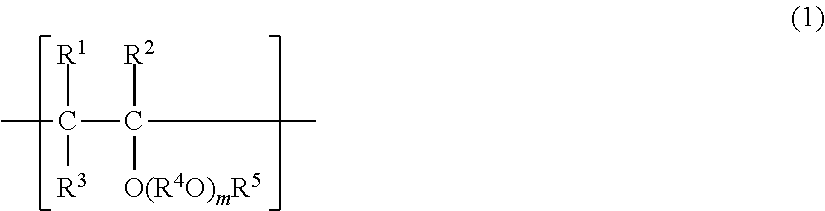Patents
Literature
421results about How to "Less influence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
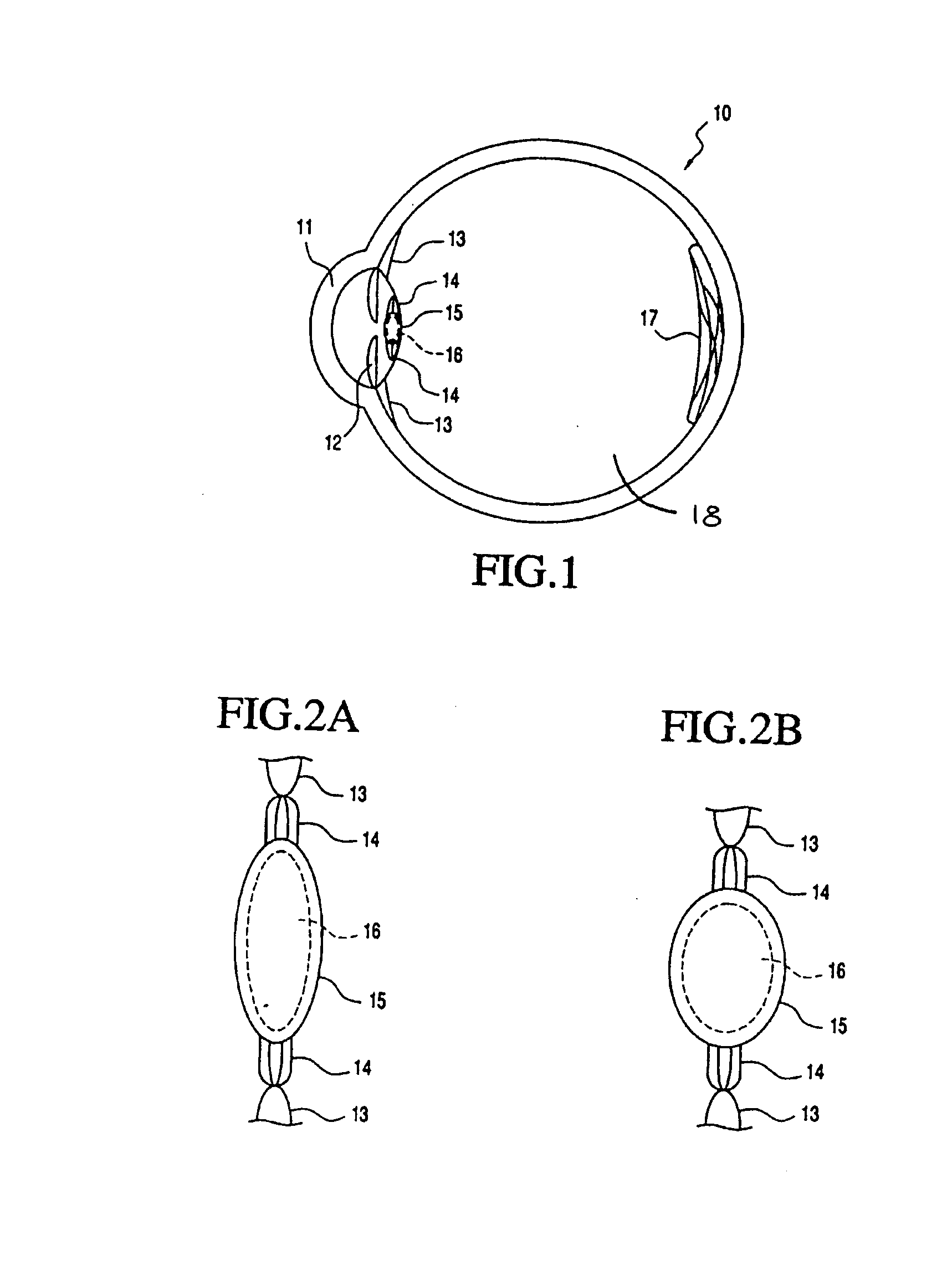
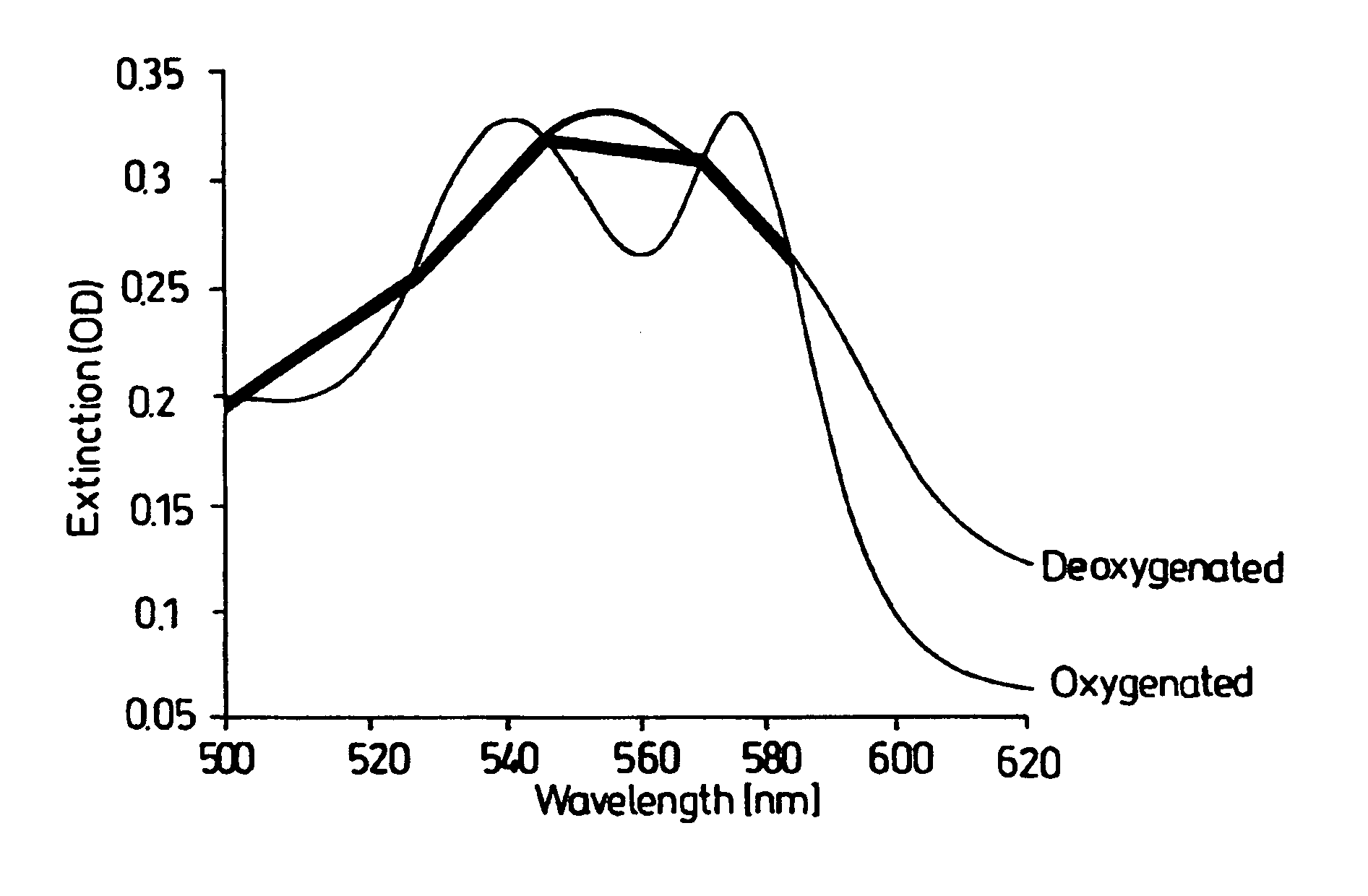
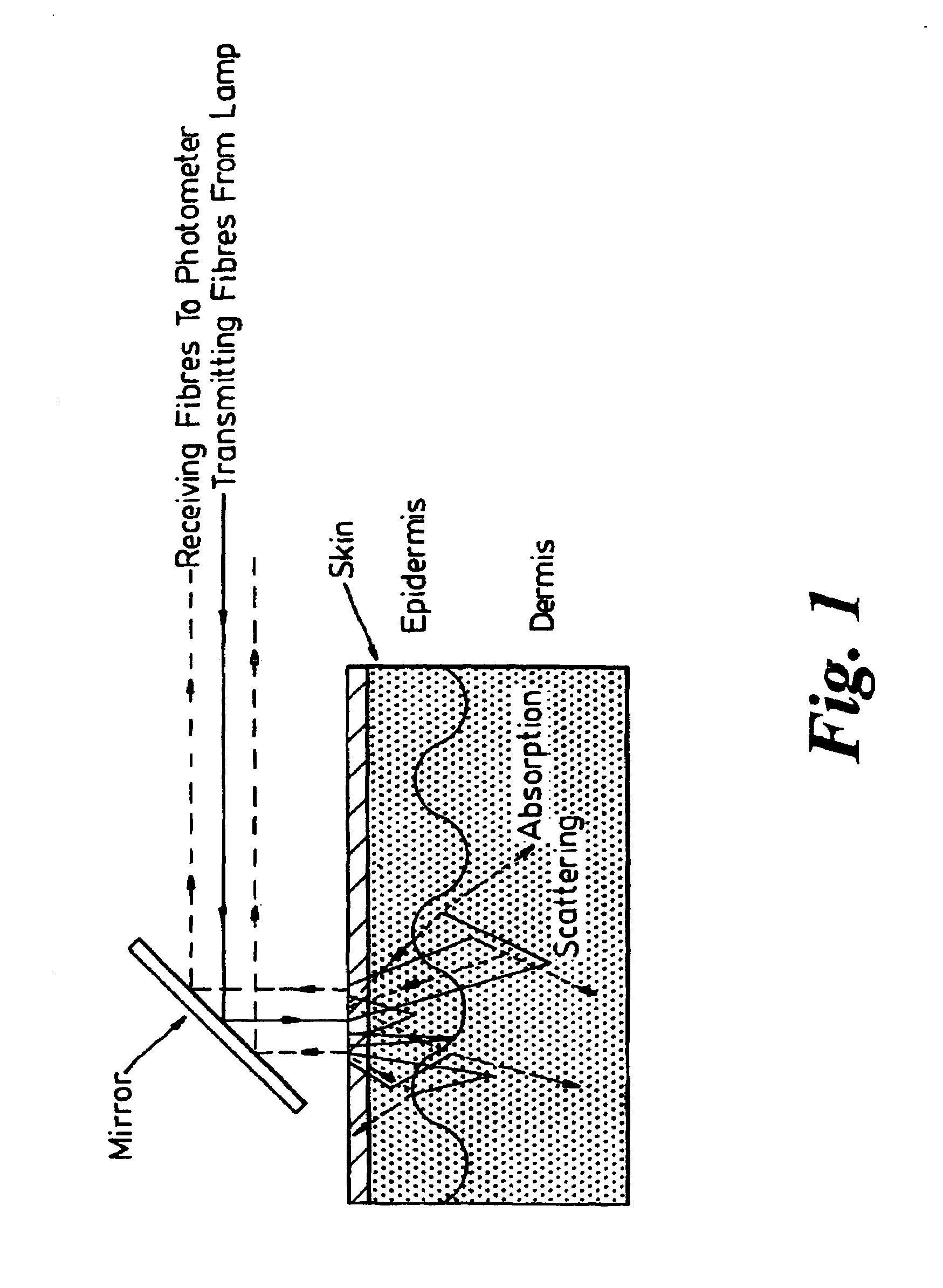
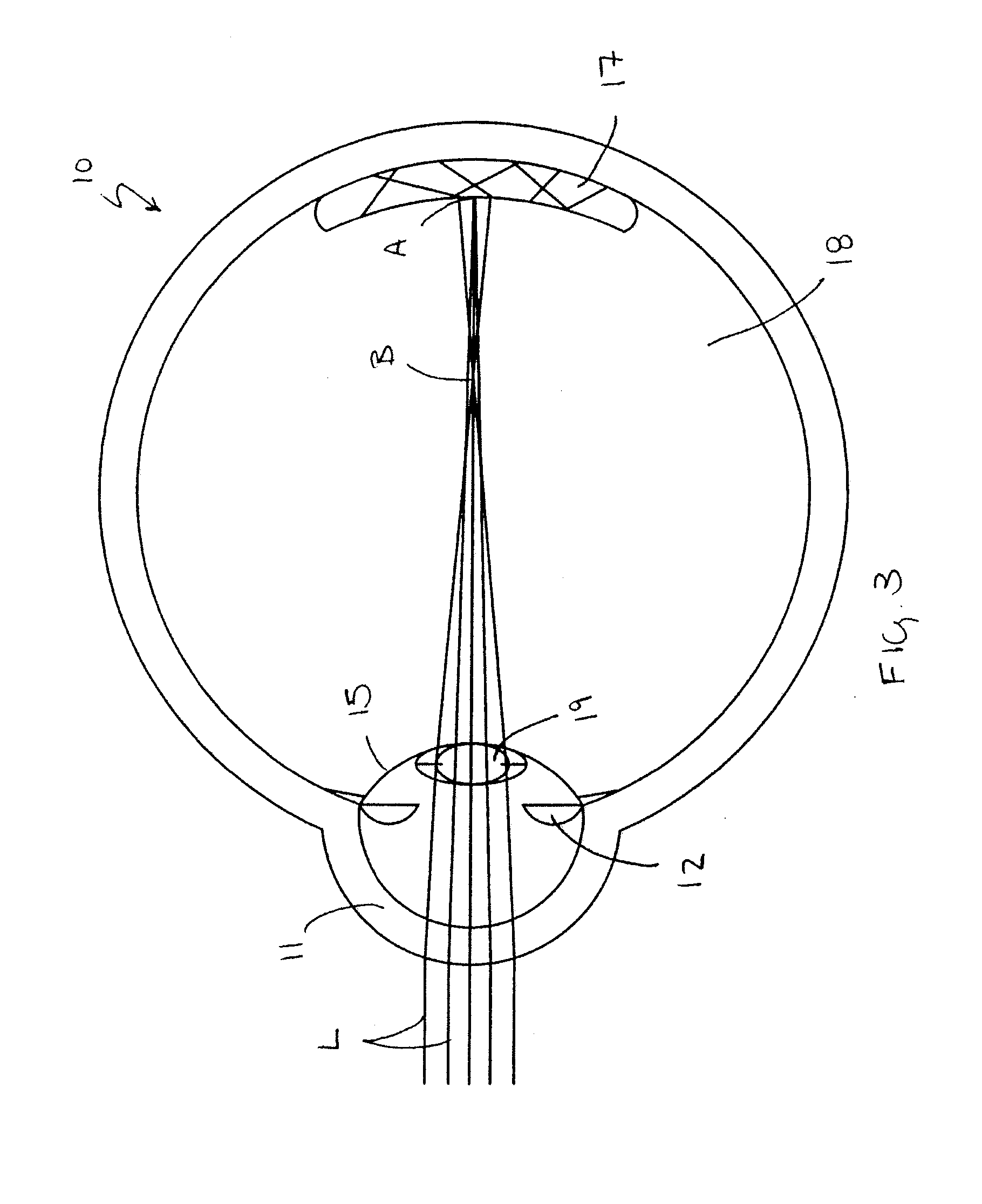
Optical device
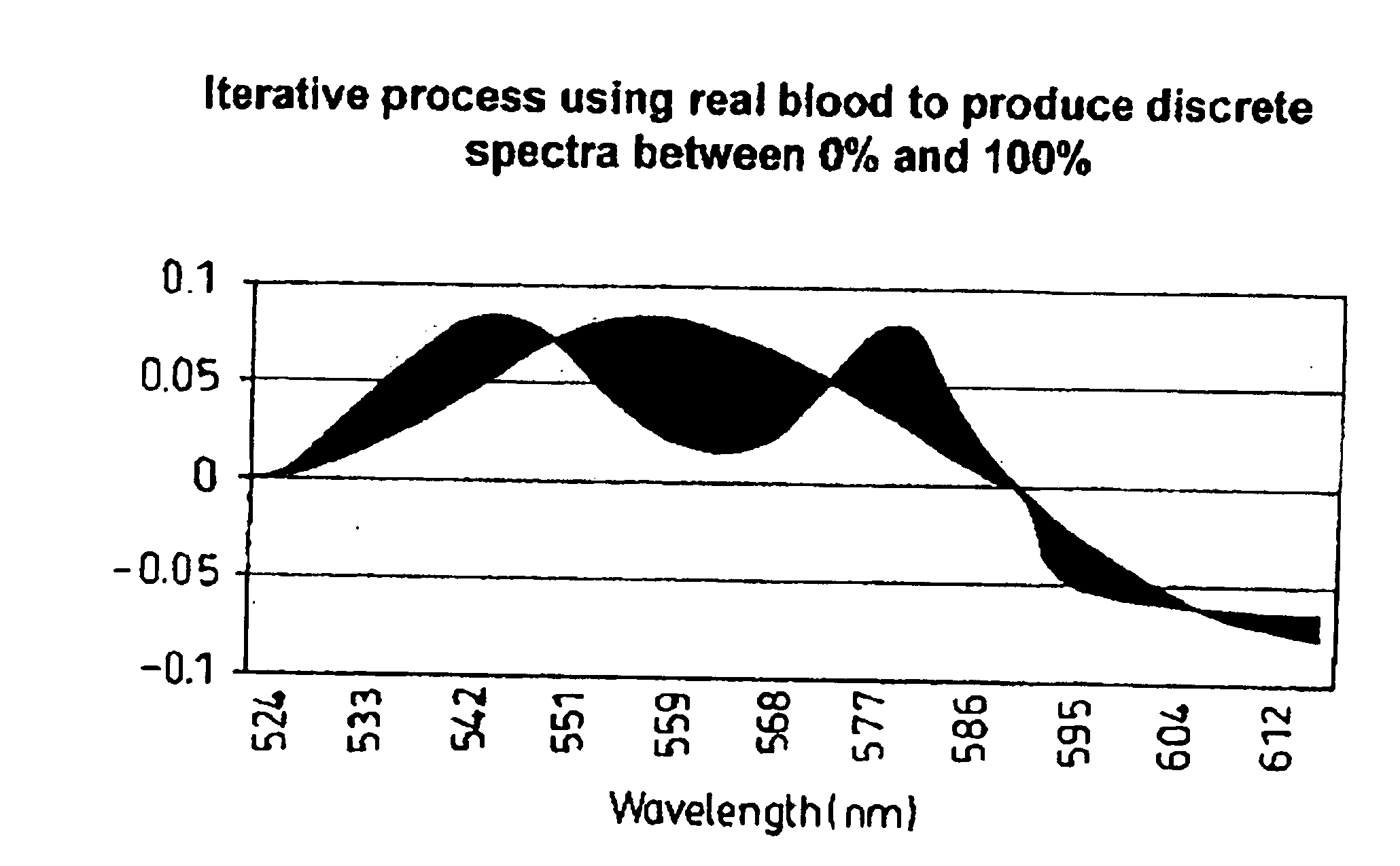
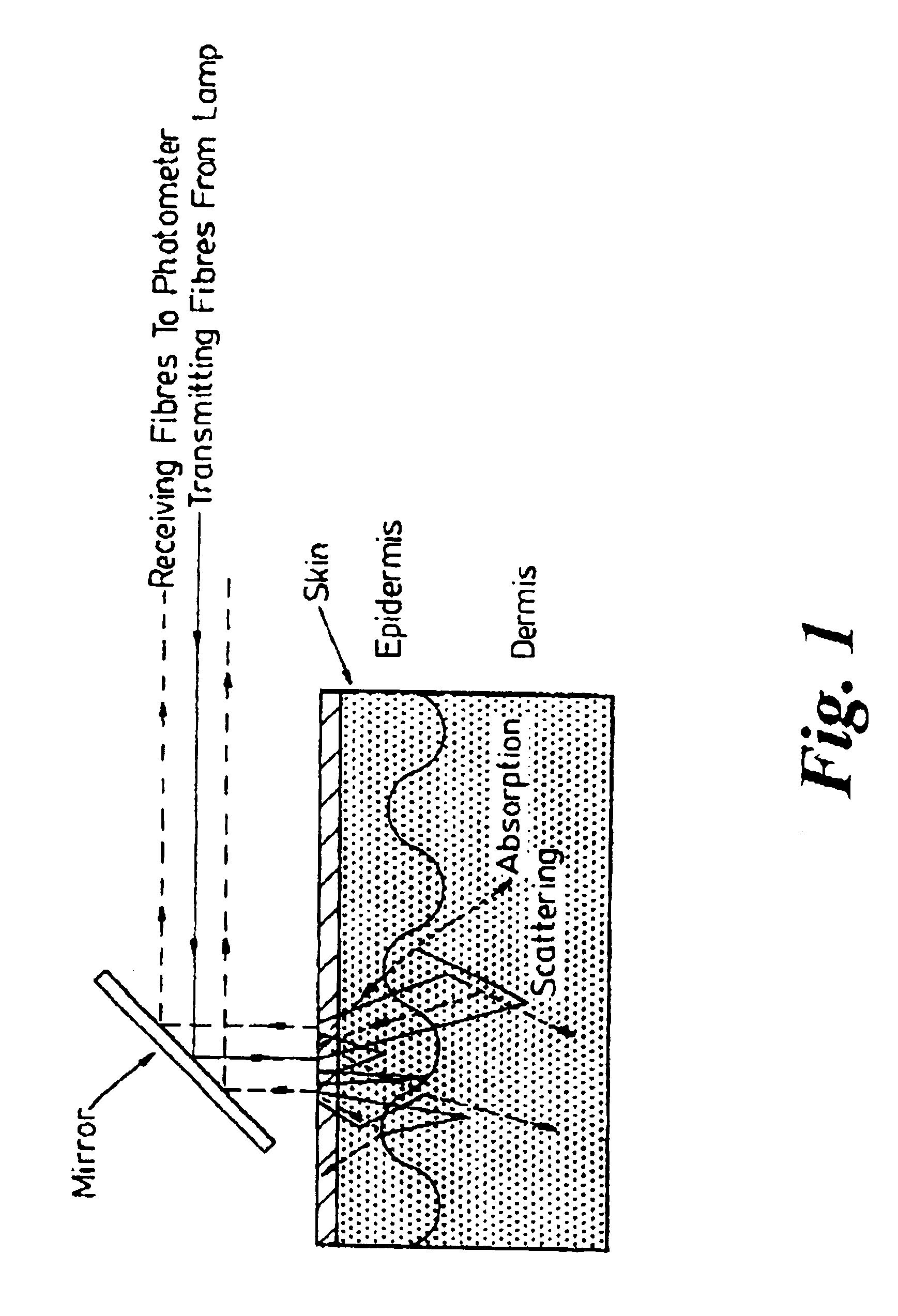
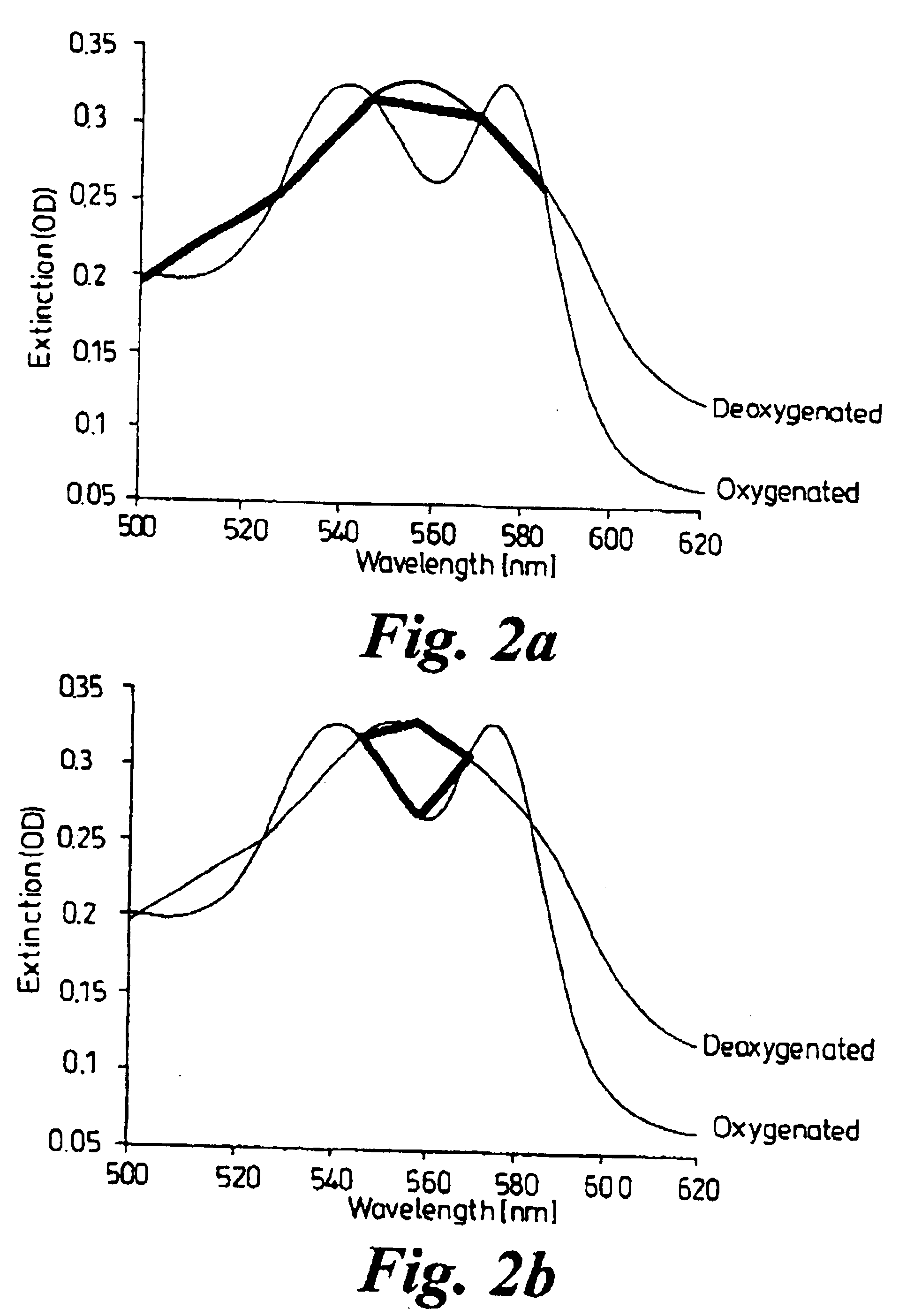
InactiveUS6842635B1Enable flexibilityStability advantageDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPhotodetectorBiological tissue
There is described a sensor device which comprises light source means for emitting a light beam, photodetector means for receiving the light beam after passing through or being reflected within living tissue and arranged to provide signals corresponding to the intensities of the respective wavelength of light received by the photodetector means characterised in that the sensor device measures blood oxygen saturation. The device can be used in conjunction with a conventional pulse oximeter. There is also described a method of measuring blood oxygen saturation.
