Patents
Literature
2615 results about "Alternator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An alternator is an electrical generator that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy in the form of alternating current. For reasons of cost and simplicity, most alternators use a rotating magnetic field with a stationary armature. Occasionally, a linear alternator or a rotating armature with a stationary magnetic field is used. In principle, any AC electrical generator can be called an alternator, but usually the term refers to small rotating machines driven by automotive and other internal combustion engines. An alternator that uses a permanent magnet for its magnetic field is called a magneto. Alternators in power stations driven by steam turbines are called turbo-alternators. Large 50 or 60 Hz three-phase alternators in power plants generate most of the world's electric power, which is distributed by electric power grids.
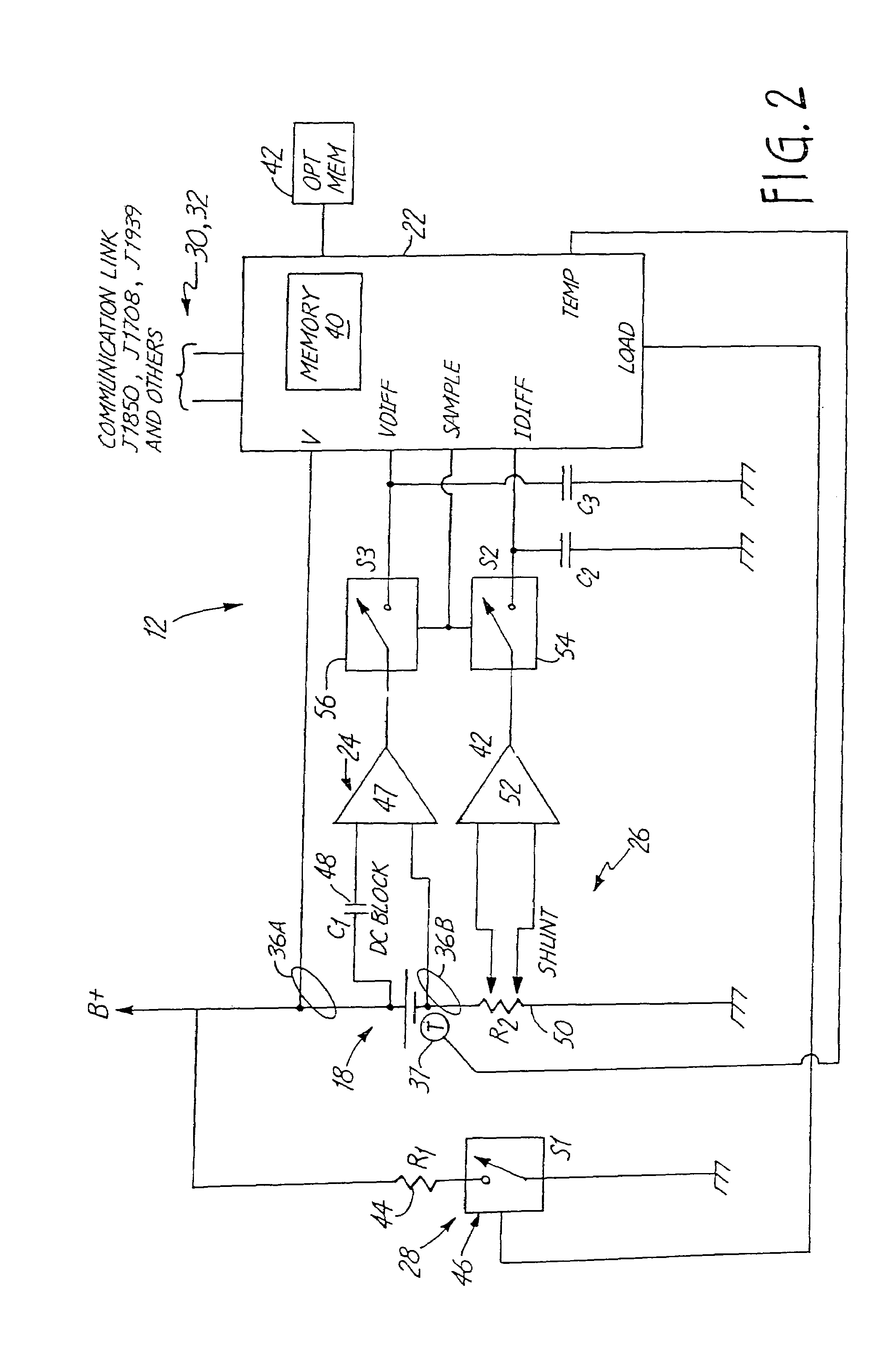
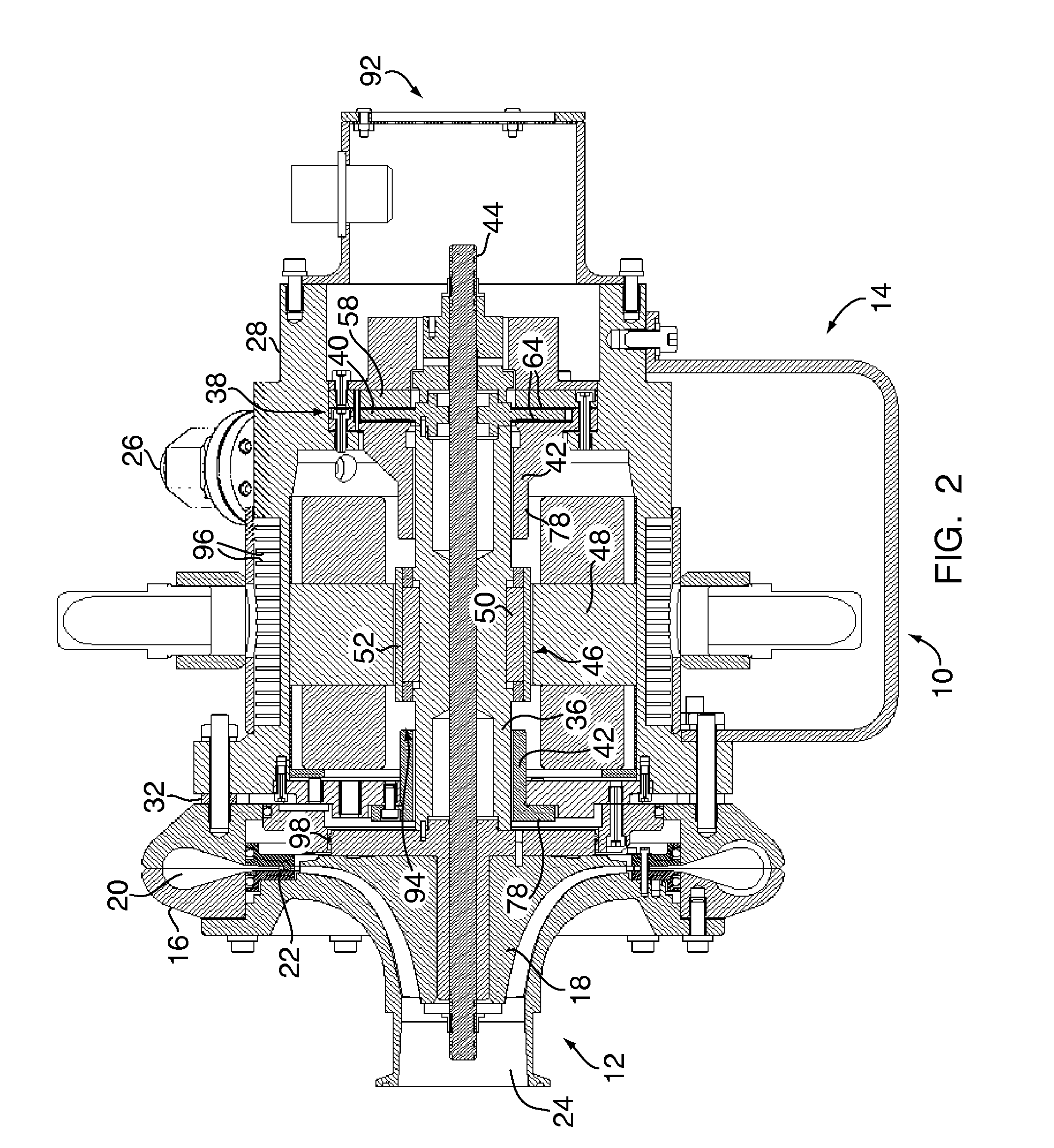
Energy management system for automotive vehicle
InactiveUS6909287B2Material analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectric powerMobile vehicleAlternator
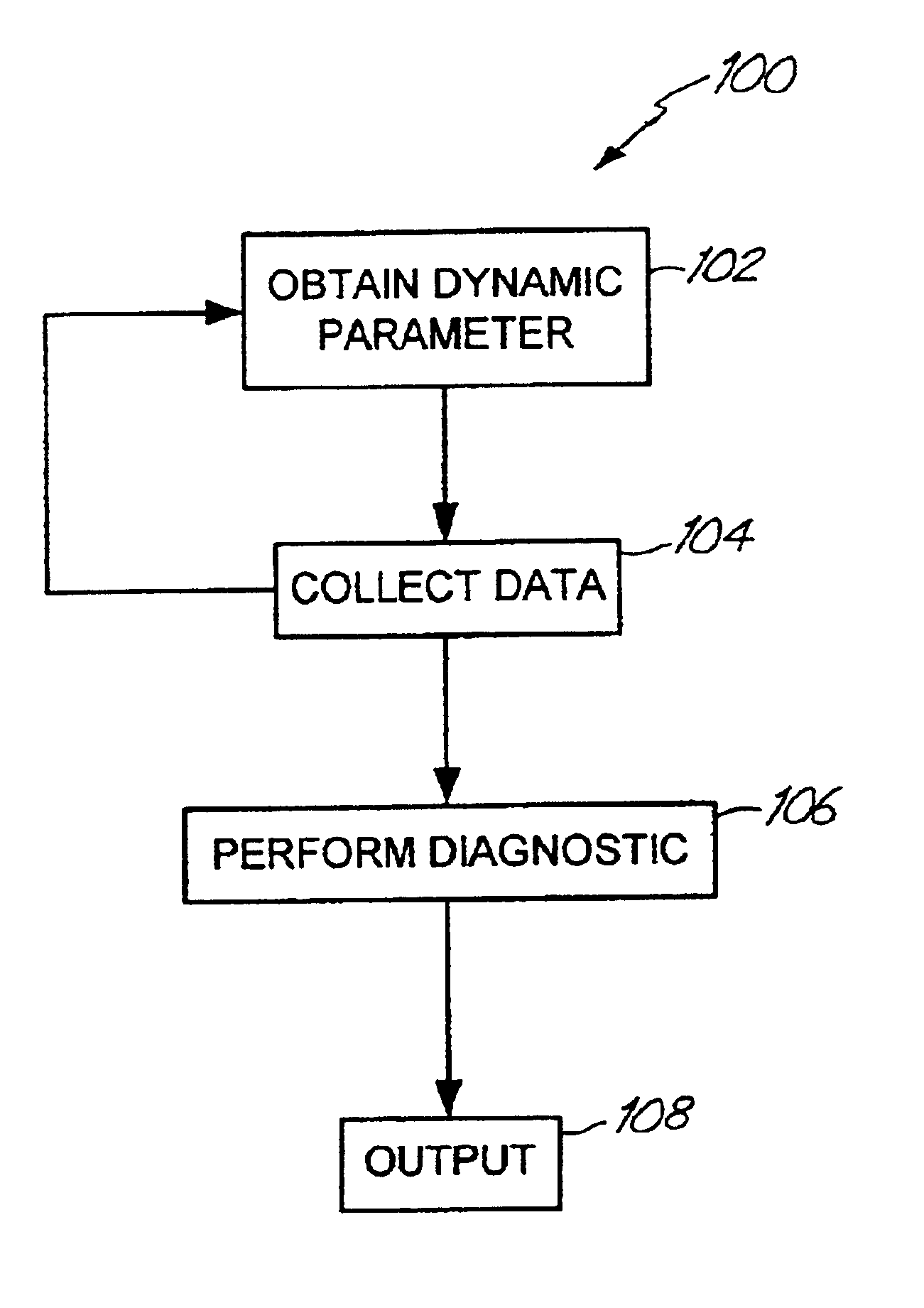
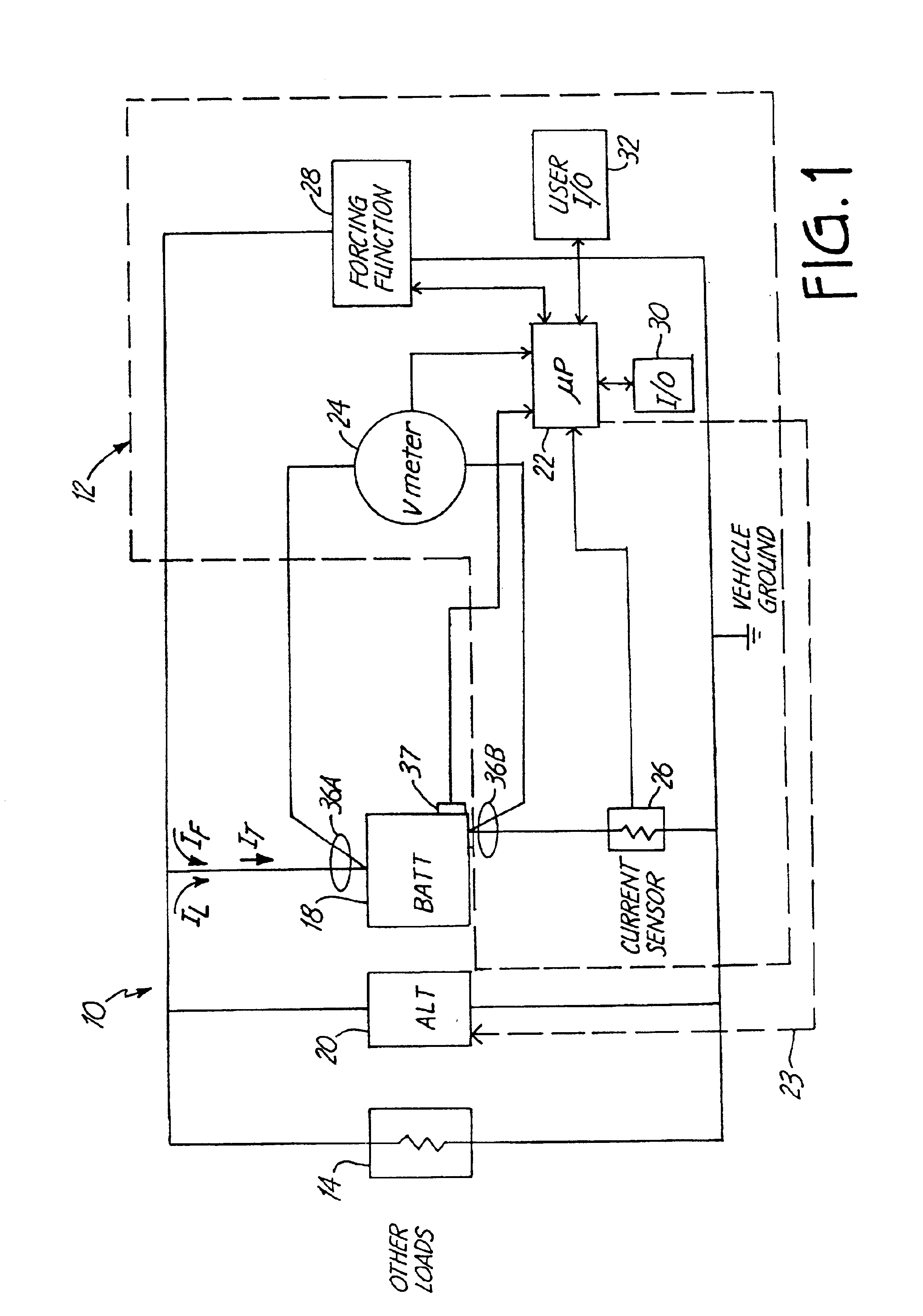
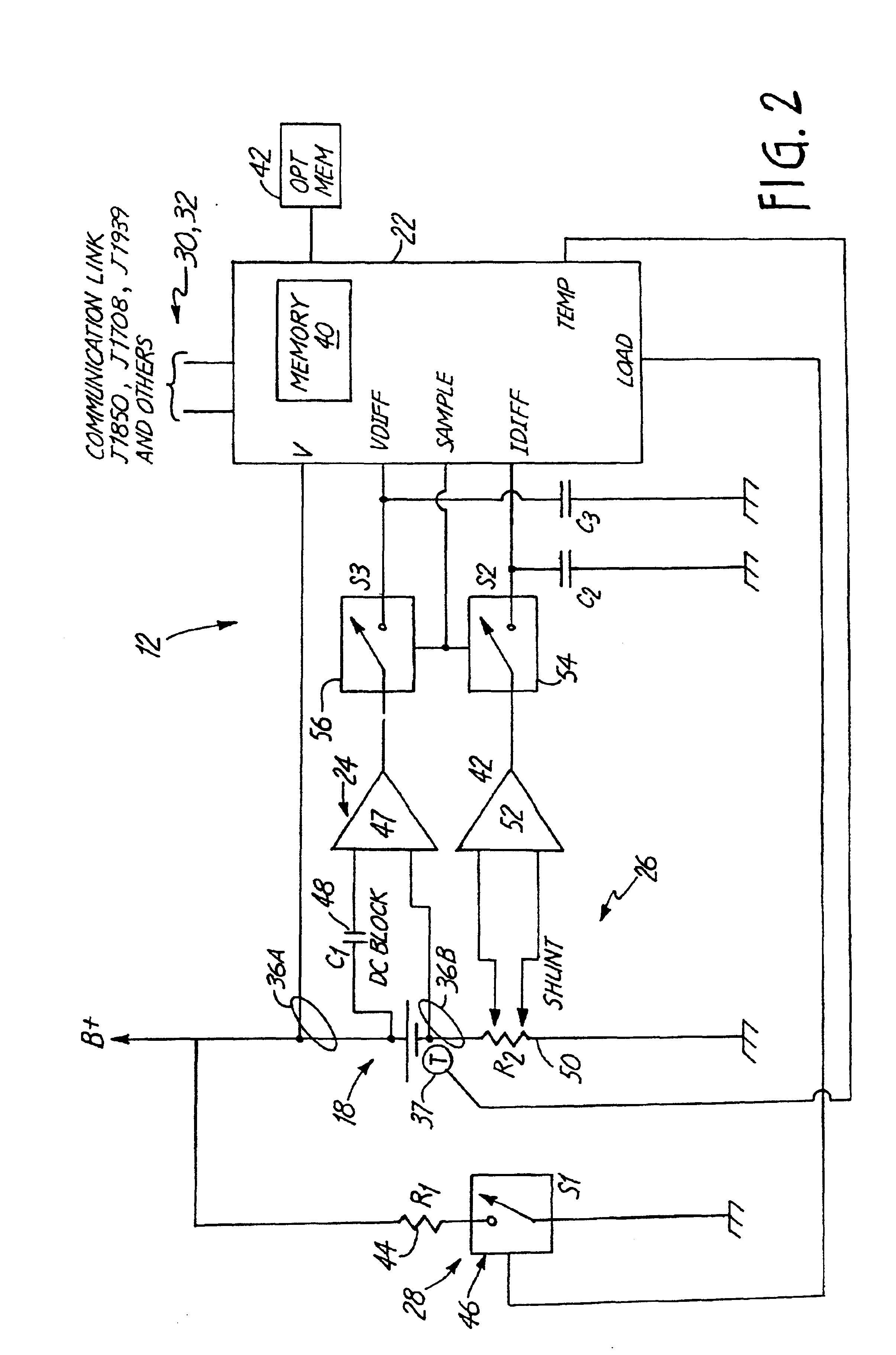
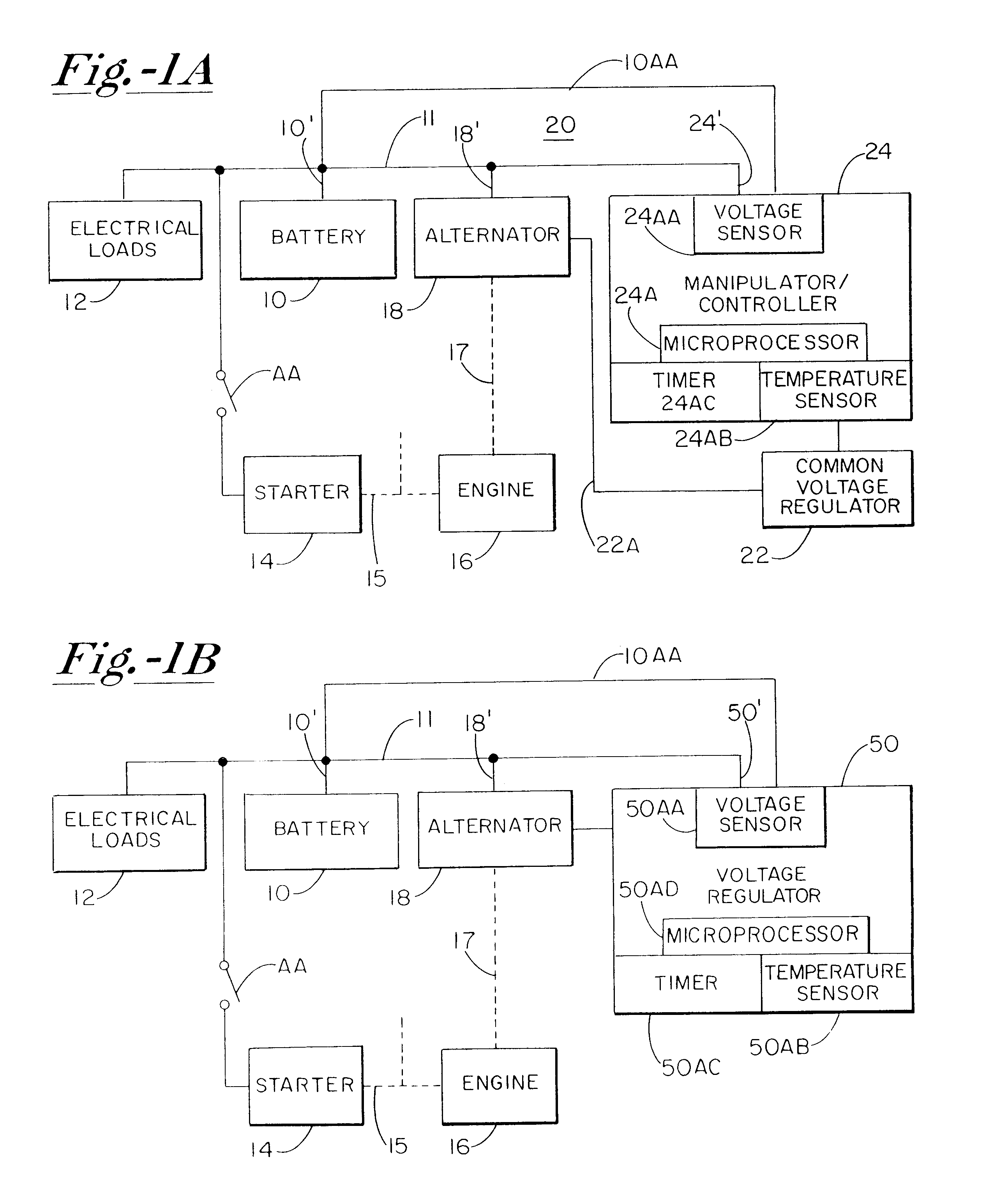
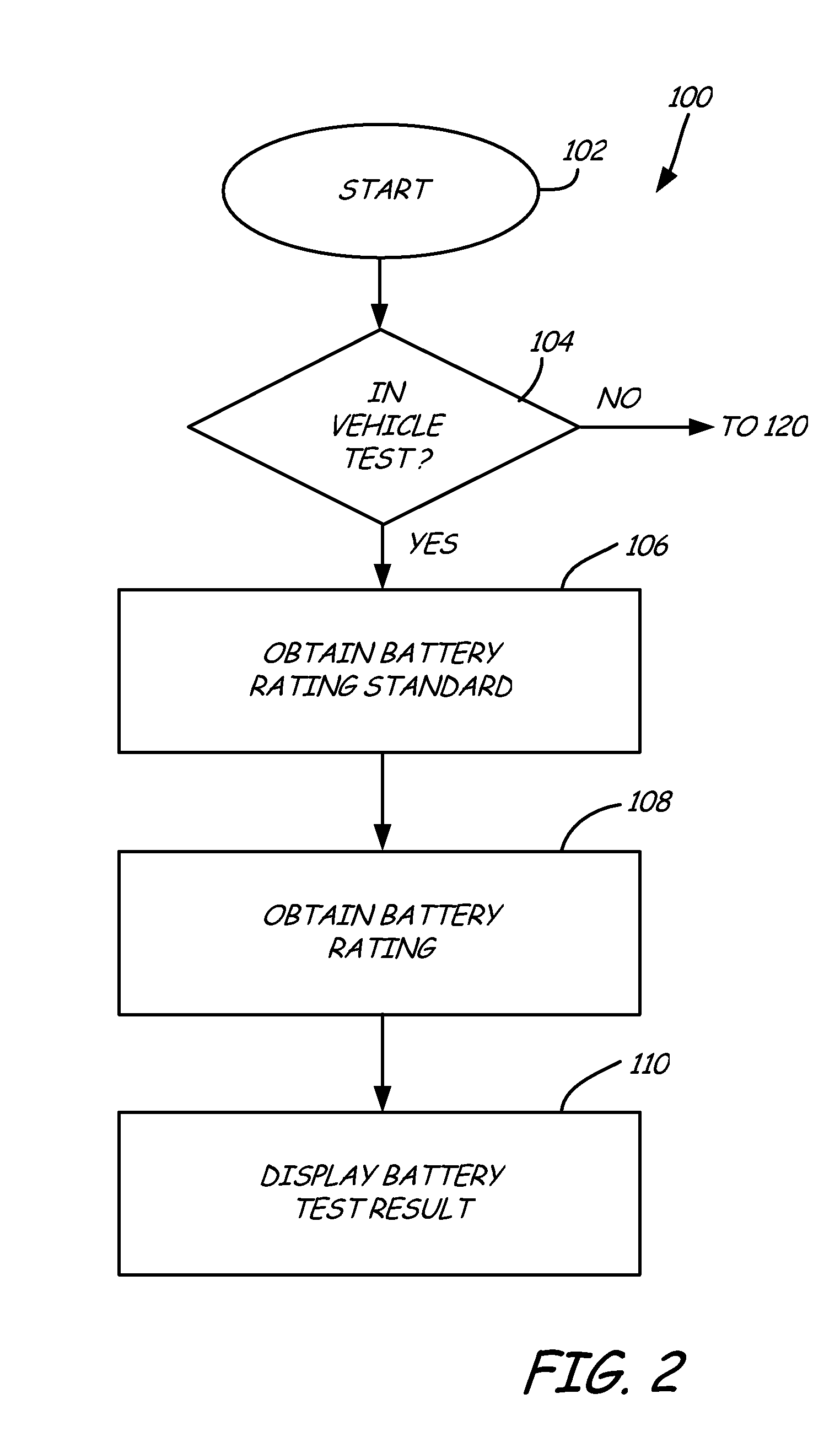
A battery monitor is provided for use with a battery of an automotive vehicle. The battery monitor can provide real time battery condition measurements and can selectively control the charging of the battery through an alternator of the vehicle based upon the measured battery condition.
