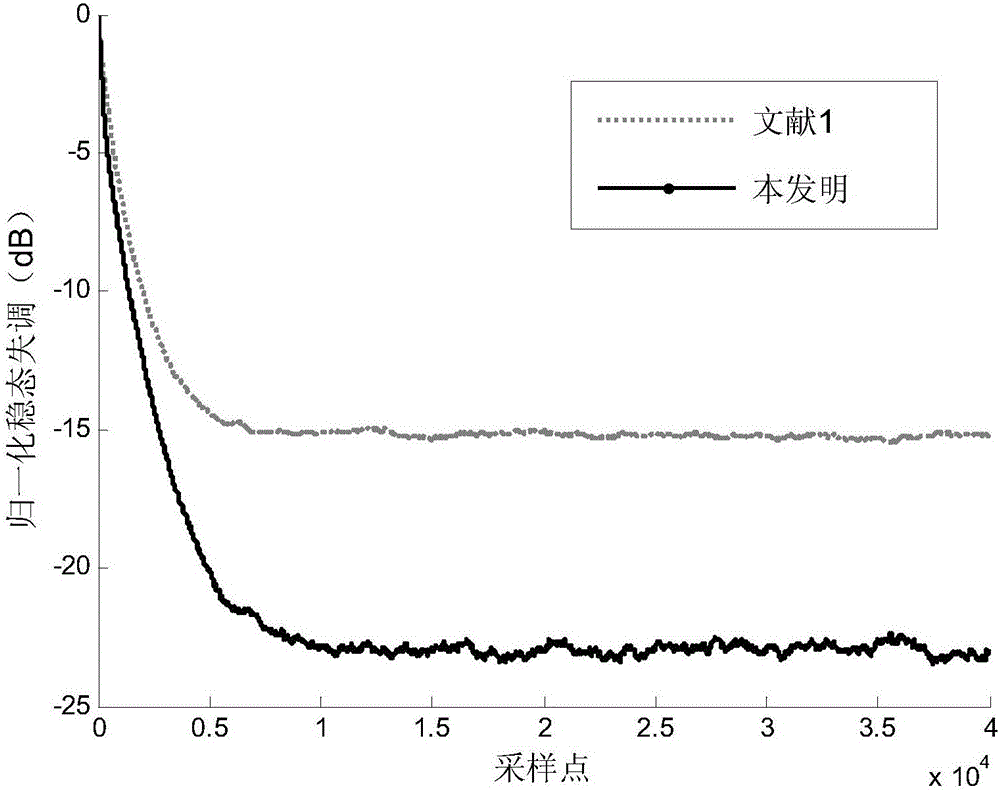
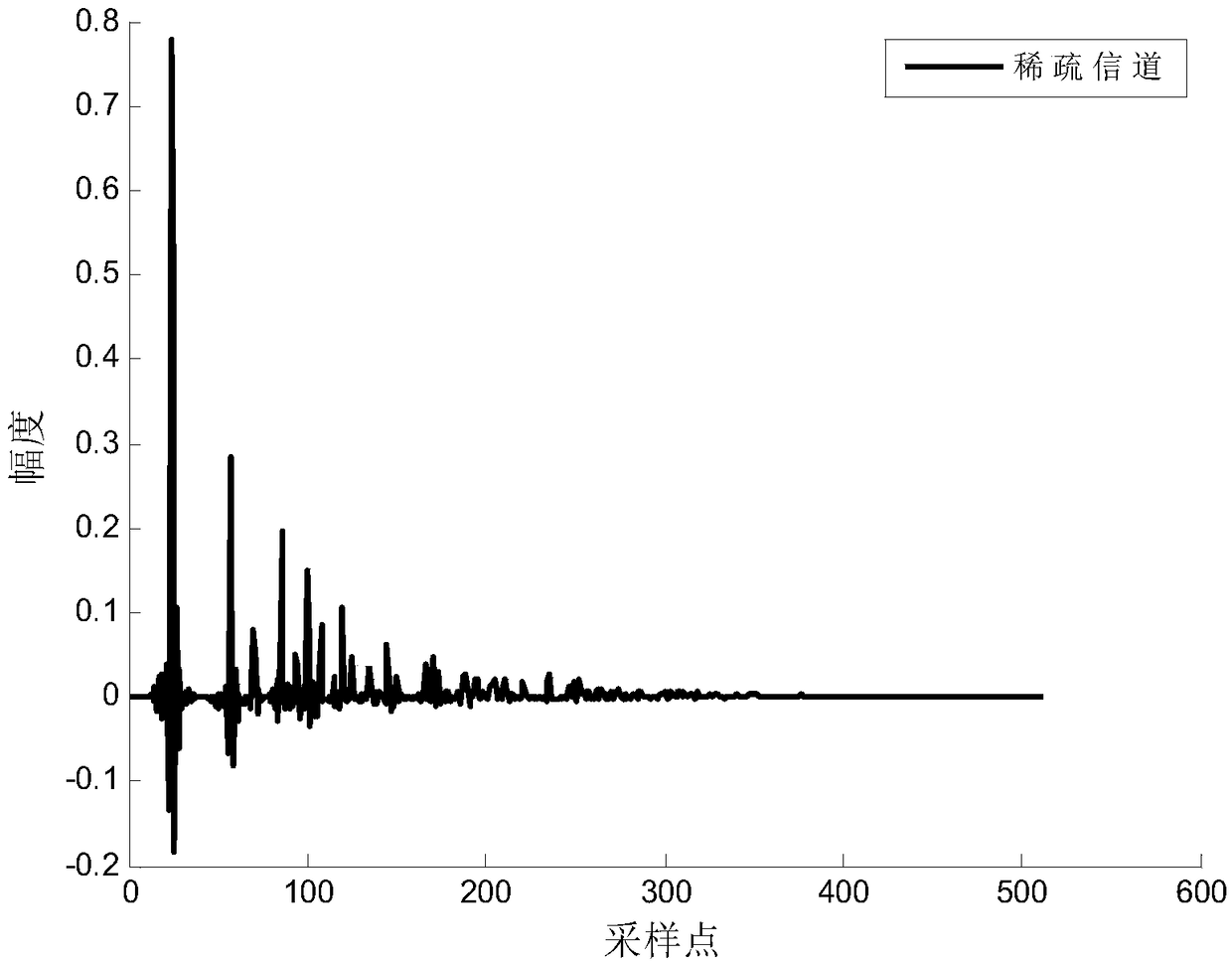
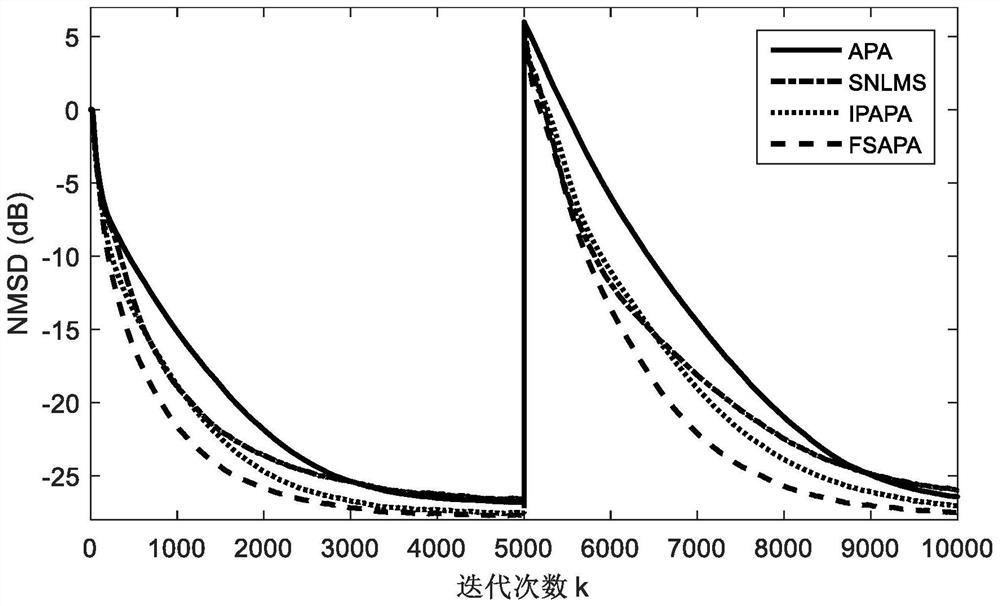
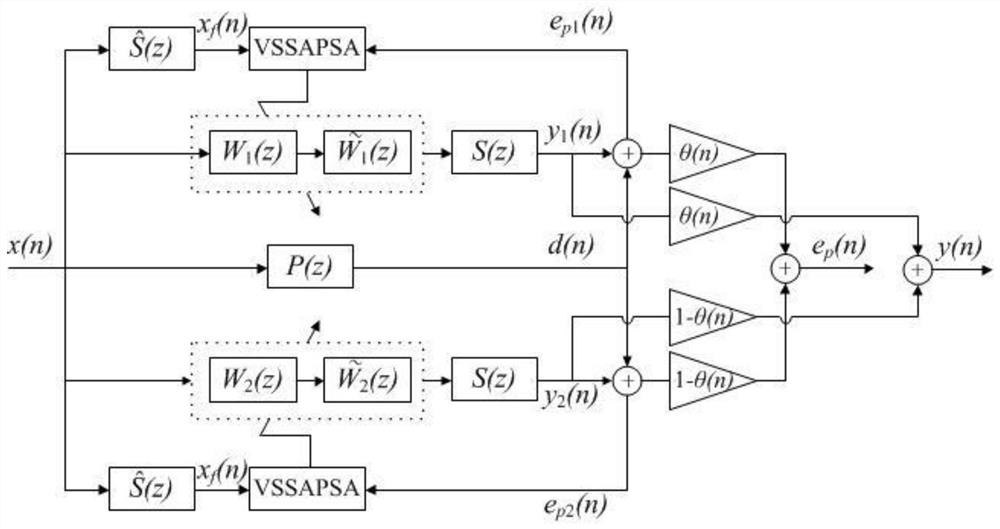
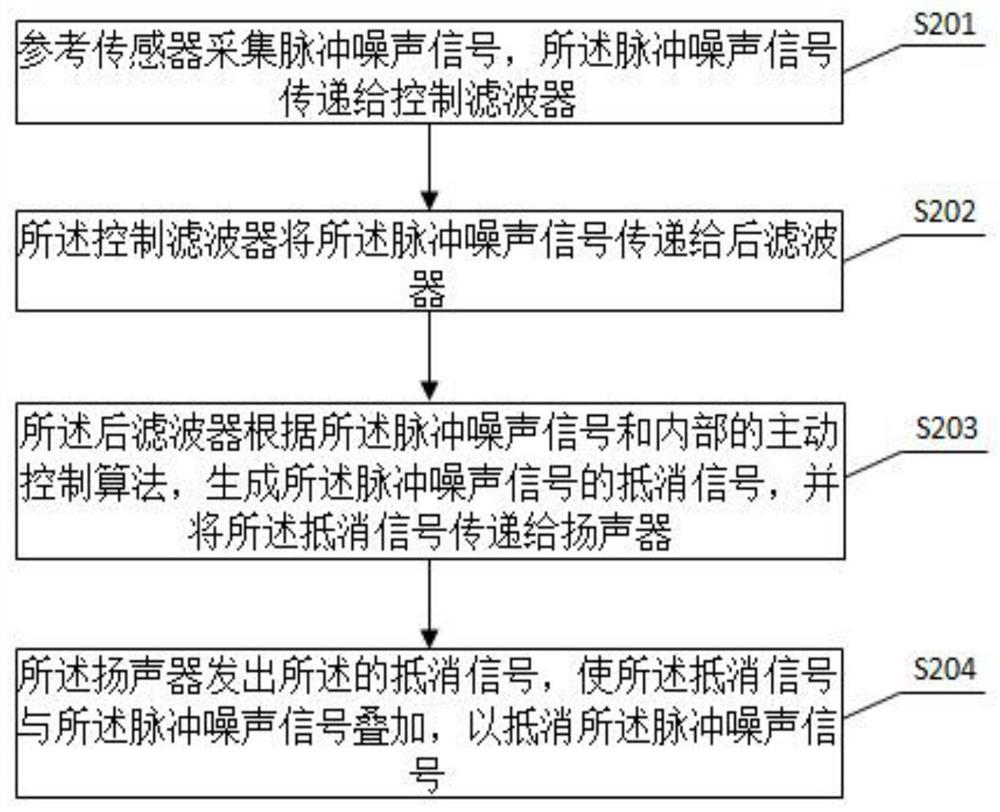
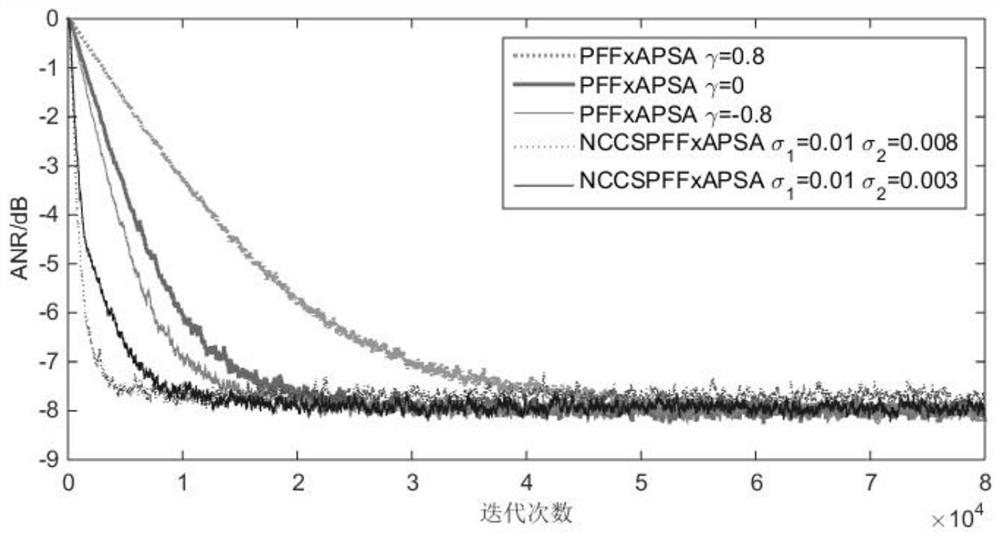
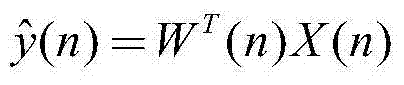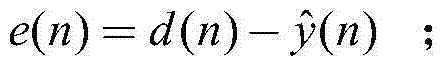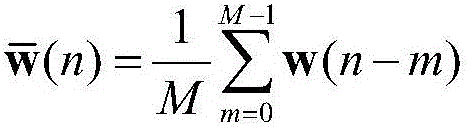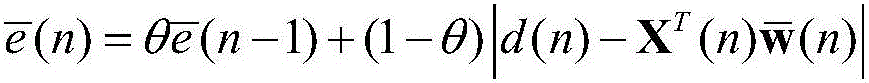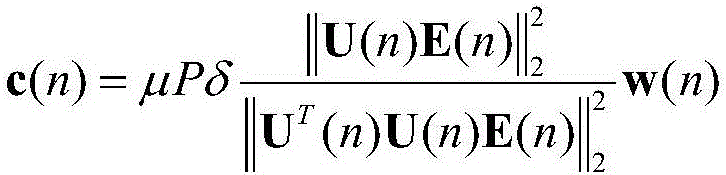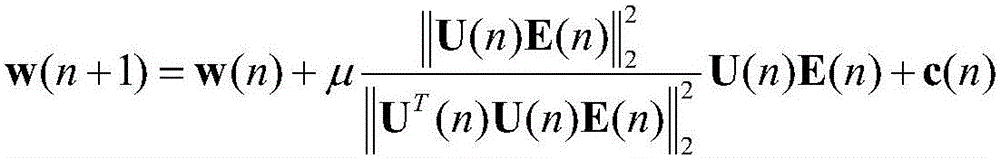Patents
Literature
59 results about "Affine projection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
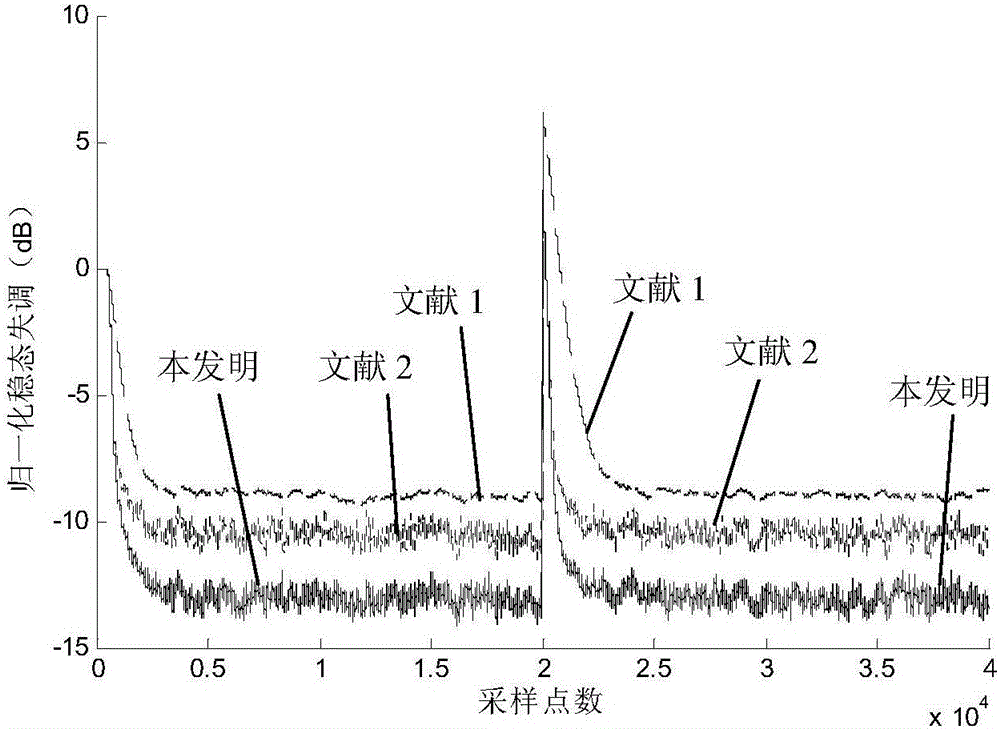
Stable adaptive filter and method
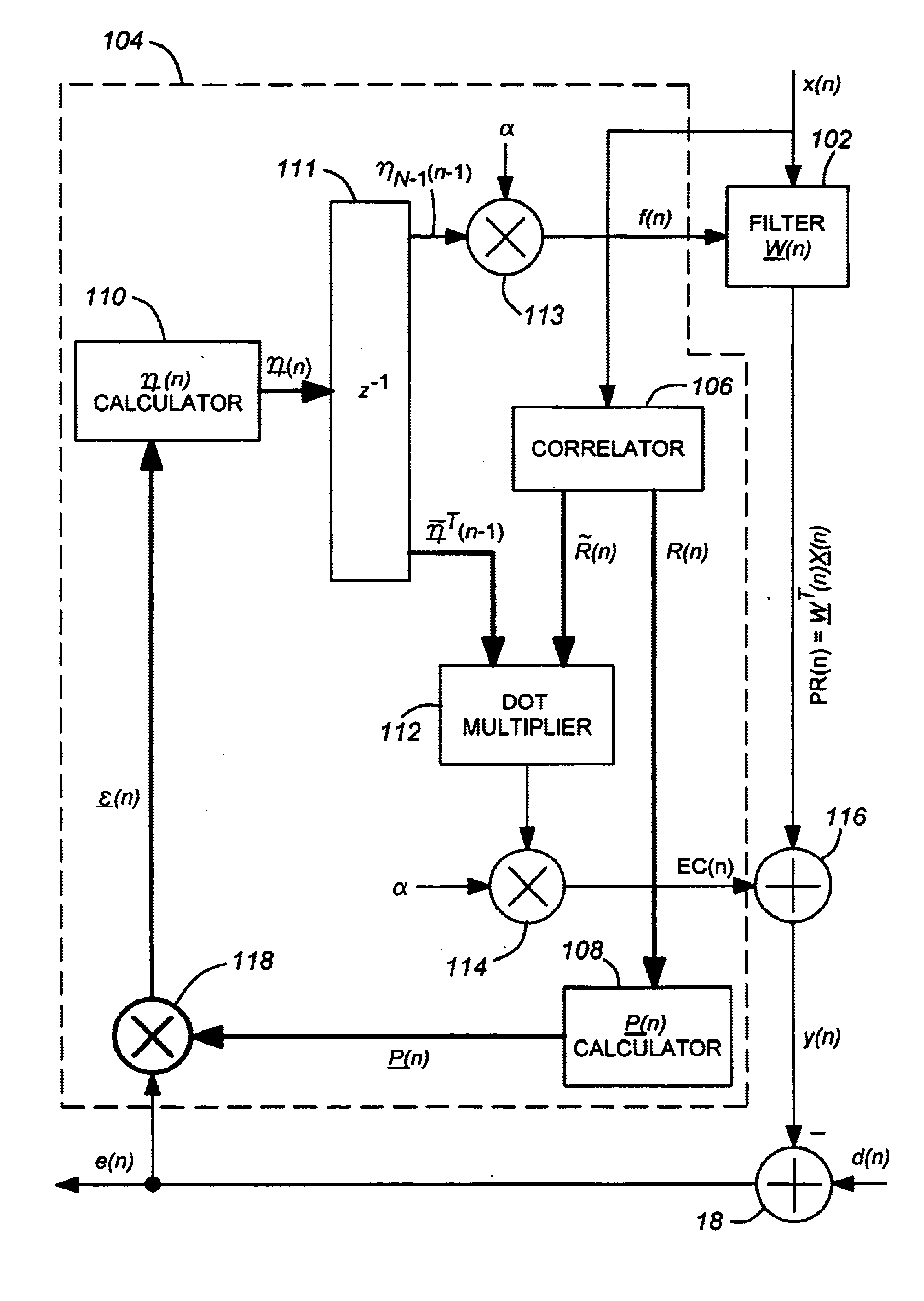
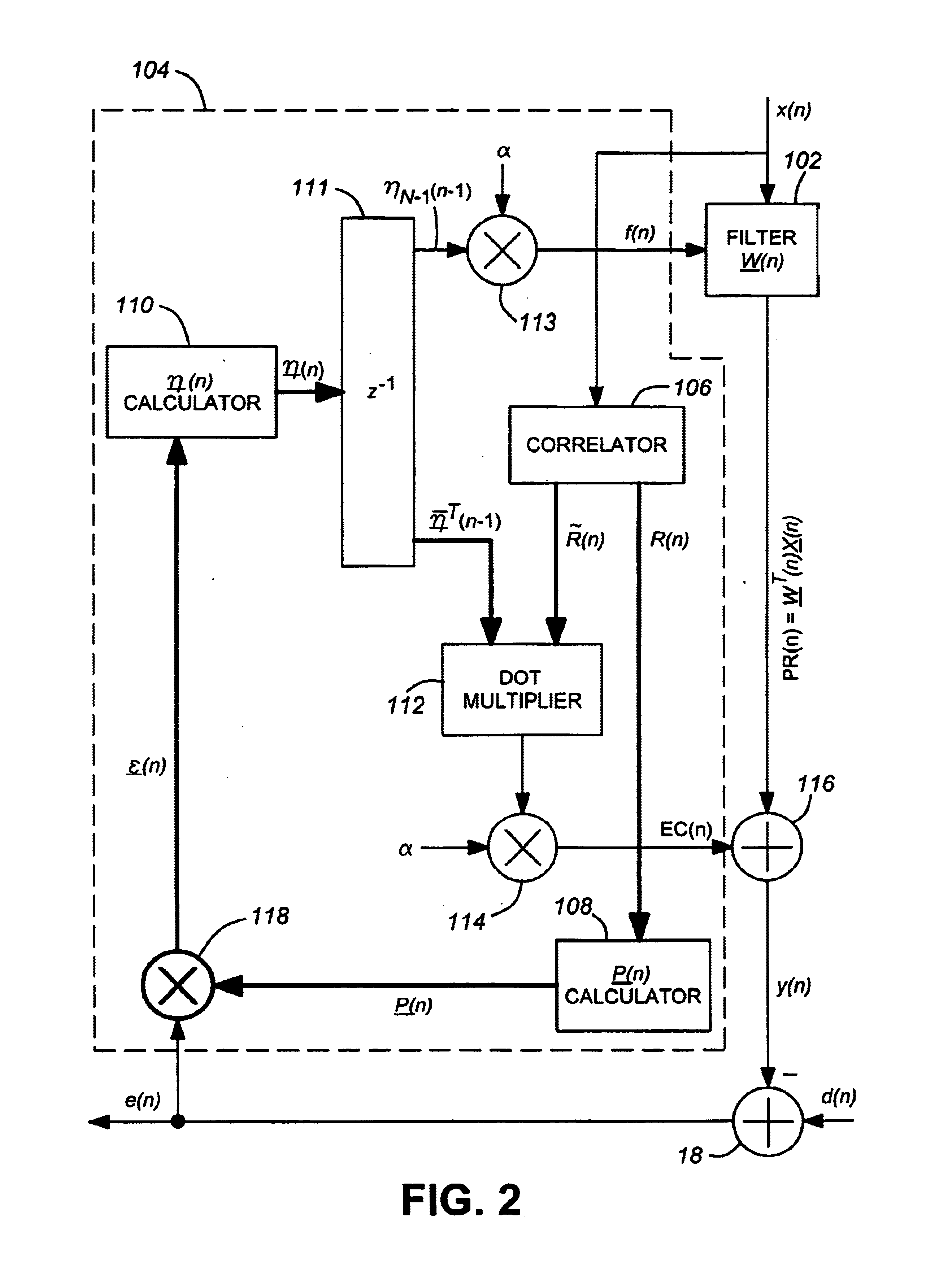
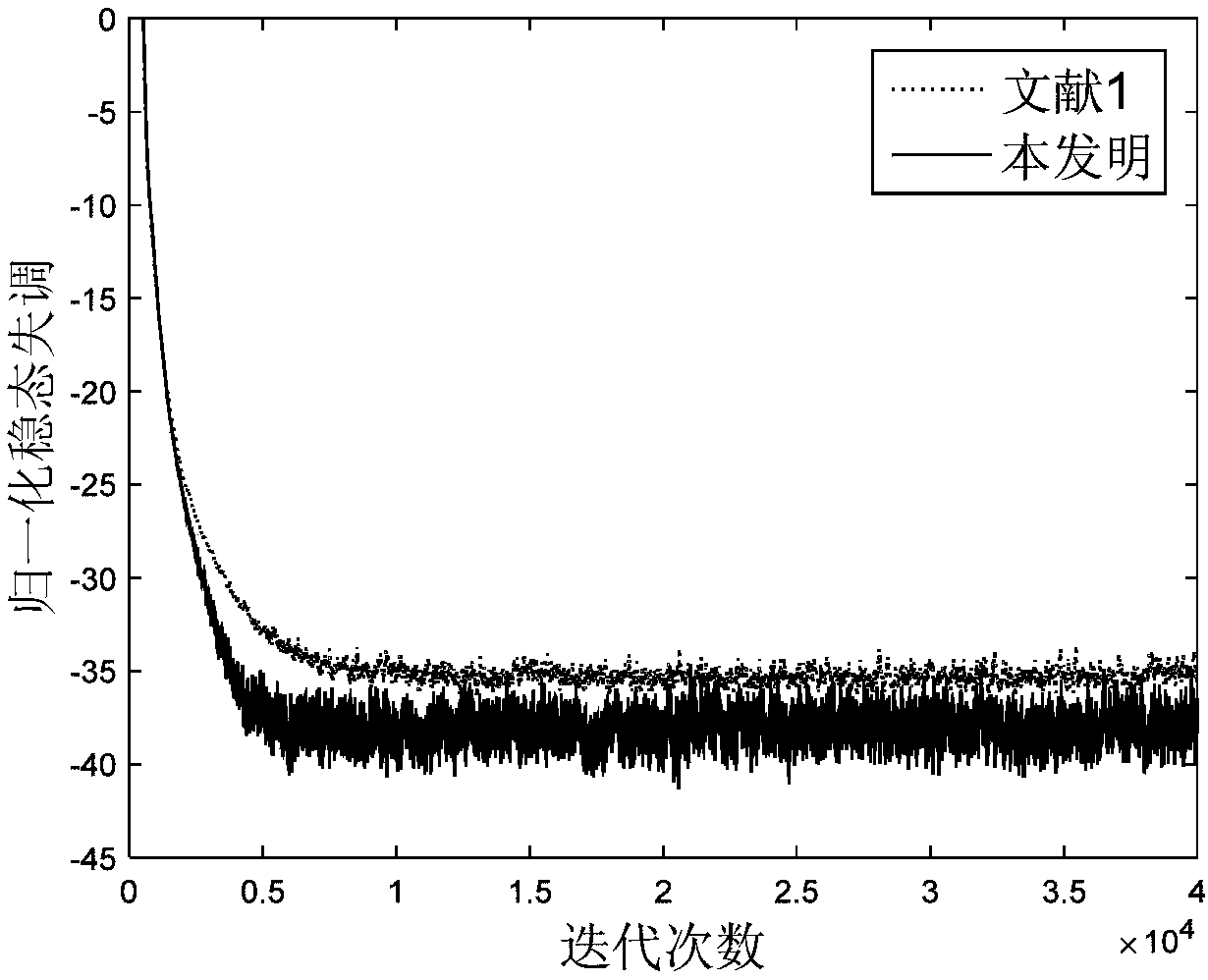
Stable adaptive filter and method are disclosed. The invention solves a problem of instability associated with Fast Affine Projection adaptive filters caused by error accumulation in an inversion process of an auto-correlation matrix. The Stable FAP uses a simplification of setting a normalized step size close to unity and reduces a problem of the matrix inversion to solving a system of linear equations whose solution coincides with a first column of the inverse auto-correlation matrix. The system of linear equations is then solved by one of descending iterative methods which provide inherent stability of operation due to intrinsic feedback adjustment. As a result, inevitable numerical errors are not accumulated, being corrected as the process goes on. In first and second embodiments of the invention the system of linear equation is solved by steepest descent and conjugate gradient methods respectively. Being immune to numerical errors, the invented method and filter are suitable for various DSP platforms, e.g., 16 and 24 bit fixed-point as well as floating point platform.
Owner:CIENA
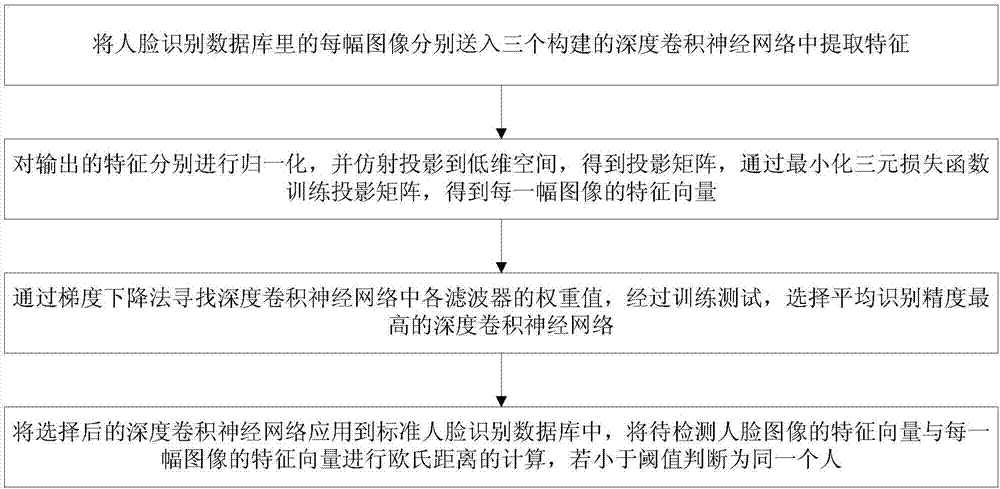
Face identification method based on deep convolutional neural network
InactiveCN107330383AAvoid dependenceReduce complexityCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesHat matrixFeature vector
The present invention discloses a face identification method based on a deep convolutional neural network. The method comprises: respectively feeding each image in a face identification database into three constructed deep convolutional neural network for feature extraction; performing normalization of output features, performing affine projection of the features to a low-dimensional space, obtaining a projection matrix, training a projection matrix through minimization of a ternary loss function, and obtaining feature vectors of each image; searching the weight value of each filter in the deep convolutional neural network through a gradient descending method, performing training test, and selecting a deep convolutional neural network having the highest average identification precision; and applying the selected deep convolutional neural network to a standard face identification database, performing Euclidean distance calculation of feature vectors of face images to be detected and each image, and if the feature vectors are smaller than a threshold value, determining that the images show the same person. Few images are used in the training, and the employed convolutional neural network is simple in structure so as to improve the face identification precision and reduce the training complexity.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
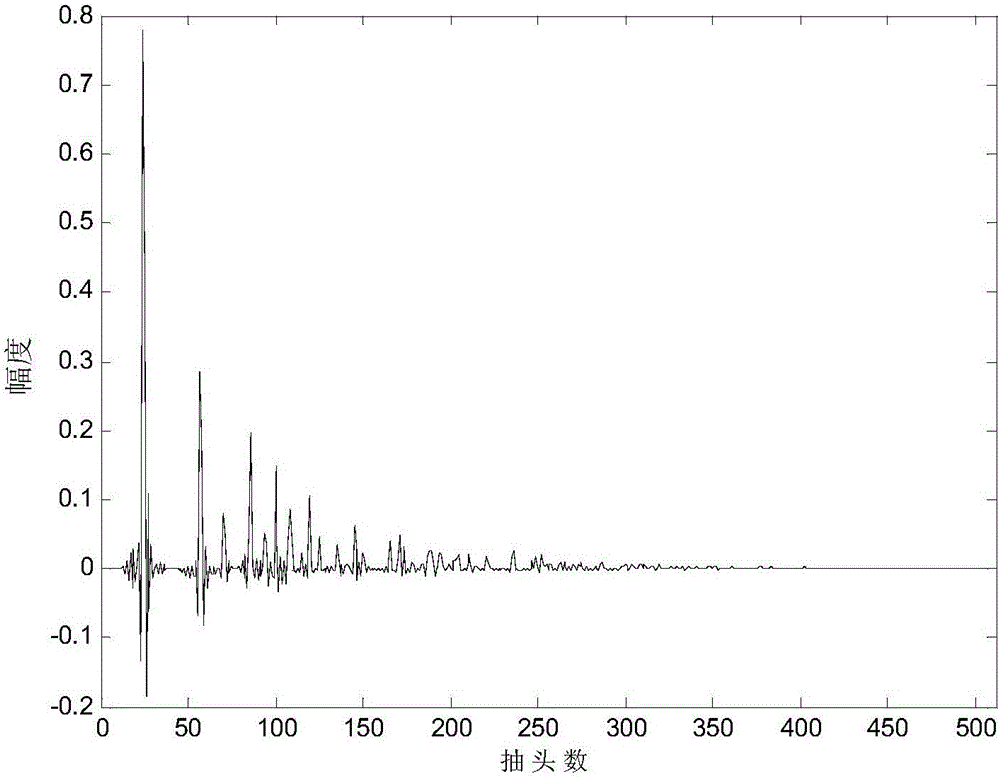
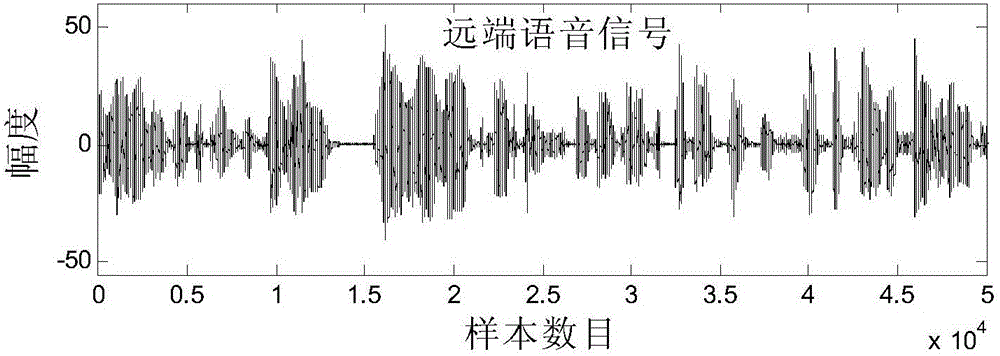
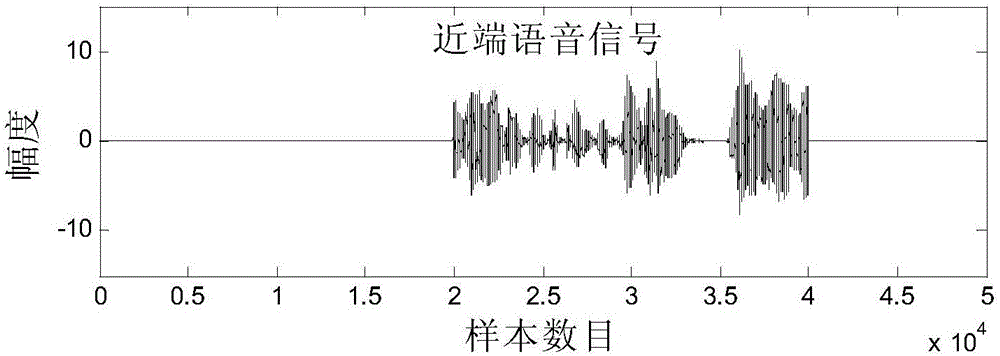
Adaptive echo cancellation method adopting memory proportionate affine projection and based on M-estimation
InactiveCN104683614AAdaptableFast convergenceTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsCommunications systemProximal point