Owner:WHITLAND RES
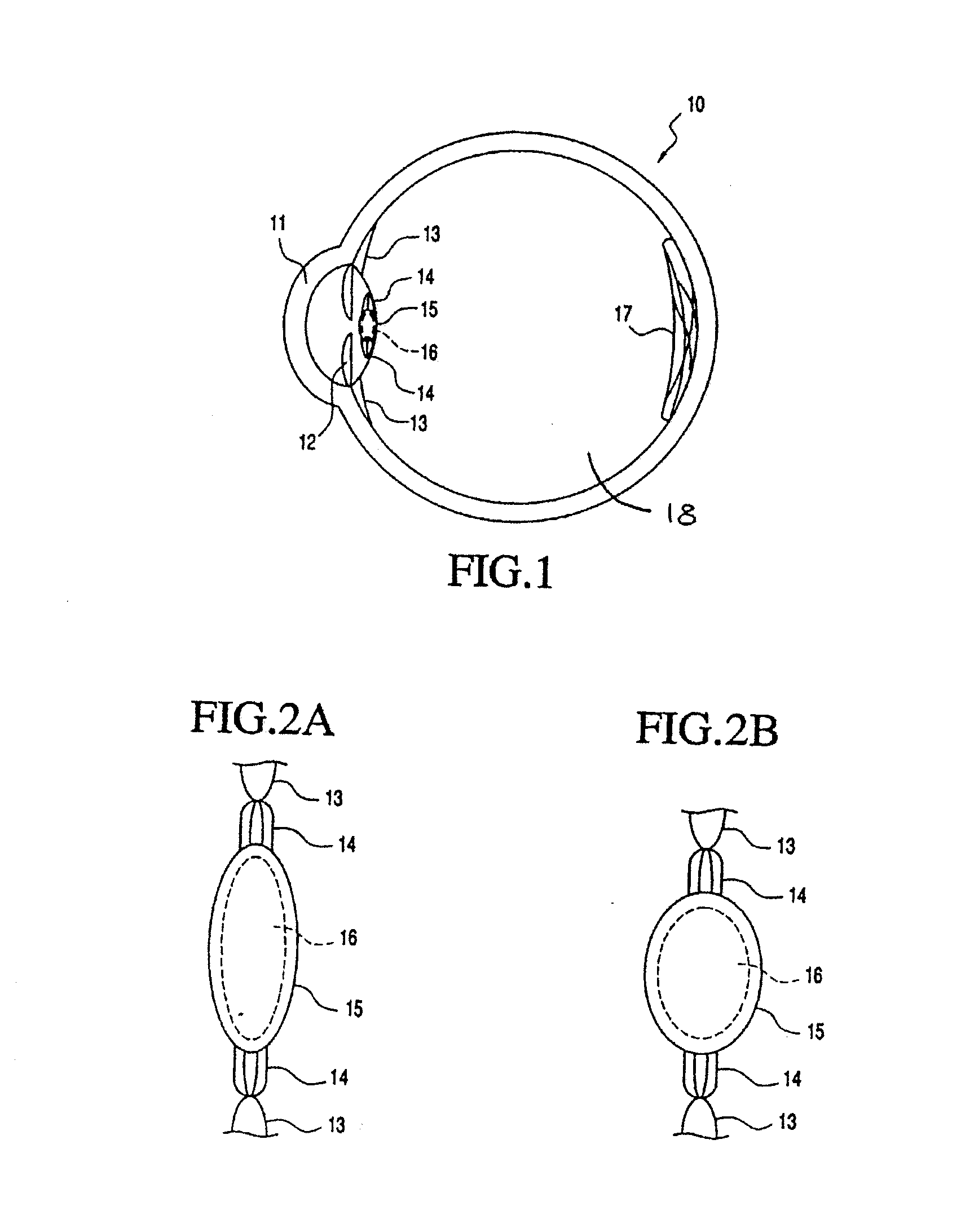
Accommodating intraocular lens system having spherical aberration compensation and method
ActiveUS20070106377A1Small internal volumeIncrease the internal volumeIntraocular lensIntraocular lensOptical power
An accommodating intraocular lens includes an optic portion, a haptic portion. The optic portion of the lens includes an actuator that deflects a lens element to alter the optical power of the lens responsive to forces applied to the haptic portion of the lens by contraction of the ciliary muscles and a secondary deflection mechanism. Movement of the lens element by the actuator causes the lens element to deform and the secondary deflection mechanism causes the lens to further deform.
Owner:ALCON INC
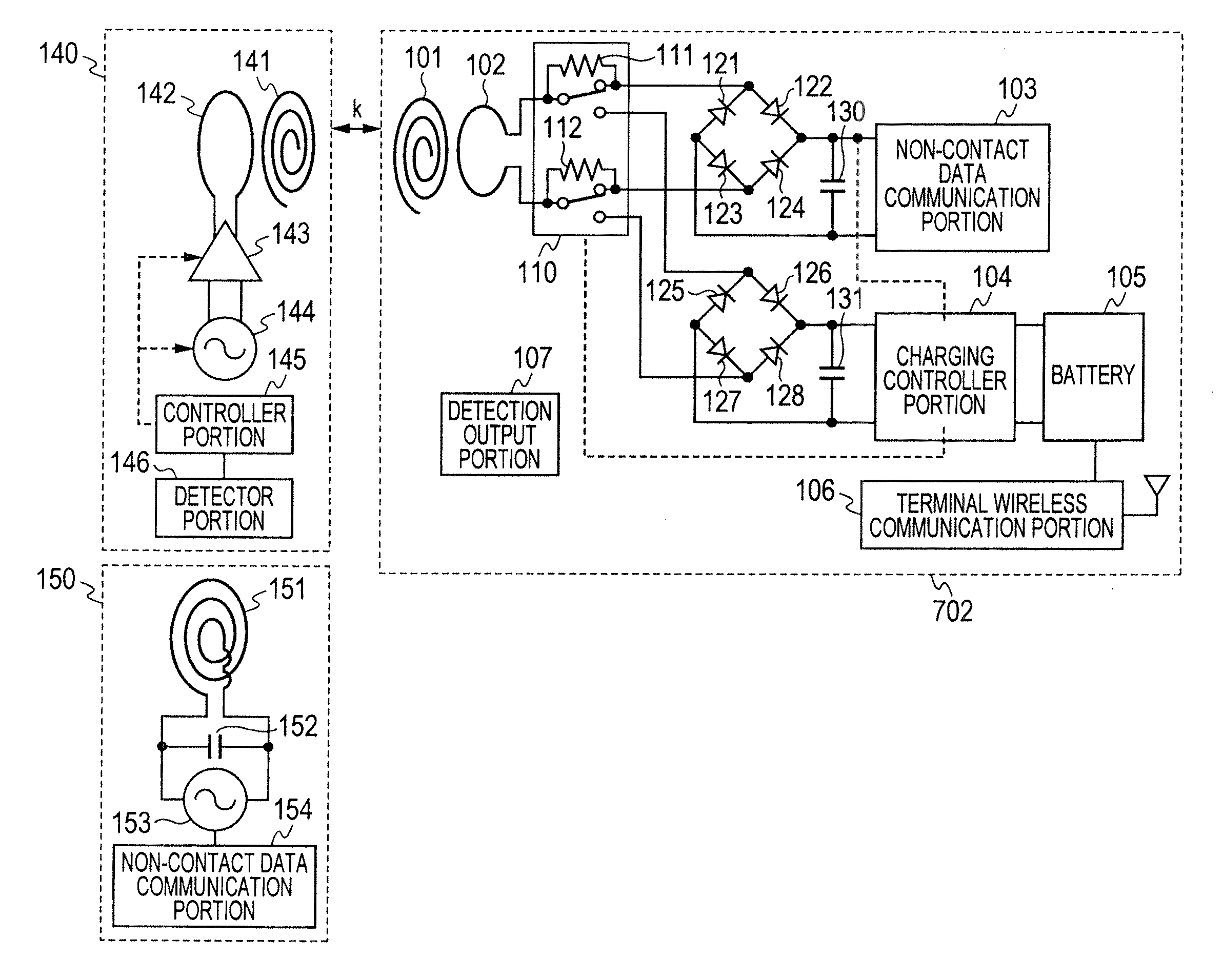
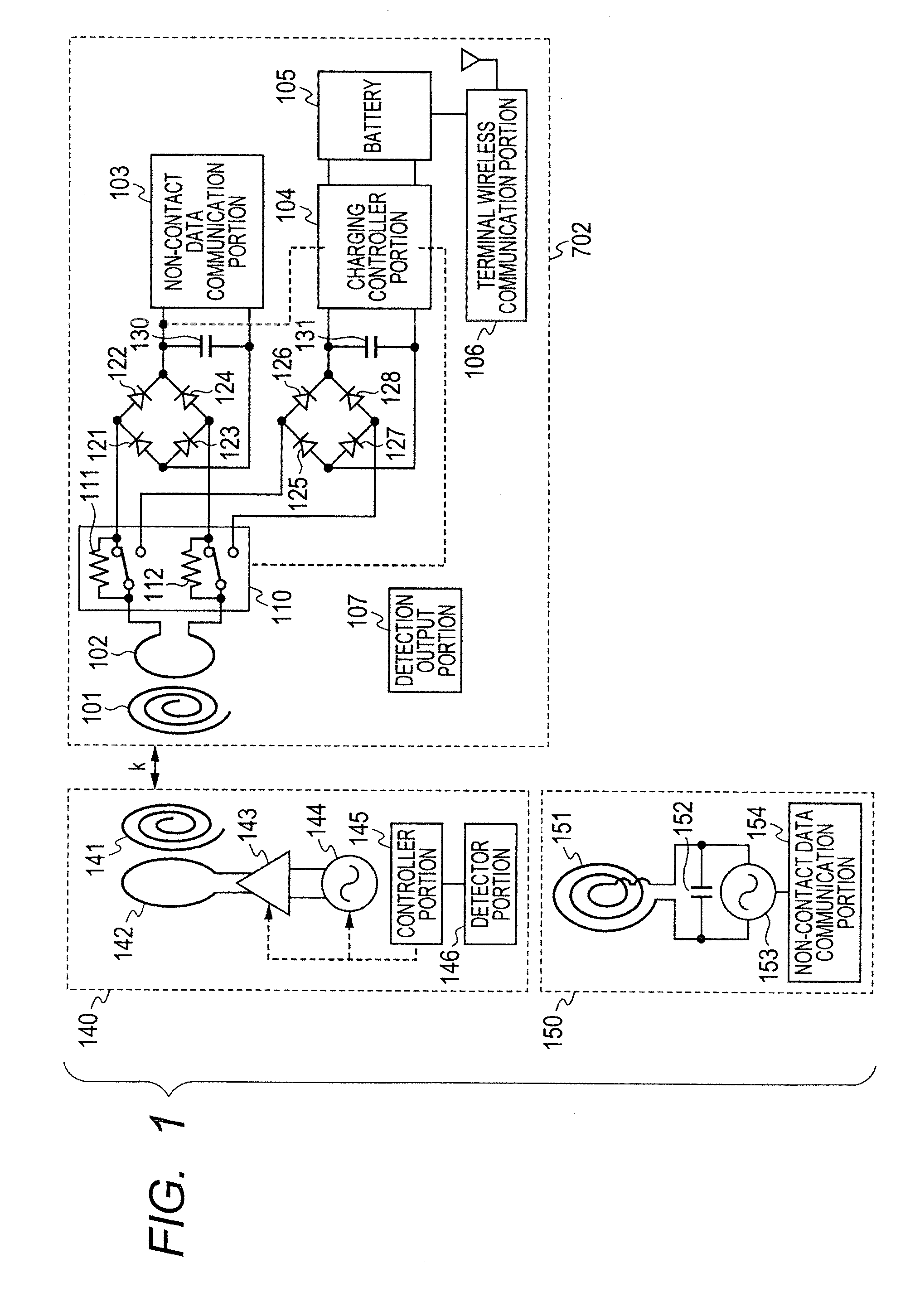
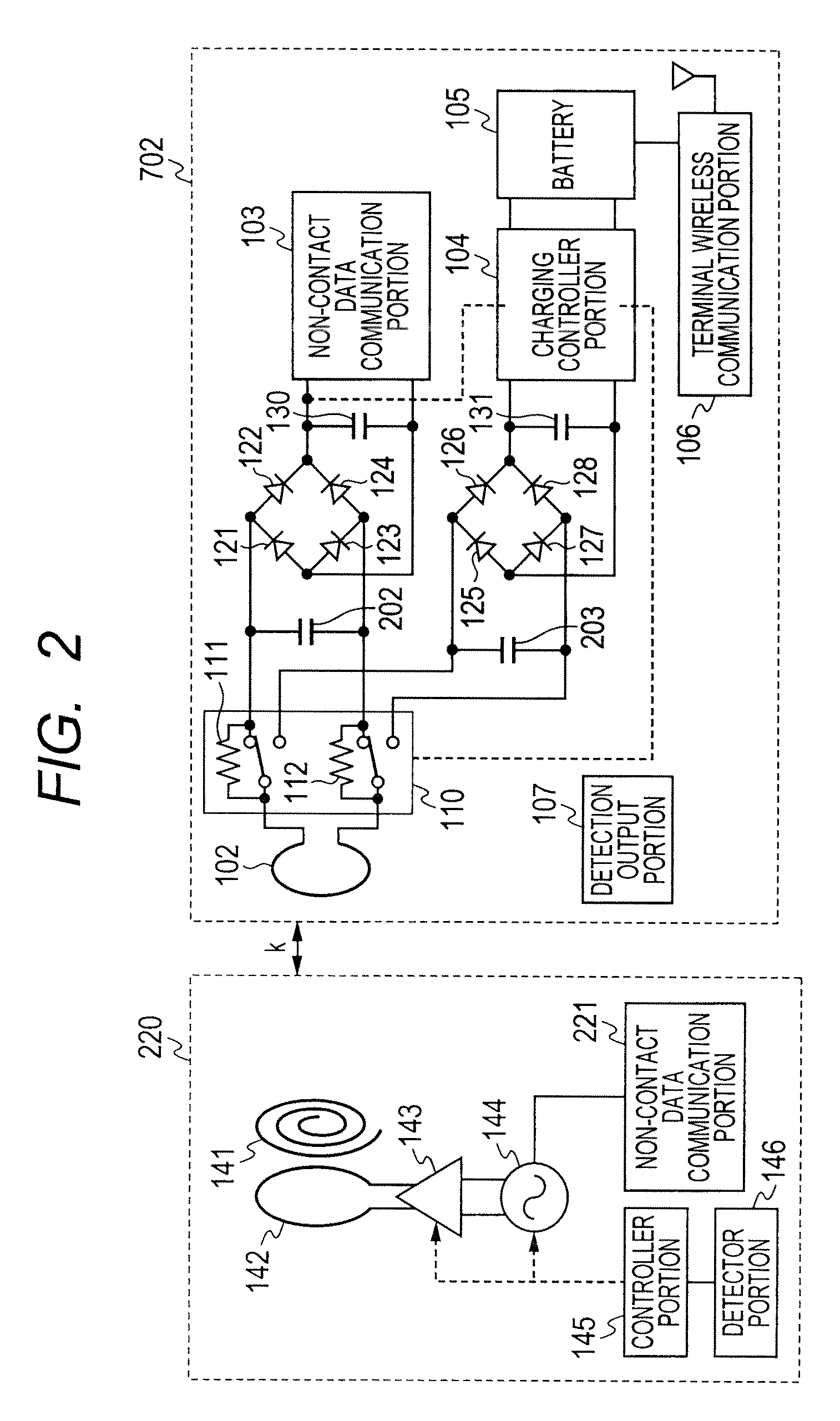
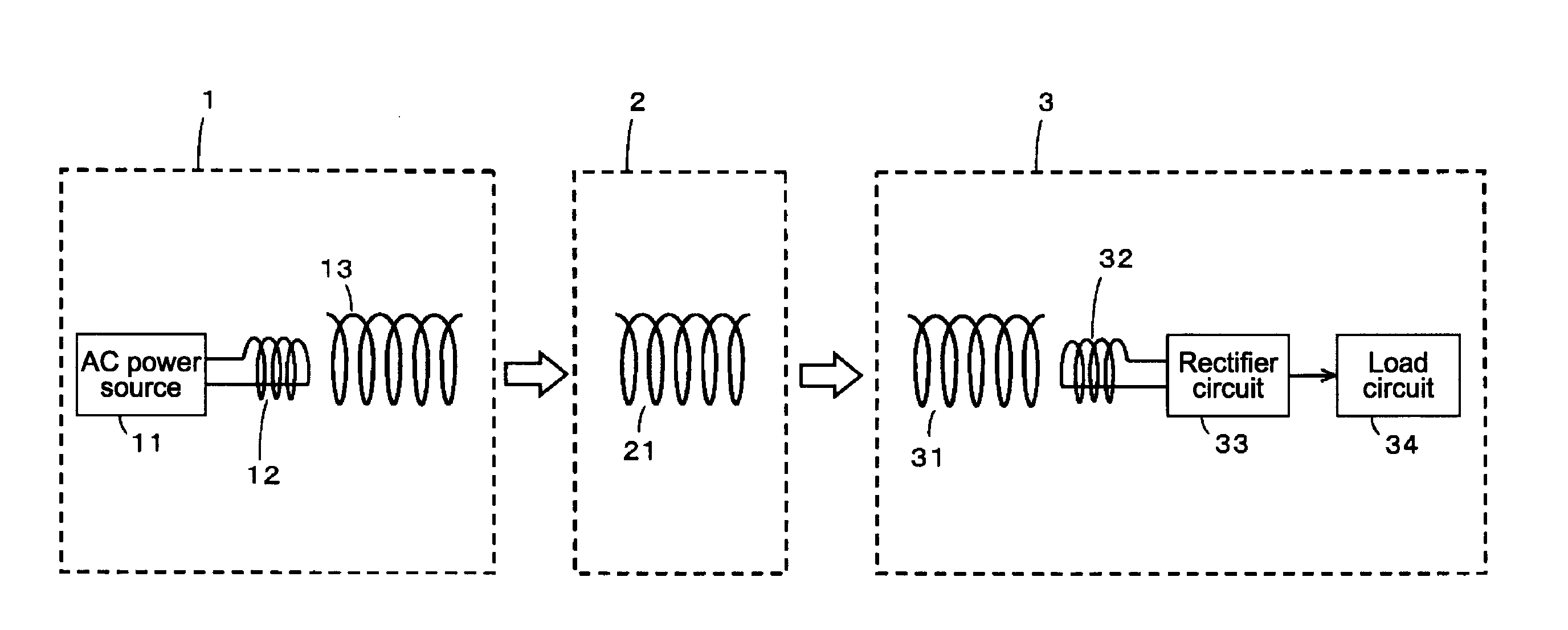
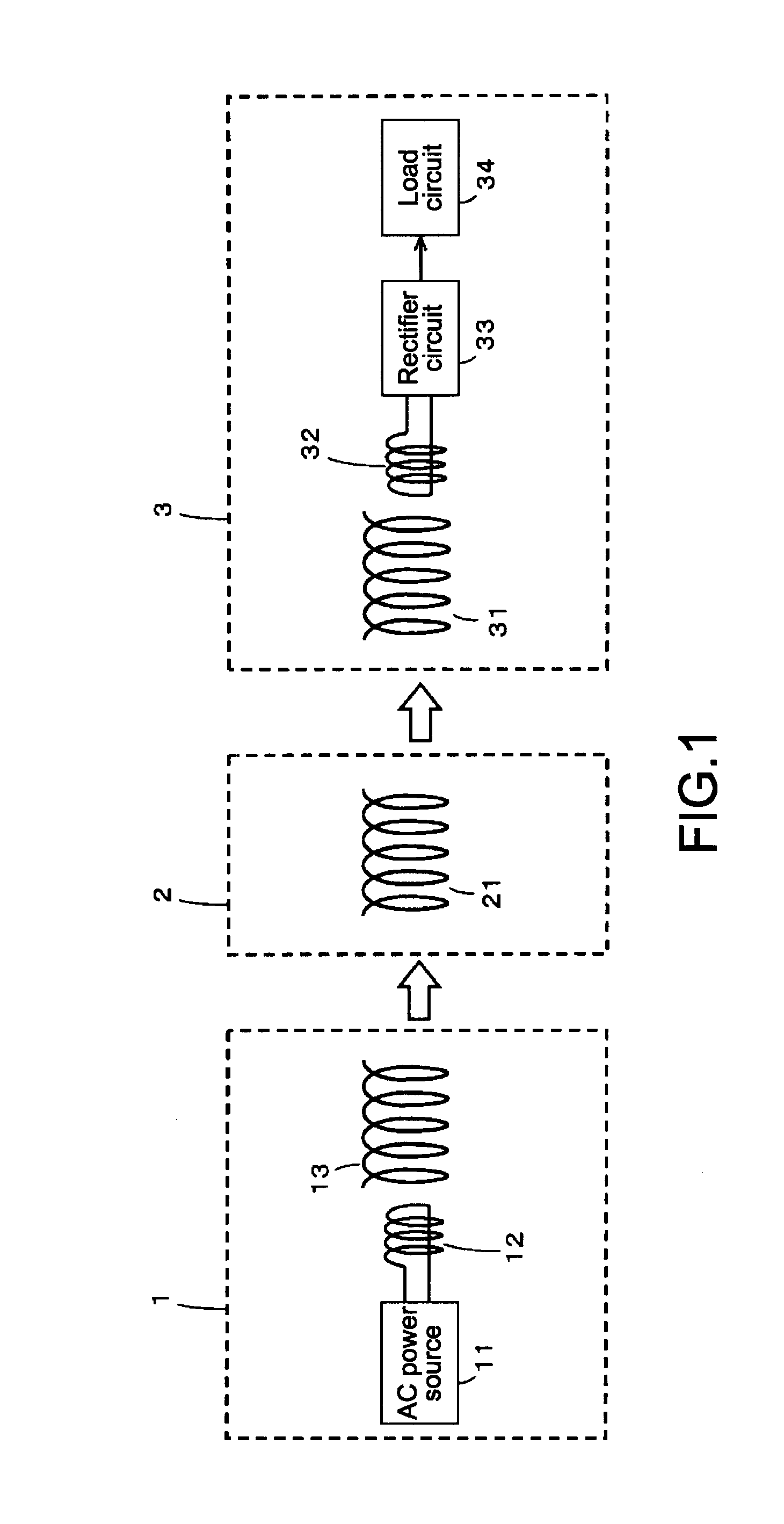
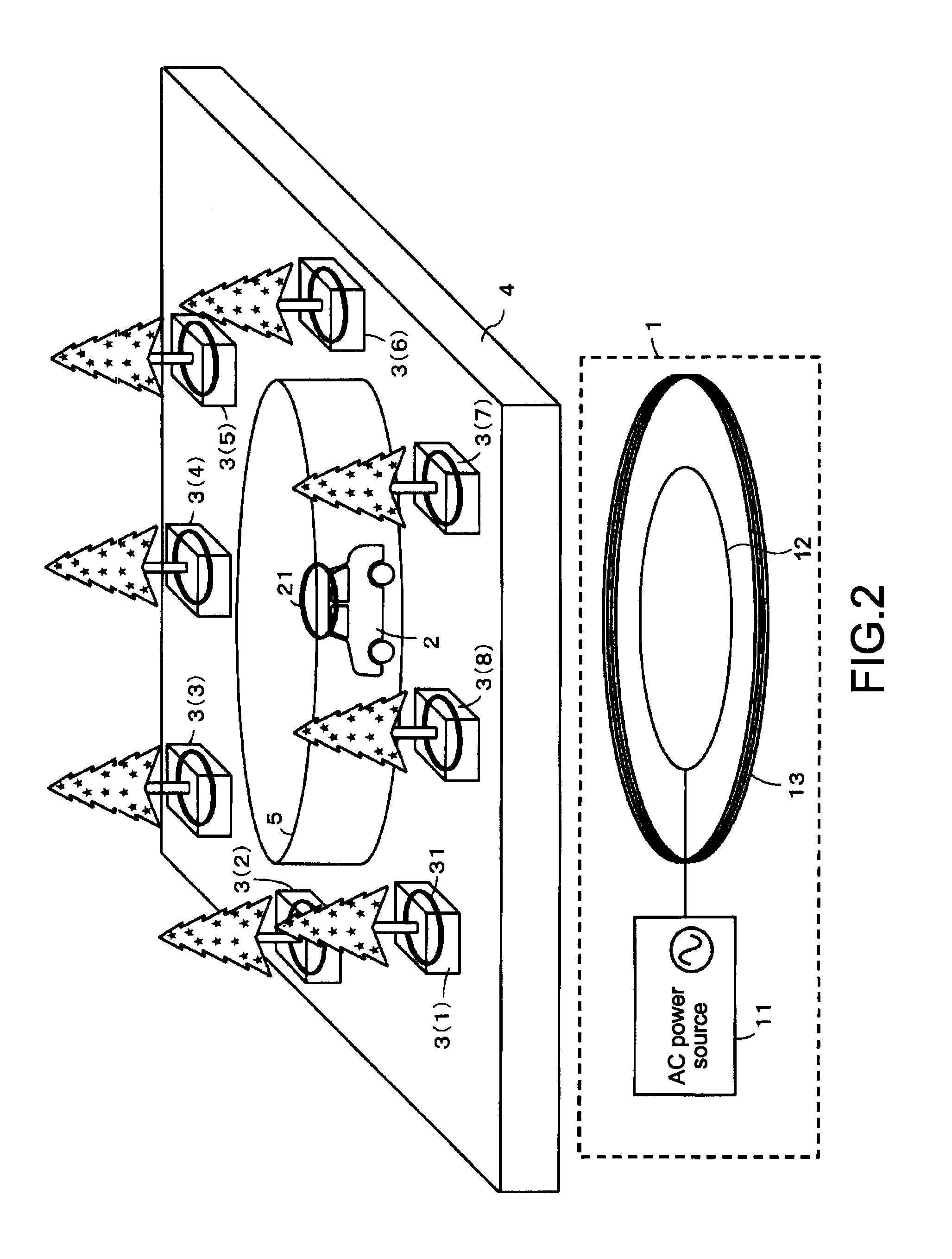
Non-contact power transmission system, receiving apparatus and transmitting apparatus
ActiveUS20120235508A1Low efficiencyGuaranteed normal transmissionCircuit authenticationCircuit monitoring/indicationElectric power transmissionElectric power system
A non-contact power transmission system comprises: a primary coil including a power supply coil and a magnetic resonance coil; and a secondary coil including a load coil, thereby transmitting an electric power from the power supply coil at a self-resonating frequency of the magnetic resonance coil, which is determined by a