Owner:MIDTRONICS
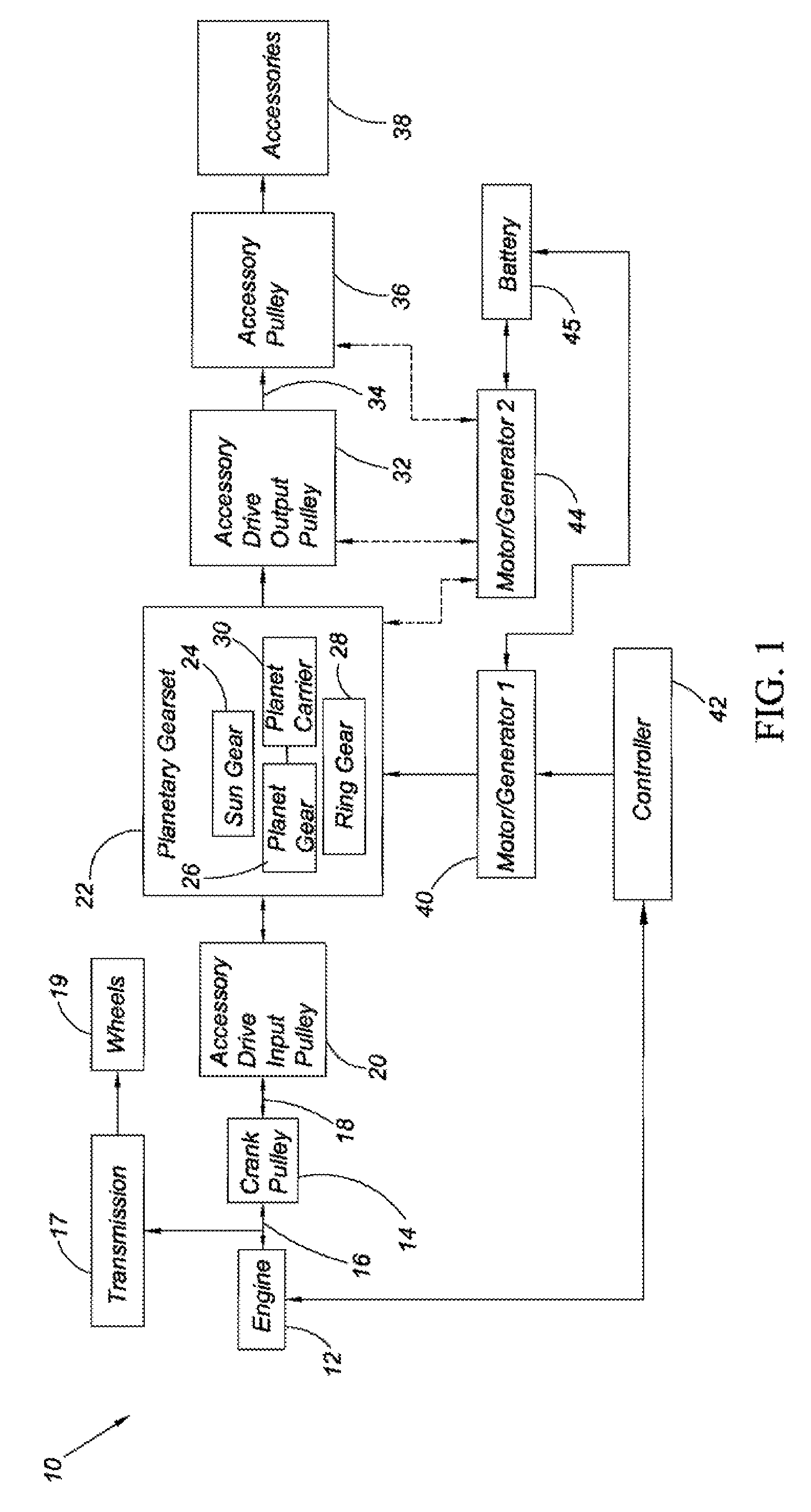
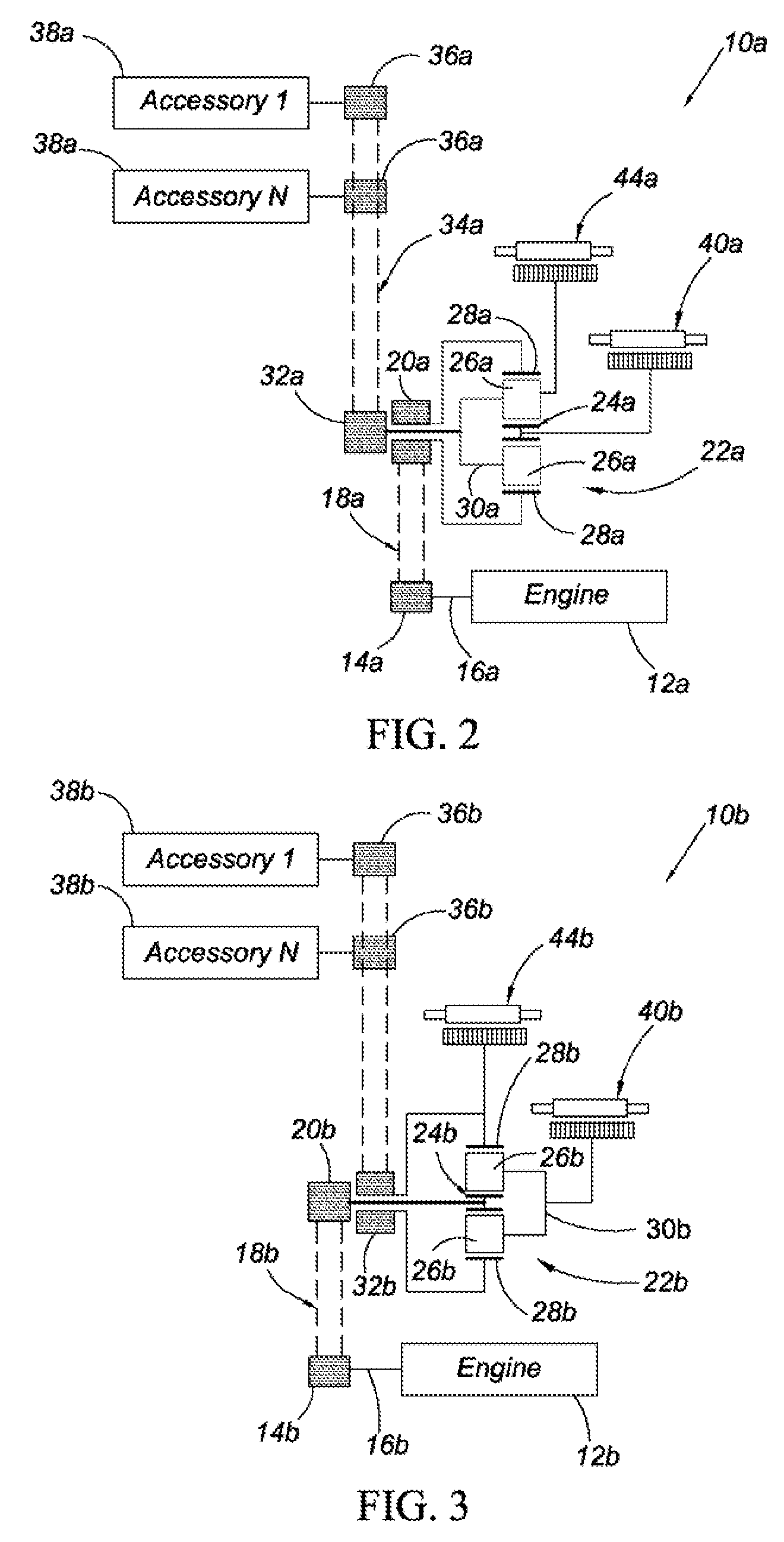
Starter alternator accessory drive system for a hybrid vehicle
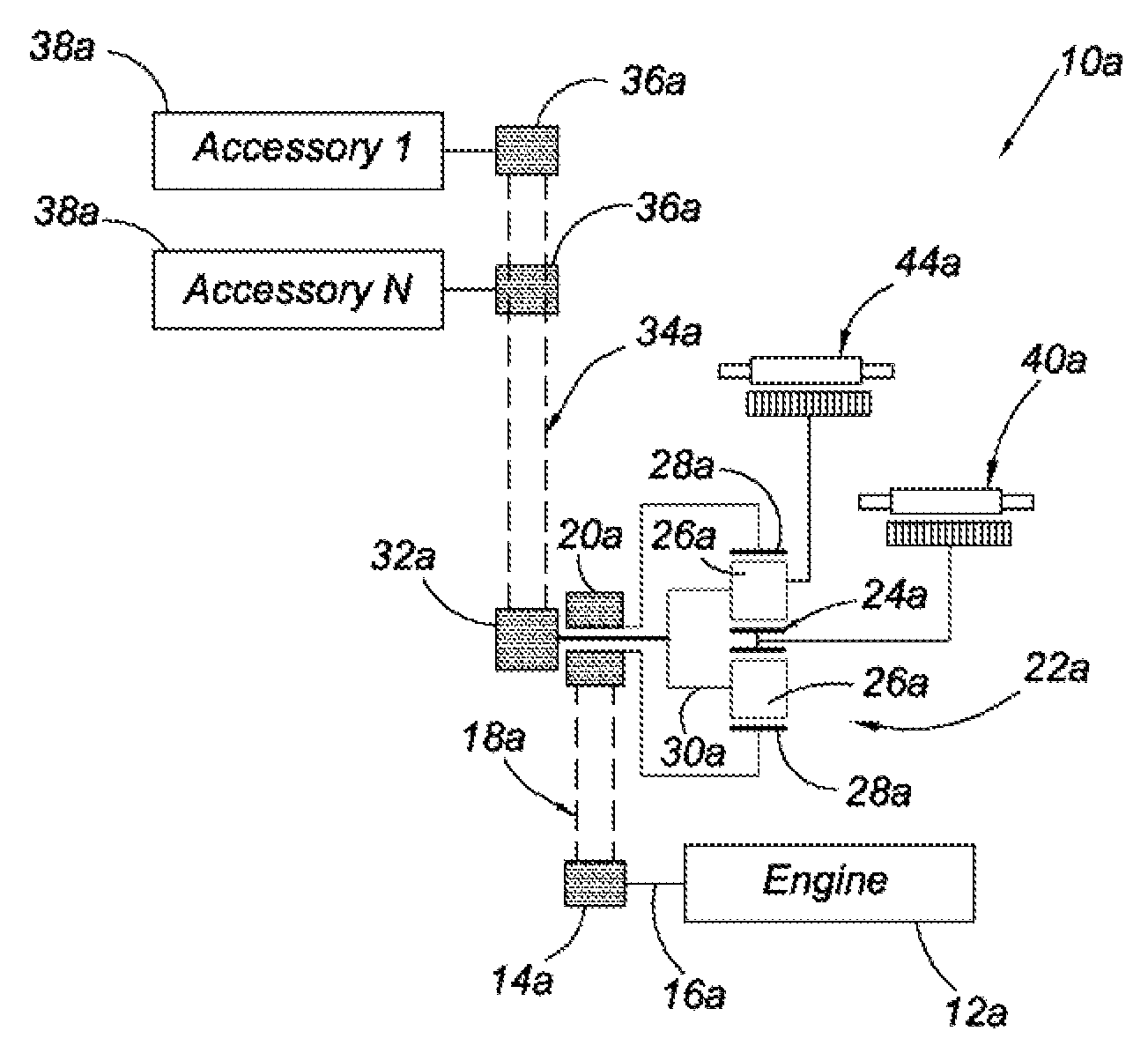
The present invention provides an alternator starter accessory drive system for a hybrid vehicle. The starter alternator accessory drive system includes a planetary gear set having a first, second, and third planetary member. An engine is operatively connected to the first planetary member, and a first motor / generator is operatively connected to the second planetary member. A torque transfer device operatively connects a plurality of accessories to the third planetary member. A second motor / generator is operatively connected to either the third planetary member or the torque transfer device. Engine output is transferable through the planetary gear set to drive the accessories at a selectable rate, and the first and second motor / generators are controllable to run the accessories while the engine is off and to re-start the engine.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
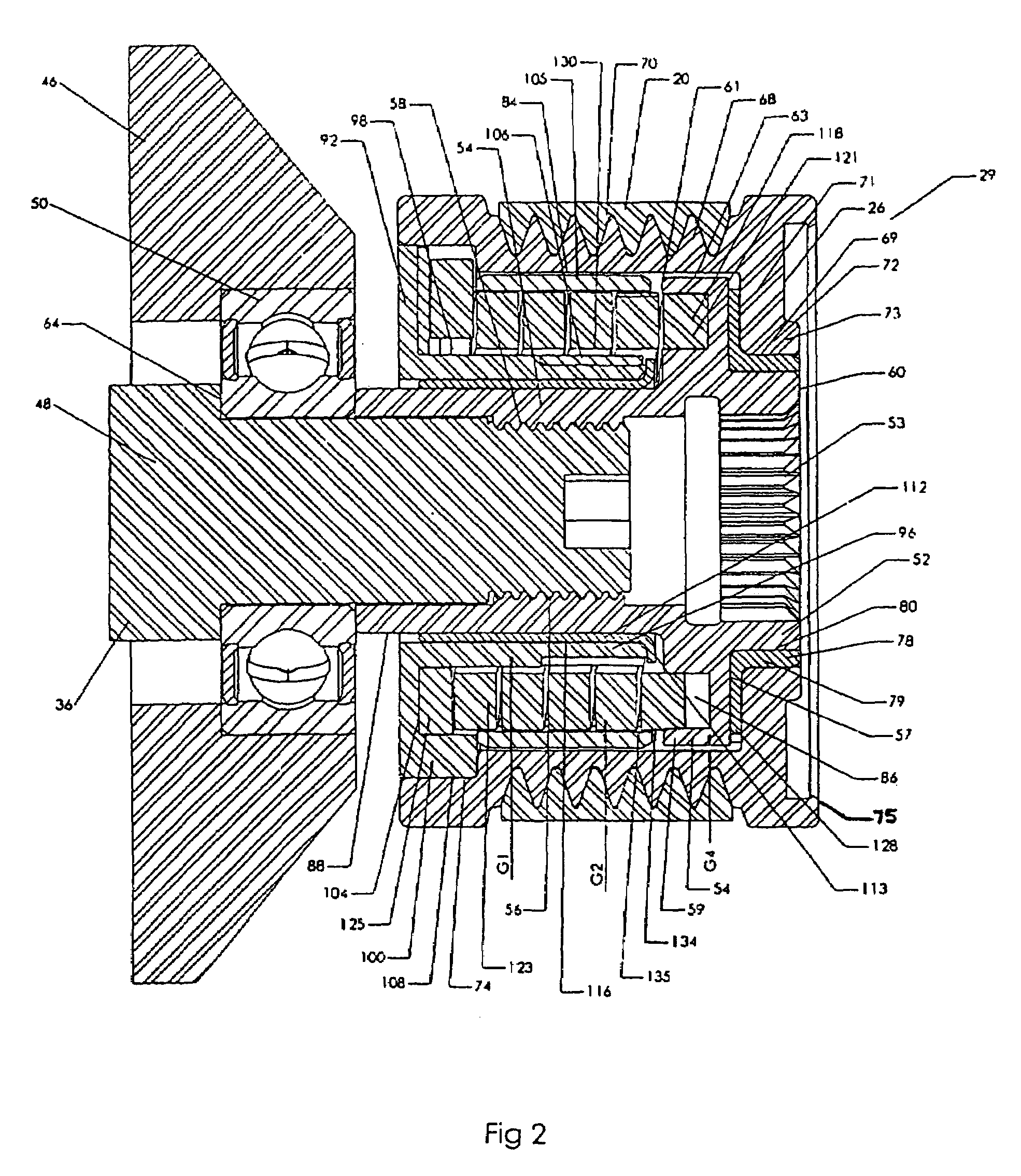
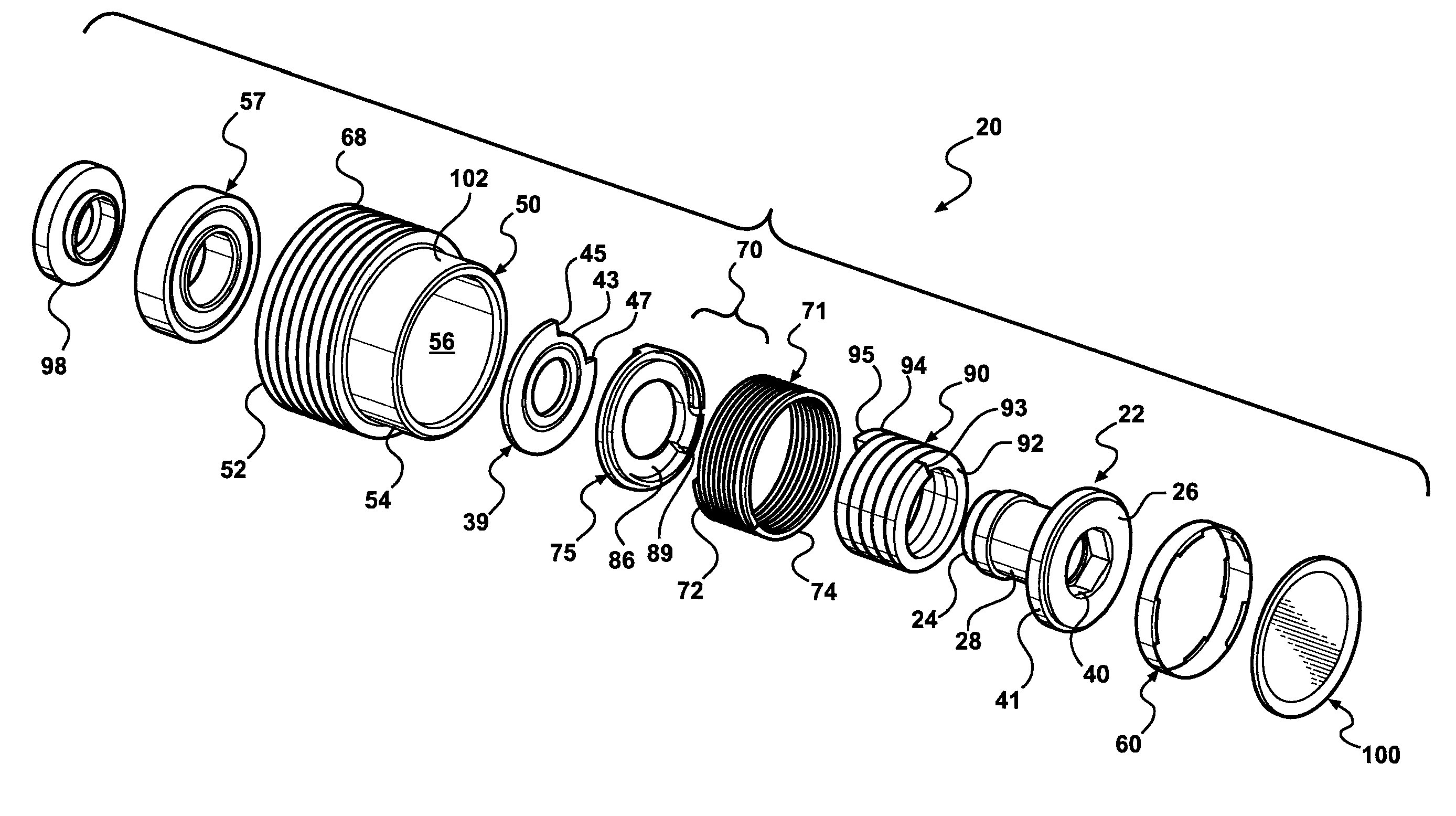
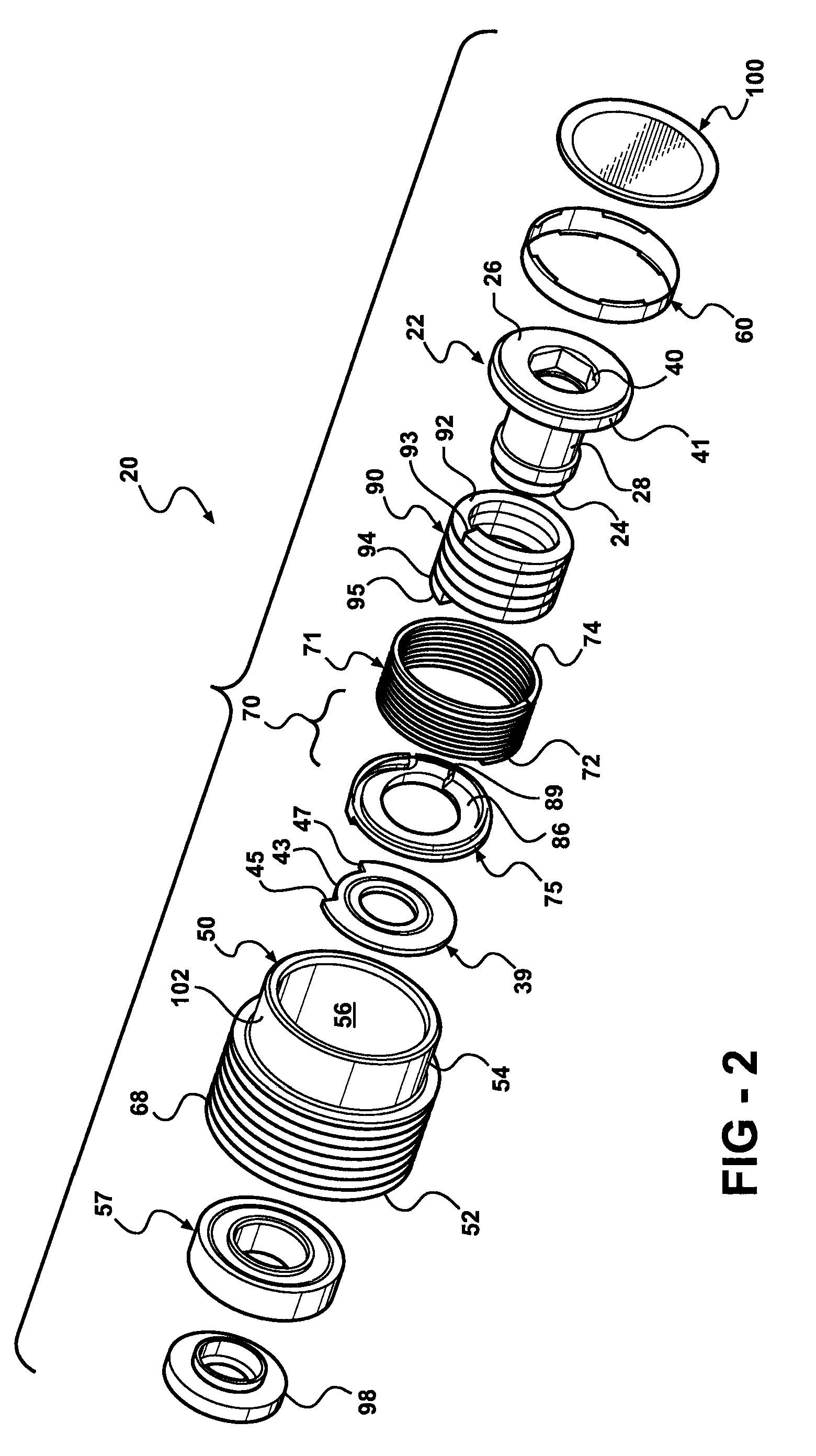
Isolator for alternator pulley
Owner:LITENS AUTOMOTIVE INC
Spring travel limiter for overrunning alternator decoupler
ActiveUS7712592B2Prevent movementPrevent rotationYielding couplingSlip couplingSerpentine beltAlternator
A decoupler assembly for transferring rotary movement between an engine driven shaft and a serpentine belt. The decoupler includes a hub configured to be assembled to the shaft. The hub has a helical first slot formed therein. A pulley is rotatably coupled to the hub. A carrier is mounted on the hub and includes a helical second slot formed therein, as well as an anti-ramp up boss formed thereon. A thrust plate is fixed to the hub and has a slot formed therein. A torsion spring is compressed between a hub end retained in the helical first slot and a carrier end retained in the helical second slot for transferring torque between the hub and carrier. The anti-ramp up boss travels within the slot formed in the thrust plate for limiting rotation between the carrier and thrust plate and preventing rotation of the torsion spring relative to the hub and carrier.
Owner:LITENS AUTOMOTIVE INC
Low inductance electrical machine
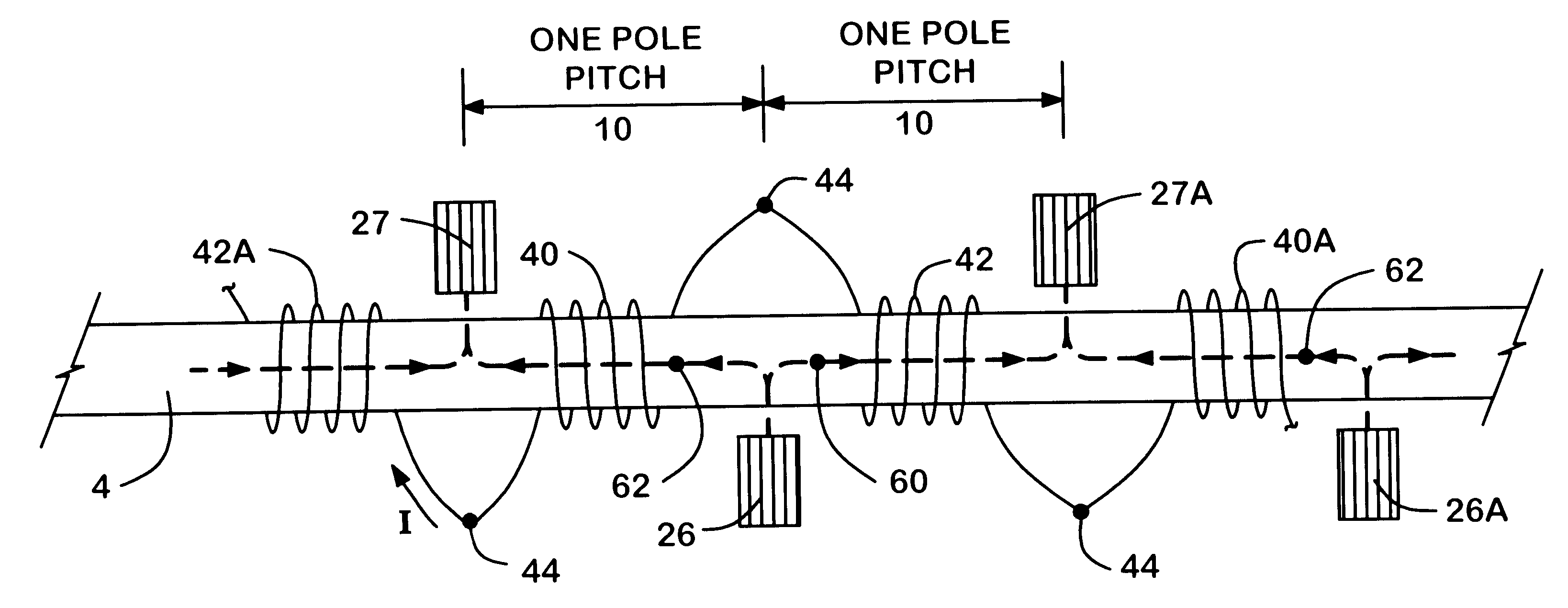
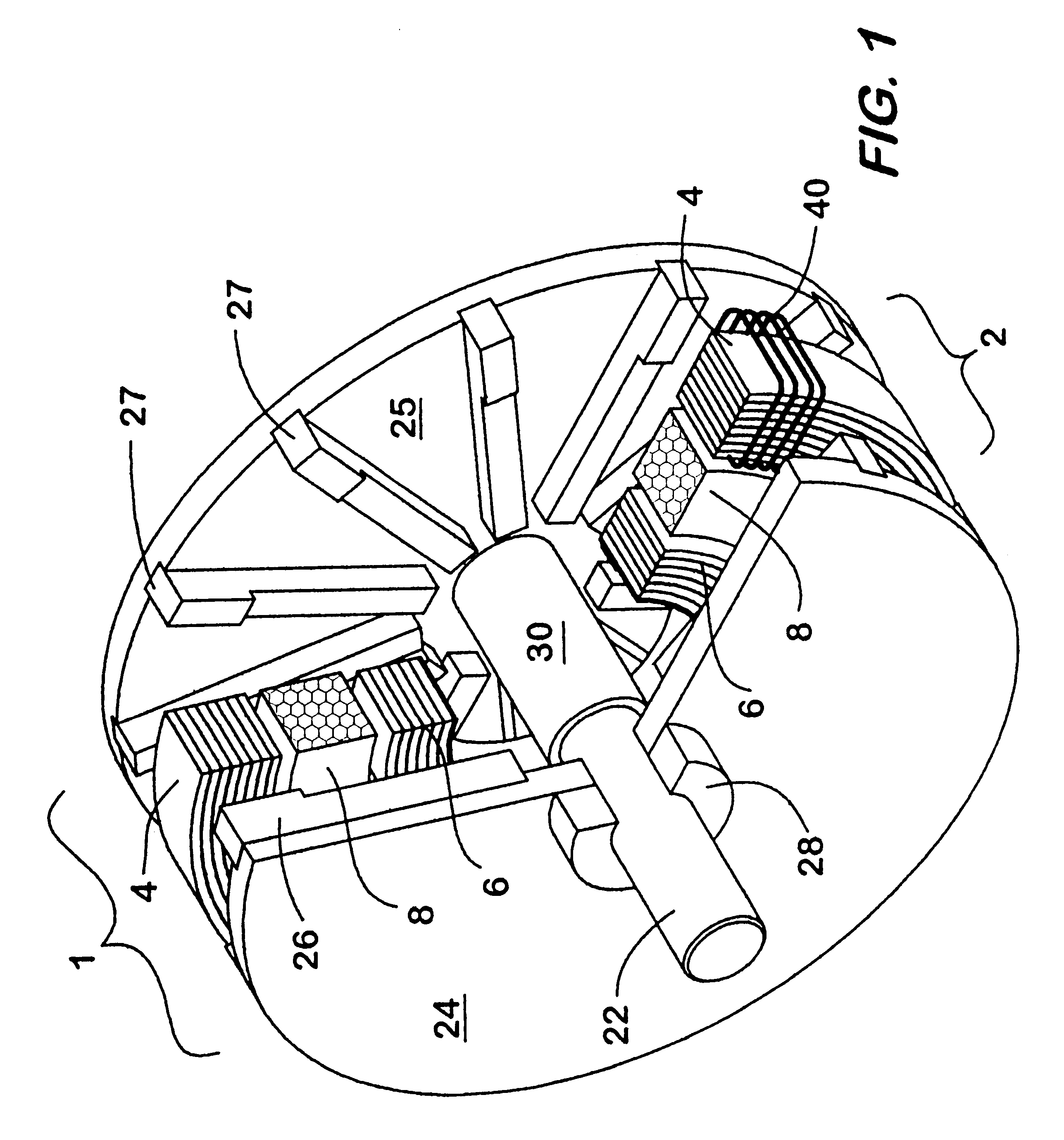
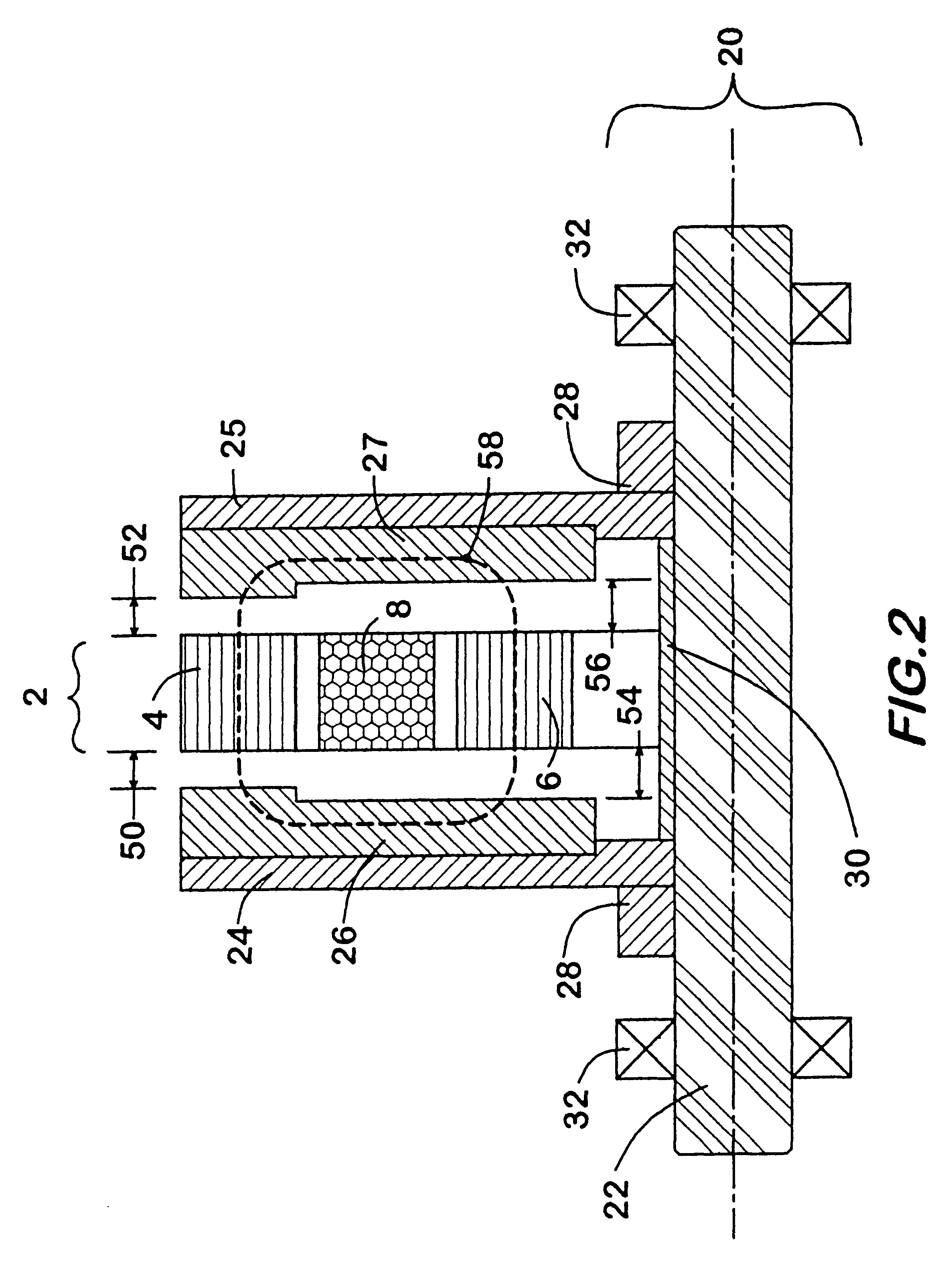
A low inductance electrical machine that may be used as an alternator or motor with low armature inductance is disclosed. Arrangements of complementary armature windings are presented in which the fluxes induced by currents in the armature windings effectively cancel leading to low magnetic energy storage within the machine. This leads to low net flux levels, low core losses, low inductance and reduced tendency toward magnetic saturation. The inclusion of additional gaps in the magnetic circuit allows for independent adjustment of air gap geometry and armature inductance. Separately excited field arrangements are disclosed that allow rotor motion to effect brush-less alternator or brush-less motor operation. An exemplary geometry includes a stator including two annular rings and a concentric field coil together with a rotor structure separated from the stator by four air gaps.