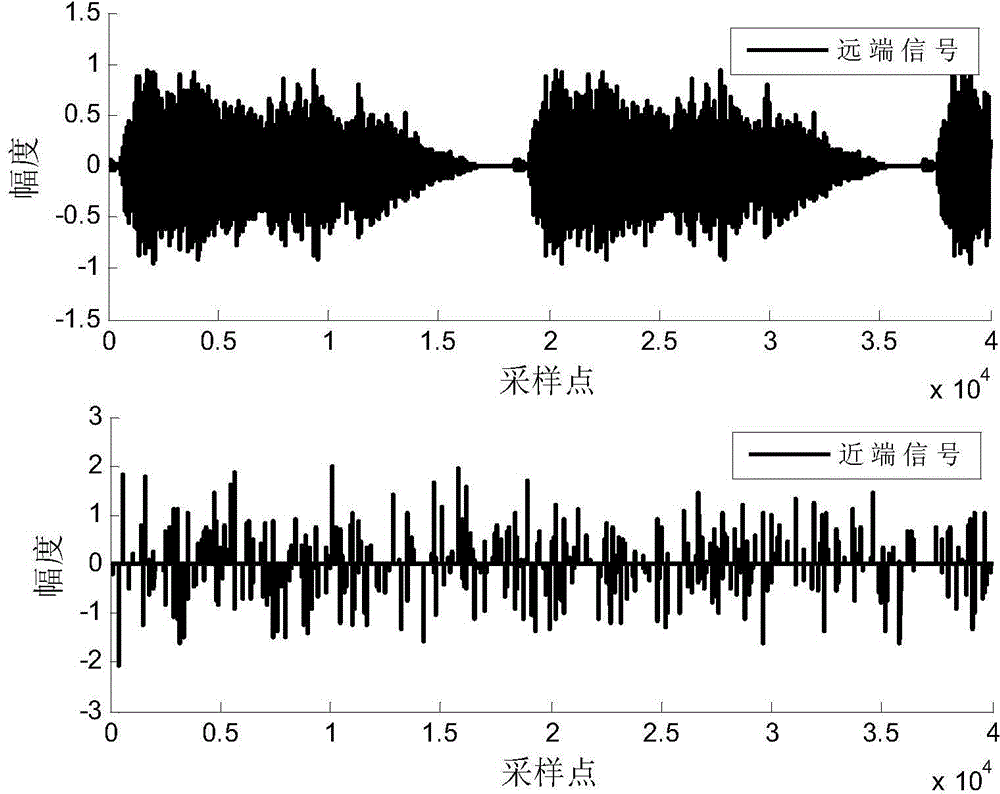
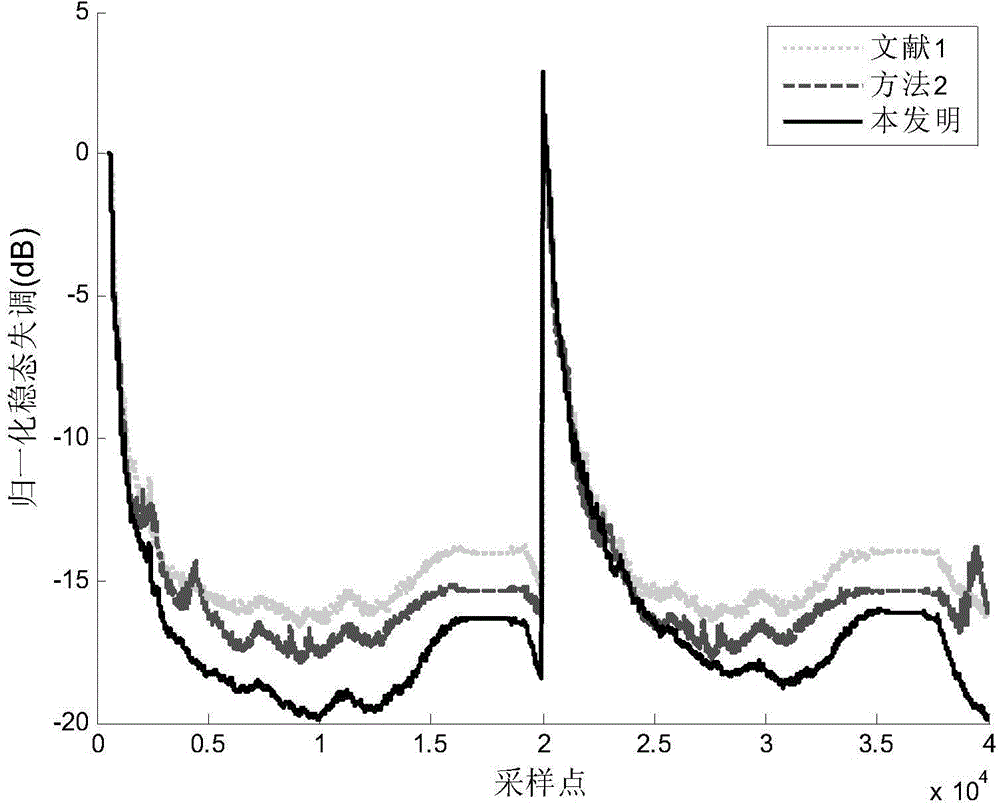
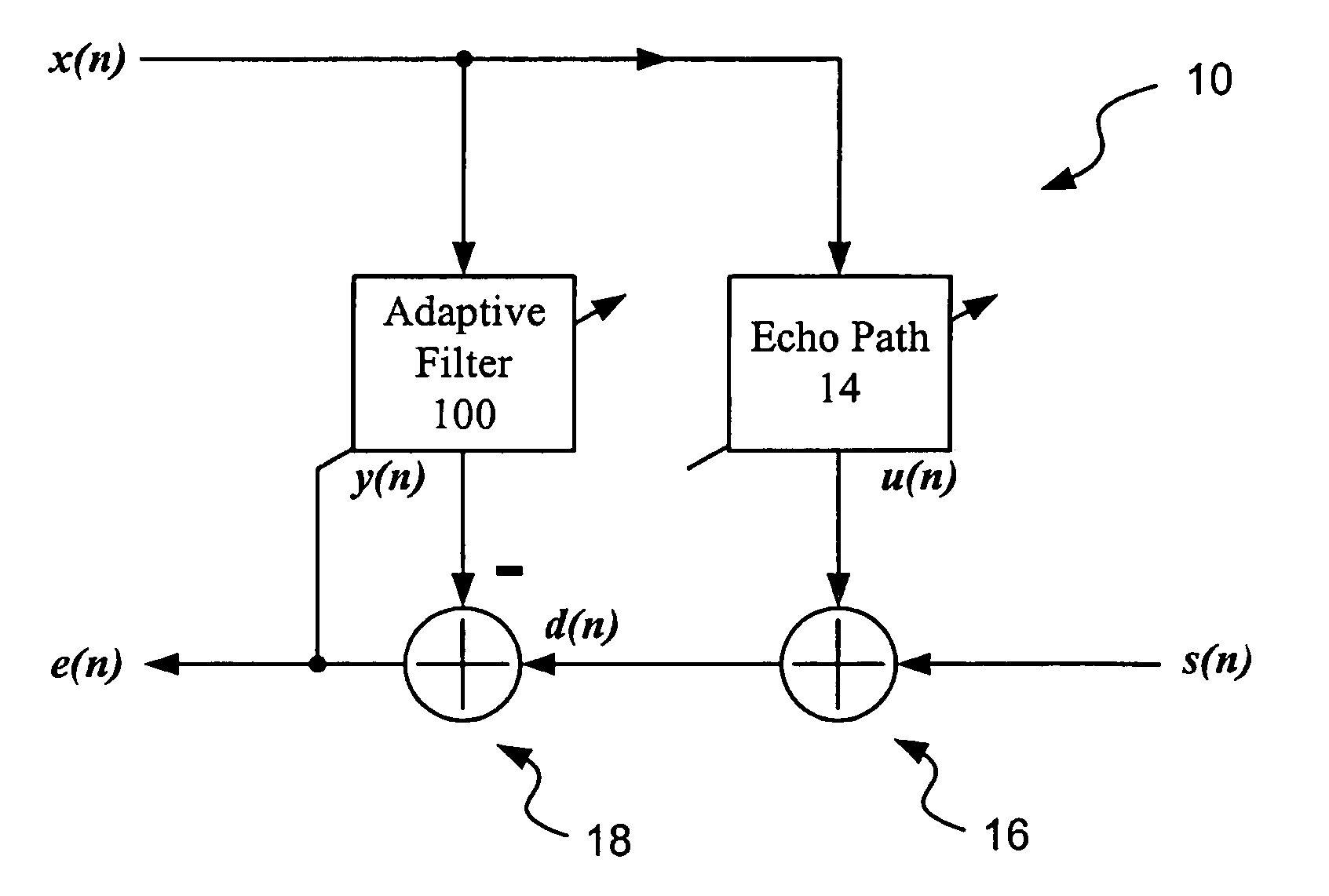
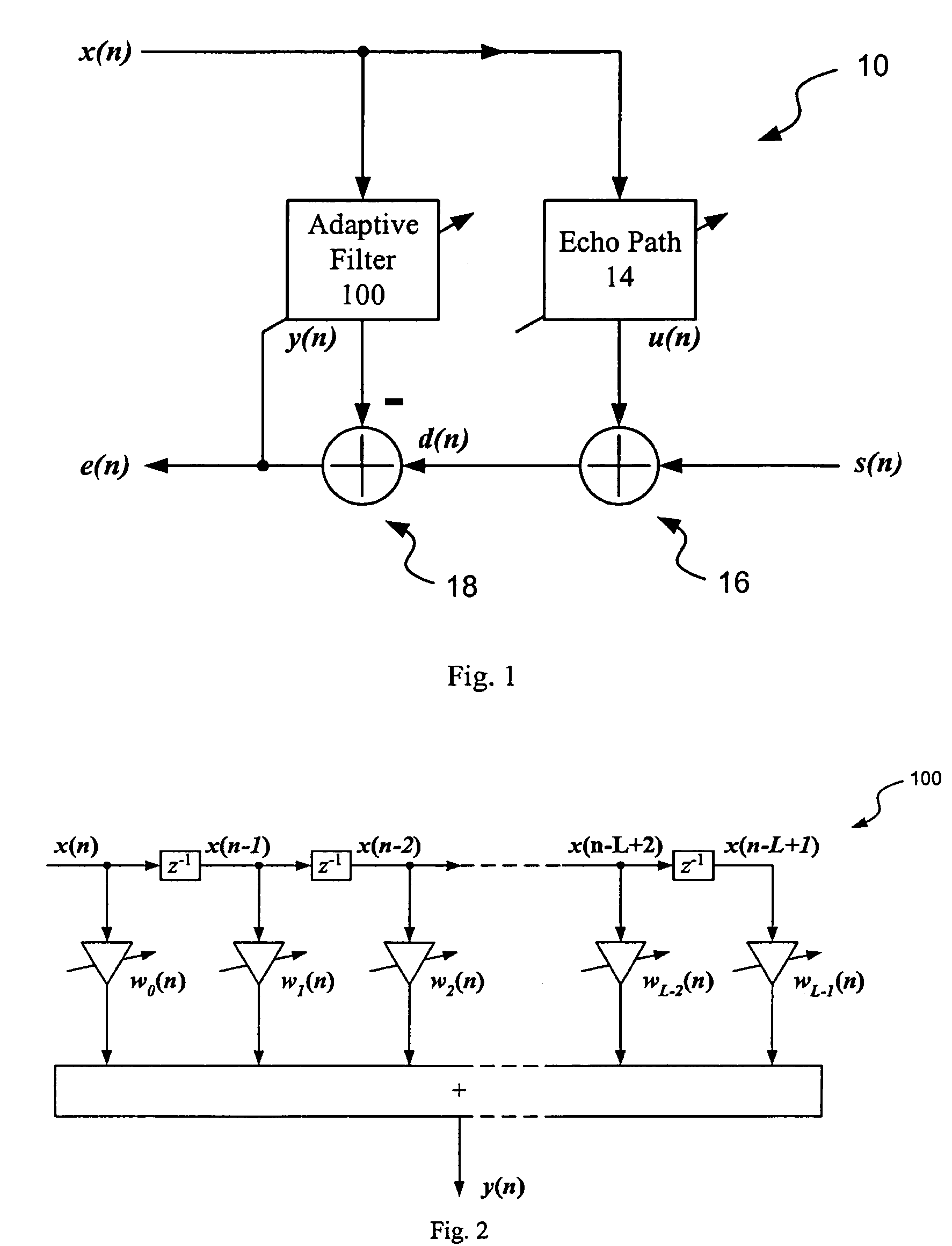
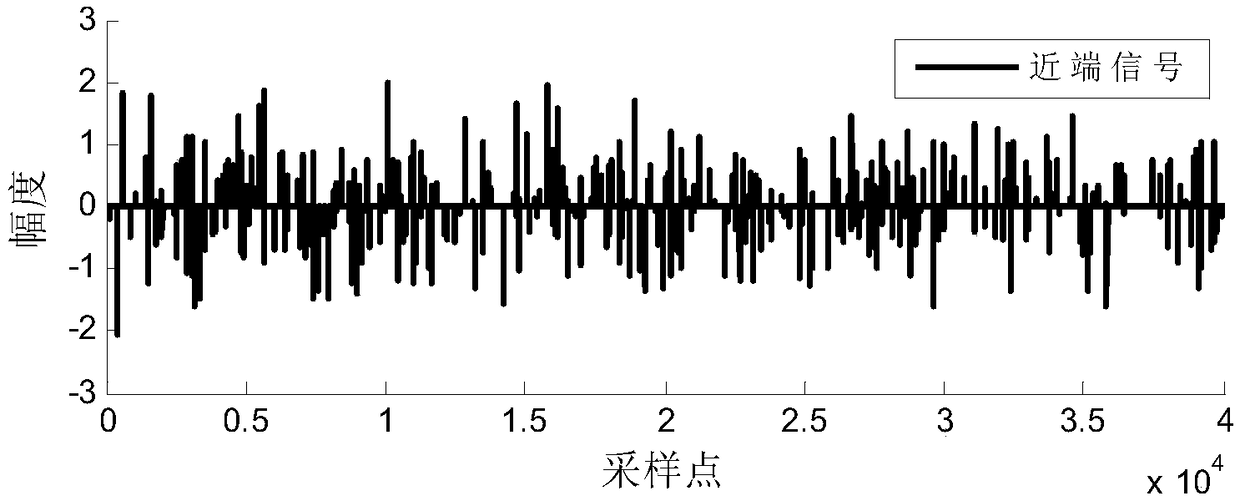
The invention discloses an adaptive echo cancellation method adopting memory proportionate affine projection and based on M-estimation. The adaptive echo cancellation method comprises the following steps: A, a remote signal is sampled; B, in echo estimation, a filter input vector X(n) passes through an adaptive filter and an output value y(n), namely an echo estimation value y(n), is obtained and equal to XT(n)w(n); C, in echo cancellation, a near-end signal d(n) with the echo, acquired by a near-end microphone and the output value y(n) of the adaptive filter are subjected to subtraction operation, and a return signal, namely a residual signal e(n), is returned to a far end and equal to d(n)-y(n); D, in updating of a tap weight vector of the filter, the method adopting memory proportionate affine projection and based on M-estimation is used and the tap weight vector w(n+1) of the adaptive filter at next moment n+1 is calculated and equal to w(n)+mu P(n)(UT(n)P(n)+delta IK)-1 psi [E(n)]; E, n is set to be n+1, and the steps B, C and D are repeated until a call is ended. The method has a good cancellation effect on an acoustic echo of a communication system and is high in convergence speed and small in steady-state error.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Adaptive echo cancellation method of affine projection maximum entropy sub-band
ActiveCN106210370AIncrease changeQuick updateTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsSpeech analysisAnti jammingSelf adaptive
The invention discloses an adaptive echo cancellation method of an affine projection maximum entropy sub-band. The adaptive echo cancellation method of the affine projection maximum entropy sub-band comprises the steps of A, far-end signal division, including, dividing a far-end signal vector U (n) into I far-end sub-band vectors Ui(n) through a first analysis filter, and dividing a near-end signal d(n) picked up by a near-end microphone into I near-end sub-band signals di(n) through a second analysis filter; B, signal extraction, including, carrying out I extraction for the far-end sub-band vectors Ui(n) through an extractor so as to obtain far-end input sub-band extraction vectors Ui(k), and carrying out I extraction for the near-end sub-band signals di(n) through the extractor so as to obtain near-end sub-band extraction signals di(k); C, affine projection; D, filter outputting, including, filtering a far-end input sub-band affine projection matrix X(k) through a filter so as to obtain an output vector Y(k); E, echo cancellation; F, tapping right vector updating, including, updating based on the maximum entropy V(k) of the current net signal vector so as to determine a right vector at the next extraction moment; and G, iteration, including, enabling k to be equal to k+1, and repeating the steps A, B, C, D, E and F until a call is ended. The echo cancellation effect is good, and the anti-jamming capability is strong.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Proportional affine projection echo elimination method based on coefficient difference
InactiveCN104270539AFast convergenceSmall steady state errorTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsComputation complexityWeight coefficient
