Patents
Literature
438results about "Optimise machine performance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
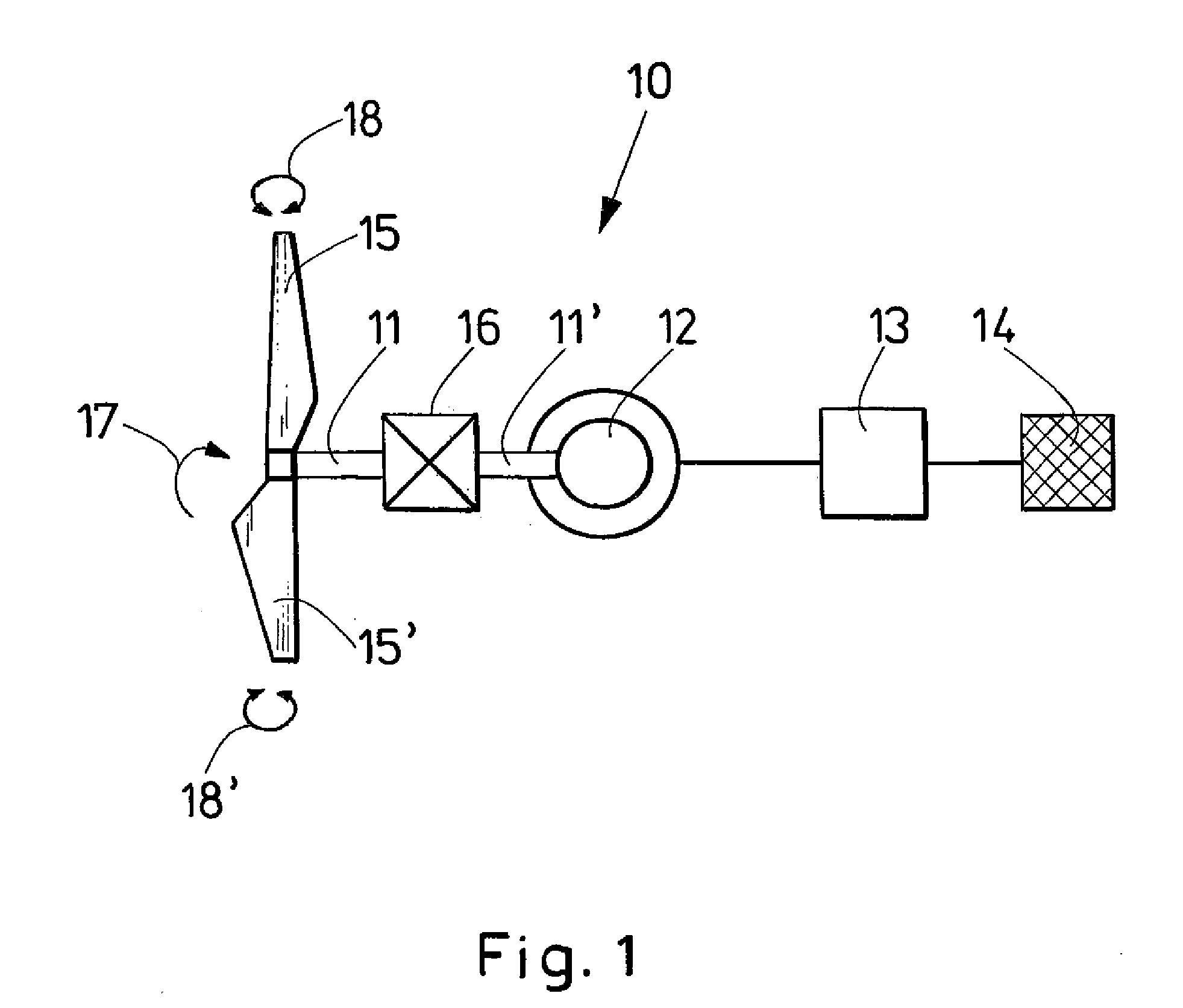
System, method and computer program product for enhancing commercial value of electrical power produced from a renewable energy power production facility
InactiveUS20050127680A1Increase power valueInherent market valueWind motor controlEngine fuctionsPower exchangeRenewable power generation
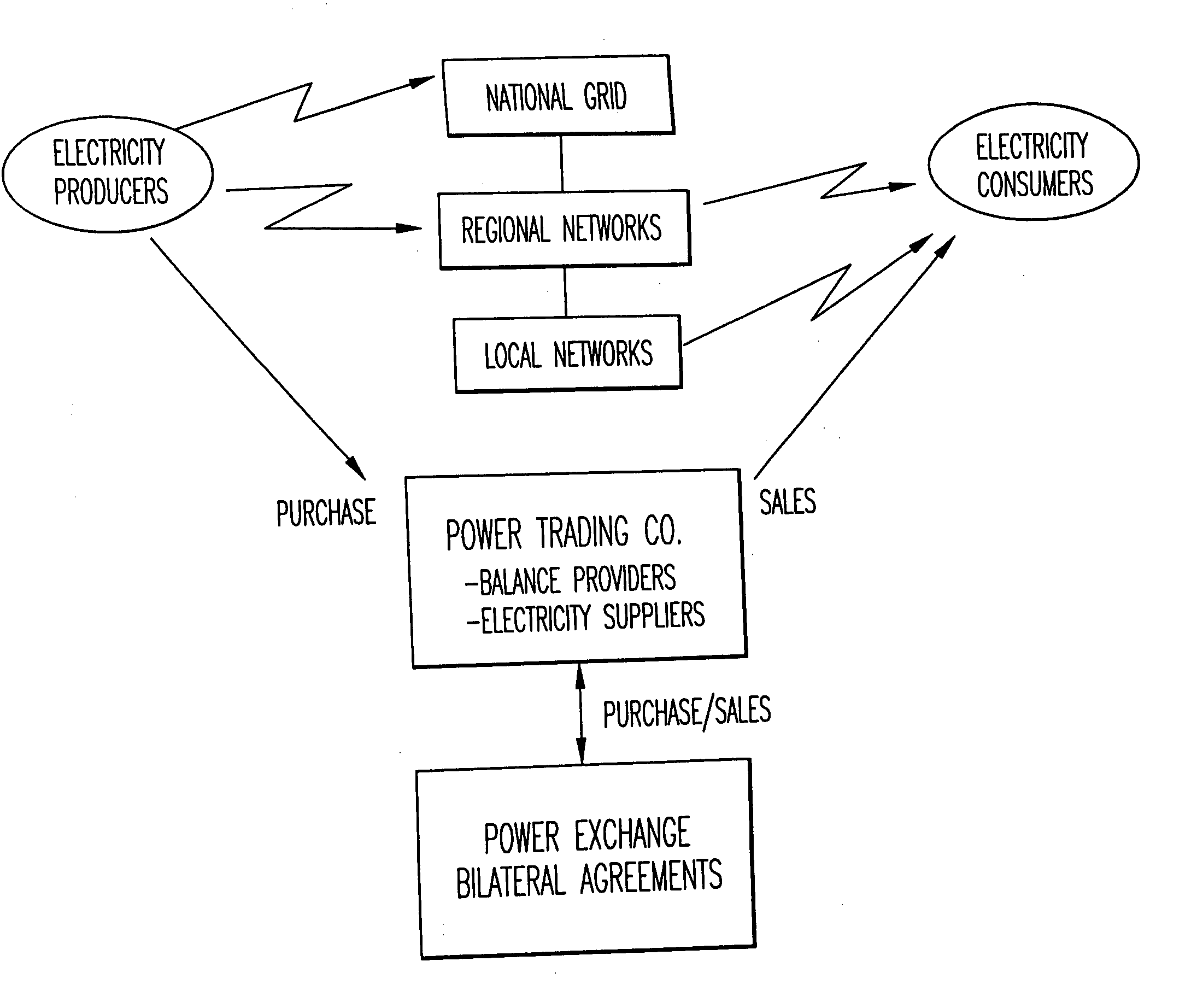
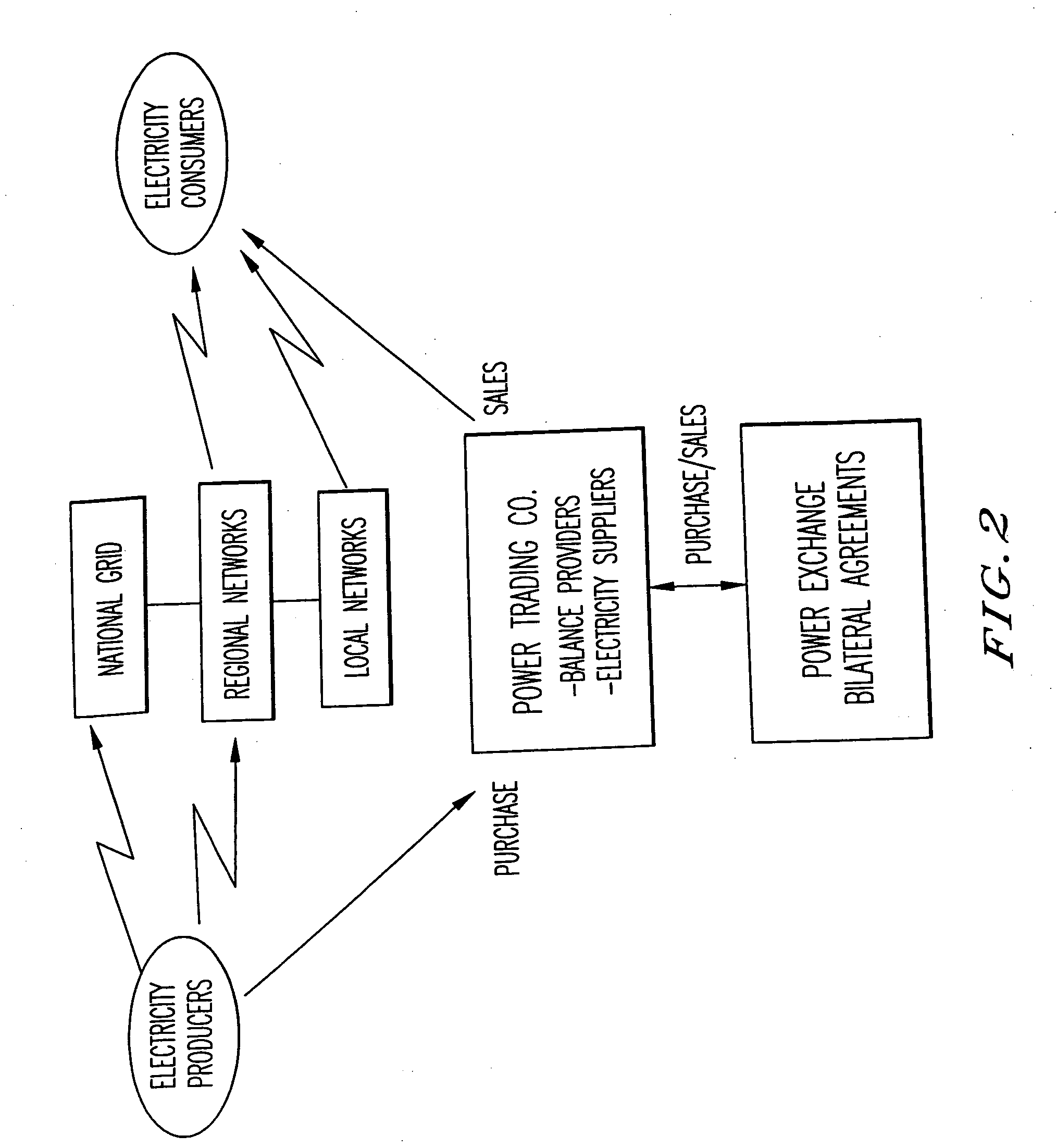
A method, system and computer program product enhance the commercial value of electrical power produced from a wind turbine production facility. Features include the use of a premier power conversion device that provides an alternative source of power for supplementing an output power of the wind turbine generation facility when lull periods for wind speed appear. The invention includes a communications infrastructure and coordination mechanism for establishing a relationship with another power production facility such that when excess electrical power is produced by the wind turbine facility, the excess may be provided to the power grid while the other energy production facility cuts back on its output production by a corresponding amount. A tracking mechanism keeps track of the amount of potential energy that was not expended at the other facility and places this amount in a virtual energy storage account, for the benefit of the wind turbine facility. When, the wind turbine power production facility experiences a shortfall in its power production output it may make a request to the other source of electric power, and request that an increase its power output on behalf of the wind turbine facility. This substitution of one power production facility for another is referred to herein as a virtual energy storage mechanism. Furthermore, another feature of the present invention is the use of a renewal power exchange mechanism that creates a market for trading renewable units of power, which have been converted into “premier power” and / or “guaranteed” by secondary sources of power source to provide a reliable source of power to the power grid as required by contract.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Wind power management system and method
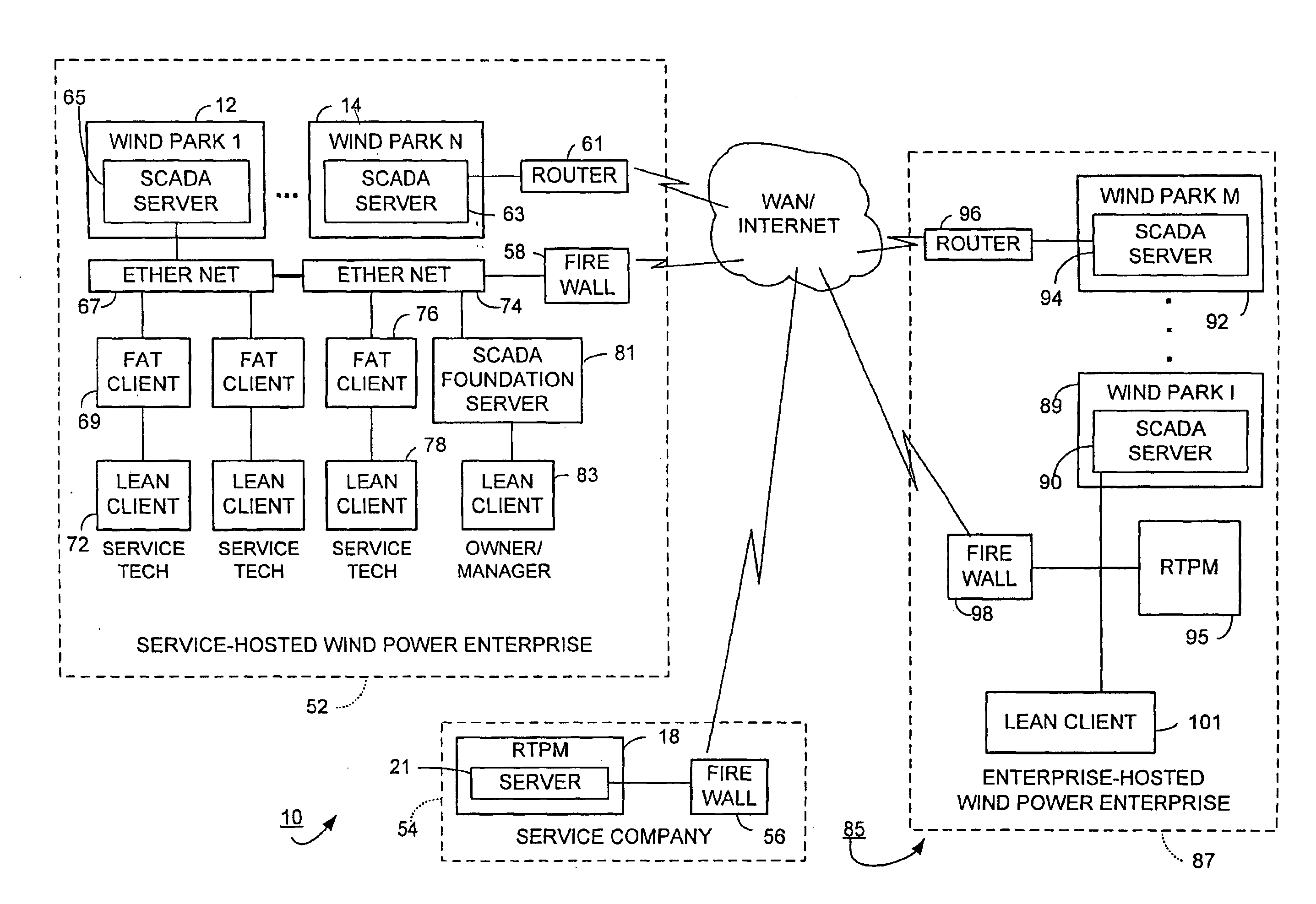
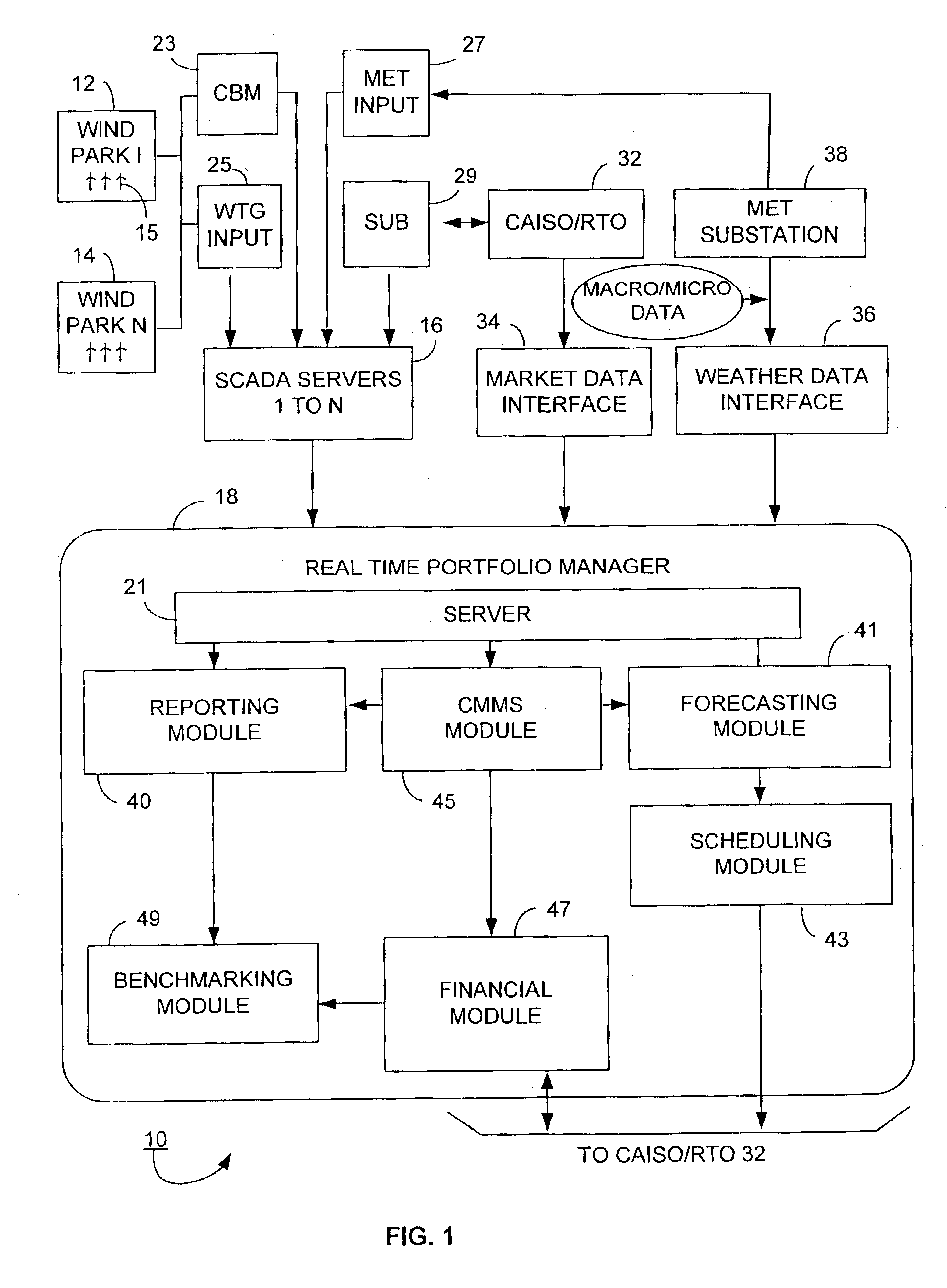
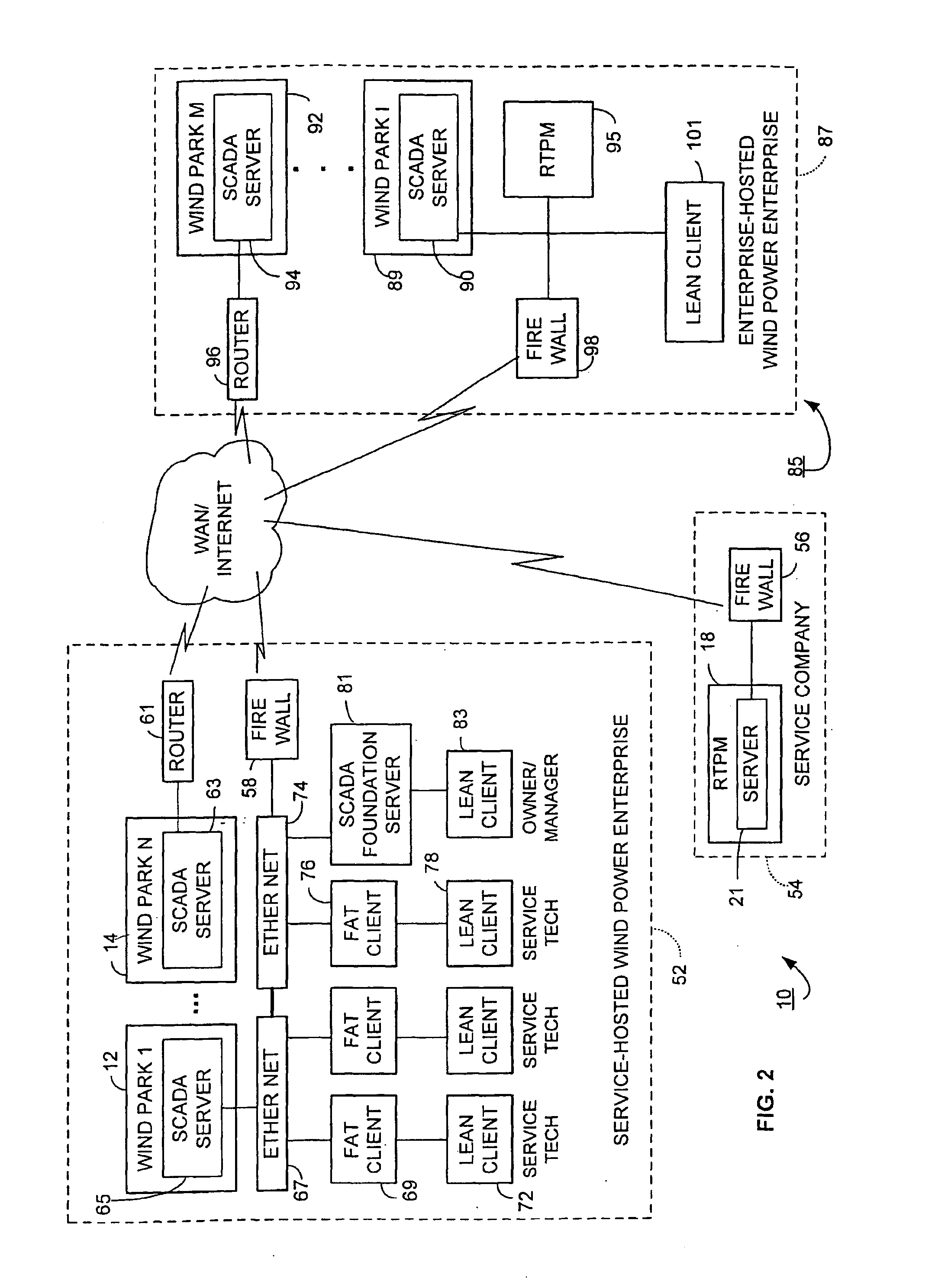
According to certain disclosed embodiments of the invention, there is provided a wind power management system to monitor performance of wind turbine generators situated in wind farms, each having a number of wind turbine generators. A real-time wind power portfolio manager receives and stores in real-time data being produced by the wind turbine generator parks. The manager has a reporting module for generating profile reports for the performance of the wind turbine generators. The manager has a server to provide the reports on-line regarding the wind turbine generators. The server stores the real-time data to enable the reports to be based on the history of the project for each one of the parks.