parasitic capacitance between wound wires of the coil and a self inductance of the coil, and taking out the electric power supplied, from the load coil of the secondary coil through magnetic coupling, with non-contact, wherein the electric power is transmitted, with non-contact, with applying magnetic coupling in coupling between the power supply coil and the magnetic resonance coil and coupling between the magnetic resonance coil and the load coil.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
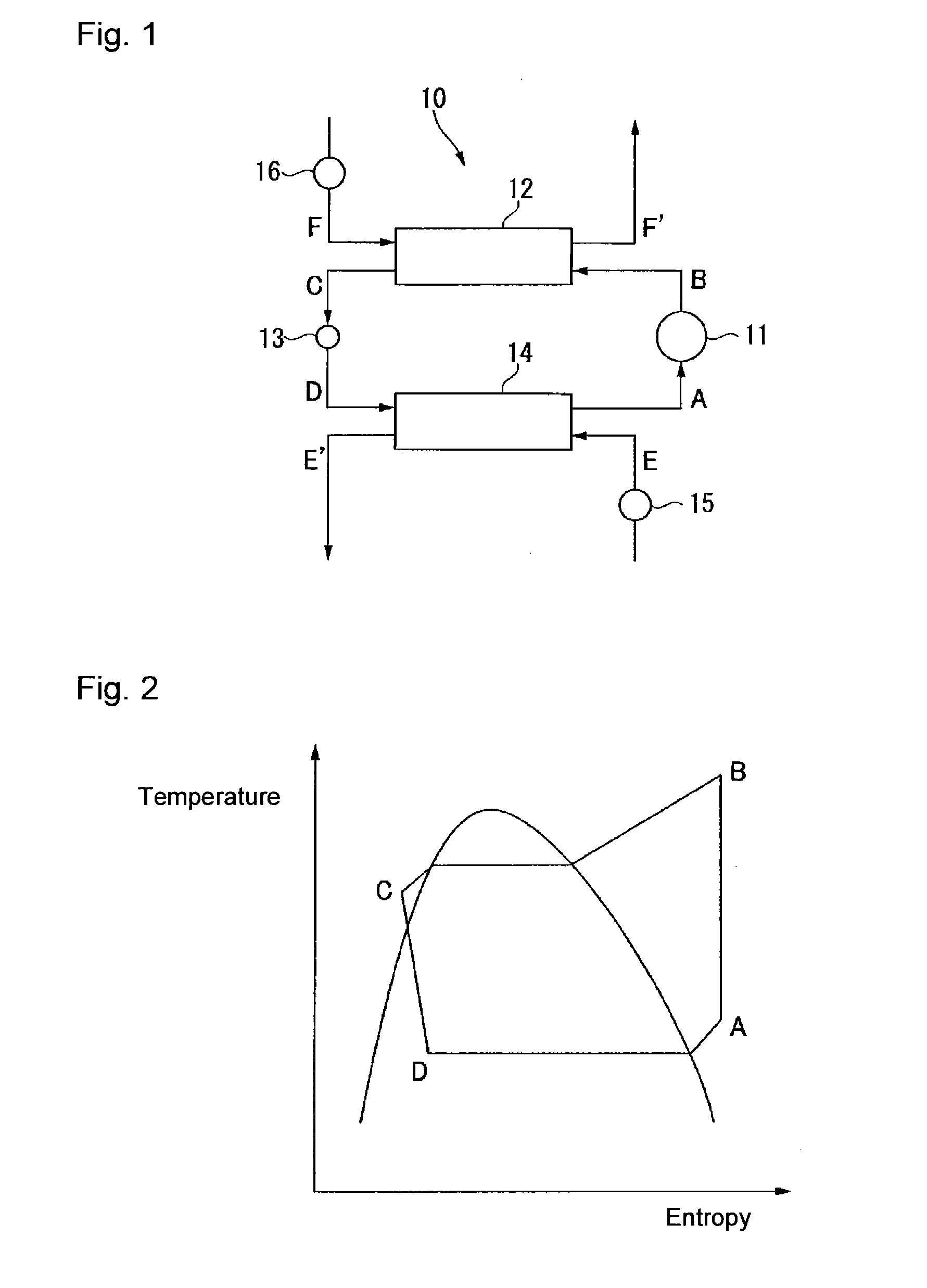
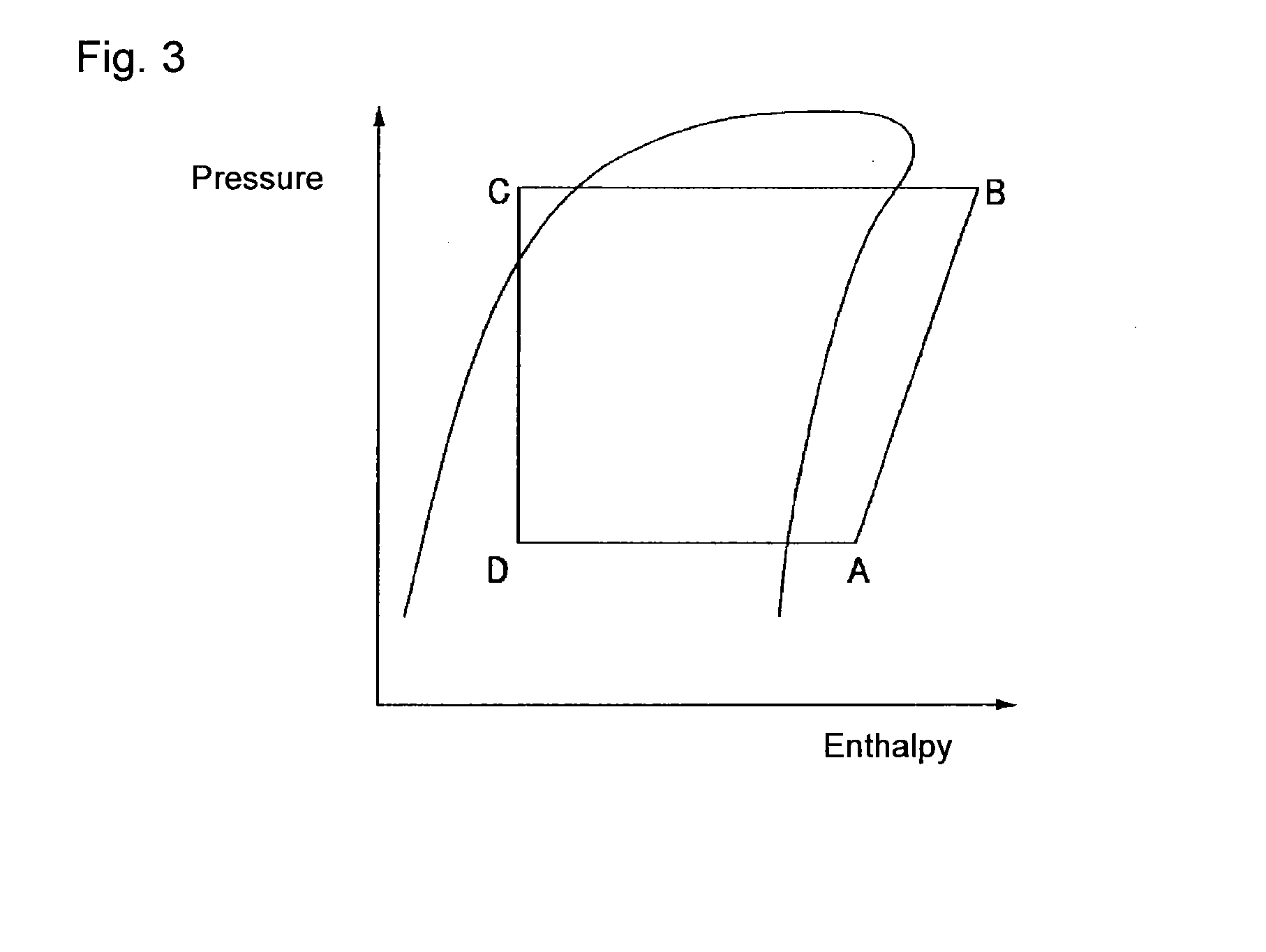
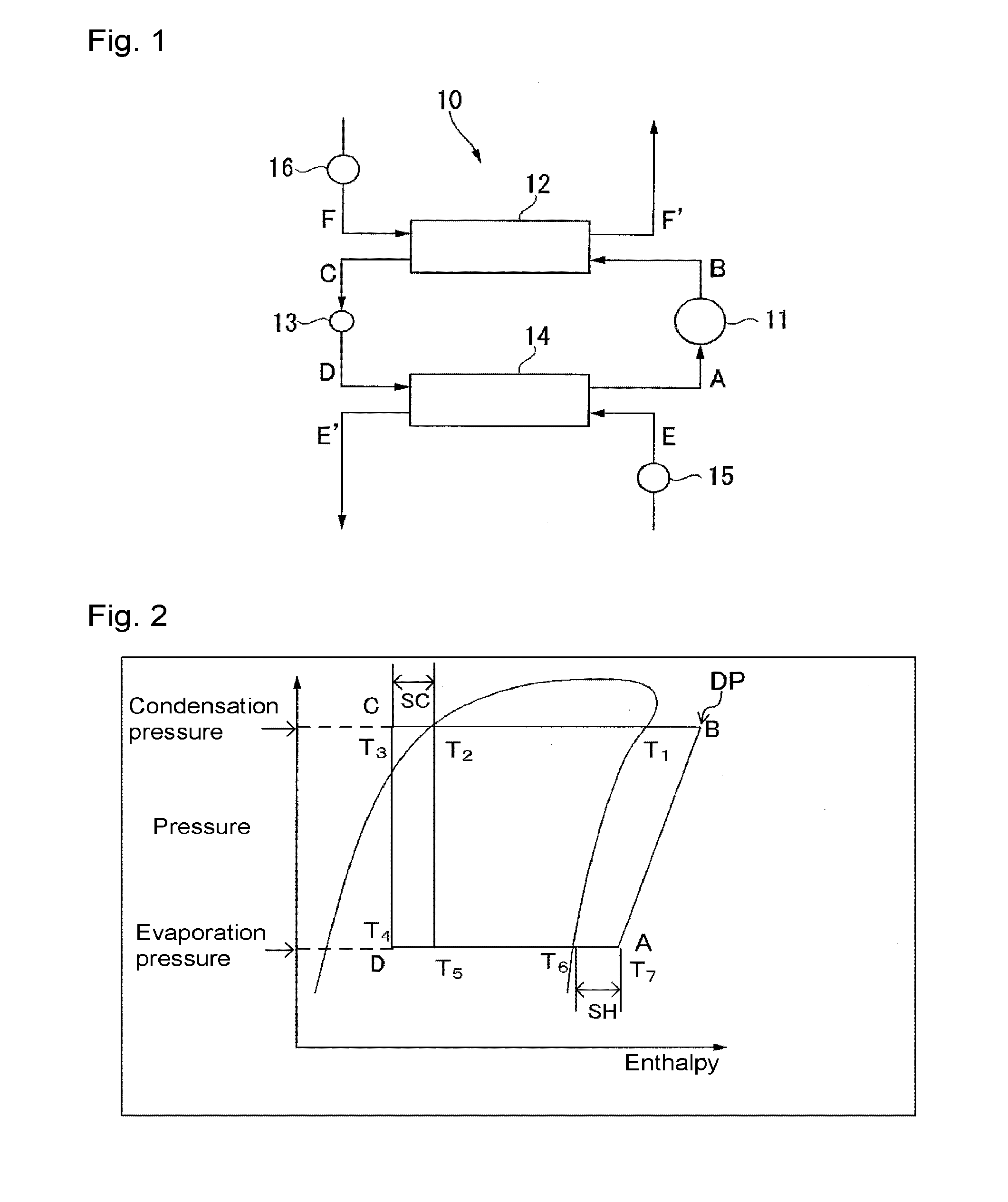
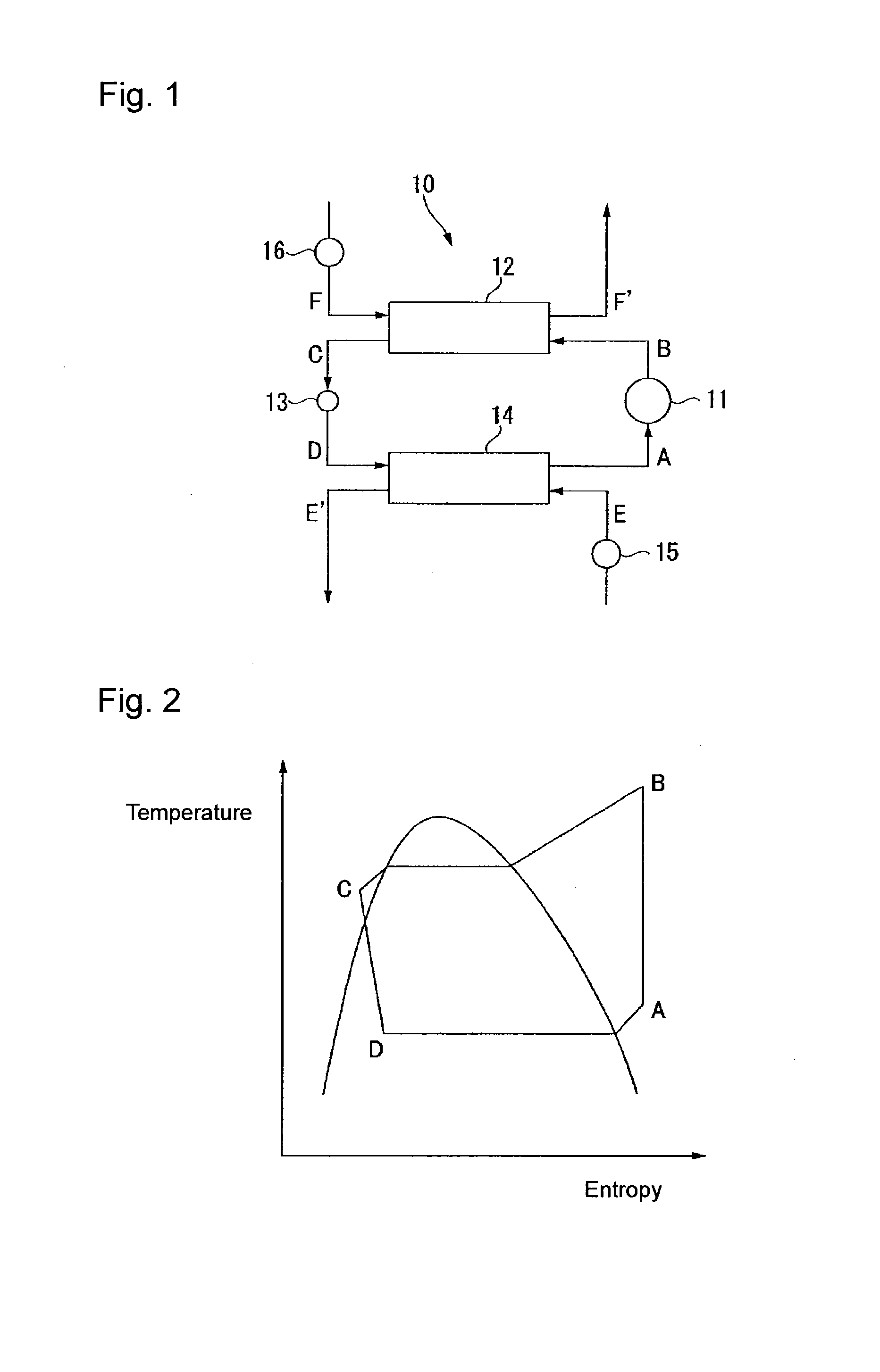
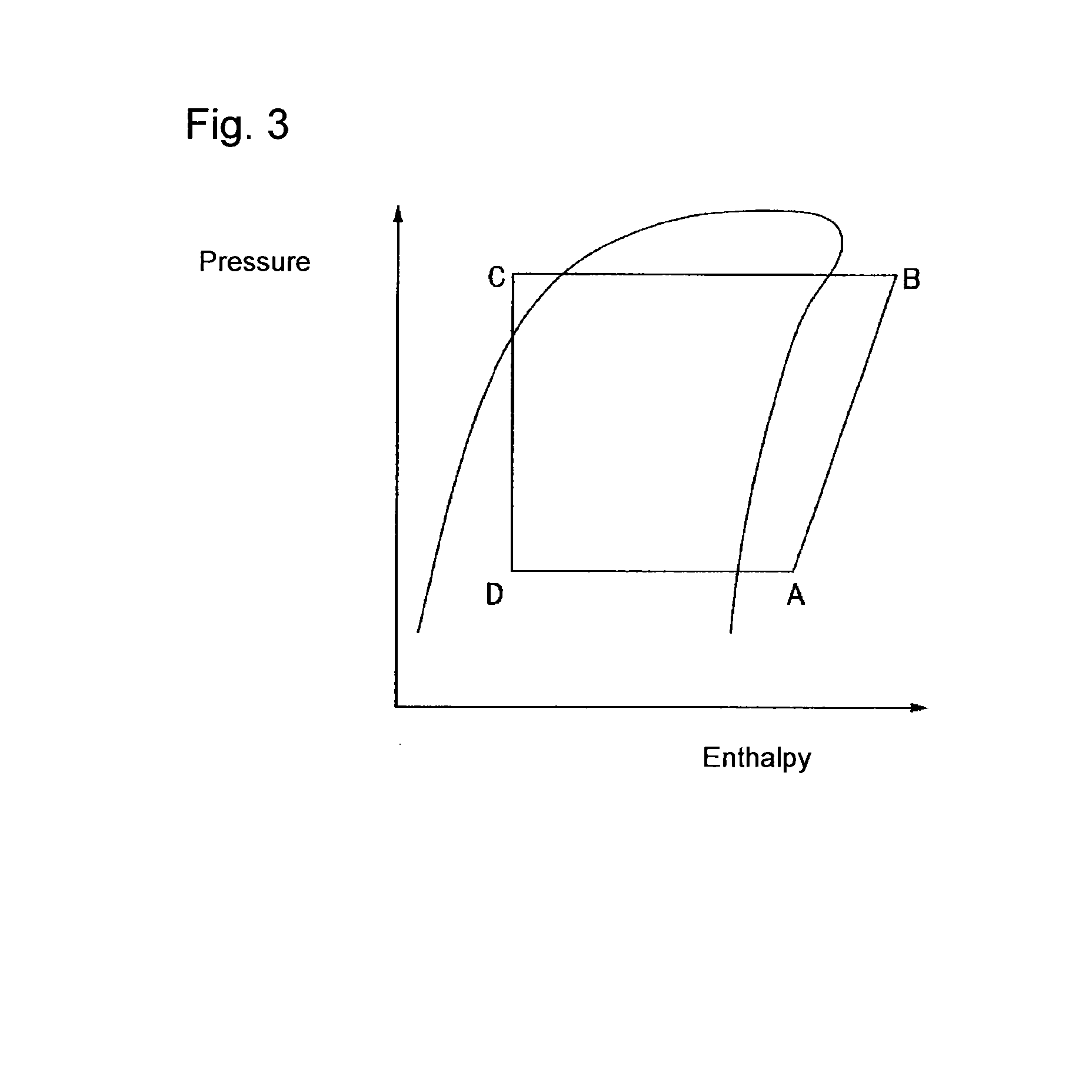
Working medium and heat cycle system
ActiveUS20140070132A1Promote decompositionLess influenceOrganic chemistryCompression machinesTransport systemOzone layer
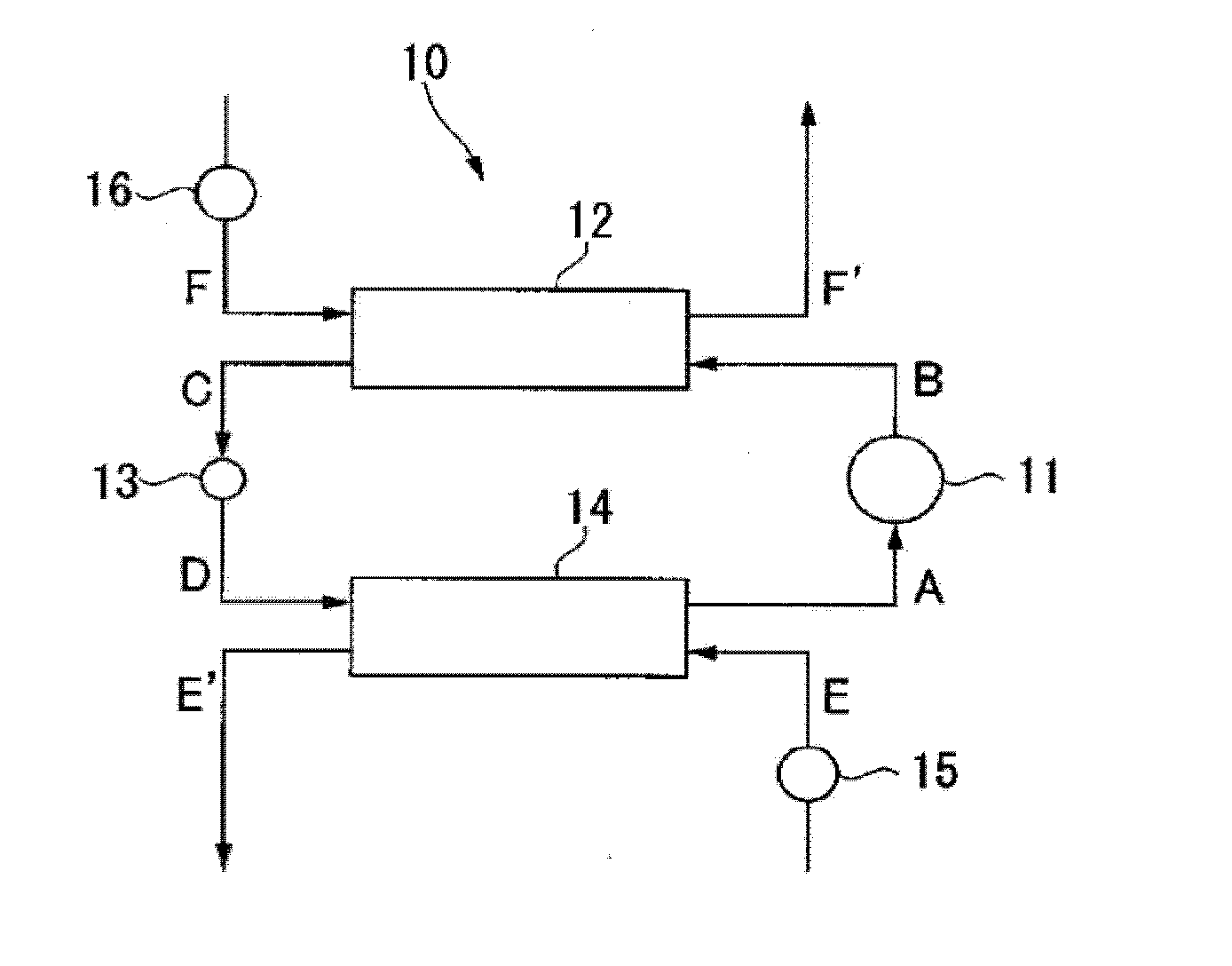
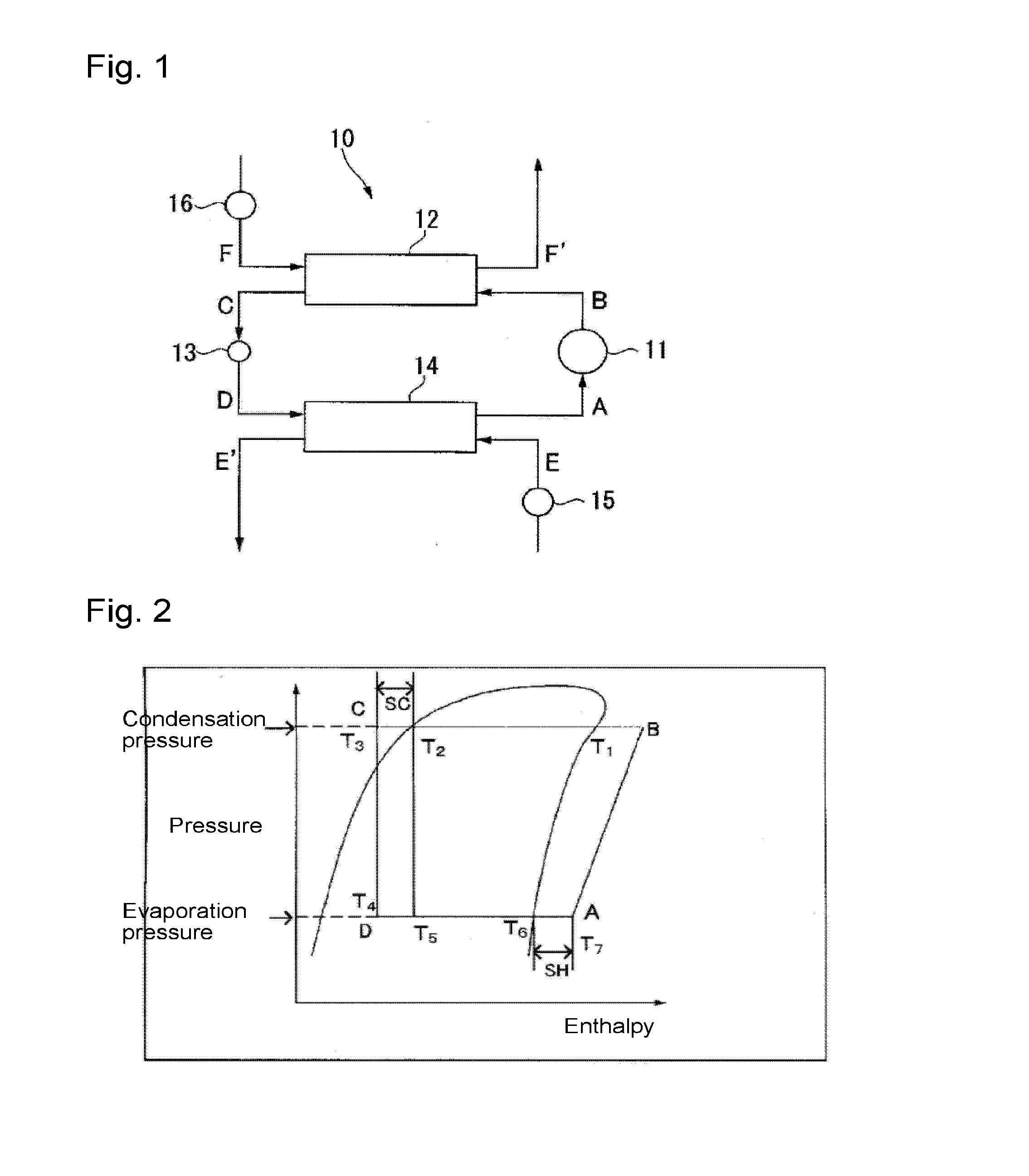
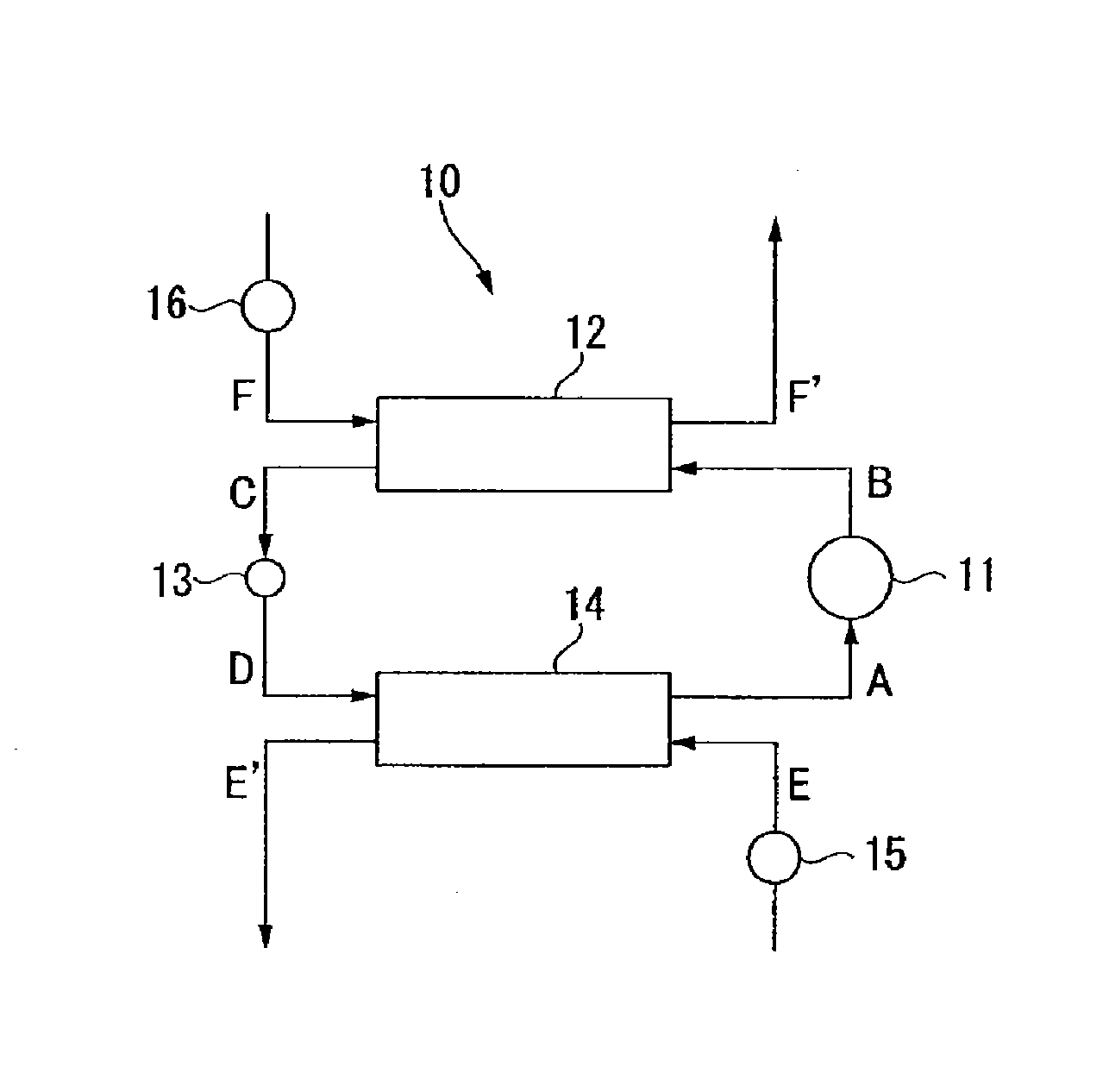
To provide a working medium for heat cycle, of which combustibility is suppressed, which has less influence over the ozone layer, which has less influence over global warming and which provides a heat cycle system excellent in the cycle performance (capacity), and a heat cycle system, of which the safety is secured, and which is excellent in the cycle performance (capacity).A working medium for heat cycle comprising 1,1,2-trifluoroethylene is employed for a heat cycle system (such as a Rankine cycle system, a heat pump cycle system, a refrigerating cycle system 10 or a heat transport system).
