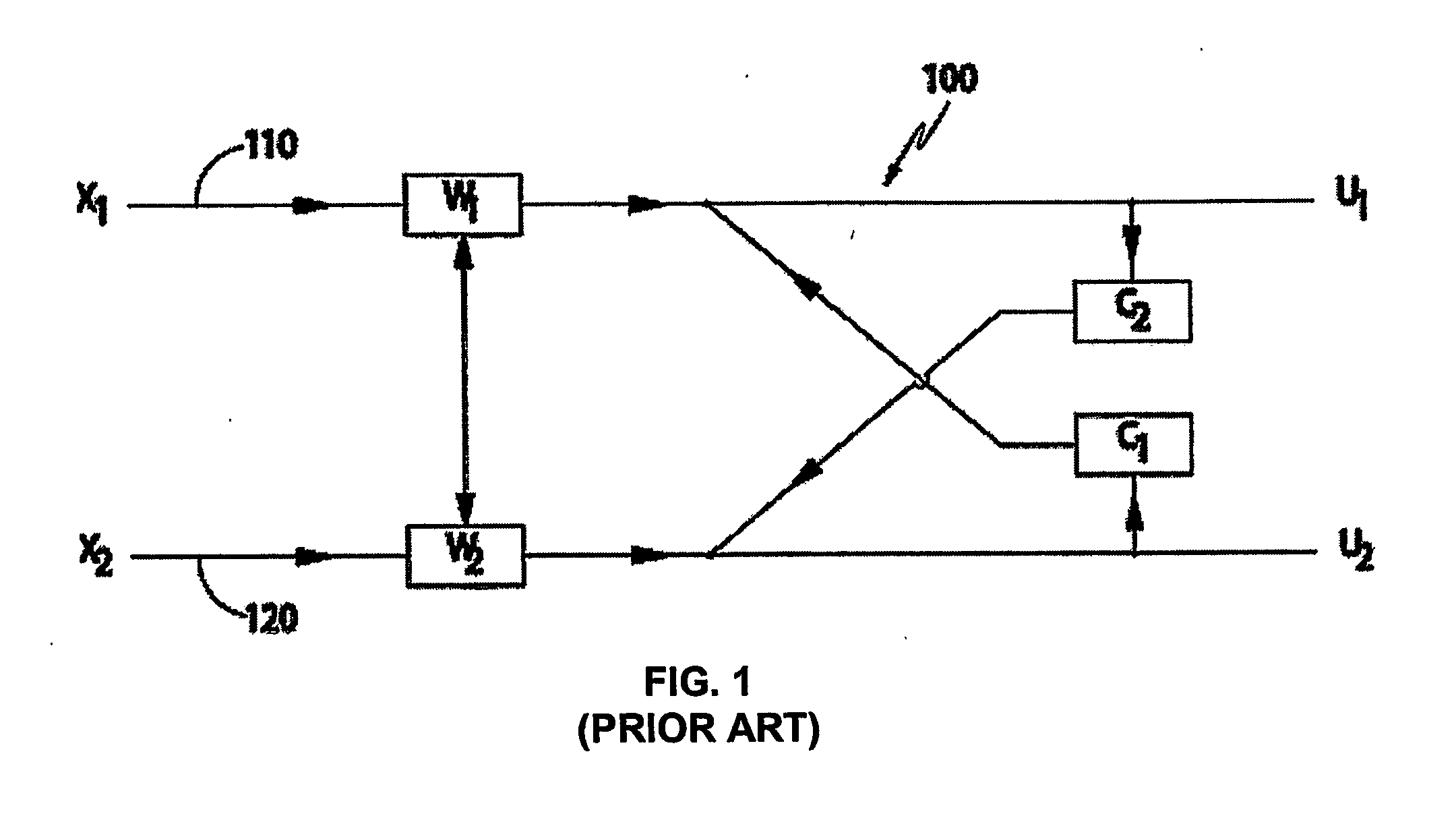
Compensating filters
InactiveUS6760451B1Eliminate phase distortionAdaptive networkAutomatic tone/bandwidth controlDigital signal processingAmplitude response
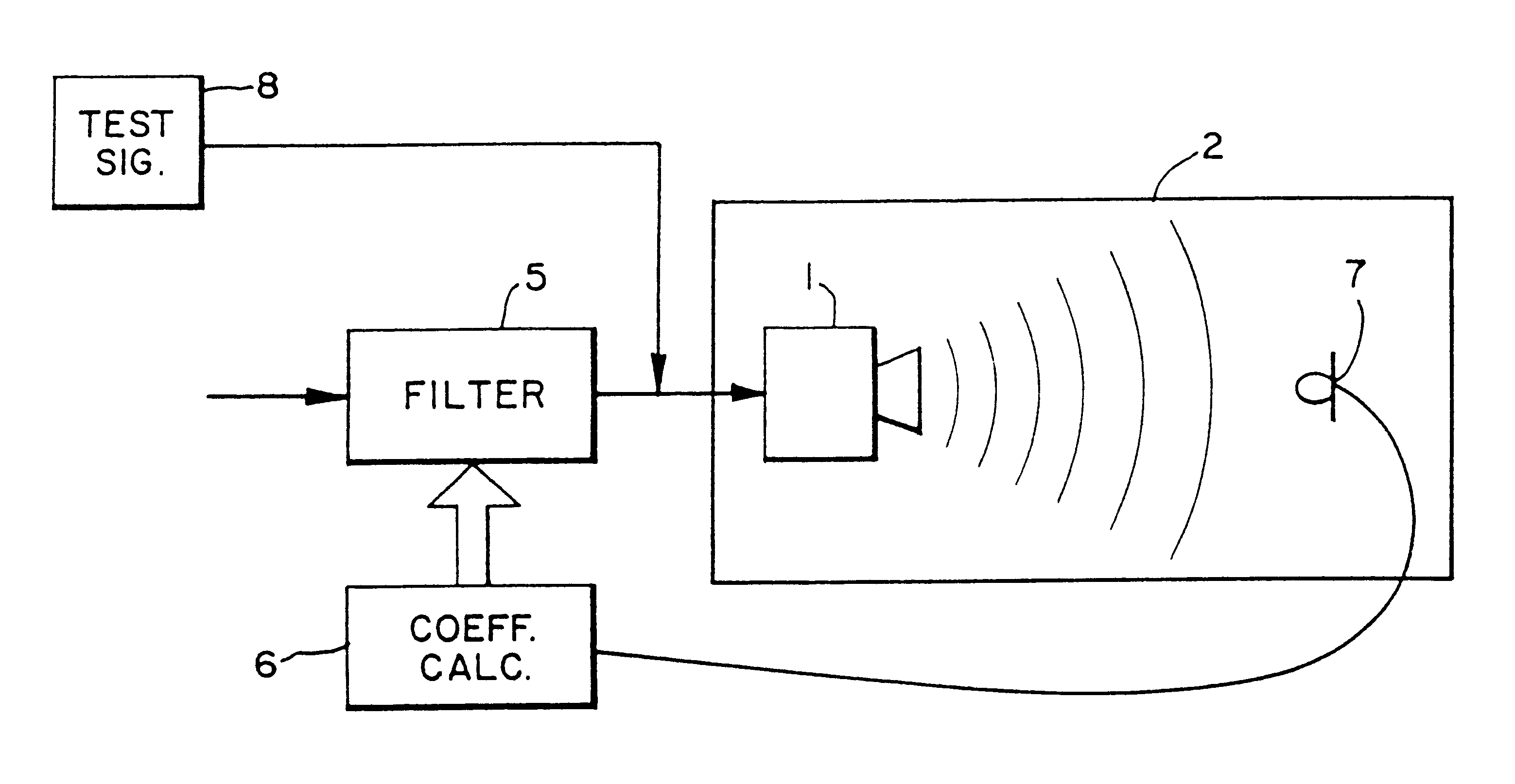
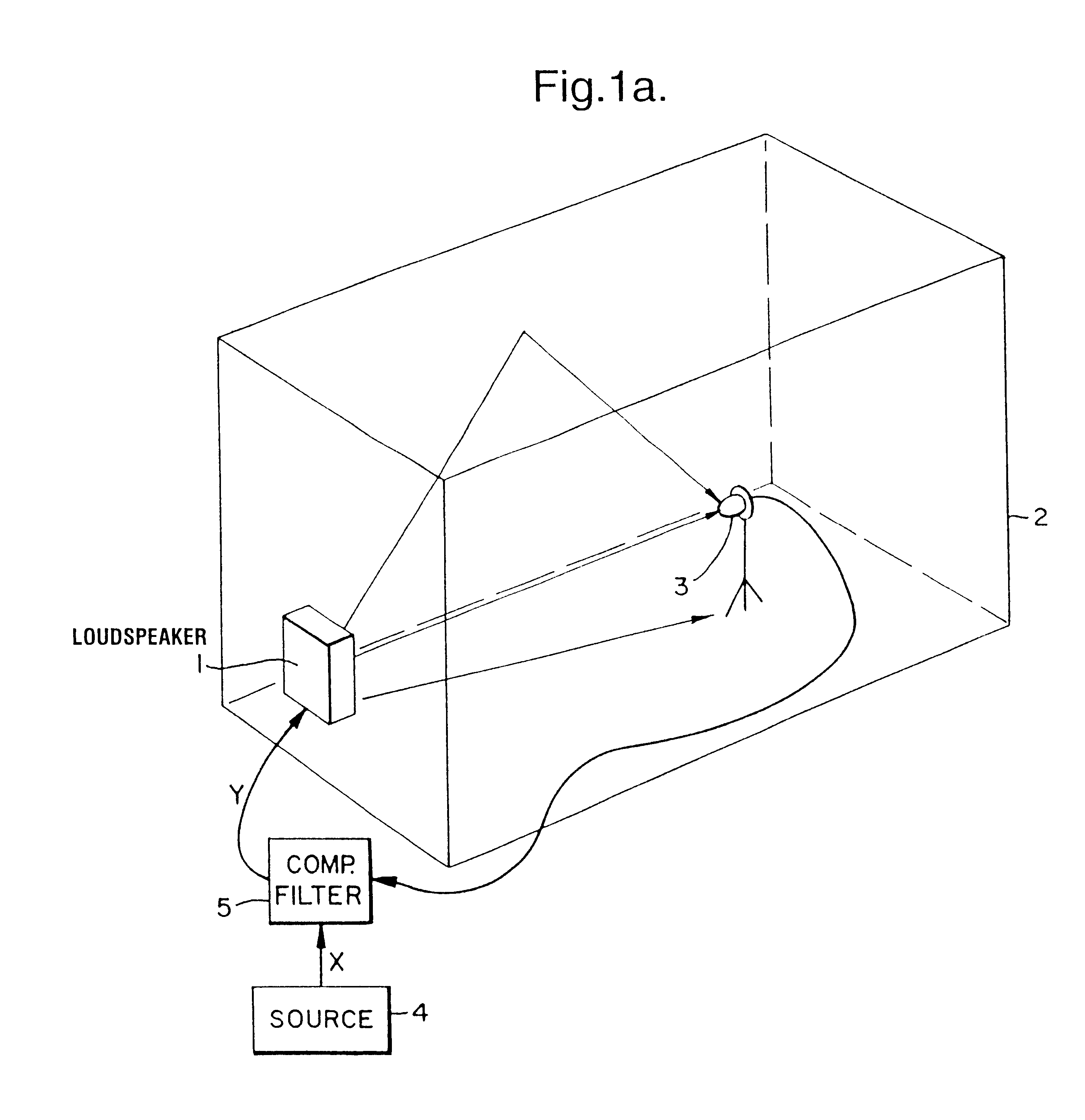
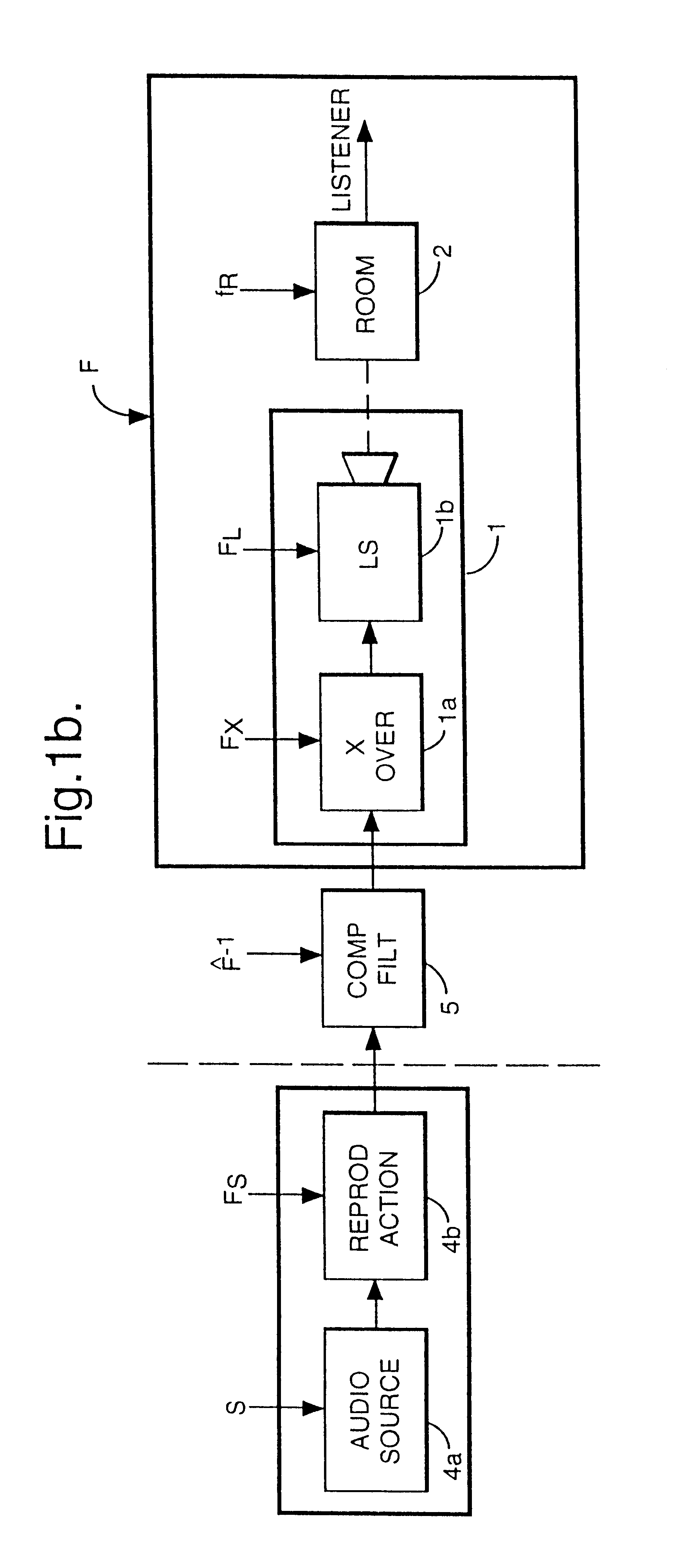
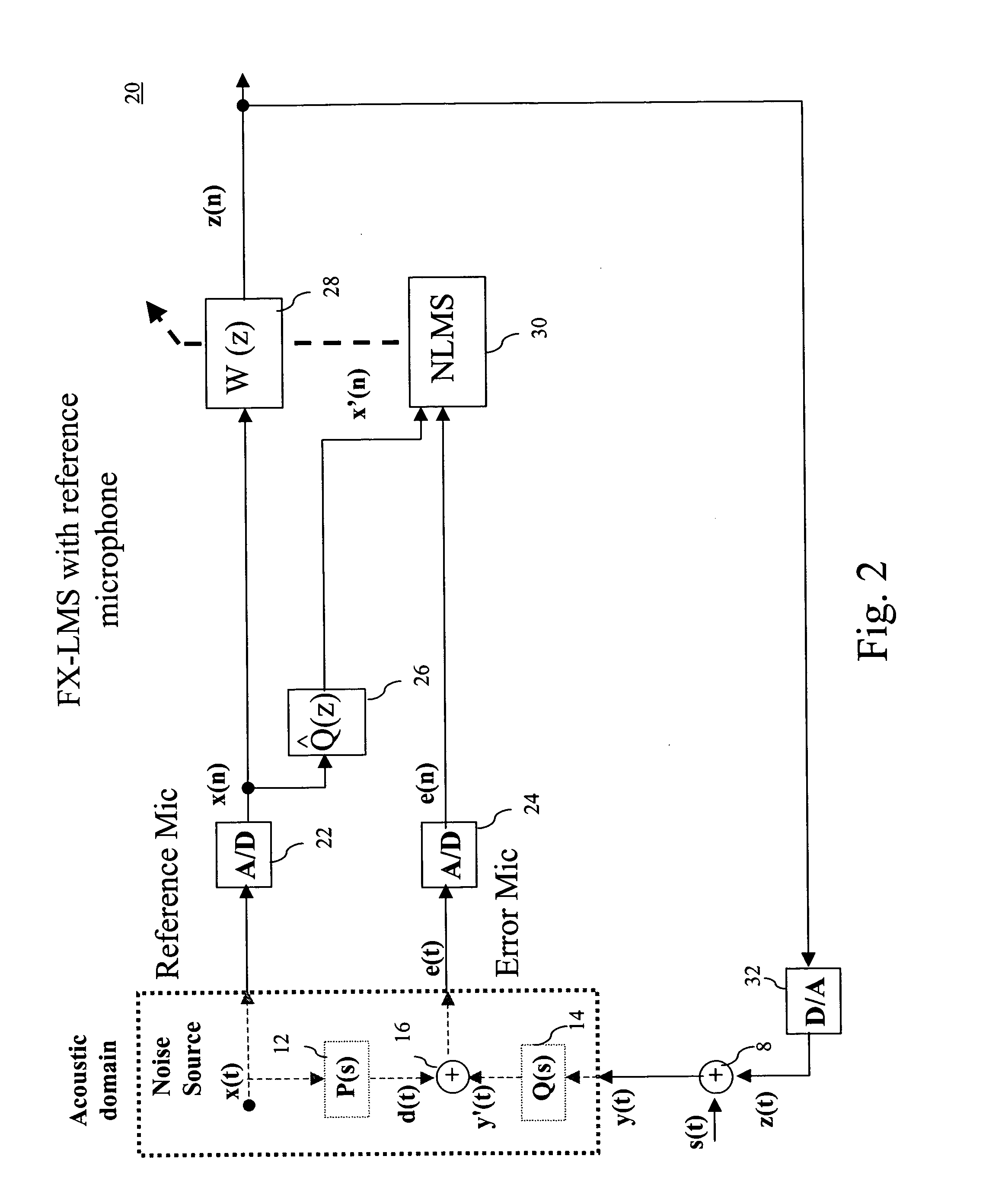
A prefilter (5) for an audio system comprising a loudspeaker (1) in a room (2), which corrects both amplitude and phase errors due to the loudspeaker (1) by a linear phase correction filter response and corrects the amplitude response of the room (2) whilst introducing the minimum possible amount of extra phase distortion by employing a minimum phase correction filter stage. A test signal generator (8) generates a signal comprising a periodic frequency sweep with a greater phase repetition period than the frequency repetition period. A microphone (7) positioned at various points in the room (2) measures the audio signal processed by the room (2) and loudspeaker (1), and a coefficient calculator (6) (e.g. a digital signal processor device) derives the signal response of the room and thereby a requisite minimum phase correction to be cascaded with the linear phase correction already calculated for the loudspeaker (1). Filter (5) may comprise the same digital signal processor as the coefficient calculator (6). Applications in high fidelity audio reproduction, and in car stereo reproduction.
Owner:CRAVEN PETER GRAHAM +1
Mitigating interference in a signal
InactiveUS7626542B2Improve performanceLower requirementAdaptive networkDigital technique networkEngineeringNon orthogonal
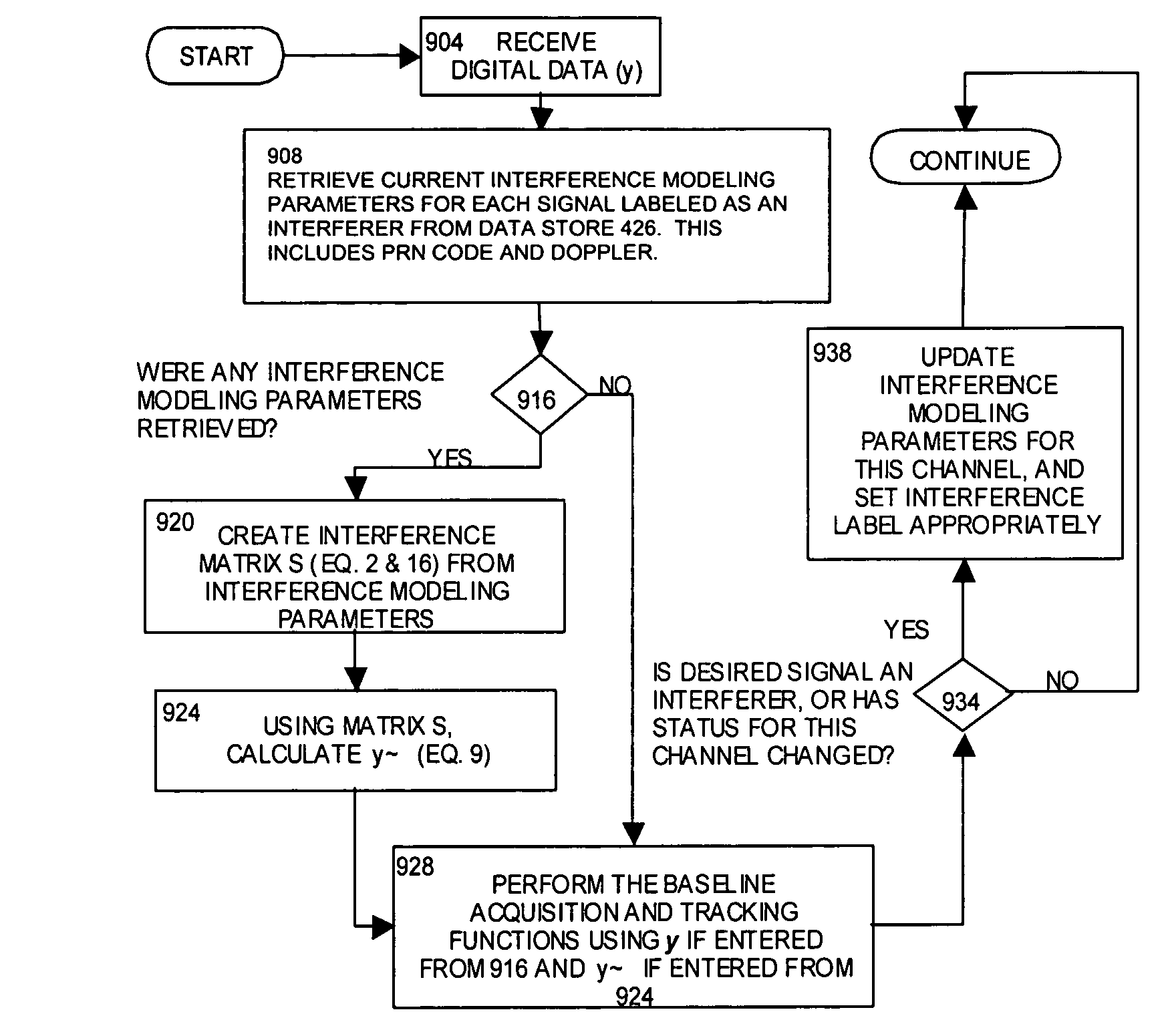
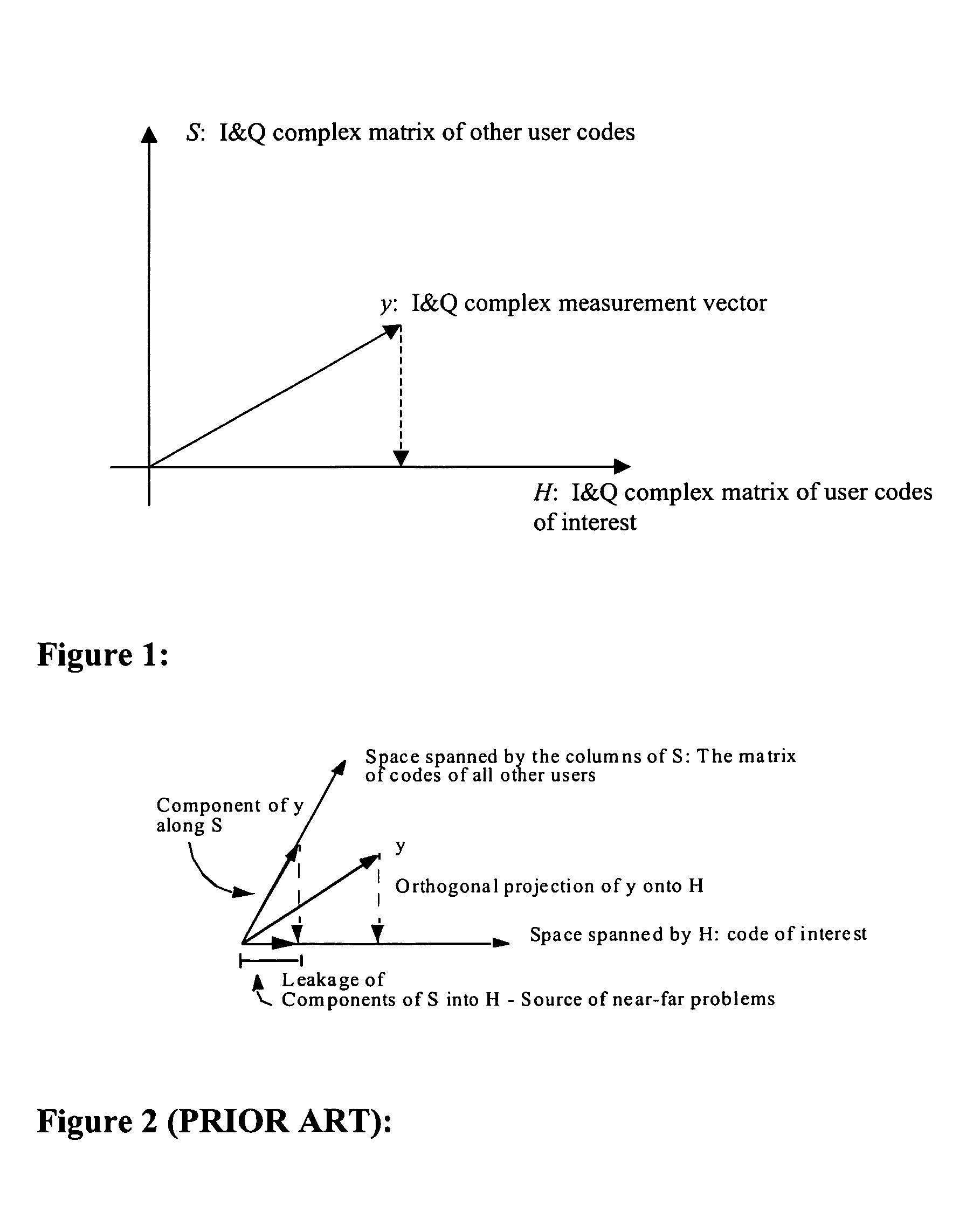
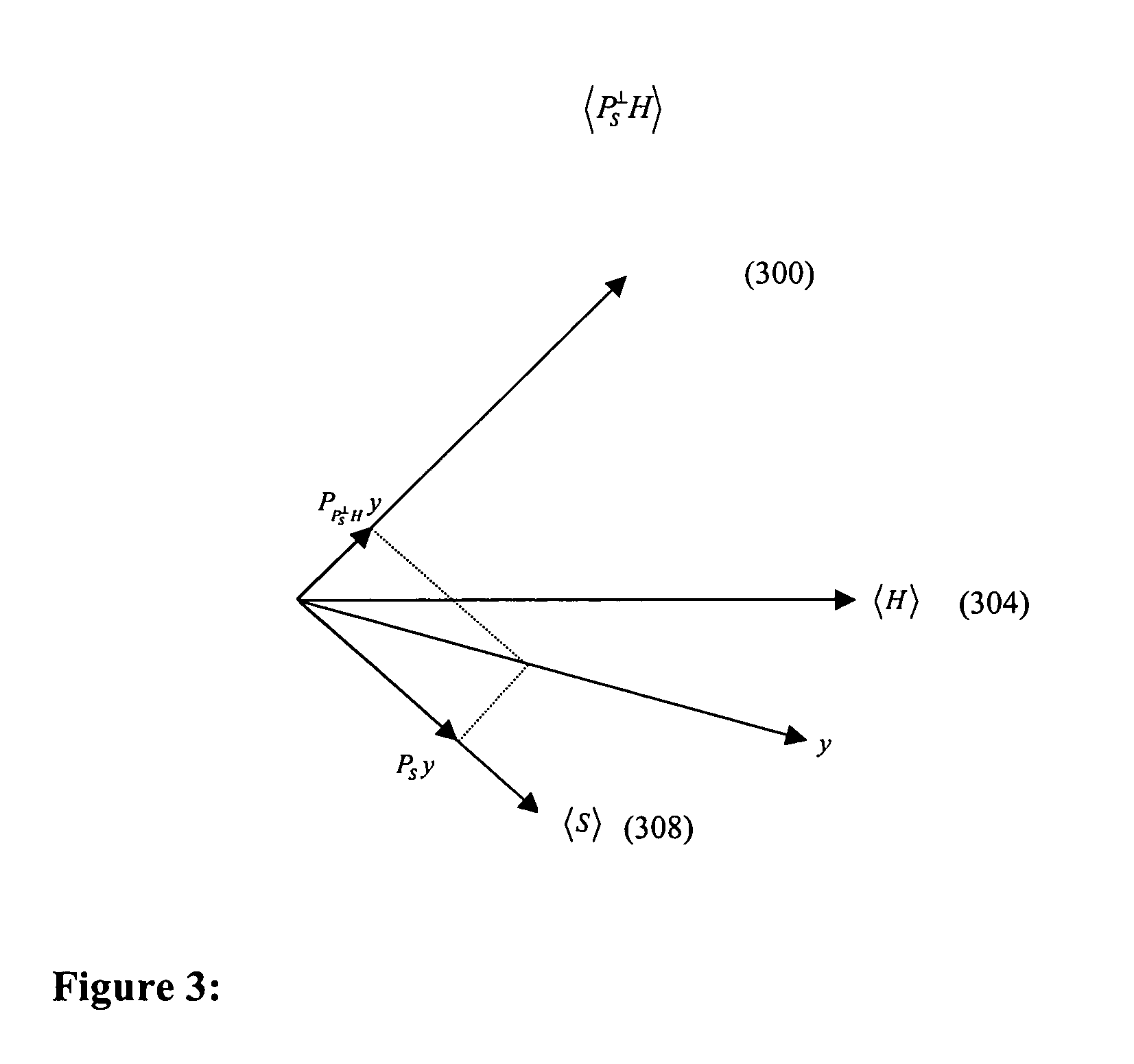
A method and receiver are disclosed for mitigating or substantially canceling signal interference between signals detected at the receiver. Once a presumed interfering signal(s) is acquired, parameters are determined that allow the interferer(s) to be modeled. The phase invariance of the process eliminates the need to acquire the interferer's phase. An orthogonal projection (for projecting onto a detection subspace which is orthogonal to a subspace spanned by the interferer(s)) is applied to the composite of all signals (y) for thereby projecting y onto the detection subspace. The interference subspace is non-orthogonal to a representation of desired (but interfered) signal of the composite signals. With the receiver properly equipped to perform this projection operation, interfering signals, multipath, multipath-like, and structured jamming signals can be effectively diminished.