Owner:SEAWEST HLDG
Wind farm supervision monitoring system
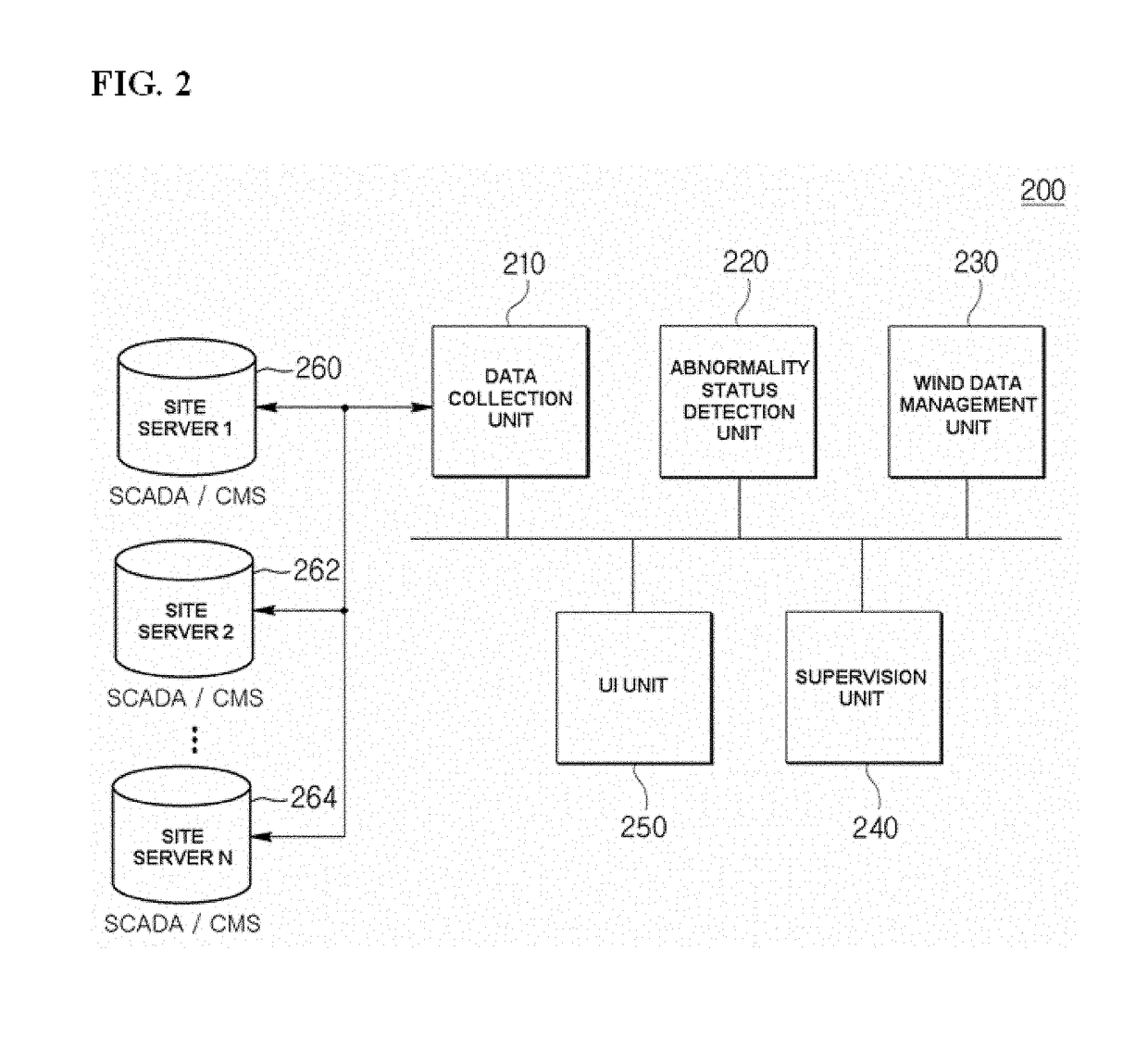
ActiveUS20170352010A1Minimize impactEarly detectionWind motor controlElectric testing/monitoringManagement unitMonitoring system
A wind farm supervision monitoring system includes: a data collection unit configured to collect data about a status monitoring of each wind turbine from at least one site server; an abnormality status detection unit configured to detect an abnormality status of each wind turbine based on the collected data about the status monitoring and issue an alarm; a wind data management unit configured to early detect a fault of each wind turbine and or monitor performance of each wind turbine based on the data about the status monitoring or the data about the abnormality status; and a supervision unit configured to manage a turbine operation status and operation and maintenance of each wind turbine and provide information for establishing an operation and maintenance plan for the detected abnormality status of the wind turbine.
Owner:DOOSAN HEAVY IND & CONSTR CO LTD
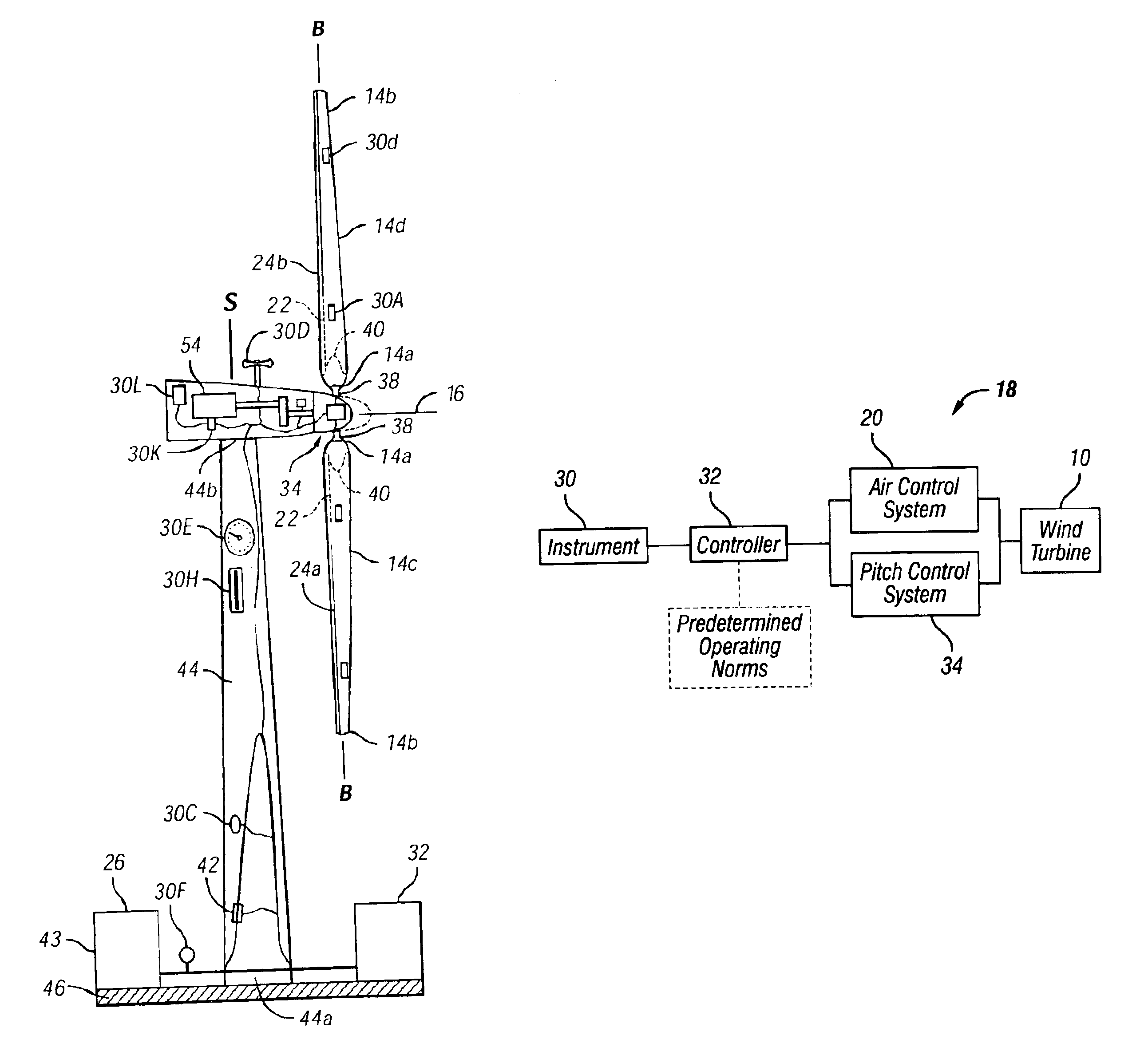
Advanced aerodynamic control system for a high output wind turbine
An advanced aerodynamic control system for a wind turbine including a drive shaft and blade. The control system includes an air control system coupled to a duct that extends from a first end toward a second end of the blade. A slot extends along a portion of a surface of the blade and is in communication with the duct. An instrument measures operating data of the wind turbine. A controller collects the operating data and compares the operating data to predetermined operating norms. The controller actuates the air control system to urge pressurized air into the duct and out of the slot at a specific air flow rate based upon the comparison between the operating data and predetermined operating norms. Control of the flow rate aids in capture of power from the wind flowing through a swept area of the wind turbine.
Owner:ADVANTEK
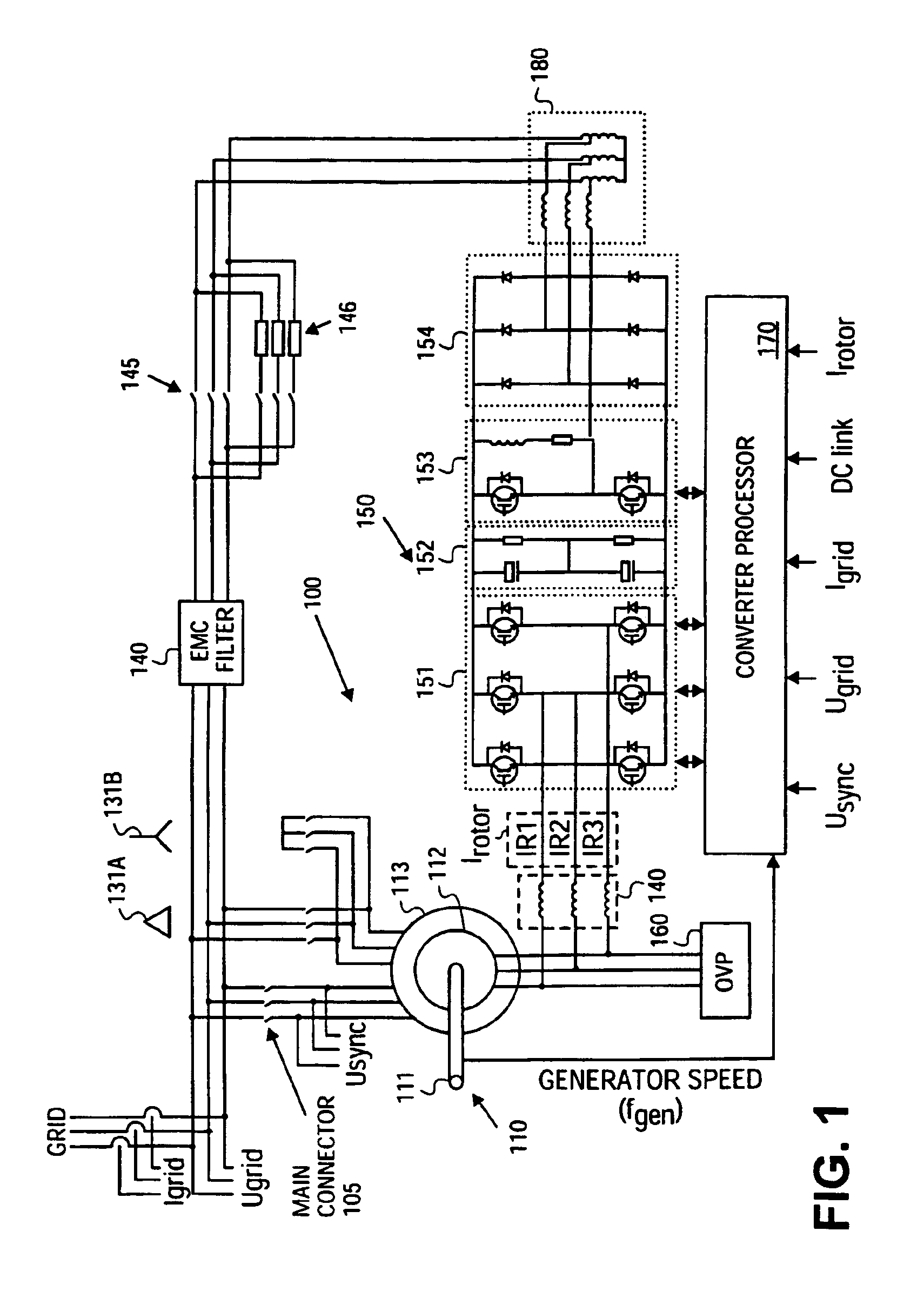
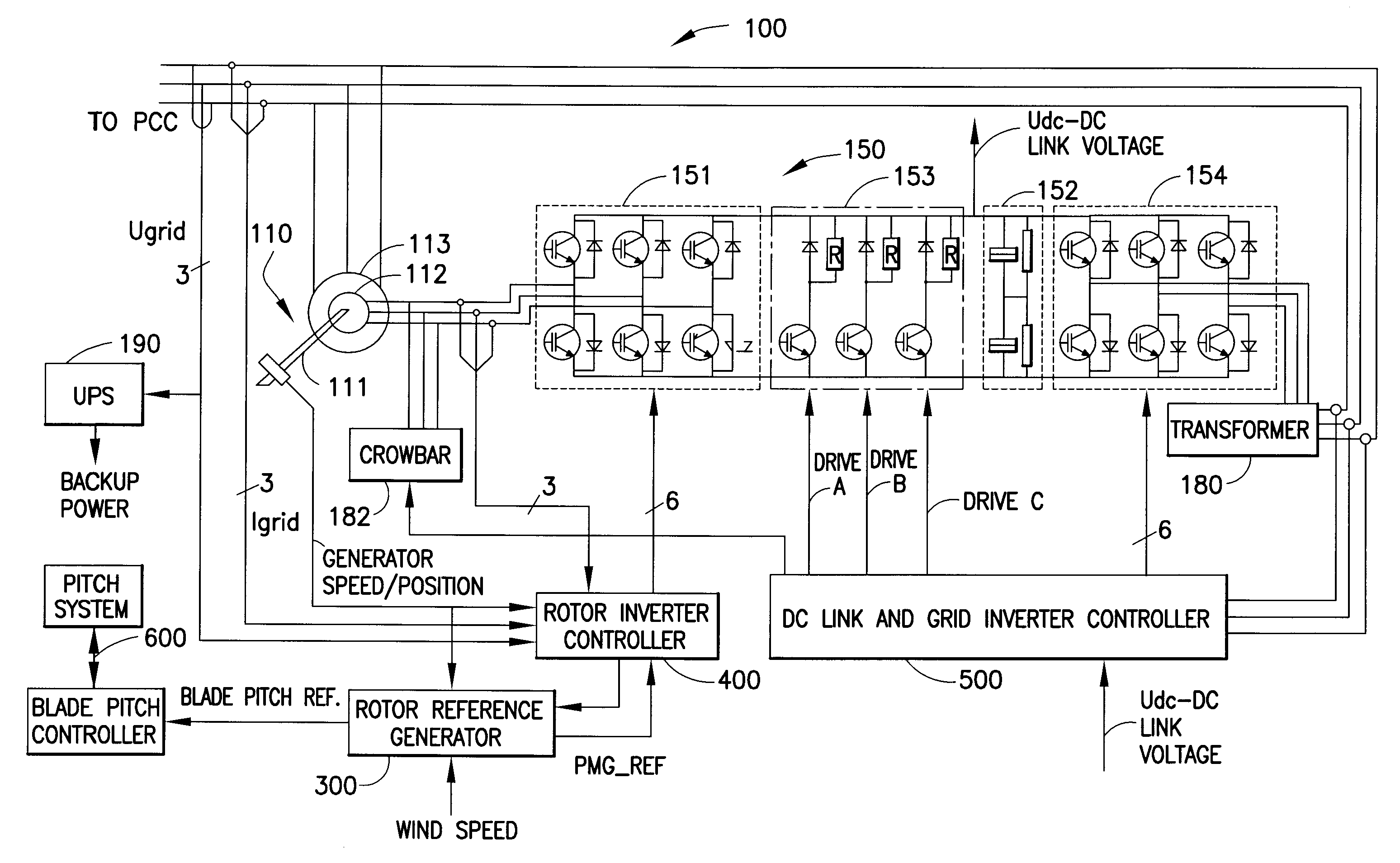
Variable speed wind turbine having a passive grid side rectifier with scalar power control and dependent pitch control
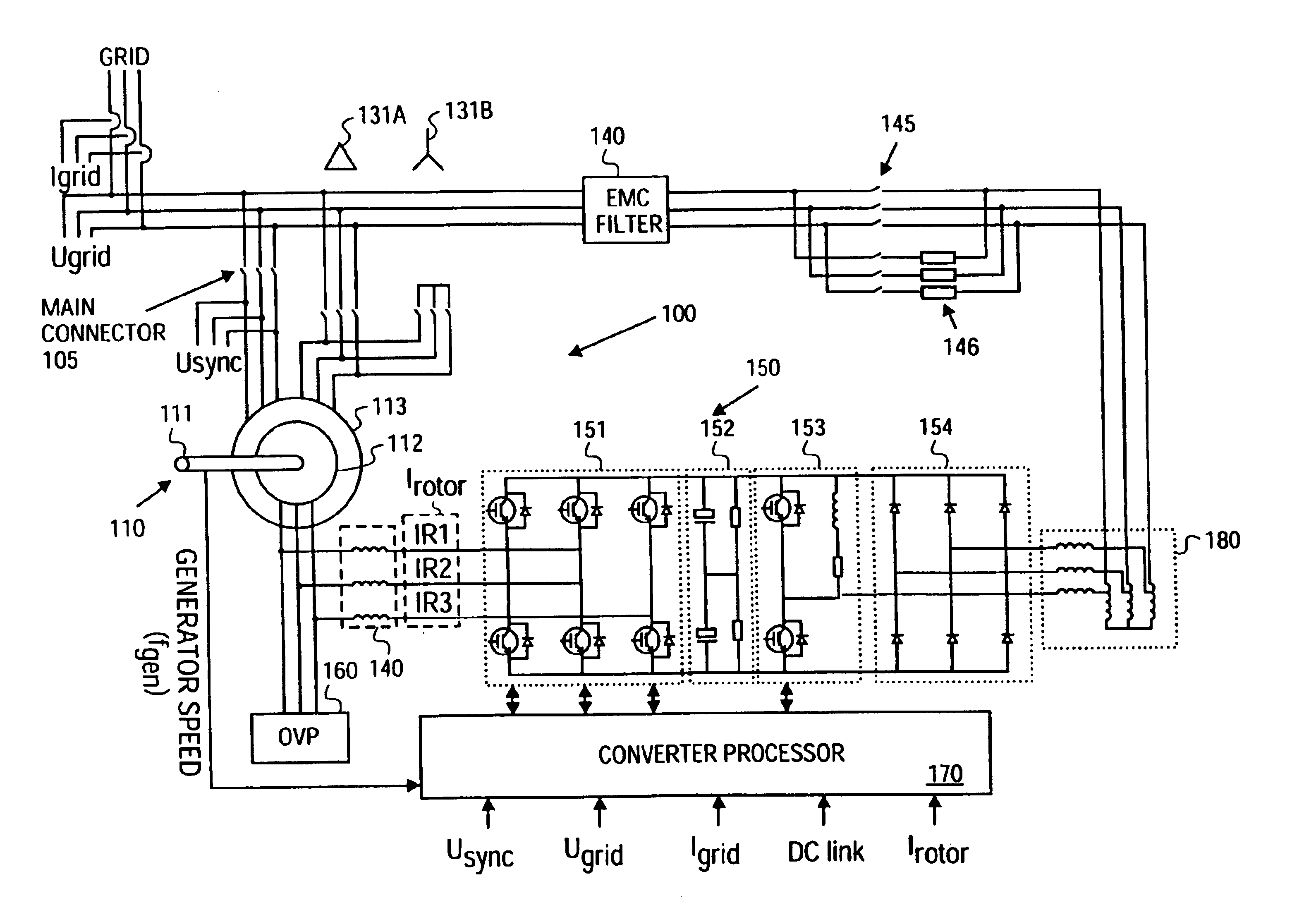
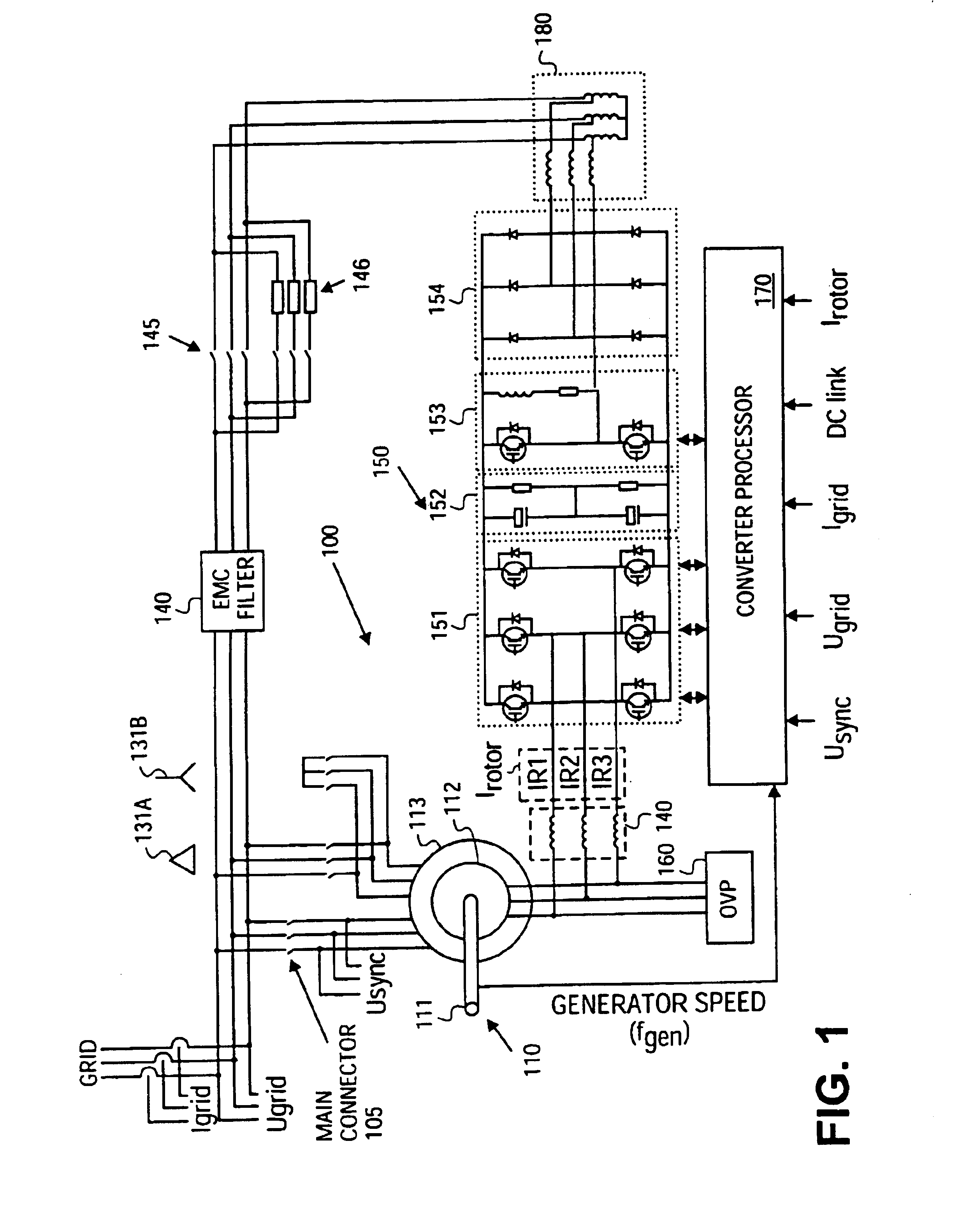
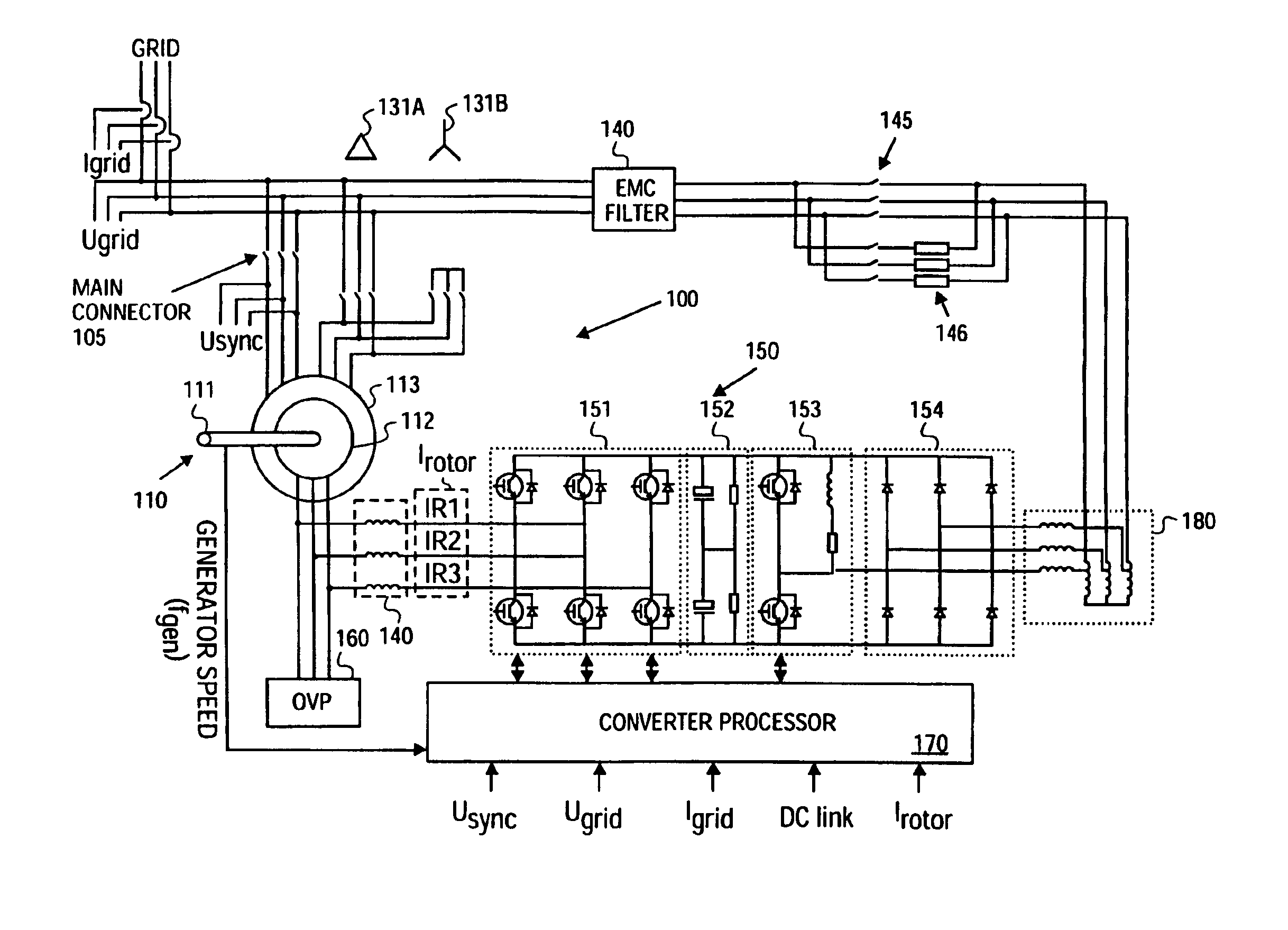
InactiveUS6933625B2Easy to controlImprove responsivenessOptimise machine performanceWind motor controlPower gridVariable speed wind turbine
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Variable speed wind turbine having a passive grid side rectifier with scalar power control and dependent pitch control
InactiveUS6856040B2Easy to controlImprove responsivenessOptimise machine performanceWind motor controlPower gridVariable speed wind turbine
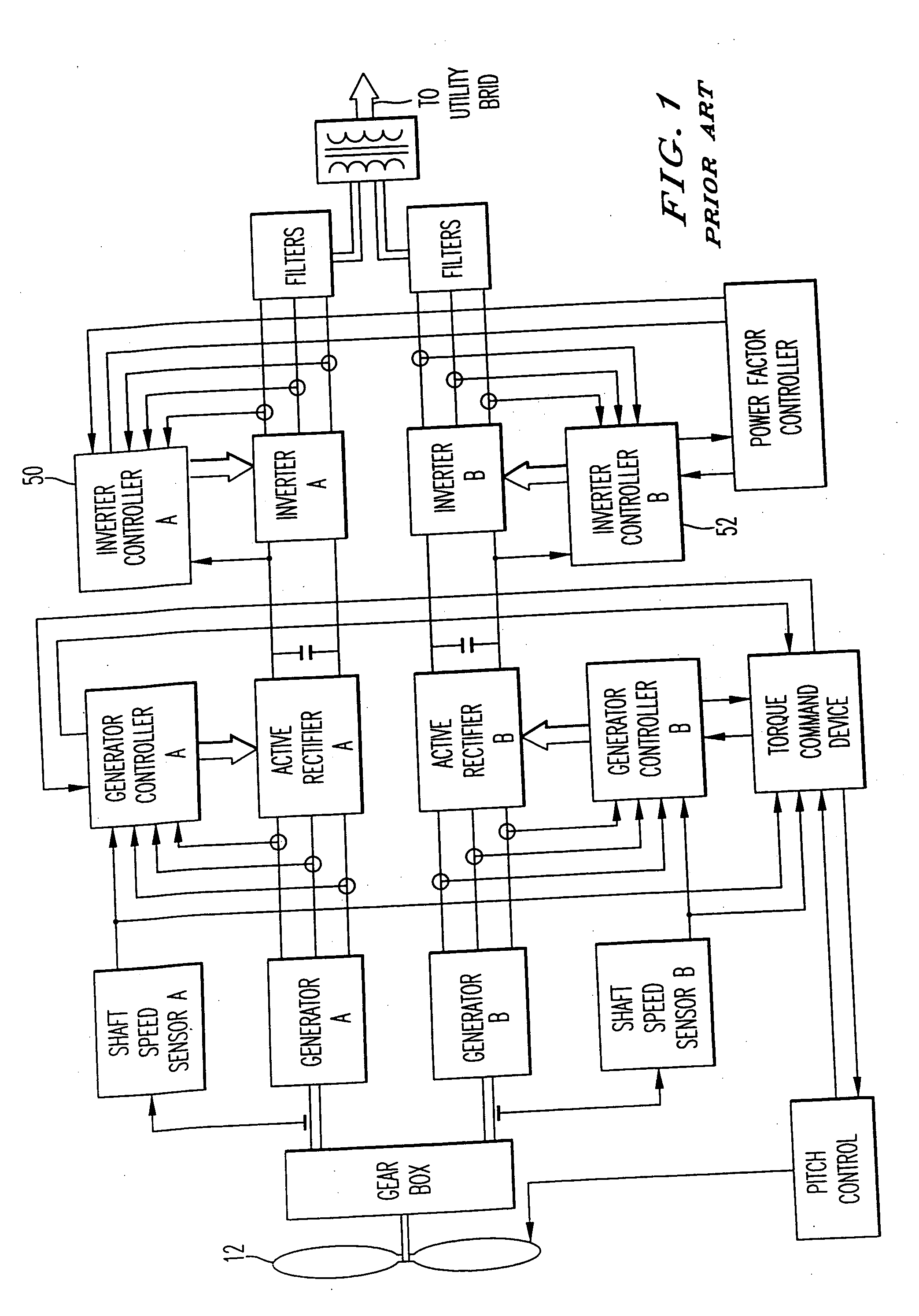
A variable speed wind turbine having a passive grid side rectifier using scalar power control and dependent pitch control is disclosed. The variable speed turbine may include an electrical generator to provide power for a power grid and a power conversion system coupled to the electrical generator. The power conversion system may include at least one passive grid side rectifier. The power conversion system may provide power to the electrical generator using the passive grid side rectifier. The variable speed wind turbine may also use scalar power control to provide more precise control of electrical quantities on the power grid. The variable speed wind turbine may further use dependent pitch control to improve responsiveness of the wind turbine.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Wind turbine with pitch control arranged to reduce life shortening loads on components thereof
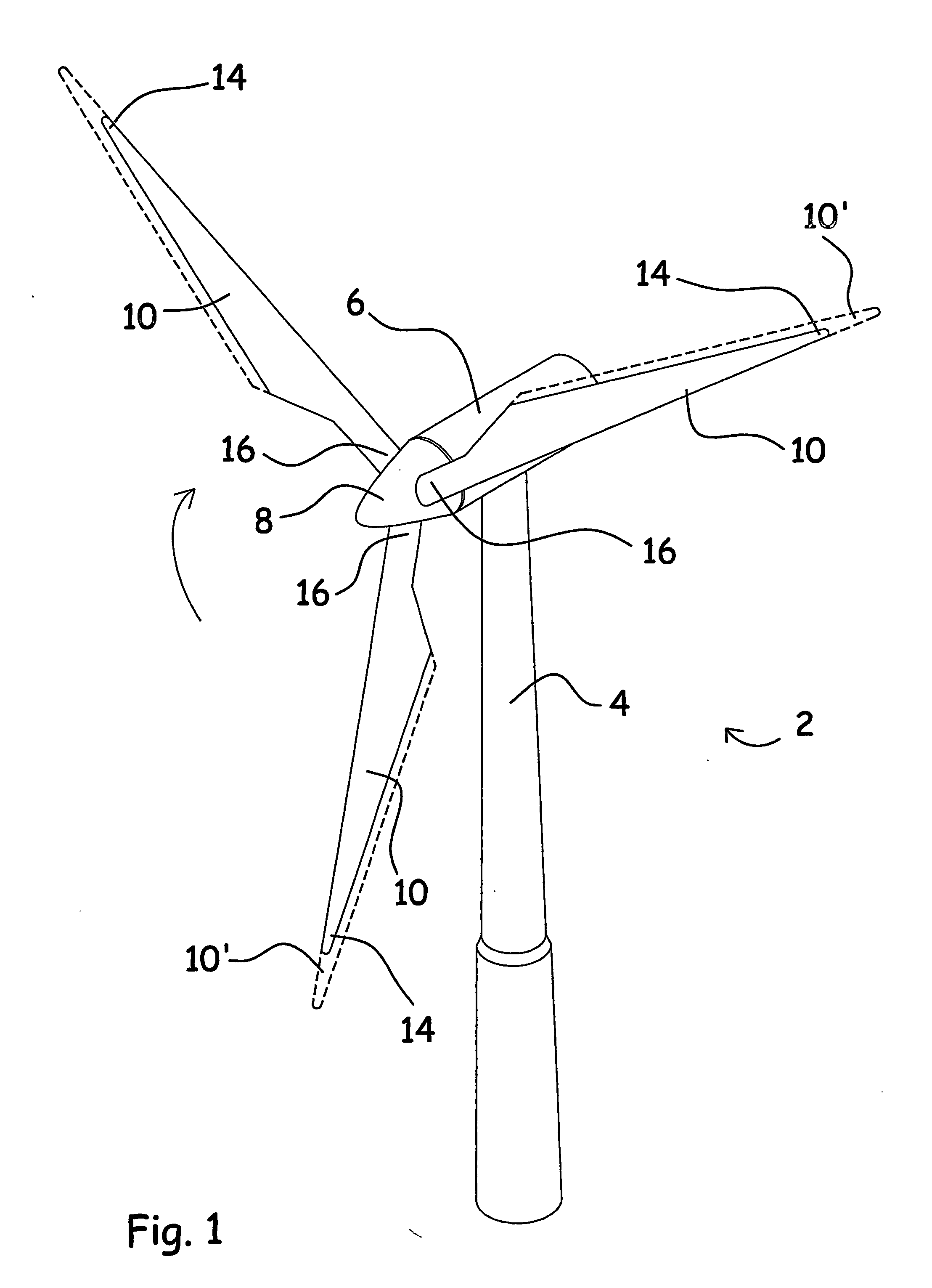
ActiveUS8096762B2Easy to operateReducing the mean bending momentPropellersPump componentsPull forceGravitational force
A wind turbine is presented where the operation lifetime of the main bearing is extended by relieving the main bearing by reducing the mean bending moment on the bearing by means of individual pitch control of the blades of the rotor so as to create an aerodynamic mean tilt moment on the rotor by means of aerodynamic forces on the blades, the tilt moment at least partly counteracting the bending moment caused by the overhang load forces on the main bearing from the gravitational pull on the rotor mass.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
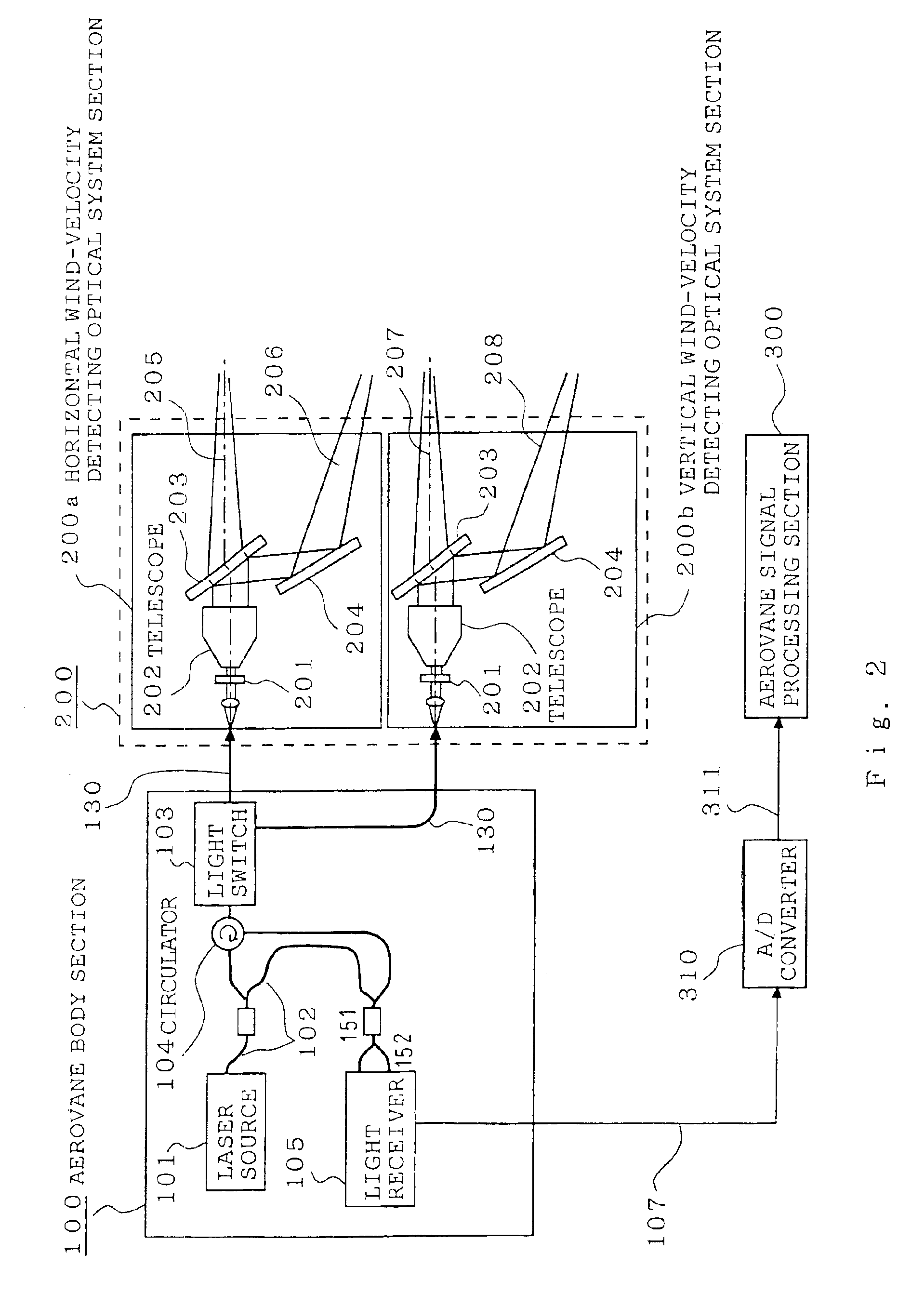
Wind power generation system