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
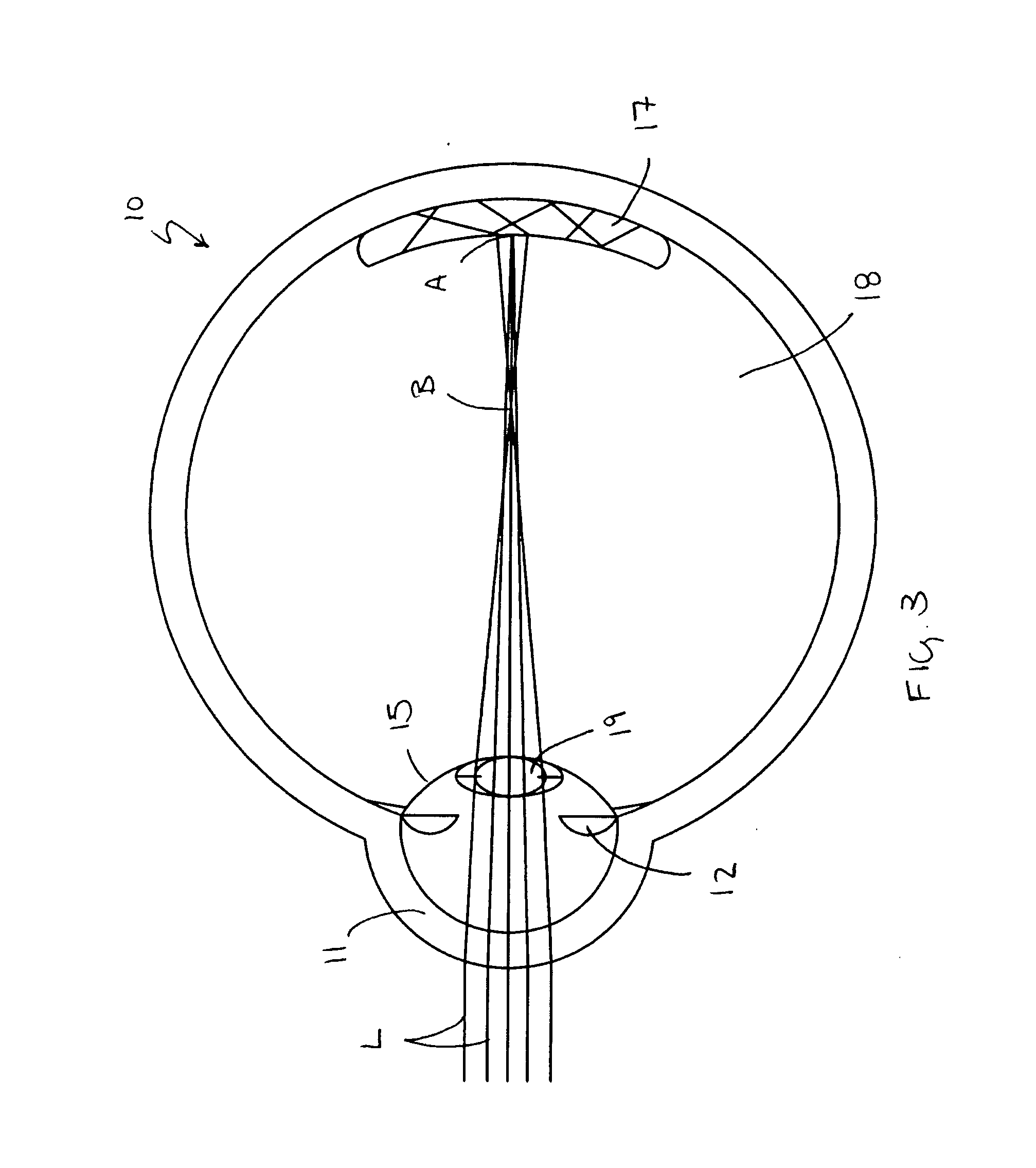
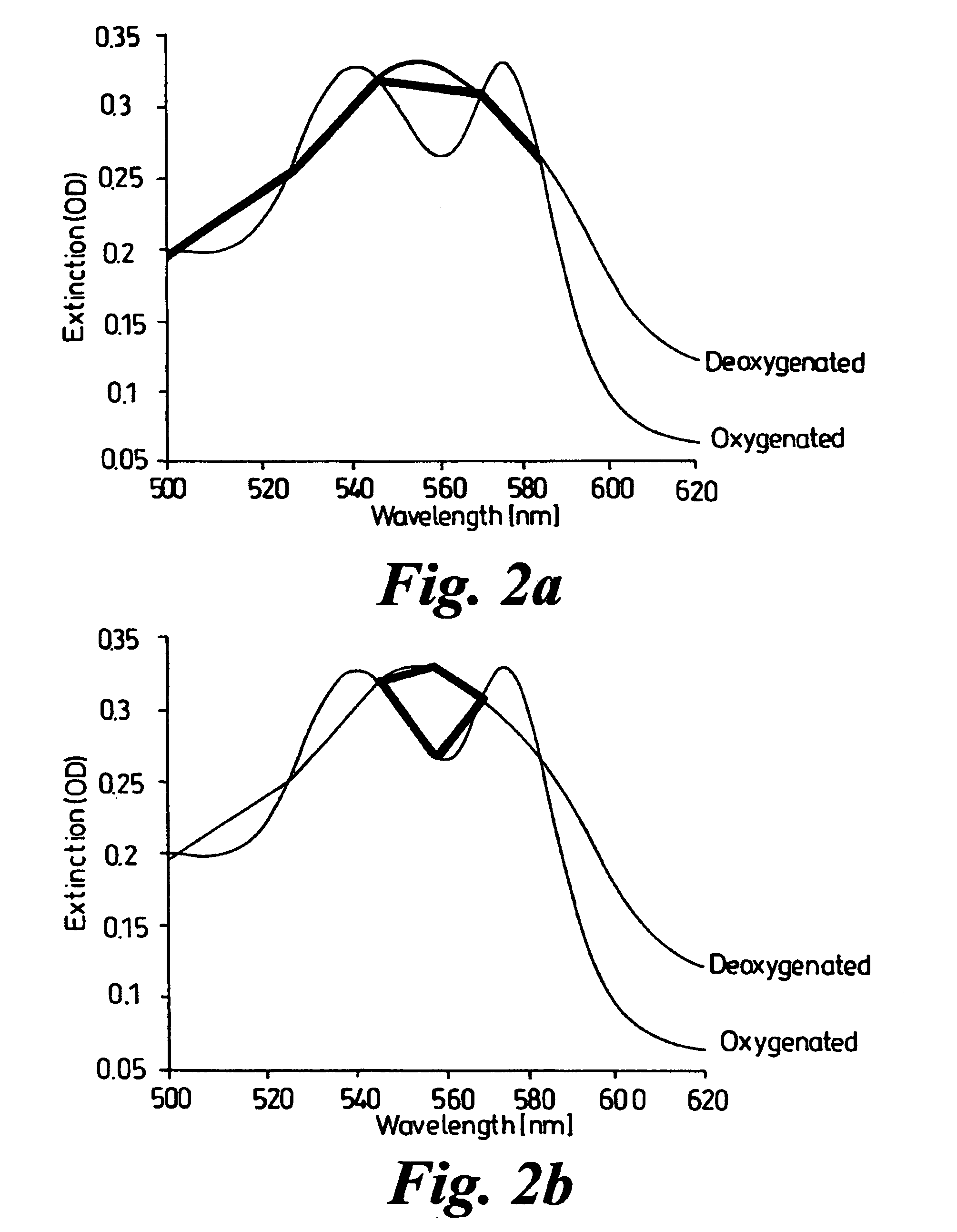
Optical device
InactiveUS7221970B2Accurate measurementReduce complexityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMedicineLength wave
Owner:WHITLAND RES
Accommodating Intraocular Lens System Having Spherical Aberration Compensation and Method
InactiveUS20080046074A1Speed up the conversion processEasy to adjustIntraocular lensIntraocular lensOptical power
An accommodating intraocular lens includes an optic portion, a haptic portion. The optic portion of the lens includes an actuator that deflects a lens element to alter the optical power of the lens responsive to forces applied to the haptic portion of the lens by contraction of the ciliary muscles and a secondary deflection mechanism. Movement of the lens element by the actuator causes the lens element to deform and the secondary deflection mechanism causes the lens to further deform.
Owner:POWERVISION
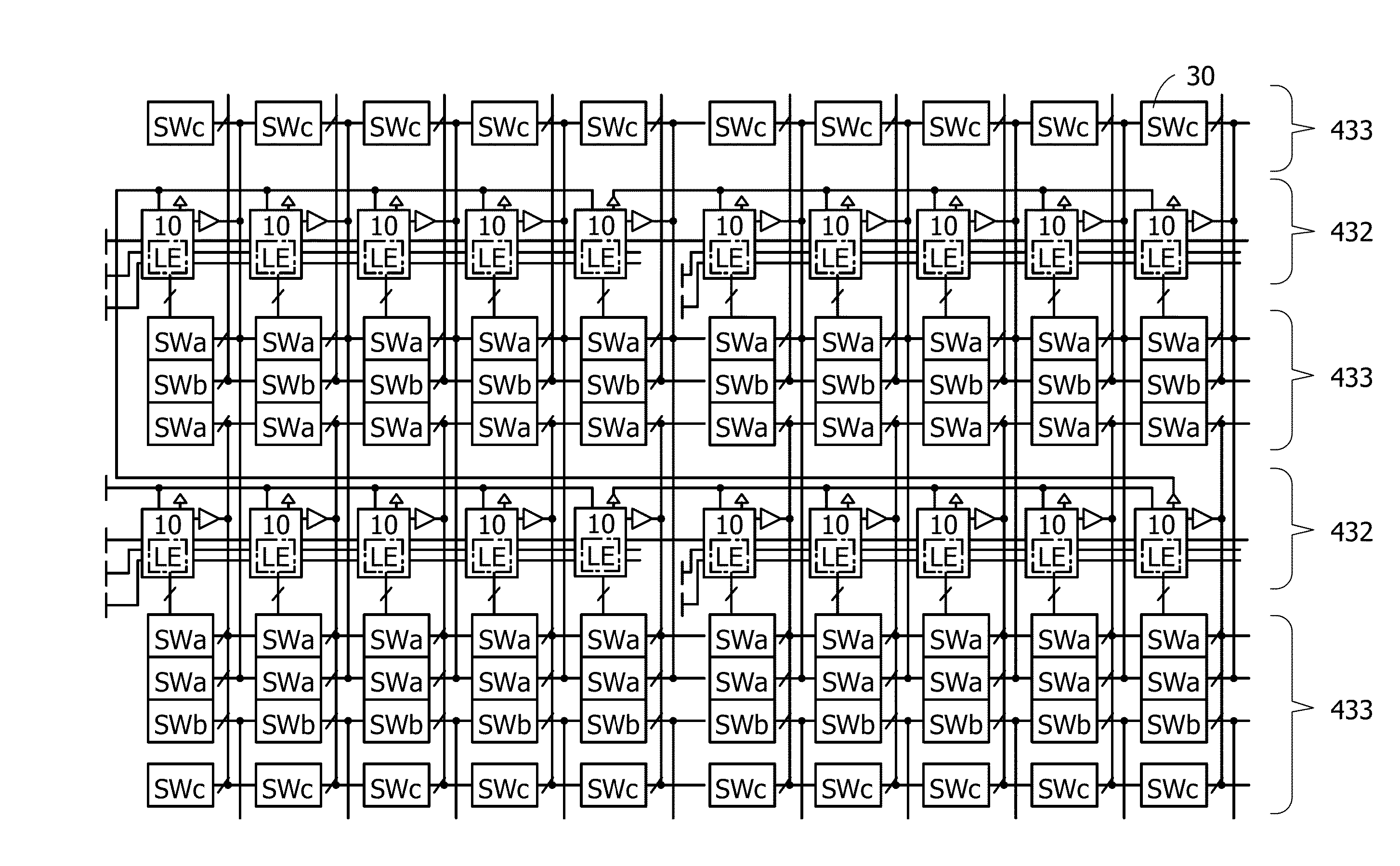
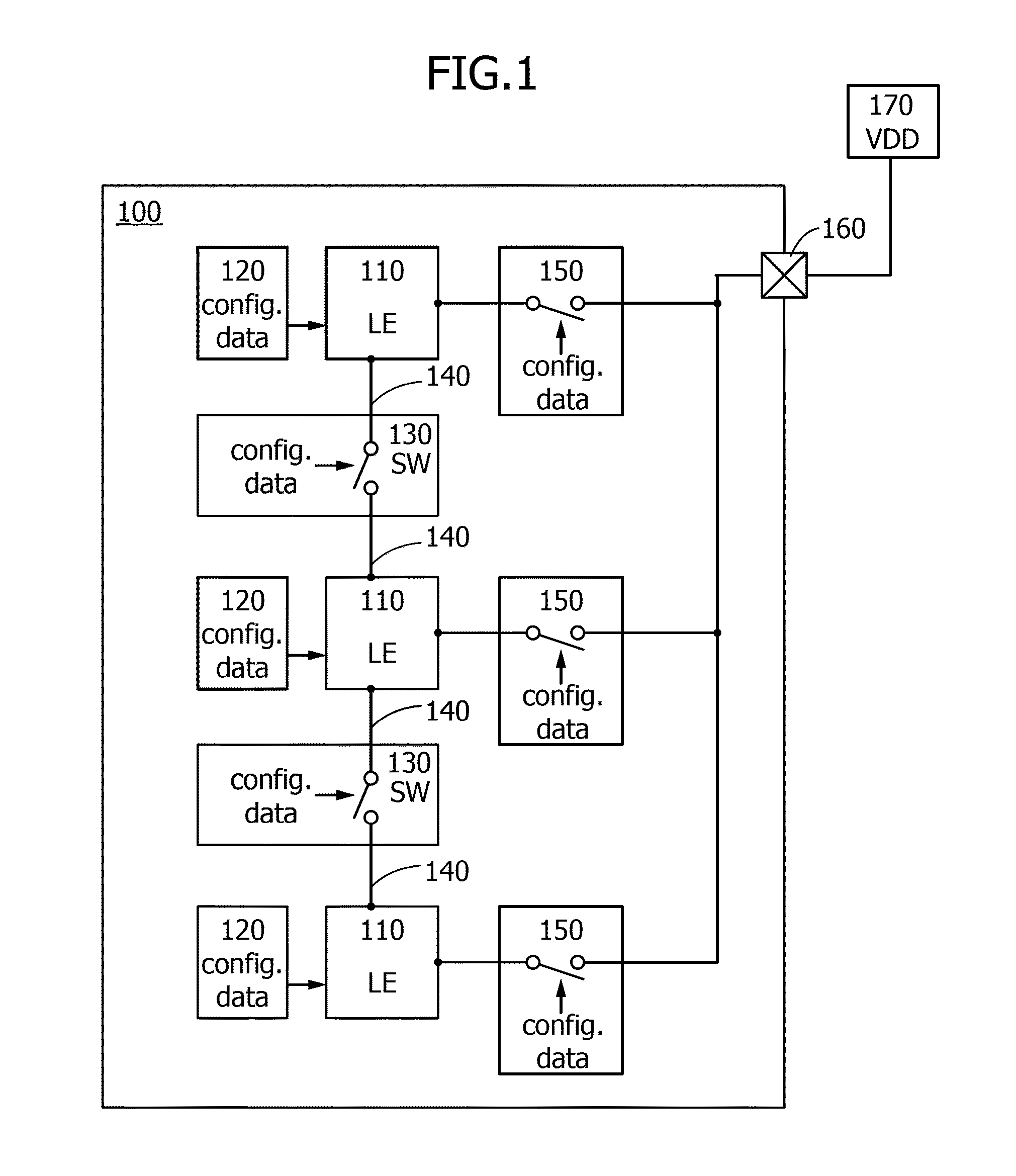
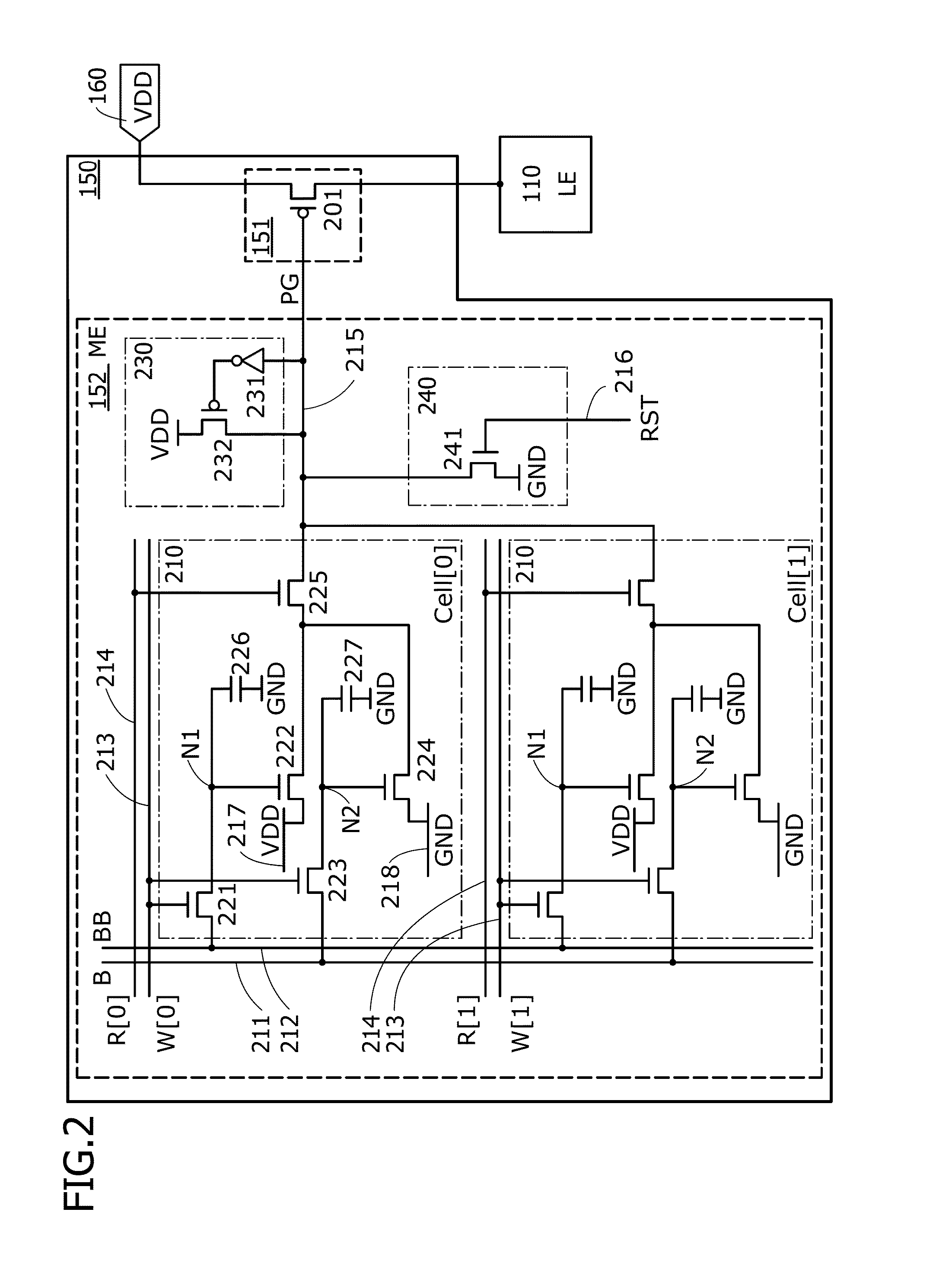
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20140159771A1Less influenceImprove reliabilityPower reduction by control/clock signalSolid-state devicesPower semiconductor deviceControl signal
A programmable logic device (PLD) that can control whether to supply power in each logic element is provided. The PLD includes at least a programmable logic element, a terminal to which a potential is input from an external power source, a switch controlling conduction between the terminal and the logic element, and a memory outputting a control signal for setting the conduction state of the switch. The memory stores pieces of configuration data for setting the conduction state of the switch. Any one of the pieces of configuration data is output as the control signal from the memory to the switch.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
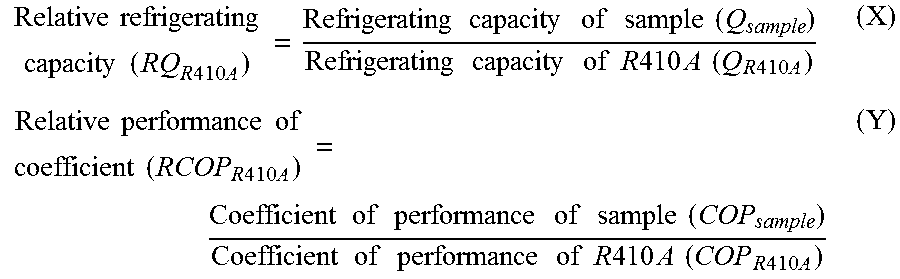
Working fluid for heat cycle, composition for heat cycle system, and heat cycle system
ActiveUS20160333243A1Stably used continuouslyCycle performance sufficientHeat-exchange elementsWorking fluidMetal working fluid
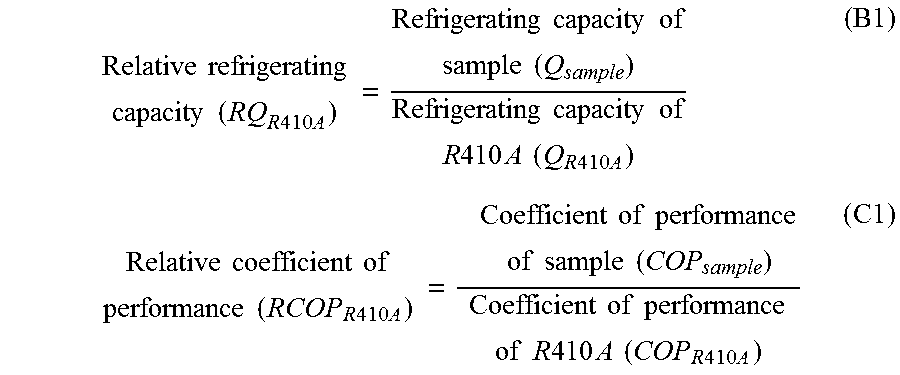
To provide a working fluid which has cycle performance sufficient as an alternative to R410A while the influence over global warming is sufficiently suppressed, which does not significantly increase the load to an apparatus as compared with a case where R410A is used, and which can be stably used continuously without any special measures, a composition for a heat cycle system comprising the working fluid, and a heat cycle system employing the composition.A working fluid for heat cycle, wherein the global warming potential is less than 300; the product of the relative coefficient of performance and the relative refrigerating capacity is at least 0.820 relative to R410A in a standard refrigerating cycle under conditions of an evaporation temperature of 0° C., a condensing temperature of 40° C., a supercoiling degree of 5° C. and a degree of superheat of 5° C.; the relative compressor discharge gas pressure is at most 1.100; the lower limit of the combustion range by method A in High Pressure Gas Safety Act is at least 5 vol %; and the pressure will not exceed 2.00 MPaG in a combustion test by method A in High Pressure Gas Safety act under 0.98 MPaG at 250° C.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
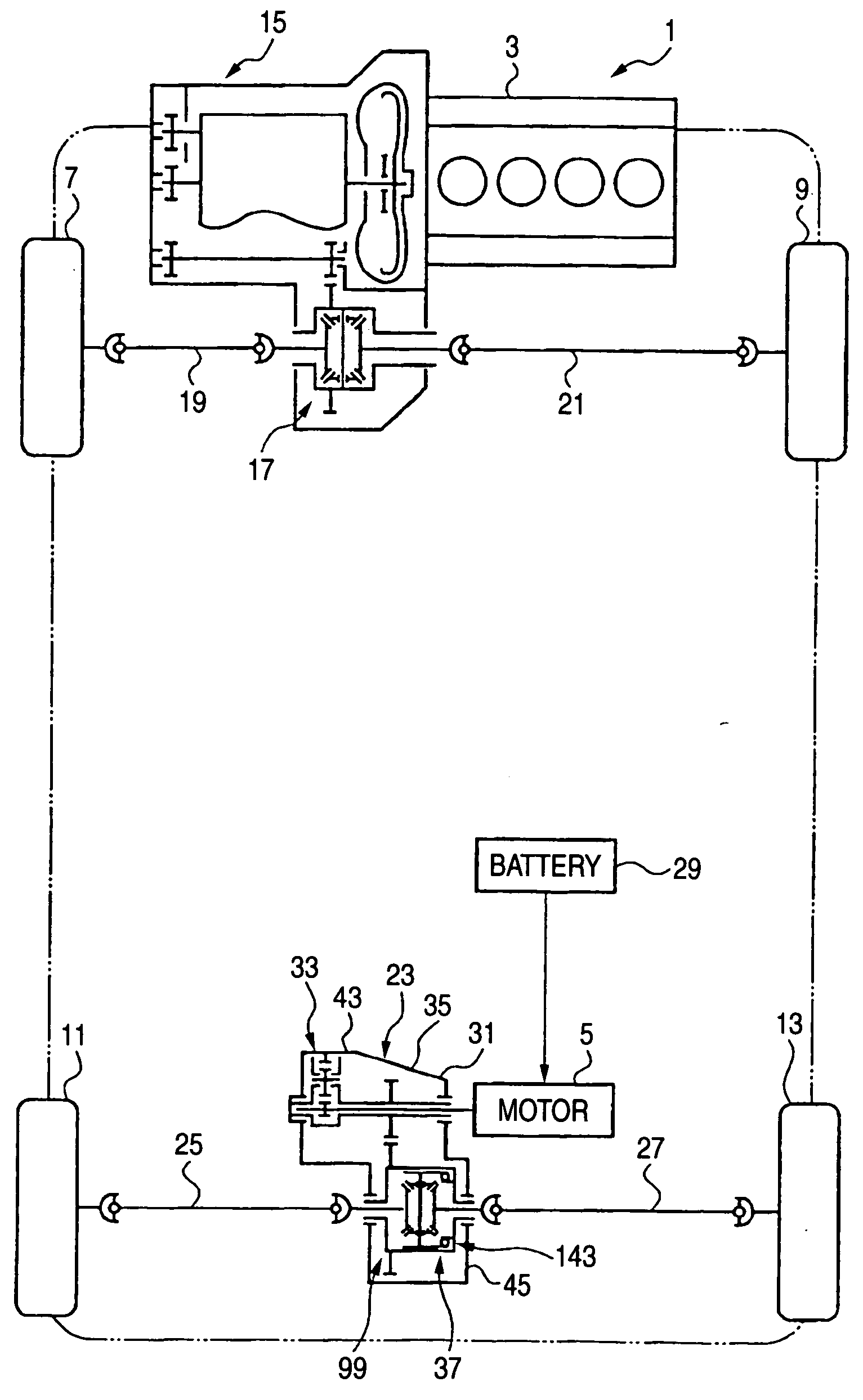
Reduction-drive device
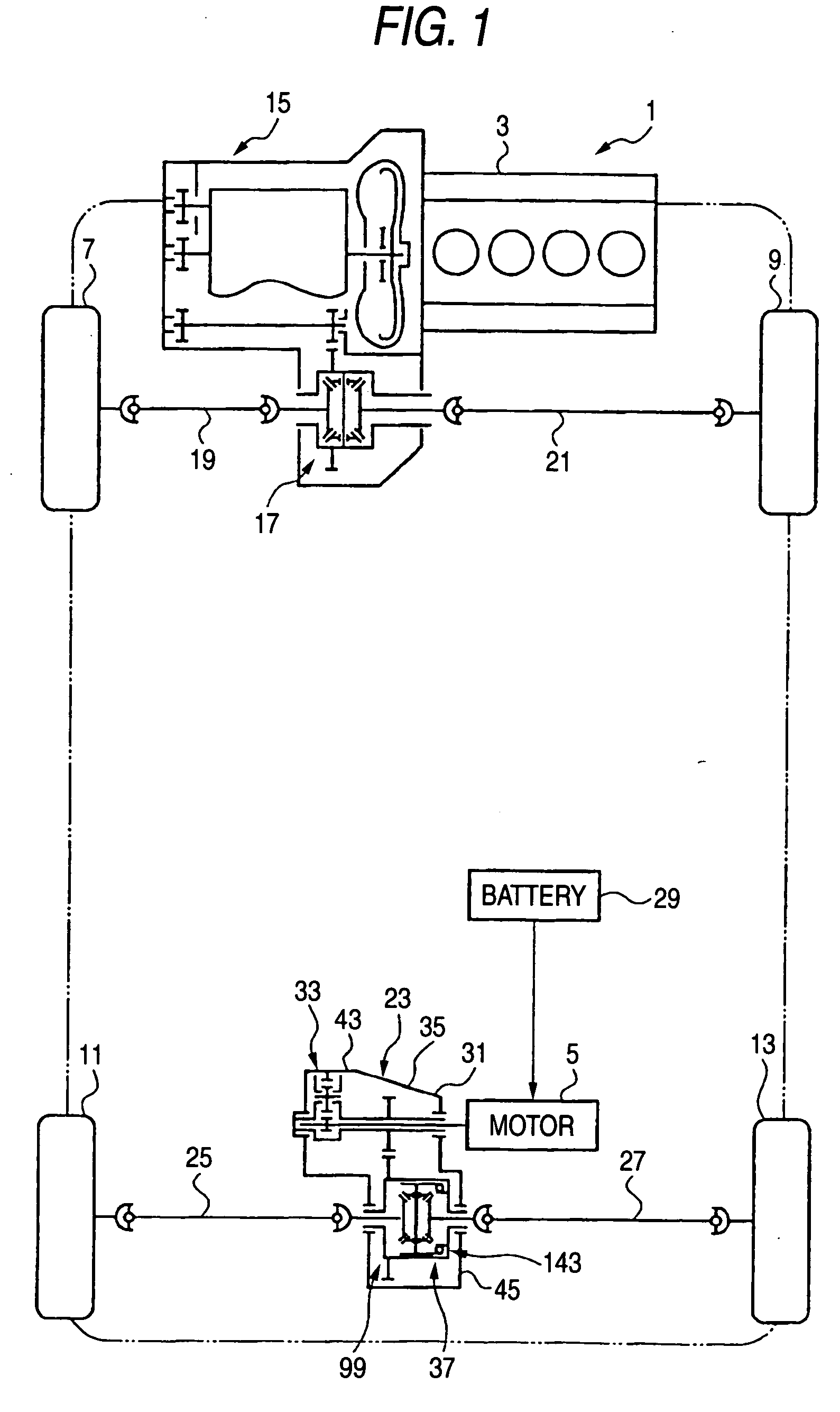
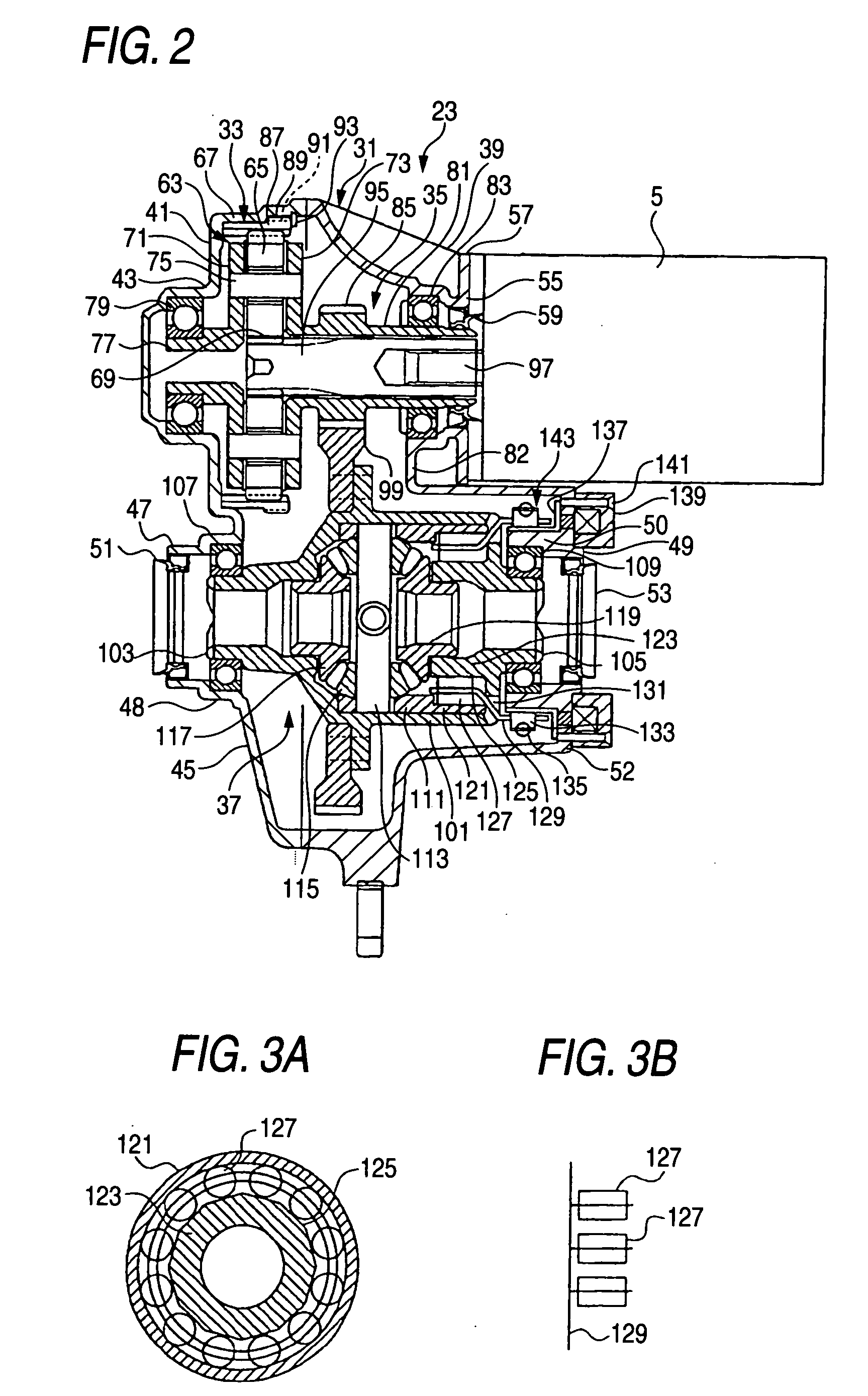
InactiveUS20050006164A1Improve sound oscillating performanceIncreased durabilityElectric propulsion mountingGas pressure propulsion mountingReduction driveEngineering
A reduction-drive device has a first and a second reduction mechanism and distribution device. The first reduction mechanism has a planetary carrier, a planetary gear rotatably supported by the planetary carrier, an internal gear in mesh with the planetary gear and a sun gear. The first reduction mechanism is supported by the housing so as to reduce driving force of the electric motor. The second reduction mechanism is positioned between the electric motor and the first reduction mechanism so as to reduce an output of the first reduction mechanism. The differential device is supported by the housing so as to distribute the output of the second reduction mechanism to a wheel side.
Owner:TOCHIGI FUJI IND CO LTD
Working fluid for heat cycle, composition for heat cycle system, and heat cycle system