Owner:DATA FUSION CORP
Methods and apparatus for reducing signal degradation
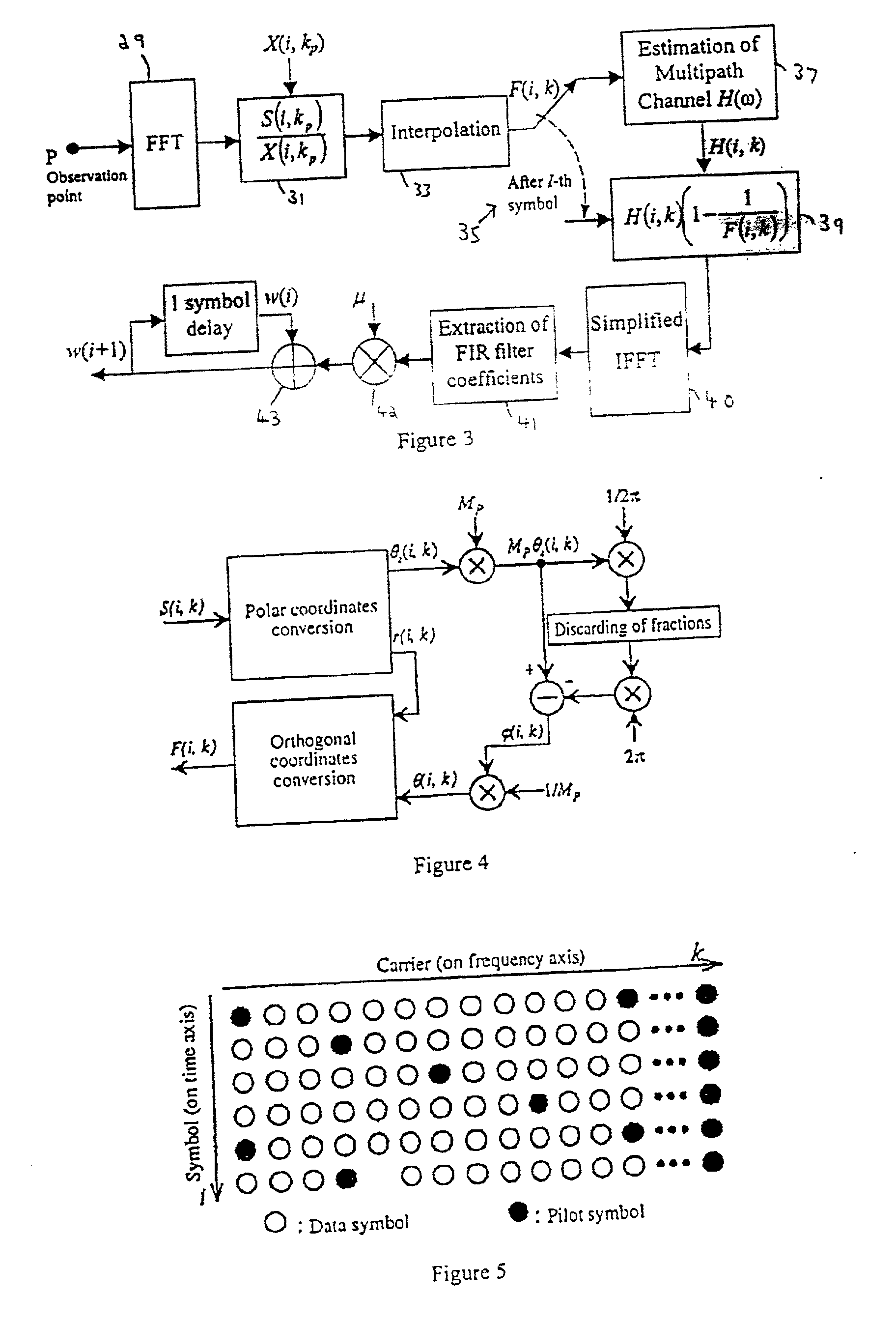
ActiveUS20020039383A1Error minimizationReduce the differencePulse transformerAdaptive networkFast Fourier transformMultipath interference
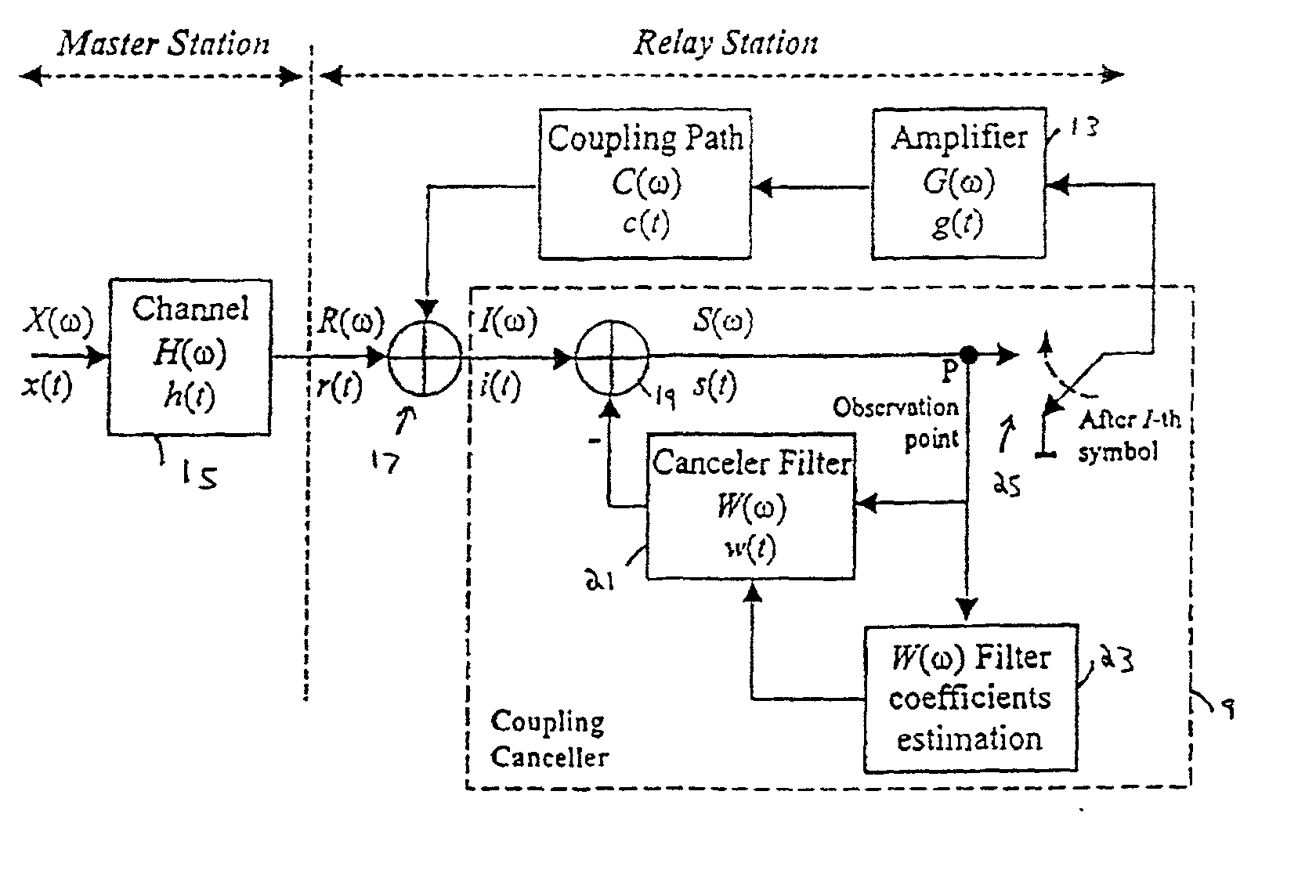
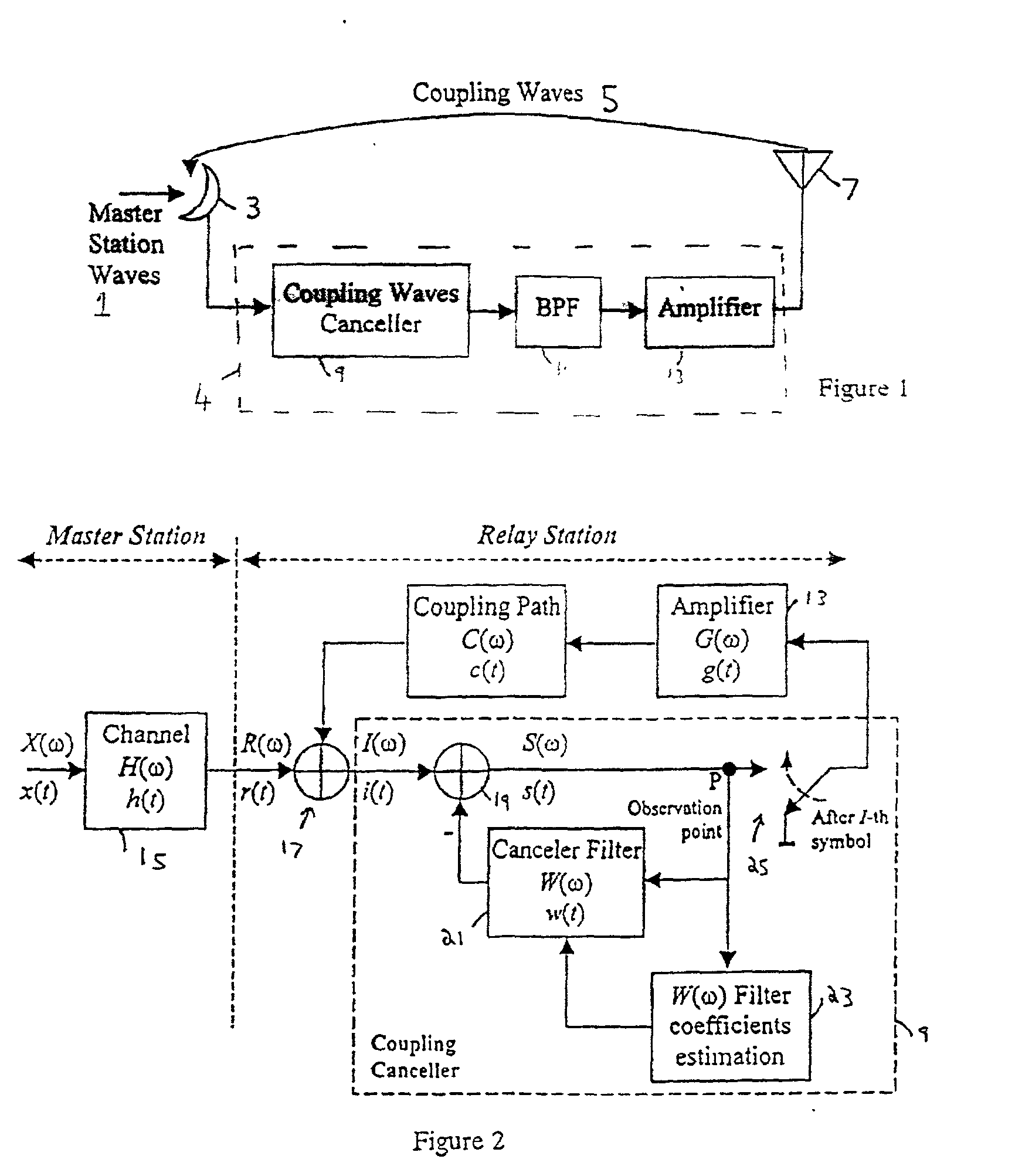
A single frequency relay station receives a signal from a master station, and retransmits it. Before retransmitting the signal, the relay station uses a digital filter to subtract from the signal components which arise from multipath interference and coupling interference. The coefficients used by the digital filter are derived from characteristics of the multipath interference and the overall transfer function of the relay station. These are derived by turning off the retransmission, so that the multipath interference can be estimated from the received signal, and commencing the retransmission again, to determine the transfer function. A simplified inverse fast Fourier transform is used to simplify the calculations.
Owner:WIPRO LTD
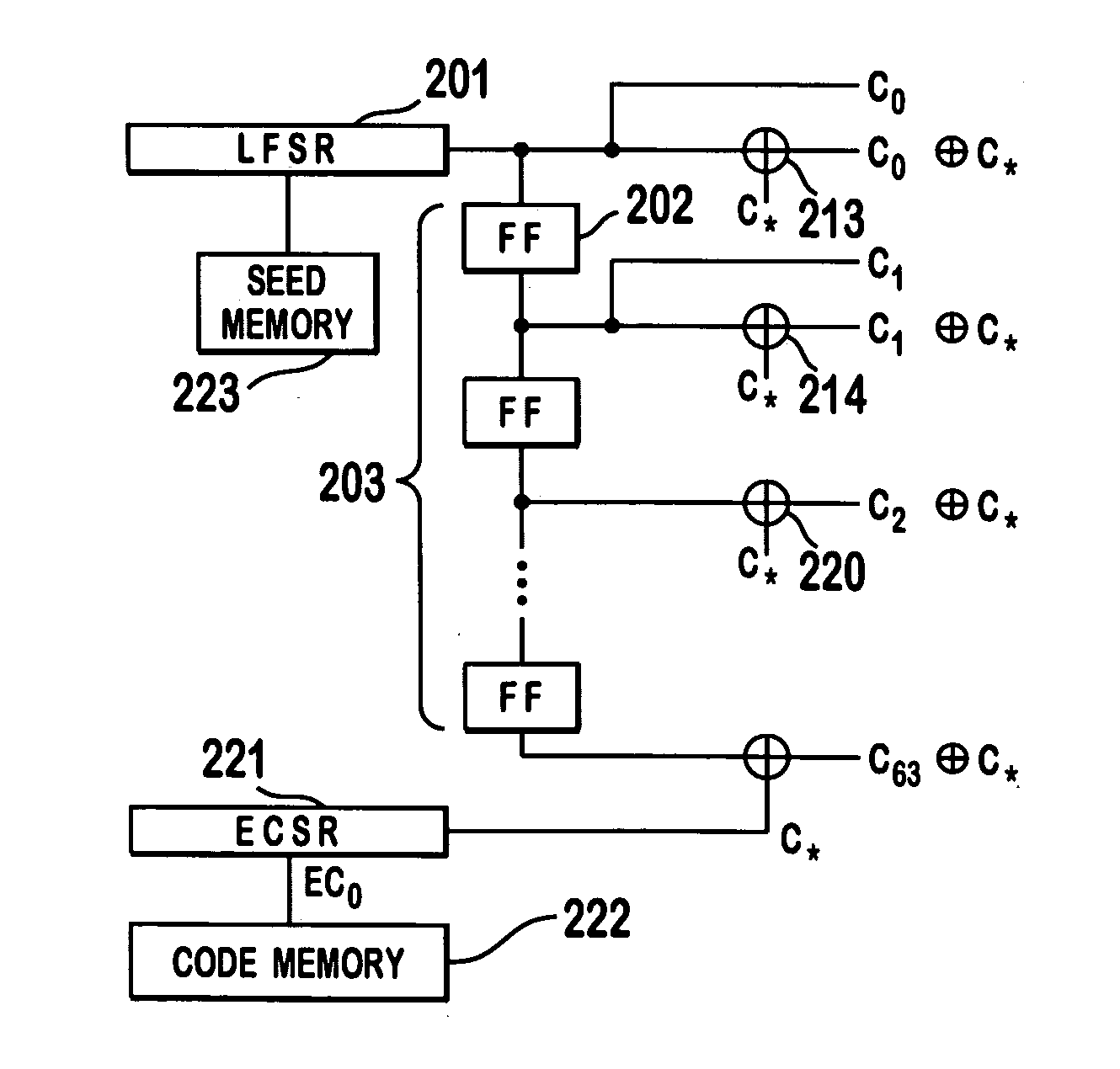
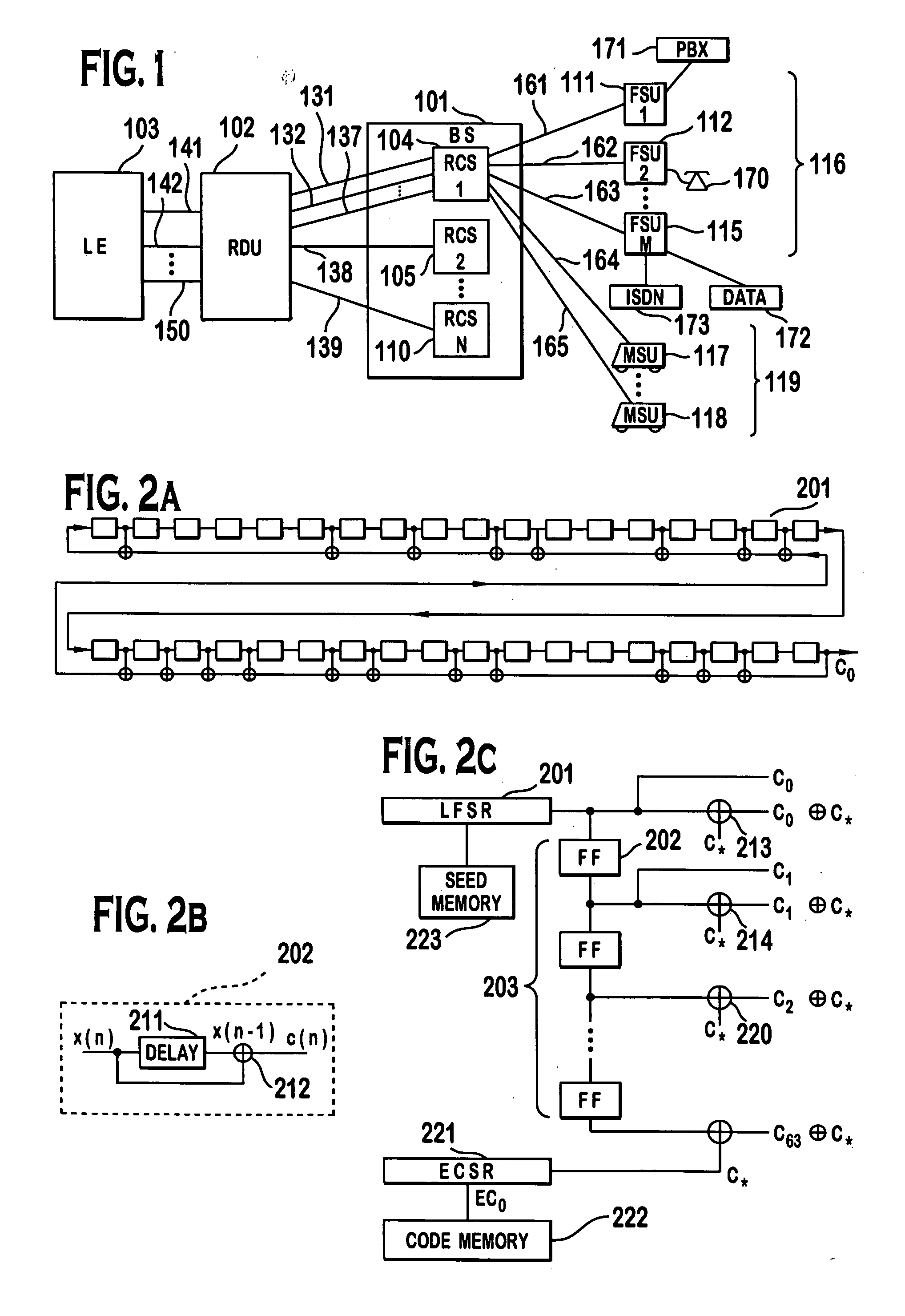
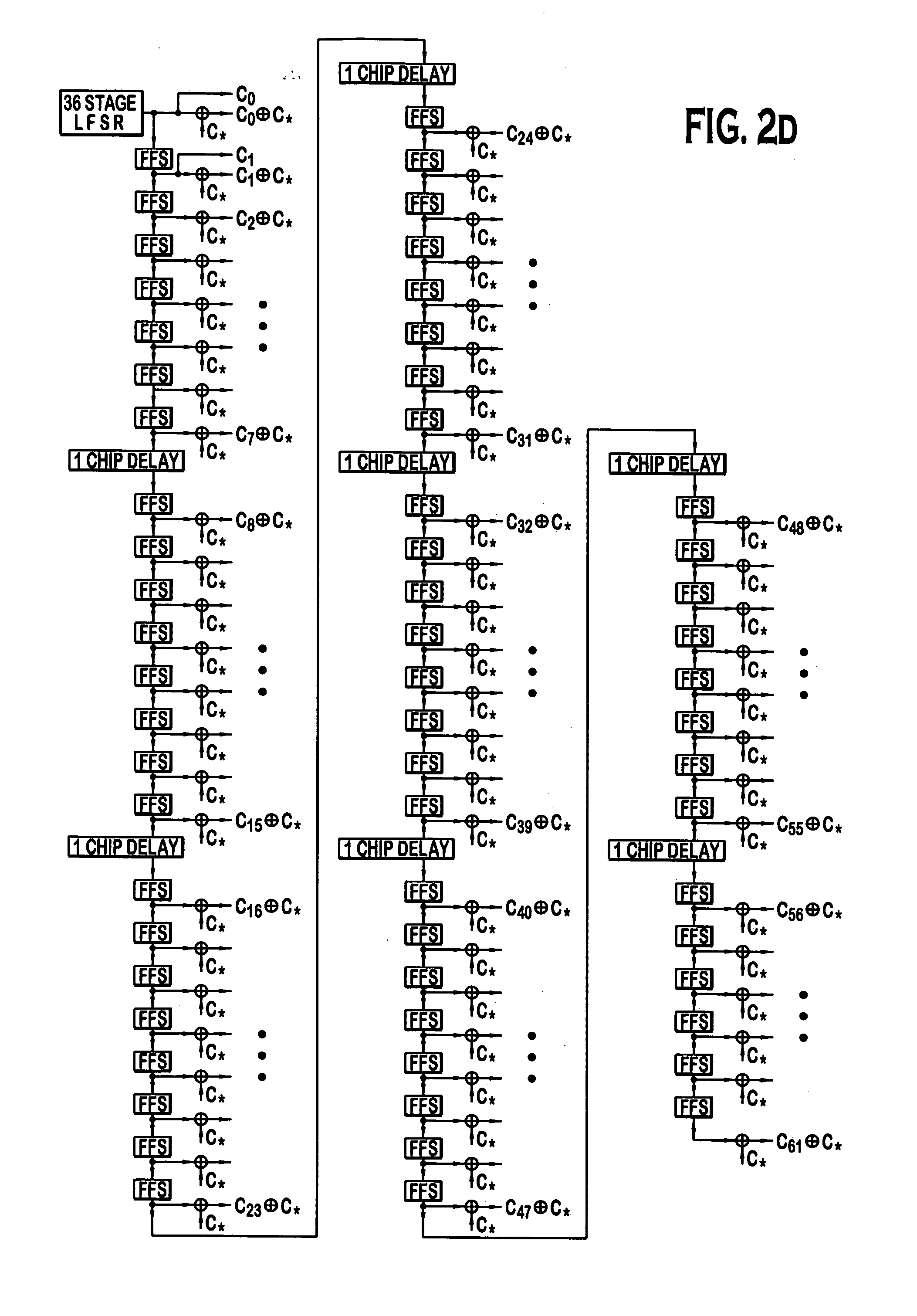
System for using rapid acquisition spreading codes for spread-spectrum communications
InactiveUS20050265430A1Increase profitEnergy efficient ICTRadio transmission for post communicationCode division multiple accessCarrier signal
A system for rapidly acquiring a spreading code, used in a code division multiple access (CDMA) system, comprises a generator for generating a first long code and a second long code, with each long code having a length of N chips. The first long code is different from the second long code. A transmitter transmits the first long code and the second long code at a first phase angle and at a second phase angle, respectively, on a carrier signal over a communications channel using radio waves. The first long code and the second long code may be transmitted at an in-phase (I) angle and at a quadrature-phase (Q) angle, respectively, on the carrier signal. From the communications channel, an I acquisition circuit and a Q acquisition circuit may acquire, in parallel, the first long code and the second long code from the I angle and the Q angle, respectively, of the carrier signal by searching, in parallel, N / 2 chips of the first long code and the second long code.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
Convergence speed, lowering the excess noise and power consumption of equalizers
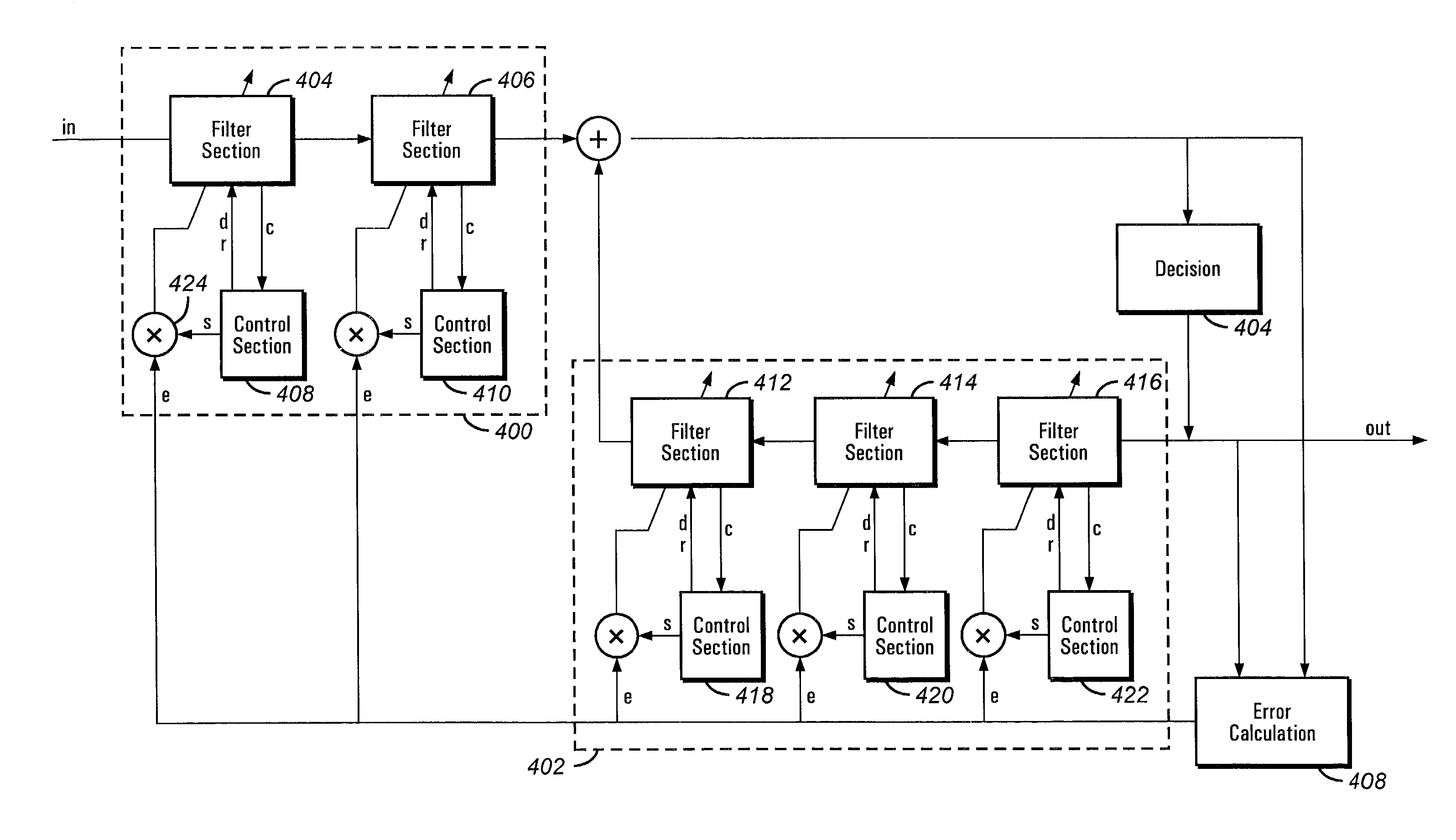
An equalizer for equalizing channel multi-path distortion includes digital filters. To improve the convergence speed and tracking ability of the equalizer while lowering noise and power consumption, the digital filters are divided into sections. Various parameters of the sections, such as step-size, shutdown and update rates can be controlled. Control of the various parameters can be realized either in software on an embedded or external processor or by dedicated hardware.
Owner:CONEXANT SYST INC
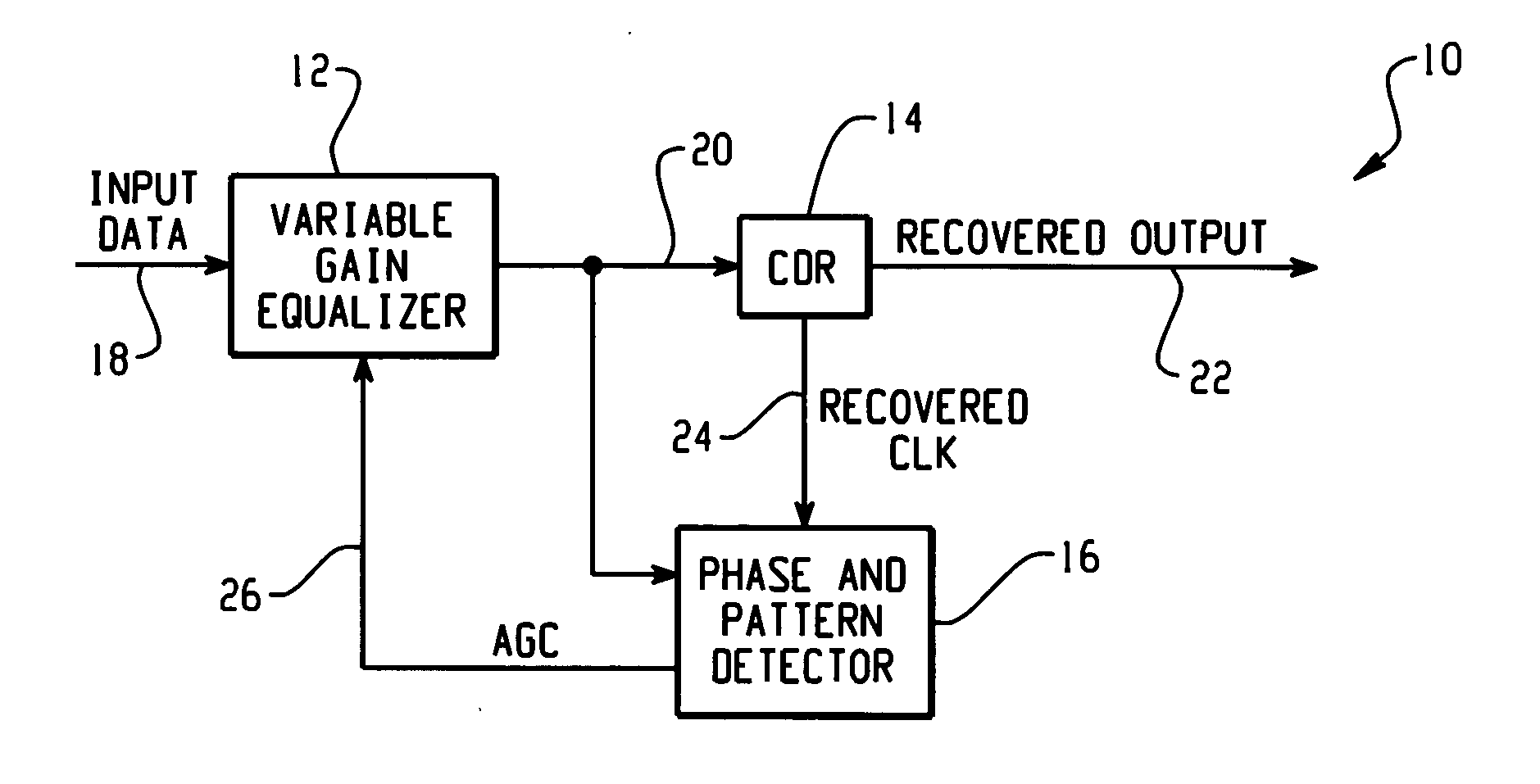
Precision adaptive equalizer
InactiveUS20050047500A1Multiple-port networksAdaptive networkDetector circuitsAutomatic gain control
In accordance with the teachings described herein, systems and methods are provided for a precision adaptive equalizer. A variable gain equalizer may be used to apply a variable gain to an input signal to generate an equalized output signal. A phase and pattern detector circuit may be coupled in a feedback loop with the variable gain equalizer. The phase and pattern detector circuit may be used to identify a high frequency data pattern in the equalized output signal and compare the high frequency data pattern with a clock signal to detect a high frequency phase error. The phase and pattern detector circuit may be further operable to generate an automatic gain control signal as a function of the high frequency phase error, the automatic gain control signal being fed back to the variable gain equalizer to control the variable gain applied to the input signal.
Owner:SEMTECH CANADA
Method and system for active noise cancellation
A method and system for active noise cancellation is provided. The system employs subband processing, and preferably implements over-sampled filterbank. The system is applicable to adaptive noise cancellation, adaptive echo cancellation for portable listening devices, such as headsets and other similar listening devices.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Audio correcting apparatus
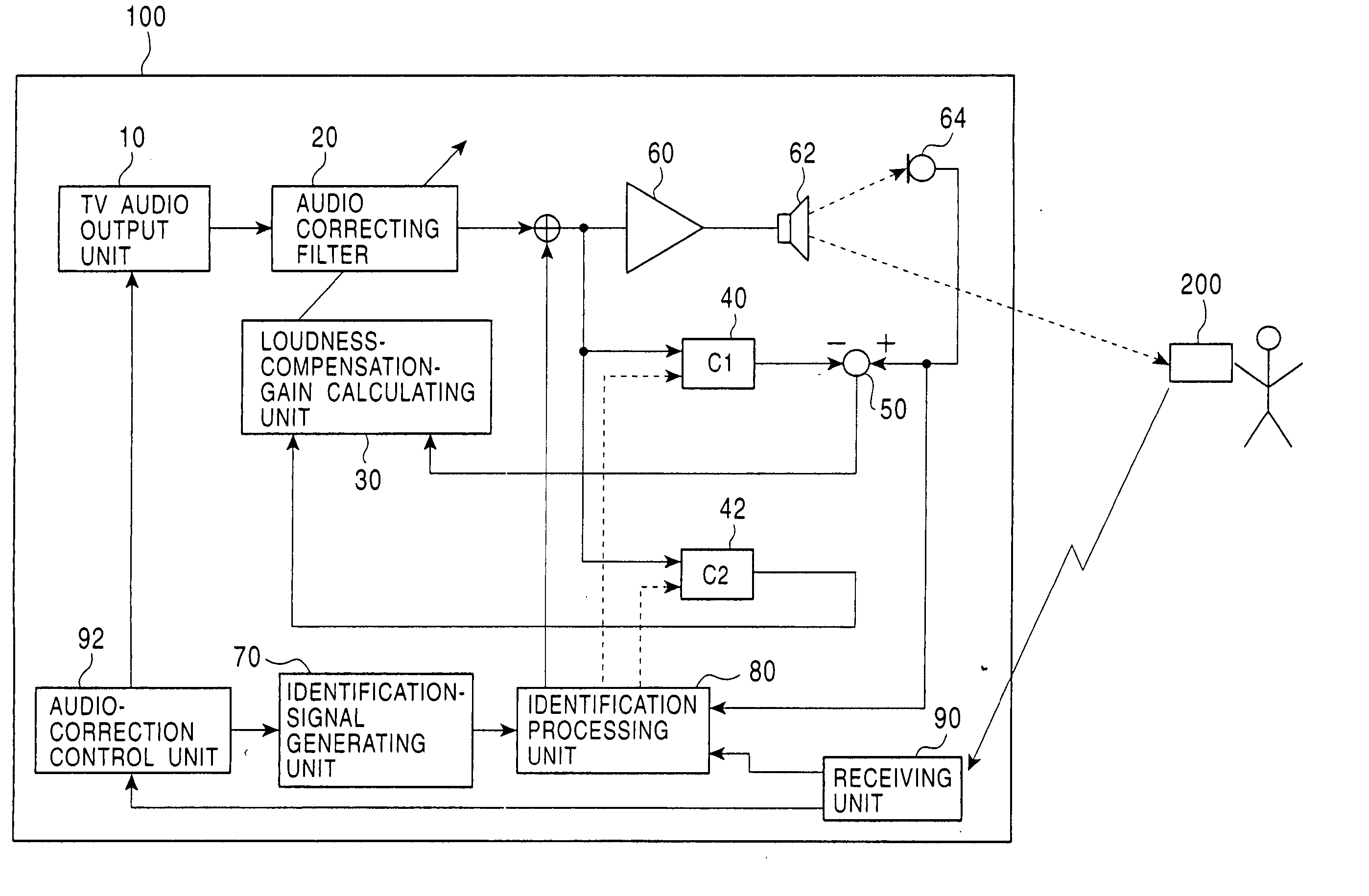
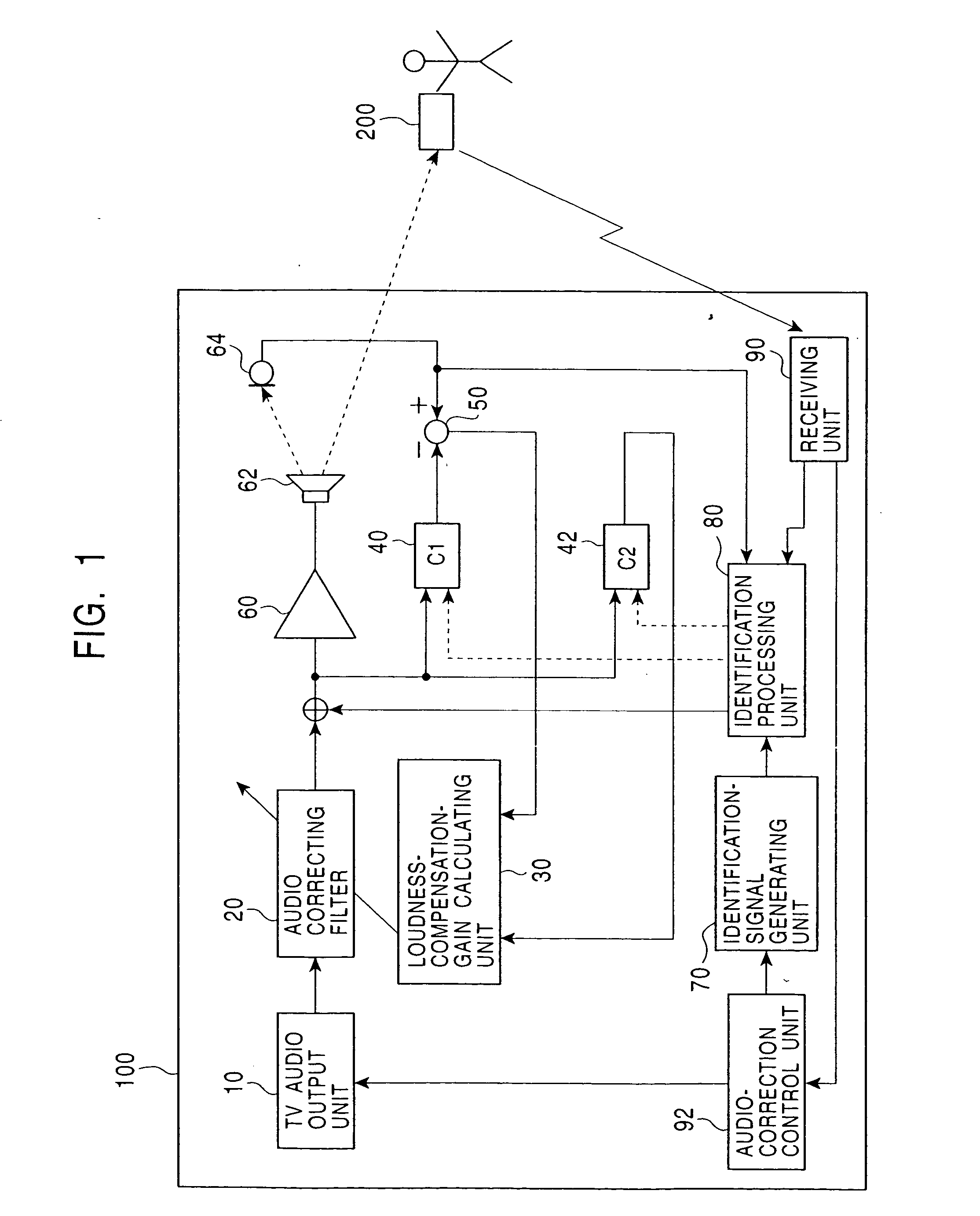
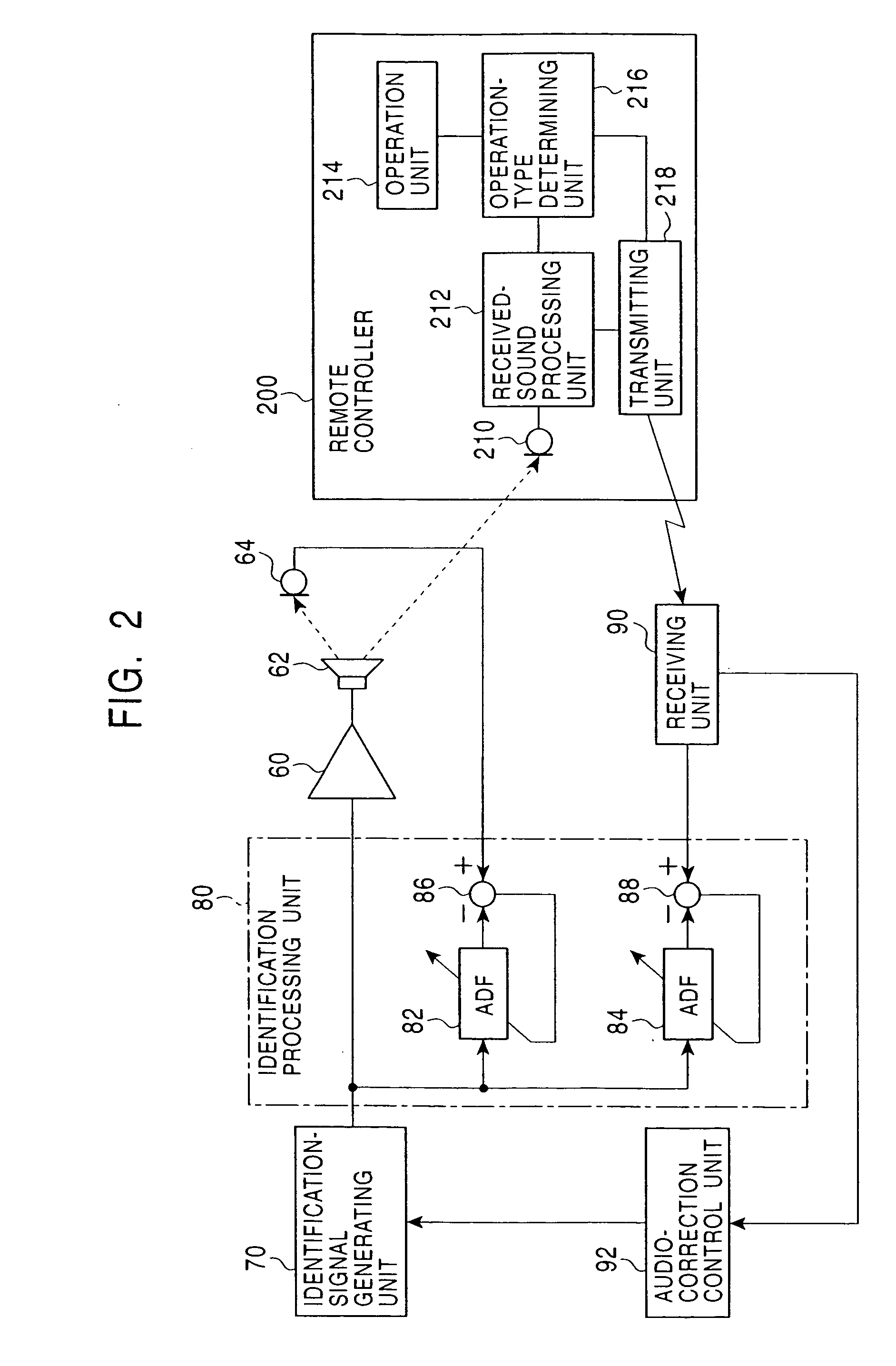
InactiveUS20050013443A1Accurate sound pressure levelListen clearlyTelevision system detailsAdaptive networkEnvironmental noiseLoudspeaker
An audio correcting apparatus includes a speaker provided on a television apparatus, a microphone provided on a remote controller, an identifying unit which identifies an acoustic characteristic from the speaker to the microphone, and an acoustic characteristic setting unit having the acoustic characteristic. A signal obtained by allowing an audio signal input to the speaker to pass through the acoustic characteristic setting unit, and a signal representing ambient noise are input to an audio-correcting filter and a loudness-compensation-gain calculating unit. Based on both signals, the sound pressure level of sound output from the speaker is corrected so that the sound output from the speaker is clearly heard when reaching the user without being affected by the ambient noise.