ActiveUS6946751B2High-efficiency operation controlAccurately suppress fluctuationPropellersWind motor controlEngineeringWind power system
A wind power generation system capable of outputting generated power at high efficiency with a smoothed output power includes a wind power generator and a laser aerovane mounted on the wind power generator or located near the wind power generator. Direction and velocity of wind blowing toward the wind power generator are observed using the laser aerovane, and a yaw angle and / or a pitch angle of the wind power generator is predicted and controlled based on the observation results. Thus, high-efficiency control of the wind power generation system, including the wind power generator, is achieved. An output-smoothing device connected to the wind power generator predicts and controls electric power input / output of the output-smoothing device based on a predicted power output of the wind power generator and smoothes the power output of the wind power generation system.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Variable Speed Wind Turbine Configured For Wind Farm Operation
InactiveUS20090206606A1Easy to controlGood effectGenerator control circuitsOptimise machine performancePower gridVariable speed wind turbine
The present invention relates to an improved wind turbine, of the type which employs doubly fed induction generators (DFIG), and a wind park including the same, which permits the use of lighter weight turbines, with the ability to have greater energy capture, more precise control of asymmetrical phases and enhanced maintenance and support of the grid during fault conditions.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
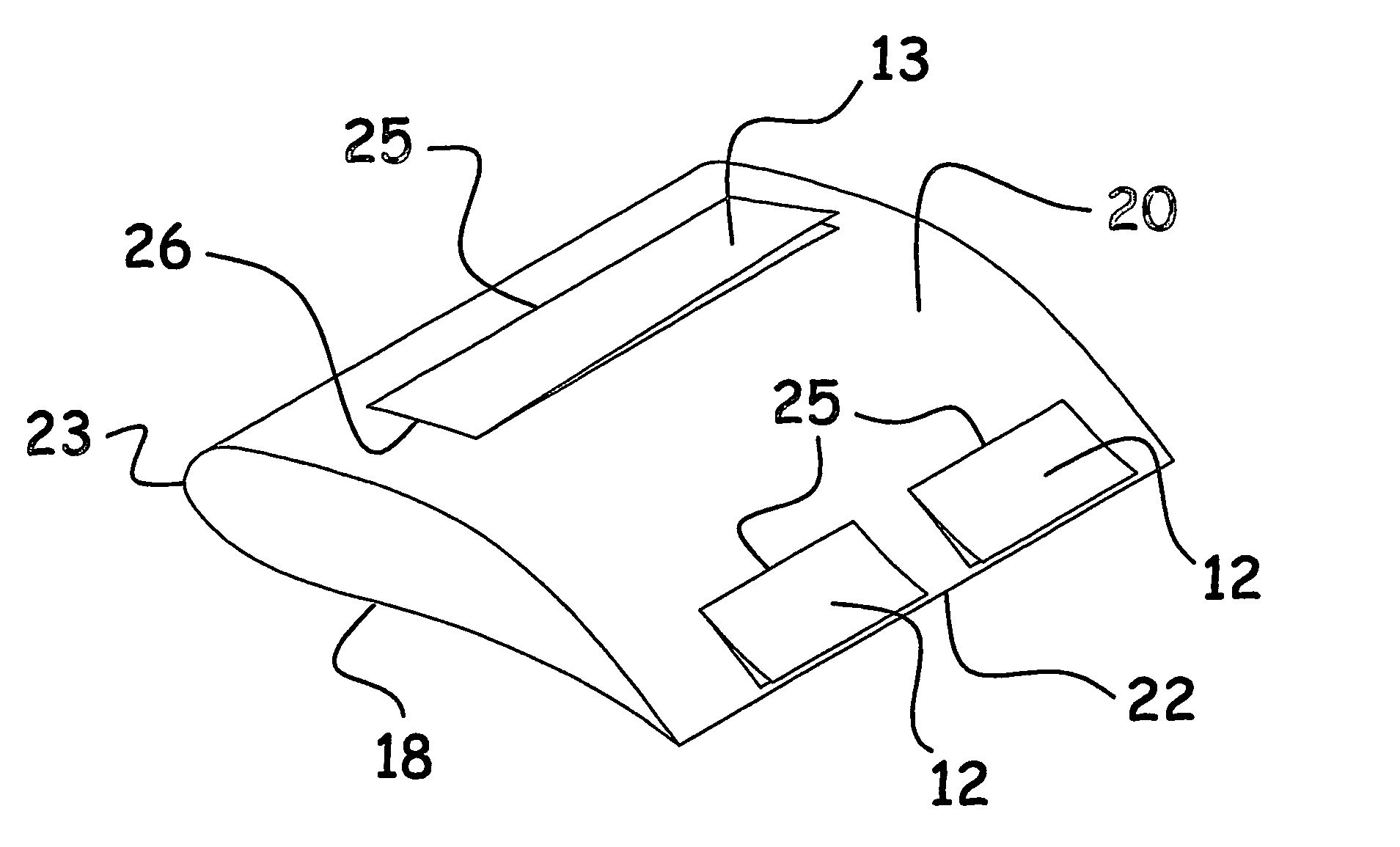
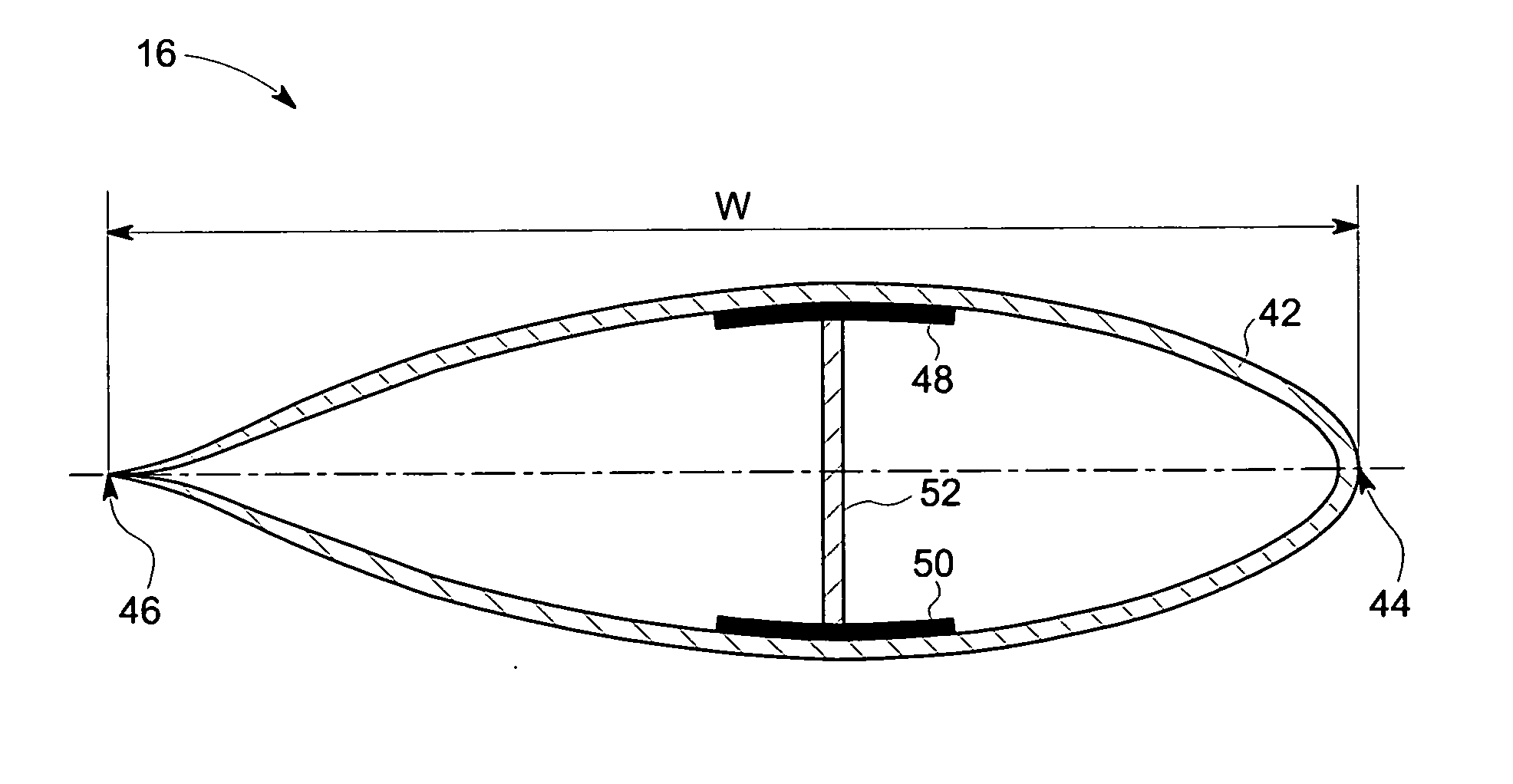
Wind turbine blade with lift-regulating means
ActiveUS7293959B2Smooth and gradual change in liftSimple wayPropellersPump componentsTurbine bladeBiological activation
Owner:LM GLASSFIBER
Control system for a wind power plant
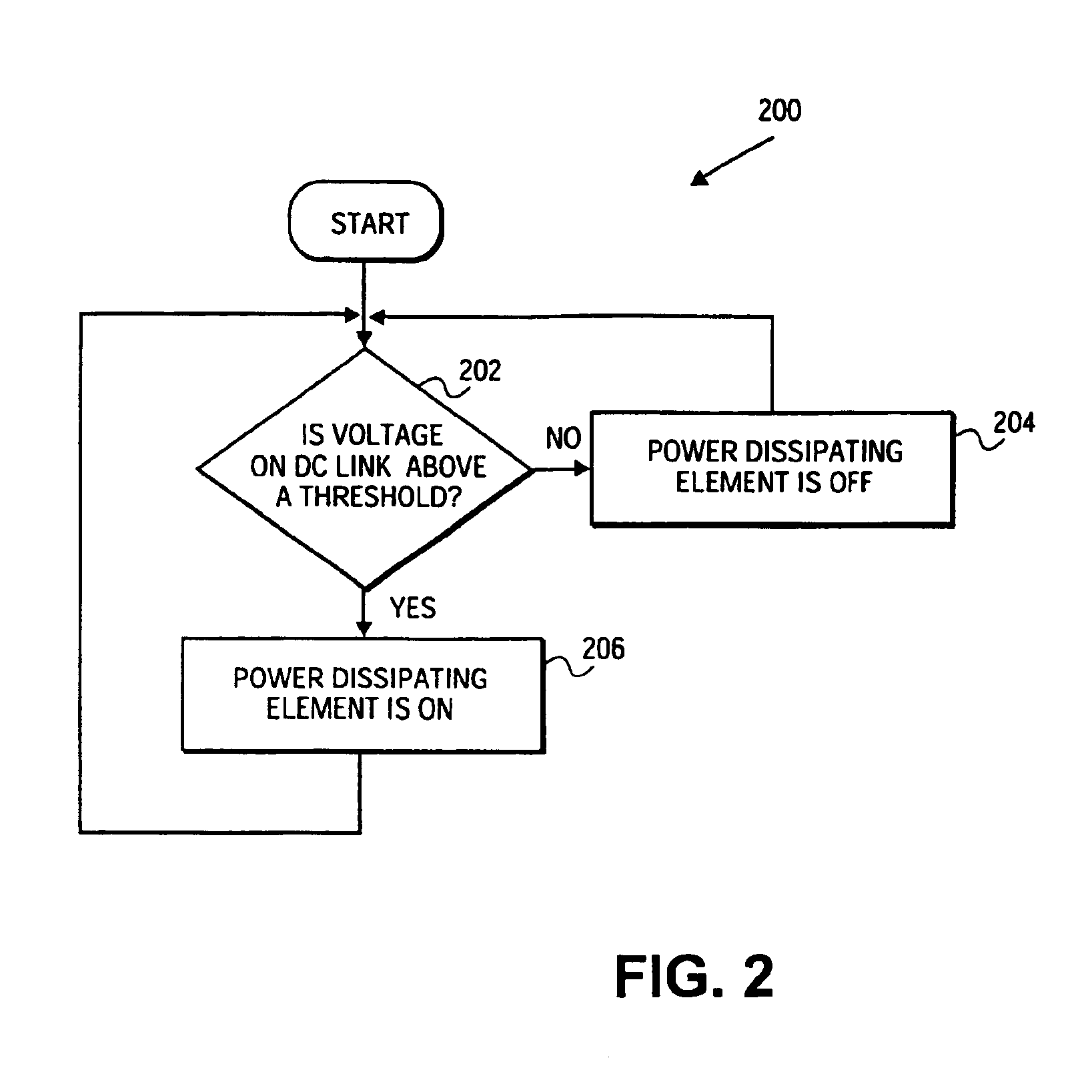
InactiveUS6850821B2Raise the ratioIncrease of component fatigueLevel controlWind motor controlPeaking power plantPower station
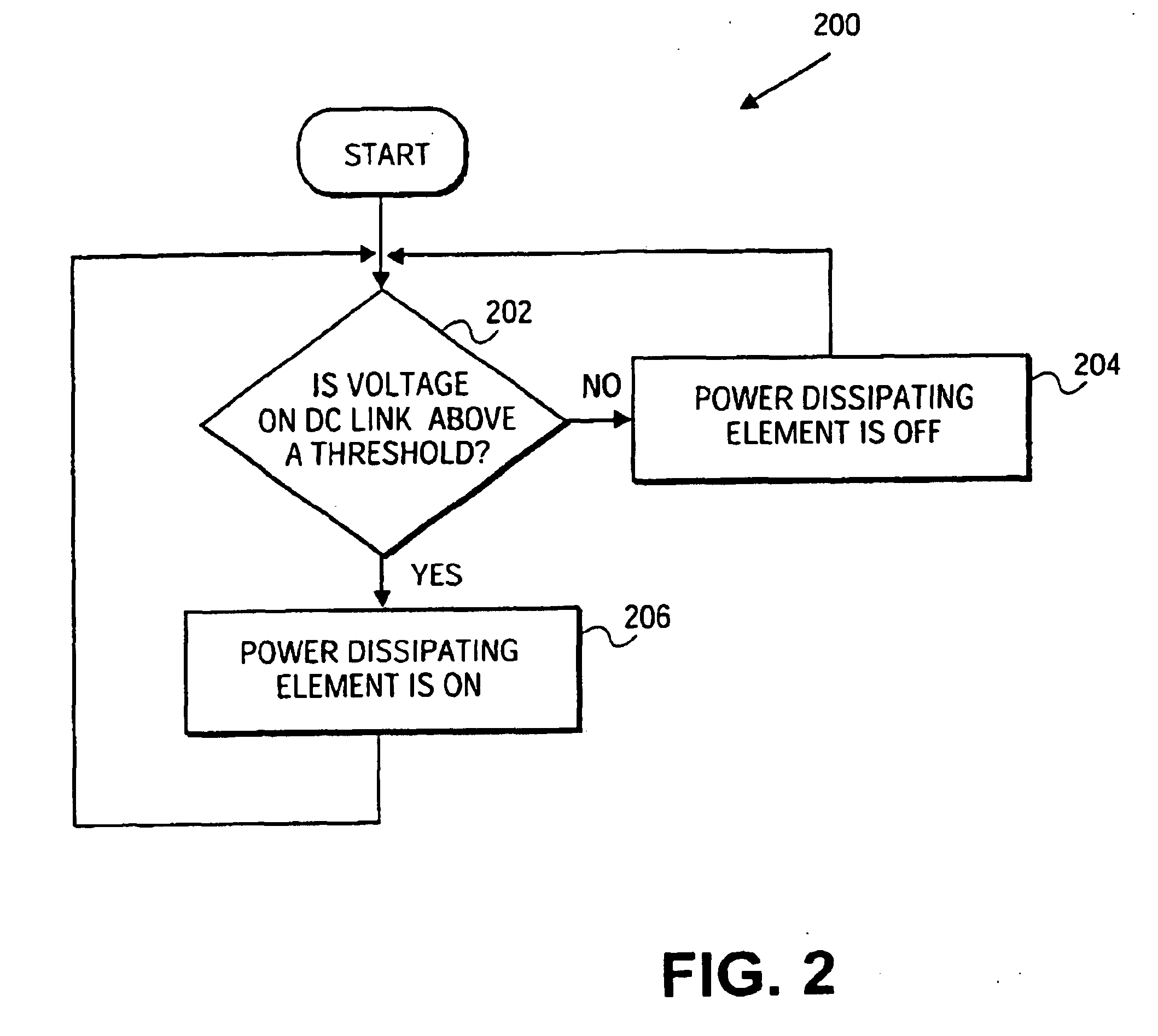
A control system for a wind power plant that includes a damage module and a control module. The damage module compares existing stress conditions on one or more component parts of the wind power plant to current energy generating costs. The control module alters electric power generated by the wind power plant based upon the comparison.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System and methods for controlling a wind turbine
A method for controlling operation of a wind turbine is described. The wind turbine includes a rotor having a plurality of rotor blades and an upwind wind condition measurement device. The method includes measuring a wind condition upwind from the rotor using the upwind wind condition measurement device and providing the measured wind condition to a processor. The method also includes determining a control algorithm parameter, based at least partially on the measured wind condition, that controls at least one of a wind turbine response bandwidth, a wind turbine response speed, and a wind turbine control error range. The method also includes determining a wind turbine operating command based at least partially on the control algorithm parameter and applying the wind turbine operating command to operation of the wind turbine.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and device for regulating a wind machine
A method and corresponding apparatus for regulating a system that produces electric power, the system including an electric alternator having a rotor integral with a rotating part of a wind machine to form a rotary assembly, and a power electronics module, the method including the steps of: producing an alternating current at output terminals of the alternator; converting the alternating current produced by the alternator into modulated pulses of direct current. Alternating electric current produced by the alternator is regulated by controlling the speed of rotation of the rotary assembly by resisting torque imposed by the alternator in response to modulating the pulses of continuous current produced by the converted the alternating current.
Owner:JEUMONT
Variable speed wind turbine having a passive grid side rectifier with scalar power control and dependent pitch control
InactiveUS6856041B2Easy to controlImprove responsivenessOptimise machine performanceWind motor controlPower gridVariable speed wind turbine