InactiveUS20170058173A1Improve stabilityCycle performance sufficientCompressorCompression machines with non-reversible cycleWorking fluidMetal working fluid
To provide a working fluid for heat cycle containing 1,2-difluoroethylene, which has high stability, and which has cycle performance sufficient as an alternative to R410A (a pseudoazeotropic mixture refrigerant of difluoromethane and pentafluoroethane in a mass ratio of 1:1) or 1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane while the influence over global warming is suppressed, a composition for a heat cycle system comprising it, and a heat cycle system employing the composition.A working fluid for heat cycle, which contains at least two members selected from a saturated hydrofluorocarbon and a hydrofluorocarbon having a carbon-carbon double bond other than 1,2-difluoroethylene, and 1,2-difluoroethylene.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Antenna, and radio timepiece using the same, keyless entry system, and rf id system
ActiveUS20060214866A1High sensitivityLess influenceLoop antennas with ferromagnetic coreAntenna supports/mountingsElectrical and Electronics engineeringRadio-frequency identification
A magnetic sensor-type antenna comprising a magnetic core and a coil wound around the magnetic core for receiving electromagnetic waves, which is disposed in a housing such that the end portion of the magnetic core is bent away from the housing or a metal portion of the housing, and a timepiece, a keyless entry system and an RFID system each comprising such an antenna.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
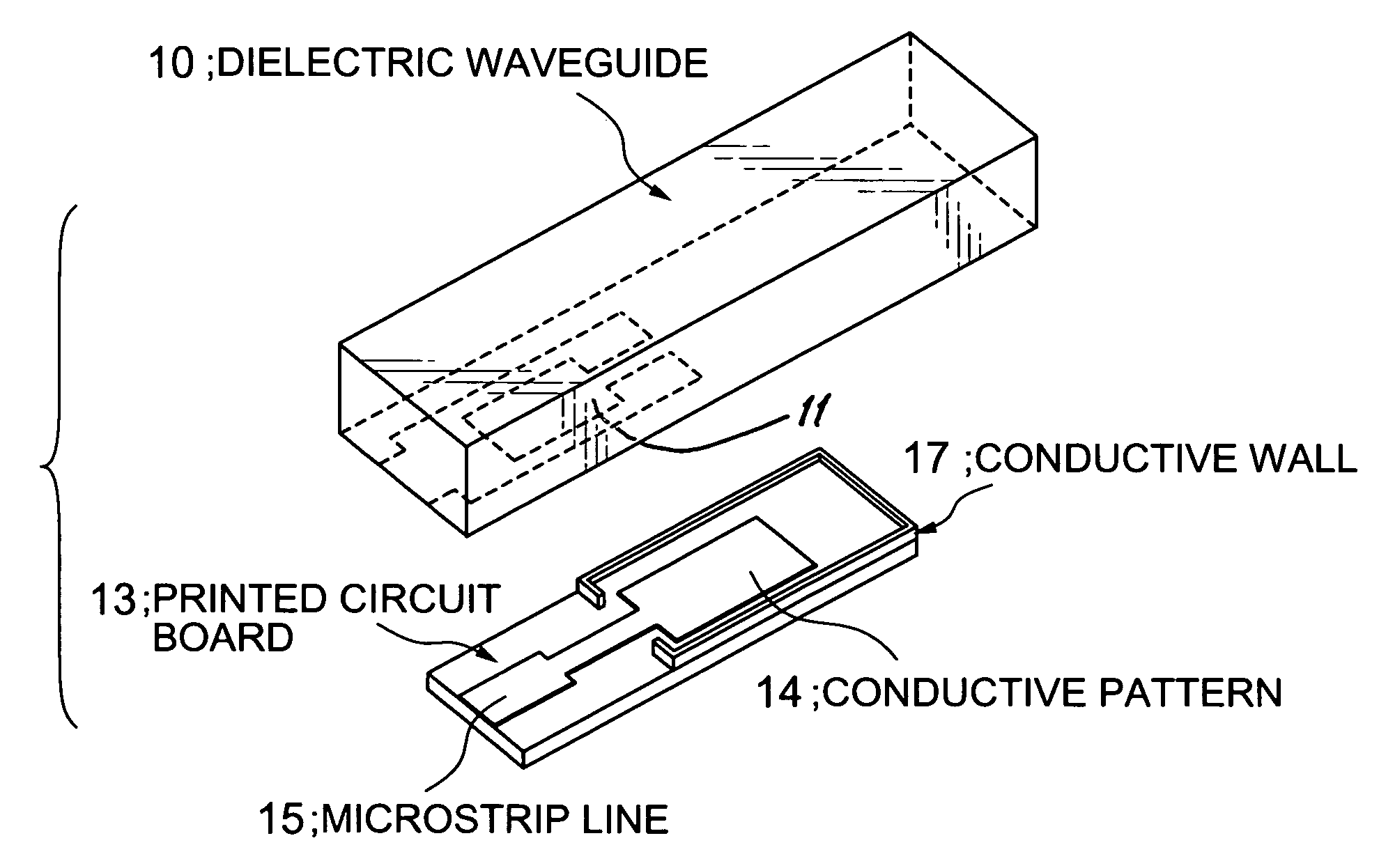
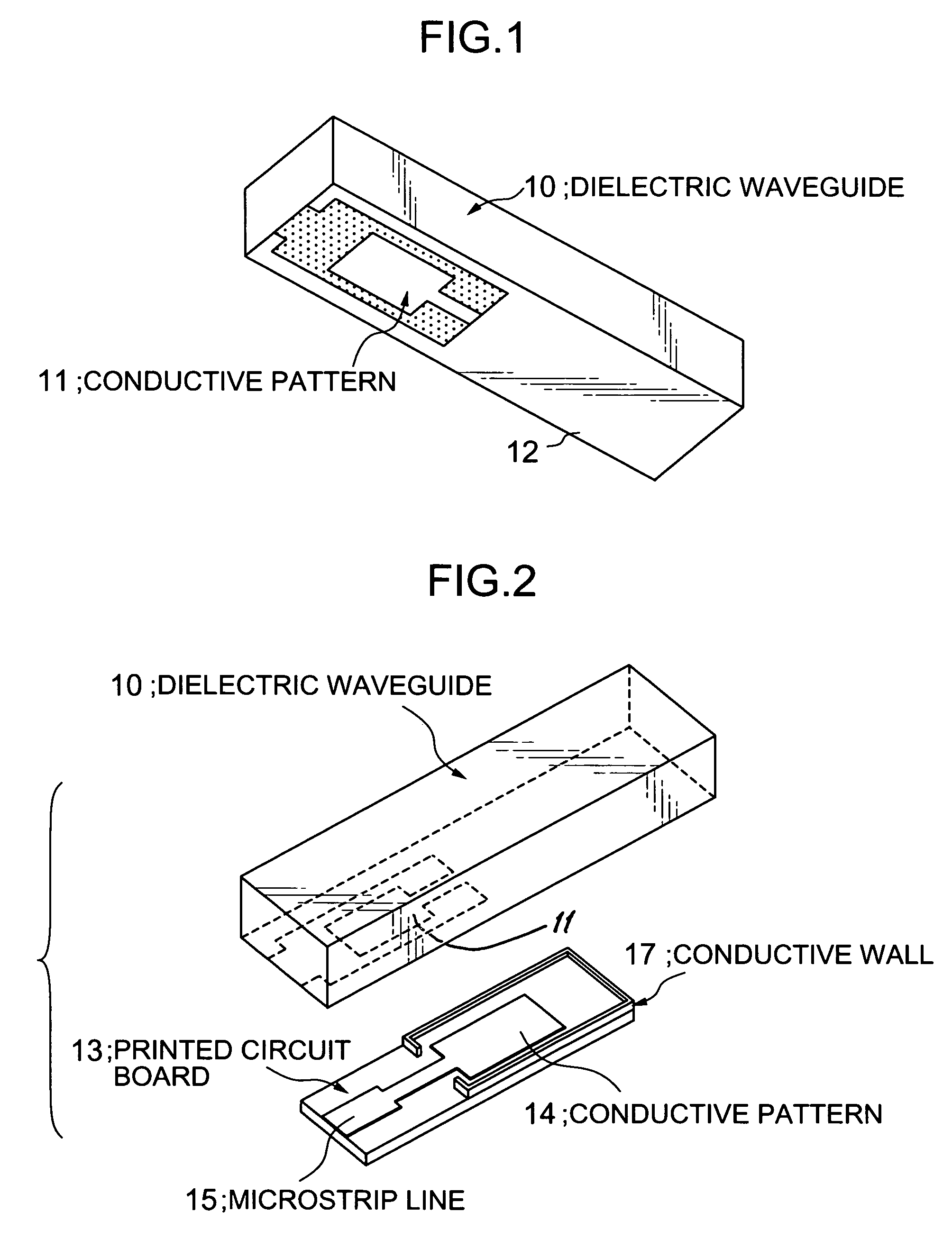
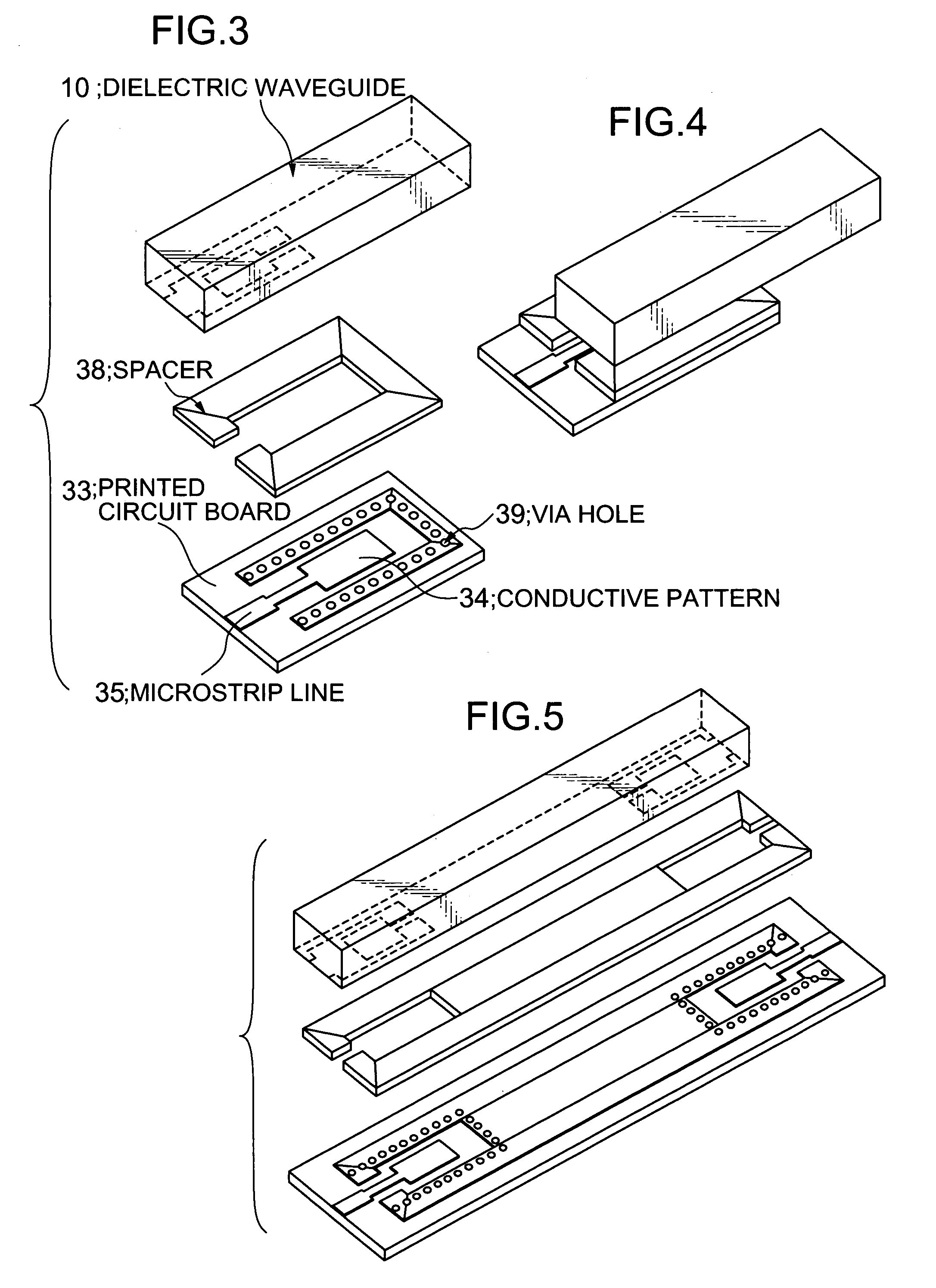
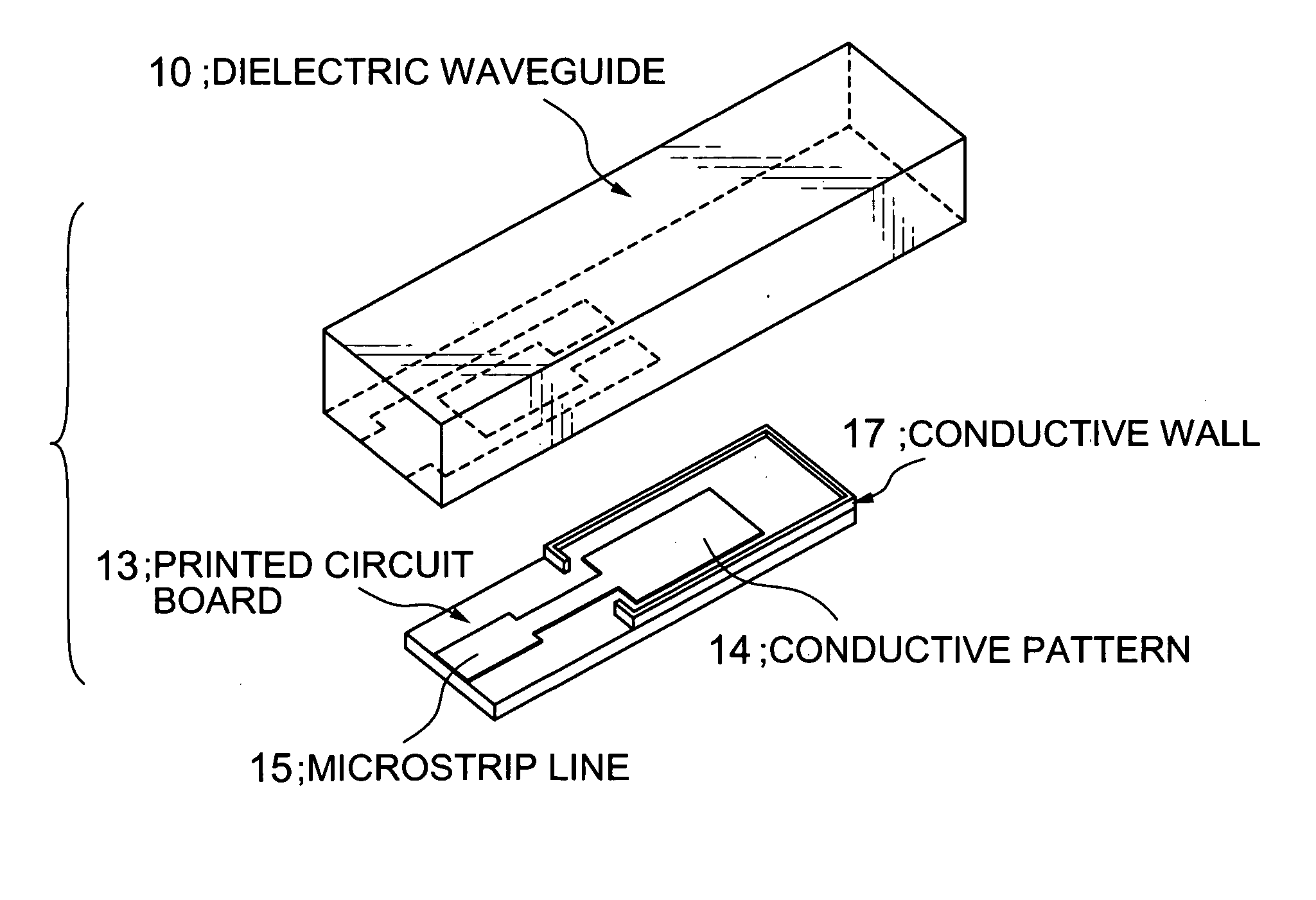
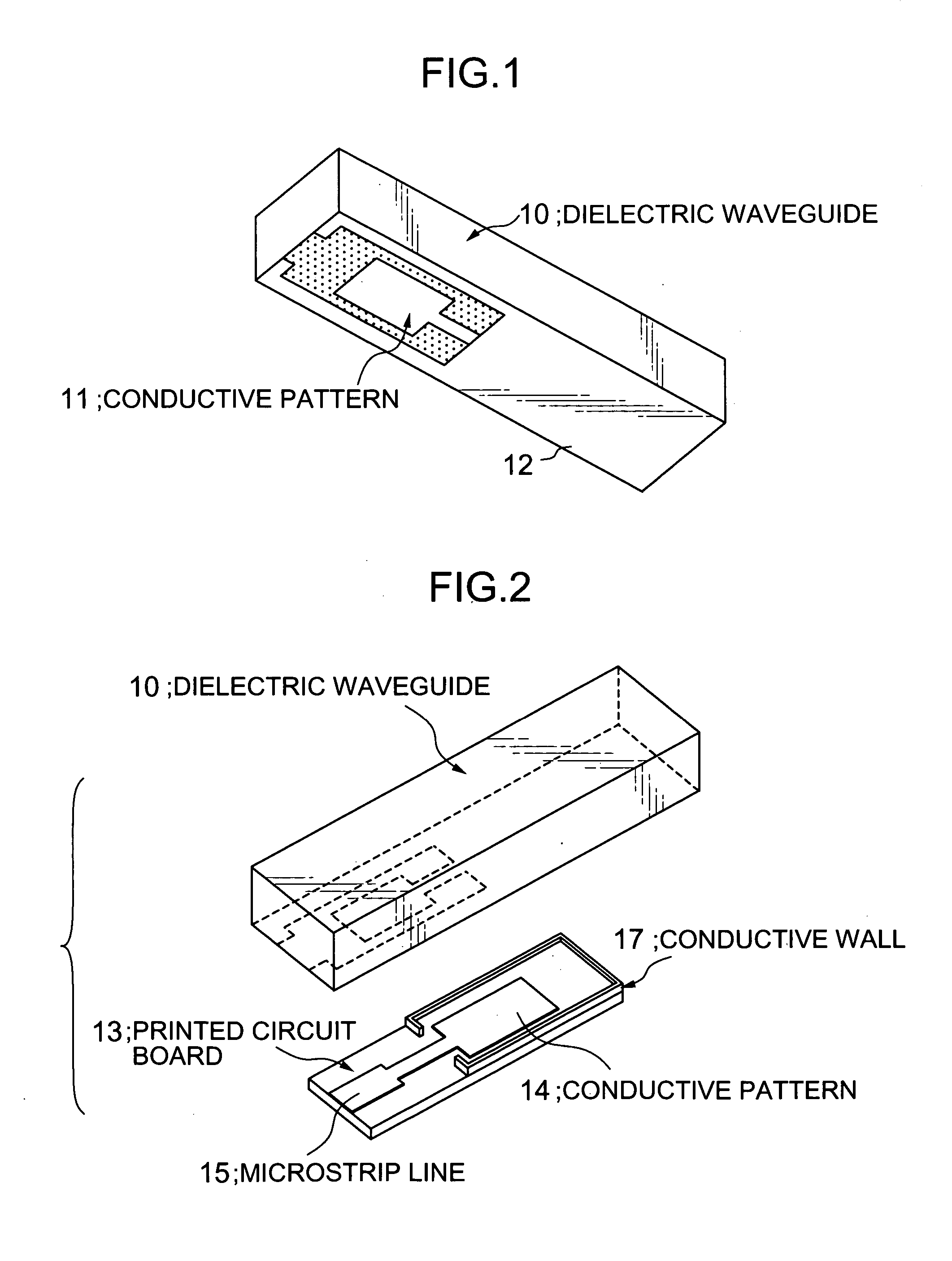
Input/output coupling structure for dielectric waveguide having conductive coupling patterns separated by a spacer
ActiveUS7132905B2Less influenceReduce leakage and less of electromagnetic energyOne-port networksResonatorsCouplingConductive materials
Disclosed is an input / output coupling structure for coupling a printed circuit board with a dielectric waveguide having a dielectric body and a conductive film covering the dielectric body. The coupling structure comprises a first conductive pattern formed on the bottom surface of the dielectric waveguide to serve as an input / output electrode, in such a manner as to be surrounded directly by an exposed portion of the dielectric body and further by the conductive film formed around the outer periphery of the exposed portion, a spacer having a surface made substantially entirely of a conductive material and a portion for defining a given space, and a second conductive pattern formed on a principal surface of the printed circuit board and electrically connected to the microstrip line. The bottom surface of the dielectric waveguide is joined to the principal surface of the printed circuit board through the spacer, to allow the first and second conductive patterns to be located in opposed relation to one another and define the space therebetween in cooperation with the spacer. The present invention can provide a simplified structure for mounting a dielectric waveguide on a printed circuit-wiring board to couple the dielectric waveguide with a microstrip line of the dielectric waveguide, and achieve a mode conversion mechanism operable in a wide frequency band and less subject to the influence of the possible displacement between the microstrip line and the dielectric waveguide.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Film-covered electric device having pressure release opening
ActiveUS20050158622A1Reduce sealEasy to set upClosuresFixed capacitor housing/encapsulationStress concentrationElectrical devices
A film-covered electric device has an electric device element and casing films. The casing films include a sealing area formed by thermally fusing the facing surfaces of the casing films together around the periphery of the electric device element, an electric device element receiving part encapsulating the electric device element inside the sealing area, and unfused portions formed in the shape of cove communicating with the electric device element receiving part. The casing films further include a stress concentrating portion touching the unfused portions for concentrating thereon the peeling stress of the casing films generated at the sealing area by the expansion of the electric device element receiving part, and a pressure releasing part is formed in the stress concentrating portion.