Owner:ALPINE ELECTRONICS INC
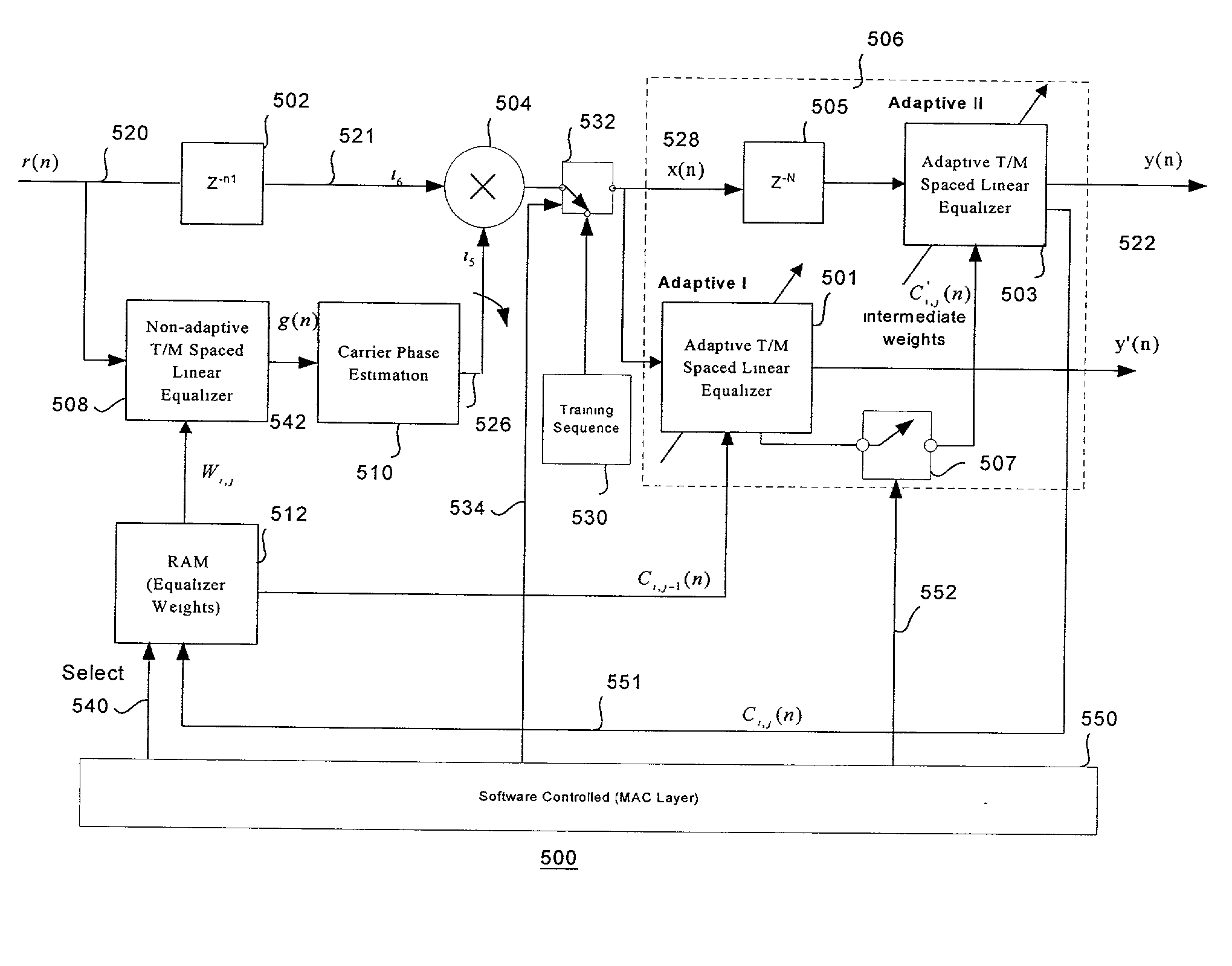
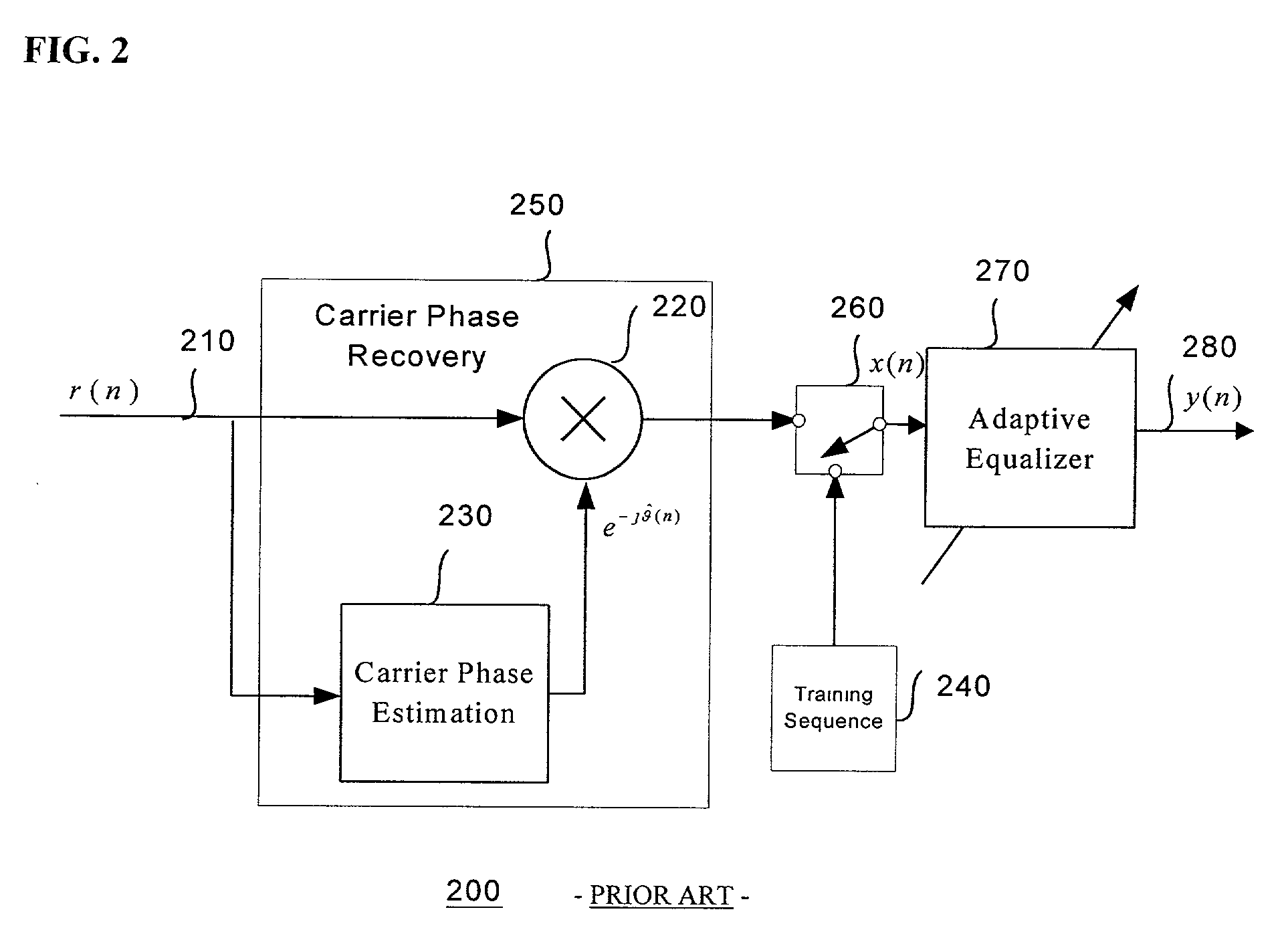
Adaptive equalizer system for short burst modems and link hopping radio networks
InactiveUS6628707B2Multiple-port networksTransmission control/equlisationPhase variationModem device
A method for an adaptive equalization apparatus in a multiple-link hopping radio system includes hopping among a plurality of radio links to receive variable-length bursts of radio signals on the plurality of radio links and equalizing amplitude and phase variations of a slow channel for each radio link from a received burst on the radio link. Further, the method includes storing the estimated tap coefficients pertinent to each radio link and using the tap weights of the current burst of the radio link to reliably pre-compensate the channel amplitude and phase distortion of a next received burst on the radio link.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Aliasing reduction using complex-exponential modulated filterbanks
ActiveUS7242710B2Signal can be impairedMitigation of impairmentMultiple-port networksAdaptive networkFrequency spectrumComputer science
The present invention proposes a new method and apparatus for the improvement of digital filterbanks, by a complex extension of cosine modulated digital filterbanks. The invention employs complex-exponential modulation of a low-pass prototype filter and a new method for optimizing the characteristics of this filter. The invention substantially reduces artifacts due to aliasing emerging from independent modifications of subband signals, for example when using a filterbank as an spectral equalizer. The invention is preferably implemented in software, running on a standard PC or a digital signal processor (DSP), but can also be hardcoded on a custom chip. The invention offers essential improvements for various types of digital equalizers, adaptive filters, multiband companders and spectral envelope adjusting filterbanks used in high frequency reconstruction (HFR) systems.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
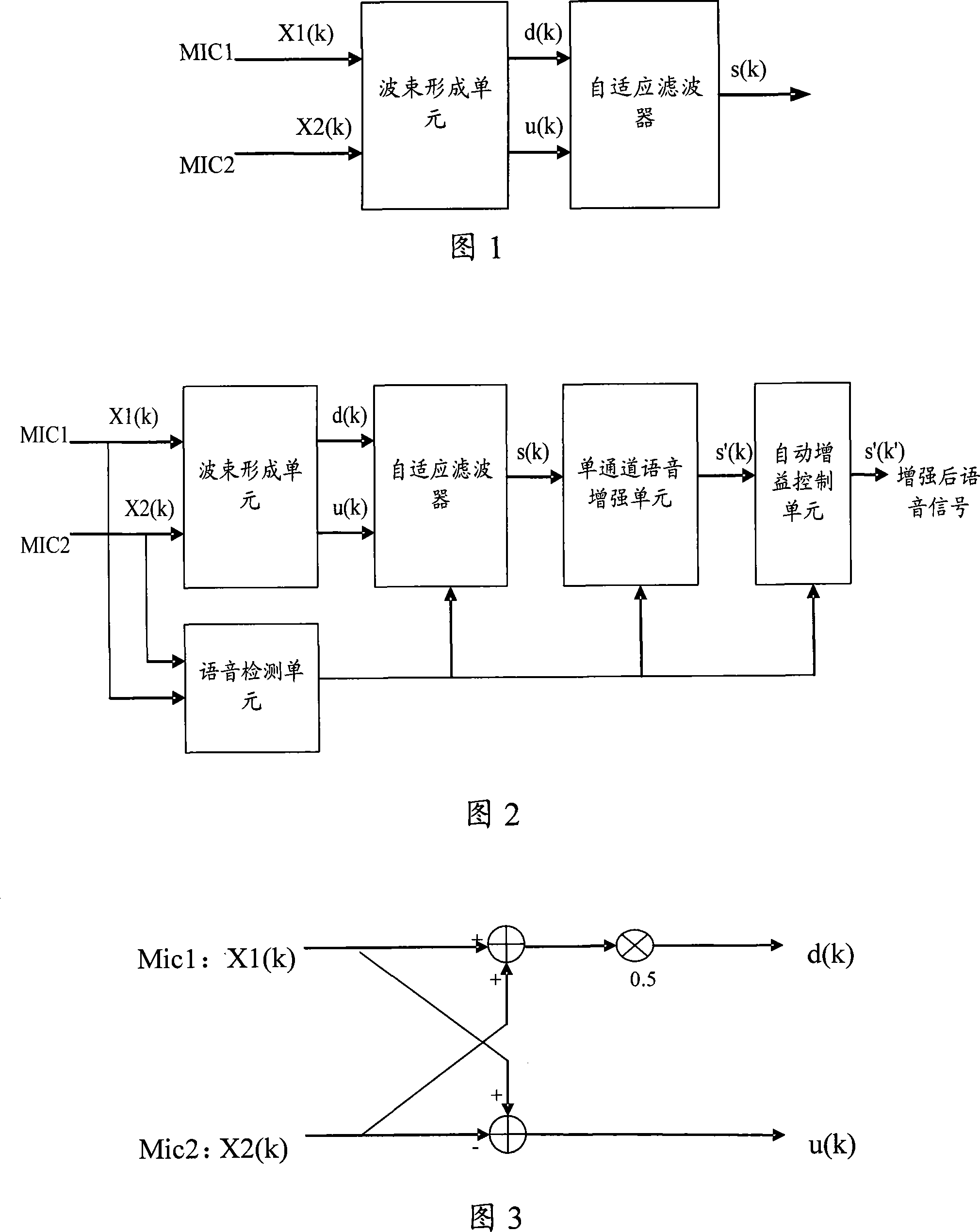
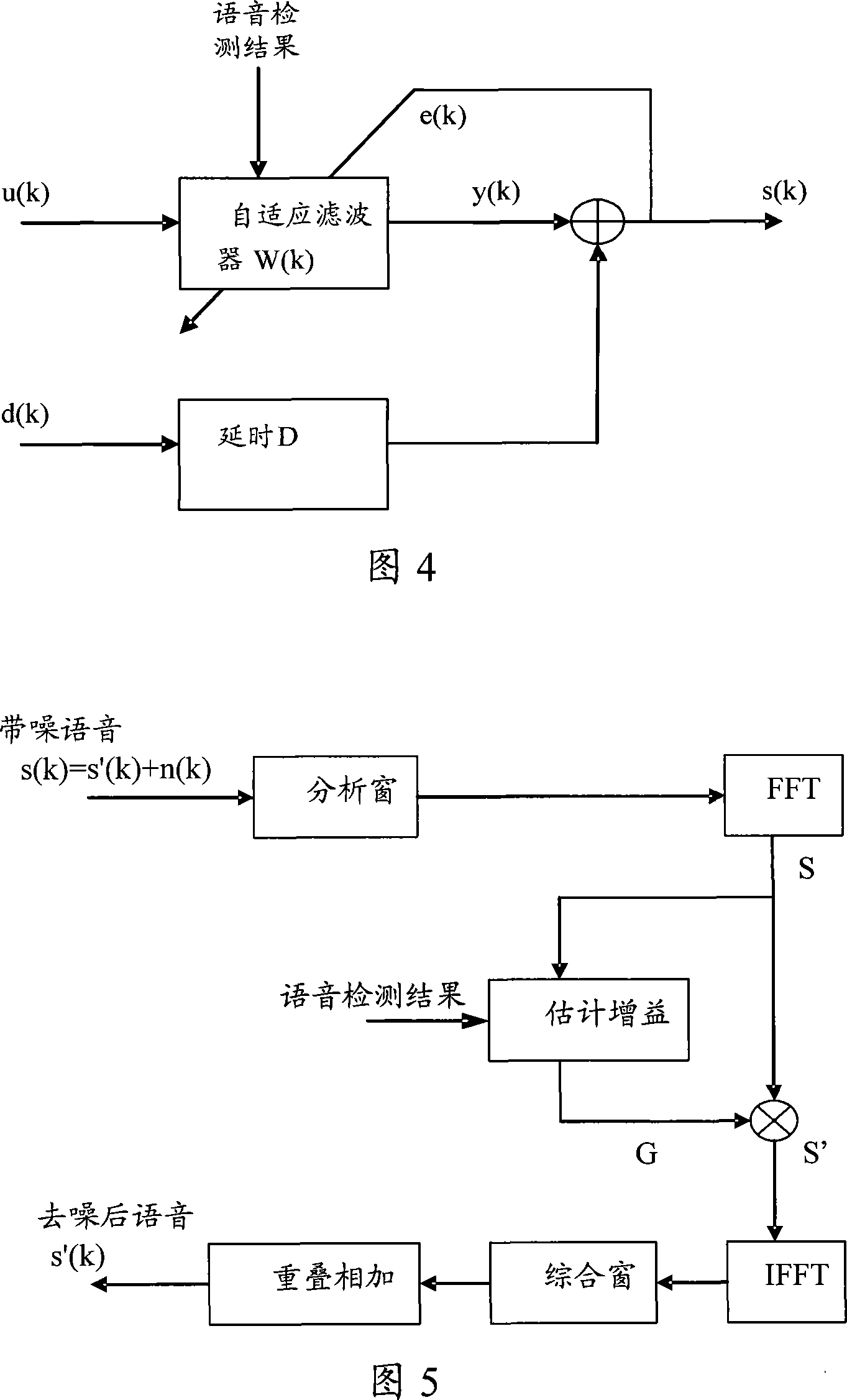
Large distance microphone array noise cancellation method and noise cancellation system
InactiveCN101192411AImprove noise cancellationImprove elimination effectAdaptive networkSpeech analysisEngineeringLarge distance
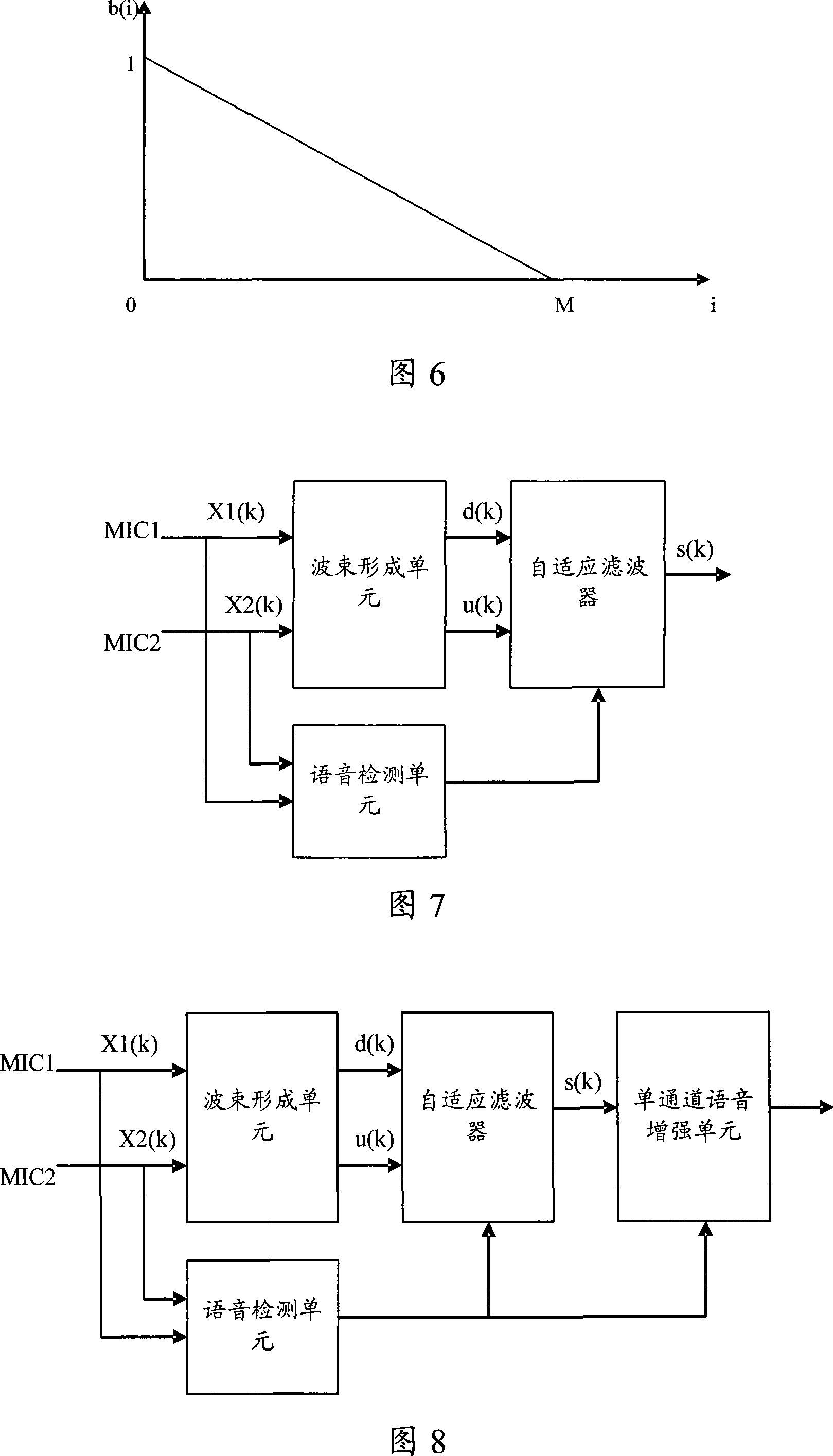
The invention discloses a method for eliminating noise of a long-distance microphone array and a noise-eliminating system. In the invention, the signals collected from two microphones are treated with respect to beam forming, and then the intensified target phonetic signals and the weakened target phonetic signals are obtained; whether target phonetic signals exist in the signals collected from the two microphones is further tested; the update of the adaptive filter coefficient is controlled based on the test result; and lastly, based on a controlled adaptive filter coefficient, the obtained intensified target phonetic signals and the weakened target phonetic signals undergo an adaptive filter process. According to the invention, the performance of noise elimination is greatly improved without affecting the quality of the target phonetics even in case that the microphones are not increased in number.
Owner:VIMICRO CORP
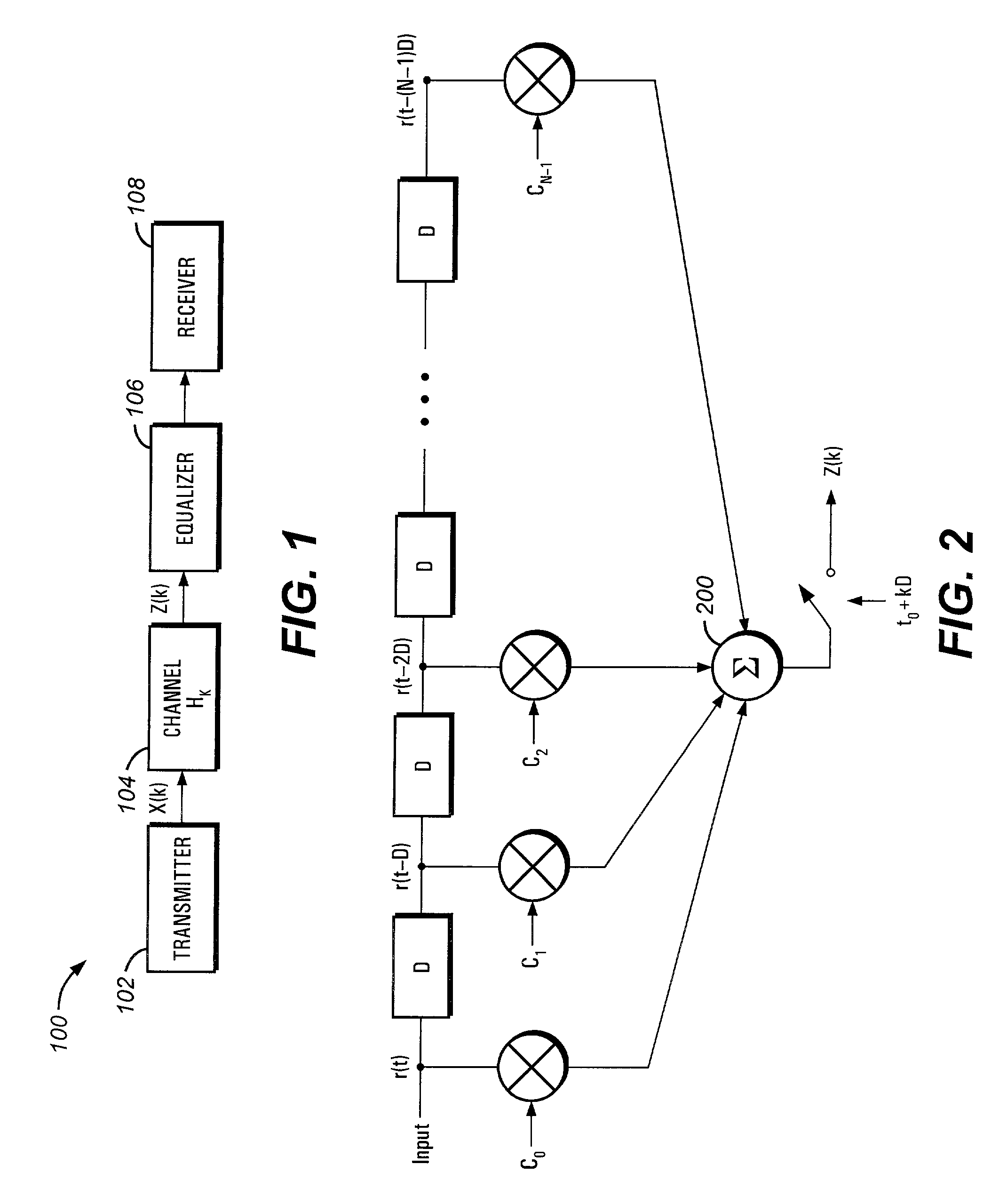
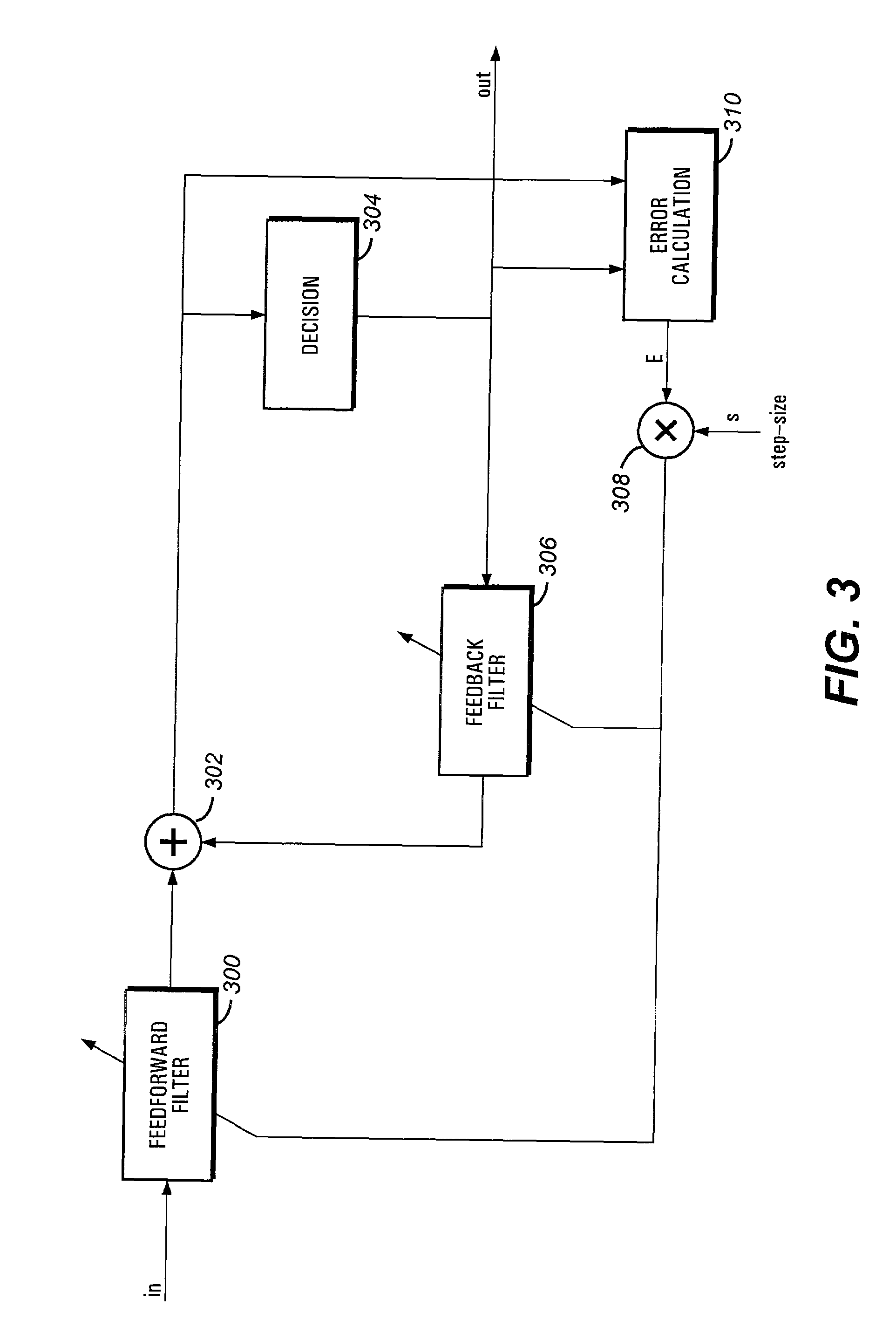
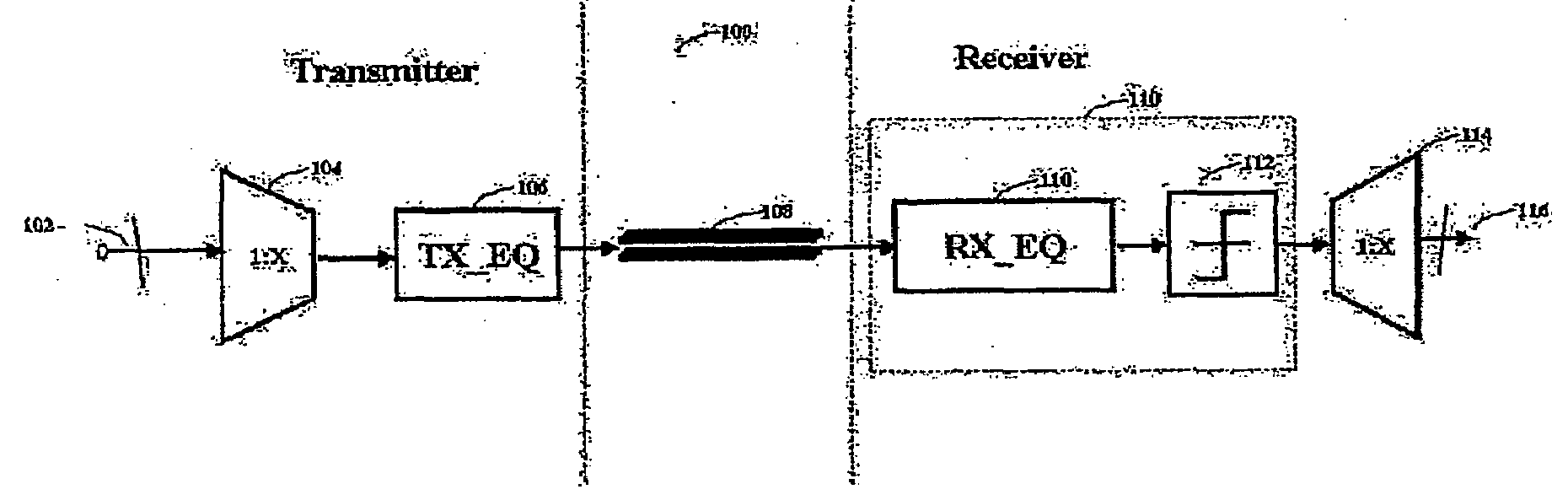
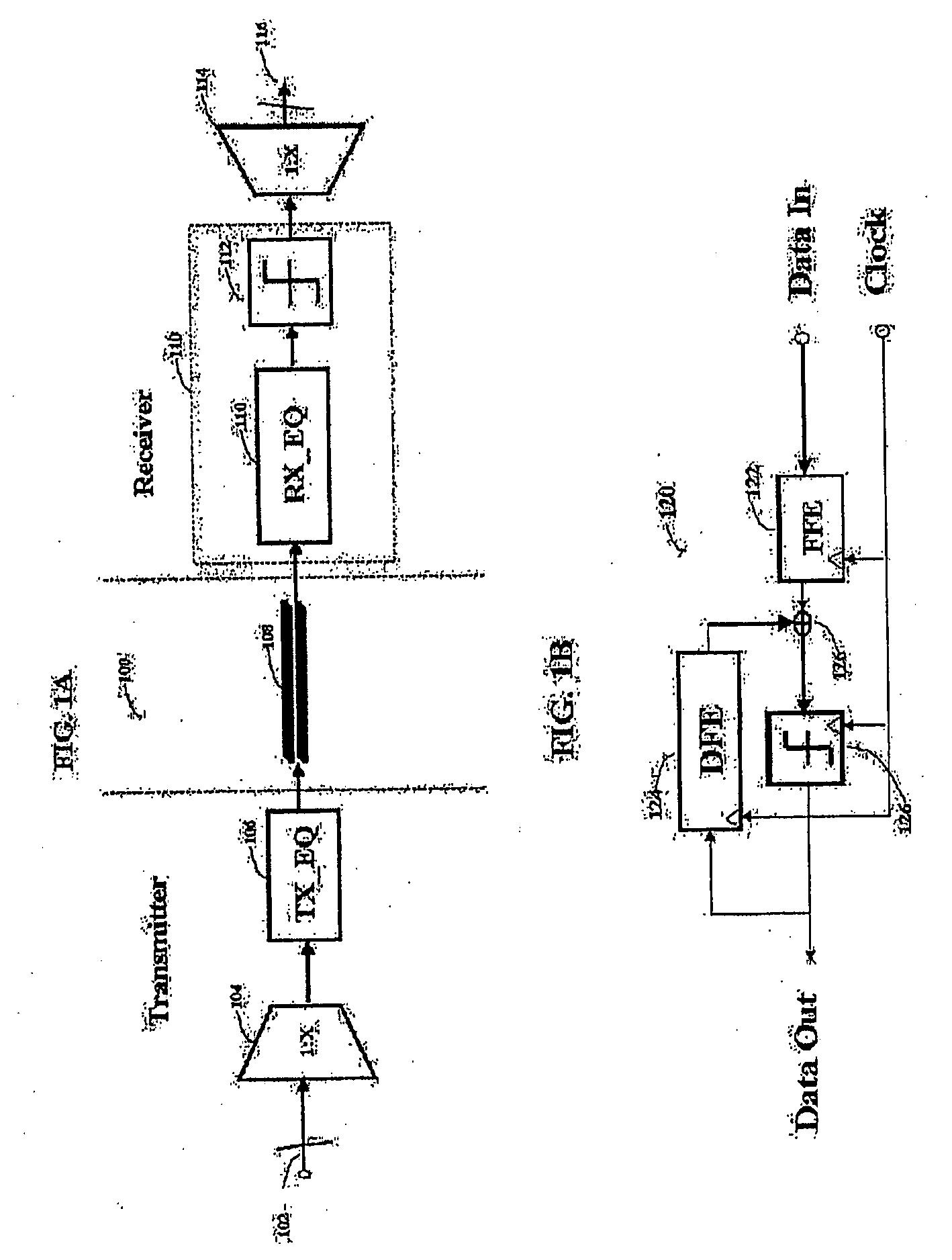
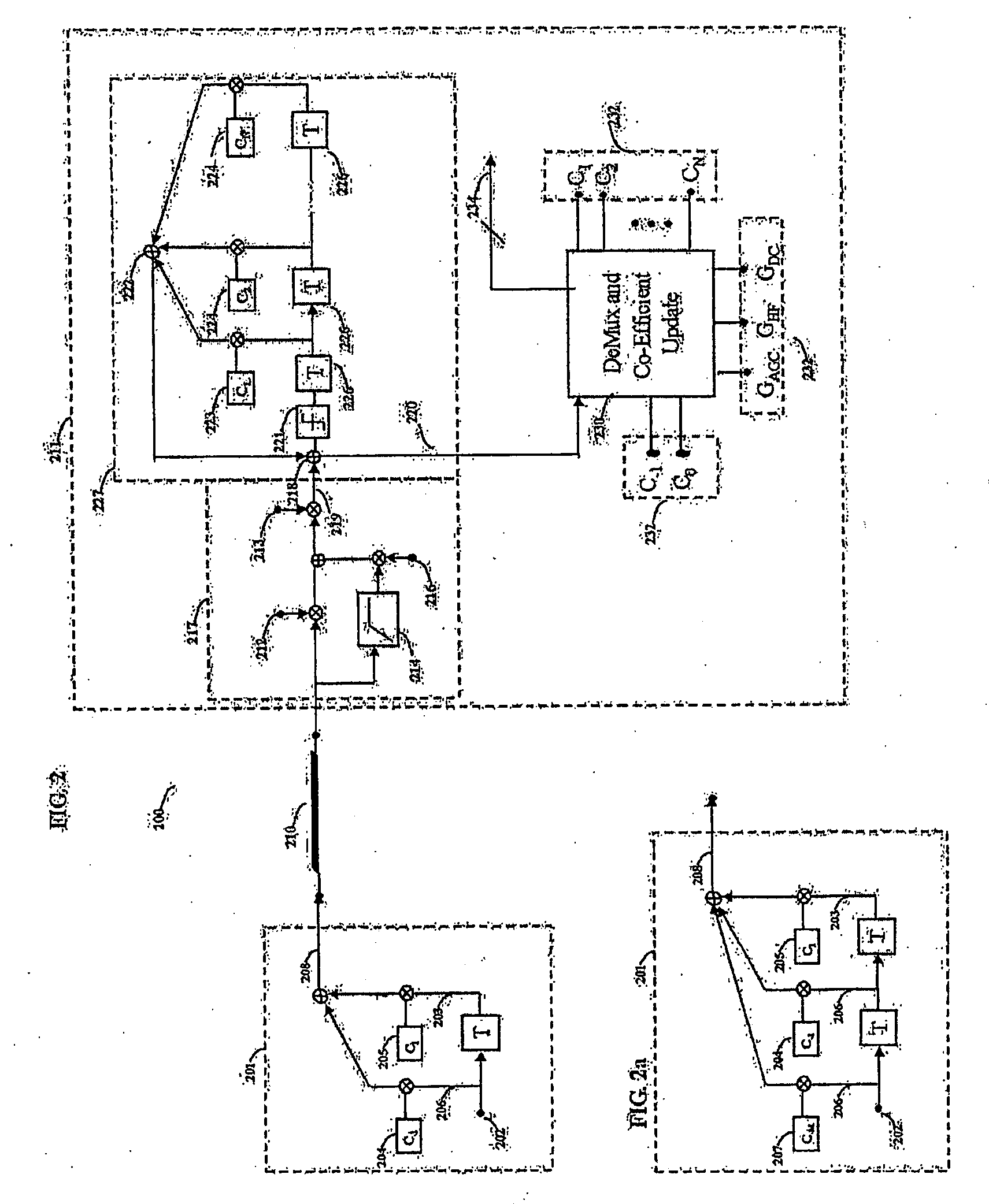
Fully adaptive equalization for high loss communications channels
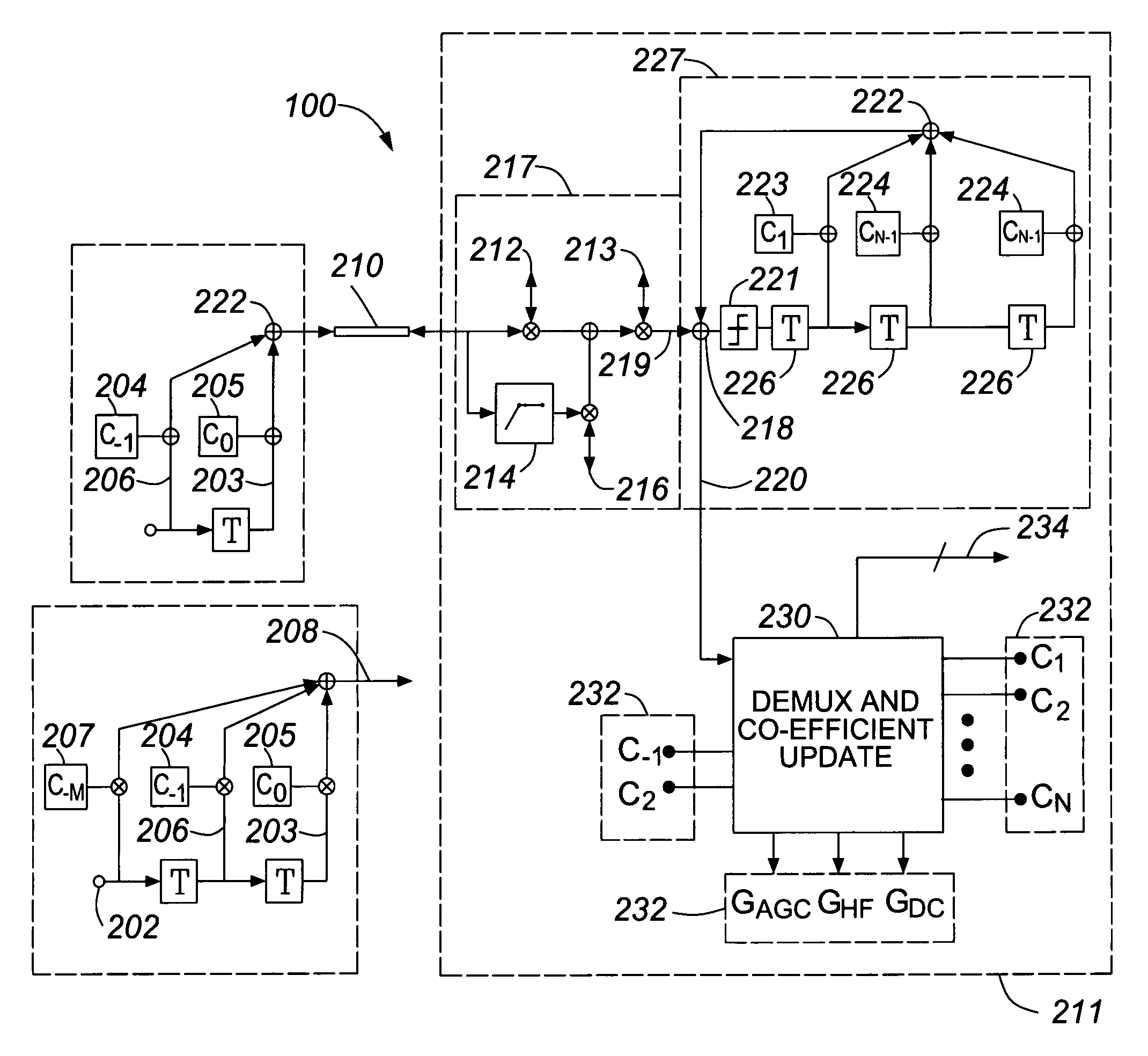
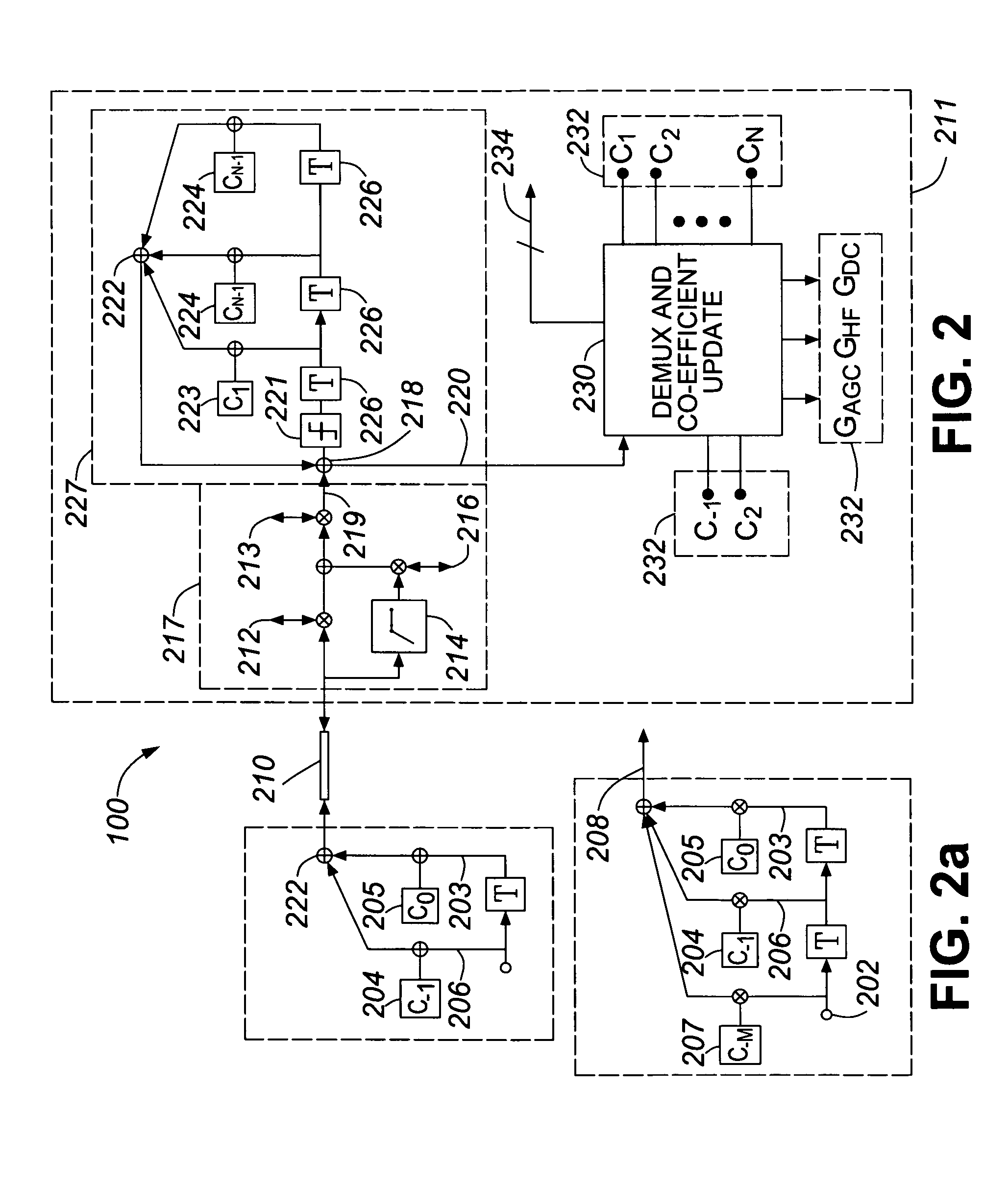
An equalization circuit is disclosed that enables high data rate transmission over high loss communications channels. Also disclosed is a set of functional blocks and update criteria that allow for the equalization function to be adapted for a large variety of different communications channels. A fully continuous adaptive equalizer is used in conjunction with a Decision Feedback Equalizer to fully equalize a large number of communications channels.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
Advanced periodic signal enhancement