Owner:RAVEN TECH
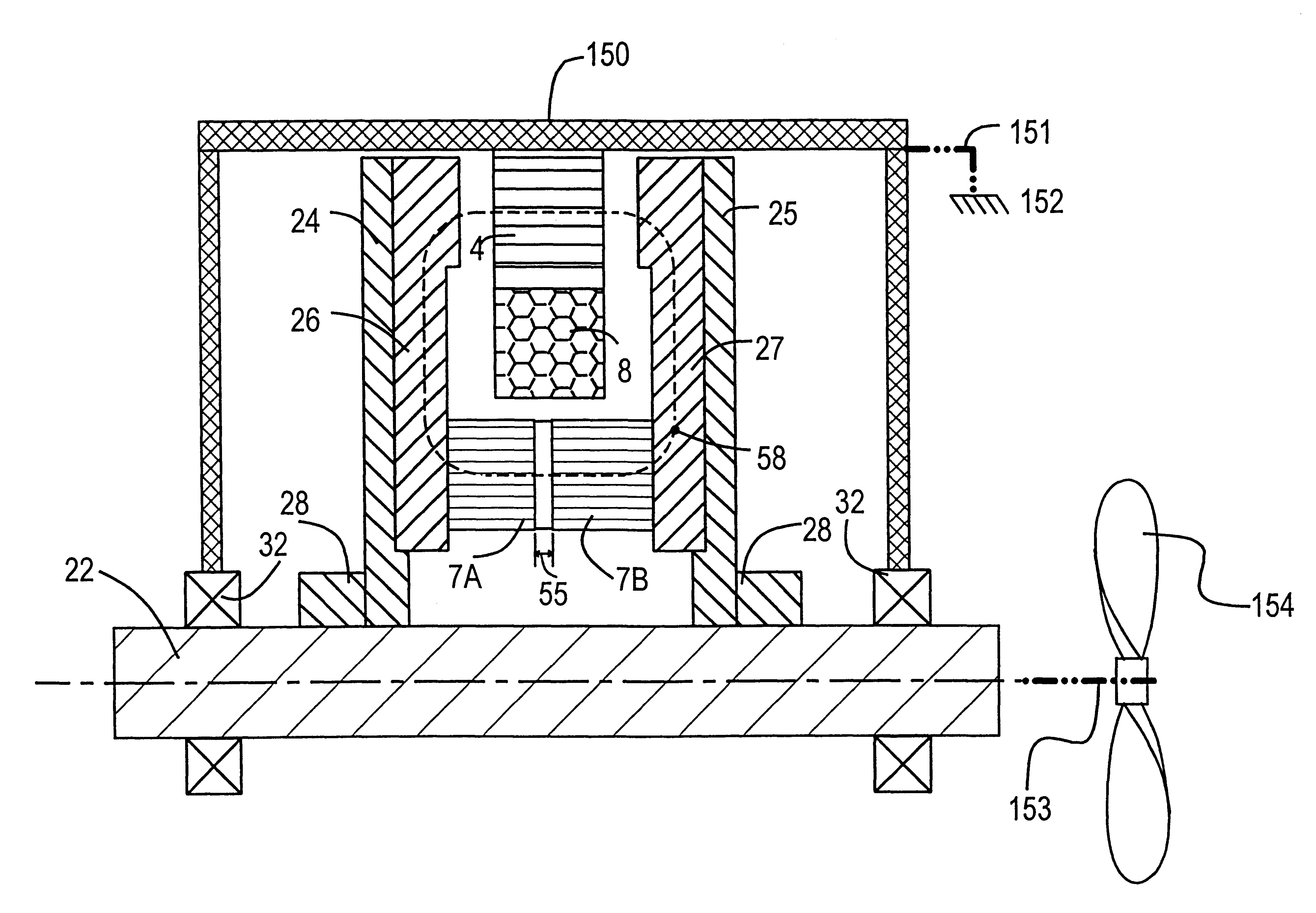
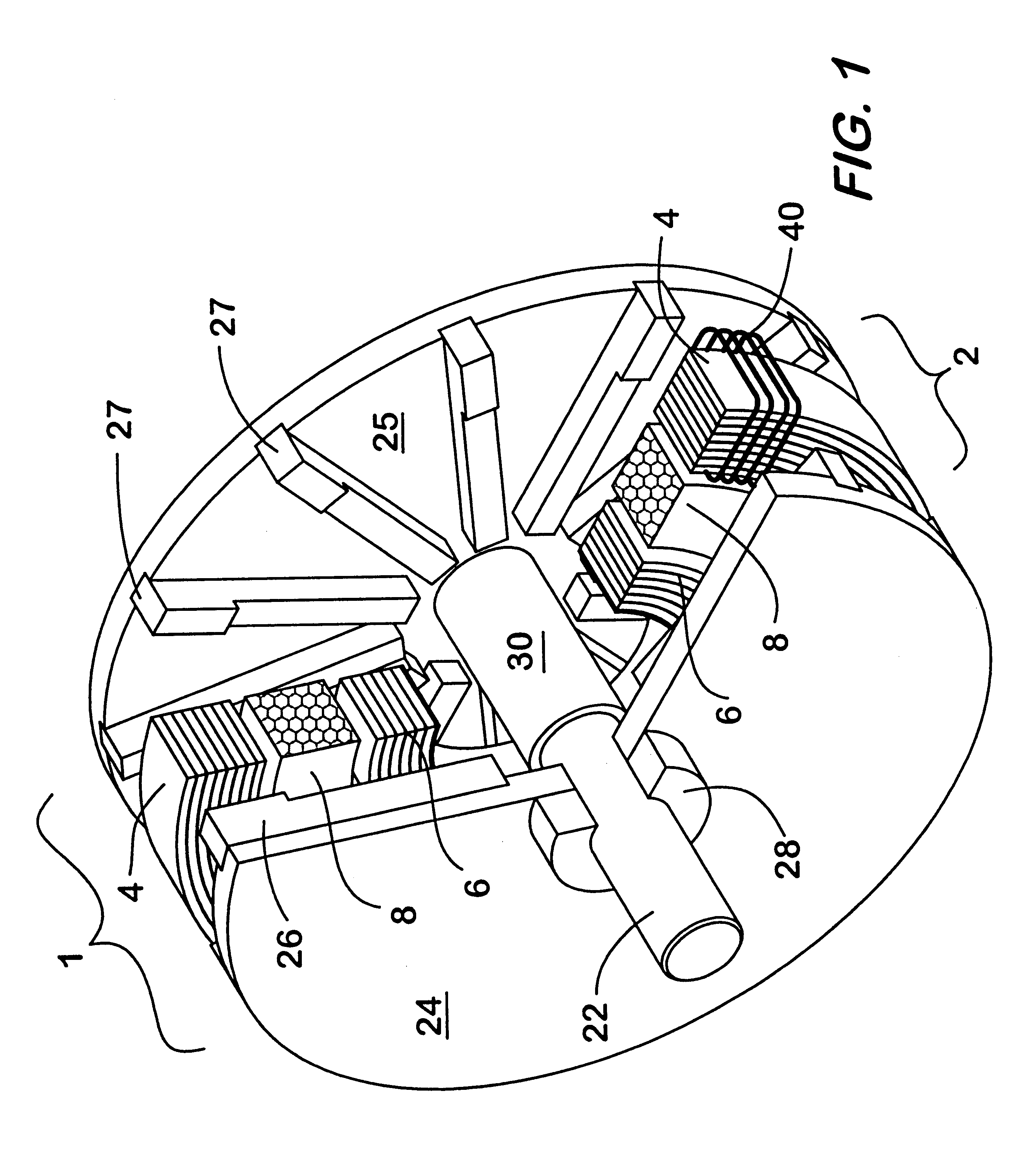
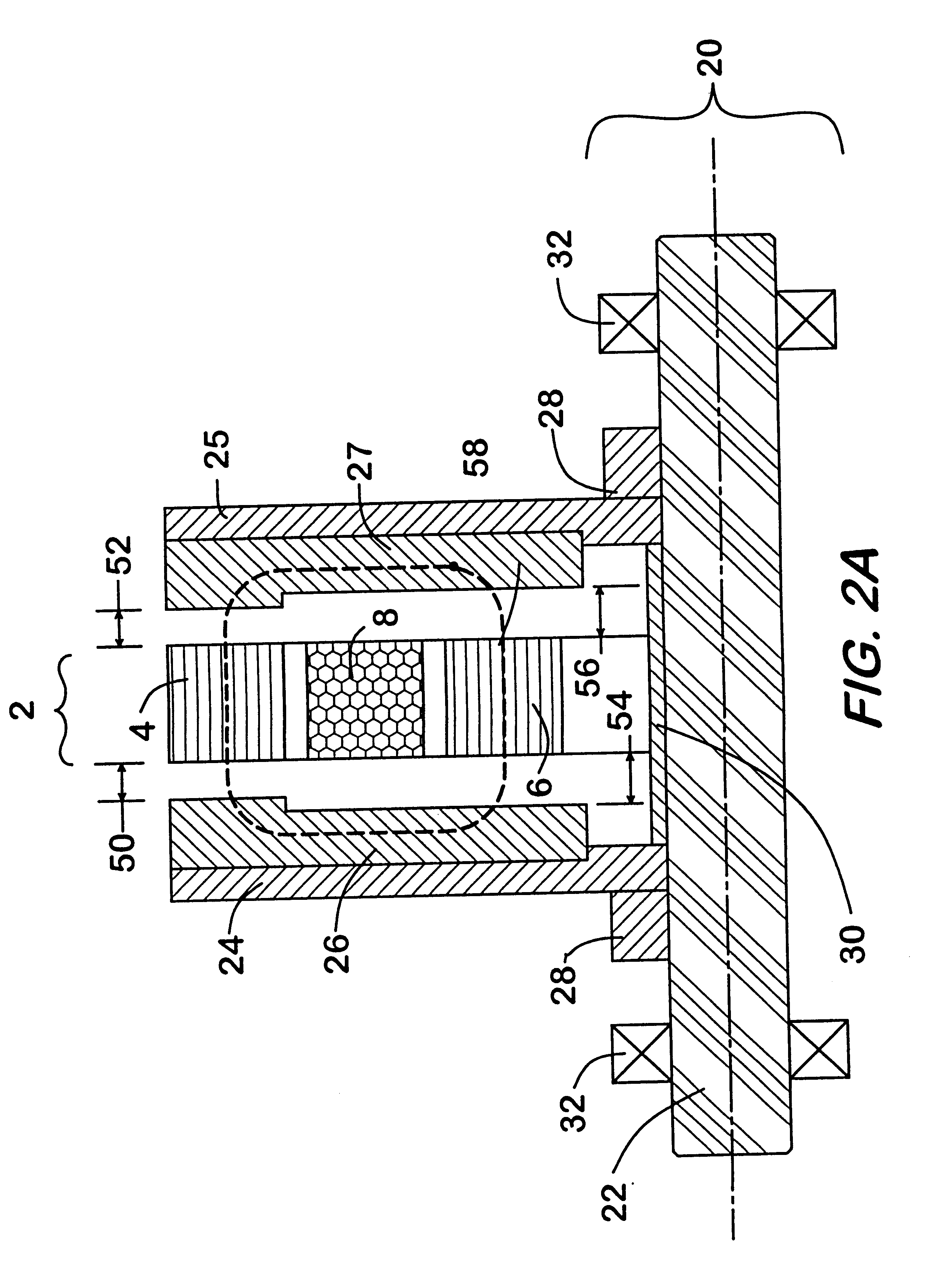
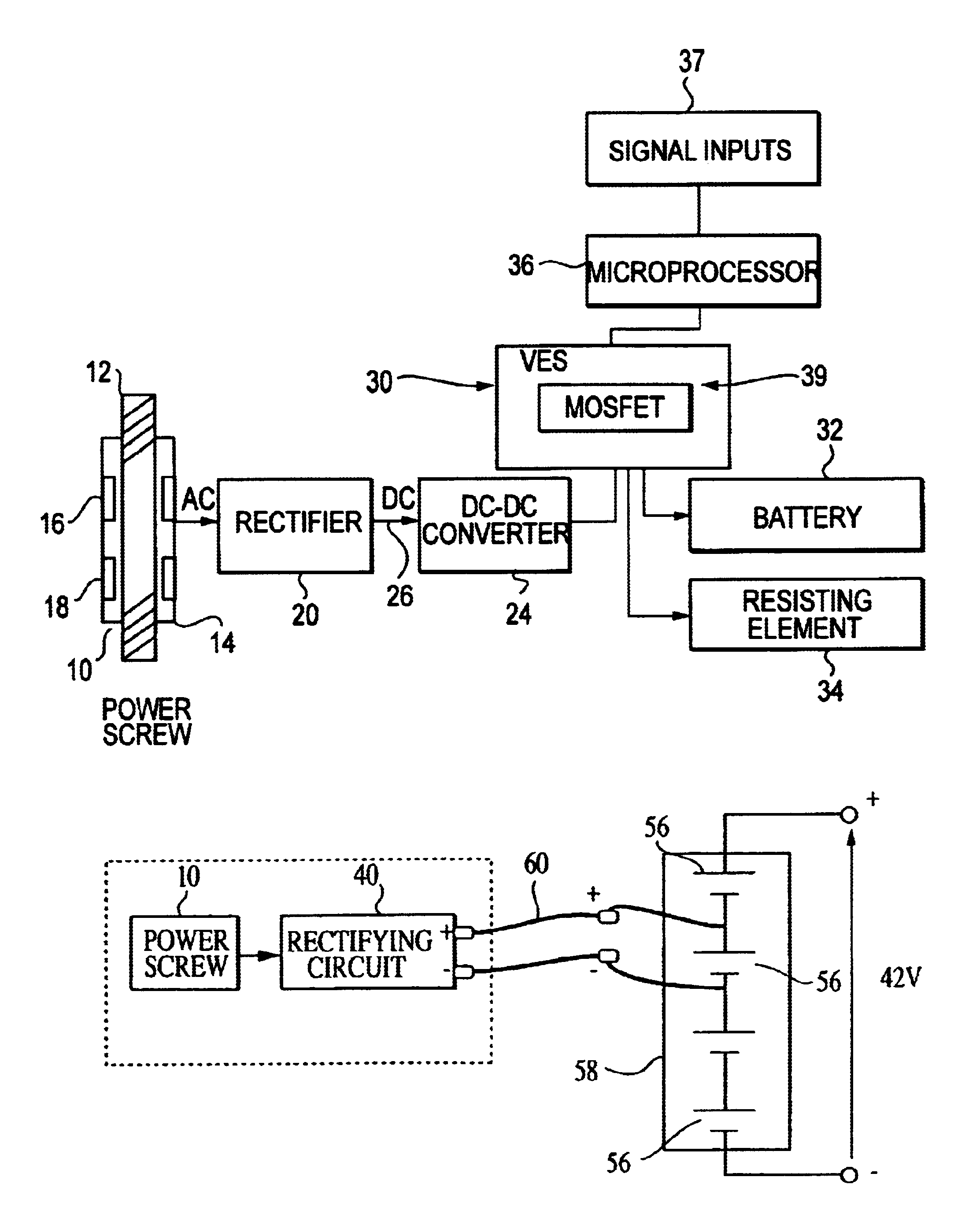
Regenerative damping method and apparatus
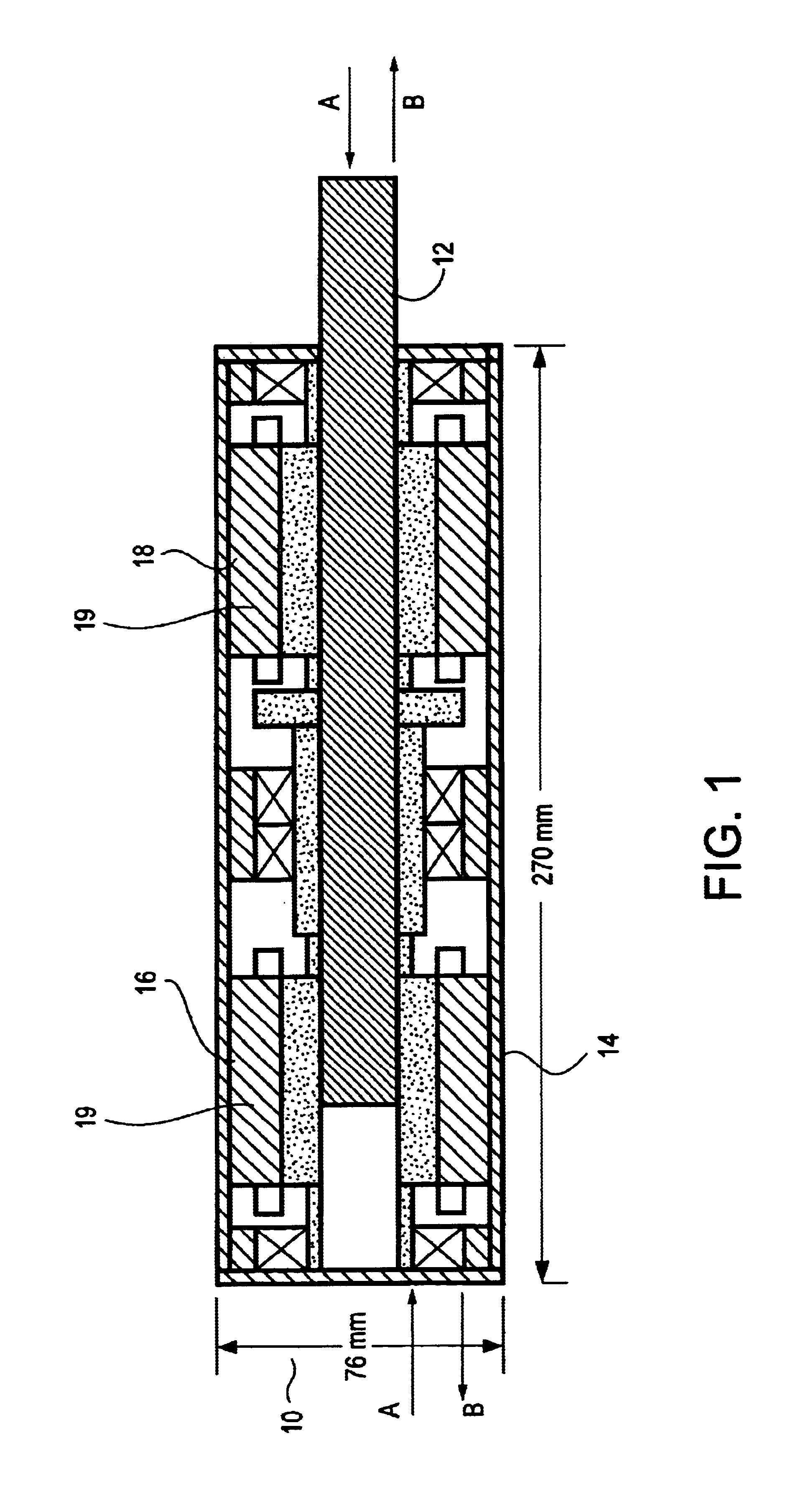
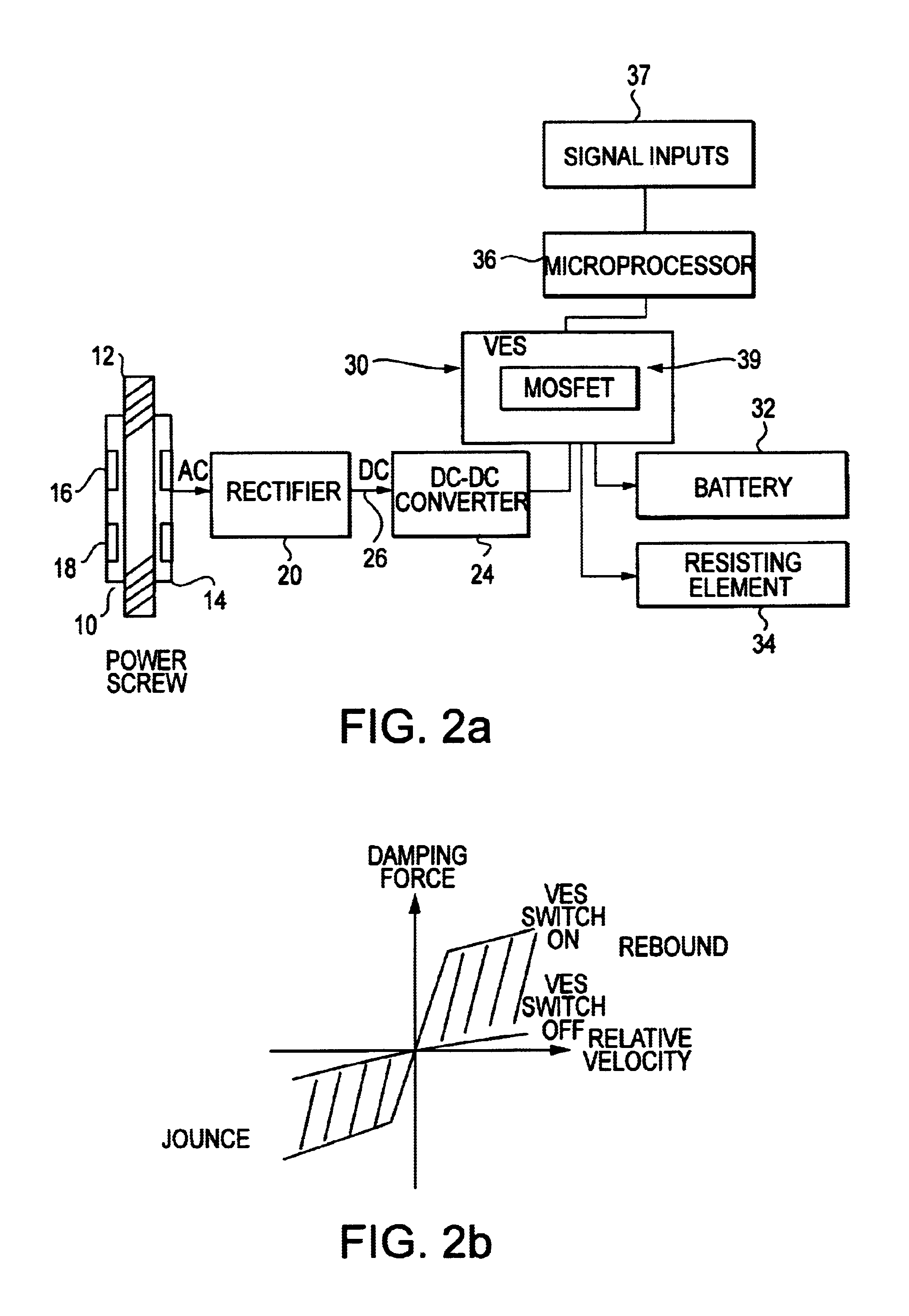
InactiveUS6920951B2Improve energy efficiencyAuxillary drivesNon-rotating vibration suppressionSemi activeElectricity
A regenerative damper and method for regenerative damping are disclosed. The regenerative damper uses the kinetic energy of undesirable vehicle motion to generate electrical current in a circuit. The electricity is generated by a power screw that operates like an alternator. Vehicle energy efficiency is increased by using the electrical current to charge a battery. The regenerative damper can be semi-active or passive. The semi-active embodiment is able to adapt to operating conditions to improve vehicle ride and handling, whereas the passive embodiment has a fixed response, regardless of operating conditions.
Owner:HANON SYST
Energy management system for automotive vehicle
Owner:MIDTRONICS
System and method for regenerating exhaust system filtering and catalyst components
InactiveUS6865883B2Increase exhaust temperatureEasy loadingElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesParticulatesAlternator
A system and method for regenerating particulate filters, catalyzed soot filters and NOx catalysts for a vehicle having a compression ignition engine. An engine control module controls engine operation and regeneration functions. The engine preferably includes an integrated starter / alternator / flywheel / retarder assembly. A load bank heater is provided in the exhaust system that is activated to directly heat exhaust gases raising the temperature thereof and approaching the temperatures required for regeneration and desulfation. Activation of the heater applies a load through the integrated starter / alternator / flywheel / retarder assembly that increases the load on the engine and in turn further increases the temperature of the exhaust to levels required for regeneration and desulfation.
Owner:DETROIT DIESEL CORP
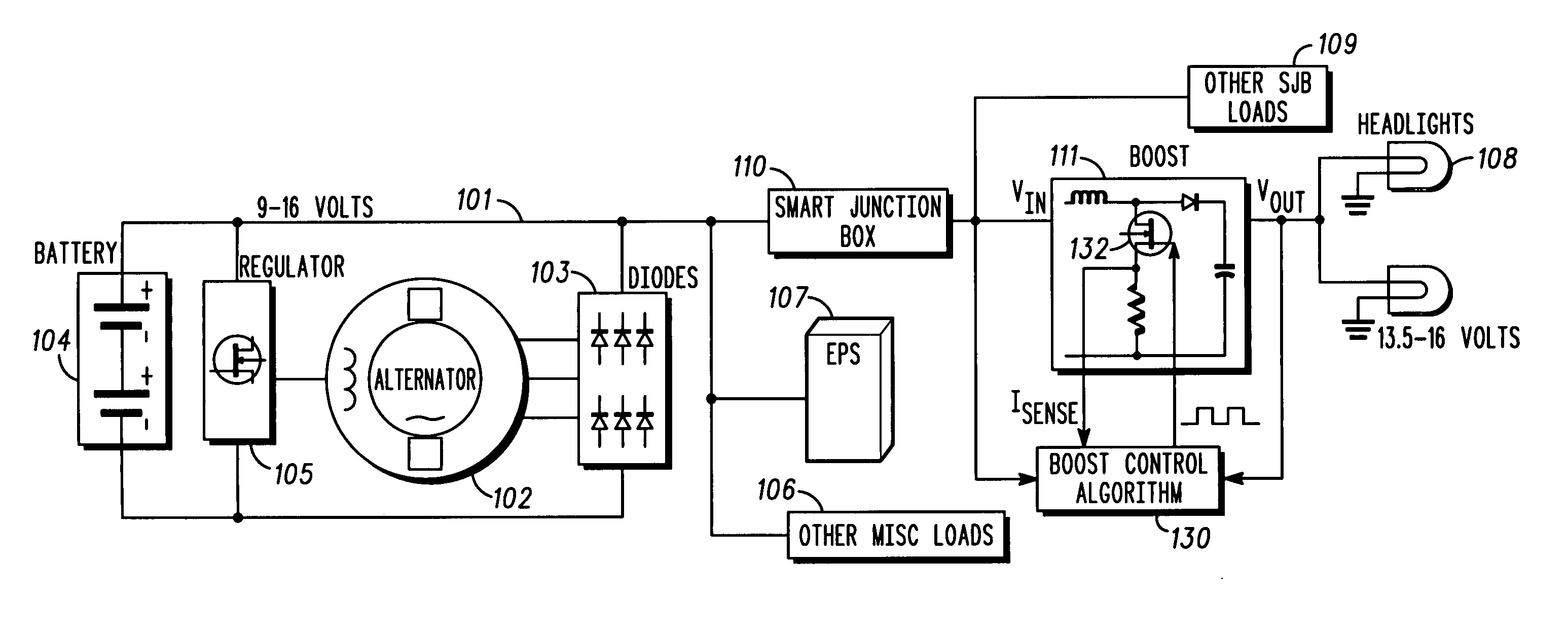
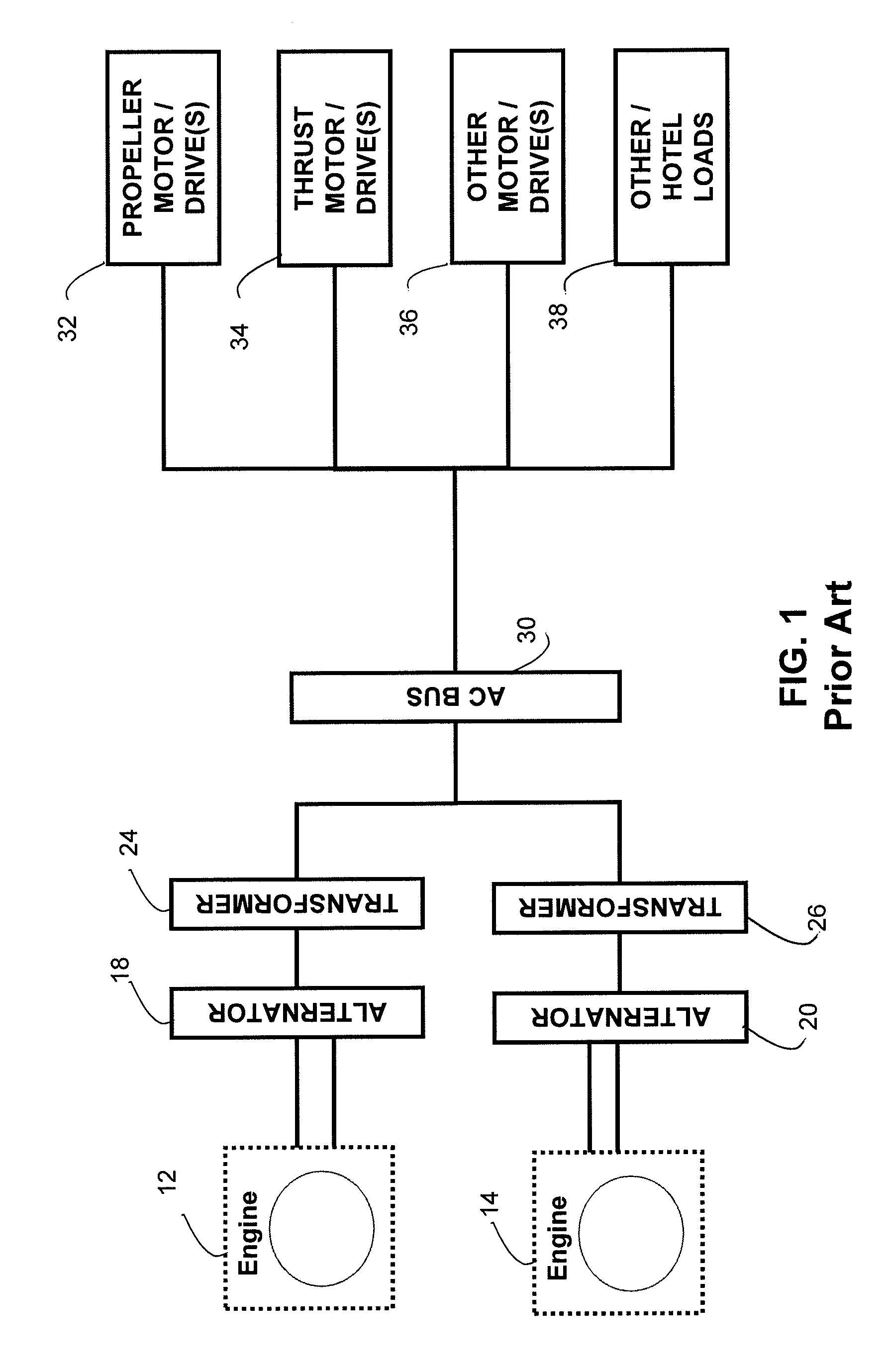
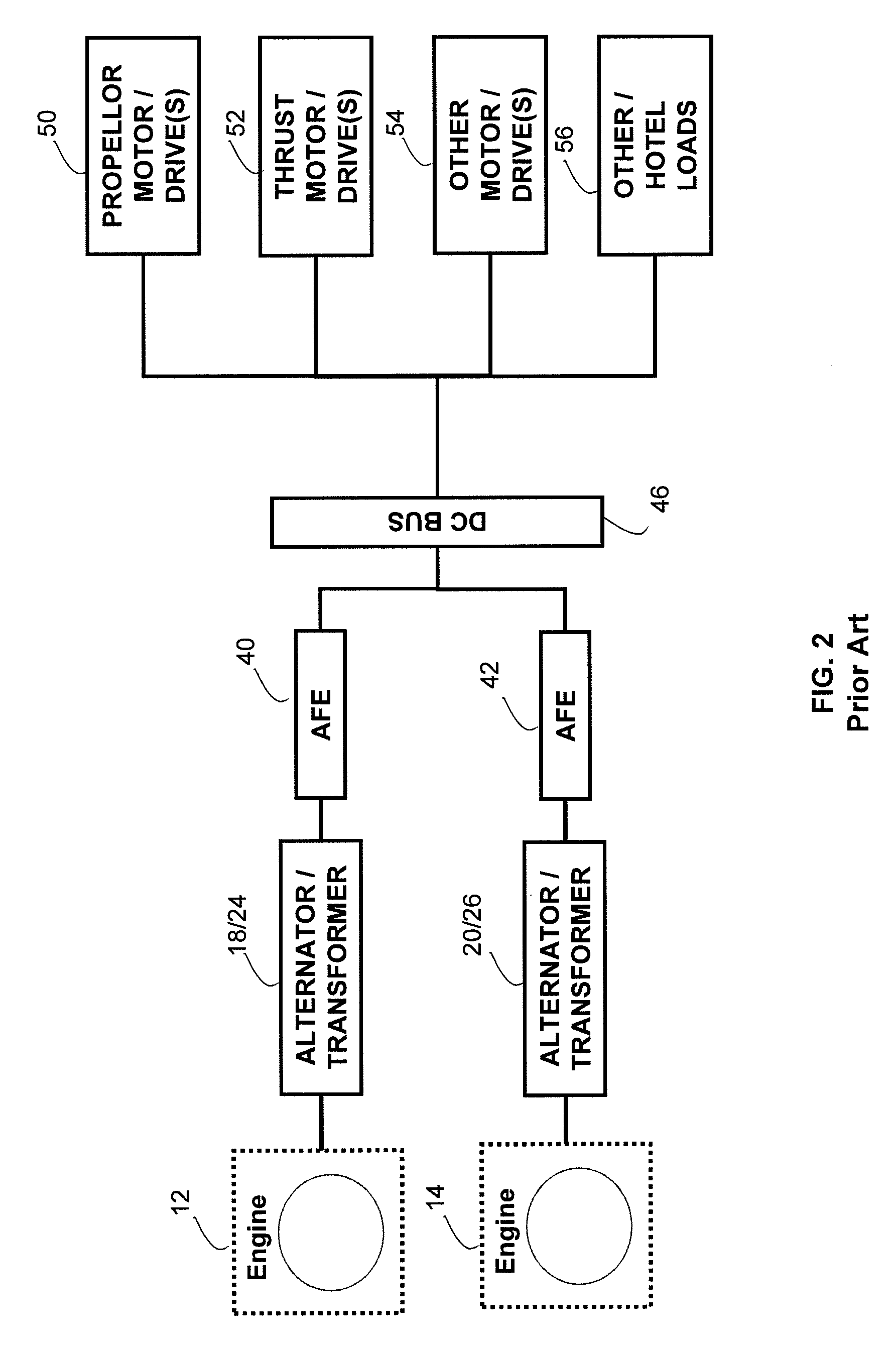
Automotive electrical system configuration using a two bus structure
InactiveUS20060043938A1Batteries circuit arrangementsEmergency protective circuit arrangementsAlternatorCritical load
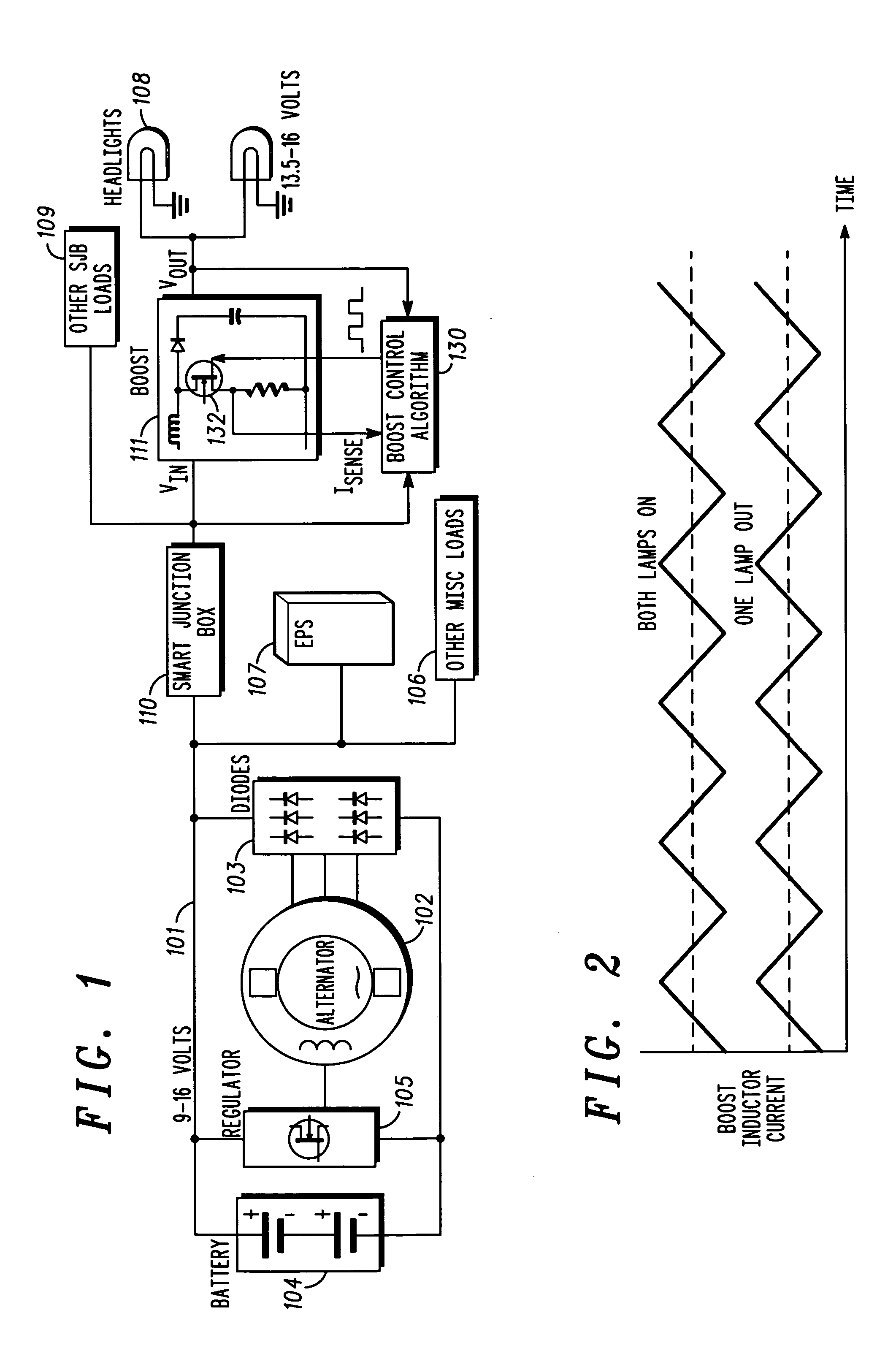
Disclosed herein are a variety of different electrical system topologies intended to mitigate the impact of large intermittent loads on a 12 volt vehicle power distribution system. In some embodiments the intermittent load is disconnected from the remainder of the system and the voltage supplied to this load is allowed to fluctuate. In other embodiments, the voltage to critical loads is regulated independently of the voltage supplied to the remainder of the system. The different topologies described can be grouped into three categories, each corresponding to a different solution technique. One approach is to regulate the voltage to the critical loads. A second approach is to isolate the intermittent load that causes the drop in system voltage. The third approach is to use a different type of alternator that has a faster response than the conventional Lundell wound field machine.
Owner:TEMIC AUTOMOTIVE OF NORTH AMERICA
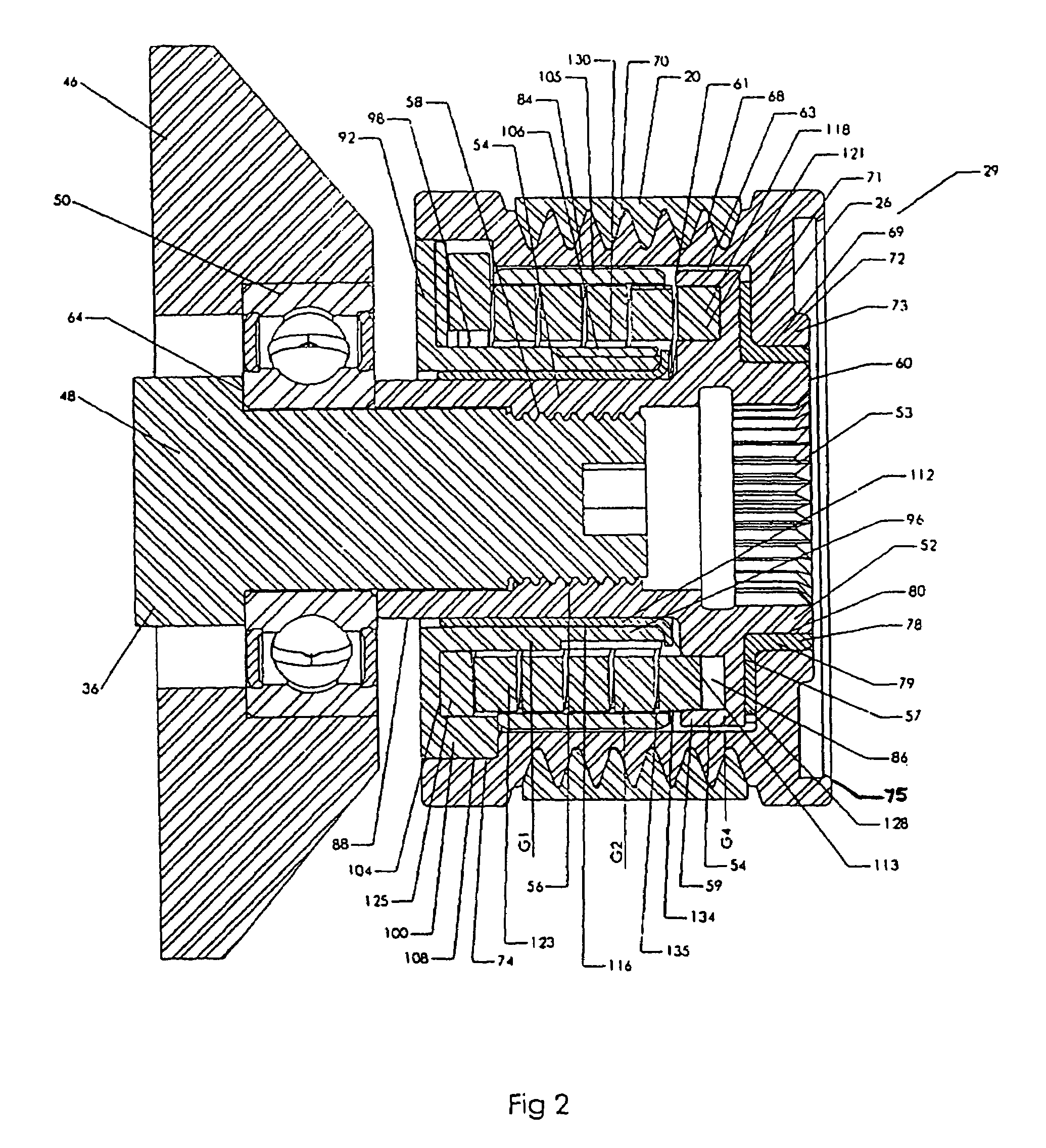
Turboalternator with hydrodynamic bearings
ActiveUS20080246281A1Recovery of wasted energyReduce pressureLiquid degasificationPump componentsStored energyAlternator
This invention provides a small, high efficiency, oil-free turbine-driven alternator (i.e. turboalternator) suitable for conversion of stored energy in a process gas to electrical power, facilitating recapture of energy during operation that would otherwise be wasted. The turboalternator includes a turbine and a generating device operatively connected together by a rotating shaft capable of rotating at high speeds. The rotating shaft is supported by foil gas bearings.