Owner:NEC CORP
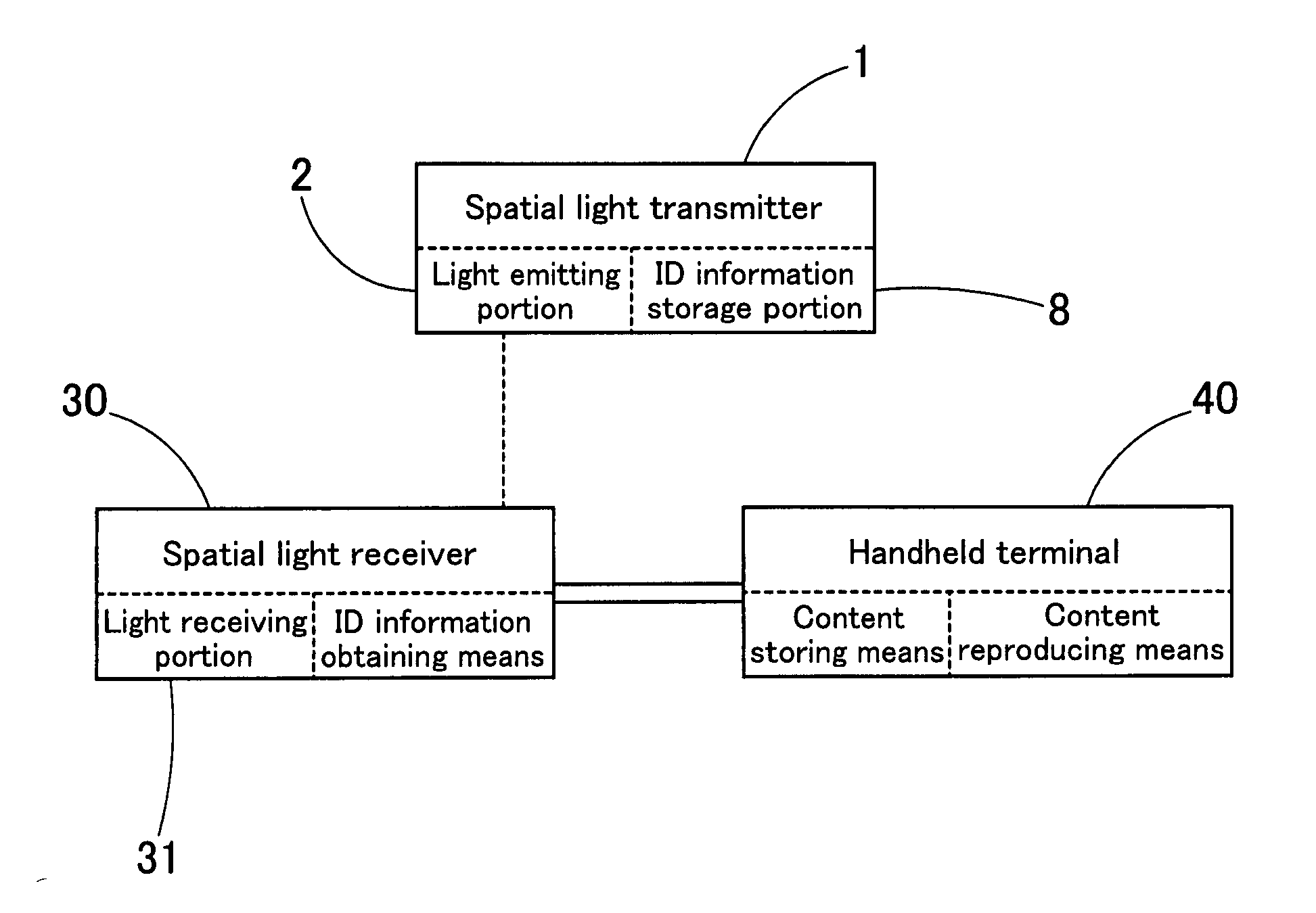
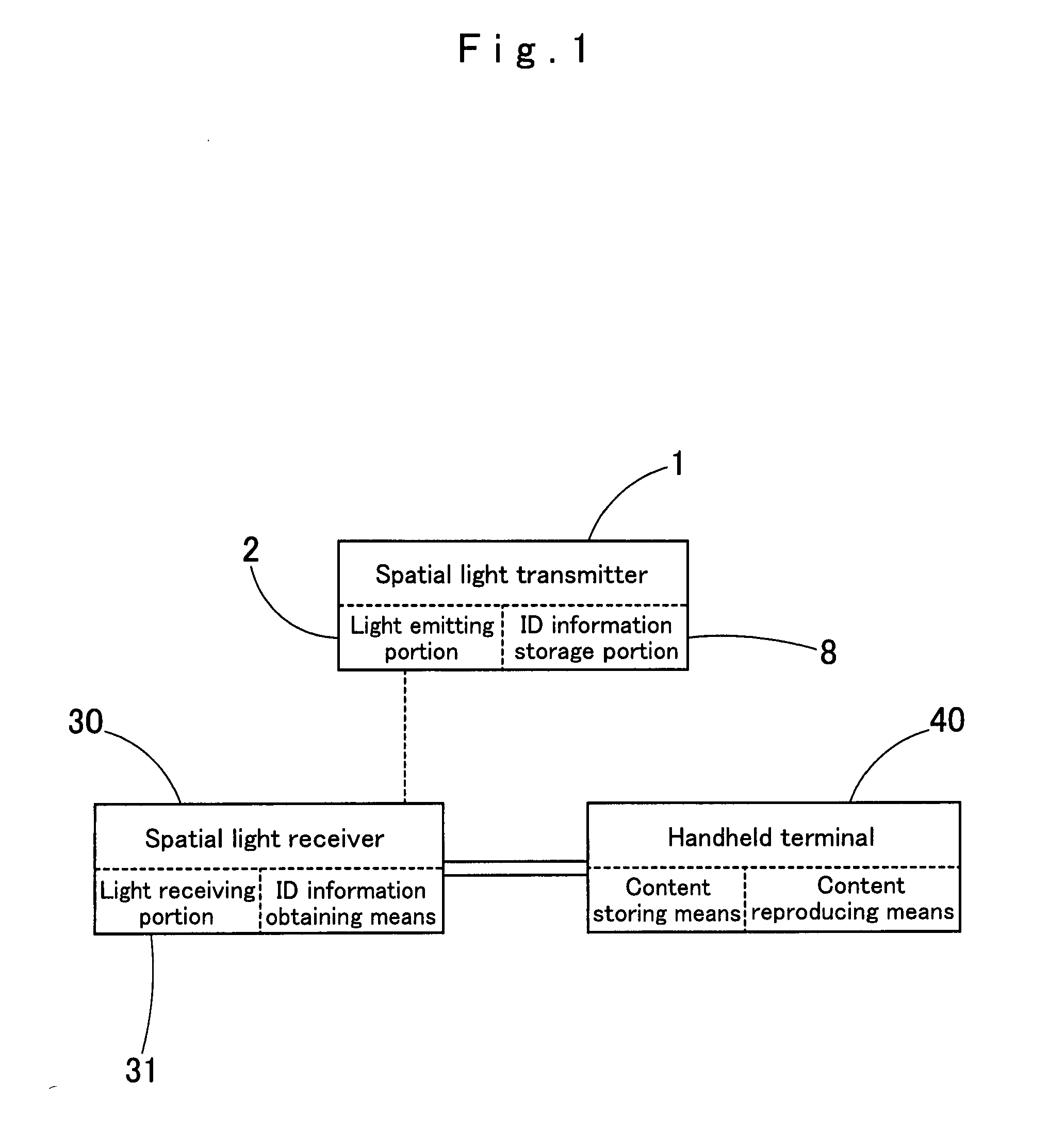
Content supplying system which uses spatial light transmission
InactiveUS20130343762A1Provide quicklySimple circuit configurationClose-range type systemsElectromagnetic transmittersLight transmissionTransmitter
A spatial light transmitter of a content supplying system stores ID information of its own and emits spatial light on which the ID information is superimposed from a light emitting portion. A spatial light receiver is used by being connected to a handheld terminal and receives spatial light emitted from the spatial light transmitter. When a user carries the handheld terminal and moves close to the spatial light transmitter, the spatial light receiver receives spatial light emitted from the spatial light transmitter, and ID information obtaining means of the spatial light receiver obtains the ID information which is superimposed on spatial light from a light receiving signal of the light receiving portion, thereby outputting the ID information to the handheld terminal. Alternatively, the ID information obtaining means of the handheld terminal obtains the ID information on the basis of the light receiving signal, and the handheld terminal reproduces the content selected on the basis of the ID information.
Owner:VLC
Accommodating intraocular lens system having spherical aberration compensation and method
InactiveUS20160262875A1Speed up the conversion processEasy to adjustIntraocular lensIntraocular lensOptical power
An accommodating intraocular lens includes an optic portion, a haptic portion. The optic portion of the lens includes an actuator that deflects a lens element to alter the optical power of the lens responsive to forces applied to the haptic portion of the lens by contraction of the ciliary muscles and a secondary deflection mechanism. Movement of the lens element by the actuator causes the lens element to deform and the secondary deflection mechanism causes the lens to further deform.
Owner:POWERVISION
Composition for heat cycle system and heat cycle system
InactiveUS20170058174A1Low global warming potentialImprove cycle performanceCompressorCompression machines with non-reversible cycleWorking fluidHeat resistance
To provide a composition for a heat cycle system, which comprises a working fluid for heat cycle which has a low global warming potential and high stability, and which can replace R410A, and a heat cycle system employing the composition.A composition for a heat cycle system, which comprises a working fluid for heat cycle containing 1,2-difluoroethylene, and a stabilizer for preventing deterioration of the working fluid for heat cycle, such as an oxidation resistance-improving agent, a heat resistance-improving agent or a metal deactivator, and a heat cycle system employing the composition for a heat cycle system.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Working medium and heat cycle system
ActiveUS20140077122A1Improve cycle performanceHigh proportion of halogenCompressorOrganic chemistryTransport systemOzone layer
To provide a working medium for heat cycle, of which combustibility is suppressed, which has less influence over the ozone layer, which has less influence over global warming and which provides a heat cycle system excellent in the cycle performance (efficiency and capacity), and a heat cycle system, of which the safety is secured, and which is excellent in the cycle performance (efficiency and capacity).A working medium for heat cycle comprising 1-chloro-2,3,3,3-tetrafluoropropene is employed for a heat cycle system (such as a Rankine cycle system, a heat pump cycle system, a refrigerating cycle system 10 or a heat transport system).
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
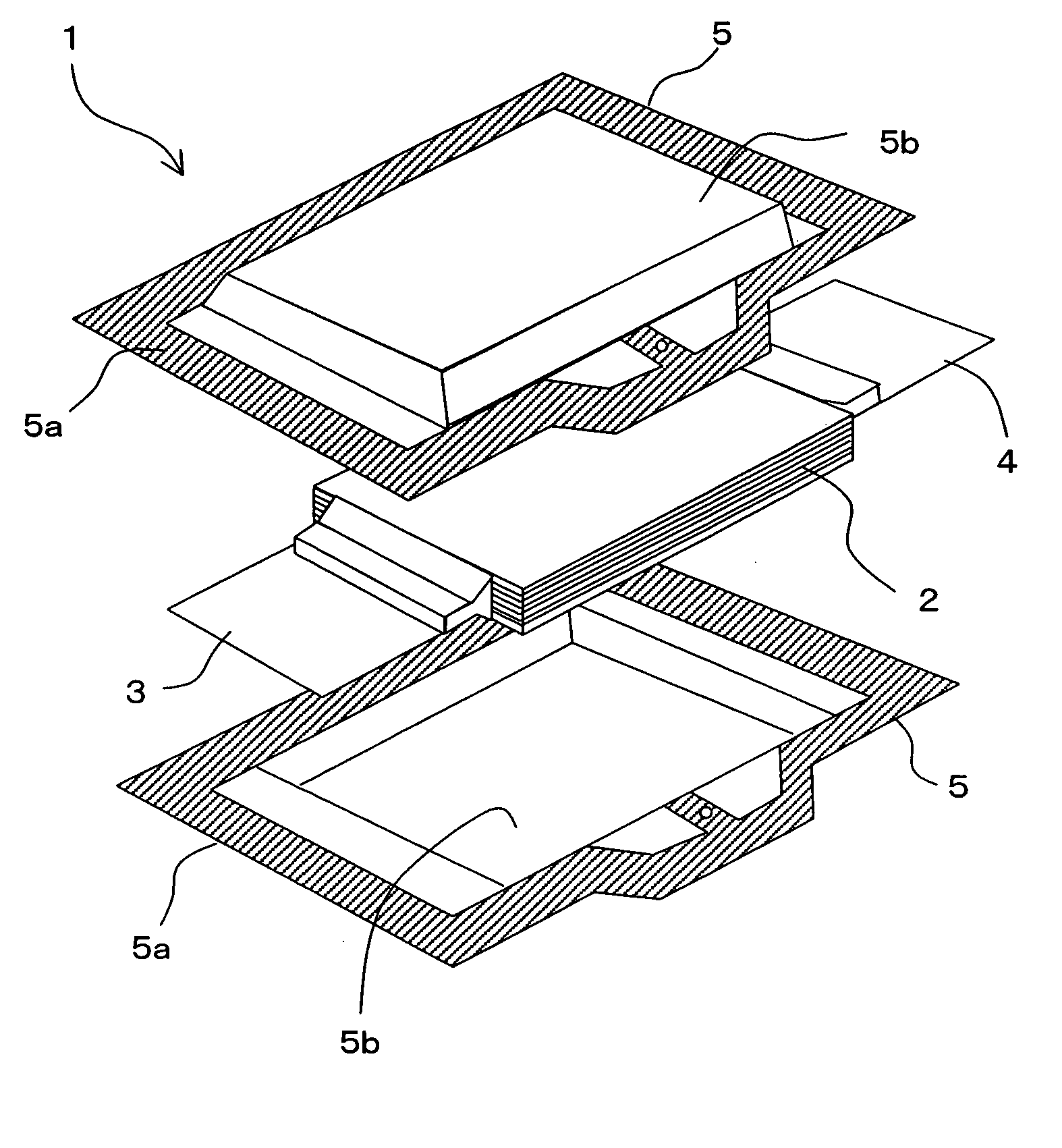
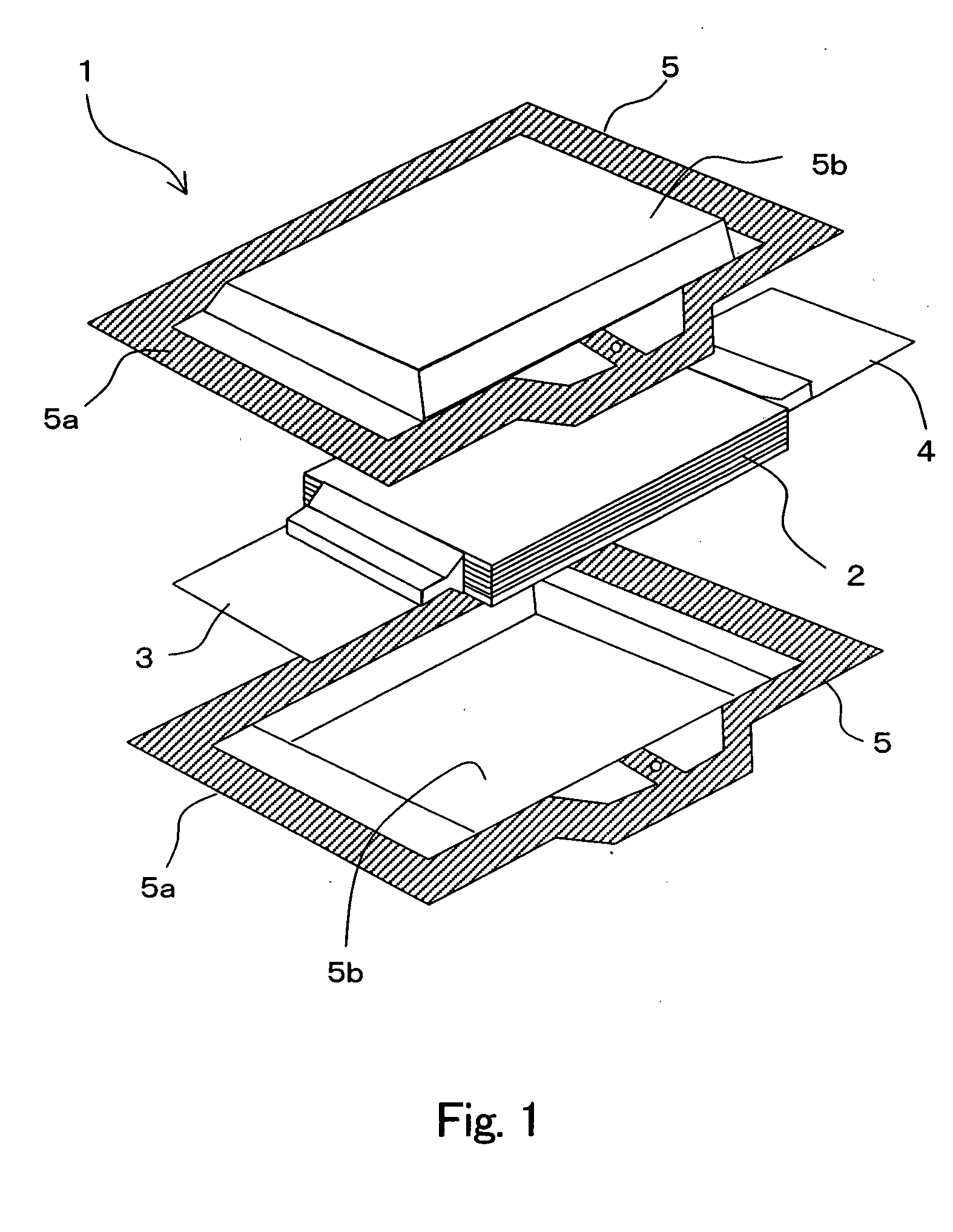
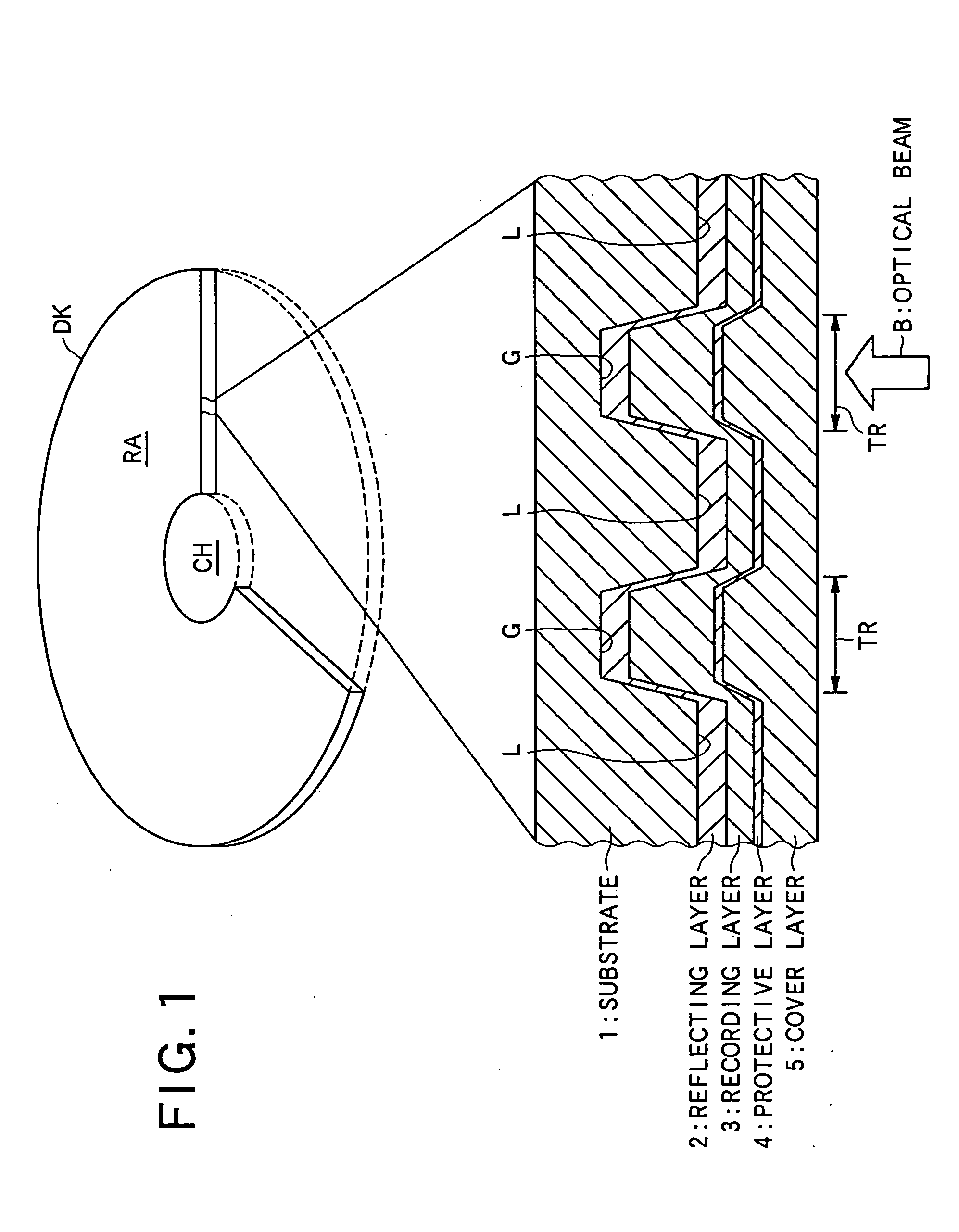
Information recording medium and information recorder
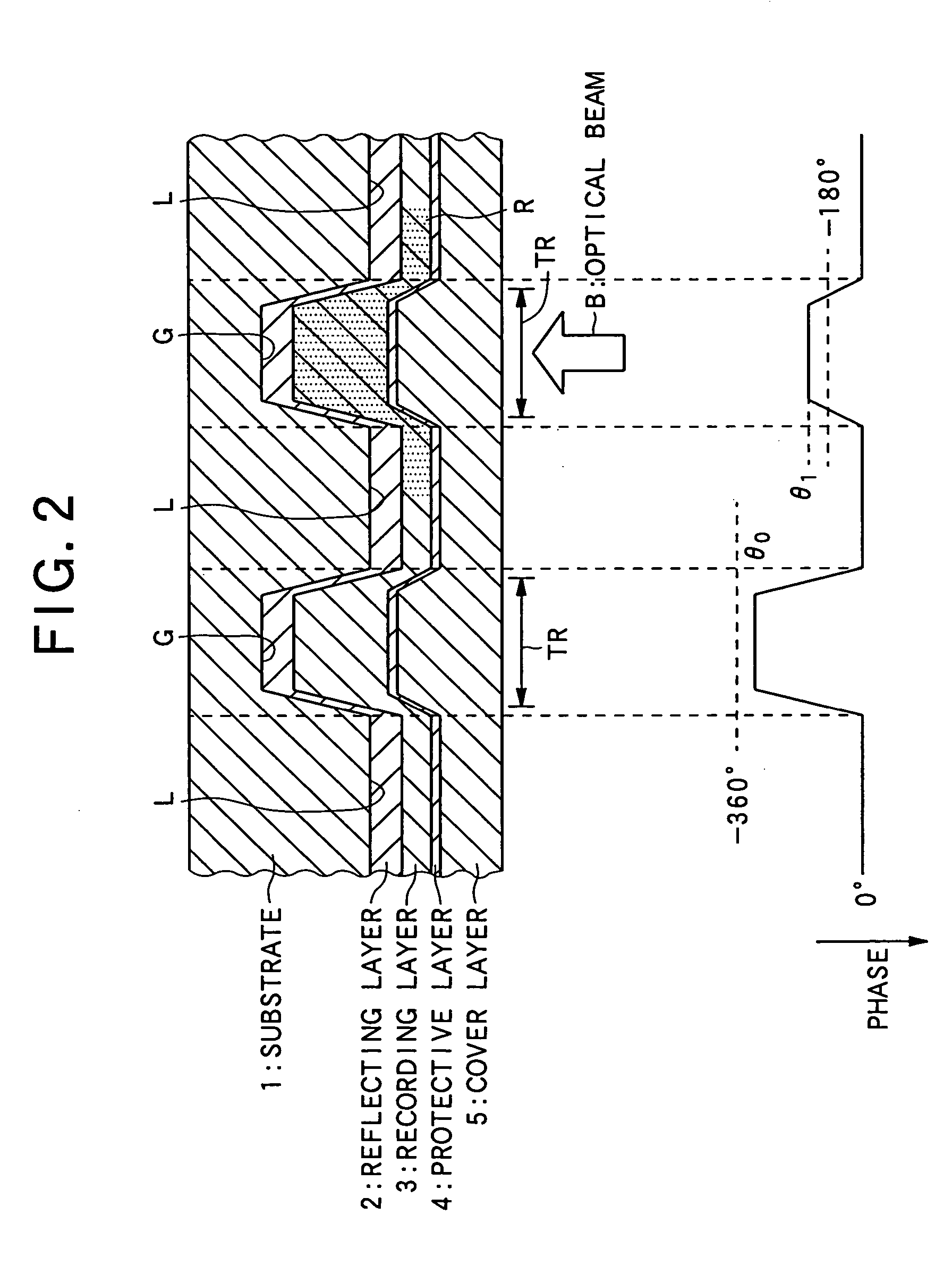
InactiveUS20050254795A1Less influenceImprove recording densityTelevision system detailsInformation arrangementRecording densityComputer science
An object of the invention is to provide an optical disc in which the influence of recording interference is reduced to make it possible to narrow the interval between adjacent recording tracks and increase the recording density of information. The optical disc comprises a substrate 1 on which the grooves G are formed, a reflecting layer 2 for reflecting an optical beam, a recording layer 3, and a cover layer 5 for protecting the recording layer 3, in which the cover layer 5, the recording layer 3, the reflecting layer 2 and the substrate 1 are disposed in this order from the side where the optical beam is applied, and the thickness of the recording layer 3 formed in an area opposed to the groove G and forming a recording track TR is greater than the thickness of the recording layer 3 formed in an area opposed to an area on the substrate 1 between two adjacent grooves G.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Object pose normalization method and apparatus and object recognition method
ActiveUS20080310720A1Less influenceLess complexImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionDistortion problem
An object pose normalization method and apparatus and an object recognition method are provided. The object pose normalization method includes: determining a pose of a non-frontal image of an object; performing smoothing transformation on the non-frontal image of the object, thereby generating a smoothed object image; and synthesizing a frontal image of the object by using the pose determination result and the smoothed object image. According to the method and apparatus, a front object image can be synthesized by using a non-frontal object image without causing an image distortion problem due to self-occlusion and non-rigid deformation.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Noncontact power feed system, noncontact relay apparatus, noncontact power reception apparatus, and noncontact power feed method
ActiveUS20110018359A1Less influenceIncrease flexibilityRail devicesElectromagnetic wave systemEngineeringCurrent source
A noncontact power feed system includes: a noncontact power feed apparatus including a power feed resonance device to supply alternate-current power to an electronic apparatus by resonance in a noncontact manner, and an alternate-current power source section to generate the alternate-current power and supply it to the power feed resonance device; a noncontact relay apparatus including a relay resonance device to receive the alternate-current power and relay it to another electronic apparatus by resonance in a noncontact manner, a relay-side rectifier circuit to form direct-current power for output, and a movement means for moving the noncontact relay apparatus by the direct-current power; and at least one noncontact power reception apparatus including a power reception resonance device to receive the alternate-current power by magnetic field resonance in a noncontact manner, a power-reception-side rectifier circuit to form direct-current power for output, and a load means driven by the direct-current power.