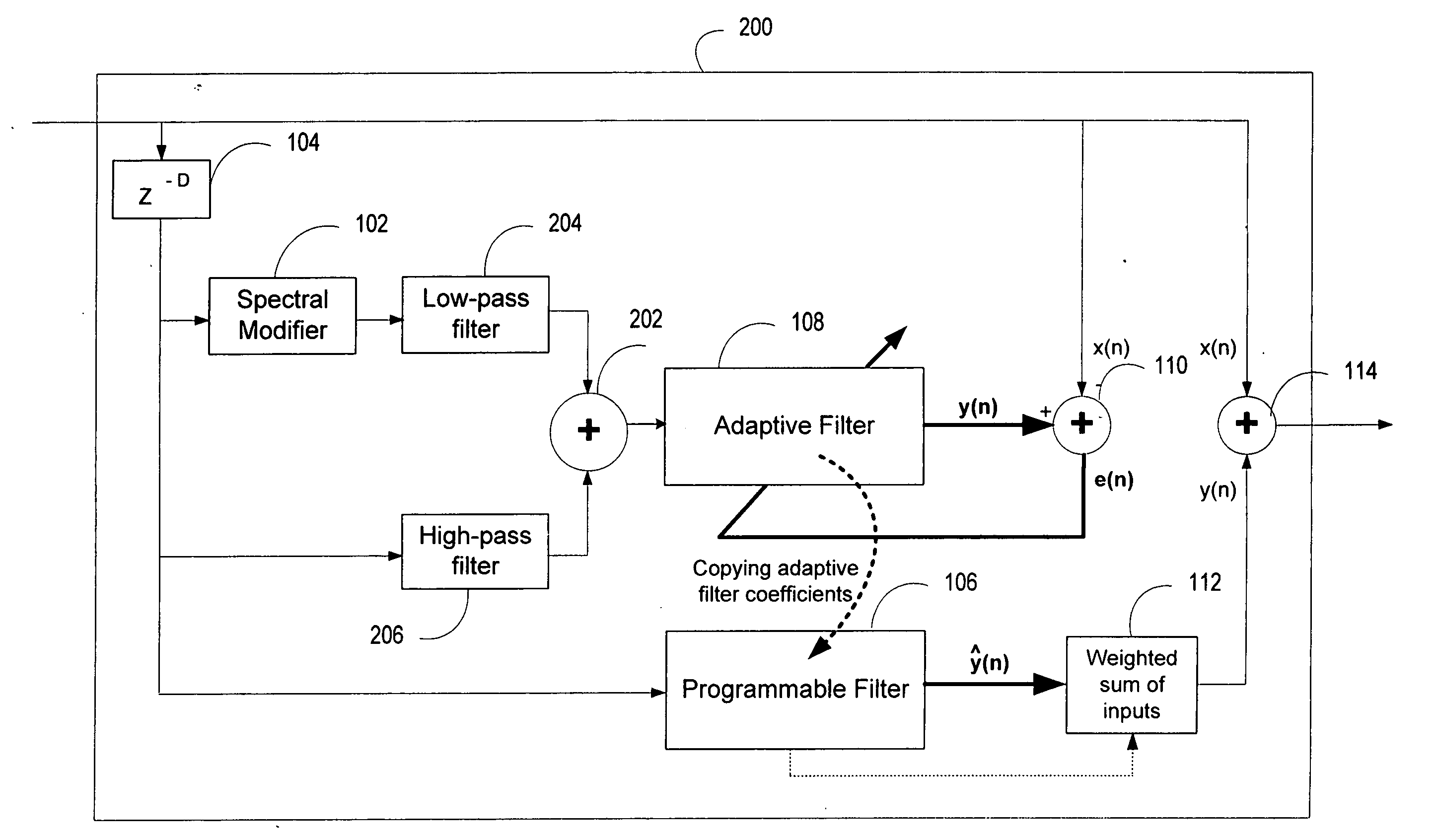
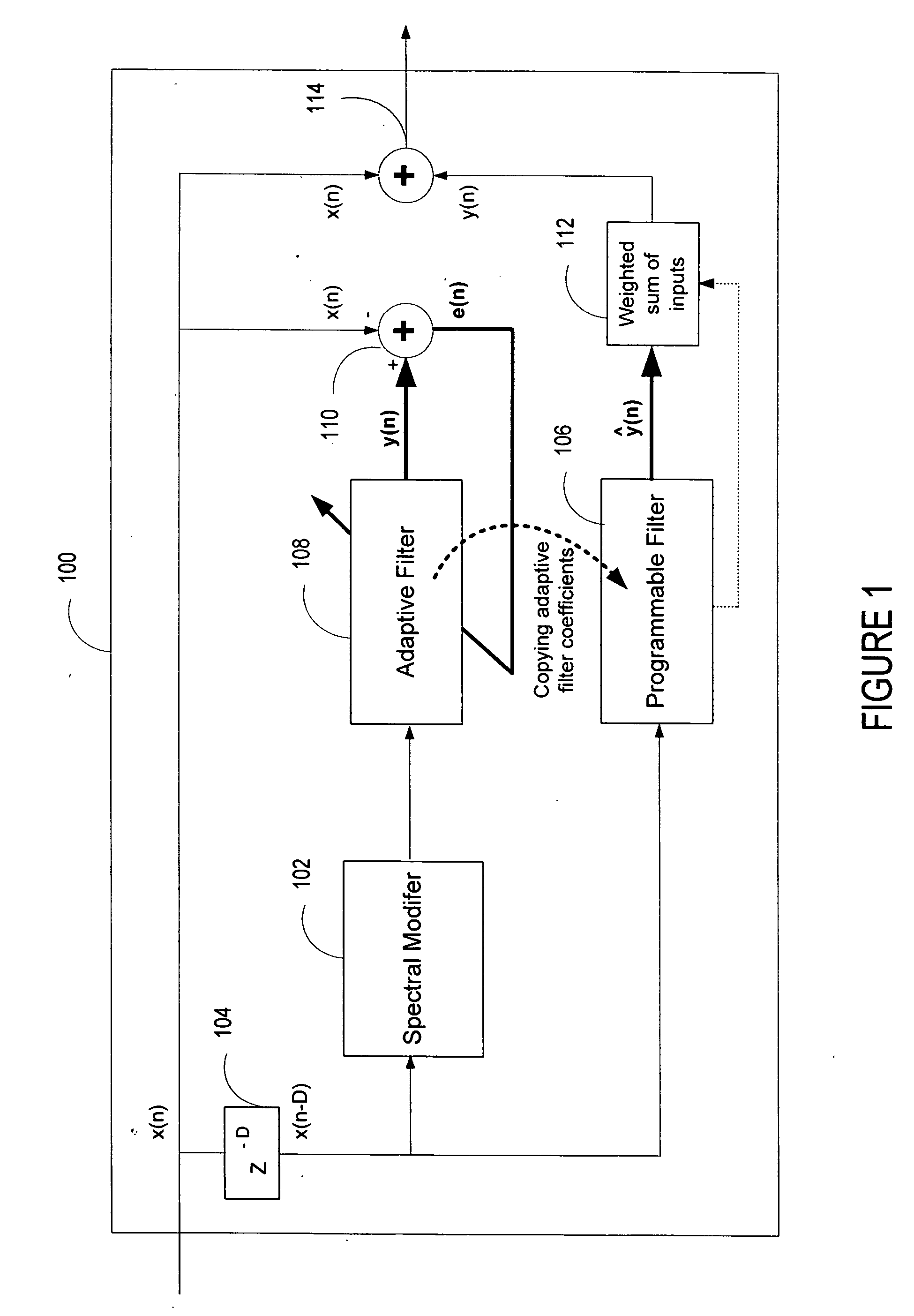
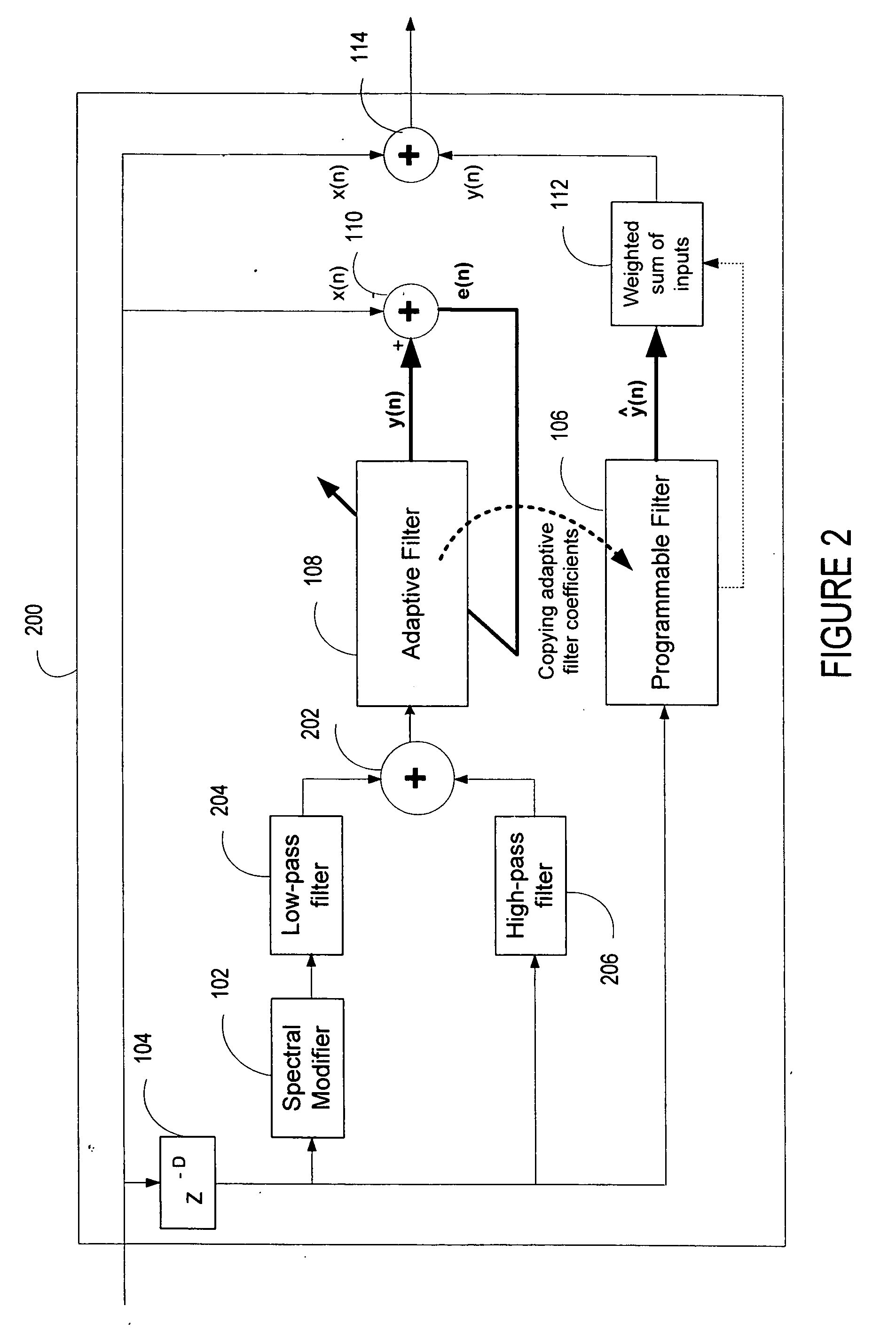
ActiveUS20060136199A1Improve processing qualityFlatten spectral character of background noiseAdaptive networkSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumProgrammable filters
An enhancement system improves the perceptual quality of a processed speech. The system includes a delay unit that delays a signal received through a discrete input. A spectral modifier linked to the delay unit is programmed to substantially flatten the spectral character of a background noise. An adaptive filter linked to the spectral modifier adapts filter characteristics to match a response of a non-delayed signal. A programmable filter is linked to the delay unit. The programmable filter has a transfer function functionally related to a transfer function of the adaptive filter.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
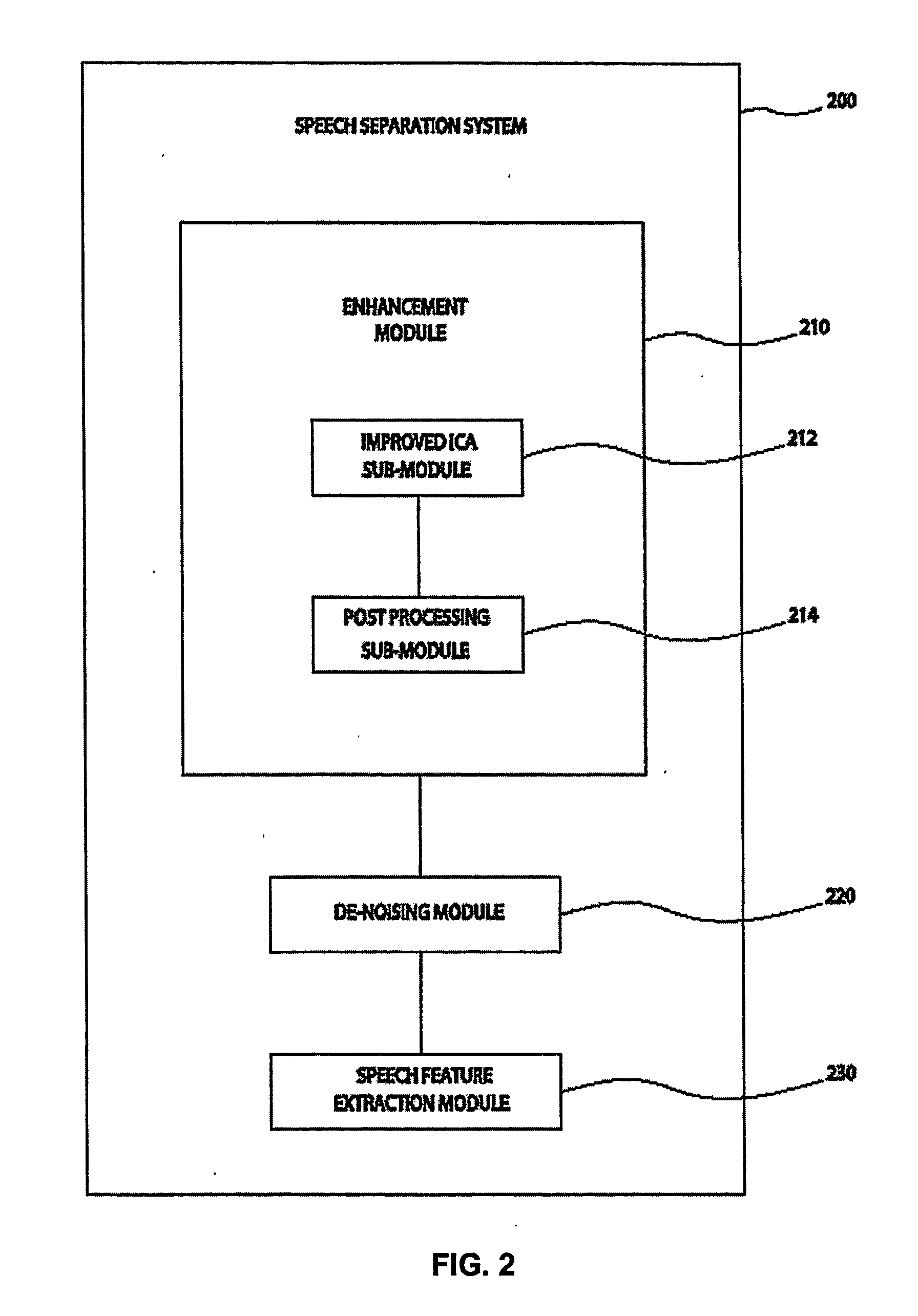
System and method for speech processing using independent component analysis under stability restraints
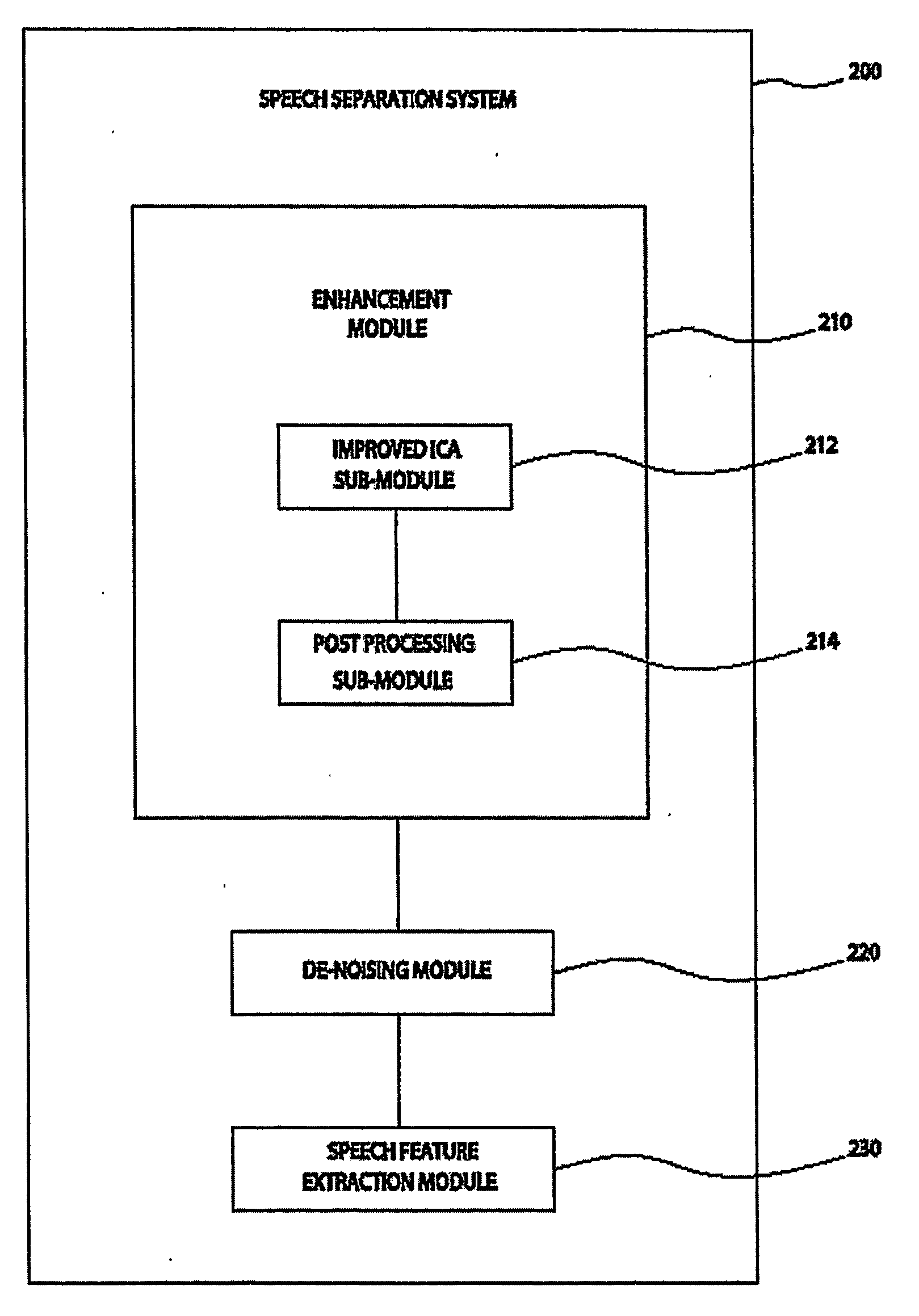
ActiveUS20060053002A1Constrain filter weight adaptation speedAvoid reverberation effectAdaptive networkSpeech analysisLearning ruleIndependent component analysis
A system and method for separating a mixture of audio signal into desired audio signals (430) (e.g., speech) and a noise sign (440) is disclosed. Microphones (310, 320) are positioned to receive the mixed audio signals, and an independent component analysis (ICA) processes (212) the sound mixture using stability constraints. The ICA process (508) uses predefined characteristics of the desired speech signal to identify and isolate a target sound signal (430). Filter coefficients are adapted with a learning rule and filter weight update dynamics are stabilized to assist convergence to a stable separated ICA signal result. The separated signals may be peripherally-processed to further reduce noise effects using post-processing (214) and pre-processing (220, 230) techniques and information. The proposed system is designed and easily adaptable for implementation on DSP units or CPUs in audio communication hardware environments.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
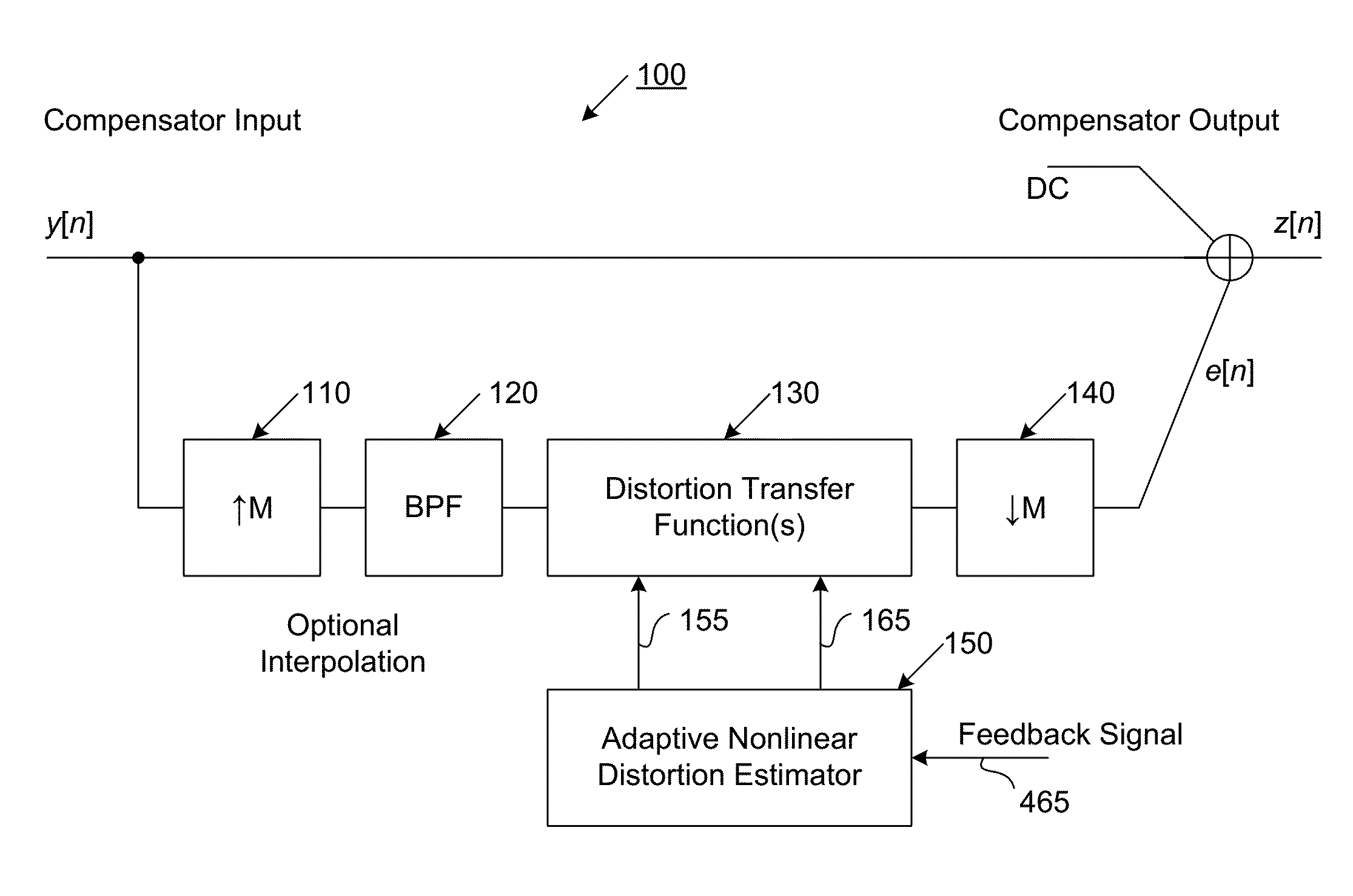
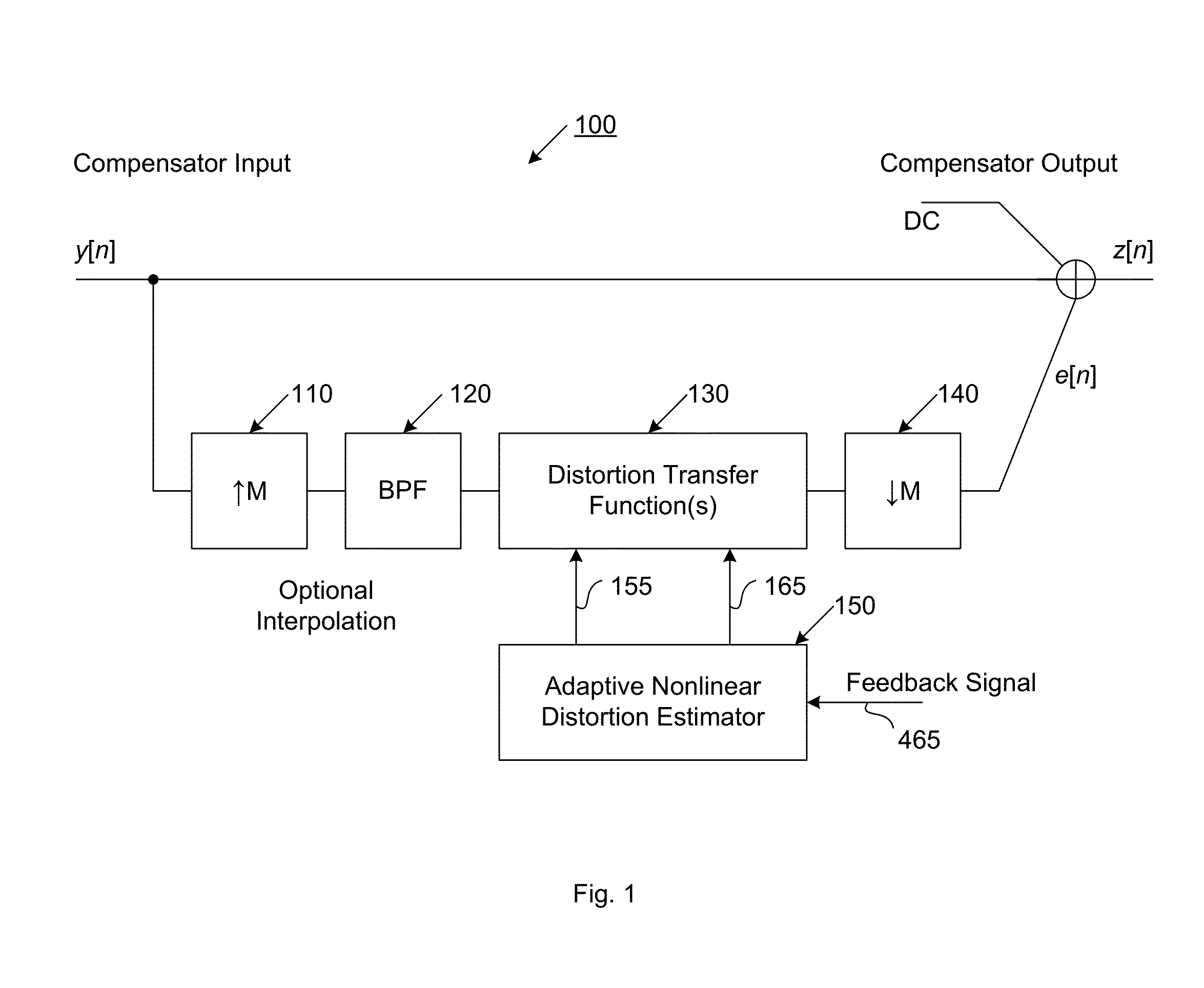
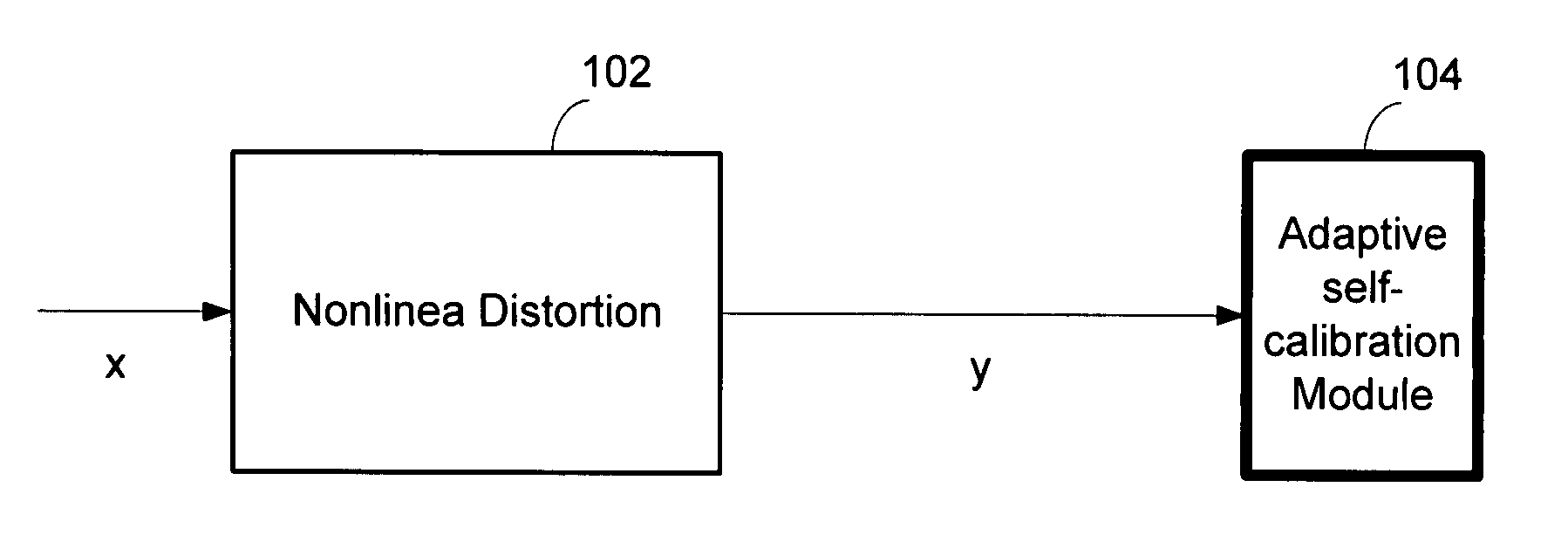
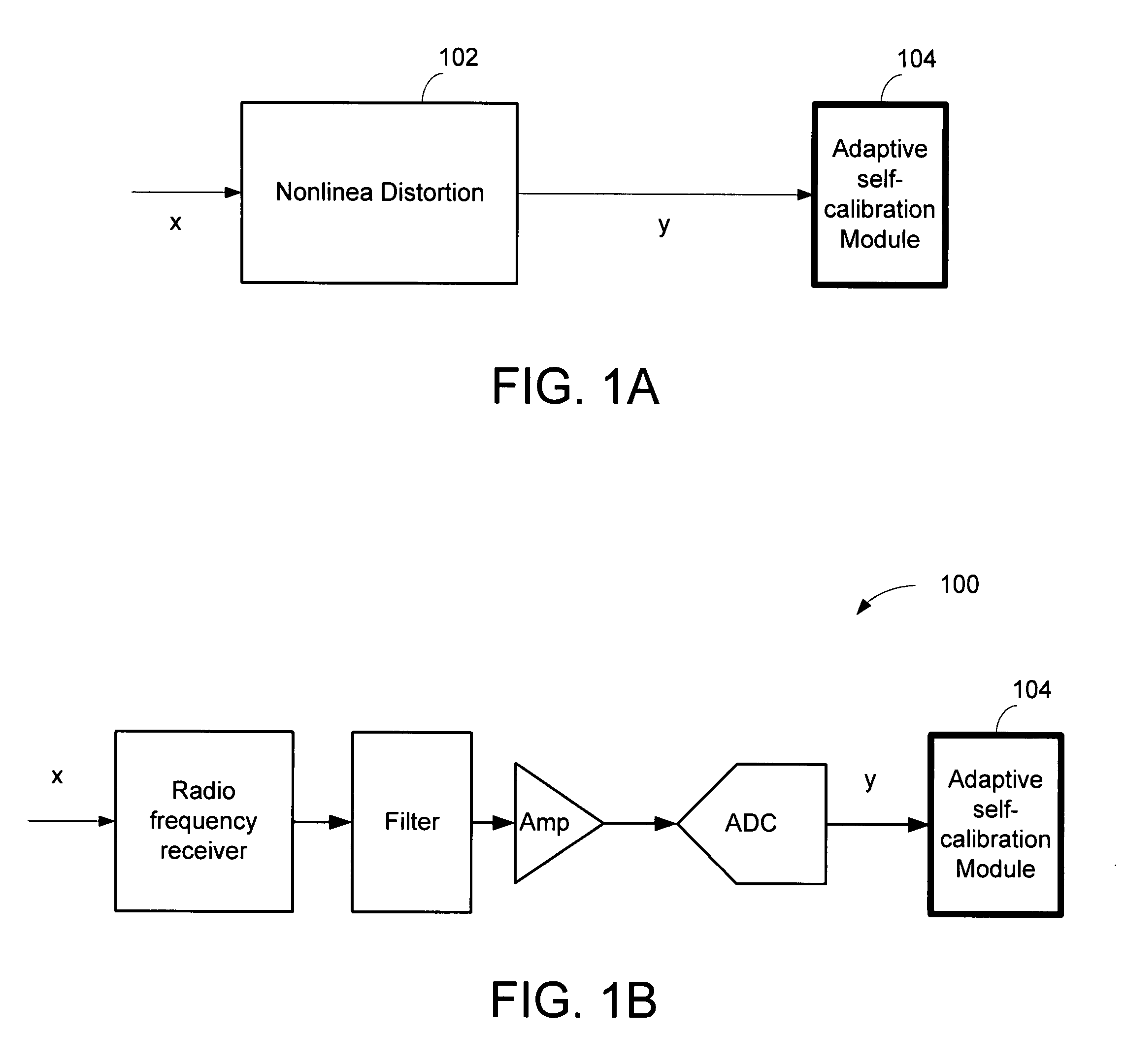
Compensator for removing nonlinear distortion
ActiveUS20160191020A1Easy to processReduce complexityChannel dividing arrangementsElectric signal transmission systemsNonlinear distortionComputation complexity
The present invention is a computationally-efficient compensator for removing nonlinear distortion. The compensator operates in a digital post-compensation configuration for linearization of devices or systems such as analog-to-digital converters and RF receiver electronics. The compensator also operates in a digital pre-compensation configuration for linearization of devices or systems such as digital-to-analog converters, RF power amplifiers, and RF transmitter electronics. The compensator effectively removes nonlinear distortion in these systems in a computationally efficient hardware or software implementation by using one or more factored multi-rate Volterra filters. Volterra filters are efficiently factored into parallel FIR filters and only the filters with energy above a prescribed threshold are actually implemented, which significantly reduces the complexity while still providing accurate results. For extremely wideband applications, the multi-rate Volterra filters are implemented in a demultiplexed polyphase configuration which performs the filtering in parallel at a significantly reduced data rate. The compensator is calibrated with an algorithm that iteratively subtracts an error signal to converge to an effective compensation signal. The algorithm is repeated for a multiplicity of calibration signals, and the results are used with harmonic probing to accurately estimate the Volterra filter kernels. The compensator improves linearization processing performance while significantly reducing the computational complexity compared to a traditional nonlinear compensator.