A variable speed wind turbine having a passive grid side rectifier using scalar power control and dependent pitch control is disclosed. The variable speed turbine may include an electrical generator to provide power for a power grid and a power conversion system coupled to the electrical generator. The power conversion system may include at least one passive grid side rectifier. The power conversion system may provide power to the electrical generator using the passive grid side rectifier. The variable speed wind turbine may also use scalar power control to provide more precise control of electrical quantities on the power grid. The variable speed wind turbine may further use dependent pitch control to improve responsiveness of the wind turbine.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Variable speed wind turbine having a passive grid side rectifier with scalar power control and dependent pitch control
InactiveUS6853094B2Easy to controlImprove responsivenessWind motor controlEmergency protective circuit arrangementsPower gridVariable speed wind turbine
A variable speed wind turbine having a passive grid side rectifier using scalar power control and dependent pitch control is disclosed. The variable speed turbine may include an electrical generator to provide power for a power grid and a power conversion system coupled to the electrical generator. The power conversion system may include at least one passive grid side rectifier. The power conversion system may provide power to the electrical generator using the passive grid side rectifier. The variable speed wind turbine may also use scaler power control to provide more precise control of electrical quantities on the power grid. The variable speed wind turbine may further use dependent pitch control to improve responsiveness of the wind turbine.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
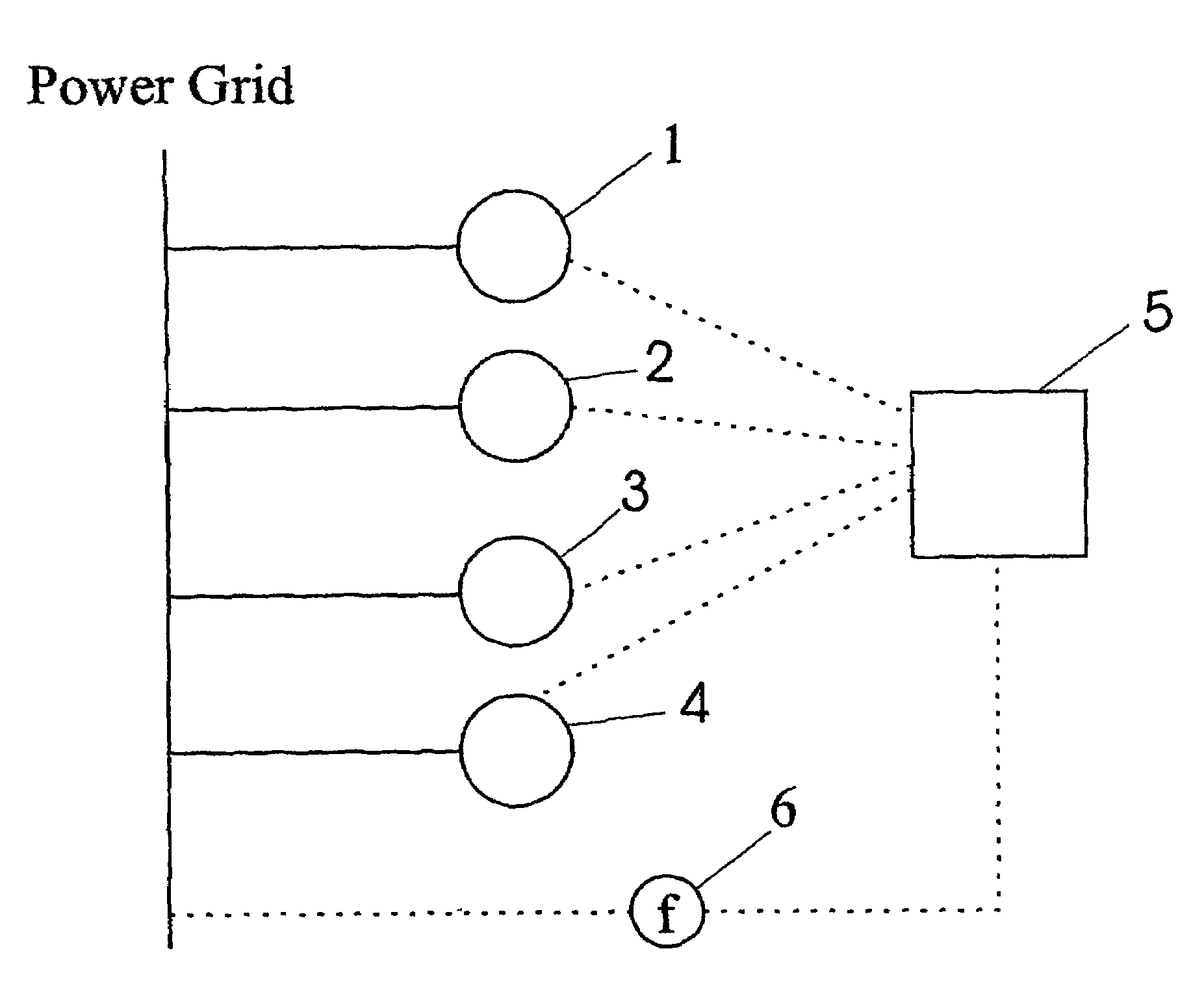
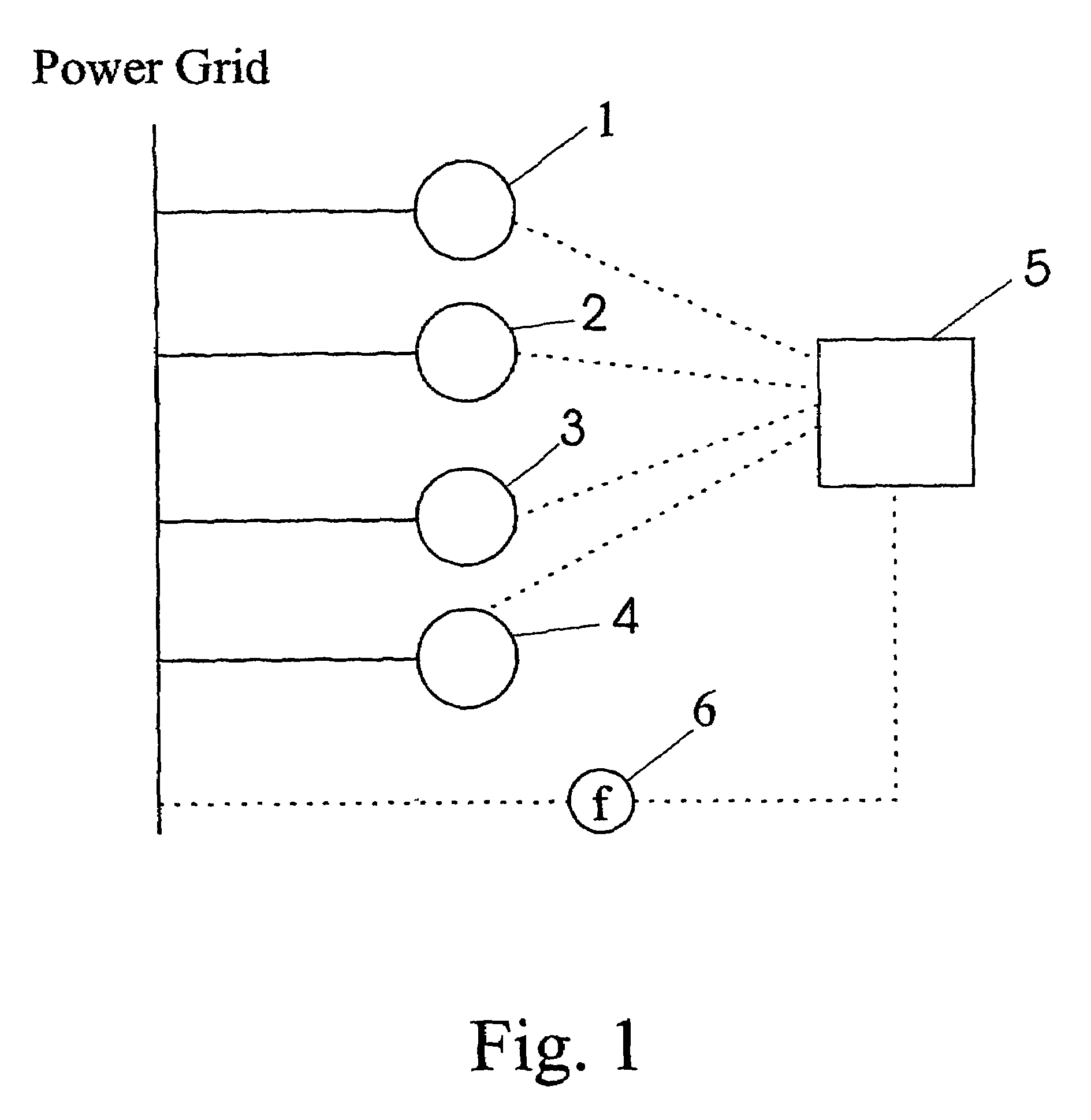
Wind farm and method for operating same
ActiveUS7372173B2Effective controlEasy to controlOptimise machine performanceWind motor controlPower gridTurbine
Owner:GE INFRASTRUCTURE TECH INT LLC
Method of operating a wind power plant
ActiveUS20130035798A1Reduce needUnbalanced loadLevel controlWind motor controlTime rangePower station
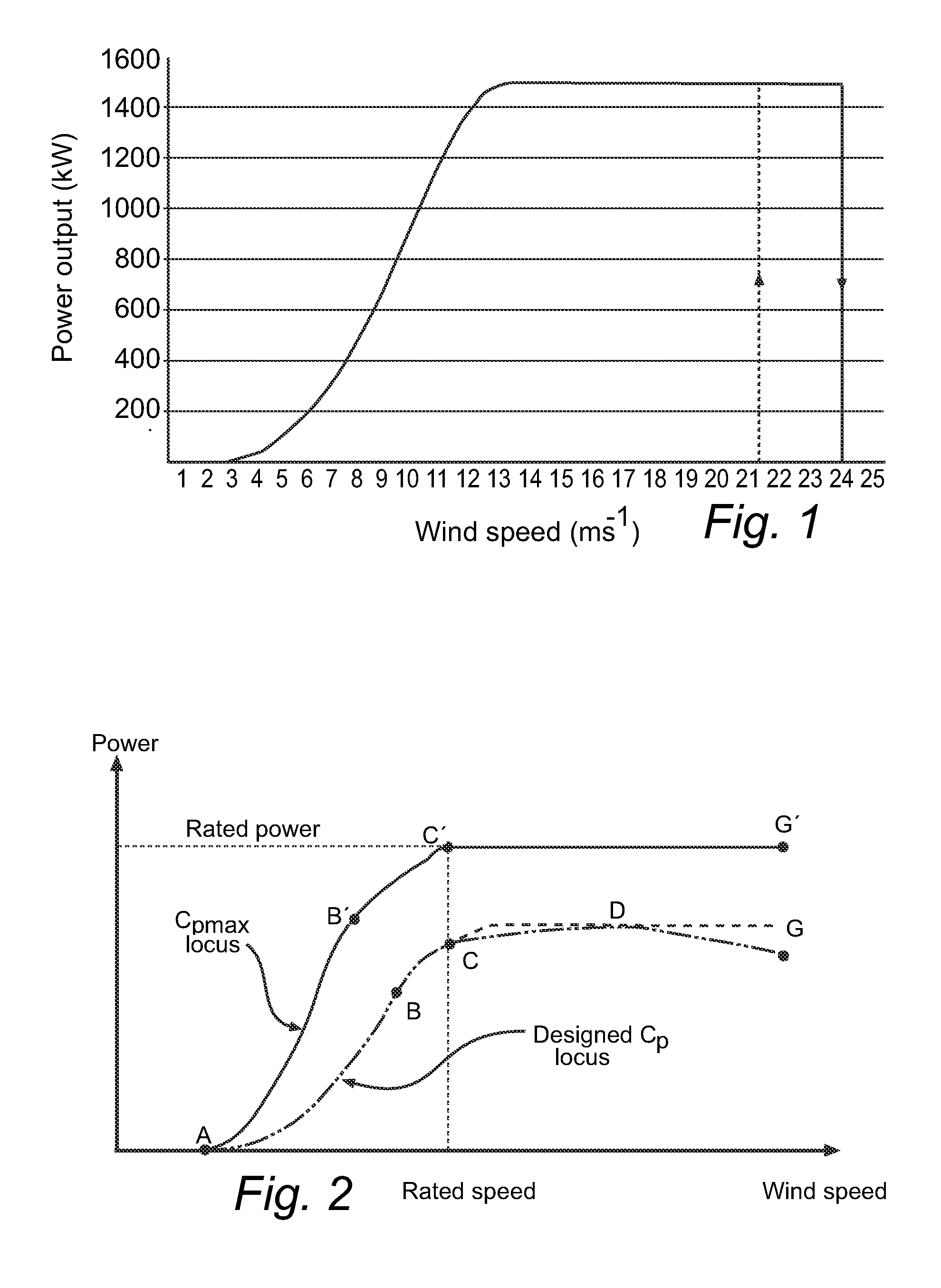
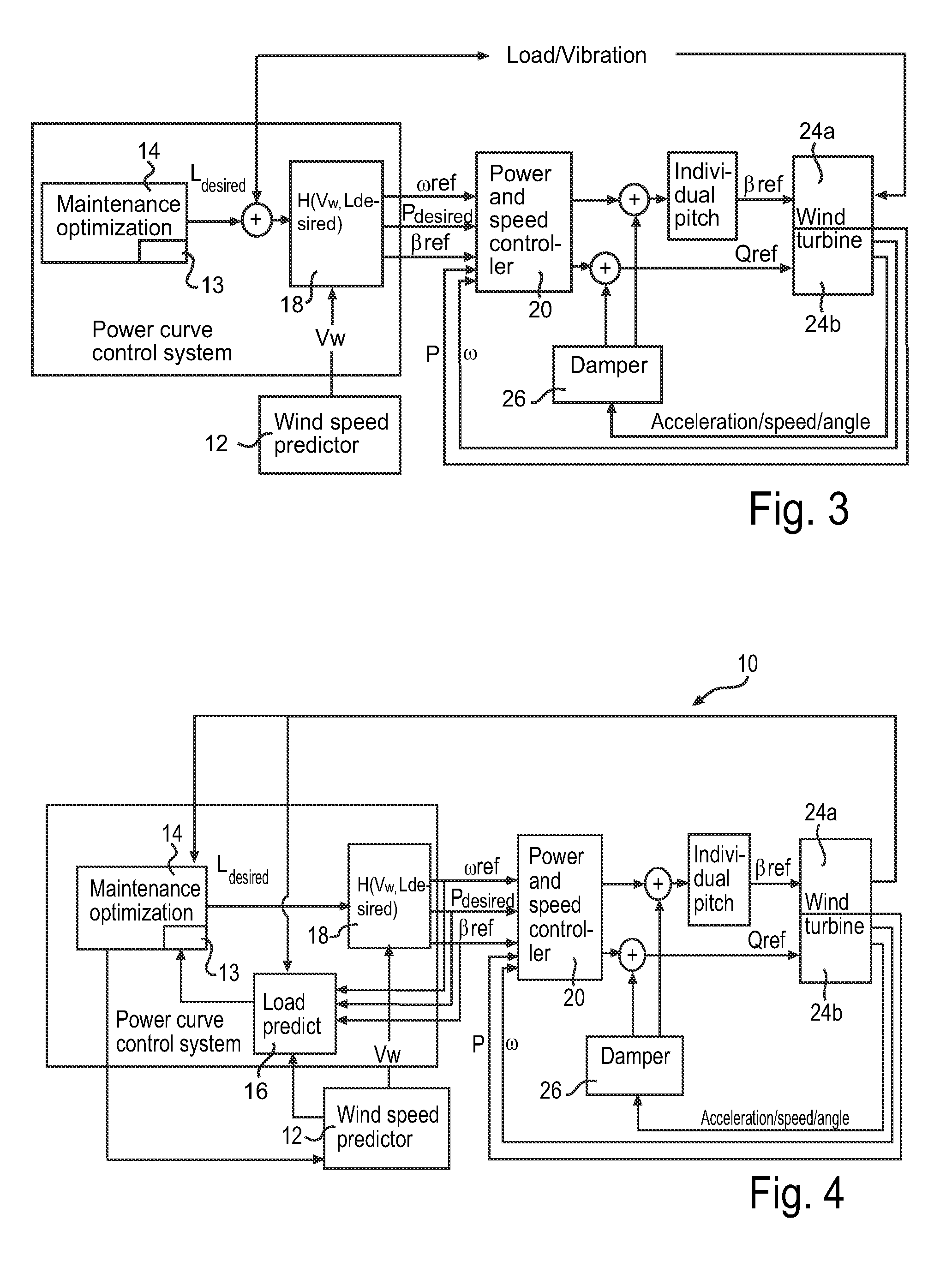
Method of operating a wind power plant including the steps of: operating the wind power plant at an current parameter schedule (Pcurrent(v)) performing a wind prediction of wind data (Vw) for a time frame (ΔT) extending to a future time T, determining a desired fatigue load level (Fdesired) of a wind power plant component at the future time T, and during operation of said wind power plant generating an updated parameter schedule (Pdesired(v)) to provide the desired fatigue load level (Fdesired) at time T if exposed to the predicted wind conditions (Vw(t)) during said time frame (ΔT)
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
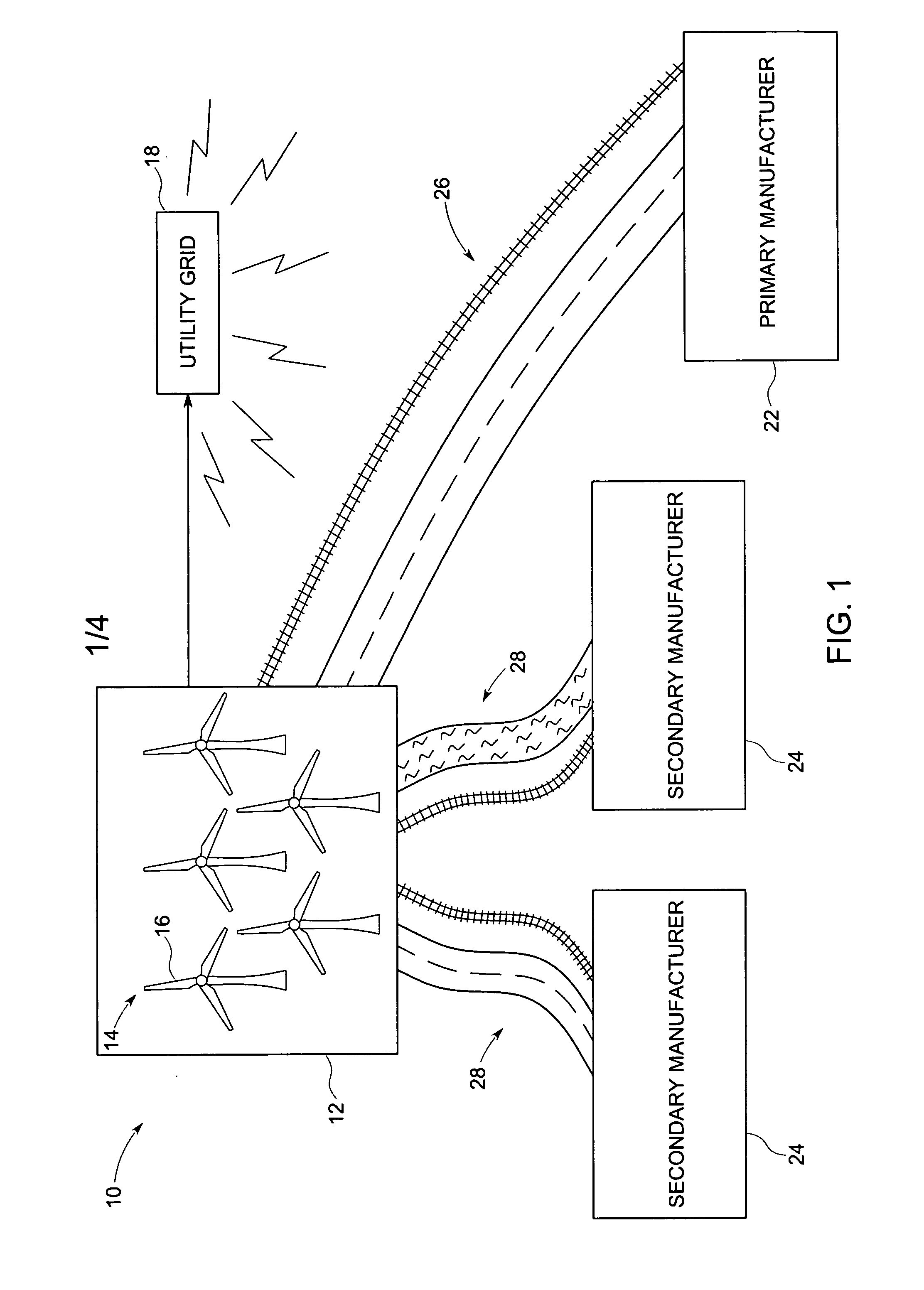
Wind blade construction and system and method thereof
A method for constructing a wind turbine blade for installation at a wind farm location is described herein. In accordance with the present method, primary components of the wind turbine blade, such as, for example, the root and the spar caps, are manufactured in a first manufacturing facility. Secondary components such as, for example, the skin, are manufactured at a second manufacturing facility, which is closer to the wind farm location than the first manufacturing facility. The manufactured primary and secondary components may be assembled in an assembly location near the wind farm.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Wind Turbine With Pitch Control Arranged To Reduce Life Shortening Loads On Components Thereof
ActiveUS20100014971A1Maximize power outputMinimizing variation of loadPropellersWind motor controlGravitational forceBlade pitch
A wind turbine is presented where the operation lifetime of the main bearing is extended by relieving the main bearing by reducing the mean bending moment on the bearing by means of individual pitch control of the blades of the rotor so as to create an aerodynamic mean tilt moment on the rotor by means of aerodynamic forces on the blades, the tilt moment at least partly counteracting the bending moment caused by the overhang load forces on the main bearing from the gravitational pull on the rotor mass.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Wind turbine having a control method and controller for performing predictive control of a wind turbine generator