The invention provides a proportional affine projection echo elimination method based on coefficient difference. The method includes the steps of (A) far-end signal sampling, (B) echo signal estimation, (C) echo signal removing, (D) updating of filter tap weight coefficients, and (E) repeating of the steps B, C and D on the condition that n is equal to n plus one, and real-time echo elimination can be achieved. When the tap weight coefficients are updated in the step D, the step length gi (n) of the ith tap weight coefficient wi (n) of a self-adapting filter at the current moment satisfies an equation shown in the text, namely, in the time period M, the step length of the tap weight coefficient of the self-adapting filter at the current moment is equal to the difference value of any tap weight coefficient at the current moment n and the tap weight coefficient at the initial moment kM of the time period, and when the weight coefficients are updated, the affine projection method of an input signal matrix formed by input signal vectors at multiple moments is adopted. According to the method, the echo elimination effect is good, environment self-adaptability is high, the convergence rate is high, steady state errors are small, meanwhile, computation complexity is low, cost of needed hardware is low, the structure is simple and the method is easy to carry out.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Adaptive filtering using fast affine projection adaptation
InactiveUS20060039458A1Multiple-port networksAdaptive networkComputation complexityAffine projection
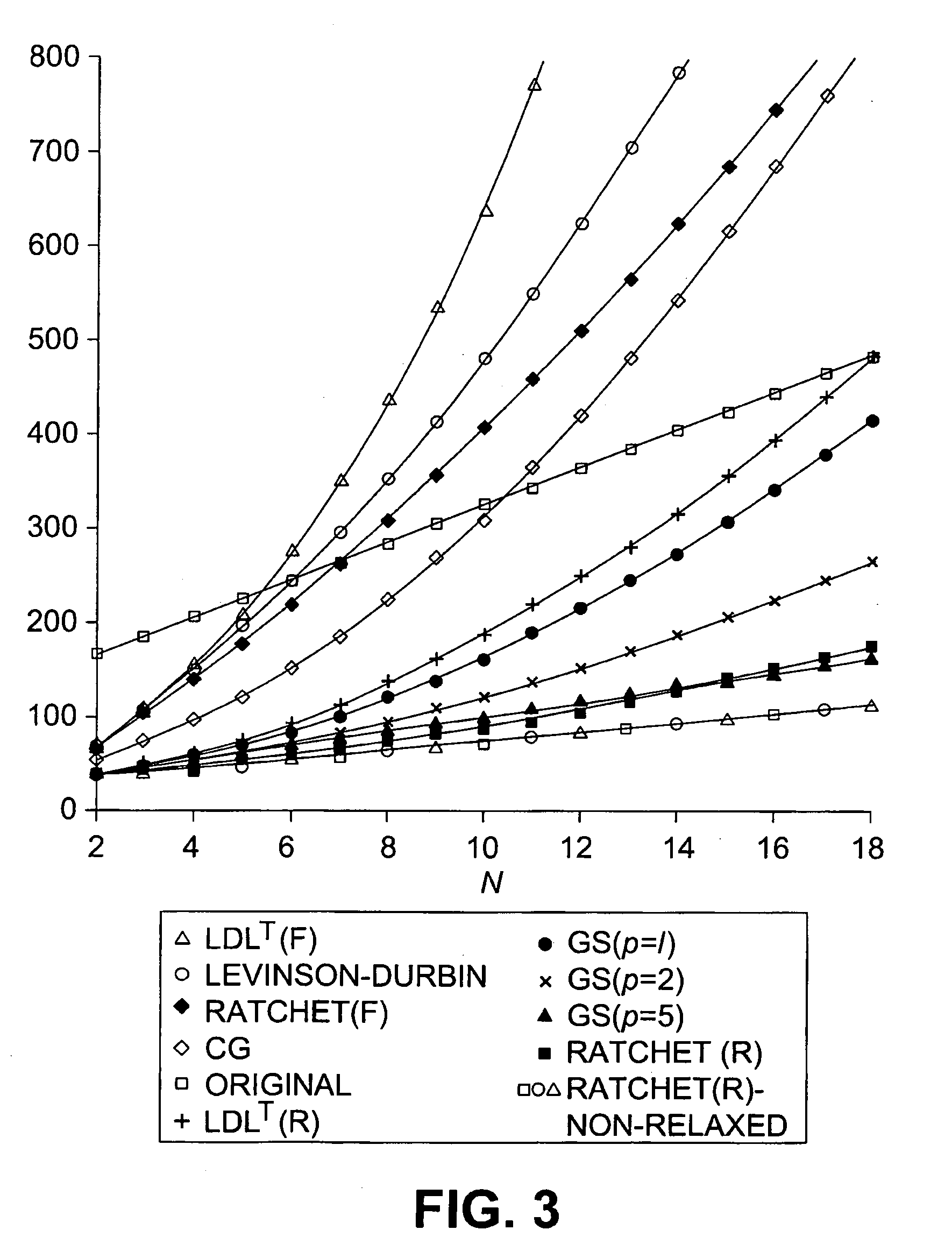
A method of adaptive filtering using fast affine projection (FAP) that allows for direct solution of the projected error vector from the autocorrelation matrix using a backward and forward recursion technique or LDLT factorization of the autocorrelation matrix followed by forward substitution, scaling and backward substitution. The method results in less computational complexity in the implementation, while still having good stability and fast convergence.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
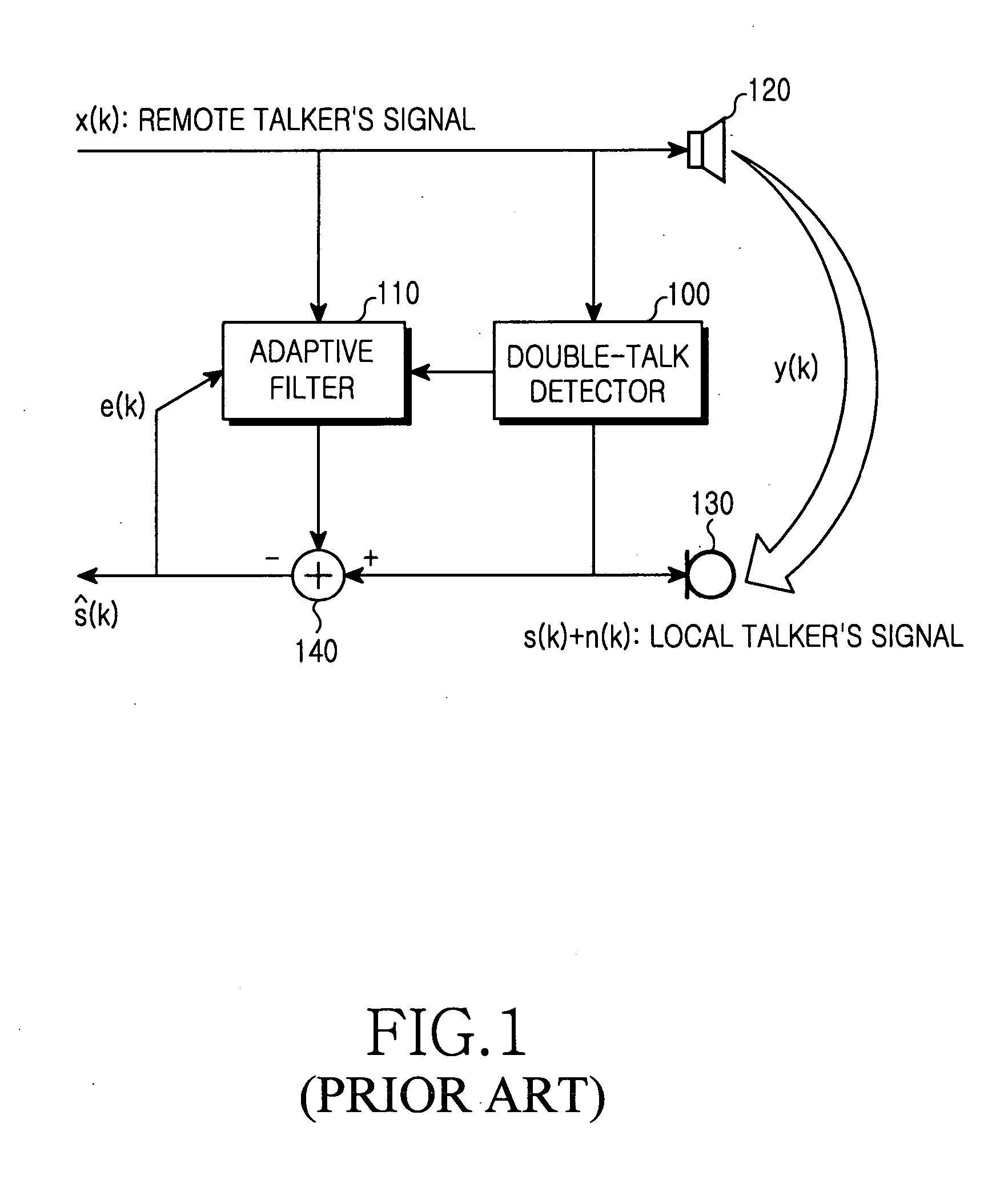
Method and apparatus for canceling acoustic echo in a double-talk period
InactiveUS20050243995A1Minimizing speech quality degradationMinimize quality degradationTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsApparel holdersMean squareDouble talk detector
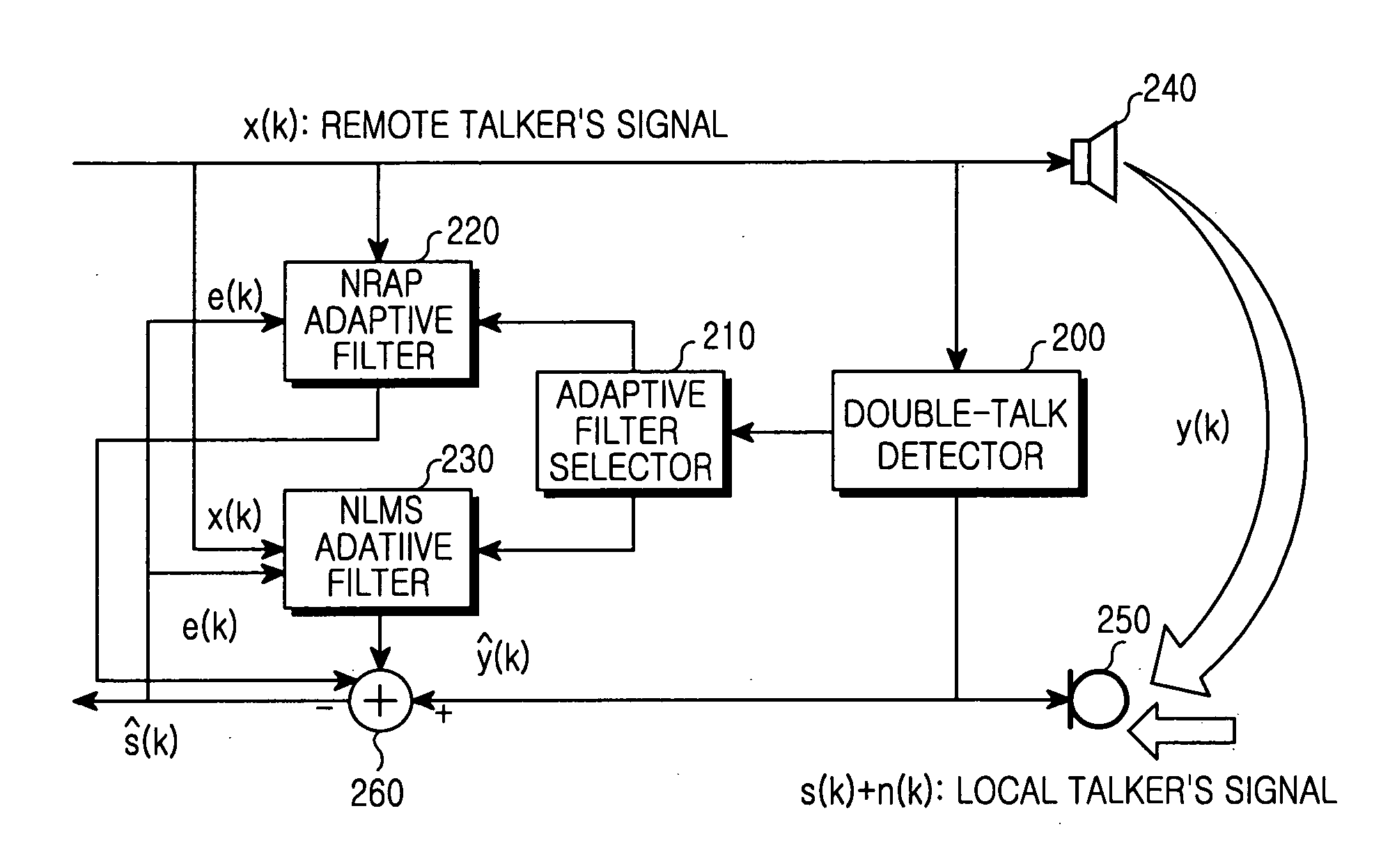
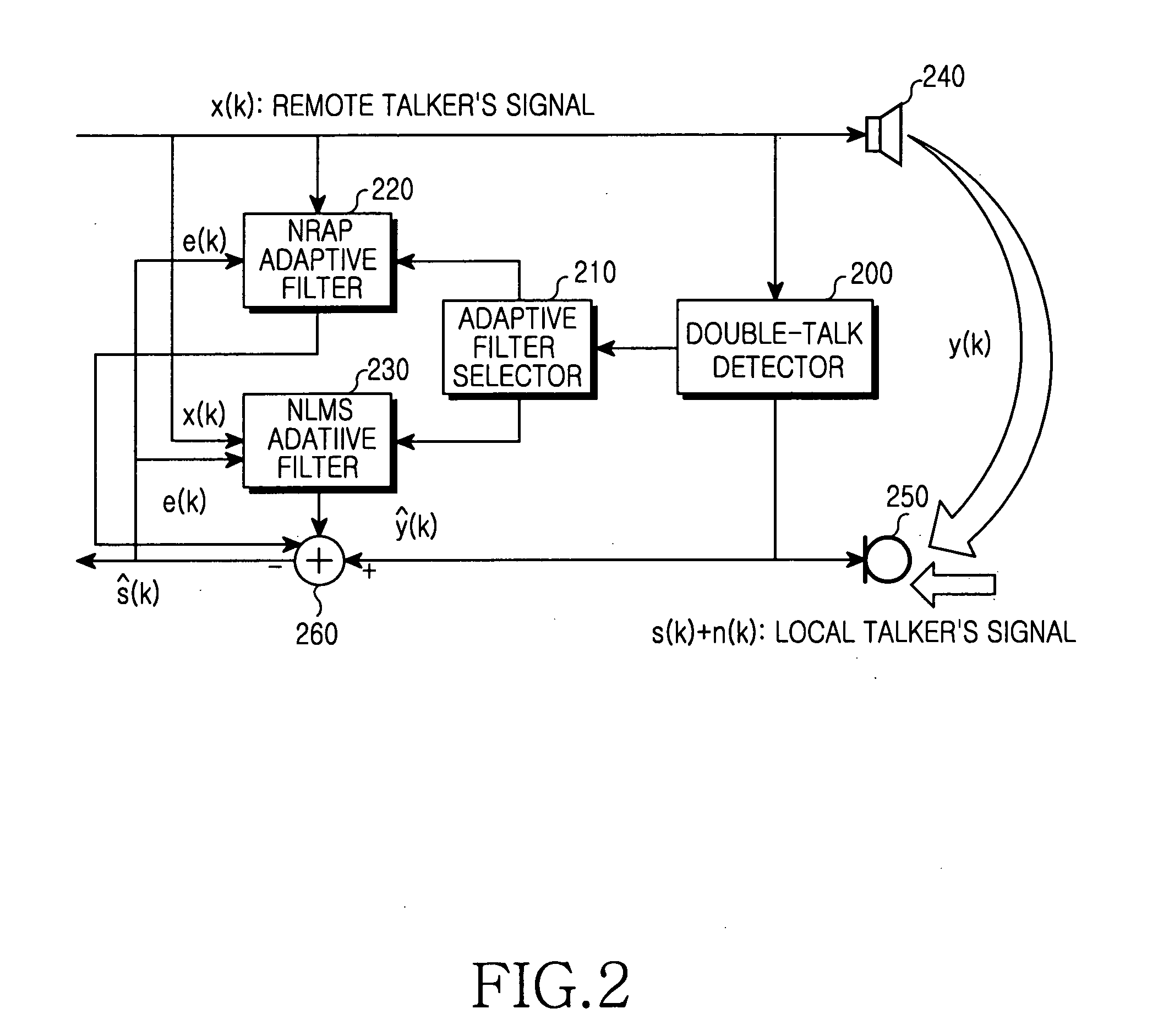
An apparatus and method for canceling an acoustic echo. In the apparatus, a double-talk detector detects whether a current period is a double-talk period or a single-talk period by determining whether a remote talker's signal and a local talker's signal are received simultaneously or at different times. A noise-robust affine projection (NRAP) adaptive filter estimates an acoustic echo included in the remote talker's signal using an NRAP algorithm if the detected current period is a double-talk period. A normalized least mean square (NLMS) adaptive filter estimates the acoustic echo included in the remote talker's signal using an NLMS algorithm if the detected current period is a single-talk period. The apparatus then generates an echo-canceled local talker's signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Convex combination adaptive echo cancellation method for affine projection sign subband adaptive filter
InactiveCN104410761AFast steady state errorSmall steady state errorTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsLine-transmissionProximal pointWeight coefficient
The invention discloses a convex combination adaptive echo cancellation method for an affine projection sign subband adaptive filter. The method mainly comprises the following steps: A, far-end signal filtering: performing far-end signal filtering to obtain the output vector Y1(n) of a large-step-length filter and the output vector Y2(n) of a small-step-length filter; B, convex combination: performing convex combination on the output vector Y1(n) and the output vector Y2(n) of the large-step-length filter and the small-step-length filter to obtain a combination filtering value