Owner:LINEARITY LLC
Adaptive equalizer system for short burst modems and link hopping radio networks
InactiveUS20020196844A1Multiple-port networksTransmission control/equlisationPhase variationModem device
A method for an adaptive equalization apparatus in a multiple-link hopping radio system includes hopping among a plurality of radio links to receive variable-length bursts of radio signals on the plurality of radio links and equalizing amplitude and phase variations of a slow channel for each radio link from a received burst on the radio link. Further, the method includes storing the estimated tap coefficients pertinent to each radio link and using the tap weights of the current burst of the radio link to reliably pre-compensate the channel amplitude and phase distortion of a next received burst on the radio link.
Owner:INTEL CORP
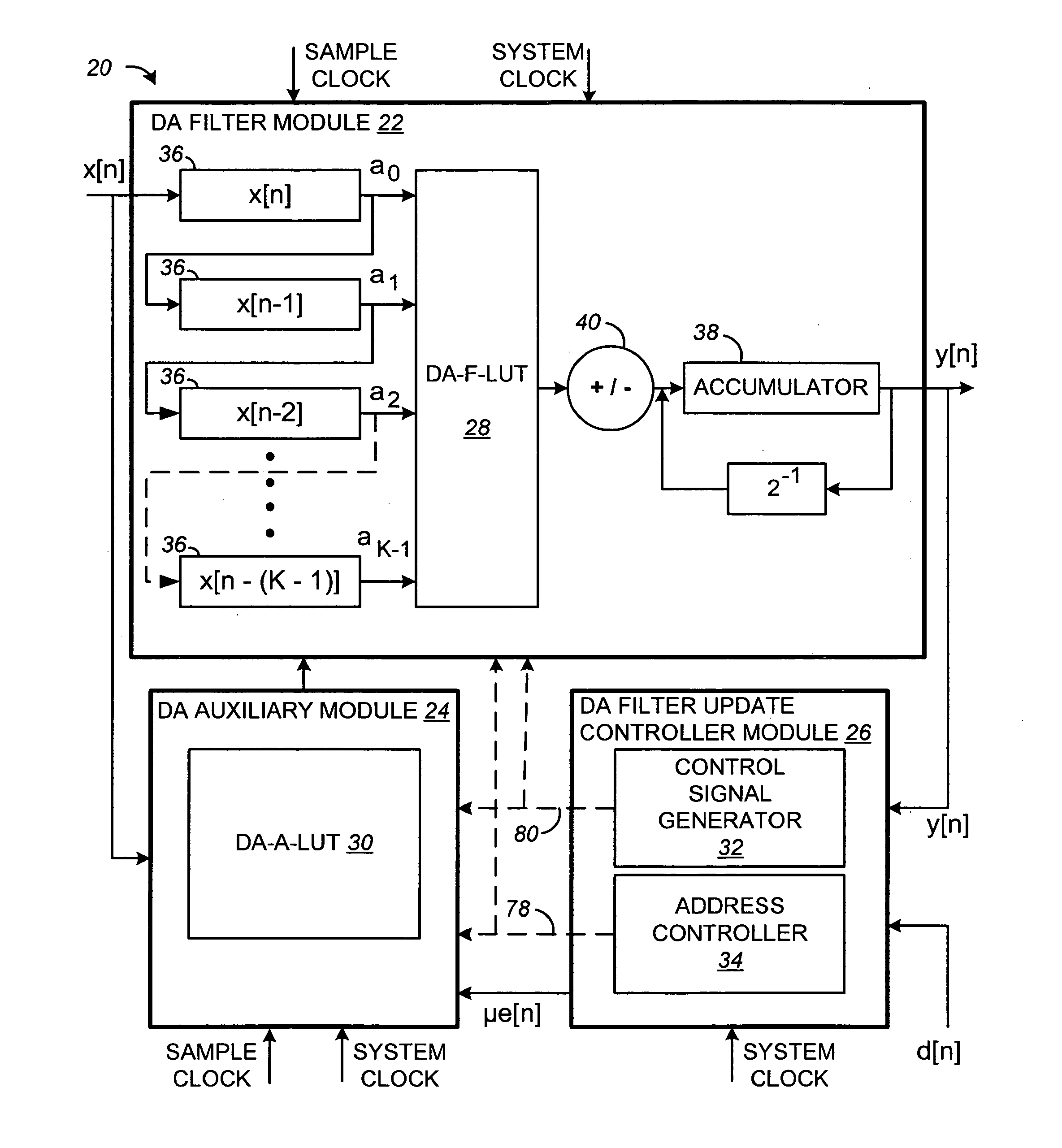
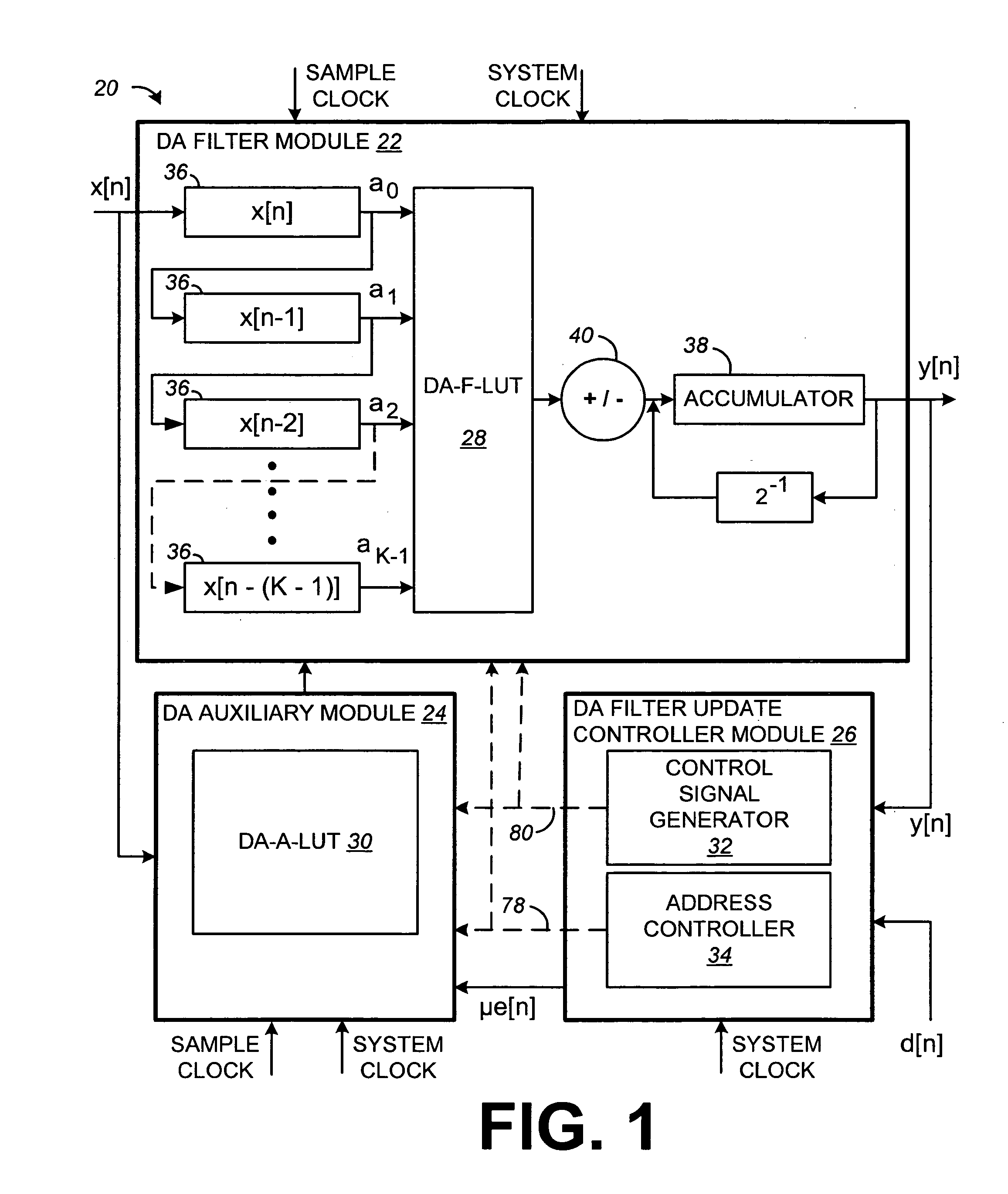
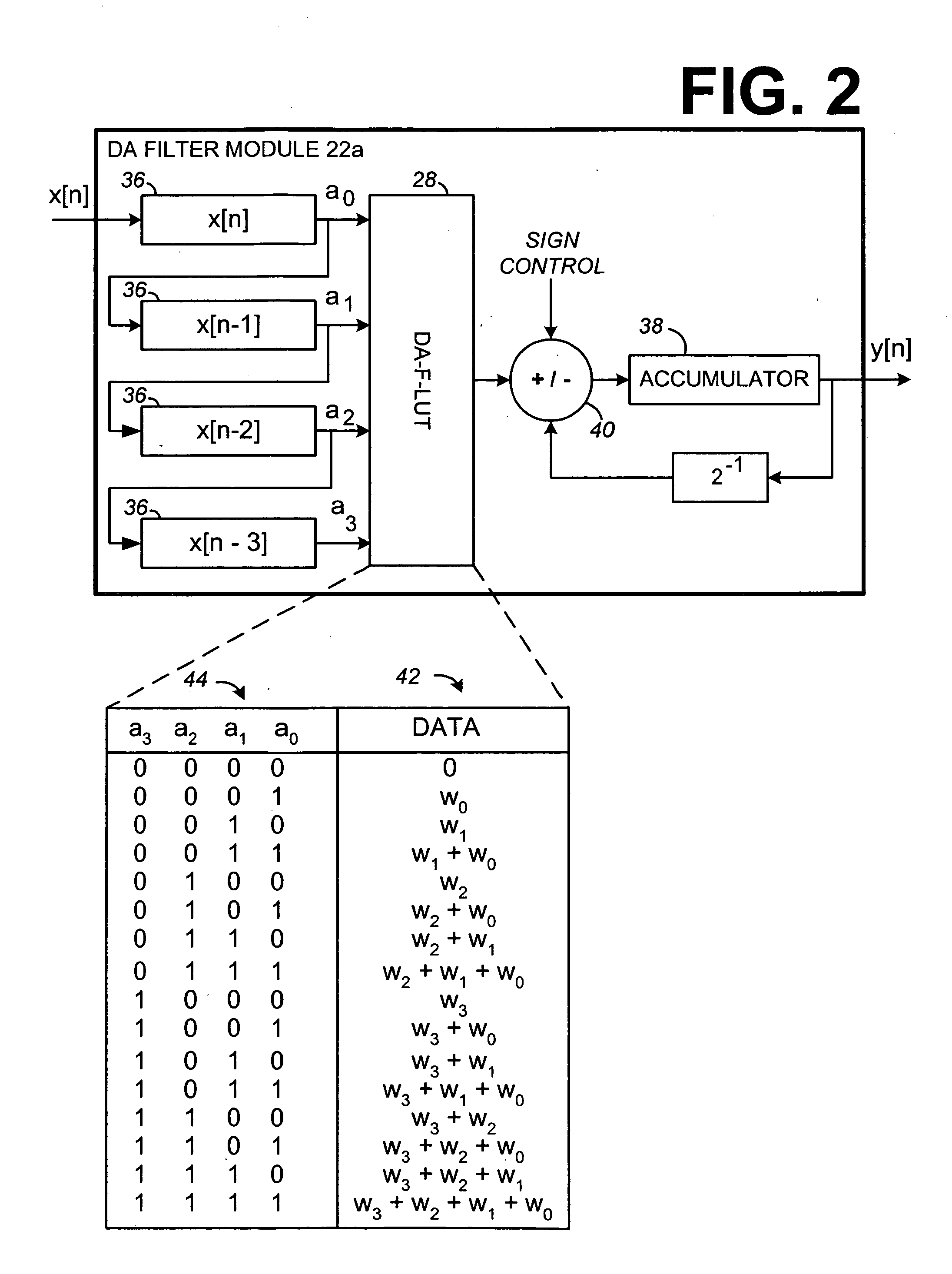
Distributed arithmetic adaptive filter and method
Systems and methods for very high throughput adaptive filtering using distributed arithmetic are disclosed. One distributed arithmetic adaptive filter may include a memory for storing a first and second lookup table. The first lookup table may include 2K filter weights addressed by the rightmost bits of each of K signal samples stored in a plurality of registers. The filter may include a controller configured to update the second lookup table with each possible combination of the sums of the K most recent input samples and update each of the 2K filter weights of the first lookup table based on the combination of the sums of the K most recent input samples stored in the second lookup table. The second lookup-table may be updated during a filtering operation that uses the first lookup-table. One filter may include a plurality of sub-filters with each sub-filter having first and second lookup tables.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
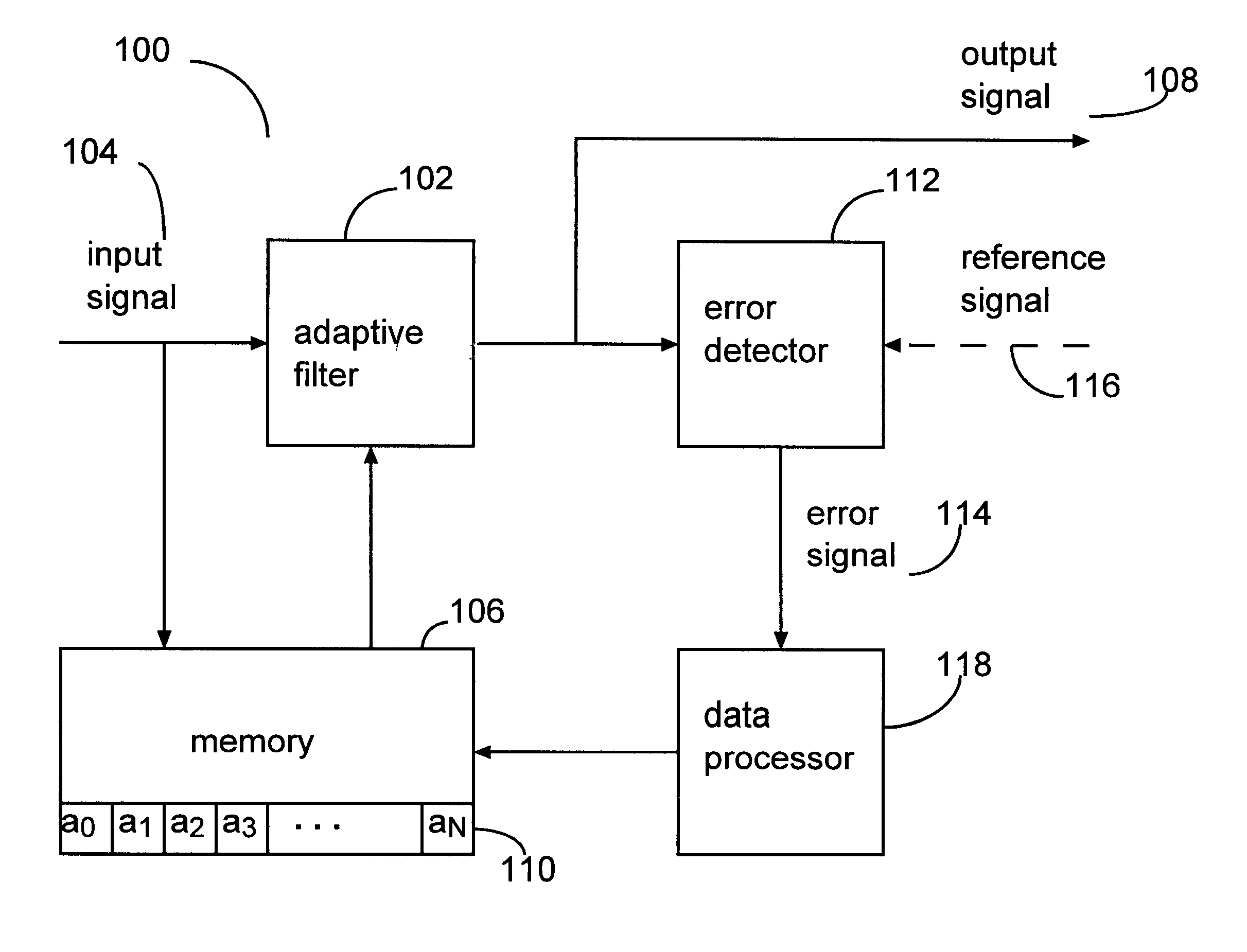
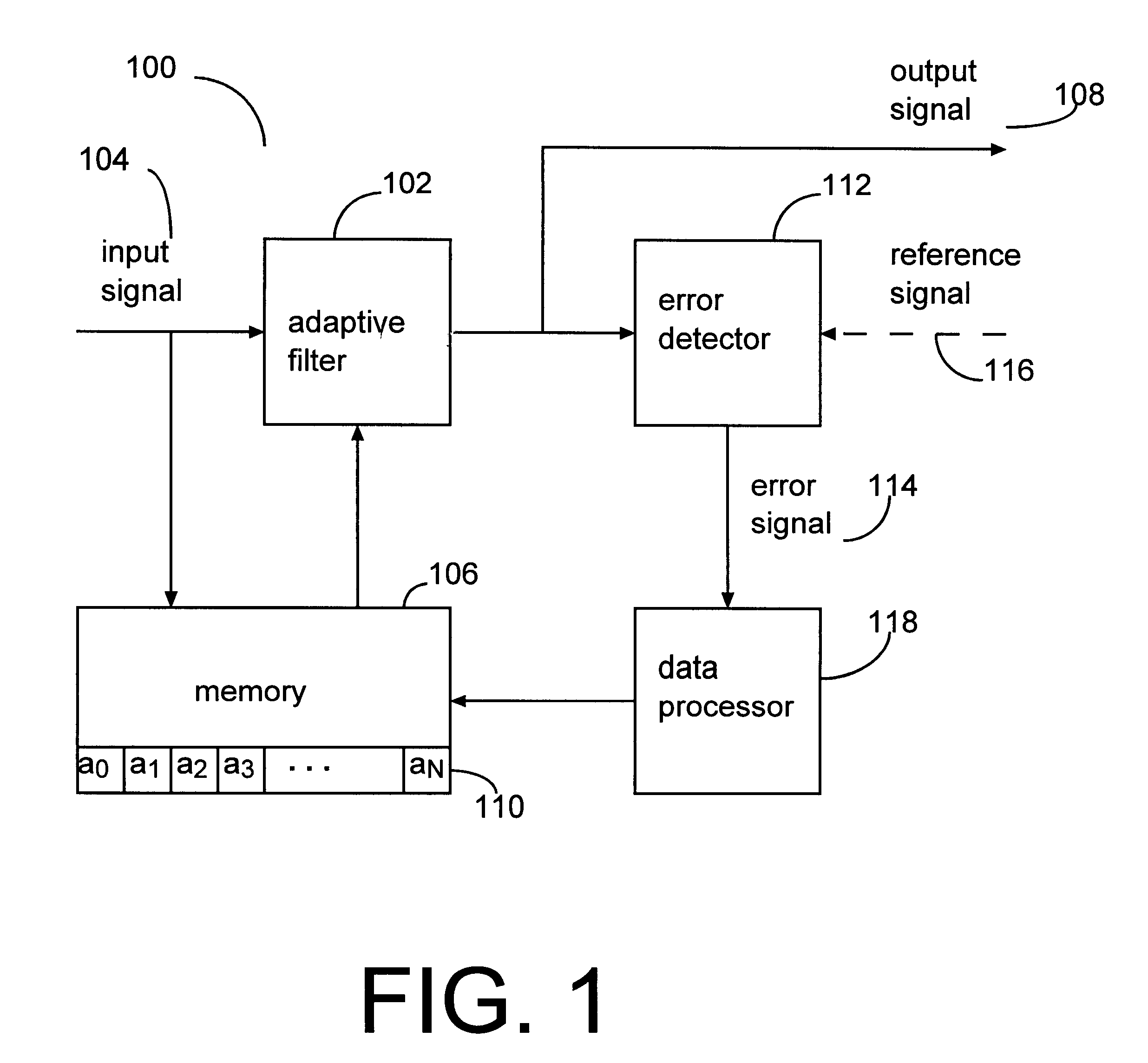
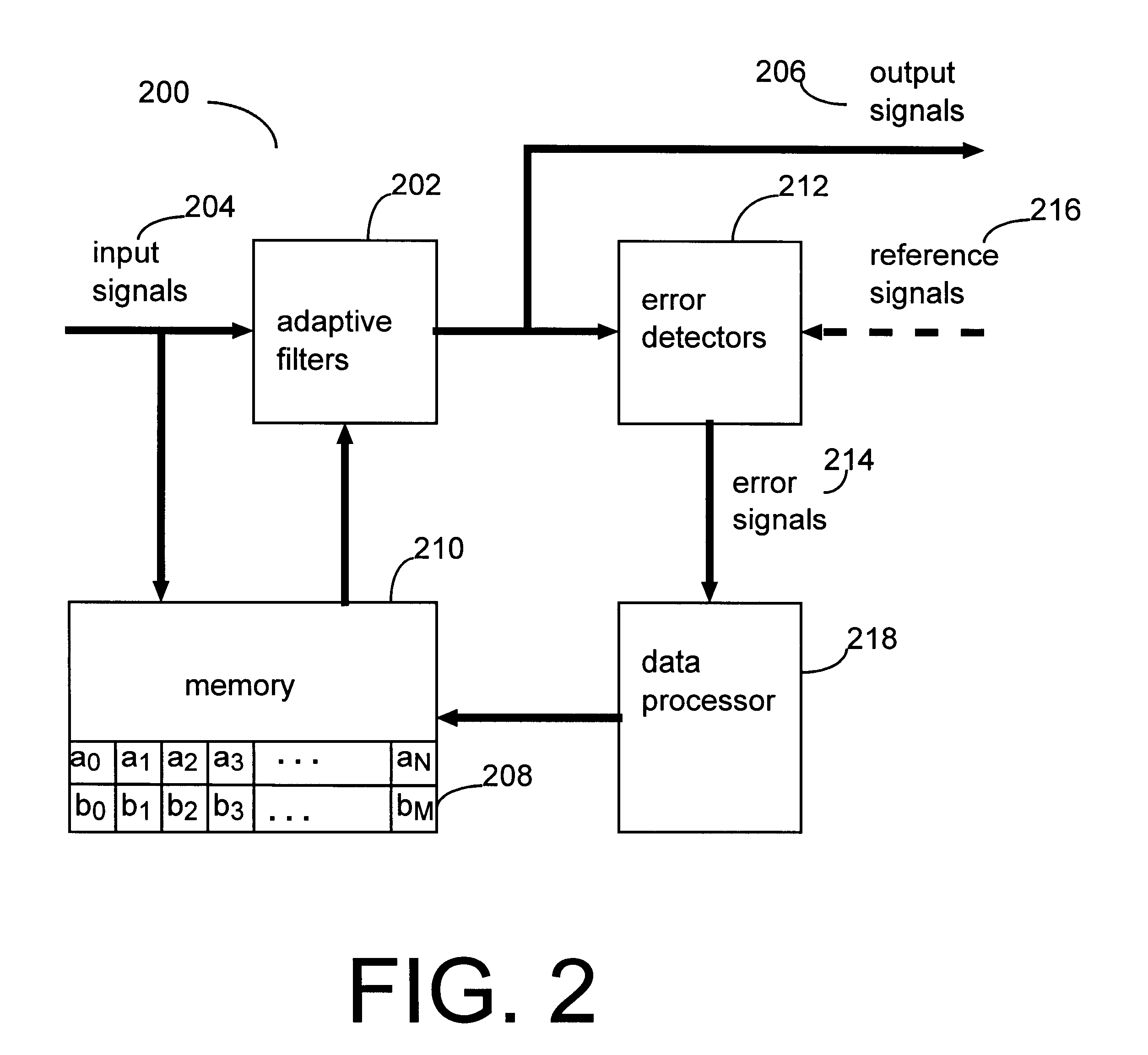
Signal processing arrangement including variable length adaptive filter and method therefor
A signal processor includes an adaptive filter that generates an output signal as a function of an input signal and of weighting coefficients stored in a memory. An error detector generates an error signal as a function of the output signal. The error signal is used in adjusting the weighting coefficients. A data processor adjusts the number of weighting coefficients of the adaptive filter and system resources used for storing the weighting coefficients as a function of a characteristic of the weighting coefficients.< / PTEXT>
Owner:MICROSEMI SEMICON U S
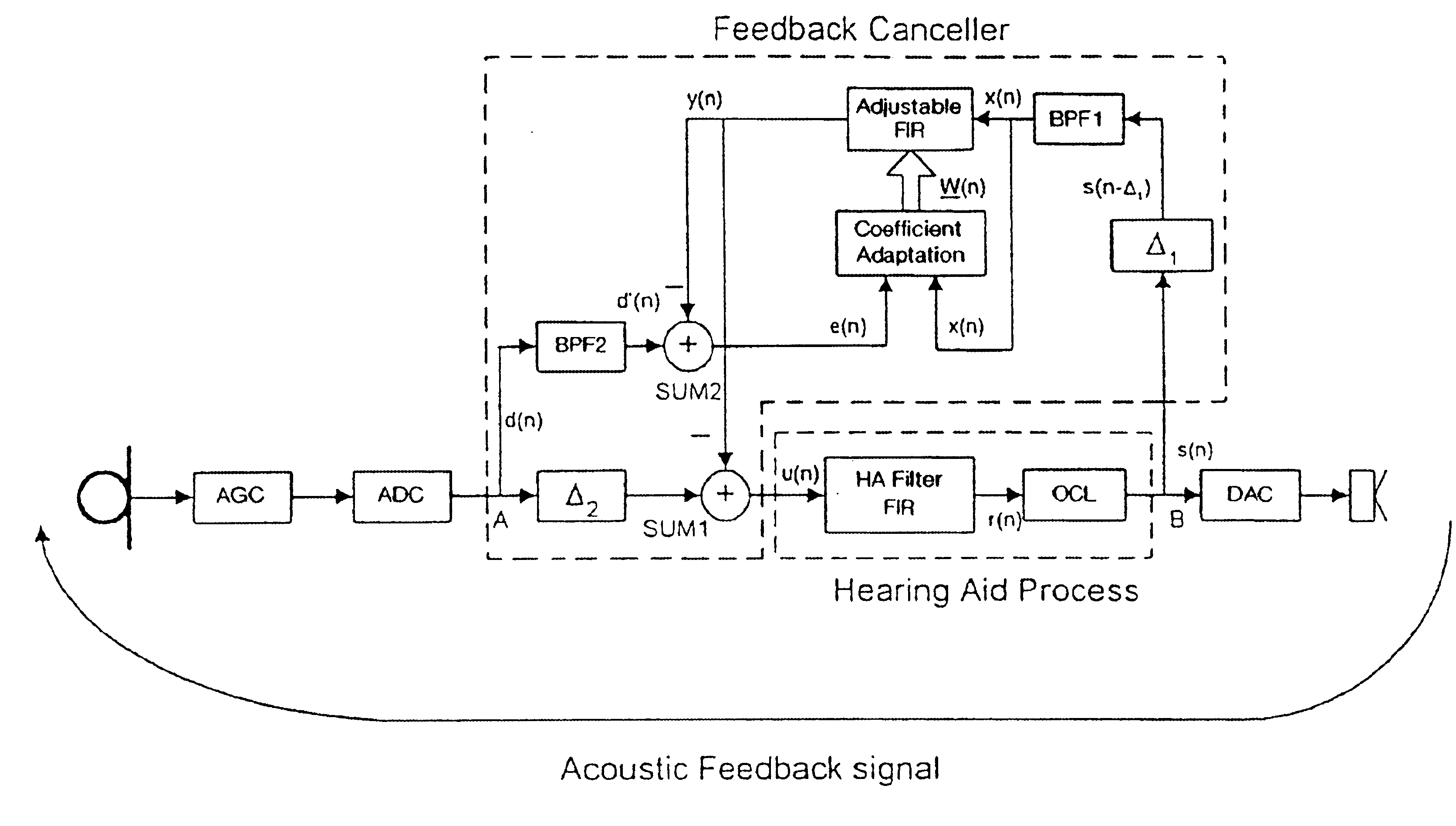
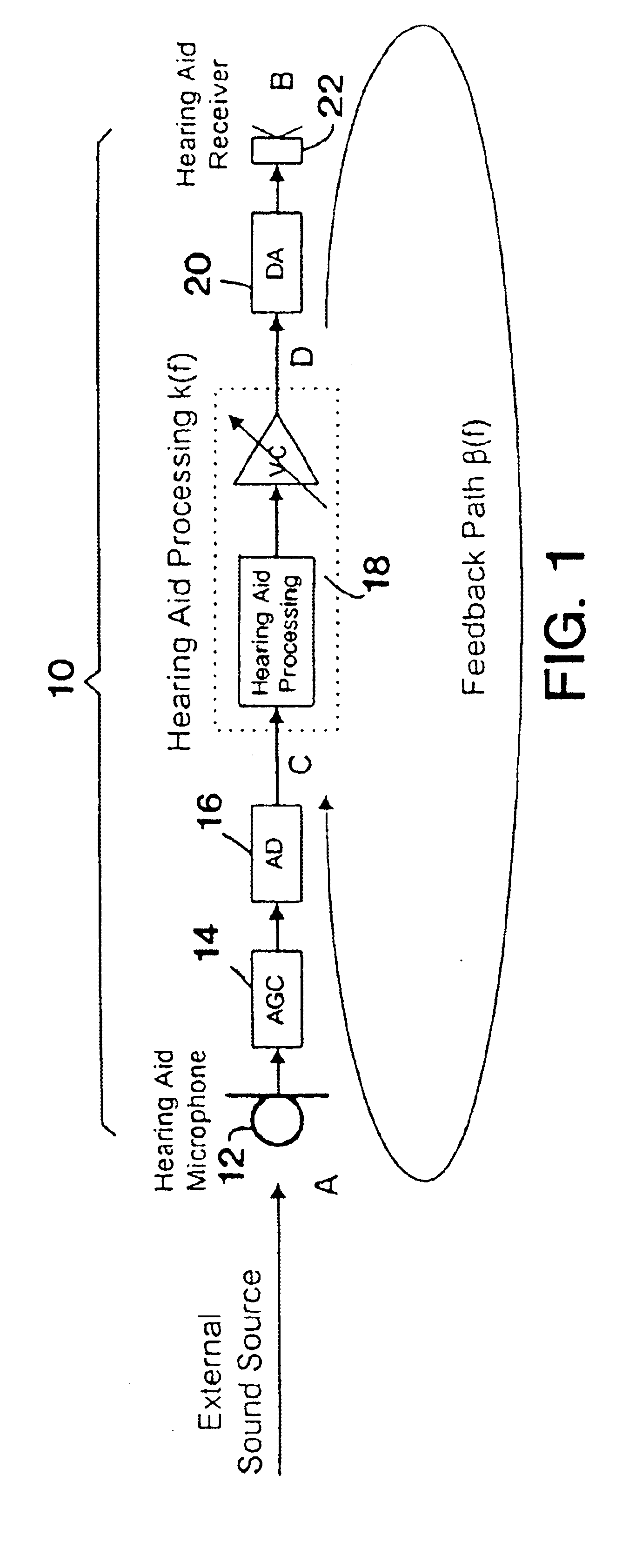
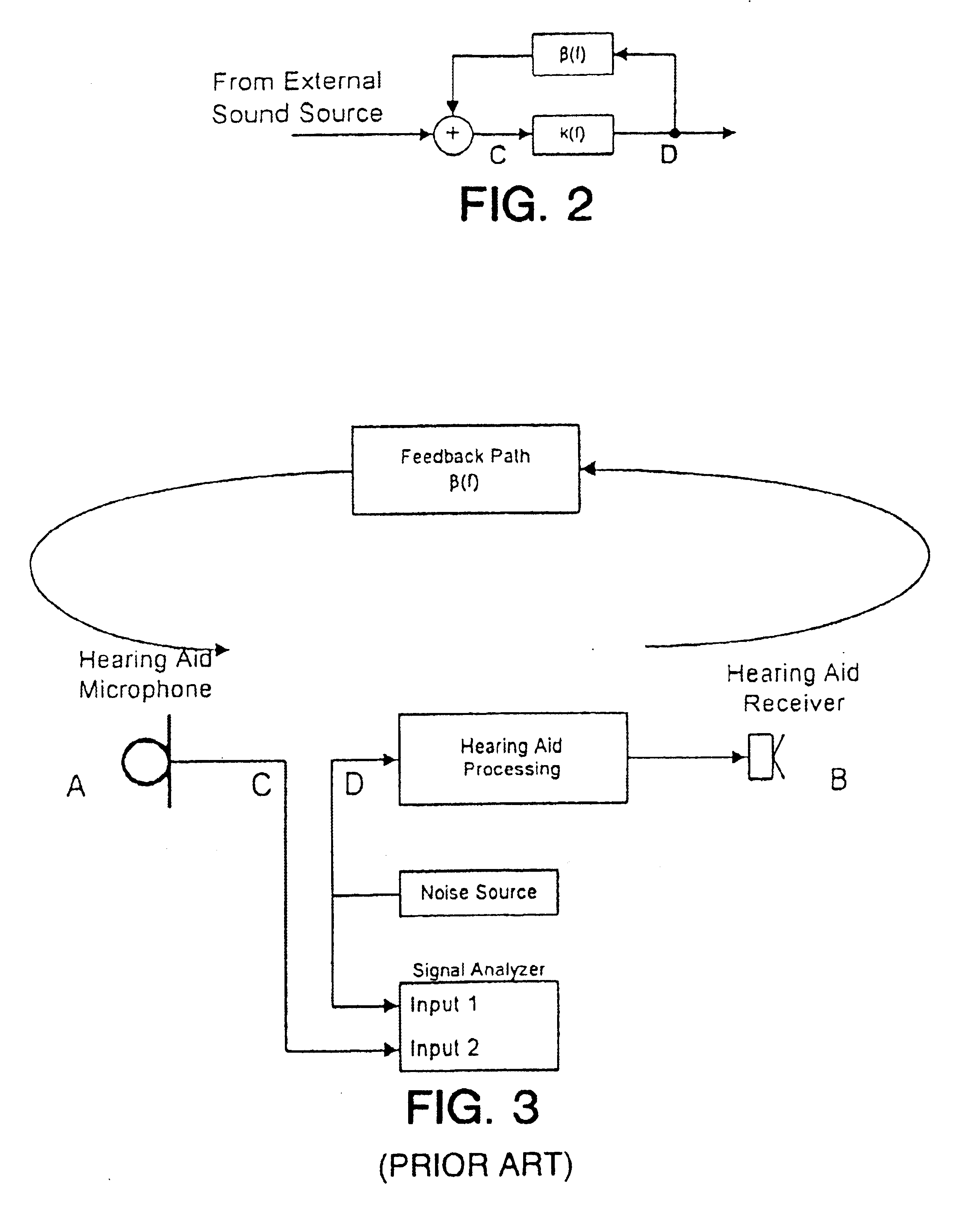
Band-limited adaptive feedback canceller for hearing aids
InactiveUS6876751B1Minimal signal distortionThe result is validSignal processingAdaptive networkEngineeringImproved method
An improved method for adaptively cancelling acoustic feedback in hearing aids and other audio amplification devices. Feedback cancellation is limited to a frequency band that encompasses all unstable frequencies. By limiting the bandwidth of the feedback cancellation signal, the distortion due to the adaptive filter is minimized and limited only to the unstable feedback regions. A relatively simple signal processing algorithm is used to produce highly effective results with minimal signal distortion.