Owner:R & D DYNAMICS
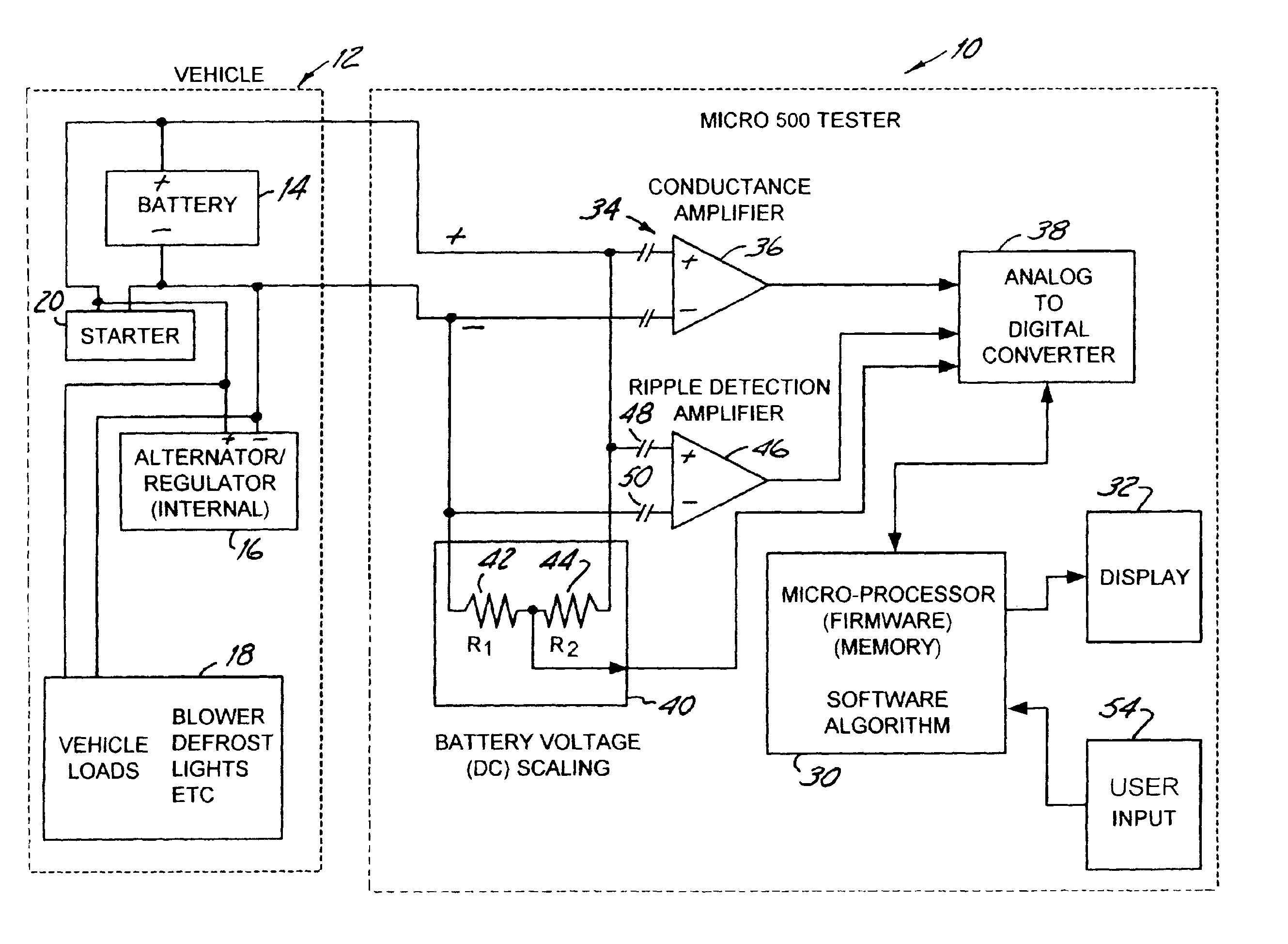
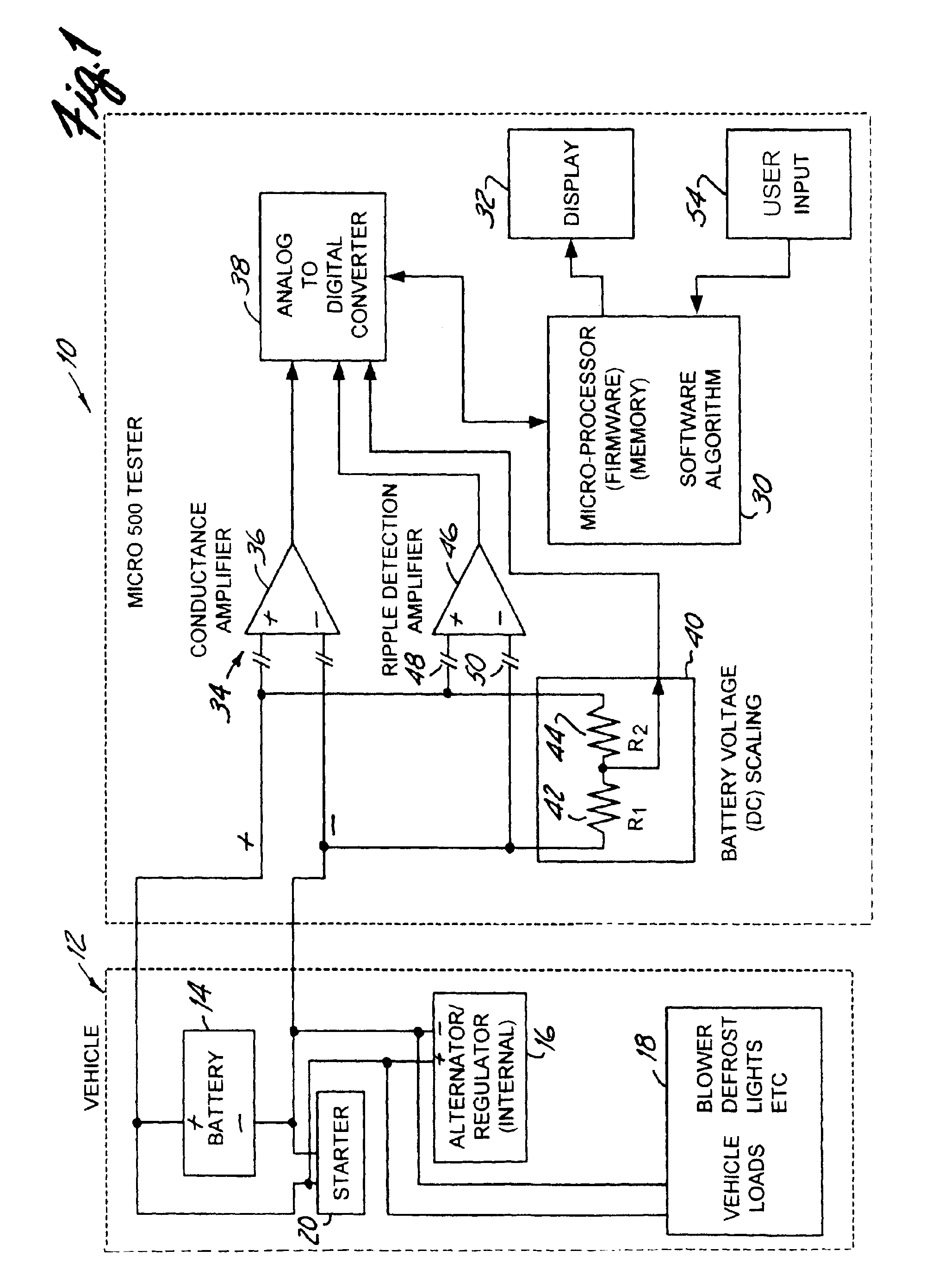
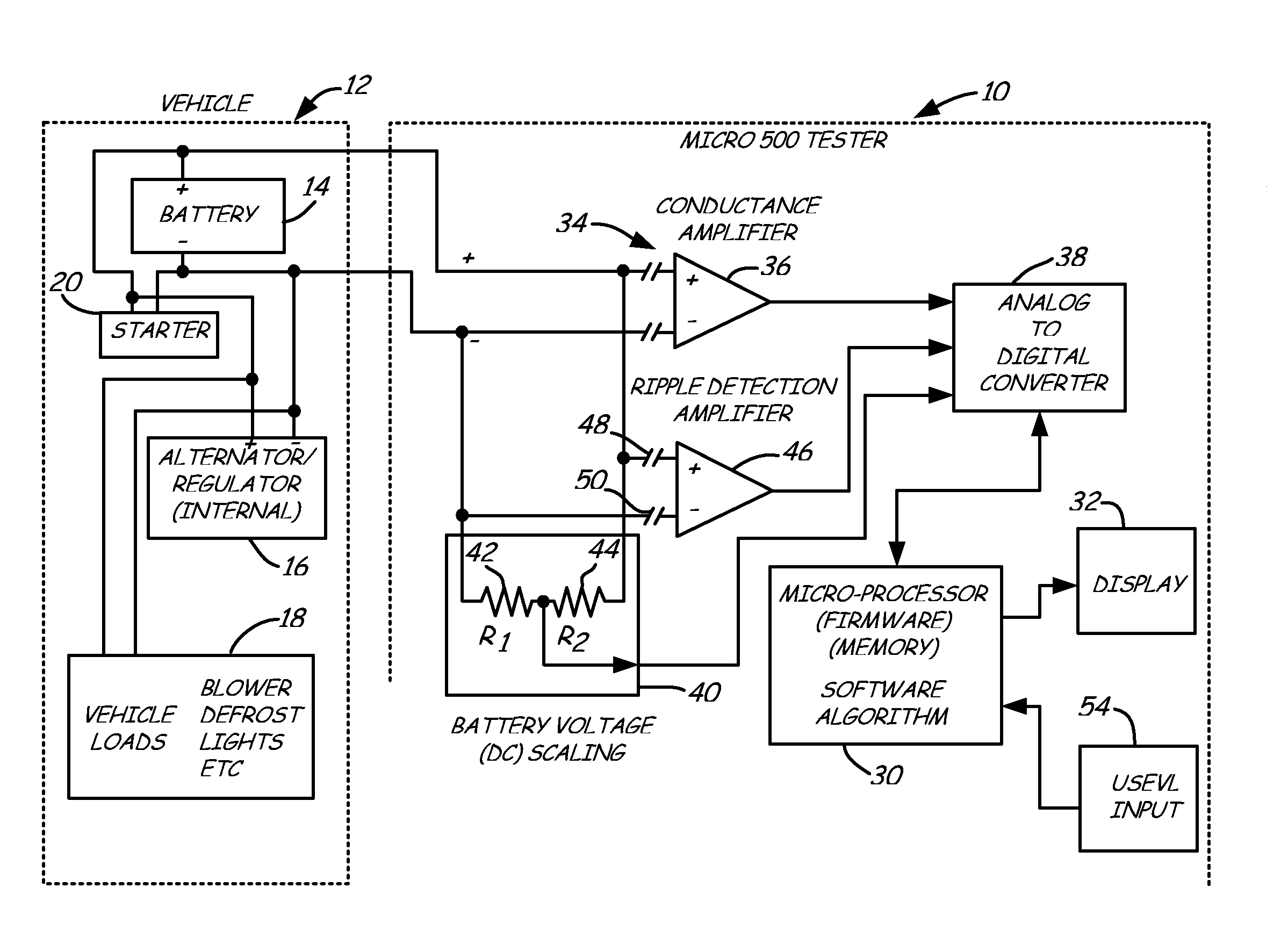
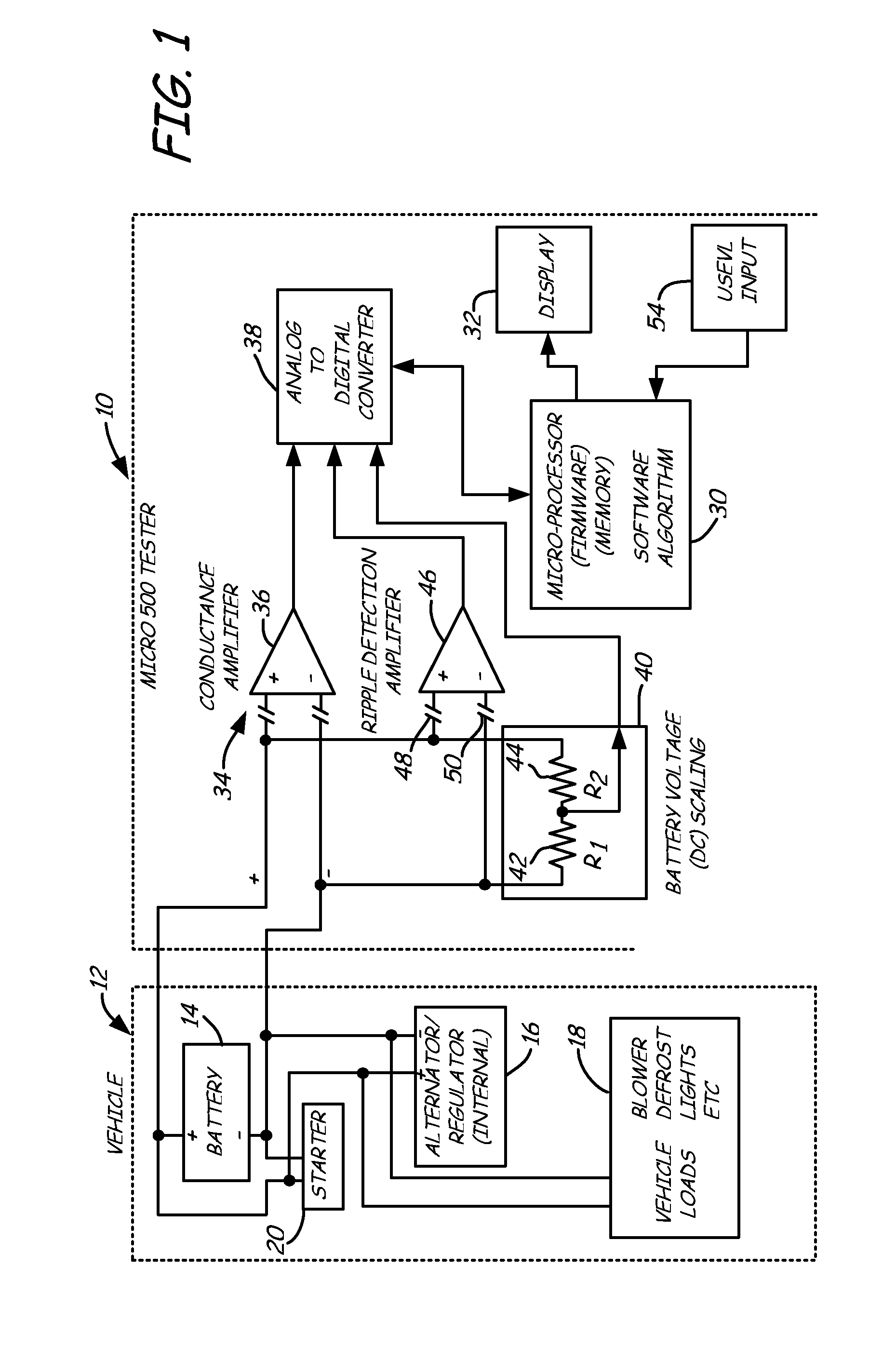
Alternator tester with encoded output
InactiveUS6914413B2Batteries circuit arrangementsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectricityAlternator
An alternator tester includes an alternator output measurement circuit configured to measure an electrical output of an alternator. A microprocessor determines a alternator condition as a function of the electrical output. The microprocessor encrypts information and provides an encrypted output which is related to the alternator electrical output. A method includes outputting such encrypted data.
Owner:MIDTRONICS
Battery capacity measuring and remaining capacity calculating system
InactiveUS6621250B1Quick calculationEnhanced advantageCircuit monitoring/indicationInternal combustion piston enginesBattery state of chargeIntegrator
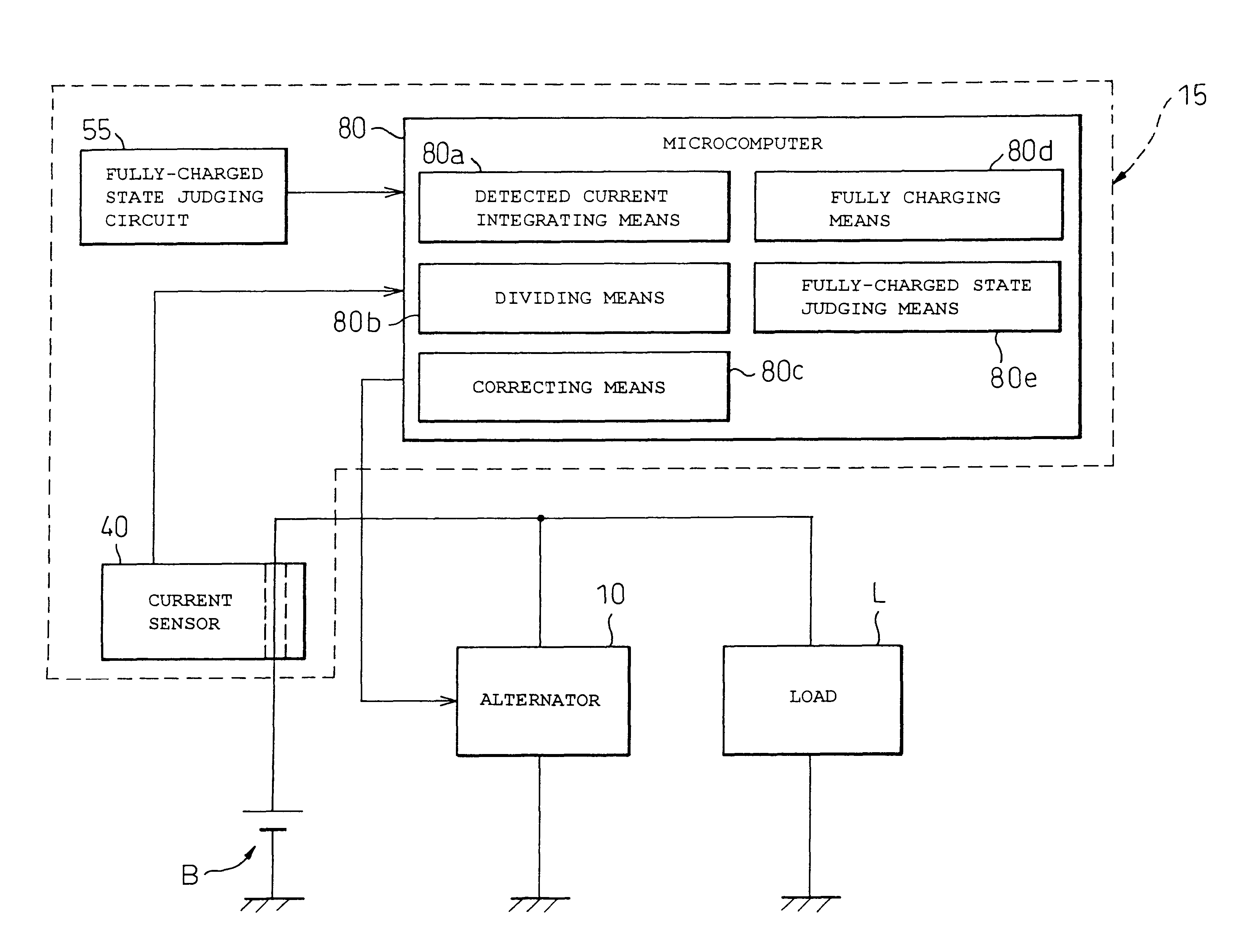
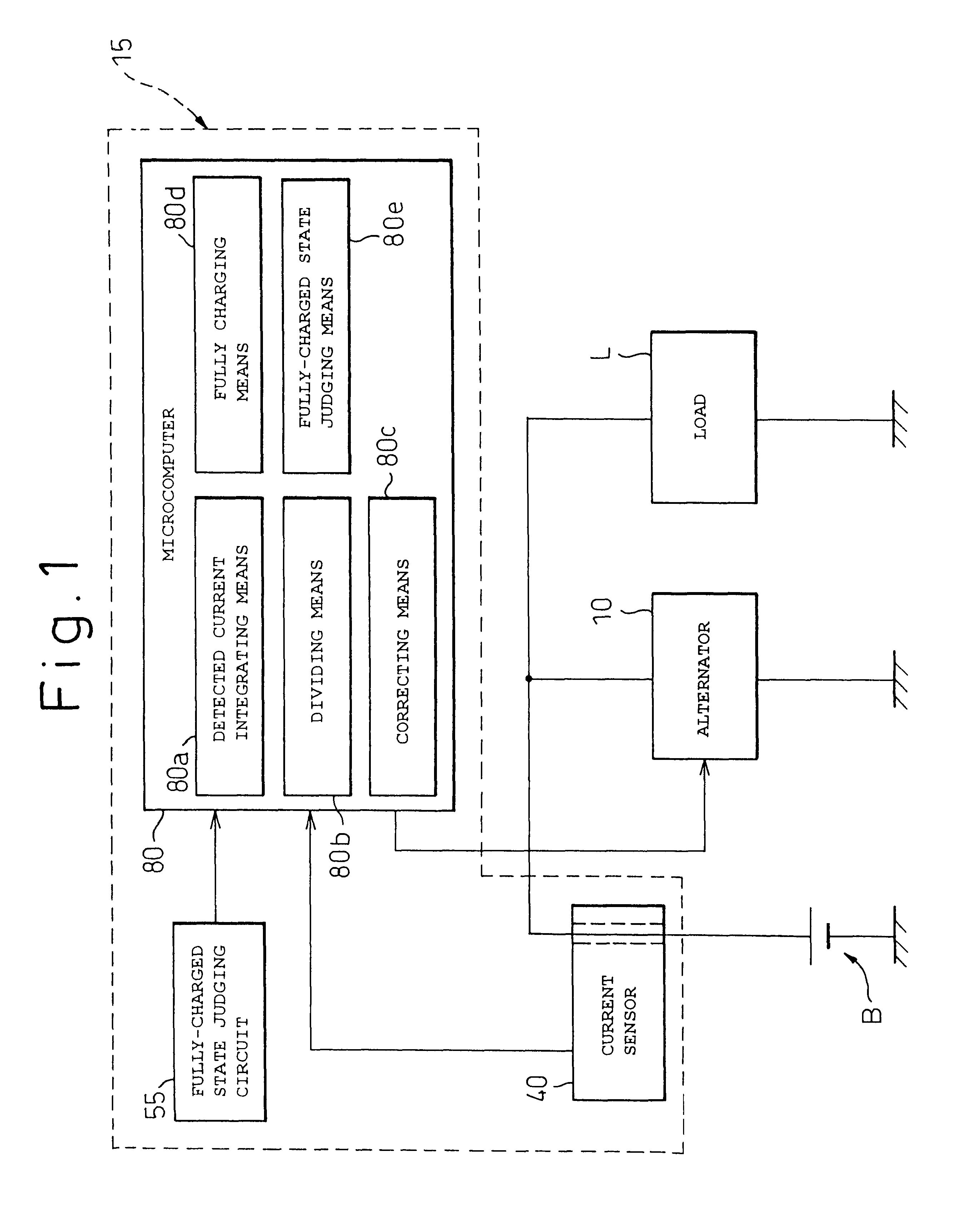
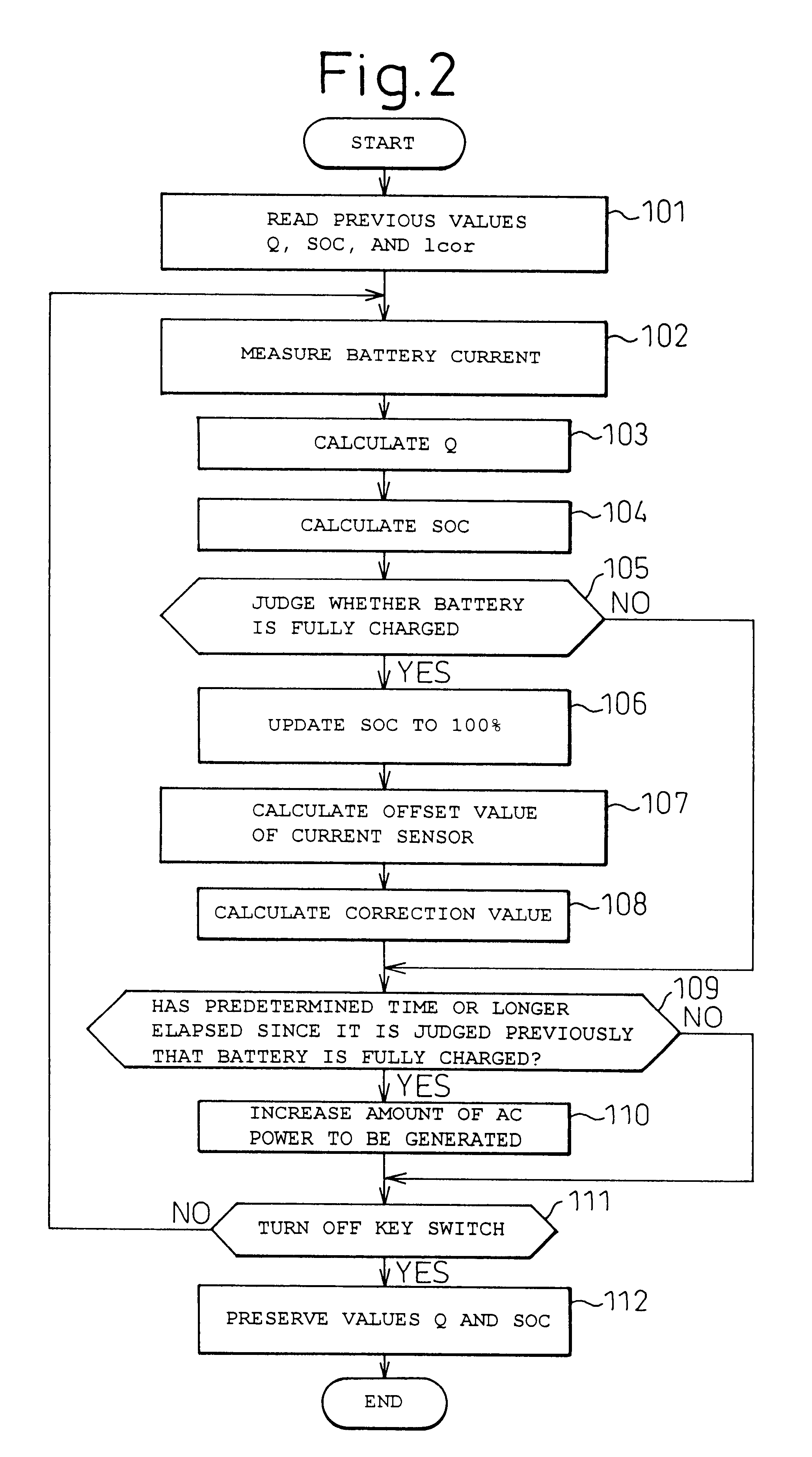
A battery capacity measuring device in accordance with the present invention has a fully-charged state detector (80e), a detected current integrator (80a), a divider (80b), and a corrector (80c) incorporated in a microcomputer (80). The fully-charged state detector detects that a battery is fully charged. The detected current integrator integrates current values that are detected by a current sensor during a period from the instant the battery is fully charged to the instant it is fully charged next. The divider divides the integrated value of detected current values by the length of the period. The corrector corrects a detected current using the quotient provided by the divider as an offset. Furthermore, a remaining battery capacity calculating system comprises a voltage detecting unit (50), a current detecting unit (40), an index calculating unit, a control unit, and a calculating unit. The voltage detecting unit detects the voltage at the terminals of a battery. The current detecting unit detects a current flowing through the battery. The index calculating unit calculates the index of polarization in the battery according to the detected current. The control unit controls the output voltage of an alternator so that the index of polarization will remain within a predetermined range which permits limitation of the effect of polarization on the charged state of the battery. When the index of polarization remains within the predetermined range, the calculating unit calculates the remaining capacity of the battery according to the terminal voltage of the battery, that is, the open-circuit voltage of the battery.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
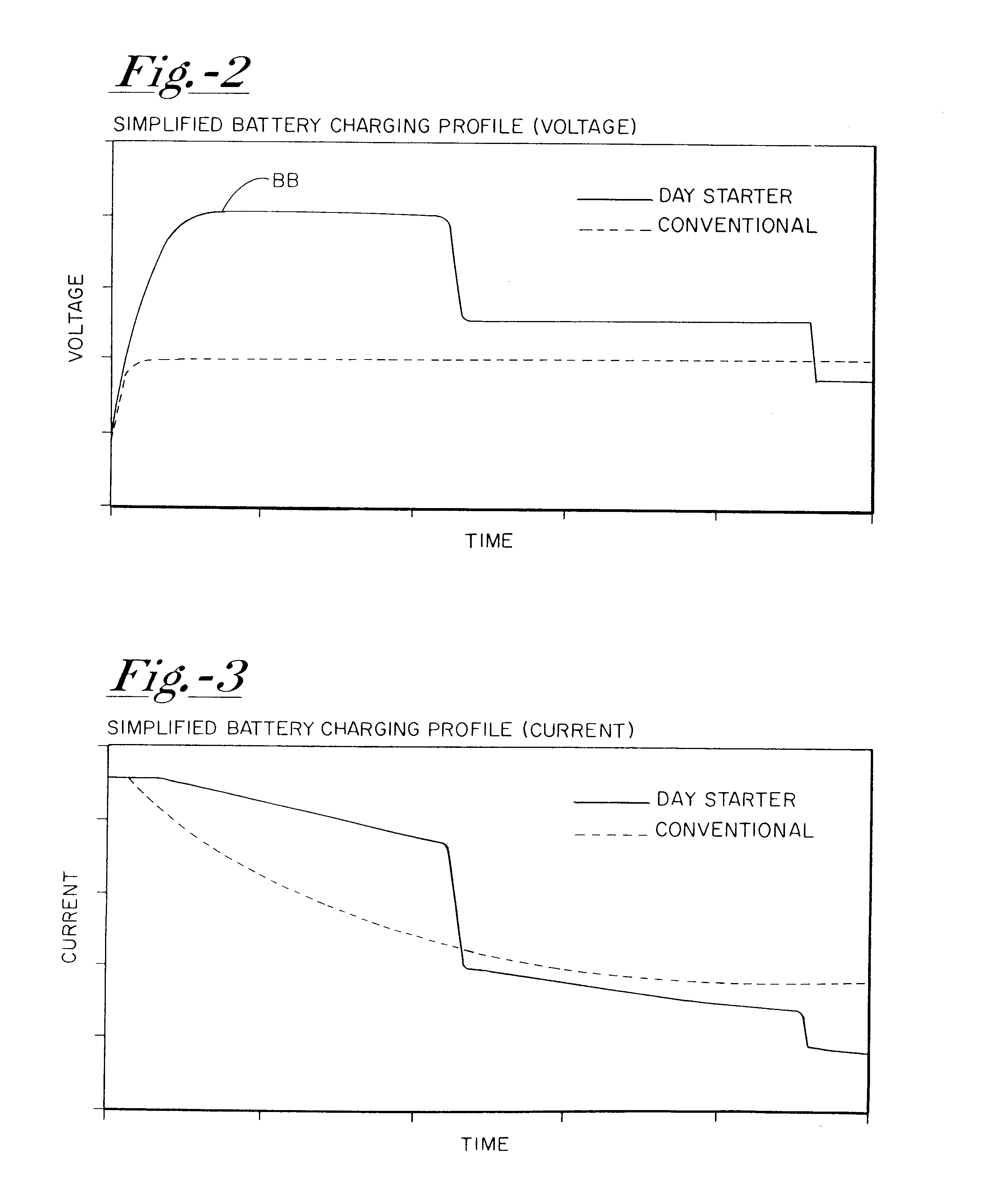
Battery charger apparatus
InactiveUS6515456B1Improve economyProlong lifeElectric powerCharge maintainance charging/dischargingBattery state of chargeAlternator
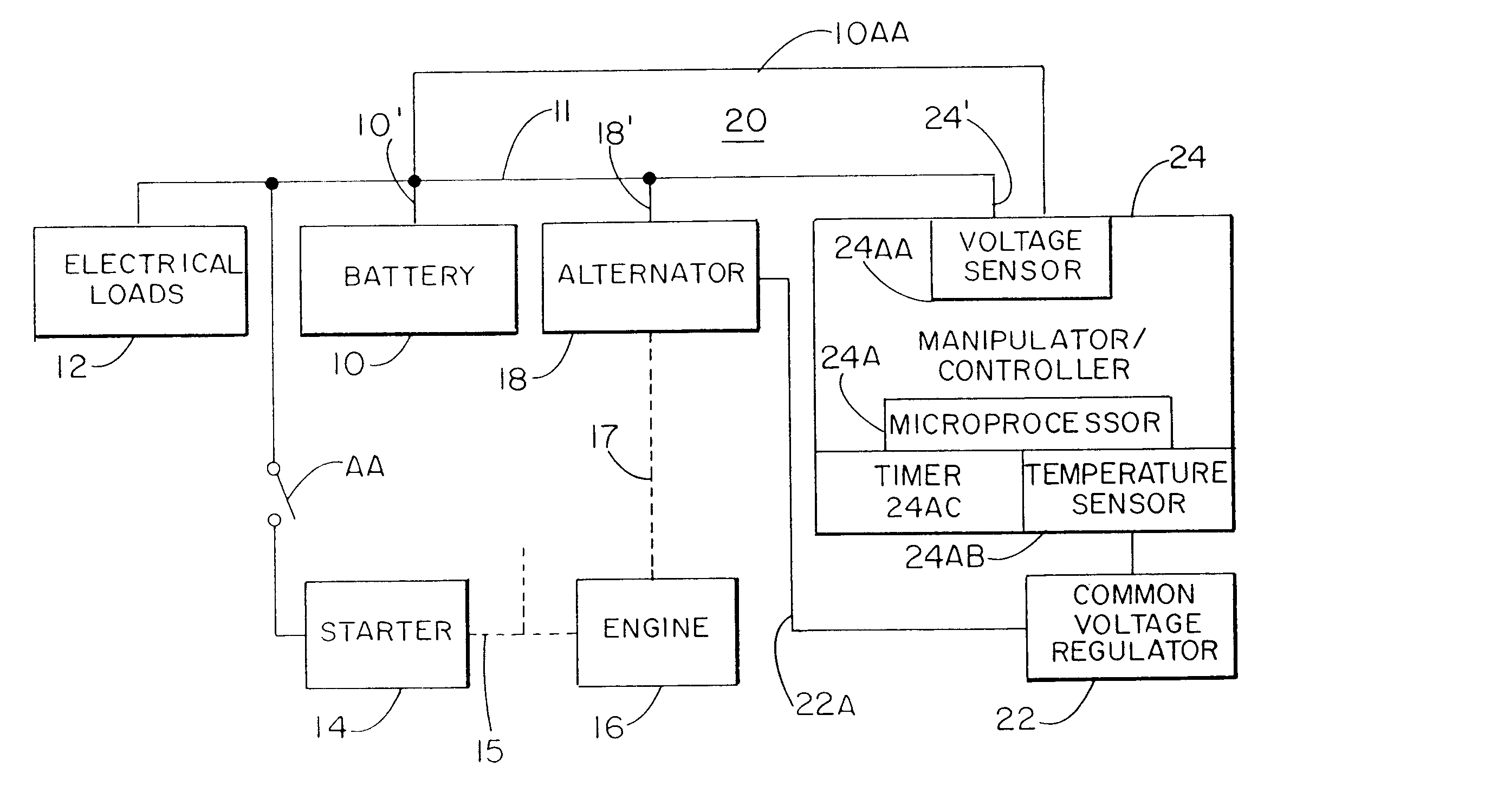
A system for actively controlling the charging profile of a battery uses a software-based alternator control unit to control the charging voltage. The system optimizes battery and alternator life. The system, on a dynamic basis, uses battery open-circuit voltage (OCV) to estimate battery state-of-charge (SOC). Also, the charging current of the battery is periodically estimated; this, after processing, provides an estimated SOC of the battery.
Owner:MIXON
Isolator for alternator pulley
InactiveUS7207910B2Dampen rotational movementIncrease damping forceYielding couplingChain/belt transmissionSerpentine beltAlternator
A decoupler for an alternator pulley in a serpentine drive system has a resilient, helical spring member that couples the alternator pulley with a hub structure through a spring retaining member. A bushing is disposed between the spring retaining member and the hub structure to facilitate sliding engagement therebetween. An annular sleeve member is disposed between the spring member and the alternator pulley to facilitate sliding engagement therebetween. The spring member is connected at one end thereof to the hub structure and connected at an opposite end thereof to the spring retaining member. The resilient spring member transmits the driven rotational movements of the alternator pulley by the serpentine belt to the hub structure such that the alternator shaft is rotated in the same direction as the alternator pulley while being capable of instantaneous relative resilient movements in opposite directions with respect to the alternator pulley during the driven rotational movement.
Owner:LITENS AUTOMOTIVE INC
Fluid driven electric power generation system
ActiveUS20080238105A1Scalable in sizeGood effectWind motor controlWind motor supports/mountsAlternatorHelical blade
A tubular housing includes at least one fixed helical vane formed onto the inner surfaces of the tubular housing in a spiral and adapted to direct fluid into a spiraled flow and focus fluid onto a fan blade assembly associated with an alternator system and located within the tubular housing before a system exhaust. A generator cone can be mounted near the center and front of the fan blade assembly facing fluid passing through the tubular housing. As fluid passes over the generator cone it experiences compression between the generator cone and housing resulting in increased pressure and velocity of the fluid, thereby increasing rotational speed of the generator blades and generator as the compressed, spiraled fluid passes through the blades and exits the tubular housing. The system can be used for fixed or mobile applications in water, wind and manually induced air flow.
Owner:MDL ENTERPRISES
Compact high power alternator
InactiveUS20050035673A1Increase surface areaImprove cooling effectMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsAlternatorRotor magnets
An apparatus for converting between mechanical and electrical energy, particularly suited for use as a compact high power alternator for automotive use and “remove and replace” retrofitting of existing vehicles. The apparatus comprises a rotor with permanent magnets, a stator with a winding, and a cooling system. Mechanisms to prevent the rotor magnets from clashing with the stator by minimizing rotor displacement, and absorbing unacceptable rotor displacement are disclosed. The cooling system directs coolant flow into thermal contact with at least one of the winding and magnets, and includes at least one passageway through the stator core. Various open and closed cooling systems are described. Cooling is facilitated by, for example, loosely wrapping the winding end turns, use of an asynchronous airflow source, and / or directing coolant through conduits extending through the stator into thermal contact with the windings.