Y(n) (Y(n)= lambda(n)Y1(n)+(1-lambda(n))Y2(n)), and performing convex combination on the tap weight vector W1(n) of the large-step-length filter and the tap weight vector W2(n) of the small-step-length filter to obtain a total filter group tap weight vector W(n) (W(n)=lambda(n)W1(n)+(1-lambda(n))W2(n); C, echo cancellation: subtracting the combination filter value Y(n) from an echo-carrying affine projection near-end signal D(n) picked up by a near-end microphone to obtain a net signal E(n) (E(n)=D(n)-Y(n)), and transmitting the net signal back to a far end; D, updating the tap weight coefficients of the filters; E, weight update of the filters: updating hybrid parameters a(n); and F, iteration: repeating the steps above under the condition that n=n+1 till the end of a conversation. The method has the advantages of high cancellation capability on the acoustic echo of a sparse communication system, high convergence speed, small steady-state error and good echo cancellation effect.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
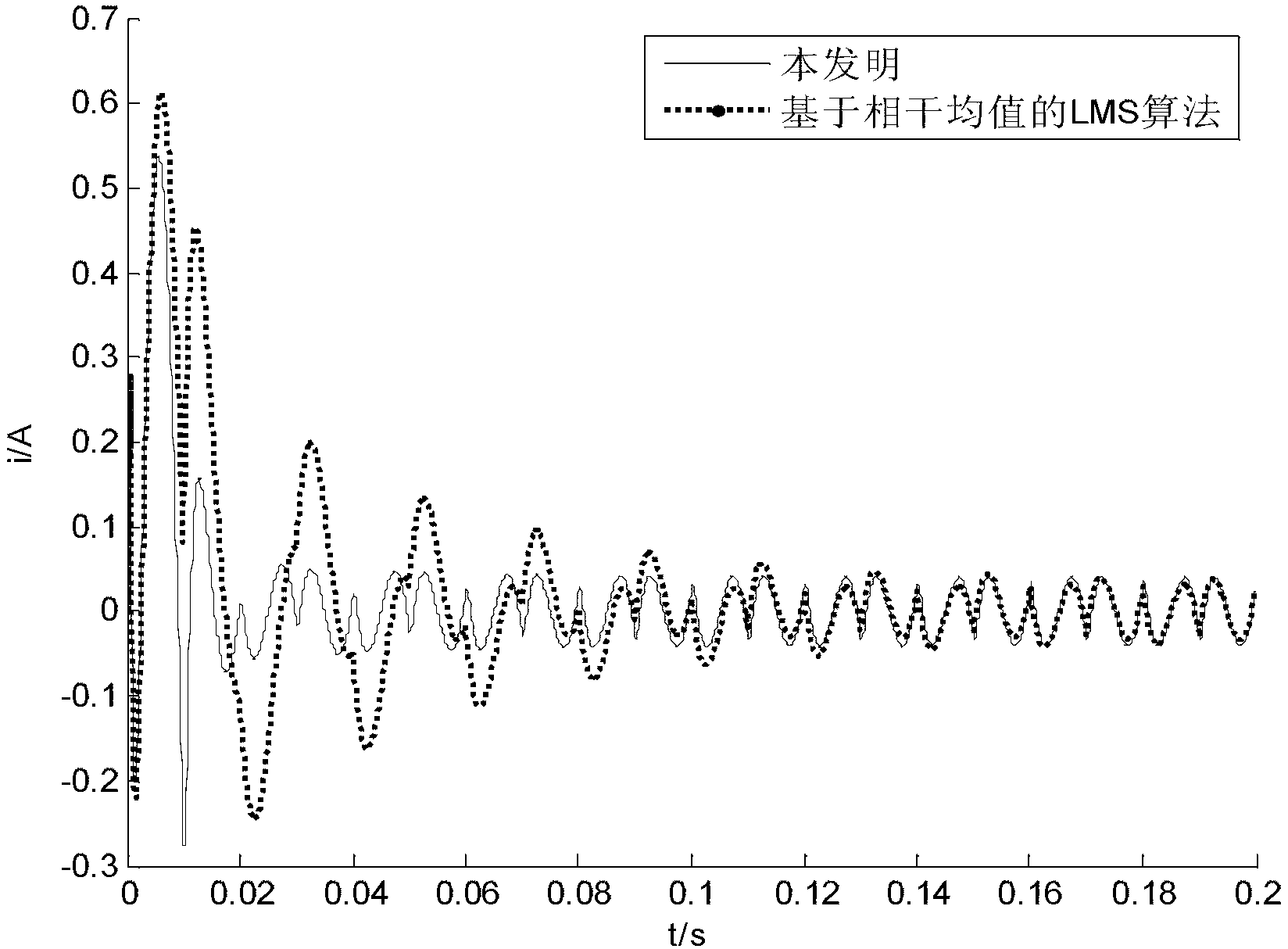
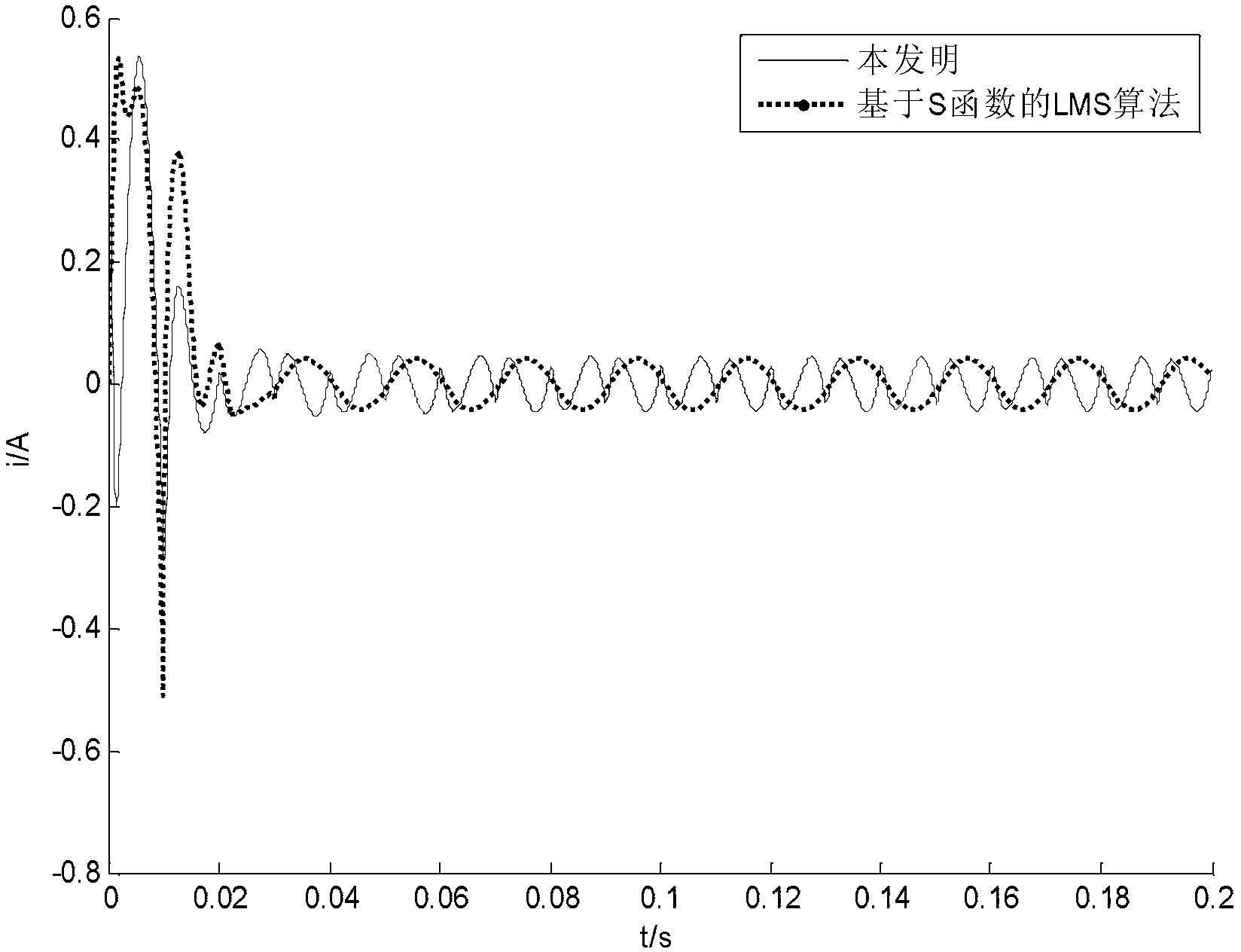
Variable step size affine projection harmonic current detection method based on time coherent average
InactiveCN103323651AFast convergenceReduce overheadSpectral/fourier analysisCurrent/voltage measurementCurrent meterHarmonic
The invention discloses a variable step size affine projection generalized harmonic current detection method based on time coherent average. The variable step size affine projection generalized harmonic current detection method based on time coherent average mainly comprises the following main steps that: a load current at the current time n and the previous (k-1) time is adopted as a column vector; the column vector subtracts the output of the time corresponding to an affine projection filter so as to obtain an error (generalized harmonic current); the step size is updated by utilizing the moving time average value of the ratio occupied in a to-be-detected signal by the error so as to eliminate the interference to the step size update by the harmonic current. The method is high in convergence rate, is high in convergence accuracy in a steady state, is high in tracking capability in jumping, and is good in timeliness.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
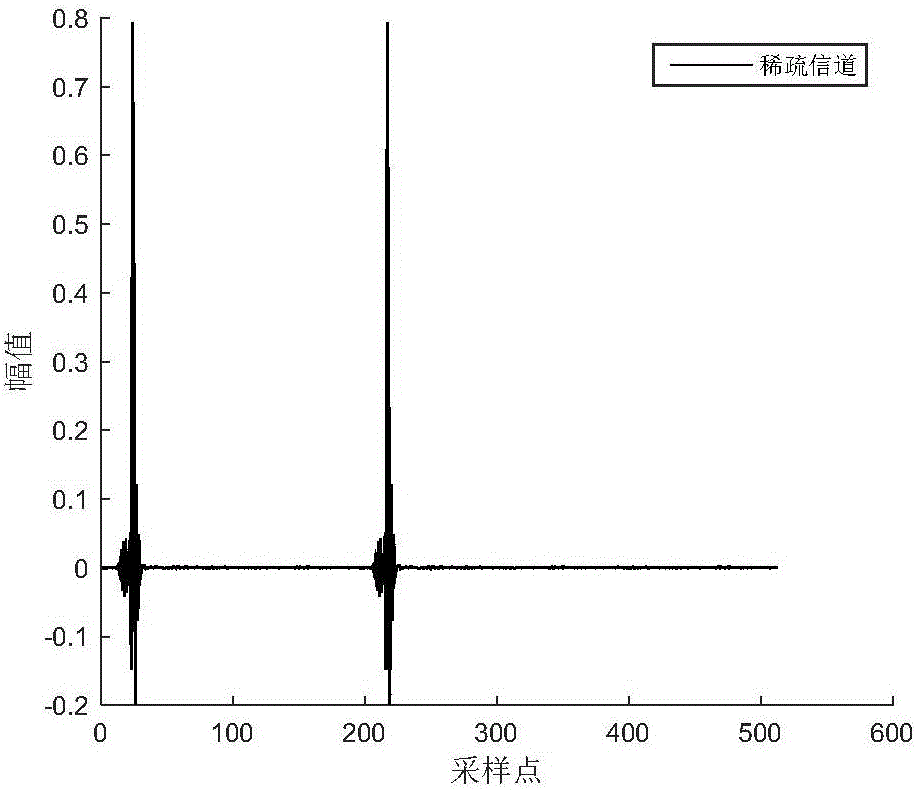
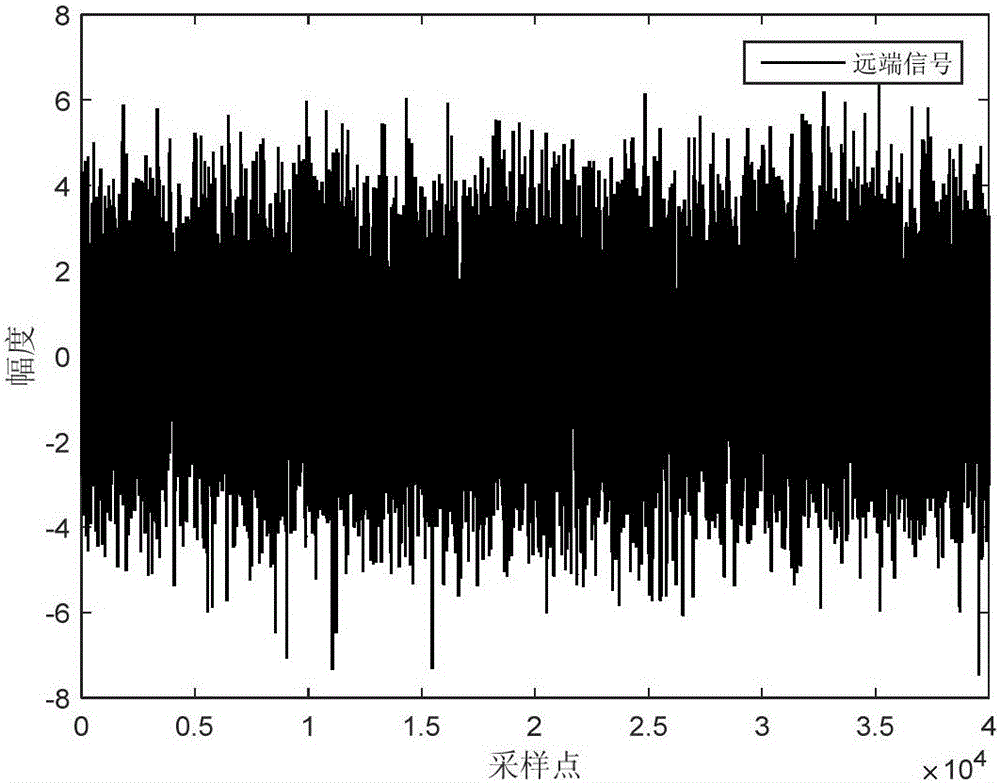
Echo cancellation method based on block-sparse proportionate reuse weight coefficient affine projection
ActiveCN105721729AStrong decorrelationImprove anti-interference abilityTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsWeight coefficientVoice communication
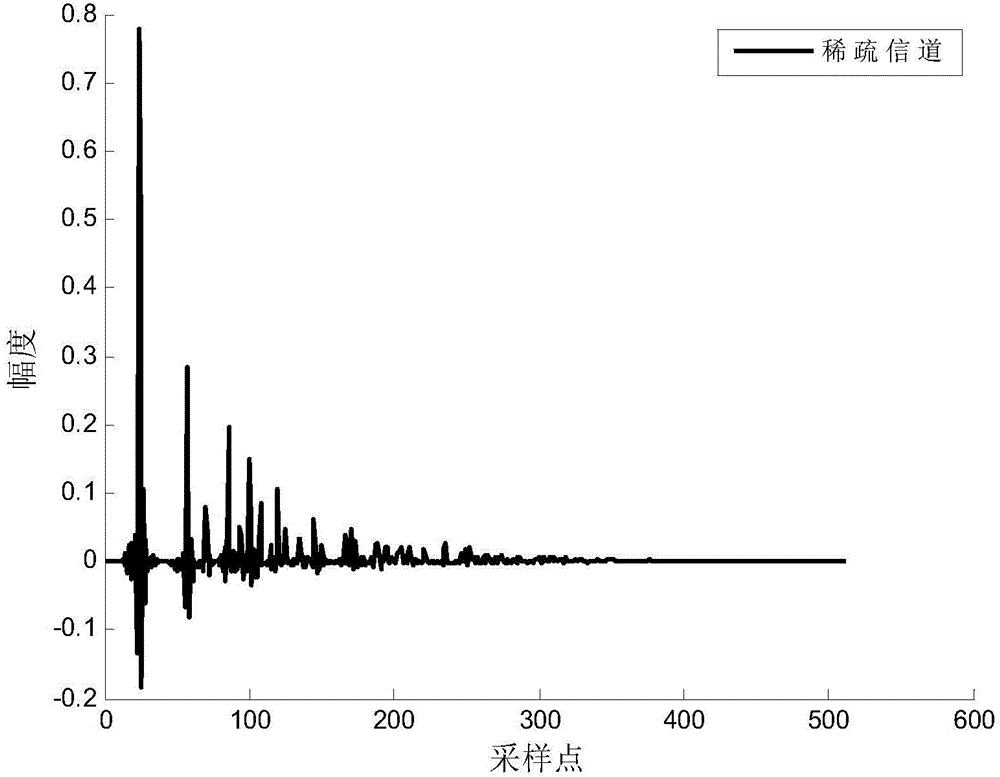
The invention discloses an echo cancellation method based on block-sparse proportionate reuse weight coefficient affine projection. The method mainly comprises following steps of A, filtering a far-end signal; obtaining an output value y (n) from a filter input vector X (n) through a self-adaptive filter; B, cancelling an echo; subtracting the output value y (n) by near-end signal d (n) which is picked up by a near-end microphone at a current moment and is equipped with the echo, thus obtaining an error as a residual signal e (n), wherein e (n) is equal to d (n)-y(n); sending back to a far-end; C, updating a filter tapping weight vector; D, assuming that n is equal to n+1, repeating steps A, B and C until finishing a call. According to the method, the echo elimination capability to the voice communication of a sparse system is high; the rate of convergence is high; the steady state error is low; and the echo elimination effect is good.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
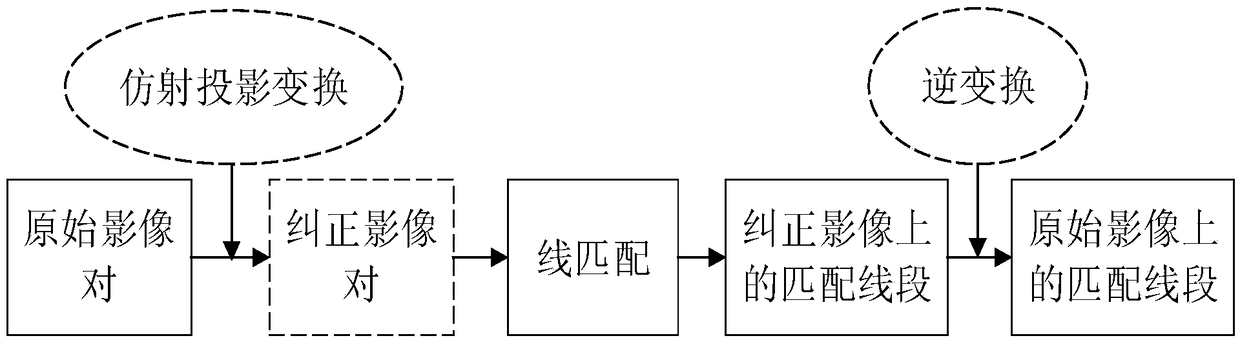
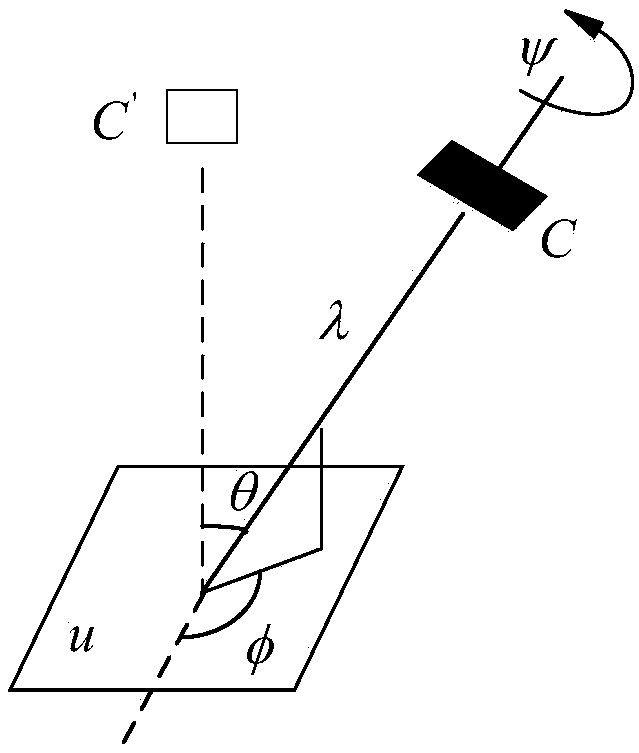