ActiveUS20130106107A1Reduced operating wearReduce tearingOptimise machine performanceWind motor controlWind forceElectric generator
The application describes a wind turbine having a control method and controller for performing predictive control of a wind turbine generator. Based on the measured instantaneous wind speed, it is known to provide control signals to a wind turbine in order to control the pitch of the wind turbine rotor blades and the speed of the generator. However, it is difficult using instantaneous wind speed measurements to achieve smooth control, due to finite response speeds of the associated electro-mechanical systems, as well as the constantly changing control system inputs. The predictive control system described in the application assumes a model of generator speed based on the values of the incident wind speed v(t) and the values of a control signal u(t) output to the wind turbine in a feed forward loop. Here, the control signal can be for one or more of controlling either the power setting of the generator, or the pitch angle of the rotor blades. The predictive controller uses a rolling time series of values for v(t) and u(t) and based on a predicted response of the generator speed w(t) optimises the time series control signal u(t). The predicted response of the generator speed w(t) is based on model, that can be refined in real time as the wind turbine operates.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Wind energy system and method of operation thereof
ActiveUS20080001409A1High yieldImprove performanceOptimise machine performanceWind motor controlLearning controllerEngineering
A method for operating a wind energy system is provided comprising the steps of setting the value of an operational parameter of the wind energy system, measuring a yield parameter of the wind energy system and measuring a condition parameter. Further, the method comprises the step of calculating an optimized value of the operational parameter based on historical data and the outcome of the measurements. The method further comprises the step of resetting the operational parameter to the optimized value of the operational parameter wherein the resetting is such that the yield parameter is optimized. Further, a wind energy system is provided having a sensor unit for measuring a yield parameter of the wind energy system, a sensor for measuring a condition parameter, an actuator for adjustment of at least one adjustable part of the wind energy system, and a self-learning controller. The self-learning controller is connected to the sensor unit and the actuator and receives measurement data from the sensor unit. The self-learning controller performs optimization calculations based on the measurement data and sends instruction signals to the actuator based on the outcome of the optimization calculations for the adjustment of the adjustable part of the wind energy system. The instruction signals are such that the yield parameter is optimized.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Monitoring and data processing equipment for wind turbines and predictive maintenance system for wind power stations
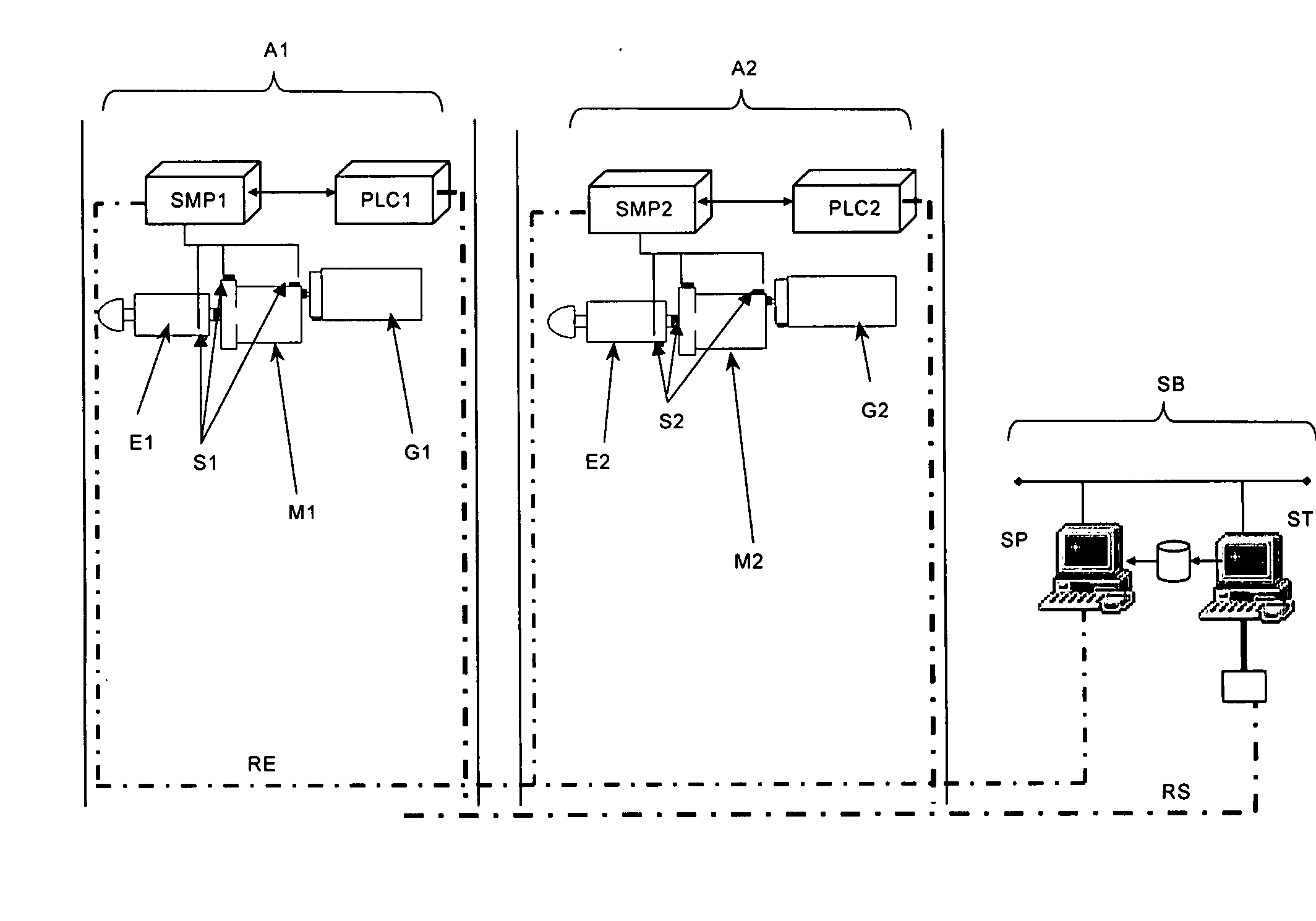
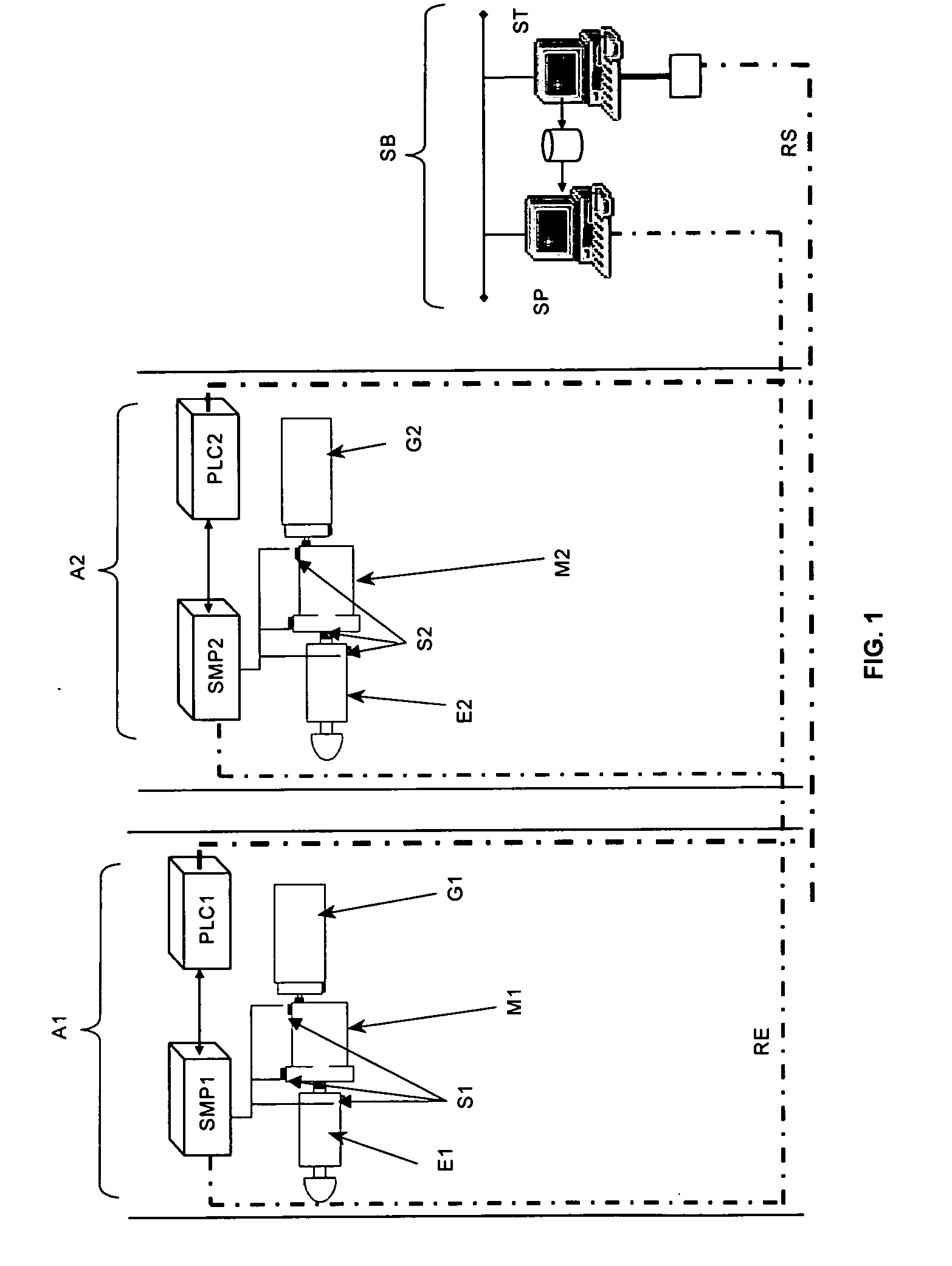
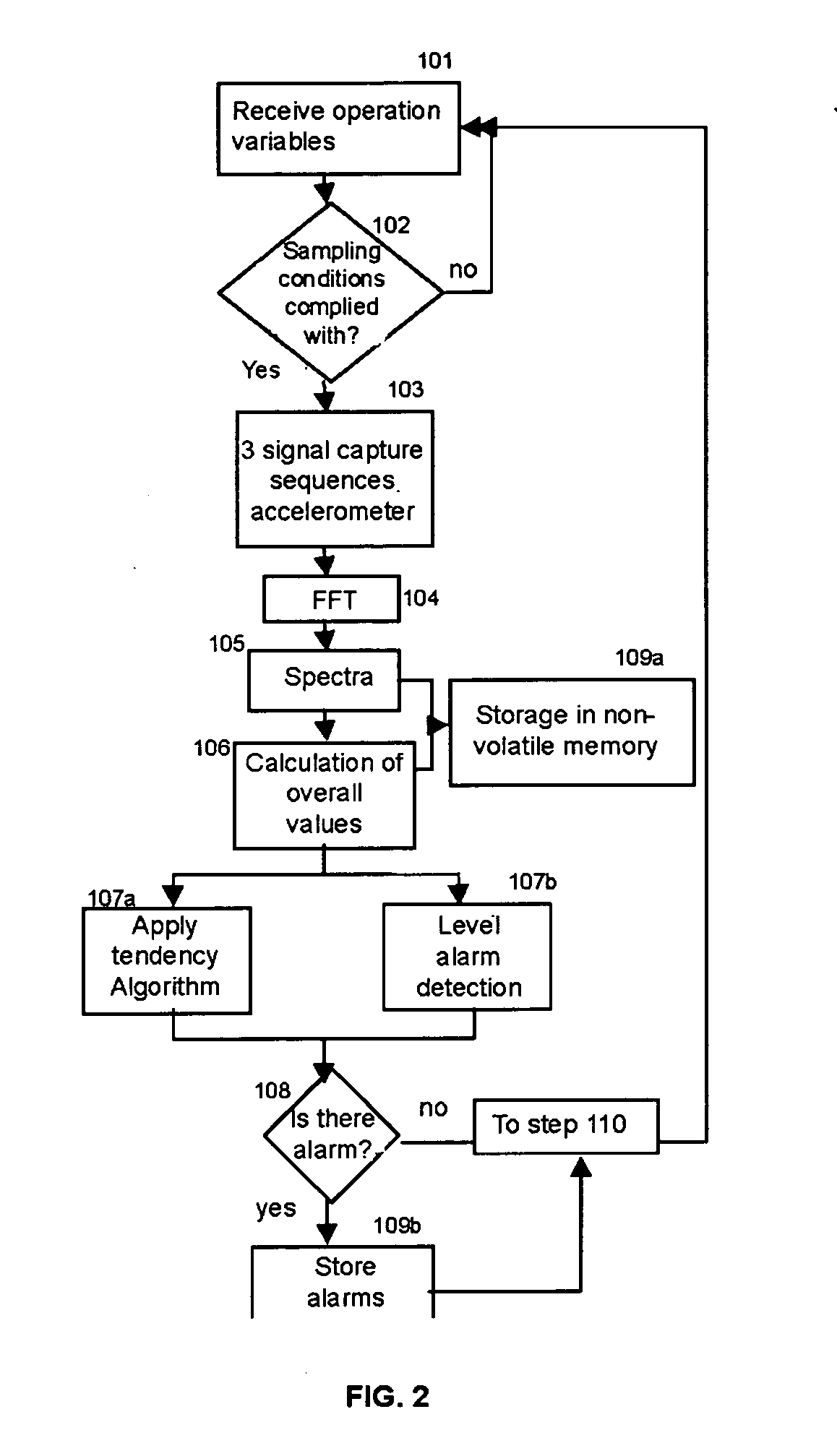
ActiveUS20070140847A1Reduce needVibration measurement in solidsWind motor controlPower stationControl system
A predictive maintenance system for wind parks, the wind park comprising a group of wind turbines (Ai), a communications network (RS) and a supervision and control system (ST) The predictive maintenance system comprises a monitoring and processing equipment (SMP) connected to the control system (PLC) of the wind turbine (Ai), such that the monitoring and processing equipment sends alarms through the control system of the wind turbine to the supervision and control system. The invention also refers to a monitoring and processing equipment (SMP) for wind turbines.
Owner:GAMESA INNOVATION & TECH SA
Wind turbine yaw control
ActiveUS20140037447A1Great power productionEasy to produceOptimise machine performancePropellersYaw systemEngineering
A method for operating a wind farm is provided. The method includes determining a wind condition, determining a wake-effect between at least two wind turbines forming at least a sub-set of the wind farm, each of the at least two wind turbines having a yaw system, and determining a desired yaw angle setpoint for each of the at least two wind turbines so that a total power production of at least the sub-set is expected to be increased compared to independently operating the yaw systems of each of the at least two wind turbines. Furthermore, a wind farm is provided