Owner:MAGNETIC APPL
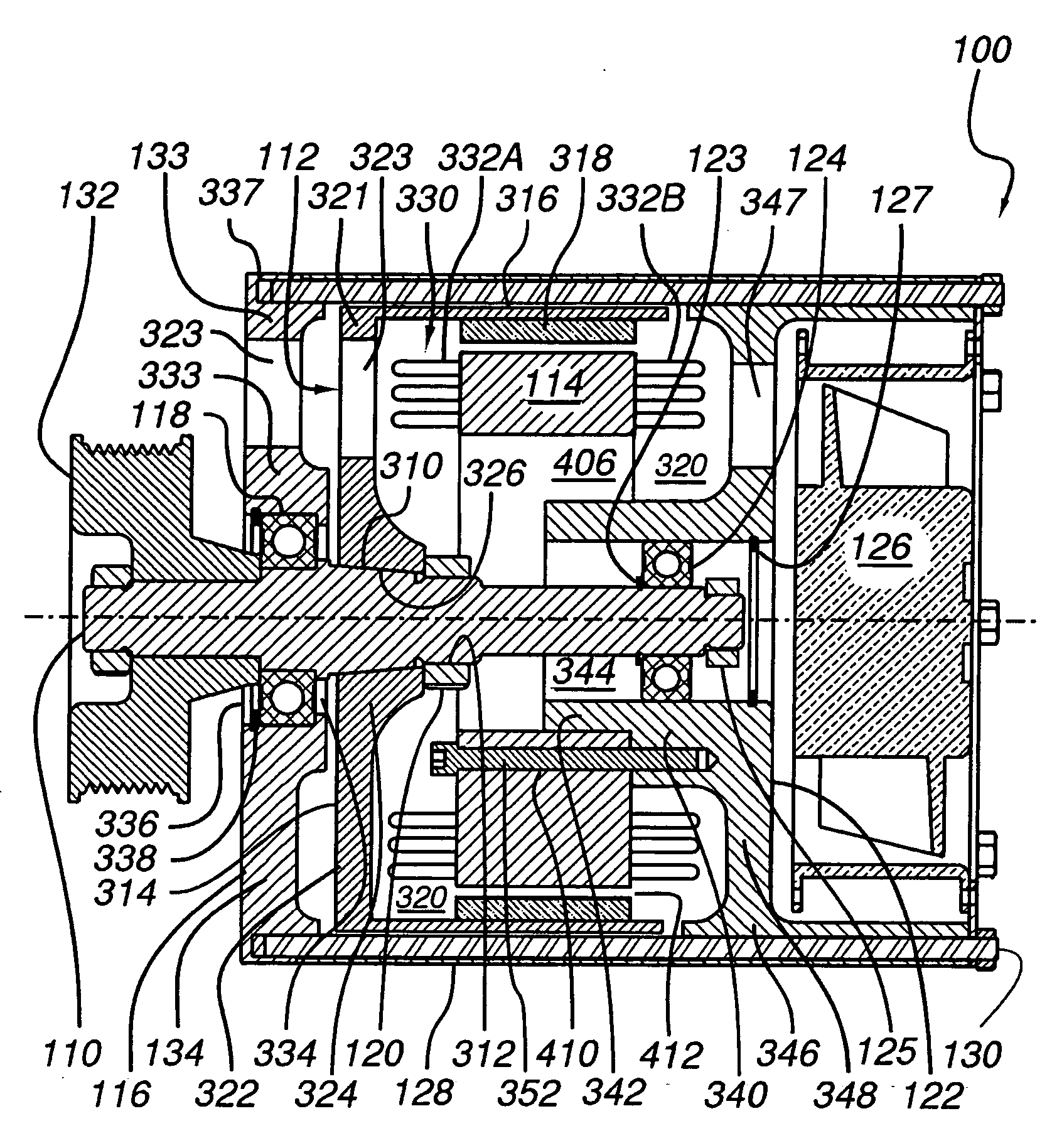
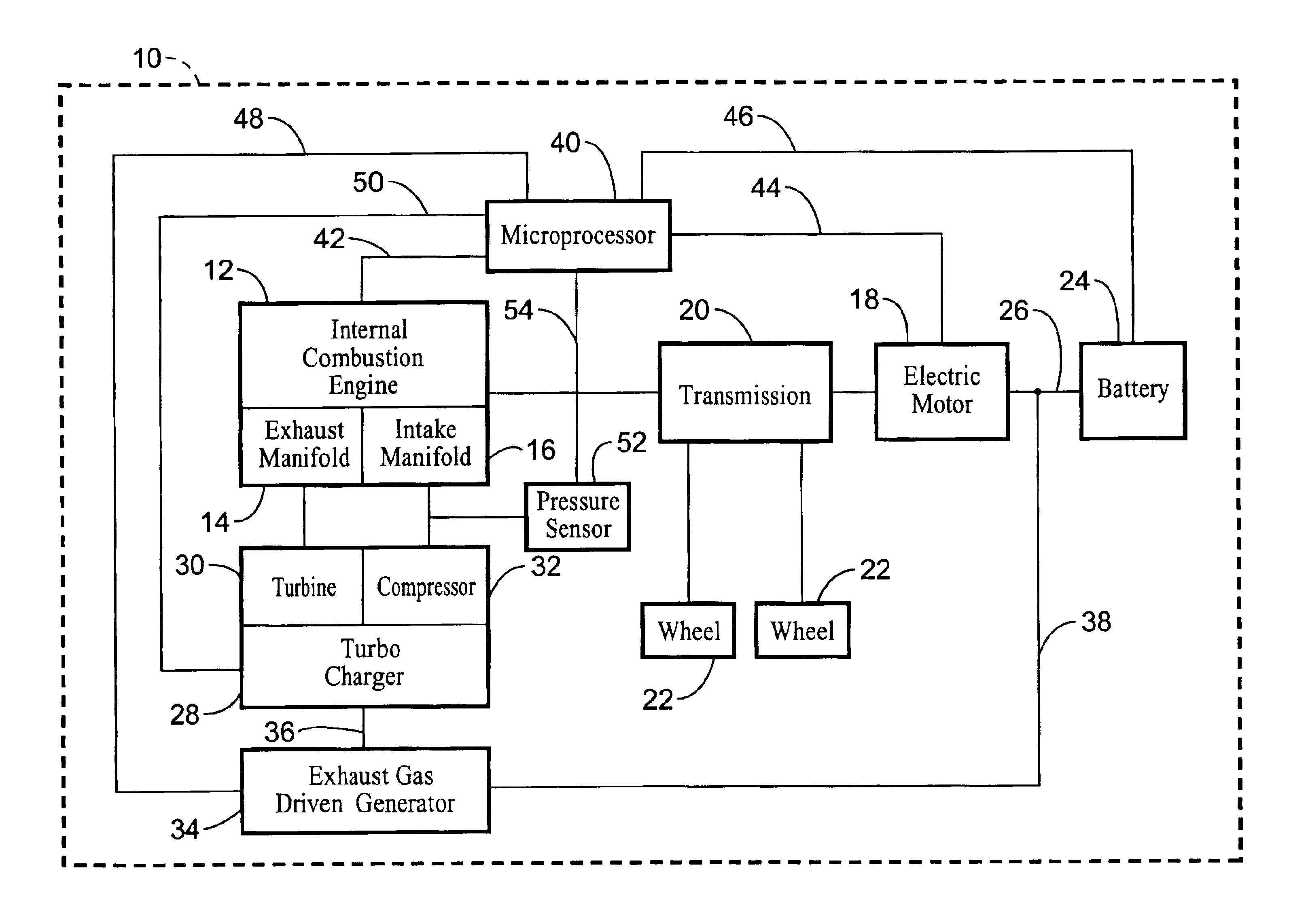
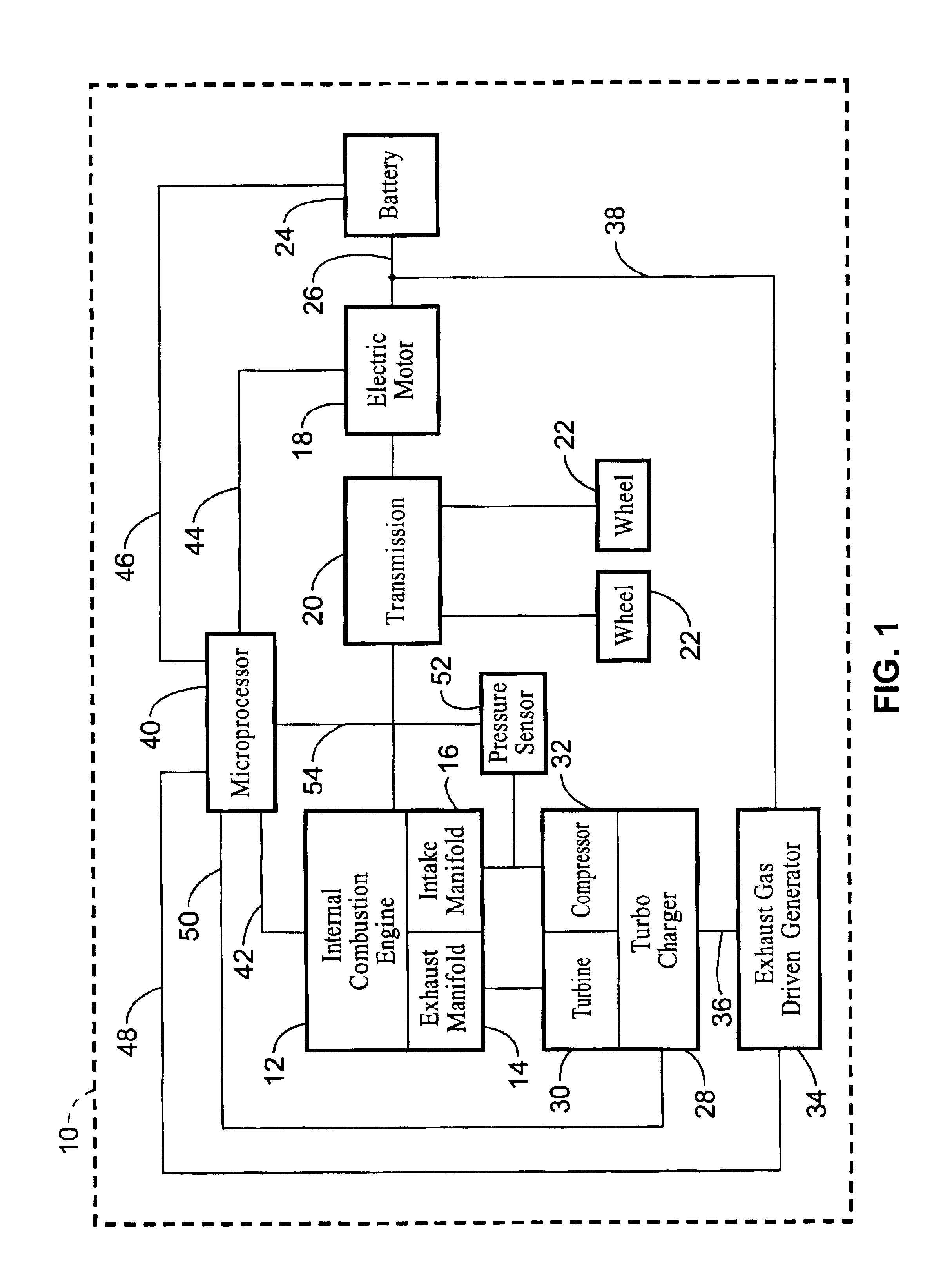
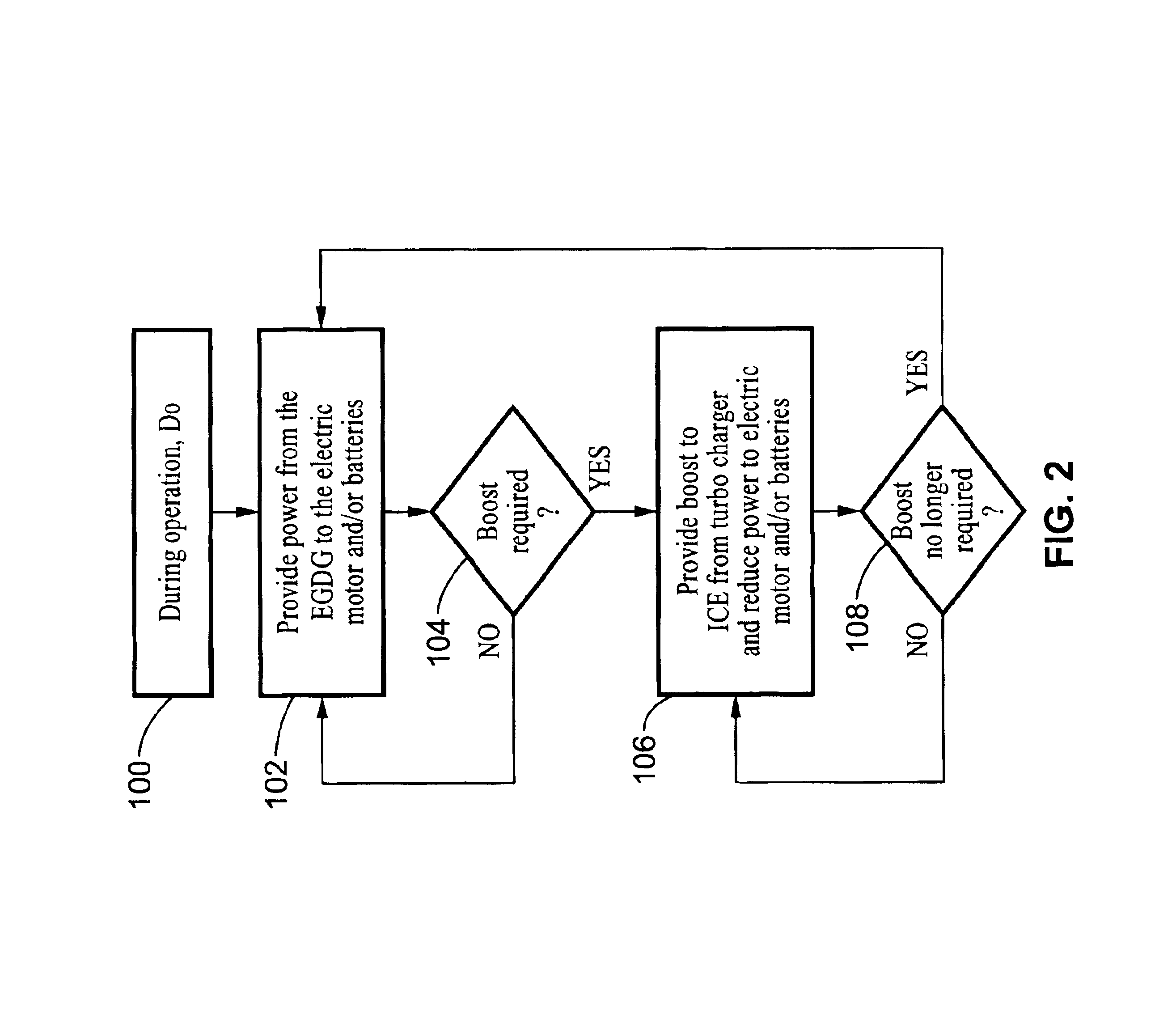
Exhaust gas driven generation of electric power and altitude compensation in vehicles including hybrid electric vehicles
InactiveUS6931850B2Improve volumetric efficiency and effective thermal efficiencyReduce fuel consumptionInternal combustion piston enginesPropulsion using engine-driven generatorsElectrical batteryTurbocharger
A hybrid electric vehicle includes an internal combustion engine, an electric motor and a transmission. A turbocharger is in fluid communication with the internal combustion engine. Moreover, a generator is mechanically coupled to the turbocharger and thereby driven by exhaust gas from the internal combustion engine. The generator can provide electricity to the motor and / or a battery while simultaneously providing altitude compensation for the internal combustion engine so that the internal combustion engine output remains at the same power and efficiency as altitude and environmental conditions change. The turbocharger can also be used for power boost if desired. The exhaust gas driven generator system can be deployed in conventional vehicles as well to charge the battery and / or power electrical accessories, thereby replacing the alternator.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
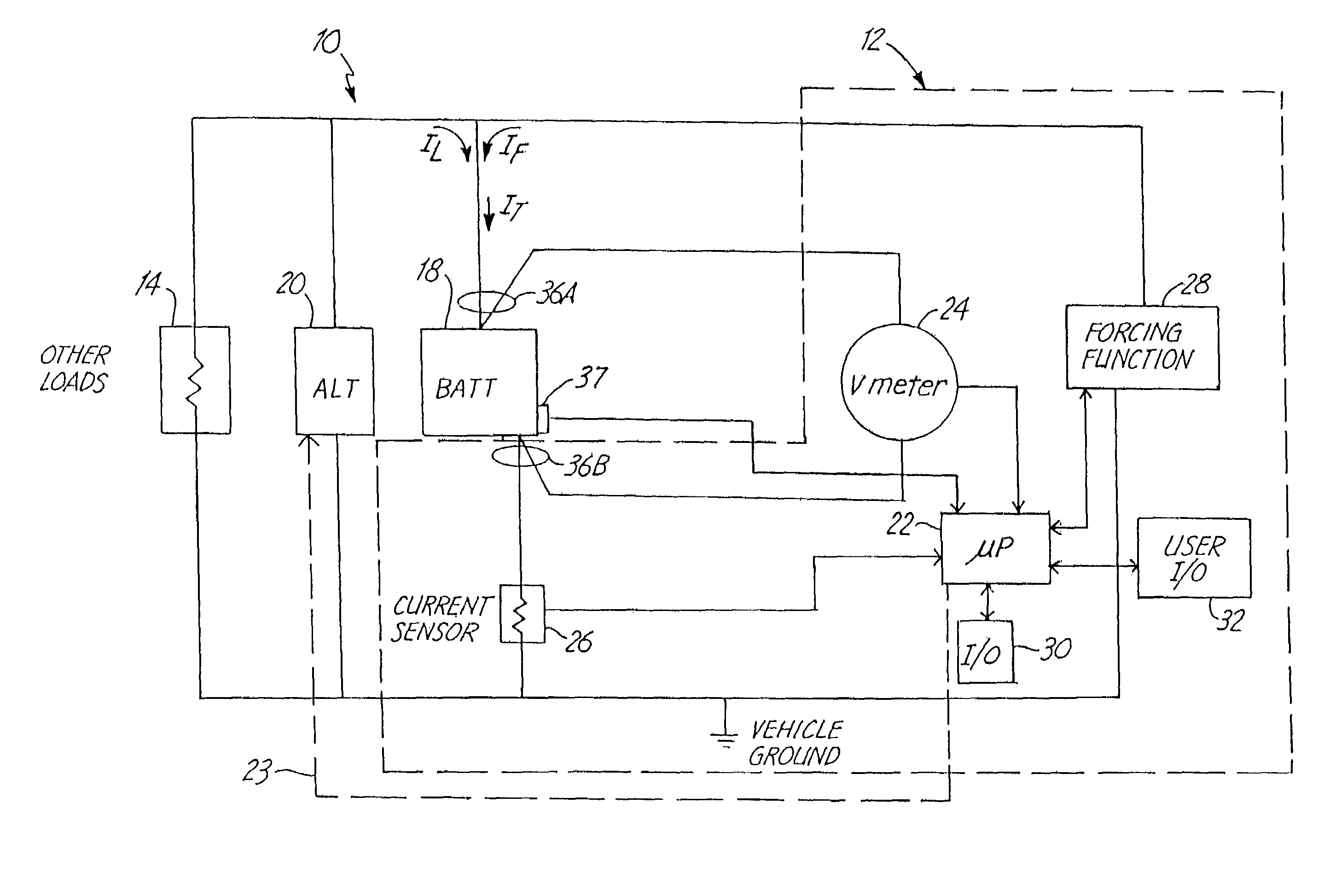
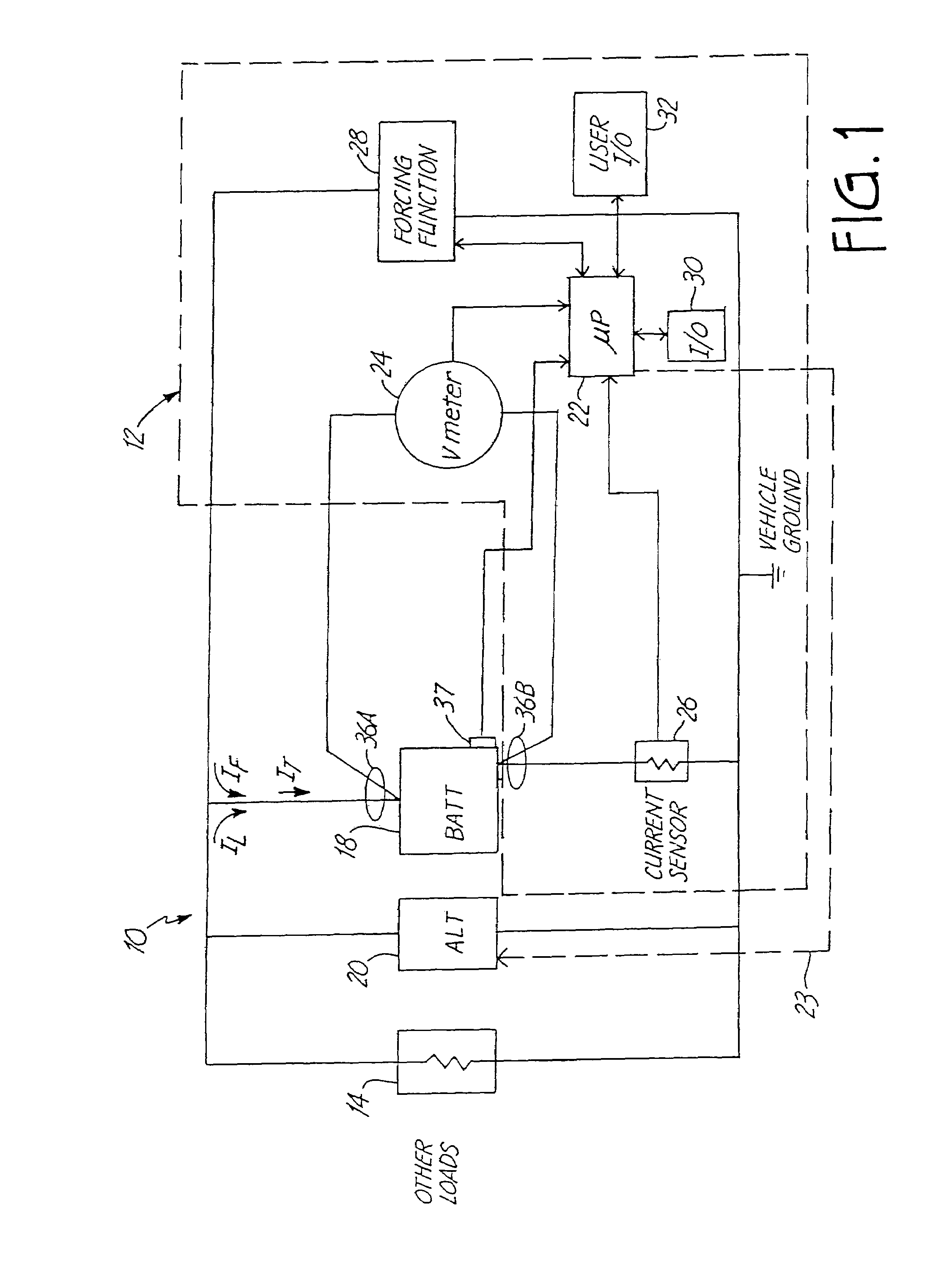
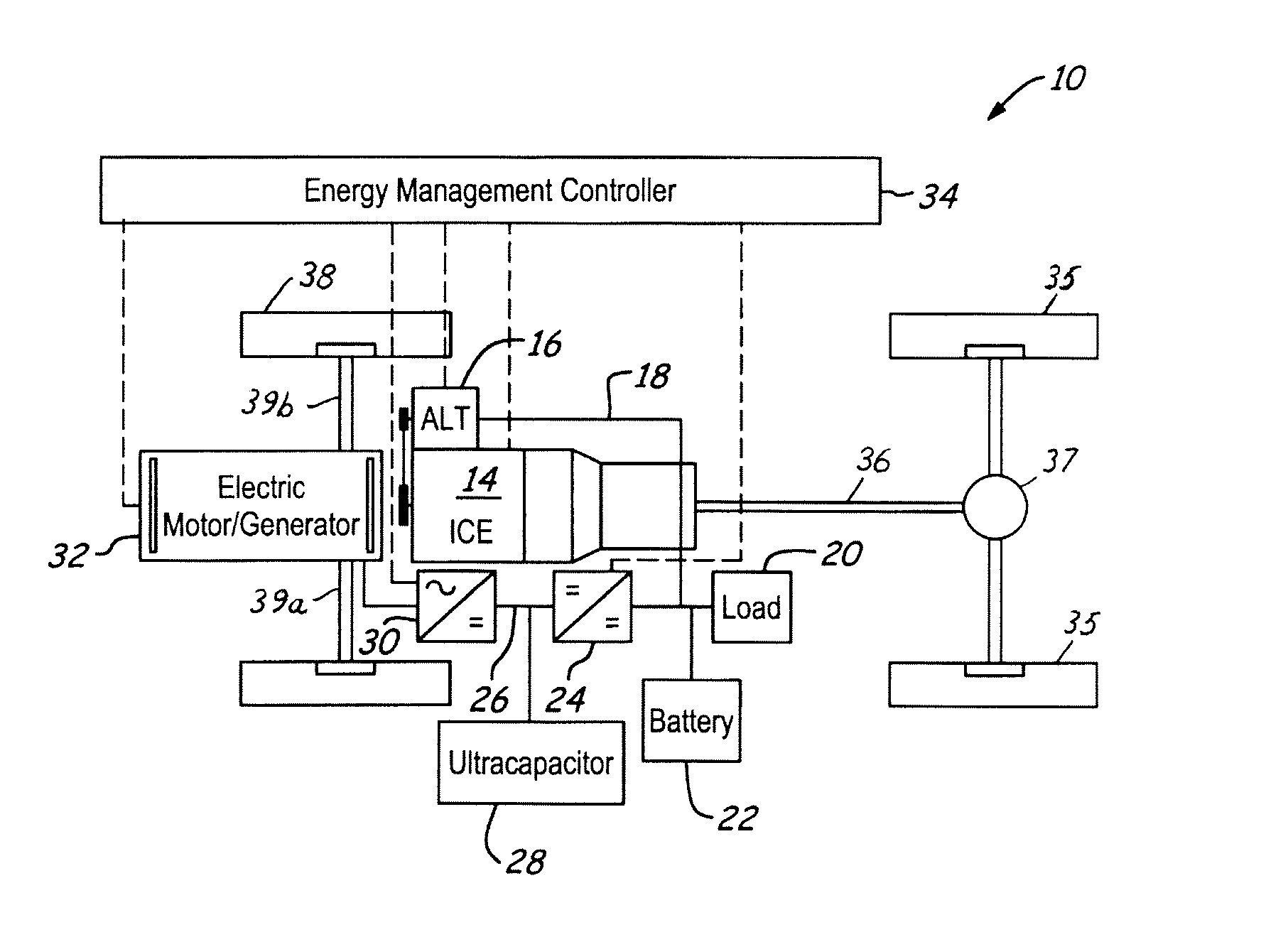
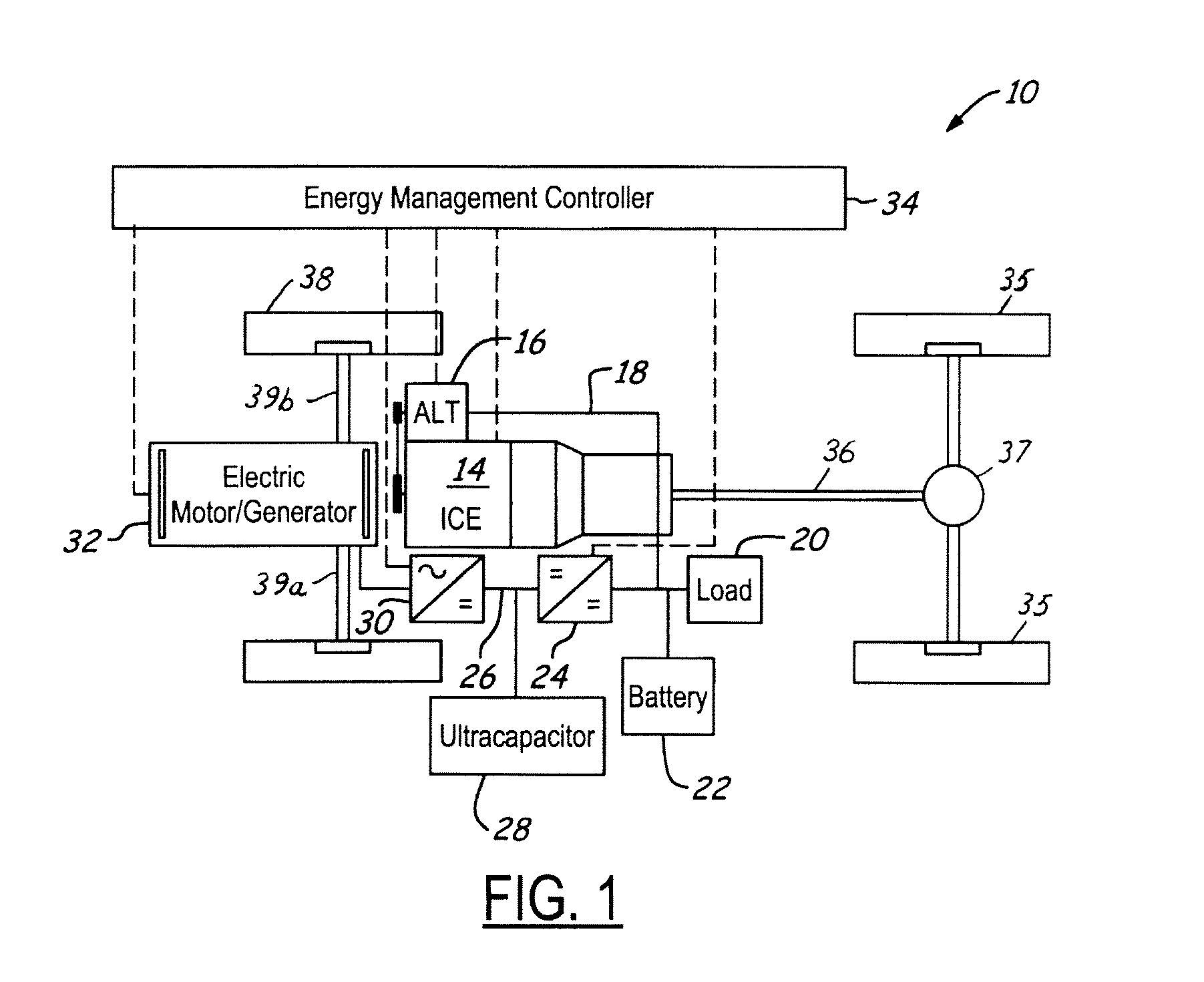
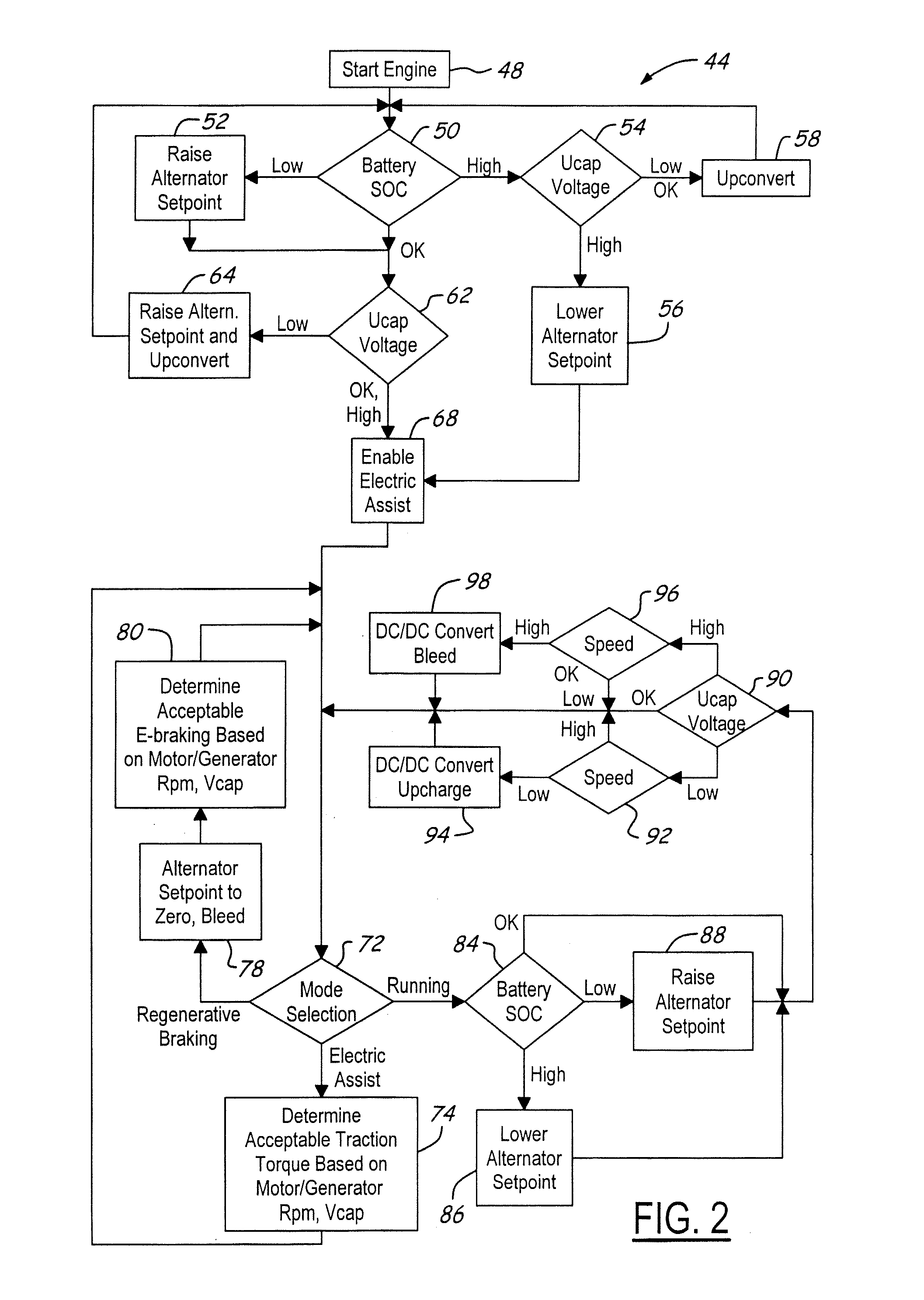
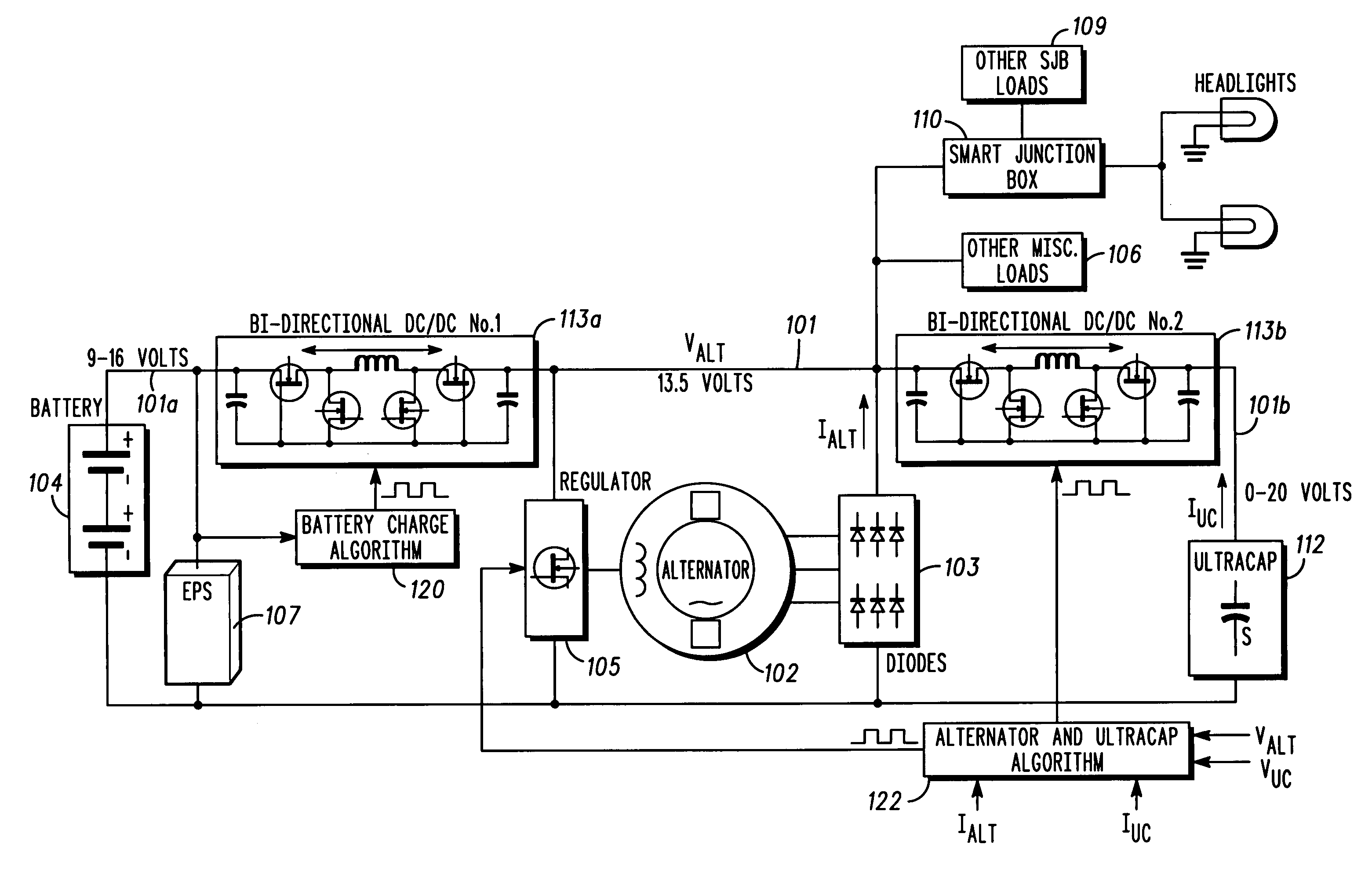
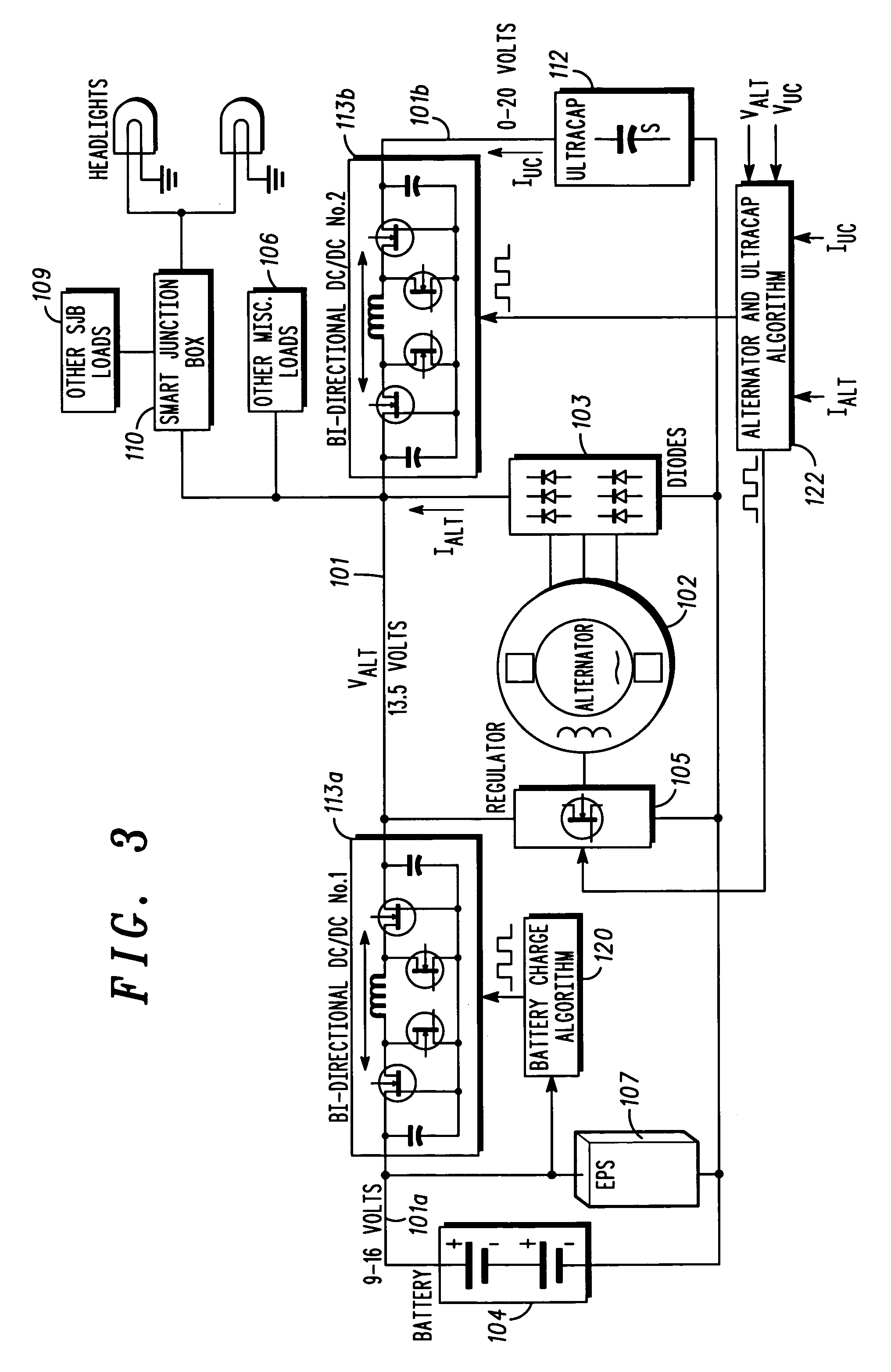
Stabilized electric distribution system for use with a vehicle having electric assist
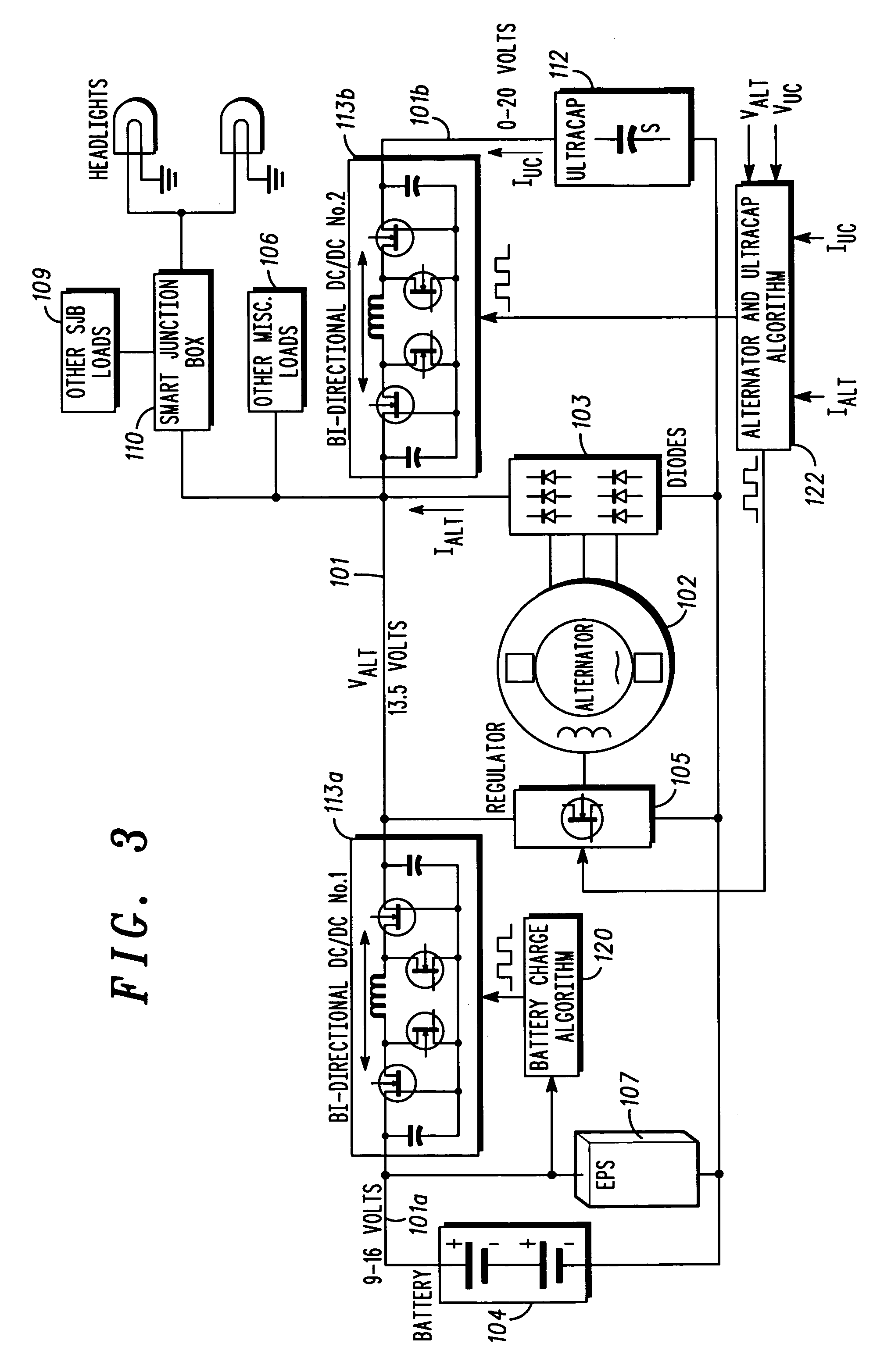
A stabilized electric distribution system for use in a vehicle having electric assist. The system electrically couples an electric assist bus to an accessory load bus while protecting the first electrical bus from electric assist and regenerative braking induced voltage variations. An energy management controller selectively controls each of a electric motor / generator, a DC / DC converter, and an alternator to affect electric energy distribution within the system. Preferably, the electric energy distribution is controlled to maintain the first electrical bus voltage within a predefined voltage range.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
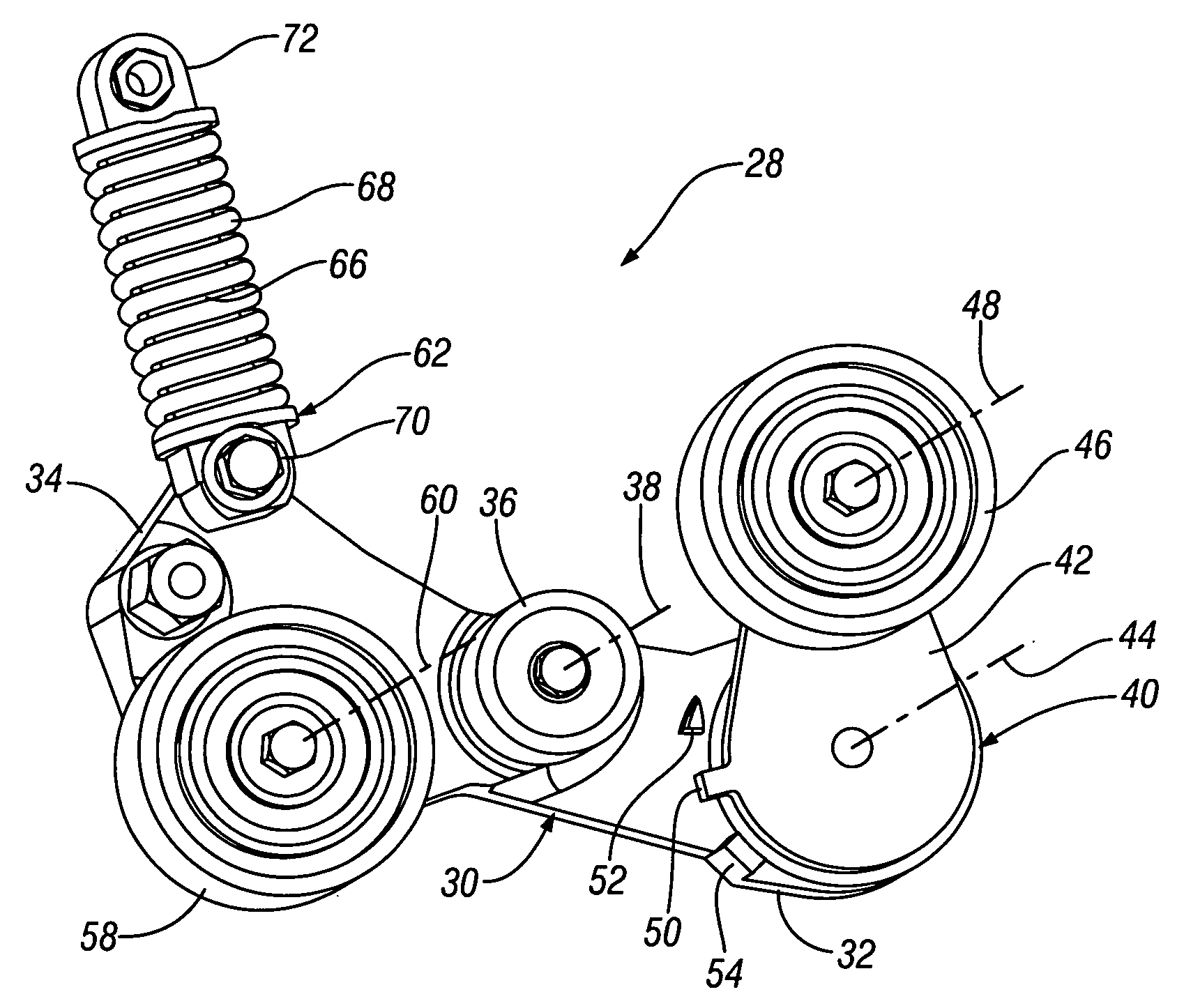
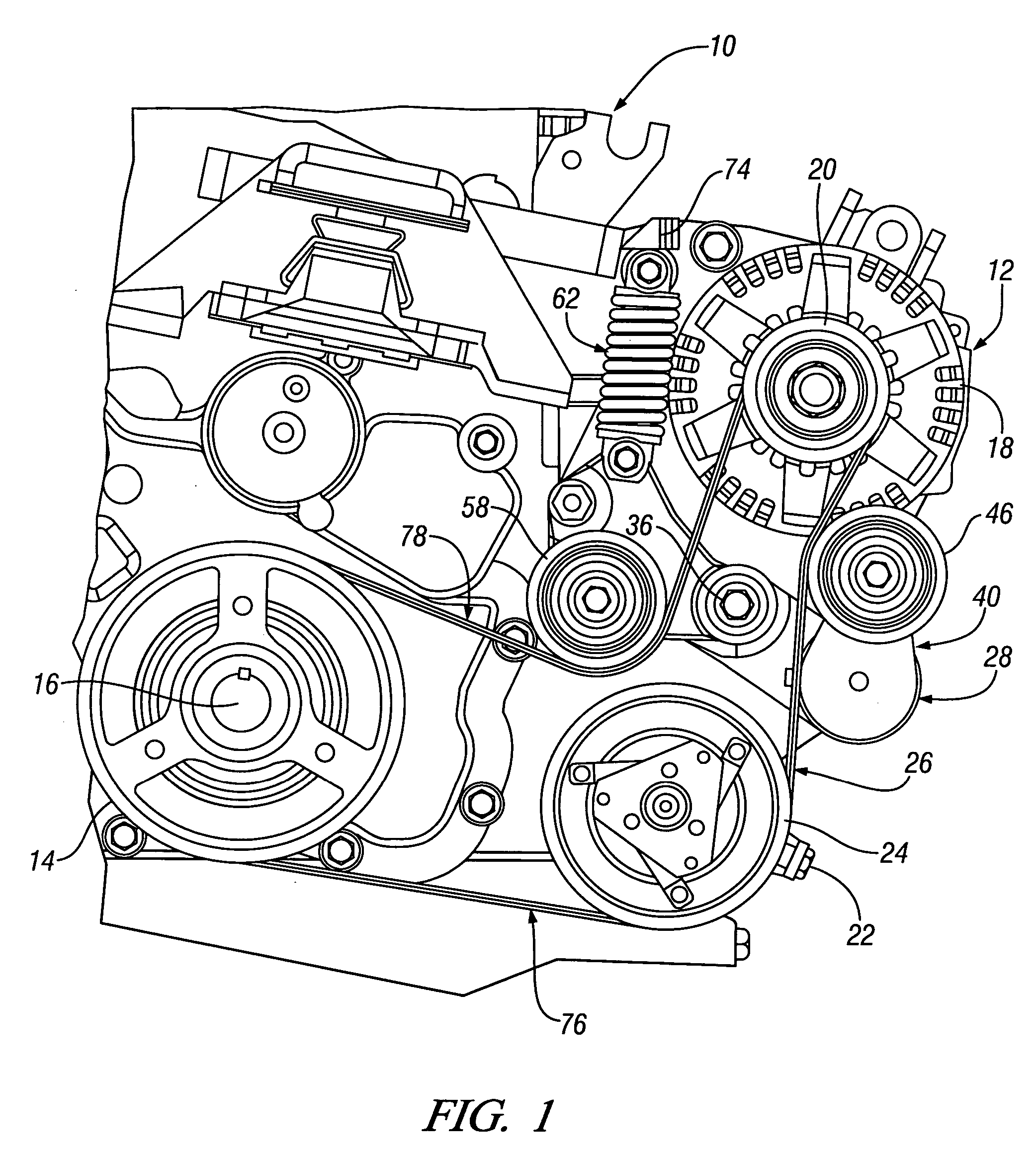
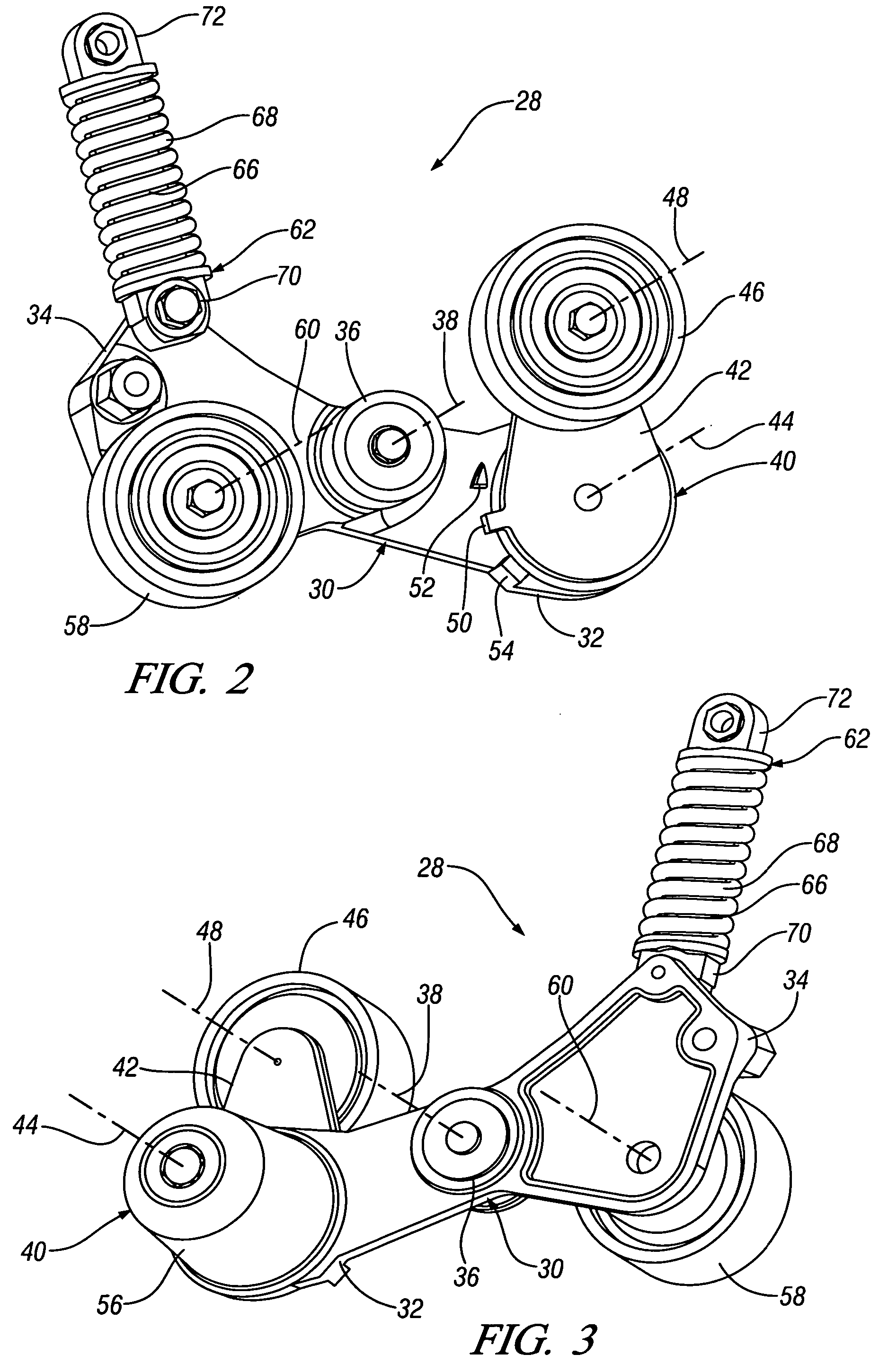
Belt alternator starter accessory drive with dual tensioner