Straight line matching method based on affine projection matrix model
PendingCN108830797AMultiple Match Line SegmentsImage analysisGeometric image transformationLine pairImage pair
The invention discloses a straight line matching method based on an affine projection matrix model. The method comprises the steps of (1) finding the affine projection matrix according to camera posture information provided by a POS system, (2) correcting an original image taken by a camera into an approximate orthomorphic image according to the affine projection matrix, (3) carrying out straightline extraction matching on the approximate orthomorphic image obtained after correction to obtain a matching straight line pair, and (4) inversely transforming the matching straight line pair by using the affine projection matrix to obtain a matching image pair of the original image. According to the method, the information of a POS sensor is fully utilized, the affine correction is carried out on oblique image data and line matching and three-dimensional reconstruction are carried out, the process such as complicated camera pose estimation is eliminated, and the method is particularly suitable for scenes with low precision requirements and high real-time requirements.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF AEROSPACE TECH
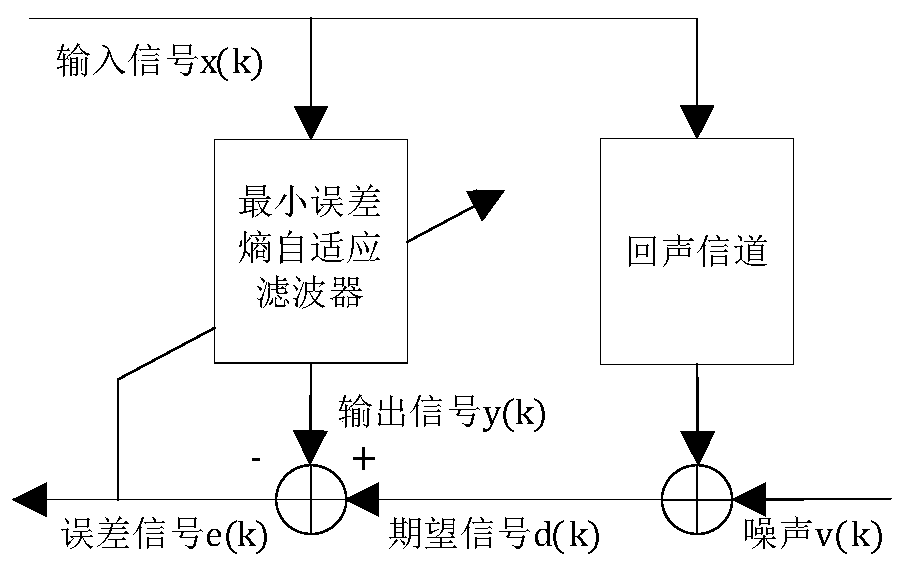
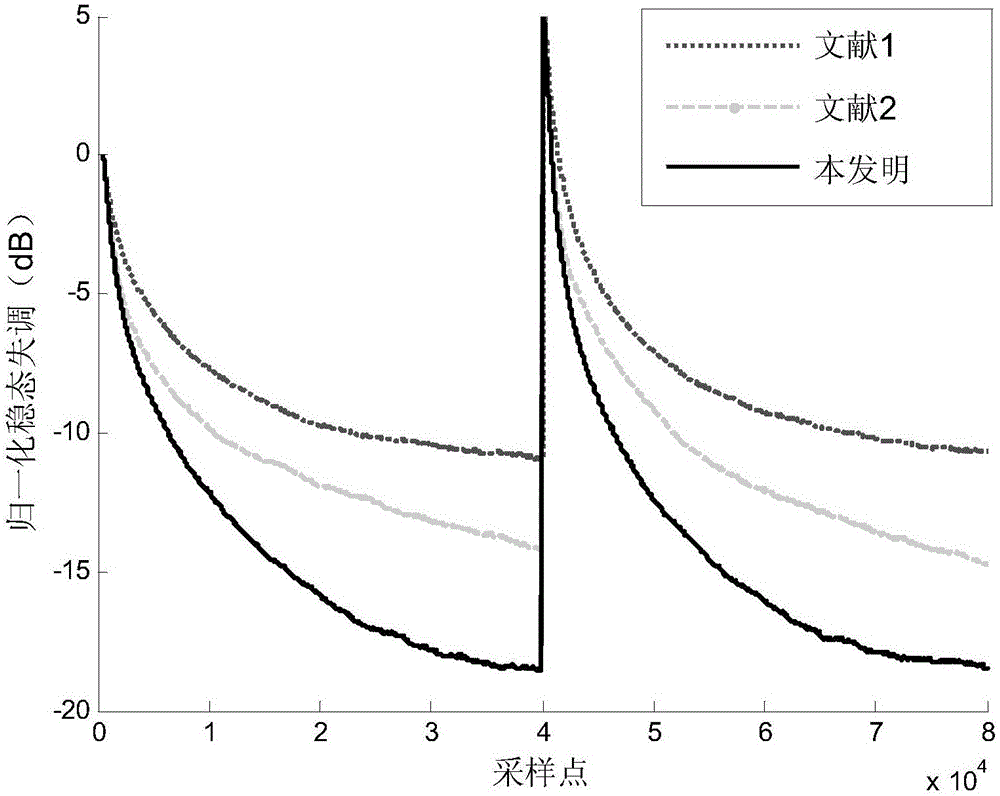
Proportional affine projection method based on minimum error entropy
InactiveCN109767779AFast convergenceBaseband system detailsSpeech analysisAdaptive filtering algorithmProjection method
The invention relates to a proportional affine projection algorithm based on a minimum error entropy. The invention discloses a novel algorithm MEE-MPAPA-Newton which is based on a Newton method framework and introduces an affine projection method into a PMEE algorithm. Such novel algorithm can better solve a problem of sparse system identification in non-Gaussian noise when a strongly correlatedsignal is input. The method, on the basis of a proportionality coefficient, a minimum error entropy criterion and a Newton method, discloses an affine projection adaptive filtering algorithm for solving the problem of sparse system identification in a non-Gaussian noise environment when the strongly correlated signal is input.
Owner:SHENYANG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Zero-norm set membership affine projection adaptive echo cancellation method based on weight vector reuse
ActiveCN106157965AReduce tap weight vector volatilitySmall steady state errorTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsSpeech analysisCommunications systemEuclidean vector
A zero-norm set membership affine projection adaptive echo cancellation method based on weight vector reuse comprises the following steps: A, remote signal sampling; B echo estimation: obtaining an output value y(n) at a current time n through an adaptive filter based on an input vector X(n) of the adaptive filter at the current time n, wherein y(n) is the estimated value of echo, and y(n)=X<T>(n)*w(n); C, echo cancellation: subtracting the output value y(n) of the adaptive filter at the current time n from a near-end signal d(n) with echo at the current time n picked up by a near-end microphone to get a residual signal e(n), wherein e(n)=d(n)-y(n), and transmitting the residual signal back to a remote end; D, filter tap weight vector updating: getting a tap weight vector w(n+1) (Please see the description for the expression) of the filter at next time n+1 using a zero-norm set membership affine projection method based on weight vector reuse; and E, letting n=n+1, and repeating the steps B, C and D until the end of the call. The method has the advantages of good cancellation effect for acoustic echo of a communication system, high convergence rate, and small steady-state error.