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
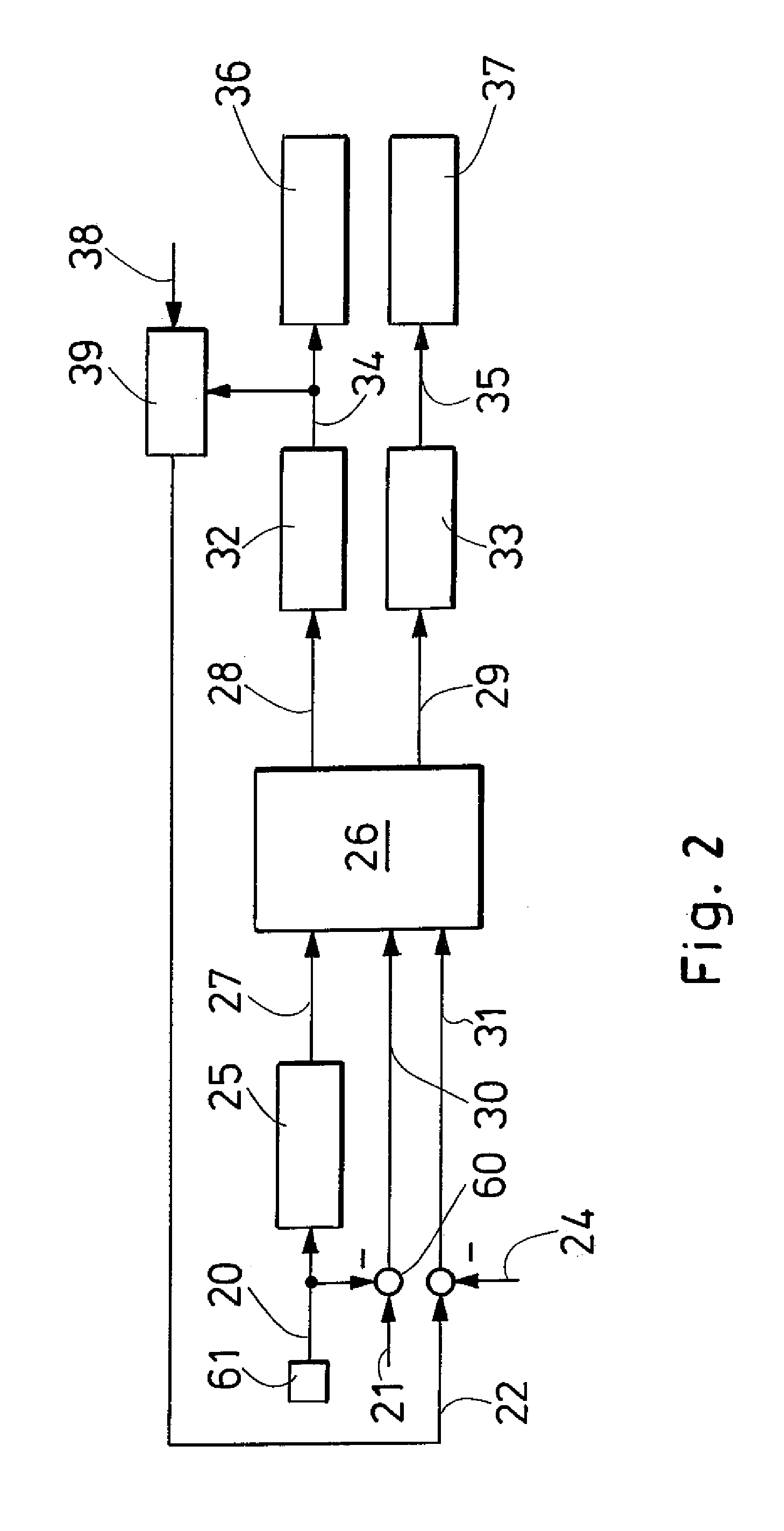
Method and system for regulation of the rotational speed of a rotor on a wind turbine
ActiveUS20080136188A1Increase energy outputEfficient identificationOptimise machine performanceWind motor controlTurbineControl theory
The invention relates to a method and a system for regulation of the rotational speed (52) of a rotor on a wind energy unit with a generator and a rotor blade. The first set parameter is a pitch angle (Pitch) of the rotor blade and the second set parameter is the torque of the generator. The system comprises a pitch angle control or regulation device (32), a torque control or regulation device (33), a first device for determination of a first rotational speed set value (28) (first rotational speed set value determination device (29)) and a second device (26) for determination of a second rotational speed set value (29) (second rotational speed set value determination device (26)). The first rotational speed set value (28) may be supplied to the pitch angle control or regulation device (32) and the second rotational speed set value (29) may be supplied to the torque control or regulation device (33), wherein the first and second rotational speed set value (28, 2)) may be different from each other.
Owner:SENVION DEUT GMBH
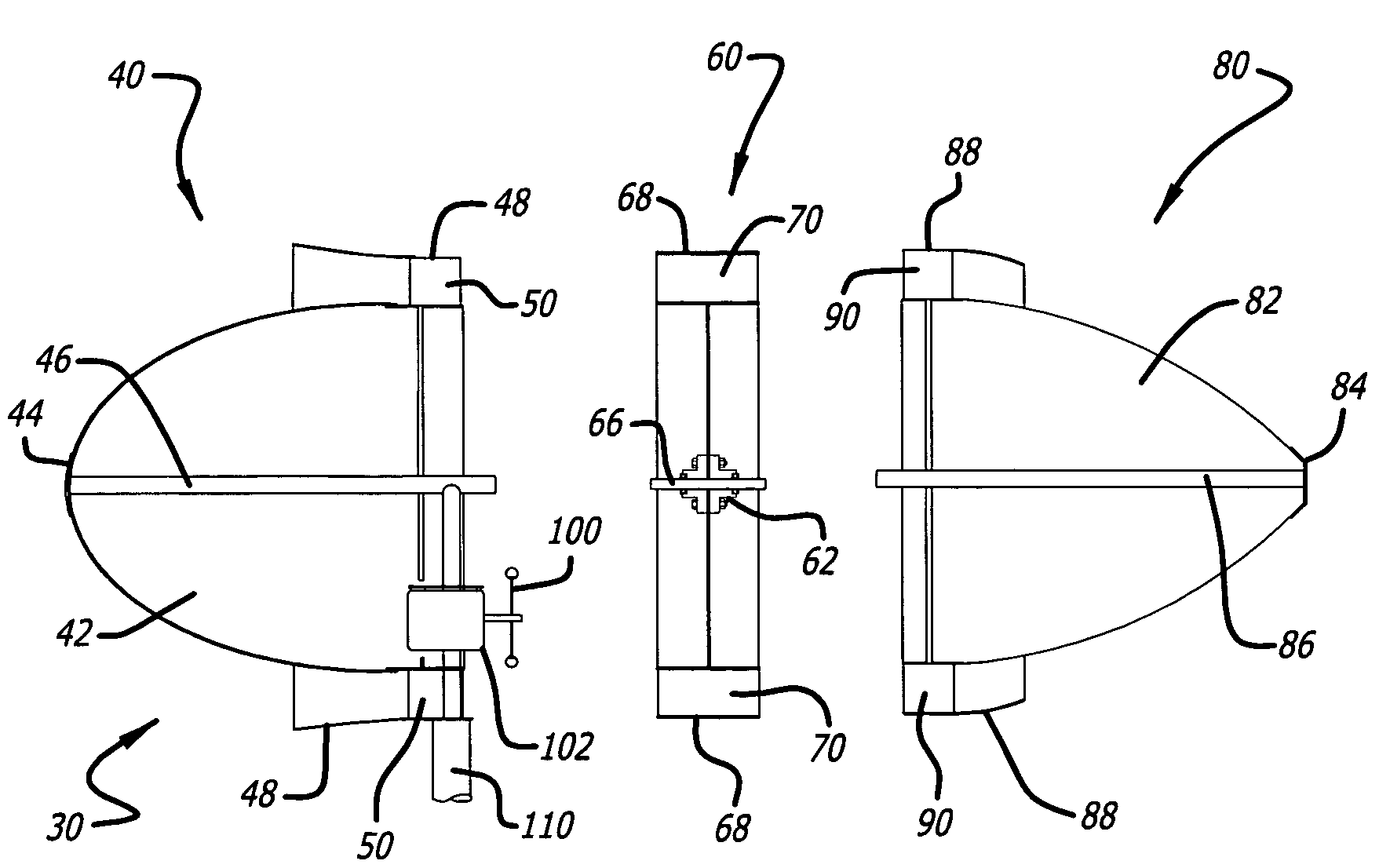
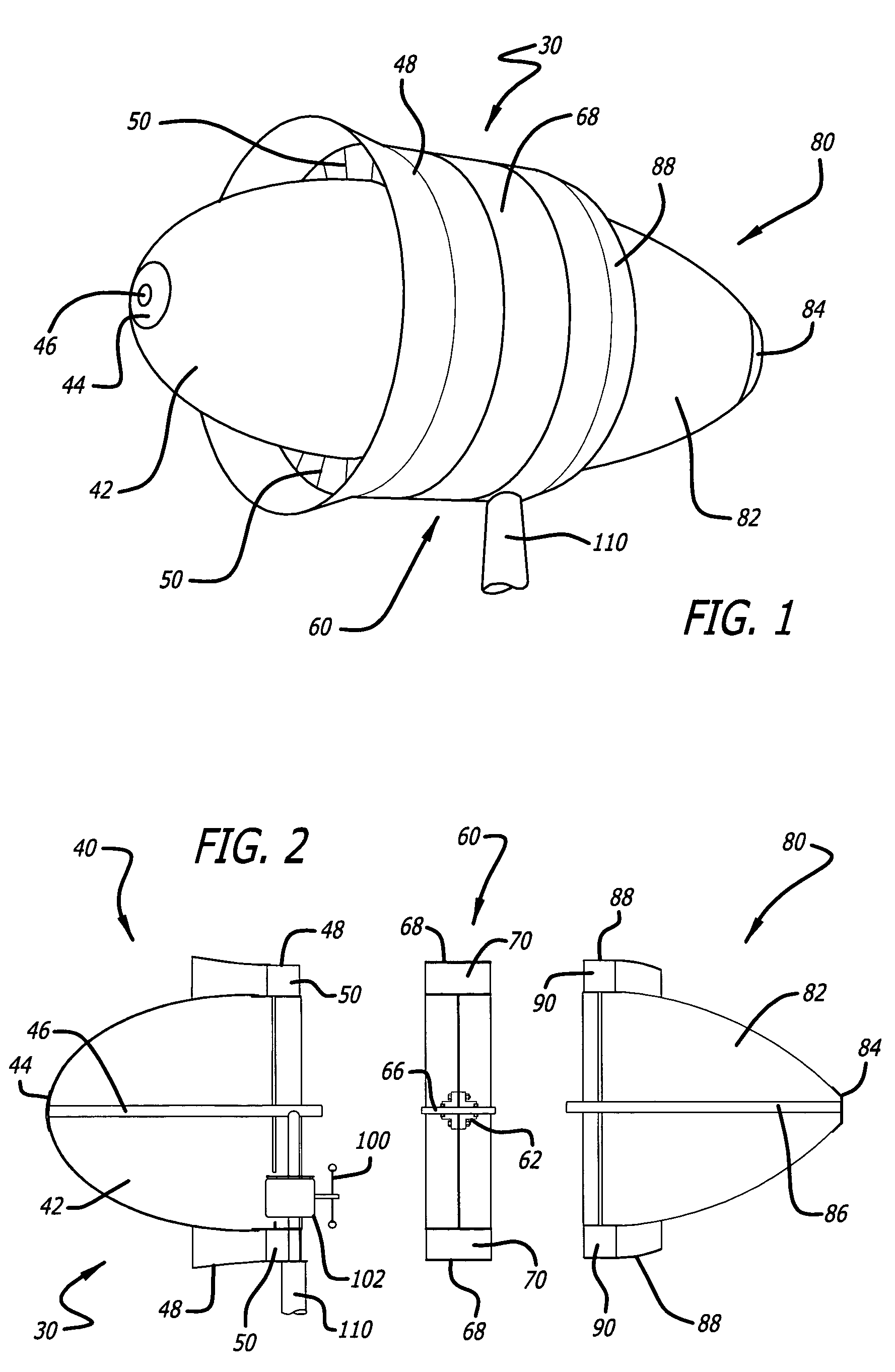
Laminar air turbine
InactiveUS7214029B2Low costMaximize rotational forcePump componentsWind motor controlWind drivenTurbine wheel
The windmill assembly is a low drag, streamlined body of revolution that captures the kinetic energy content of the accelerated laminar air surrounding the body. The assembly includes a power-generating, wind-driven turbine that is compact, lightweight and capable of producing a substantially greater output than a conventional windmill with a comparable size rotor. The turbine includes a protruding aerodynamic nose and outer cowling that provide a streamlined, wind-collecting inlet section that constricts the incoming air stream and increases its velocity through the turbine blades. The turbine further includes an exit section designed to exhaust the air stream with a minimum of turbulence. One or more generators are coupled to a turbine wheel, and are electrically switched on and off to maximize the energy capture over the full range of ambient winds. The wind turbine assembly may be configured around a blimp-type body having counter-rotating turbine assemblies.
Owner:RICHTER DONALD L
Method for adapting a wind energy installation to given wind conditions
InactiveUS20070067067A1Short response timeFull adjustmentPropellersLevel controlAngle of incidenceTemporal resolution
A method for operating a wind energy installation, in particular for adapting a wind energy installation (10) to given wind conditions, the wind energy installation (10) having a rotor (16), which can be driven by wind, with at least two rotor blades (20), whose respective angles of incidence of the wind can be adjusted by means of at least one adjustment device, and having a generator for converting the mechanical energy of the rotor (16) to electrical energy. During operation of the wind energy installation, parameters are measured with spatial and / or temporal resolution on the side of the wind energy installation (10) facing the wind, said parameters describing the wind conditions in the measurement region, preferably the wind speed and / or the wind direction. The wind parameters are measured at various vertical distances from the ground, namely various heights, and at horizontal distances from the rotor (16), which are selected such that the angles of incidence of the wind on the individual rotor blades (20) can be adapted in response to the measured wind parameters before the wind on which the wind parameters are based, in particular a wind front or a gust of wind, reaches the rotor (16). Values are predicted or calculated, in particular continuously or periodically, from the measured wind parameters—prognosis values—which describe wind conditions occurring in the future at the rotor blades for various heights. The angles of incidence of the wind on the individual rotor blades (20) are adjusted individually and independently of one another, preferably a plurality of times during a complete revolution of a rotor blade, depending on these predicted or calculated prognosis values at the various heights.