An accessory drive for an engine has a belt driven starter generator adapted for driving and being driven by the engine. In an exemplary embodiment, the drive includes a first engine drive pulley and a second starter drive pulley. A drive belt engages the drive pulleys for driving either pulley from the other. A dual belt tensioner made as a preassembled unit has a carrier with a central pivot mounted to the engine and first and second carrier arms extending radially from the central pivot. A first tensioner mounted on the first arm carries a first tensioner pulley biased against a first belt run adjacent the second drive pulley that is slack during engine starting. A second tensioner pulley carried on the second arm is biased against a second belt run adjacent the second drive pulley that is taut during engine starting A hydraulic strut connected to the second arm, and preferably included in the preassembled unit, provides moderate biasing for the second tensioner pulley during normal engine operation and velocity sensitive resistance, to increased belt forces, that limits reactive movement of the second tensioner pulley during engine starting and transient engine operation.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Low inductance electrical machine for flywheel energy storage
InactiveUS6175178B1Synchronous generatorsMagnetic circuit rotating partsBrushless motorsFlywheel energy storage
A low inductance electrical machine which may be used as an alternator or motor with low armature inductance is disclosed. Arrangements of complementary armature windings are presented in which the fluxes induced by currents in the armature windings effectively cancel leading to low magnetic energy storage within the machine. This leads to low net flux levels, low core losses, low inductance and reduced tendency toward magnetic saturation. Separately excited field arrangements are disclosed that allow rotor motion to effect brushless alternator or brushless motor operation. An exemplary geometry includes a stator including two toroidal rings and a concentric field coil together with a rotor structure separated from the stator by four air gaps. An alternate embodiment allows for counter-rotation of two rotor elements for use as a flywheel energy storage system in which the external gyroscopic effects cancel.
Owner:RAVEN TECH
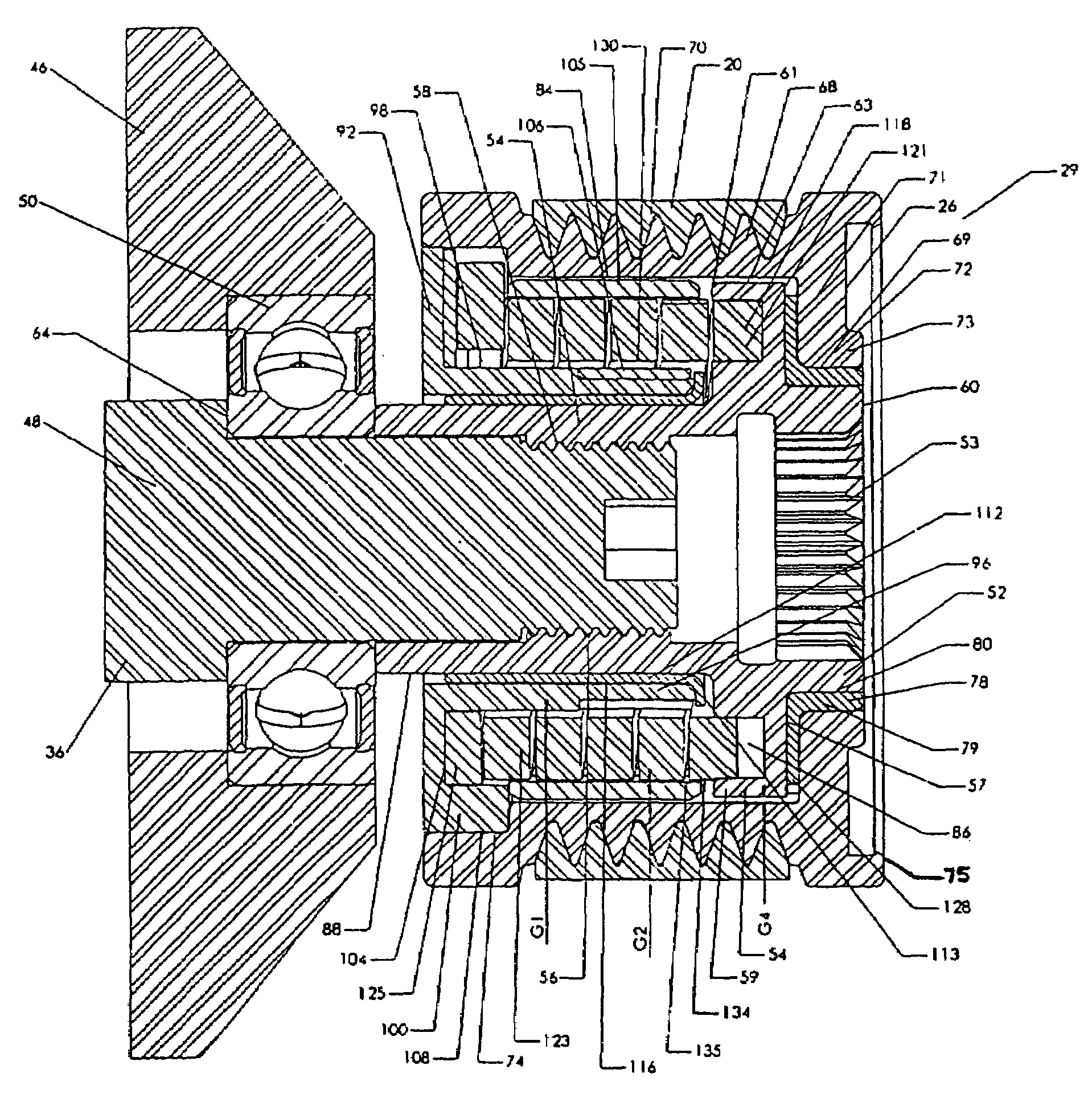
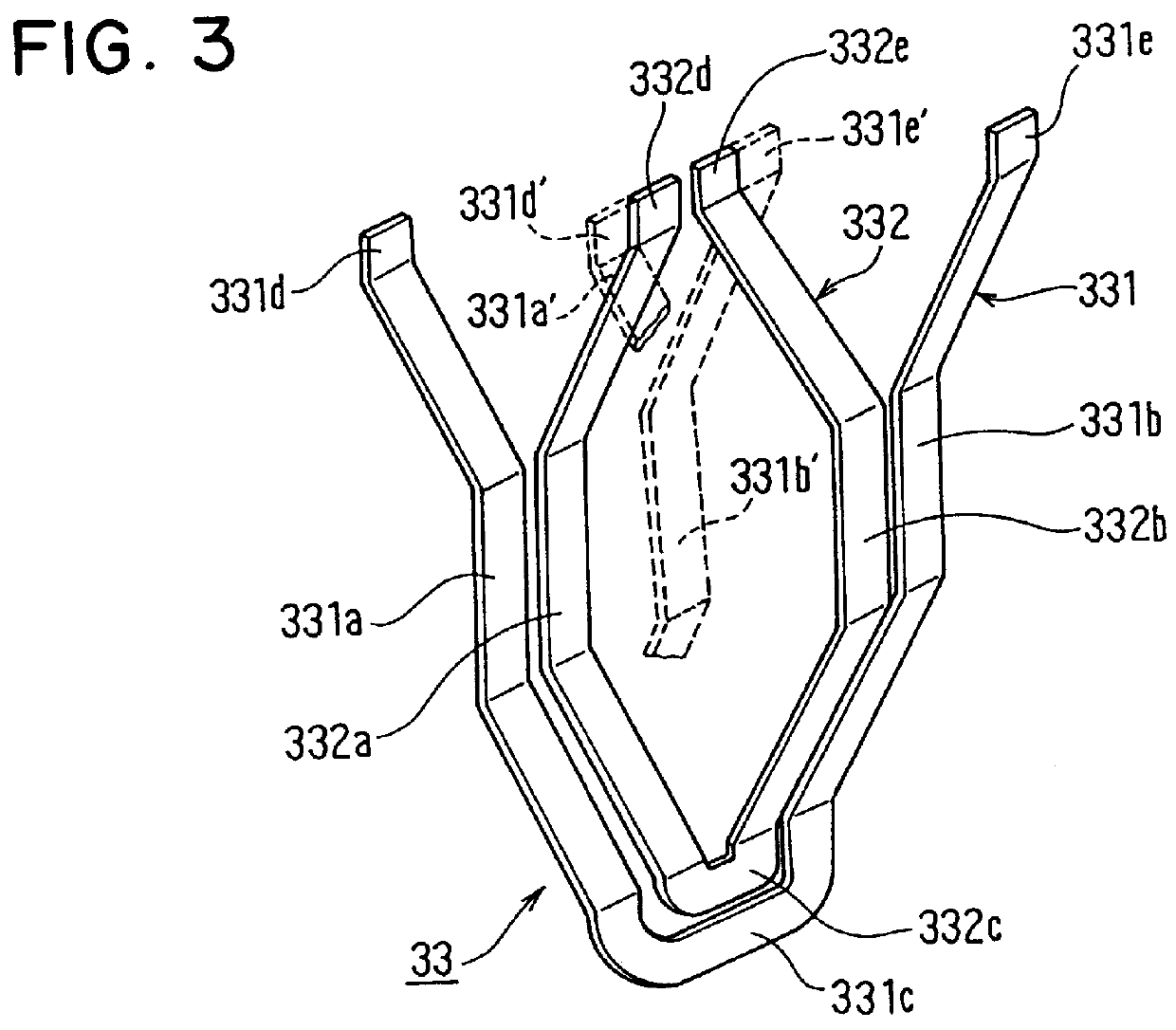
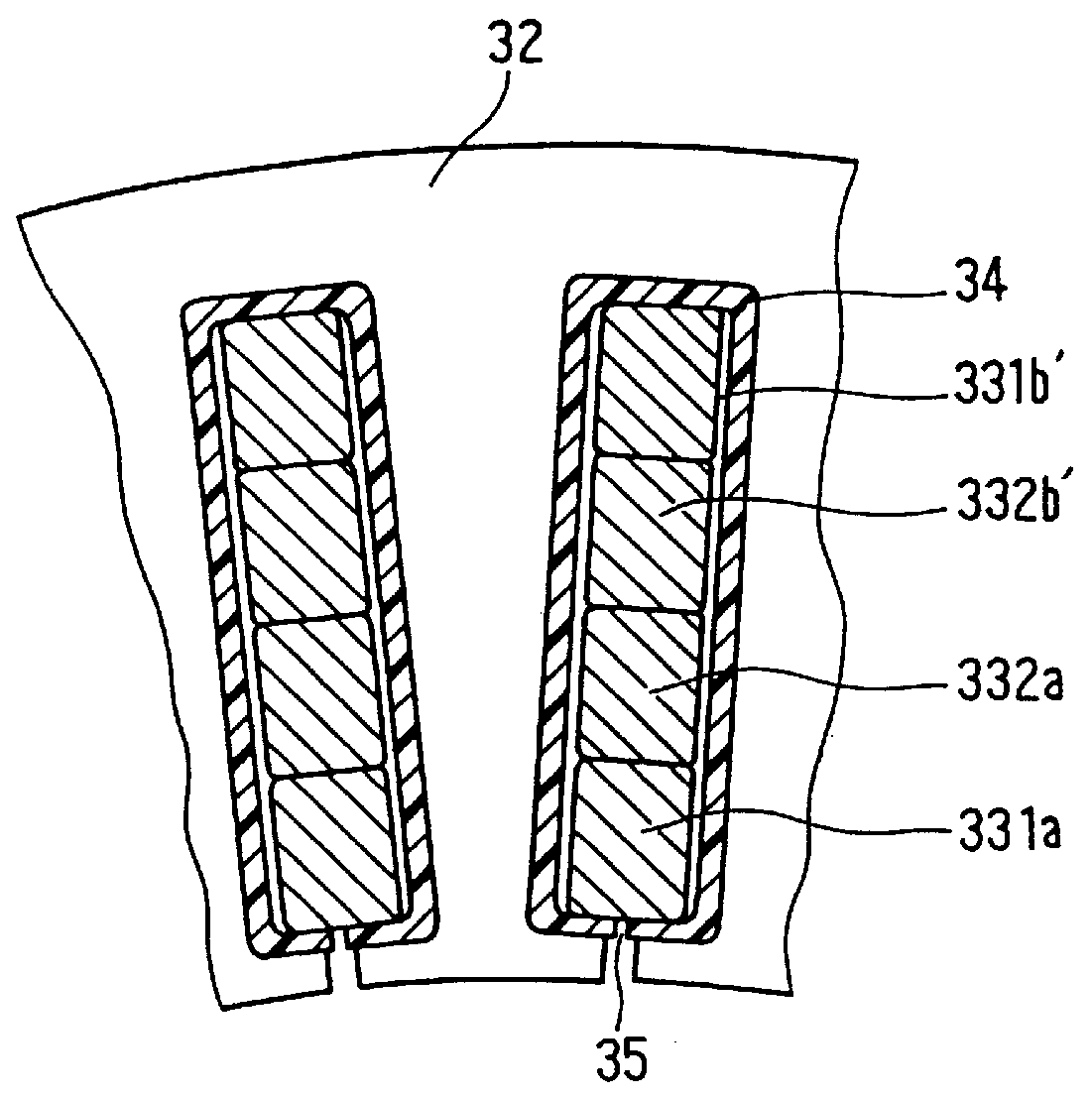
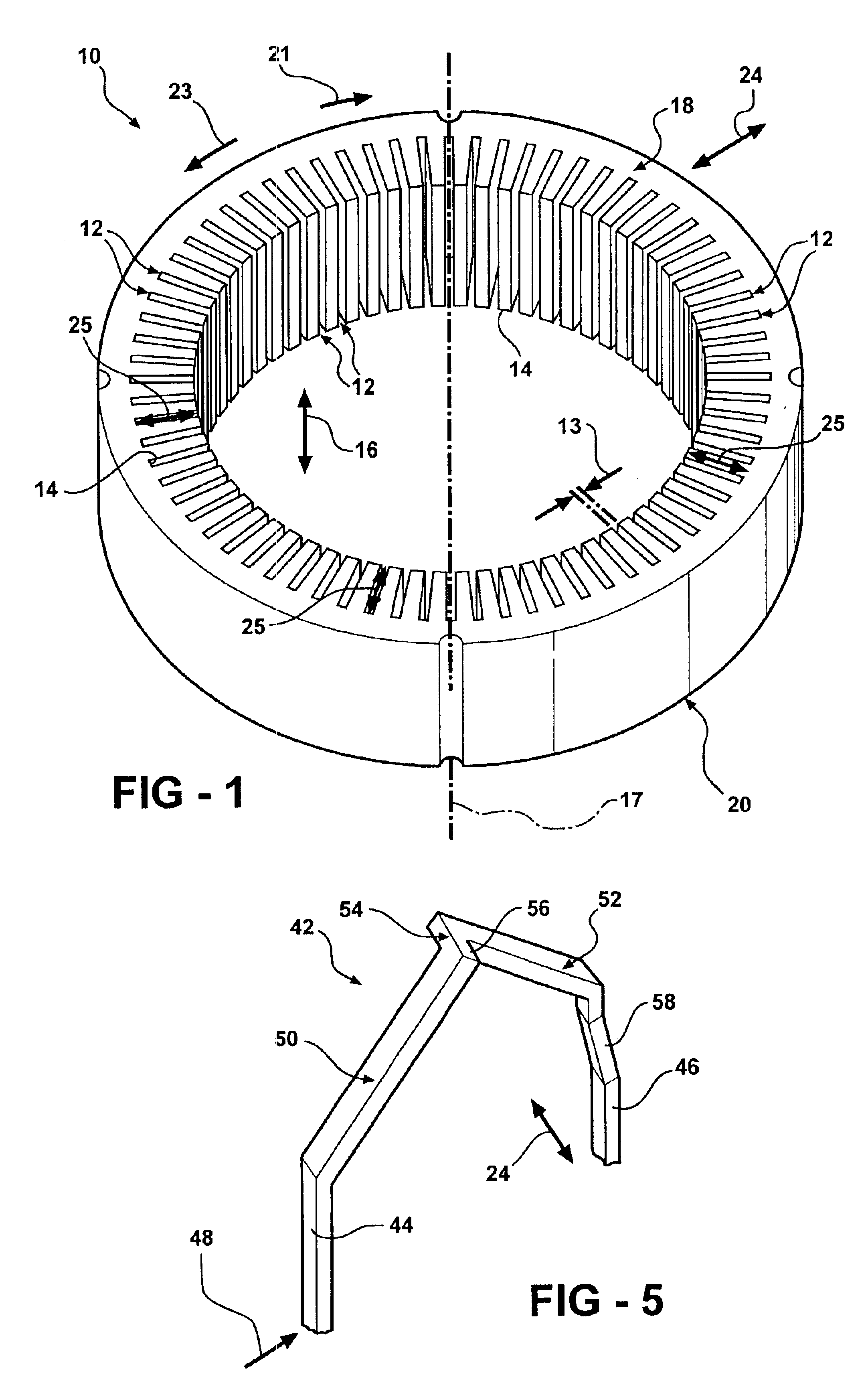
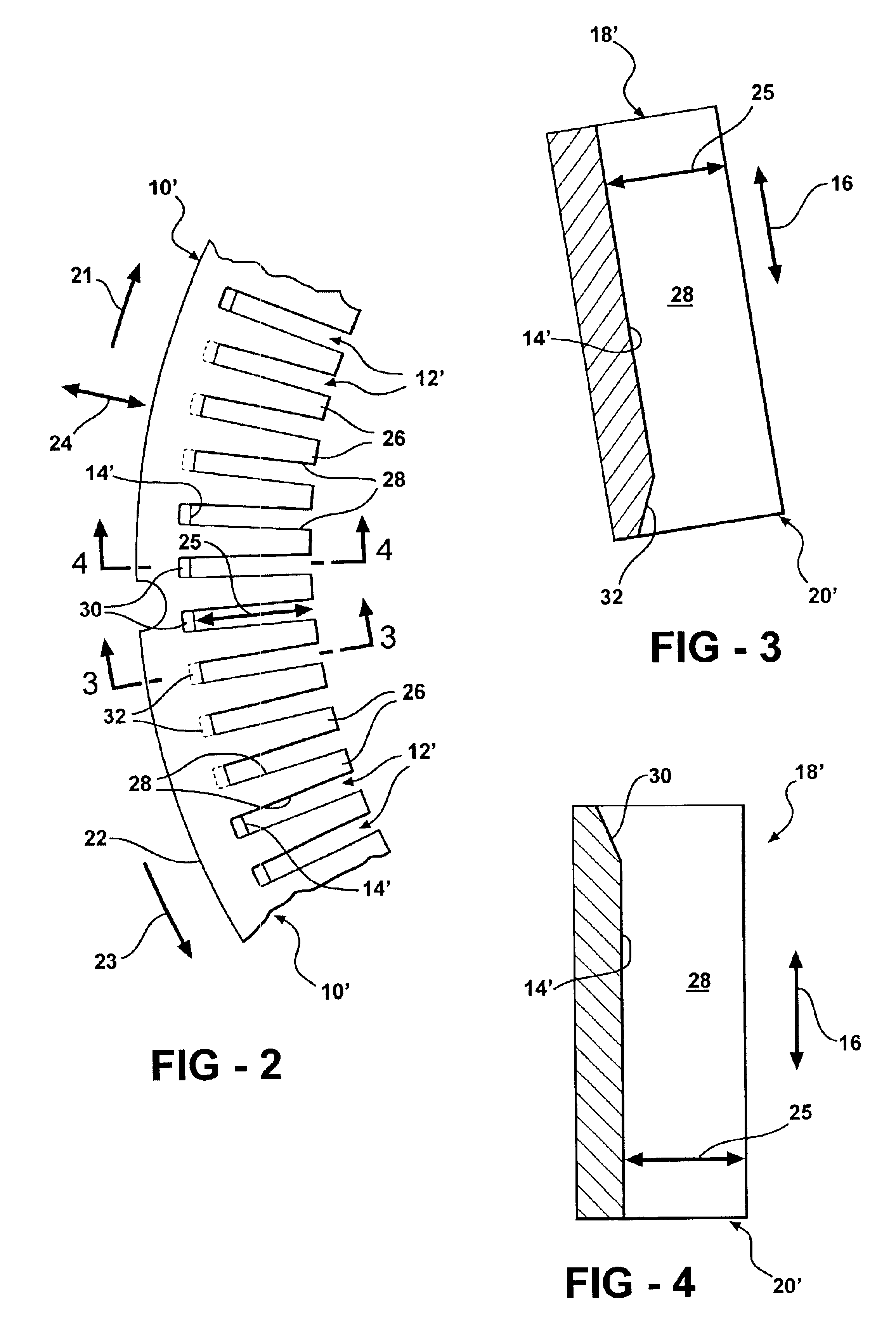
Stator arrangement of alternator for vehicle
InactiveUS6144136ASynchronous generatorsMagnetic circuit rotating partsAlternatorElectrical conductor
In a stator of an alternator for a vehicle including a stator core and a multi-phase stator winding, the stator winding is composed of a plurality of conductor segments having a pair of conductor members connected with one another to form a first coil-end group disposed on one axial end of the stator core so that first U-turn portions of the conductor segments are surrounded by second U-turn portions of the conductor segments and a second coil-end group disposed on the other axial end of said stator core so that ends of said conductor segments are connected to form lap windings.