Owner:HOUSE EAR INSTITUTE
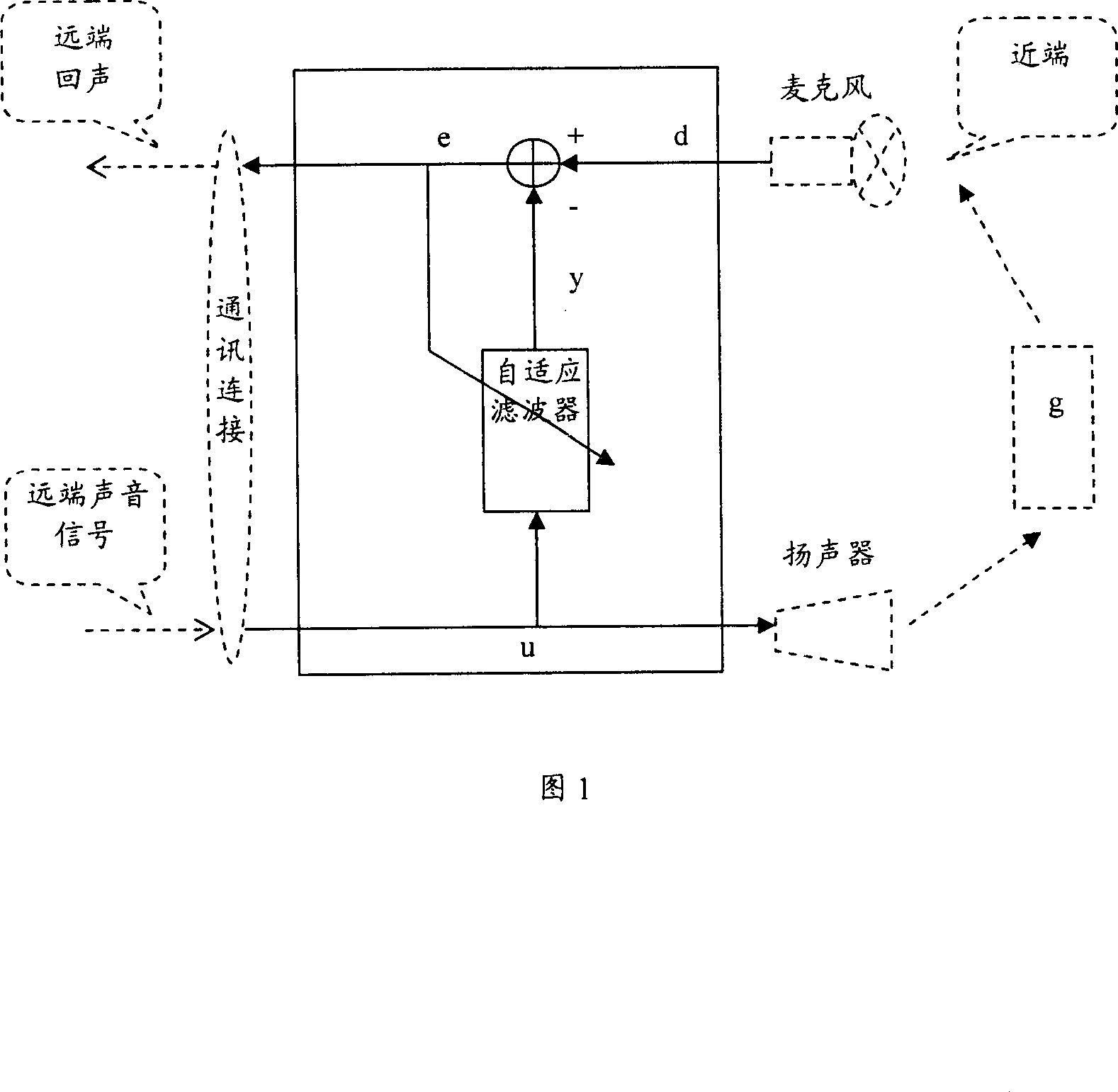
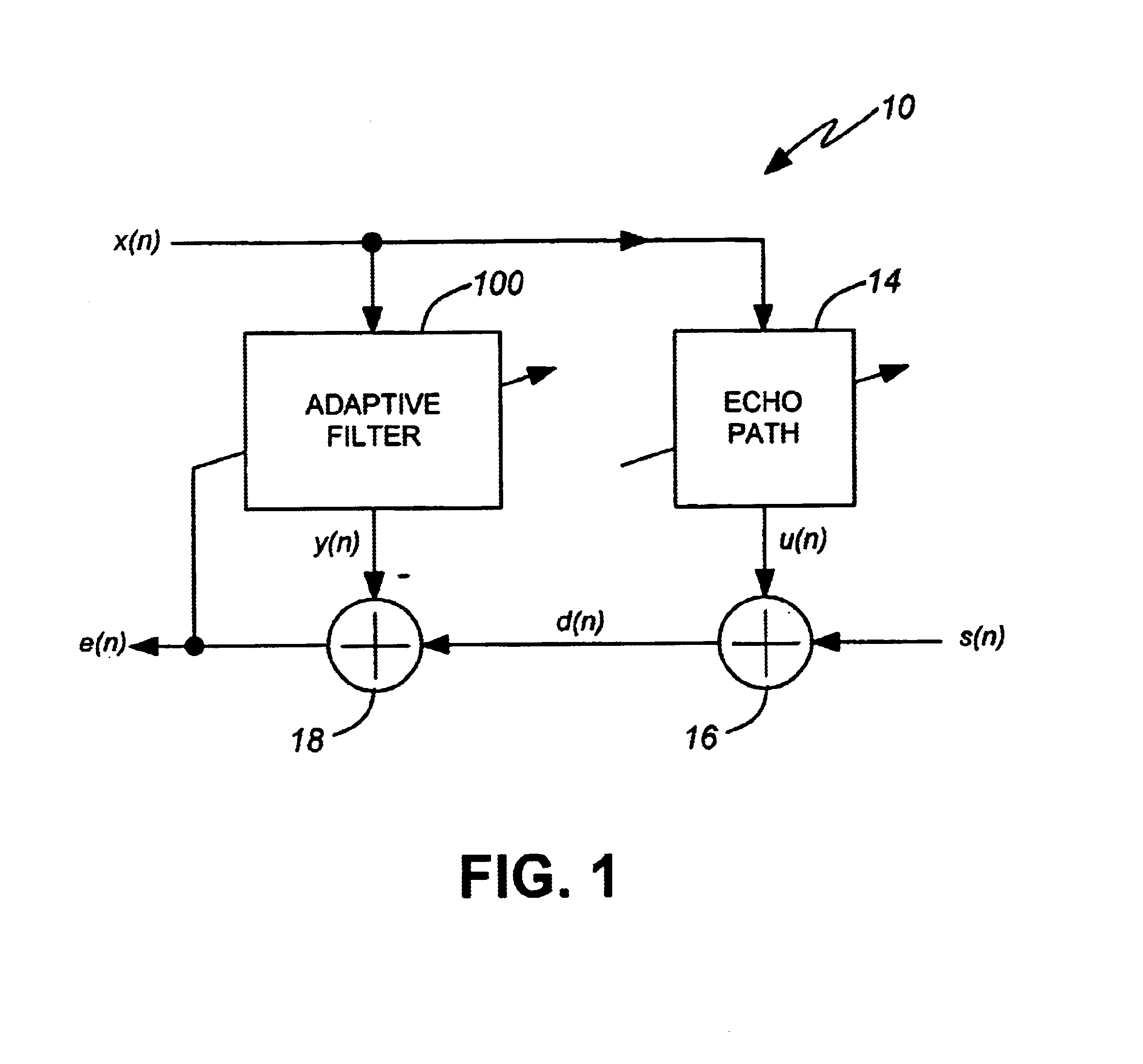
Digital adaptive filter and acoustic echo canceller using the same
InactiveUS6842516B1Improve performanceImprove matchTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsAdaptive networkAdaptive filterComputer science
To achieve an improved convergence behaviour for, e.g., echo cancellation there is provided a digital adaptive filter which includes a filter coefficient update means to successively update filter coefficients in accordance with an input signal, an estimated power of the input signal, and an error signal between the input signal filtered in the digital adaptive filter and the input signal propagated along an external path being modelled by the digital adaptive filter. Here, an input signal power estimation means is adapted to perform recursive smoothing for an increasing input power and a decreasing input power in an asymmetric fashion with different smoothing factors. In case the estimation is carried out in the frequency domain the step size for the update of filter coefficients may be calculated for each frequency band individually.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Adaptive equalizer, decoding device, and error detecting device
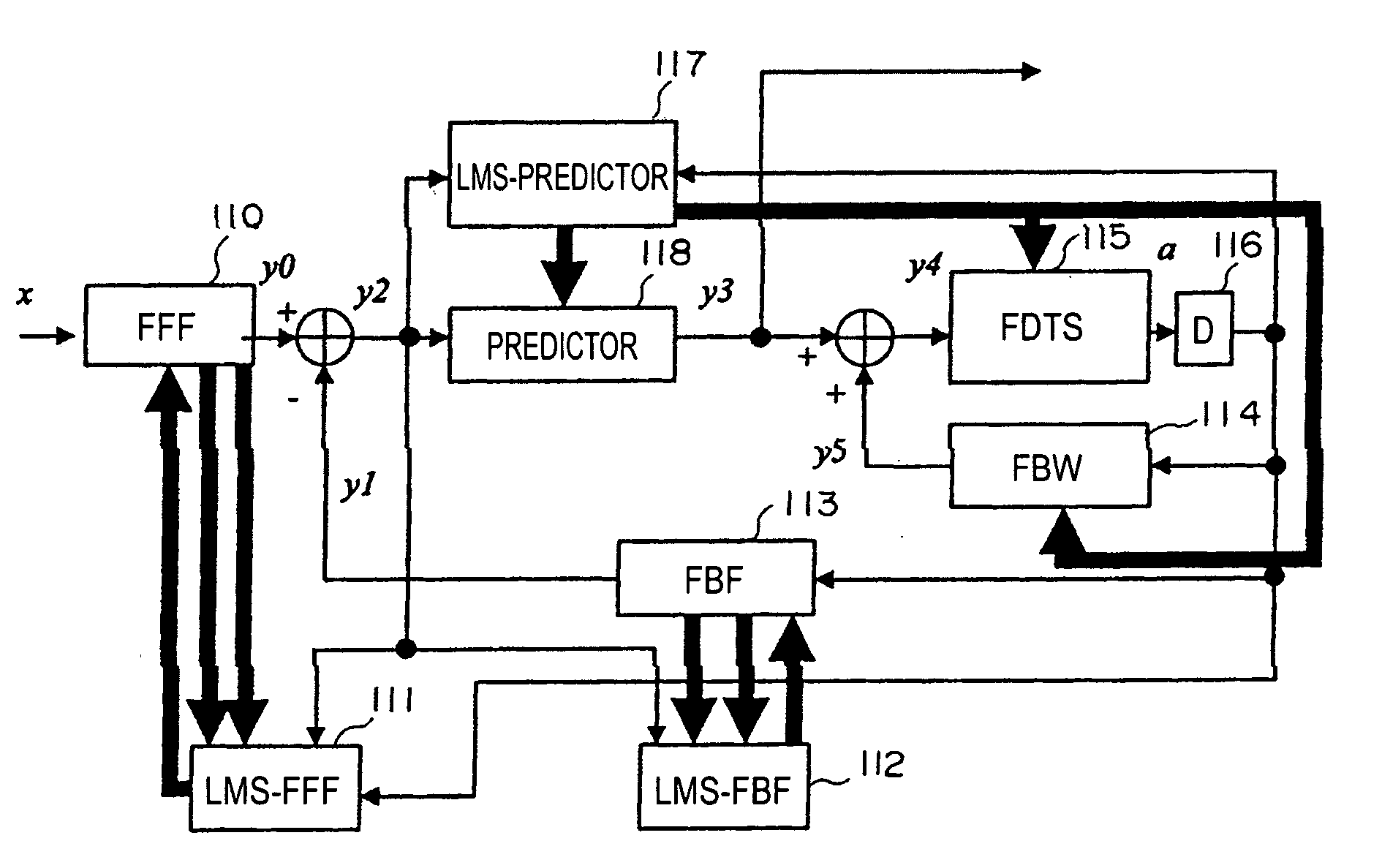
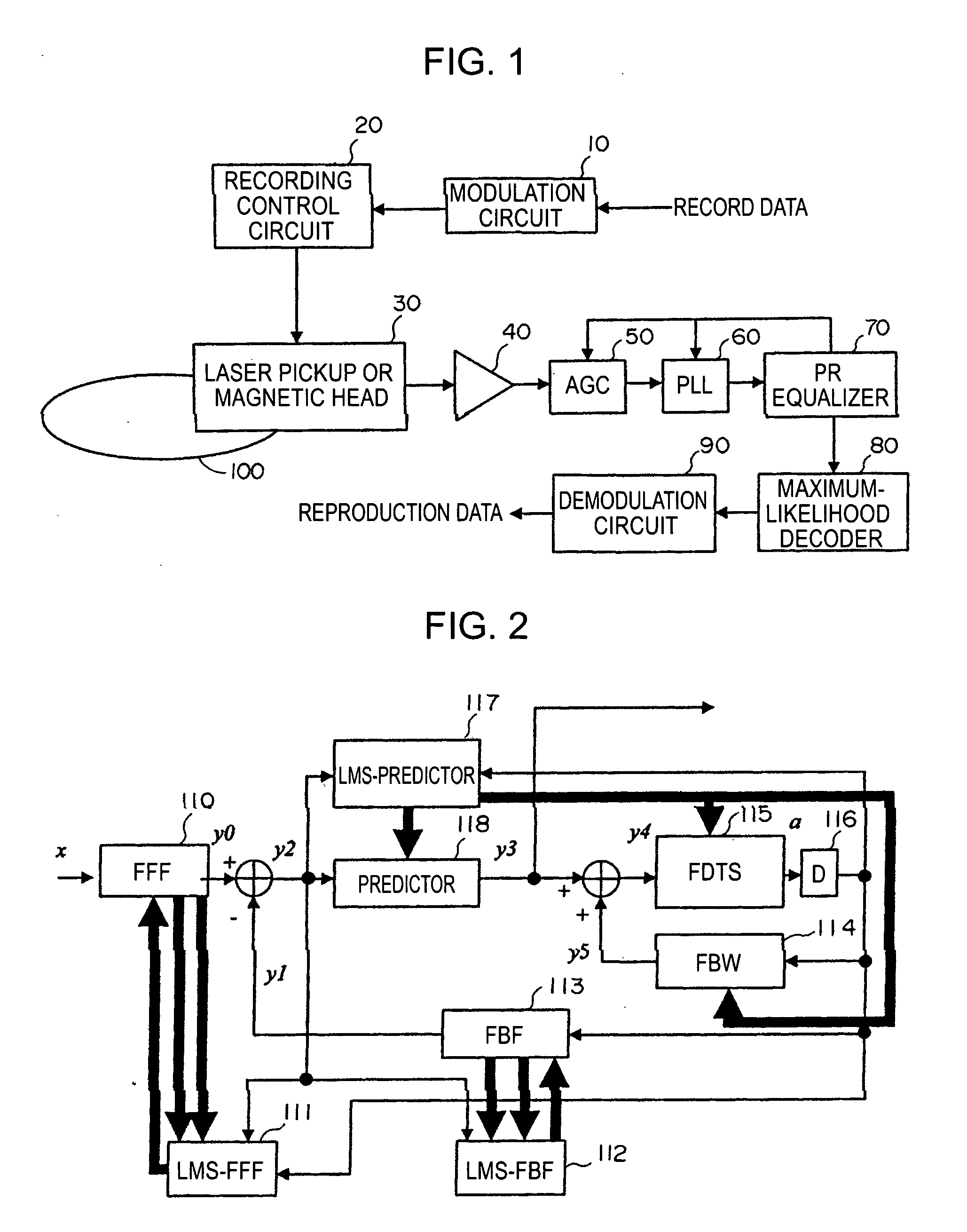
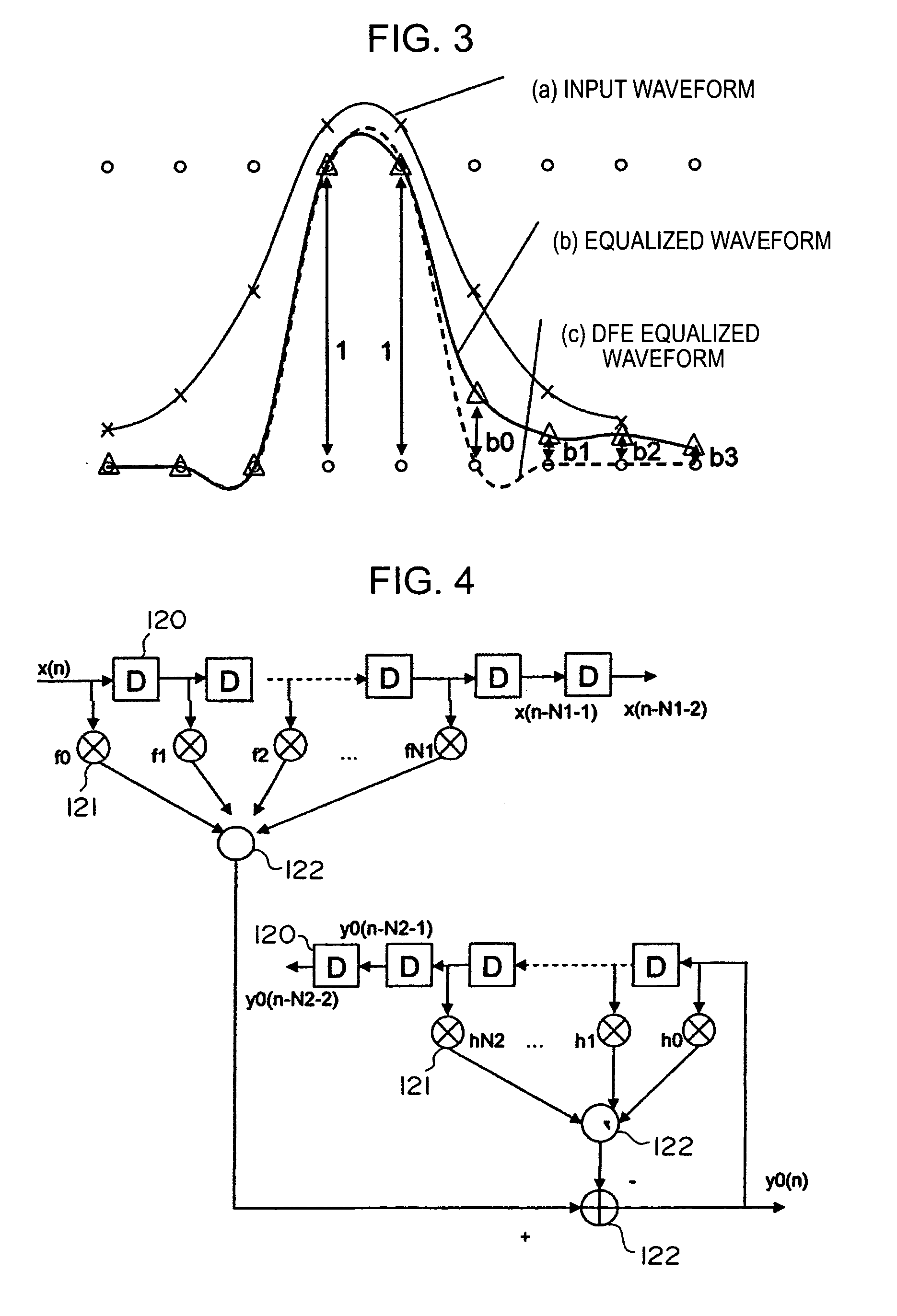
InactiveUS20050135472A1Adequate equalization processingExtra processingMultiple-port networksModification of read/write signalsEqualizationOptical recording
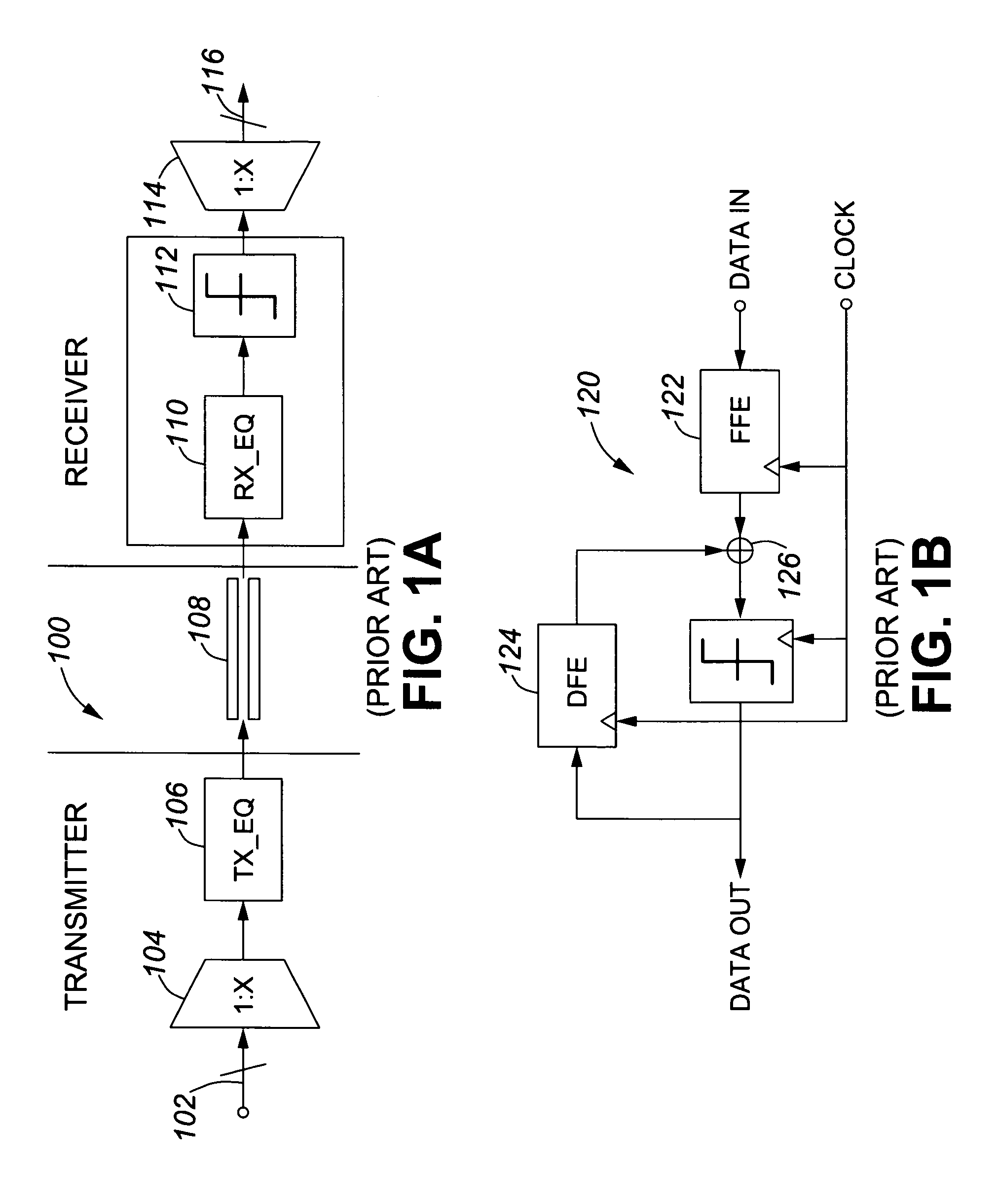
In a waveform equalizer for a communication apparatus, a magnetic recording apparatus, or an optical recording / reproducing apparatus, a feed-forward filter (FFF) is provided and, at a subsequent stage, a decision feedback equalizer (DFE) or a fixed delay tree search / decision feedback equalizer (FDTS / DFE) employing FDTS for a determination unit is provided. Partial response (PR) is performed on only a first portion of inter-symbol interference (ISI) of a waveform equalized by the FFF and equalization that does not consider subsequent response (i.e., trailing-edge ISI) is performed. A feed-back filter (FBF) generates a response for the trailing-edge ISI and the DFE structure subtracts the generated response from a response provided by the FFF so that a result becomes a partial response.
Owner:SONY CORP
Echo elimination device for microphone and method thereof
InactiveCN1953060AMeet the delay requirementsGuaranteed to workAdaptive networkSpeech analysisComputer moduleSelf adaptive
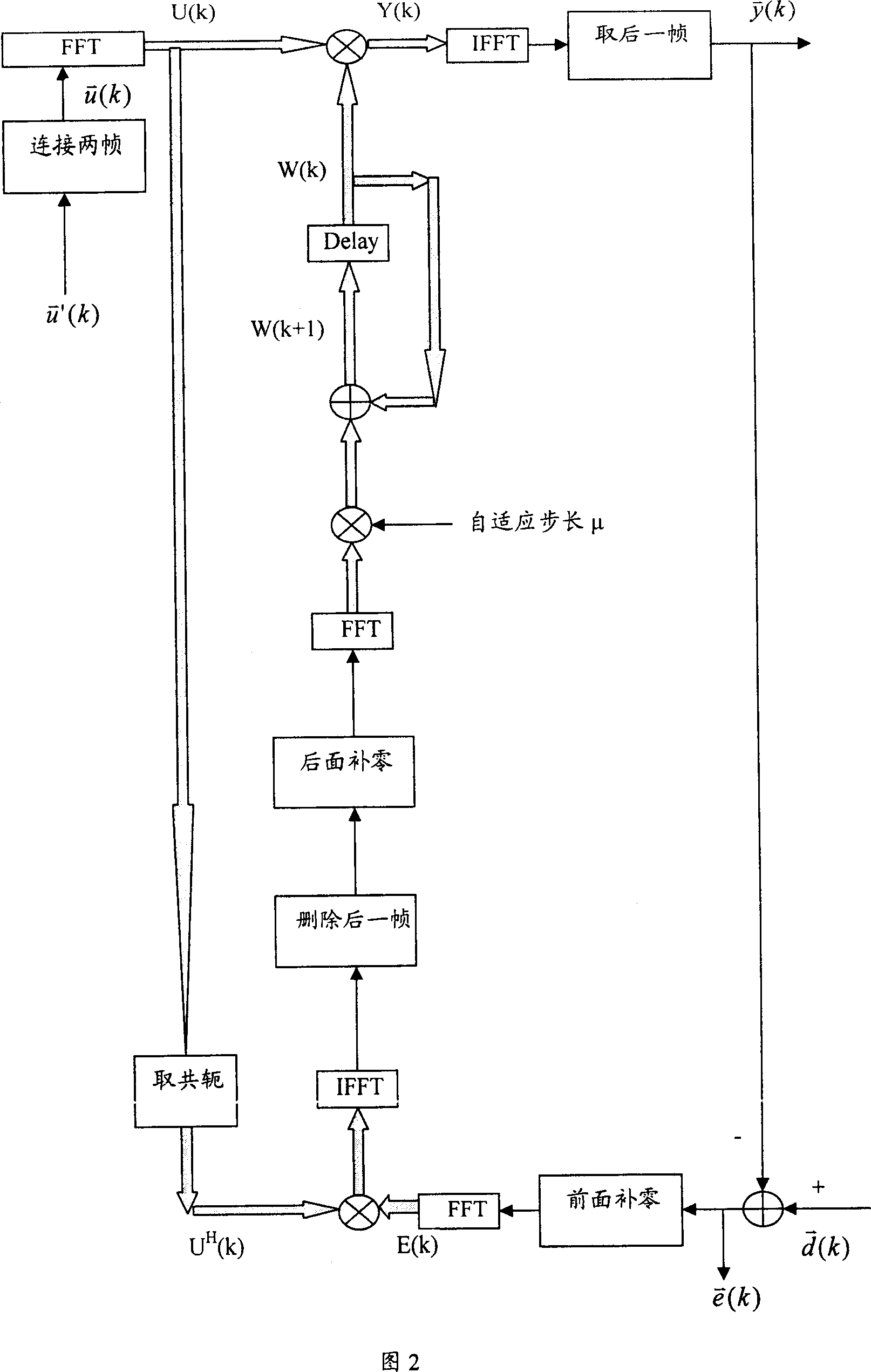
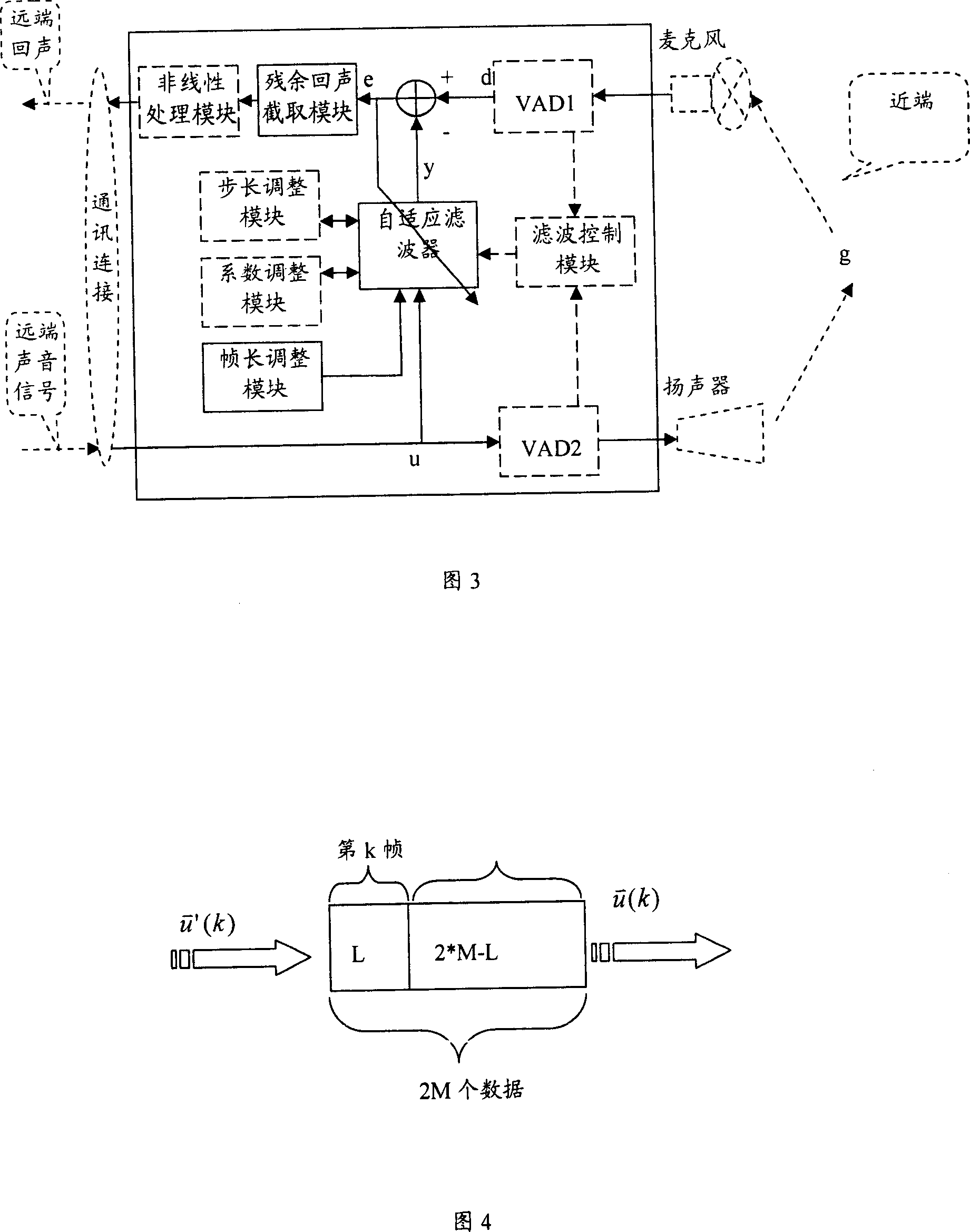
This invention discloses a microphone echo elimination device and method, which eliminates echo between microphone and sound circuit, wherein, the device comprises long frame adjust module to combine one self adaptive filter parameter data frame for self adapting filter.