Owner:SONY CORP
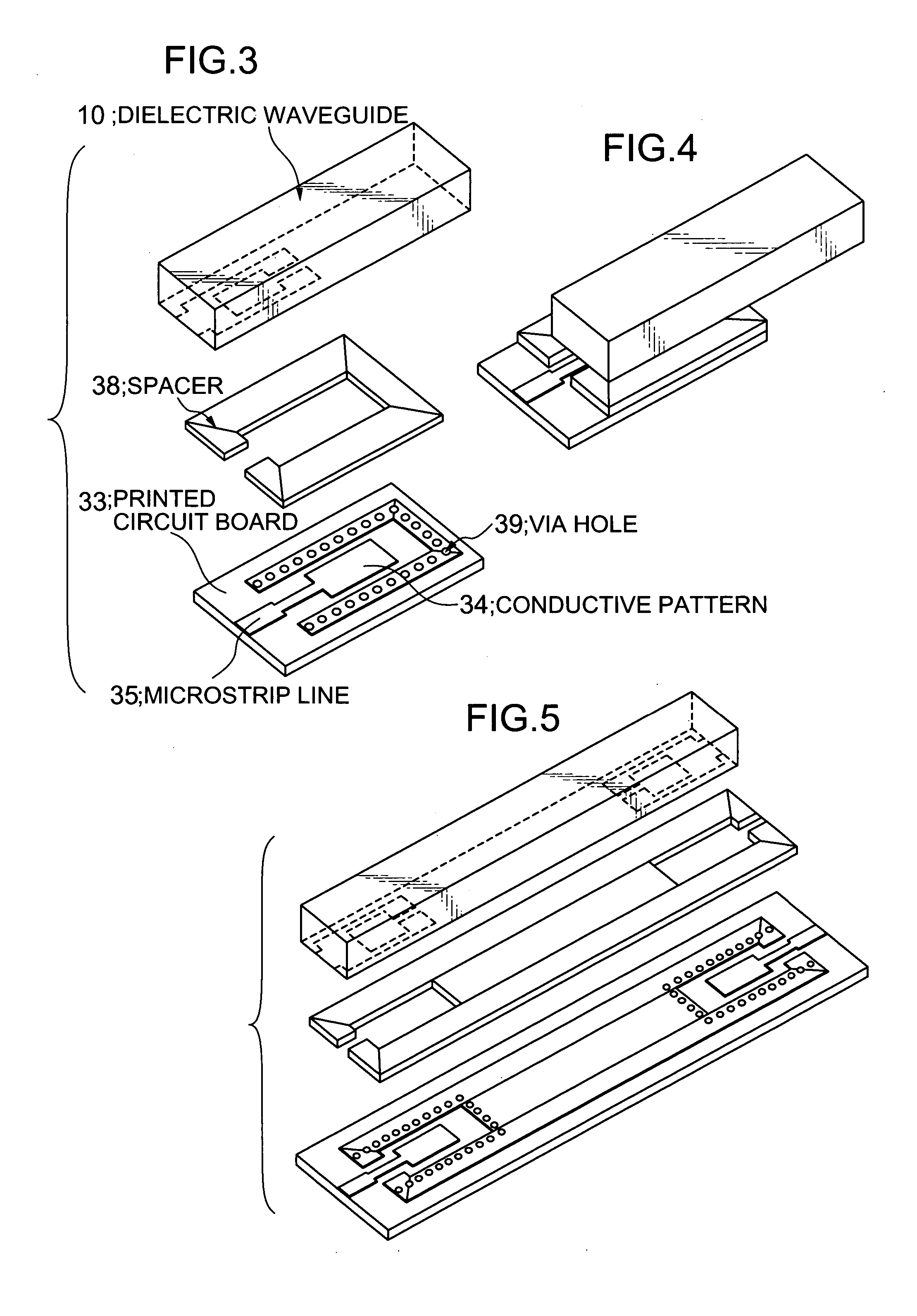
Input/output coupling structure for dielectric waveguide
ActiveUS20050099242A1Reduce leakageReduce lessOne-port networksResonatorsCouplingConductive materials
Disclosed is an input / output coupling structure for coupling a printed circuit board with a dielectric waveguide having a dielectric body and a conductive film covering the dielectric body. The coupling structure comprises a first conductive pattern formed on the bottom surface of the dielectric waveguide to serve as an input / output electrode, in such a manner as to be surrounded directly by an exposed portion of the dielectric body and further by the conductive film formed around the outer periphery of the exposed portion, a spacer having a surface made substantially entirely of a conductive material and a portion for defining a given space, and a second conductive pattern formed on a principal surface of the printed circuit board and electrically connected to the microstrip line. The bottom surface of the dielectric waveguide is joined to the principal surface of the printed circuit board through the spacer, to allow the first and second conductive patterns to be located in opposed relation to one another and define the space therebetween in cooperation with the spacer. The present invention can provide a simplified structure for mounting a dielectric waveguide on a printed circuit-wiring board to couple the dielectric waveguide with a microstrip line of the dielectric waveguide, and achieve a mode conversion mechanism operable in a wide frequency band and less subject to the influence of the possible displacement between the microstrip line and the dielectric waveguide.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
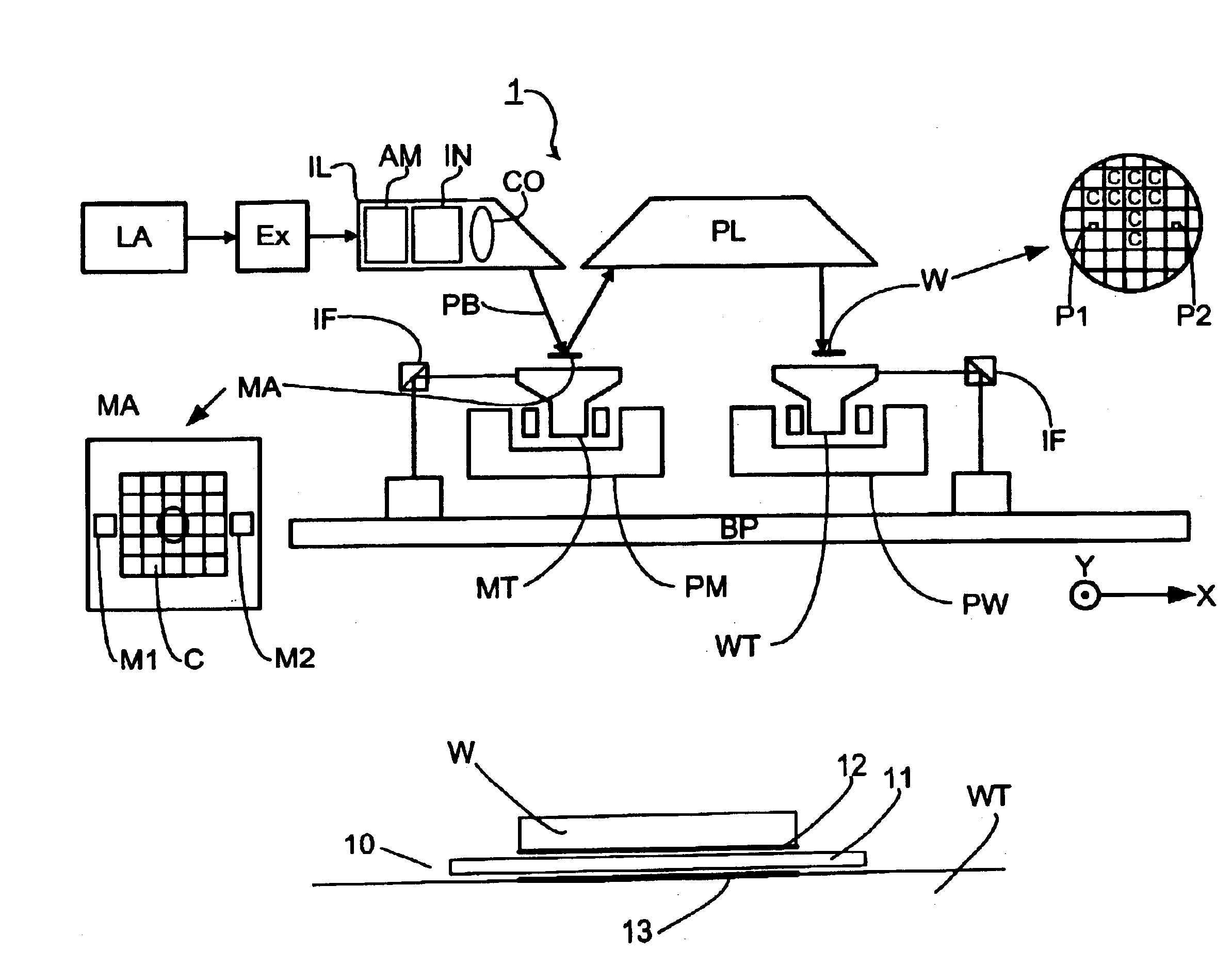
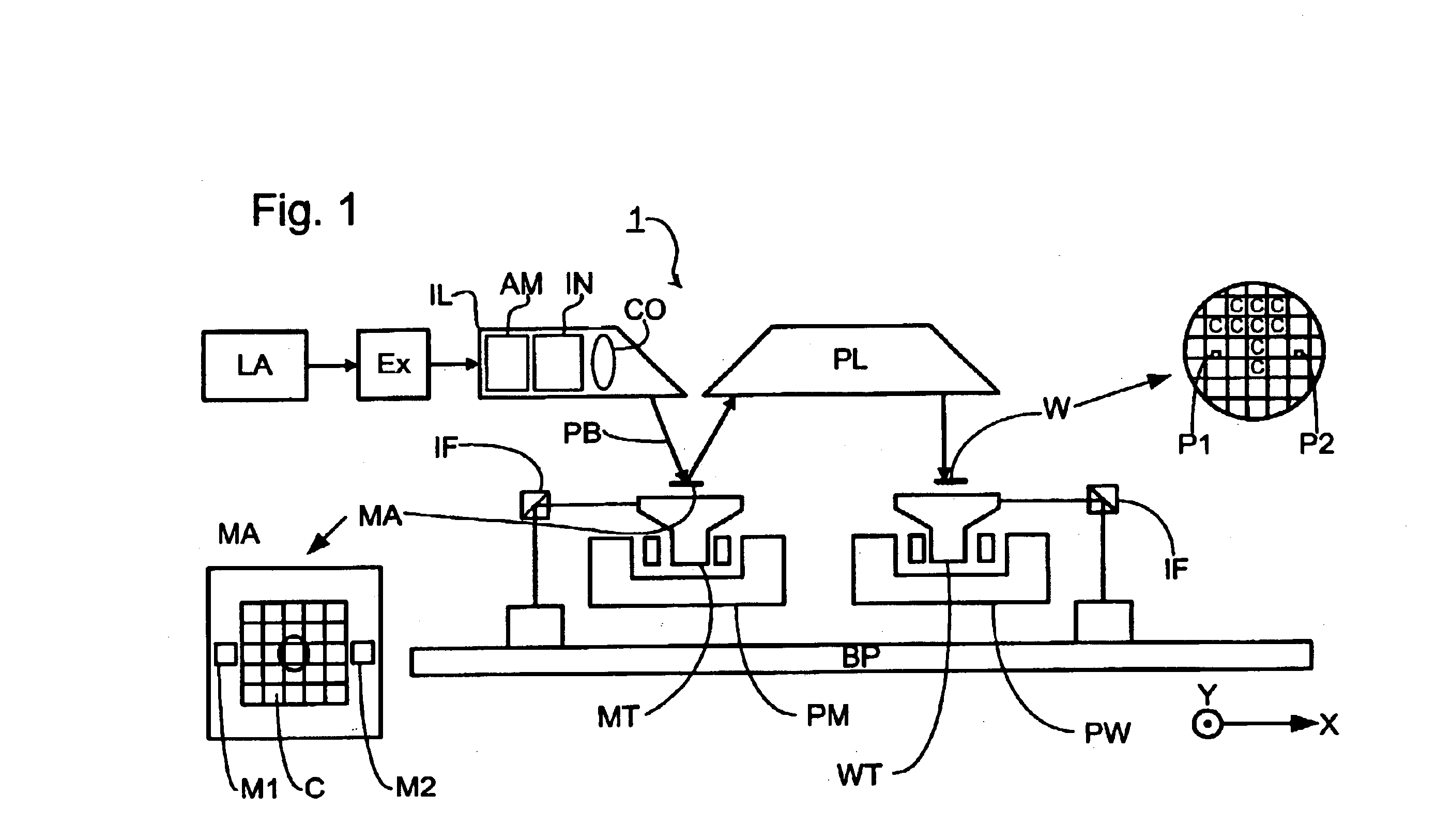
Chuck, lithographic projection apparatus, method of manufacturing a chuck and device manufacturing method
InactiveUS6864957B2Easy to disassembleReduction factorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusDielectricPotential difference
A lithographic projection apparatus with a chuck in which a dielectric element of the electrostatic chuck has a specific resistivity of at least 1016 Ωcm so that once the potential difference between electrodes of the chuck is removed the force on the article to be clamped reduces below a predetermined minimum level quickly. The dielectric element also has a coefficient of thermal expansion of less than 0.02×10−6K−1. A method of manufacturing a chuck includes joining a first glass ceramic element with a second glass element with an electrode therebetween in which a current is passed through the second glass element.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Multilayer insulated wire and transformers made by using the same
InactiveUS6329055B1Good effectLowered in electric propertyPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsPolymer sciencePolyetherimide
There is disclosed a multilayer insulated wire which comprises a conductor and solderable extrusion-insulating layers made up of two or more layers for covering the conductor, wherein at least one insulating layer is formed by a mixture comprising 100 parts by weight of a resin (A), of at least one selected from the group consisting of polyetherimide resins and polyethersulfone resins, 10 parts by weight or more of a resin (B), of at least one selected from the group consisting of polycarbonate resins, polyarylate resins, polyester resins, and polyamide resin, and 15 to 200 parts by weight of an inorganic filler (C). There is also disclosed a transformer which utilizes the multilayer insulted wire. The multilayer insulated wire is excellent in heat resistance, solderability, high-frequency characteristic, and coilability, and it is favorably suitable for industrial production. Further, the transformer utilizing the multilayer insulated wire is excellent in electrical properties and high in reliability, since when used at high frequencies, electric properties are not lowered and influence by the generation of heat can be prevented.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Organosilicon compounds
ActiveUS20040266968A1Less influencePrevulcanization behaviour is also improvedSilicon organic compoundsOrganic chemistry methodsAlcoholSilanes
Organosilicon compounds of the general formula I are produced by catalytically reacting silanes of the general formula II with alcohols of the general formula R'-OH, with the elimination of R<IV>OH, wherein the molar ratio of R-OH to R<IV>OH- groups is at least 1 and R<IV>OH is removed continuously or discontinuously from the reaction mixture. The organosilicon compounds may be used as coupling agents in filler-reinforced rubber mixtures.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
Anode and battery
ActiveUS20050191547A1Improving impedanceVariation in characteristicElectrode thermal treatmentFinal product manufactureLithium carbonateVapor phase
Provided are an anode capable of preventing an increase in impedance and variations in characteristics and a battery using the anode. An anode active material layer includes at least one kind selected from the group consisting of simple substances, alloys and compounds of silicon and the like capable of forming an alloy with Li. The anode active material layer is formed by a vapor-phase deposition method or the like, and is alloyed with an anode current collector. A coating including lithium carbonate is formed on at least a part of a surface of the anode current collector. Thereby, an increase in impedance can be prevented. Moreover, the anode is less subject to an influence by a difference in a handling environment or storage conditions, so variations in impedance can be prevented.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Semiconductor device and display device utilizing the same
InactiveUS7345657B2Small currentSmall valueStatic indicating devicesDigital storageElectrical resistance and conductanceCapacitance