Owner:VOLKSWIND
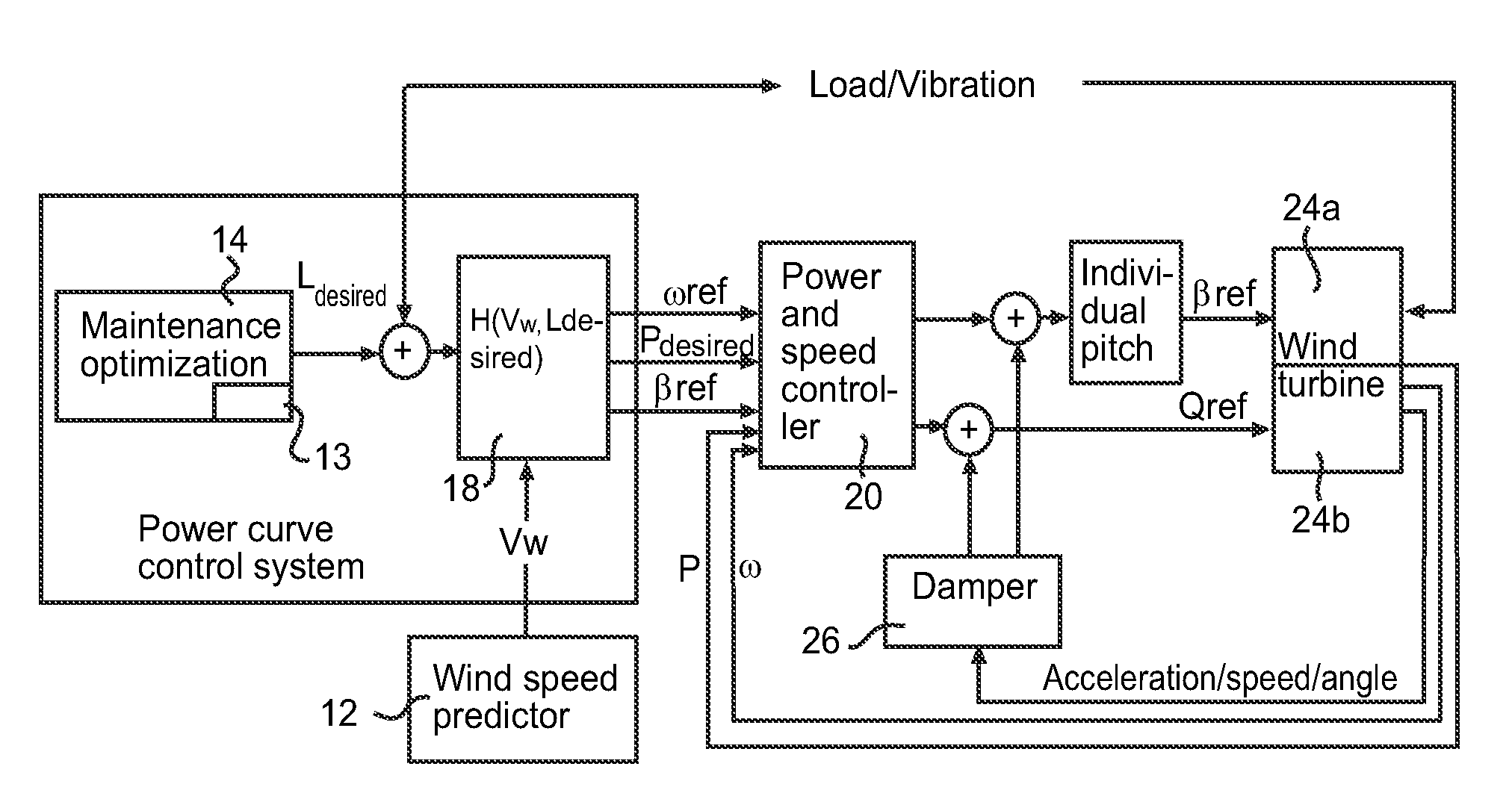
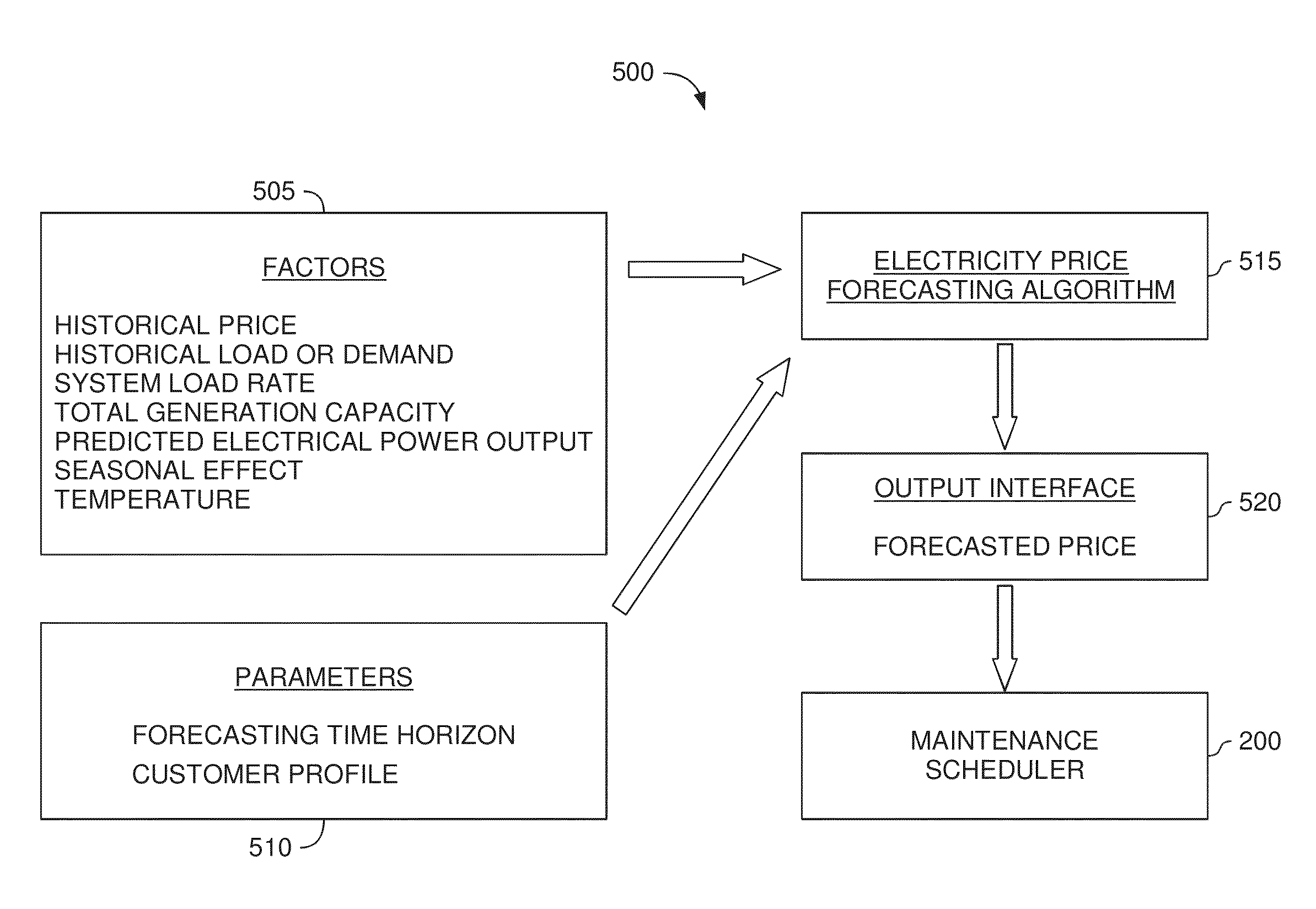
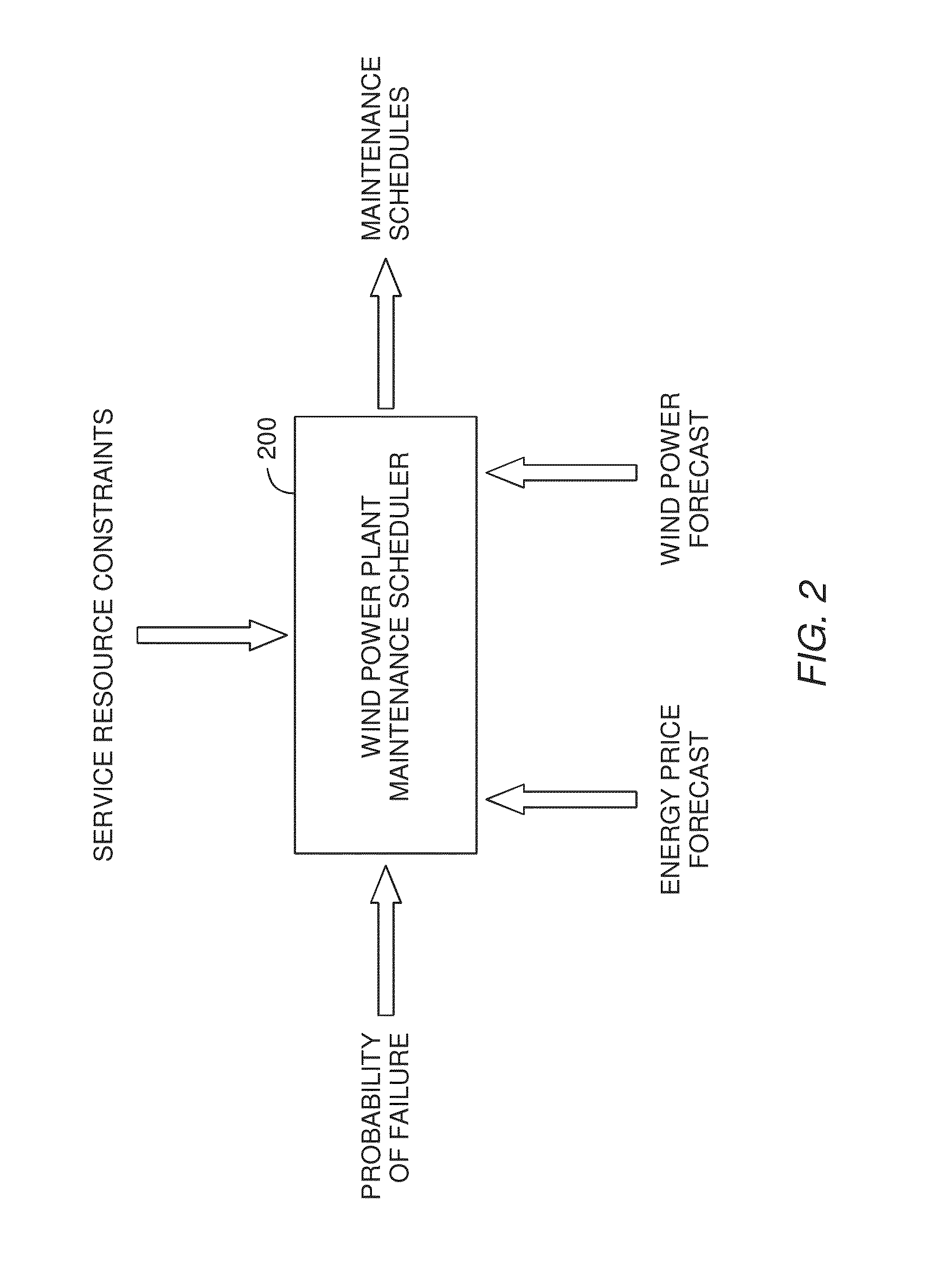
Wind turbine maintenance optimizer
Determining when to perform preventative maintenance is an important consideration for maximizing the revenue of a wind turbine. For example, performing preventative maintenance may be cheaper than replacing turbine components when they fail. When determining to perform preventative maintenance, a maintenance scheduler may consider multiple factors. These factors may include the probability of failure, the predicted price of energy, predicted wind power production, resource constraints, and the like. Specifically, the maintenance scheduler may predict the future values of these factors which are then integrated into a net present value (NPV) for each of the components. Based on the respective NPVs, the maintenance scheduler may determine which maintenance actions to perform and in what order.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
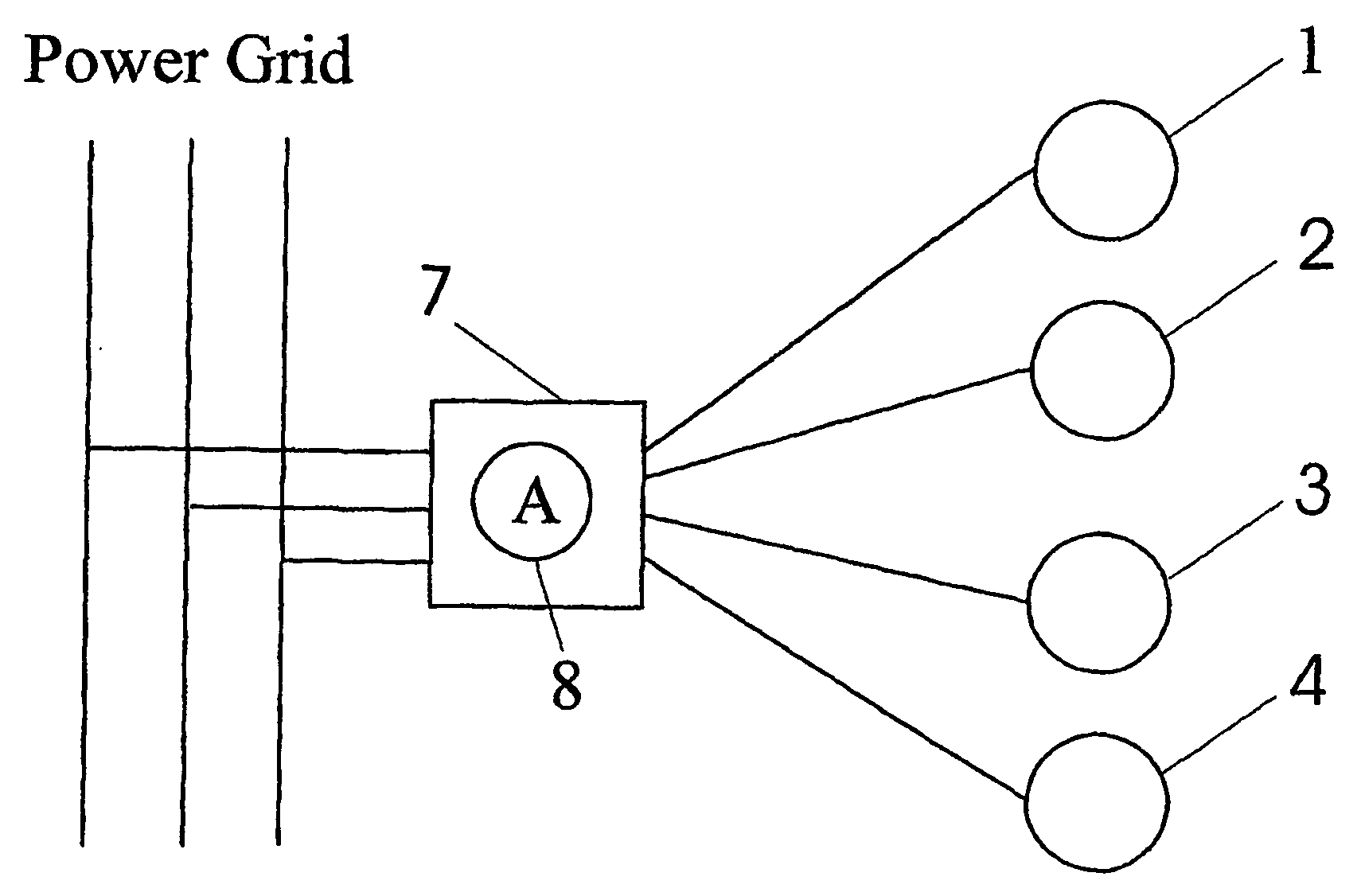
Wind farm and method for operating same
ActiveUS20070047163A1Effective controlEasy to controlOptimise machine performanceWind motor controlPower gridTurbine
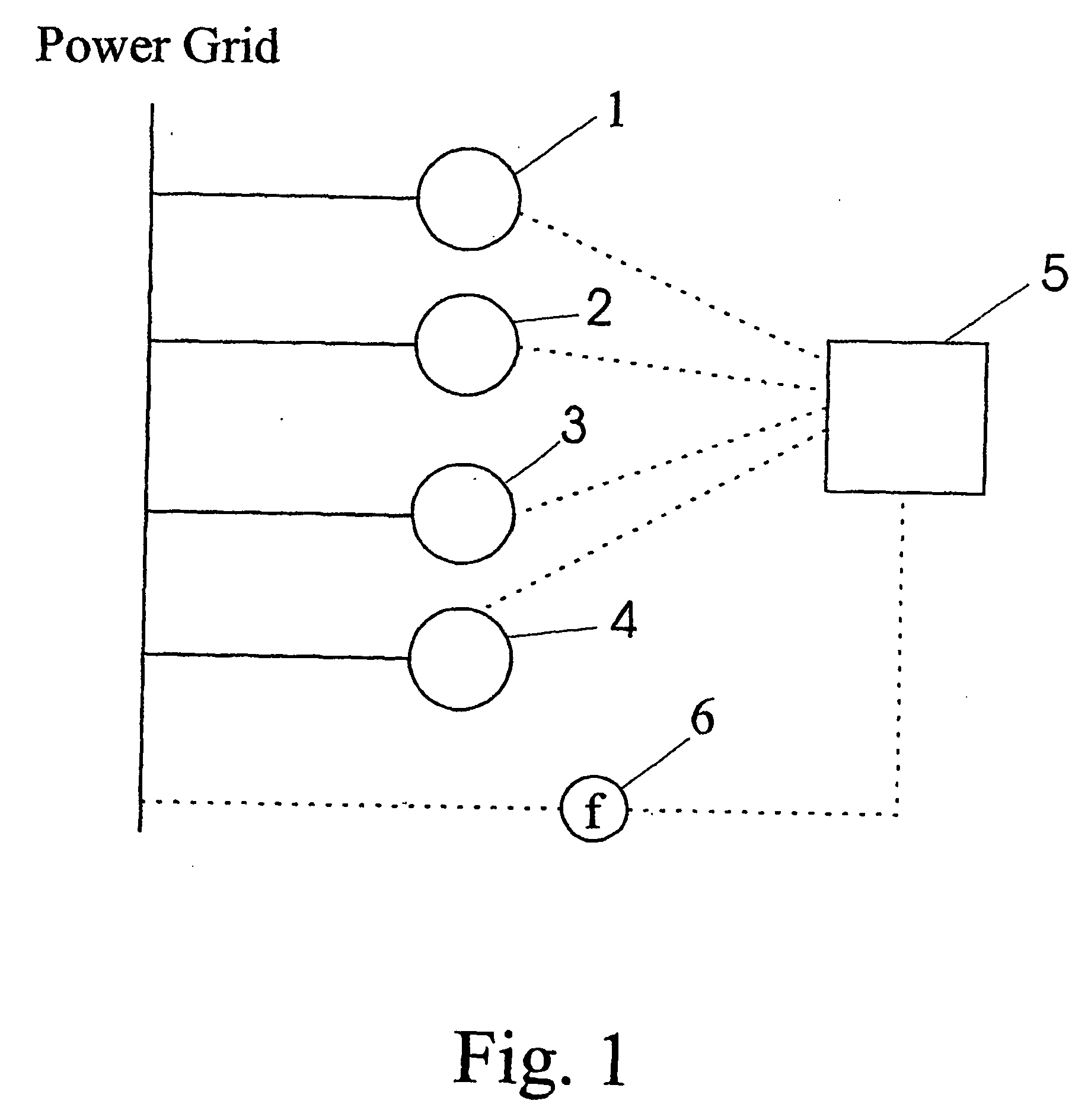
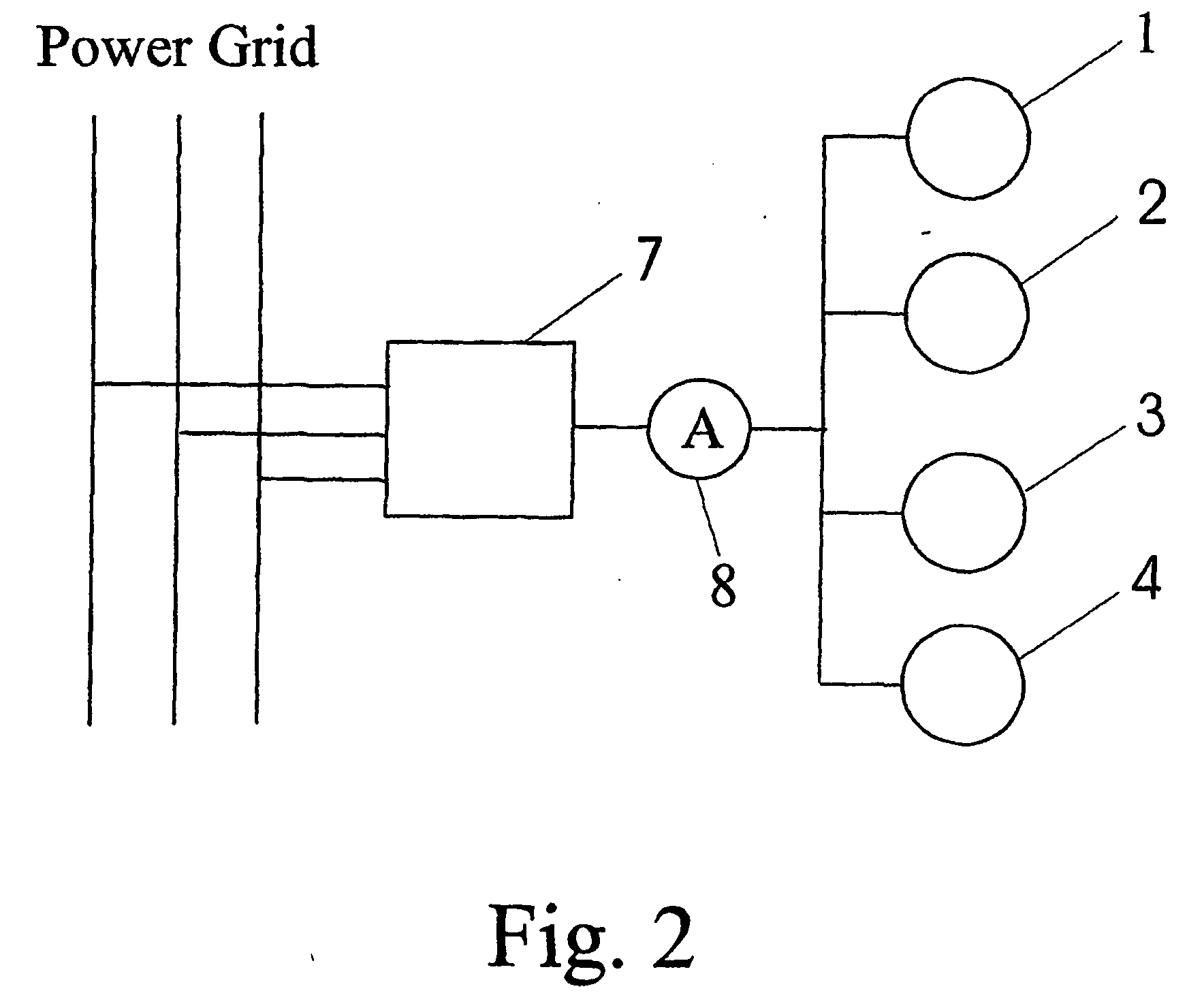
A wind farm with at least two wind turbines (1, 2, 3, 4) connected to a power grid is provided, said wind farm further comprising a control unit (5) connected to said at least two wind turbines (1, 2, 3, 4), and a sensor unit (6) connected to said power grid and said control unit (5), wherein said sensor unit (6) is adapted to measure the grid frequency of said power grid and to transmit said measured grid frequency to said control unit (5), and wherein said control unit (5) is adapted to control the output of real power of said wind farm according to said measured grid frequency. Furthermore, a method for operating a wind farm is proposed, said method comprising the steps of measuring the grid frequency with a sensor unit, transmitting said measured grid frequency to a centralized control unit, determining whether the measured grid frequency lies outside a predetermined range, and, if the measured grid frequency lies outside said predetermined range, selecting at least one out of the at least two wind turbines comprised in said wind farm by said centralized control unit and regulating the power output of said selected at least one wind turbine.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Wind turbine blade wirh lift-regulating means
ActiveUS20070003403A1Smooth and gradual change in liftSimple wayPropellersPump componentsTurbine bladeBiological activation
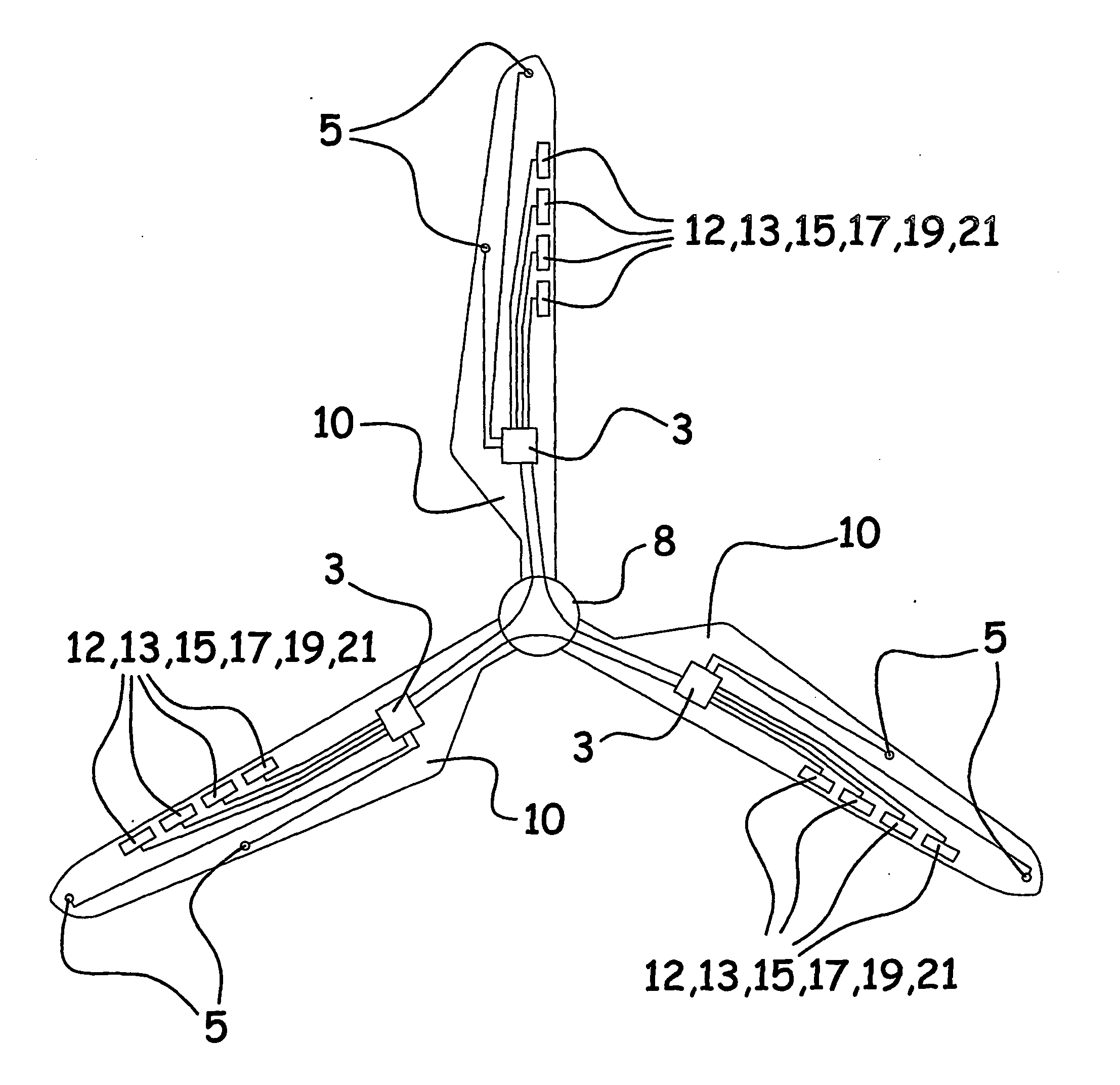
Wind turbine blade (10) including adjustable lift-regulating means (12, 13, 15, 17, 19, 21) arranged on or at the surface of the wind turbine blade (10), said lift-regulating means being provided with activating means by means of which they can be adjusted and thus alter the aerodynamic properties of the blade (10). The lift-regulating means (12, 13, 15, 17, 19, 21) and the activating means are adapted and arranged such that by activation of the activating means, the lift can be reduced in a zone extending in the longitudinal direction of the blade (10) from a first position adjacent the blade tip (14) to a second position between the first position and the blade root (16) and this second position is variable in the longitudinal direction of the blade (10) by adjusting the activate means. The lift-regulating means are formed of at least one flexible flap (12, 13, 15, 17, 19, 21). The invention further relates to a wind turbine rotor including such wind turbine blades, to a wind turbine and to a method of controlling the wind turbine.