Owner:DENSO CORP
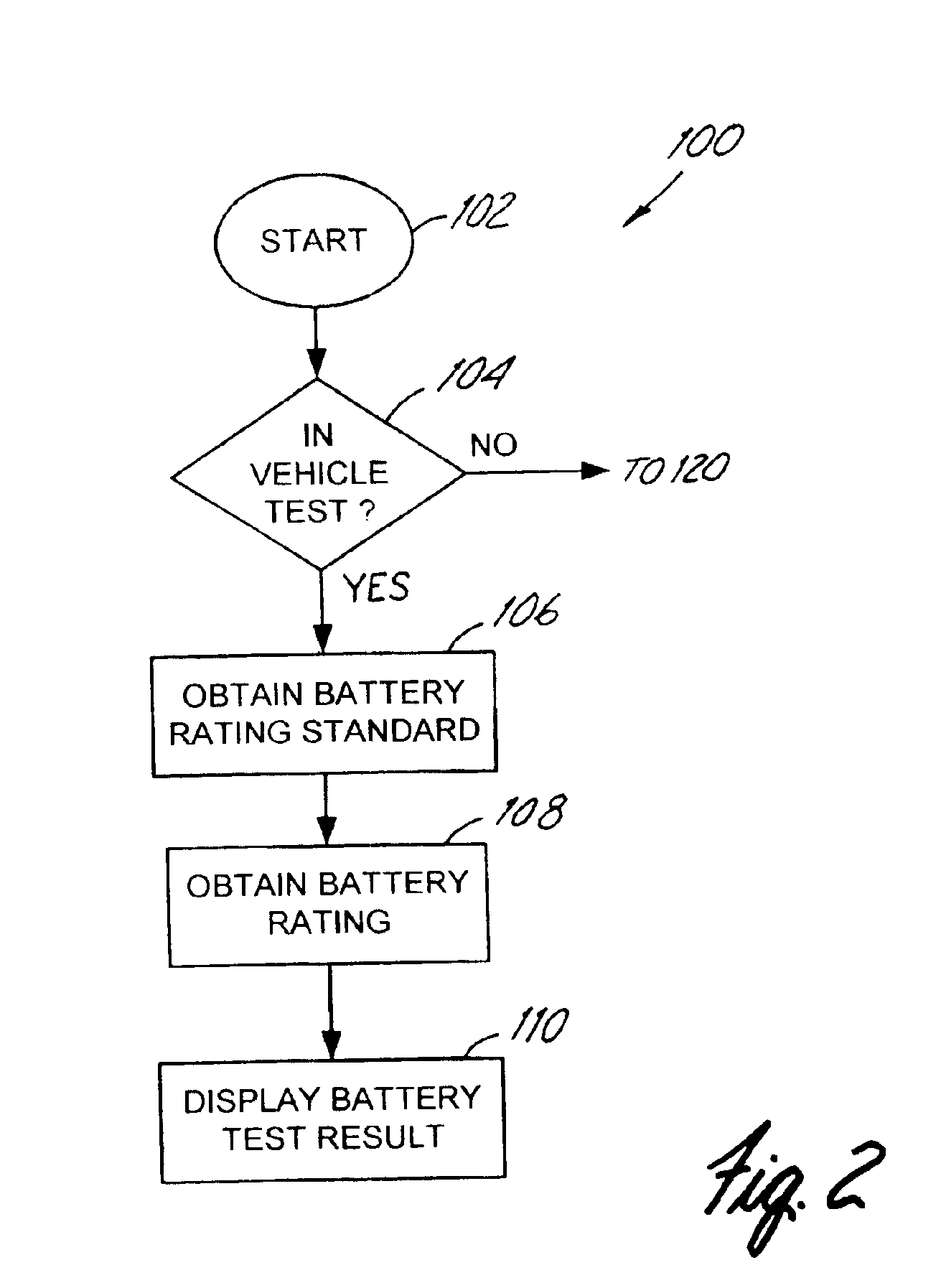
Alternator tester
An alternator tester is provided for testing an alternator of a vehicle while the alternator is coupled to the vehicle. A sensor is configured to couple to the vehicle and sense a signal related to operation of the alternator. A memory contains data related to operator instructions for performing an alternator tester of a function of vehicle type. A processor configured to provide an output indication of alternator condition based upon the sensed signal. An extra load or connection can be provided for coupling to the electrical system.
Owner:MIDTRONICS
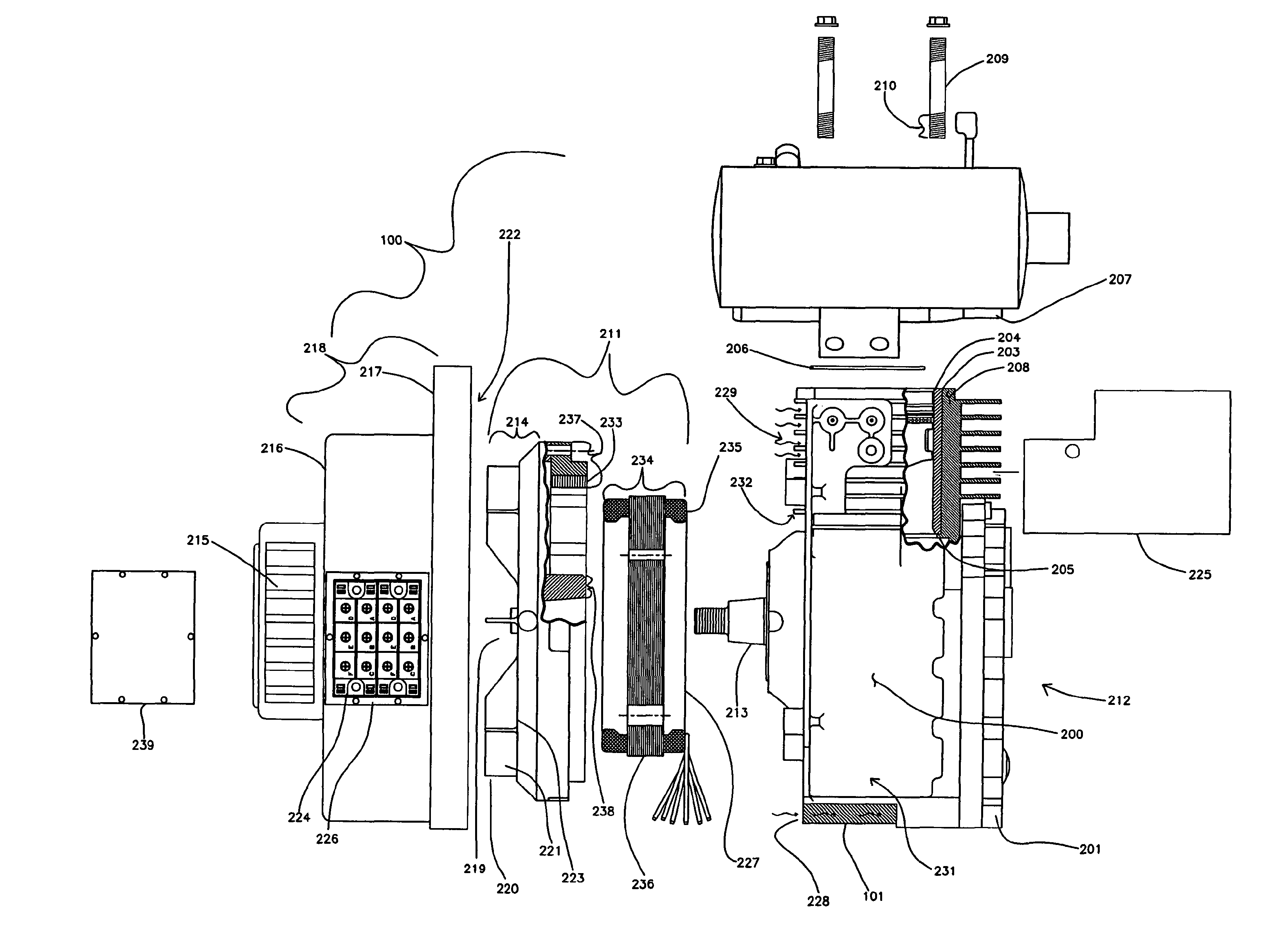
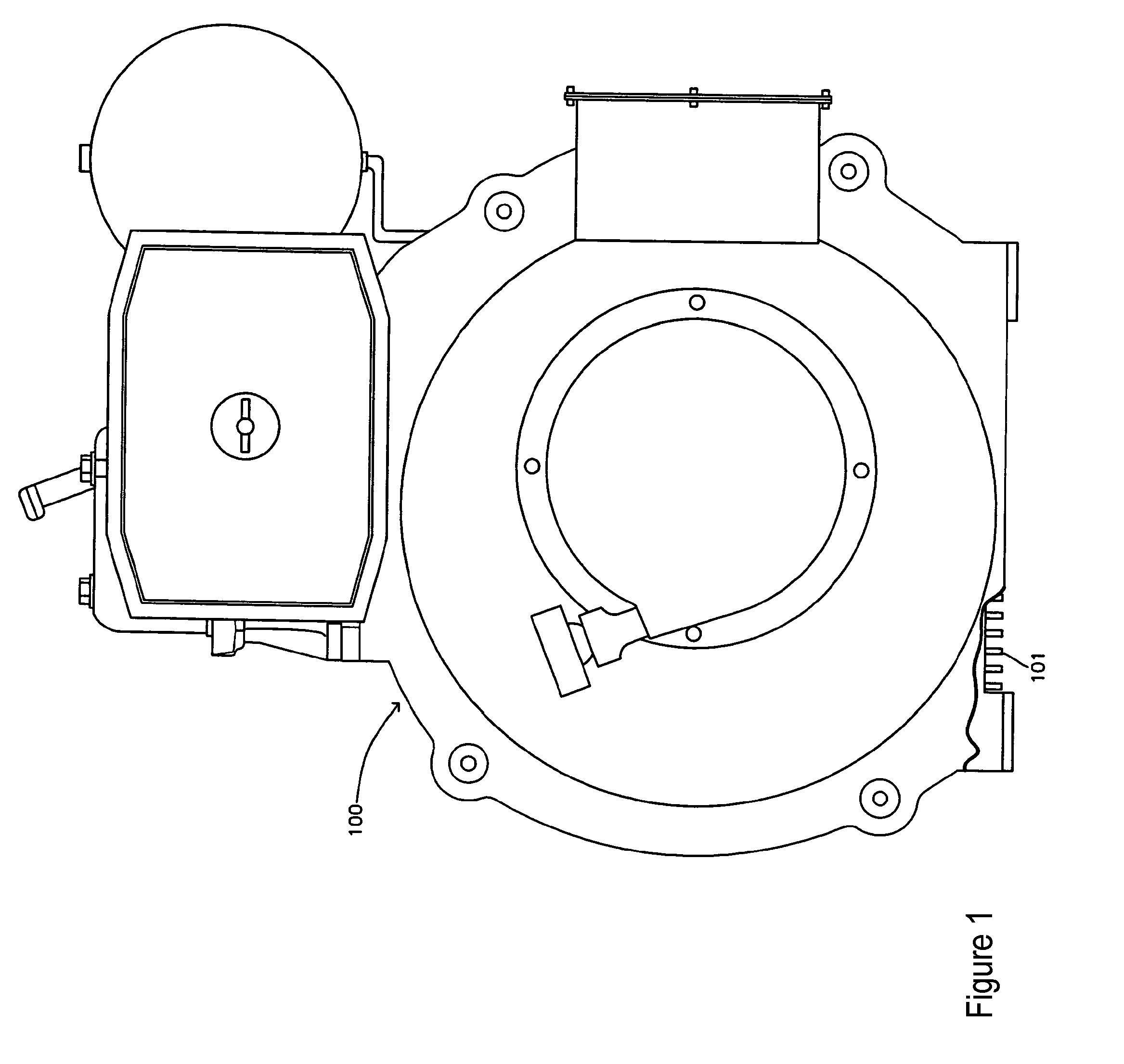
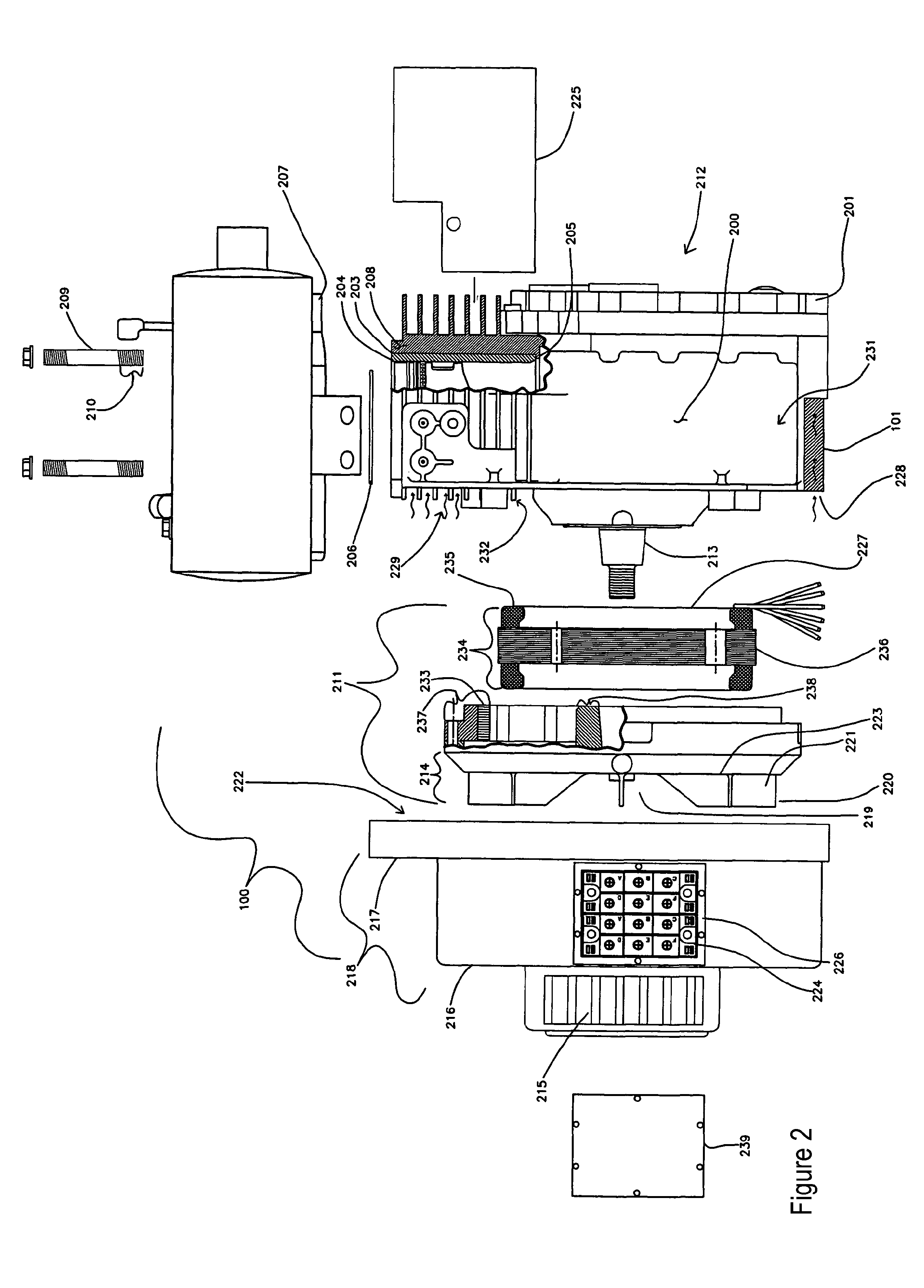
Lightweight Portable Electric Generator with Integrated Starter/Alternator
ActiveUS20070227470A1Improve torque performanceLow costMagnetic circuit rotating partsAir coolingAlternatorFuel efficiency
A compact and lightweight electric generator for portable power applications employs a new engine design and integration approach for reducing engine, generator, and starter weight. A unique flywheel alternator / starter configuration that generates electrical power, rotates the engine for starting, provides inertia for smooth engine operation, pressurized air for cooling, and inertia for the alternator. An engine cowling provides rotating component protection, a fan shroud mechanism, cooling air ducts, and a cooling mechanism for handling large quantities of heat produced by rectified power conversion. An electrical hook up that allows the generator to provide transient surge capacity for starting inductive loads, or improved load leveling and fuel efficiency.
Owner:MAINSTREAM ENG
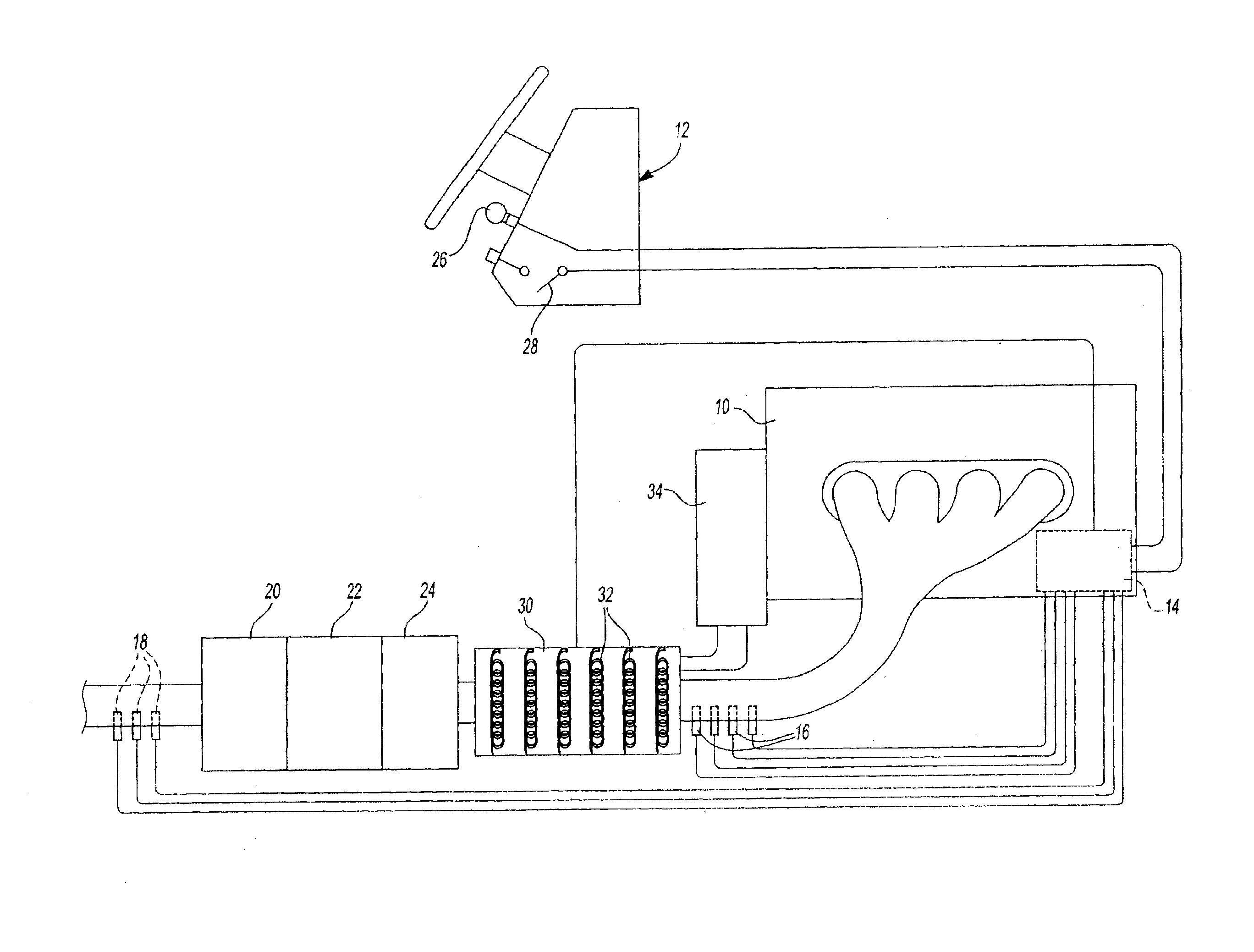
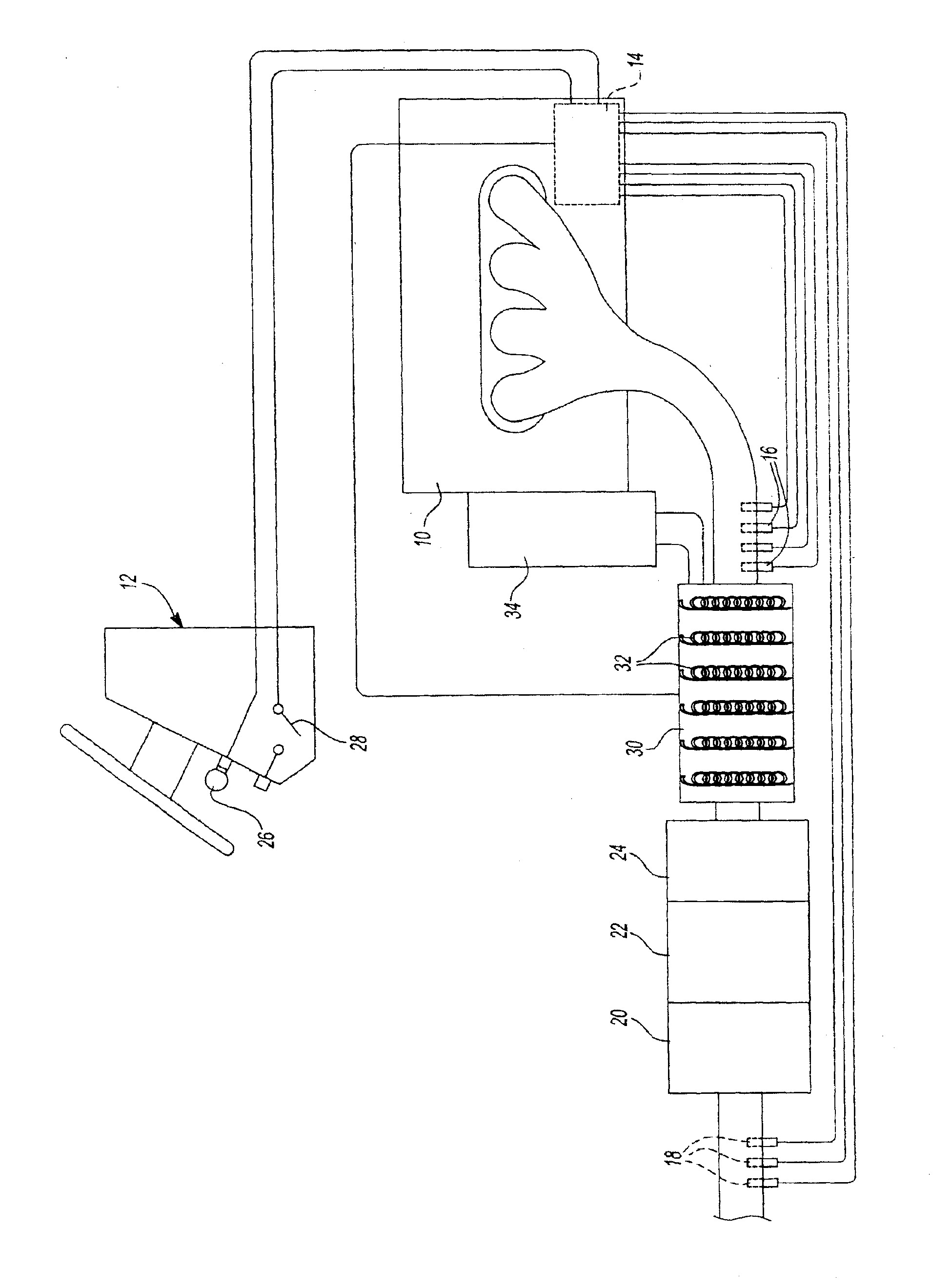
Vehicle auxiliary power unit, assembly, and related methods
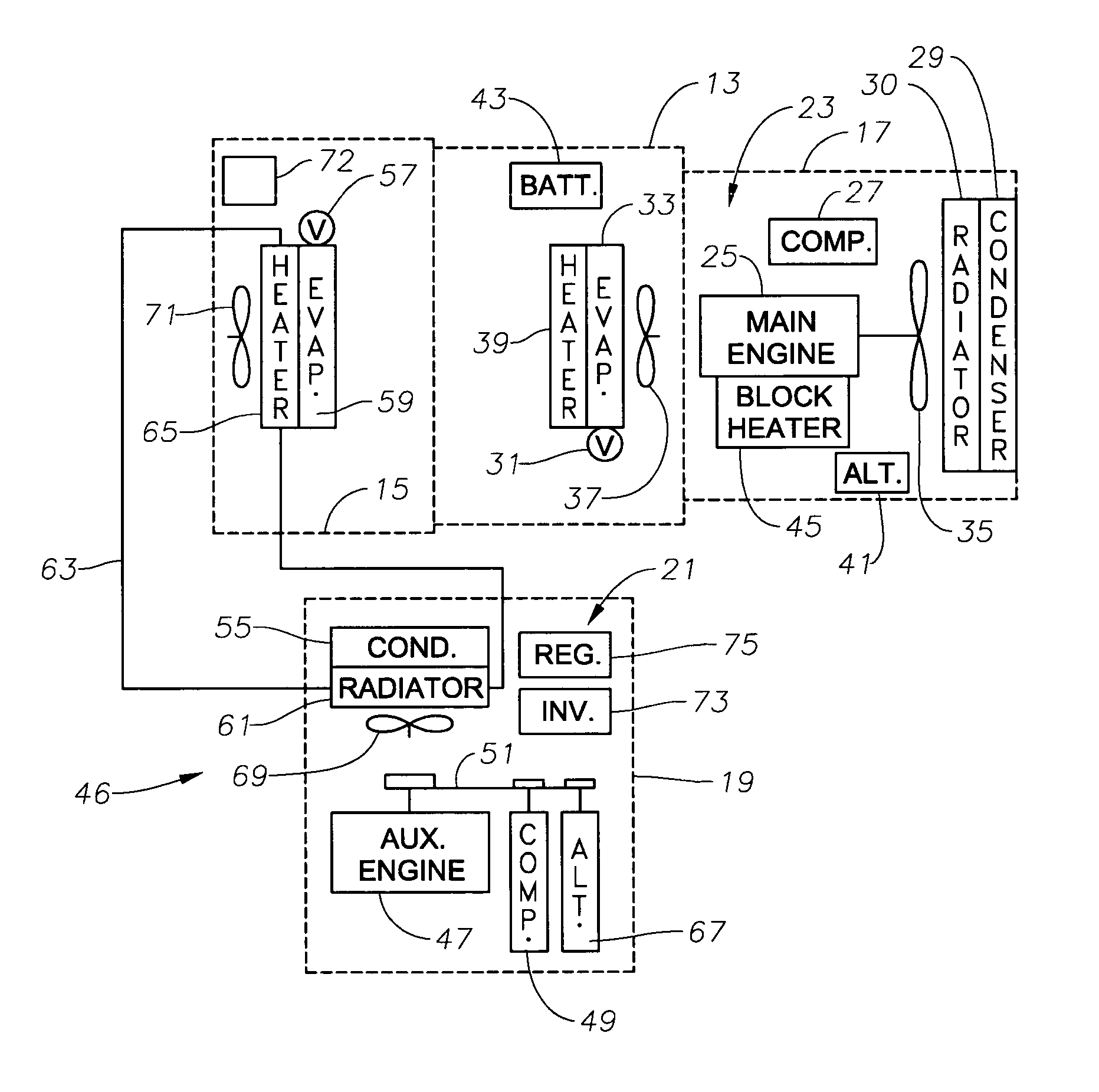
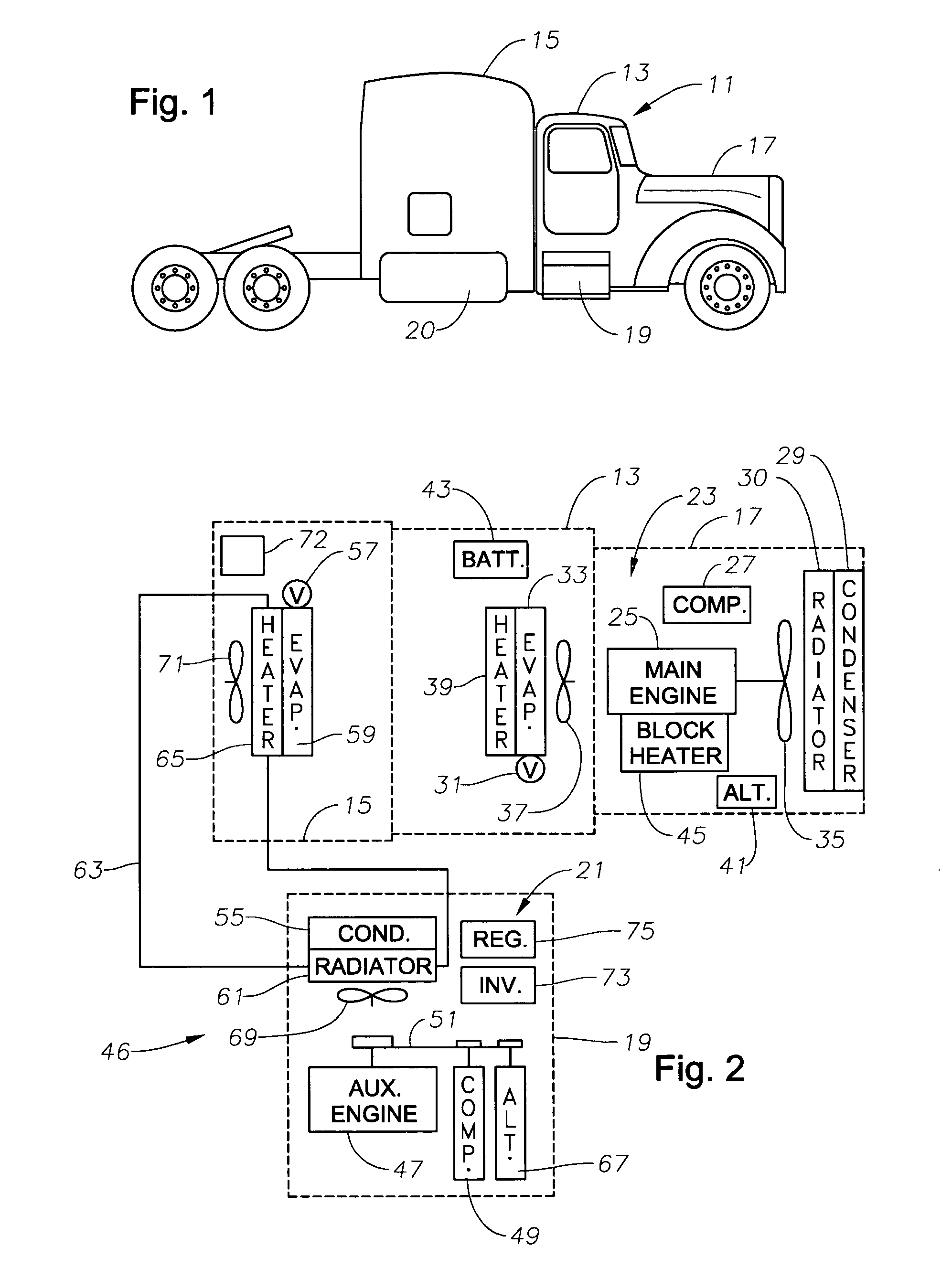
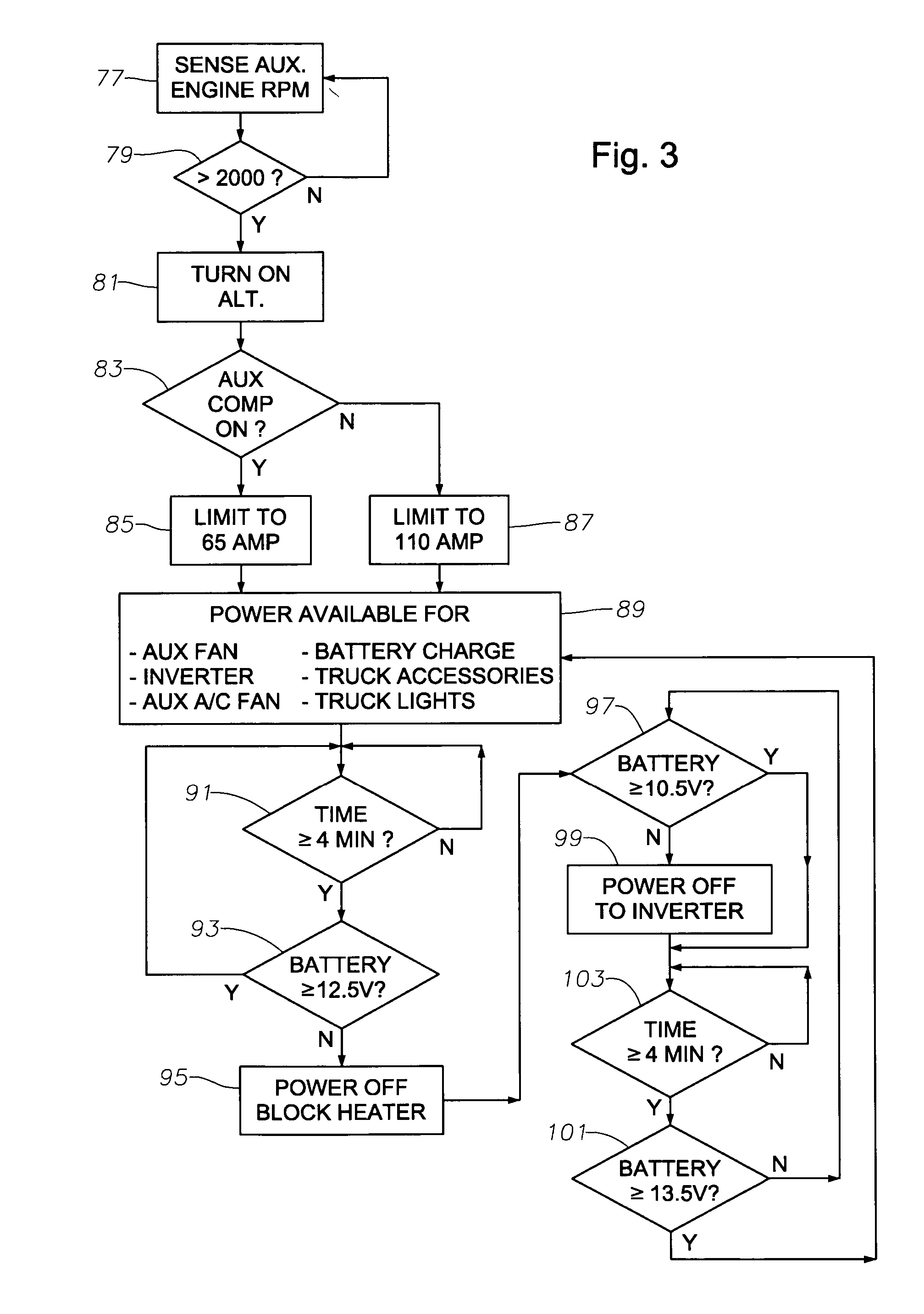
InactiveUS20050035657A1Avoid OverloadingPrevent excessive vehicle battery depletionAir-treating devicesRailway heating/coolingElectrical batteryAuxiliary power unit
A truck includes an auxiliary power unit having components specifically selected such that they form a stand-alone unit that can fit within an auxiliary compartment of a vehicle and deliver heating, cooling, and additional electric power to the vehicle. Included is an auxiliary engine, an auxiliary alternator, and an auxiliary condenser to provide coolant for a personnel compartment mounted evaporator. An auxiliary voltage regulator provides a ramp-up feature to minimize excessive start-up loads, limits maximum available current from the auxiliary alternator when the auxiliary compressor is engaged, and selectively disables power to electrical components in the event of low vehicle battery voltage. The auxiliary engine includes a radiator system to provide heated fluid for a personnel compartment mounted heat exchanger.