Owner:聊城来通国际贸易有限公司
Method for eliminating combined step length proportional affine projection echo
ActiveCN107105111AFast convergenceSmall steady state errorTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsSpeech analysisLoudspeakerAffine projection
A method for eliminating combined step length proportional affine projection echo comprises the following steps of A, acquiring a sound signal x(n) transmitted from a far end at a telephone loudspeaker and acquiring an expected signal d(n) at a telephone microphone; B, using the sound signal x(n) as an input of an adaptive filter, and using the output of the adaptive filter as an estimated value d<^>(n) of an echo signal; C, performing echo offset, namely using an error signal e(n) obtained through subtracting d<^>(n) from d(n) as a clean signal after echo offset and transmitting the error signal to the remote end; D, calculating an error vector of the adaptive filter; E, calculating a weight updating increment deltaw(n) of the adaptive filter; F, calculating a combined step length mu(n); G, updating the weight vector w(n+1)=w(n)+mu(n)deltaw(n) of the adaptive filter; and H, setting n=n+1, repeating the steps A, B, C, D, E, F, G until the calling is finished. The method has advantages of high convergence speed and low steady-state error.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
A proportional affine projection-like adaptive echo cancellation method based on M estimation is proposed
ActiveCN109040497AFast convergenceGood echo cancellationTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsCommunications systemEuclidean vector
The invention discloses a proportional affine projection-like adaptive echo cancellation method based on M estimation. The method comprises: A,a far end signal is collected; B, an echo is estimated, wherein the input vector X (n) of the filter is passed through an adaptive filter to obtain an output value y (n), i. E., an estimate value y (n) of the echo, y (n) = WT (n) X (n); C, echo is cancelled, the output value y (n) of the adaptive filter is subtracted from the near-end signal d (n) picked up by the near-end microphone and sent back to the far-end, and the return signal is the residual signal e (n), e (n) = d (n)- Y (n); D, the filter tap weight vector is updated, Using the method of proportional affine projection-like based on M estimation, the adaptive filter tap amount W (n) at time n is calculated, E, n is set as n+1, the steps of A, B, C, D are repeated until the call ends. The method is effective in eliminating the acoustic echo of communication system with fast convergencespeed and small steady-state error.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Affine-projection-like self-adaptive echo cancellation method with biased compensation
InactiveCN106161821ADecrease tap weight vectorReduce the deviation from the expected valueTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsCommunications systemProximal point
The invention discloses an affine-projection-like self-adaptive echo cancellation method with biased compensation. The affine-projection-like self-adaptive echo cancellation method comprises the steps of: A, sampling a remote signal; B, estimating an echo, wherein a self-adaptive filter input vector X (n) at a current moment n passes through a self-adaptive filter to obtain an output value y (n) at the current moment n, namely an echo estimation value y(n) is obtained and equal to XT(n)w(n); C, cancelling the echo, wherein a near-end signal d (n) with an echo at the current moment n which is picked up by a near-end microphone and the output value y(n) at the current moment n of the self-adaptive filter are subjected to subtraction operation, and a return signal, namely a residual signal e(n), is returned to a far end and equal to d(n)-y(n); D, updating a tapping weight vector of the filter, wherein an affine-projection-like method with biased compensation is adopted to calculate the tapping weight vector w(n+1) of the self-adaptive filter at a next moment n+1 by adopting a formula shown in description; E, and assuming that n is equal to n+1, repeating the steps B, C and D until a call is ended. The method has a good cancellation effect on the acoustic echo of a communication system, and is high in convergence speed and small in steady-state error.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Zero attraction based adaptive echo elimination method of affine projection
ActiveCN109151237AFast convergenceSuppress interferenceTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsHat matrixWeight coefficient
The invention discloses a zero attraction based adaptive echo elimination method of affine projection. The method comprises the following steps of A) far-end signal processing in which a far-end signal from the far end is sampled to obtain a far-end signal discrete value x(n) of present time n, and an adaptive filter input vector X(n) and an affine projection matrix U(n) of the present time are constructed; B) echo estimation in which an output value y(n), namely an echo estimated value y(n) is obtained by an adaptive filter from the filter input vector X(n); C) echo offset in which a near-endmicrophone picks up a near-end signal d(n) with an echo at the present time n, and the near-end signal d(n) with the echo at the present time n is subtracted from the output value y(n) of the adaptive filter at the present time n to obtain a residual error signal e(n); D) construction of a proportional affine projection matrix; E) calculation of a zero attraction factor; F) update of a weight coefficient vector, and G) repetition. The method is high in identification capability and convergence speed, low in stable error and good in echo elimination effect.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
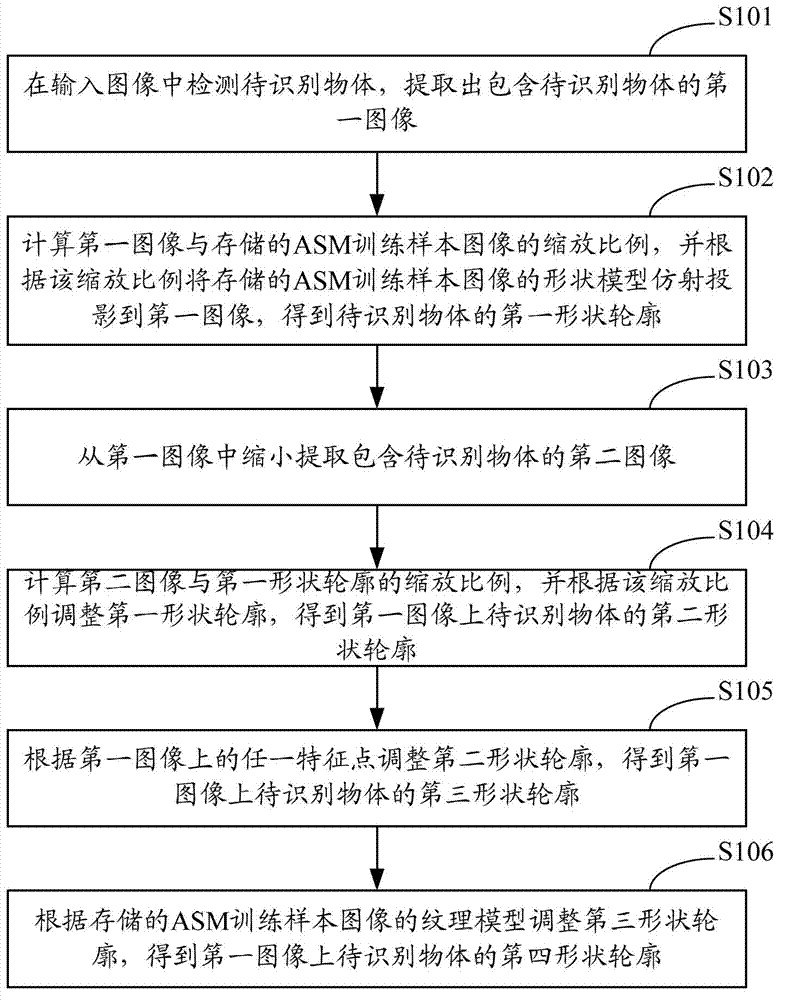
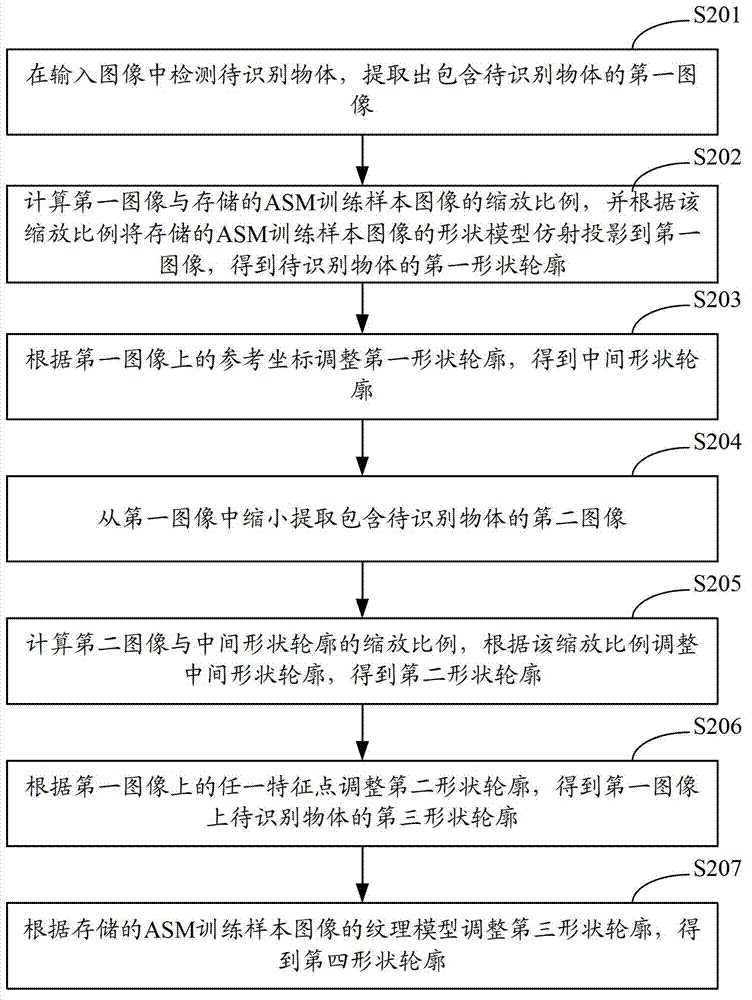
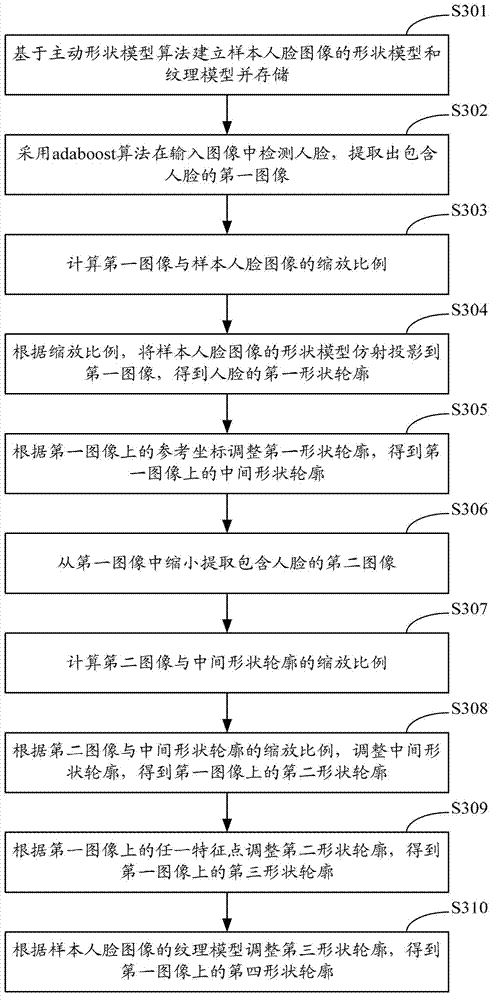
Method and system for extracting outlines
ActiveCN102779278AImprove extraction accuracyAvoid precisionCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingStorage management
The invention relates to the technical field of image processing and provides a method and a system for extracting outlines. The method includes: extracting a first image containing an object to be identified from input images; performing affine projection of shape models of automatic storage management (ASM) training sample images onto the first image according to scaling so as to obtain a first shape outline; narrowing and extracting a second image containing the object to be identified from the first image, adjusting a previous shape outline according to scaling so as to obtain a second shape outline, and adjusting the second shape outline according to any feature point on the shape models so as to obtain a third shape outline. Due to the fact that the object to be identified is extracted at least two times, correspondingly the shape models of the ASM training sample images are adjusted automatically at least two times according to the scaling, and the method and the system for extracting outlines guarantee and optimize extraction accuracy, simultaneously avoid problems of poor extraction accuracy and long extraction time when an initial mobile coordinate and scaling coefficients are set in manual mode, and are particularly suitable for extraction of outlines of remote objects to be identified.