A source-drain voltage of one of two transistors connected in series becomes quite small in a set operation (write signal), thus the set operation is performed to the other transistor. In an output operation, two transistors operate as a multi-gate transistor, therefore, a current value can be small in the output operation. In other words, a current can be large in the set operation. Therefore, the set operation can be performed rapidly without being easily influenced by an intersection capacitance and a wiring resistance which are parasitic on a wiring and the like. Further, an influence of variations between adjacent ones can be small as one same transistor is used in the set operation and the output operation.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method and device for determining the pressure in brake systems
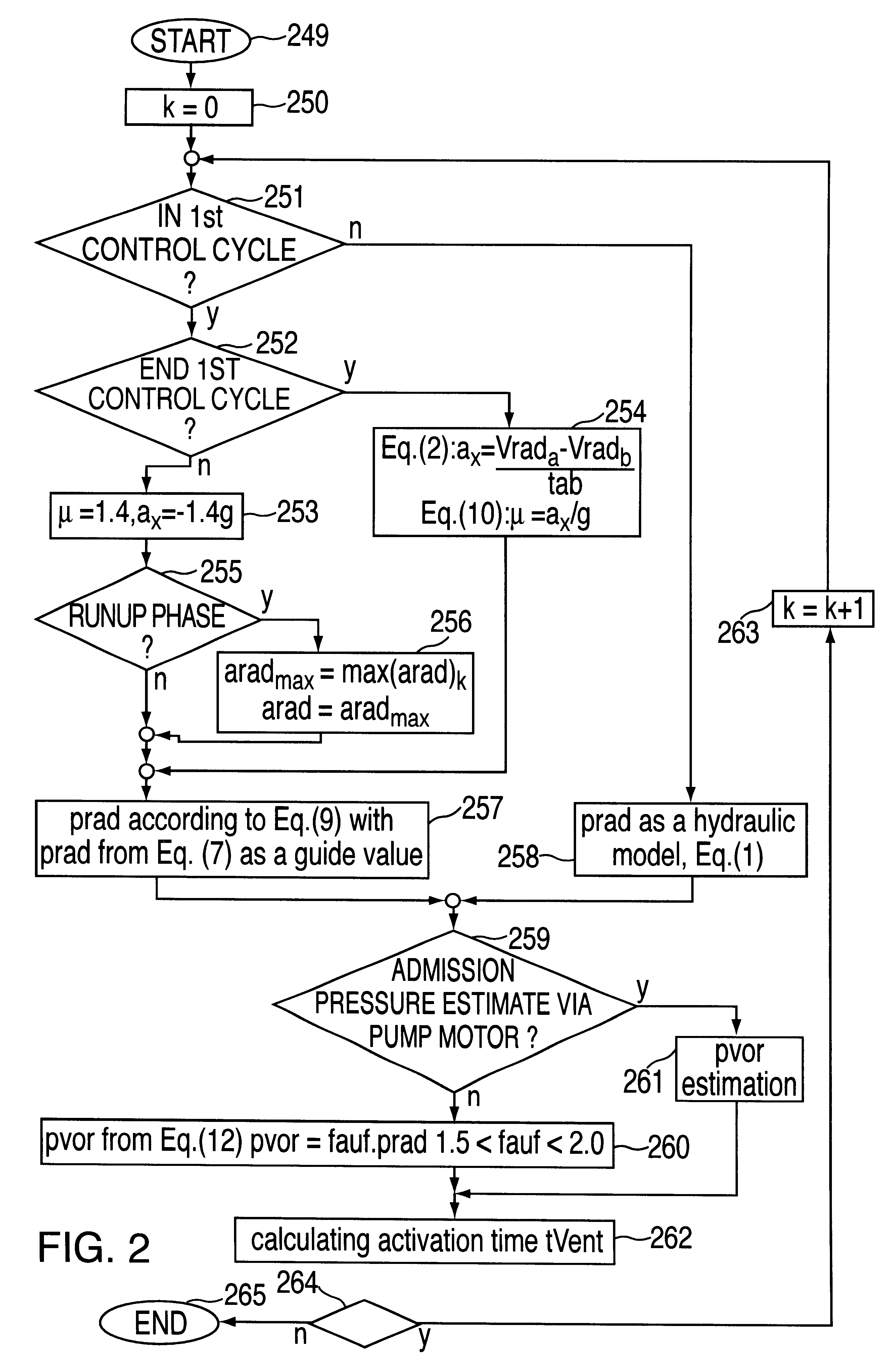
InactiveUS6446490B1Improve driving stabilityImprove securityFluid braking transmissionApplication and release valvesEngineeringActuator
Device and method for determining a wheel braking pressure and / or an admission pressure in a braking system in which pressure medium is introduced from a reservoir for the pressure medium having an admission pressure into a wheel brake through at least one shutoff device for inlet and / or outlet and / or passage of a pressure medium, it being possible to remove pressure medium from the wheel brake through at least one means delivering the pressure medium. In so doing, a pressure quantity representing the admission pressure is estimated, at least one operating state of at least one actuator in the braking system is detected and the wheel braking pressure is estimated as a function of the estimated admission pressure and the detected operating states.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
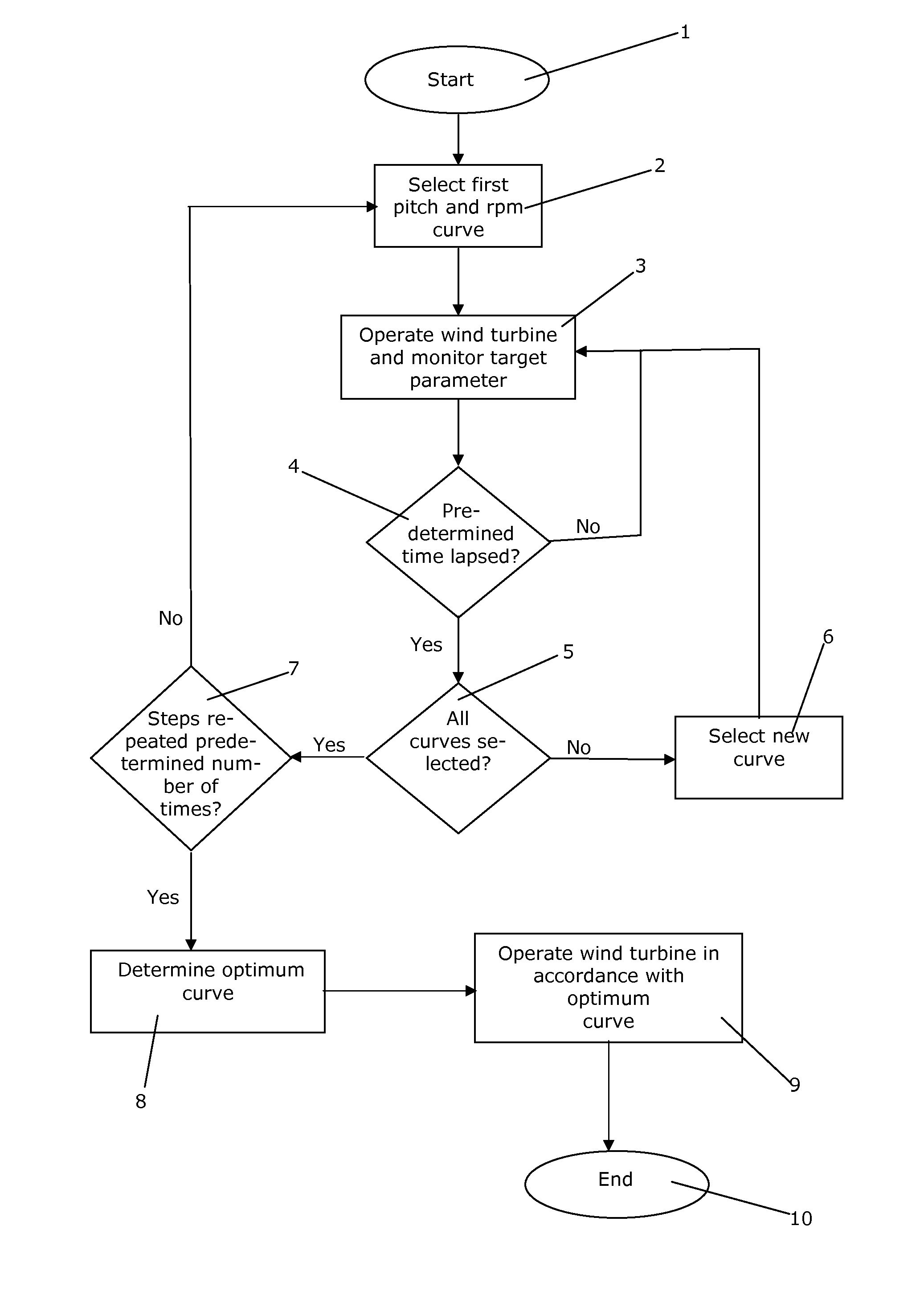
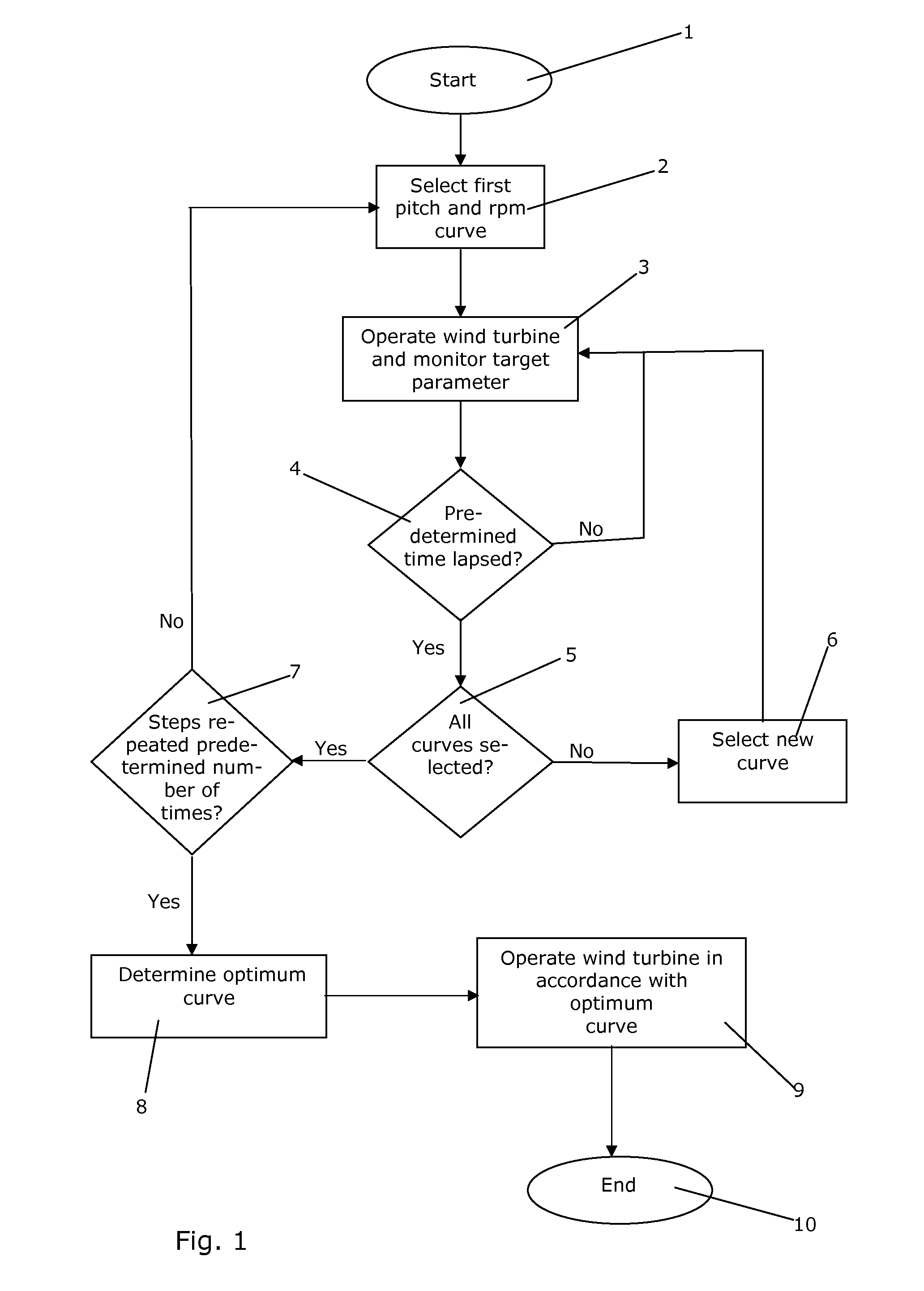
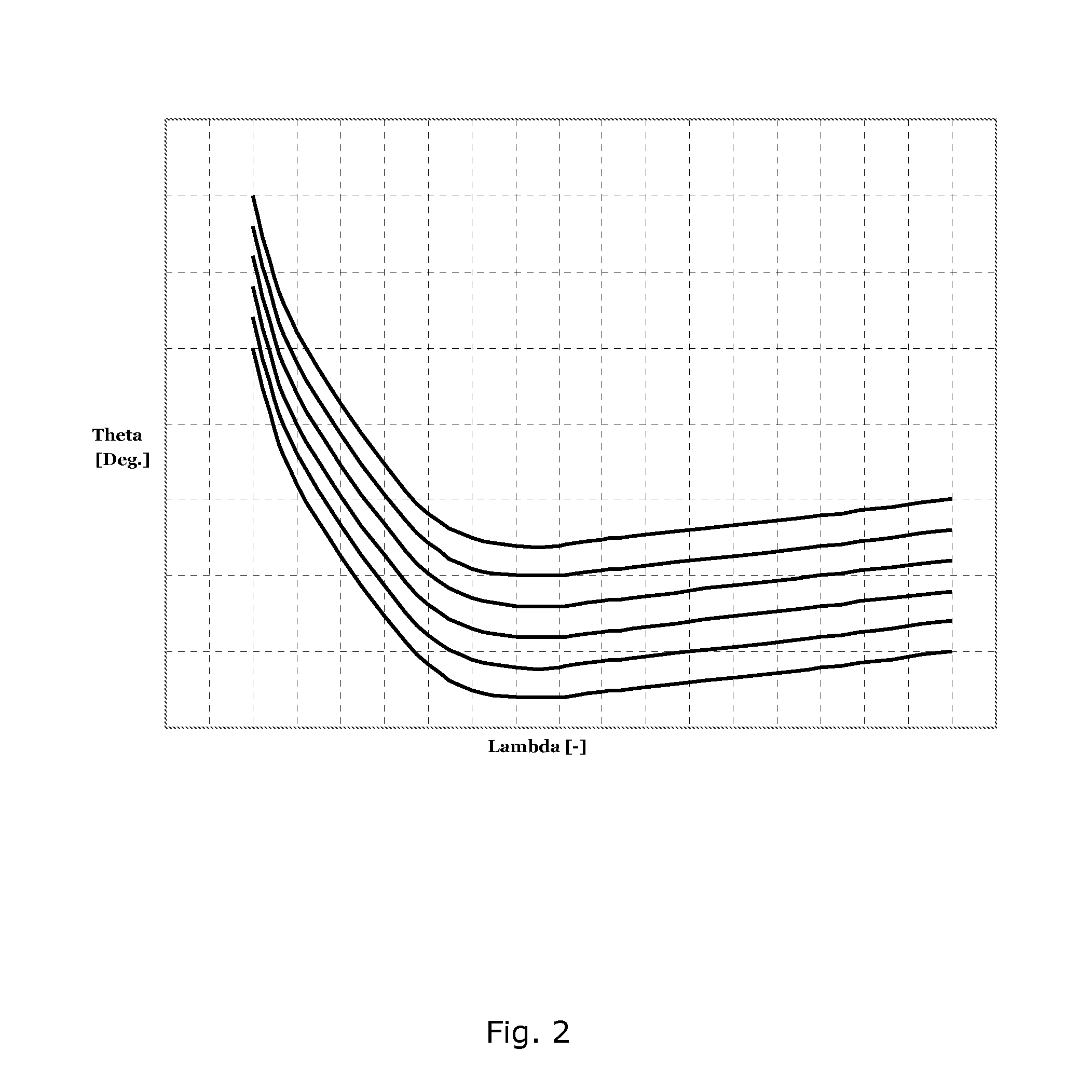
Method for controlling operation of a wind turbine
ActiveUS20110309621A1Less influenceRaise the possibilityOptimise machine performanceWind motor controlEngineeringTurbine
A method for controlling operation of a wind turbine and a method for controlling operation of a plurality of wind turbines positioned in a wind farm are disclosed. According to the method, a pitch and rotational speed curve, e.g. a θ versus λ curve, is selected from a group of pitch and rotational speed curve, and the wind turbine is operated in accordance with the selected curve for a short period, while monitoring at least one target parameter, e.g. power production or loads on one or more components. This is repeated for each of the curves of the group of pitch and rotational speed curves. This is also repeated a predetermined number of times, i.e. each curve is selected in turn a predetermined number of times. Based on the monitored target parameters an optimum curve is determined from the group of pitch and rotational speed curve, and the wind turbine is operated in accordance with this optimum curve. The method ensures that the applied curve is in fact optimal for the specific wind turbine, at the specific site and under the specific conditions. Thereby the wind turbine can be operated in a more optimal manner, e.g. with respect to power production and / or loads or wear on components.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Developing device and process cartridge
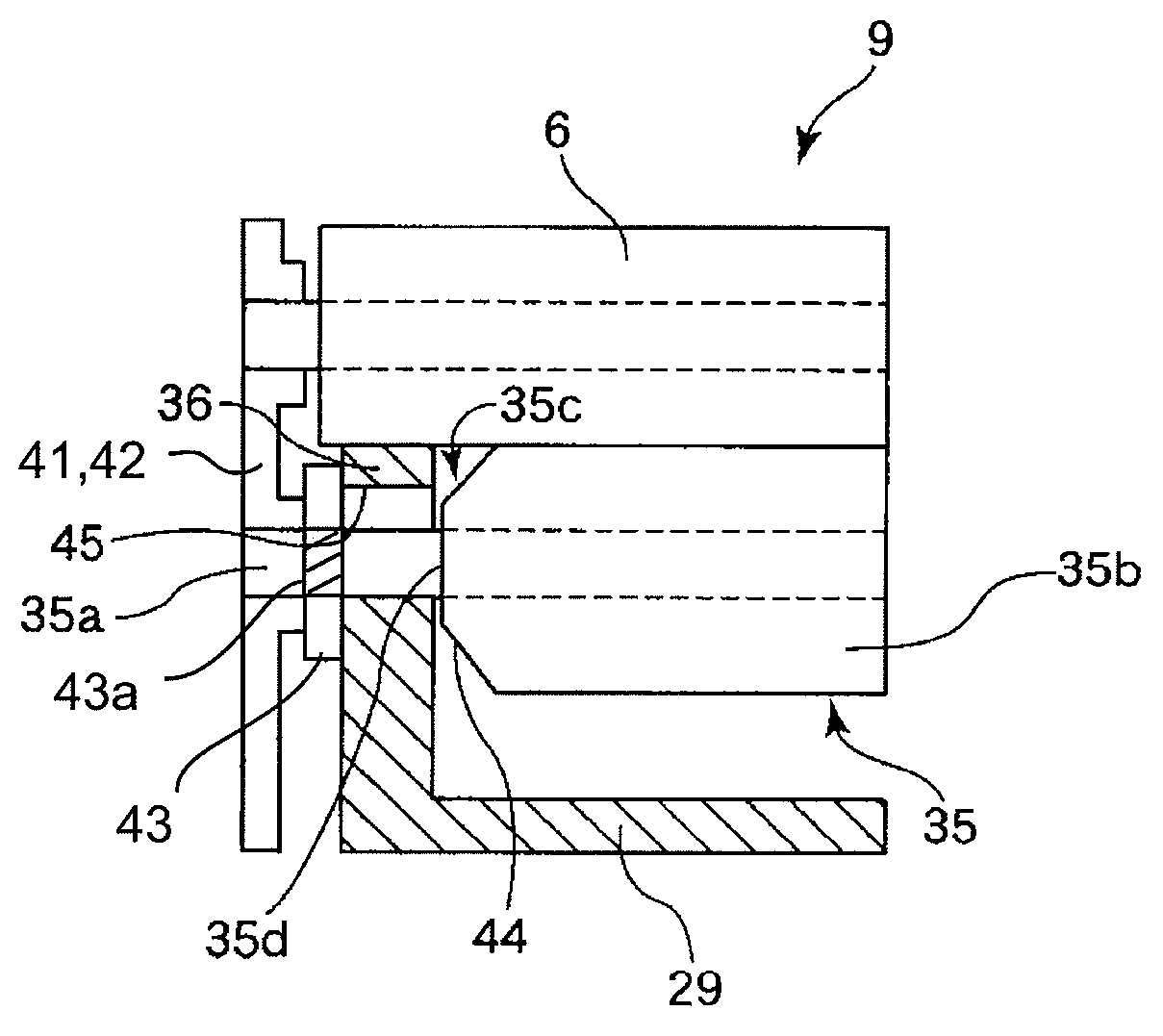
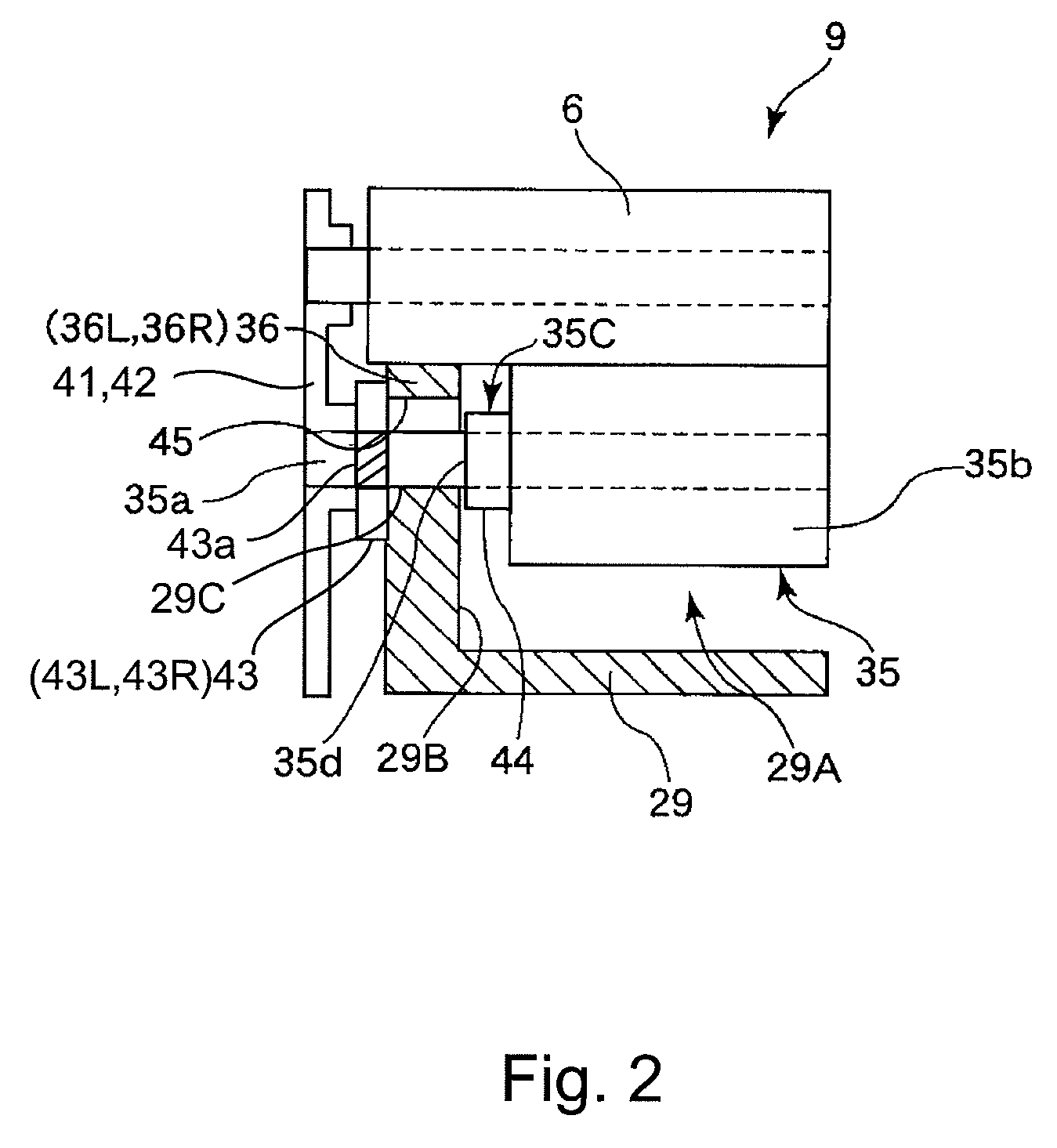
InactiveUS8583001B2Less influencePrevent Toner LeakageElectrographic process apparatusEngineeringMechanical engineering
A developing device includes a developing container, provided with an opening, for containing a developer; a developing roller, provided at the opening, for forming a developer image on an image bearing member; a seal member, provided at the opening along an end portion of the developing roller, for preventing toner leakage from a gap between the opening and the developing roller; and a developer supplying roller, including a core material and a cylindrical elastic member which is provided around the core material and is contacted to the developing roller, for supplying the developer to the developing roller. The cylindrical elastic member has an end surface and a central portion with respect to a longitudinal direction thereof. The end surface has an outer diameter larger than that of the central portion so as to be in non-contact with the seal member.
Owner:CANON KK
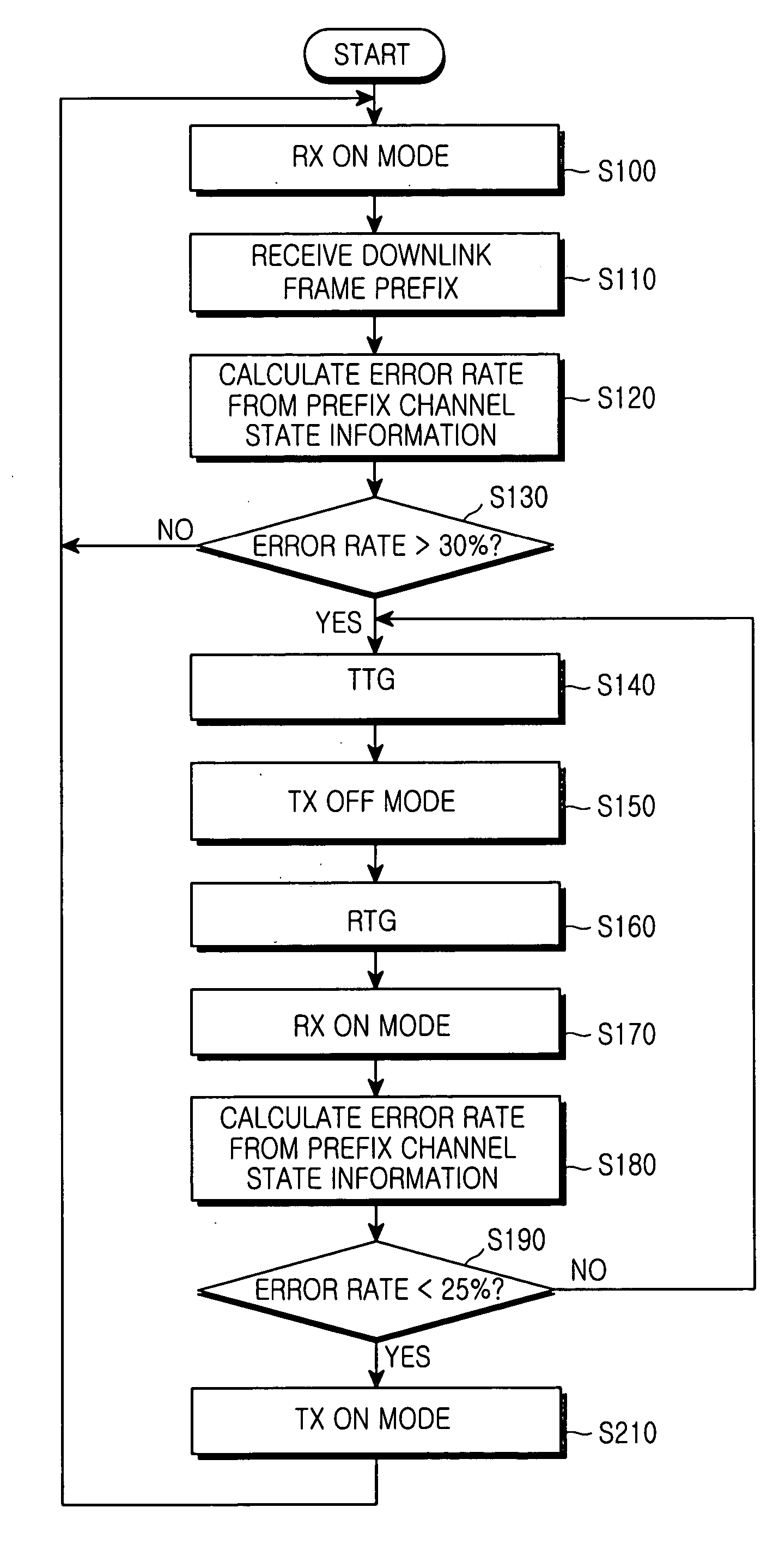
Method for saving power in a user terminal after synchronization loss in broadband wireless access communication system
InactiveUS20050120282A1Reduce transmissionReduce unnecessary power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTPower managementBroadbandReal-time computing
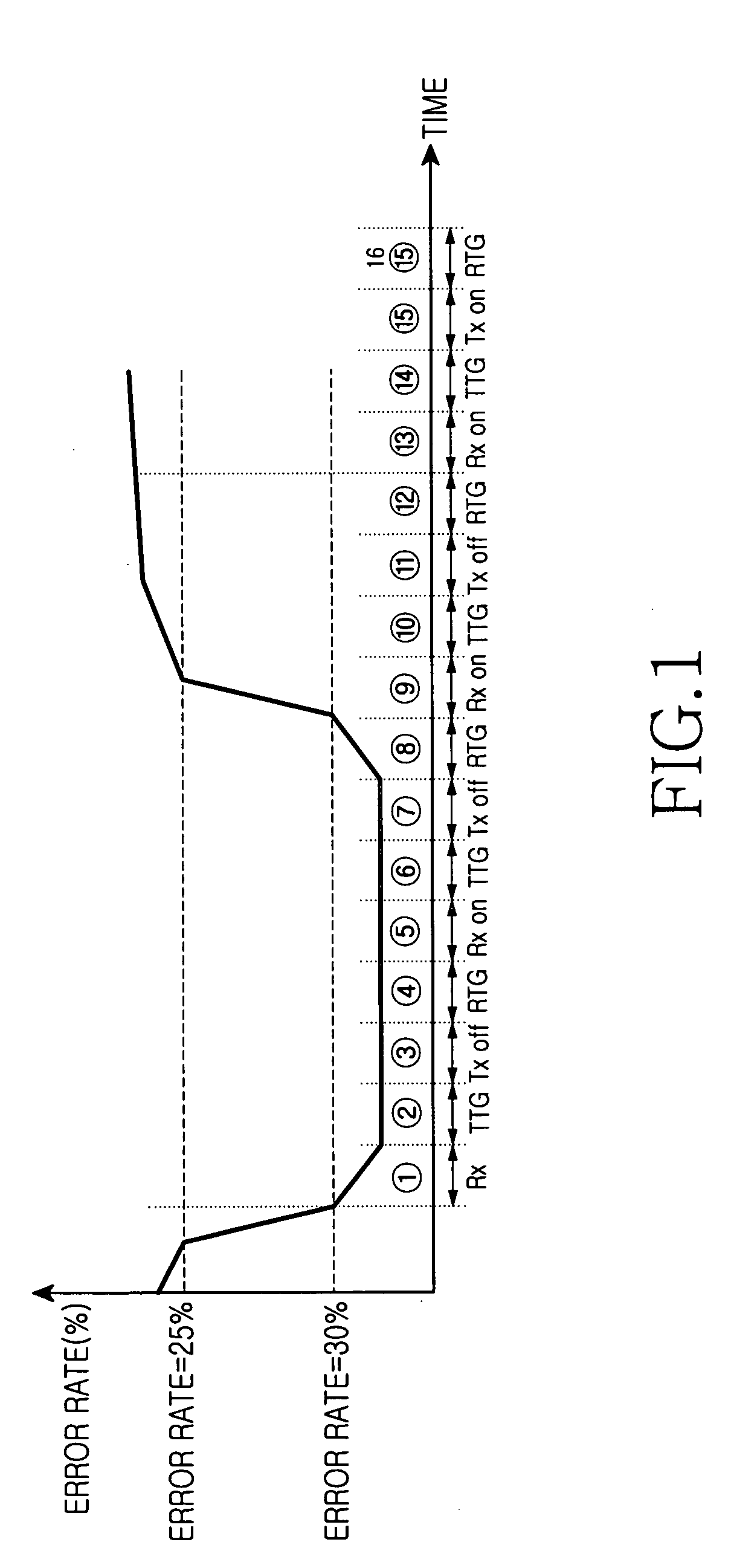
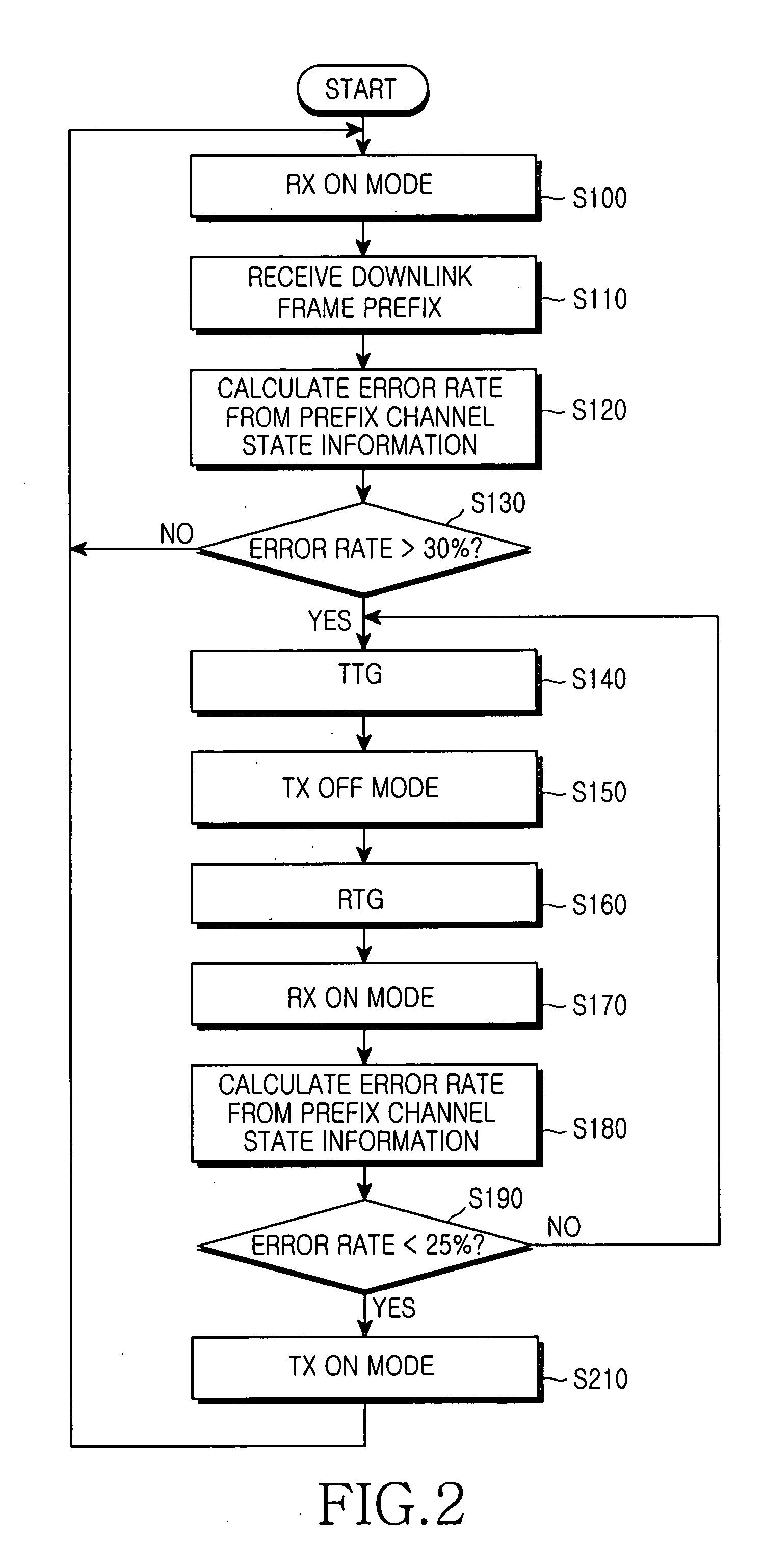
Disclosed is a method for reducing power consumption of a user terminal when synchronization between a user terminal and a base station is disrupted in a broadband wireless access communication system. The method comprises the steps of: calculating first error rate (E) based on first channel state information included in a signal transmitted from the base station; comparing the first error rate (E) with a first threshold value; determining that the synchronization is disrupted and maintaining a transmission-off mode for a predetermined period of time if the first error rate (E) is greater than the first threshold value; maintaining a reception-on mode during a period of time set for a reception mode after the transmission-off mode is performed; receiving from the base station second channel state information during the reception-on mode; calculating a second error rate (E1) based on the second channel state information; comparing the second error rate (E1) with a second threshold value; and determining that the synchronization has been reestablished and maintaining the transmission mode in a transmission-on mode if the second error rate (E1) is less than the second threshold value.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com