Owner:LONGHORN SCSF LTD +1
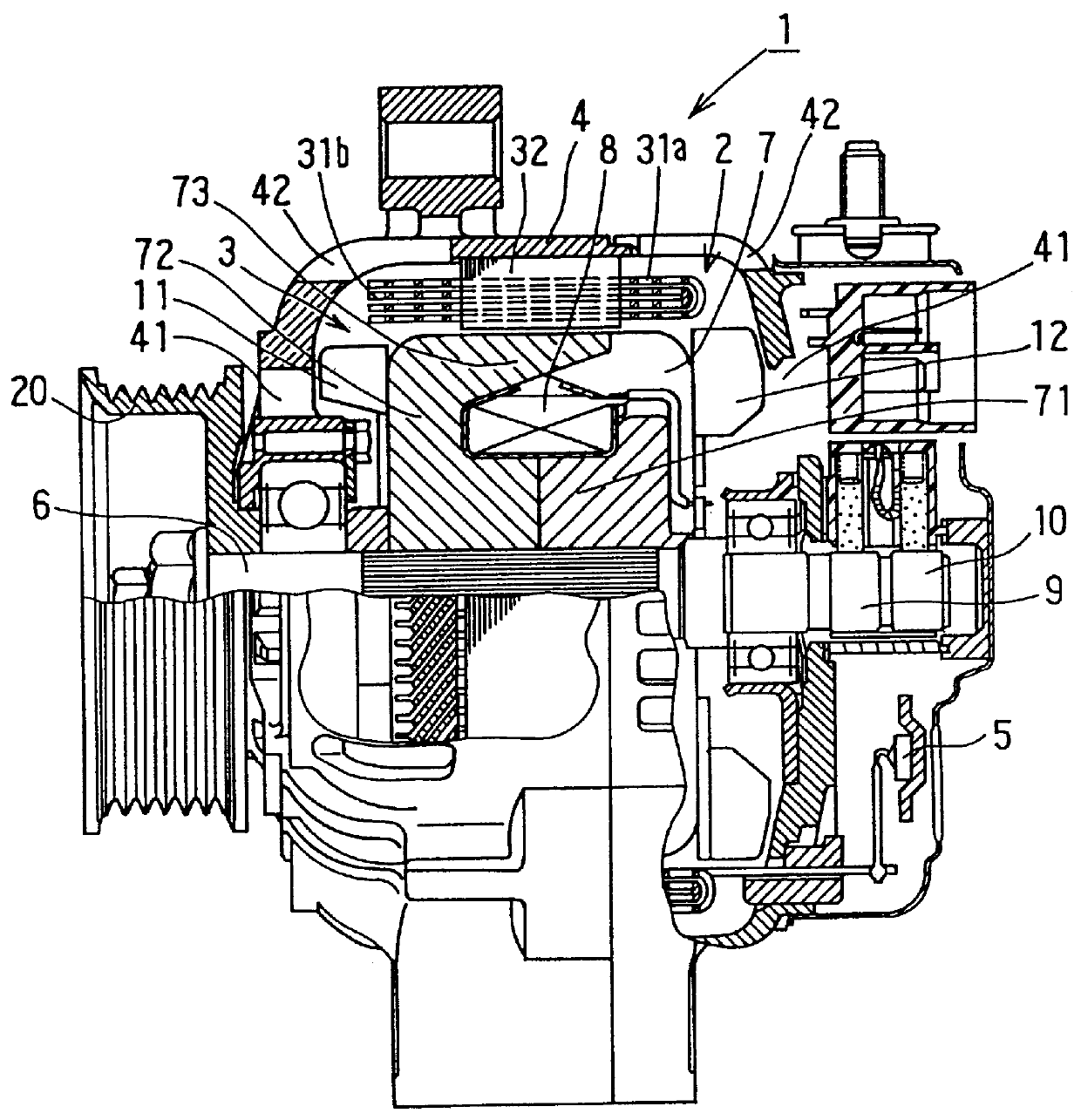
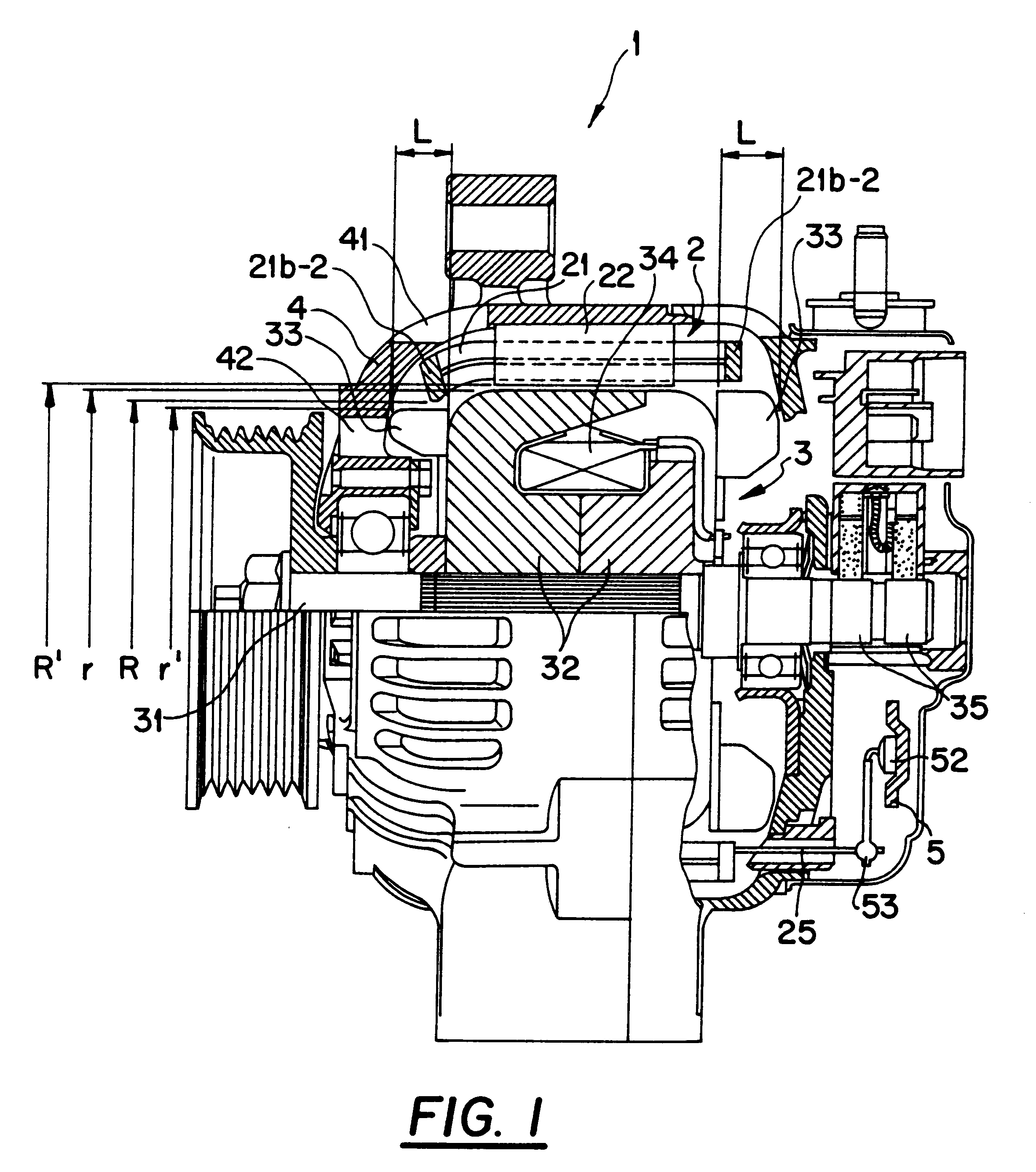
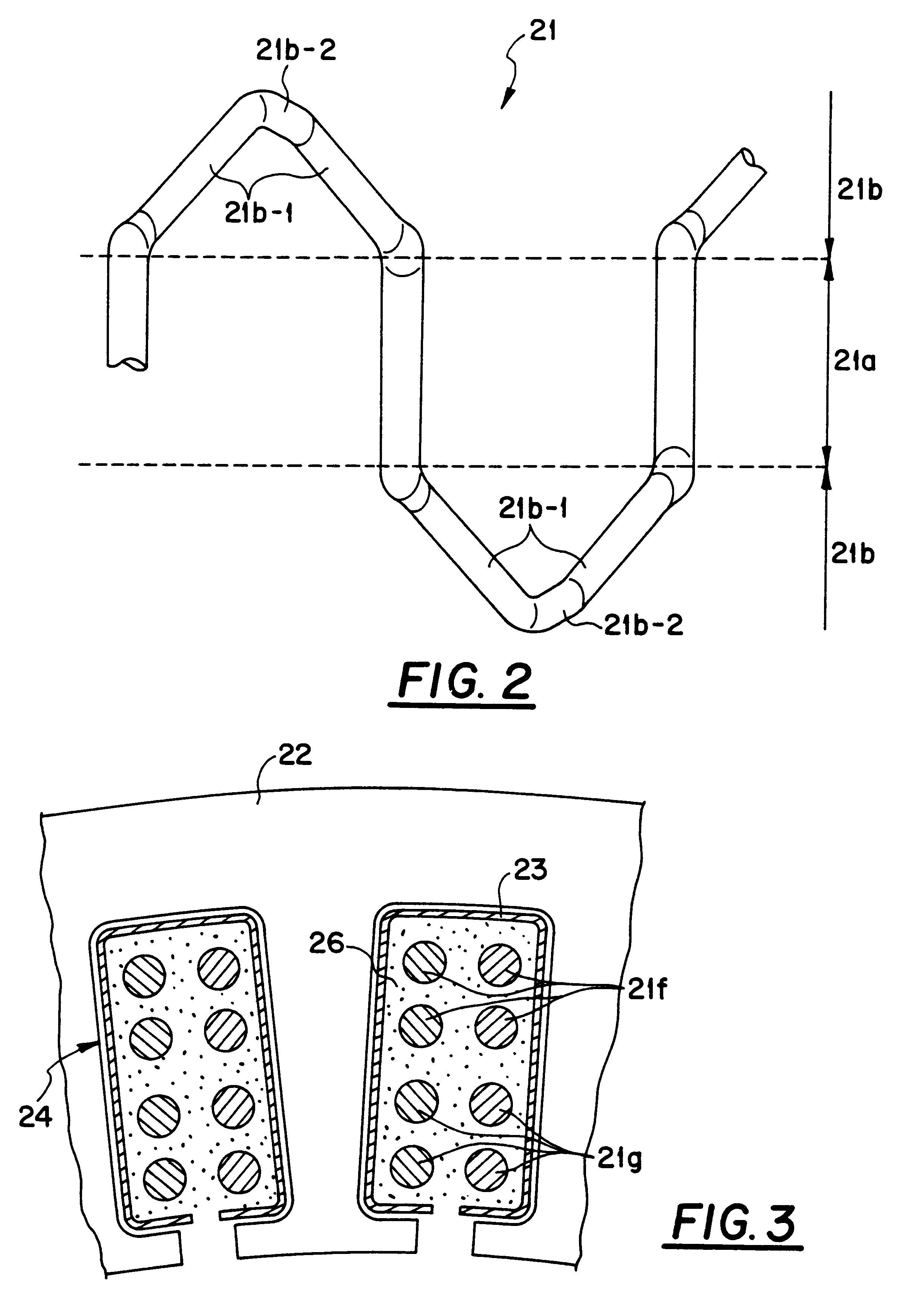
Alternator for vehicle
InactiveUS6181045B1Heat resistantIncrease heat radiationSynchronous generatorsWindings insulation shape/form/constructionElectrical conductorAlternator
It is an object of this invention to provide an alternator for a vehicle in which all electric conductors forming bridge portions are sufficiently exposed to cooling winds so that the cooling performance is remarkably improved. It is another object of this invention to provide an alternator for a vehicle which is excellent in cooling performance, insulating characteristic, and heat resisting property. An alternator for a vehicle includes a stator. The stator includes an iron core 22, an electric conductor 21, and an insulator 23. The electric conductor 21 forms a winding on the iron core 22. The insulator 23 provides electric insulation between the electric conductor 21 and the iron core 22. The stator is supported by a housing. The dimension of openings of slots in the iron core 22 is smaller than the distance between inner side surfaces of the slots. The electric conductor 21 has accommodated portions accommodated in the slots, and bridge portions connecting the accommodated portions. Pieces of the electric conductor which extend out of the slots are approximately separated into a conductor groups 21f located on outer radial sides of the slots and a conductor group 21g located on inner radial sides of the slots, and form the bridge portions. Predetermined gaps are provided between pieces of the electric conductor in the bridge portions. The bridge portions have ridge portions inclined in a same circumferential direction in each of the outer radial side and the inner radial side, and top portions connecting the ridge portions along an axial and radial direction.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Automotive electrical system configuration using a two bus structure
InactiveUS7075273B2Batteries circuit arrangementsLoad balancing in dc networkAlternatorCritical load
Disclosed herein are a variety of different electrical system topologies intended to mitigate the impact of large intermittent loads on a 12 volt vehicle power distribution system. In some embodiments the intermittent load is disconnected from the remainder of the system and the voltage supplied to this load is allowed to fluctuate. In other embodiments, the voltage to critical loads is regulated independently of the voltage supplied to the remainder of the system. The different topologies described can be grouped into three categories, each corresponding to a different solution technique. One approach is to regulate the voltage to the critical loads. A second approach is to isolate the intermittent load that causes the drop in system voltage. The third approach is to use a different type of alternator that has a faster response than the conventional Lundell wound field machine.
Owner:TEMIC AUTOMOTIVE OF NORTH AMERICA
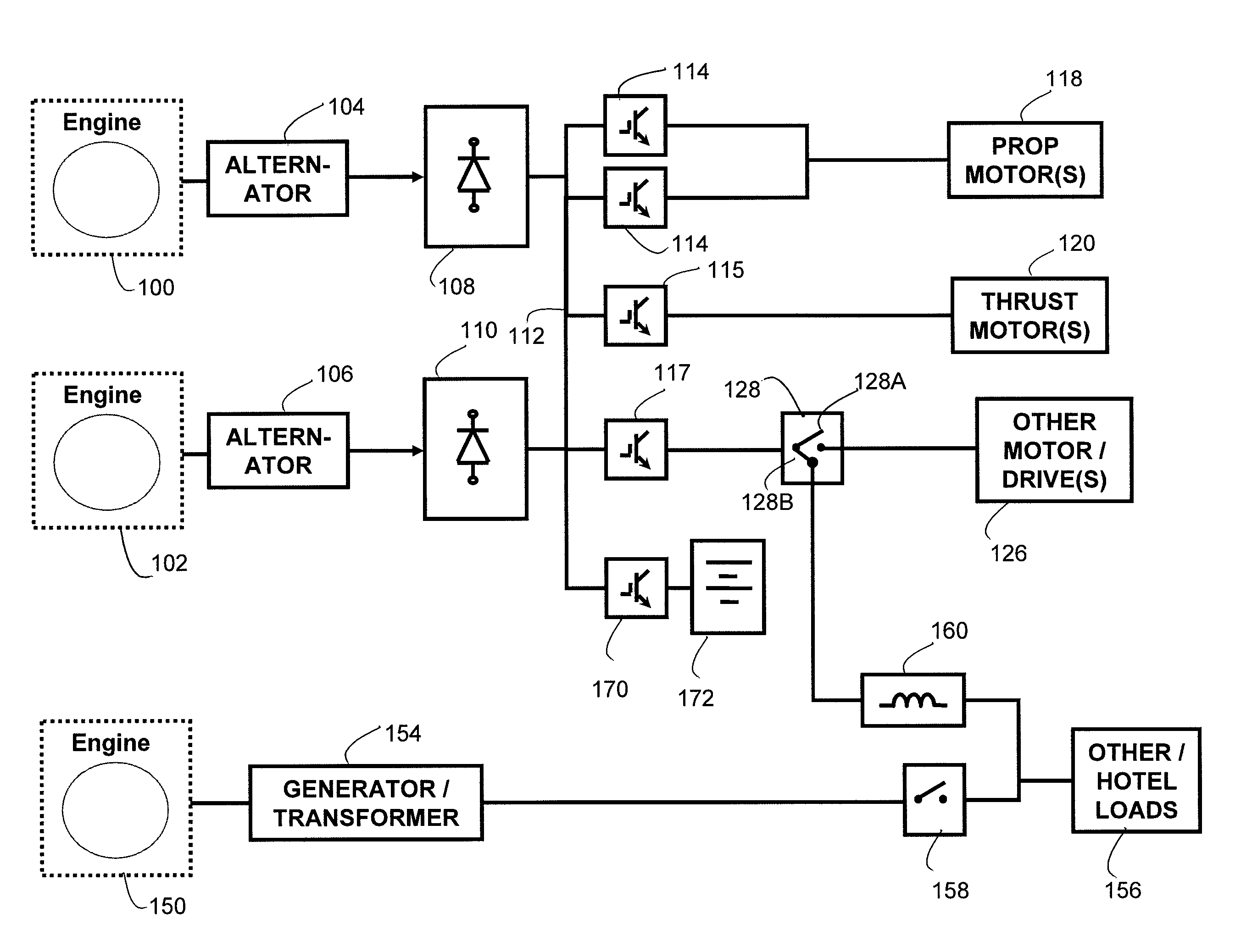
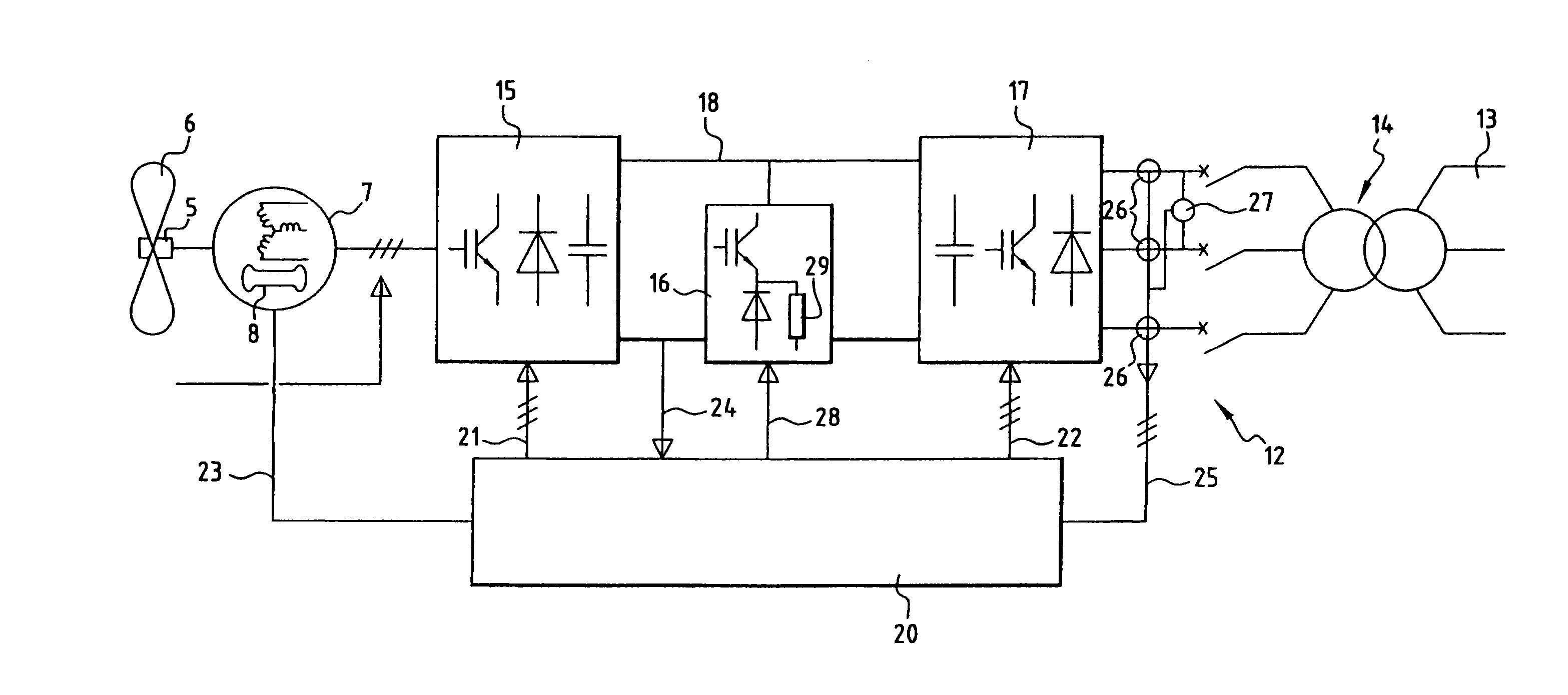
Power generation apparatus
ActiveUS20110080040A1Ac-dc network circuit arrangementsPlural diverse prime-mover propulsion mountingElectricityAlternator
An apparatus including an alternator that is drivable by an engine for producing a first AC electric current, a rectifier in electrical communication with the alternator for producing a DC electric current, an inverter in electrical communication with the rectifier for producing a second AC electric current where the second AC electric current having an acceptable frequency and / or voltage, and the inverter in electrical communication with one or more electric loads responsive to the second AC electric current, and an energy storage device that is able to electrically couple to the alternator, rectifier, and / or inverter.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
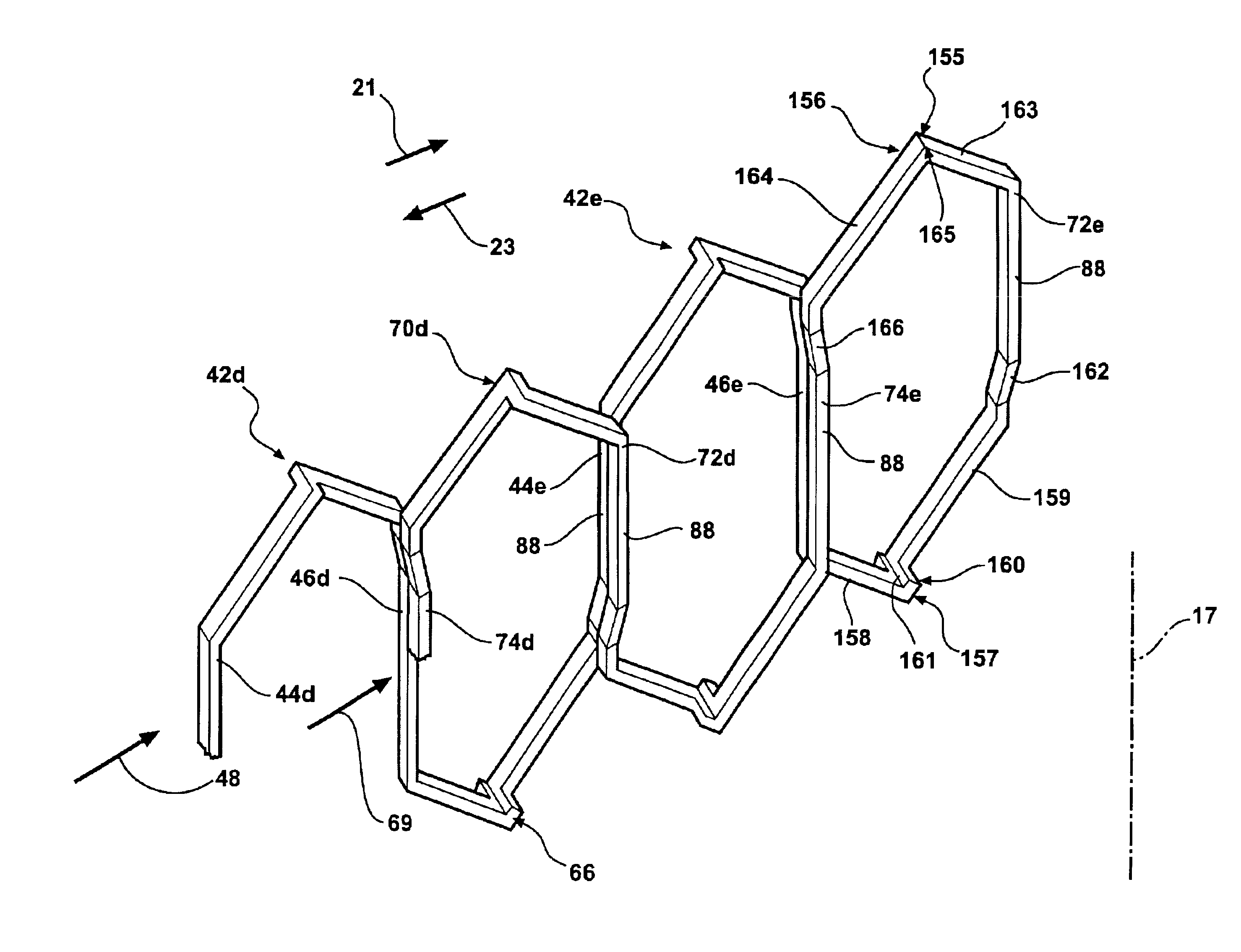
Stator winding having cascaded end loops
An alternator stator having cascaded end loop segments includes a multi-phase stator winding that is adapted to be placed in a plurality of circumferentially spaced axially-extending core slots in a surface of a stator core. The stator winding includes a plurality of straight segments alternately connected at the first and second ends of the stator core by a plurality of end loop segments to form the winding. The end loop segments include first and second sloped portions meeting at an apex portion. Each of the end loop segments includes a radial outward adjustment and a radial inward adjustment and forms a cascaded winding pattern.
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
Method and device for regulating a wind machine
A method and corresponding apparatus for regulating a system that produces electric power, the system including an electric alternator having a rotor integral with a rotating part of a wind machine to form a rotary assembly, and a power electronics module, the method including the steps of: producing an alternating current at output terminals of the alternator; converting the alternating current produced by the alternator into modulated pulses of direct current. Alternating electric current produced by the alternator is regulated by controlling the speed of rotation of the rotary assembly by resisting torque imposed by the alternator in response to modulating the pulses of continuous current produced by the converted the alternating current.
Owner:JEUMONT
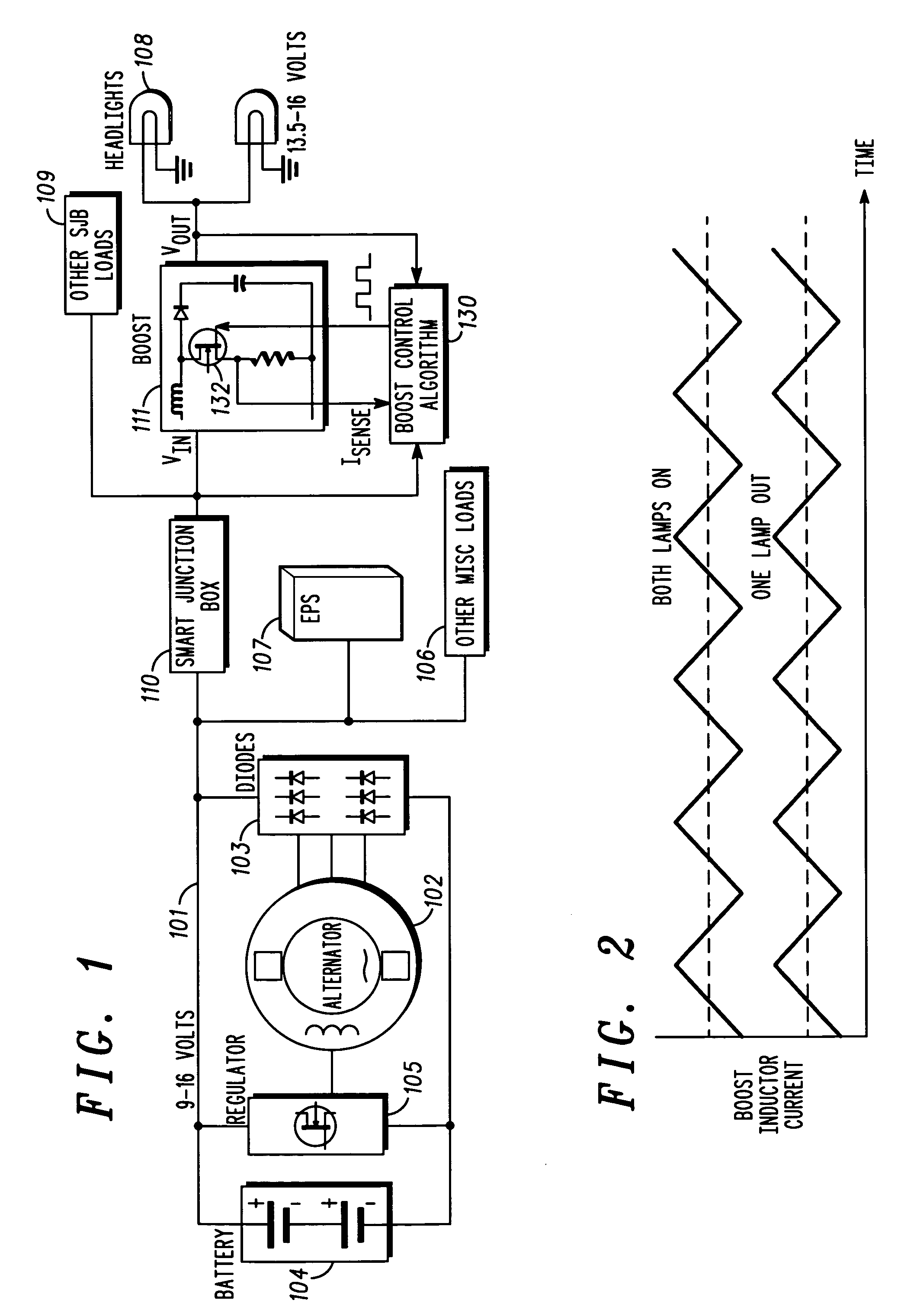
Controller for permanent magnet alternator
InactiveUS7176658B2Improve conversion efficiencyReduce radio frequency interferenceDc network circuit arrangementsEmergency protective circuit arrangementsAlternatorControl system
The invention is a control system that, among other things, controls a permanent magnet alternator and provides relatively accurate voltage regulation. The control system may include one or more of the following: (1) a rectification system to rectify and regulate the output voltage of an alternator, (2) a rectifier / limiter used as an electrical power source to a boost type regulator, (3) a multimode rectifier / limiter, (4) a DC to AC inverter bridge, and (5) power switches employed in the system to minimize the switching energy that would otherwise be dissipated in the power switches as heat.
Owner:MAGNETIC APPL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com