Owner:LM GLASSFIBER
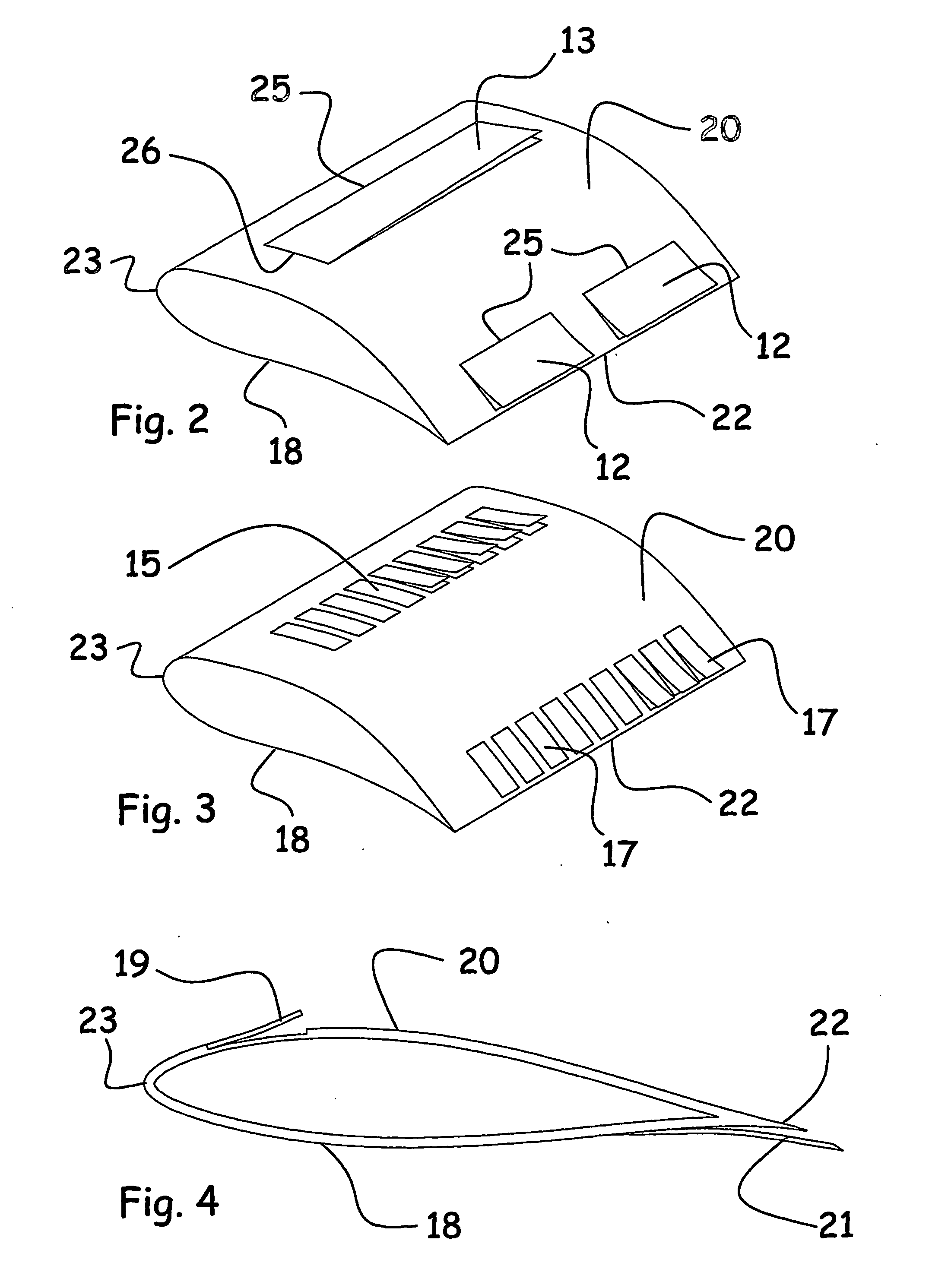
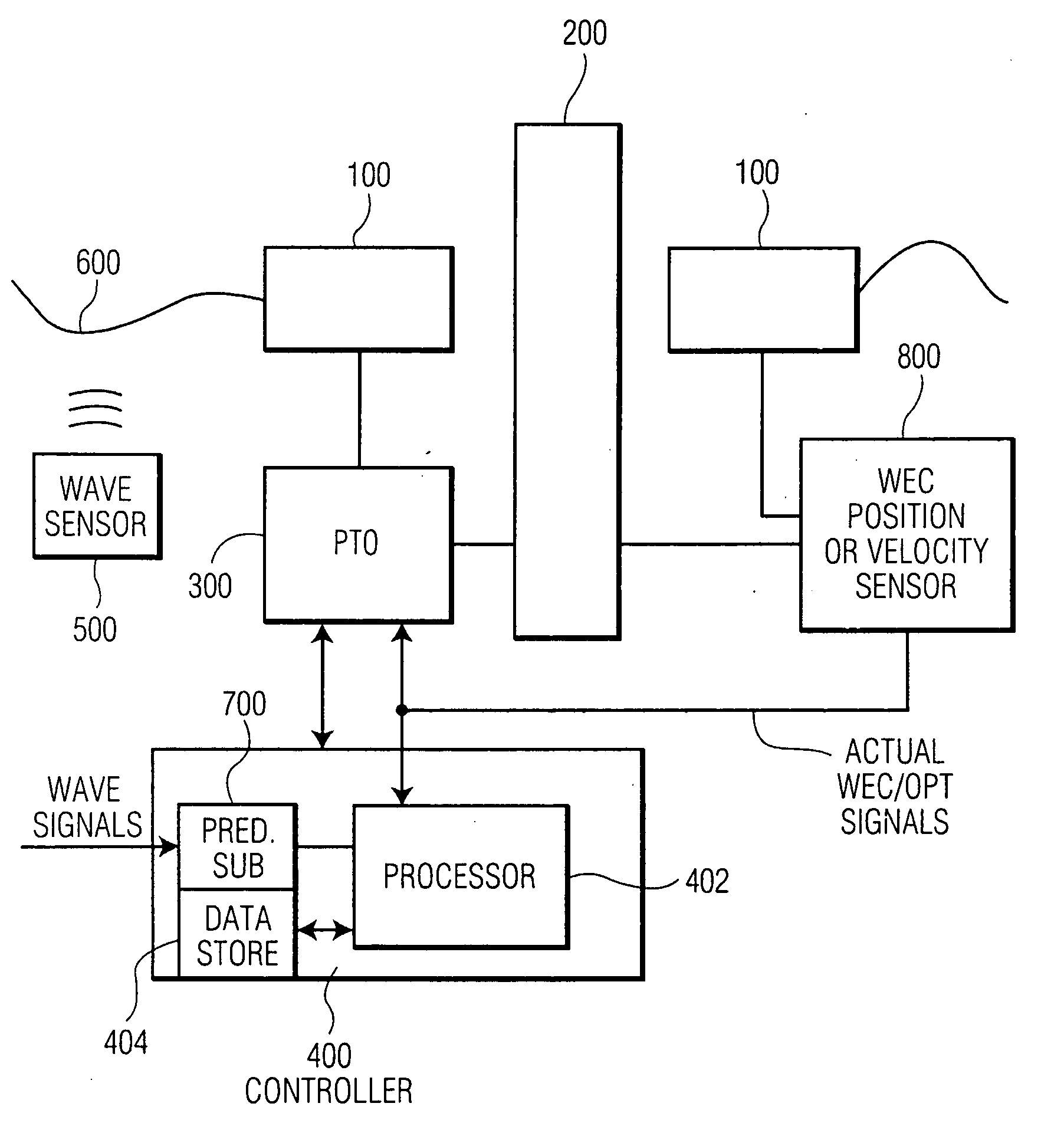
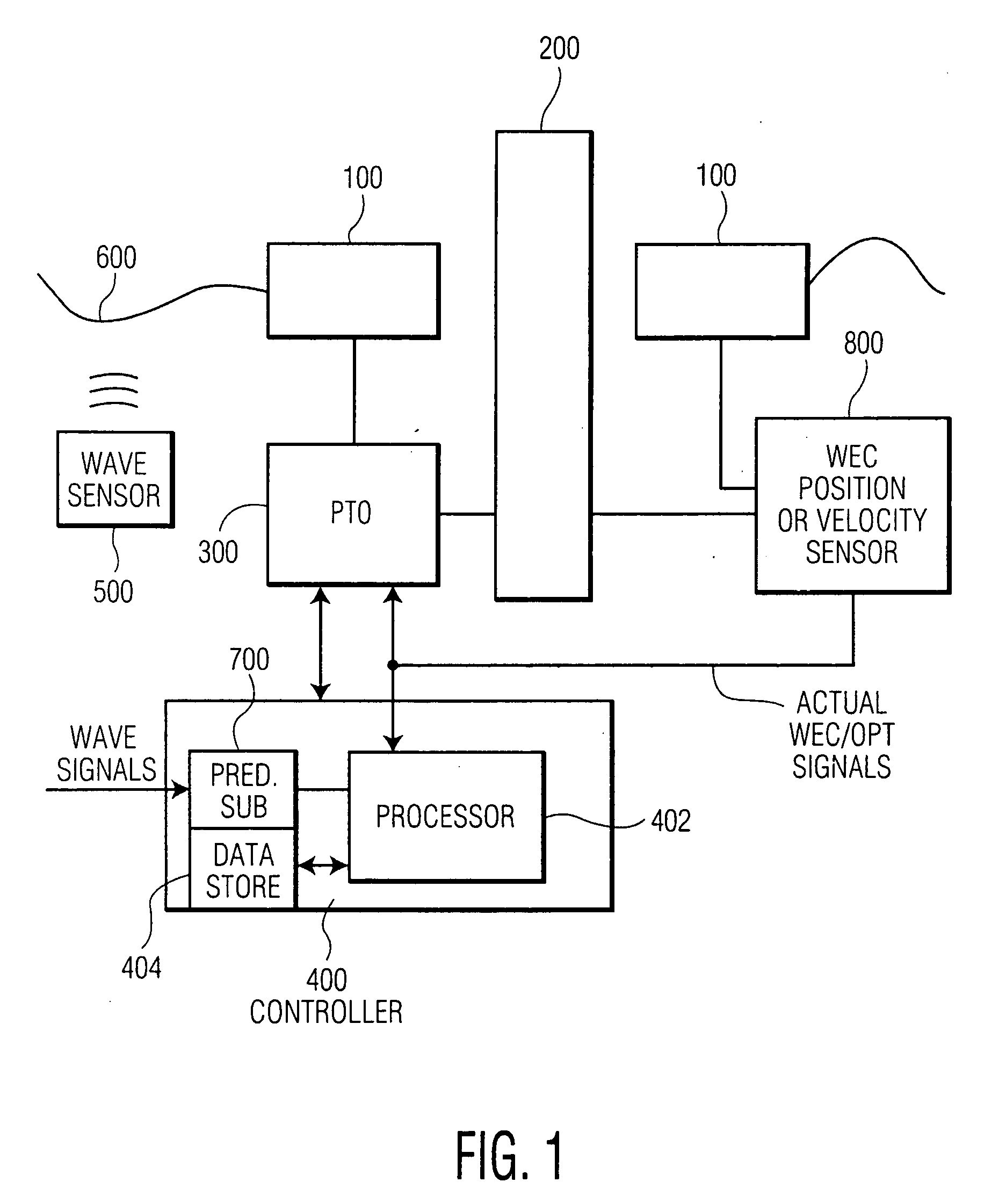
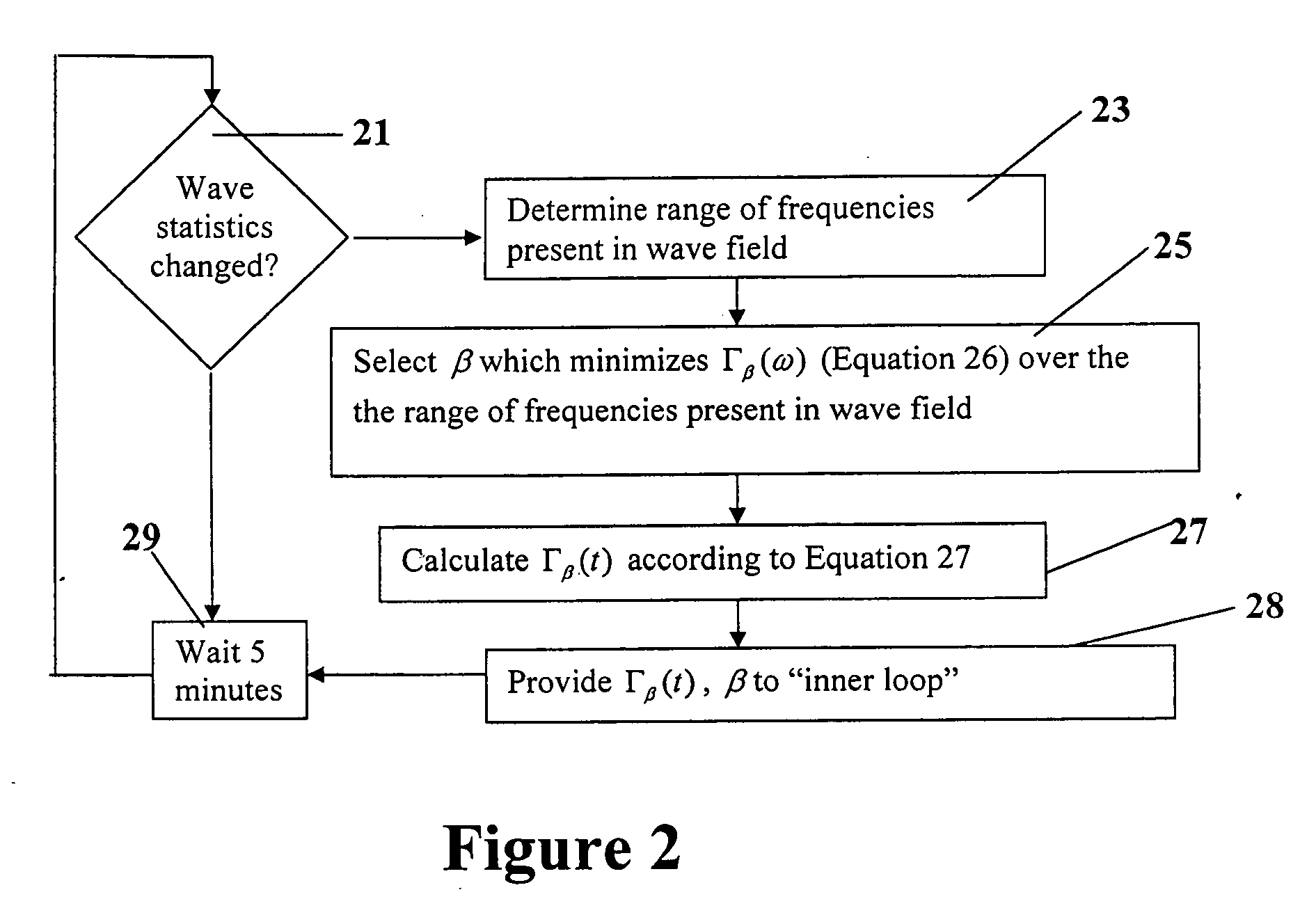
Advanced wave energy converter control
ActiveUS20100148504A1Simple control systemLess errorOptimise machine performanceEngine fuctionsRelative motionEngineering
A wave energy converter (WEC) system includes first and second bodies which can move relative to each other in response to waves and a power-take-off (PTO) device coupled between the two bodies to convert their relative motion into energy. A sensor is used to sense selected characteristics of an incoming wave and produce signals which are applied to a control computer for predicting the impact of the incoming waves on the WEC. Simultaneously, signals indicative of the actual conditions (e.g. the velocity) of the WEC are also supplied to the control computer which is programmed to process the predicted and actual information in order to generate appropriate signals (forces) to the components of the WEC such that the average wave power captured by the PTO is maximized.
Owner:OCEAN POWER TECHNOLOGIES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com