Owner:VIMICRO CORP
Canceller circuit and controlling method
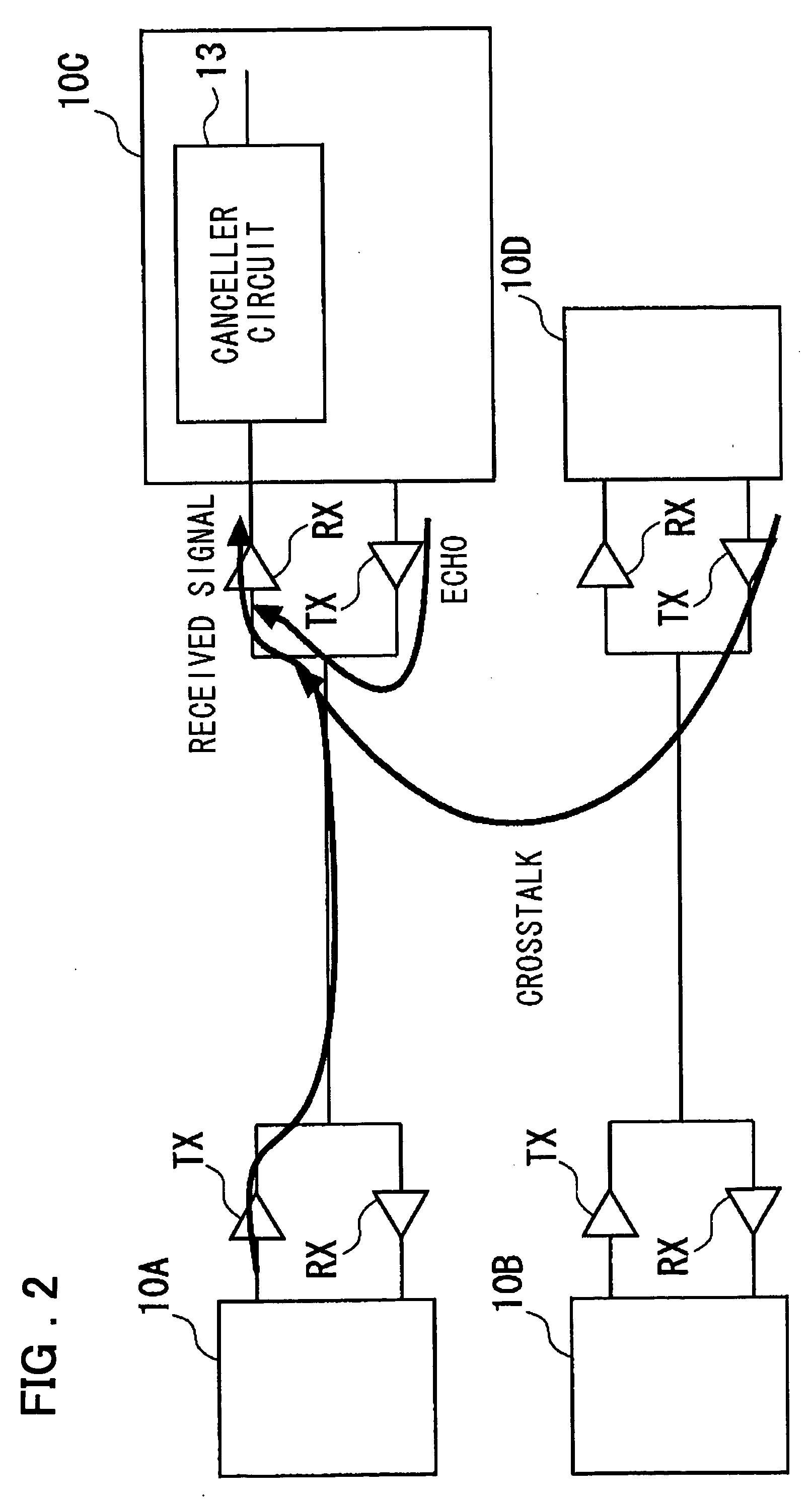
InactiveUS20050099967A1Easy to integrateAdaptive networkCross-talk reductionAdaptive filterEngineering
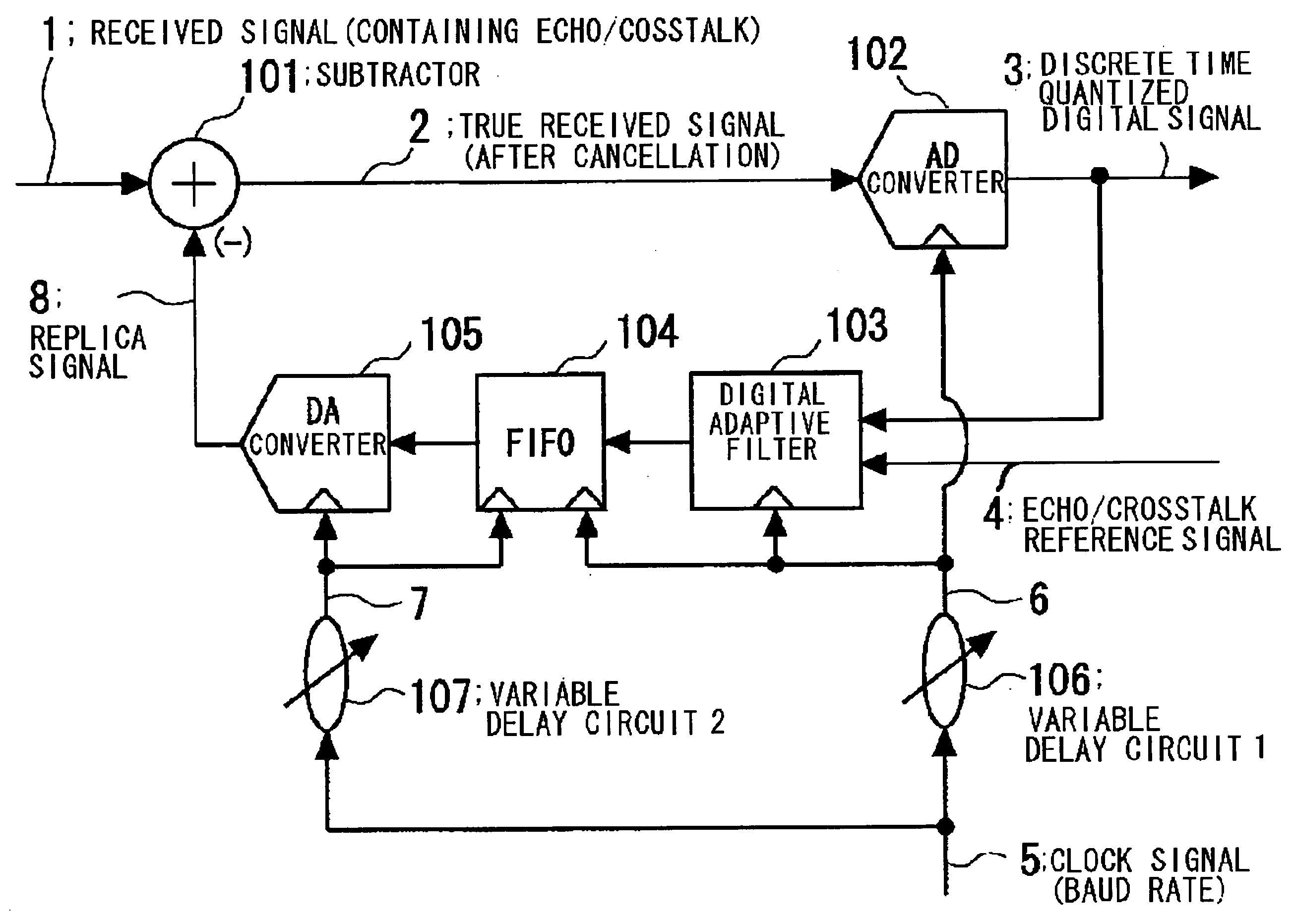
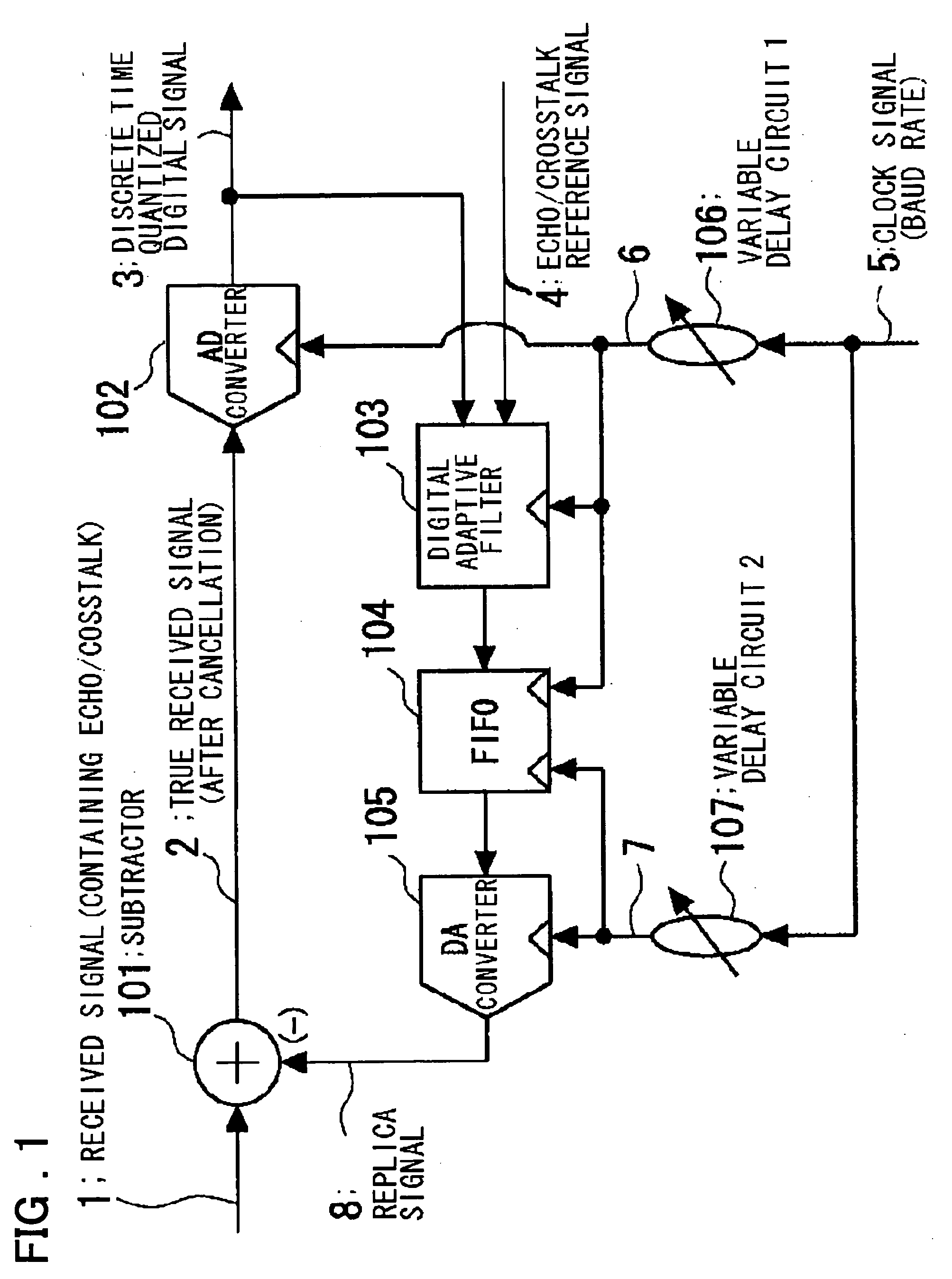
Disclosed is a device in which overasampling is not needed and in which the echo / crosstalk of a continuous time analog waveform may be canceled at a baud rate. There are provided a continuous time analog subtractor, an AD converter for converting an analog signal from a subtractor to a digital signal, an adaptive filter receiving a digital output signal from the AD converter and an echo / crosstalk reference signal and having adaptively variable filter coefficients, a FIFO in which a digital output signal from the FIFO is written in first-in first-out and in which a write and read clocks are interchanged, a D / A converter for converting the digital output signal from the FIFO to an analog signal to output the analog signal, and first and second variable delay circuits for variably delaying an input clock signal to output the delayed signals as first and second clock signals. The first clock signal is supplied to the AD converter, adaptive filter and to the FIFO, while the second clock signal is supplied to the FIFO and to the DA converter as sampling clock. A received signal, containing the echo-crosstalk, and a replica signal of the echo-crosstalk, output from the D / A converter, is supplied to the subtractor. A true received signal, which is the received signal from which the echo / crosstalk has been cancelled, is supplied to the AD converter.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Method and system for on-line blind source separation
InactiveUS6898612B1Efficient separationAdaptive networkSpeech analysisNO storageFinite impulse response
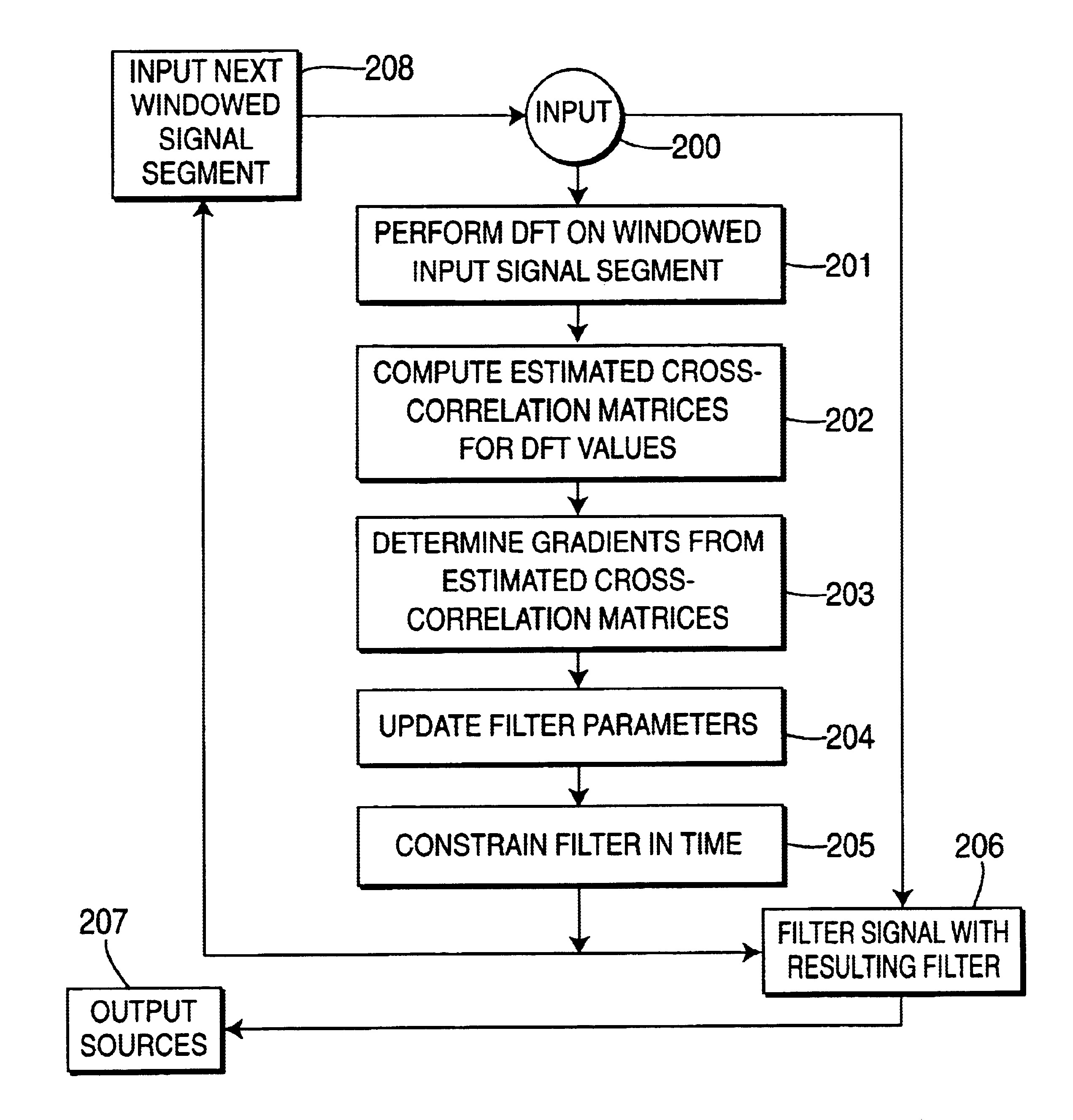
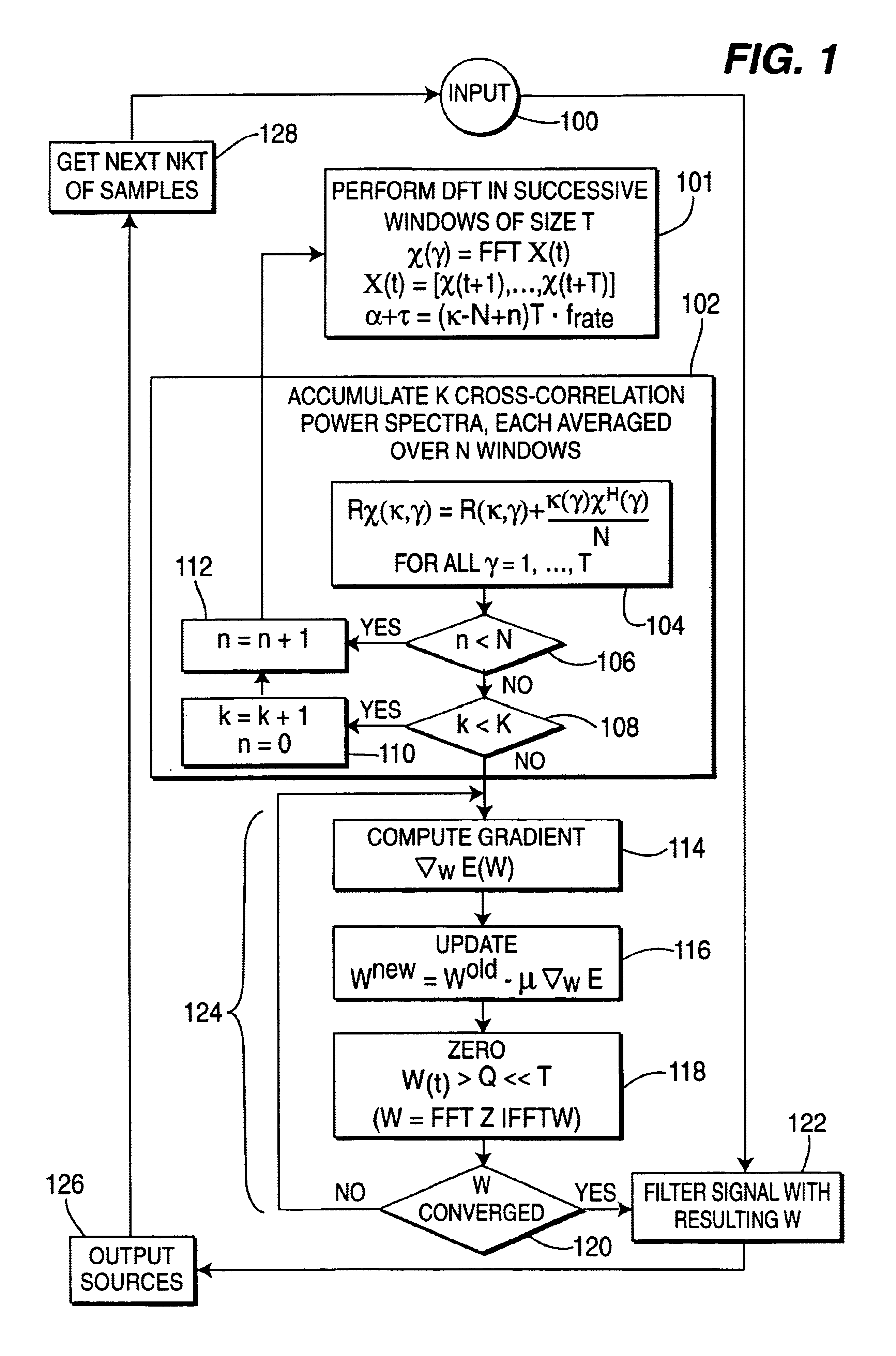
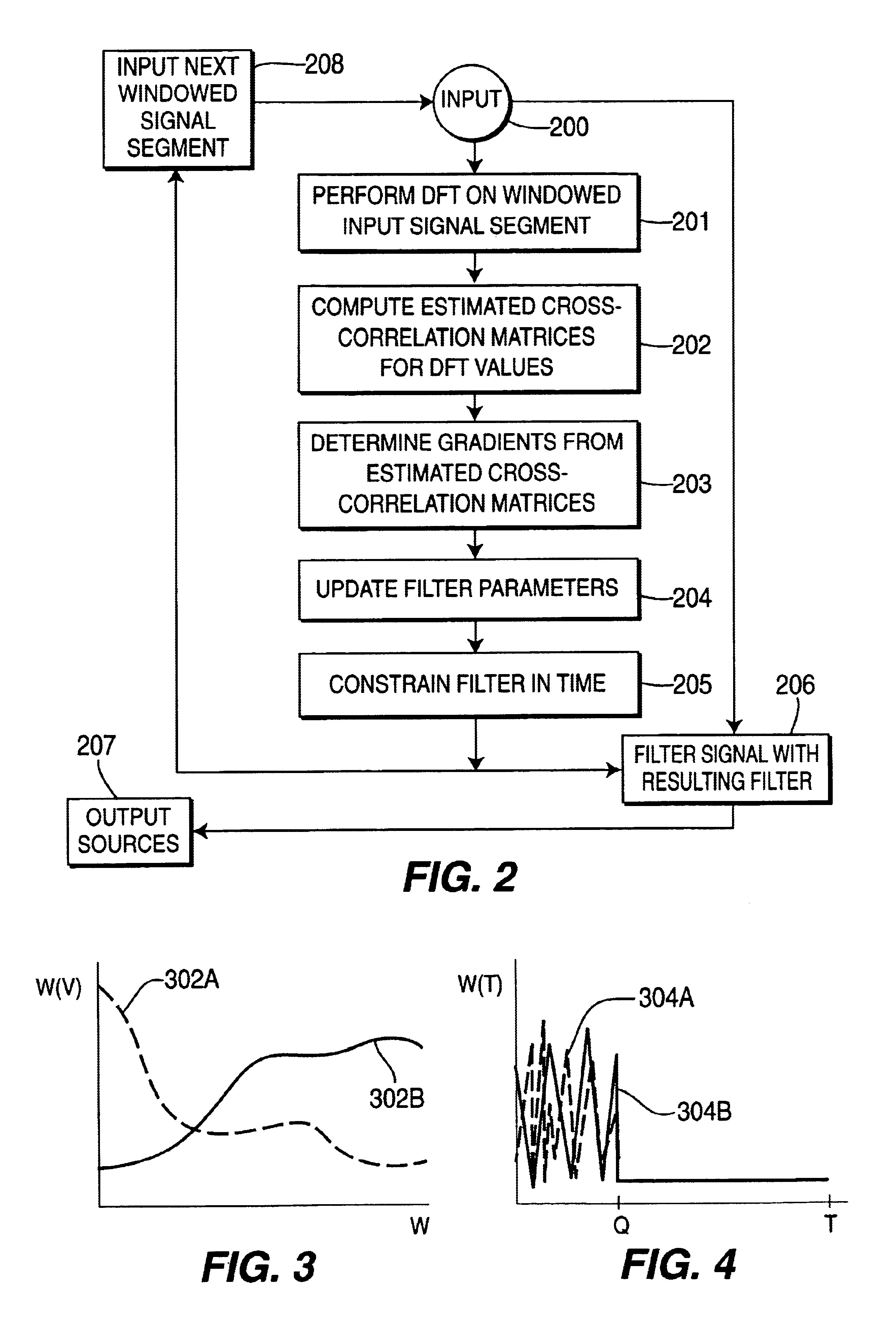
A method and apparatus is disclosed for performing blind source separation using convolutive signal decorrelation. For a first embodiment, the method accumulates a length of input signal (mixed signal) that includes a plurality of independent signals from independent signal sources. The invention then divides the length of input signal into a plurality of T-length periods (windows) and performs a discrete Fourier transform (DFT) on the, signal within each T-length period. Thereafter, estimated cross-correlation values are computed using a plurality of the averaged DFT values. A total number of K cross-correlation values are computed, where each of the K values is averaged over N of the T-length periods. Using the cross-correlation values, a gradient descent process computes the coefficients of a finite impulse response (FIR) filter that will effectively separate the source signals within the input signal. A second embodiment of the invention is directed to on-line processing of the input signal—i.e., processing the signal as soon as it arrives with no storage of the signal data. In particular, an on-line gradient algorithm is provided for application to non-stationary signals and having an adaptive step size in the frequency domain based on second derivatives of the cost function. The on-line separation methodology of this embodiment is characterized as multiple adaptive decorrelation.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Nonlinear digital signal processor
InactiveUS20080080644A1Multiple-port networksAdaptive networkDigital signal processingPhase response
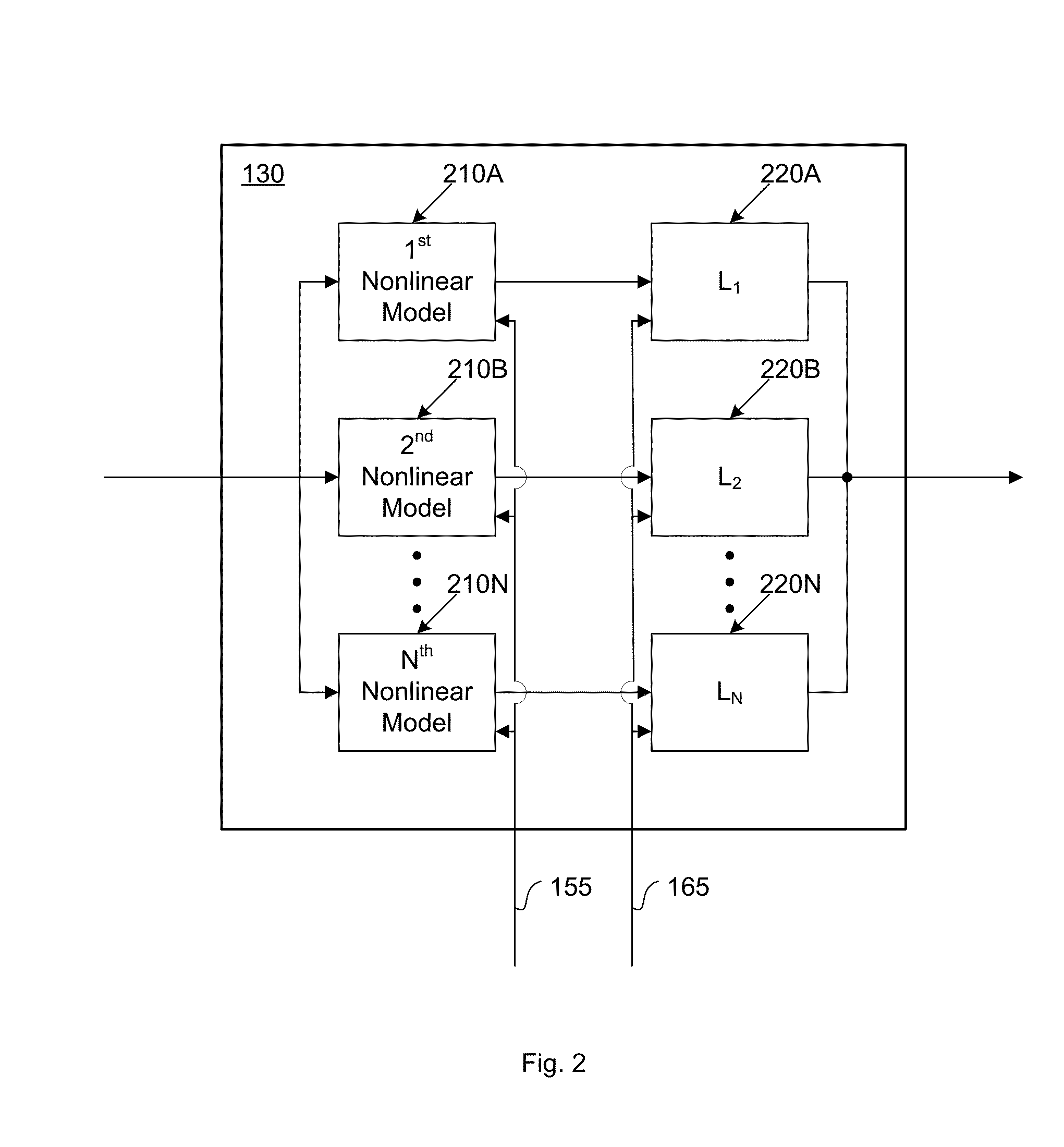
A digital signal processor (DSP) comprises an input terminal configured to receive an input, an adaptive nonlinear phase filter coupled to the input terminal, the adaptive nonlinear phase filter having a time-varying phase response, and an adaptive nonlinear amplitude filter coupled to the input terminal, the adaptive nonlinear amplitude filter having a time-varying amplitude response.A method of processing a signal comprises receiving the signal, sending the signal to an adaptive nonlinear phase filter, the adaptive nonlinear phase filter having a time-varying phase response, and sending the signal to an adaptive nonlinear amplitude filter, the adaptive nonlinear amplitude filter having a time-varying amplitude response.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Tunable filter and portable telephone
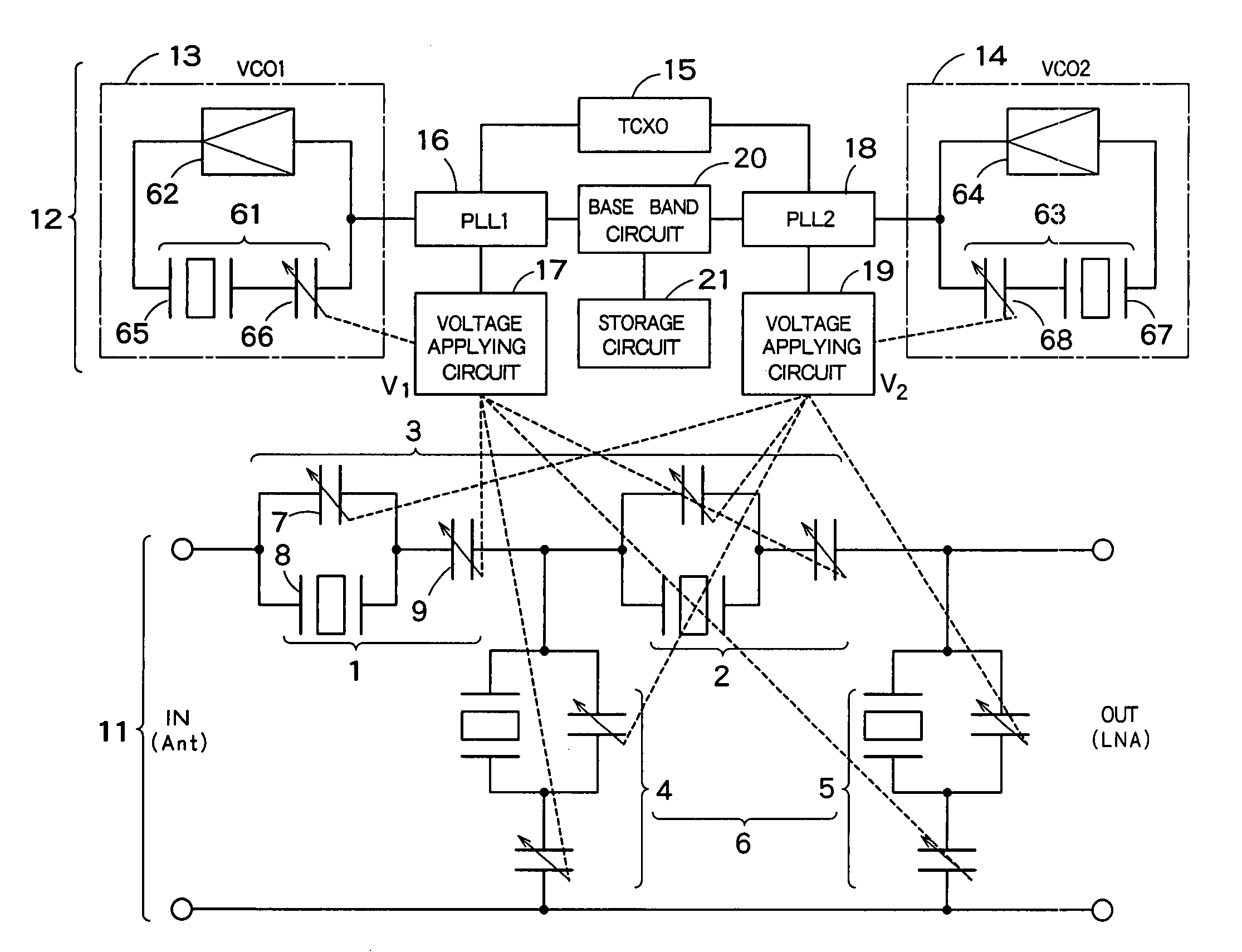
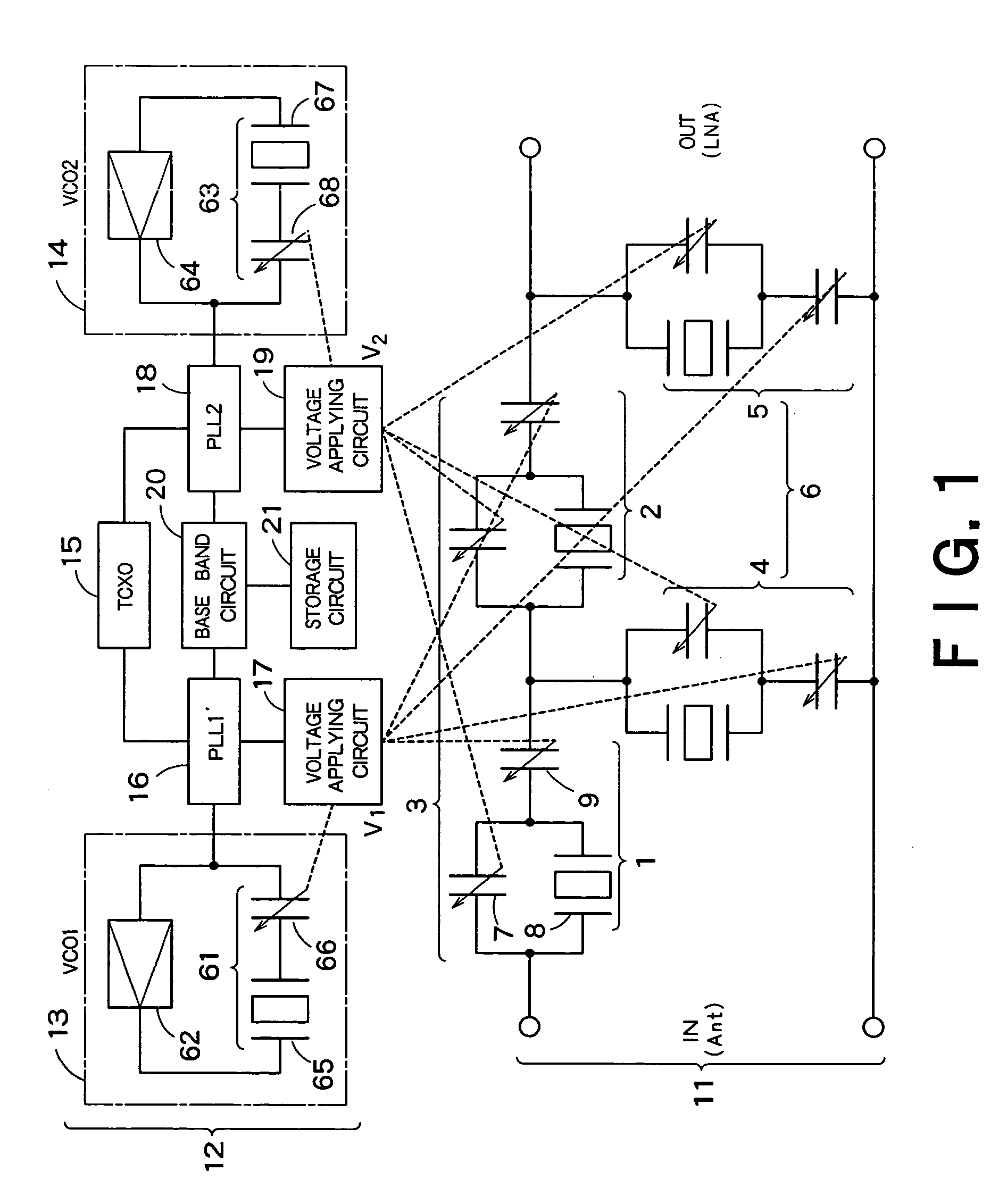
InactiveUS7135940B2Good reproducibility and reliabilityLow insertion lossMultiple-port networksTransmission control/equlisationCapacitanceInductor