Owner:TCL CORPORATION
Affine projection symbol echo cancellation method based on orthogonal transformation
ActiveCN105788605ASimplified Update ComputationFast convergenceSpeech analysisAffine projectionOrthogonal transformation
The present invention discloses an affine projection symbol echo cancellation method based on orthogonal transformation. The method mainly comprises the steps of A acquiring a voice signal x(n) transmitted from a far-end and a desired signal d(n) collected by a near-end microphone; B calculating the output y(n) of an adaptive filter; C carrying out the echo cancellation, namely, taking an error signal e(n) obtained by subtracting y(n) from d(n) as a clean signal after the echo cancellation to transmit to the far-end; D orthogonally transforming an input matrix X(n) of the adaptive filter into a decorrelation matrix U(n); E updating a tap weight vector of the adaptive filter; F defining n=n+1, and repeating the steps of A, B, C, D and E until the conversation is ended. The method has the advantages of fast convergence speed and low steady-state error except having the good robustness for the doubletalk.
Owner:杭州东南吉通网络有限公司
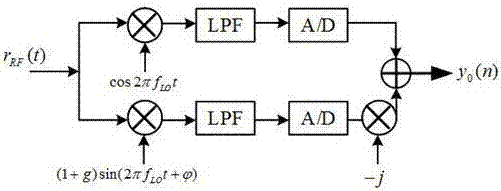
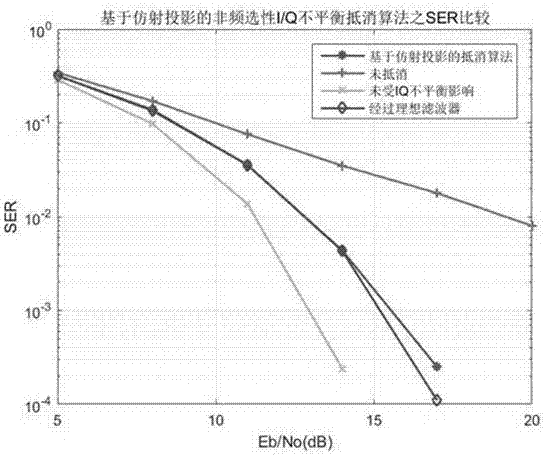
I/Q imbalance cancellation algorithm based on affine projection adaptation
ActiveCN106961402AIntegrity guaranteedGuaranteed correctnessTransmitter/receiver shaping networksLinear modelSelf adaptive
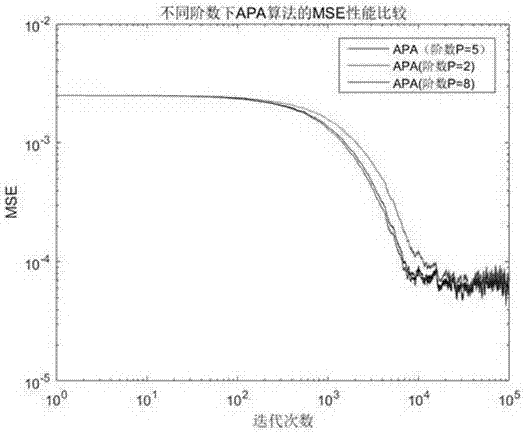
The invention provides an I / Q imbalance cancellation algorithm based on affine projection adaptive filtering, relating to a blind cancellation algorithm without training sequences. The whole cancellation process is modeled as an adaptive filtering mode, a wide linear model is used as the filtering structure prototype of a neutralizing filter, the restoration the 'moderation' of signals disturbed by I / Q imbalance is taken as the goal, and an adaptive process of the filter is deduced based on the principle of affine projection adaptation, which means that an update iteration rule of filter tap weights is obtained. Additionally, combined with some improvements of I / Q imbalance situations, the algorithm can be applied to engineering practices; and finally, the overall operation flow of the cancellation algorithm can be obtained; and computer simulation results can verify that the impact of the I / Q imbalance on the signals can be effectively canceled by the algorithm, and meanwhile, compared with a traditional cancellation algorithm, the algorithm provided by the invention has a faster convergence rate and more stable MSE performance.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Proportional affine projection echocancellation method of convex combination coefficient differences
ActiveCN106060295AFast initial convergenceFast convergenceTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsSpeech analysisWeight coefficientAffine projection
The invention discloses a proportional affine projection echocancellation method of convex combination coefficient differences. The method includes the following steps: A. far-end signals sampling and filtering, A1. a far-end dispersion input signal constitutes an input vector X (n) of a convex combination adaptive filtering echocancellation filter; A2. inputting a filter to the vector X (n) to obtain filtering values y1 (n) and y2 (n) of a large step length and a small step length; B. echo offsetting, subtracting a near-end signal d (n) and a combination filter output value y (n) to obtain a total residual signal e (n) after echocancellation, and transmitting the total residual signal e (n) to a far end; C. conducting convex combination, conducting convex combination on the output value y1 (n) and y2 (n) of the large step length and the small step length through a weight [lambda] to obtain a combination output value y (n), and conducting convex combination on tap weight coefficients W1 (n) and W2 (n) through the weight [lambda] to obtain a tap weight coefficient W (n) of a tap filter; D. updating a tap weight vector of a filter; E. updating the weight of the filter; F. limiting the weight of the filter; G. repeating the steps of A, B, C, D, E, F, thus realizing echocancellation. The method has strong identification capability, rapid convergence, strong tracking capability, low stability error rate, and excellent effects of echocancellation.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
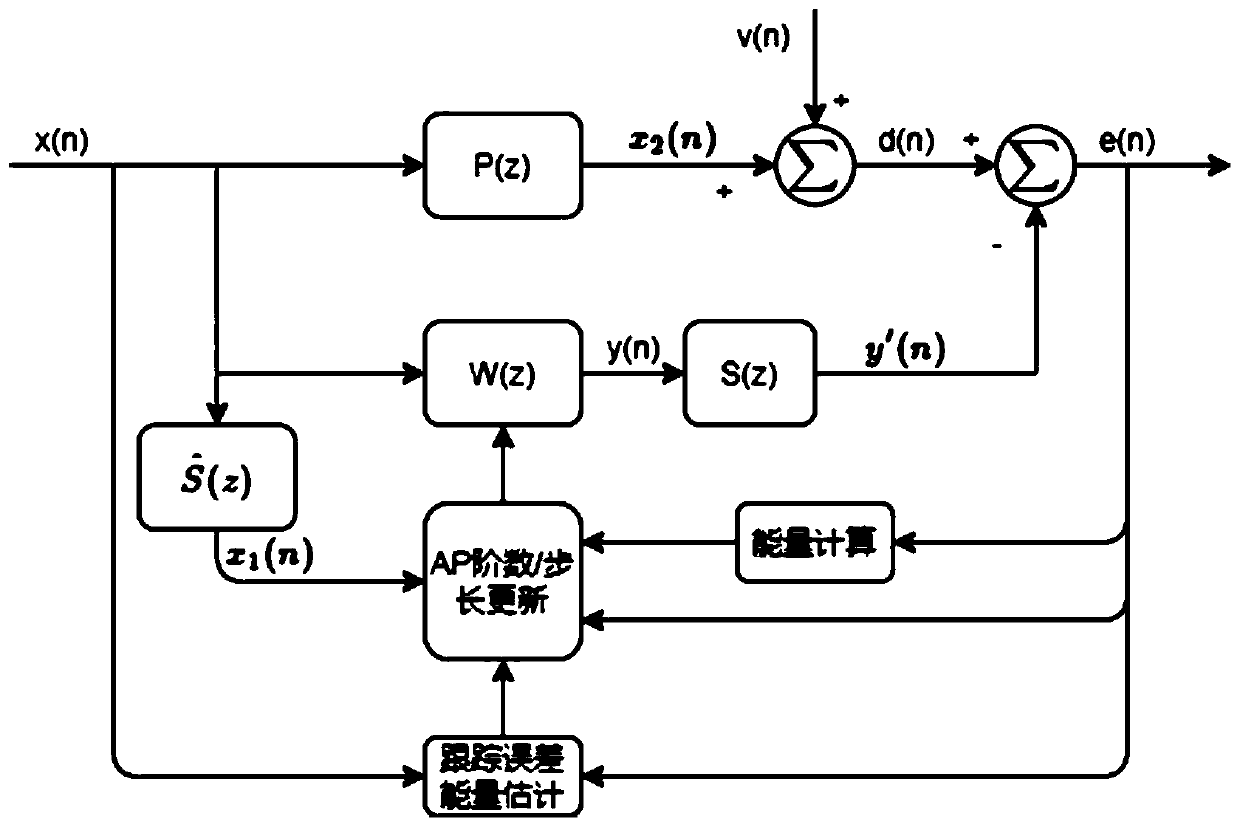
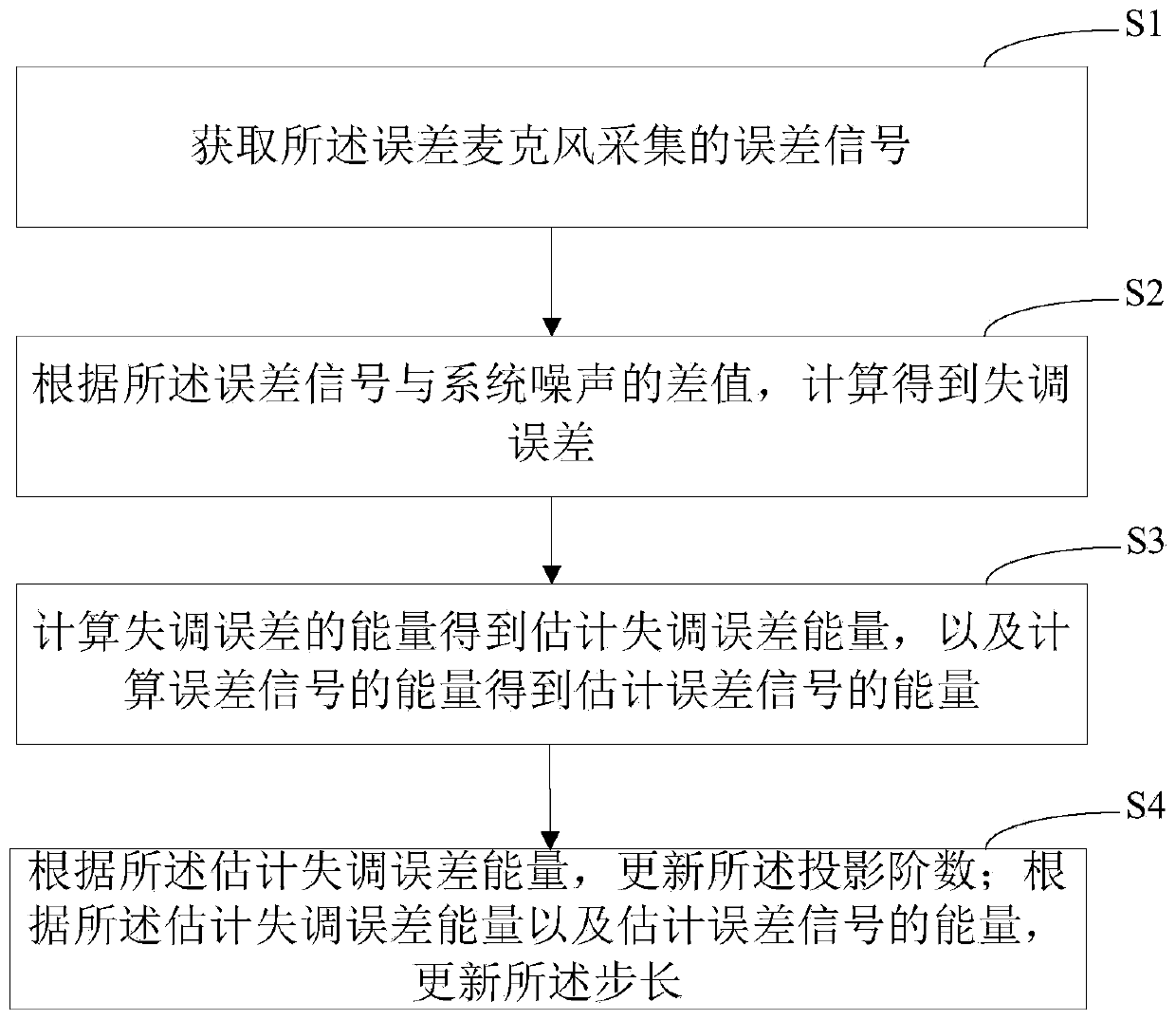
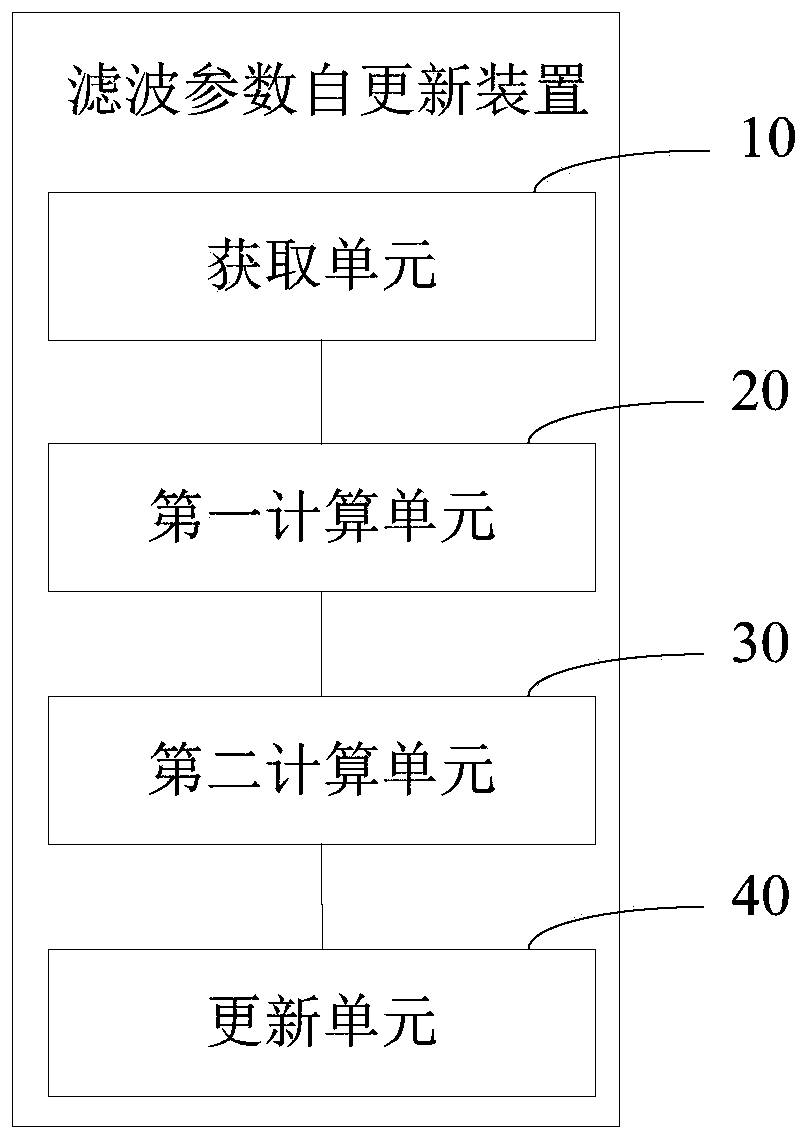
Filtering parameter self-updating method, filter, equipment and storage medium
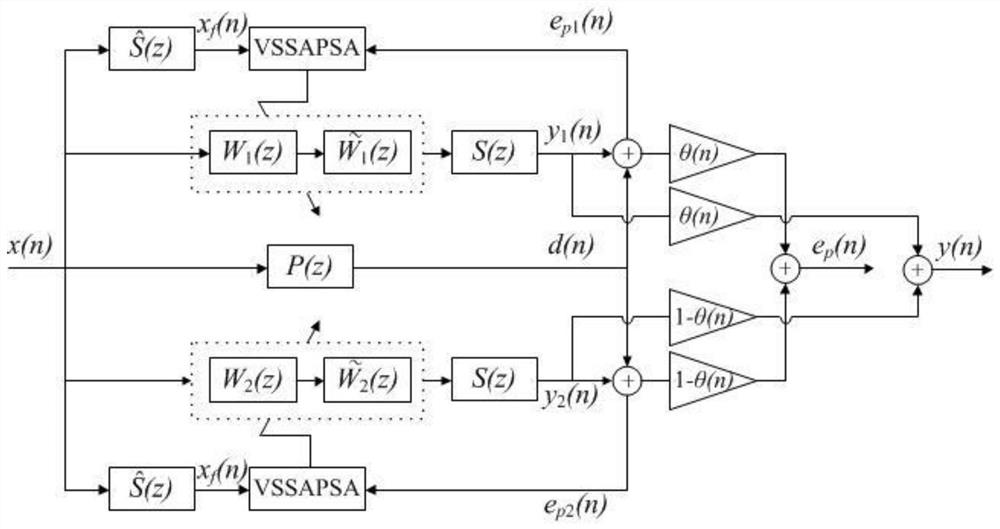
ActiveCN111508464AFast convergenceGuaranteed stabilitySound producing devicesActive noise controlNoise reductionAffine projection
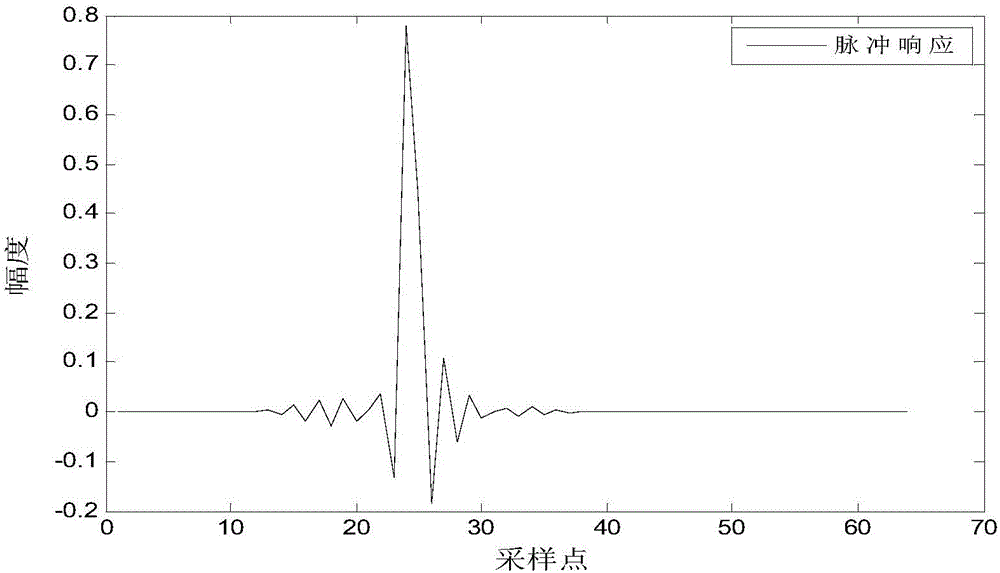
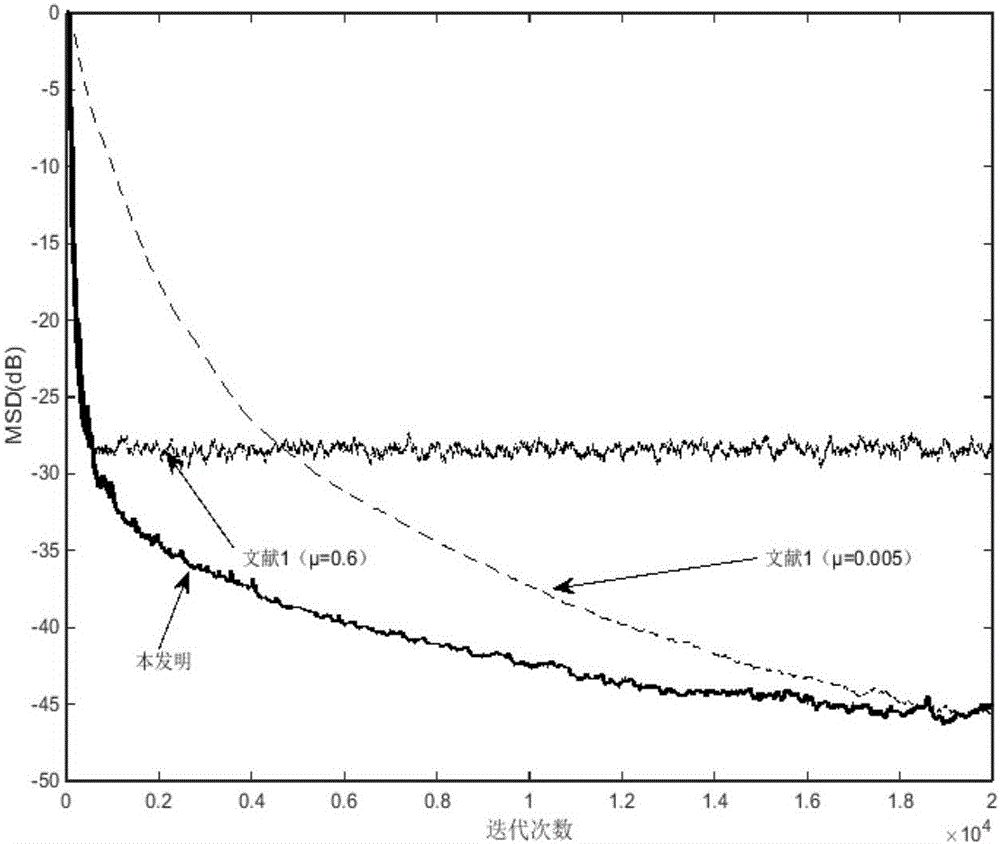
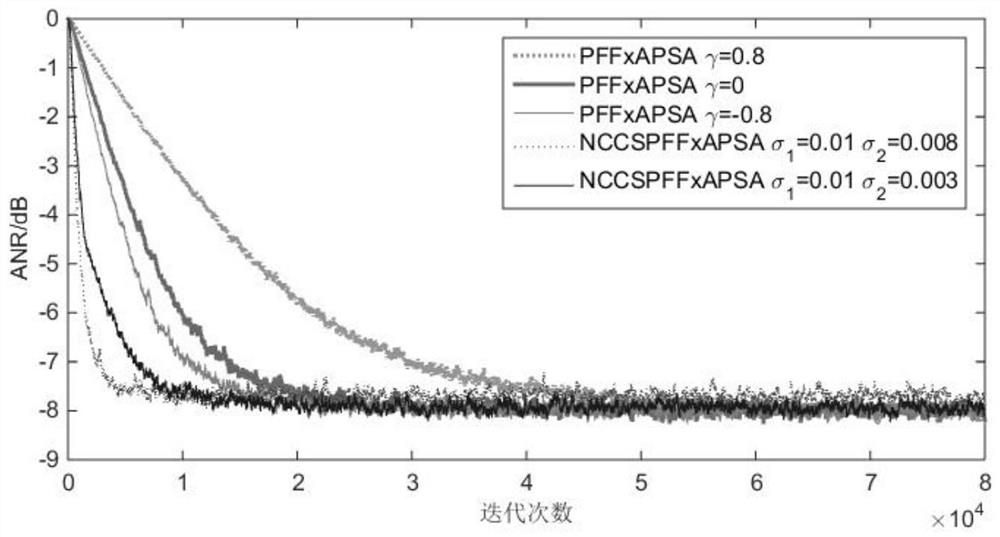
The invention provides a filtering parameter self-updating method, a filter, equipment and a storage medium, which are applied to an affine projection filter in an active noise reduction system with an error microphone, the projection order of the filter is updated based on the energy of an offset error, and the offset error is the difference between an error signal and system noise; the step length is updated based on the energy of the offset error and the energy of the error signal; when the active noise reduction system starts to work, the estimated offset error energy is very large, at themoment, the projection order is updated to be maximum, the step length is updated to be close to the step length maximum value under the projection order, the convergence speed is increased, and thesystem stability is guaranteed; and when the estimated maladjustment error energy is very small, the projection order is updated to the minimum, and the step length is updated to be close to the minimum step length value under the projection order, so that the steady-state error is smaller. According to the invention, the projection order is dynamically adjusted, and the calculated amount is small.
Owner:深圳市友杰智新科技有限公司
Complex affine projection adaptive signal processing method based on kernel function
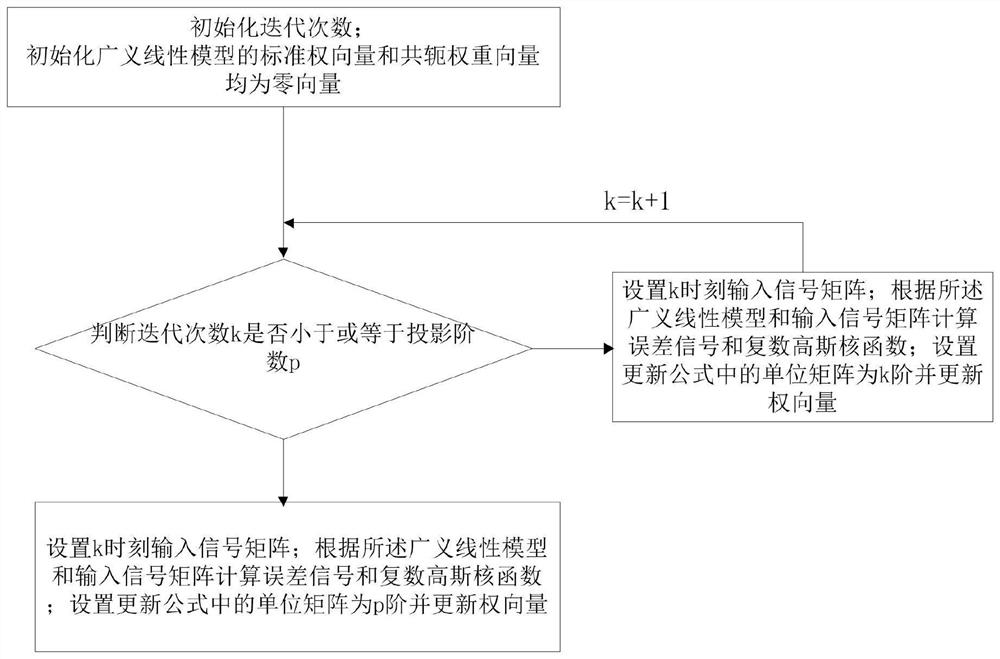
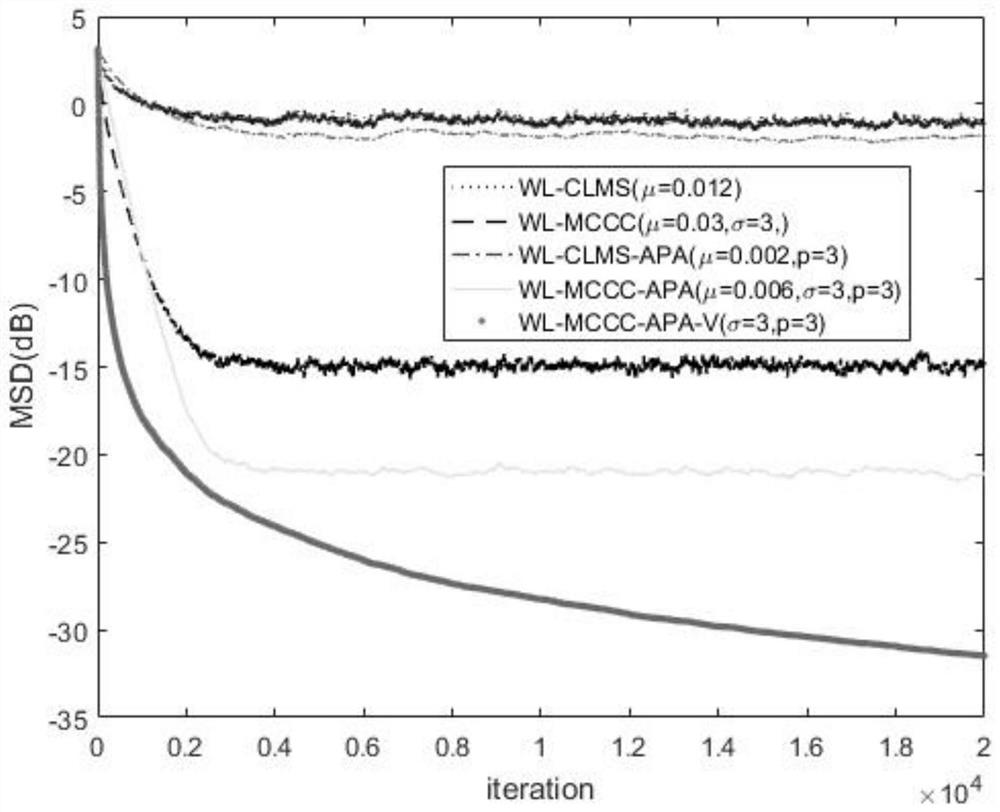
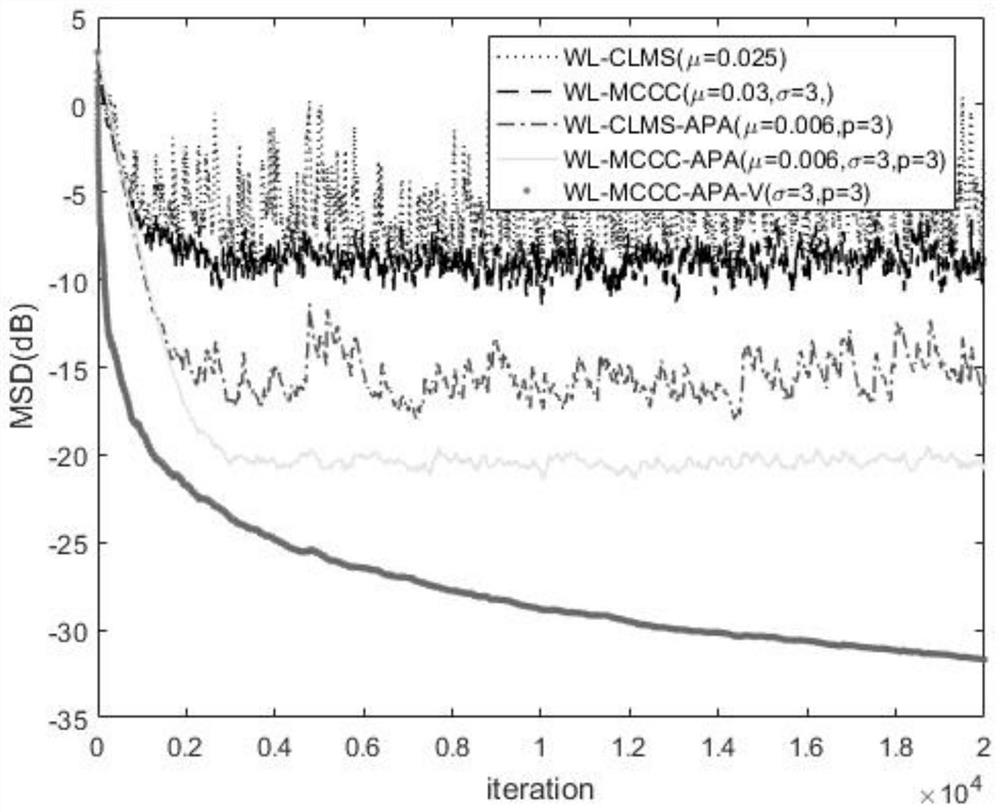
PendingCN113872567AImprove signal qualityImprove stabilityAdaptive networkAffine projectionSelf adaptive