A tunable filter has a plurality of variable capacitors and a plurality of inductor elements, each being formed on a common substrate, a filter circuit formed by using at least a portion of the plurality of variable capacitors and a portion of the plurality of inductor elements, a monitor circuit formed by using at least a portion of the plurality of variable capacitors and a portion of the plurality of inductor elements, a detecting circuit which detects a prescribed circuit constant of the monitor circuit, a storage which stores information relating to a reference circuit constant of the monitor circuit, and a capacitance control circuit which controls capacitance of the variable capacitors in the monitor circuit and capacitance of the variable capacitors in the filter circuit, based on a result detected by the detecting circuit and information stored in the storage.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Fully Adaptive Equalization for High Loss Communications Channels
InactiveUS20080260016A1Multiple-port networksTransmission control/equlisationEngineeringEqualization
An equalization circuit is disclosed that enables high data rate transmission over high loss communications channels. Also disclosed is a set of functional blocks and update criteria that allow for the equalization function to be adapted for a large variety of different communications channels. A fully continuous adaptive equalizer is used in conjunction with a Decision Feedback Equalizer to fully equalize a large number of communications channels.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
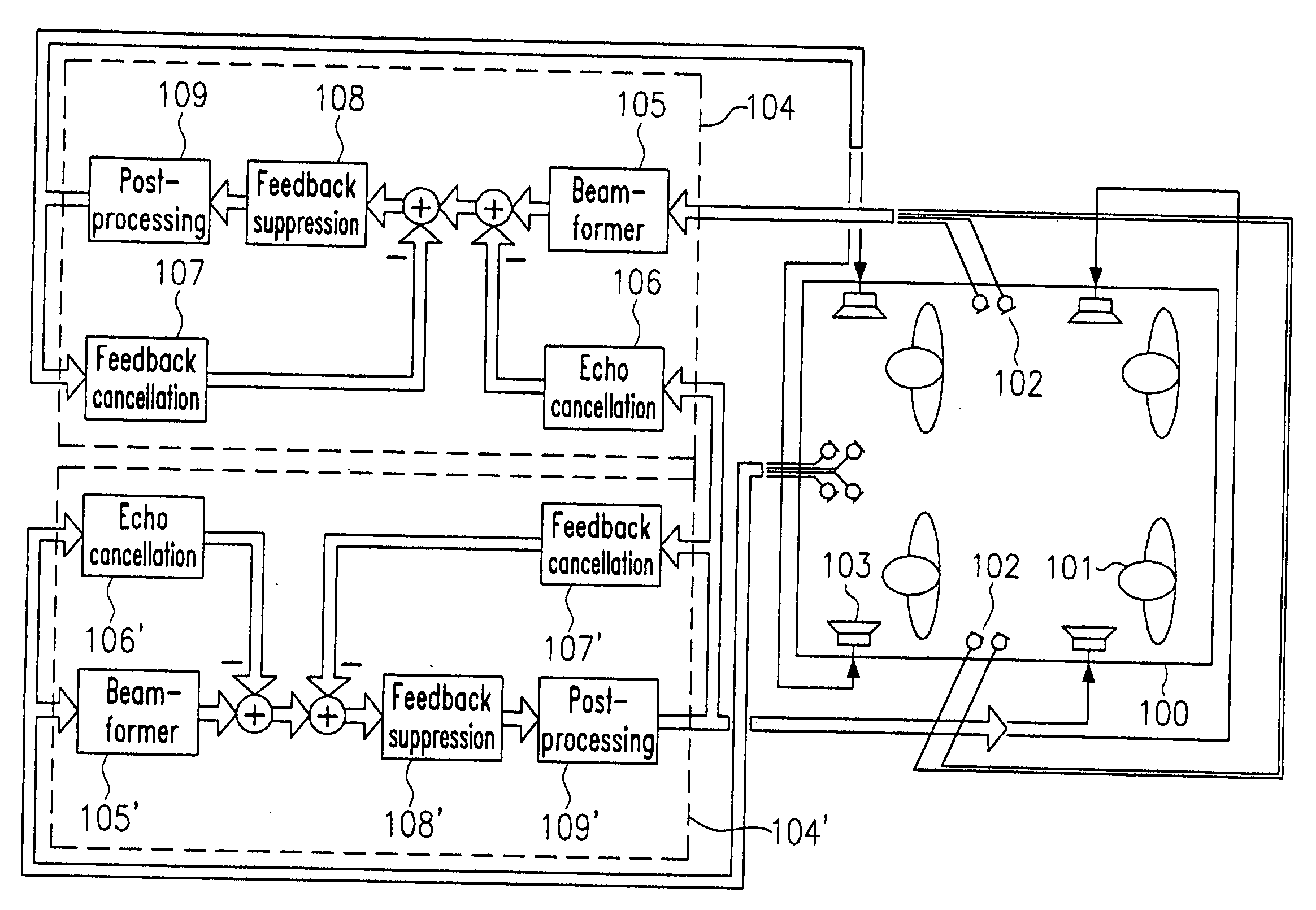
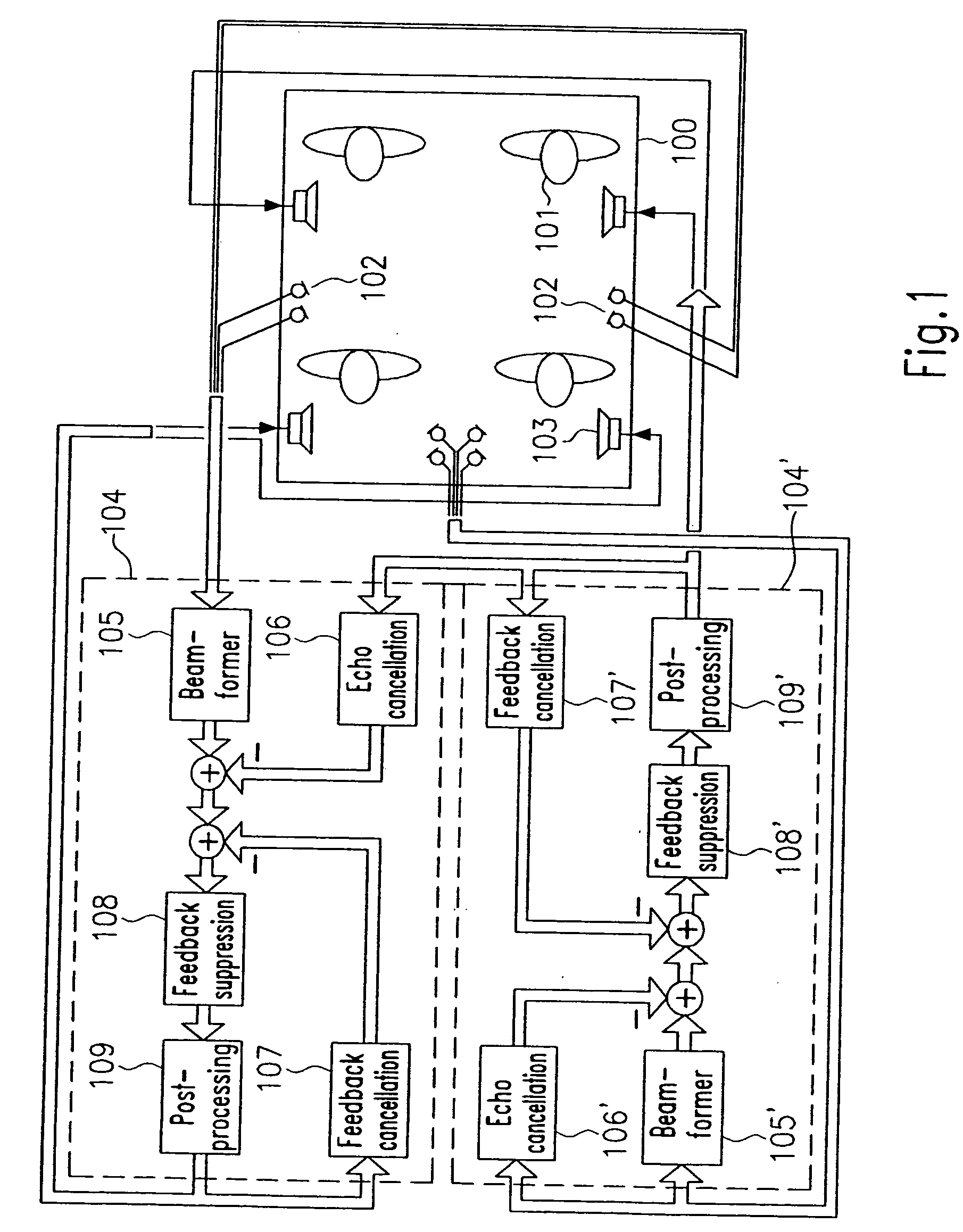
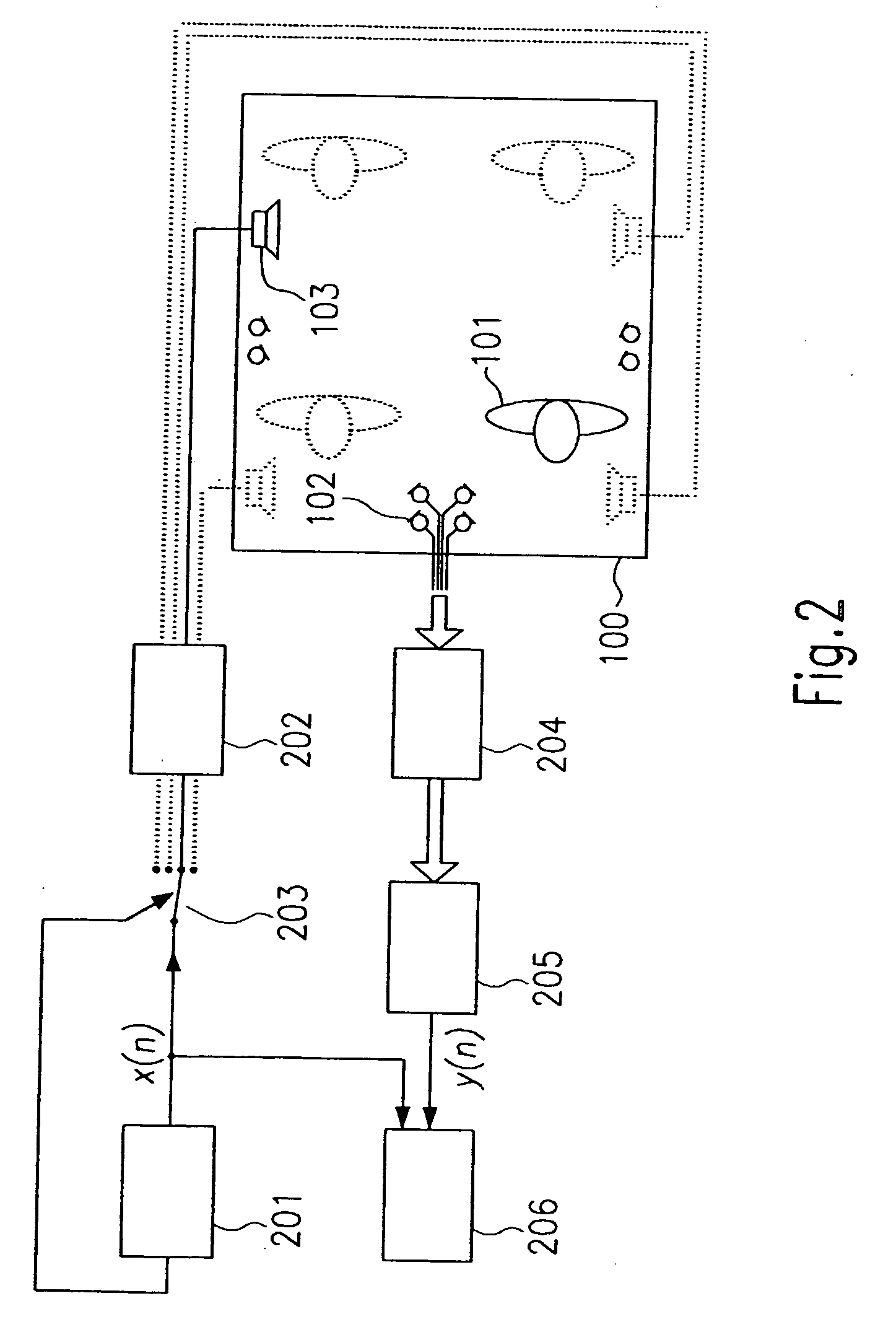
Indoor communication system for a vehicular cabin
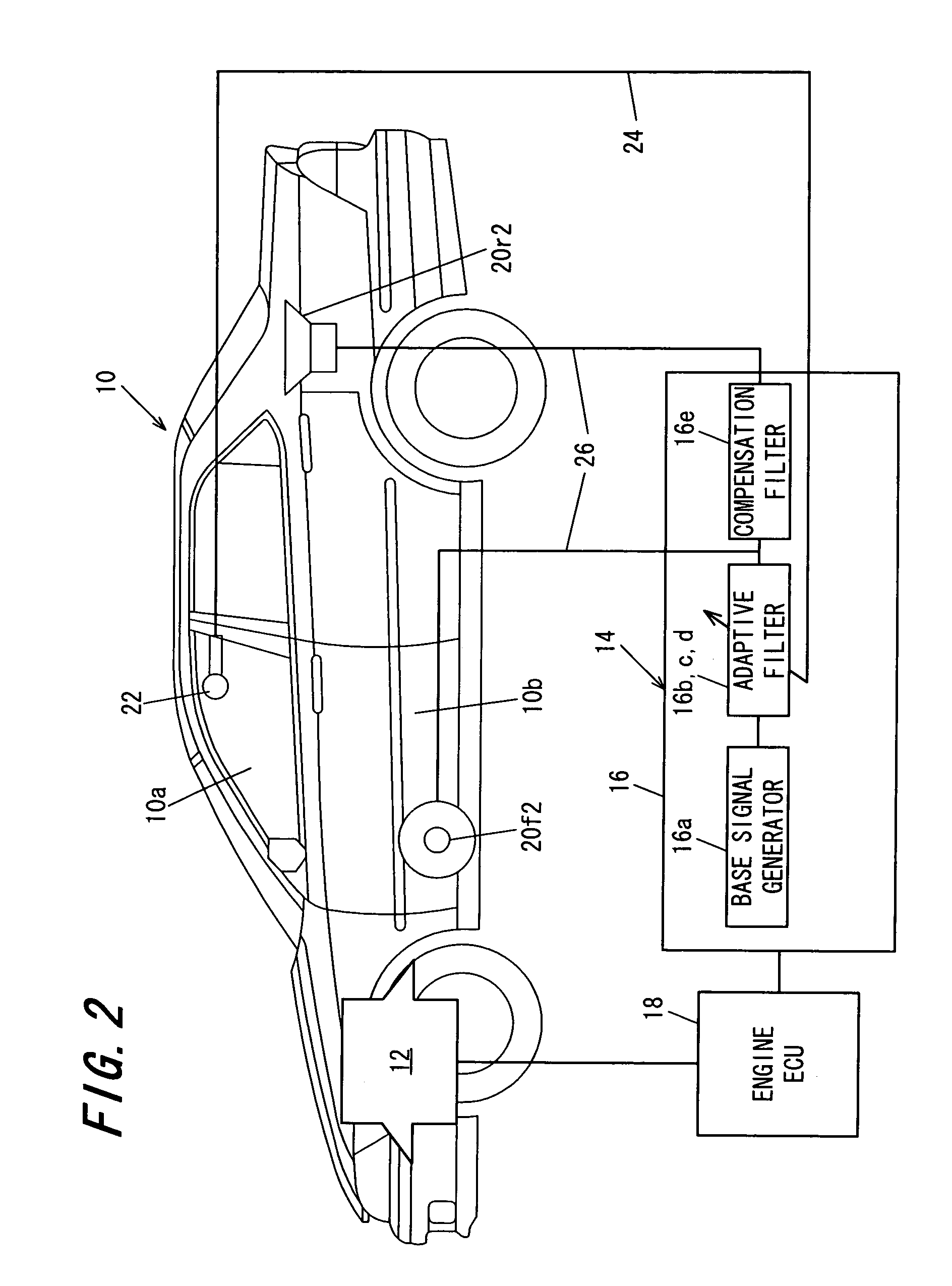
A system automatically determines an equalizing filter characteristic for a communication system within a vehicle. The communication system includes a loudspeaker and a microphone or microphone array. The system transmits a predetermined test signal through the loudspeaker and receive the test signal through the microphone or microphone array. Based on the predetermined test signal and the received test signal, a transfer function is developed. The equalizing filter characteristic is then developed from the transfer function.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
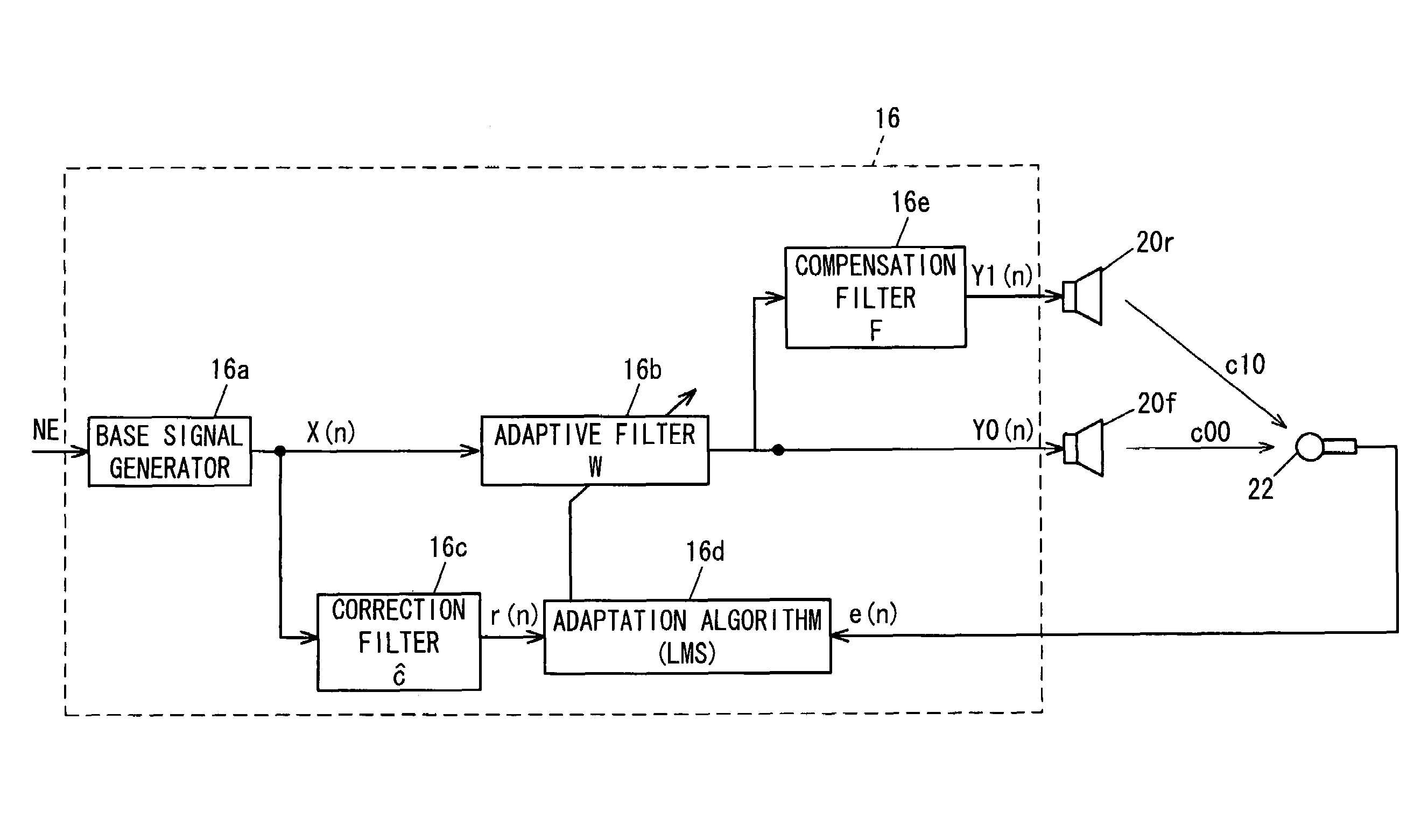
Active noise cancellation system
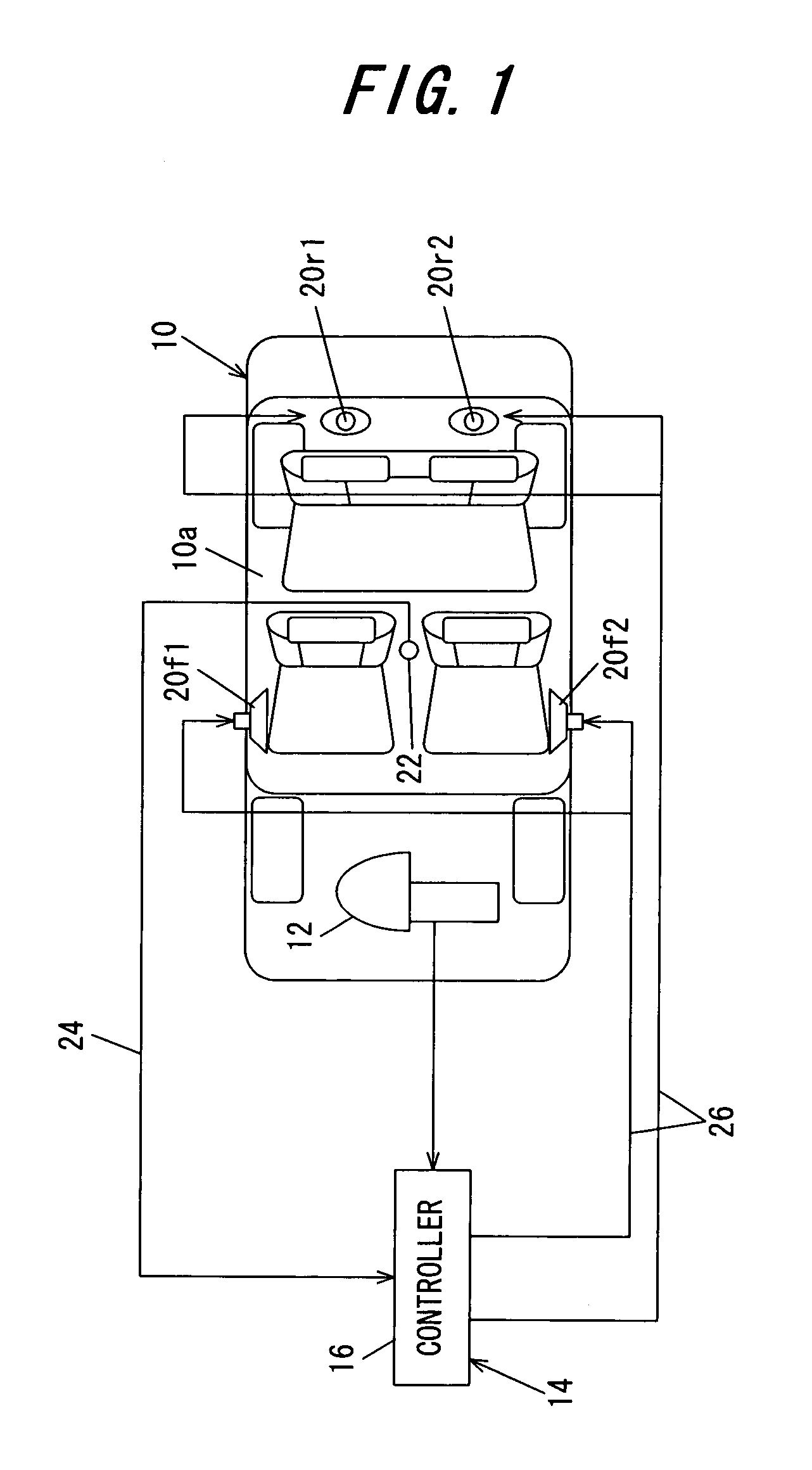
ActiveUS7536018B2Reduce noiseIncrease the number ofVibration measurement in fluidAdaptive networkControl signalEngineering
In an active noise cancellation system having an adaptive filter that outputs a control signal, first and second speakers that emit a canceling signal generated based on the control signal, a microphone that detects an error signal, a correction filter that corrects the base signal by a correction value to generate a reference signal and a filter coefficient updater that successively updates the adaptive filter coefficient based on the error signal and reference signal such that the error signal is minimized, the correction value of the correction filter is set to a sum obtained by adding the transfer characteristic from the first speaker to the microphone, and a product obtained by multiplying the transfer characteristic from the second speaker to the microphone by the prescribed value, thereby enabling to reduce the number of microphones and avoid the increase in parts, the amount of work to provide complicated wiring to the microphones, and the computational load involved in updating the adaptive filter coefficient, while enabling to maintain an area in which noise can be reduced to the same level as that obtained before reducing the number of microphones.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD +1
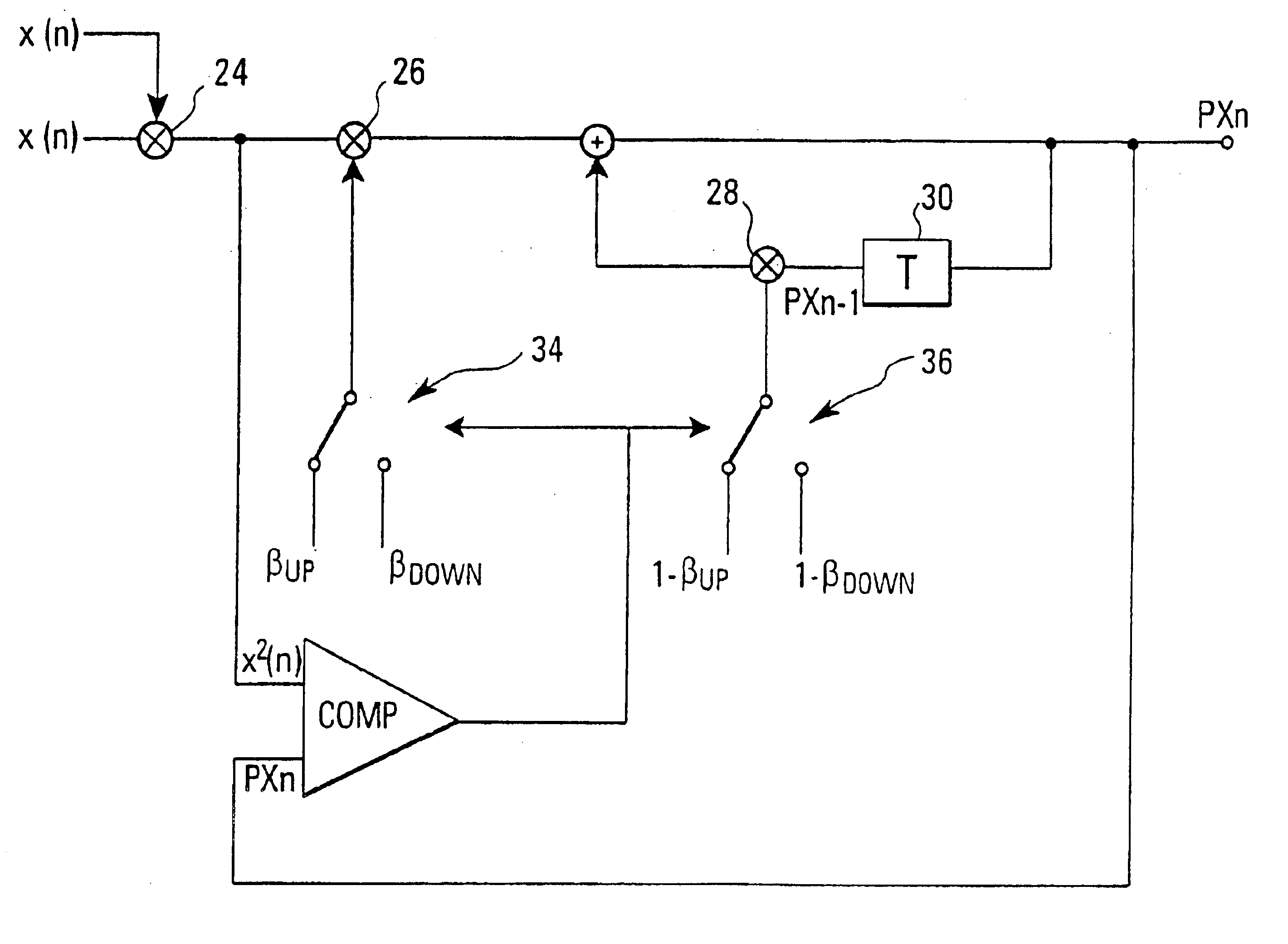
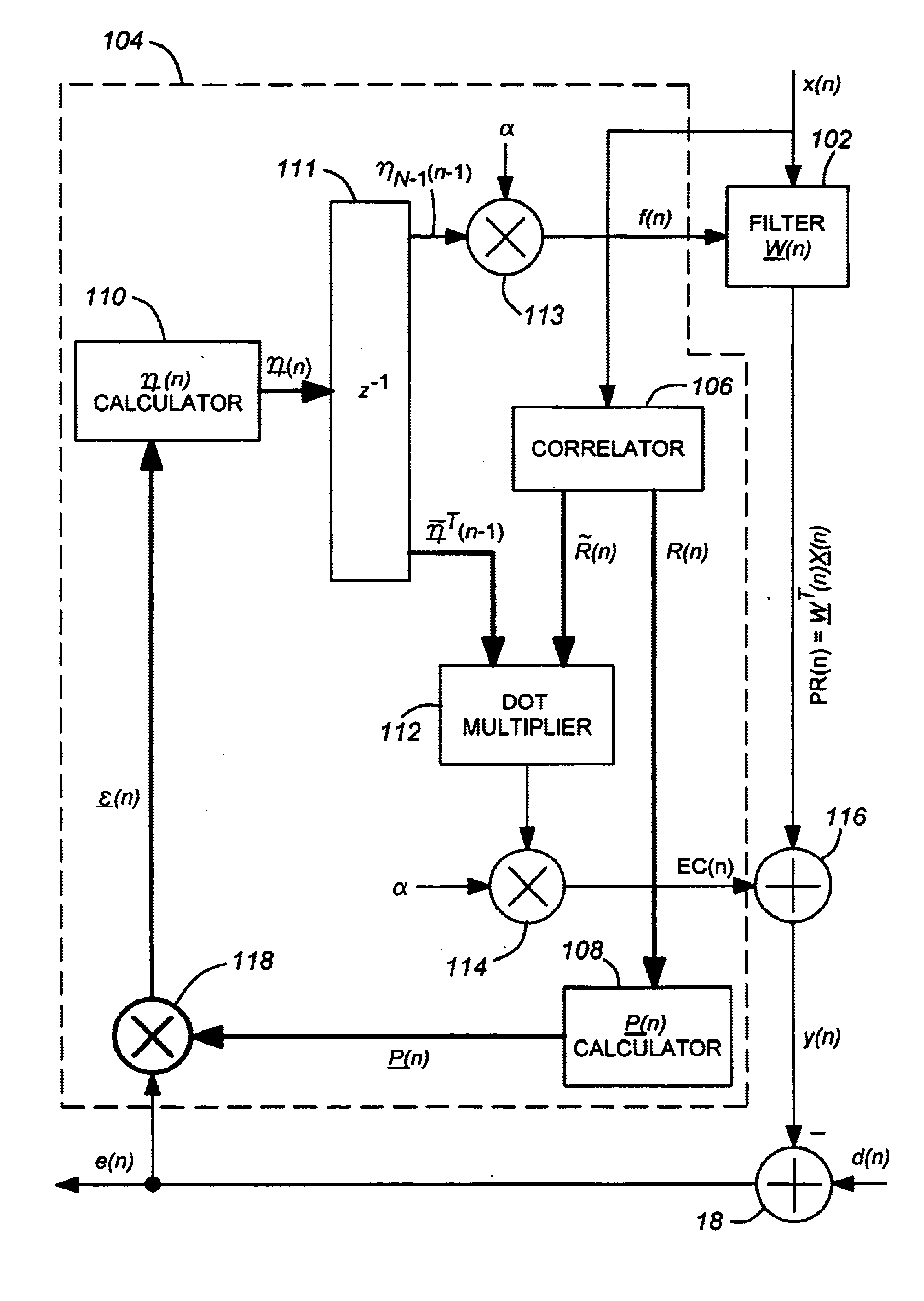
Stable adaptive filter and method
Stable adaptive filter and method are disclosed. The invention solves a problem of instability associated with Fast Affine Projection adaptive filters caused by error accumulation in an inversion process of an auto-correlation matrix. The Stable FAP uses a simplification of setting a normalized step size close to unity and reduces a problem of the matrix inversion to solving a system of linear equations whose solution coincides with a first column of the inverse auto-correlation matrix. The system of linear equations is then solved by one of descending iterative methods which provide inherent stability of operation due to intrinsic feedback adjustment. As a result, inevitable numerical errors are not accumulated, being corrected as the process goes on. In first and second embodiments of the invention the system of linear equation is solved by steepest descent and conjugate gradient methods respectively. Being immune to numerical errors, the invented method and filter are suitable for various DSP platforms, e.g., 16 and 24 bit fixed-point as well as floating point platform.
Owner:CIENA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com