The invention discloses a complex affine projection adaptive signal processing method based on a kernel function, a complex Gaussian kernel function is applied to a generalized linear affine complex projection algorithm, and the robustness of an adaptive filtering system is improved by using the excellent performance of the Gaussian kernel function in a non-Gaussian environment, especially an impulse noise environment. When the number k of iterations is small, the unit matrix in the formula is updated to k order; when k is large, the unit matrix in the formula is updated to be p-order, and the accuracy of weight vector calculation is improved; and a variable step size method is used, so that the convergence speed is improved, and the offset error is reduced.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
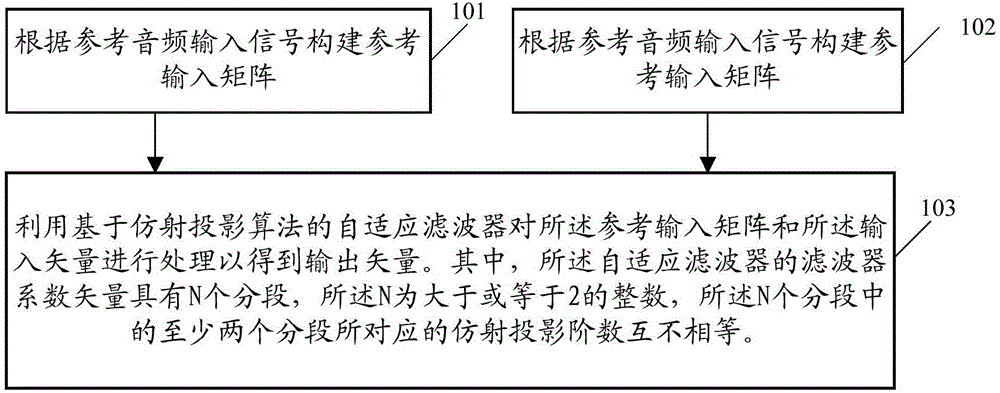
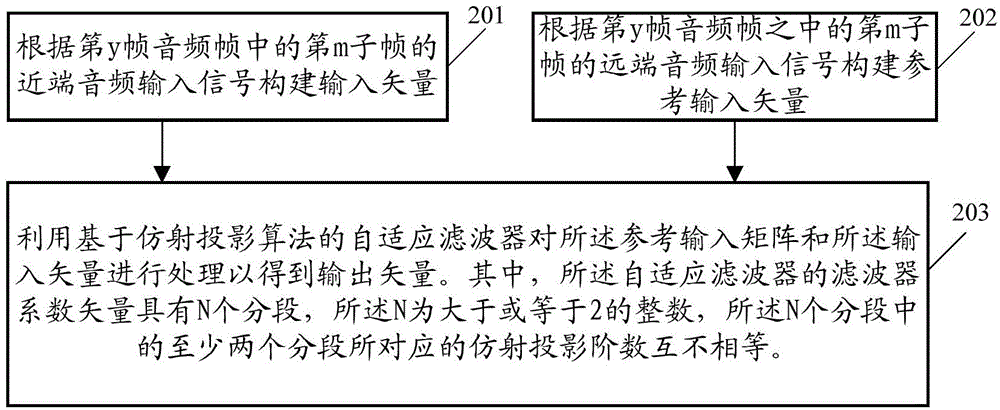
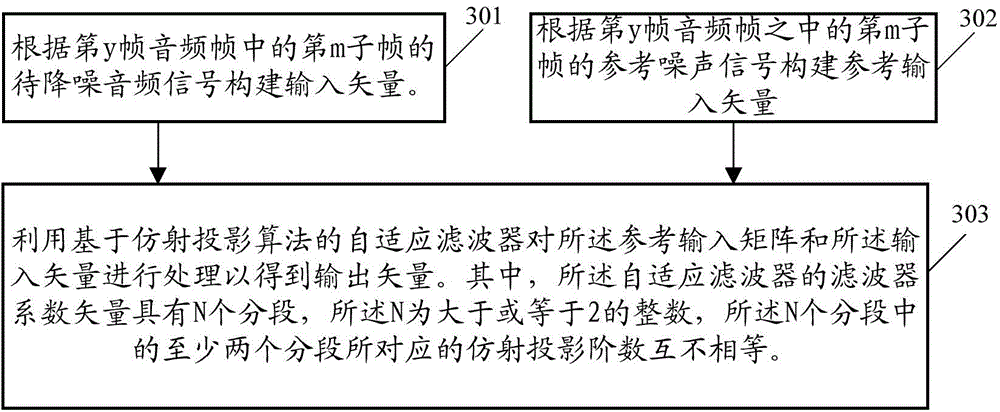
Audio signal processing method and related device
InactiveCN104392727ALarge adjustment rangeFast convergenceSpeech analysisAffine projectionComputer science
The embodiment of the invention provides an audio signal processing method and a related device. The audio signal processing method includes the steps of establishing an input vector according to an audio input signal, establishing a reference input matrix according to a reference audio input signal, and processing the reference input matrix and the input vector through an adaptive filter on the basis of the affine projection algorithm so as to obtain an output vector, wherein the coefficient vector of a filter body of the adaptive filter has N segments, N is an integer larger than or equal to 2, and the affine projection orders of at least two segments in the N segments are not equal. By means of the scheme, the expansion of the adjustment range of the update rates of the portions, with different filter coefficient vectors, of the adaptive filter is facilitated.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Filter reference affine projection symbol active control method based on variable step size
ActiveCN113285692AGuaranteed stabilitySolve the problem of further improvement of convergence performanceAdaptive networkSound producing devicesNoiseEngineering
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Optical signal processing apparatus, optical signal processing method and computer program
PendingUS20220329343A1Less influenceOptical mode multiplex systemsElectromagnetic receiversFilter (signal processing)Linear filter
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
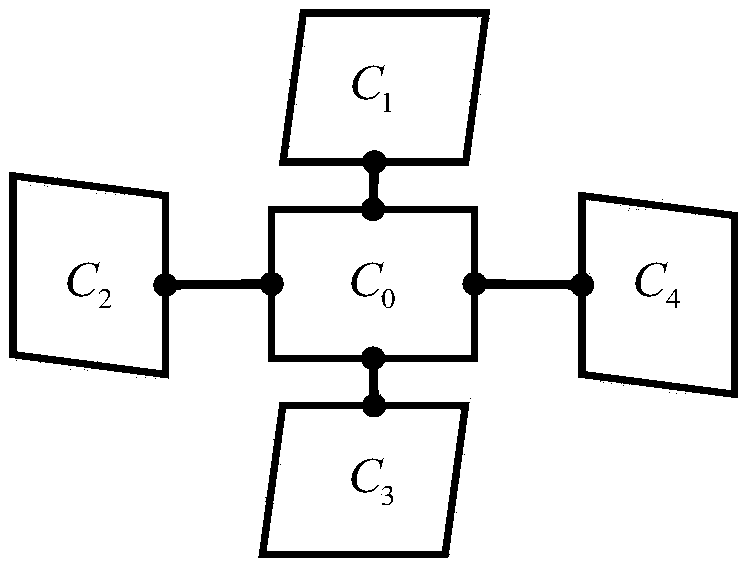
Object projection method and object projection system
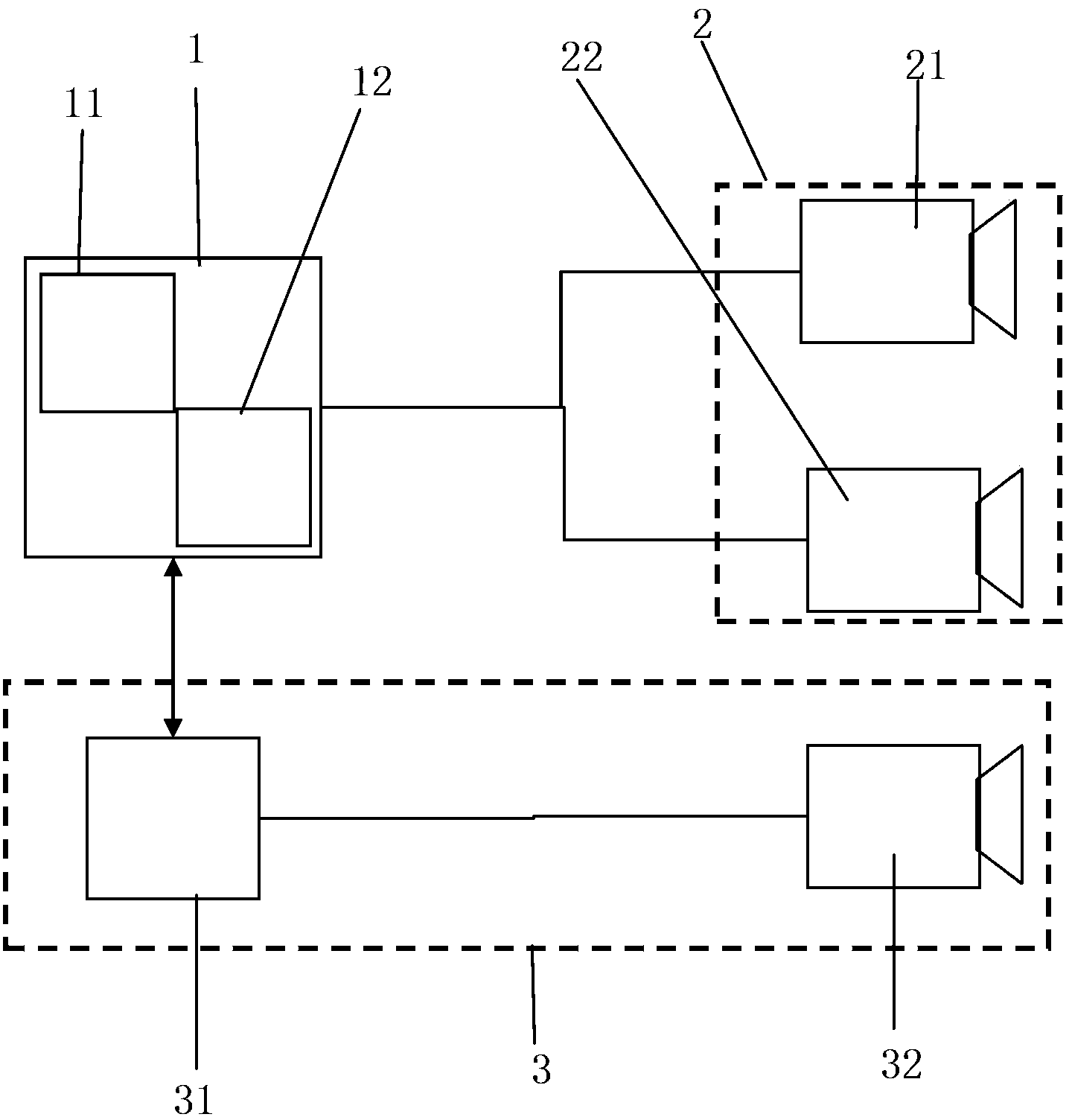
ActiveCN102939562BAccurately establishedParallel correction is validStereoscopic photographyProjection systemAffine projection
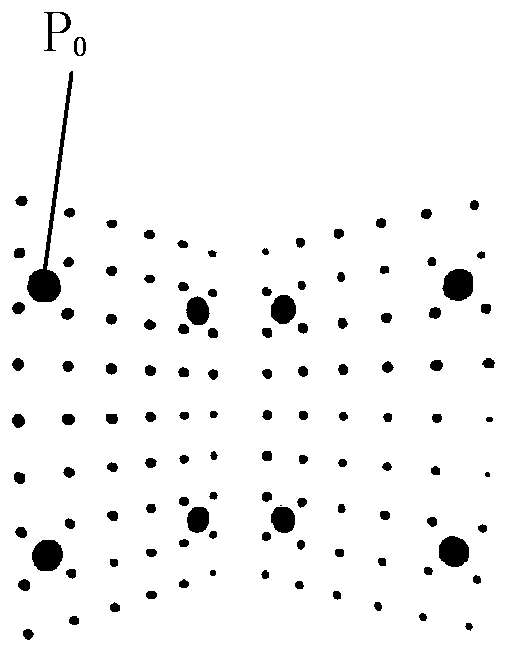
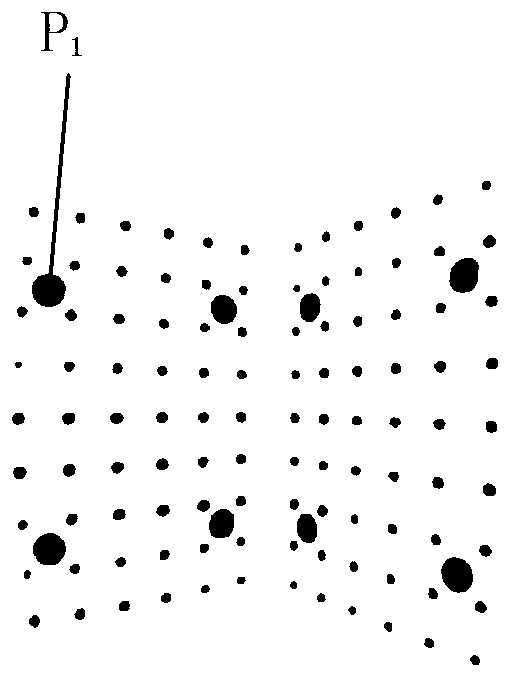
An object projection method includes: acquiring the three-dimensional coordinates corresponding to the matching point-pair (P0 and P1) of the object in the first video camera (21) and the second video camera (22); acquiring the affine projection matrix of the third video camera (32); calculating the theoretical barycentric coordinates of the object in the third video camera (32); calculating the theoretical projection size of the object in the third video camera (32); acquiring the actual barycentric coordinates of the projection of the object in the third video camera (32); acquiring the actual projection size of the object in the third video camera (32); and judging whether the three-dimensional coordinates corresponding to the matching point-pair (P0 and P1) is right or not. An object projection system using the method is also provided.
Owner:SHENZHEN TAISHAN SPORTS TECH CO LTD
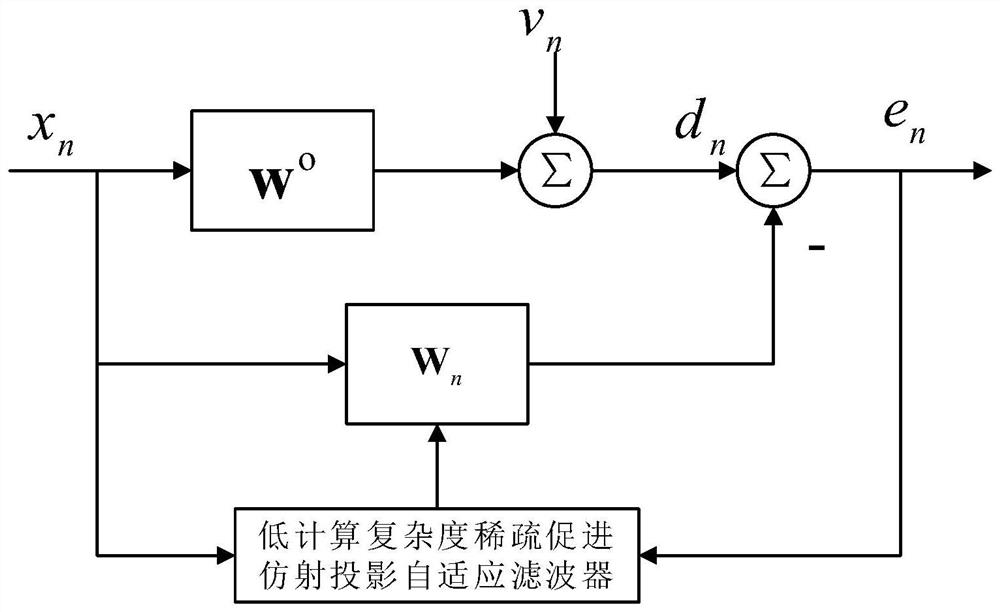
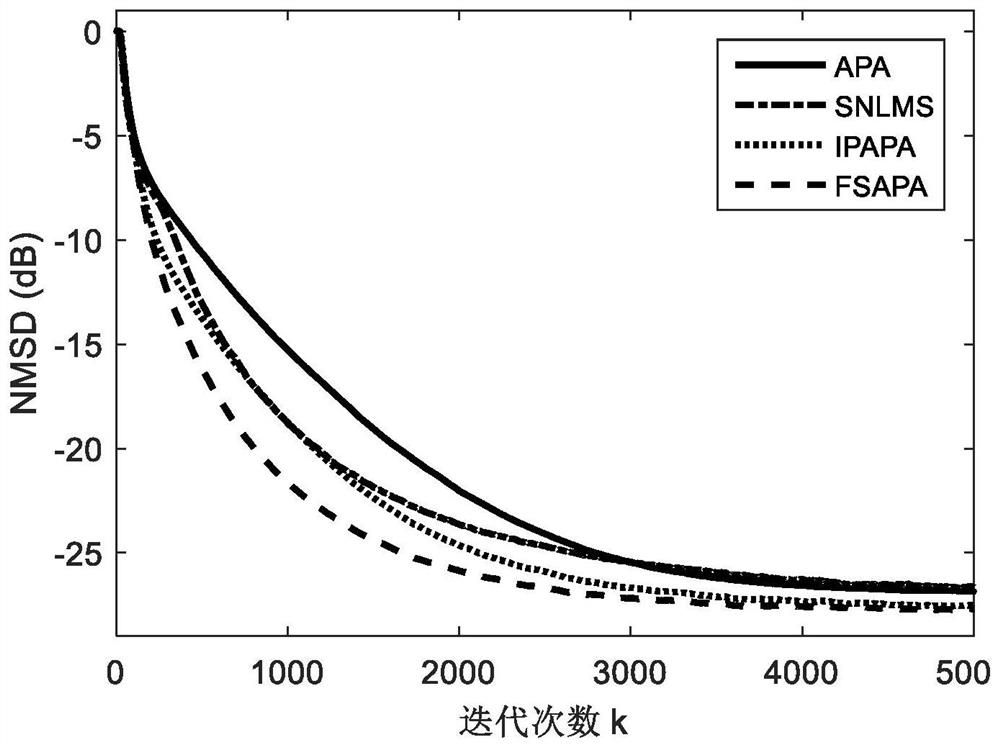
Sparse promotion affine projection adaptive filter with low computational complexity
ActiveCN113225045APerformance is not affectedFast convergenceAdaptive networkHigh level techniquesComputation complexityCommunications system
The invention discloses a sparse promotion affine projection adaptive filter with low calculation complexity, and belongs to the field of digital filter design. The filter is provided by the application of a sparse regularization technology in the sparse signal recovery (SSR) field in an affine projection algorithm (APA). A sparse promotion matrix under different diversity estimation conditions is mainly adopted, so that the adaptive filter can better approach a sparse linear system. In addition, the sparse promotion matrix strategy is periodically updated, so that the calculation cost of the filter can be reduced, and the performance of the filter is not influenced. The sparse promotion affine projection adaptive filter with low computational complexity disclosed by the invention can be applied to electronic and communication systems with sparse characteristics.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Filter -based filter reference reference to the projection symbol active control method
ActiveCN113285692BGuaranteed stabilitySolve the problem of further improvement of convergence performanceAdaptive networkSound producing devicesControl engineeringControl impulse
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
An Affine Projection Maximum Entropy Subband Adaptive Echo Cancellation Method
ActiveCN106210370BIncrease changeQuick updateTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsSpeech analysisAnti jammingAffine projection
A kind of affine projection maximum entropy sub-band adaptive echo cancellation method, its steps are: A, far-end signal segmentation, the far-end signal vector U (n) is divided into 1 far-end sub-band vector U through analysis filter i (n), at the same time, the near-end signal d(n) picked up by the near-end microphone is divided into 1 near-terminal band signals d through the analysis filter i (n); B, signal extraction, the remote terminal with vector U i (n) carry out I extraction through extractor; Obtain far-end input sub-band extraction vector U i (k); also for near terminal with signal d i (n) I extraction is performed by the extractor to obtain the near-terminal strip extraction signal d i (k); C, affine projection, D, filter output, the far-end input subband affine projection matrix X(k) is filtered by a filter to obtain an output vector Y(k); E, echo cancellation, F, The tap weight vector is updated, based on the maximum entropy V(k) update of the current net signal vector to determine the weight vector at the next extraction moment, G, iteration, let k=k+1, repeat A, B, C, D, E, Step F, until the end of the call. It has good echo cancellation effect and strong anti-interference ability.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com